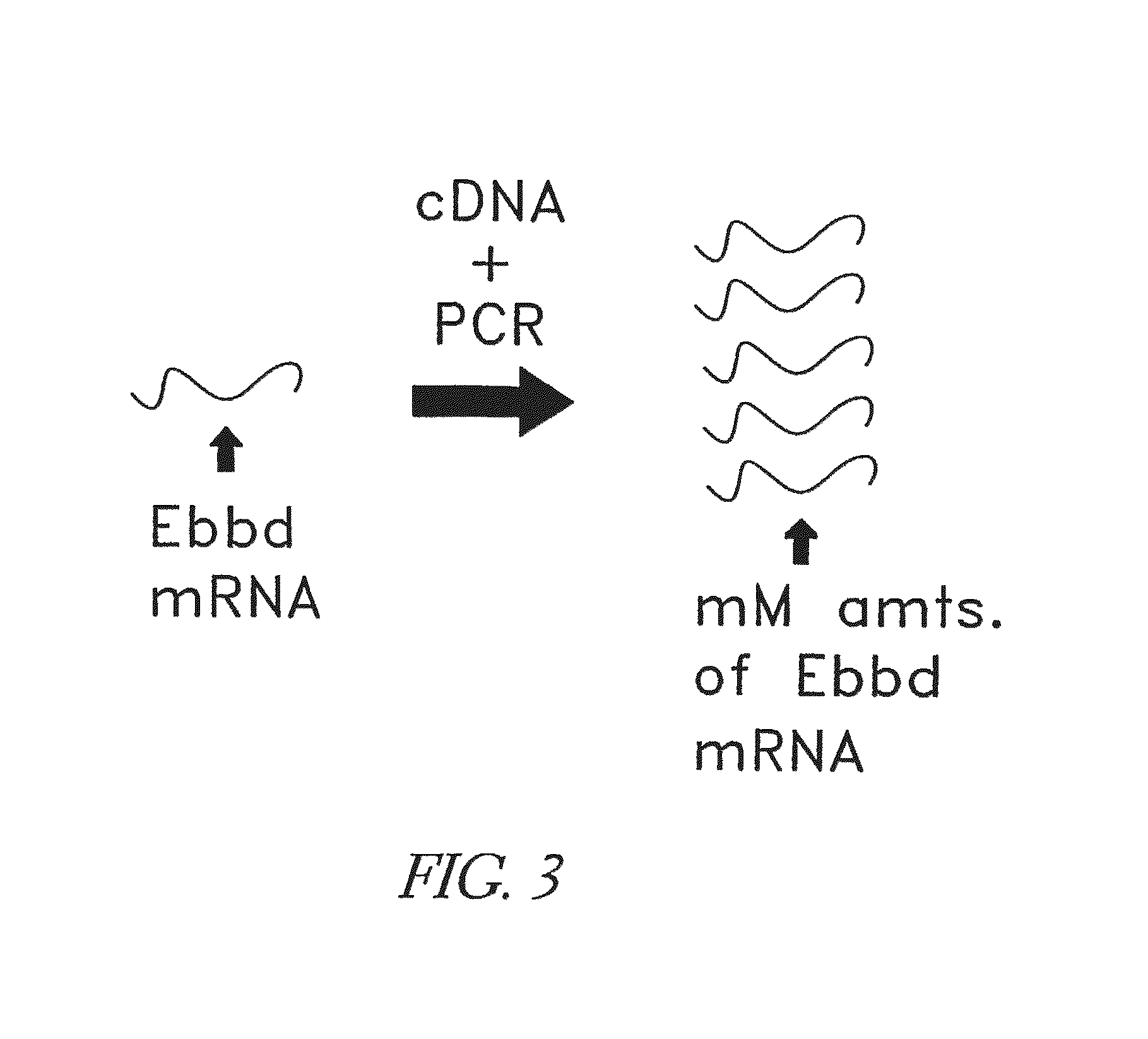
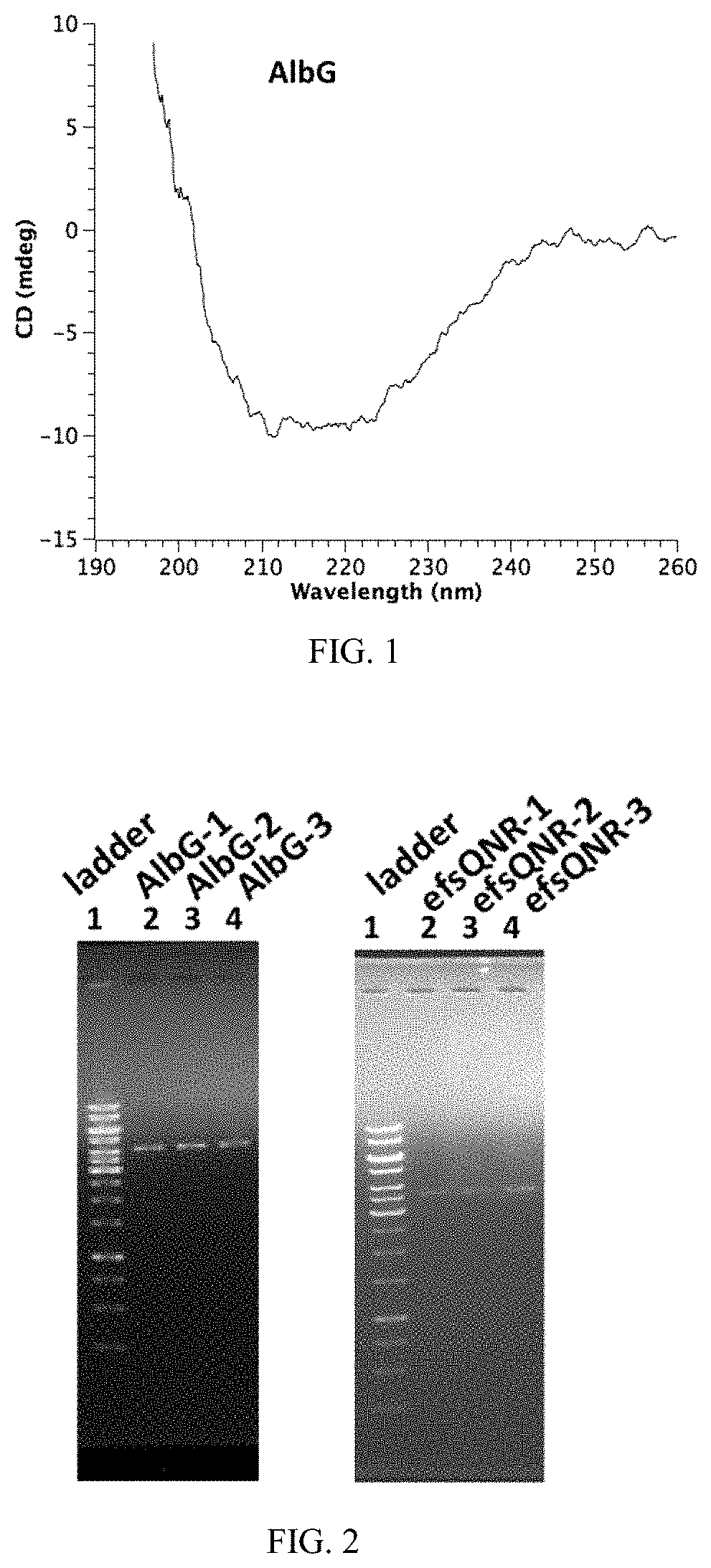
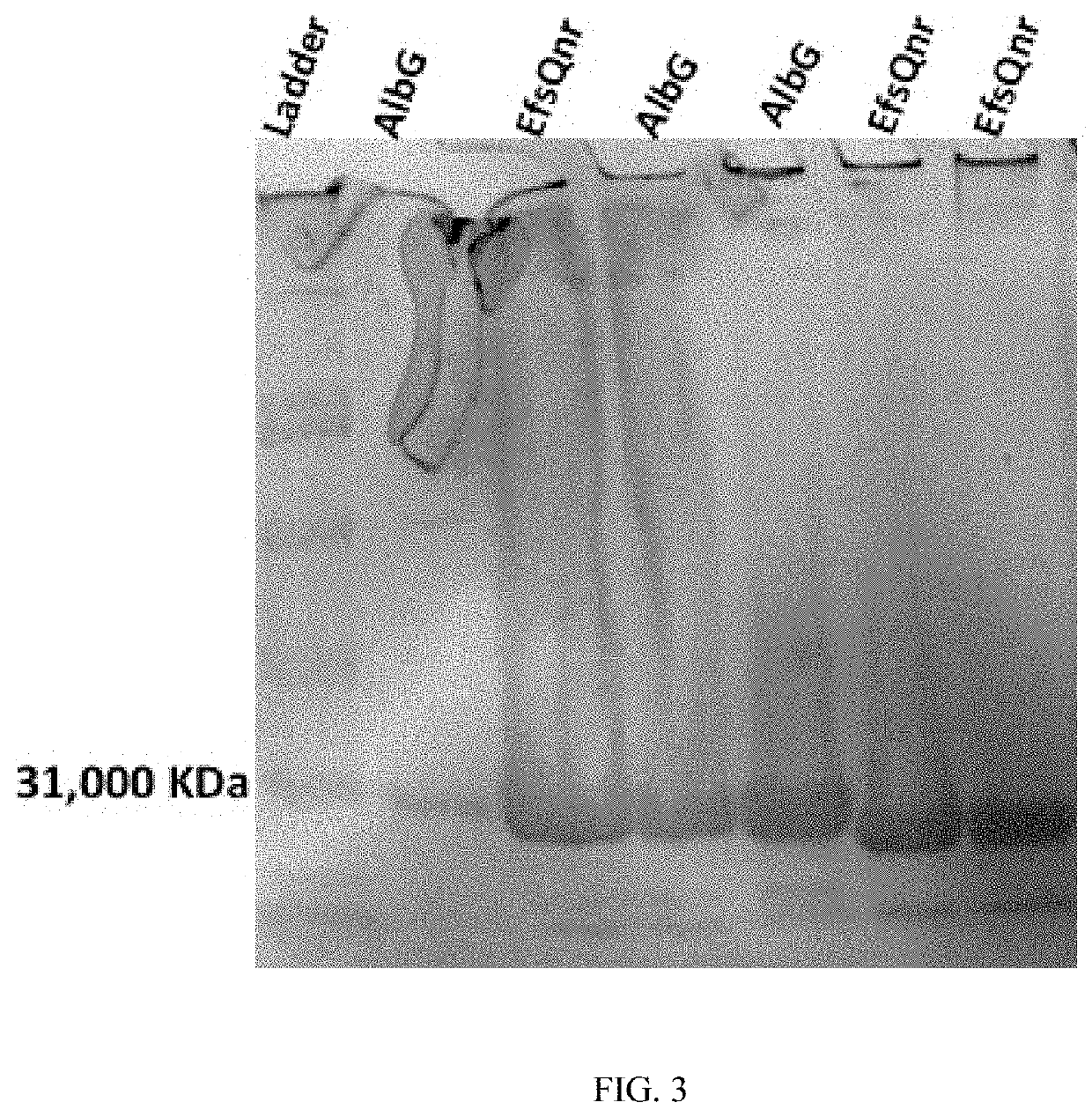
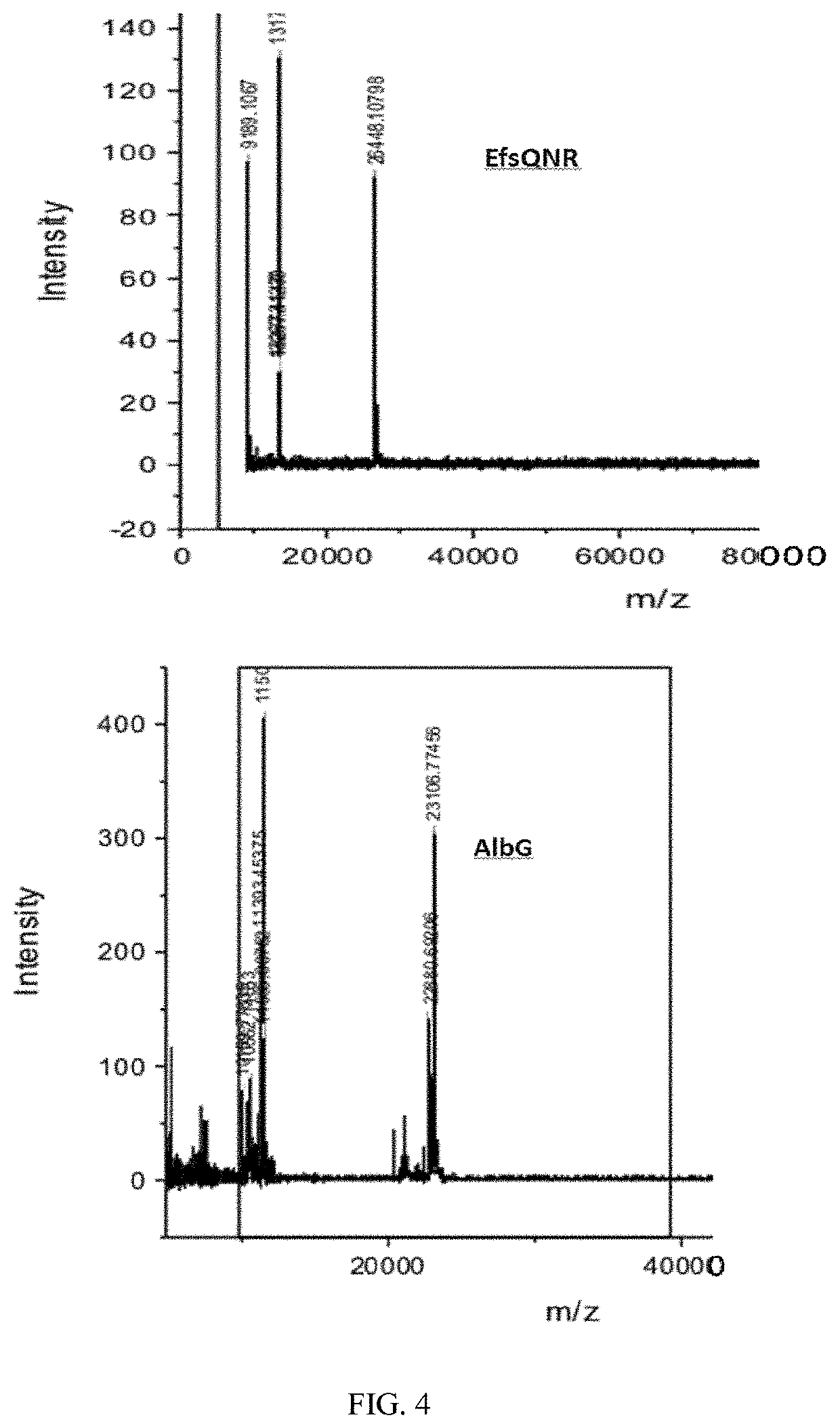
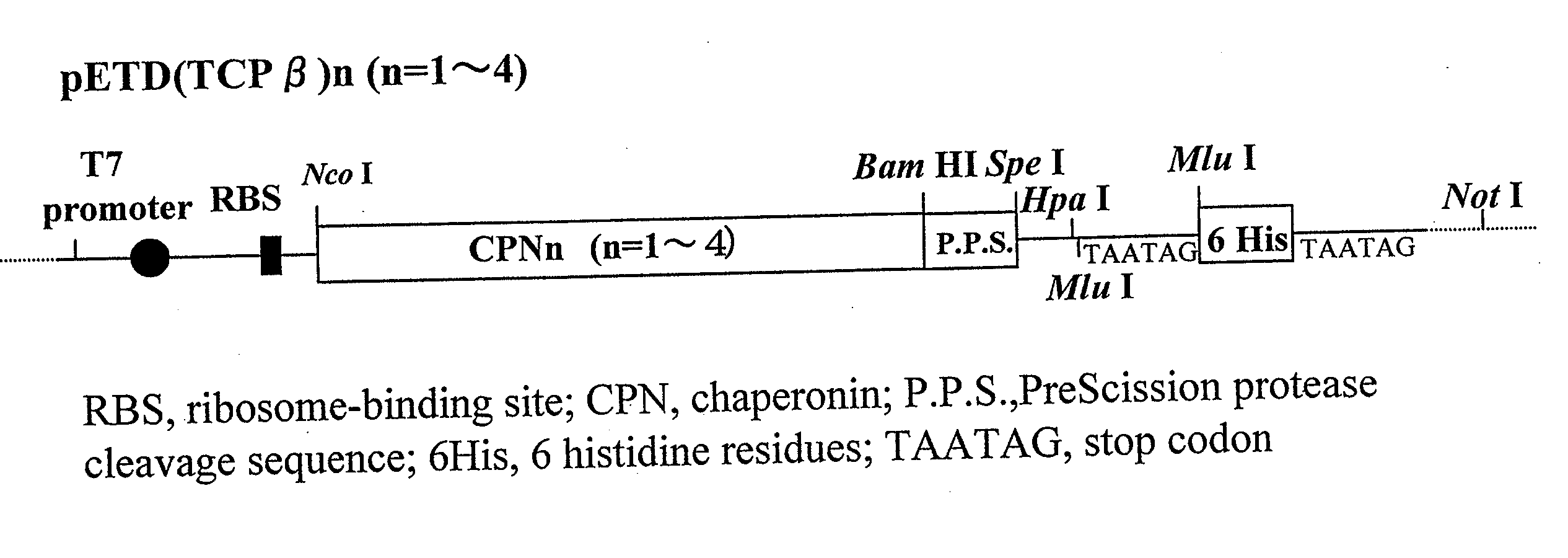
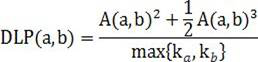Patents
Literature
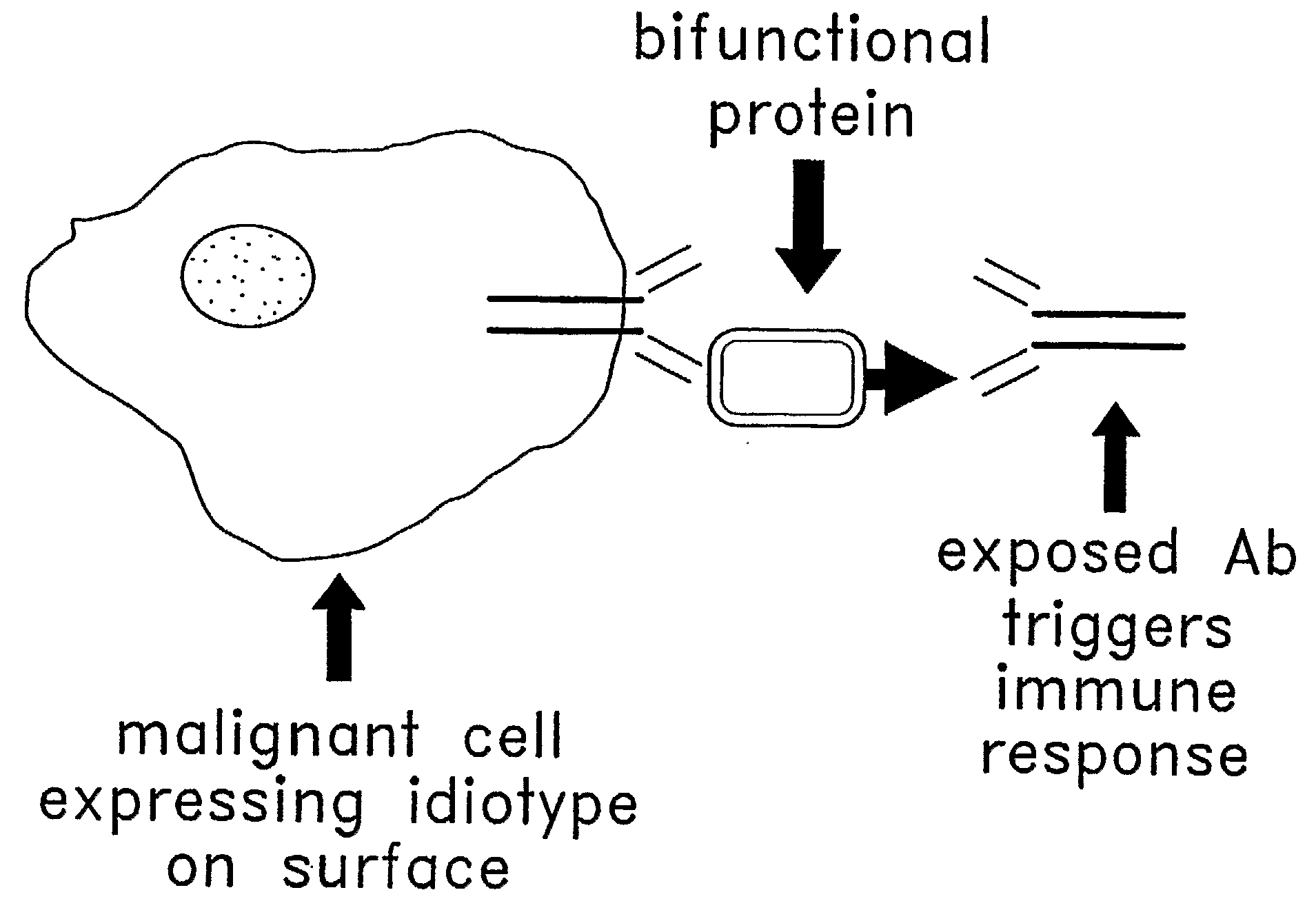
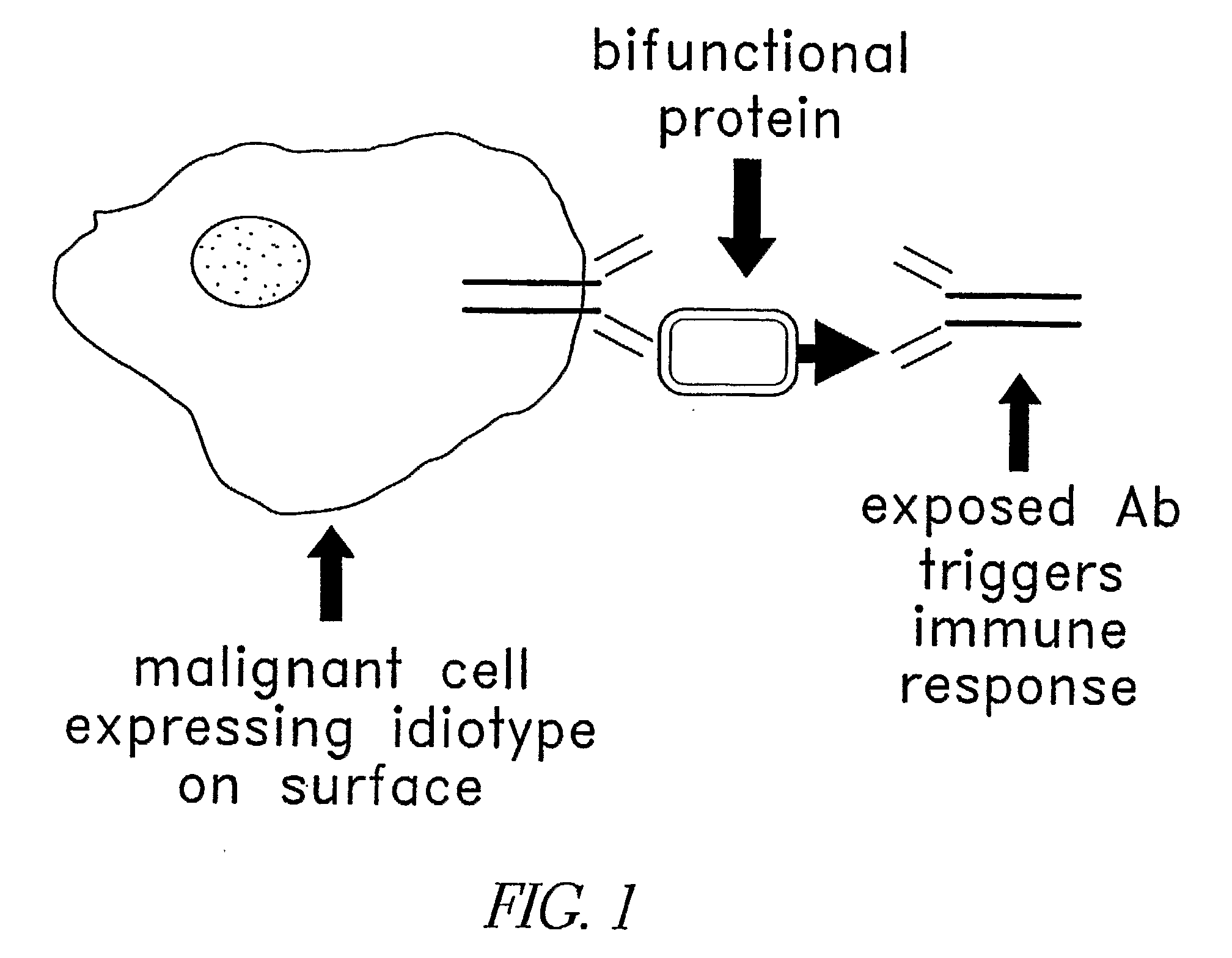
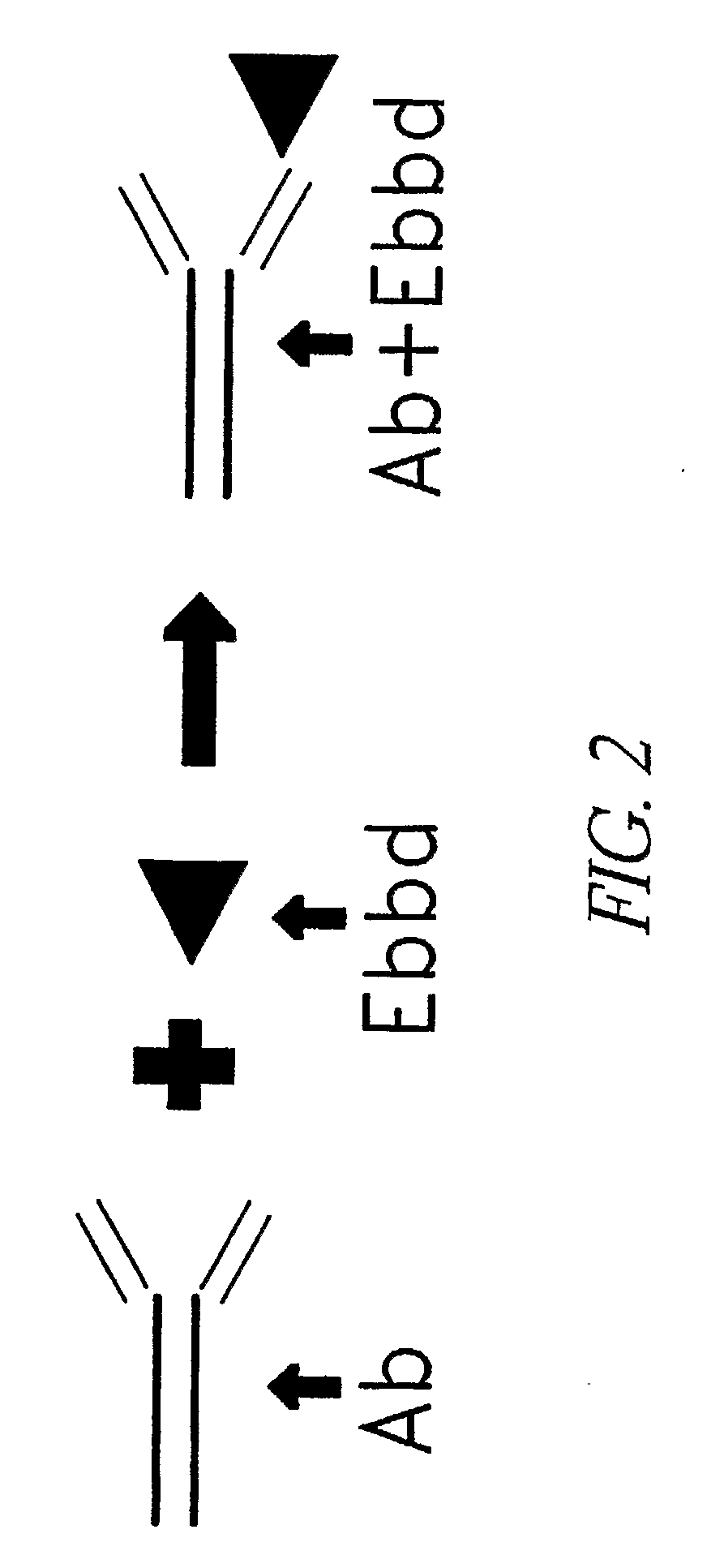
37 results about "Protein link" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
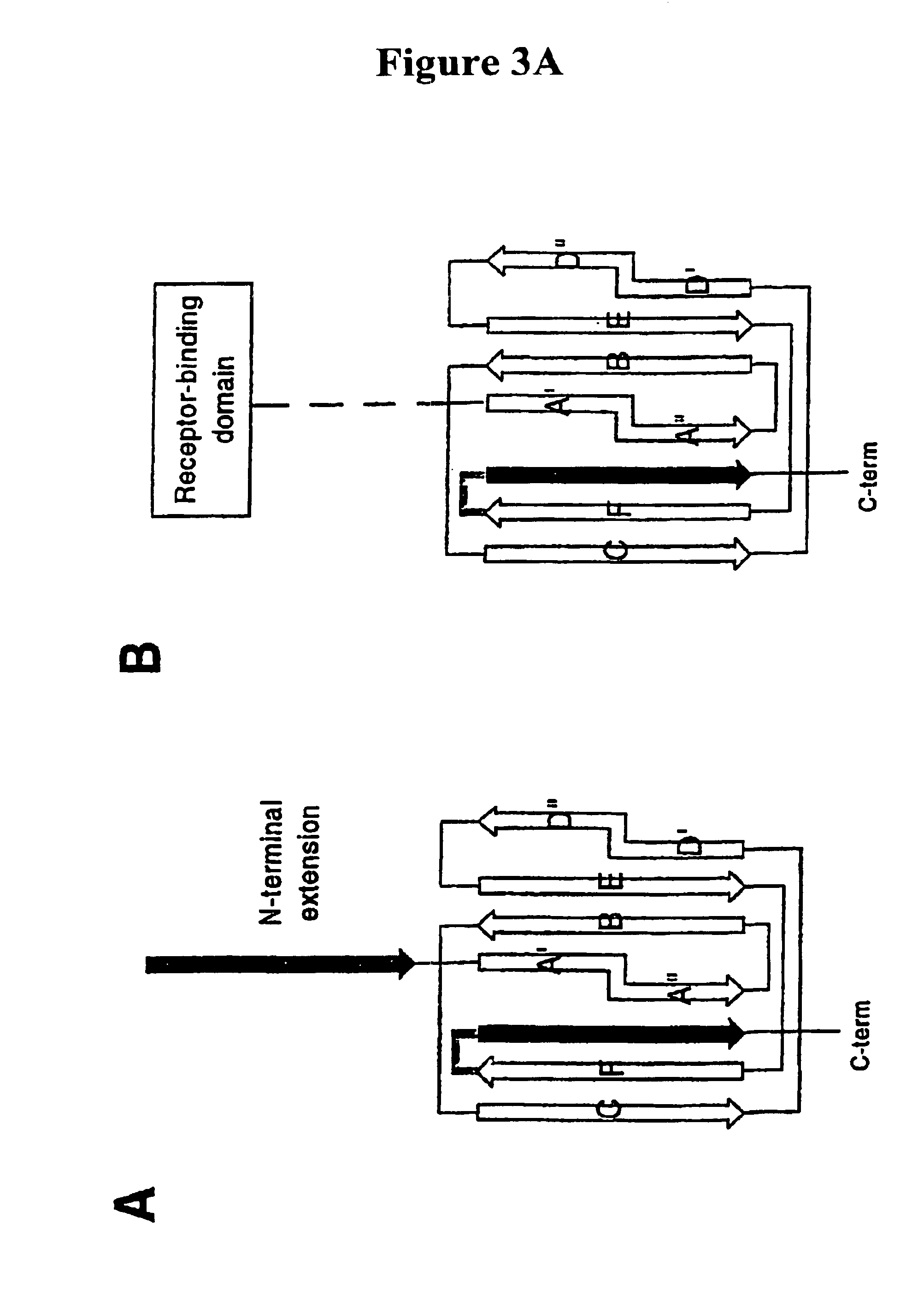
In nervous system: Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators …activation by receptor proteins of linking proteins, which move across the membrane, bind to channel proteins, and open the channels. Another system is the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) system.
Reduction of non-specific binding in assays
Methods and compositions are disclosed for reducing non-specific binding in a binding assay for the determination of an analyte in a sample where one of the reagents for conducting the binding assay comprises a solid support comprising a polysaccharide. The method comprises including in an assay medium for conducting the binding assay a soluble compound comprising a protein linked to a polysaccharide. Also disclosed are methods and compositions for determining the presence and / or amount of an analyte in a sample suspected of containing the analyte. The methods include as reagents a solid support comprising a polysaccharide and a soluble compound comprising a protein linked to a polysaccharide.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
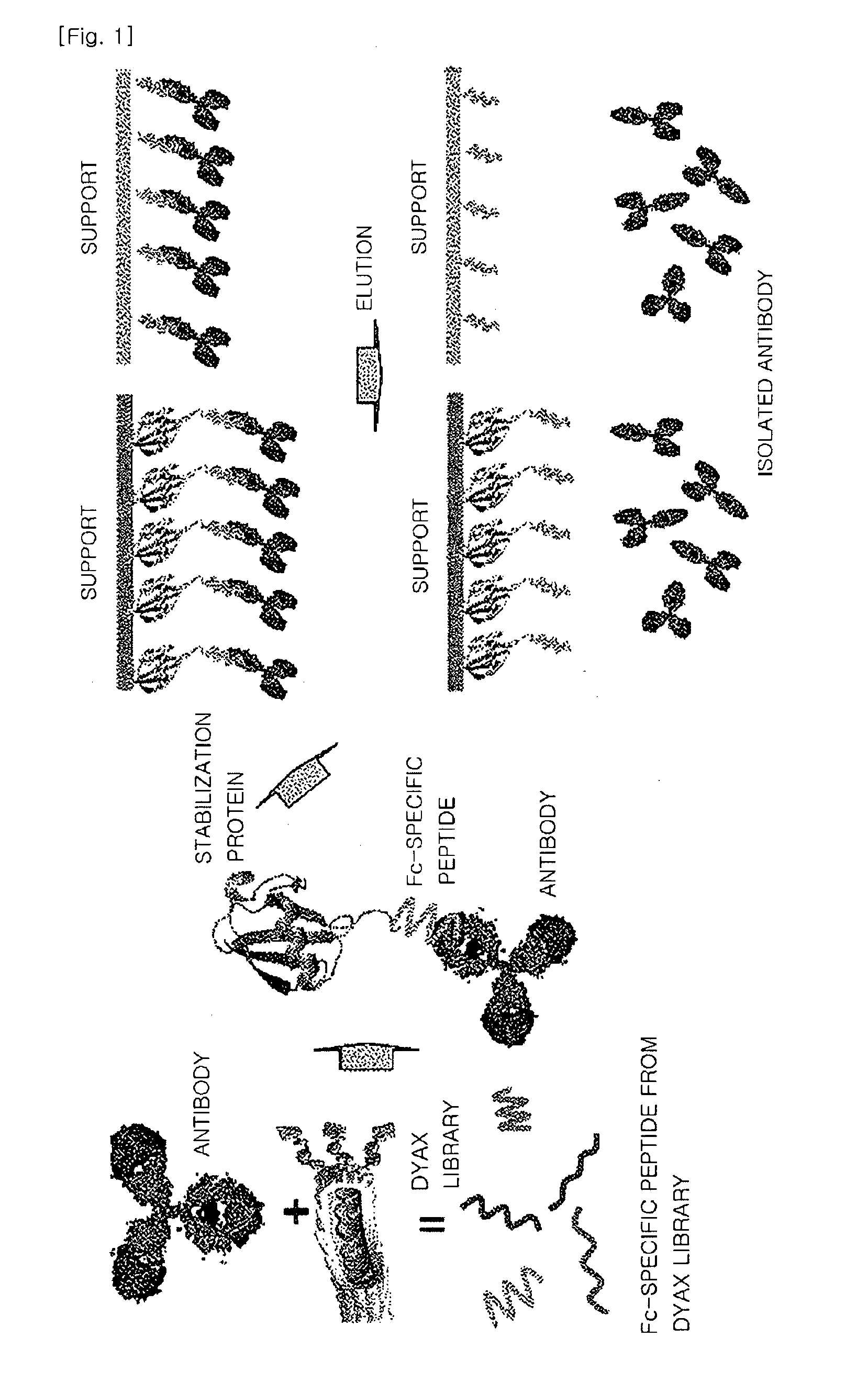
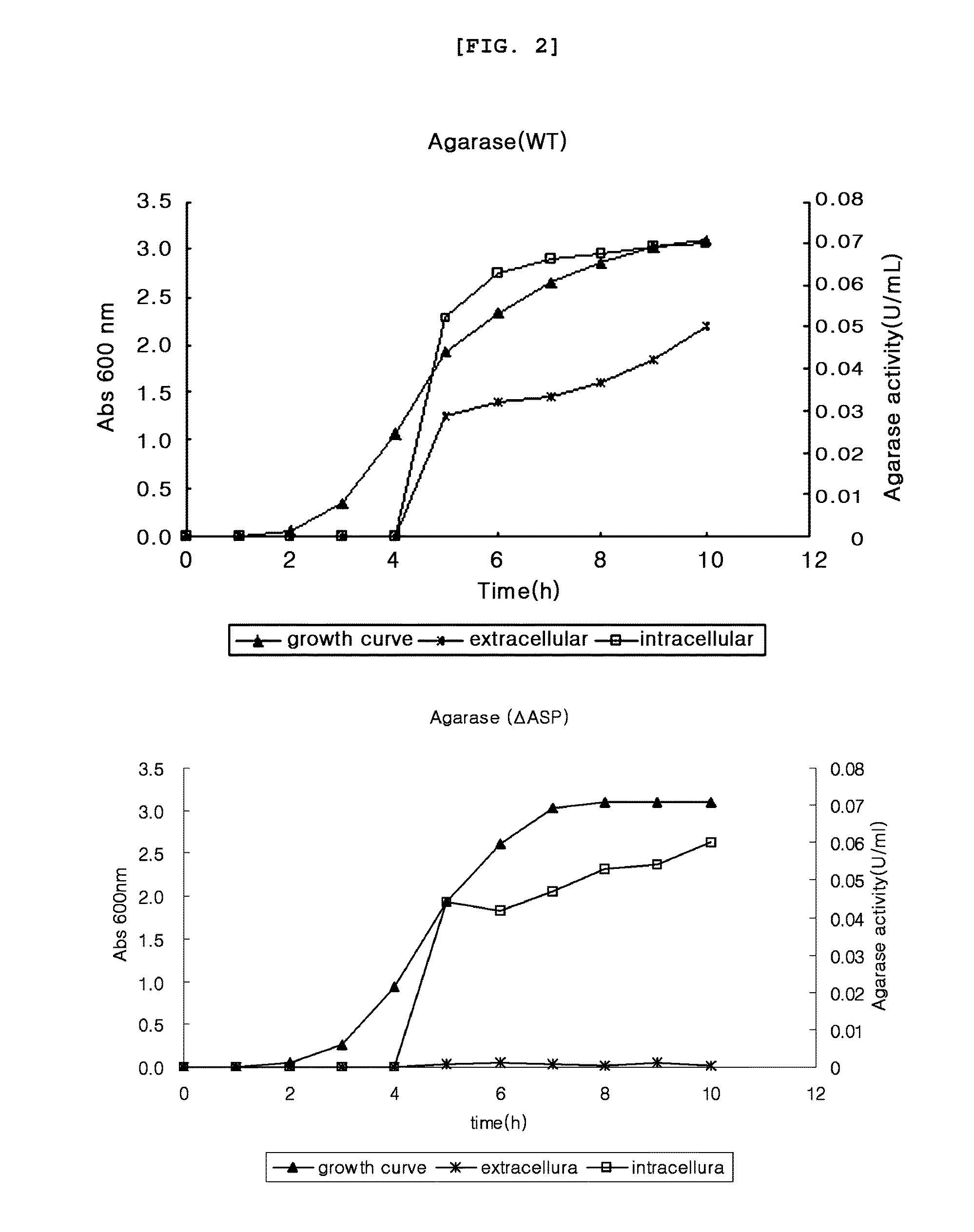
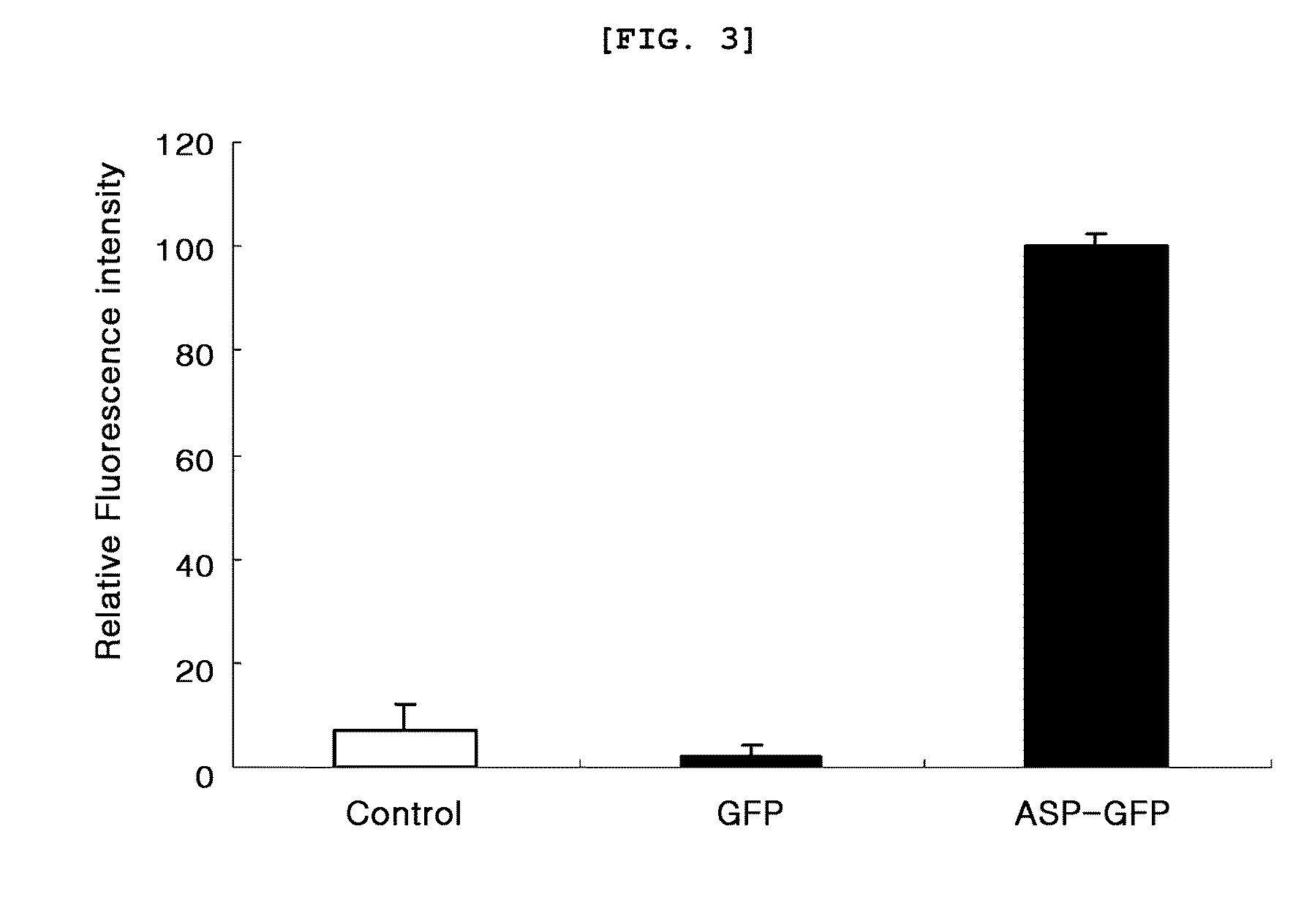
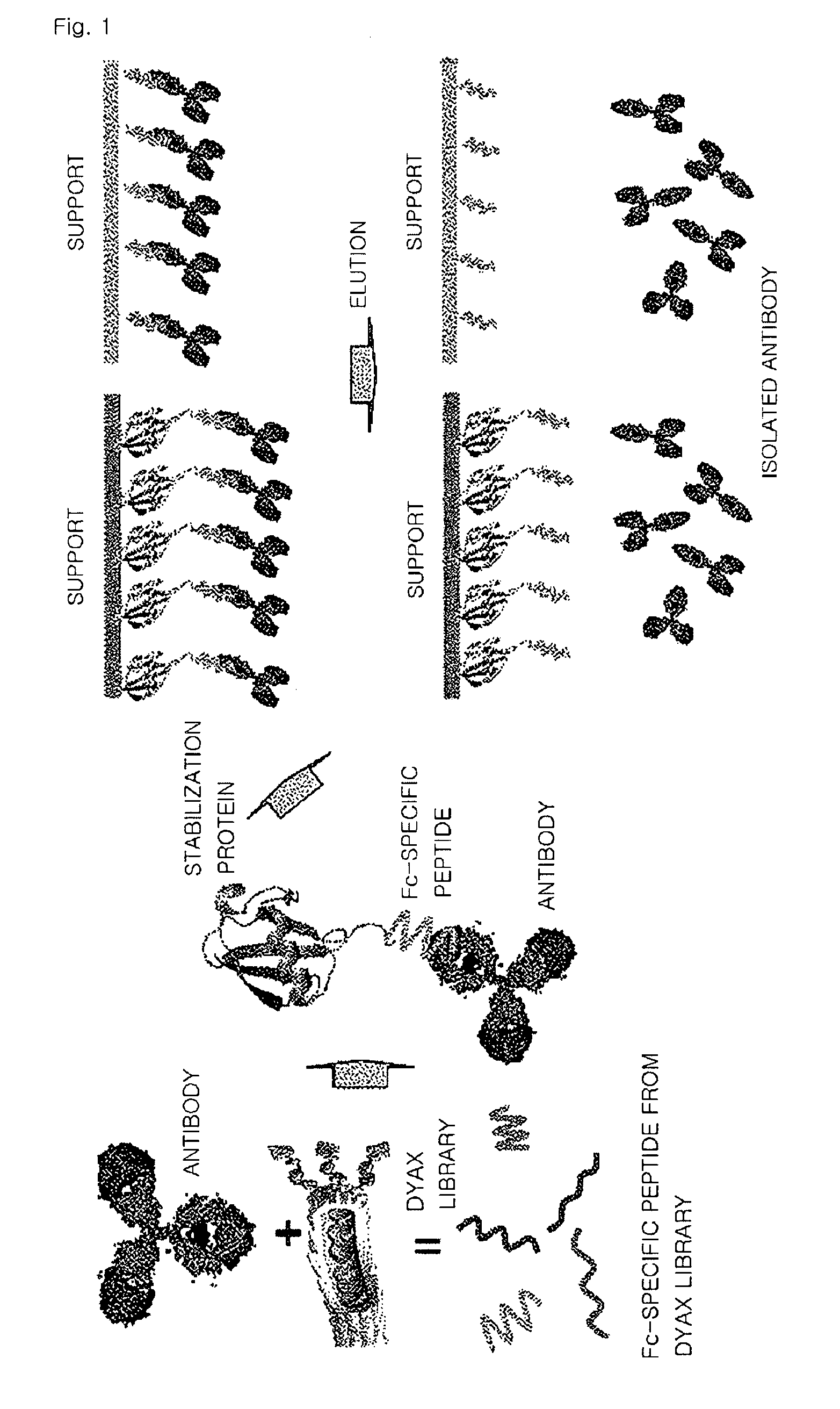
Fusion protein binding specifically to constant region of antibody, method of preparing the fusion protein, and method of isolating antibody using the fusion protein
A fusion protein that includes a polypeptide binding specifically to a constant region of an antibody and a stabilization protein linked to a terminus of the polypeptide, a polynucleotide encoding the fusion protein, a cell including the polynucleotide, a method of preparing the fusion protein, and a method of isolating an antibody by using the fusion protein.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
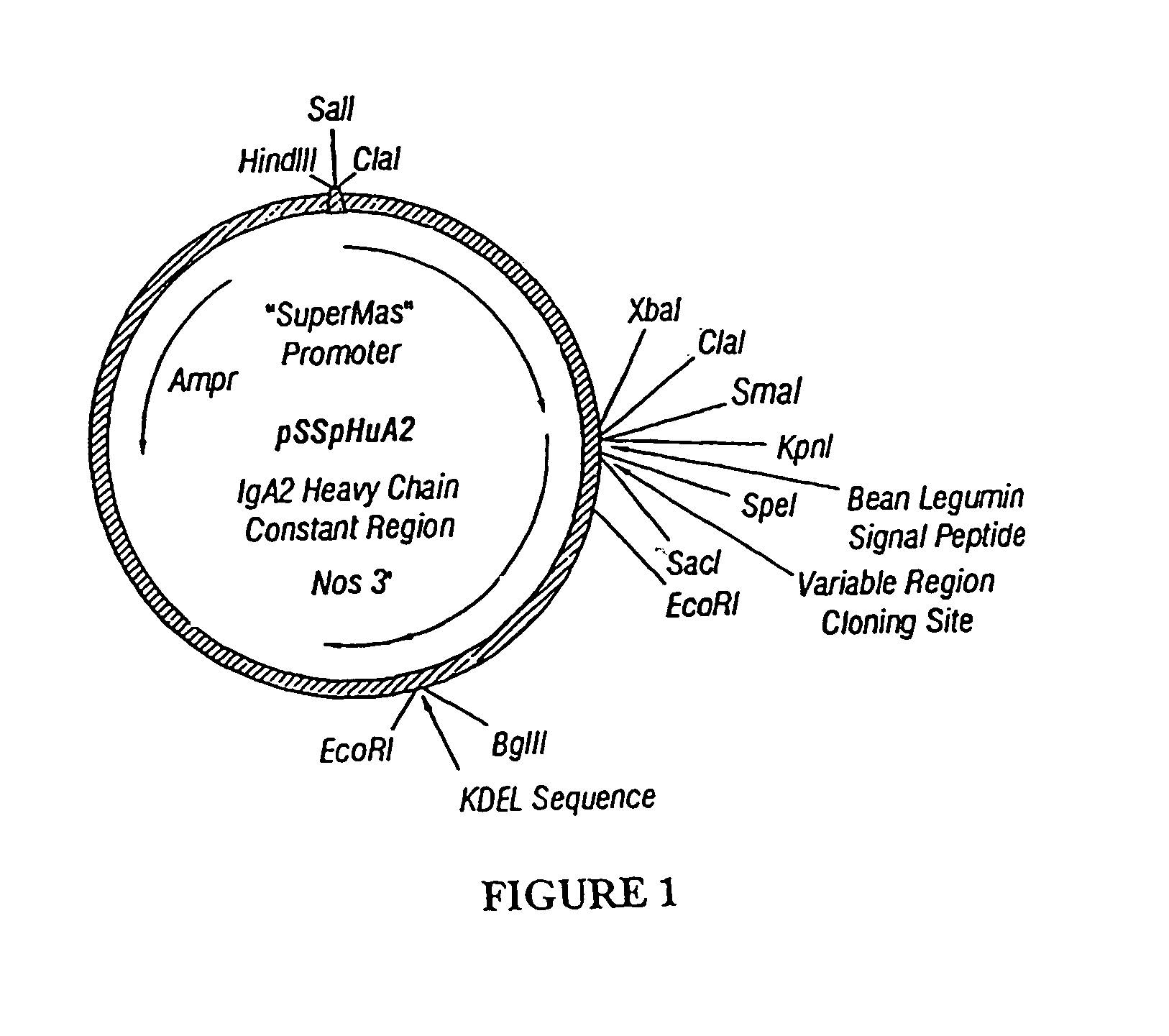
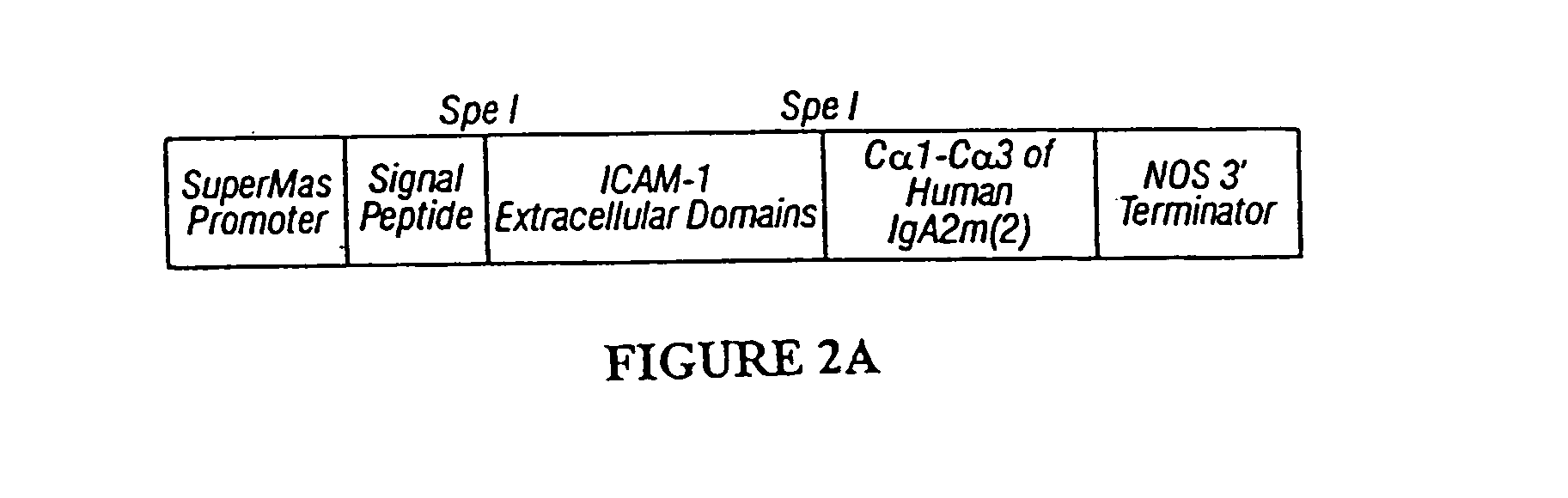
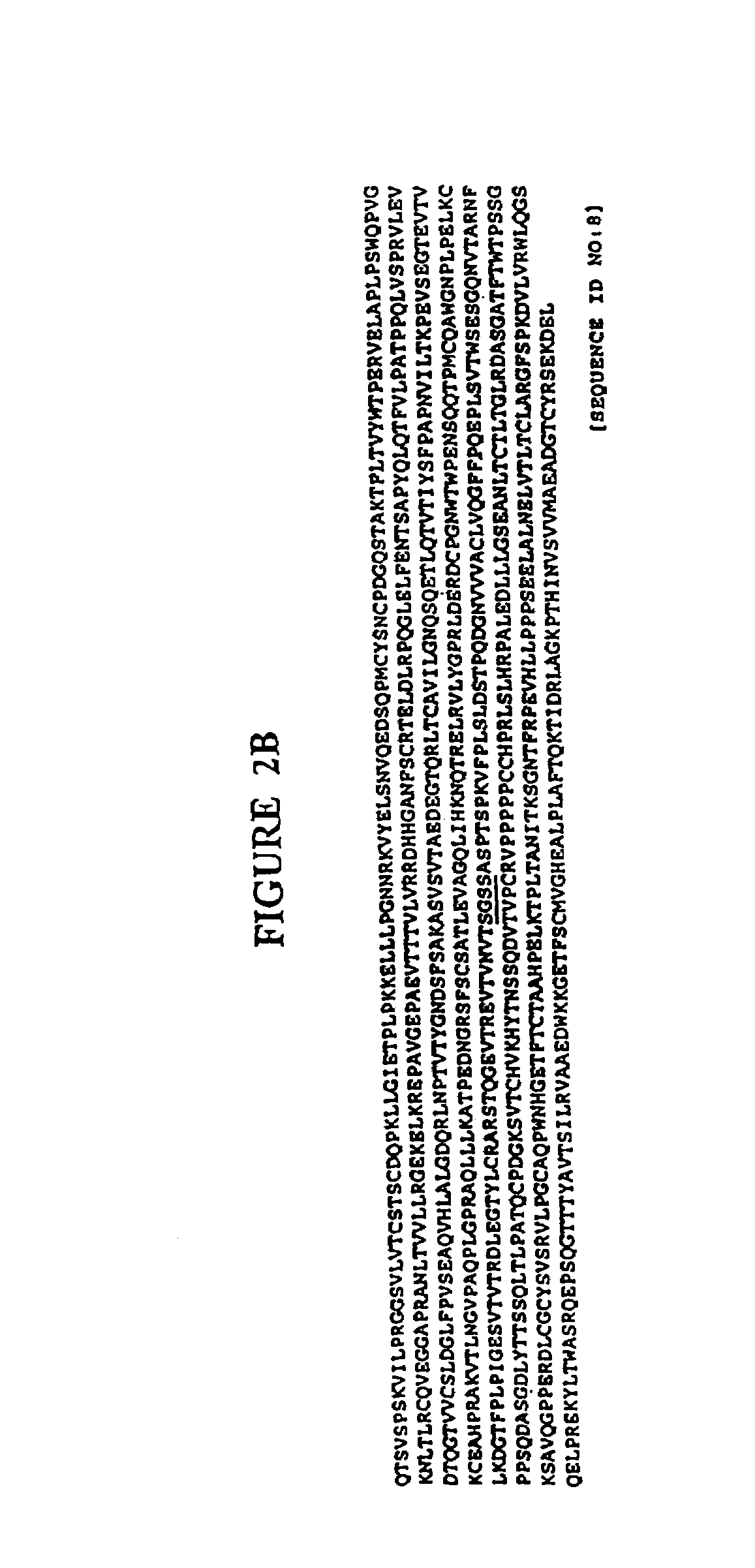
Immunoadhesin comprising a chimeric ICAM-1 molecule produced in a plant
InactiveUS7951378B2Improve efficiencyIncrease in valencySsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsMammalADAMTS Proteins
The immunoadhesions of the present invention are useful in treating rhinovirus infections. The immunoadhesions contain a chimeric ICAM molecule and may optionally also contain J chain and secretory compounds. The chimeric ICAM molecule is a fusion protein that has a rhinovirus receptor protein linked to an immunoglobulin protein. This invention also includes the greatly increased and improved method of producing immunoadhesions in plants. Each of the components of an immunoadhesin is produced in a plant cell and thereby assembles within the plant cell. This method of producing the immunoadhesions of the present invention results in the efficient and economic production of these molecules. The present invention also contemplates the production of immunoadhesions in a variety of eukaryotic cells including plants and mammalian cells. The immunoadhesions of the present invention are useful as a therapeutic against the common cold in humans which is caused by rhinoviruses.
Owner:PLANET BIOTECH
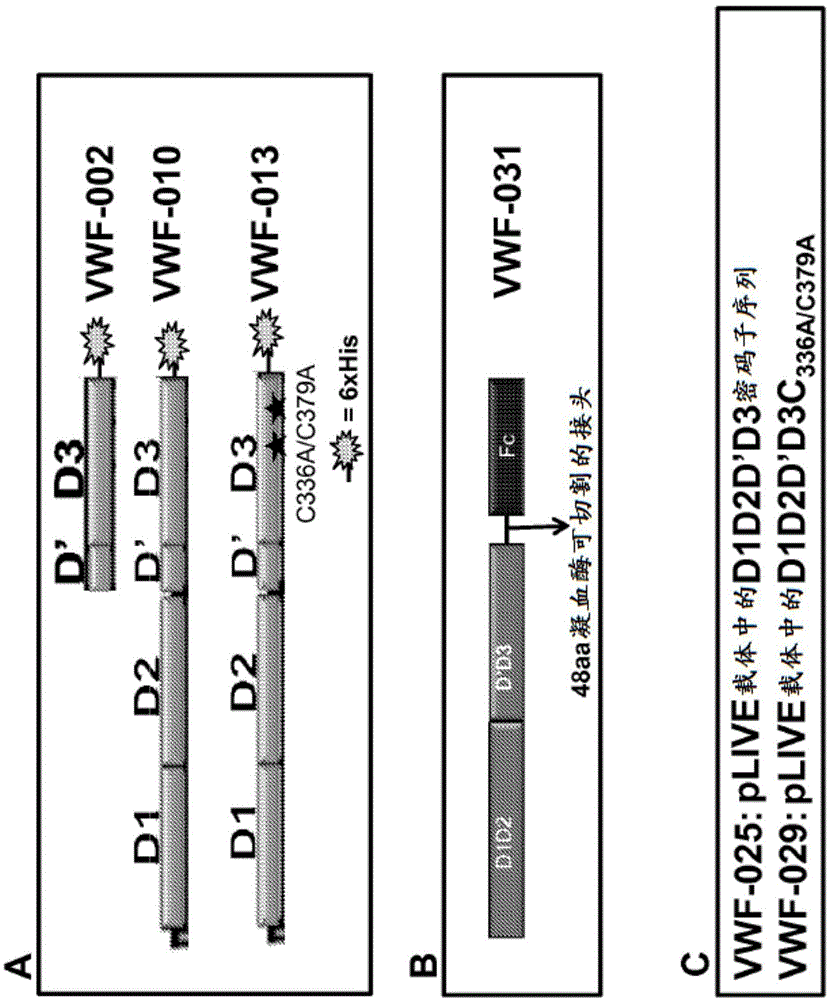
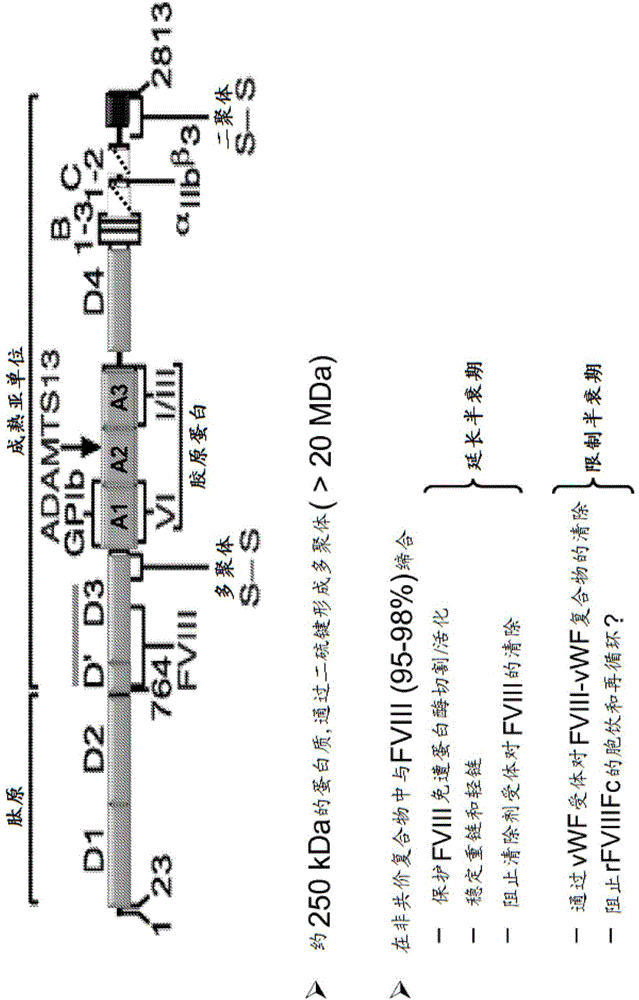
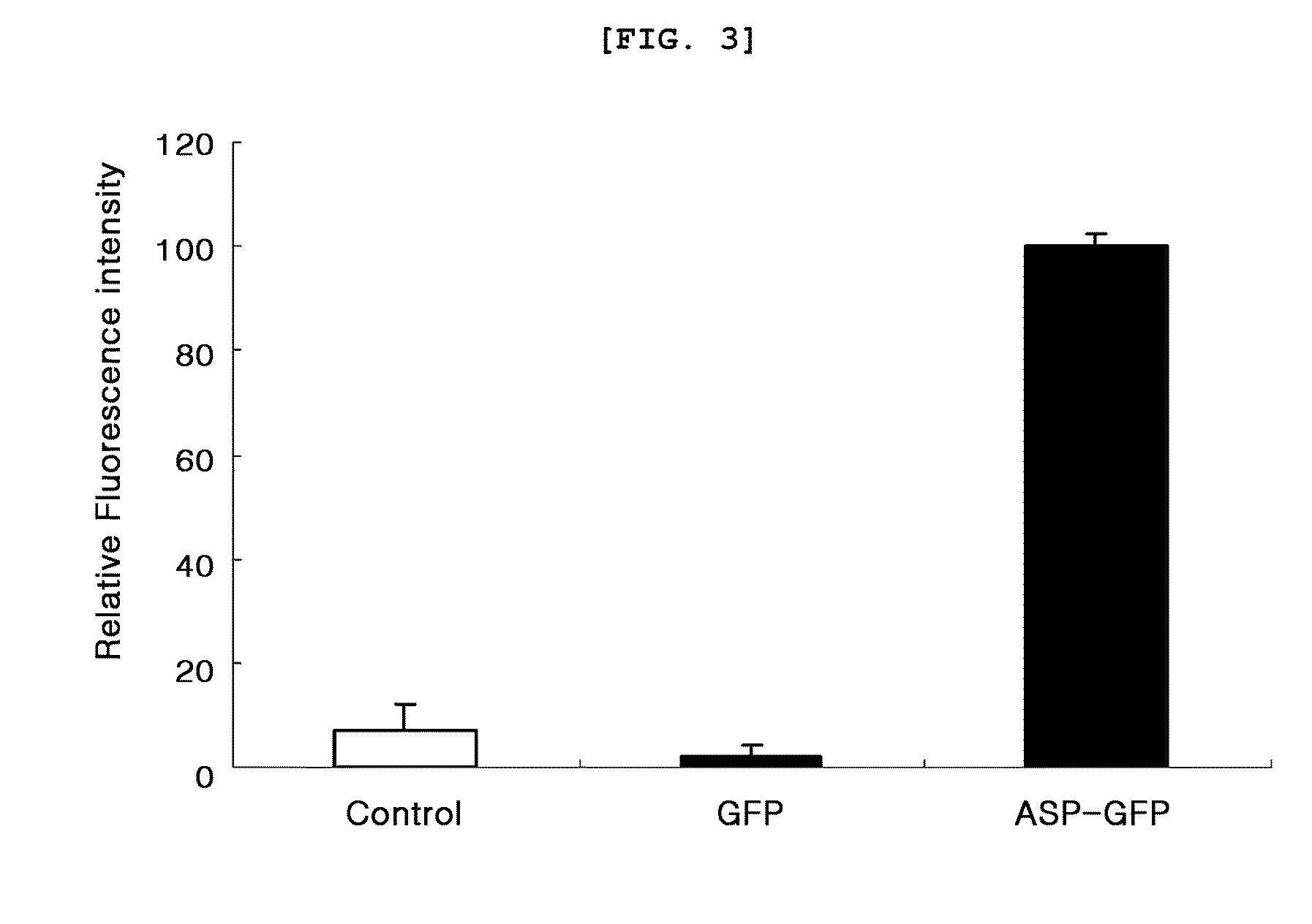
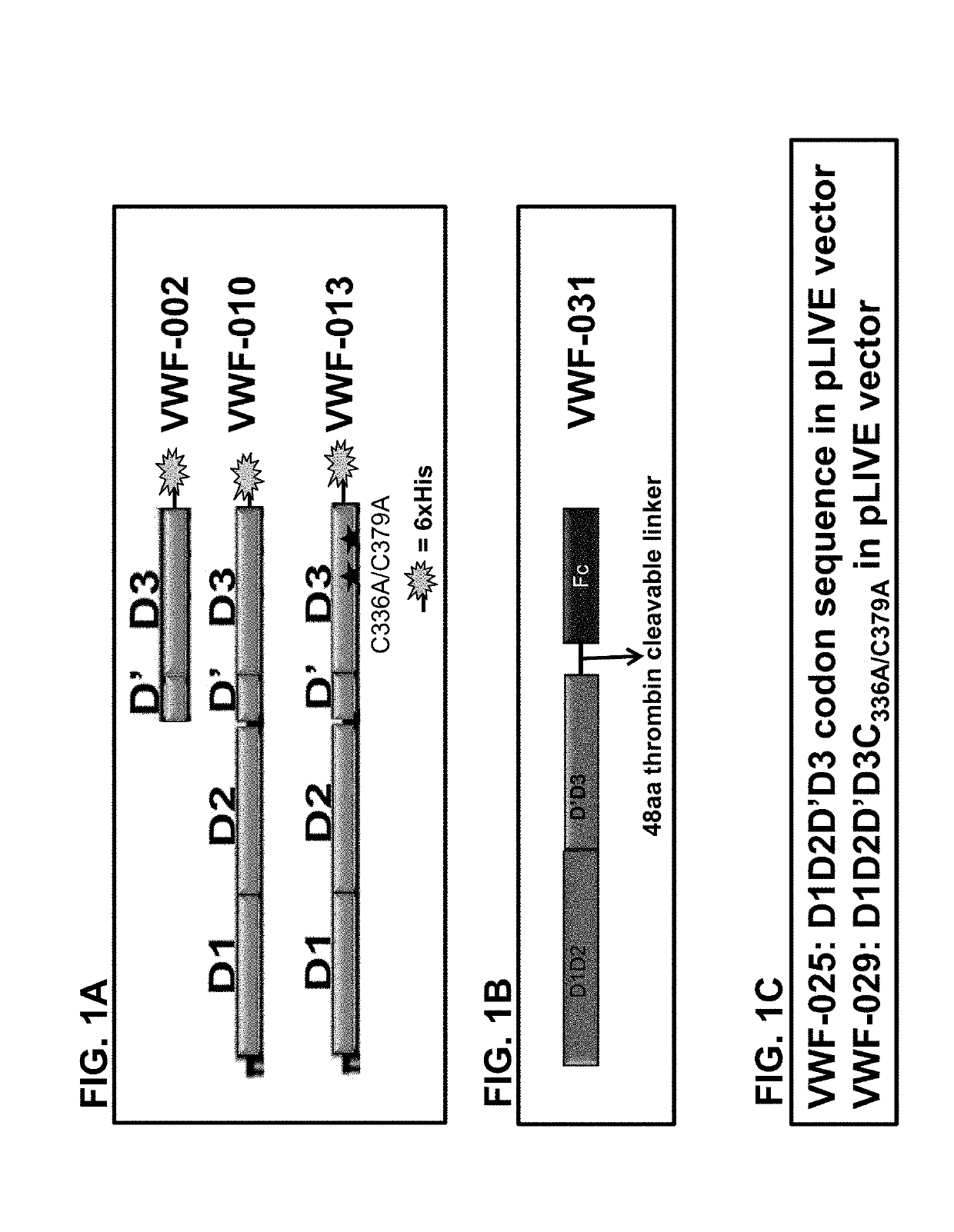
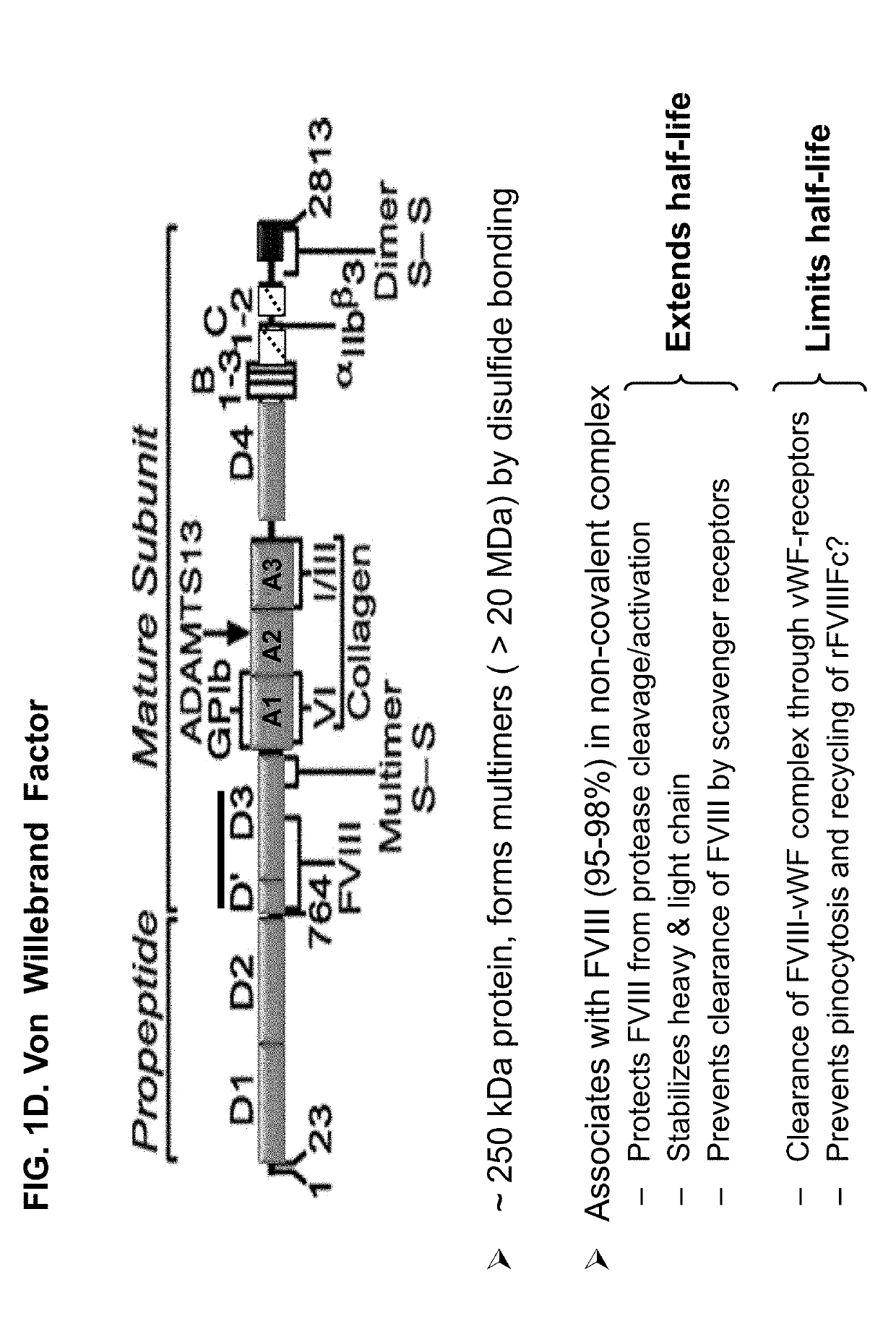
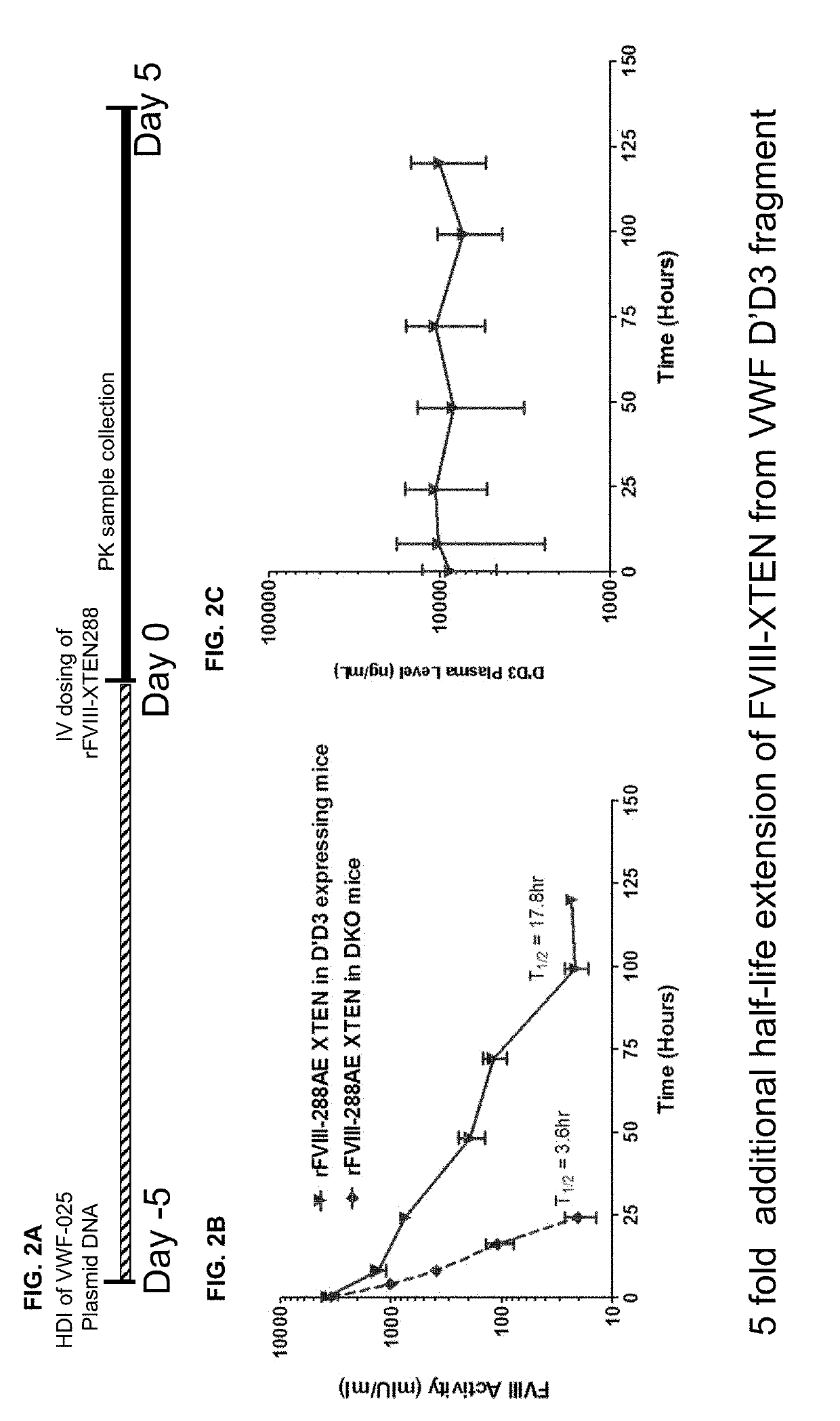
Factor VIII complex with XTEN and von willebrand factor protein, and uses thereof
The present invention includes a chimeric protein comprising a VWF protein with D' domain and D3 domain ofVWF, one or more XTEN sequence, and a FVIII protein, wherein the VWF fragment, the XTEN sequence, or the FVIII protein are linked to or associated with each other. The chimeric protein can further comprise one or more Ig constant region or a portion thereof (e.g., an Fc region). A polypeptide chain of a VWF fragment is associated with a FVIII polypeptide chain linked to an XTEN sequence. The VWF fragment polypeptide chain can prevent or inhibit binding of endogenous VWF toFVIII protein linked to the XTEN sequence. By preventing or inhibiting binding of endogenous VWF to FVIII protein, VWF fragment can extend half-life of chimeric protein comprising FVIII protein. The invention includes nucleotides, vectors, host cells, use of VWF fragment, or chimeric proteins.
Owner:BIOVERATIV THERAPEUTICS INC
Therapeutic compounds structurally-linked to bacterial polypeptides
InactiveUS6913750B2Stabilizing the pilus-protein portionBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroorganismProtein subunit
A protein construct comprising a pilus protein portion, preferably a structurally stabilized pilus-protein, and an additional, or effector, portion other than a pilus protein or chaperone and wherein said effector portion serves to stabilize the pilus protein portion and to confer a therapeutic activity, such as vaccine activity or anti-microbial or anticancer activity, on the protein construct is disclosed. Such effector portion commonly comprises a donor strand complementary segment capable of structurally stabilizing a pilus protein subunit and attaching the auxiliary portion to said subunit to form the pilus protein analog of the invention. Methods of using said protein constructs are also disclosed as well as the formation and use of analogs comprising fragments of a pilus protein linked to effector components to produce immunogenic and / or therapeutic activity.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC +1
Method for Making Targeted Therapeutic Agents
InactiveUS20080199499A1Rapid and efficient identification and isolation and productionEffective and low methodAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLibrary screeningDisease markersCross linker
Provided herein are methods and kits for making a targeted therapeutic for treating a disease or condition. The therapeutic agents can be targeted to patient-specific disease markers. In one of these methods, the method includes obtaining a biological sample from a patient having the disease or condition, or who is at risk for developing the disease or condition. In this particular method, the sample includes a population of diseased cells, screening a library comprising proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs to identify mRNA-protein pairs that bind to the diseased cells, isolating one or more proteins from the identified mRNA-protein pairs, and conjugating the isolated protein(s) to a therapeutic agent. Some of the methods further include preparing a library with proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs. In certain of these methods, the preparation of the library includes providing at least two candidate mRNA molecules in which each of the mRNA molecules includes a cross-linker, translating at least two of the candidate mRNA molecules to generate at least one translated protein, and linking at least one of the candidate mRNA molecules to its corresponding translated protein via the cross-linker to form at least one cognate pair.
Owner:PROTEONOVA
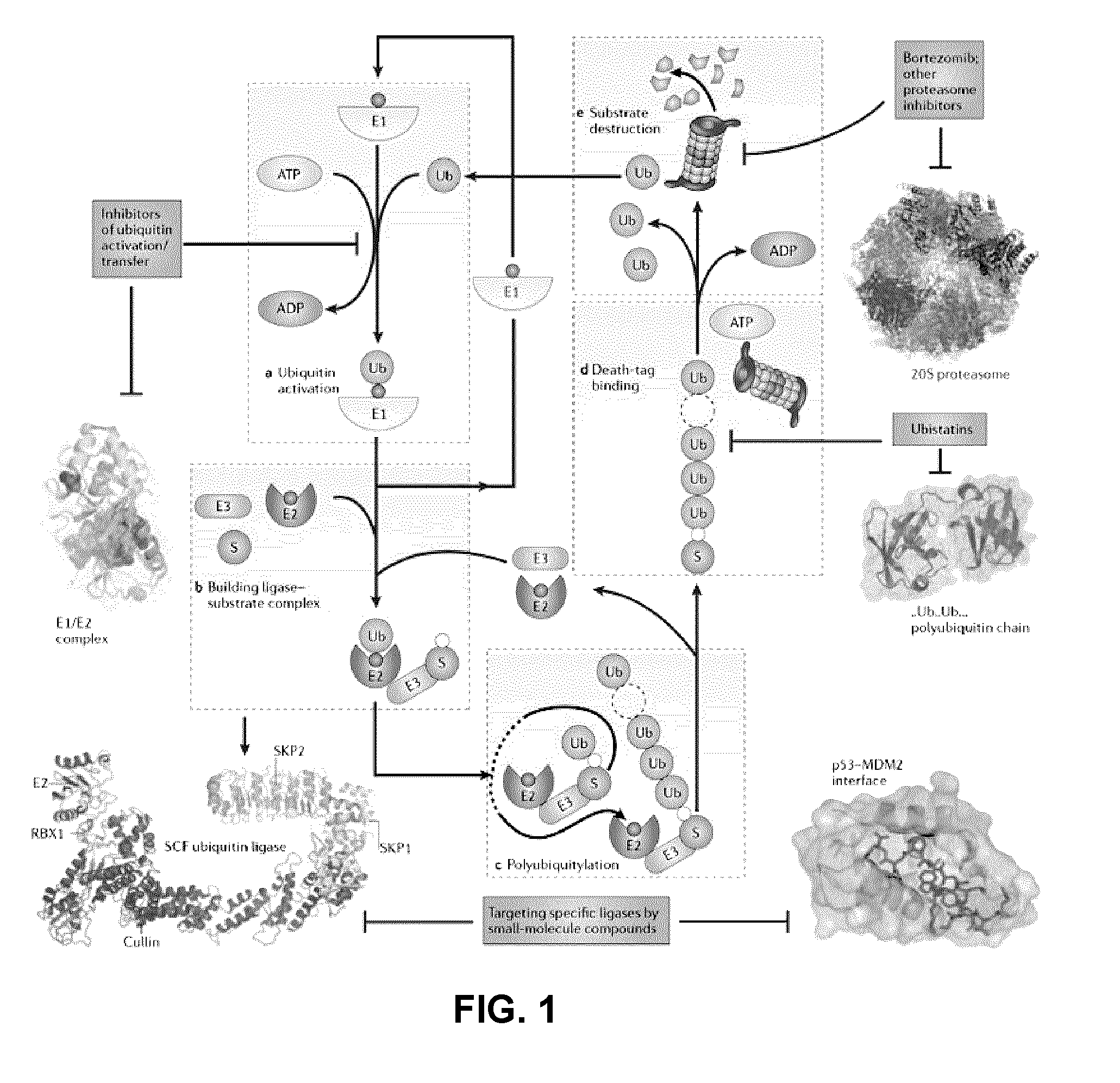
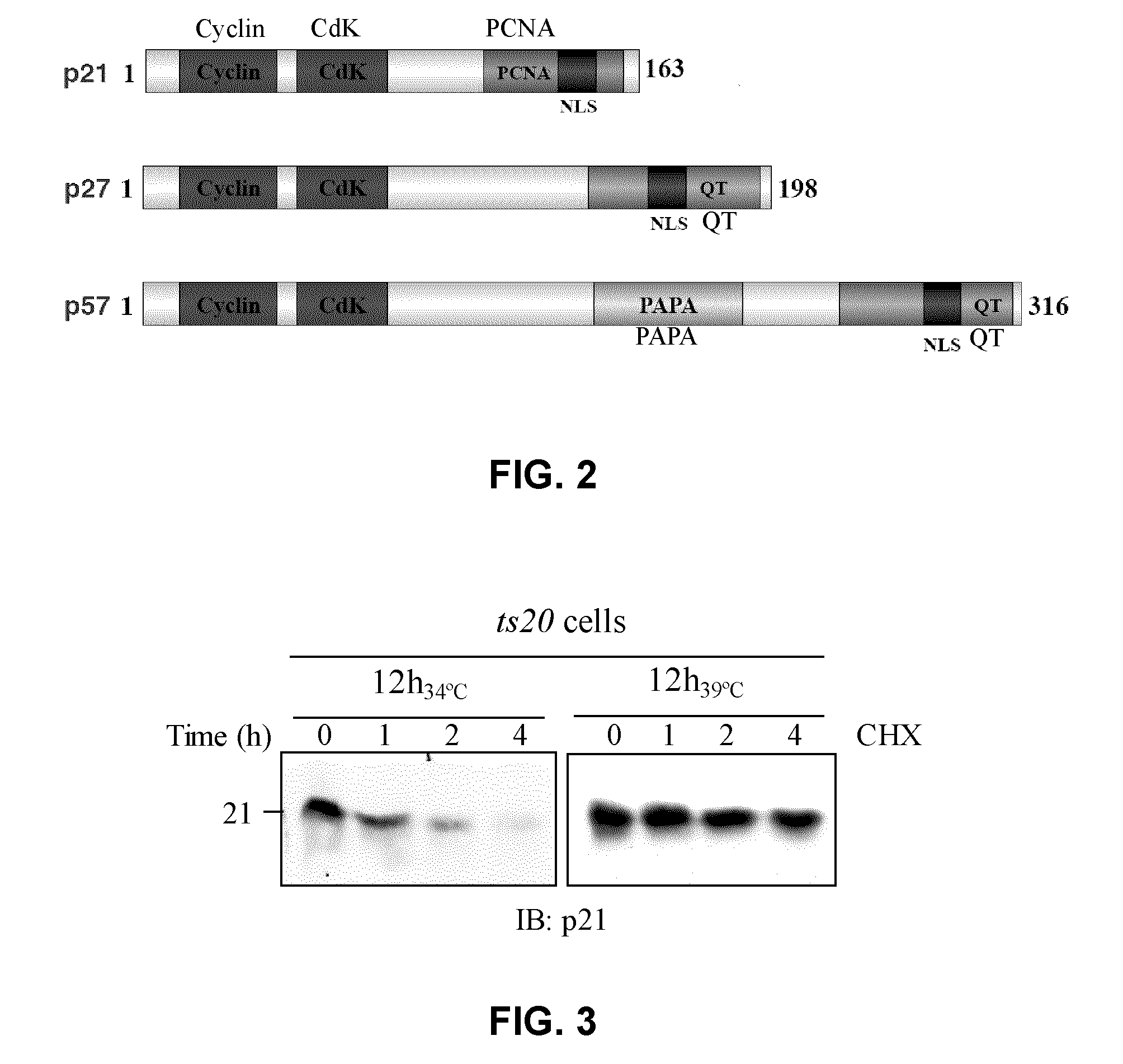
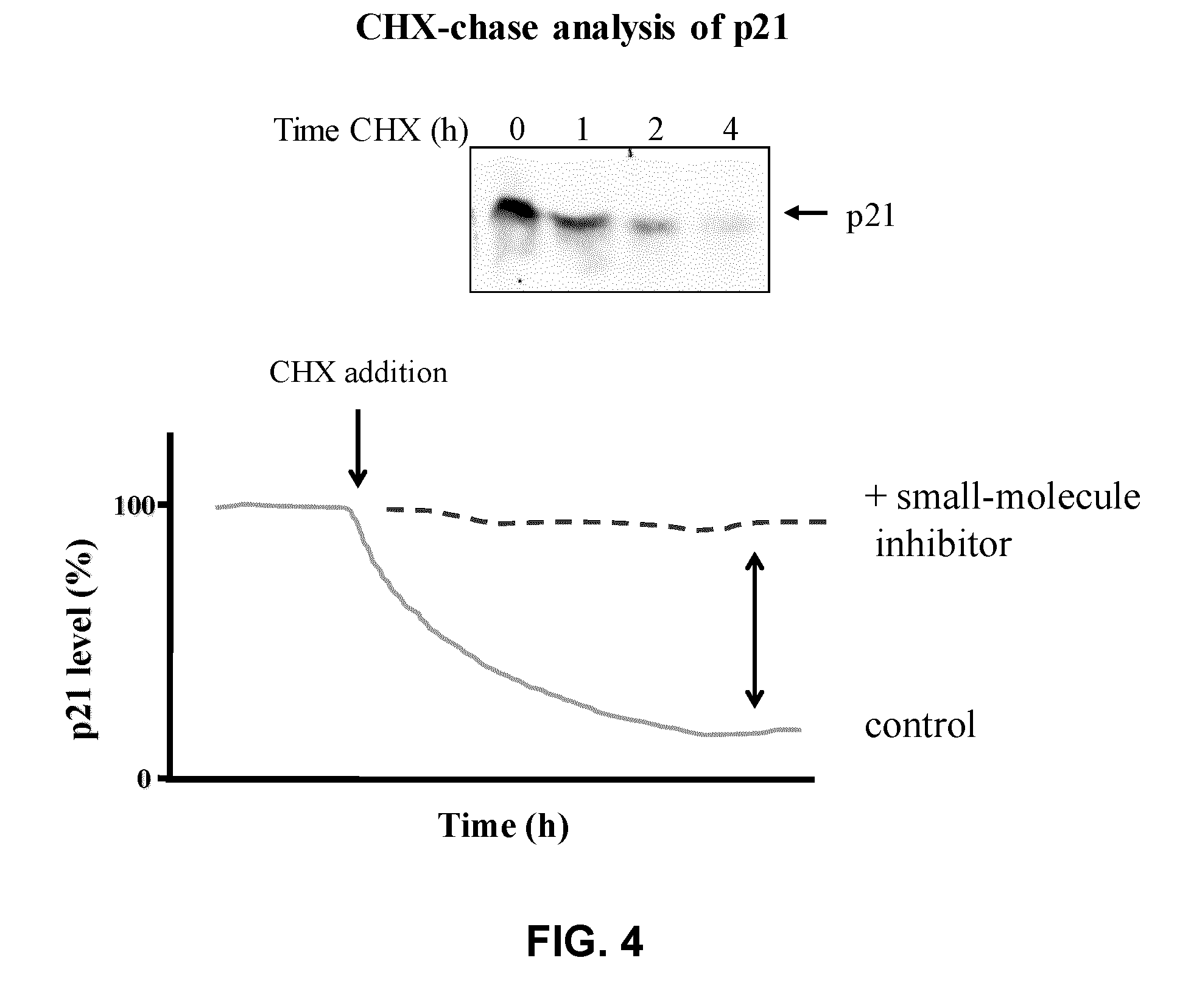
Assay for inhibitors of CIP/KIP protein degradation
An assay and system compatible with high throughput screening (HTS) that is capable of identifying inhibitors, such as small-molecule inhibitors, of the degradation of the Cdk inhibitor p21, are described. The assay is based on the use of fusion protein comprising (i) a p2 polypeptide; and (i) a reporter protein linked to the C-terminal of said p21 polypeptide, wherein the fusion protein has a half-life that is similar to that of the p21 polypeptide. Inhibitors identified by this assay may be useful to inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells, and thus for the treatment of cancers.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL
Functional screening
Screening methods for identifying molecules that interact with and / or regulate accumulation and stabilization of unstable proteins are provided. The screening methods involve generation of chimeric proteins comprising a region of an unstable protein linked to a region of a marker gene product. Changes in the levels of the unstable protein, due to accumulation, and / or stabilization and / or hyperaccumulation are then determined by analyzing the change in the marker gene product level. The marker gene product can be an antibiotic resistance gene that confers antibiotic resistance by stoichiometrically binding to the antibiotic or it can be a fluorescent protein region. Thus, antibiotic resistance screening or fluorescence imaging or cell sorting methods can be used to detect changes in the levels of the unstable chimeric proteins. Unstable proteins suitable for this screening method include, but are not limited to, membrane proteins such as ion channels, receptors, or presenilins.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF THE
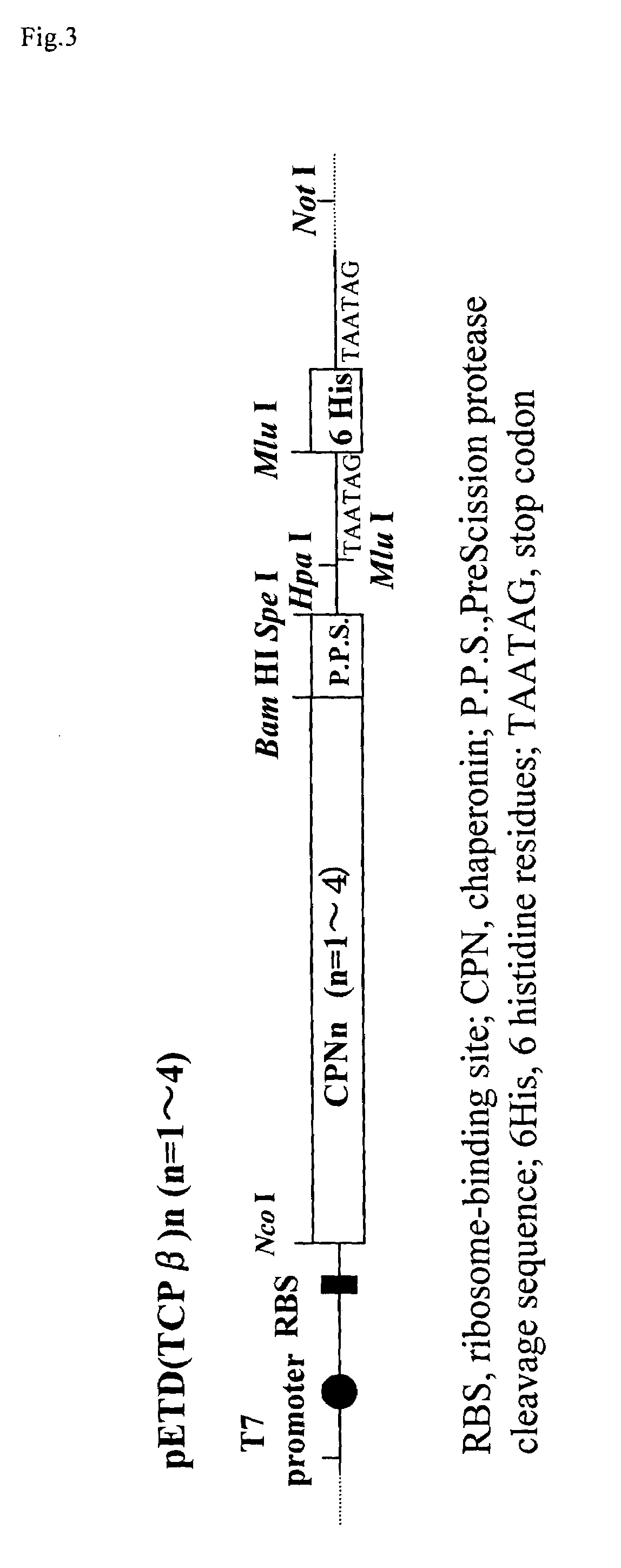
Process for production of a recombinant protein and a fusion protein
InactiveUS7276355B2Avoid toxicityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFusions for enhanced expression stability/foldingThermosomesFusion Protein Expression
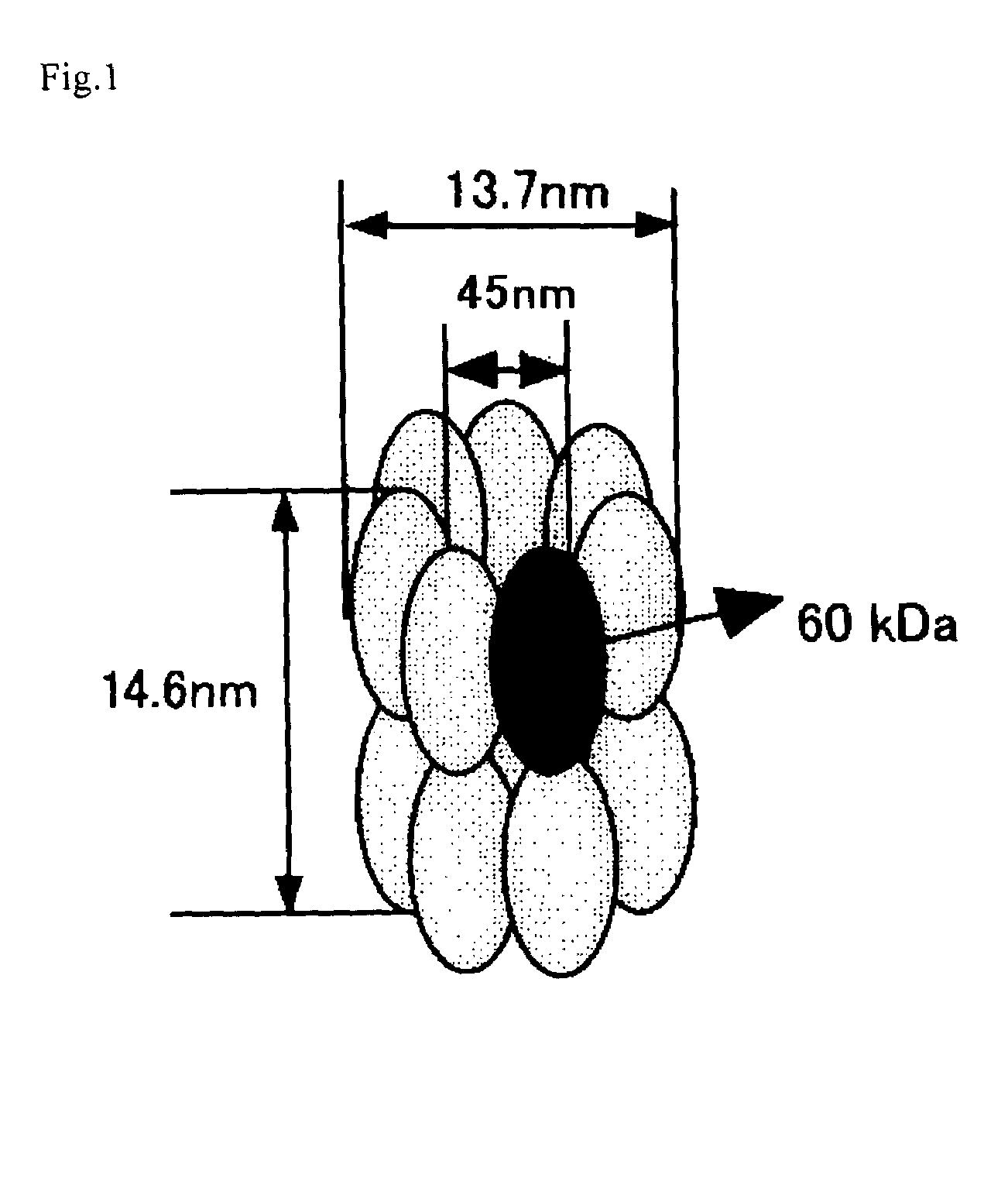
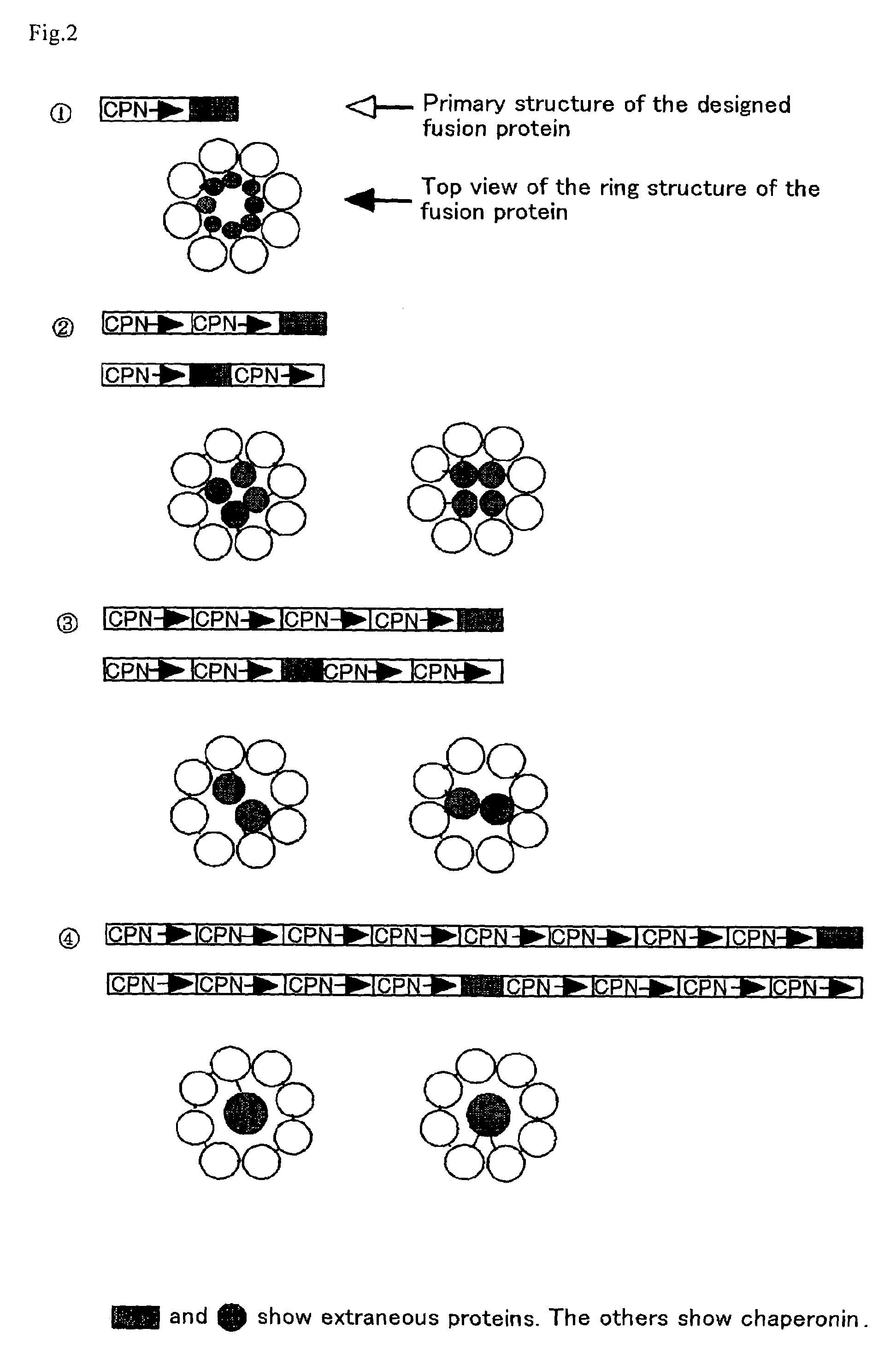
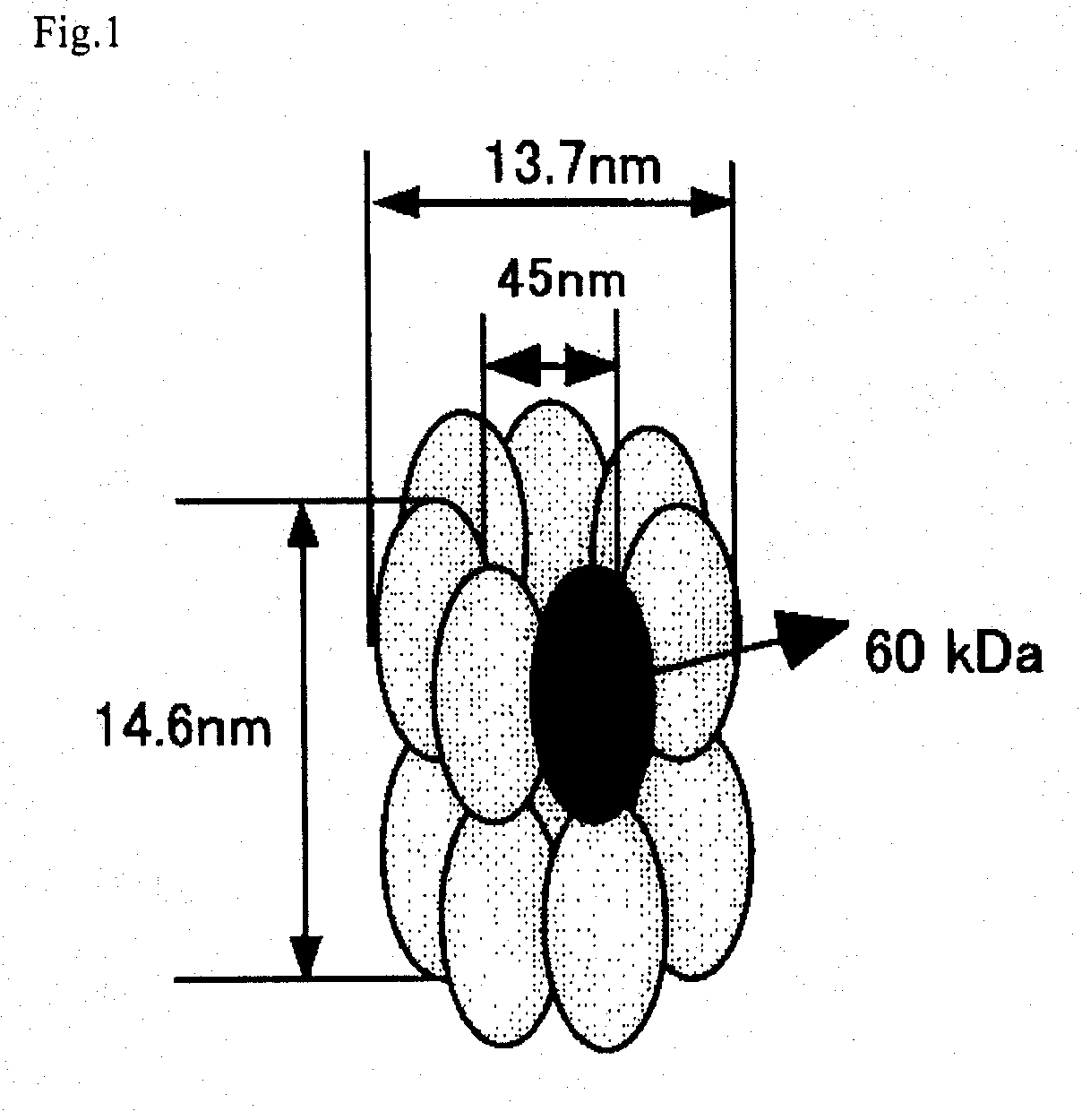
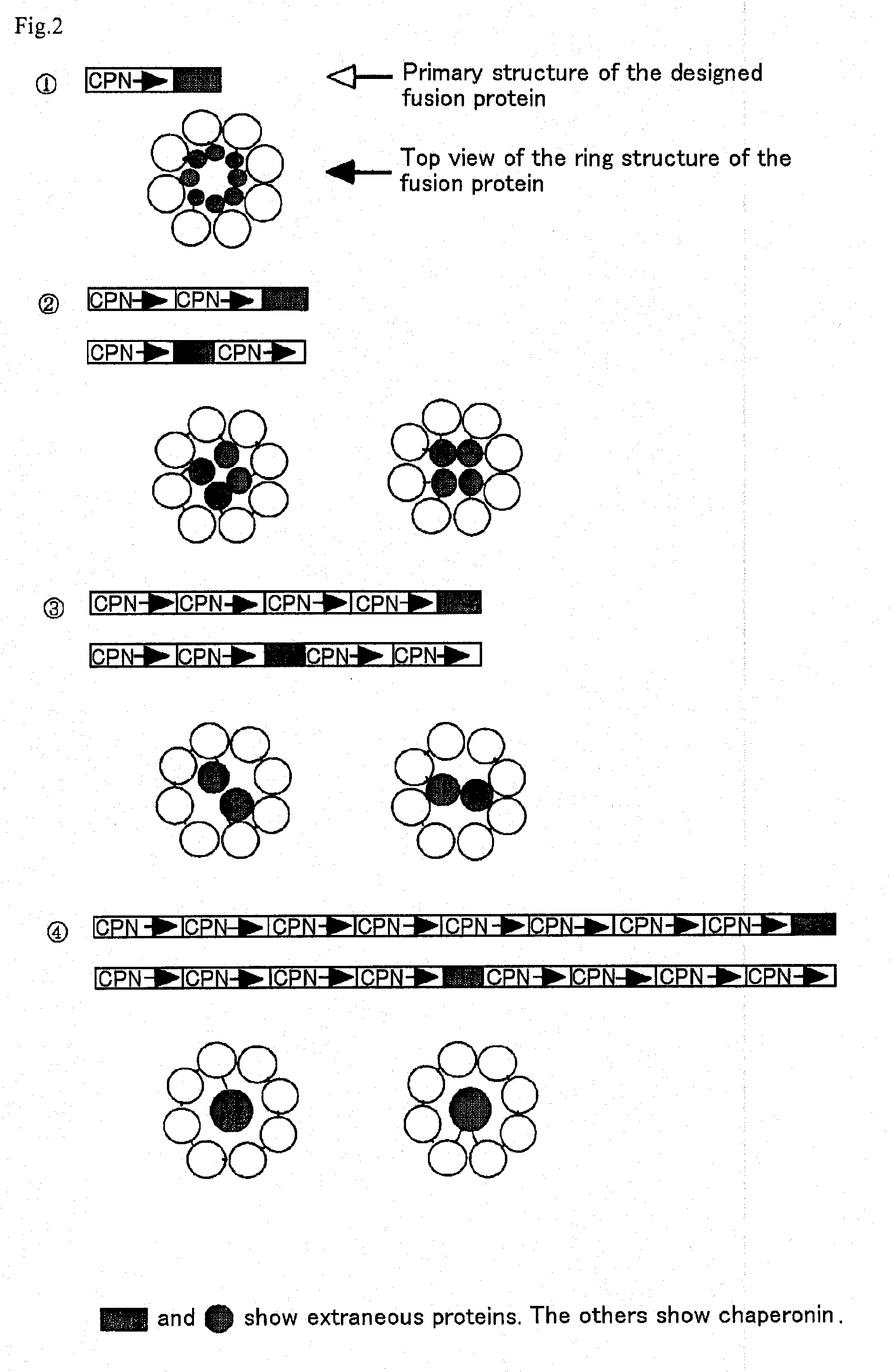
This invention provides a recombinant protein expression system using a host and cell-free translation system, and is capable of universally expressing a large amount of any protein as soluble protein, while preventing toxicity in hosts, formation of inclusion bodies, and decomposition with proteases. Such may be achieved by expressing the desired protein as a fusion protein with chaperonins, such as about 60 kDa molecular chaperones, 60 kDa heat shock proteins, or thermosomes, and accommodating the desired protein inside of a stereostructure of a chaperonin. The present invention provides a process for producing a protein, which comprises transcribing and translating a gene containing a gene encoding the linked chaperonin subunits and a gene encoding a desired protein thereby synthesizing a fusion protein having the desired protein linked via a peptide linkage to the linked chaperonin subunits.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Method for making targeted therapeutic agents
ActiveUS20110212114A1Rapid and efficient identification and isolation and productionEffective and low methodAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDisease markersCross linker
Provided herein are methods and kits for making a targeted therapeutic for treating a disease or condition. The therapeutic agents can be targeted to patient-specific disease markers. In one of these methods, the method includes obtaining a biological sample from a patient having the disease or condition, or who is at risk for developing the disease or condition. In this particular method, the sample includes a population of diseased cells, screening a library comprising proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs to identify mRNA-protein pairs that bind to the diseased cells, isolating one or more proteins from the identified mRNA-protein pairs, and conjugating the isolated protein(s) to a therapeutic agent. Some of the methods further include preparing a library with proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs. In certain of these methods, the preparation of the library includes providing at least two candidate mRNA molecules in which each of the mRNA molecules includes a cross-linker, translating at least two of the candidate mRNA molecules to generate at least one translated protein, and linking at least one of the candidate mRNA molecules to its corresponding translated protein via the cross-linker to form at least one cognate pair.
Owner:PROTEONOVA
Vacuole targeting peptide and nucleic acid
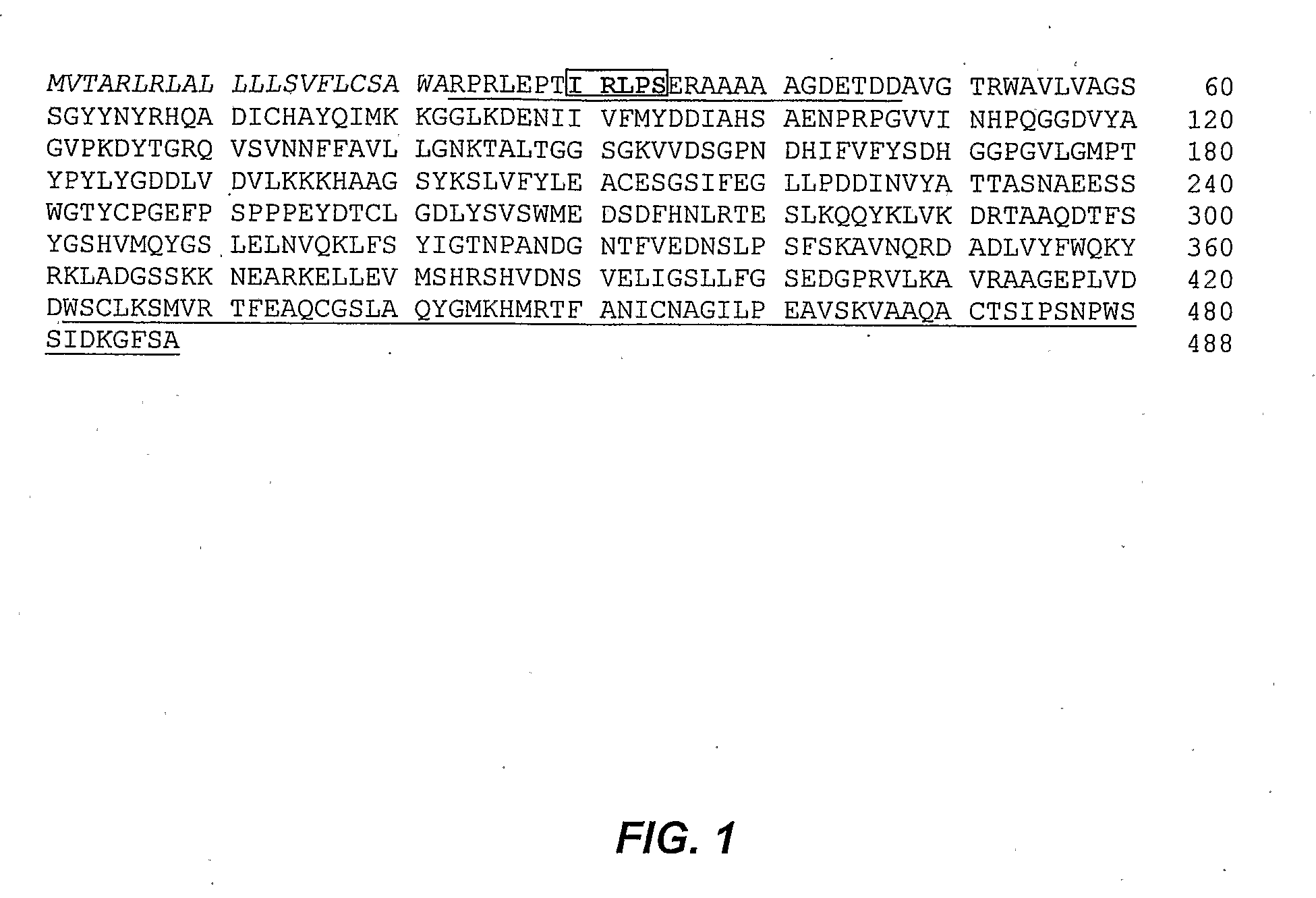
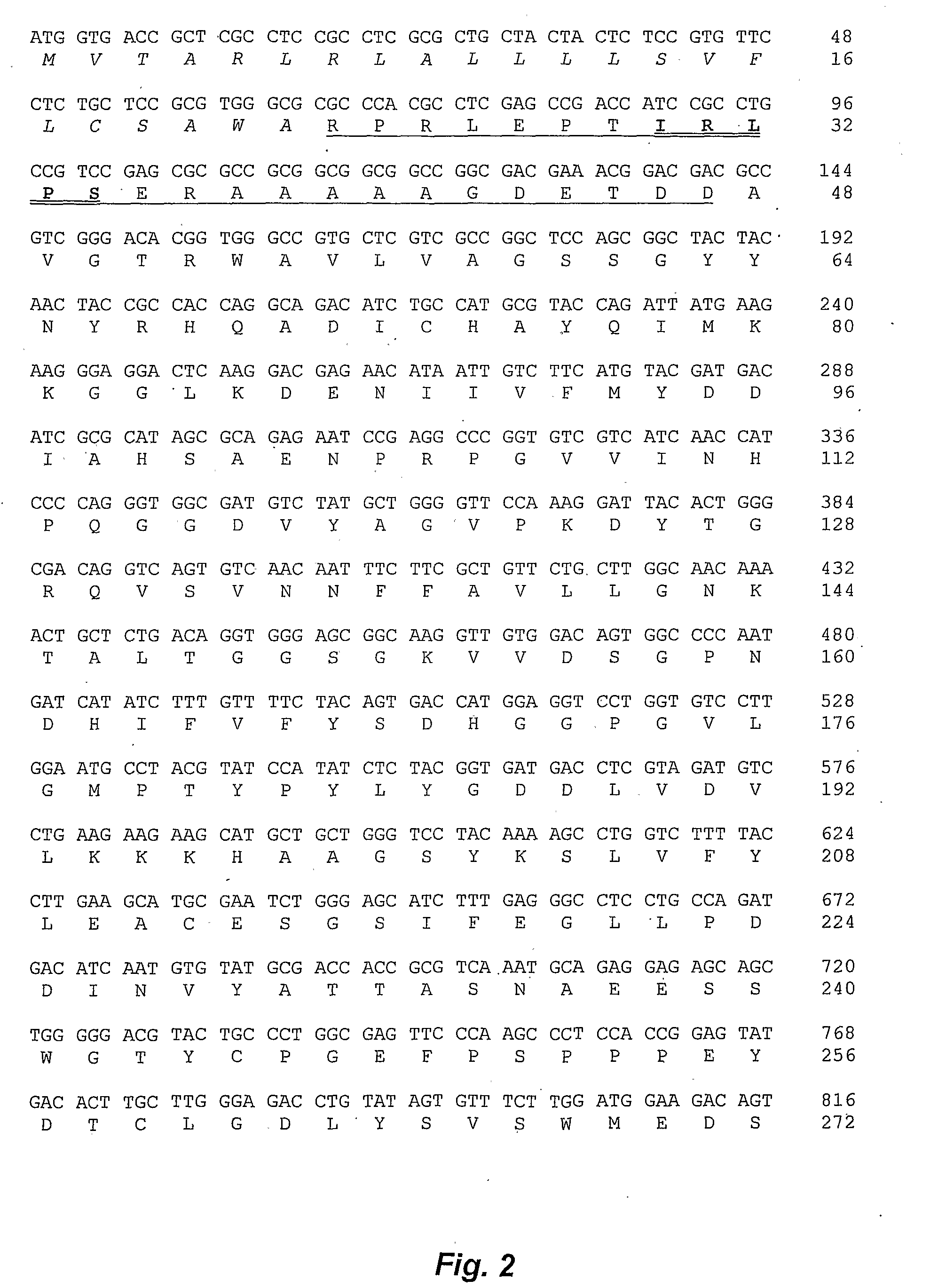
The present invention relates to a plant vacuole targeting sequence X1X2X3PX4 wherein X1 is a hydrophobic amino acid, X2 is a basic amino acid, X3 is a hydrophobic amino acid, P is proline; and X4 is a hydrophilic amino acid, such as the sequences IRLPS, IKLPS, LRLPS and LKLPS. The vacuole targeting sequence may be present in a chimeric protein linked to an amino acid sequence of a heterologous protein to facilitate vacuole vacuole targeting of the expressed chimeric protein in a plant cell. The invention is applicable to production of expressed, chimeric proteins in monocots and dicots, and in particular monocots such as cereals and sugarcane.
Owner:SUGAR IND INNOVATION
Blocking method for activated quantum dots
The invention provides a blocking method for activated quantum dots. The activated quantum dots are blocked by adopting polymer inert protein formed by cross-linking reaction of 1-ethyl-3-3-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDC) and inert protein. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that effective blocking of the surfaces of the activated quantum dots can be ensured and protein linking in the blocking process is firmer, and thereby the sensitivity and the stability of a reagent are improved and basic performance of the quantum dot immunochromatography reagent is improved. The invention also aims at providing application of the method in an immunofluorescence assay kit for the quantum dots.
Owner:NANJING VAZYME MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
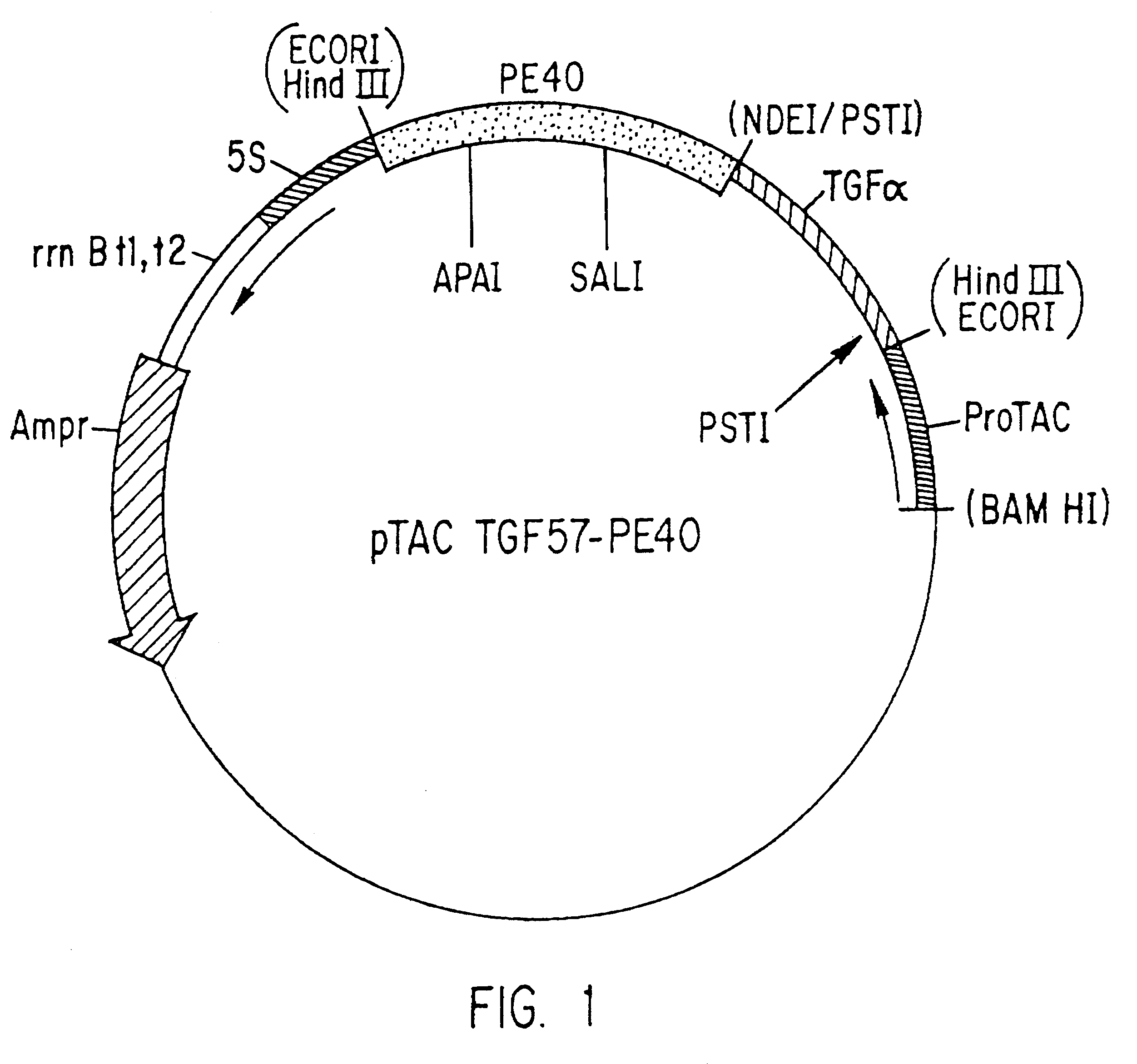
Modified PE40 toxin fusion proteins
InactiveUS6207798B1Improve purification effectEffective combinationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsToxinReceptor for activated C kinase 1
We have modified PE40 toxin by removing at least two of its four cysteine amino acid residues and have formed hybrid molecules containing modified PE40 linked to a cell recognition protein that can be an antibody, a growth factor, a hormone, a lymphokine, or another polypeptide cell recognition protein for which a specific cellular receptor exists whereby the modified PE40 toxin is directed to cell types having receptors for the cell recognition protein linked to the modified PE40.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
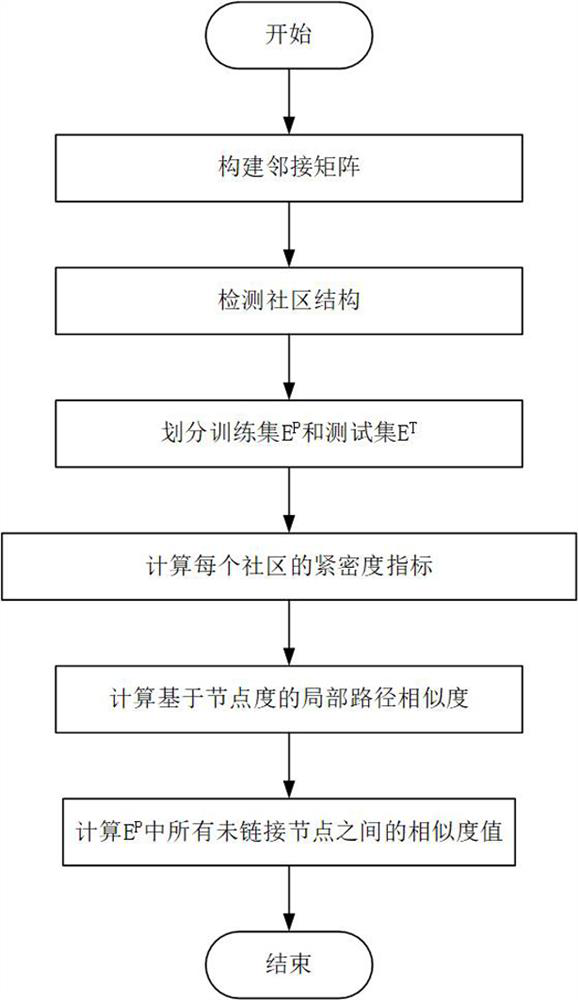
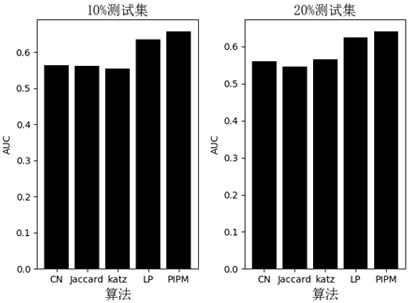
Protein link prediction algorithm fusing community structure and node degree local path similarity
The invention discloses a protein link prediction algorithm fusing community structure and node degree local path similarity. The purpose of the algorithm is to predict potential links in a protein interaction network. The method mainly comprises the following steps: constructing an adjacent matrix; detecting a community structure; constructing a training set and a test set; calculating communitycompactness indexes; calculating local path similarity based on the node degree; and calculating similarity values among all the nodes which are not linked. Existing link prediction methods mostly utilize common neighbor information of nodes, and do not consider contribution of protein community structure information to link prediction. Therefore, the defects of a method based on local informationsimilarity and a protein interaction prediction method based on a community structure are considered; the invention provides a protein link prediction method fusing community structure and node degree local path similarity, and link prediction is carried out in combination with a topological structure between proteins while community information in a protein interaction network is considered.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Cell membrane penetrating conjugates
A cell penetrating conjugate comprising a recombinant beta helical protein linked to a functional molecule wherein the beta helical protein length is in the range of from 5nmto 25nm, suitably, from 10nm to 15nm and width is in the range of from 1nmto 5nm, suitably,from 1nm to 3nm.Processes for preparing said conjugates and uses thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:싸이카온코솔루션즈리미티드
Method for the secretory production of heterologous protein in escherichia coli
InactiveUS20110033890A1Improve secretion efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifEnzyme stabilisationHeterologousEscherichia coli
The present invention relates to a signal sequence peptide for the improvement of extracellular secretion efficiency of a heterologous protein in E. coli. More particularly, the present invention relates to a gene construct for the improvement of extracellular secretion efficiency of the said heterologous protein in E. coli, which comprises a polynucleotide encoding a recombinant protein composed of the heterologous protein linked to C-terminal of the signal sequence peptide represented by SEQ. ID. NO. 3. The present invention contributes to the improvement of extracellular secretion efficiency of a recombinant protein, so that it can be effectively applied to the production of a recombinant protein.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
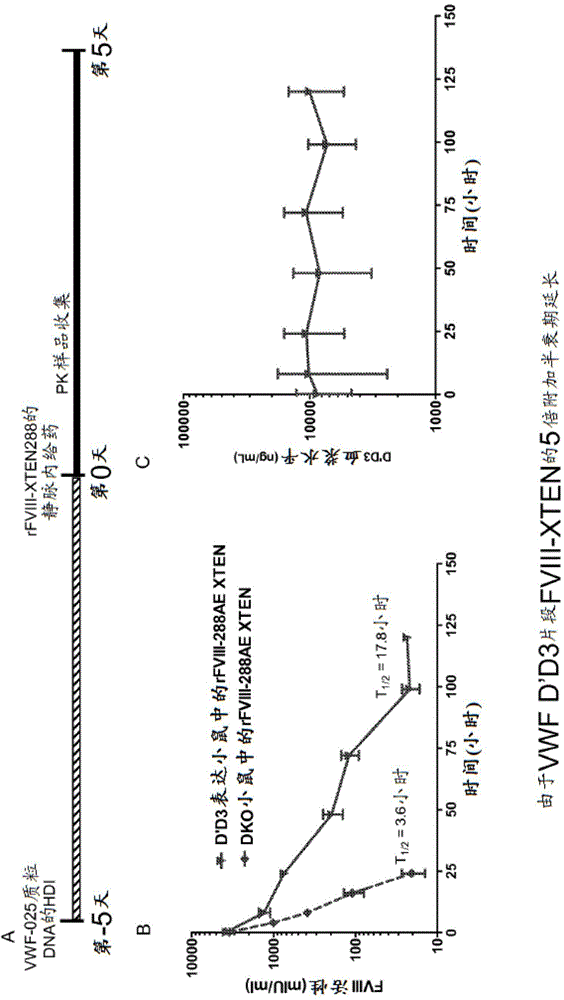
Factor viii complex with xten and von willebrand factor protein, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190169267A1Avoid clearingReduce gapFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIII vWFNucleotide
The present invention provides a chimeric protein comprising a VWF protein comprising the D′ domain and D3 domain of VWF, one or more XTEN sequence, and a FVIII protein, wherein the VWF fragment, the XTEN sequence, or the FVIII protein are linked to or associated with each other. The chimeric protein can further comprise one or more Ig constant region or a portion thereof (e.g., an Fc region). A polypeptide chain comprising a VWF fragment of the invention binds to or is associated with a polypeptide chain comprising a FVIII protein linked to an XTEN sequence and the polypeptide chain comprising the VWF fragment can prevent or inhibit binding of endogenous VWF to the FVIII protein linked to the XTEN sequence. By preventing or inhibiting binding of endogenous VWF to the FVIII protein, which is a half-life limiting factor for FVIII, the VWF fragment can induce extension of half-life of the chimeric protein comprising a FVIII protein. The invention also includes nucleotides, vectors, host cells, methods of using the VWF fragment, or the chimeric proteins.
Owner:BIOVERATIV THERAPEUTICS INC
Cell penetrating protein-antibody conjugates and methods of use thereof
ActiveCN108135958BImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSaccharide peptide ingredientsIntracellularAntibody conjugate
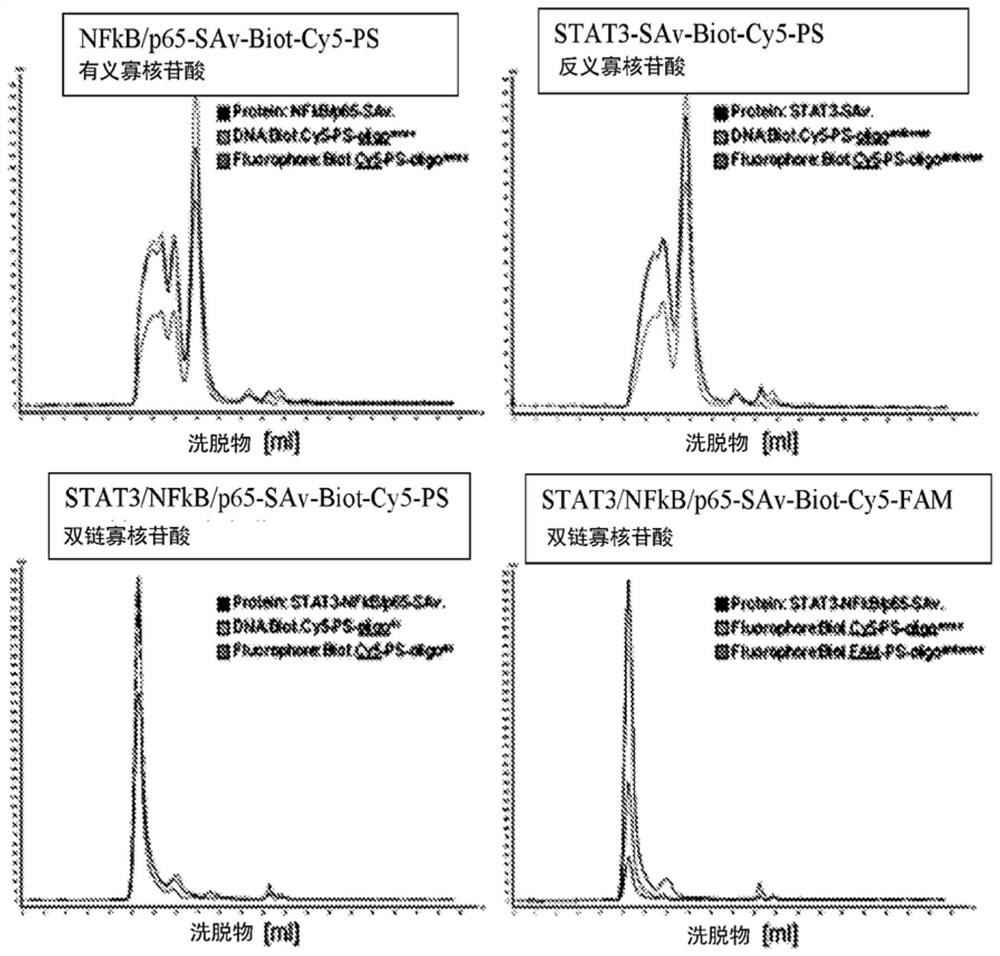
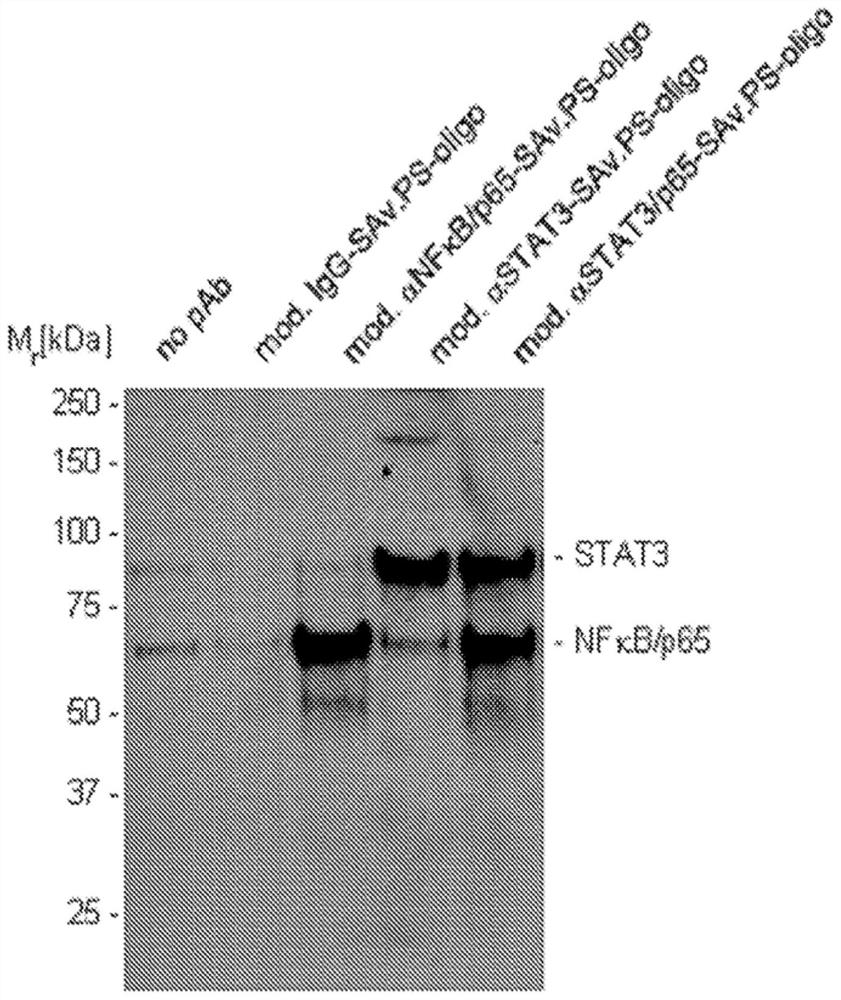
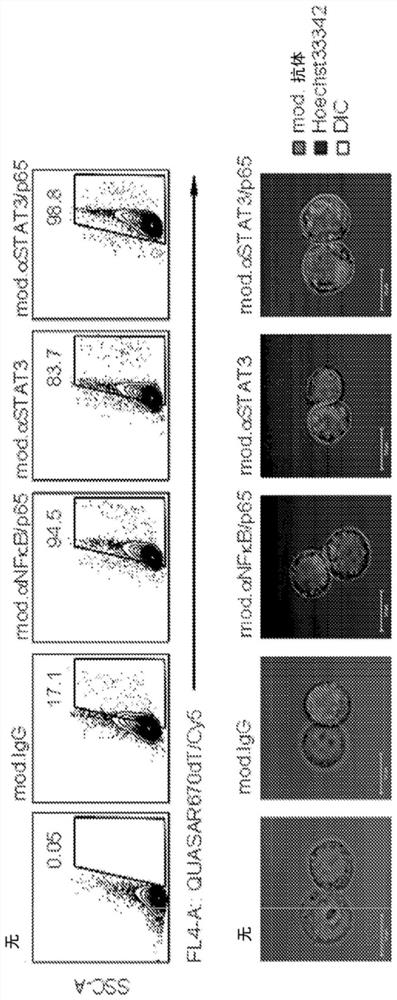
The present aspect provides cell penetrating conjugates. The conjugate includes the non-cell-penetrating protein linked by a phosphorothioate nucleic acid, wherein the phosphorothioate nucleic acid enhances intracellular delivery of the non-cell-penetrating protein. The invention also provides methods and kits comprising the conjugates provided herein.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Protein identification method and system
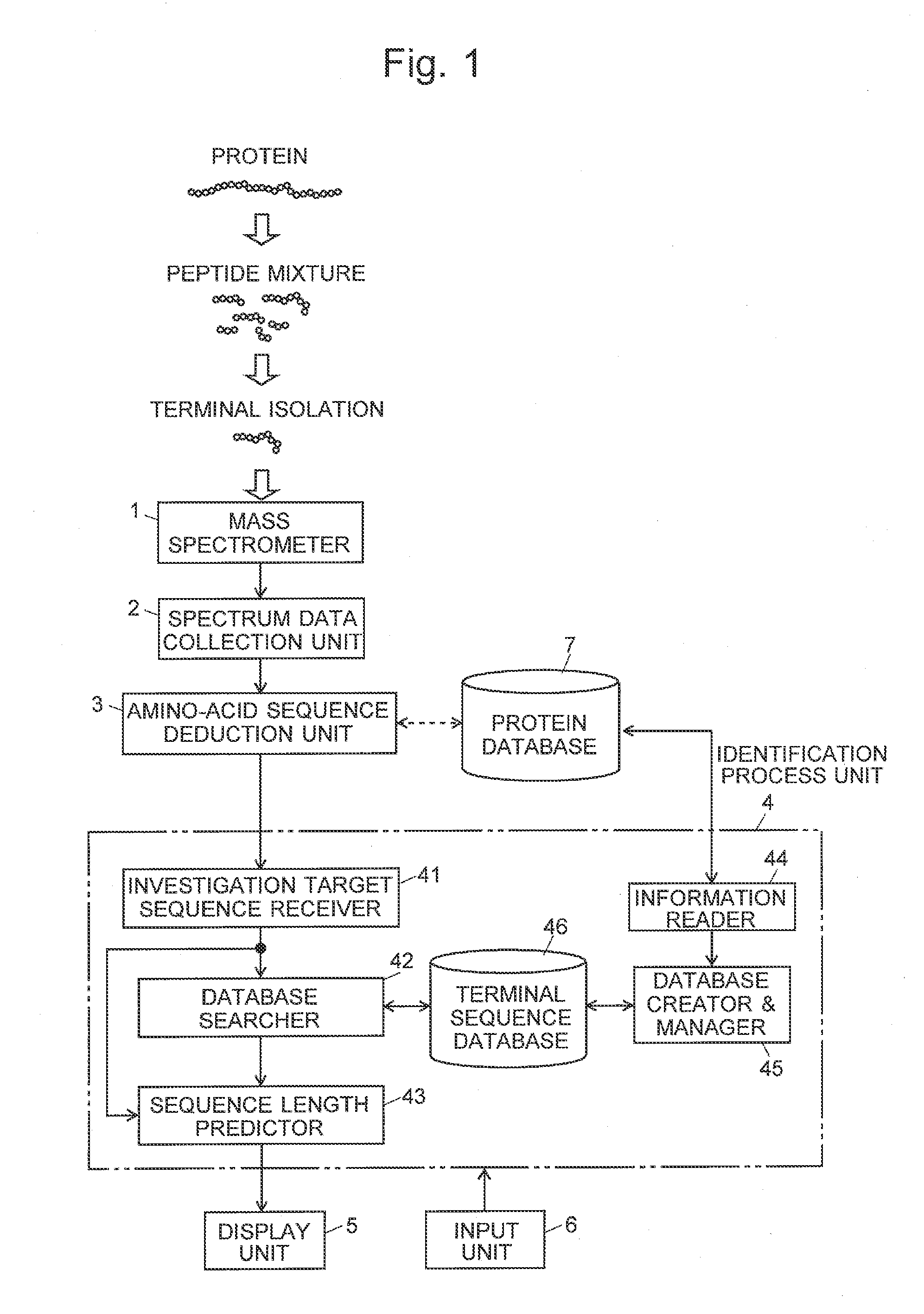
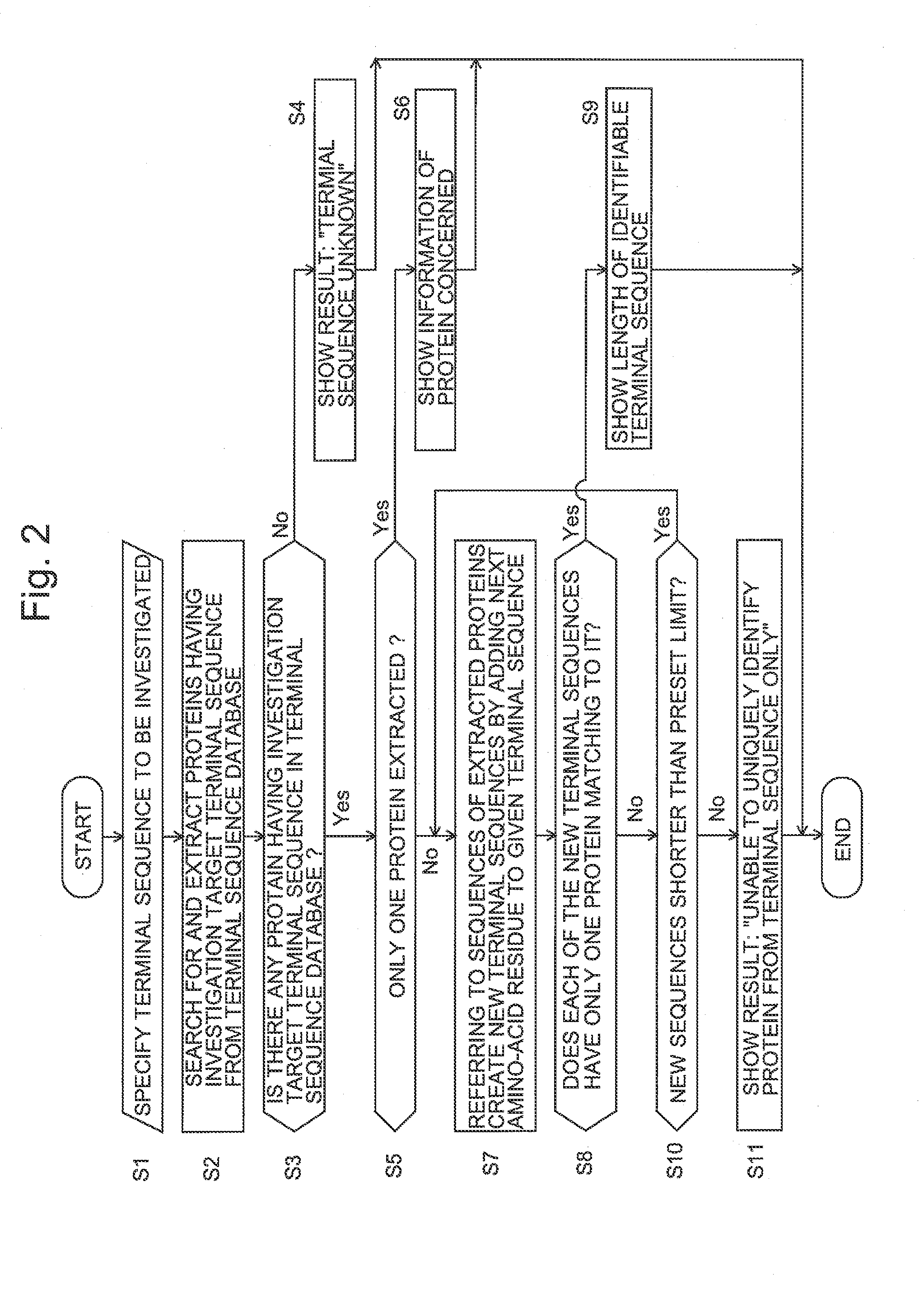
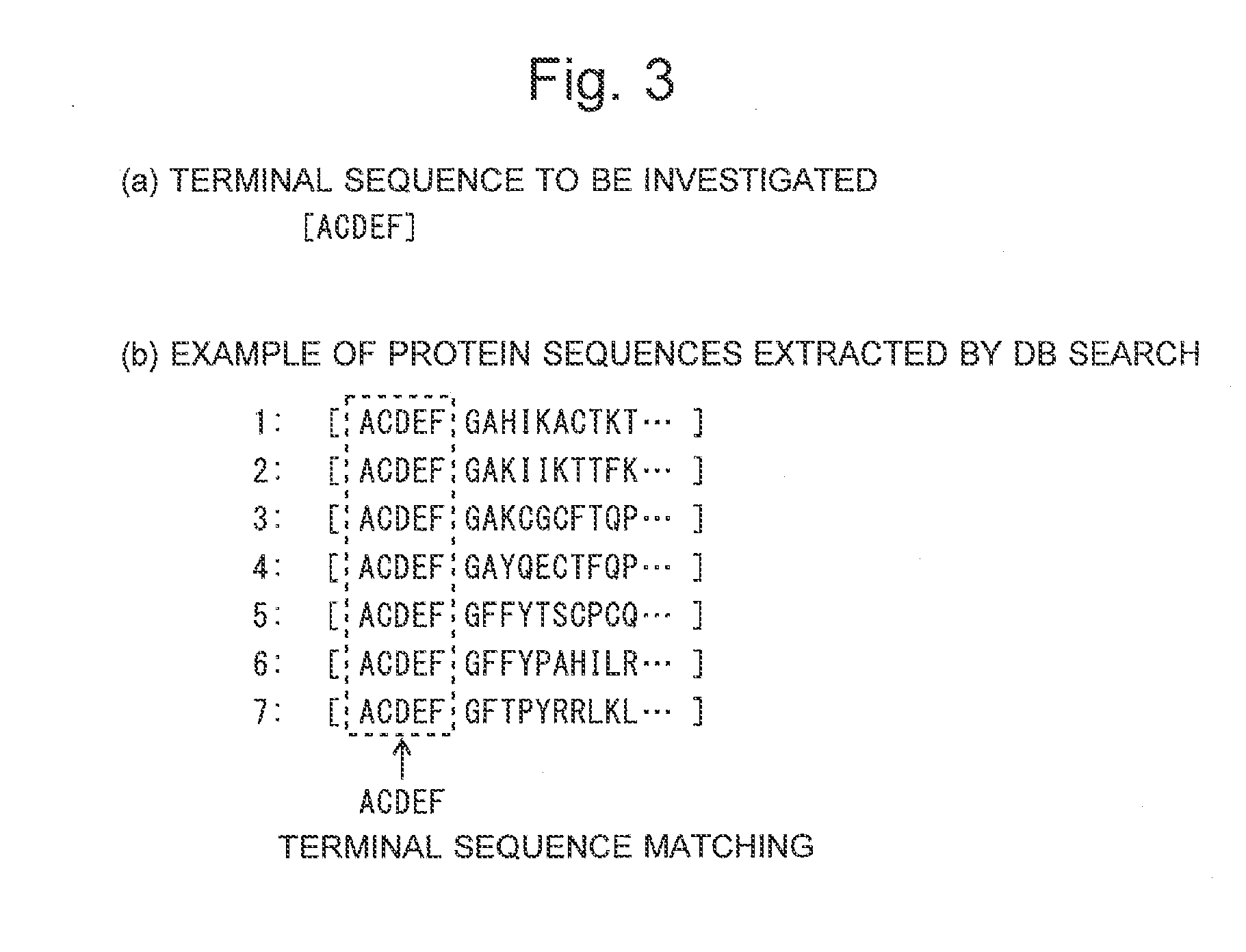
When a terminal sequence to be investigated is specified (S1), a corresponding protein is extracted from a database containing known proteins linked with terminal sequences (S2). If one protein cannot be uniquely identified (“No” in S5), amino-acid residues to be bonded to the target terminal sequences are selected, and new terminal sequences with the selected amino-acid residues respectively added are created for further investigation (S7). Each new terminal sequence is examined as to whether or not one protein can be uniquely identified from it, and if not so, another amino-acid residue is added. While such processes are repeated, if it has been found that the protein can be uniquely identified before the sequence length reaches an upper limit, the sequence length is displayed (S9). If the sequence length has reached the upper limit without successful identification, a message saying that the protein cannot be identified is displayed (S11).
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method for making targeted therapeutic agents
ActiveUS9193795B2Rapid and efficient identification and isolation and productionEffective and low methodAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDisease markersCross linker
Provided herein are methods and kits for making a targeted therapeutic for treating a disease or condition. The therapeutic agents can be targeted to patient-specific disease markers. In one of these methods, the method includes obtaining a biological sample from a patient having the disease or condition, or who is at risk for developing the disease or condition. In this particular method, the sample includes a population of diseased cells, screening a library comprising proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs to identify mRNA-protein pairs that bind to the diseased cells, isolating one or more proteins from the identified mRNA-protein pairs, and conjugating the isolated protein(s) to a therapeutic agent. Some of the methods further include preparing a library with proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs. In certain of these methods, the preparation of the library includes providing at least two candidate mRNA molecules in which each of the mRNA molecules includes a cross-linker, translating at least two of the candidate mRNA molecules to generate at least one translated protein, and linking at least one of the candidate mRNA molecules to its corresponding translated protein via the cross-linker to form at least one cognate pair.
Owner:PROTEONOVA
Modular targeted therapeutic agents and methods of making same
ActiveUS20190231870A1Induces muscle paralysisPrevents blood clottingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLibrary screeningADAMTS ProteinsProtein pair
Provided herein are methods for making targeted therapeutics. In several embodiments, the therapeutics are directed against soluble agents such as toxins, venoms, and / or other factors that alter physiological biopathways as well as methods of using such therapeutics to treat patients or patient populations to reduce, eliminate, or inactivate, detrimental soluble agents that such patients or patient populations have been exposed to. In several embodiments, the therapeutics are directed to patient-specific disease markers. In several embodiments, the methods comprise screening a library comprising proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs to identify mRNA-protein pairs that bind to the diseased cells, isolating one or more proteins from the identified mRNA-protein pairs, and conjugating the isolated protein(s) to a therapeutic agent.
Owner:PROTEONOVA
Cell membrane penetrating conjugates
ActiveUS20200338204A1Well formedPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHybrid peptidesCell membraneProtein length
A cell penetrating conjugate comprising a recombinant β helical protein linked to a functional molecule wherein the β helical protein length is in the range of from 5 nm to 25 nm, suitably, from 10 nm to 15 nm and width is in the range of from 1 nm to 5 nm, suitably, from 1 nm to 3 nm. Processes for preparing said conjugates and uses thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:CYGENICA LTD
Process for production of a recombinant protein and a fusion protein
This invention provides a recombinant protein expression system using a host and cell-free translation system, and is capable of universally expressing a large amount of any protein as soluble protein, while preventing toxicity in hosts, formation of inclusion bodies, and decompositions with proteases. Such may be achieved by expressing the desired protein as a fusion protein with chaperoning, such as about 60 kDa molecular chaperons, 60 kDa heat shock proteins, or thermosomes, and accommodating the desired protein inside of a stereostructure of a chaperonin. The present invention provides a process for producing a protein, which comprises transcribing and translating a gene containing a gene encoding the linked chaperonin subunits and a gene encoding a desired protein thereby synthesizing a fusion protein having the desired protein linked via a peptide linkage to the linked chaperonin subunits.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Method of Producing Protein-Carbohydrate Vaccines Reduced in Free Carbohydrate
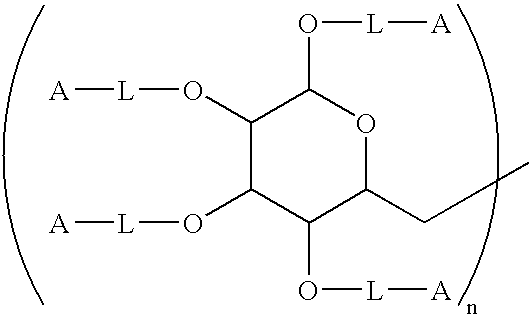
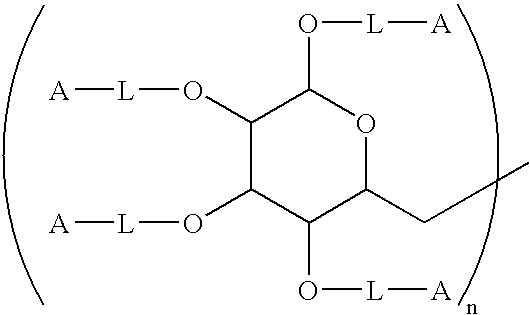
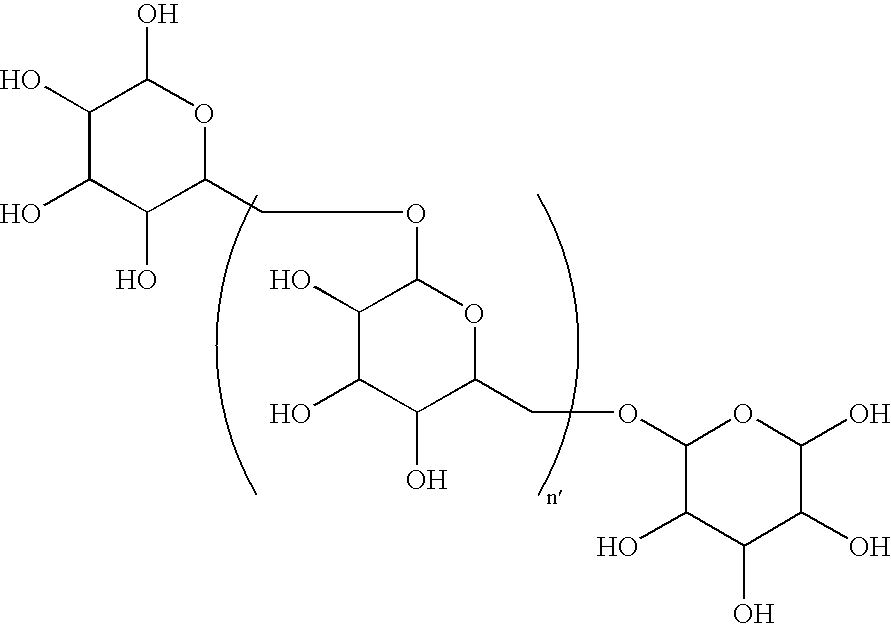
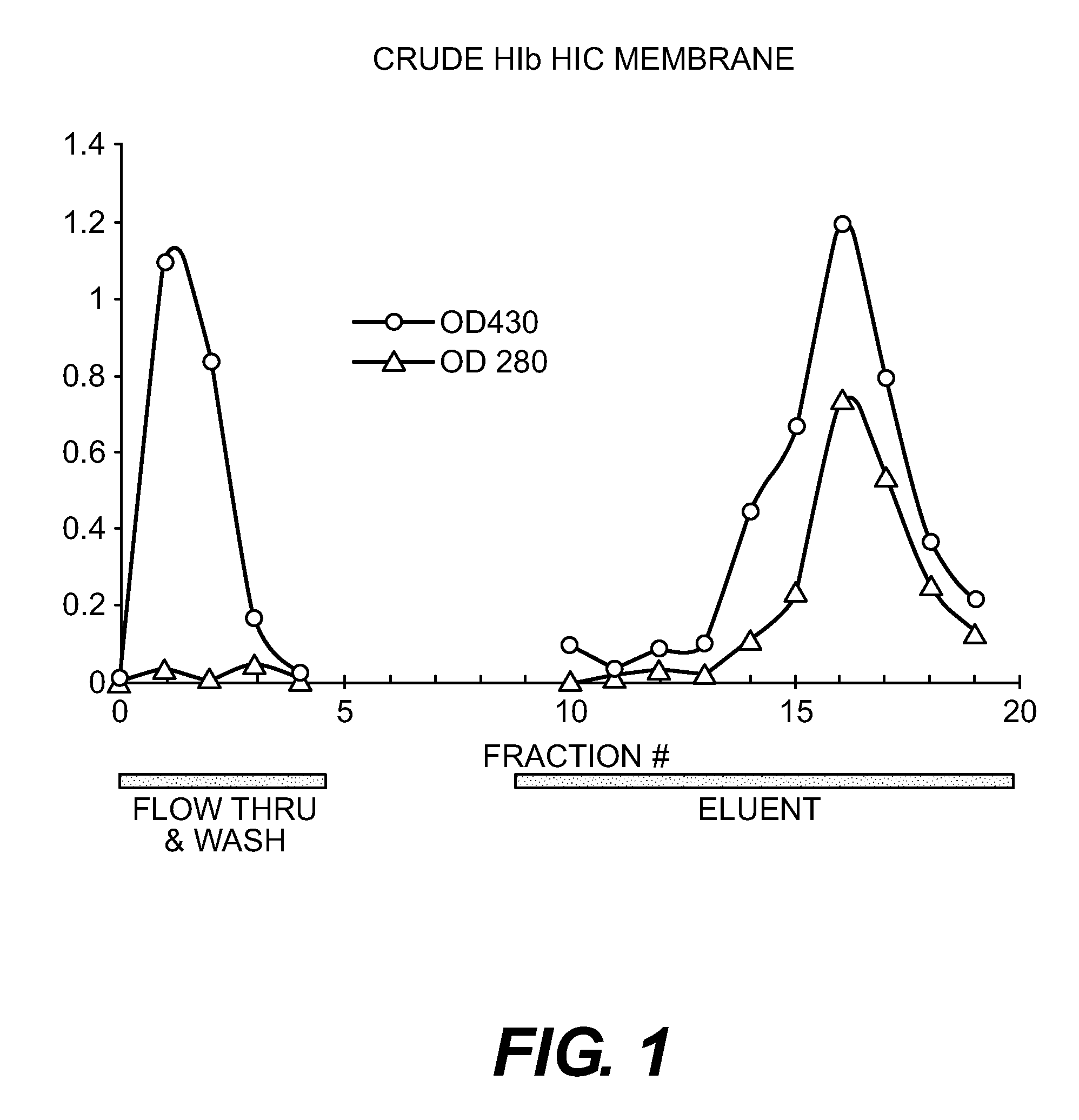
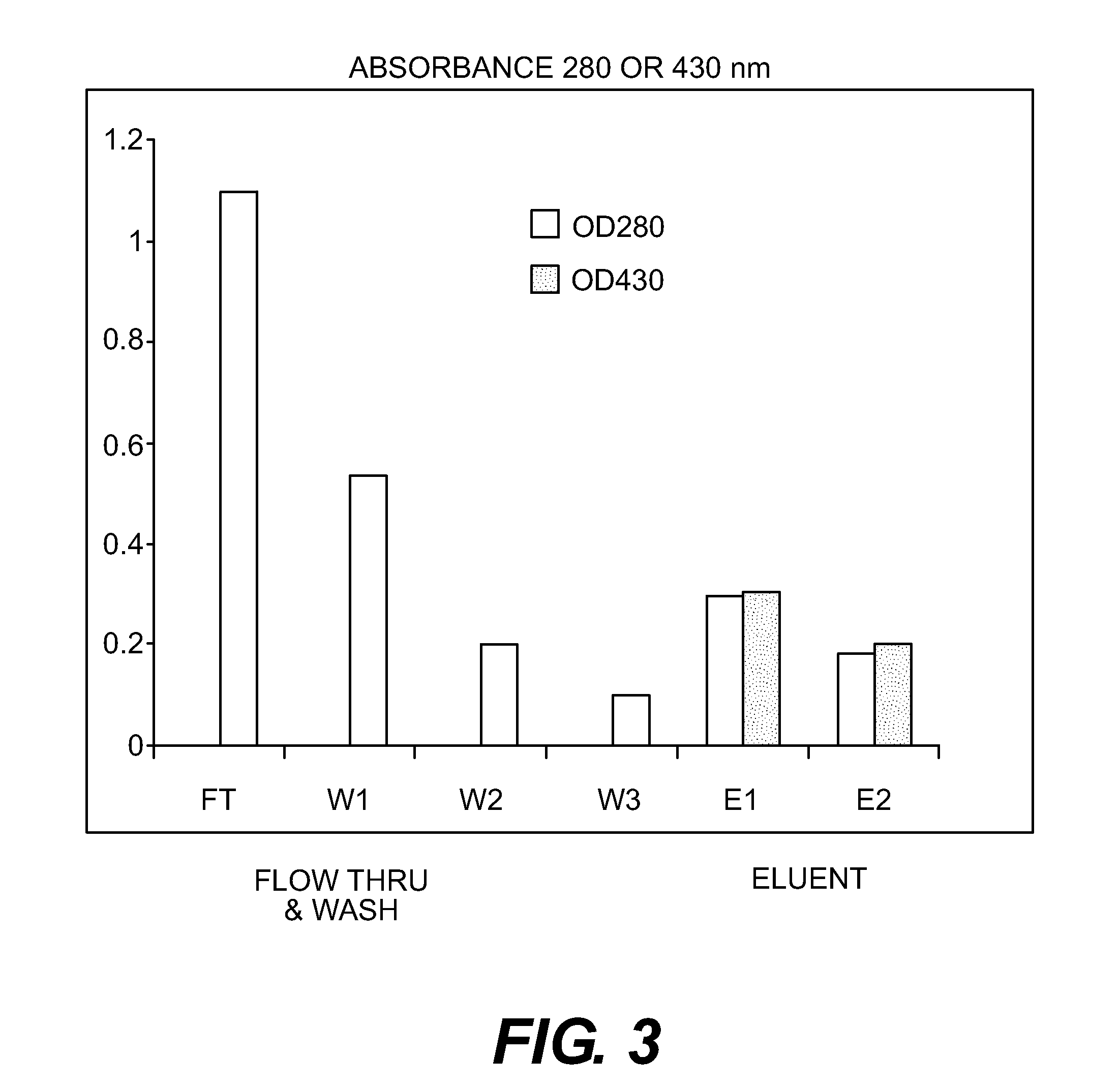
InactiveUS20120135030A1Lower Level RequirementsMethod is newAntibacterial agentsPeptide preparation methodsProtein linkChemistry
This invention is directed to processes for reducing the level of free carbohydrate from a solution of protein-linked carbohydrate (conjugate) and non-linked carbohydrate. In this process, the conjugate is adsorbed to a hydrophobic membrane while the carbohydrate is not. The conjugate is then desorbed from the membrane, yielding a solution that is substantially reduced in free carbohydrate.
Owner:FINA BIOSOLUTIONS
Cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogels comprising proteins
PendingUS20220160938A1Reduce adverse effectsPromote natural blood clottingOintment deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHyaluronic acid
The invention relates to the field of derivatized cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogels having blood-derived proteins linked into their structure, as well as preparation and uses thereof.
Owner:LACERTA TECH
Method for the secretory production of heterologous protein in Escherichia coli
InactiveUS8304210B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifEnzyme stabilisationHeterologousEscherichia coli
The present invention relates to a signal sequence peptide for the improvement of extracellular secretion efficiency of a heterologous protein in E. coli. More particularly, the present invention relates to a gene construct for the improvement of extracellular secretion efficiency of the said heterologous protein in E. coli, which comprises a polynucleotide encoding a recombinant protein composed of the heterologous protein linked to C-terminal of the signal sequence peptide represented by SEQ. ID. NO. 3. The present invention contributes to the improvement of extracellular secretion efficiency of a recombinant protein, so that it can be effectively applied to the production of a recombinant protein.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Fusion protein binding specifically to constant region of antibody, method of preparing the fusion protein, and method of isolating antibody using the fusion protein
A fusion protein that includes a polypeptide binding specifically to a constant region of an antibody and a stabilization protein linked to a terminus of the polypeptide, a polynucleotide encoding the fusion protein, a cell including the polynucleotide, a method of preparing the fusion protein, and a method of isolating an antibody by using the fusion protein.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of producing protein-carbohydrate vaccines reduced in free carbohydrate
InactiveUS8647621B2Lower Level RequirementsAntibacterial agentsPeptide preparation methodsProteinProtein link
This invention is directed to processes for reducing the level of free carbohydrate from a solution of protein-linked carbohydrate (conjugate) and non-linked carbohydrate. In this process, the conjugate is adsorbed to a hydrophobic membrane while the carbohydrate is not. The conjugate is then desorbed from the membrane, yielding a solution that is substantially reduced in free carbohydrate.
Owner:FINA BIOSOLUTIONS
Modular targeted therapeutic agents and methods of making same
ActiveUS10206998B2Induces muscle paralysisPrevents blood clottingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLibrary screeningDisease markersMedicine
Provided herein are methods for making targeted therapeutics. In several embodiments, the therapeutics are directed against soluble agents such as toxins, venoms, and / or other factors that alter physiological biopathways as well as methods of using such therapeutics to treat patients or patient populations to reduce, eliminate, or inactivate, detrimental soluble agents that such patients or patient populations have been exposed to. In several embodiments, the therapeutics are directed to patient-specific disease markers. In several embodiments, the methods comprise screening a library comprising proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs to identify mRNA-protein pairs that bind to the diseased cells, isolating one or more proteins from the identified mRNA-protein pairs, and conjugating the isolated protein(s) to a therapeutic agent.
Owner:PROTEONOVA
ELISA detection method of dioscin content
The present invention relates to the method of detecting dioscin content in plant body or relevant sample, and is ELISA detection method. Protein link coupled dioscin is used as antigen to obtain dioscin and its relevant saponin antibody, and the dioscin and its relevant saponin antibody is used as solid antigen in competitive enzynme linked immunological detection of the dioscin content in plant body or relevant sample. The method is simple, low in cost and high in sensitivity, and may be used in different departments.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com