Patents
Literature
236 results about "Brake wear" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
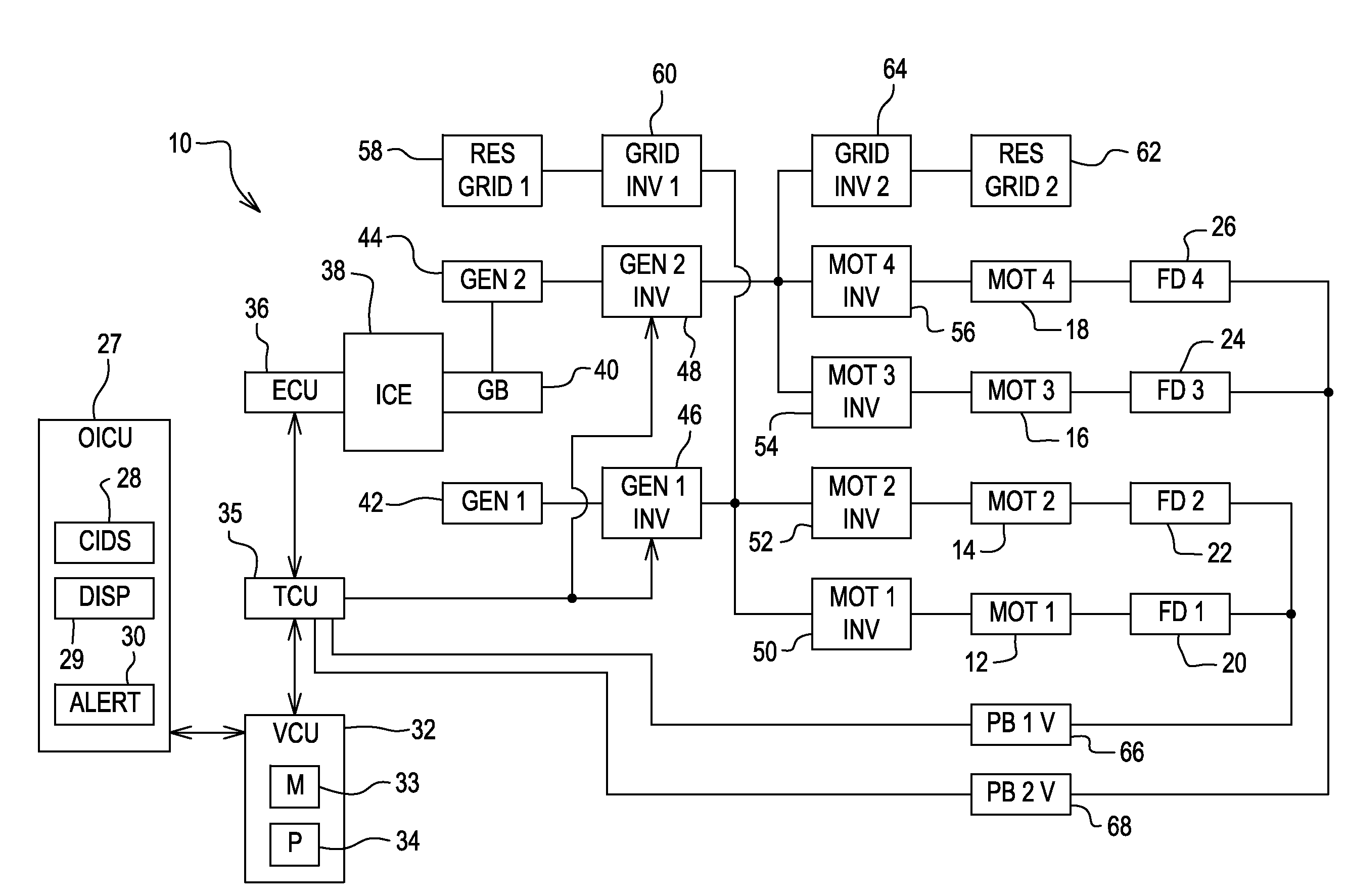
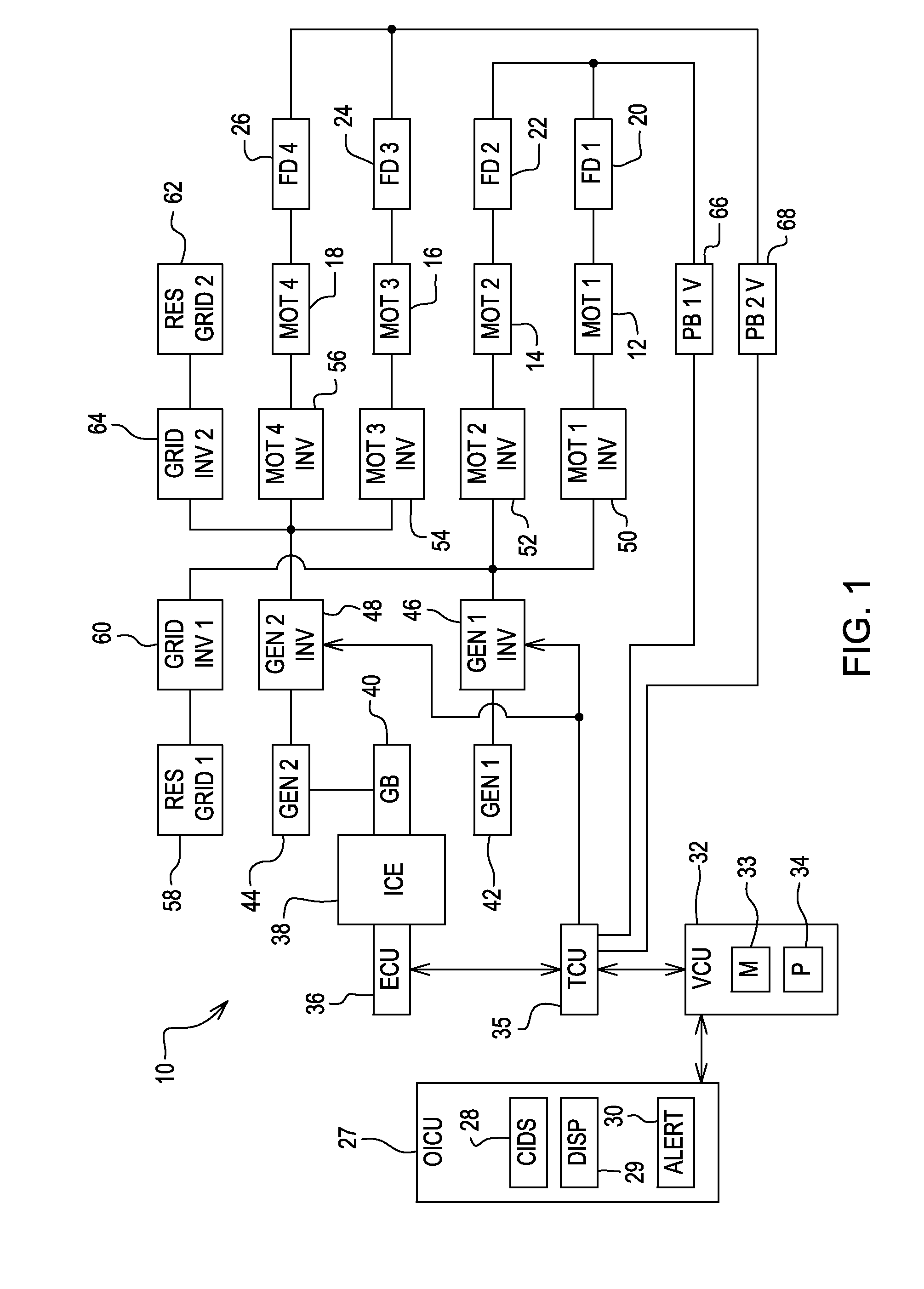
Method and apparatus for a hybrid battery configuration for use in an electric or hybrid electric motive power system
InactiveUS7049792B2Optimize power systemImprove power densityMotor/generator/converter stoppersBatteries circuit arrangementsHigh energyElectric vehicle
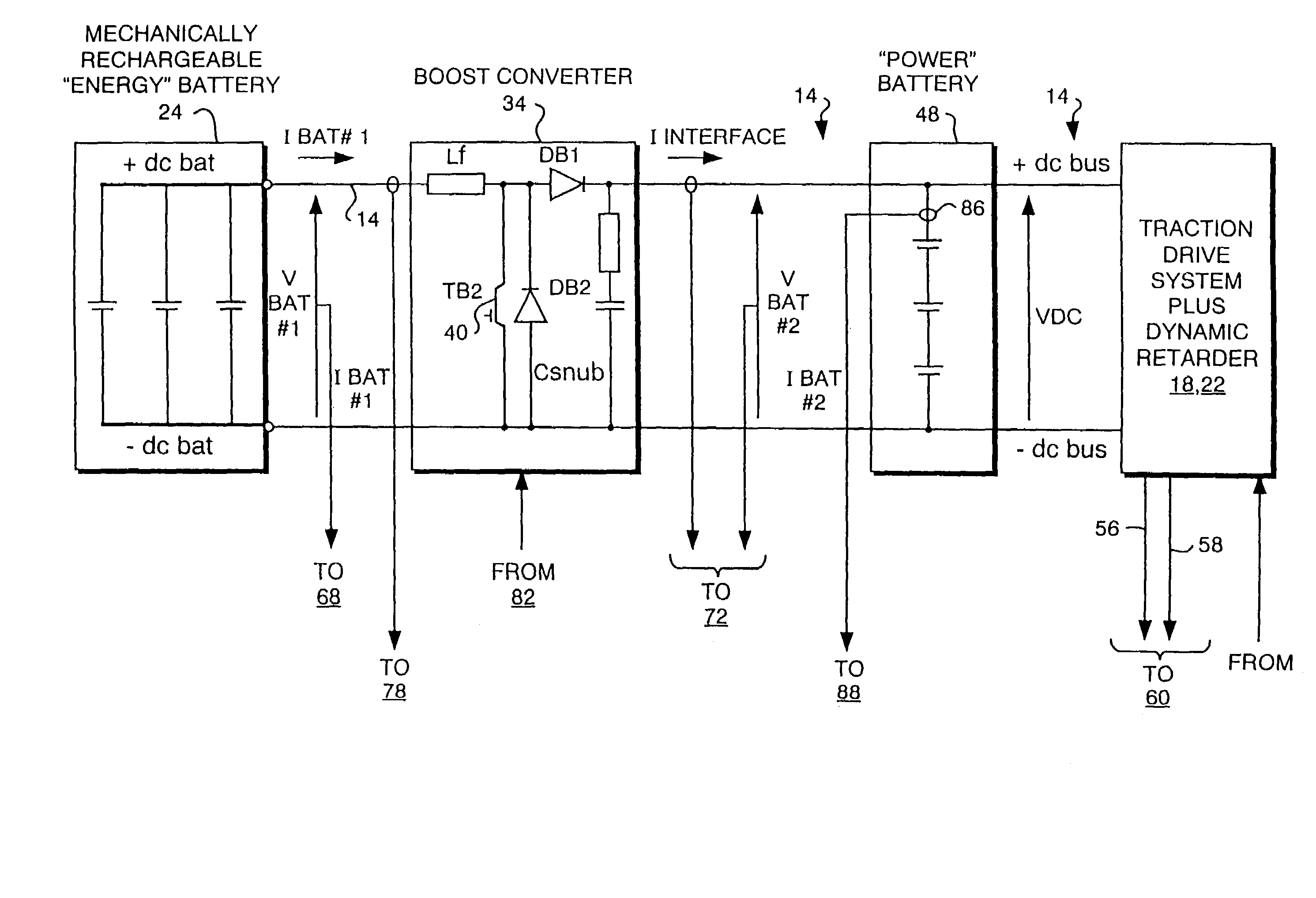
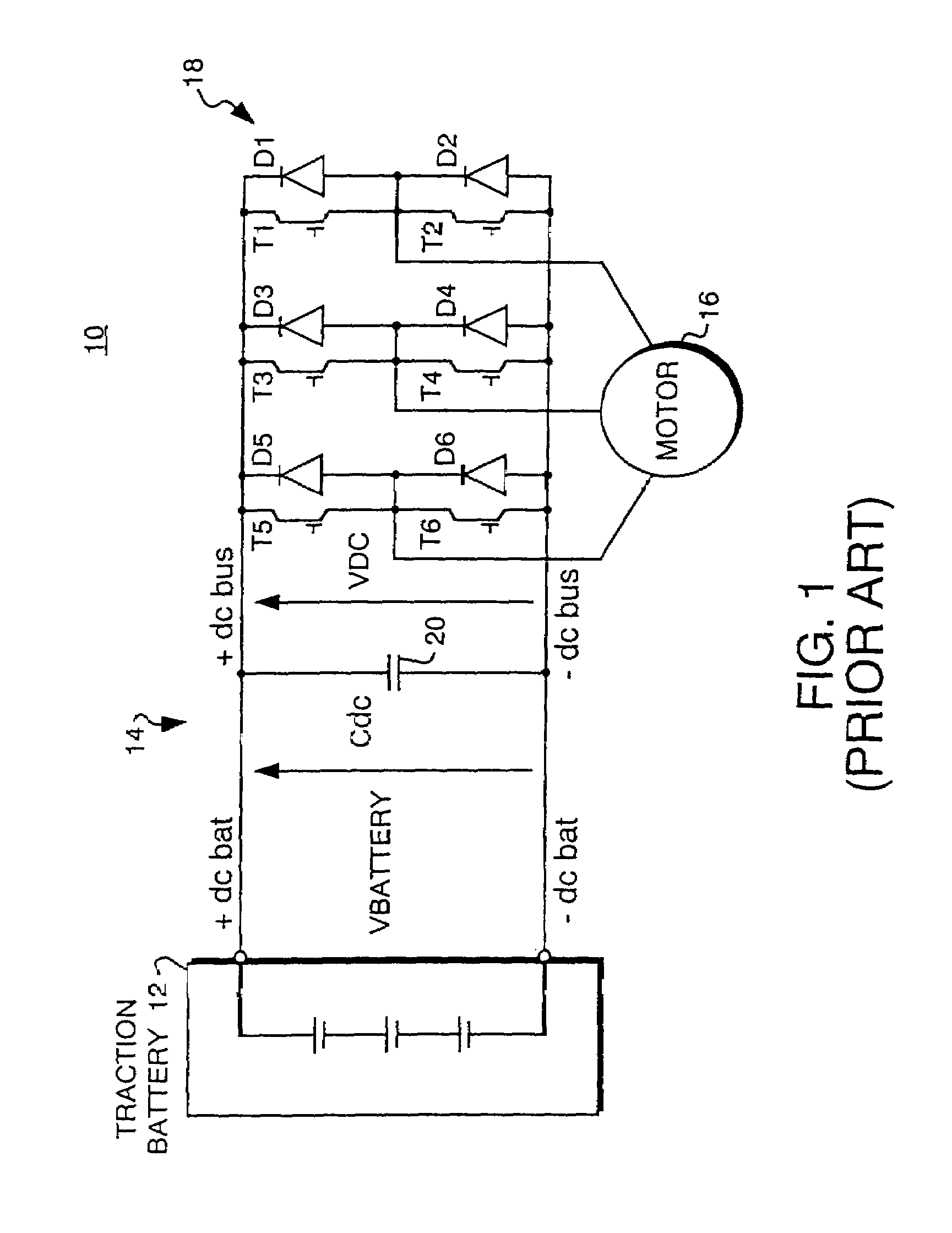
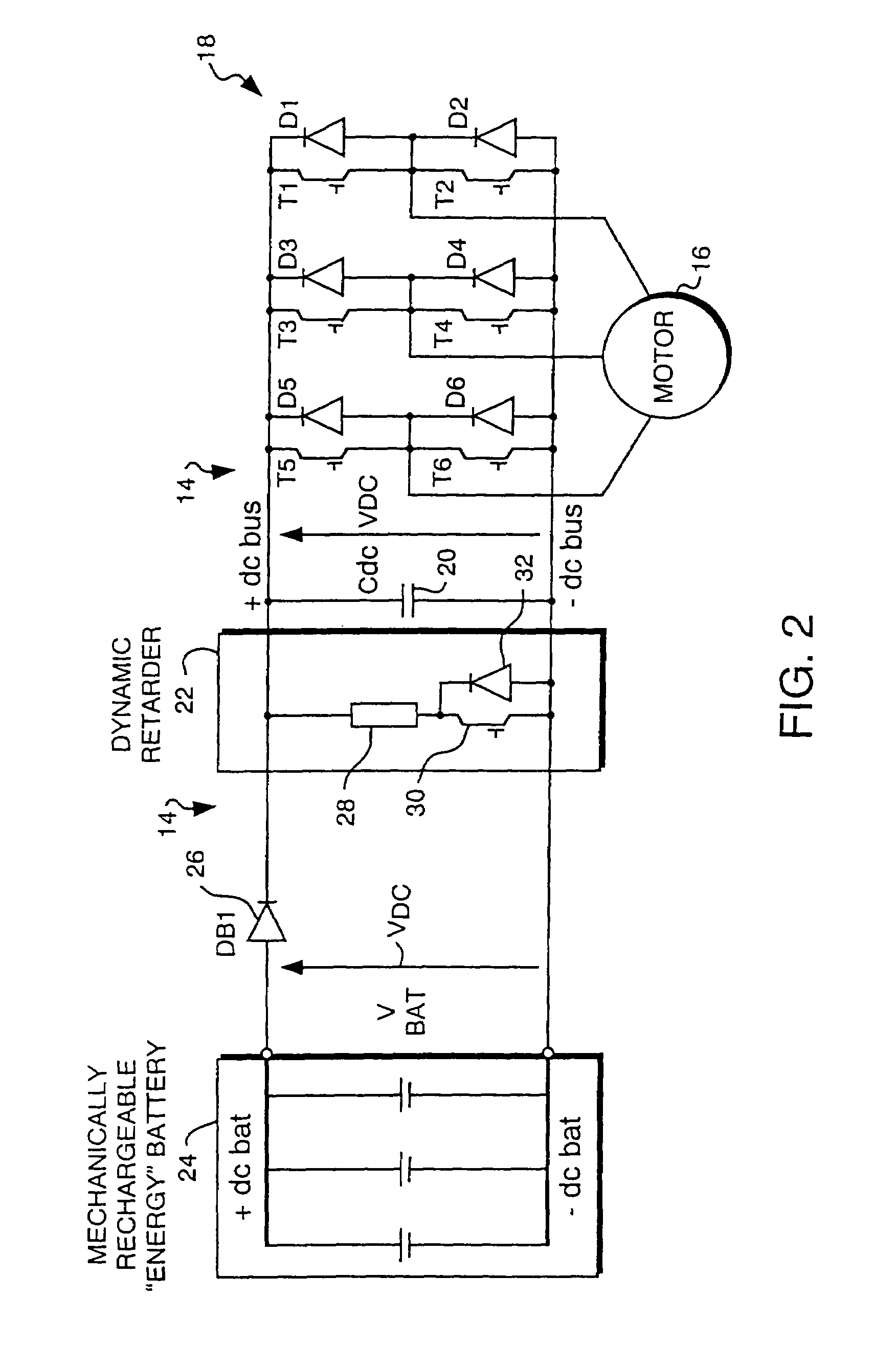
A power system for an electric motor drive such as may be used in an electrically propelled vehicle incorporates the combination of a high power density battery and a high energy density battery to provide an optimal combination of high energy and high power, i.e., a hybrid battery system. The hybrid battery system in one form includes components which prevent electrical recharge energy from being applied to the high energy density battery while capturing regenerative energy in the high power density battery so as to increase an electric vehicle's range for a given amount of stored energy. A dynamic retarding function for absorbing electrical regenerative energy is used during significant vehicle deceleration and while holding speed on down-hill grades, to minimize mechanical brake wear and limit excessive voltage on the battery and power electronic control devices. The high energy density battery coupled in circuit with a boost converter, a high power density battery, a dynamic retarder, and an AC motor drive circuit. The hybrid battery system is controlled by a hybrid power source controller which receives signals from a vehicle system controller using current and voltage sensors to provide feedback parameters for the closed-loop hybrid battery control functions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
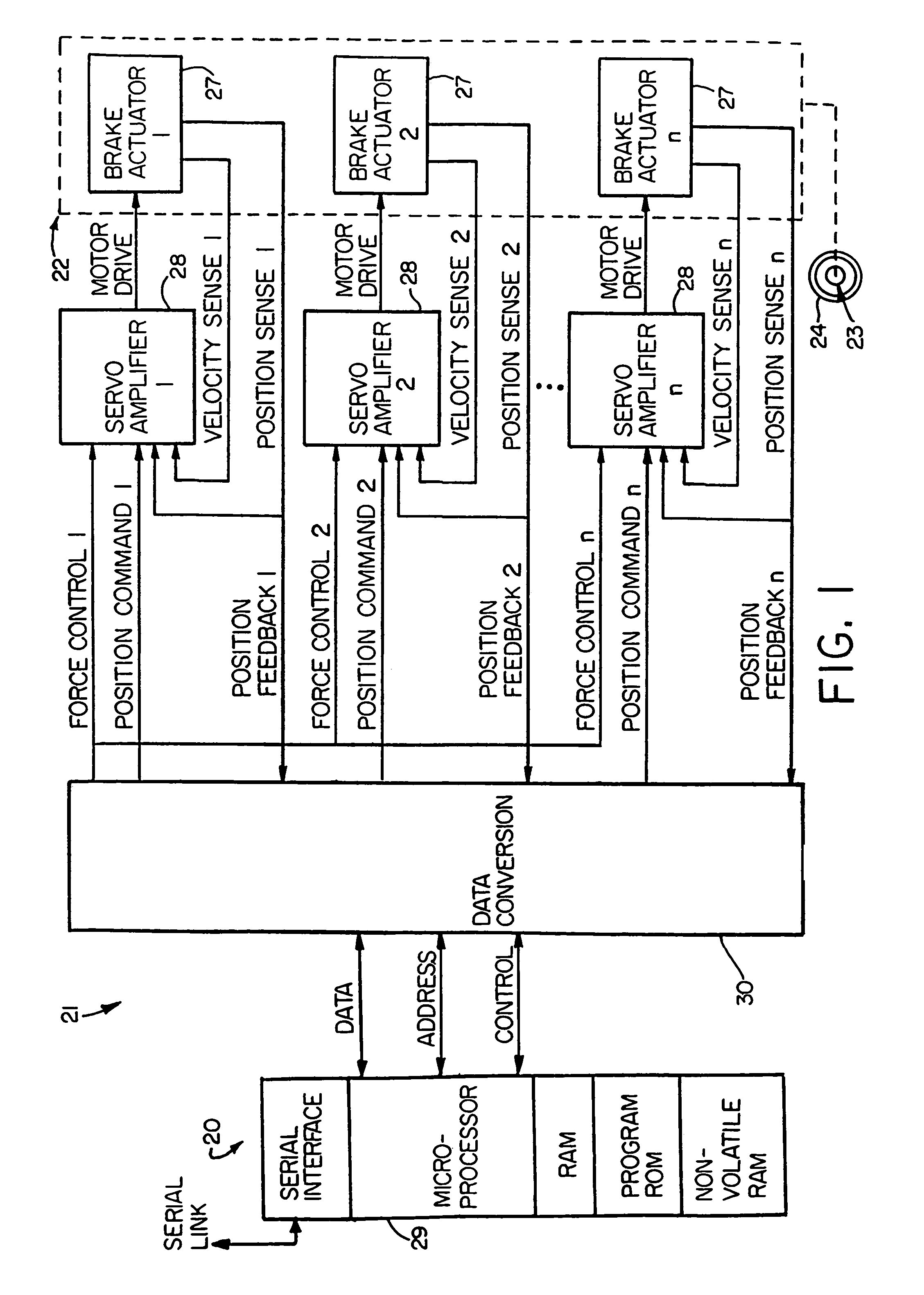
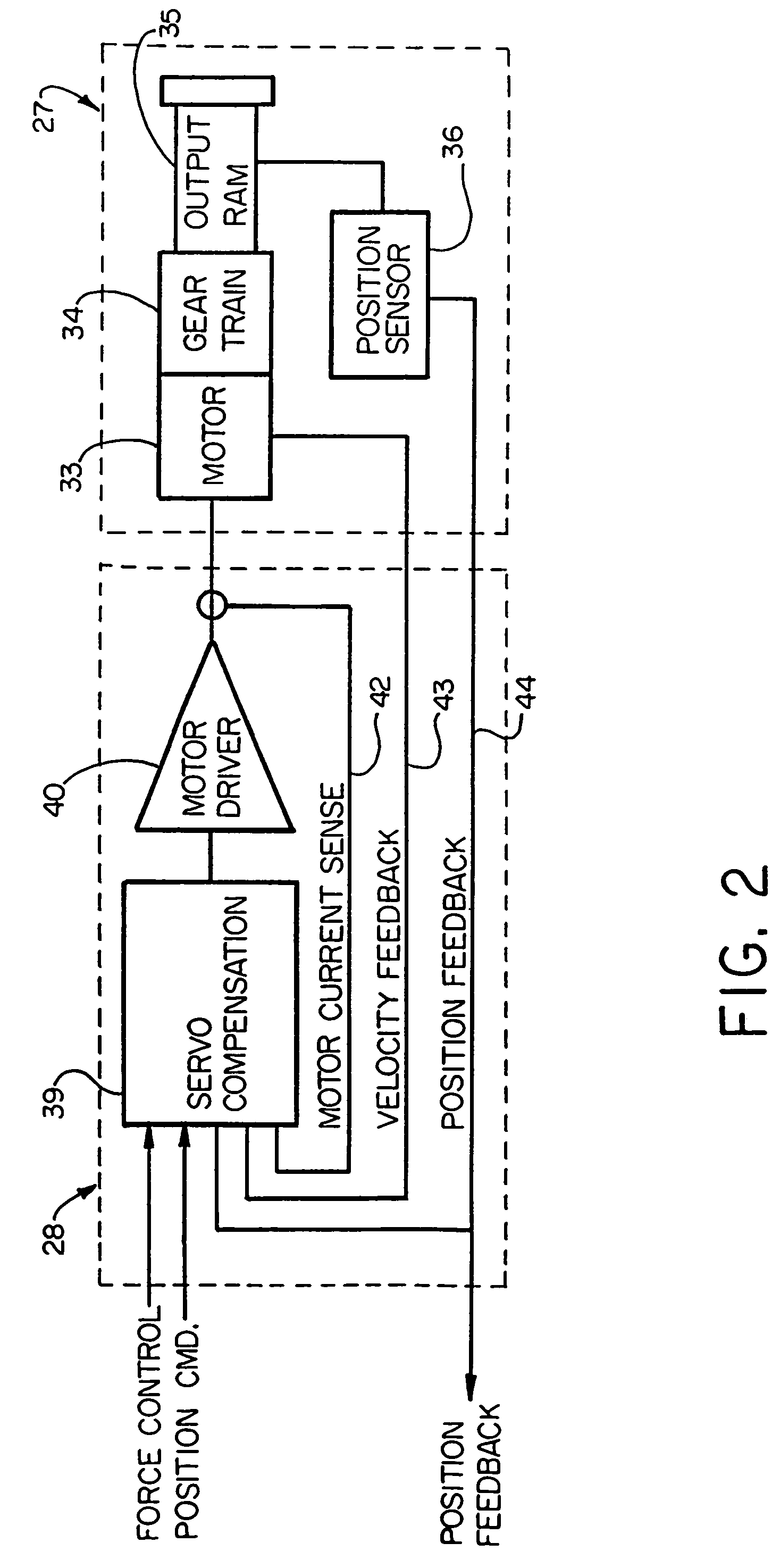
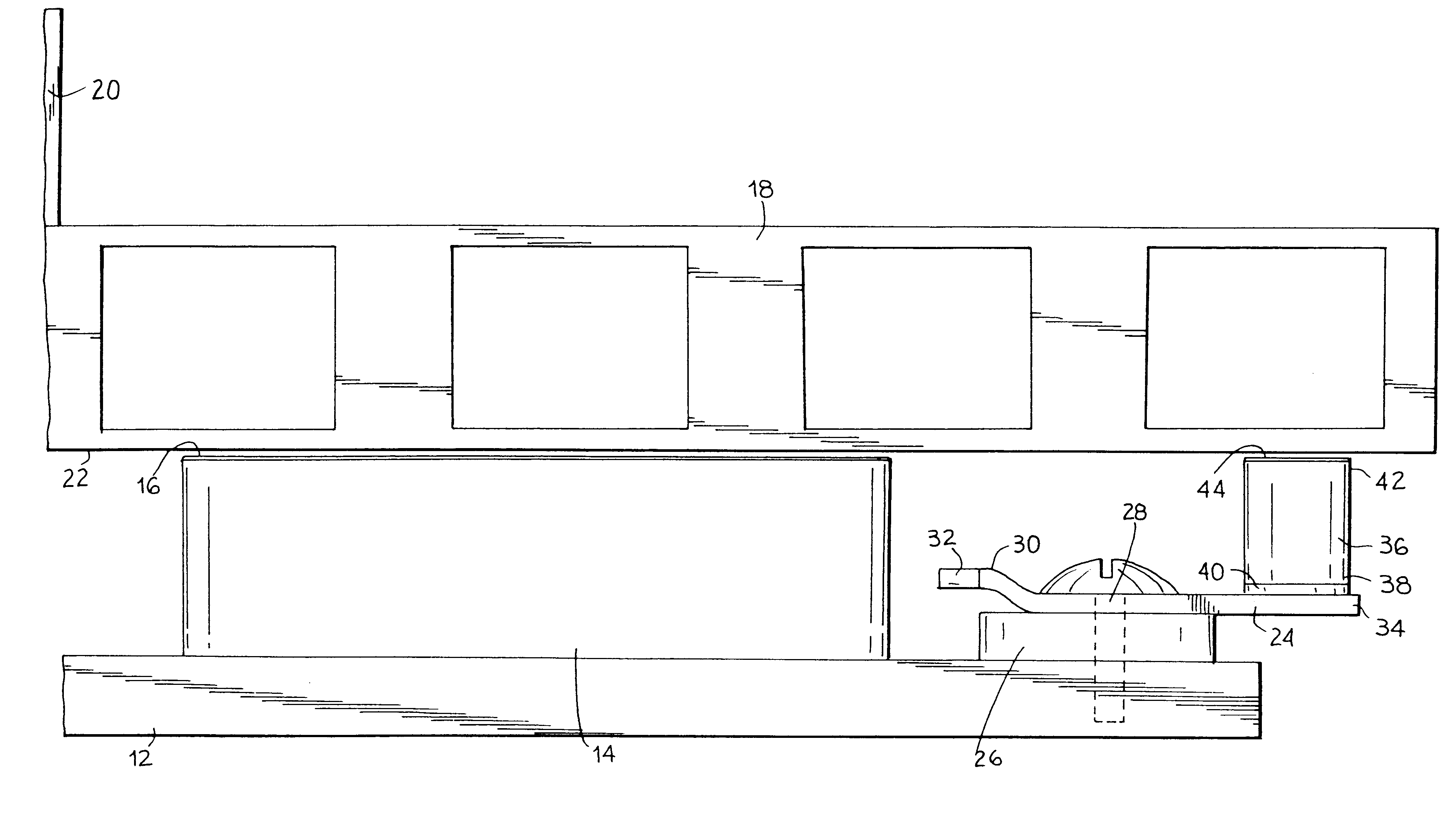
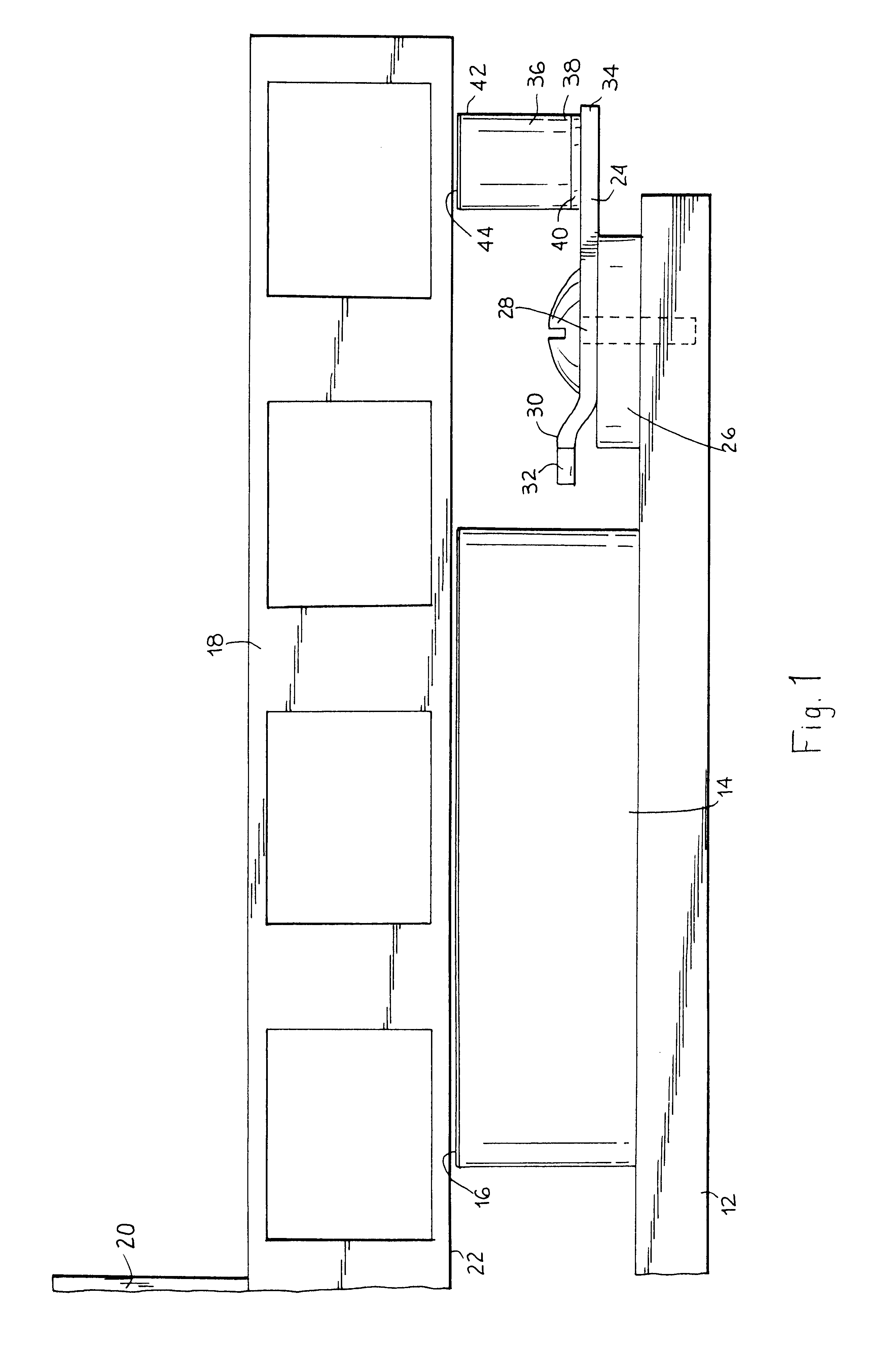
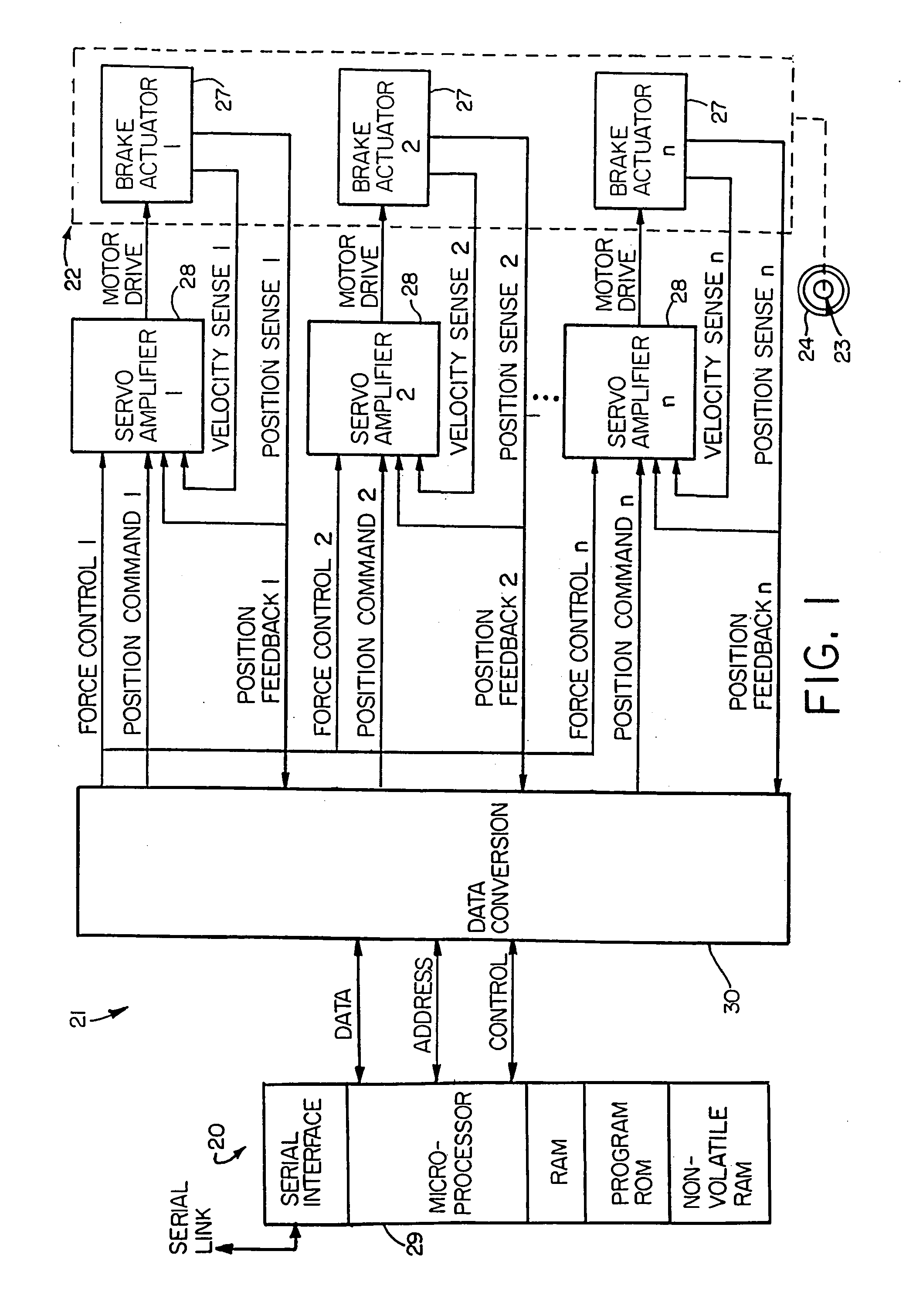
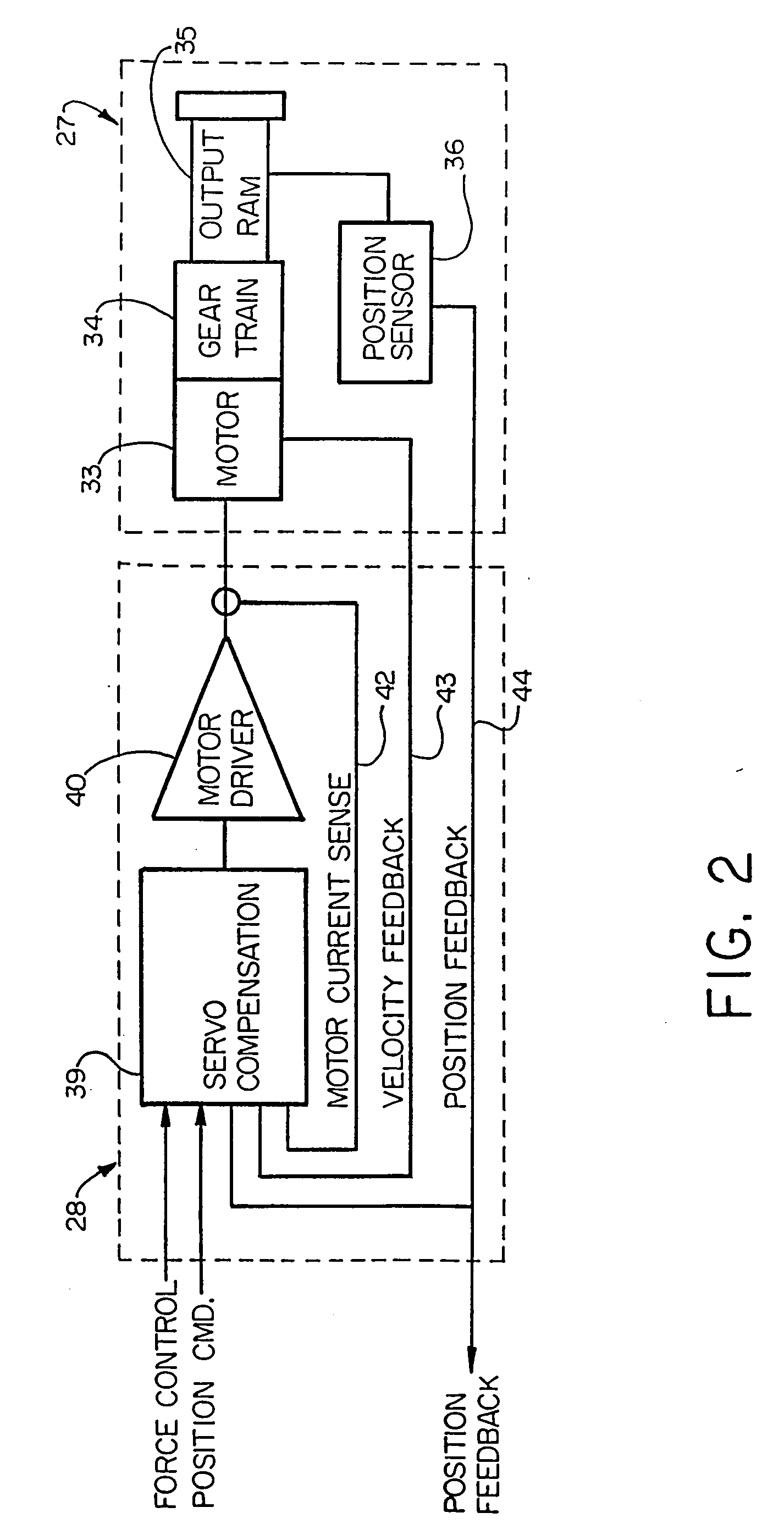
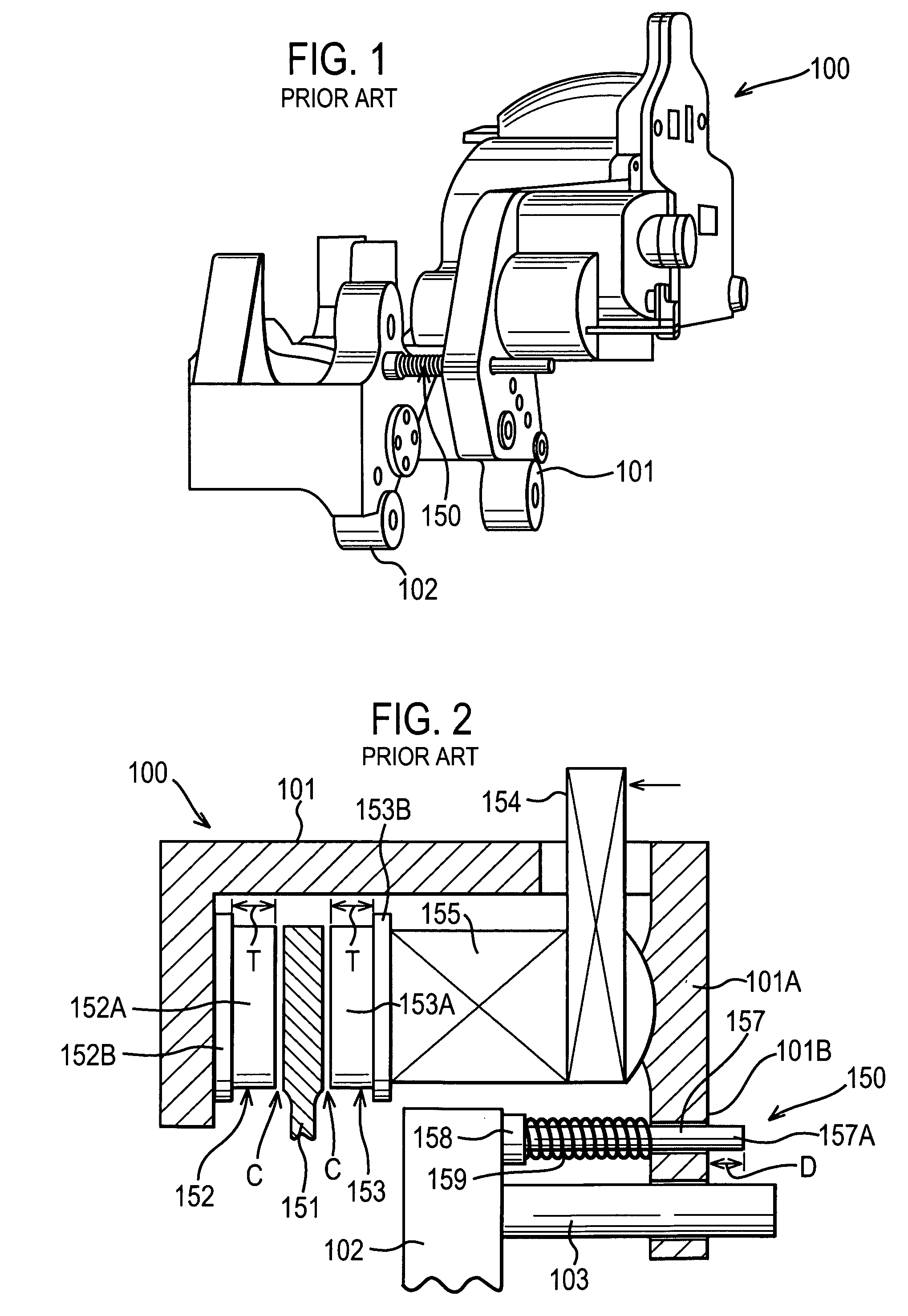
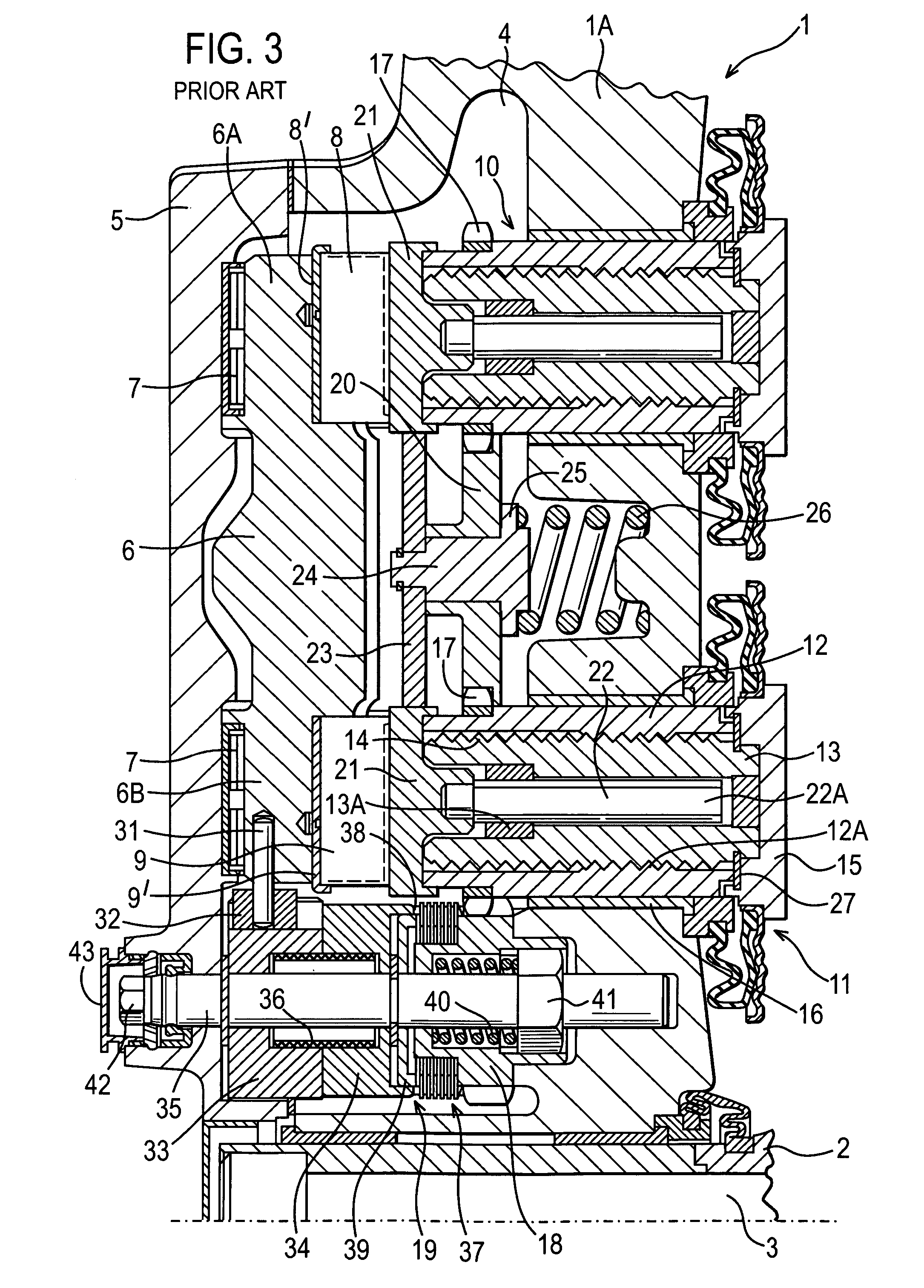
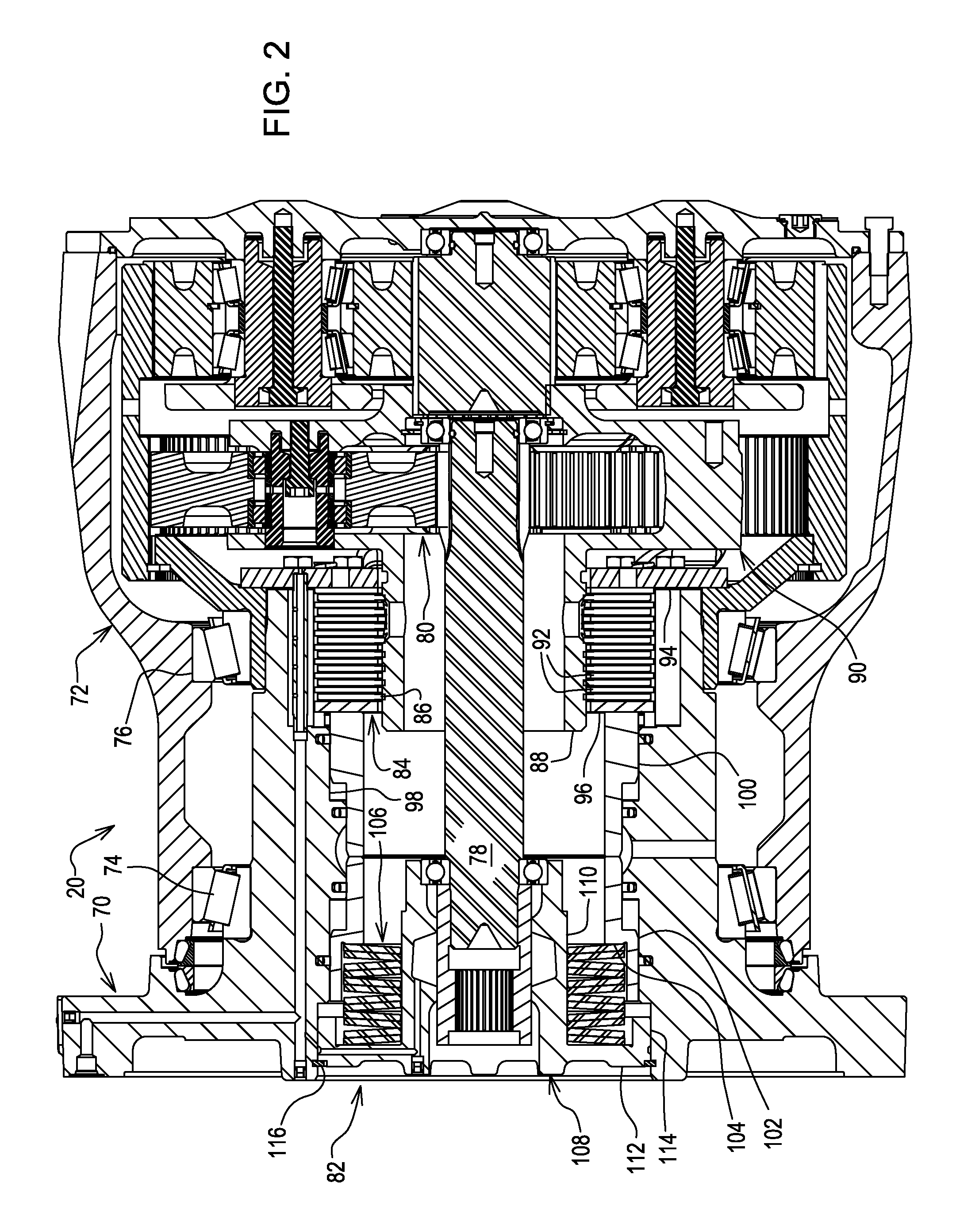
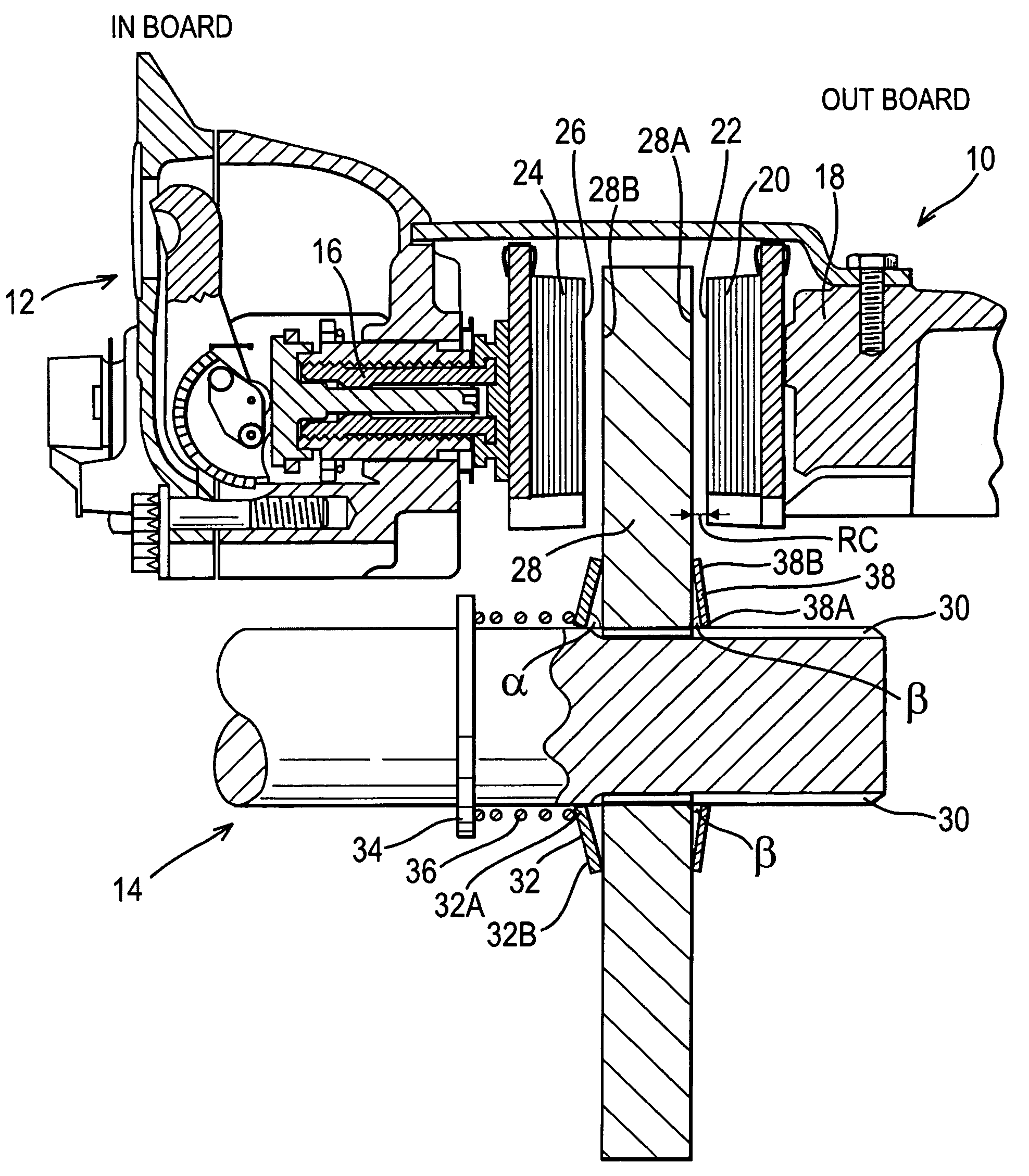
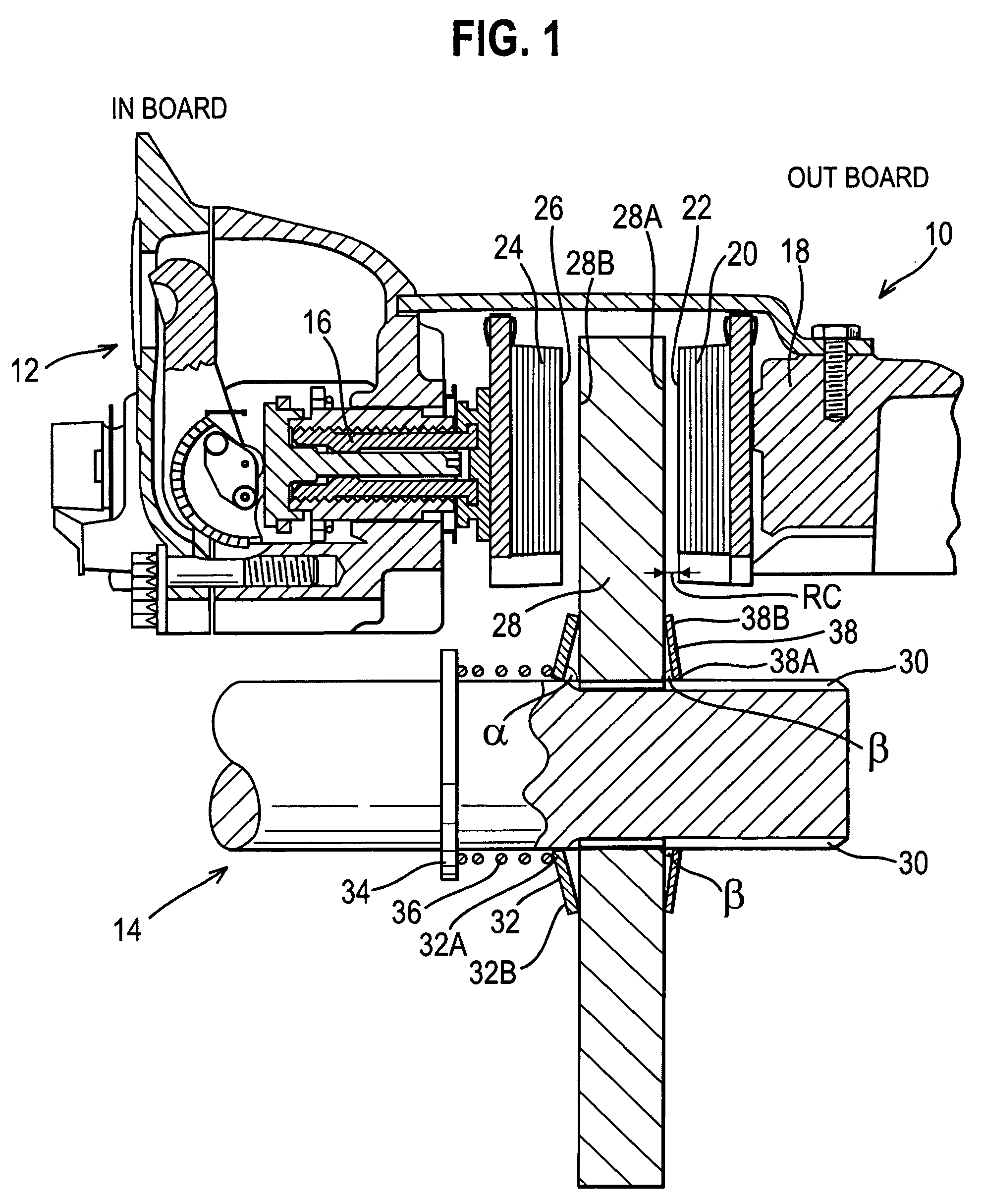
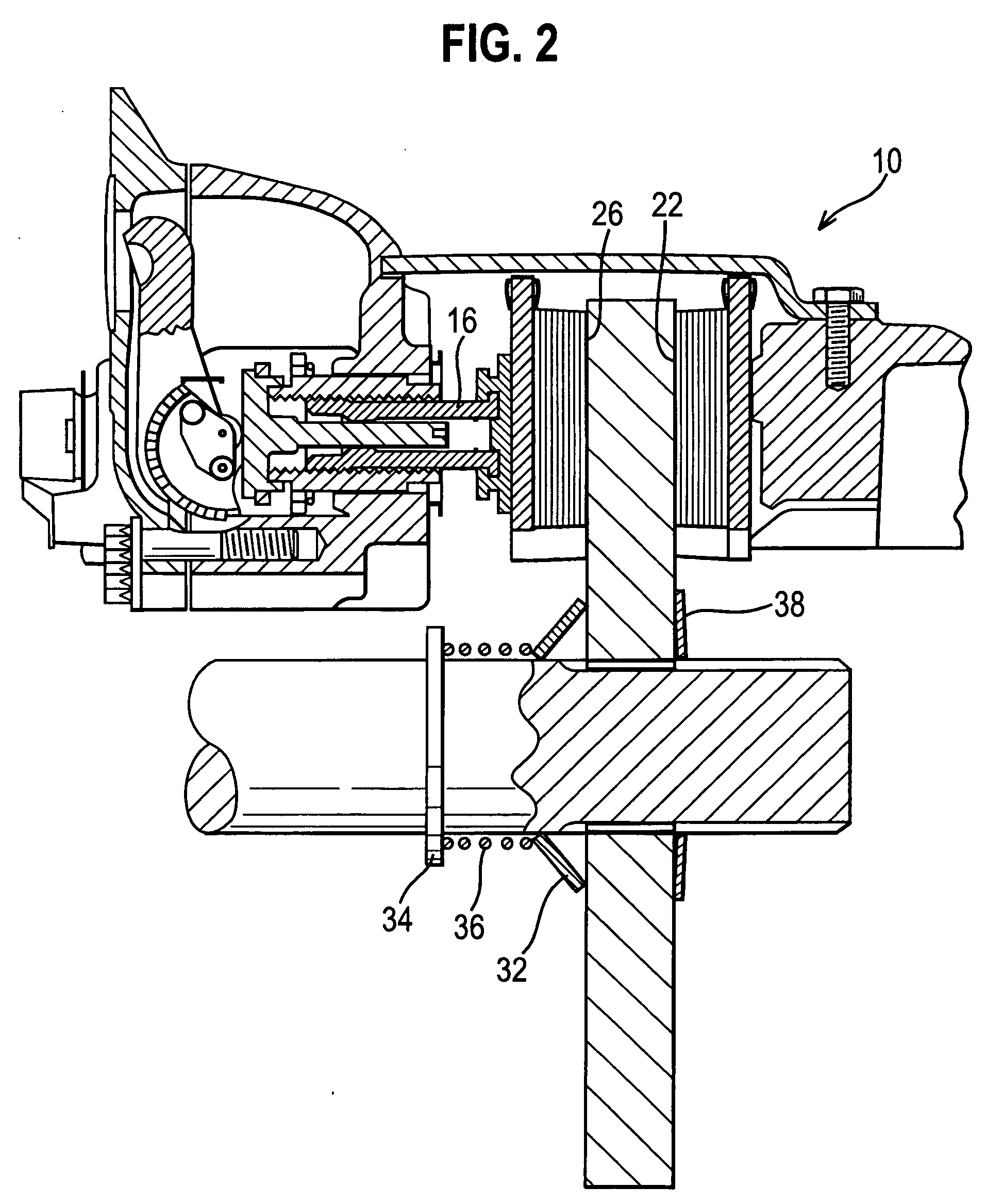
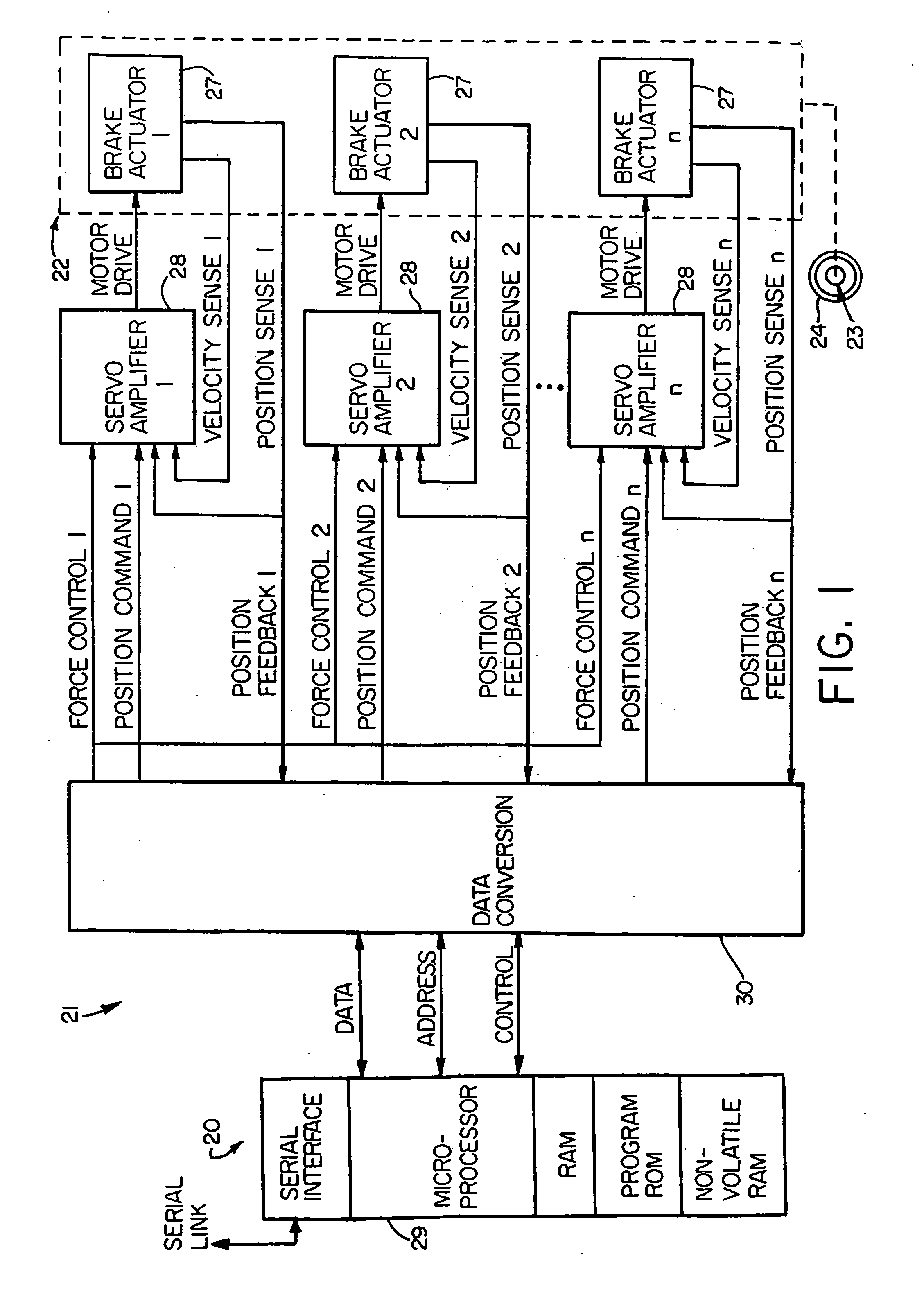
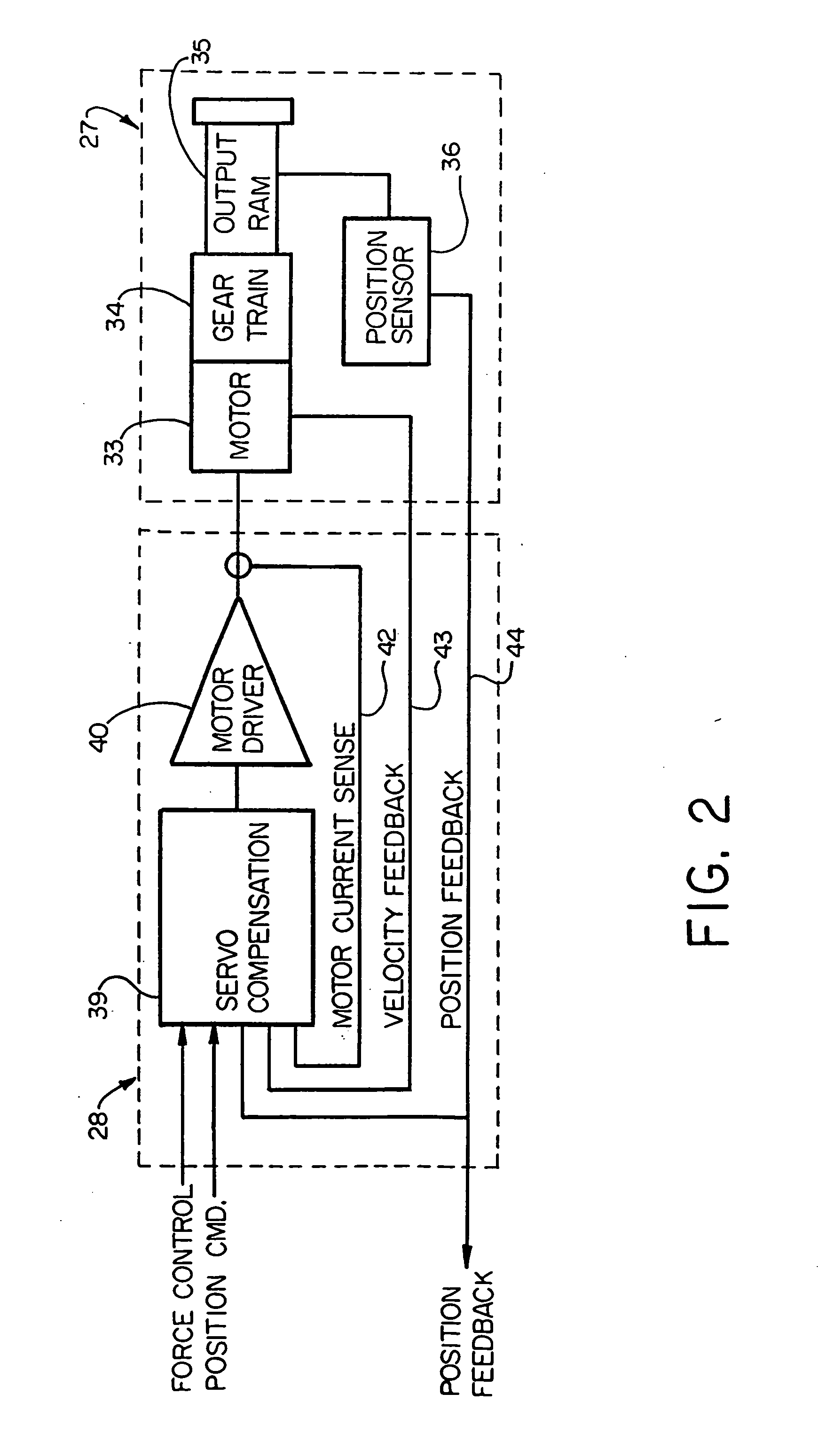
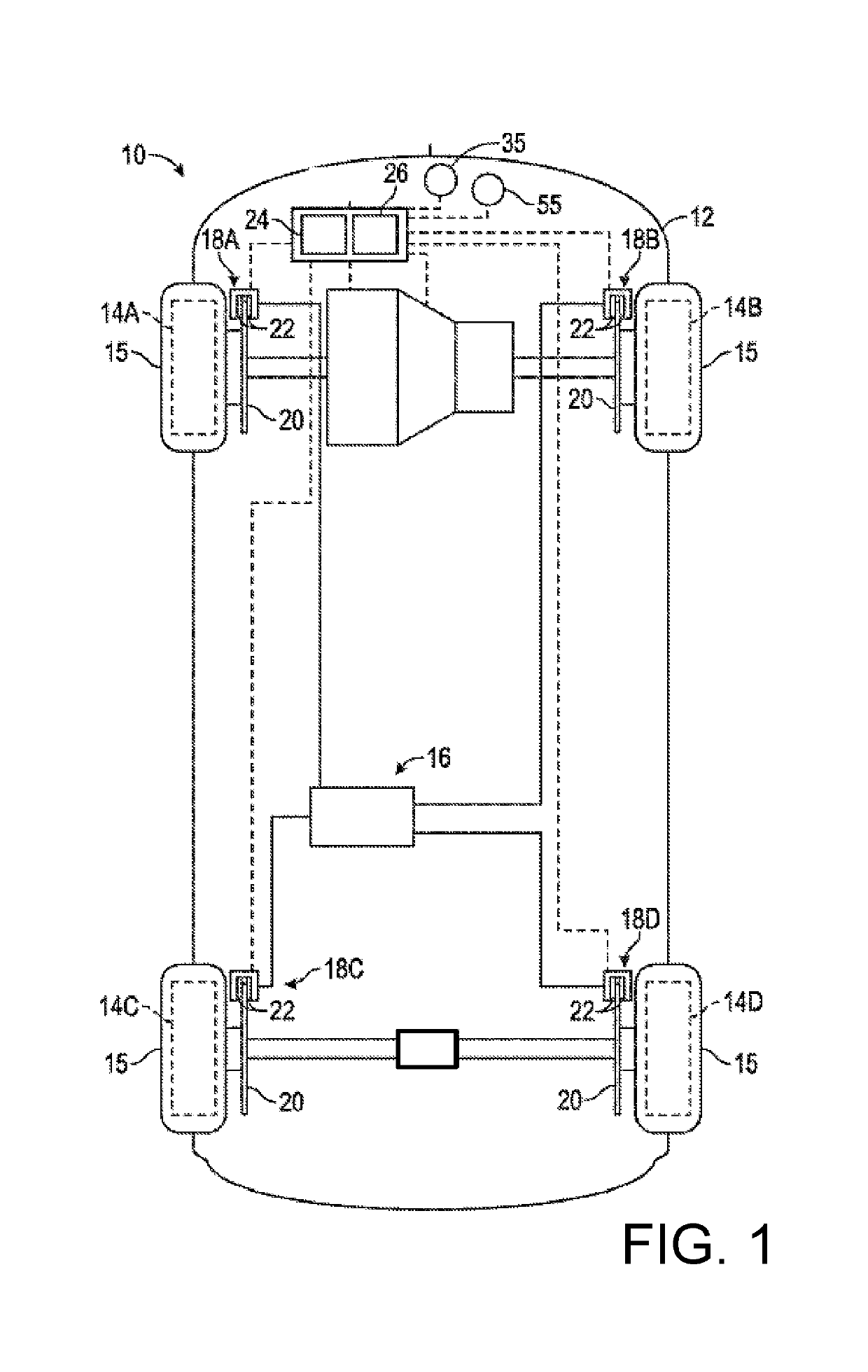
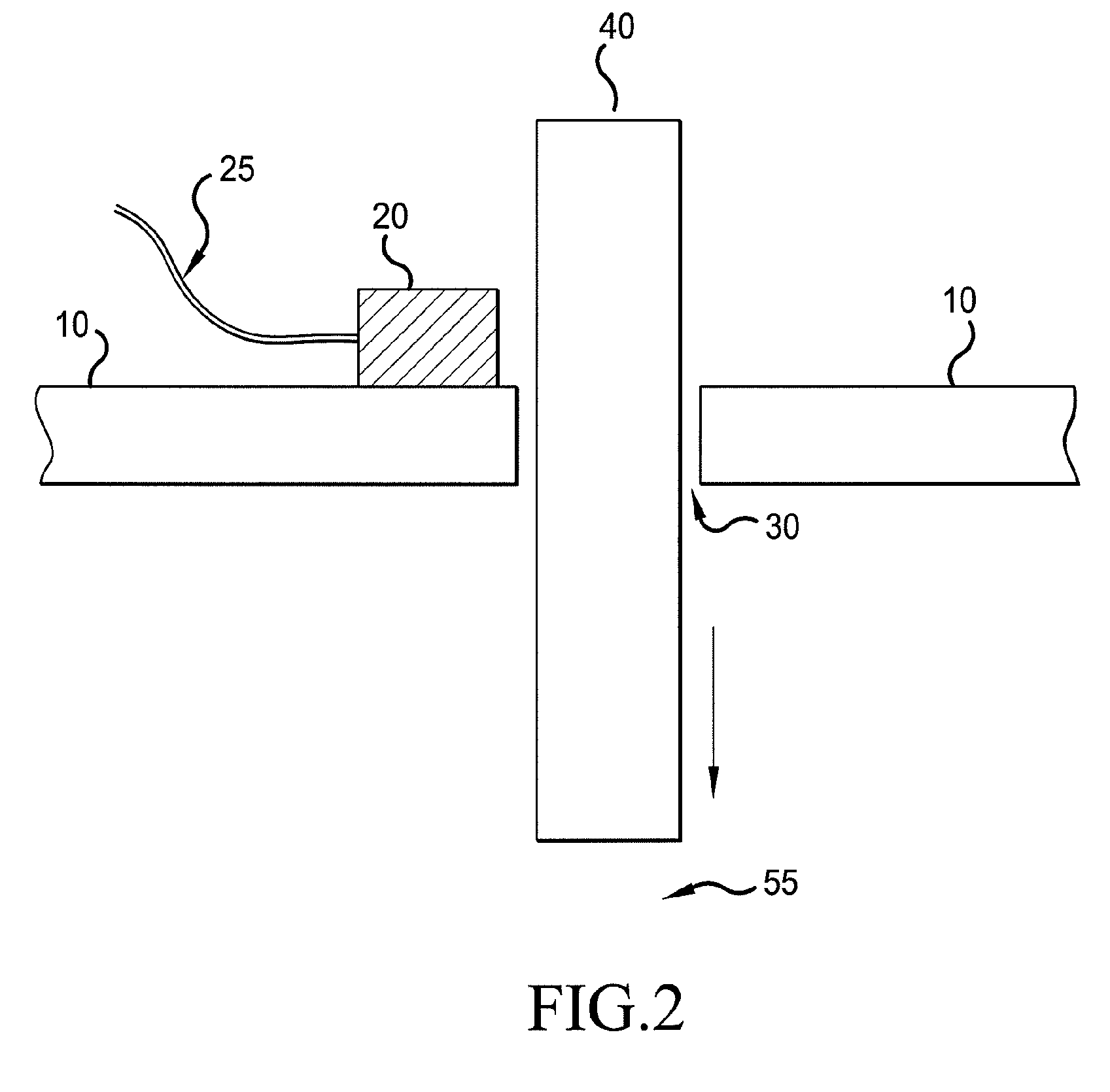
Electronic aircraft braking system with brake wear measurement, running clearance adjustment and plural electric motor-actuator ram assemblies
InactiveUS7108107B2Easy maintenanceIncrease weightAxially engaging brakesBraking action transmissionElectric aircraftActuator
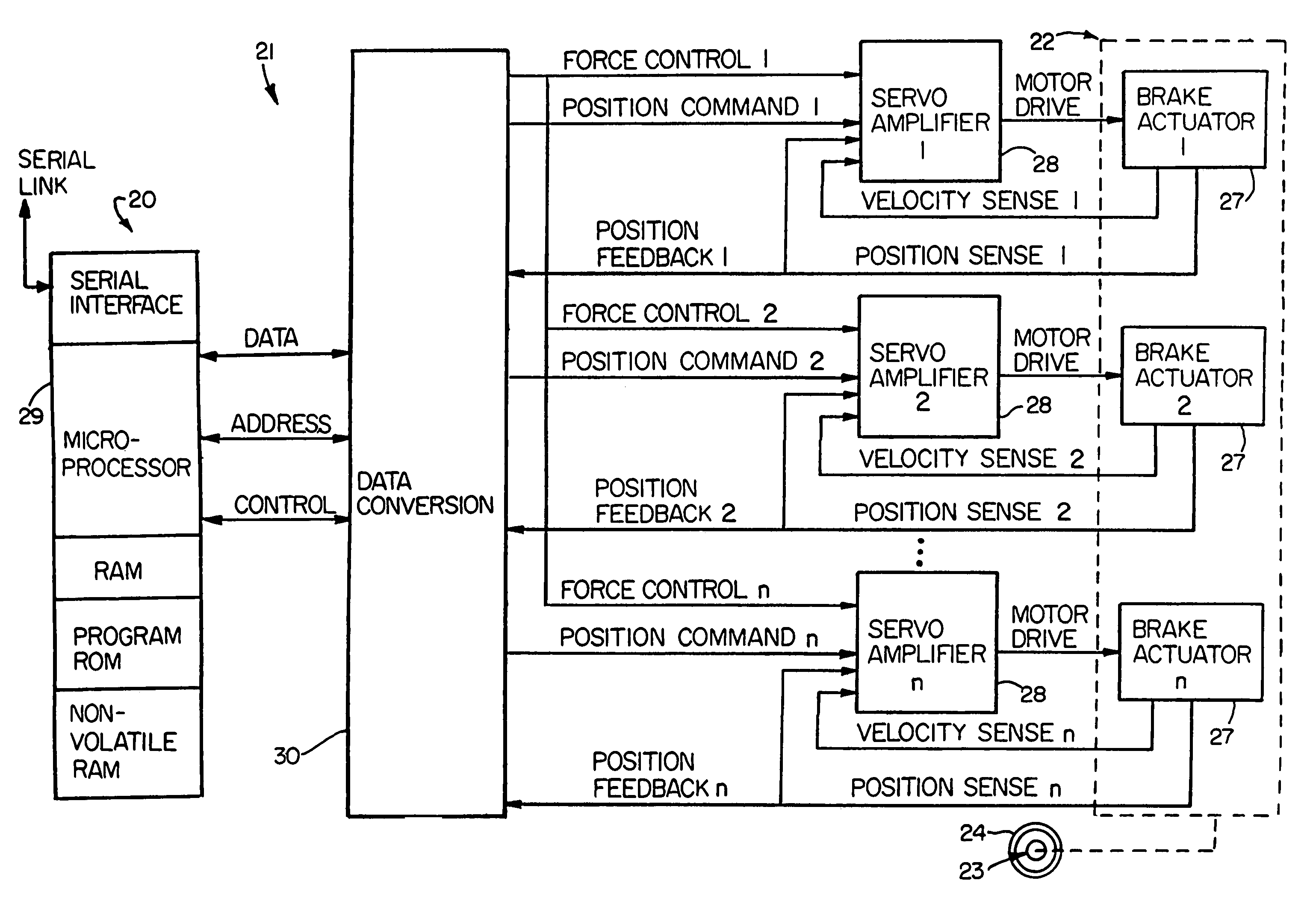
An electrically actuated aircraft brake system and method which provides for brake wear measurement, brake running clearance adjustment, ram position-based control and improved construction and operation. Brake wear and running clearance measurement are obtained by analyzing the output of position sensing circuitry. The position sensing circuitry, preferably including a LVDT position sensor, is also used to determine braking load, a brake controller including circuitry for effecting displacement of one or more reciprocating rams to load a brake disk stack by a predetermined amount based on a present displacement value of the position signal obtained from the position sensor. The position sensor preferably includes a LVDT transducer connected between the reciprocating ram and a brake housing, and the motive device preferably includes a servo motor. Also provided is an actuator housing including a guideway for each ram, the guideway and ram having the same polygonal cross-section, whereby the ram nut is guided and restrained from rotation by the guideway as it is translated by a ball screw in threaded engagement with the ram nut for selective movement into and out of forceful engagement with the brake disk stack for applying and releasing braking force on a rotatable wheel. An electric motor is drivingly connected to each ball screw by a first gear integral with the ball screw, a second gear in mesh with the first gear, and a pinion on a rotating drive shaft of the electric motor.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
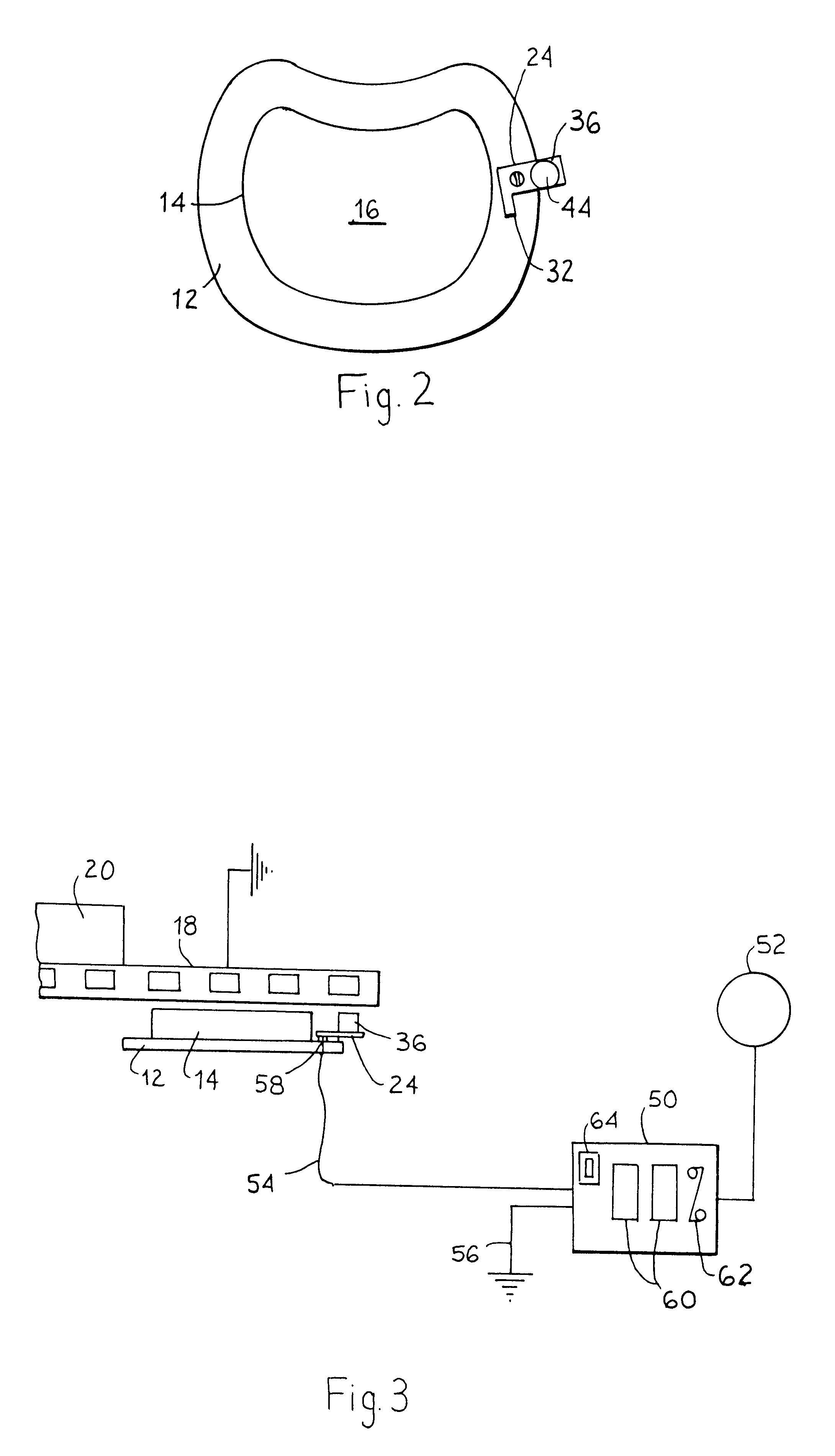
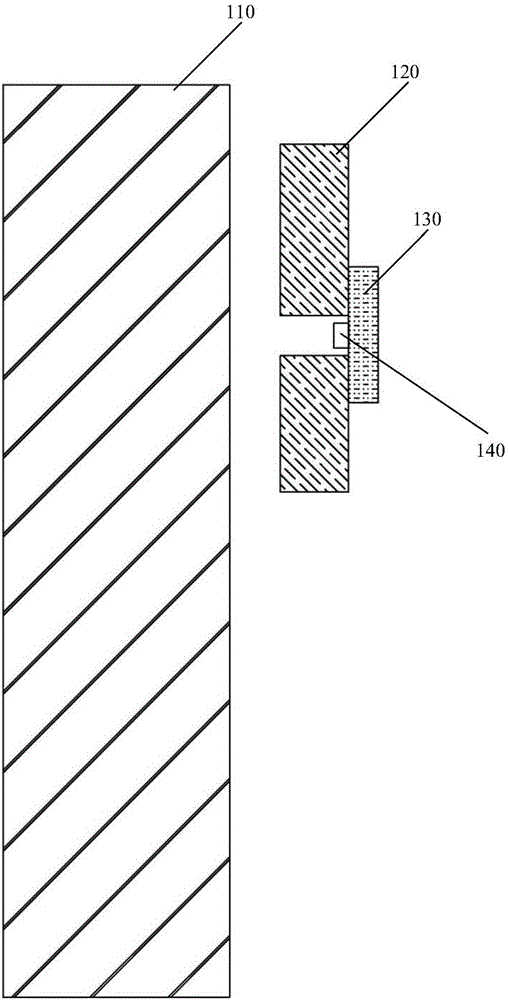
Brake pad wear sensor
A sensor is attached to a backing plate of a brake pad. The sensor comprises a metal arm extending to one side of the brake pad. The metal arm is electrically insulated from the backing plate. A tab made from a dielectric material projects from a free end of the arm in the same direction that the brake pad extends from the backing plate. The tab is bonded to the arm by an electrically conductive paste. The tab has a wear face spaced from the backing plate the same distance as a brake surface of the brake pad. When a brake is applied by a vehicle operator, both the brake pad brake surface and the tab wear face frictionally engage a brake rotor fixed to a wheel hub. The dielectric material is selected so the tab wears at the same rate as the brake pad. A lead wire connected to the arm enables the capacitance of the tab to be measured by a grounded capacitance meter when the brake is applied. The capacitance changes as the dielectric material wears away. The capacitance is used to indicate the remaining amount of brake pad life on a digital readout.
Owner:YAZAKI NORTH AMERICA
System and method for detecting thickness of automobile brake pad in real time
ActiveCN102774373AEffective use of thicknessImprove detection accuracyBrake safety systemsDriver/operatorSafety control
The invention discloses a system and a method for detecting the thickness of an automobile brake pad in real time, belonging to the field of automobile brake systems. Each pair of brake calipers of the detection system is provided with two eddy current sensors for detecting the thickness signal of the brake pad in real time; after being sequentially connected with a sampling resistor and a sensor power switch in series, the eddy current sensors are connected into the two sides of a sensor power supply; a current signal collected by the eddy current sensors is converted into a voltage signal by the sampling resistor; the sampling resistor is accessed into the input end of a signal processing module; the signal processing module is used for calculating the thickness of the brake pad; a display module is connected with the signal processing module for displaying the thickness information of the brake pad; and the output end of the signal processing module is connected with an audio and video alarm device. The detection system has the advantages of simple structure, high measurement precision, convenience in implementation and high popularity, compared with a brake pad abrasion detection system using a contact type switch principle, more key information can be provided, and the safety control capability of a driver is improved.
Owner:马鞍山市安工大智能装备技术研究院有限公司
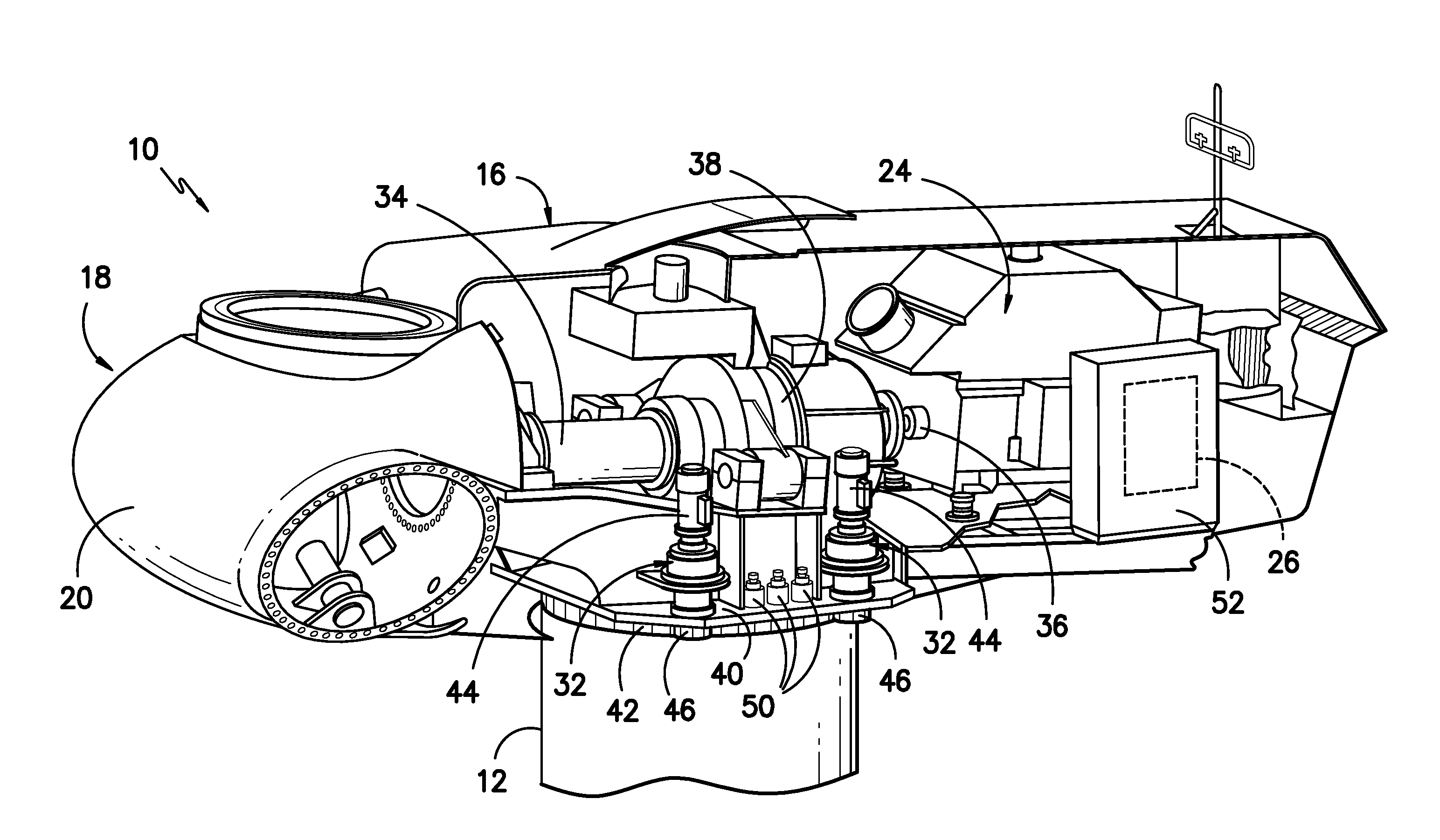
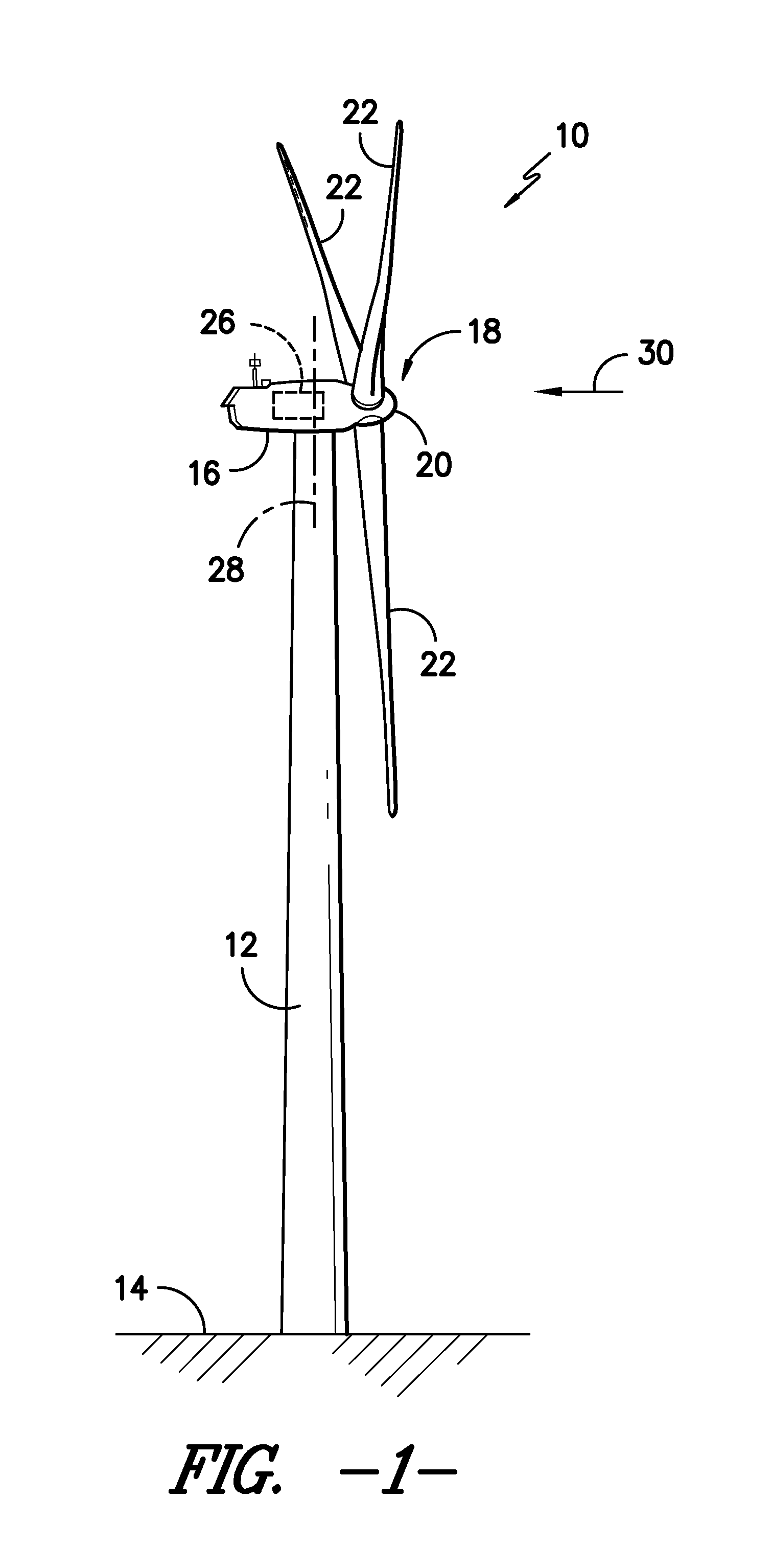
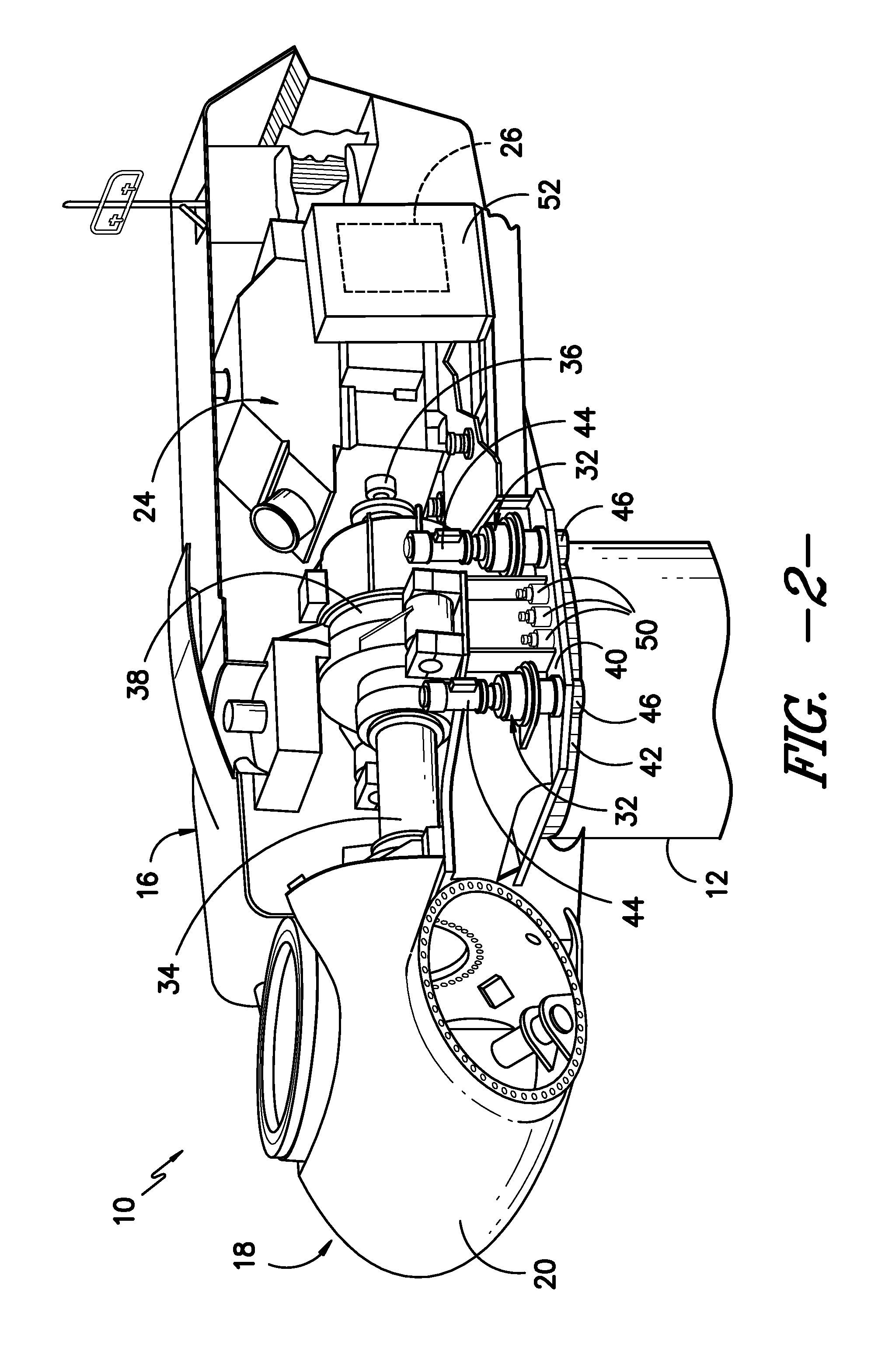
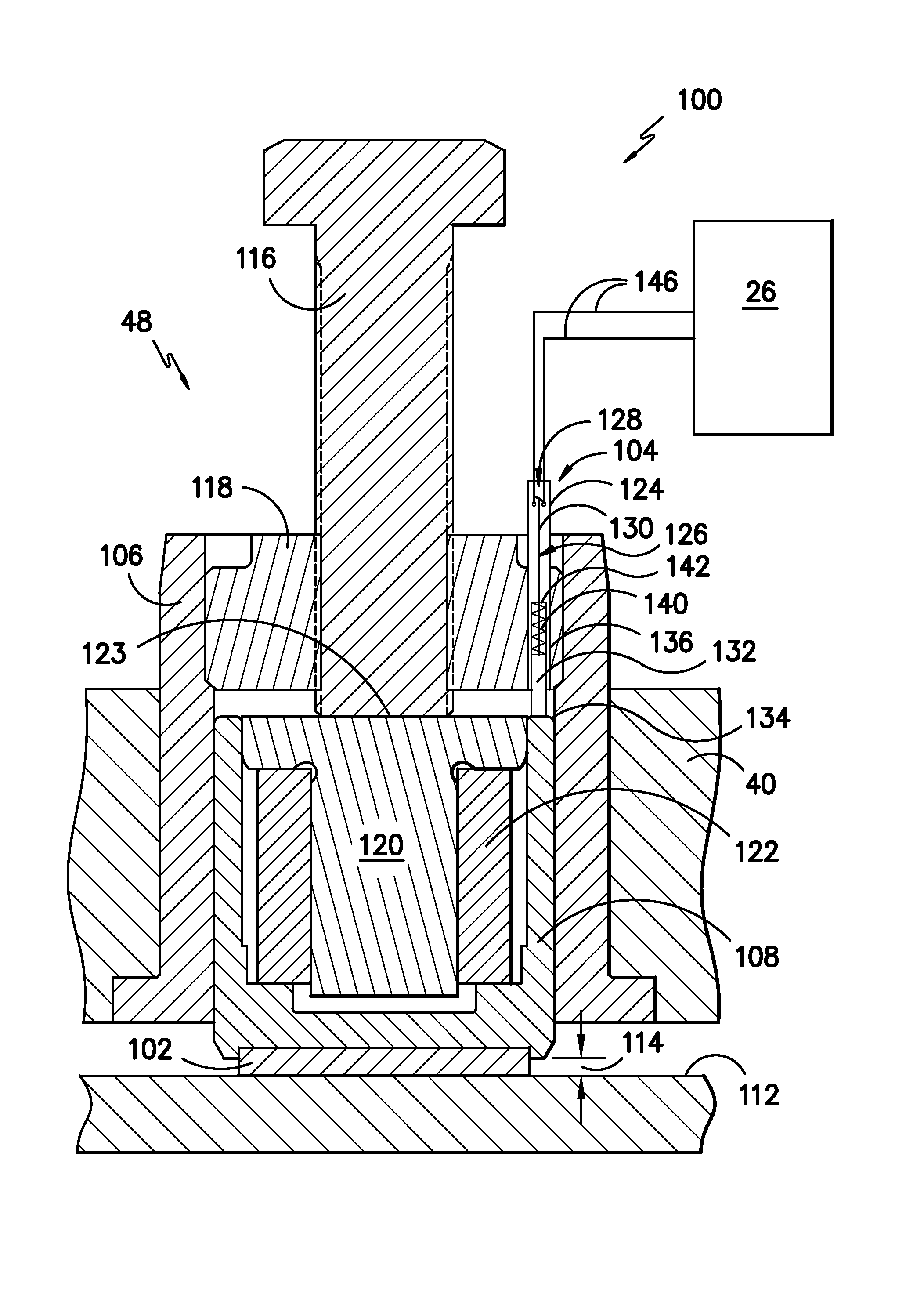
System for actively monitoring wear on wind turbine brake pads and related methods
A system for monitoring wear on a brake pad of a wind turbine is disclosed. The system may include a brake assembly having a brake pad and a moveable component. The brake pad may be configured to engage a friction surface of the wind turbine. The movable component may be configured to move relative to the friction surface as the brake pad wears. Additionally, the system may include a sensor at least partially mounted within the brake assembly. The sensor may be configured to detect a position of the movable component relative to the sensor or a position of the friction surface relative to the sensor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electronic aircraft braking system with brake wear measurement, running clearance adjustment and plural electric motor- actuator ram assemblies
InactiveUS20070125607A1Easy maintenanceIncrease weightBraking action transmissionMechanically actuated brakesGear wheelActuator
An electrically actuated aircraft brake system and method which provides for brake wear measurement, brake running clearance adjustment, ram position-based control and improved construction and operation. Brake wear and running clearance measurement are obtained by analyzing the output of position sensing circuitry. The position sensing circuitry, preferably including a LVDT position sensor, is also used to determine braking load, a brake controller including circuitry for effecting displacement of one or more reciprocating rams to load a brake disk stack by a predetermined amount based on a present displacement value of the position signal obtained from the position sensor. The position sensor preferably includes a LVDT transducer connected between the reciprocating ram and a brake housing, and the motive device preferably includes a servo motor. Also provided is an actuator housing including a guideway for each ram, the guideway and ram having the same polygonal cross-section, whereby the ram nut is guided and restrained from rotation by the guideway as it is translated by a ball screw in threaded engagement with the ram nut for selective movement into and out of forceful engagement with the brake disk stack for applying and releasing braking force on a rotatable wheel. An electric motor is drivingly connected to each ball screw by a first gear integral with the ball screw, a second gear in mesh with the first gear, and a pinion on a rotating drive shaft of the electric motor.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
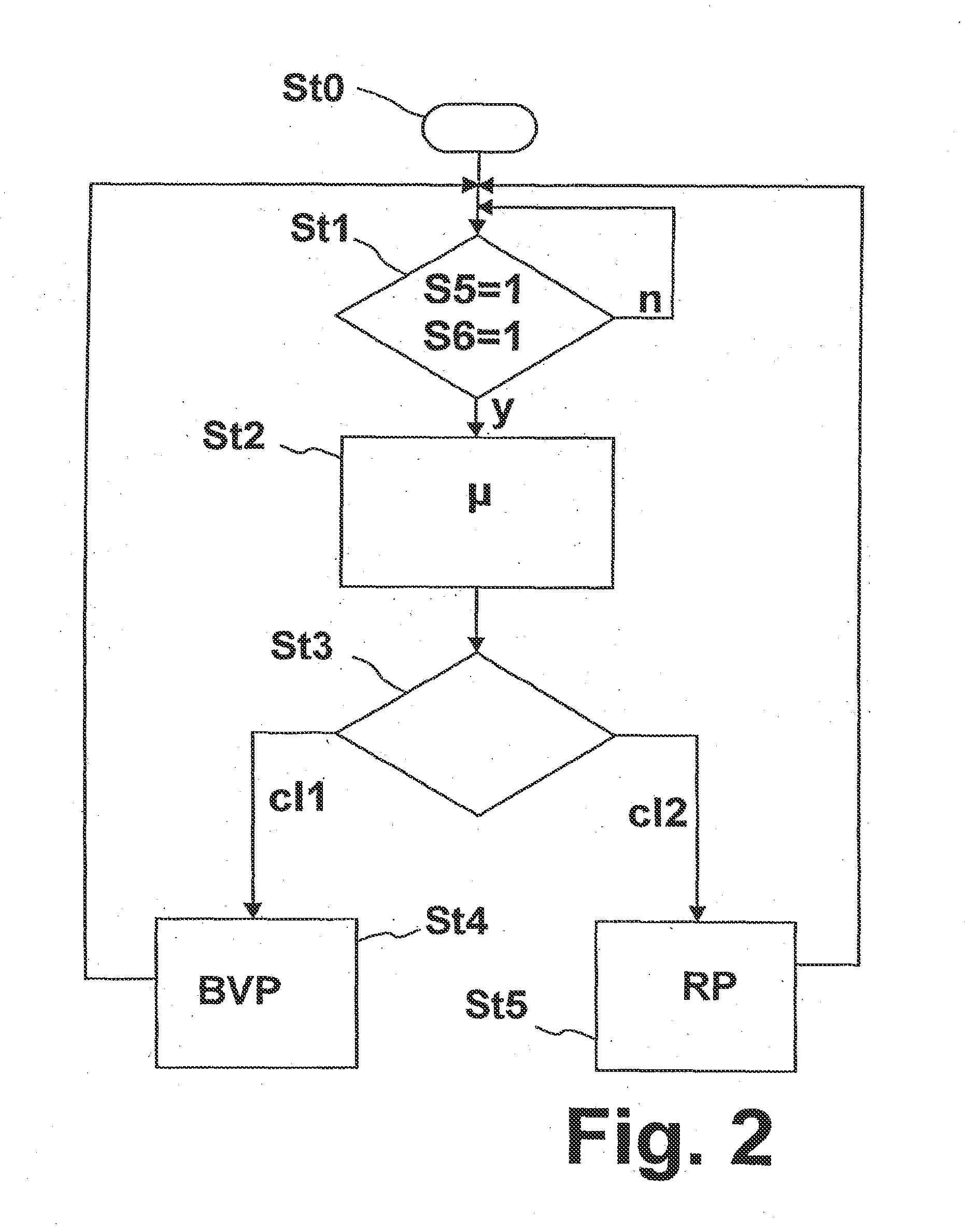
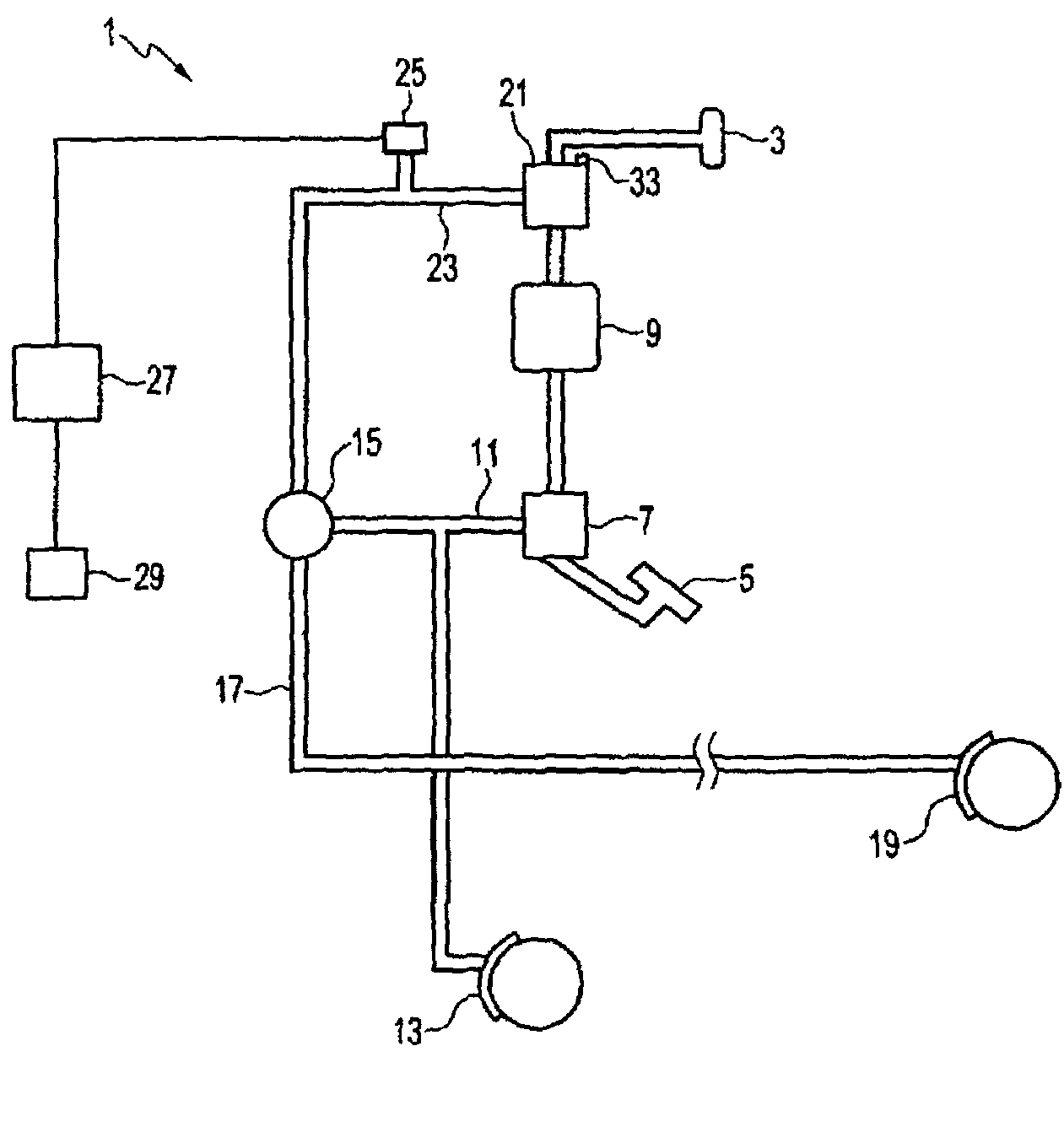
Method and Control Device fort Open-Loop or Closed-Loop Control of a Vehicle Brake System
ActiveUS20140188363A1Guaranteed uptimeImprove distributionAnalogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsLoop controlClosed loop
A method for carrying out closed-loop or open-loop control of a vehicle brake system includes, when a braking request signal is present, setting brake pressures at brakes on axles and / or wheels of the vehicle by distributing brake pressure. Before braking is initiated on the basis of current, received or detected data relating to friction conditions or grip conditions between the roadway surface and tire surfaces of the vehicle, a determination is made as to whether, or to what extent, the distribution of brake pressure occurs in a brake wear pressure distribution or in a frictional engagement pressure distribution for the subsequent initiation of the braking process.
Owner:ZF CV SYST EURO BV
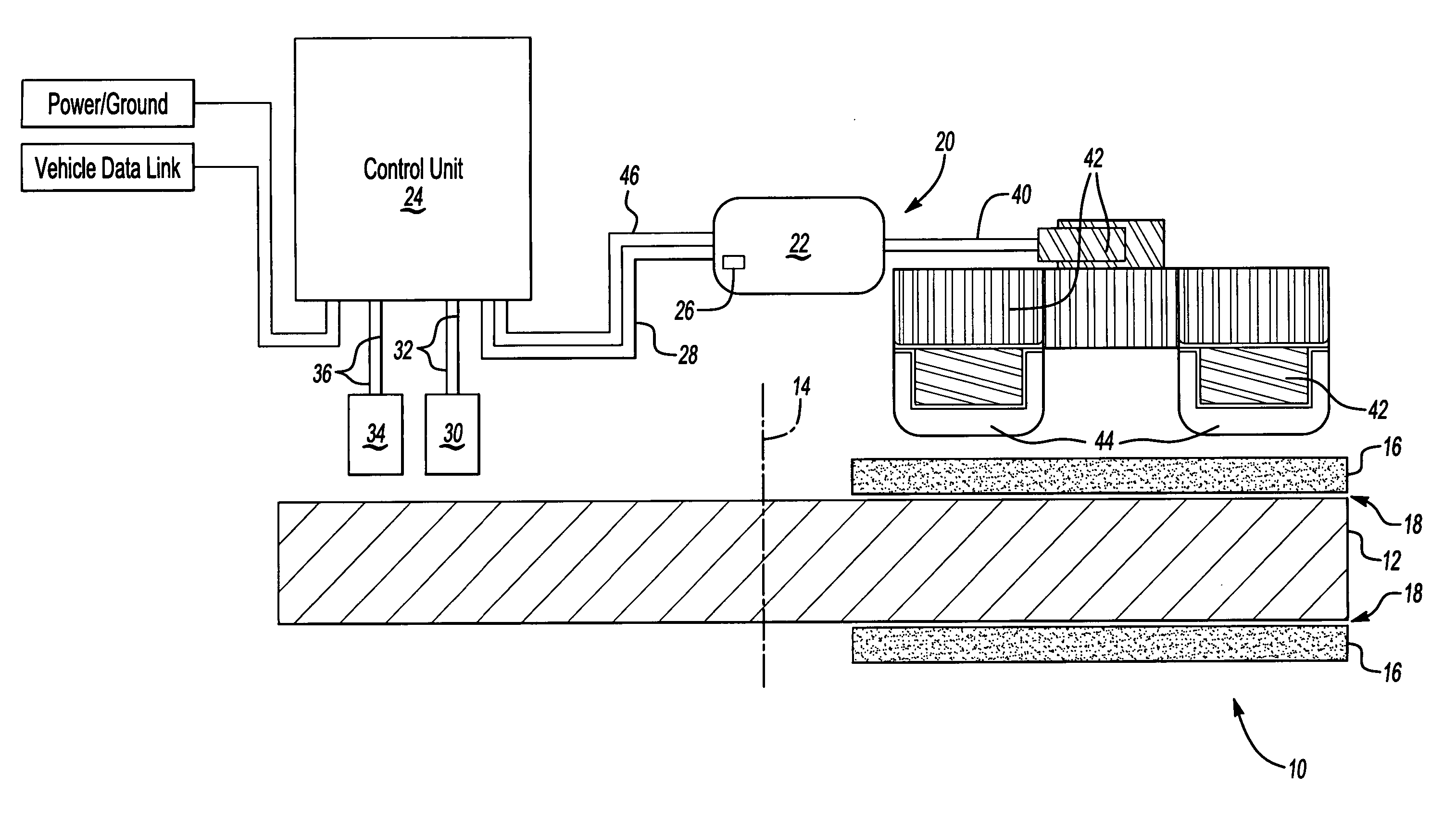
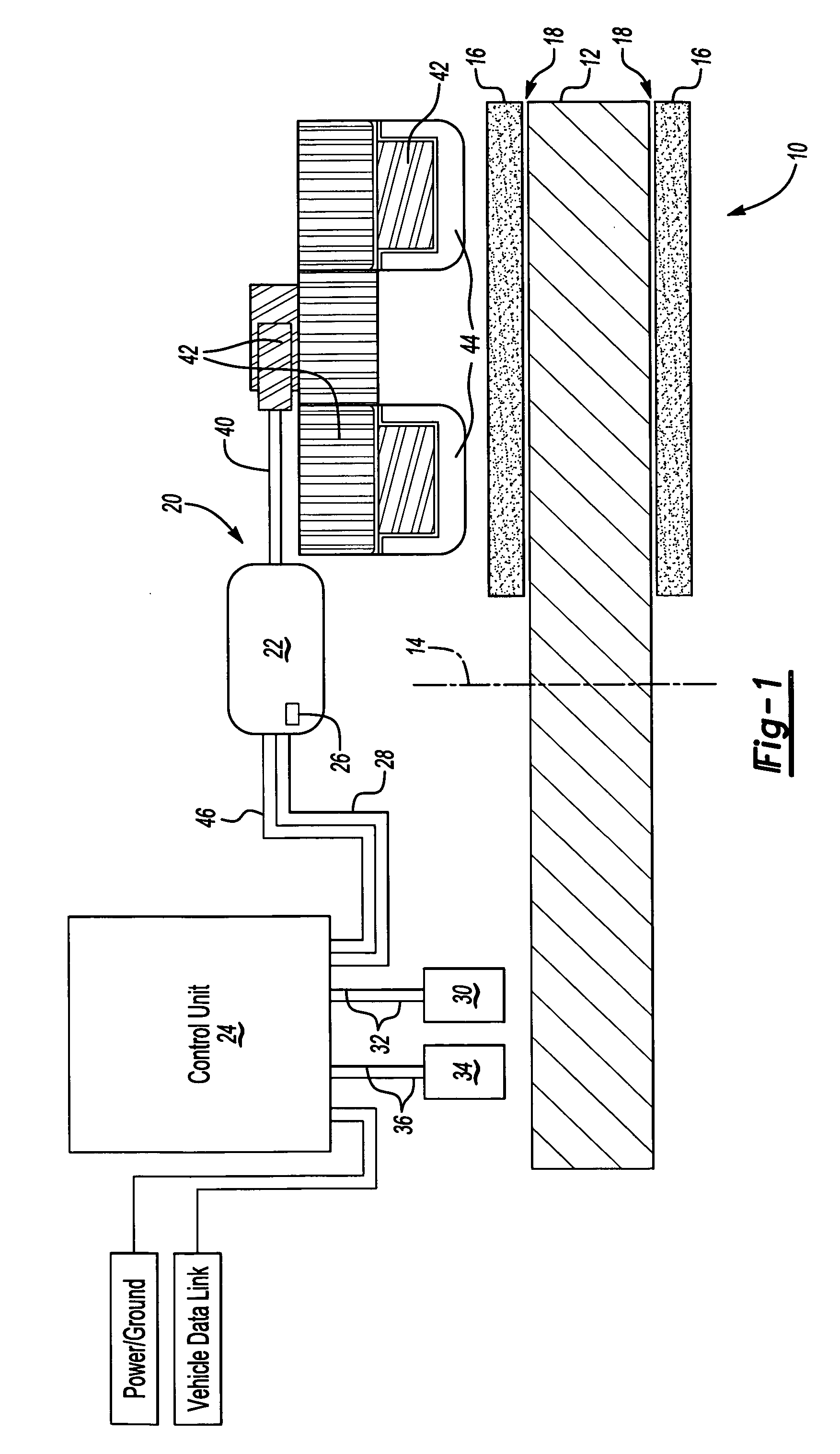
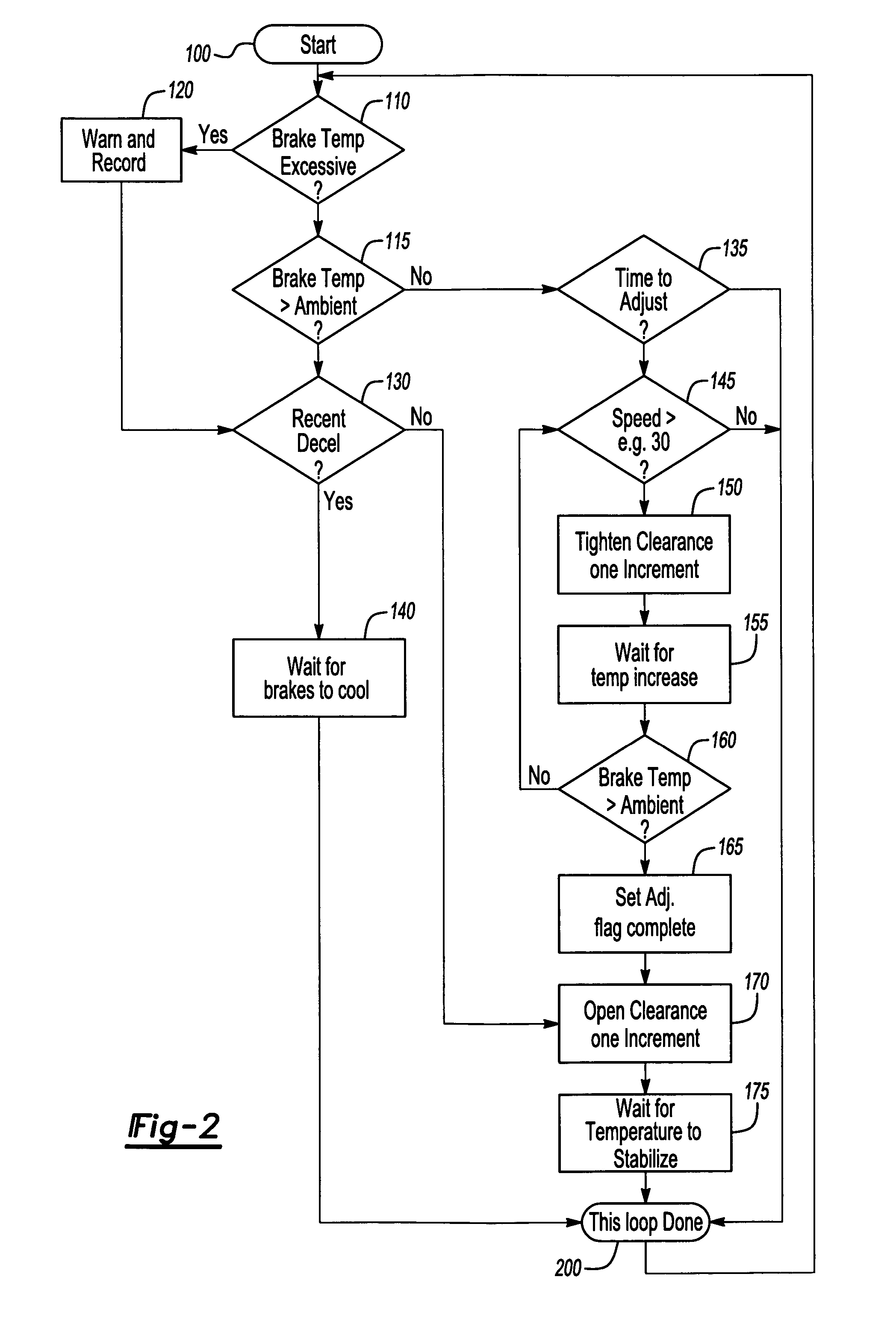
Temperature based clearance control for vehicle brake
InactiveUS20070235268A1Optimize brake clearanceIncrease the gapAxially engaging brakesBraking elementsData transmissionVehicle brake
An adjustment mechanism for a vehicle brake uses an electric motor to adjust brake clearance based on brake temperature and wheel speed. A temperature sensor transmits brake temperature data to a controller. If a brake is dragging during non-braking events, the controller identifies an increase in brake temperature and actuates the electric motor to increase brake clearance. The controller also adjusts brake clearance to accommodate for brake wear. When wheel speed is above a predetermined speed value, the controller actuates the electric motor to move a non-rotating brake component toward a rotating brake component until a predetermined temperature increase is sensed. Once the predetermined temperature increase is identified, the electric motor moves the non-rotating brake component away from the rotating brake component to provide an optimized brake clearance.
Owner:ARVINMERITOR TECH
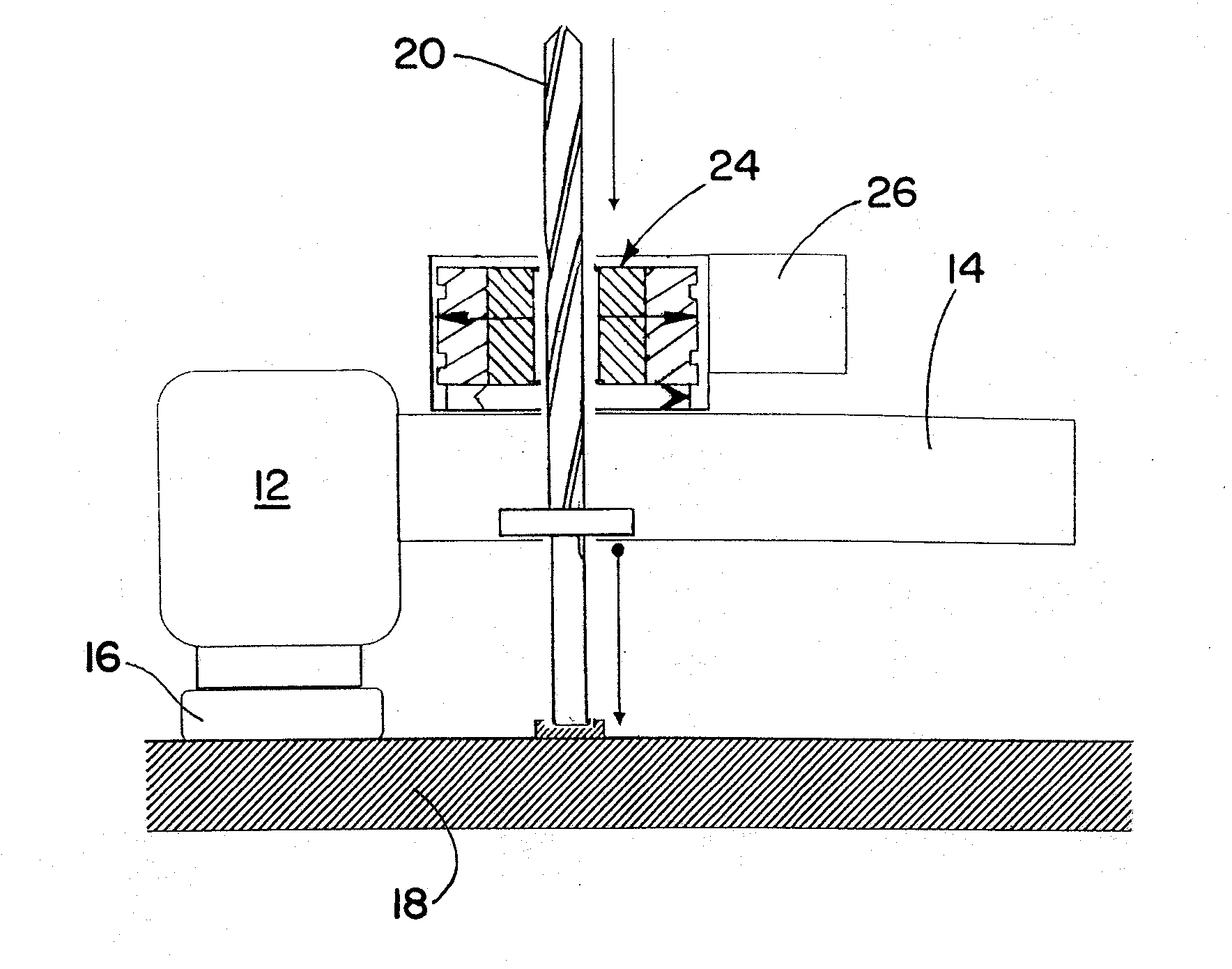
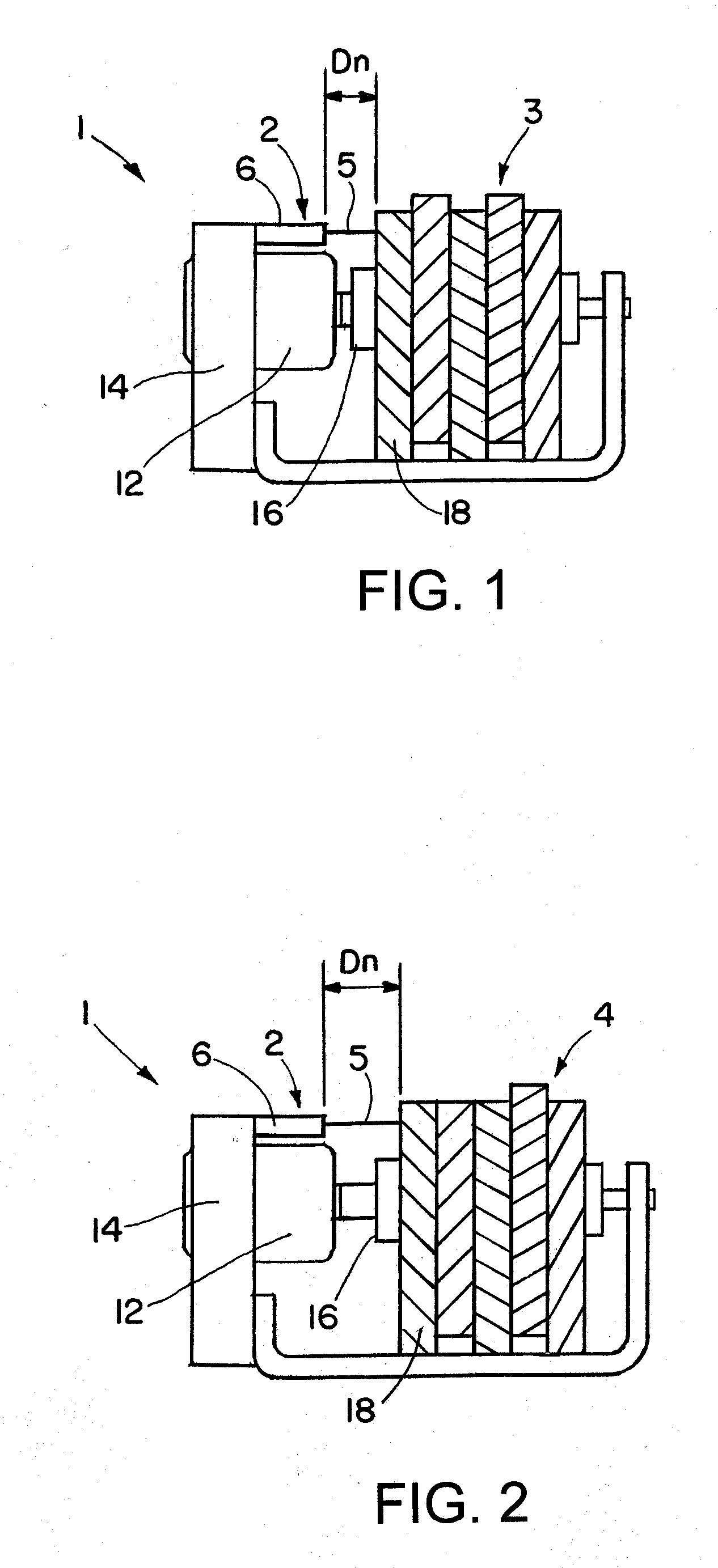
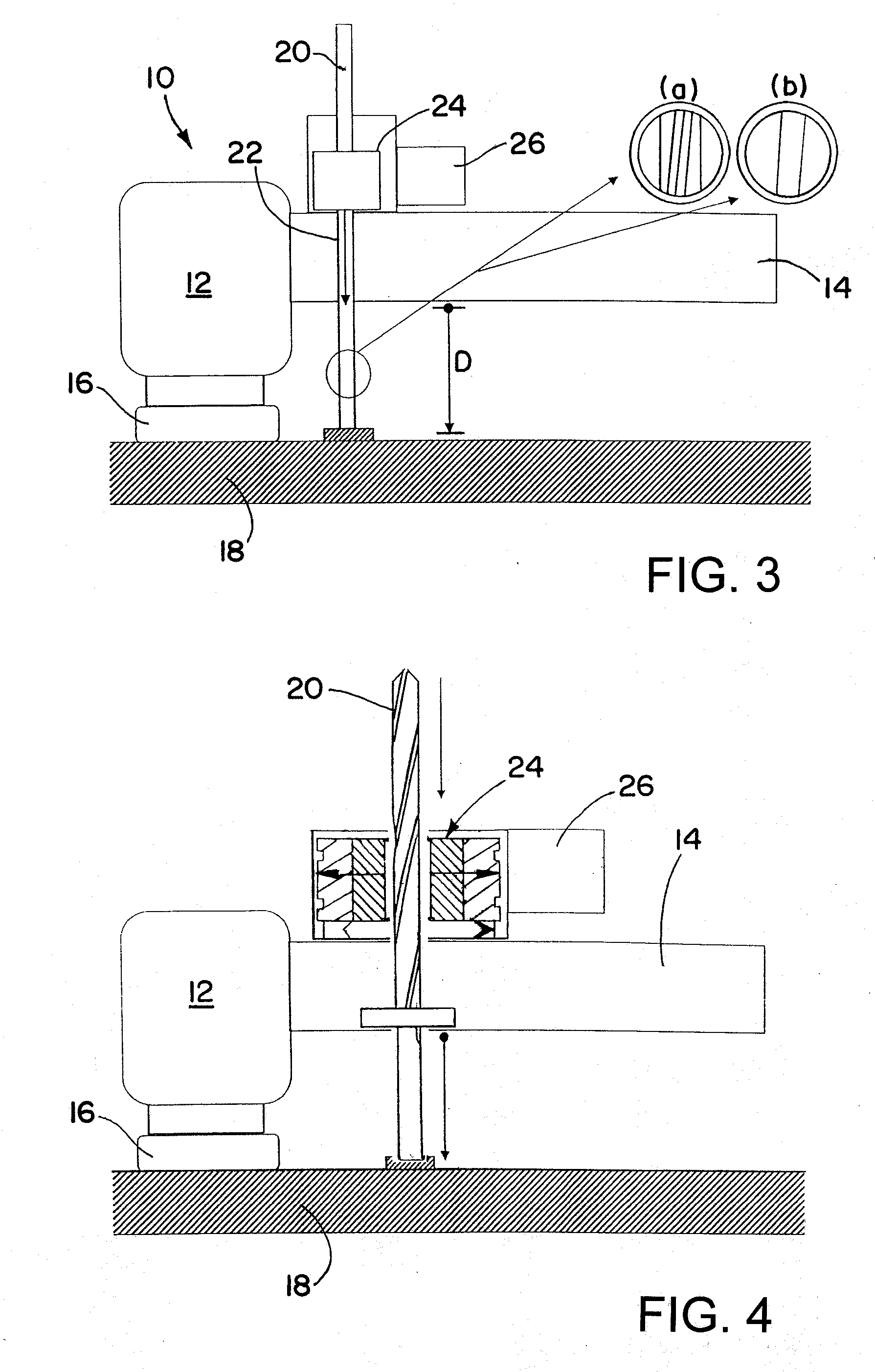
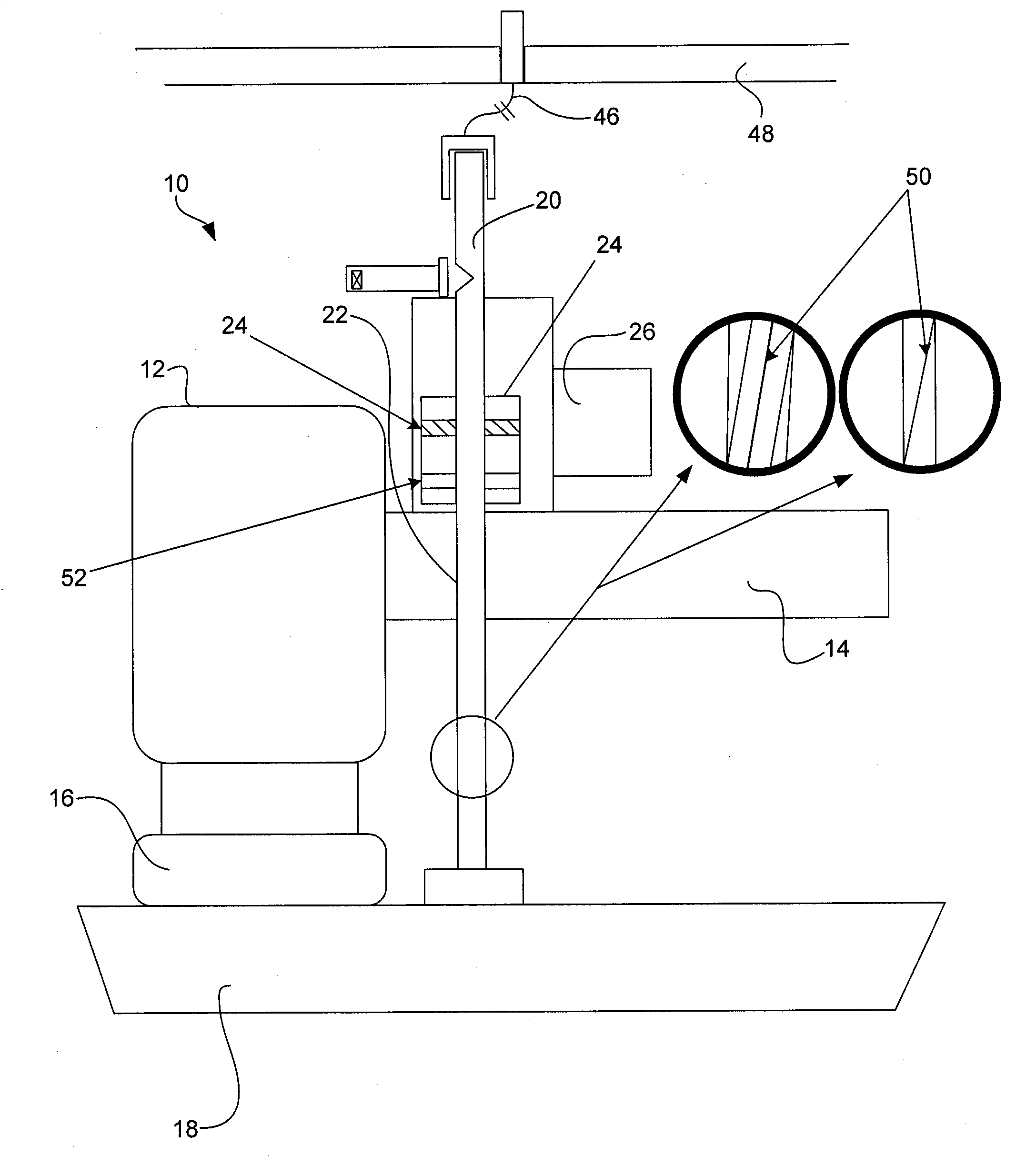
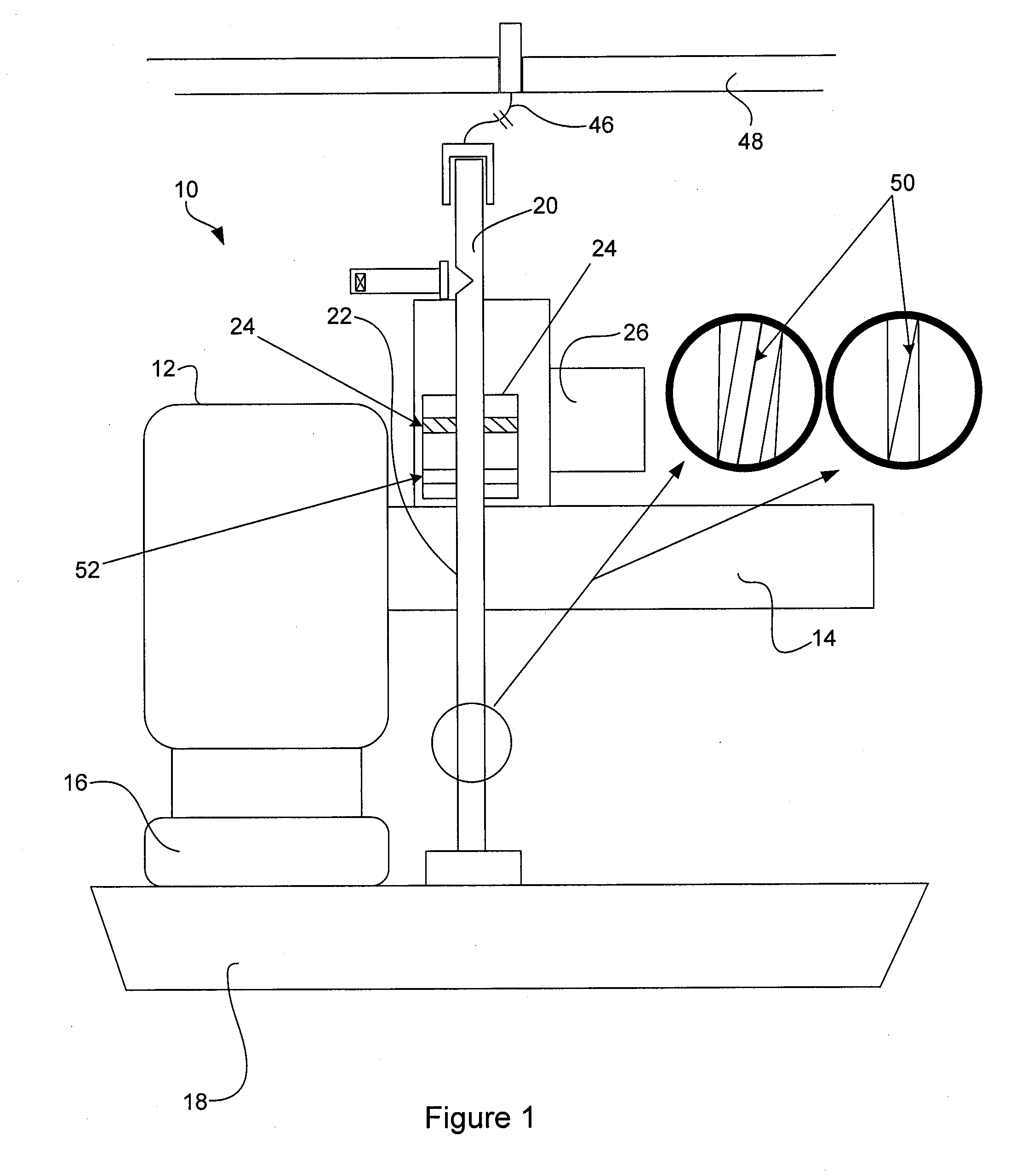
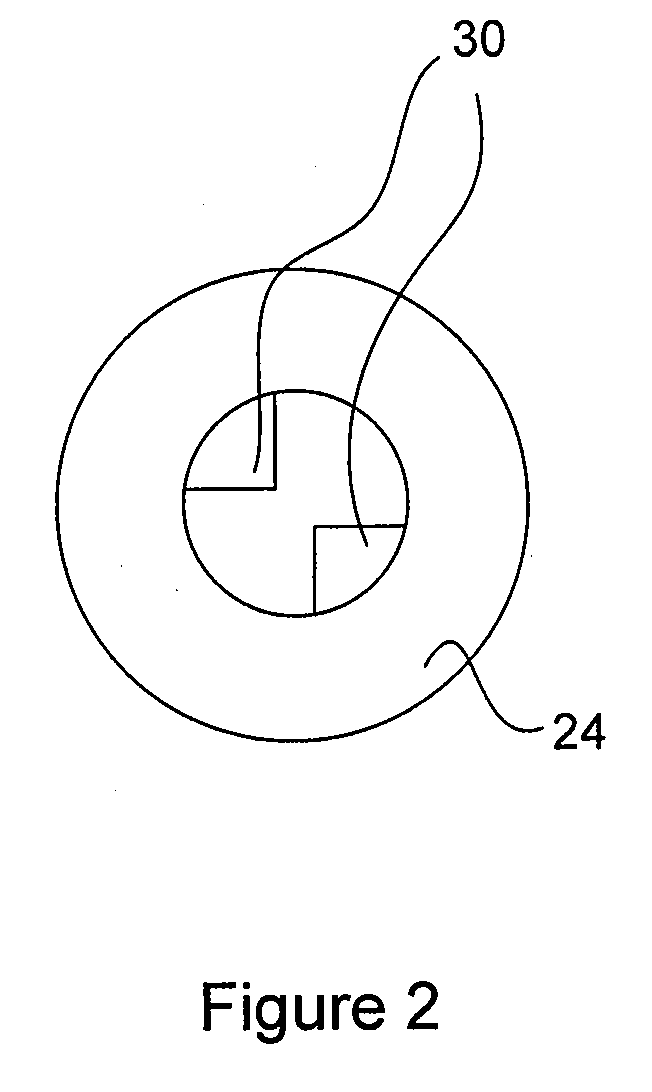
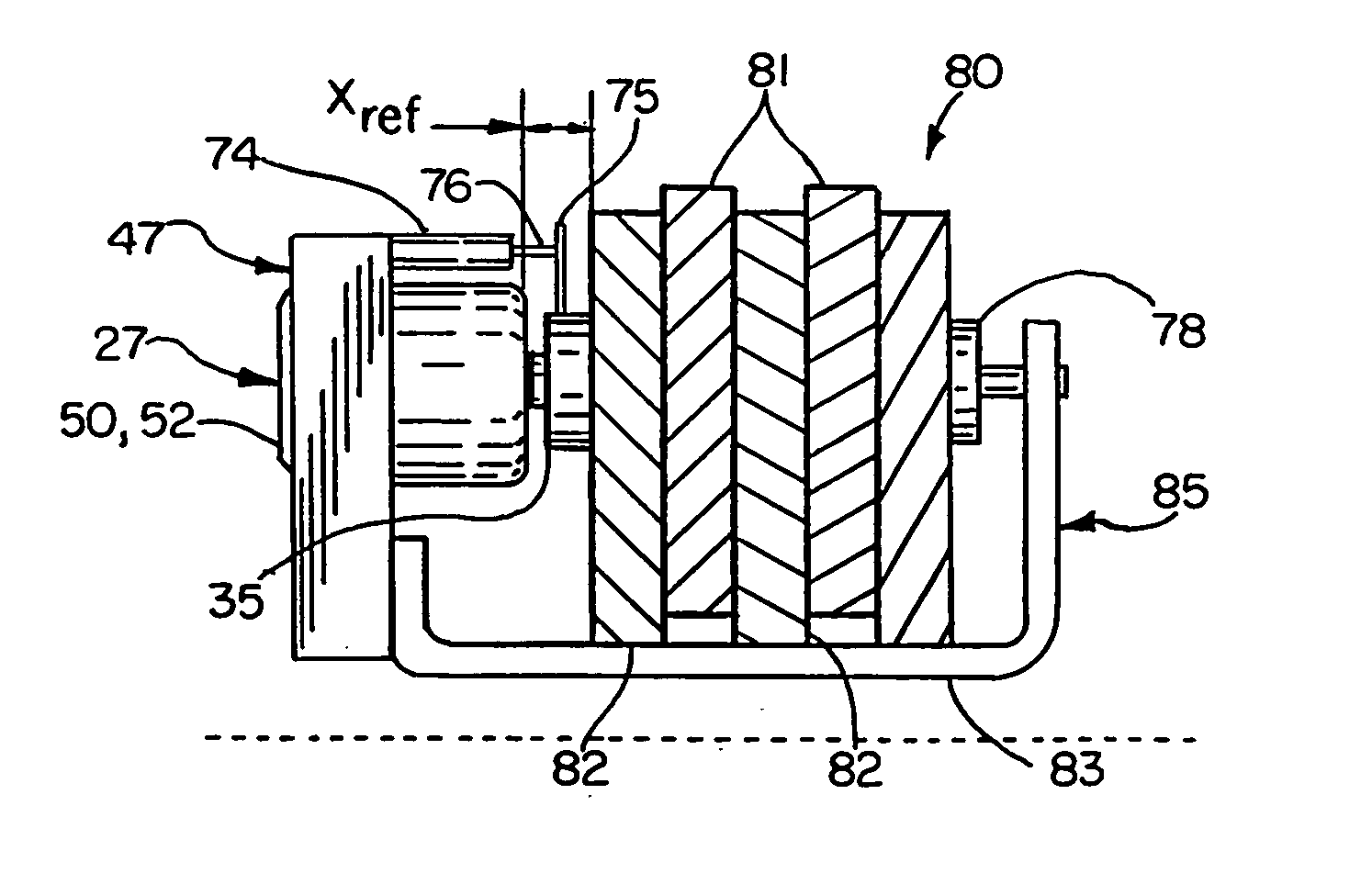
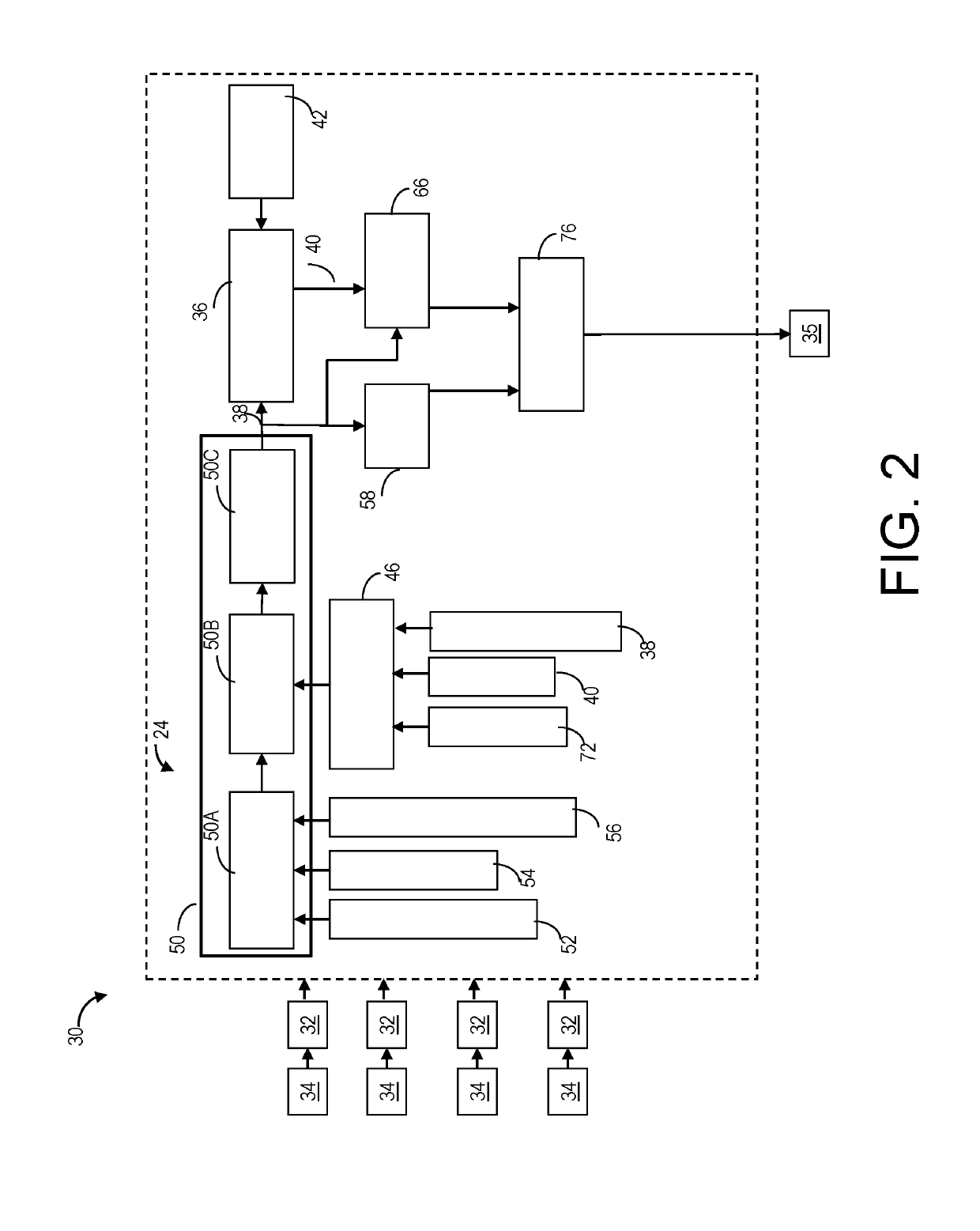
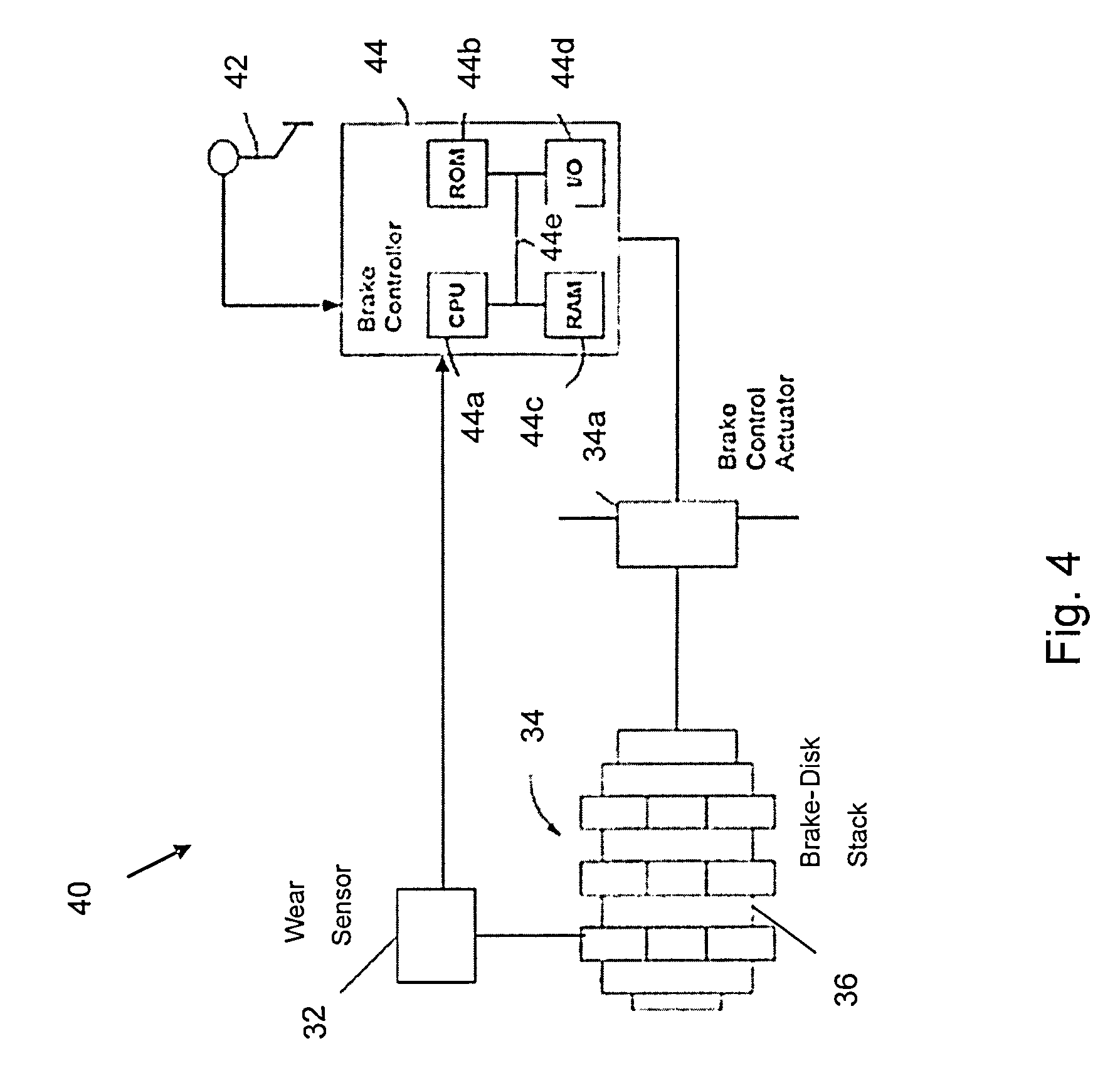
Brake wear measurement system
ActiveUS20090205910A1Small linear displacementMechanically actuated brakesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementEngineeringLinear displacement
A brake measurement system that utilize angular and / or linear displacement sensors to measure movement of a member operatively coupled to a movable member of a brake, wherein displacement of the movable member of the brake is indicative of brake wear. The system can include a twisted spline member operatively coupled to a moveable member of a brake assembly, and an angular displacement sensor operatively coupled to the twisted spline member. Movement of the moveable member is converted by the twisted spline member into an angular displacement sensed by the angular displacement sensor.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Brake pad wear indicator
A brake assembly includes a caliper, a brake pad, an actuator to force the brake pad into engagement with a rotor and an adjuster mechanism to compensate for wear of the brake pad. The adjuster mechanism includes a rotating component that rotates substantially in proportion to wear of the brake pad and is manually operable to deadjust the adjuster mechanism when replacement of the brake pad is required. The rotating component is operably coupled to a pad wear indicator mounted on the caliper which visually indicates an amount of brake pad wear.
Owner:MERITOR HEAVY VEHICLE BRAKING SYST (UK) LTD
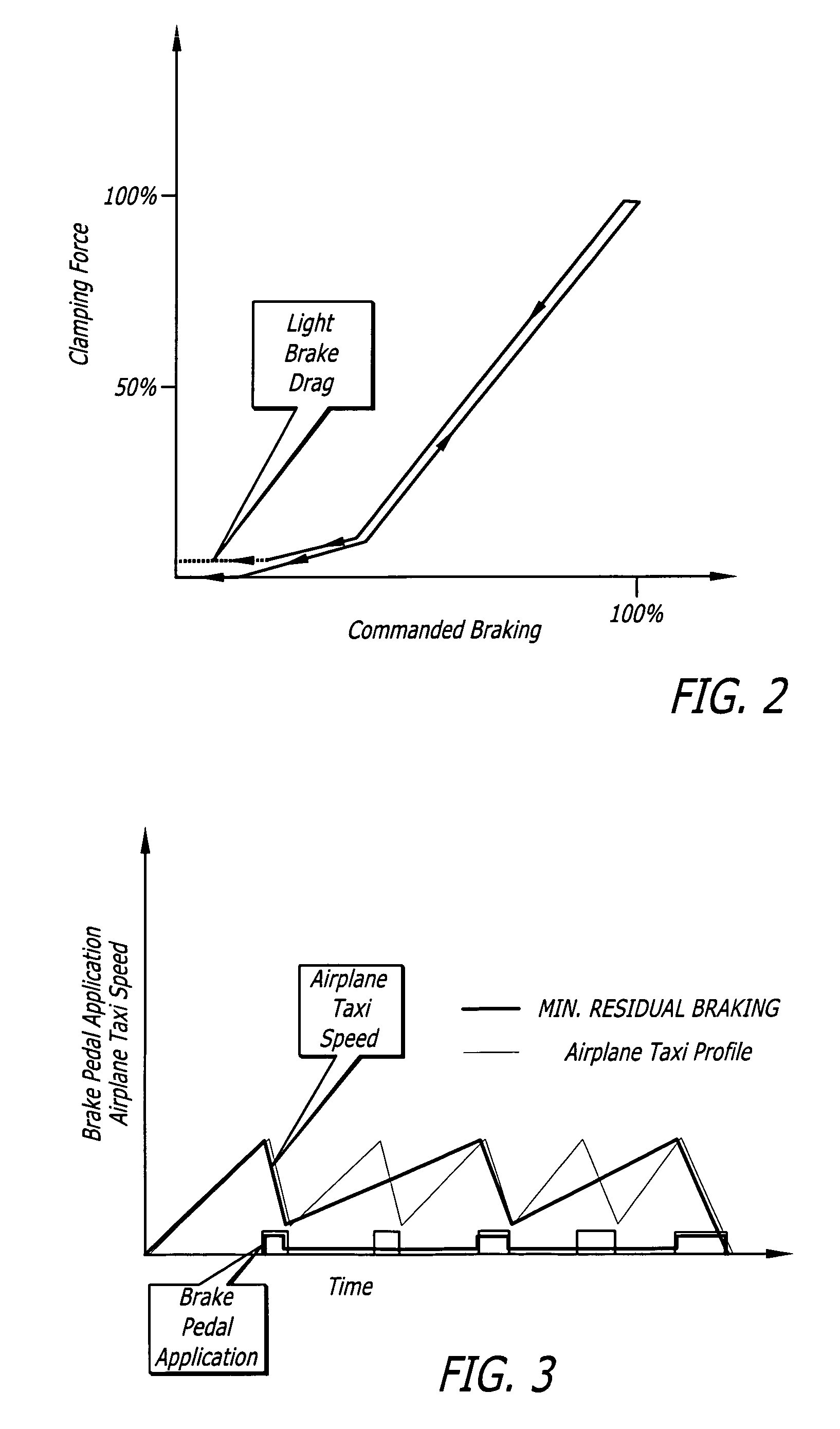
Method to reduce carbon brake wear through residual brake force
ActiveUS20060186736A1Reduced brake wearAvoid excessive frictionAutomatic braking sequenceBraking action transmissionAirplaneBrake force
The method for reducing aircraft carbon brake wear involves monitoring the commanded initiation of braking, and setting a residual brake clamping force to a predetermined minimum residual brake clamping force, which is maintained following the commanded initiation of braking to prevent release of braking during taxiing of the aircraft. The minimum residual brake clamping force is applied despite a commanded release of braking until at least one predetermined control logic condition occurs.
Owner:HYDRO AIRE AEROSPACE CORP
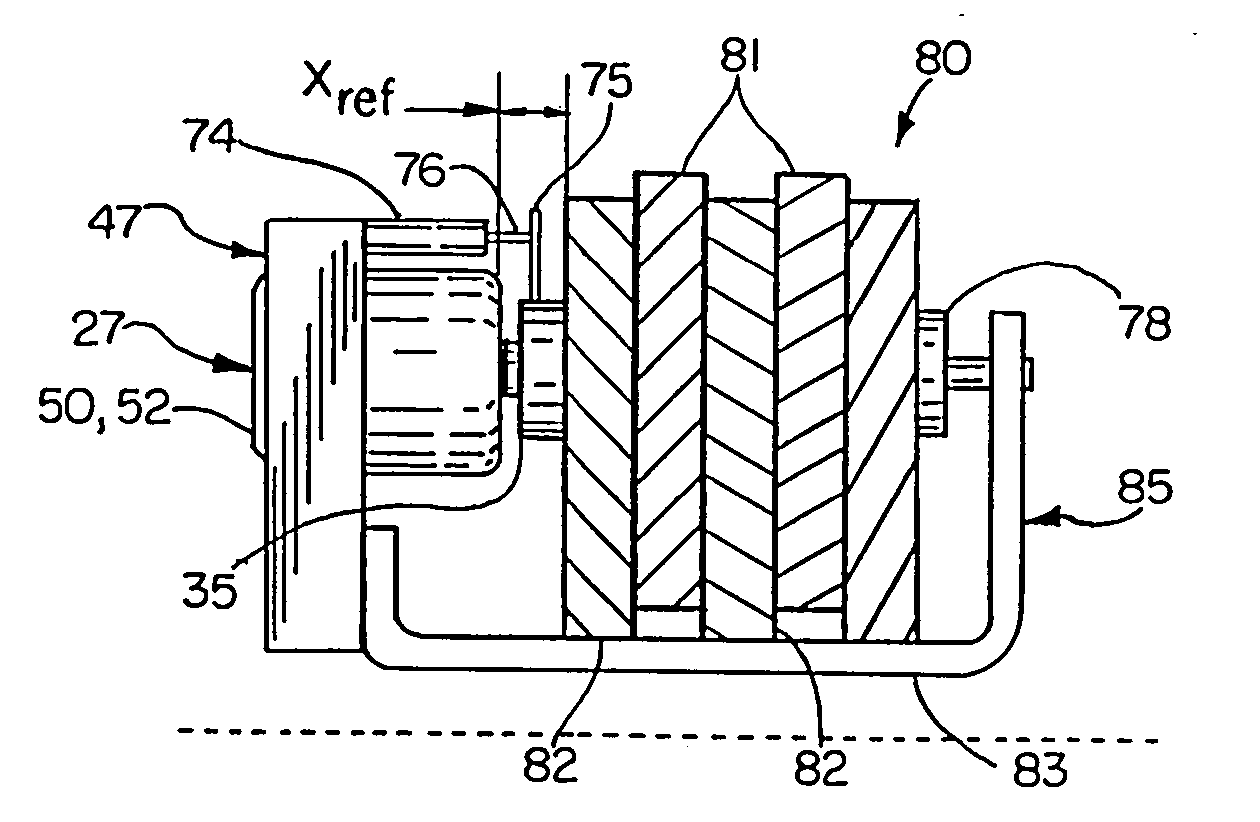
Measuring Brake Wear
ActiveUS20120221184A1Easy to exportBraking element arrangementsAnalogue computers for trafficElectrical controlEngineering
A final drive assembly is driven by an electric motor and includes a park and service brake arrangement including a shared disc brake pack that is compressed by a preload exerted by a compression spring arrangement defined by a stack of Belleville springs for establishing an engaged park brake condition in the absence of pressurized brake actuating fluid being routed to a park brake piston. An electrical control is provided for computing disc brake pack wear based on a stored load curve of the stack of Belleville springs containing information correlating preload amounts to various compressed heights of the stack of Belleville springs, and on the magnitude of a drive signal sent to the electric motor for causing sufficient drive torque to be developed for causing the rotor discs of the engaged disc brake pack to slip relative to the stator discs.
Owner:DEERE & CO
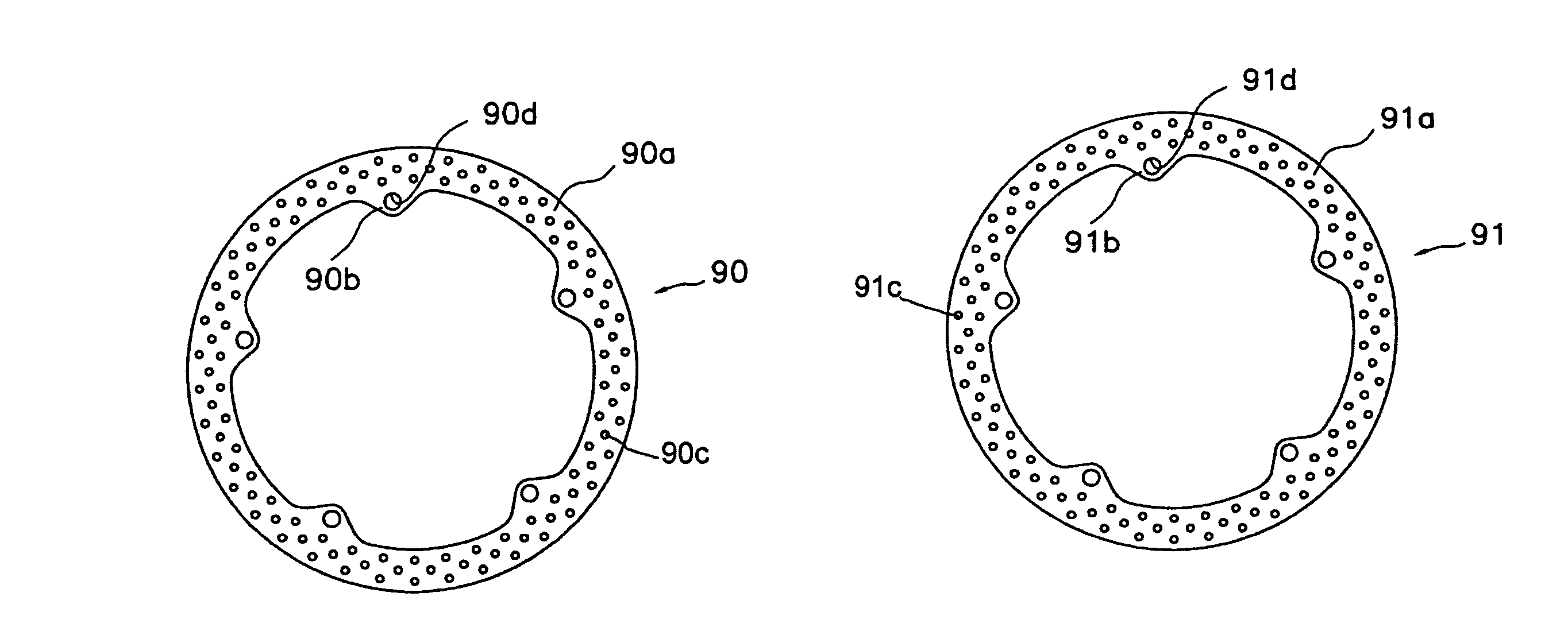
Disc sliding mechanism
A brake system includes a brake disc having a first disc face and a second disc face on a first side and a second side, respectively, of the brake disc. The brake disc is mounted rotatably fast with but longitudinally slidable on a rotatable shaft. The brake disc is clampable between a first friction surface of a fixed brake pad positioned on the first side of the brake disc and a second friction surface of a moveable brake pad positioned on the second side of the brake disc. The system further includes a disc positioner operable to define a running clearance between the first disc face and the first friction surface. The disc positioner is adjustable to maintain the running clearance as the fixed brake pad wears. A biasing member located on the second side of the brake disc maintains contact between the disc positioner and first disc face of the brake disc.
Owner:MERITOR HEAVY VEHICLE BRAKING SYST (UK) LTD
Method for establishing non-exhaust-pipe particulate matter emission inventory of road moving source
InactiveCN103810398AEmission reductionReduce pollutionSpecial data processing applicationsParticulatesEmission inventory
The invention discloses a method for establishing a non-exhaust-pipe particulate matter emission inventory of a road moving source, which comprises the following steps: S10, measuring traffic flow of a road section to be measured and vehicle speeds V according to vehicle types; S20, calculating a particulate matter emission factor correction coefficient ST (V) of the vehicle speeds of vehicles on tire wear of the vehicles; S30, calculating a particulate matter emission factor correction coefficient SB (V) of the vehicle speeds of the vehicles on brake wear; S40, calculating a tire wear particulate matter emission factor after the vehicle speeds are corrected, a brake wear particulate matter emission factor after the vehicle speeds are corrected and a pavement wear particulate matter emission factor after the vehicle speeds are corrected; S50, calculating a non-exhaust-pipe particulate matter emission load of the road moving source. The method for establishing the non-exhaust-pipe particulate matter emission inventory of the road moving source, which is disclosed by the invention, can accurately reflect time and space variation of the non-exhaust-pipe particulate matter emission of the road moving source.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL RES INST OF ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION
Vanadium-contained semimetallic brake block
ActiveCN105240429ANot easy to produceReduce wear rateOther chemical processesFriction liningAluminum silicateCellulose fiber
The invention discloses a vanadium-contained semimetallic brake block. The vanadium-contained semimetallic brake block includes, by weight, 5-7 parts of red copper fibers, 3-6 parts of potassium hexatitanate whiskers, 4-5 parts of barium sulfate, 15-25 parts of ferrovanadium powder, 4-6 parts of frictional powder, 13-15 parts of short stainless steel fibers, 6-10 parts of graphite, 2-4 parts of cellulosic fibers, 7-9 parts of coke blacking, 1-5 parts of modified resin nitrile fibers, 3-7 parts of chromite ore fine, 1-5 parts of nitrile rubber, 5-9 parts of ceramic adhesive agents and 8-10 parts of spray-bounded aluminum silicate fibers. The brake block obtained by material mixing, steel backing treatment, press molding, heat treatment, packaging and storage is low in wear rate, not prone to being dusty, high in density, good in heat dissipation, small in vibration, low in noise and high in corrosion resistance. The whole manufacturing process is simple, stability is good, cost is low and the cost-performance ratio is high.
Owner:盐城加能汽车部件有限公司
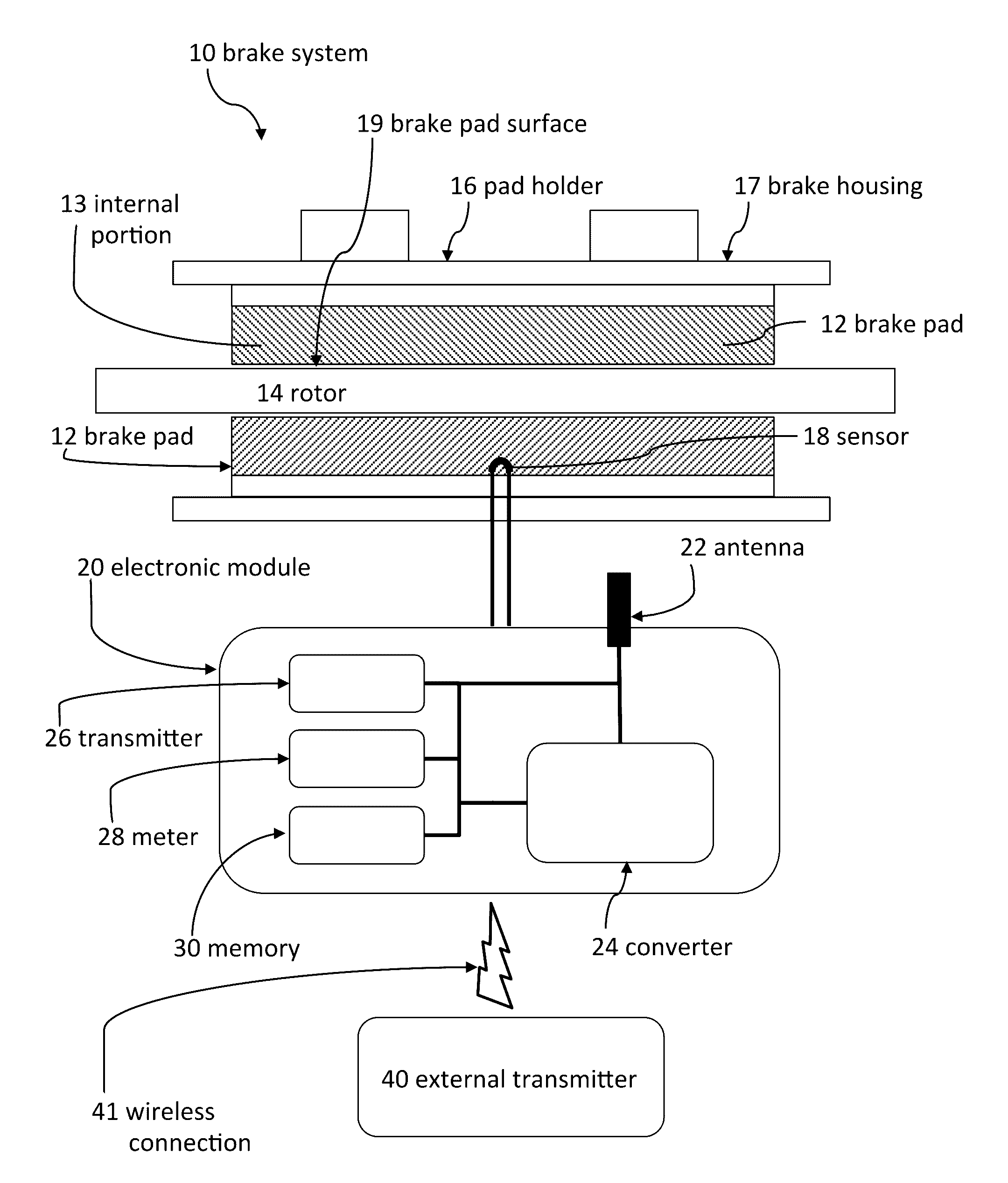
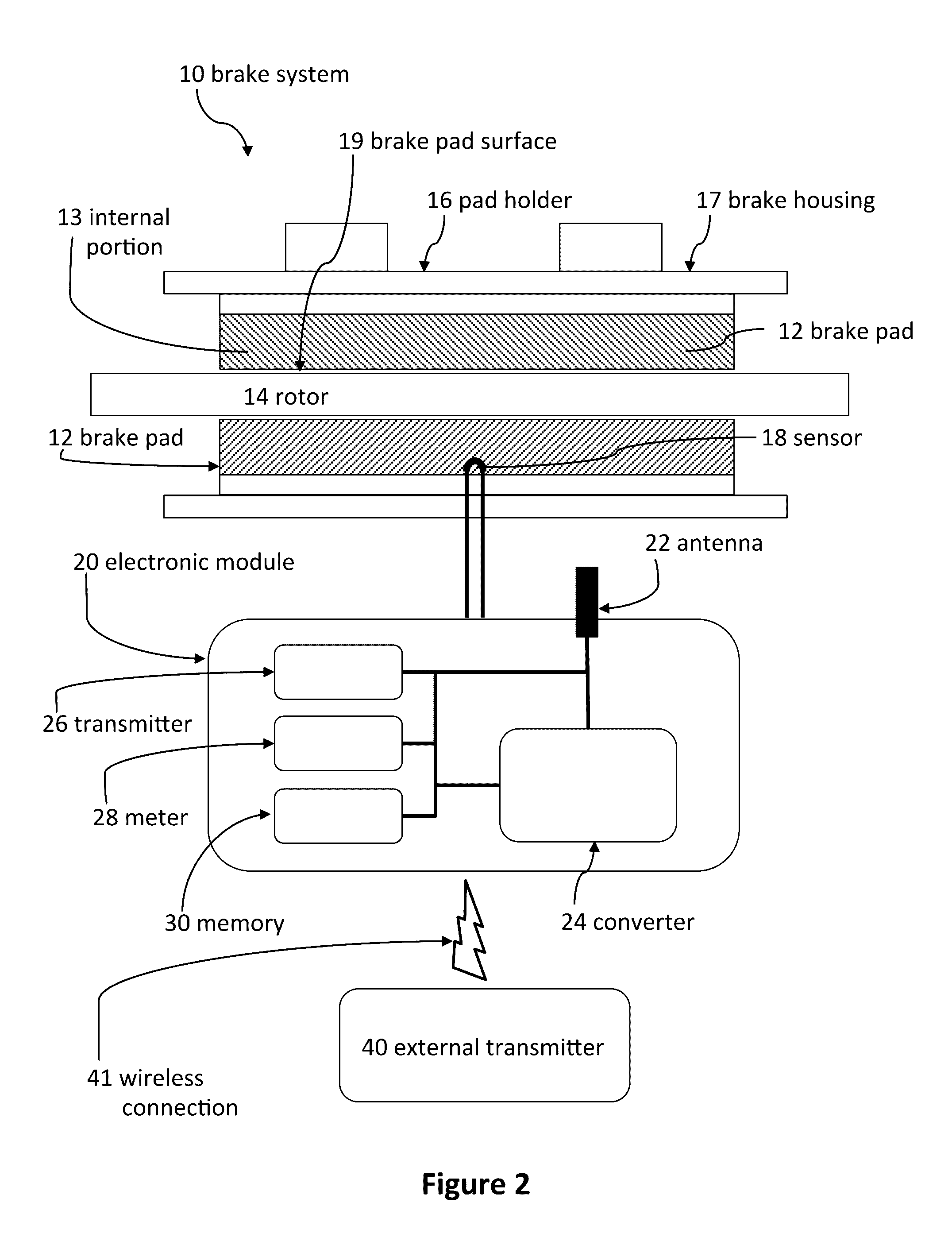
Systems and methods for detecting wear of brake pads
A system can be used to indicate wear of a brake pad. The system can include a brake housing, a brake pad mechanically coupled to the brake housing, and a sensor mechanically coupled to the brake pad. The sensor can determine when the brake pad has been worn to a predetermined location. The system can also include an electronic module electrically coupled to the sensor and mechanically coupled to the vehicle. The electronic module can include a radio frequency antenna configured to wirelessly transmit radio frequency information to an external receiver, a battery, memory, and an internal transmitter coupled to the battery. The internal transmitter can be configured to wirelessly transmit information from the sensor and the memory to the external receiver via the radio frequency antenna.
Owner:EDEN GIDEON
Brake wear measurement system and method
A brake measurement system comprising a measurement mechanism for measuring brake wear operatively coupled to a moveable member of a brake assembly is provided. The system further includes a displacement sensor and a visual indicator. The displacement sensor is operatively coupled to the measurement mechanism, wherein movement of the moveable member is converted by the measurement mechanism into a displacement sensed by the displacement sensor. The visual indicator is operatively connected to the measurement mechanism, wherein the visual indicator displays the movement of the moveable member and consequently the wear of the brake stack at a point on the exterior of an aircraft brake housing for inspection.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Electronic aircraft braking system with brake wear measurement, running clearance adjustment and plural electric motor-actuator ram assemblies
InactiveUS20050109565A1Easy maintenanceIncrease weightAxially engaging brakesBraking action transmissionEngineeringActuator
An electrically actuated aircraft brake system and method which provides for brake wear measurement, brake running clearance adjustment, ram position-based control and improved construction and operation. Brake wear and running clearance measurement are obtained by analyzing the output of position sensing circuitry. The position sensing circuitry, preferably including a LVDT position sensor, is also used to determine braking load, a brake controller including circuitry for effecting displacement of one or more reciprocating rams to load a brake disk stack by a predetermined amount based on a present displacement value of the position signal obtained from the position sensor. The position sensor preferably includes a LVDT transducer connected between the reciprocating ram and a brake housing, and the motive device preferably includes a servo motor. Also provided is an actuator housing including a guideway for each ram, the guideway and ram having the same polygonal cross-section, whereby the ram nut is guided and restrained from rotation by the guideway as it is translated by a ball screw in threaded engagement with the ram nut for selective movement into and out of forceful engagement with the brake disk stack for applying and releasing braking force on a rotatable wheel. An electric motor is drivingly connected to each ball screw by a first gear integral with the ball screw, a second gear in mesh with the first gear, and a pinion on a rotating drive shaft of the electric motor.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
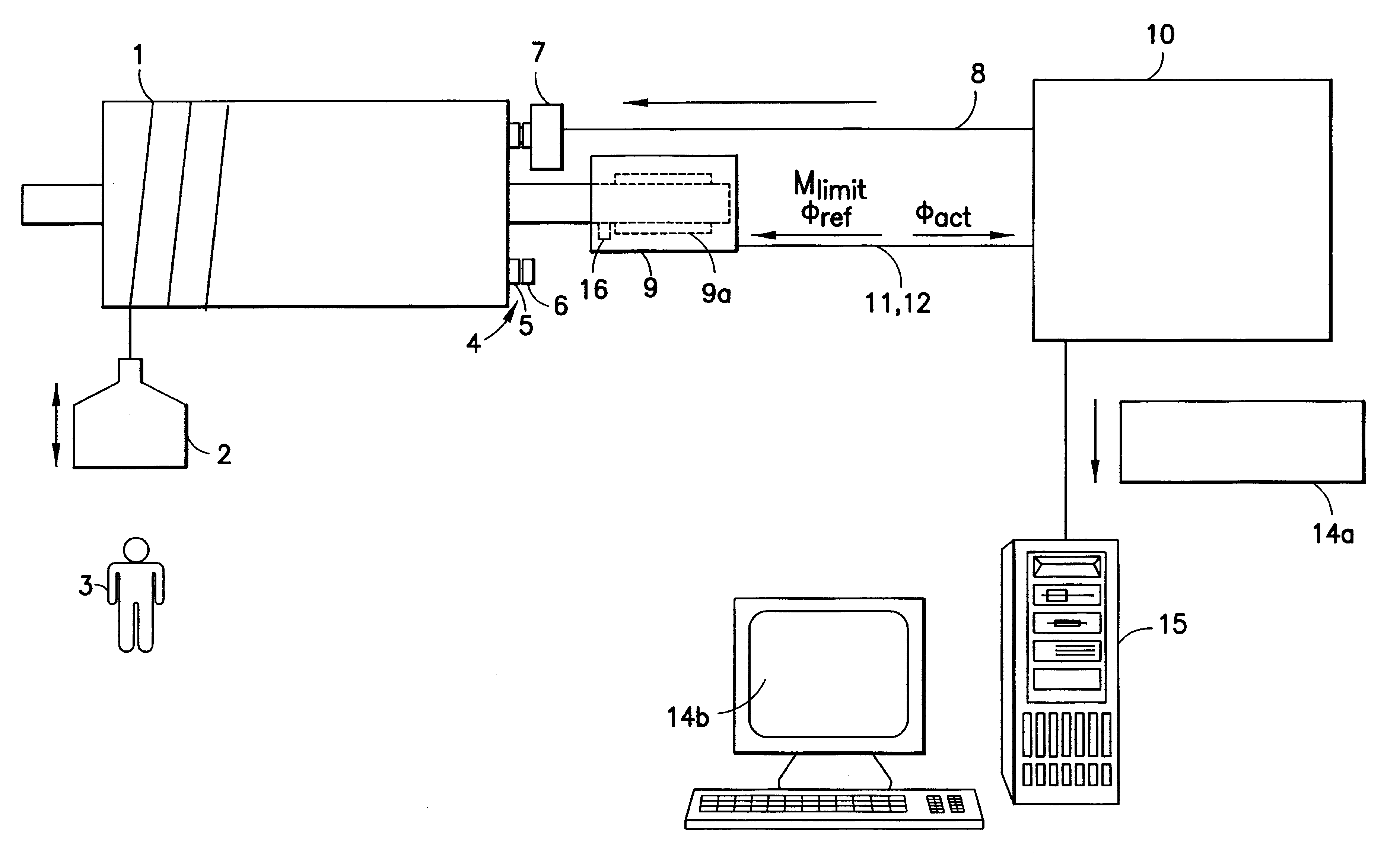
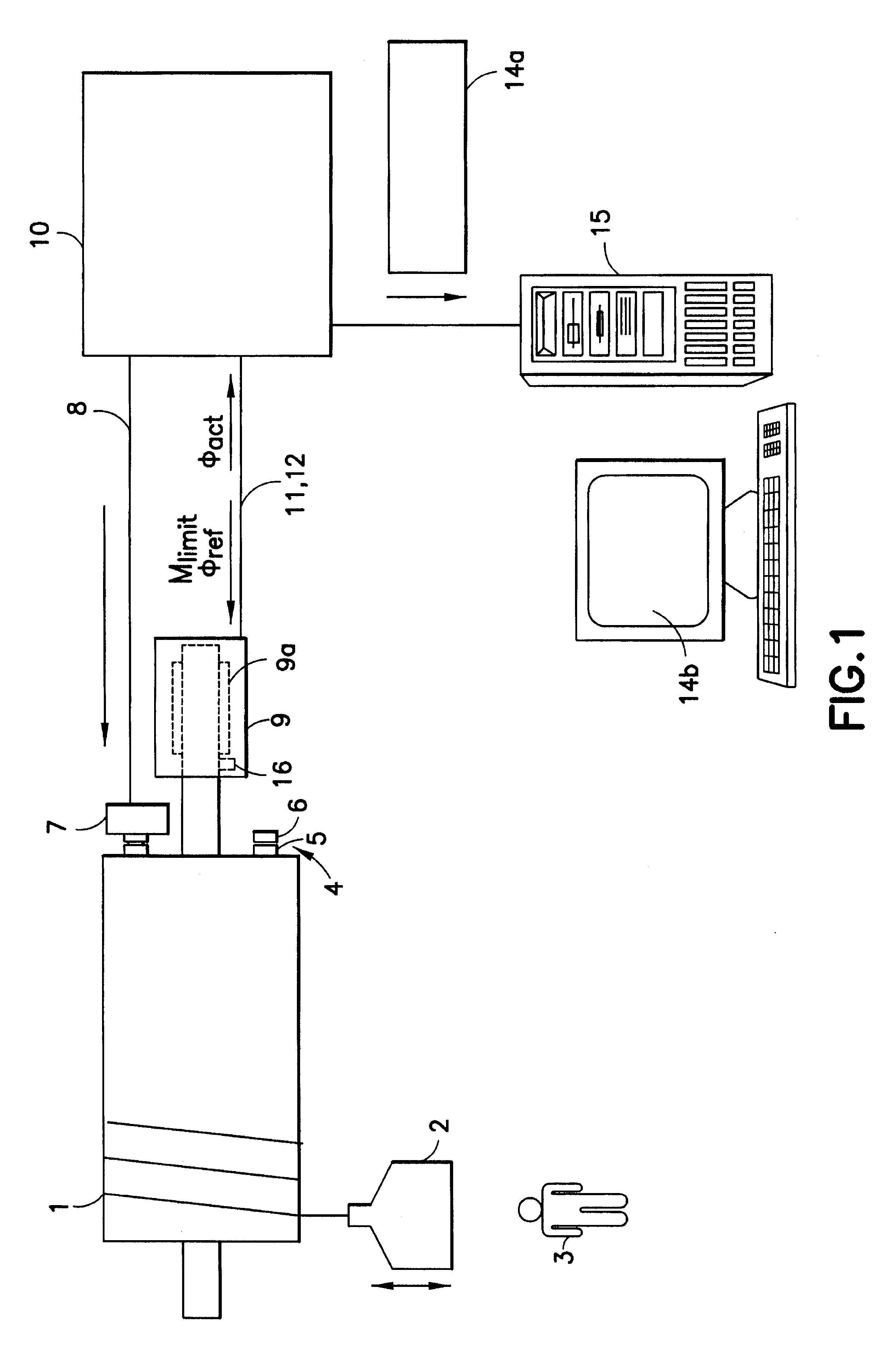
Means for monitoring holding brake wear
A highly dependable process and device for monitoring wear for a holding brake is performed via an electronically controlled brake test. A shaft which is drivable by a motor can be braked by the holding brake. A reference angular position which is to be traveled by the motor during the brake test and which deviates from the current actual angular position of the motor is preset along with a maximum limit torque to be applied by the motor during the brake test are preset for the motor. During the brake test, the actual angular position of the shaft is monitored to determine whether the shaft rotates. The existence of wear in the holding brake is evidenced by rotation of the shaft during the brake test.
Owner:MANNESMANN AG
Brake pad wear estimation
Technical solutions are described for determining thickness of a vehicle brake pad. An example method for estimating brake pad wear on a vehicle includes computing a corner torque for a brake based on corner brake pressure applied to the brake. The method also includes computing a corner power for the brake based on the corner torque. The method also includes computing a rotor temperature of a rotor of the brake based on the corner power. The method also includes determining a brake pad wear rate per unit of power based on the rotor temperature and the corner power. The method also includes computing a brake pad wear based on the brake pad wear rate and the corner power.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Bicycle disk brake apparatus with laminated components
A bicycle disk brake rotor apparatus comprises a generally circular first rotor member and a generally circular first second rotor member. The first rotor member has a first fixing component structured to mount the first rotor member to a hub mounting member, and the first second rotor member has a first fixing component structured to mount the first second rotor member to the hub mounting member. The first rotor member is attached to a side of the first second rotor member, and the first second rotor member is formed of a material having greater braking wear resistance than the first rotor member.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
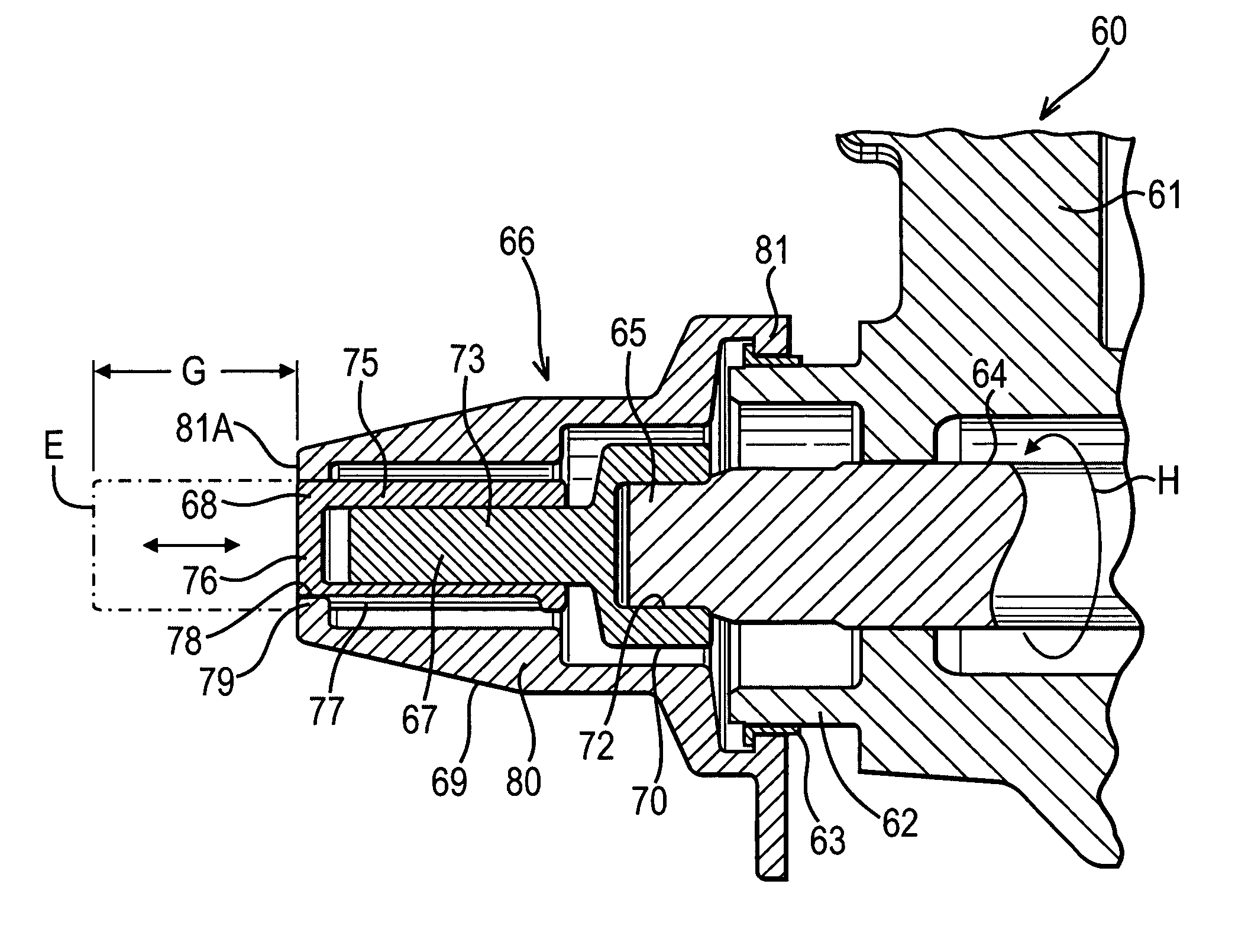
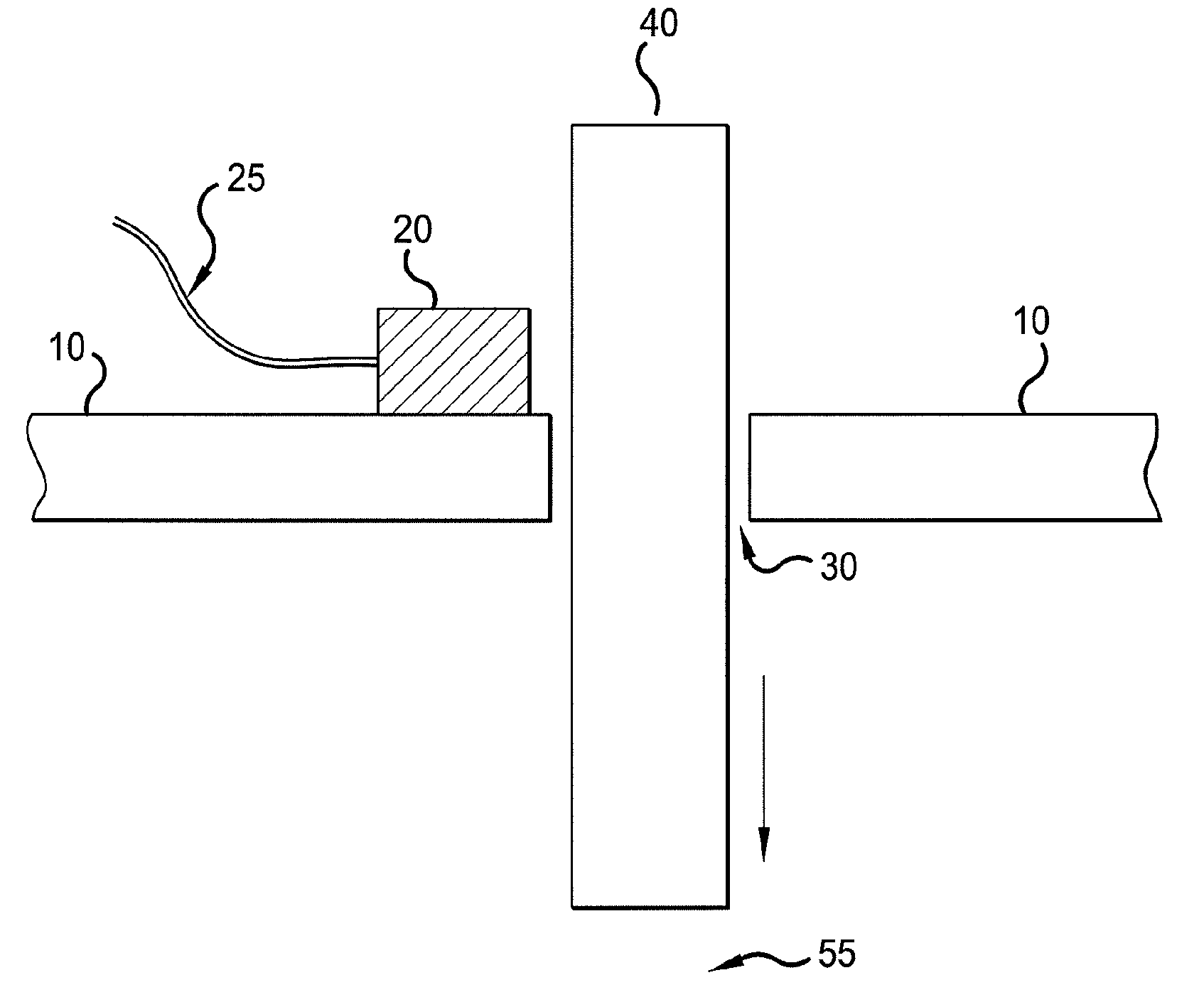
Proximity sensor for brake wear detection
ActiveUS9441692B2Analogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsProximity sensorEngineering
A proximity sensor 20, 21, 22 and method for detection of wear in a brake disc stack 55 on an aircraft including a wear pin 40, 43, 50 for moving in a first direction as the brake wears, and a switch 20, 21, 22 for measuring movement of the wear pin in the first direction. When the wear pin 40, 43, 50 moves in the first direction to a predetermined position, the switch 20, 21, 22 signals that the brake disc stack 55 has worn the predetermined amount.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
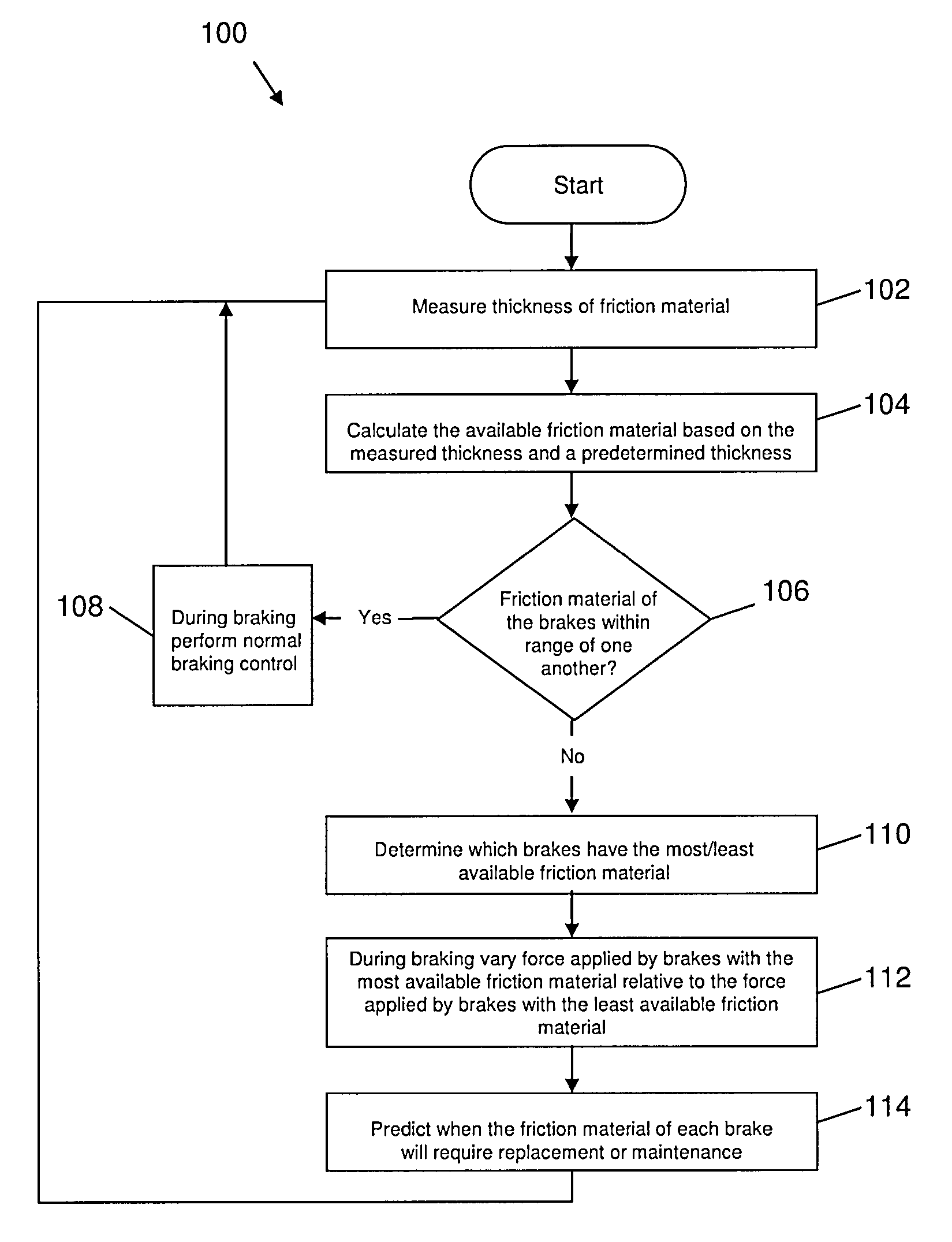
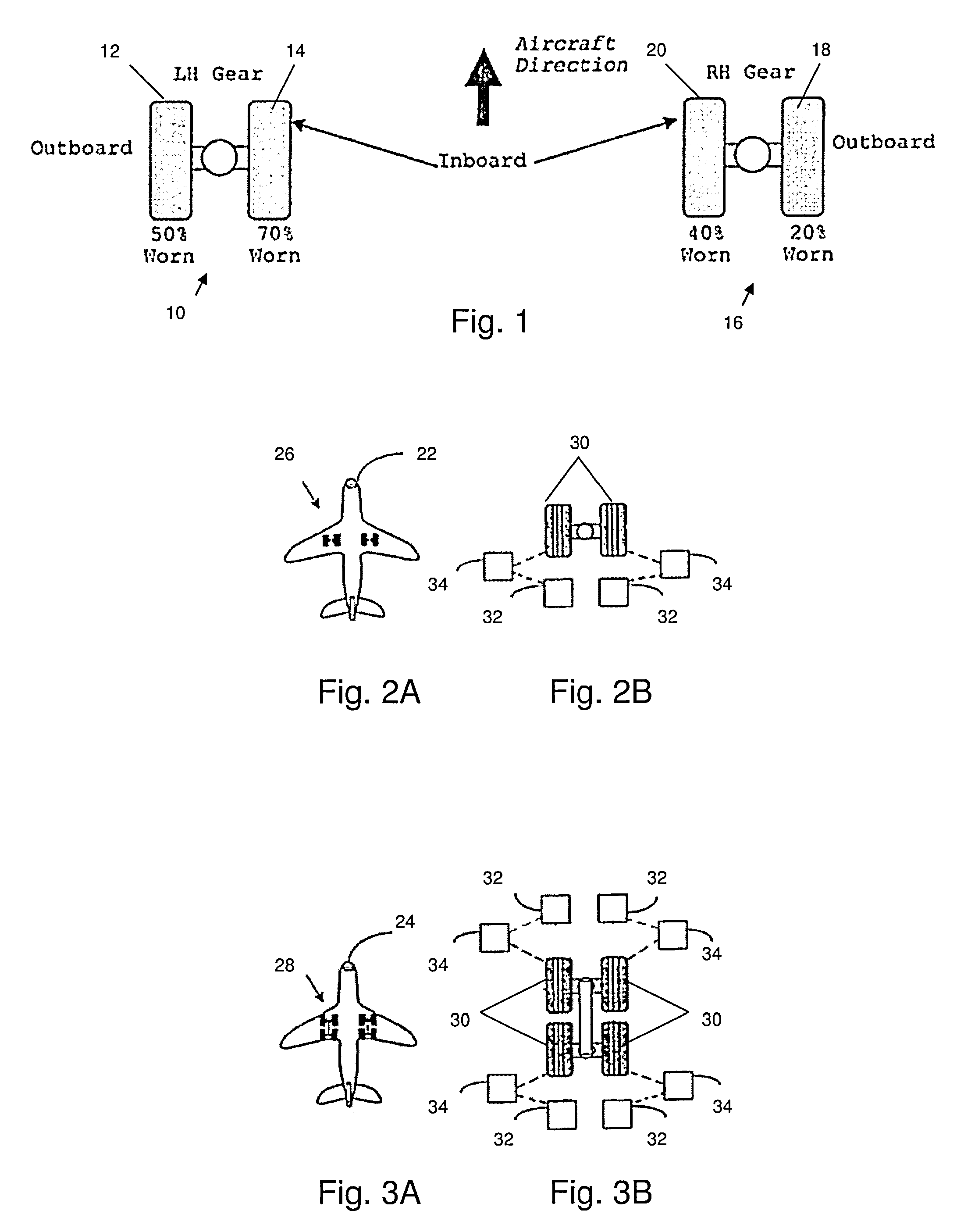
Brake wear control system
ActiveUS8634971B2Frequent inspectionFrequent maintenanceMechanically actuated brakesDigital data processing detailsControl systemEngineering
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
System for actively monitoring wear on wind turbine brake pads and related methods
A system for monitoring wear on a brake pad of a wind turbine is disclosed. The system may include a brake assembly having a brake pad and a moveable component. The brake pad may be configured to engage a friction surface of the wind turbine. The movable component may be configured to move relative to the friction surface as the brake pad wears. Additionally, the system may include a sensor at least partially mounted within the brake assembly. The sensor may be configured to detect a position of the movable component relative to the sensor or a position of the friction surface relative to the sensor.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Monitor for manual trailer brake activation
ActiveUS8127600B2Reducing wear and incidenceSave wearBraking action transmissionHand actuated initiationsTrailer brake controllerBiological activation
In a highway tractor trailer vehicle, a brake control sensor is operative to detect each activation of the manual trailer brake control, and a recorder receives and stores data comprising a speed of the tractor at each manual trailer brake control activation. Trailer brake wear is reduced by penalizing an operator of the tractor for each unauthorized activation of the manual trailer brake control. Testing of the connection of the tractor to the trailer is encouraged by tracking the activation of the manual trailer brake control and penalizing the operator for failure to test the connection.
Owner:MEIER CLAY +1
Disc-shaped braking unit based on pressure rotation
The invention belongs to the technical field of automobile braking, and particularly relates to a disc-shaped braking unit based on pressure rotation. The disc-shaped braking unit based on pressure rotation comprises a brake disc, a first braking unit, a second braking unit and telescopic structures, wherein the first braking unit and the second braking unit are connected by a braking unit connecting shell and are positioned at both sides of the brake disc. Extension and retraction of hydraulic columns mounted on a braking unit hydraulic shell are controlled by a hydraulic pressure; each telescopic structure is formed in a manner that a telescopic inner rod is embedded inside a telescopic outer sleeve and the telescopic inner rod and the telescopic outer sleeve can slide in a mutual embedding manner; the telescopic outer sleeves can move along with a power plate in the axis directions of the telescopic sleeves under the extending and retracting action of the hydraulic columns; meanwhile, screw threads on the outer surfaces of the telescopic outer sleeves are matched with screw thread holes on first supporting plates fixed on a braking unit hydraulic shell to enable the brake disc to be supported and driven to rotate. According to the disc-shaped braking unit disclosed by the invention, by utilizing difference in worn positions of a brake pad in the light braking process and the heavy braking process, people not only can realize that the brake pad needs to be replaced, but also can utilize heavy braking to continuously and safely drive when light braking is invalid.
Owner:龙口富元机械有限公司
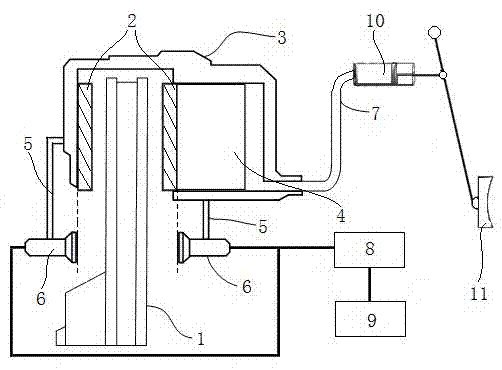
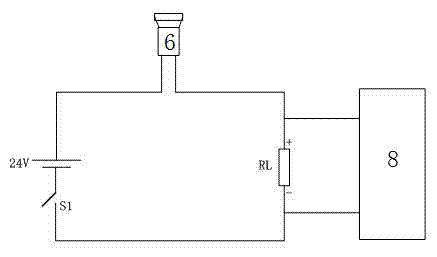
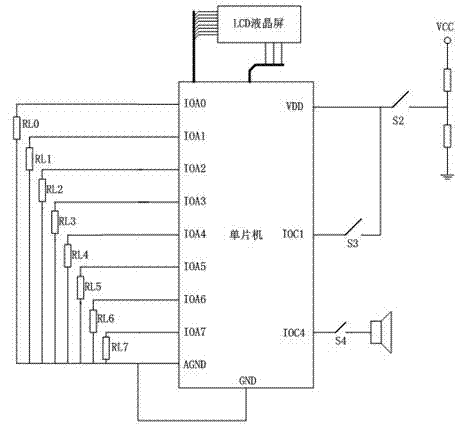
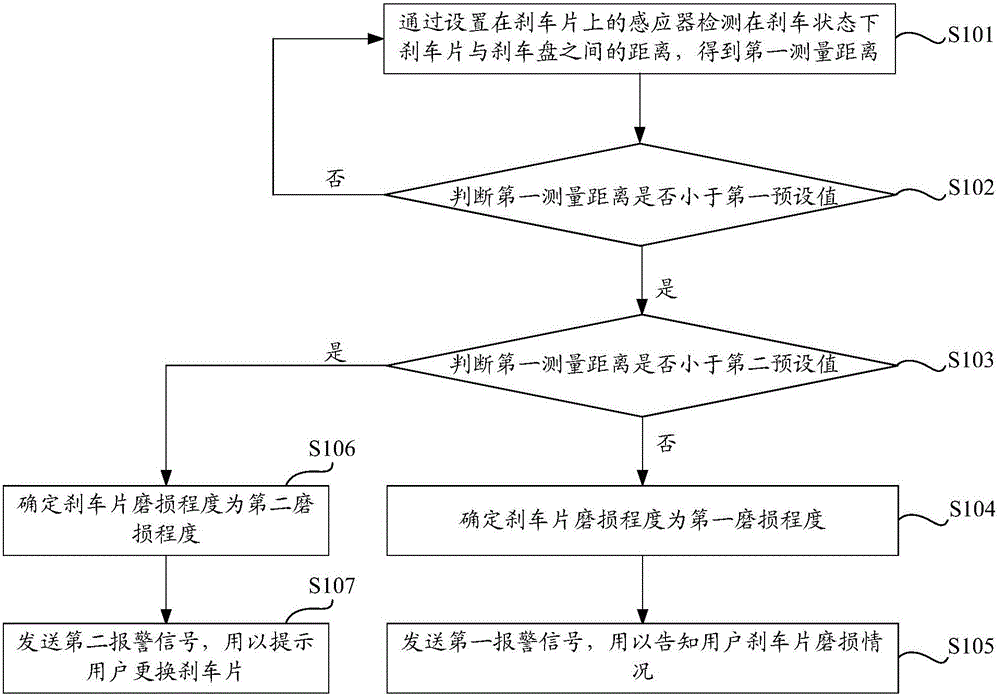
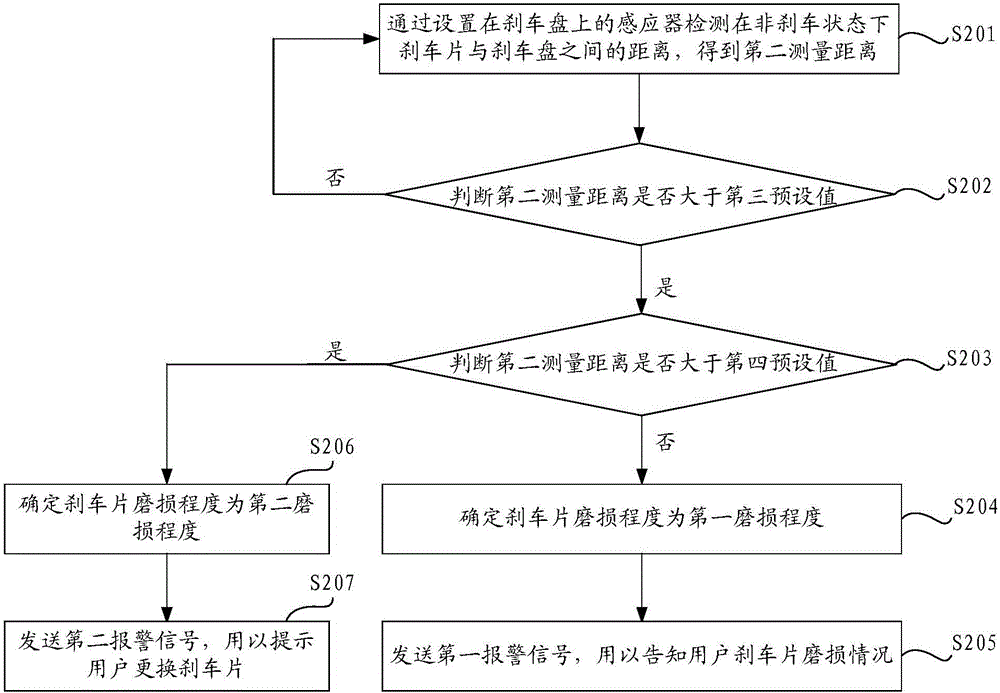
Brake pad wear warning method and device
The invention discloses a brake pad wear warning method and device. The brake pad wear warning method comprises the following steps: detecting the distance between a brake pad and a brake disc by an inductor to obtain a measured distance; analyzing according to the obtained measured distance to acquire the wear degree of the brake pad; and sending a warning signal according to the wear degree of the brake pad. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, a user can conveniently know wear of the brake pad without examining the brake pad, so that convenience is brought to replace the brake pad in time, the convenience in learning about wear of the brake pad is improved, and potential safety hazards during driving, caused by the excessively thin brake pad, are avoided.
Owner:LETV HLDG BEIJING CO LTD +1
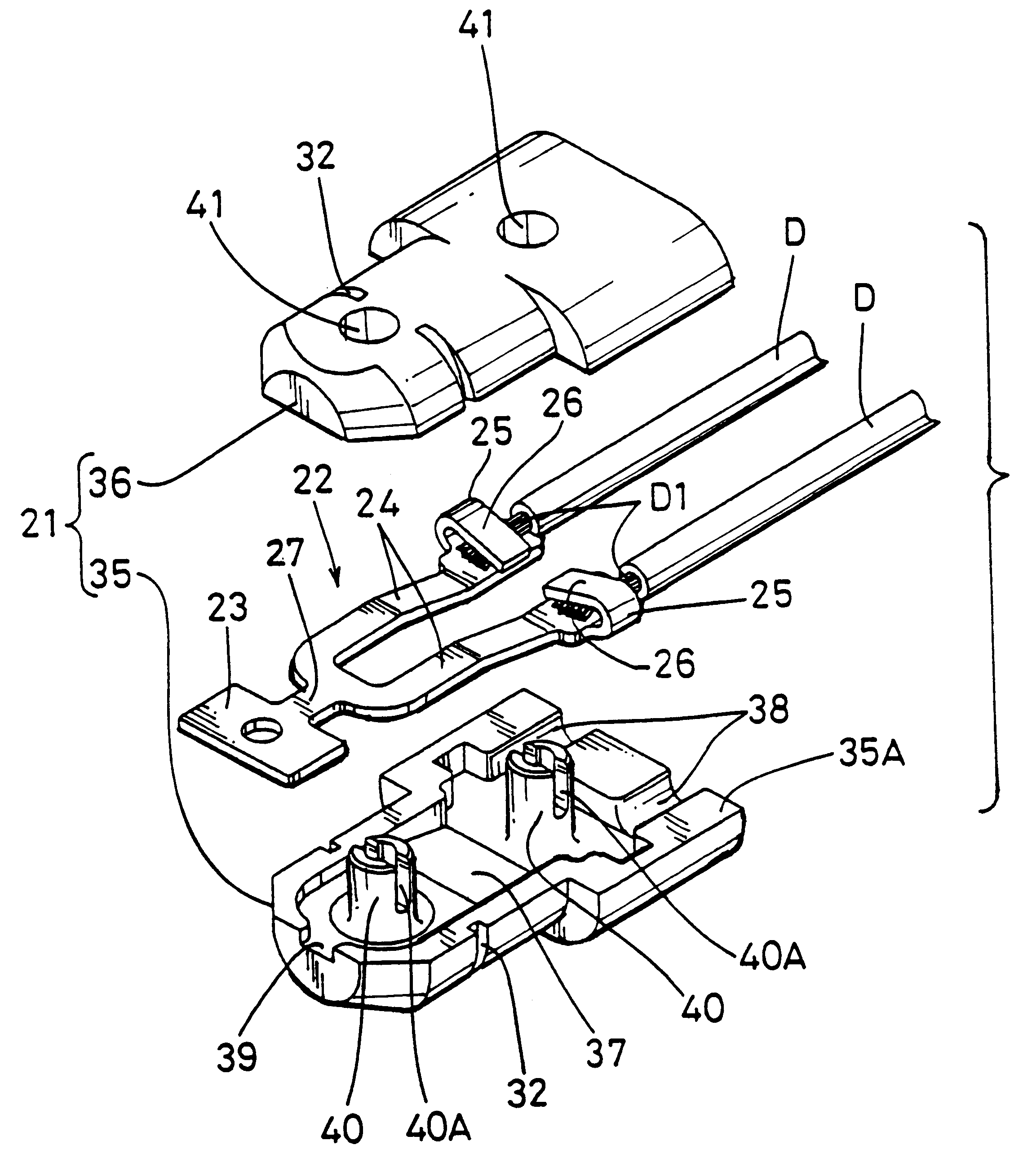
Abrasion detecting probe for a brake pad
The invention provides an abrasion detecting probe for a brake pad which does not require insert-moulding and in which production costs are low.A probe 20 is housed in base components 35 and 36, which are snap-fitted together. In this manner, the terminal 22 can be attached within the base member 21 in a precise predetermined position by the simple operation of joining the base components 35 and 36 together. Therefore, as opposed to a conventional probe, insert-moulding is not required and the probe can be manufactured simply and cheaply. A sleeve 50 may provide an audible brake wear warning.
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
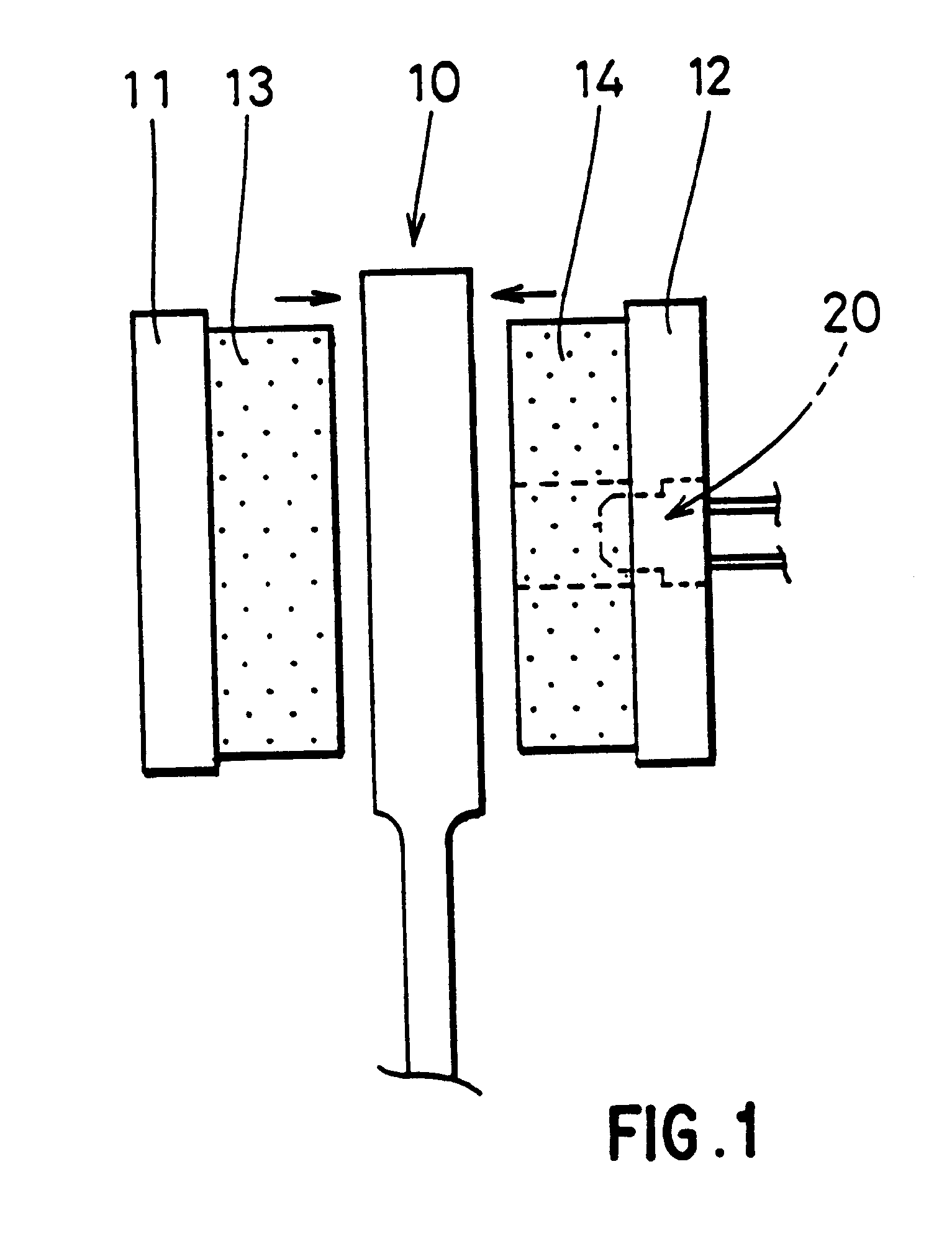
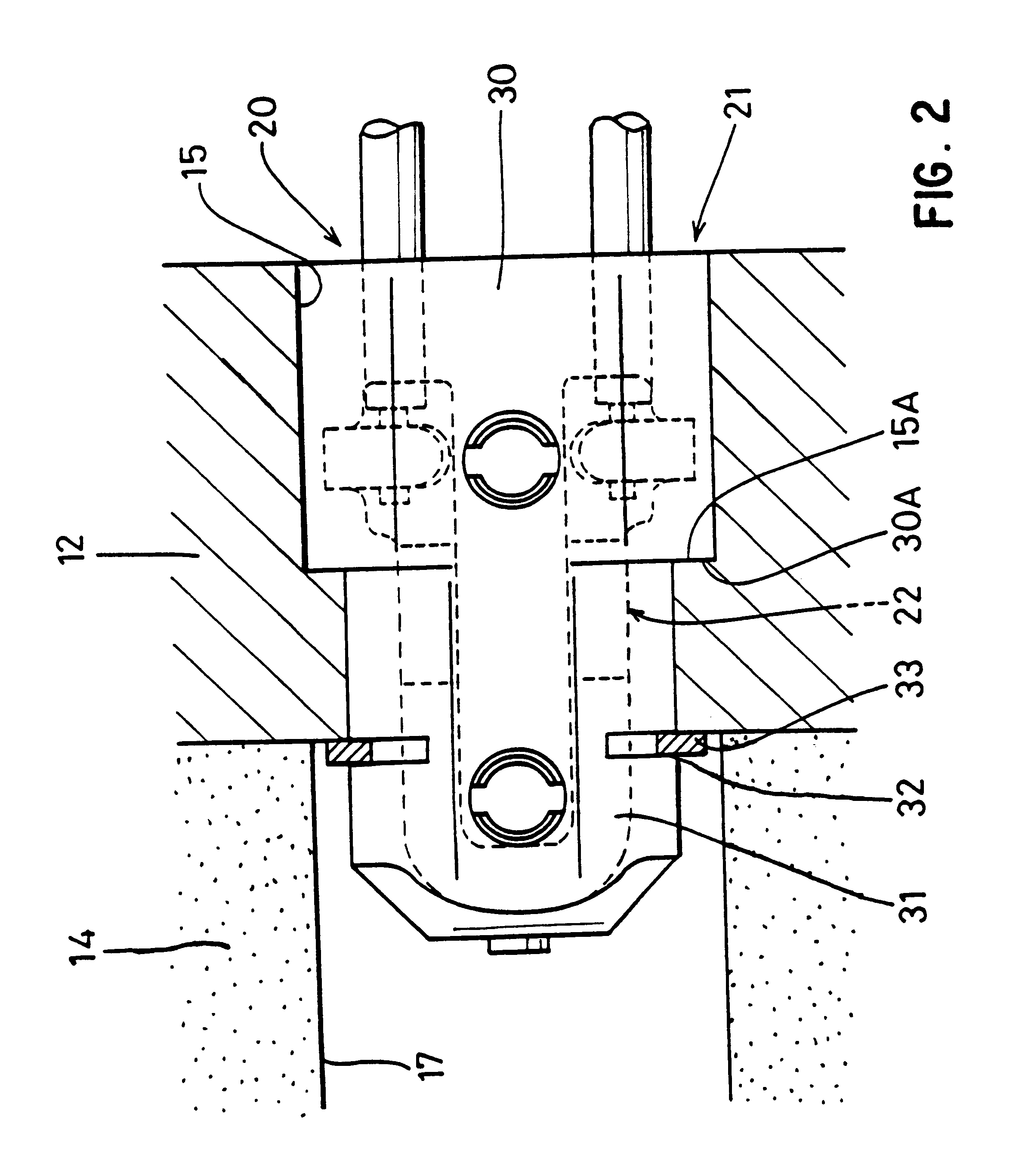
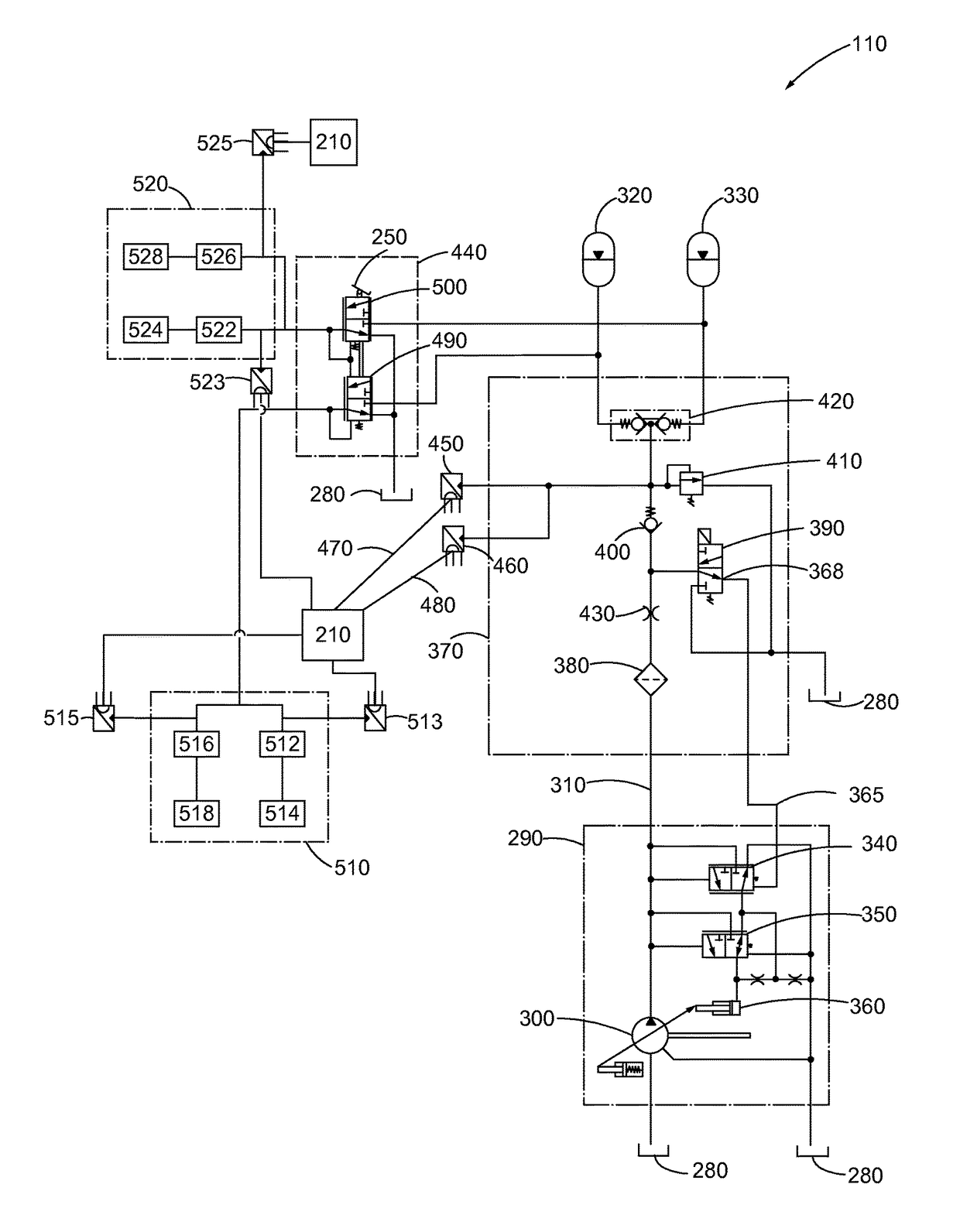
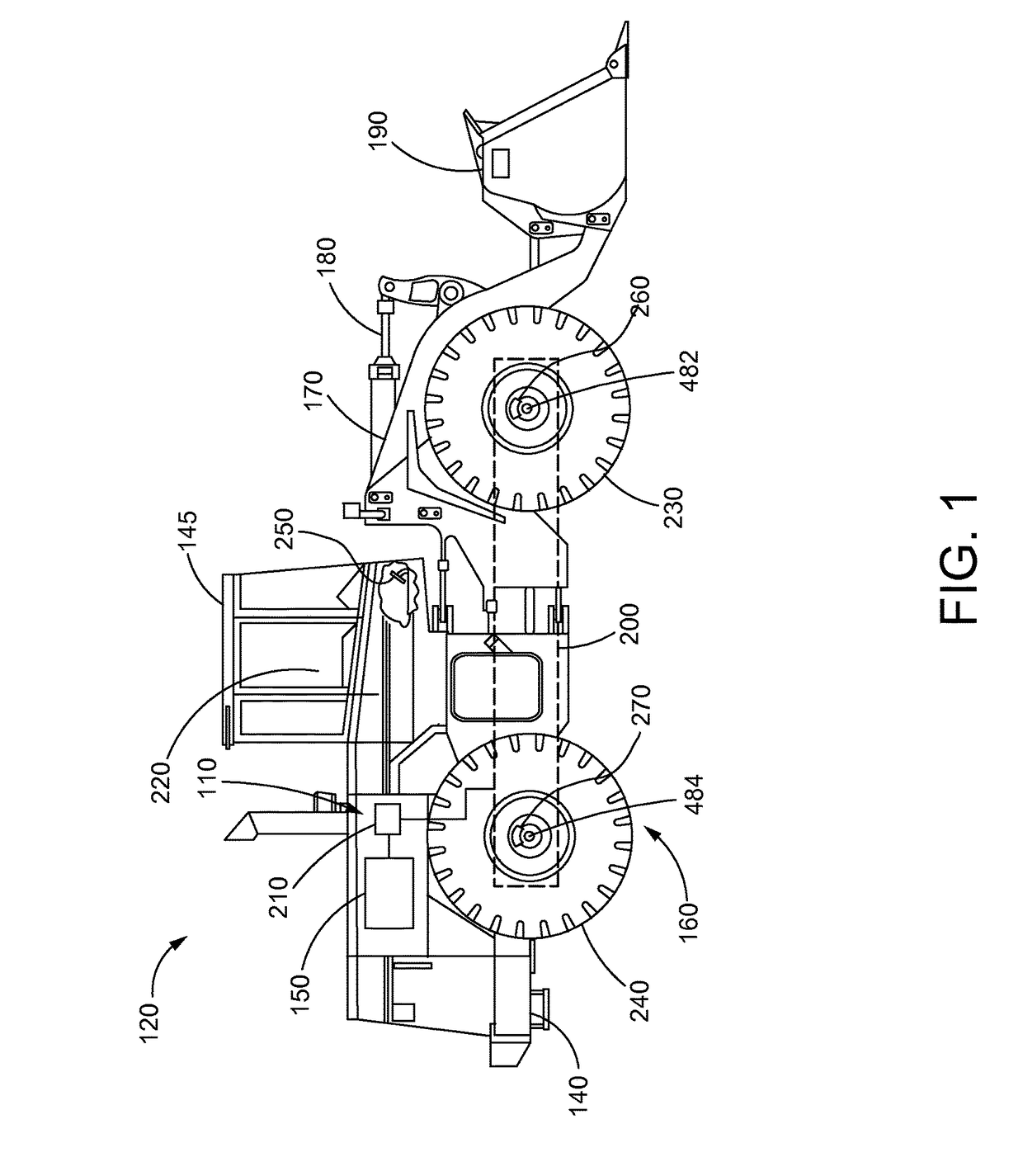
Brake Wear Analysis System
A brake wear analysis system is presented for use within a work machine. The brake wear analysis system includes a brake charge system as well as at least one accumulator connected to the brake charge system. The at least one accumulator operable to flow a fluid from the accumulator to a brake control valve based on an executed braking action. A change of pressure within the at least one accumulator being received by a pressure sensor connected to the brake charge system and transmitted to a brake wear analysis module within the controller of the work machine. The brake wear analysis module being configured to compare the flow of fluid from the at least one accumulator with a predetermined condition resulting in a determination of whether or not a braking mechanism of the work machine is functioning in a worn condition.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Adaptive compensation method for an anti-lock brake control
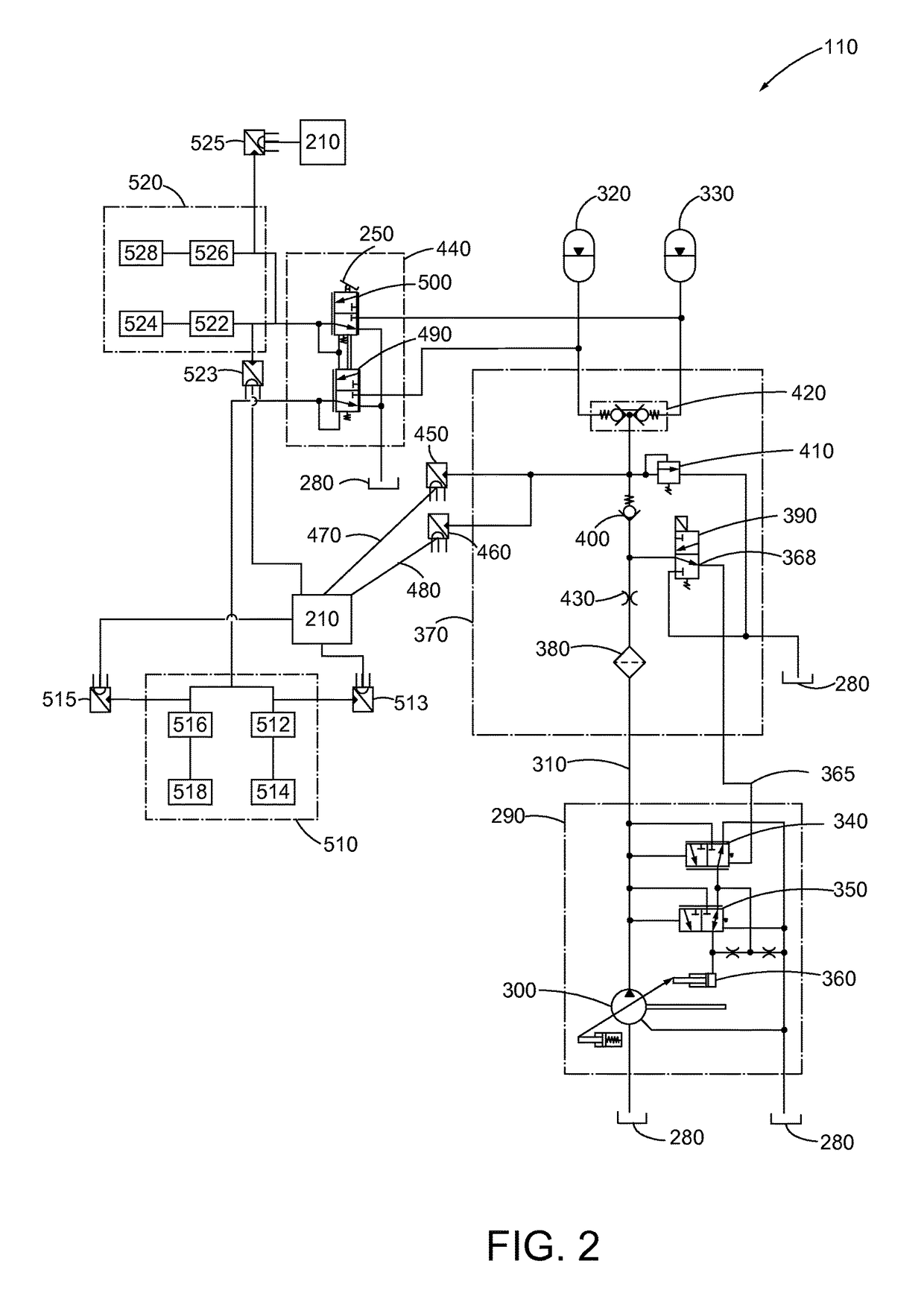
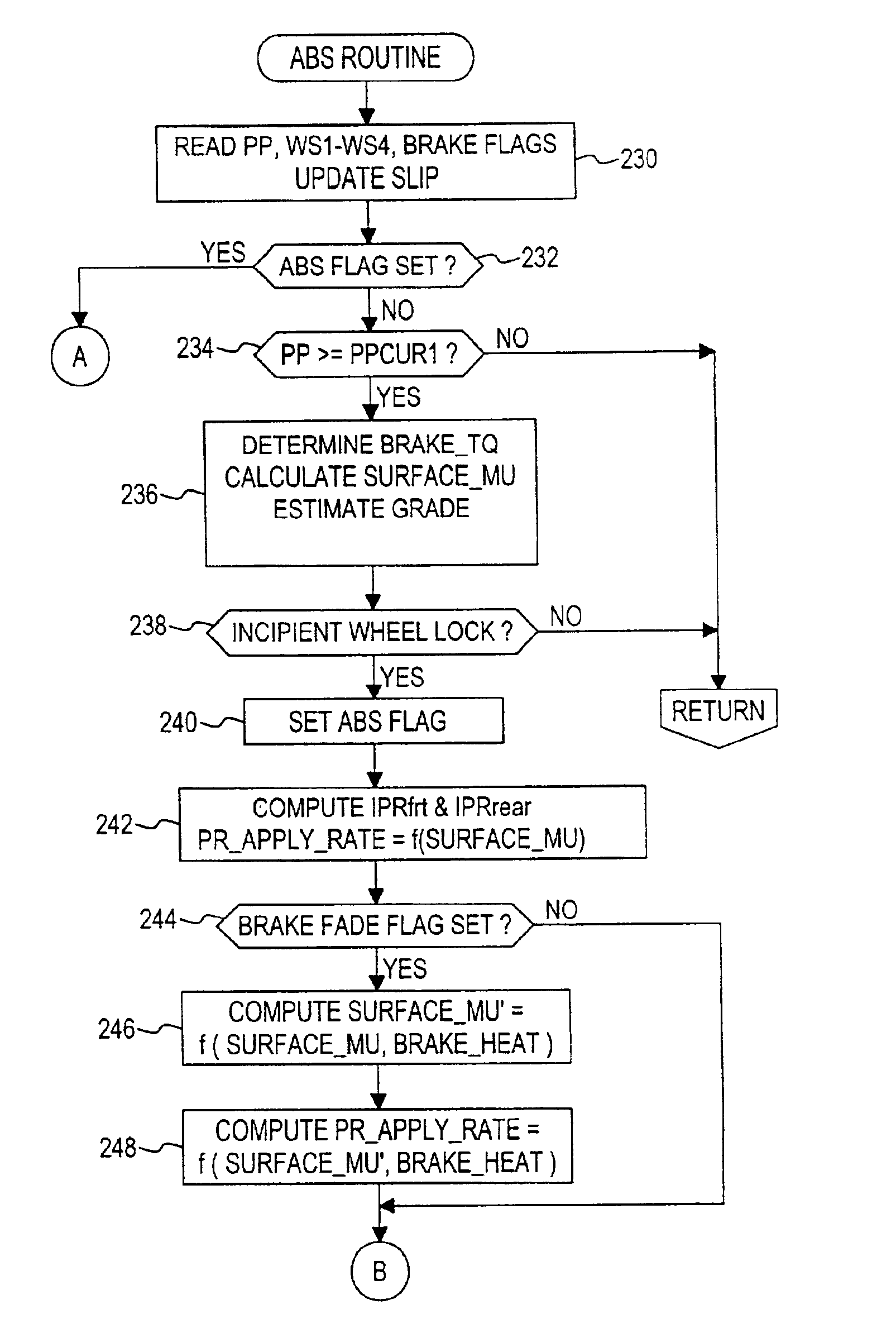
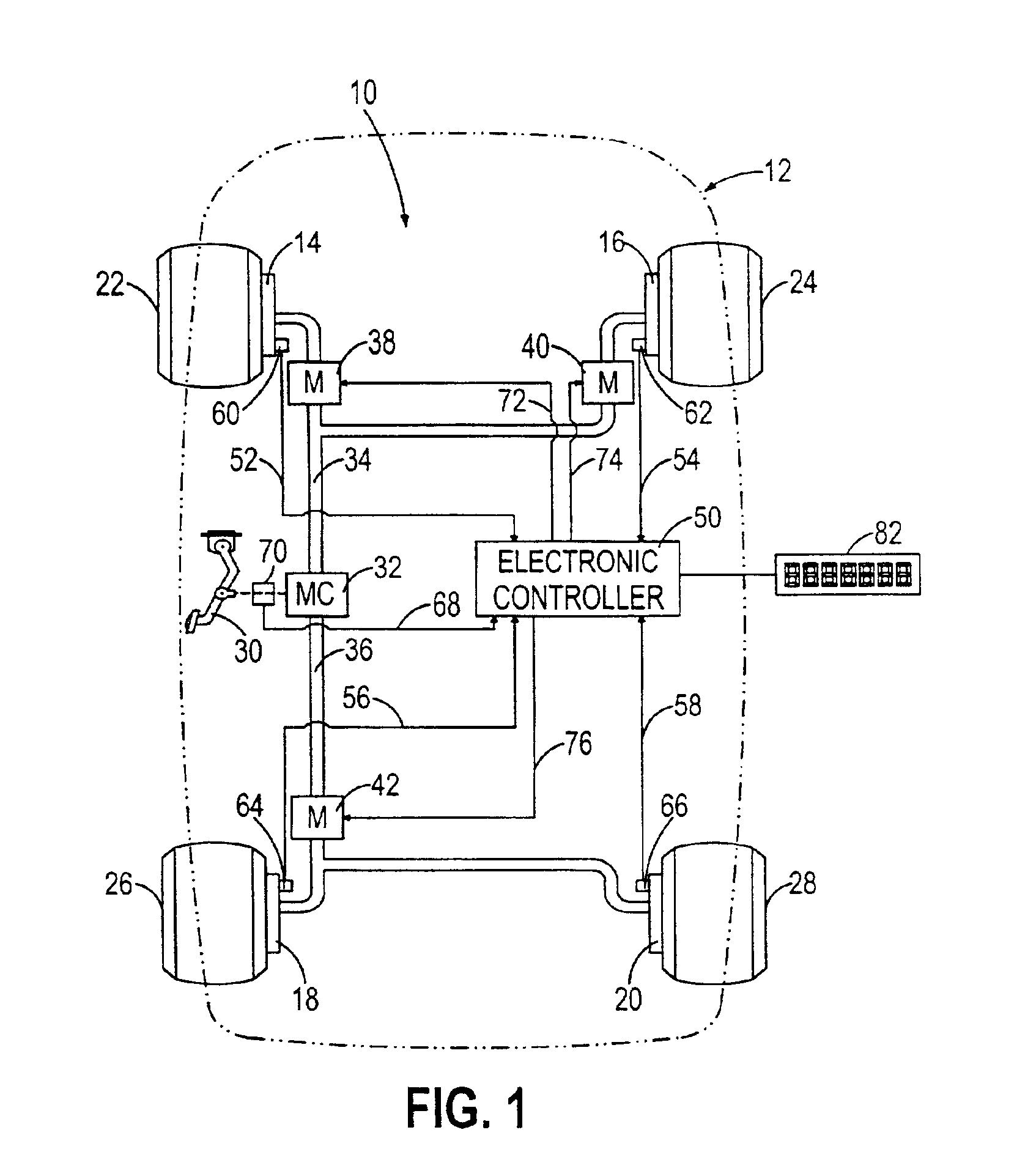
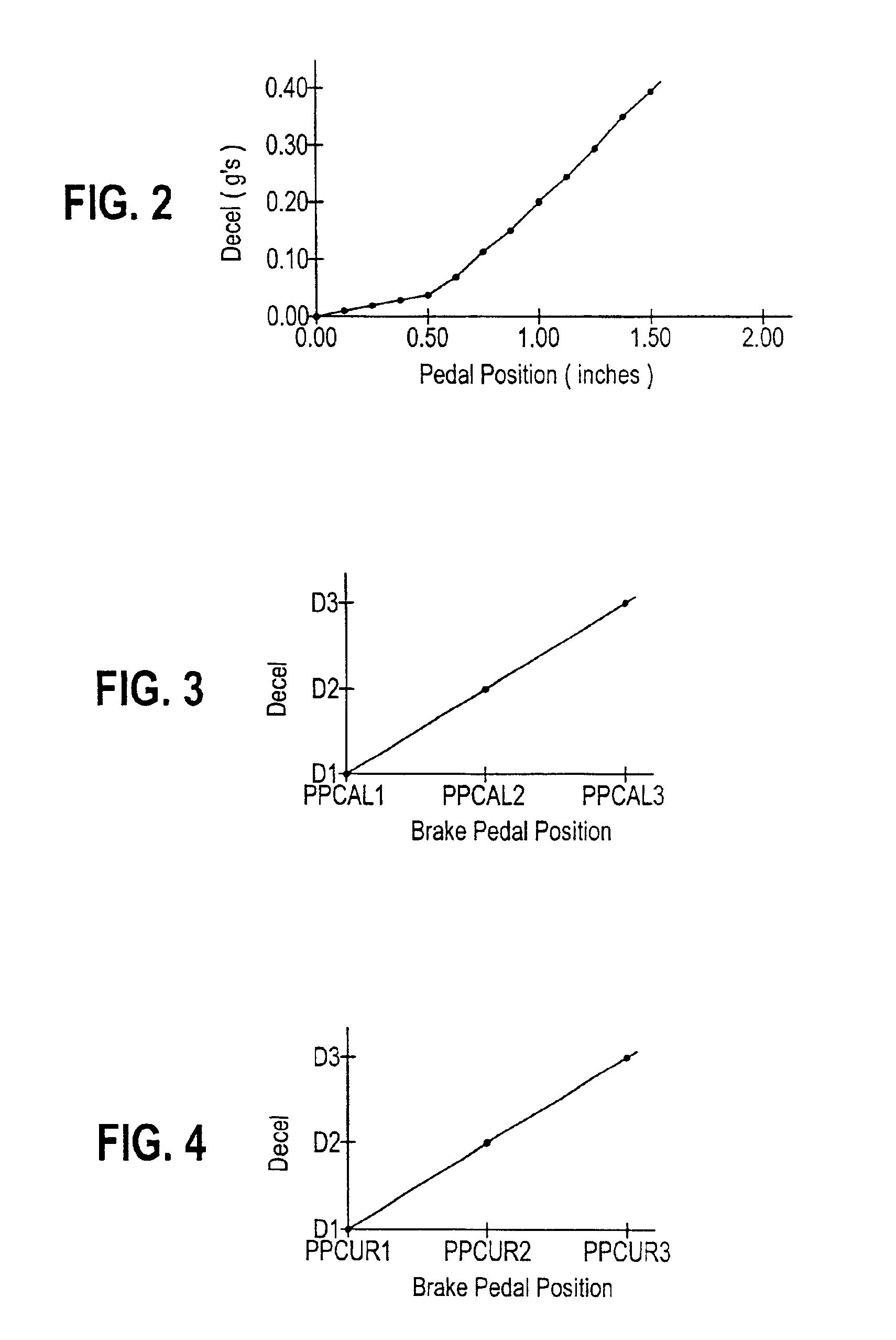
InactiveUS6859712B2Optimal control methodGreat tractionBraking action transmissionDigital data processing detailsEngineeringSelf adaptive
An improved anti-lock control method for a vehicle brake system identifies various factors that degrade the effectiveness of the brake system and adaptively adjusts a brake apply rate during anti-lock brake control to compensate for the identified degradation so that the optimal tractive force during anti-lock brake control is more nearly realized. The identified factors include fading due to brake heating, hydraulic leakage, mis-adjusted and non-releasing rear brakes, brake wear and excessive vehicle weight.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com