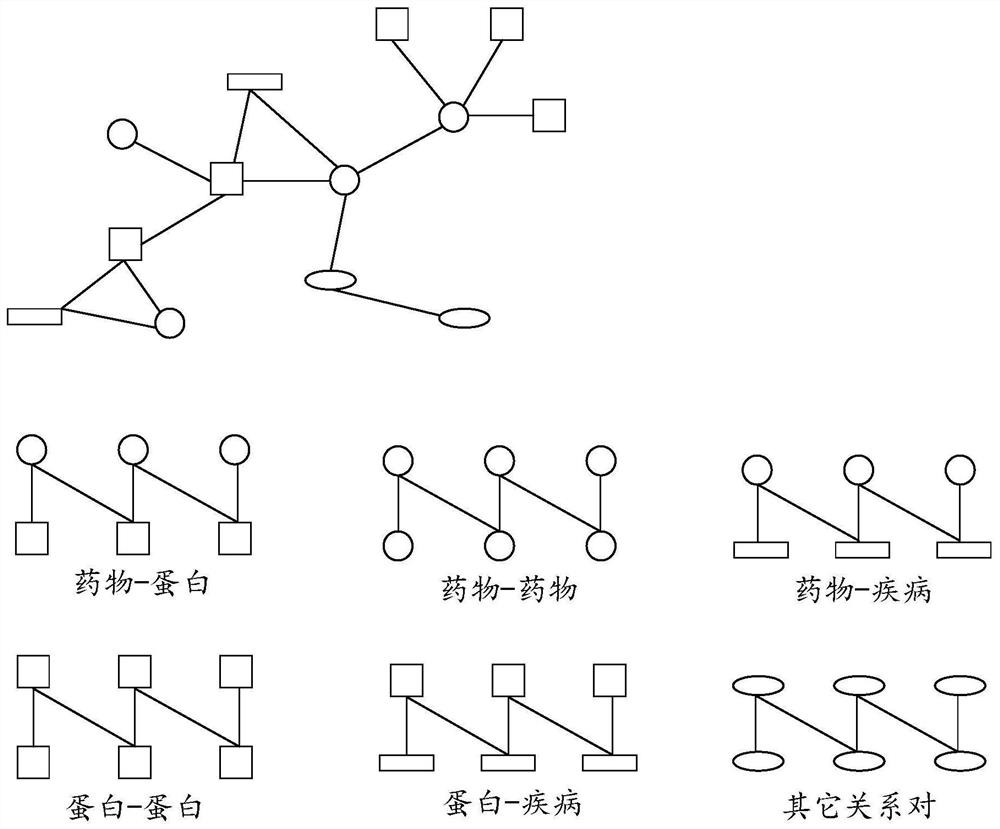
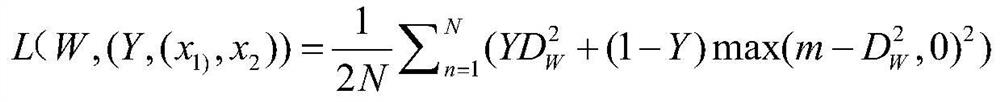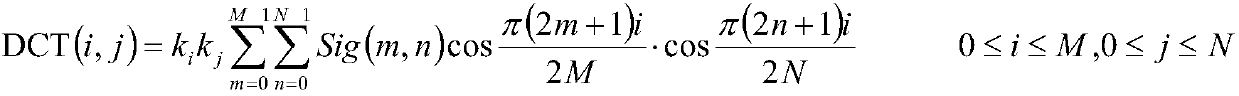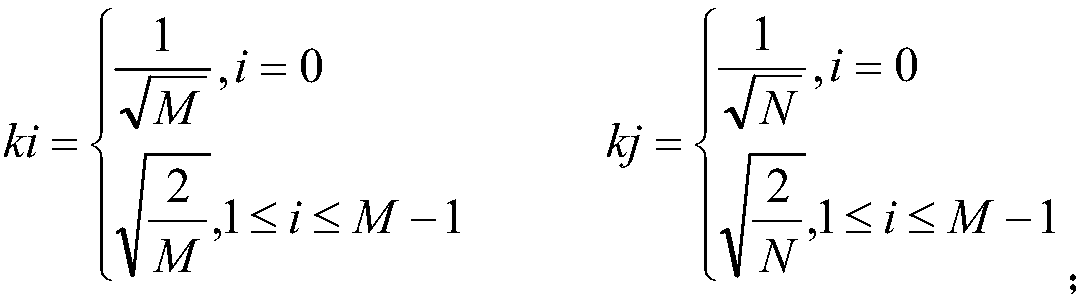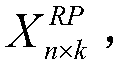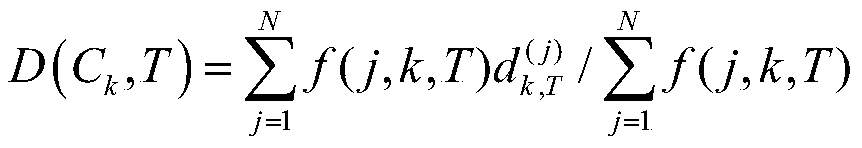Patents
Literature
87 results about "Protein pair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aim to always pair a protein and complex carbohydrate together at meal and snack times. Proteins help with satiety and carbohydrates help increase blood sugars. For example, a good snack would be whole-grain crackers (carb) and hummus (protein), or apple slices (carb) and peanut butter (protein).
Method, apparatus, media and signals for identifying associated cell signaling proteins
Methods, apparatus, media and signals for identifying associated cell signaling proteins are disclosed. The method involves producing and storing a comparison value for each pair of the cell signaling proteins in response to data values representing physical properties of respective cell signaling proteins. The method further involves identifying cell signaling protein pairs having comparison values satisfying a condition indicative of an association between the cell signaling proteins.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
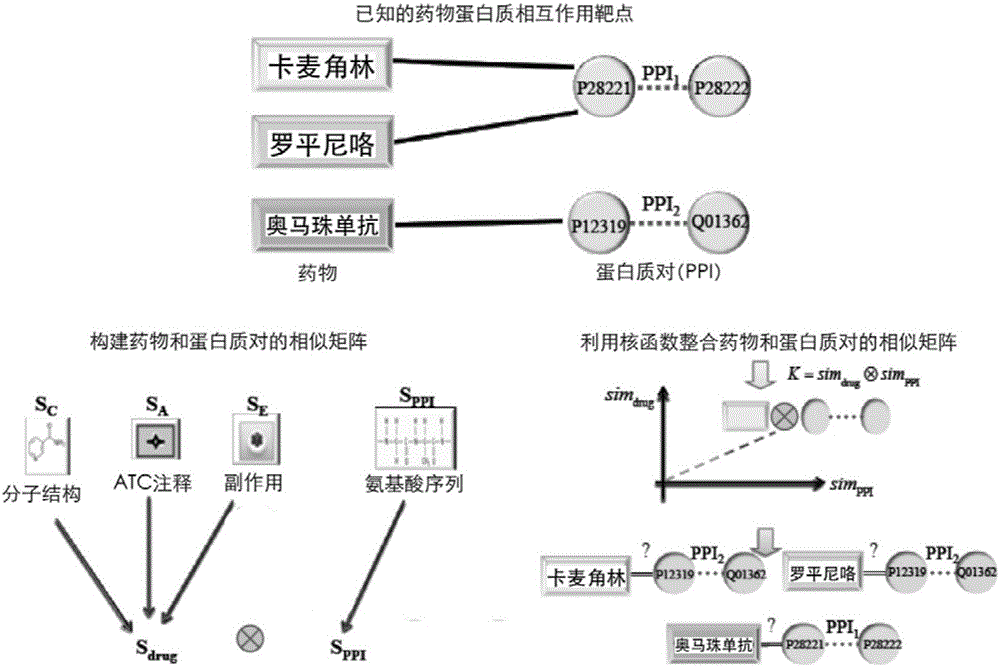
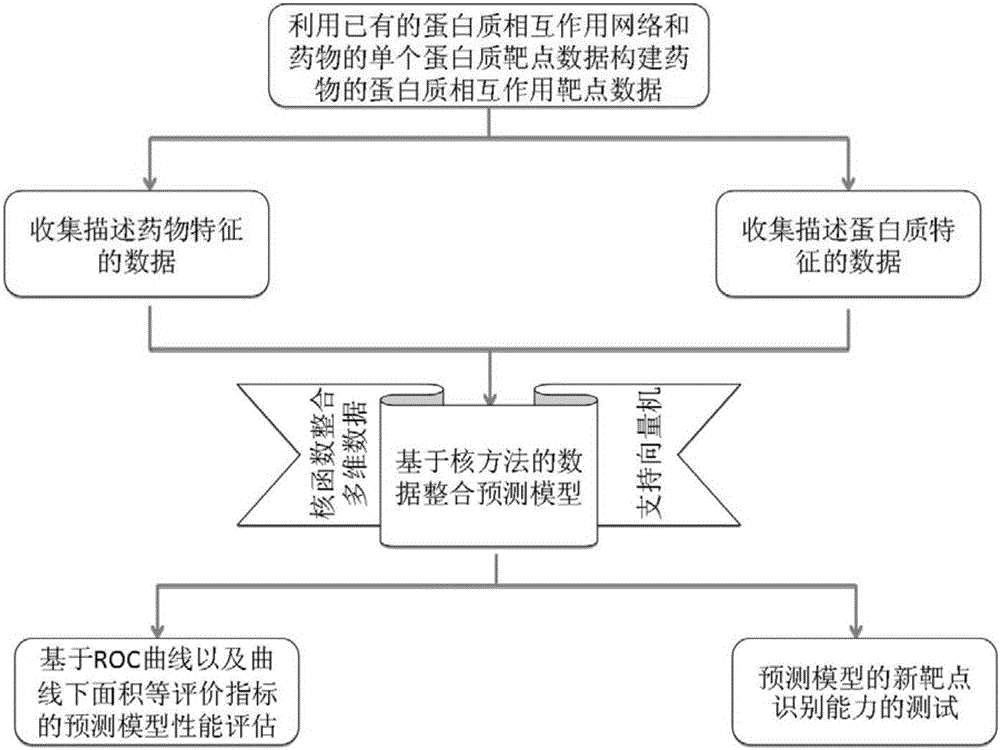
Method and system for predicting protein interaction target point of drug
InactiveCN105160206AWiden the search spaceImprove classification effectSpecial data processing applicationsEvolutionary biologyProtein targetData set
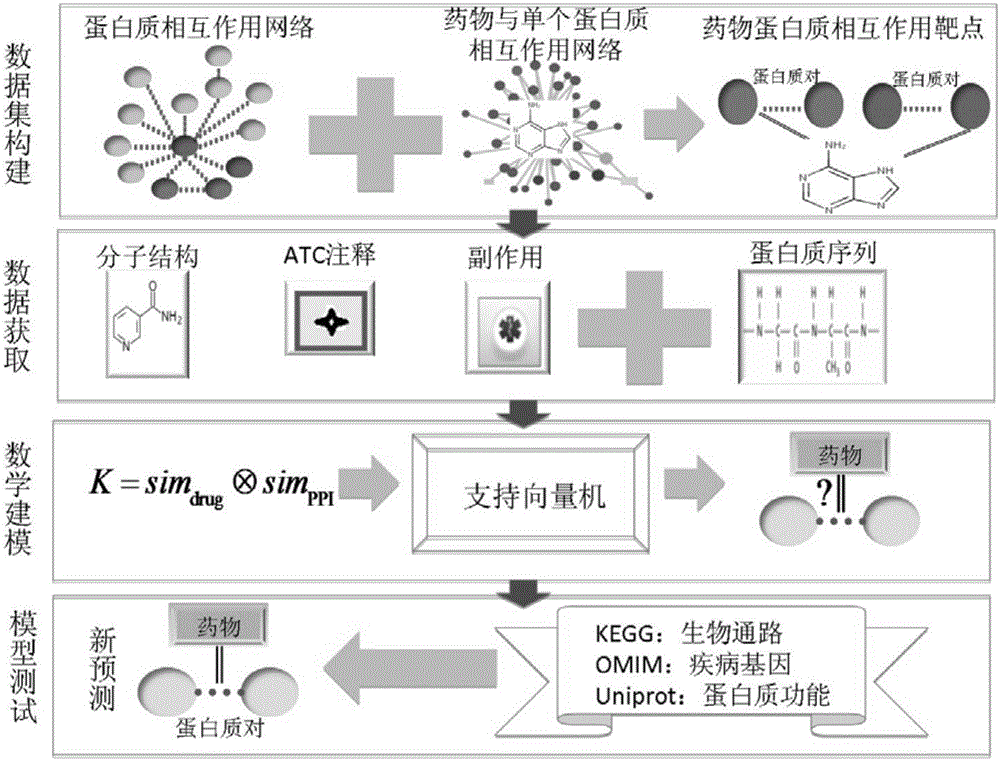
The invention relates to a method and a system for predicting a protein interaction target point of a drug. The method comprises: 1) collecting a human protein interaction network and single protein target point data of the drug, and constructing an interactive protein target point data set of the drug; 2) obtaining description data of the drug and proteins; 3) constructing a bigraph for representing an interactive relationship between the drug and a protein pair, constructing a similar matrix for representing drug similarity and protein pair similarity, establishing a kernel function for correlating the similar matrix of the drug and the protein pair, and establishing a prediction model through a machine learning algorithm; and 4) performing independent set testing by utilizing unknown drug and interactive protein pair, and predicting a possibly existent unknown drug protein interaction target point, and verifying a prediction result through database and document retrieval. According to the method and the system, the search space of the drug target point can be expanded and the more specific drug protein interaction target point with the best classification performance can be obtained.
Owner:ACAD OF MATHEMATICS & SYSTEMS SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
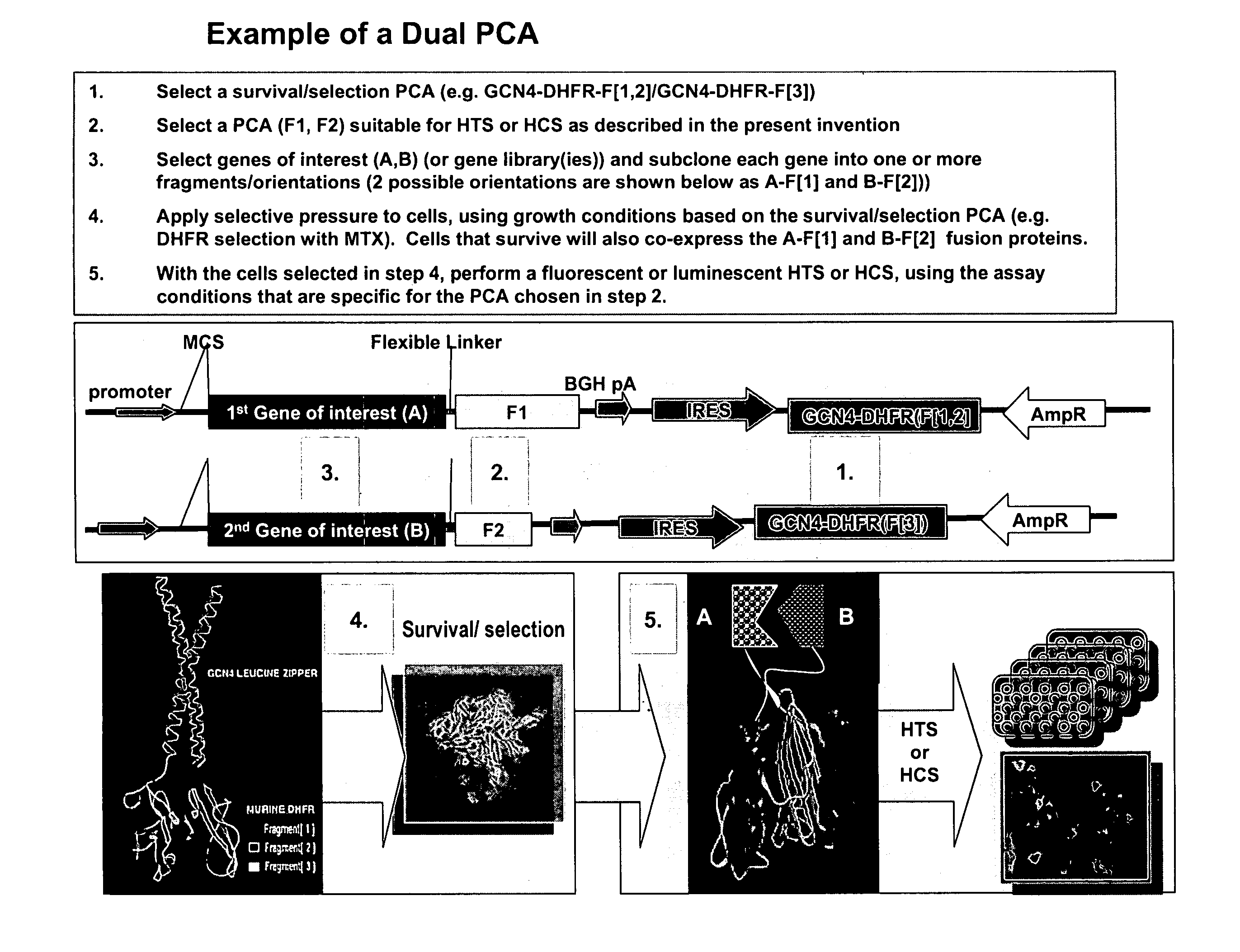
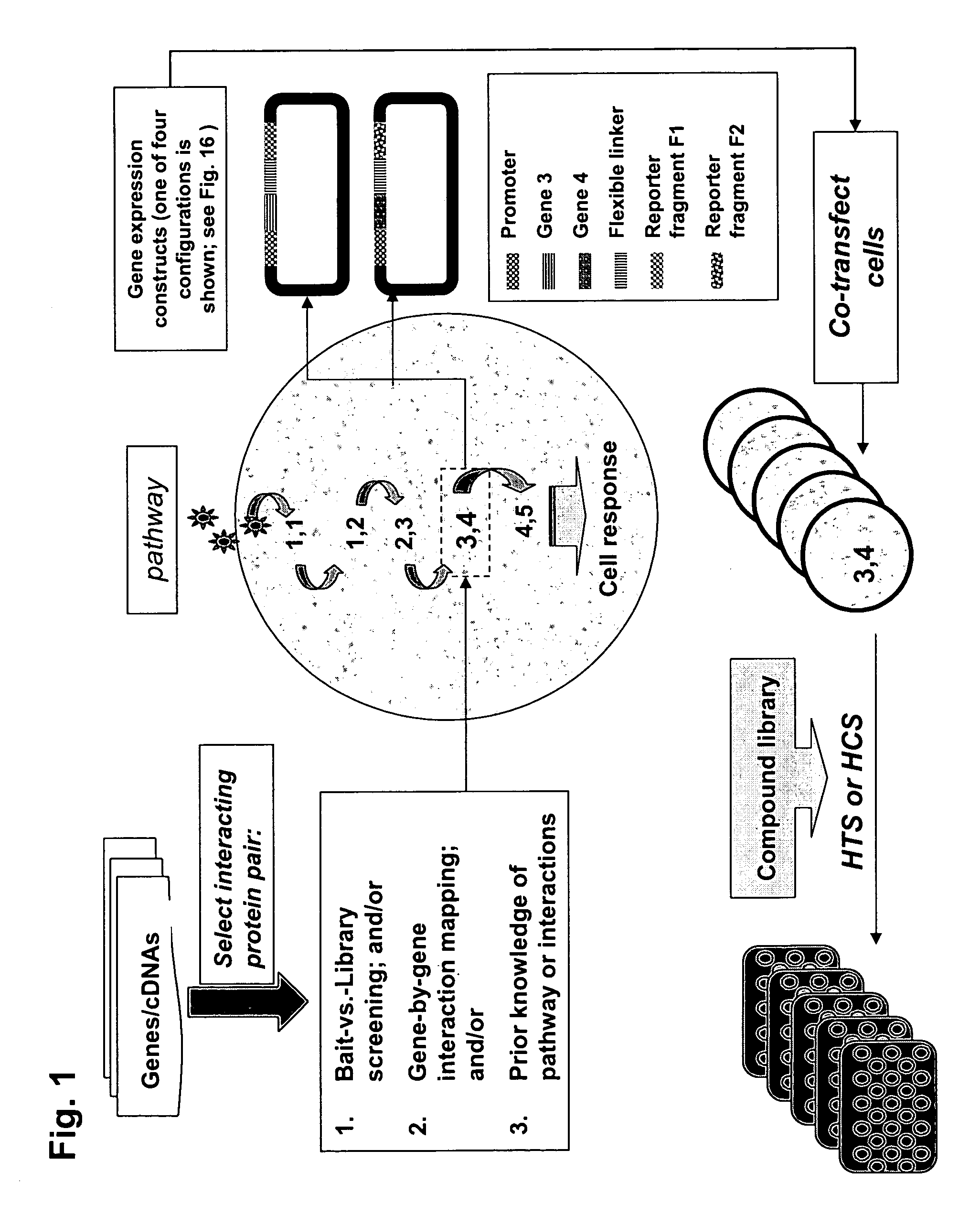
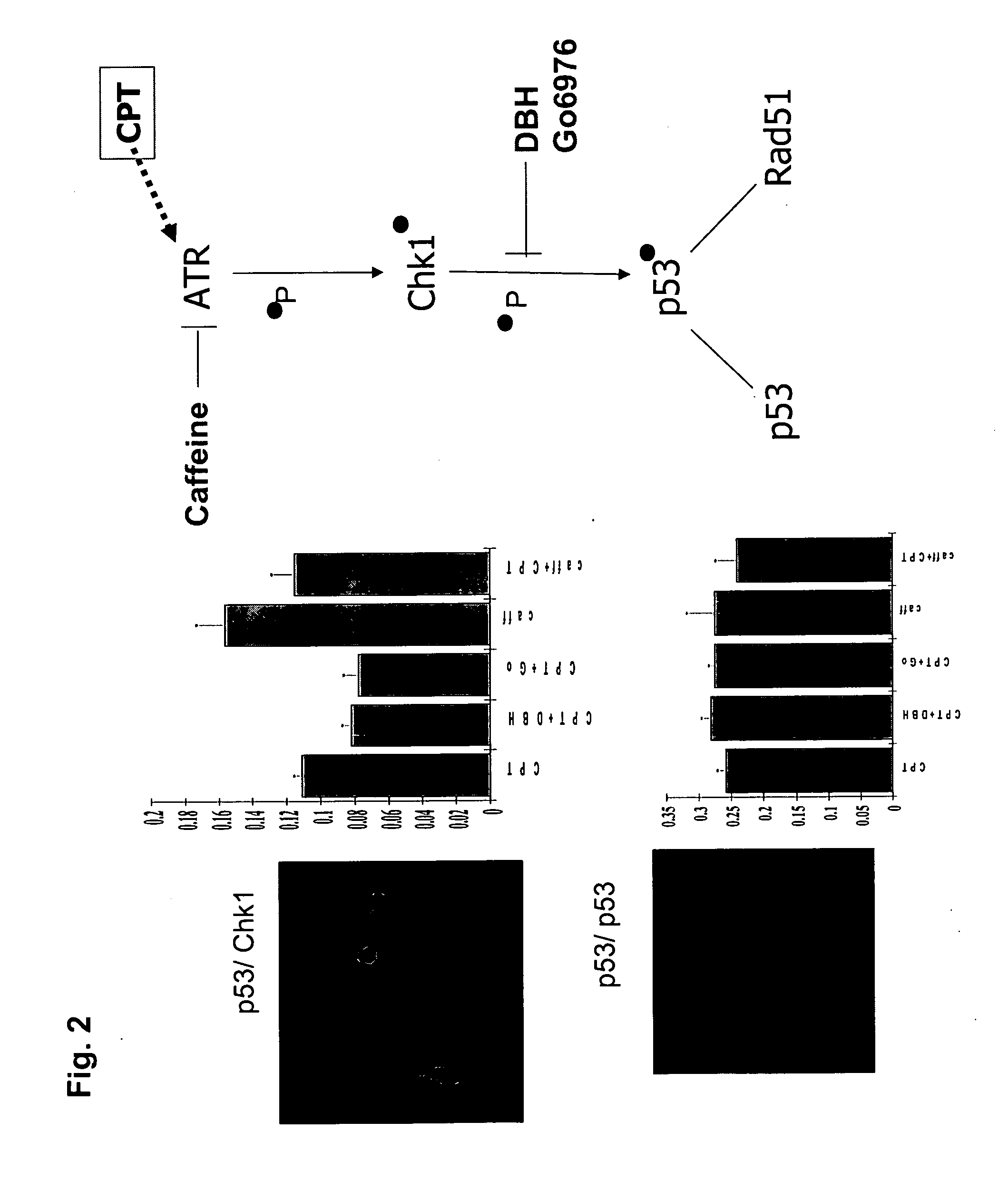
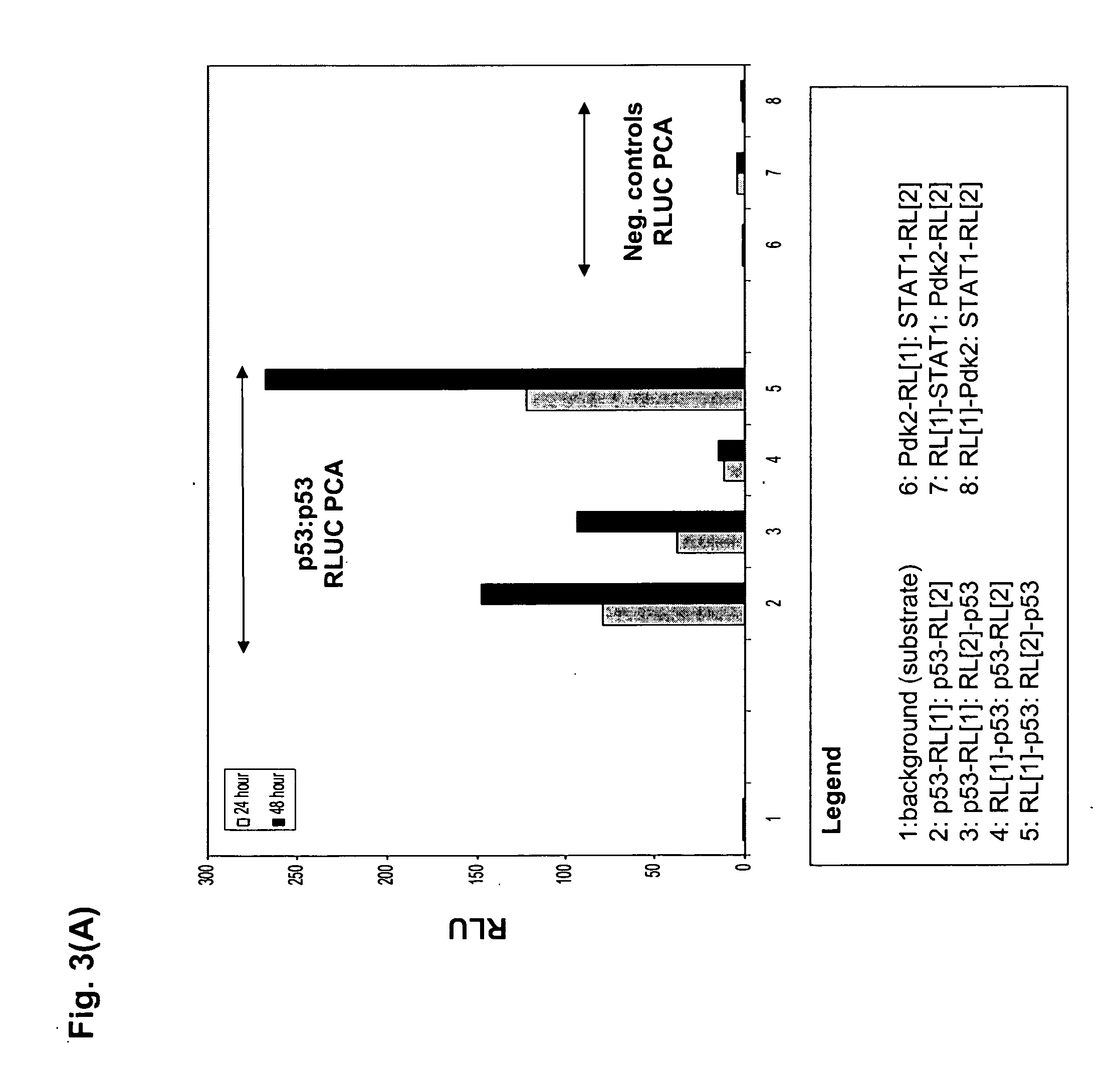
Protein fragment complementation assays for high-throughput and high-content screening
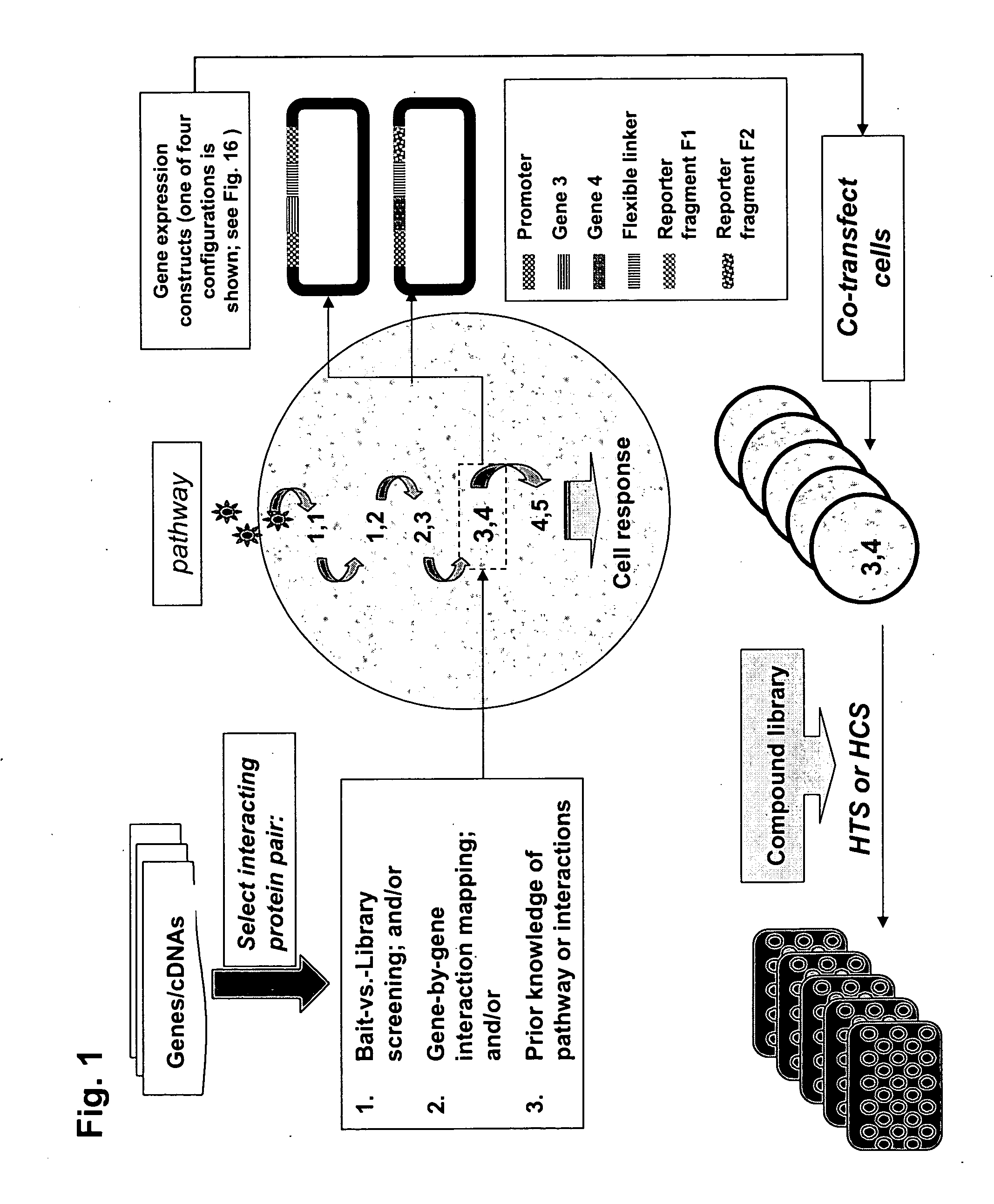
The present invention provides protein fragment complementation assays for drug discovery, in particular to identify compounds that activate or inhibit cellular pathways. Based on the selection of an interacting protein pair combined with an appropriate PCA reporter, the assays may be run in high-throughput or high-content mode and may be used in automated screening of libraries of compounds. The interacting pair may be selected by cDNA library screening; by gene-by-gene interaction mapping; or by prior knowledge of a pathway. Fluorescent and luminescent assays can be constructed using the methods provided herein. The selection of suitable PCA reporters for high-throughput or high-content (high-context) assay formats is described for a diversity of reporters, with particular detail provided for examples of monomeric enzymes and fluorescent proteins. Methods are described for constructing such assays for one or more steps in a biochemical pathway; testing the effects of compounds from combinatorial, natural product, peptide, antibody, nucleic acid or other diverse libraries on the protein or pathway(s) of interest; and using the results of the screening to identify specific compounds that activate or inhibit the protein or pathway(s) of interest. Single-color and multi-color assays are disclosed. Further disclosed are universal expression vectors with cassettes that allow the rapid construction of assays for a large and diverse number of gene / reporter combinations. The development of such assays is shown to be straightforward, providing for a broad, flexible and biologically relevant platform for drug discovery.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Compounds and assays for controlling Wnt activity
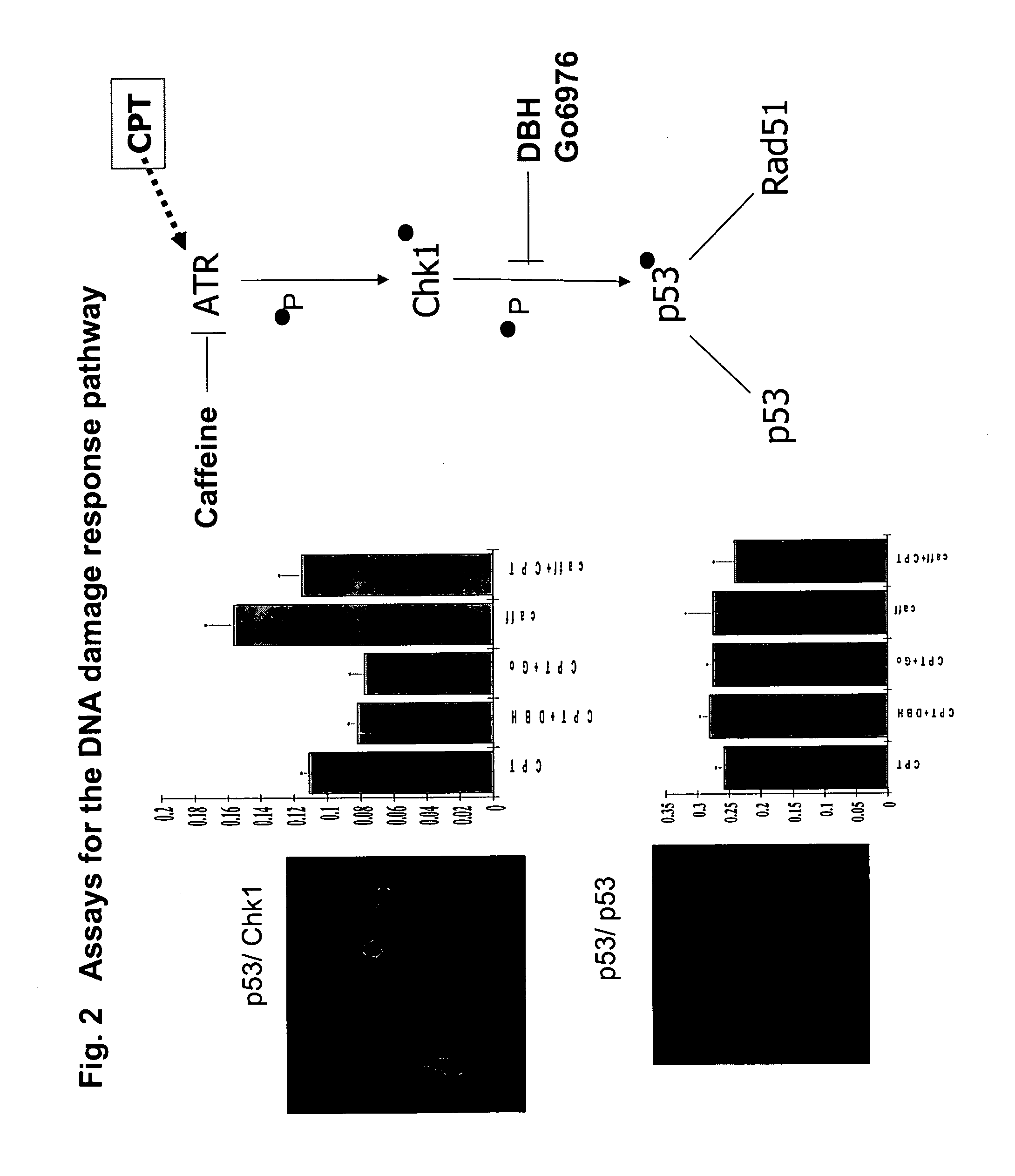
The present invention relates to the field of therapeutic methods to screen for compounds on the basis of their ability to influence Wnt activity. The screening process is applied to both a physical library of a series of compounds and a virtual library of compounds that affect Wnt activity. In one aspect, the virtual screening process could be carried out where a permutational library of small peptides is substituted for the small organic molecules. The inventive methods may be used to empirically test for effects on Wnt activity and may also be applied to any pair of proteins involved in protein-protein interactions.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
Process for producing well-preserving low-lactose or lactose-free milk product
InactiveUS20100215828A1Extension of timeWeakening of nutritional valueMilk preparationMilk preservationLactose free milkEnzyme system
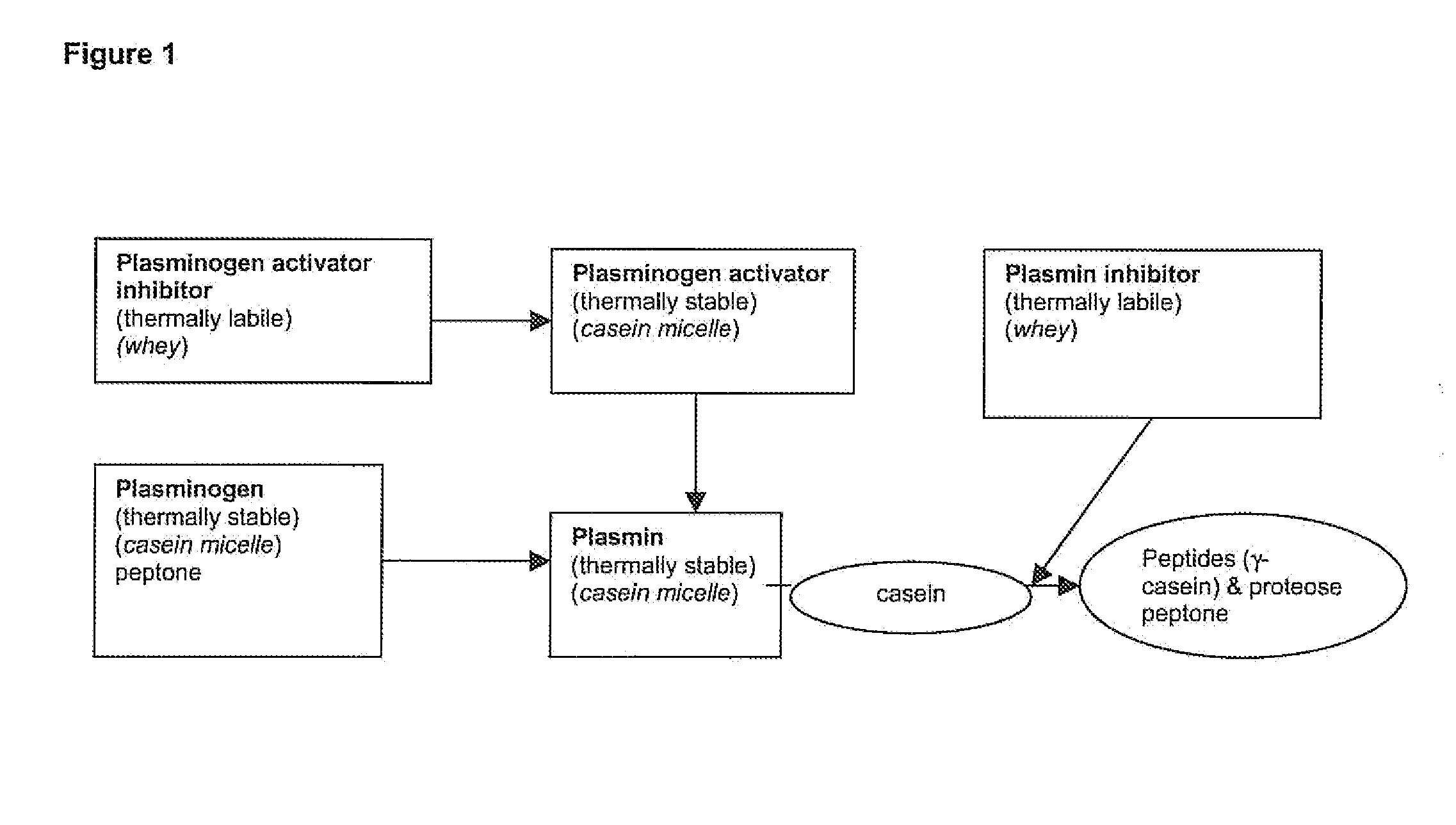
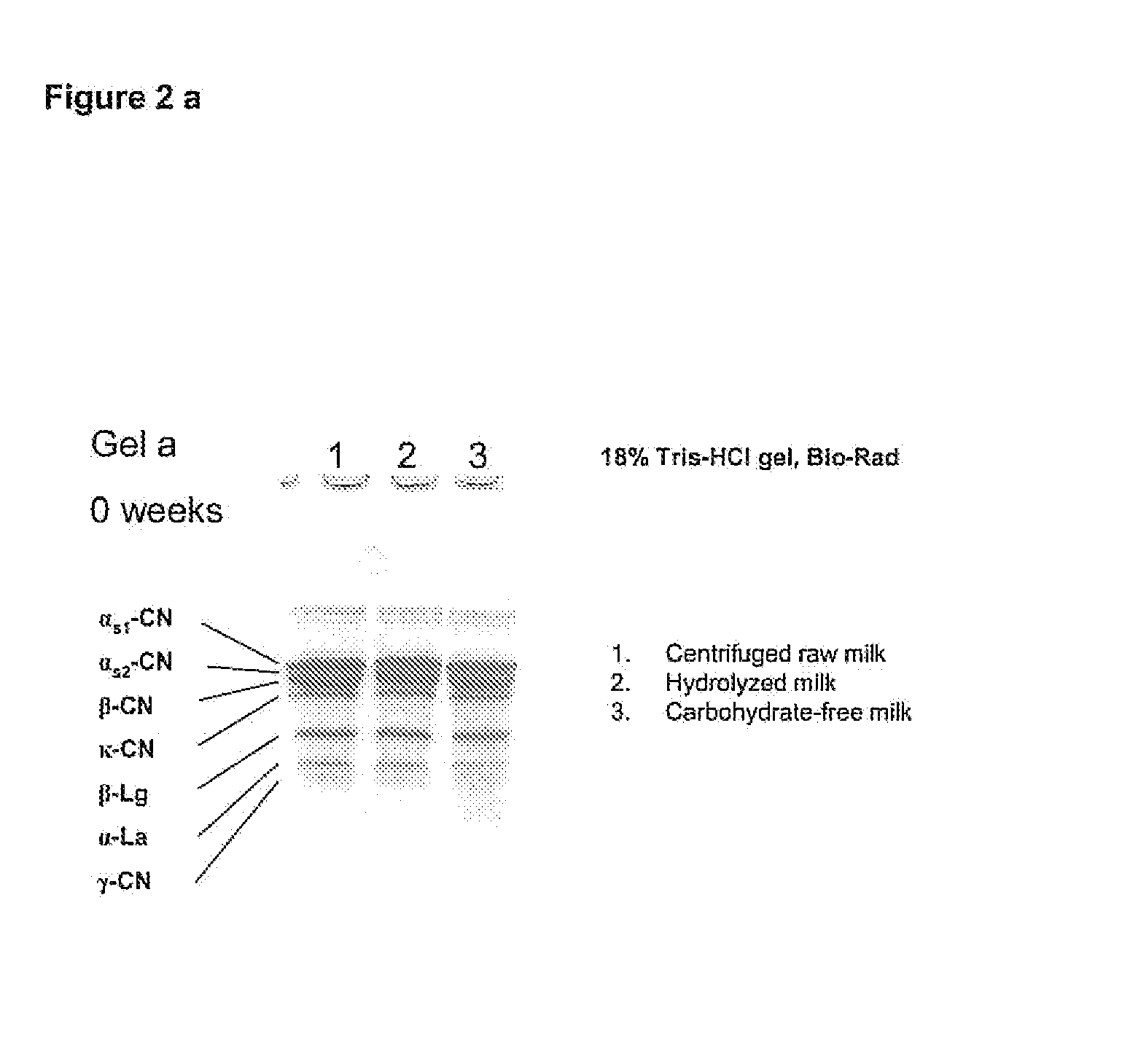
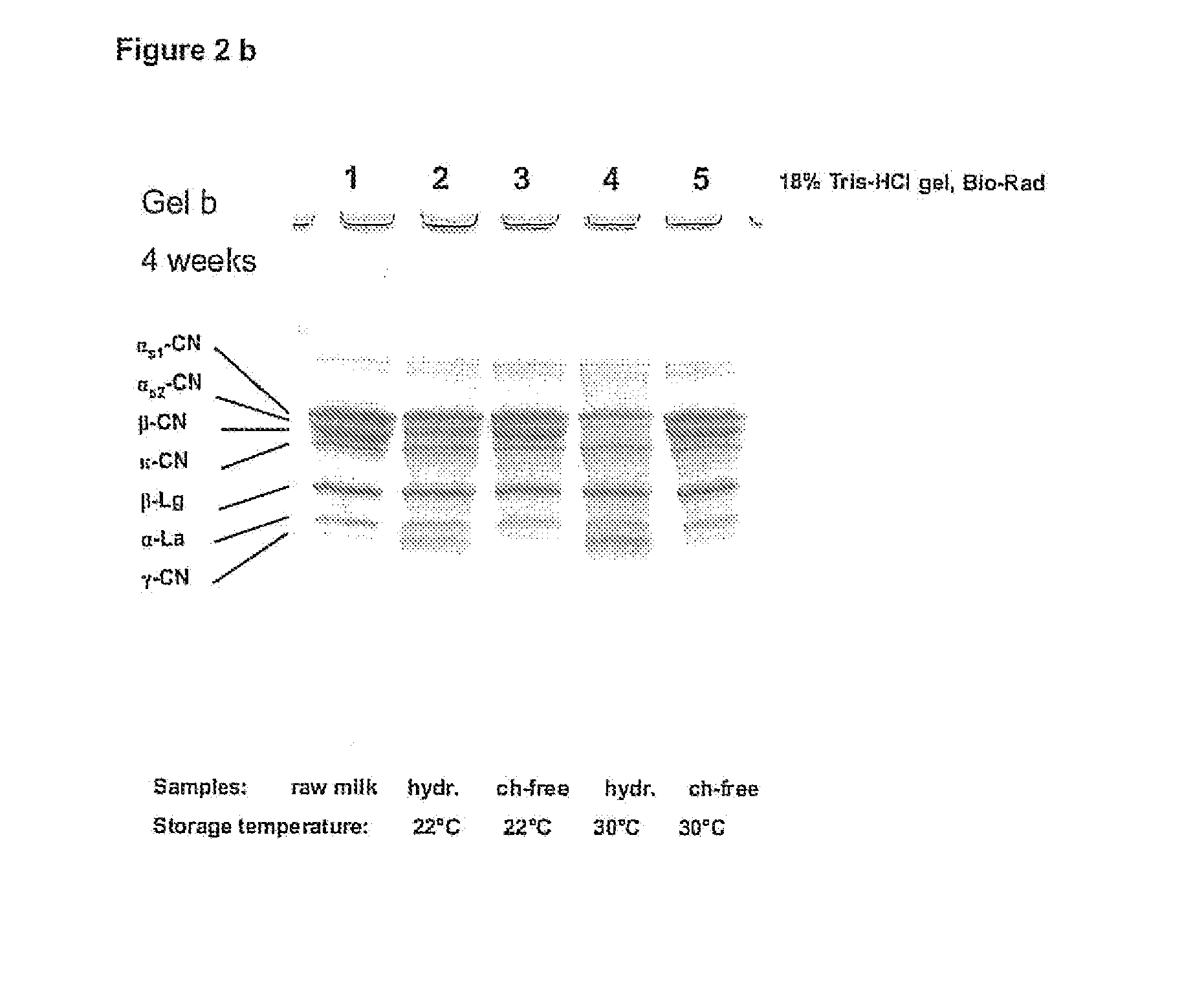
The invention relates to a process for the production of well-preserving lactose-free and low-lactose milk products. The process of the invention is characterized by separating the sugars and proteins in a raw material, thermally treating them in such a manner that the plasmin enzyme system and other proteolytic enzymes are inactivated, and combining the fractions and other preparation agents into a drink with a required composition and properties.
Owner:VALIO LTD
Protein fragment complementation assays for high-throughput and high-content screening
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Method for improving bioavailability of iron and zinc elements of broad beans
InactiveCN103229962AHigh nutritional valueImprove bioavailabilityFood preparationBiotechnologyIn vitro digestion
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant processing and in particular relates to a method for improving the bioavailability of iron and zinc elements of broad beans. The broad beans are low in cost, contain abundant microelements and proteins and have a certain advantage to dietary nutrition of people. Phytic acid which is contained in cotyledons of the broad beans can be combined with proteins and metal ions to reduce the bioavailability of the proteins and the metal elements. The deficiency of iron and zinc elements has certain universality, and the iron and zinc elements play an important role in intelligence development of children and physical health of adults. Most people take vegetarian diet as staple food in China, wherein the broad beans are popular bean crops, and carrots and spinaches are popular vegetables. The carrots and spinaches contain beta-carotene; and according to the method disclosed by the invention, the fact that the bioavailability of the iron and zinc elements in the broad beans can be improved by adding the carrots and spinaches into raw broad bean flour or cooked broad bean flour is discovered by using the carrots, spinaches and the broad bean flour to do an in-vitro digestion experiment, and therefore the nutritional value in use of the broad beans is increased.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
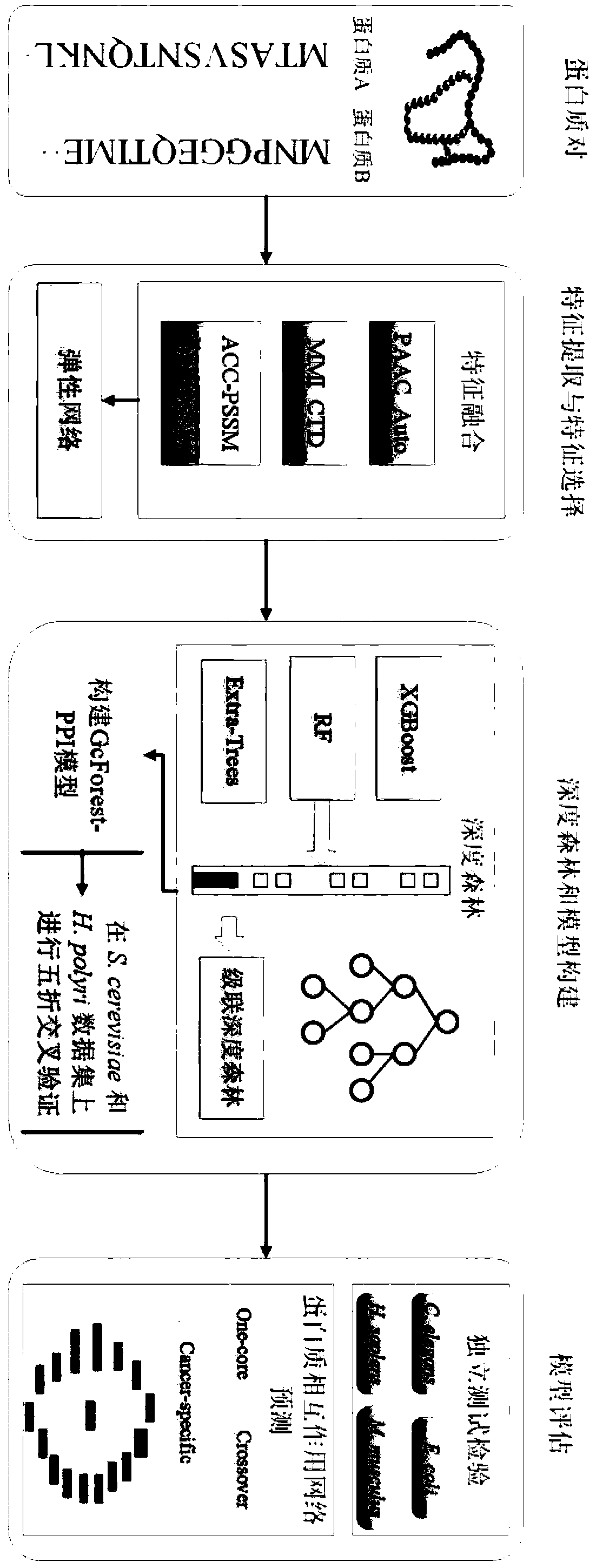
Protein-protein interaction prediction method based on deep forest
ActiveCN111210871AReduce complexityImprove forecast accuracyBiostatisticsProteomicsDipeptideDrug target
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of biological information, discloses a protein-protein interaction prediction method based on a deep forest. According to the method, pseudo amino acid composition, a mutual information descriptor, composition, and distribution, a conversion descriptor, an amino acid composition position specificity score matrix and a dipeptide composition position specificity score matrix are fused to convert a protein sequence into a numerical vector; sequence information, physicochemical property information and evolution information of the protein pair are fused as initial characteristics of a sample; an elastic network is used for feature selection, and redundant and irrelevant features are removed; and a fused optimal feature vector is inputted intoa constructed multi-granularity cascade depth forest to predict protein-protein interaction. The method is simple and effective, the deep forest can represent the high-level feature information of the protein pair, the results of the training set and the test set are obviously superior to those of other prediction methods, and a certain reference can be provided for drug target prediction and human disease treatment.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
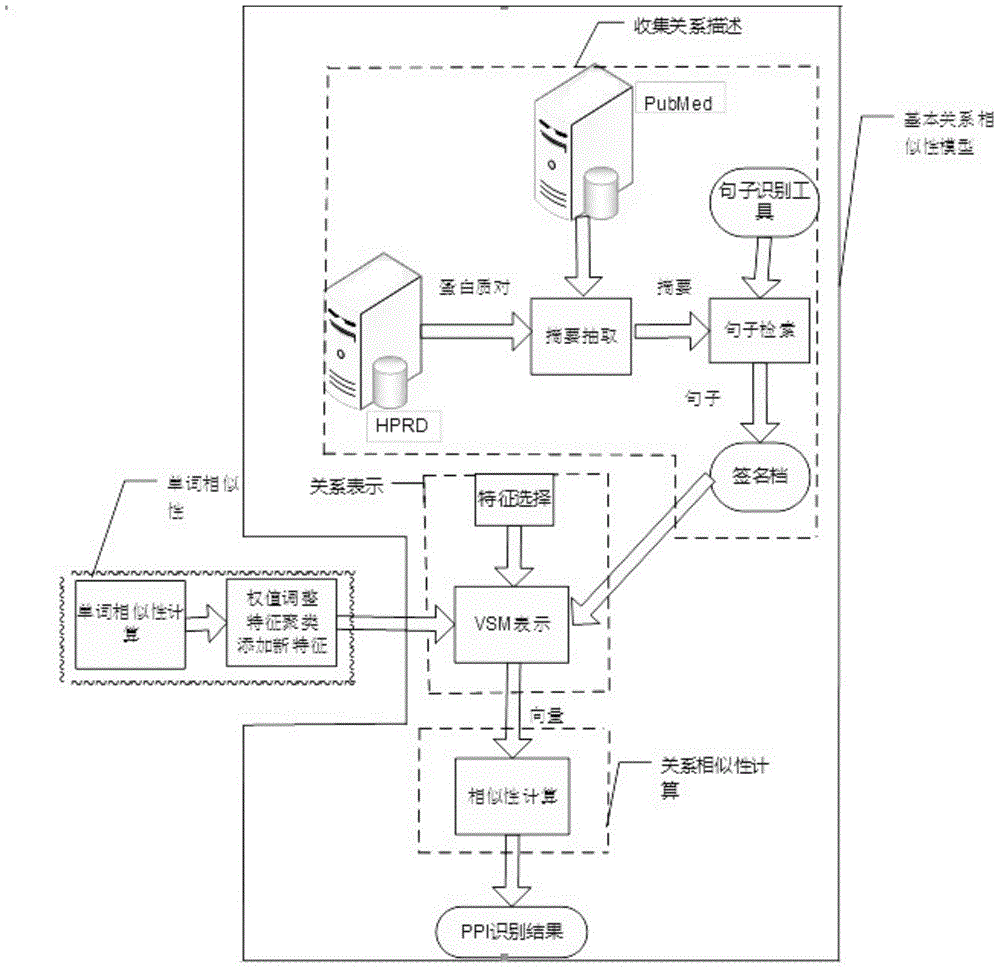
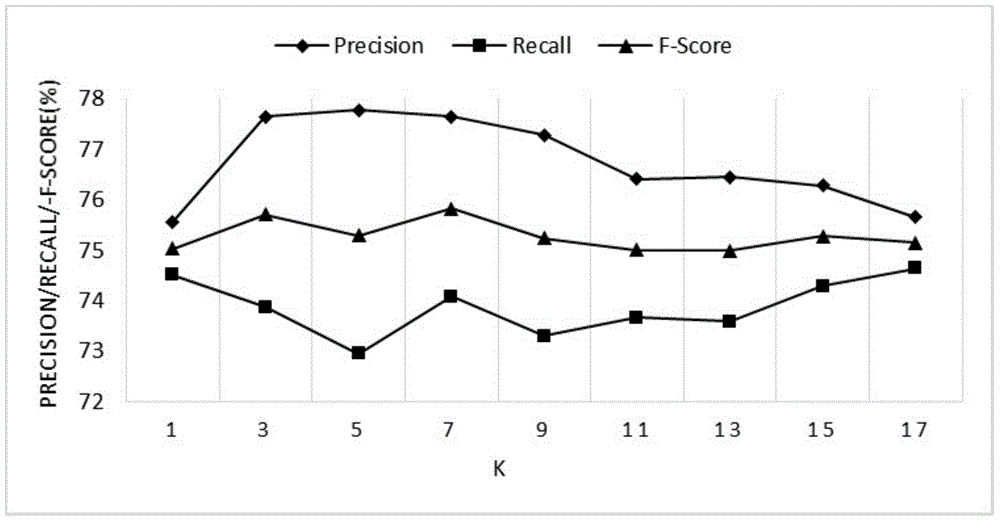
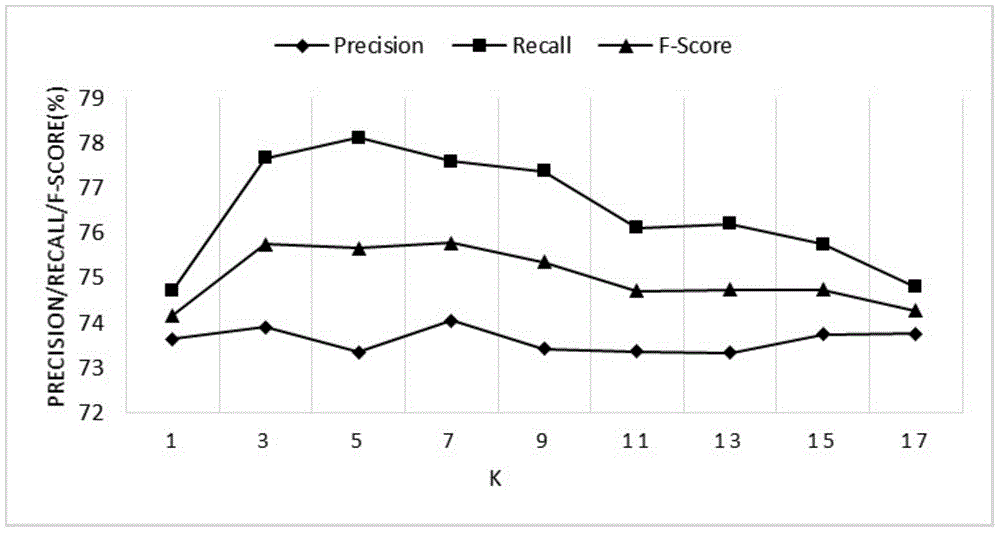
Protein interactive relationship identification method based on text relationship similarity
InactiveCN104537280AHigh precisionImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorProtein target
The invention discloses a protein interactive relationship identification method based on the text relationship similarity. The protein interactive relationship identification method includes the following steps: (1) sentences of protein pair keywords in a text set are obtained, and all the sentences are gathered to obtain signature files S, wherein each protein pair is (p1, p2), and each target protein pair corresponds to the corresponding signature file; (2) the relationships between p1 and p2 are denoted through characteristic vectors; (3) the relationship similarity is calculated, wherein similarity calculation comparing is carried out on the vectors for denoting the relationships between the target protein pairs and the characteristic vectors of the protein pairs with the known interactive relationships, and the most similar characteristic vectors are found and signed to serve as signs of the target protein pairs; (4) a word similarity matrix is calculated; (5) a word similarity model is introduced into a basic relationship similarity model to form a new mixed model. By means of the protein interactive relationship identification method, according to abundant context information in a text, the interactive relationship characteristics are more comprehensively obtained, and the identification accuracy is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
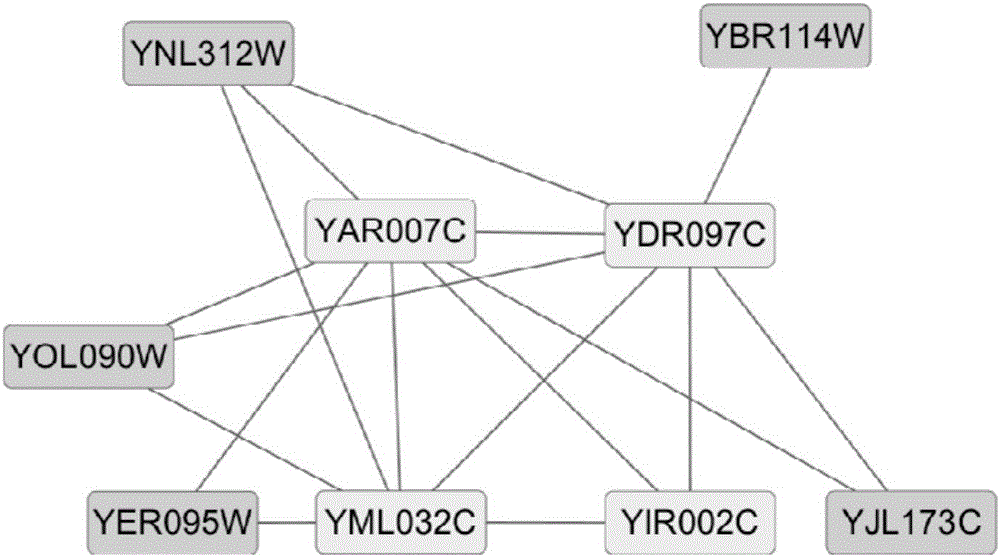
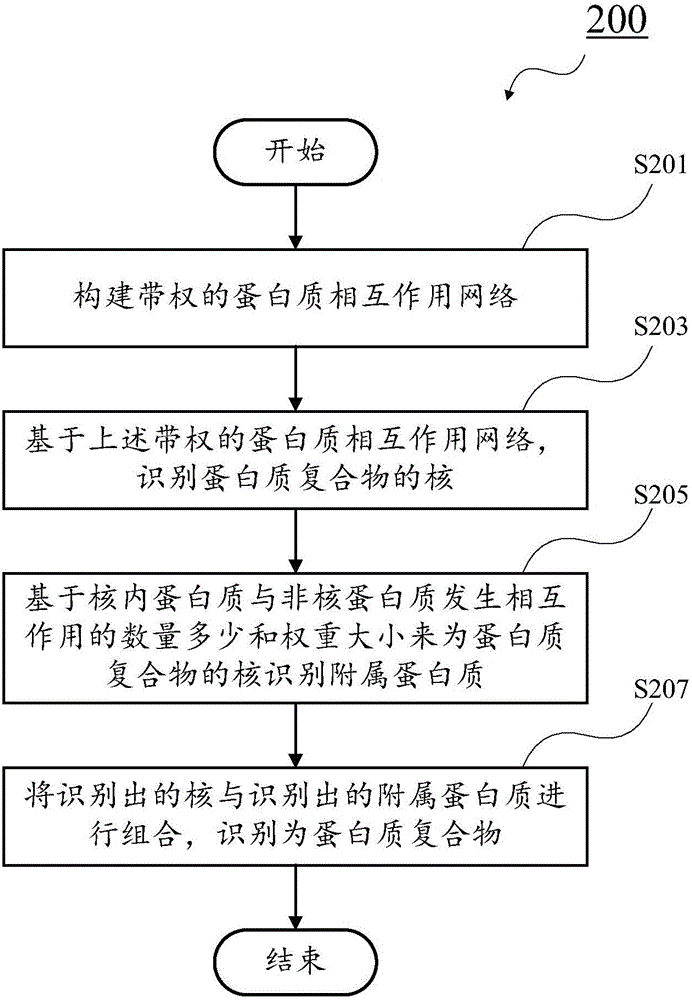
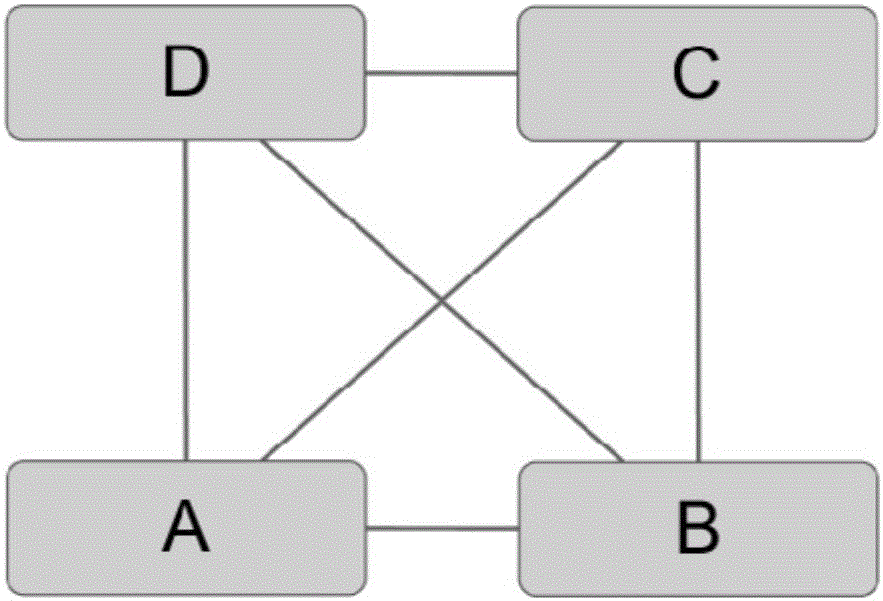
Recognition method of protein complexes
The invention discloses a recognition method of protein complexes. The method comprises following steps: constructing a weighted protein-protein interaction network, wherein weight value represents similarity between gene representing modes corresponding to proteins with codes interacting each other; recognizing nucleuses of protein complexes based on the weighted protein-protein interaction network; recognizing accessory proteins for the nucleuses of protein complexes based on the number of nuclear proteins interacting with non-nuclear proteins and weight; and combining recognized nucleuses and recognized accessory proteins to recognize the protein complexes. The method does not take internal structures of protein complexes into consideration and utilizes the feature of code interaction with high protein gene expression. Therefore, the method is capable of recognizing protein complexes with overlapping structures and the recognized protein complexes reflect actual internal structures of protein complexes.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF URBAN CONSTR
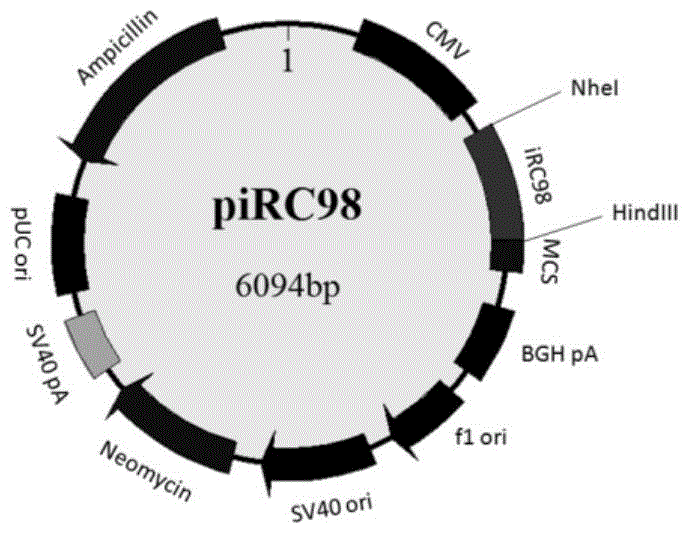
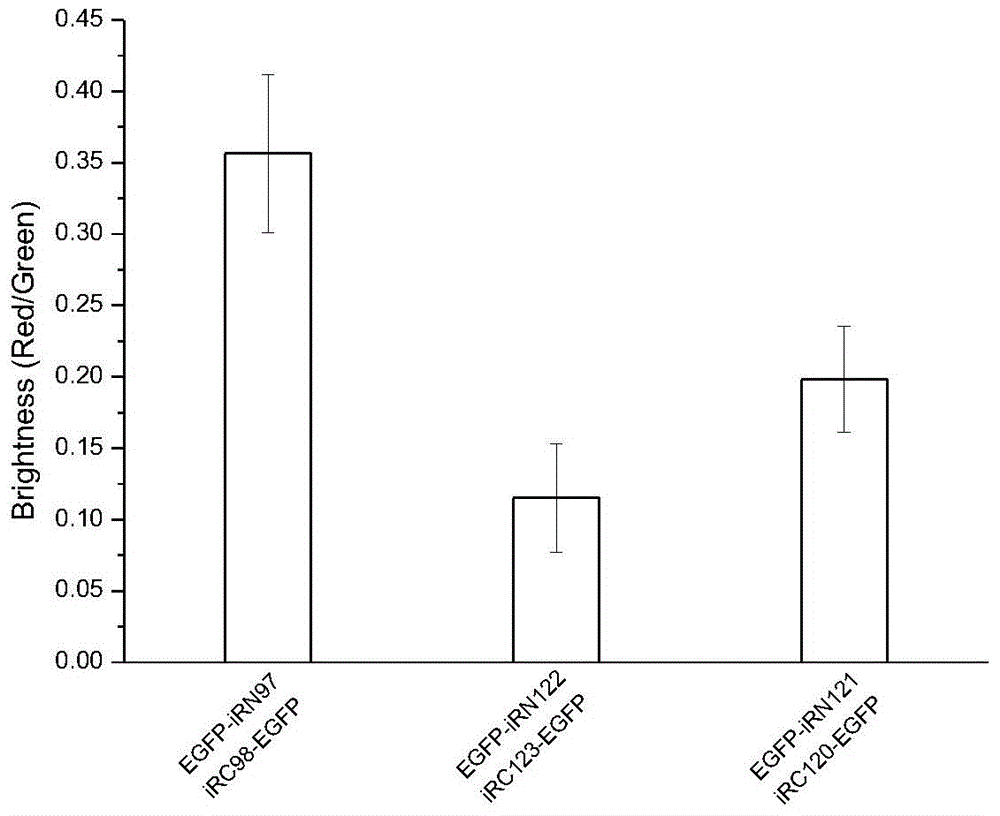
Fluorescent protein iRFP-based dimolecular fluorescent fragment complementary system, and applications
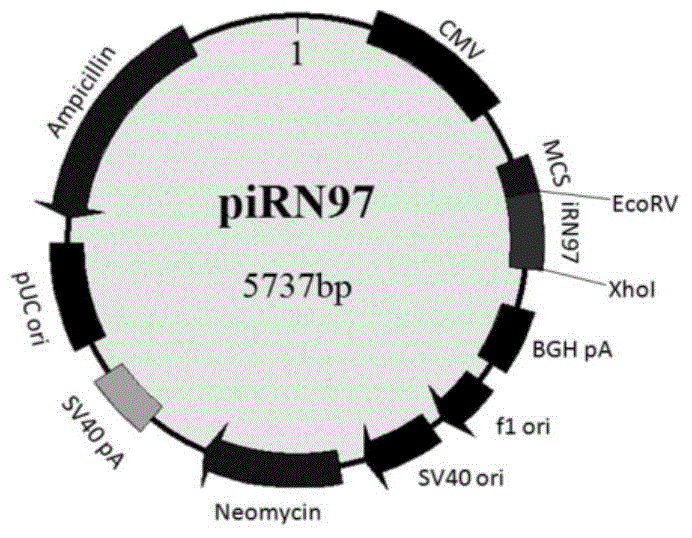
ActiveCN105624178AEnhanced inhibitory effectEase of evaluationFluorescence/phosphorescenceVector-based foreign material introductionProtein pairPhytochrome
The invention discloses a fluorescent protein iRFP-based dimolecular fluorescent fragment complementary system, and applications. According to the fluorescent protein iRFP-based dimolecular fluorescent fragment complementary system, phytochrome fluorescent protein iRFP is taken as a template, and is divided into a non-fluorescent nitrogen terminal fragment iRN97 and a non-fluorescent carbon terminal fragment iRC98 at the amino acid 97-98 sites; when fusion expression of the two fragments with protein pairs with interactions is realized, the two non-fluorescent fragments are drawn to be close to generate iRFP fluorescence; fusion expression of iRN97 with human immunodeficiency virus integrase IN, and fusion expression of iRC98 with cell protein P75 are realized respectively, the interaction between IN and p75 is studied in living cells via fluorescent complementation of iRN97 with iRC98; when a drug is capable of inhibiting the protein-protein interaction, it is impossible for iRN97 and iRC98 to be drawn to be close, so that fluorescence recovery is inhibited. The fluorescent protein iRFP-based dimolecular fluorescent fragment complementation system is a simple, effective, and convenient evaluation system of drugs used for inhibiting protein interactions.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
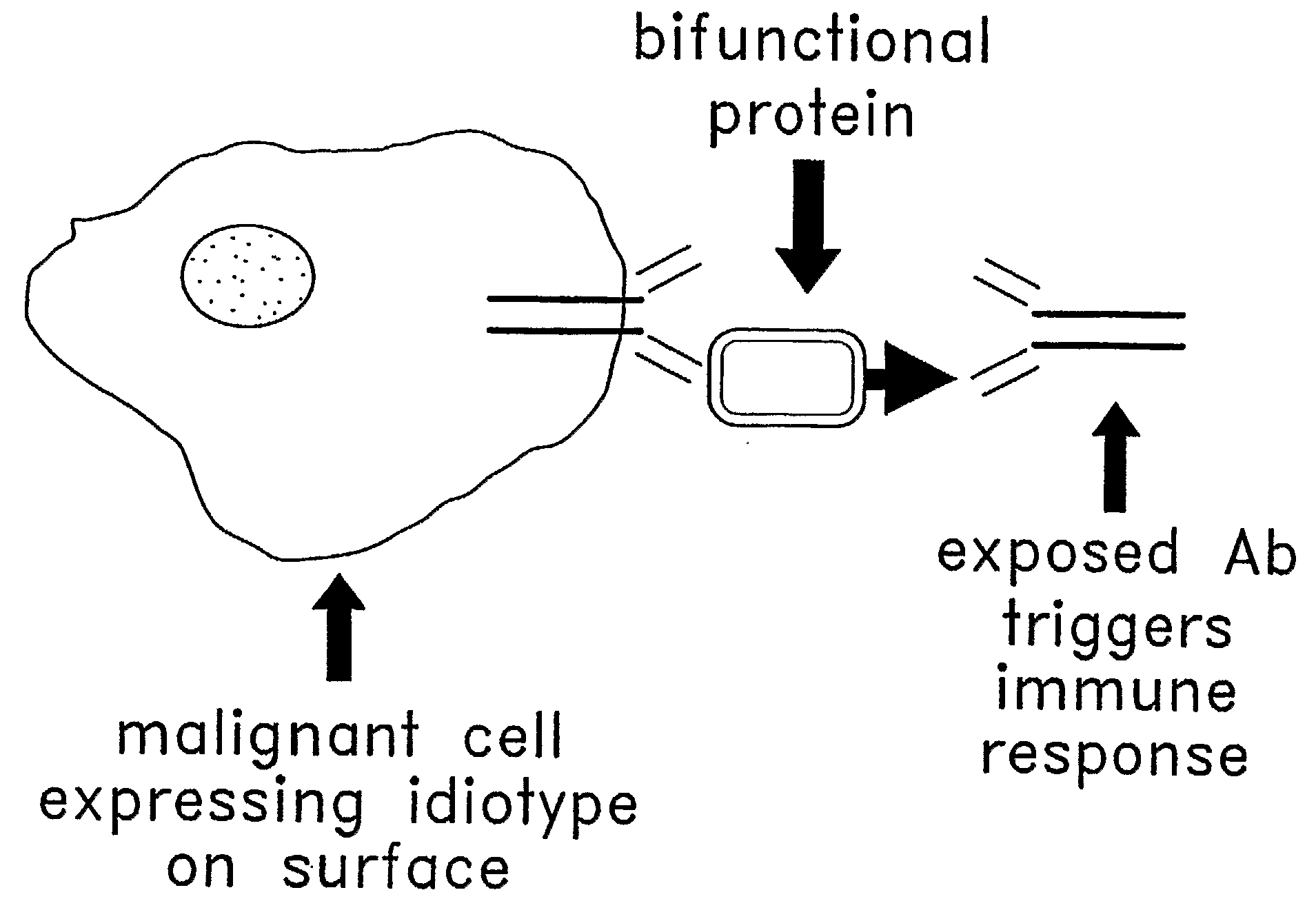
Method for Making Targeted Therapeutic Agents
InactiveUS20080199499A1Rapid and efficient identification and isolation and productionEffective and low methodAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLibrary screeningDisease markersCross linker
Provided herein are methods and kits for making a targeted therapeutic for treating a disease or condition. The therapeutic agents can be targeted to patient-specific disease markers. In one of these methods, the method includes obtaining a biological sample from a patient having the disease or condition, or who is at risk for developing the disease or condition. In this particular method, the sample includes a population of diseased cells, screening a library comprising proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs to identify mRNA-protein pairs that bind to the diseased cells, isolating one or more proteins from the identified mRNA-protein pairs, and conjugating the isolated protein(s) to a therapeutic agent. Some of the methods further include preparing a library with proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs. In certain of these methods, the preparation of the library includes providing at least two candidate mRNA molecules in which each of the mRNA molecules includes a cross-linker, translating at least two of the candidate mRNA molecules to generate at least one translated protein, and linking at least one of the candidate mRNA molecules to its corresponding translated protein via the cross-linker to form at least one cognate pair.
Owner:PROTEONOVA
Protein folding identification method based on deep metric learning
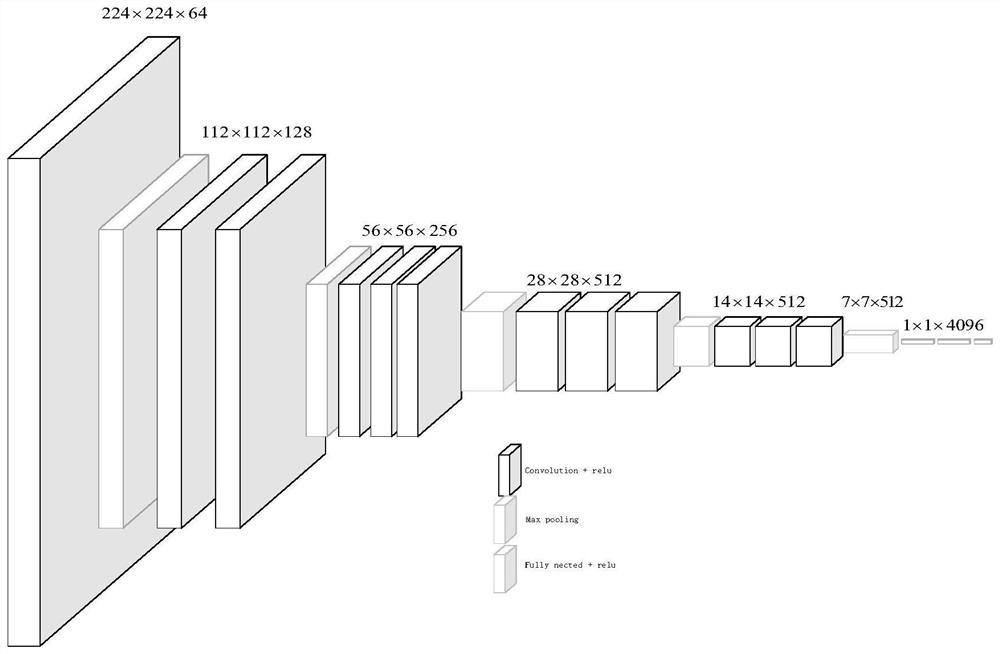
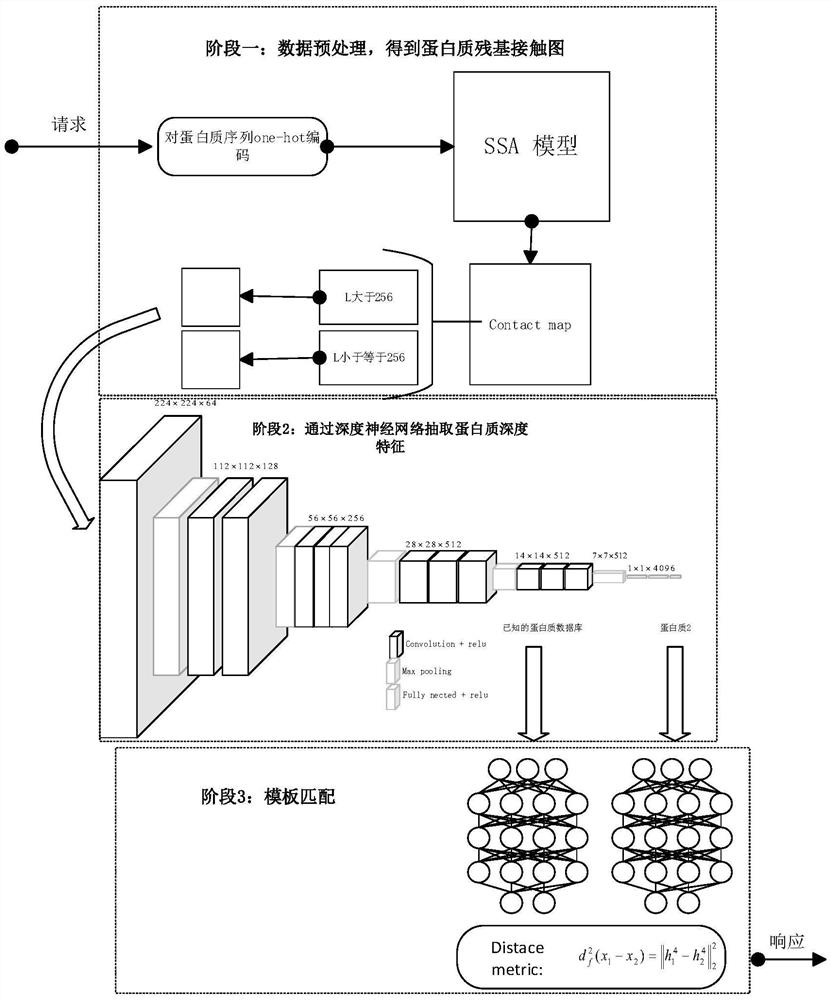
ActiveCN112116950AImprove recognition accuracyHigh precisionNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsAlgorithmProtein Feature
The invention discloses a protein folding identification method based on deep metric learning. The method comprises the following steps of encoding protein to obtain digital expression of a protein sequence, inputting the digital expression of the protein sequence into an SSA model to obtain a potential relational graph of protein residues, and fixing the relational graph to a set size, inputtingthe relational graph into a trained convolutional neural network, and obtaining the output of the previous layer of the classification layer as a depth feature, inputting the depth features into a trained twin network to obtain final protein features, and calculating the Euclidean distance between the query protein and the template protein based on the protein characteristics, and allocating the folding type of the template protein closest to the query protein to the query protein. A twin network is used, so that the distance between protein pairs of the same folding type is closer, and the distance between protein pairs of different folding types is farther.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for enzymatic cross-linking of a protein
InactiveUS20110086014A1Improve accessibilityPrevent precipitationSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsCross-linkEnzymatic hydrolysis
A method for cross-linking albumin for use as a sealant or glue for a biological system, for example to induce hemostasis and / or prevent leakage of any other fluid from a biological tube or tissue, such as lymph for example. The cross-linked albumin may optionally and preferably be applied as part of a bandage for example. In other embodiments, the present invention provides a method of enzymatically cross-linking globular proteins, by altering the structure of the protein to improve the accessibility of the protein to the cross-linking enzyme.
Owner:LIFEBOND
Methods of protein docking and rational drug design
Aspects of the present disclosure relate to computing systems and computational methods for docking a library of compounds against a massive amount of conformations of a protein of interest.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method for determining interaction between proteins based on random projection integrated classification
InactiveCN107607723AResolving Unpredictable Protein InteractionsAddressing Disease-Related QuestionsBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseProtein pair
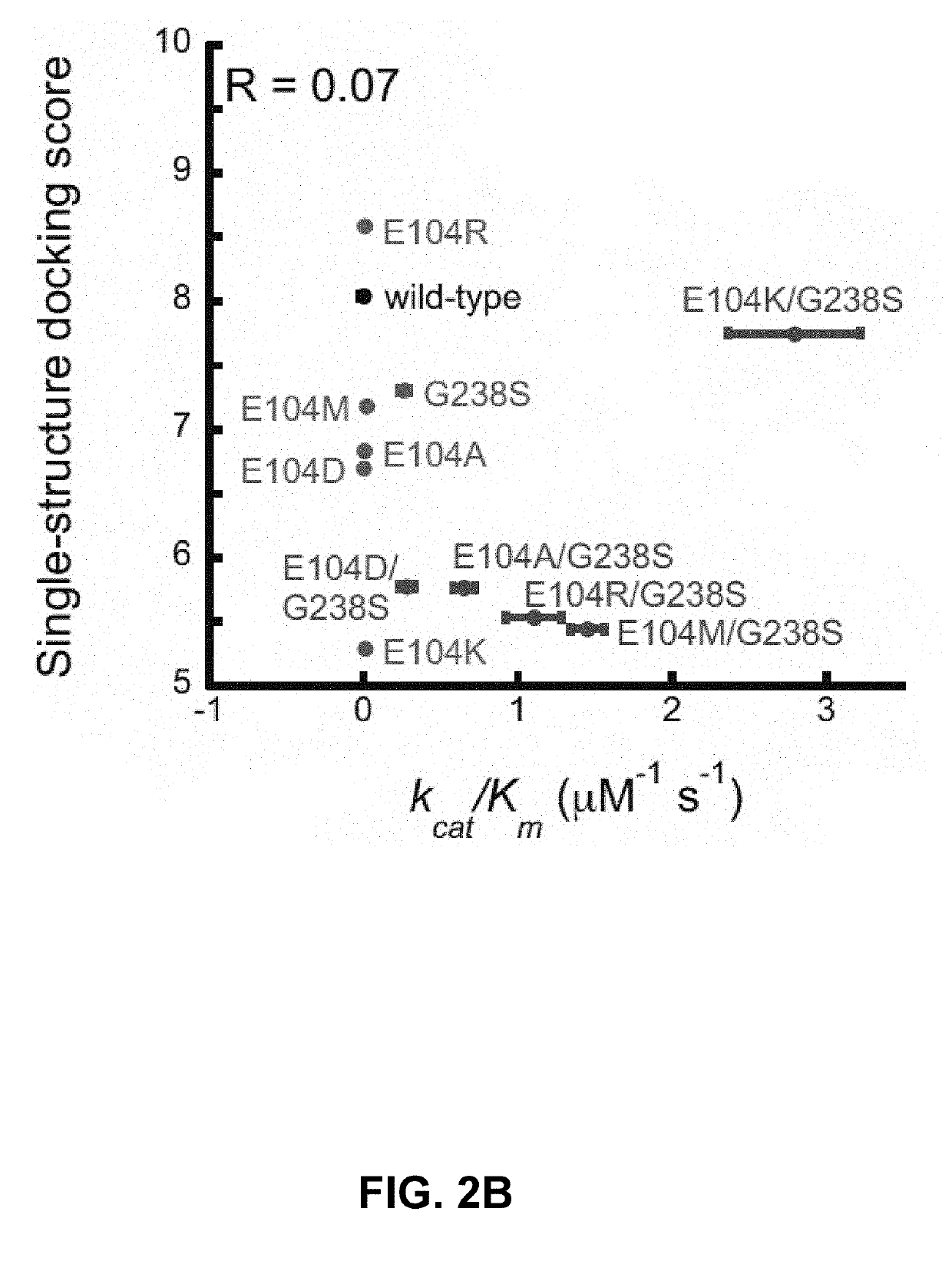
The invention relates to the field of biology and particularly relates to a method for determining the interaction between proteins based on random projection integrated classification. The method comprises A, protein data screening, B, substitution matrix characterization, C, discrete cosine transformation, D, establishment of random projection integrated model and E, model determination. The method can acquire a prediction model of interaction between proteins according to classification characteristics of interaction between proteins and the prediction model is used for detecting interaction between proteins related to diseases so that the problem that the prior art cannot predict interaction between proteins and disease correlation and prediction of interaction between proteins and disease correlation is realized. The method is suitable for screening animal and strain protein pairs, builds a random projection integrated model for later analysis through substitution matrix characterization and discrete cosine transformation and provides accurate effect display and expression. Compared with the traditional method, the method provided by the invention has the better accuracy rate,sensitivity, a positive predictive value and stability and accuracy of Matthews correlation coefficient measurement.
Owner:LANZHOU JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Method of anticipating interaction between proteins
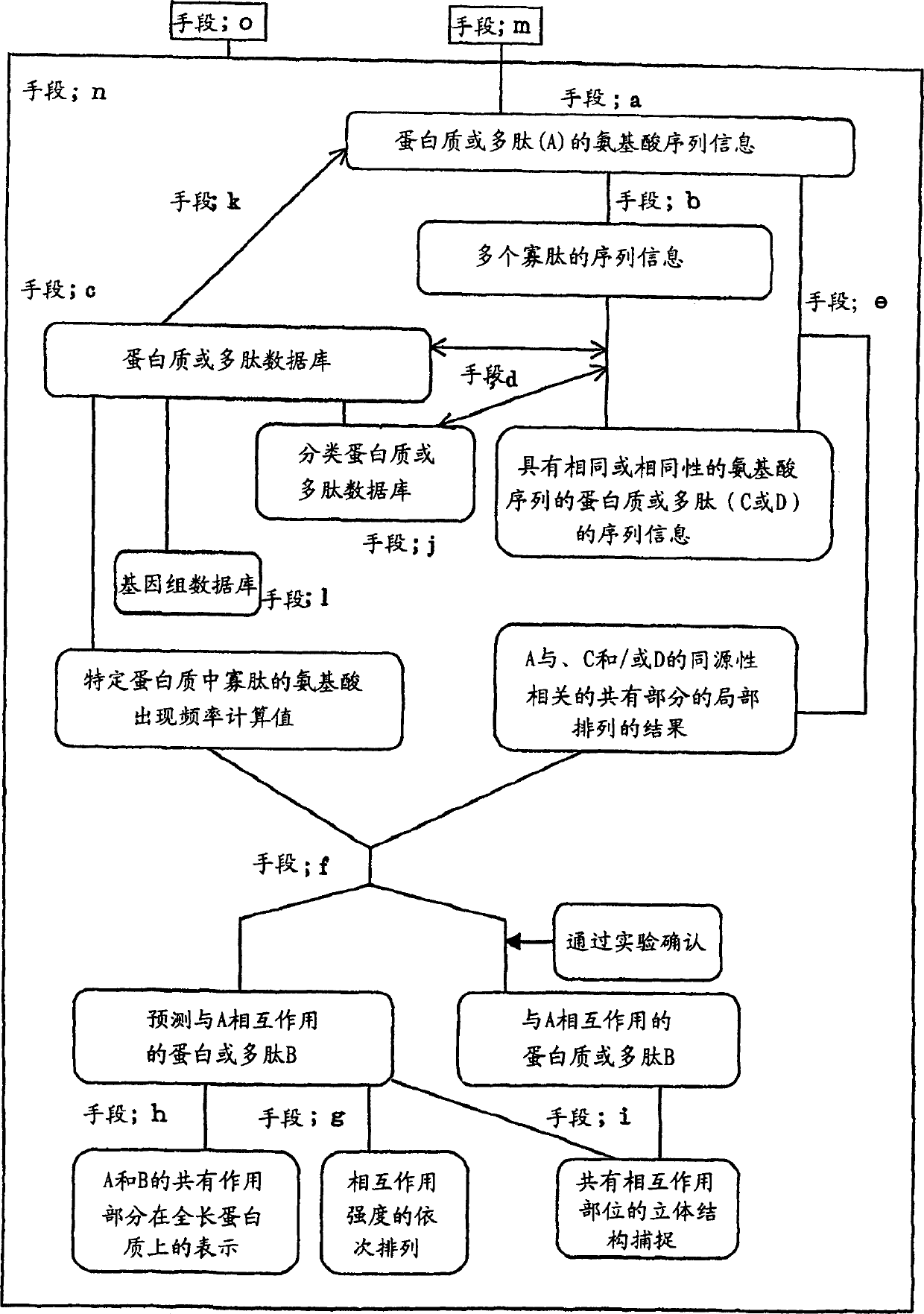
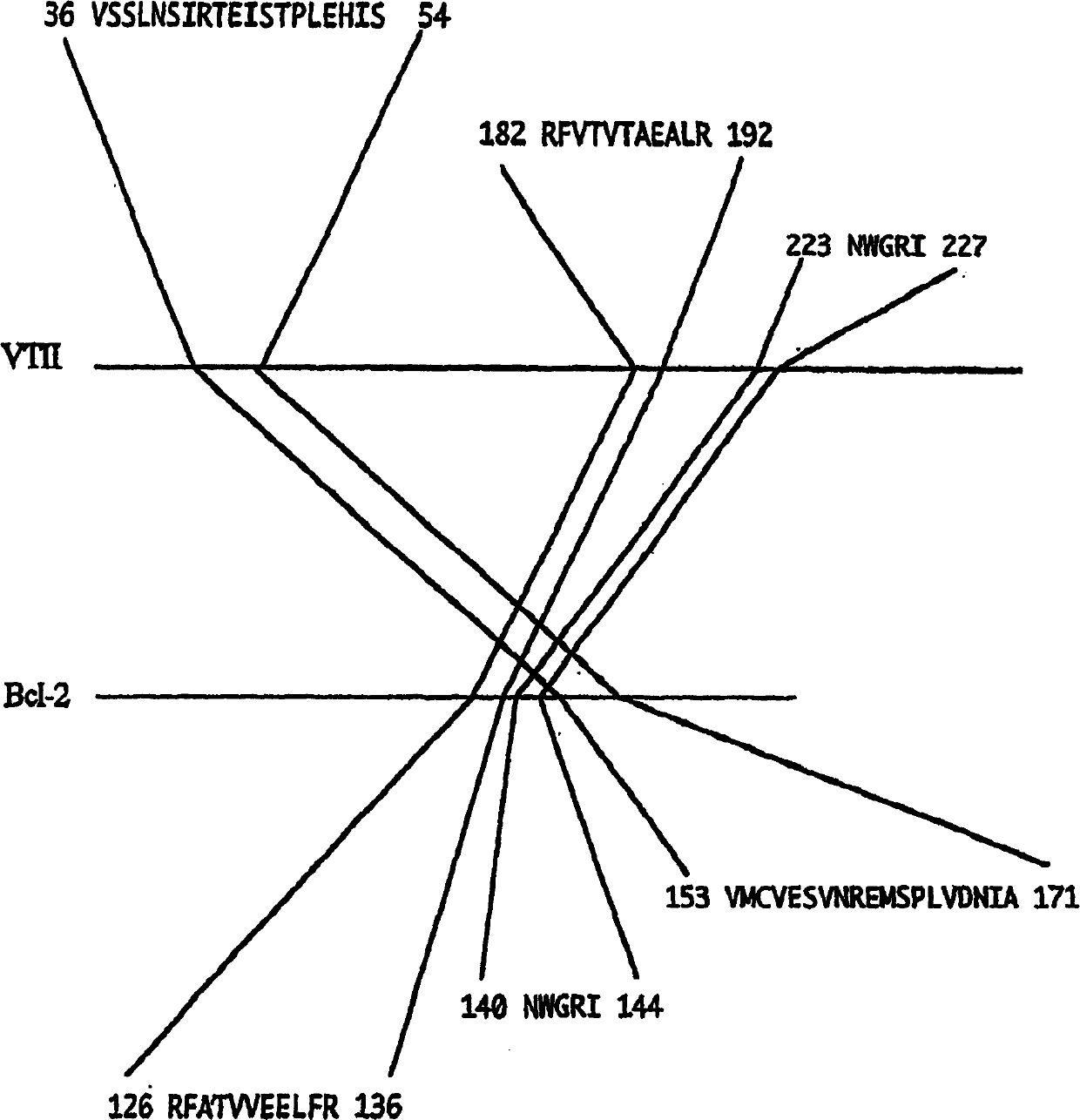
InactiveCN1416549ALibrary screeningPeptide preparation methodsProtein DatabasesAmino acid sequence alignment
The present invention relates a method for predicting a protein or polypeptide (B) that interacts with a specific protein or polypeptide (A), wherein the method is characterized by comprising: 1) decomposing the amino acid sequence of protein or polypeptide (A) into a series of oligopeptides having a pre-determined length as sequence information; 2) searching, within a database of protein or polypeptide amino acid sequences, for a protein or polypeptide (C) comprising an amino acid sequence for each member of the series or for a protein or polypeptide (D) comprising an amino acid sequence homologous to an amino acid sequence for each member of the series; 3) carrying out local amino acid sequence alignment between said protein or polypeptide (A) and the detected protein or polypeptide (C) or detected protein or polypeptide (D); and 4) predicting whether the detected protein or polypeptide (C) and / or protein or polypeptide (D) is a protein or polypeptide (B) that interacts with the protein or polypeptide (A) based on the results of the local amino acid sequence alignment and a value calculated from a frequency of amino acids and / or a frequency of said oligopeptides in said amino acid sequence database; and to a recording medium for carrying out the above method, a device comprising the recording medium, and proteins obtained thereby.
Owner:DAIICHI SEIYAKU CO LTD +1
Labeled protein and method for obtaining the same
InactiveUS20110009601A1Easy to purifyImprove purification effectDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsChemistryProtein target
It is an object of the present invention to obtain a labeled protein, and specifically, to separate a labeled protein and the same unlabeled protein. There is provided a labeled protein including: a protein to be labeled having a target protein, at least one or more affinity interaction domains for binding to an affinity support, and at least one or more labeling sites; and a labeling reagent binding to at least one of the labeling sites; wherein the affinity of the labeled protein for the affinity support is difference from that of the protein to be labeled for the affinity support.
Owner:CANON KK
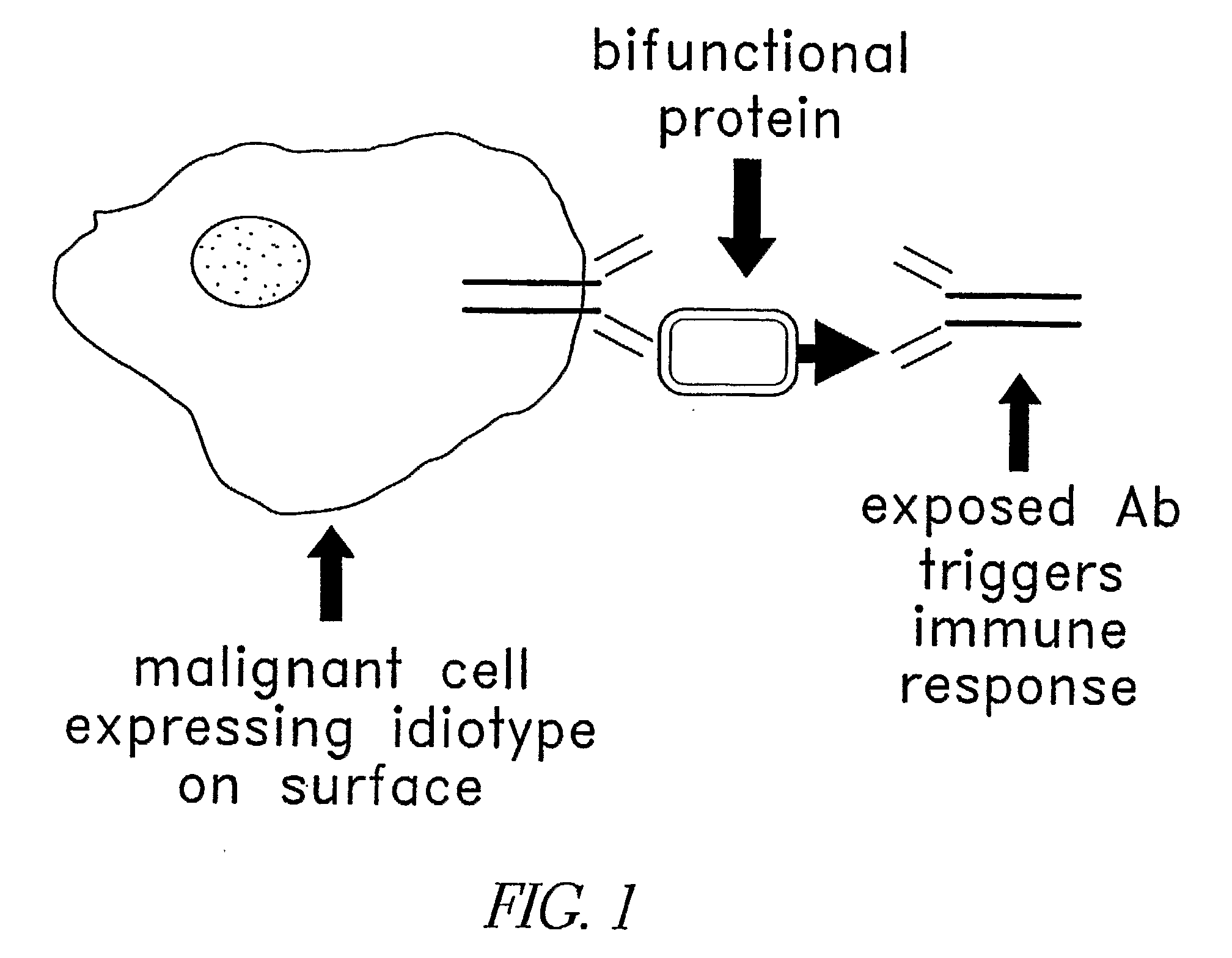
Method for making targeted therapeutic agents
ActiveUS20110212114A1Rapid and efficient identification and isolation and productionEffective and low methodAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDisease markersCross linker
Provided herein are methods and kits for making a targeted therapeutic for treating a disease or condition. The therapeutic agents can be targeted to patient-specific disease markers. In one of these methods, the method includes obtaining a biological sample from a patient having the disease or condition, or who is at risk for developing the disease or condition. In this particular method, the sample includes a population of diseased cells, screening a library comprising proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs to identify mRNA-protein pairs that bind to the diseased cells, isolating one or more proteins from the identified mRNA-protein pairs, and conjugating the isolated protein(s) to a therapeutic agent. Some of the methods further include preparing a library with proteins linked to their cognate mRNAs. In certain of these methods, the preparation of the library includes providing at least two candidate mRNA molecules in which each of the mRNA molecules includes a cross-linker, translating at least two of the candidate mRNA molecules to generate at least one translated protein, and linking at least one of the candidate mRNA molecules to its corresponding translated protein via the cross-linker to form at least one cognate pair.
Owner:PROTEONOVA
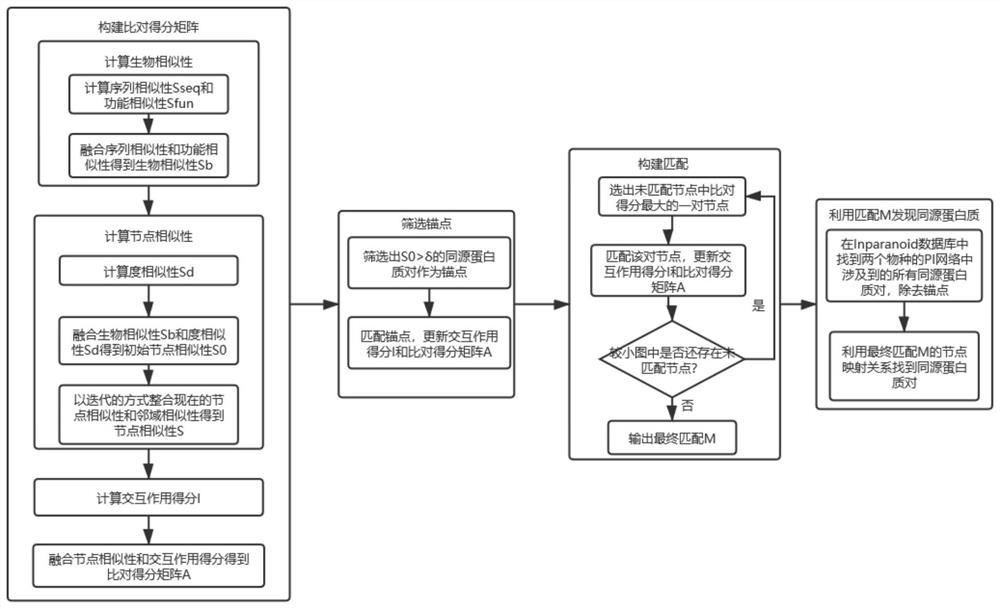
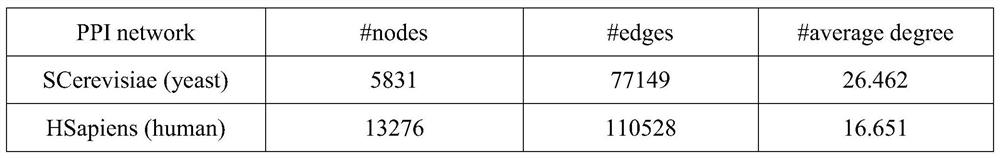
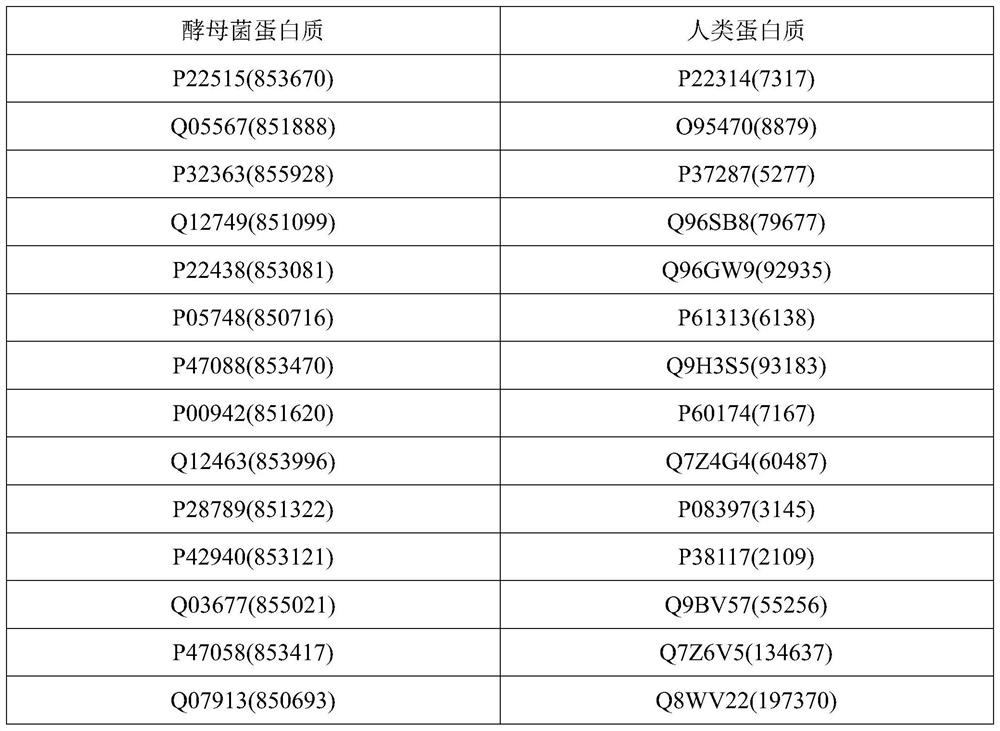
Homologous protein detection method based on biological protein information network comparison
ActiveCN112582027AEasy to integrateQuality improvementSequence analysisSystems biologyProtein detectionBiological studies
The invention discloses a homologous protein detection method based on biological protein information network comparison, and aims to solve the problem of false positive of homologous protein discovered by adopting a traditional sequence-based method, and the problem that the topology quality and the biological function quality of the matching result cannot be well balanced by the existing biological protein information network comparison algorithm. According to the method, the biological similarity, the network structure similarity and interaction information can be well fused, and more homologous protein pairs among different species can be found, so that the method has guiding significance for biologically researching the homologous relationship among the proteins and predicting the proteins with unknown functions.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for improving meat product flavor
InactiveCN111480800AEasy to operateMeet the needs of different tastesFood ingredient as flavour affecting agentAnimal proteins working-upBiotechnologyMonosodium glutamate
The invention relates to application of meat product processing, meat protein glycosylation and flavor regulation. According to the related application, the purpose of regulating and controlling the adsorption capacity of meat protein to flavor substances is achieved through glycosylation with reducing sugar and meat protein are used as raw materials, so that the adsorption capacity of the proteinto flavor substances such as aldehyde, ketone and ester can be enhanced through glycosylation of the meat protein. Compared with the addition of flavor enhancers such as monosodium glutamate, synthetic essence and the like, the method has the characteristics of safety, greenness and health; on the premise of reducing harm to human bodies, the requirements of people for different flavors of meat products can be met, and the method has a theoretical guidance effect on regulating and controlling the adsorption capacity of flavor substances through glycosylation in the processing process of the meat products so as to improve the flavor of the meat products.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
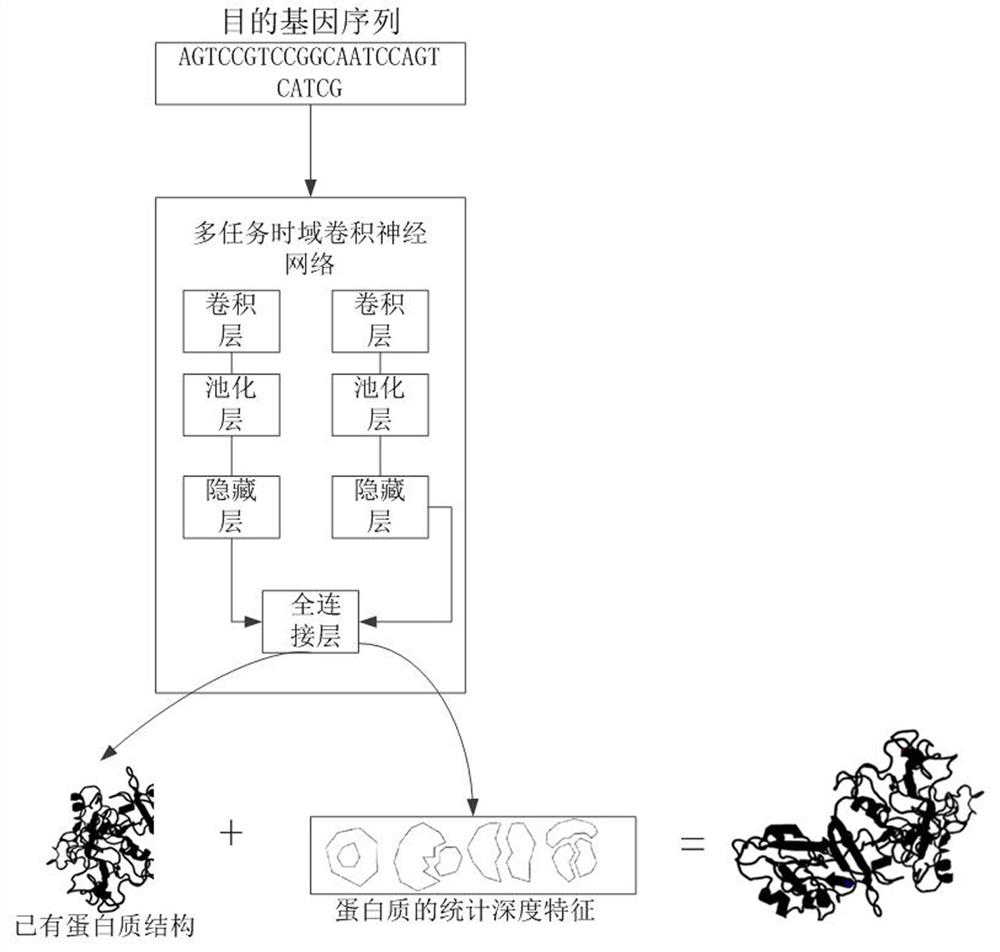
Protein structure prediction method and device based on multi-task time domain convolutional neural network
ActiveCN112289370AReduce dimensionalityReduce complexityBiostatisticsNeural architecturesProtein DatabasesA-DNA
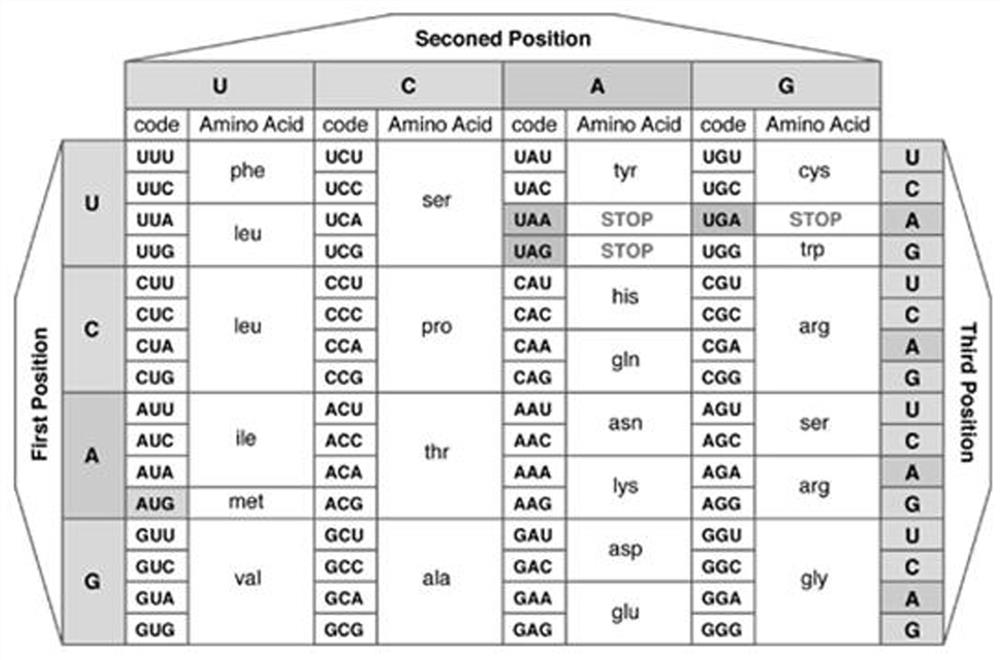
The invention relates to a protein structure prediction method and device based on a multi-task time domain convolutional neural network. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining a target gene sequence and a protein database; establishing a DNA RNAamino acid ternary sequence data set corresponding to each protein according to the genetic code table and a protein database; establishing a multiple regression equation according to the residue depth and physicochemical properties of amino acids in the protein database to obtain statistical depth characteristics of each protein; clustering theternary sequence data set and mapping the ternary sequence data set into a multi-dimensional feature vector; taking the multi-dimensional feature vector and the statistical depth feature of the protein as the input of a multi-task time domain convolutional neural network, and training the multi-task time domain convolutional neural network; and predicting the protein structure by utilizing the statistical depth characteristics of the protein. According to the invention, the statistical depth characteristics of the protein are combined with the multi-task time domain convolutional neural network, so that the complexity of the model is reduced, and the generalization and the fitting degree are improved.
Owner:WUHAN GENECREATE BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD
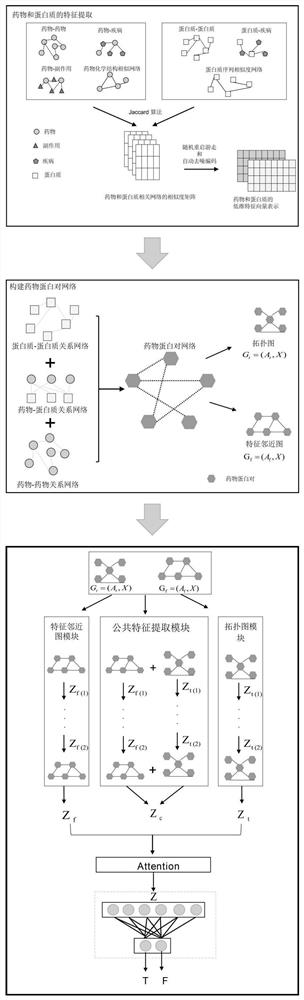
Drug target interaction prediction method based on multi-channel graph convolutional network
ActiveCN112863693AImprove accuracyOvercome the problem of relying on manual feature extractionBiostatisticsDrug referencesPharmaceutical drugProtein Feature
The invention discloses a drug-target interaction prediction method based on a multi-channel graph convolutional network, and belongs to the technical field of drug-target relationship prediction. According to the method, the problem that the accuracy of drug target interaction prediction is poor due to the fact that the existing method depends on inaccurate features extracted manually is solved. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a drug protein pair network according to an obtained drug feature matrix and an obtained protein feature matrix, performing feature extraction on a topological relation between drug protein pairs in the drug protein pair network and a proximity relation between drug protein pair features by adopting a multichannel graph convolutional network, and obtaining topological relation embedding and feature proximity relation embedding; processing topological relation embedding and feature proximity relation embedding to obtain common embedding; and finally, fusing topological relation embedding, feature proximity relation embedding and common embedding through an attention mechanism, and inputting a fusion result into a multi-layer perceptron to predict the drug target relation. The method can be applied to prediction of the relationship between the drug and the target.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
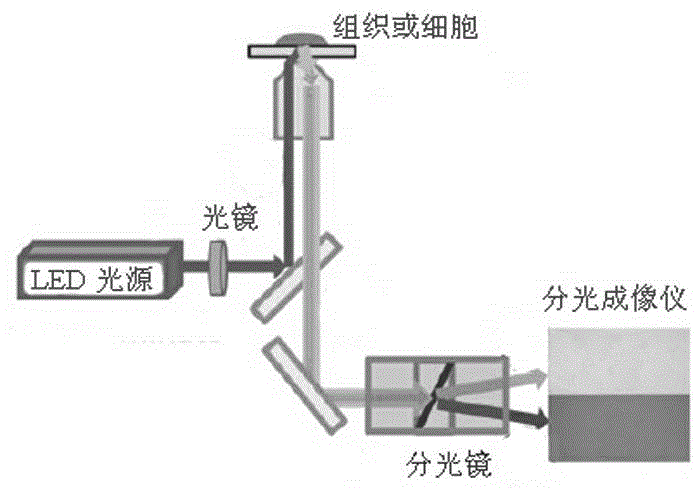
Preparation and application of real-time living cell structural mechanics fluorescent detection probe real-time living cell structural mechanics detection method and application of the method
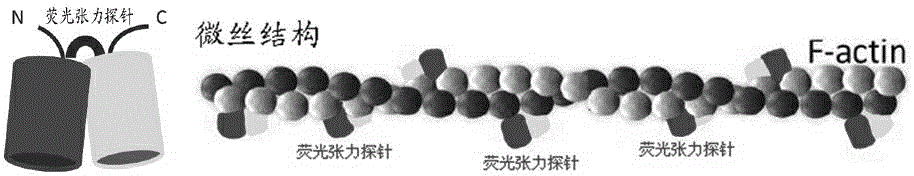
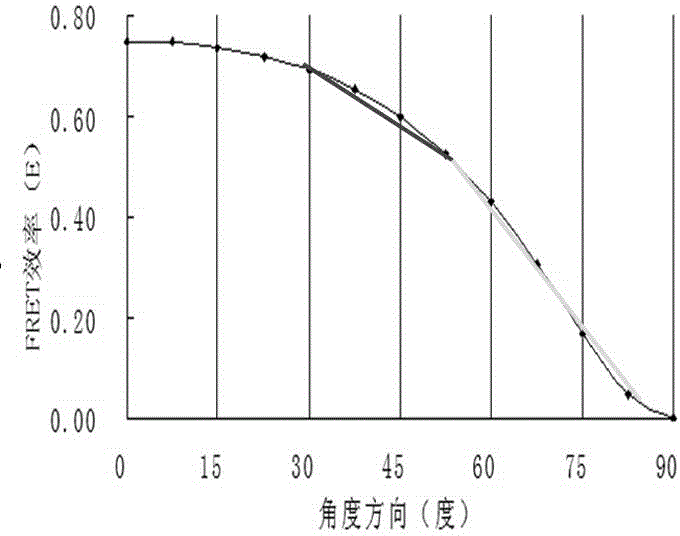
InactiveCN104634769ARealize continuous observationBreaking through the limitations of surface mechanics testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsProtein pairBio engineering
The invention relates to a real-time living cell structural mechanics detection method and application of the method, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: selecting fluorescent protein pairs capable of being subjected to fluorescence resonance energy transfer, connecting the protein pairs to angle positions by using short peptide chains, and constructing a mechanical detection probe by utilizing the fluorescence resonance energy transfer caused by the angle change of the protein pairs; and integrating the probe into the cell skeleton proteins by adopting a molecular cloning method and by connecting the probe with a skeleton protein. The fluorescence energy transfer is detected, so that the mechanical change of cell skeleton transfer can be estimated. The lengths of short peptide chains are changed, the initial angles of the protein pairs can be regulated, the sensitivity of the fluorescence probe is improved, and research on a mechanism related to the cell structure mechanics is effectively realized. The improved probe has the detection characteristics of slight influence on a culture medium, rapidness, micro amount, sensitivity, accuracy and high flux and can be used for constructing a cell platform for screening drugs related to the cell structure mechanics.
Owner:郭军
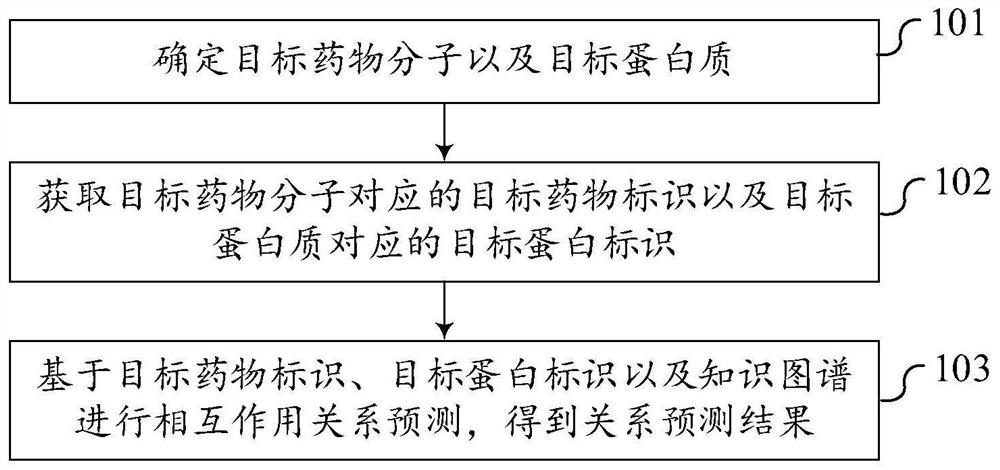
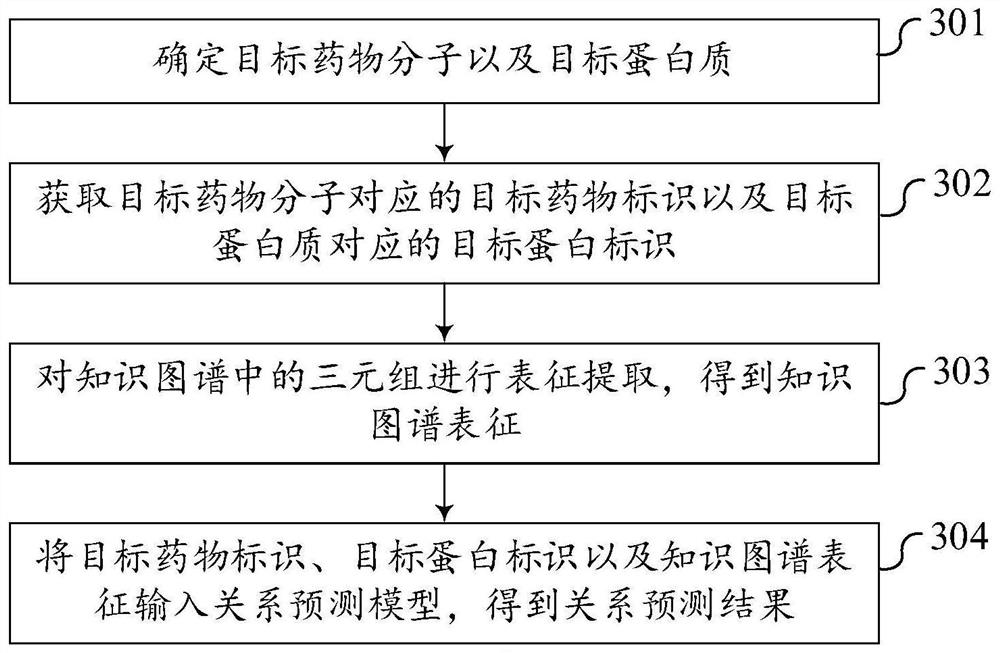
Drug target relationship prediction method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN113470741AImprove forecast accuracyRich sourcesBiostatisticsKnowledge representationDrug protein interactionsProtein target
The embodiment of the invention discloses a drug target relationship prediction method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of machine learning. The method comprises the following steps: determining a target drug molecule and a target protein; obtaining a target drug identifier corresponding to the target drug molecule and a target protein identifier corresponding to the target protein; and performing interaction relationship prediction based on the target drug identifier, the target protein identifier and the knowledge graph to obtain a relationship prediction result. At least one kind of omics data is introduced, the knowledge graph is formed in combination with the known drug target interaction pair, and drug target relationship prediction is performed based on the knowledge graph, so that information sources of relationship prediction are enriched, the defect that relationship prediction is performed only by depending on known prior knowledge such as drug protein interaction is overcome, and the prediction accuracy of the correlation between the drug molecules and the proteins is improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
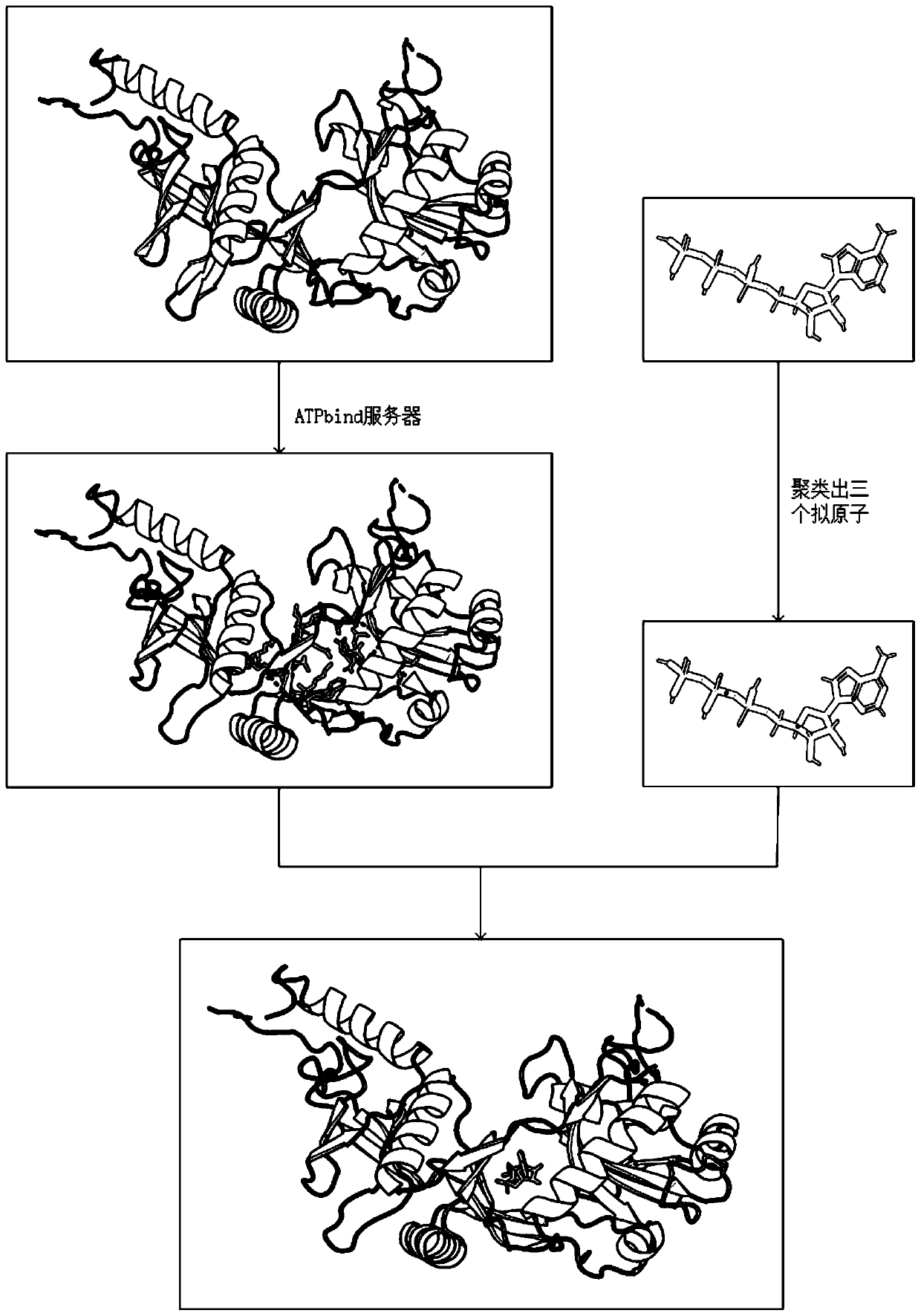
Differential evolution-based protein ATP docking method
ActiveCN110197700AImprove forecast accuracyReduce computational costBiostatisticsArtificial lifeSpatial structureComputer science
Disclosed is a differential evolution-based protein ATP docking method. First, an ATPbind server is used to predict protein-ATP binding residue information, which improves the prediction accuracy of acomplex molecular spatial structure. Then, the original protein-ATP structure prediction problem is transformed into an optimal problem of searching for the optimal individual through the design of the individual population, which reduces the computational cost. Finally, by the differential evolution algorithm is used to search for the optimal individual, which improves the prediction accuracy ofthe protein-ATP complex structure. The invention provides a differential evolution-based protein ATP docking method with low computational cost and high search efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
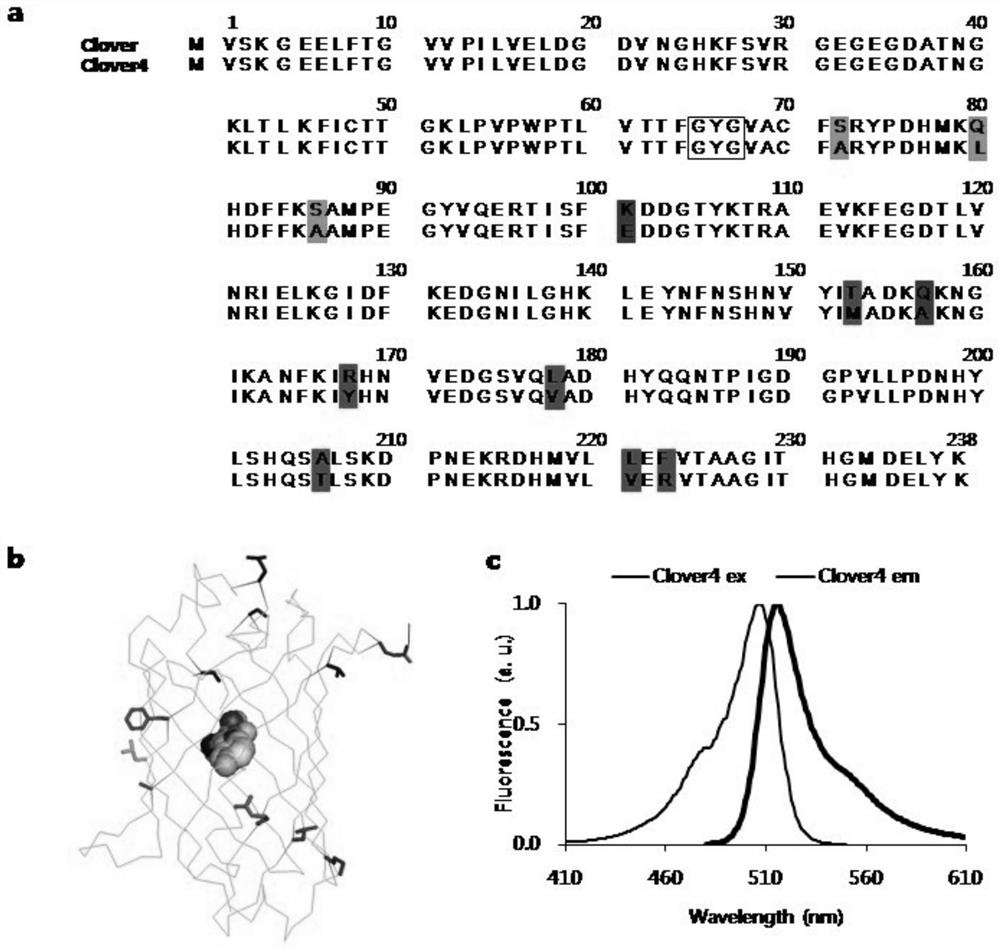
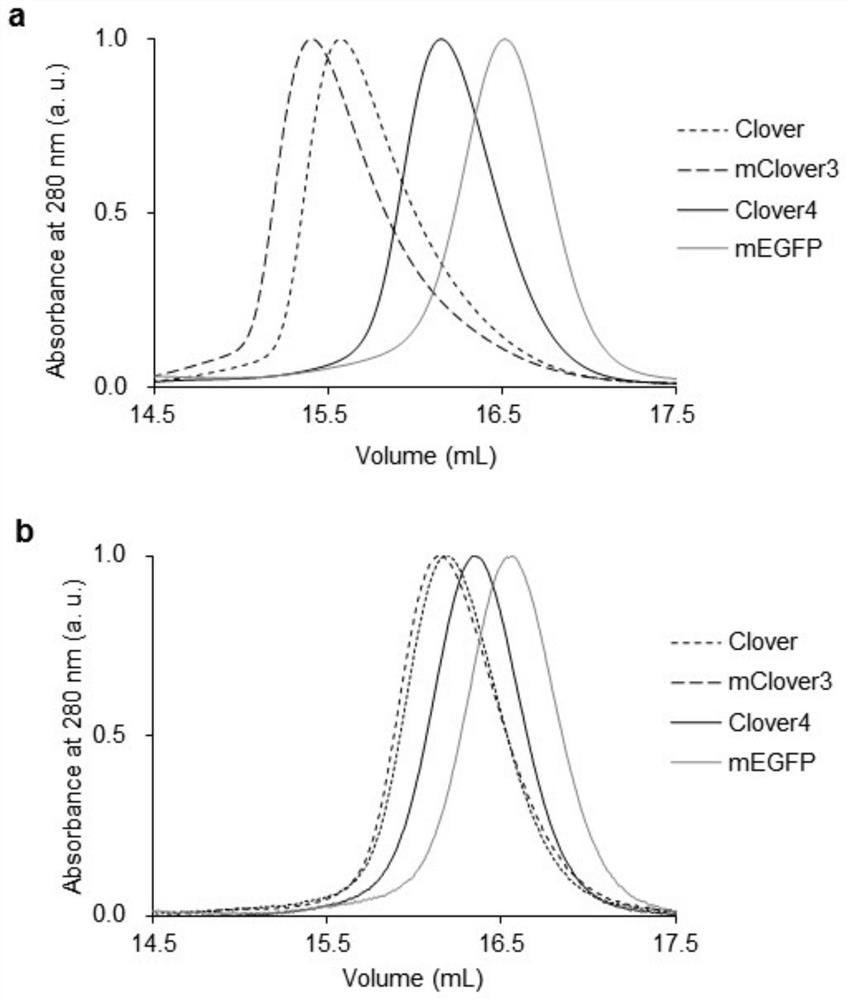
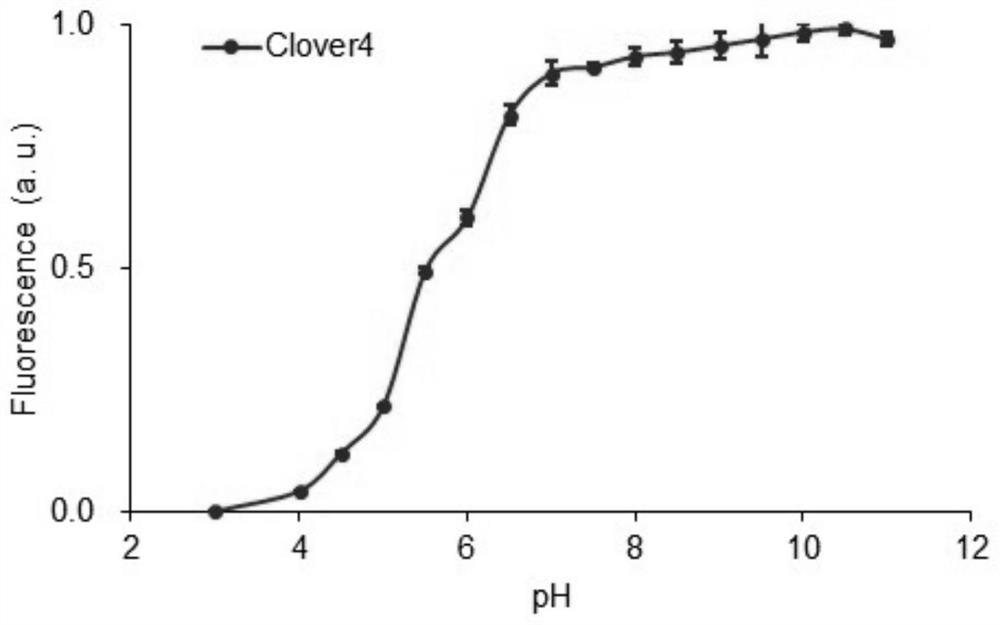
Green fluorescent protein Clover4, probe derived from green fluorescent protein Clover4 and based on bioluminescence resonance energy transfer and application of green fluorescent protein Clover4
ActiveCN113201058AIncrease brightnessImprove monotonyBiological testingGenetic engineeringProtein pairFluorescent protein
The invention relates to a green fluorescent protein Clover4, a probe derived from green fluorescent protein Clover4 and based on bioluminescence resonance energy transfer and application of green fluorescent protein Clover4 In particular, the invention discloses a green fluorescent protein Clover 4, and compared with an amino acid sequence of Clover, an amino acid sequence of the green fluorescent protein has 11 mutation sites. The invention discloses a protein pair containing the green fluorescent protein and used for bioluminescence resonance energy transfer detection and a probe based on bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. After the green fluorescent protein is used for a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer probe, the detection limit is reduced, the detection sensitivity is improved, the detection dynamic range is widened, an antibody can be detected in a lower-concentration antibody environment, and early diagnosis is facilitated.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Use of reg4 and pharmaceutical composition thereof
InactiveUS20130244954A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical drugTherapeutic effect
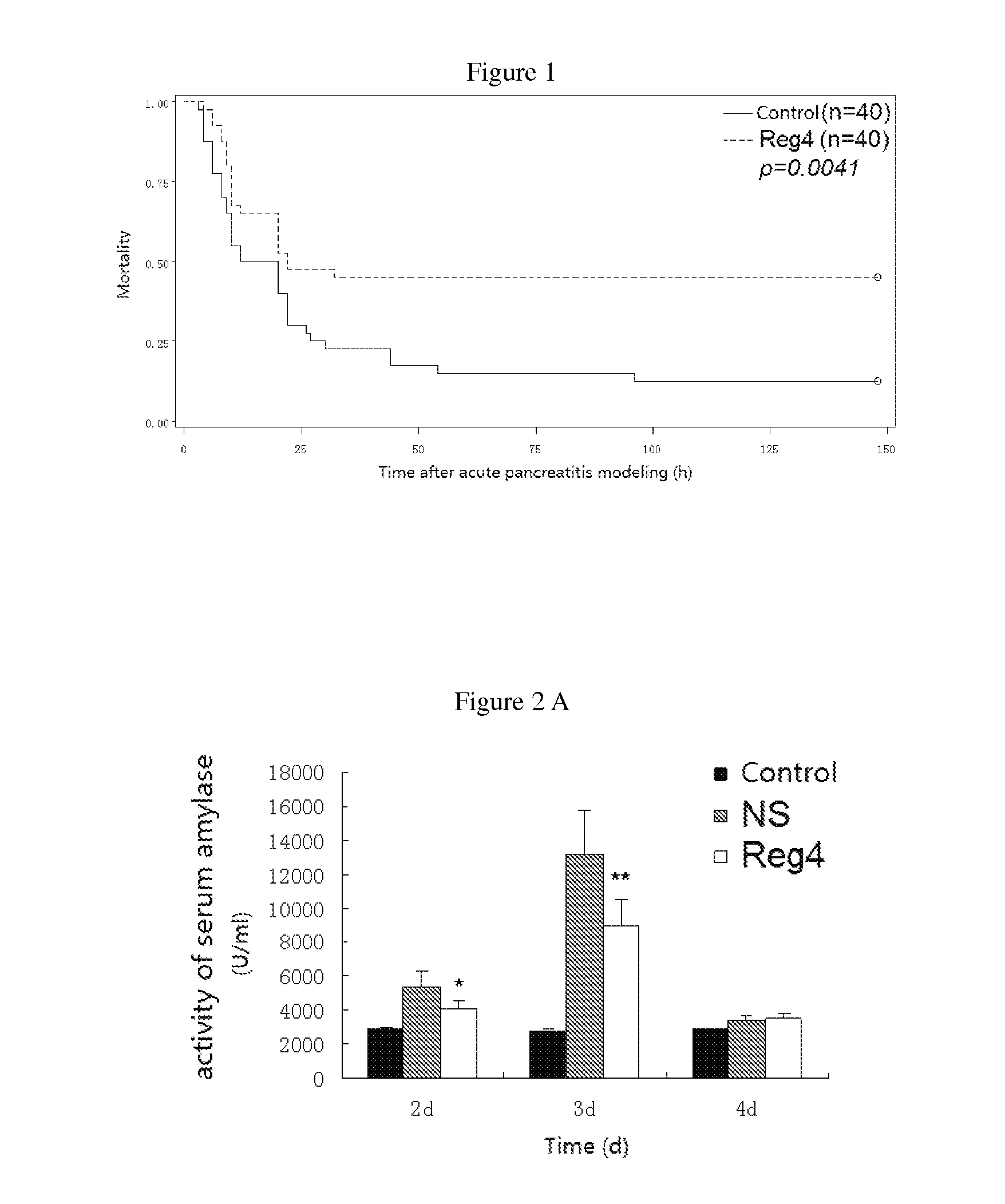
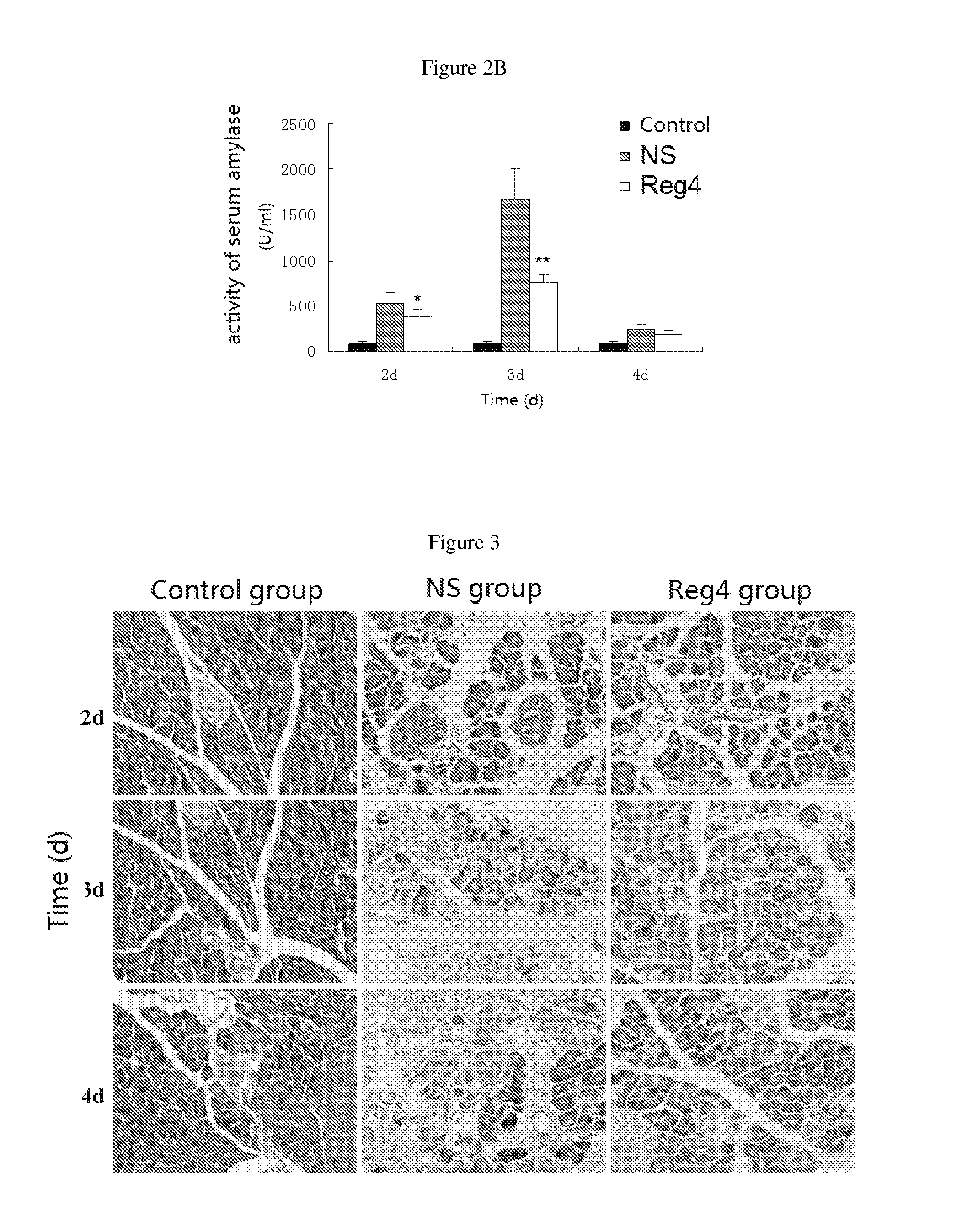
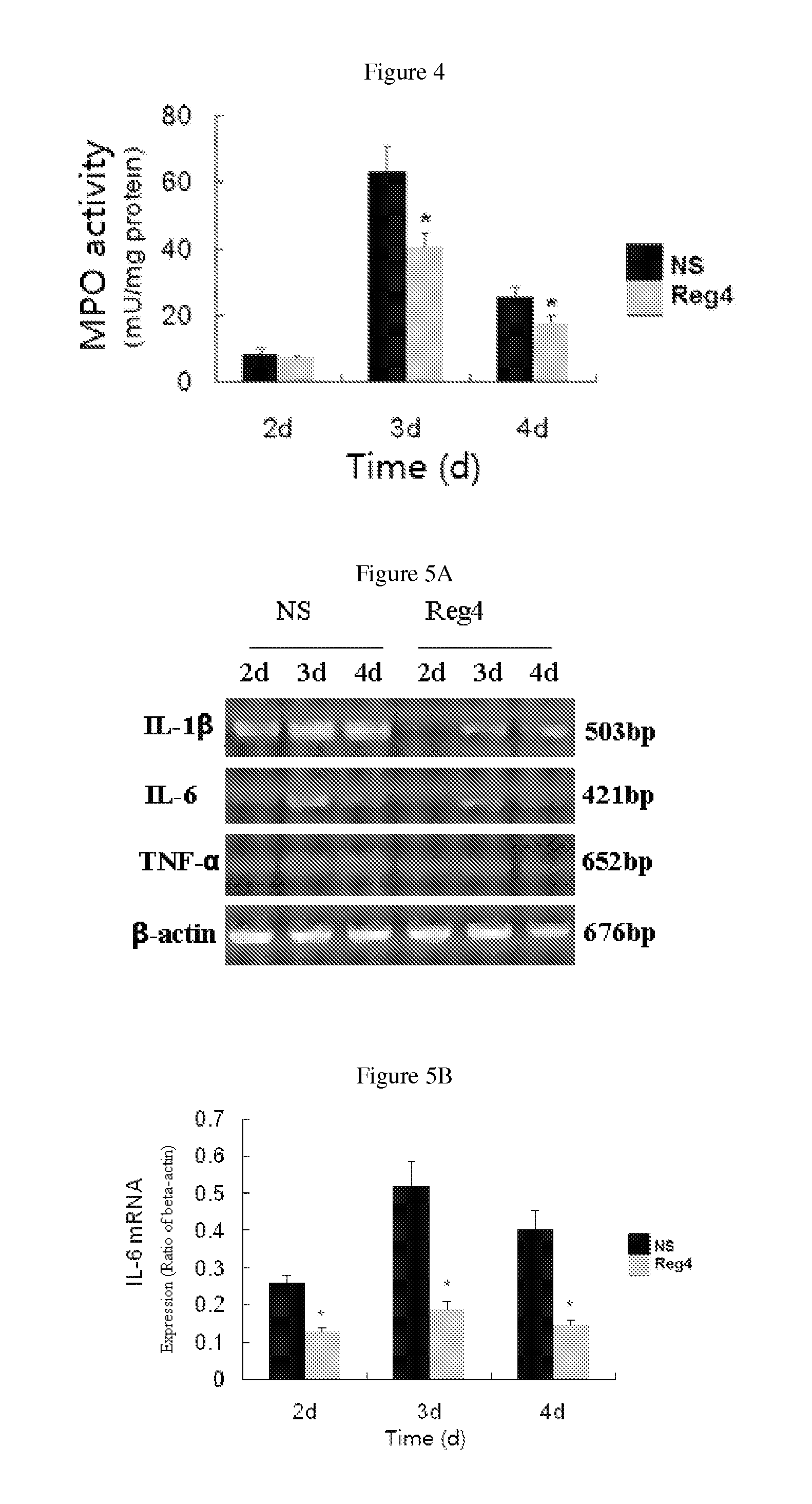
The invention is in the field of biotechnology. Specifically it describes the application and pharmaceutical composition of Reg4. The invention describes the applications of the protein as following in (a) or (b) in preparing drugs for treating acute pancreatitis: (a) the protein whose amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, or bioactive fragments, or analogs; (b) the proteins whose amino acid sequence have at least 70% homology comparing with amino acid sequence described in (a) and have activity for treating acute pancreatitis. The protein described in this invention treats acute pancreatitis effectively and may provide new therapy for treating acute pancreatitis clinically.
Owner:SHANGHAI WUYANG BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
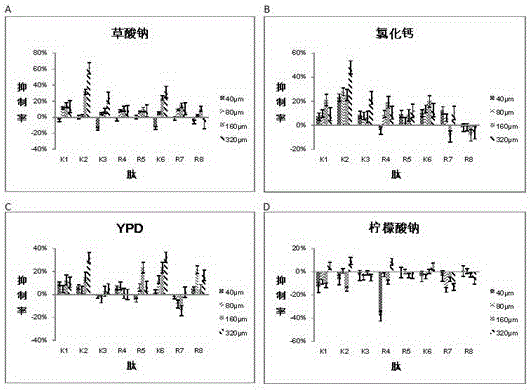
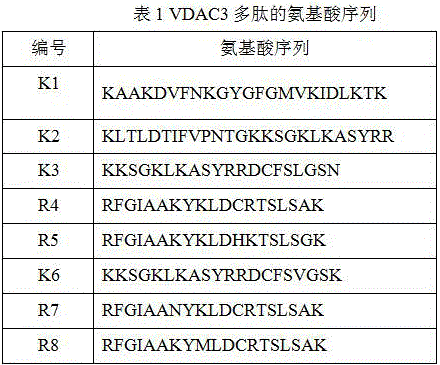
Application of VDAC protein to cell growth inhibition by utilizing oxalic acid or calcium salt and earthquake prediction
InactiveCN106432461AAccurate forecastPrevention and Mitigation of Natural DisastersAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsWater birdEarthquake prediction
According to the invention, the affinity of VDAC3 protein on oxalic acid or calcium salt is proved by experiments. The calcium concentration can be reduced due to formation of organic acid calcium, such as calcium oxalate and the like, and related phenomena, such as spasm and the like, can be caused by reduction of the calcium concentration and the hard and insoluble organic acid calcium salt. Continental or offshore earthquake can be predicted accurately according to inhibition behavior activities and abnormal phenomena that animals suffer from spasm, refuse food, cannot stand and are easy to capture, water birds refuse to go in the water, and seabirds fear spasm and fly towards the mainland; therefore, the invention also provides application of the VDAC3 polypeptide to earthquake prediction, and a simple, convenient and effective earthquake prediction method is established and has great benefit of preventing and reducing natural hazard in the country and even the world.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
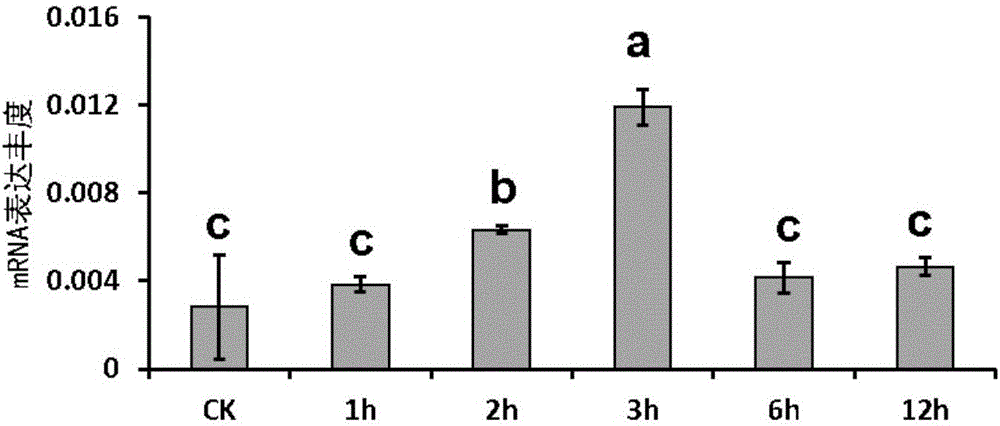
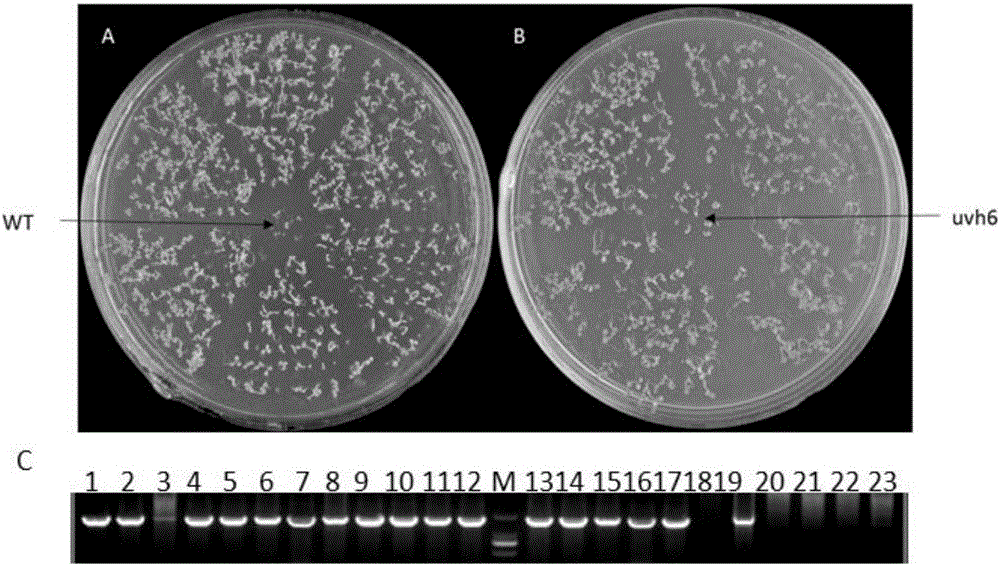
Plant heat resistance related protein TaXPD and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106317214AImprove heat resistanceIncreased Breeding Heat TolerancePlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceGMO Plants
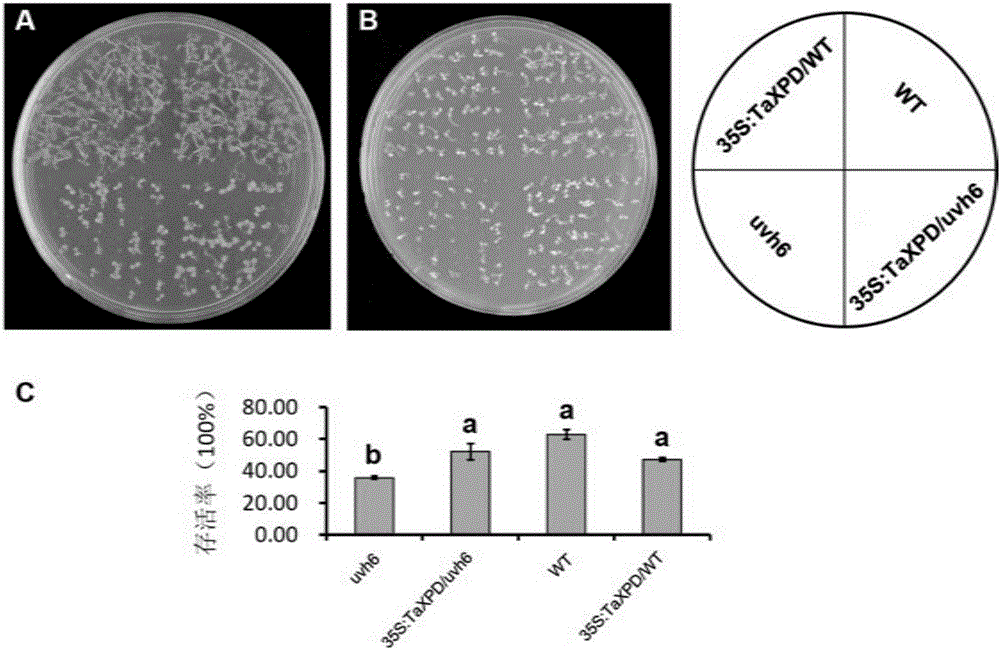
The invention discloses plant heat resistance related protein TaXPD and coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is a1) or a) or a3: a) amino acid sequence and is a protein as shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table; a) is fusion protein which is obtained by connecting label to an end N or / and an end C of the protein as shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table; and a3) is protein which is related to plant heat resistance and is obtained by substitution and / or deficiency and / or addition of one or several amino acid residues of the protein as shown in a1) or a2). Experiments prove that the coding gene of the protein is guided into an arabidopsis mutant uvh6-1 to obtain a transgenic plant of which the survival rate is increased and / or the extension length of a hypocotyledonary axis is increased and / or the ion leakage rate is reduced. Therefore, the protein provided by the invention has important theoretical significance and practical value on cultivation of plants of which heat resistance are improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com