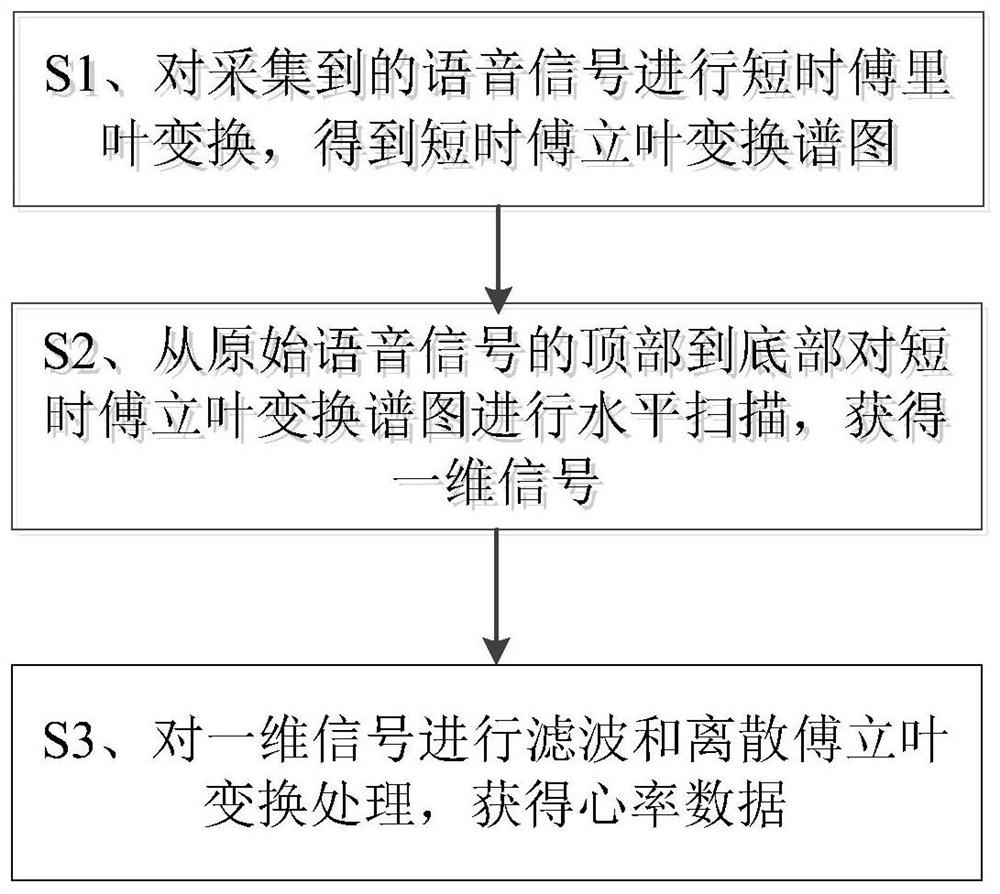
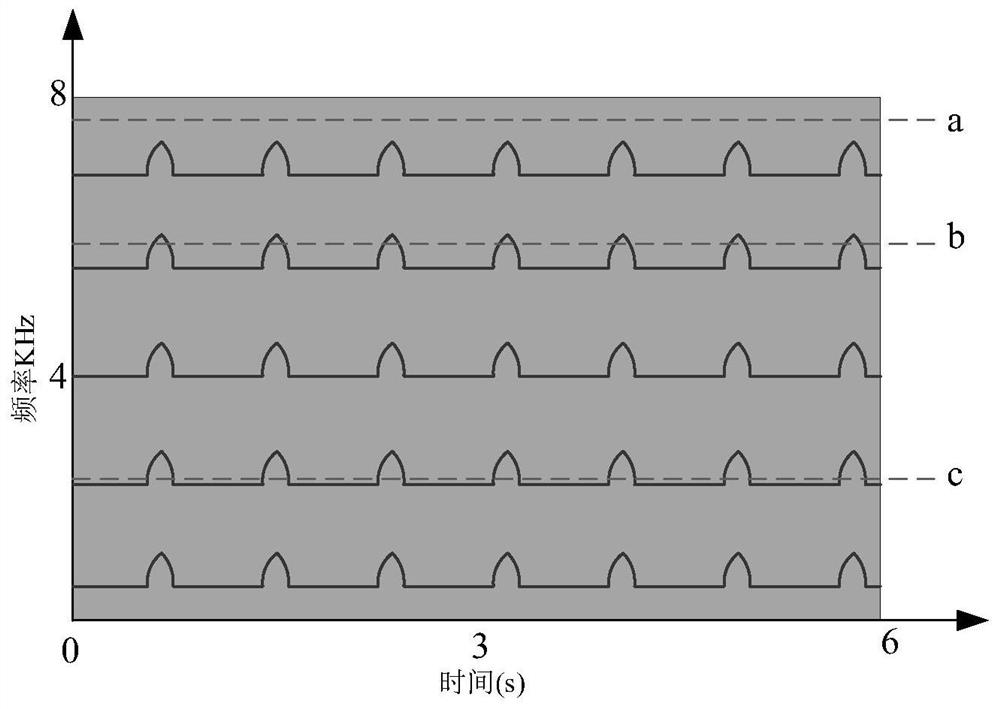
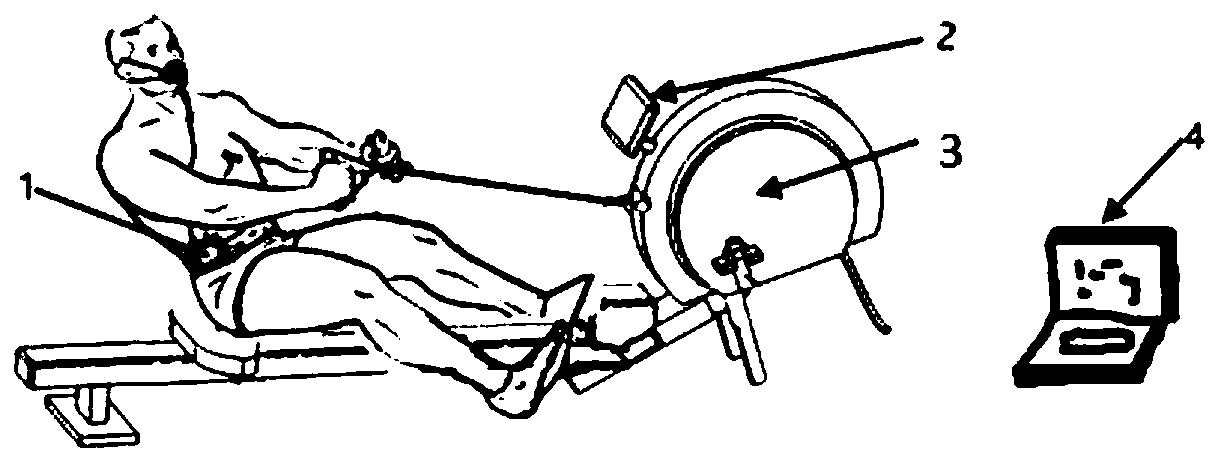
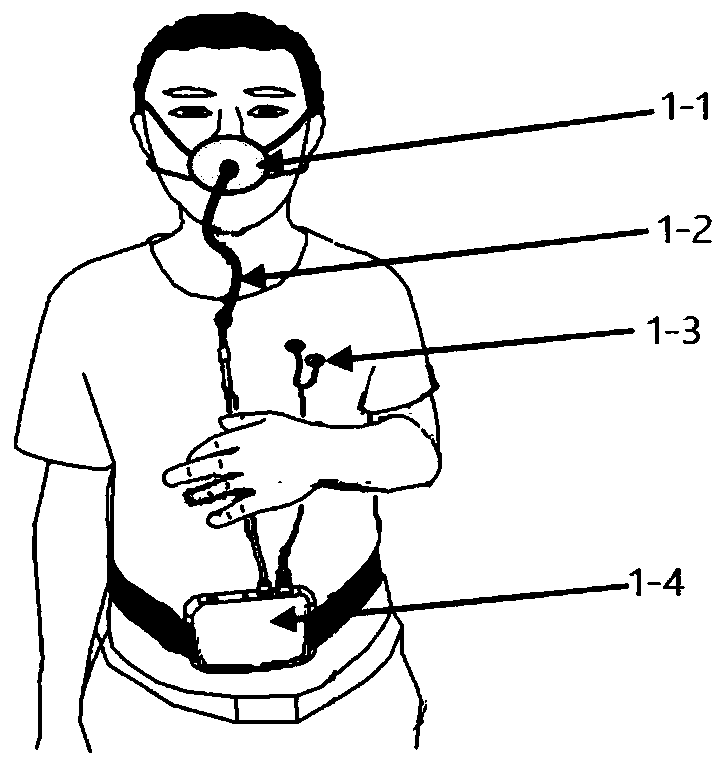
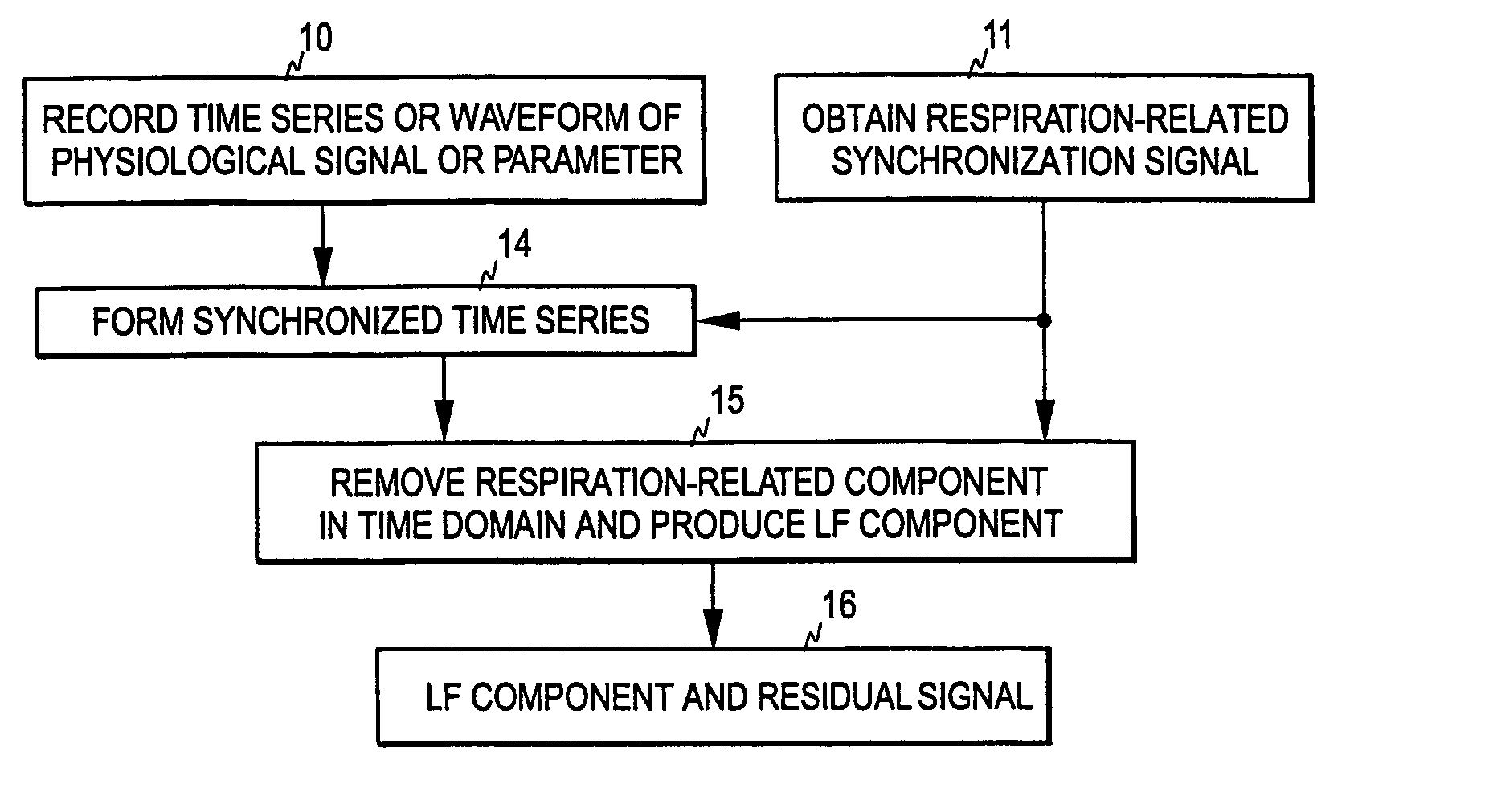
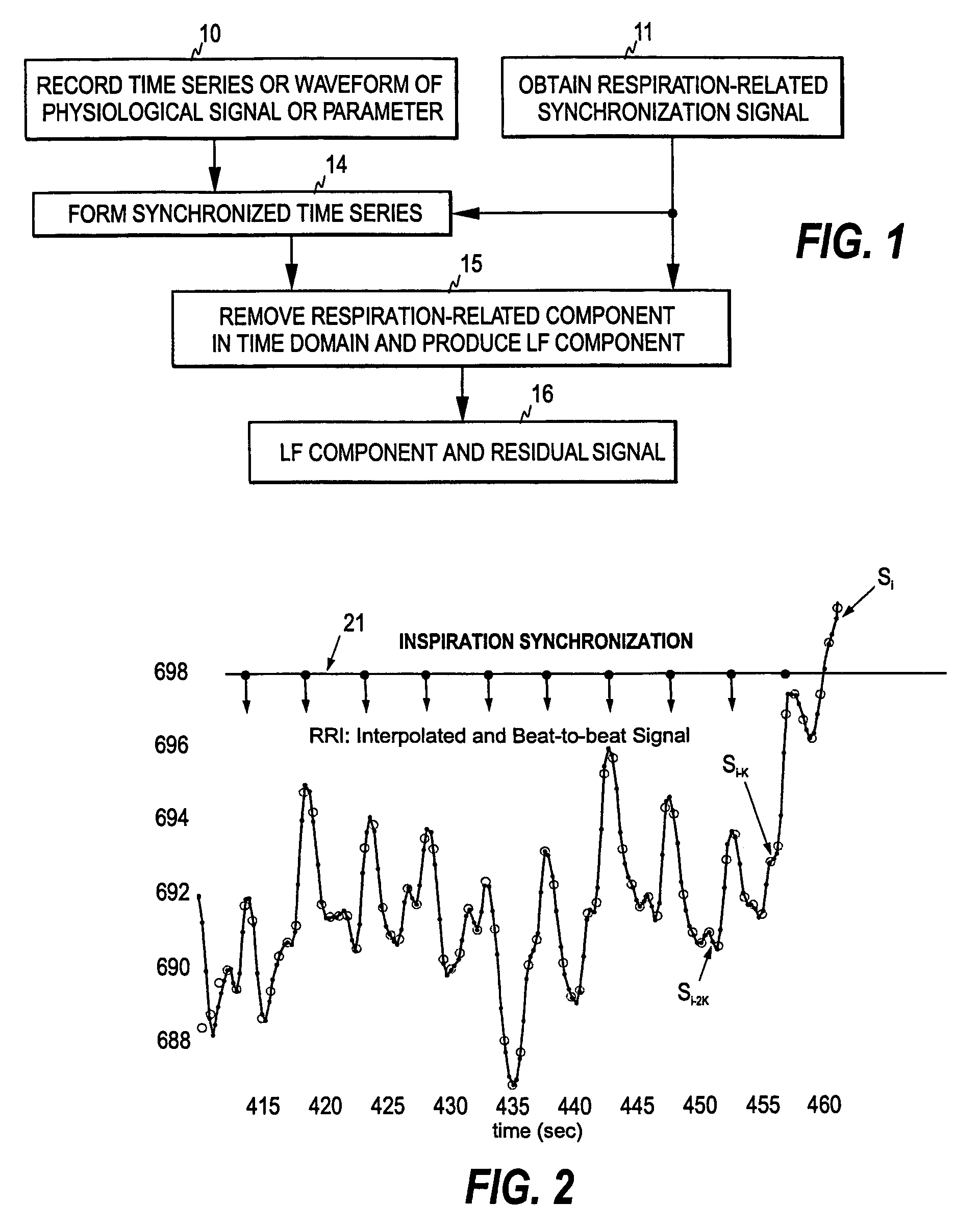
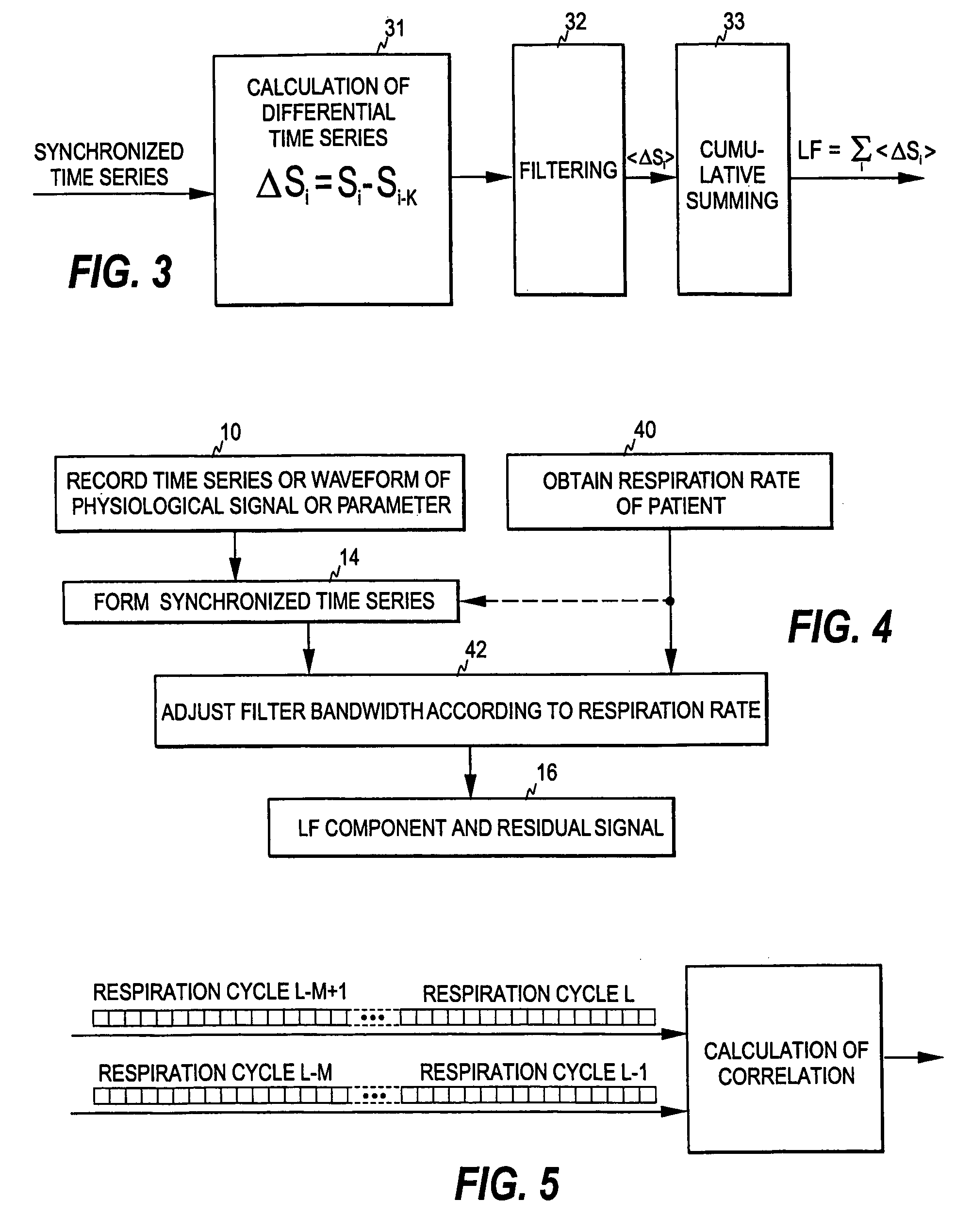
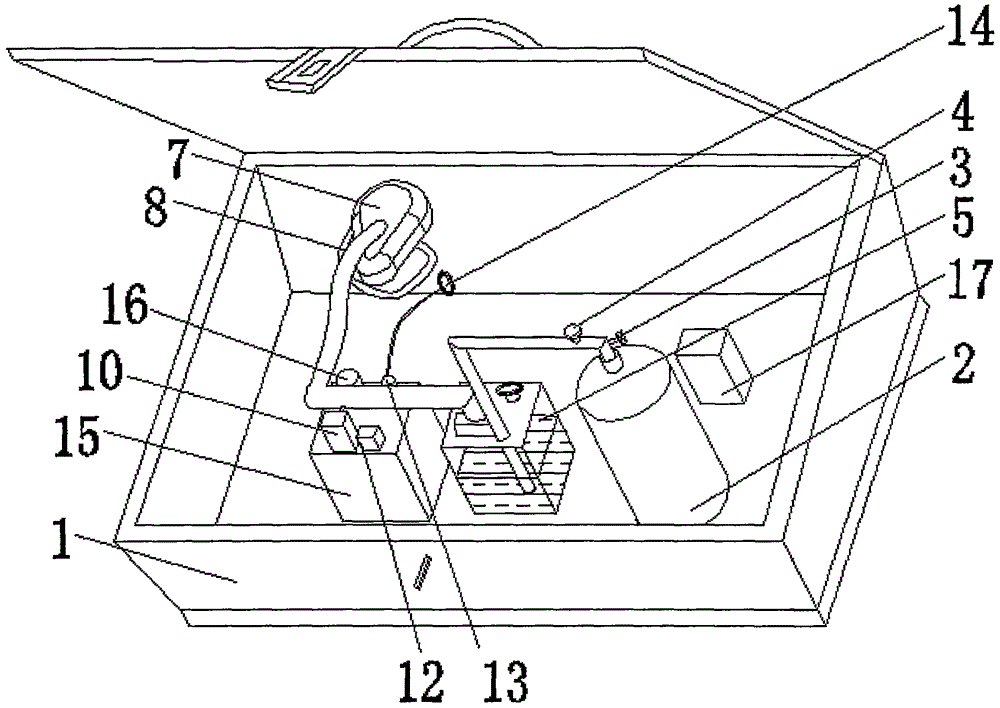
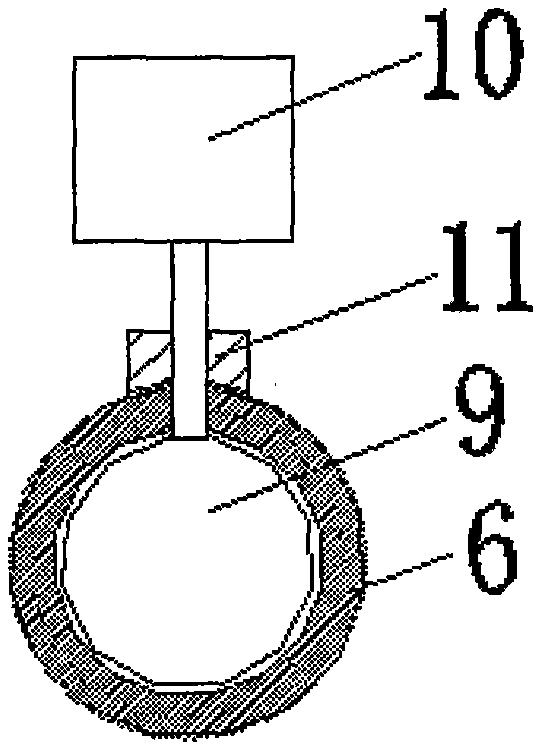
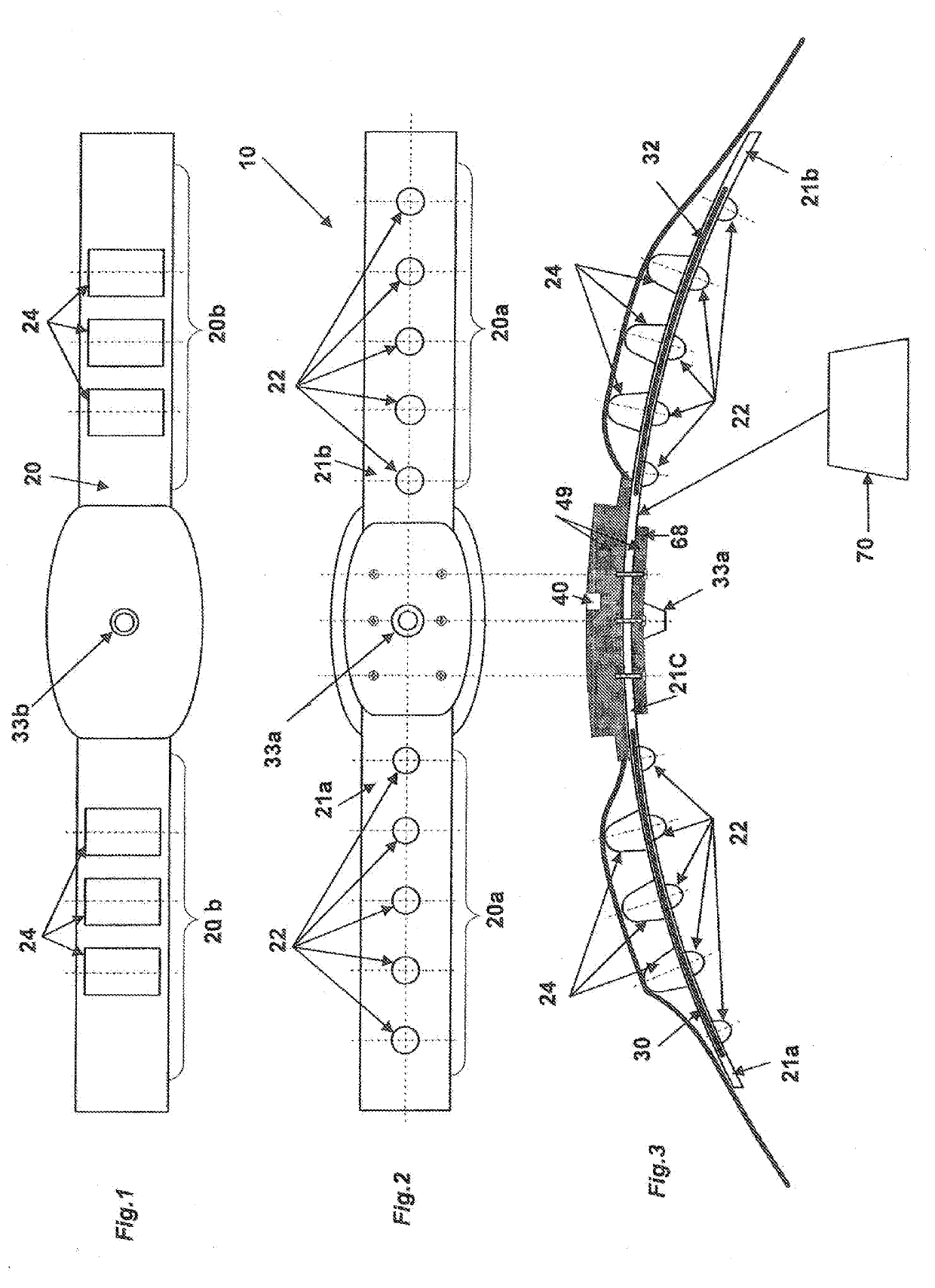
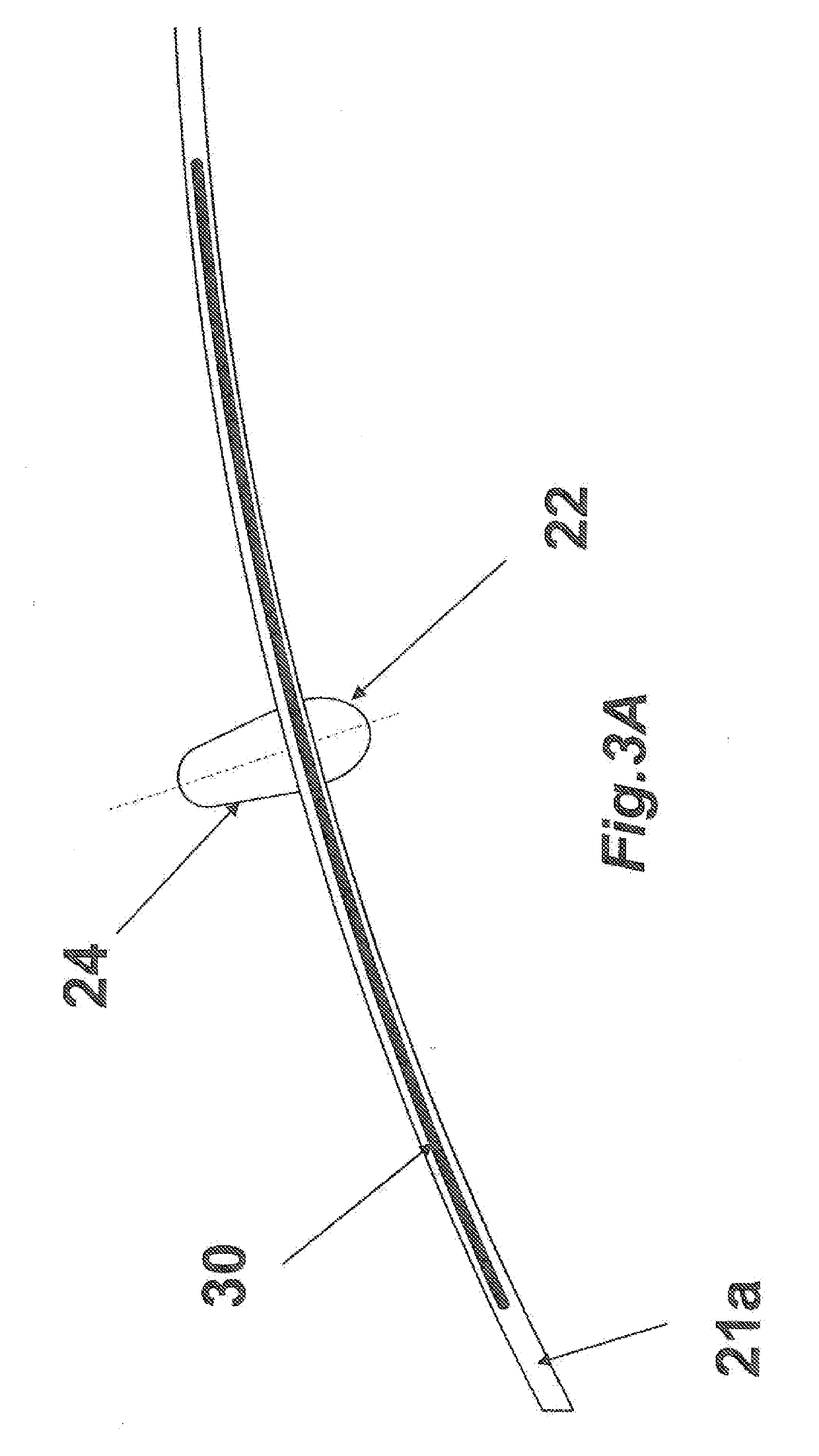
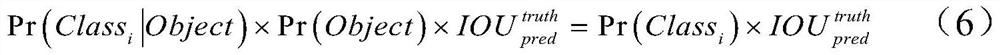Patents
Literature
93 results about "Respiration rhythm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Respiratory rhythm. a regular, oscillating cycle of inspiration and expiration, controlled by neuronal impulses transmitted between the respiratory centers in the brain and the muscles of inspiration in the chest and diaphragm.
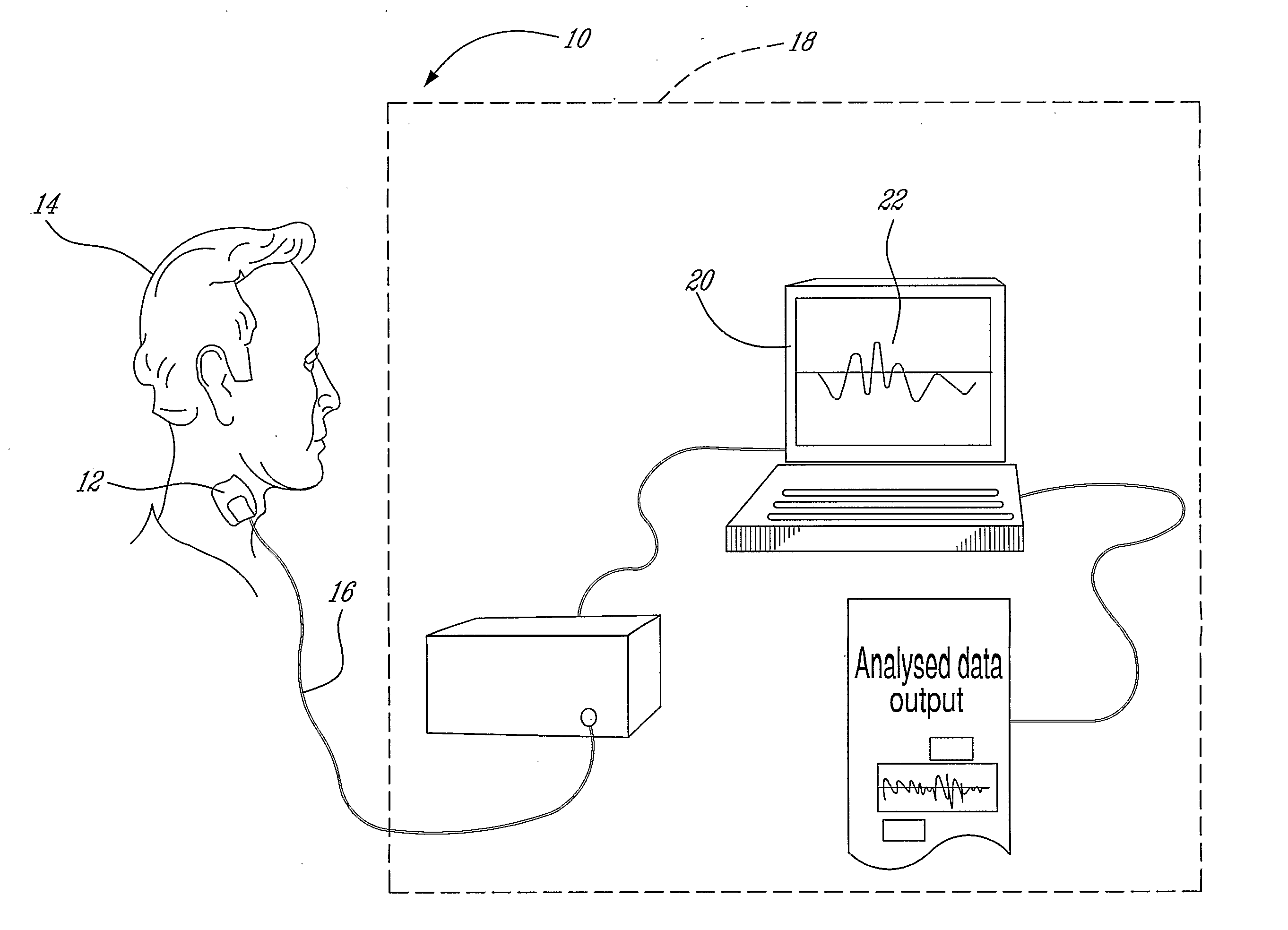
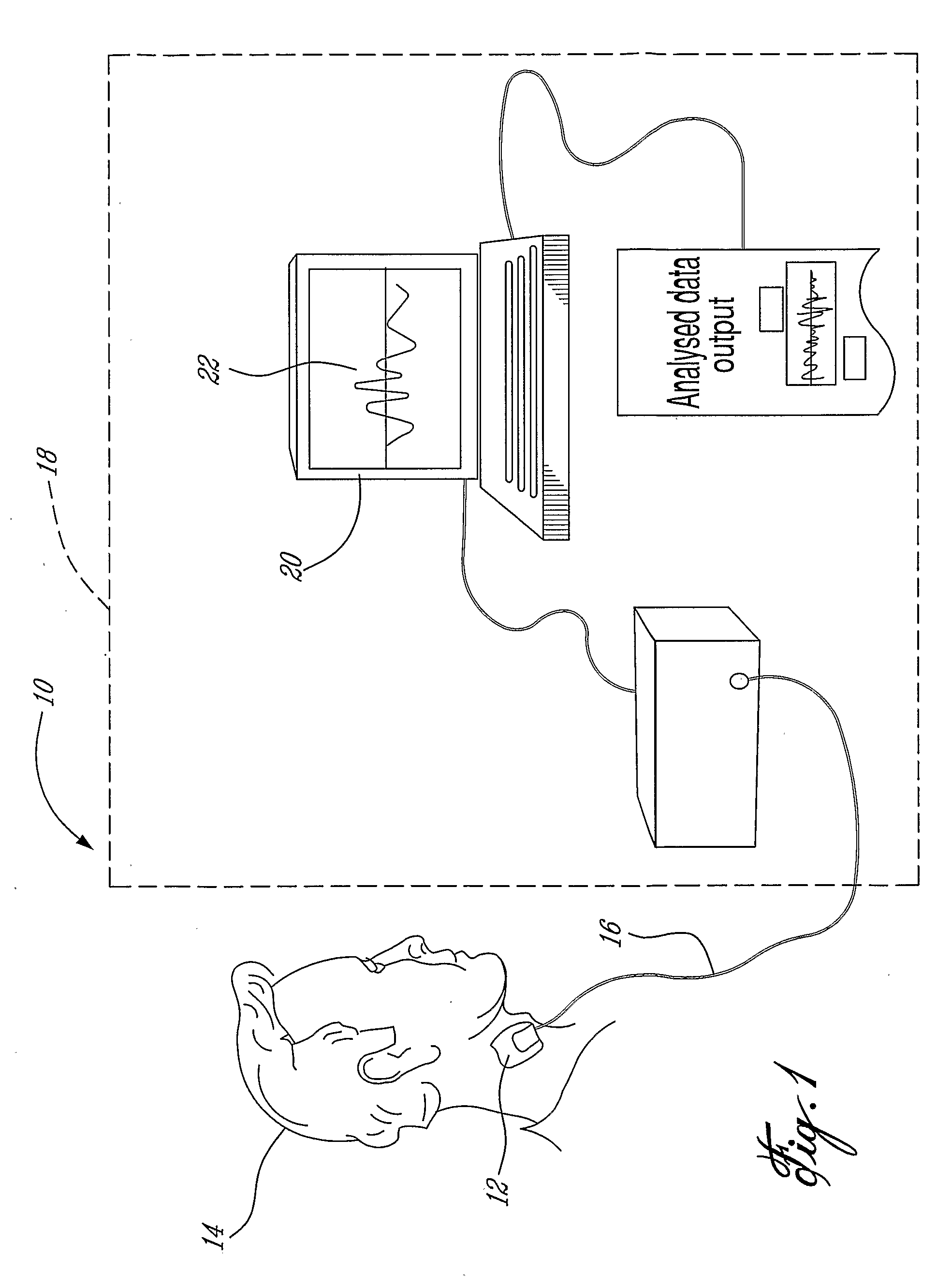
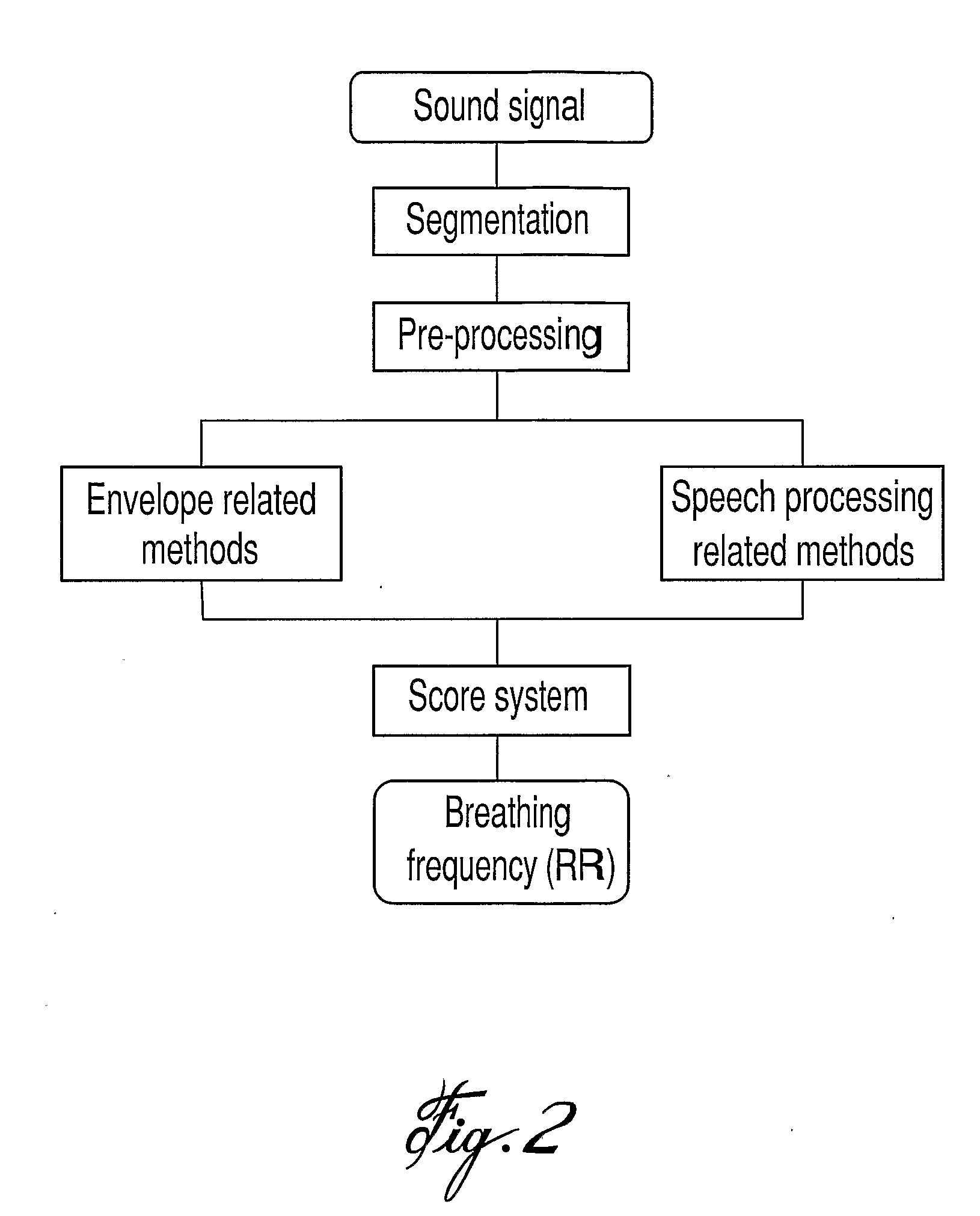
Non-Invasive Monitoring of Respiratory Rate, Heart Rate and Apnea
A method and apparatus for estimating a respiratory rate of a patient. The method comprises the steps of recording respiratory sounds of the patient, deriving a plurality of respiratory rates from the recorded sounds using a plurality of respiratory rate estimating methods and applying a heuristic to the plurality of derived respiratory rates, the heuristic selecting one of the derived respiratory rates. The selected respiratory rate is the estimated respiratory rate. The apparatus comprises at least one sensor recording respiratory sounds of the patient, a plurality of respiratory rate processors, each of the processors comprising a respiratory rate calculating method, a heuristic means for selecting one of the calculated respiratory rates and a display means for displaying the selected respiratory as the estimated respiratory rate.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Device for monitoring breathing during sleep and ramped control of CPAP treatment
InactiveUS20020007127A1Decrease air pressureImprove sound qualityElectrocardiographyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTraffic volumeEngineering
A CPAP apparatus including: a variable pressured air source and means to vary the air pressure delivered therefrom; a nose piece for sealed air communication with a patient's respiratory system; an air communication line from the air source to the nose piece; a sound transducer adapted to be in sound communication with the patient's respiratory system; and a feedback system controlling the output pressure of the air source in response to an output from the transducer so as to increase the output air pressure from said air source, in response to detection of sound indicative of snoring, in accordance with a predefined procedure. The sound transducer, in its most general form, comprises a pressure transducer which, in addition to detecting snoring sounds, can detect other respiratory parameters such as the rate of breathing, inhaled air flow volume, and inhaled air flow rate. Output air pressure from air source is increased in response to one or more of these parameters in accordance with a pre-defined procedure.
Owner:RESMED LTD
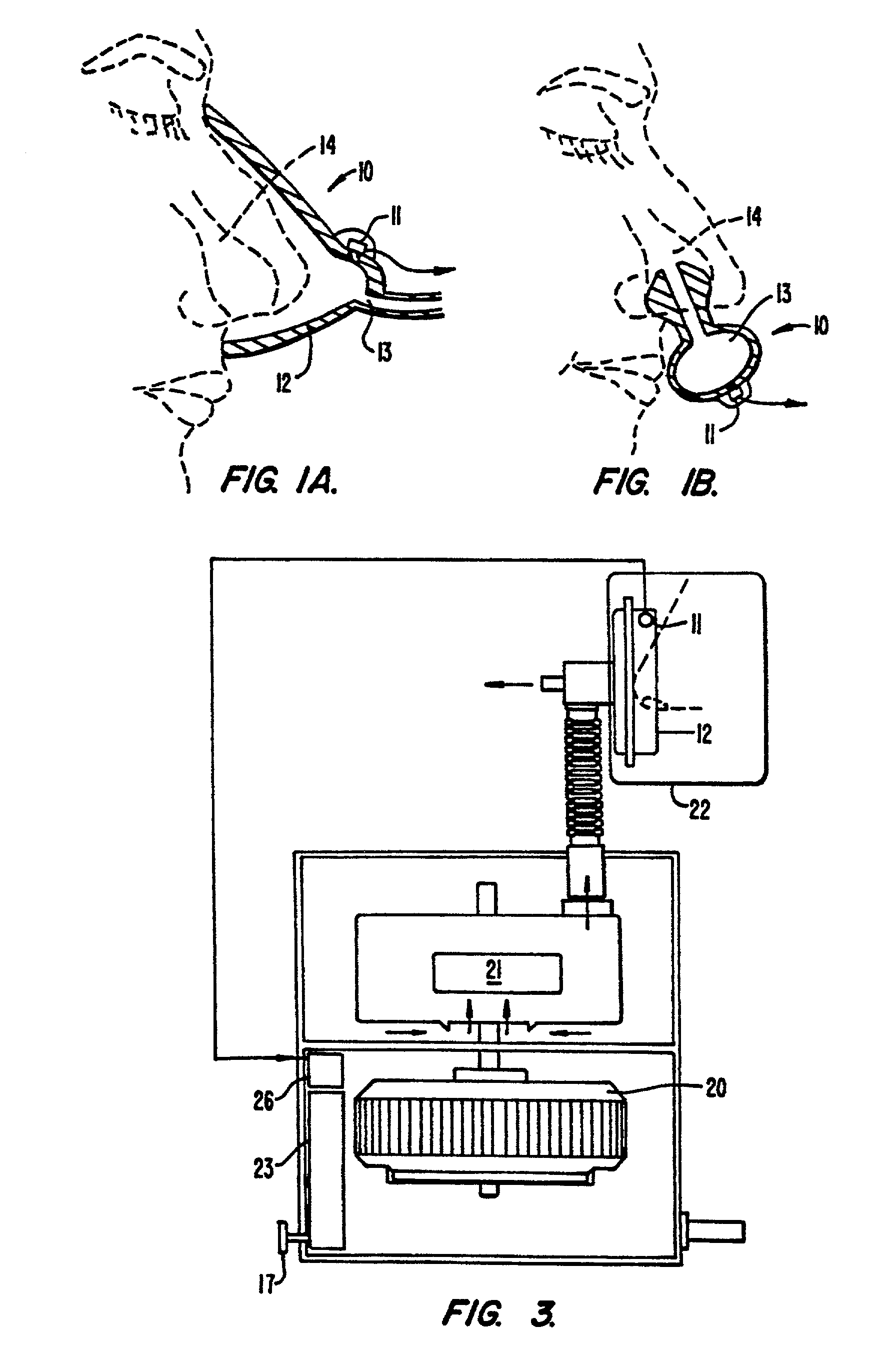
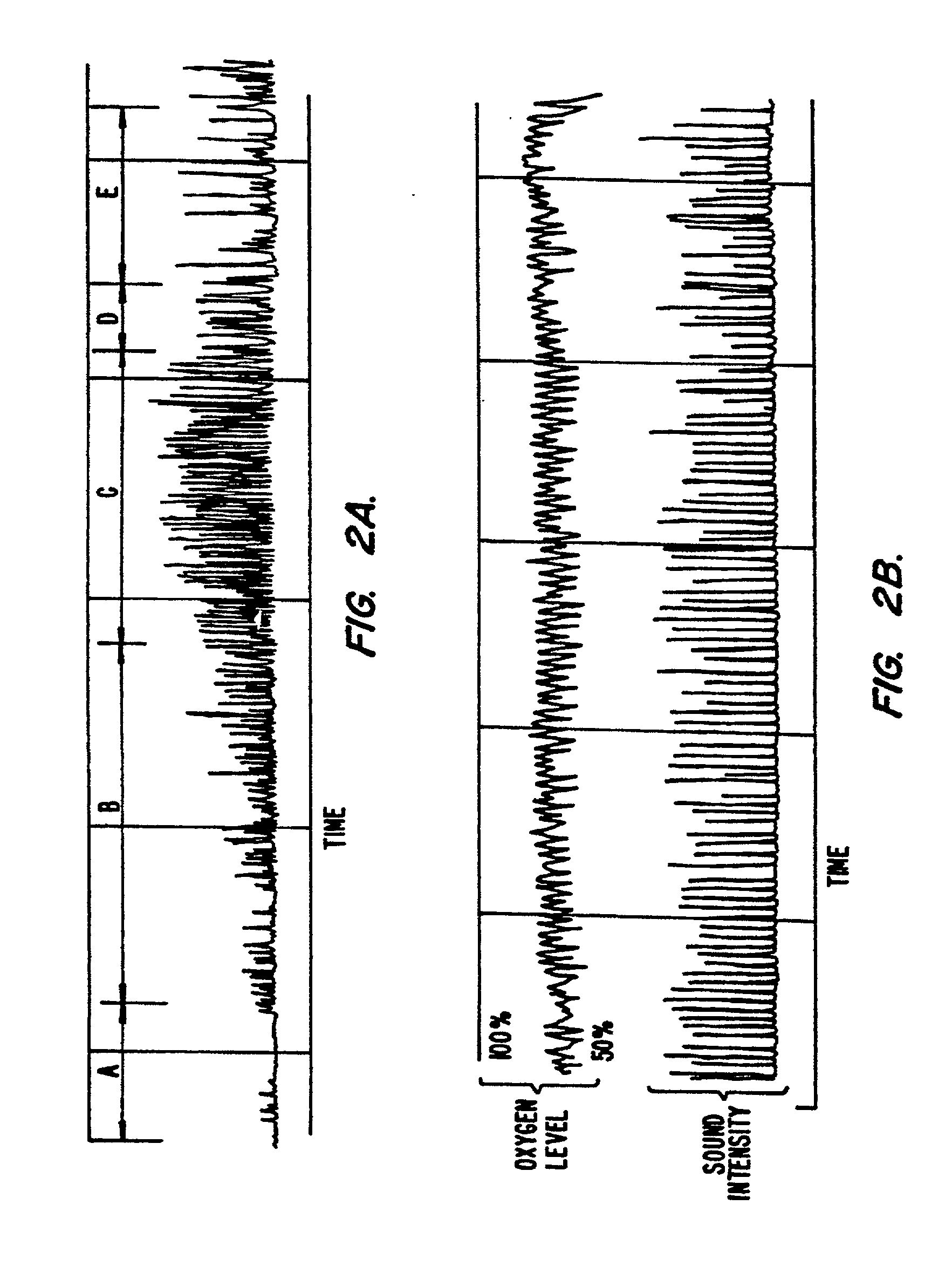
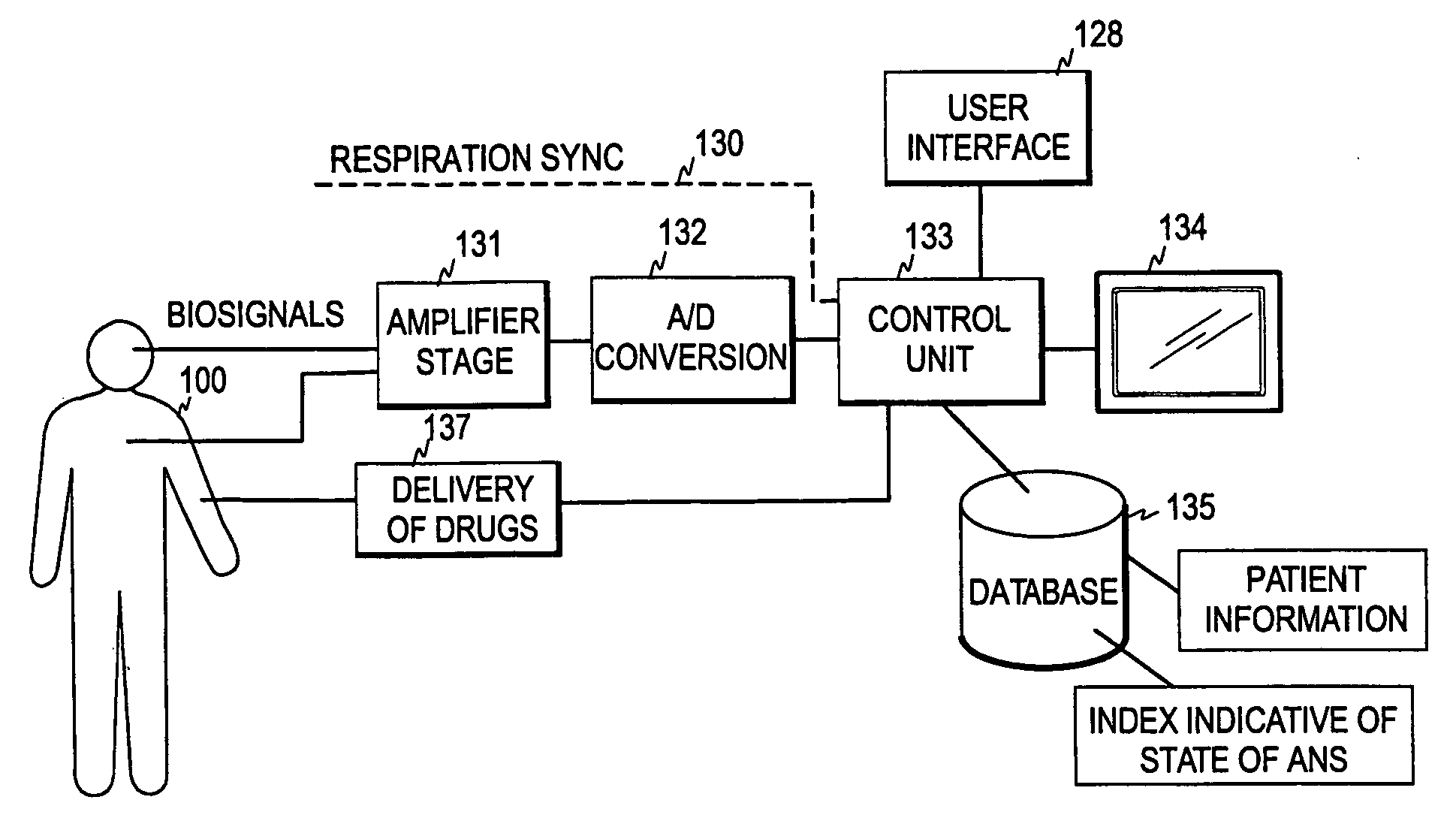
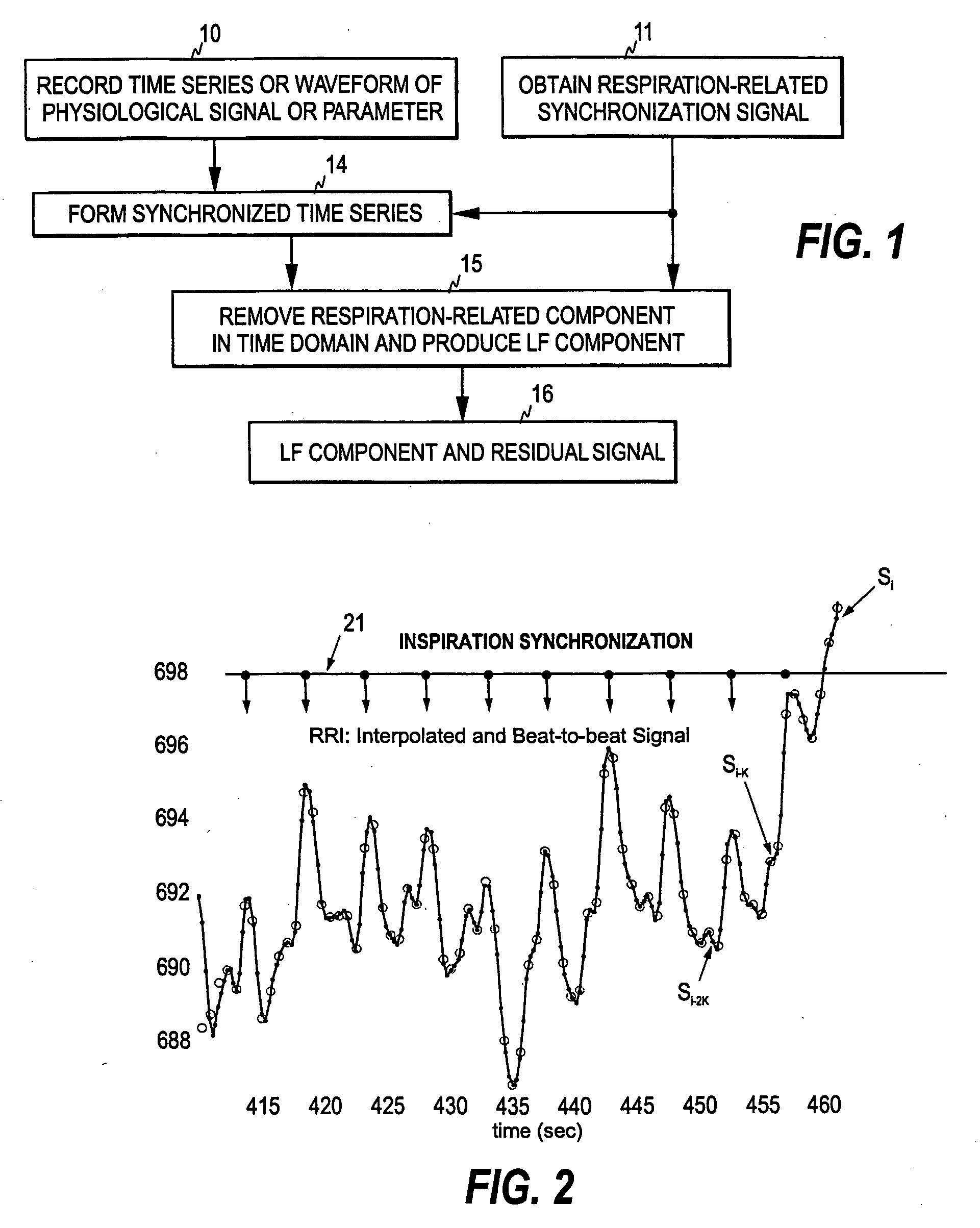
Real-time monitoring of the state of the autonomous nervous system of a patient
InactiveUS20060074333A1Reliable resultsElectrocardiographyRespiratory organ evaluationNervous systemMedicine
The invention relates to a method and arrangement for monitoring the state of the autonomous nervous system (ANS) of a patient. A first measurement signal is acquired from a patient, the first measurement signal representing a physiological signal measured from the patient. In order to enable real-time monitoring of the state of the ANS, a second measurement signal indicative of a respiration rhythm of the patient is acquired and at least one indicator signal is generated by means of the first and second measurement signals. The at least one indicator signal may then be used to obtain an indication of the state of the autonomous nervous system of the patient.
Owner:INSTRUMENTARIUM CORP
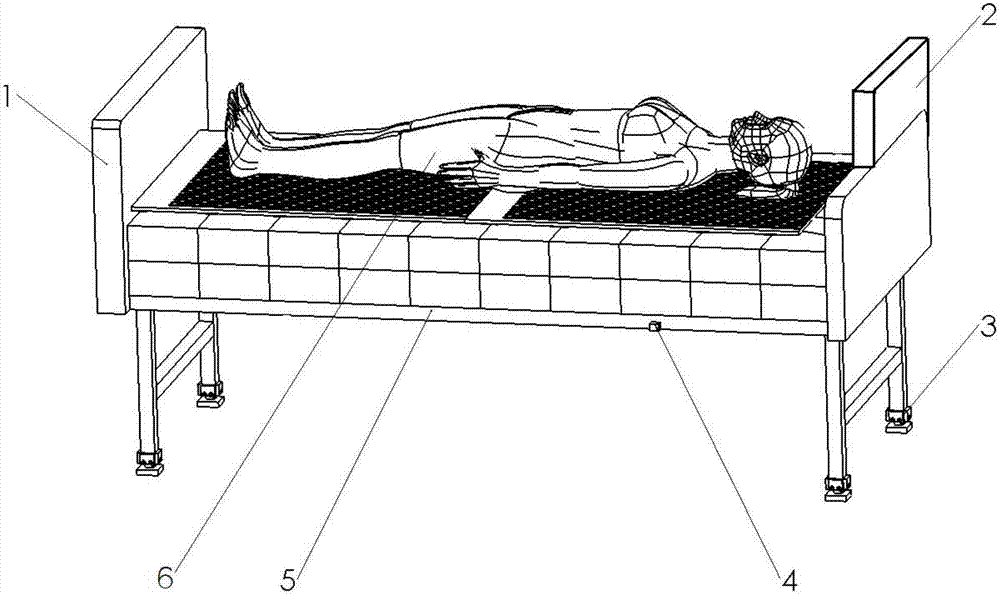
Method and intelligent bed for detecting respiration rates and heart rates without constraints
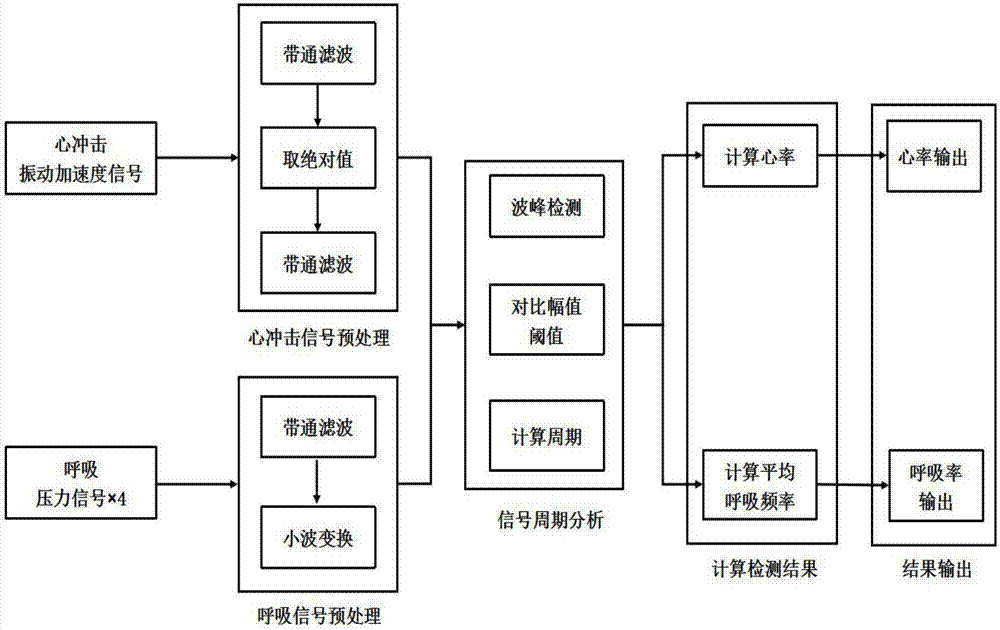
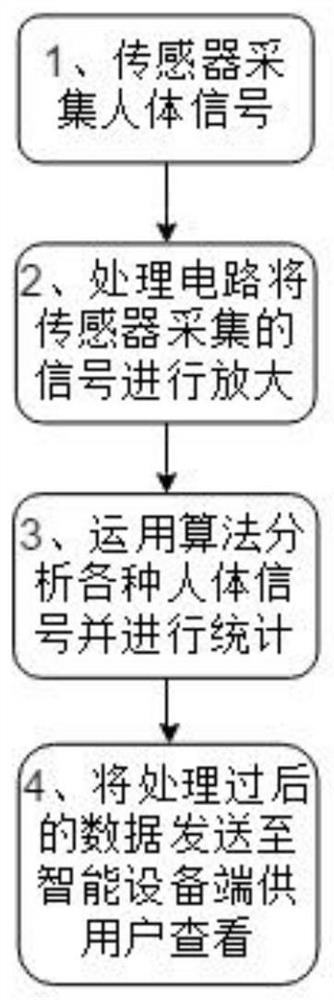
The invention relates to a method and an intelligent bed for detecting respiration rates and heart rates without constraints. The method includes steps of 1), preprocessing heart impact signals; 2), preprocessing respiration signals; 3), analyzing signal cycles, to be more specific, detecting wave peaks of 2n preprocessed pressure signals and preprocessed acceleration signals and carrying out threshold judgment on the preprocessed pressure signals and the preprocessed acceleration signals to obtain respiration and heartbeat cycles of users; 4), computing the heart rates and the respiration rates, to be more specific, dividing the heartbeat cycles obtained at the step 3) by 60 to obtain the heart rates of the users, acquiring 2n respiration cycles by 2n pressure sensors by the aid of the step 3), computing average values of the 2n respiration cycles to obtain average respiration cycles, and dividing the average respiration cycles by 60 to obtain the respiration rates of the users. The method and the intelligent bed have the advantages that vibration acceleration of a bed can change by the aid of heart impact, the heart rates can be extracted by the aid of the change of the vibration acceleration of the bed, the respiration rates can be extracted by the aid of change of pressures which are applied by the thoracic cavities to the bed in respiration movement, and accordingly the heart rates and the respiration rates can be detected without the constraints; the method and the intelligent bed are high in output accuracy and recognition speed and good in real-time performance.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Monitoring physiological parameters based on variations in a photoplethysmographic signal
InactiveCN1646055AFunction increaseEvaluation of blood vesselsSurgical instrument detailsNervous systemRR interval
A method and apparatus are disclosed for using photoplethysmography to obtain physiological parameter information related to respiration rate, heart rate, heart rate variability, blood volume variability and / or the autonomic nervous system. In one implementation, the process involves obtaining (2502) a pleth, filtering (2504) the pleth to remove unwanted components, identifying (2506) a signal component of interest, monitoring (2508) blood pressure changes, monitoring (2510) heart rate, and performing (2512) an analysis of the blood pressure signal to the heart rate signal to identify a relationship associated with the component of interest. Based on this relationship, the component of interest may be identified (2514) as relating to the respiration or Mayer Wave. If it is related to the respiration wave (2516), a respiratory parameter such as breathing rate may be determined (2520). Otherwise, a Mayer Wave analysis (2518) may be performed to obtain parameter information related to the autonomic nervous system.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
Acoustically Enhanced Pet Animal Collar for Health & Vital Signs Monitoring, Alert and Diagnosis
An acoustically enhanced collar for monitoring vital signs of a pet animal, may comprise an elastic band having a working surface configured to wrap around a neck of a pet animal and an oppositely faced rear surface, at least one sensor element situated along a circumference of the band and configured to measure at least one bioparameter from the following bioparameters: temperature, heart rate, respiration rate, movement; at least one acoustic concentrator projecting as a bump toward the neck from the working surface on a first side of the at least one sensor element; at least one acoustic concentrator projecting as a bump toward the portion from the working surface on a second side of the at least one sensor element and acoustic balancers projecting from the rear surface at least partly behind the acoustic concentrators. Preferably, the acoustic concentrators and balancers have a base end having an “X” shape.
Owner:PETPACE
Patient monitoring
ActiveUS20190343456A1Appropriate arrangementReduce processing requirementsAuscultation instrumentsCatheterVeinMedicine
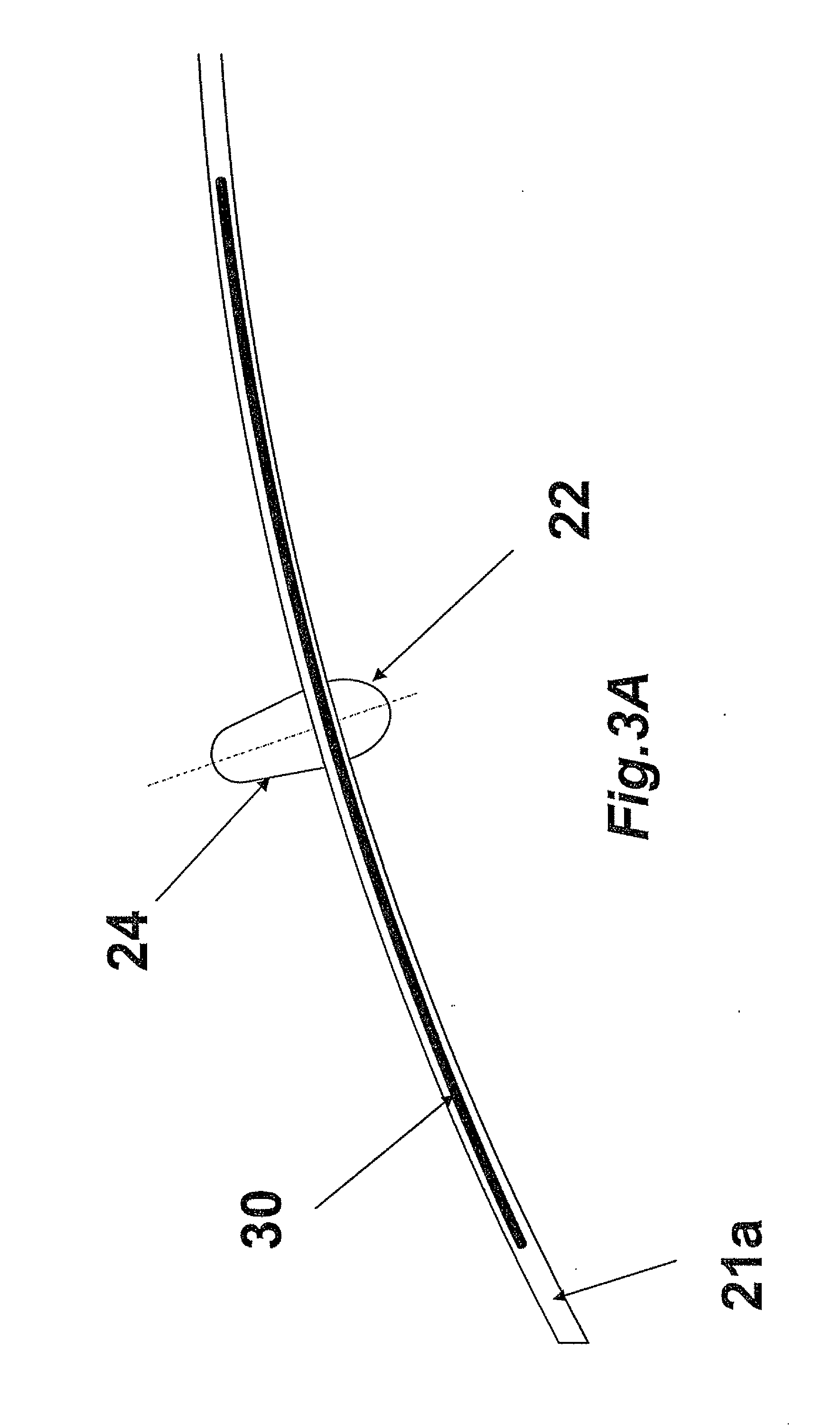
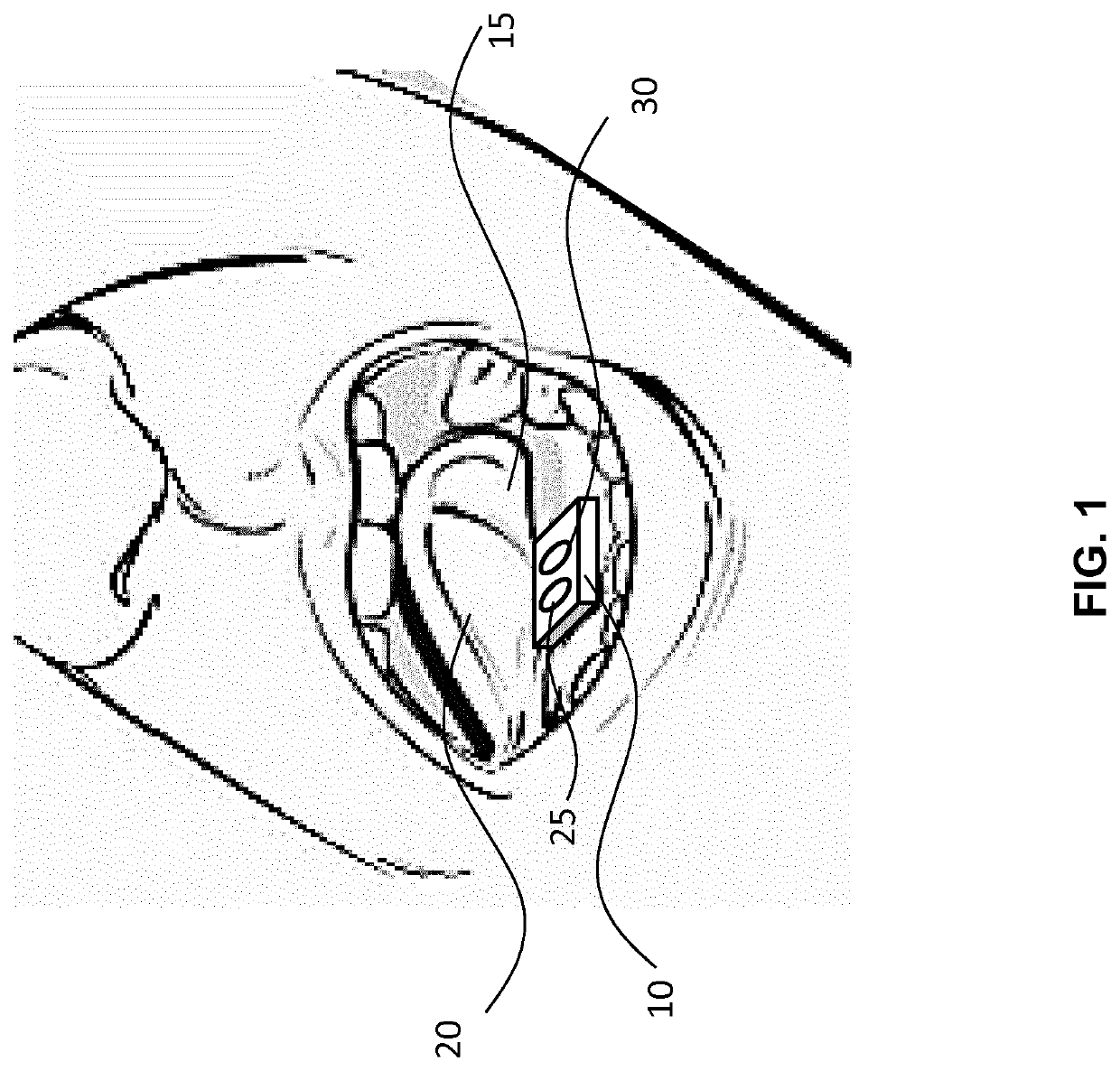
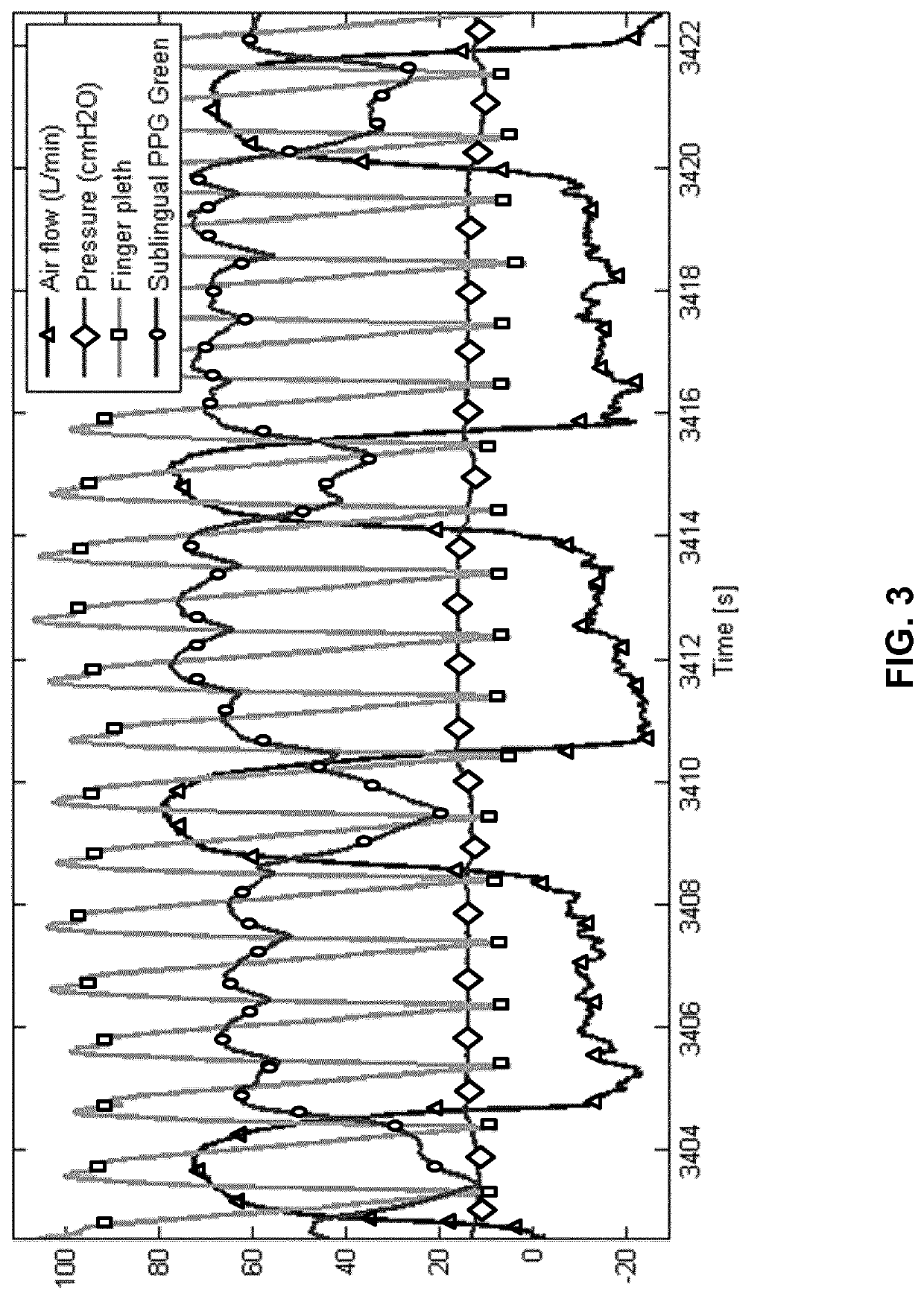
Presented are concepts for monitoring cardio-respiratory function of a patient. One such concept comprises detecting light or sound from the sublingual vasculature using a sublingual sensor unit adapted to be positioned at a sublingual vasculature of the patient's tongue and to generate a sensor output signal based on the detected light or sound. A processing unit adapted to receive at least one of the sensor unit output signal, wherein the sensor unit and the processing unit are arranged to analyze the venous component in the sensor output signal. An output signal from the sublingual sensor may then be used to provide information on cardio-respiratory parameters like respiration rate and respiration rate variability, for example.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Abdominal respiration training aid
InactiveCN103341254ACultivate awareness of abdominal breathingCorrect breathing methodGymnastic exercisingAbdominal respirationNose
An abdominal respiration training aid comprises an inflatable abdominal belt, a nose cover, a respiration pipeline, an air pump, an extension-type air bag and a main machine circuit, wherein the extension-type air bag is connected with an air cushion in the inflatable abdominal belt through a first way air guide pipeline and a second way air guide pipeline, the air cushion in the inflatable abdominal belt is connected with the air pump through a third way air guide pipeline, at least the first way air guide pipeline and the second way air guide pipeline are provided with valves, the nose cover is connected with the respiration pipeline, the respiration pipeline is connected with a sensor, the sensor is used for detecting respiration frequency, the main machine circuit opens or closes the valves according to detection signals fed back by the sensor, and the air cushion in the inflatable abdominal belt can exhaust air into the extension-type air bag according to respiration rhythms, or the air cushion in the inflatable abdominal belt can store air from the extension-type air bag. The abdominal respiration training aid can help people to carry out abdominal respiration training and to develop an accurate respiration mode, and plays significant roles in increasing vital capacity, oxygen delivery capacity and a cardio-pulmonary function, discharging abdominal waste, improving abdominal blood circulation, and prolonging the life.
Owner:徐赤坤
Non-contact motion and body measurement data acquisition system
PendingCN112232256AImprove accuracyHeart rate real-time monitoringImage enhancementImage analysisFrequency spectrumData acquisition
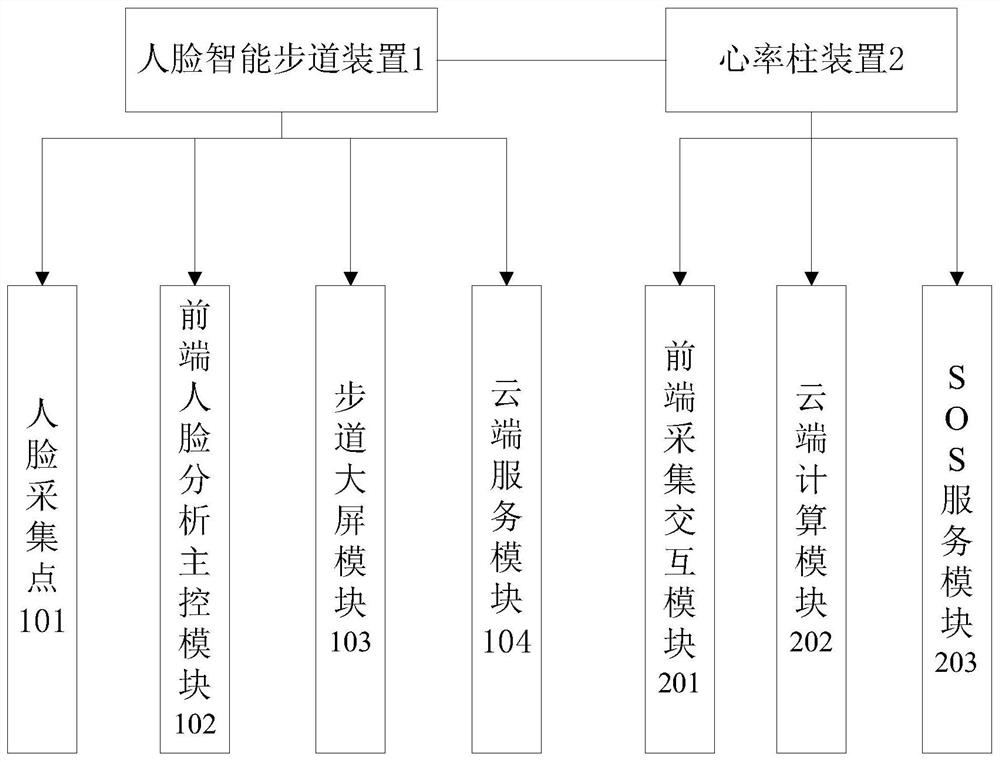
The invention provides a non-contact motion and body measurement data acquisition system, and aims to solve the technical problems of low accuracy and limited usage scenarios of a non-contact heart rate and respiratory rate measurement method in the prior art. The system comprises a human face intelligent footpath device and a heart rate column device, the heart rate column device calculates heartrate data of a to-be-tested person by analyzing frequency spectrum peaks in voice data, and the heart rate data of the to-be-tested person is calculated by processing facial image data through a multiple linear regression method. Lung image data is processed through a selective integrated aggregation method to calculate respiratory rate data of the to-be-tested person. The motion data and the body side data of the personnel can be efficiently and stably acquired in a non-contact mode, the accuracy is high, and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING DIGITAL FITNESS TECH
Respiratory muscle training system in motion state and using method thereof
ActiveCN111013104AImprove training effectRealize dynamic optimizationGymnastic exercisingRespiratory flowTraining plan
The invention discloses a respiratory muscle training system in a motion state and a using method thereof. The respiratory muscle training system comprises a wearable respiratory monitoring module, aninteractive display module, a sports apparatus and a respiratory training management system. The wearable respiration monitoring module monitors parameters such as a respiration rate, a respiration flow rate, a respiration flow and heart rate of a subject in real time through a flow sensor and an electrocardio-electrode and transmits the parameters to the interactive display module. The interactive display module receives a training mode and training parameters issued by the training management system, compares the training mode and training parameters with respiratory and heart rate information obtained from the wearable respiratory monitoring module, and reminds a subject to adjust the respiratory rhythm and respiratory depth in real time; the sports apparatus is used for assisting a subject to keep respiratory training under set exercise intensity, so that the training effect can be improved; the respiratory training management system is a management tool for a rehabilitation doctor to sign and issue a training scheme and is used for making a respiratory training plan, setting differentiated training parameters, tracking and managing respiratory training process data and realizing continuous optimization of the respiratory training scheme.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System for inducing a subject to fall asleep
InactiveCN102015001AImprove sleepingElectrocardiographyMedical devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
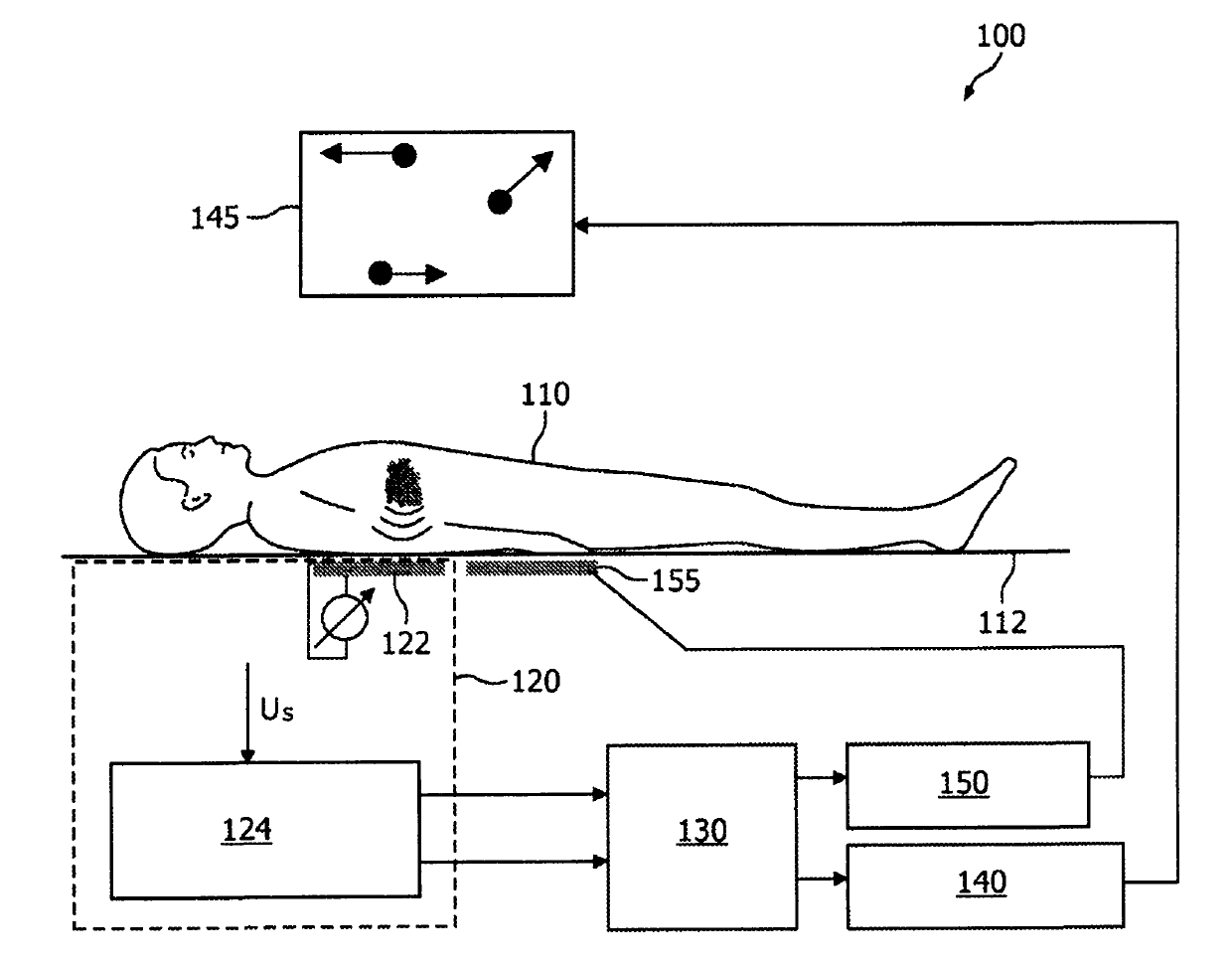
A system (100) for inducing a subject (110) to fall asleep comprises a monitor (120) for monitoring heart rate and breathing rate of the subject (110), a coherence assessing device (130) coupled to the monitor (120) for assessing a degree of coherence between the heart rate and the breathing rate, and an output device (140, 150) coupled to the coherence assessing device (130). The output device (140, 150) may comprise a light pattern generator (140) for generating a light pattern (145) in view of the subject (110) based on the degree of coherence. The output device (140, 150) may alternatively or additionally comprise an instructing system (150) for instructing the subject on a breathing pattern, and wherein the instructions are given based on the degree of coherence.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
Apparatus for monitoring a subject
InactiveUS20200281523A1Few false alarmFew false alarmsSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateMedicineEngineering
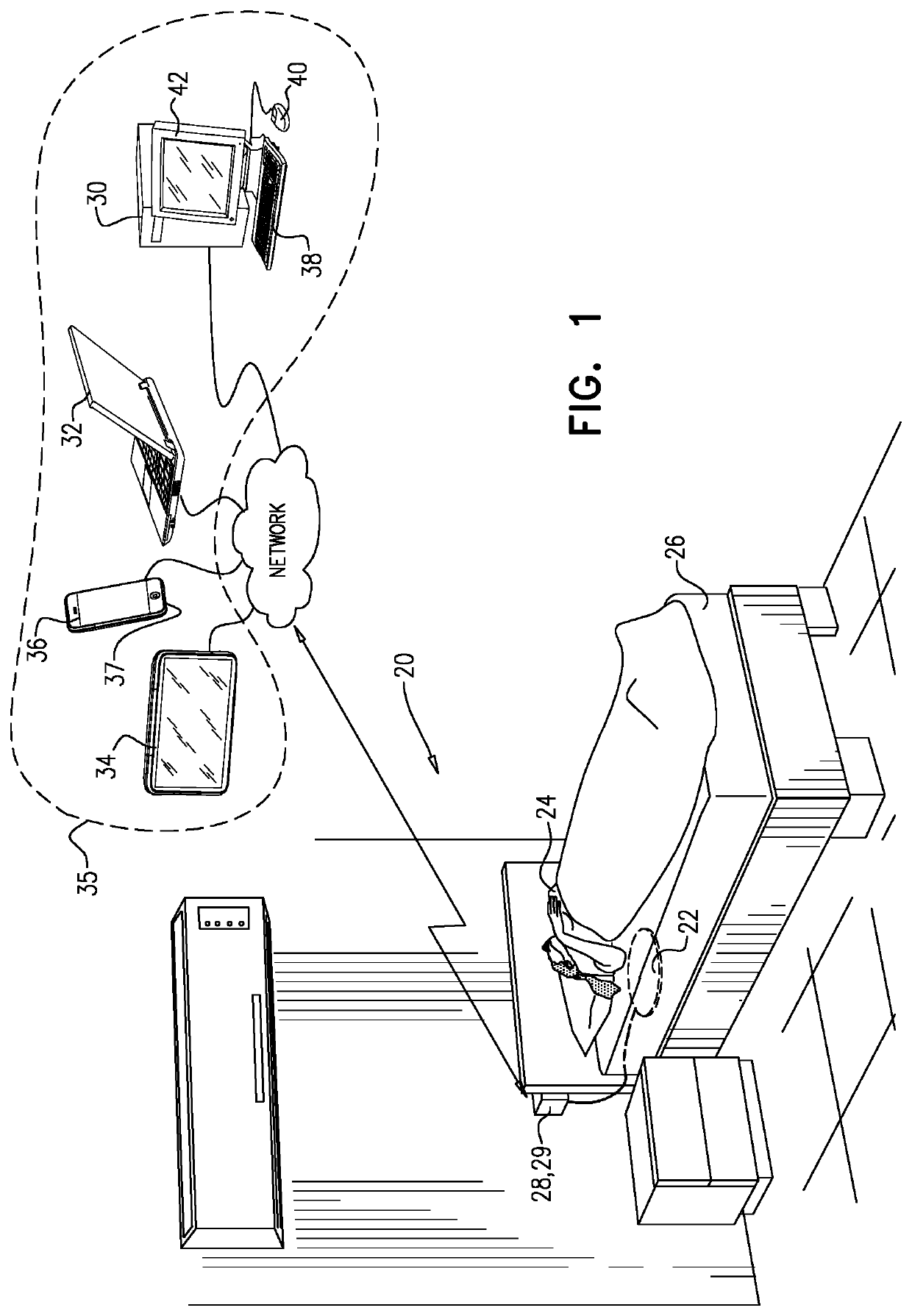
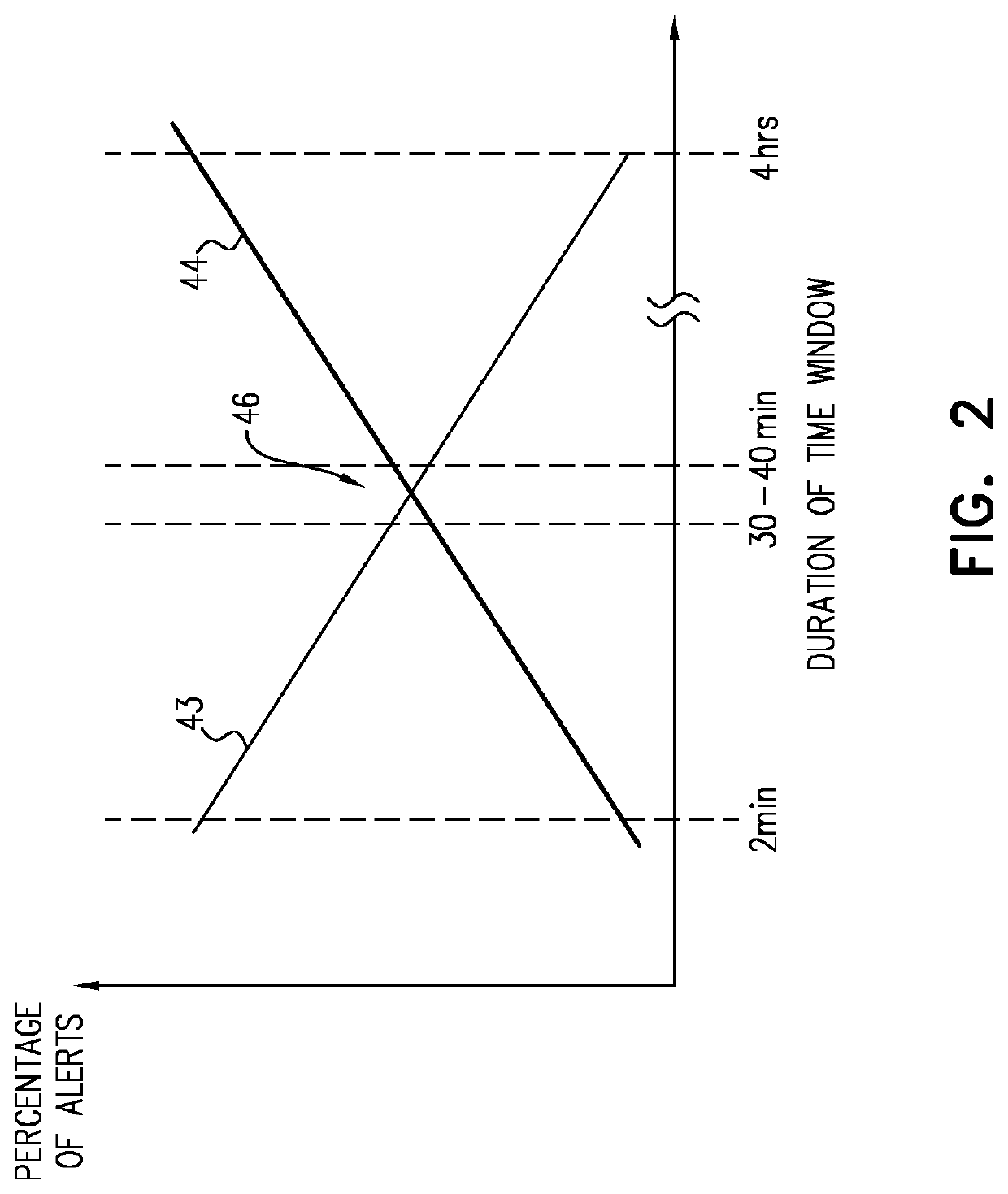
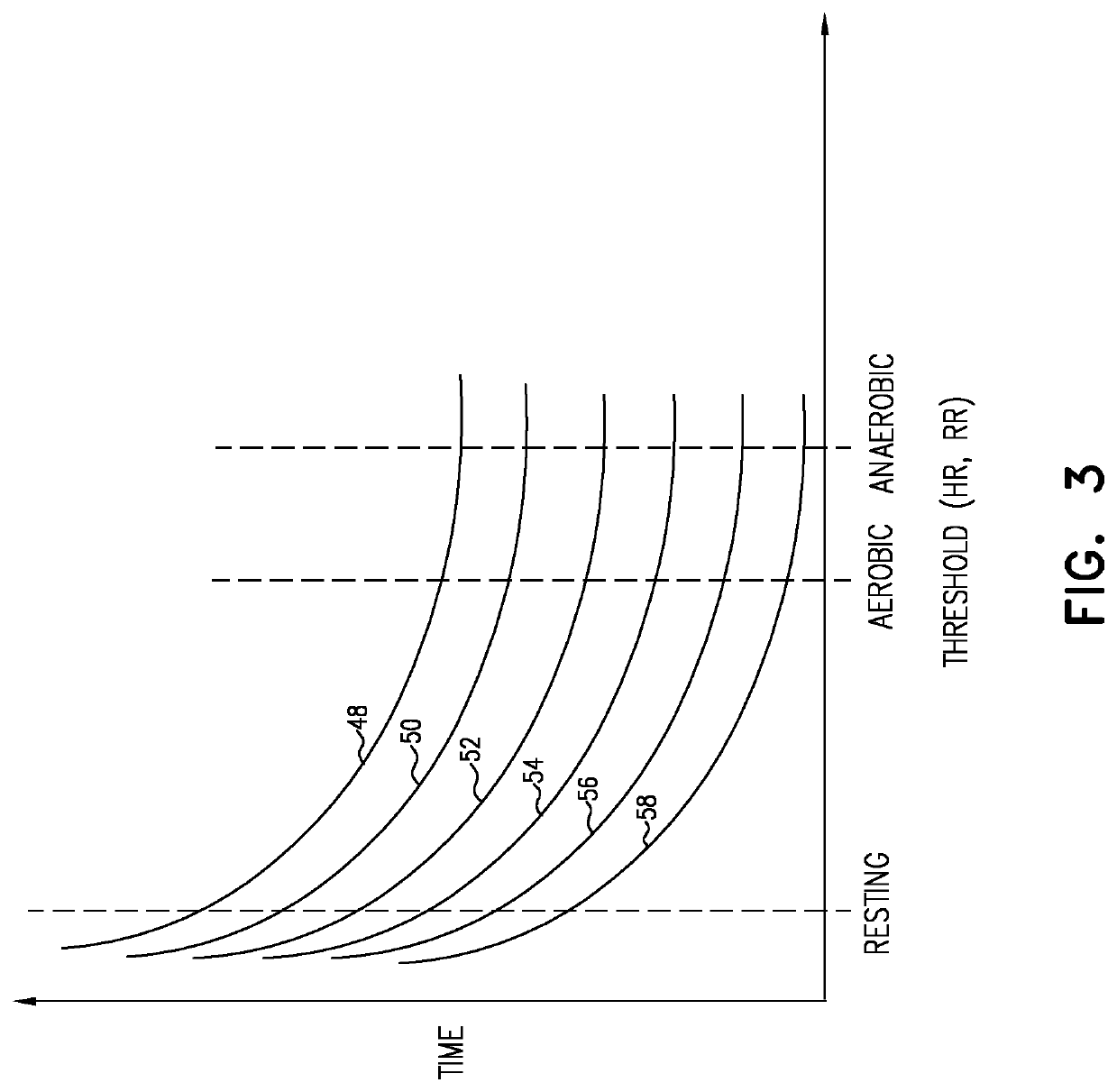
A sensor monitors a subject and generates a signal. A computer processor receives the signal, derives therefrom data related to a heart rate of the subject and / or a respiration rate of the subject, derives from the signal at least one subject status indication that the subject is: awake and not moving, moving and asleep, not moving, asleep, awake and moving and in a bed, in a particular sleep stage while asleep, and / or has been continuously in a bed over a previous in-bed period of at least 15 hours, determines a threshold of at least 0.7 times an aerobic heart rate threshold and / or at least 0.7 times an aerobic respiratory rate threshold, and generates an alert if the signal indicates that the physiological parameter of the subject exceeds the threshold for an amount of time determined in response to the subject status indication. Other applications are also described.
Owner:HILL ROM SERVICES
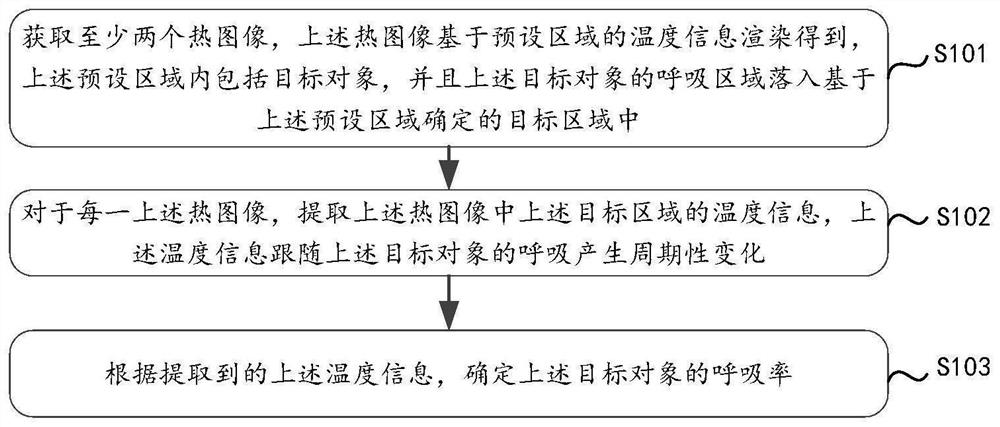
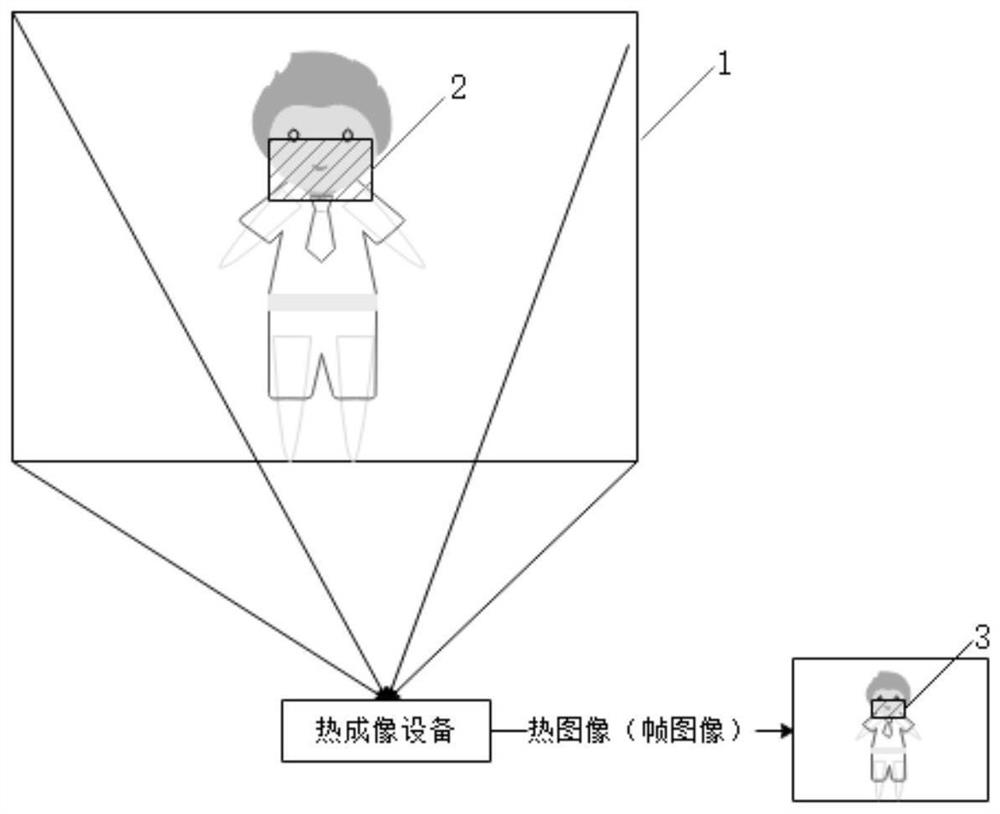
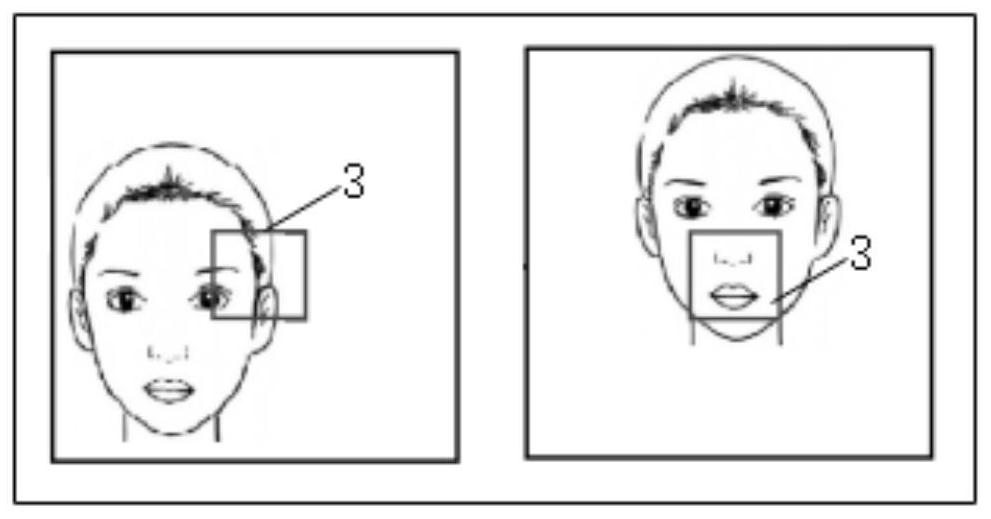
Respiratory rate detection method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment
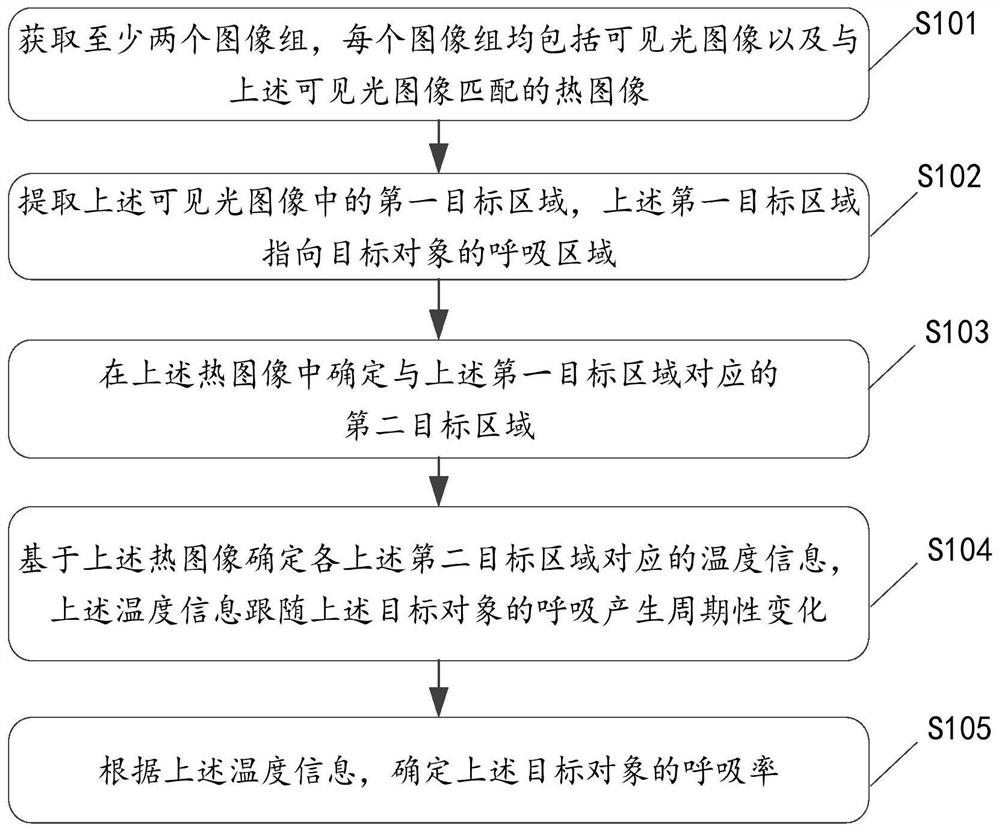
The invention relates to a respiratory rate detection method and device, a storage medium and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring at least two image groups, wherein each image group comprises a visible light image and a thermal image matched with the visible light image; extracting a first target area in the visible light image, wherein the first target area points to a breathing area of a target object; determining a second target area corresponding to the first target area in the thermal image; determining temperature information corresponding to each second target area on the basis of the thermal image, wherein the temperature information periodically changes along with respiration of the target object; and determining the breathing rate of the target object according to the temperature information. According to the method, the respiratory rate detection result can be obtained under the condition that the target object is not contacted, non-contact detection is achieved, and the good detection speed and detection accuracy are achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN SENSETIME TECH CO LTD
Digital respiration following oxygen supply system and oxygen supply method thereof
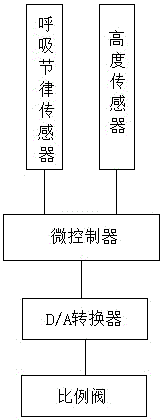
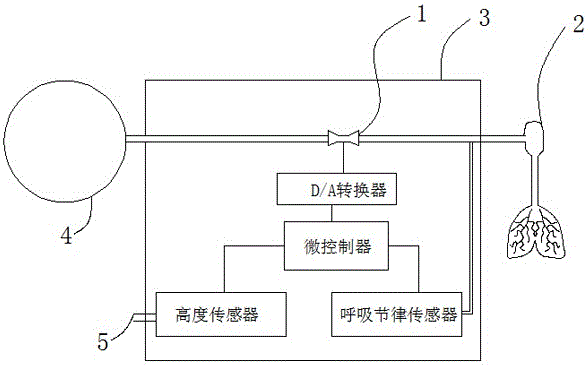
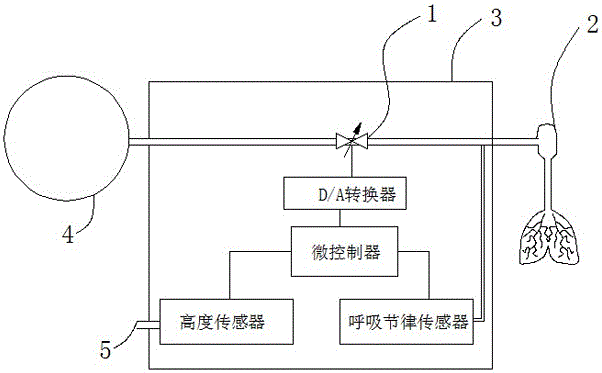
ActiveCN106039607ASolve wasteSolve pollutionBreathing masksFire rescueMicrocontrollerMathematical model
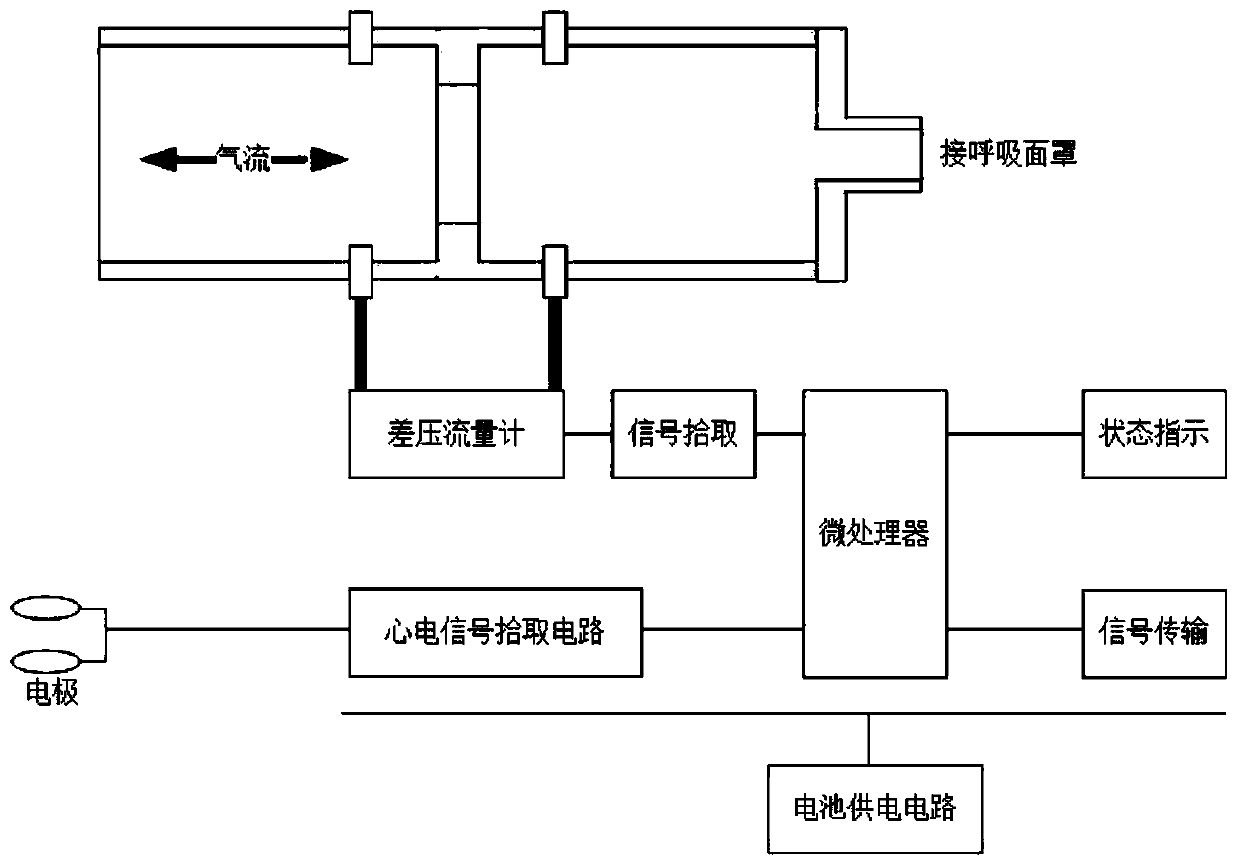
The invention discloses a digital respiration following oxygen supply system. The digital respiration following oxygen supply system comprises a respiration rhythm sensor, a height sensor, a microcontroller, a D / A converter and proportional valves. The input end of the microcontroller is connected with the height sensor and the respiration rhythm sensor, and the proportional valves communicate with an oxygen source and an oxygen mask through oxygen transmitting pipelines. The invention further discloses an oxygen supply method of the digital respiration following oxygen supply system. The method includes the following steps that the pulmonary respiration depth P of a human body is detected; the pulmonary respiration cycle T of the human body is detected; the pulmonary ventilation flow sigma and the needed oxygen flow (O2) are worked out through a mathematical model preset in a microprocessor according to the respiration depth P and the respiration cycle T; the microcontroller converts the obtained pulmonary ventilation flow sigma and needed oxygen flow (O2) into electric signals which are then sent to the D / A converter; and the opening degree of the proportional valves is controlled according to the intensity of the electric signals through the D / A converter. The oxygen utilization rate is increased and the comfort level is improved for an oxygen user.
Owner:四川海特亚美航空技术有限公司
Real-time monitoring of the state of the autonomous nervous system of a patient
The invention relates to a method and arrangement for monitoring the state of the autonomous nervous system (ANS) of a patient. A first measurement signal is acquired from a patient, the first measurement signal representing a physiological signal measured from the patient. In order to enable real-time monitoring of the state of the ANS, a second measurement signal indicative of a respiration rhythm of the patient is acquired and at least one indicator signal is generated by means of the first and second measurement signals. The at least one indicator signal may then be used to obtain an indication of the state of the autonomous nervous system of the patient.
Owner:INSTRUMENTARIUM CORP
A novel oxygen filter respiration device for emergency internal medicine
InactiveCN105688316AChange breathing rhythmAvoid secondary damageRespiratorsMedical devicesEngineeringBottle
The invention provides a novel oxygen filter respiration device for emergency internal medicine. The novel oxygen filter respiration device comprises a box body; the bottom surface of the inner side of the box body is provided with an oxygen bottle; a pressure gauge is arranged at the outlet of the oxygen bottle; the outlet of the oxygen bottle is connected with the inlet end of a filter via a pipeline; the pipeline is provided with a throttle valve between the outlet end of the oxygen bottle and the inlet end of the filter; the outlet end of the filter is connected with a mask via a pipeline; the mask is provided with a fasting belt; the filter is arranged on the left side of the oxygen bottle; a support table is arranged on the left side of the filter; the filter and the support table are fixedly installed on the bottom surface of the inner side of the box body; a servo motor is fixedly installed on the front portion of the upper surface of the support table. By adjusting the rotating speed of the servo motor, the oxygen supply frequency can best match the respiration frequency of a patient, so that the patient does not need to change the respiration rhythm forcibly and secondary injury to the patient is prevented. The device is simple and efficient to operate, and is great in safety and practicability.
Owner:台培春
Non-contact respiratory rate detection method based on an infrared thermal imager
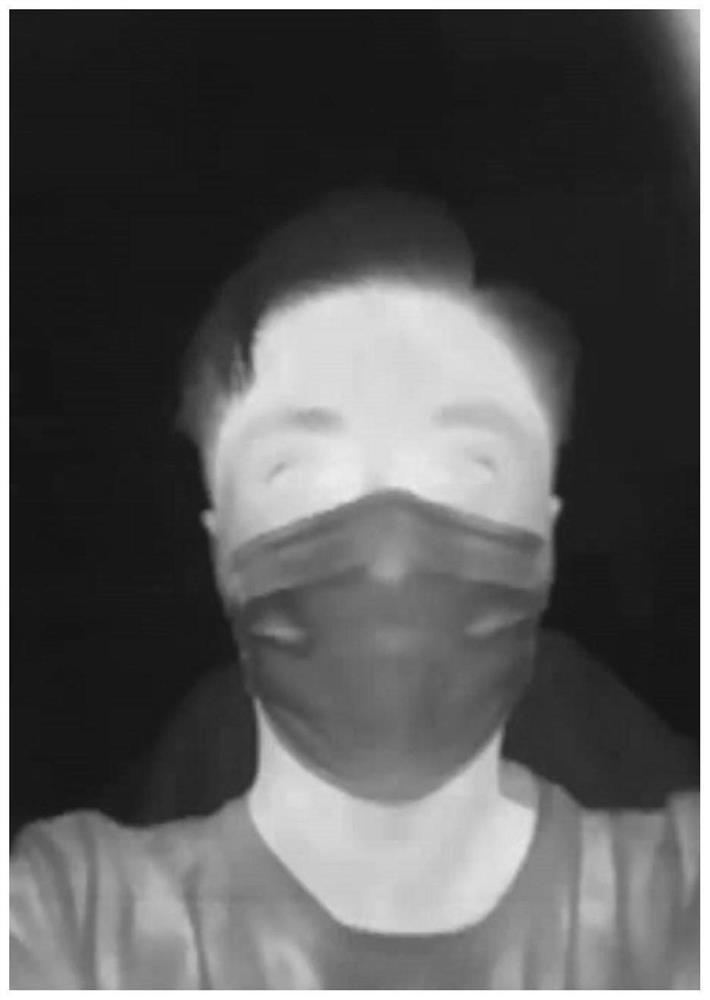
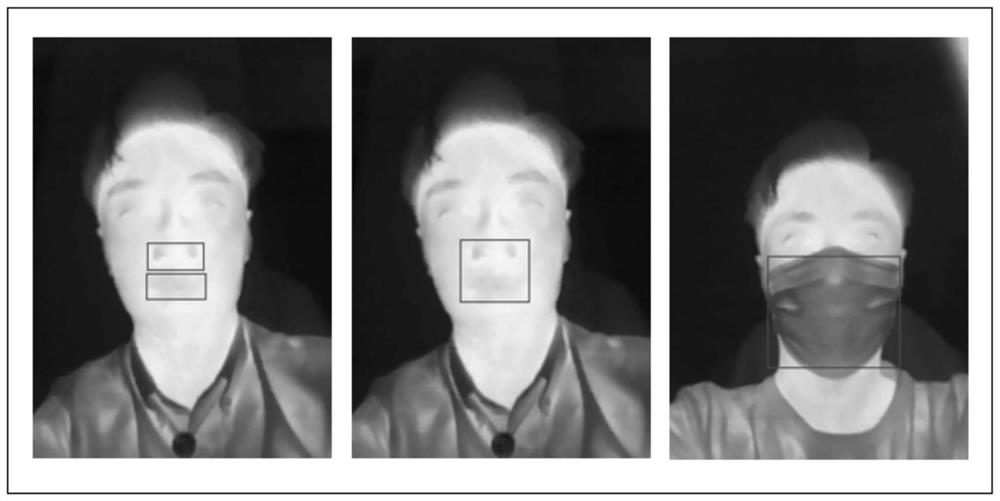
PendingCN113793300AAvoid harmAvoid discomfortImage enhancementDiagnostic signal processingNostrilMedicine
The invention relates to the technical field of non-contact respiratory rate measurement, in particular to a non-contact respiratory rate detection method based on an infrared thermal imager, which comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring an infrared image sequence of a human face at least comprising a nose area as a training set; (2) marking a nostril area in the face infrared image in the training set, and recording the nostril area as ROI; (3) performing model training on the marked parameters by using a deep learning YOLO V3 method; (4) acquiring a to-be-measured face infrared image sequence as a measurement set, detecting each frame of image in the measurement set by using the model obtained by training, outputting a positioned ROI coordinate, and calculating a temperature average value of a positioned ROI region of each frame of image to obtain a curve of temperature changing along with time; (5) filtering the curve by using a low-pass filter; and (6) calculating to obtain the respiratory rate. According to the invention, the thermal infrared imager is used as measuring equipment, the temperature value can be directly obtained, the precision is quite high, and the measuring accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
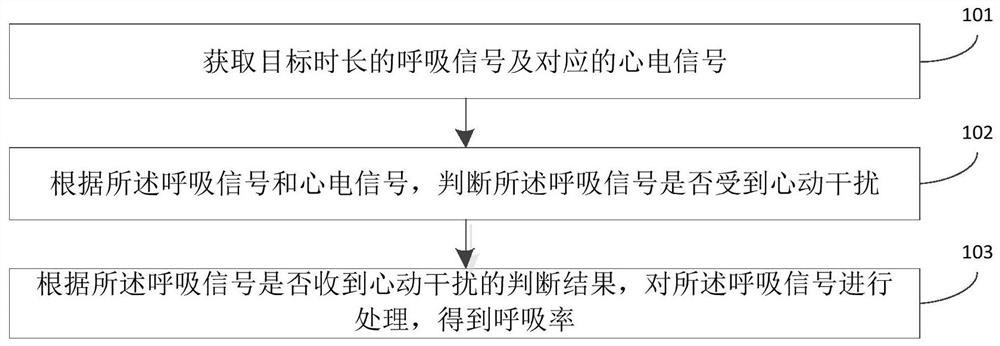
Respiratory rate detection method and device and medical equipment
PendingCN113397523AImprove accuracyImprove detection efficiencyRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsMedical equipmentEmergency medicine
The invention discloses a respiratory rate detection method and device and medical equipment, and relates to the technical field of medical signal processing. The respiratory rate detection method comprises the steps that a respiratory signal of target duration and a corresponding electrocardiosignal are acquired; according to the respiratory signal and the electrocardiosignal, whether the respiratory signal is subjected to cardiac interference or not is judged; and according to the judgment result of whether the respiratory signal is subjected to cardiac interference or not, the respiratory signal is processed, and the respiratory rate is obtained. The acquired respiratory signal and the electrocardiosignal are combined for cardiac interference judgment, and the respiratory signal is processed according to the judgment result. Compared with the prior art that the respiratory signal is processed blindly, the respiratory rate detection accuracy is improved, and meanwhile the respiratory rate detection efficiency is further improved by selectively processing the respiratory signal.
Owner:EDAN INSTR
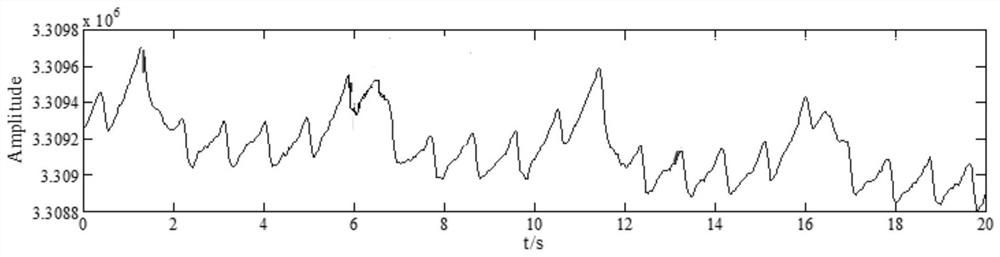
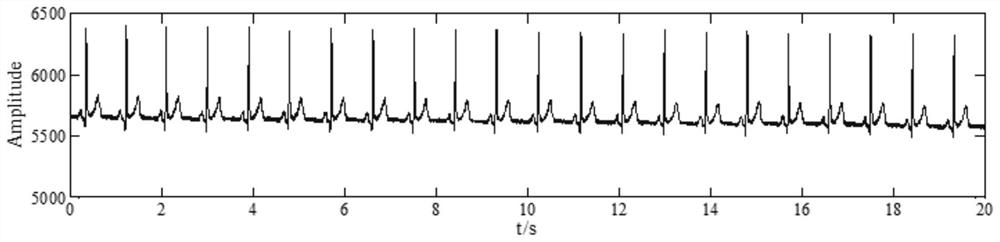
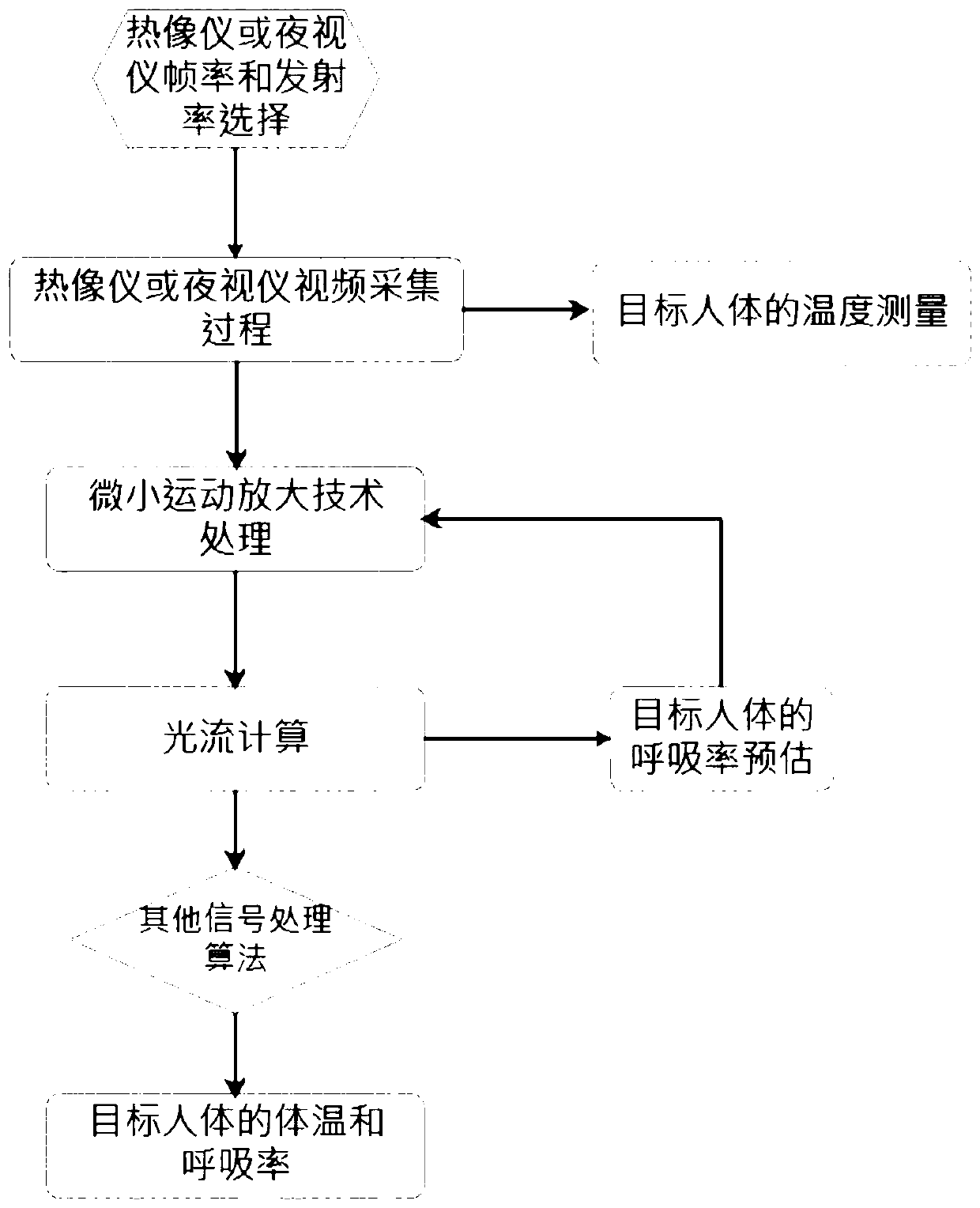
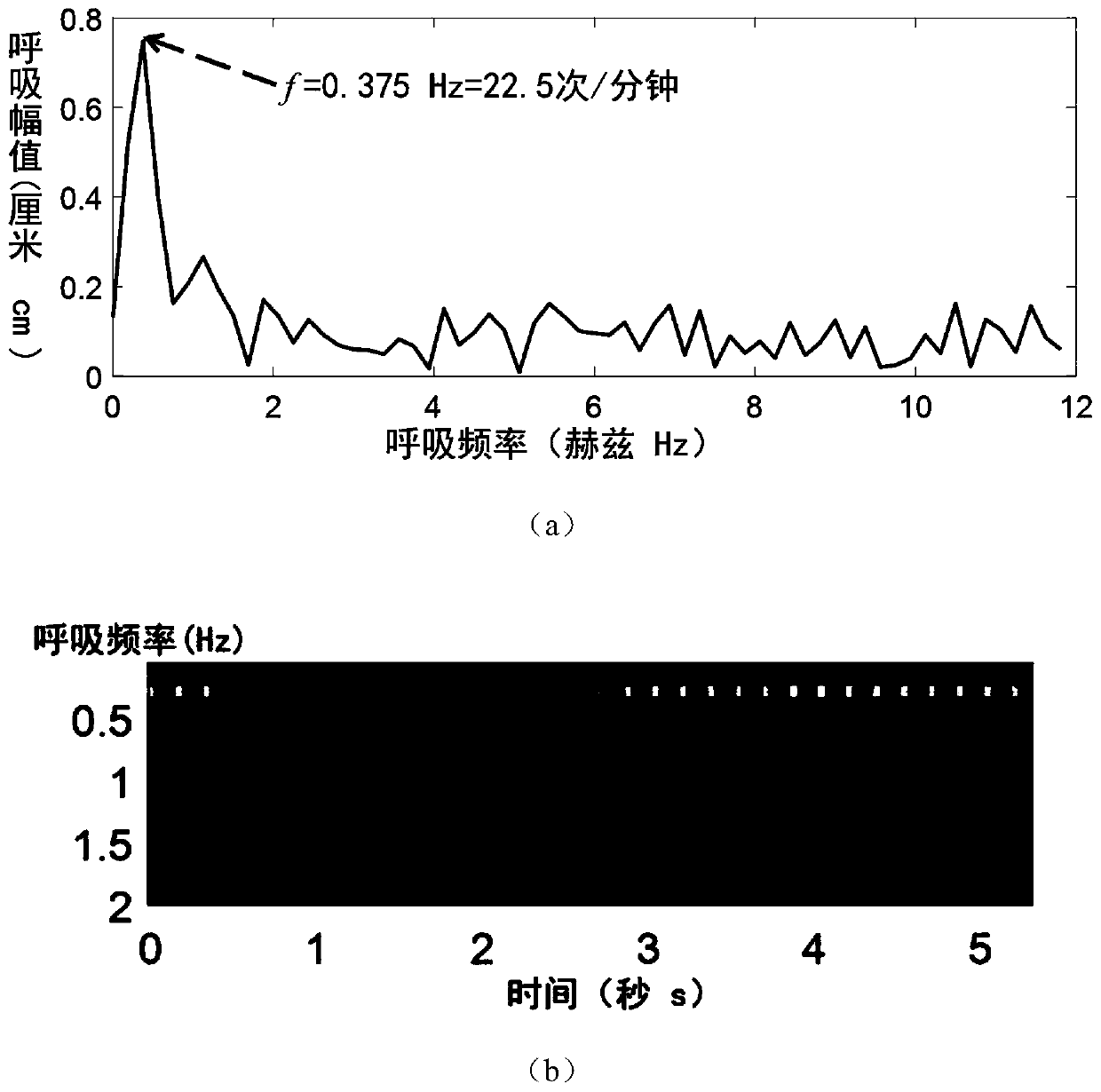
Non-contact body temperature and respiration rate combined detection method
The invention provides a non-contact body temperature and respiration rate combined detection method. The method comprises the steps of acquiring video image data under the target background of a human body by a thermal imager or a night vision device, wherein the video image data comprise temperature field information in a scene, and the temperature of the human body can be directly read in the thermal imager or the night vision device; amplifying the acquired video image data by using a micro motion amplification technology; and carrying out optical flow calculation on the amplified video image data to finally obtain an accurate value of respiration rate. According to the method, infrared video images are captured by the thermal imager or the night vision device, the body temperature andthe respiration rate of the crowd are jointly detected, and even under the condition that the body temperature is normal due to the fact that a specific target crowd takes antipyretics, the specifictarget crowd can be identified through the characteristic change of the respiration rate of the specific target crowd and an alarm is given.
Owner:智方达(天津)科技有限公司
Vital sign extraction algorithm based on piezoelectric film sensor and system thereof
InactiveCN113017559AReduce computing power requirementsEliminate inaccurate measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodyAlgorithm
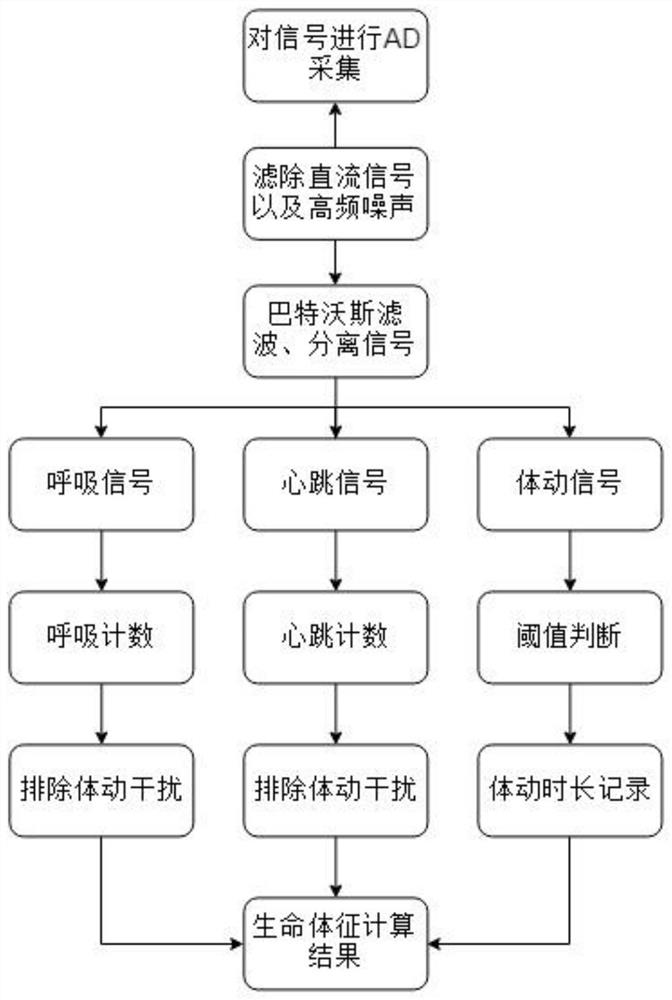
The invention relates to a vital sign extraction algorithm based on a piezoelectric film sensor technology, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: amplifying and filtering measured original heartbeat and respiration signals mixed with body movement signals; dividing the obtained signals into heartbeat, breathing and body movement signals; finding out a peak point in the data, and solving the corresponding heart rate and respiration rate. According to the algorithm, a heartbeat signal is separated from a breathing signal and a body movement signal by utilizing a signal, collected by a piezoelectric film, of a human body during sleep, so that an MCU can conveniently obtain vital sign parameters of a user during sleep. By adopting the compensation algorithm, the heart rate and the breath which are not collected can be compensated, so that the calculation result is more accurate.
Owner:青岛中物云传智能科技有限公司
Thermal stimulation apparatus for vehicles
InactiveCN101378802AReduce fatigueEnhance physical fitnessVehicle seatsMedical devicesThermal stimulationEngineering
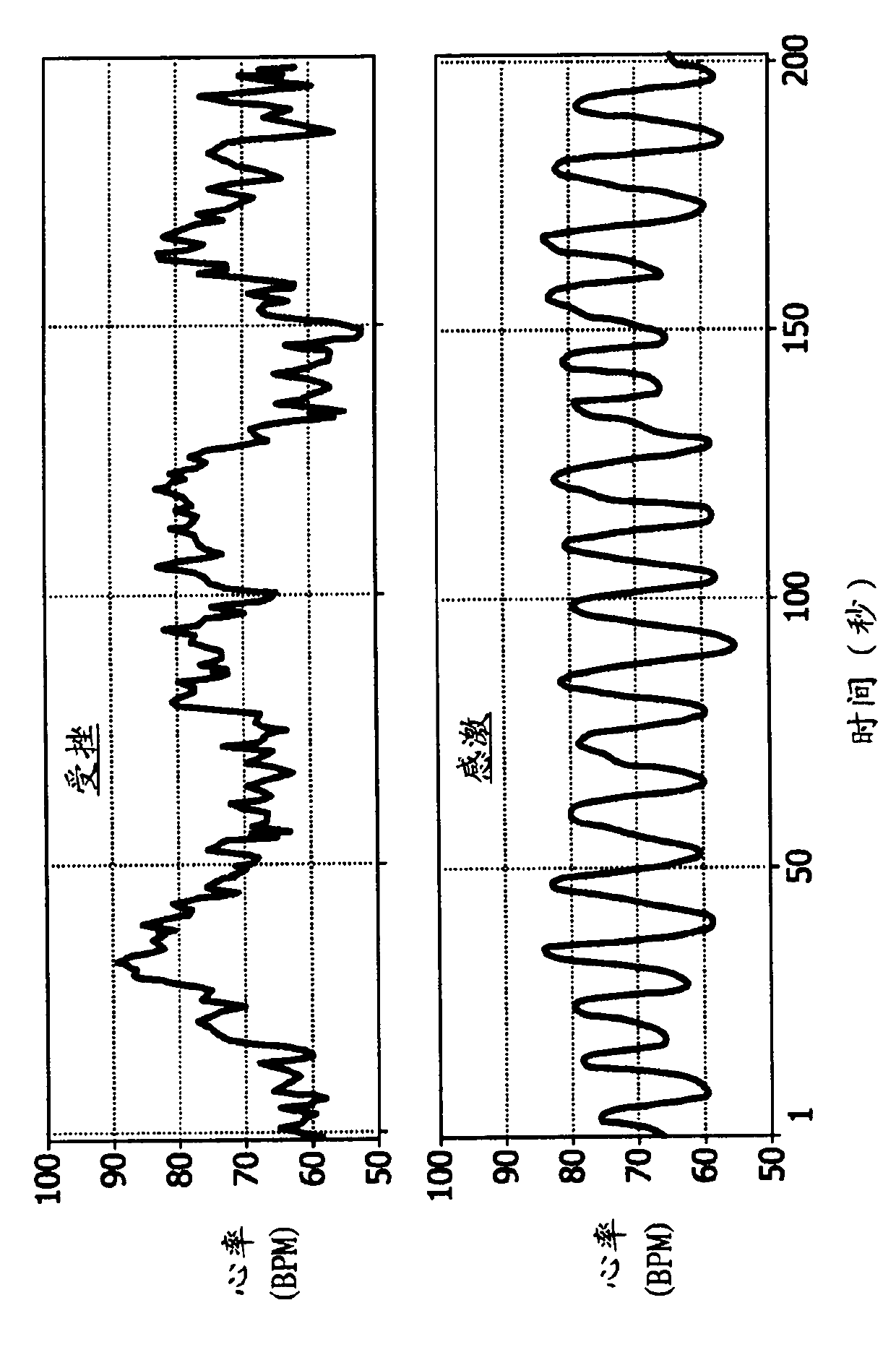
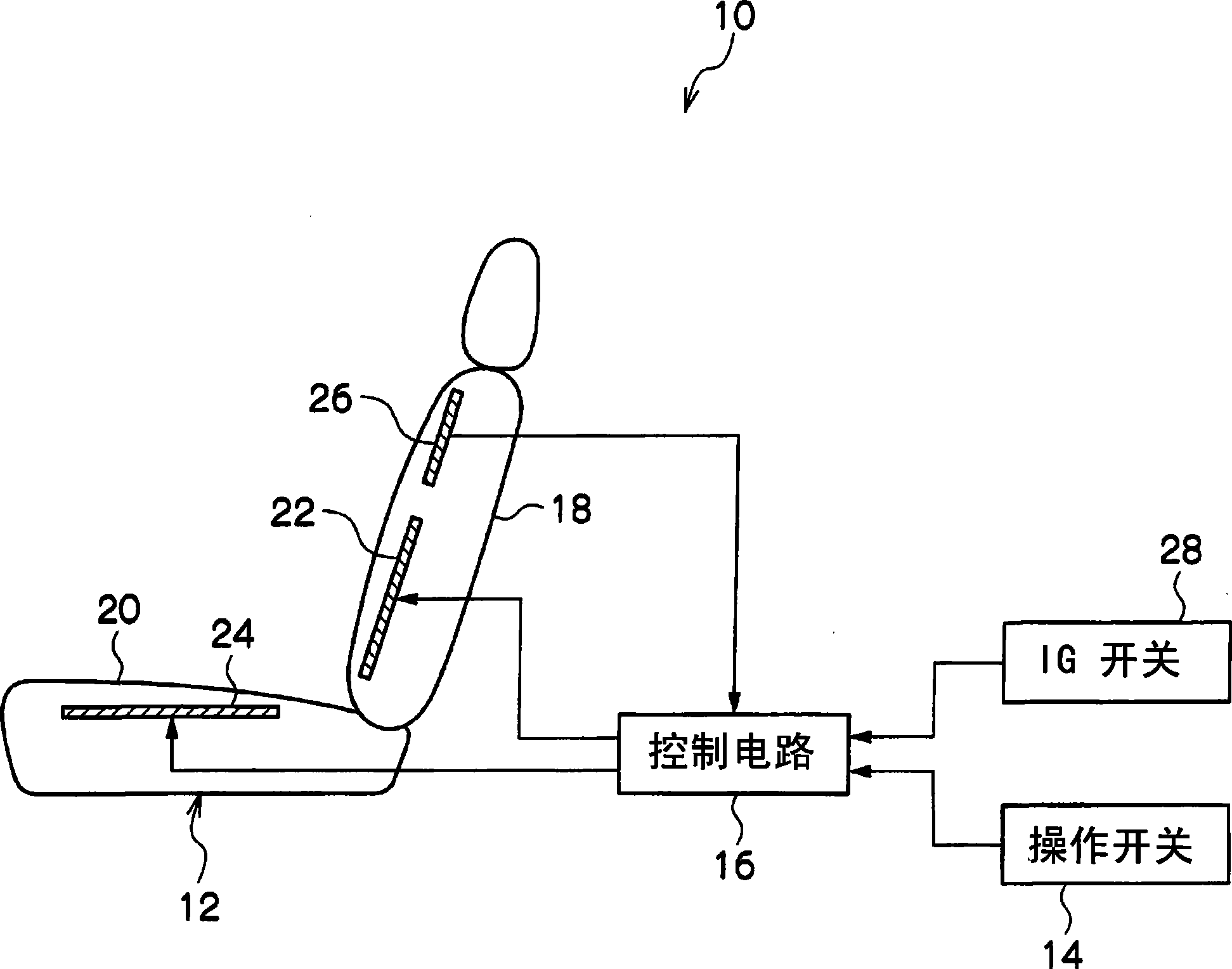
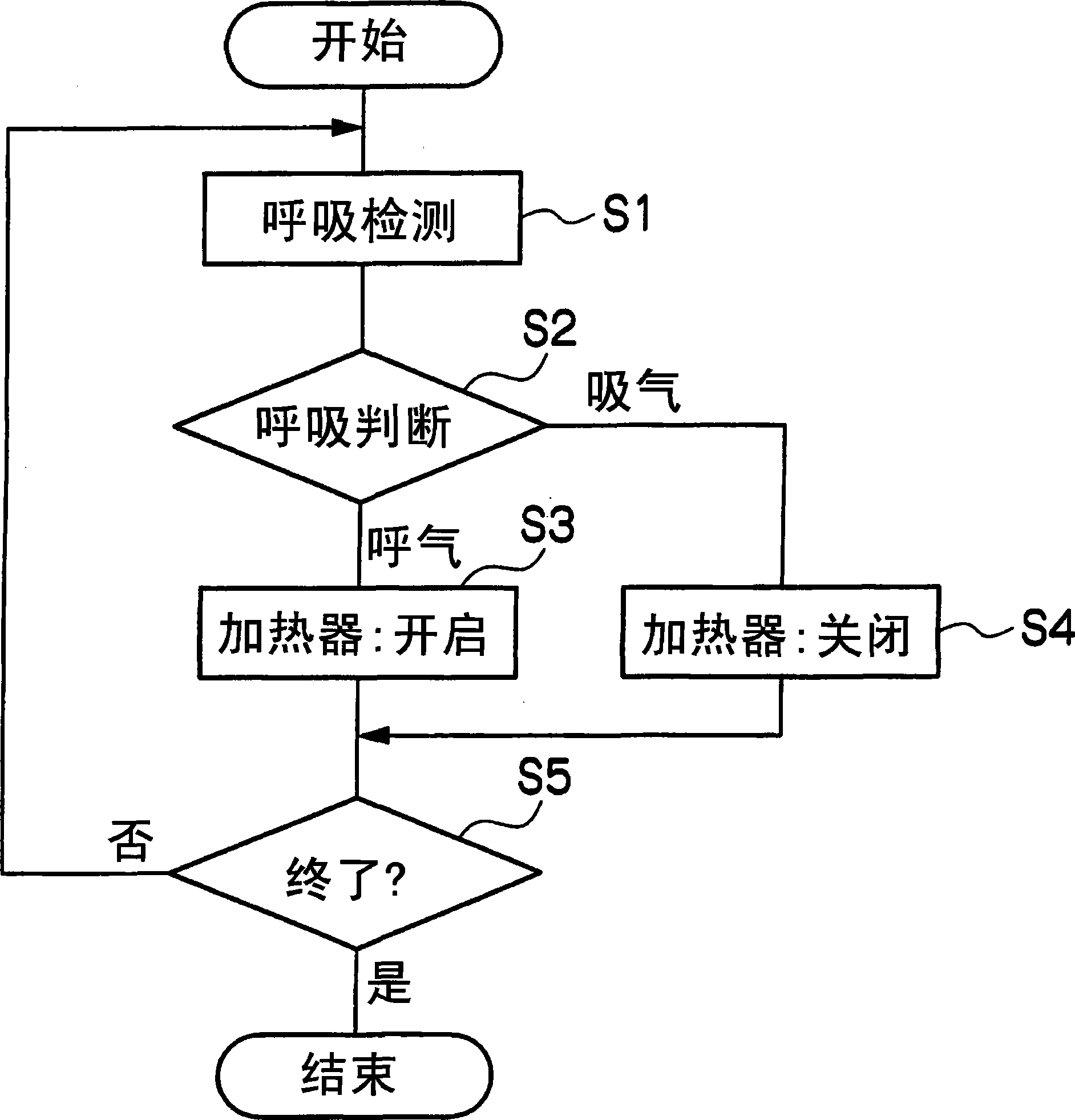
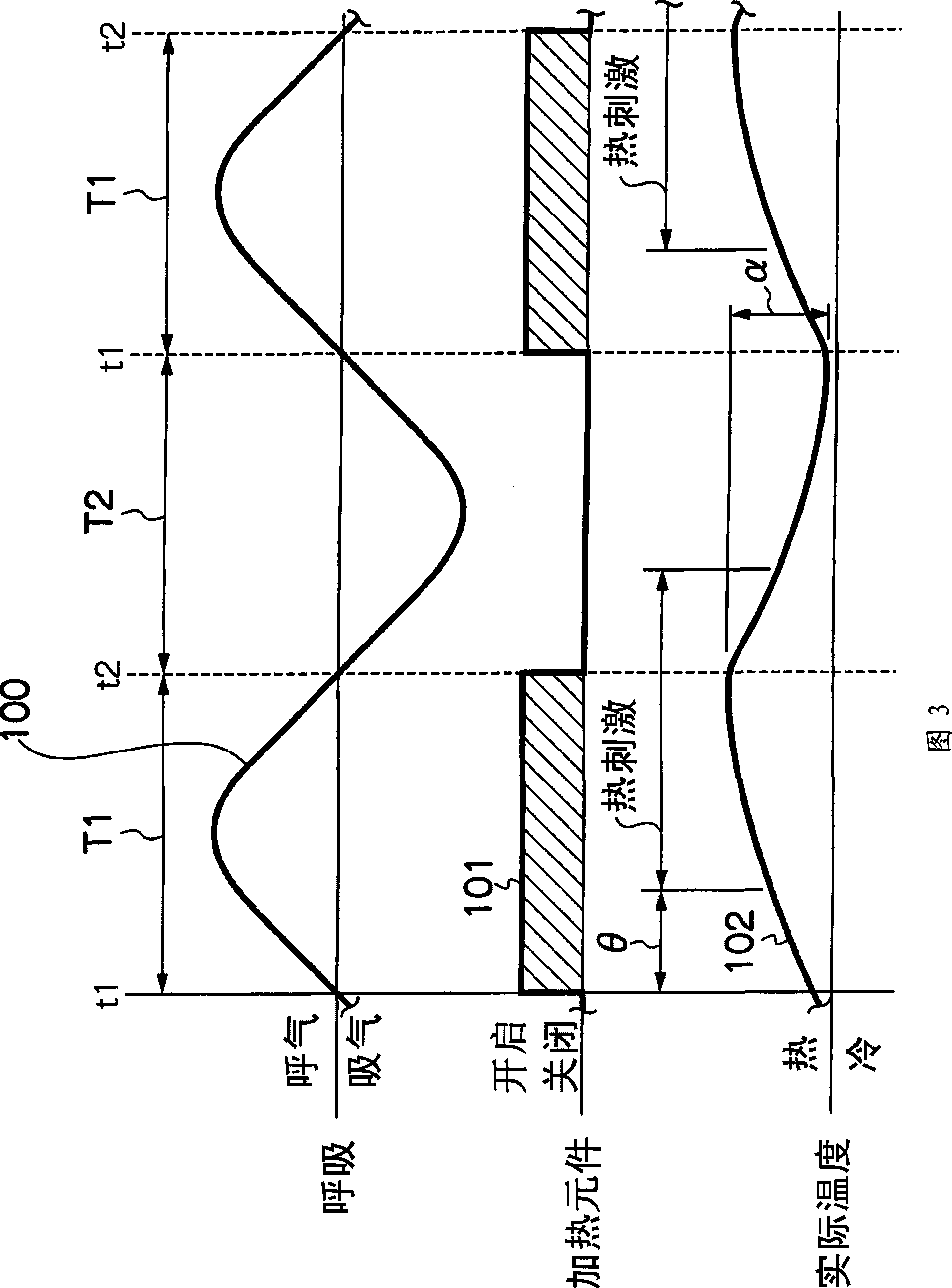
It is intended to provide a thermal stimulation apparatus for vehicles which can exert effects of, for example, reducing fatigue and improving physical conditions on a crew member in a vehicle. In a thermal stimulation apparatus for vehicles (10), when the biorhythm (for example, respiration rhythm) with periodical changes of a crewmember is detected by a piezoelectric sensor (26), heater elements (22, 24) are switched on by a control circuit (16) based on the detection data and thus thermal stimuli synchronizing the respiration rhythm of the crew member are provided to the crew member by switching on / off the heater element (22, 24). As a result, the autonomic nerve (parasympathetic nerve) activity of the crew member can be enhanced. Therefore, it becomes possible to exert effects of, for example, reducing fatigue and improving physical conditions on a crew member in a vehicle.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Respiration rate detection method and device based on thermal imaging and electronic equipment
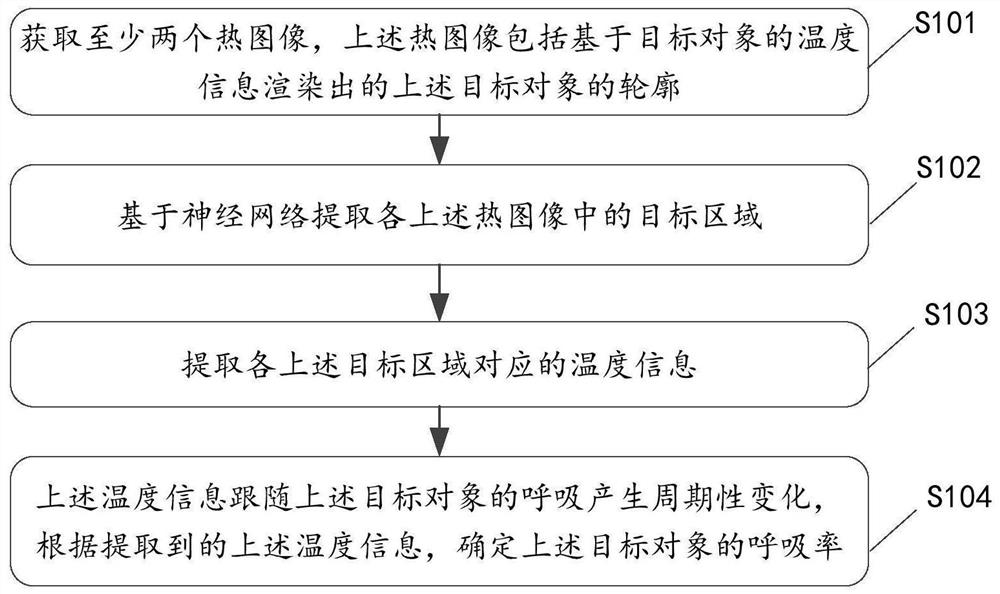
The invention relates to a respiratory rate detection method and device based on thermal imaging and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring at least two thermal images comprising the contour of a target object rendered based on the temperature information of the target object; extracting a target area in each thermal image based on a neural network; extracting temperature information corresponding to each target area; the temperature information periodically changing along with respiration of the target object, and determining the respiration rate of the target object according to the extracted temperature information. According to the method and the device, the breathing rate of the target object can be determined by analyzing the thermal image shot by the thermal imaging camera, so that the breathing rate detection result is obtained under the condition that the target object is not contacted, non-contact detection is realized, the blank of a non-contact detection scene is filled, and the method and the device have good detection speed and detection accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN SENSETIME TECH CO LTD
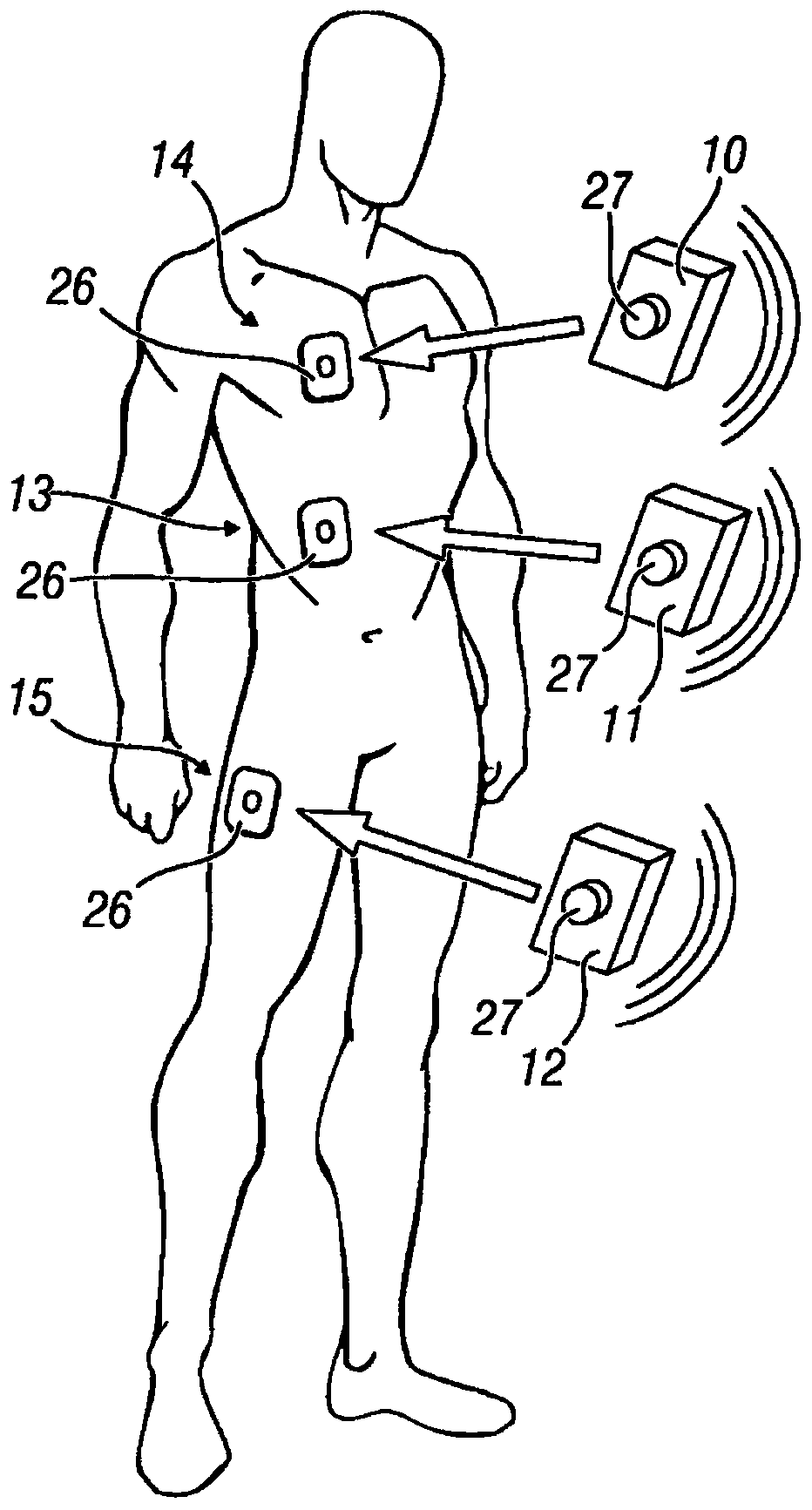
Wearable device for continuously monitoring respiratory rate
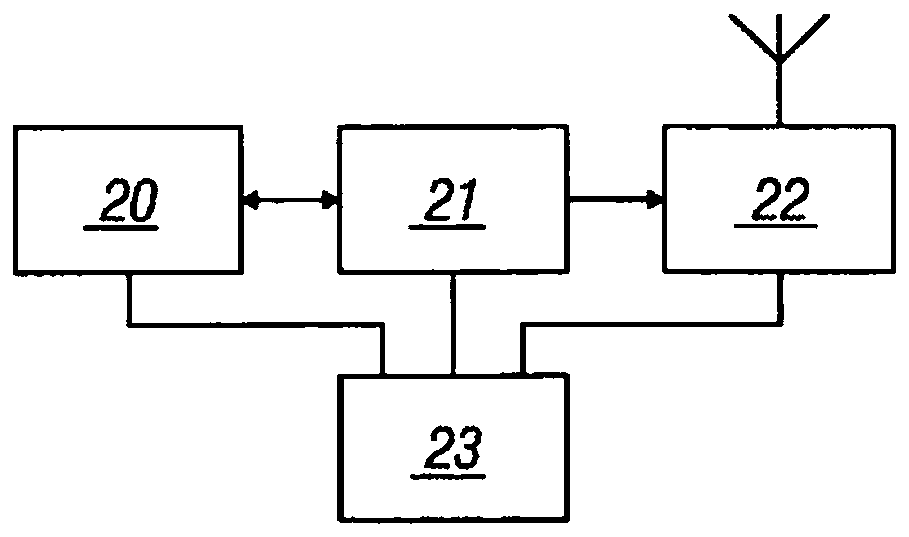
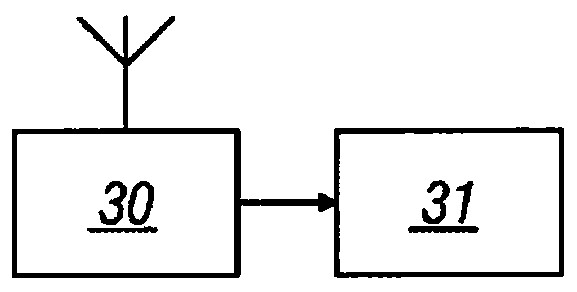
A wearable device for continuously monitoring the respiratory rate of a patient, comprises three inertial sensors (10, 11, 12), the first inertial sensor (10) is positioned on the abdomen (13), the second inertial sensor (11) is positioned on the thorax (14), and the third inertial sensor (12) is positioned on a part of the body (15) not subject to respiratory movements, fixed with respect to thetorso. Each inertial sensor (10, 11, 12) comprises an accelerometer, a magnetometer, and a gyroscope. Each inertial sensor (10, 11, 12) comprises a microprocessor (21) connected to the accelerometer,magnetometer, and gyroscope. The microprocessor (21) is connected to a transmitter (22) and is configured to process the signals and supply to the transmitter (22) a signal represented by a quaternionthat describes the orientation of the three inertial sensors with respect to the Earth's reference system. A receiver (30) connected to a control centre (31) is configured to receive the abdominal quaternion of the first inertial sensor, the thoracic quaternion of the second inertial sensor, and the reference quaternion of the third inertial sensor and is configured to send them to the control centre (31). The control centre (31) is configured to process the quaternions received, so that the abdominal quaternion and the thoracic quaternion will be referenced to the reference quaternion. The control centre (31) comprises a band-pass adaptive filter (55, 56) that filters the signals represented by the abdominal quaternion and by the thoracic quaternion to eliminate the residual components linked to the movements of the patient. The control centre (31) is configured to calculate the respiratory rate from the signals represented by the filtered abdominal quaternion and the filtered thoracic quaternion.
Owner:米兰综合工科大学
Anti-motion-interference non-contact respiratory signal measuring method
ActiveCN111402201AInterference will notInterference will not be affectedImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyThoracic structure
The invention discloses an anti-motion-interference non-contact respiratory signal measurement method, which does not need to be in contact with a human body for measurement, is simple to implement and is not interfered by detection equipment, and the measurement precision is greatly improved. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1, shooting N frames of thoracic cavity position images;2, processing a first frame of thoracic cavity position image; 3, processing the second to Nth frames of thoracic cavity position images; 4, obtaining a curve of each side length and each diagonal length changing with time through the obtained side lengths and diagonal lengths of the N polygons on the N frames of thoracic cavity position images; and 5, carrying out filtering processing on the curve of each side length and each diagonal length changing with time so as to obtain a respiration signal and a respiration rate.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Breath guiding device and breath guiding method
The invention discloses a breath guiding device and a breath guiding method. The breath guiding device comprises an ideal entropy feedback device, a life entropy corrector and a respiratory wave guidedevice, wherein the ideal entropy feedback device and the life entropy corrector are connected in series so as to form a self-excitation breath guide closed loop, and the ideal entropy feedback device and the respiratory wave guide device are used in combination so as to form a mutual excitation breath guide open link. According to the breath guiding method, the heart rate and respiratory rate signals of a human body are obtained through a remote sensing detection radar; and analysis is performed so as to obtain corrected entropies, and a signal feedback path is established. According to thebreath guiding device and the breath guiding method of the invention, self-excitation control is performed on the breath guiding device on the basis of the rule of corrected entropy minimization, so that intervention intensity can be learned and corrected, and therefore, an intervention effect can be improved, co-frequency guidance and resonance guidance are connected in series, and the co-frequency and resonance mutual excitation effect of a group can be optimized.
Owner:北京喜马医疗科技有限公司
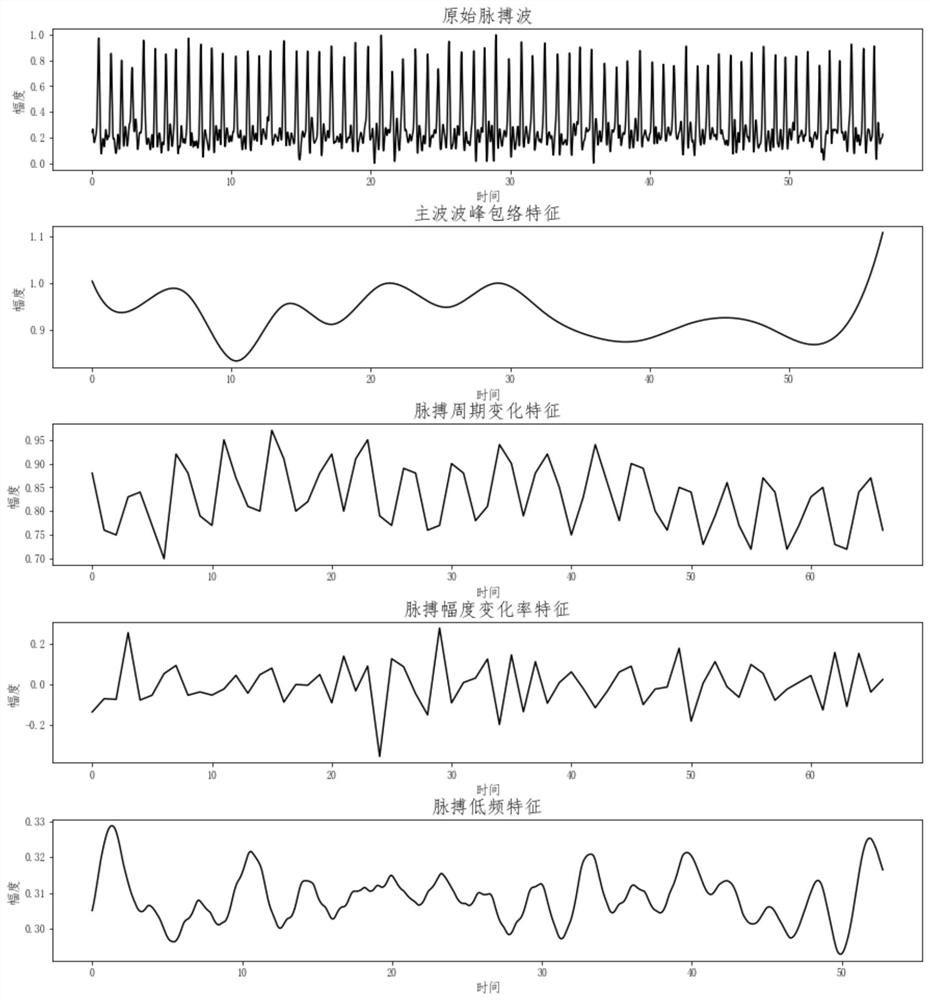
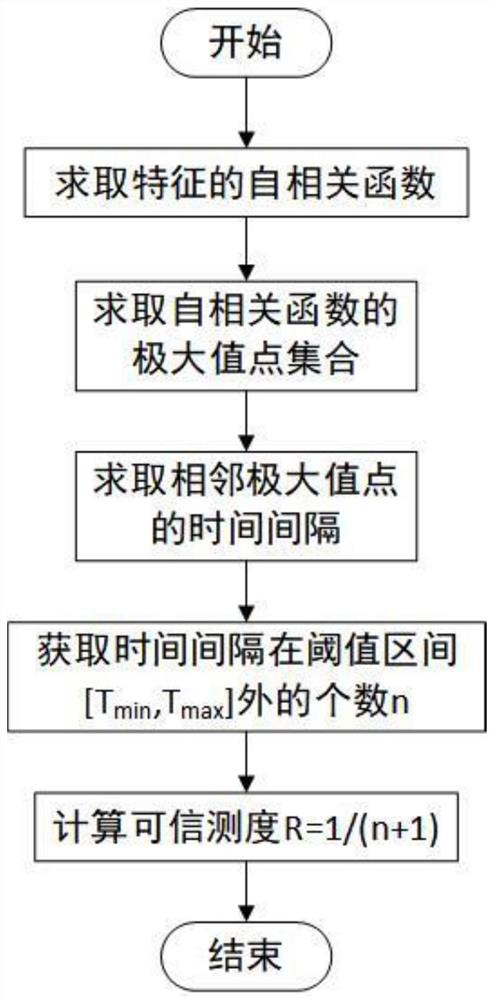
Pulse wave multi-feature fusion-based respiratory rate extraction method
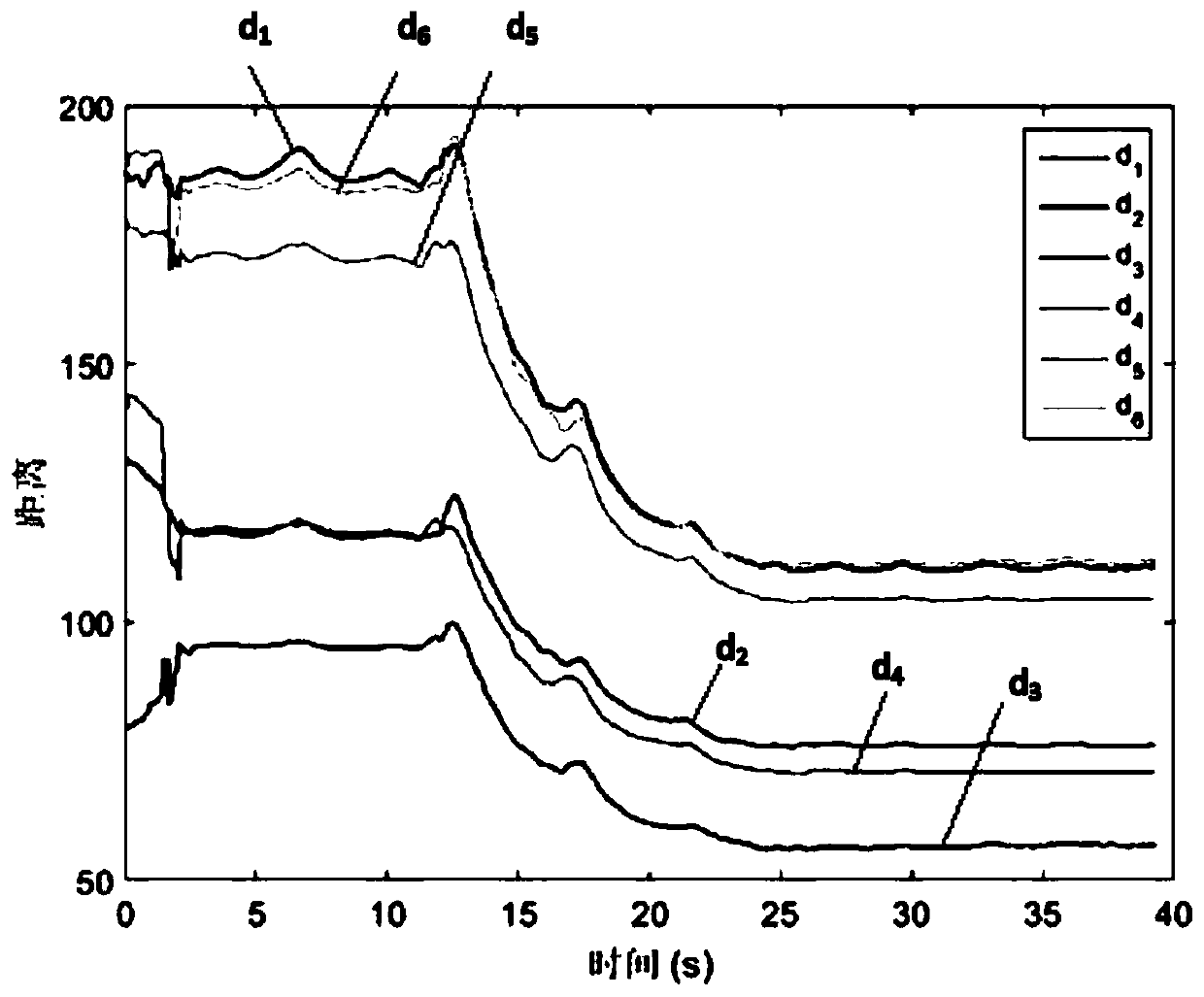
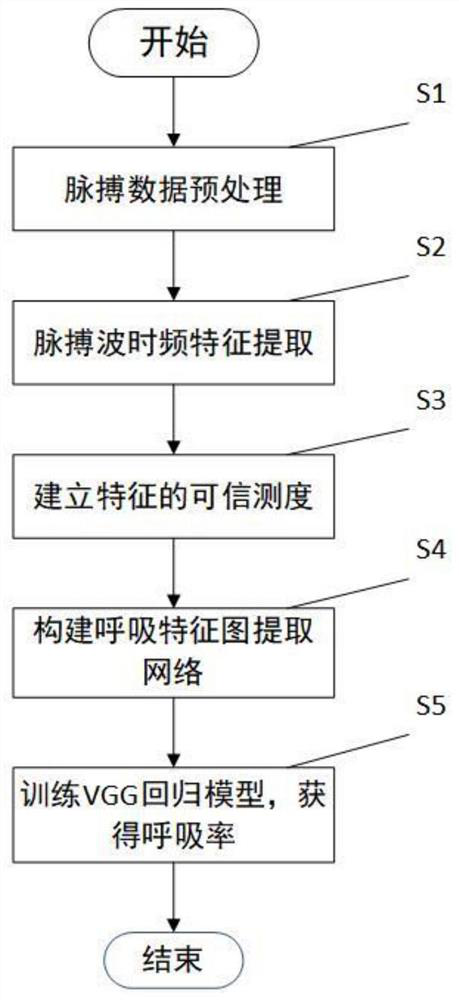
ActiveCN112998690AResolve uncertaintyImprove accuracyRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsMulti feature fusionData pre-processing
The invention discloses a pulse wave multi-feature fusion-based respiratory rate extraction method, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring signals at the wrist and fingers of a user by using an array pulse wave acquirer to obtain a multi-channel pulse wave file, and performing data preprocessing on the pulse wave file to obtain a multi-channel fused pulse wave; multiple time-frequency characteristics of the fused pulse waves are extracted; constructing a credible measure of each time-frequency feature through time domain analysis; taking the credible measure of each feature as the learning weight of each feature in a neural network by using an attention mechanism, and extracting a respiration feature map by using a convolutional neural network; and fusing the extracted breathing feature maps, and inputting the fused breathing feature maps into a VGG regression model to obtain a final breathing rate. According to the method, on the basis of credible measurement of multiple features, the respiration feature map is better extracted in combination with an attention mechanism of the neural network, and the accuracy of pulse wave respiration rate extraction under the condition of big data is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
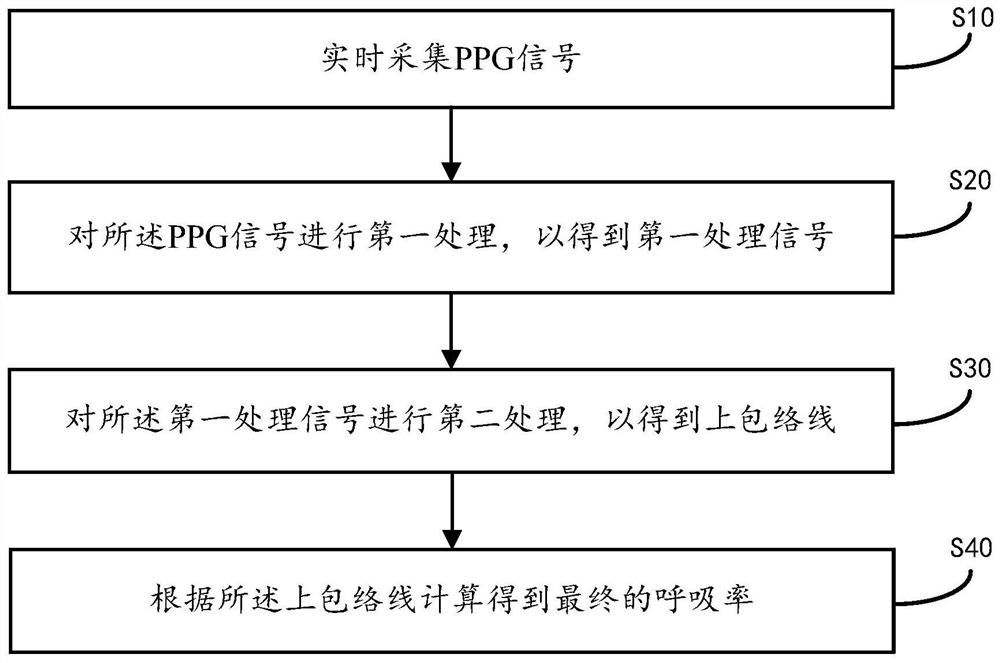
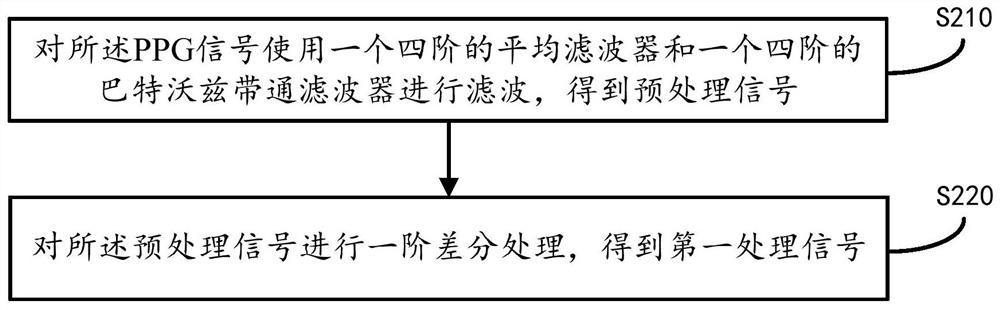
PPG signal based respiratory rate measurement method and device
PendingCN112494008ALess affected by the outside worldEasy to operateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringEmergency medicine
The invention provides a PPG signal based respiratory rate measurement method and device. The method includes the following steps: collecting PPG signals in real time; performing first processing on the PPG signals so as to obtain a first processing signal, wherein the first processing includes filtering and differential processing; performing second processing on the first processing signal so asto obtain an upper envelope; and calculating final respiratory rate according to the upper envelope. In addition, a PPG signal based respiratory rate measurement device is also provided. Through theprovided measurement method and device, the measurement of the respiratory rate can be realized through the PPG based signals; and compared with existing respiratory rate measurement methods, the measurement method and device are small in influences from the outside, wide in application scenario, simple in operation, easy to carrying and faster in measurement.
Owner:SHENZHEN FENDA SMART TECH LTD
Respiration rate detection method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment
The invention relates to a respiratory rate detection method and device, a storage medium and electronic equipment. The method comprises the steps that at least two thermal images are acquired, the thermal images are obtained through rendering based on temperature information of a preset area, the preset area comprises a target object, and a breathing area of the target object falls into a target area determined based on the preset area; for each thermal image, temperature information of the target area in the thermal image is extracted, and the temperature information periodically changes along with respiration of the target object; and the breathing rate of the target object is determined according to the extracted temperature information. According to the method, the respiratory rate of the target object can be determined by analyzing the temperature information of the target area of the thermal image, so that non-contact detection is realized, and the method has good detection speed and detection accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN SENSETIME TECH CO LTD
Acoustically Enhanced Pet Animal Collar for Health & Vital Signs Monitoring, Alert and Diagnosis
An acoustically enhanced collar for monitoring vital signs of a pet animal, may comprise an elastic band having a working surface configured to wrap around a neck of a pet animal and an oppositely faced rear surface, at least one sensor element situated along a circumference of the band and configured to measure at least one bioparameter from the following bioparameters: temperature, heart rate, respiration rate, movement; at least one acoustic concentrator projecting as a bump toward the neck from the working surface on a first side of the at least one sensor element; at least one acoustic concentrator projecting as a bump toward the portion from the working surface on a second side of the at least one sensor element and acoustic balancers projecting from the rear surface at least partly behind the acoustic concentrators. Preferably, the acoustic concentrators and balancers have a base end having an “X”shape.
Owner:PETPACE
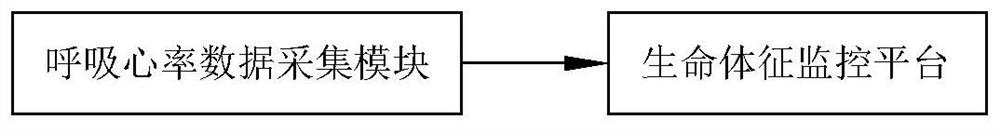
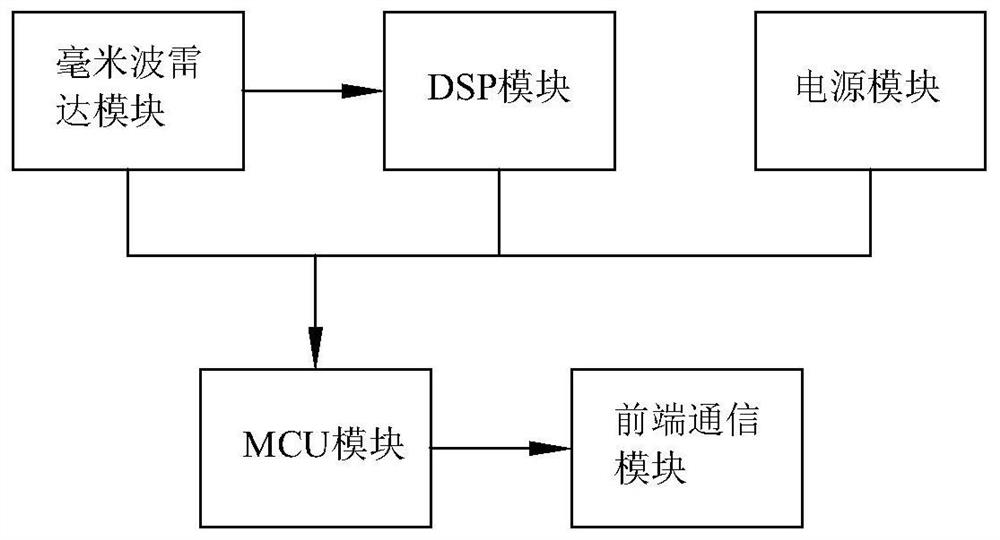
Multi-target respiratory heart rate monitoring method and system based on millimeter wave radar technology
ActiveCN111481184BNo invasion of privacyImprove reliabilityDigital data authenticationSensorsEngineeringEmergency medicine
The present invention relates to a multi-target breathing and heart rate monitoring method and system based on millimeter-wave radar. The millimeter-wave radar module performs non-contact heart rate and respiration rate detection, which avoids cumbersome contact monitoring procedures and does not offend the detected ones. user's privacy. Compared with the non-contact detection technology in the prior art, the present invention improves the detection accuracy and greatly enhances the reliability of the measurement. The present invention monitors and analyzes the breathing and heart rate data of the monitoring object in real time through the vital signs monitoring platform, which can prevent the monitoring object from sudden unexpected diseases, or provide timely alarms in the event of an emergency; medical staff can timely monitor the vital signs through the vital signs monitoring platform Master the vital signs data of the monitoring object, timely evaluate the physical condition of the monitoring object and give professional opinions and suggestions; the family members of the monitoring object can obtain the health report of the monitoring object through the vital signs monitoring platform, and follow the professional guidance. Nursing the monitoring objects.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com