Patents
Literature
58 results about "Multilevel security" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
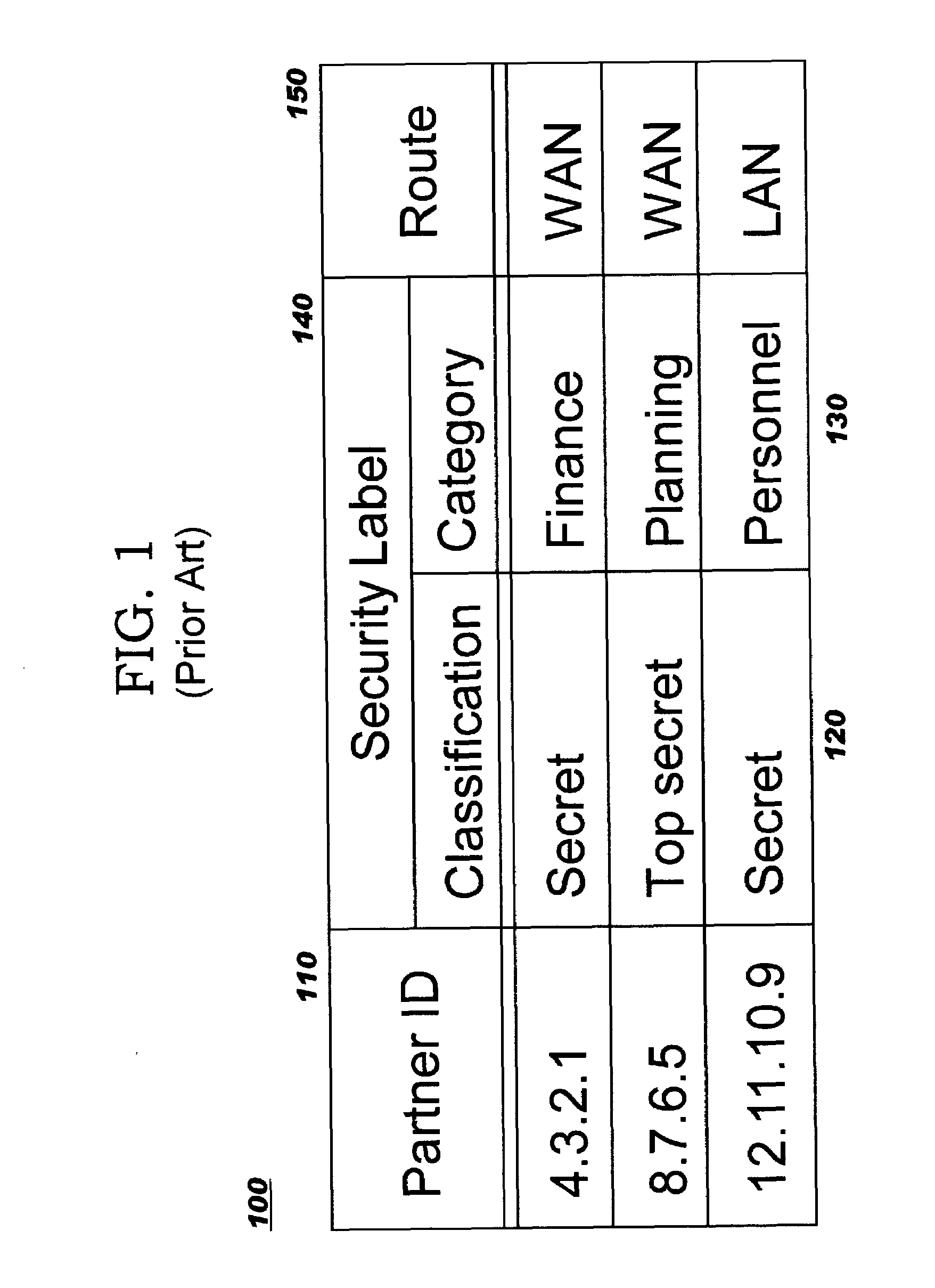
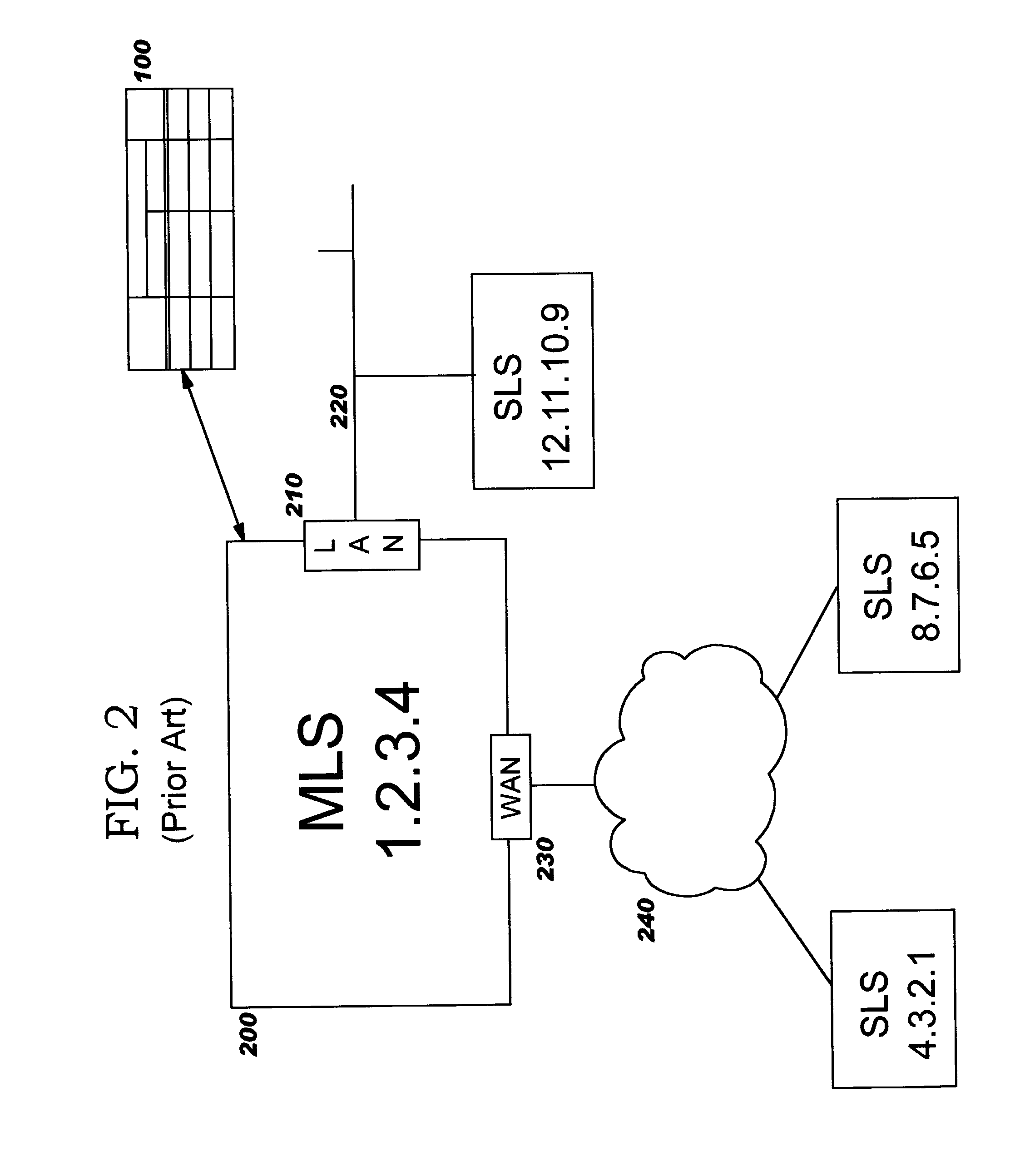
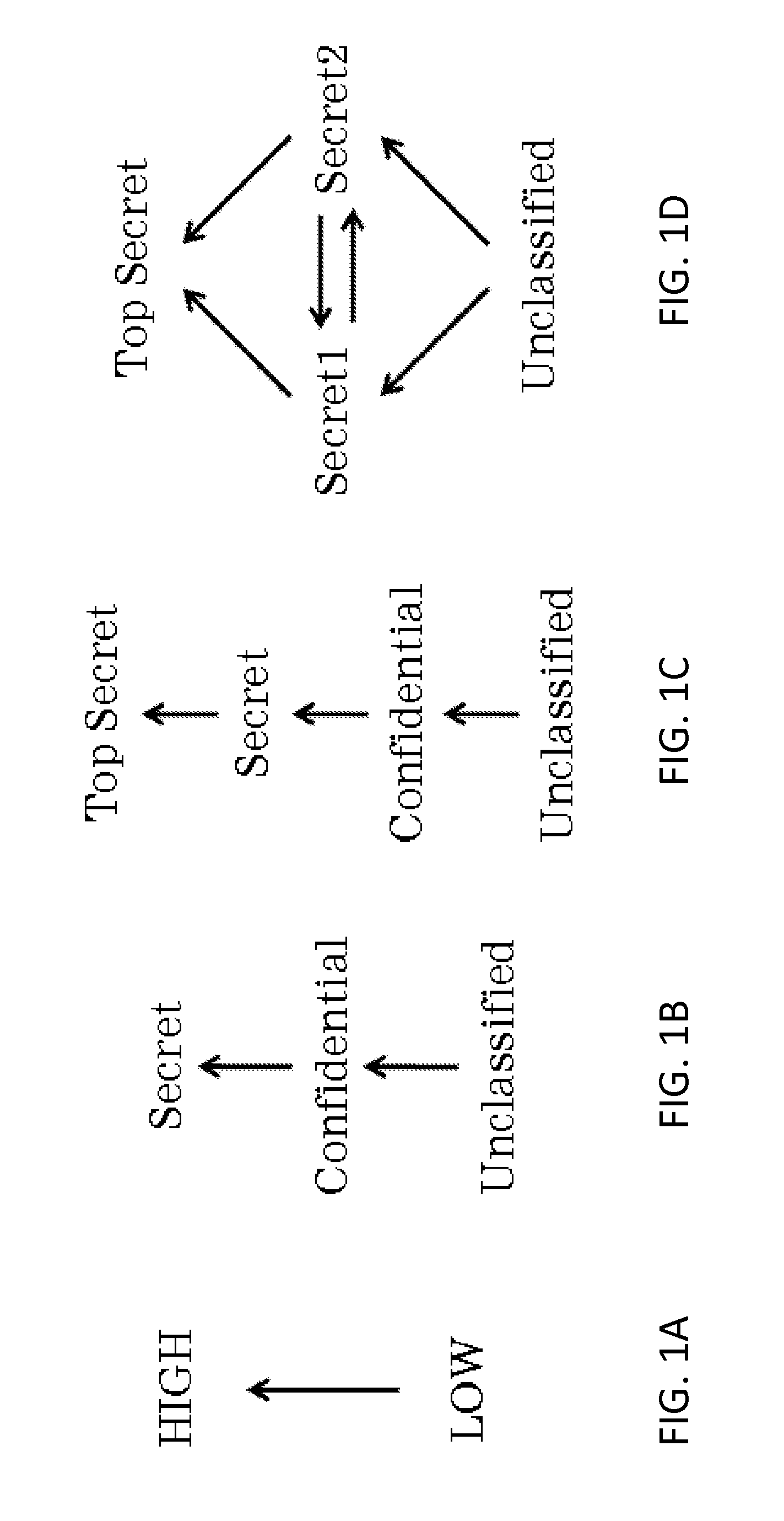
Multilevel security or multiple levels of security (MLS) is the application of a computer system to process information with incompatible classifications (i.e., at different security levels), permit access by users with different security clearances and needs-to-know, and prevent users from obtaining access to information for which they lack authorization. There are two contexts for the use of multilevel security. One is to refer to a system that is adequate to protect itself from subversion and has robust mechanisms to separate information domains, that is, trustworthy. Another context is to refer to an application of a computer that will require the computer to be strong enough to protect itself from subversion and possess adequate mechanisms to separate information domains, that is, a system we must trust. This distinction is important because systems that need to be trusted are not necessarily trustworthy.
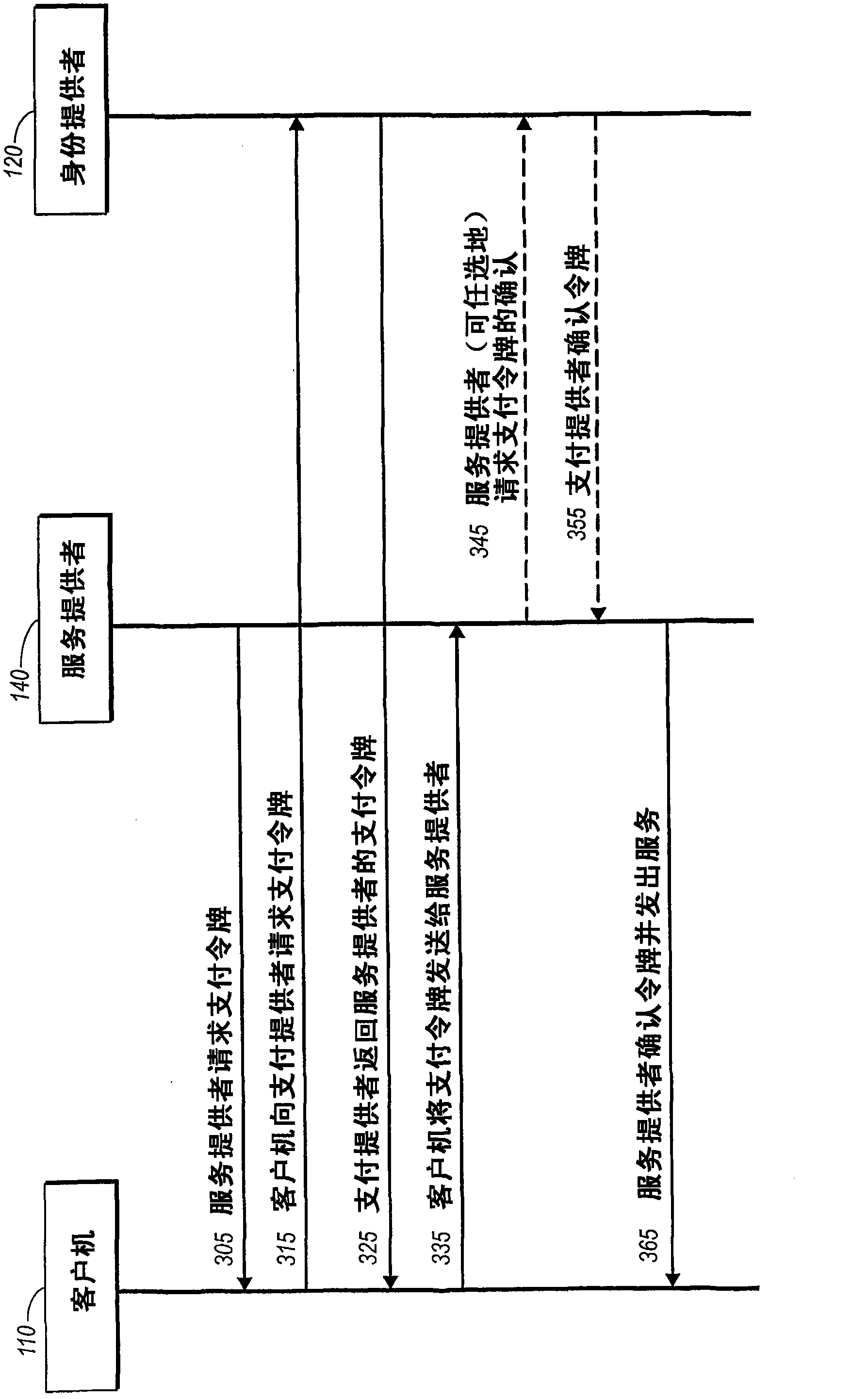
Secure network commercial transactions
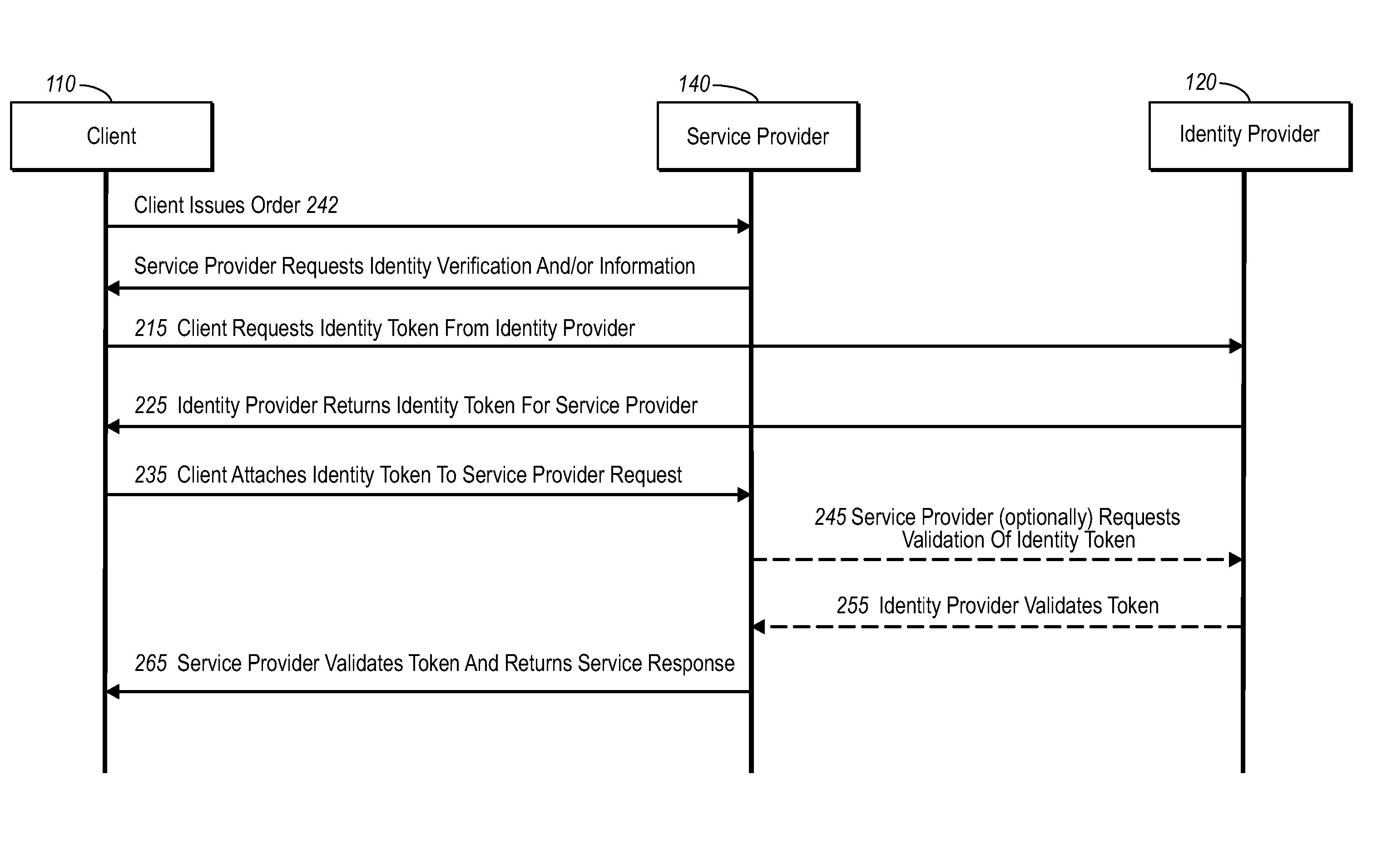
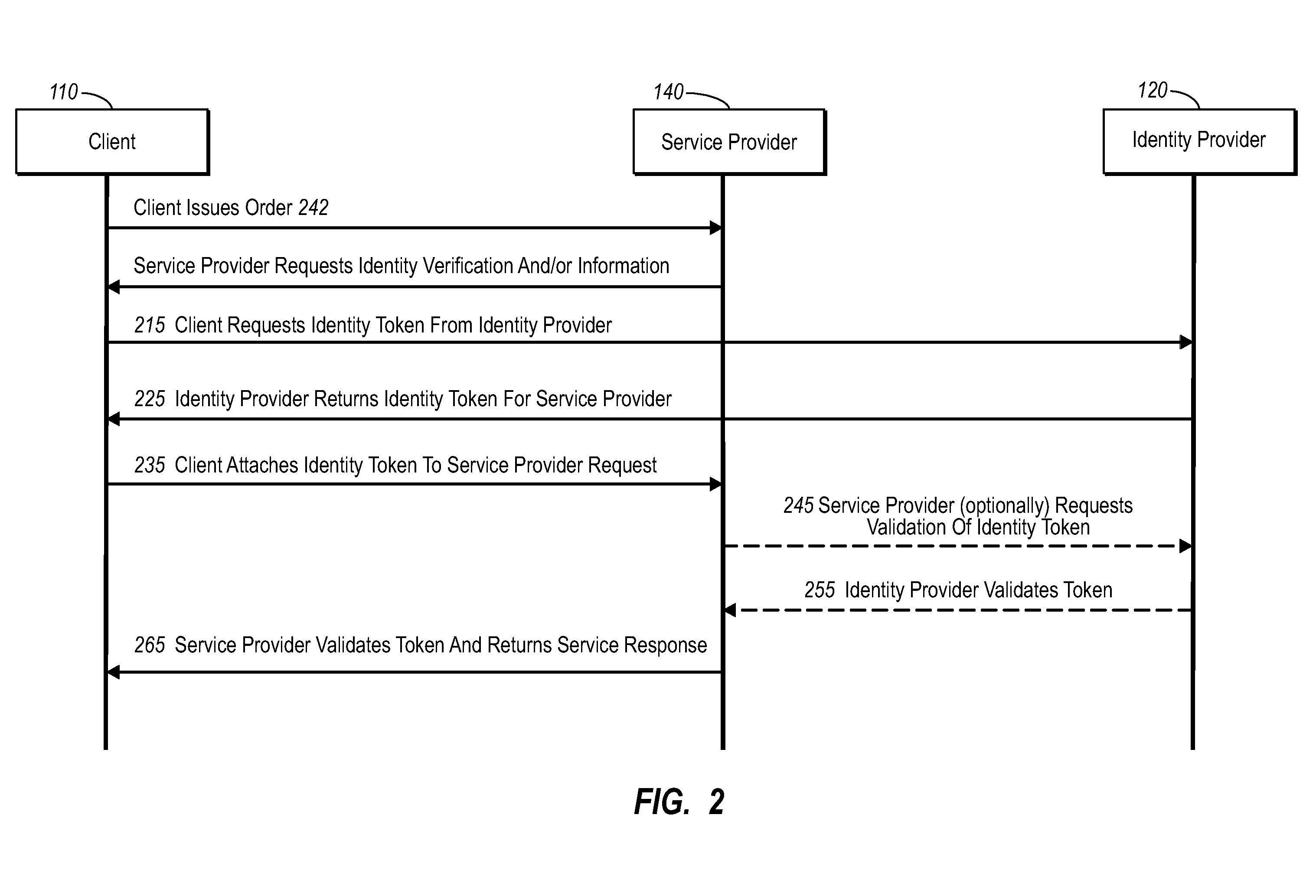
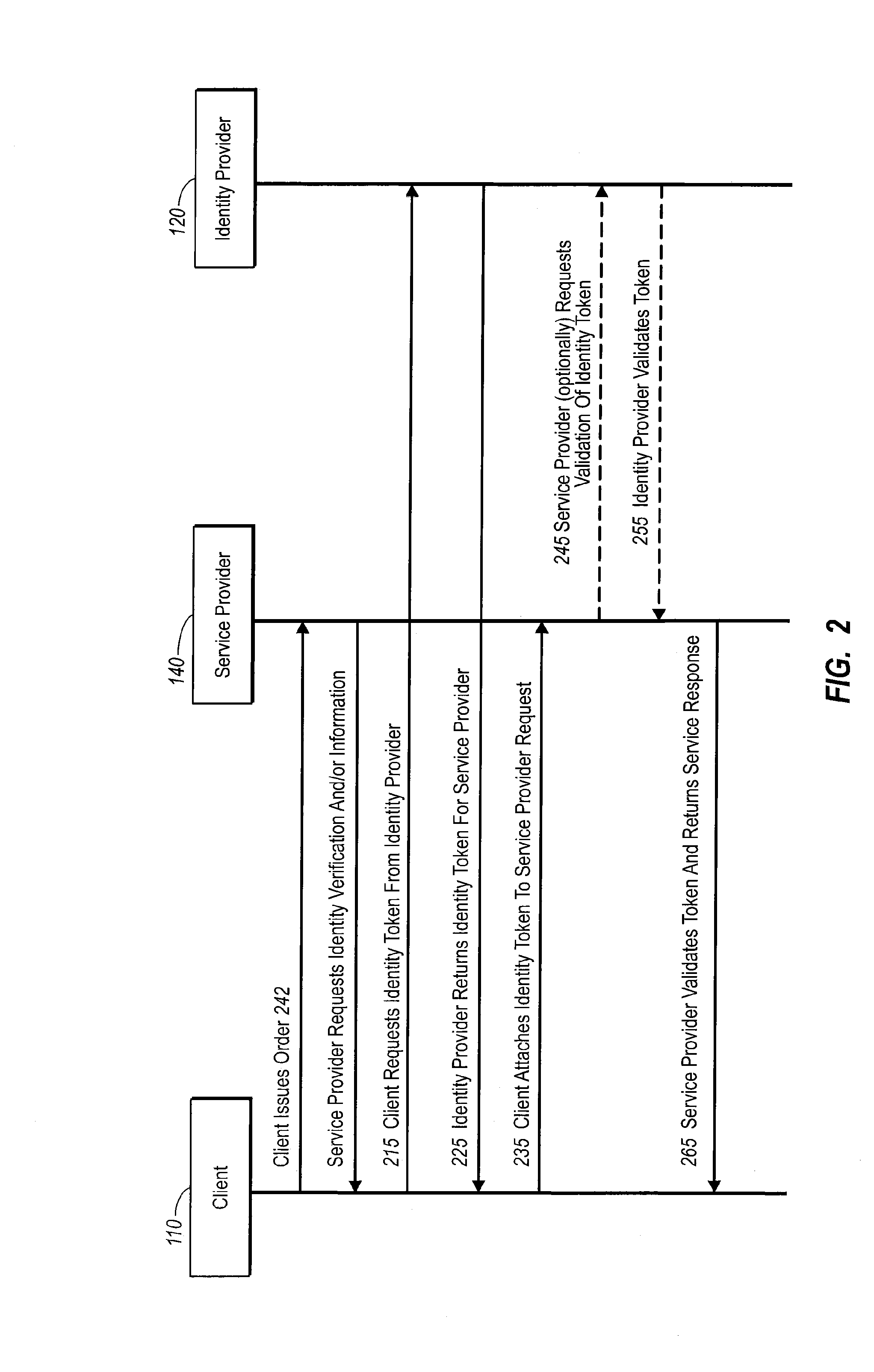
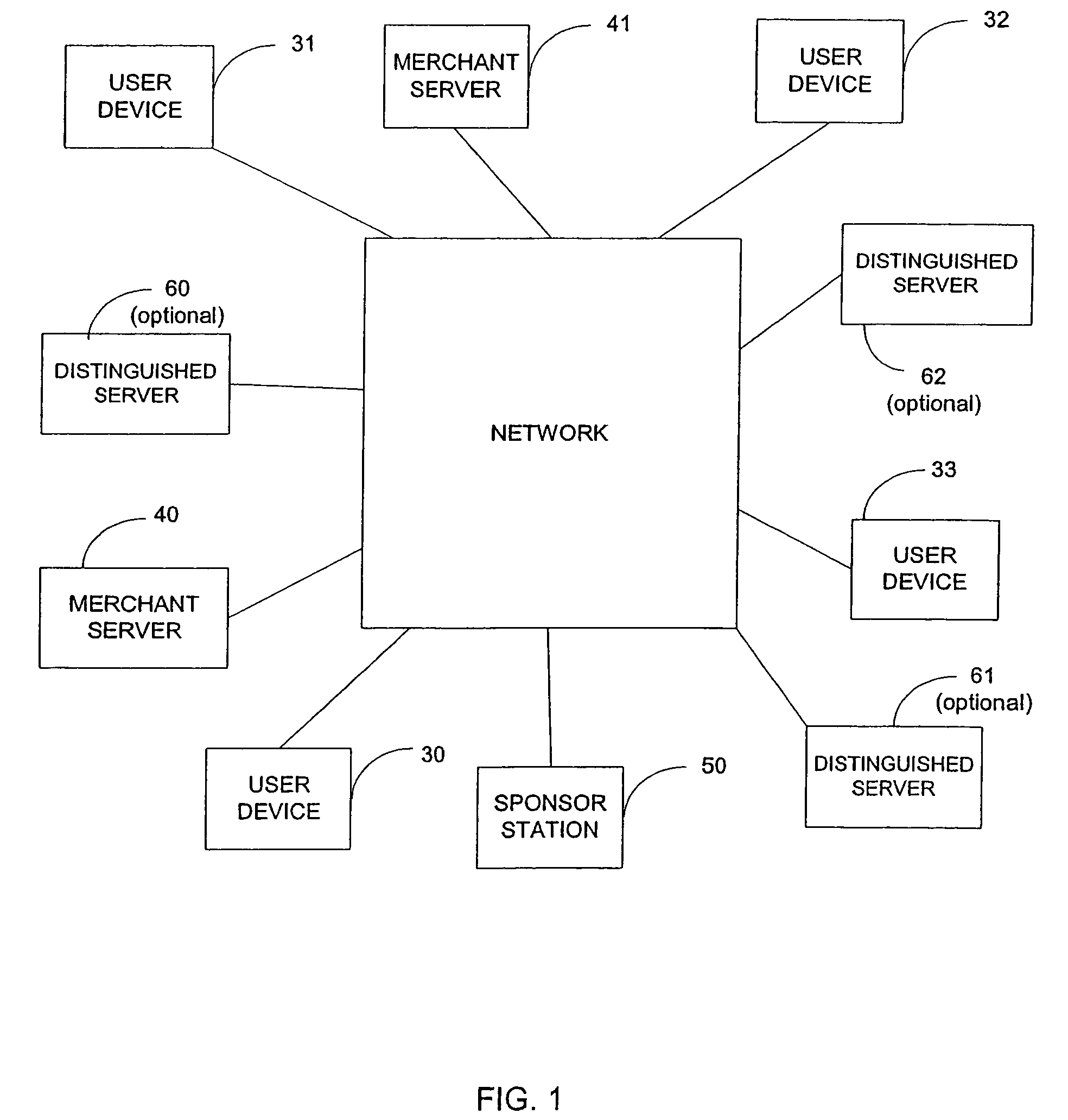
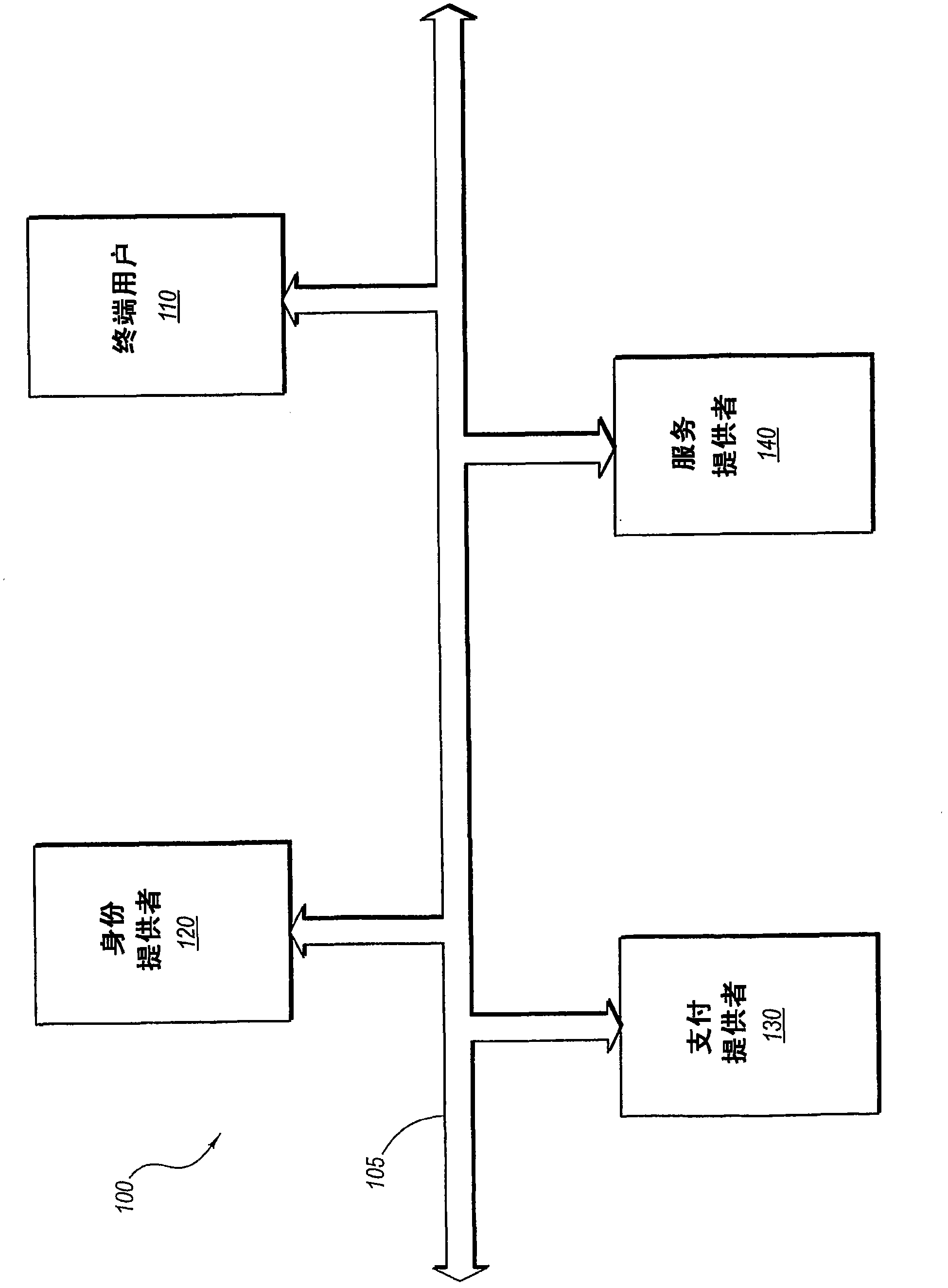
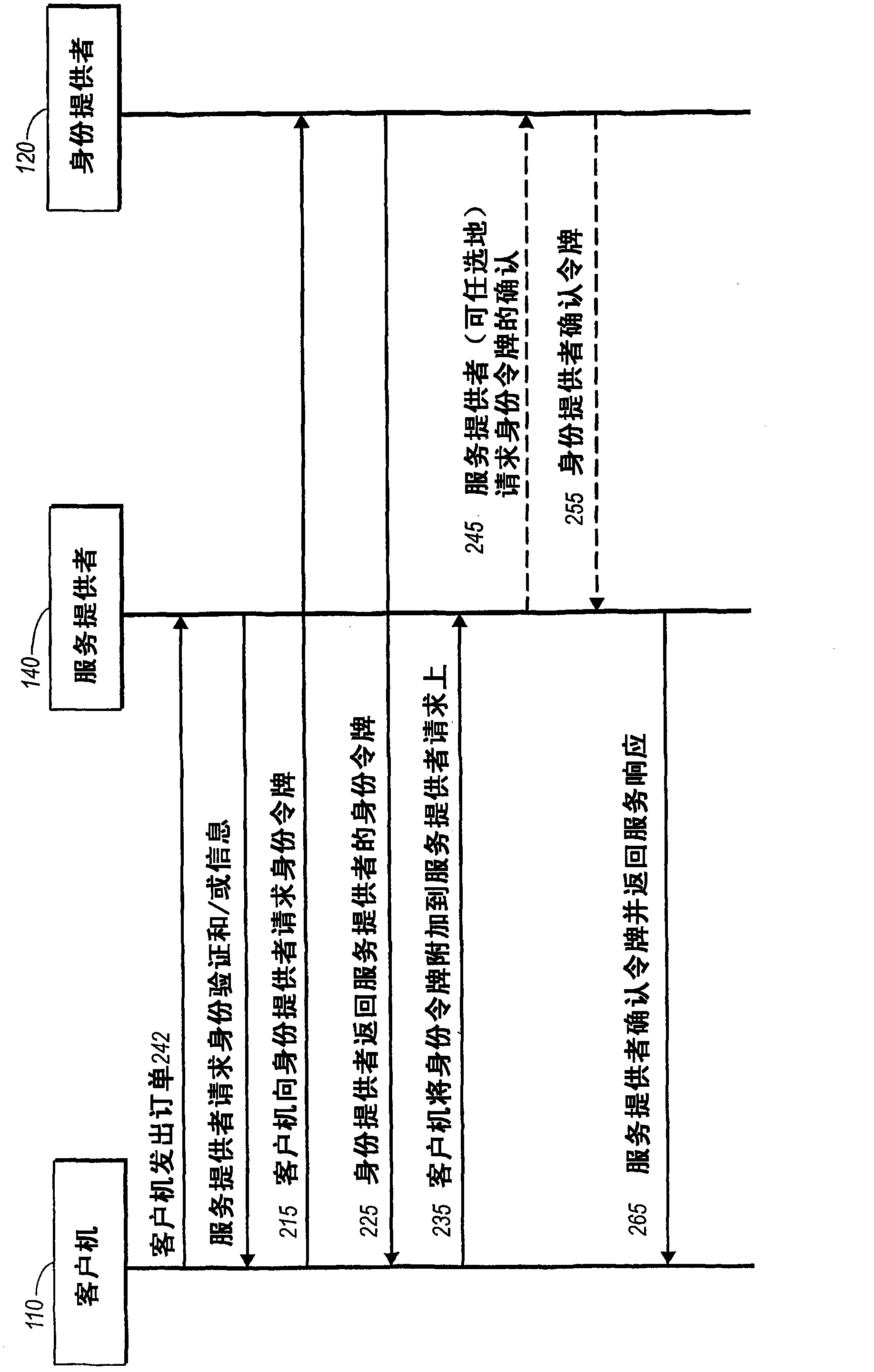
InactiveUS20060235795A1Reduce the burden onSimpler and more secure online commercial transactions frameworkFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPaymentSecure communication
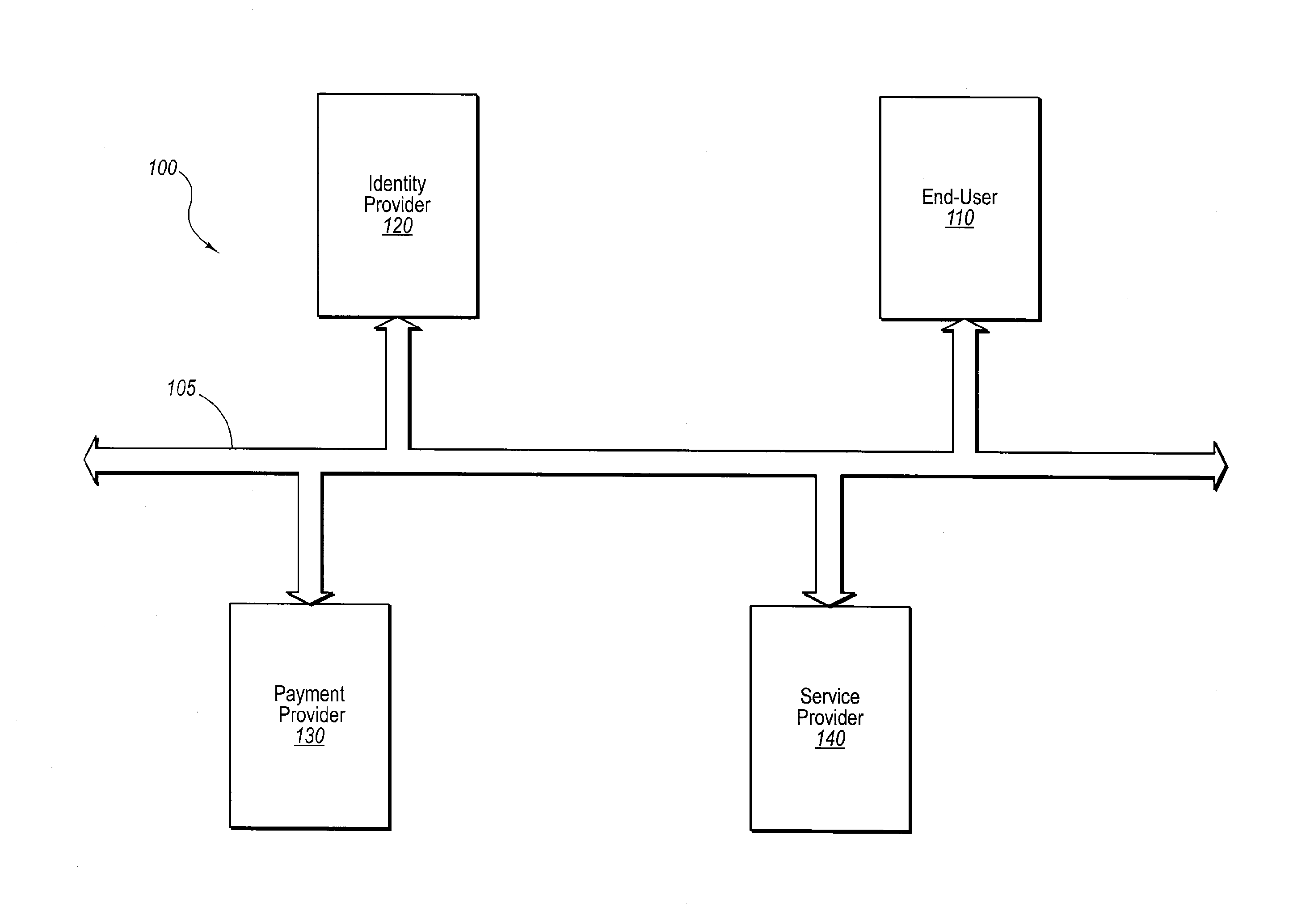
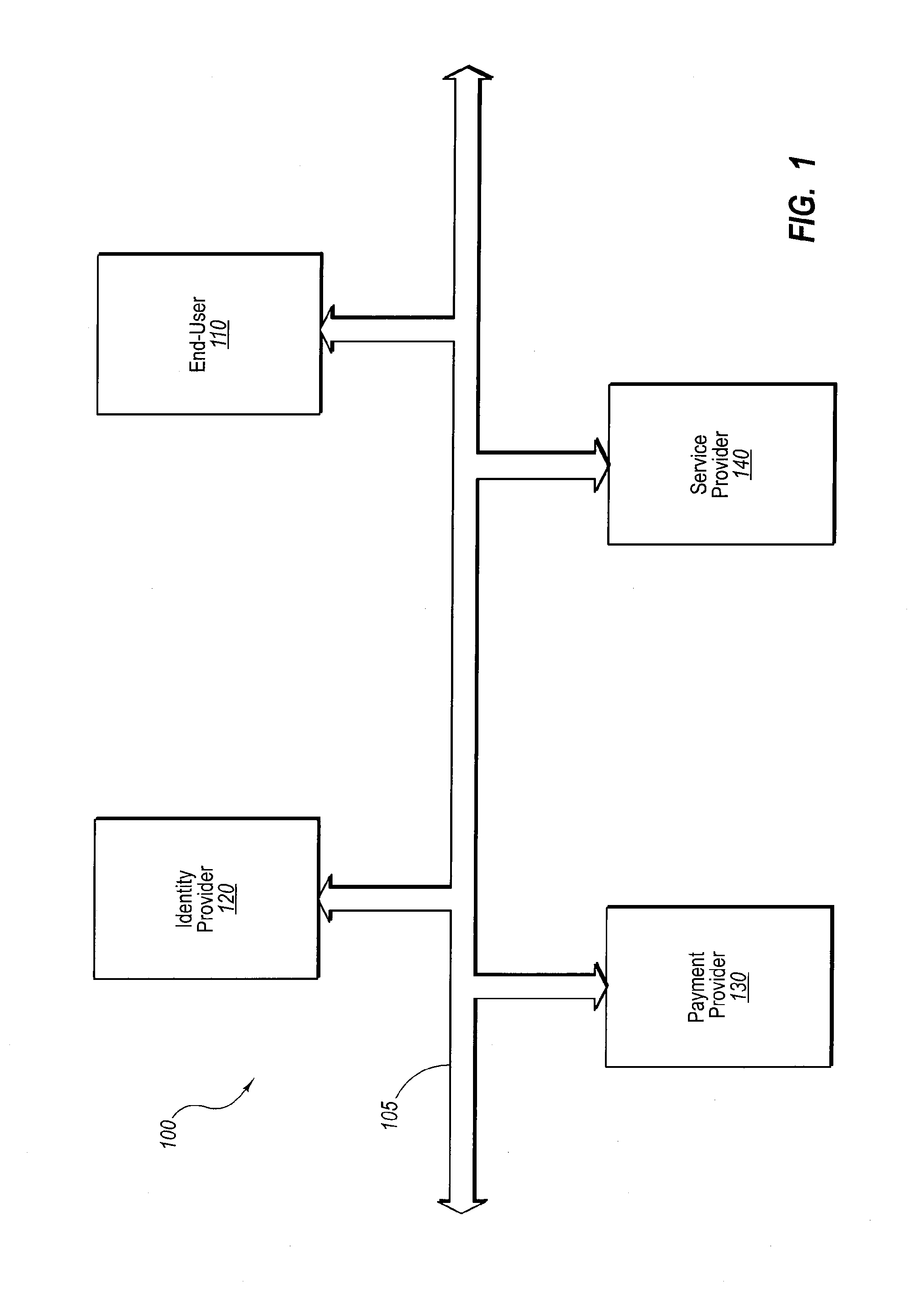
Current embodiments provide for authorization and payment of an online commercial transaction between a purchaser and a merchant including verification of an identity of the purchaser and verification of an ability of the purchaser to pay for the transaction, where the identity provider and the payment provider are often different network entities. Other embodiments also provide for protocols, computing systems, and other mechanisms that allow for identity and payment authentication using a mobile module, which establishes single or multilevel security over an untrusted network (e.g., the Internet). Still other embodiments also provide for a three-way secure communication between a merchant, consumer, and payment provider such that sensitive account information is opaque to the merchant, yet the merchant is sufficiently confident of the consumer's ability to pay for requested purchases. In yet another embodiment, electronic billing information is used for authorization, auditing, payment federation, and other purposes.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
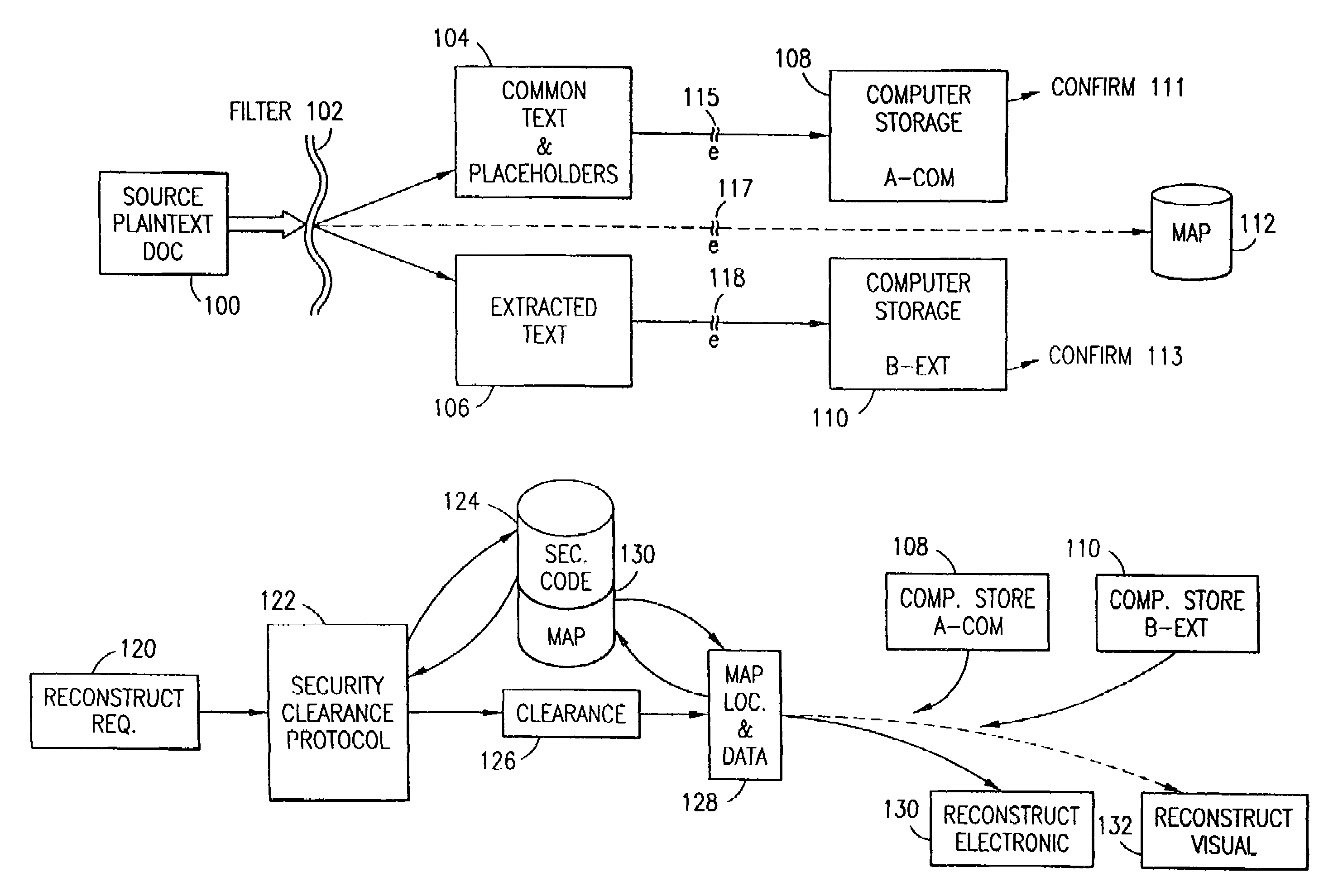
Data security system and method associated with data mining
ActiveUS7322047B2Ease overhead performanceHigh overhead performancePeptide/protein ingredientsMultiple keys/algorithms usagePlaintextInternet privacy
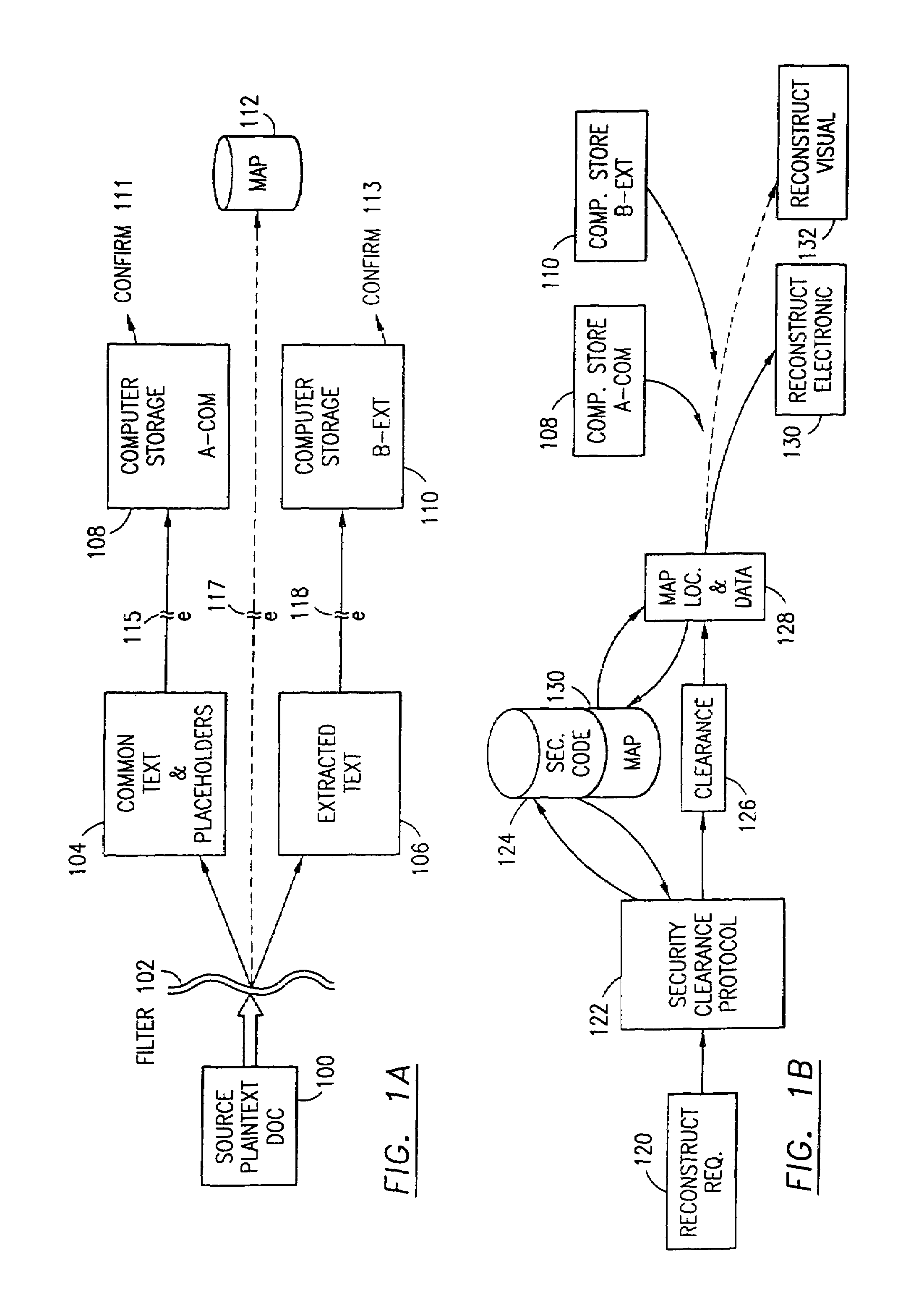
The data security method, system and associated data mining enables multiple users, each having a respective security clearance level to access security sensitive words, data objects, characters or icons. The method extracts security sensitive words, data objects, characters or icons from plaintext or other source documents to obtain (a) subsets of extracted data and (b) remainder data. The extracted data is, in one embodiment, stored in a multilevel security system (MLS) which separates extract data of different security levels with MLS guards. Some or all of the original data is reconstructed via one or more of the subsets of extracted data and remainder data only in the presence of a predetermined security level. In this manner, an inquiring party, with the proper security clearance, can data mine the data in the MLS secured storage.
Owner:DIGITAL DOORS
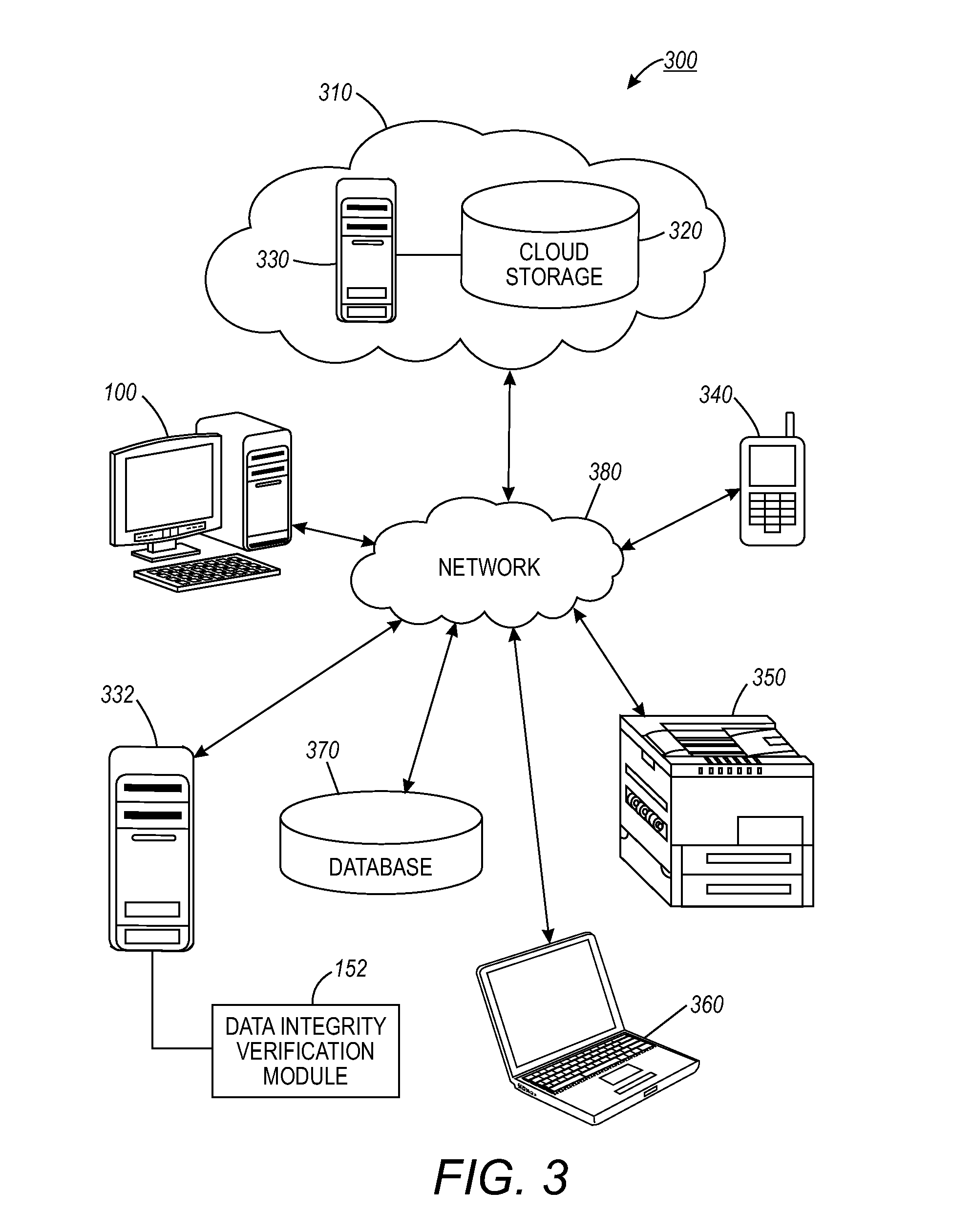
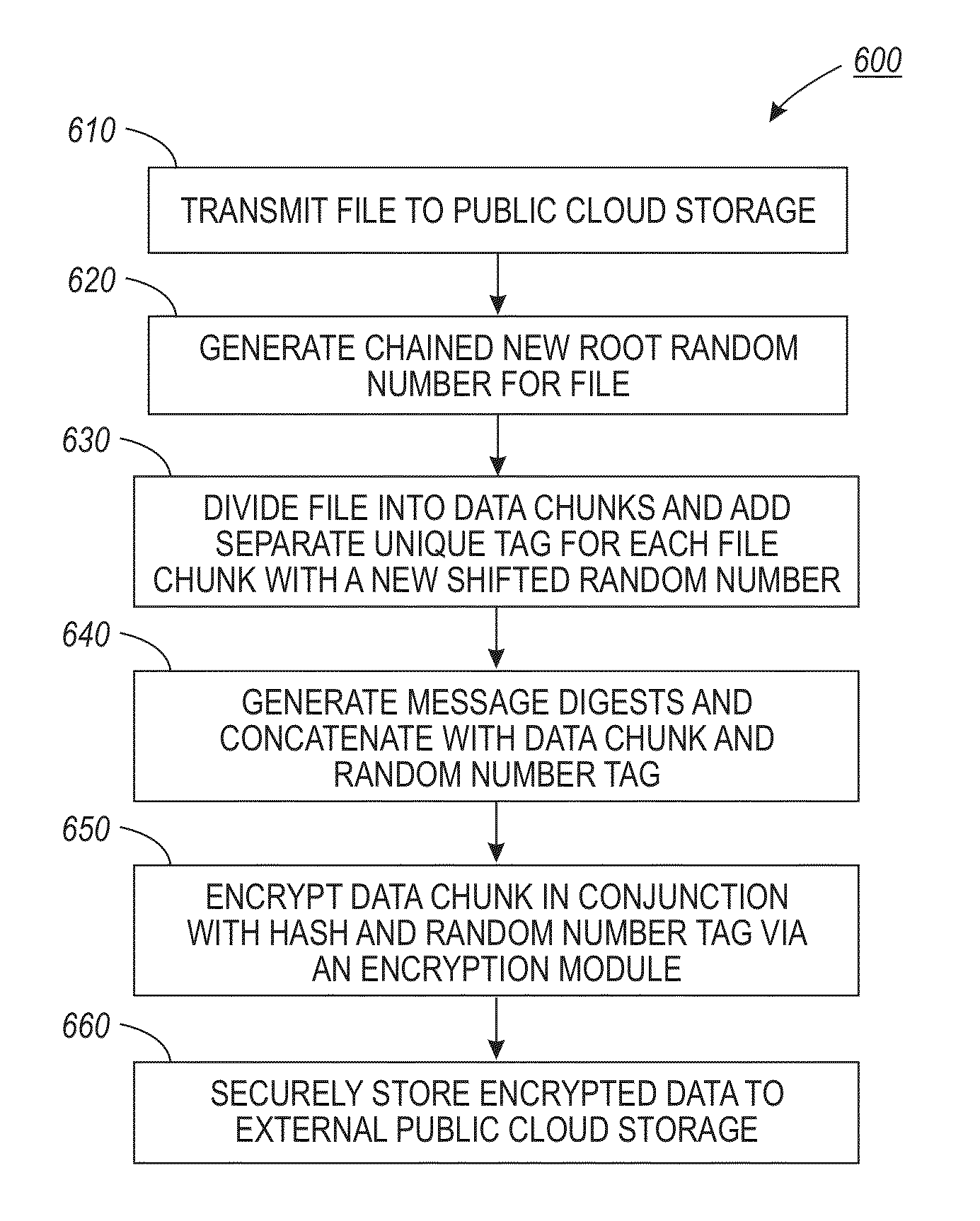
Random number based data integrity verification method and system for distributed cloud storage
InactiveUS20110246433A1Less computing powerSimple hardwareDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsHash functionData integrity
A data integrity verification method and system based on a root random number to ensure secure distributed data storage on a public cloud. A new root random number can be generated in response to receiving a file for storage to the public cloud. A unique random number tag for each data chunk associated with the file can be calculated via a shift operation and the tag can be added to the data chunk. A hash function (message digests) can be then generated and concatenated with the data chunk and the random number tag. The data chunk in conjunction with the hash and the random number tag can be encrypted by an encryption module and stored to the public cloud in order to provide multiple levels of security with respect to the distributed public cloud storage. Upon file retrieval, the encryption module decrypts all data chunks and recalculates the hash in order to verify the data integrity of the file.
Owner:XEROX CORP
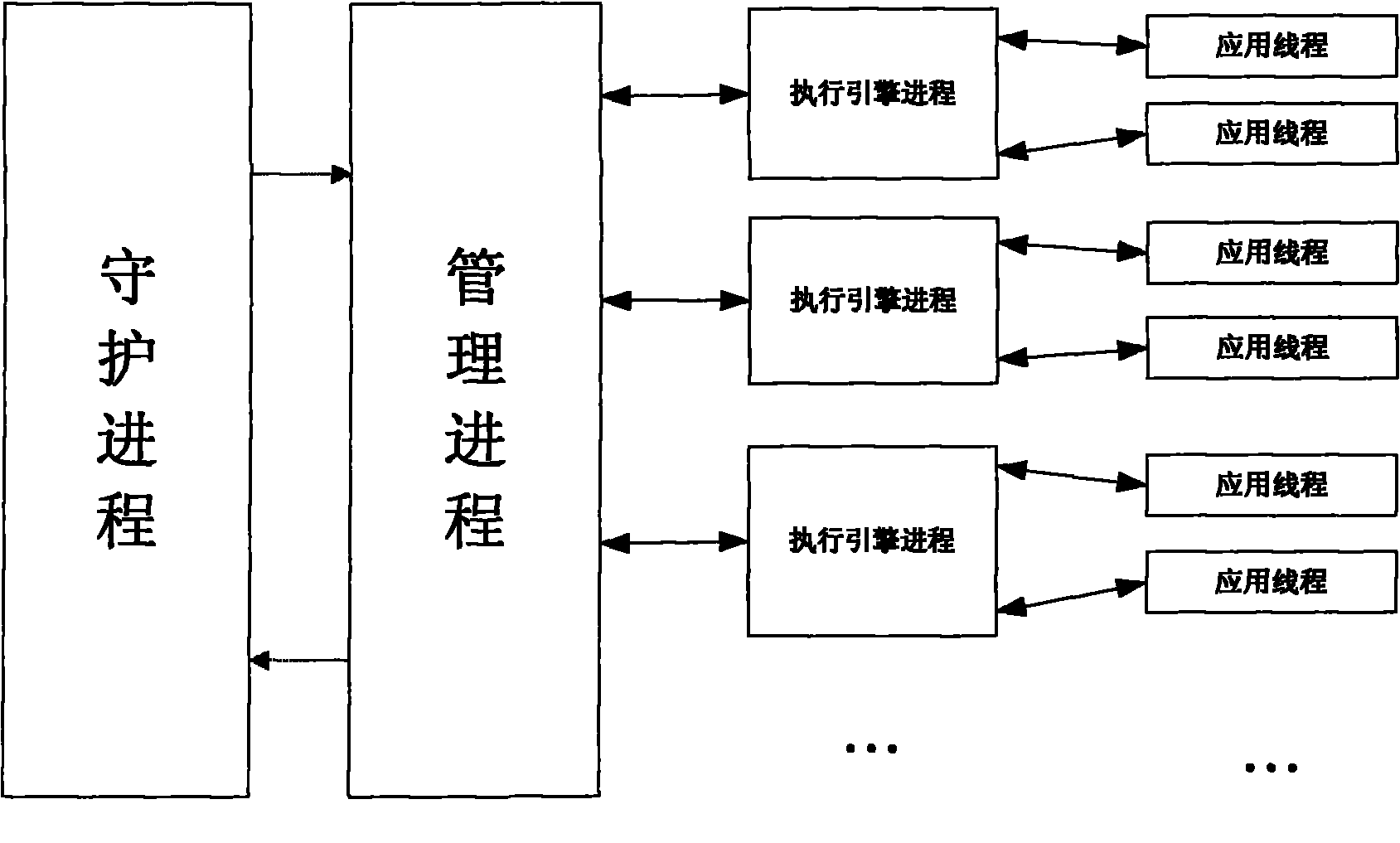
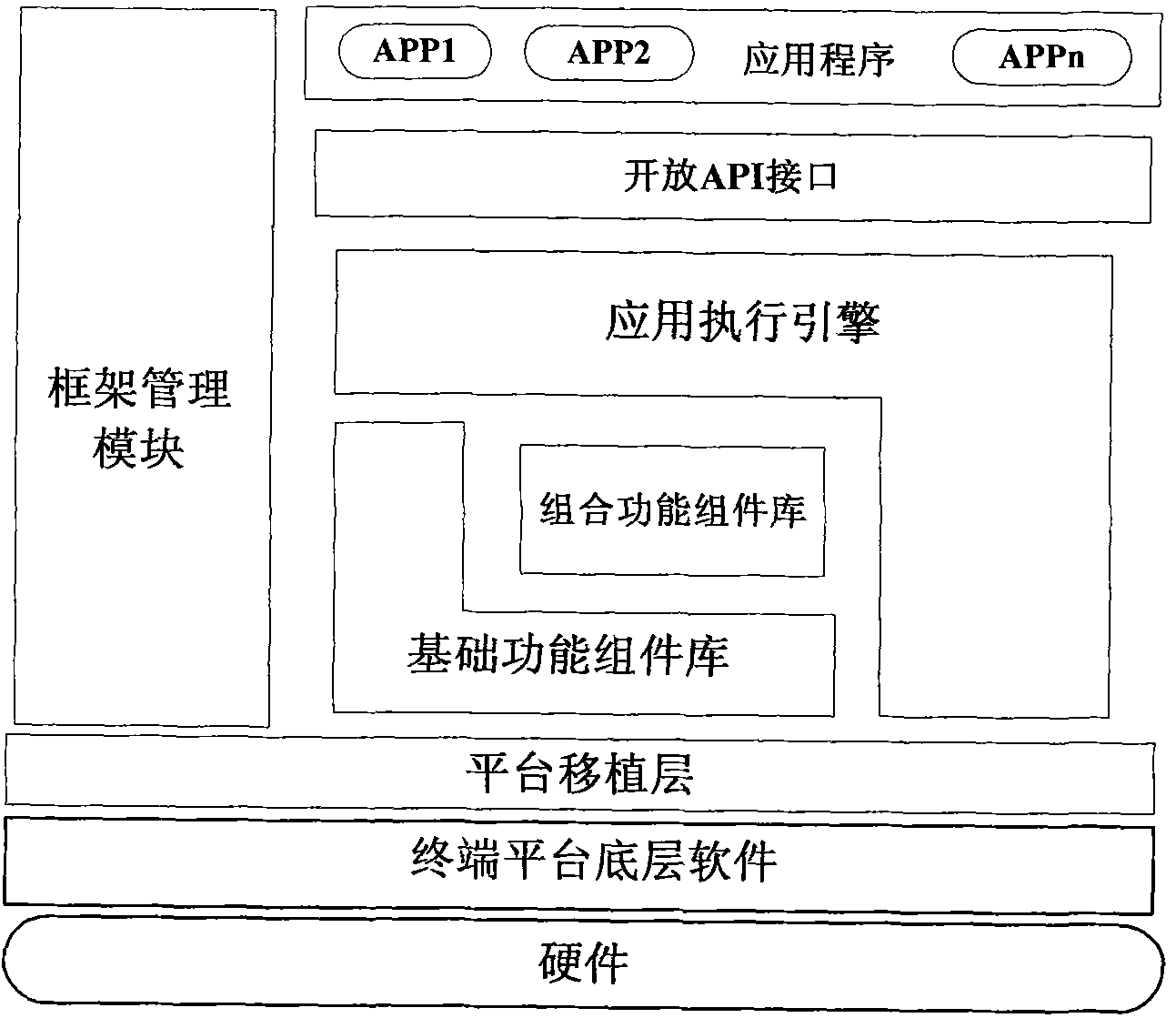
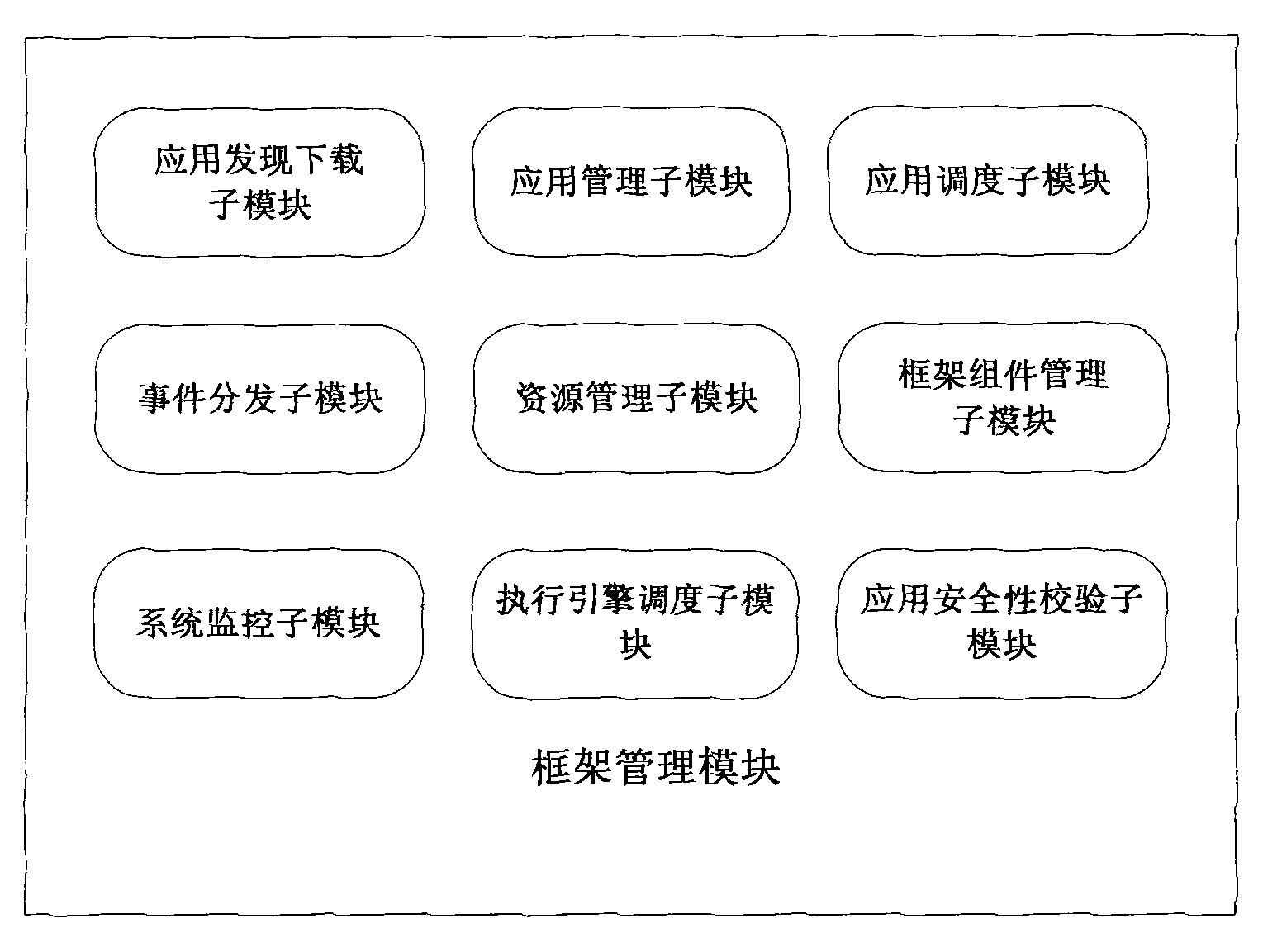
Embedded system supporting dynamic loading operation of application programs
InactiveCN101833465ARich developmentPromote rapid developmentProgram loading/initiatingThree levelUser needs
The invention relates to an embedded system supporting dynamic loading operation of application programs. The system comprises a frame management module, an application execution engine module, a basic functional unit library module and an API module, wherein the API module, the application execution engine module and the basic functional unit library module are orderly arranged from top to bottom; the frame management module is the core management unit and used for implementing the unified management and dispatching on the terminal software and hardware resources; the frame management moduleis used for providing a system resource acquisition and release interface for the loaded application program, thereby implementing the unified management and dispatching on the system software and hardware resources; the basic functional unit library module is used for being called by other units or application execution engine; and the basic functional unit is distributed onto the terminal accessible server, so that the frame management module can remotely load the basic functional unit according to user needs when the terminal operates. The embedded system of the invention also comprises a multilevel security management module which comprises process management submodules at three levels.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
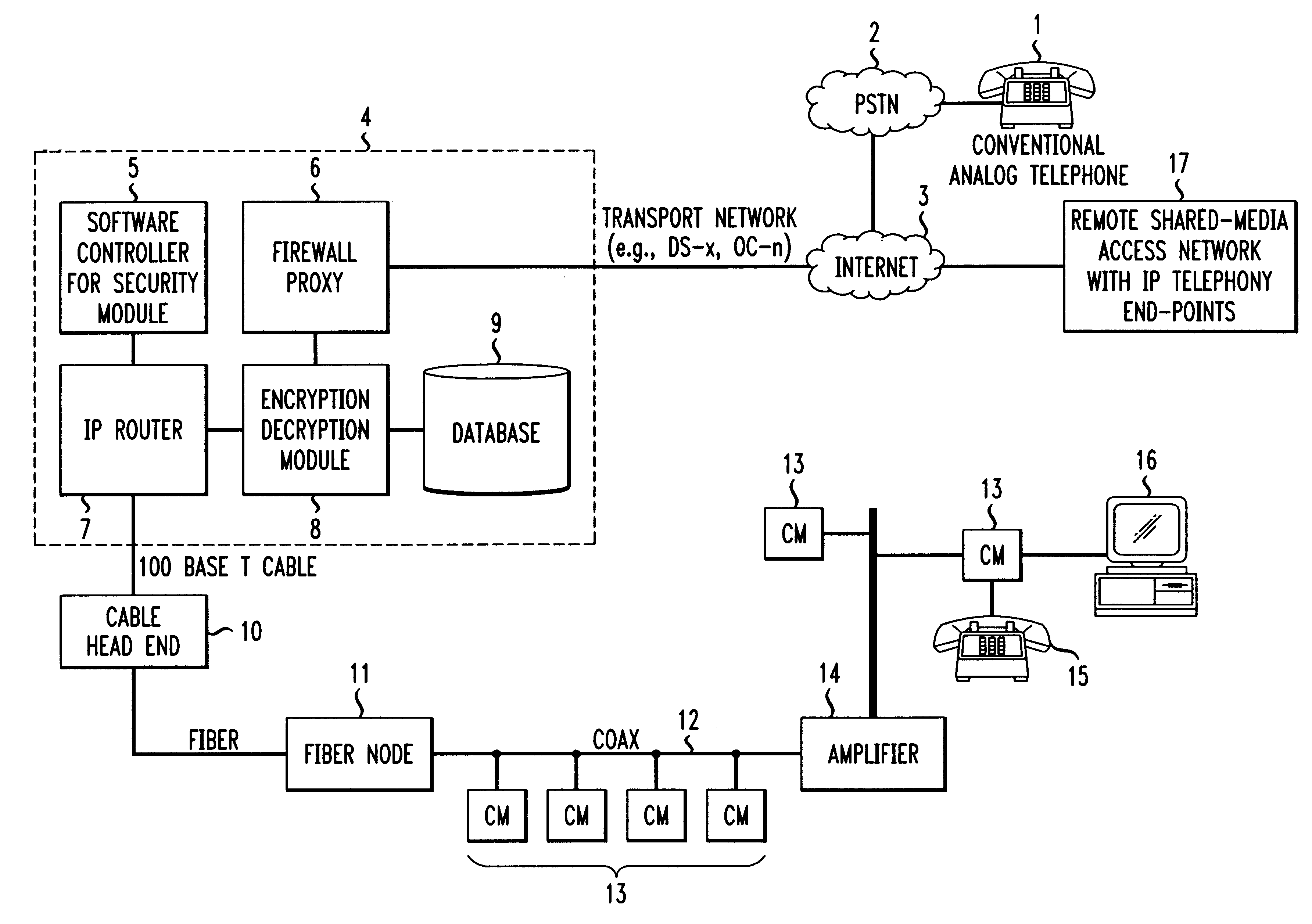
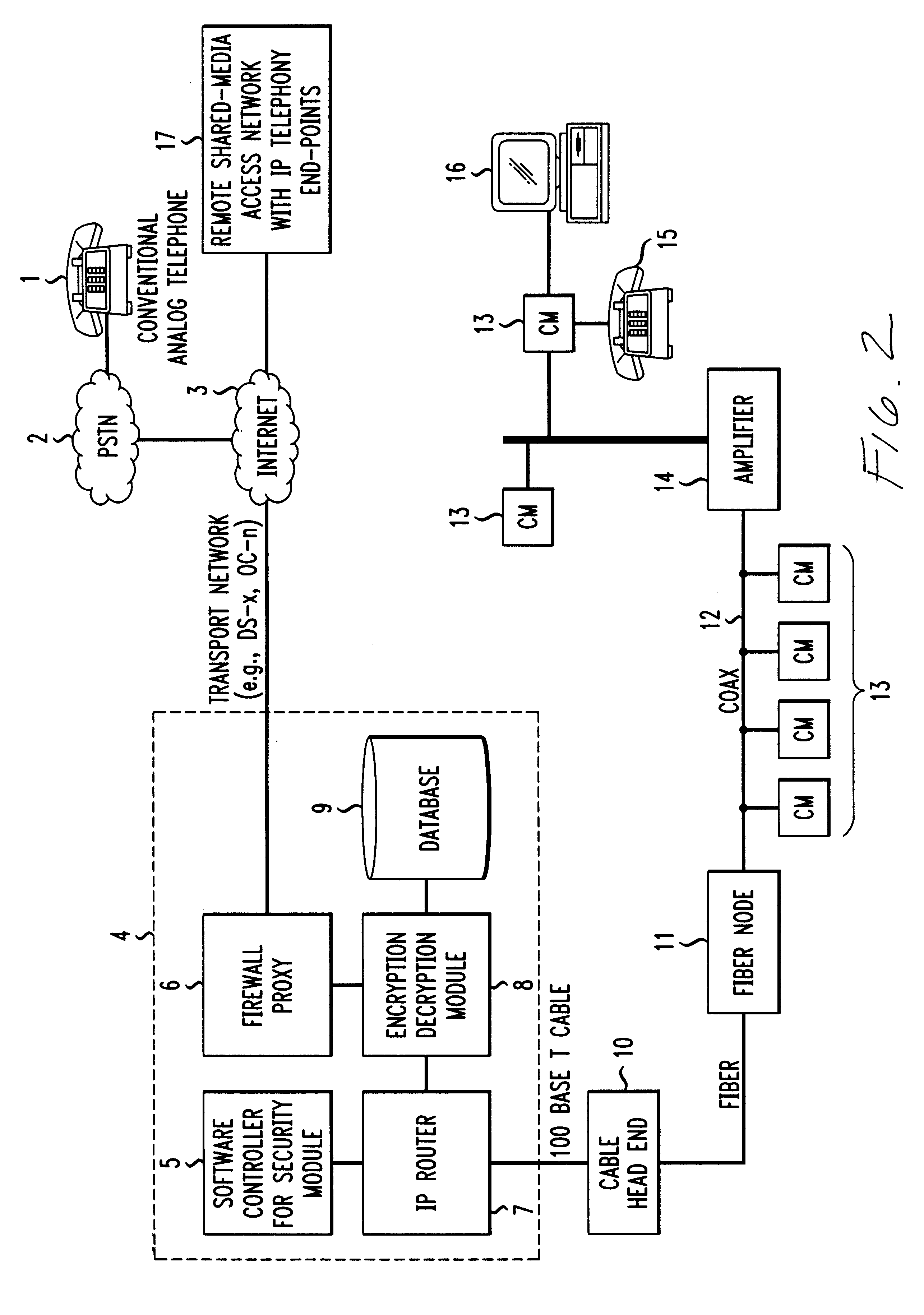
Billing method for customers having IP telephony service with multiple levels of security
InactiveUS6363150B1Justify costEnsuring privacyUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringHigh rateSecurity level
A method for initiating a security and billing feature request at the beginning or during an active telephone call. The telephone subscriber can select one of a plurality of security levels that may be required to ensure privacy during a call. Since each level of security is based on a different encryption and authentication algorithm, the levels of security can be incrementally priced. Thus, selecting an algorithm which is deemed to be very secure can be billed to the subscriber at a higher rate than an algorithm that is deemed to be less secure.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
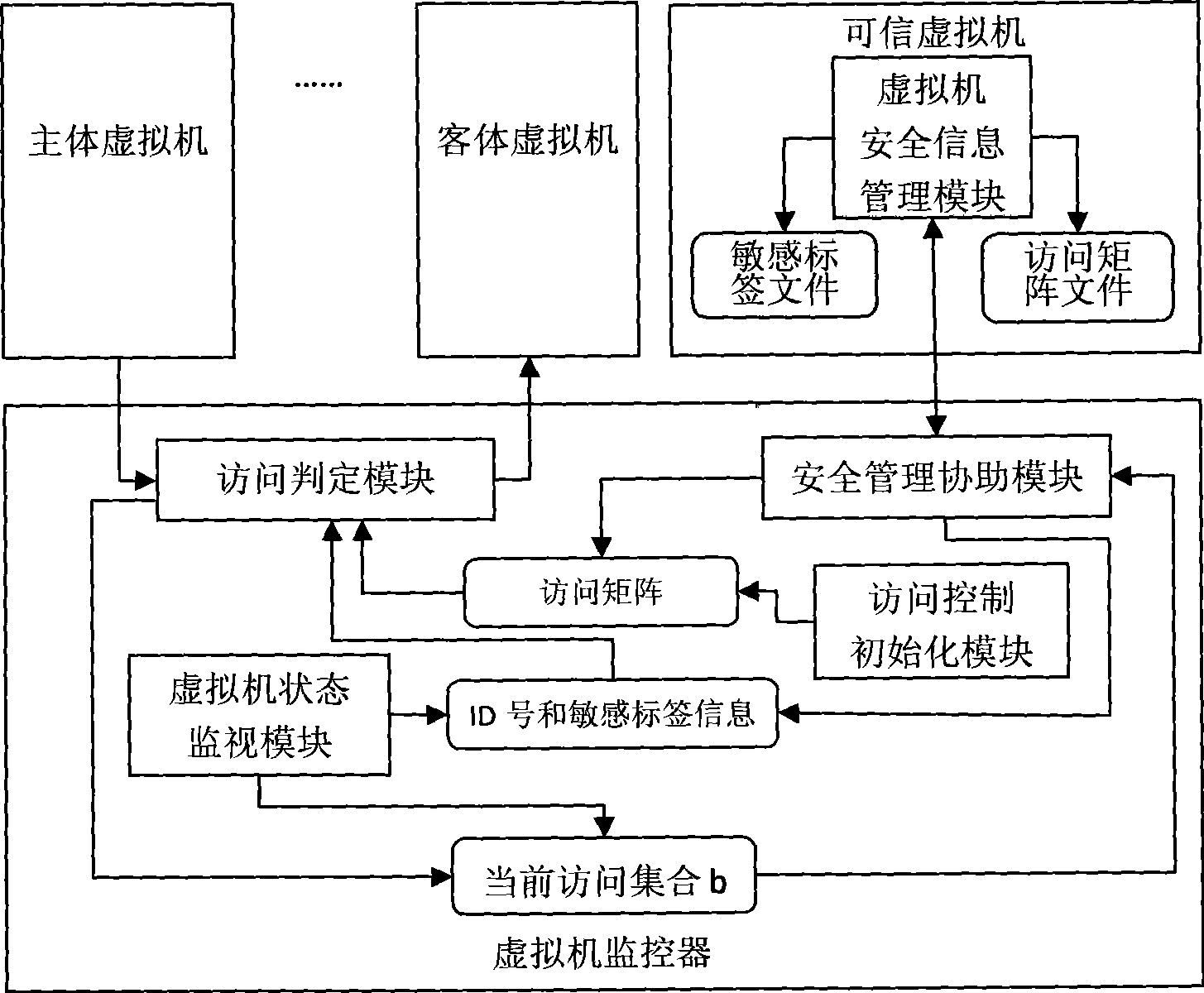
Forced access control method and apparatus in virtual environment
InactiveCN101452397AMeet security needsShare blockingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtualizationSecurity level
The invention relates to a forced access control method and a device applied to a virtual environment in the technical field of computer application. The method comprises: designating a virtual machine in a virtual environment as a credible virtual machine with security management authority, in which, the credible virtual machine uses security classification and security category as a sensitive label to identify the security level of a single virtual machine; establishing an access matrix and setting the access type set of each virtual machine to other virtual machines; and when a certain virtual machine main body gets access to a certain virtual machine object in a certain access type, judging whether the access is permitted according to the sensitive label of both the main body and the object and the access type set of the main body to the object in the access matrix. The device comprises an access control initializing module, a virtual machine state monitoring module, an access judgment module, a security management assisting module and a virtual machine security information management module in the credible virtual machine. The forced access control method and the device can effectively control communication and resource sharing between virtual machines in a virtual environment of multilevel security.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
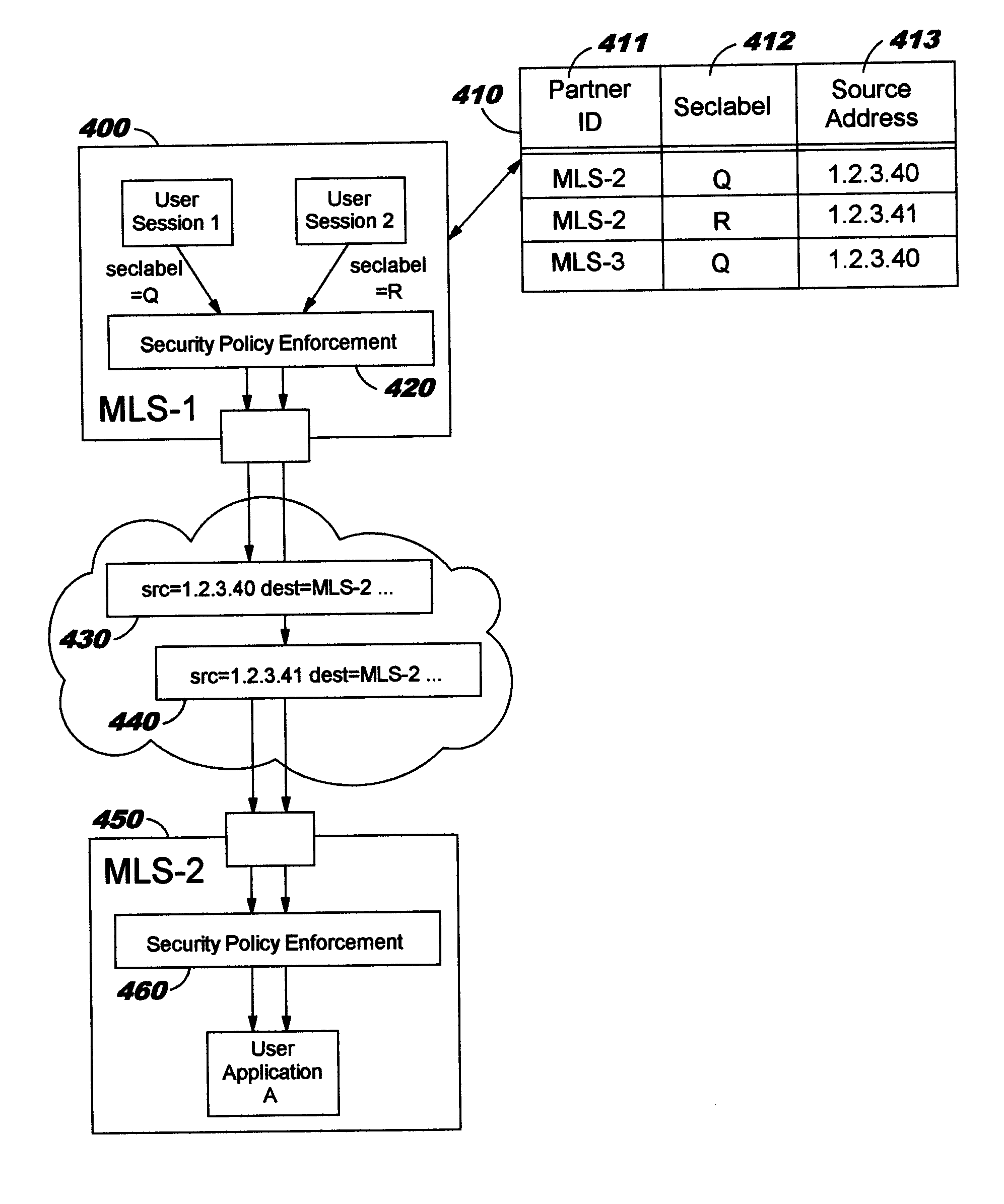
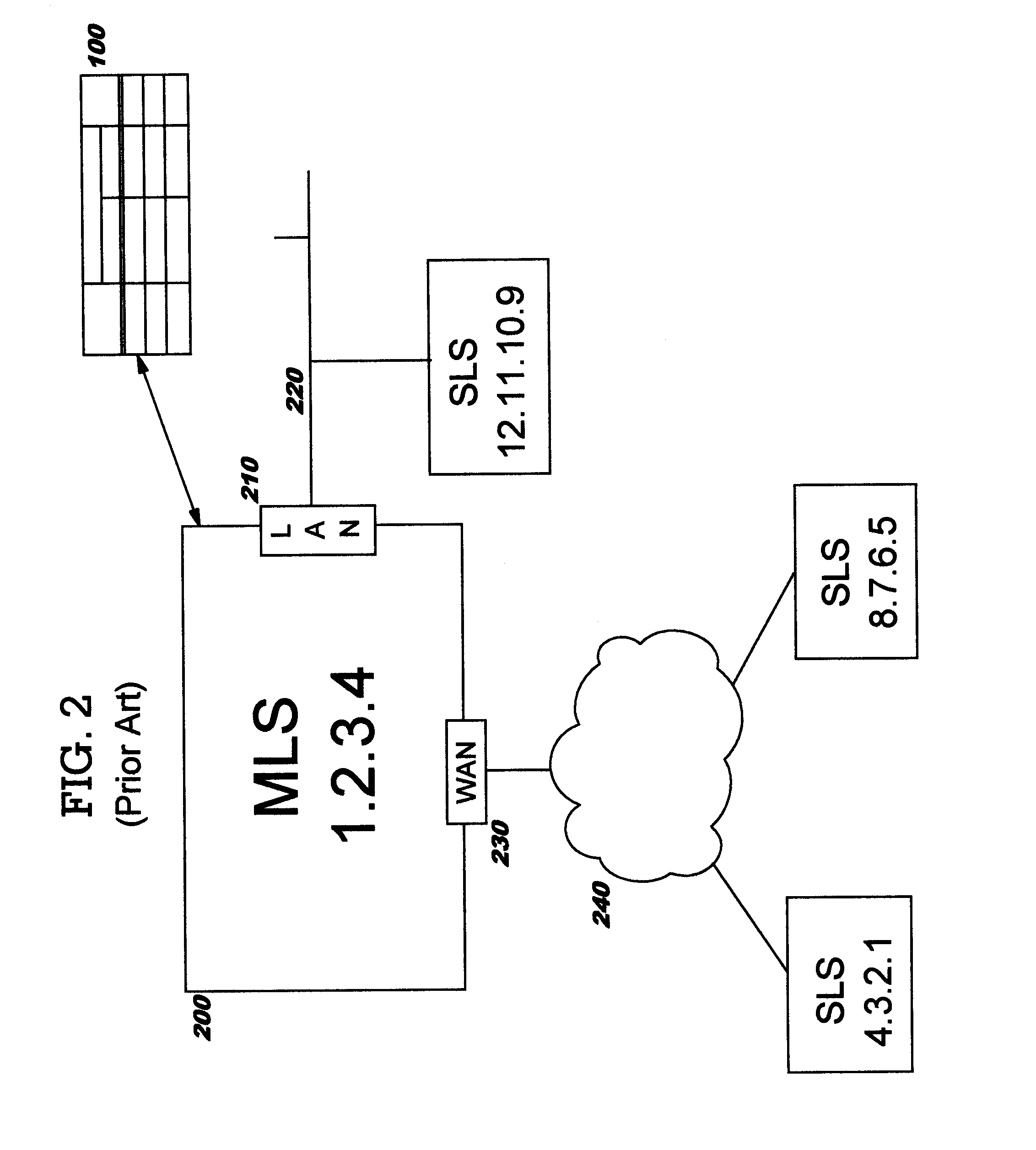
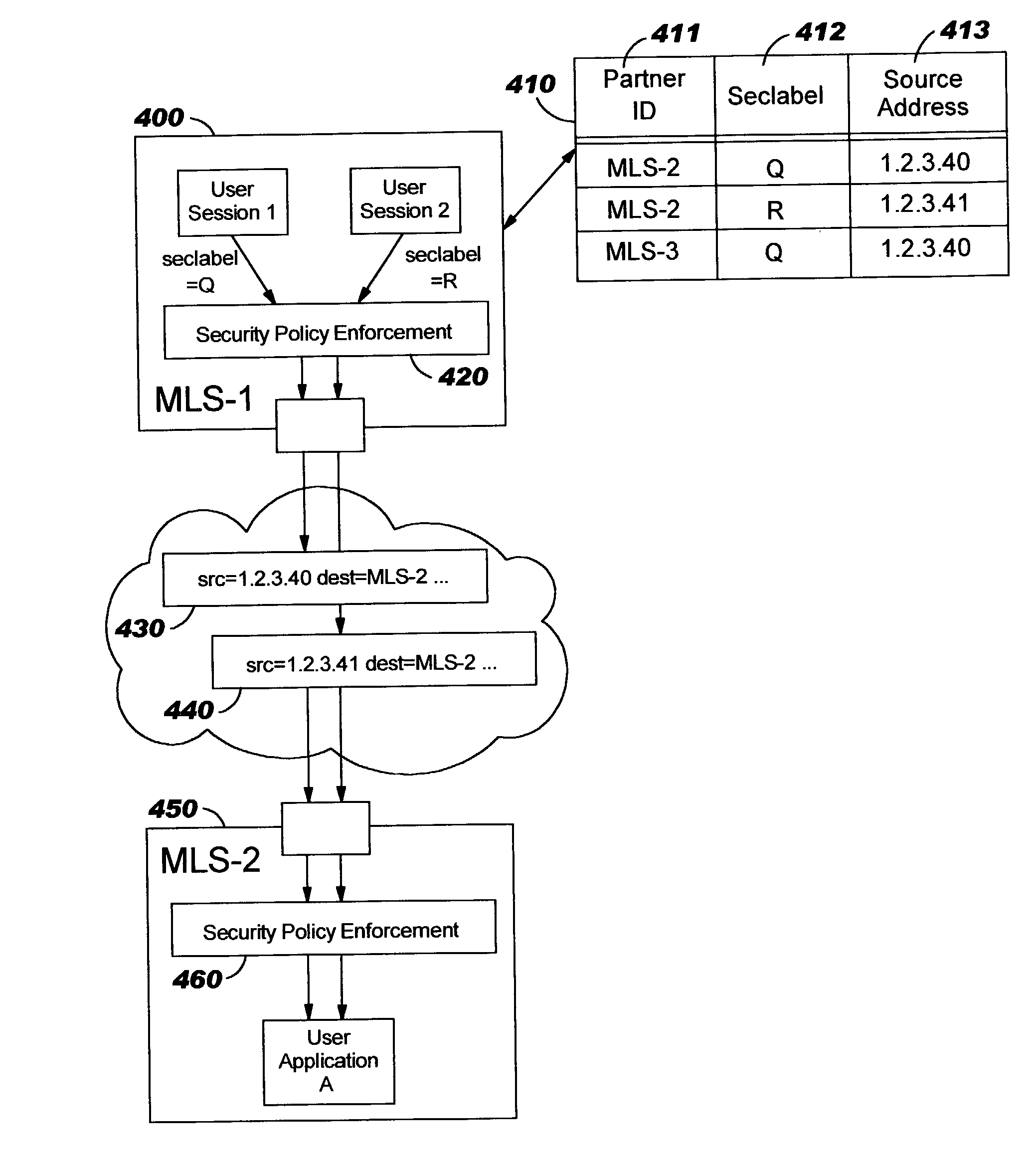
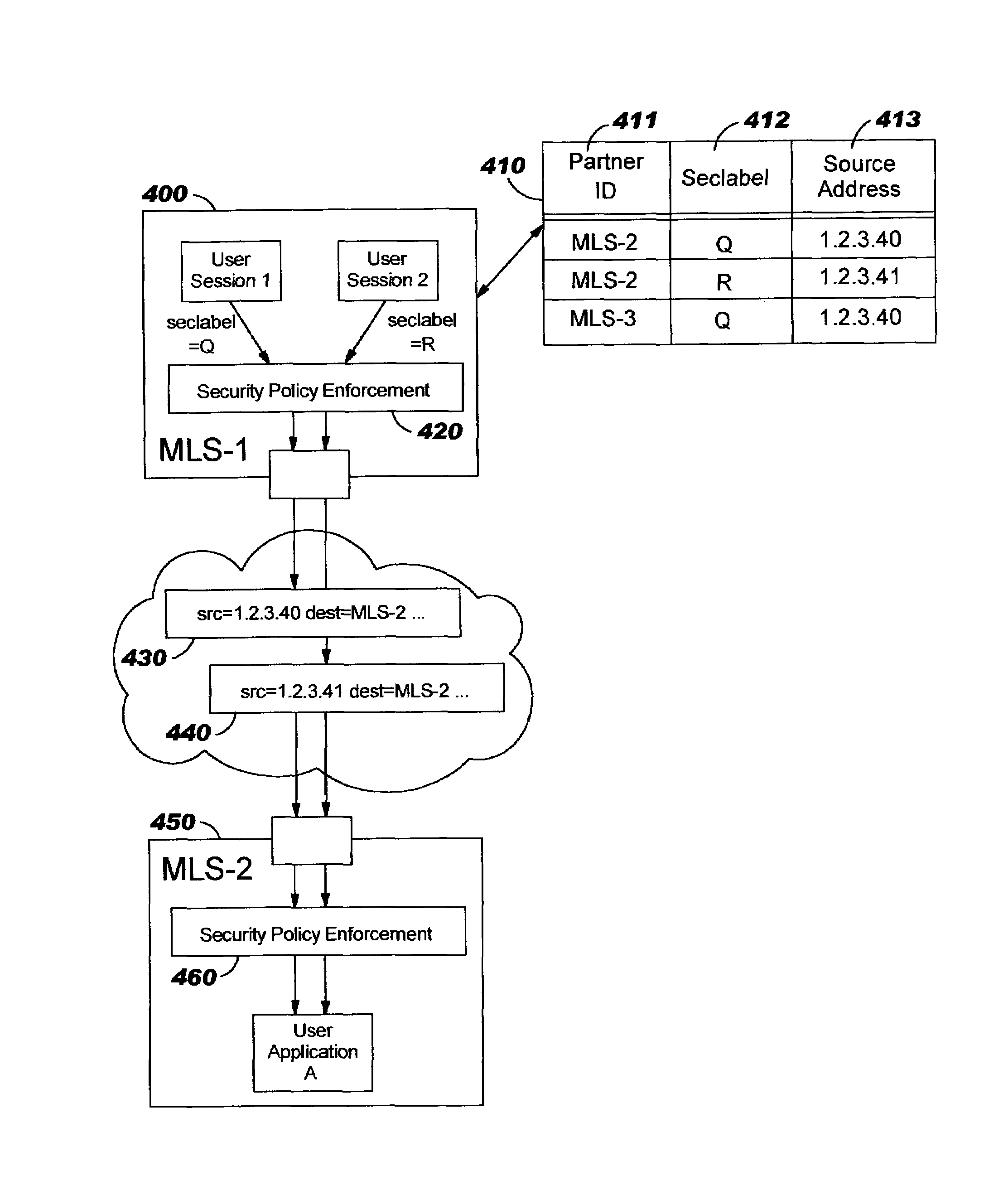
Multi-Level Security Systems
InactiveUS20070250921A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPath lengthSingle level
Techniques are disclosed for multi-level security (“MLS”) in computing systems. Communication between MLS systems in the prior art requires explicitly tagging each packet with its security classification. The packet tags comprise variable-length bit patterns inserted into packet headers. This results in a number of drawbacks, including increased path length and code complexity, as well as reduced interoperability. An MLS system according to the present invention simulates a cluster or collection of single-level security systems, and thereby avoids packet tagging. For each security classification used by an MLS system, a distinct source address is defined. This source address is used for outbound packets having that security classification, such that the packet's source address implicitly identifies the packet's security classification.
Owner:IBM CORP
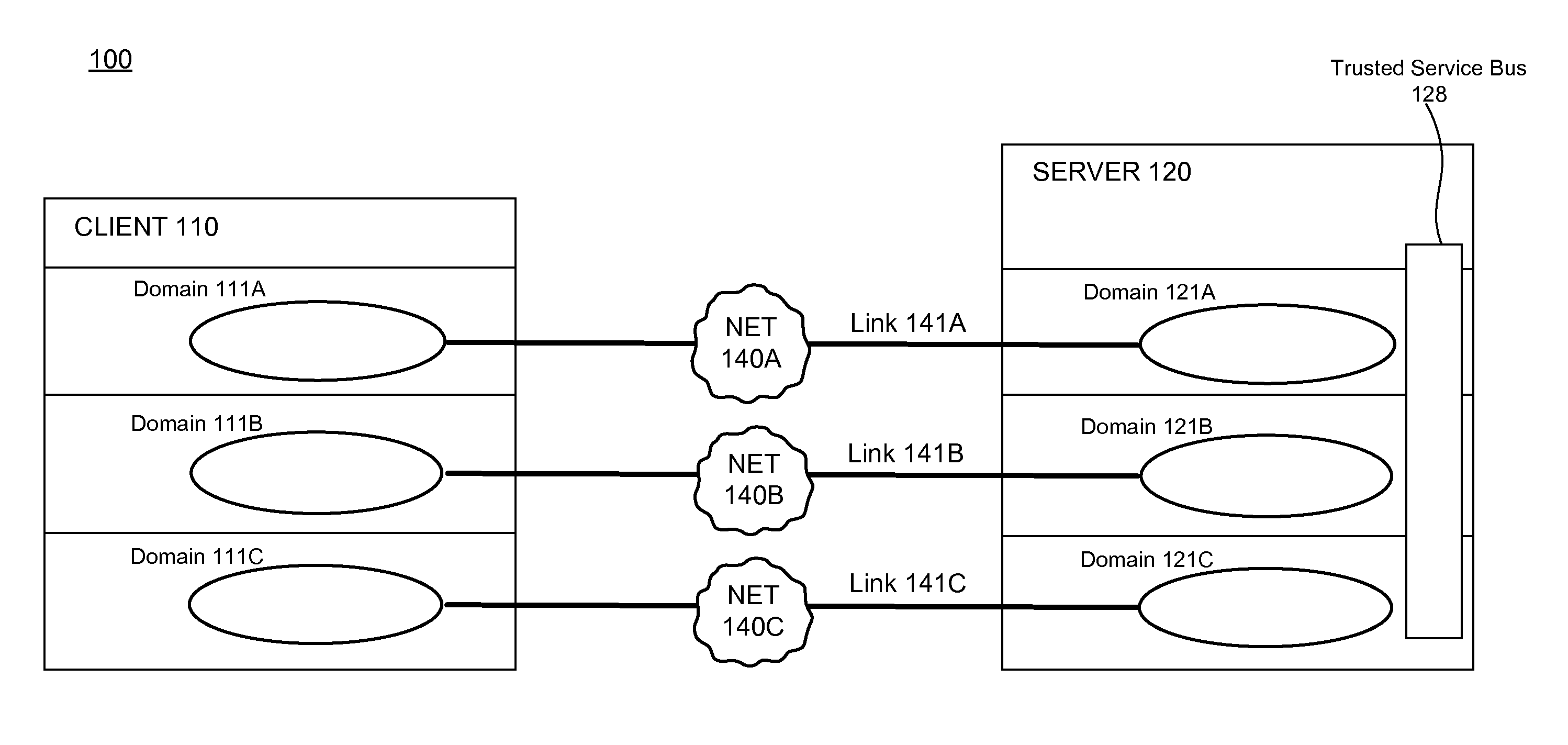
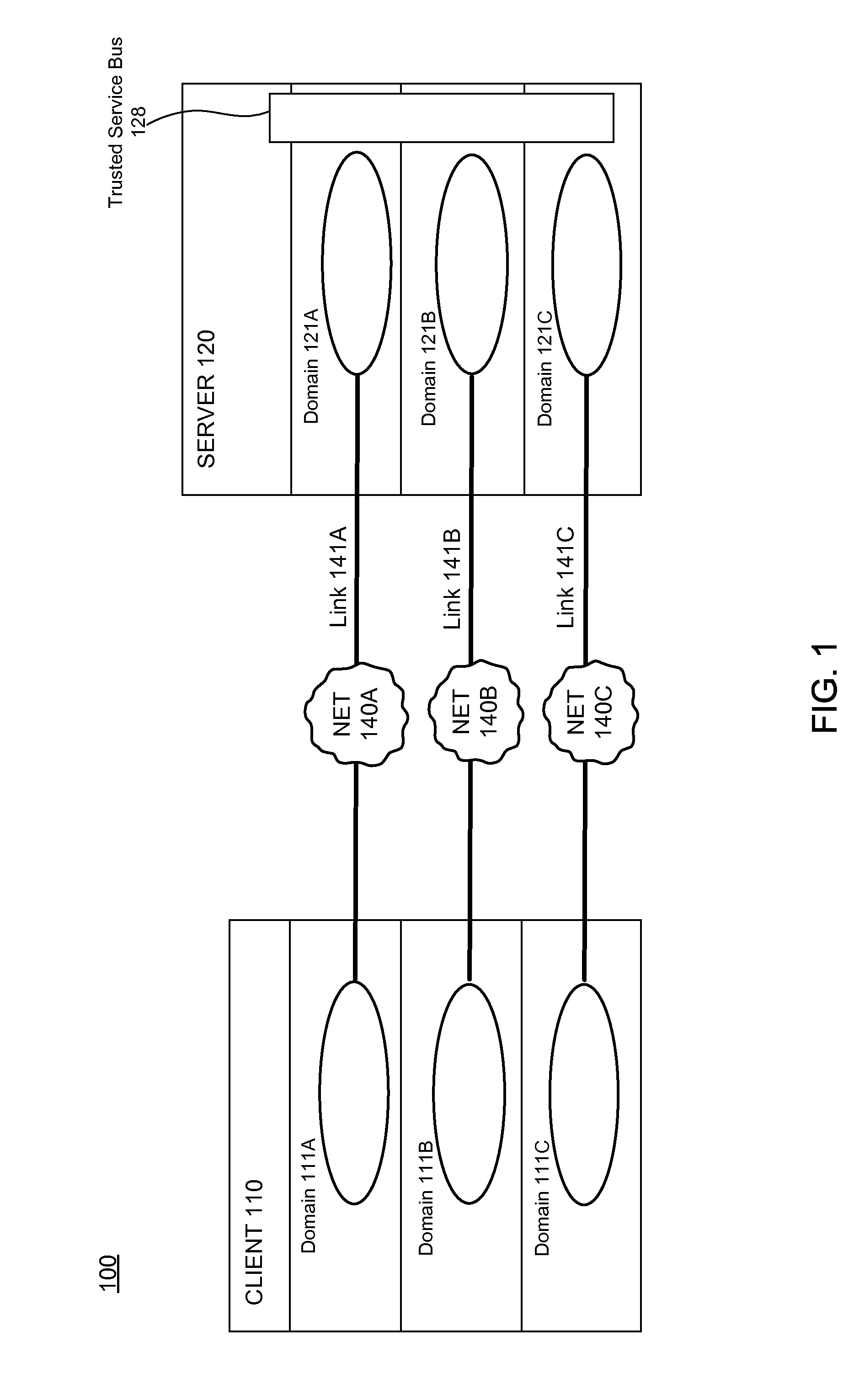
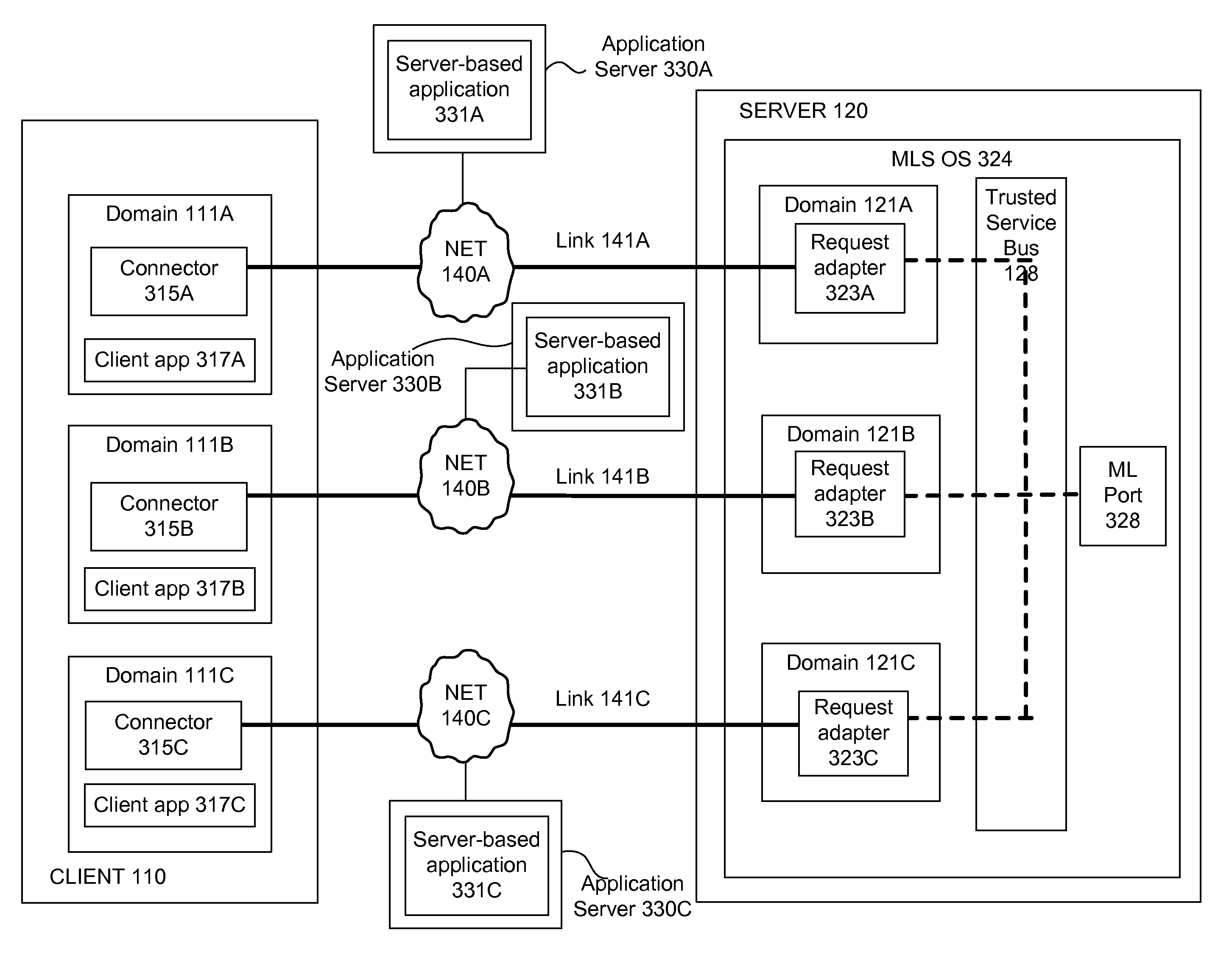
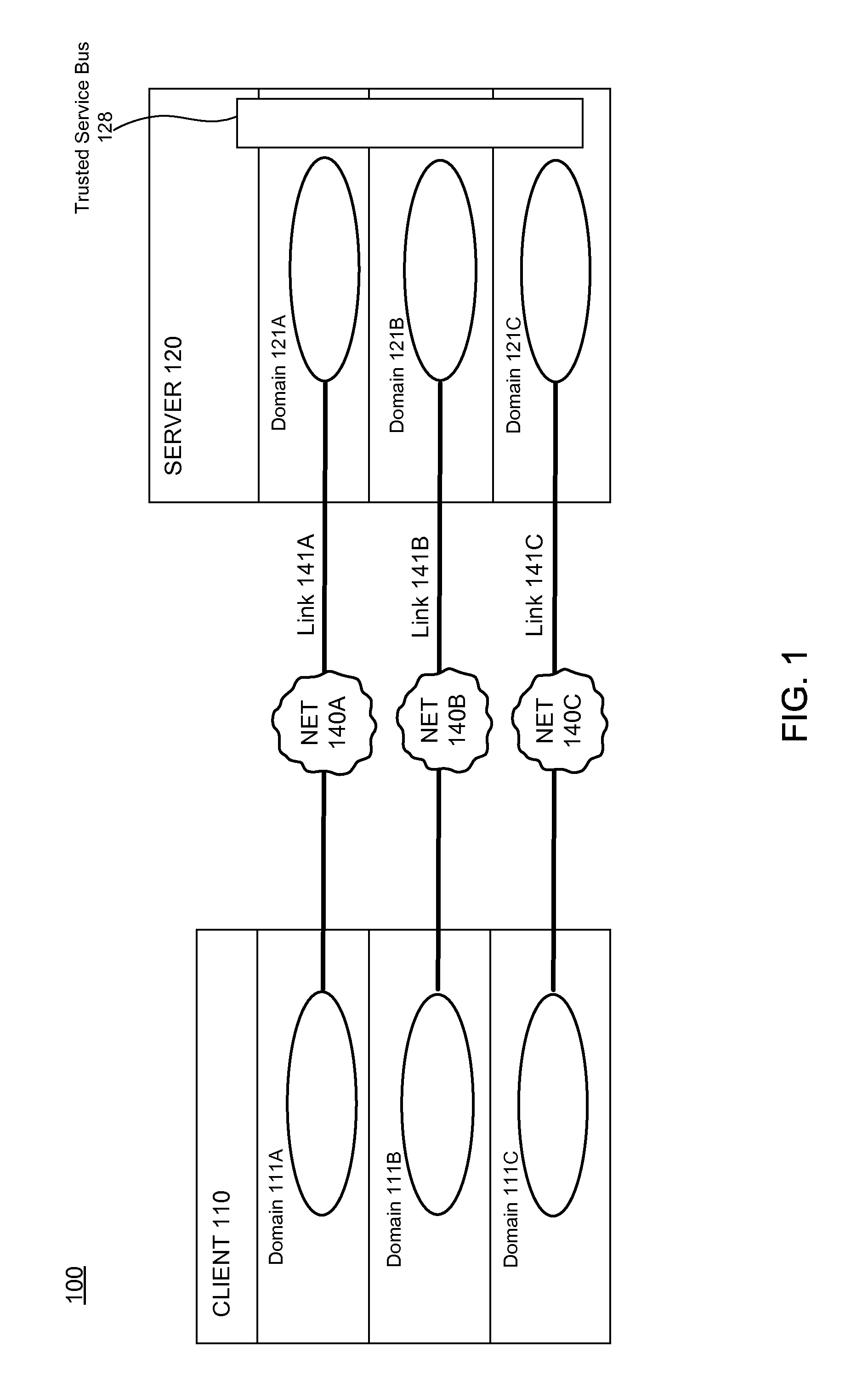
Server-based architecture for securely providing multi-domain applications
ActiveUS8584211B1Improve securityGood security riskDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInternet privacySecurity domain
A Multilevel Security (MLS) server provides MLS functionality to single-level applications running on a remote Multiple Independent Level Security (MILS) or MLS client device. More specifically, the MLS server provides a plurality of different security domains in which applications can execute. The client device executes a single-level application in a first security domain, the single-level application not natively capable of communicating with other domains. The single-level application in the first security domain sends a request to the MLS server. The MLS server receives the request, passing it to all applicable domains, including a second security domain, where it is duly executed. The MLS server then provides the results of the request execution—if any—back to an appropriate application on the client device. For example, the single-level application in the first security domain can display the aggregated results obtained from multiple distinct security domains, or an application running in the second security domain can display the results.
Owner:STERLING COMP
Systems and methods for configuring digital storage media with multiple access privileges
InactiveUS20050125678A1Great control and auditImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationInternal/peripheral component protectionAccess methodInternet privacy
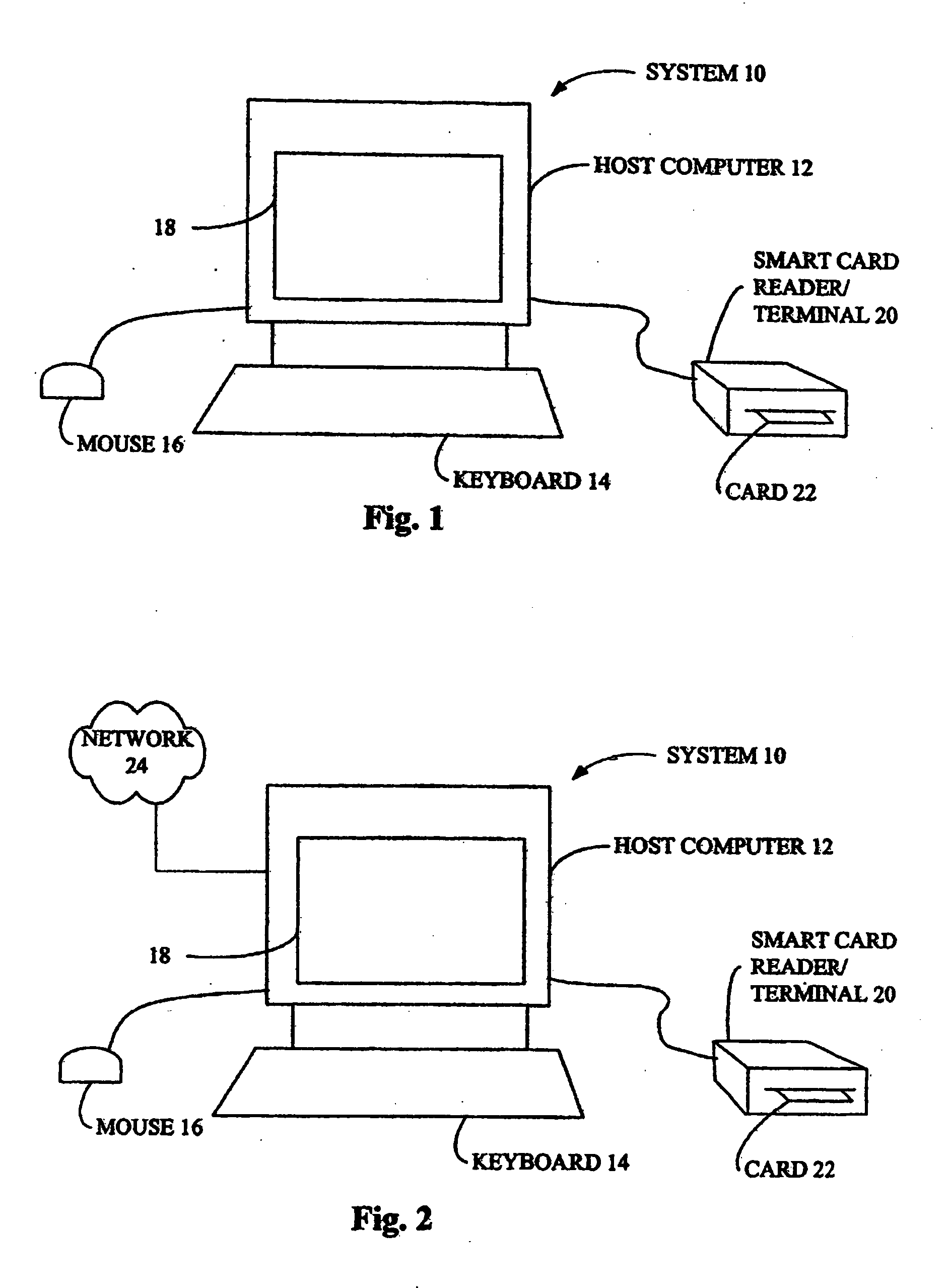
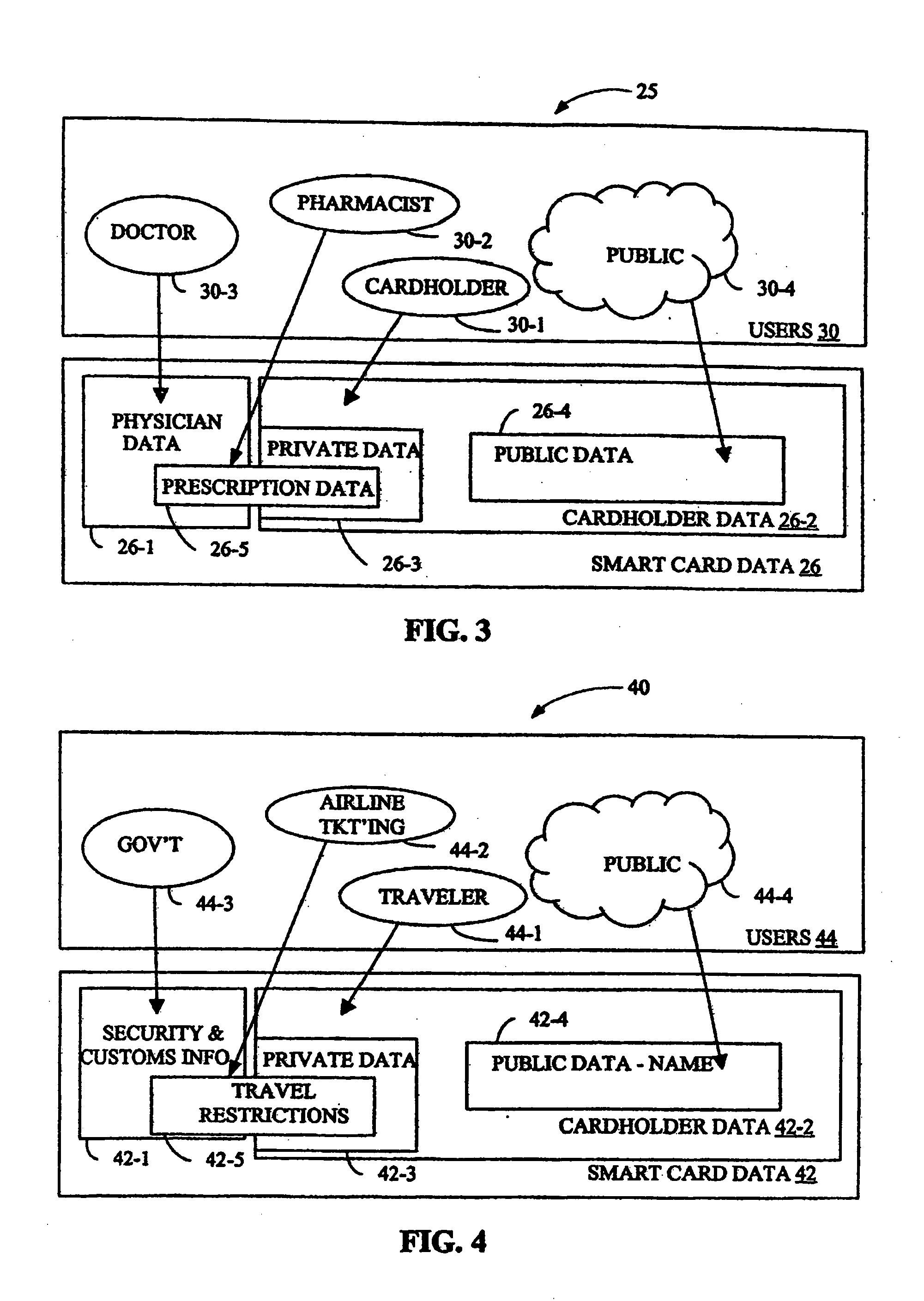
Disclosed is a system for accurately storing and reading digital identifications and permissions with an access rights management component that protects the privacy and integrity of the data stored. Aspects of the invention enable effective use of smart cards for applications such as air travelers identity, medical information such as history and prescriptions, or secure employee access cards. Multiple levels of security are permitted to ensure that users of the data, programs, and other resources stored on the card may access only that data that they have been authorized to. The use of a single card for multiple user roles may be used in conjunction with multiple access methods.
Owner:JANSSEN SCOPE
Technique for providing multiple levels of security
ActiveUS20070055878A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsInternet privacyEngineering
Techniques for authentication are provided. A first authentication request transformed with a private portion of a first type split private key is received. A first user is authenticated for a first level of network access based upon the first request being transformed with the first type of split private key. A second authentication request that is transformed with a private portion of a second type private key is also received. A second user is authenticated for a second level of network access based upon the second request being transformed with the second type of split private key.
Owner:VMWARE INC
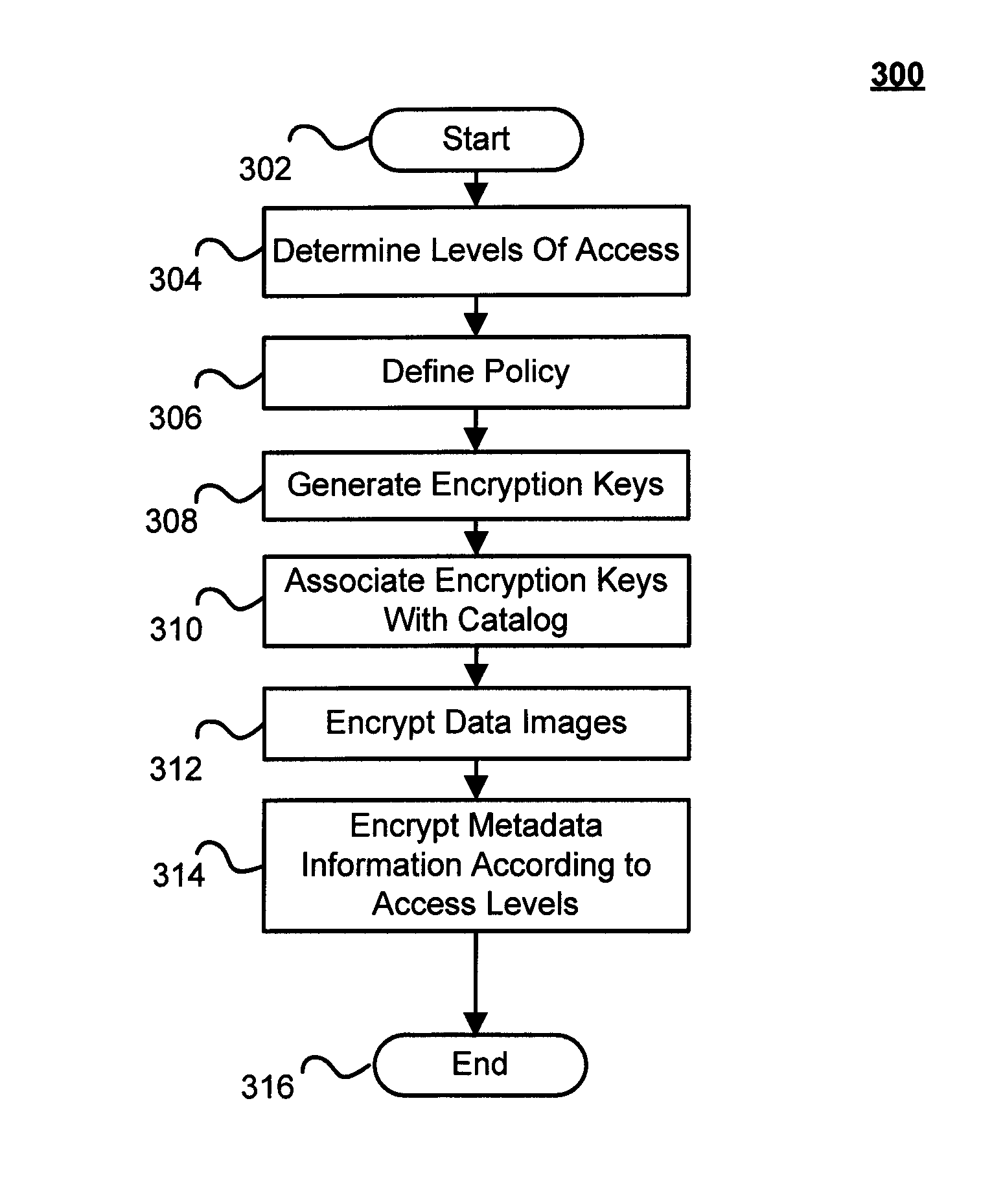
Techniques for providing multiple levels of security for a backup medium
Techniques for providing multiple levels of security for backups are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as a method for providing multiple levels of security for a backup medium comprising protecting a data portion of the backup medium with a first security mechanism, and protecting a metadata portion of the backup medium with a second security mechanism.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Multi-level security systems
InactiveUS20070277034A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsPath lengthSingle level
Techniques are disclosed for improving multi-level security (“MLS”) in computing systems. Communication between MLS systems in the prior art requires explicitly tagging each packet with its security classification. The packet tags comprise variable-length bit patterns inserted into packet headers. This results in a number of drawbacks, including increased path length and code complexity, as well as reduced interoperability. An MLS system according to the present invention simulates a cluster or collection of single-level security systems, and thereby avoids packet tagging. For each security classification used by an MLS system, a distinct source address is defined. This source address is used for outbound packets having that security classification, such that the packet's source address implicitly identifies the packet's security classification.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multi-level security systems
InactiveUS7356695B2Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsPath lengthSingle level
Techniques are disclosed for improving multi-level security (“MLS”) in computing systems. Communication between MLS systems in the prior art requires explicitly tagging each packet with its security classification. The packet tags comprise variable-length bit patterns inserted into packet headers. This results in a number of drawbacks, including increased path length and code complexity, as well as reduced interoperability. An MLS system according to the present invention simulates a cluster or collection of single-level security systems, and thereby avoids packet tagging. For each security classification used by an MLS system, a distinct source address is defined. This source address is used for outbound packets having that security classification, such that the packet's source address implicitly identifies the packet's security classification.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Authentication for a commercial transaction using a mobile module
InactiveUS20140351146A1Reduce the burden onSimpler and more secure online commercial transactions frameworkMarketingPayments involving neutral partySecure communicationPayment
Current embodiments provide for authorization and payment of an online commercial transaction between a purchaser and a merchant including verification of an identity of the purchaser and verification of an ability of the purchaser to pay for the transaction, where the identity provider and the payment provider are often different network entities. Other embodiments also provide for protocols, computing systems, and other mechanisms that allow for identity and payment authentication using a mobile module, which establishes single or multilevel security over an untrusted network (e.g., the Internet). Still other embodiments also provide for a three-way secure communication between a merchant, consumer, and payment provider such that sensitive account information is opaque to the merchant, yet the merchant is sufficiently confident of the consumer's ability to pay for requested purchases. In yet another embodiment, electronic billing information is used for authorization, auditing, payment federation, and other purposes.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multi-Level User Device Authentication System for Internet of Things (IOT)
ActiveUS20180183779A1Reduce insecurityDigital data authenticationTransmissionUser deviceInternet privacy
The present invention describes the user authentication system comprising of multiple levels of security which is used to authorize the user. The system uses more than one levels of authentication process which receives the credentials from the user and authorizes them to allow access to the IoT devices which are used by the user.The connected devices represent individual targets, for the cyber-criminals who 20 would hack the devices to retrieve the secure information of the users. Such insecurities about the IoT, devices and the system are eliminated by using the multiple level user authentication system which is described in the present invention.
Owner:KRISHAN BALDEV
Server-based architecture for securely providing multi-domain applications
ActiveUS9021559B1Facilitate data exchangeDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInternet privacySecurity domain
A Multilevel Security (MLS) server provides MLS functionality to single-level applications running on a remote Multiple Independent Level Security (MILS) or MLS client device. More specifically, the MLS server provides a plurality of different security domains in which applications can execute. The client device executes a single-level application in a first security domain, the single-level application not natively capable of communicating with other domains. The single-level application in the first security domain sends a request to the MLS server. The MLS server receives the request, passing it to all applicable domains, including a second security domain, where it is duly executed. The MLS server then provides the results of the request execution—if any—back to an appropriate application on the client device. For example, the single-level application in the first security domain can display the aggregated results obtained from multiple distinct security domains, or an application running in the second security domain can display the results.
Owner:STERLING COMP
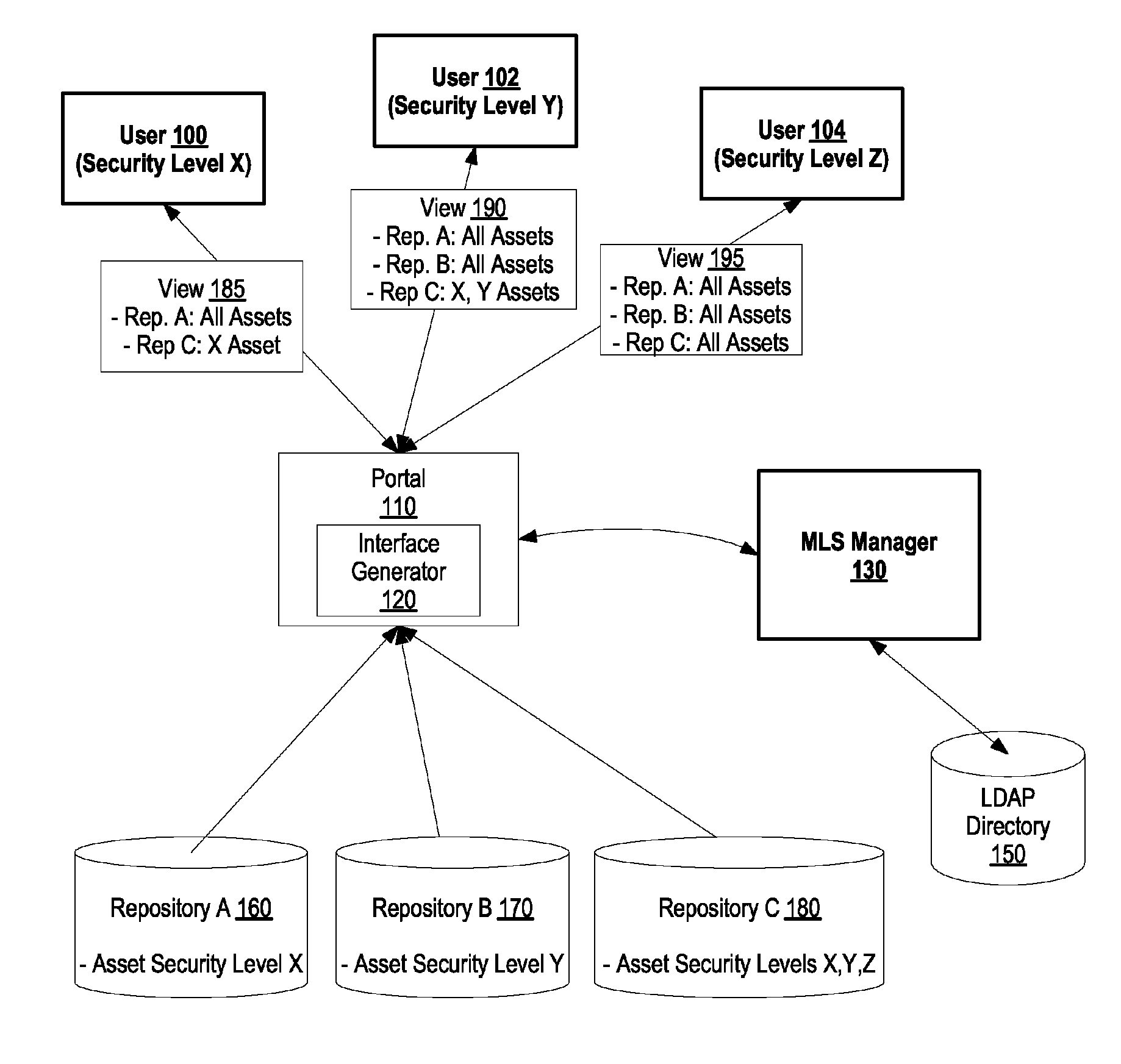
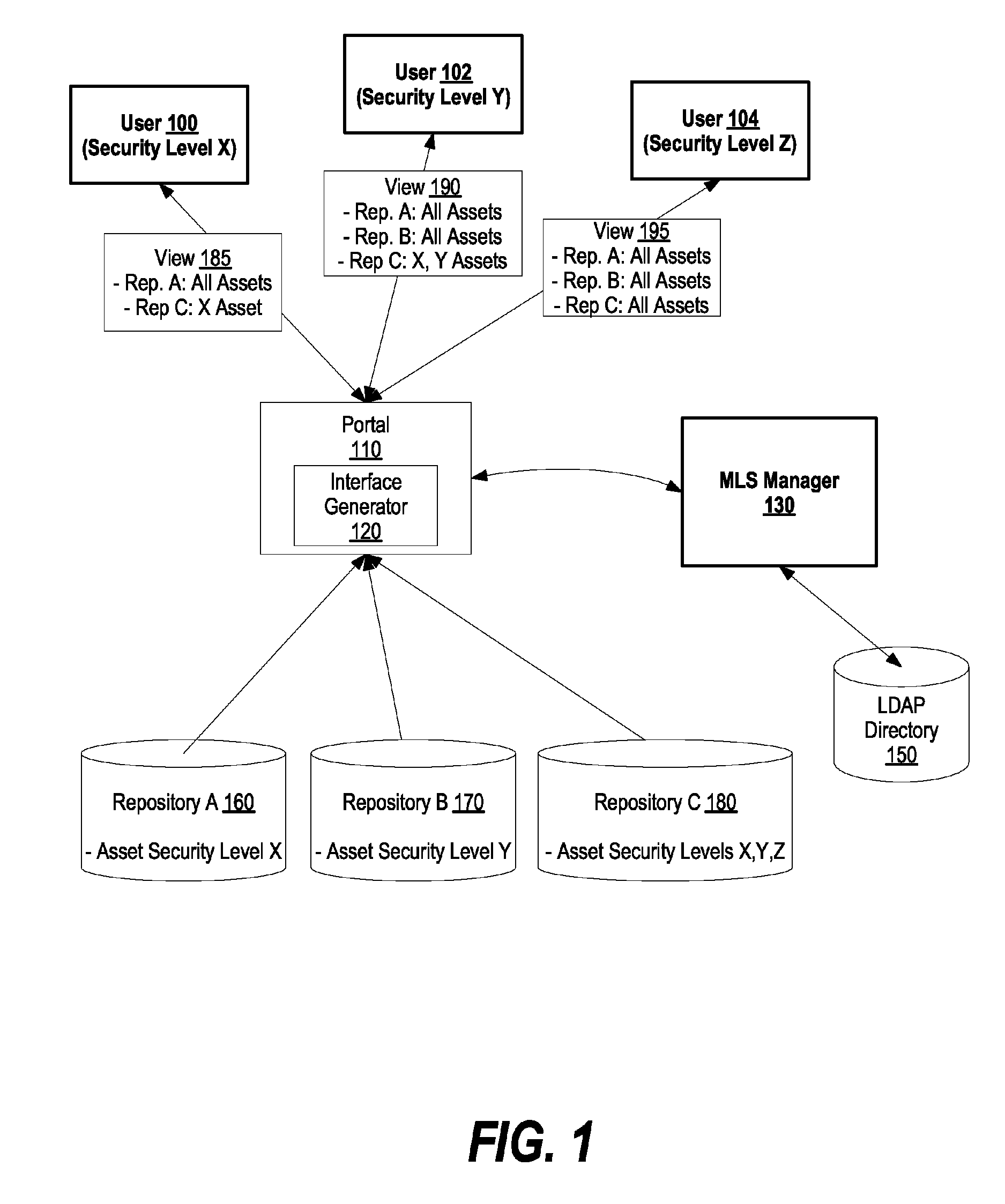
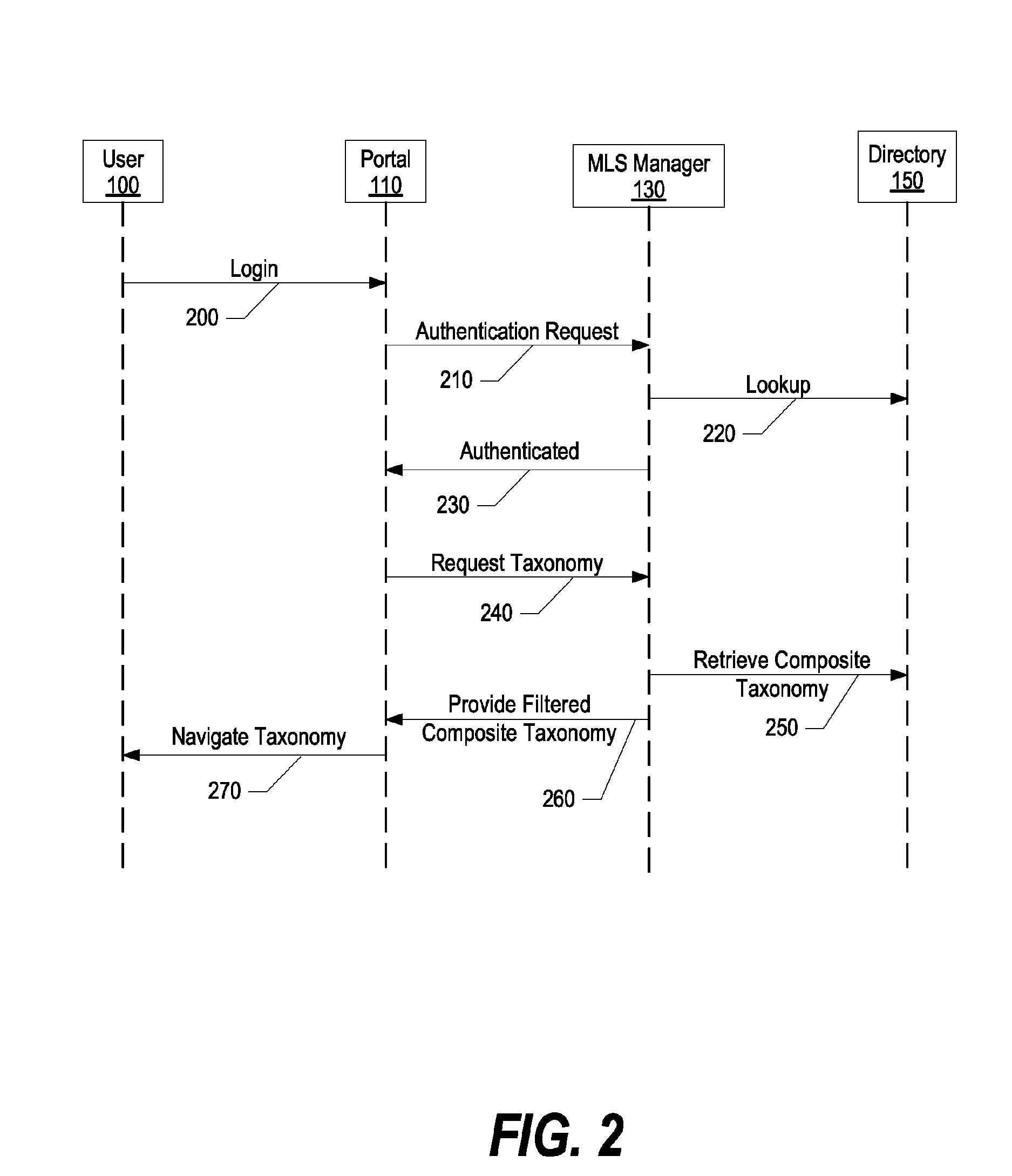
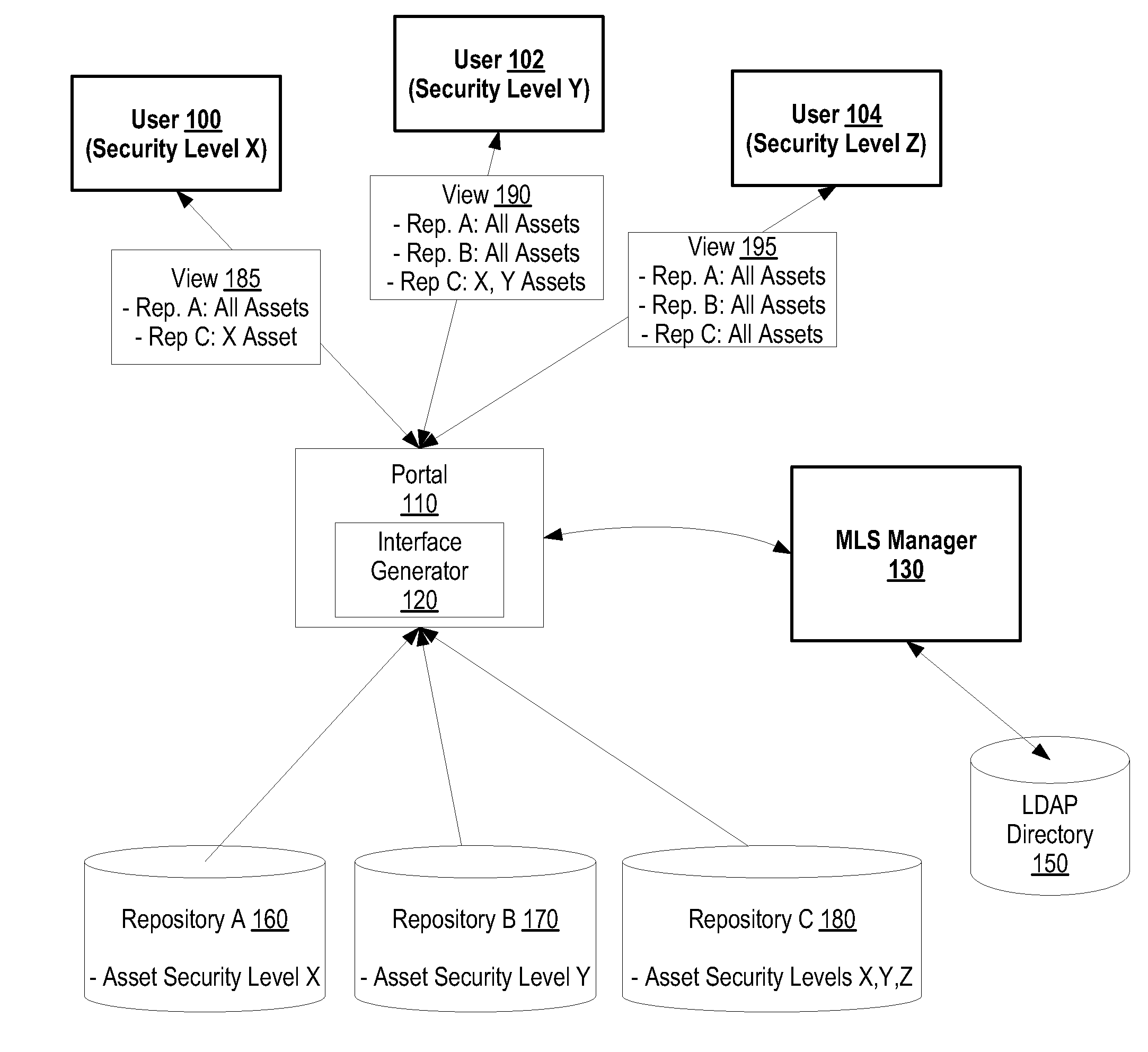
System and method for adding multi-level security to federated asset repositories
InactiveUS7962516B2Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsView basedUser identifier
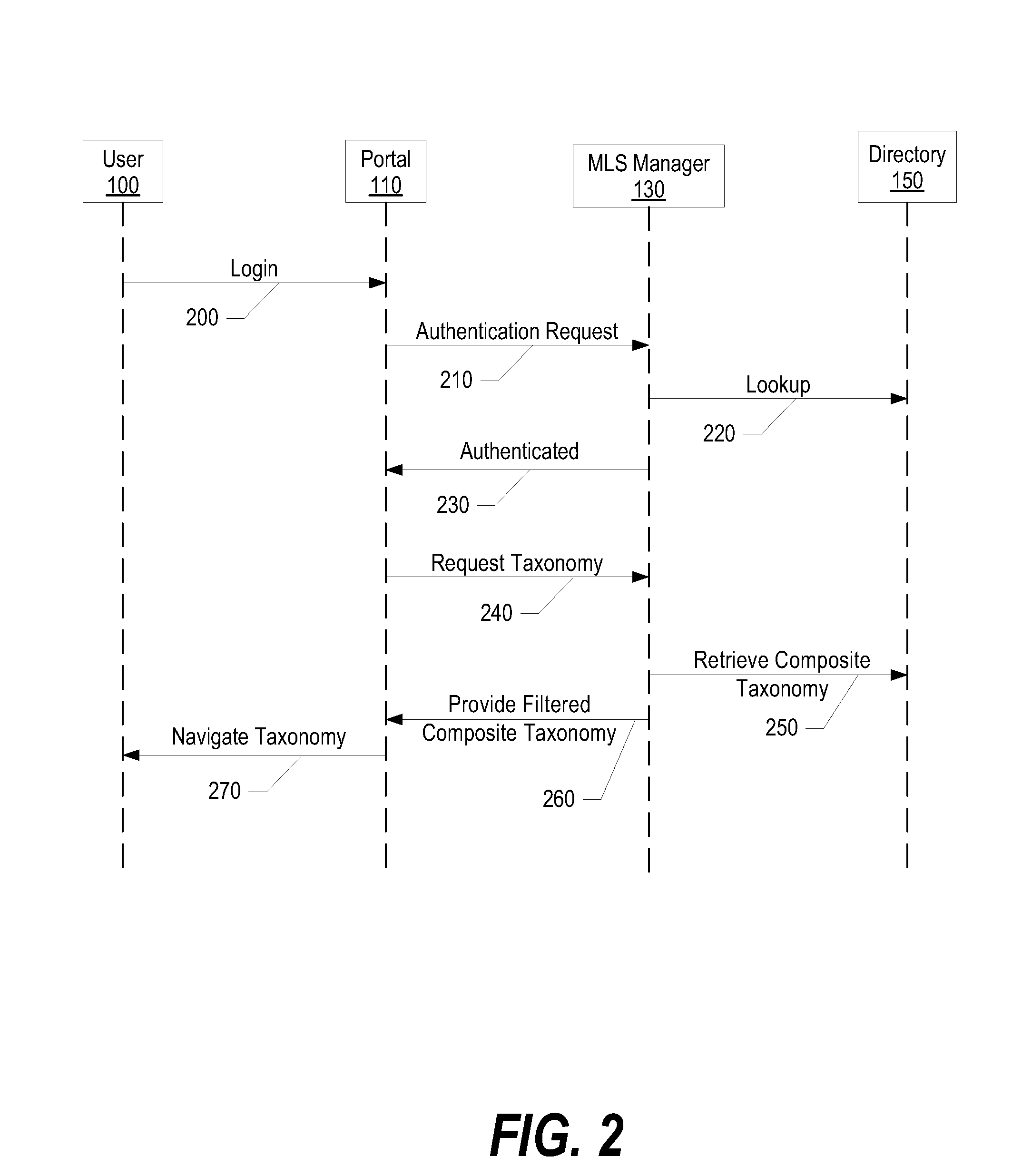
A system and method for adding multi-level security to federated asset repositories is provided. A multi-level security (MLS) manager receives normalized taxonomies from repository managers, which manage repositories that include assets assigned various security levels. In turn, the MLS manager integrates the taxonomies into a composite taxonomy. When a portal receives a request from a user, the portal sends a taxonomy request to the MLS manager that includes the user's user identifier. The MLS manager retrieves the composite taxonomy, identifies the user's security level, filters the composite taxonomy based upon the user's security level, and provides the filtered composite taxonomy to the portal. In turn, the portal generates a user interface view based upon the filtered composite taxonomy and provides the user interface view to the user, which utilizes the user interface view to request and receive access to assets from one or more federated repositories.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and system for a multi-level security association lookup scheme for internet protocol security
InactiveUS20090178104A1Computer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer networkSecurity association
Methods and systems for data communication are disclosed and may include utilizing a multi-level lookup process for determining IPsec parameters from a security association database. The security association database may be stored in content addressable memory, and may include an Internet protocol address table, a security association lookup table, and a security association context table. The security association lookup and security association context tables may include a single table. An Internet protocol address table index may be looked up in the Internet protocol address table for a first lookup of the multi-level lookup process. A security protocol index may be looked up utilizing the Internet protocol address table index for a second lookup of the multi-level lookup process. The Internet protocol security parameters may be determined utilizing the security protocol index. IPsec processing may be performed utilizing the determined Internet protocol security parameters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Technique for providing multiple levels of security
ActiveUS7596697B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsMultilevel securityAuthentication
Owner:VMWARE INC
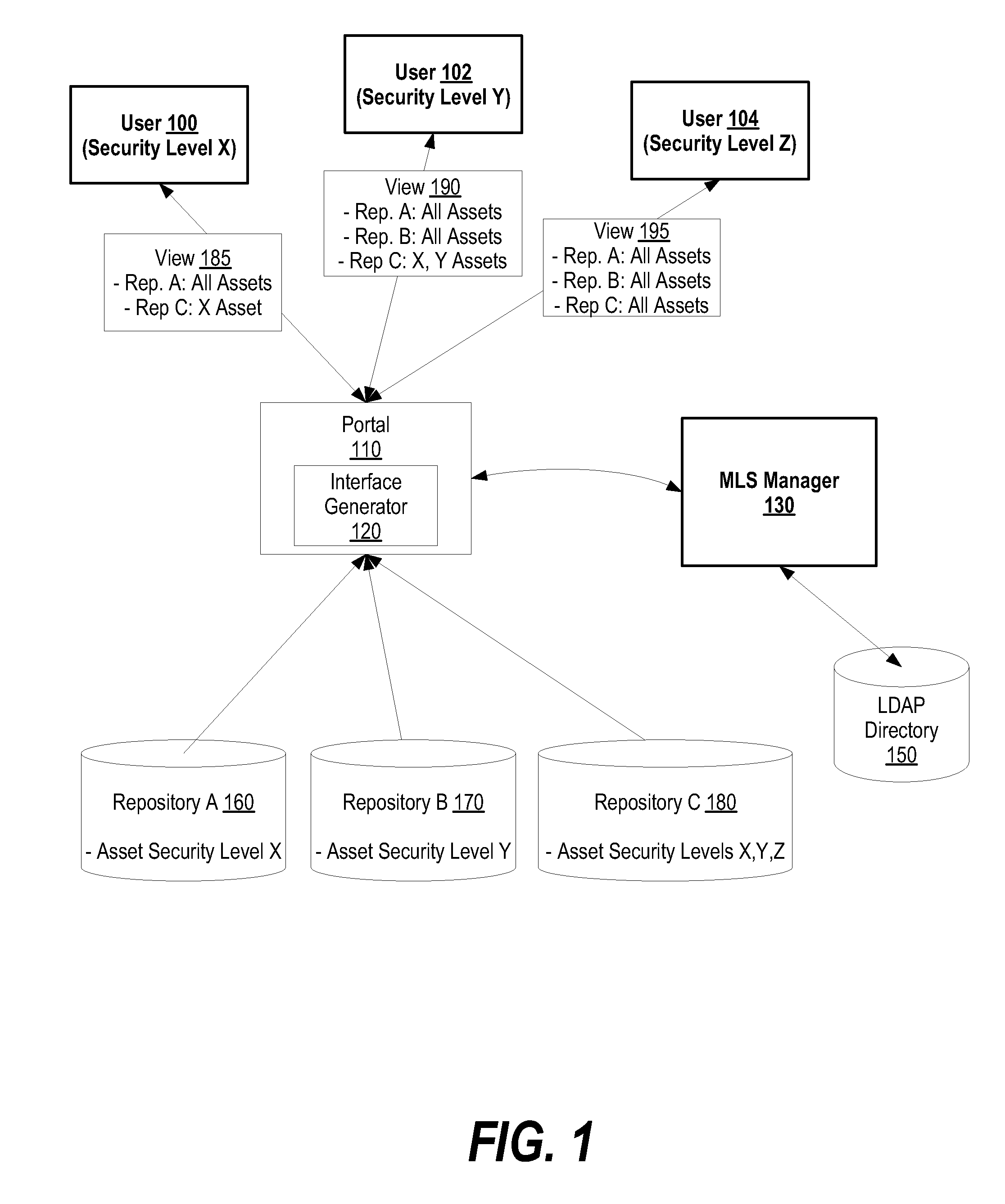
System and Method for Adding Multi-Leval Security to Federated Asset Repositories
InactiveUS20090198698A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsView basedUser identifier
A system and method for adding multi-level security to federated asset repositories is provided. A multi-level security (MLS) manager receives normalized taxonomies from repository managers, which manage repositories that include assets assigned various security levels. In turn, the MLS manager integrates the taxonomies into a composite taxonomy. When a portal receives a request from a user, the portal sends a taxonomy request to the MLS manager that includes the user's user identifier. The MLS manager retrieves the composite taxonomy, identifies the user's security level, filters the composite taxonomy based upon the user's security level, and provides the filtered composite taxonomy to the portal. In turn, the portal generates a user interface view based upon the filtered composite taxonomy and provides the user interface view to the user, which utilizes the user interface view to request and receive access to assets from one or more federated repositories.
Owner:IBM CORP
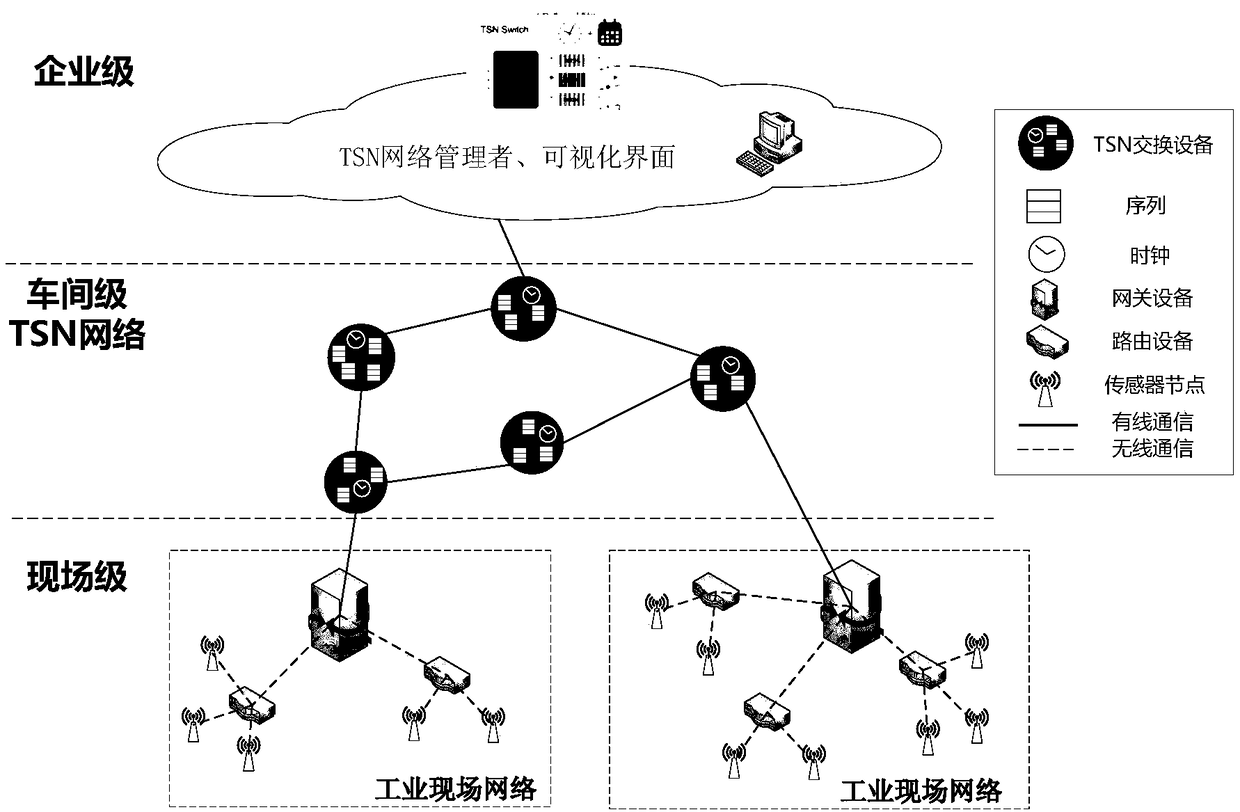
Industrial time sensitive network multilevel security data scheduling method
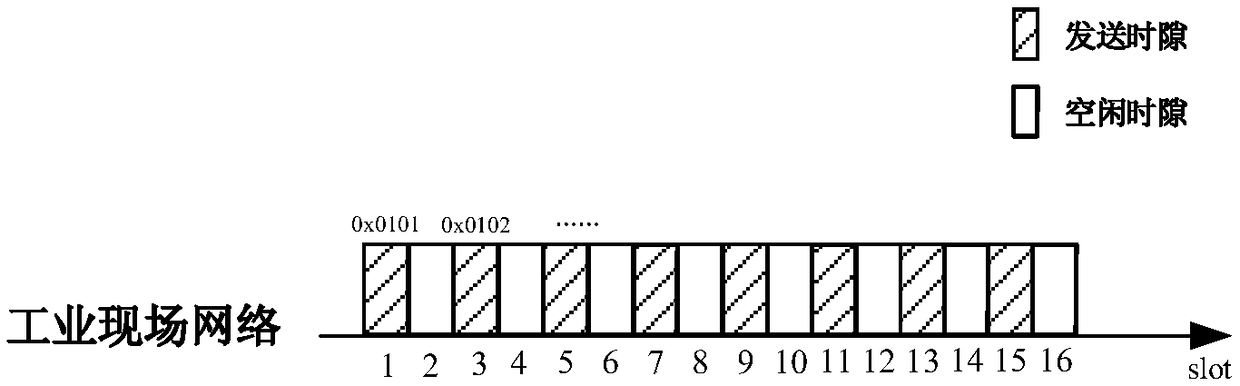
ActiveCN109450943ABalancing Security NeedsBalanced Data Transfer EfficiencyTransmissionData transmissionTime sensitive
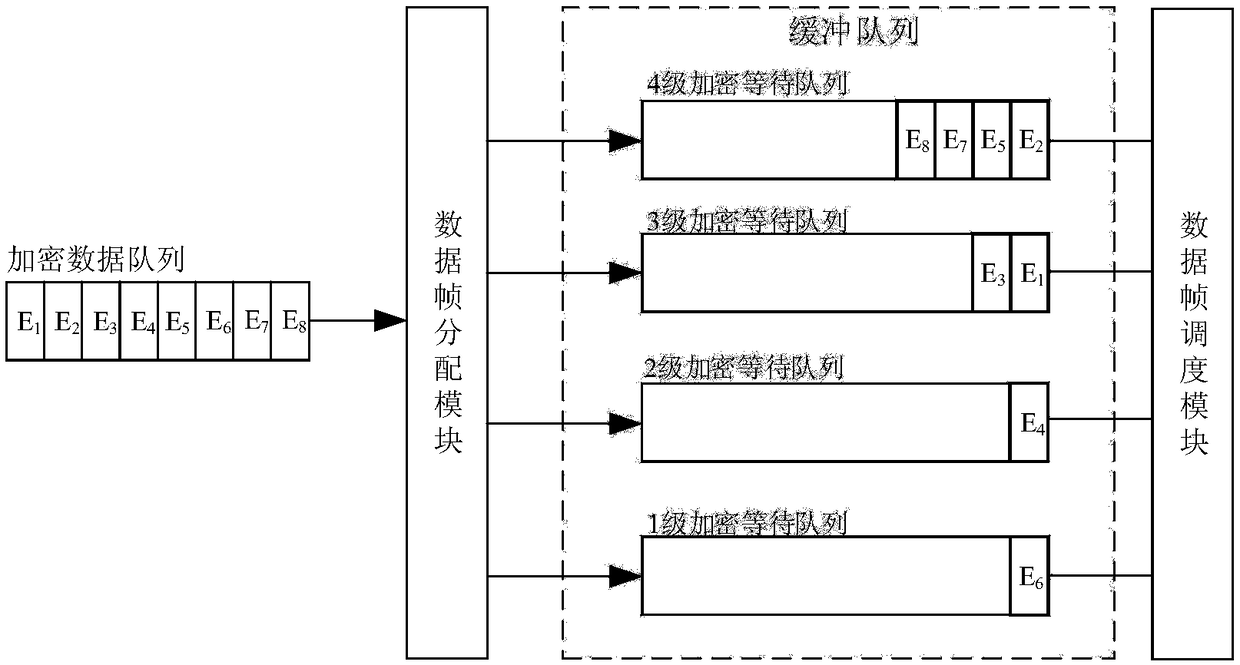
The invention relates to an industrial time sensitive network multilevel security data scheduling method, and belongs to the field of communication networks. The method comprises the steps that S1, agateway device is used as a network manager to allocate priorities for data frames sent by field nodes; S2, the industrial wireless network field nodes generate a data frame information table; S3, thenodes perform encryption of different strength grades on the data frames about to be sent, and update the data frame information table; S4, a TSN switching device builds a multilevel security data scheduling model, and comprises a data frame allocation module, a buffer queue module and a data frame scheduling module; the data frame distribution module divides a buffer queue into four grades of encryption waiting queues according to the data frame encryption grades; and S5, the data frame scheduling module performs internal scheduling on the data frames in the encryption waiting queues according to comprehensive priorities. The method meets the requirements of the determinacy of industrial wireless network data transmission and the real-time performance of high-priority data transmission.
Owner:KYLAND TECH CO LTD
Random number based data integrity verification method and system for distributed cloud storage
InactiveUS8694467B2Less computing powerSimple hardwareDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsHash functionData integrity
A data integrity verification method and system based on a root random number to ensure secure distributed data storage on a public cloud. A new root random number can be generated in response to receiving a file for storage to the public cloud. A unique random number tag for each data chunk associated with the file can be calculated via a shift operation and the tag can be added to the data chunk. A hash function (message digests) can be then generated and concatenated with the data chunk and the random number tag. The data chunk in conjunction with the hash and the random number tag can be encrypted by an encryption module and stored to the public cloud in order to provide multiple levels of security with respect to the distributed public cloud storage. Upon file retrieval, the encryption module decrypts all data chunks and recalculates the hash in order to verify the data integrity of the file.
Owner:XEROX CORP
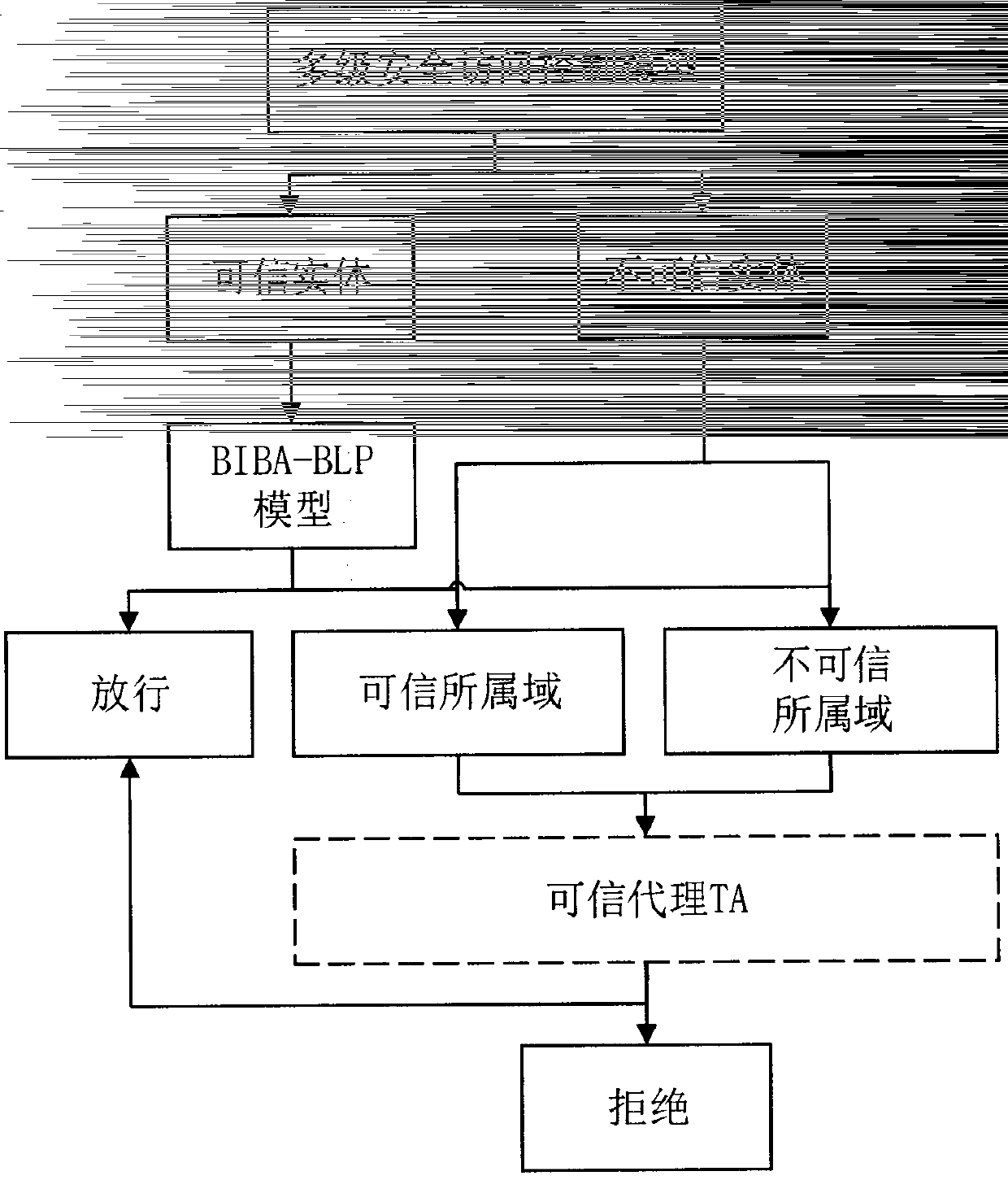
Multilevel security access control model based on information flow
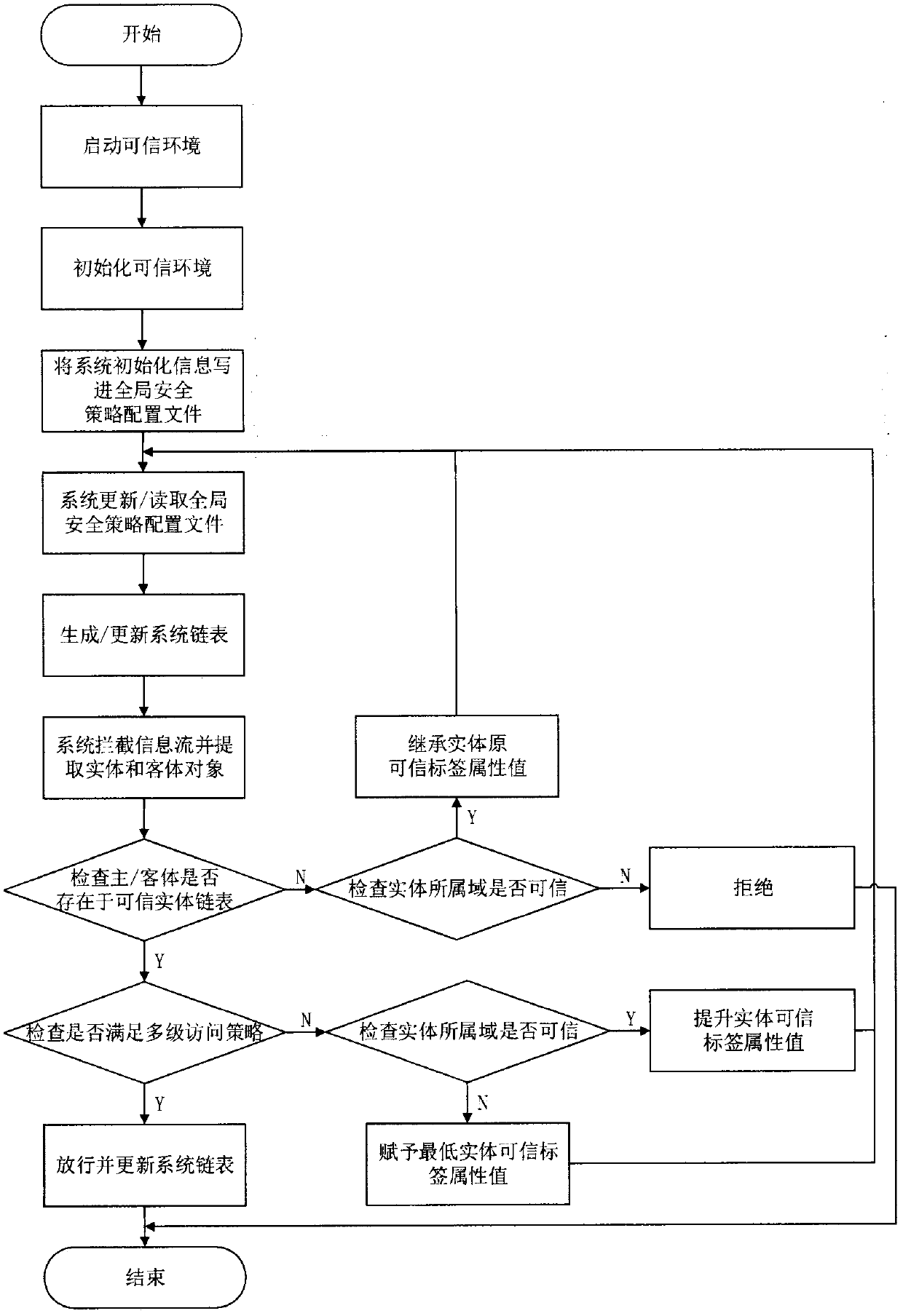
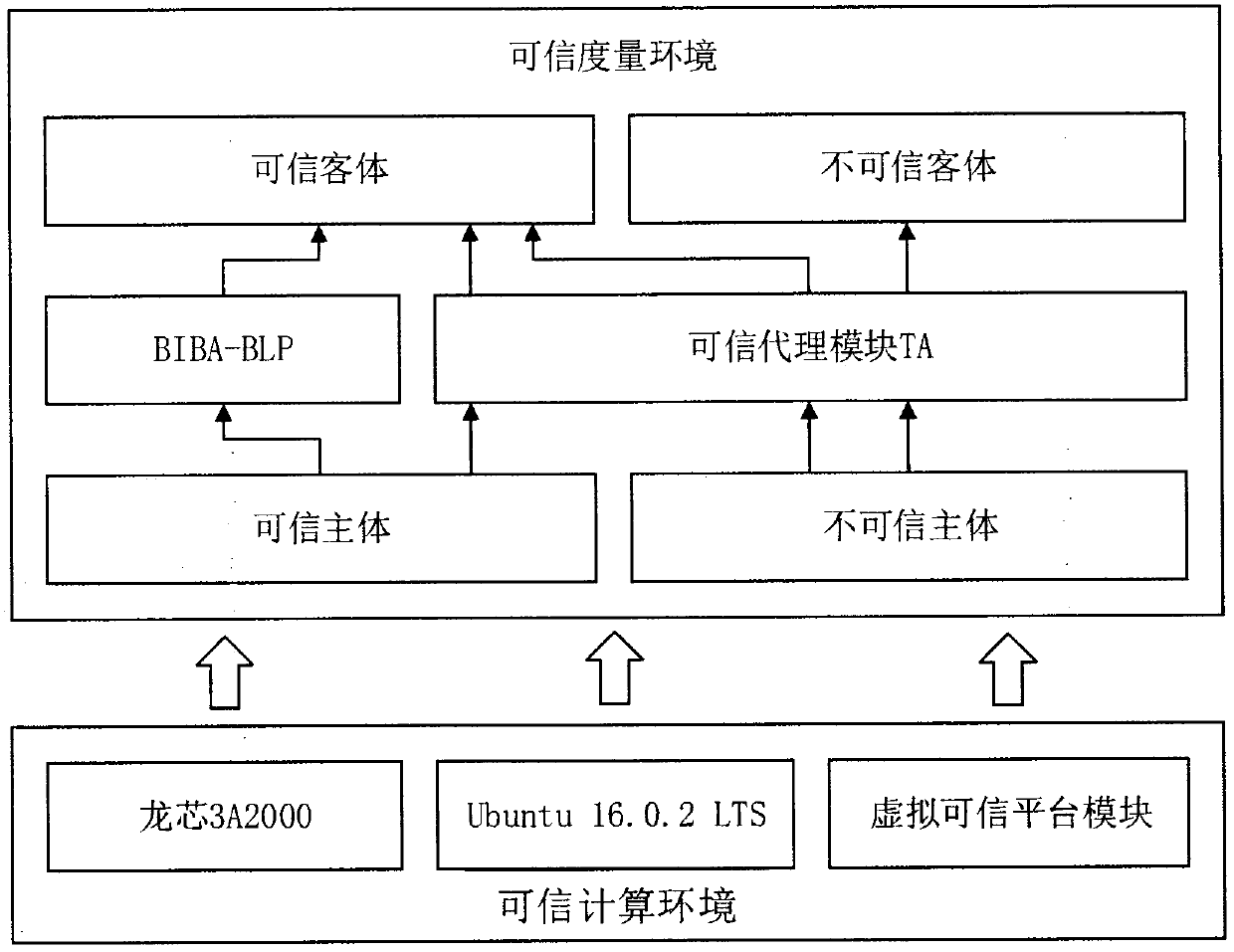
InactiveCN107612929ATo solve the "monotonicity defectTransmissionDesign informationMultilevel security
The invention provides a multilevel security (MLS) access control model based on information flow on the basis of the information flow forced access strategy. By analyzing relations and emphases on two multilevel security strategy BIBA and BLP models, the multilevel security though design information flow access rules are utilized, monotonic defects of existing models are considered, a trusted agent (TA) module for implementing access rules for specific information is designed, the limiting condition for information flow transmission is expanded, and meanwhile the system can still keep the original credible grade. The model has the good information flow access control effect and is applicable to cross-domain system information flow transmission.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Network commercial transactions
The present invention describes network commercial transactions. Current embodiments provide for authorization and payment of an online commercial transaction between a purchaser and a merchant including verification of an identity of the purchaser and verification of an ability of the purchaser to pay for the transaction, wherein the identity provider and the payment provider are often different network entities. Other embodiments also provide for protocols, computing systems, and other mechanisms that allow for identity and payment authentication using a mobile module, which establishes single or multilevel security over an untrusted network (e.g., the Internet). Still other embodiments also provide for a three-way secure communication between a merchant, consumer, and payment provider such that sensitive account information is opaque to the merchant, yet the merchant is sufficiently confident of the consumer's ability to pay for requested purchases. In yet another embodiment, electronic billing information is used for authorization, auditing, payment federation, and other purposes.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
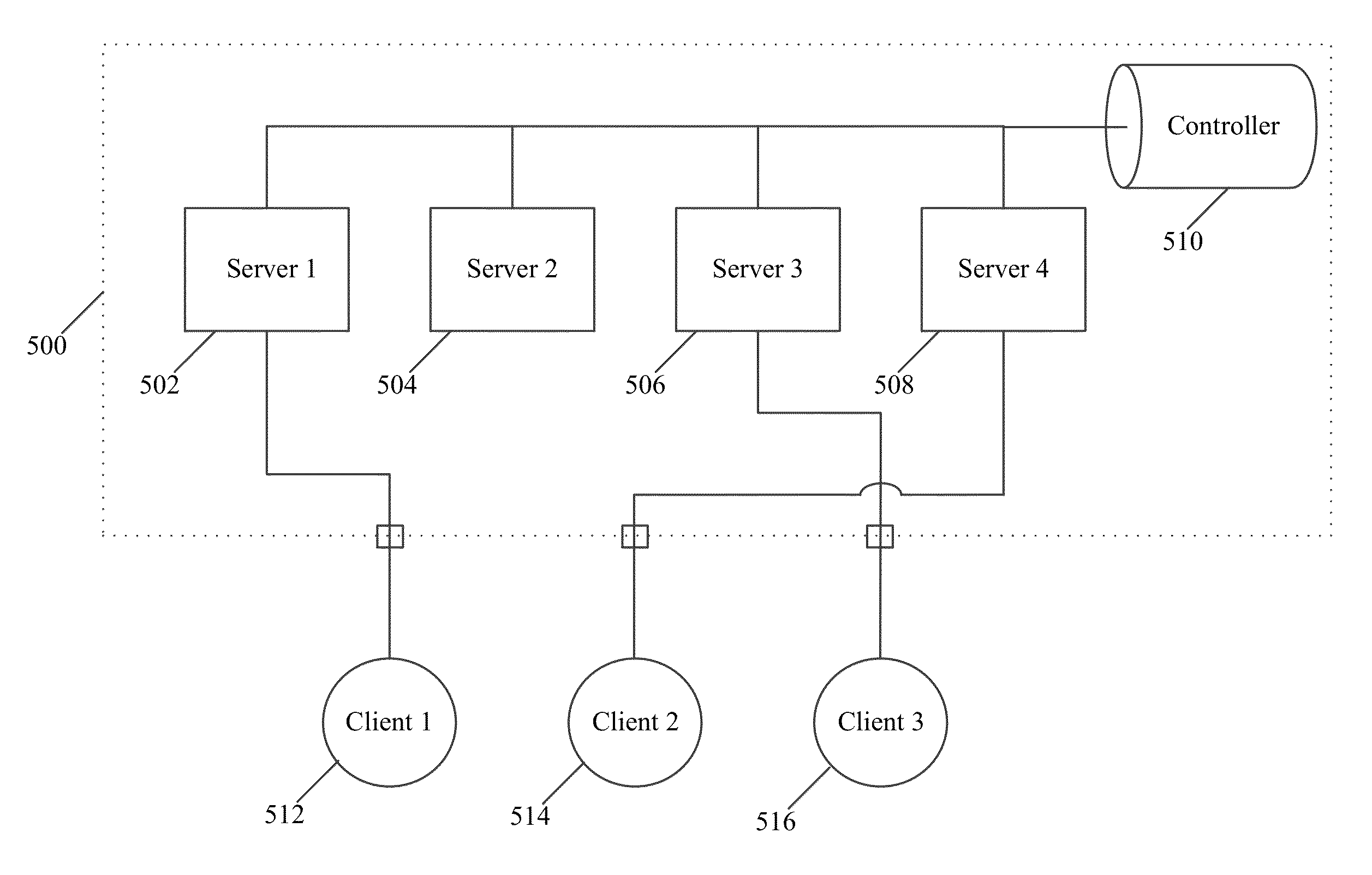
Methods and systems for dynamically specializing and re-purposing computer servers in an elastically scaling cloud computing infrastructure
InactiveUS20150089062A1Facilitate workload requestSimple processDigital computer detailsProgram controlResource poolWorkload
Methods and systems for dynamically repurposing and elastically scaling cloud computing networks and infrastructures in response to user workload requirements. The system receives, via a network interface, a workload request to manage a workload, determines workload requirements, and assigns the workload to an appropriate server in a server resource pool. Server capabilities and the server resource pool can be dynamically modified to satisfy current or expected workload requirements. An isolated gateway is provided such that data to and from the cloud computing network is physically segregated, thus providing data security. The cloud computing network is structured to provide multi-level security for workloads and workload owners.
Owner:VERTISCALE INC
Multilevel security policy conversion method
InactiveCN101763476AReduce labor costsImprove efficiencyDigital data protectionData descriptionSecurity policy
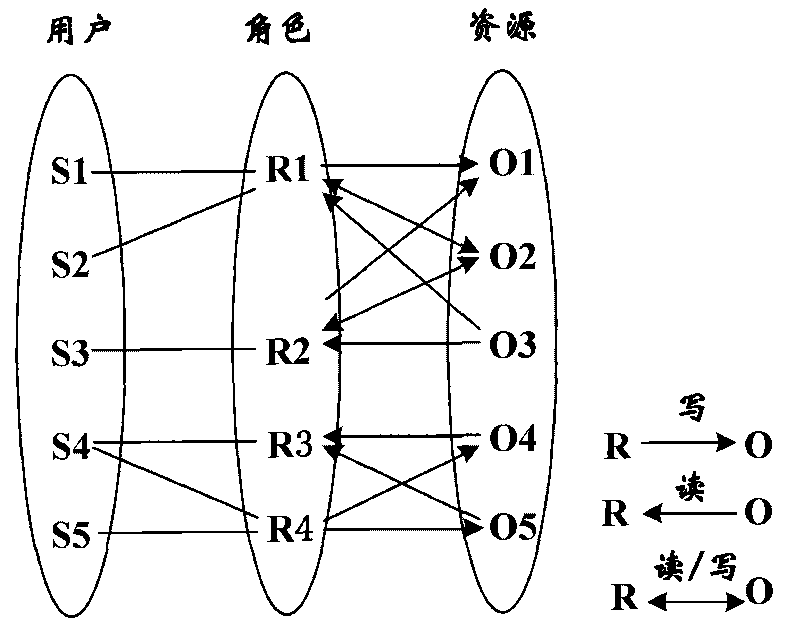
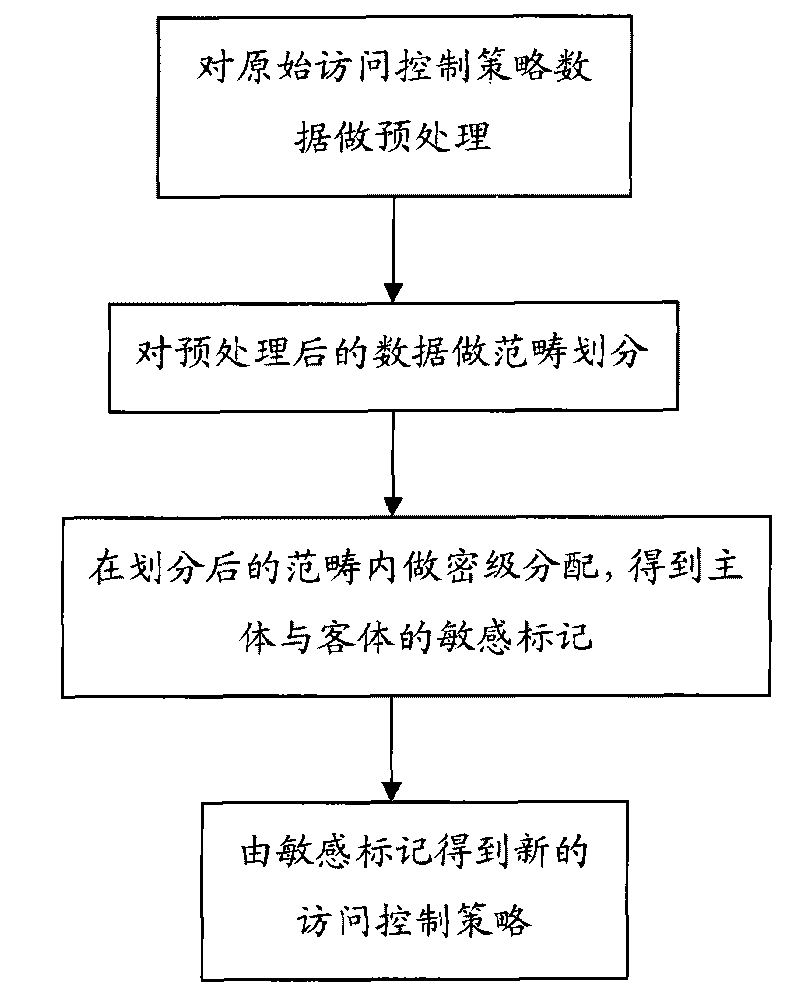
The invention provides a multilevel security policy conversion method, comprises the steps: reading, in an original system, original authorized policy data which describes the authority of host to access relative guests in the original system; classifying the guests in the original system and clustering the classes so as to construct the membership between category and the guests; then combining the membership between the category and the guests with the original authorized policy to construct the membership between the host and the category; within each of the resultant categories, calculating an optimal security classification assignment way of the host to the guests to result I the security classification between the host and the guests so as to obtain a sensitive mark; and according to the sensitive mark of the host and the guests and the access authority of a system to be migrated, generating authorized policy data of the system to be migrated. The method according to the invention can be suitable for the conversion of security policy in large-scale system.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
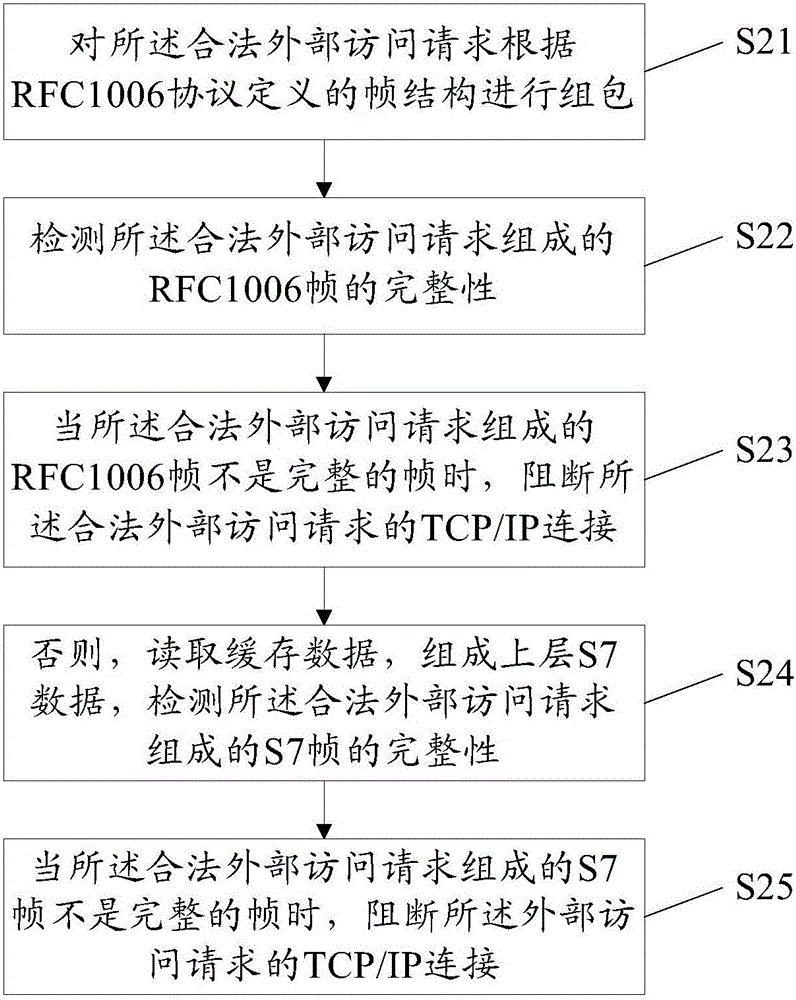
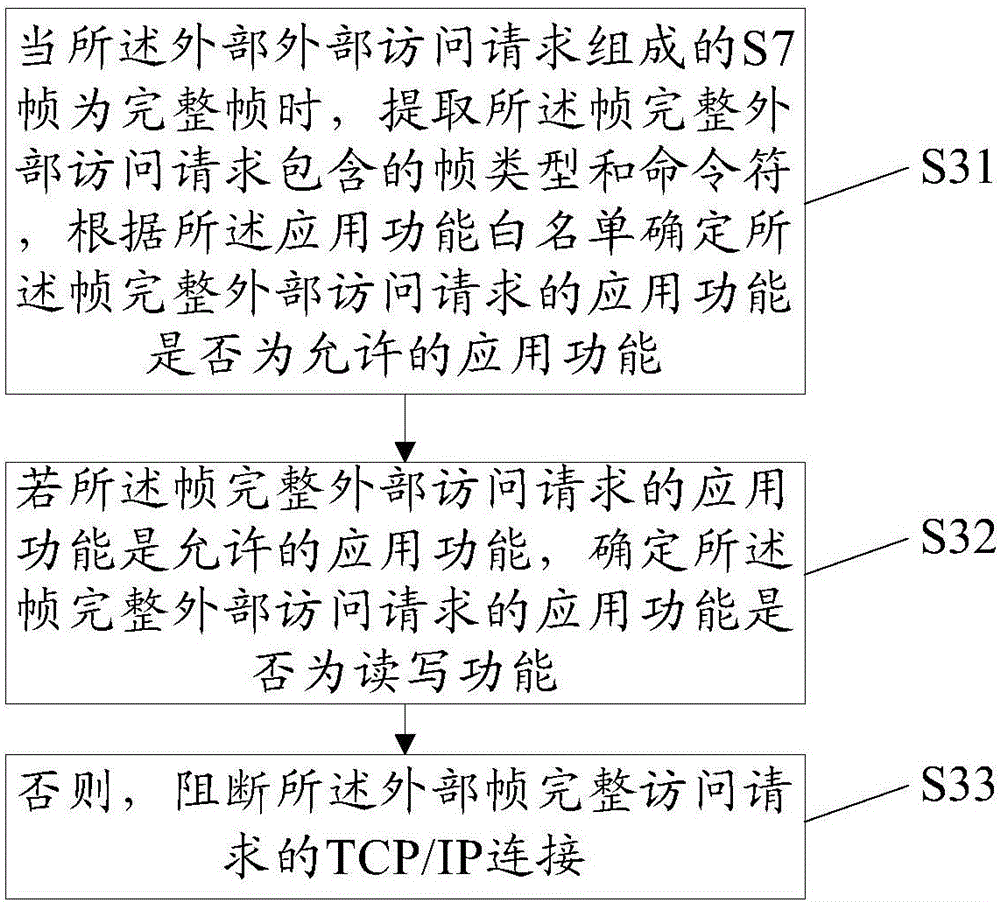
Security protection method and system for industrial control system using S7 protocol
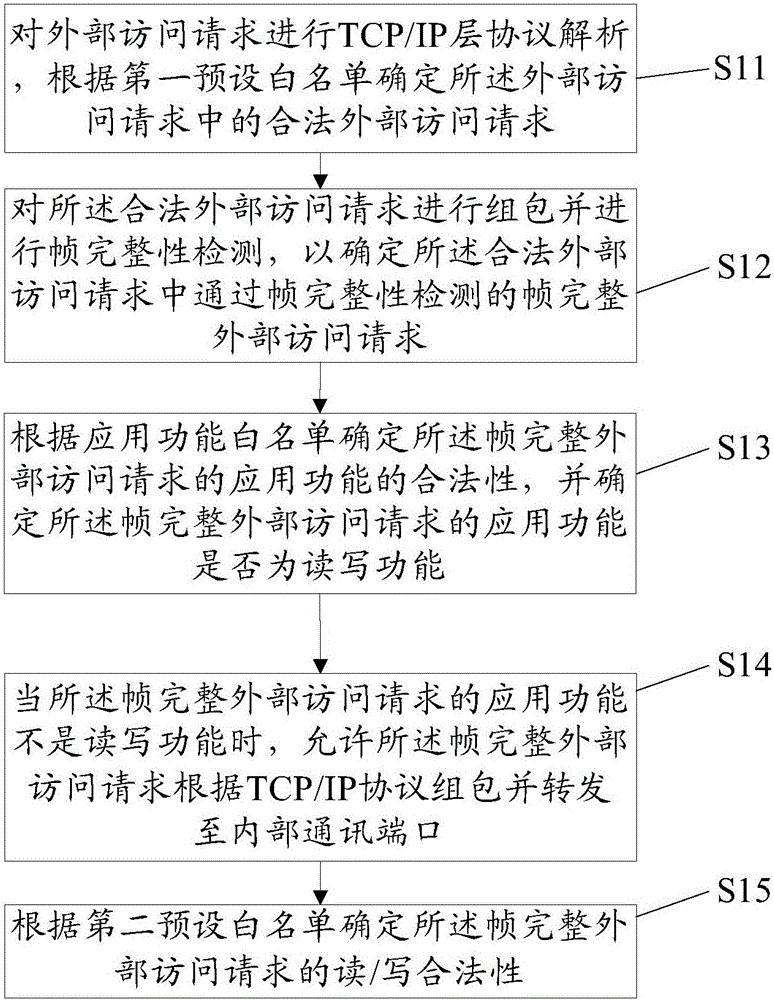
The invention provides a security protection method for an industrial control system using an S7 protocol. The method includes the following steps that: TCP / IP layer protocol analysis is performed on an external access request from a client, the IP address and port number of the client are determined, so that the validity of the external access request can be determined according to a client address white list; the external access request is packetized, the integrity of frames formed by the external access request is detected; the validity of the external access request is determined according to an application function white list, and whether the application function of the external access request is a read-write function is determined; and when the application function of the external access request is a read-write function, the validity of the external access request is determined according to a second preset white the list. The invention also provides a corresponding security protection system. According to the security protection method and the security protection system of the invention, multilevel security protection is carried out in a TCP / IP layer and an application layer, and therefore, a variety of attacks at an industrial control device or system adopting an S7 protocol can be effectively resisted, and security risks caused by the lack of security prevention mechanisms in the prior art can be avoided effectively.
Owner:INSECTECH BEIJING CO LTD
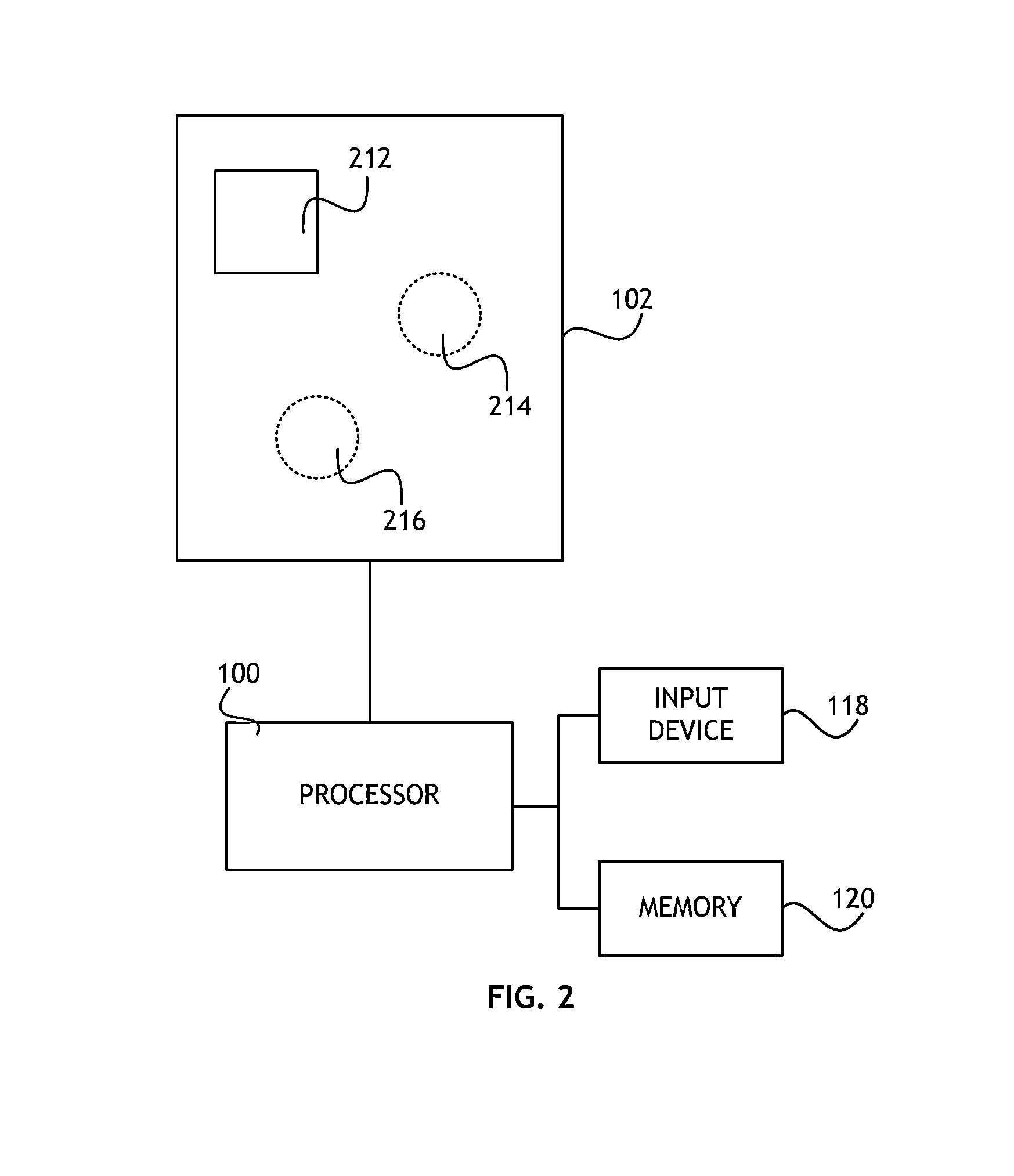
High assurance classification level disambiguation for displays
ActiveUS8875226B1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionAmbiguityDisplay device
A method for disambiguating entities on a multi-level security display includes receiving a selection of a particular security level and rendering entities having a different security level in a visually distinct way. Visual distinction may include not drawing the entities on the multi-level security display.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
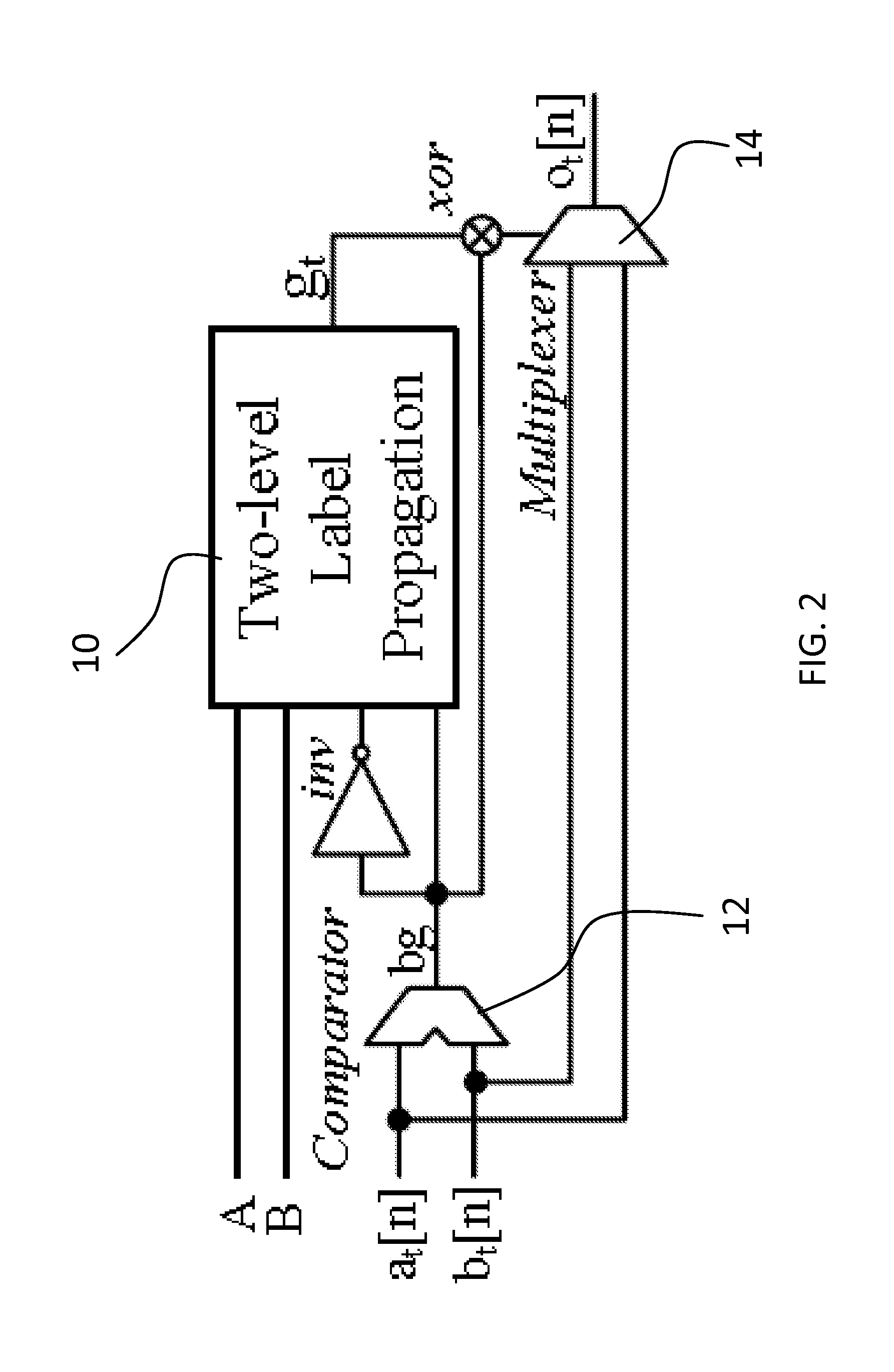
Method and system providing mutli-level security to gate level information flow
ActiveUS20160026801A1Easy to trackWide rangeDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsComputer hardwareSecurity level
A preferred method for providing multi-level security to a gate level information flow receives or specifies a security lattice having more than two security levels. The security lattice defines how security levels relate to each other. A hardware design implementing information flows including flows having security levels specified by the security lattice is received. Logic is created for testing the hardware design in view of the security lattice. A logic function is created based upon the hardware design and the logic for testing to implement the security lattice. Another method receives a hardware design in a hardware description language. At least a portion of the hardware design is synthesized to gate level primitives. Functional component tracking logic supporting more than two-security levels is built from the gate level primitives. Functional components in the hardware design are simulated with the functional component tracking logic.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Network access control system and method using adaptive proxies
InactiveUS20130246627A1Eliminating short comings thereofDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationControl systemNetwork Access Control
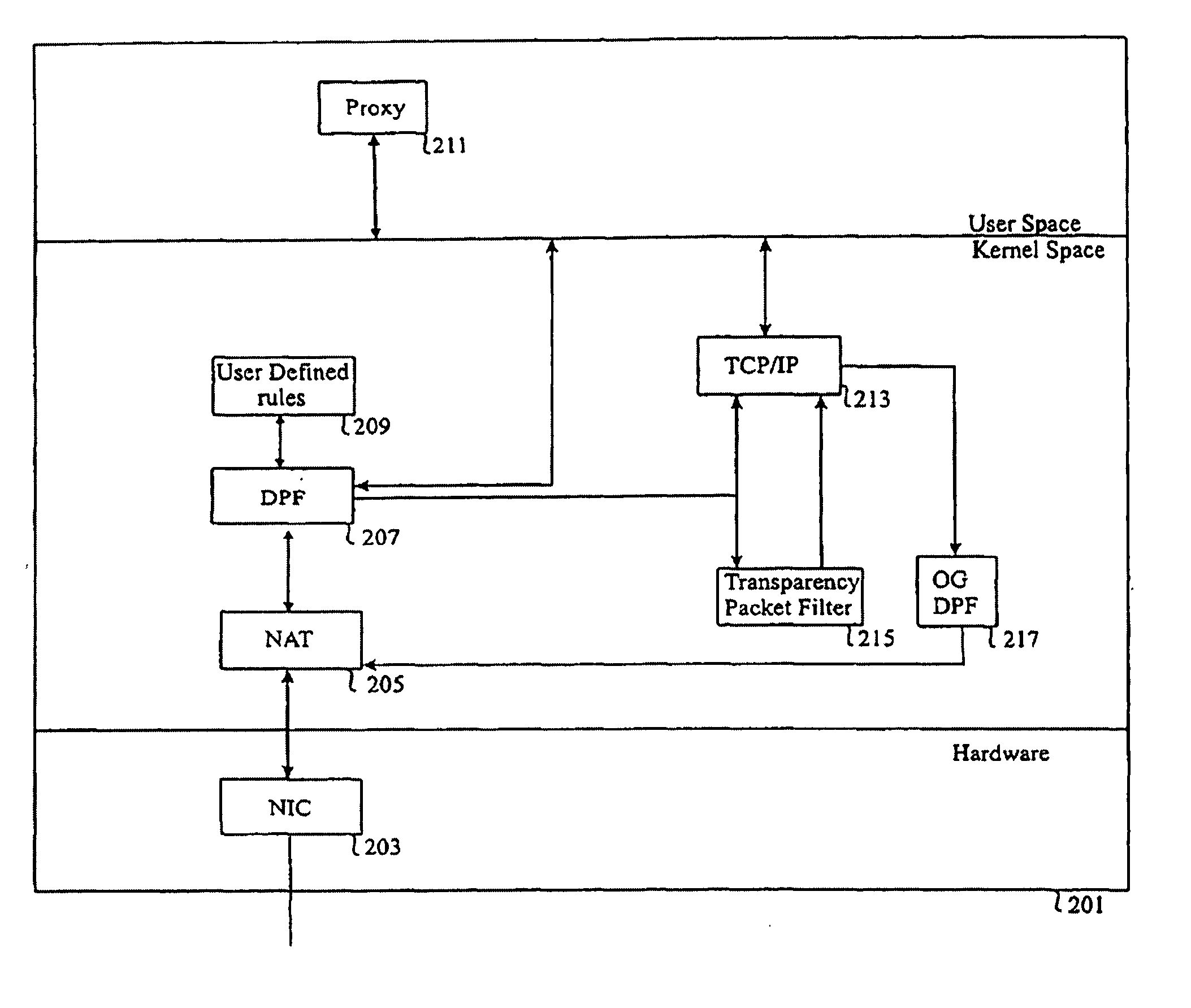
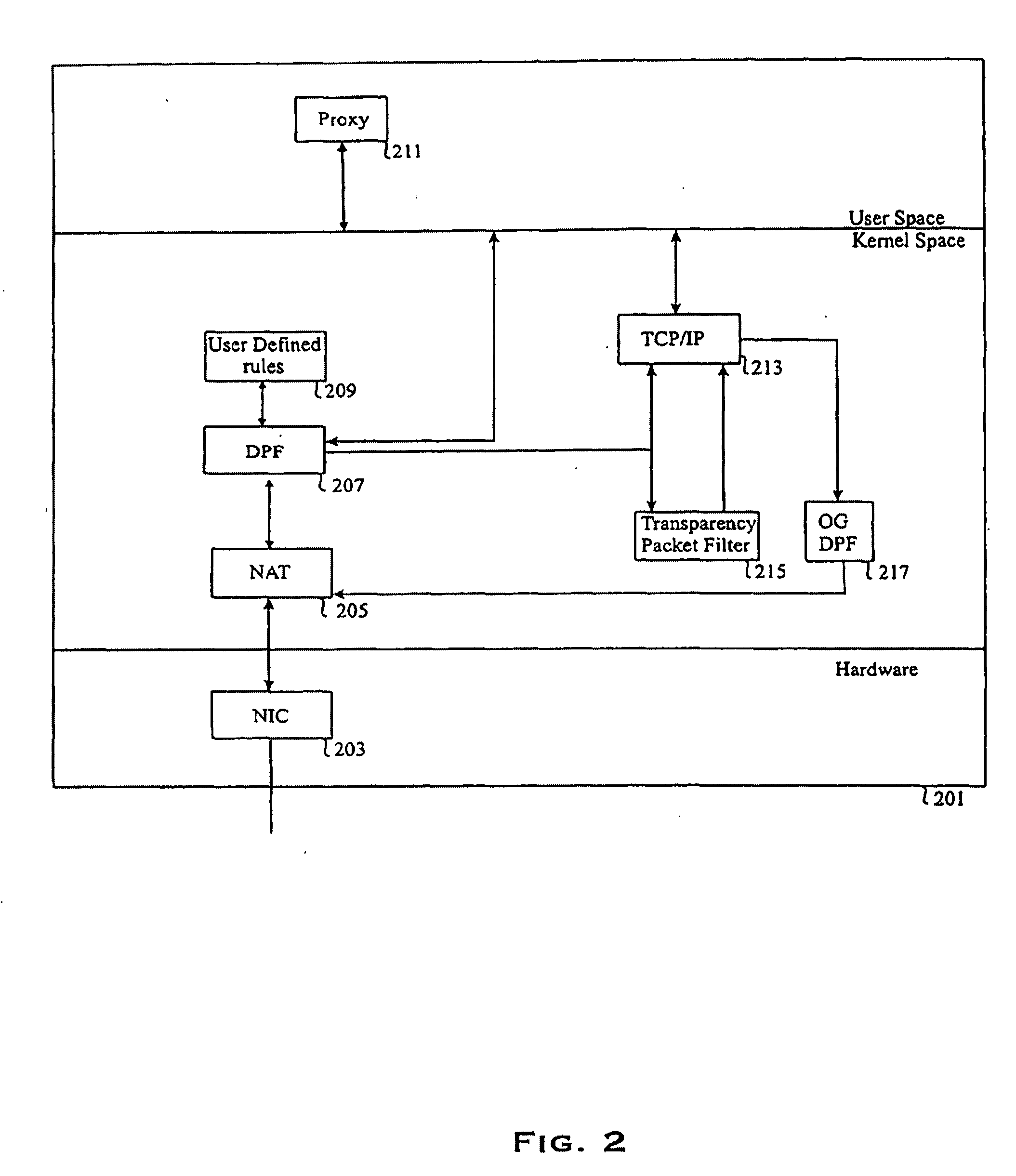
A method, system and computer program for providing multilevel security to a computer network. The method comprises the step of receiving a first communication packet on at least one network interface port from an outside network. The method further includes the steps of filtering the first packet in one of at least two levels of security comprising a first level of security which examines the content information of the packet and a second level of security which examines the first packet excluding the content information of the packet. The system includes a first packet filter configured to filter its input packets by examining content information of its packets and a second packet filter configured to filter its input packets by examining the header information without examining the content information of its packets. The system further includes a third filter which is configured to forward a number of packets to one of the first and second filters, thereby providing security to the computer network. The computer program includes a first module located in an application layer, a second module located in a network layer, and a third module located in a kernel space and configured to examine a number of packets received by the computer network from at least one outside network and to forward the number of packets to one of the first and second modules after examining the number of packets.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com