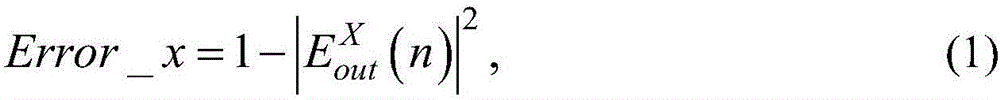Patents
Literature
81 results about "Time domain equalization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
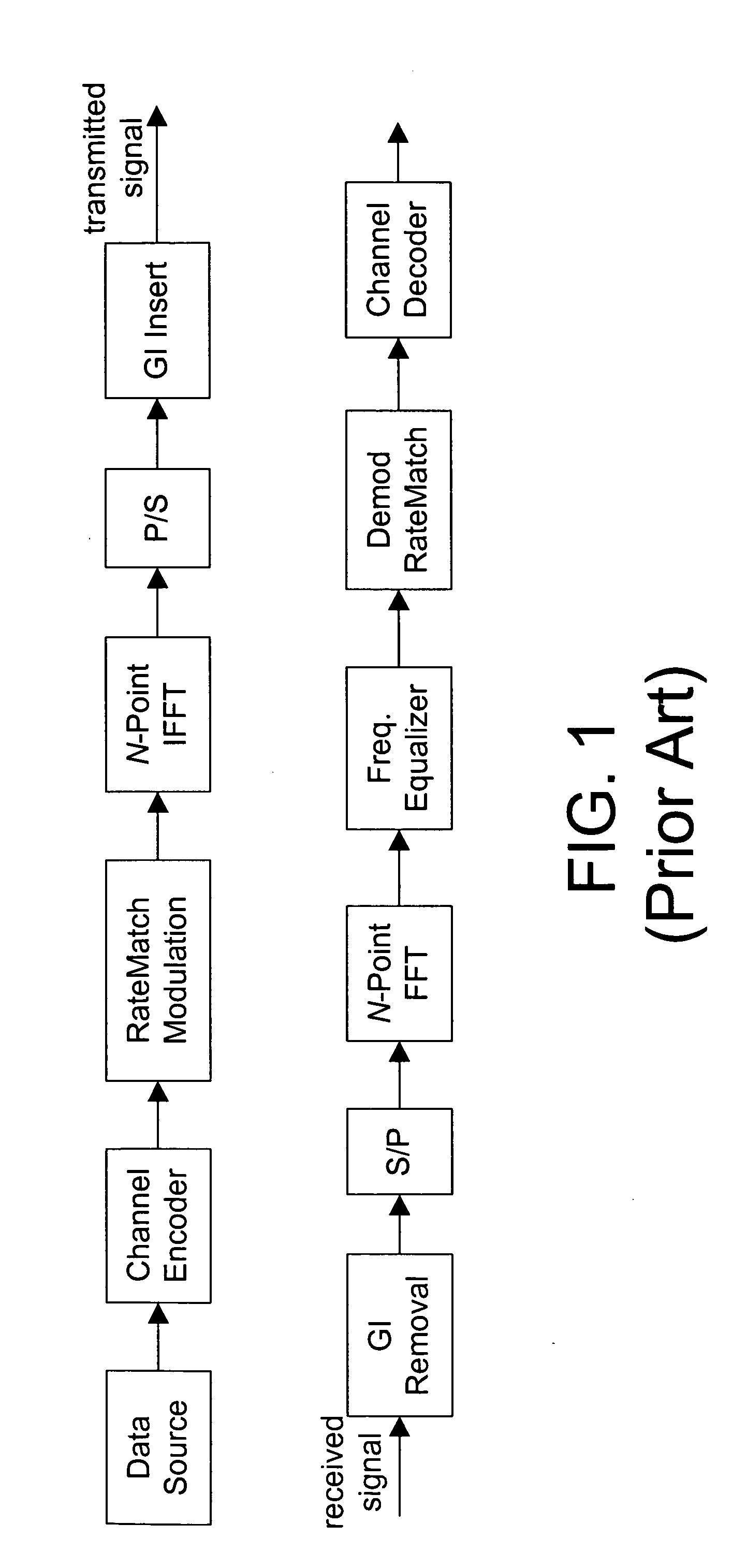
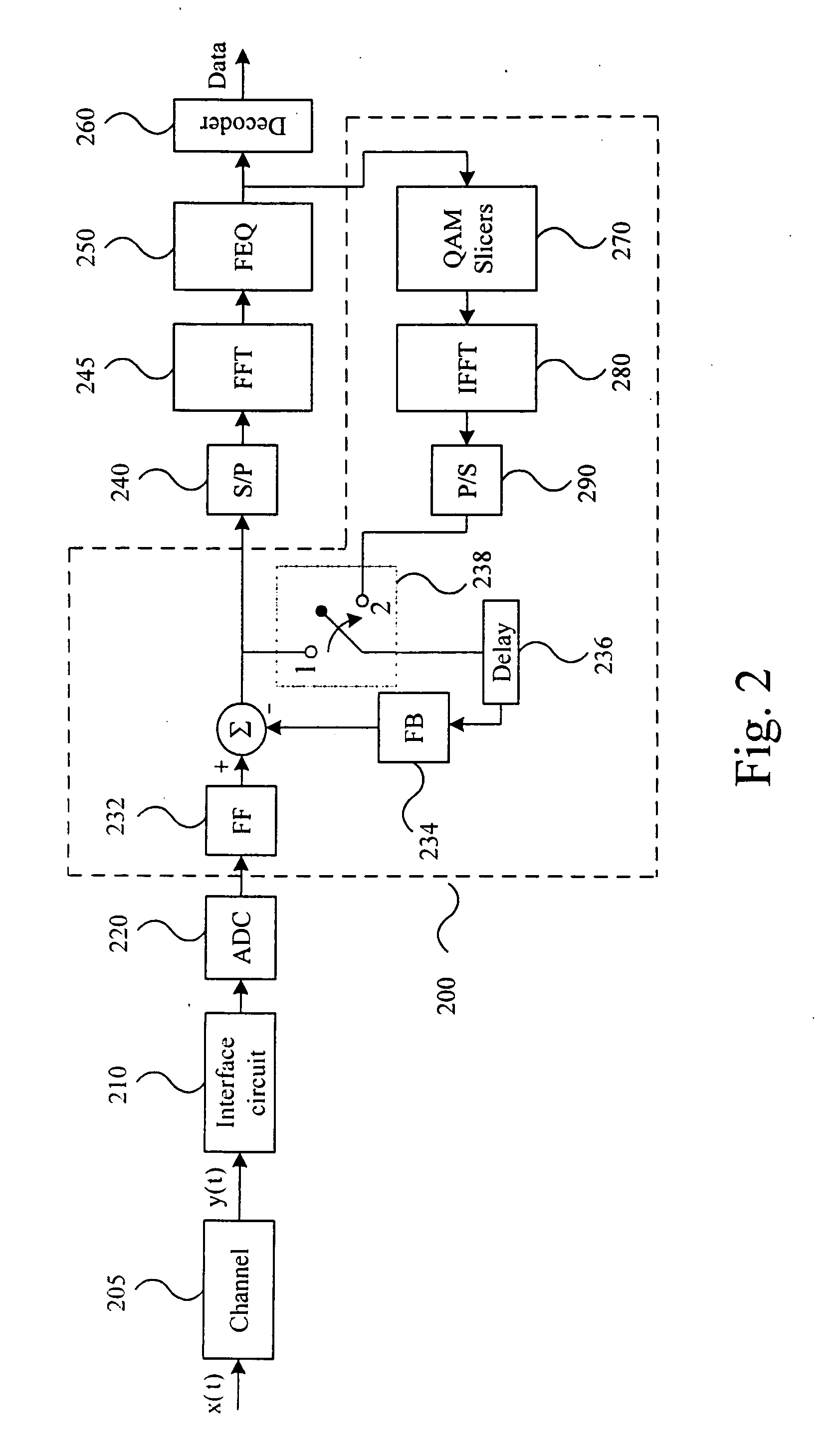
TIME-DOMAIN EQUALIZATION. In Time domain equalization technique, a window function is applied to the data in time domain obtained after performing IFFT operation. For the correlative polynomial (1-D) used in the section 4, the window function proposed to use for ICI suppression is (1-exp (j2πn/N)) (Chin et al., 2006).
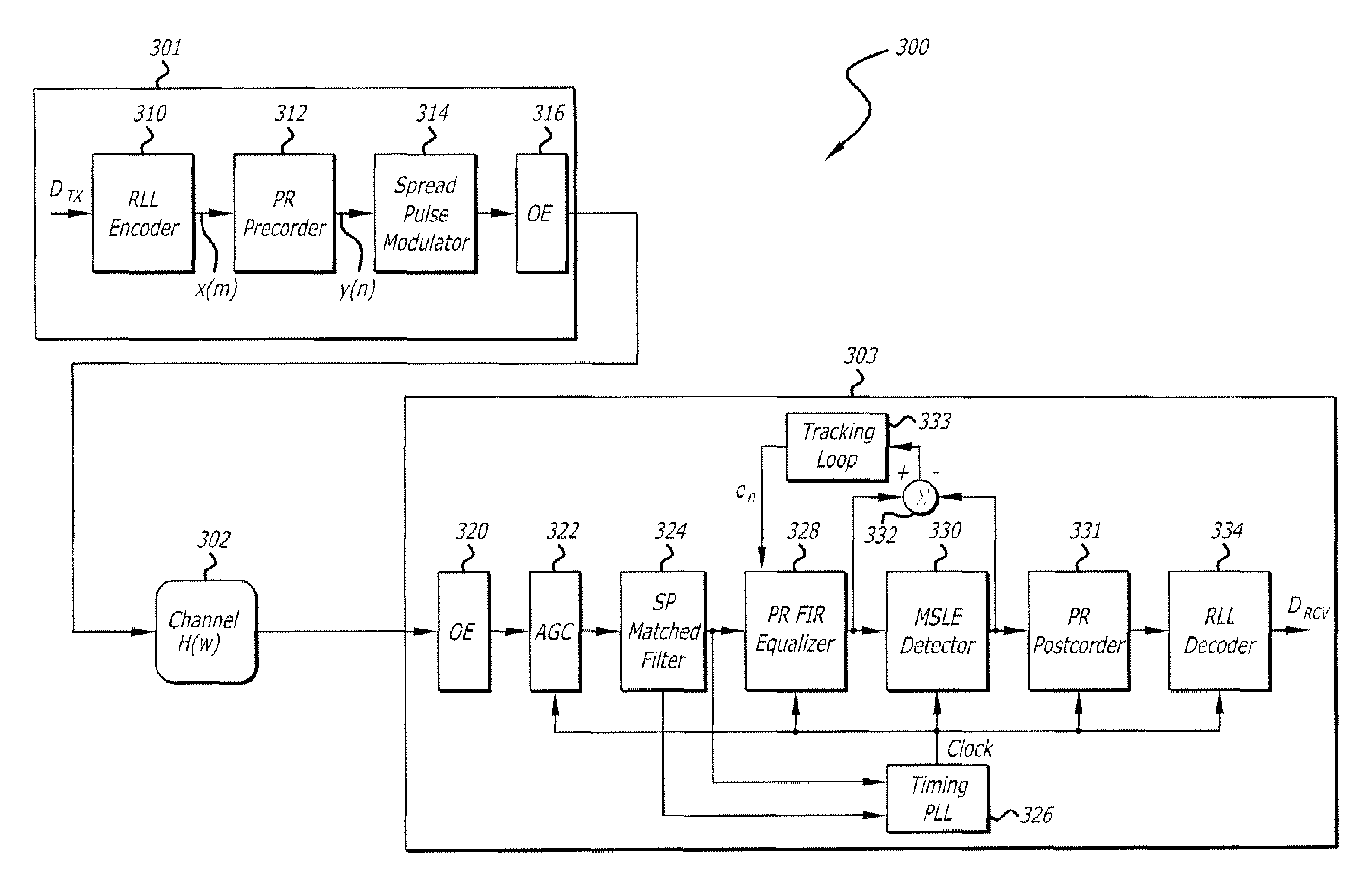
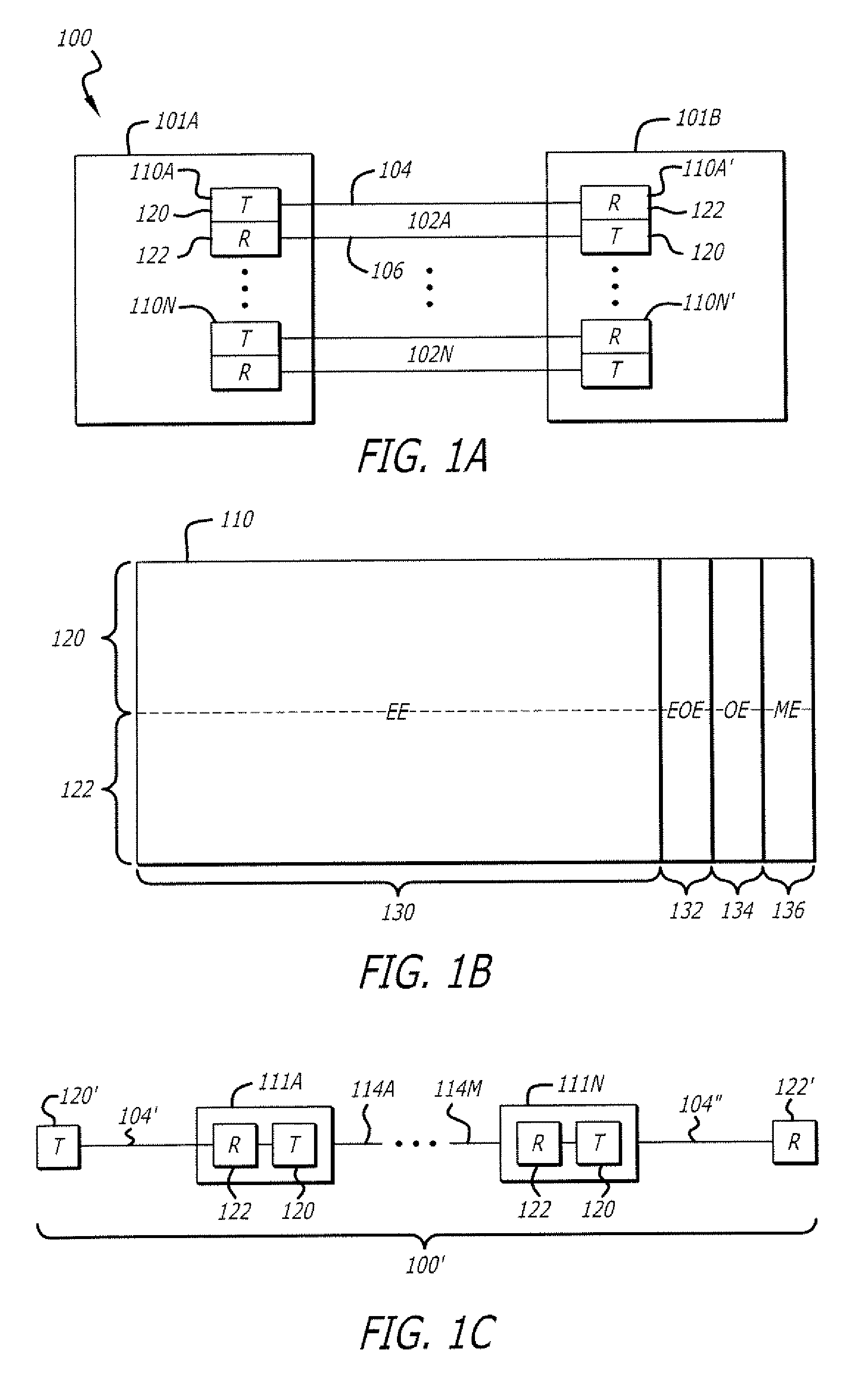
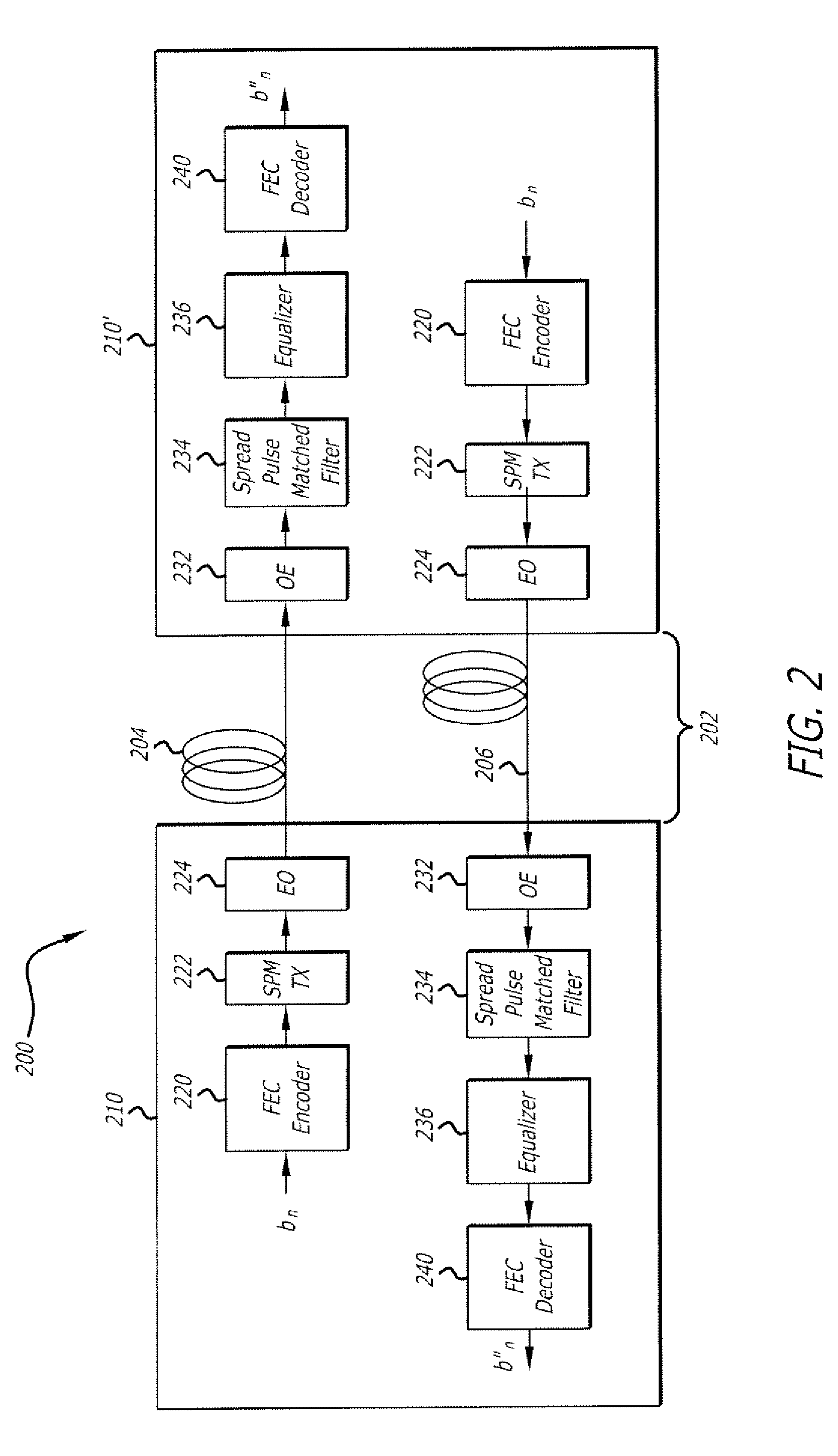
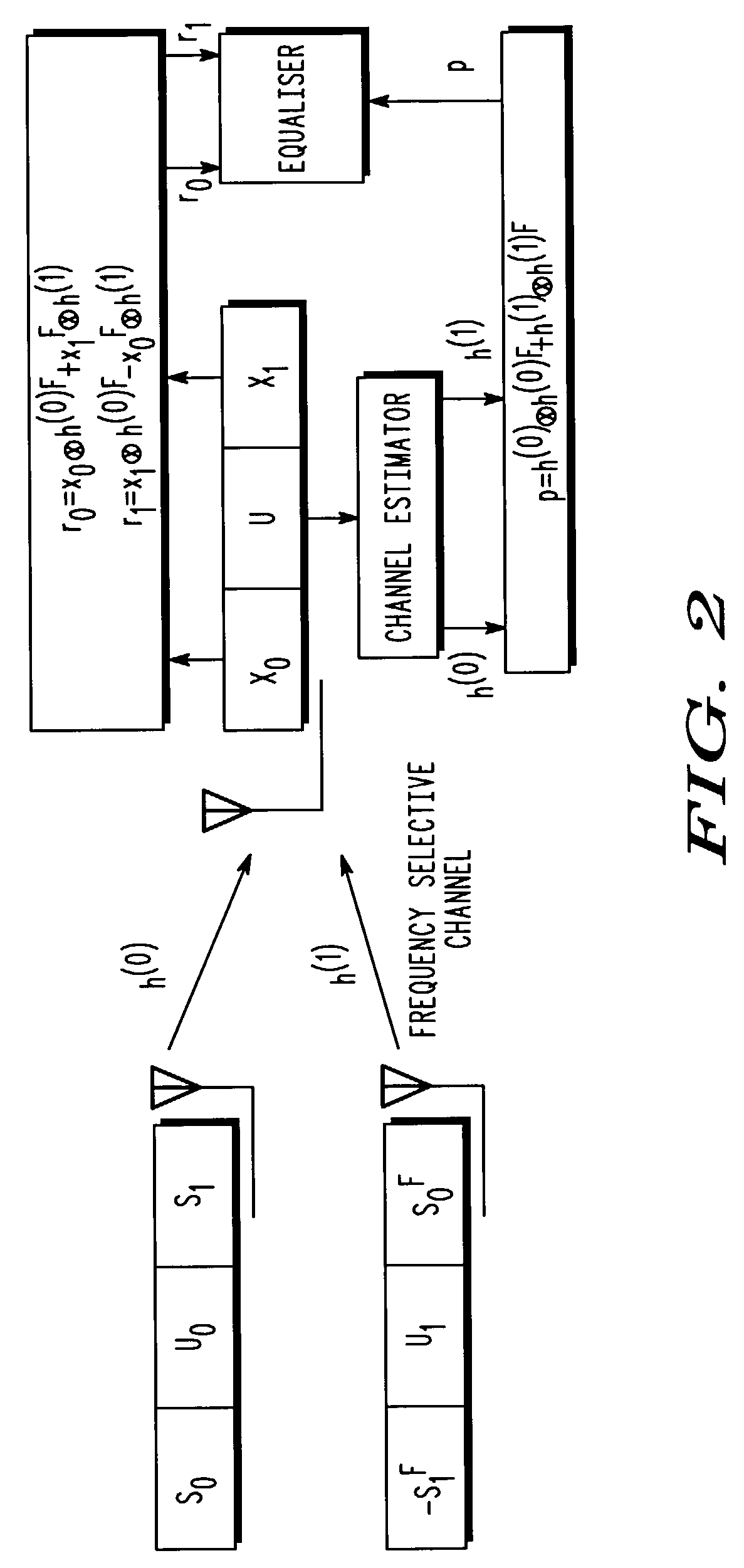
Methods of spread-pulse modulation and nonlinear time domain equalization for fiber optic communication channels
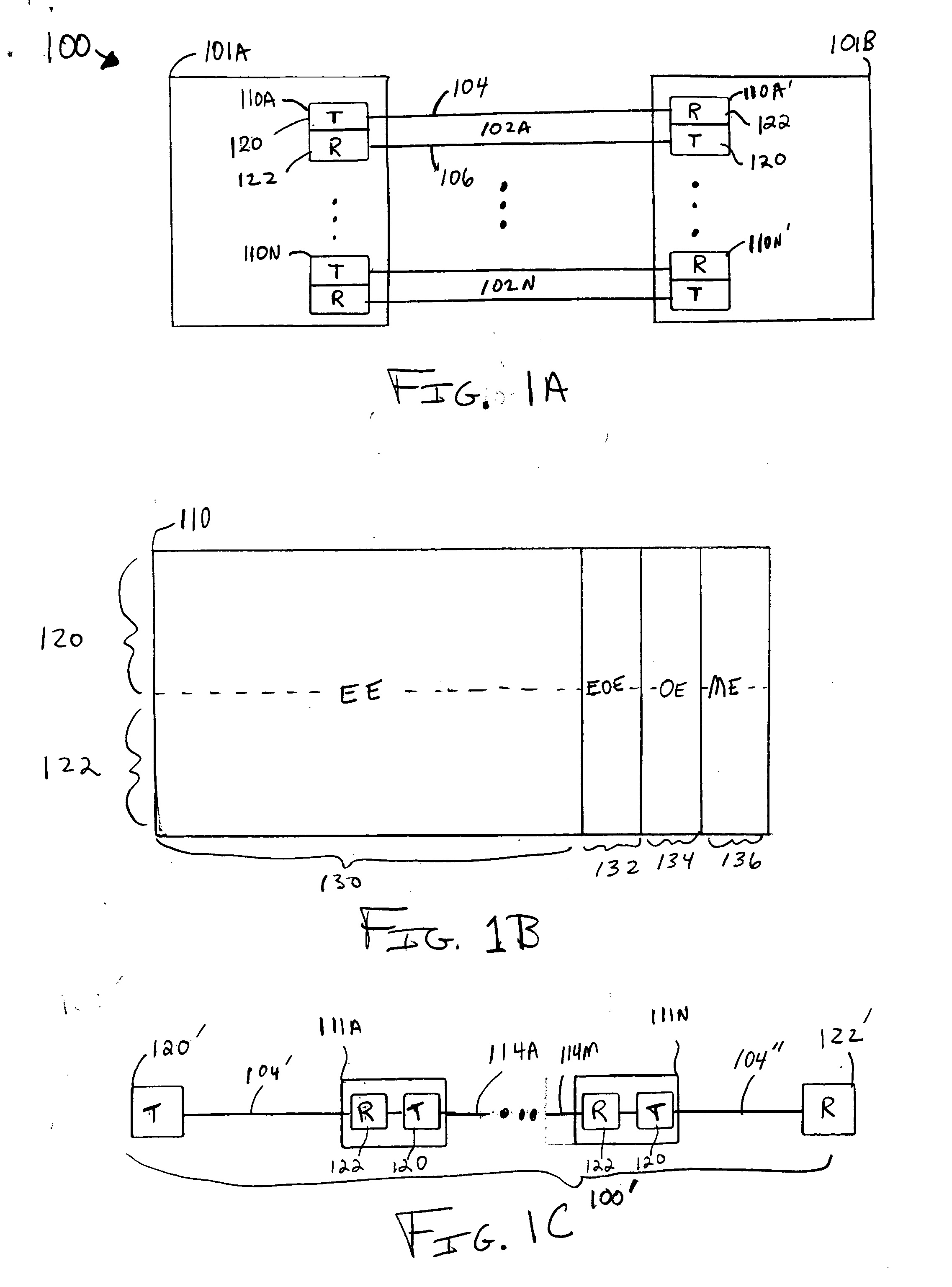
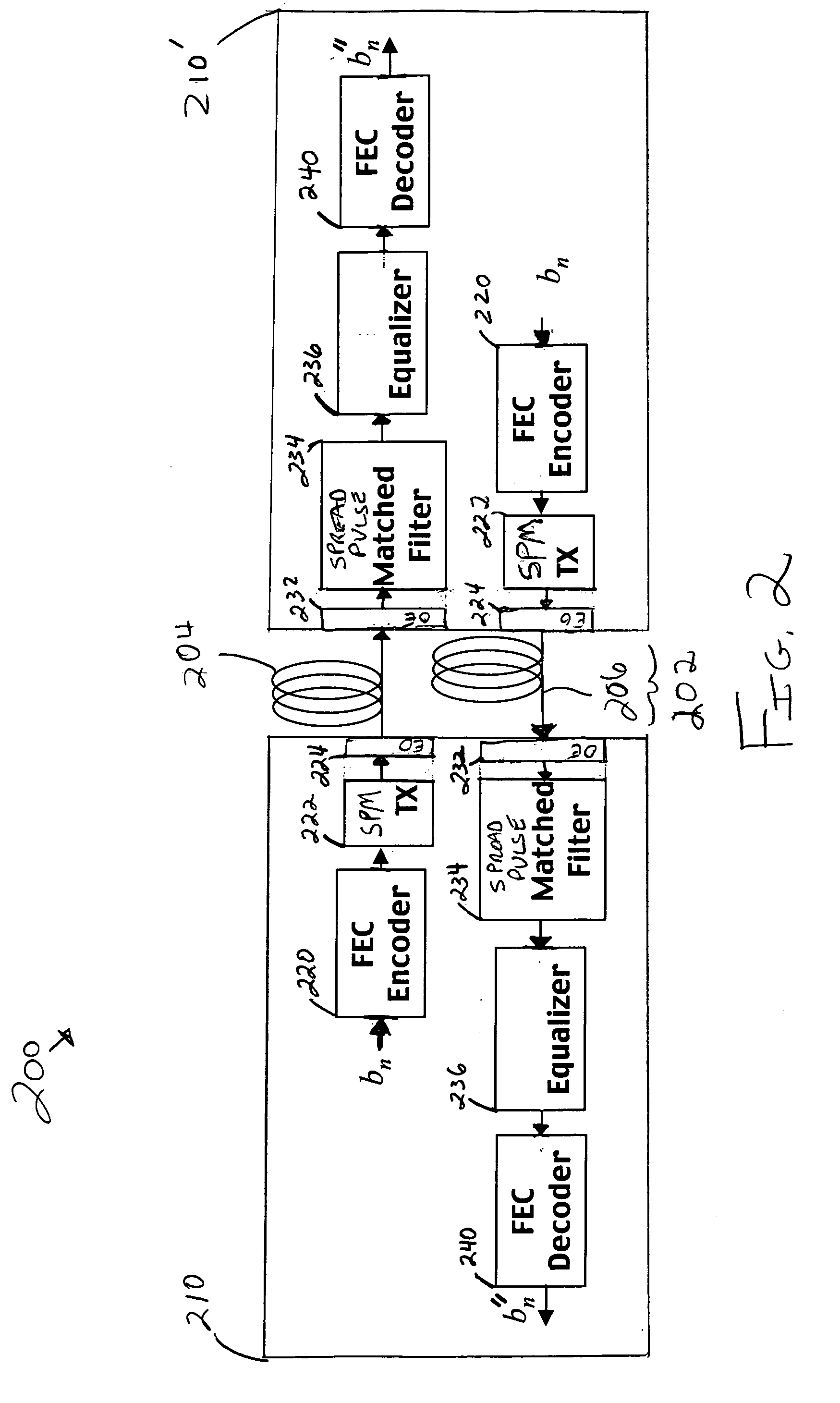
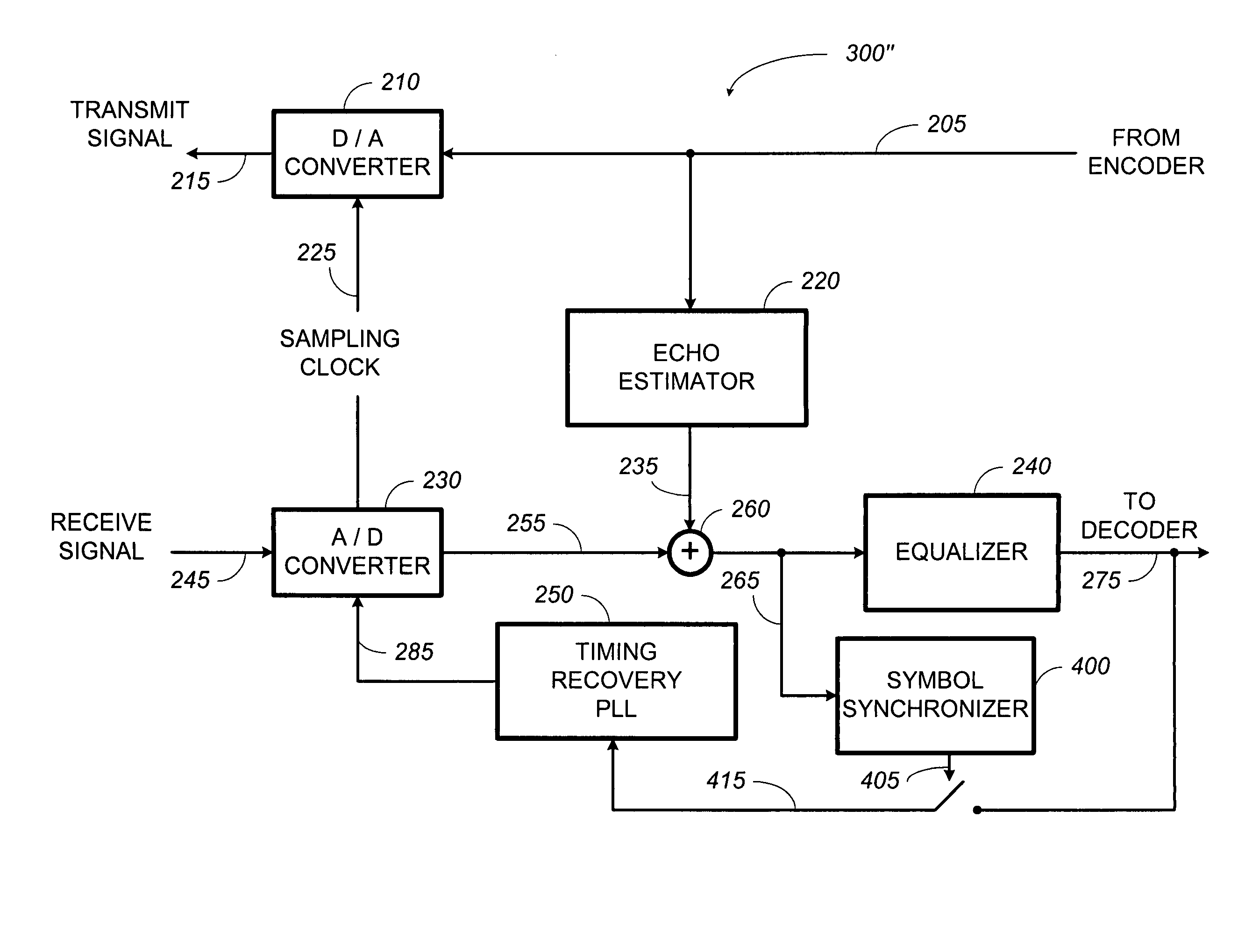
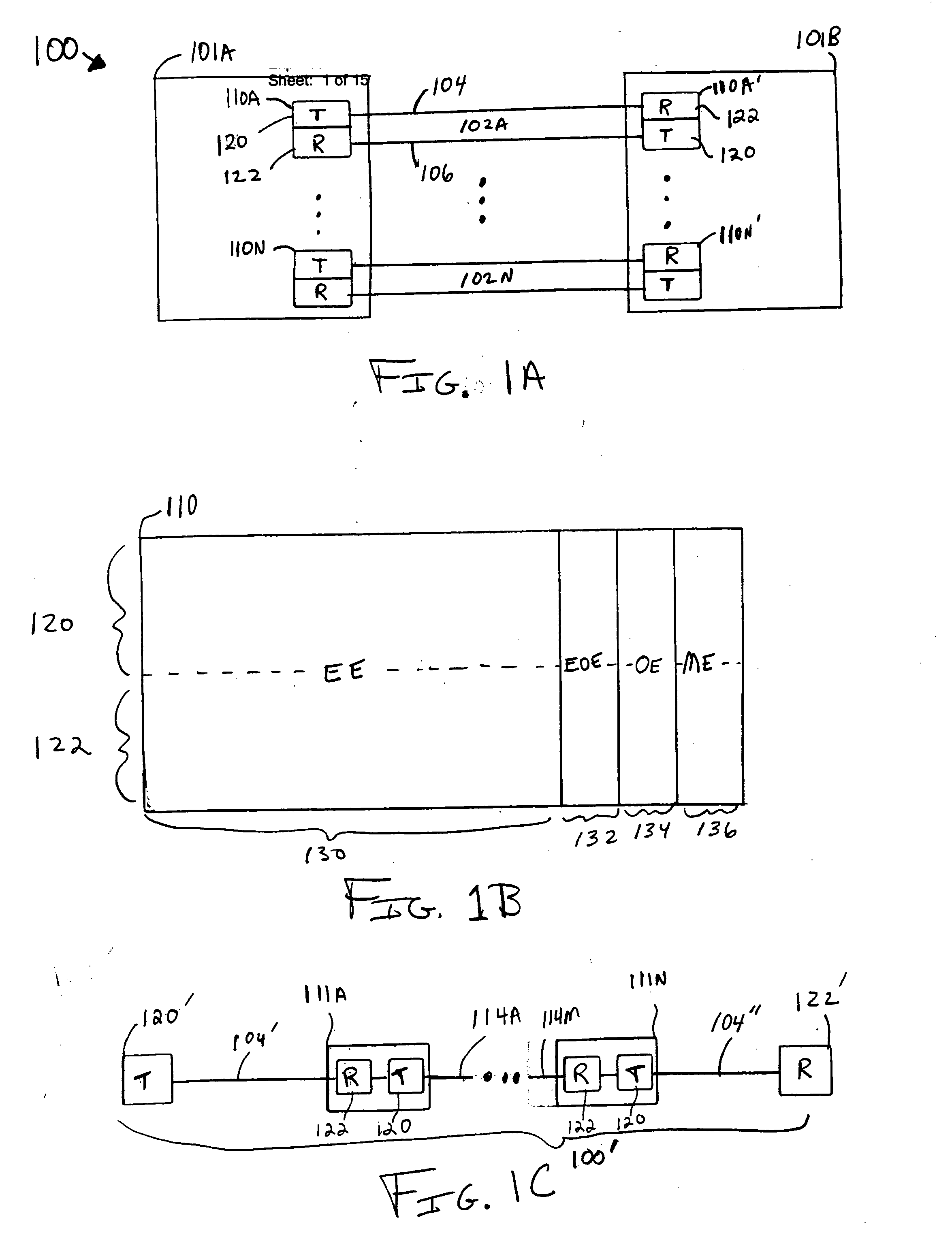
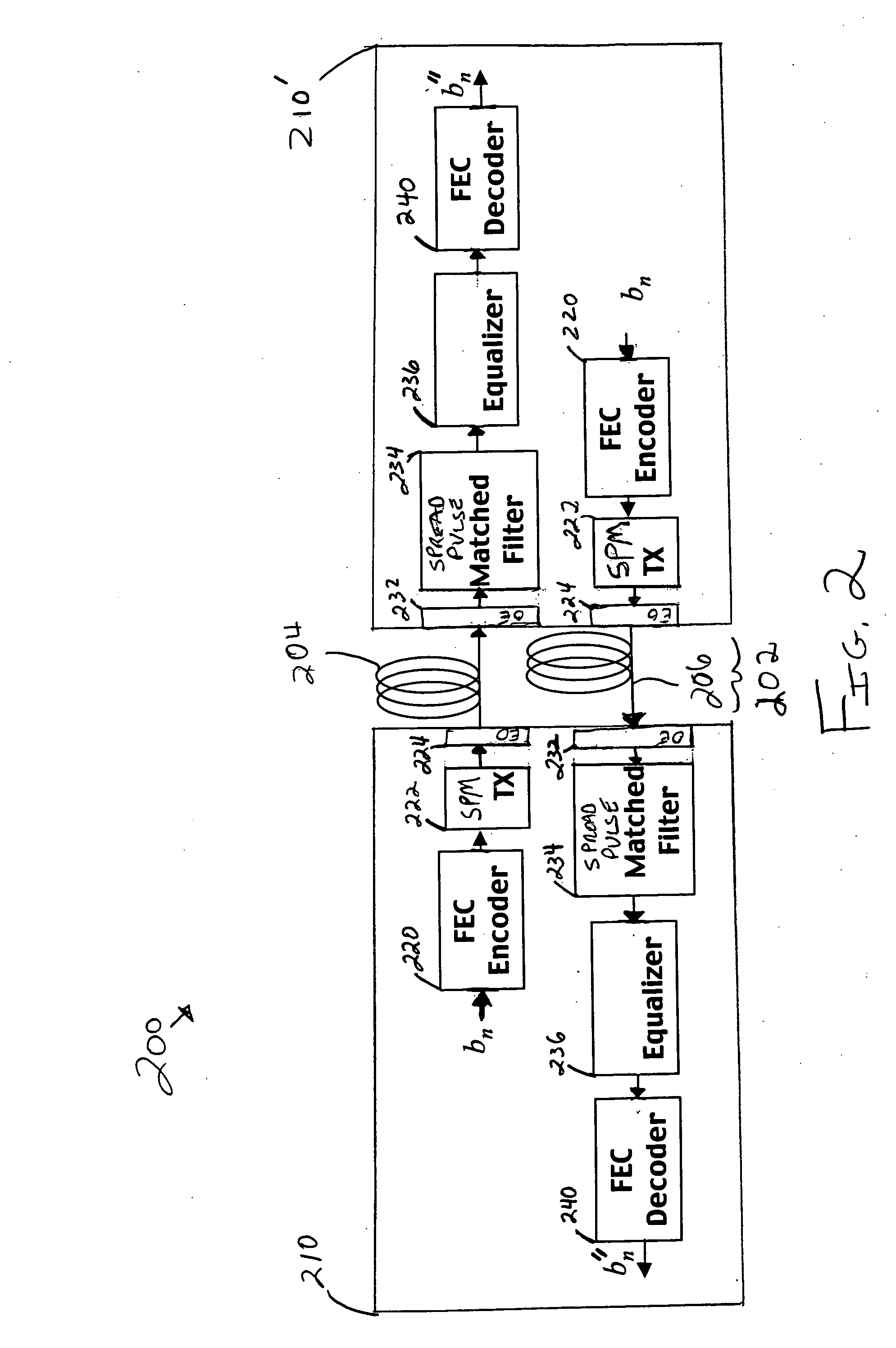
Methods, apparatus, and systems for an optical communication channel. A data signal is preconditioned prior to transmission over a fiber optic cable to minimize signal distortion and transmitted over a fiber optic cable. Preconditioning may include none, one or more, or all of the following: encoding the data signal using a run length limited code, correlating bits of the data signal, and spreading out the pulses in the time-domain in the data signal. The pulse spreading function can be implemented either in the electrical domain prior to the electrical-to-optical conversion; in the optical domain during and / or after the electrical-to-optical conversion; or a combination of both. During reception, the data signal and clock are recovered. Recovery may include maintaining an amplitude in an electrical signal, filtering the electrical signal, shaping the electrical signal, and removing distortions and intersymbol interference (ISI) from the received electrical signal.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
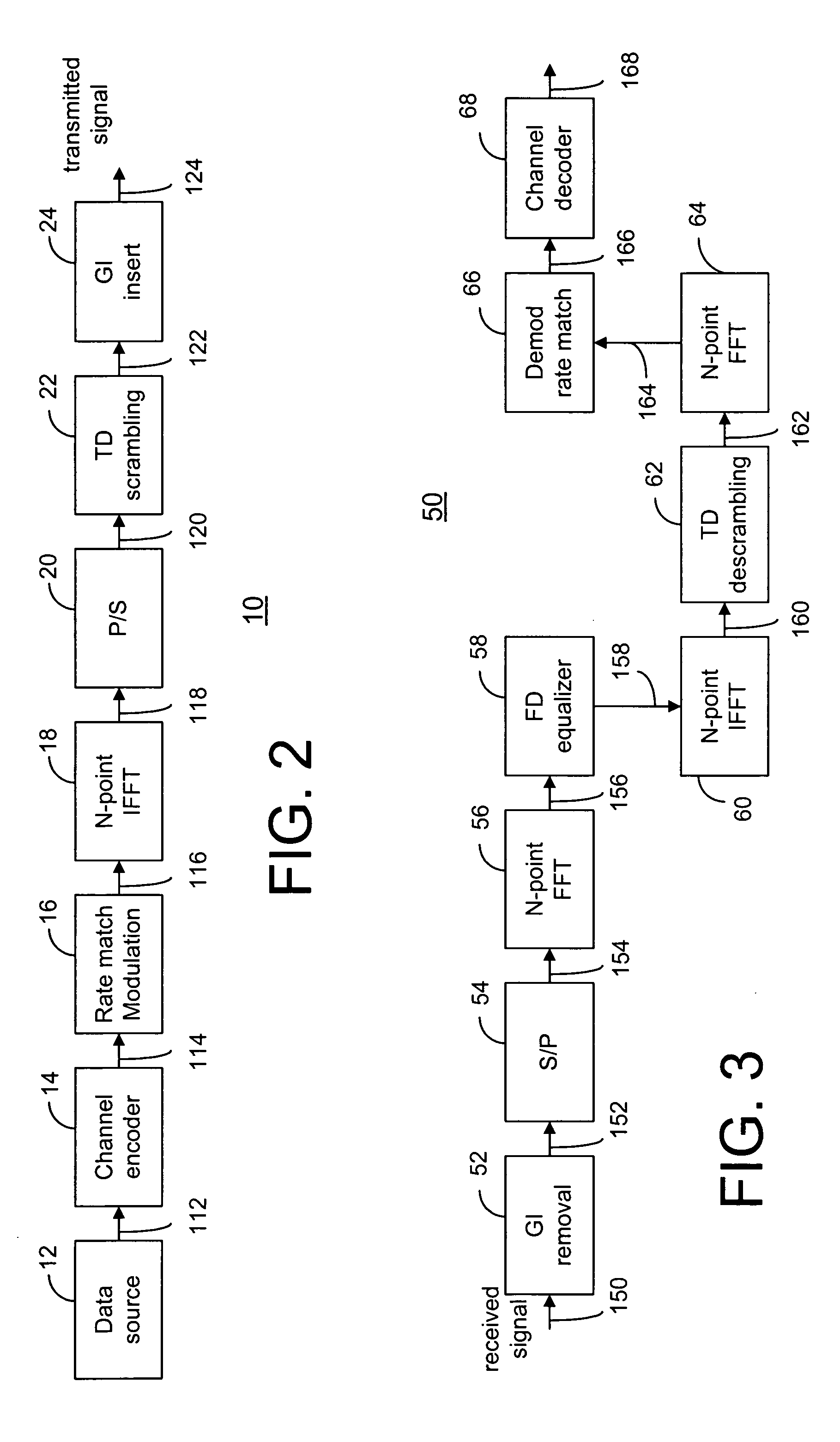
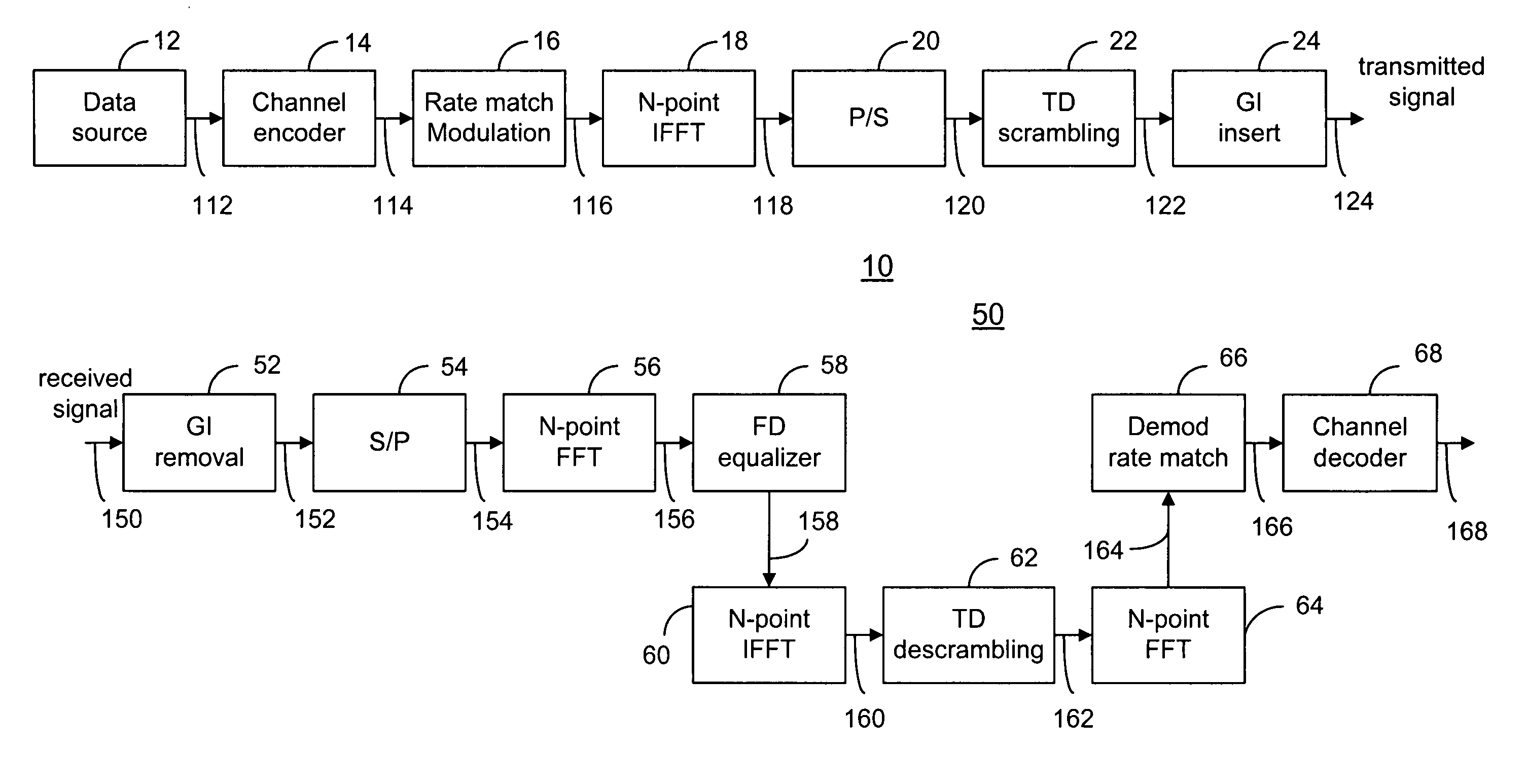
OFDM transceiver structure with time-domain scrambling
InactiveUS20050180311A1Suppression of interference effectsIncrease frequency diversitySpectral gaps assessmentEqualisersTime domainTransceiver
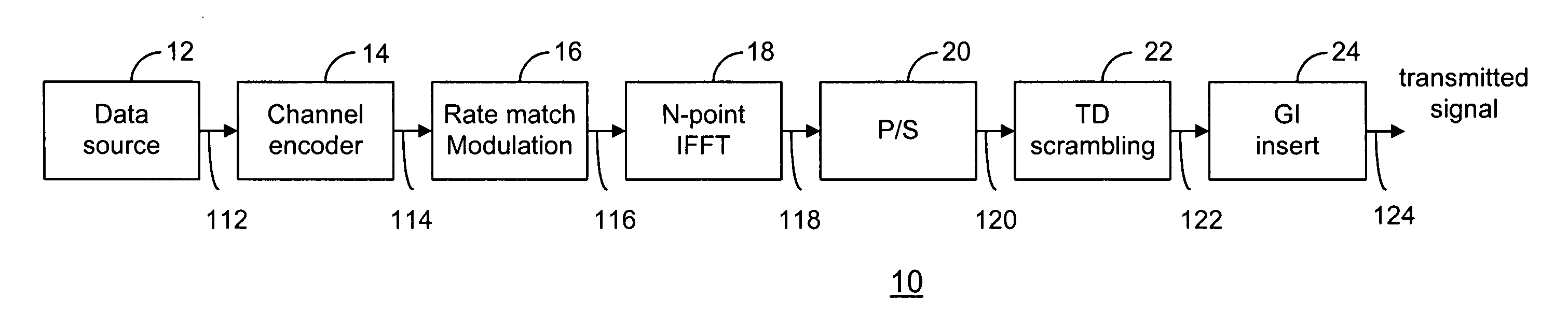
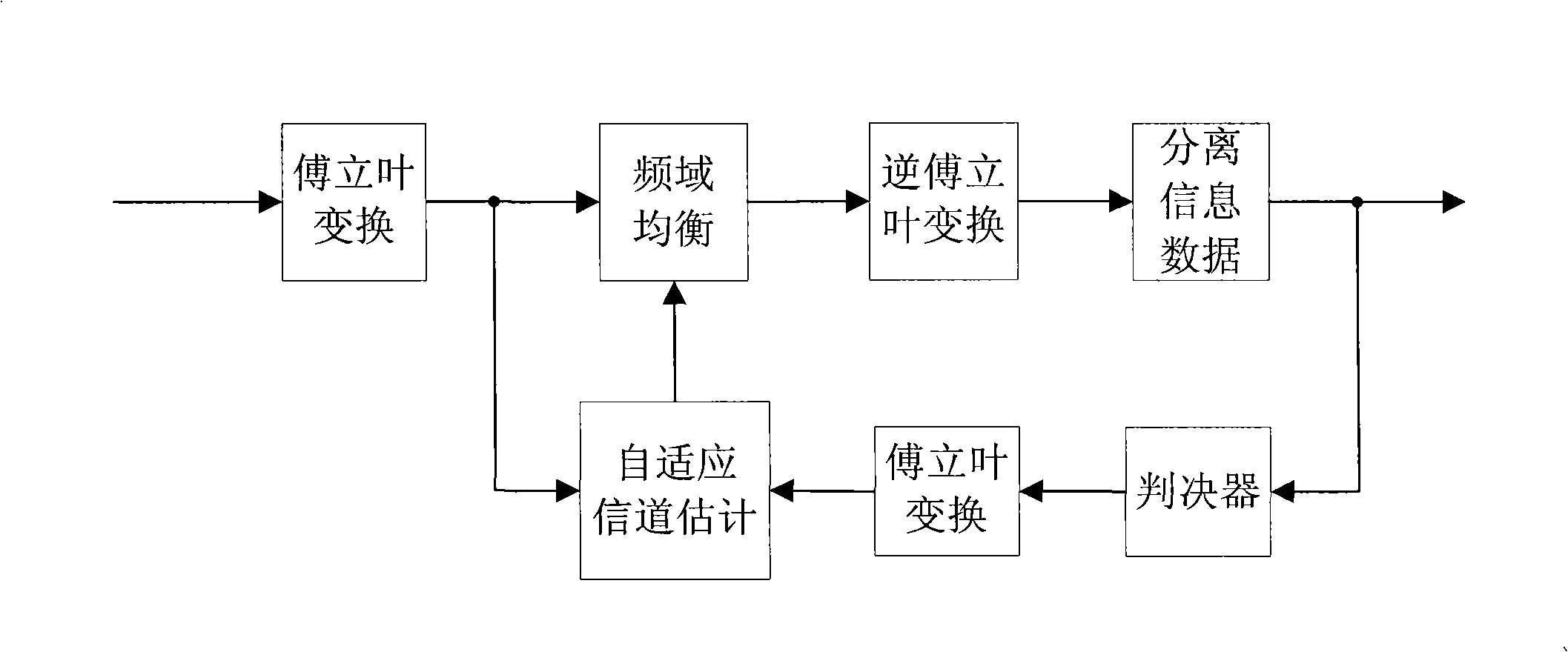
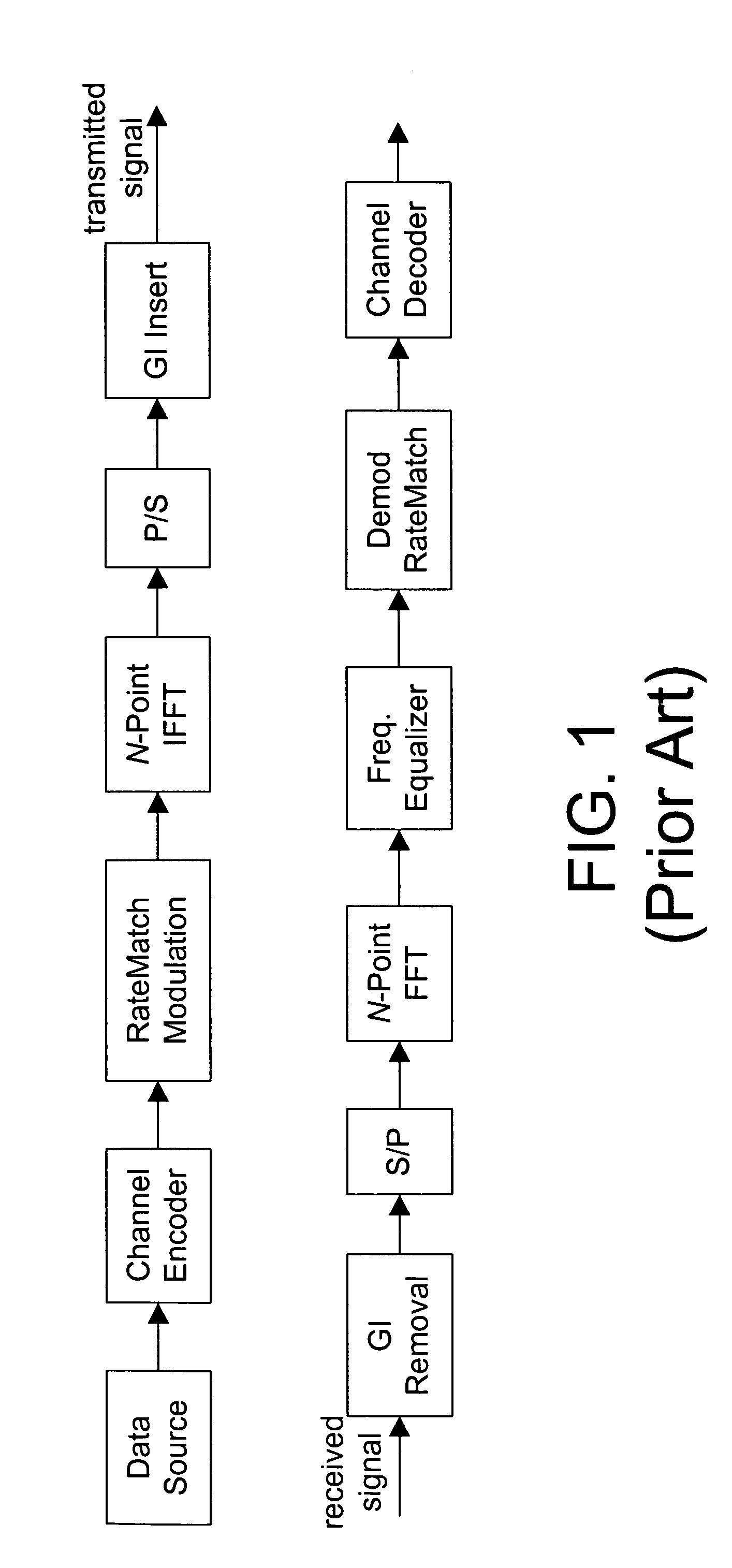
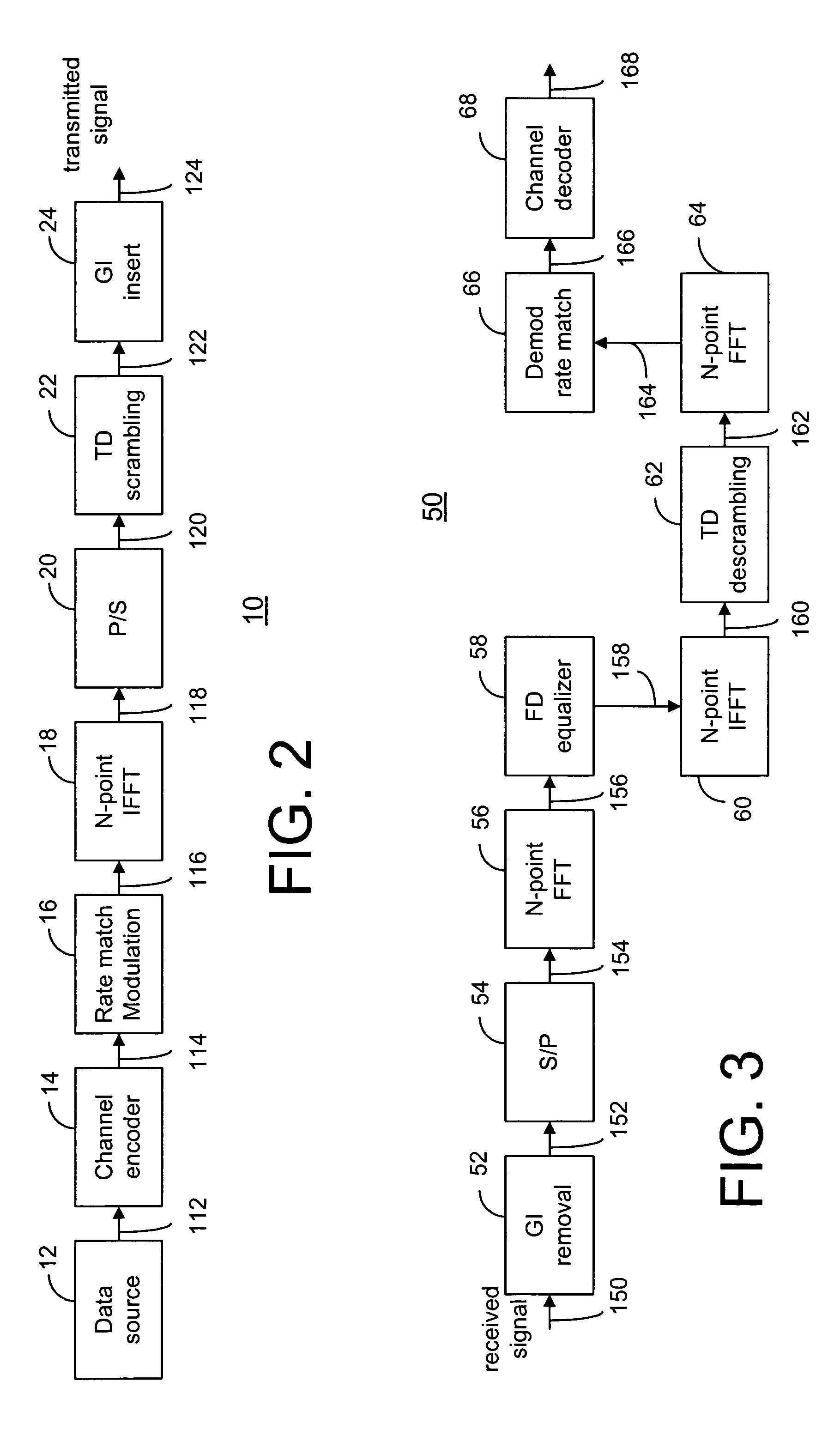
A method and transceiver for wireless multicarrier communications. At the transmitter side, conventional OFDM symbols, after inverse fast Fourier Transform, are scrambled in time domain and then guard-interval (GI) inserted, up-converted at the carrier frequency for transmission. At the receiver side, after GI removal and frequency domain channel equalization, the received signal is transformed into time-domain by inverse fast Fourier Transform. The time-domain equalized signal is descrambled in time domain and then transformed back to the frequency domain before it is rate-matched, demodulated and decoded. This time-domain scrambling and descrambling method can be used in a wireless OFDM system such as WLAN, cellular OFDM, and MC-CDMA.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
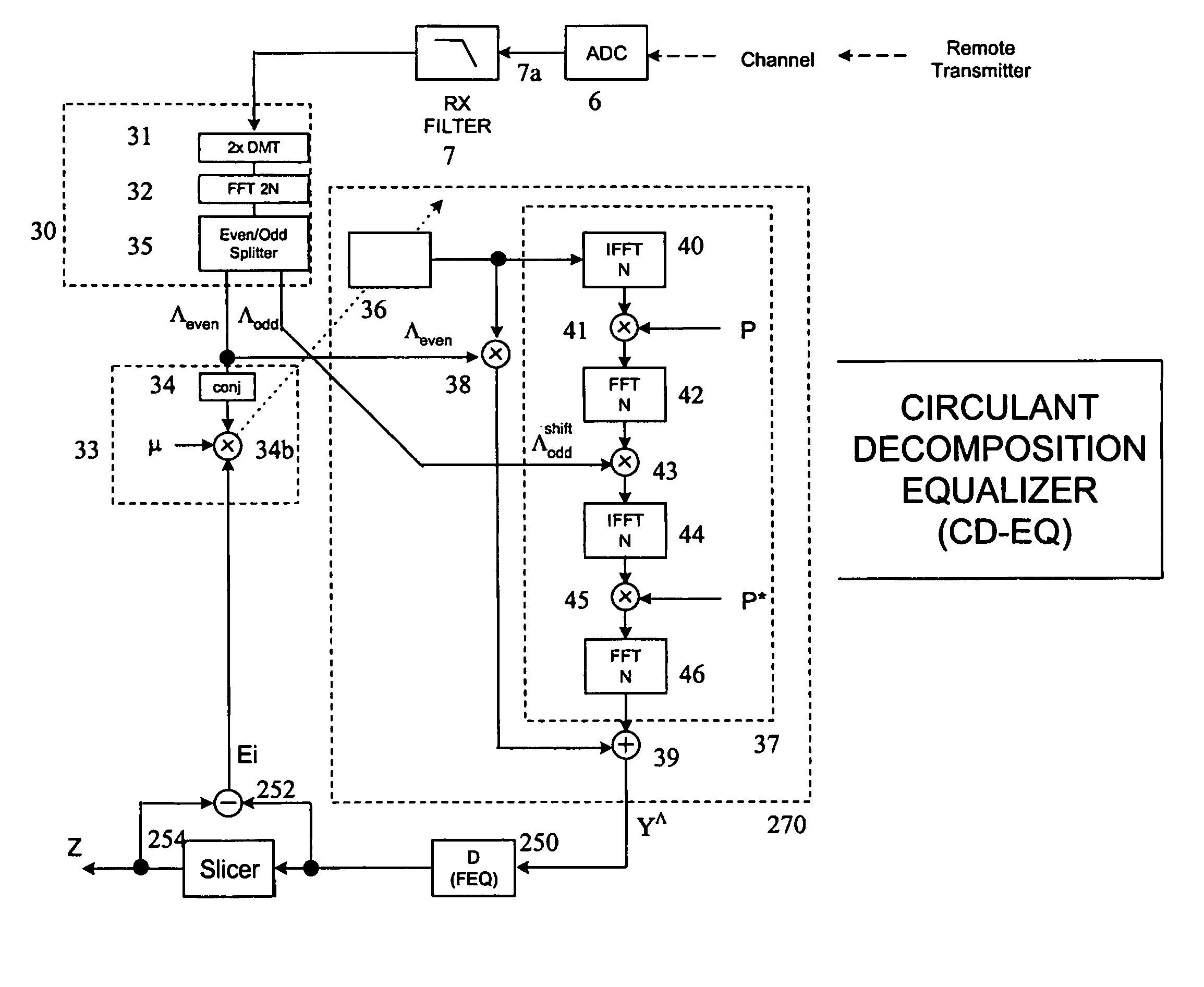
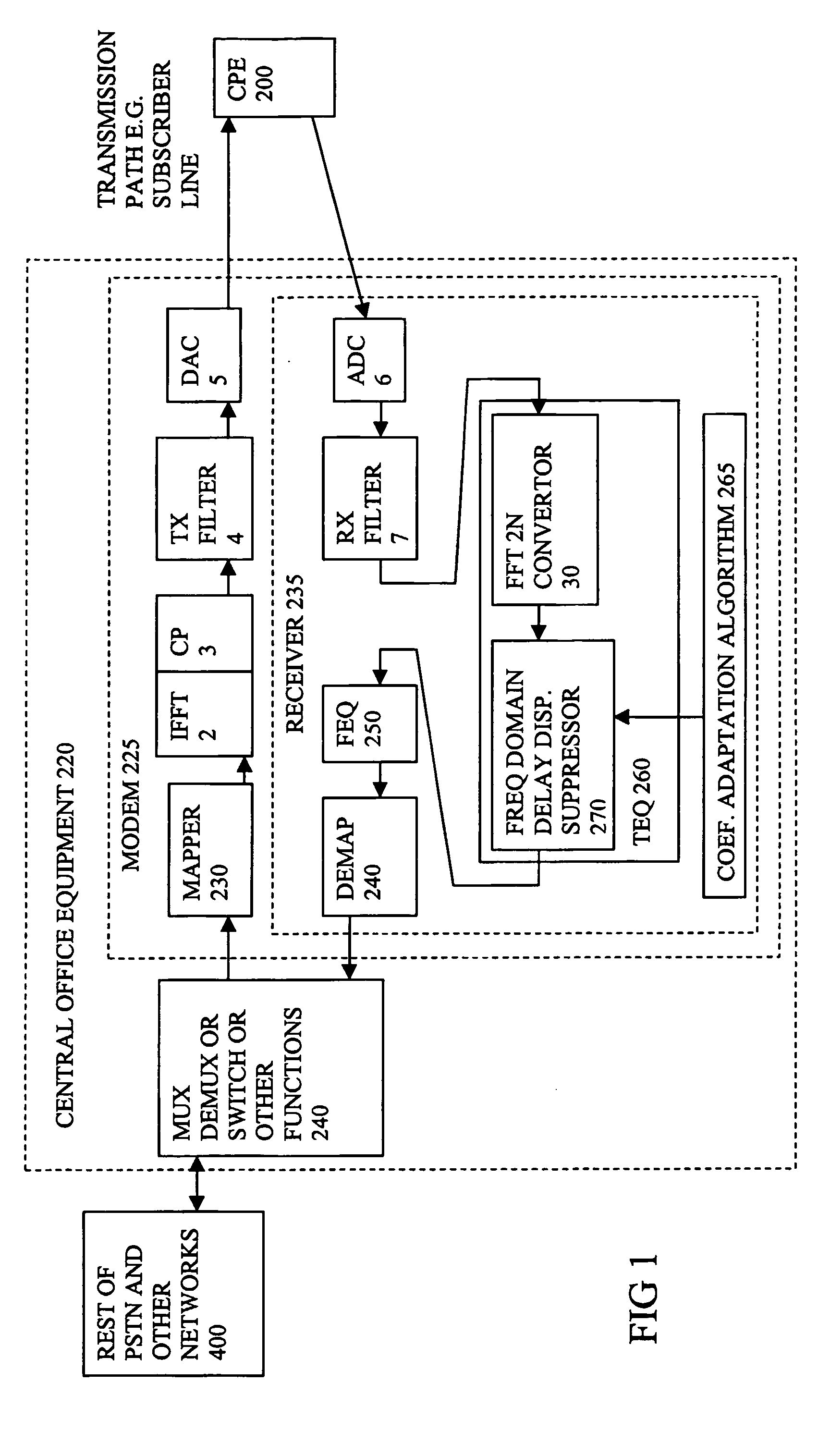
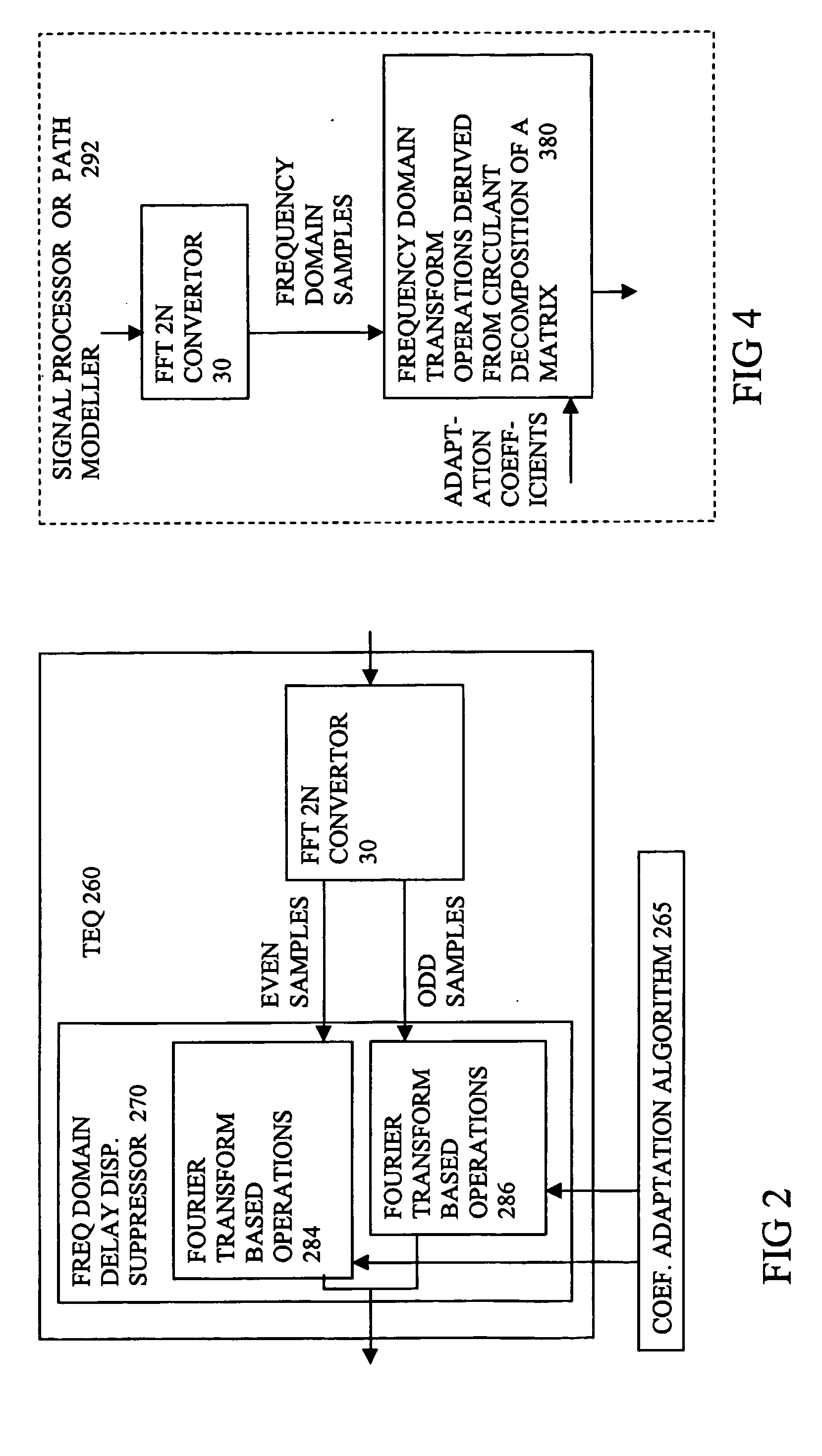
Time domain equalization using frequency domain operations
InactiveUS20050175112A1Better networkLarge capacityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainTime domain equalization
An equalizer for a multi carrier transmission system, converts a transmitted multi carrier signal into sampled frequency domain signals, and suppresses time domain delay dispersion, on the sampled frequency domain signals. It exploits circulant decomposition of a Toeplitz matrix to enable the computationally heavy evaluation of a matrix multiplied by a vector, to be avoided. Increased precision arises from the frequency domain processing being equivalent to a longer time domain FIR filter than is normally practical. The amount of compensation for different carriers can be adjusted, which can lead to increased precision.
Owner:PROTON WORLD INT +1
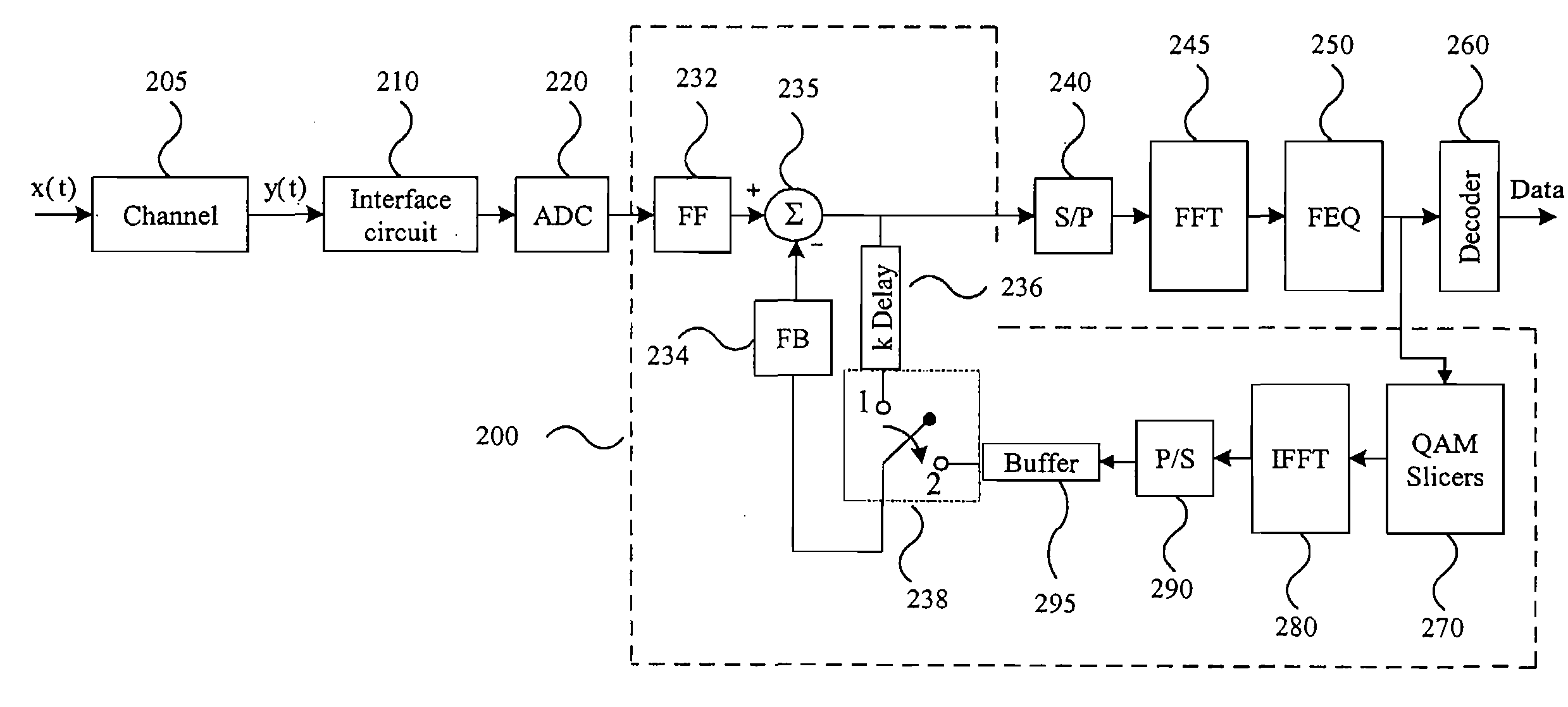
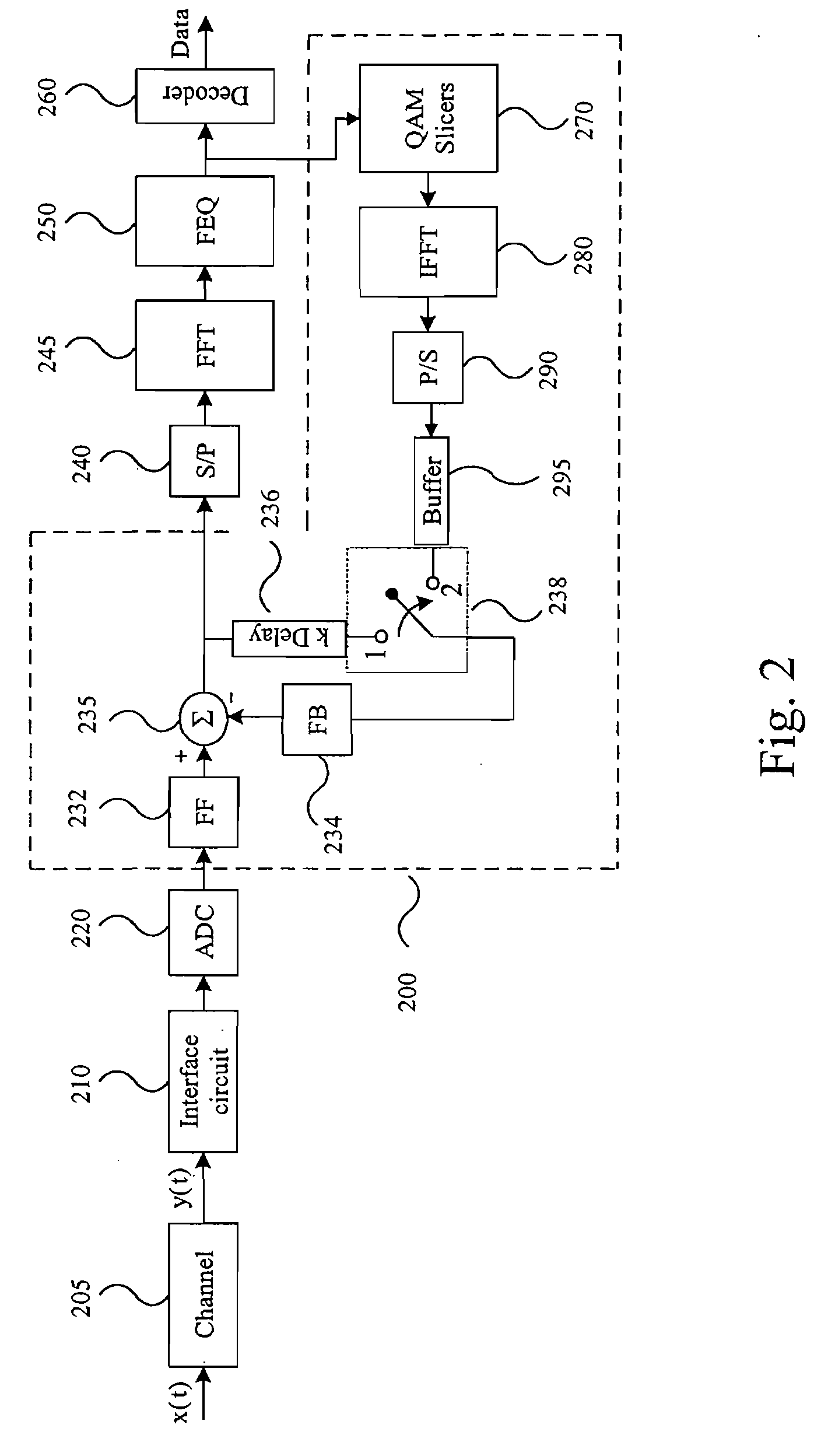
System and Method for Time-Domain Equalization in Discrete Multi-tone Systems
InactiveUS20070121718A1Minimal lengthAvoid Intersymbol InterferenceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainFir system
A novel time-domain equalizer (TEQ) is provided for the receiver of a Discrete Multi-tone (DMT) system to shorten the length of the effective channel impulse response. The TEQ is based on a variant of the conventional decision-feedback equalizer (DFE) structure along with a training method for the TEQ settings. By using this DFE-based TEQ for DMT systems, the data symbols transmitted through the effective shortened channel would be more reliable.
Owner:PROSCEND COMM
System and method for timing recovery in a discrete multi-tone system
InactiveUS6985548B1Phase offsets in the pilot tone are minimizedReduce distractionsModulated-carrier systemsAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionTime domainTransceiver
A system and method for performing pilot tone based timing recovery in a communication system using the discrete multi-tone (DMT) modulation. In DMT modulation, interference is introduced to the phase of the pilot tone in the transmitter due to the cyclic prefix. Broadly, a receiver is configured to detect and apply a phase offset to the pilot tone in a phase locked-loop upon recognition of far-end signal segments during transceiver initialization. The output of the phase locked-loop is then used to control the timing of the analog-to-digital (A / D) and digital-to-analog (D / A) conversions. In alternative embodiments, the receiver is configured to detect and remove the cyclic prefix from the far-end signal either prior to, or after, time-domain equalization. In a similar manner, the resulting signal stream is applied to the input of the timing recovery phase locked-loop (PLL). The output of the PLL is used to control the timing of the A / D and D / A converters. In a further alternative embodiment, a phase error on the pilot tone is estimated in the frequency domain. The phase error is then applied to the input of a modified timing recovery PLL to reduce phase interference on the pilot tone.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
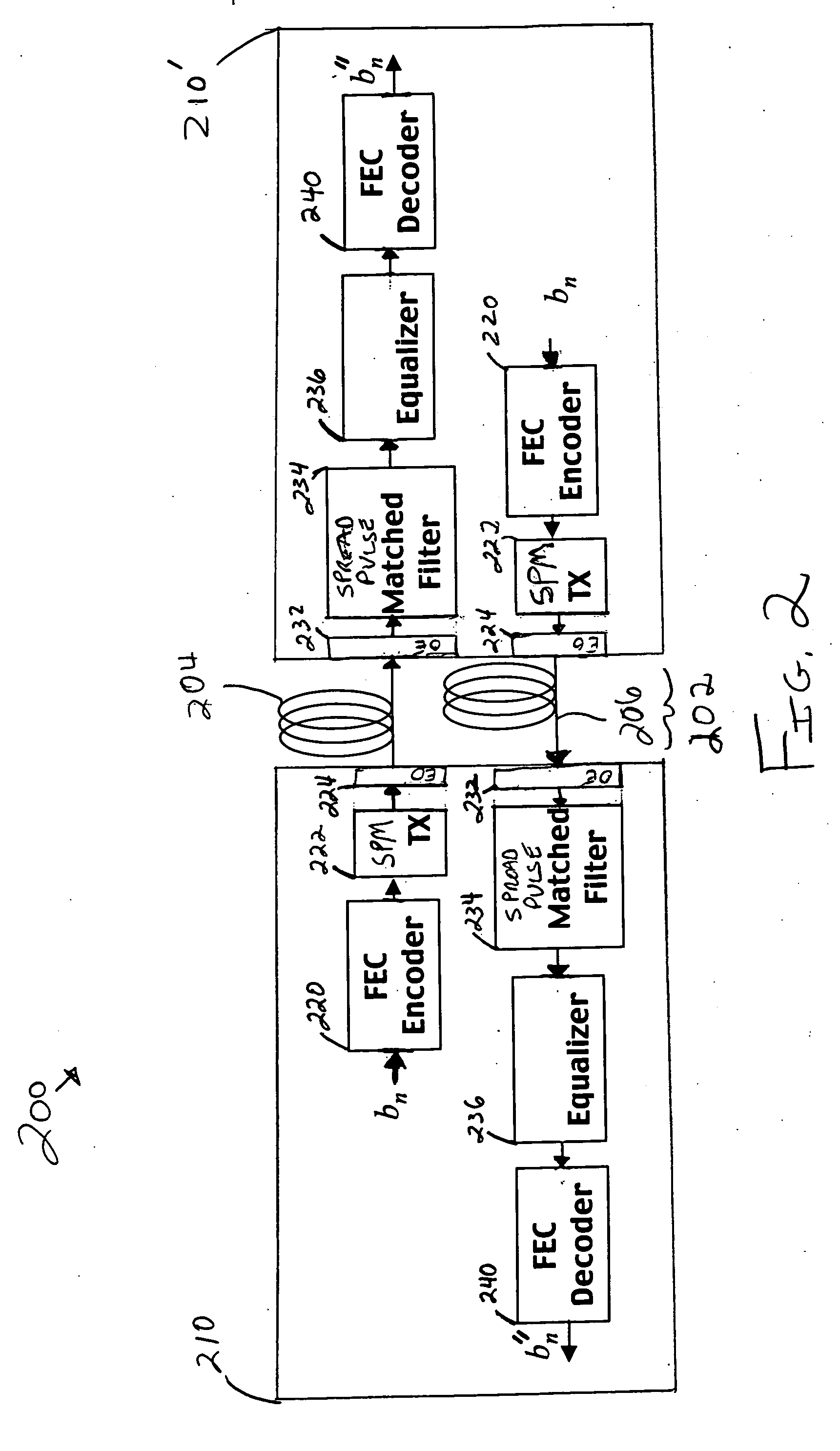
Apparatus with spread-pulse modulation and nonlinear time domain equalization for fiber optic communication channels
ActiveUS7286762B2Modulated-carrier systemsTime-division optical multiplex systemsFinite impulse responseTransceiver
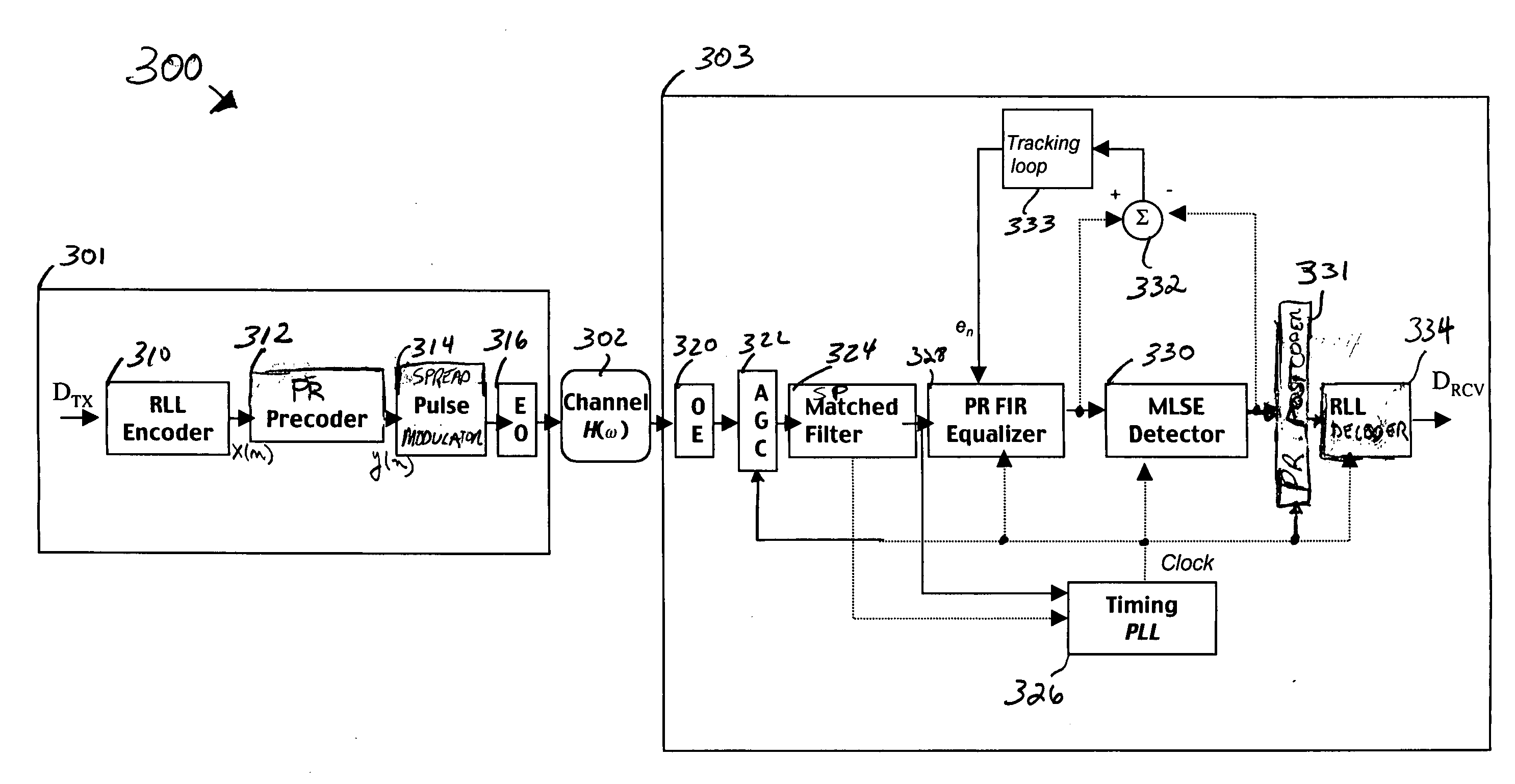
A transmitter and transceiver for an optical communication channel may include a data encoder, a partial response (PR) precoder, a pulse filter, and an electrical-to-optical converter to transmit a spread pulse signal over an optical communication channel. The data encoder to encode the transmit data into coded data. The precoder to correlate bits of the coded data together into a precoded signal at the output of the precoder. The pulse filter to spread out the pulses in the precoded signal into a spread-pulse signal at the output of the pulse-shaping filter. The electrical-to-optical converter to convert an electrical spread-pulse signal into light pulses at its optical output. A transceiver may further include an optical-to-electrical converter, an automatic gain controller, a matched filter, a PR finite impulse response equalizing filter, a maximum likelihood sequence estimation detector, and a data decoder in order to decode and recover the data.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
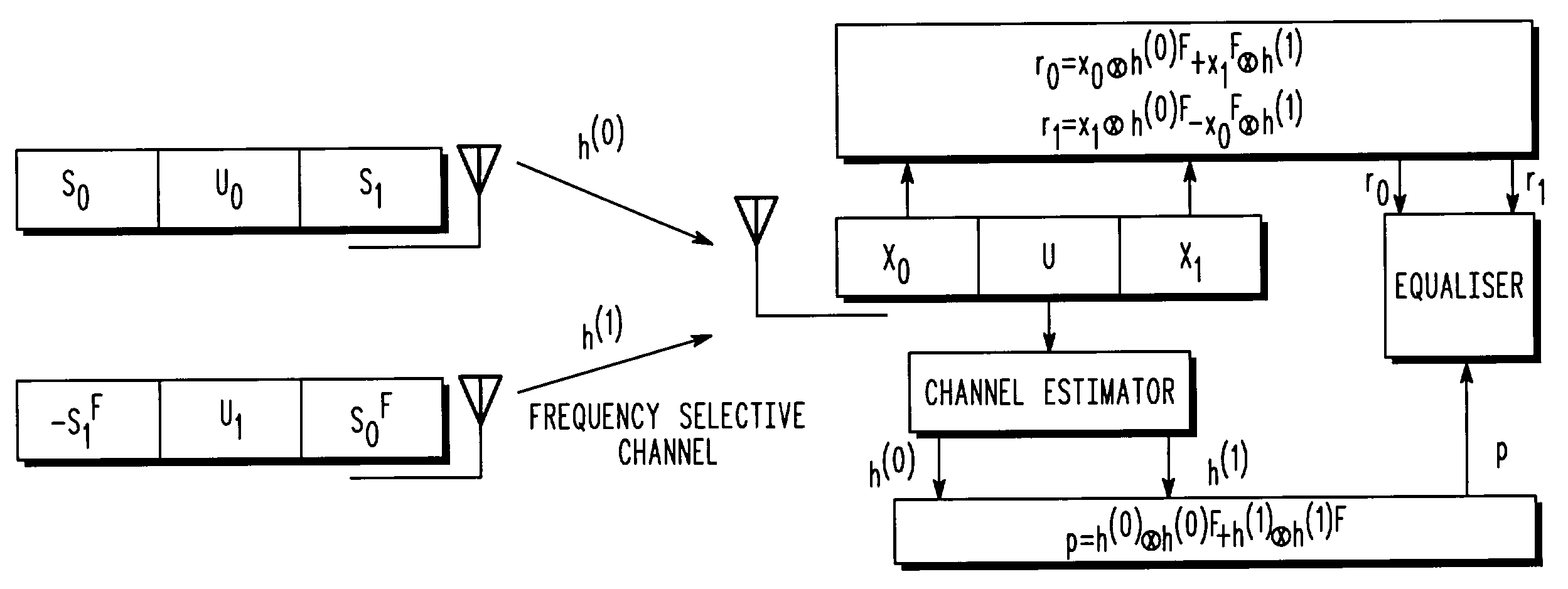
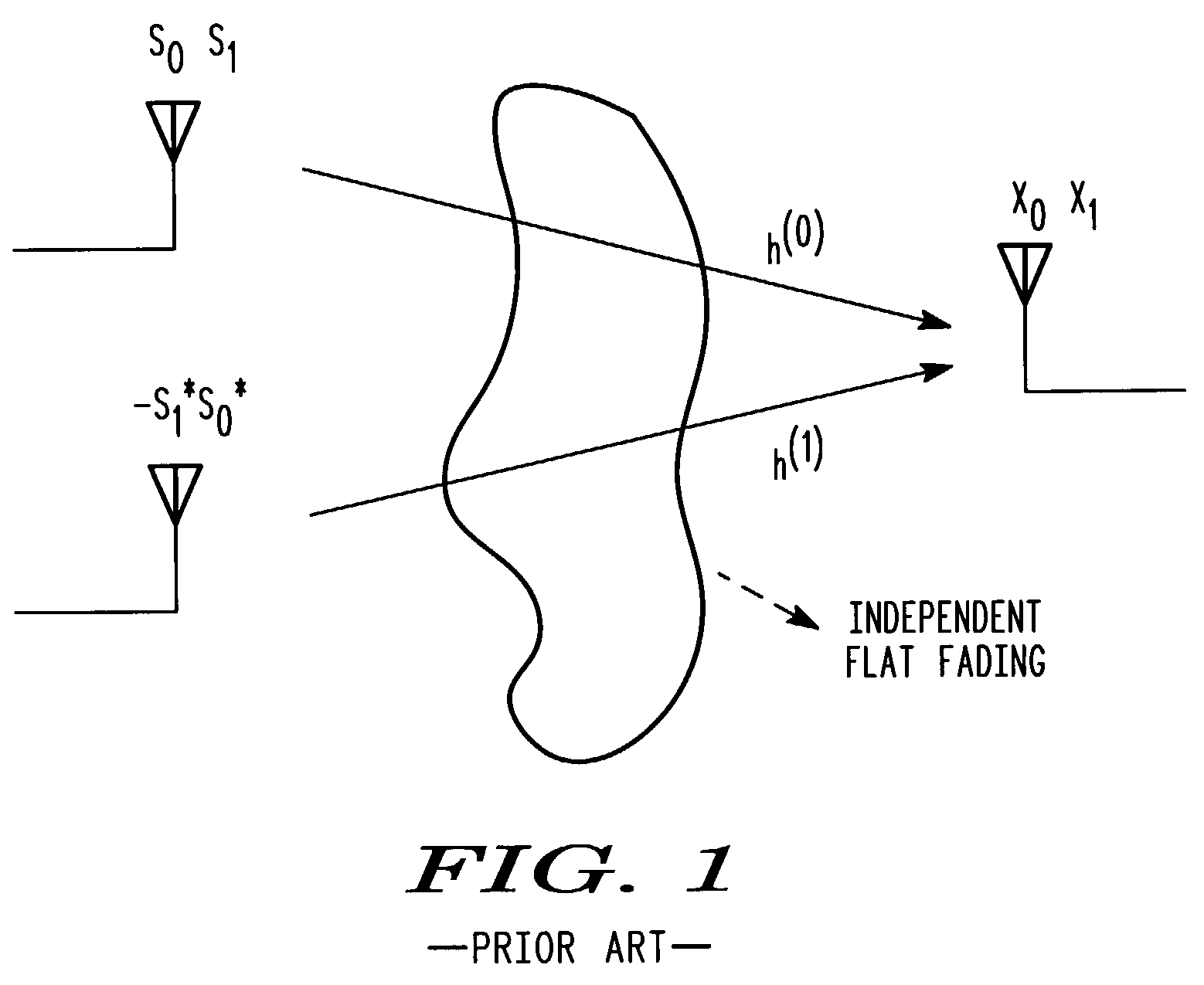
Space-time transmit diversity scheme for time-dispersive propagation media
InactiveUS7471734B2Modulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationTime domainSpace time transmit diversity
This invention extends Alamouti's scheme for wideband TDMA systems; it then works in conjunction with time-domain equalization. In fact, the present invention envisages time-domain DFE or MLSE equalization (which is more robust than linear frequency-domain equalization) via the use of a training mid-amble to separate adjacent sub-blocks; this mid-amble is used in equalizer training and its direct and inter-symbol interference contributions to the received signal, are subtractively eliminated to facilitate the detection process itself. This approach may be applied to all systems in time-dispersive propagation media, where the burst or slot length is short enough that the fading can be considered time-invariant over its duration.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Apparatus with spread-pulse modulation and nonlinear time domain equalization for fiber optic communication channels
ActiveUS20060245757A1Modulated-carrier systemsTime-division optical multiplex systemsFinite impulse responseTransceiver
A transmitter and transceiver for an optical communication channel may include a data encoder, a partial response (PR) precoder, a pulse filter, and an electrical-to-optical converter to transmit a spread pulse signal over an optical communication channel. The data encoder to encode the transmit data into coded data. The precoder to correlate bits of the coded data together into a precoded signal at the output of the precoder. The pulse filter to spread out the pulses in the precoded signal into a spread-pulse signal at the output of the pulse-shaping filter. The electrical-to-optical converter to convert an electrical spread-pulse signal into light pulses at its optical output. A transceiver may further include an optical-to-electrical converter, an automatic gain controller, a matched filter, a PR finite impulse response equalizing filter, a maximum likelihood sequence estimation detector, and a data decoder in order to decode and recover the data.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Receiving end equilibrium method and system based on frequency domain communication channel estimation
ActiveCN103338171AReduce complexityGood estimateChannel estimationMulti-frequency code systemsPhase noiseFiber chromatic dispersion
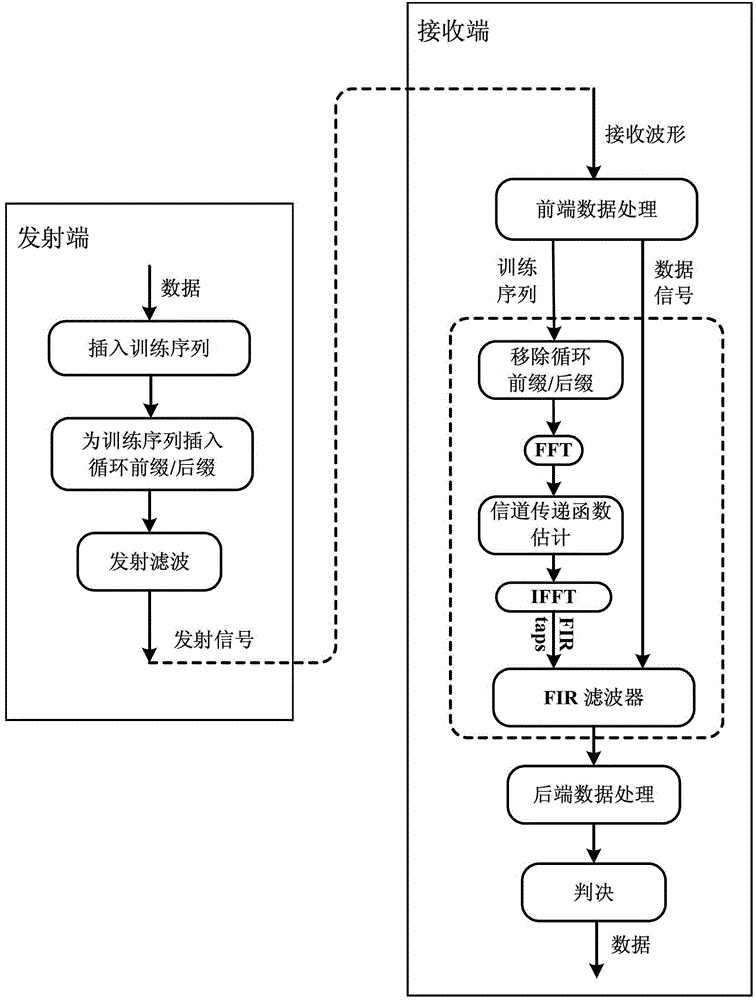
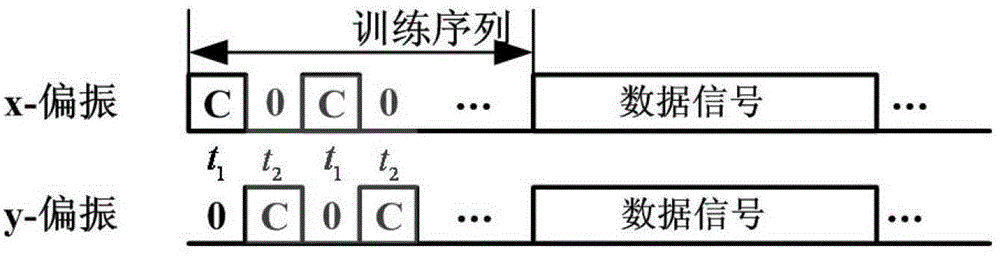
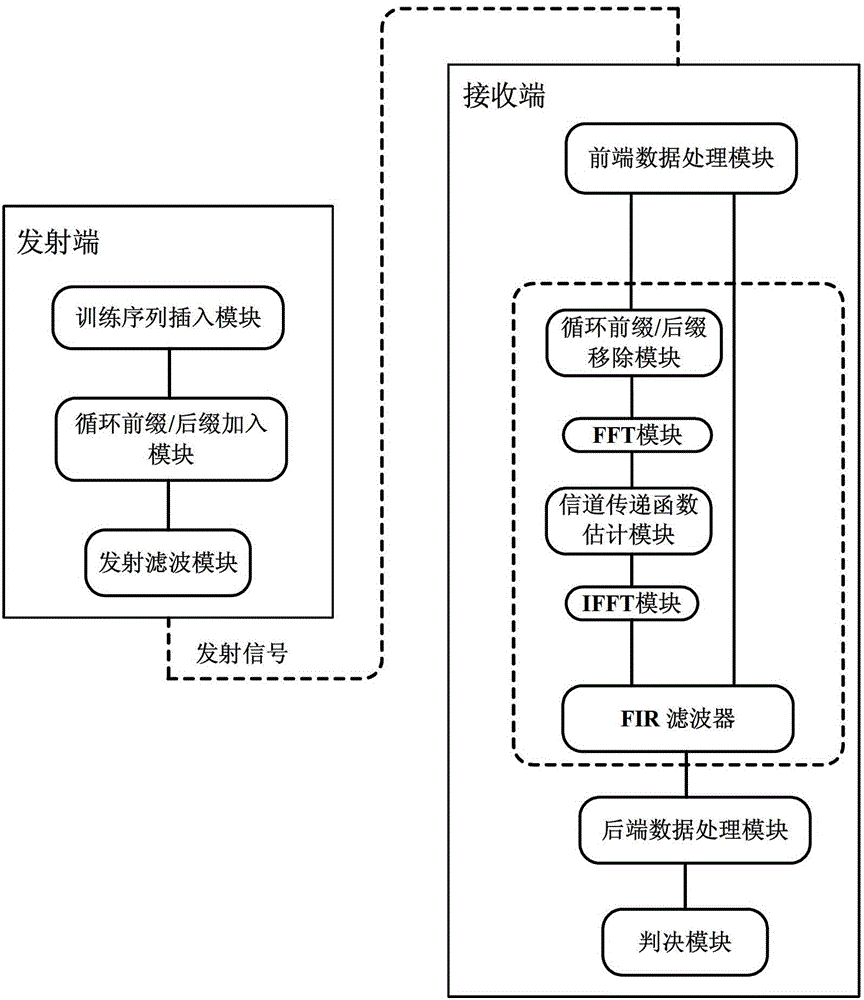
The invention relates to a receiving end equilibrium method and system based on frequency domain communication channel estimation. The method comprises the following steps: training sequences with flat spectrum characteristics are inserted into signals at the transmitting terminal, the received training sequences are transformed into the frequency domain at the receiving end through fast Fourier transformation, the transfer function of a communication channel is obtained through dividing the ideal spectrum corresponding to the frequency domain, and then the reciprocal of the transfer function is taken and is transformed into the time domain through the fast Fourier transformation so as to obtain time domain filter tapping coefficient; thereafter, filtering is performed to data signals in the time domain through utilizing the time domain filter tapping coefficient, so that signaling equilibrium is realized. The system includes various modules realizing the corresponding functions. The method and the system combine characteristic of avoidance in cost caused by inserting cyclic prefix / suffix of time domain equilibrium and the characteristic of simple communication channel estimation of the frequency domain equilibrium; on the condition that the optical fiber dispersion is smaller or the dispersion is compensated by other arithmetic, the phase noise compensation is efficiently performed; the arithmetic complexity is small; the calculation time can be saved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
An OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) underwater acoustic communication method with high spectral efficiency under a time-varying double-spread channel condition
ActiveCN109743118AImprove reliabilityReduce complexityMulti-frequency code systemsBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
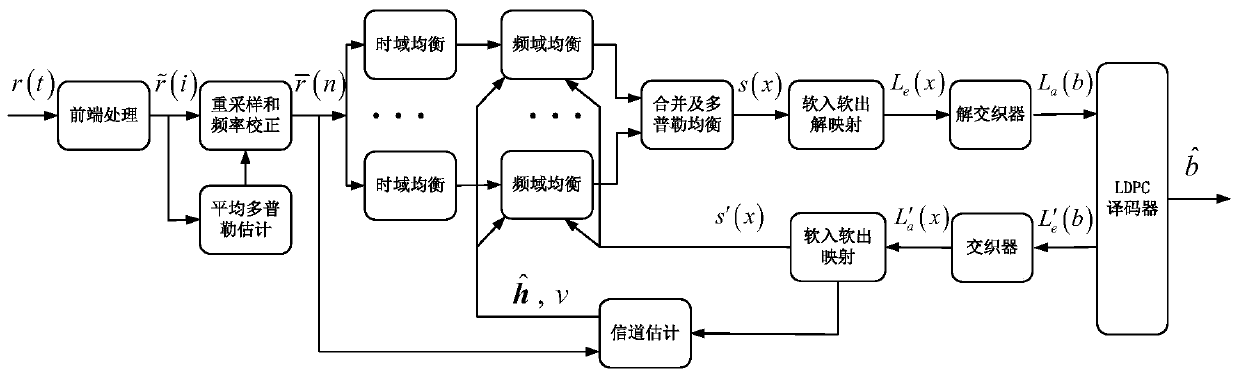
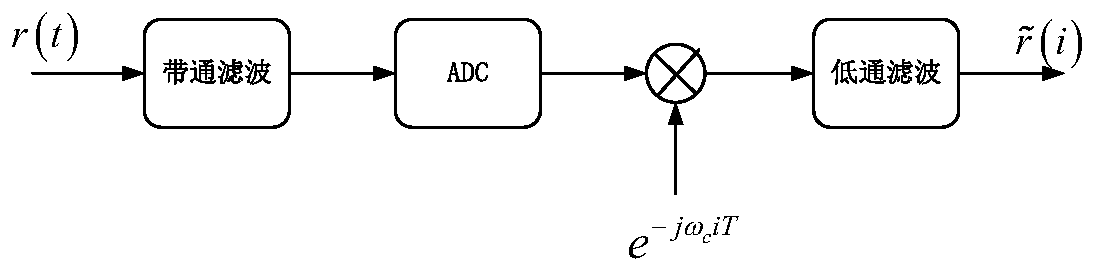
The invention discloses an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) underwater acoustic communication method with high spectral efficiency under a time-varying double-spread channel condition, and belongs to the technical field of underwater acoustic communication. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out band-pass filtering on a received signal r (k), carrying out front-endprocessing such as ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) conversion into a digital signal, carrying out down-conversion and low-pass filtering, estimating average Doppler by utilizing a fuzzy function method, carrying out resampling and frequency correction, multiplexing the signal, carrying out time domain equalization and frequency domain equalization, carrying out diversity combination, and then adopting the OMP-DCD algorithm to perform residual Doppler compensation. an iterative signal processing technology is adopted, an LDPC decoder and an equalizer are cascaded through soft-in soft-out mapping / demapping and an interleaver / deinterleaver, close information interaction is achieved in the two modules, soft information transmitted in a reciprocating mode is fully utilized, and interferenceof a time-varying double-spread channel is effectively resisted. According to the method, the complexity and the performance can be well compromised, and serious inter-symbol interference, inter-carrier interference and pilot frequency-pilot frequency interference in the transmission process are efficiently solved. And the method is low in complexity and can be realized on the DSP in real time.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
Self-adaptive time domain equalization system and in-band full-duplex wireless communication system
InactiveCN108494497AEnhanced inhibitory effectReal-time adaptive processingElectromagnetic receiversDuplex signal operationSelf interferenceTime domain
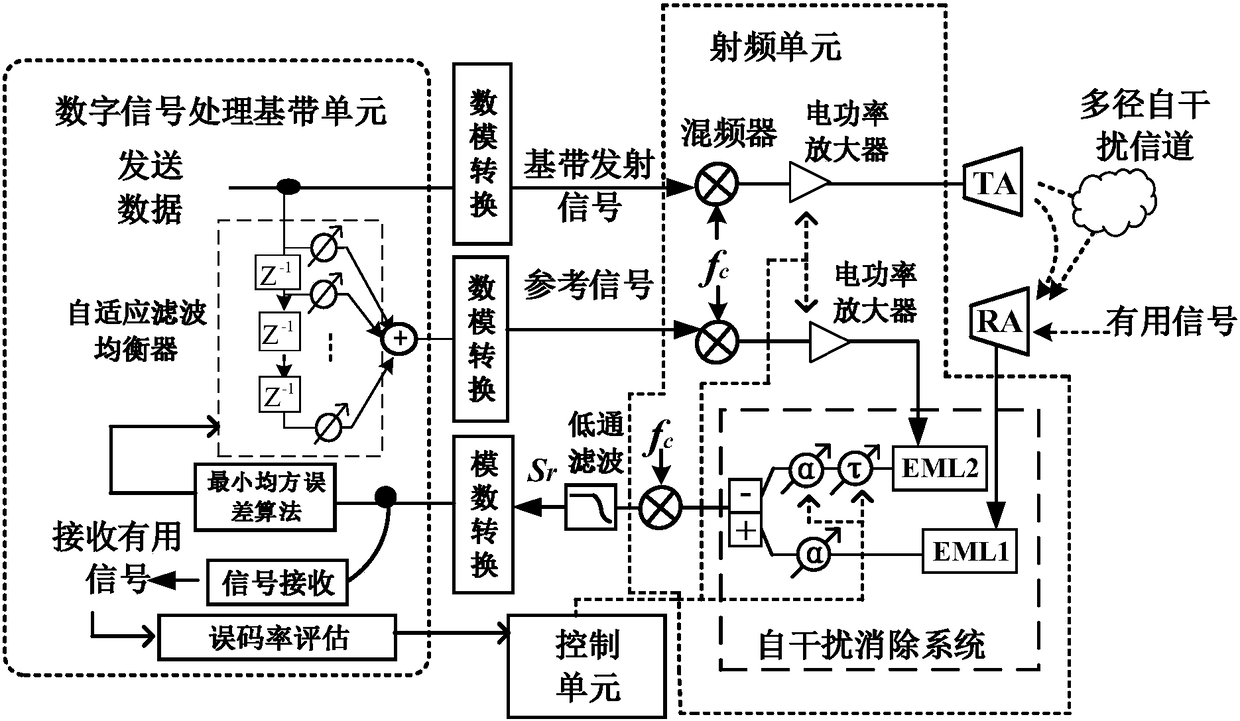
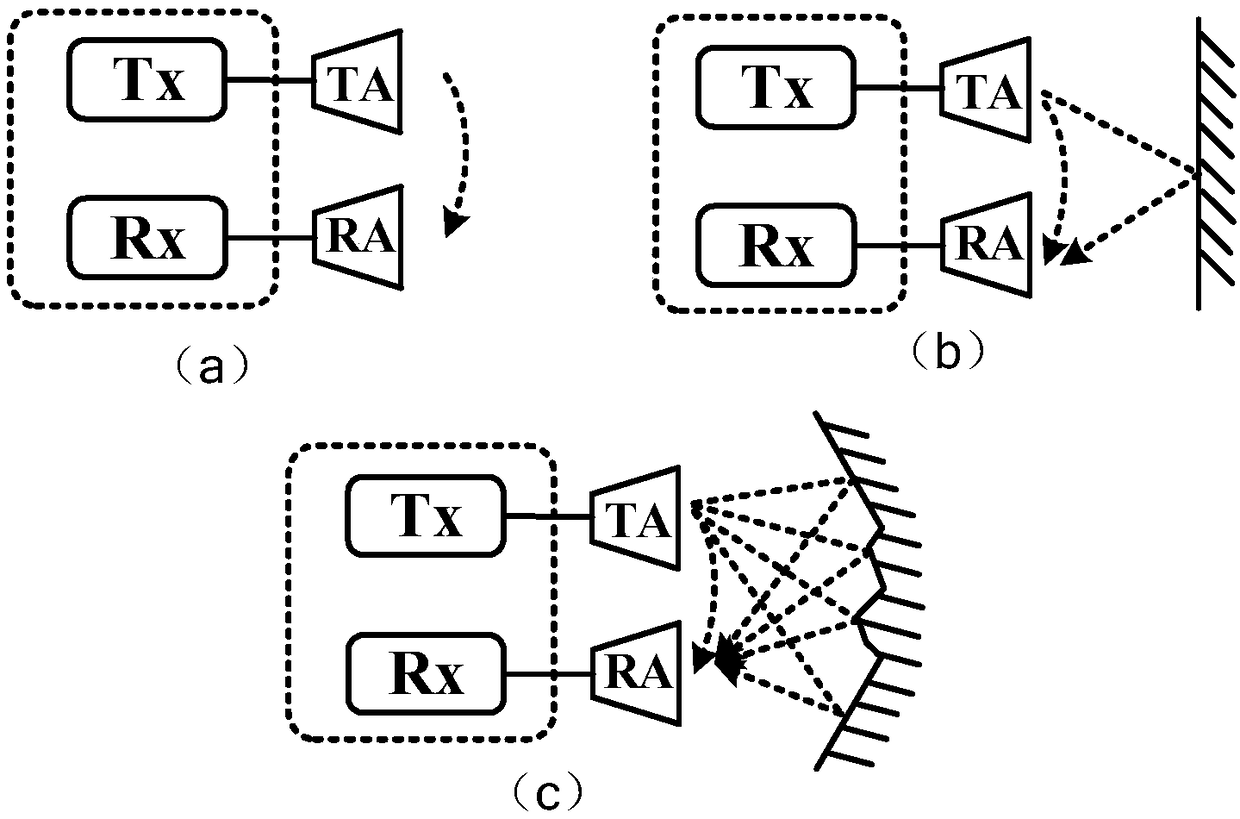
The invention provides a self-adaptive time domain equalization system for a multi-path self-interference channel in an optical self-interference cancellation system. A self-adaptive time domain equalization module is used for carrying out self-adaptive training adjustment on a reference signal; an optical self-interference cancellation module is used for receiving a mixed signal and the referencesignal, realizing cancellation of a self-interference signal, and outputting an optical signal; and a control module is used for controlling reception of the optical signal and state switching of theself-adaptive training of the optical signal in a process of carrying out self-adaptive training adjustment on the reference signal by the self-adaptive time domain equalization module. Meanwhile, the invention provides an in-band full-duplex wireless communication system. Through the self-adaptive time domain equalization system, a problem that the suppressing bandwidth is severely reduced due to the multi-path self-interference channel is solved, the bandwidth of a passband can be expanded, and a better self-interference suppression ratio can be obtained in the selected passband.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
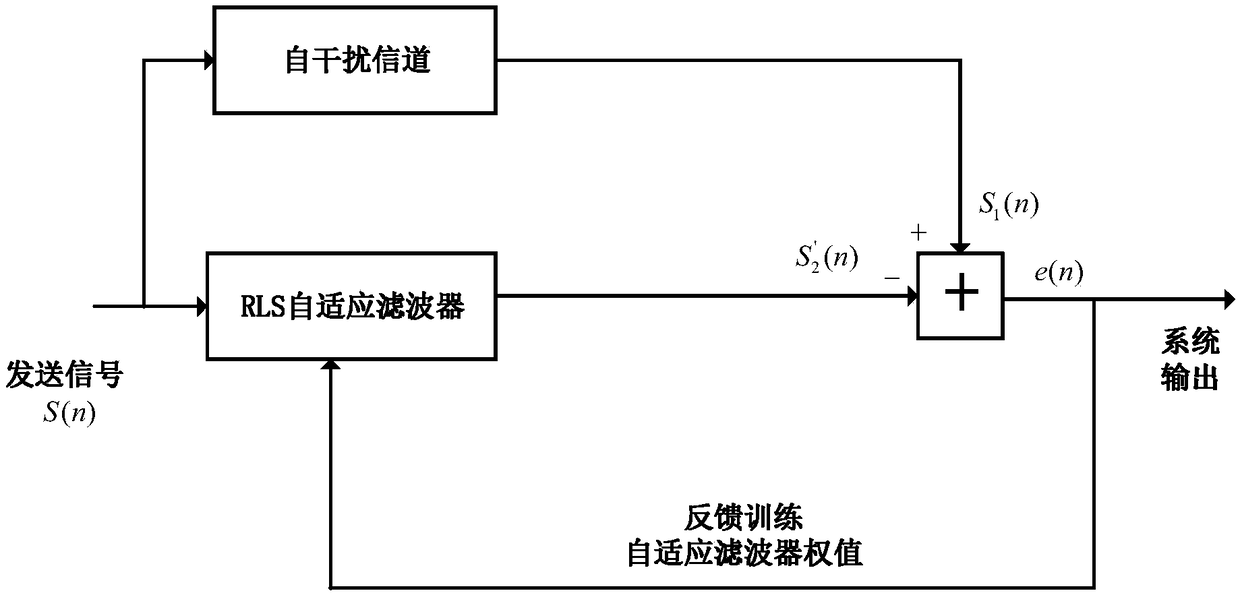
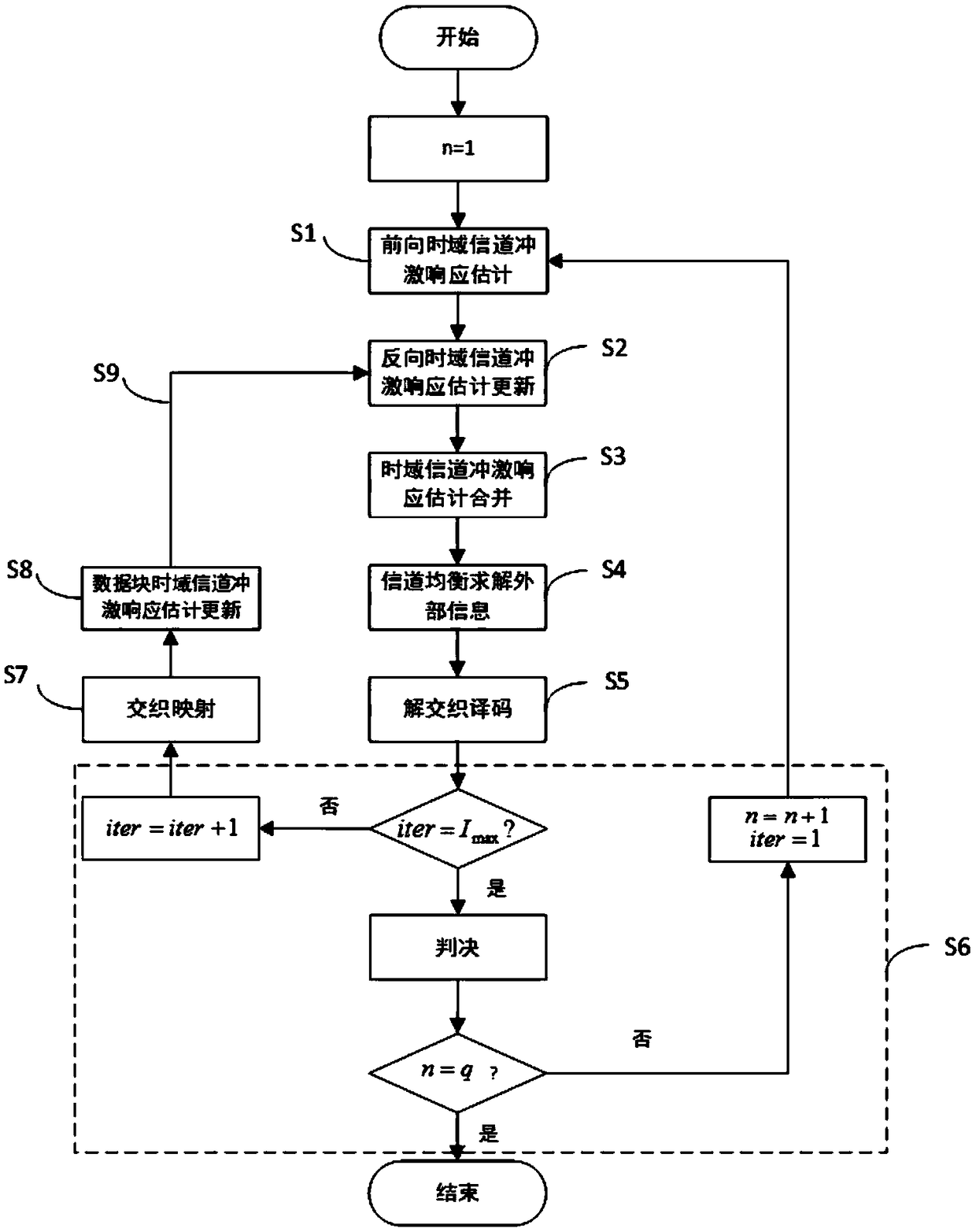
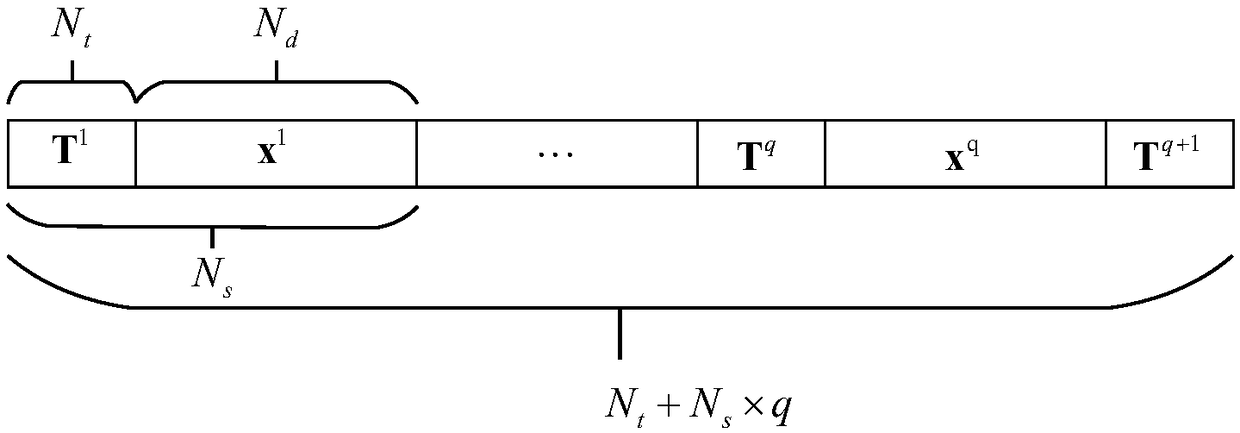
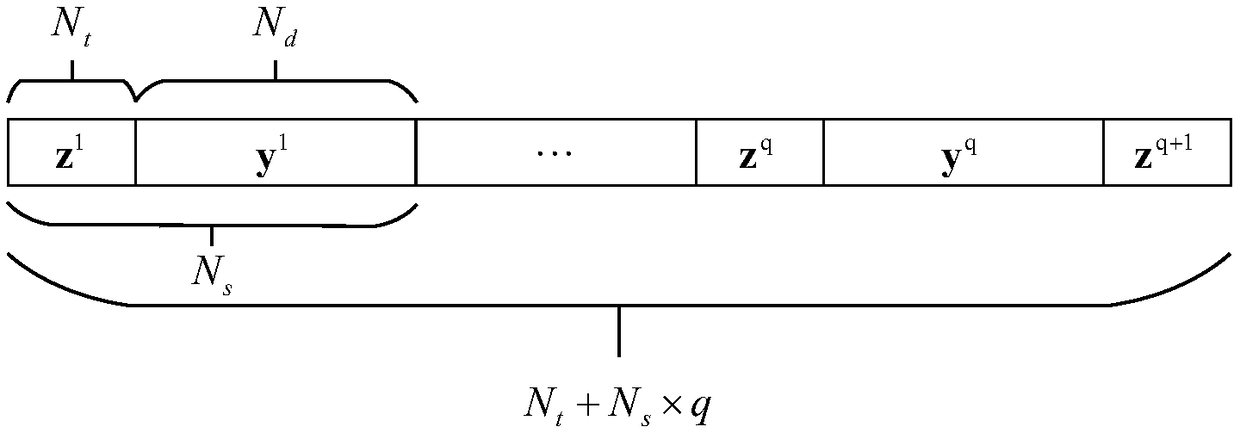
Soft information iterative receiving method based on bidirectional time domain equalization
ActiveCN109246039AAvoid lossReduce time complexityChannel estimationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainComputation complexity
The invention discloses a soft information iterative receiving method based on bidirectional time domain equalization, and the method is suitable for a super Nyquist (FTN) transmission system. Based on the forward and reverse channel estimation of a channel in a time domain, the method employs a weighted combining equalization method, and adopts a soft information iterative equalization (Turbo equalization) structure. Through the iterative exchange of soft information, the method makes the most of the error correction gain of the channel coding to effectively improve the error performance of the system. Meanwhile, the method employs an estimated mean value for transmitting a data symbol in the Turbo iteration for the channel estimation, so the method can better track channel changes. Compared with other methods, the method of the invention can more effectively eliminate the inter-symbol interference brought by the channel, can effectively resist the inter-symbol interference carried bythe FTN transmission system, and has lower computational complexity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
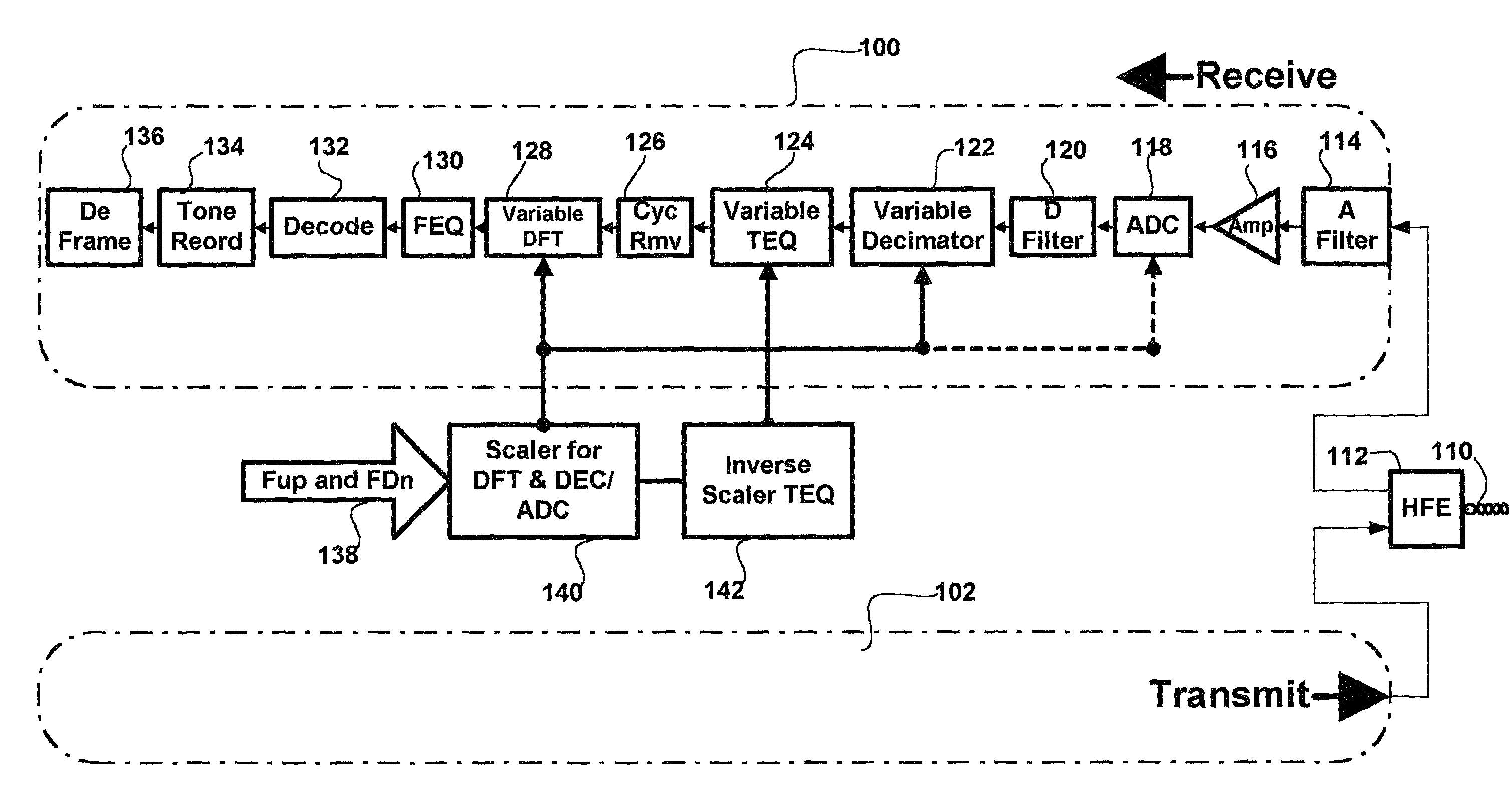
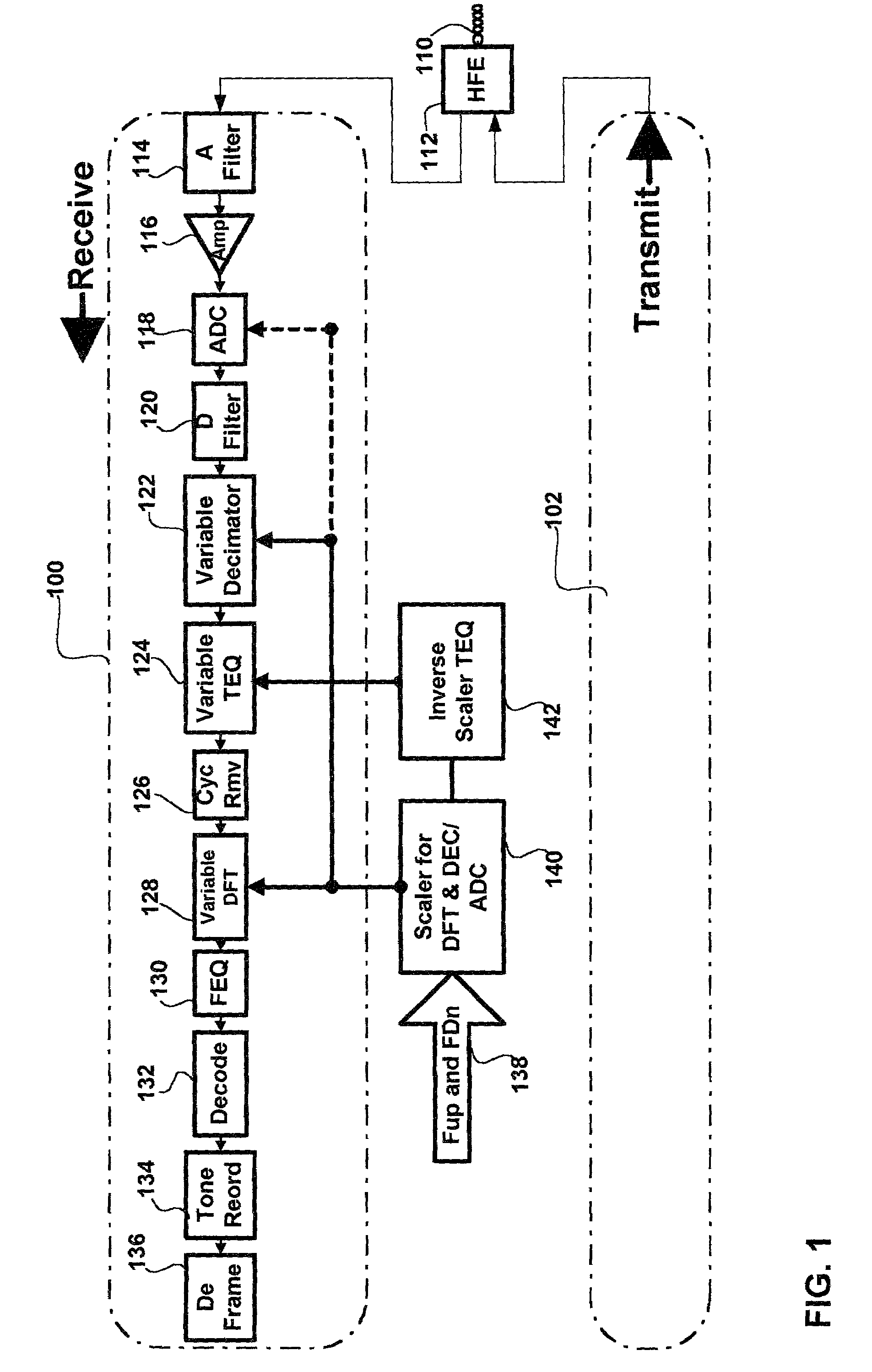
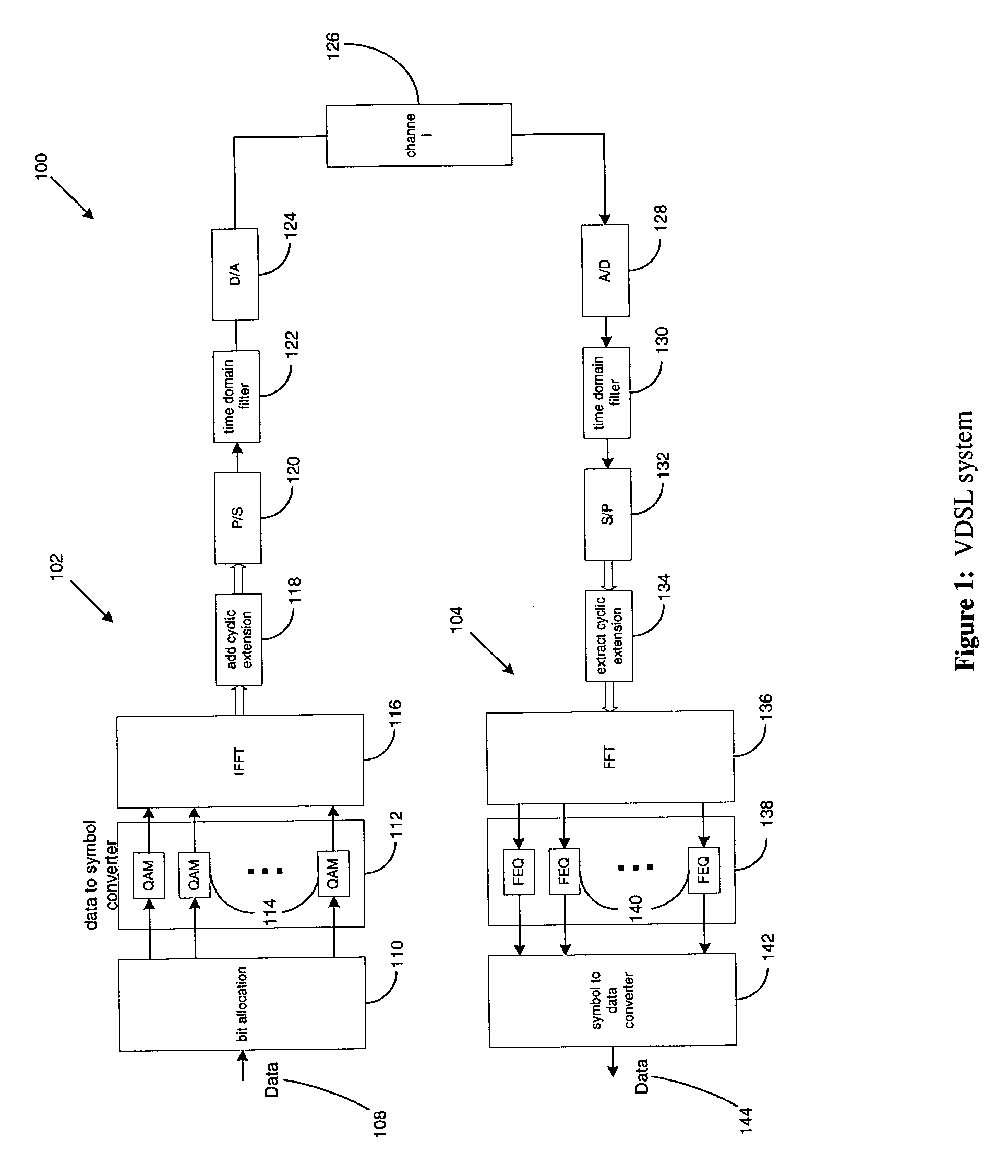
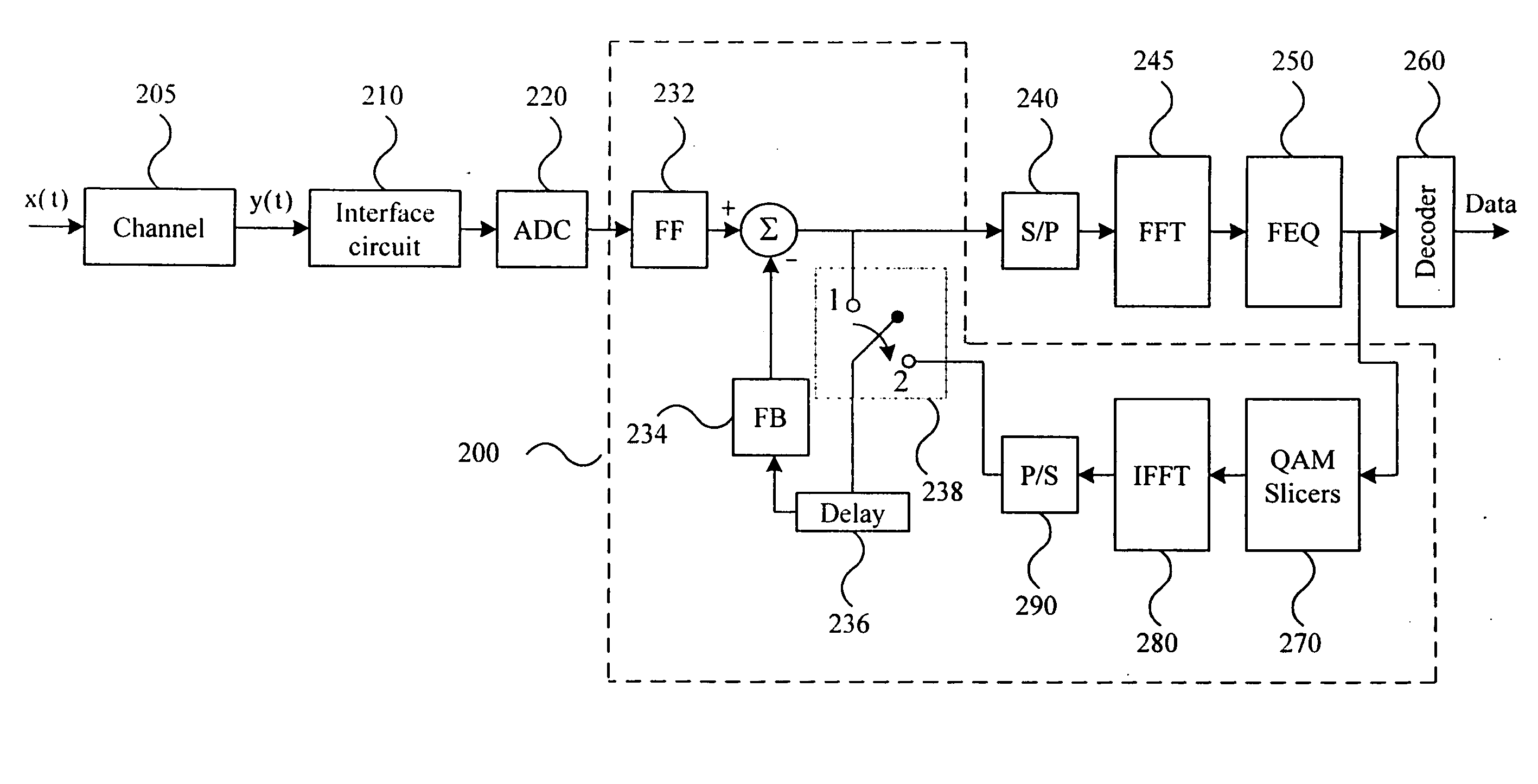
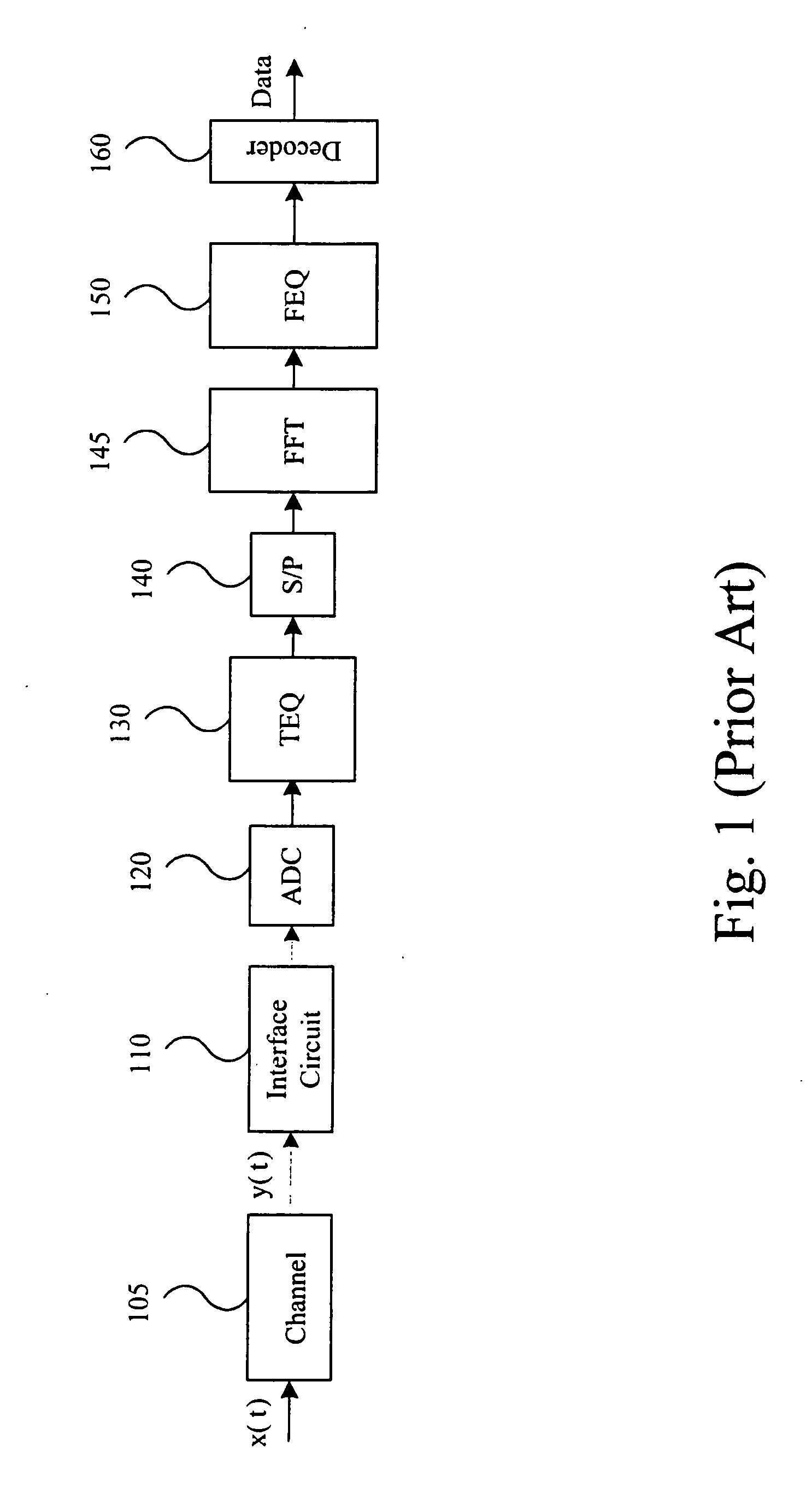
Method and apparatus for time domain equalization in an XDSL modem
InactiveUS7076010B1Minimize intersymbol interferenceSevere interferenceMultiple-port networksError preventionModem deviceTime domain equalization
The current invention provides a method and apparatus for time domain equalization in an XDSL modem. A received communication channel is analyzed to determine the highest frequency component thereof. Typically, there is an inverse relationship between the length of a subscriber line and the highest frequency component over which communications can be supported. In response to the frequency determination, the sampling rate for the channel is reduced to the lowest sample rate consistent with maintaining signal integrity on the highest frequency component of the channel. The sampling rate reduction may accomplished in the analog portion of the receive path, e.g. the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or in a digital decimator coupled thereto. Concurrently the demodulator complexity is also scaled back. Where the XDSL protocol is digital multi-tone (DMT) the input sample size to the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) engine is reduced accordingly. With these adjustments in place TEQ resources may be scaled inversely. Thus as line length increases and the available bandwidth on the subscriber line is reduced more TEQ resources are made available to deal with the increased delay interval over which intersymbol interference is evidenced. Scaling of TEQ resources may be accomplished using a TEQ architecture which allows either the length or the tap line or the delay between taps to be varied.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
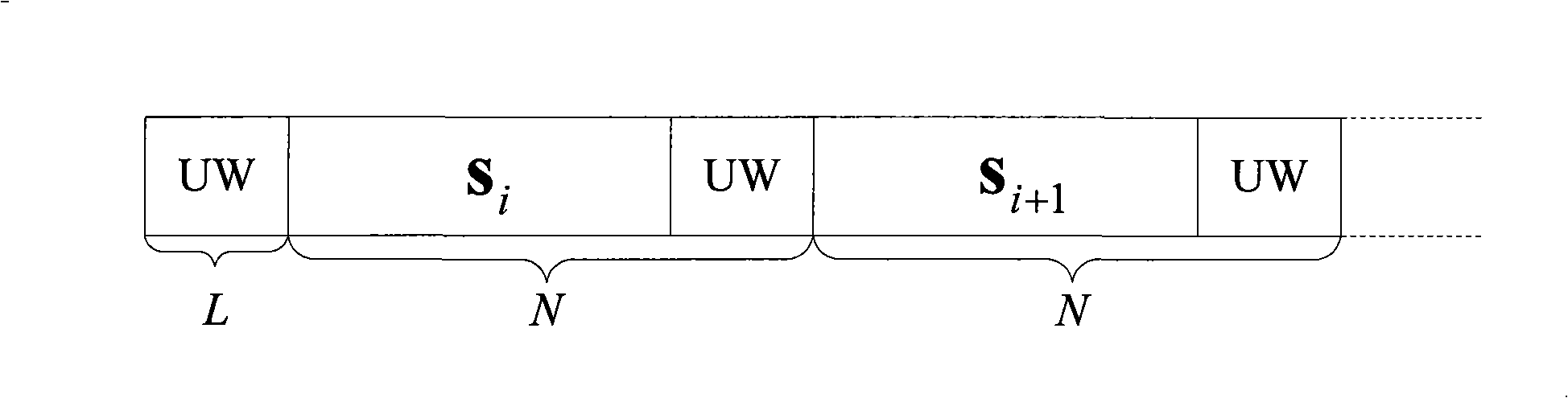
Adaptive equalization method for single carrier system
InactiveCN101404631AReduce the impact of noiseSmall amount of calculationMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksData segmentComputation complexity
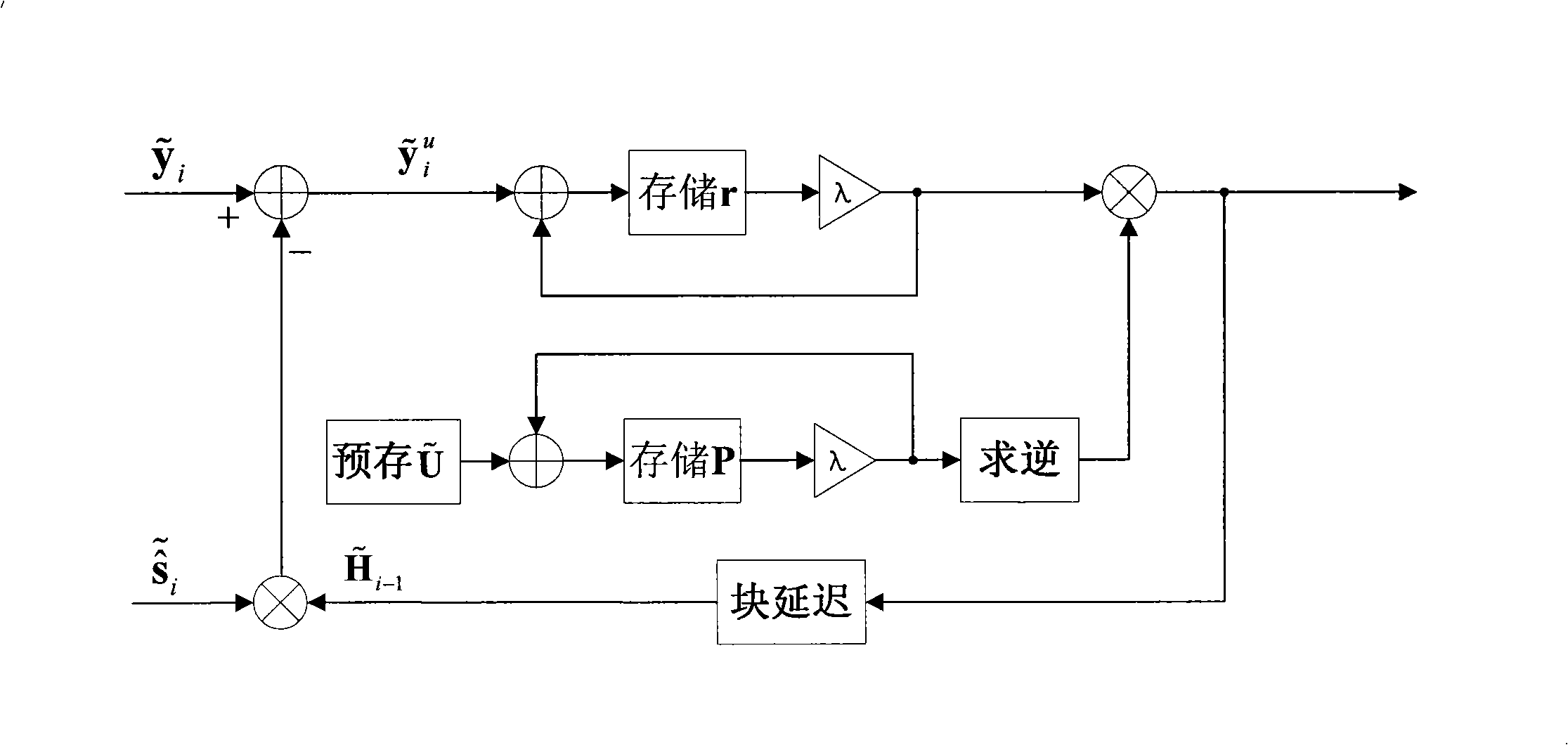
The invention provides an adaptive equalization method of a single-carrier system. The method includes the following steps: step A: the received signal is converted to frequency-domain data by fourier transformation; step B: the time-domain equalization data are obtained after frequency-domain equalization and inverse fourier transformation; wherein, each data section xi with length N in the transmission structure consists of an information section si with length N-L and a known UW section u with fixed length L as cyclic prefix; step C: UW section with length L is separated from the time-domain equalization data and the equalized signal and the own error signal are used as the input variables of adaptive channel estimation. The invention can restrict the error measurement in the UW section and reduce the noise impact and also has the advantages of low calculation complexity and small calculation amount.
Owner:北京韦加航通科技有限责任公司
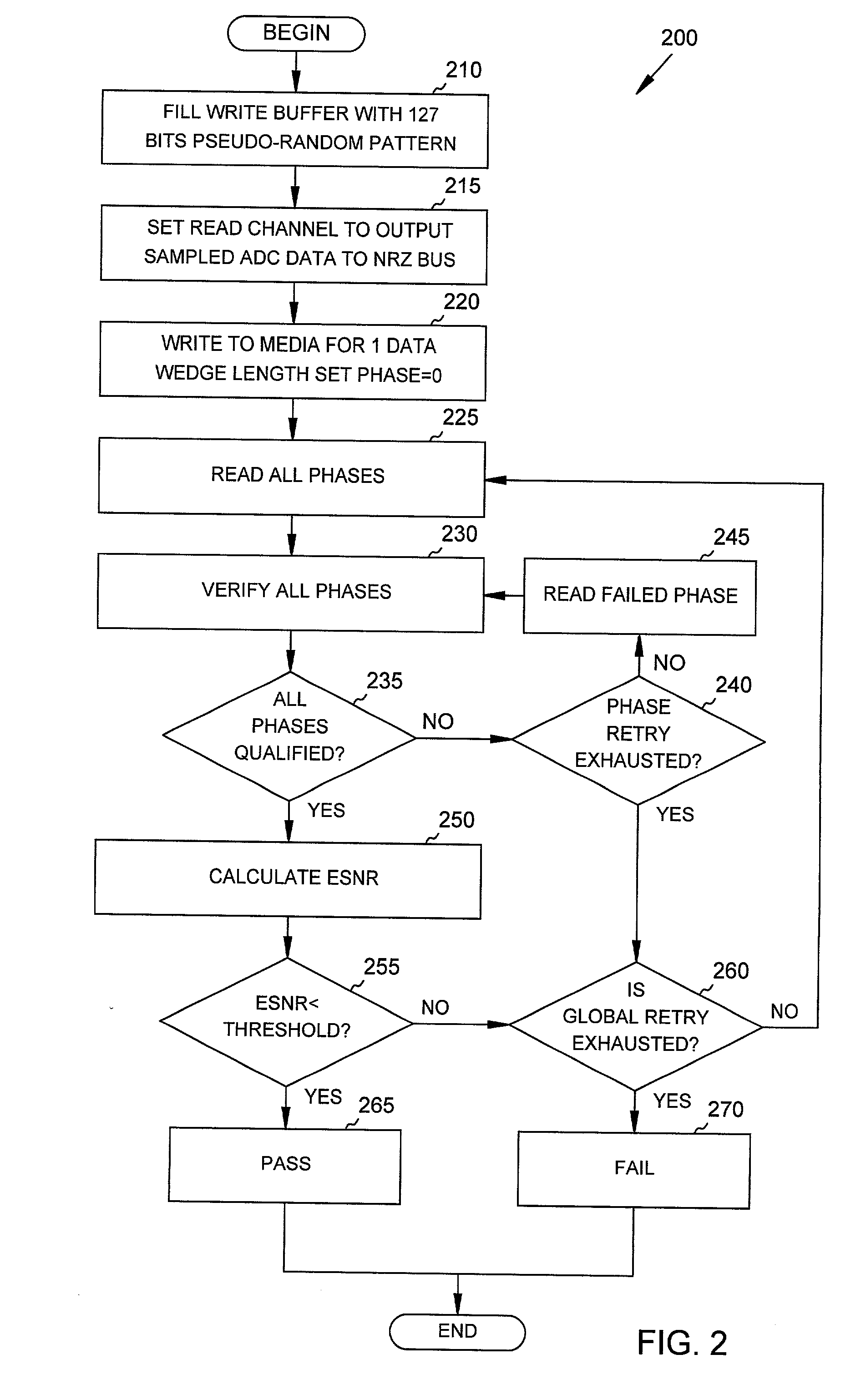
System and method to determine the time domain equalized signal-to-noise ratio of a mass storage device
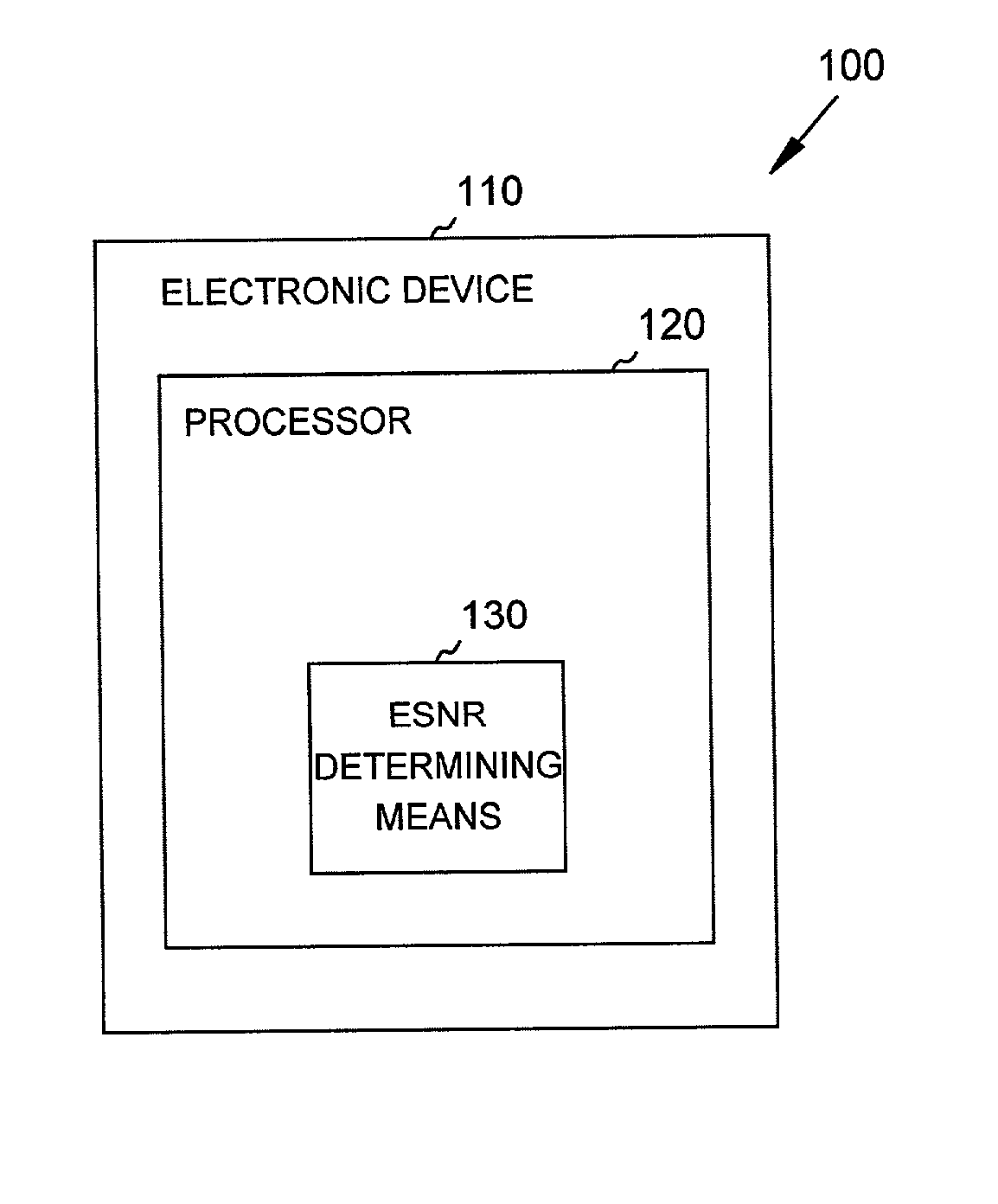
InactiveUS20020128787A1Accurate measurementLess timeDisc-shaped record carriersError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTime domainMass storage
Systems and methods are provided through which a time domain equalized signal-to-noise-ratio (ESNR) of an electronic device is determined by executing ESNR determining firmware in the electronic device. The ESNR is used to perform rejection / acceptance testing of the electronic device during manufacturing of the device, and / or to perform read channel tuning and optimization. In one embodiment, determination of the ESNR includes both phase level retry and global level retry.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Apparatus for time-domain pre-emphasis and time-domain equalization and associated methods
InactiveUS20100027607A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainTime domain equalization
An integrated circuit (IC) includes a transmitter. The transmitter includes a pre-emphasis circuit. The pre-emphasis circuit pre-distorts an input signal by moving in time a sampling point of the input signal. The input signal is thus pre-distorted before transmission to a communication channel. The IC may optionally include a receiver. The receiver includes an equalization circuit. The equalization circuit equalizes a signal received from a communication channel by moving in time a sampling point of the signal received from the communication channel.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
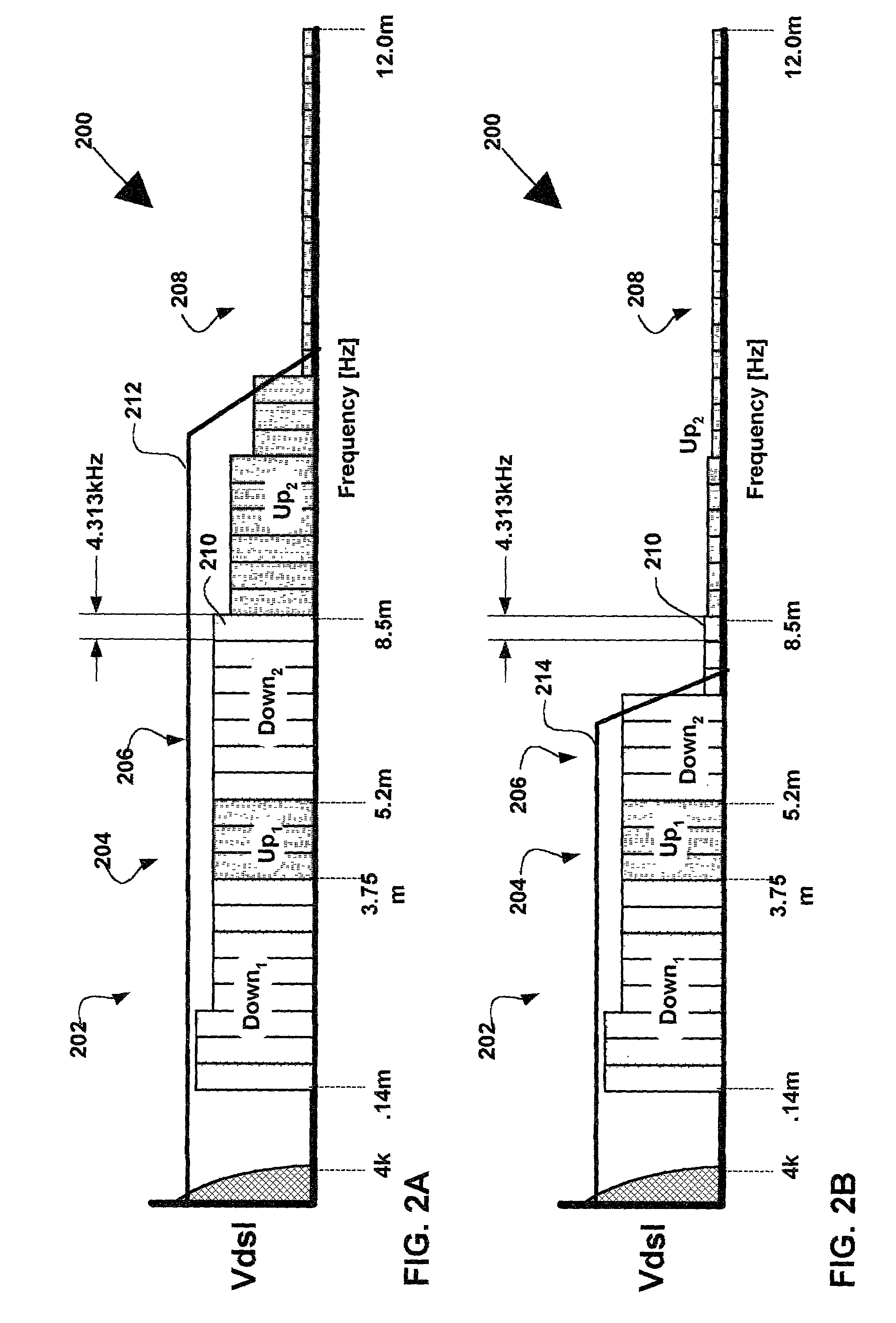
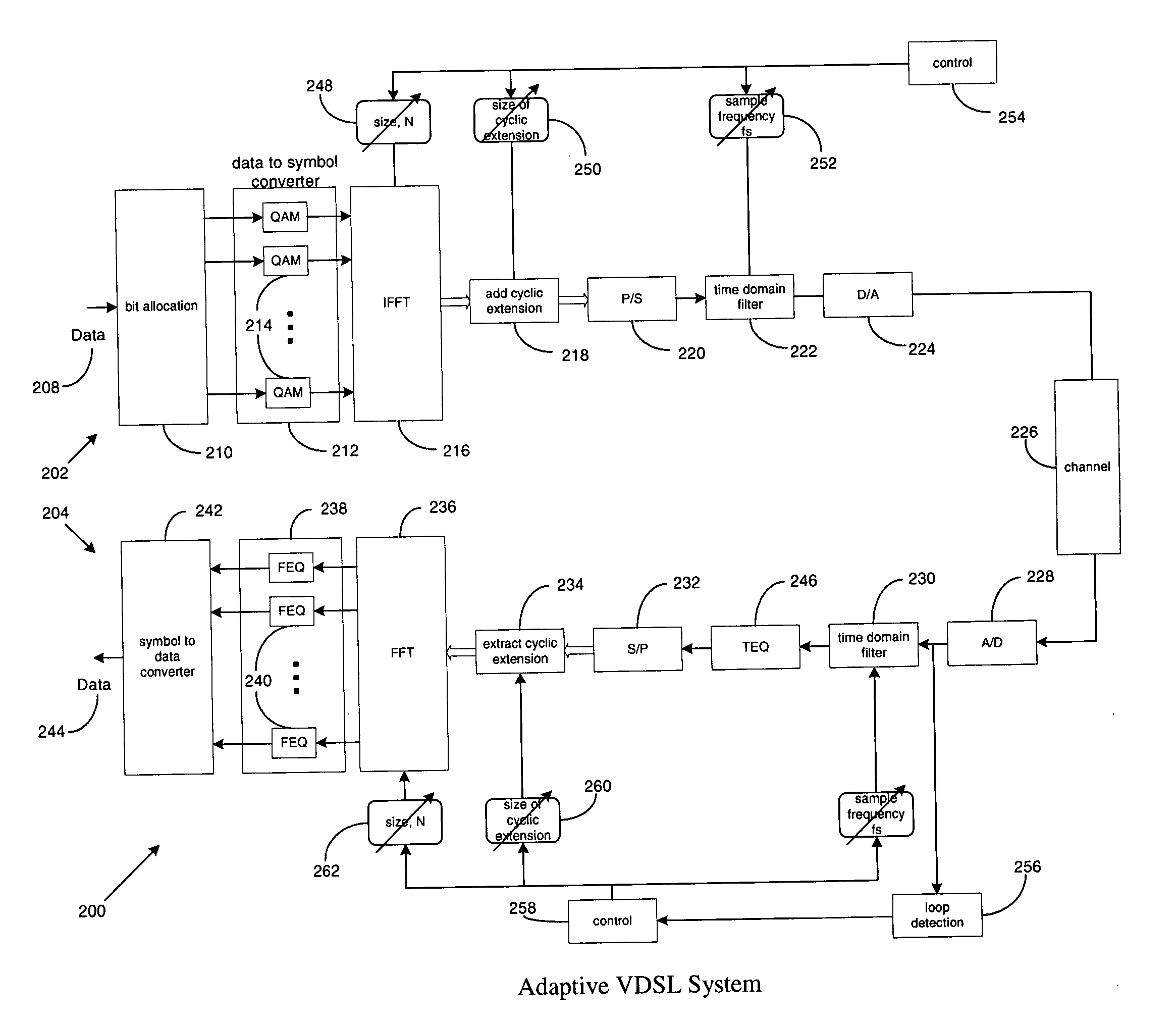
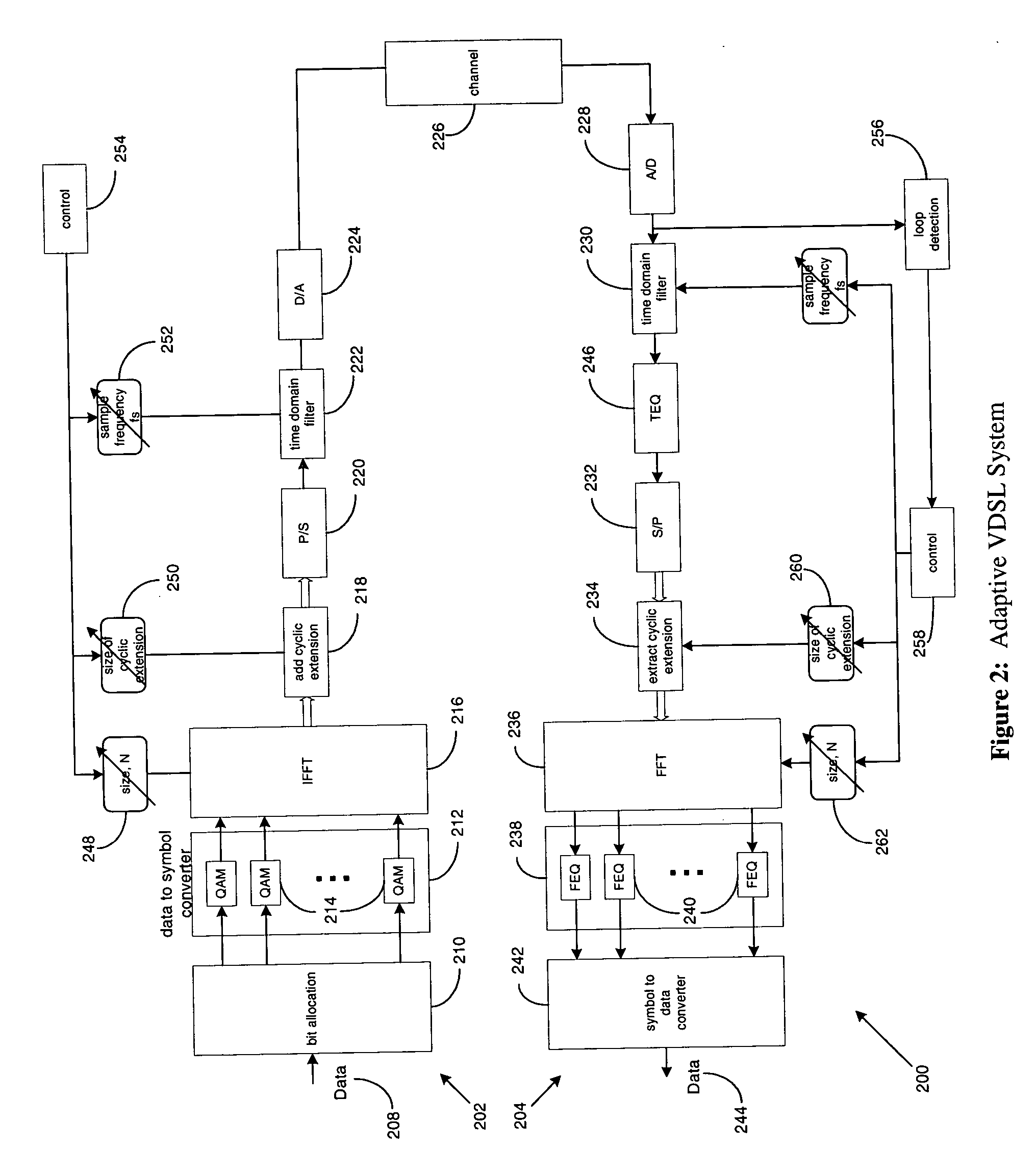
Systems and methods for adaptive VDSL with variable sampling frequency and time-domain equalizer
InactiveUS20060104339A1Lighten the computational burdenImprove system performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsLoop lengthTime domain equalization
A method and system for enhancing reach-performance of a multi-carrier VDSL System estimates loop length, estimates maximum available bandwidth that can be utilized at that particular loop length, optimally selects an FFT size and sampling rate, and decides whether to apply a time domain equalization to its receiver and if so, selects a cyclic extension size. To minimize the implementation complexity, the sampling frequencies at receiver and transmitter are lowered to match the actual usable bandwidth. The FFT / IFFT sizes in the implementation are also required to set appropriately accordingly.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
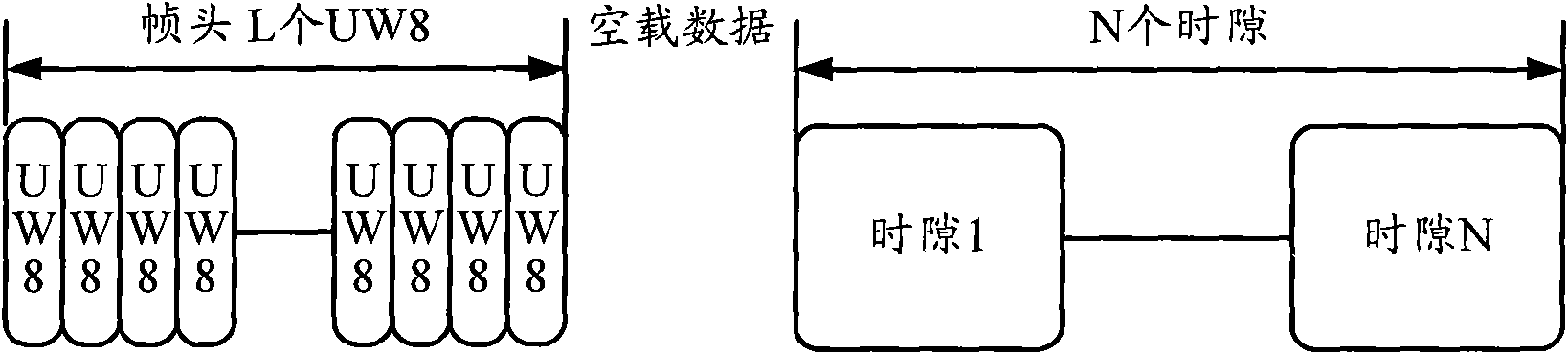
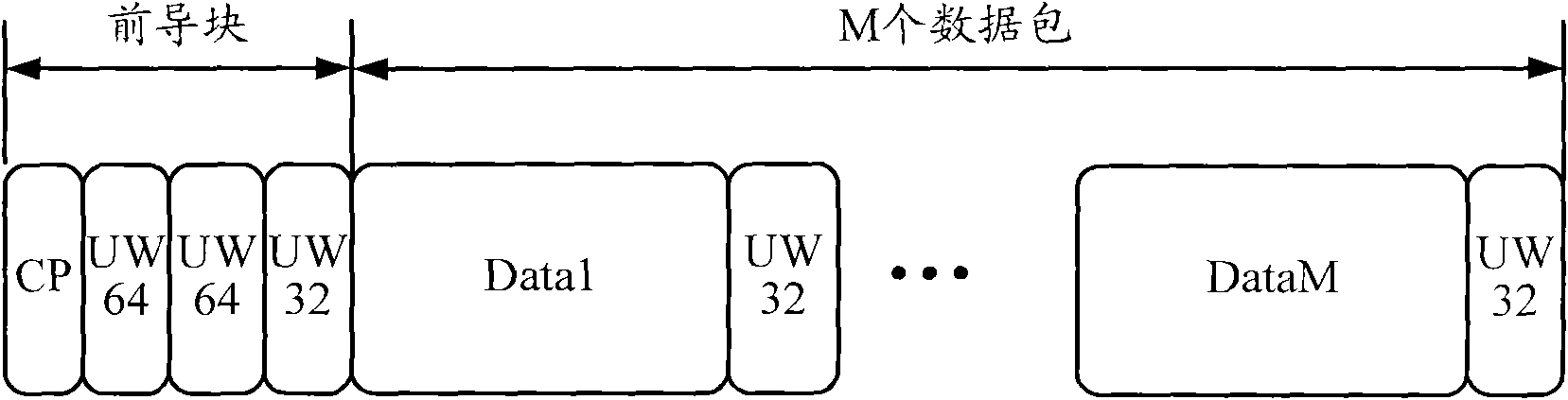
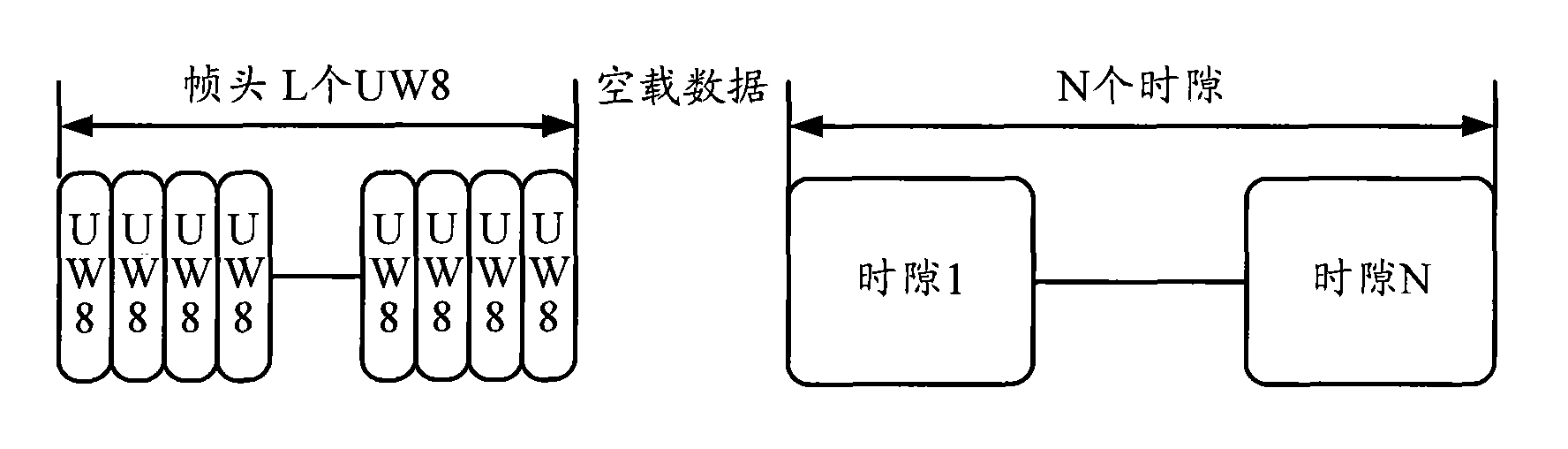
Single carrier frequency domain equalization frame structure aiming at short-wave communication channel
InactiveCN101778062AImprove balanceBalance complexity reductionRadio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTime delaysTime domain equalization
The invention discloses a single carrier frequency domain equalization frame structure aiming at a short-wave communication channel. The frame structure comprises a frame header and a plurality of time slots, wherein each time slot further includes a front guide block and a plurality of packets. The single carrier frequency domain equalization frame structure aiming at the short-wave communication channel utilizes adaptive frequency domain equalization for carrying out equalization treatment and achieves excellent equalization effect; and furthermore, along with the increment of multipath time delay spread, the equalization complexity is greatly reduced compared with time domain equalization. Compared with a parallel system, the single carrier frequency domain equalization frame structure has low peak-to-average ratio (PAR), strong frequency selective fading resisting capability as well as higher transmission speed and lower bit error rate (BER) under the same condition.
Owner:北京韦加航通科技有限责任公司
System and method for time-domain equalization in discrete multi-tone system
InactiveUS20060034363A1Shorten the lengthImprove performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainChannel impulse response
A novel structure for the TEQ in a DMT system receiver to shorten the length of the effective channel impulse response is provided. A time-domain equalizer, based on the decision-feedback filter structure, along with a training method is disclosed. In accordance with the DFE-based TEQ in the DMT system, the data symbols that transmitted through the effective shortened channel would be more reliable.
Owner:WANG CHIN LIANG +2
Flexible optical network time domain equalization method and system based on composite neural network
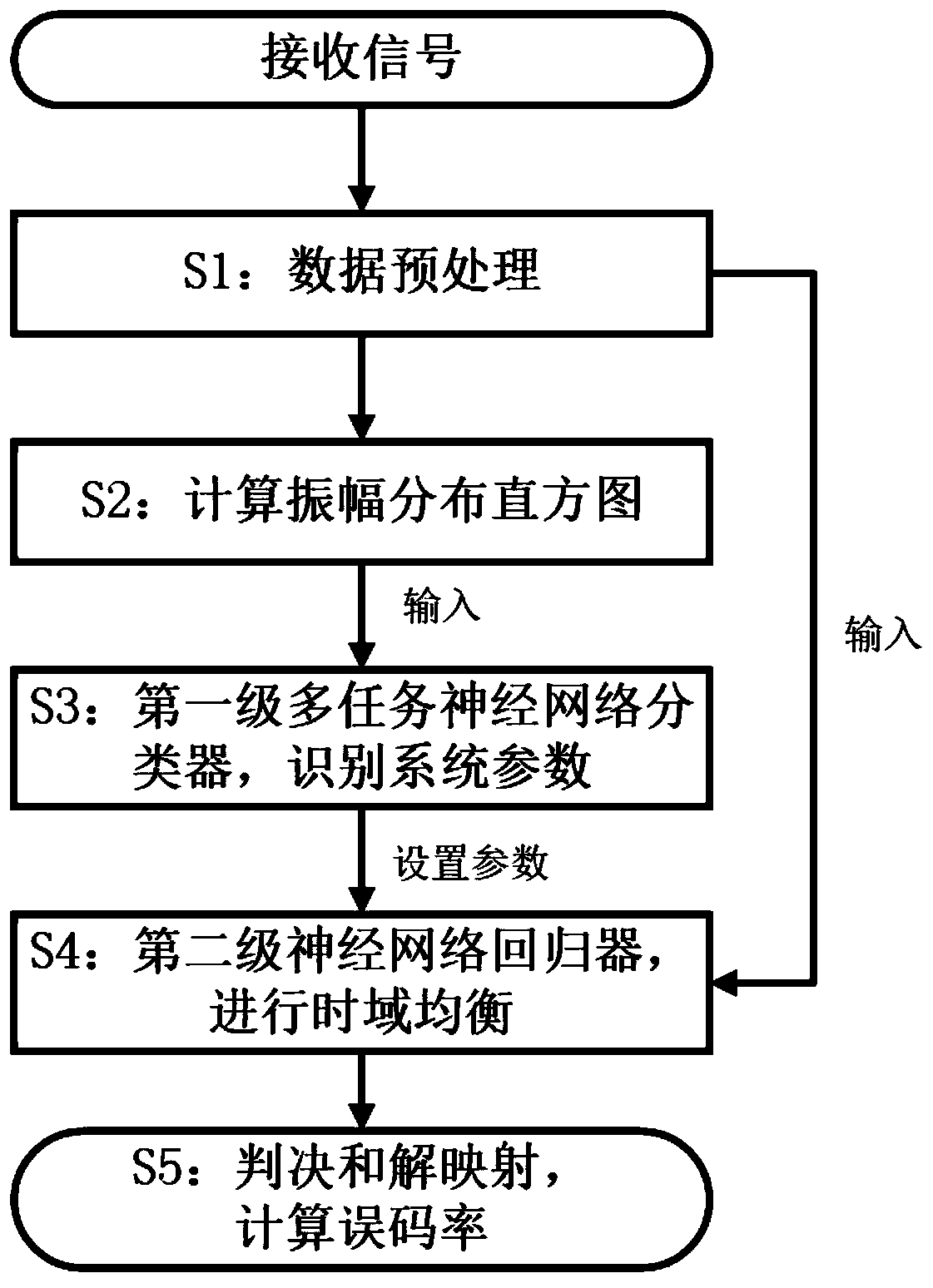
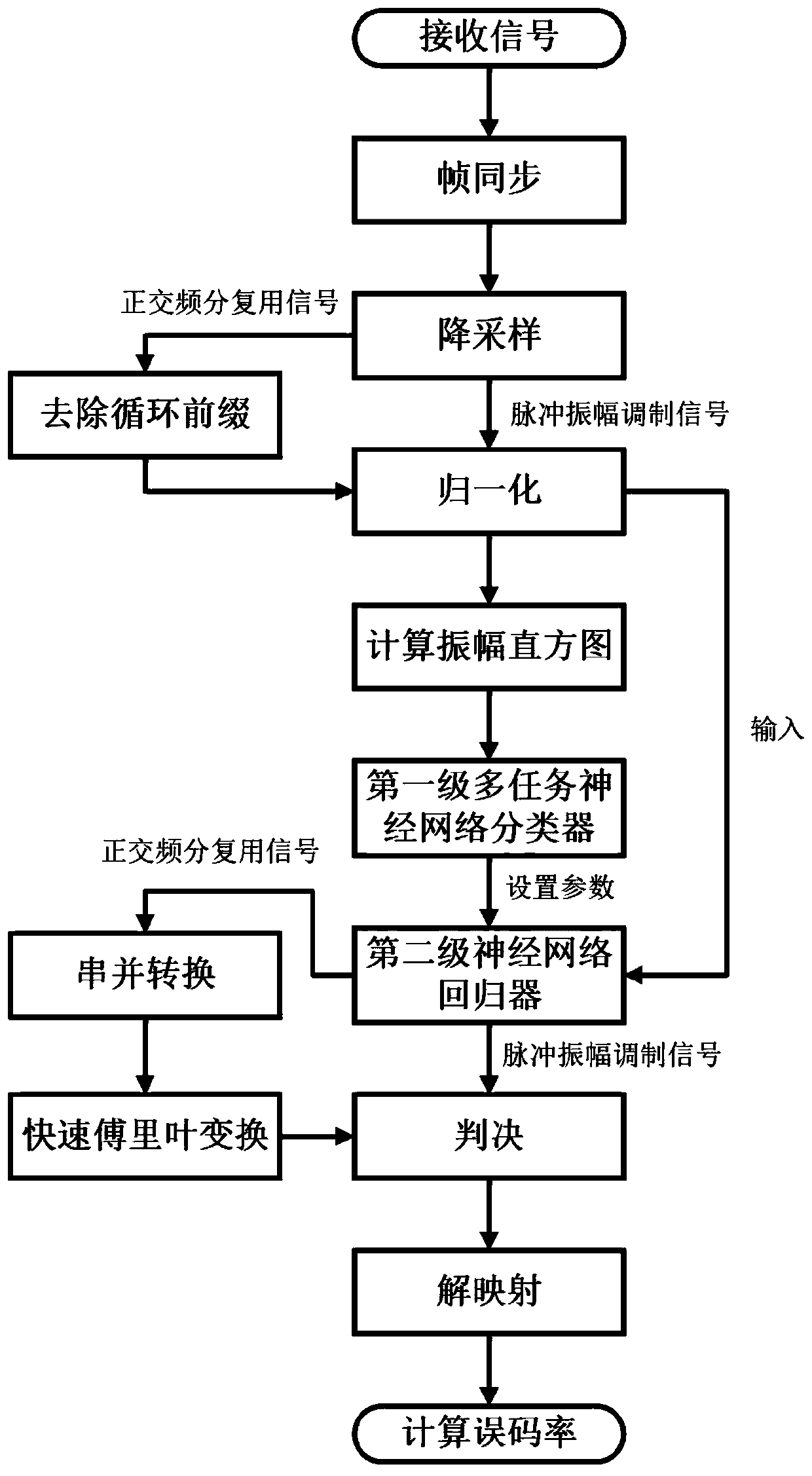
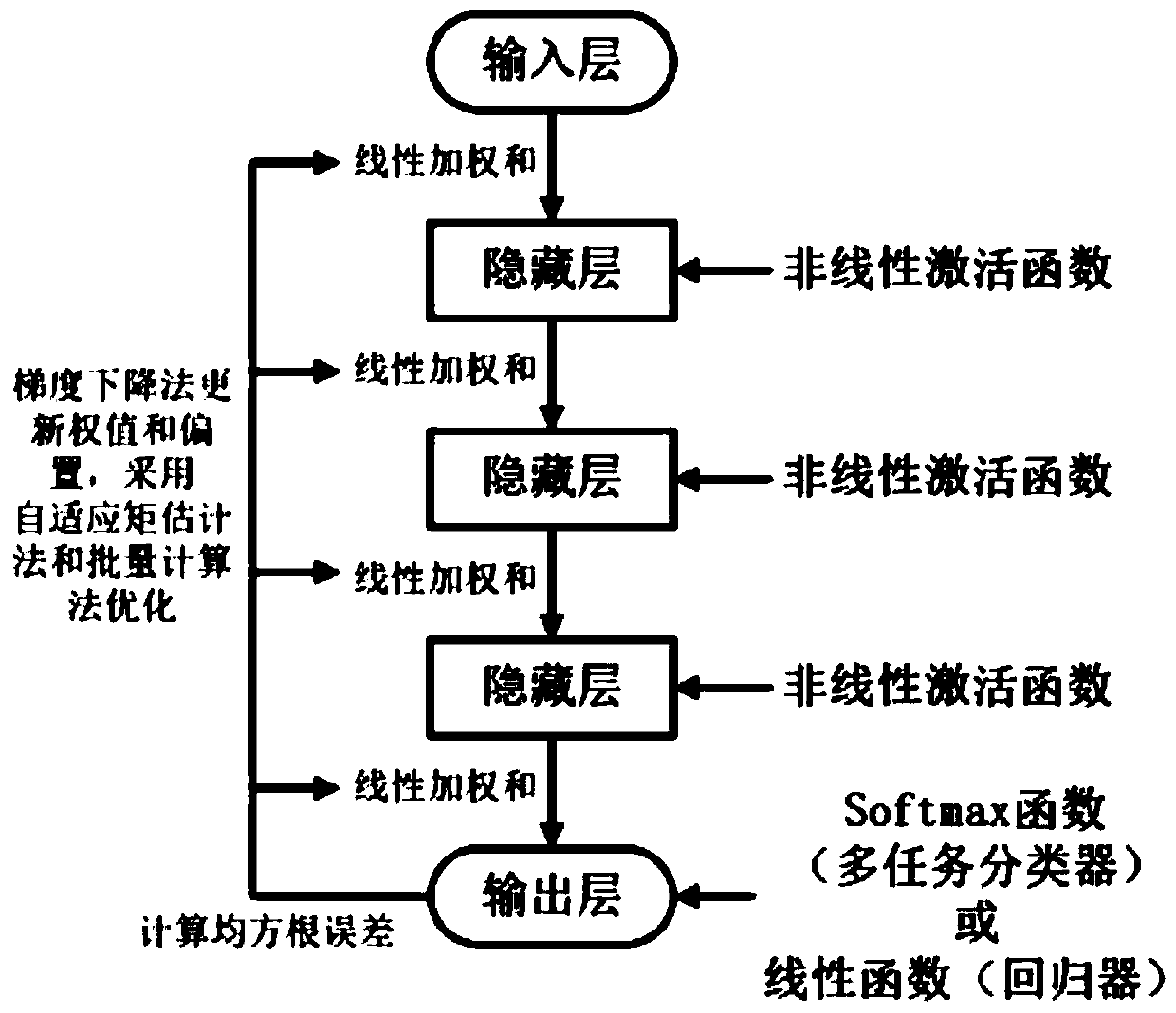
ActiveCN111093123AAvoid failureGood channel equalization effectMultiplex system selection arrangementsNeural architecturesAlgorithmTime domain equalization
The invention discloses a flexible optical network time domain equalization method and system based on a composite neural network, and belongs to the field of optical fiber communication systems, andthe method comprises the steps: (1) preprocessing a received signal transmitted by a flexible optical network; (2) calculating an amplitude distribution histogram of the preprocessed received signal;(3) inputting the amplitude distribution histogram into a first-stage multi-task neural network classifier, and outputting transmission parameters of the flexible optical network; (4) setting a weightand an offset parameter of a second-stage neural network regression device according to the transmission parameter of the flexible optical network; (5) carrying out time domain equalization on the preprocessed received signal by adopting a second-stage neural network regression device, wherein the number of input neurons of the first-stage multi-task neural network classifier is the same as the number of groups of amplitude histograms, and the number of output neurons of the first-stage multi-task neural network classifier is the same as transmission parameters of the flexible optical network. The time domain equalization method and system disclosed by the invention are wider in application range.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multistage time domain blind equalization method of OFDM signals
InactiveCN103957177AImplement blind equalizationSimple calculationMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainTime domain equalization
The invention relates to a multistage time domain blind equalization method of OFDM signals. The method comprises the following steps that the frame format of received signals of a receiving sequence is determined through the correlated peak searching method; frame synchronization symbol information of the OFDM signals is used for completing the first stage of time domain equalization on the received signals, a cyclic prefix sequence of the OFDM signals is used for completing the second stage of time domain equalization on the received signals, and signals after the second stage of time domain equalization are output signals which can be used for subsequent processing of signals. According to the method, in the process of determining equalizer coefficients, inherent repeatability of the frame format of the OFDM signals is fully utilized, and under the condition without prior information of the received signals, signal blind equalization is achieved, and the equalization effect is good; the method has the advantages of being simple in calculation and quick in processing to the OFDM signals with multiple sub carriers.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Systems with spread-pulse modulation and nonlinear time domain equalization for fiber optic communication channels
ActiveUS20060245758A1Modulated-carrier systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationTime domain equalizationMatched filter
Embodiments of fiber optic communication systems are disclosed. In one embodiment, the system includes an optical channel having a channel response, a pulse-shaping transmitter coupled to a first end of the optical channel, and a receiver coupled to a second end of the optical channel. The transmitter includes a spread pulse modulator to shape pulses of data prior to transmission and an electrical to optical converter to transmit electrical data signals as the light signals over the optical channel. The receiver includes an optical to electrical converter to receive light signals from the optical channel and generate electrical data signals and a matched filter to receive and filter the electrical data signals with a response substantially matching a combined response of the transmitter and the channel response to increase a signal to noise ratio thereof.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
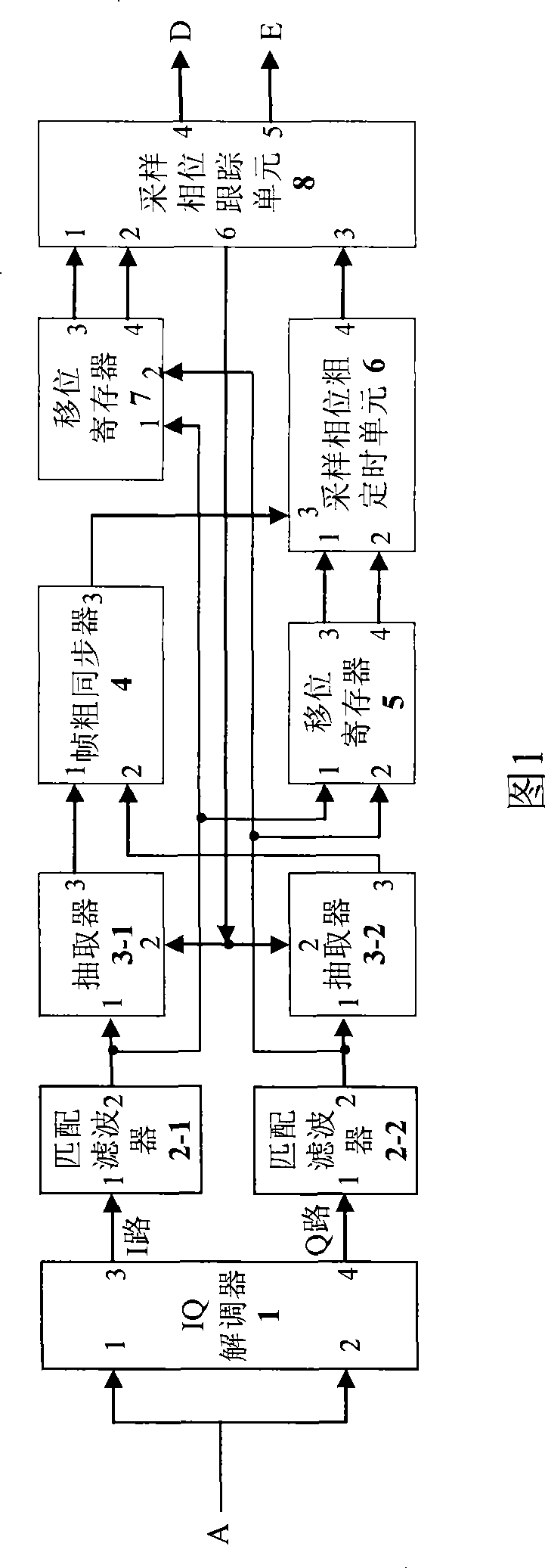
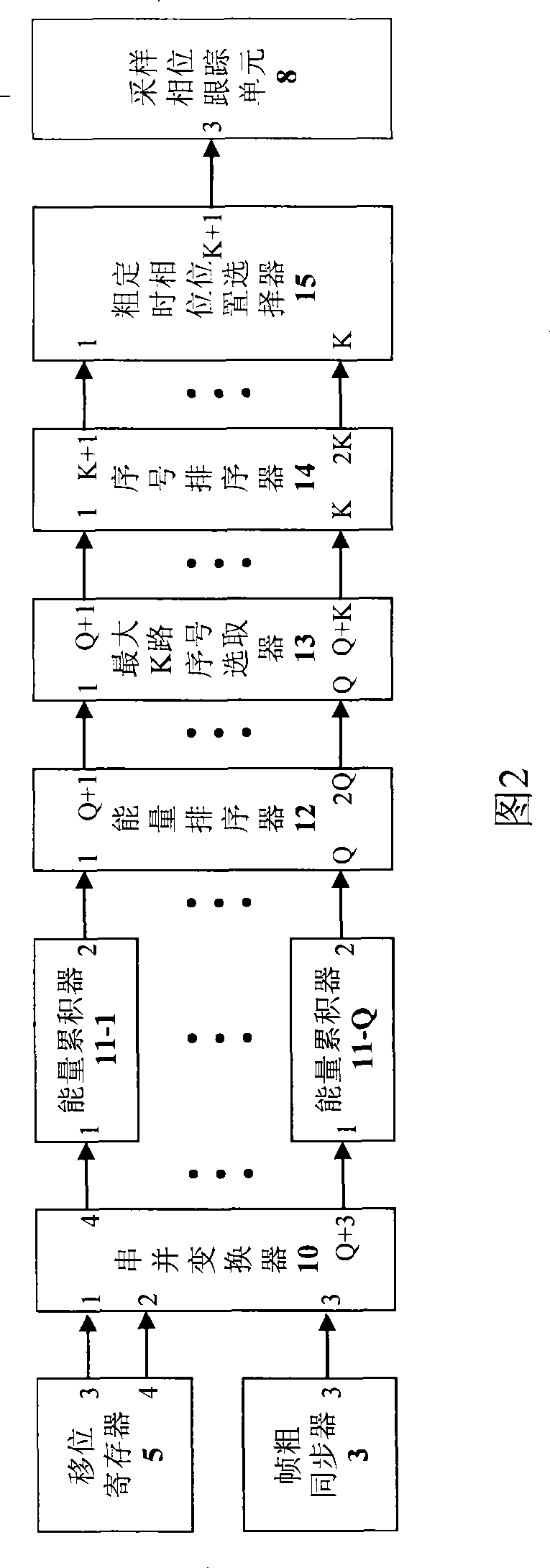
Multi-path symbol resistant timing synchronization device
ActiveCN101420405AStrong anti-multipath abilityEasy to implementMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainCommunications system
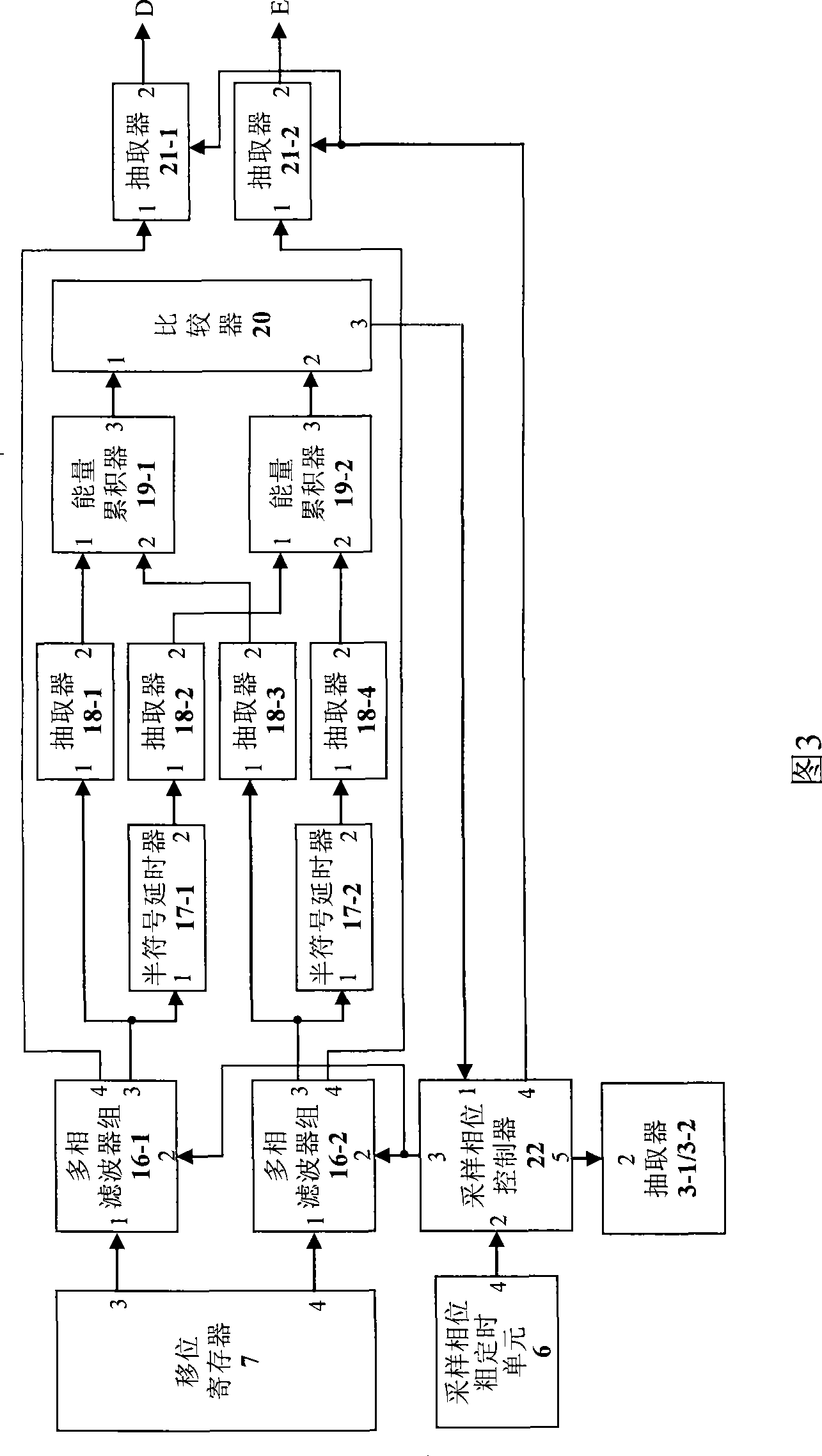
The present invention discloses a multipath symbol resistant timing synchronizing device which relates to wideband single carrier modulation continuous communication in communication field and a symbol timing synchronizing device in burst communication. The multipath symbol resistant timing synchronizing device adjusts the timing phase based on the accumulated energy of a plurality of symbol sample values and not the energy of a single symbol sample value. The timing synchronizing of symbol is realized through a blind estimation method in which a coarse symbol timing estimation and a symbol timing tracking are combined. The multipath symbol resistant timing synchronizing device according to the invention has the characteristics of strong multipath resistance, quick synchronizing speed, adaptability for time domain equalization system, adaptability for frequency domain equalization system, full digital circuit realization, etc. The multipath symbol resistant timing synchronizing deviceis especially suitable for being applied for high-speed data communication system of wideband frequency selectively fading wireless channel.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
LMS (least mean square) method for updating coefficient of self-adaptive equalizer without frequency difference and phase difference feedback
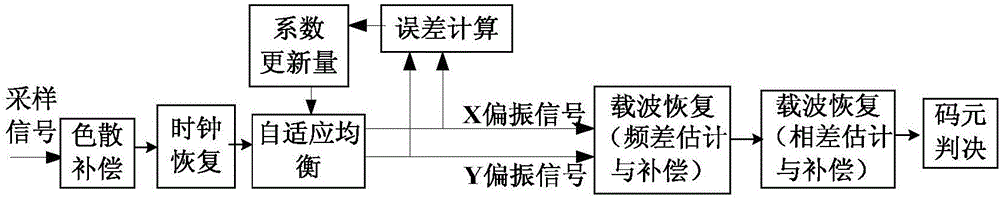
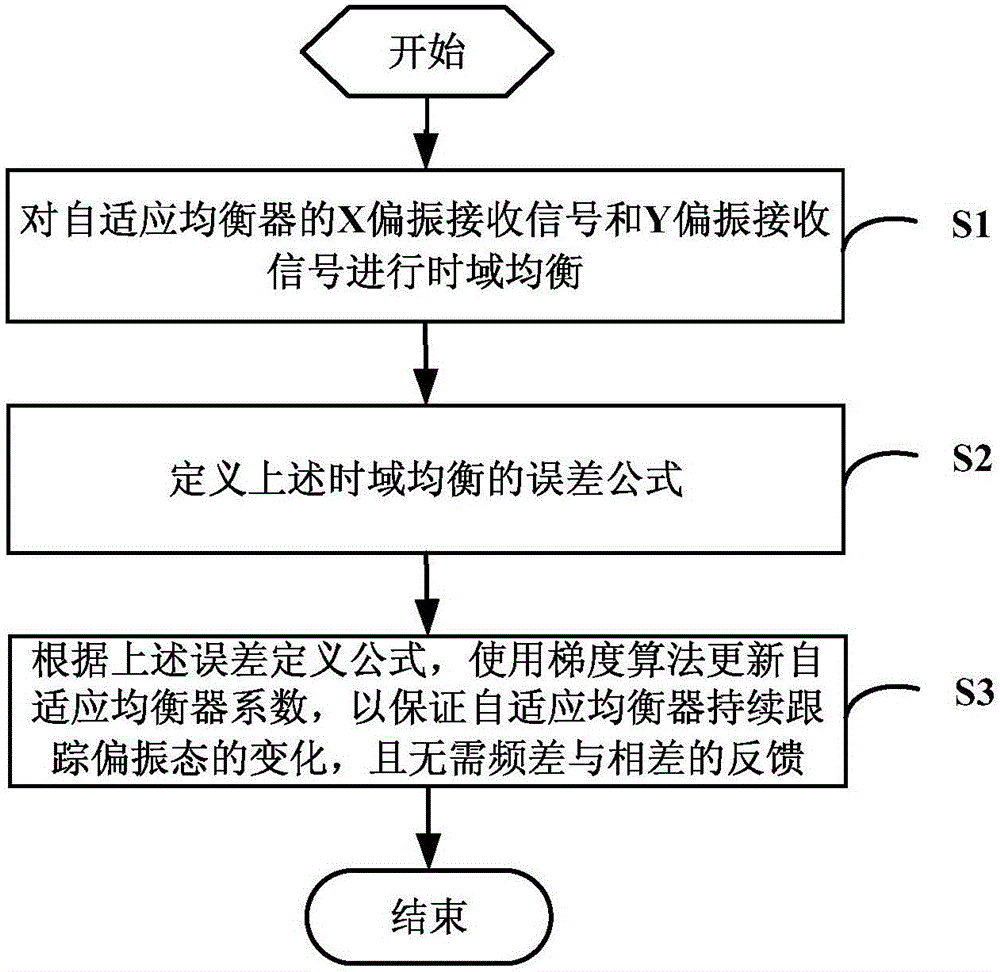
ActiveCN106789793AAccurate trackingGuaranteed robustnessEqualisersElectromagnetic transmissionTime domainCommunications system
The invention discloses an LMS (least mean square) method for updating a coefficient of a self-adaptive equalizer without frequency difference and phase difference feedback and relates to the technical field of coherent light communication. The LMS method comprises steps as follows: an X polarization receipt signal and a Y polarization receipt signal of the self-adaptive equalizer are subjected to time domain equalization; the error formula of time domain equalization is defined; the coefficient of the self-adaptive equalizer is updated with a gradient algorithm according to the error definition to guarantee that the self-adaptive equalizer constantly tracks changes of the polarization state and frequency difference and phase difference feedback is not required. With the adoption of the LMS method, updating of the coefficient of the self-adaptive equalizer does not depend on frequency difference and phase difference feedback any more, a coherent light communication system can correctly track the changes of the polarization state or even extreme changes of the polarization state, and the robustness of the system is guaranteed.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
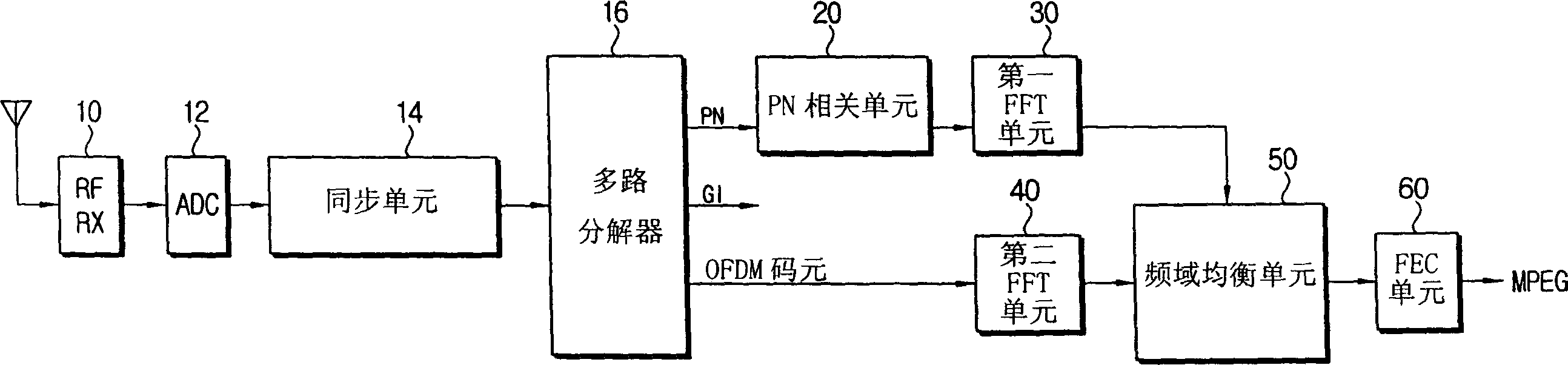
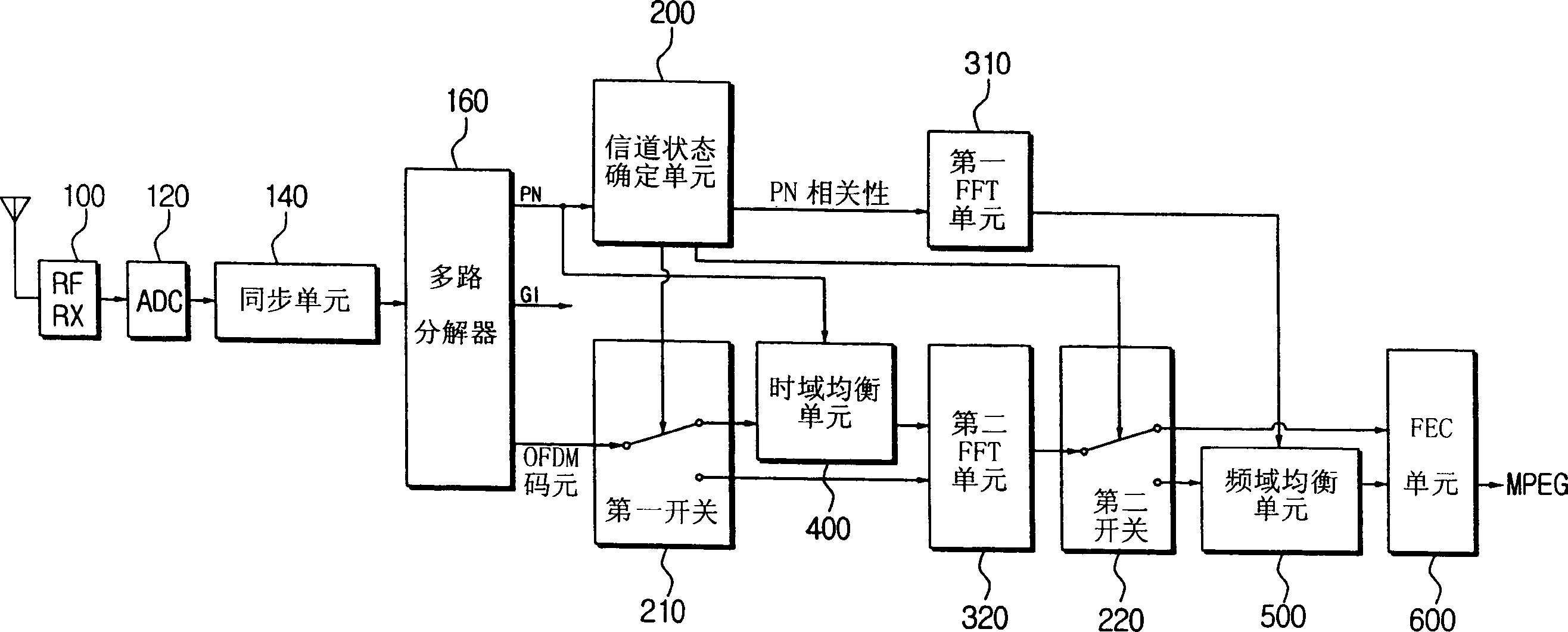
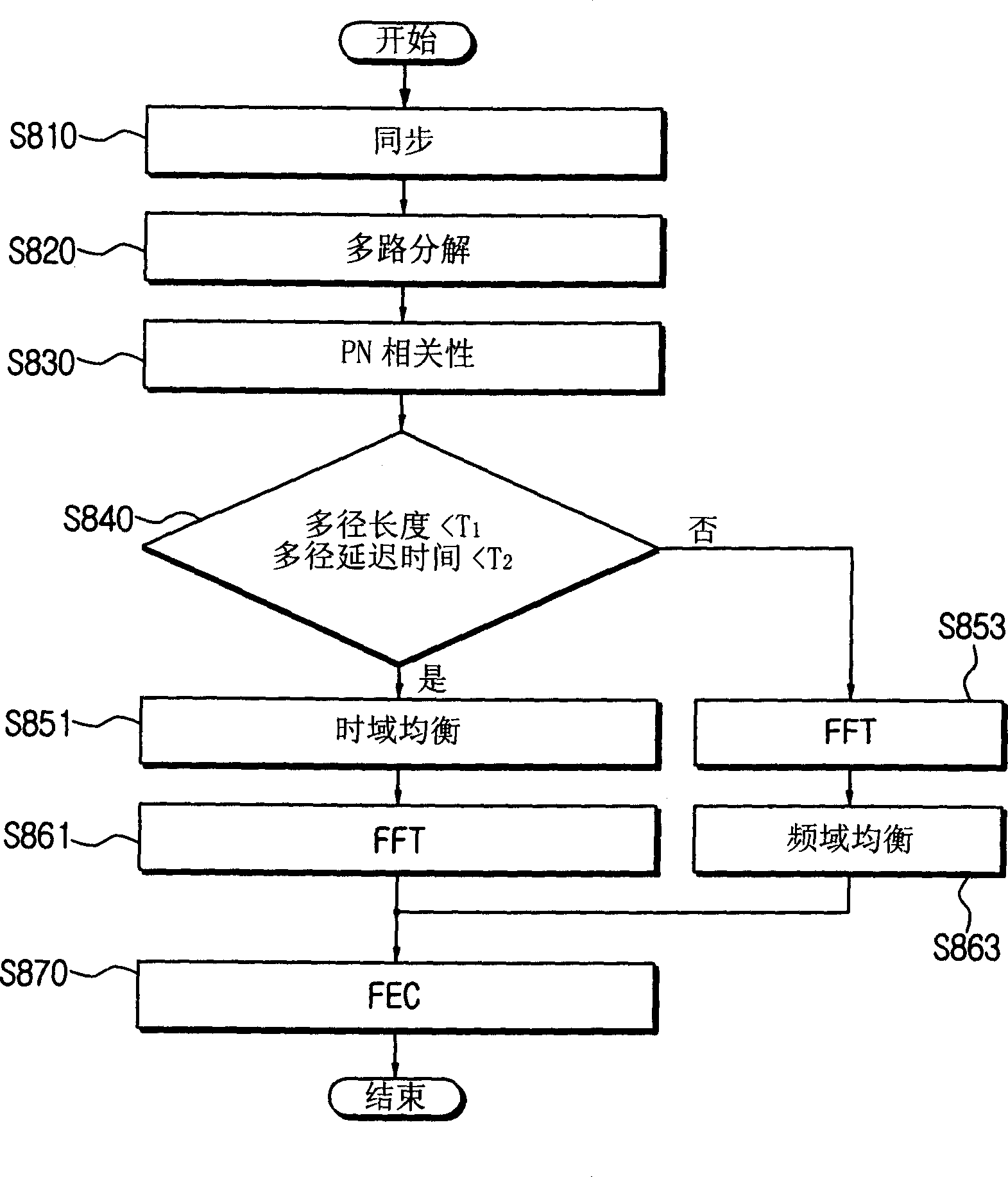
Time domain synchronous orthogonal frequency division multiplex receiving device and equalization method thereof
InactiveCN1574820AImprove receiving efficiencyTransmission control/equalisingEqualisersTime domainTime domain equalization
The invention relates to a TDS-OFDM receiving device using different equalizing methods according to channel status and a equalizing method, which comprises: a synchronous unit which is used to enable the OFDM signal according to the receiving of the antenna, transformation to baseband and the analog-digital conversion to be synchronous; a demultiplexer which is used to decompose the OFDM signal received from the synchronous element to a plurality of signals comprising the synchronous information and the OFDM code elements; a time domain equilibrium element which is used to use the OFDM code elements in the synchronous information equilibrium time domain; a first FFT unit which is used to transform the correlation of the synchronous information by the FFT; a second FFT unit which is used to transform the OFDM code elements by the FFT; a frequency domain equilibrium unit which is used to use the correlation of the synchronous information transformed in the first FFT unit to balance the OFDM code elements transformed in the second FFT unit; and a channel state confirmation unit which is used to calculate the correlation of the synchronous information to estimate the channel state, and choose one of the time domain equilibrium unit and the frequency domain equilibrium unit for equilibrium based on the estimated channel state. So the receiving function is improved by choosing one of the time and the frequency domain equilibrium units according to channel state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for carrying out equalization on 100M magnitude broadband reception signal
InactiveCN102594374AImprove adaptabilityHigh speedEnergy efficient ICTTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalizationTime domain equalization
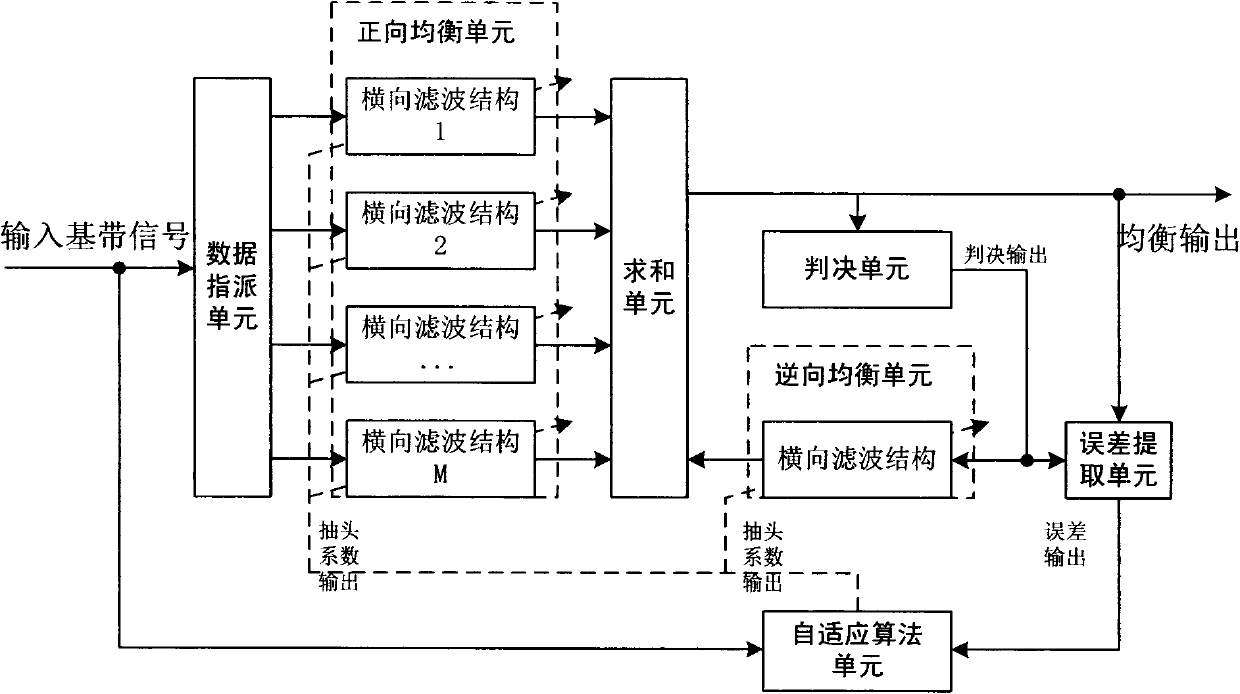
The invention provides a method for carrying out equalization on a 100M magnitude broadband reception signal, and is aimed at providing a method for using a simple time domain parallel structure to carry out time domain equalization on the broadband signal with small resource consumption, a fast operation speed, and no need of changing a transmission system. The method is realized through the following technical scheme: (1) employing a fraction interval adaptive blind equalization digital logic circuit with decision feedback, and receiving over-sampling baseband signal to be equalized in parallel; (2) carrying out addition of output of all transverse filtering structures as equalization output, and sending the baseband signal to be equalized into the transverse filtering structures in a forward direction equalization unit according to a corresponding phase relationship; (3) judging an equalization output result with a decision unit, and solving an error signal e(n) of the output result and a decision result; after e(n) is adjusted through an error convergence factor, carrying out gradient estimation and equalization coefficient updating, and sending an updated equalization coefficient to each transverse filtering structure to carry out an equalization operation. According to the method, contradiction between generating the equalization results and carrying out the equalization coefficient updating simultaneously in a code element is solved.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Systems and methods for frequency domain realization of non-integer fractionally spaced time domain equalization
Various systems and methods are described for performing fractionally spaced time domain equalization (TEQ). One embodiment is a method implemented in a communication system for training a fractionally spaced time domain equalizer (TEQ). The method comprises performing an initialization phase, averaging a received signal in the system to reduce effects of noise in a channel, determining a channel estimate, and aligning an ideal reference signal with the received signal. The method further comprises updating a target response filter according to a non-integer multiple of a base sampling rate, determining an adaptation error based on useful information both inside and outside a Nyquist band of the TEQ, and updating the TEQ according to the adaptation error.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
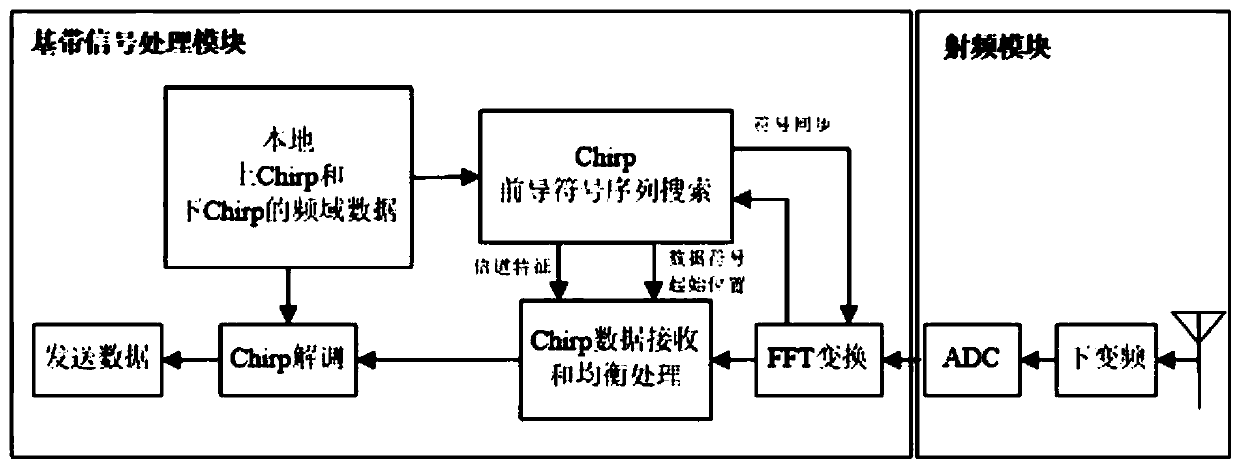
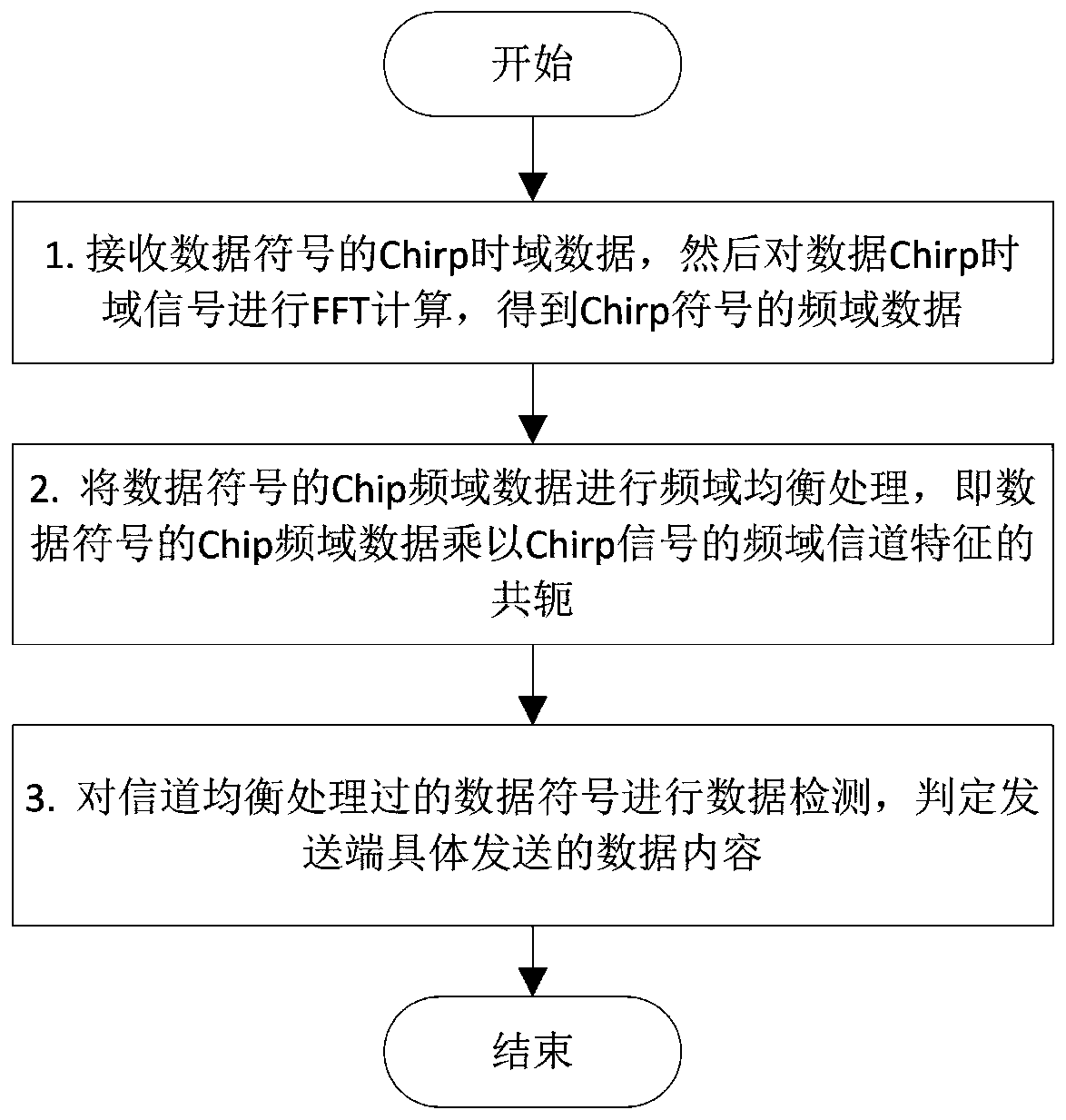
Channel estimation and equalization method for Chirp modulation signals
ActiveCN110572337ASolve the problem of frequency selective fadingImprove accuracyChannel estimationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainFast Fourier transform
The invention relates to a channel estimation and equalization method for Chirp modulation signals, and belongs to the technical field of Internet of Things. In the Chirp signal receiving and transmitting process, due to the modulation characteristic of Chirp signals, the amplitude of signals received by a receiver is fixed, time domain equalization processing can be completed through automatic gain control (AGC), and therefore channel estimation and equalization cannot be conveniently and directly carried out on the received time domain Chirp signals. In the invention, the received time domain Chirp signal is firstly subjected to fast Fourier transform, and the time domain Chirp signal is transformed to the frequency domain for channel estimation and equalization, which is beneficial to solving the problem of frequency selective fading in the wireless channel.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
OFDM transceiver structure with time-domain scrambling
InactiveUS7564906B2Suppression of interference effectsSame peak data rateSpectral gaps assessmentEqualisersTime domainTransceiver
A method and transceiver for wireless multicarrier communications. At the transmitter side, conventional OFDM symbols, after inverse fast Fourier Transform, are scrambled in time domain and then guard-interval (GI) inserted, up-converted at the carrier frequency for transmission. At the receiver side, after GI removal and frequency domain channel equalization, the received signal is transformed into time-domain by inverse fast Fourier Transform. The time-domain equalized signal is descrambled in time domain and then transformed back to the frequency domain before it is rate-matched, demodulated and decoded. This time-domain scrambling and descrambling method can be used in a wireless OFDM system such as WLAN, cellular OFDM, and MC-CDMA.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Audio equalizing method and device
InactiveCN101567673AAvoid the disadvantages of the applicationImprove sound qualityTone controlTime domainTime domain equalization
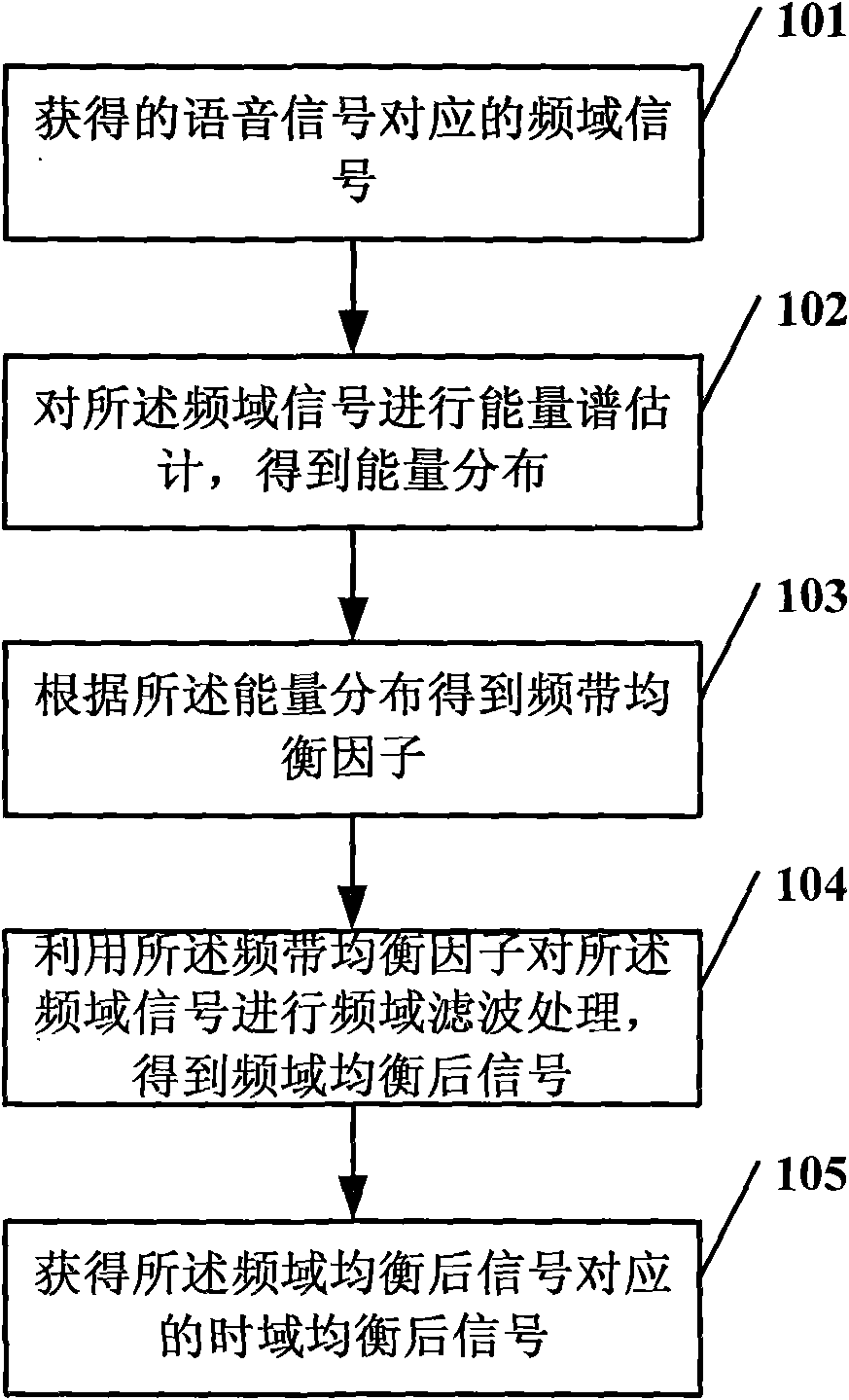
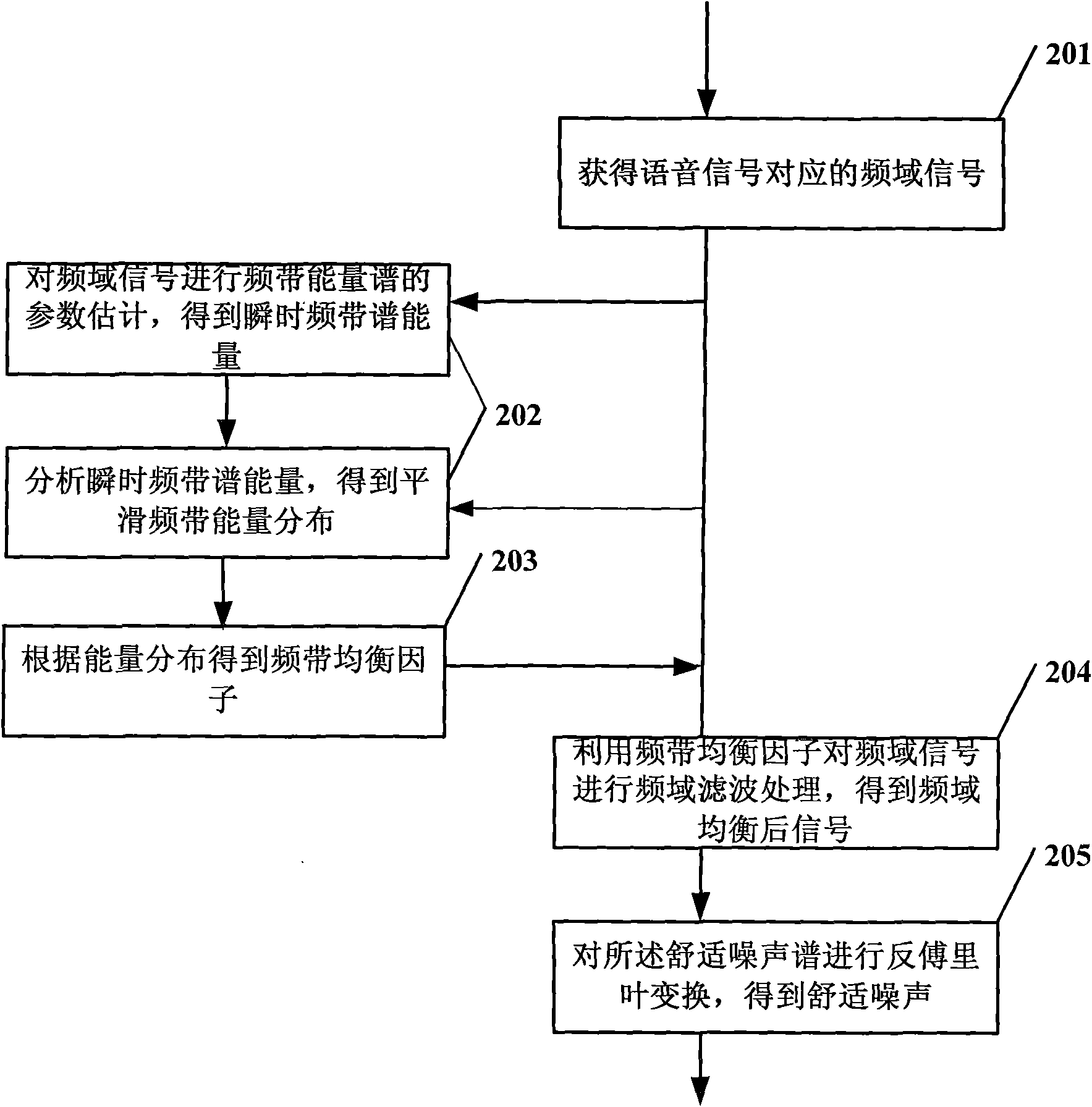
The invention embodiment relates to an audio equalizing method, which includes the following steps: executing energy spectrum estimation for frequency domain signal corresponding to the obtained speech signal, obtaining energy distribution, and then obtaining frequency band equalizing factor according to the energy distribution, executing frequency domain filtering process for the frequency domain signal using the frequency band equalizing factor, obtaining the signal after frequency domain equalization, obtaining signal after time-domain equalization corresponding to the signal after frequency domain equalization. In addition, the invention embodiment also provides an audio equalizing device. The invention embodiment can avoid application disadvantage of pattern equalizing technique in speech signal environment with dynamic real time variation, thereby compensating or strengthening speech signal corresponding to certain frequency band, and has the advantages of superior acoustic quality, simplicity and practicality and remarkable effect.
Owner:深圳市顺畅声学科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com