Patents
Literature
404results about "ABS control systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
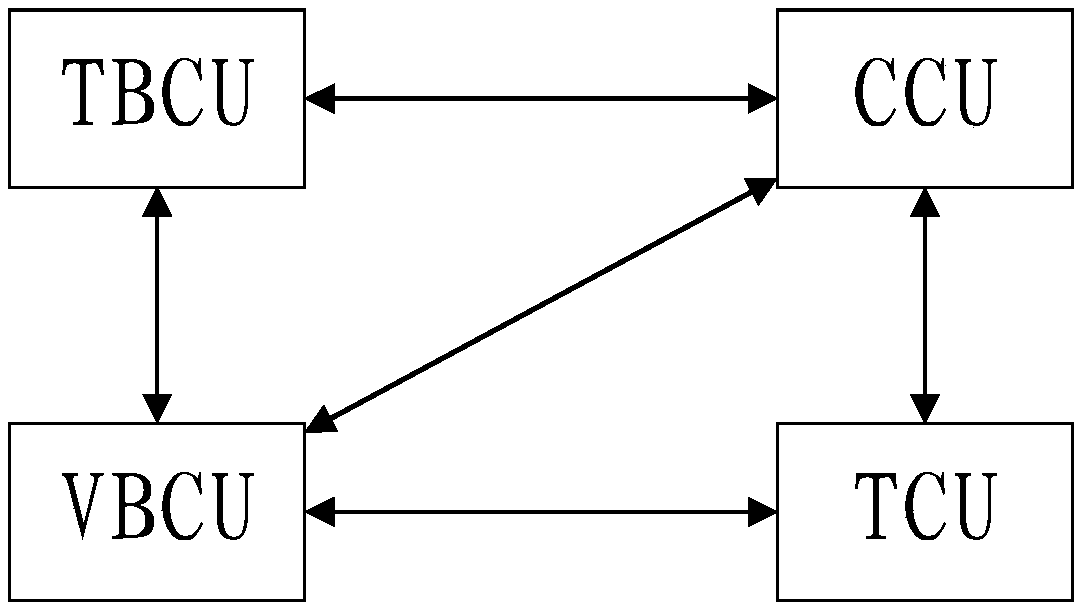
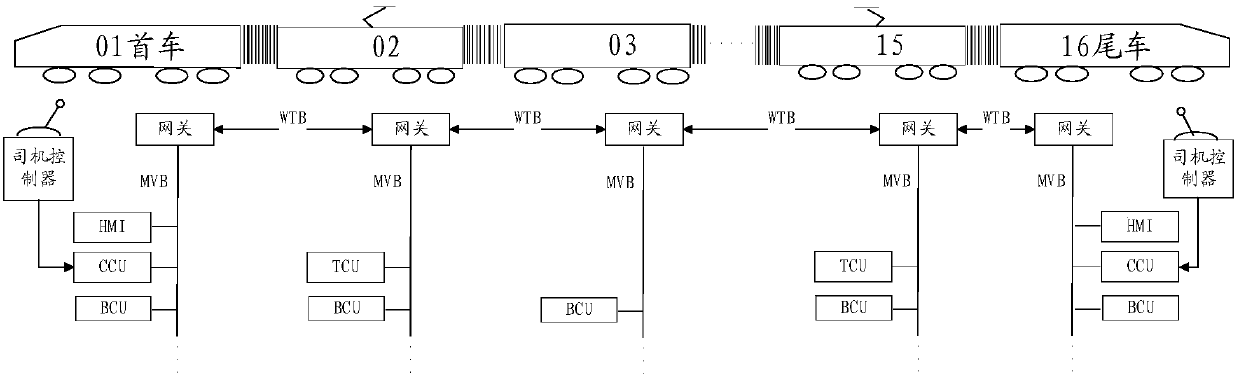
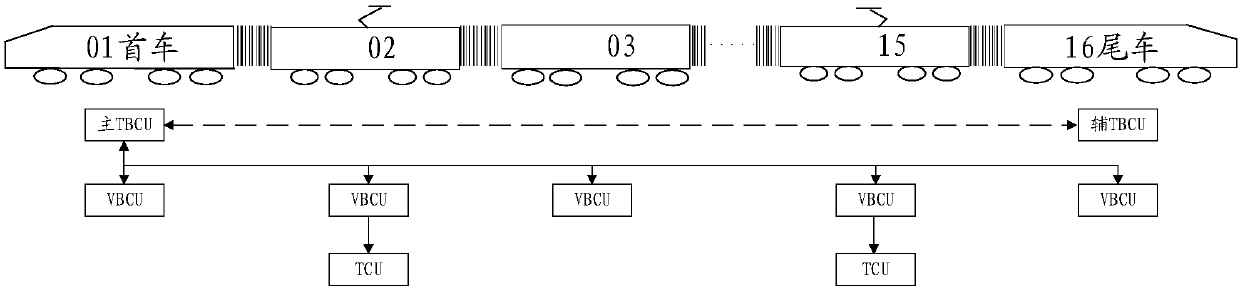
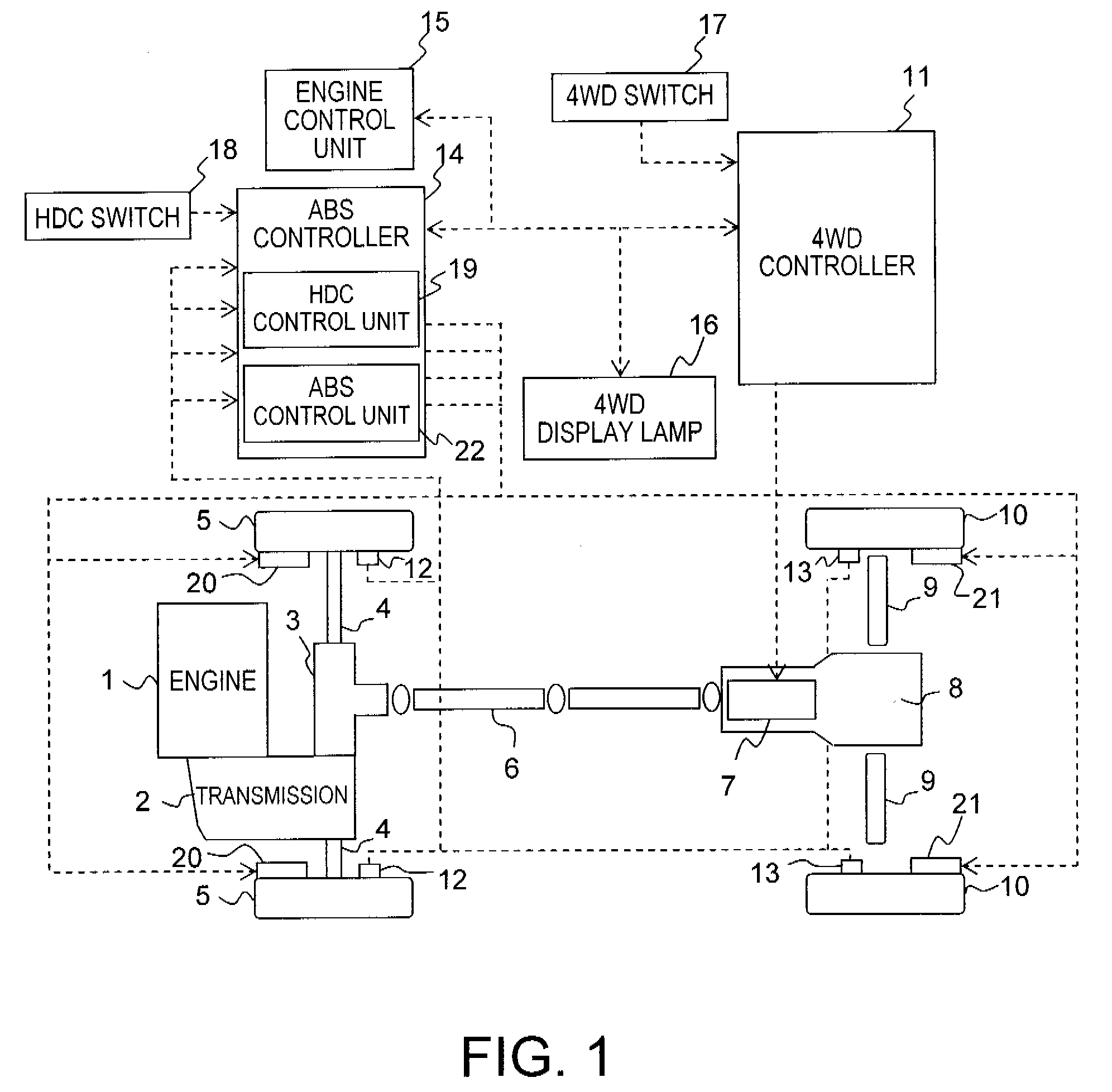
Rail train brake control system and train
ActiveCN109795518AFlexible groupingSpeed controllerElectric devicesControl systemCommunication control
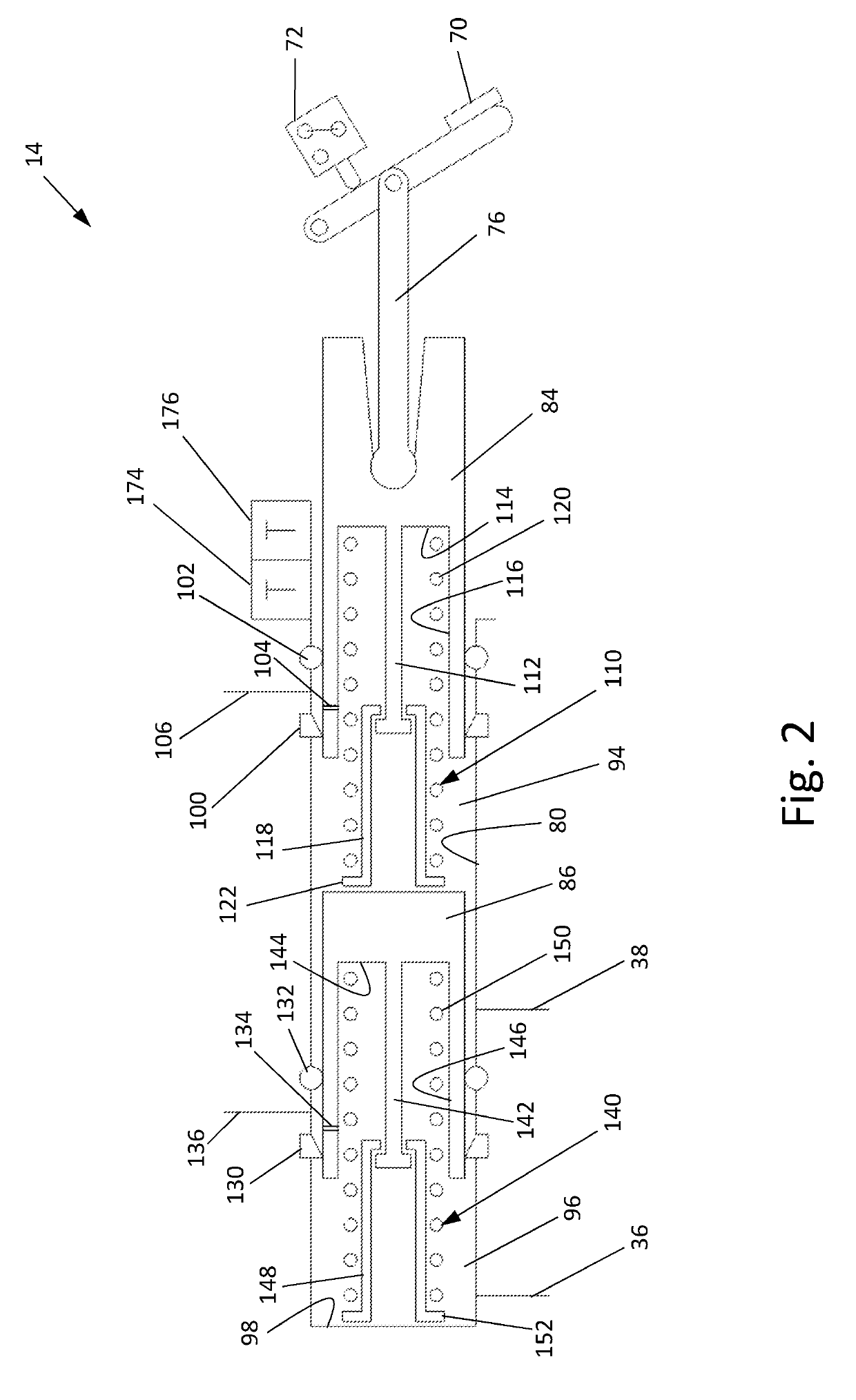
The embodiment of the invention provides a rail train brake control system and relates to the field of rail transit. The rail train brake control system comprising a single brake control unit, a wholetrain brake control unit, a traction control unit and a communication control unit is characterized in that the single brake control unit is arranged in each carriage of a rail train; the whole trainbrake unit and the communication control unit are arranged in the carriages located on both ends of the rail train; the traction control unit is arranged in power cars of multiple carriages; the single brake control unit, the whole train brake control unit, the traction control unit and the communication control unit realize communication through gateway. Further provided is a train comprising the above-mentioned system. The rail train brake control system has the advantage of realizing flexible grouping of the train with each carriage provided with the single brake control unit to apply airbraking force, each power car provided with the traction control unit to apply electric braking force, and the whole train brake control unit adopted to conduct centralized control.
Owner:CRRC TANGSHAN CO LTD
Running red lights avoidance and virtual preemption system
InactiveUS20160328968A1Low costImprove efficiencyBrake system interactionsRoad vehicles traffic controlIn vehicleAutomatic braking
The present invention integrates the in-car traffic light system of Elsheemy with the vehicle's automatic braking system to significantly reduce running red lights which causes outrageous accidents rates, injuries rates, death rates and damage rates at intersections, the present invention also provides a virtual preemption system integrated with the in-car traffic light system for both emergency vehicles and also civilians vehicles.
Owner:ELSHEEMY MOHAMED ROSHDY
Regenerative braking system based on ESC hardware and control method of regenerative braking system
ActiveCN105150858ALow costEasy to implementBraking action transmissionElectrodynamic brake systemsRegenerative brakeWheel speed sensor
The invention discloses a regenerative braking system based on ESC hardware. The system comprises a brake pedal unit, a vacuum booster unit, a brake master cylinder unit, a hydraulic execution unit, four wheel cylinders, four wheel speed sensors, an ESC control unit, a vehicle control unit, a motor control unit and a battery control unit. The brake pedal feeling the same as that of a traditional hydraulic braking system can be guaranteed, no brake pedal travel simulator needs to be additionally mounted, when the ESC hardware fails, backup braking the same as that of the traditional hydraulic braking system can be provided, and the braking safety is guaranteed. Regenerative braking is finished through a drive motor, the hydraulic execution unit is used for finishing hydraulic braking, and a braking scheme which is low in cost and easy to implement and integrates regenerative braking and ESC is provided.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
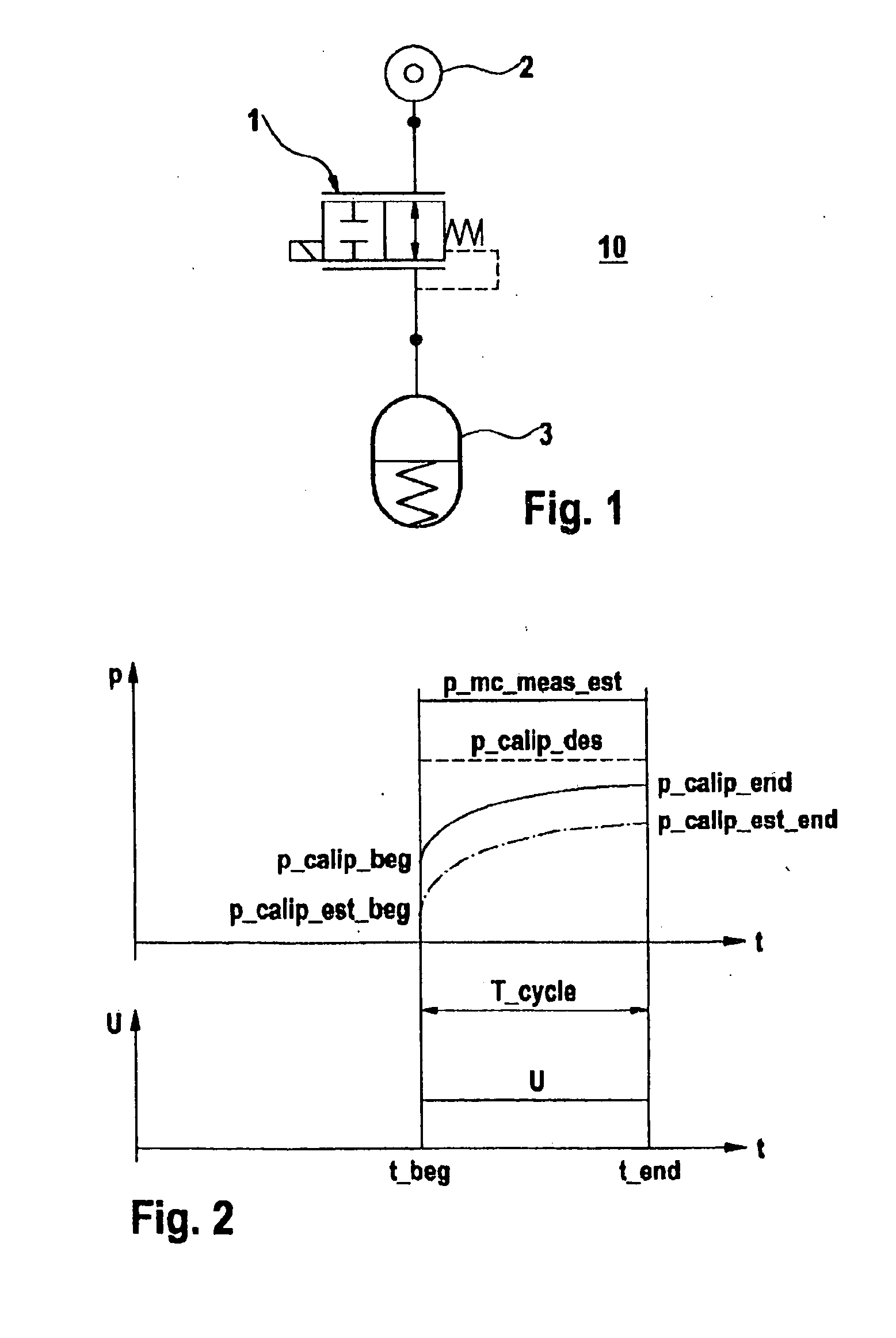
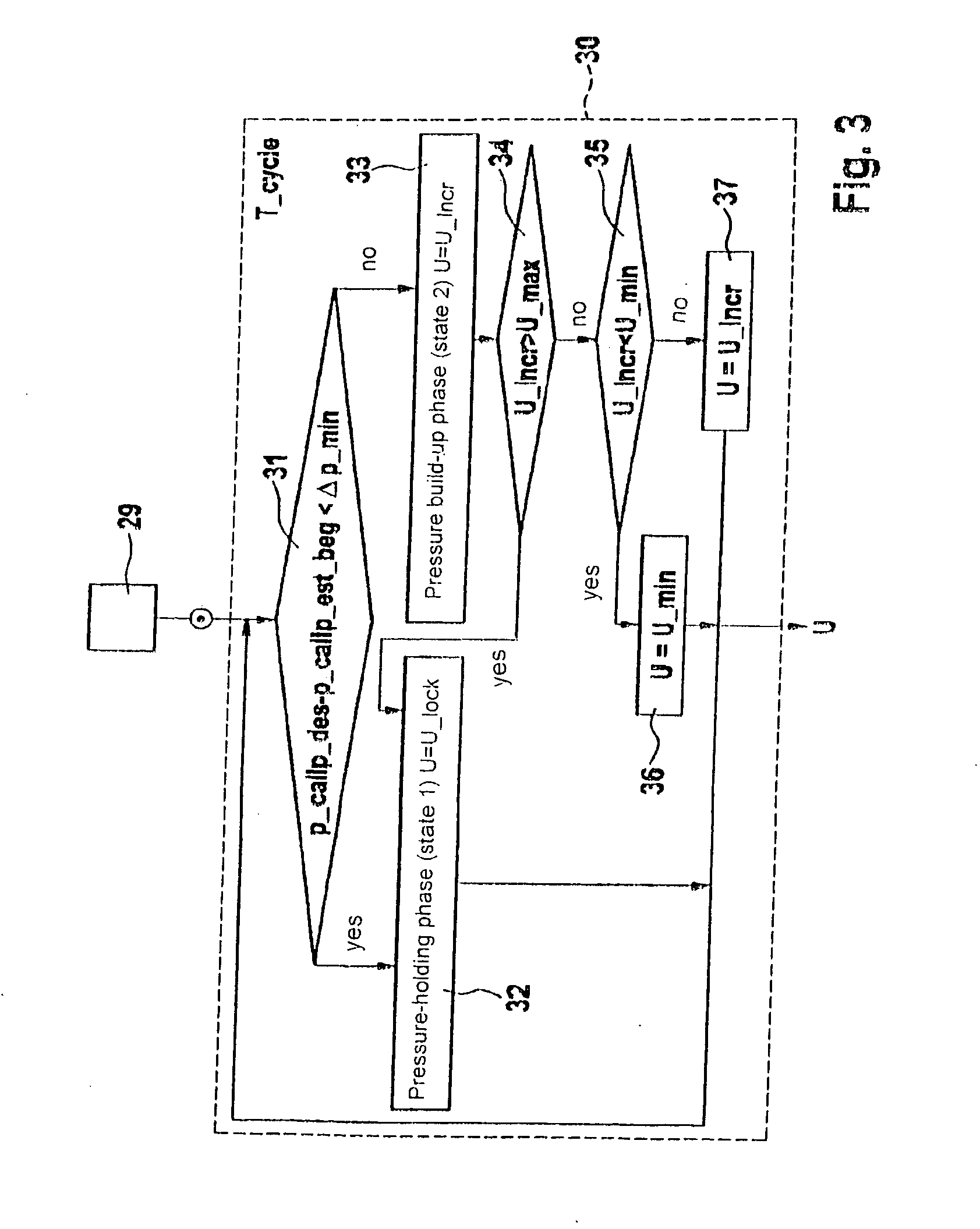
Method for determining parameters
InactiveUS6901789B1Stable conditionImprove pressure resistanceHand manipulated computer devicesAnalogue computers for trafficTime limitEngineering
A method for determining parameters for the viscosity or temperature of a brake fluid of a vehicle by way of a predetermined pressure build-up within time limits in at least one defined section of a brake circuit and for detecting a pressure in the said section and / or a time which is required for the build-up of the said pressure.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
System and method for determining whether a trailer is attached to a vehicle
ActiveUS20170305436A1Improve accuracyIncrease ratingsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsNavigation instrumentsControl systemAutomotive engineering
A control system for a vehicle for determining whether a trailer is attached to the vehicle, the system being configured to receive an input of pitch data for the vehicle and to determine from the pitch data whether a trailer is attached to the vehicle.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
Electric power-assisted braking system with composite functions
PendingCN105774788AShock suppressionSmall pressure fluctuationsBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsElectric power systemLiquid storage tank
The invention relates to the field of vehicle engineering and discloses an electric power-assisted braking system with composite functions. The electric power-assisted braking system comprises a brake pedal displacement sensor, a brake pedal, a pedal travel simulator, an electric power-assisted assembly, a main cylinder, a wheel cylinder, a hydraulic control unit, a liquid storage tank, a motor, a deceleration and torque increment mechanism, an electronic control unit, a normally open electromagnetic valve, a normally closed electromagnetic valve and a vehicle-mounted other sensor. By designing the pedal travel simulator, decoupling of friction braking force and regenerated braking force can be achieved, and continuous variable crural feeling is provided; a motor assisting device, a brake anti-lock system and the hydraulic control unit can be integrated, and an active braking function is achieved; and no interference exits between motor input and driver input, active braking can be achieved through the motor, and the electric power-assisted braking system can serve as a brake actuating mechanism of intelligent automobiles and unmanned automobiles.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
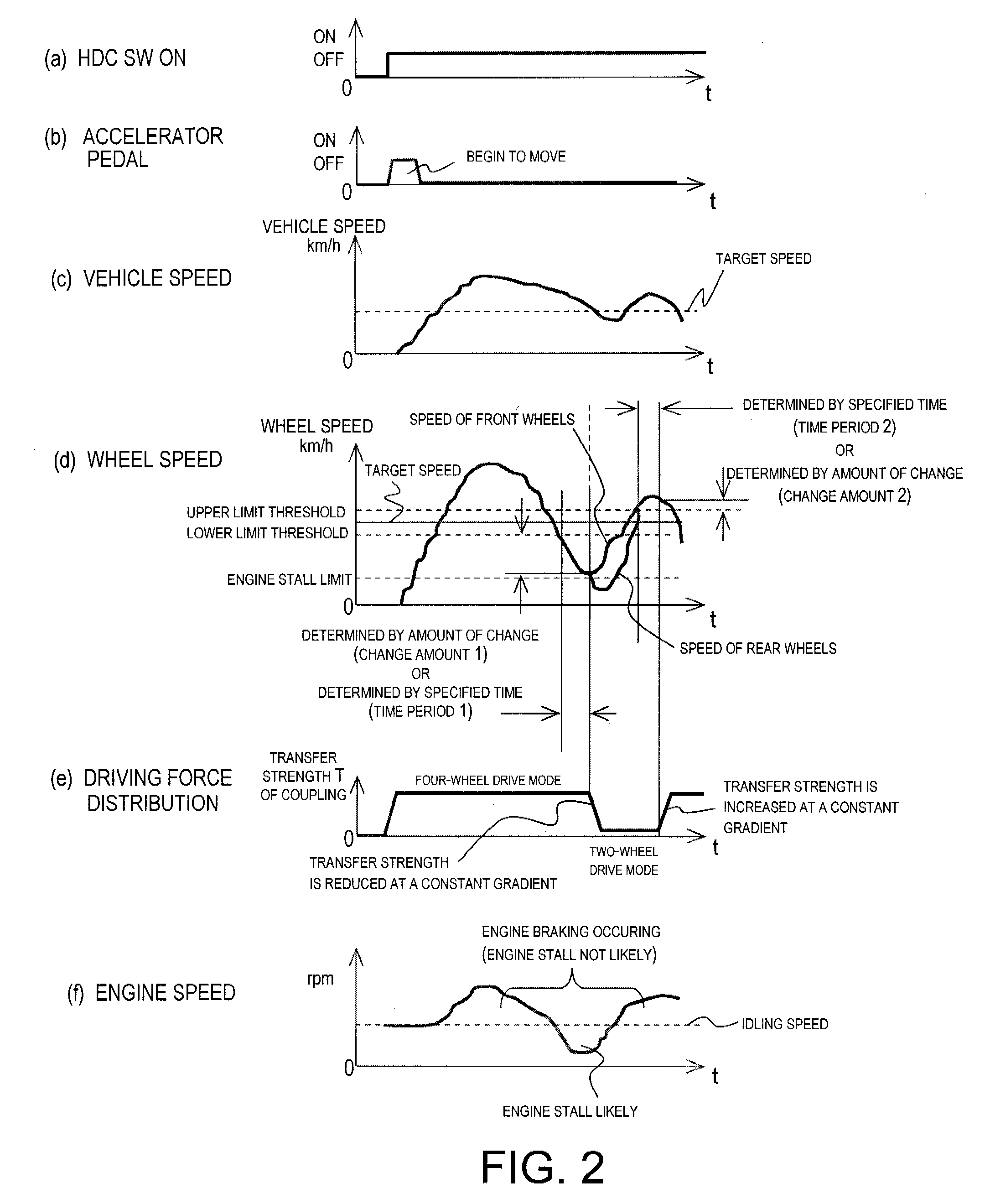
Vehicle driving force control apparatus
A driving force control apparatus is configured to automatically apply a braking force to a plurality of wheels in order to descend down a hill at a constant speed, such that the wheels can be prevented from being locked by the braking force, and the vehicle speed can be prevented from increasing. In order for a vehicle to travel at a preset speed, the vehicle driving force control apparatus detects the speeds of the wheels subjected to a braking force, and switches the vehicle from a four-wheel drive (4WD) mode in which driving force is distributed to all of the wheels to a two-wheel drive (2WD) mode in which driving force is distributed to only the front wheels. The switch is made when the vehicle speed is equal to or less than a lower limit threshold. The front wheels are prevented from locking, and increases in the vehicle speed are suppressed.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
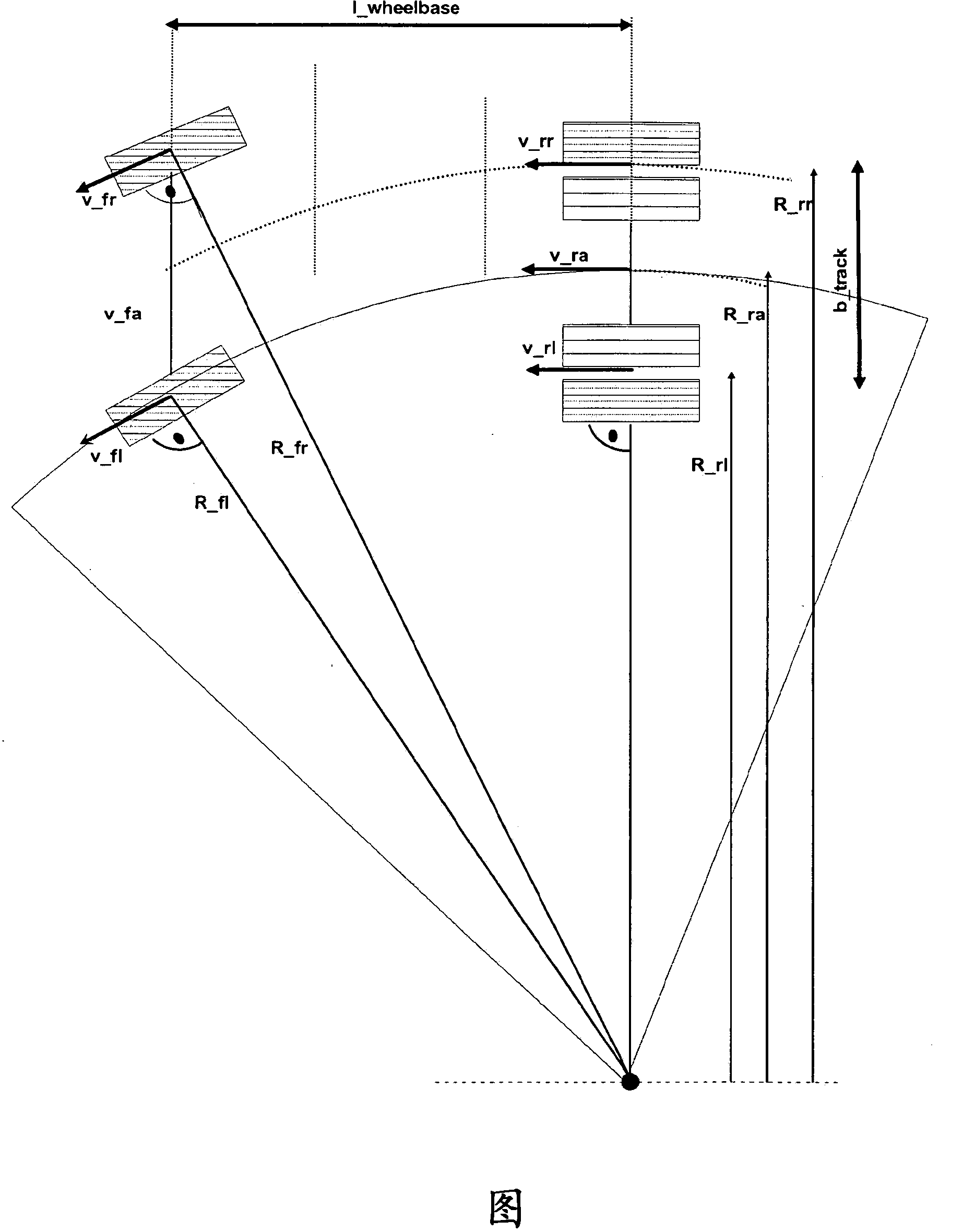
Method for operating a wheel slip control apparatus with compensated wheel speeds
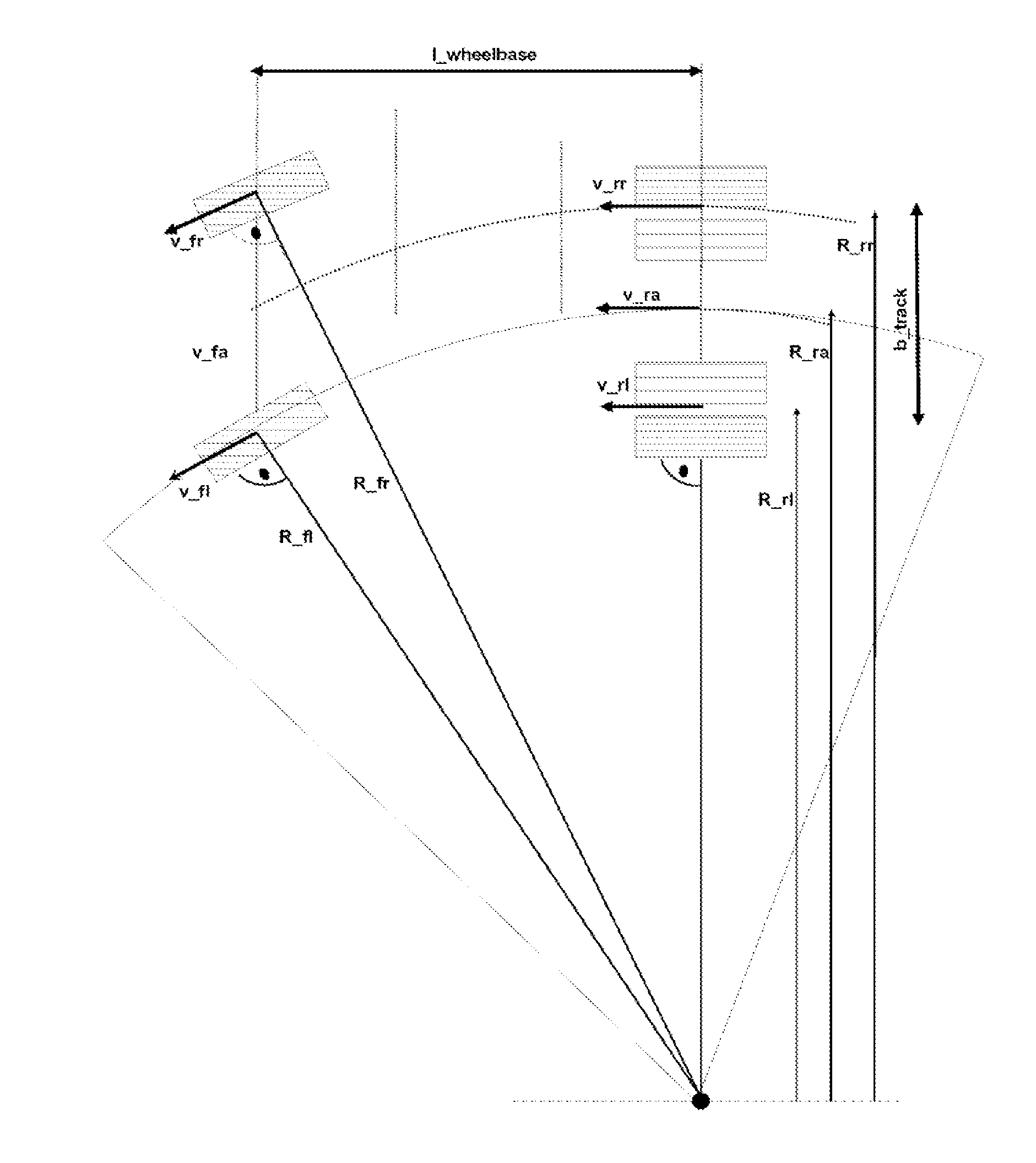
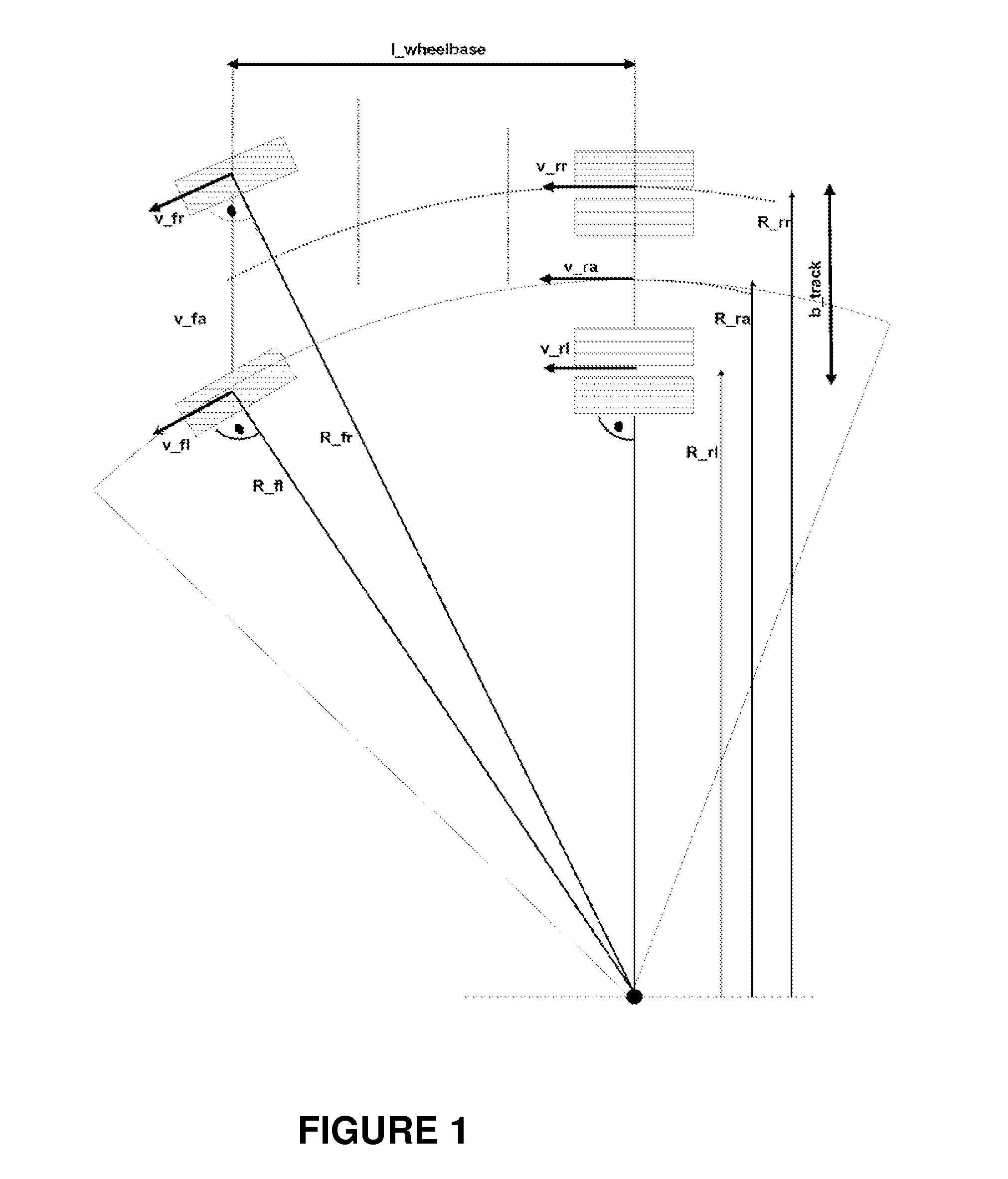
ActiveCN104411550AEliminate the effect of speed differenceImprove adjustment qualityABS control systemsSpeed/accelaration controlAutomotive engineering
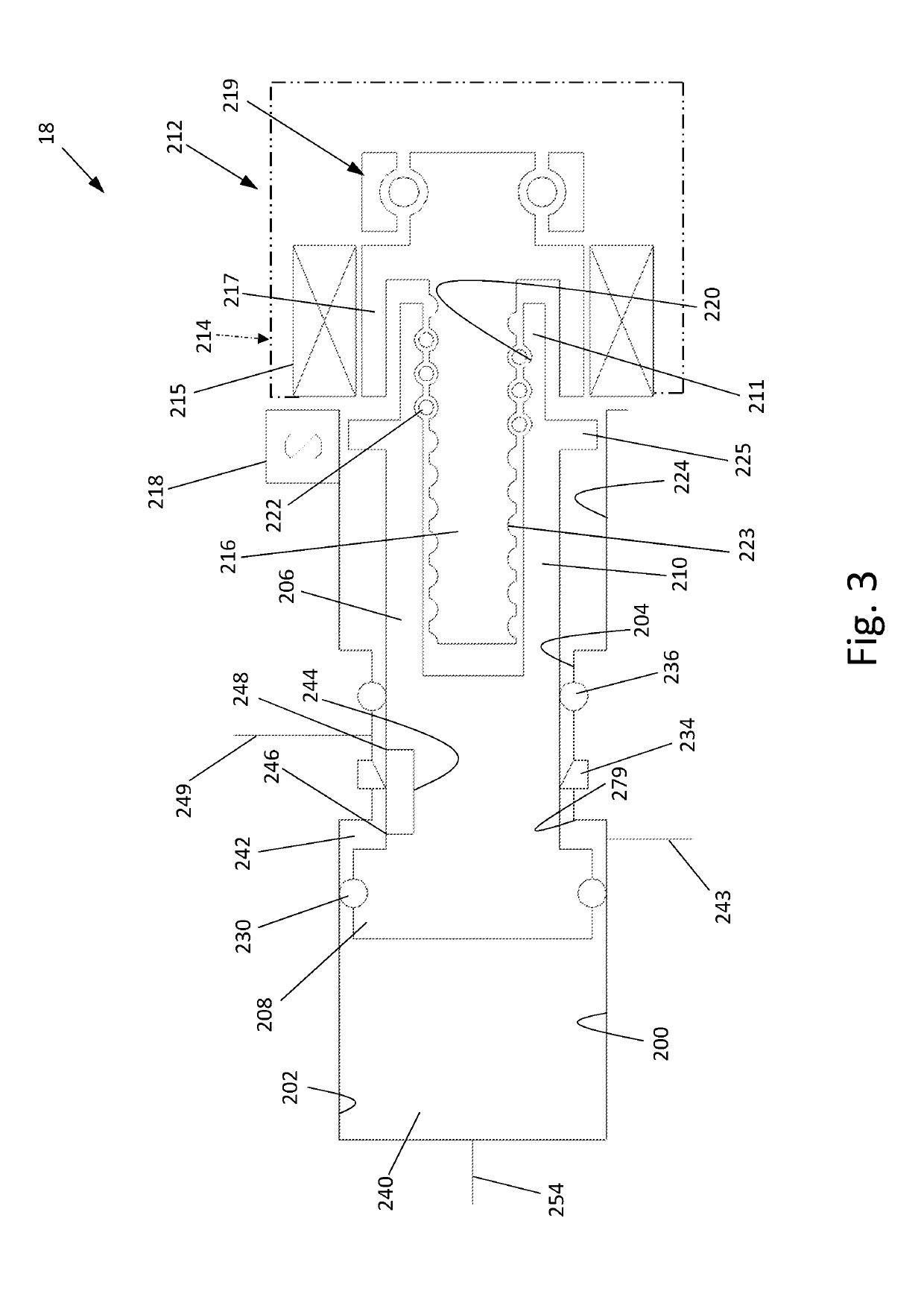
The invention relates to a method for operating a wheel slip control apparatus of a vehicle, including determining wheel speeds (Vfl_C, Vfr_C, Vrr_C, Vrl_C) of wheels of the vehicle as input variables for the wheel slip control apparatus, said wheel speeds being compensated for in terms of wheel speed differences during travel around curves, wherein: a) a neutral-steering, understeering or oversteering driving condition of the vehicle is determined from the driving characteristics of said vehicle during travel around curves; b) based on the determined neutral-steering, understeering or oversteering driving condition of said vehicle, either the reference yaw rate (omegaz_ ref) or the actual yaw rate (omegaz_meas) is used for calculating a curve radius (Rra_ref or Rra_meas) related to a selected point on said vehicle; c) wheel-related curve radii (Rrl, Rrr, Rfl, Rfr) for at least some of said wheels of said vehicle are determined from said curve radius (Rra_ref or Rra_meas) related to the selected point; d) reference factors (kfl, kfr, krl, krr) are determined from said wheel-related curve radii (Rrl, Rrr, Rfl, Rfr) and a common reference curve radius (Rra) for the at least some of said wheels of said vehicle; e) the compensated wheel speeds (Vfl_C, Vfr_C, Vrr_C, Vrl_C) are determined in each case from said reference factors (kfl, kfr, krl, krr) and measured wheel speeds (Vrl, Vrr, Vfl, Vfr) for the at least some of said wheels of said vehicle, and f) for the at least some of said wheels of said vehicle said compensated wheel speeds (Vfl_C, Vfr_C, Vrr_C, Vrl_C) are used as input variables for said wheel slip control apparatus.
Owner:KNORR BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Vehicle Brake System With Secondary Brake Module
A brake system has a wheel brake and is operable under a non-failure normal braking mode and a manual push-through mode. The system includes a master cylinder operable by a brake pedal during a manual push-through mode to provide fluid flow at an output for actuating the wheel brake. A first source of pressurized fluid provides fluid pressure for actuating the wheel brake under a normal braking mode. A secondary brake module includes a plunger assembly for generating brake actuating pressure for actuating the wheel brake under the manual push-through mode.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Anti-lock braking system as well as control method and control device thereof
ActiveCN107303820AQuick responseAchieve recyclingSpeed controllerElectric devicesBrake torqueControl theory
The invention discloses an anti-lock braking system as well as a control method and a control device thereof. The method comprises the steps of controlling working states of wheel hub motors according to an SOC signal of a battery and wheel speed signals of various wheels, distributing total target braking torque of various wheels according to different working states of the wheel hub motors, transmitting the distributed total target braking torque of various wheels to corresponding slave braking controllers and controlling output torque of corresponding motors by the corresponding slave braking controllers according to the distributed total target braking torque, wherein each slave braking controller comprises a first slave braking controller and a second slave braking controller; each first slave braking controller controls the output torque of a corresponding electromechanical brake according to the distributed total target braking torque; each second slave braking controller controls the output torque of the corresponding wheel hub motor according to the distributed total target braking torque. By using the method, the response speed and the brake accuracy of the anti-lock braking system can be improved.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR
Electric brake system
ActiveUS20190366997A1Effectively performing emergency brakingEfficient executionBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsHydraulic control unitWheel cylinder
An electronic brake system of the present disclosure is disclosed. The an electronic brake system may include a reservoir to store oil: a master cylinder having a master piston connected to a brake pedal and a master chamber for discharging oil by a displacement of the master piston; a hydraulic pressure supply apparatus generating hydraulic pressure by an electrical signal output corresponding to a displacement of the brake pedal to supply to wheel cylinders of the respective wheels; a hydraulic control unit transmitting the hydraulic pressure discharged from the hydraulic pressure supply apparatus to the wheel cylinders of the respective wheels; and a redundancy control apparatus generating hydraulic pressure using a motor and a pump to transmit to at least one of the wheel cylinders.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Abs strategy for hybrid brake actuators
ActiveUS20180229705A1Efficient deliveryPotential failureBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsActuatorBrake force
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
Brake system with two pressure sources, and two methods for operating a brake system
ActiveUS20190308601A1Improve the level ofReduce spendingBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsOn boardInlet valve
A brake system, including four hydraulically actuatable wheel brakes. Each wheel brake is assigned in each case one outlet valve which is closed when electrically deenergized. Each wheel brake is assigned in each case one inlet valve which is open when electrically deenergized. The brake system furthermore includes a simulator which is actuatable by a brake pedal, wherein two pressure provision devices are provided for actively building up pressure in the wheel brakes, two brake circuits are hydraulically formed, wherein, in each brake circuit, in each case one pressure provision device is hydraulically connected to two wheel brakes, and wherein two separate on-board electrical systems are provided, and wherein each pressure provision device is fed in each case by one of the two on-board electrical systems.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Wire driven hydraulic parking braking system for full-wheel steering electric-wheel car
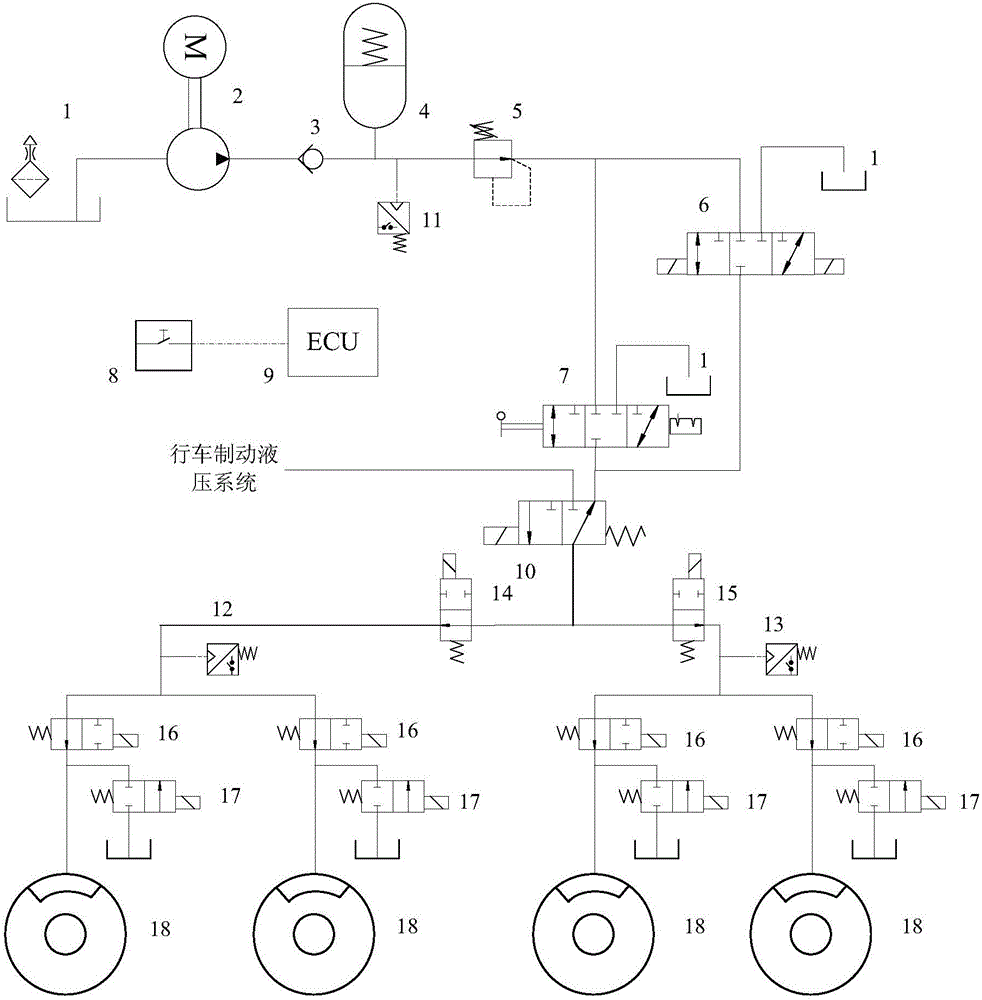
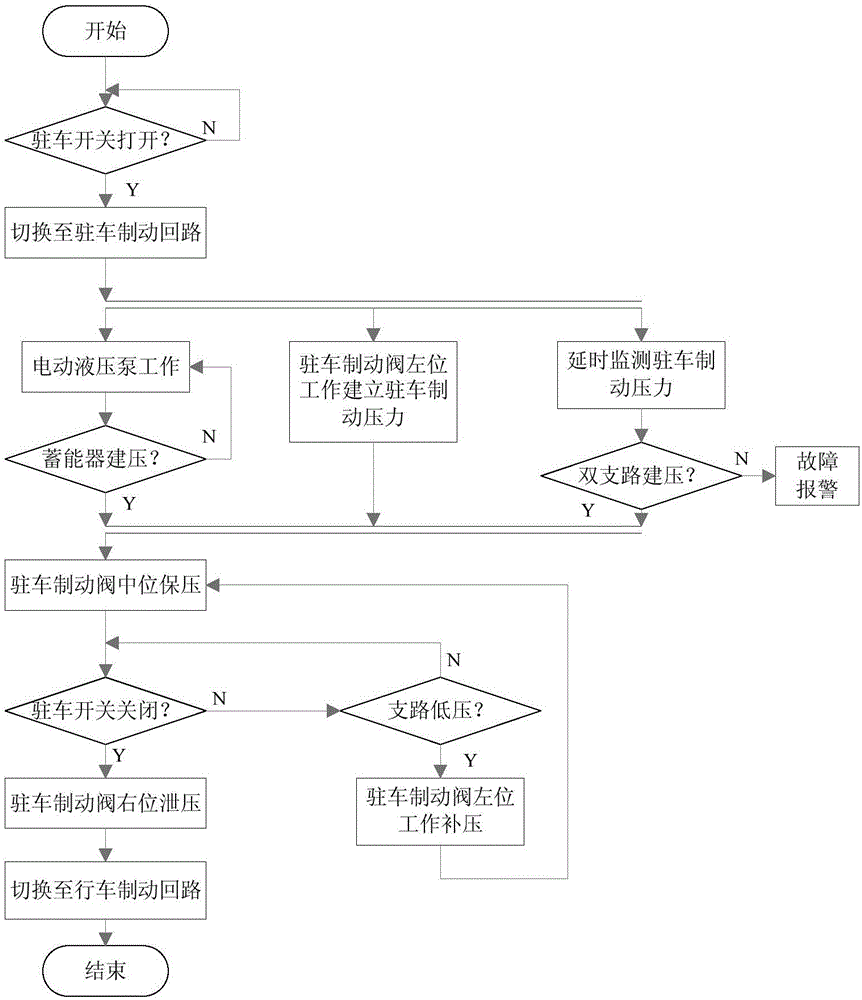
InactiveCN105667477AUse less frequentlyEasy to save energyFluid braking transmissionABS control systemsElectro hydraulicHydraulic pump
The invention discloses a wire driven hydraulic parking braking system for a full-wheel steering electric-wheel car. The system comprises an electric hydraulic pump (2), an energy accumulator (4) and a pressure reducing valve (5) which are connected in sequence through a pipeline, wherein the pressure reducing valve (5) is connected with a parking braking valve (6) and a manual parking valve (7) through pipelines respectively, and the parking braking valve (6) and the manual parking valve (7) are connected with a traveling / parking switching valve (10) through pipelines respectively; the traveling / parking switching valve (10) is connected with wheel brakes (18) of a front wheel and a rear wheel through pipelines respectively. The system further comprises a parking braking switch (8) and a parking braking electronic control unit (9), wherein the parking braking switch (8) and the parking braking electronic control unit (9) are connected, and the parking braking electronic control unit (9) is used for acquiring sensor information and controlling electric execution components. A wire driven hydraulic parking scheme is adopted to be adapted to the characteristic of independent steering of wheels; parking pressure increase, parking pressure maintaining and parking pressure relief are controlled by the wire driven electromagnetic hydraulic valve, and response is quick; parking brake fluid pressure is generated through cooperation of the electric hydraulic pump, the energy accumulator and a pressure regulating valve, and braking force can be adjusted flexibly; by the adoption of the system, the ABS function and the ESP function can be integrated.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Full-hydraulic ABS braking system based on hybrid power and braking method thereof
InactiveCN106564486AFull hydraulic brake realizationRealize independent braking functionBraking action transmissionElectrodynamic brake systemsHydraulic brakeEnergy storage
The invention provides a full-hydraulic ABS braking system based on hybrid power and a control method for braking energy recycling. The system comprises energy storage devices, a liquid charging valve, an electronic pedal, proportioning valves and a braking controller. The energy storage devices are connected with the liquid charging valve through pipelines. Pressure sensors are arranged on the pipelines. The proportioning valves are connected with the pipeline between the energy storage devices and the liquid charging valve. The electronic pedal is connected with the braking controller which is connected with the proportioning valves and wheel edge brakes. The objectives of the invention are to achieve the ABS function and braking energy recycling while adopting a novel hydraulic driving braking system. A traditional hydraulic booster is replaced, so a double-loop function is achieved, space occupation of the system is reduced and response time of the braking system of the whole vehicle is extended.
Owner:CHINA NORTH VEHICLE RES INST
Method for controlling a solenoid valve
ActiveUS20110010067A1Simple methodImprove accuracyAnalogue computers for trafficABS control systemsSolenoid valveEngineering
In a method for controlling a proportional solenoid valve in a hydraulic system, a model of the hydraulic system is formed, control cycles are predefined, and an estimate is made of the pressure prevailing in the hydraulic system at the end of the control cycle and of the coil current applied to the coil of the solenoid valve based on the variables prevailing at the start of the control cycle, the physical parameters of components of the hydraulic system, and the temperature of the hydraulic fluid.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
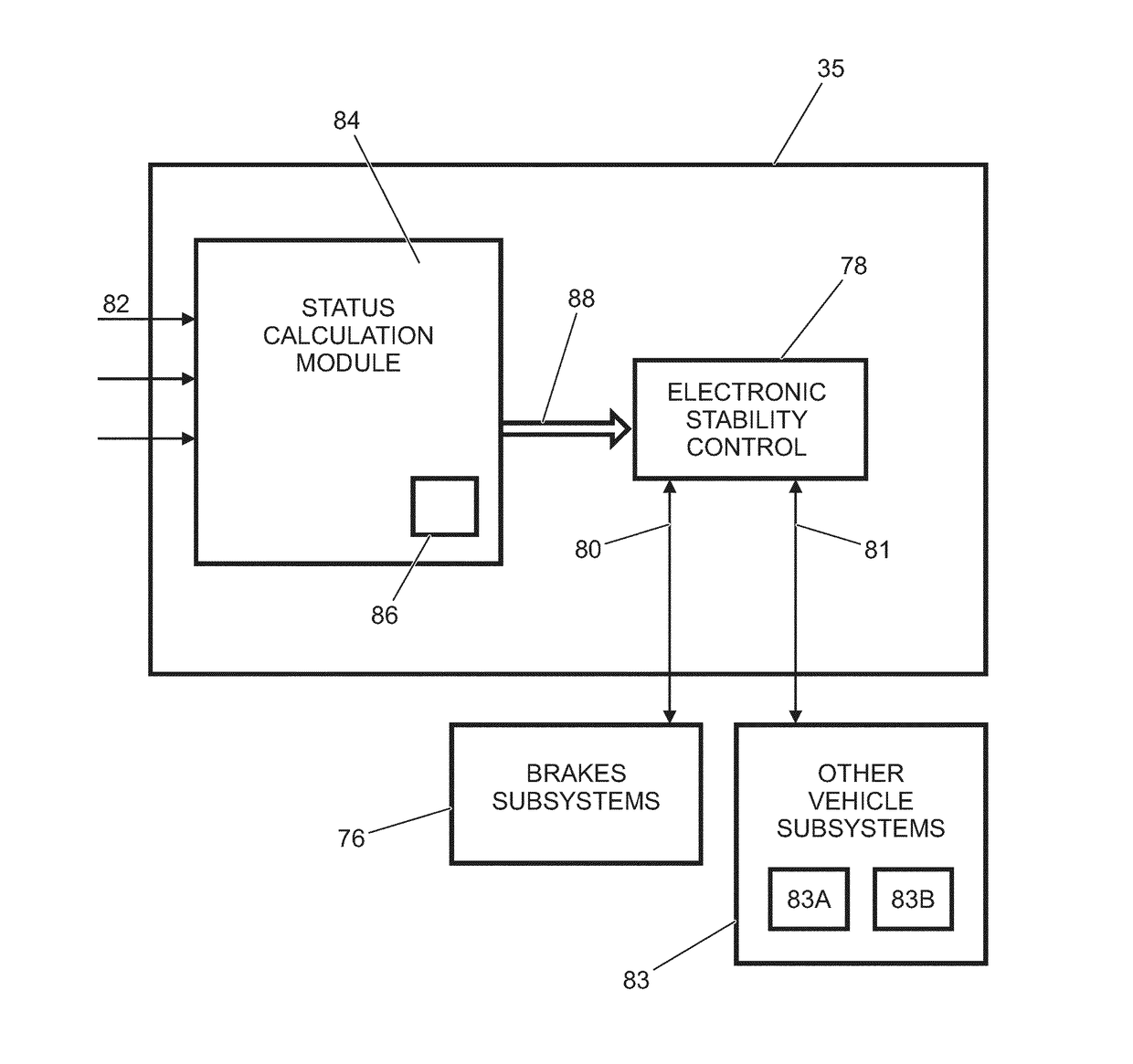
System And Method For Capturing A Rear Part Of A Vehicle
ActiveUS20170140228A1Reliably determinedIncrease profitRoad vehicles traffic controlVehicle sub-unit featuresEngineeringMechanical engineering
A system for a vehicle (13) having a driver's cabin (15) and a rearward extending portion (14) that is pivotable with respect to the driver's cabin (15), for capturing a rear part (17) of the rearward extending portion (14), the system having at least two wheel sensors (2, 3) located on opposite ends of an axis (18, 19) of the rearward extending portion (14), for acquiring information on a rotational movement of wheels attached to the ends of the axis (18, 19), and a control unit (4) connected with the wheel sensors (2, 3), which control unit determines the rear part (17) of the rearward extending portion (14) based on the acquired information on the rotational movement of the wheels.
Owner:MEKRA LANG GMBH & CO KG
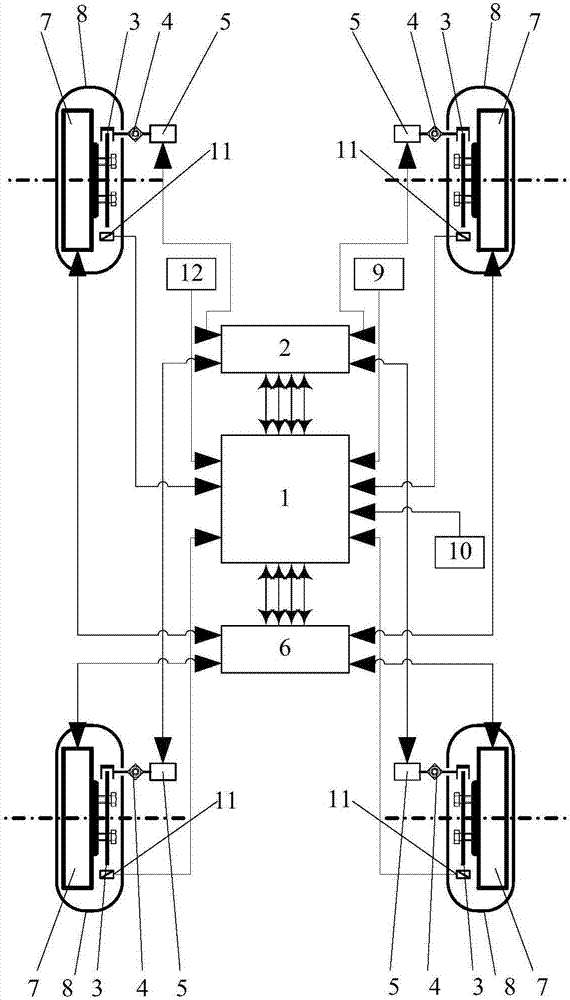
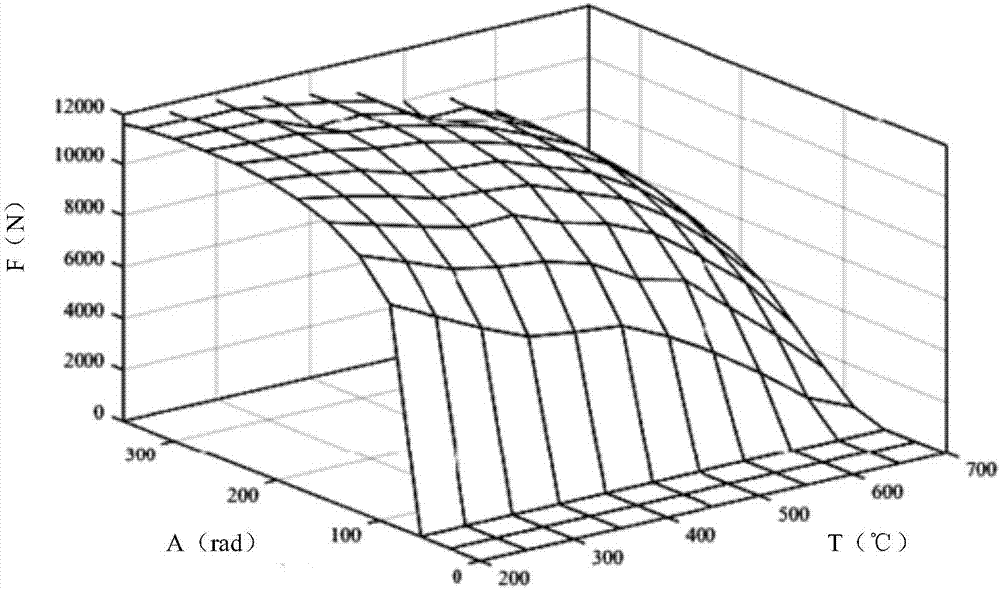
Vehicle antiskid control system and method based on datum combination
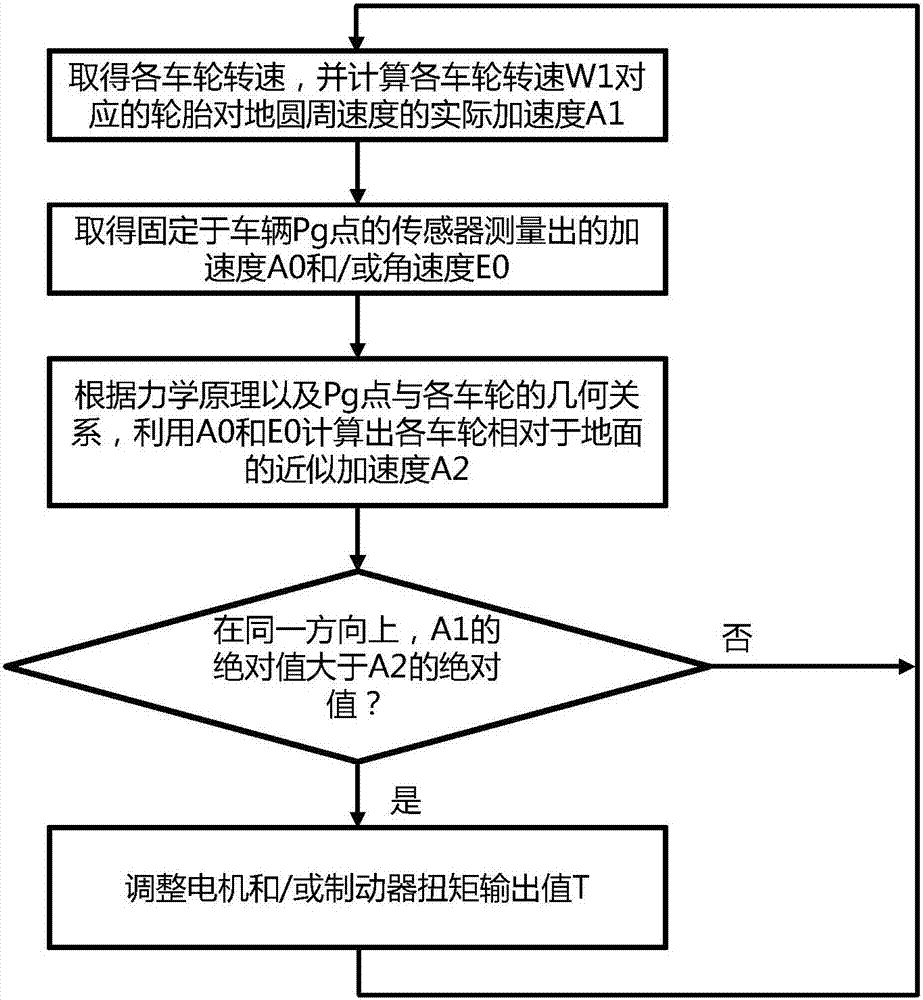
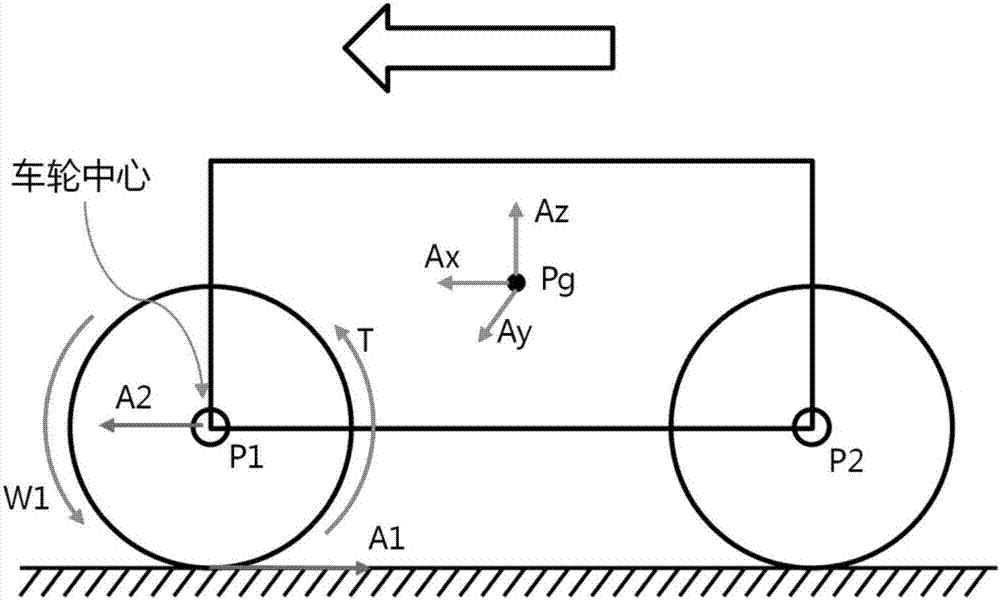
The invention provides a vehicle antiskid control system based on datum combination. The vehicle antiskid control system comprises at least one acceleration sensor and an angular velocity sensor which are fixed to a vehicle body. According to the control system, by using the geometrical relation between the sensors and wheels, an approximate acceleration value A2 over the ground near the wheel landing places is calculated based on the mechanics principle, and the relation of the acceleration value A2 and an acceleration value A1 of the actual circumference velocity of the wheels near the landing places is used to control and drive the torque output of the wheels, so that all the wheels have a good antiskid control effect in any state.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Anti-lock braking device of steering drive axle hub brake and design method thereof
InactiveCN105752061AIncrease widthAvoid interferenceABS control systemsWheel speed sensorSpatial structure
The invention relates to an automotive anti-lock braking system (ABS) technology, in particular to an anti-lock braking device of a steering drive axle hub brake and an ABS anti-lock braking structure for a steering drive front axle with a hub brake.The anti-lock braking device is structurally characterized by further comprising a gear ring and a wheel speed sensor, the gear ring is a cylindrical gear rotor installed on a peripheral face of one side end, provided with an oil seal and a spacer bush, of a hub, the internal diameter of the cylindrical gear rotor is in interface fit with the external diameter of the hub, and the cylindrical gear rotor is installed on the hub in a pressing mode; the wheel speed sensor is installed on the inner side face of a brake bottom plate and is parallel to the center axis of the hub, the sensing end of the wheel speed sensor is of a flat head structure distributed parallel to a gear crest of the cylindrical gear rotor.The anti-lock braking device has the advantages that the infinite space is fully utilized without affecting the assembly intensity, the steering drive front axle ABS anti-lock braking device is realized; the interval precision of the sensor and the cylindrical gear rotor is accurate and does not need to be adjusted; the flat head wheel speed sensor is more sensitive in sensing.
Owner:福建省晋江市东石肖下连盛机械配件厂(普通合伙)
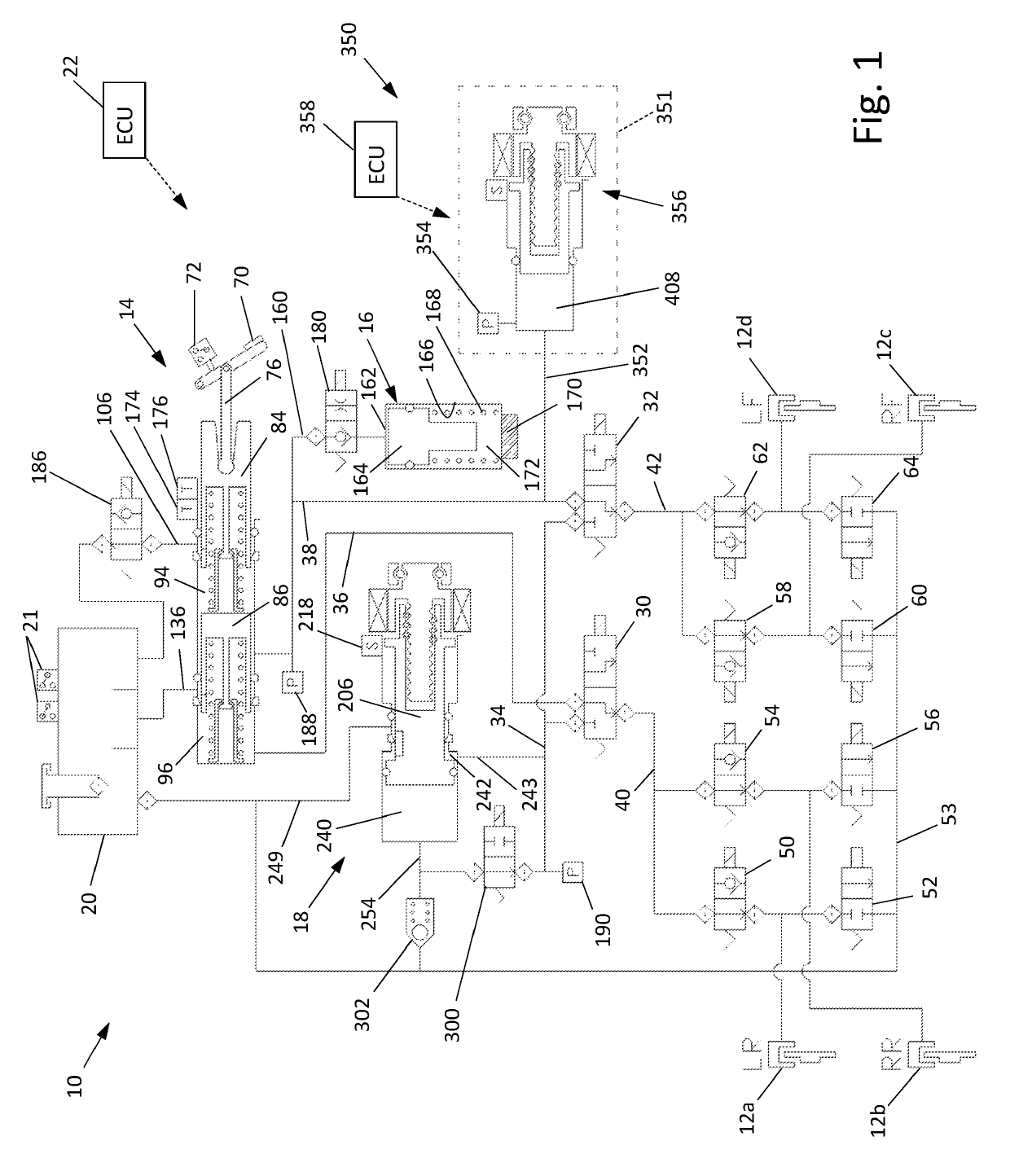
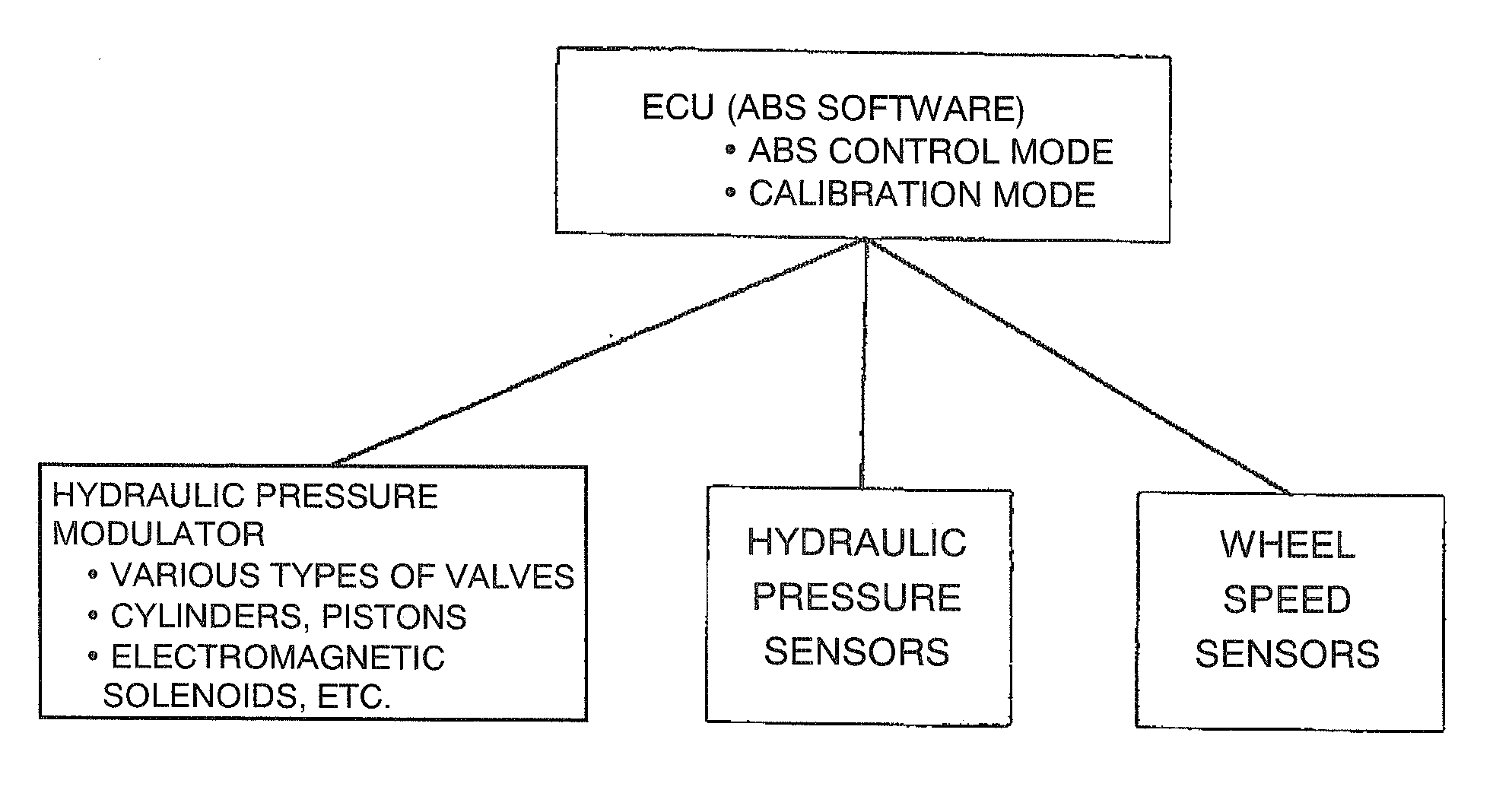
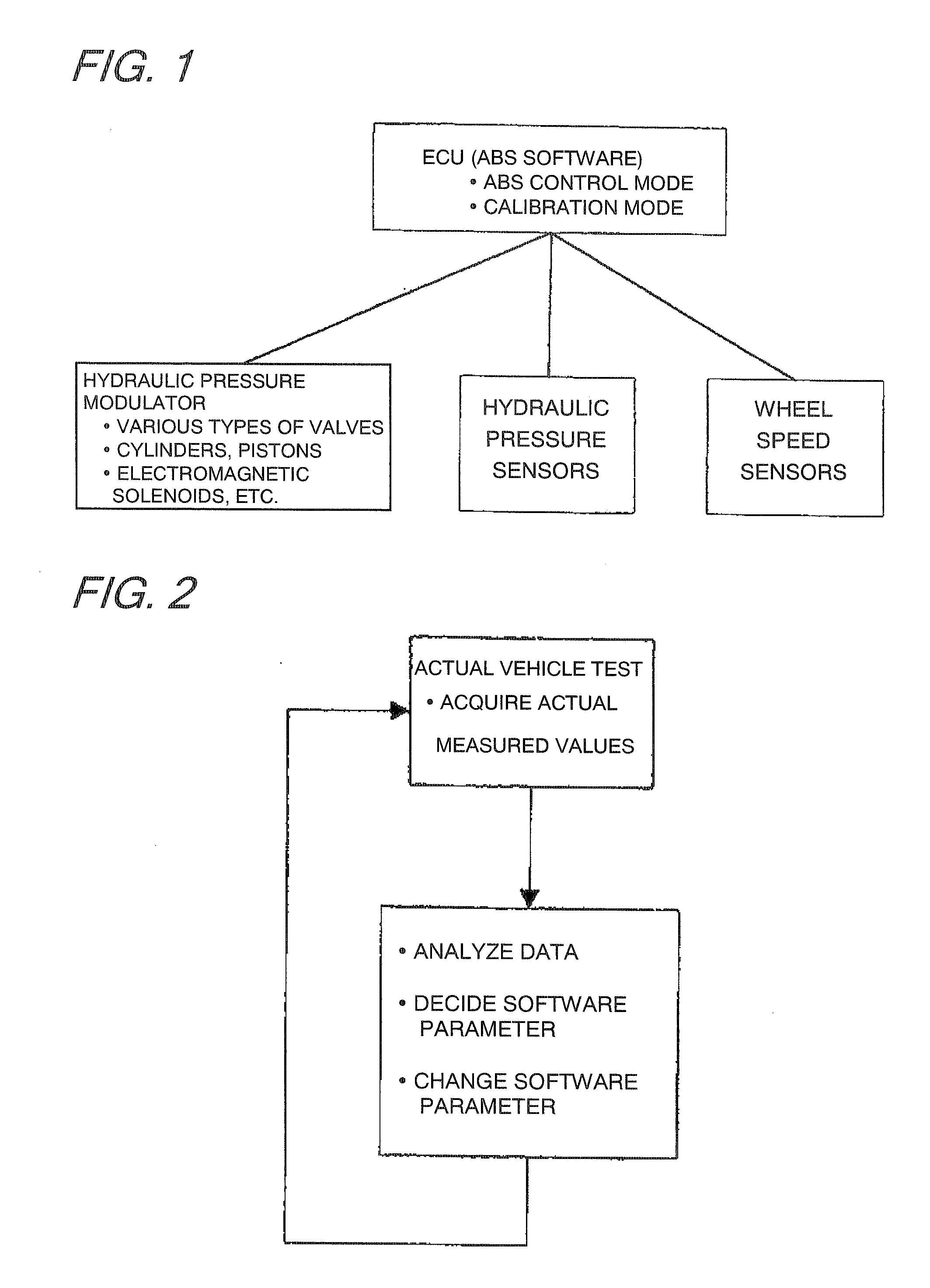
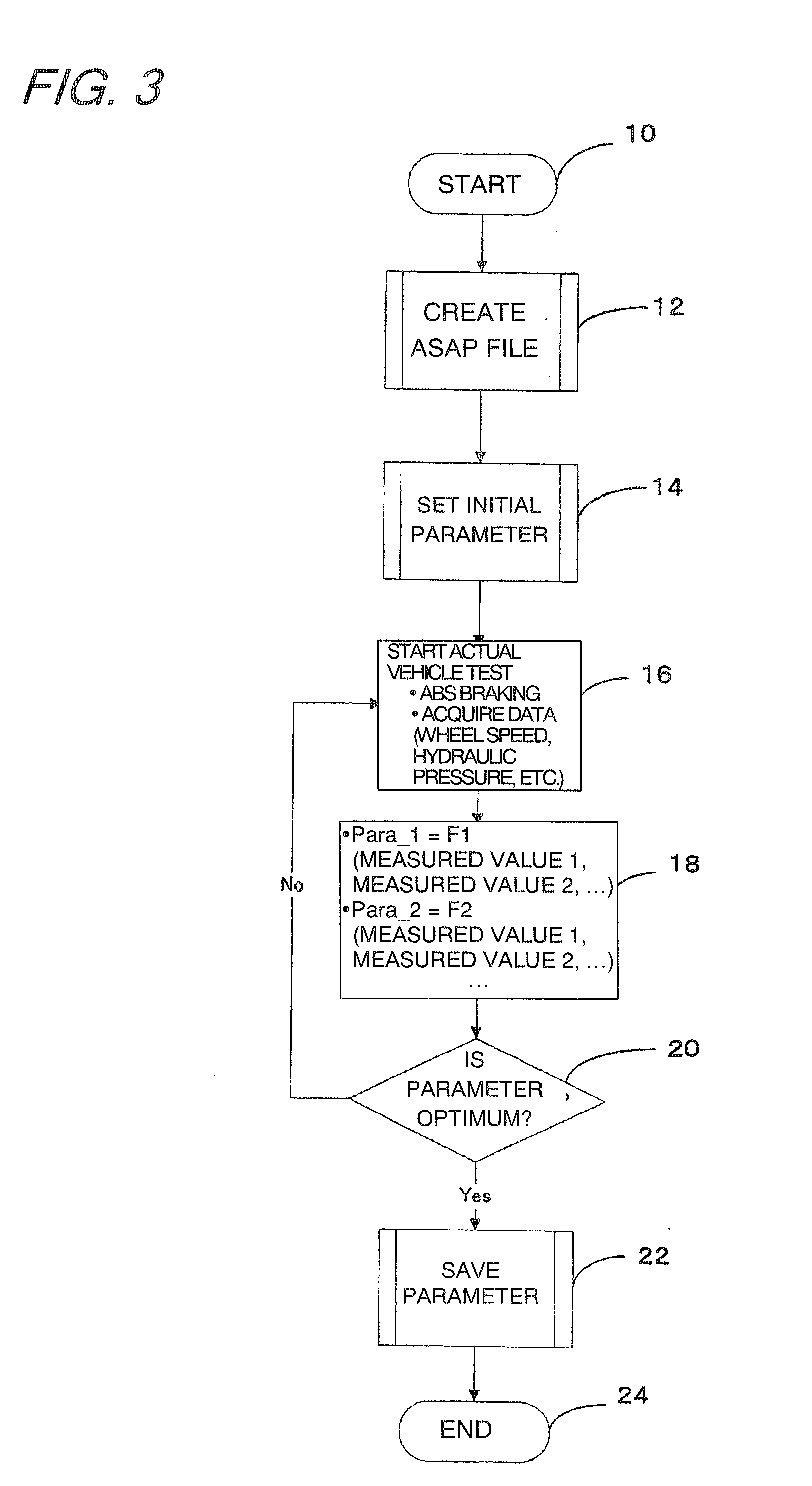
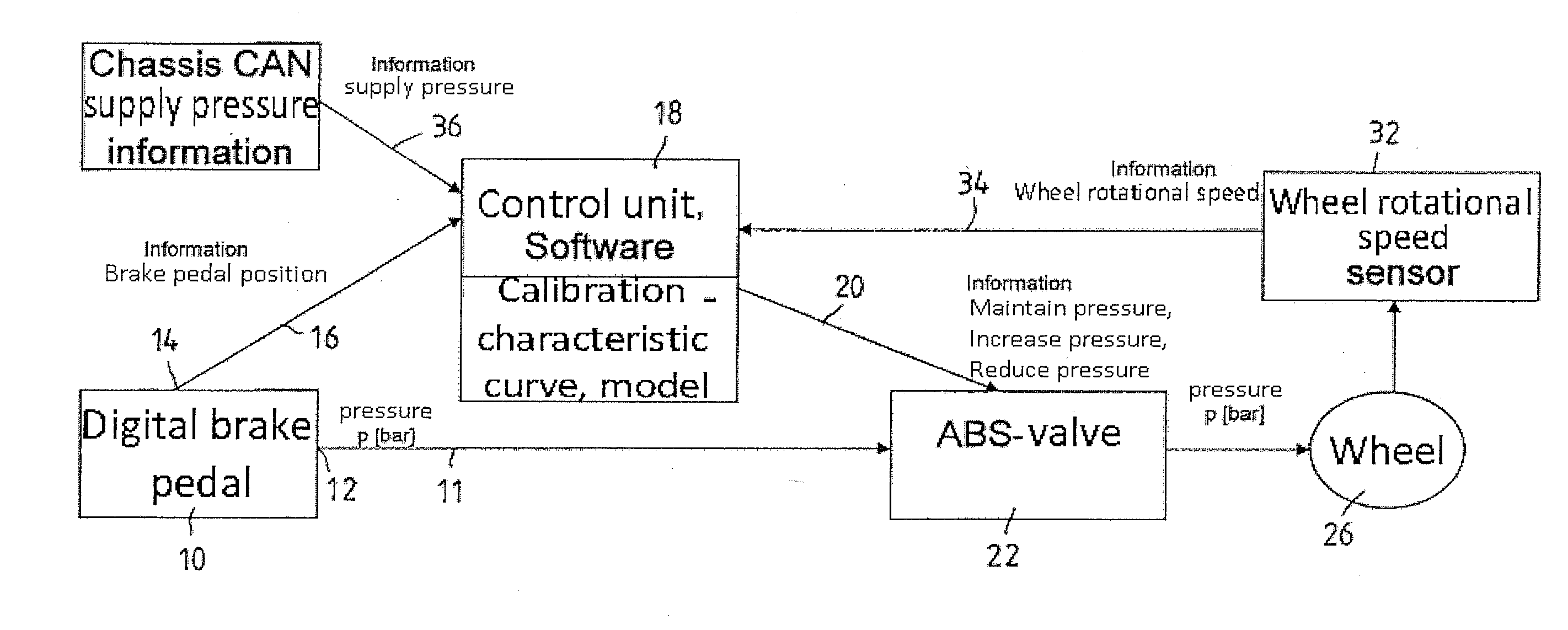
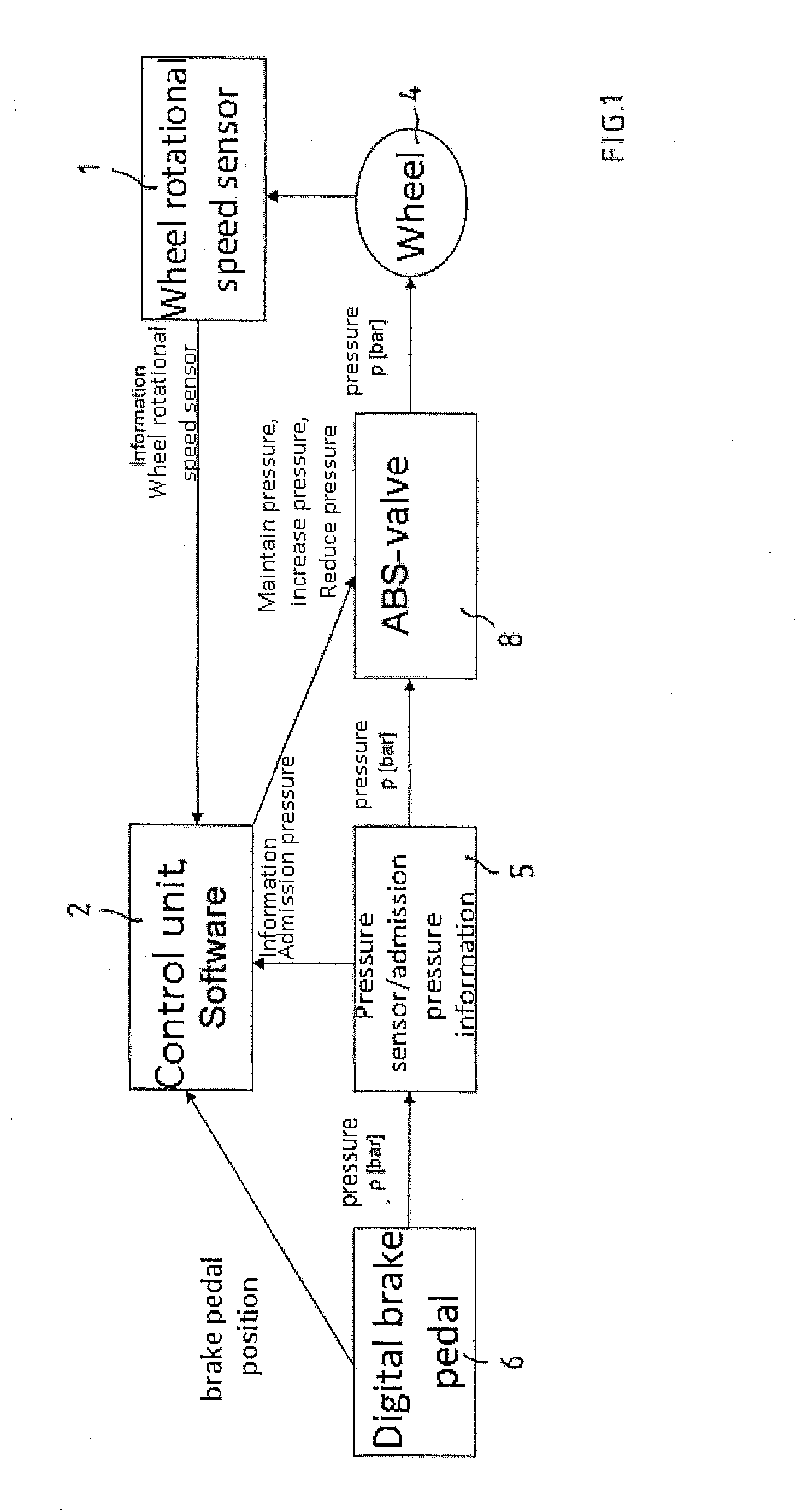
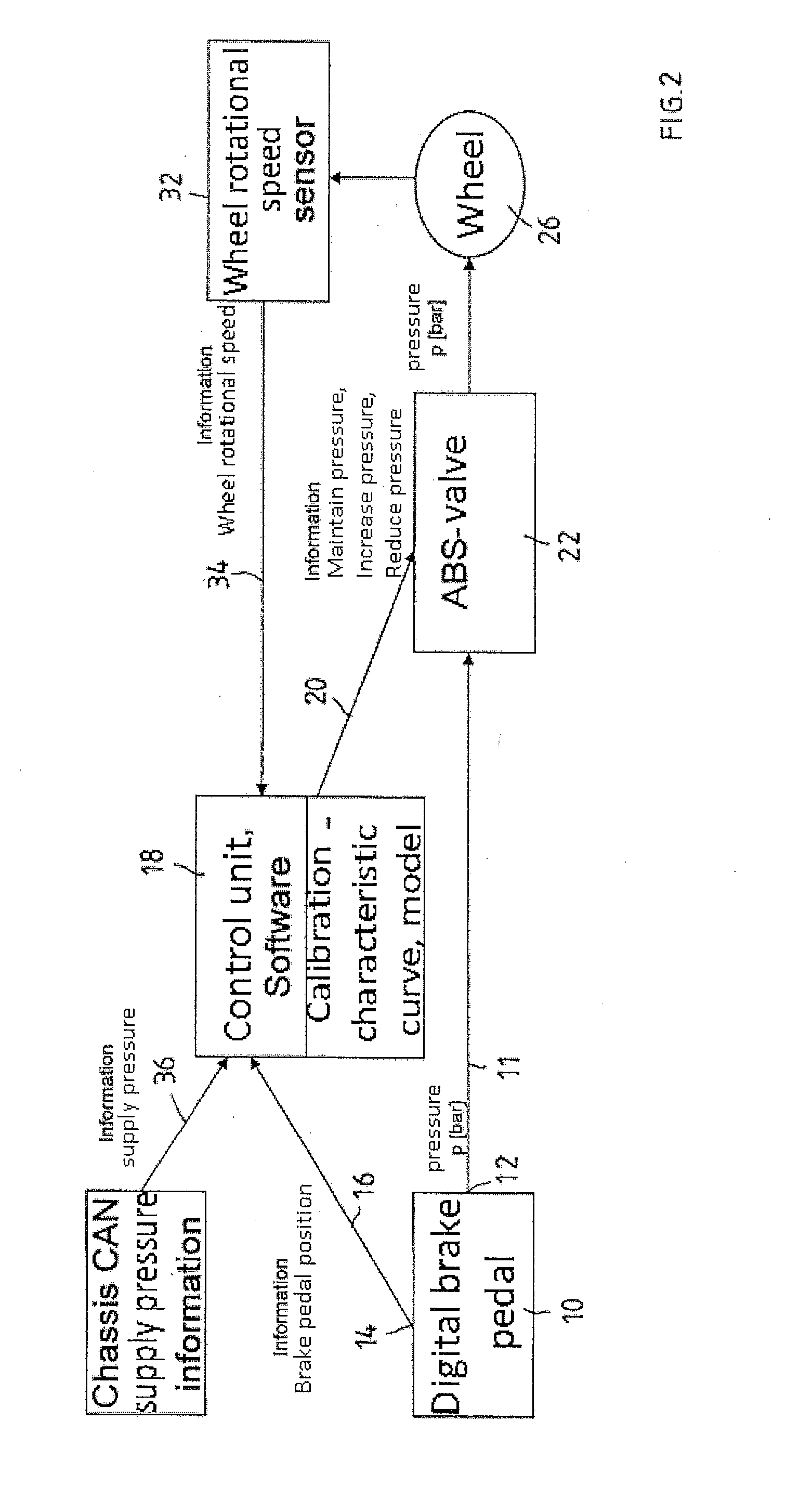
Vehicular abs control system with internal parameter automatic calibration function
ActiveUS20110071744A1Digital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsWheel speed sensorControl system
To provide an ABS control system and software with an automatic parameter calibration function. An ABS control system according to the present invention includes an electronic control unit (ECU), a wheel speed sensor, and a brake pressure sensor. The wheel speed sensor and the brake pressure sensor measure wheel speed and brake pressure during ABS braking, and the ABS control system automatically calibrates an internal parameter used in ABS control in response to the wheel speed and brake pressure measurement results.
Owner:BOSCH CORP
Method for operating a wheel slip control apparatus with compensated wheel speeds
ActiveUS20150191158A1Control is carry-outAccurately carry-outHand manipulated computer devicesDigital data processing detailsProcess engineeringSlew rate
A method and device for operating a wheel slip control apparatus, including determining wheel speeds of wheels compensated with respect to wheel speed differences during a turn as input variables for the wheel slip control apparatus, with which a) a neutral steering, understeering or oversteering driving condition of the vehicle is determined from the driving behavior during a turn, b) depending on the determined condition of the vehicle, either the reference or actual yaw rate is used to calculate a turn radius related to a selected point on the vehicle, c) wheel-related turn radii for at least some wheels are determined from the turn radius related to the selected point, d) reference factors are determined from the wheel-related turn radii and a common reference turn radius for at least some wheels, and e) the compensated wheel speeds are each determined from the reference factors and measured wheel speeds for at least some wheels, and f) the compensated wheel speeds are used as input variables for a wheel slip control apparatus.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Electronically controlled pneumatic braking system in a commercial vehicle, and method for electronically controlling a pneumatic braking system
ActiveCN107921945AMaximum predetermined brake pressureAverage scheduled brake pressureBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsControl signalControl manner
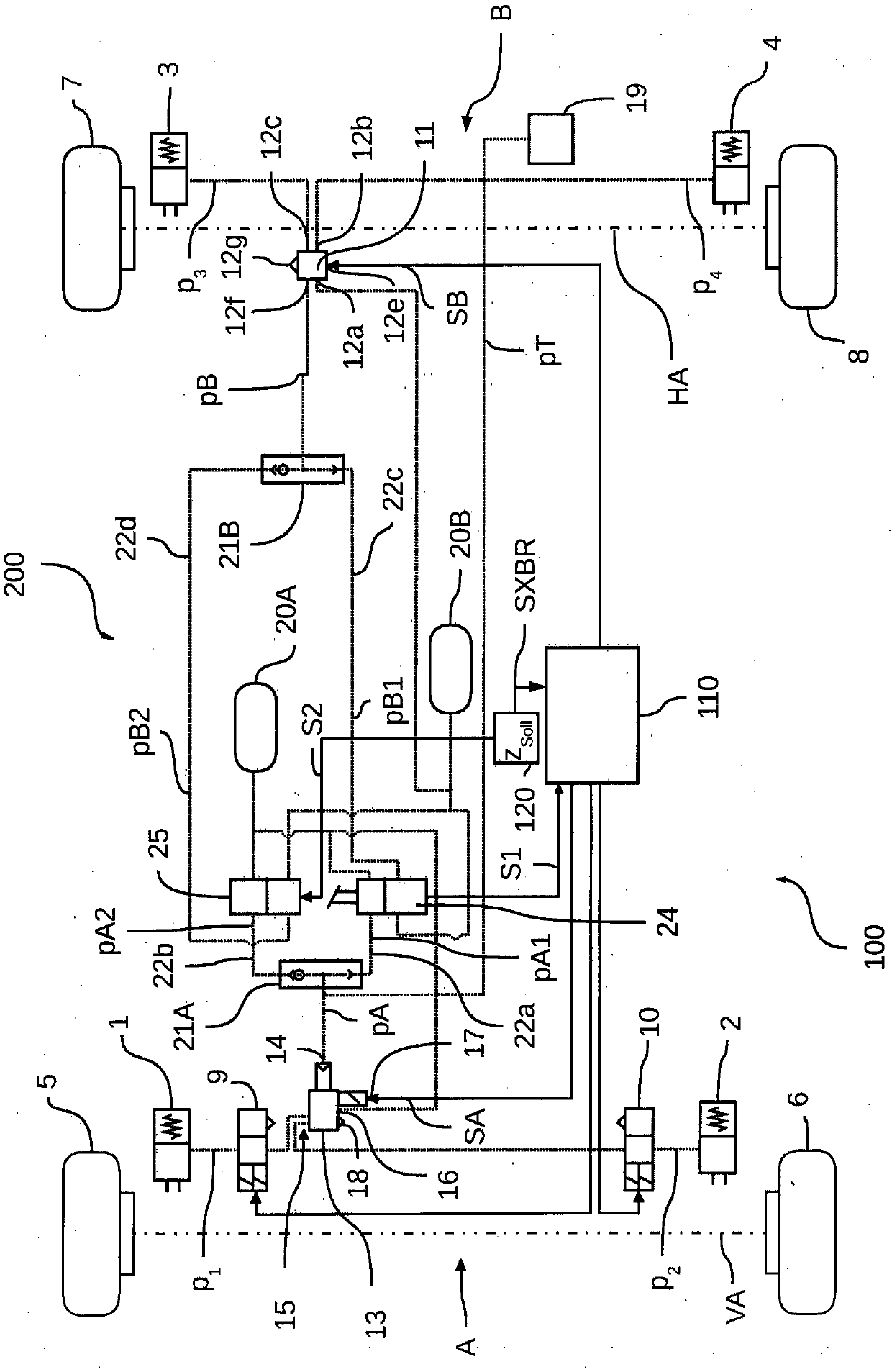
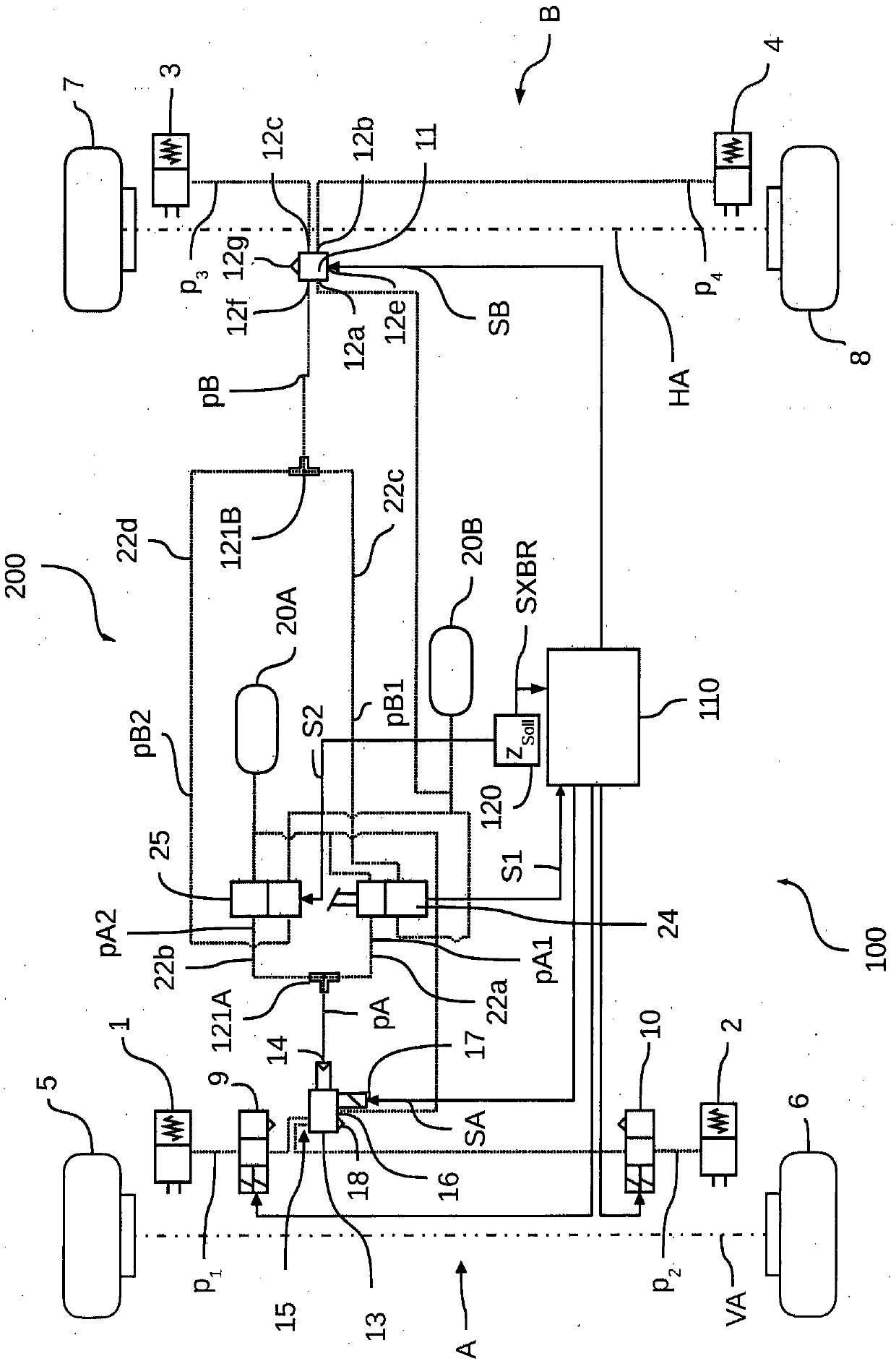
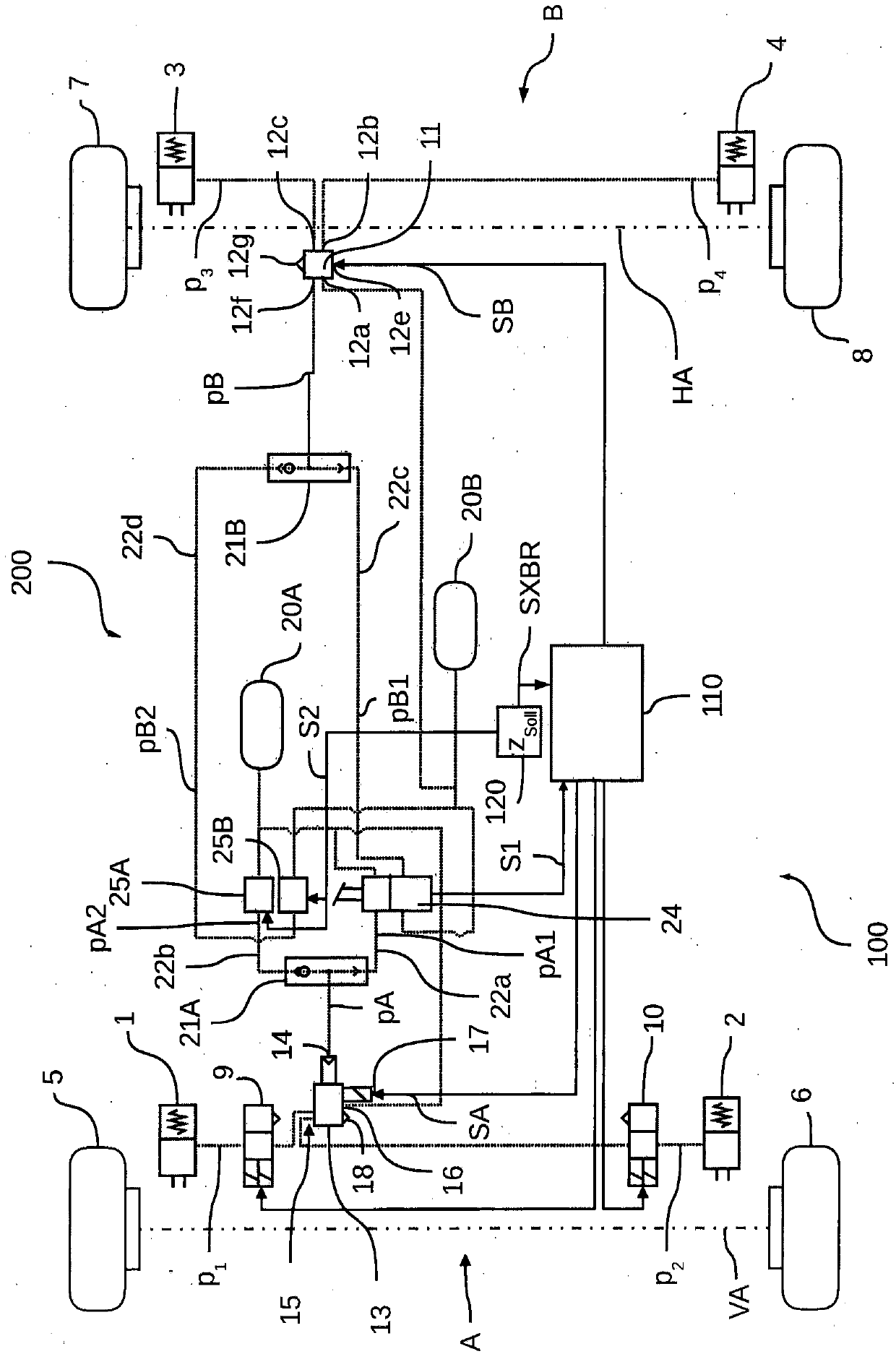
The invention relates to an electronically controlled pneumatic braking system (100) comprising at least one braking circuit (A, B) with which at least one control valve (13, 11) for adjusting brakingpressures (p1, p2, p3, p4) is associated, the at least one control valve (13, 11) being controllable electronically in accordance with a control signal (SA, SB) and pneumatically in accordance with acontrol pressure (pA, pB). According to the invention, a second brake valve (25) is provided in addition to a first brake valve (24), the second brake valve (25) being able to output a pneumatic second brake valve control pressure (pA2, pB2) in an electronically controlled manner. The first brake valve (24) can, in addition to an actuation signal (S1), pneumatically output a first brake valve control pressure (pA1, pB1). The two brake valves (24, 25) are disposed in the pneumatic braking system (100) in such a way that the first brake valve control pressure (pA1, pB1) of the first brake valve(24) and / or the second brake valve control pressure (pA2, pB2) of the second brake valve (25) is / are output as the control pressure (pA, pB) to the at least one control valve (13, 11) in order for the at least one control valve (13, 11) to be pneumatically controlled, and the second brake valve (25) can be electronically controlled when the at least one control valve (11, 13) is prevented from being electrically controlled, such that an electronically-pneumatically controlled redundancy is created.
Owner:ZF CV SYST EURO BV
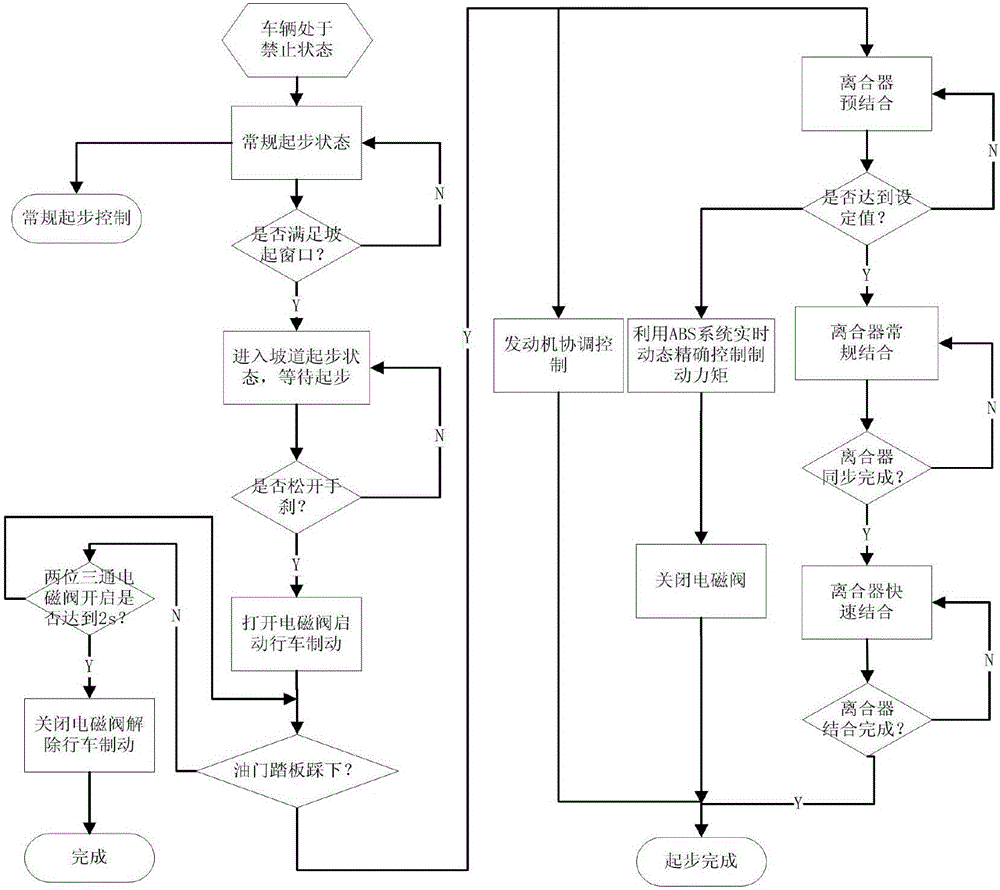
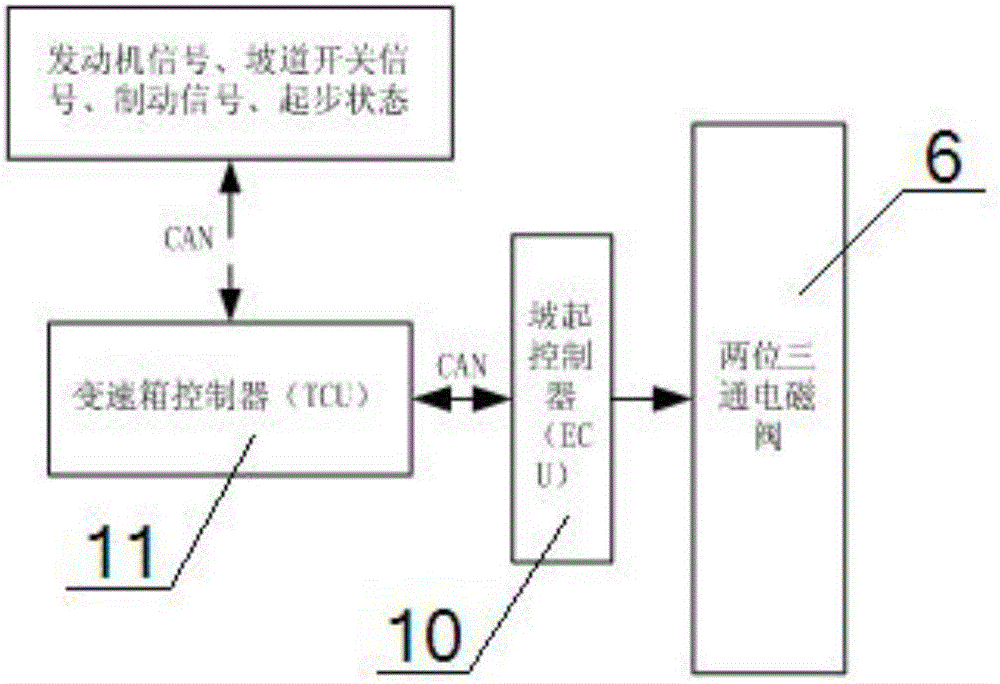
Hill starting system and use method thereof
ActiveCN106427961AAvoid slippery slopesQuick responseInternal combustion piston enginesBraking action transmissionLoad sensingEngineering
The invention provides a hill starting system. The hill starting system comprises a two-position three-way electromagnetic valve, a load sensing valve, an ABS valve, a gearbox controller and a hill starting switch. An air inlet of the two-position three-way electromagnetic valve is sequentially communicated with an air outlet of an air compressor through a foot valve, an air cylinder, a four-protection valve and a drier, an exhaust port of the two-position three-way electromagnetic valve is communicated with an air inlet of the ABS valve through the load sensing valve, the two-position three-way electromagnetic valve and the ABS valve are in signal connection with a hill starting controller, and the gearbox controller is in signal connection with the hill starting controller, the hill starting switch and an engine. During use, firstly the hill starting switch is pressed, a manual valve is switched off, an accelerator is trodden, the hill starting controller automatically controls the engagement depth of a clutch and coordinates the output torque of the engine according to hill resistance, currently needing to be overcome, obtained through calculation, and a vehicle is made to be started smoothly. By means of the design, the structure is simplified, the starting response speed is increased, and integrated control of a brake, the clutch and the engine is achieved.
Owner:DONGFENG COMML VEHICLE CO LTD
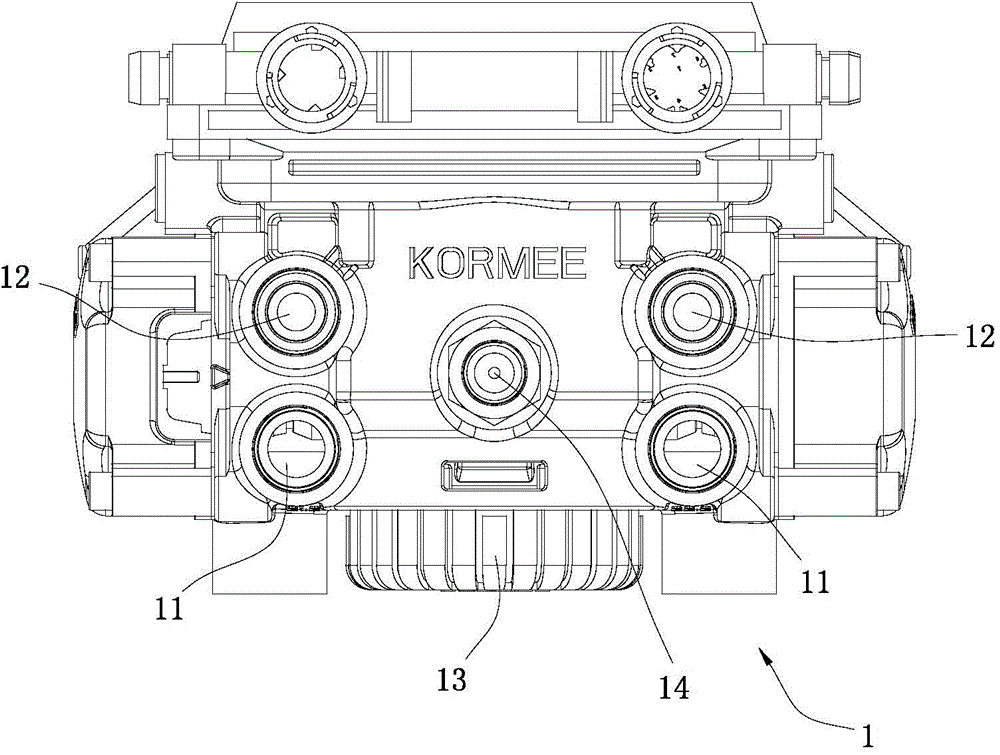
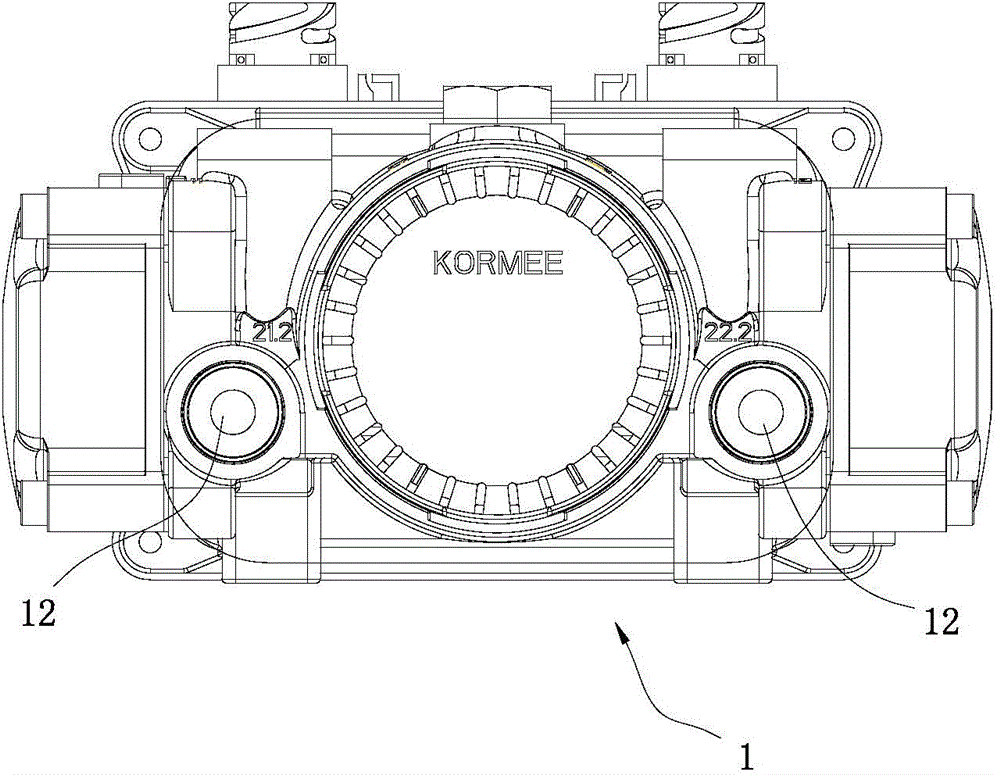
Electronic control relay valve assembly of anti-lock brake system
InactiveCN104309601APedal responsiveAccurate judgmentABS control systemsApplication and release valvesDriver/operatorSolenoid valve
The invention discloses an electronic control relay valve assembly of an ABS (anti-lock brake system). The electronic control relay valve assembly of the ABS comprises a valve body and a solenoid valve group; a pressure sensor used for detecting the pressure of brake air chambers is arranged in the valve body; the valve body comprises two main air inlets, four air outlets and an exhaust port; two air chambers are symmetrically distributed in the valve body; one of the two brake chambers is respectively communicated with one of the two main air inlets, two of the four air outlets and the exhaust port; a valve capable of controlling whether the main air inlet is communicated with the corresponding air outlets or not is arranged in each air chamber; a main control piston capable of abutting on the corresponding valve is arranged in each air chamber; the valves are controlled by the solenoid valve group connected with the valve body; the internal valve operation of the valve body is controlled through the solenoid valve group, and the pressurization working condition, the pressure-maintained working condition and the pressure-reduced working condition are realized through an internal logic operation method and threshold value control; the electronic control relay valve assembly is adapted to various working conditions; as an electronic control air brake vehicle is adopted, the reaction to stepping of a driver is more sensitive, and judgment on brake performance is more accurate; brake can be realized more rapidly, and the defects that the mechanical brake response time is slow, the brake comfort is poor and the like are eliminated.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KORMEE AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS CONTROL TECH
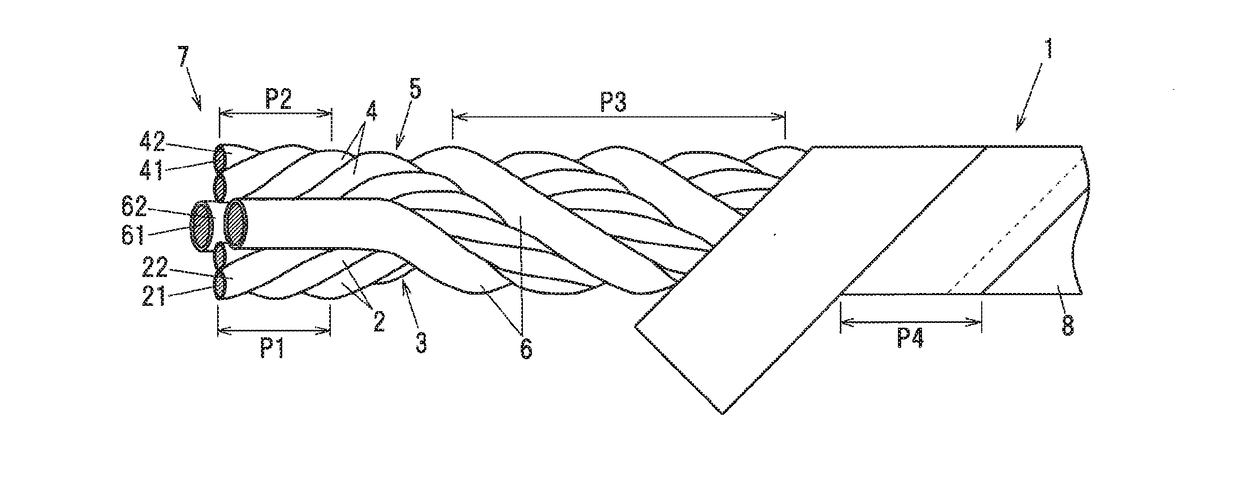
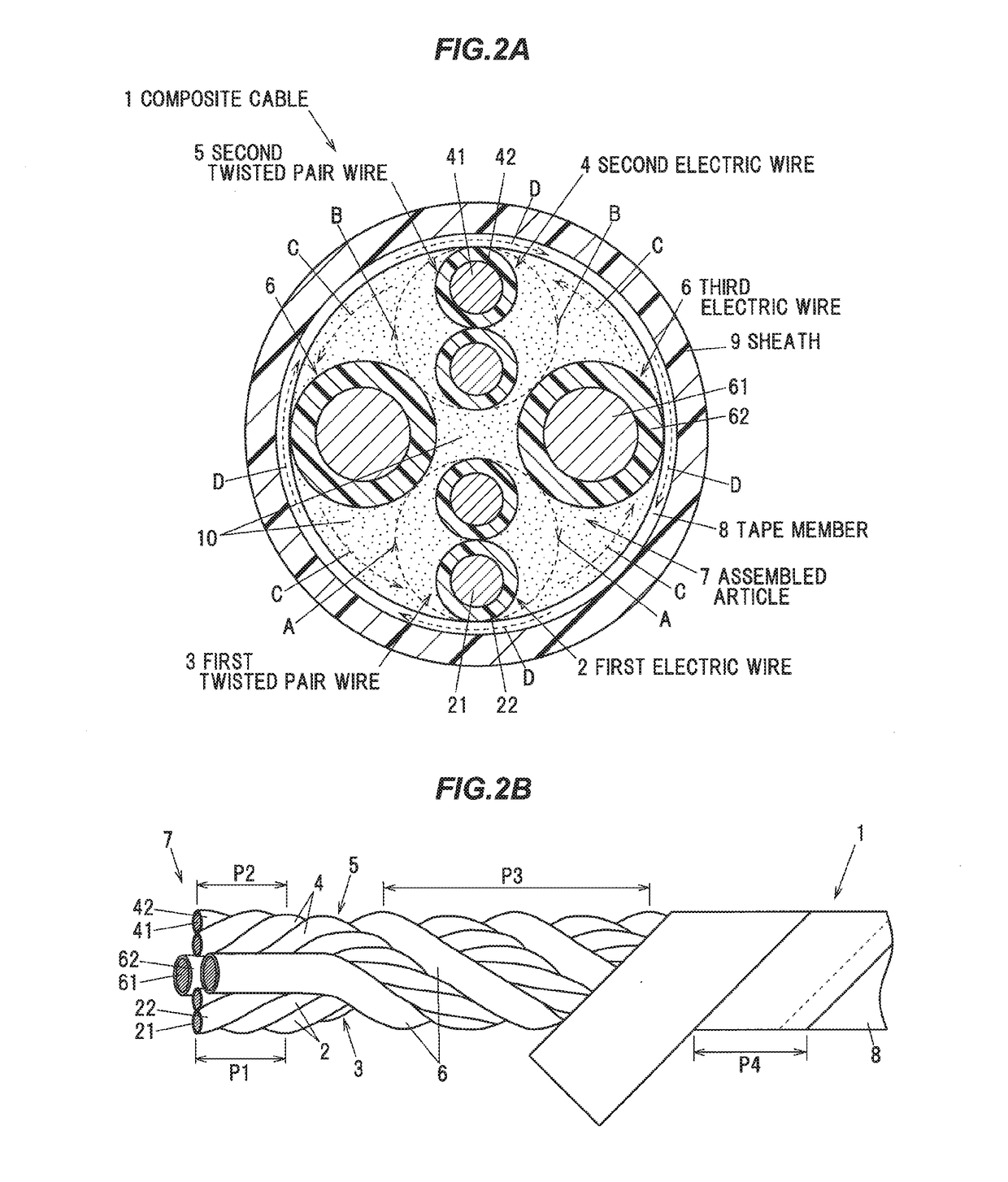
Composite cable and composite harness
ActiveUS20170263353A1Inhibit deteriorationBraking action transmissionInsulated cablesTwisted pairElectric wire
A composite cable includes a first twisted-pair wire formed by twisting a pair of first electric wires, a second twisted-pair wire formed by twisting a pair of second electric wires, a pair of third electric wires arranged between the first and second twisted-pair wires in a circumferential direction, each third electric wire having a larger outer diameter than the first and second electric wires, and a tape member spirally wound around an assembled article that is formed by twisting the first twisted-pair wire, the second twisted-pair wire and the pair of third electric wires together. The two twisted-pair wires have the same twist direction, the twist direction of the two twisted-pair wires is different from a twist direction of the assembled article, and the twist direction of the assembled article is different from a winding direction of the tape member.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Method for determining a brake pressure value on the basis of characteristic curves
A method for determining a value of a brake pressure modulated by a pneumatic channel of a braking value encoder having at least one electrical channel, in a braking device of a vehicle, including: (a) a first characteristic curve, in which the dependence of the signals, modulated by the at least one electrical sensor, on the degree of activation of the braking value encoder is represented, is determined and stored; (b) a second characteristic curve, in which the dependence of the brake pressure values, modulated by the channel, on the electrical signals detected by the sensor is represented, is determined and stored; and (c) the brake pressure value corresponding to a specific braking request as a result of activation of the encoder is determined based on the first and second characteristic curves.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
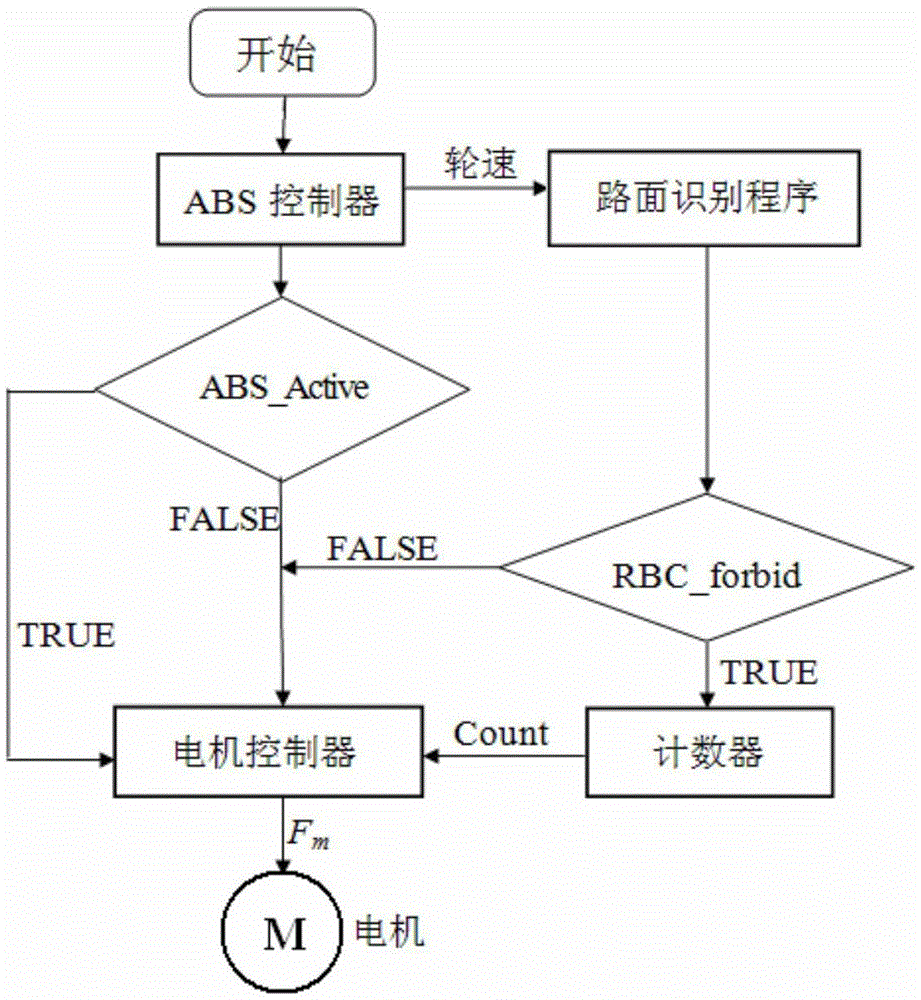
Braking energy recovery system and control method based on system
ActiveCN105644536AEnsure driving safetyImprove braking energy recoveryElectrodynamic brake systemsABS control systemsAdhesion coefficientRecognition algorithm
The invention discloses a braking energy recovery system. The system comprises an ABS controller, a motor controller and a motor, wherein the braking energy recovery system is provided with a pavement recognition module, and a signal input end of the pavement recognition module is connected with a wheel speed signal output signal in the ABS controller; the signal output end of the pavement recognition module is connected with the motor controller. The invention further discloses a control method of the system. Through the adoption of the above technical scheme, a pavement recognition algorithm program module is added to enable the braking energy recovery function to directly quit while recognizing the emergency brake; under the normal brake, the relatively maximum motor braking force is provided according to the pavements with different adhesion coefficients in the premise of preferably guaranteeing the vehicle travelling security, thereby guaranteeing the relatively maximum braking energy recovery rate. The technical scheme provided by the invention is low in cost.
Owner:WUHU BETHEL AUTOMOTIVE SAFETY SYST
Method for detecting fluid leakage
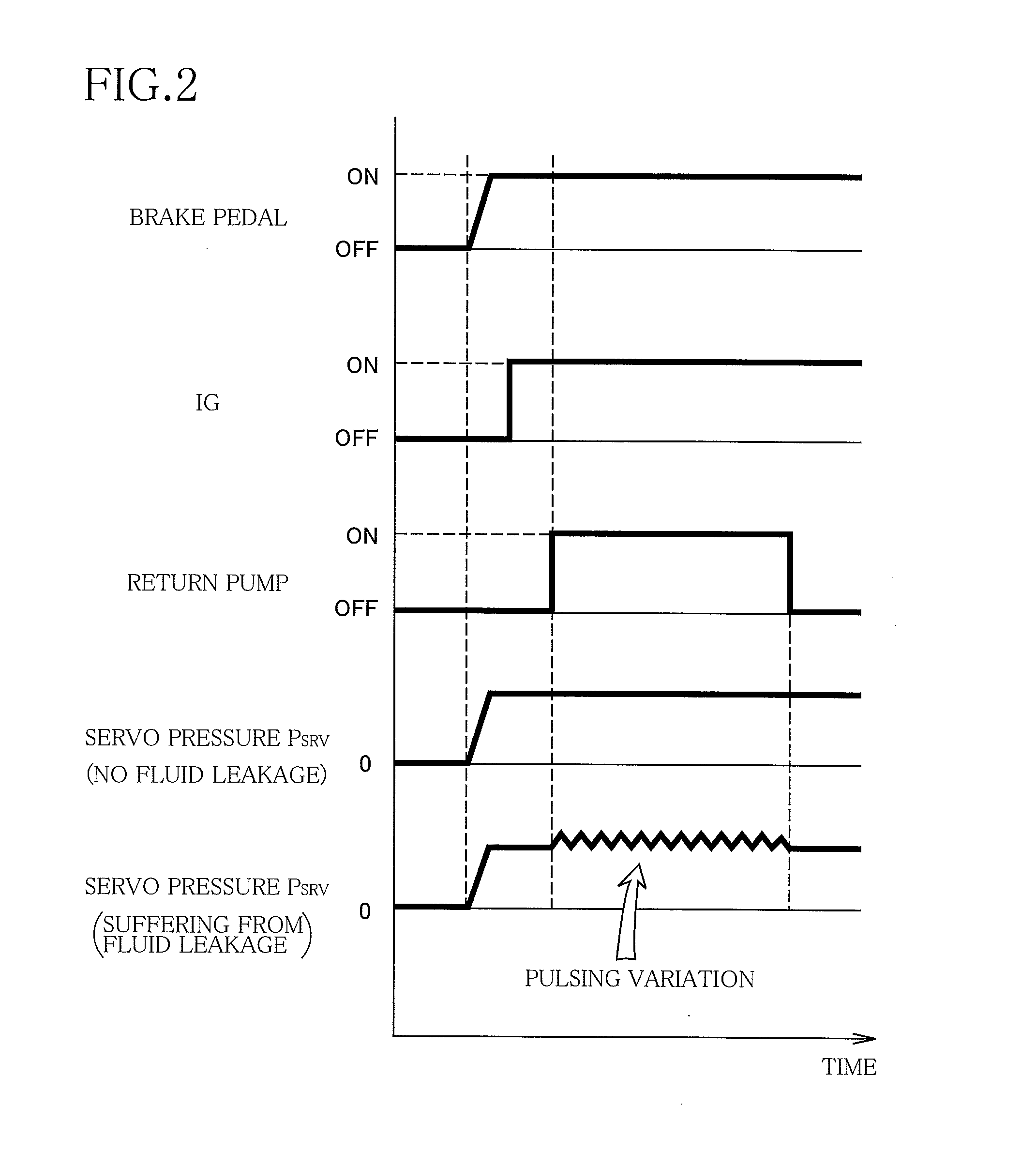
InactiveUS20160059839A1Easy to detectEasily fluid leakageMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateABS control systemsPressure decreaseWorking fluid
A method for detecting fluid leakage from a pressure-decrease valve in a hydraulic brake system having an ABS device including: a shutoff valve for shutting off supply of a working fluid from a fluid-pressure supply source to a brake device provided for a wheel; the pressure-decrease valve for discharging the working fluid from the brake device; a reservoir for storing the working fluid discharged from the pressure-decrease valve; and a return pump for returning the working fluid stored in the reservoir to a portion between the shutoff valve and the fluid-pressure supply source, the method including the steps of: activating the return pump in a state in which the hydraulic brake system is not in ABS operation, and detecting the fluid leakage from the pressure-decrease valve based on a variation in a pressure of the working fluid in the fluid-pressure supply source caused when the return pump is activated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Solenoid valve and hydraulic braking system for vehicle
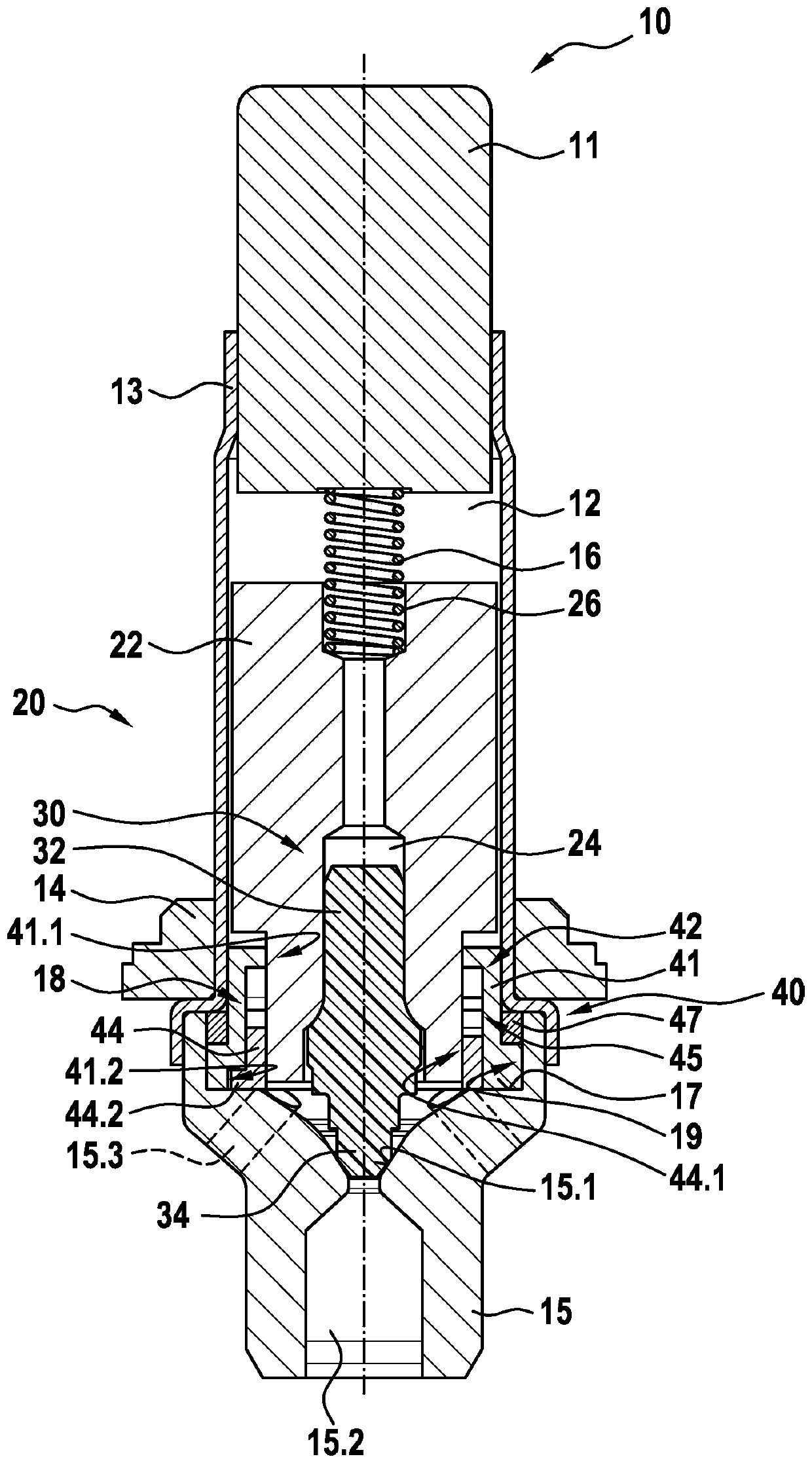
ActiveCN109863068AReduce complexityLow costOperating means/releasing devices for valvesABS control systemsMagnetic tension forceSolenoid valve
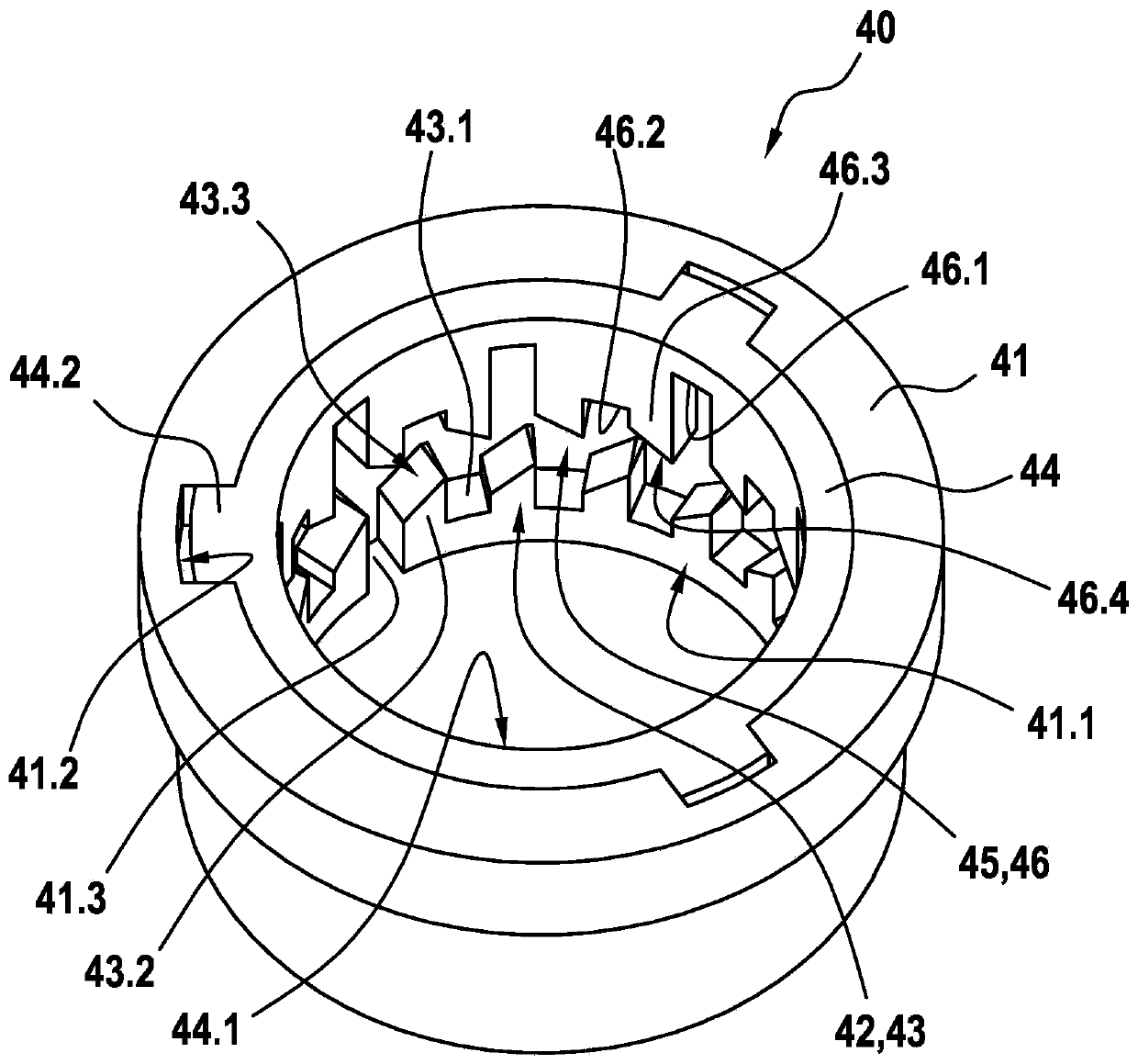
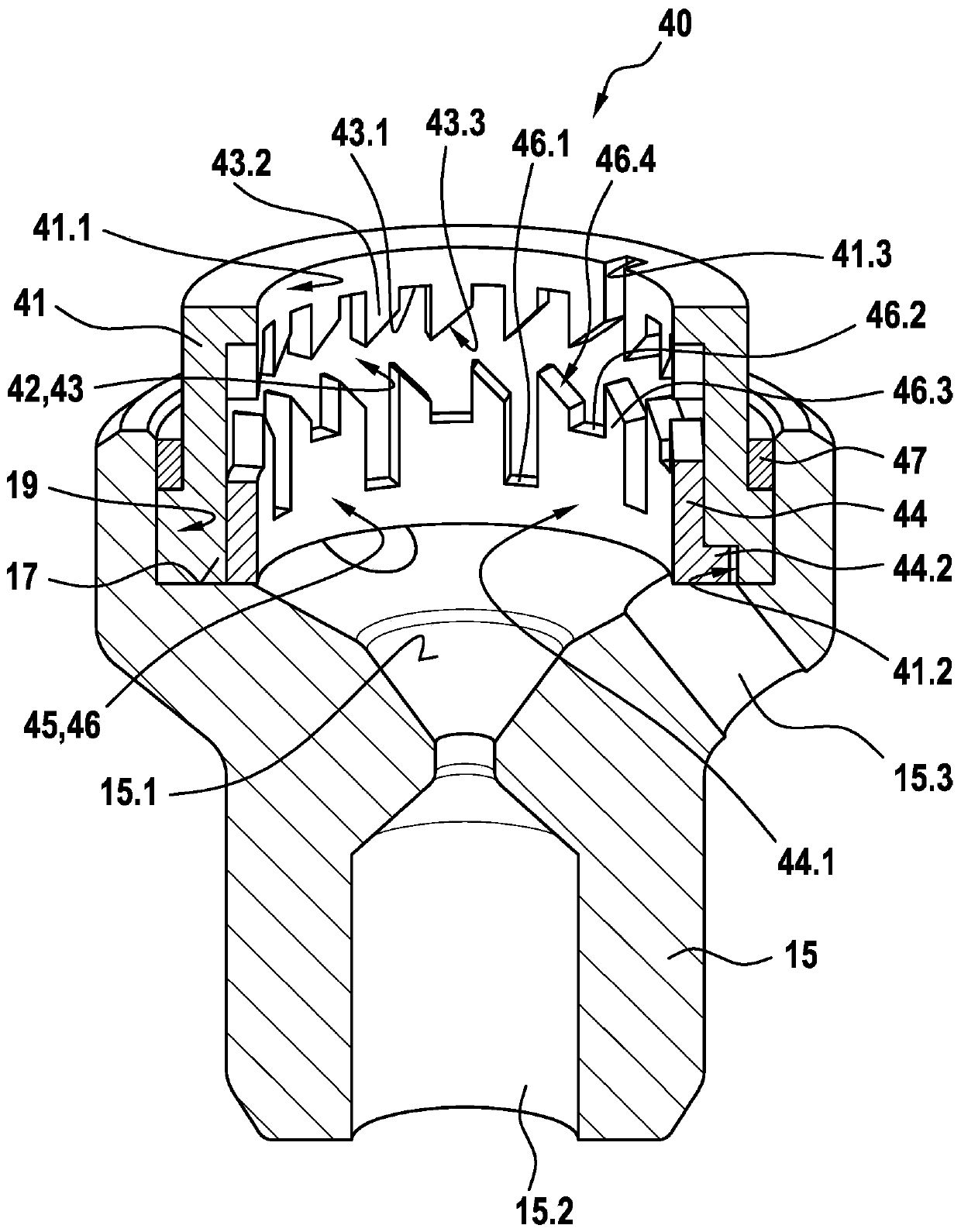
The invention relates to a solenoid valve (10) for a hydraulic braking system, comprising: a magnetic assembly; a pole core (11); a guide sleeve (13) joined to the pole core (11); a valve armature (20) running axially movably within the guide sleeve (13), the armature being drivable in opposition to a force of a restoring spring (16) by means of a magnetic force produced by the magnetic assembly,or being drivable by the force of the restoring spring (16), and said armature moving a plunger (30) comprising a closing element (34); and a valve body (15) connected to the guide sleeve (13) and comprising a valve seat (15.1) that is located between at least one first flow opening (15.2) and at least one second flow opening (15.3), the plunger (30) being fixedly connected to the valve armature (20). The invention also relates to a hydraulic braking system comprising a solenoid valve (10) of this type. The valve body (15) has a receiving region (19) which at least partially accommodates a guide assembly (40), the valve armature (20) running axially through at least one through-opening (41.1, 44.1) of the guide assembly (40), a mechanical detent device (18) being formed between the guide assembly (40) and the valve armature (20), the detent device releasing the valve armature (20) when the latter is in a de-energised closed position, such that the restoring spring (16) drives the valvearmature (20) and pushes the closing element (34) sealingly into the valve seat (15.1) to produce a sealing function, and said detent device fixes the valve armature (20) in a de-energised open position against the force of the restoring spring (16) in an axial detent position, such that the closing element (34) is raised from the valve seat (15.1).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
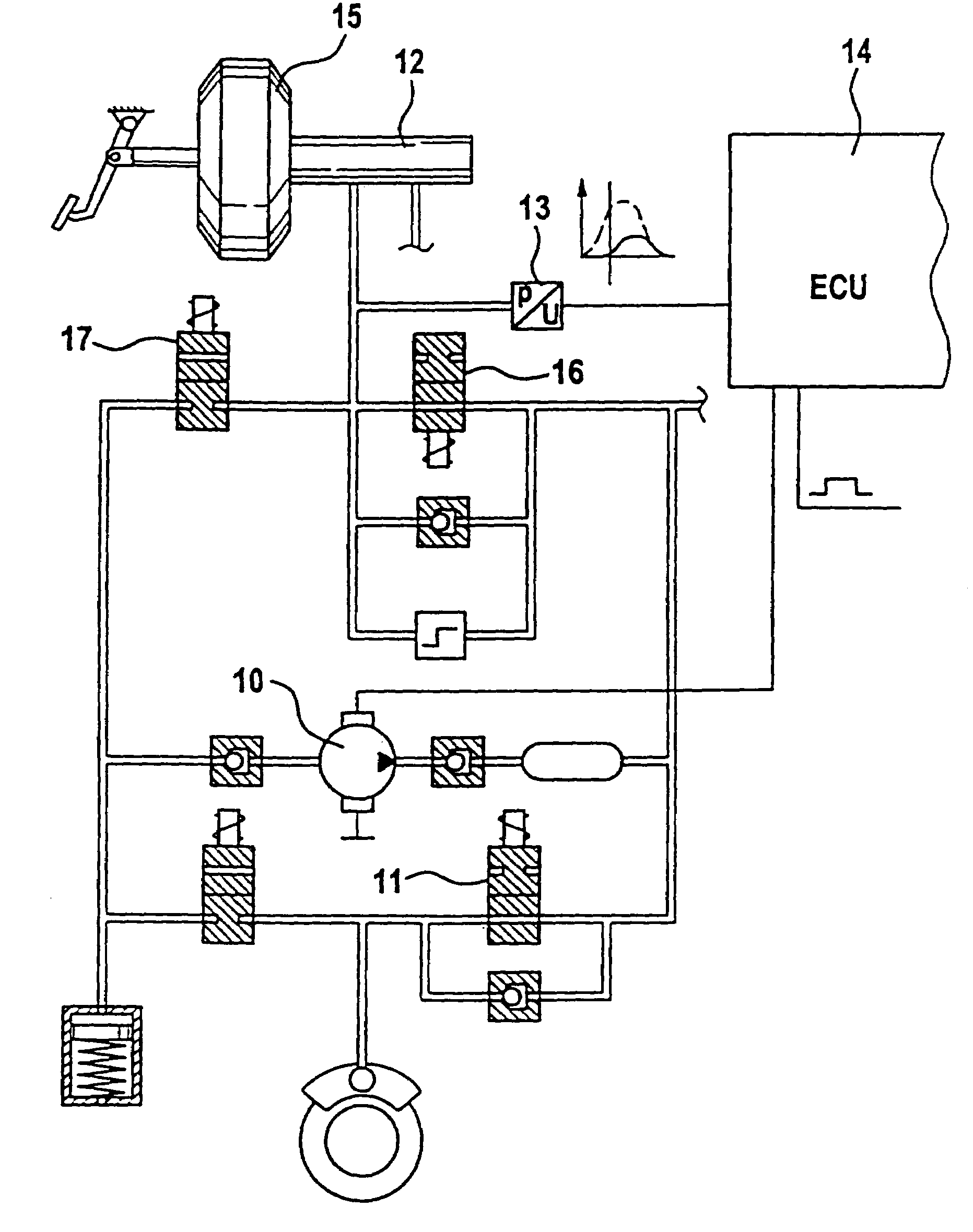
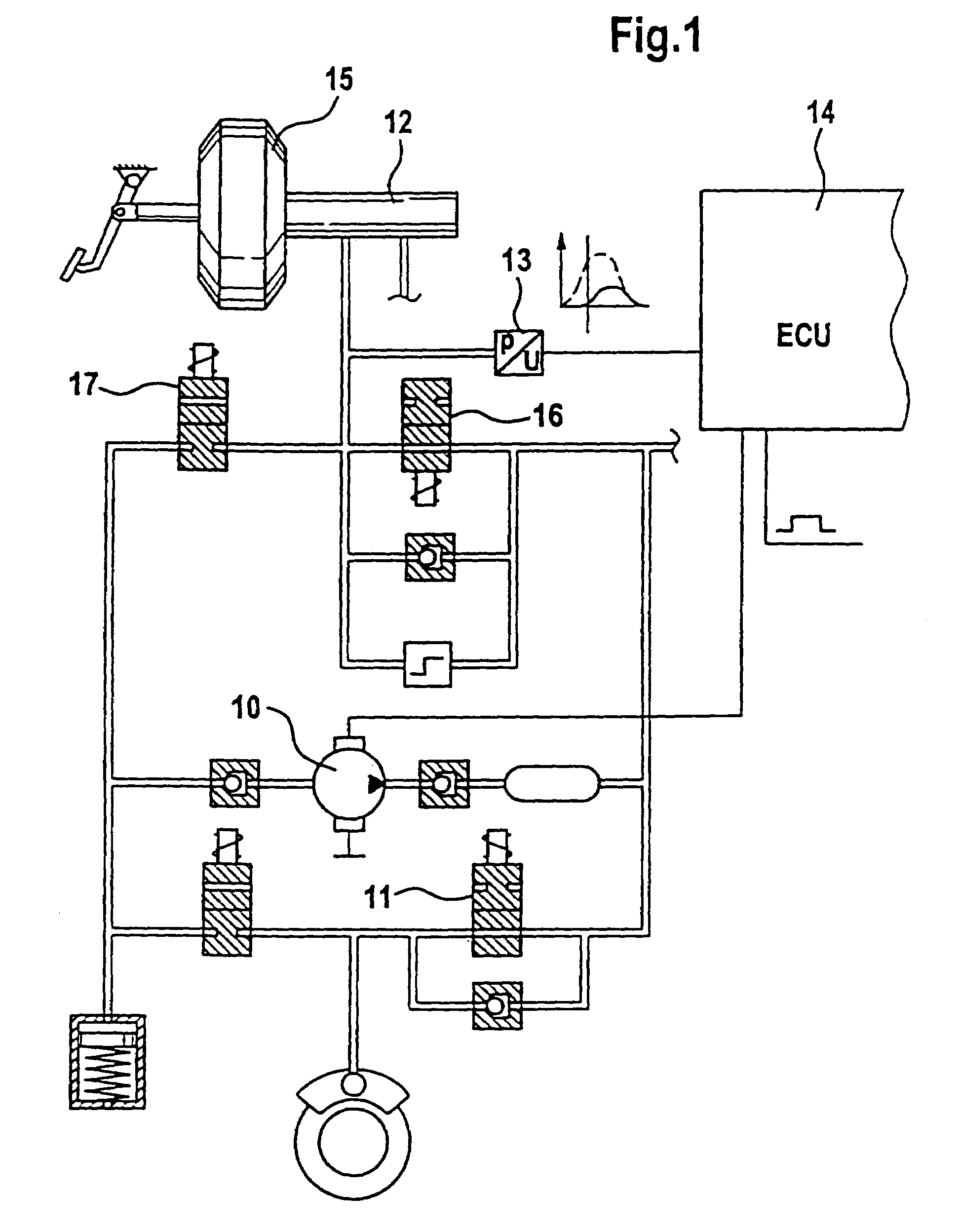
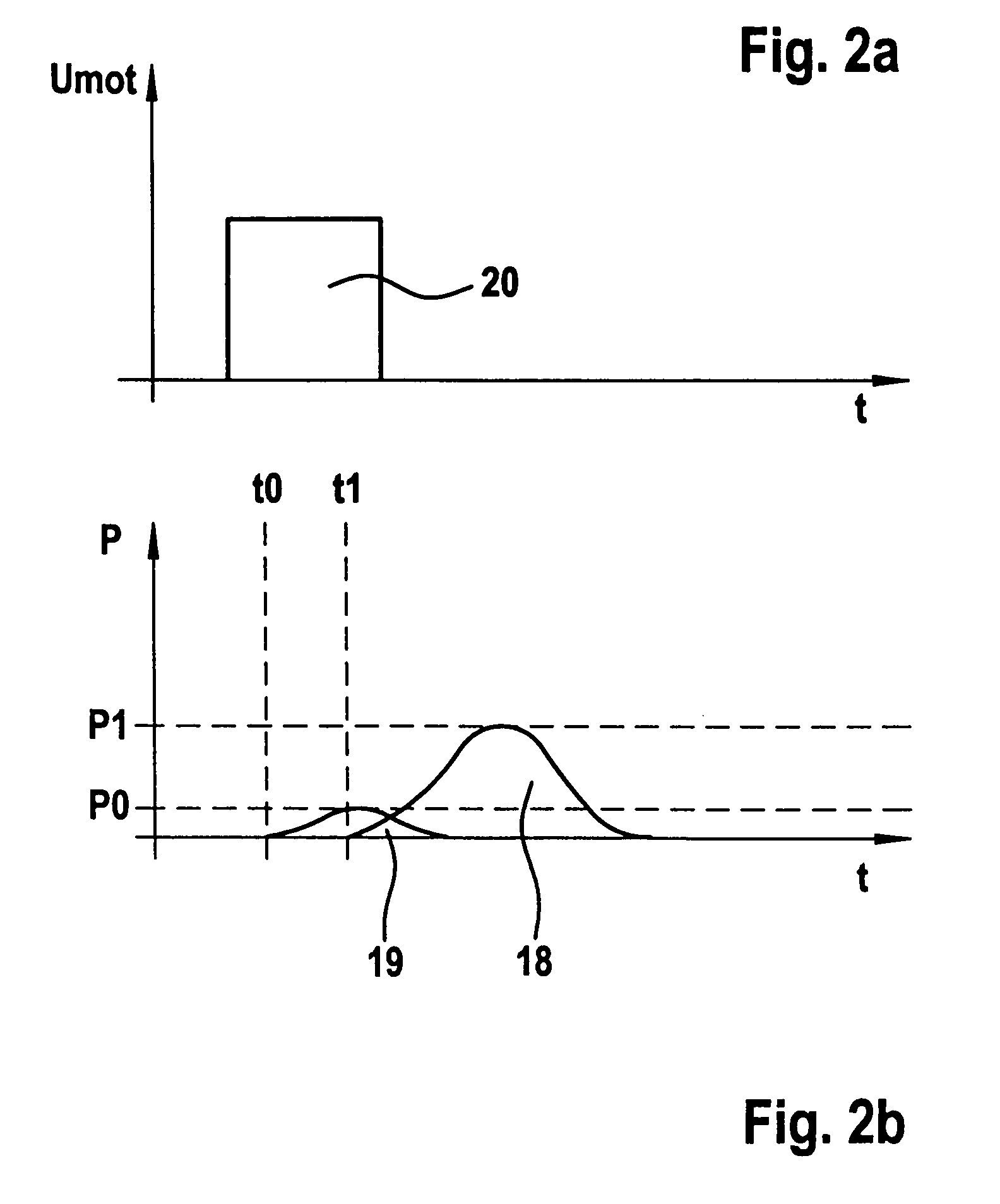
Method for determining a model upstream pressure by means of a mathematical model in an electronically regulated motor vehicle brake system
InactiveCN103857570ADecrease the integral valueHigh precisionABS control systemsTemporal changeLow-pass filter
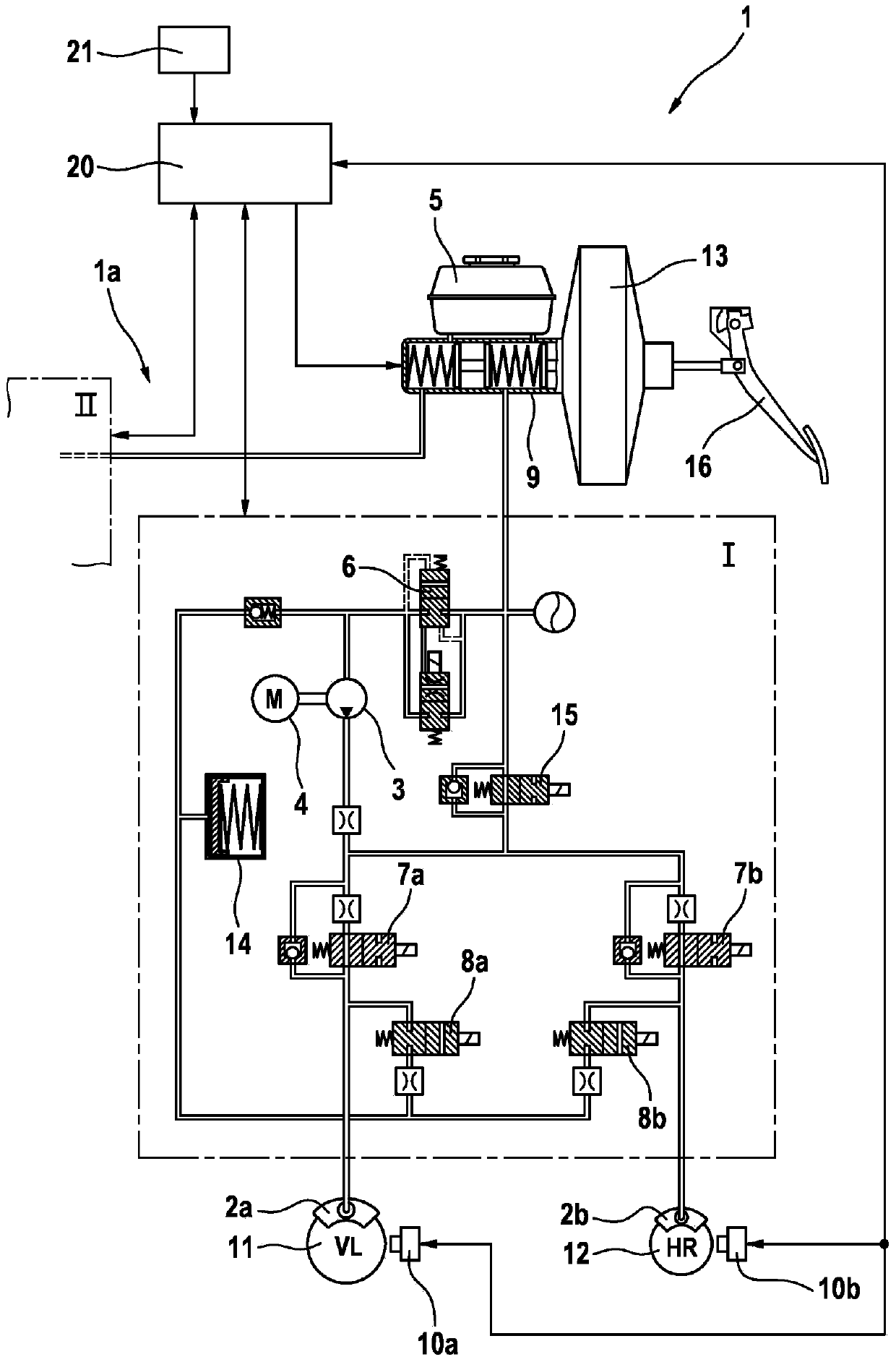
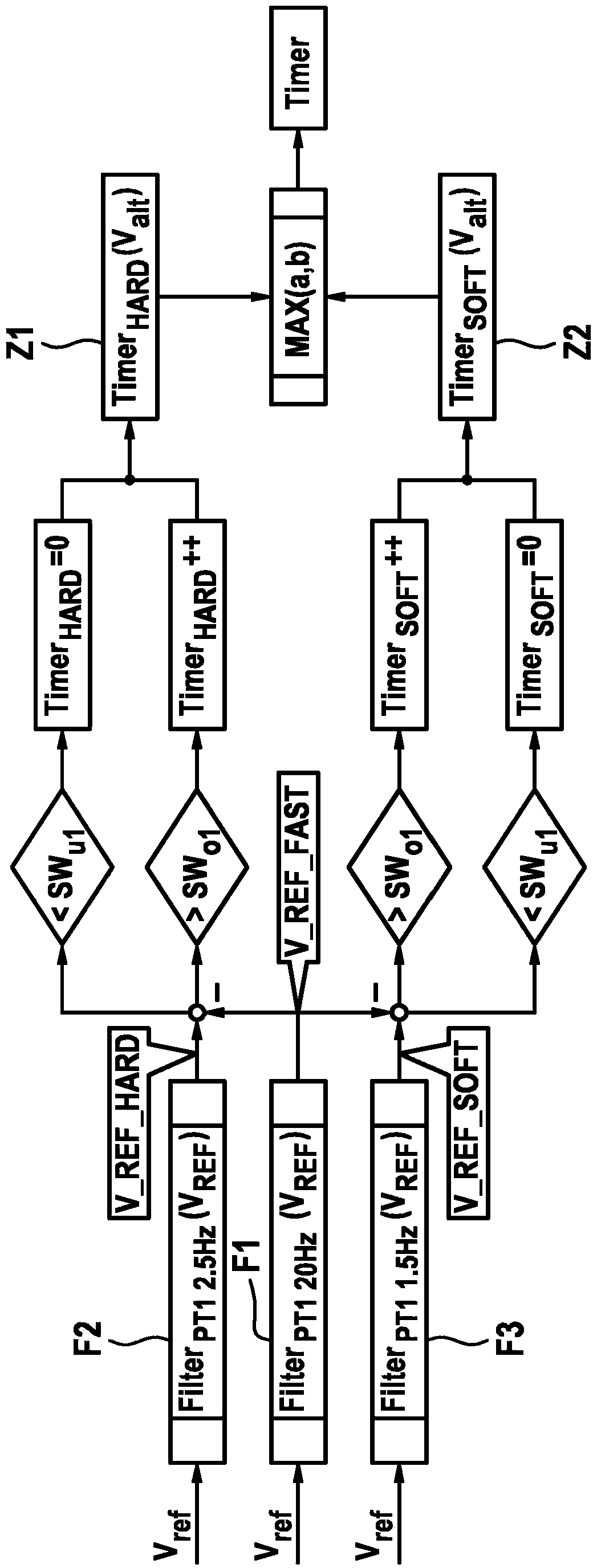
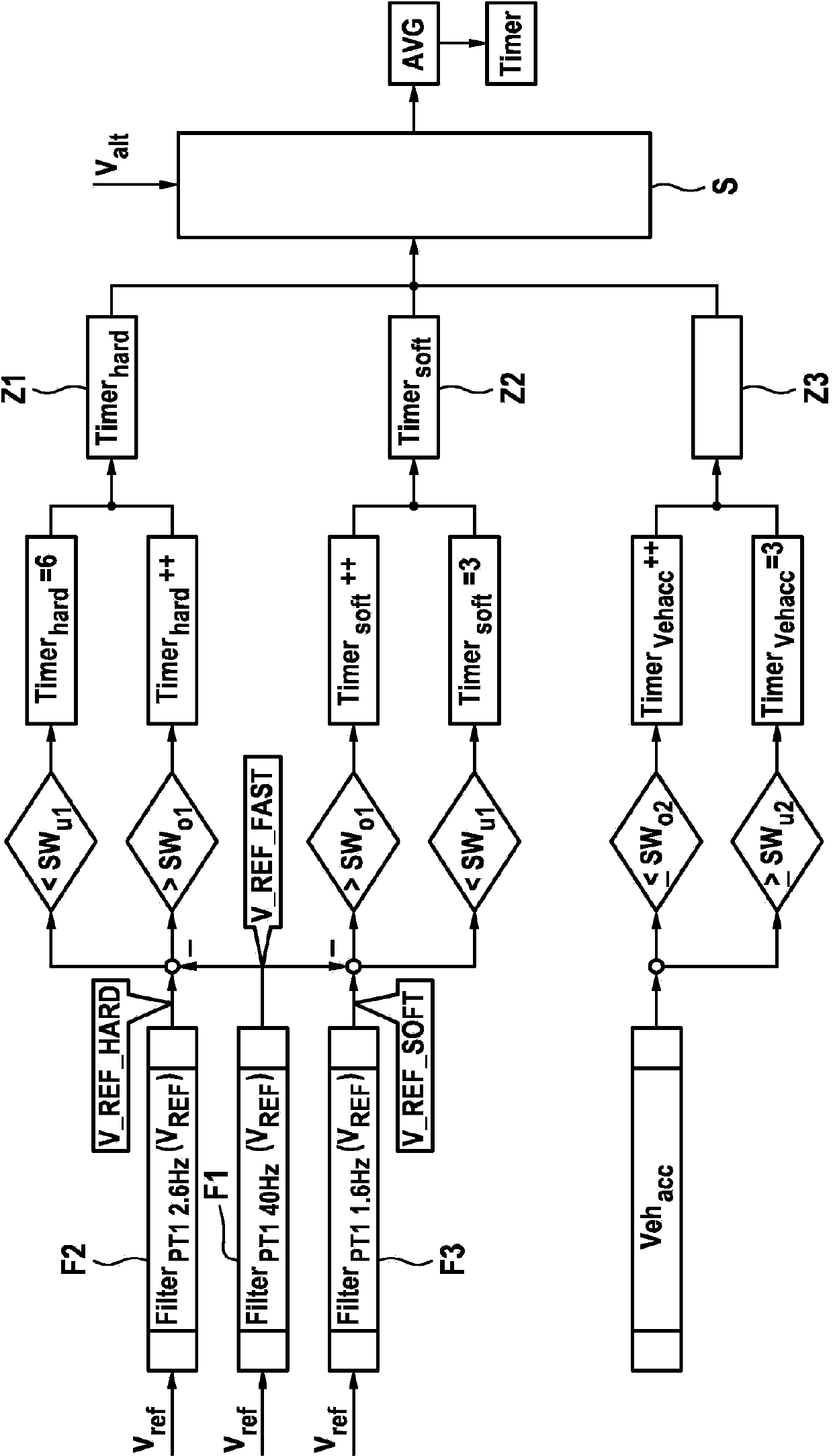
The invention relates to a method for determining a model upstream pressure (PTHZ-mod) by means of a mathematical model in an electronically regulated motor vehicle brake system (1), in which method a regulation of an electrically controllable hydraulic brake valve (7a, 7b) effecting a braking pressure buildup on at least one wheel brake (2a, 2b) is performed using the model upstream pressure (PTHZ-mod) as at least one parameter, and wheel sensors (10a, 10b) for determining a vehicle speed signal indicating the vehicle speed, and an operable brake pedal (16) are provided; according to the invention at least one first low-pass filtered speed signal (vref-fast, Vref-hard, Vref-soft) is generated from the vehicle speed signal (Vref) by means of a low-pass filter (F1, F2, F3) with a first limit frequency (fg1, fg2, fg3), from the temporal progression of which filtered signal the time (t1) of a significant decrease of speed is detected, which is used as a starting criterion to determine a period of time (timer) beginning with a vehicle deceleration initiated by a braking process and ending at the time (t2) when regulation of the braking process begins, and to classify the actuation speed of the brake pedal (16), the period of time (Timer) is compared to at least one first threshold value (SW1, SW2), and finally a model upstream pressure (PTHZ-mod) is determined by means of the mathematical model on the basis of the comparison result.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com