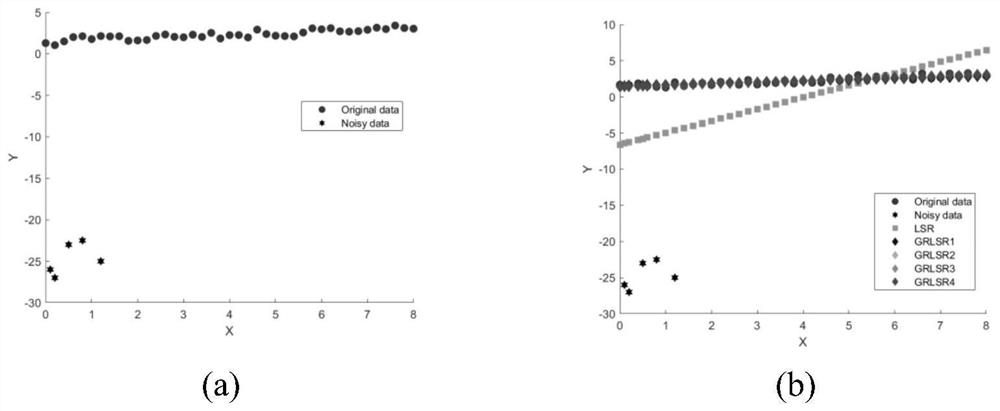
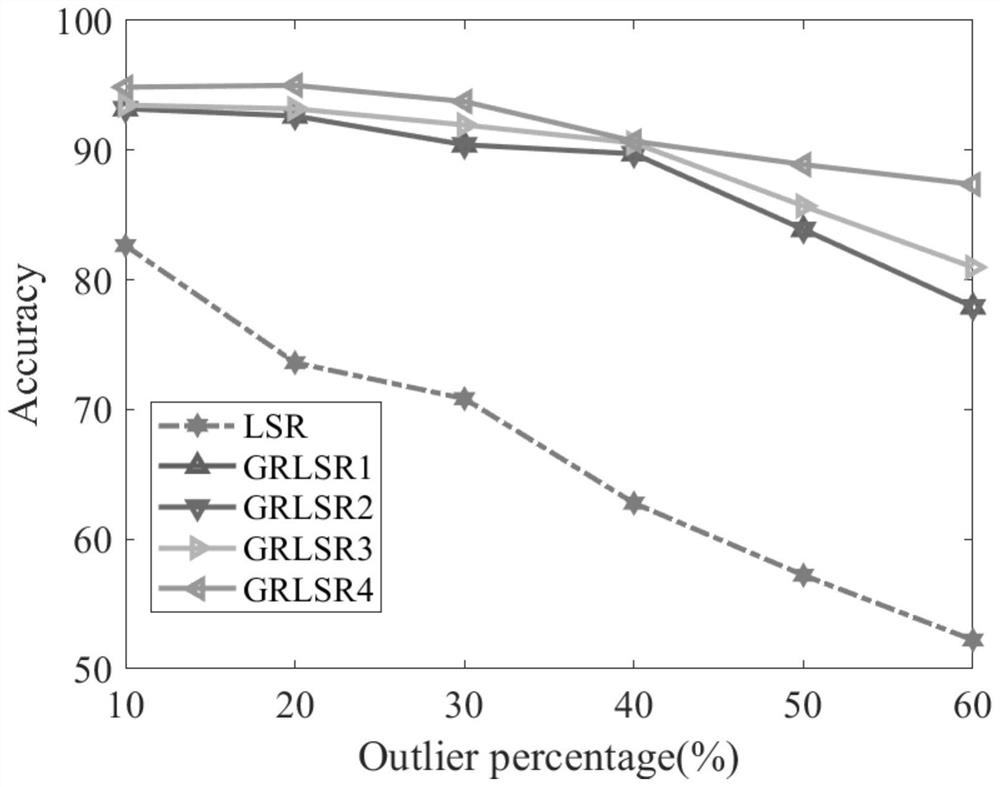
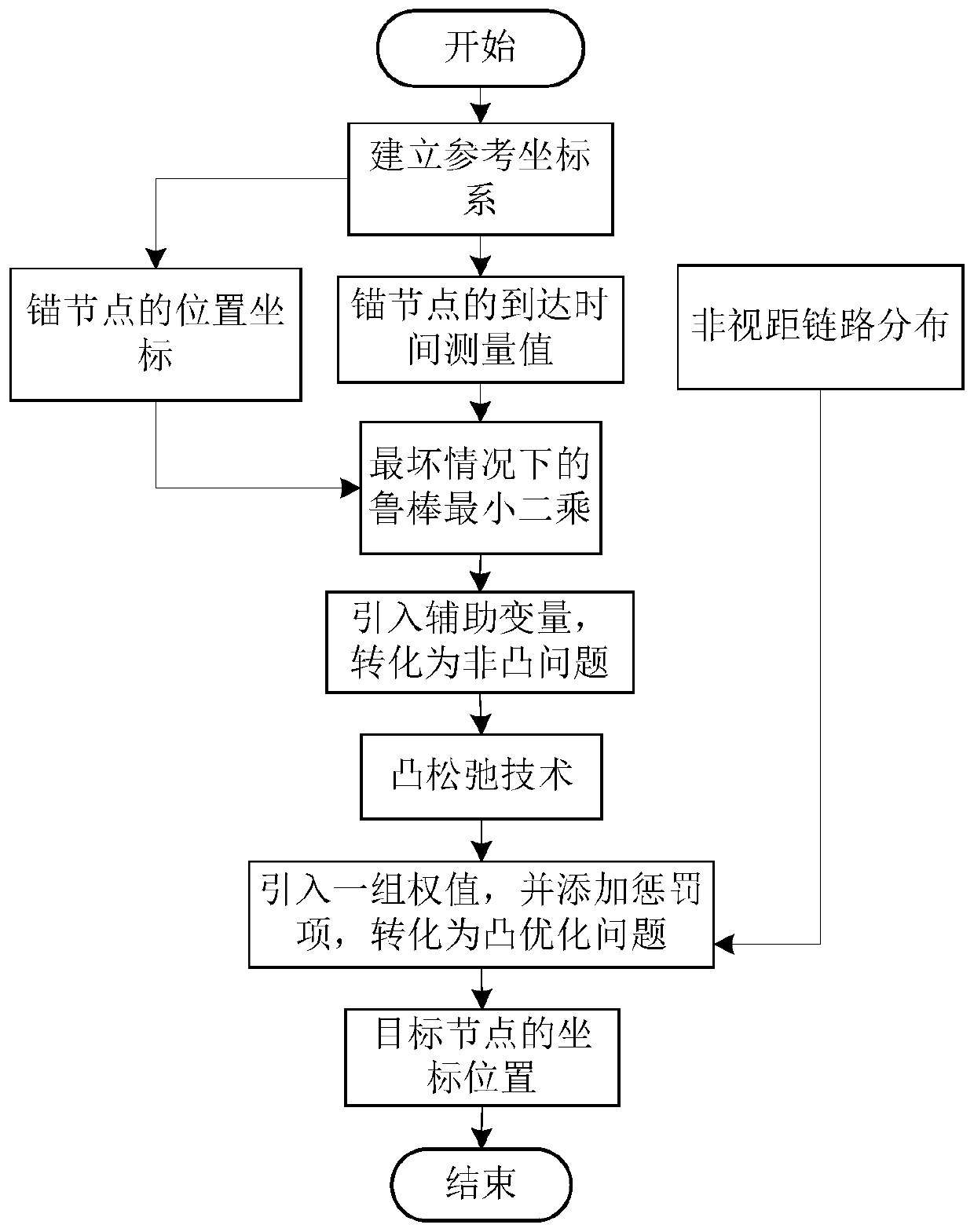
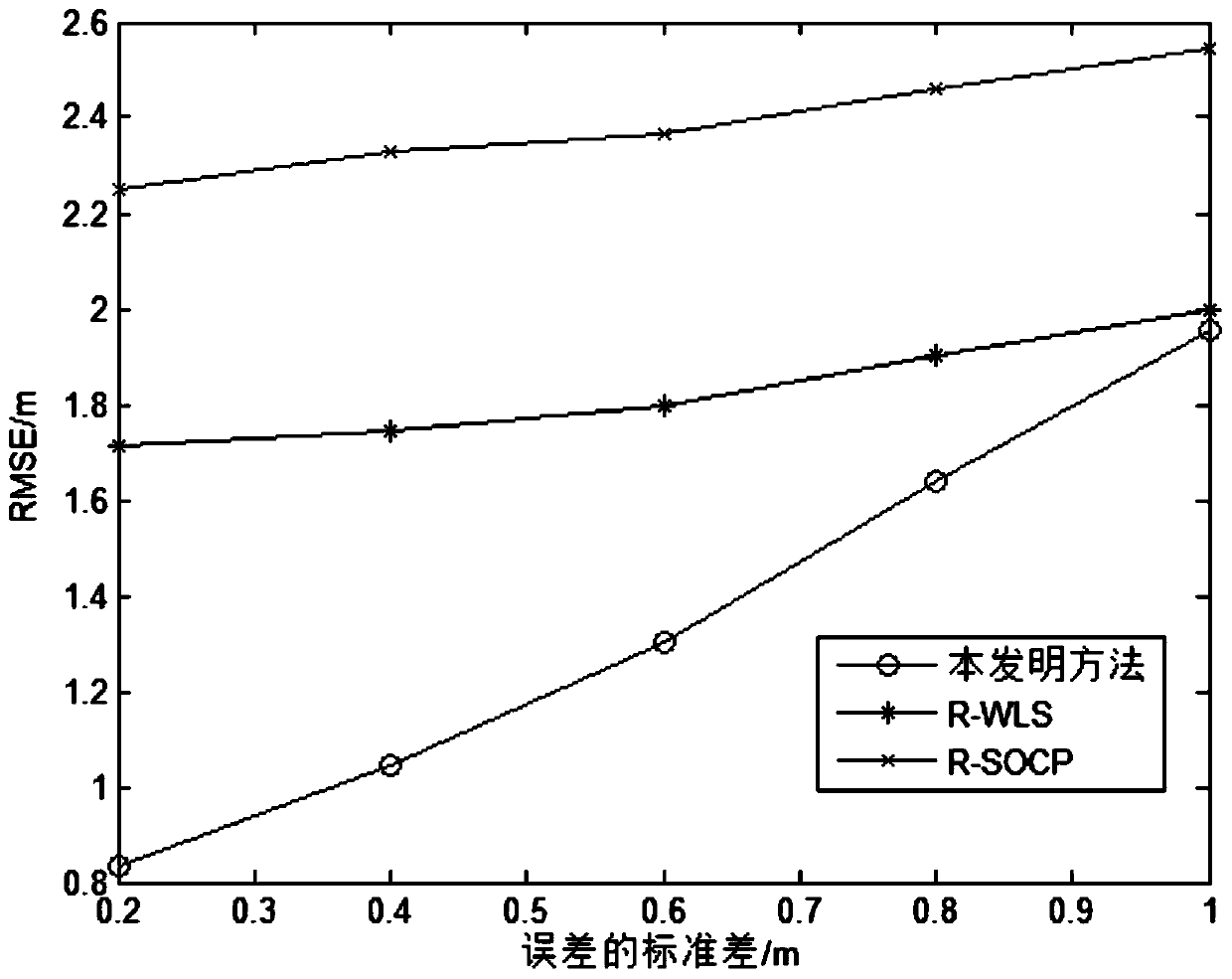
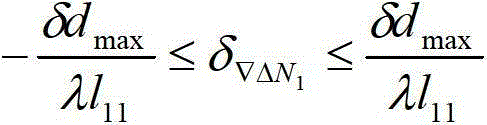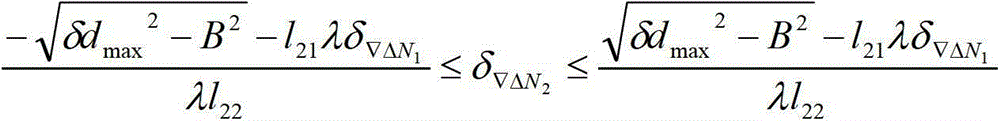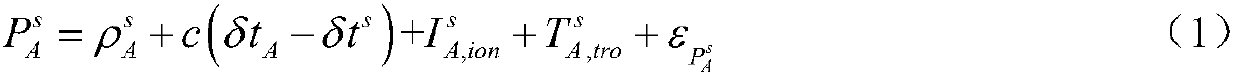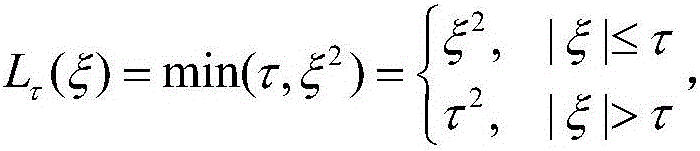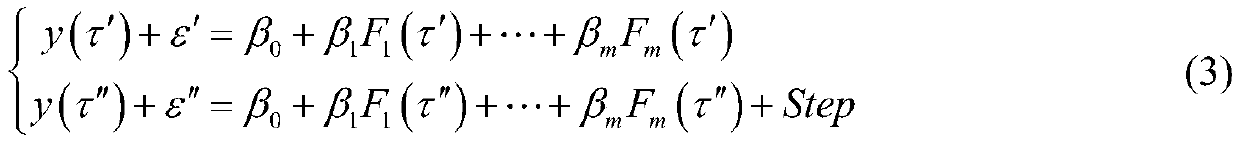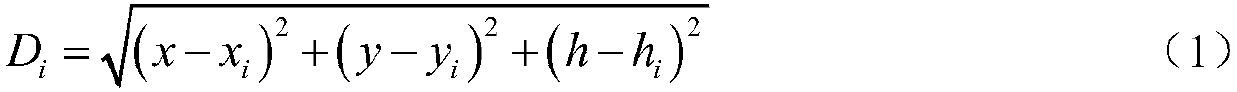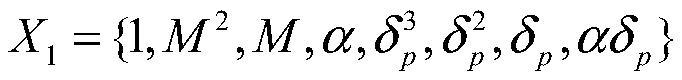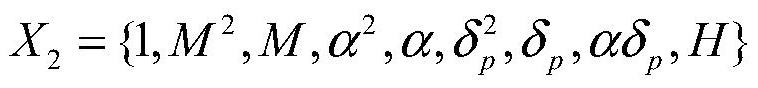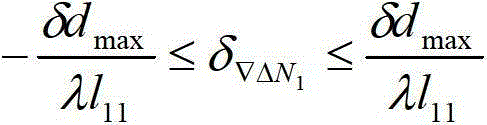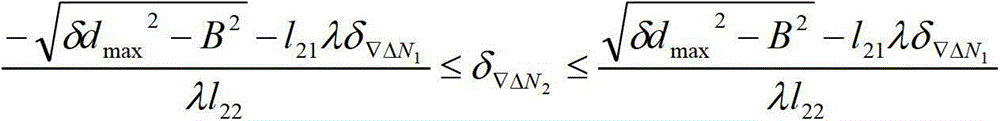Patents
Literature
45 results about "Robust least squares" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
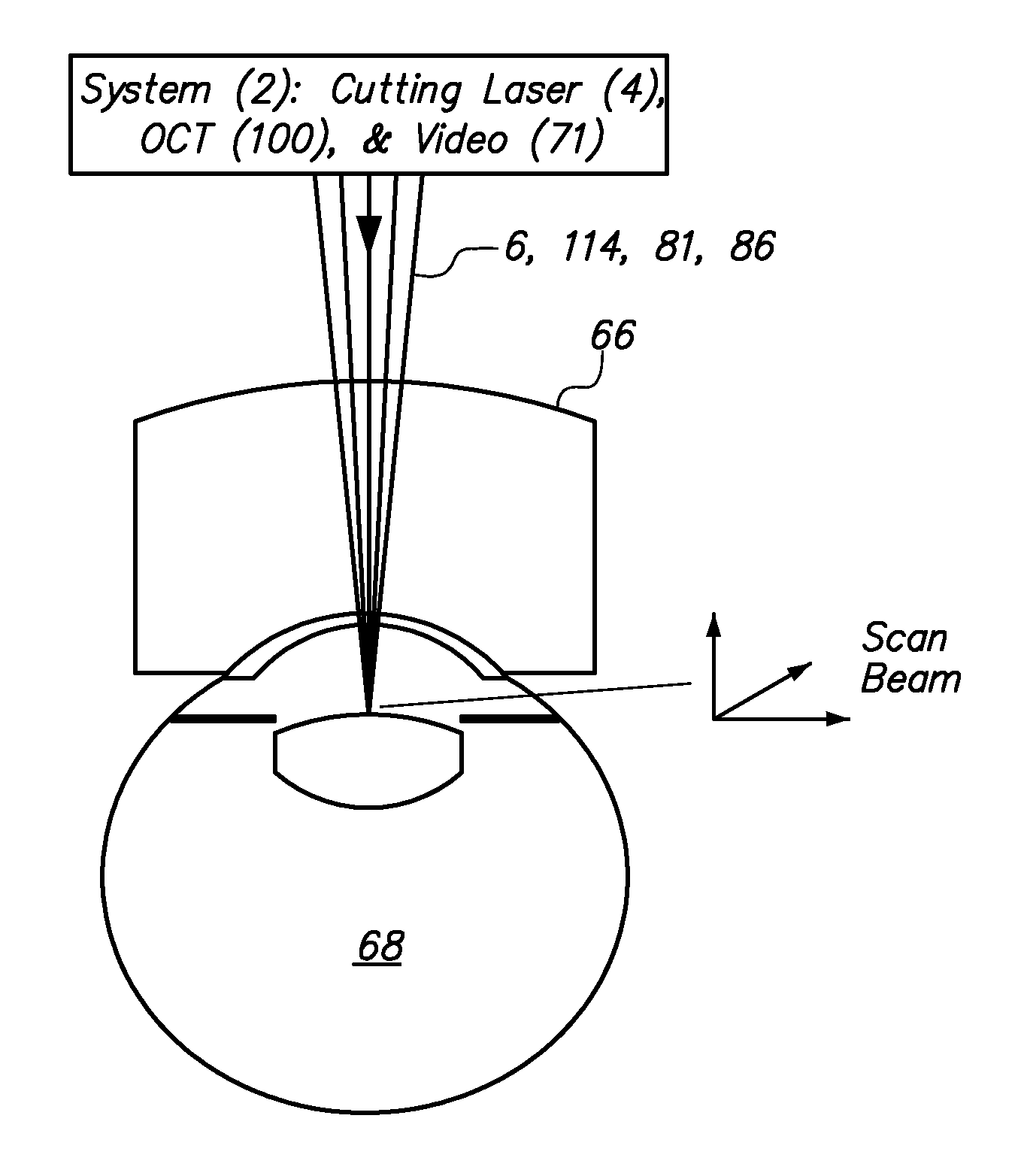
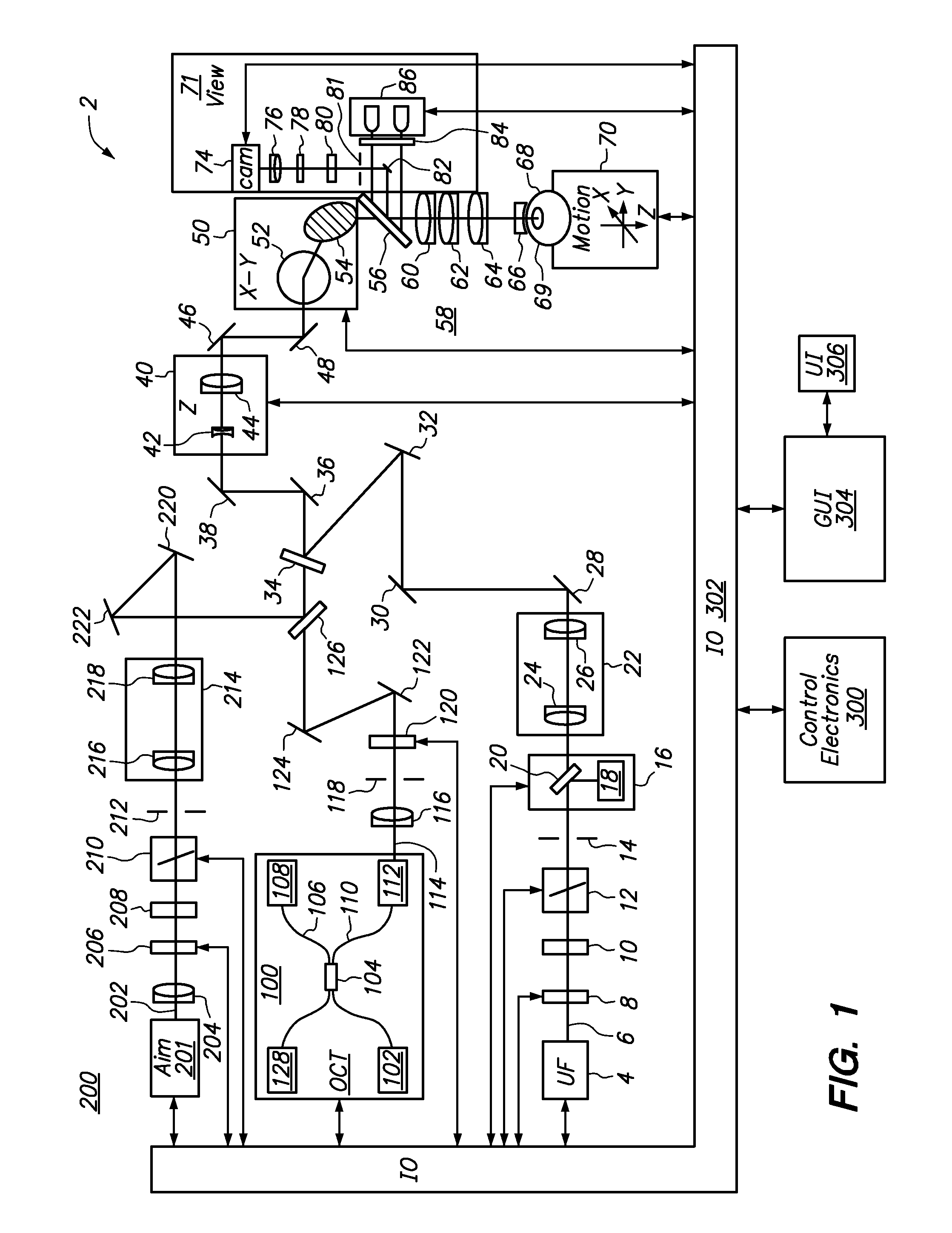
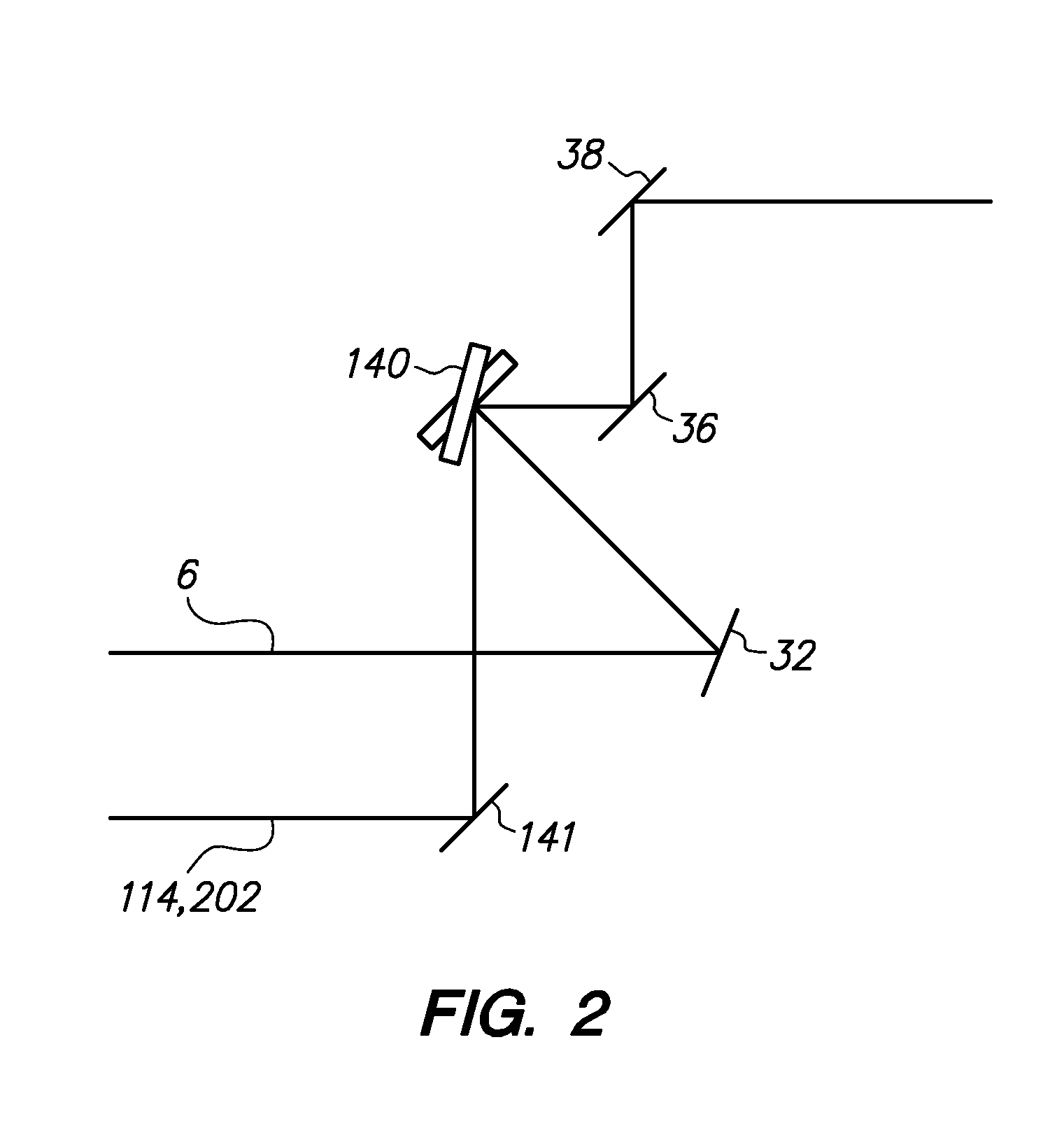
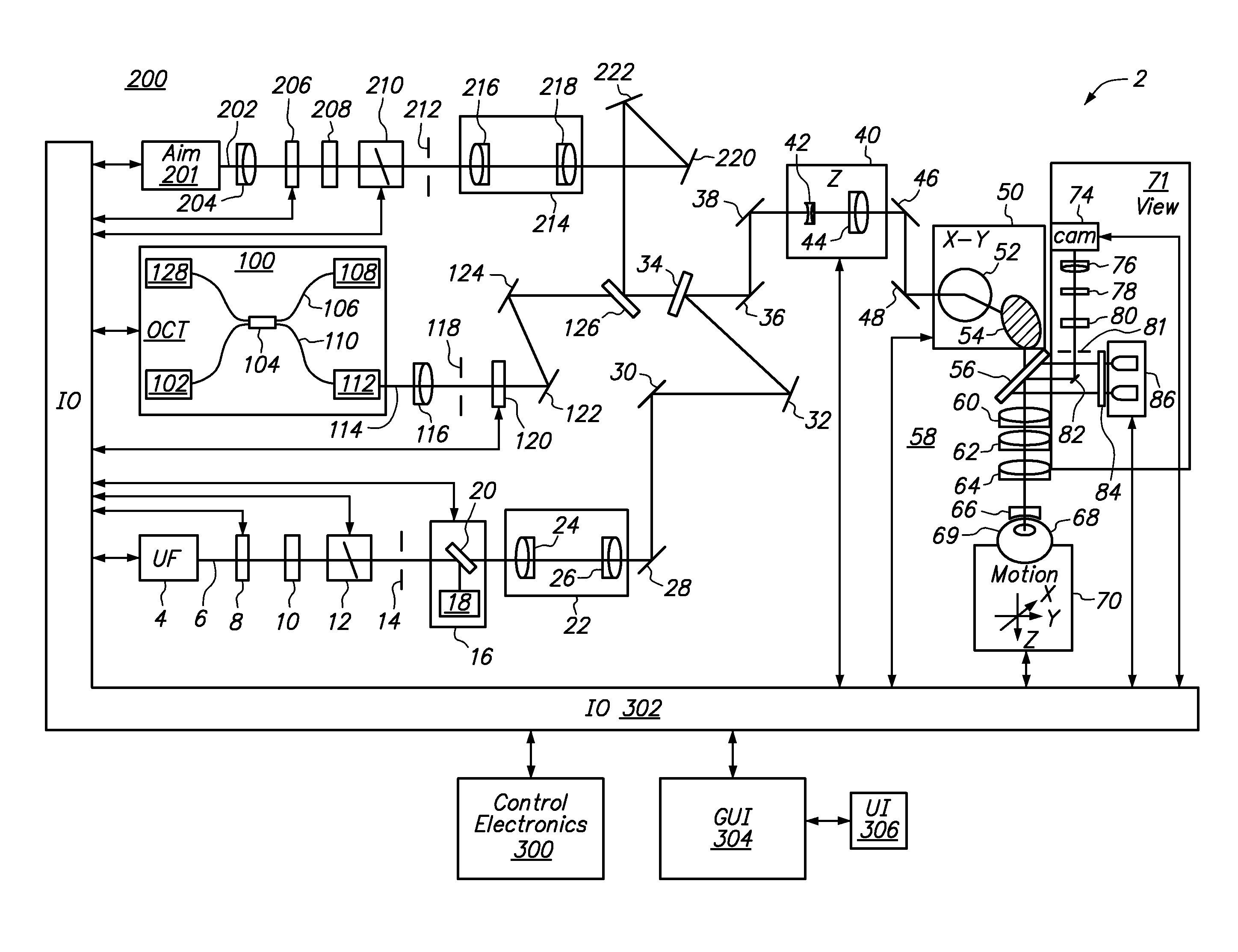
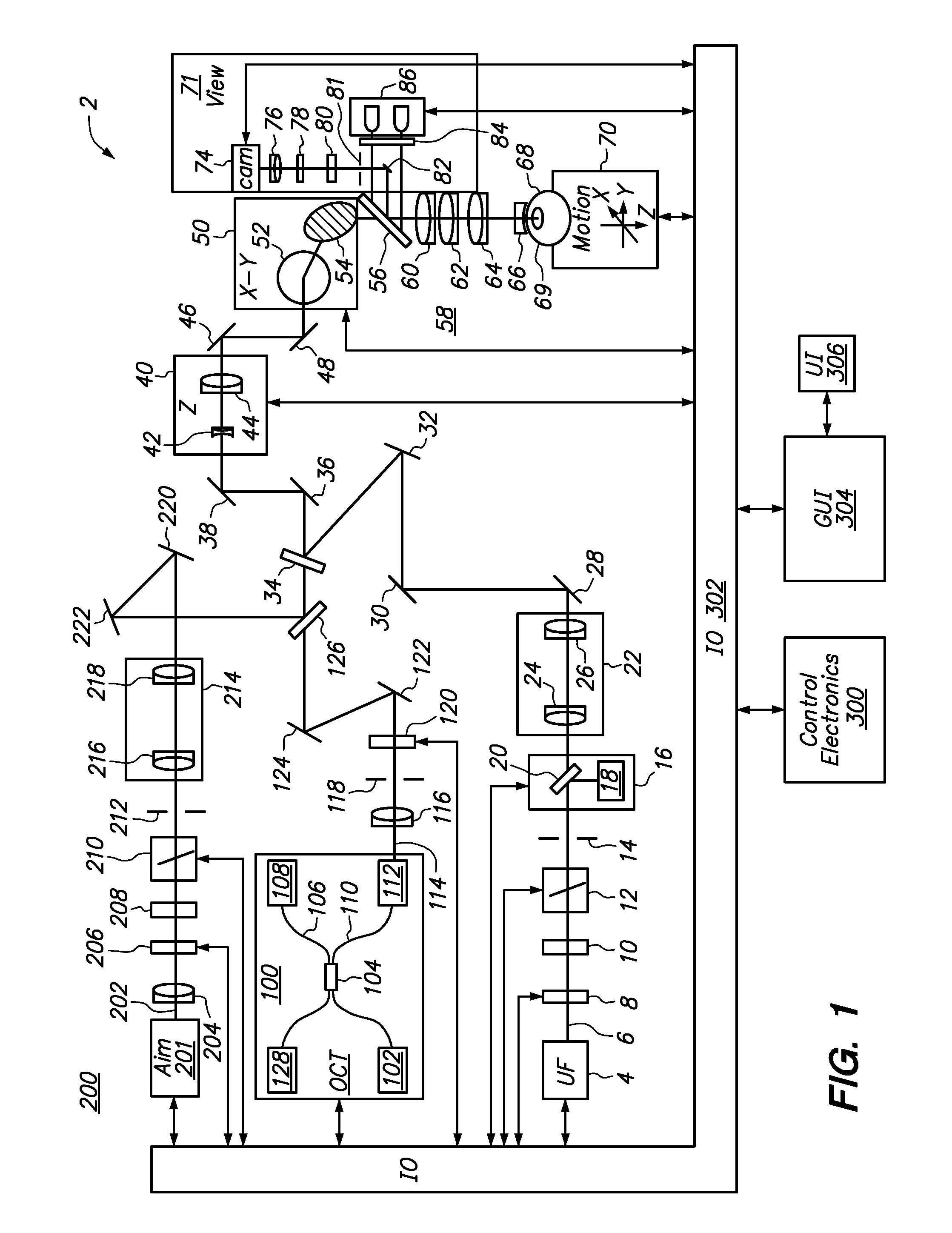
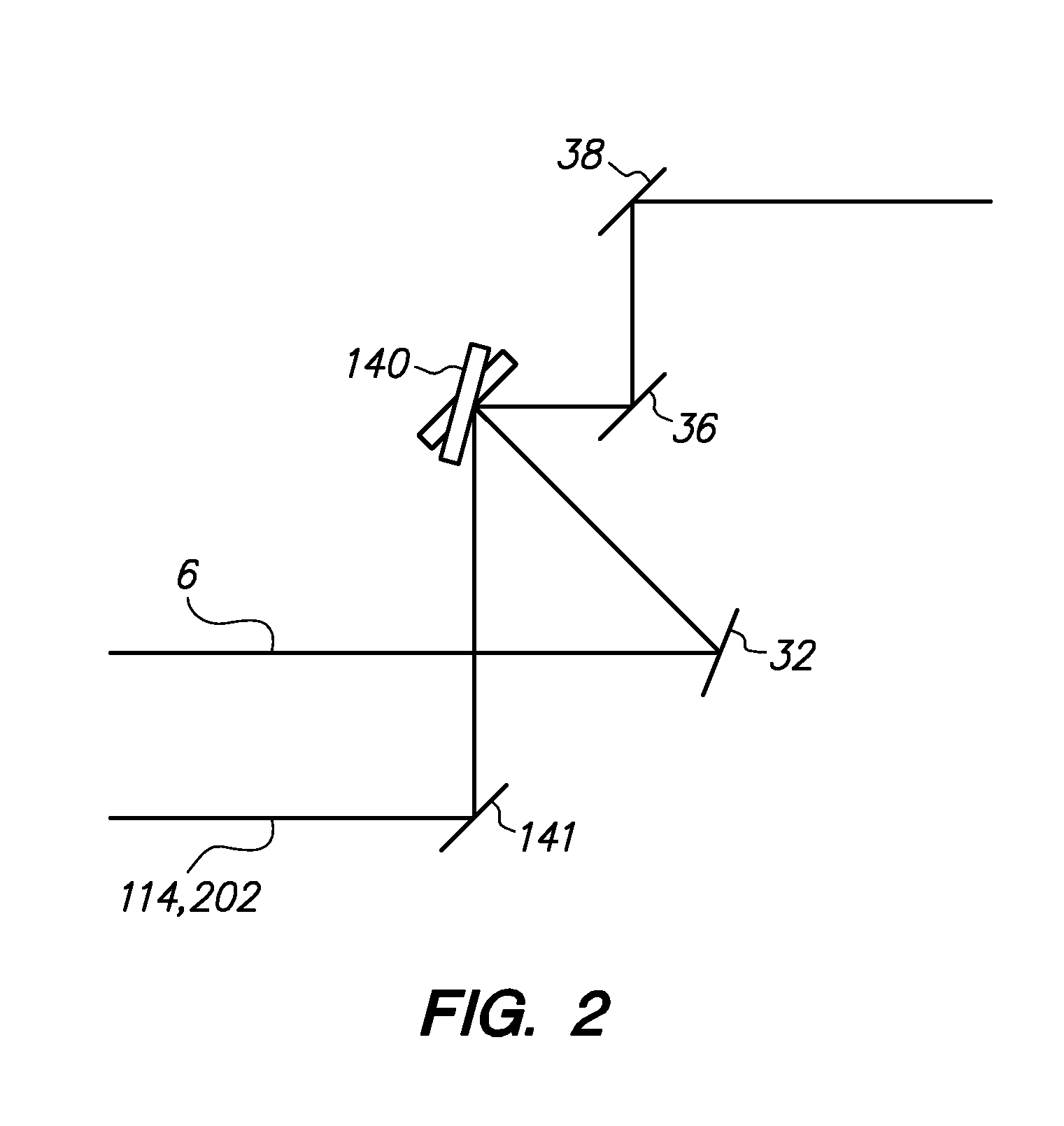
Method and apparatus for automated placement of scanned laser capsulorhexis incisions
ActiveUS20110202046A1Easy to implantLaser surgeryImage enhancementAnatomical structuresRobust least squares
Systems and methods are described for cataract intervention. In one embodiment a system comprises a laser source configured to produce a treatment beam comprising a plurality of laser pulses; an integrated optical system comprising an imaging assembly operatively coupled to a treatment laser delivery assembly such that they share at least one common optical element, the integrated optical system being configured to acquire image information pertinent to one or more targeted tissue structures and direct the treatment beam in a 3-dimensional pattern to cause breakdown in at least one of the targeted tissue structures; and a controller operatively coupled to the laser source and integrated optical system, and configured to adjust the laser beam and treatment pattern based upon the image information, and distinguish two or more anatomical structures of the eye based at least in part upon a robust least squares fit analysis of the image information.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Method and apparatus for automated placement of scanned laser capsulorhexis incisions
ActiveUS8845625B2Easy to implantLaser surgeryImage enhancementAnatomical structuresRobust least squares
Systems and methods are described for cataract intervention. In one embodiment a system comprises a laser source configured to produce a treatment beam comprising a plurality of laser pulses; an integrated optical system comprising an imaging assembly operatively coupled to a treatment laser delivery assembly such that they share at least one common optical element, the integrated optical system being configured to acquire image information pertinent to one or more targeted tissue structures and direct the treatment beam in a 3-dimensional pattern to cause breakdown in at least one of the targeted tissue structures; and a controller operatively coupled to the laser source and integrated optical system, and configured to adjust the laser beam and treatment pattern based upon the image information, and distinguish two or more anatomical structures of the eye based at least in part upon a robust least squares fit analysis of the image information.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
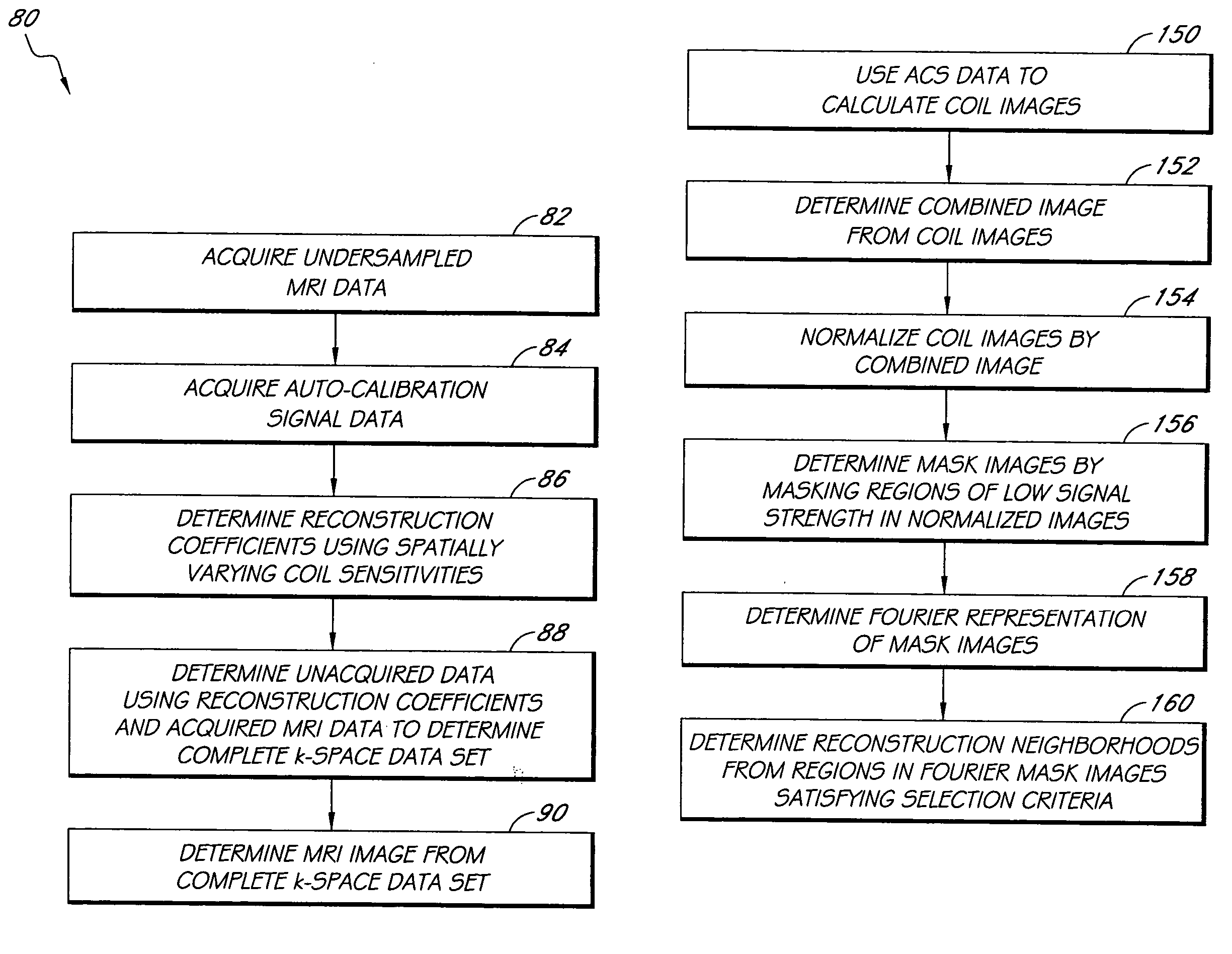
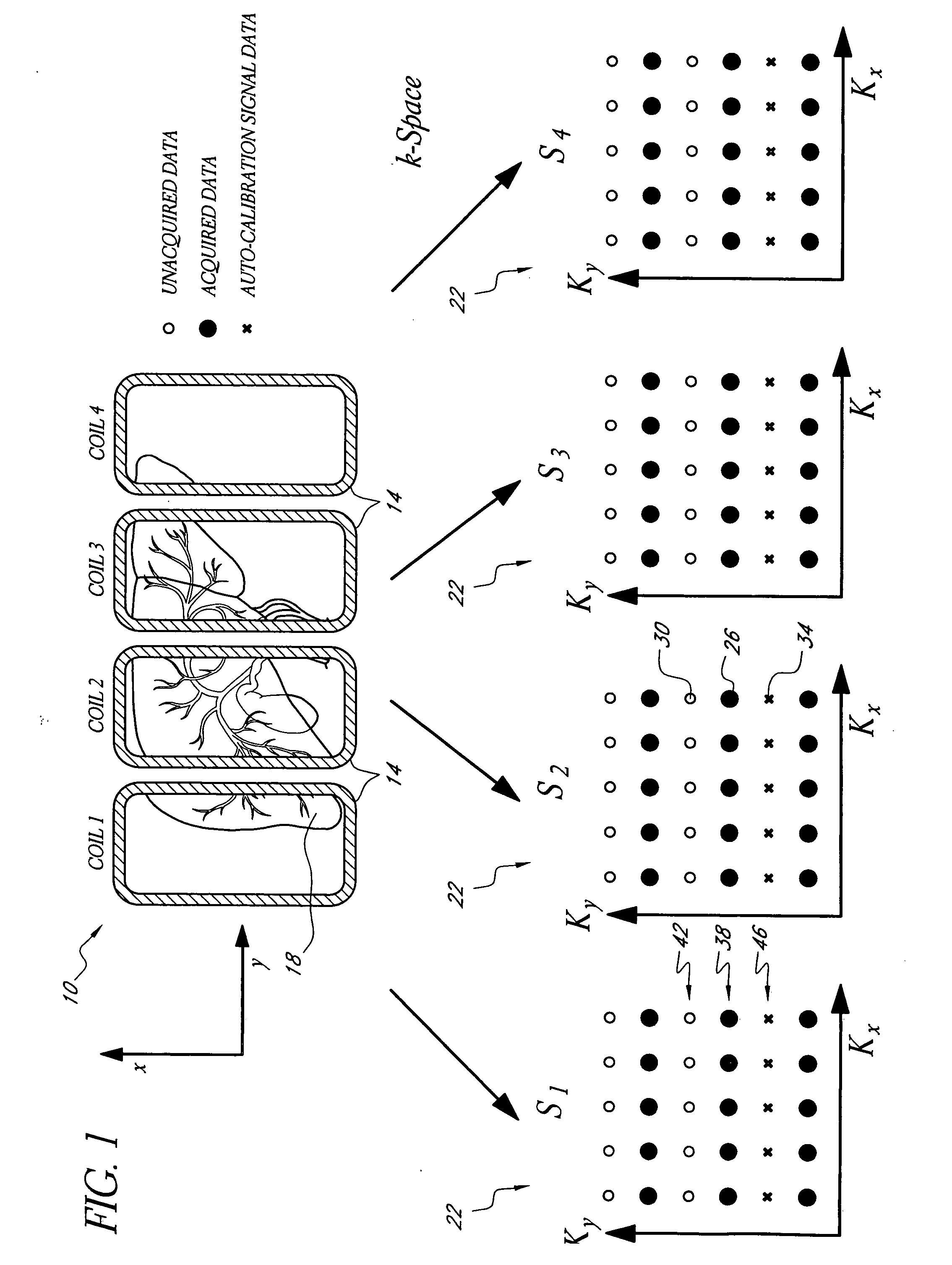
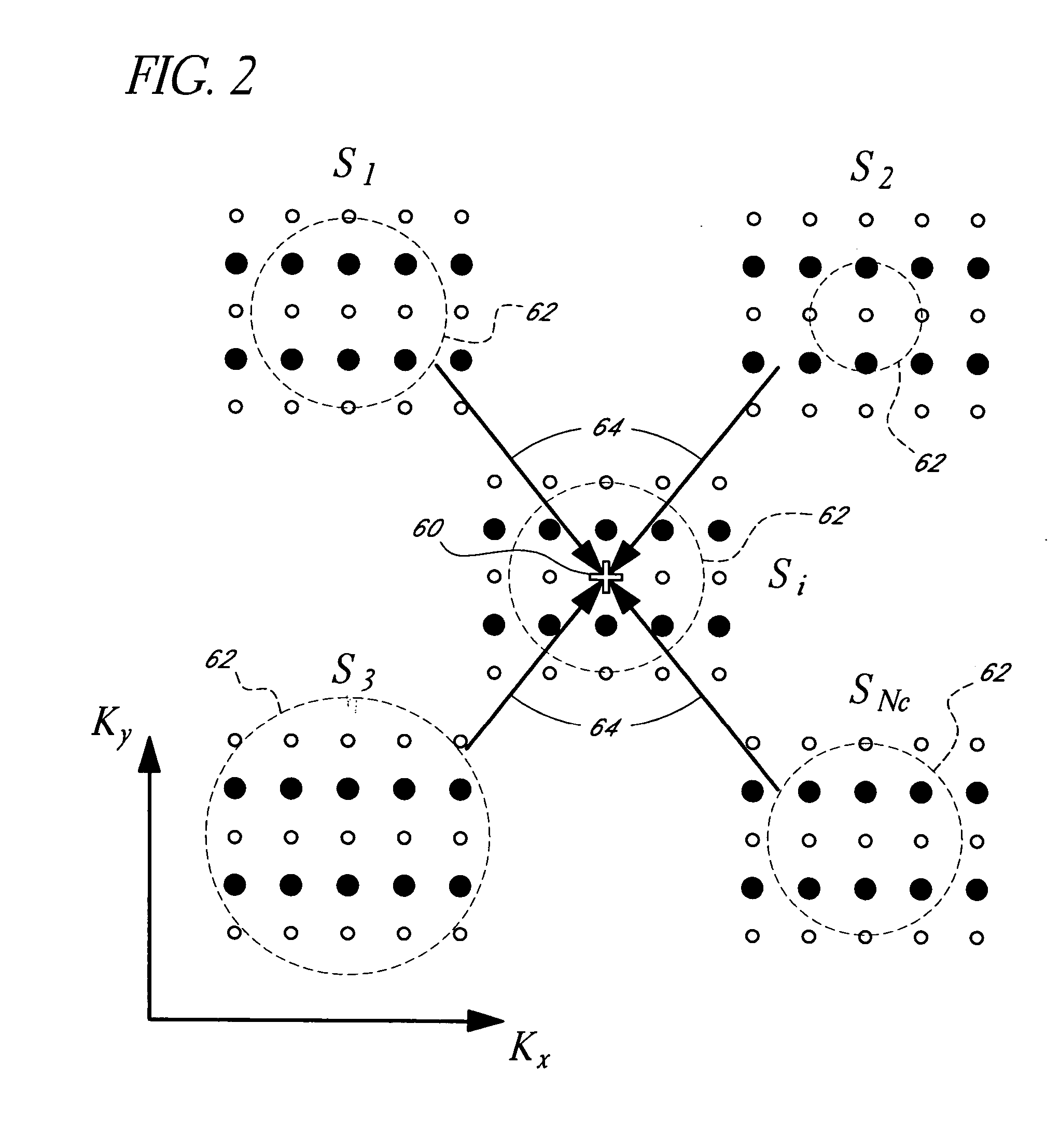
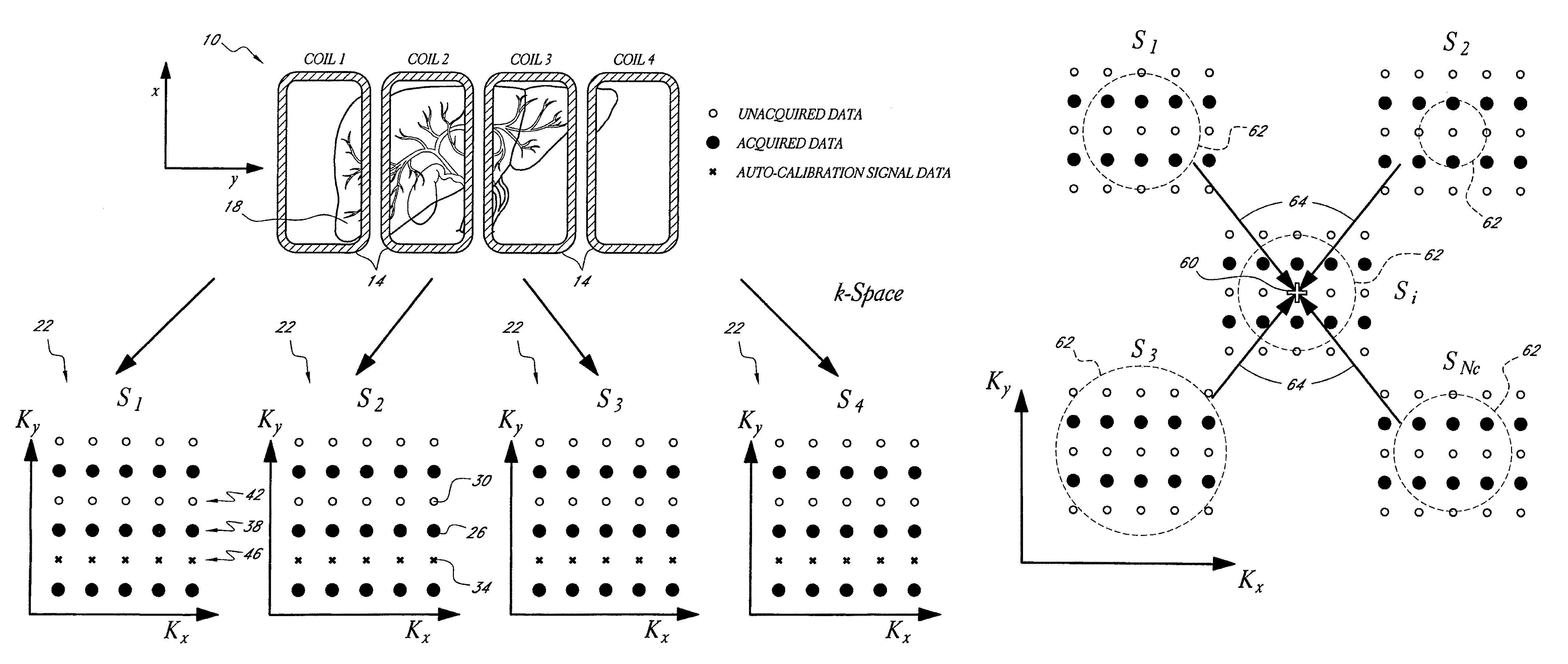
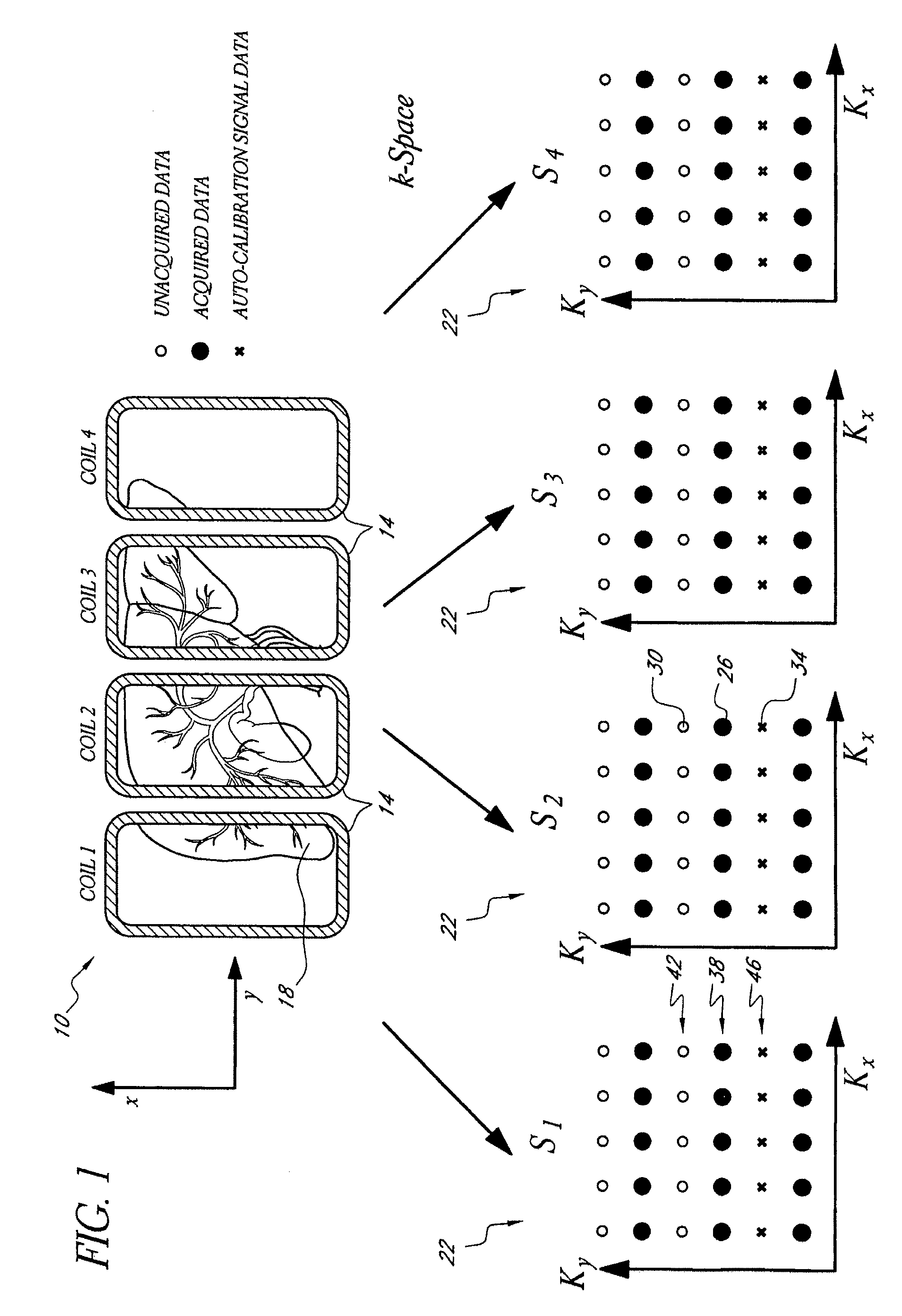
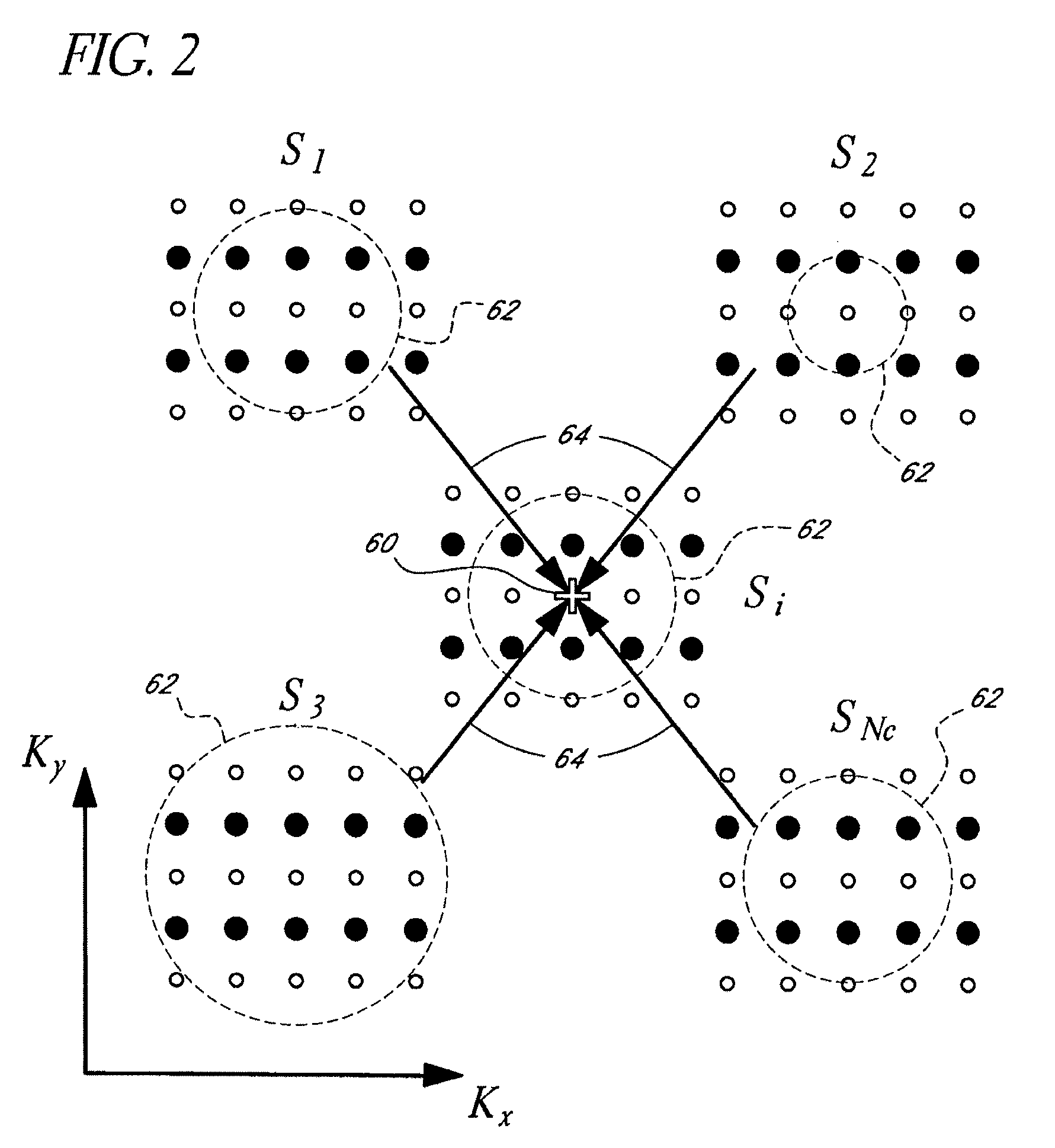
Systems and methods for image reconstruction of sensitivity encoded MRI data
Methods and systems in a parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system utilize sensitivity-encoded MRI data acquired from multiple receiver coils together with spatially dependent receiver coil sensitivities to generate MRI images. The acquired MRI data forms a reduced MRI data set that is undersampled in at least a phase-encoding direction in a frequency domain. The acquired MRI data and auto-calibration signal data are used to determine reconstruction coefficients for each receiver coil using a weighted or a robust least squares method. The reconstruction coefficients vary spatially with respect to at least the spatial coordinate that is orthogonal to the undersampled, phase-encoding direction(s) (e.g., a frequency encoding direction). Values for unacquired MRI data are determined by linearly combining the reconstruction coefficients with the acquired MRI data within neighborhoods in the frequency domain that depend on imaging geometry, coil sensitivity characteristics, and the undersampling factor of the acquired MRI data. An MRI image is determined from the reconstructed unacquired data and the acquired MRI data.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Systems and methods for image reconstruction of sensitivity encoded MRI data
ActiveUS7511495B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel magnetic resonance imagingData set
Methods and systems in a parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system utilize sensitivity-encoded MRI data acquired from multiple receiver coils together with spatially dependent receiver coil sensitivities to generate MRI images. The acquired MRI data forms a reduced MRI data set that is undersampled in at least a phase-encoding direction in a frequency domain. The acquired MRI data and auto-calibration signal data are used to determine reconstruction coefficients for each receiver coil using a weighted or a robust least squares method. The reconstruction coefficients vary spatially with respect to at least the spatial coordinate that is orthogonal to the undersampled, phase-encoding direction(s) (e.g., a frequency encoding direction). Values for unacquired MRI data are determined by linearly combining the reconstruction coefficients with the acquired MRI data within neighborhoods in the frequency domain that depend on imaging geometry, coil sensitivity characteristics, and the undersampling factor of the acquired MRI data. An MRI image is determined from the reconstructed unacquired data and the acquired MRI data.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
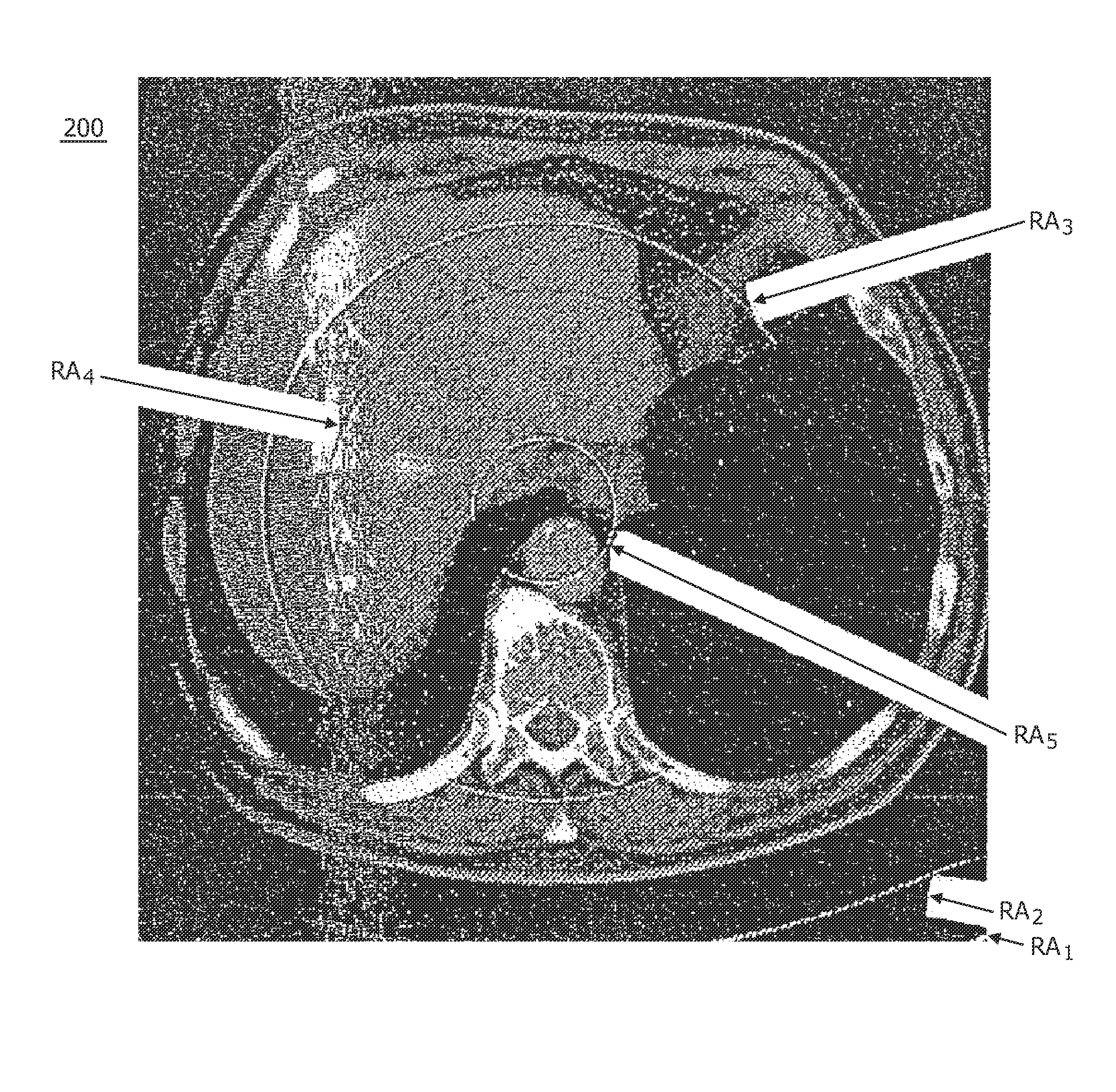
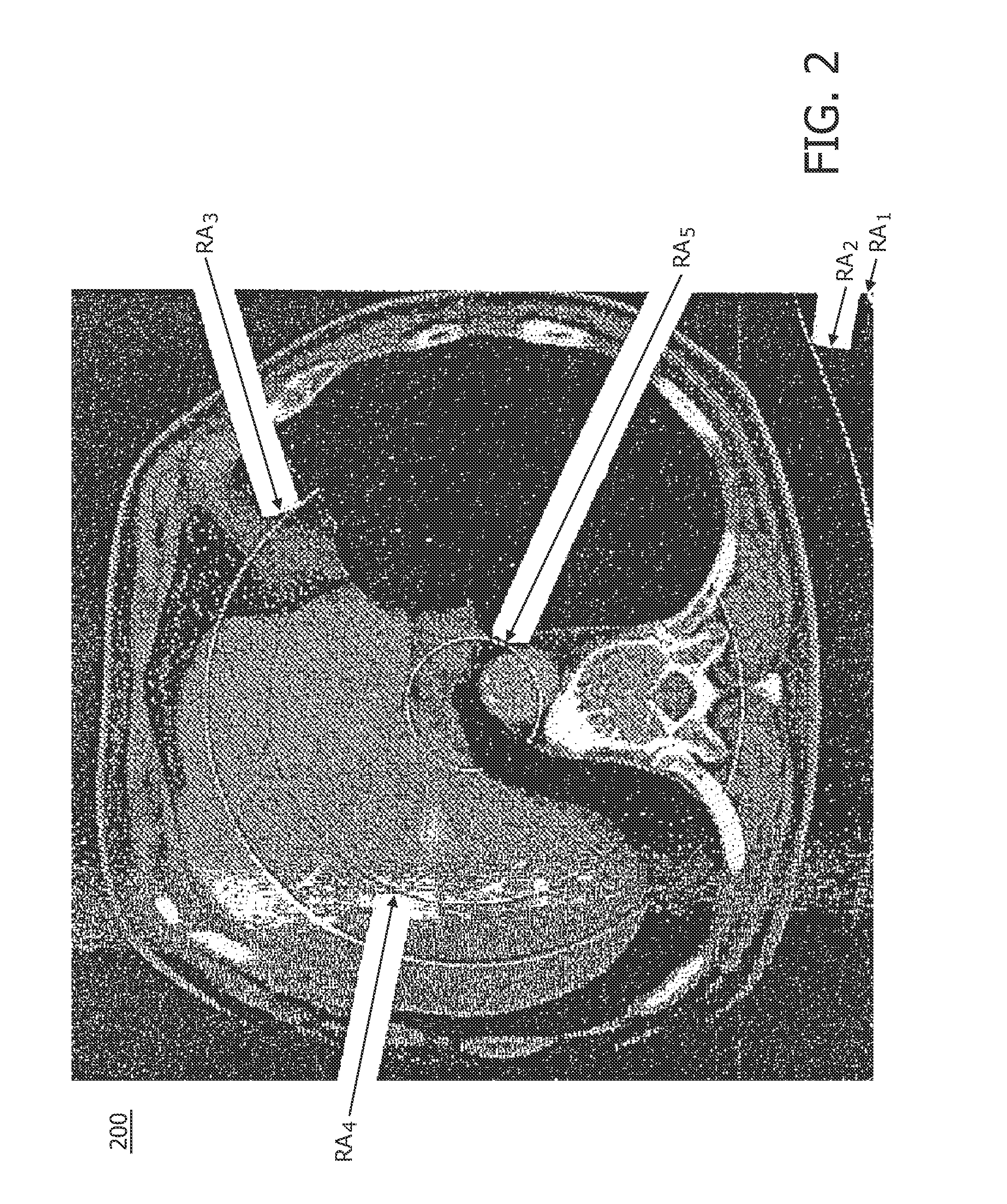
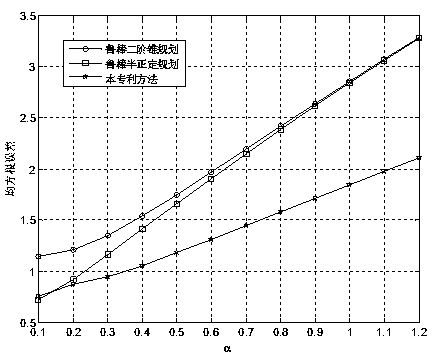
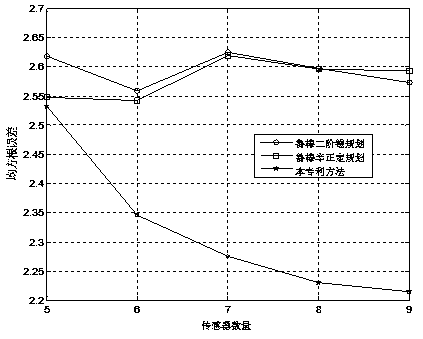
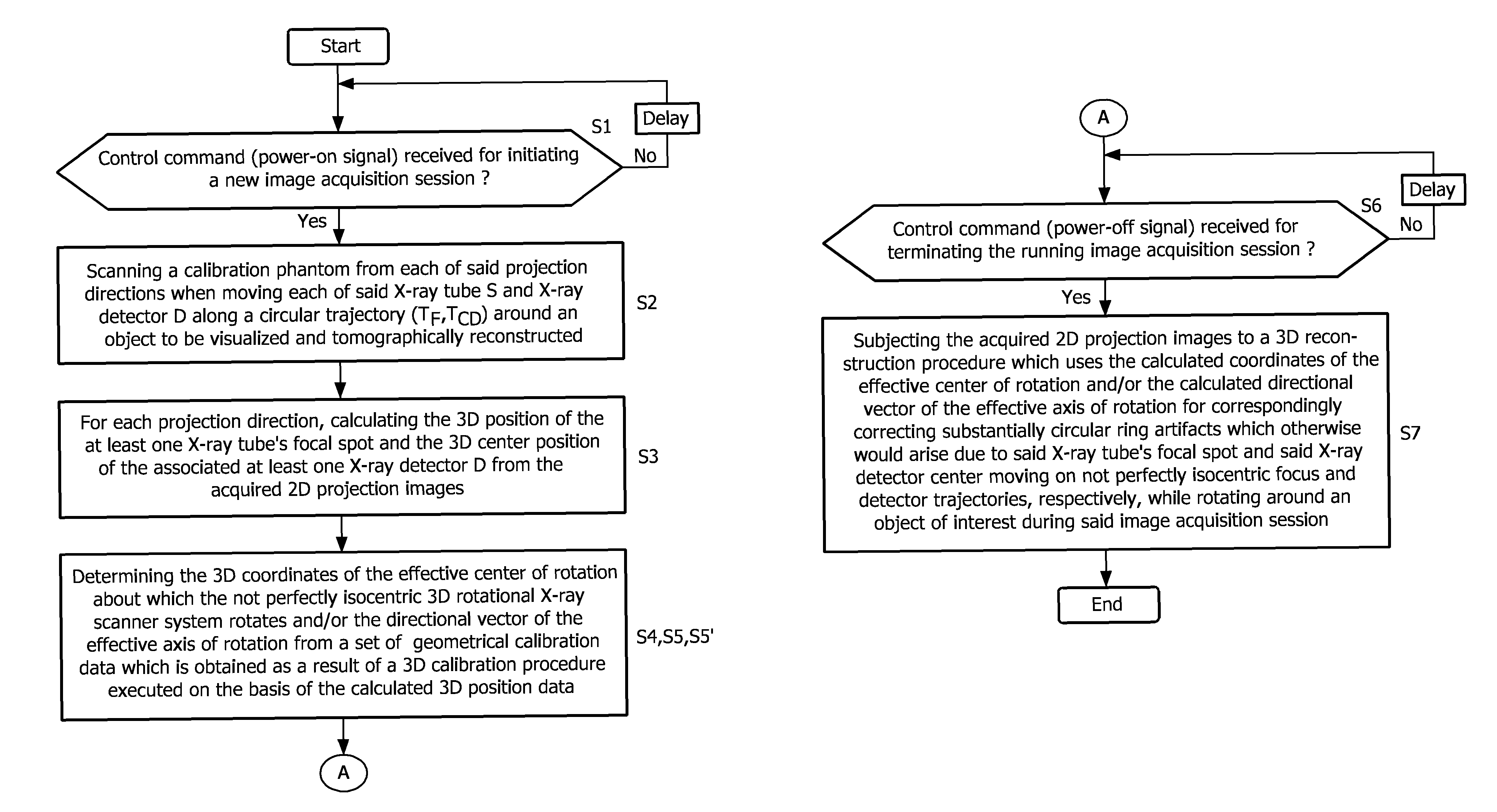
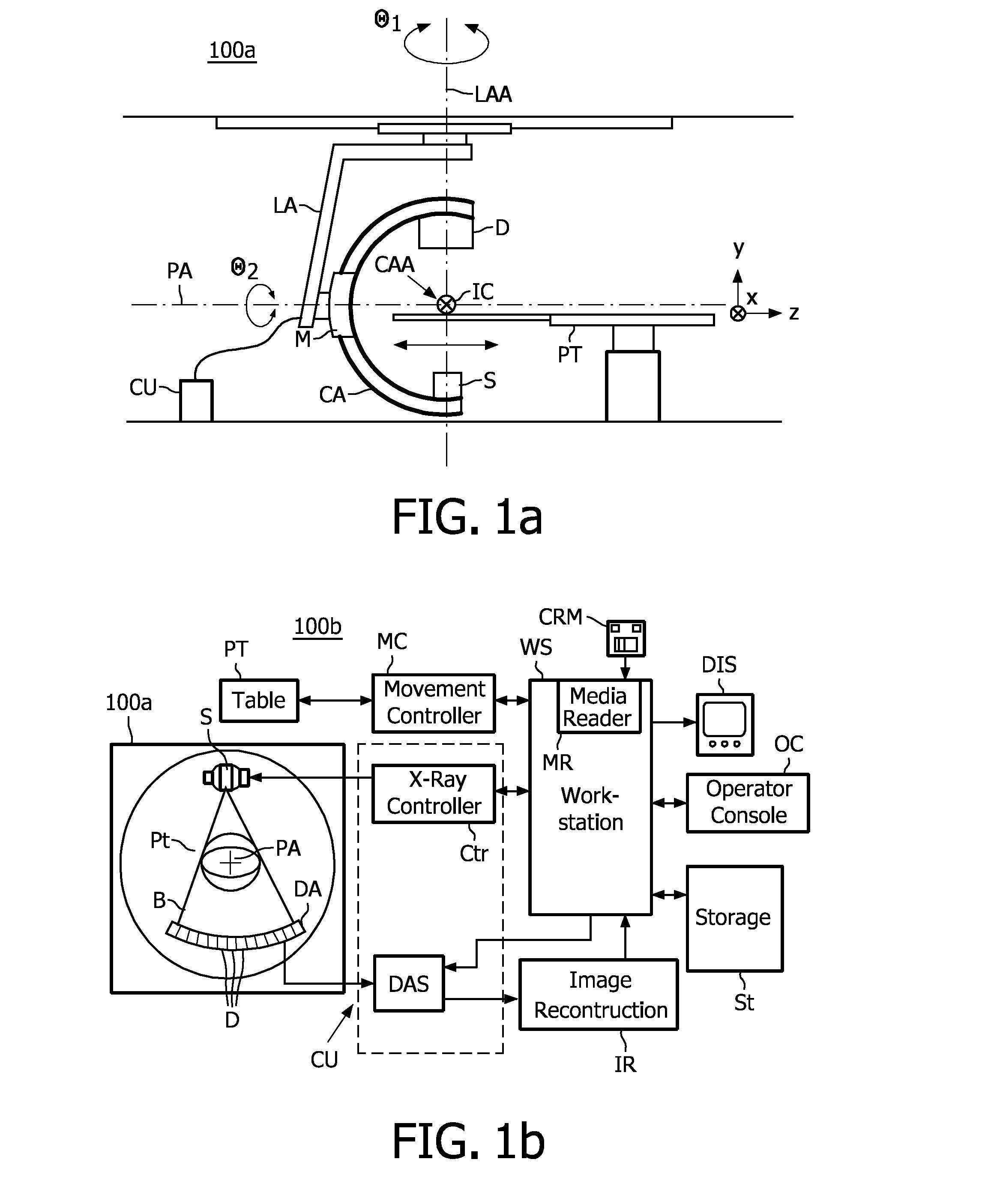
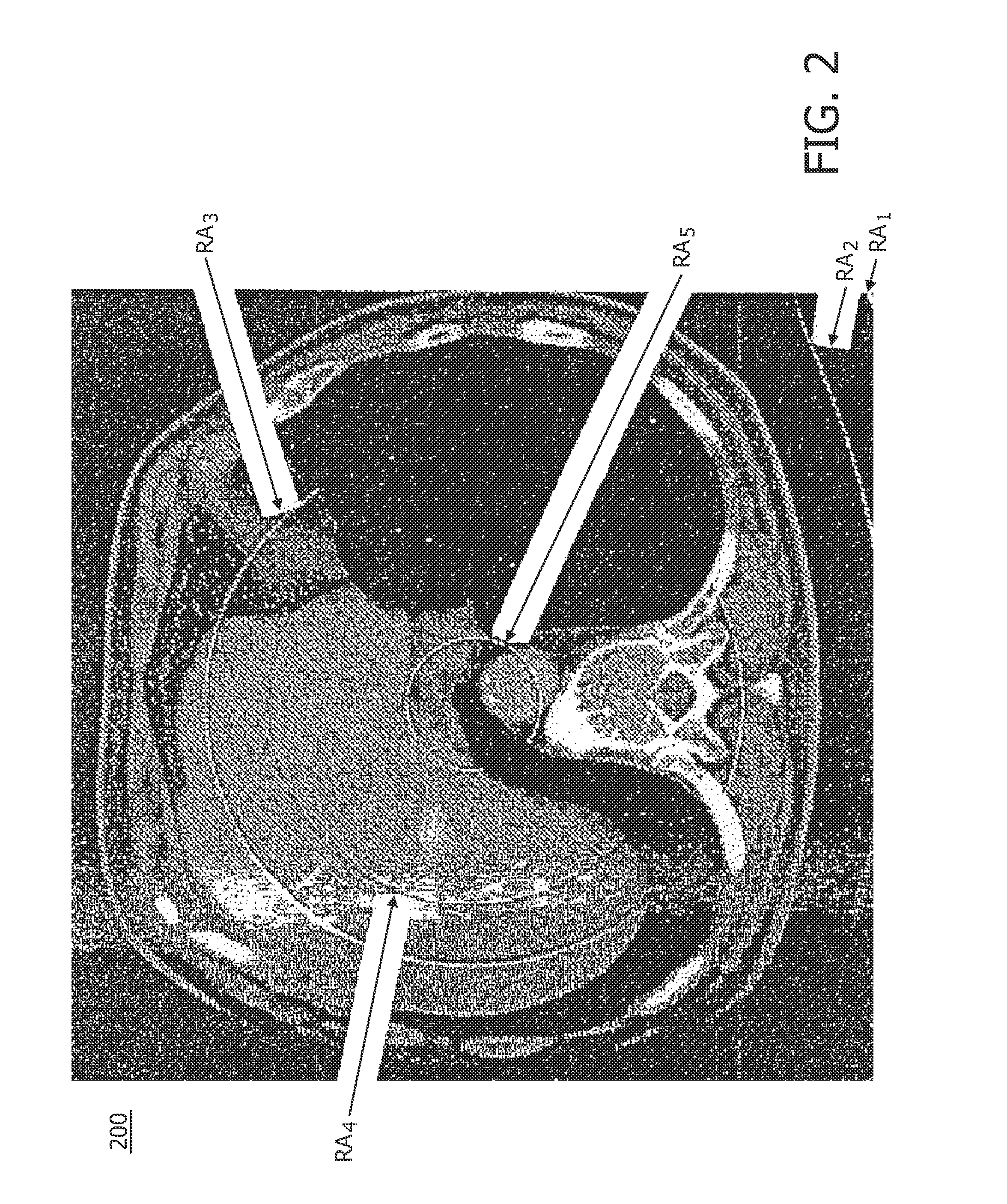
Calibration method for ring artifact correction in non-ideal isocentric 3D rotational x-ray scanner systems using a calibration phantom based rotation center finding algorithm
InactiveUS20110135053A1Eliminate artifactsEasy to correctMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersX-ray
The present invention refers to 3D rotational X-ray imaging systems for use in computed tomography (CT) and, more particularly, to a fast, accurate and mathematically robust calibration method for determining the effective center of rotation (I) in not perfectly isocentric 3D rotational C-arm systems and eliminating substantially circular ring artifacts (RA) which arise when using such a CT scanner system for acquiring a set of 2D projection images of an object of interest to be three-dimensionally reconstructed. For this purpose, a C-arm based rotational CT scanner comprising at least one radiation detector (D) having an X-radiation sensitive surface exposed to an X-ray beam emitted by at least one X-ray tube (S), each rotating along a non-ideal circular trajectory (TF, TCD) about an object of interest to be three-dimensionally reconstructed from a set of 2D projection images is used for providing geometrical calibration data by scanning a calibration phantom from a plurality of distinct projection directions and calculating, for each projection direction, the 3D positions of the X-ray tube's focal spot and the X-ray detector's center. For approximating the exact 3D position and angular direction of the axis of rotation about which the at least one X-ray tube and the at least one radiation detector rotate, a circular regression technique using a number of mathematically robust least squares fits is applied.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
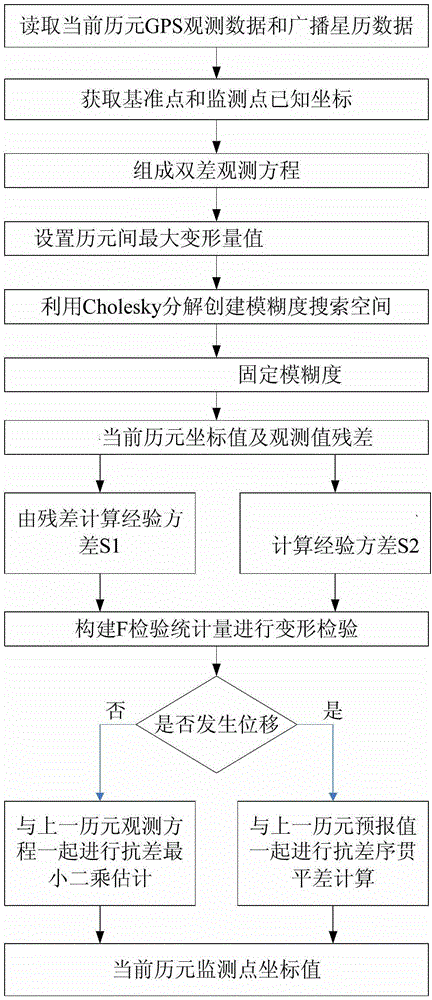
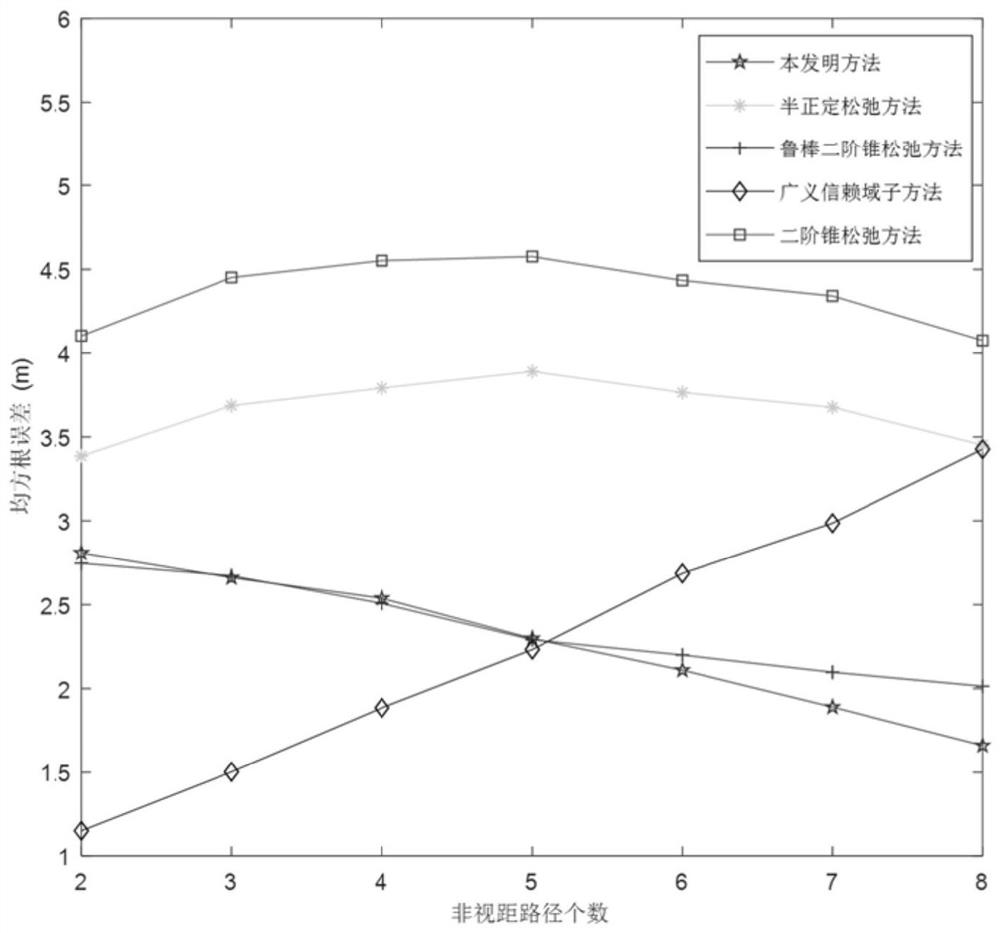
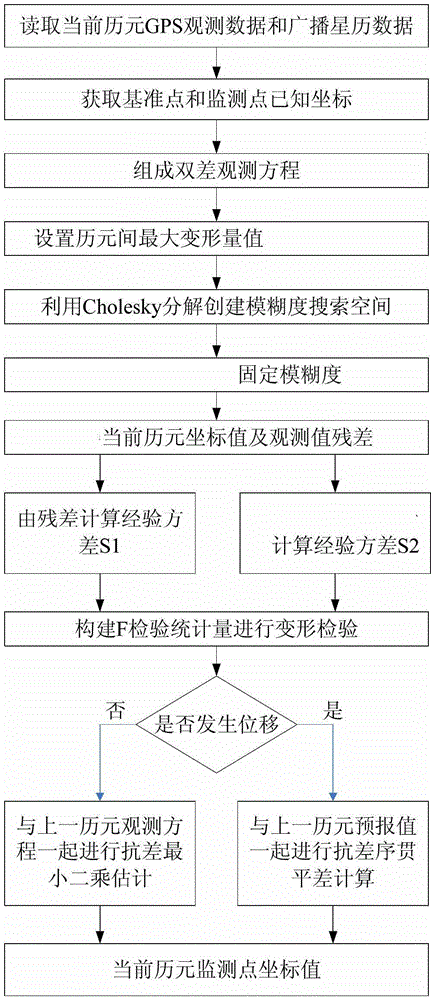
Method for processing global position system (GPS) deformation monitoring data
ActiveCN103148813AImprove processing efficiencyImprove reliabilityUsing wave/particle radiation meansDouble differenceObservation data
The invention provides a method for processing global position system (GPS) deformation monitoring data. The method for processing the GPS deformation monitoring data comprises (1) obtaining present epoch observation data and broadcast ephemeris data of a base station and a monitoring station, and forming a double-difference observation equation by using phase observation values; (2) setting a maximum deformation quantity between two epochs; (3) adopting a Cholesky to resolve and construct an ambiguity search space; (4) searching the ambiguity, and enabling a variance ratio to be larger than 3; (5) obtaining fixed solution coordinates X, Y and Z of a single epoch whole cycle ambiguity and a convariance matrix of the single epoch whole cycle ambiguity of a monitoring point; (6) using an average gap method to carry out deformation detection on a deformation value between a present epoch and a previous epoch; (7) after finishing the detection of (6), using a robust least square static solution by superposition of two epoch observation equations as a result of the present epoch, or obtaining a result of the present epoch according to a robust sequential adjustment. The method for processing the GPS deformation monitoring data is accurate.
Owner:HUNAN ZHILI ENG SCI & TECH
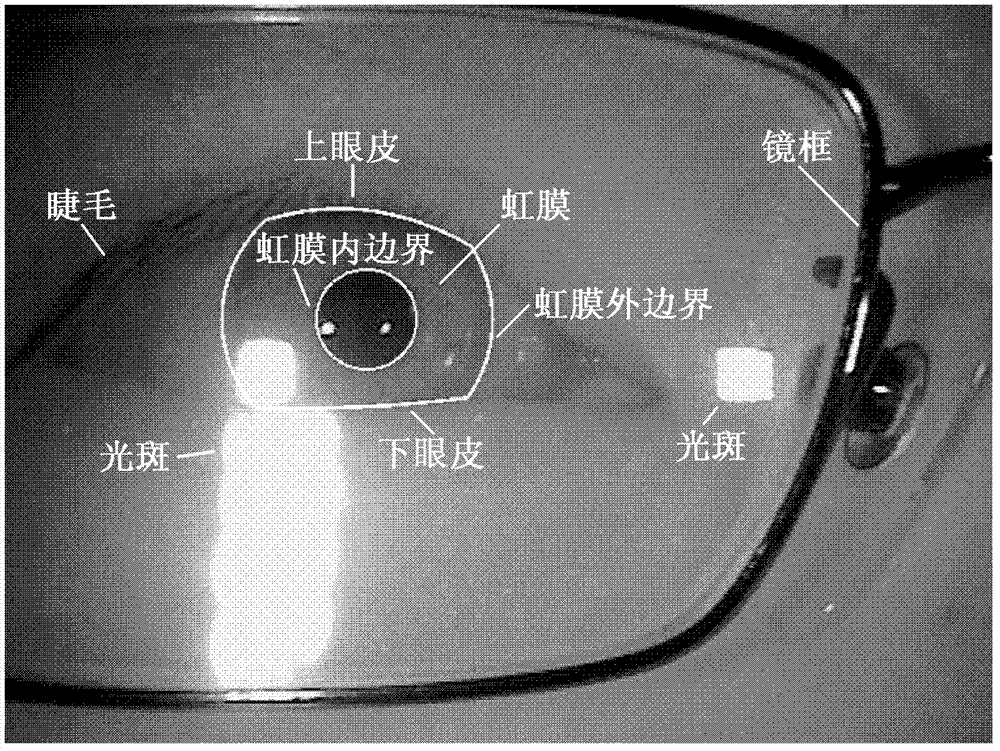
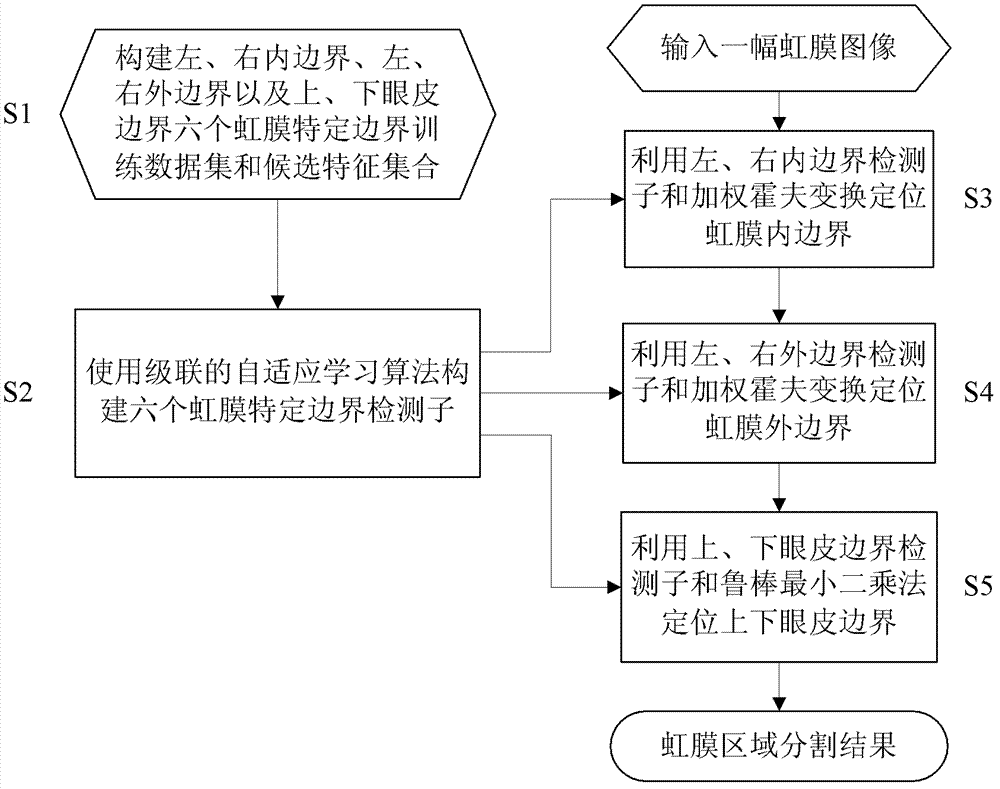
Robust iris region segmentation method based on specific boundary detectors
ActiveCN102629319AHigh precisionImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature setData set
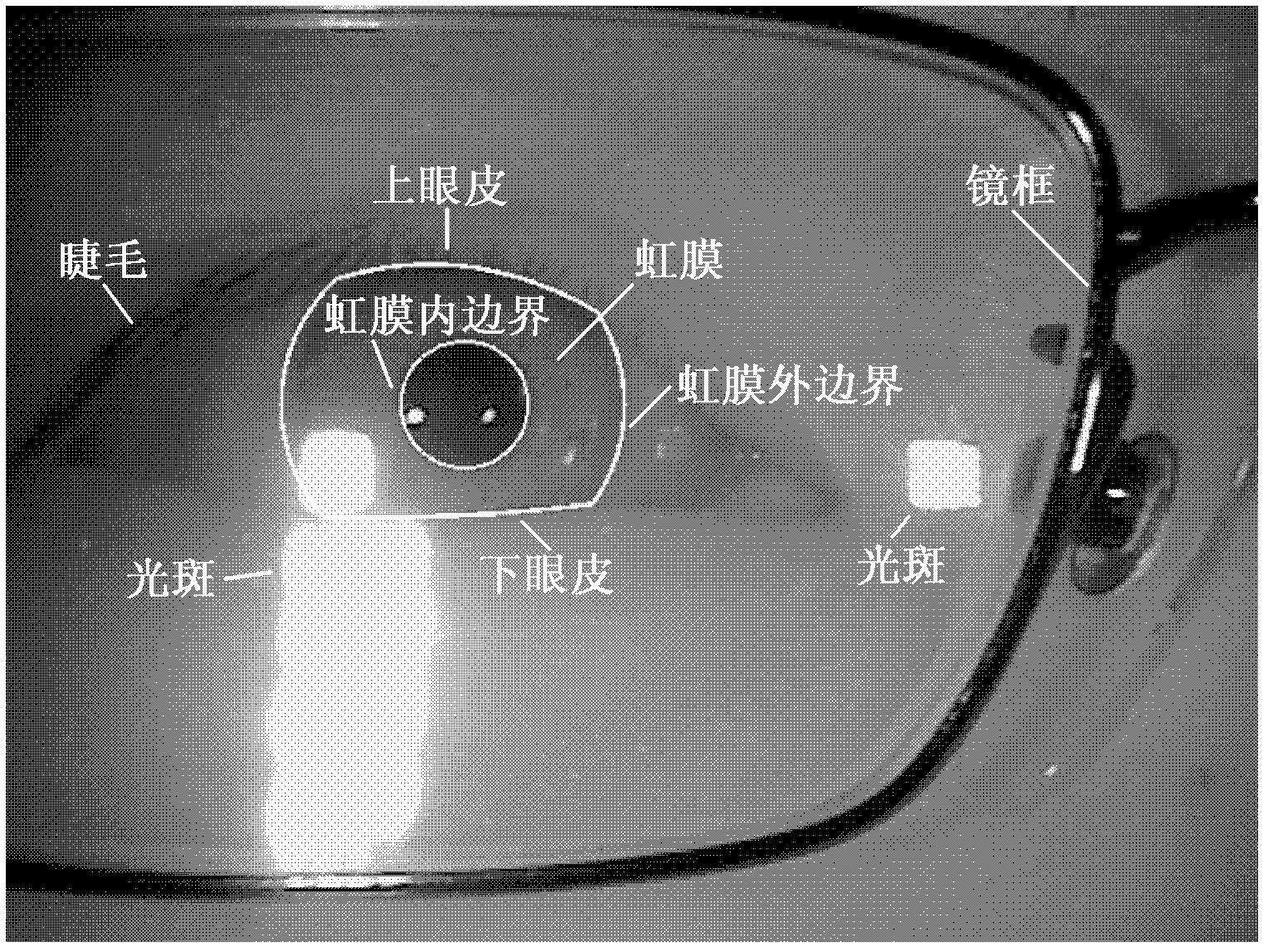
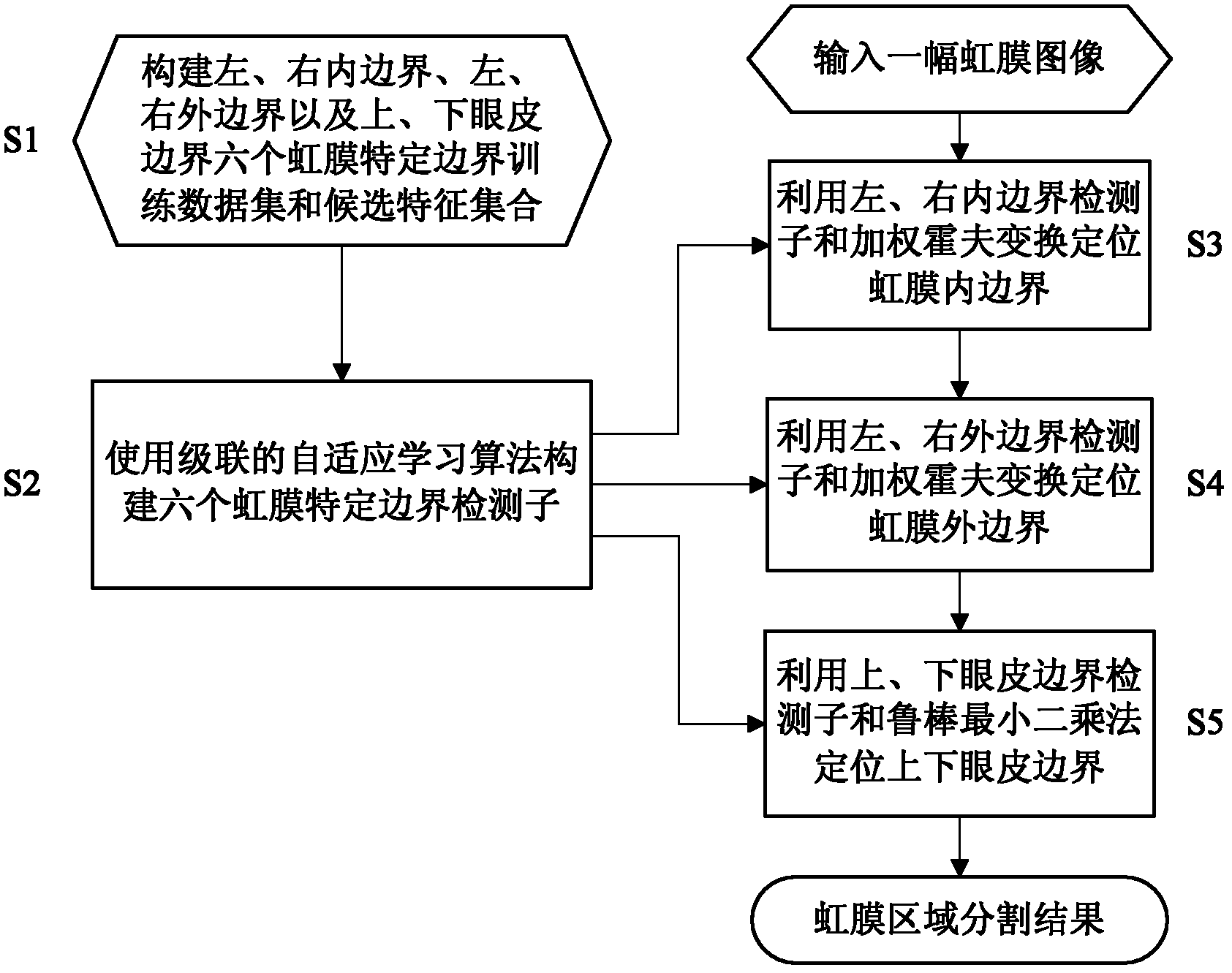
The invention discloses a robust iris region segmentation method based on specific boundary detectors, which comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a left and right inner boundary, left and right outer boundary and upper and lower eyelid boundary iris specific boundary training data set and a candidate feature set; S2, constructing the six iris specific boundary detectors by using a cascaded self-adaptive learning algorithm; S3, positioning an iris inner boundary by utilizing the left and right inner boundary detectors and weighted Hough transform; S4, positioning an iris outer boundary by utilizing the left and right outer boundary detectors and the weighted Hough transform; and S5, positioning an upper eyelid boundary by utilizing the upper and lower eyelid boundary detectors and a robust least square method. By utilizing the robust iris region segmentation method, an iris effective area can be accurately segmented in an iris image containing a lot of noise, so that the accuracy, the robustness and the usability of an iris identification system are improved. The robust iris region segmentation method can be widely applied to various application systems for identity recognition and security defense by using iris recognition.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
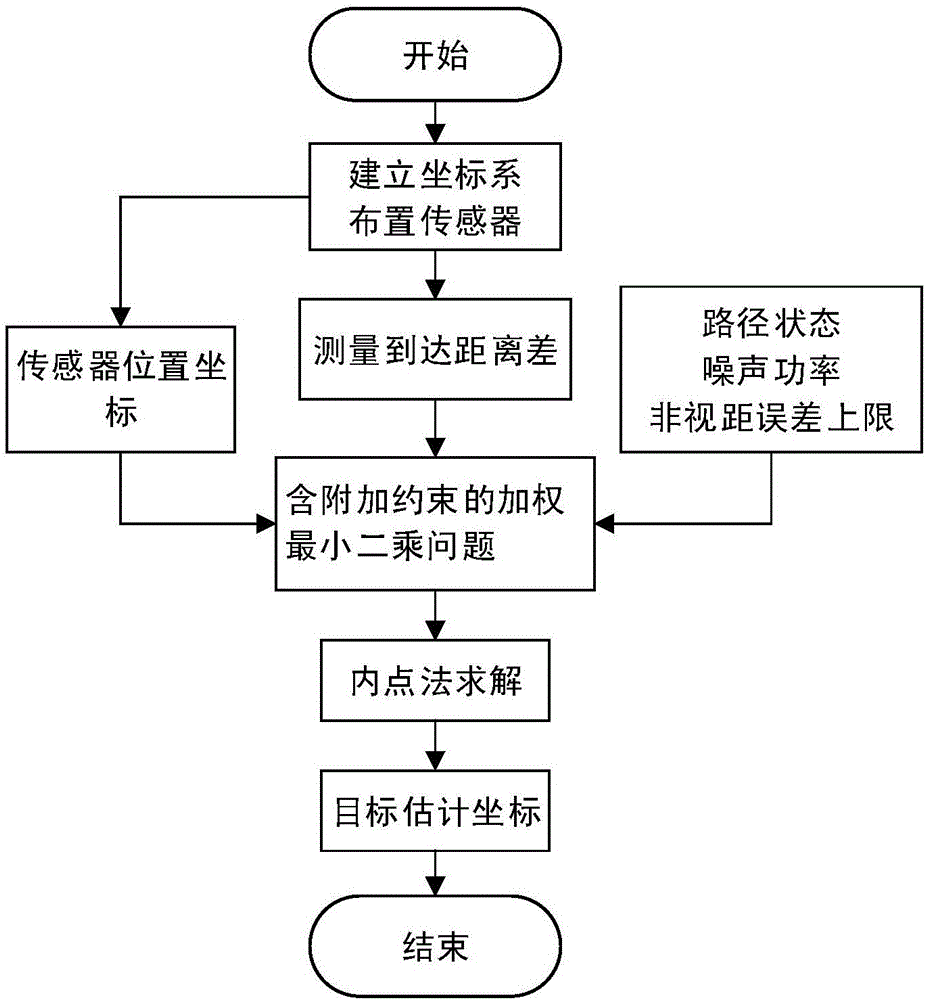
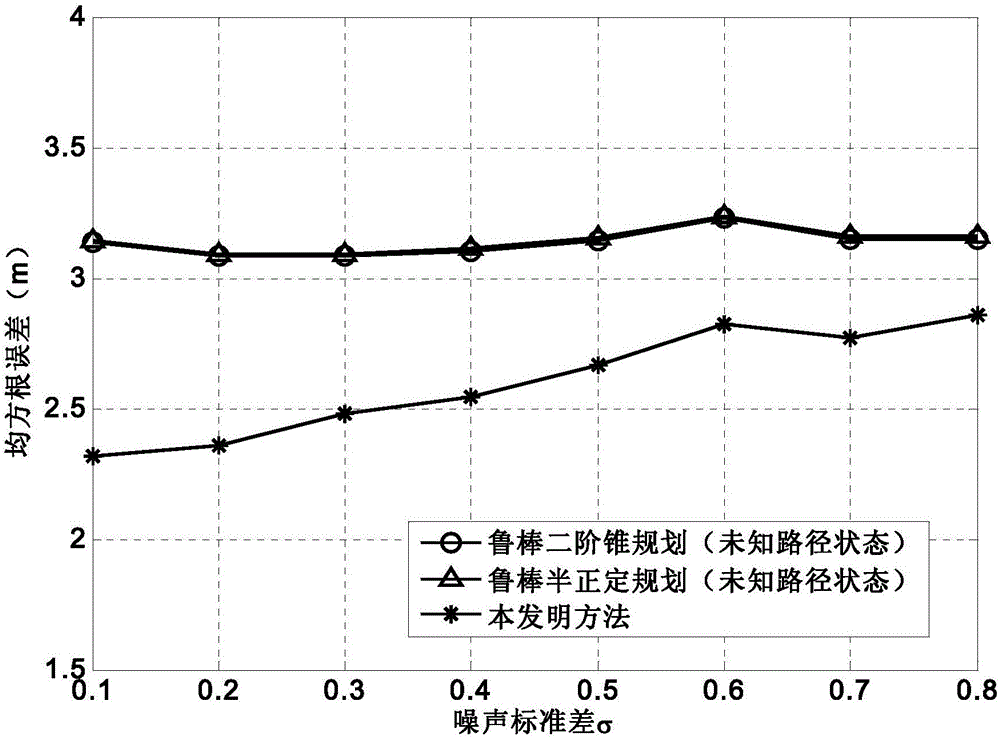
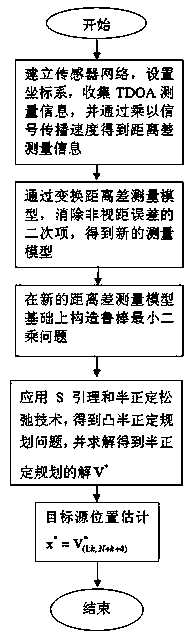
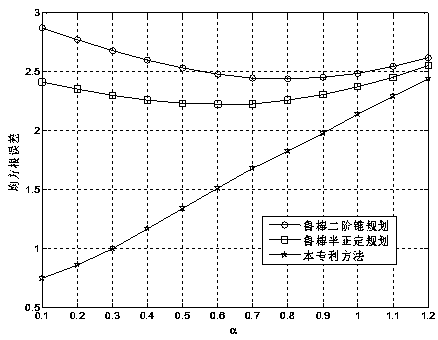
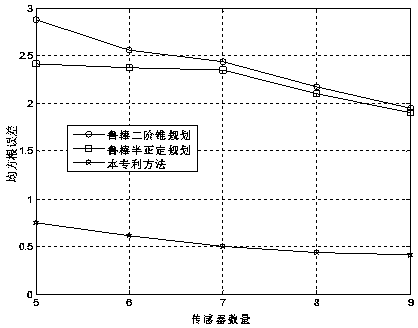
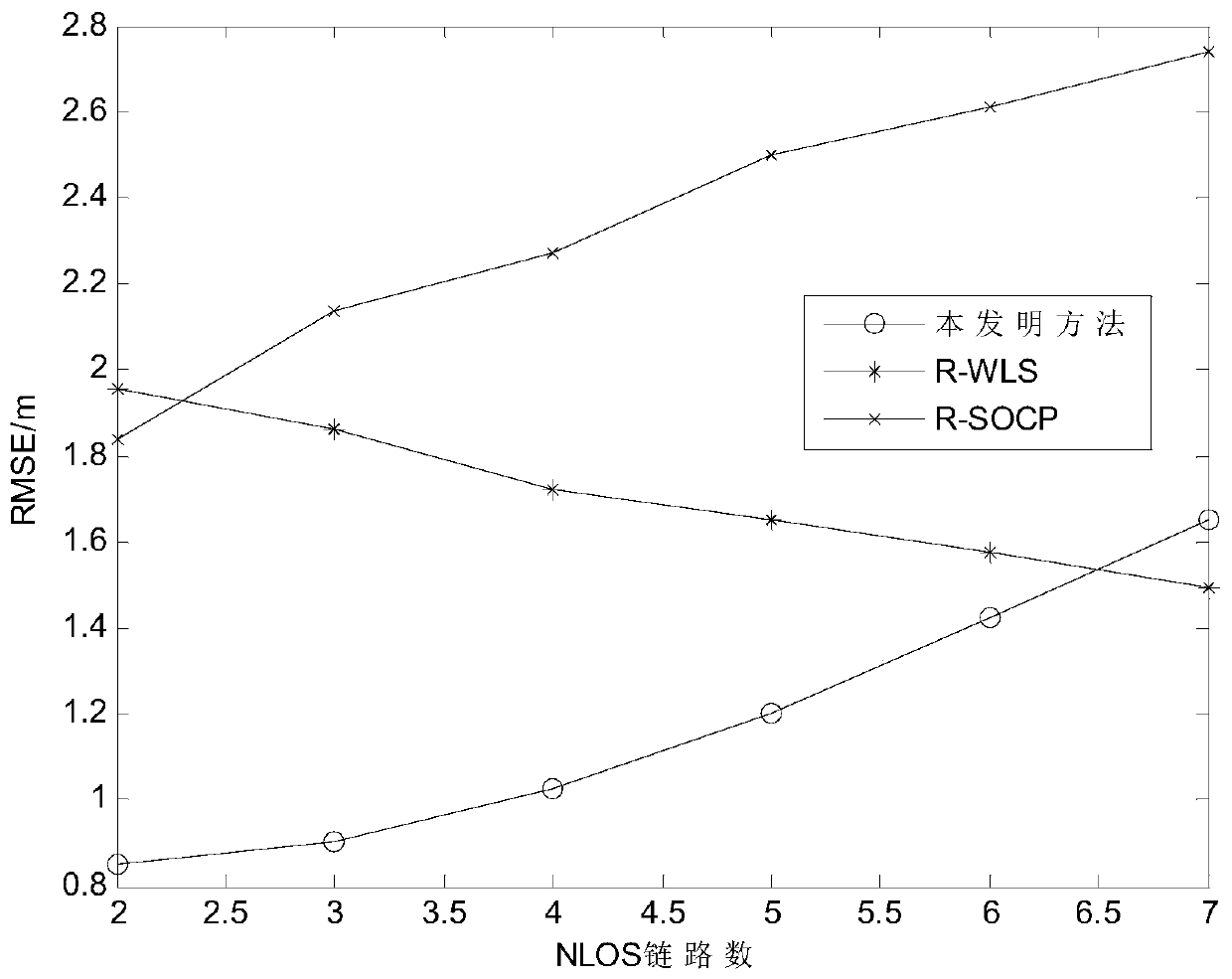
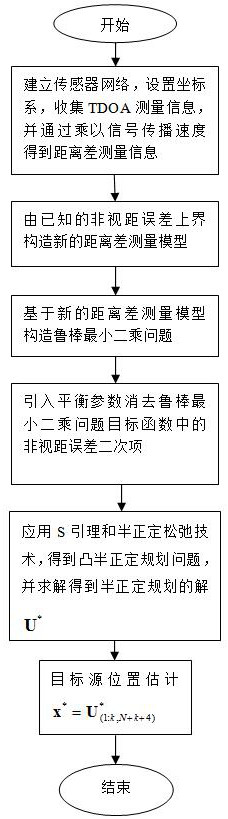
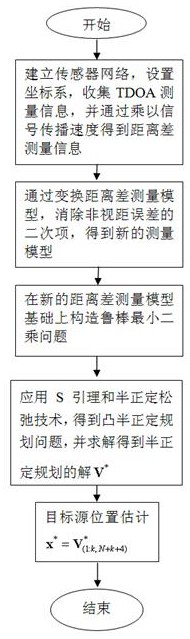
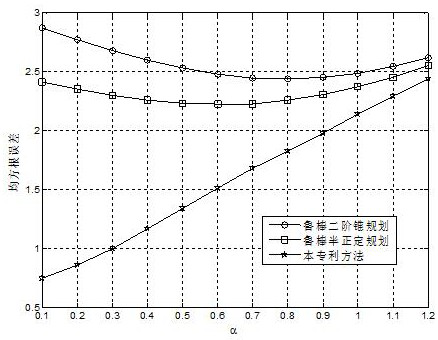
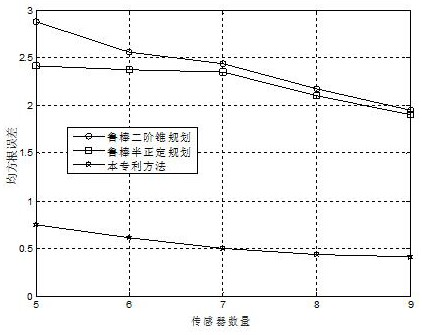
Steady positioning method based on time difference of arrival in sight distance and non-sight-distance mixed environment
ActiveCN106842121ATake advantage ofFully play the rolePosition fixationRobust least squaresMultilateration
The invention discloses a steady positioning method based on time difference of arrival in sight distance and non-sight-distance mixed environment. The method comprises the following steps: separately processing a distance difference measurement model under the sight distance environment and a distance difference measurement model under the non-sight-distance environment, building a robust least-squares problem under the worst case, and designing the specific constraint in allusion to two causes under the non-sight-distance environment that the reference path is the sight distance and the normal path is the non-sight-distance and the reference path is the non-sight-distance and the normal path is the sight distance, realizing the concrete analysis in allusion to the particular case, and adequately using the state information of the path. In allusion to the unbalancedness problem of the distance difference measurement model processing under the sight distance environment and the distance difference measurement model processing under the non-sight-distance environment, and based on the difference of the positional accuracy under the sight distance and the non-sight-distance environment, an effective weight value is designed, the robust least-squares problem under the worst case is adjusted to a weighting least-squares problem, so the function of the sight distance path is adequately developed, and the positional accuracy is further improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
GNSS satellite selection method based on robust least square
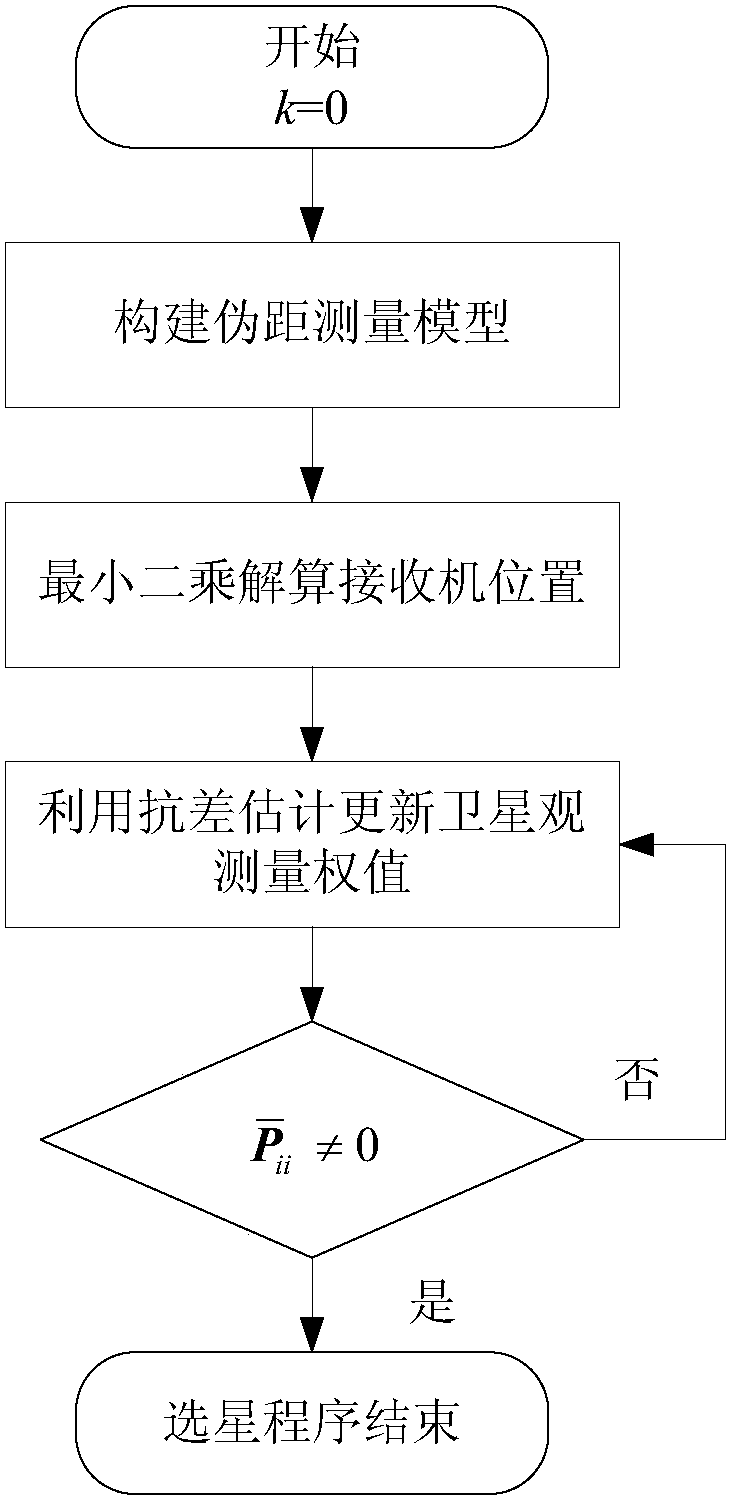
InactiveCN107765269AImprove computing efficiencyImprove real-time performanceSatellite radio beaconingRobust least squaresEquivalent weight
The invention discloses a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) satellite selection method based on robust least square, which comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a pseudo range measurement model; (2) setting the priori value of a weight matrix, and solving the pseudo range measurement model constructed in step (1) by using the least square technology to get the receiver position solution and the clock error; (3) calculating the standard residual according to the receiver position solution and the clock error, and using a robust equivalent weight coefficient to update the weight matrix; and (4) judging and analyzing the weight of each satellite according to the updated weight matrix; if the weight of a satellite is equal to 0, eliminating the satellite from the pseudo rangemeasurement model, extracting the corresponding element of the weight matrix, recalculating the receiver position solution and the clock error by using the least square technology, and transferring the receiver position solution and the clock error to step (3) to make iterative analysis; and if the weights of all satellites are not equal to 0, outputting available satellites, and ending the satellite selection program. Through the method, the weight of each observation satellite can be adaptively adjusted, and satellites with poor observation quality can be eliminated.
Owner:CHINESE AERONAUTICAL RADIO ELECTRONICS RES INST
Method for obtaining sparse solution of robust least square support vector machine
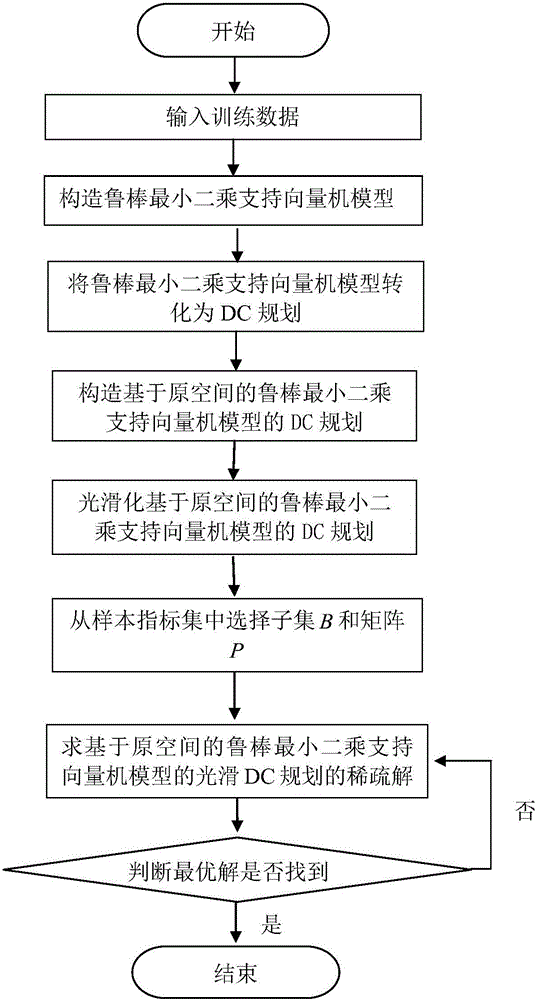
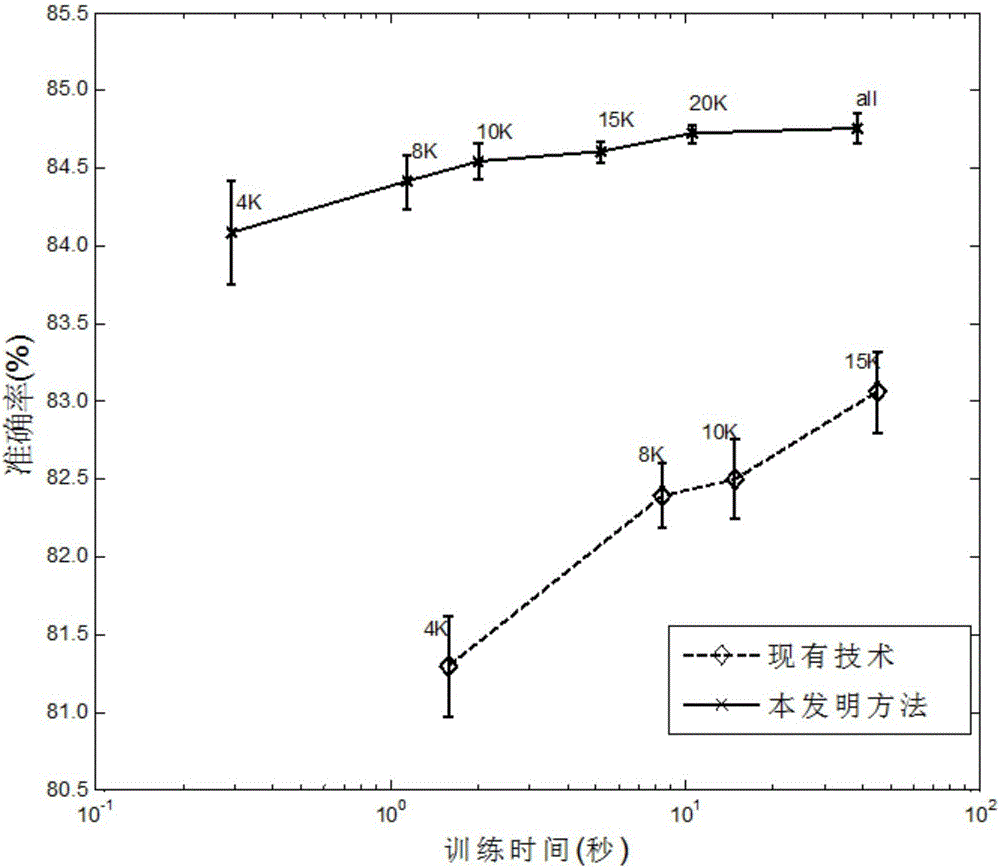
InactiveCN106126482ASparseImprove the speed of solvingCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmLeast squares support vector machine
The invention provides a method for obtaining a sparse solution of a robust least square support vector machine. The method is used for solving the technical problem of solution lack sparsity existing in an obtaining method of a solution of the robust least square support vector machine and comprises the implementation steps that training data is input; a robust least square support vector machine model is constructed; the robust least square support vector machine model is converted into a DC plan; the DC plan of the robust least square support vector machine model based on original space is constructed; the DC plan of the robust least square support vector machine model based on the original space is smoothed; a subset B and a matrix P are selected from a sample index set; the sparse solution of the smoothed DC plan of the robust least square support vector machine model based on the original space is obtained; whether an optimal solution is sought or not is judged. According to the method, the sparse solution of the robust least square support vector machine can be obtained, and the method can be applied to the fields of classification and regression of big data with noise.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
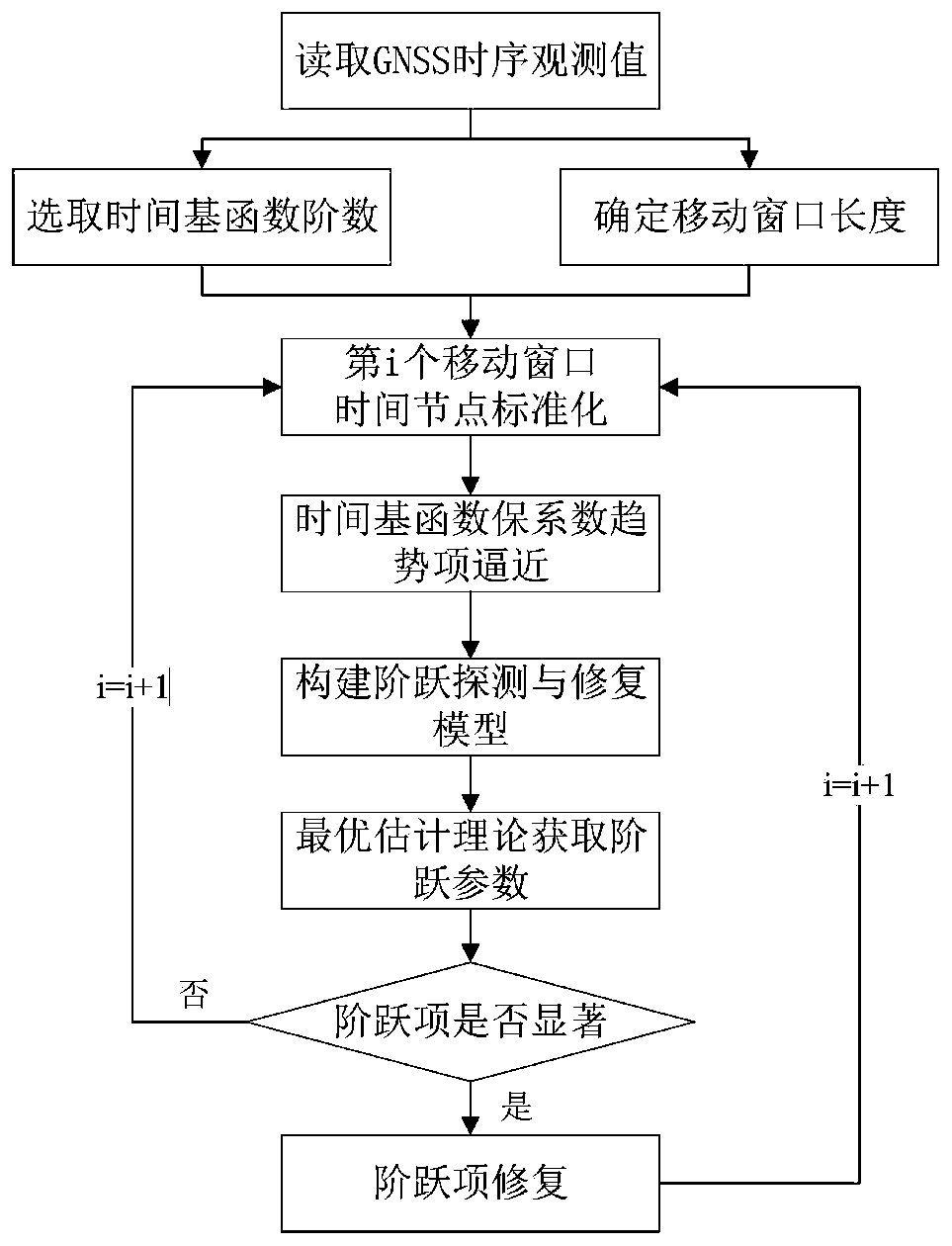
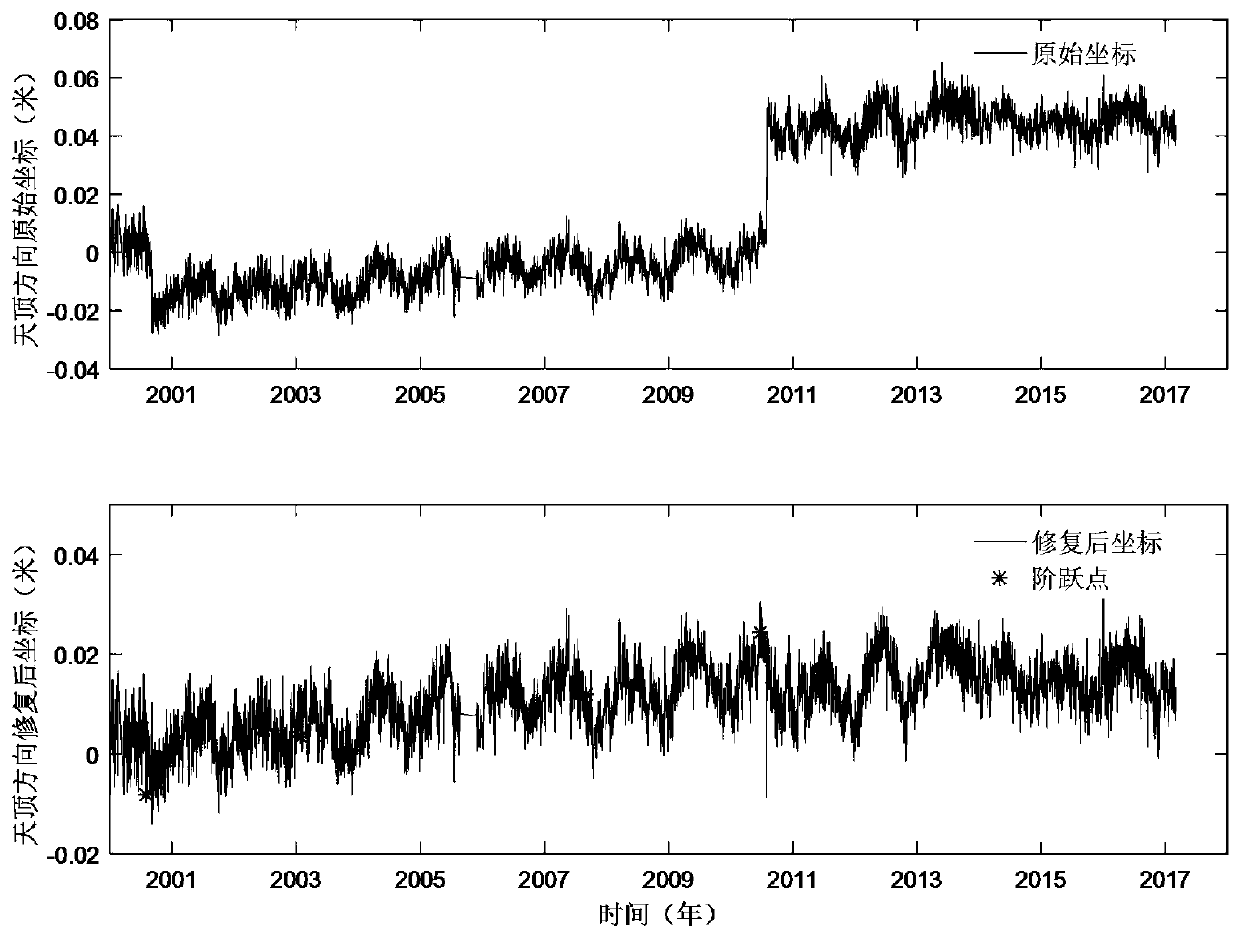
GNSS time sequence step detection and restoration method
ActiveCN110632625AImprove step detection accuracyAchieve separationSatellite radio beaconingRestoration methodAlgorithm
The invention discloses a GNSS time sequence step detection and restoration method. In view of the GNSS time sequence step problem, a step detection and restoration model is constructed through a moving window method and a time-based function guaranteed coefficient trend term approximation mode by utilizing the trend invariance characteristic in a continuous time window before and after the step of a time sequence, step parameter estimation and variance-covariance estimation are performed by adopting robust least squares, generalized least squares or other optimal estimation theories, and stepparameter significance test and step restoration are performed through statistical hypothesis test. The method is suitable for detection and restoration of multiple types of GNSS time sequences underunequal time intervals or data missing. The step detection and restoration estimation theory is strict and easy to program. The detection result has the optimal statistical property, and the restoration result has statistical reliability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method for preparation of biogas and combined production of organic fertilizer through processing peat by dilute acid
InactiveCN103275745AEasy to adjustIn line with industrial policyBio-organic fraction processingWaste based fuelRobust least squaresOrganic fertilizer
The present invention refers to 3D rotational X-ray imaging systems for use in computed tomography (CT) and a fast, accurate and mathematically robust calibration method for determining the effective center of rotation (I) in not perfectly isocentric 3D rotational C-arm systems and eliminating substantially circular ring artifacts (RA) which arise when using such a CT scanner system. For this purpose, a C-arm based rotational CT scanner comprising at least one radiation detector (D) having an X-radiation sensitive surface exposed to an X-ray beam emitted by at least one X-ray tube (S), each rotating along a non-ideal circular trajectory (TF, TCD) about an object of interest to be three-dimensionally reconstructed from a set of 2D projection images is used for providing geometrical calibration data by scanning a calibration phantom from a plurality of distinct projection directions and calculating, for each projection direction, the 3D positions of the X-ray tube's focal spot and the X-ray detector's center. For approximating the exact 3D position and angular direction of the axis of rotation about which the at least one X-ray tube and the at least one radiation detector rotate, a circular regression technique using a number of mathematically robust least squares fits is applied.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
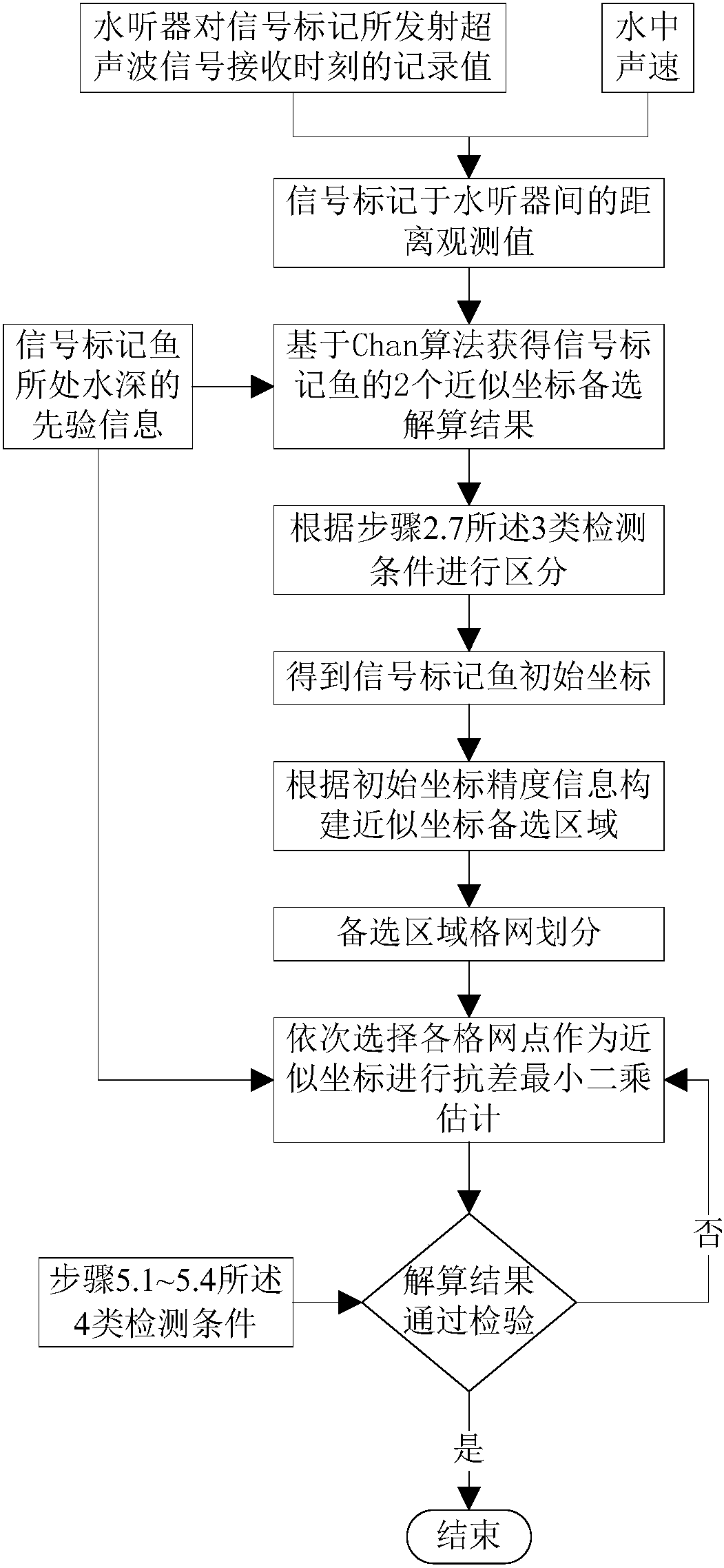
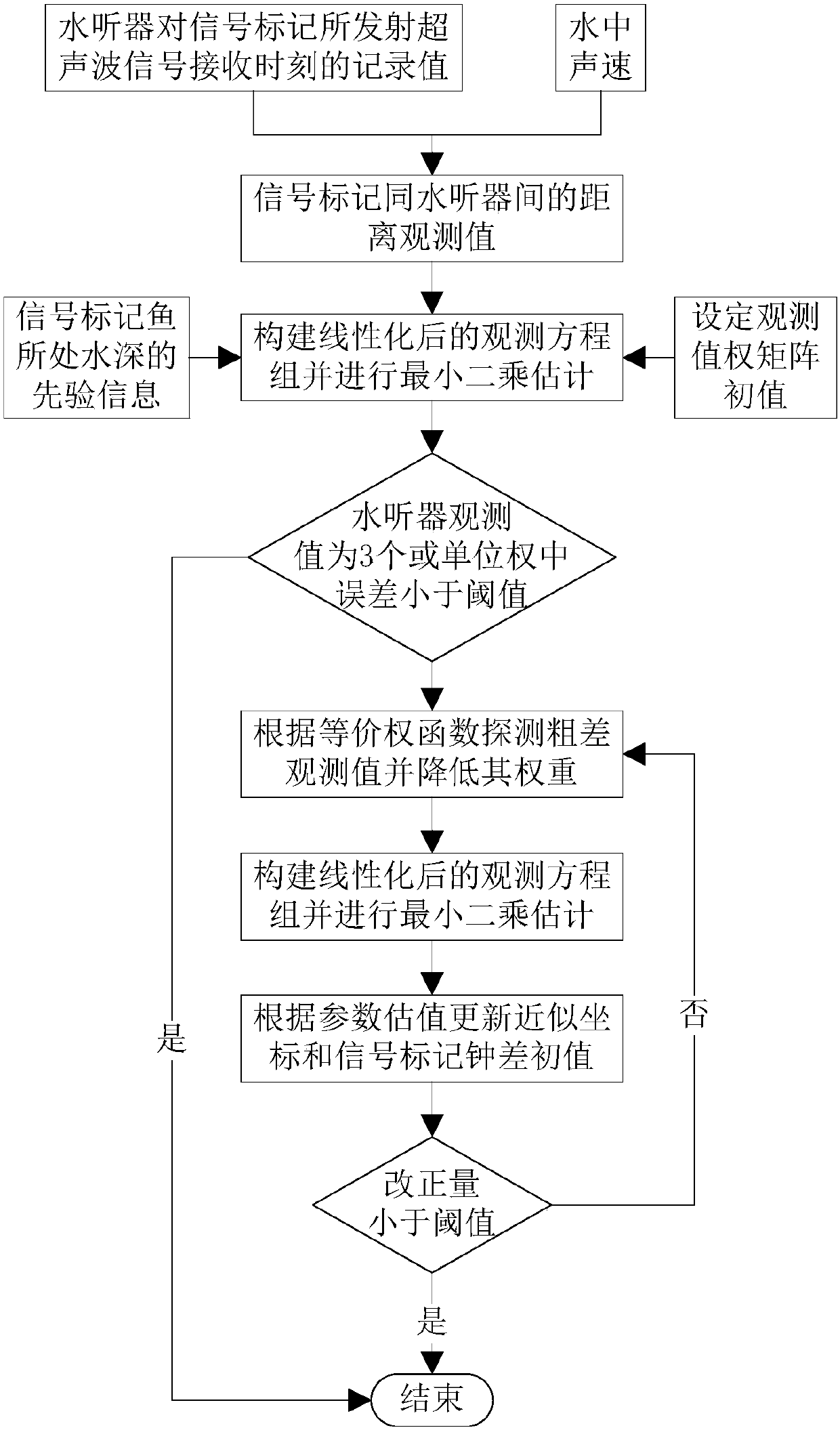
Fish ultrasonic wave marker precise positioning method and system suitable for complex water environment
ActiveCN107942336AImprove applicabilityEffective development and utilizationAcoustic wave reradiationHydrophoneRobust least squares
The invention discloses a fish ultrasonic wave marker precise positioning method and system suitable for a complex water environment. The method comprises the steps of S1, collecting the time when a signal marker fish arrives at each hydrophone in a hydrophone monitoring network or the time difference between arrivals at two hydrophones; S2, estimating approximate coordinates and a signal emissiontime of the signal marker fish by using a Chan algorithm; S3, taking the approximate coordinates of the signal marker fish as the center, constructing an approximate coordinate alternative interval,and dividing the approximate coordinate alternative interval into sub-nets; S4, taking a node position of one subnet as a position initial value of the signal marker fish, and carrying out the signalmarker positioning calculation by using the robust least-square estimation; and S5, evaluating a positioning calculation result obtained in the step S4, if the evaluation passes, determining the position calculation result as the precise positioning result of the signal marker fish, and otherwise, repeating the step S4. The method of the invention can effectively realize the accurate capture of fish movement trajectories with high precision and high reliability.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Robust positioning method based on arrival time difference under non-line-of-sight error condition
ActiveCN110221244APrecise positioningSolve the problem of the upper bound of the non-line-of-sight errorPosition fixationRobust least squaresArrival time
The invention discloses a robust positioning method based on arrival time difference under a non-line-of-sight error condition, which solves the problem of robust least square by taking a target position and a reference path non-line-of-sight error as estimation parameters. A method for introducing balance parameters is provided to eliminate non-line-of-sight error quadratic terms in an objectivefunction, then auxiliary variables are introduced, and S lemma and a semi-definite relaxation technology are adopted to obtain a convex semi-definite programming problem; and finally, the semi-definite programming problem is solved by using a common inner point method solving tool so as to obtain an estimated value of the position of the target source in the established coordinate system. The method overcomes the unreasonable non-line-of-sight error upper bound in the existing robust method and the negative influence caused by applying the triangular inequality, and greatly improves the positioning accuracy of the existing method in the dense non-line-of-sight environment.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Calibration method for ring artifact correction in non-ideal isocentric 3D rotational X-ray scanner systems using a calibration phantom based rotation center finding algorithm
InactiveUS8249213B2Easy to correctImprove image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersX-ray
The present invention refers to 3D rotational X-ray imaging systems for use in computed tomography (CT) and, more particularly, to a fast, accurate and mathematically robust calibration method for determining the effective center of rotation (I) in not perfectly isocentric 3D rotational C-arm systems and eliminating substantially circular ring artifacts (RA) which arise when using such a CT scanner system for acquiring a set of 2D projection images of an object of interest to be three-dimensionally reconstructed. For this purpose, a C-arm based rotational CT scanner comprising at least one radiation detector (D) having an X-radiation sensitive surface exposed to an X-ray beam emitted by at least one X-ray tube (S), each rotating along a non-ideal circular trajectory (TF, TCD) about an object of interest to be three-dimensionally reconstructed from a set of 2D projection images is used for providing geometrical calibration data by scanning a calibration phantom from a plurality of distinct projection directions and calculating, for each projection direction, the 3D positions of the X-ray tube's focal spot and the X-ray detector's center. For approximating the exact 3D position and angular direction of the axis of rotation about which the at least one X-ray tube and the at least one radiation detector rotate, a circular regression technique using a number of mathematically robust least squares fits is applied.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
TOA-based sensor position error suppression method in asynchronous network
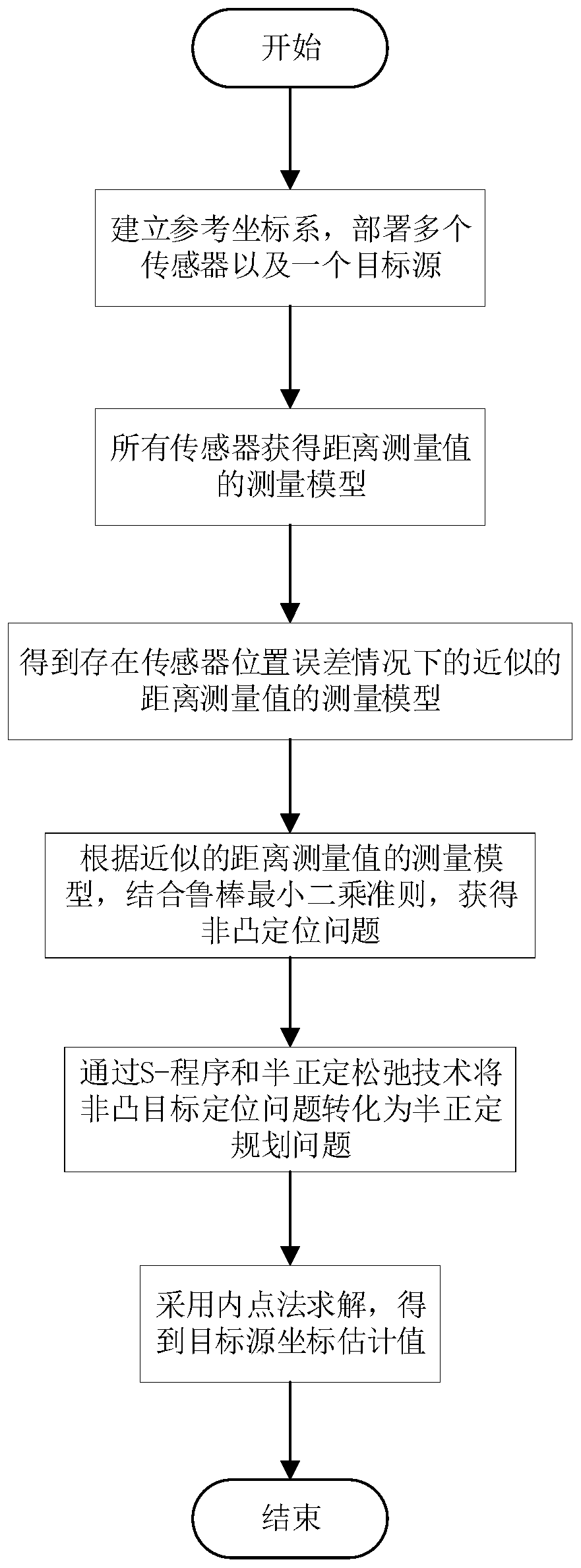
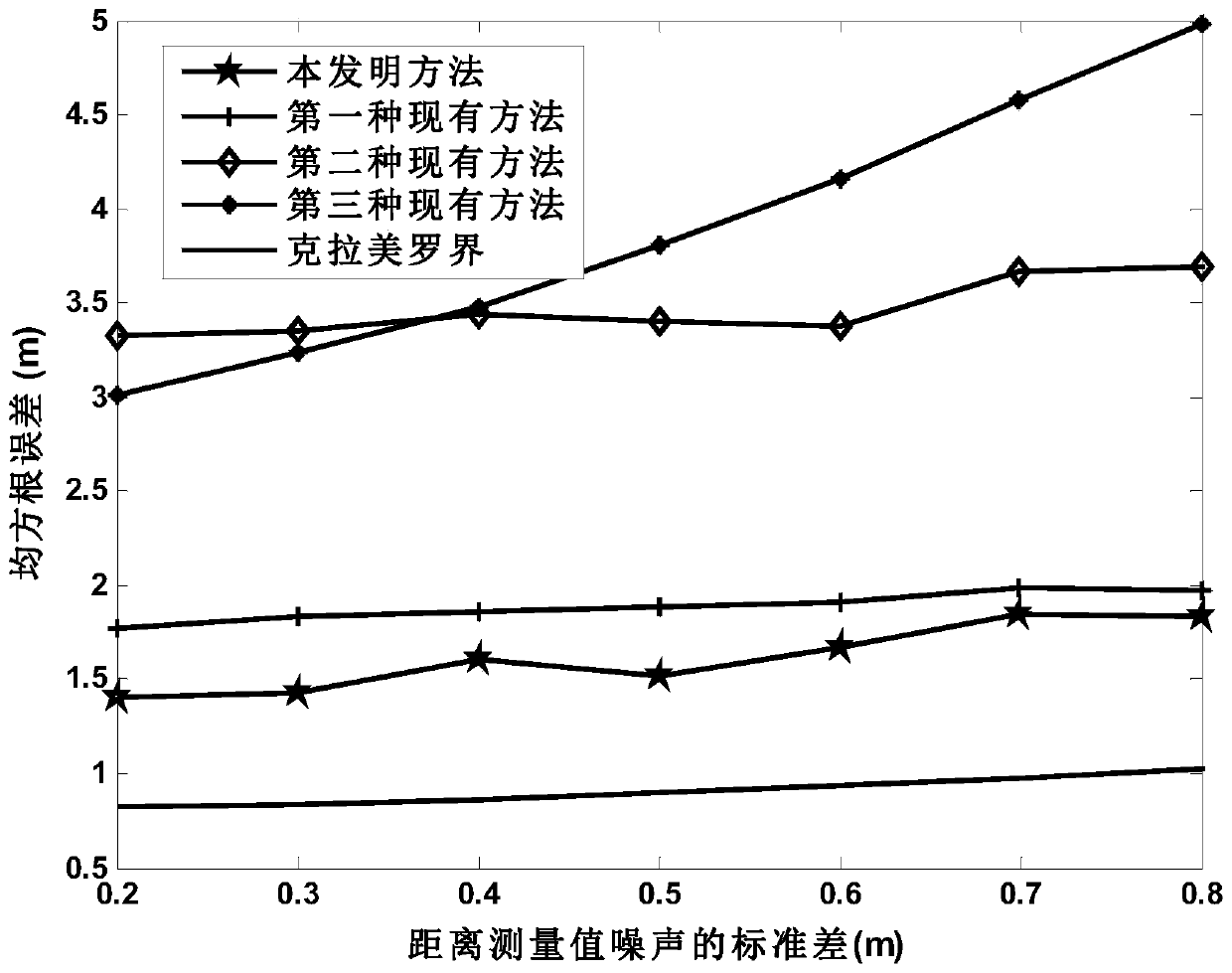
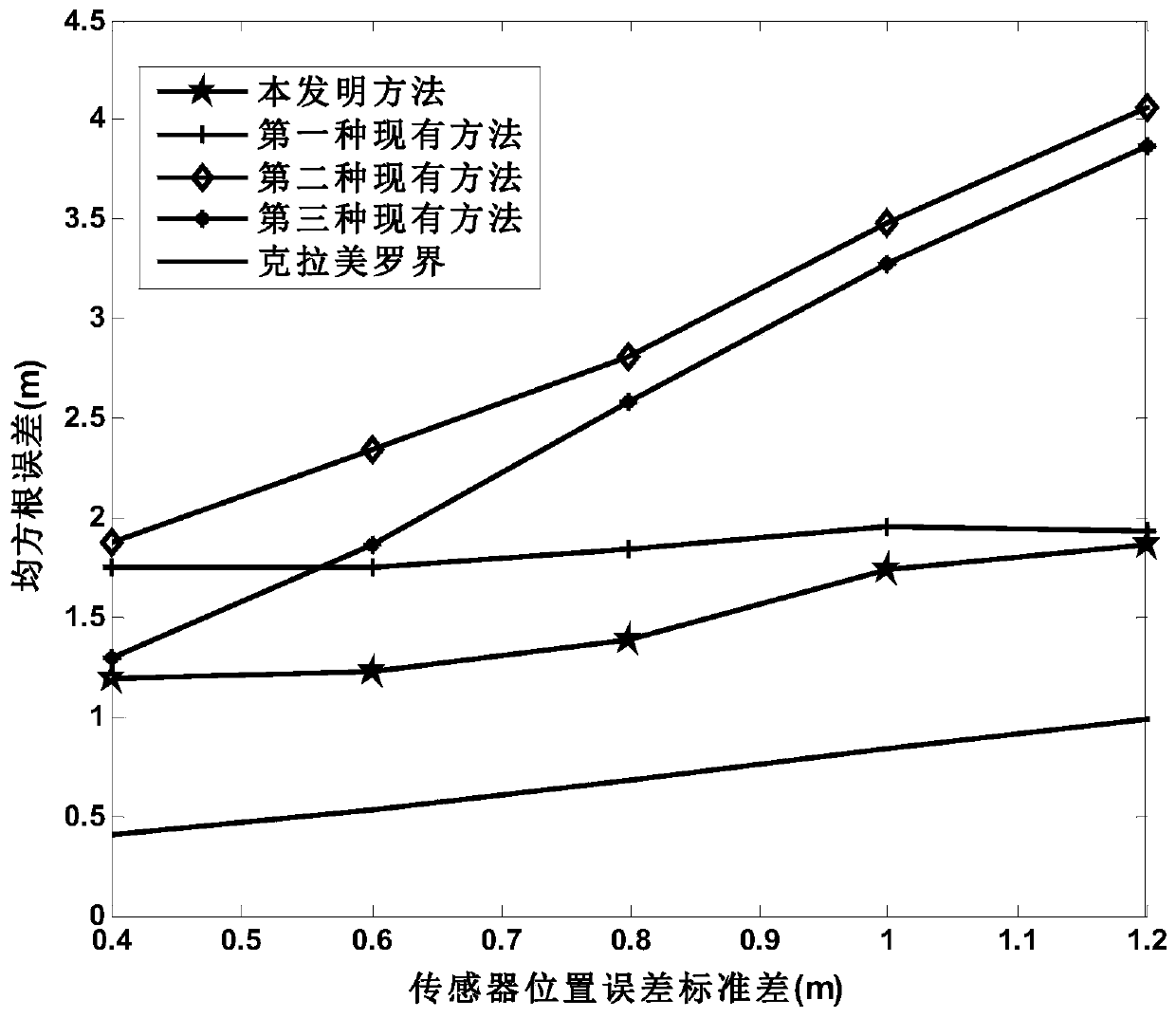
ActiveCN111157943AHigh positioning accuracyLow cost of executionPosition fixationInterior point methodAsynchronous network
The invention discloses a TOA-based sensor position error suppression method in an asynchronous network. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a measurement model of a distance measurement value obtained by a sensor, and combining an actual coordinate position model of the sensor in a reference coordinate system and a robust least square criterion to obtain a non-convex positioning problem for solving a target source position and initial sending time; importing a relaxation variable and an auxiliary variable into a non-convex positioning problem, combining an S-program and a positive semidefinite relaxation technology, and relaxing the non-convex positioning problem into a positive semidefinite programming problem for solving a target source position and initial sending time; solving the positive semidefinite programming problem for solving the position of the target source and the initial sending time by adopting an interior point method to obtain an estimated value of the position of the target source. The method has the advantages that the influence of sensor position errors can be effectively reduced, the performance is still stable under the condition of largesensor position errors, and the positioning precision is high.
Owner:宁波市大学科技园发展有限公司
Positioning method based on arrival time under unknown sight distance and non-sight-distance distribution condition
ActiveCN110673089AEasy to solveImprove target positioning accuracyNetwork topologiesPosition fixationWireless sensor networkingEngineering
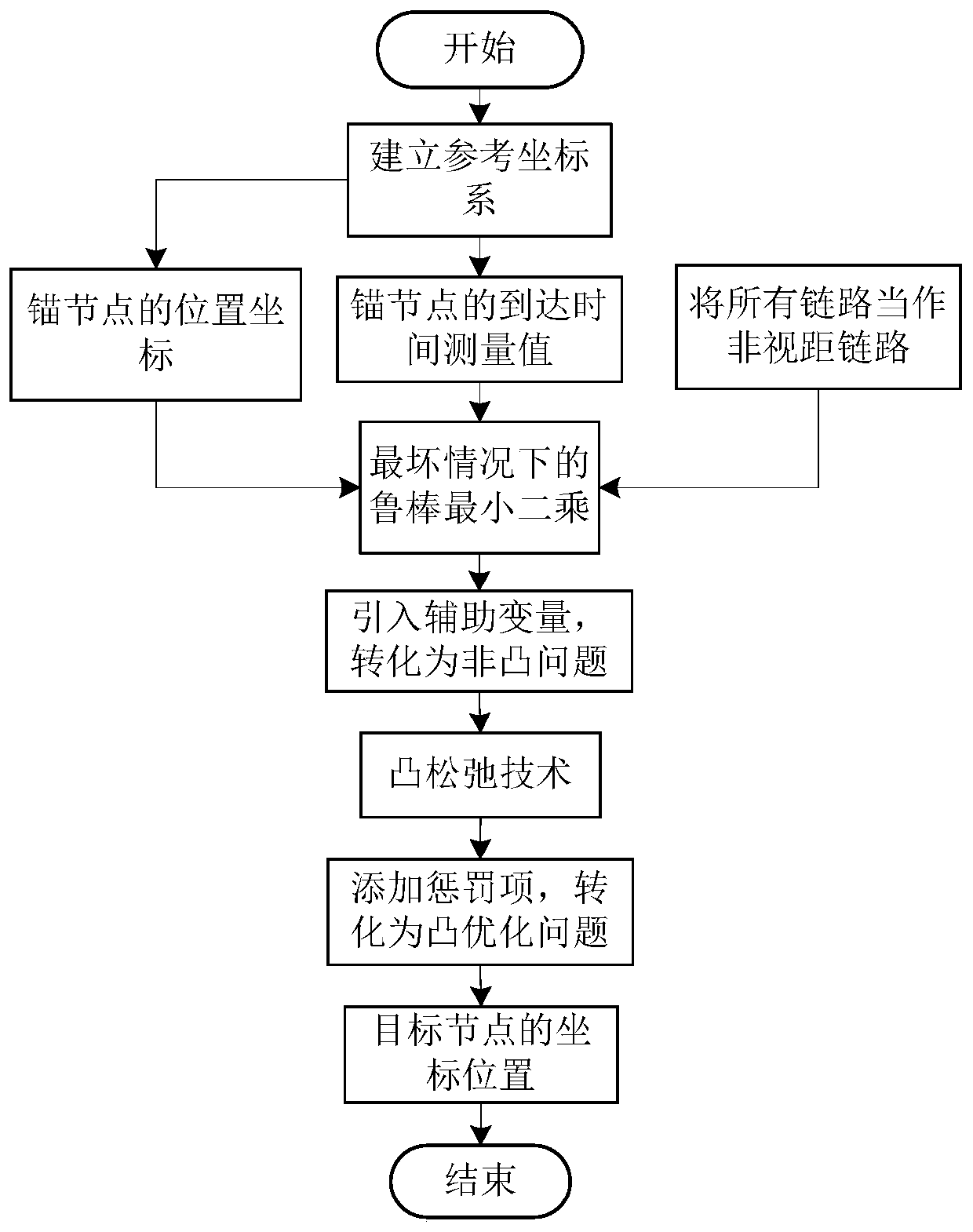
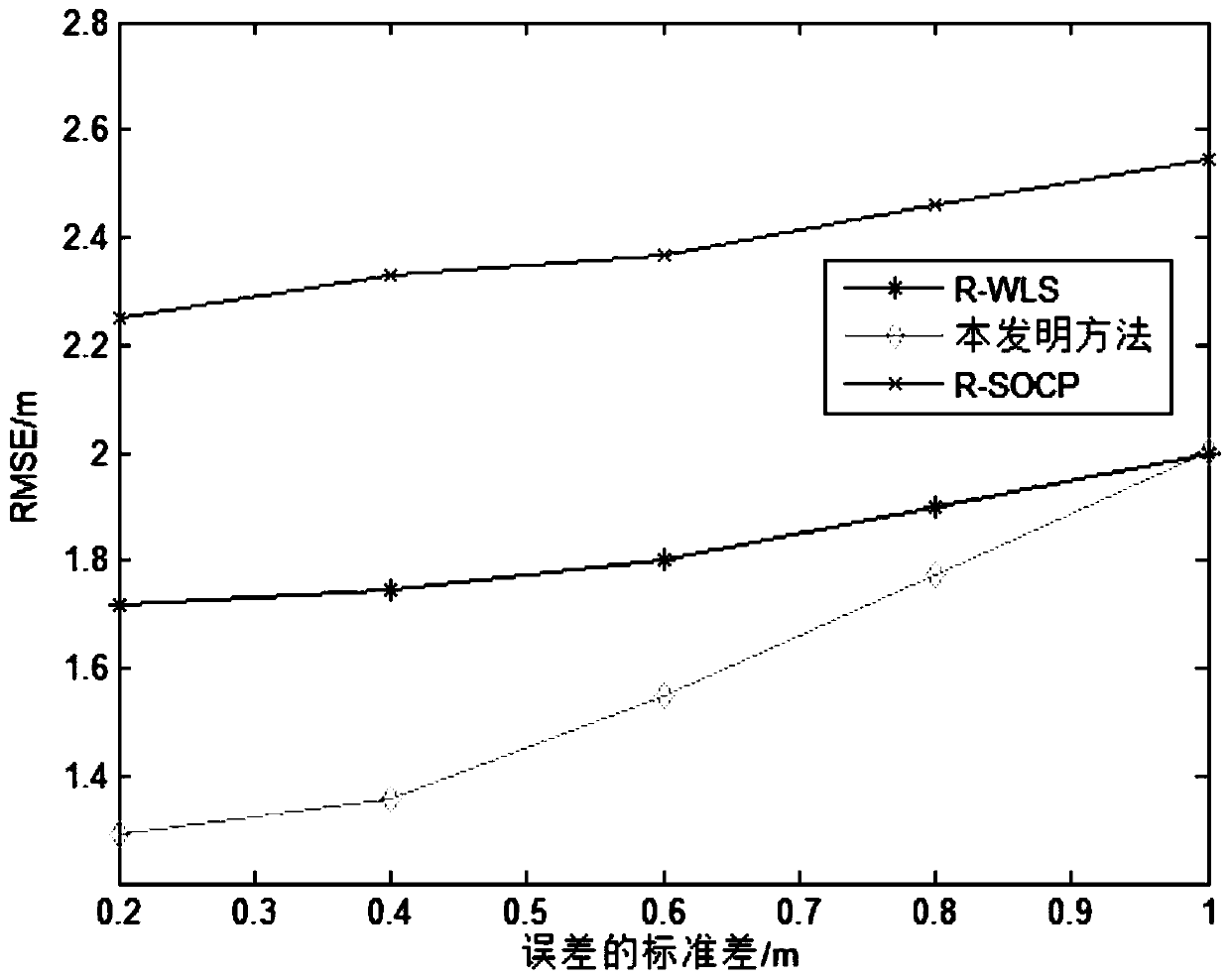
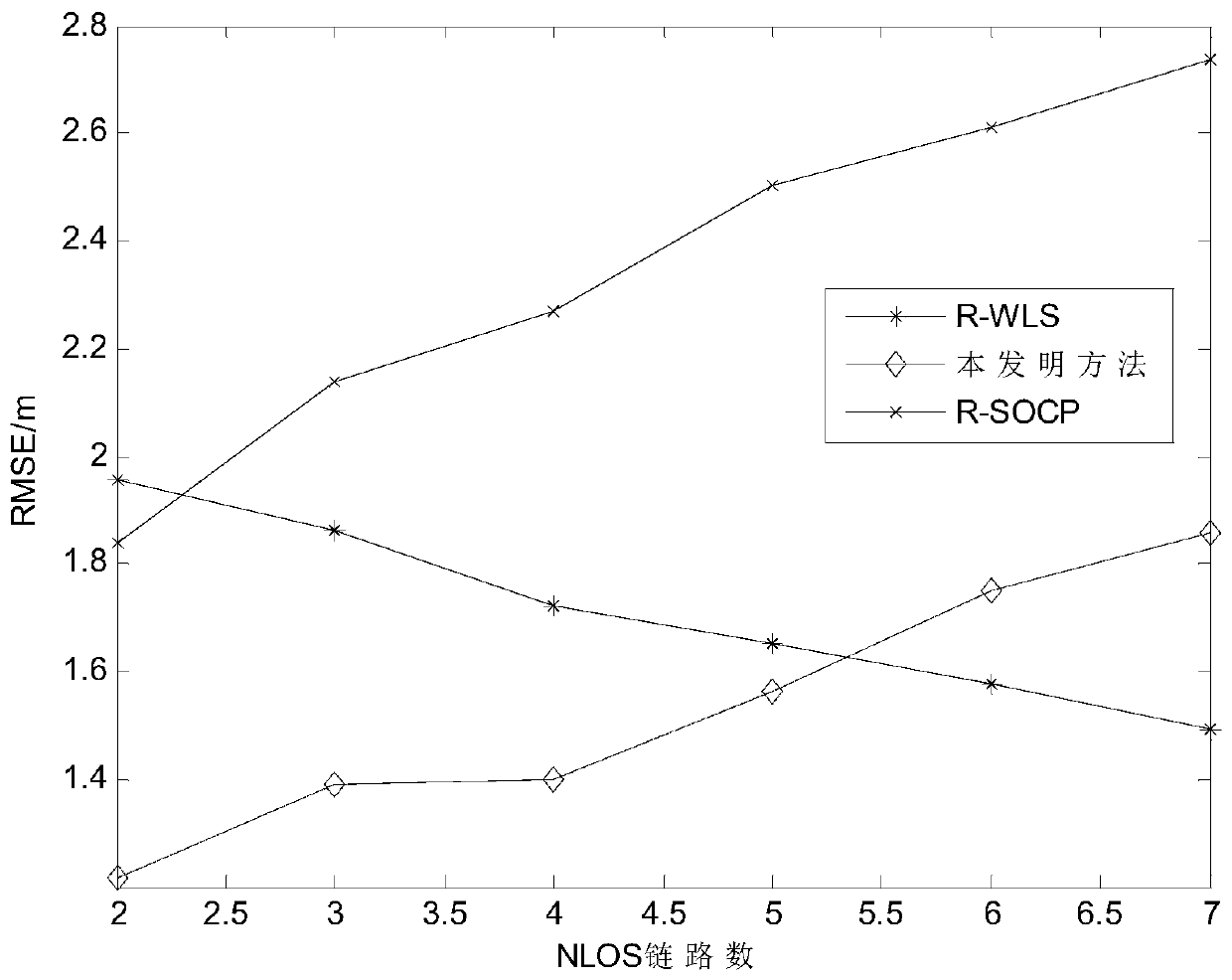
The invention discloses a positioning method based on an arrival time under an unknown sight distance and non-sight-distance distribution condition. All sight distance links in a wireless sensor network are regarded as non-sight-distance links, and a distance measurement model between a target node and each anchor node is established. A minimization problem is obtained by adopting a robust least square method under a worst condition according to an approximate expression of the distance measurement model. An auxiliary variable is introduced and a function is converted into a non-convex problem; constraint conditions in the non-convex problem are relaxed through a convex relaxation technology, a penalty term is introduced, and the problem is converted into a convex optimization problem; andthe convex optimization problem is solved to obtain a position estimation value of the target node. The method has the advantages that the distribution conditions of the sight distance links and thenon-sight-distance links are not need to be known, and the positioning precision is high.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
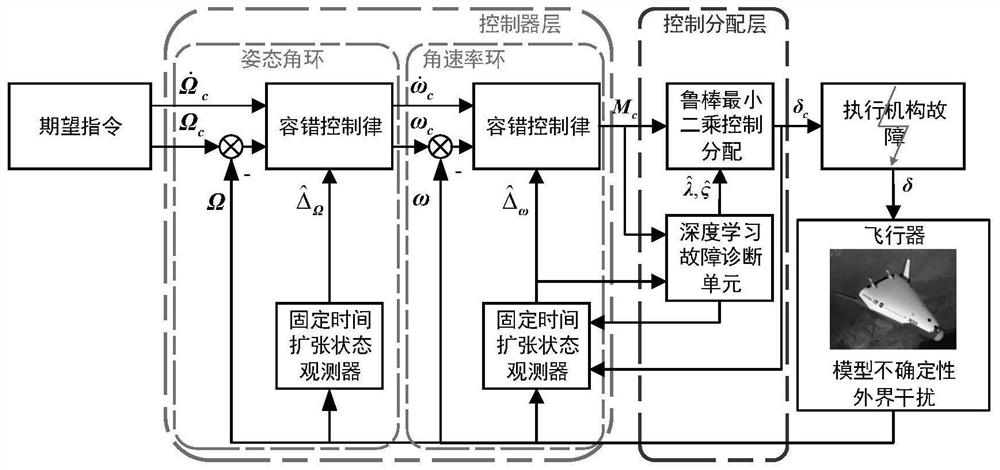
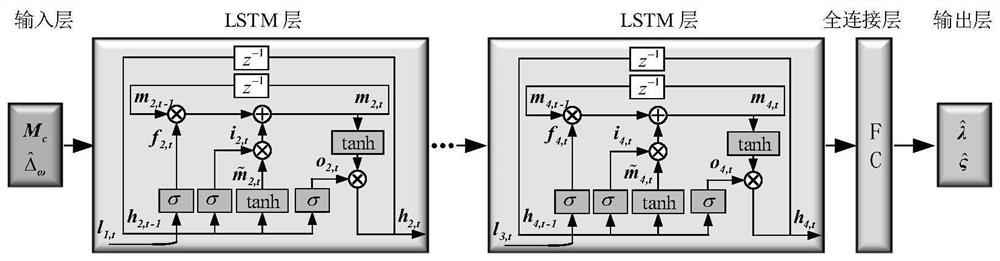
Aircraft hierarchical fault-tolerant control method based on deep learning fault diagnosis
ActiveCN113485304AImprove controllabilityImprove fault toleranceProgramme controlSustainable transportationFlight vehicleState observer
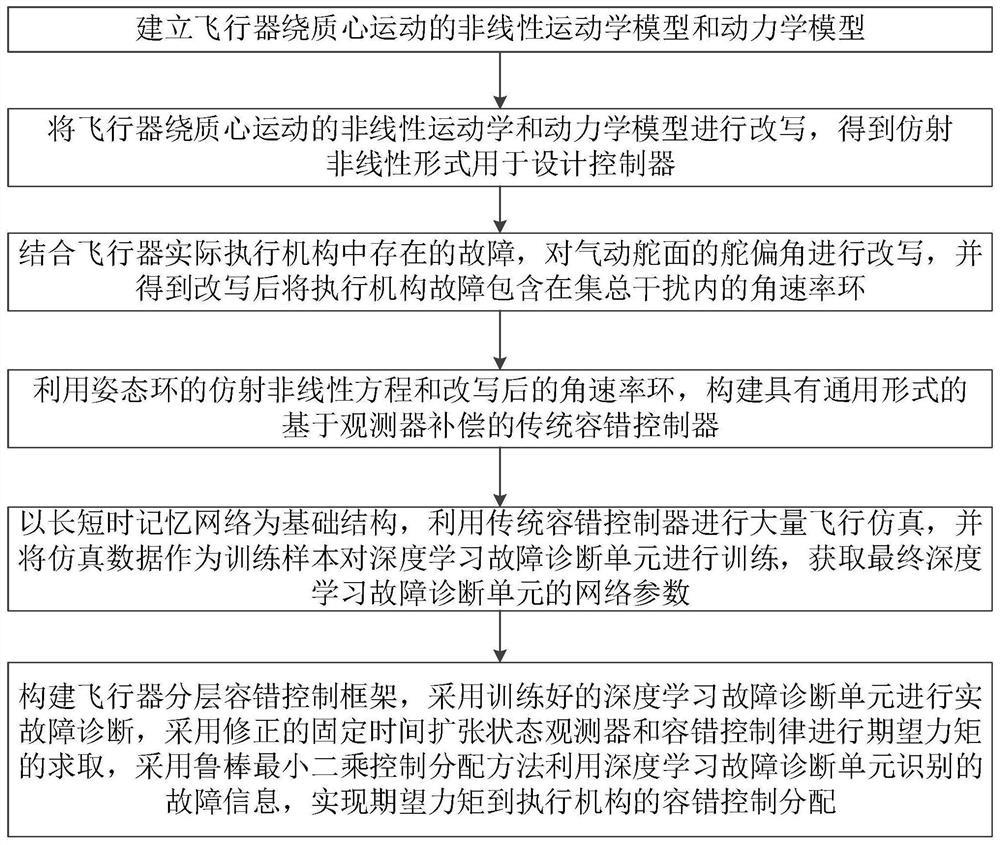
The invention discloses an aircraft hierarchical fault-tolerant control method based on deep learning fault diagnosis, and belongs to the field of aircraft control. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing an aircraft mathematical model and writing the aircraft mathematical model into affine nonlinear forms of an attitude ring and an angular rate ring; further considering possible faults of an execution mechanism, taking the possible faults as lumped interference, and rewriting an angular rate ring; combining a fixed time expansion state observer and a quadratic programming control distribution method to form a traditional fault-tolerant controller; then, using a traditional fault-tolerant controller for carrying out mass flight simulation, and training and using a deep learning fault diagnosis unit for diagnosing fault parameters; and finally, combining the corrected fixed time extended state observer, the corrected fault-tolerant control law and robust least square control distribution to form a control framework of the aircraft hierarchical fault-tolerant control method, and distributing the final control surface deflection angle to each execution mechanism after the fault is considered. According to the invention, the control performance and the fault-tolerant performance are improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
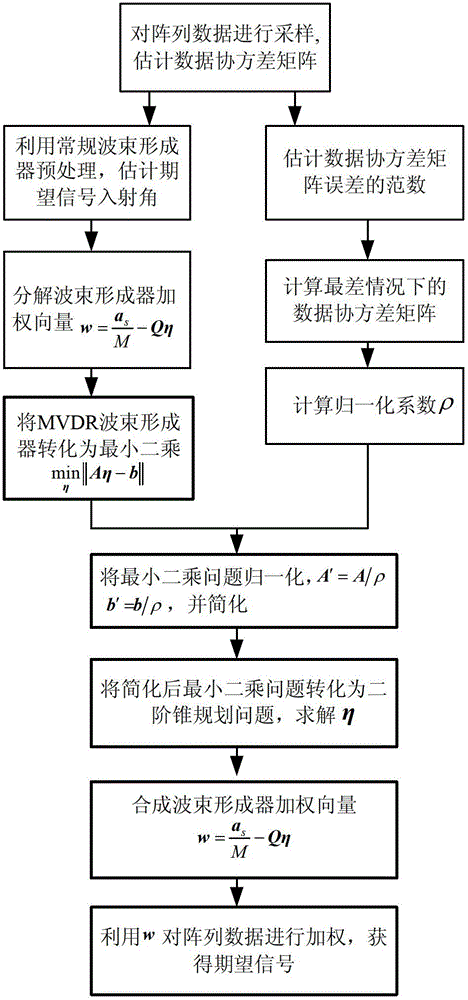
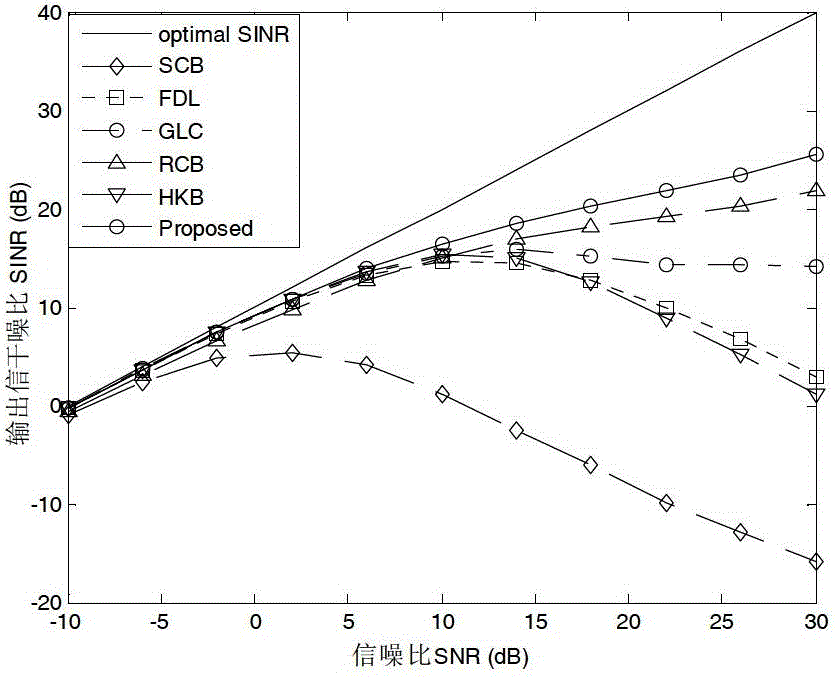
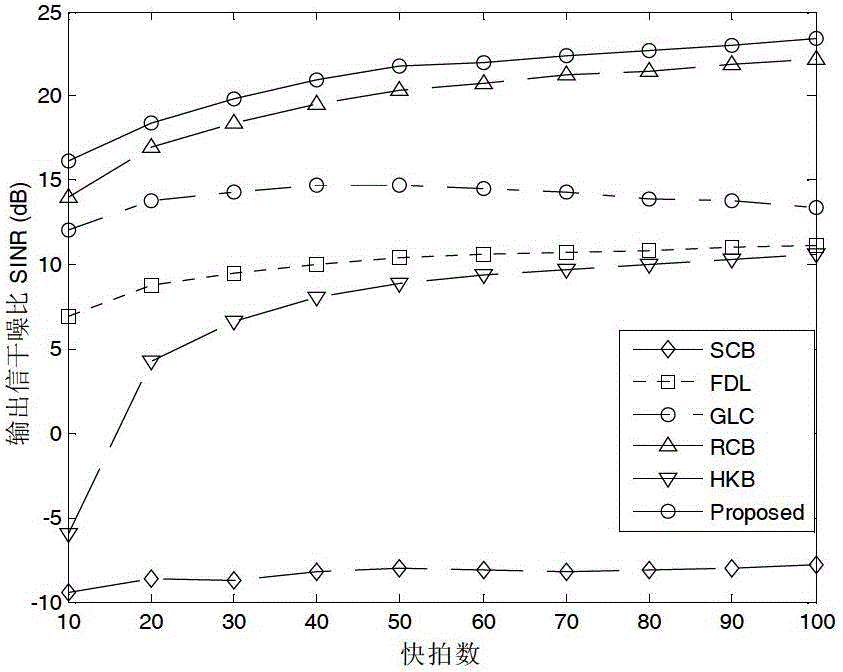
Robust beam forming method based on robust least-square
InactiveCN103245941BRemove uncertaintyImprove robustnessSpatial transmit diversityWave based measurement systemsInterior point methodBeam pattern
The invention provides a robust beam forming method based on a robust least-square. The method has the following steps: decomposing the weight of a beam forming device into two parts of static stage weight and self-adaptive weight by utilizing a generalized sidelobe cancellation device, transforming the standard MVDR (Minimum Variance Distortionless Response) beam forming device expression into a least-square form, acquiring data covariance matrix in the worst condition under the norm restrict of real data covariance matrix and estimated data covariance matrix error, utilizing the data covariance matrix to modify the least-square problem and to transform the problem into a robust least-square problem, further transforming the problem into a second order cone planning problem, and acquiring an optimal solution by utilizing an efficient interior point method. The method has better performances in the following aspects: (1) the output signal interference noise ratio and the power estimated accuracy when the existence conditions are mismatched, (2) the nulling depth of the interference direction in the beam pattern, (3) low mismatching sensibility to the parameter needed to be estimated in advance in the arithmetic. The method has certain the oretical meaning and utility value.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Robust iris region segmentation method based on specific boundary detectors
ActiveCN102629319BCalculation speedDetection speedCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature setData set
The invention discloses a robust iris region segmentation method based on specific boundary detectors, which comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a left and right inner boundary, left and right outer boundary and upper and lower eyelid boundary iris specific boundary training data set and a candidate feature set; S2, constructing the six iris specific boundary detectors by using a cascaded self-adaptive learning algorithm; S3, positioning an iris inner boundary by utilizing the left and right inner boundary detectors and weighted Hough transform; S4, positioning an iris outer boundary by utilizing the left and right outer boundary detectors and the weighted Hough transform; and S5, positioning an upper eyelid boundary by utilizing the upper and lower eyelid boundary detectors and a robust least square method. By utilizing the robust iris region segmentation method, an iris effective area can be accurately segmented in an iris image containing a lot of noise, so that the accuracy, the robustness and the usability of an iris identification system are improved. The robust iris region segmentation method can be widely applied to various application systems for identity recognition and security defense by using iris recognition.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
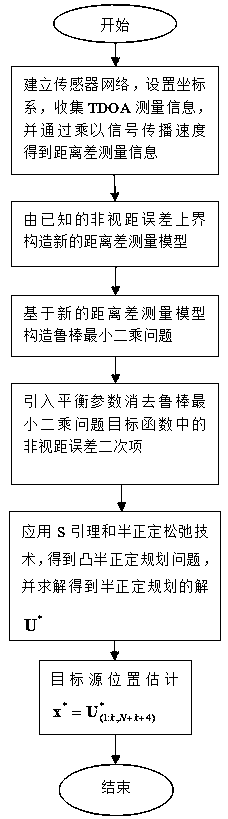
Robust TDOA positioning method for jointly estimating target position and non-line-of-sight error
The invention relates to a robust TDOA positioning method for jointly estimating a target position and a non-line-of-sight error, and the method eliminates a non-line-of-sight error quadratic term byconverting an original measurement model. According to the converted measurement model, a robust least square problem which takes target position and reference path non-line-of-sight errors as estimation parameters is constructed; then, an S lemma and a positive semi-definite relaxation technology are adopted to obtain a convex positive semi-definite planning problem; finally, the positive semi-definite planning problem is solved by using a common inner point method solving tool so as to obtain an estimated value of the position of a target source in an established coordinate system; and the robust TDOA positioning method for jointly estimating the target position and the non-line-of-sight error has the advantages that the problems caused by overlarge non-line-of-sight error upper bound and application of a triangular inequality in the existing robust method are solved, and the positioning accuracy of the existing method in a non-line-of-sight environment is improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
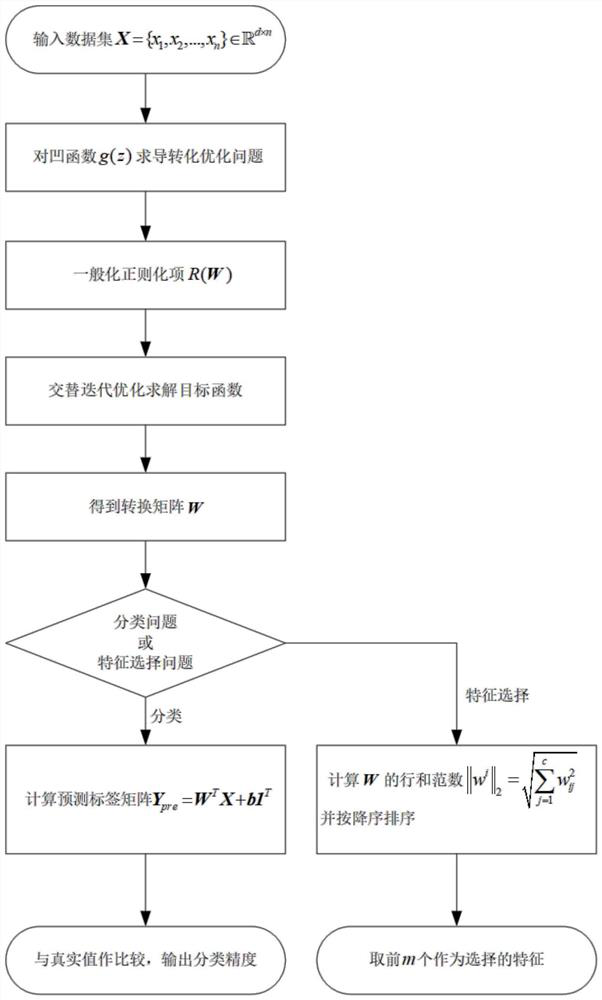
Image classification and feature selection method based on robust least two regression framework
PendingCN114037860AImprove robustnessHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionRobust least squaresFeature selection
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Target positioning method based on arrival time in mixed sight distance and non-sight distance environment
ActiveCN110673088AEasy to solveImprove target positioning accuracyPosition fixationEngineeringRobust least squares
The invention discloses a target positioning method based on an arrival time in a mixed sight distance and non-sight distance environment. The method comprises a step of establishing different distance measurement models according to a link type between a target node and an anchor node, a step of obtaining a minimization problem through approximate expressions of two different distance measurementmodels by adopting a robust least square method under a worst condition, and further converting the minimization problem into a target function, a step of introducing an auxiliary variable in the target function to be converted into a non-convex problem, a step of relaxing a constraint condition in the non-convex problem by using a convex relaxation technology and introducing a weight and a penalty term to obtain a convex optimization problem, and a step of solving the convex optimization problem to obtain a position estimation value of the target node. The method has high positioning precision.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
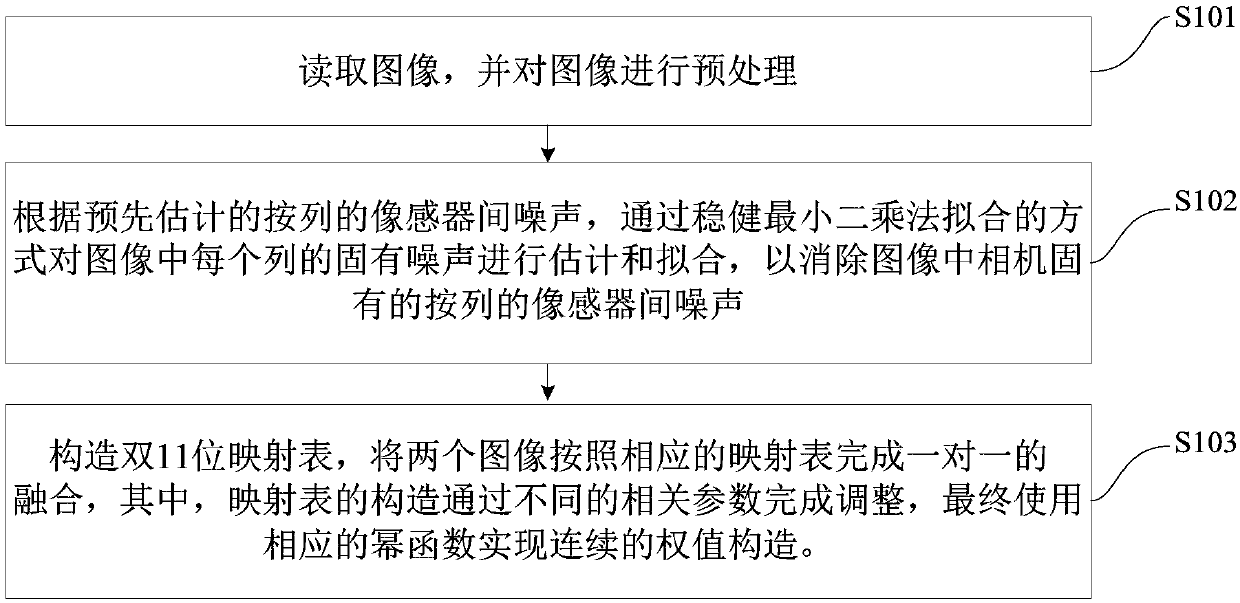
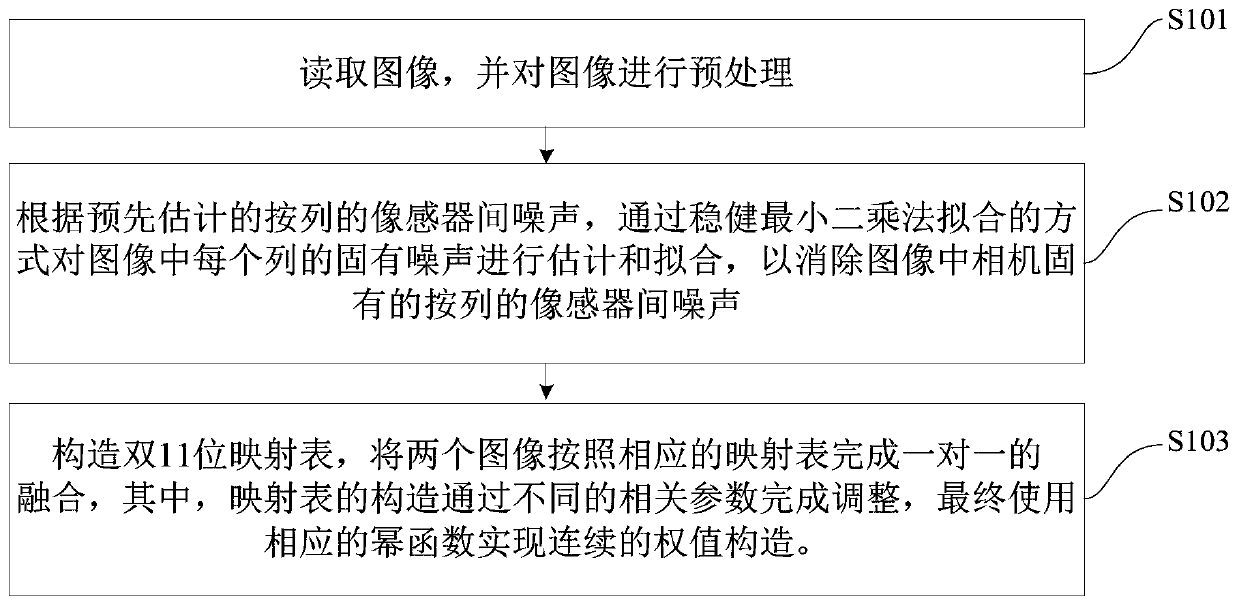
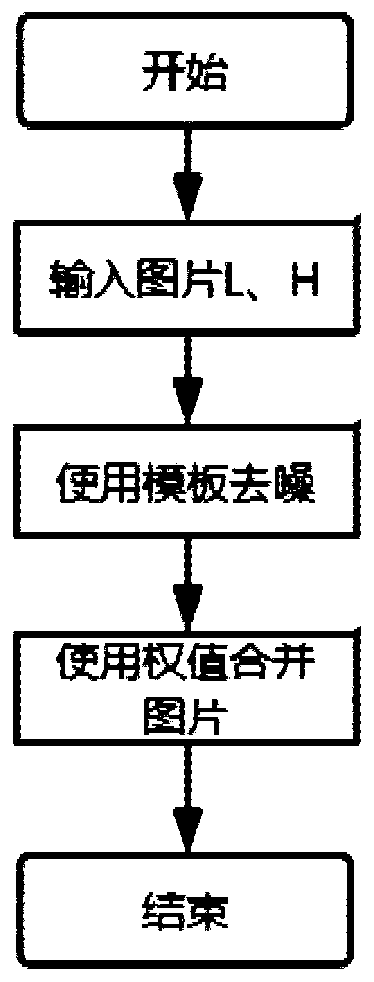
Image denoising fusion method and system based on high and low bit data of camera
ActiveCN107909559ASolve the noise problemAvoid problems such as poor synthesis effectImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingPattern recognition
The invention discloses an image denoising fusion method and system based on high and low bit data of a camera. The method comprises the steps of reading an image, and performing preprocessing on theimage; estimating and fitting the inherent noise of each column in the image through a mode of robust least square fitting according to pre-estimated per-column noise between camera sensors so as to eliminate the inherent per-column noise between the camera sensors of the camera in the image; constructing double 11-bit mapping table, accomplishing one-to-one fusion on two images according to the corresponding mapping table, wherein adjustment for the construction of the mapping tables is accomplished through different relevant parameters, and finally realizing continuous weight construction byusing a corresponding power function. According to the method, problems such as poor image synthesis effect caused by the inherent noise of the sensors can be effectively avoided, smooth fusion of high and low bit images is realized, and problems such as generation of synthesis seams are avoided.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
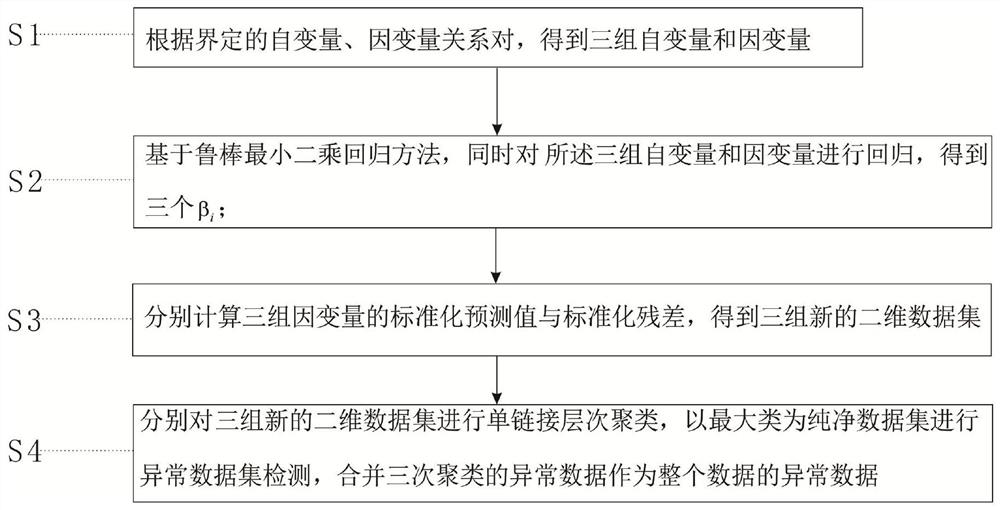
An abnormal data detection method for aerodynamic data sets
ActiveCN111241481BSolving Modeling DifficultiesReduce computational complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsData setAlgorithm
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Robust positioning method based on time difference of arrival under non-line-of-sight conditions
ActiveCN110221244BPrecise positioningSolve the problem of the upper bound of the non-line-of-sight errorPosition fixationInterior point methodRobust least squares
The invention discloses a robust positioning method based on time difference of arrival under the condition of non-line-of-sight error. The method constructs a robust least square problem with the non-line-of-sight error of the target position and the reference path as estimation parameters. A method of introducing a balance parameter is proposed to eliminate the quadratic term of the non-line-of-sight error in the objective function, and then an auxiliary variable is introduced, and the convex semi-definite programming problem is obtained by using the S lemma and positive semi-definite relaxation technique; finally, the commonly used interior point method is used to solve the tool Solve the semi-positive definite programming problem to obtain the estimated value of the target source position in the established coordinate system. The invention overcomes the unreasonable upper bound of the non-line-of-sight error in the existing robust method and the negative impact brought by the application of the triangle inequality, and greatly improves the positioning accuracy of the existing method in a dense non-line-of-sight environment.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Target positioning method based on robust TOA/RSS in non-line-of-sight environment
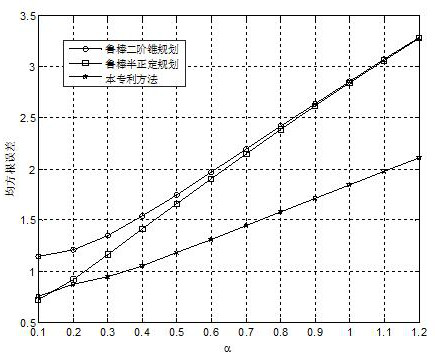
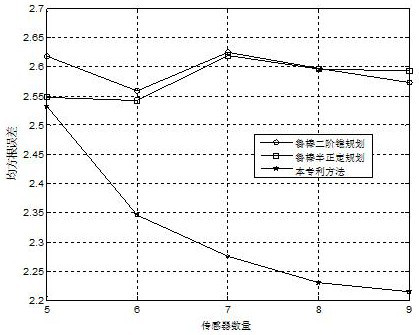
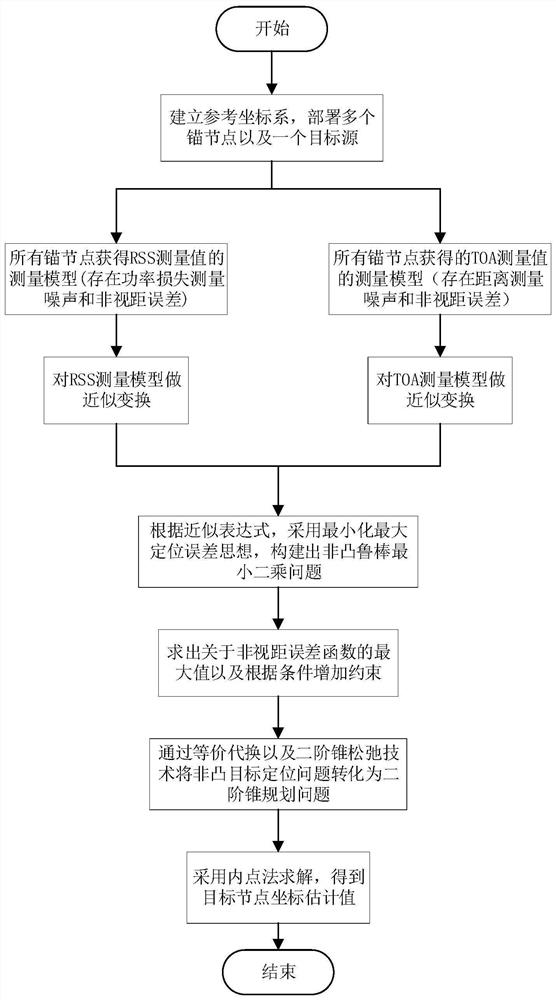
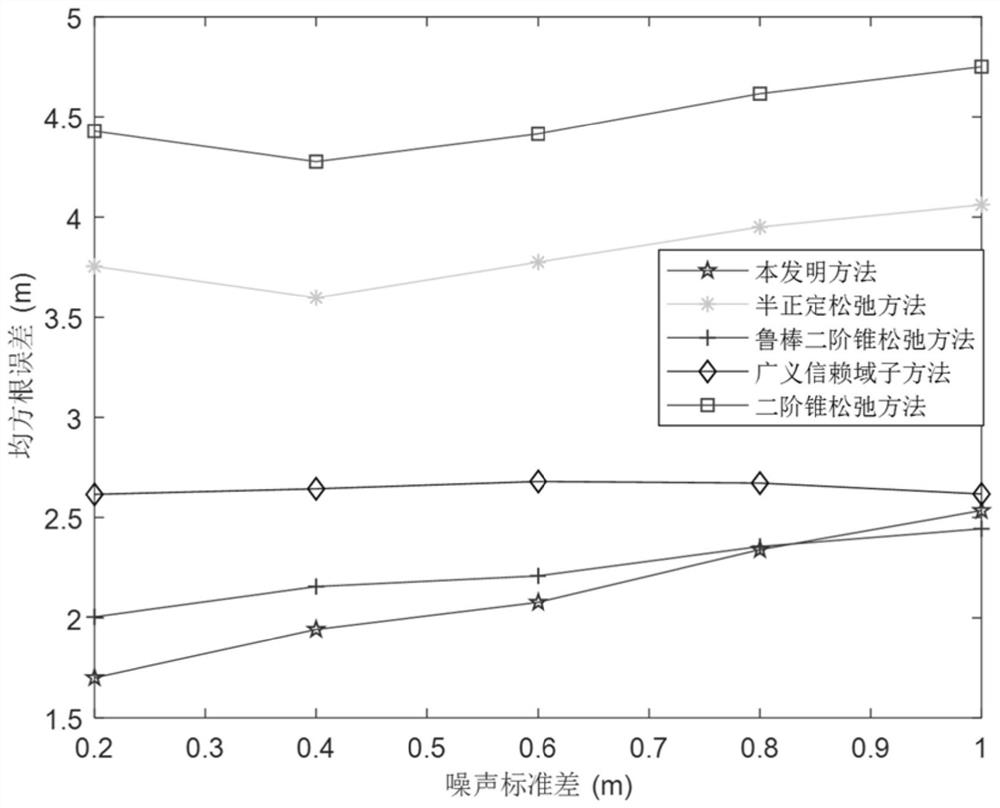
PendingCN114779165APrecise positioningAccurate estimatePosition fixationSlack variableInterior point method
The invention discloses a target positioning method based on robust TOA / RSS in a non-line-of-sight environment. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out approximate transformation on a measurement model of an RSS measurement value and a measurement model of a TOA measurement value; obtaining a non-convex positioning problem according to the two approximate expressions by adopting a robust least square criterion; combining the maximum value of the function about the non-line-of-sight error during RSS measurement and the maximum value of the function about the non-line-of-sight error during TOA measurement, and introducing a slack variable and an auxiliary variable to obtain an equivalence problem of the non-convex positioning problem; a second-order cone relaxation method is adopted, and the equivalence problem of the non-convex positioning problem is converted into a second-order cone programming problem; solving the second-order cone programming problem by adopting an interior point method to obtain a position estimation value of the target node in the reference coordinate system; the method has the advantages that two kinds of measurement information of the received signal strength and the arrival time are fully utilized, and a global optimal solution can be obtained, so that the target positioning accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for processing gps deformation monitoring data
ActiveCN103148813BImprove processing efficiencyImprove reliabilityUsing wave/particle radiation meansDouble differenceObservation data
The invention provides a method for processing global position system (GPS) deformation monitoring data. The method for processing the GPS deformation monitoring data comprises (1) obtaining present epoch observation data and broadcast ephemeris data of a base station and a monitoring station, and forming a double-difference observation equation by using phase observation values; (2) setting a maximum deformation quantity between two epochs; (3) adopting a Cholesky to resolve and construct an ambiguity search space; (4) searching the ambiguity, and enabling a variance ratio to be larger than 3; (5) obtaining fixed solution coordinates X, Y and Z of a single epoch whole cycle ambiguity and a convariance matrix of the single epoch whole cycle ambiguity of a monitoring point; (6) using an average gap method to carry out deformation detection on a deformation value between a present epoch and a previous epoch; (7) after finishing the detection of (6), using a robust least square static solution by superposition of two epoch observation equations as a result of the present epoch, or obtaining a result of the present epoch according to a robust sequential adjustment. The method for processing the GPS deformation monitoring data is accurate.
Owner:HUNAN ZHILI ENG SCI & TECH
Robust tdoa localization method for joint estimation of target position and non-line-of-sight error
ActiveCN110221245BPrecise positioningHigh precisionPosition fixationInterior point methodEngineering
The invention relates to a robust TDOA positioning method for jointly estimating the target position and the non-line-of-sight error, and eliminates the quadratic item of the non-line-of-sight error by transforming the original measurement model. According to the transformed measurement model, a robust least squares problem is constructed with the non-line-of-sight error of the target position and the reference path as the estimated parameters; then, the convex positive semi-definite programming problem is obtained by using the S lemma and positive semi-definite relaxation technique; Utilize the interior point method solving tool commonly used at last to solve the semi-positive definite programming problem, thereby obtain the estimated value of the target source position in the established coordinate system; The advantage of the present invention is to overcome the non-line-of-sight error in the existing robust method The problems caused by the excessive boundary and the application of the triangle inequality have improved the positioning accuracy of the existing methods in the non-line-of-sight environment.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Image denoising fusion method and system based on camera high and low bit data
ActiveCN107909559BSolve the noise problemAvoid problems such as poor synthesis effectImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage denoising
The invention discloses an image denoising fusion method and system based on camera high and low bit data. The method includes the following steps: reading the image and preprocessing the image; based on the pre-estimated column-wise inter-image sensor noise , estimate and fit the inherent noise of each column in the image through robust least squares fitting to eliminate the column-by-column inter-sensor noise inherent to the camera in the image; construct a double 11-bit mapping table to combine the two Each image is fused one-to-one according to the corresponding mapping table. The construction of the mapping table is adjusted through different relevant parameters, and finally the corresponding power function is used to achieve continuous weight construction. This method can effectively avoid problems such as poor image synthesis effects caused by the inherent noise of the sensor, achieve smooth fusion of high and low-bit images, and avoid problems such as the generation of synthesis seams.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com