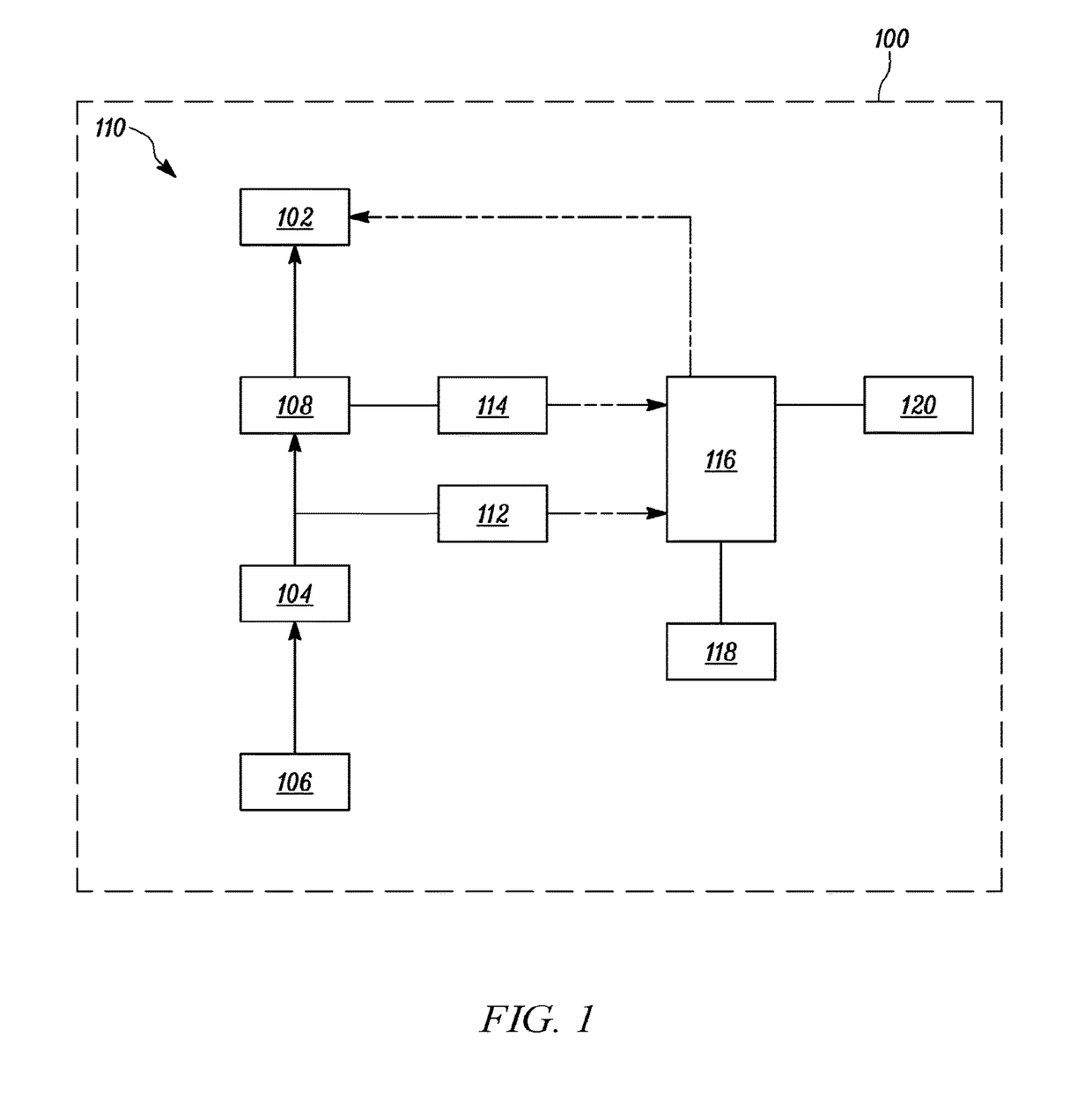
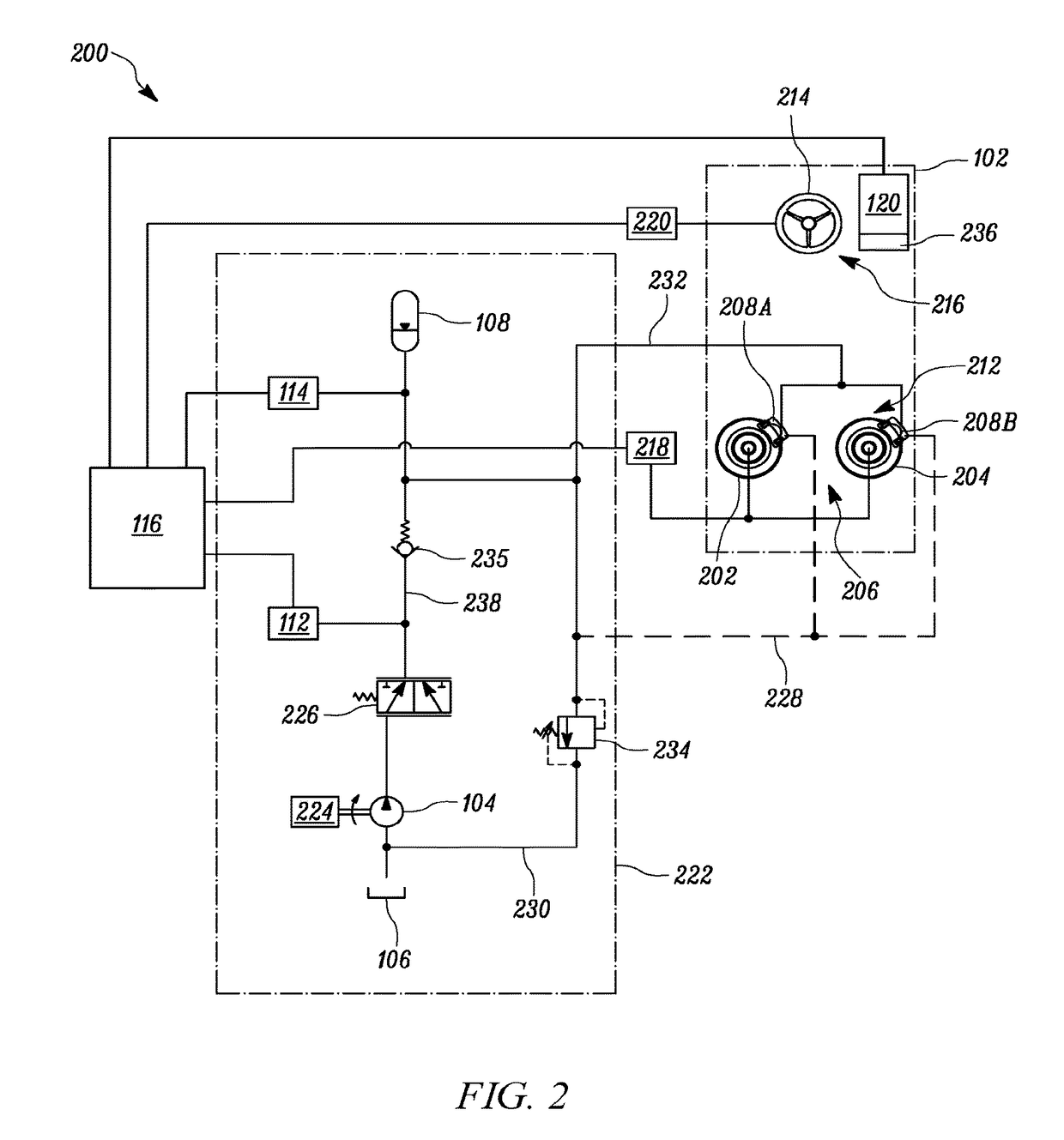
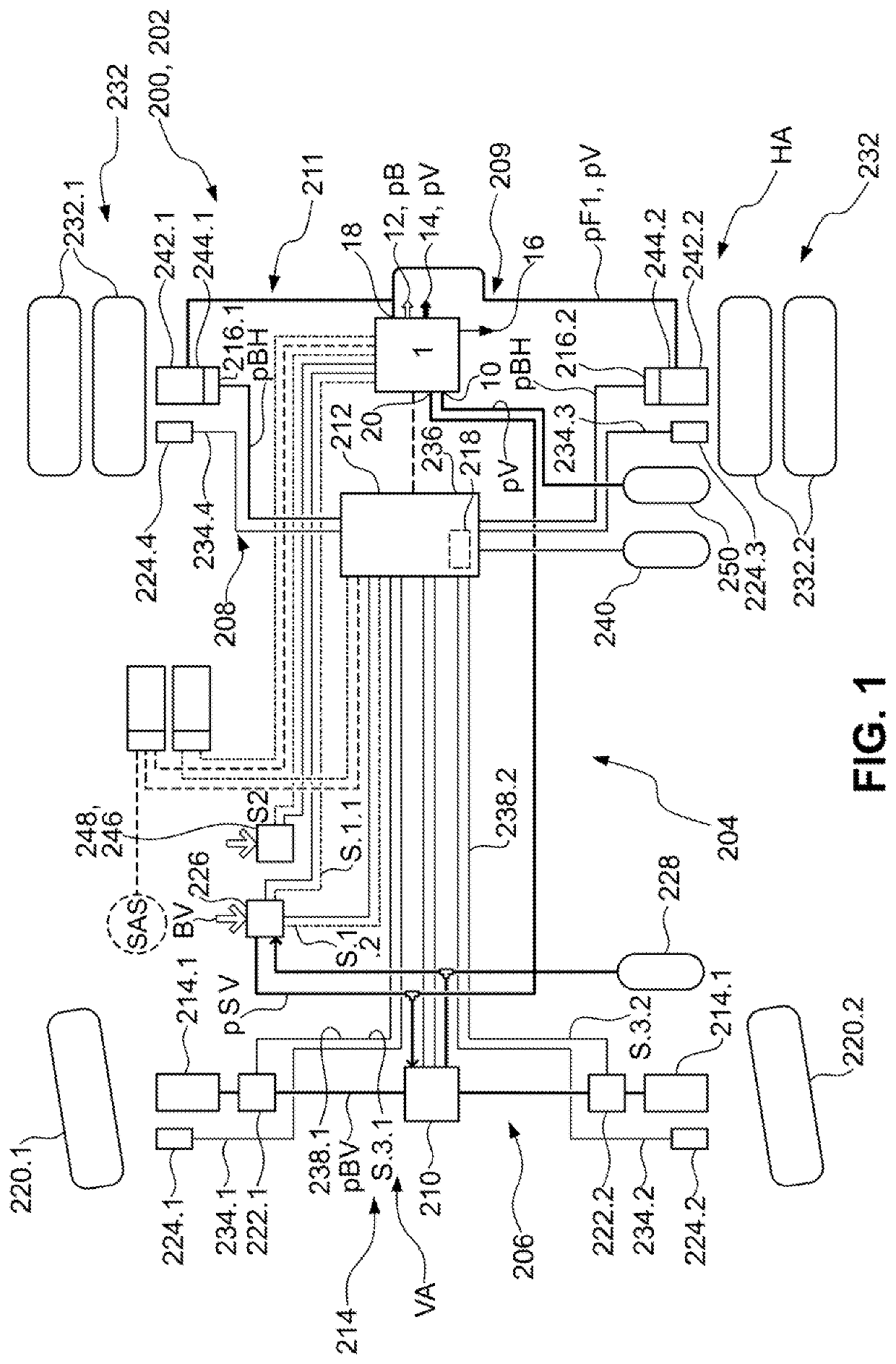
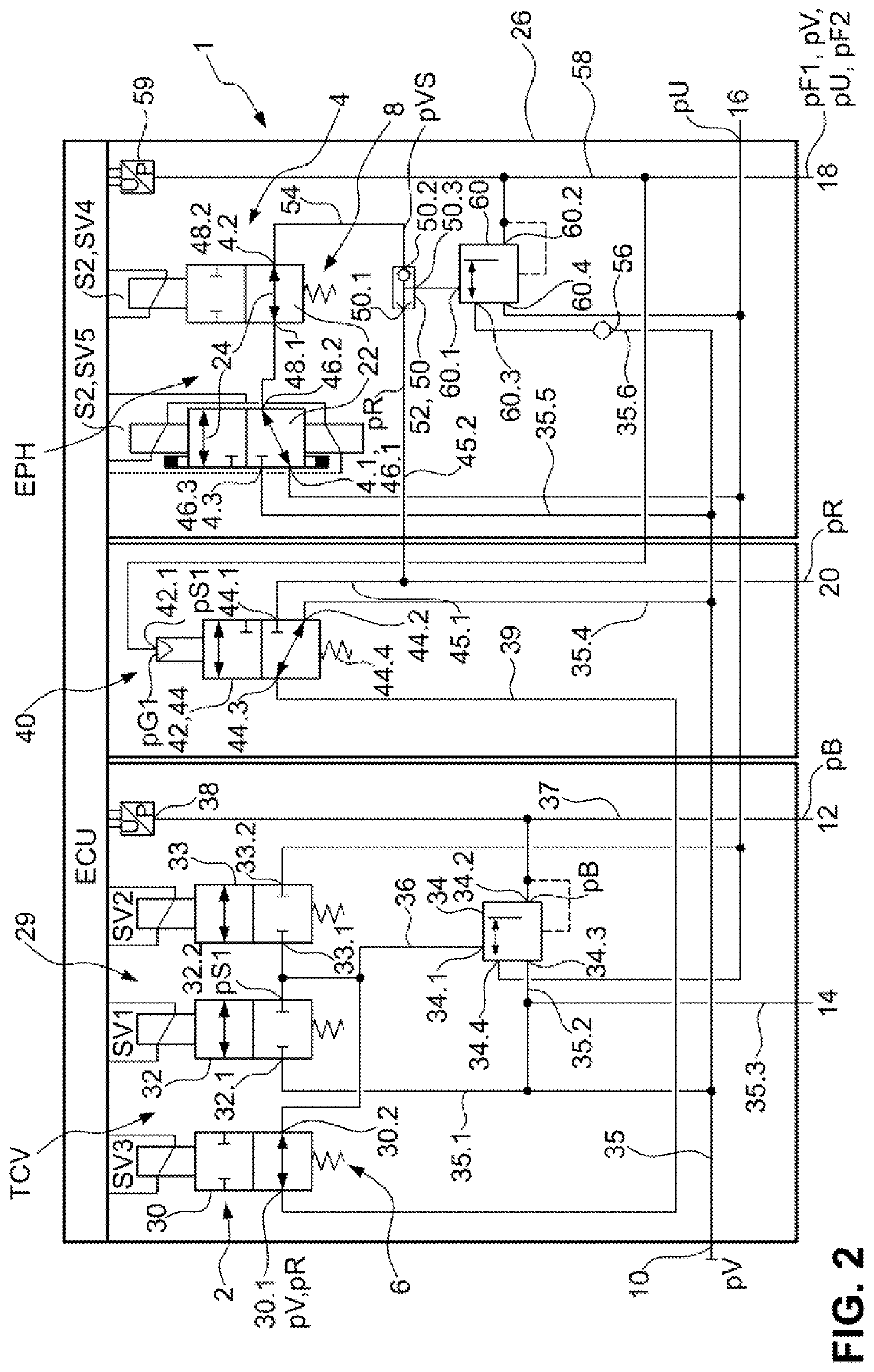
Patents
Literature
129results about "Braking pressure measurements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
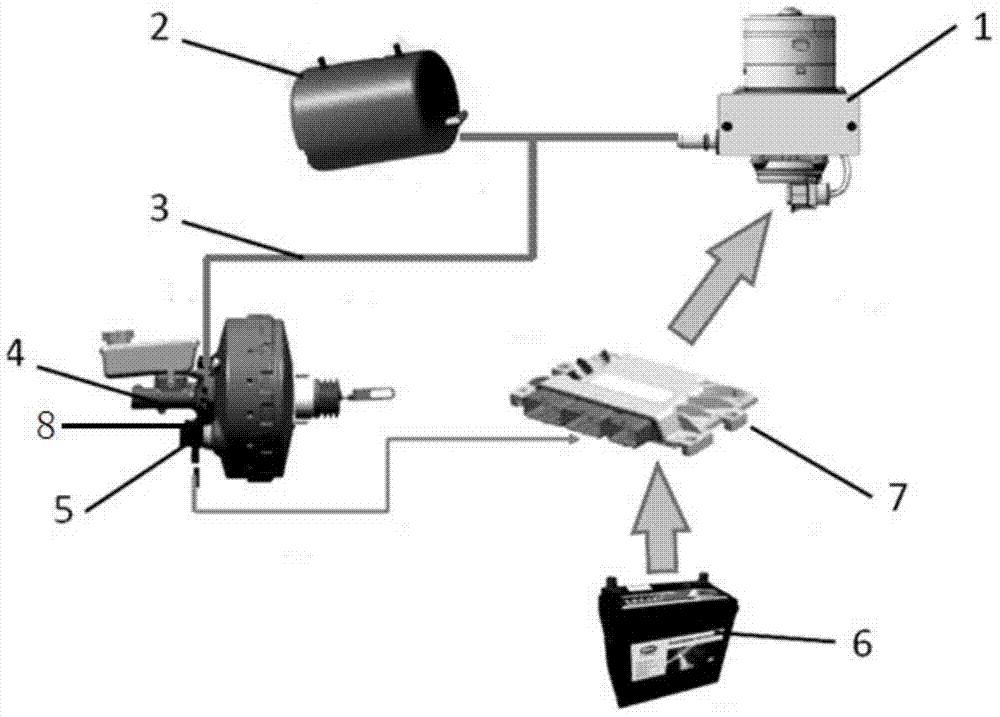
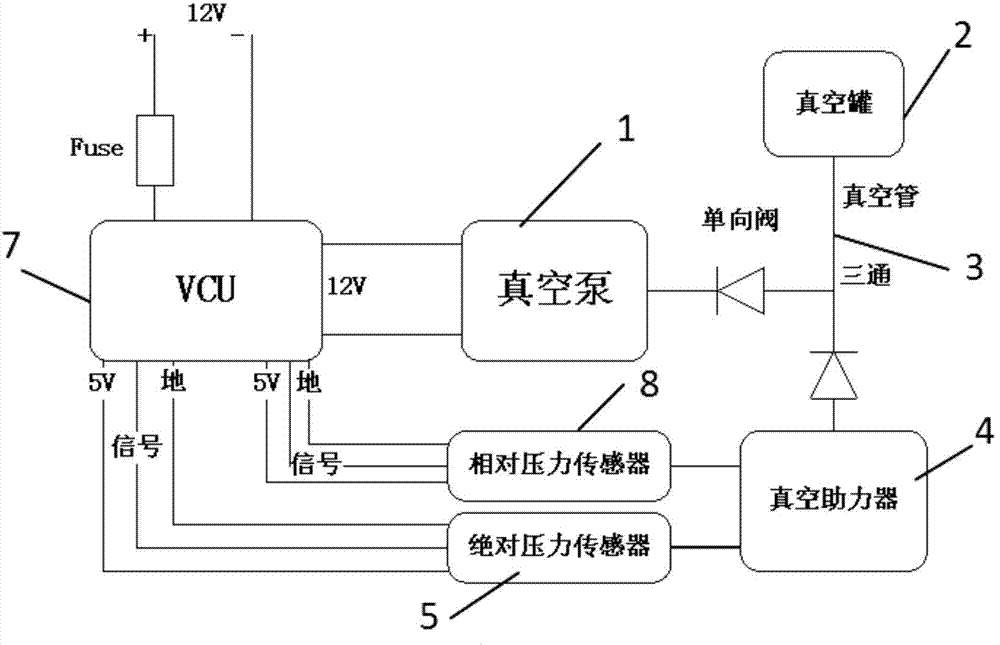
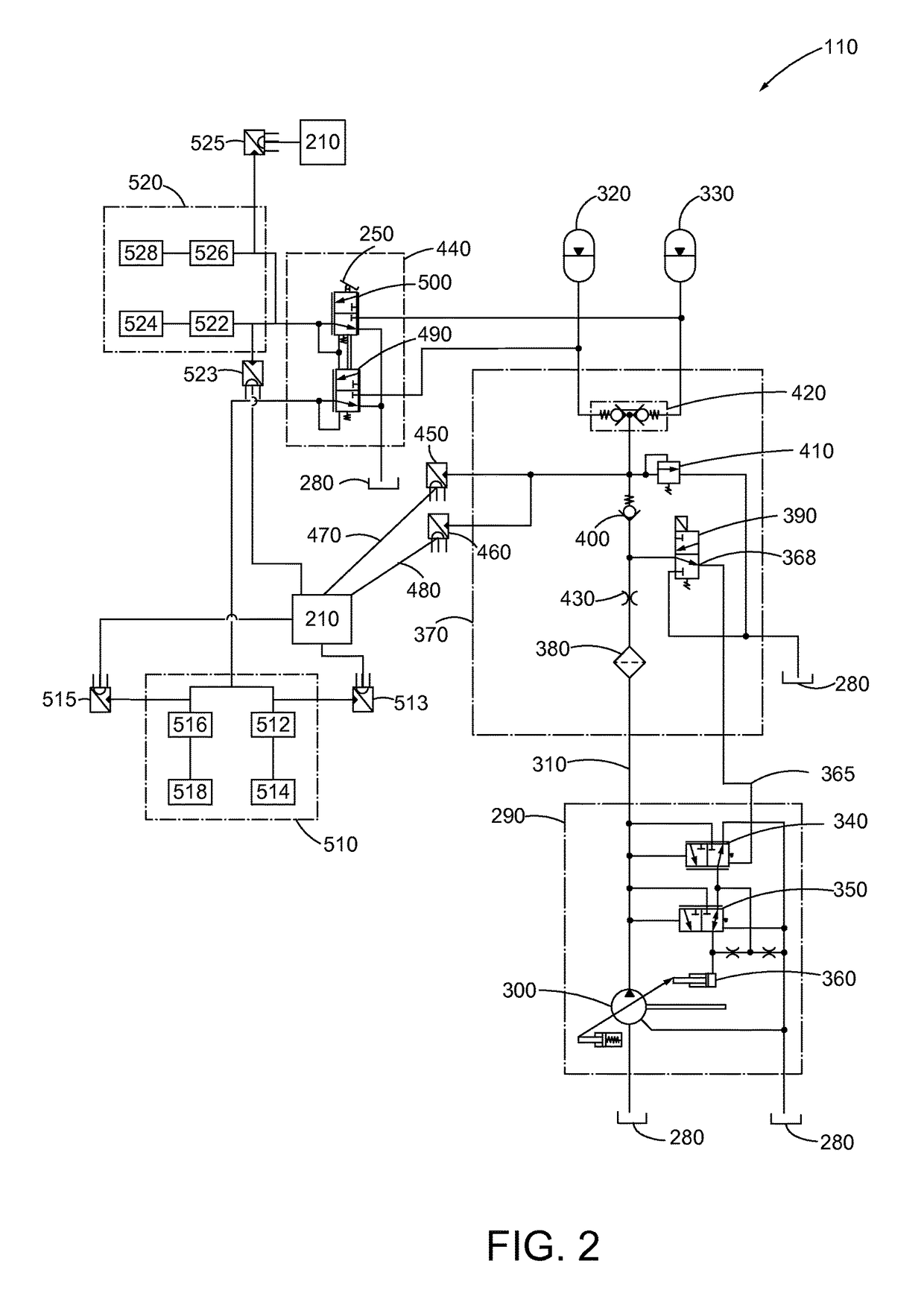
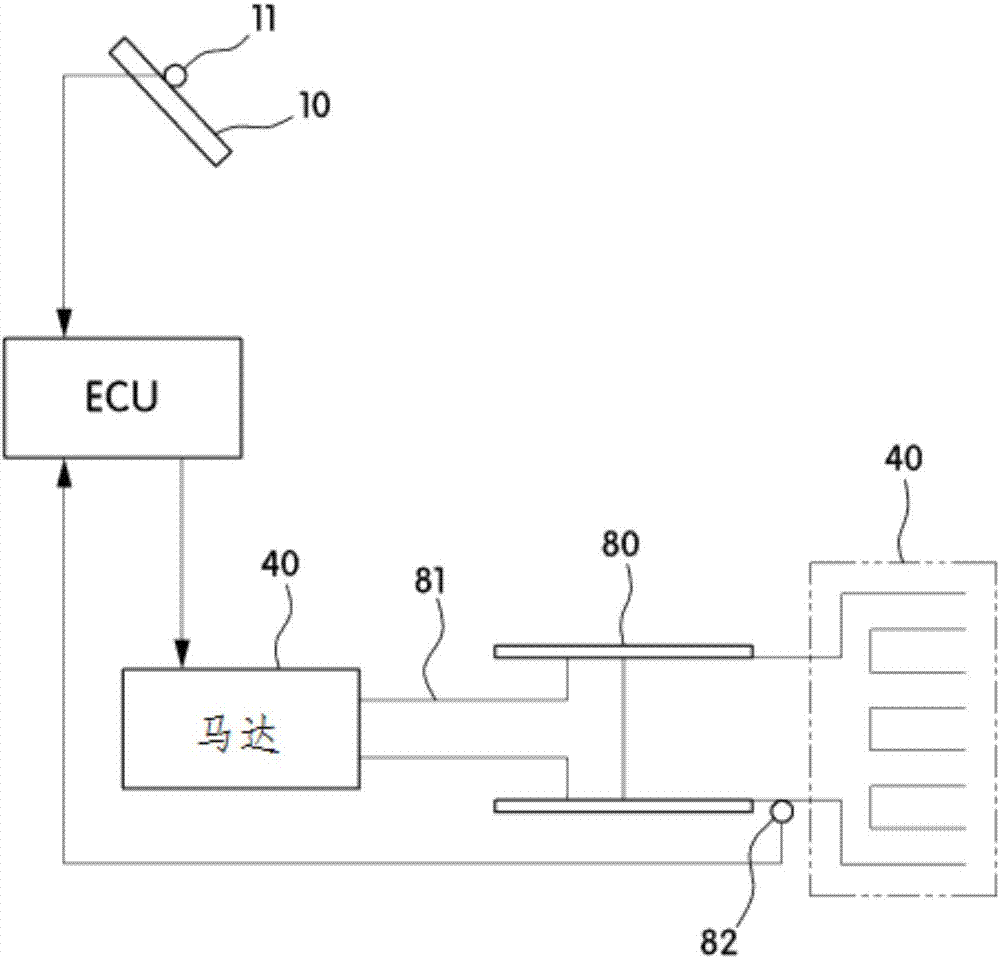
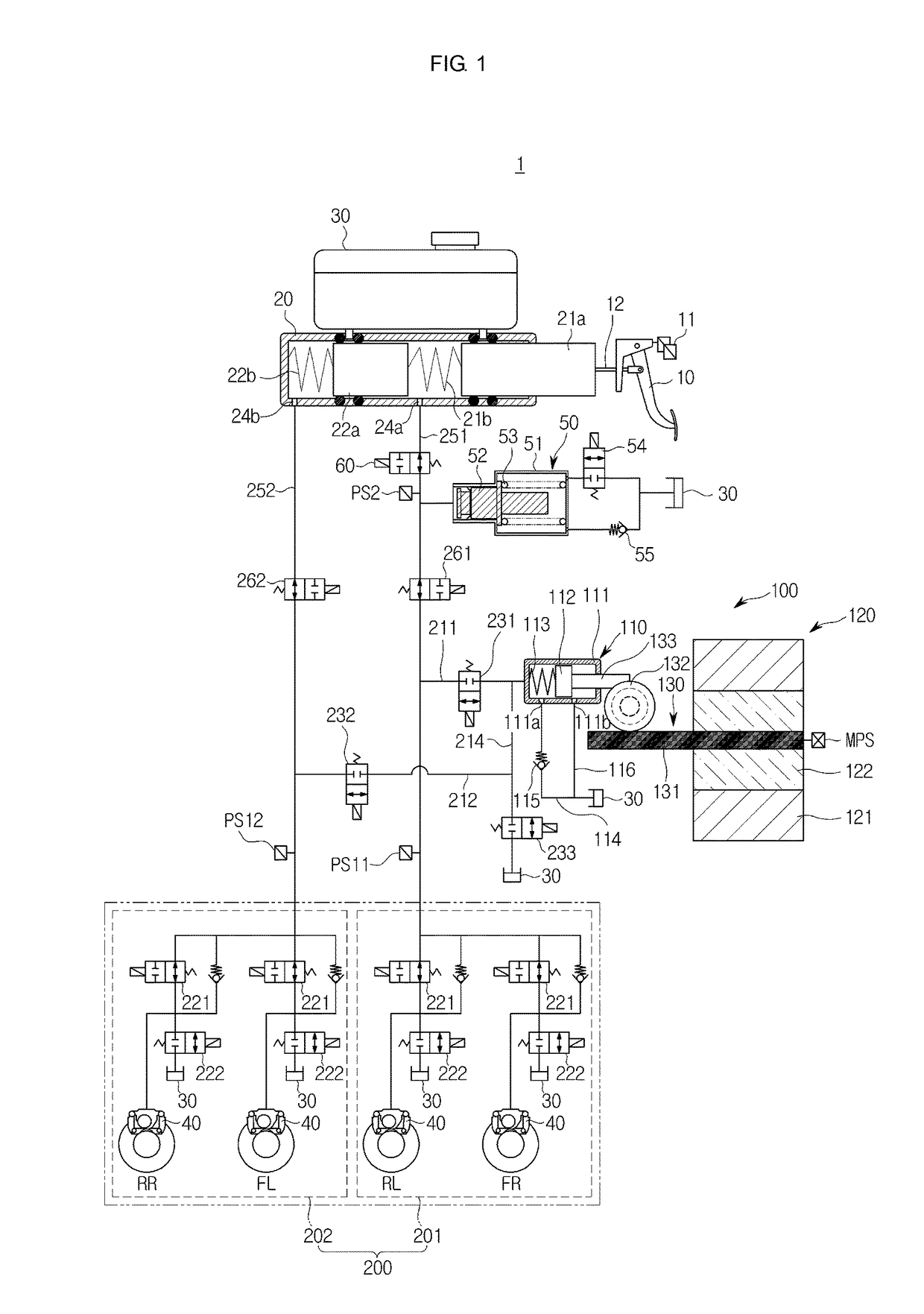
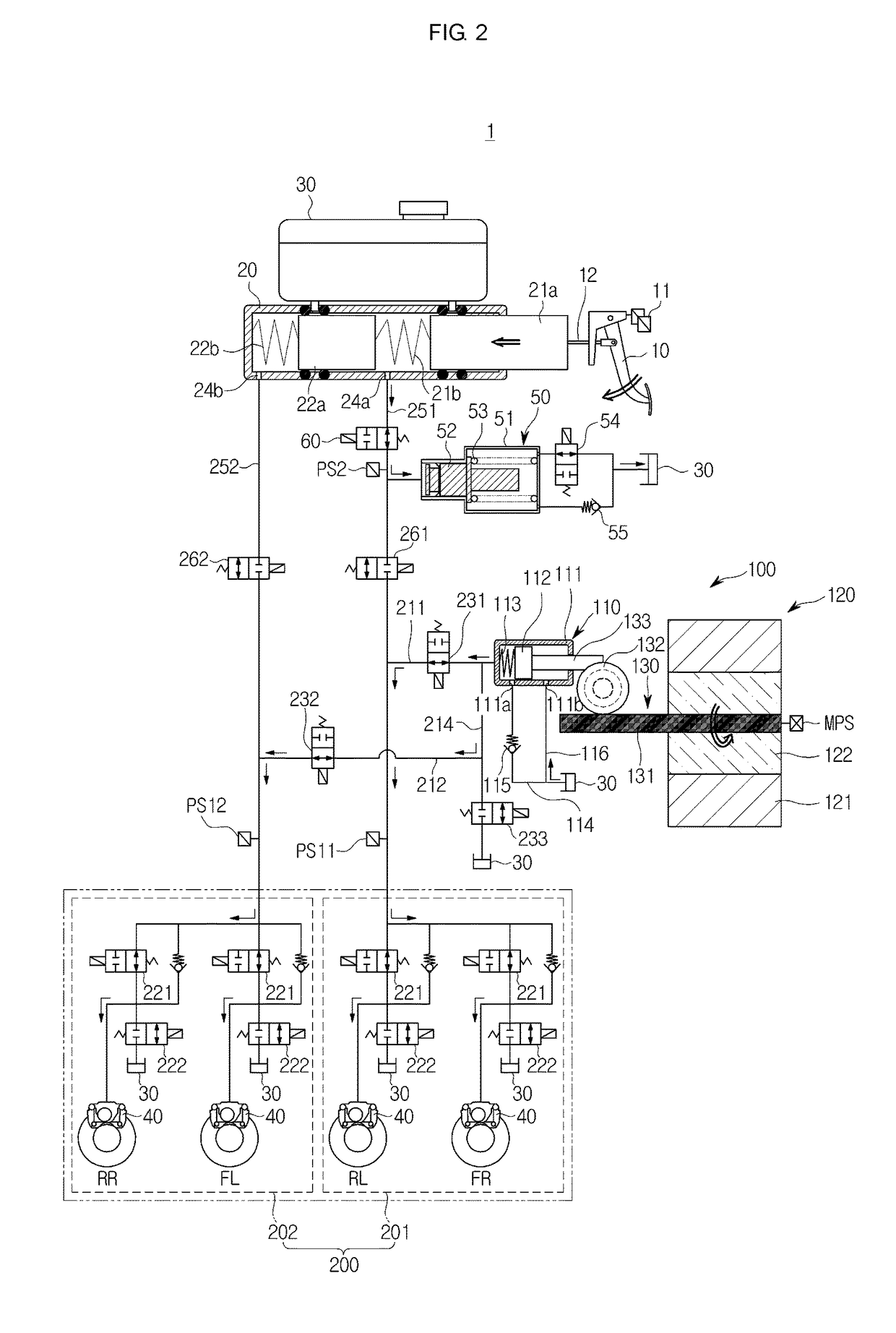
Vacuum booster system of electric automobile and pressure measurement method of system
ActiveCN104842987AAccurate measurementEfficient measurementBraking action transmissionBraking pressure measurementsRelative pressureAtmospheric pressure
An embodiment of the invention provides a vacuum booster system of an electric automobile and a pressure measurement method of the system. The system mainly includes that a relative pressure sensor and an absolute pressure sensor are oppositely arranged on a vacuum booster, sensor signals of the relative pressure sensor and the absolute pressure sensor are connected into a vehicle control unit through cables, and the relative pressure sensor and the absolute pressure sensor are used for measuring absolute pressure and atmospheric pressure in the vacuum booster system. According to the vacuum booster system of the electric automobile and the pressure measurement method of the system, the relative pressure sensor and the absolute pressure sensor are oppositely arranged on the vacuum booster, and the sensor signals are connected into the vehicle control unit, so that the absolute pressure and atmospheric pressure in the vacuum booster system of the electric automobile can be accurately and effectively measured, and by the aid of the redundant design of double sensors, the safety and reliability of the vacuum booster system of the electric automobile can be ensured.
Owner:BEIJING ELECTRIC VEHICLE
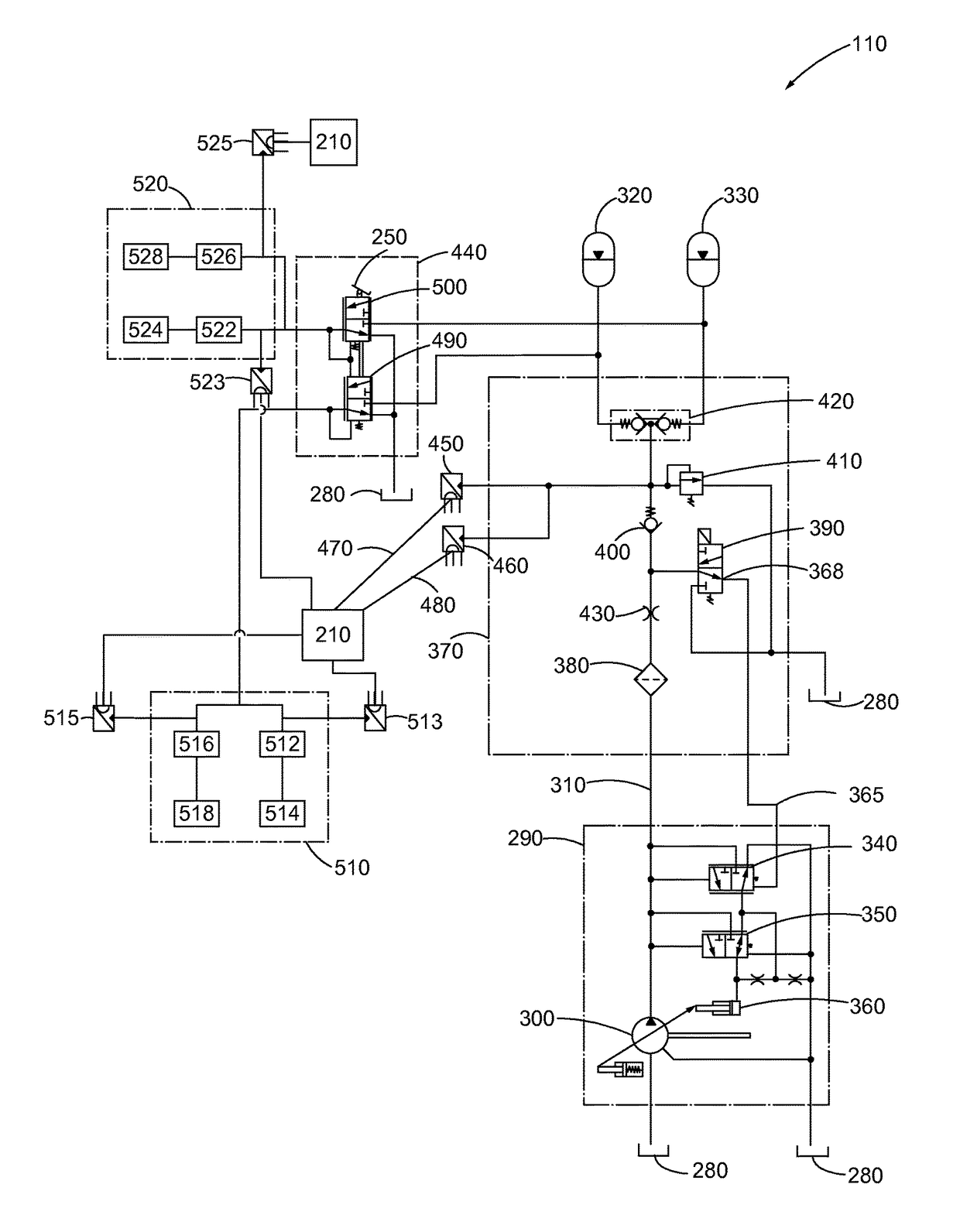
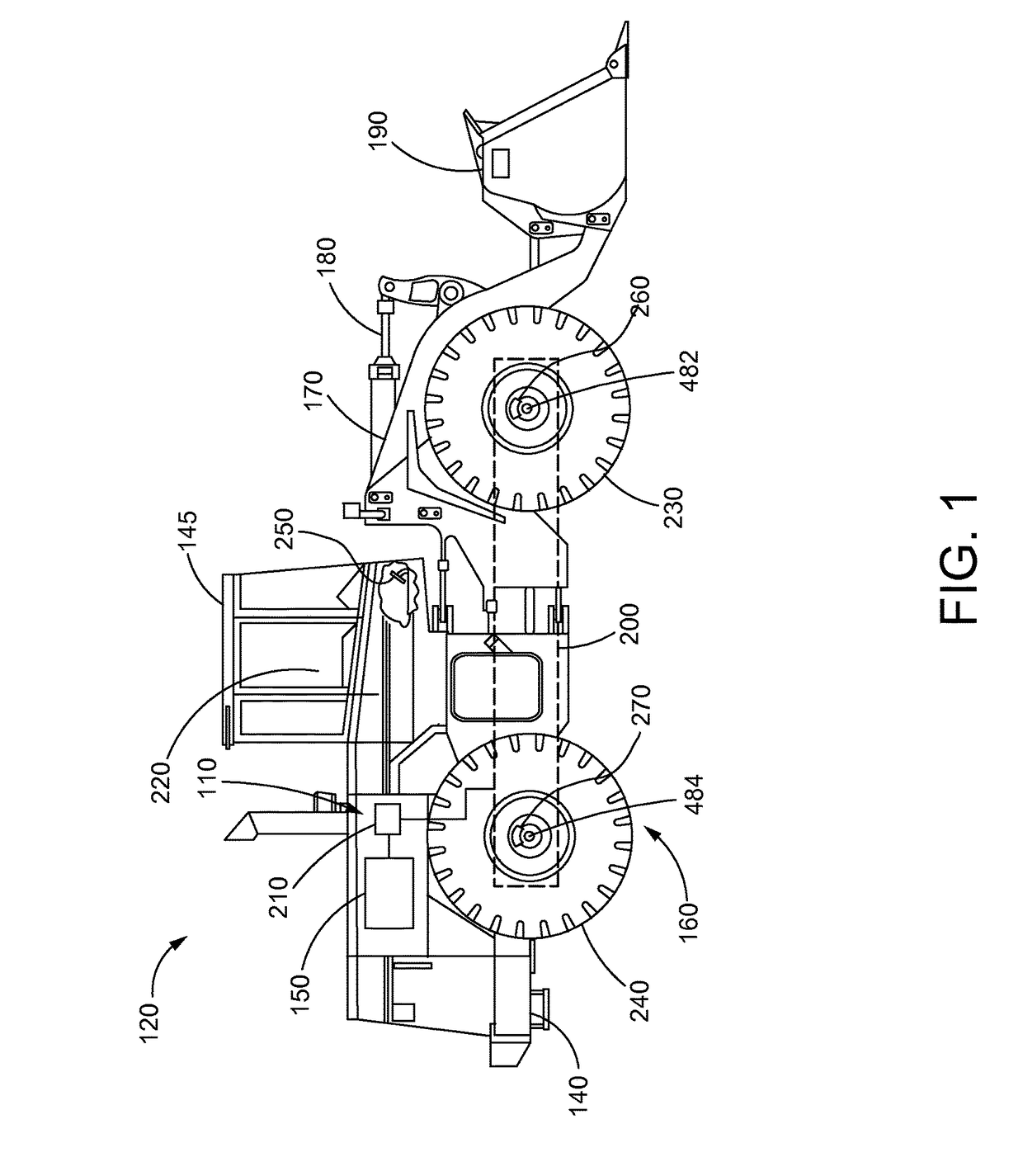
Brake Wear Analysis System
A brake wear analysis system is presented for use within a work machine. The brake wear analysis system includes a brake charge system as well as at least one accumulator connected to the brake charge system. The at least one accumulator operable to flow a fluid from the accumulator to a brake control valve based on an executed braking action. A change of pressure within the at least one accumulator being received by a pressure sensor connected to the brake charge system and transmitted to a brake wear analysis module within the controller of the work machine. The brake wear analysis module being configured to compare the flow of fluid from the at least one accumulator with a predetermined condition resulting in a determination of whether or not a braking mechanism of the work machine is functioning in a worn condition.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Locomotive brake control system and method
ActiveCN111634304ATo achieve mutual cooperationHigh control precisionAerodynamic brakesRail brake actuationControl systemCylinder pressure
The invention belongs to the field of locomotive brake control and relates to a locomotive brake control system and control method. The locomotive brake control system comprises an average pipe control system and a brake cylinder control system, wherein the average pipe control system can compare the brake cylinder pre-control pressure with the average pipe pre-control pressure, and outputs a large pressure as the average pipe pressure, the brake cylinder control system can compare the brake cylinder pre-control pressure with the average pipe pressure and output large pressure to serve as thebrake cylinder pressure to achieve braking. The locomotive brake control system is advantaged in that redundancy of two control systems can be realized.
Owner:CRRC QINGDAO SIFANG ROLLING STOCK RES INST +1
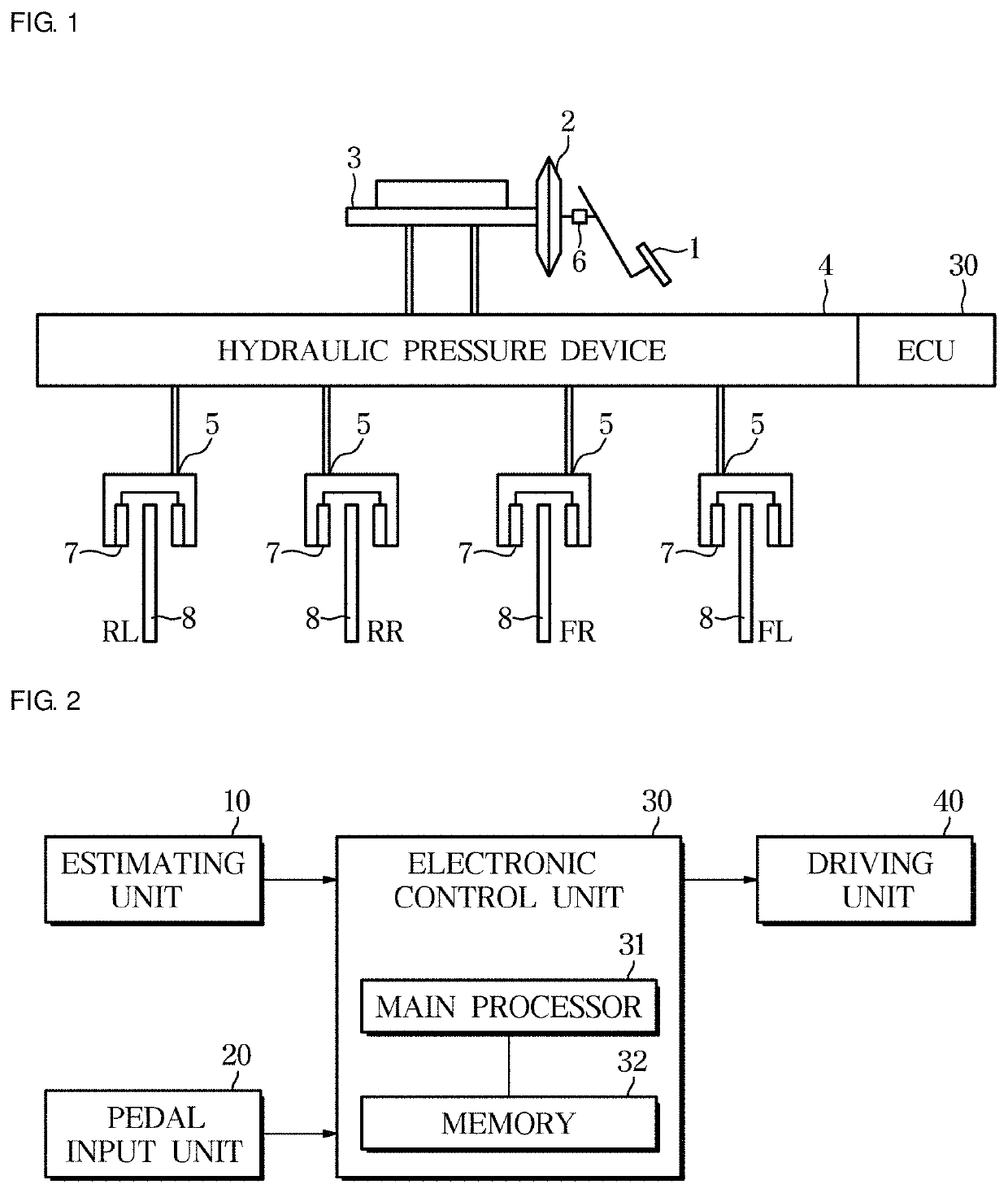
Electronic brake system
ActiveUS20190092174A1Braking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionDriver/operatorBraking system
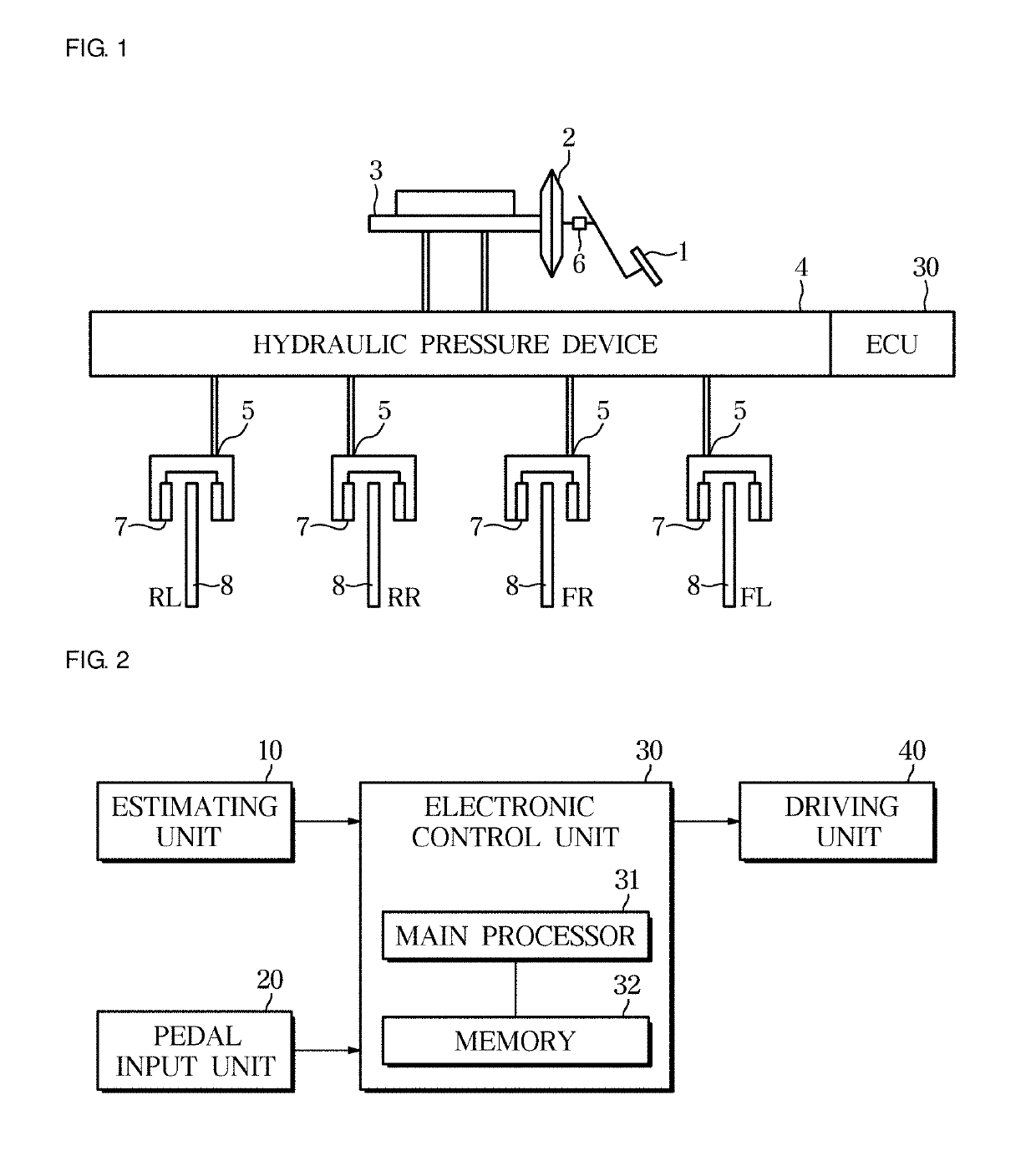
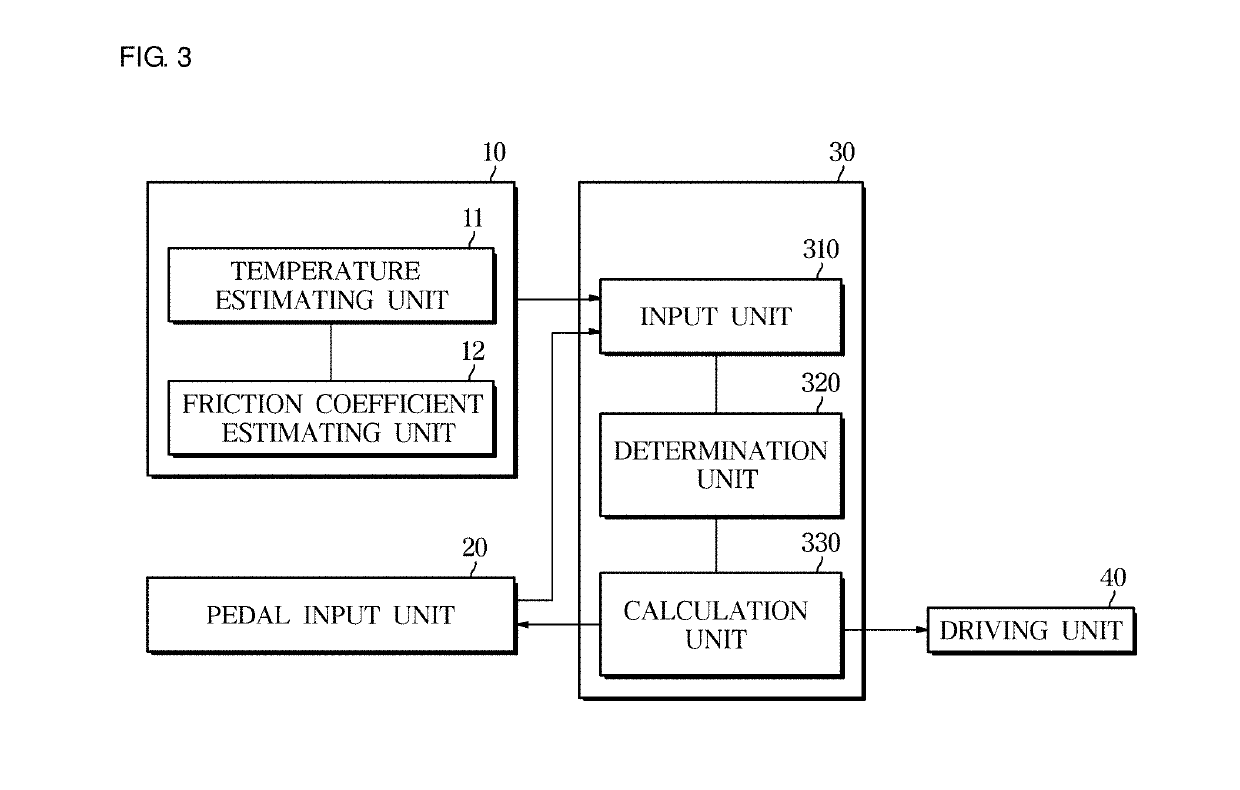
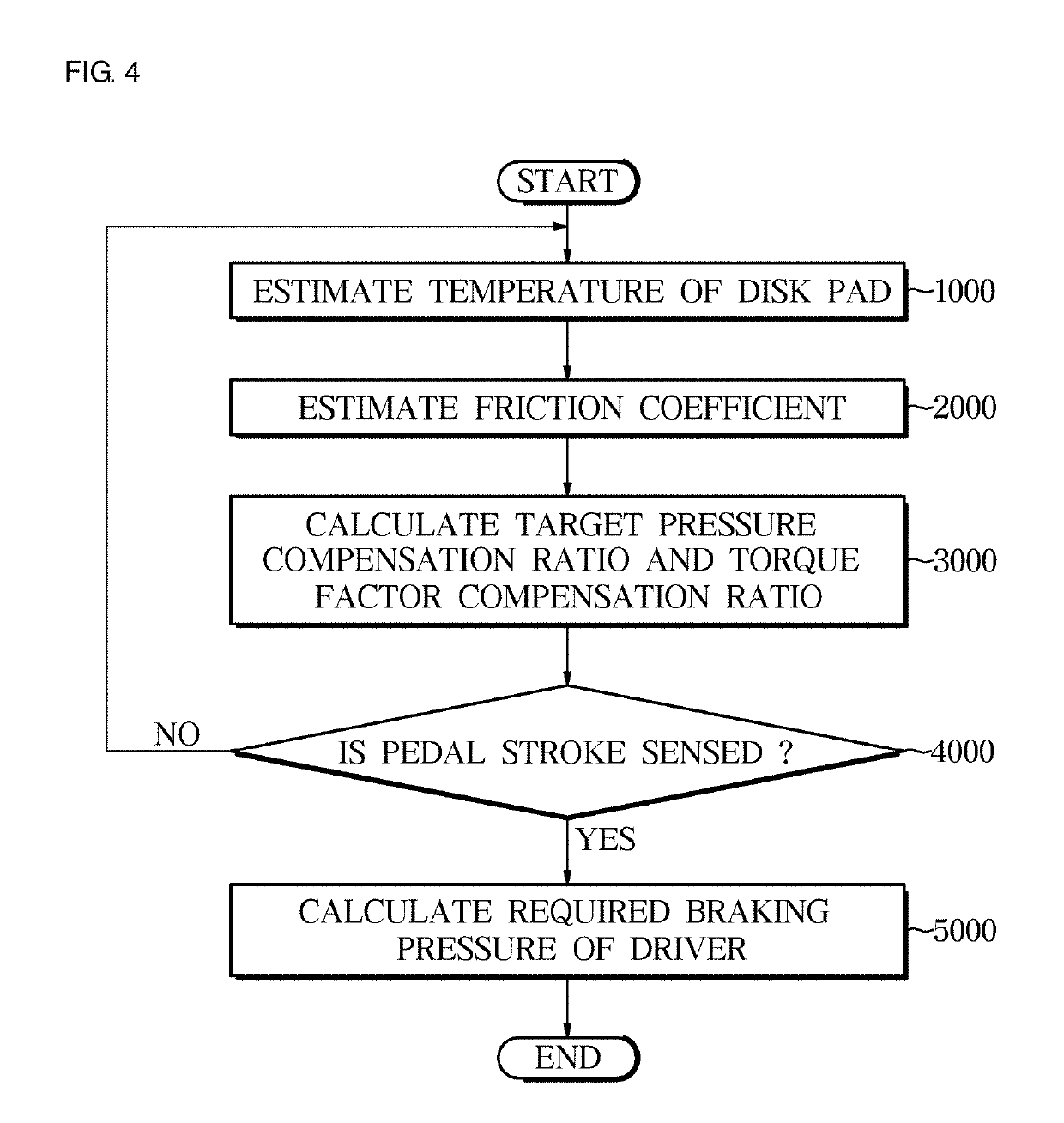
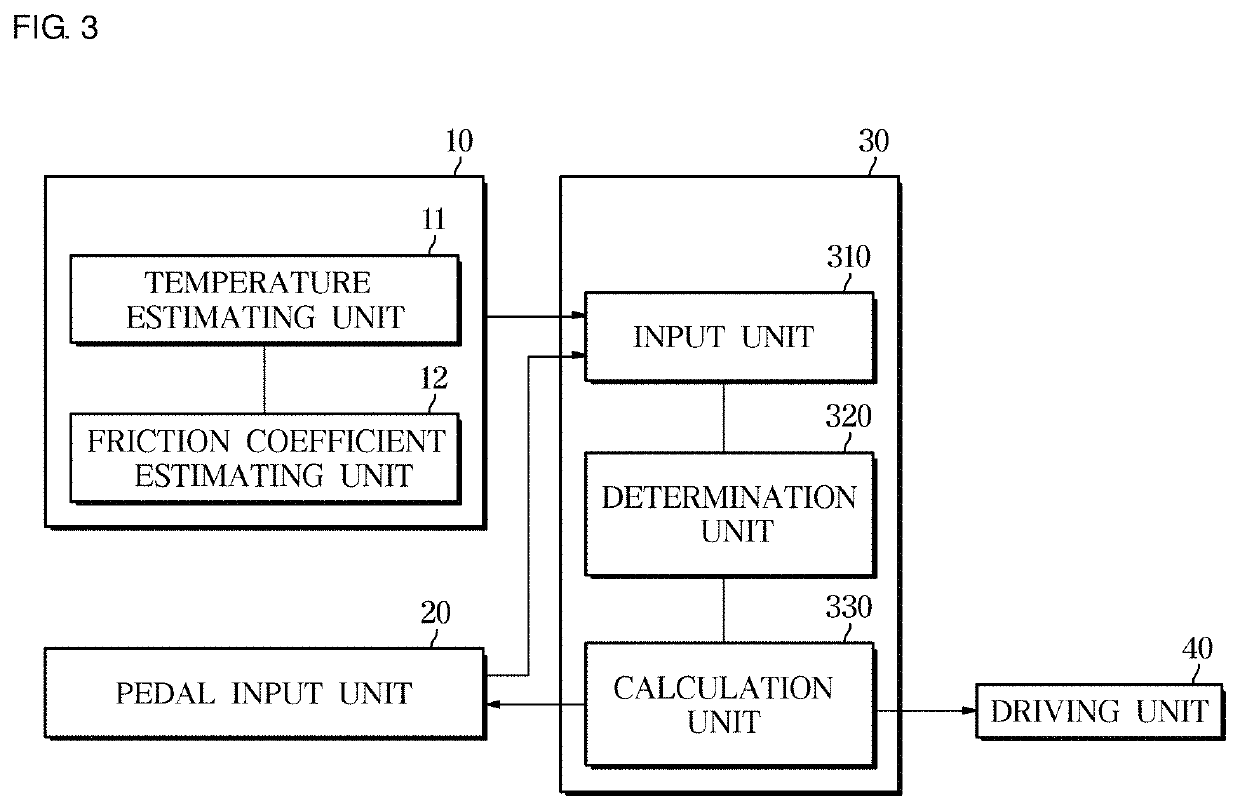
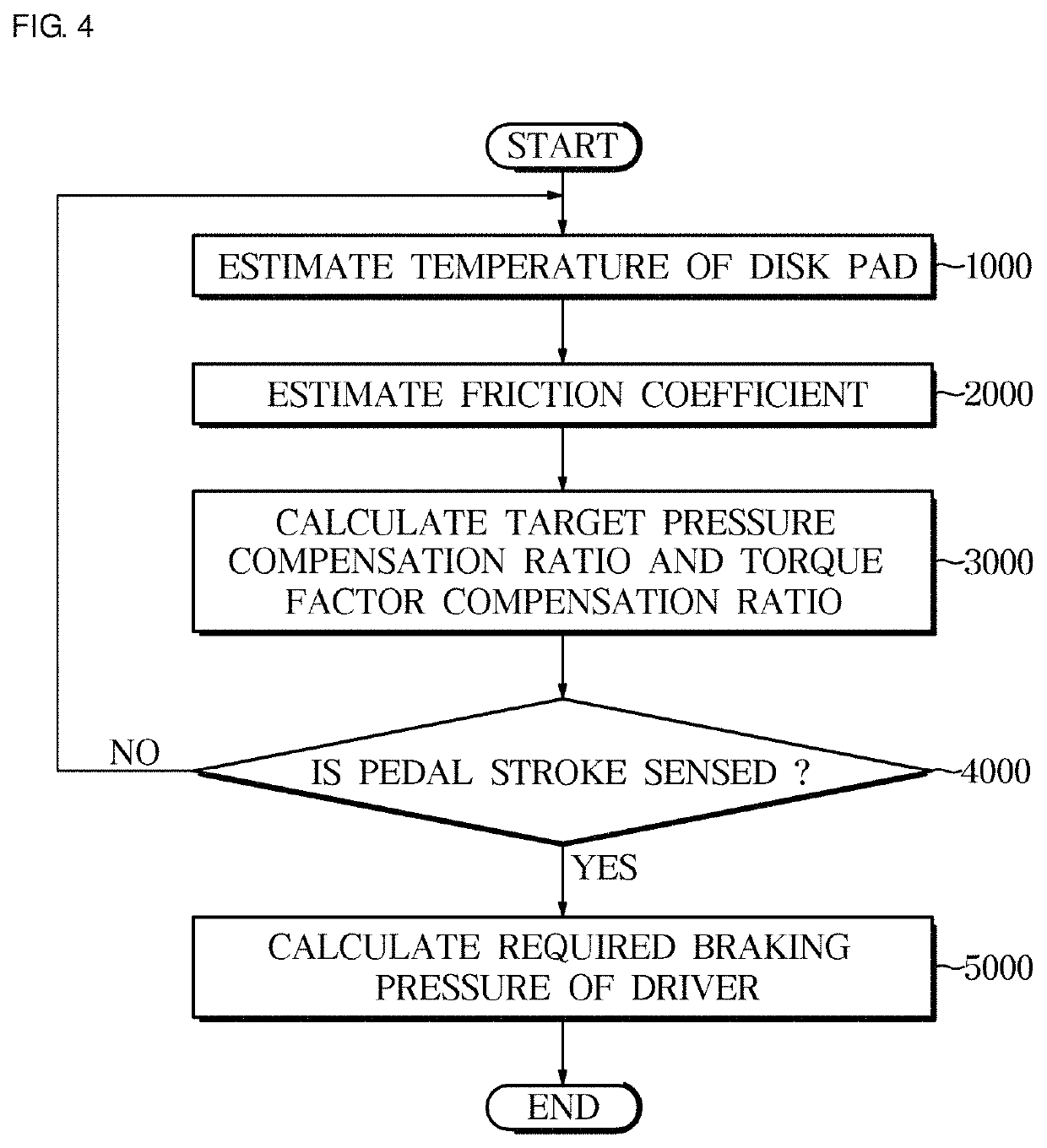
Provided are an electronic brake system and a method of controlling the same. The electronic brake system includes a pedal input unit configured to receive a pedal force according to a driver's braking intention, an estimating unit configured to estimate a temperature and a friction coefficient of a brake disk pad, and a control unit configured to correct a braking target pressure according to the driver's braking intention on the basis of the estimated temperature and friction coefficient of the brake disk pad.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Apparatus and method for controlling braking pressure of powered booster brake system
ActiveCN107444381AReduce computing loadImprove controllabilityBraking action transmissionPump/compressor arrangementsControl theoryMechanical engineering
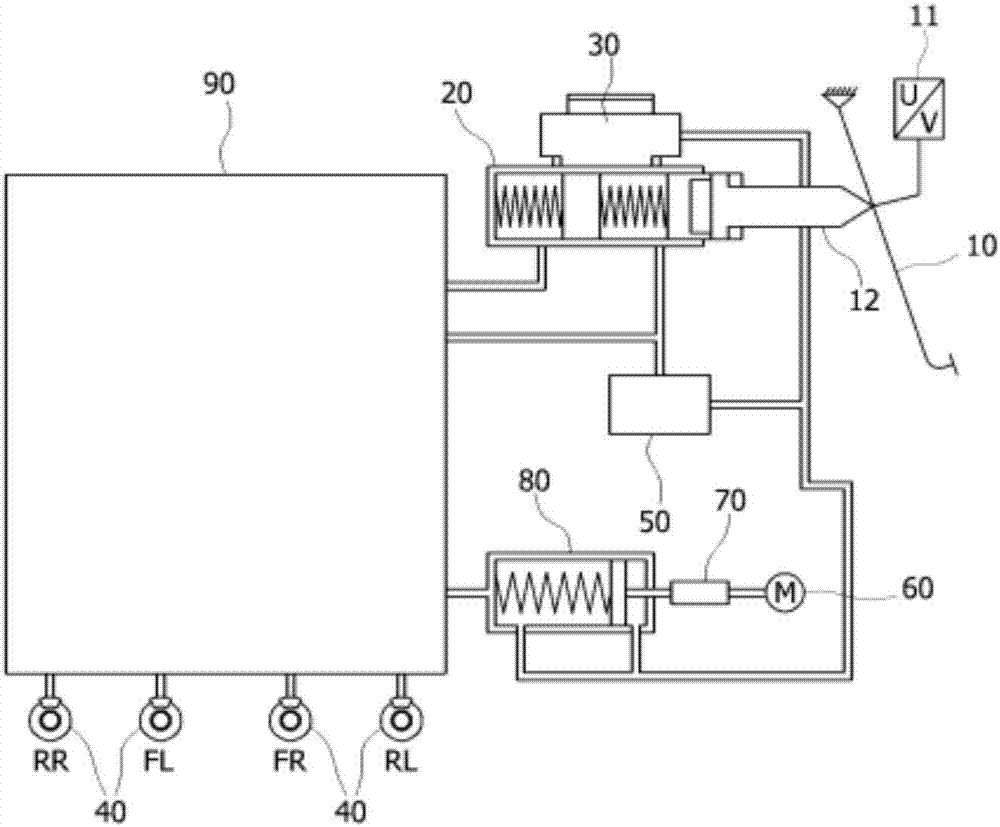
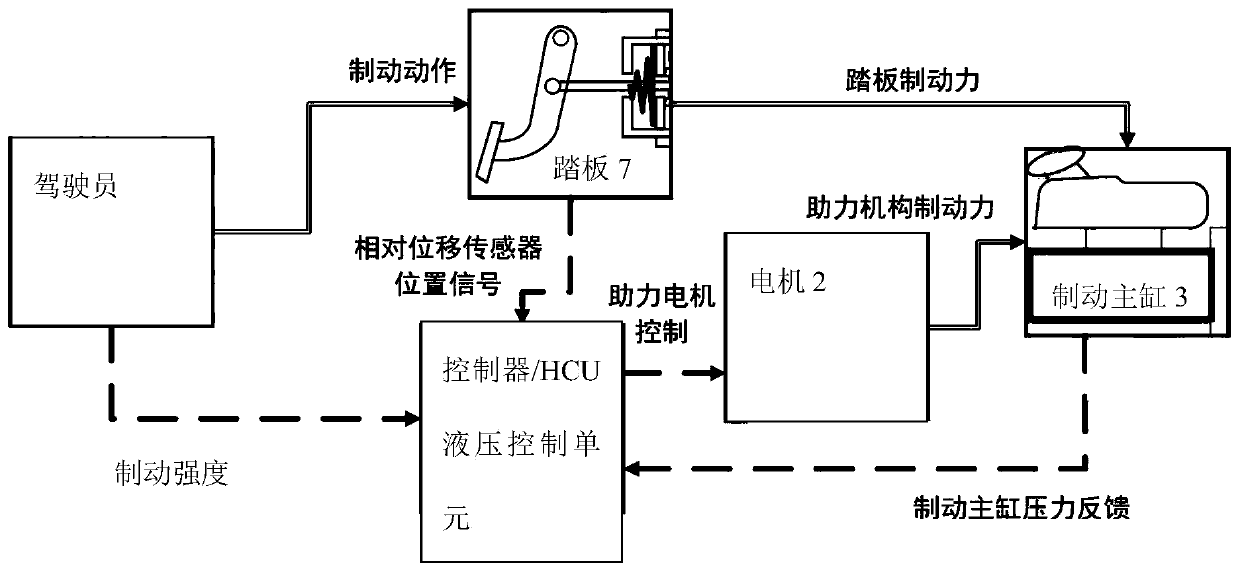
The present disclosure relates to an apparatus and a method for controlling a braking pressure of a powered booster brake system, the apparatus including a pedal stroke sensor configured to detect a manipulation degree of a brake pedal; an electronic control unit (ECU) configured to calculate a braking pressure using the detection result of the pedal stroke sensor; and a motor configured to move a piston inside a pump to perform a braking operation under control of the ECU, wherein the ECU determines a first position of the piston, which corresponds to the braking pressure, and controls the motor on the basis of a position of the piston.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
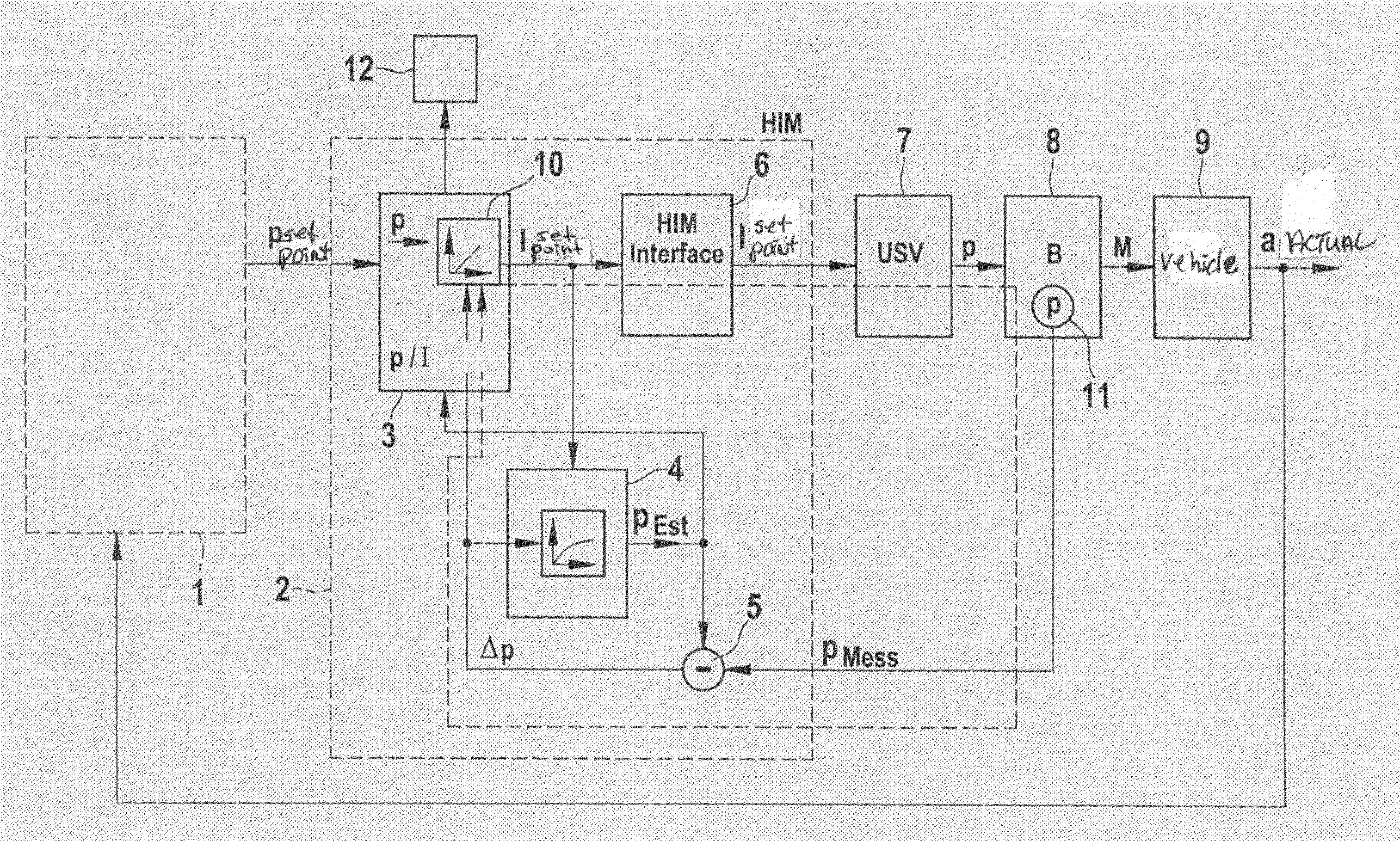
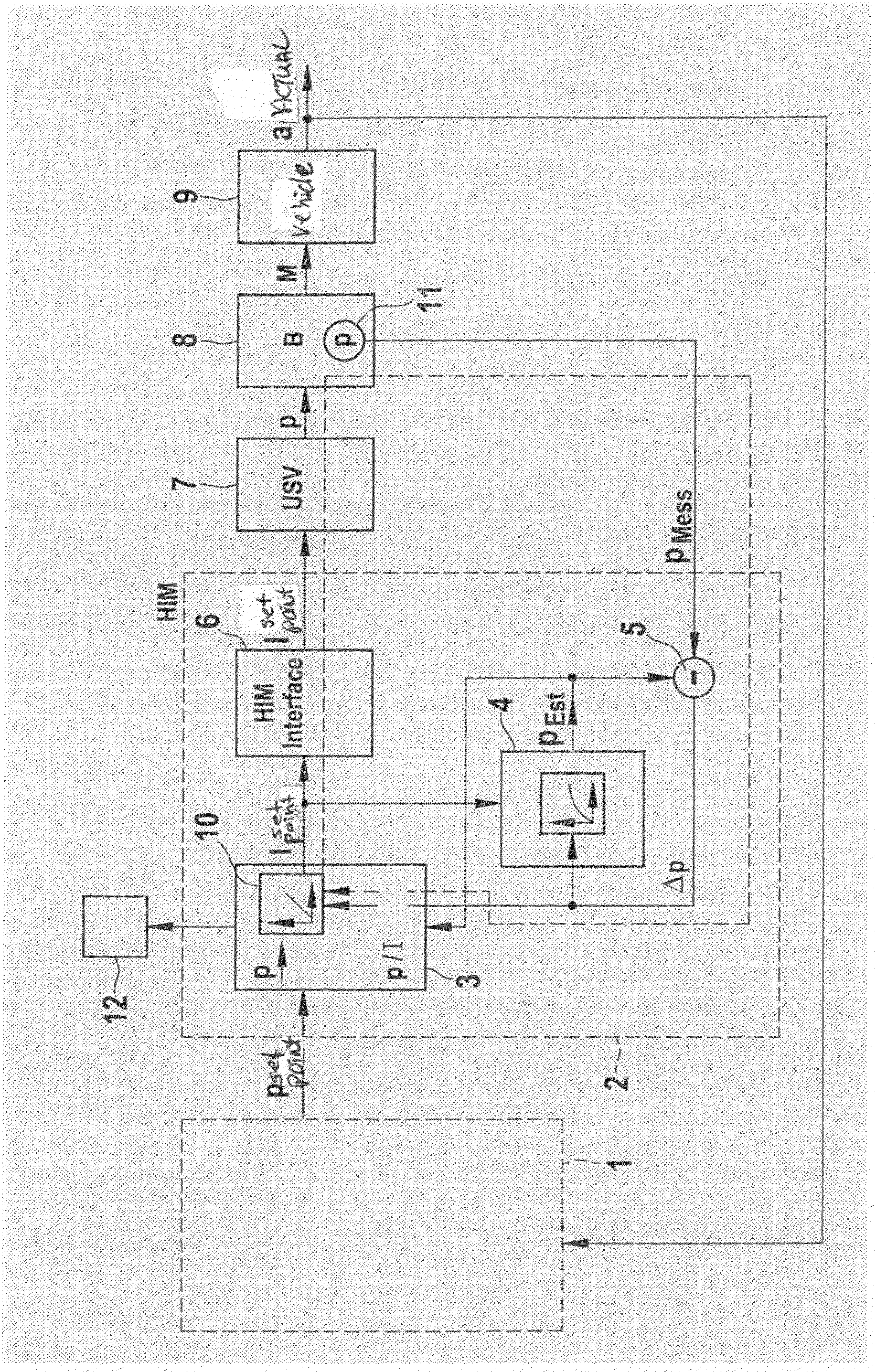
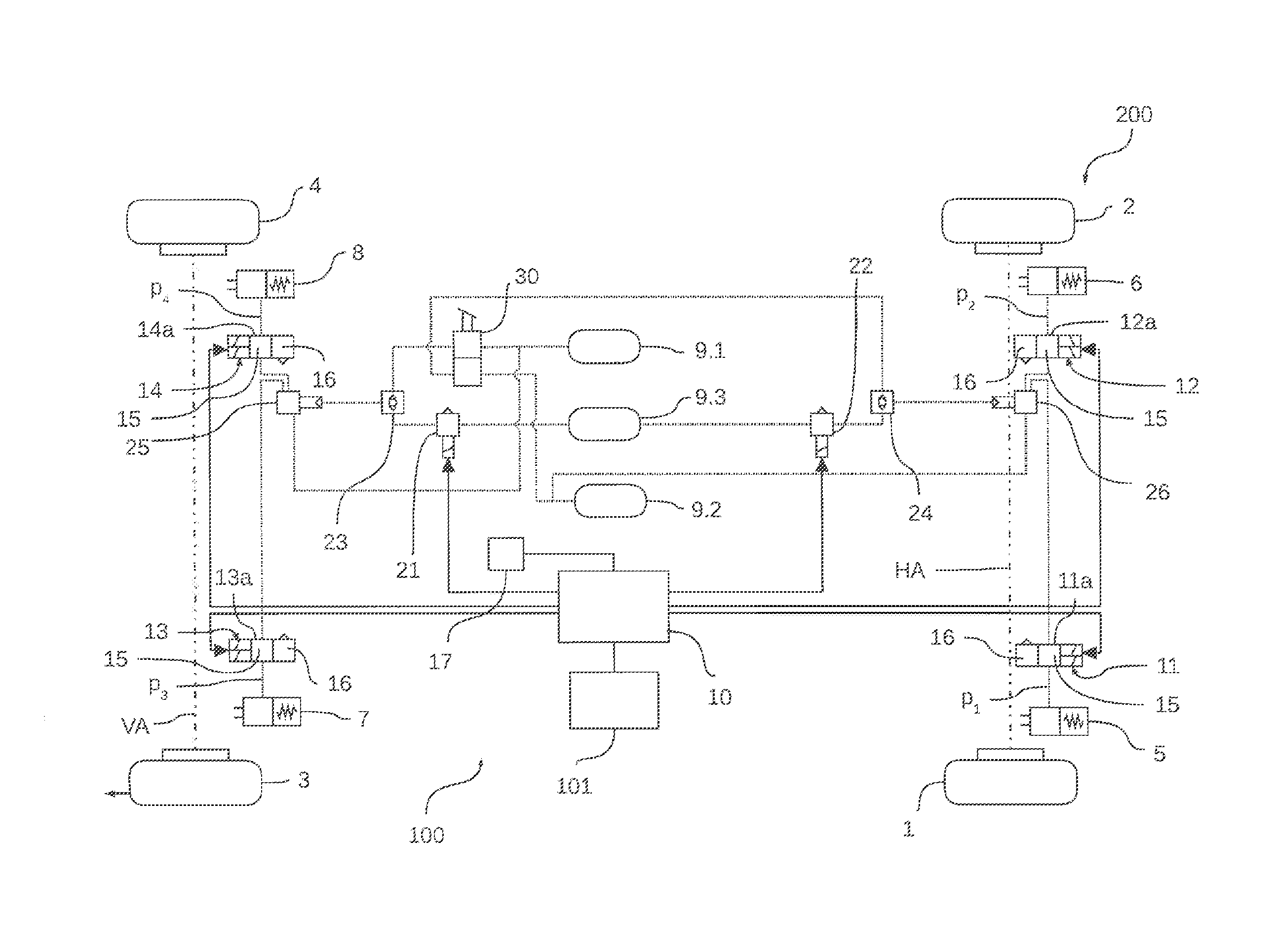
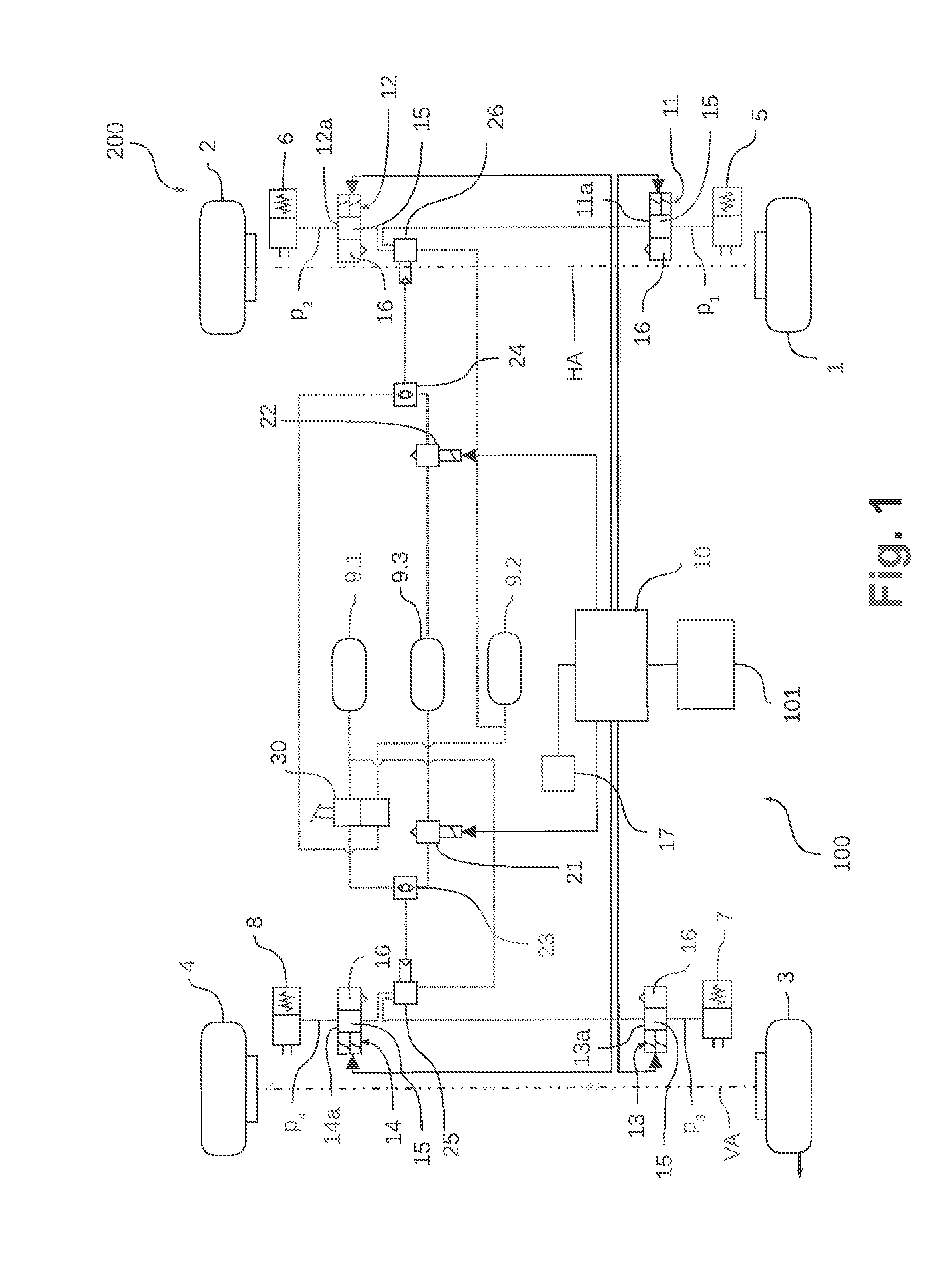
Closed-Loop Control of Brake Pressure Using a Pressure-Limiting Valve
InactiveUS20090210127A1Quality improvementQuality is easy to controlDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsLoop controlClosed loop
A device for controlling the brake pressure in a hydraulic brake system with the aid of a pressure-limiting valve that limits the brake pressure to a predefined threshold value, and to that end is driven by an electronic device in accordance with a valve characteristic curve. The setting accuracy can be improved considerably if an estimating unit for estimating the brake pressure, a sensor system for measuring the brake pressure, a unit for determining a pressure difference between the measured brake pressure and the estimated brake pressure, as well as a controller unit which drives the pressure-limiting valve as a function of the pressure difference are provided.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Electronic brake system and control method thereof
ActiveUS20180229707A1Pressure of wheel cylinder be increasedIncrease hydraulic pressureBraking action transmissionVehicle sub-unit featuresHydraulic control unitWheel cylinder
Disclosed herein is an electronic brake system. An electronic brake system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure, which is an electronic brake system including a pedal displacement sensor configured to sense displacement of a brake pedal according to a pedal effort of the brake pedal, a hydraulic pressure supply device configured to generate a hydraulic pressure using a rotational force of a motor operated by an electrical signal output from the pedal displacement sensor, and a hydraulic control unit configured to transmit a hydraulic pressure discharged from the hydraulic pressure supply device to wheel cylinders provided on respective wheels, includes a plurality of valves configured to adjust the hydraulic pressures transmitted to the wheel cylinders, a pressure measurer configured to measure hydraulic pressures of the wheel cylinders and a hydraulic pressure of the hydraulic control unit, and a controller configured to control an electromagnetic force of the valve when a difference between the measured hydraulic pressure of the wheel cylinder and the measured hydraulic pressure of the hydraulic control unit is more than a preset first threshold value during an anti-lock braking system (ABS) operation.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
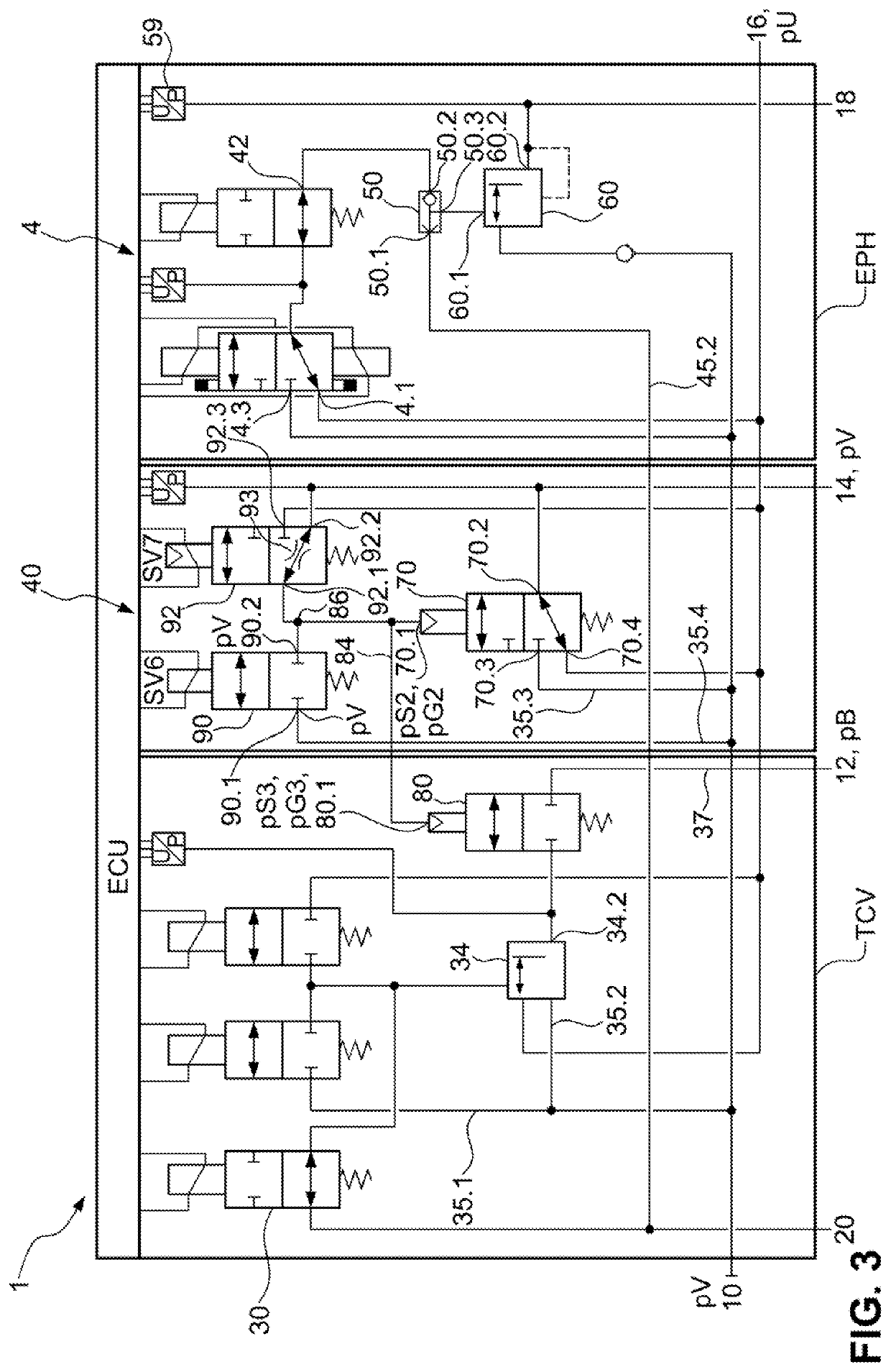
Multi-mode electronic hydraulic brake boosting system and control method
InactiveCN111497811ASteady braking feelIncrease stiffnessBraking action transmissionBrake action initiationsDriver/operatorMaster cylinder
The invention discloses a multi-mode electronic hydraulic brake boosting system and a control method. When the power assisting system fails, an emergency mechanical braking mode is achieved through structural redundancy, under the normal power assisting mode, common braking and emergency braking are divided according to the strength requirement of a brake, and the common braking power assisting mode and the emergency active pressurizing mode are controlled respectively. Accurate assistance can be provided during general braking so that the pressure of the brake master cylinder can accurately follow the target pressure, pressure buildup of the brake master cylinder can be completed more quickly during emergency braking, braking force is output to the maximum extent, the system response timeof the emergency braking working condition is shortened, the braking capacity is improved, and traffic accidents are avoided. The design of the multi-mode power assisting system can accurately trackthe braking intention of a driver, the intelligent degree of switching between different power assisting modes is high, the rapidity and accuracy of braking response and the safety of a vehicle are improved, and the multi-mode power assisting system has very high practical application value.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Electric apparatus of vehicle having an at least partly electric braking and steering device
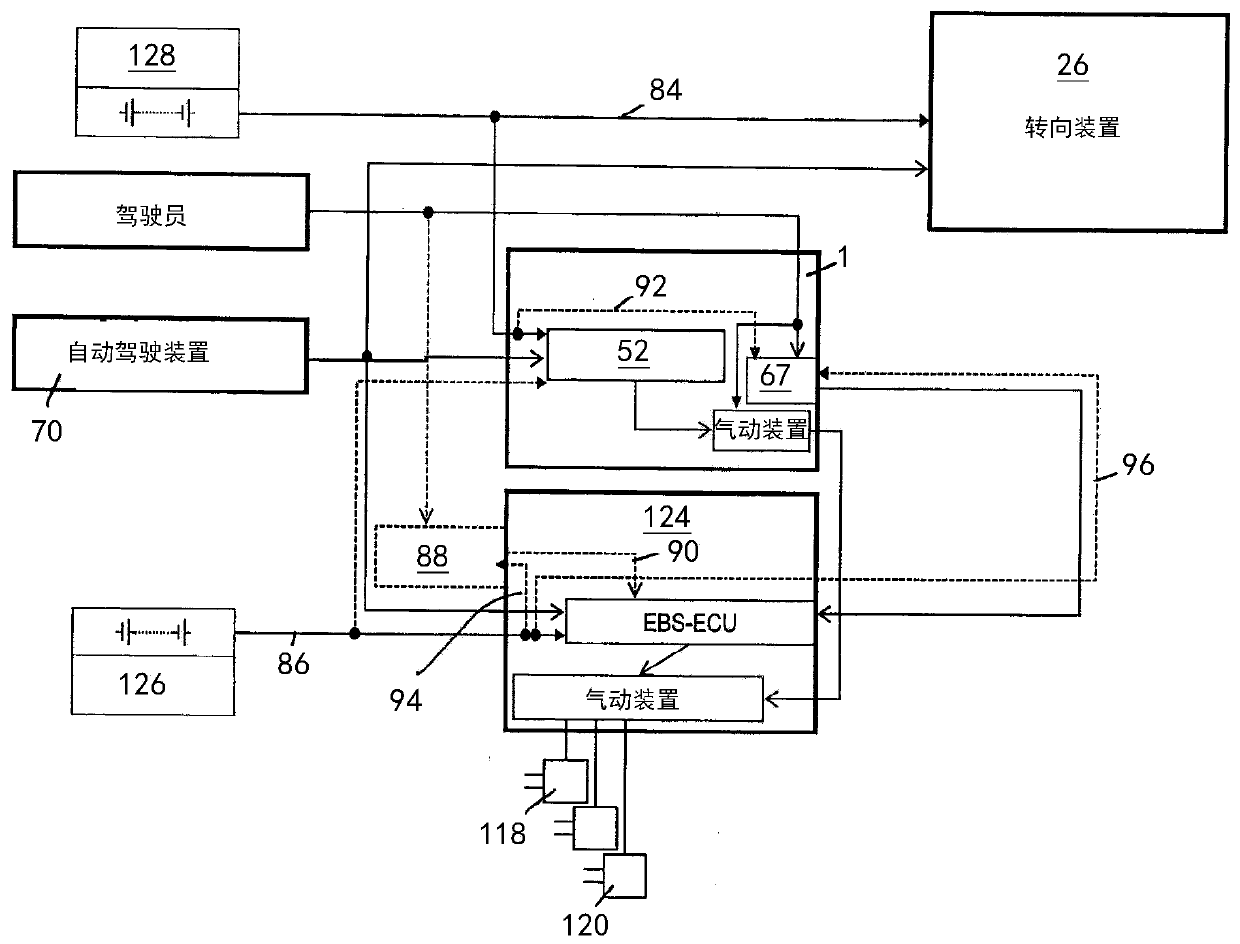
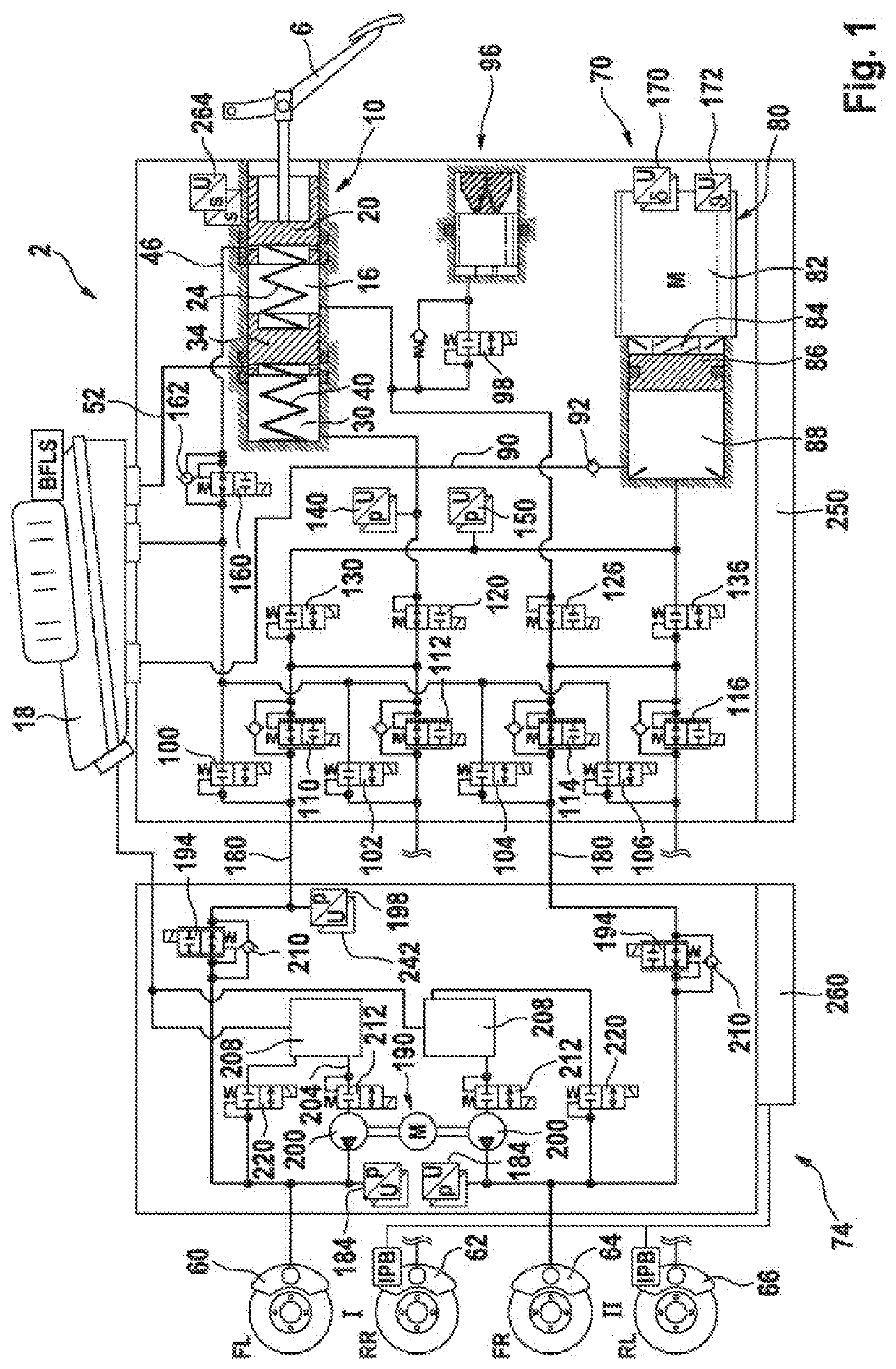
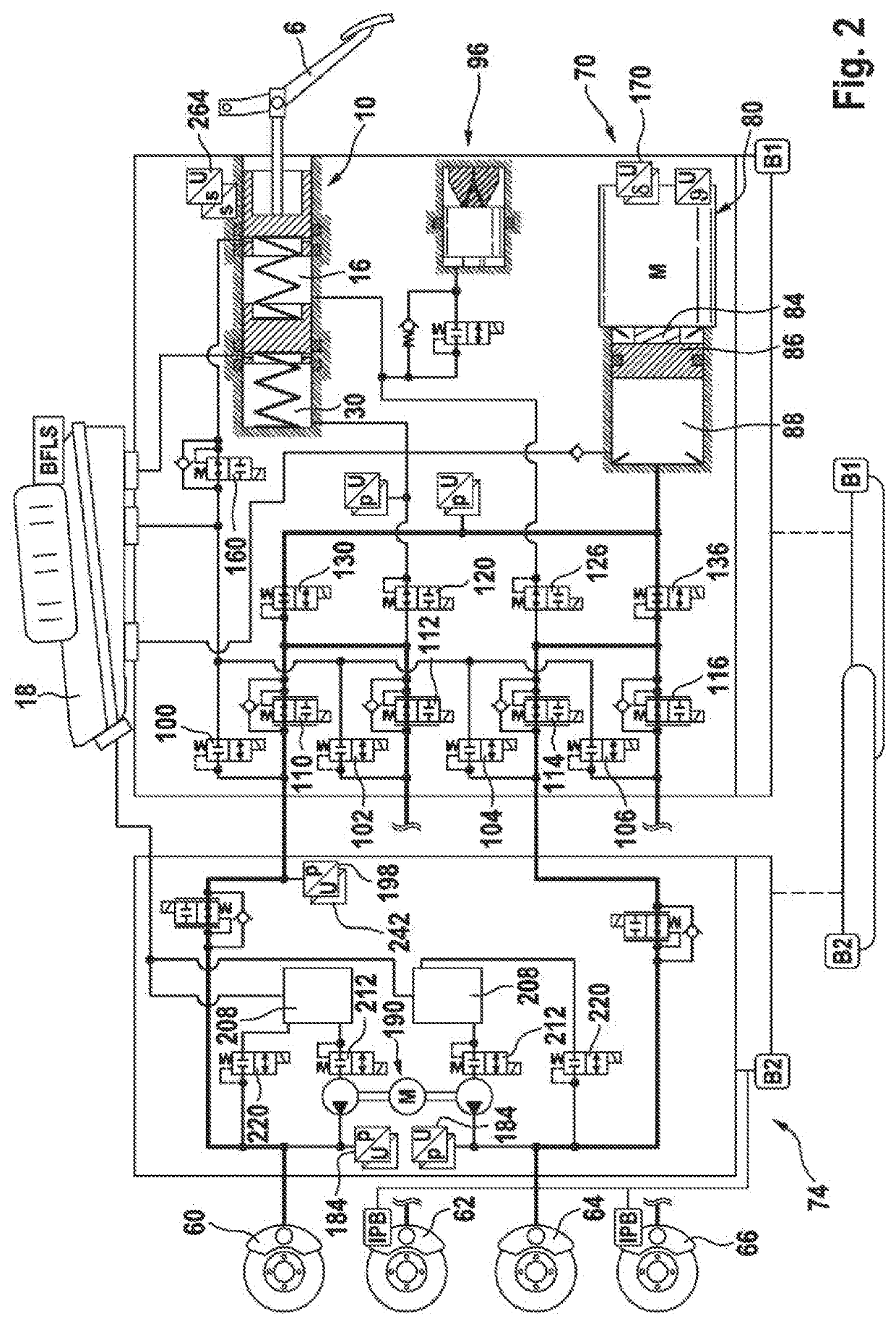
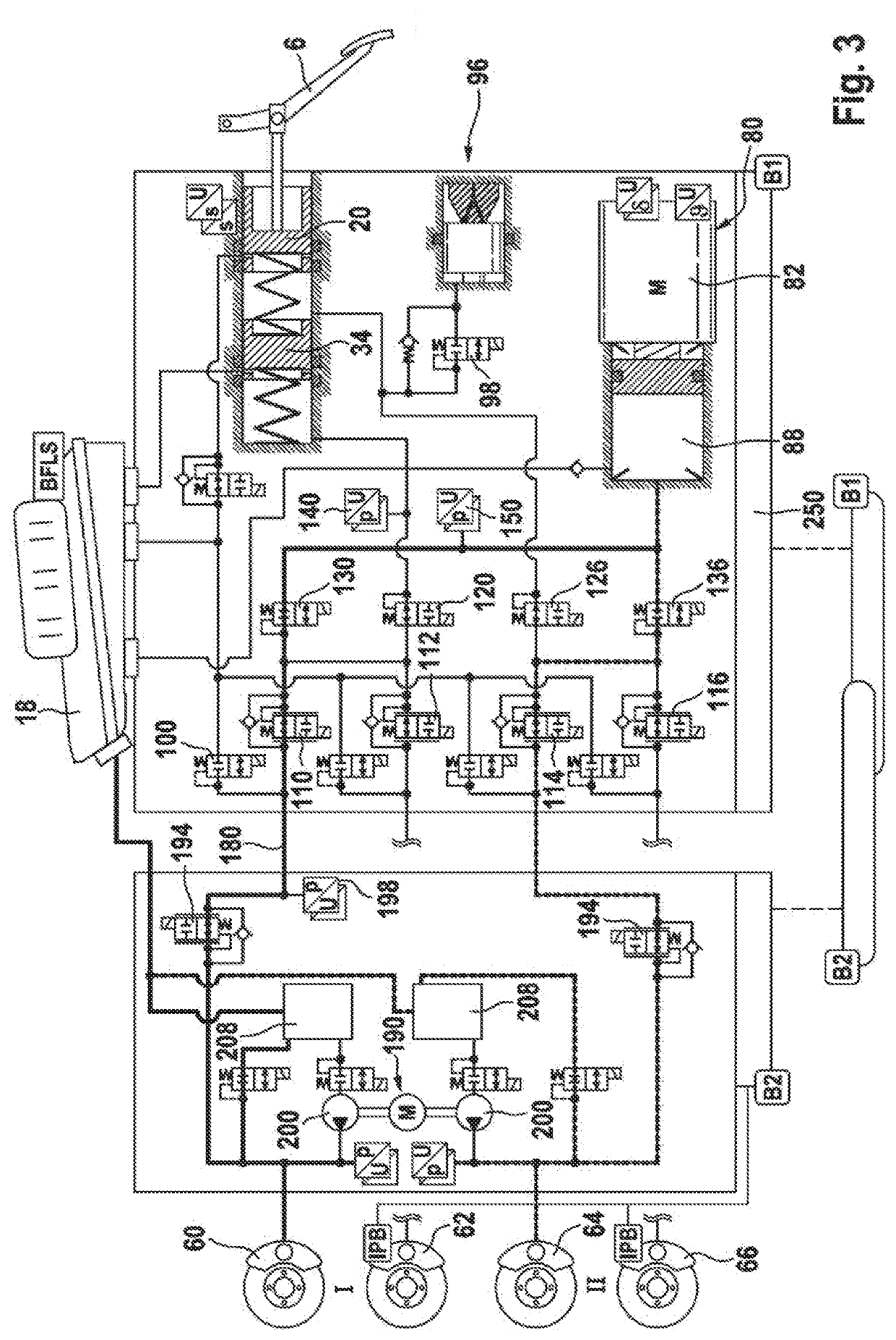
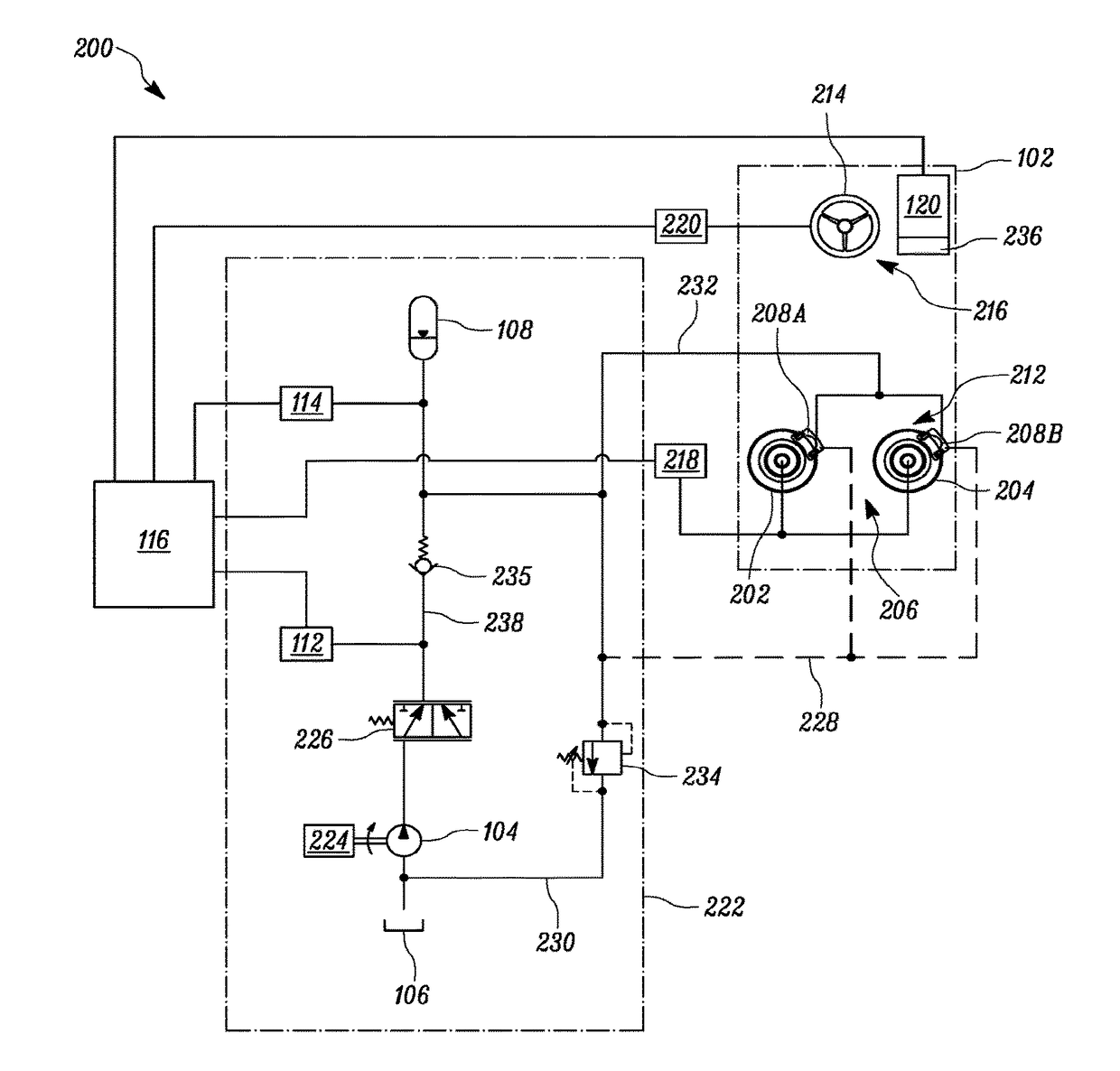
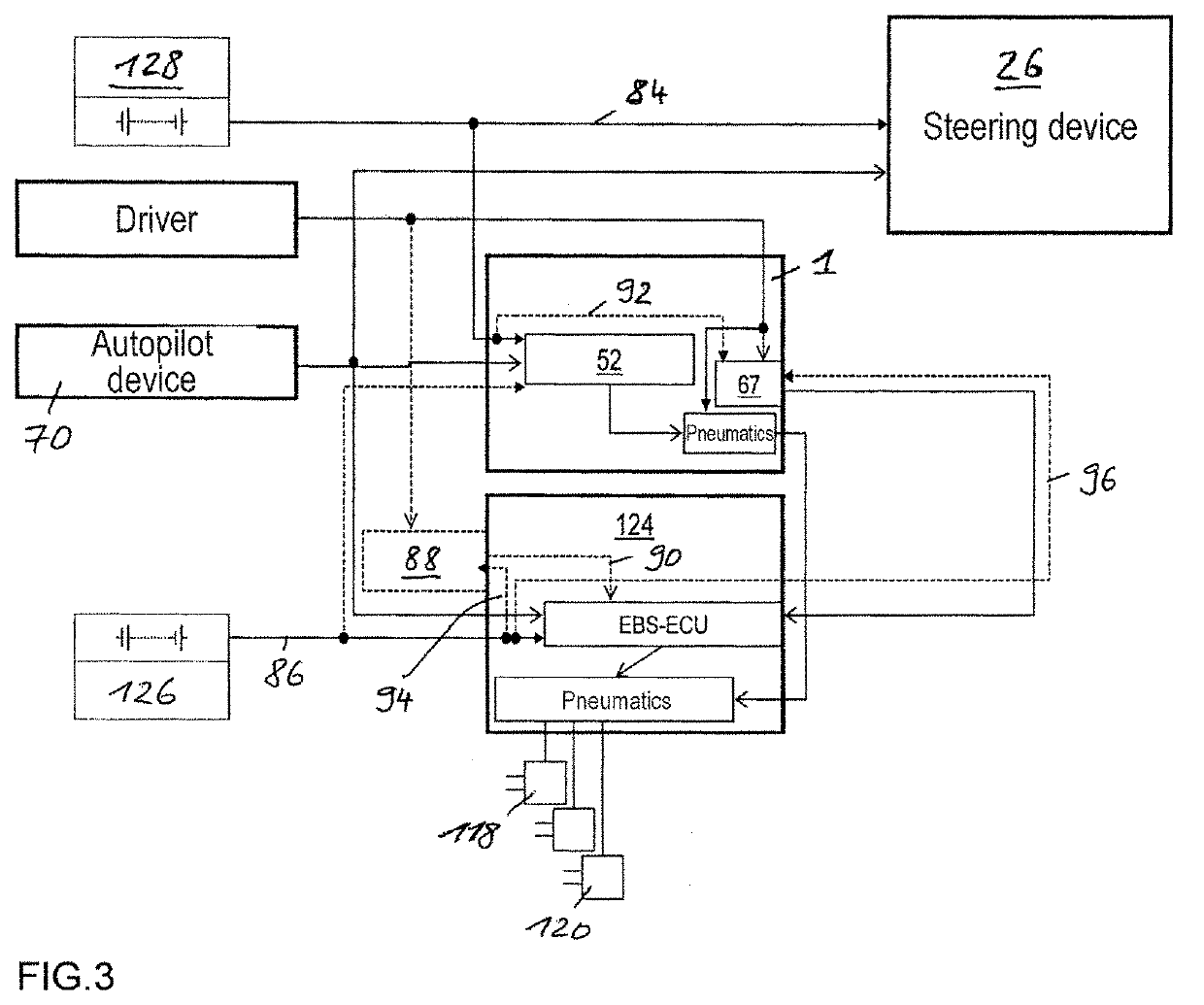
ActiveCN110248854AHigh precisionBrake system interactionsBraking action transmissionElectricitySteering wheel
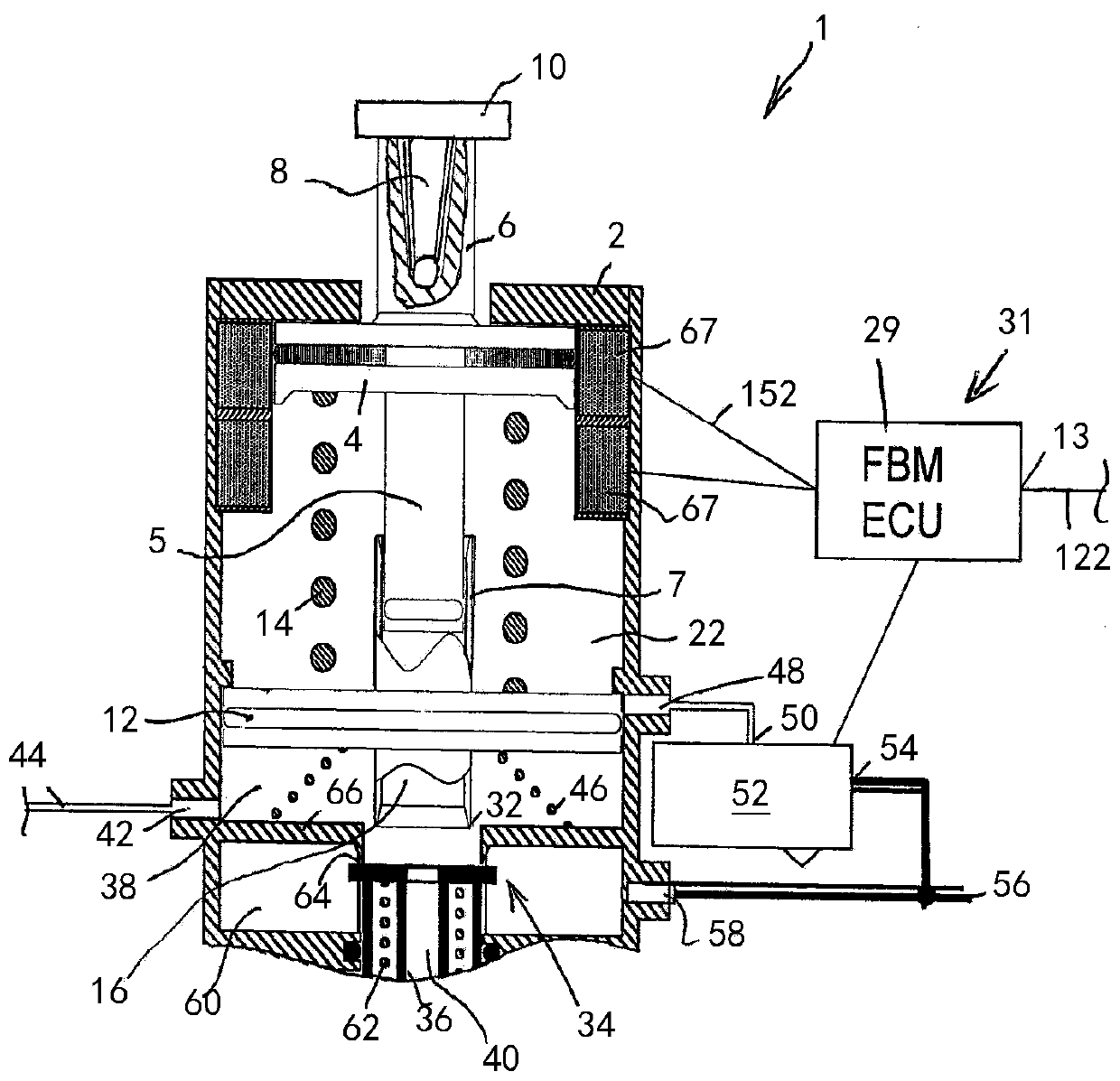
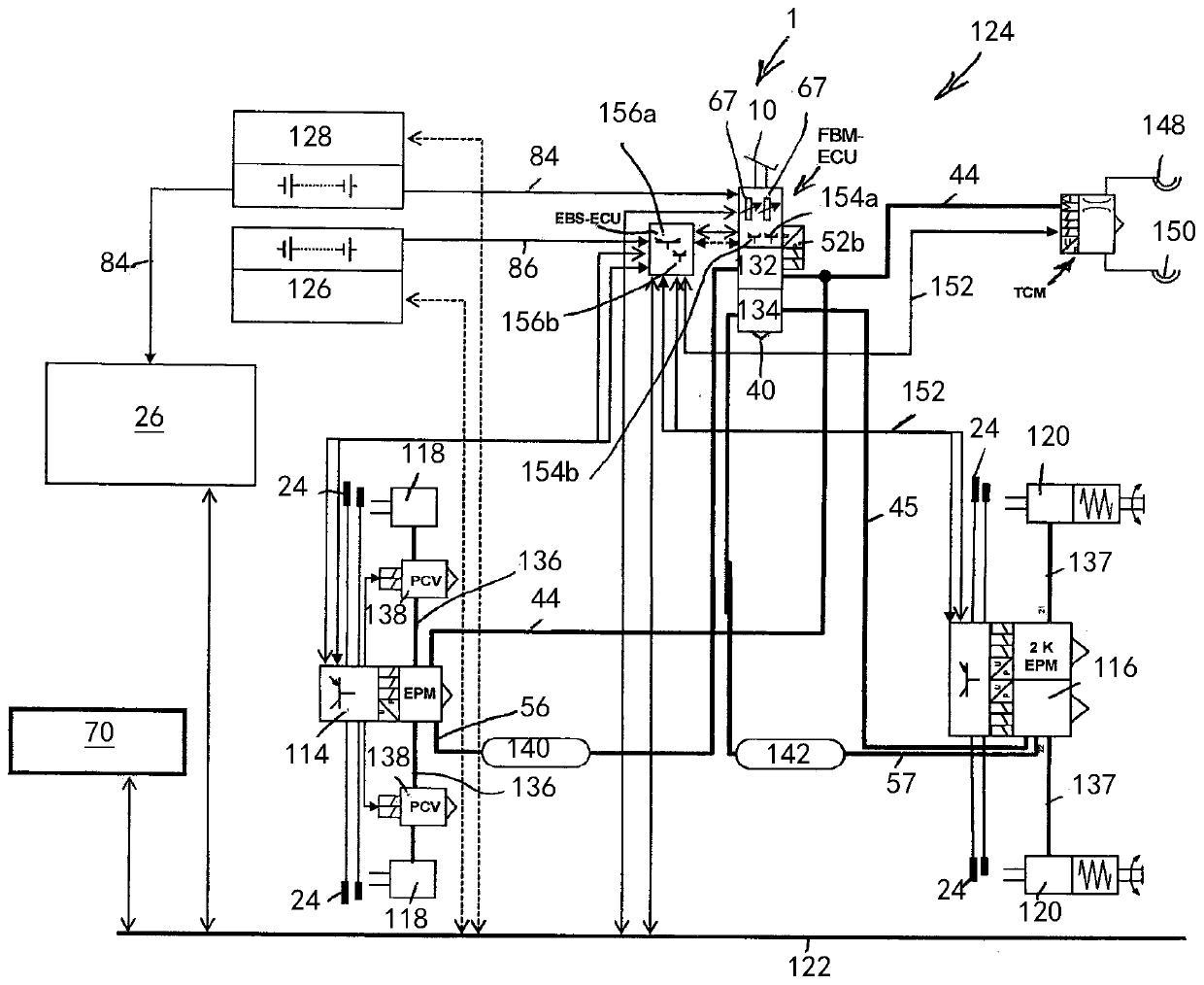
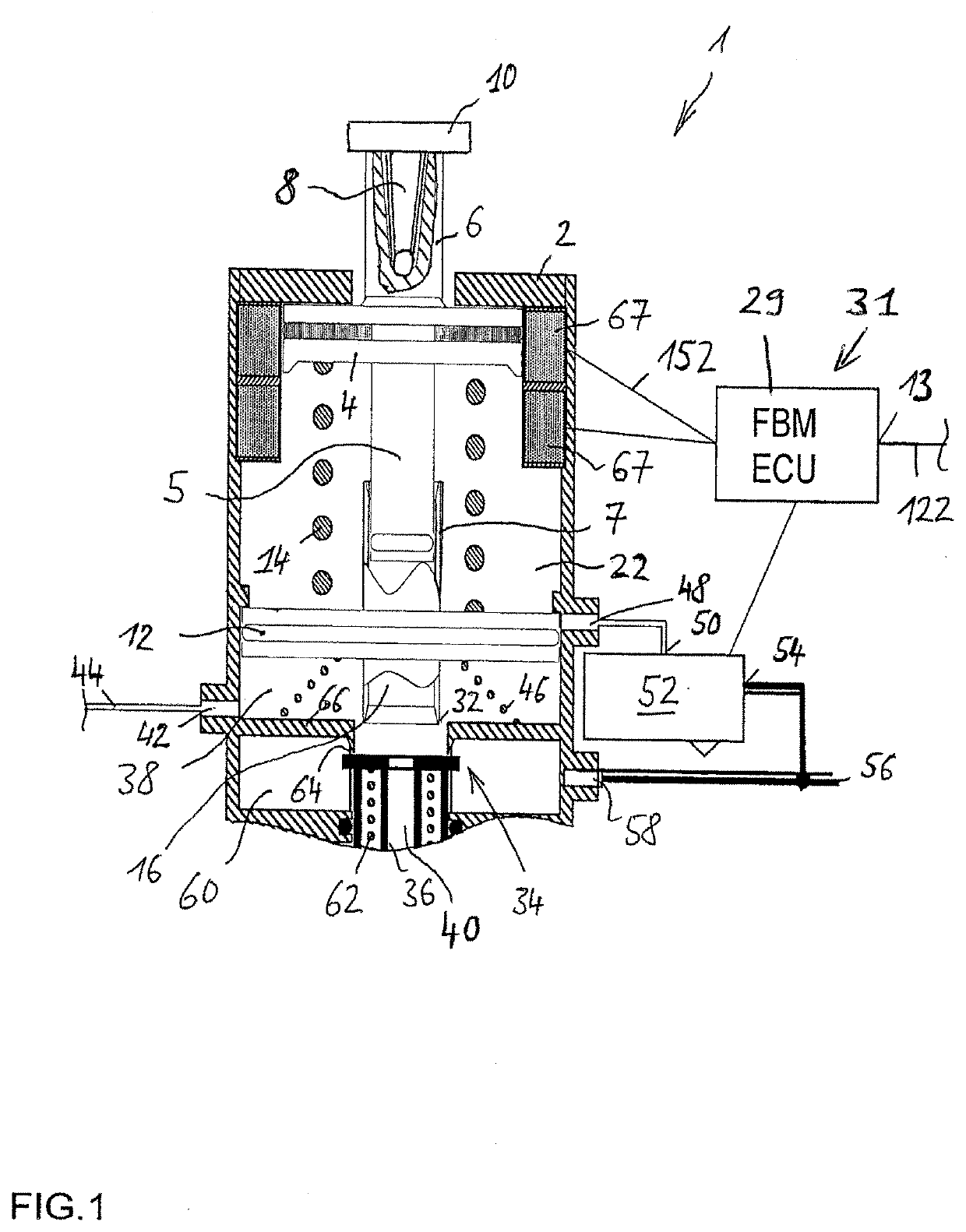
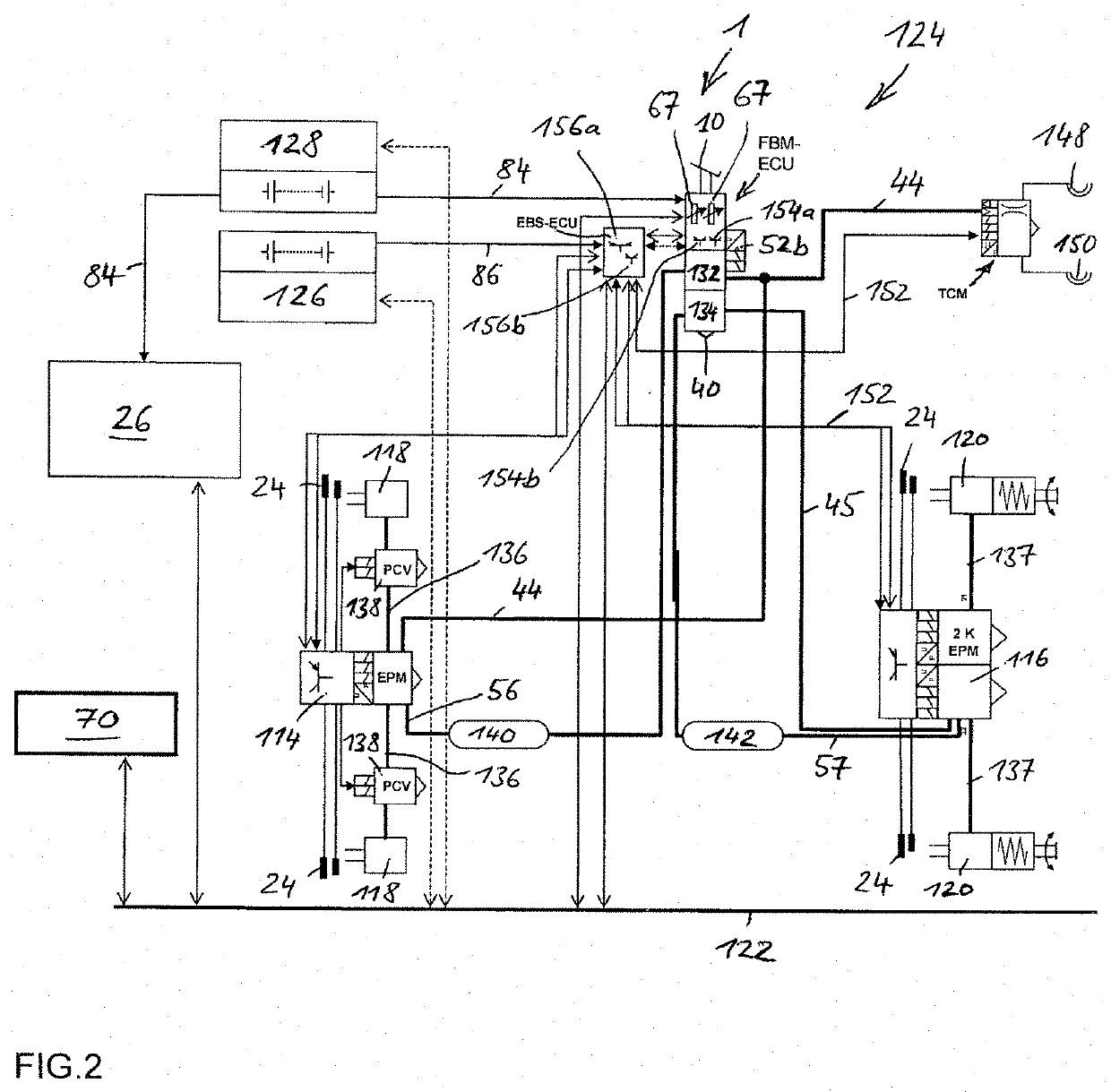
The invention relates to an electric apparatus of a vehicle having an at least partly electric braking and steering device comprising an electric or electromechanical steering device (26) with or without a continuous mechanical connection between a steering wheel (28) and a steering gear (30) and having an electronic steering control device and an electric steering actuator (72), and an electropneumatic service brake device (124) which comprises an electropneumatic service brake valve device (1), an electronic brake control device (EBS-ECU), electropneumatic modulators (114, 116) and pneumatic wheel brake actuators (118, 120), wherein the electropneumatic service brake valve device (1) has a service brake actuating member (10) and, within at least one electric service brake circuit, at least one electric channel (130) with at least one electric brake transducer (67) which can be actuated by the service brake actuating member (10) in order to output actuating signals in a manner which is dependent on an actuation of the service brake actuating member (10), and at least one electronic evaluation device (FBM-ECU) which receives the actuating signals and inputs brake request signals into the electronic brake control device (EBS-ECU) in a manner which is dependent on the actuating signals. The invention is characterized in that the electronic evaluation unit (FBM-ECU) is integrated into the electronic steering control device, or the electronic steering control device is integrated into the electronic evaluation device (FBM-ECU).
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Brake control system used in a vehicle and control method thereof
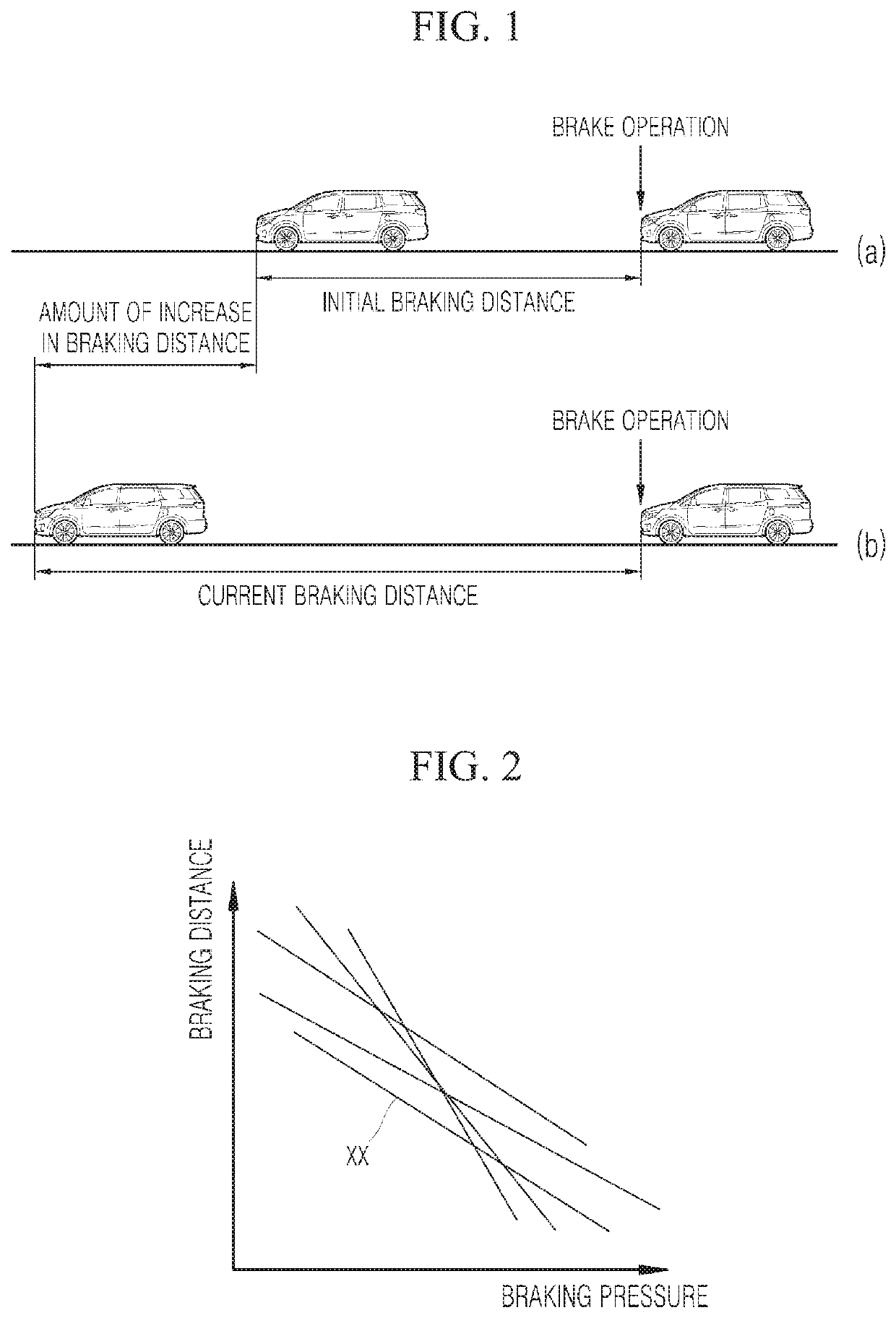
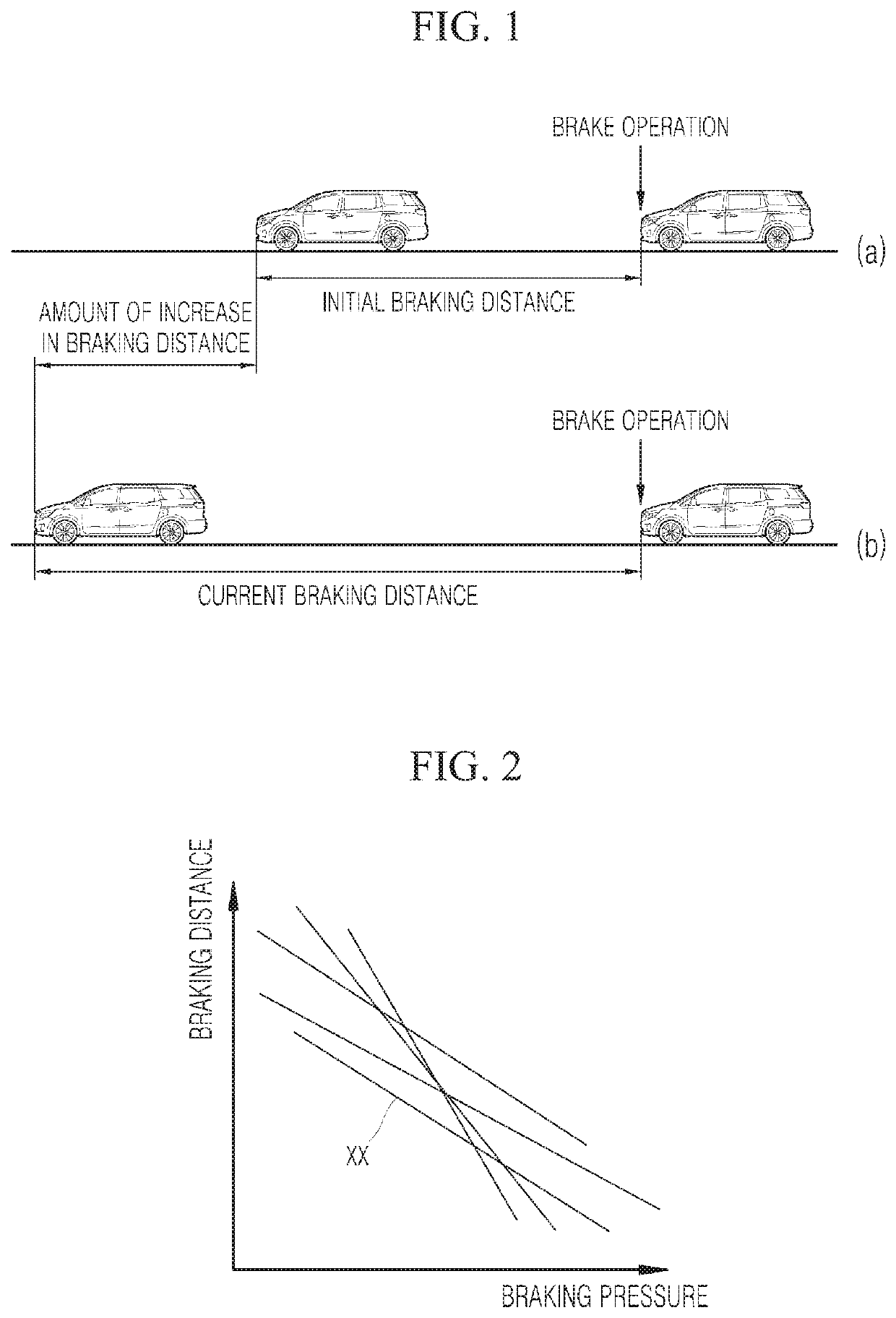
ActiveUS20190389442A1Increase brake pressureShorter braking distanceBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesControl systemBraking distance
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
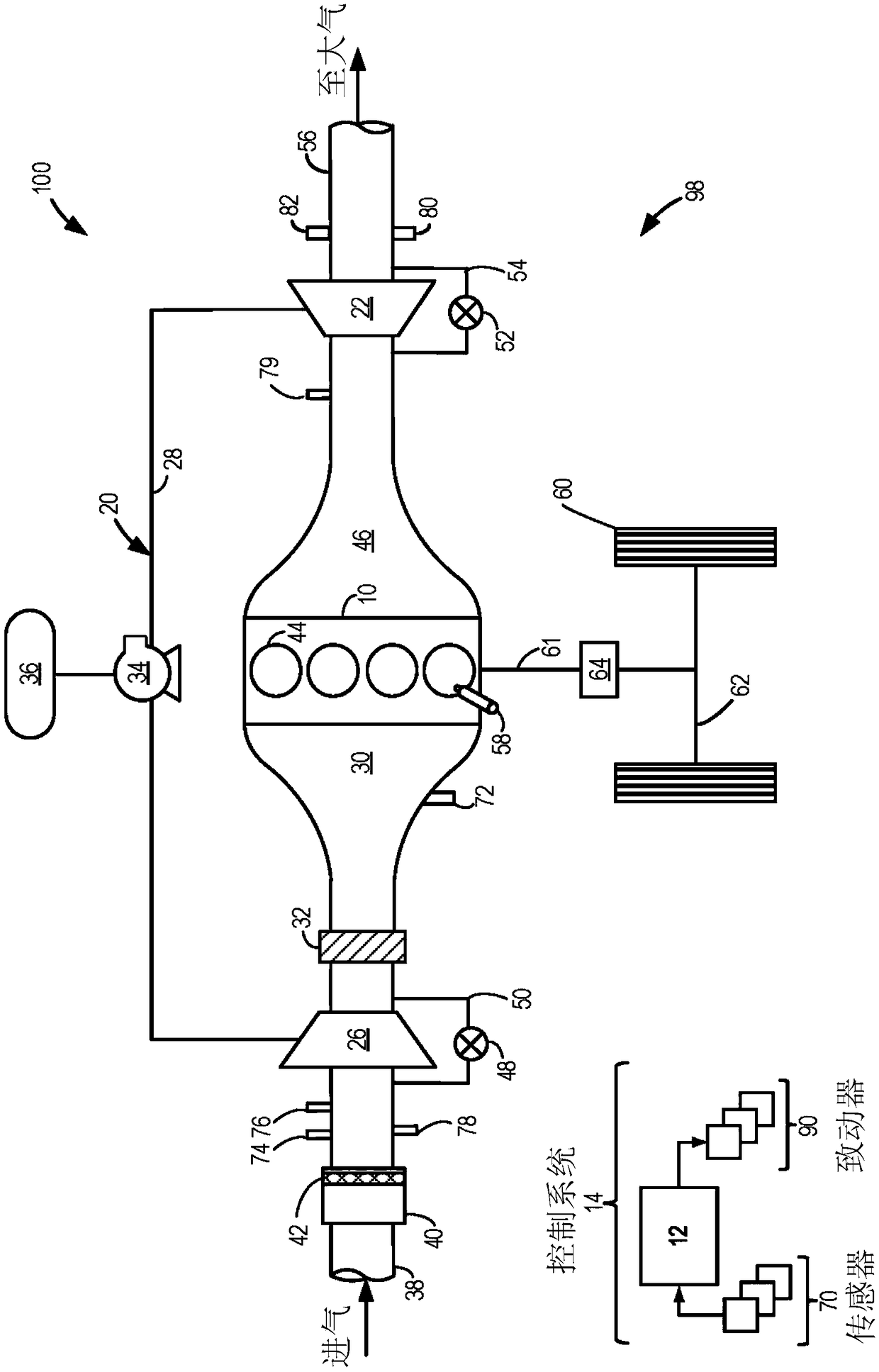
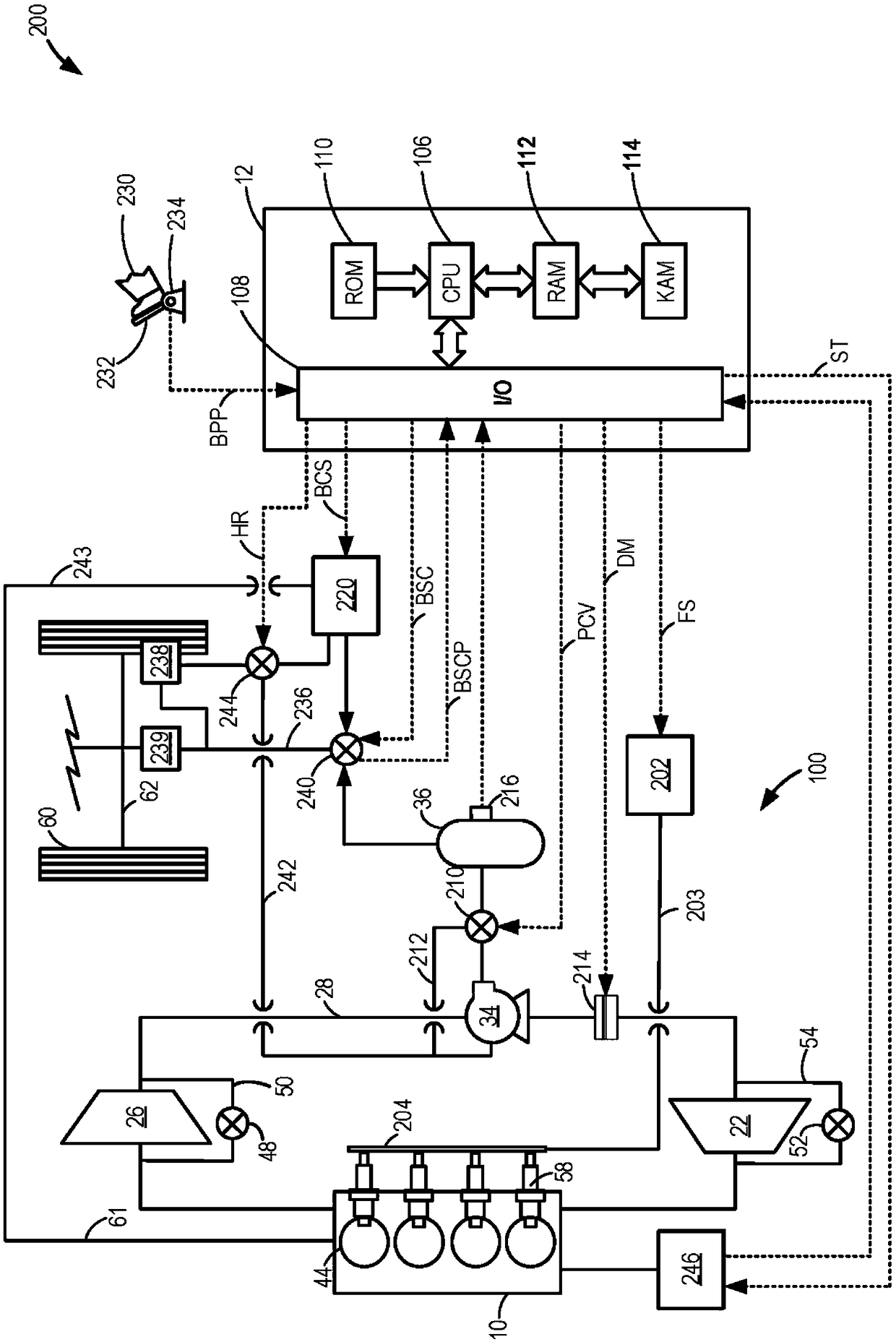
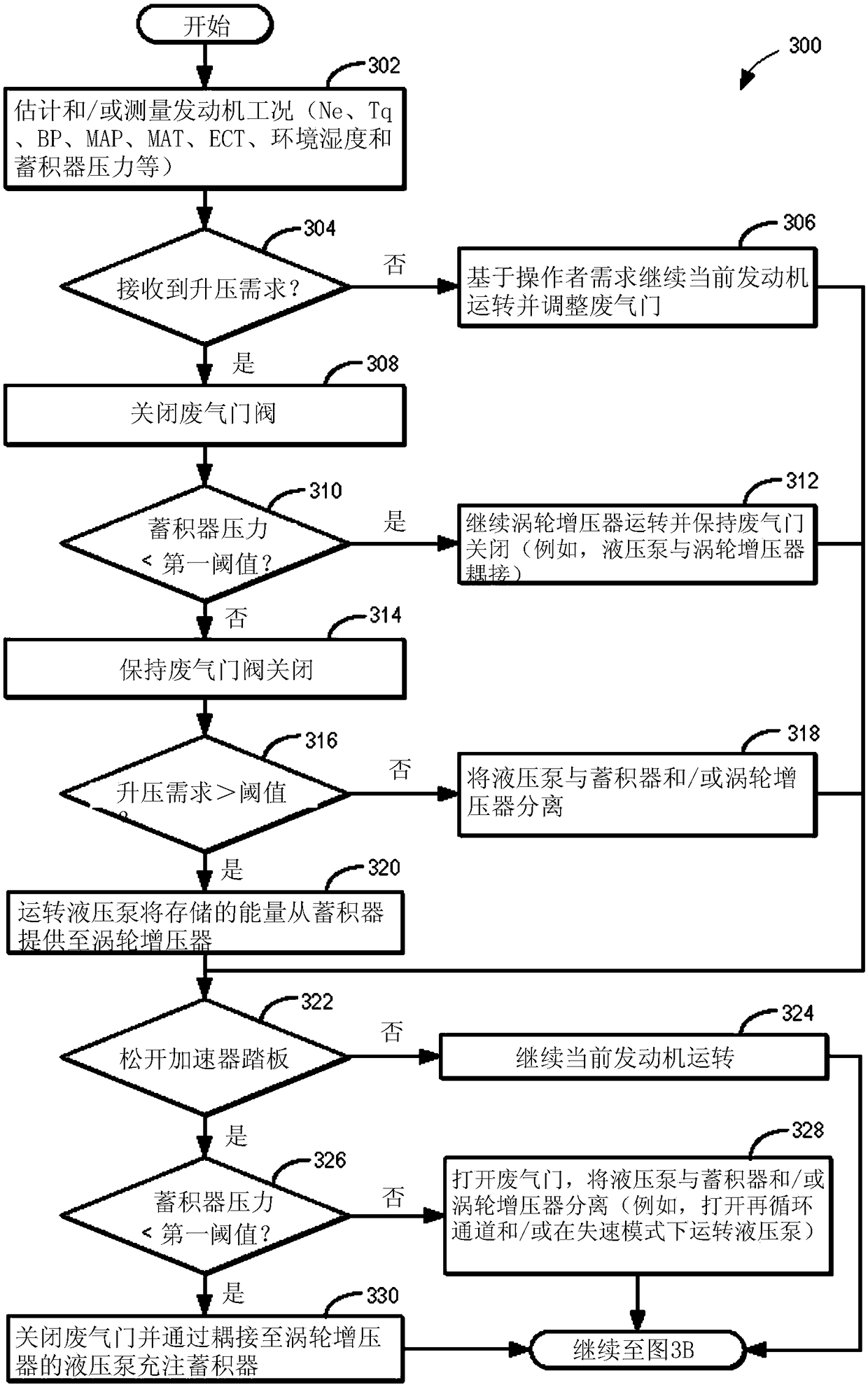
Hydraulic turbocharged engine with automatic start-stop
The invention relates to a hydraulic turbocharged engine with automatic start-stop. Methods and systems are provided for a vehicle engine including a turbocharger coupled to a hydraulic pump and a hydraulic accumulator. In one example, a method may include, in response to the vehicle coming to a stop, supplying pressure to a hydraulic braking system of the vehicle from the accumulator coupled to ahydraulic pump coupled to a shaft of a turbocharger of an engine installed in the vehicle, and automatically shutting down the engine while the vehicle is stopped.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Brake system of automobile, automobile and control method of brake system
PendingCN112572380AIncrease redundancyBraking action transmissionBrake action initiationsNew energyControl valves
The invention provides a brake system of an automobile, the automobile and a control method of the brake system so as to improve the redundancy performance of the brake system. The scheme of the invention is suitable for intelligent automobiles, new energy automobiles or traditional automobiles and the like. Specifically, the scheme of the invention relates to the improvement of the brake system in the automobile. According to the brake system, a first control valve 130 is connected with a first brake pipeline 111 and a second brake pipeline 121, so that when the first control valve 130 is ina conducting state, the first brake pipeline 111 is communicated with the second brake pipeline 121, brake fluid between the two brake pipelines can circulate, and the redundancy performance of the brake system can be improved. The situation that in an existing braking system, the first brake pipeline 111 and the second brake pipeline 121 are two independent brake pipelines, and after a pressure providing device (a pressurizing device and a braking main cylinder) on one brake pipeline fails, the automobile loses half of braking force is avoided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
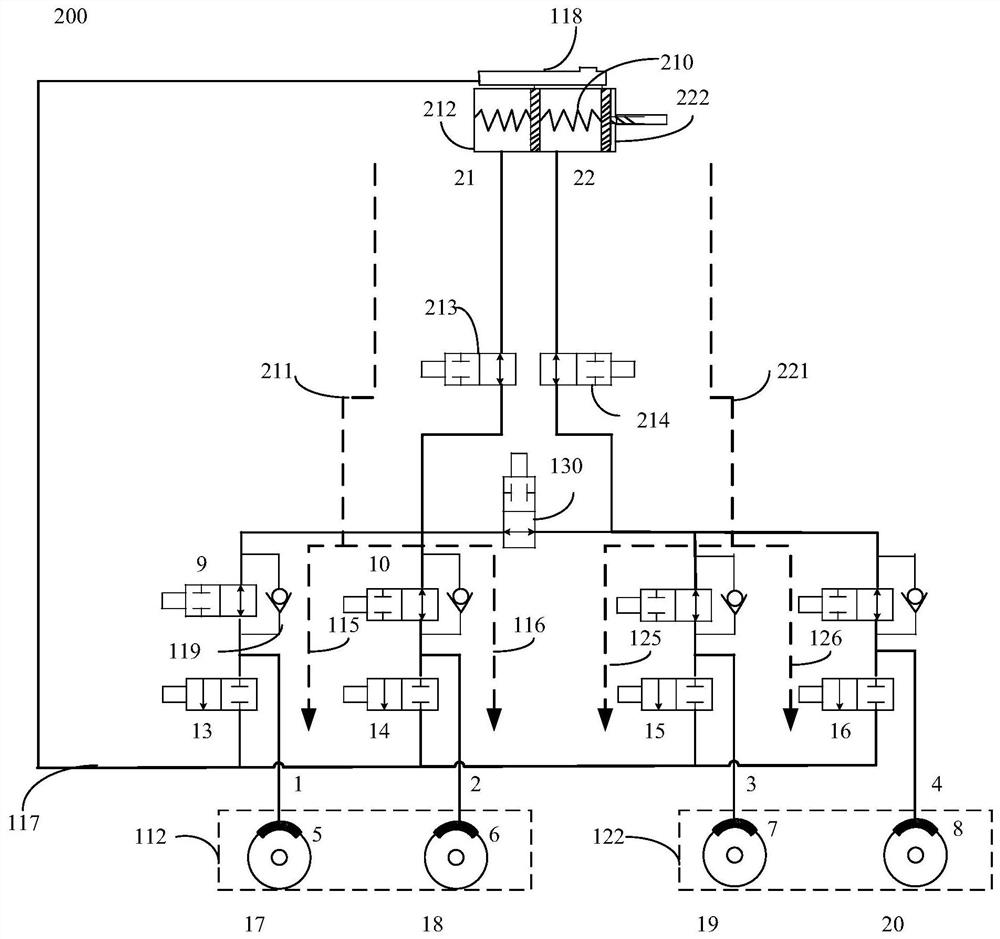
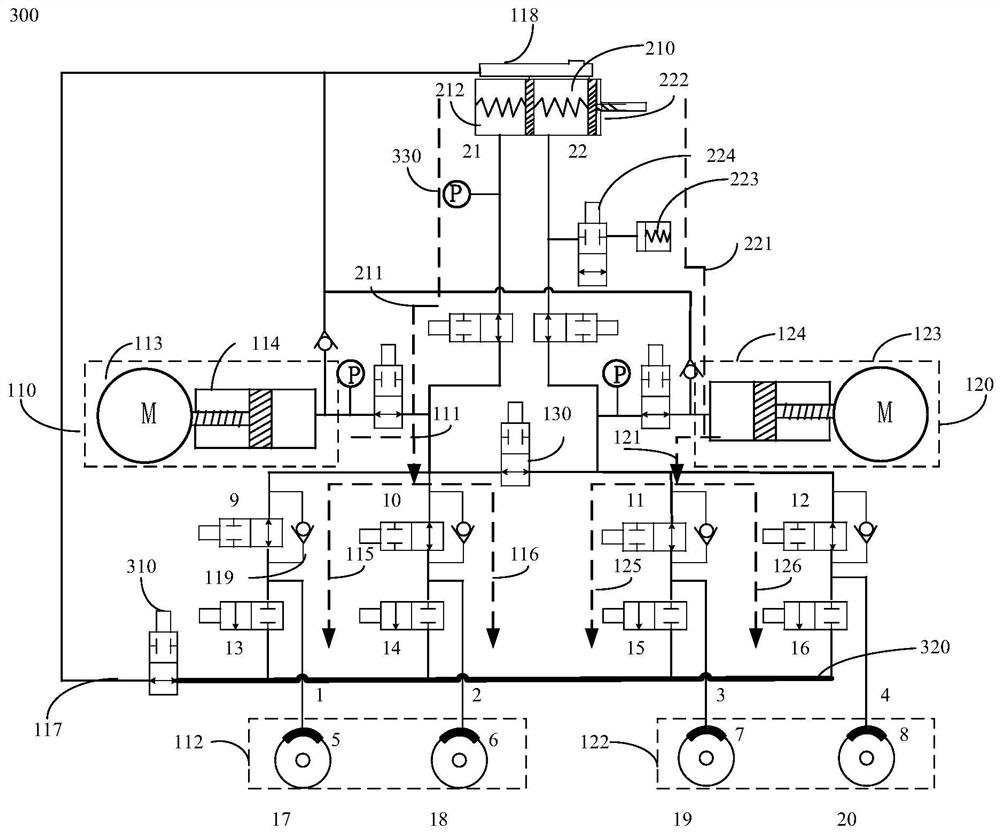
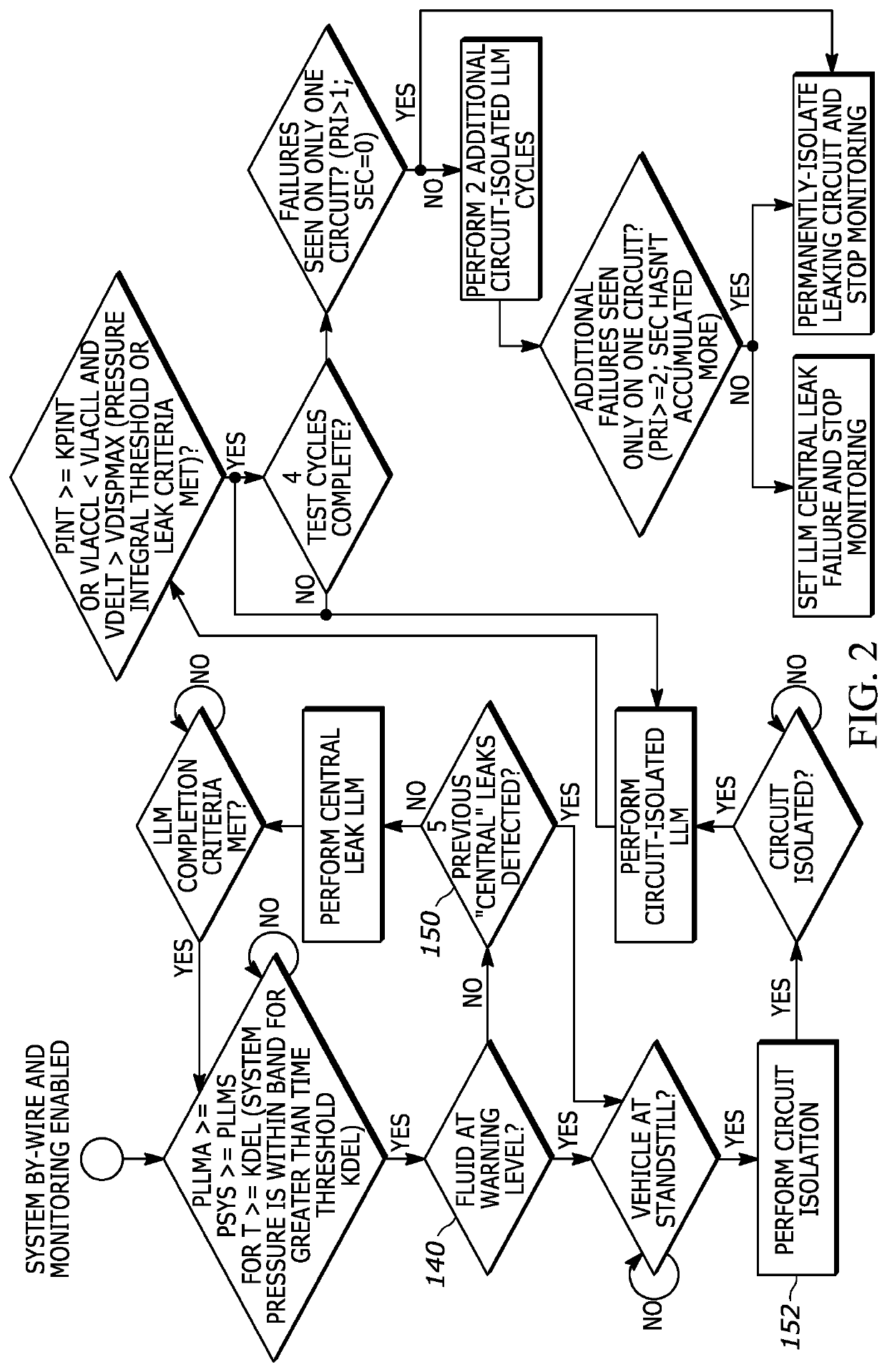
Small hydraulic leak detection and related methods
ActiveUS20210318199A1Measurement of fluid loss/gain rateBrake action initiationsControl engineeringControl theory
A method for detecting a small hydraulic leak of braking fluid in a vehicle, the vehicle having at least a first braking circuit and a second braking circuit, the method includes determining whether system braking pressure falls within a predetermined range, determining whether leakage exists in the braking circuits, determining whether the vehicle is in secure standstill, monitoring small leakage of a braking circuit while the vehicle is in secure standstill if leakage was detected and the vehicle is in the secure standstill, and isolating at least one of the braking circuits if a leakage exists in one of the braking circuits.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
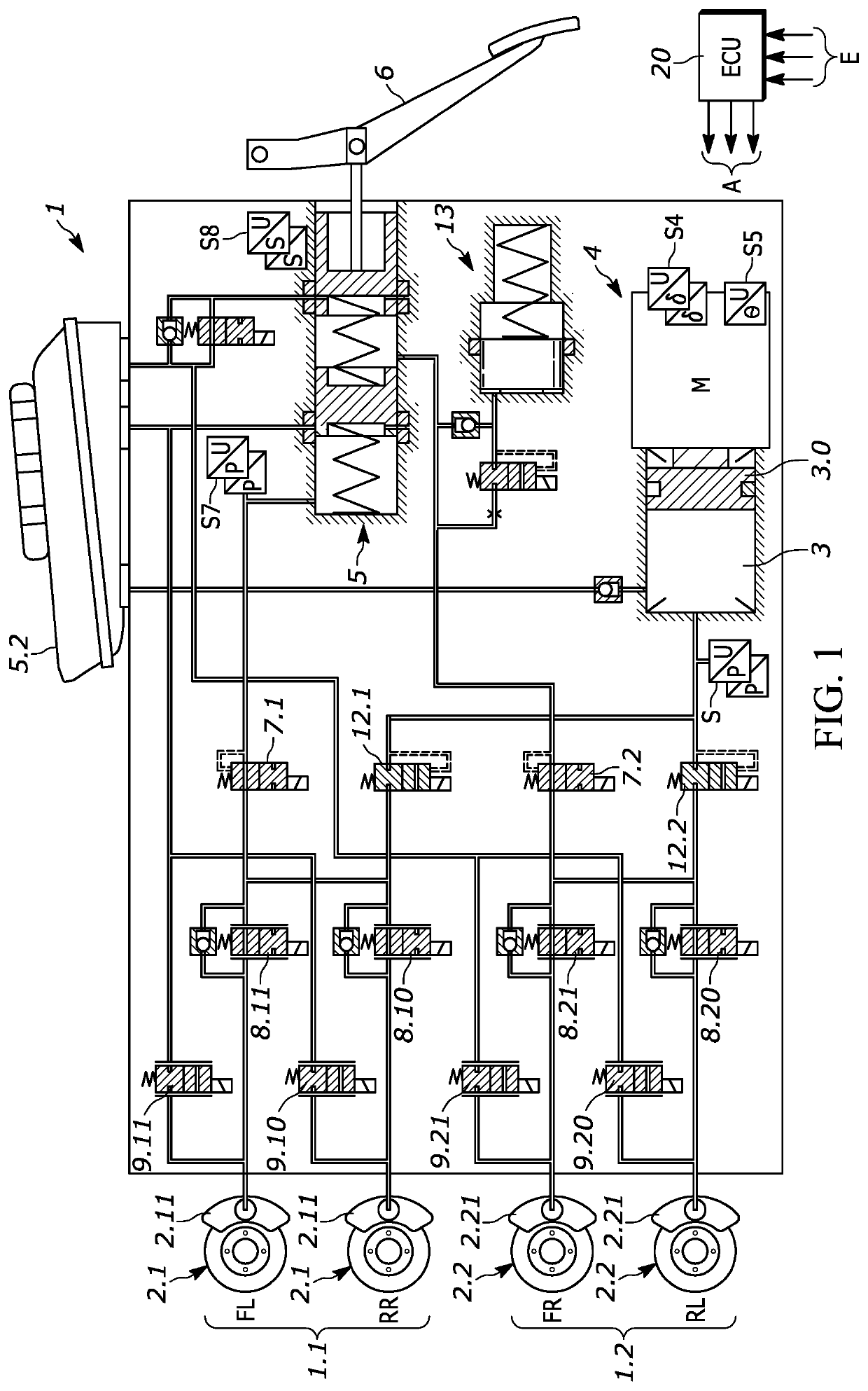
Method for checking the functionality of a braking system, and braking system
ActiveUS20200361439A1Improve robustnessIncrease costBraking action transmissionVehicle sub-unit featuresIsolation valveControl theory
A method for checking functionality of a motor vehicle braking system. The braking system has a main module, including: hydraulically actuatable wheel brakes, pairs being assigned to respective brake circuits; at least one electrically actuatable wheel valve per wheel brake sets wheel-specific brake pressures; a pressure provision device actively builds up pressure in the wheel brakes; a pressure-medium reservoir at atmospheric pressure, and an auxiliary module, which has for each of two wheel brakes: a pressure sensor for measuring pressure in a wheel brake line; an open when deenergized isolating valve in the wheel brake line; a pump. At least one variable is measured to assess functionality of the braking system. Using least one acceptance criterion, and checked whether the variable satisfies the acceptance criterion. Determining at least one variable representing the viscosity of the brake fluid, and the at least one acceptance criterion depends on a variable representing viscosity.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Systems, apparatuses, and methods for monitoring pressure in a hydraulic system
ActiveUS20180005462A1Braking action transmissionRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesHydraulic pumpEngineering
A method, system, and apparatus to determine a malfunction or an abnormal pressure condition in a hydraulic system over a time period are provided. The method, system, and apparatus include monitoring hydraulic accumulator charge time, hydraulic accumulator discharge time, and hydraulic pump pressure over the time period, and determining whether the monitored hydraulic accumulator charge time, hydraulic accumulator discharge time, and hydraulic pump pressure are within respective predetermined ranges. A maintenance notification is output responsive to at least one of the monitored hydraulic accumulator charge time, hydraulic accumulator discharge time, and hydraulic pump pressure being outside the respective predetermined ranges during the time period.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Electropneumatic control module
PendingUS20220227342A1Easy constructionLow costBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsControl engineeringElectrical control
An electropneumatic control module has a trailer control unit, which has a trailer brake pressure port and a trailer feed pressure port, a holding brake unit, which has a spring-type actuator port and a holding brake pilot control unit, and an electronic control unit, which switches a holding brake pilot control unit into a ventilation position, wherein a second holding brake pilot control port is connected in pressure-conducting manner to a first holding brake pilot control port and the spring-type actuator port is connectable to a vent. The holding brake unit is connected to a redundancy port and is configured to output a first holding brake pressure at the spring-type actuator port when the holding brake pilot control unit is in the ventilation position and a redundancy pressure is provided. The trailer control unit outputs a brake pressure at the trailer brake pressure port when a redundancy pressure is provided.
Owner:ZF CV SYST EURO BV
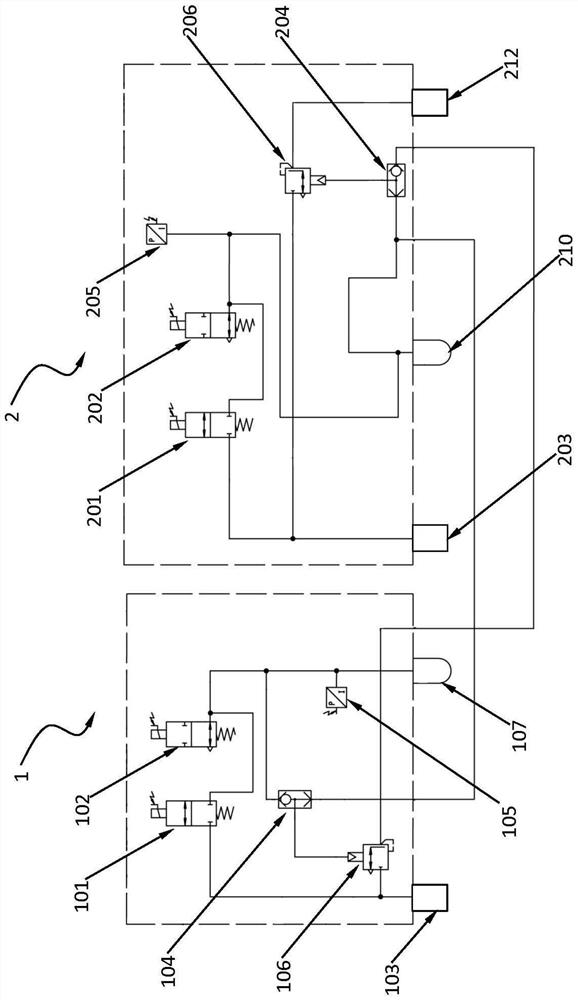
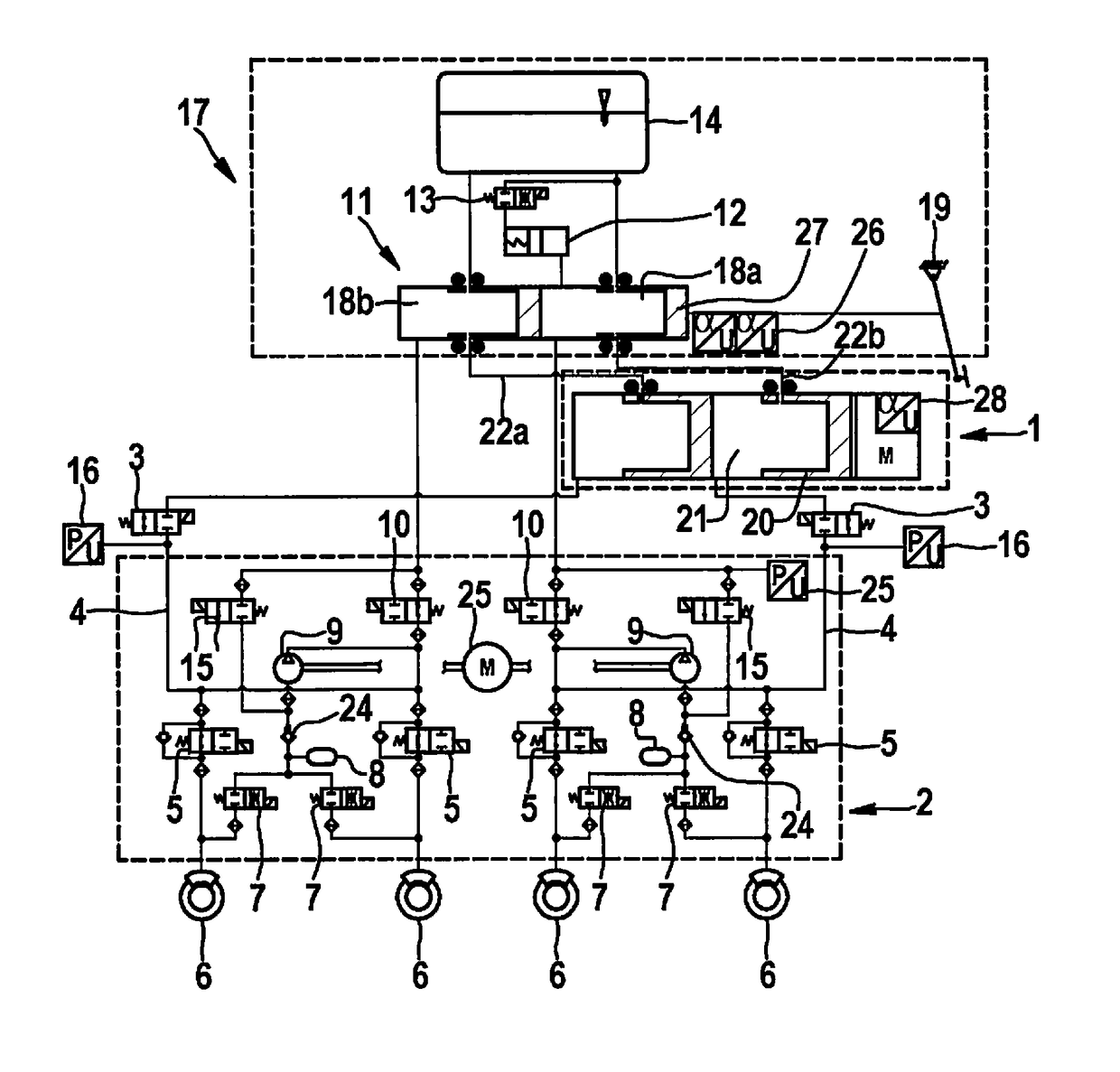
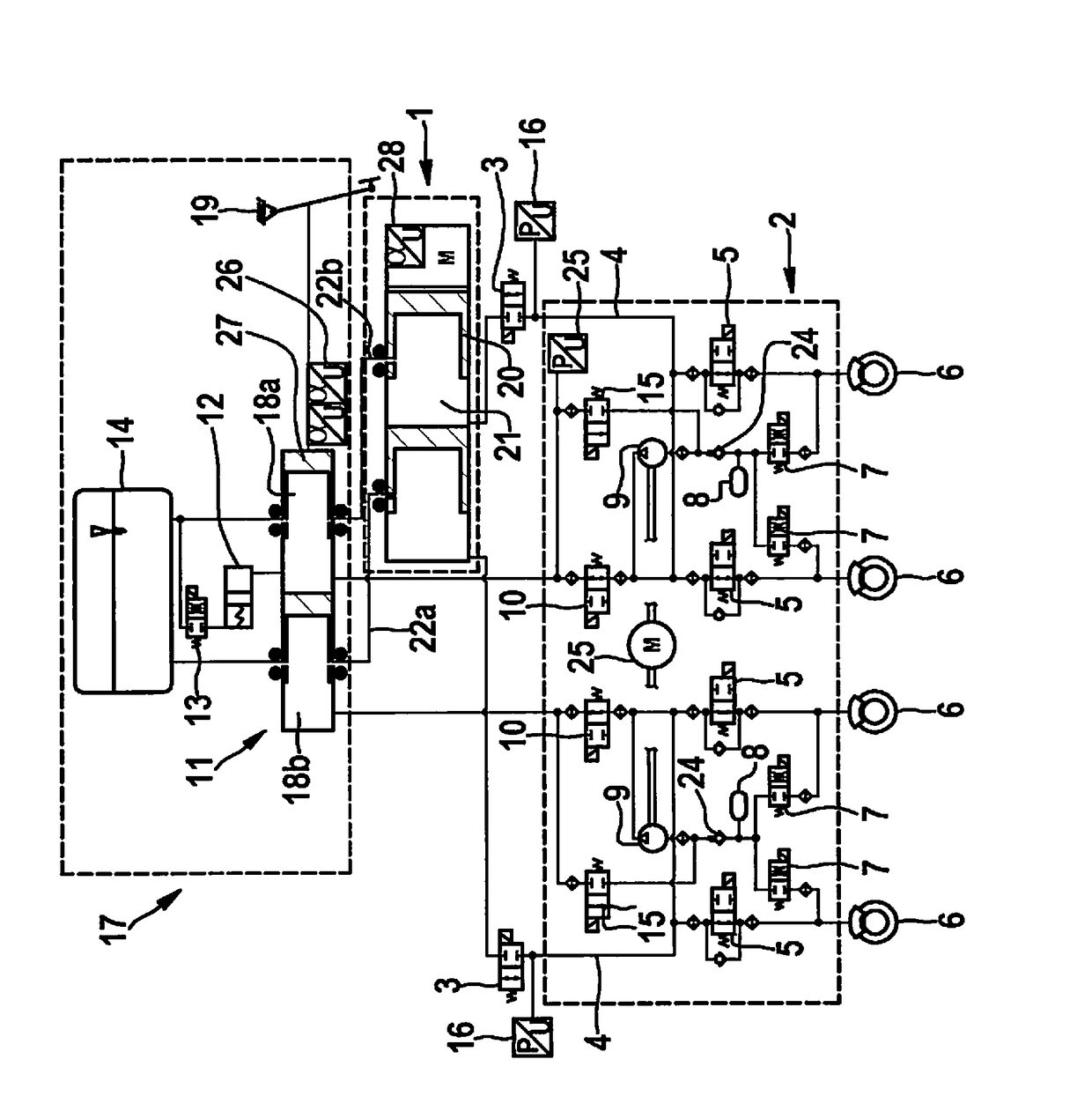
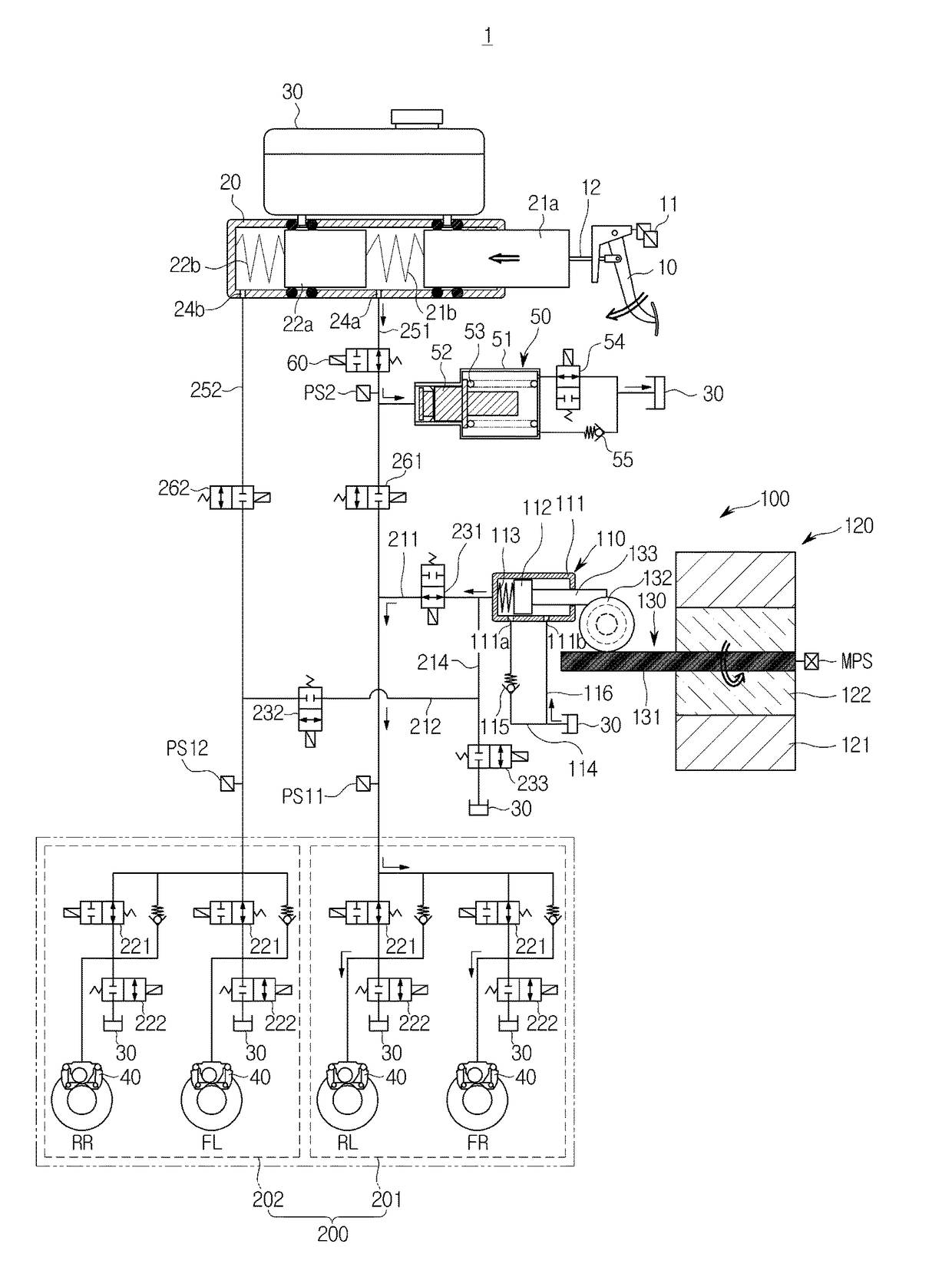
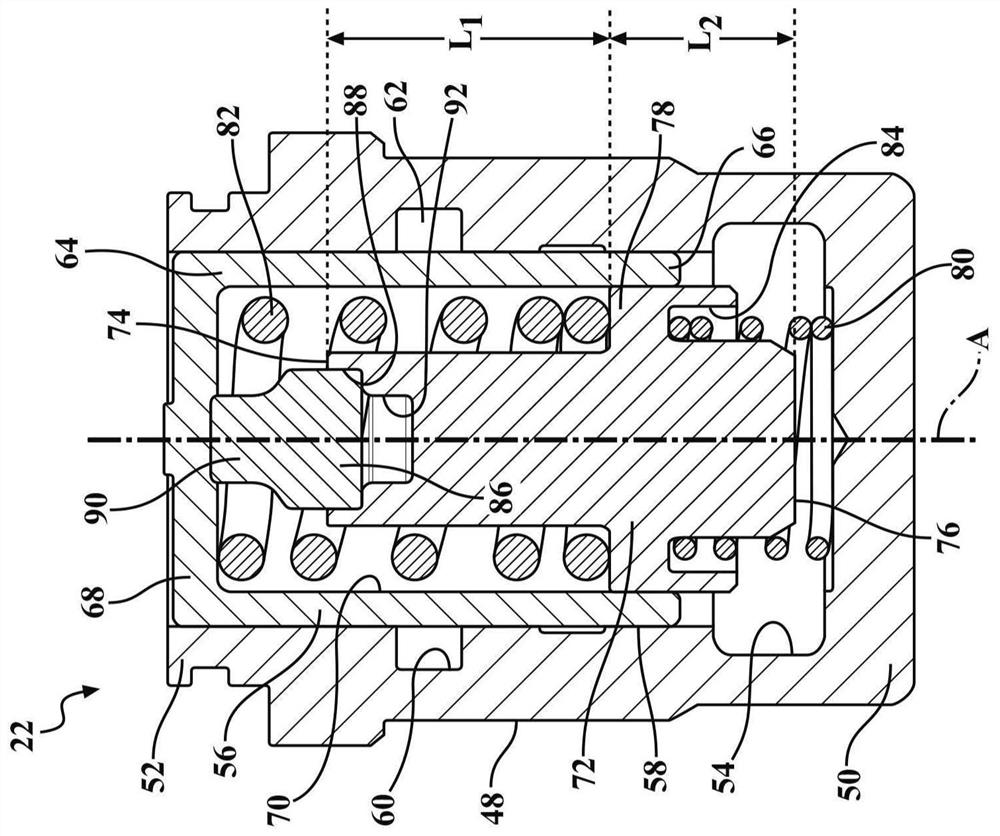
Hydraulic brake system and method for operating a hydraulic brake system
InactiveUS9914440B2Completely isolatedInhibitionVehicle sub-unit featuresBraking pressure measurementsHydraulic brakeBraking system
A hydraulic braking system and a method for operating the hydraulic braking system. The hydraulic braking system has a first pressure generating unit and a second pressure generating unit. The first pressure generating unit is hydraulically interruptibly and uncircumventably connected to the second pressure generating unit via a first interrupting element in such a way that with the first interrupting means in a closed position, a hydraulic connection between the first and second pressure generating unit is no longer possible.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
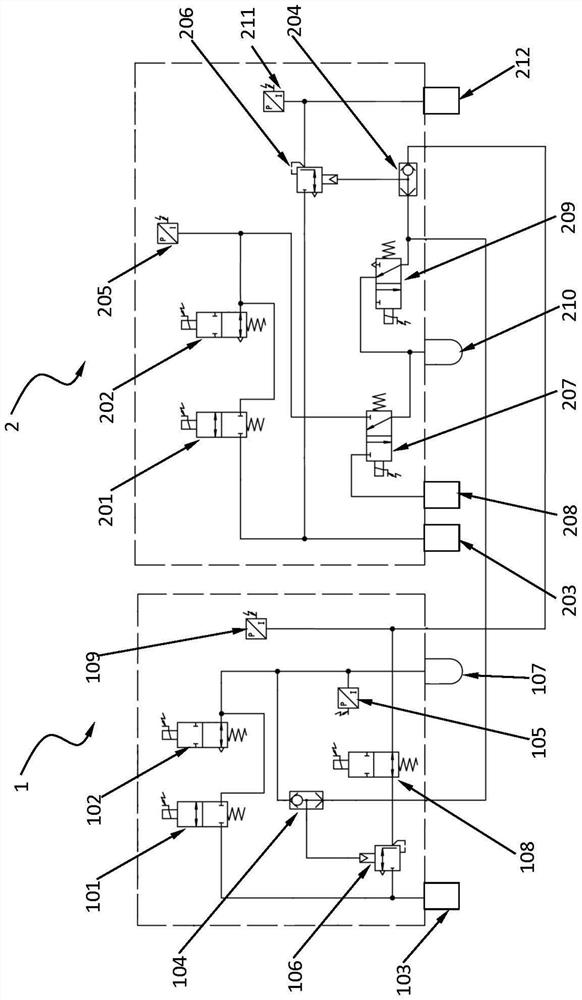
Electronic brake system
ActiveUS10857891B2Braking element arrangementsBraking action transmissionDriver/operatorControl theory
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Electric apparatus of a vehicle having an at least partly electric braking and steering device
InactiveUS20210129831A1Simple equipmentSatisfies fault toleranceBrake system interactionsVehicle sub-unit featuresDriver/operatorSteering wheel
An electric equipment component of a vehicle having an electric braking / steering device, including: a) an electric steering device with / without a continuous mechanical connection between a steering wheel and a steering gear mechanism, and an electronic steering control device and an electric steering actuator; an electropneumatic service brake device having an electropneumatic service brake valve device, an electronic brake control device, electropneumatic modulators and pneumatic wheel brake actuators; and a device having the electronic evaluation device of the electropneumatic service brake valve device and generating a second activation force independently of a driver's braking request, the further device acting on the control piston in the same or opposite direction to the first activation force when a braking request, independent of the driver's request, is present; the electronic evaluation device being integrated into the electronic steering control device, or the electronic steering control device being integrated into the electronic evaluation device.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Brake control system used in a vehicle and control method thereof
ActiveUS11225231B2Increase brake pressureInhibitionBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesControl systemMechanical engineering
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
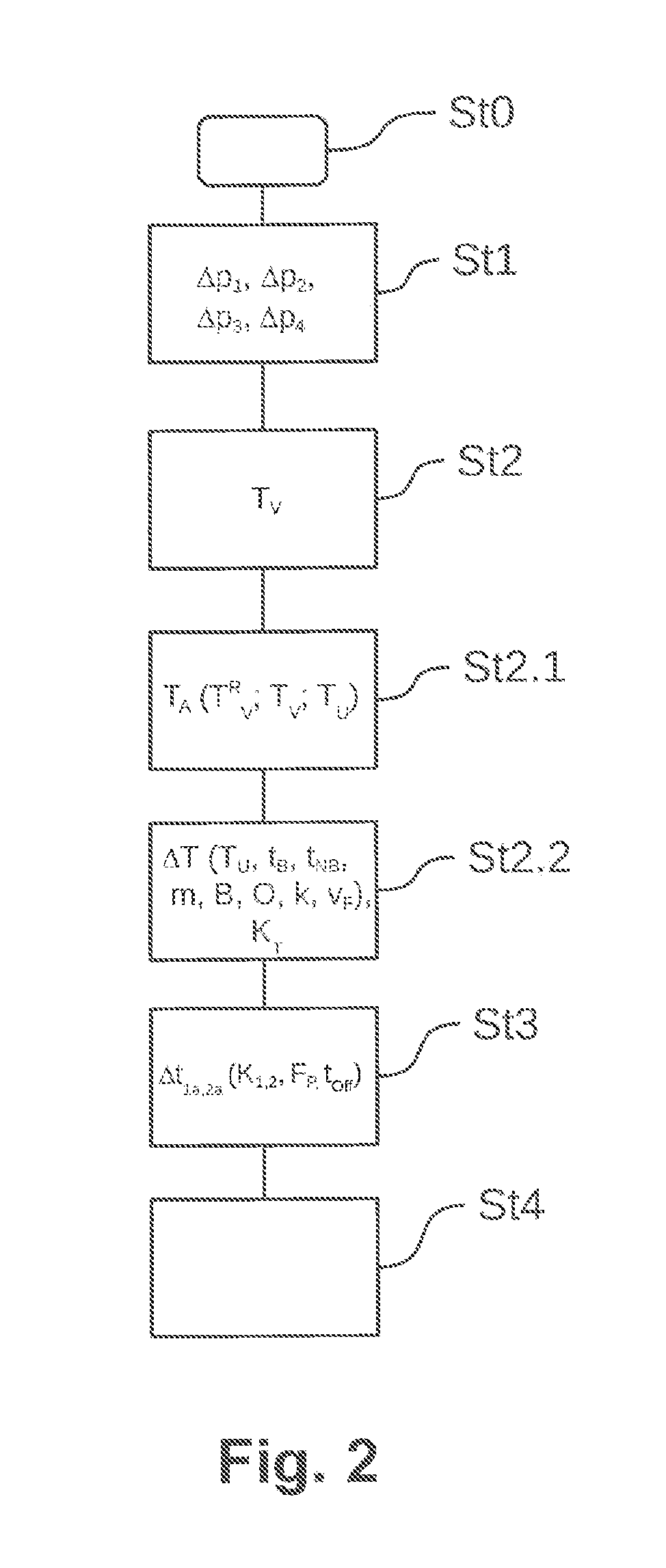
Method for the temperature-dependent control of a pressure control valve and a control device therefore
ActiveUS20170036655A1Application and release valvesBraking pressure measurementsInlet valvePressure difference
A method for the temperature-dependent control of a pressure control valve of a vehicle comprising an inlet valve and an outlet valve includes detecting a predefined pressure difference to be controlled by the pressure control valve, determining a present valve body temperature, wherein, for this purpose, a temperature change proceeding from a starting temperature is considered depending on at least one detected valve body influencing variable, determining, depending on the pressure difference to be controlled and on the determined present valve body temperature, at least one of a temperature-adjusted pulse duration for the inlet valve and a temperature-adjusted pulse duration for the outlet valve, and controlling at least one of the inlet valve and the outlet valve of the pressure control valve via the particular temperature-adjusted pulse duration in order to effectuate the detected pressure difference at the determined valve body temperature.
Owner:ZF CV SYST EURO BV
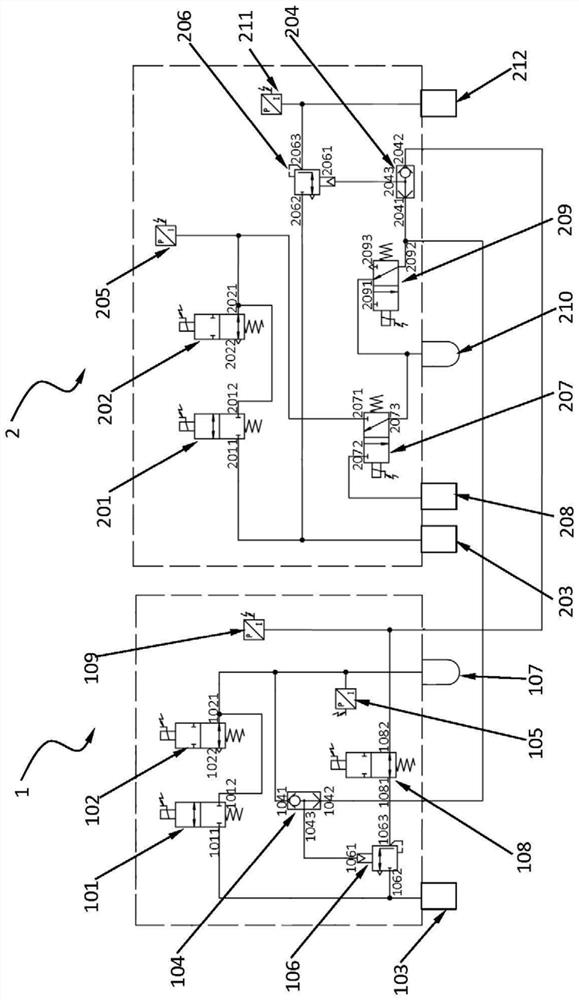
Electronic brake system and control method thereof
ActiveUS20180118179A1Braking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsWheel cylinderPressure measurement
Disclosed herein is an electronic brake system, which includes at least one or more valves provided to control a hydraulic pressure delivered to wheel cylinders provided in wheels, a pressure measurer configured to measure the hydraulic pressure delivered to the wheel cylinders provided in the wheels, and a controller configured to open at least one or more valves that deliver the hydraulic pressure to a corresponding wheel cylinder and close at least one or more valves that deliver the hydraulic pressure to the remaining wheel cylinders other than the corresponding wheel cylinder when the at least one or more valves are detected as being opened or closed a predetermined number of times or more during a predetermined time period, and synchronize the measured hydraulic pressure with a hydraulic pressure of the wheel cylinder having all of the at least one or more valves open.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
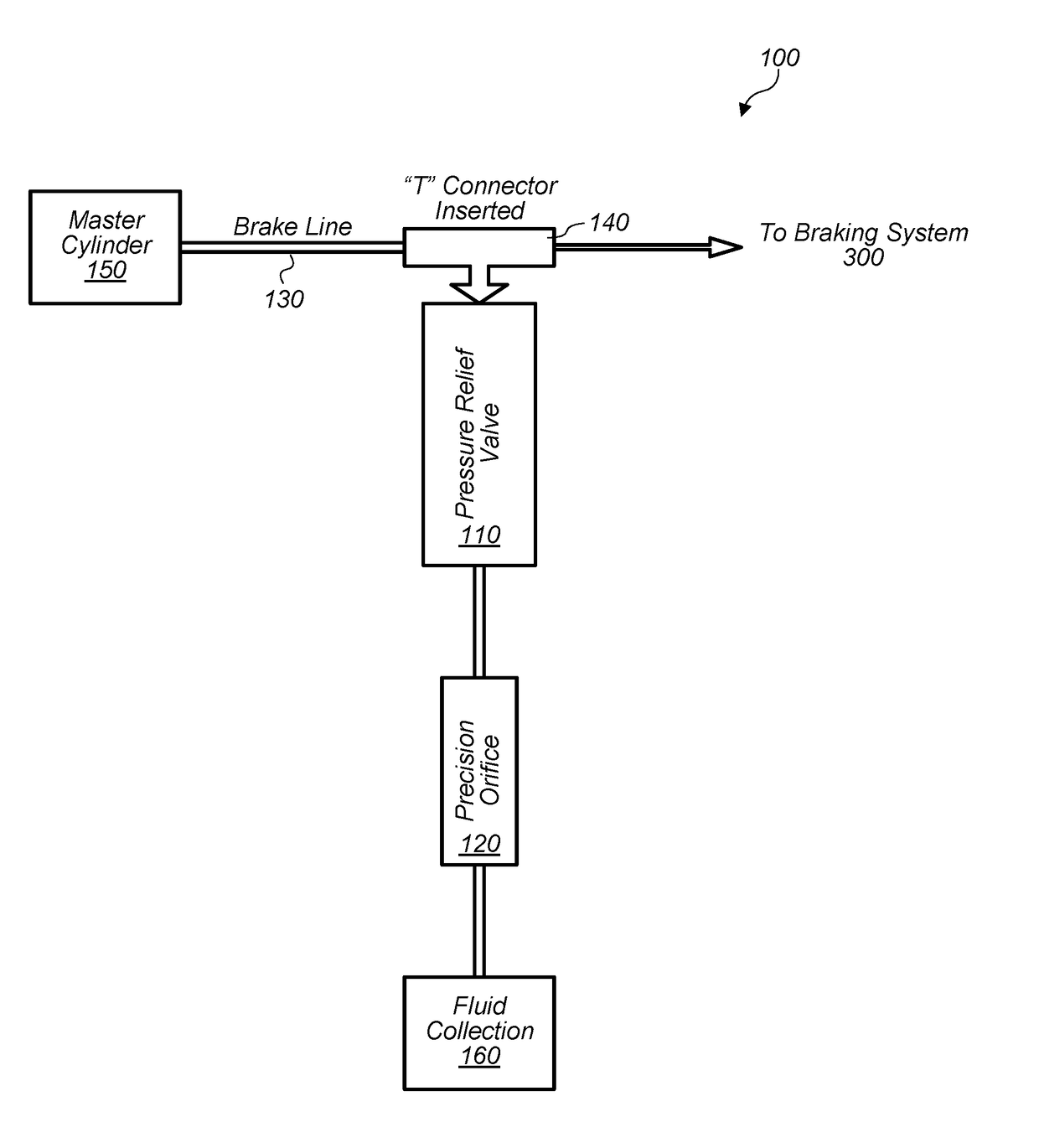
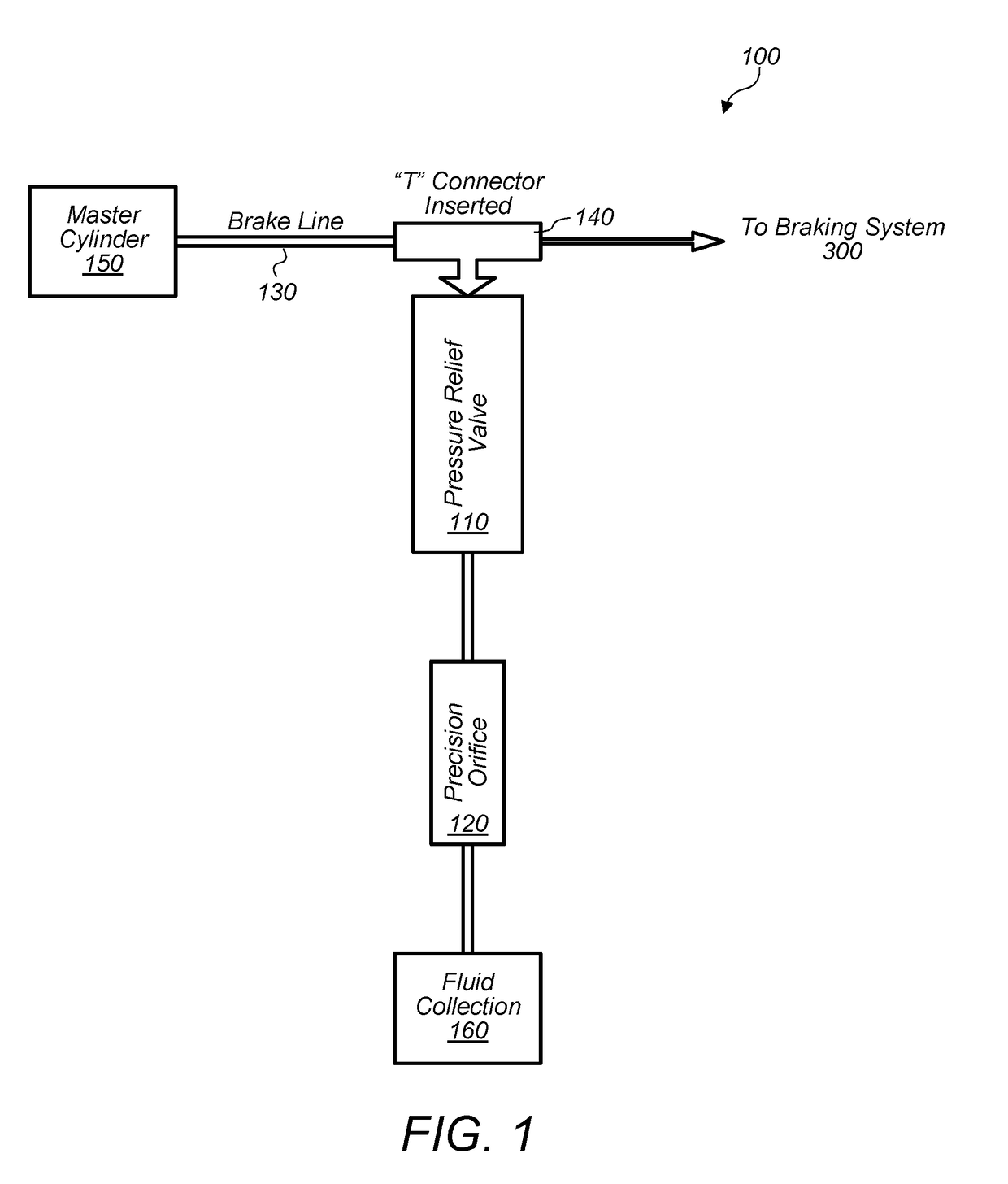
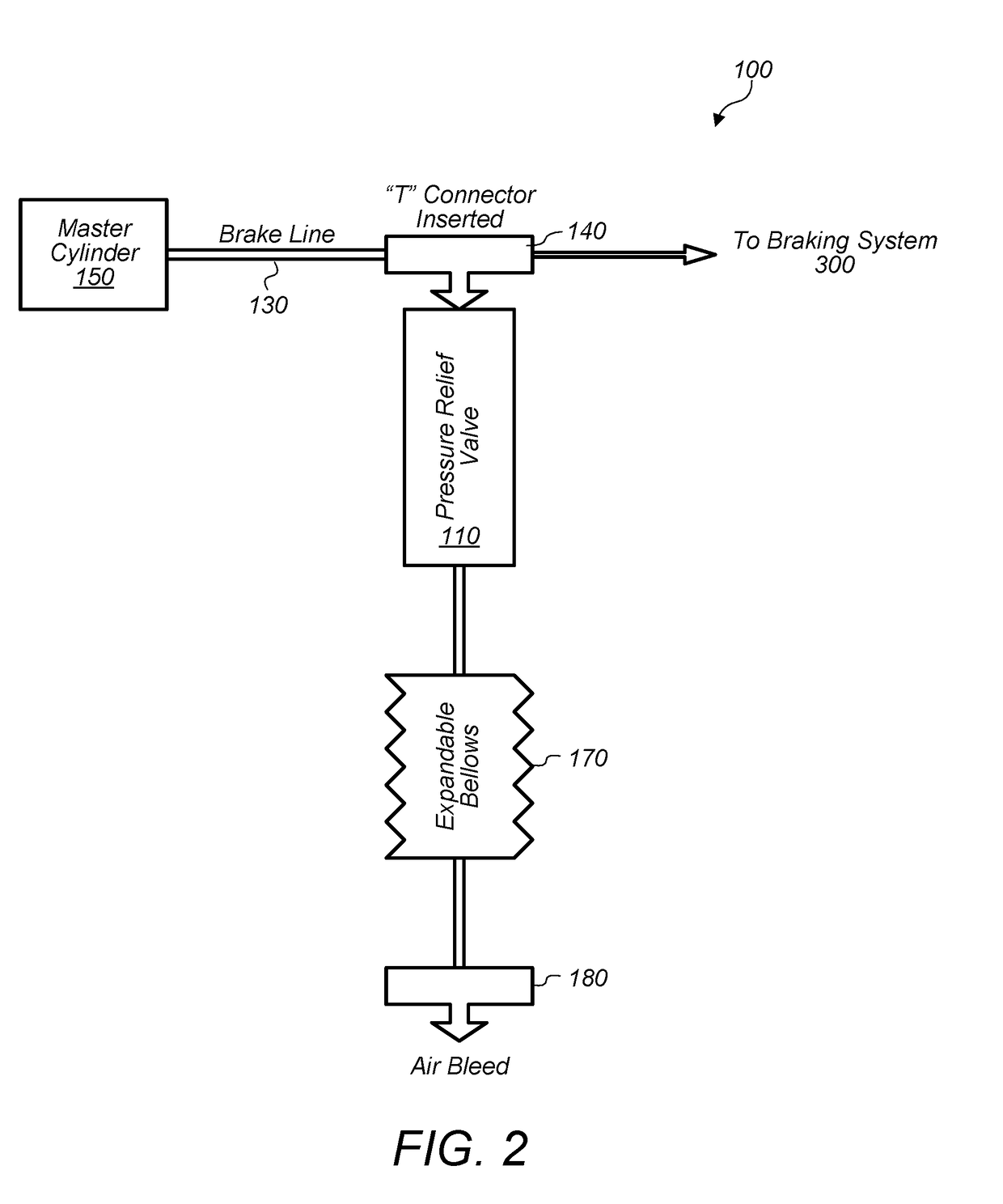
Pressure relief designs for vehicle braking system to prevent injuries
InactiveUS20180118175A1Reduce certain injuries resultingReduce fluid pressureBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsEngineeringPreventing injury
In some embodiments, a system and / or method may reduce certain injuries resulting from a vehicle collision. The method may include opening a valve in a pressurized brake line of a brake system of a vehicle in response to a trigger. The trigger may include a set pressure value of a fluid in the pressurized brake line. The method may include allowing the fluid in the pressurized brake line to flow through a sized opening accessible through the opened valve. The sized opening may reduce a fluid pressure in the pressurized brake line verses time. The sized opening may be dimensioned to allow a flow rate of the fluid conveying through the sized opening such that the fluid pressure reduces over a period of time. The method may include reducing backpressure on a brake pedal coupled to the pressurized brake line.
Owner:STOCKBAUER FRED S
Railway Brake Cylinder Monitoring System and Method
ActiveUS20200079342A1Braking action transmissionWireless architecture usageMonitoring systemControl theory
A system and method for monitoring air pressure applied to a brake cylinder of a braking assembly of a railway vehicle, including an empty-load device, and an RFID transducer in communication with the empty-load device, wherein the RFID transducer is configured to measure the air pressure delivered to the brake cylinder of the braking assembly, and generate data on the air pressure delivered to the brake cylinder of the braking assembly; and a remote data monitor configured to read data from the RFID transducer.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
Method for detecting malfunctions of an electro-actuated brake apparatus of a motor vehicle
A method for detecting malfunctions of a motor vehicle electro-actuated brake apparatus may include the steps of providing, in an electronic control unit, a functional control block and a first functional block having a numerical model representative of the electro-actuated brake caliper. The method may also include providing a target signal to the functional control block for generating the control signal to operate the electro-actuated brake caliper. The method may also include providing the target signal to the first functional block for generating a first signal. In the method, the first signal may be compared with a feedback signal for generating an error signal to be sent to the electronic control unit. Further, the method may include performing, by the second functional block, an error validation check to provide information on the operating state of the electro-actuated brake caliper to the electronic control unit.
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
Method for detecting malfunctions of an electro-actuated brake apparatus of motor vehicle
ActiveCN112955357ASuitable for operating conditionsBraking action transmissionBrake typesControl signalTarget signal
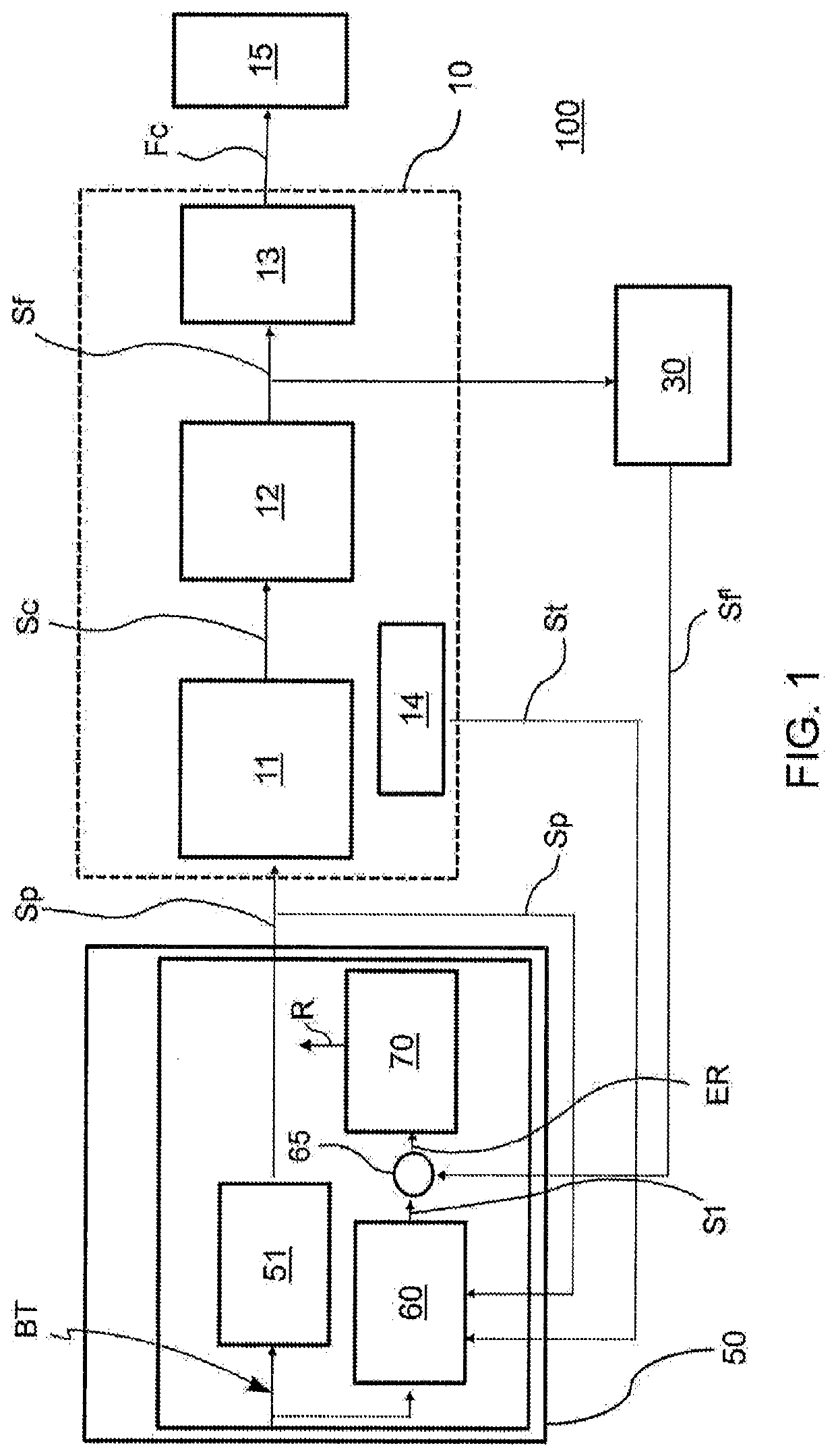
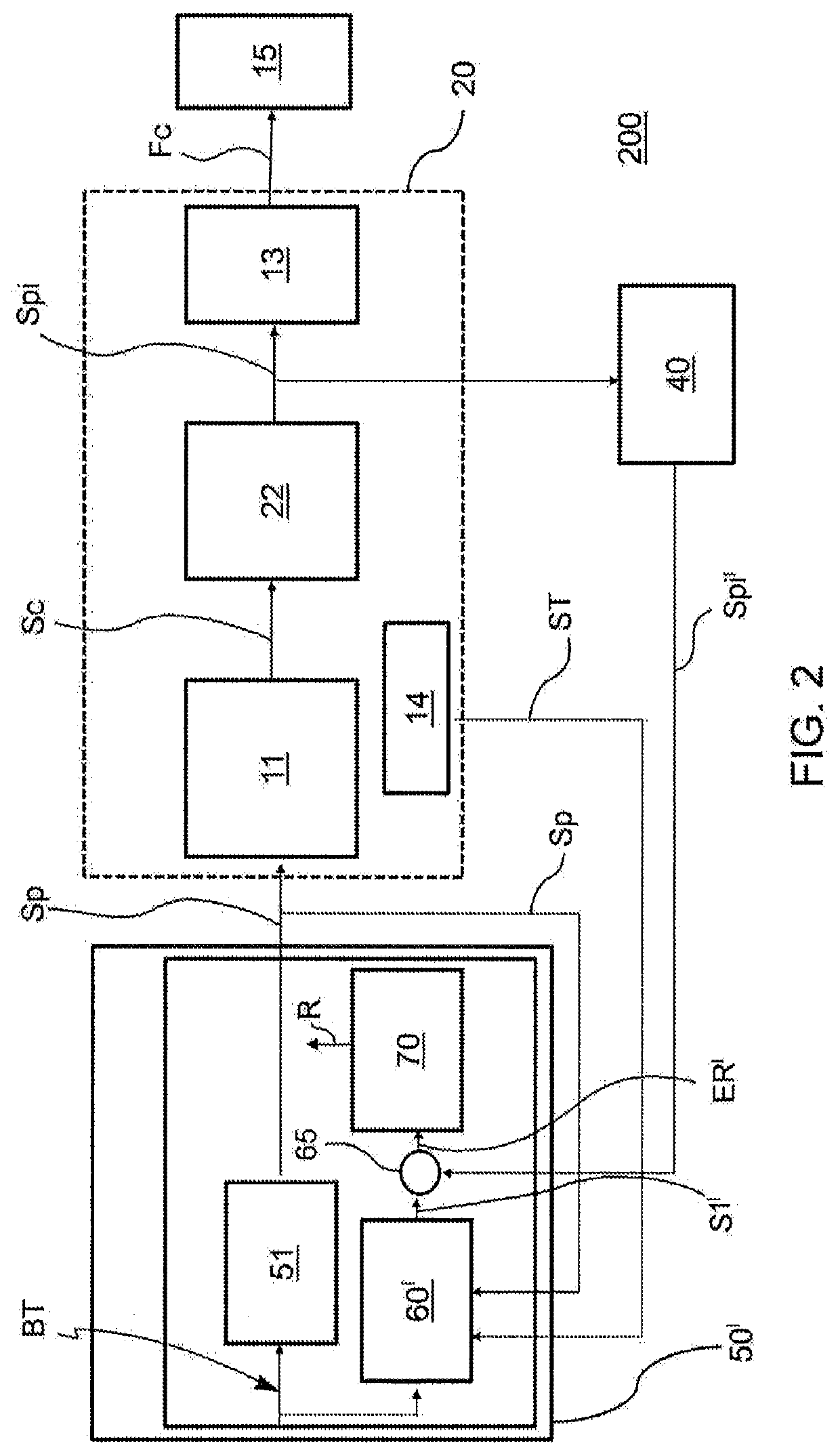
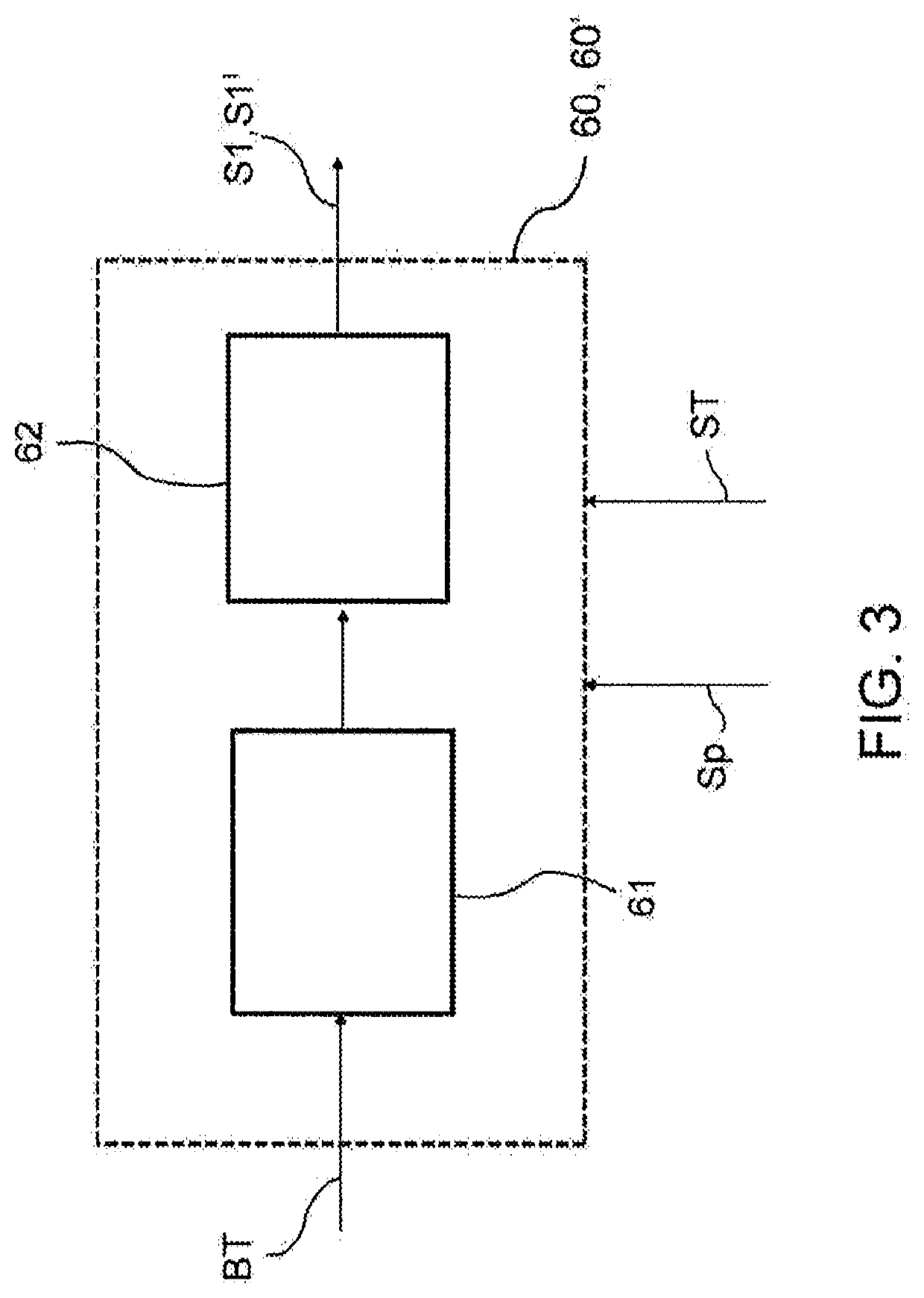
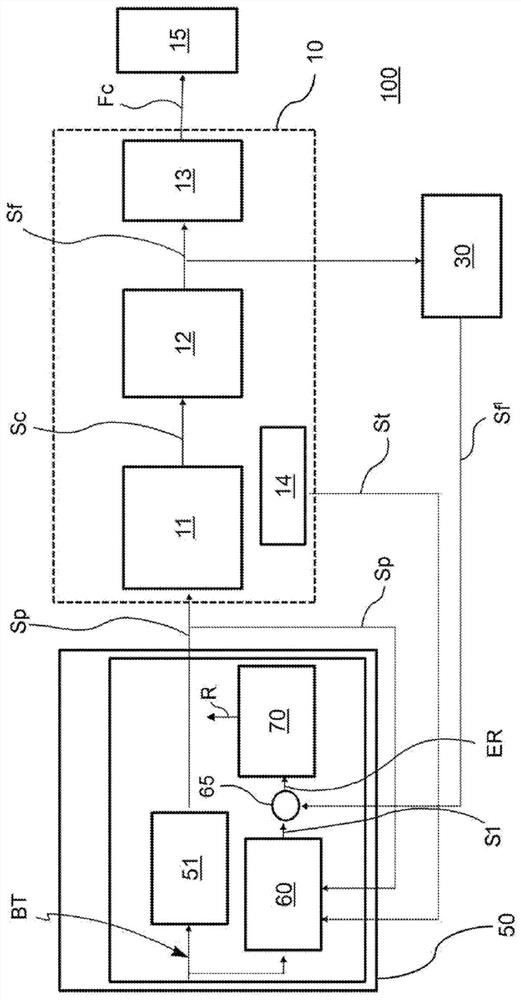
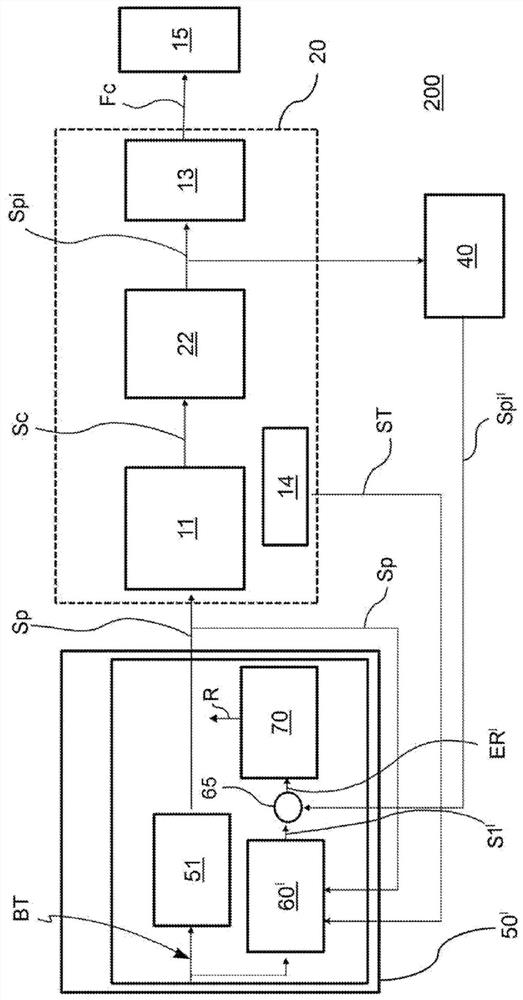
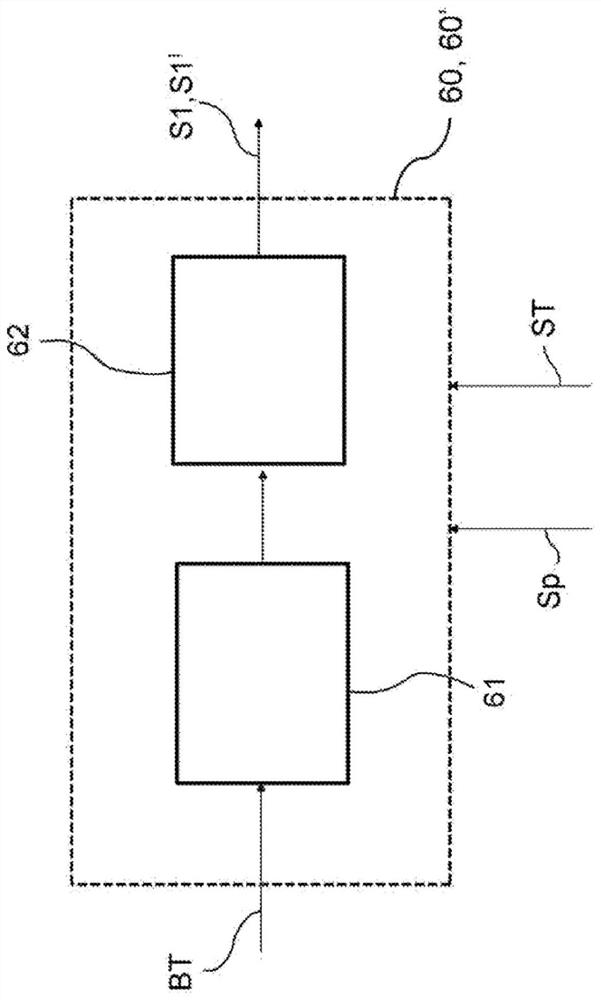
The invention relates to a method for detecting malfunctions of an electro-actuated brake apparatus (100; 200) of a motor vehicle. The apparatus includes: an electronic control unit (50; 50'); an electro-actuated brake caliper (10; 20) electrically actuated by the electronic control unit for generating a clamping force (Fc) on a disc (15) of the brake apparatus in response to a control signal (Sp) generated by the electronic control unit. The method comprising the steps of: providing, in the electronic control unit, a functional control block (51) and a first functional block (60; 60') consisting of a numerical model representative of the electro- actuated brake caliper; providing a target signal (BT) to the functional control block for generating said control signal to operate the electro-actuated brake caliper; providing said target signal to the first functional block for generating a first signal (S1; S1') representative of a theoretical quantity associated with the numerical model representative of the electro-actuated brake caliper; comparing said first signal with a feedback signal (Sf'; Spi') representative of a real operating quantity associated with the electro-actuated brake caliper for generating an error signal to be sent to a second functional block (70) of the electronic control unit; performing, by said second functional block, an error validation check to provide information (R) on the operating state of the electro-actuated brake caliper to the electronic control unit.
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
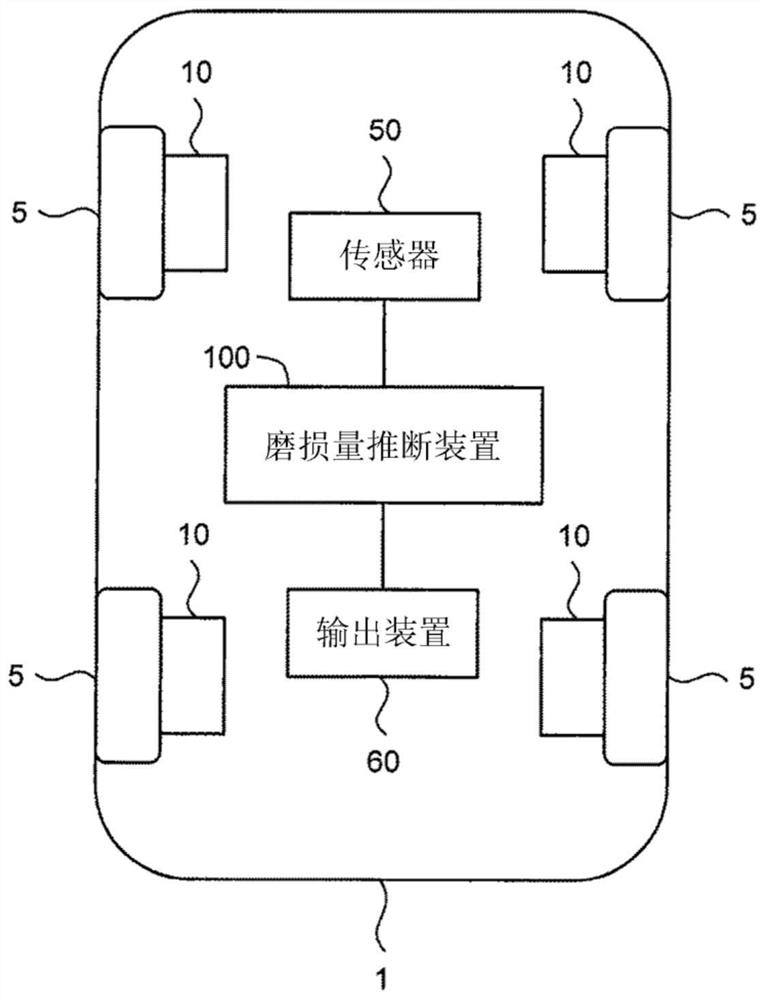
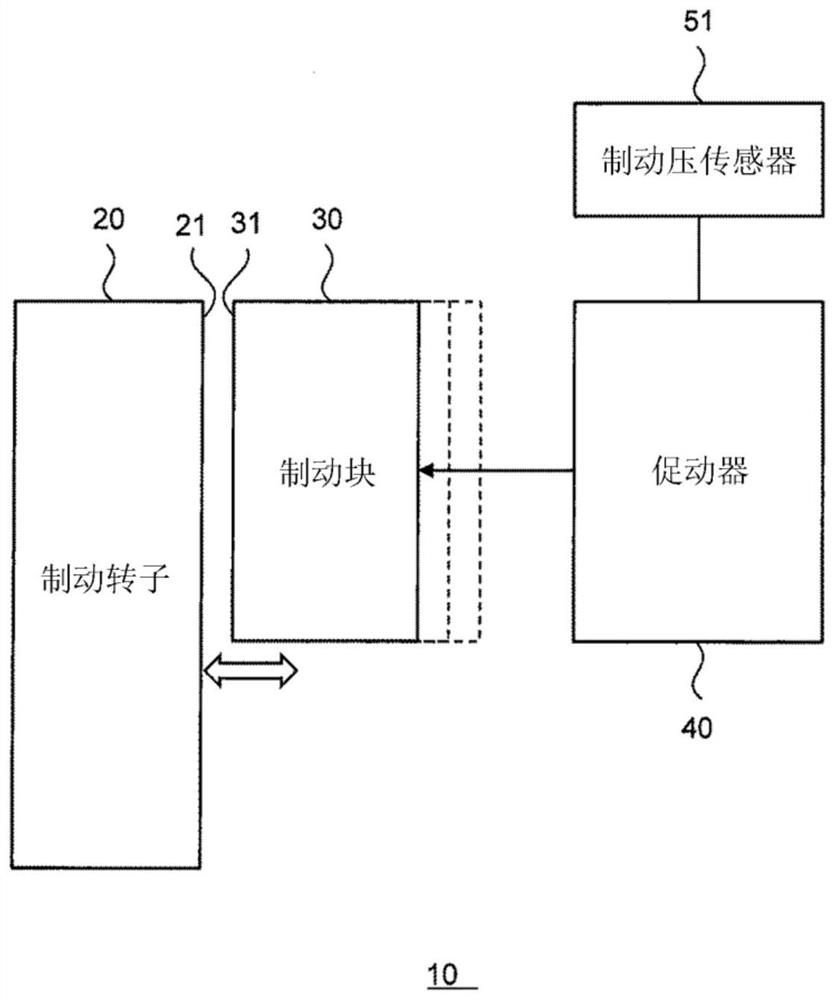
Wear amount estimation device, wear amount estimation method, and wear amount estimation program
PendingCN114060439AImprove inference accuracyBraking elementsBraking pressure measurementsControl theoryMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a wear amount estimation device, a wear amount estimation method, and a wear amount estimation program for improving the estimation accuracy of the wear amount of a brake pad of a vehicle. The amount of wear function represents the amount of wear as a function of vehicle speed, brake pressure, and brake duration. When the vehicle is braked, the wear amount estimation device executes a wear amount calculation process for calculating a wear amount corresponding to the vehicle speed, the brake pressure, and the brake duration by using the wear amount function. In addition, the wear amount estimation device estimates the temperature of the contact portion of the brake pad in contact with the brake rotor on the basis of the vehicle speed, the brake pressure, and the brake duration. On the basis of the temperature of the contact part, the wear amount estimation device updates temperature history information indicating at least the temperature history of the contact part. In the wear amount calculation process, the wear amount function is variably set on the basis of the temperature history of the contact portion indicated by the temperature history information obtained at the time of the last braking.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for decelerating a vehicle train and combination of pneumatic brake systems of the vehicles of a vehicle train
ActiveCN109789859AReduce slipBrake pressure boostABS control systemsBraking pressure measurementsInlet valveEngineering
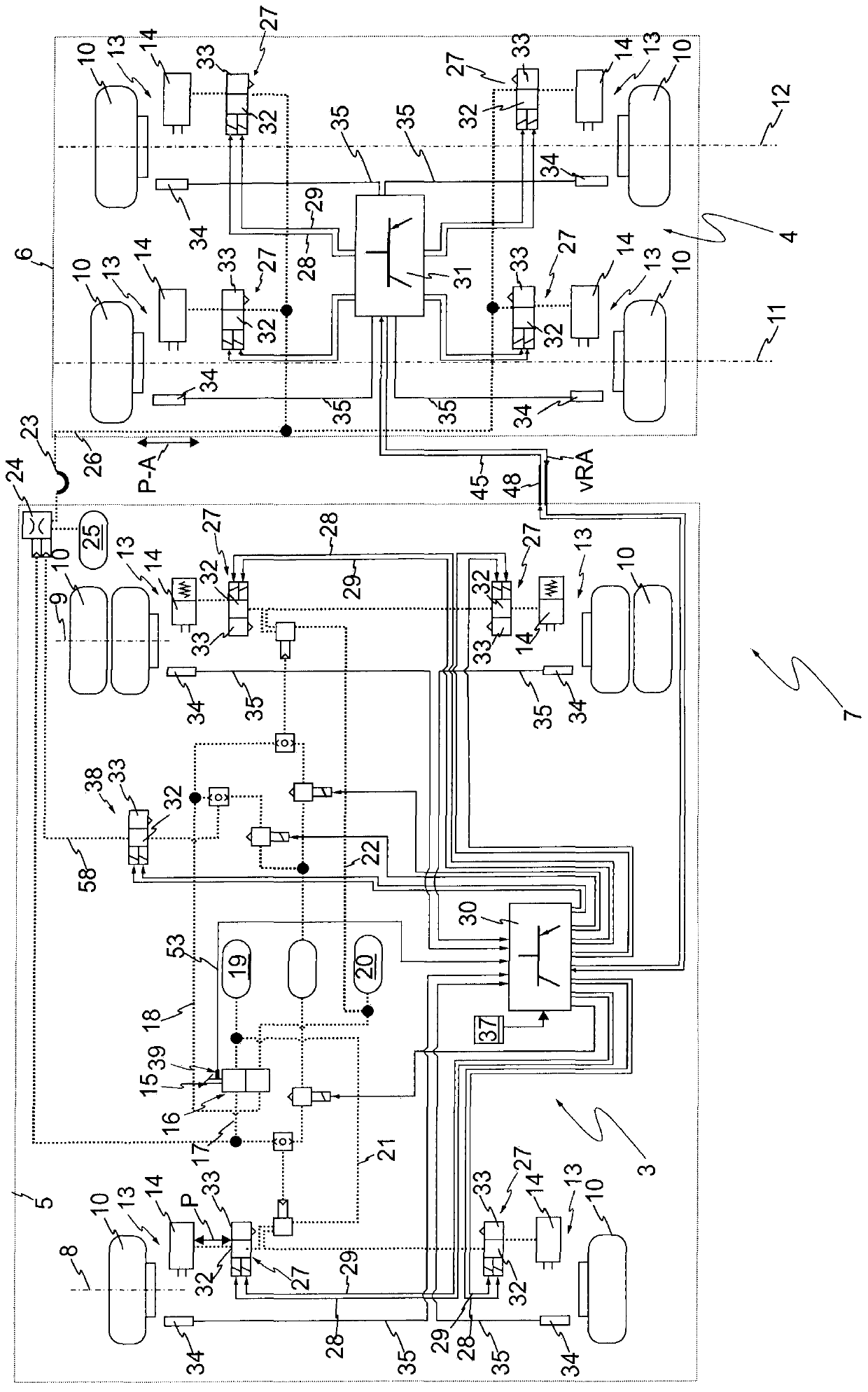
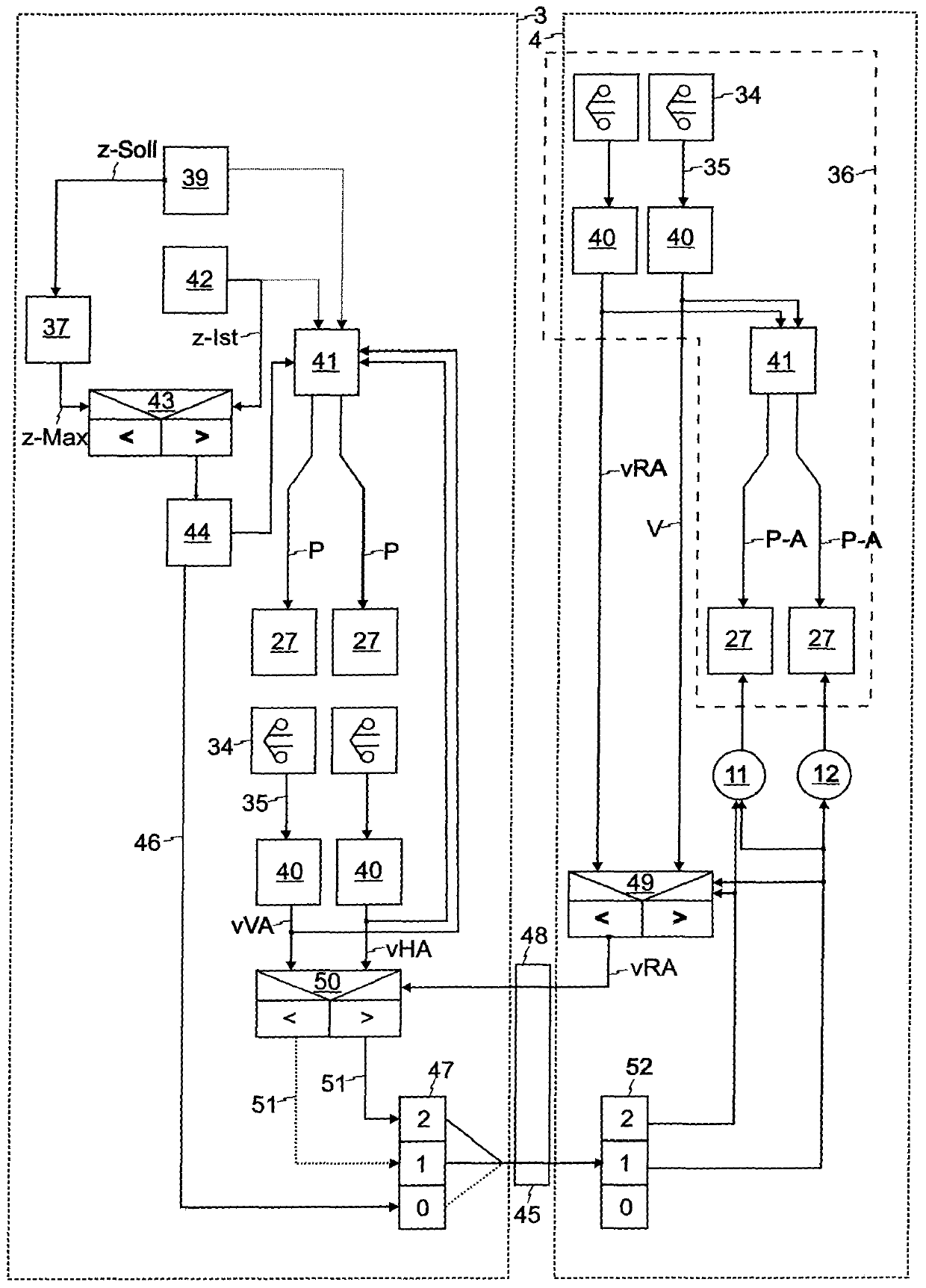
The invention relates to a method for decelerating a vehicle train with a traction vehicle and at least one trailer vehicle with an anti-lock brake system, and to a combination of pneumatic brake systems of the vehicles of a vehicle train. In order to improve the braking behaviour of a vehicle train, the invention provides that an electronic brake control unit (30) of the traction vehicle brake system (3) detects a current vehicle deceleration actual value (z-lst), continuously compares the vehicle deceleration actual value (z-lst) with a maximum deceleration (z-Max) and in the event of the vehicle deceleration actual value (z-lst) reaching or exceeding the maximum deceleration (z-Max) limits the brake pressure (P) and makes available an information signal (45) for the respective brake electronics (31) of each trailer vehicle (6), which information signal (45) represents at least one piece of limiting status information (46), wherein the respective brake electronics (31) of a trailer brake system (4) acquire measurement signals (35) from rotational speed sensors (34), and set the brake pressure (P-A) at the wheel brakes (13) as a function of the measurement signals (34) by actuating pressure control valves (27) receive (52) the information signal (45), and, when limitation (44) of the brake pressure in the traction vehicle (5) is detected on the basis of the measurement signals(34) for each trailer axle (11, 12), determine a dynamic slip variable value (v, vRA) which represents the slip, compare (49) slip variable values (v, vRA) of all the trailer axles (11, 12) with oneanother, and close the inlet valves (32) of the respective pressure control valves (27) at least at those trailer axles (12) with the higher slip values than a control axle (11) and the currently lowest slip.
Owner:WABCO EURO BVBA SPRL
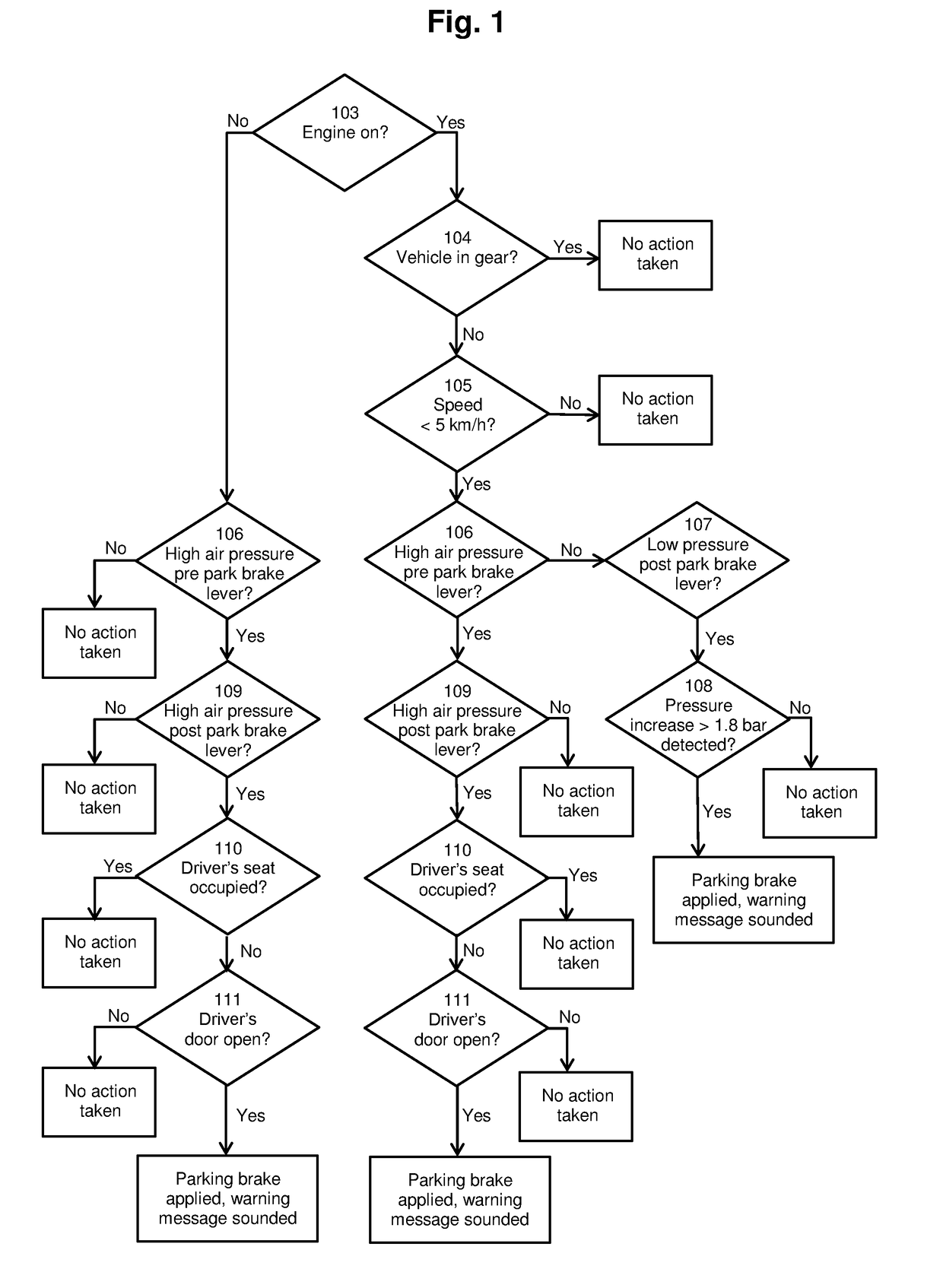
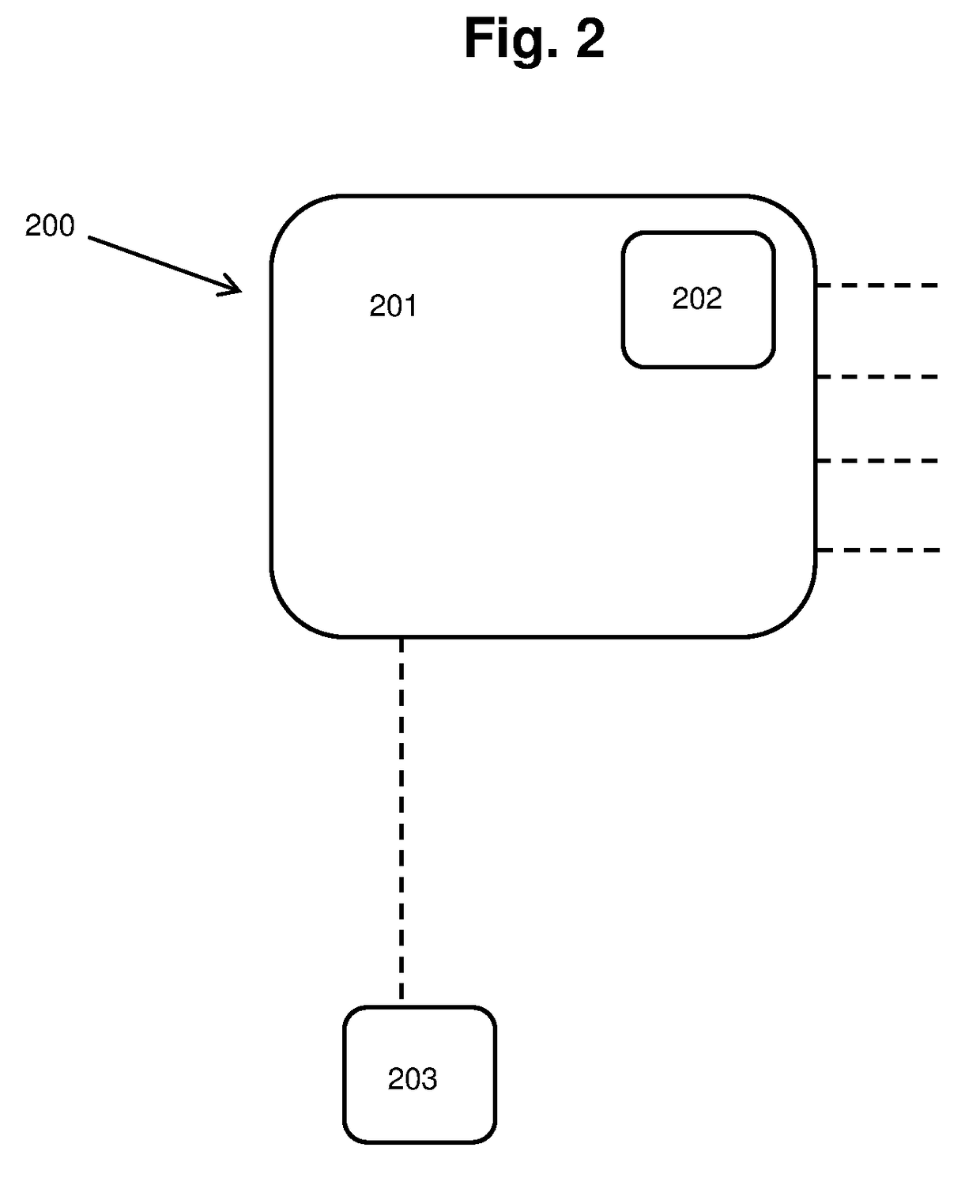
Vehicle safety braking system
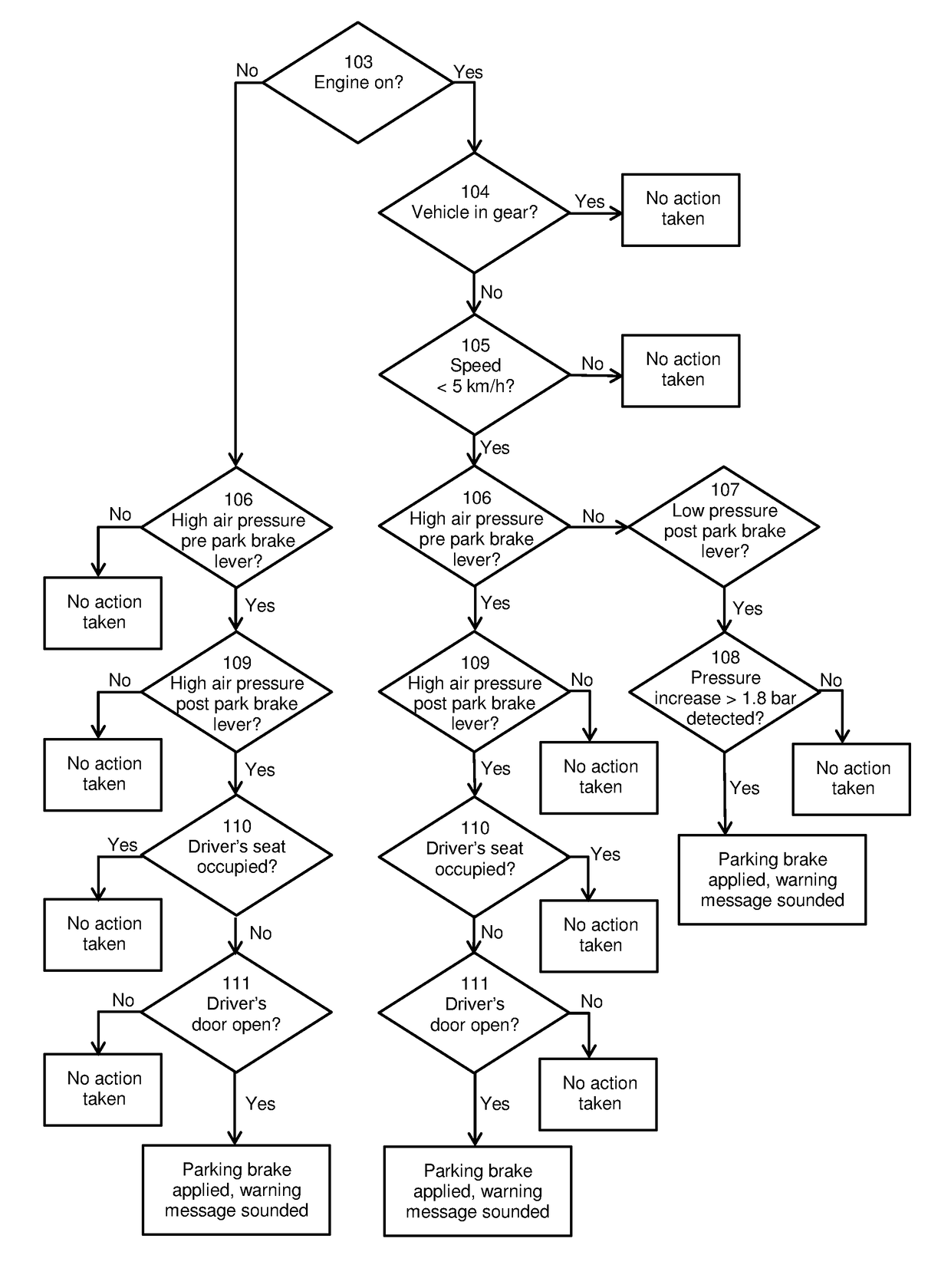
InactiveUS20180319379A1Possible to moveReduce riskAutomatic initiationsABS control systemsParking brakeCommercial vehicle
A vehicle safety device (200) for preventing an unoccupied vehicle moving uncontrollably. The device comprises a control module (201) and a brake module (203). The device (200) is configured to detect when a driver leaves said vehicle. The device (200) is also configured to activate, through the brake module (203), a braking system when the device detects that said driver has left the vehicle. The device may improve the safety of a vehicle in which it is fitted. A system (300) comprising the device (200) and a vehicle (400) comprising the system (300) are also described. A method of preventing an unoccupied vehicle moving is also described. The device, system, vehicle and method are particularly useful for preventing accidents in large commercial vehicles caused by a driver leaving the vehicle without engaging a parking brake.
Owner:VISION TECH (GRP) LTD
Pedal feeling simulator assembly and brake system
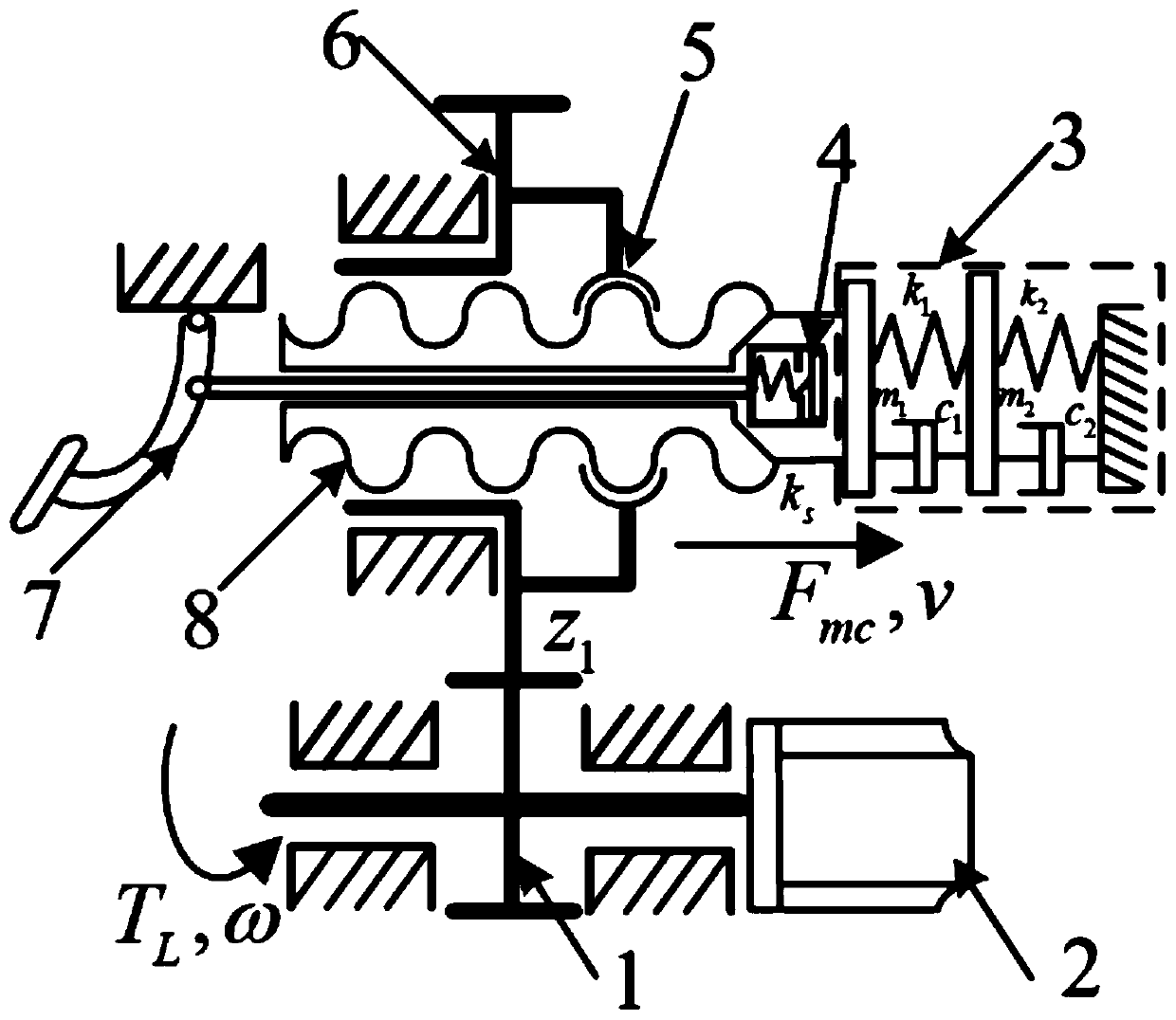
The invention provides a pedal feeling simulator assembly and a brake system. The pedal feel simulator includes a housing extending along a central axis between a closed end and an open end and defining a chamber extending between the closed end and the open end. A first piston is slidably disposed in the chamber. The first piston defines a compartment in fluid communication with the chamber. A second piston is slidably disposed in the compartment. A spring seat extends radially outward from the second piston. A first resilient member is located in the chamber and extends between the spring seat and the closed end. A second resilient member is located in the compartment and extends between the spring seat and the first piston. The third elastic component is located between the second piston and the first piston. The utility model further discloses a brake system comprising the pedal feeling simulator.
Owner:BWI (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com