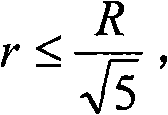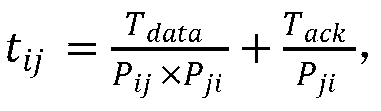Patents
Literature
34 results about "End to end throughput" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
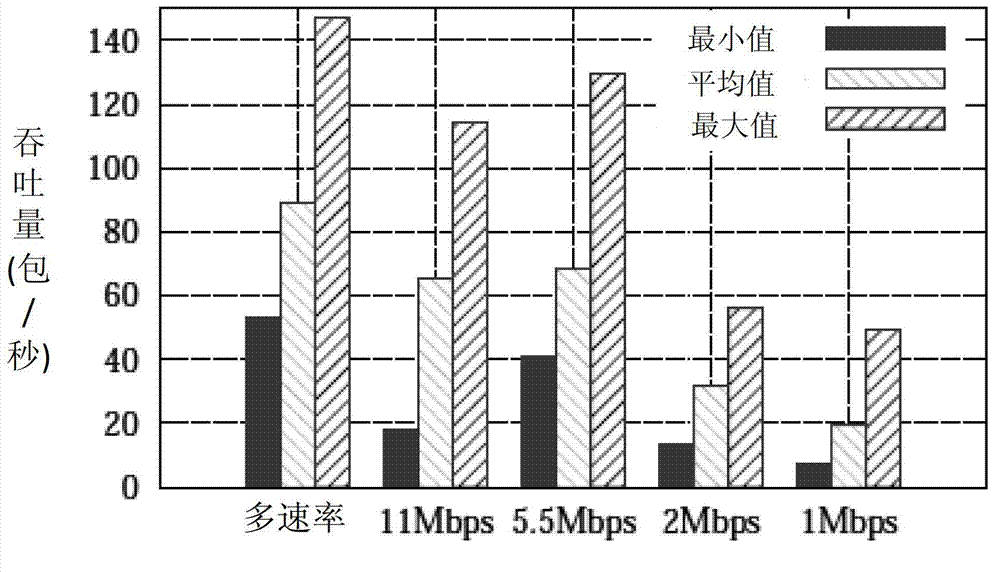
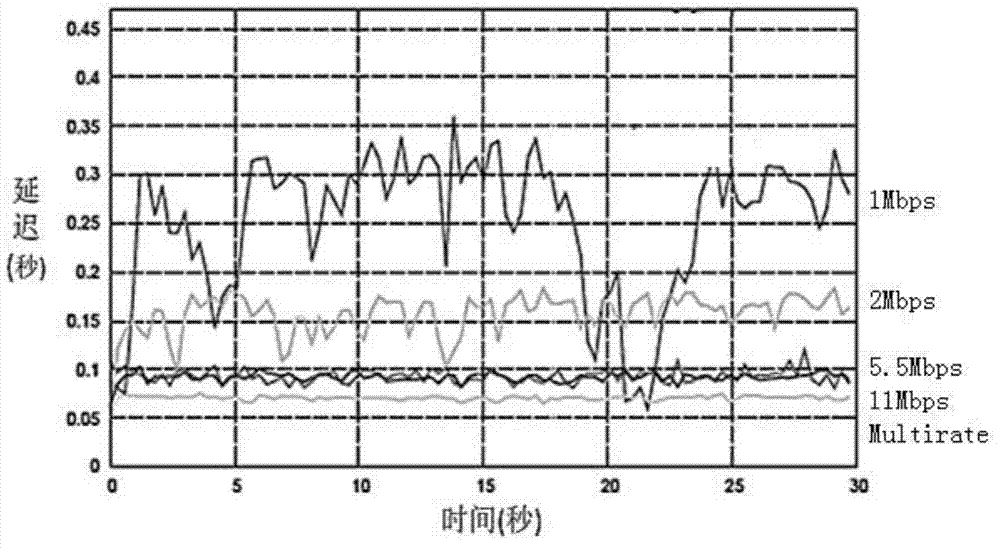
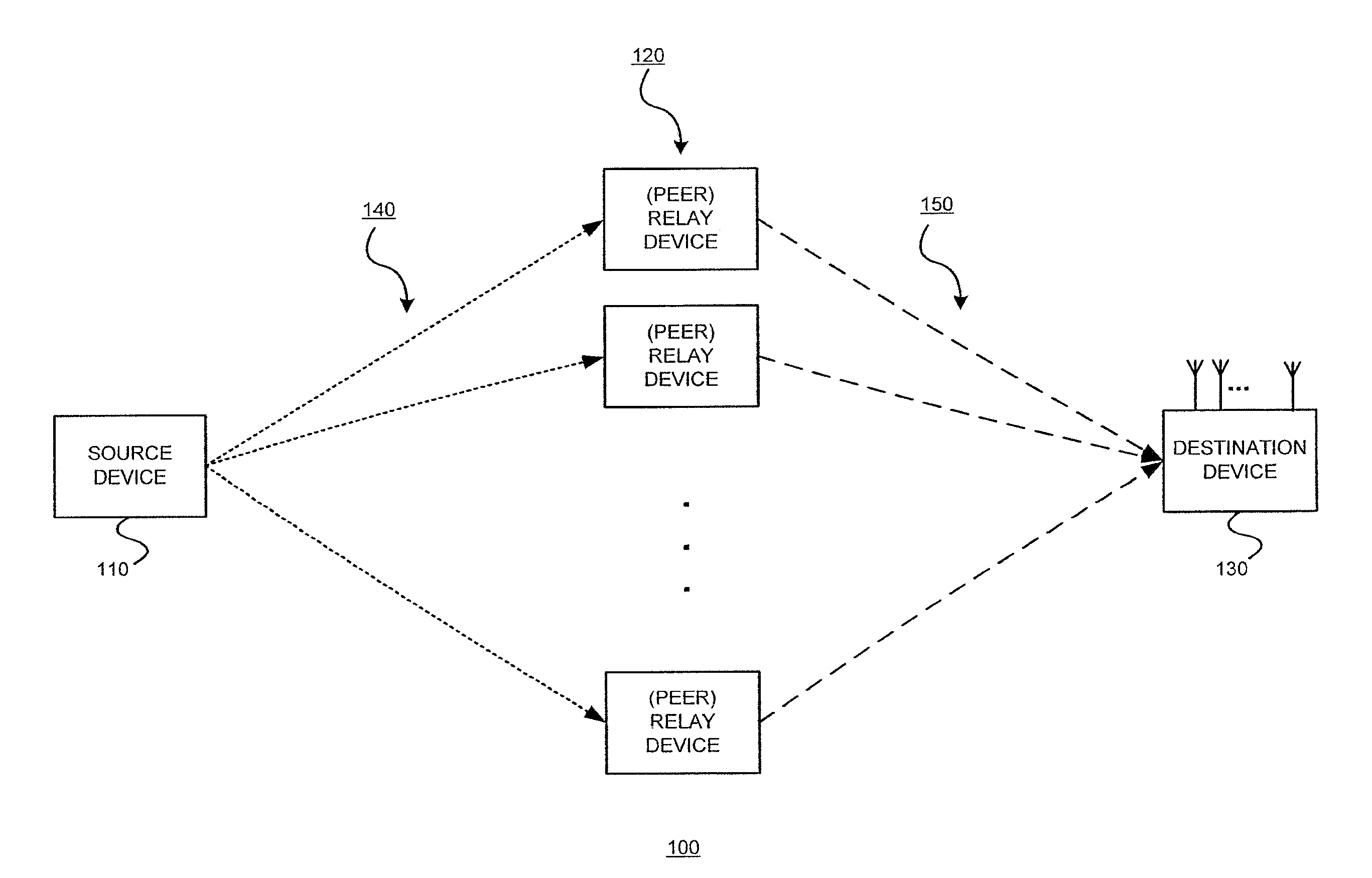
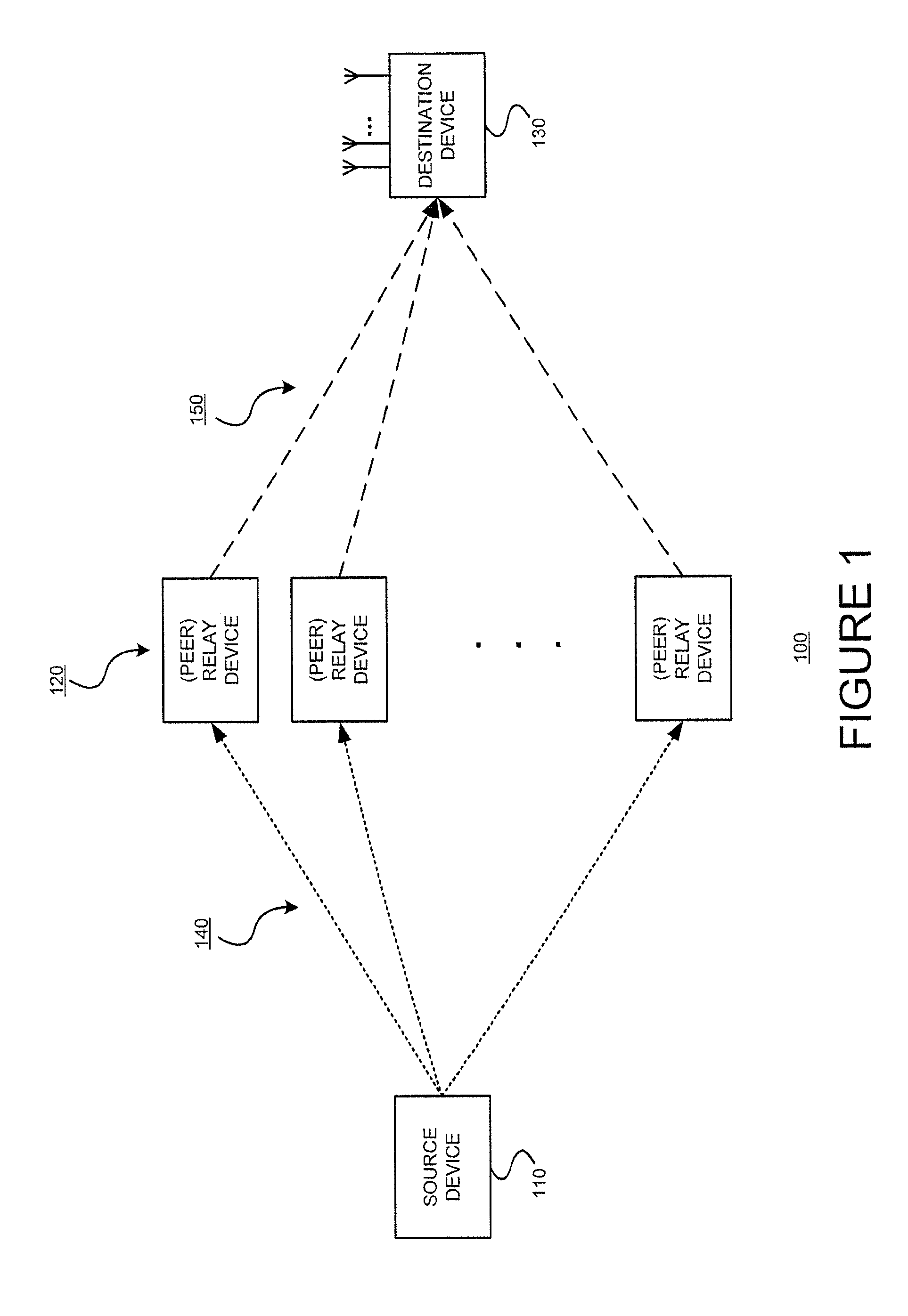
Throughput is a measure of how fast we can actually send data through a network. End to end delay is the sum of time taken from the source to the destination for a packet to reach. End to end delay is the time taken by a packet to travel from source to destination. Delay depends on number of hops and congestion on the network.
Packet based communications
InactiveUS20100014510A1Raise the ratioImprove efficiencyNetwork connectionsData trafficCommunication endpoint
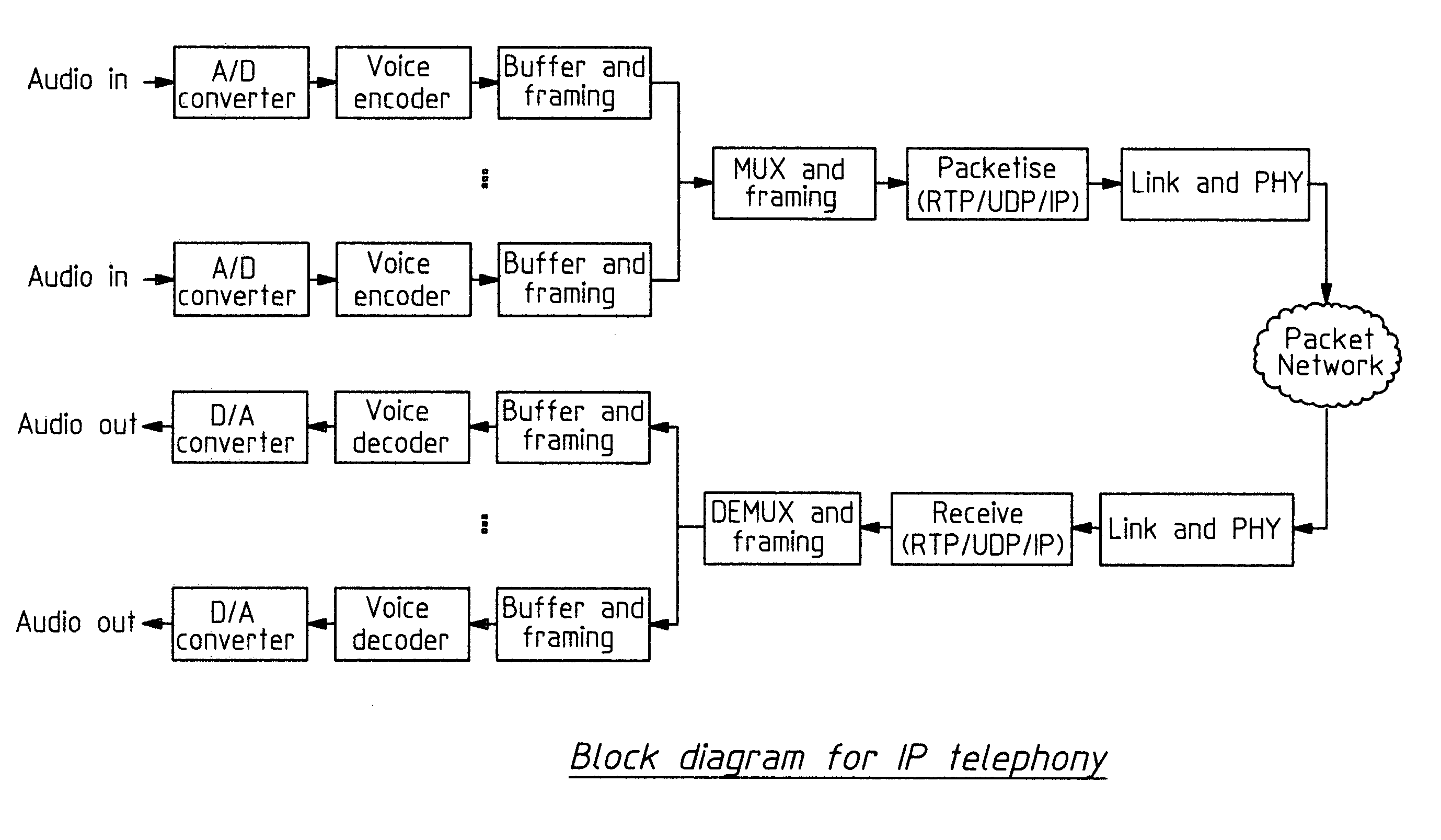
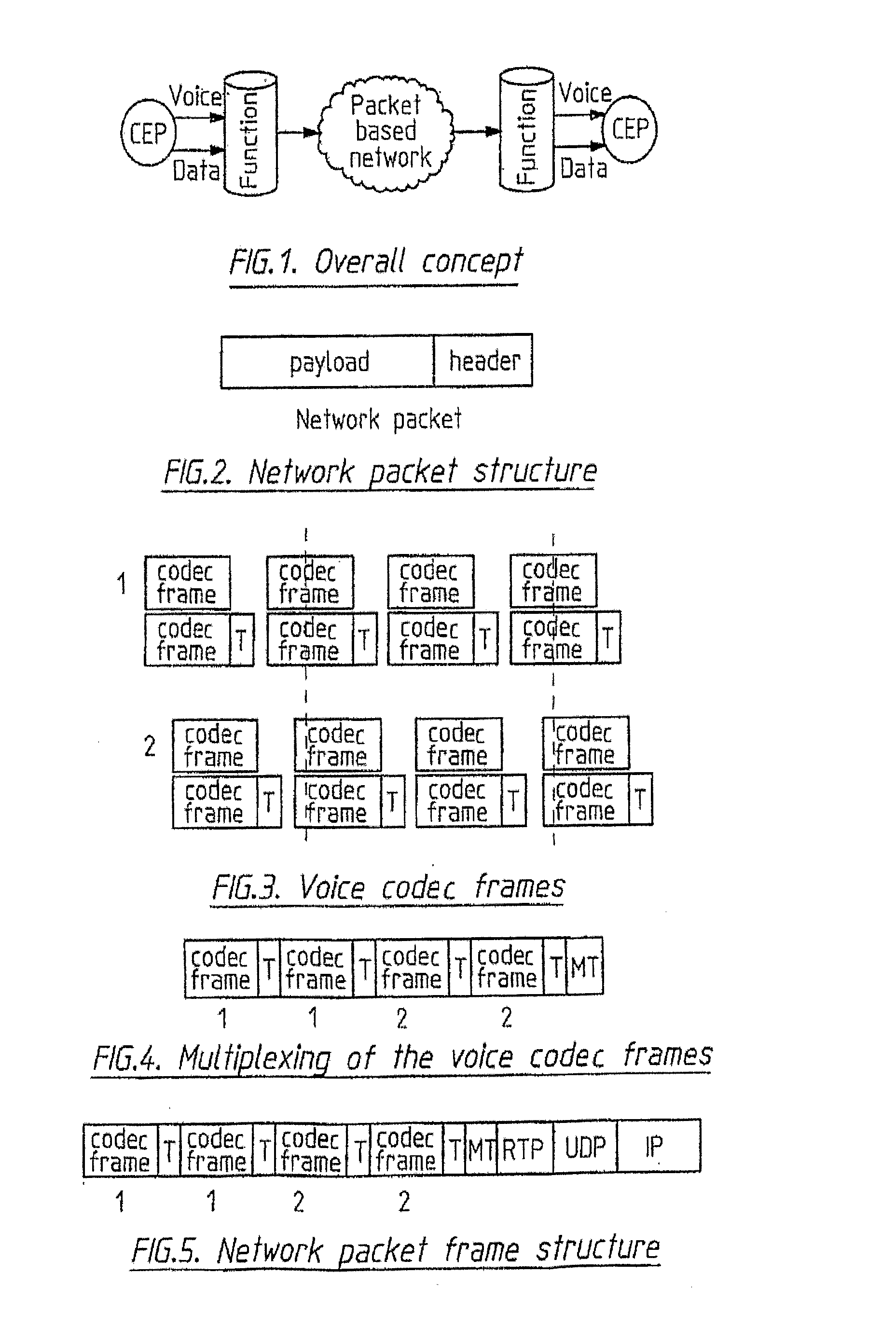
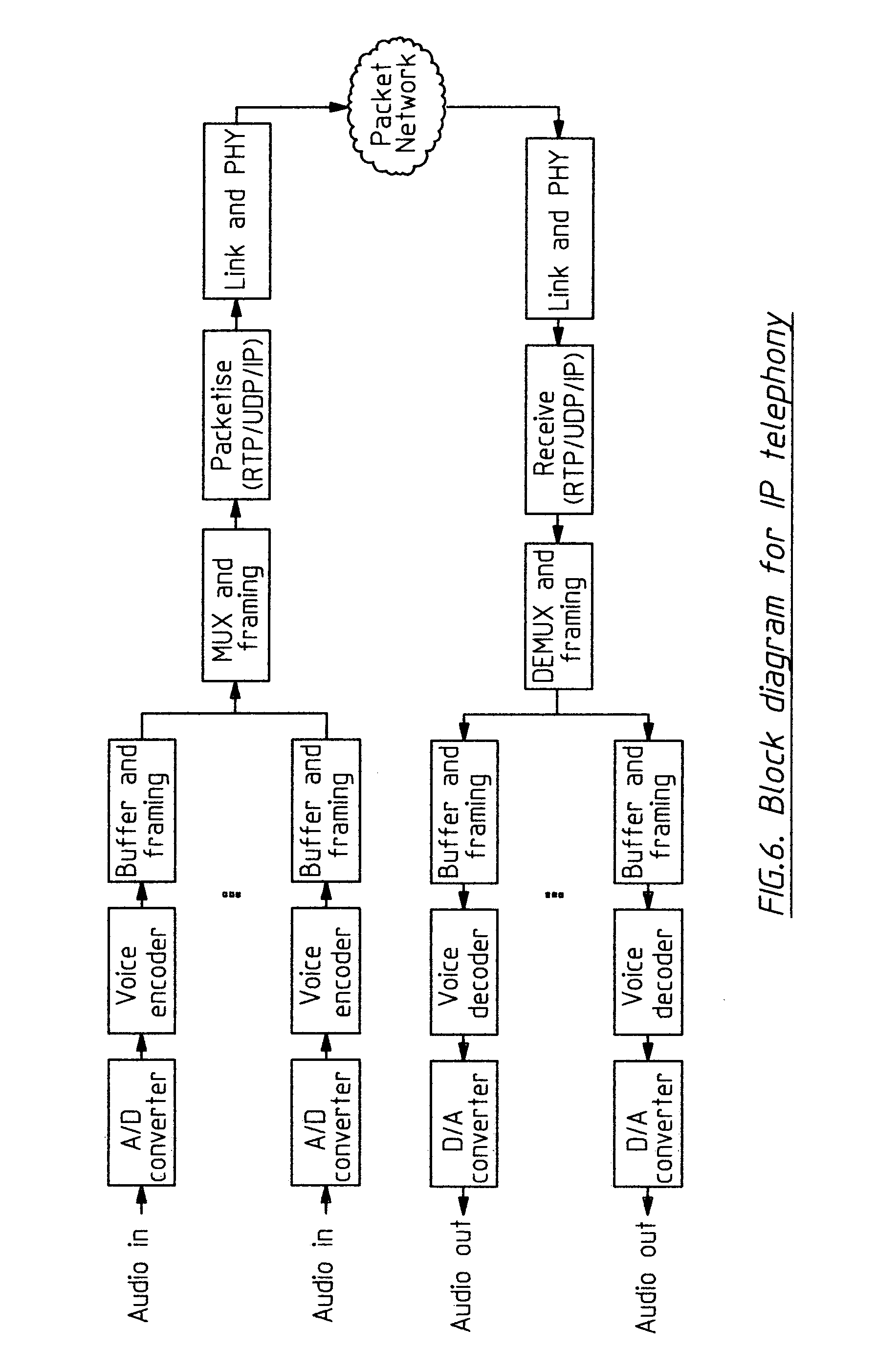
This invention is applicable to packet based, rate limited radio links, such as satellite or terrestrial wireless digital communications systems. These communications networks concurrently carry time-critical traffic, such as voice or multimedia, and non time-critical traffic, such as generic data traffic, between two or more communication end points. The communication end points may be connected through a number of heterogenous networks and the end to end throughput characteristics may vary over time. A first aspect of the invention concerns a method for generating packets. In other aspects the invention concerns a computer system for use in packet based communications, a computer protocol for packet based communications and a communications packet. The invention involves determining a “time slice” packet size from the link speed and the interval of time extending between the times at which packets are selected for output from a buffer to the transmission interface. It also involves creating a network packet from frames of time-critical data generated during the interval, where the packet is synchronised to both existing timing requirements of the time-critical frames and the link speed. Then, adding non time-critical data to the network packet if its size had not exceeded the determined “time slice” packet size.
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
Coopmax: a cooperative mac with randomized distributed space time coding for an IEEE 802.16 network
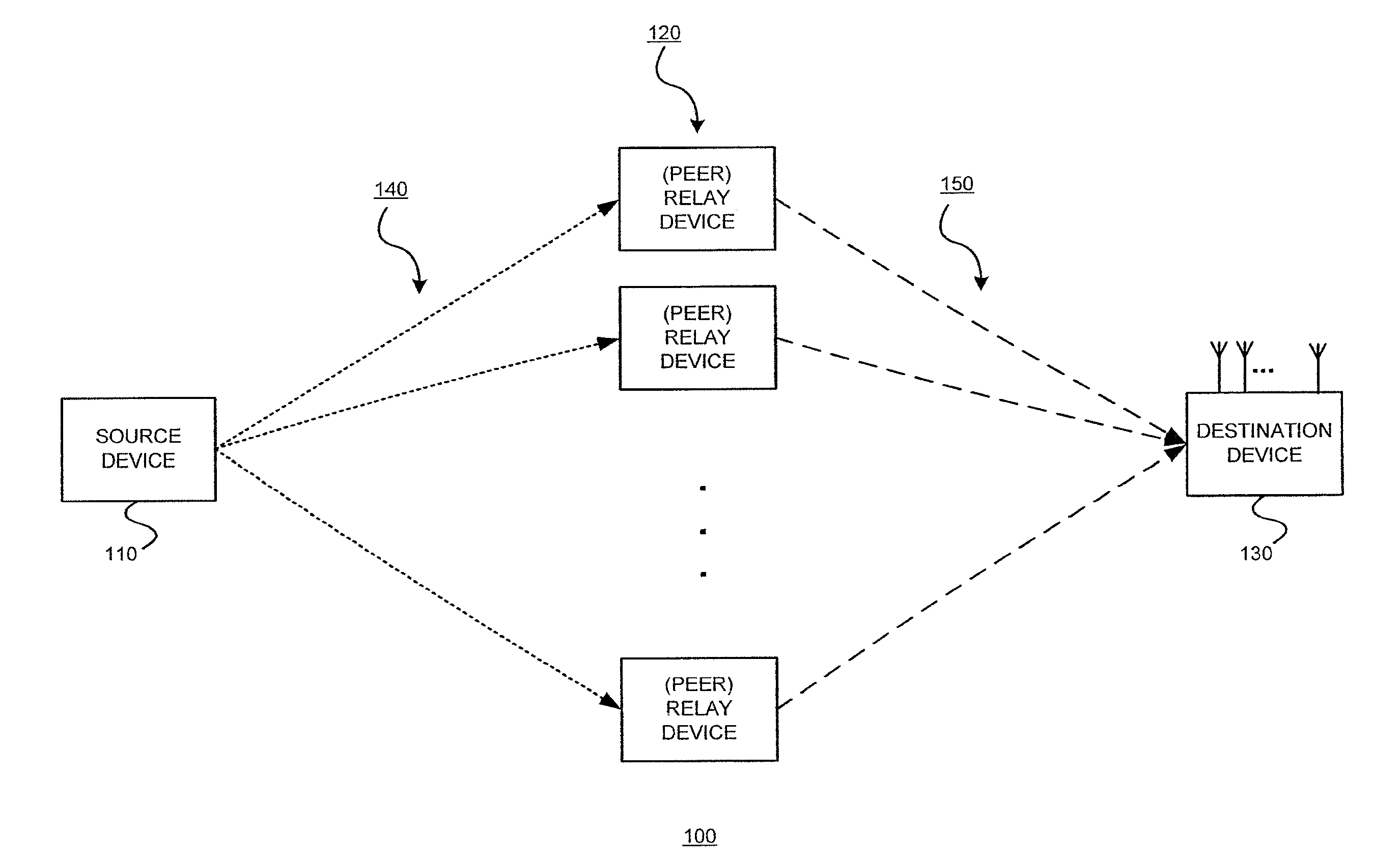
Cooperative communication is a technique that can be employed to meet the increased throughput needs of next generation WiMAX systems. In a cooperative scenario, multiple stations can jointly emulate the antenna elements of a multi-input multi-output system in a distributed fashion. A framework for a randomized distributed space-time coding (“R-DSTC”) technique in the emerging relay-assisted WiMAX network, and the development of a cooperative medium access control (“MAC”) layer protocol, called CoopMAX, for R-DSTC deployment in an IEEE 802.16 system, is described. The technique described couples the MAC layer with the physical (PHY) layer for performance optimization. The PHY layer yields significant diversity gain, while the MAC layer achieves a substantial end-to-end throughput gain.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Power management for throughput enhancement in wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS20080132264A1Reduce power consumptionExpand the transmission rangeEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsTransmitted power
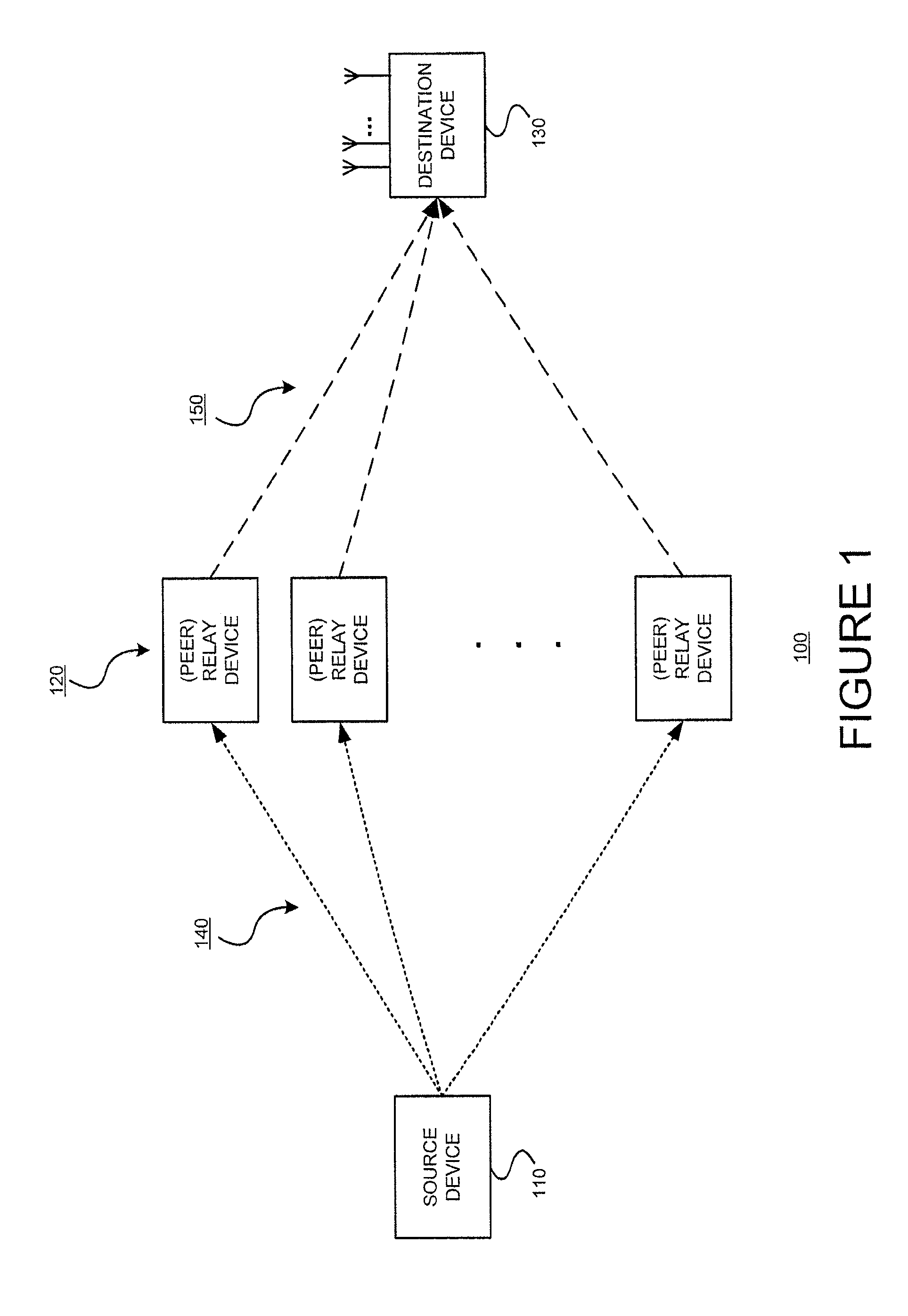
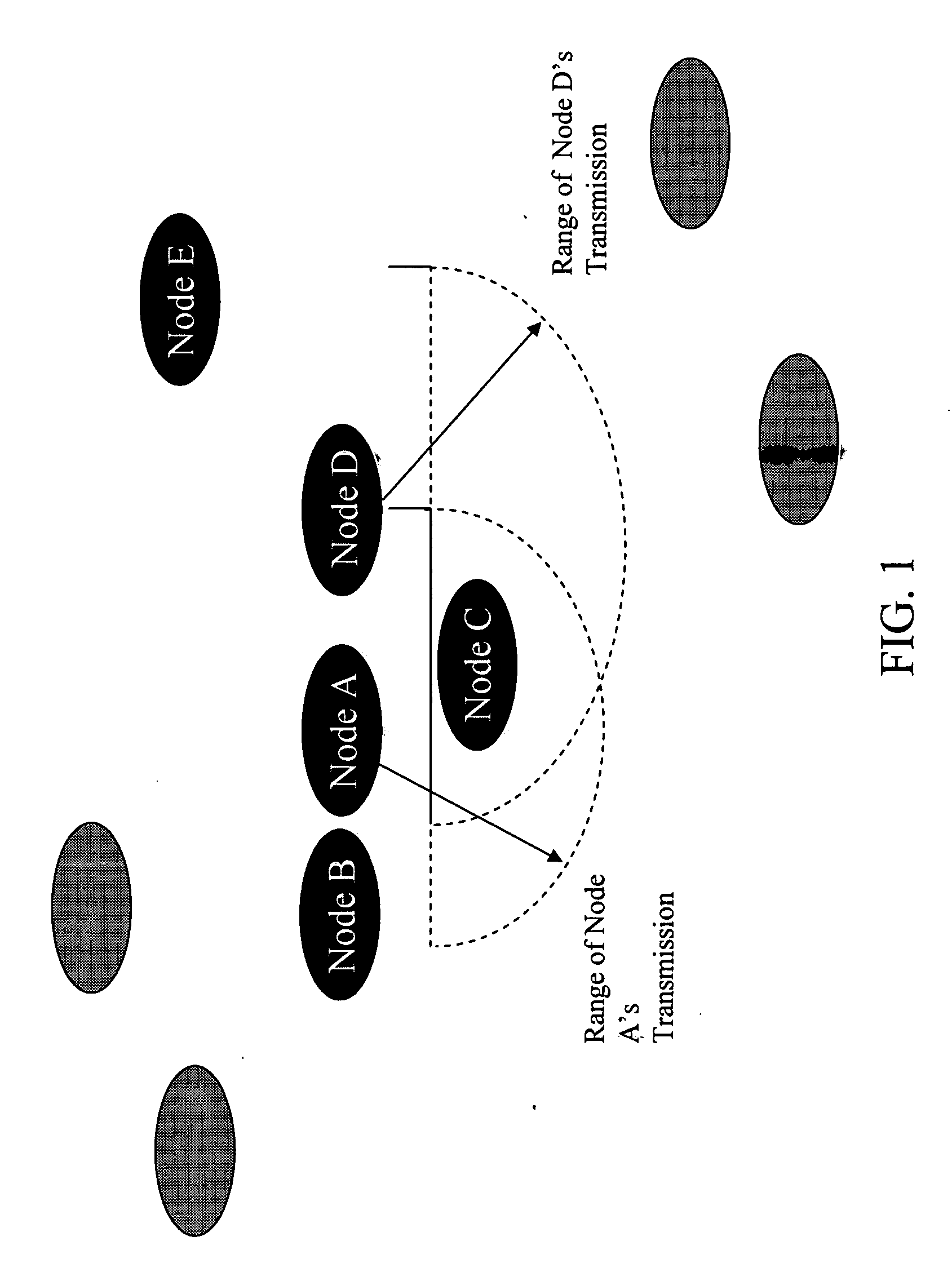
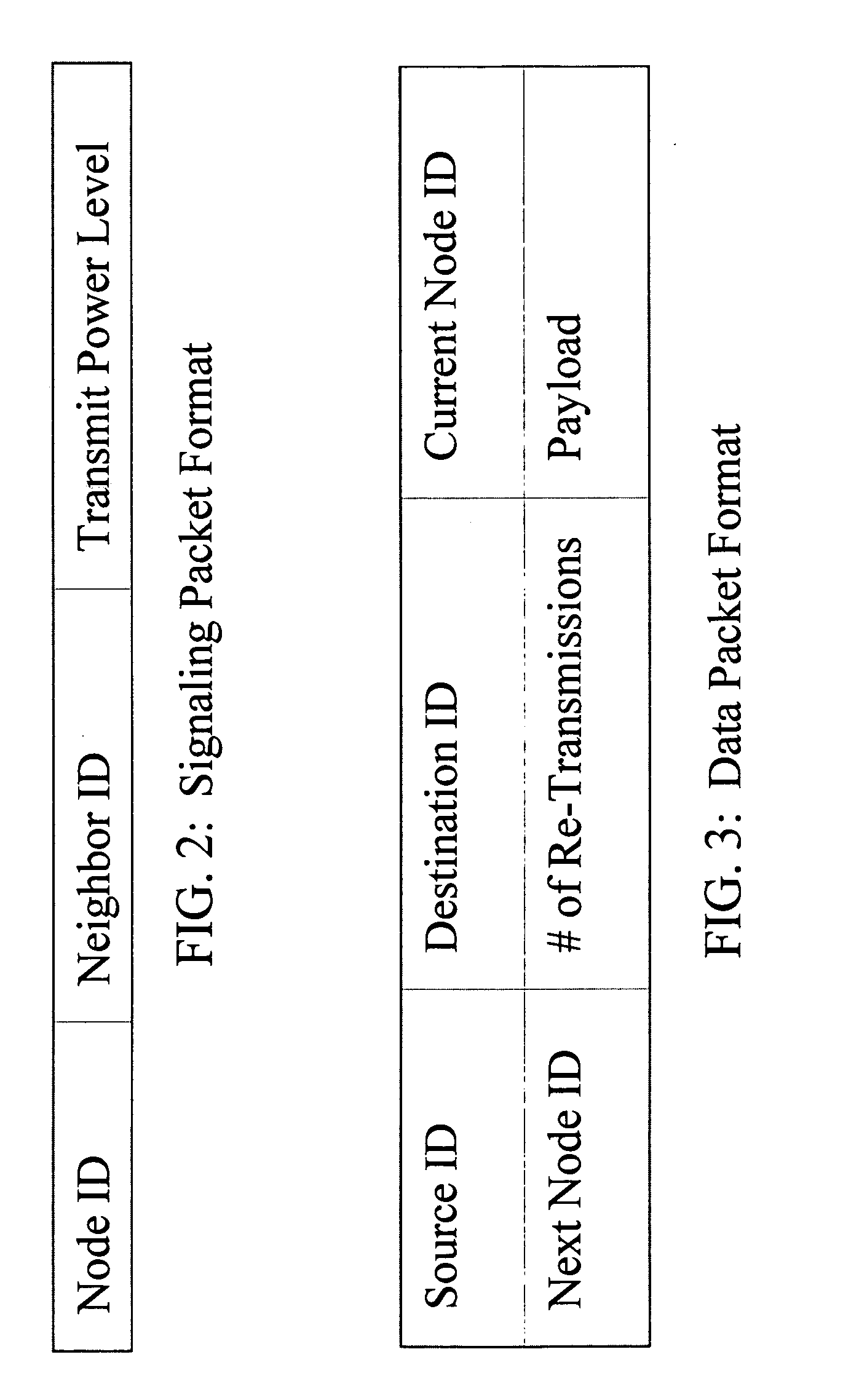
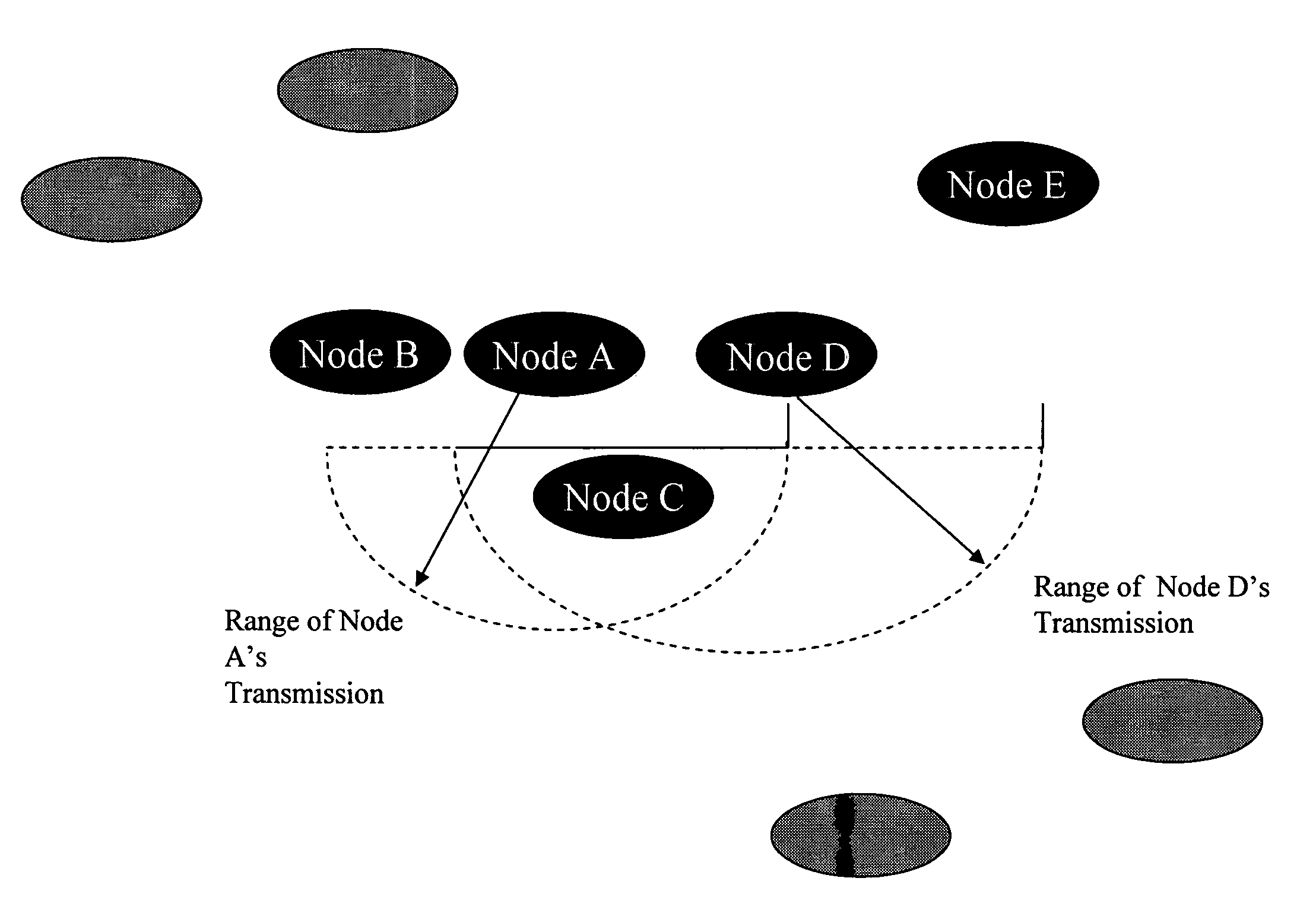
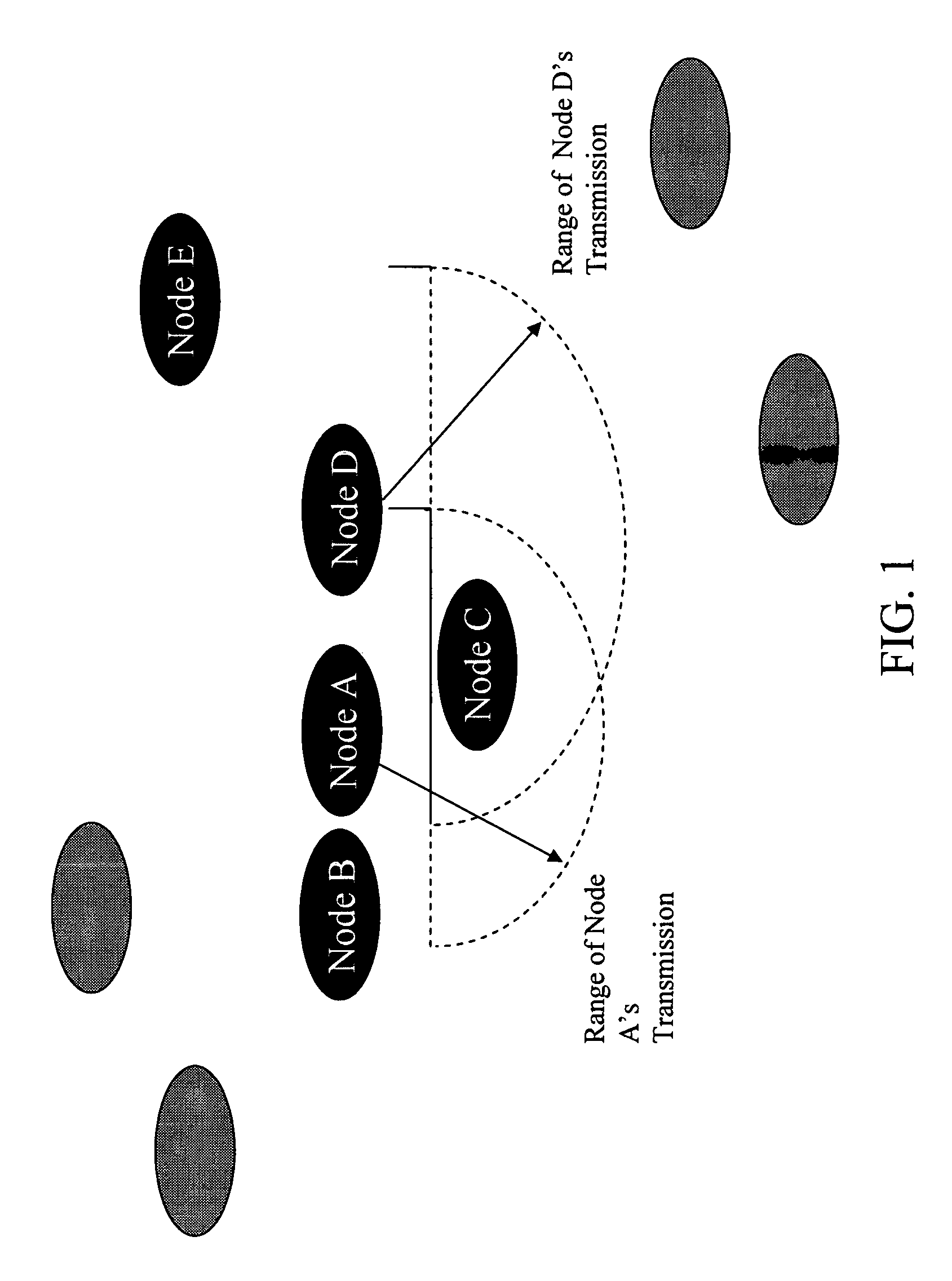
The present invention relates to power management within the context of wireless ad-hoc networks. More specifically to the effects of using different transmit powers on the average power consumption and end-to-end network throughput in a wireless ad-hoc environment. This power management approach reduces the system power consumption and thereby prolongs the battery life of mobile nodes. Furthermore, the invention improves the end-to-end network throughput as compared to other ad-hoc networks in which all mobile nodes use the same transmit power. The improvement is due to the achievement of a tradeoff between minimizing interference ranges, reduction in the average number of hops to reach a destination, reducing the probability of having isolated clusters, and reducing the average number of transmissions including retransmissions due to collisions. The present invention provides a network with enhanced end-to-end throughput performance, and lower transmit power.
Owner:HRL LAB
Power management for throughput enhancement in wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS7668127B2Improve network throughputReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsTransmitted power
Owner:HRL LAB
Wireless sensor network opportunistic routing protocol based on grid clustering
InactiveCN101577668AEnergy efficient ICTData switching networksWireless sensor networkingDependability
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless network protocols, in particular relates to an opportunistic routing method based on grid clustering in a wireless sensor network. The invention adopts a grid-type clustering method and the opportunistic routing algorithm to fully take advantages of the energy effectiveness of a clustering topology control method and the advantage of an opportunistic routing in the aspect of end-to-end throughput, thereby ensuring that the sensor network achieves effective optimization in the aspects of data throughput, transmission reliability, and the like on the premise of energy saving.
Owner:北京循天行信息技术有限公司
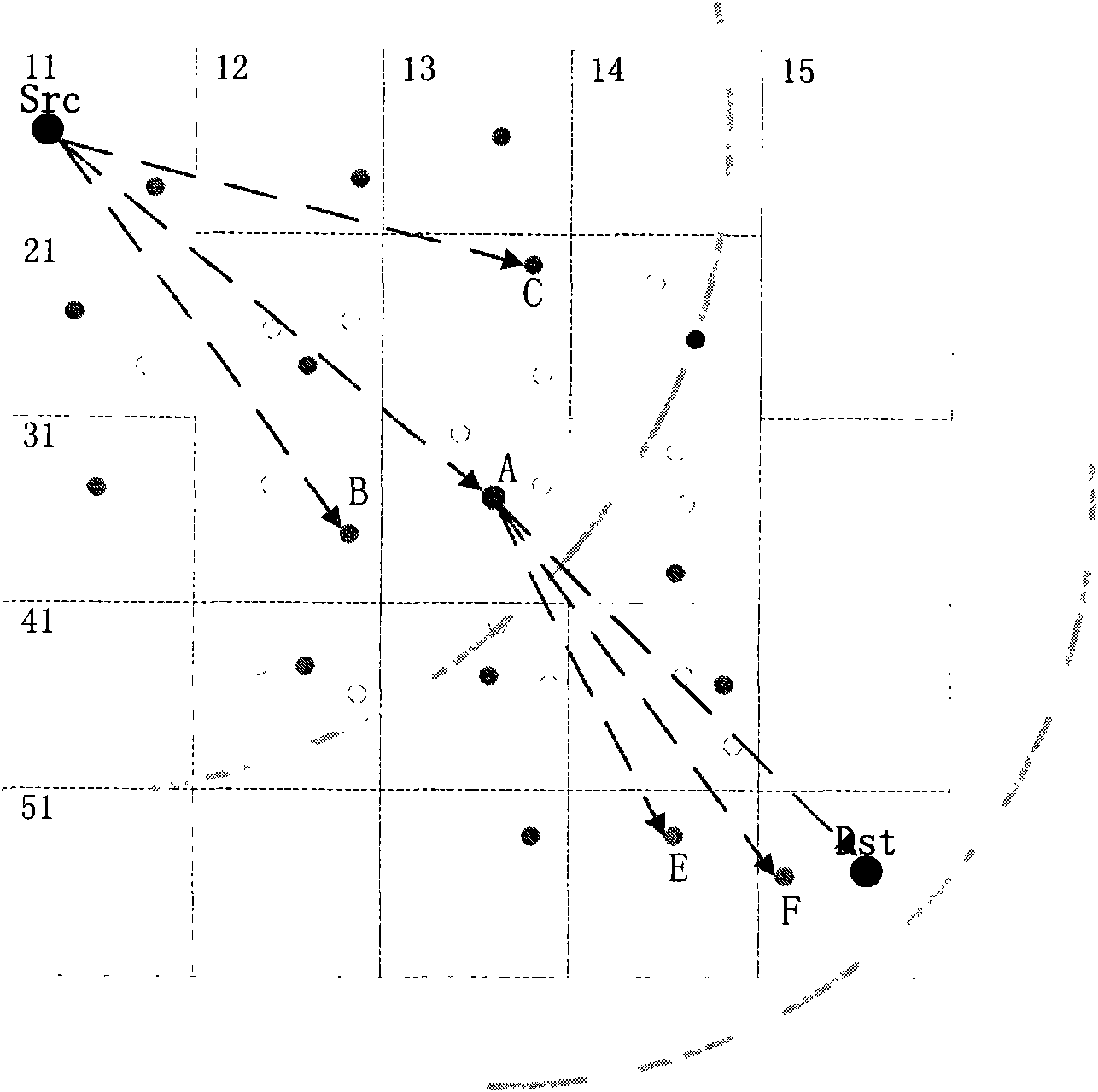
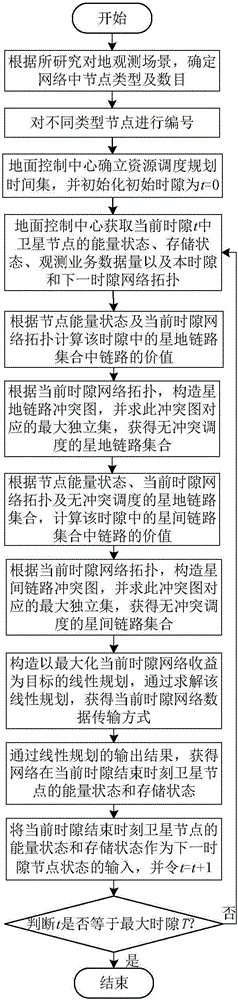
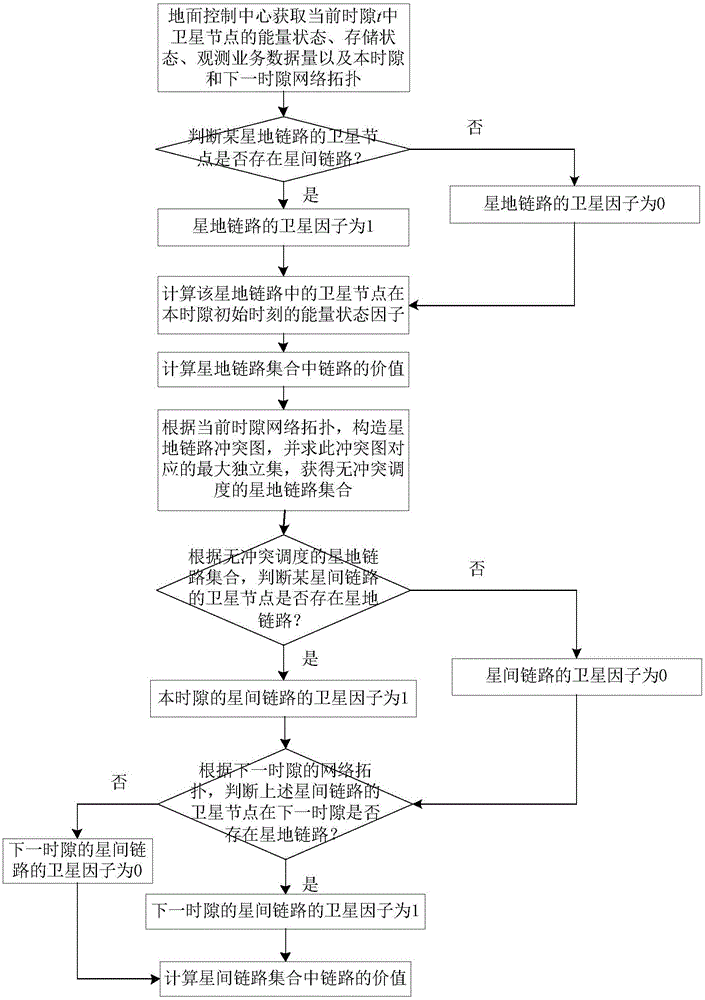
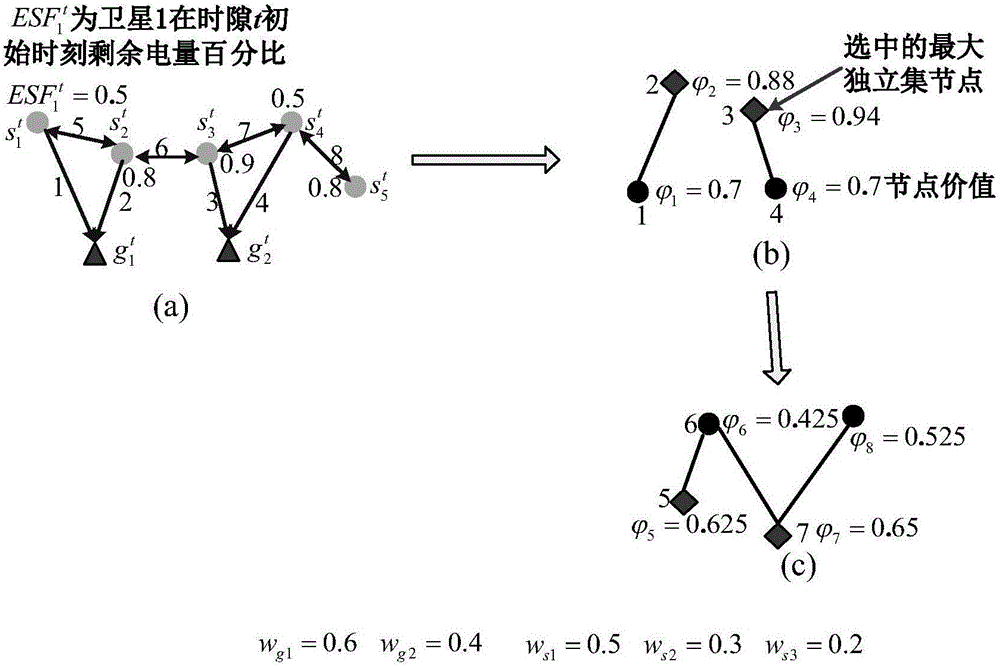
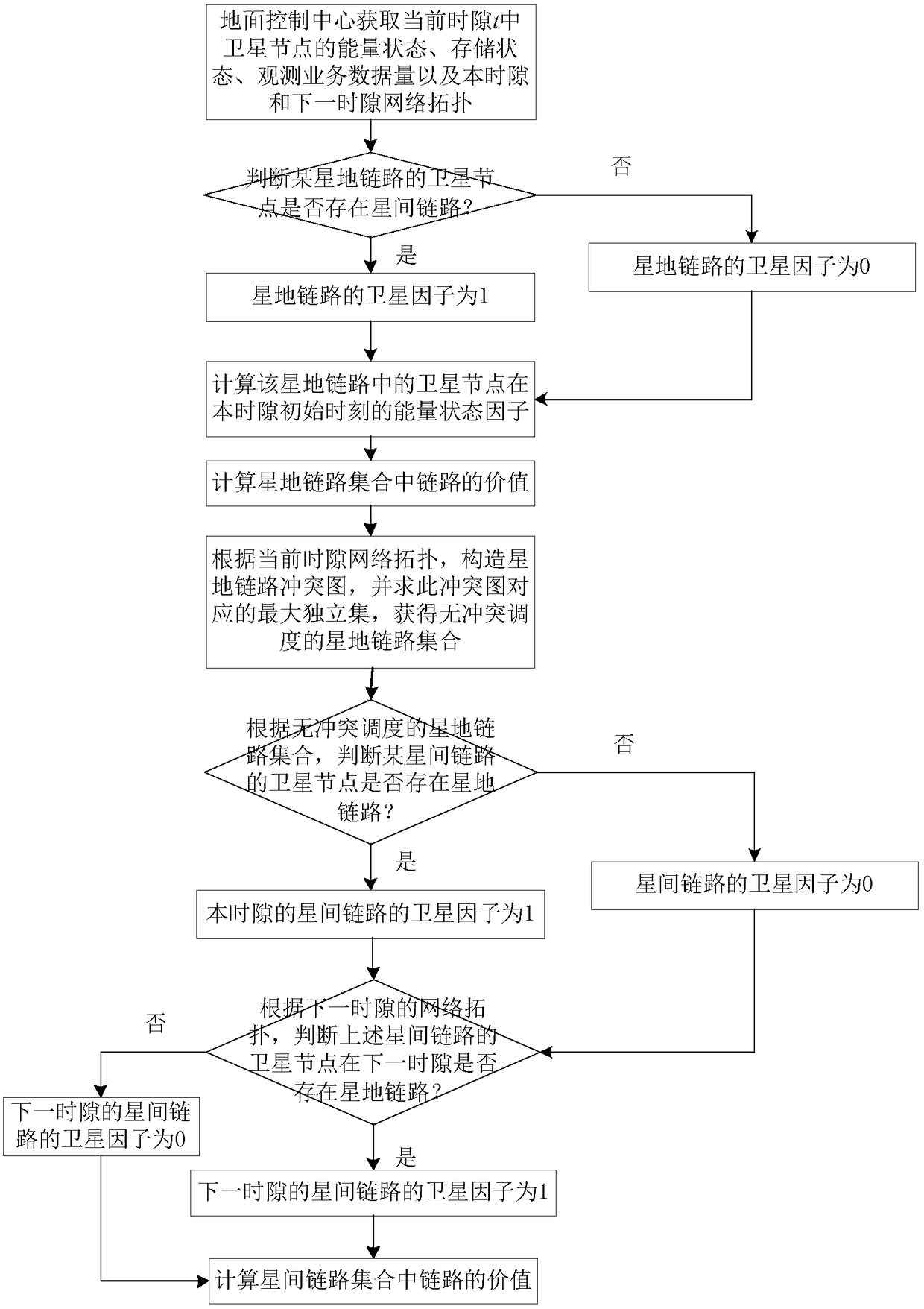
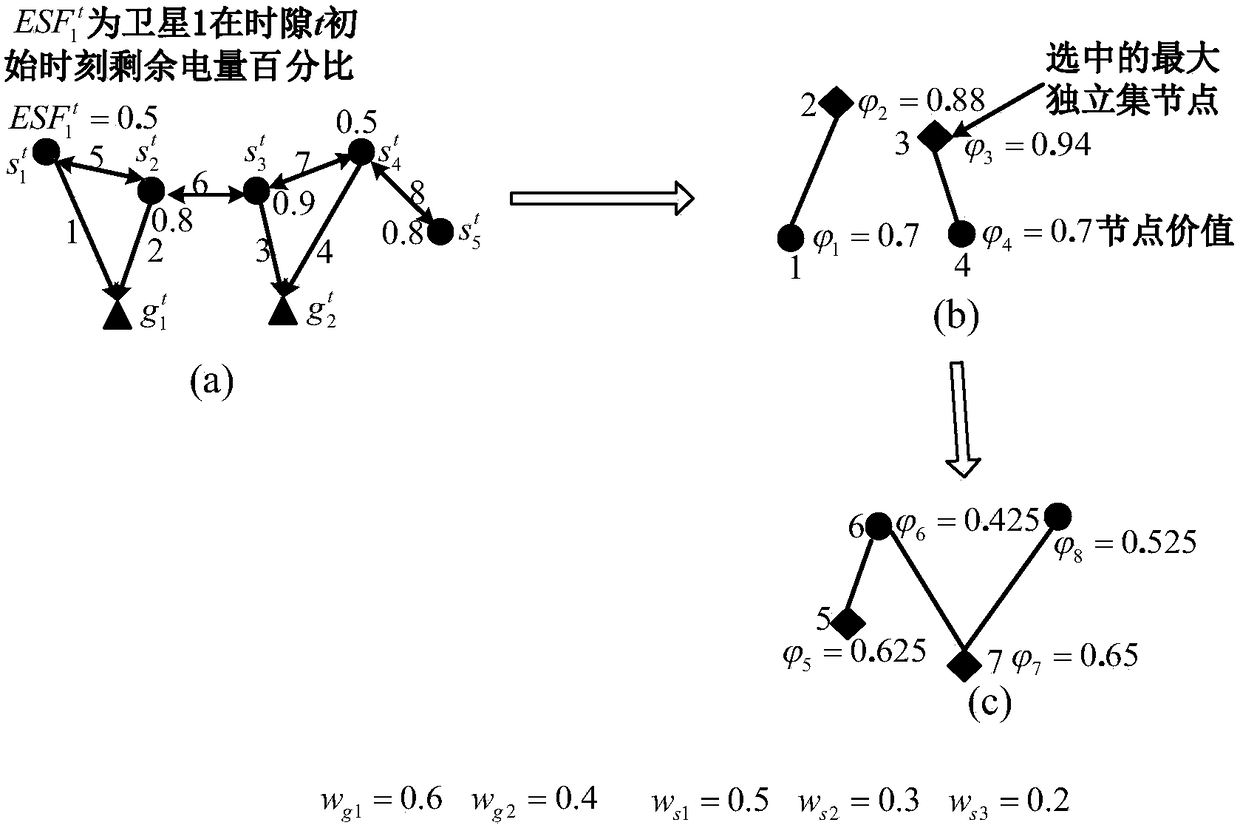
Method for scheduling efficient resource of minisatellite network based on earth observation tasks
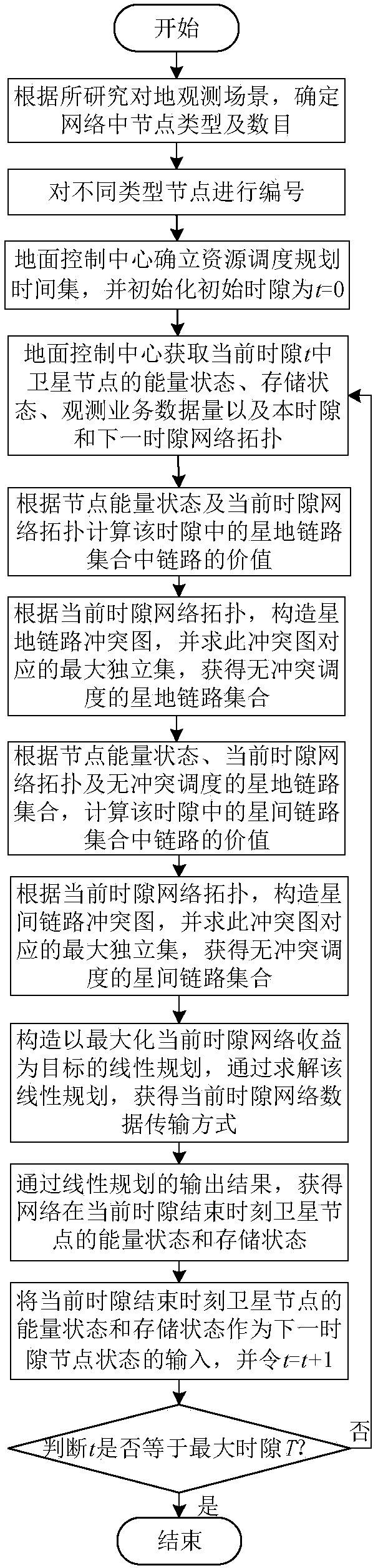
ActiveCN106100719AImprove resource utilization efficiencyImprove return efficiencyRadio transmissionEarth observationMaximal independent set
This invention discloses a method for scheduling efficient resource of a minisatellite network based on earth observation tasks, and solves the problems that the end-to-end throughput capacity is low and the utilization efficiency of the network resource is low because the network resource is not fully considered during the scheduling process in the earth observation scene of the resource-limited minisatellite network. The method comprises the implementation processes of: according to an initial network topology, determining a node number; at the same time, initializing a network resource scheduling planning time set; according to current network state and resource scheduling conflict restraint, constructing a link scheduling conflict graph by a ground control center; solving a maximal independent set corresponding to the conflict graph to acquire a network conflict-free scheduling link set; by using the link set and a linear programming, solving a resource allocation scheme and a data transmission method capable of mostly optimizing the network efficiency till a time slot is ended. The method improves the resource utilization ratio, increases the returning efficiency of important task data, improves the earth observation network performance of the minisatellite, and is used for scheduling the efficiently transmitted resource of earth observation system data.
Owner:陕西丝路天图卫星科技有限公司
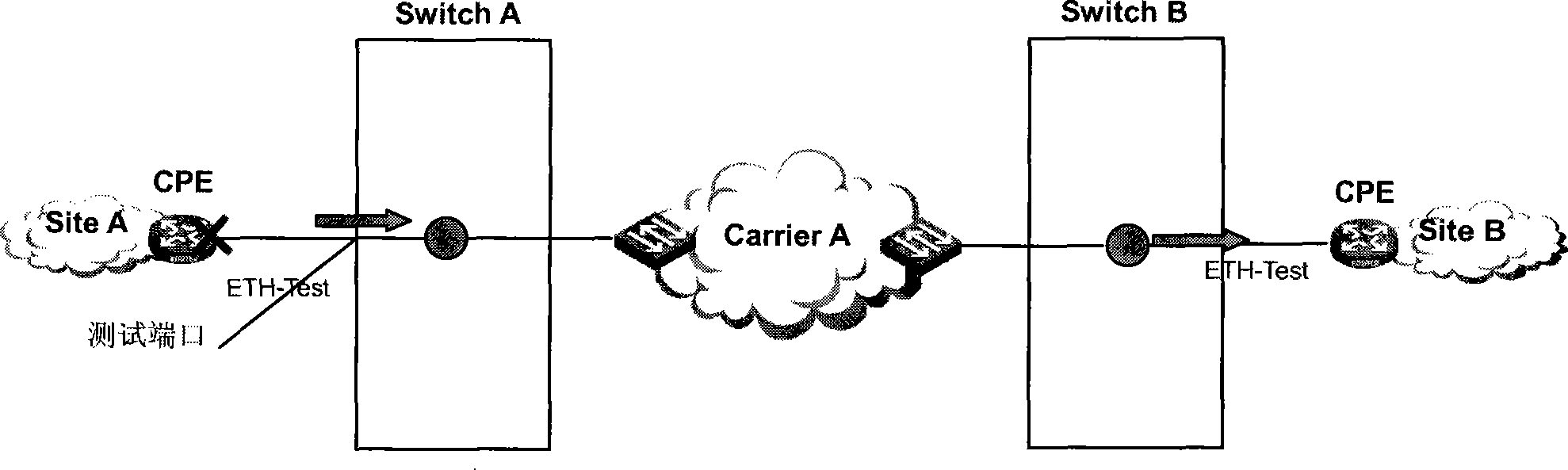
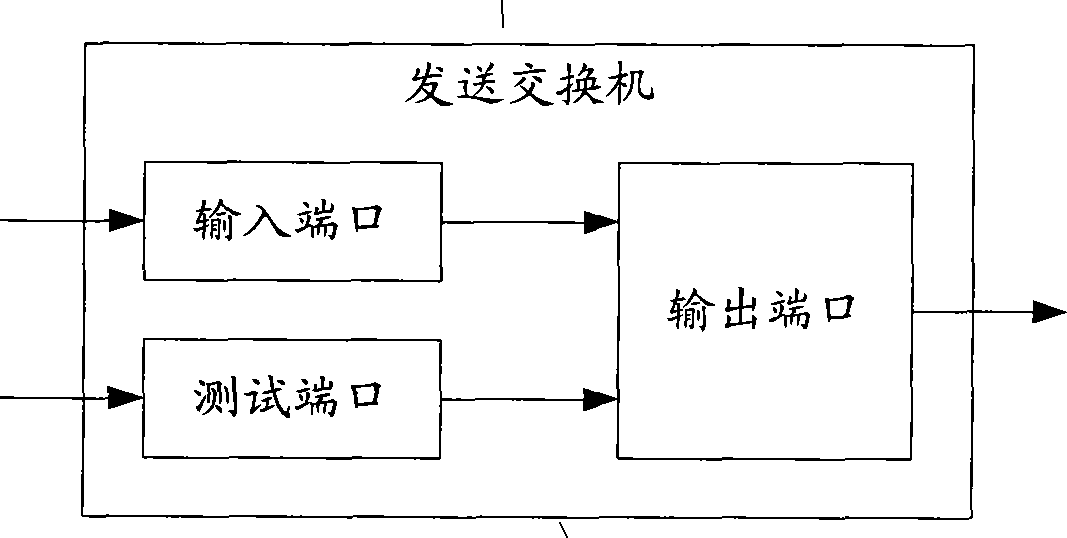
An end-to-end throughput measuring method and device
InactiveCN101242321ADoes not affect normal forwardingData switching networksEnd to end throughputBandwidth measurement
The invention provides an end-to-end flux measurement method, comprising: a sending exchange receives a data message of a pending measurement user, and acquires the test message at a test port, wherein the test message takes with an identification of the pending measurement user; when the bandwidth occupied by the data message of the pending measurement user is less than an appointed speed of a pending measurement flux, the exchange transmits the data message and test message of the pending measurement user at an output port to make the total bandwidth occupied by the data message and the test message equal to the appointed speed of a pending measurement flux and to make the test message transmit in a priority lower than that of the data message; a receiving exchange receives and accounts the total bandwidth occupied by the data message and the test message of the pending measurement user at an input port based on the identification of the pending measurement user as an end to end actual flux bandwidth. The invention further provides a sending exchange and a receiving exchange for an end to end flux measurement. The invention can achieve an end to end flux bandwidth measurement in a condition without breaking the user data message.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
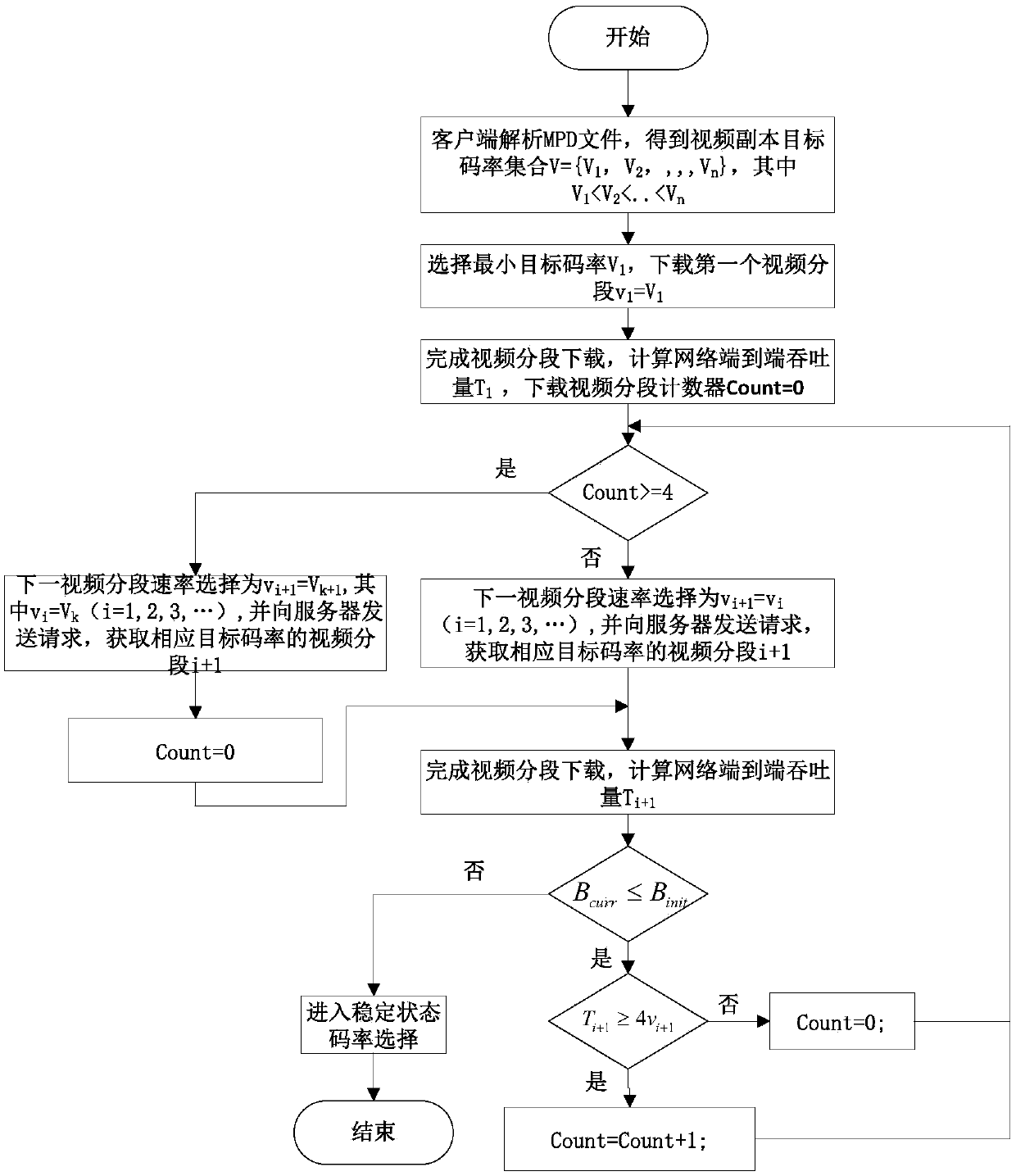
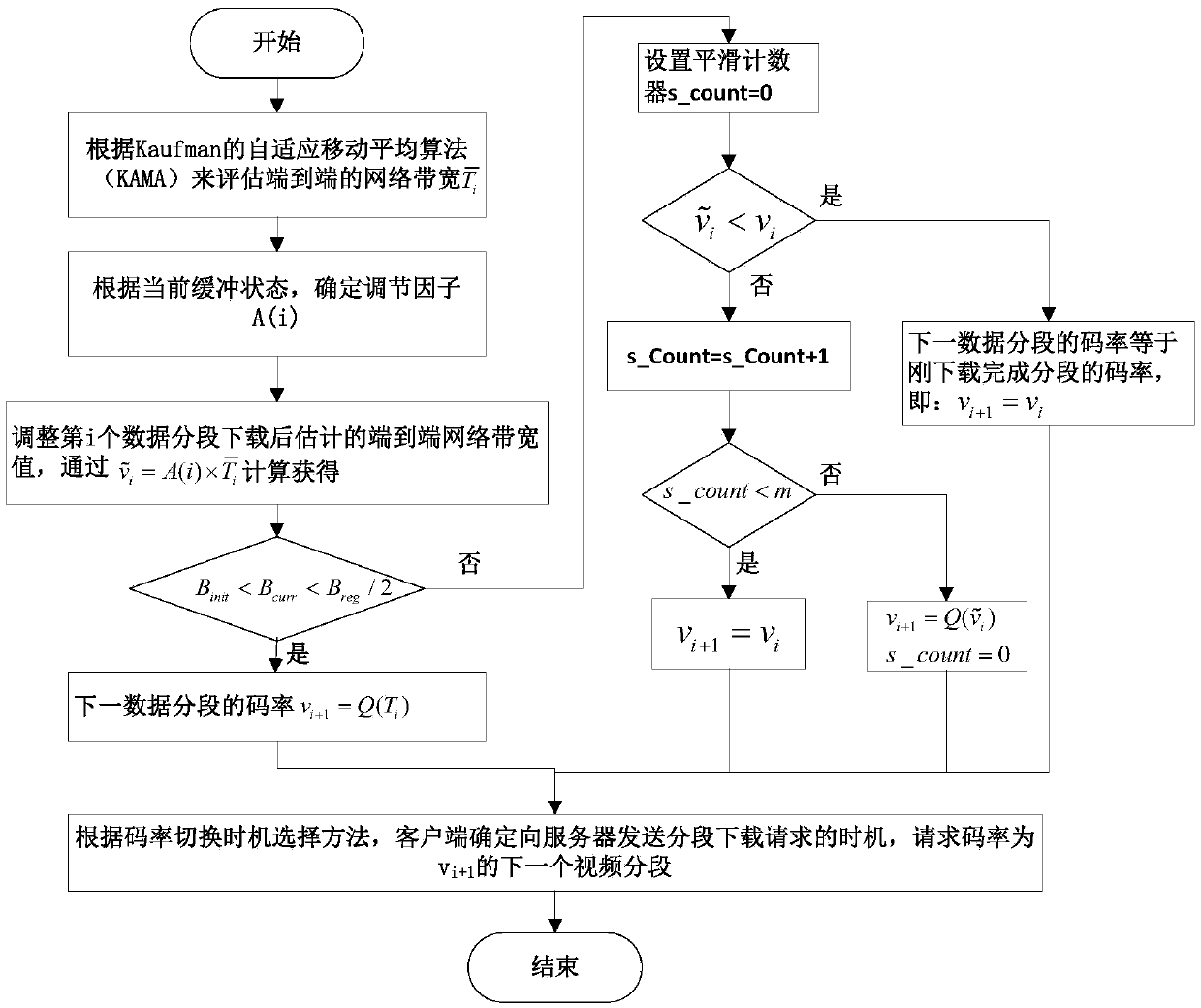
Two-stage client code rate selection method of DASH transmission system
ActiveCN108184152AAddress quality of experienceSolve UtilizationSelective content distributionTransmission protocolMoving average
The invention belongs to the technical field of audio and video transmission, and discloses a two-stage client code rate selection method of a DASH transmission system. Under a system framework basedon an HTTP dynamic adaptive media transmission protocol, a client dynamically adjusts a video playing code rate according to estimated network end-to-end throughput and buffer area state information.According to the method disclosed by the invention, at a playing startup stage, the utilization rate of a network bandwidth is improved while ensuring a low startup delay and the playing smoothness byusing a code rate selection method similar to TCP slow start; at a stable playing stage, the network end-to-end throughput is estimated by using a Kaufman-based adaptive moving average algorithm, thereby reducing the impact of the instantaneous change of the network bandwidth on the code rate; and meanwhile, a code rate switching time selection method of a random factor is imported to reduce thevideo quality jitter problem caused by the frequent change of the code rate in a video playing process, and thus the user experience is improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
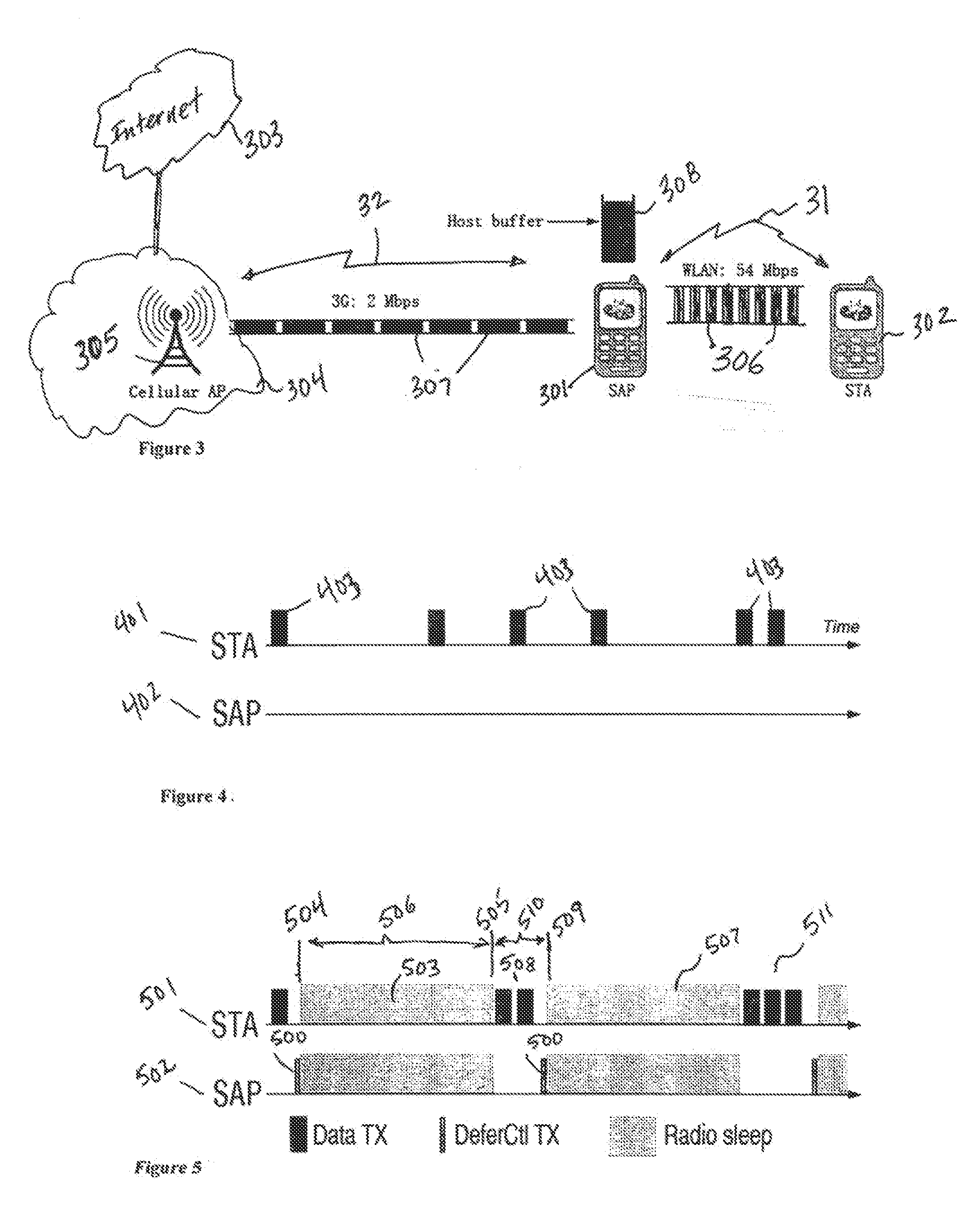
Power Efficiency and Packet Delivery Ratio Through Micro Rate Control at Access Point Functionality Enabled Devices
InactiveUS20110158115A1Reduce energy consumptionImproves packet delivery ratioEnergy efficient ICTPower managementQuery throughputComputer science
Embodiments of the invention provide a method to allow a software access point (SAP)-enabled device to go to sleep as much as possible without sacrificing throughput and latency across networks. The SAP-enabled device defers transmissions from client stations if maximum end-to-end throughput that can be supported by the networks is below the maximum throughput supported by a connection to the client station.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
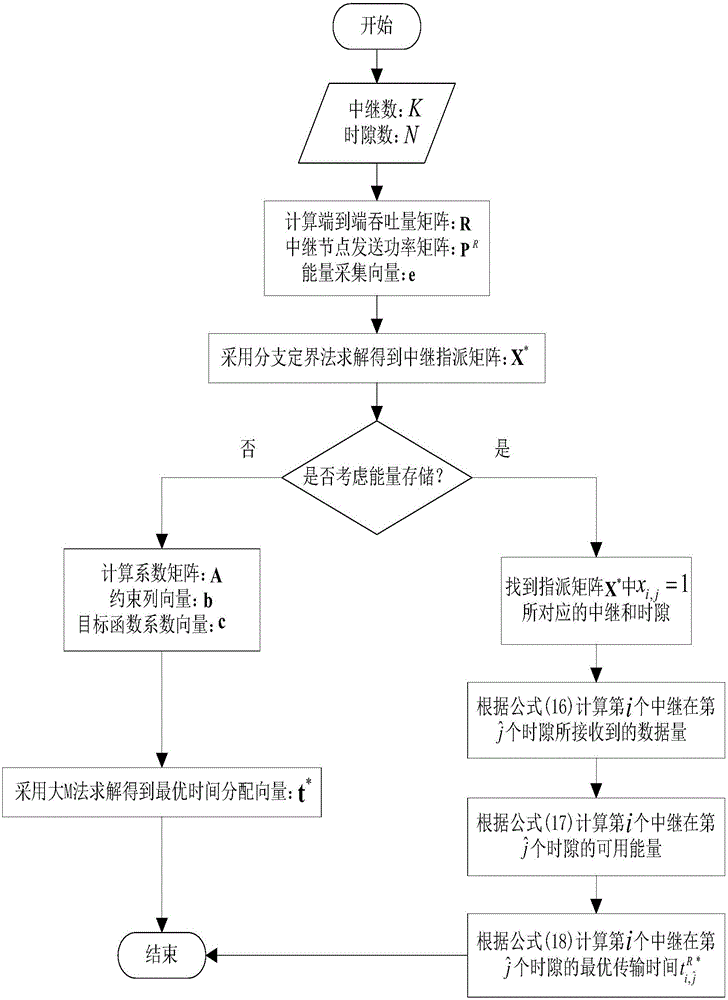
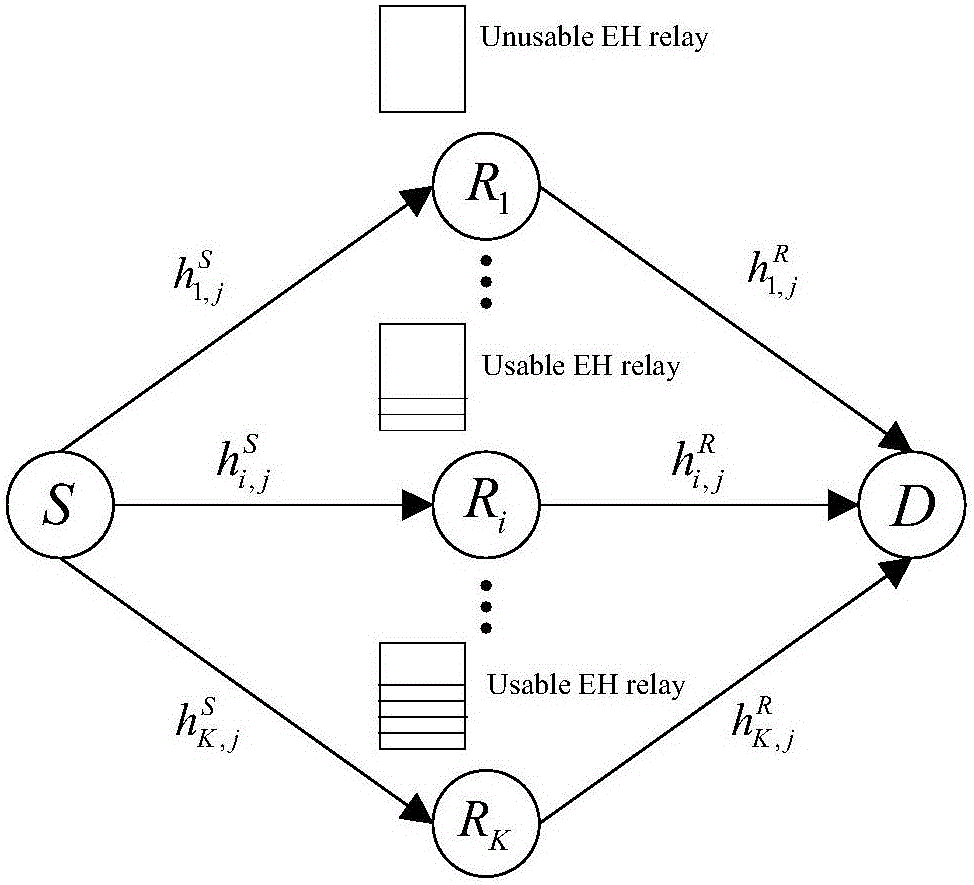
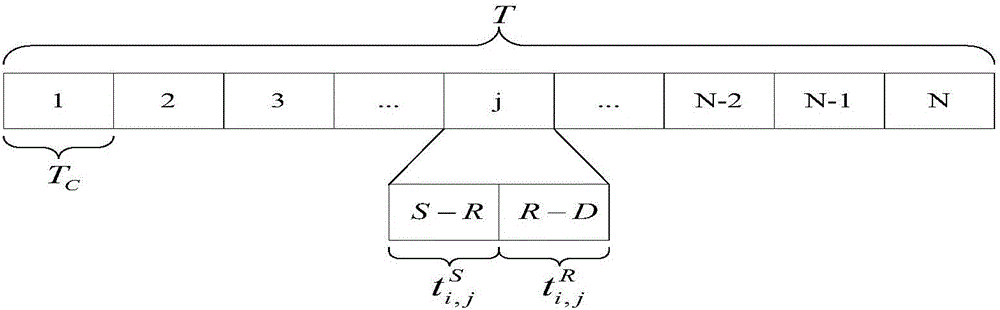
Method for optimal distribution of time of energy harvesting relay system based on relay selection
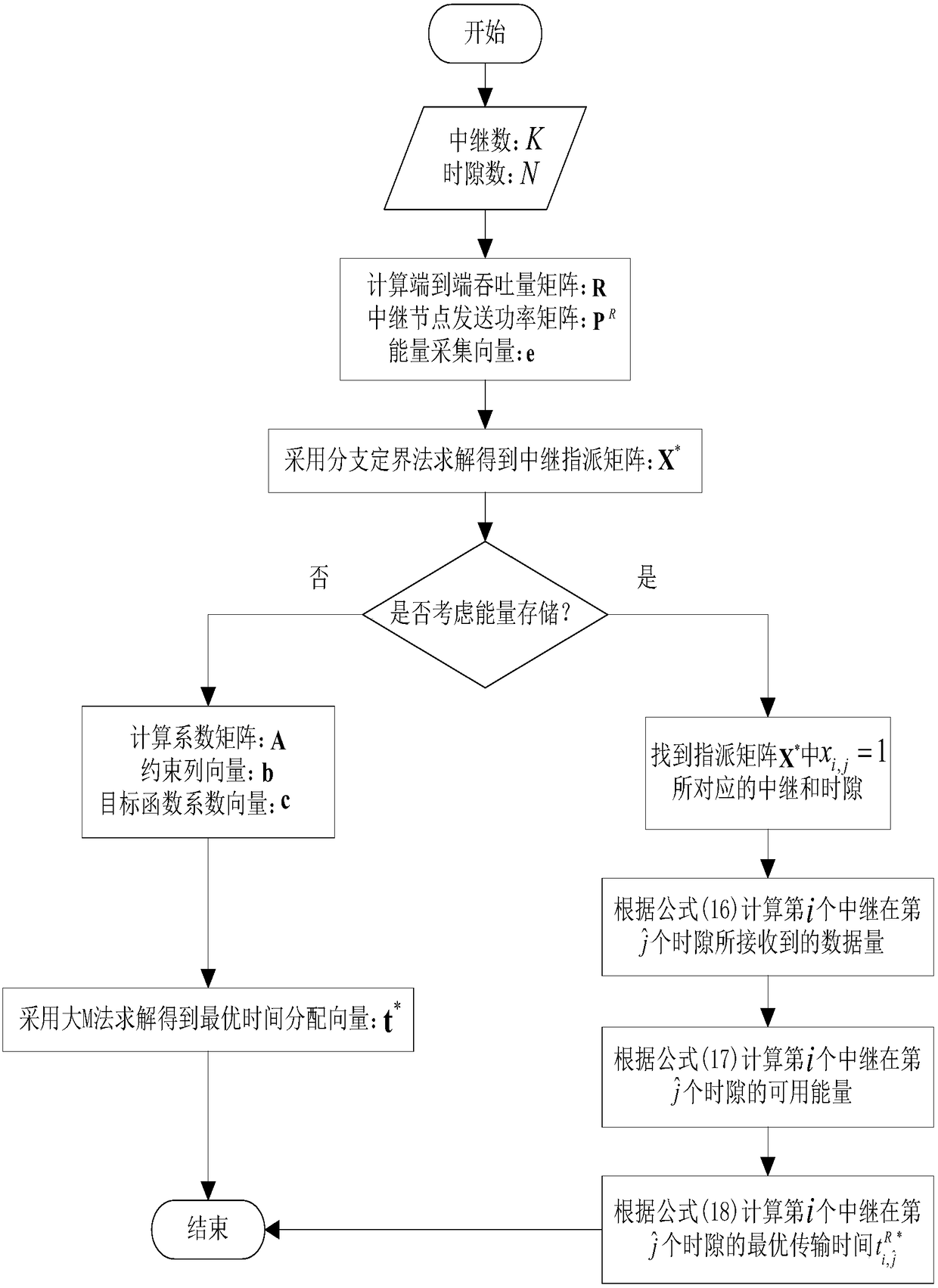
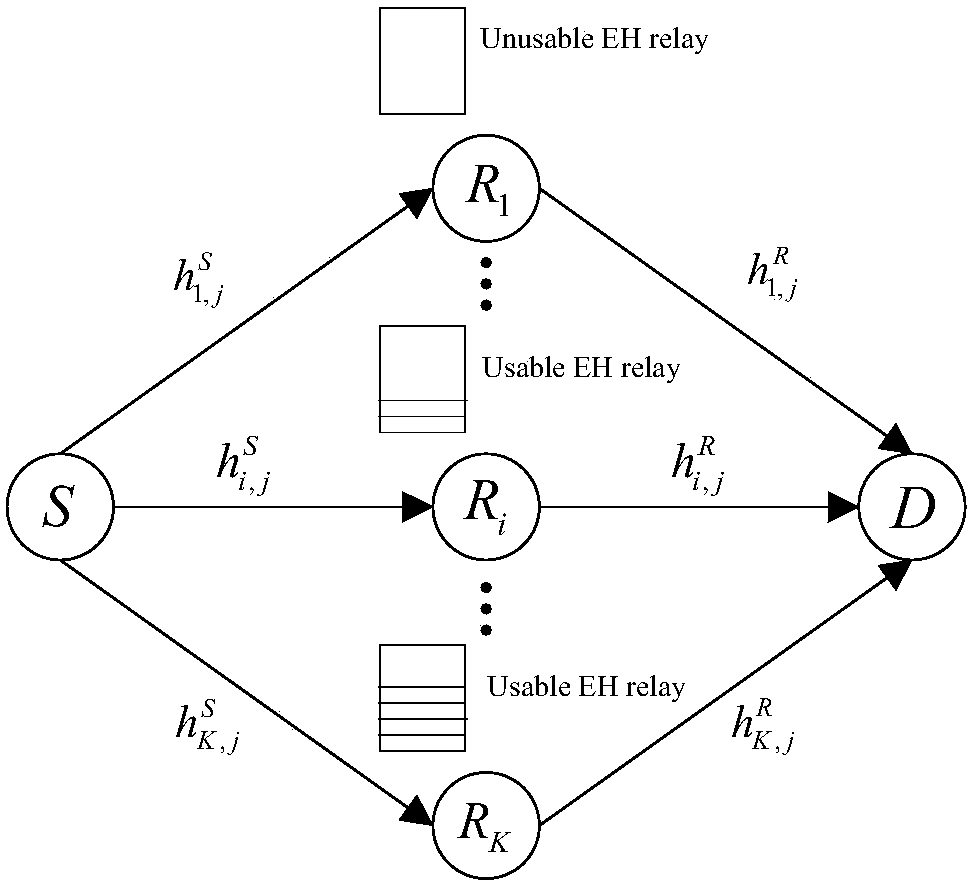
ActiveCN105744629AThe result of relay selection is reasonableMeet the needs of practical applicationsRadio transmissionWireless communicationSimplex algorithmEngineering
The invention aims at a multi-relay system with an energy harvesting function and provides a method for optimal distribution of time of an energy harvesting relay system based on relay selection. In the method, a plurality of relay nodes work under an energy harvesting mode of wireless energy transmission (WET), an optimization model with maximum system end-to-end throughput is constructed based on the limitations of energy causality and data causality, and a branch and bound method is adopted to select the relay node used by each time slot. A simplex method and an independent solution method are respectively adopted to carry out optimal distribution on the transmission time of the source node and the relay node in each time slot for different service conditions of the relay node about the residual energy, so that the data quantity received by the target node is improved. According to the method, pairing of the relay node and the transmission time slot during multi-relay cooperation and optimal distribution of the transmission time of the source node and the relay node are realized, so that the system throughput performance is effectively improved, and the method has an advantage that the energy consumption expenditure is saved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Cognitive routing protocol for heterogeneous wireless return network
InactiveCN102143549AReduce overheadOptimize end-to-end performanceHigh level techniquesWireless communicationHeterogeneous wireless networkRouting protocol
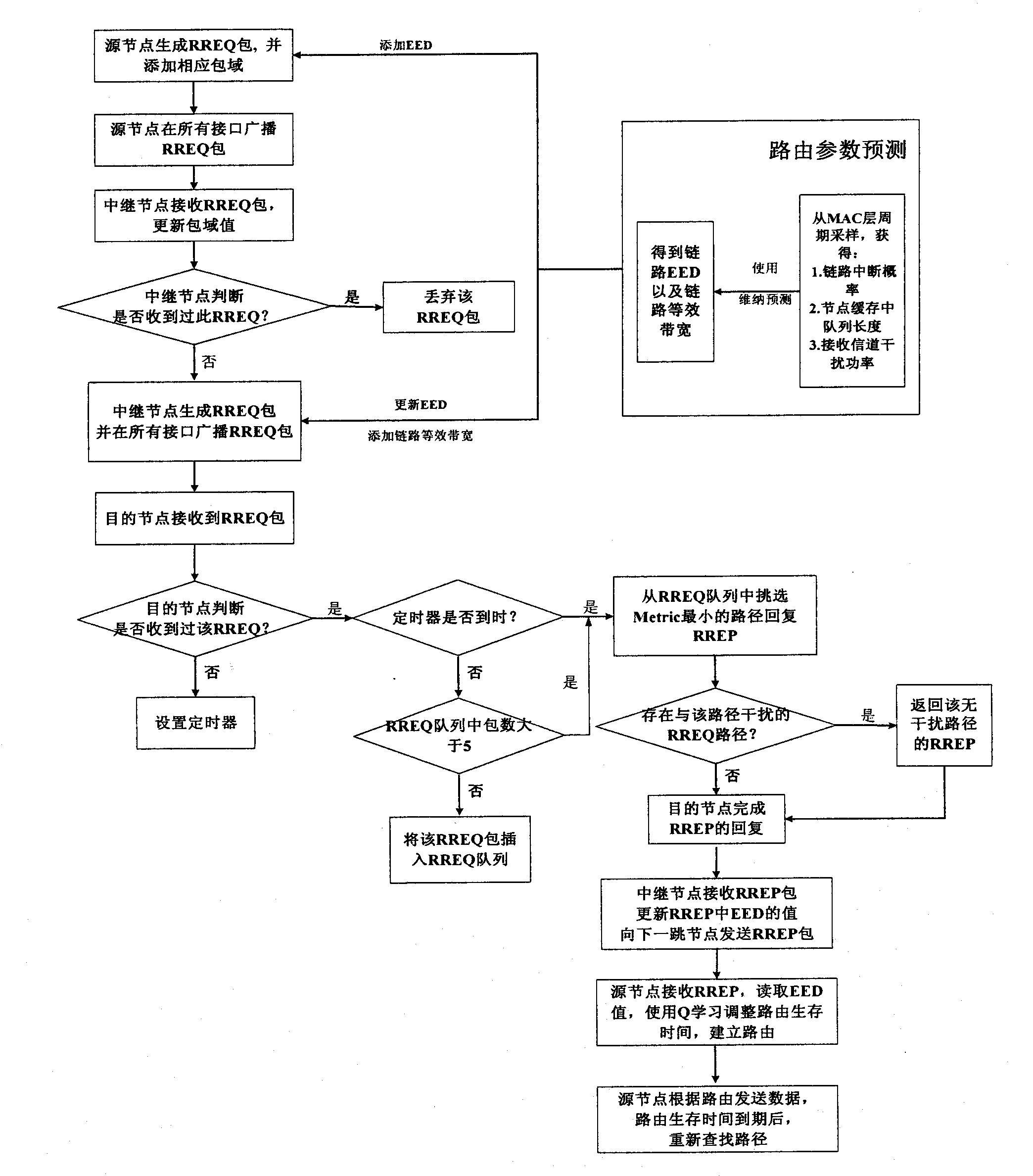
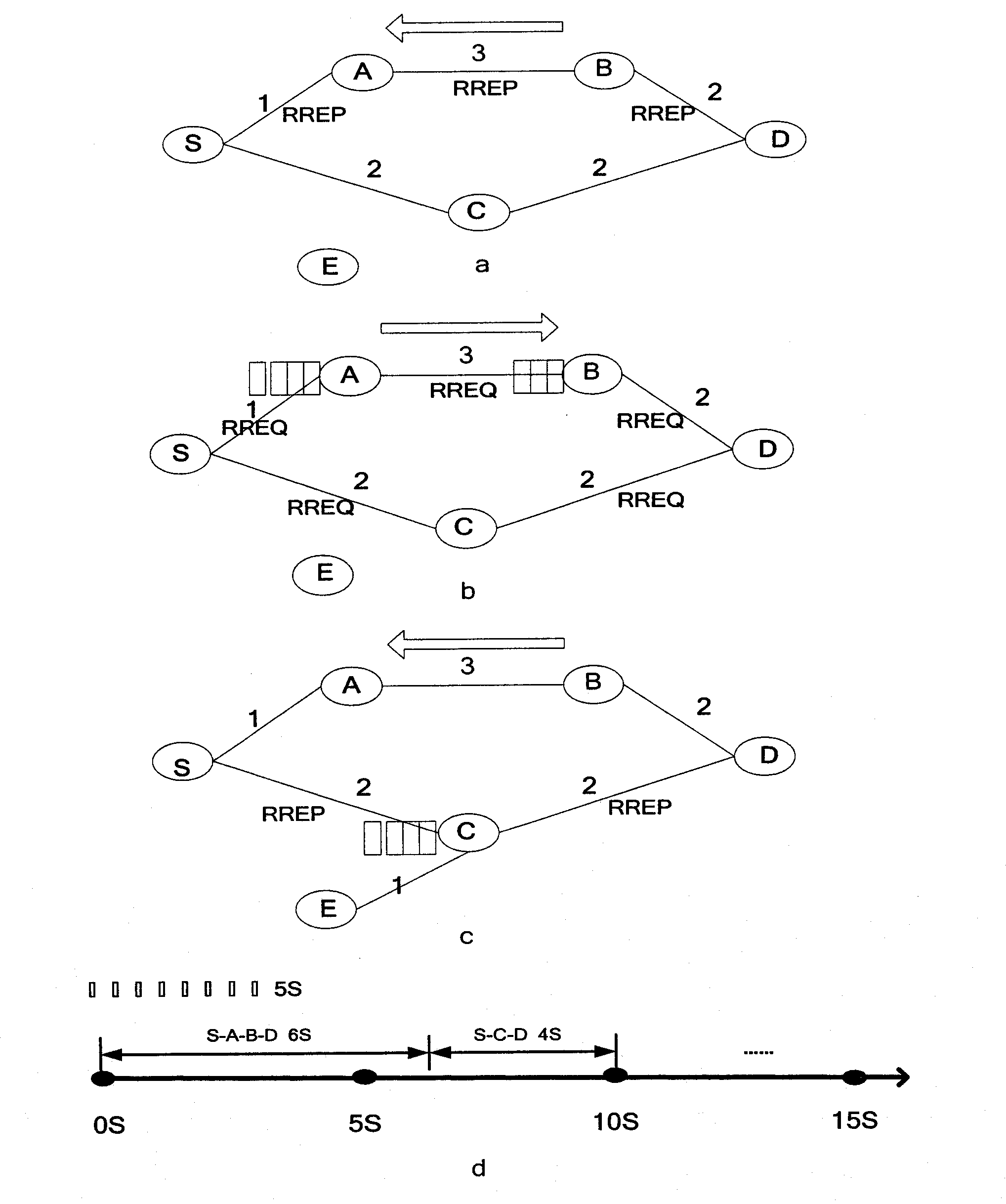
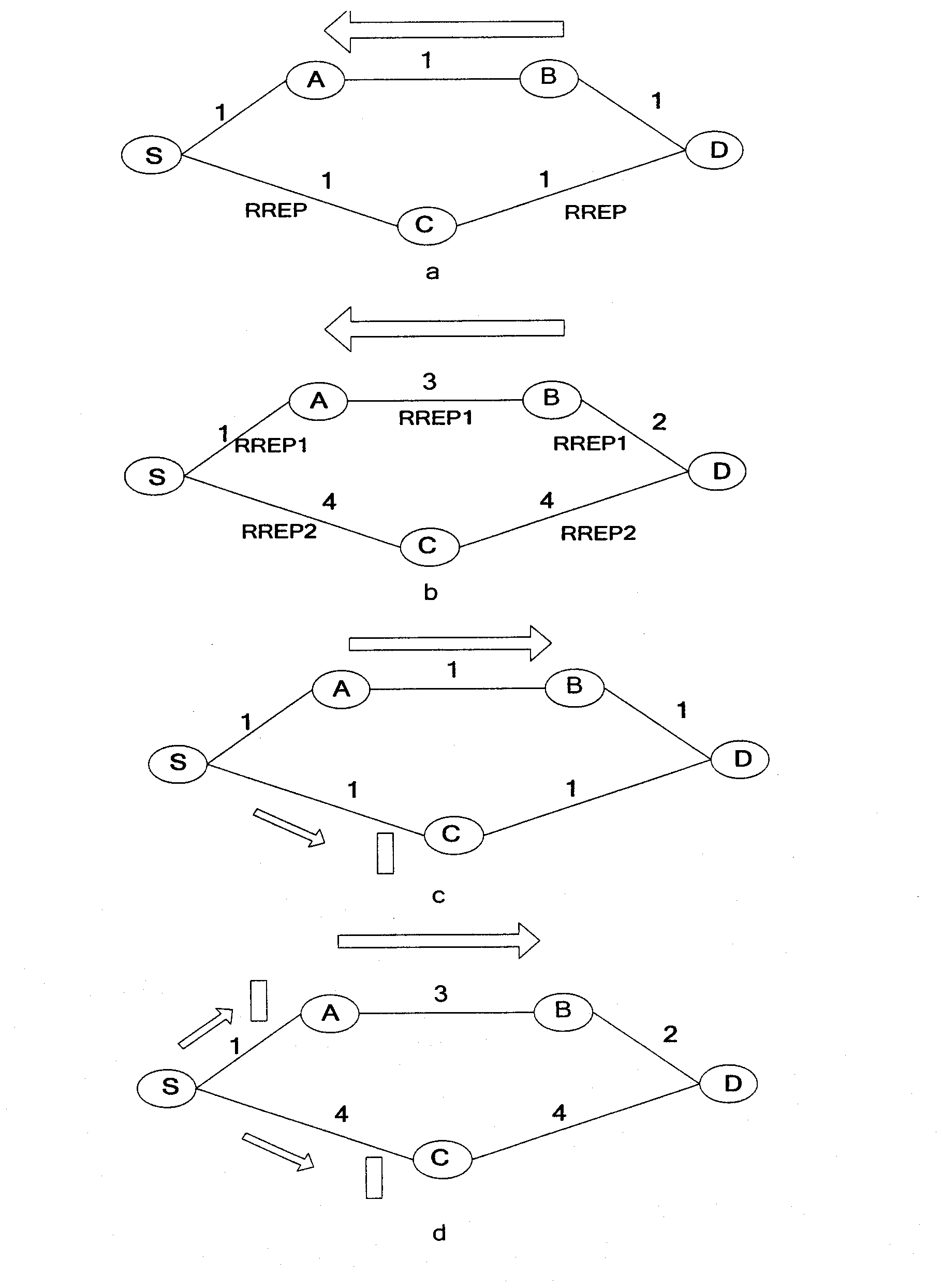
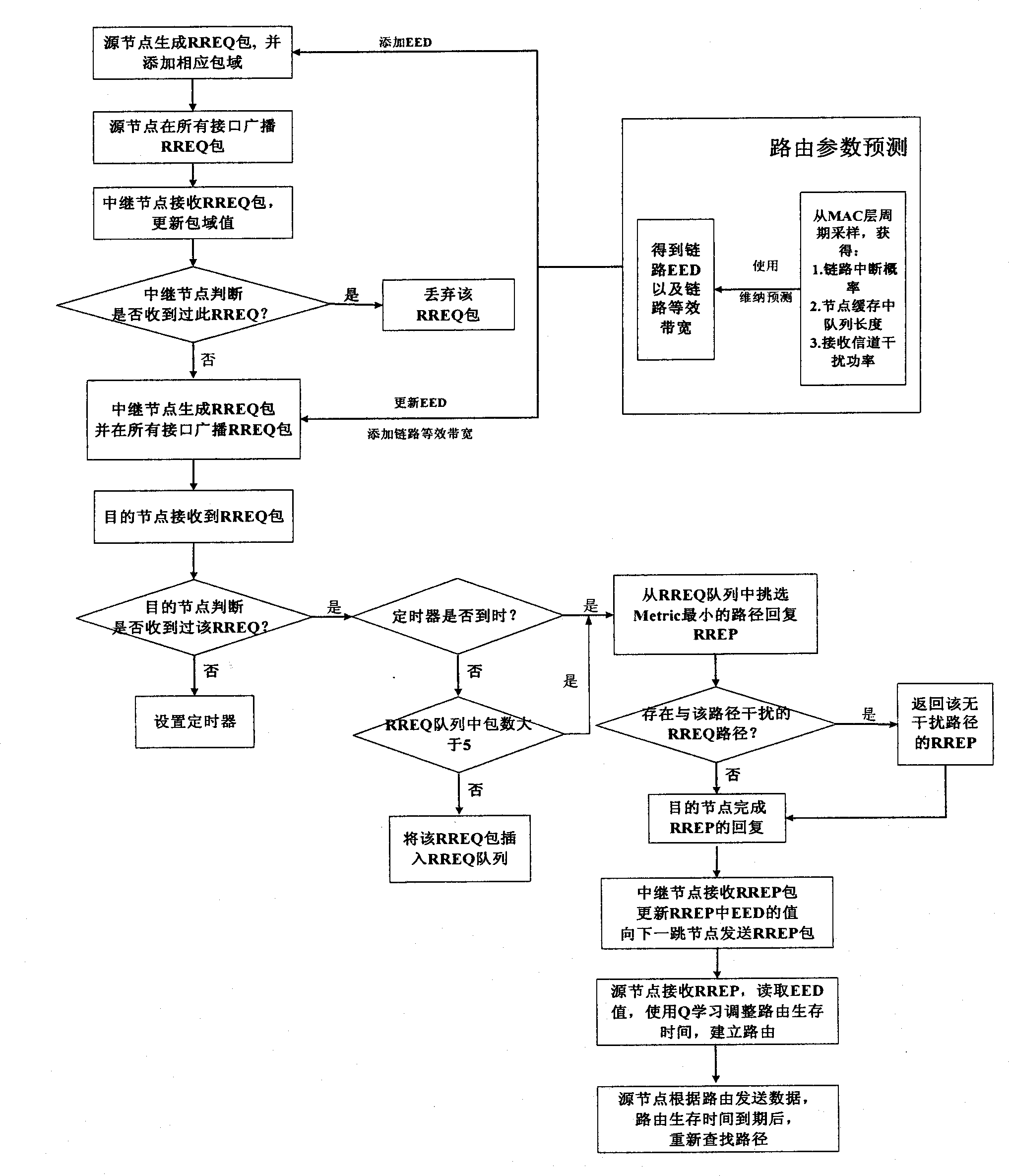
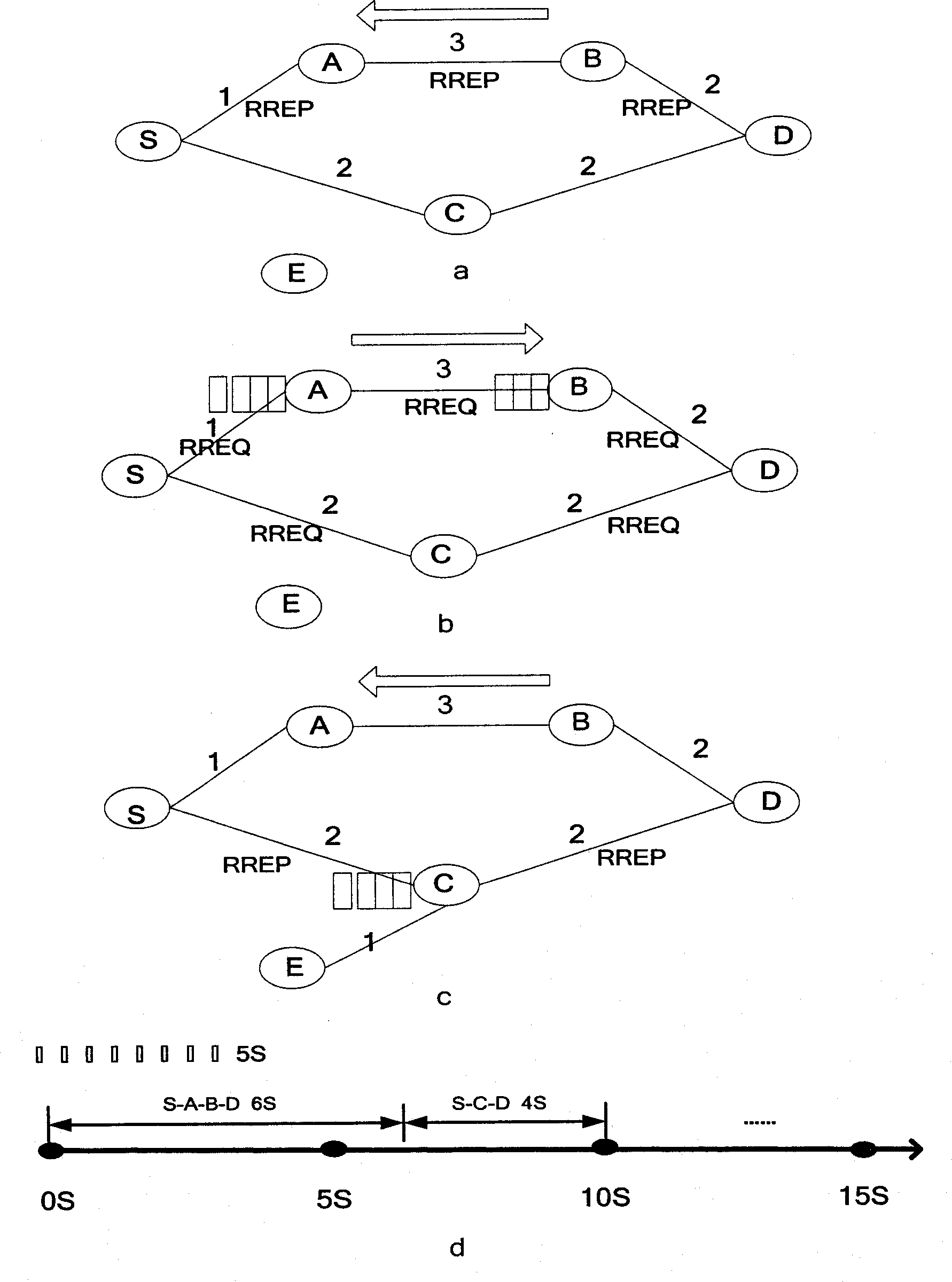
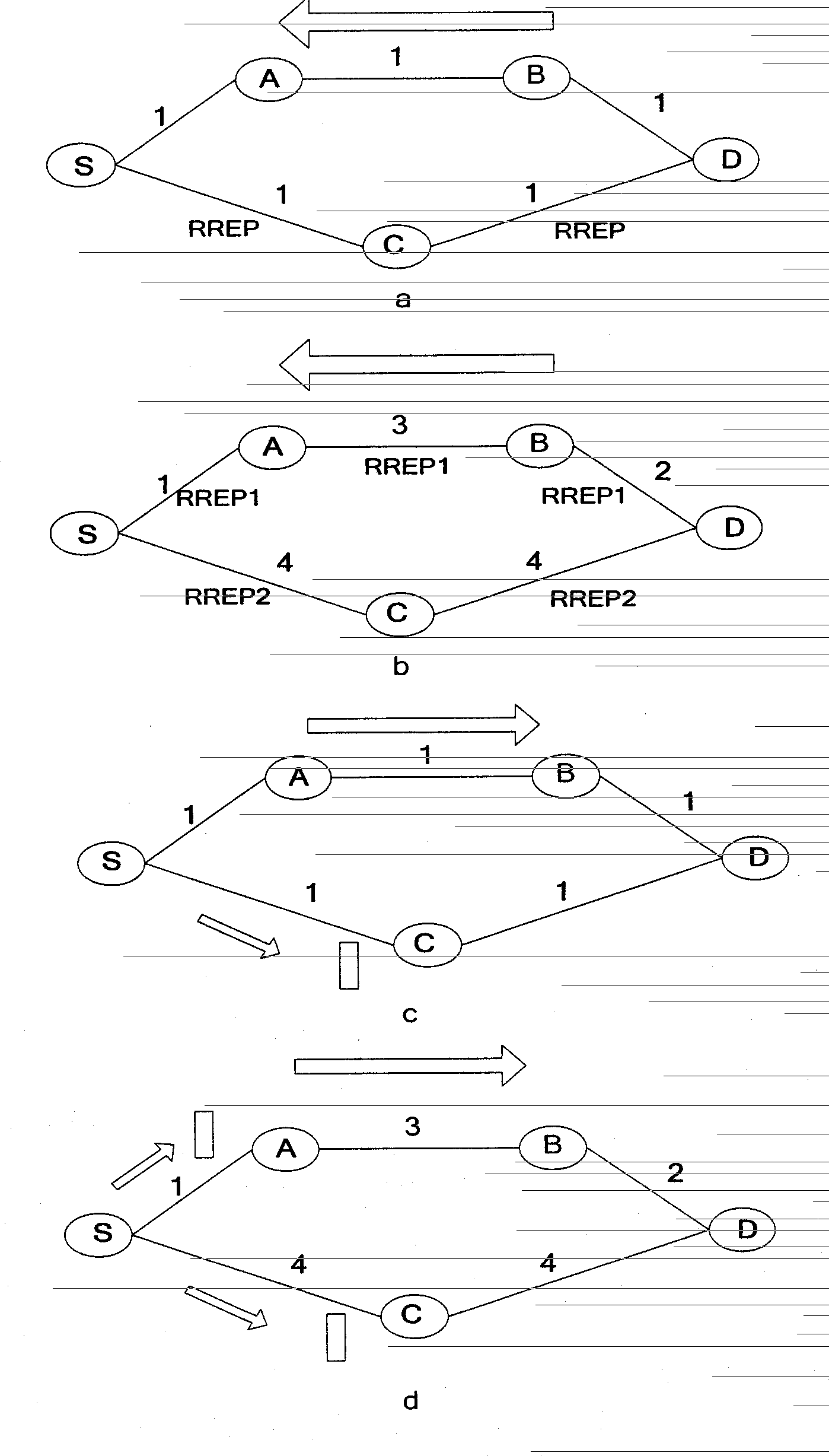
The invention discloses a cognitive routing protocol suitable for a heterogeneous wireless return network, belonging to the field of wireless communication. The cognitive routing protocol mainly solves the problem of how to effectively select the path aiming to the difference of the nodes in the heterogeneous network. When a source node sends a RREQ (route request) and an intermediate node receives the RREQ, an acquired link delay EED and a link equivalent bandwidth ABITF are added into the RREQ by Wiener forecasting according to the message transmitted by a MAC (media access control) layer. A destination node selects a path for response in consideration of queuing delay, transmission delay, interference, link frequency diversity and other factors according to the routing information carried by the RREQ. After receiving the returned RREQ, the source node dynamically adjust the routing life time according to the forecasted end-to-end delay, so as to improve the effective utilization rate of the path. The cognitive routing protocol selects the routing in comprehensive consideration of frequency diversity and link interference according to the characteristics of the heterogeneous network by introducing Wiener forecasting and Q learning. Therefore, the end-to-end throughput is improved, the routing overhead is reduced, and the network resources are fully used.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Transmitting method based on parallel batch network coding
InactiveCN104243098AReduce negative impactFlexible organizationError preventionWireless communicationData streamWireless mesh network
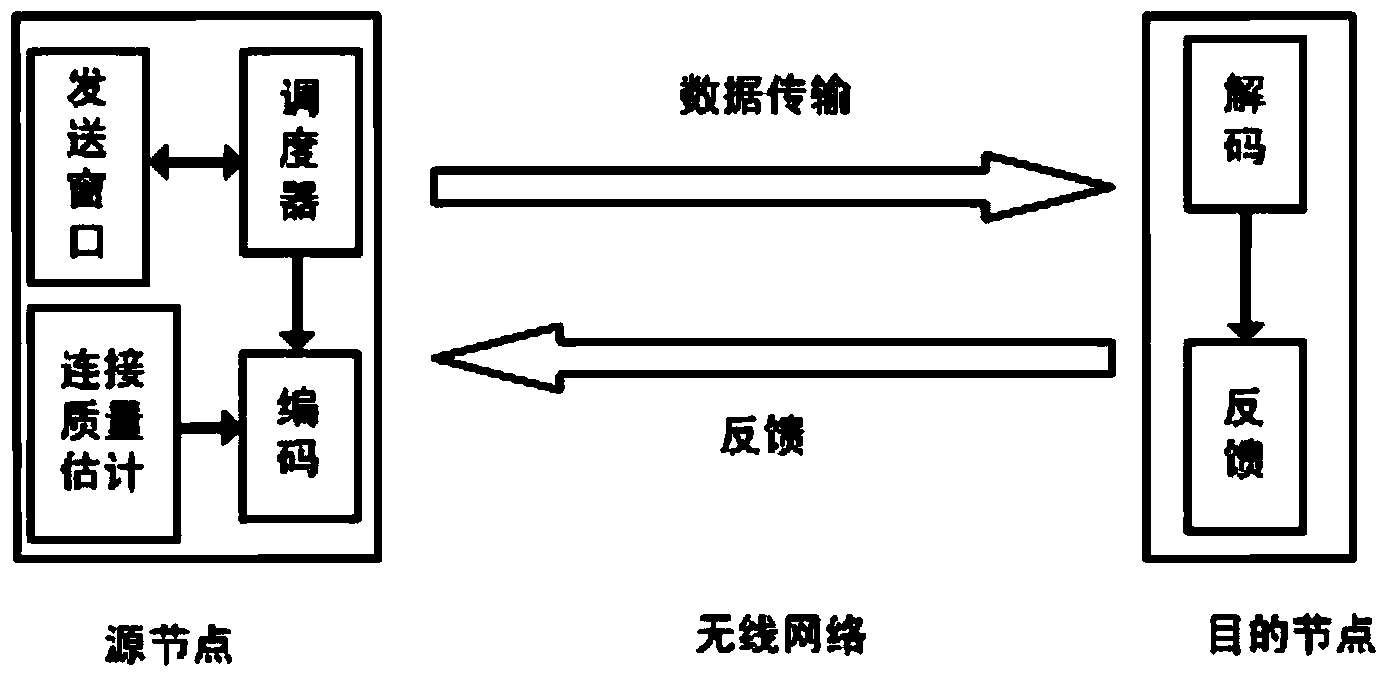
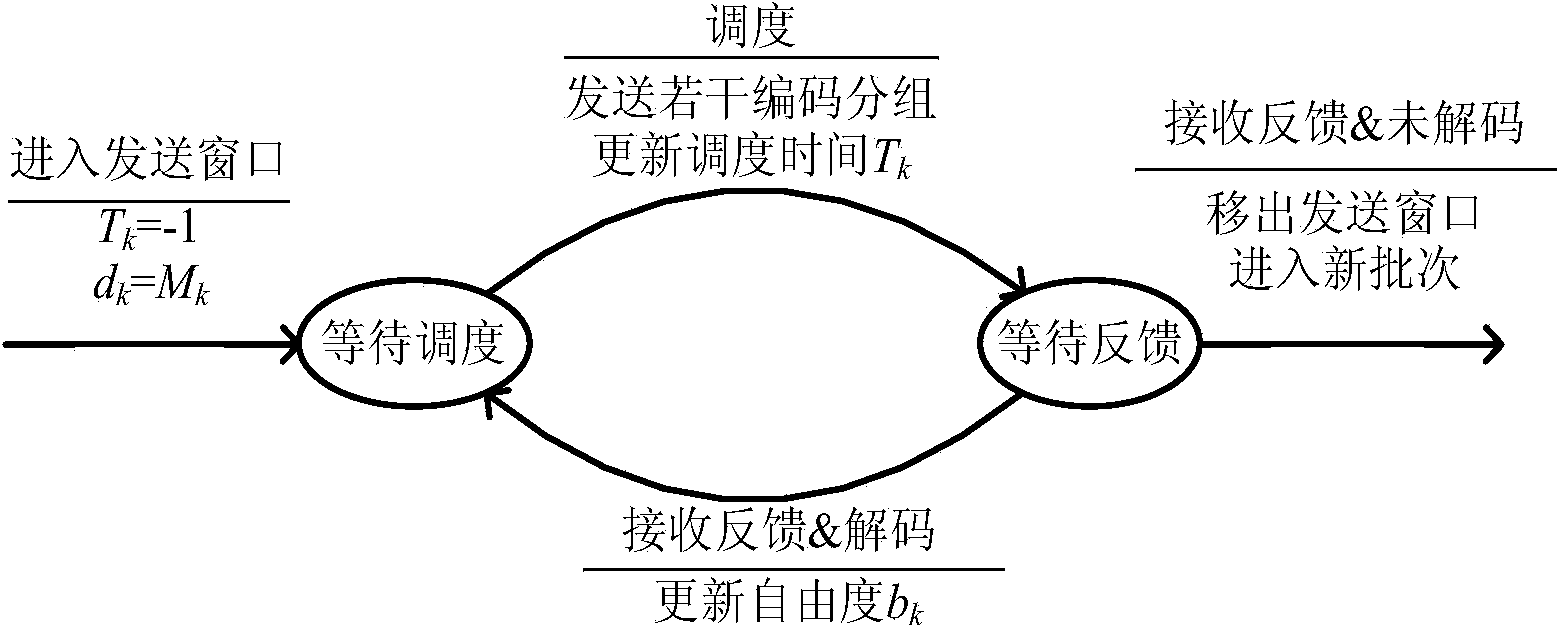
The invention relates to a transmitting method based on parallel batch network coding. According to the transmitting method, network coding is used for transmitting data, data flow to be transmitted is divided into batches comprising the same number of groups, the groups in each coding batch are coded and transmitted together, and a target node can decode one batch after receiving the enough number of the coded groups. The method can be applied to a wireless Mesh network, and provides reliable and efficient data transmission service; network coding is utilized for improving the transmission efficiency; to overcome the defect of low efficiency caused by an existing research and use stop wait strategy, the invention provides a parallel transmission method; a sending window which can dispatch a plurality of batches at the same time is maintained on a source node, and parallel dispatching of the multiple batches is controlled according to feedback information; in comparison with an existing research result, batch transmission can be organized more flexibly and efficiently, and then the end-to-end handling capacity is improved.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method, device and terminal for selective response packet transmission
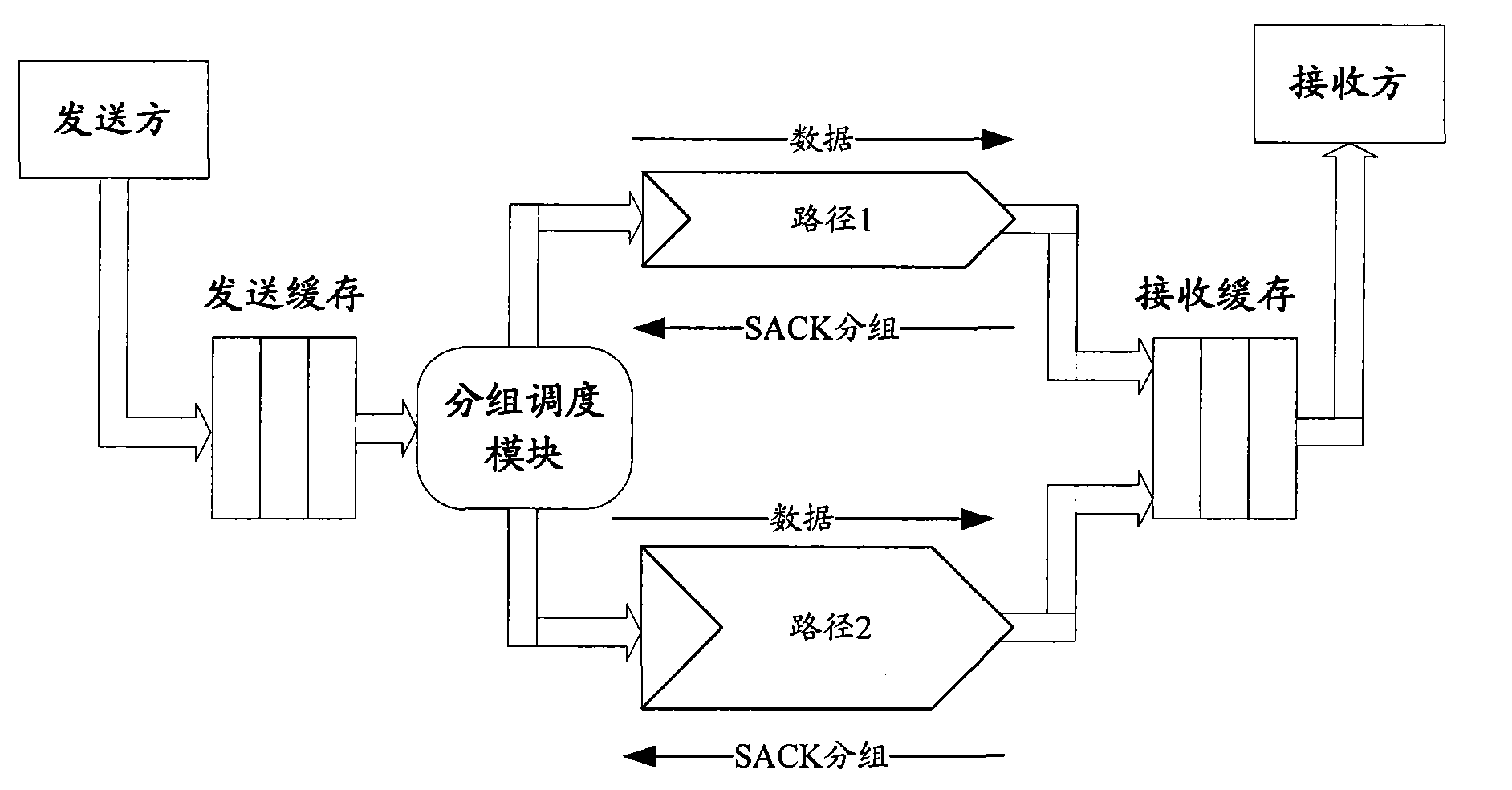
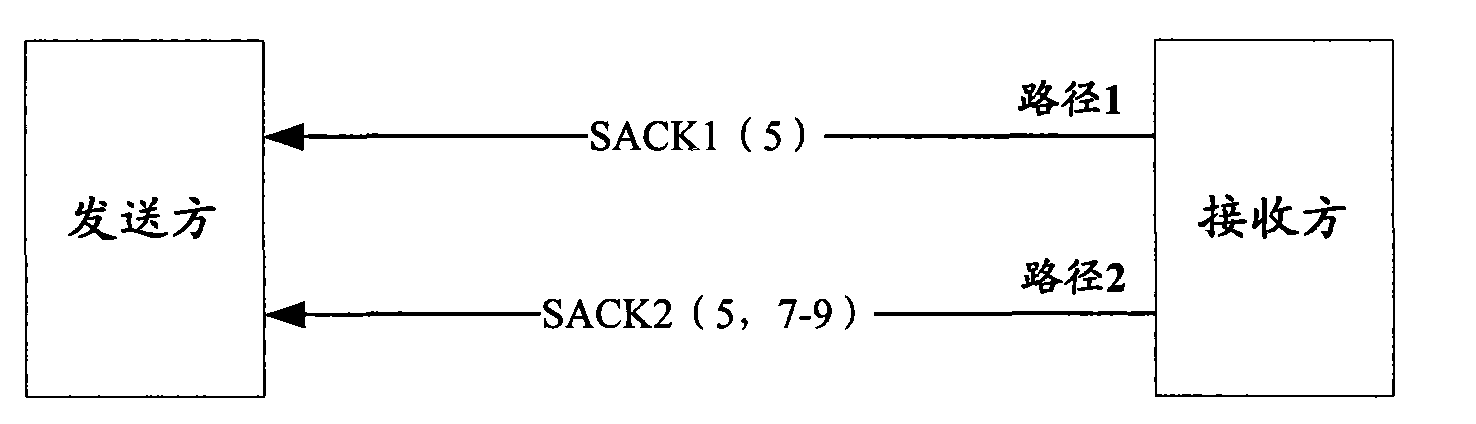
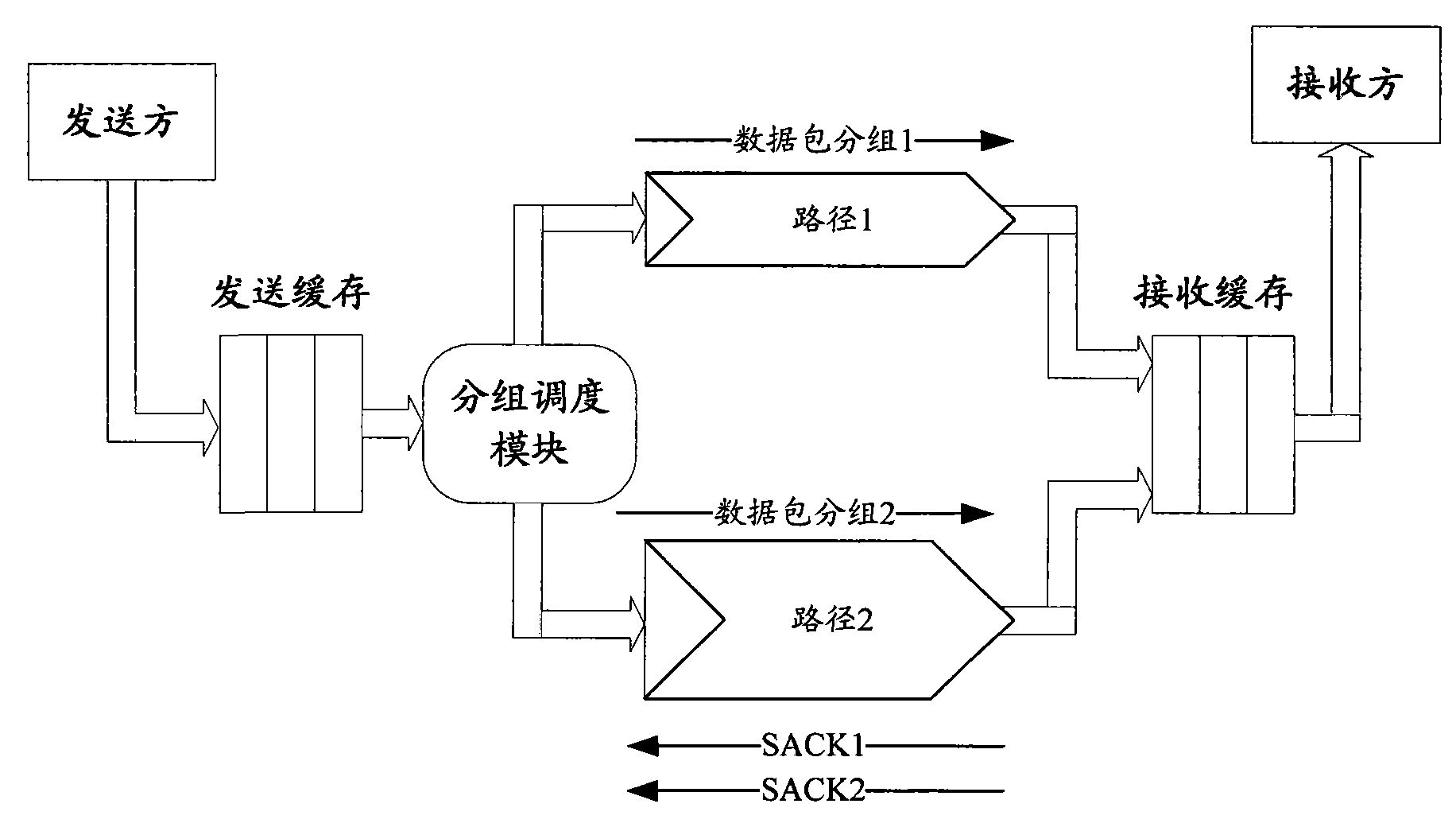
InactiveCN101631357AAvoid disorderImprove throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission protocolMulti path
The invention relates to the field of mobile communication, in particular to a technique for transmitting selective response SACK packets in multi-path transmission protocols. A selective response packet transmission method comprises the steps of determining one single path among a plurality of paths as a selective response SACK packet transmission path and transmitting the SACK packets through the SACK packet transmission path. The invention also provides a selective response packet transmission device. As one path is selected from a plurality of paths as the SACK packet transmission path and all the SACK packets are sent to a sender through the SACK packet transmission path, that the earlier sent SACK packets arrive earlier can be ensured so as to avoid the disorder of the SACK packets arriving at the sender. In addition, as the path with minimum round-trip delay is selected as the SACK packet transmission path, the SACK packets can be accelerated to arrive at the sender so as to improve the end-to-end throughput of multi-path concurrent transmission.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Load-Balancing Structure for Packet Switches and Its Constructing Method
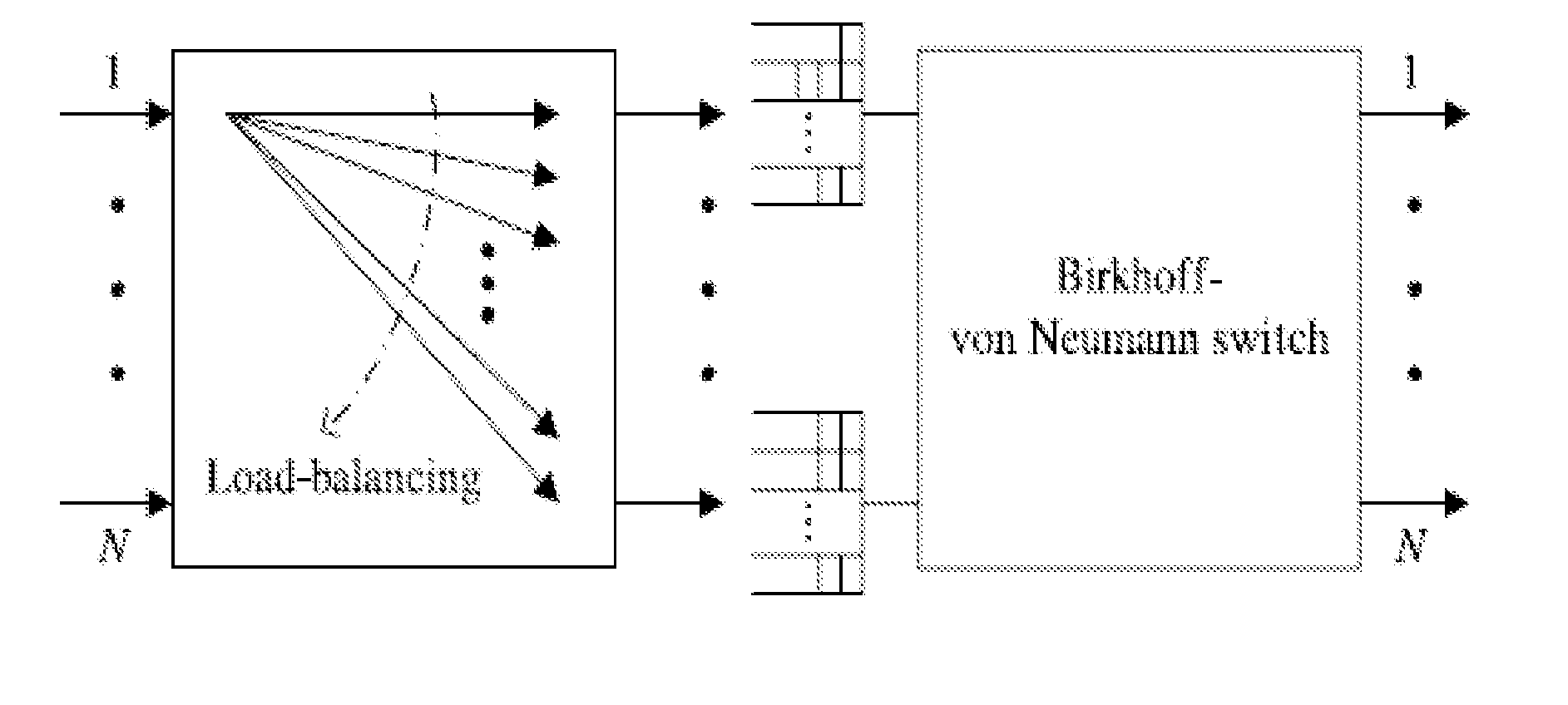
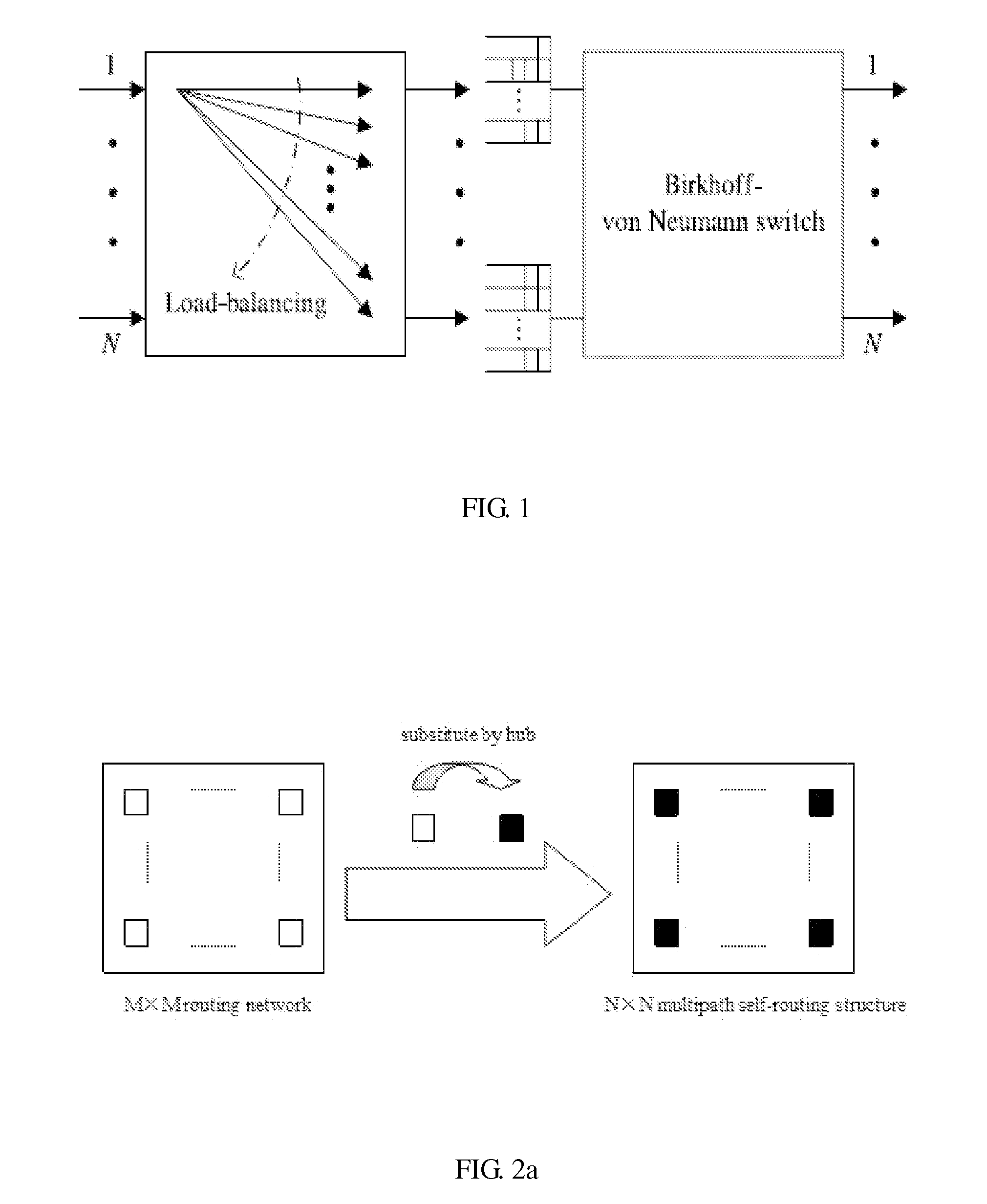
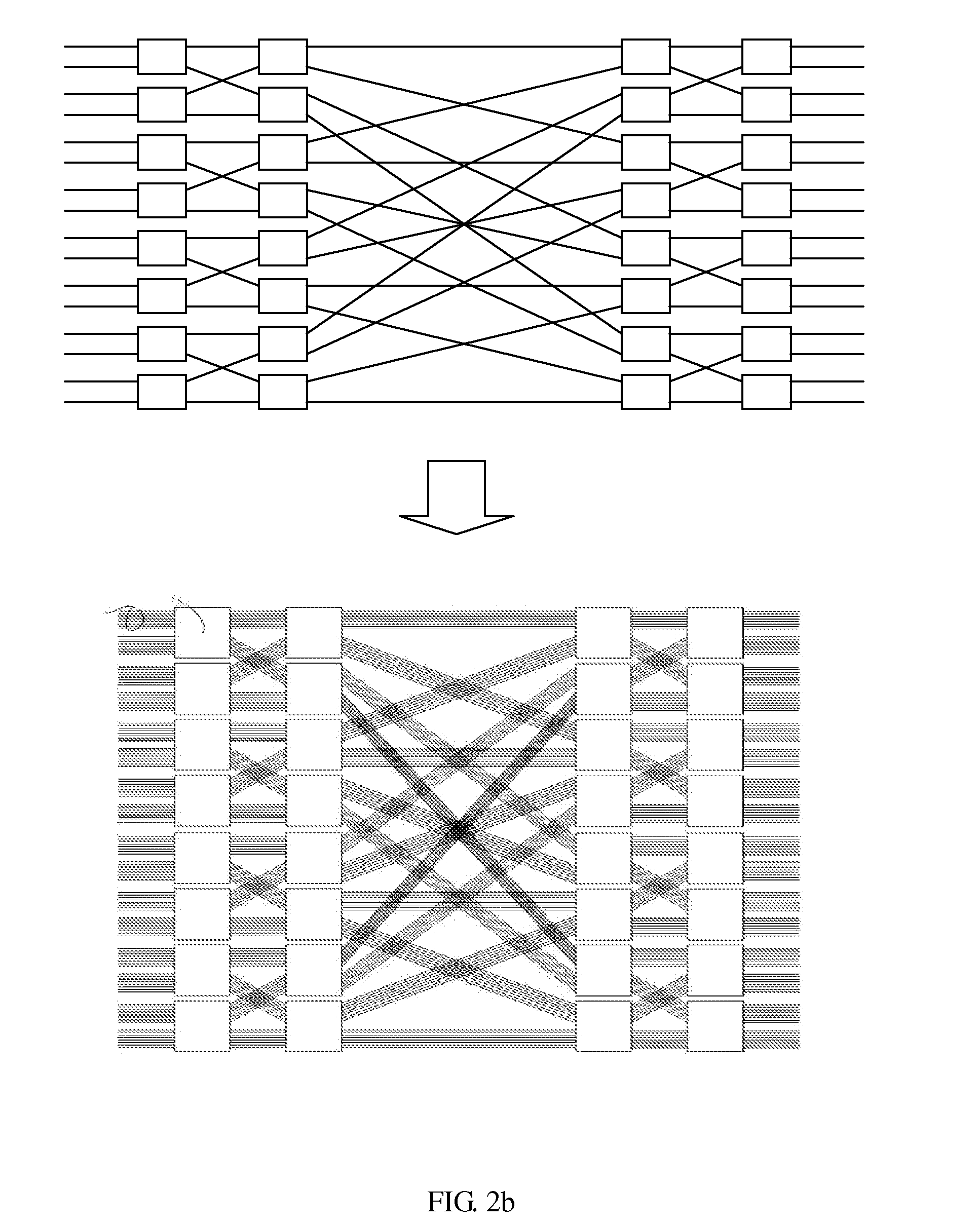
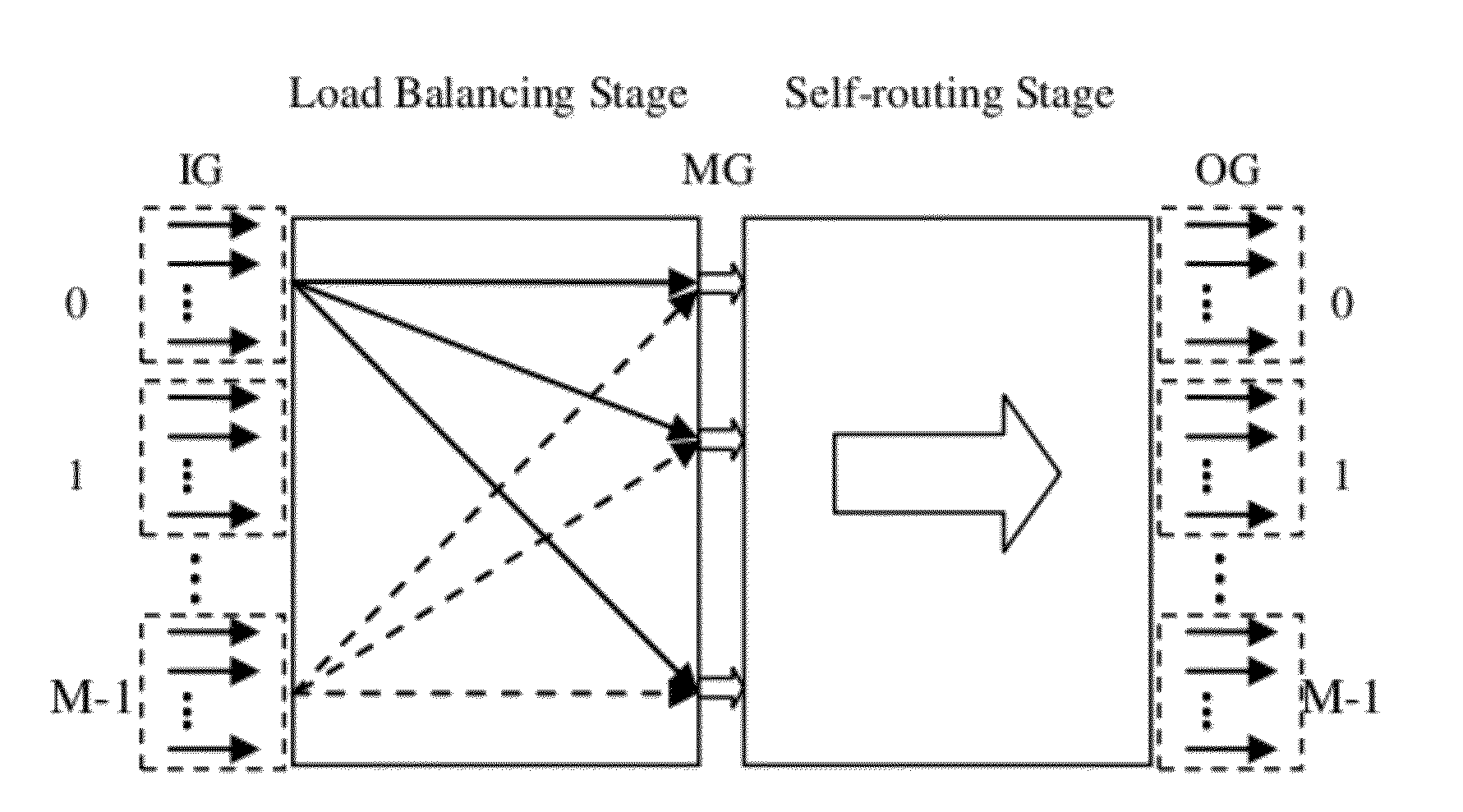
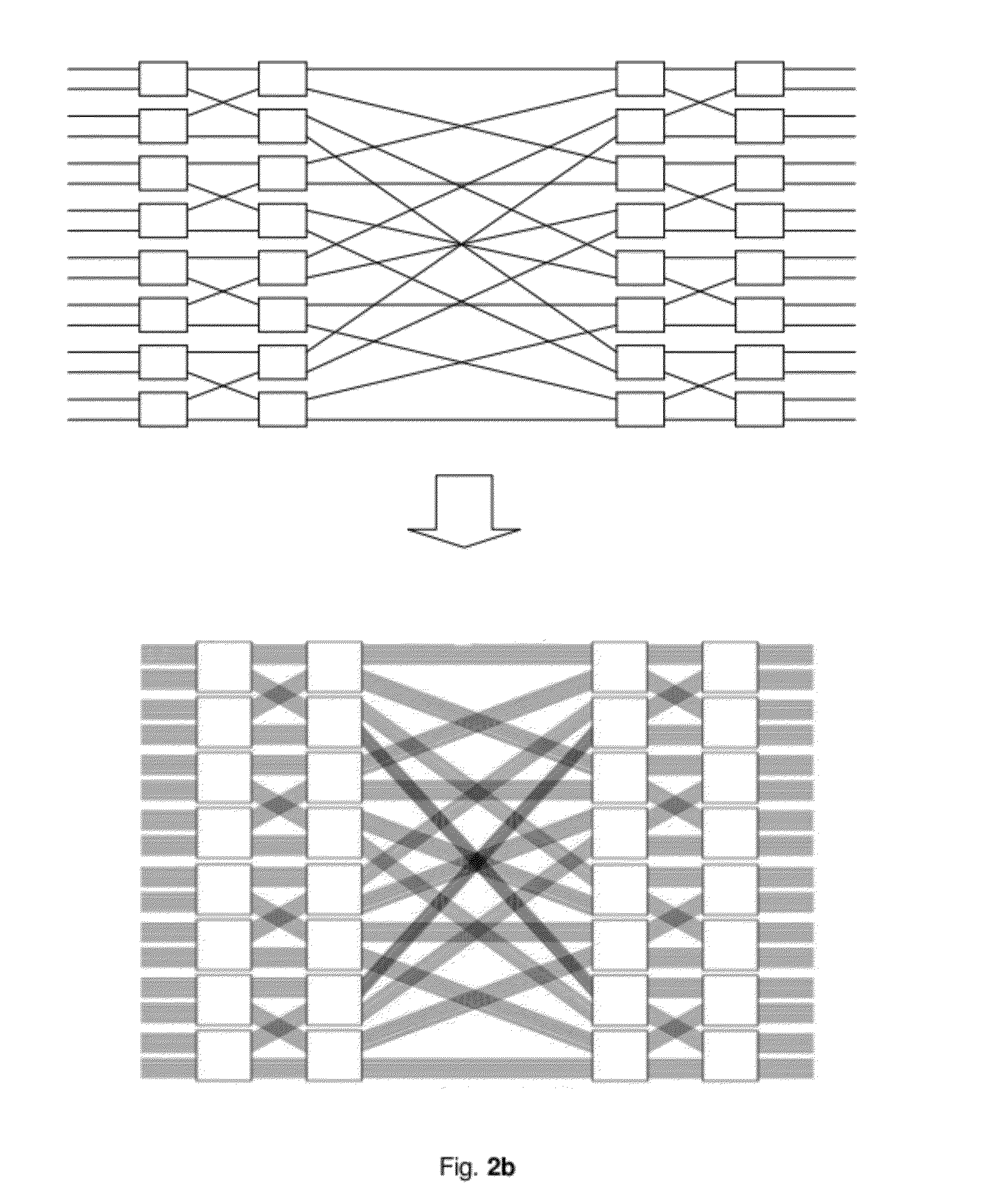
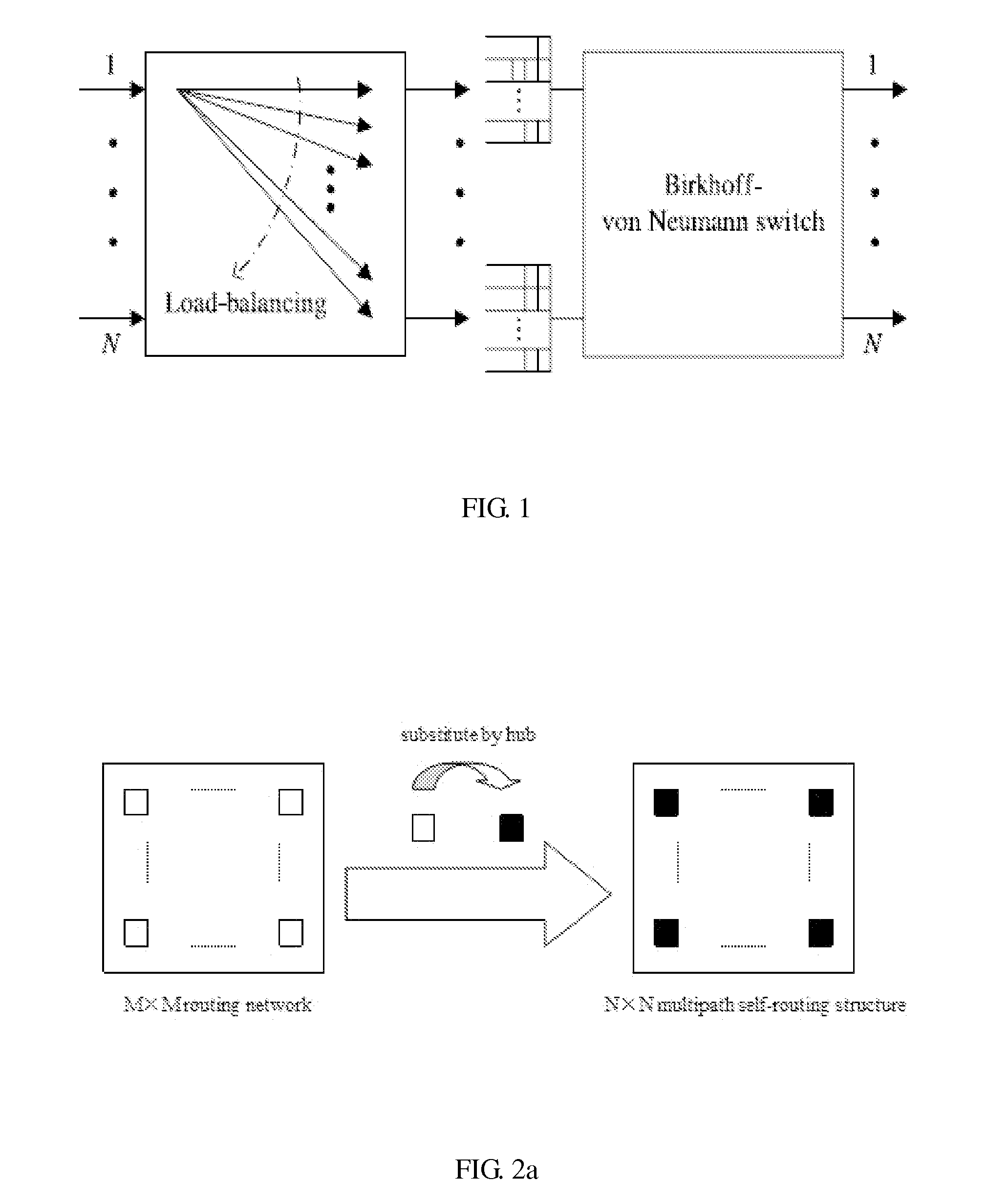
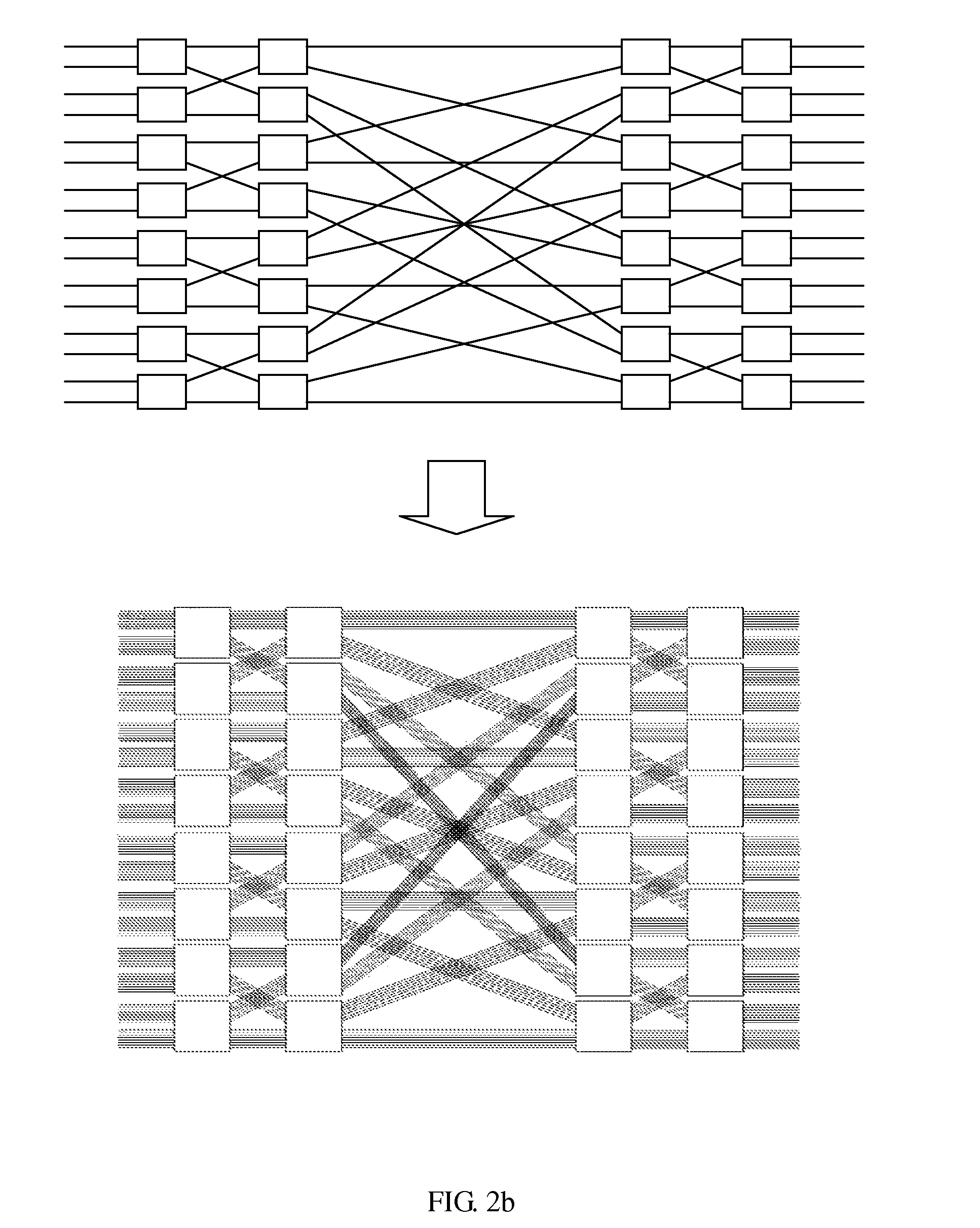
InactiveUS20110176425A1Improve end-to-end throughputSolve the real problemError preventionTransmission systemsSelf routingStructure of Management Information
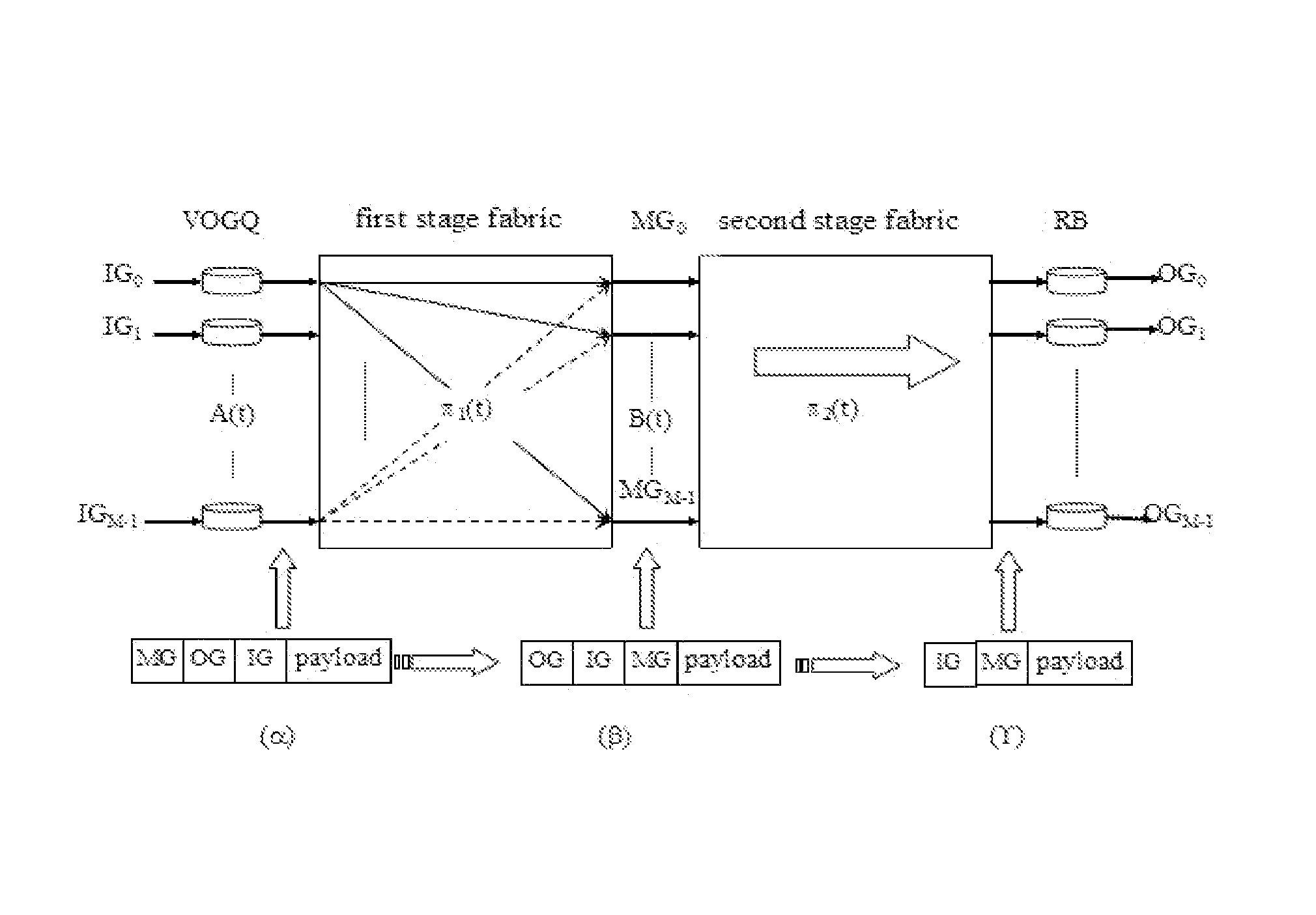
This invention provides a load-balancing structure for packet switches and its constructing method. In this method, the structure based on self-routing concentrators is divided into two stages, that is, a first stage and a second stage fabric. A virtual output group queue (VOGQ) is appended to each input group port of the first stage fabric, and a reordering buffer (RB) is configured behind each output group port of the second stage fabric. Packets stored in the VOGQ are combined into data blocks with preset length, which is divided into data slices of fixed size, finally each data slice is added an address tag and is delivered to the first stage fabric for self-routing. Once reaching the RB, data slices are recombined into data blocks. This invention solves the packet out-of-sequence problem in the load-balancing Birkhoff-von Neumann switching structure and improves the end-to-end throughput.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +2
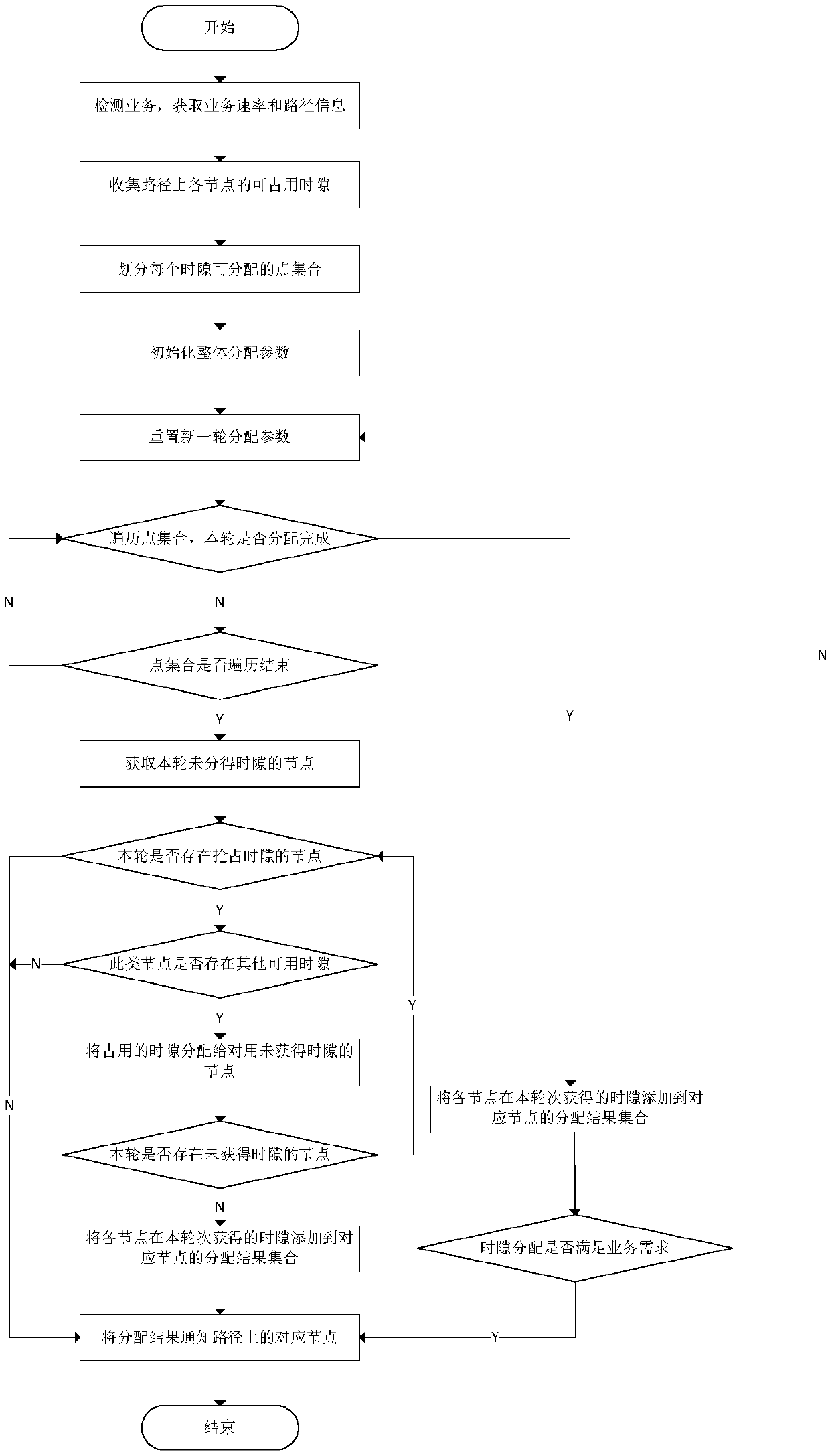
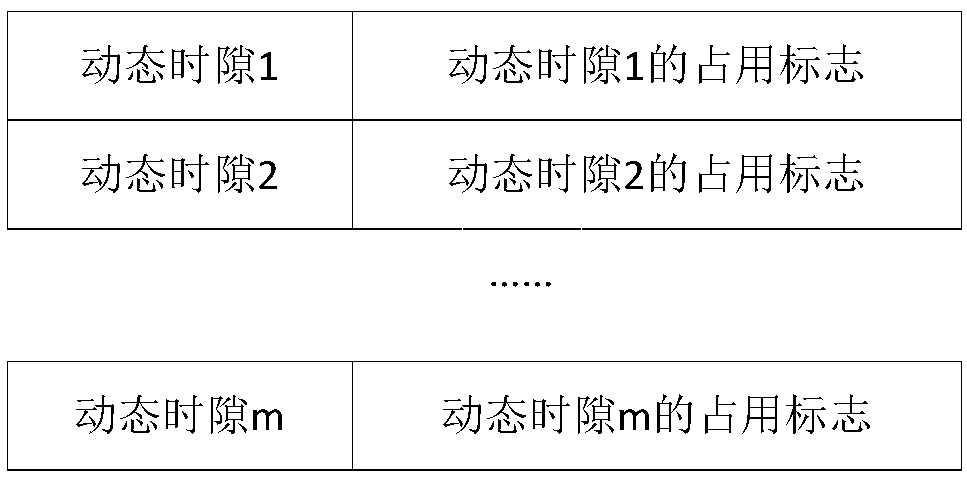
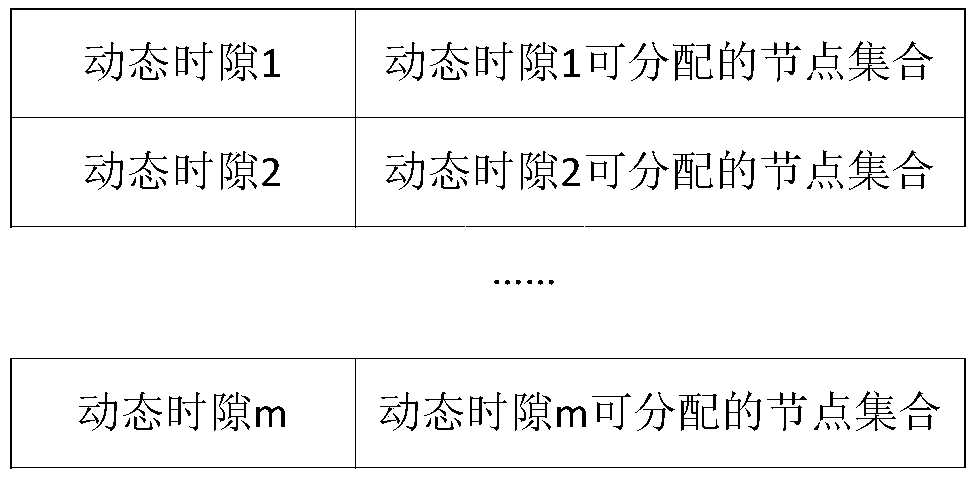
Dynamic time slot allocation method based on service flow path in TDMA ad-hoc network
ActiveCN109547148AReduce allocation timeImprove effective utilizationTime-division multiplexData switching networksService flowEnd to end throughput
The invention discloses a dynamic time slot allocation method based on a service flow path in a TDMA ad-hoc network, which solves a problem that dynamic time slot allocation time is too long when multi-hop transmission is executed, and a non-bottleneck node occupies an invalid time slot. A scheme provided by the invention is as follows: detecting services at a service flow source node, summarizingdynamic time slot occupation conditions of each node to the last hop node on the service flow path and allocating all the time slots; executing allocation round by round, guaranteeing that the numberof the dynamic time slots allocated to each node on the path is equal after allocation is completed, using a one-step backspacing mode while executing allocation round by round, and increasing the number of time slots which can be occupied by a bottleneck node. Design of the method provided by the invention comprises that a source node detects the service path, the last hop node on the path summarizes information of each node and performs time slot allocation, service detection and time slot allocation time is reduced, and by allocating round by round and the one-step backspacing mode, a buckets effect is avoided, time slot utilization rate is improved, end-to-end throughput is increased, and the method is used in the field of the TDMA ad-hoc network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Directional antenna-based multi-rate multi-path route optimization method
InactiveCN103402235AImprove throughputLower latencyWireless communicationTime delaysDirectional antenna
The invention discloses a directional antenna-based multi-rate multi-path route optimization method in the technical field of wireless network. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining higher end-to-end throughput by selecting a directional antenna forward direction; selecting a forward rate for each node provided with a directional antenna so as to obtain higher end-to-end throughput at the same time; and finally selecting a forward set for each node provided with the directional antenna so as to obtain higher end-to-end throughput by using a multi-path route mode. According to the method, the problems of selection of the direction of the directional antenna in multi-path routing and selection of the optimal transmission rate to obtain higher end-to-end throughput are effectively solved. The multi-path route mode obtained by a DSMA (Multi-rate Any-path Routing with Directional Antennas) algorithm is optimized. Compared with a single-rate multi-path route mode, the DSMA has the advantage that higher end-to-end throughput can be obtained. The end-to-end average time delay can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Load-Balancing Structure for Packet Switches with Minimum Buffers Complexity and its Building Method
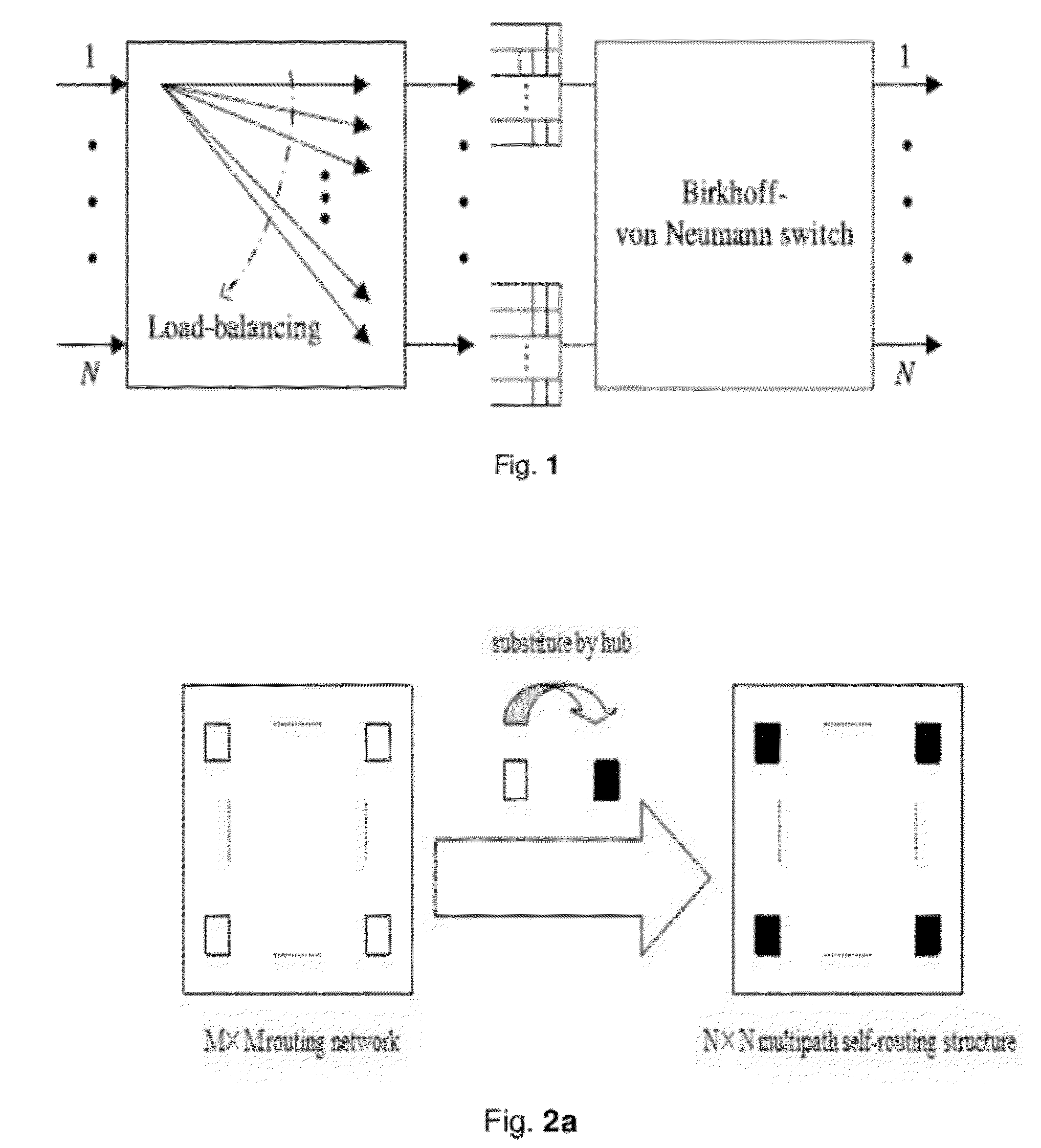
InactiveUS20120207020A1Improve end-to-end throughputReduce complexityError preventionTransmission systemsLoad SheddingRound complexity
This invention provides a structure of load-balancing packet switches with minimum buffers complexity and its concomitant methodology. It abandons the VOQ between the first stage and the second stage fabrics, which has no problems of queue delay and packets out-of-sequence. Therefore, this invention solves the packets out-of-sequence problem in load-balancing Birkhoff-von Neumann switching structure and improves the end-to-end throughput. Moreover, it greatly reduces the buffer complexity to O(N).
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +1
CoopMAX: a cooperative MAC with randomized distributed space time coding for an IEEE 802.16 network
Cooperative communication is a technique that can be employed to meet the increased throughput needs of next generation WiMAX systems. In a cooperative scenario, multiple stations can jointly emulate the antenna elements of a multi-input multi-output system in a distributed fashion. A framework for a randomized distributed space-time coding (“R-DSTC”) technique in the emerging relay-assisted WiMAX network, and the development of a cooperative medium access control (“MAC”) layer protocol, called CoopMAX, for R-DSTC deployment in an IEEE 802.16 system, is described. The technique described couples the MAC layer with the physical (PHY) layer for performance optimization. The PHY layer yields significant diversity gain, while the MAC layer achieves a substantial end-to-end throughput gain.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Multithread cooperation routing method for sensing interference
ActiveCN104144461AAddressing Interfering EffectsMaximize end-to-end throughputWireless communicationData streamMode selection
The invention discloses a multithread cooperation routing method for sensing interference. According to the research on the method that cooperative transmission and direct transmission can be adopted among the nodes in a multi-hop cooperative wireless network, through combination of relay selection and channel distribution, the problem of cooperative routing sensitive in interference is researched, and a distributed and cooperative routing method design is provided. According to the method, in the process of building cooperative routing, channel distribution, optimal transmission mode selection and optimal cooperation node selection are finished. By means of the method, the optimal cooperative routing with the least interference is selected for multiple data flows in the network, and meanwhile, reasonable distribution of multiple channels in the wireless network in the multiple data flows is determined, so that end-to-end handling capacity of the network data flow is maximized, and the network delay is lowered.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
A method and apparatus for spectrum allocation optimization
ActiveCN109005593AMeet diverse needsHigh level techniquesWireless communicationFrequency spectrumData stream
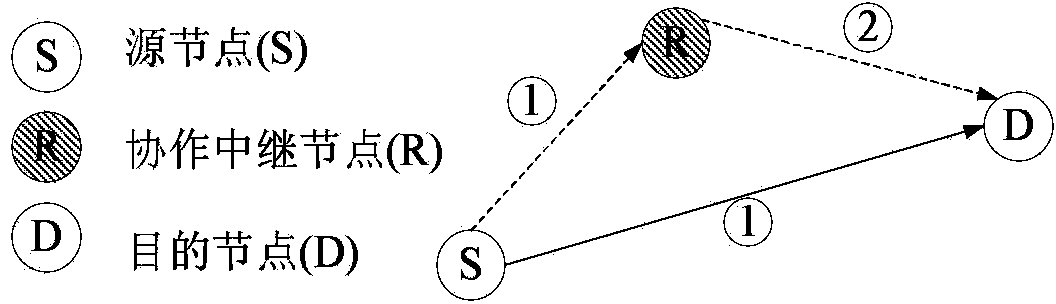
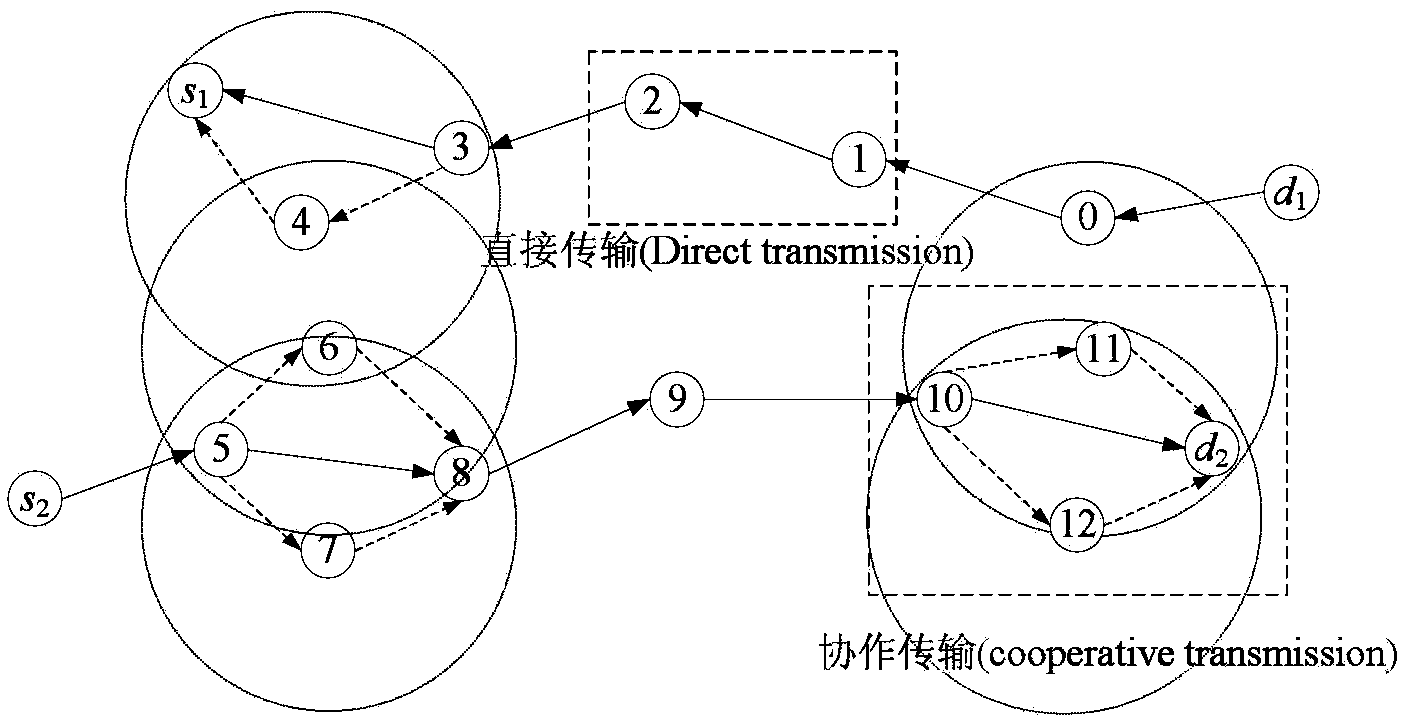
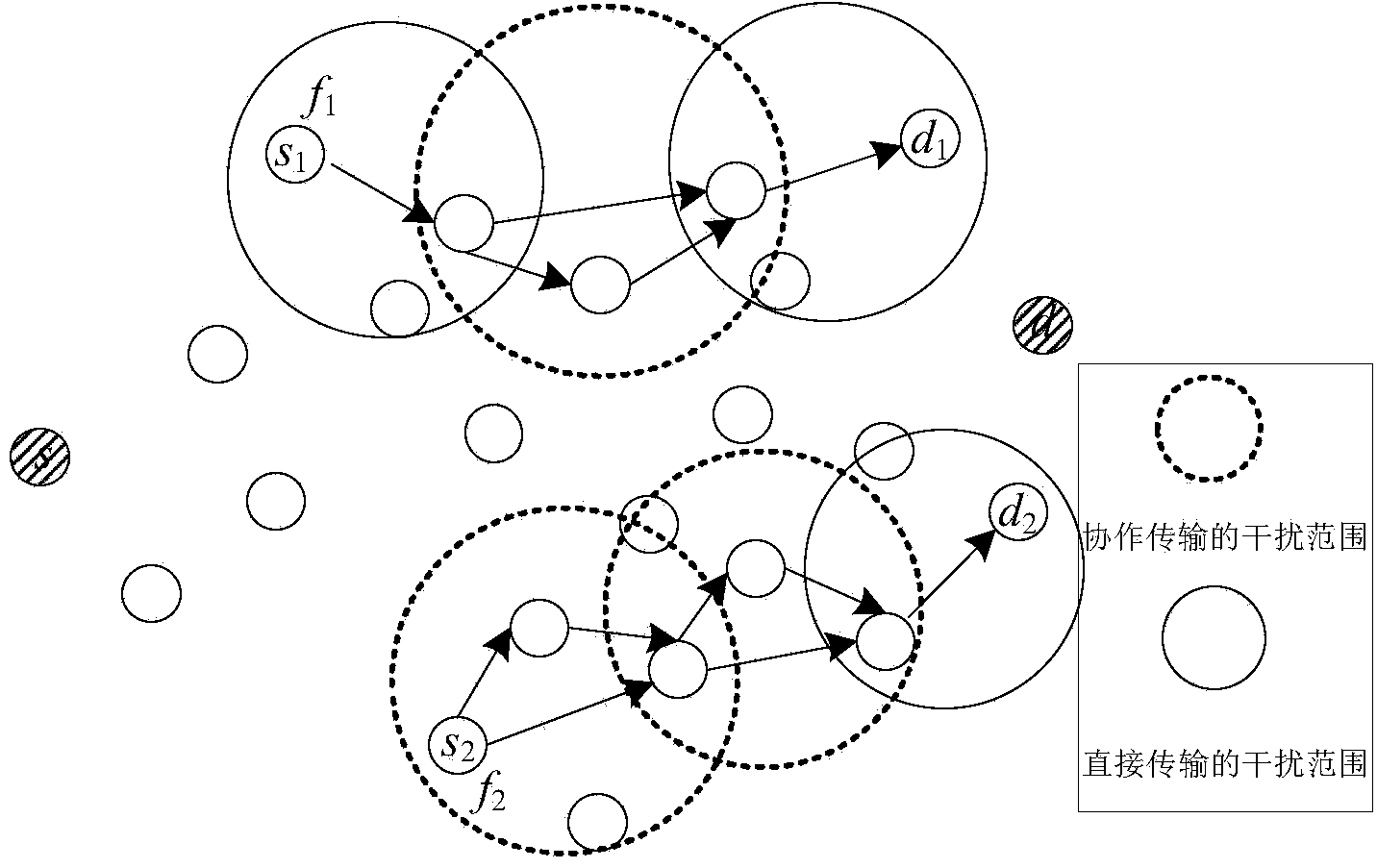
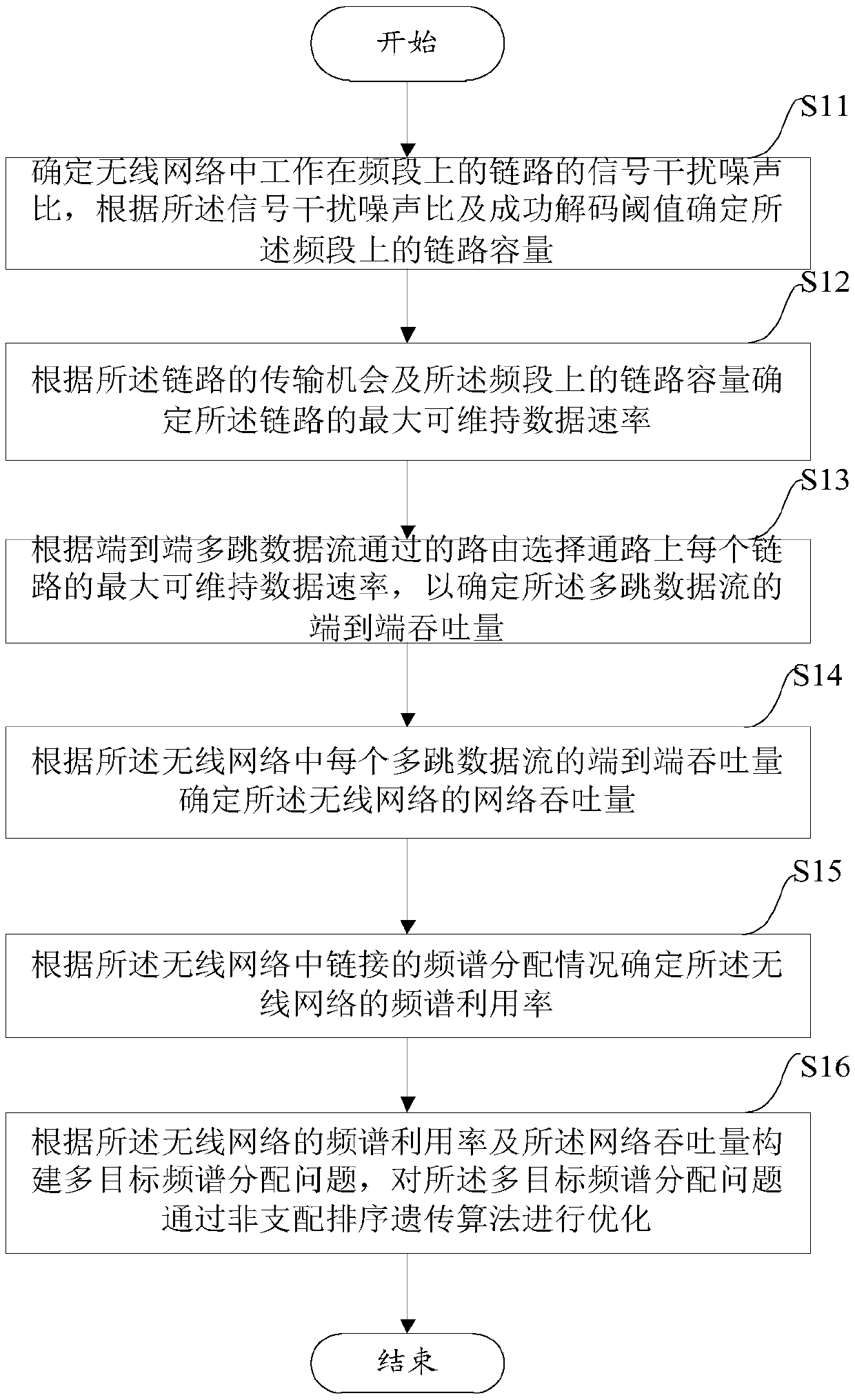
An object of the present application is to provide an optimized method and apparatus for spectrum allocation. The method comprises: determining a link capacity on a frequency band by determining a signal-to-interference-to-noise ratio of a link operating on the frequency band in a wireless network according to the signal-to-interference-to-noise ratio and a successful decoding threshold; determining a maximum maintainable data rate of the link according to a transmission opportunity of the link and a link capacity on the frequency band; determining an end-to-end throughput of the data stream according to a maximum sustainable data rate to determine a network throughput of the wireless network; determining a spectrum utilization rate of the wireless network according to a spectrum allocation situation of links in the wireless network; constructing a multi-objective spectrum allocation problem according to spectrum utilization and network throughput, and optimizing the multi-objective spectrum allocation problem by non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. Maximum allowable network throughput can be achieved and spectrum efficiency can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Distributed scheduling method based on successive interference cancellation in MIMO wireless network
InactiveCN110336596AImprove throughputTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionBroadcastingDistributed computing
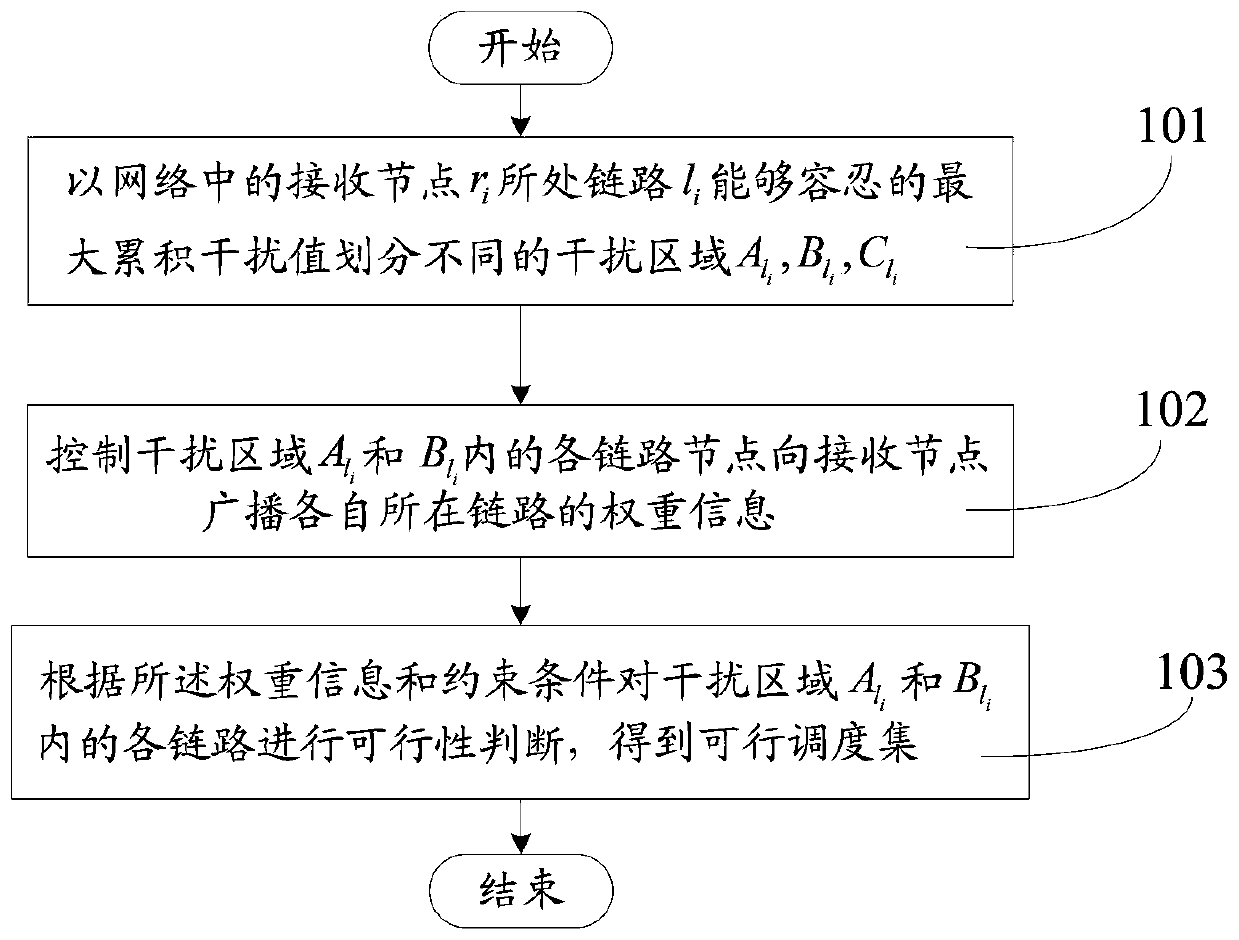
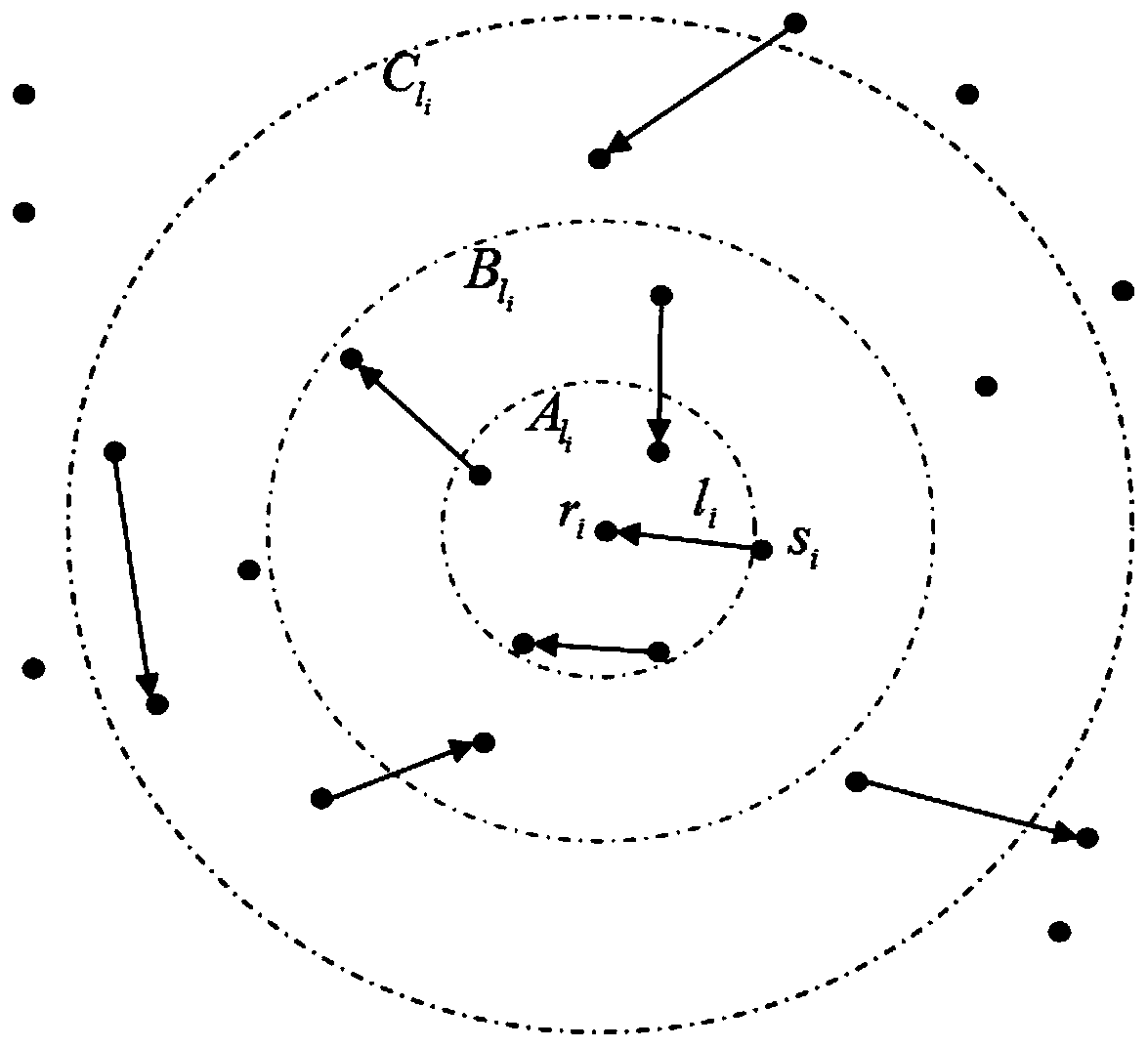
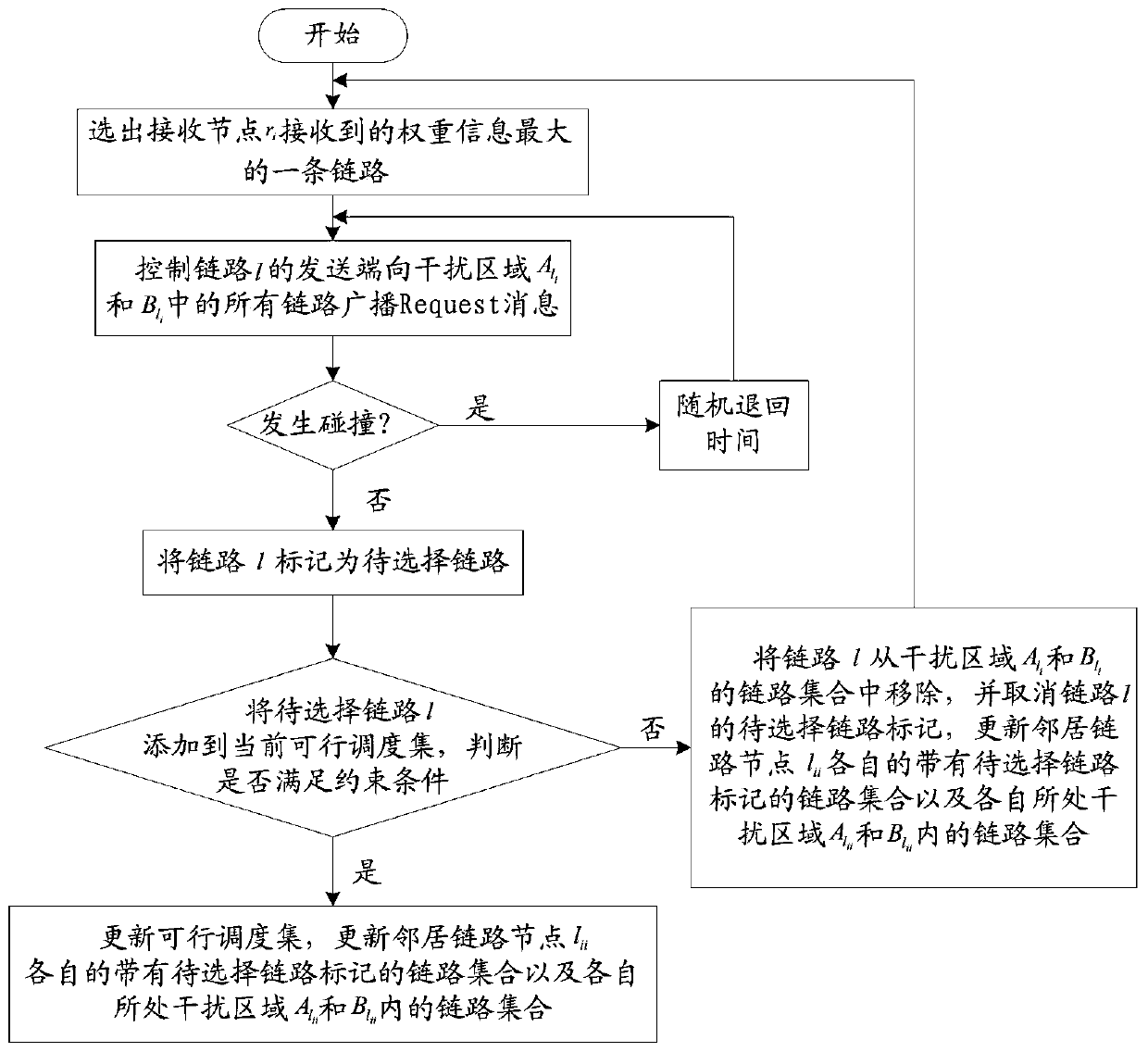
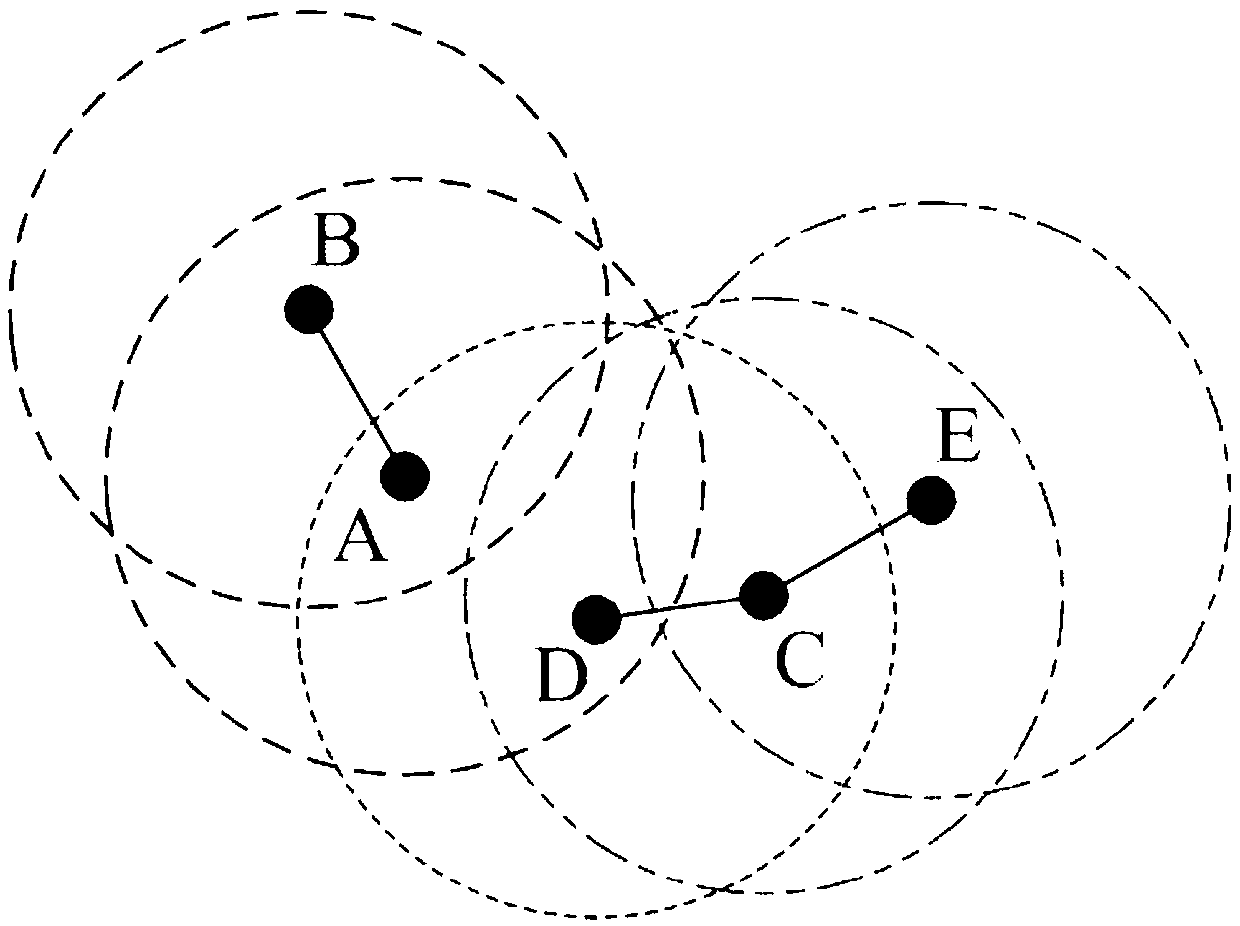
The invention discloses a distributed scheduling method based on successive interference cancellation in an MIMO wireless network. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing different interference regions Ali, Bli and Cli according to a maximum cumulative interference value tolerable by a link li where a receiving node ri in a network is located; controlling each link node in the interference areas Ali and Bli to broadcast weight information of respective link to a receiving node ri; and performing feasibility judgment on each link in the interference areas Ali and Bli according tothe weight information and constraint conditions, so as to obtain a feasible scheduling set, wherein the constraint conditions are conditions satisfying SINR and SIC and maximizing the minimum reachable end-to-end throughput. According to the method, the constraint conditions are set to meet the conditions of SINR, SIC and maximum minimum reachable end-to-end throughput, distributed scheduling iscarried out according to the weight information and the constraint conditions, the purpose of maximizing the minimum reachable end-to-end throughput is achieved, and the network throughput is improved.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
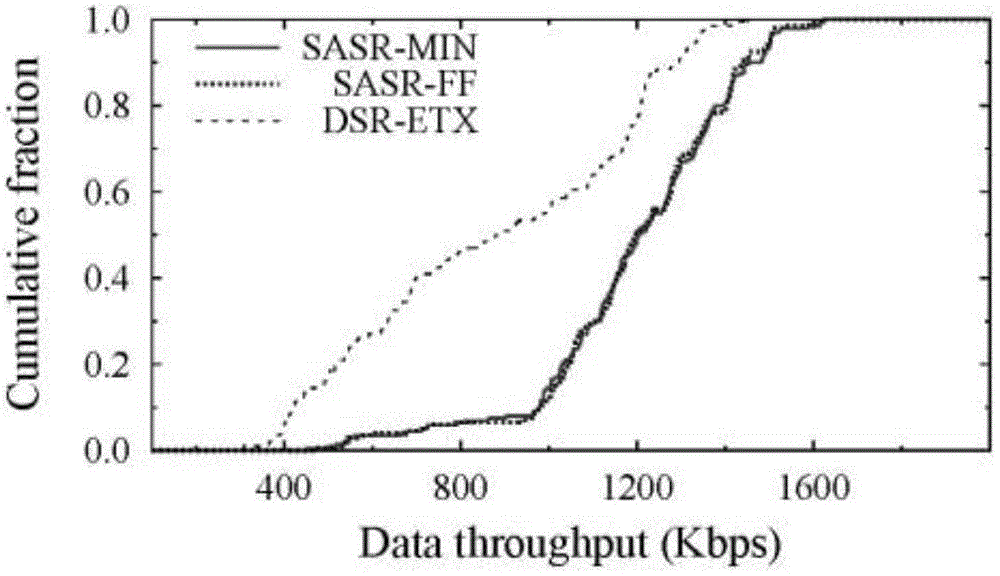
Single-path routing method using reusability of spectrum spaces
InactiveCN103347289AImprove end-to-end throughputReduce consumptionHigh level techniquesWireless communicationFrequency spectrumReusability
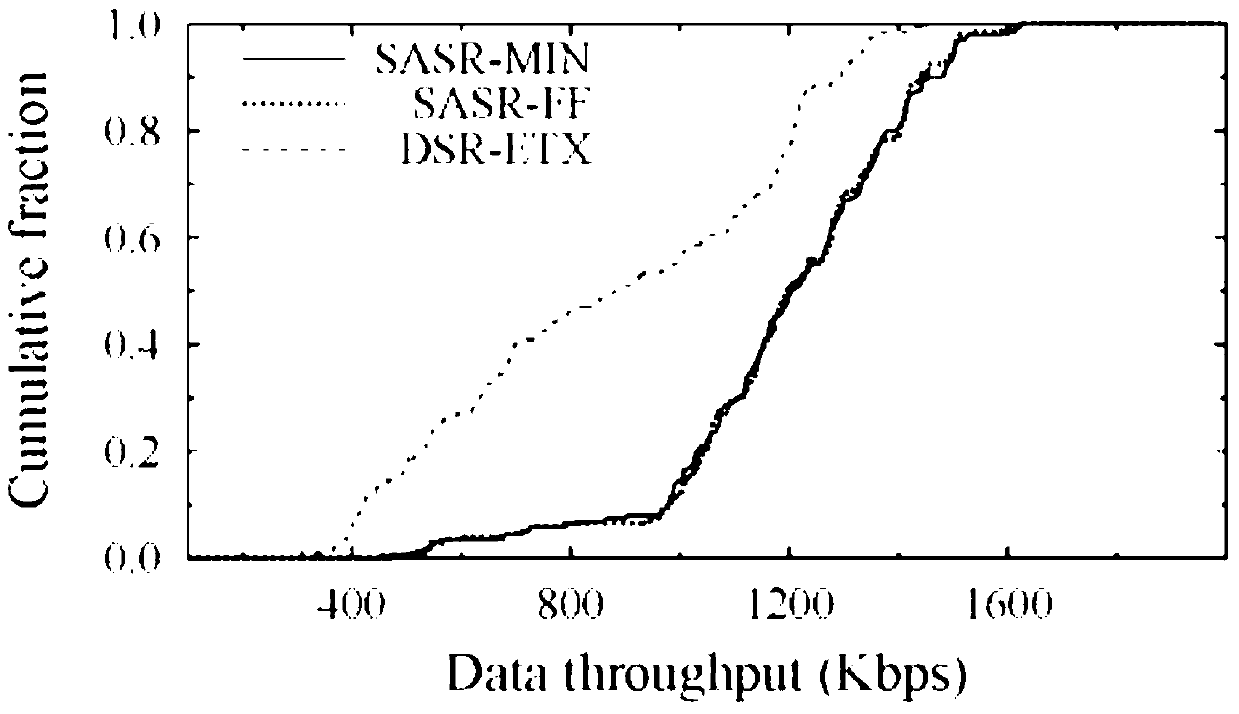
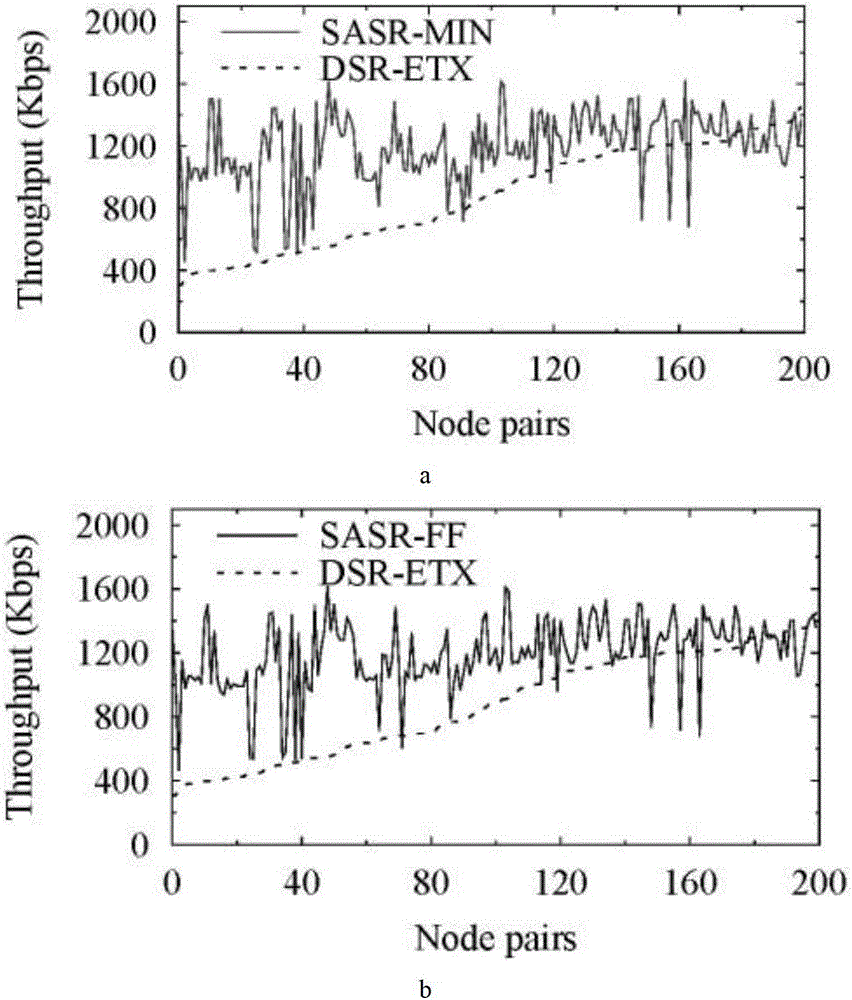
The invention belongs to the technical field of a multi-hop wireless network, and provides a single-path routing method using the reusability of spectrum spaces. The method comprises the steps that whether the spaces of links are reusable or not is judged, the reusability of the spectrum spaces among the links is quantized to obtain the routing metric value of a reusable unit; then modeling is conducted on the routing metric value of the reusable unit; an SASR-MIN algorithm or an SASR-FF algorithm is used for calculating the routing metric value of a path; at last, a destination node finds out a final path used for transmitting a data package and conducts data transmission according to the routing metric value. The reusability of the spaces among the links is considered when the routing metric value of the path is determined, a chosen routing path is made to achieve higher end-to-end throughput, and excess energy consumption is not extra introduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cognitive routing protocol for heterogeneous wireless return network
InactiveCN102143549BReduce overheadOptimize end-to-end performanceHigh level techniquesWireless communicationHeterogeneous networkQ-learning
The invention discloses a cognitive routing protocol suitable for a heterogeneous wireless return network, belonging to the field of wireless communication. The cognitive routing protocol mainly solves the problem of how to effectively select the path aiming to the difference of the nodes in the heterogeneous network. When a source node sends a RREQ (route request) and an intermediate node receives the RREQ, an acquired link delay EED and a link equivalent bandwidth ABITF are added into the RREQ by Wiener forecasting according to the message transmitted by a MAC (media access control) layer. A destination node selects a path for response in consideration of queuing delay, transmission delay, interference, link frequency diversity and other factors according to the routing information carried by the RREQ. After receiving the returned RREQ, the source node dynamically adjust the routing life time according to the forecasted end-to-end delay, so as to improve the effective utilization rate of the path. The cognitive routing protocol selects the routing in comprehensive consideration of frequency diversity and link interference according to the characteristics of the heterogeneous network by introducing Wiener forecasting and Q learning. Therefore, the end-to-end throughput is improved, the routing overhead is reduced, and the network resources are fully used.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
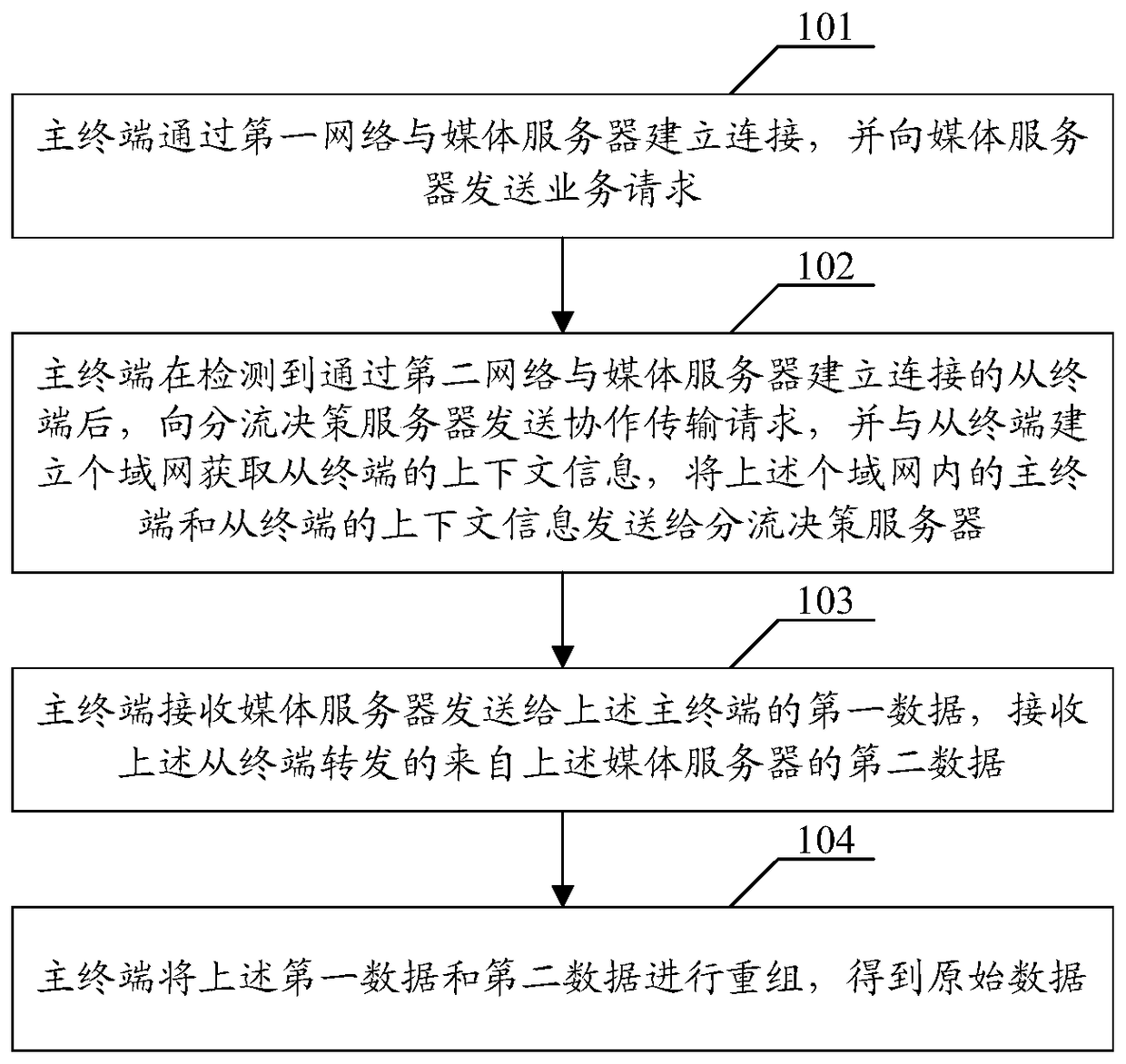
A multi-stream concurrent transmission method, device and system
A multi-stream concurrent transmission method, device and system, wherein the realization of the method includes: the master terminal establishes a connection with the media server through the first network, and sends a service request to the media server; After the connected slave terminal is established, send a cooperative transmission request to the distribution decision server, and establish a personal area network with the slave terminal to obtain the context information of the slave terminal, and send the context information of the master terminal and the slave terminal in the personal area network to the distribution decision server ; The context information of the master terminal and the slave terminal is used to execute the distribution decision; the result of the distribution decision is used to split the original data corresponding to the service request into first data and second data; the master terminal receives the first data sent by the media server to the master terminal One data, receiving the second data from the media server forwarded by the slave terminal; the master terminal reassembles the first data and the second data to obtain the original data. It can improve end-to-end throughput and network resource utilization.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
A Time Optimal Allocation Method for Energy Harvesting Relay System Based on Relay Selection
ActiveCN105744629BThe result of relay selection is reasonableMeet the needs of practical applicationsRadio transmissionWireless communicationSimplex algorithmService condition
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multi-rate multi-path routing optimization method based on directional antenna
InactiveCN103402235BImprove throughputLower latencyWireless communicationDirectional antennaComputer science
The invention discloses a directional antenna-based multi-rate multi-path route optimization method in the technical field of wireless network. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining higher end-to-end throughput by selecting a directional antenna forward direction; selecting a forward rate for each node provided with a directional antenna so as to obtain higher end-to-end throughput at the same time; and finally selecting a forward set for each node provided with the directional antenna so as to obtain higher end-to-end throughput by using a multi-path route mode. According to the method, the problems of selection of the direction of the directional antenna in multi-path routing and selection of the optimal transmission rate to obtain higher end-to-end throughput are effectively solved. The multi-path route mode obtained by a DSMA (Multi-rate Any-path Routing with Directional Antennas) algorithm is optimized. Compared with a single-rate multi-path route mode, the DSMA has the advantage that higher end-to-end throughput can be obtained. The end-to-end average time delay can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Load-balancing structure for packet switches and its constructing method
InactiveUS8902887B2Improve throughputError preventionTransmission systemsSelf routingStructure of Management Information
This invention provides a load-balancing structure for packet switches and its constructing method. In this method, the structure based on self-routing concentrators is divided into two stages, that is, a first stage and a second stage fabric. A virtual output group queue (VOGQ) is appended to each input group port of the first stage fabric, and a reordering buffer (RB) is configured behind each output group port of the second stage fabric. Packets stored in the VOGQ are combined into data blocks with preset length, which is divided into data slices of fixed size, finally each data slice is added an address tag and is delivered to the first stage fabric for self-routing. Once reaching the RB, data slices are recombined into data blocks. This invention solves the packet out-of-sequence problem in the load-balancing Birkhoff-von Neumann switching structure and improves the end-to-end throughput.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +2
An Efficient Resource Scheduling Method for Small Satellite Networks Based on Earth Observation Missions
ActiveCN106100719BImprove efficiencyReduce complexityRadio transmissionEarth observationMaximal independent set
This invention discloses a method for scheduling efficient resource of a minisatellite network based on earth observation tasks, and solves the problems that the end-to-end throughput capacity is low and the utilization efficiency of the network resource is low because the network resource is not fully considered during the scheduling process in the earth observation scene of the resource-limited minisatellite network. The method comprises the implementation processes of: according to an initial network topology, determining a node number; at the same time, initializing a network resource scheduling planning time set; according to current network state and resource scheduling conflict restraint, constructing a link scheduling conflict graph by a ground control center; solving a maximal independent set corresponding to the conflict graph to acquire a network conflict-free scheduling link set; by using the link set and a linear programming, solving a resource allocation scheme and a data transmission method capable of mostly optimizing the network efficiency till a time slot is ended. The method improves the resource utilization ratio, increases the returning efficiency of important task data, improves the earth observation network performance of the minisatellite, and is used for scheduling the efficiently transmitted resource of earth observation system data.
Owner:陕西丝路天图卫星科技有限公司
A Single Path Routing Method Exploiting Spectrum Spatial Reusability
InactiveCN103347289BImprove end-to-end throughputReduce consumptionEnergy efficient ICTHigh level techniquesData packPathPing
The invention belongs to the technical field of a multi-hop wireless network, and provides a single-path routing method using the reusability of spectrum spaces. The method comprises the steps that whether the spaces of links are reusable or not is judged, the reusability of the spectrum spaces among the links is quantized to obtain the routing metric value of a reusable unit; then modeling is conducted on the routing metric value of the reusable unit; an SASR-MIN algorithm or an SASR-FF algorithm is used for calculating the routing metric value of a path; at last, a destination node finds out a final path used for transmitting a data package and conducts data transmission according to the routing metric value. The reusability of the spaces among the links is considered when the routing metric value of the path is determined, a chosen routing path is made to achieve higher end-to-end throughput, and excess energy consumption is not extra introduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com