Patents
Literature
32 results about "Muscular force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
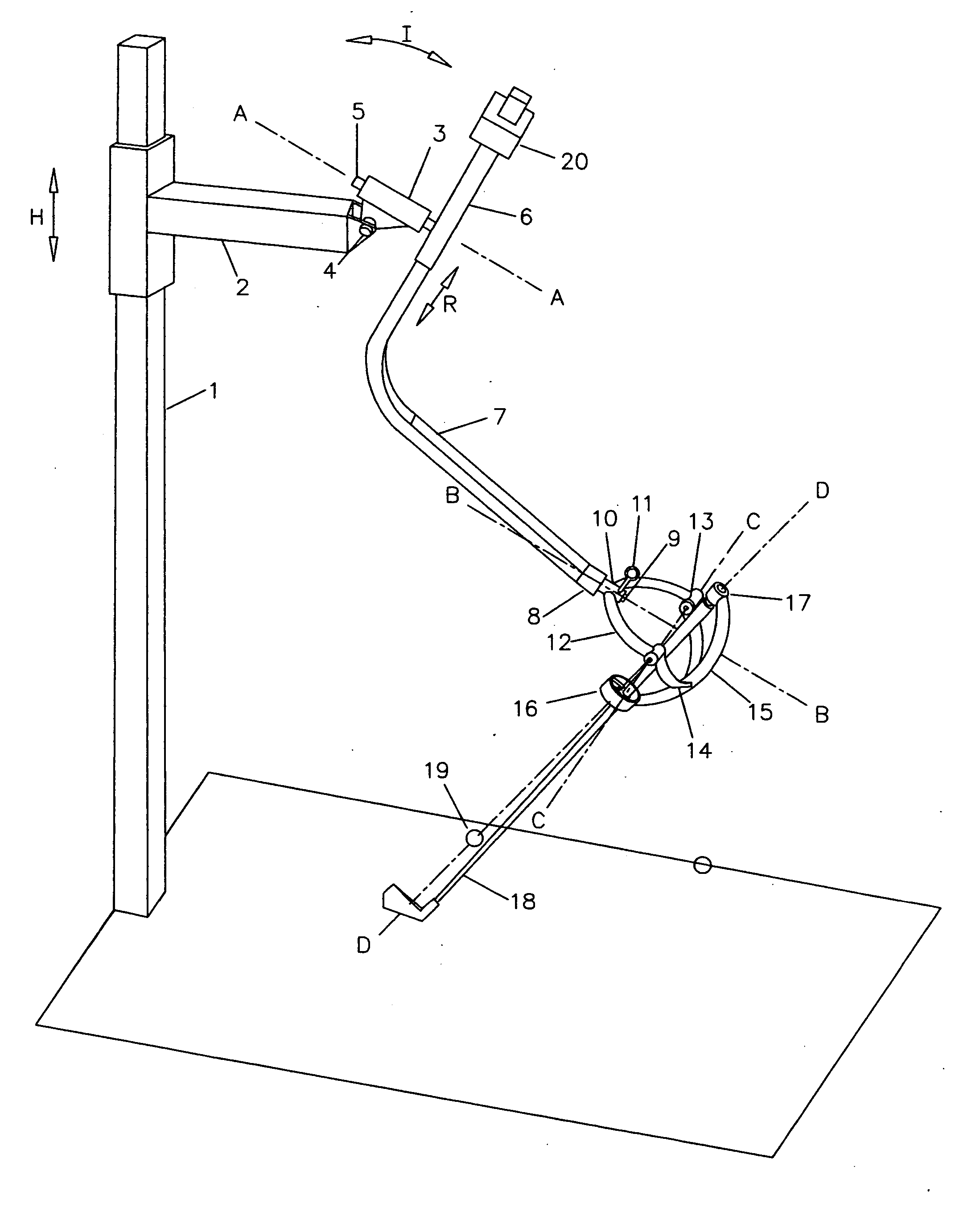
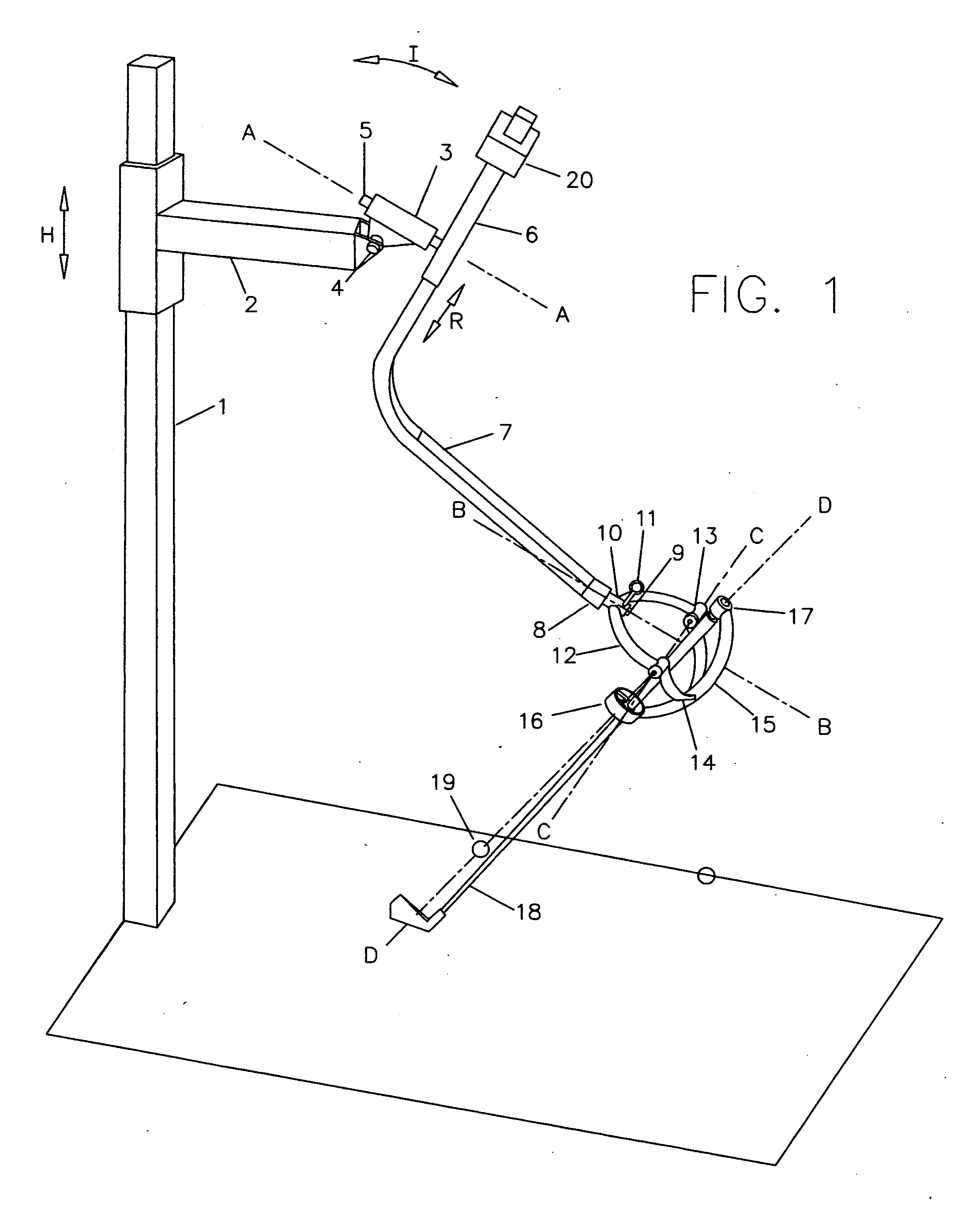
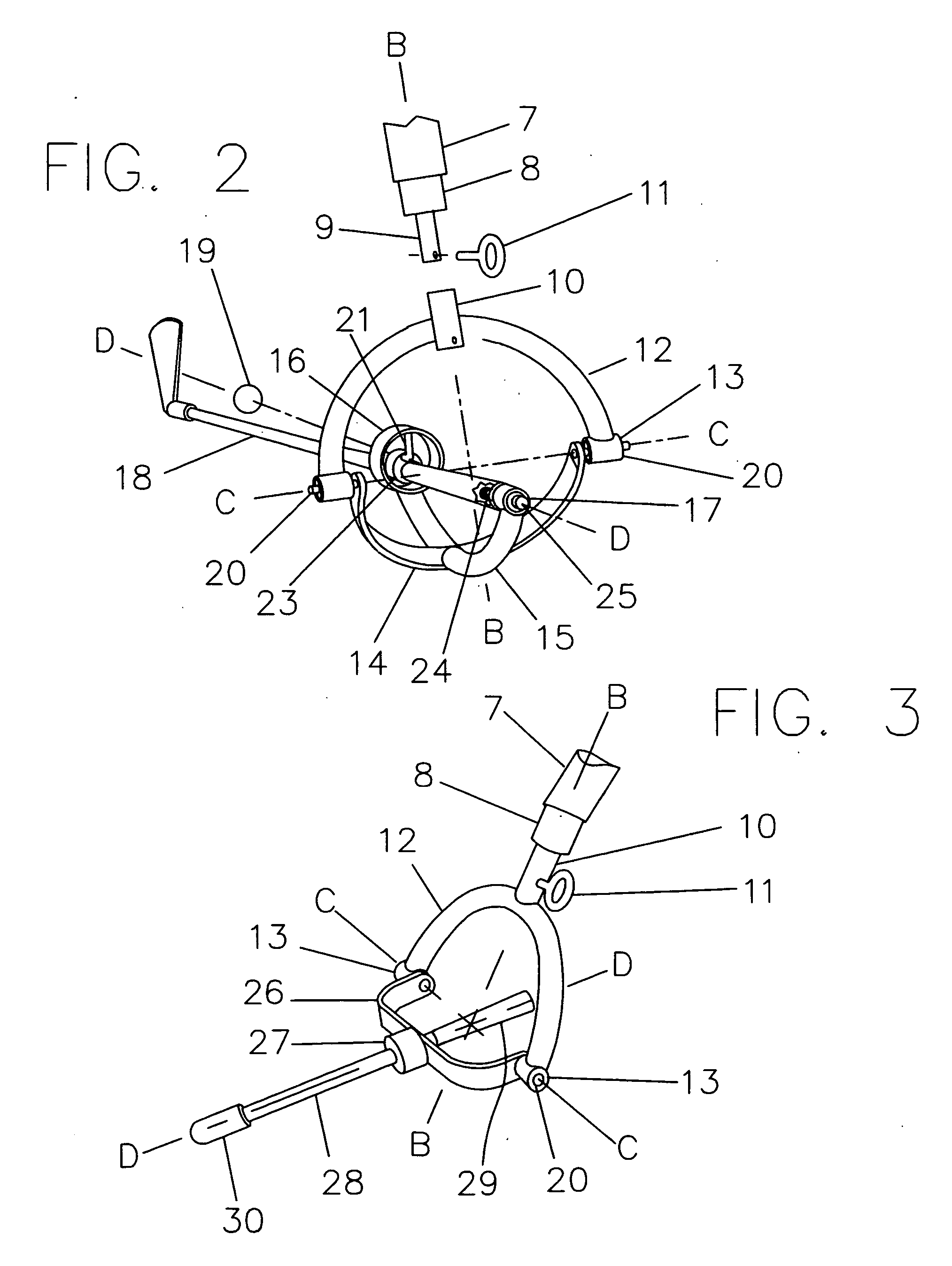
A Method, a Computer Program, and Device for Controlling a Movable Resistance Element in a Training Device
ActiveUS20100069202A1Short response timeFast trainingClubsMuscle exercising devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceMuscular force
A method for controlling a movable resistance element belonging to a training device. The resistance element is influenced by a user with a muscular force. A device is adapted to generate a reference signal for controlling a power conversion device coupled to and controlling a movable resistance element belonging to a training device, and which is influenced by a user with a muscular force. A computer program for carrying out the method and a use of the device.
Owner:SENSYACT
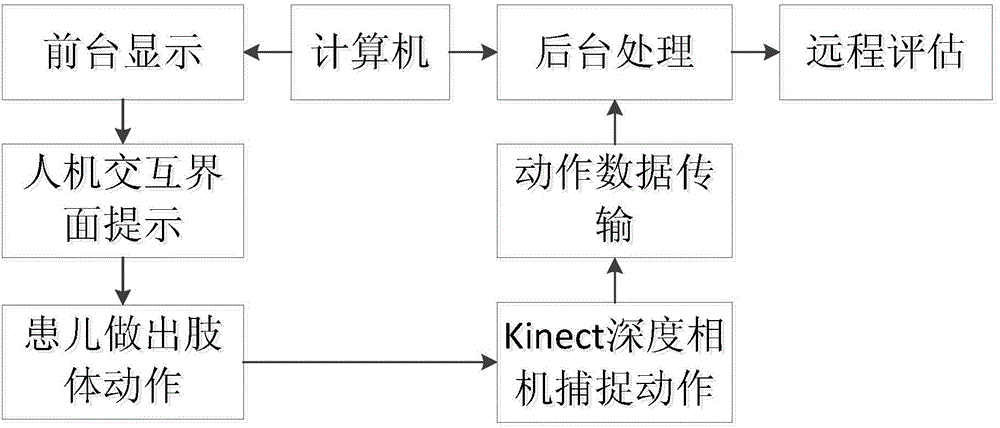
Cerebral palsy child rehabilitation training method based on Kinect sensor
InactiveCN104524742AAccurate detection of coordinated actions in real timeImprove coordinationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCerebral paralysisMuscular force
The invention discloses a cerebral palsy child rehabilitation training method based on a Kinect sensor. The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring skeleton point data of a child; S2, carrying out limb movement training and judging the tilting angle and uplifting angle of skeleton points of the child, wherein after the child conducts a movement, the movement of the child is captured, and the tilting angle and uplifting angle of the joint points of the head, the upper limbs and the lower limbs are judged; S3, carrying out robust interactive processing on the movement of the child; S4, connecting a game engine and sending child skeleton data obtained after robust interactive processing in the step S3 to the game engine; S5, feeding back the movement of the child in a voice mode to remind the child of non-standard movements and encourage the child to conduct standard movements; S6, estimating the progress of rehabilitation training of the child. According to the method, the movement behavior characteristics of the child in training are acquired based on microsoft Kinect, so that the cardiovascular endurance, muscular endurance, muscular force, balance and flexibility of the child are comprehensively developed.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Resistance and power monitoring device and system for exercise equipment
InactiveUS7351187B2Enhance physical fitnessWeightsMovement coordination devicesMuscular forceImpeller
An exercise device includes pedals, a belt and a hydro-kinetic brake. A user applies muscular force to the pedals and the pedal belt transfers the motion of the pedals to a flywheel shaft of the fluid brake. The pedals may be configured to accept force from a hand, foot, arm, leg and / or neck of the user. The amount of work performed by the user is derived by measuring the relative rotational speeds of two radial-blade impellers of the fluid brake. The wattage exhibited by the fluid brake during the exercise session may be recorded and associated with an identified user, whereby records of the exercise performance of an individual may be updated.
Owner:SELIBER JOSEPH
Control stick adapter
ActiveUS7993203B1Feel goodGaming more comfortableCathode-ray tube indicatorsVideo gamesMuscular forceEngineering
A control mechanism adapter for a game console having a circular base with an upper surface, an under surface, and a central opening, wherein the central opening allows a user's finger to rest directly on the control mechanism of a game console. There are legs on the under surface of said base, and attachment elements on the legs to attach the base to a control mechanism of a game console. The base has two raised control elements on the upper surface and on opposing sides of the base. The open center allows the user's thumb to rest on the same standard control geometry that the user is accustomed to using. The user has the option to press against the raised elements, either laterally or with the tip of the thumb. The raised element feature allows the user to manipulate the control lever with less downward muscular force and with improved dexterity.
Owner:STEELSERIES
Automated surgical rod cutter and bender including a power-base, assembly for rod cutting, and assembly for rod bending
InactiveUS20120186411A1Linear changeStock shearing machinesForging press detailsMuscular forceEngineering
A rod manipulator including power-base and various assemblies, interchangeably attaching to the base. The power-base is composed of a pneumatic cylinder and piston which affects the function of various assemblies. The piston moves the central component of an assembly toward the fixed portion of that assembly. A bending assembly containing mobile pivots around which a surgical metal rod can be bent. A cutting assembly containing blades in central and fixed portions between which a surgical metal rod can be cut. The distal end of the cut rod is retained by replaceable, sterilizable, eject-grips during and immediately after the cutting operation. The general object of the invention is to provide an improved surgical rod cutter and surgical rod bender, capable of performing both tasks with one power source, requires one-person operation, eliminates the need for significant muscular forces and eliminates the opportunity for an unsafe projectile in the operating room.
Owner:LODAHI SEBSTIAN +2
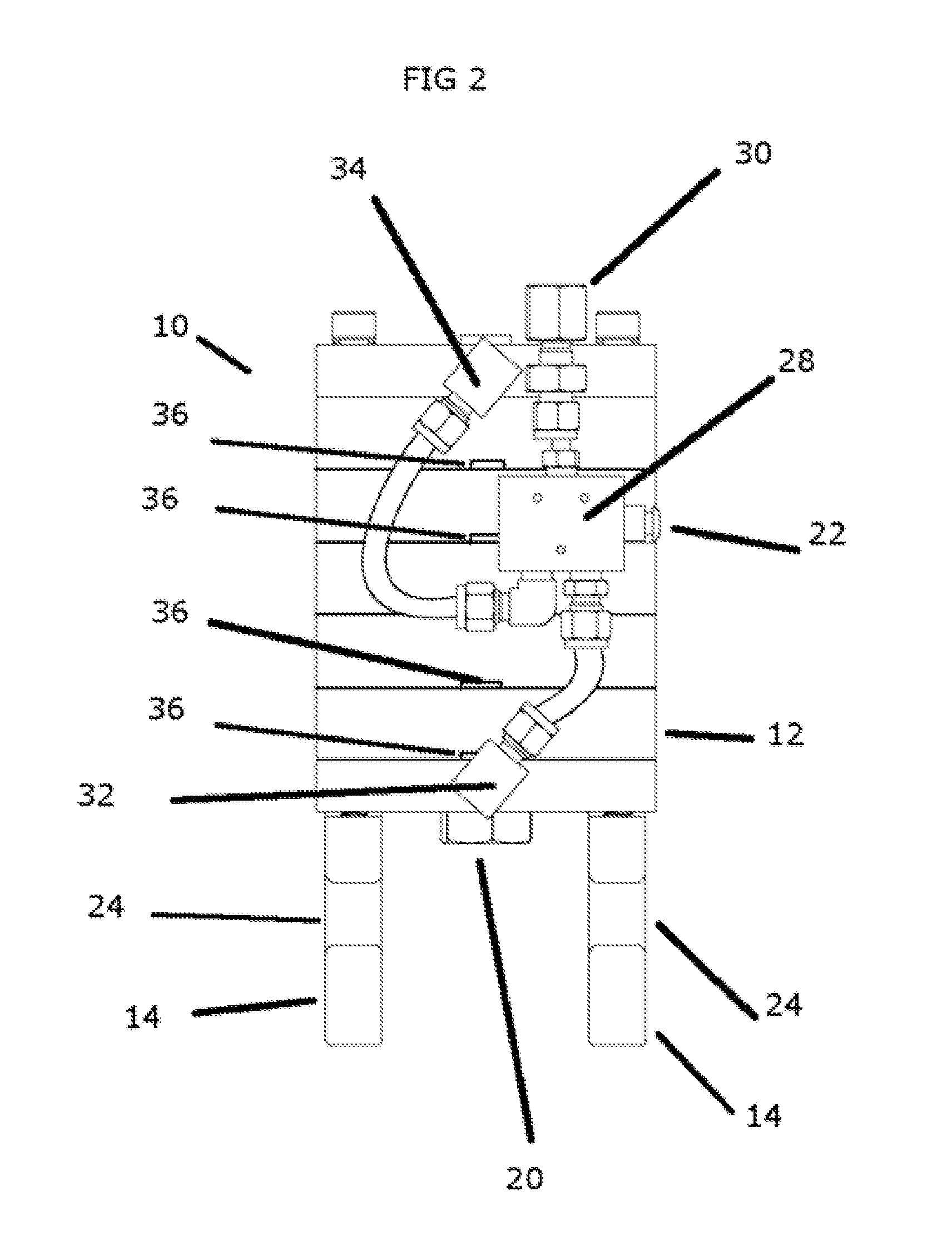
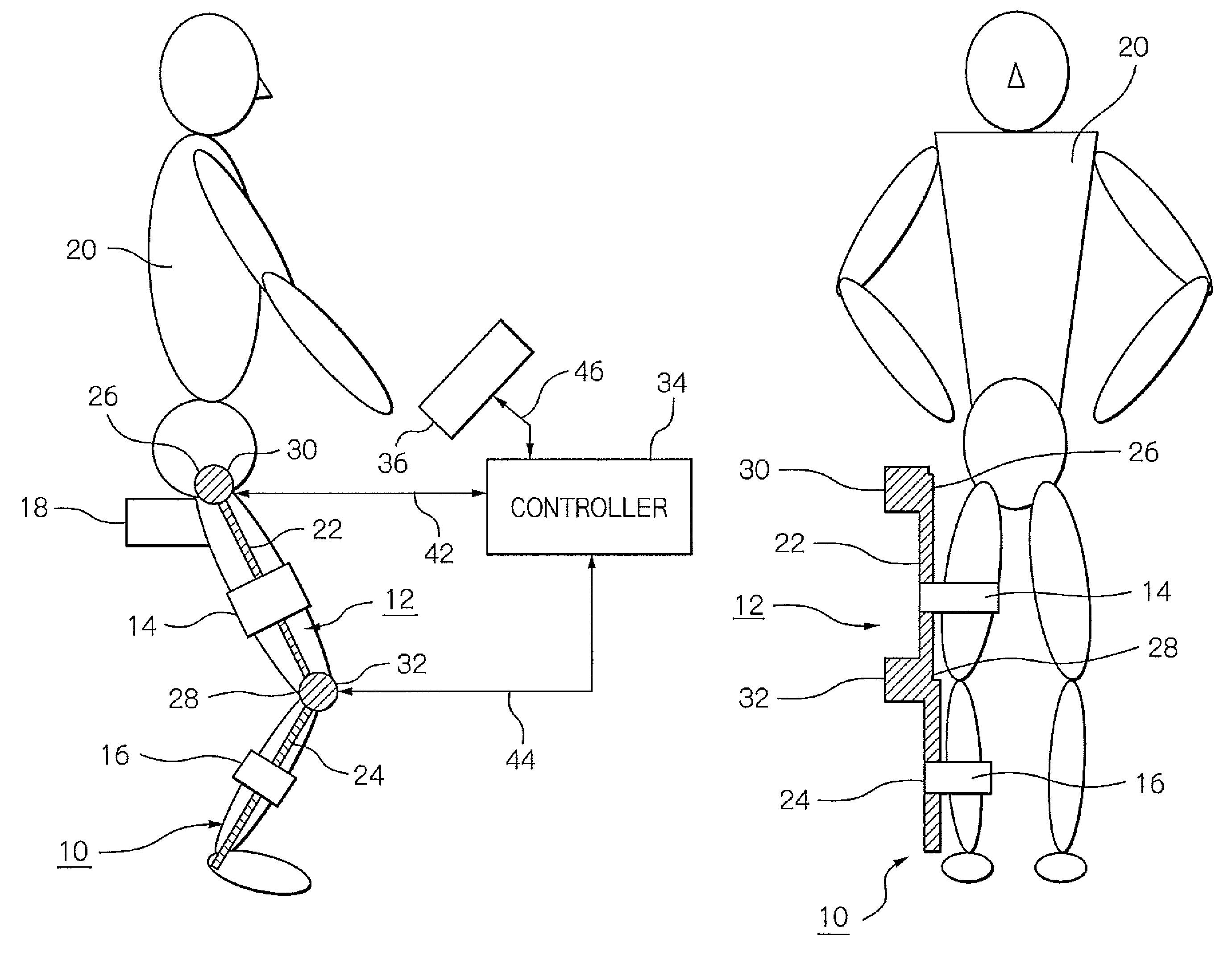
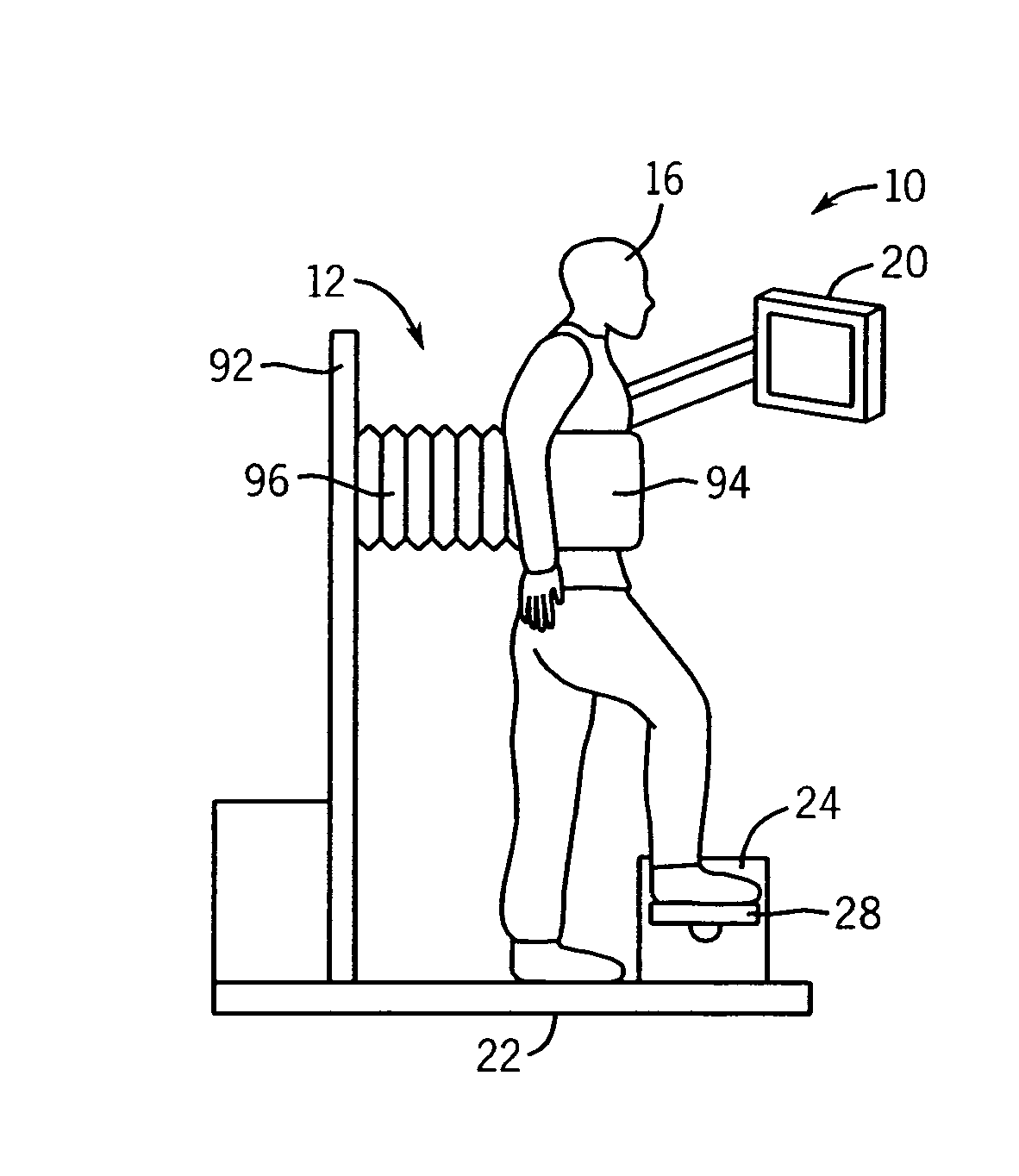
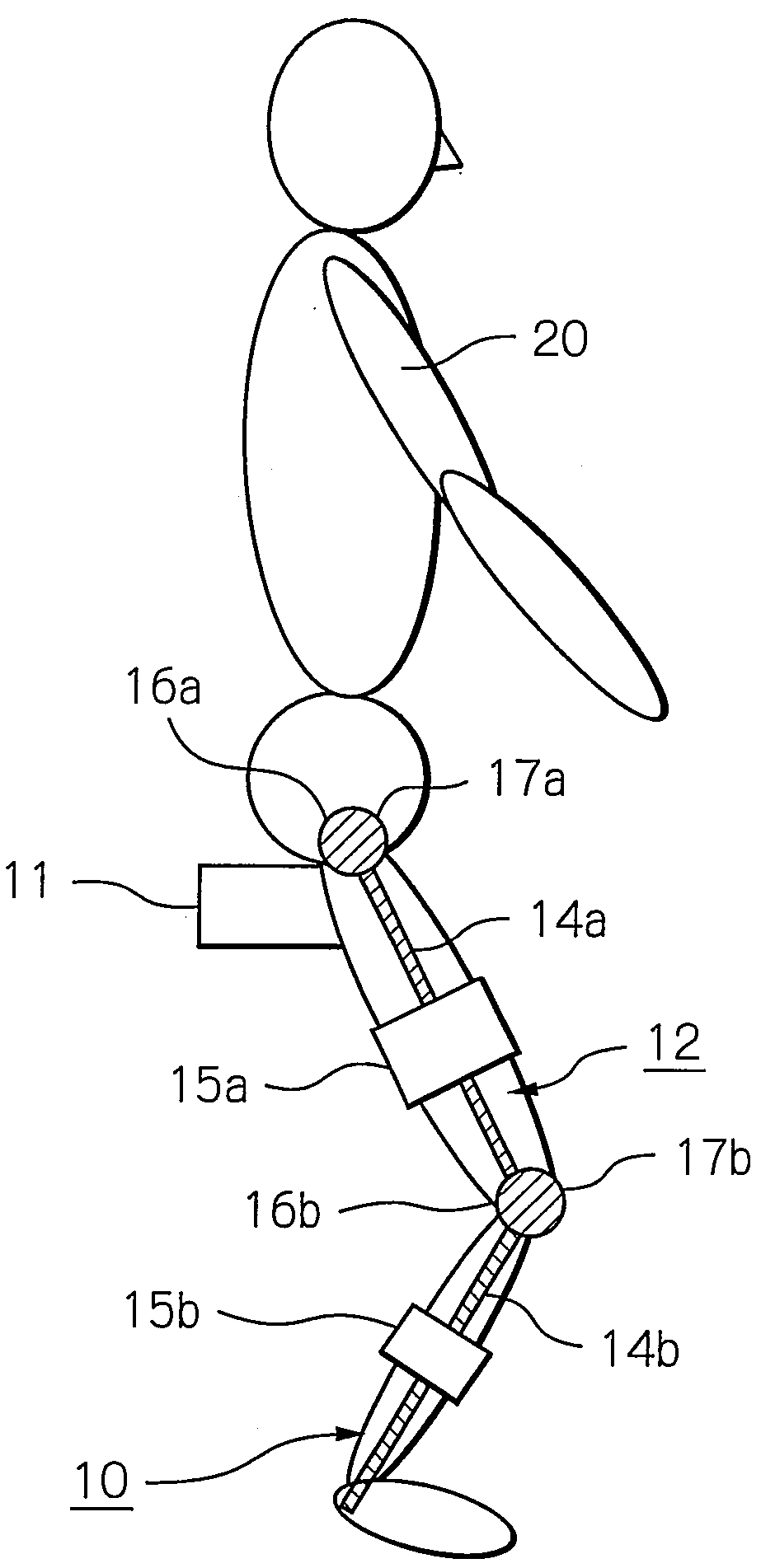
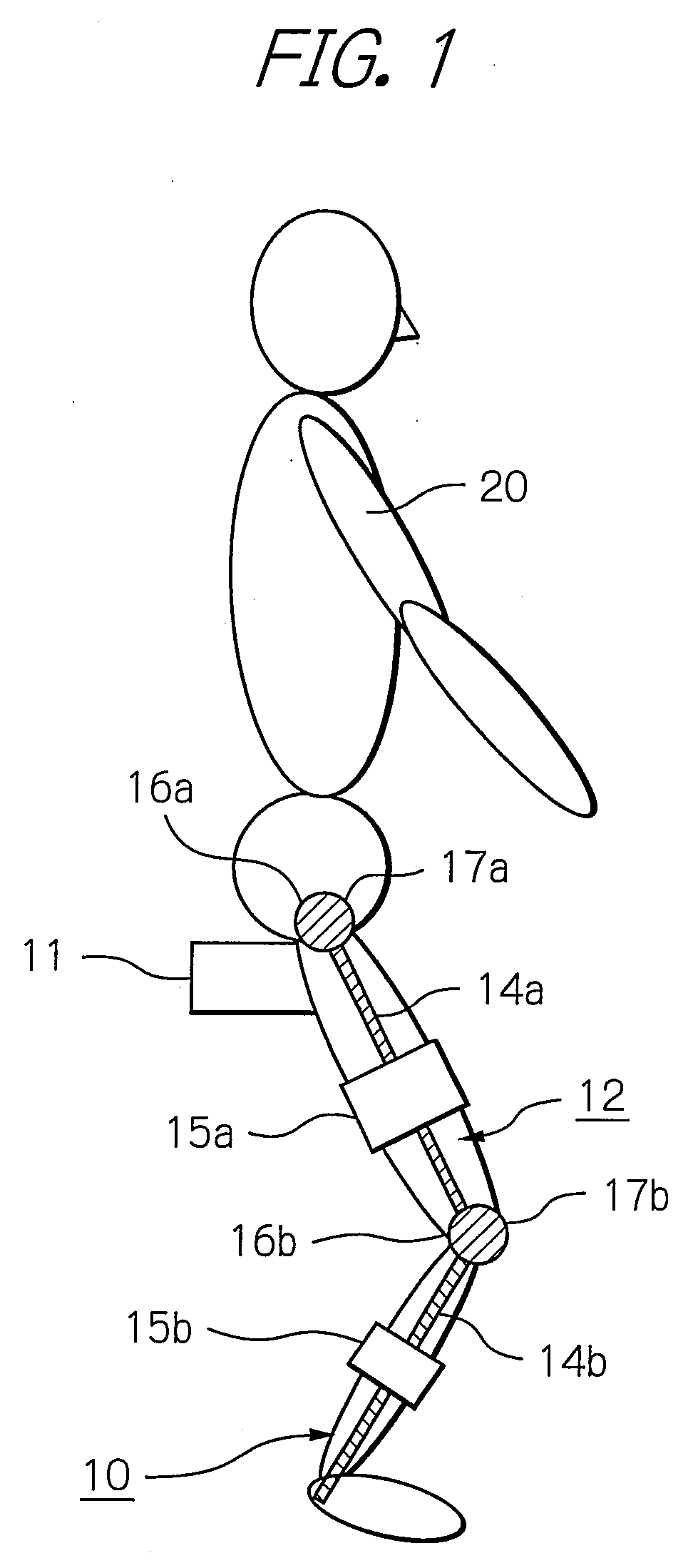
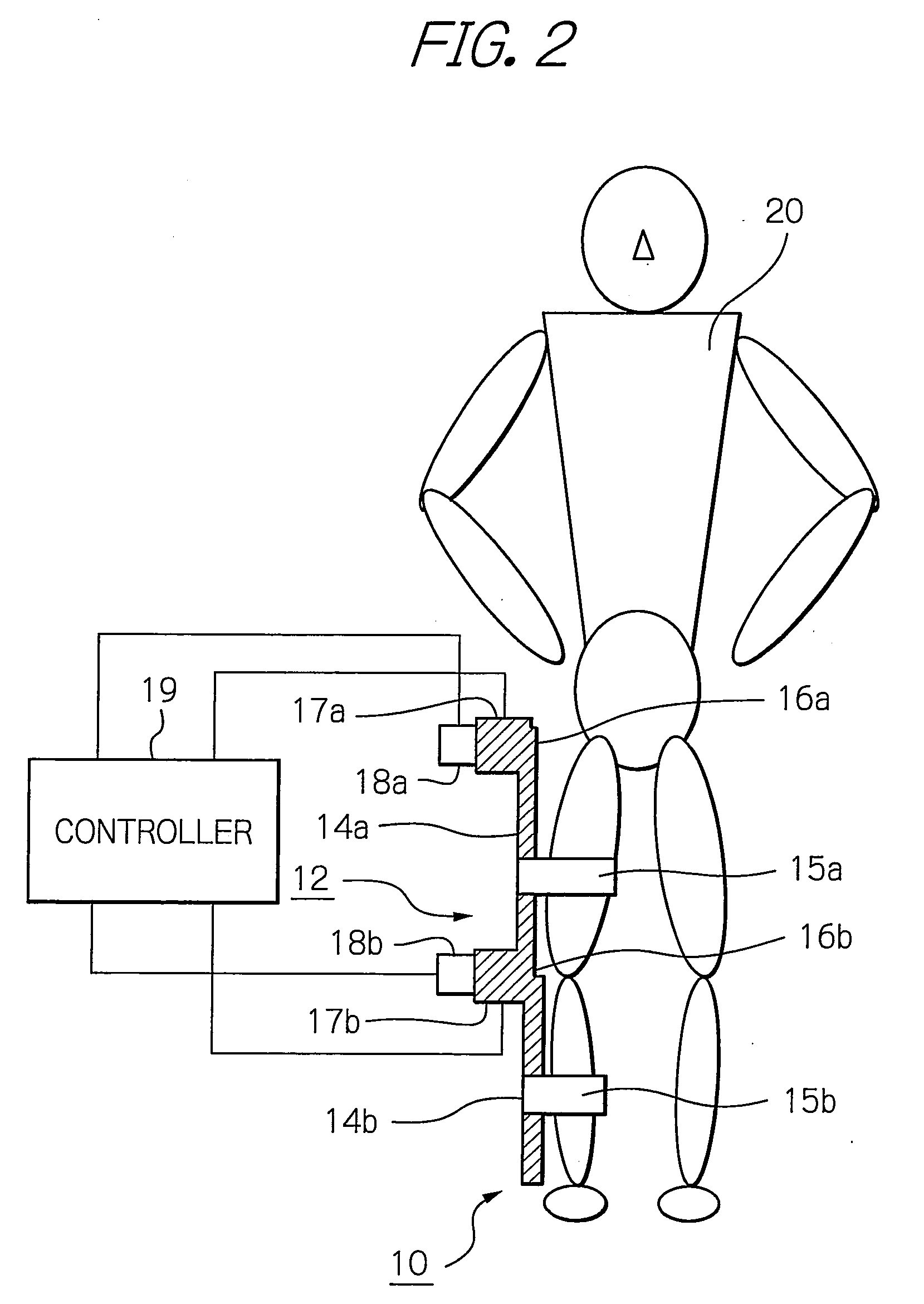
Muscle training device with muscular force measurement function for controlling the axial torque of a joint axle
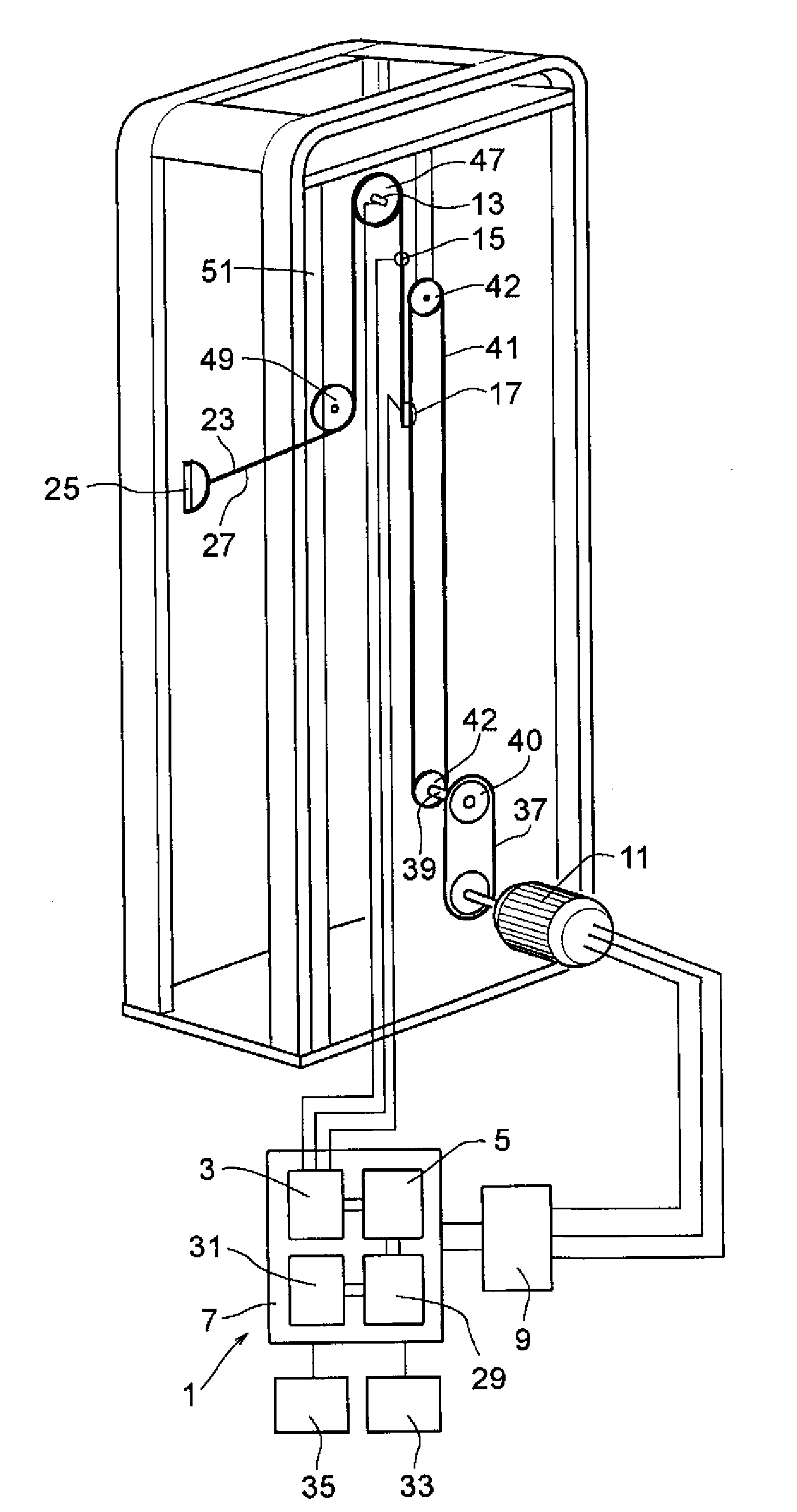
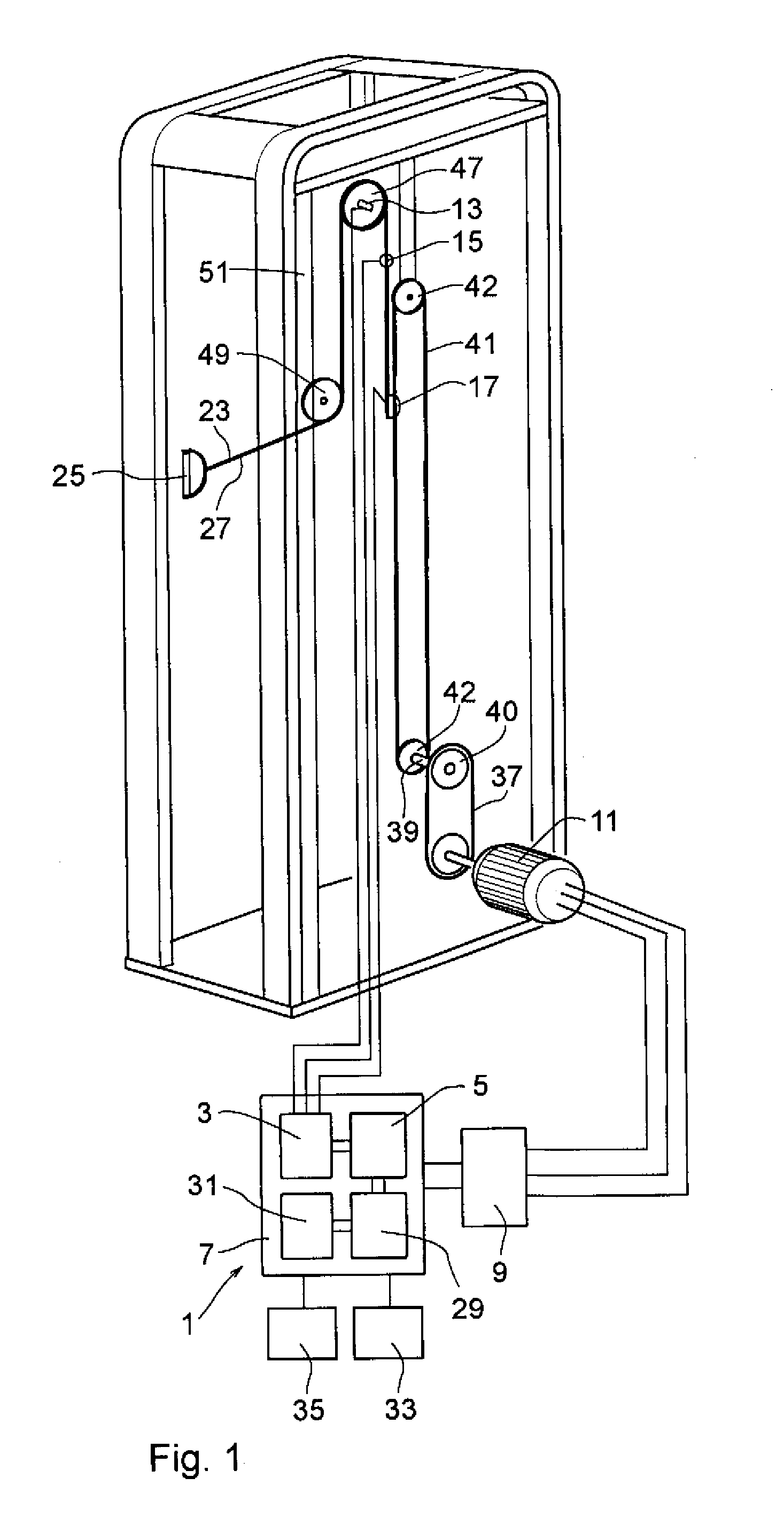
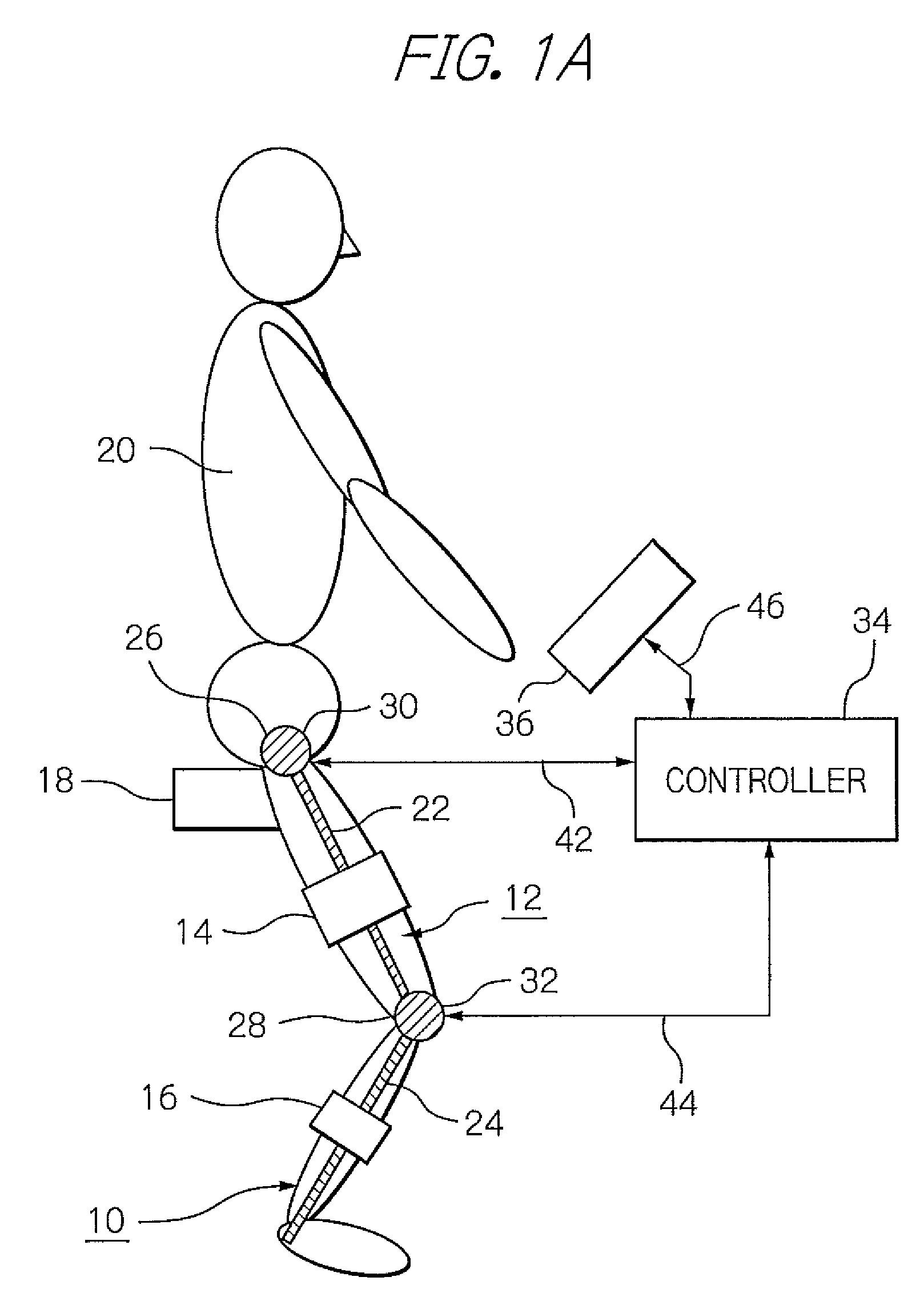
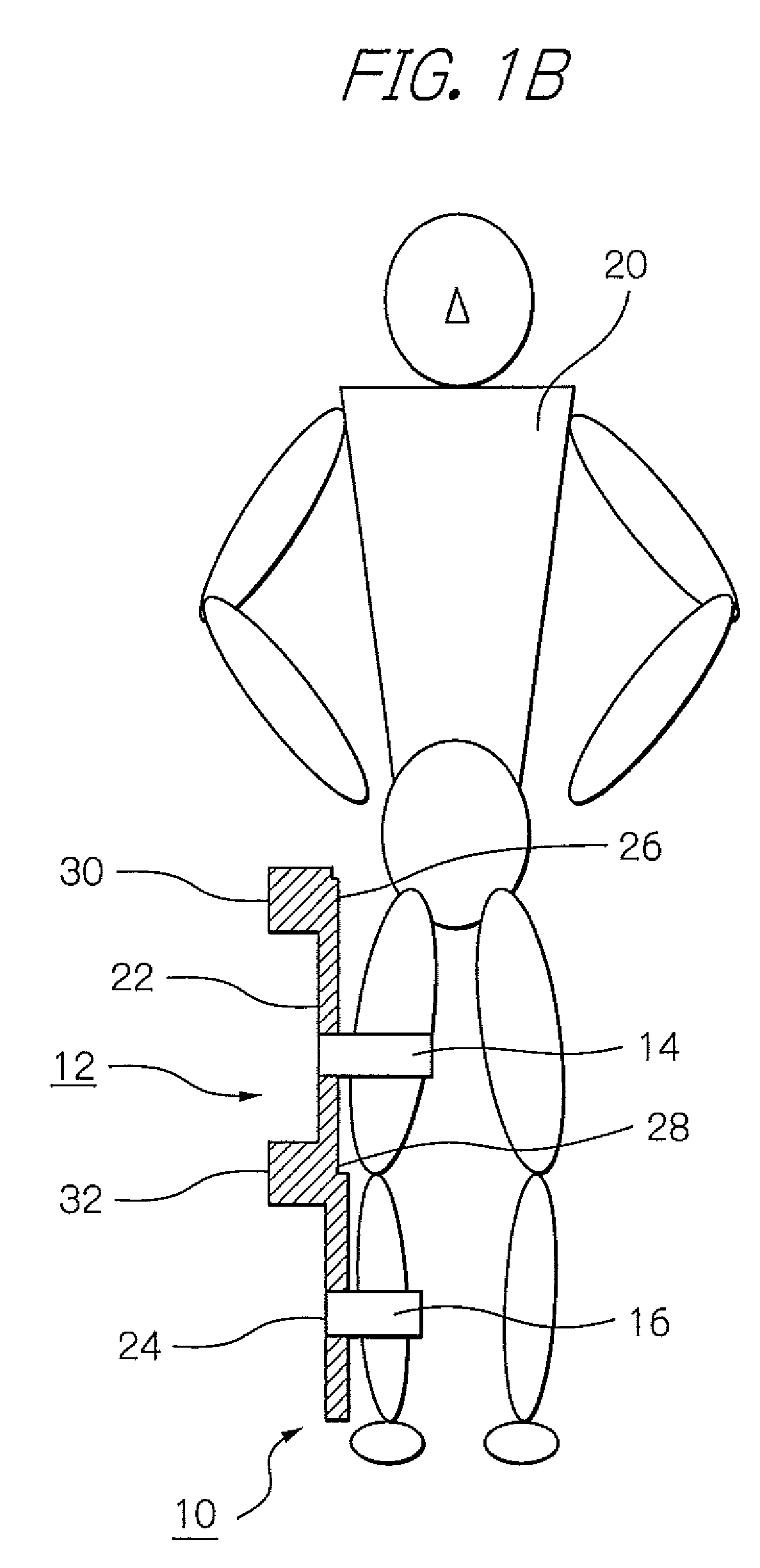
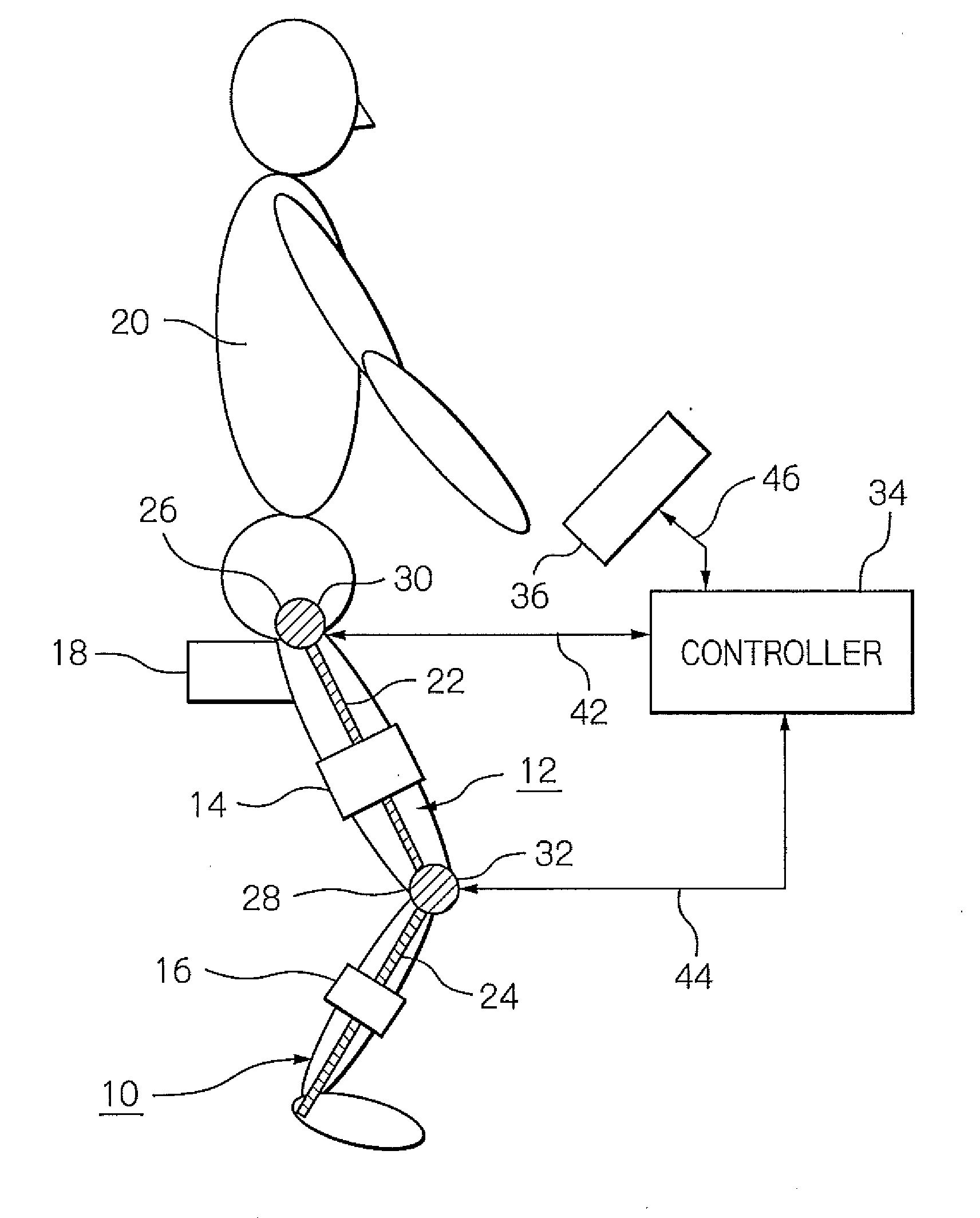
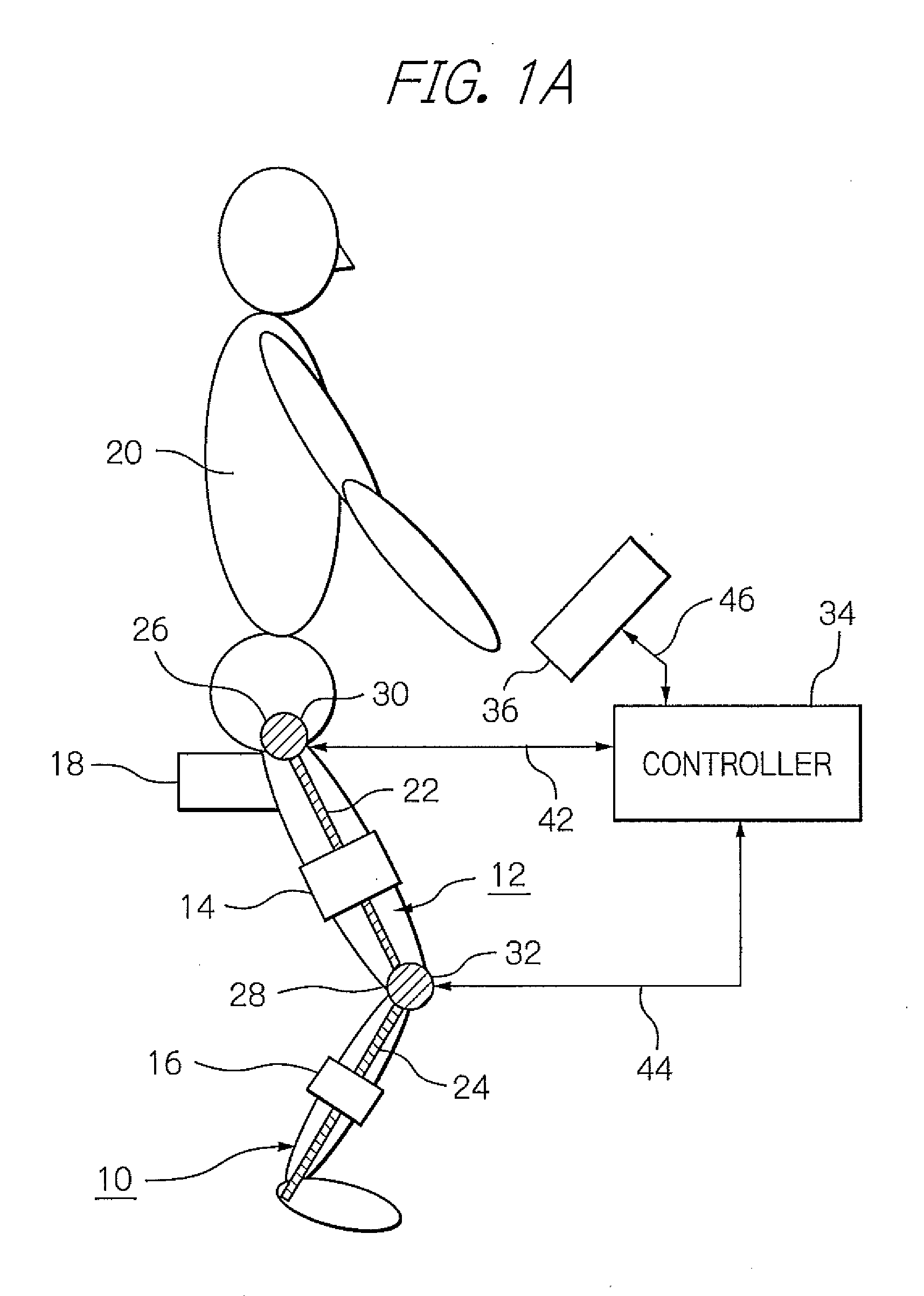
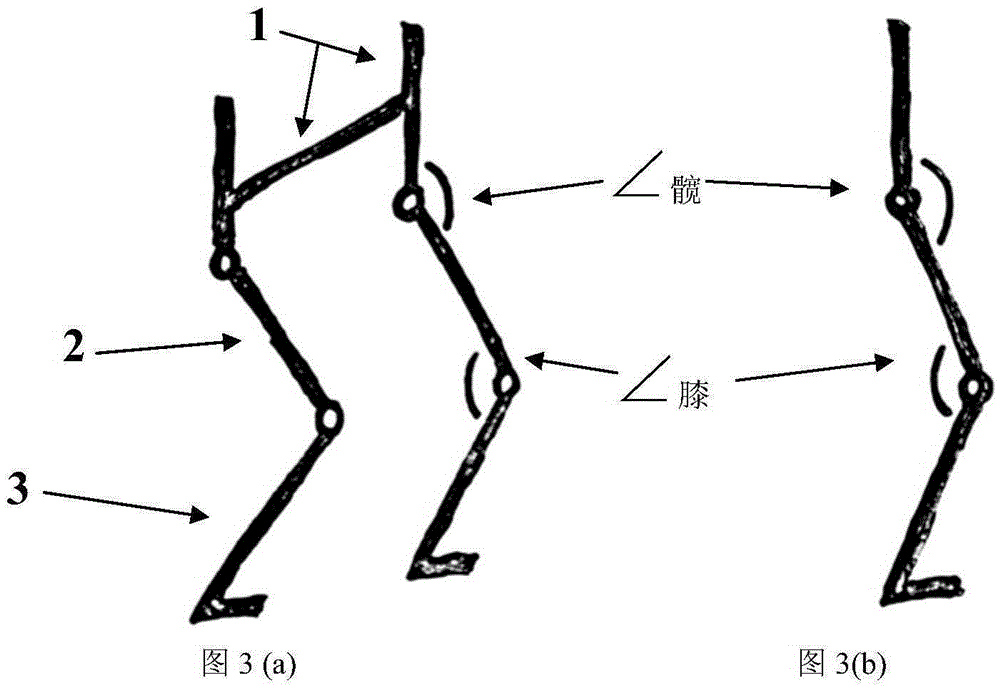
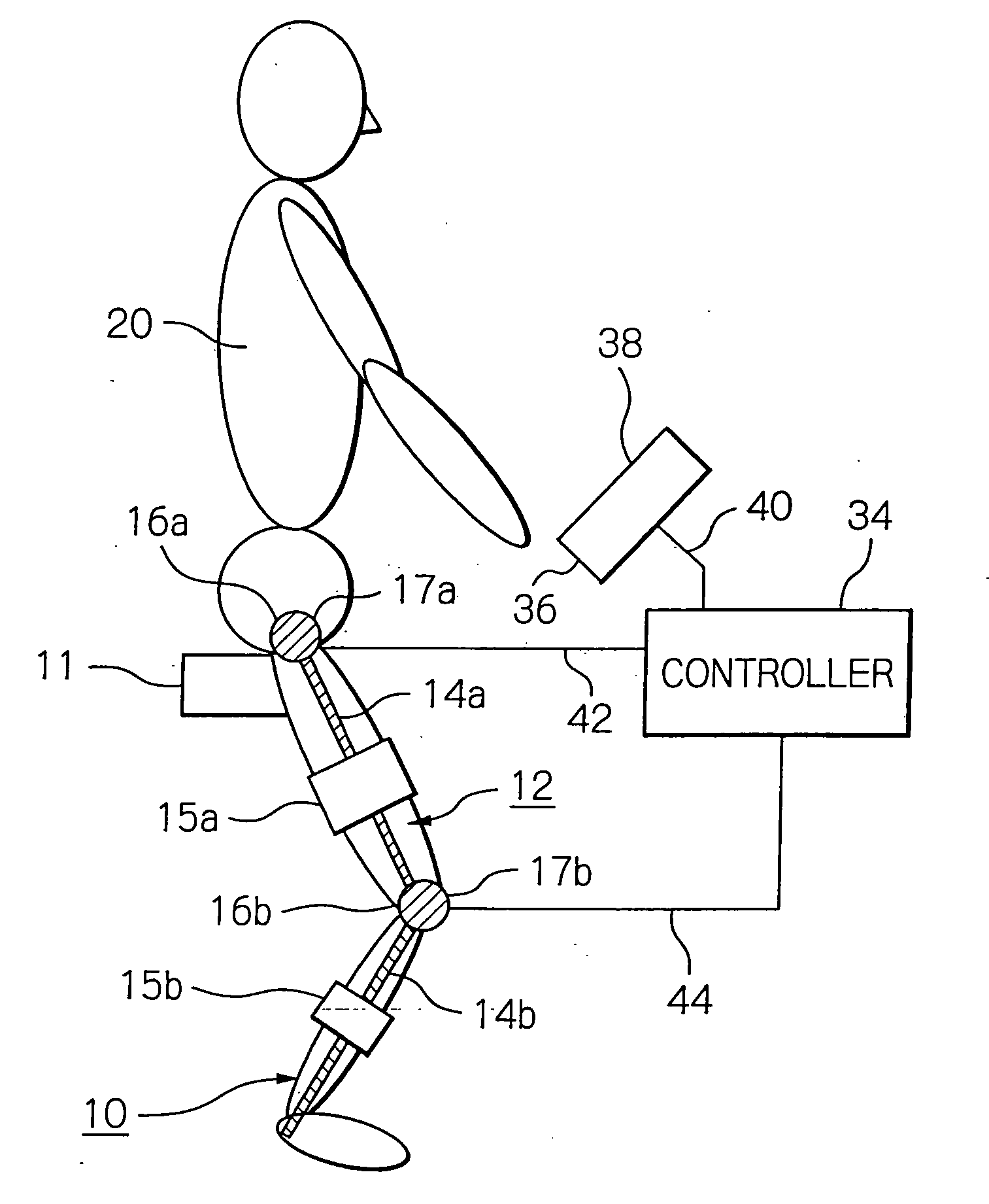
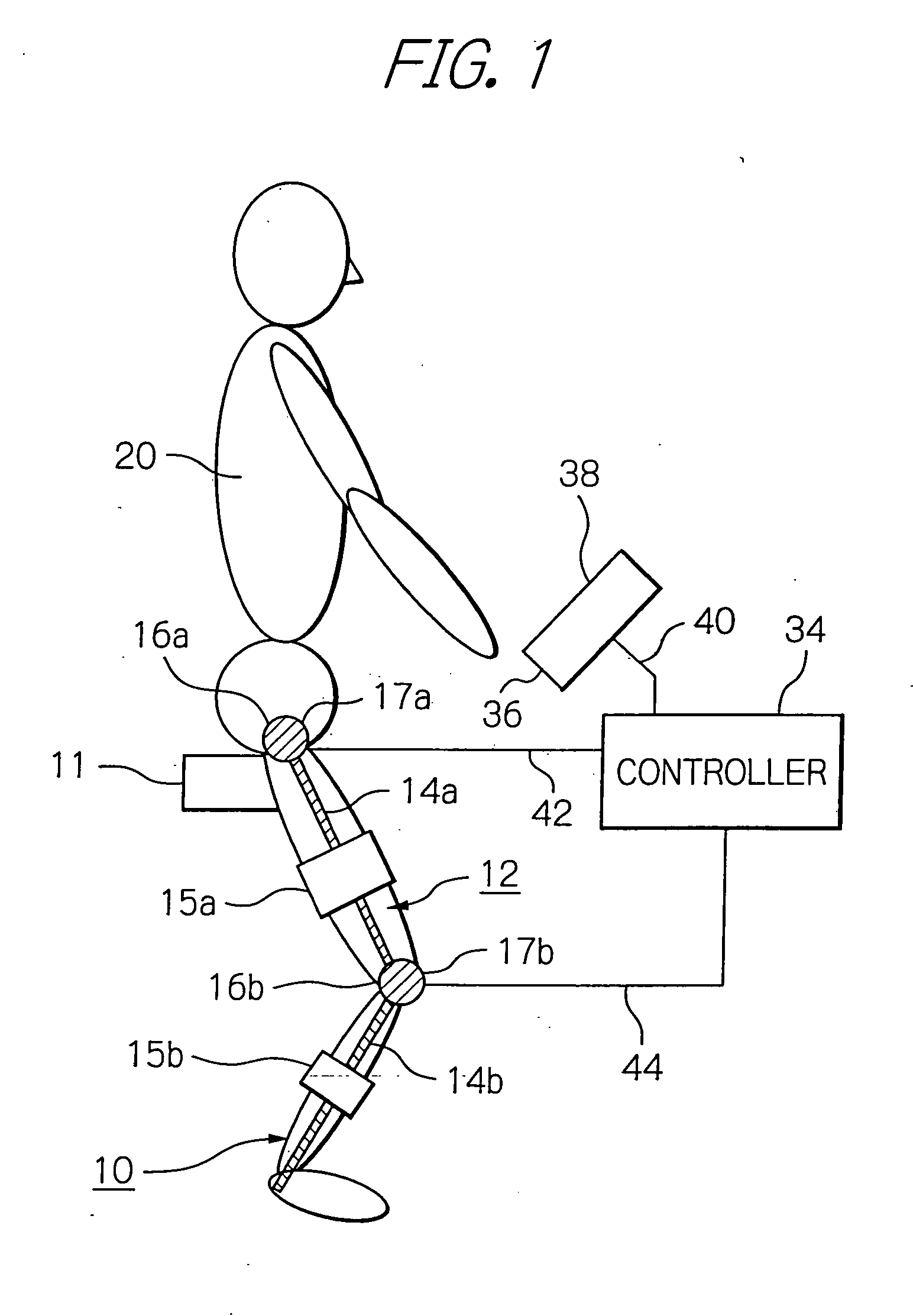
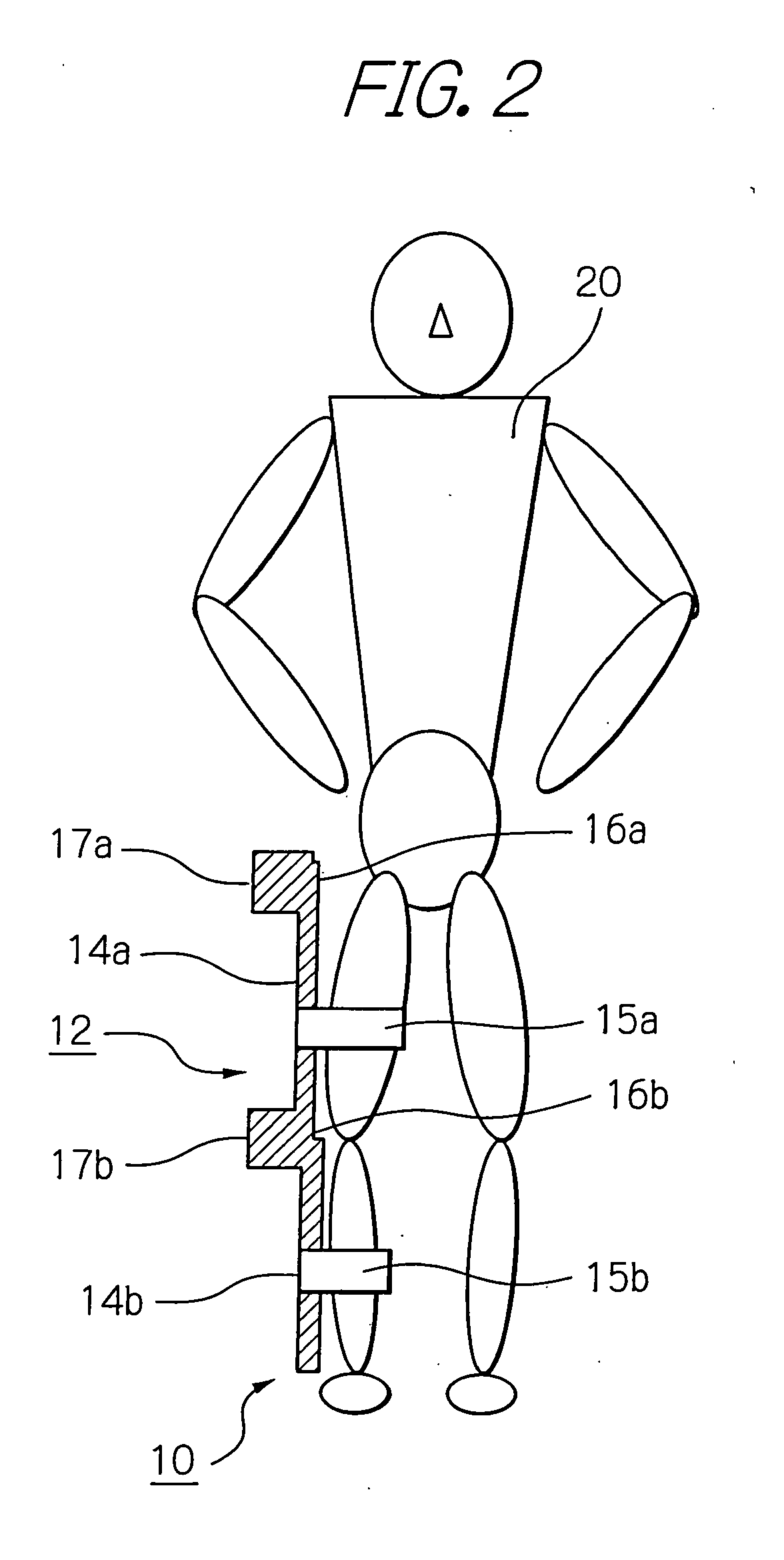
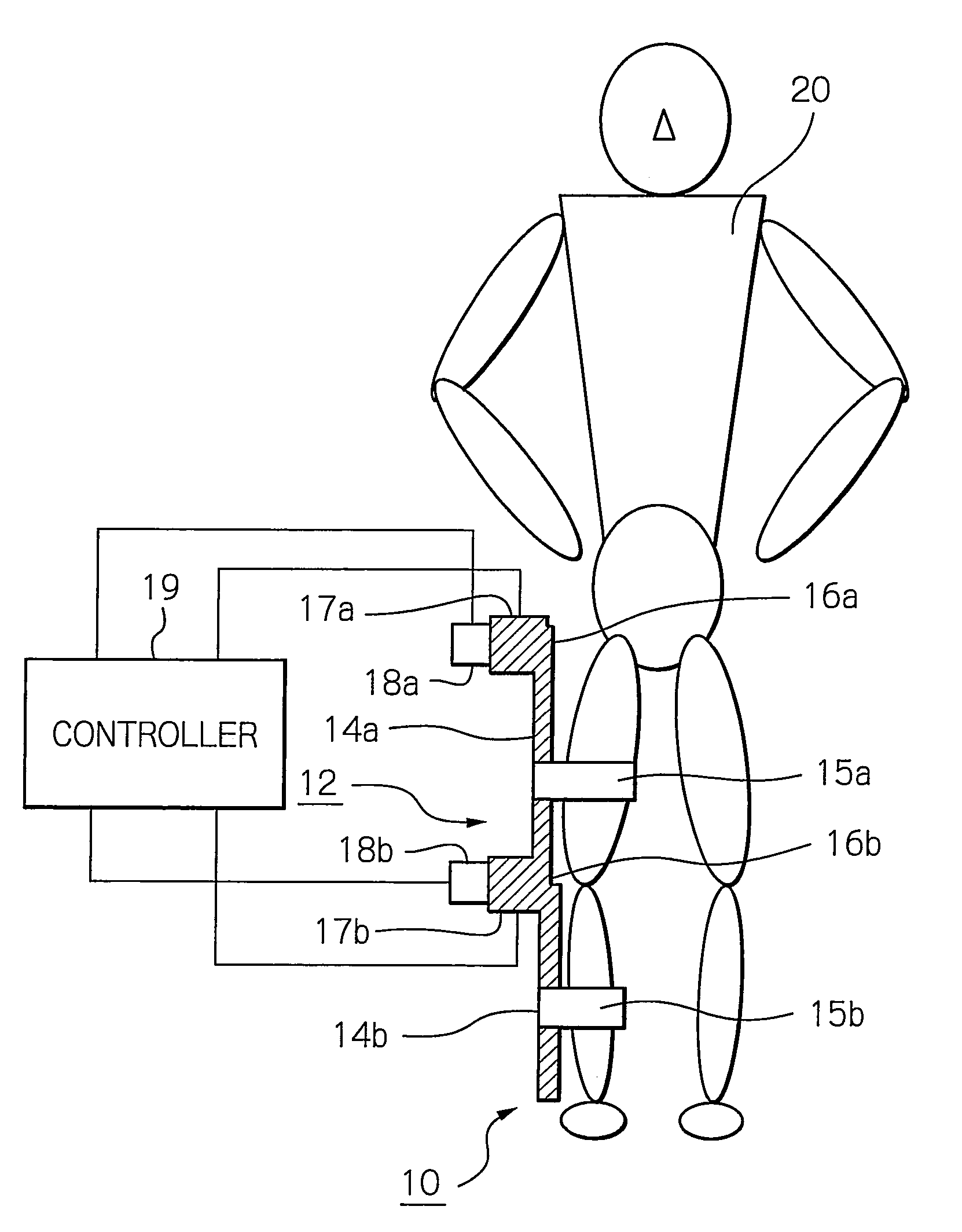
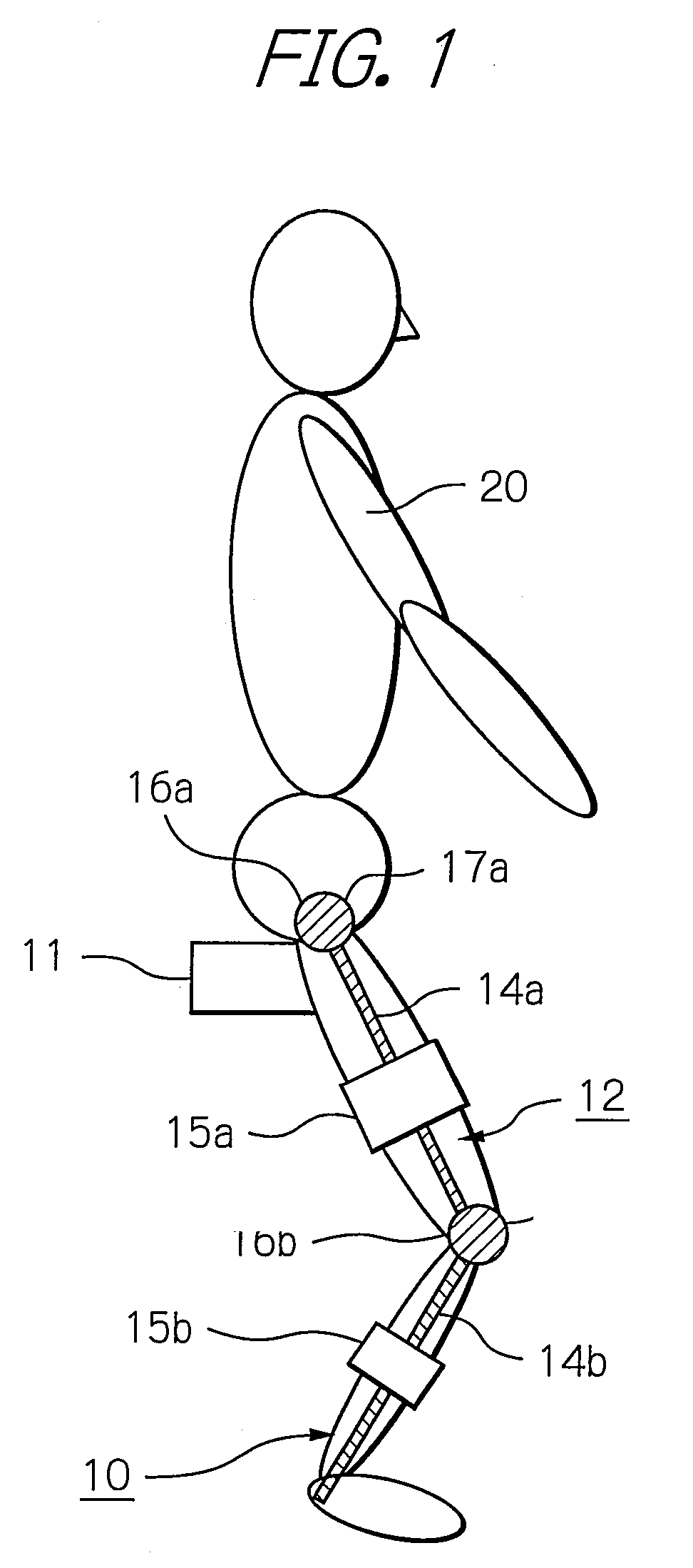
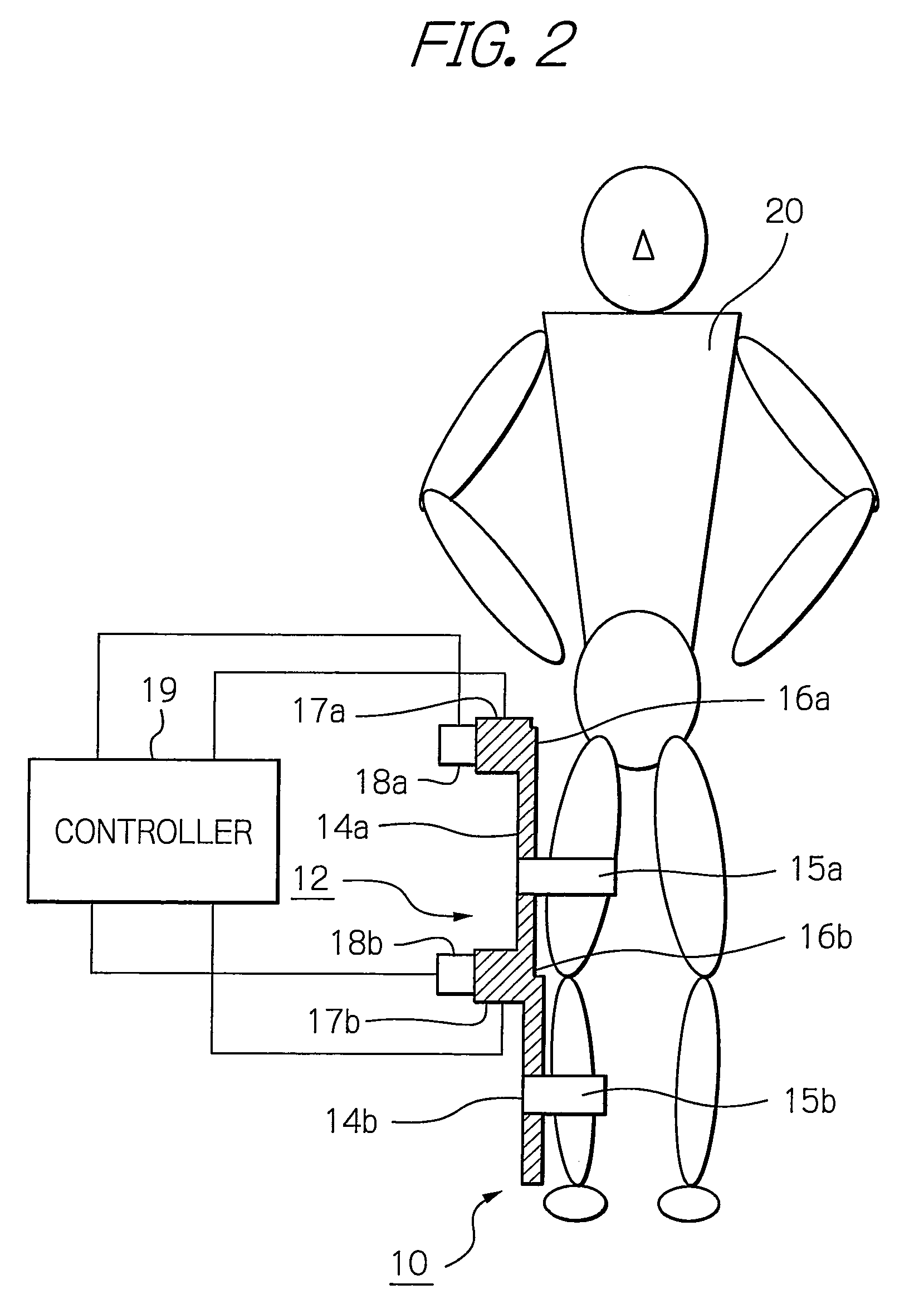
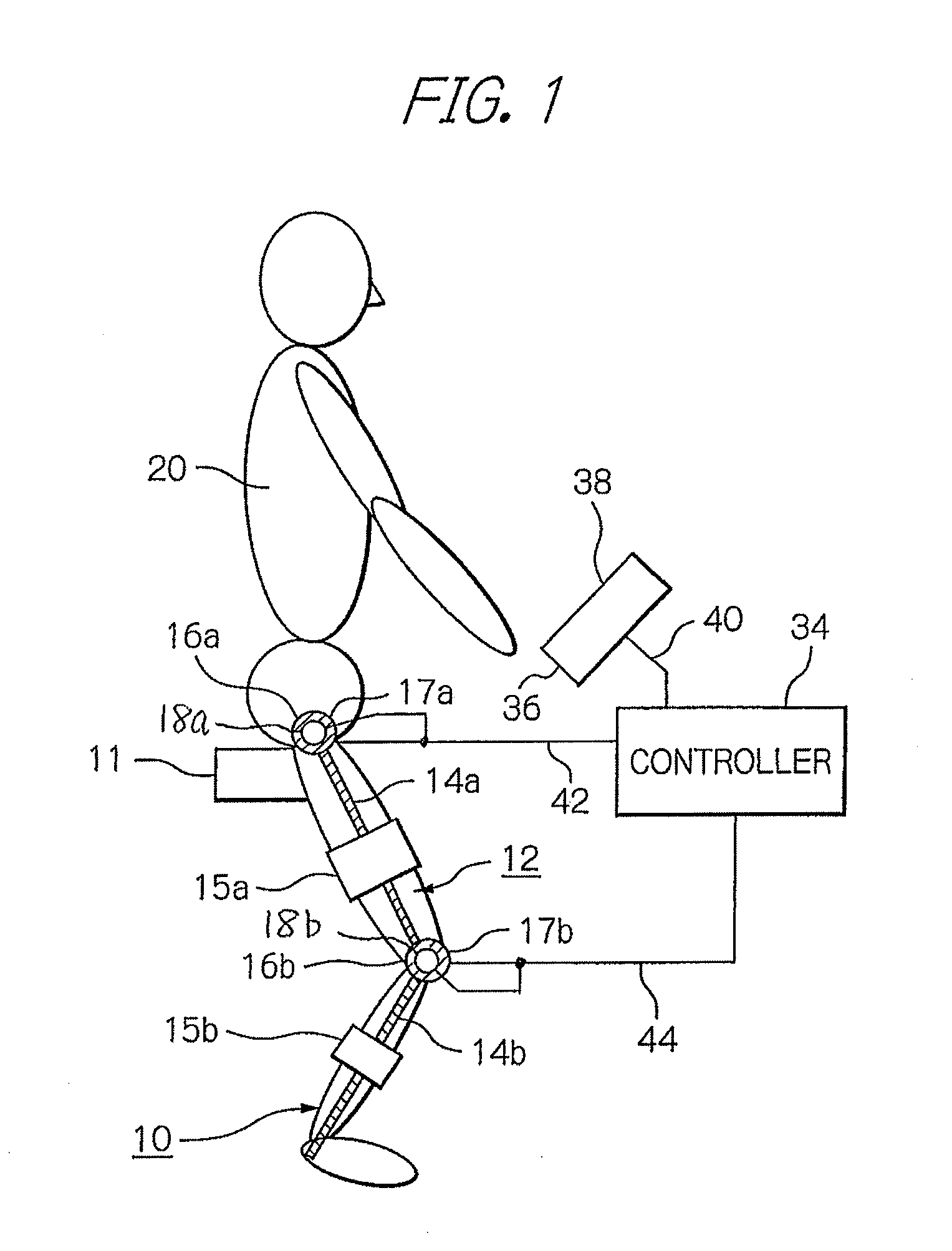
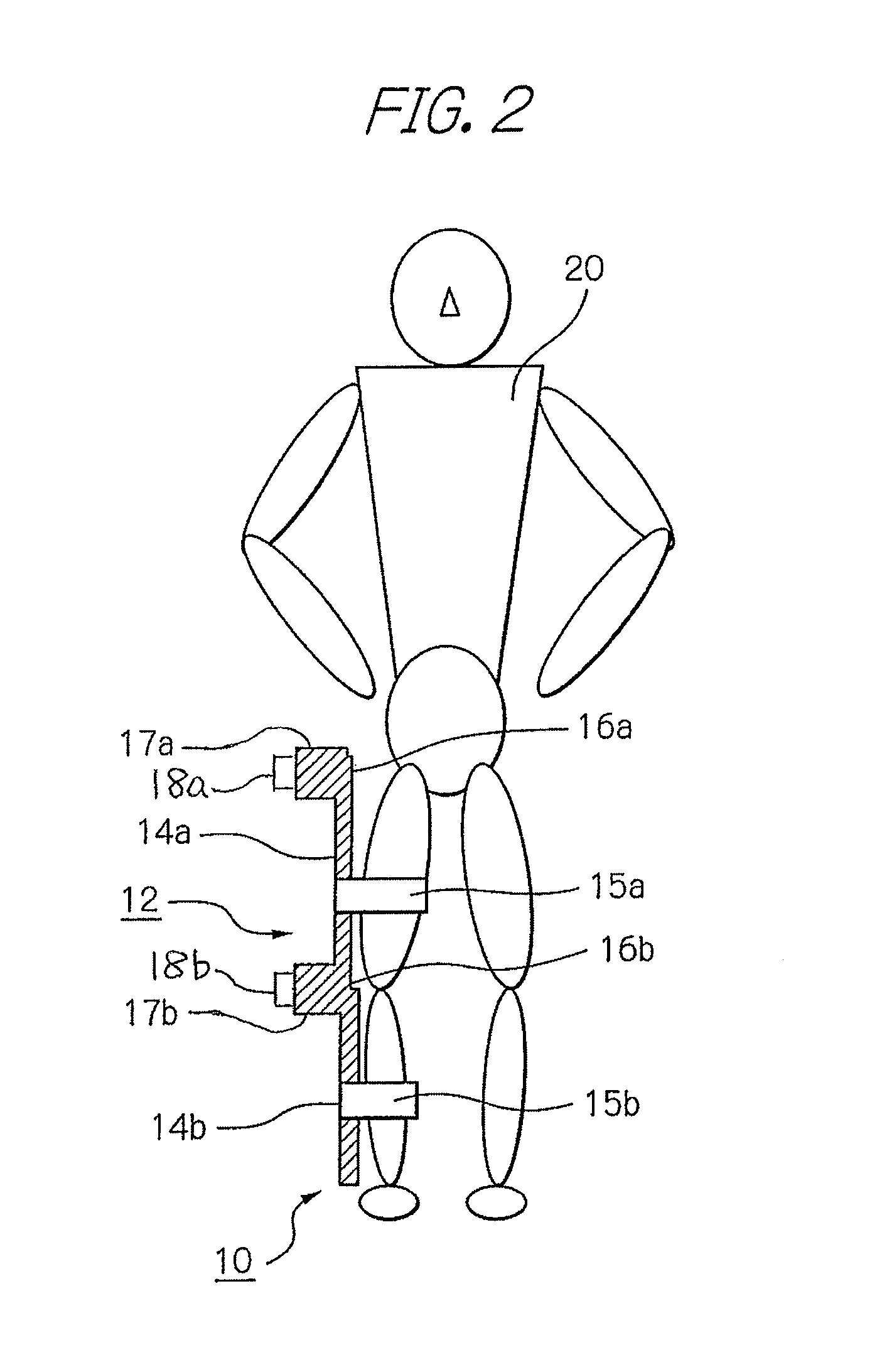
ActiveUS8181520B2Safe measurement and training of muscular forceAccurate measurementChiropractic devicesWork measurementMuscular forceMuscle training
A training device measures, after its robot arm is mounted on a trainee, a change in angle of the joint axles of a limb of the trainee with angular sensors. Based on the angular change measured, a controller calculates an angular rate in the direction in which a load is applied, stores as the maximum muscular force a load at the time when the angular rate has exceeded a predetermined value, and stops applying the loads.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Muscle training device with muscular force measurement function for controlling the axial torque of a joint axle
ActiveUS20100050765A1Measure securityEnsure training safetyChiropractic devicesWork measurementMuscular forceMuscle training
A training device measures, after its robot arm is mounted on a trainee, a change in angle of the joint axles of a limb of the trainee with angular sensors. Based on the angular change measured, a controller calculates an angular rate in the direction in which a load is applied, stores as the maximum muscular force a load at the time when the angular rate has exceeded a predetermined value, and stops applying the loads.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Skeletal muscle mechanical behavior multiscale modeling method
InactiveCN106202739ARealize macro and micro geometry modelingRealize simulationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMuscle tissueMuscular force
The invention relates to a skeletal muscle mechanical behavior multiscale modeling method and aims at solving the problem in the prior art that a complete process from cell electrophysiologic action potential activation to skeletal muscle mechanical output cannot be simulated. The method comprises the steps of S1, determining positions and attitudes of muscle fibers; S2, establishing a skeletal muscle macroscopic geometric model and a skeletal muscle microcosmic geometric model according to the S1; S3, carrying out grid division on the geometric models established in the S2; S4, carrying out skeletal muscle electrophysiologic property modeling according to the S3; S5, carrying out multiscale calculation between cells and muscle tissues according to the S3 and S4; S6, establishing a skeletal muscle multiscale biomechanics model according to the S5; and S7, predicting muscular force according to the S6. The method is applied to the field of biomedical engineering.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Sport beverage containing protein
InactiveCN101015384AGood effectIncrease synthesisFood preparationMuscular forceIsomaltooligosaccharide
The invention discloses a sport beverage with protein, which contains saccharose, glucose, fructose, oligomisomaltose, lactalbumin, arginine, vitamin and minerals, wherein the beverage comprises is characterized by the following: (1) enhancing insuline effect; supplementing muscular glycogen rapidly; (2) releasing energy gradiently; maintaining to supplement muscular glycogen; (3) accelerating the repairation and regeneration of muscular tissue; (4) improving hormone synthesized level and muscular force for athletes; (5) supplementing lost electrolyte rationally in the sport; (6) supplementing vitamin in the sport.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF SPORTS SCI RES
Multifunctional training apparatus for the lower limb muscles
InactiveUS20110263389A1Easy to useSimple structureMuscle exercising devicesMuscular forceVertical plane
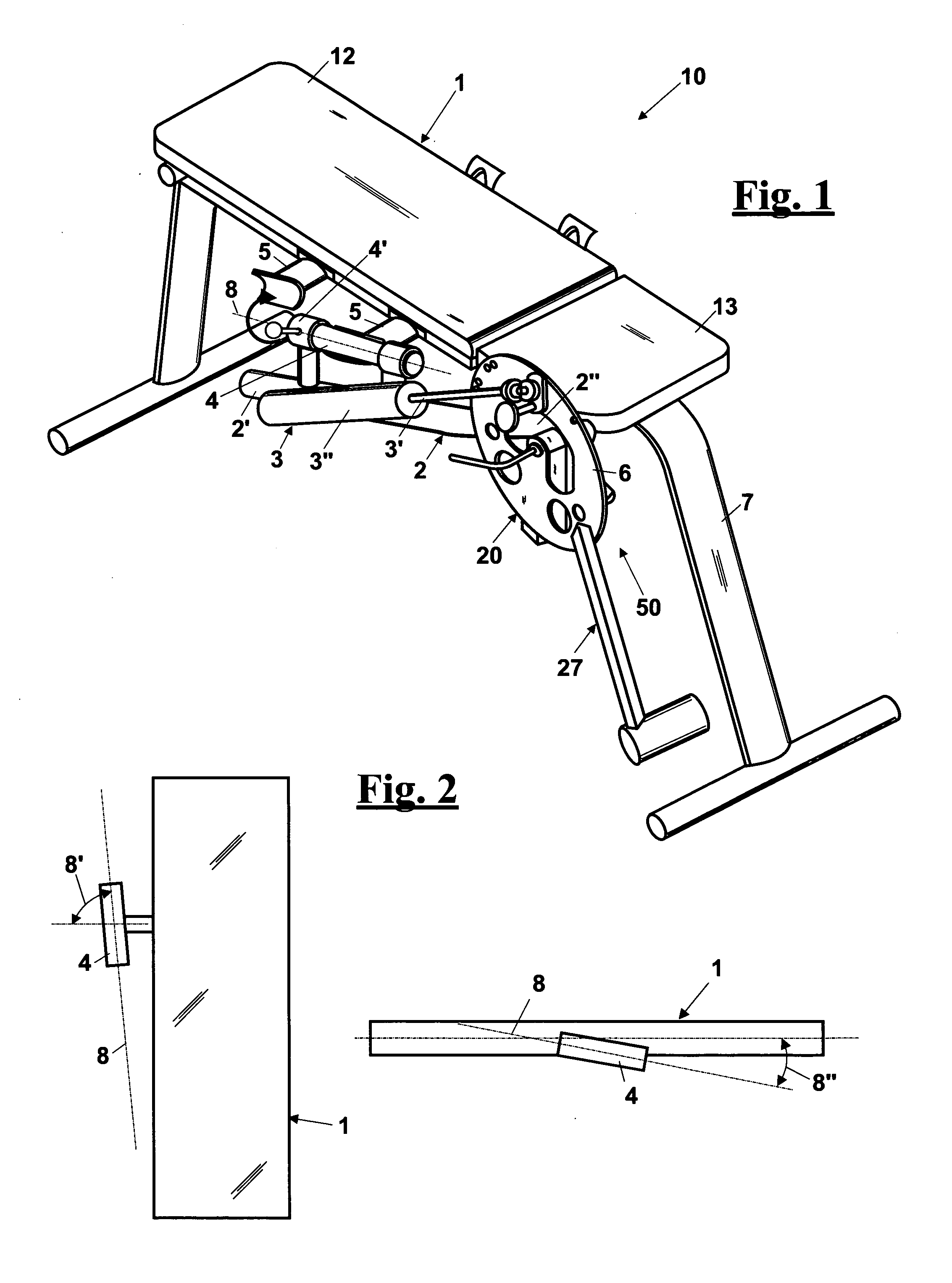
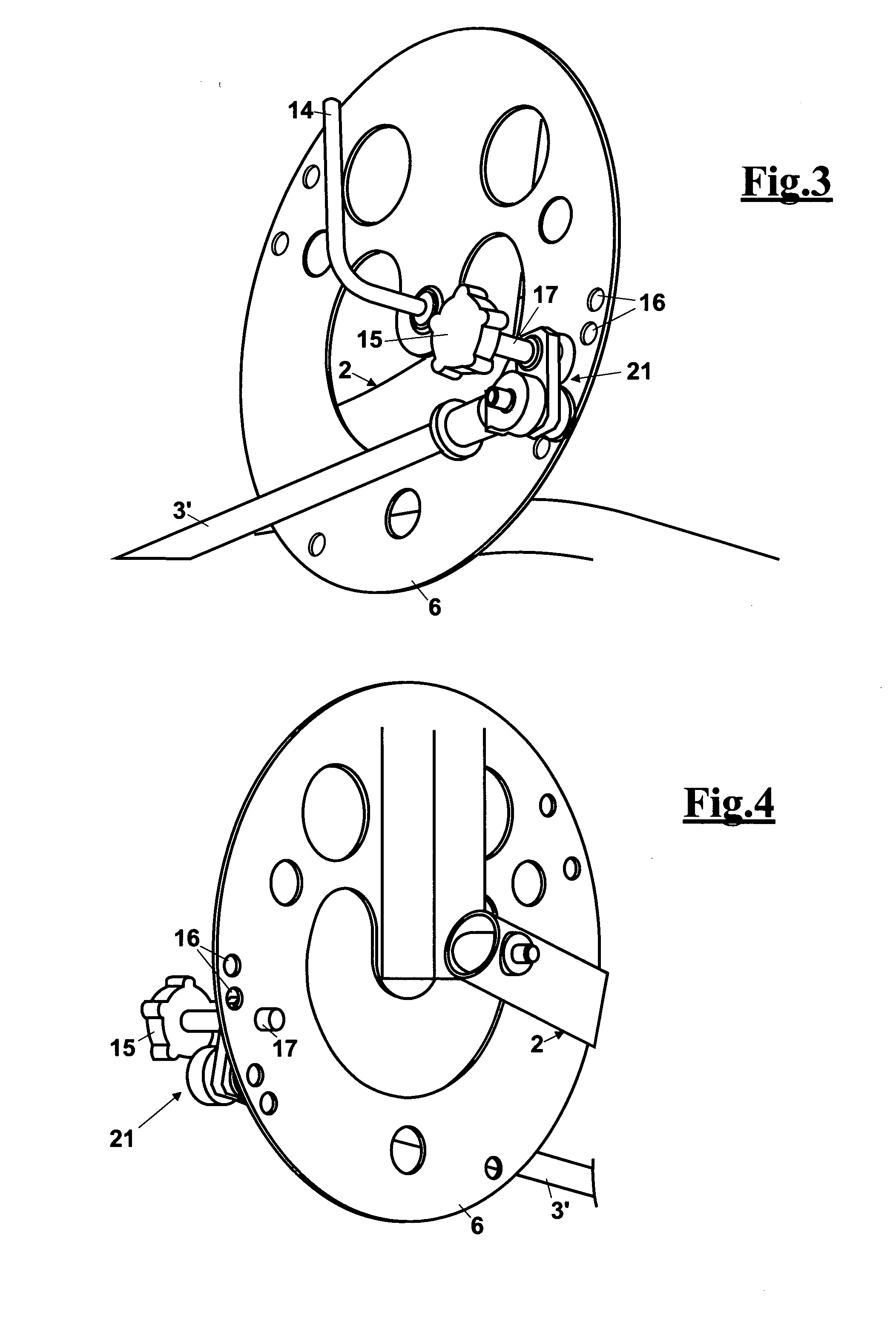
A multifunctional training apparatus for training the lower limb muscles includes a training bench adapted to support a user in a desired training position, a movable rotatable support unit for resisting a muscular force of a lower limb which is caused by a reciprocating movement, a contrast member that is adapted to provide a resistance force against the movement of the movable support unit, and a support element that is adapted to pivotally support the movable support unit and the contrast member. The support element is mounted on the training bench by a rotatable coupling about an axis that is at an angle with respect to the training bench, such that the movable support unit can rotate from a first substantially vertical position to a second substantially horizontal position. In this way, training movements of the lower limbs are possible according to movement in a vertical plane and in a horizontal plane, using a single training device.
Owner:BURGASSI RINALDO +3
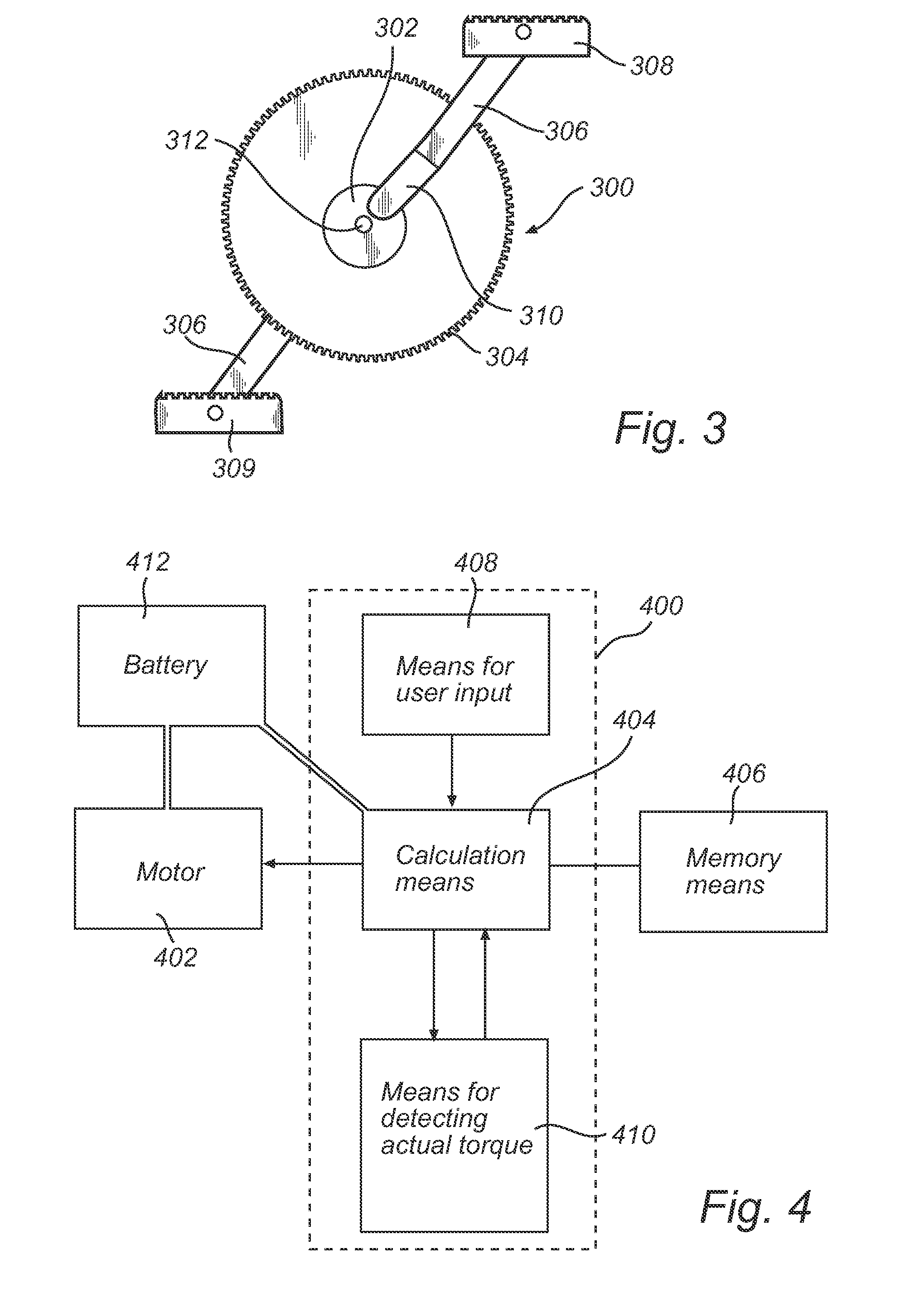
Control system
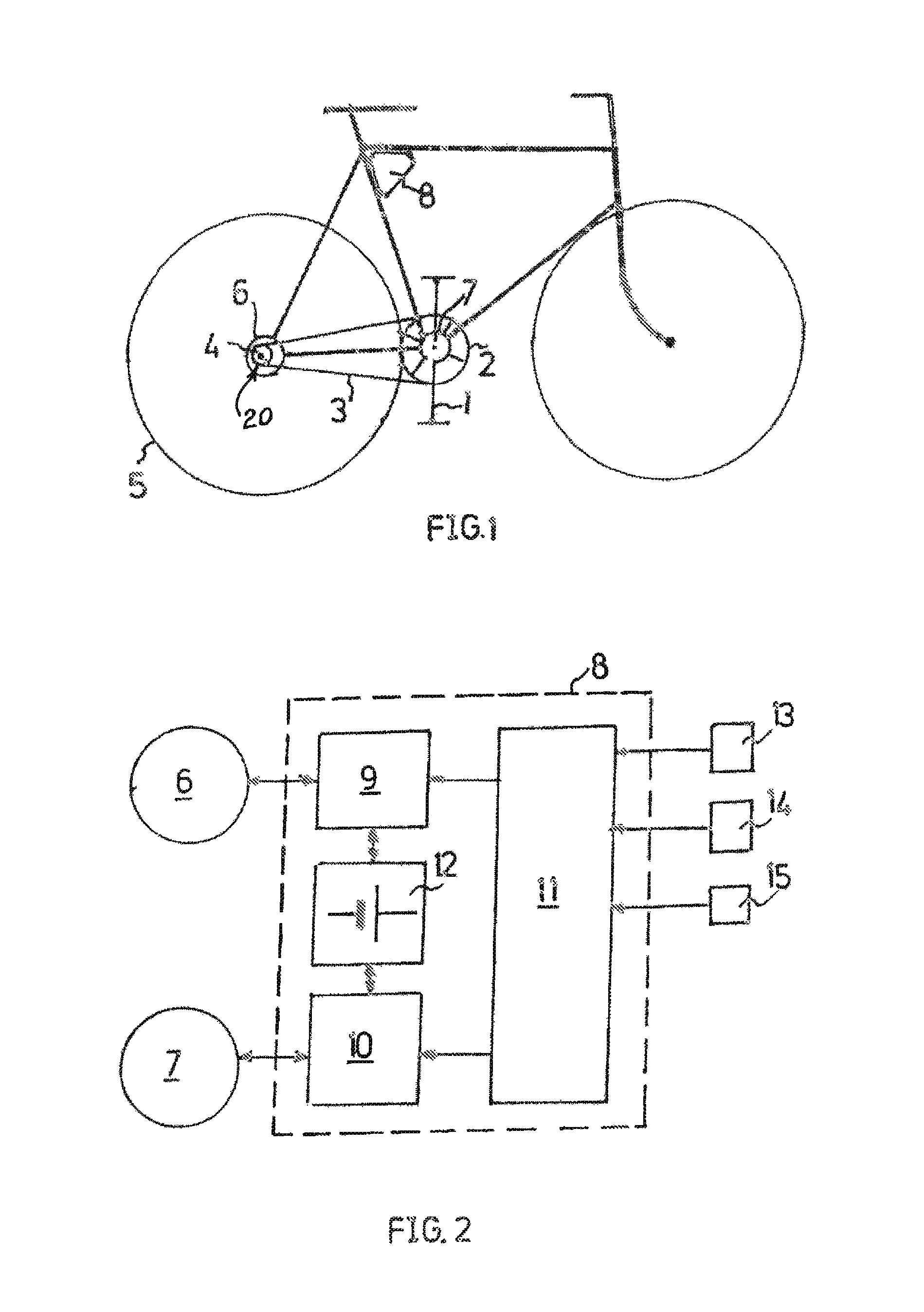
InactiveUS20140365013A1Mechanical power/torque controlSampled-variable control systemsMuscular forceControl system
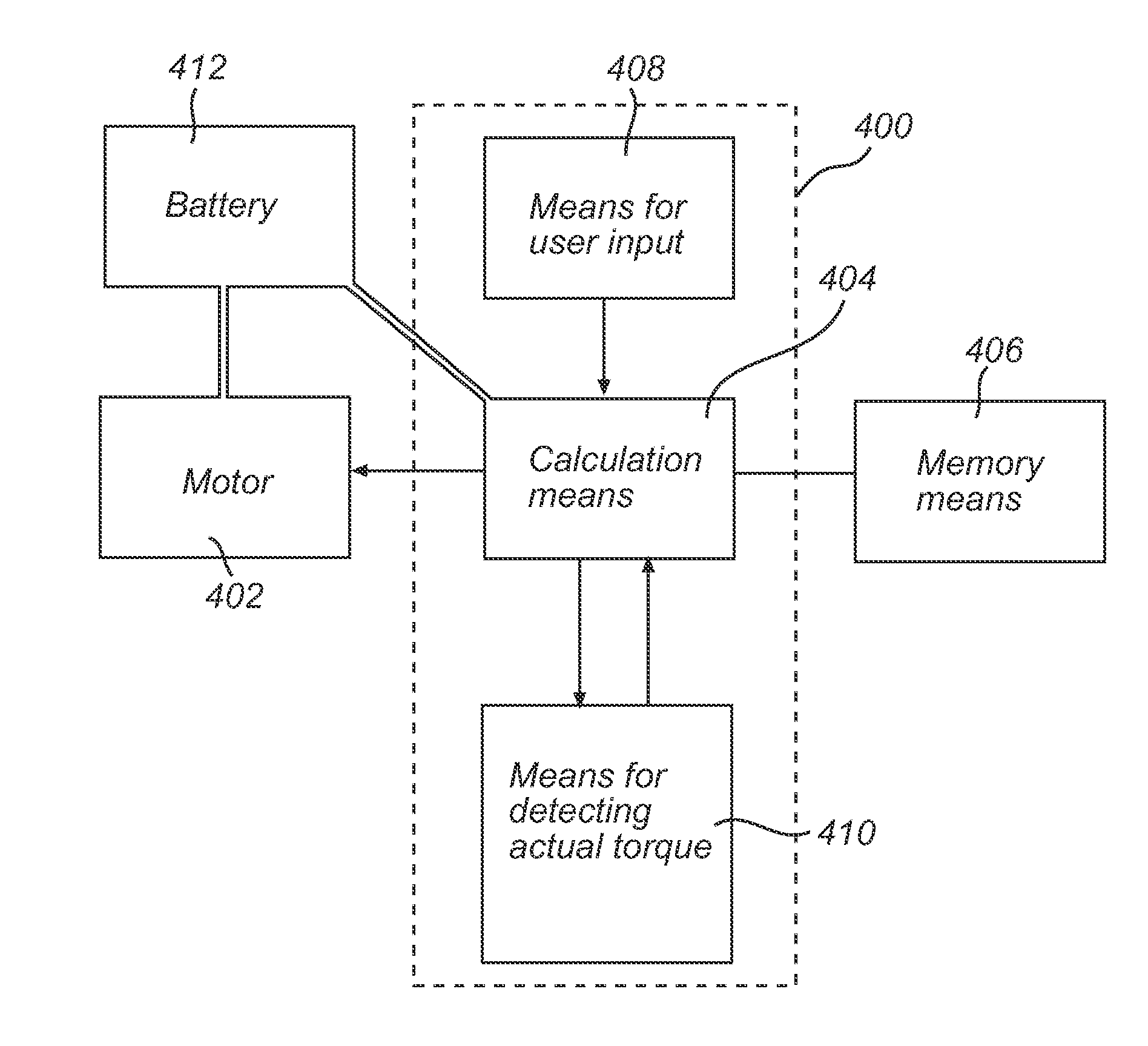
A method for controlling and regulating an electrical auxiliary motor suitable for a pedal-driven vehicle including a crank axle, such as a bicycle, in such a way that said electrical auxiliary motor assists a user in rotating said crank axle by muscular force, the method including: a) receiving information about the specific torque TPSet said user would like to generate when rotating said crank axle by muscular force; b) determining the actual torque TP generated by the user on the crank axle; and c) for each TP, adjusting the torque generated by the electrical auxiliary motor TM in such a way that: TM is increased in case TP is higher than TPSet; TM is not changed in case TP is equal to TPSet; TM is reduced in case TP is lower than TPSet; and TM is 0 in case TP is 0.
Owner:HOGANAS AB
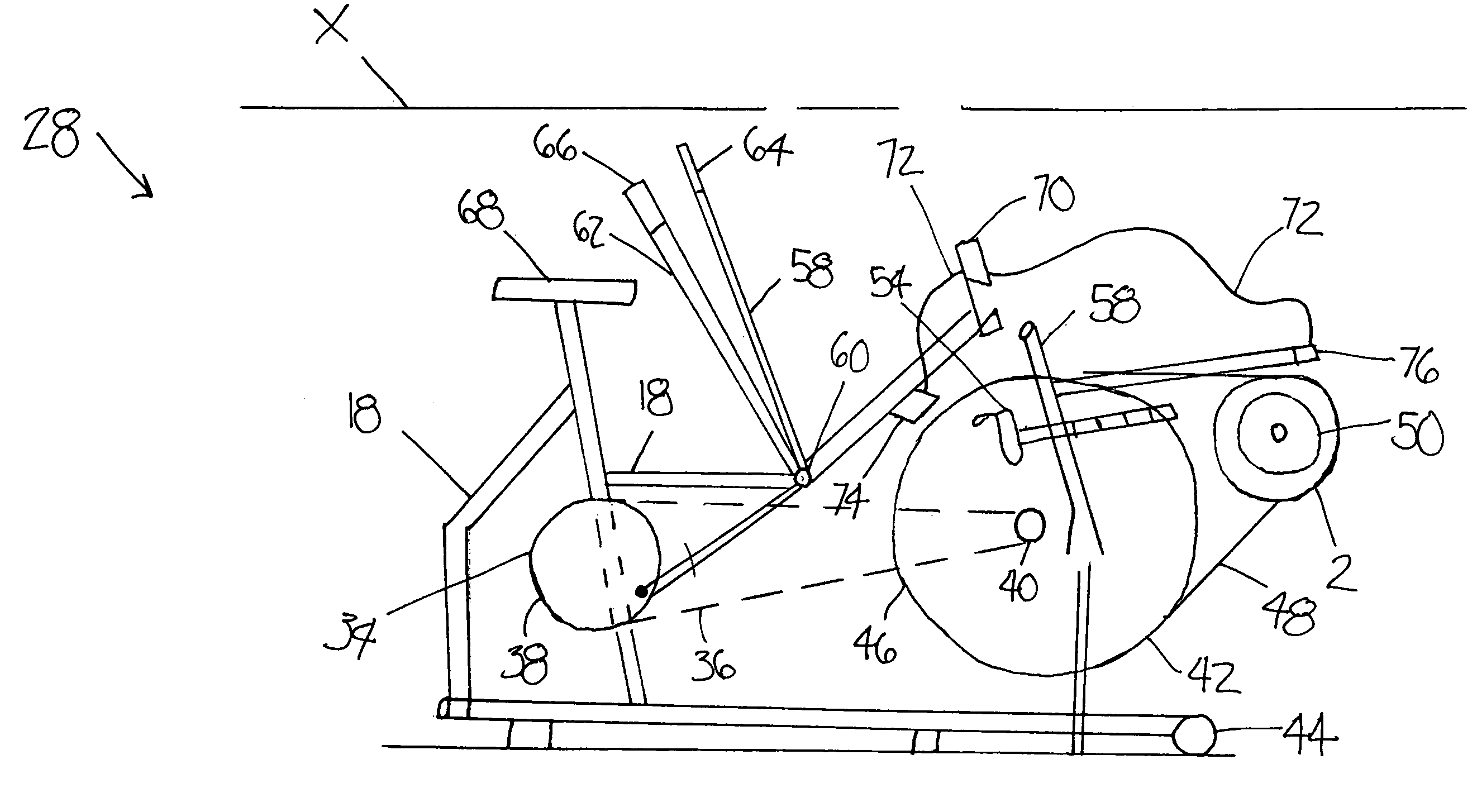
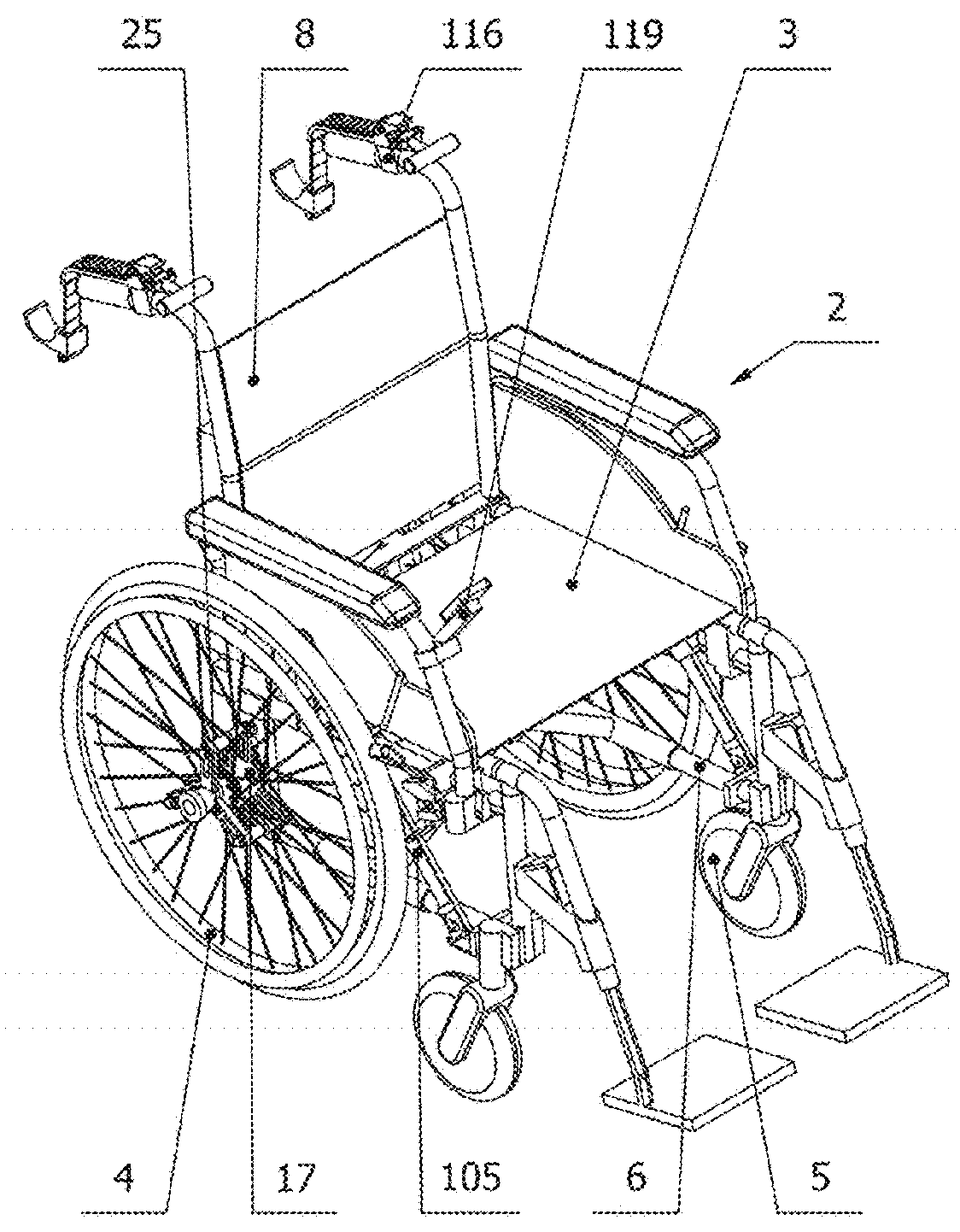
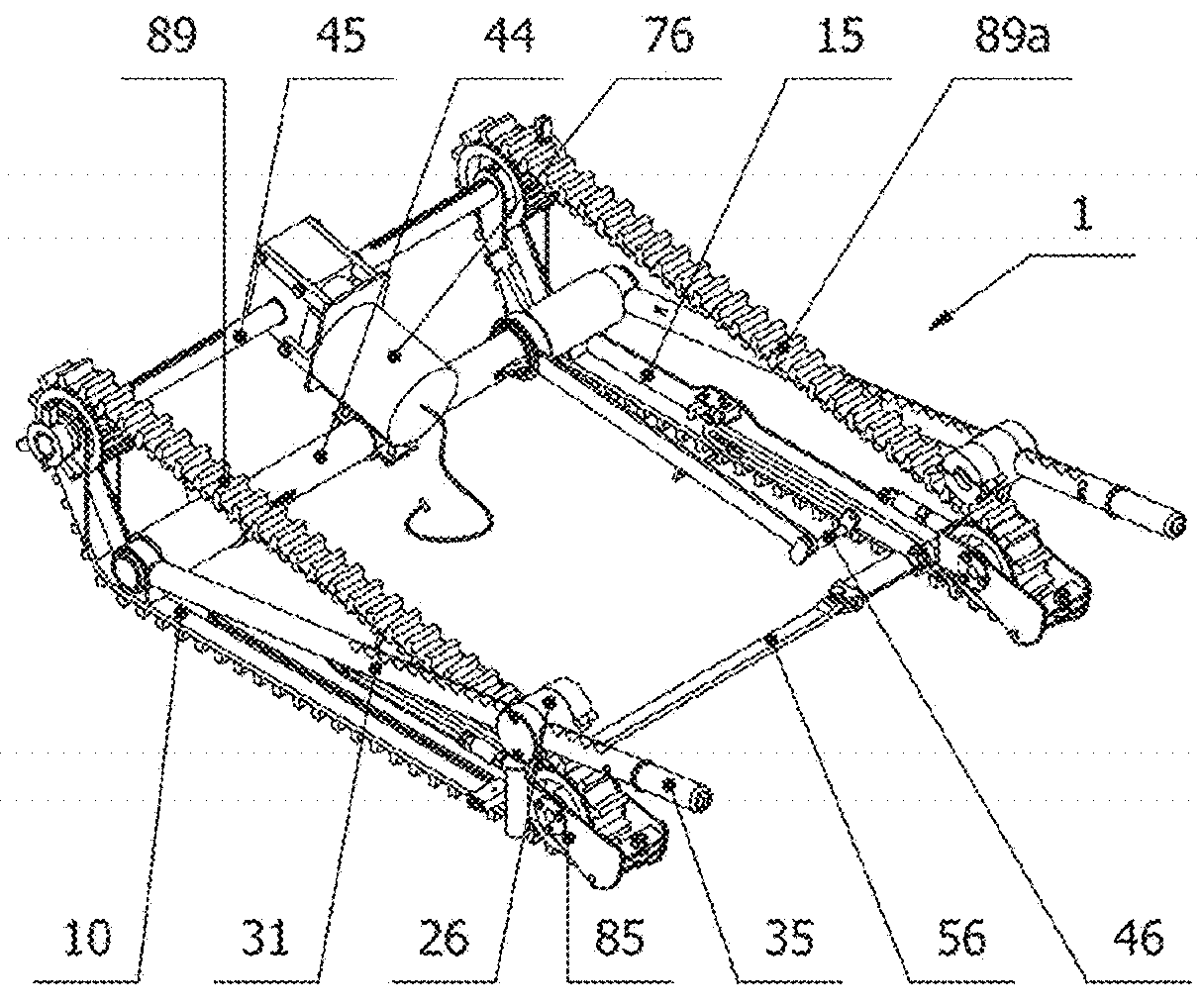
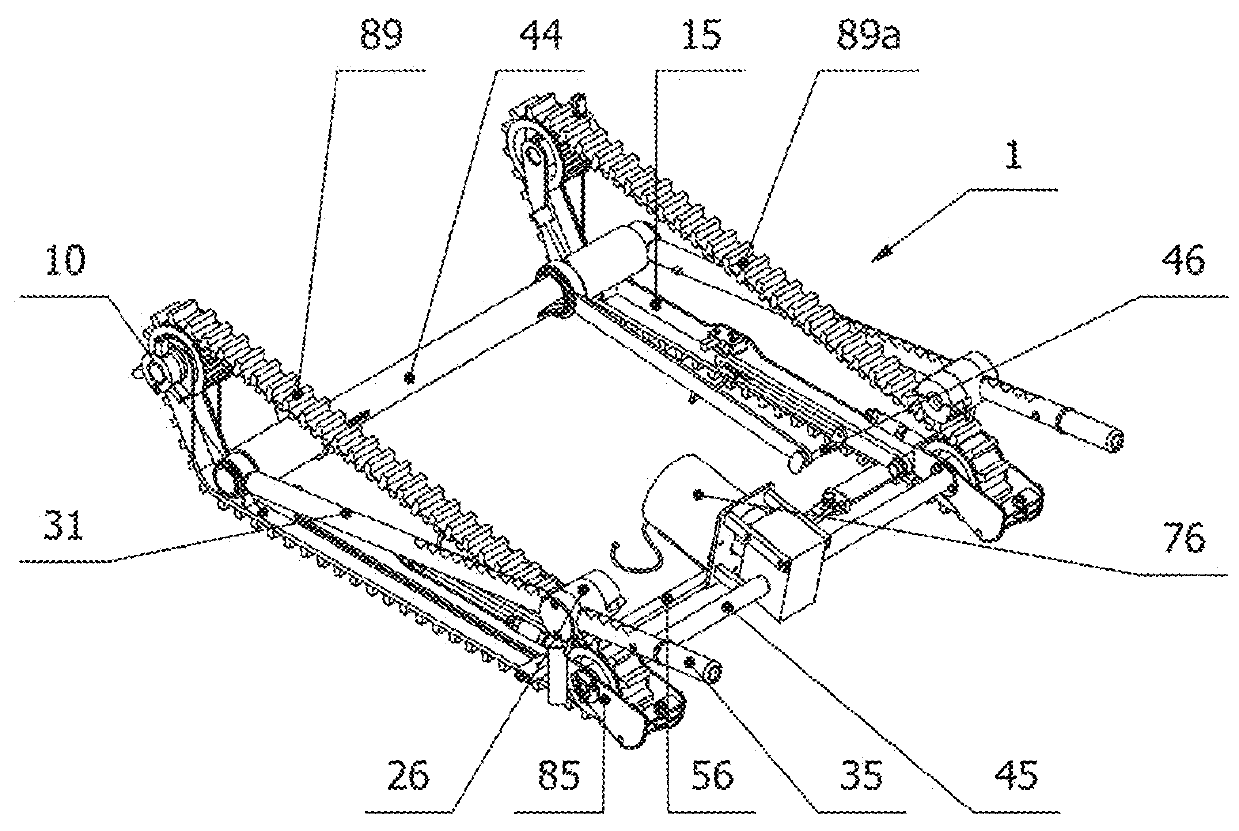
A stair-climbing device for a wheelchair, a wheelchair suitable for installing such a stair-climbing device and a wheelchair equipped with such a stair-climbing device
InactiveUS20190209404A1Suitable for installationThe process is convenient and fastWheelchairs/patient conveyanceThird partyMuscular force
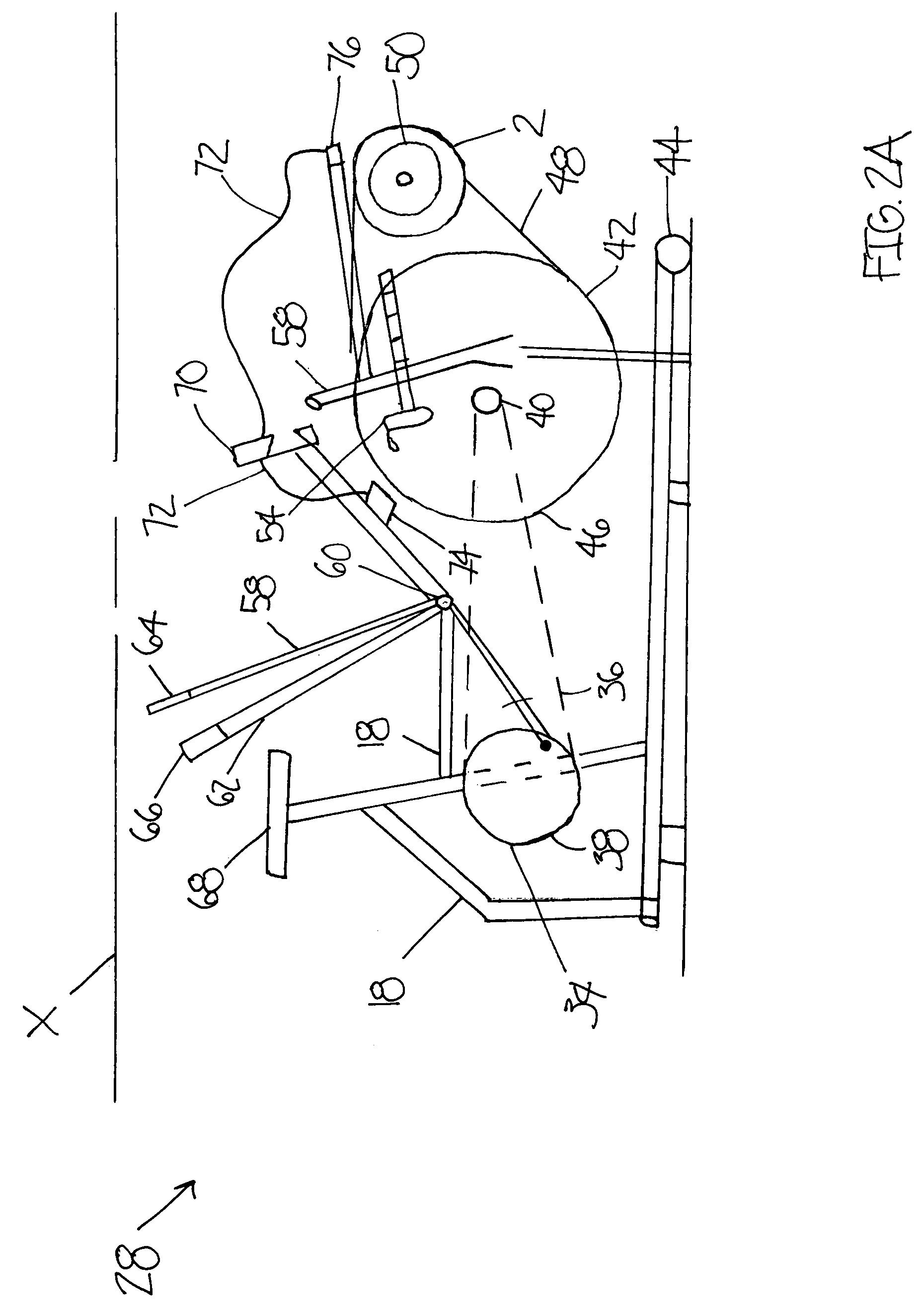
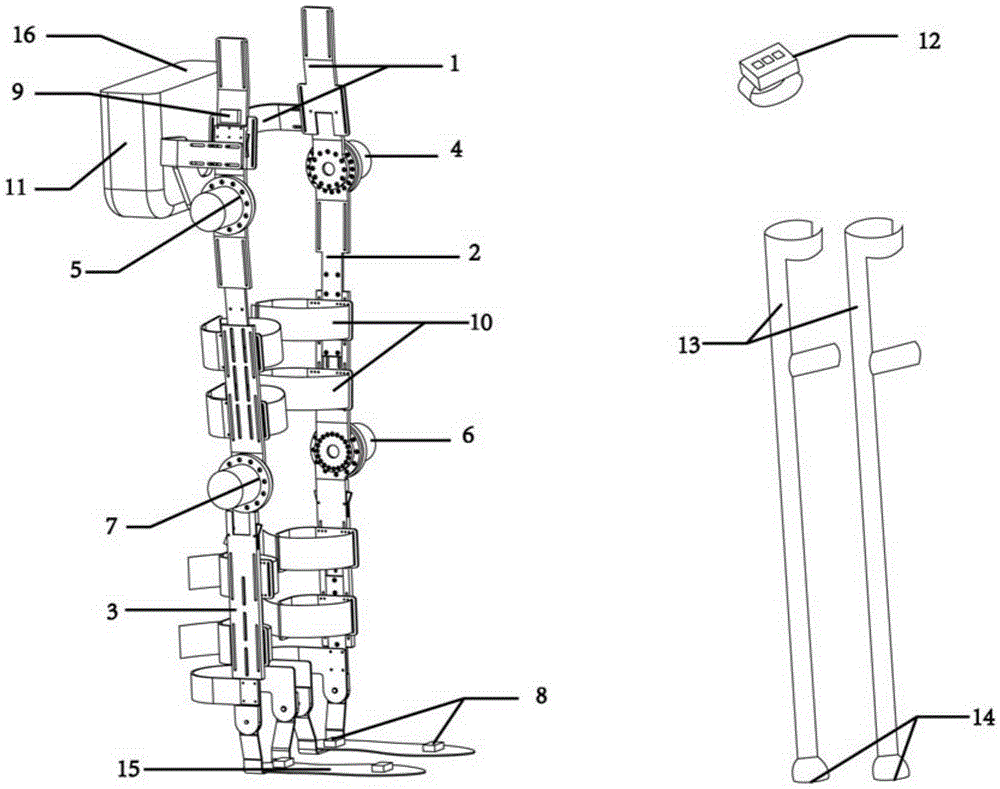
The object of the invention is a stair-climbing device (1) for moving a wheelchair (2) on stairs by means of muscular force of a person sitting on the wheelchair (2) or by means of an electric drive assembly (76) without the assistance of third party. The stair-climbing device (1) comprises two crawler units (89), which are connected with each other by a drive axle (44); connecting units comprising an attachment devices (17) mountable on each hub of the main wheel (4) of the wheelchair (2) and a holders (26) for rotational mounting on the main wheel (4) to each attachment device (17) and comprising main arms (31) mounted slidingly in the holders (26) and rotationally connected at one its end with the main axle (44) for manual changing a position of the stair-climbing device (1) in relation to the wheelchair (2) between a transport mode position, stair-climbing mode position and optionally landing mode, if the landing mode is present; a levelling units (105) for setting the attached wheelchair (2) in a horizontal position during stair climbing. The invention also includes a wheelchair (2) suitable for attaching a stair-climbing device (1), wherein the wheelchair (2) comprises a frame (6), main wheels (4), front wheels (5), a seat (3) and a back-rest (8). Moreover, the invention includes a wheelchair (2) with a mounted stair-climbing device (1).
Owner:WHEELSTAIR SP ZOO
Golf swing training machine
A golf swing training device, in which a golf club or golf club simulating device is propelled by the arms and hands of a person along a desired arcuate trajectory under an optimal amount of muscular force, maintains the hands of the user on a single optimal plane, while allowing the club to travel on a separate plane through a structure containing a plurality of rotational means allowing all necessary anatomically desireable movements. A movable user platform allows hysteresis in the swing when a user shifts their weight.
Owner:MENEGHINI JAMES R
Training device for muscle activation patterns
ActiveUS8257284B2More immediate and accurate feedbackSimple methodClubsChiropractic devicesMuscular forceEngineering
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Sitting mode control method for wearable bionic exoskeleton mechanical leg rehabilitation device
InactiveCN105326625AImprove adaptabilityHigh activityDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesThighMuscular force
The invention discloses a sitting mode control method for a wearable bionic exoskeleton mechanical leg rehabilitation device. The method comprises the steps as follows: a control module judges whether a posture of a user simultaneously meets trigger conditions C1, C2, C3 and C4 or not through collected signals; if the control module detects that the user meets the sitting trigger conditions, the control module sends out an instruction to a hip motor and a knee motor; the hip motor begins to constantly speed up to a speed v0 from stillness at an accelerated speed a0 and rotates at the speed v0, the angle<hip> is reduced, and a trunk and thighs of the user are driven to generate a relative angle motion; and meanwhile, the knee motor also begins to constantly speed up to the speed v0 from stillness at the accelerated speed a0 and then rotates at the constant speed v0, the angle<knee> is reduced, and the thighs and shanks of the user are driven to generate the relative angle motion. The sitting mode control method is capable of helping a patient carry out sitting training at an initial stage, so that the joint range of motion and the muscular force can be strengthened; and meanwhile, gradual improvement of the adaptability of the patient to the exoskeleton is facilitated, and thus a foundation is laid for later walking motion.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Resistance training device exerting a constant load without depending upon position
InactiveUS20080026923A1Efficient executionEffective trainingClubsMuscle exercising devicesMuscular forceConstant load
A resistance training device effectively training the muscular force of a desired muscle includes a saddle for a user to sit on, a robot arm adjustable to the length of a limb of the user, a fastener for securing the robot arm to the limb, a controller for controlling the torque of a driving source driving a joint of the robot arm, and an input operating unit for the user to input a driving condition. When the user inputs a training load and an output direction of the distal end of the limb to be trained, the value of a torque necessary for generating the training load is calculated. The robot arm generates the torque of the calculated magnitude acting in a direction opposite to the output direction in such a manner that a constant training load is exerted to the user without dependency on the position of the user.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
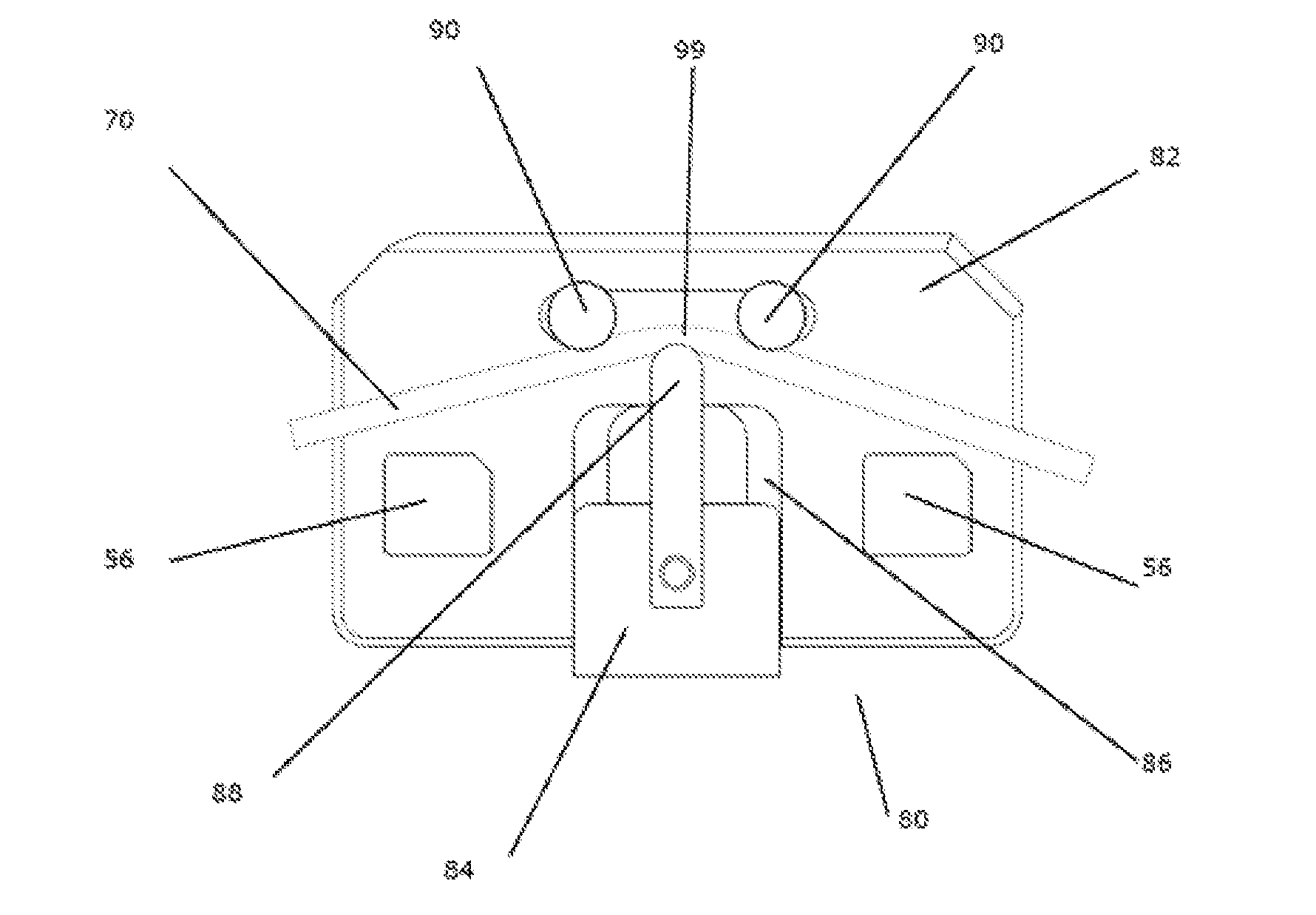
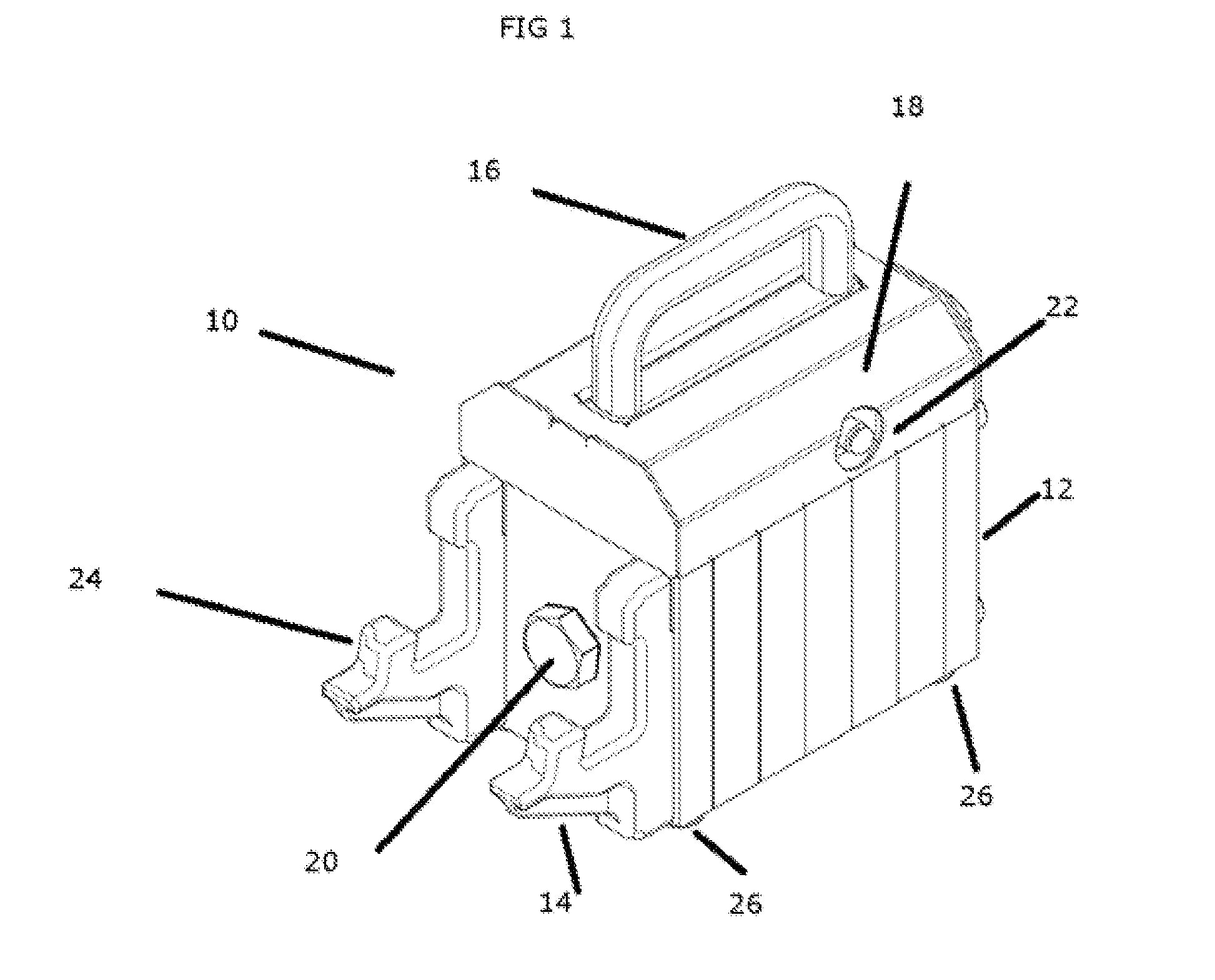
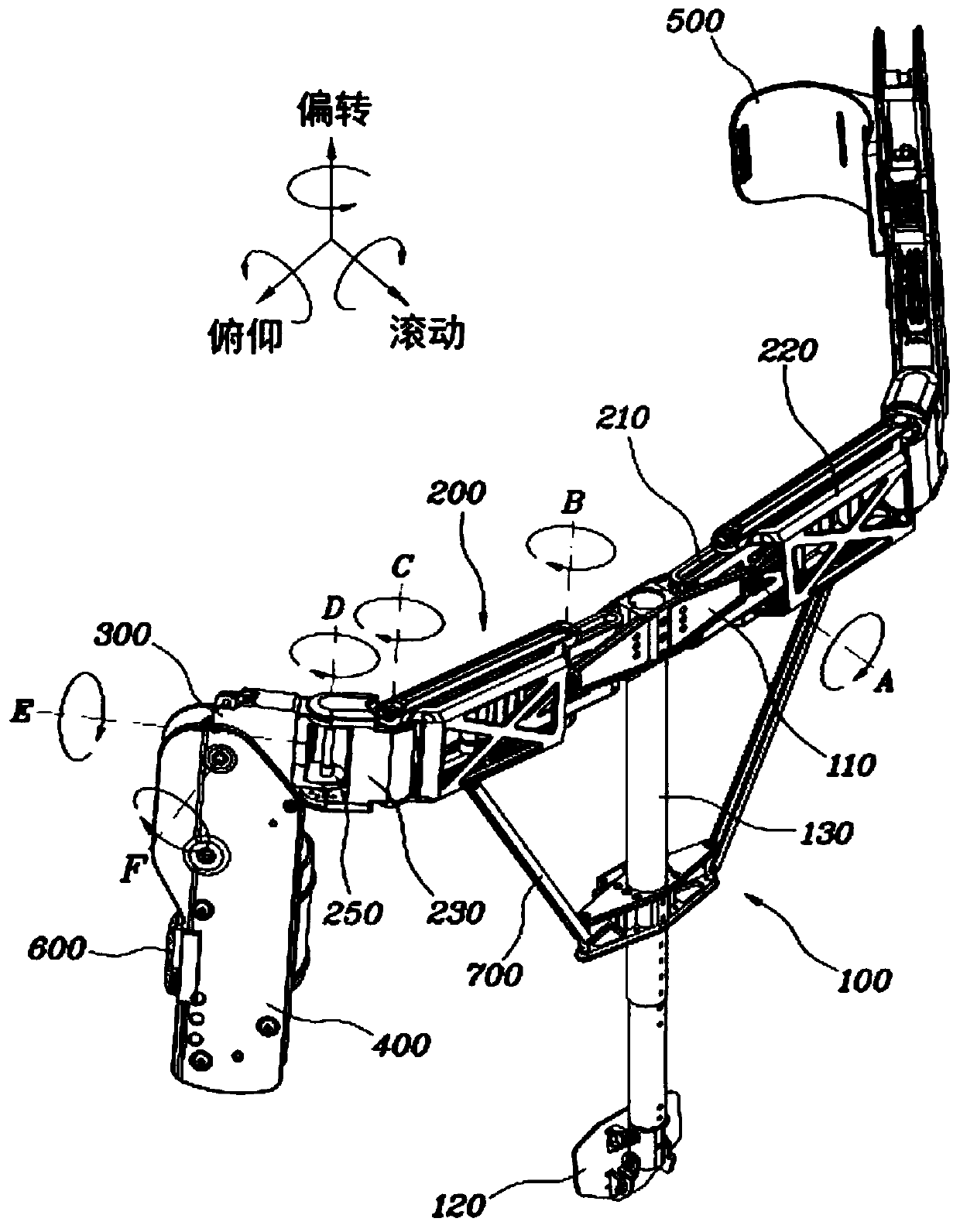
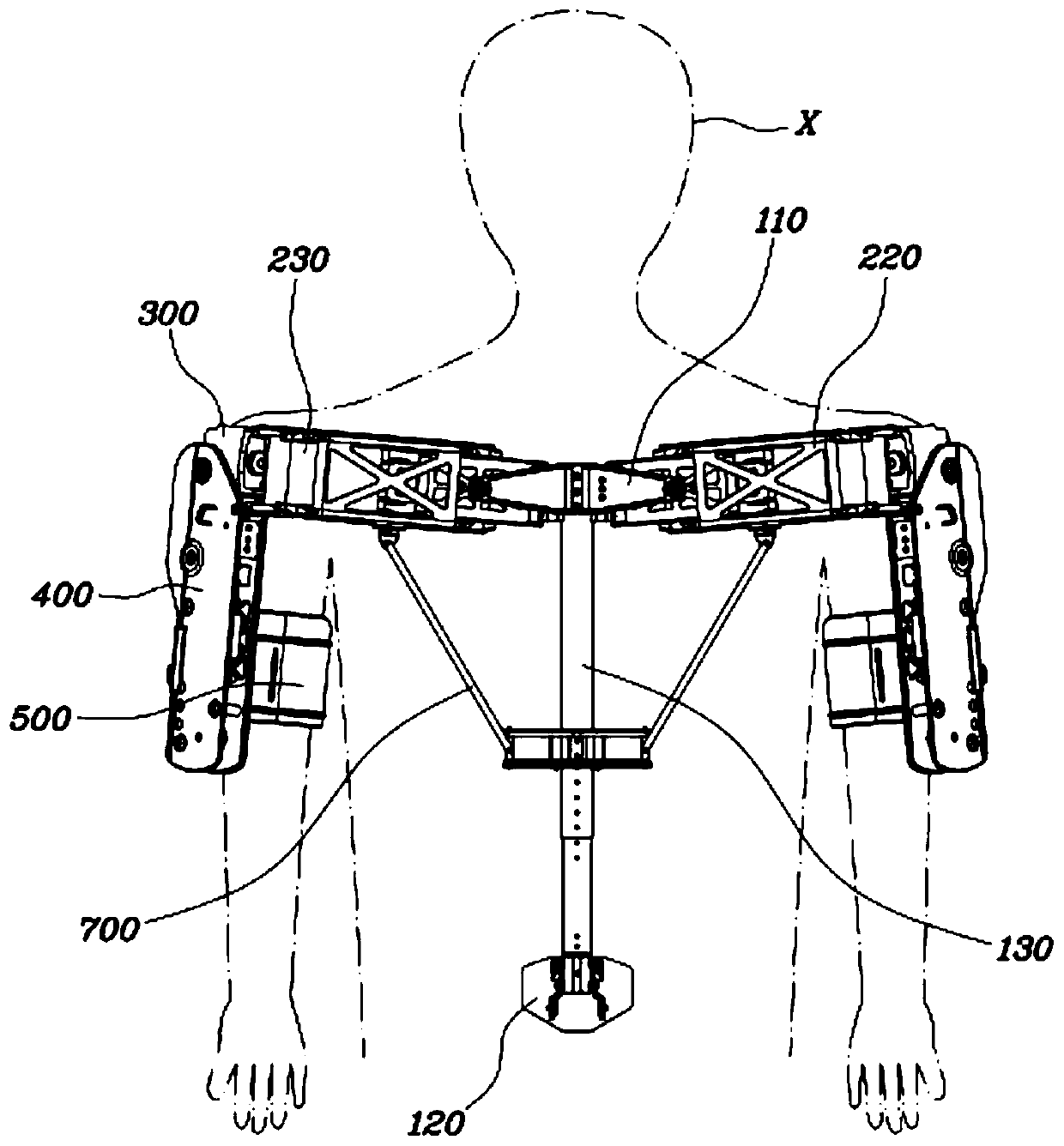
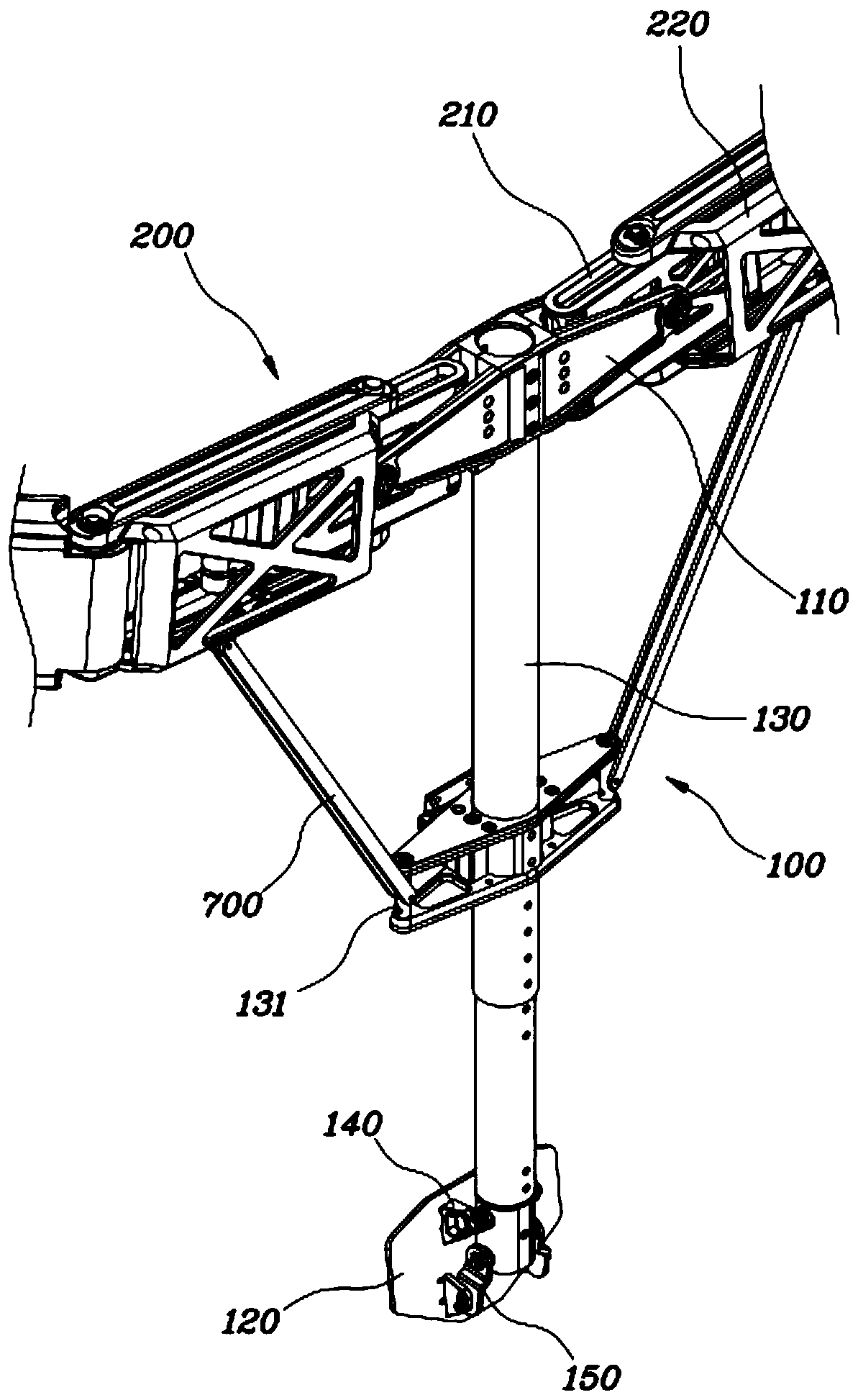
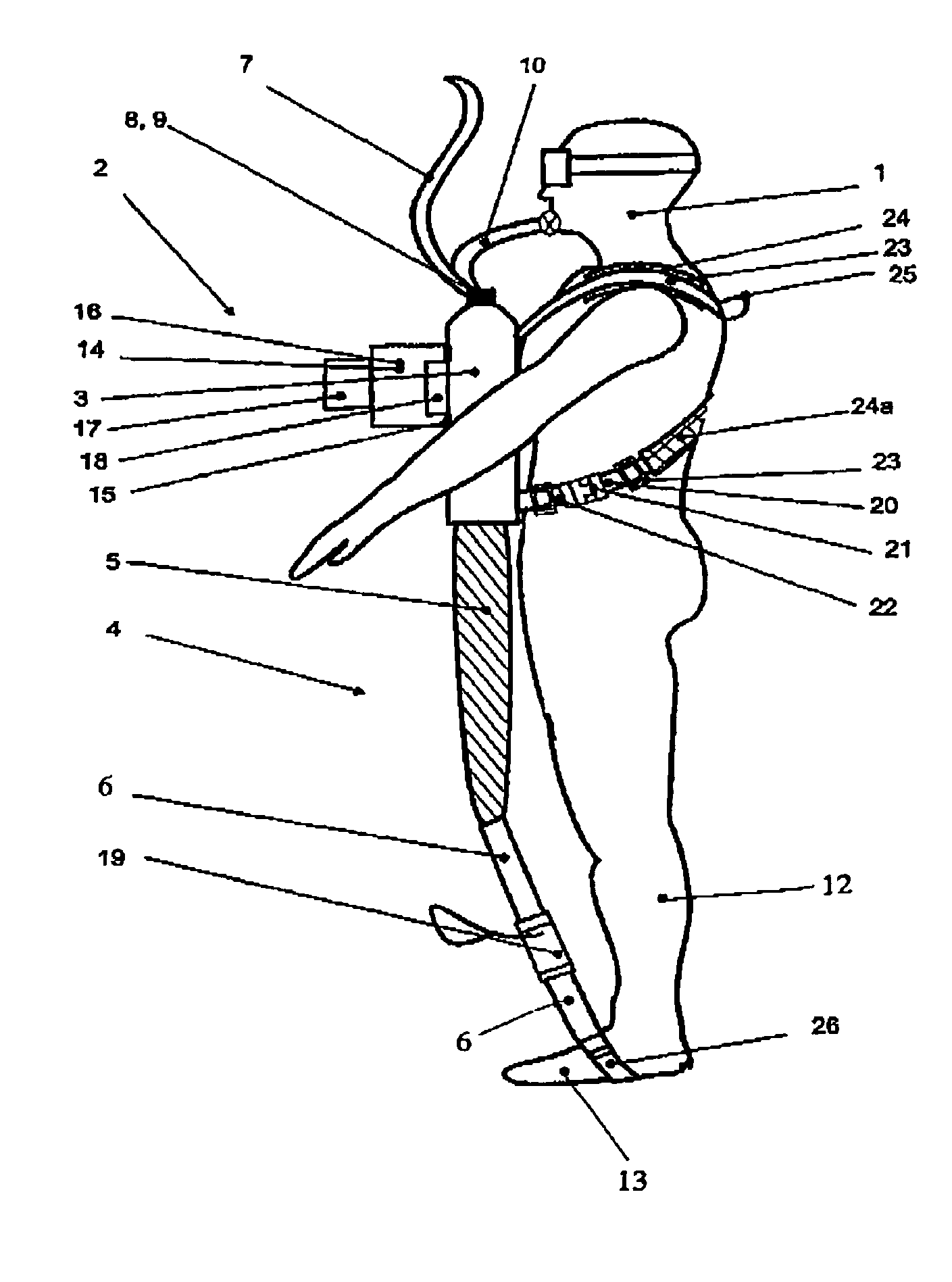
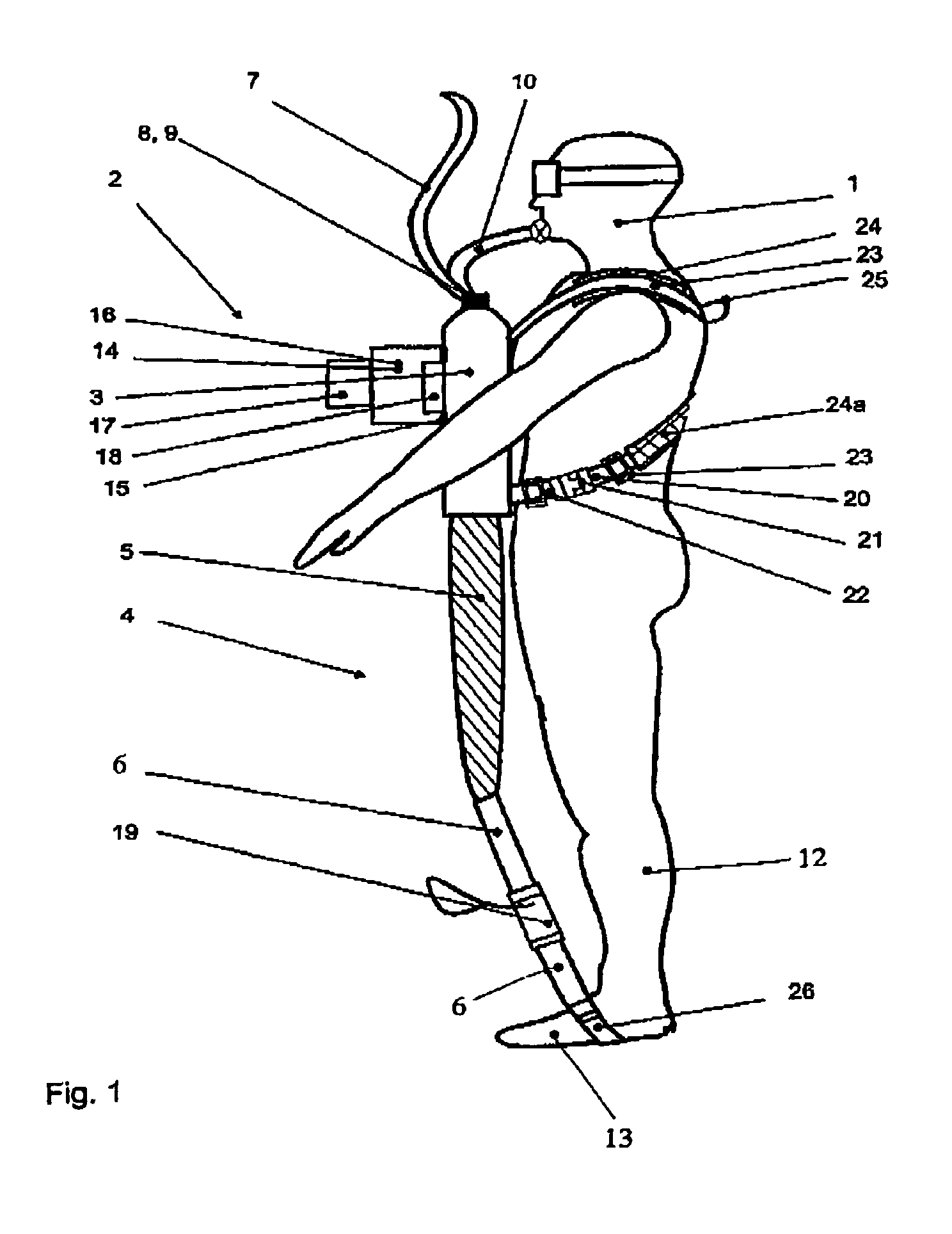
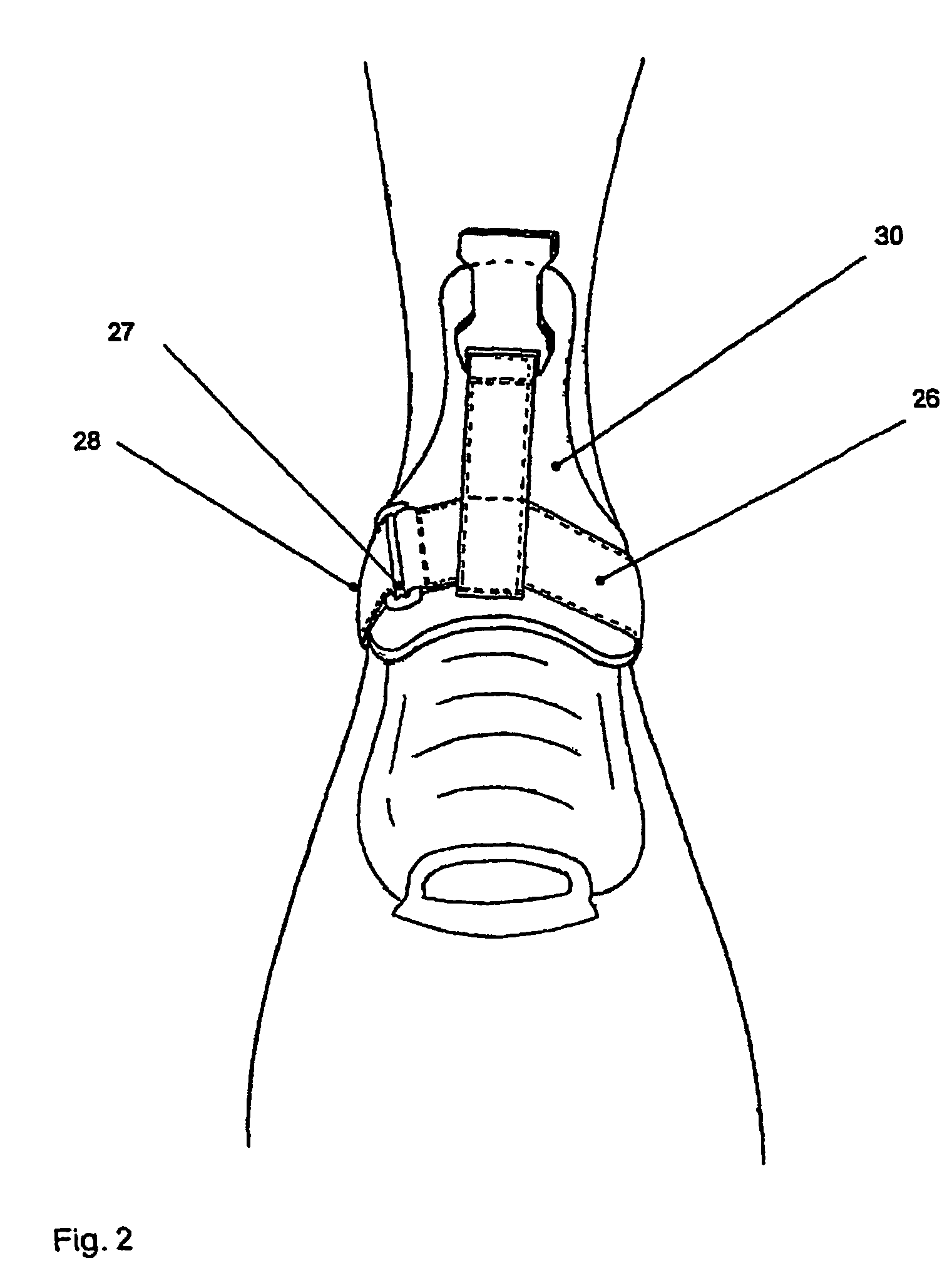
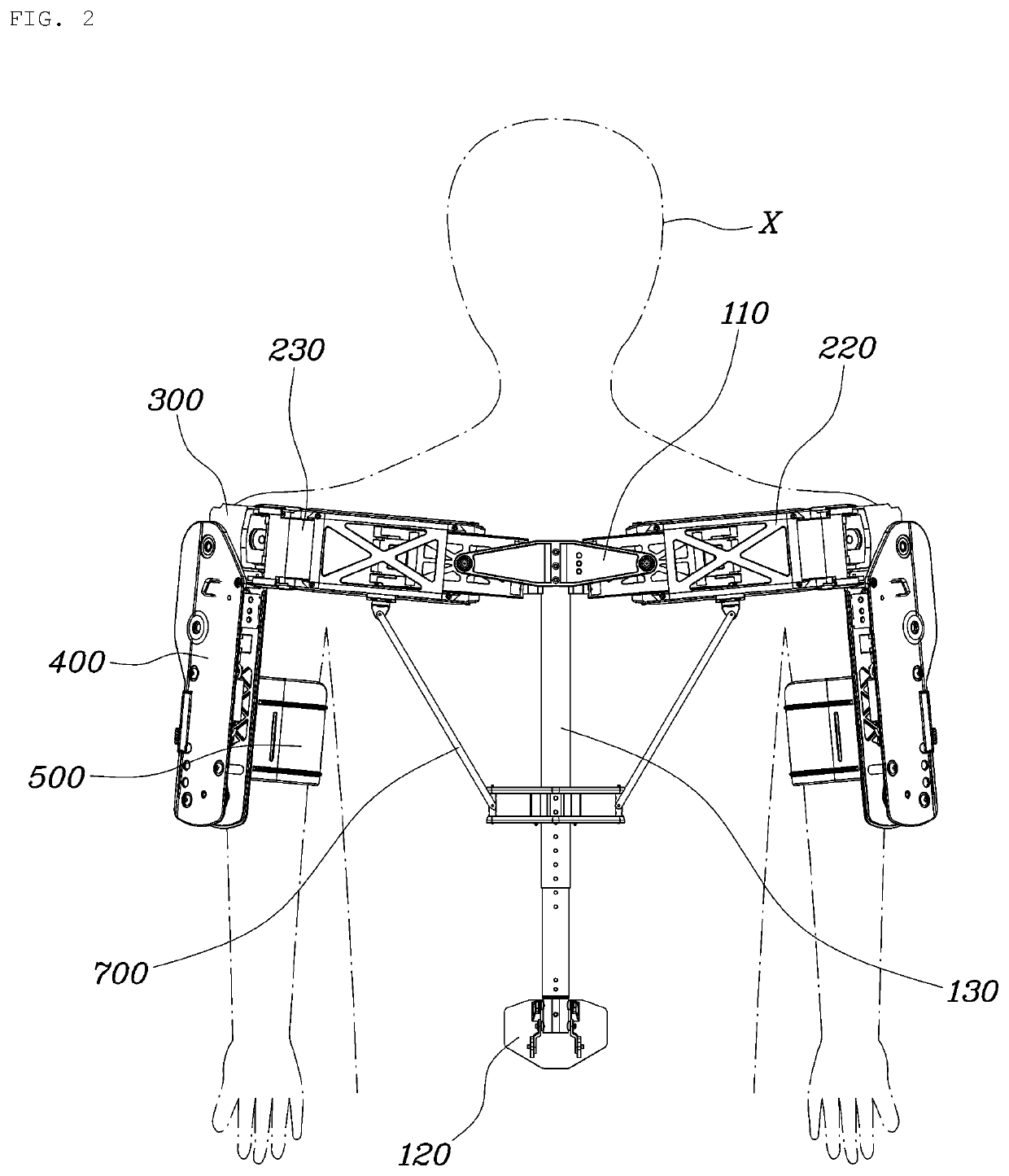
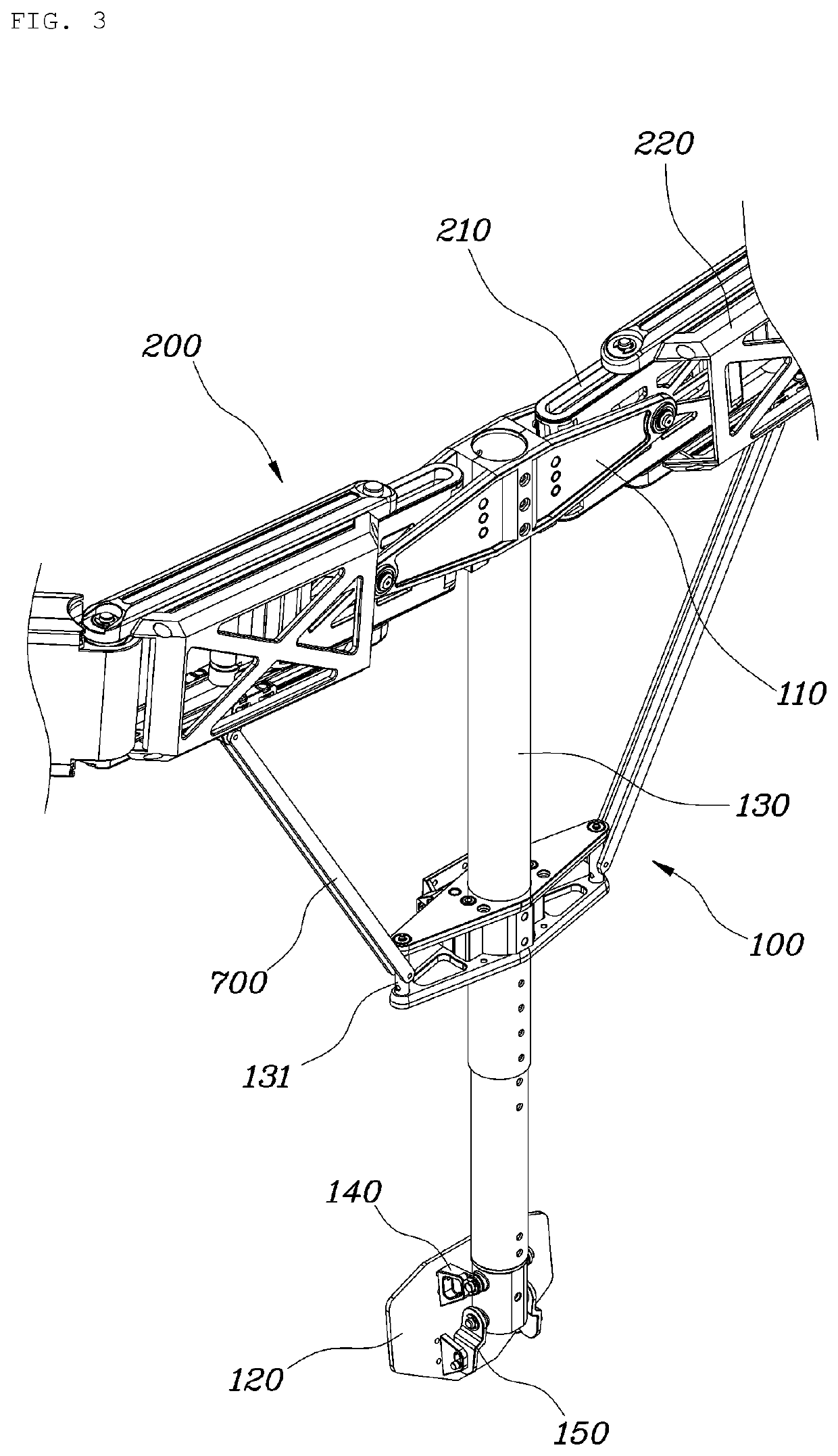
Wearable apparatus for increasing muscular force
PendingCN111300378ANatural movementAchieve twisting actionProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesMuscular forcePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A wearable apparatus for increasing muscular force includes: a mount body coupled to an upper body of a wearer; a shoulder frame coupled at one end thereof to the mount body at the dorsal surface of the wearer and which is rotatable in up and down direction; a mounting frame coupled at one end thereof to the other end of the shoulder frame to be torsionally rotated; a supporter, which surrounds part of an upper arm of the wearer to support the upper arm of the wearer; and a compensation frame, which is integrally coupled to the supporter to be rotated together with the supporter about a shoulder joint of the wearer. The compensation frame capable of generating supporting force that varies depending on the angle to which the compensation frame is rotated.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
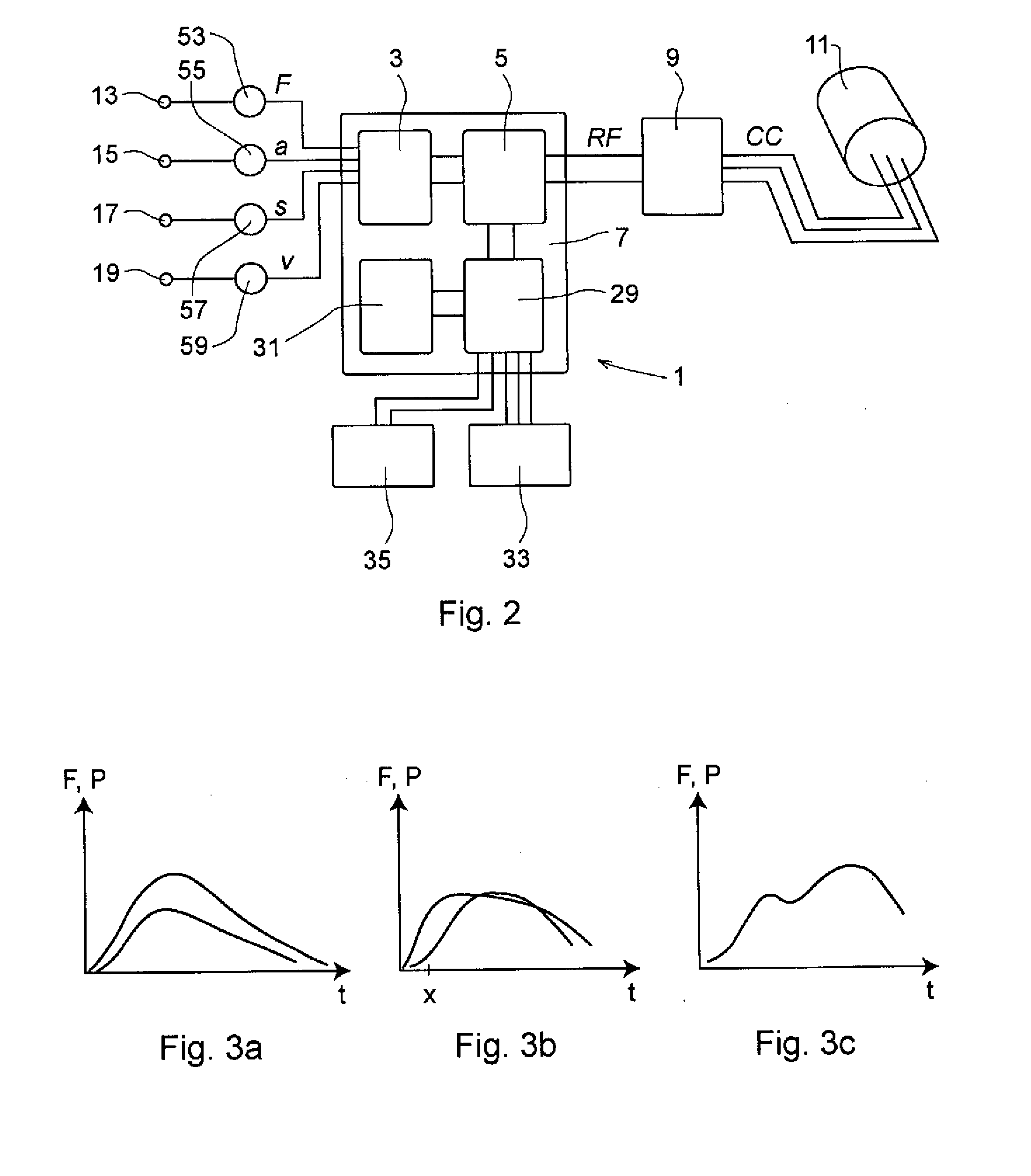
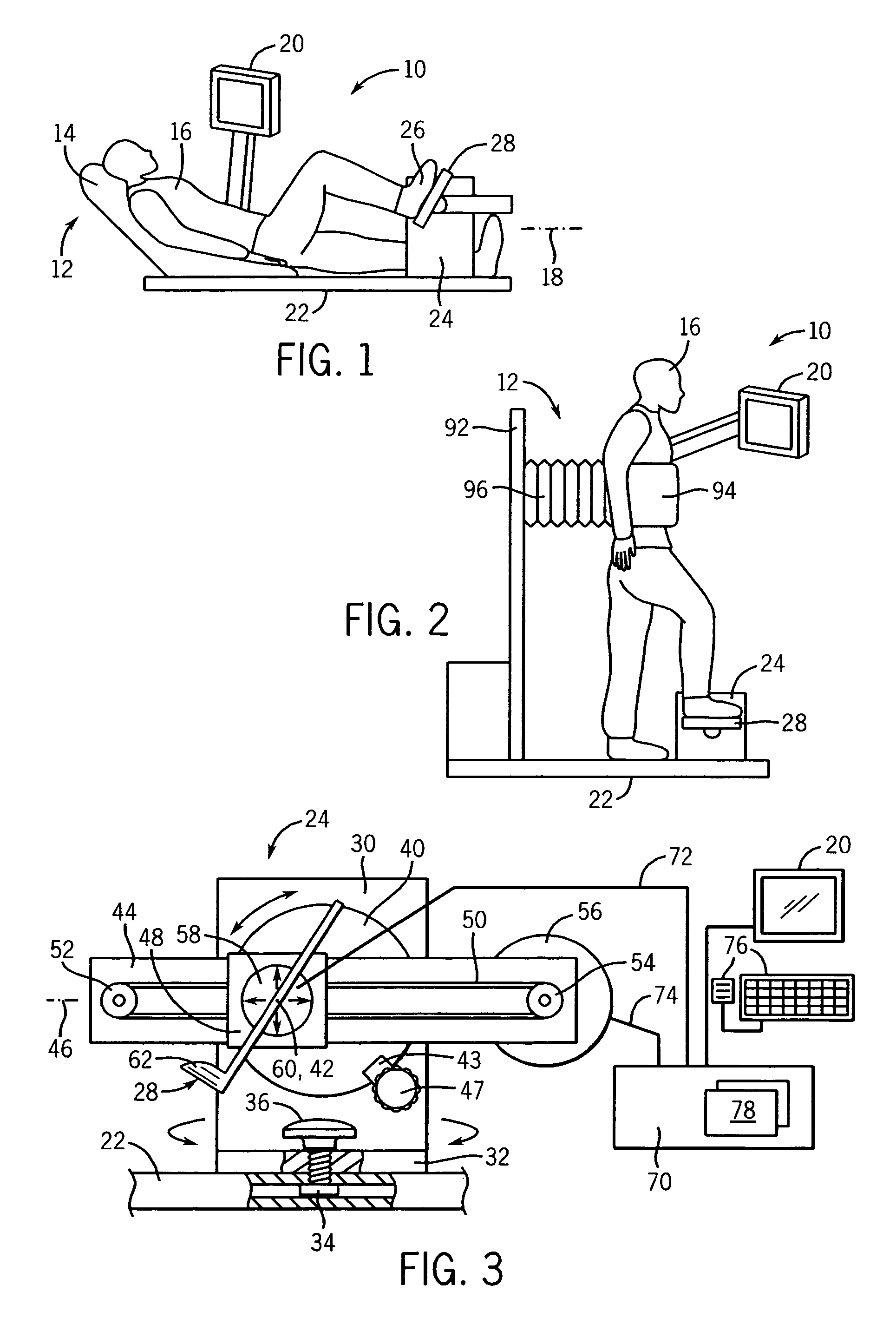
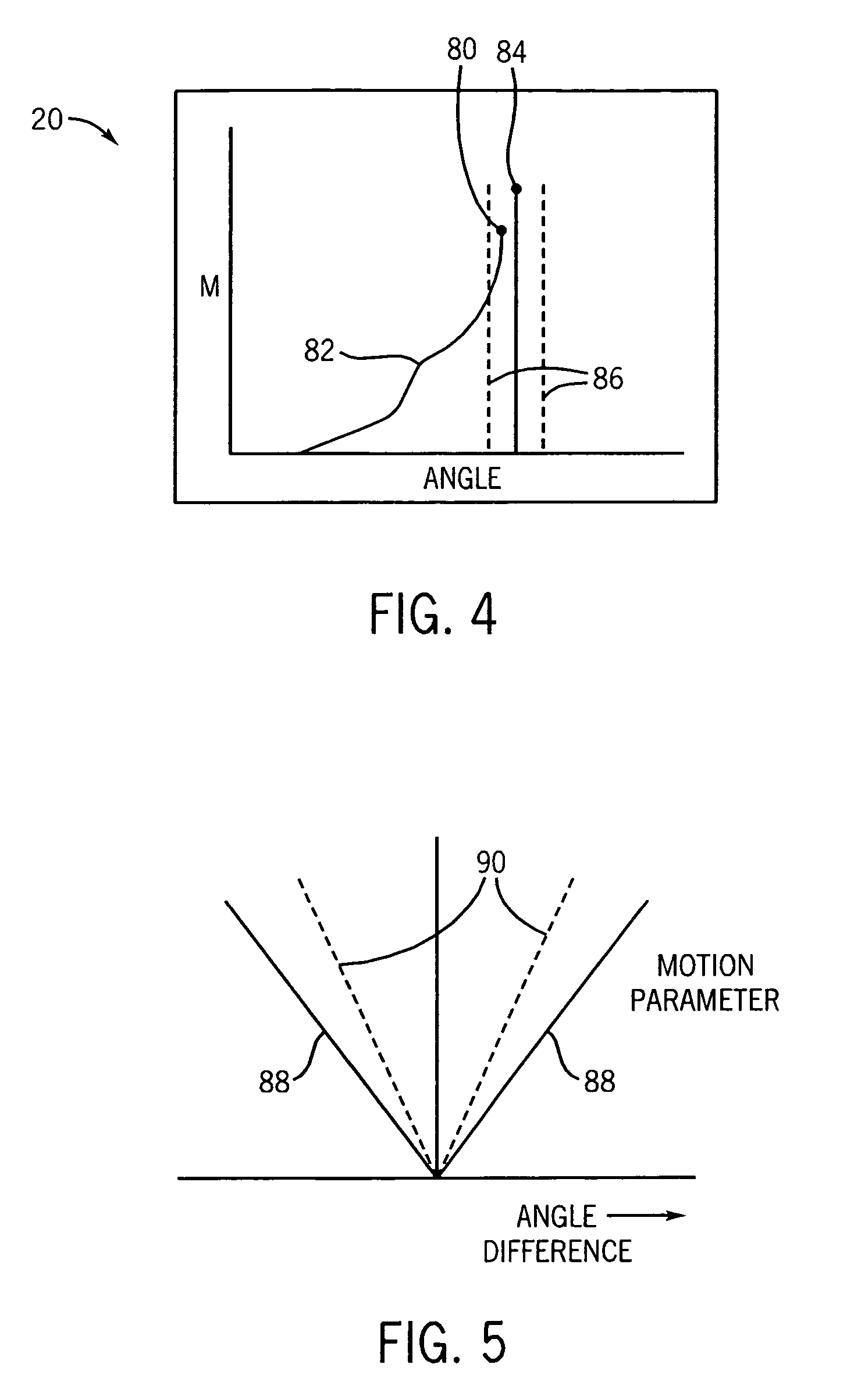
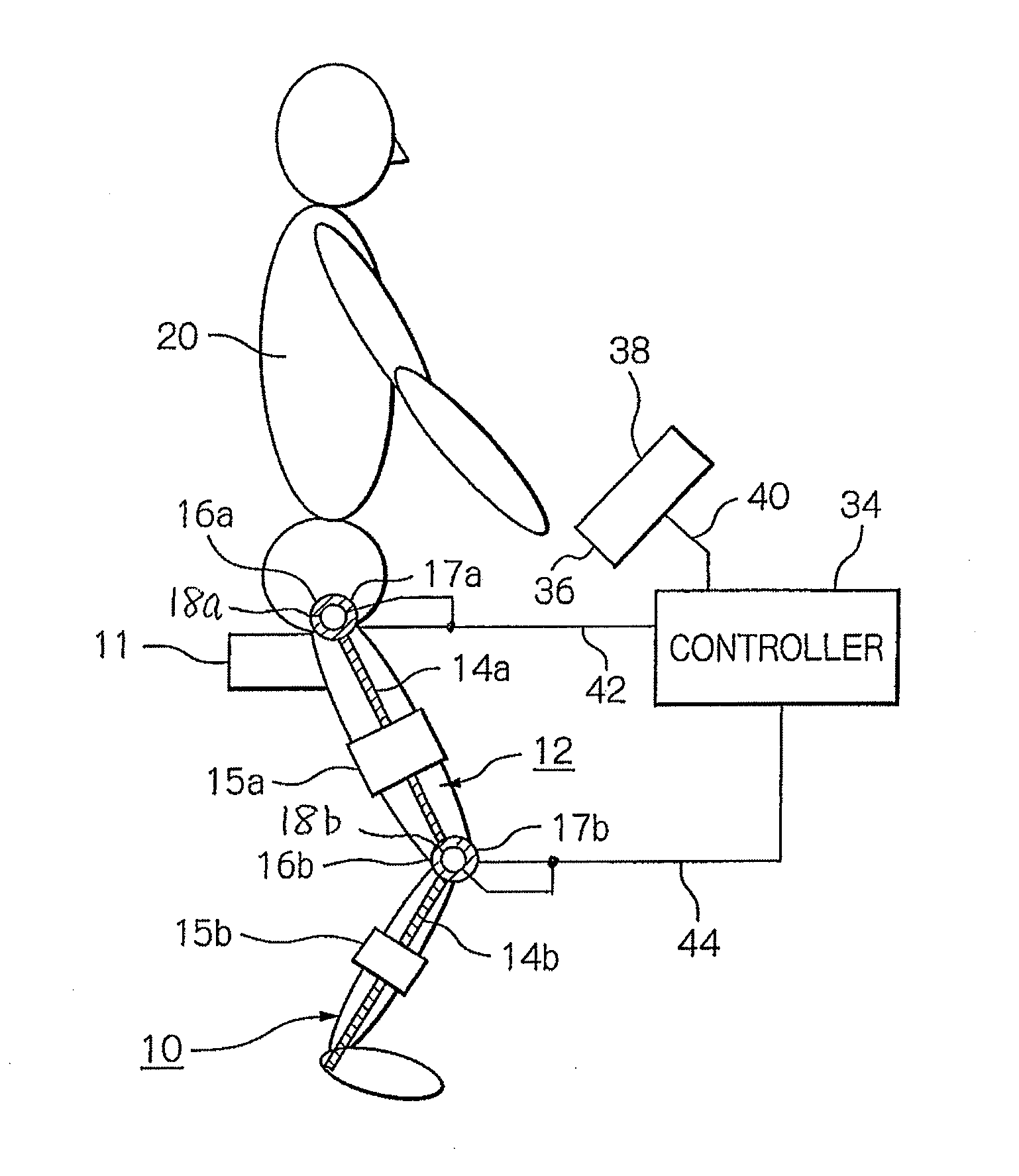
Apparatus and method for resistance-based muscular force evaluation using a hexagonal diagram of output distribution
InactiveUS20080202232A1Improve accuracyAccurately evaluate muscular forceWork measurementSensorsMuscular forceEngineering
The torques at the first and second joints of a test subject are measured, which may be generated simultaneously by the coordinate action of the antagonistic mono- and bi-articular muscles. A hexagonal diagram of the output distribution is formulated on a plane formed by two axes corresponding to torques at the first and second joints as. Based on the diagram, the muscular force of the subject, changing through training, may accurately be evaluated, without the necessity of specifying the force of individual function-based muscles of praxis, even if the subject changes his or her position or joint angle. The torques at the first and second joints are measured, which are generated simultaneously by the coordinate action of the antagonistic mono- and bi-articular muscles. The muscular force of the bi-articular link mechanism of the subject is thus measured by the diagram.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Birthing aid: method of using musculoskeletal repositioning device
InactiveUS20110186056A1Increase muscle strengthDecreased muscular tensionImpression capsEar treatmentChild birthMuscular tension
The present embodiment relates to the use of a musculoskeletal repositioning device in the birthing process by causing increased muscular strength and decreased muscular tension especially during the “push” phase of child birth. The device guides the condyles and articulating discs of the temporomandibular joint from a neutral or passive position into an active power position.
Owner:RAMPUP
Resistance-based muscular force evaluation and training utilizing elasticity following angular change of first and second joints
ActiveUS8181519B2Accurately indicatedResilient force resistorsWork measurementMuscular forceEngineering
In an apparatus for resistance-based muscular force evaluation and training, elasticity at the distal end of a robot arm is made to follow changes caused in the force exerted by the muscles of praxis as a result of changes in angle at the first and second joints. Even when the trainee changes his or her position, he or she may be indicated of and may positively comprehend the direction in which he or she is to exert the force. The robot arm have its distal end secured to the distal end of the link mechanism has elasticity variable with directions. The elasticity is varied to follow changes caused in the force exerted on the distal end of the link mechanism by a set of antagonistic mono-articular muscles and a set of antagonistic bi-articular muscles, as a result of changes in angle at the first and second joints.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Apparatus and method for resistance-based muscular force evaluation using a hexagonal diagram of output distribution
InactiveUS7748271B2Improve accuracyAccurately evaluate muscular forceWork measurementSensorsMuscular forceEngineering
The torques at the first and second joints of a test subject are measured, which may be generated simultaneously by the coordinate action of the antagonistic mono- and bi-articular muscles. A hexagonal diagram of the output distribution is formulated on a plane formed by two axes corresponding to torques at the first and second joints as. Based on the diagram, the muscular force of the subject, changing through training, may accurately be evaluated, without the necessity of specifying the force of individual function-based muscles of praxis, even if the subject changes his or her position or joint angle. The torques at the first and second joints are measured, which are generated simultaneously by the coordinate action of the antagonistic mono- and bi-articular muscles. The muscular force of the bi-articular link mechanism of the subject is thus measured by the diagram.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Resistance training device exerting a constant load without depending upon position
InactiveUS8002670B2Efficient executionEffective trainingClubsMuscle exercising devicesMuscular forceConstant load
A resistance training device effectively training the muscular force of a desired muscle includes a saddle for a user to sit on, a robot arm adjustable to the length of a limb of the user, a fastener for securing the robot arm to the limb, a controller for controlling the torque of a driving source driving a joint of the robot arm, and an input operating unit for the user to input a driving condition. When the user inputs a training load and an output direction of the distal end of the limb to be trained, the value of a torque necessary for generating the training load is calculated. The robot arm generates the torque of the calculated magnitude acting in a direction opposite to the output direction in such a manner that a constant training load is exerted to the user without dependency on the position of the user.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
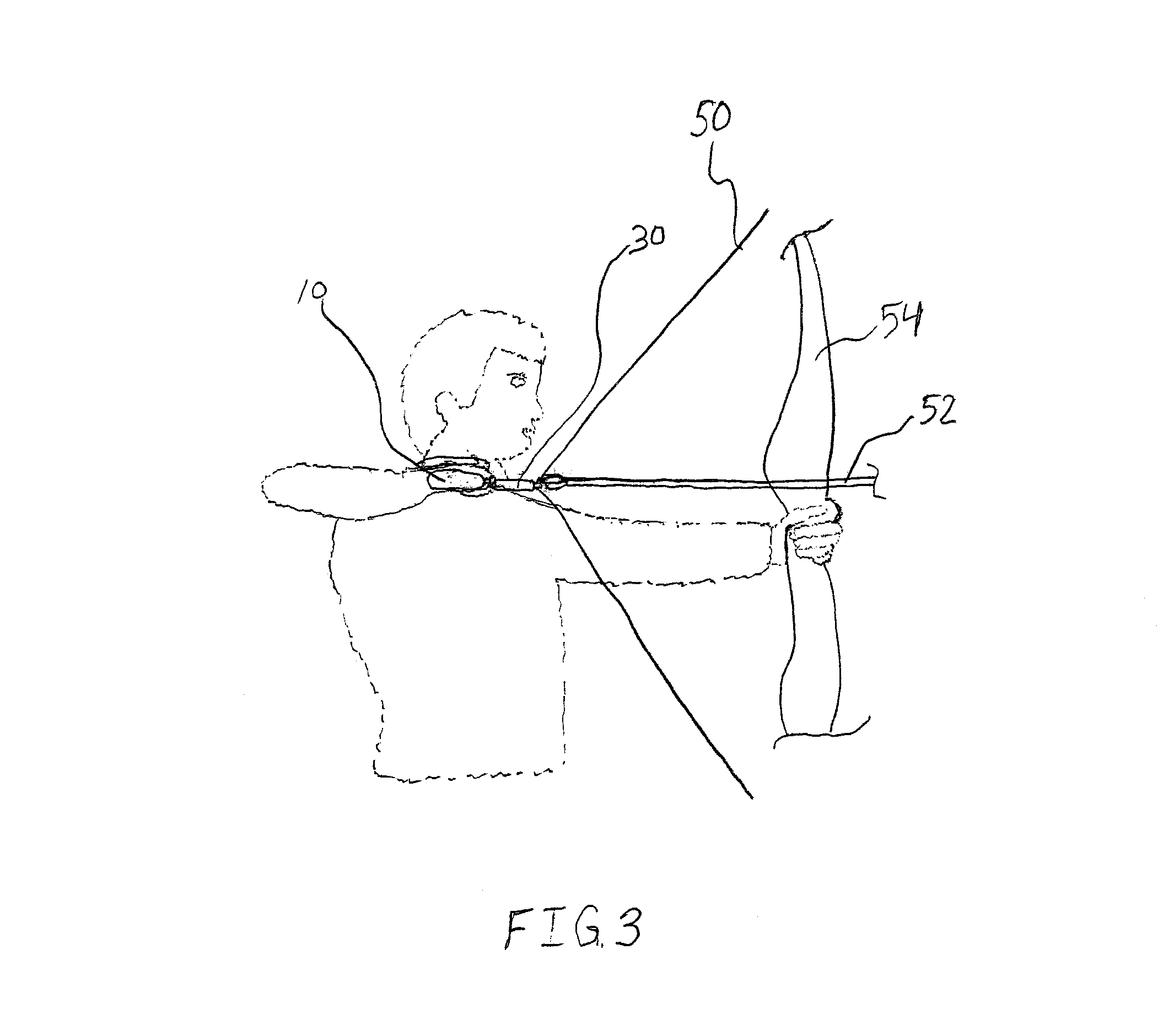
Archery apparatus and method
InactiveUS8733335B2Little strengthReduce fatigueFiring/trigger mechanismsBows/crossbowsMuscular forceBowstring
An archery apparatus includes a combined adjustable neck support, handle and release mechanism for reducing the amount of force exerted by an archer to maintain a bowstring and associated arrow in a generally fully drawn position. In operation, the release mechanism is secured to the bowstring, the handle is grasped by the drawing hand of the archer, with the other hand of the archer on the bow frame, the bowstring is drawn by the archer to the generally fully drawn position so that the release mechanism is proximate the side of the head of the archer and the neck support is selectively and supportably disposed against the archer's neck. Thus, both the manual muscular force exerted by the drawing arm of the archer and the force supplied by the neck support are available in tandem for maintaining a bowstring and associated arrow in a generally fully drawn position. The release mechanism is then actuated to provide the normal proper triggering of the arrow into flight.
Owner:PIERCE JIM
Diving apparatus
InactiveUS7258509B2Improve securityEasy to separateLife-buoysUnderwater equipmentMuscular forceFresh air
A diving apparatus includes a pump that is actuated by muscular force. Diving weights are fastened to a fresh-air tank by surface zip fasteners. A traction element lies between the pump and the diver's limbs and to which it is attached a quick-release device. A float is surrounded by a net, the float having a seat located below the surface of the water and each of the straps, which are used to fasten the fresh-air tank to the diver, has at least one quick fastener which can be opened by the diver.
Owner:ELLWITZ MARTIN
Muscular tension-elevating agent
InactiveCN1917894ALittle side effectsImprove securityMetabolism disorderMuscular disorderMuscular forceMuscular tension
It is intended to provide a muscular tension-elevating agent obtained from a fruit, i.e., a muscular tension-elevating agent and a body fat-controlling agent originating in a natural material which reinforces muscular force and shows effects of reducing body fat and inhibiting body fat accumulation without lowering the skeletal muscle amount or the inner organ weight. More specifically speaking, it is intended to obtain polyphenol from a fruit and utilize the same in a muscular tension-elevating agent, a body fat-controlling agent or a drink, a food and a drug for elevating muscular tension, reducing body fat and inhibiting body fat accumulation. Namely, a muscular tension-elevating agent or a body fat-controlling agent containing, as the active ingredient, polyphenol originating in a fruit which is efficacious in elevating muscular tension and a drink, a food and a drug containing the same.
Owner:ASAHI BREWERIES LTD
Vehicle, particularly a bicycle, comprising an electrical auxiliary drive
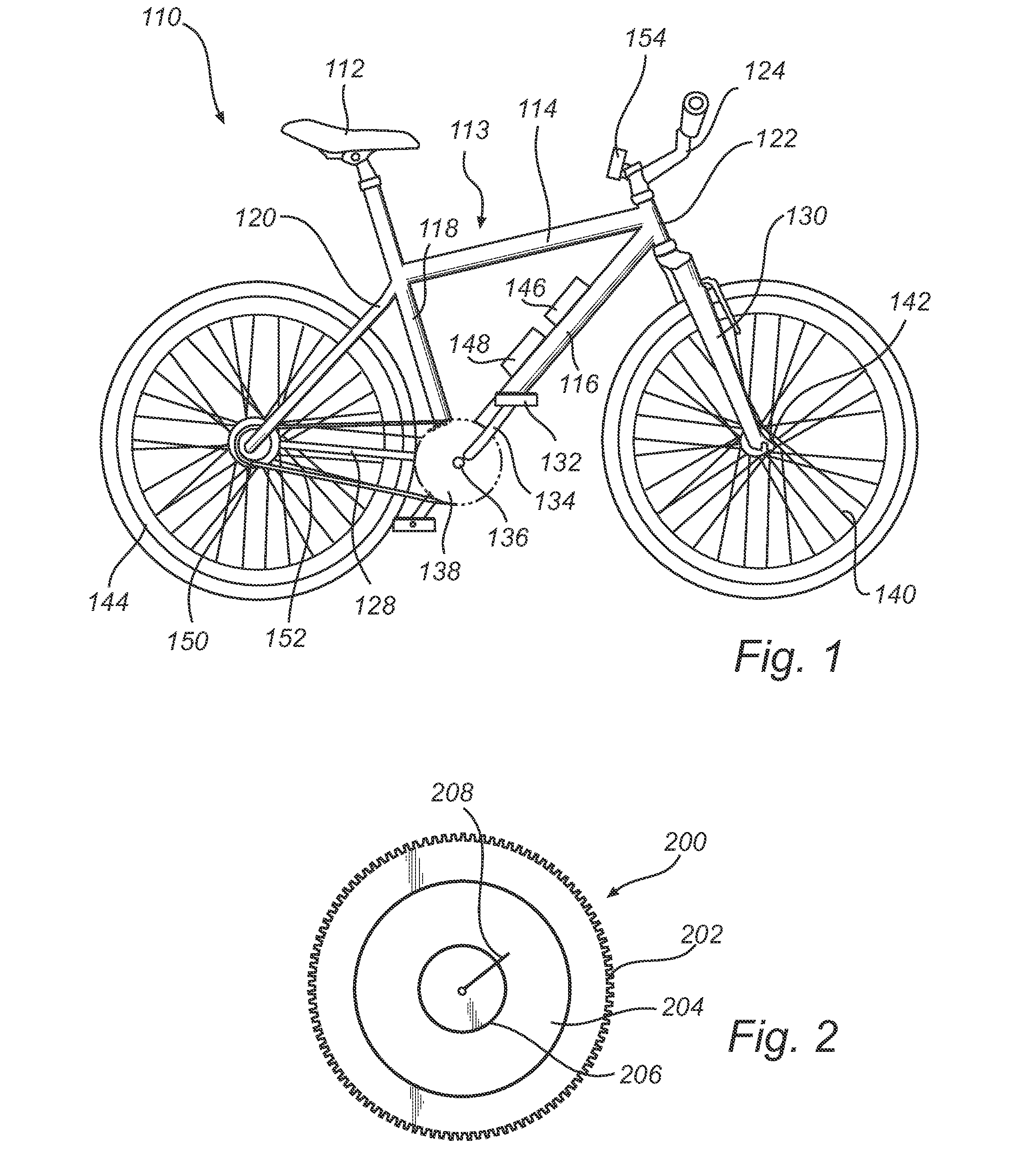
A vehicle, particularly a bicycle, including a crank drive that is to be actuated by muscular force and that is disconnectably drive-connected to at least one driven wheel, and also including an electrical auxiliary drive for assisting the crank drive. The vehicle can be driven solely by the auxiliary drive when the drive connection between the crank drive and the wheel is disconnected. In addition, a control device for the auxiliary drive is preferably connected to a sensor which detects the crank rotational speed.
Owner:STROTHMANN ROLF
Wearable apparatus for increasing muscular force
ActiveUS20200188212A1Attracting forceProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesMuscular forcePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A wearable apparatus for increasing muscular force includes: a mount body coupled to an upper body of a wearer; a shoulder frame coupled at one end thereof to the mount body at the dorsal surface of the wearer and which is rotatable in up and down direction; a mounting frame coupled at one end thereof to the other end of the shoulder frame to be torsionally rotated; a supporter, which surrounds part of an upper arm of the wearer to support the upper arm of the wearer; and a compensation frame, which is integrally coupled to the supporter to be rotated together with the supporter about a shoulder joint of the wearer. The compensation frame capable of generating supporting force that varies depending on the angle to which the compensation frame is rotated.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
A Multiscale Modeling Method for Skeletal Muscle Mechanical Behavior
InactiveCN106202739BRealize macro and micro geometry modelingRealize simulationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMuscle tissueMuscular force
The invention relates to a skeletal muscle mechanical behavior multiscale modeling method and aims at solving the problem in the prior art that a complete process from cell electrophysiologic action potential activation to skeletal muscle mechanical output cannot be simulated. The method comprises the steps of S1, determining positions and attitudes of muscle fibers; S2, establishing a skeletal muscle macroscopic geometric model and a skeletal muscle microcosmic geometric model according to the S1; S3, carrying out grid division on the geometric models established in the S2; S4, carrying out skeletal muscle electrophysiologic property modeling according to the S3; S5, carrying out multiscale calculation between cells and muscle tissues according to the S3 and S4; S6, establishing a skeletal muscle multiscale biomechanics model according to the S5; and S7, predicting muscular force according to the S6. The method is applied to the field of biomedical engineering.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Sitting mode control method of wearable bionic exoskeleton mechanical leg rehabilitation device
InactiveCN105326625BImprove adaptabilityHigh activityDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesThighMuscular force
The invention discloses a sitting mode control method for a wearable bionic exoskeleton mechanical leg rehabilitation device. The method comprises the steps as follows: a control module judges whether a posture of a user simultaneously meets trigger conditions C1, C2, C3 and C4 or not through collected signals; if the control module detects that the user meets the sitting trigger conditions, the control module sends out an instruction to a hip motor and a knee motor; the hip motor begins to constantly speed up to a speed v0 from stillness at an accelerated speed a0 and rotates at the speed v0, the angle<hip> is reduced, and a trunk and thighs of the user are driven to generate a relative angle motion; and meanwhile, the knee motor also begins to constantly speed up to the speed v0 from stillness at the accelerated speed a0 and then rotates at the constant speed v0, the angle<knee> is reduced, and the thighs and shanks of the user are driven to generate the relative angle motion. The sitting mode control method is capable of helping a patient carry out sitting training at an initial stage, so that the joint range of motion and the muscular force can be strengthened; and meanwhile, gradual improvement of the adaptability of the patient to the exoskeleton is facilitated, and thus a foundation is laid for later walking motion.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Wearable muscular strength assisting device and upper arm module thereof
PendingCN111791217AIncreased durabilityImprove AssemblabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesMuscular forcePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present invention discloses an upper arm module of a wearable muscle strength assisting device, comprising: a base part connected to the body of a wearer and provided corresponding to the upper end part of the upper arm of the wearer; an upper arm part having one end rotatably coupled to the base part about a fixed point, extending to correspond to an upper arm of the wearer, and coupled to the upper arm of the wearer; an elastic body having one end fixedly coupled to a position spaced apart from one end of the upper arm portion in a direction in which the upper arm portion extends; a first link, one end of which is rotatably coupled to the base portion at an action point provided apart from the fixed point, and which is coupled to the upper arm portion so as to guide the other end tomove when the upper arm portion rotates about the fixed point; and a second link rotatably coupled to the other end of the first link at a first point, coupled to the upper arm portion to guide movement of a second point spaced apart from the first point when the upper arm portion rotates about the fixed point, and coupled to the other end of the elastic body at a third point spaced apart from thefirst point and the second point.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com