Patents
Literature
192 results about "Access register" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
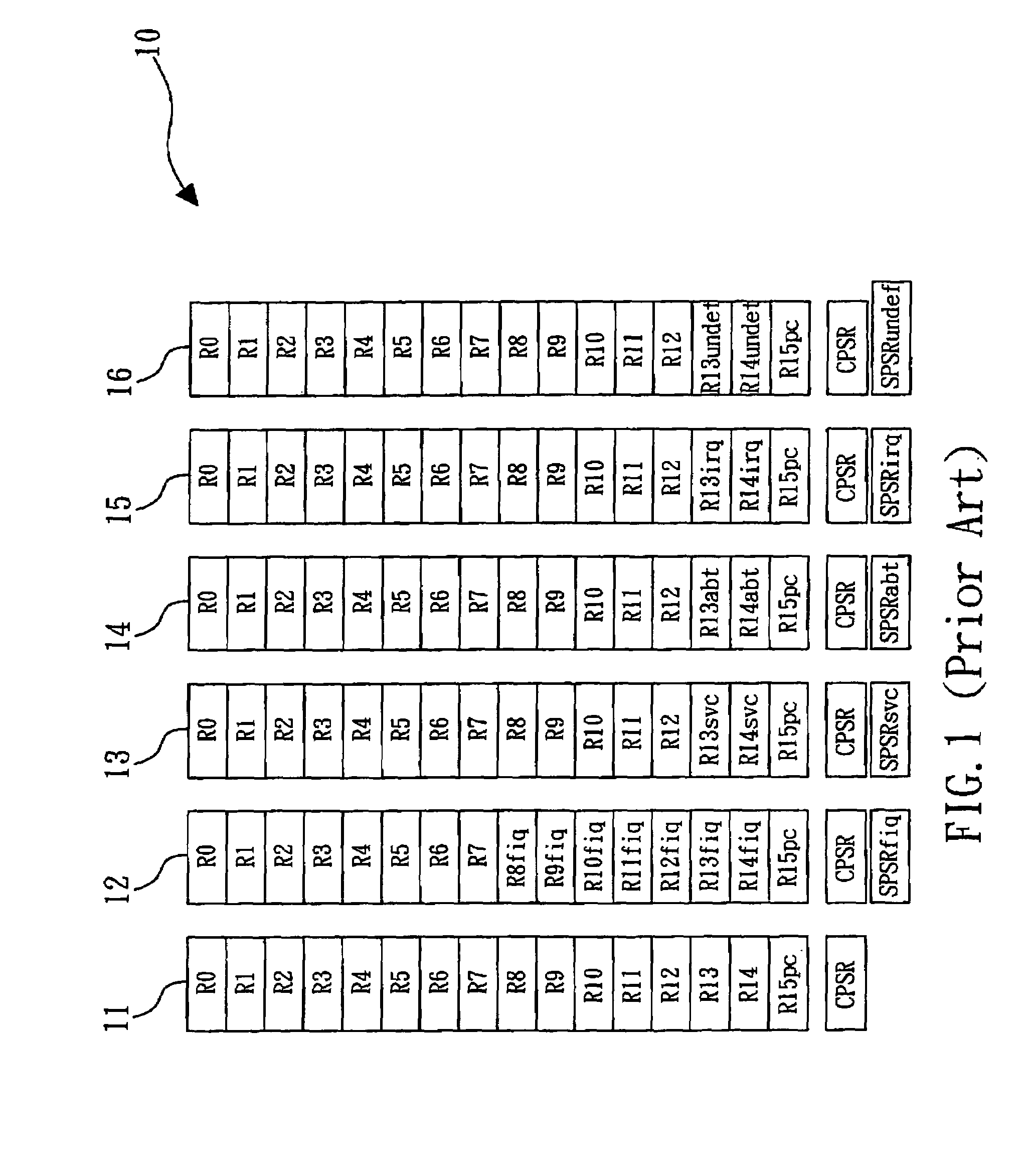
In IBM terminology, Access Registers are hardware registers in the processor. They work in conjunction with the general purpose registers, giving the address space access to its data spaces and to other address spaces in order to retrieve data. ARs were introduced with MVS/ESA.
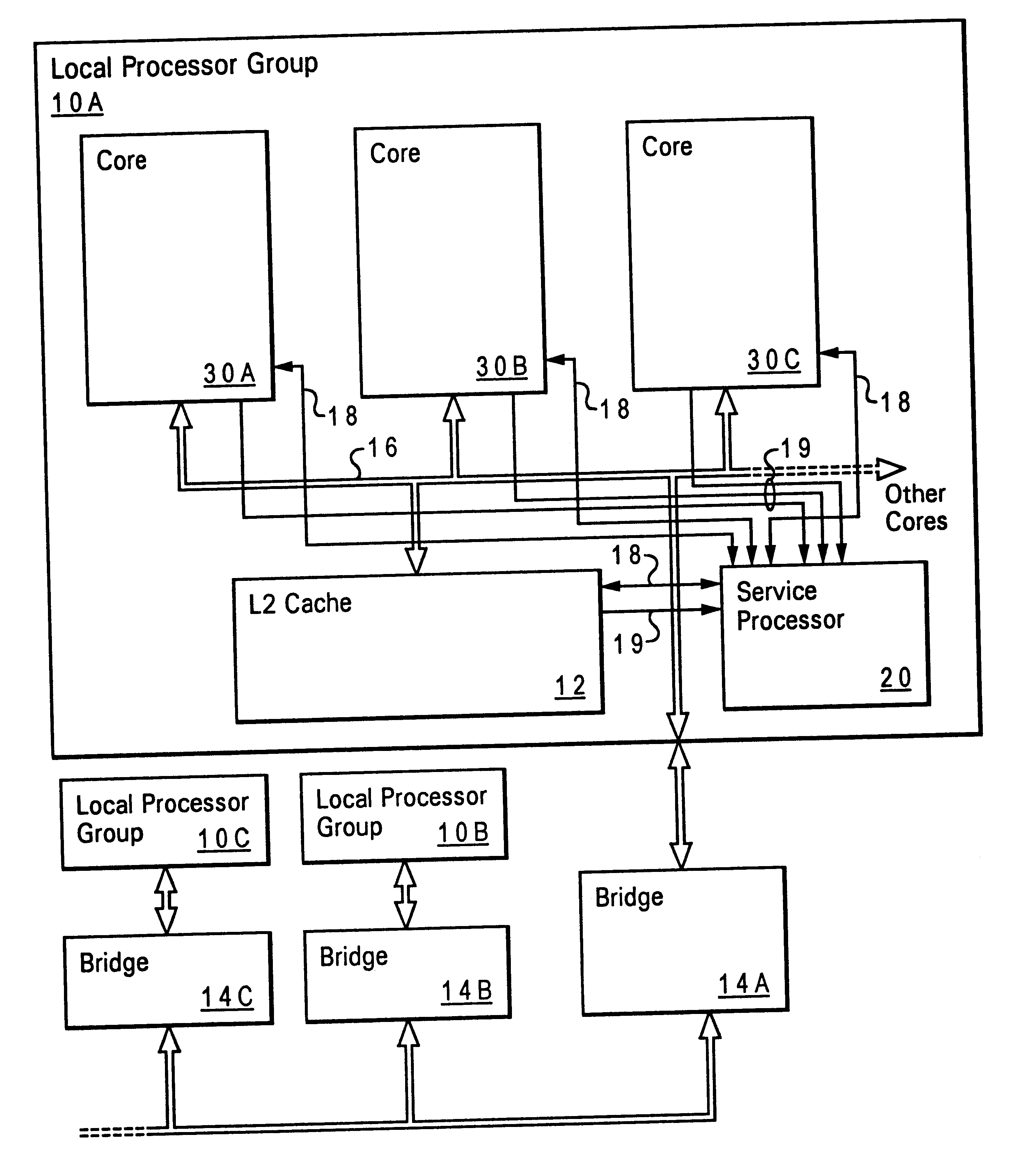
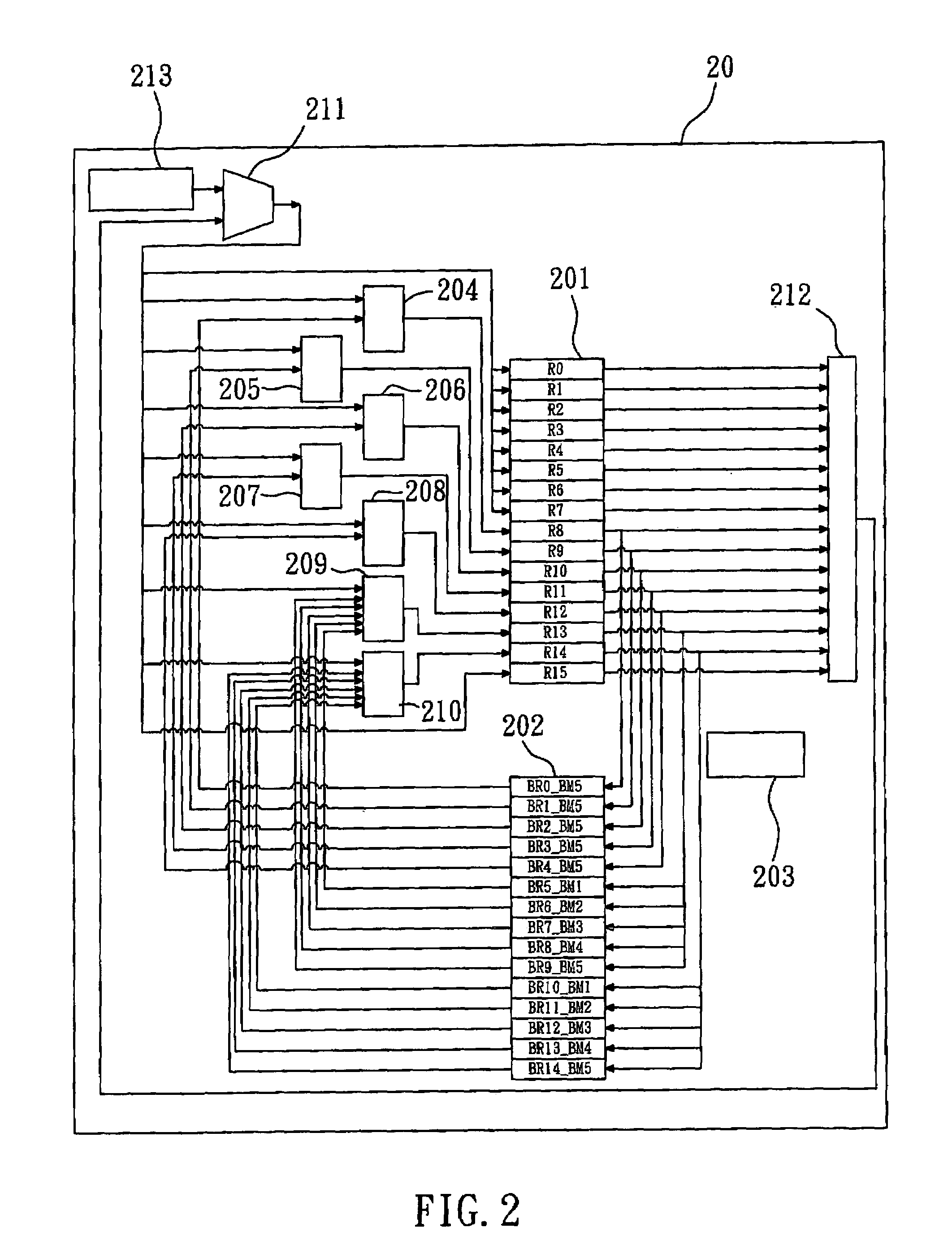
FPGA with register-intensive architecture
ActiveUS7028281B1Minimize resourceReduce consumptionSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designProcessor registerMultiplexer
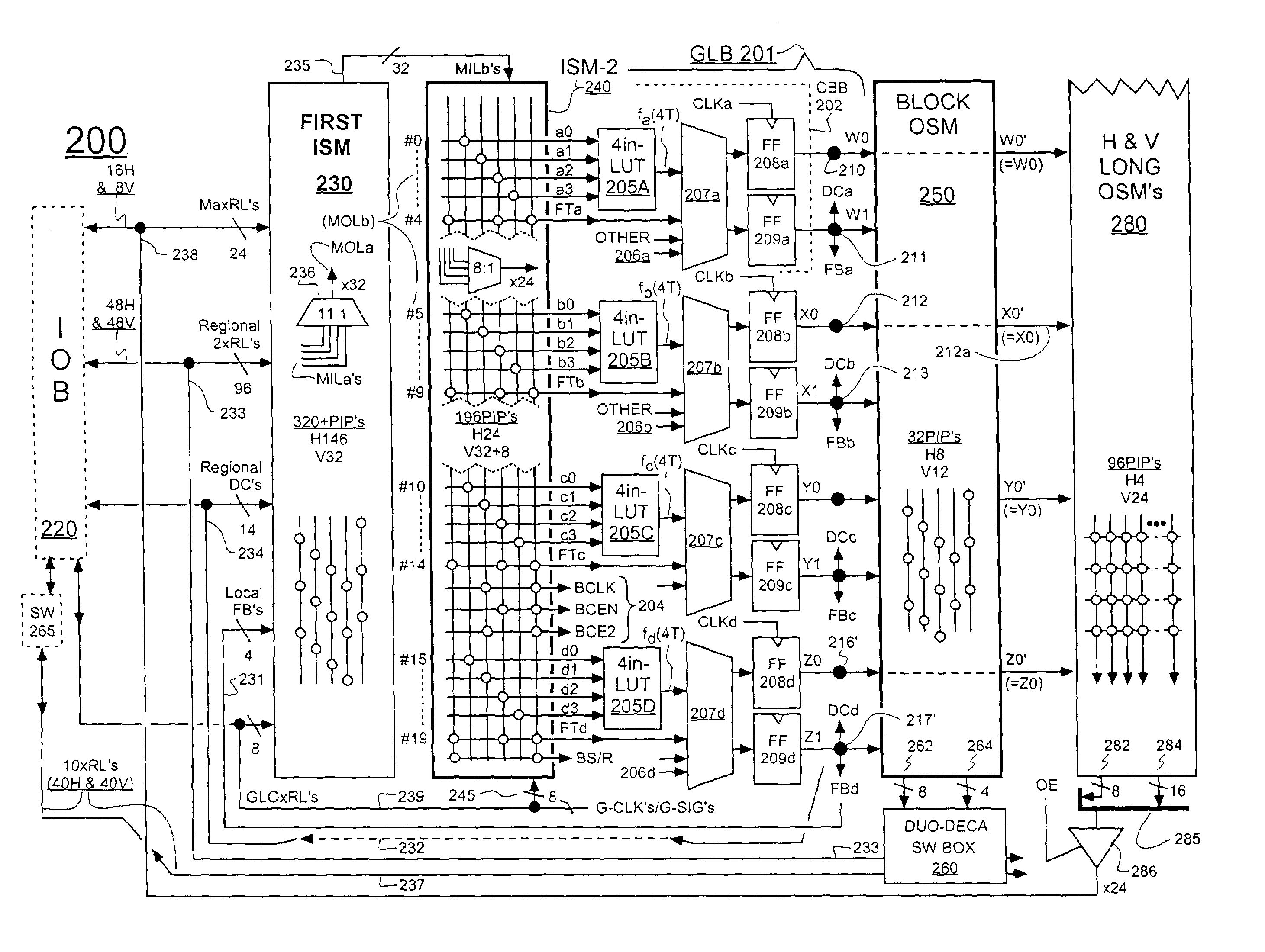
Field programmable gate arrays (FPGA's) may be structured in accordance with the disclosure to have a register-intensive architecture that provides, for each of plural function-spawning LookUp Tables (e.g. a 4-input, base LUT's) within a logic block, a plurality of in-block accessible registers. A register-feeding multiplexer means may be provided for allowing each of the plural registers to equivalently capture and store a result signal output by the corresponding, base LUT of the plural registers. Registerable, primary and secondary feedthroughs may be provided for each base LUT so that locally-acquired input signals of the LUT may be fed-through to the corresponding, in-block registers for register-recovery purposes without fully consuming (wasting) the lookup resources of the associated, base LUT. A multi-stage, input switch matrix (ISM) may be further provided for acquiring and routing input signals from adjacent, block-interconnect lines (AIL's) and / or block-intra-connect lines (e.g., FB's) to the base LUT's and / or their respective, registerable feedthroughs. Techniques are disclosed for utilizing the many in-block registers and / or the registerable feedthroughs and / or the multi-stage ISM's for efficiently implementing various circuit designs by appropriately configuring such register-intensive FPGA's.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
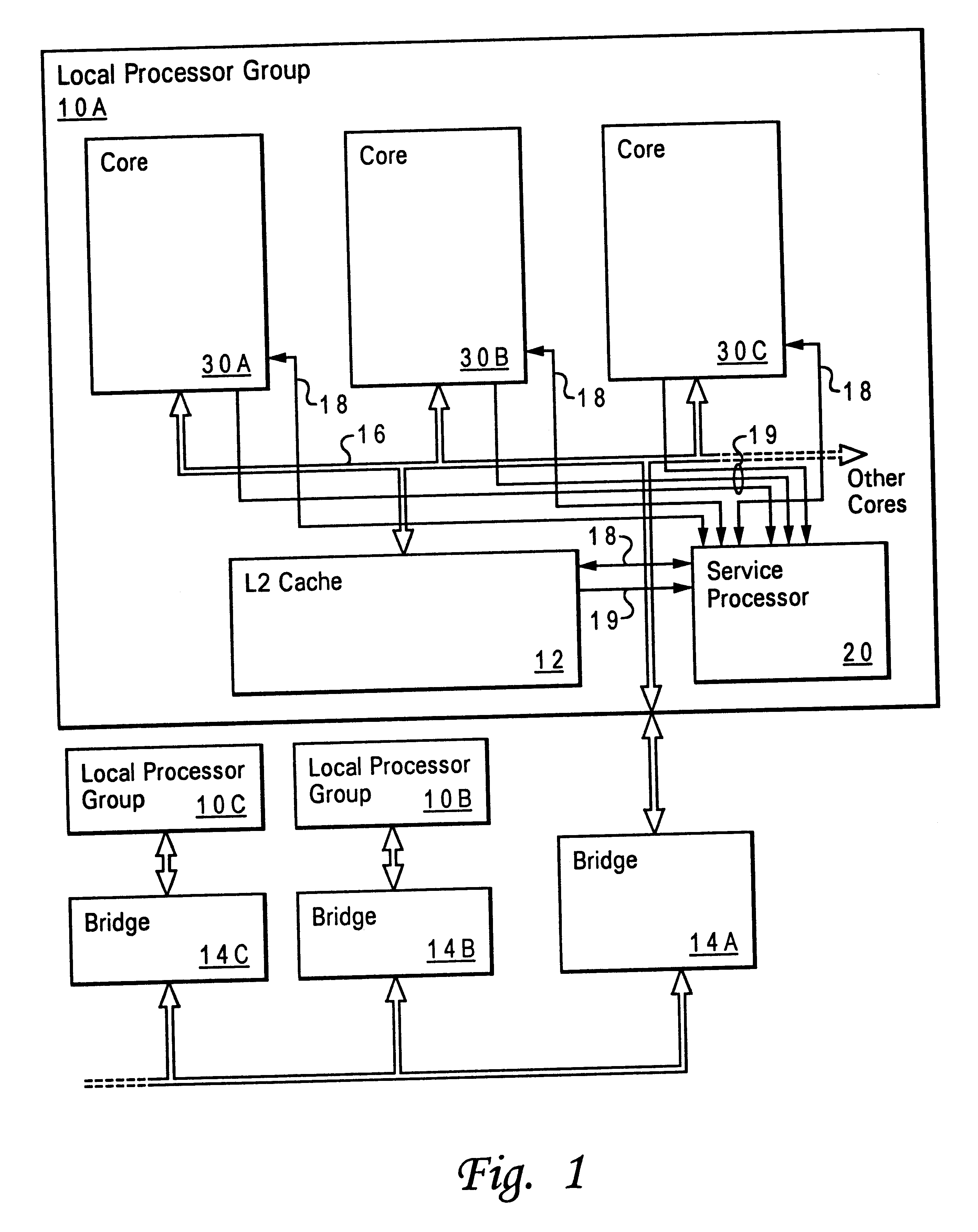
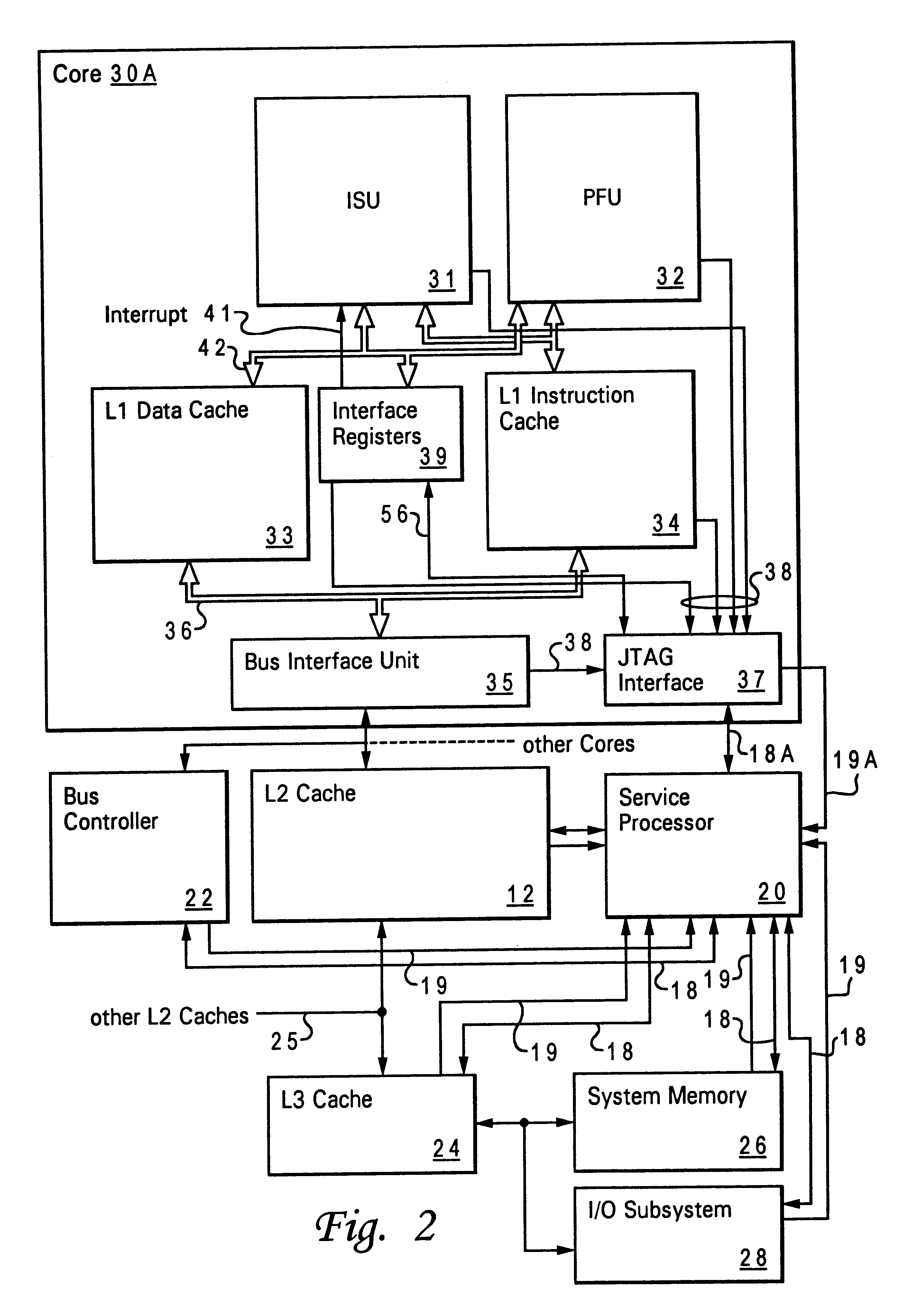
Method and apparatus for servicing a processing system through a test port
InactiveUS6629268B1Error detection/correctionMemory systemsProcessor registerJoint Test Action Group
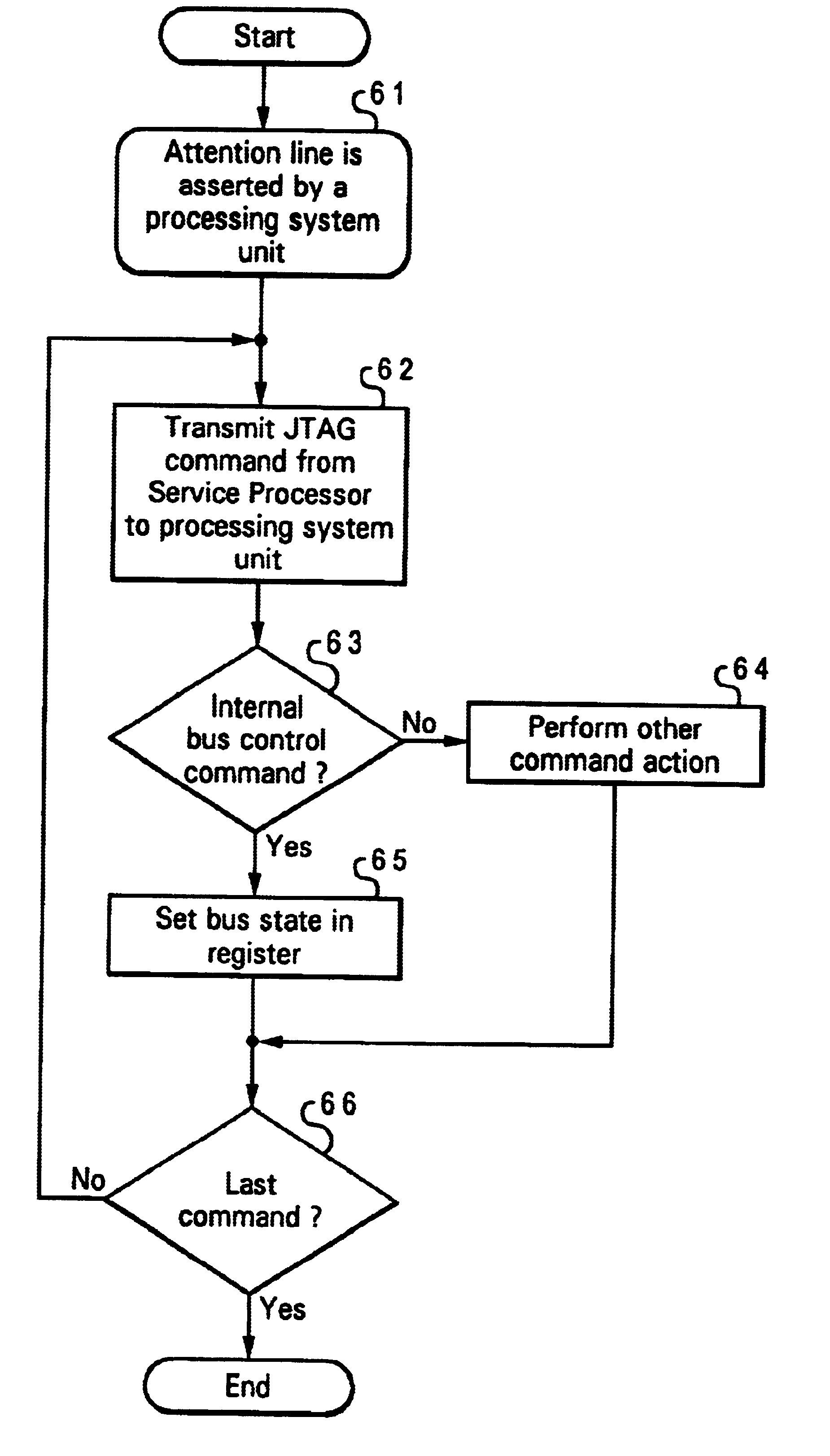
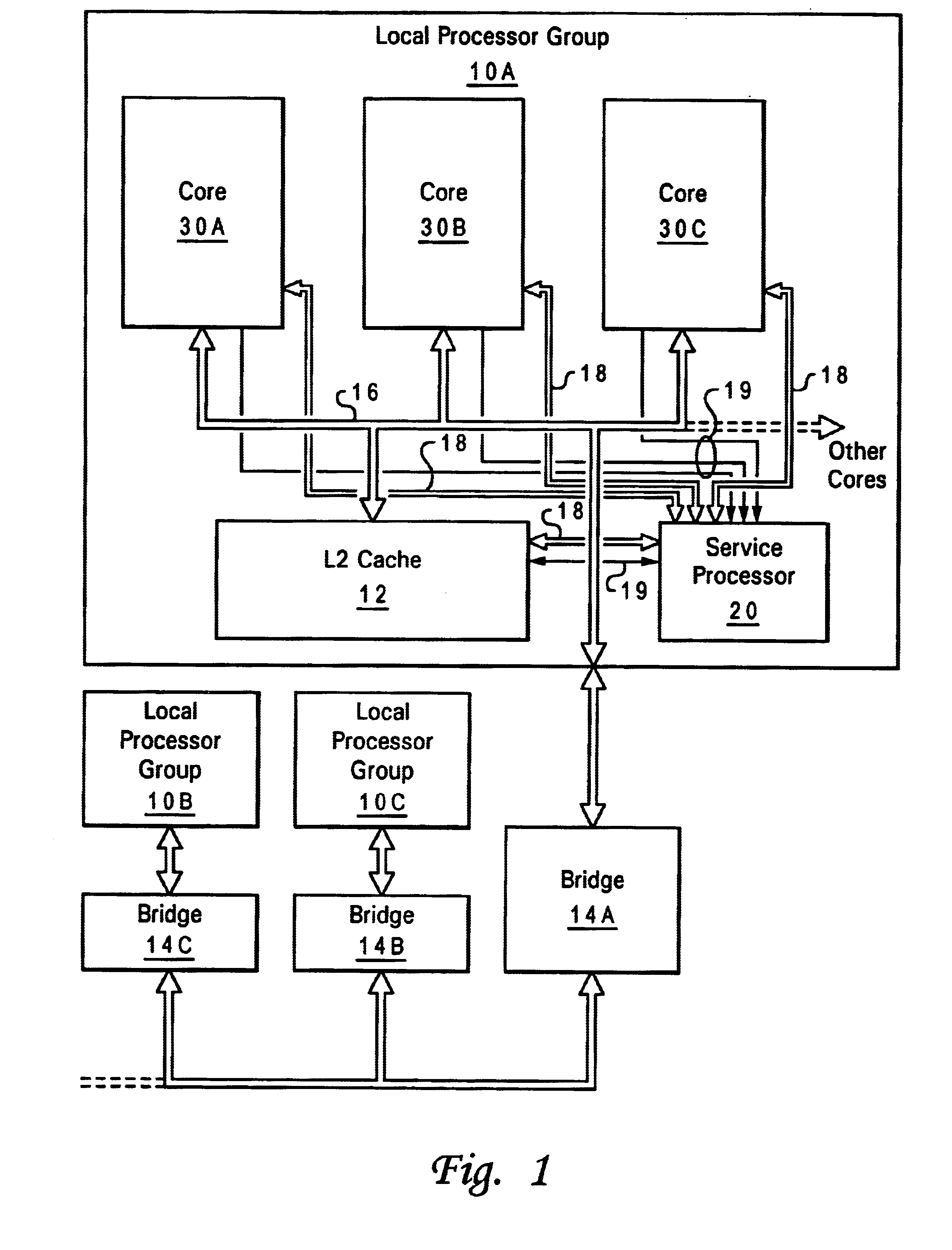
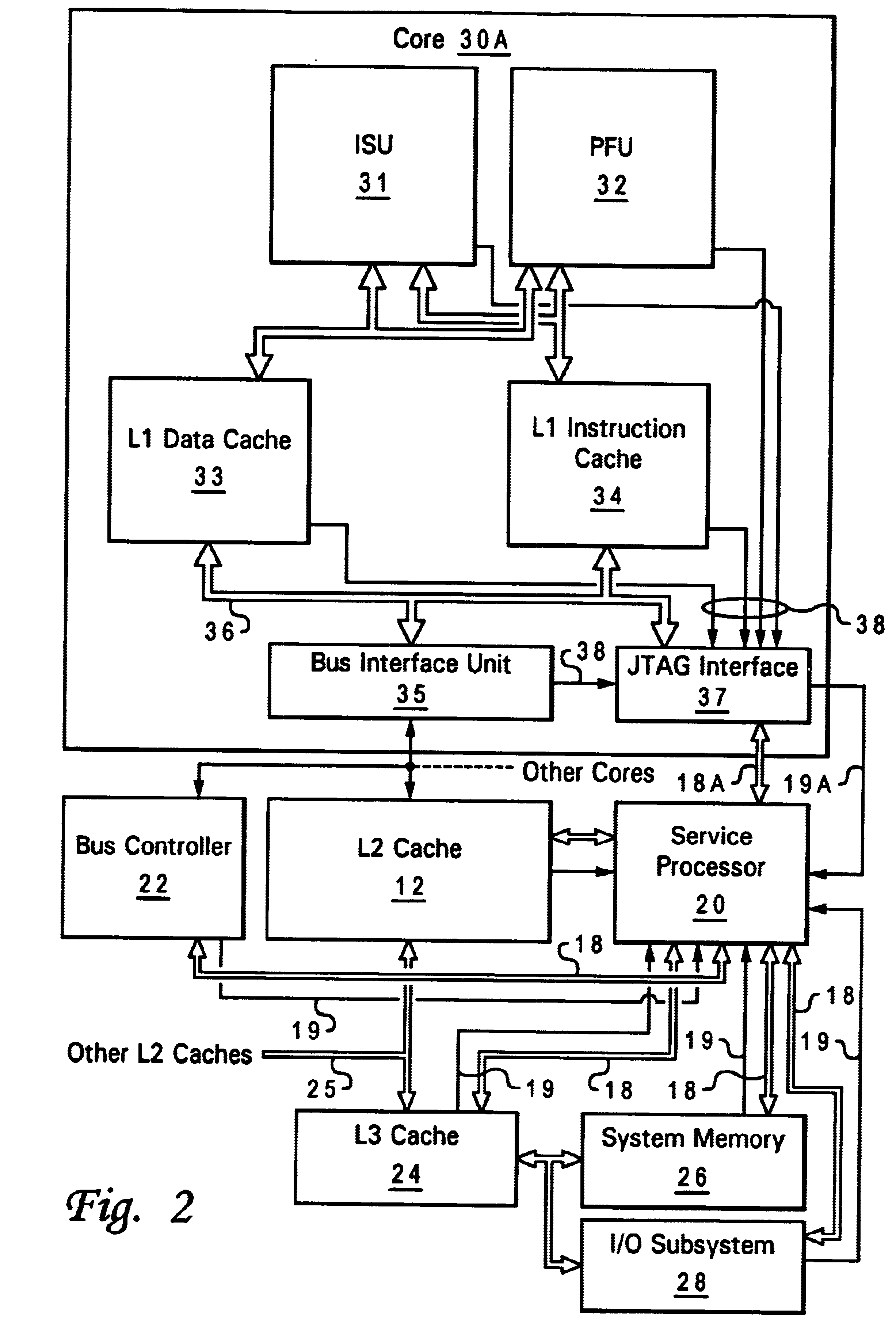
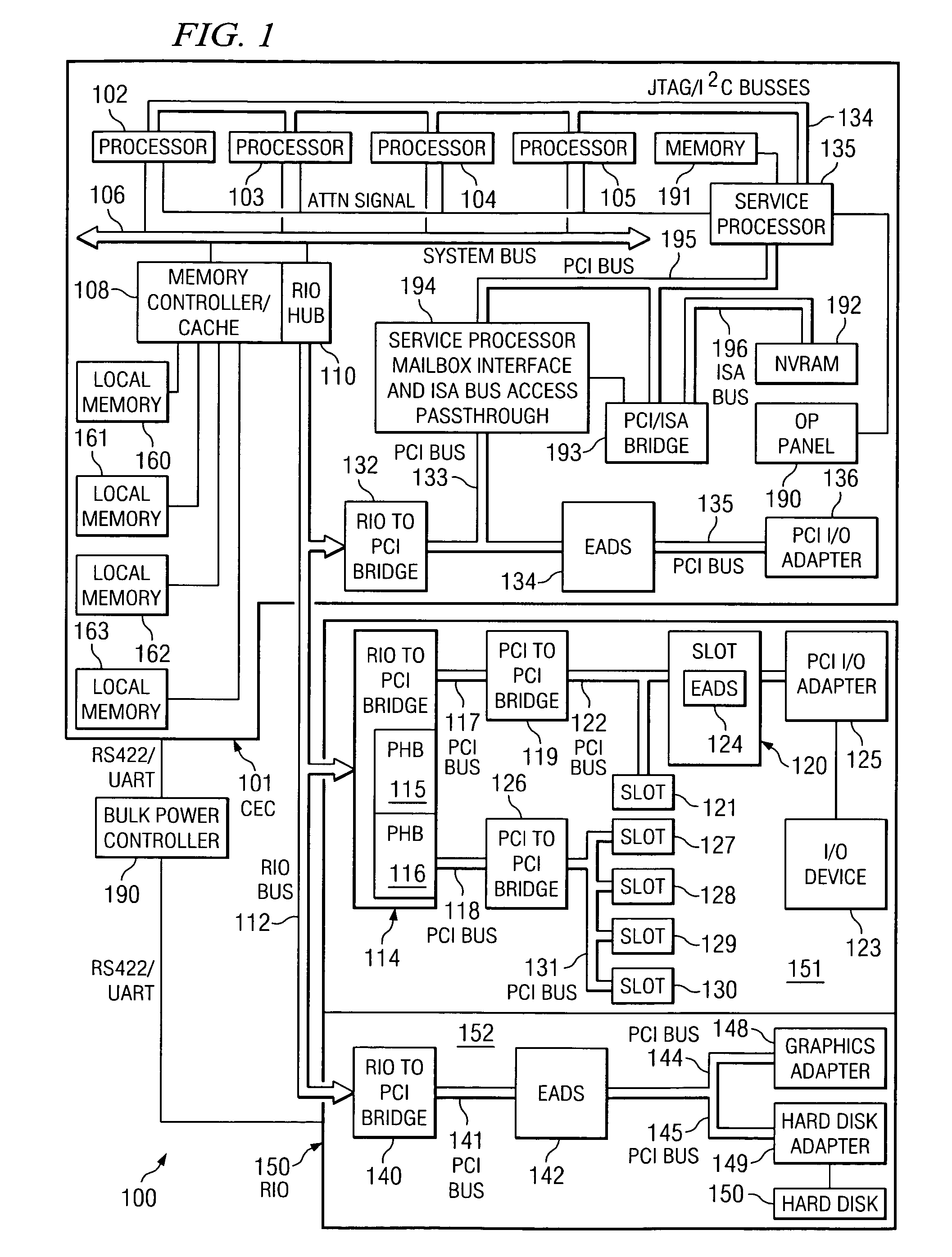
A method and apparatus for servicing a processing system through a test port allow initialization and fault recovery capability including the ability to coherently access cache memory while the processing system is operating. A JTAG standard interface is used to access registers in a main processing component and has the additional capability to generate internal bus transactions to access registers, cache and memory both within the main processor, and externally by causing a bus interface in the main processor to generate external bus transactions. The service processor can coherently access cache by this mechanism, allowing fault tolerant recovery from operations in which the cache must be coherently flushed in order to maintain proper system operation.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Techniques for hardware-assisted multi-threaded processing
ActiveUS20070294694A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsThread schedulingProcessor register
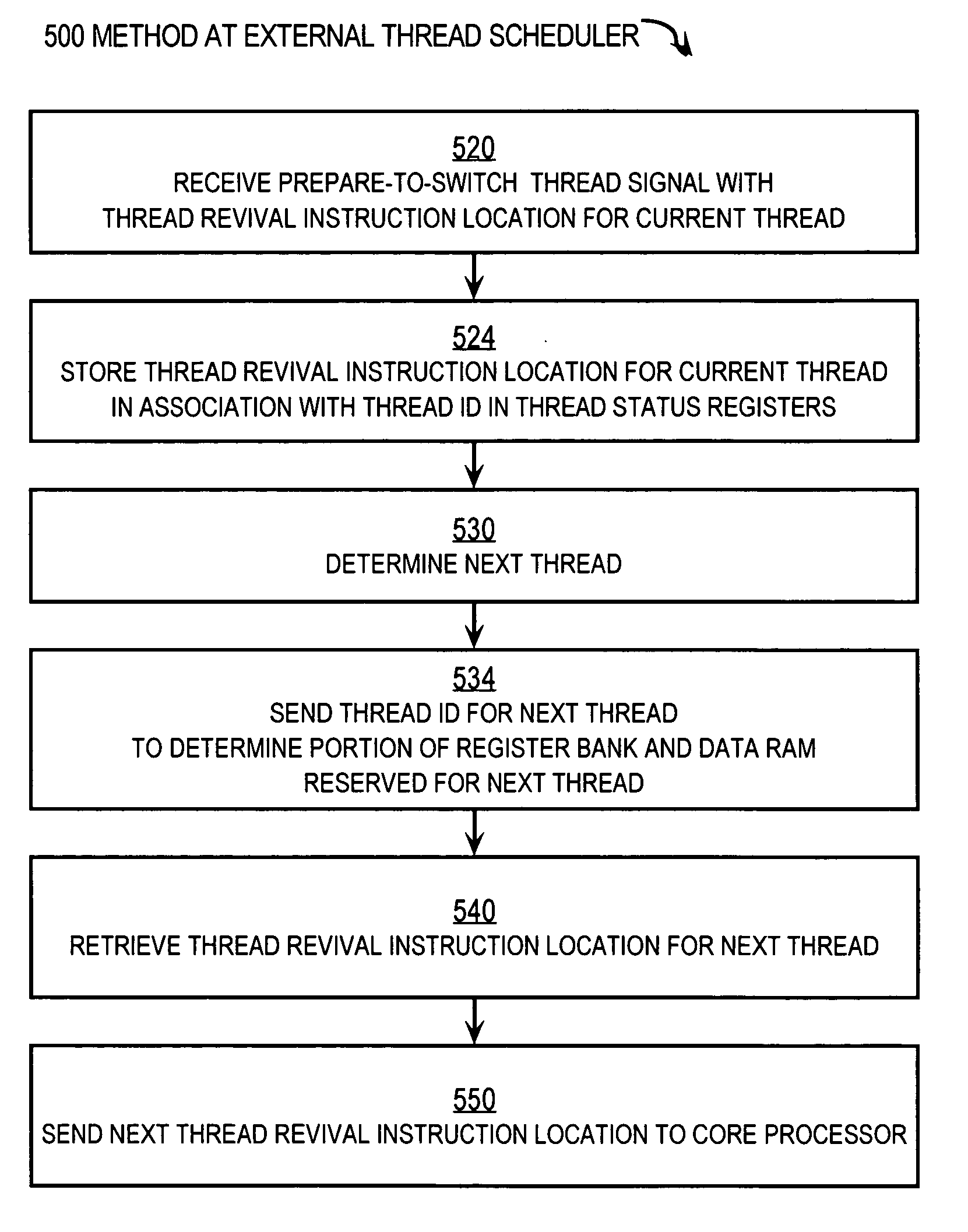
Techniques for processing each of multiple threads that share a core processor include receiving an intra-thread register address from the core processor. This address contains C bits for accessing each of 2c registers for each thread. A thread ID is received from a thread scheduler external to the core processor. The Thread ID contains T bits for indicating a particular thread for up to 2T threads. A particular register is accessed in a register bank that has 2(C+T) registers using an inter-thread address that includes both the intra-thread register address and the thread ID. The particular register holds contents for the intra-thread register address for a thread having the thread ID. Consequently, register contents of all registers of all threads reside in the register bank. Thread switching is accomplished rapidly by simply accessing different slices in the register bank, without swapping contents between a set of registers and memory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
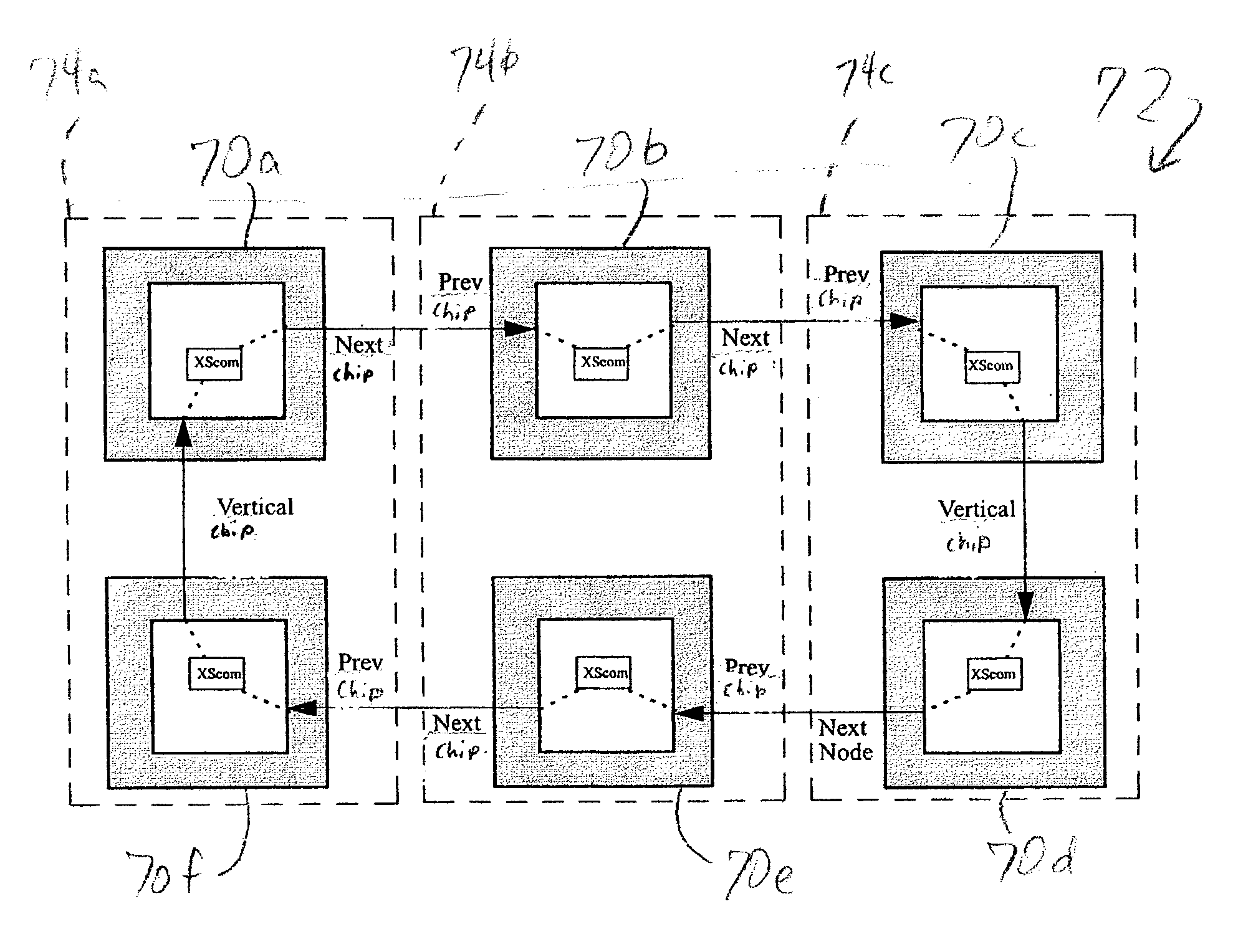
Cross-chip communication mechanism in distributed node topology
InactiveUS20040215929A1Promote disseminationSubstation/switching arrangement detailsElectric digital data processingTransmission protocolMain processing unit
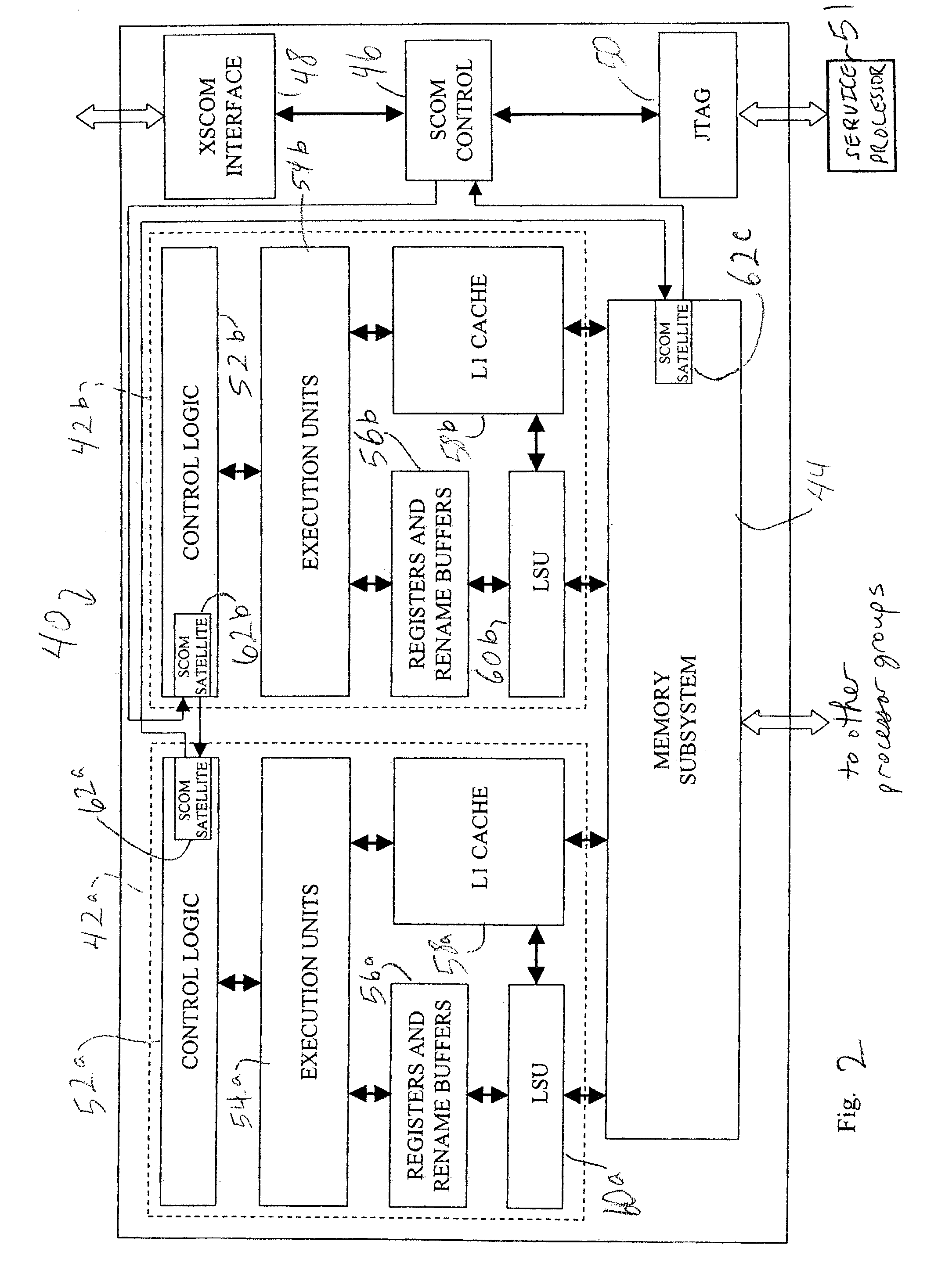
A method of communicating between processing units on different integrated circuit chips in a multi-processor computer system by issuing a command from a source processing unit to a destination processing unit, receiving the command at the destination processing unit while the destination processing unit is processing program instructions, and accessing registers in clock-controlled components of the destination processing unit without interrupting processing of the program instructions by the destination processing unit. The access may be a read from status or mode registers of the destination processing unit, or write to control or mode registers. Many processing units can be interconnected in a ring topology, and the access command can be passed from the source processing unit through several other processing units before reaching the destination processing unit. Each of the processing units is assigned a respective, unique identification number (PID) in addition to one or more optional "special" tags which are not necessarily unique, and an external command (XSCOM) interface on a given chip recognizes only those commands that include the corresponding chip tag, unless the command is a broadcast. Commands may be directed to subgroups of processors by implementing masks against the PID, selected portion of the PID, or other "special" tag in a broadcast fashion. The XSCOM interface also has the ability to block any broadcast command (e.g., reset) to itself when that command was issued by its associated processing unit (a "Block Self" mode). The processing units are interconnected via a fabric bus, and the XSCOM interface preferably uses an additional communications line that follows the topology of the fabric bus or could alternately use command / data packets across the existing fabric transmission protocol. The service processor has access to this command interface through an external port (e.g. JTAG) and assembly code running on the processing unit has access to the command interface via special assembly code sequences.
Owner:IBM CORP
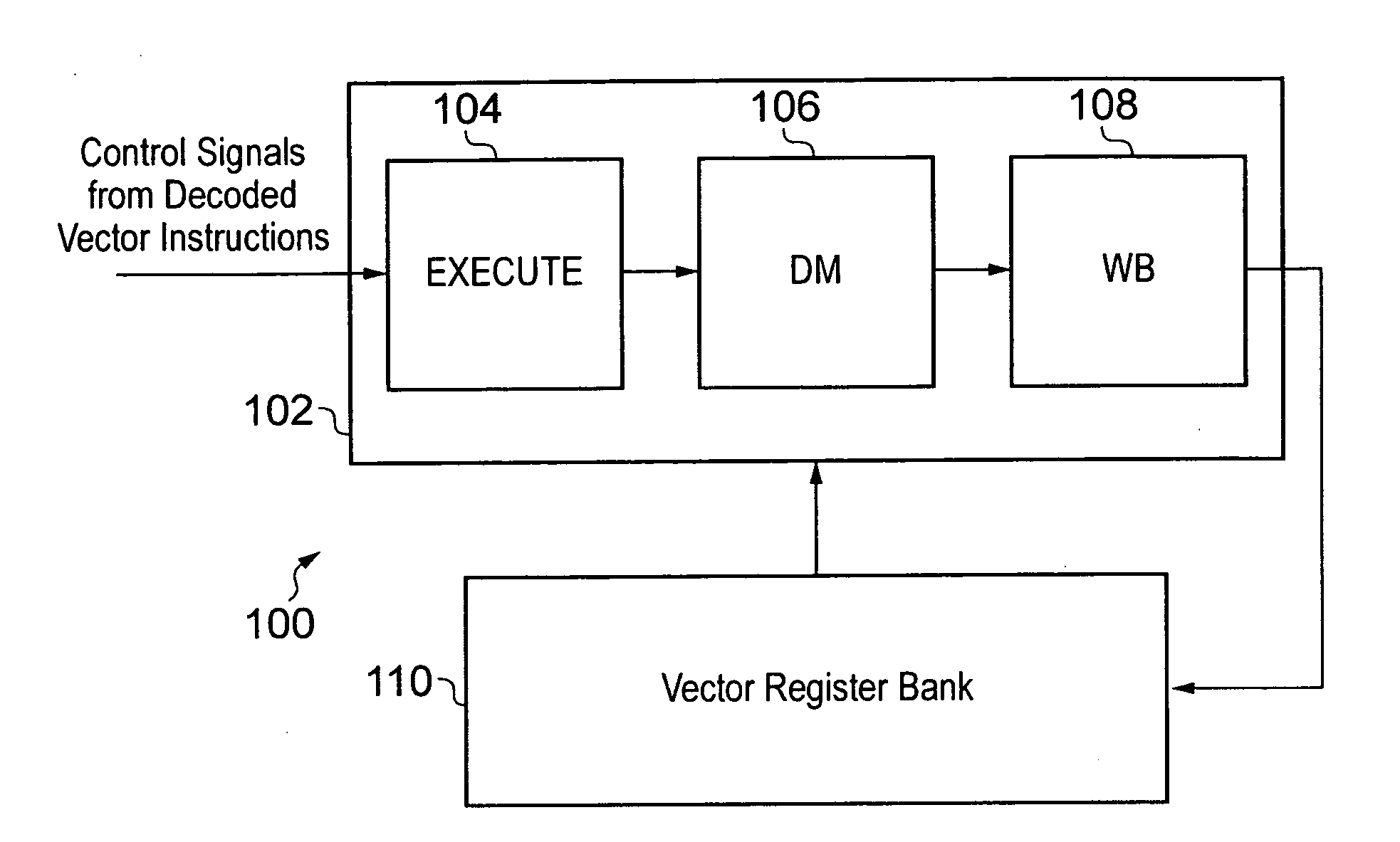
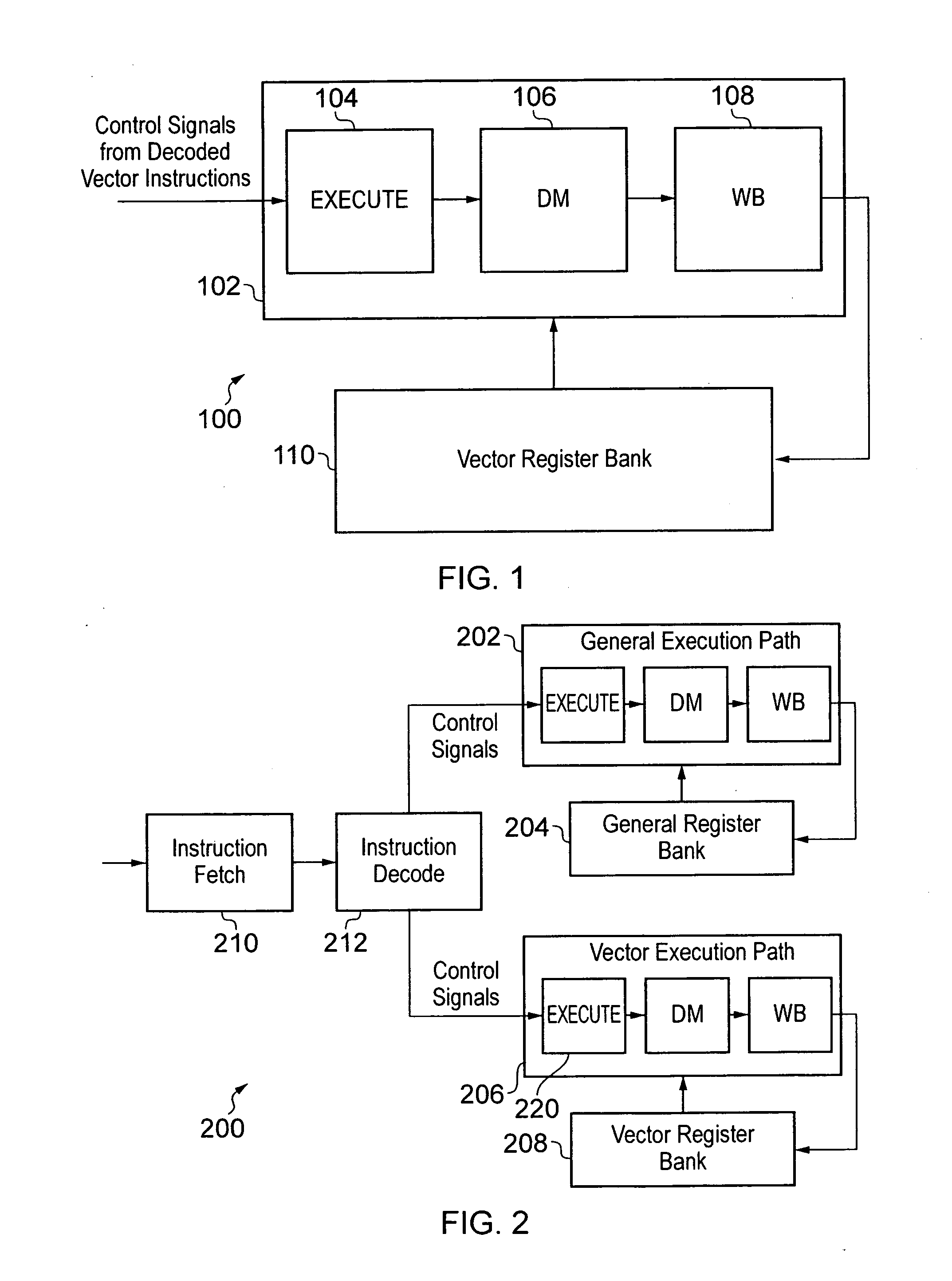
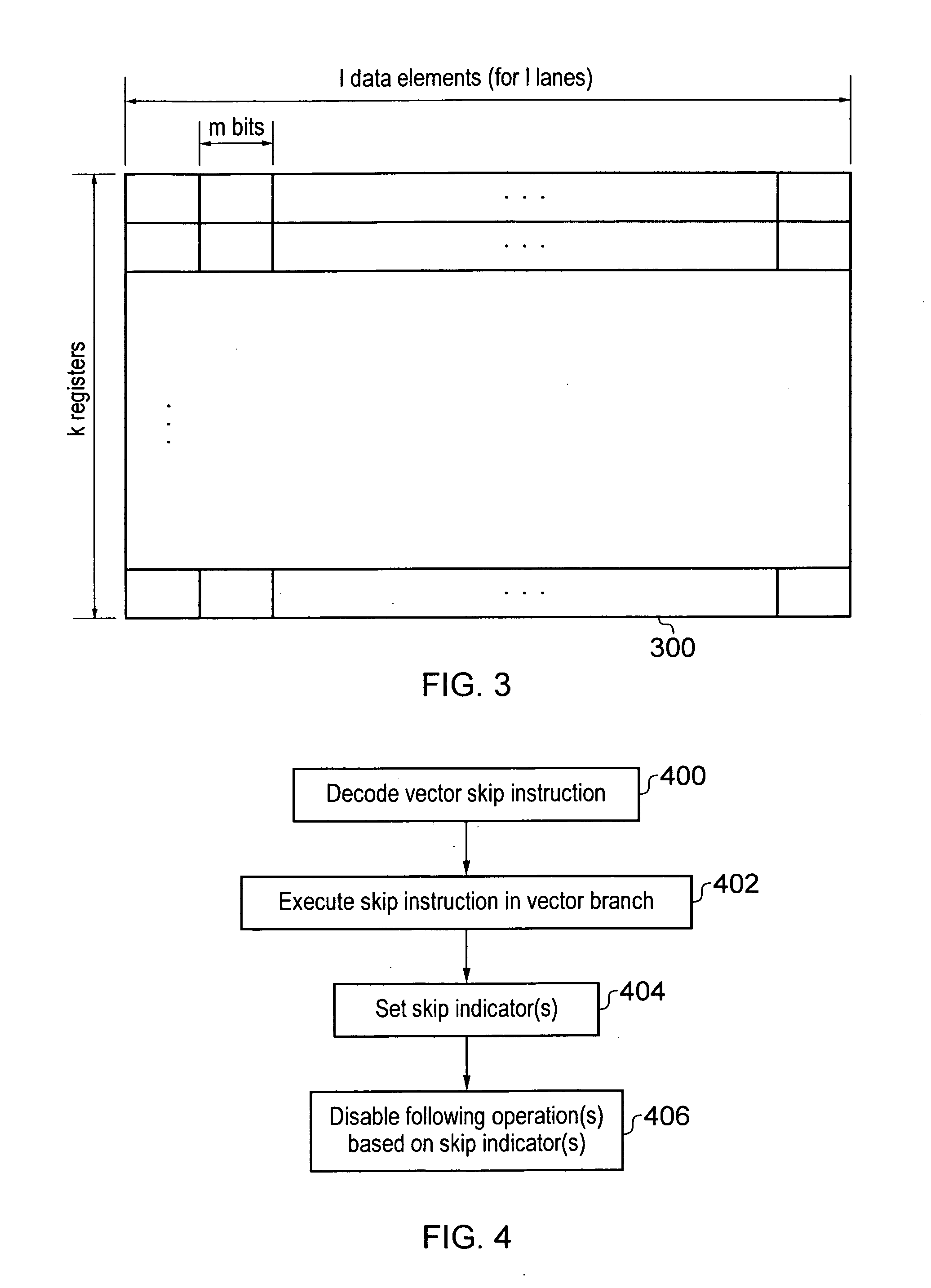
Data processing apparatus and method for handling vector instructions
ActiveUS20100312988A1Complex nestingIncrease profitGeneral purpose stored program computerProgram controlProcessor registerData element
A data processing apparatus and method and provided for handling vector instructions. The data processing apparatus has a register data store with a plurality of registers arranged to store data elements. A vector processing unit is then used to execute a sequence of vector instructions, with the vector processing unit having a plurality of lanes of parallel processing and having access to the register data store in order to read data elements from, and write data elements to, the register data store during the execution of the sequence of vector instructions. A skip indication storage maintains a skip indicator for each of the lanes of parallel processing. The vector processing unit is responsive to a vector skip instruction to perform an update operation to set within the skip indication storage the skip indicator for a determined one or more lanes. The vector processing unit is responsive to a vector operation instruction to perform an operation in parallel on data elements input to the plurality of lanes of parallel processing, but to exclude from the performance of the operation any lane whose associated skip indicator is set. This allows the operation specified by vector instructions to be performed conditionally within each of the lanes of parallel processing without any modification to the vector instructions that are specifying those operations.
Owner:ARM LTD
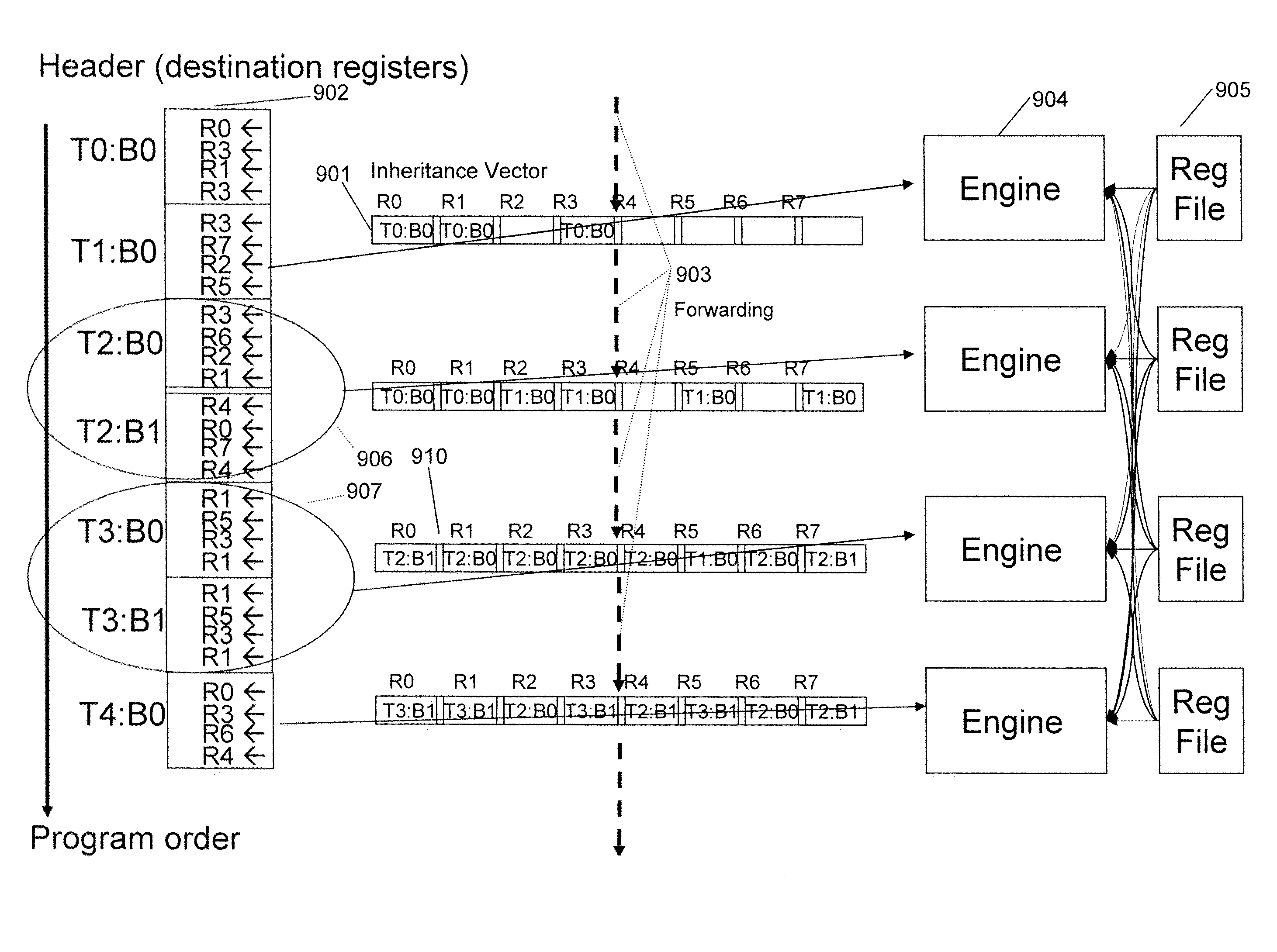
Parallel processing of a sequential program using hardware generated threads and their instruction groups executing on plural execution units and accessing register file segments using dependency inheritance vectors across multiple engines
ActiveUS8677105B2Efficient switchingInstruction analysisDigital computer detailsProcessor registerExecution unit
A unified architecture for dynamic generation, execution, synchronization and parallelization of complex instructions formats includes a virtual register file, register cache and register file hierarchy. A self-generating and synchronizing dynamic and static threading architecture provides efficient context switching.
Owner:INTEL CORP
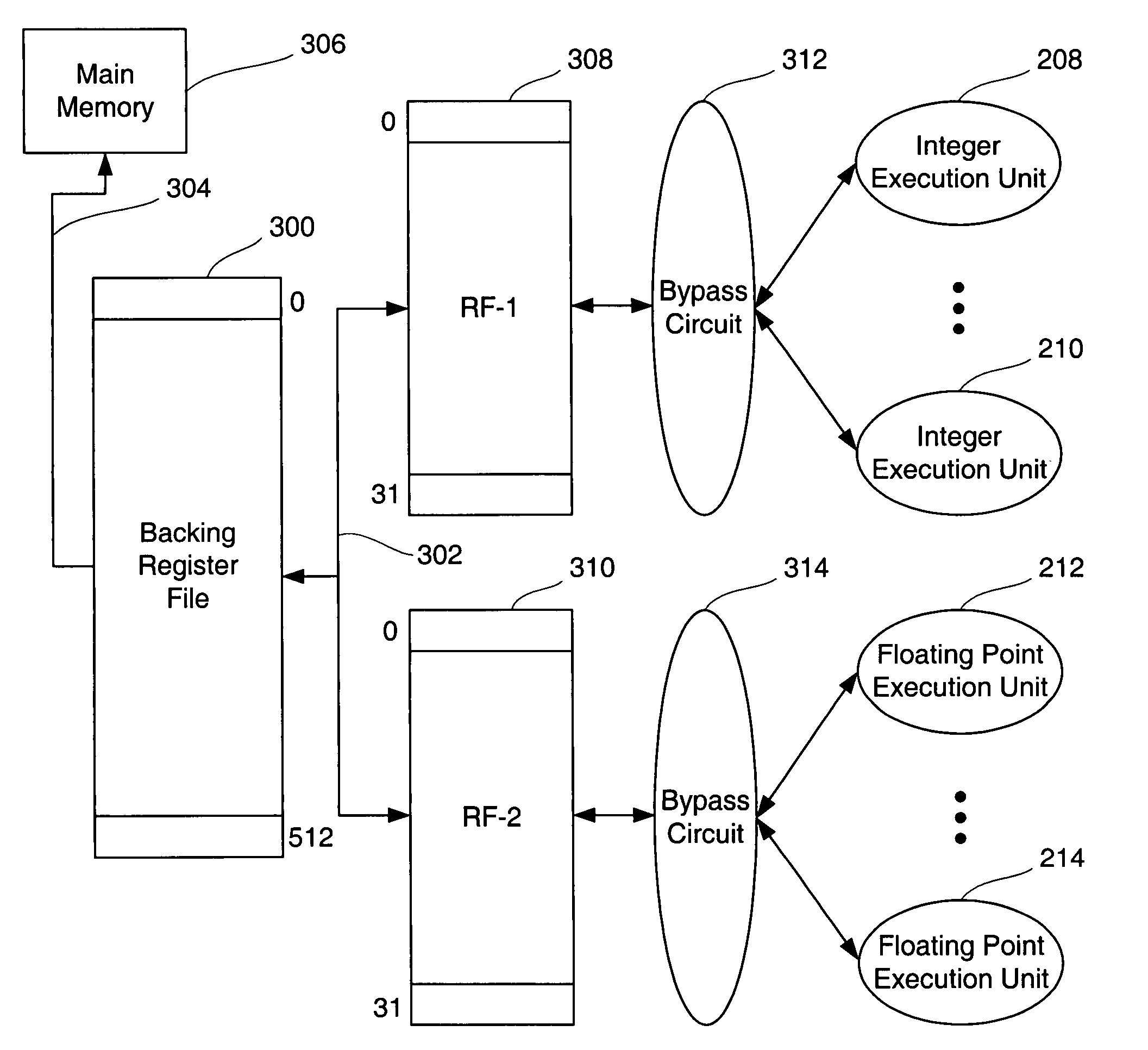
Backing Register File for processors
InactiveUS7206925B1Improve throughputConsiderable timeDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsProcessor registerExecution unit
A processor is defined by a new architectural feature called a Backing Register File, where a Backing Register File is a set of randomly accessible registers capable of holding values, and further are directly connected to the processor's register files. The processor's register files are in turn connected to the processor's execution units. A Backing Register File is visible and controllable by users, allowing them to make use of a larger local address space increasing execution unit throughput thereby, while not changing the size of the processor's register files themselves.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
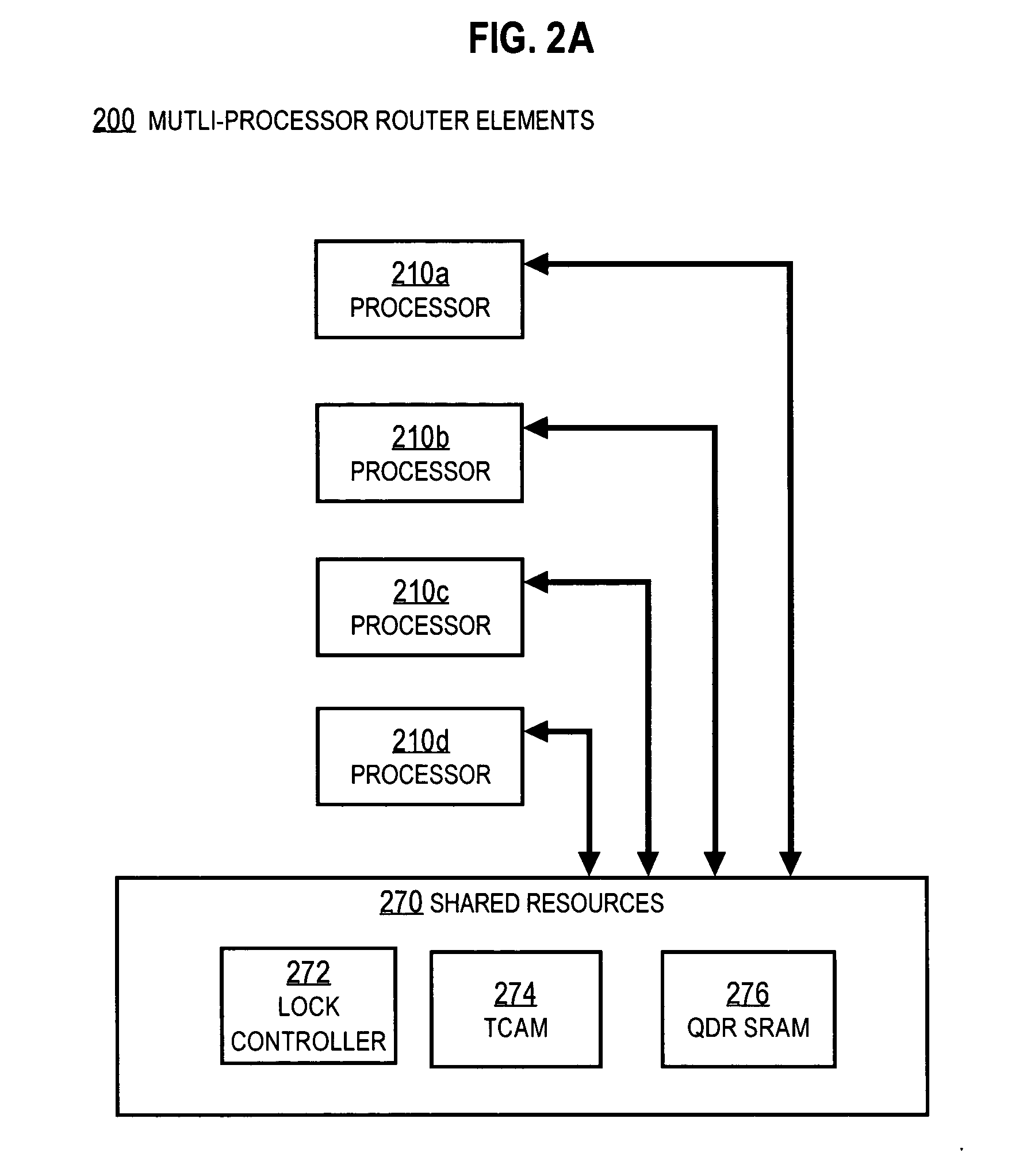
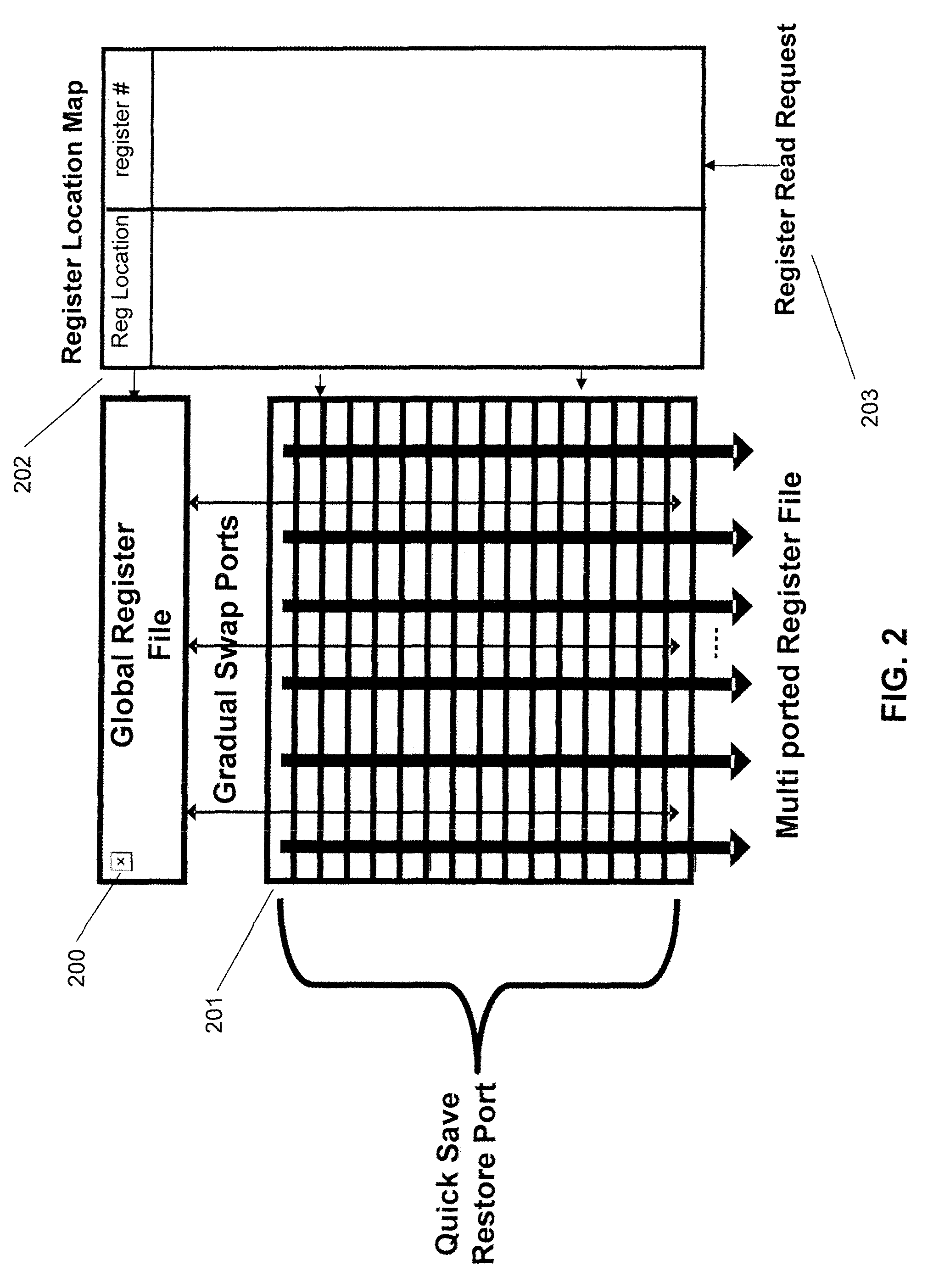
System for negotiating access to a shared resource by arbitration logic in a shared resource negotiator
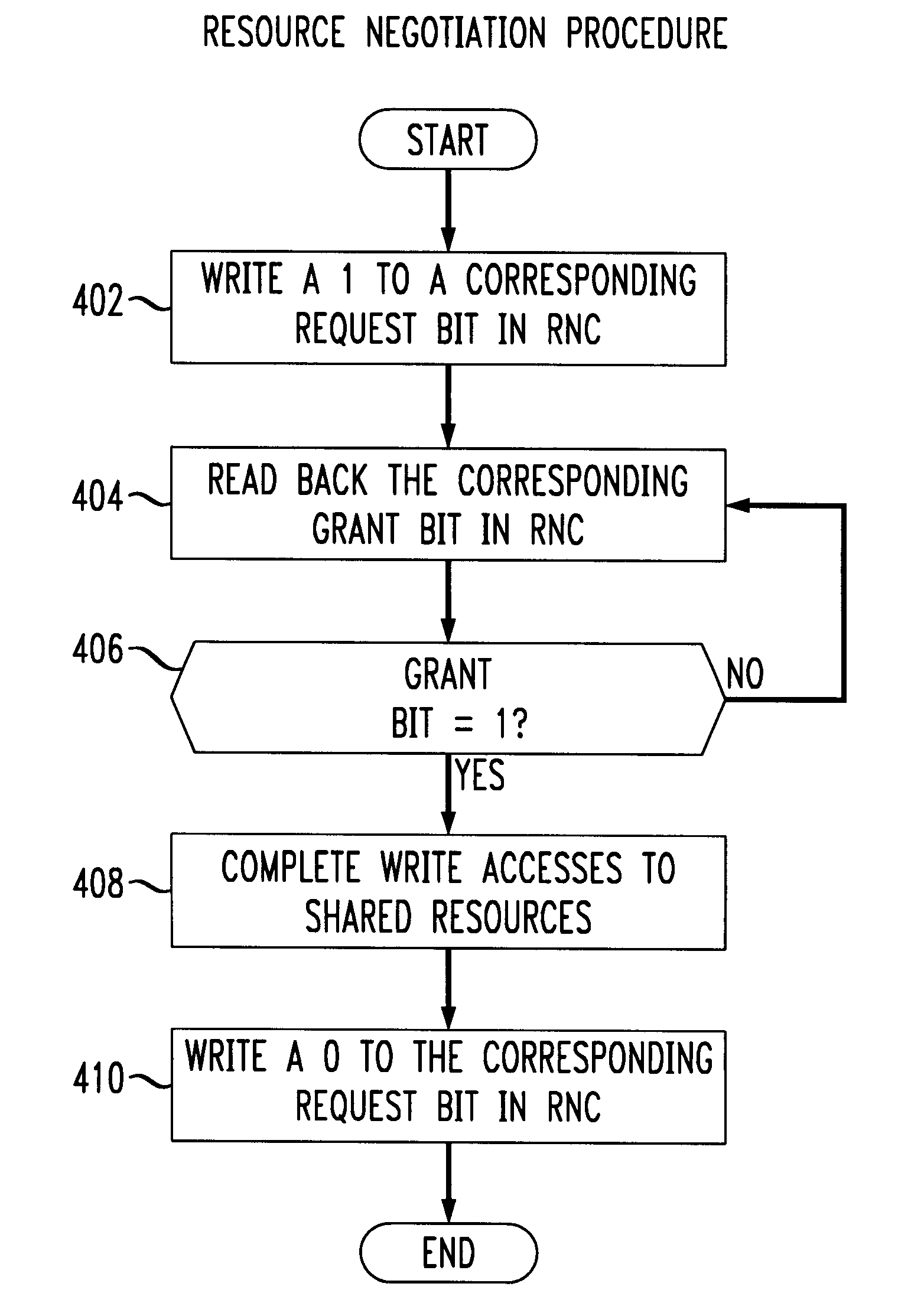
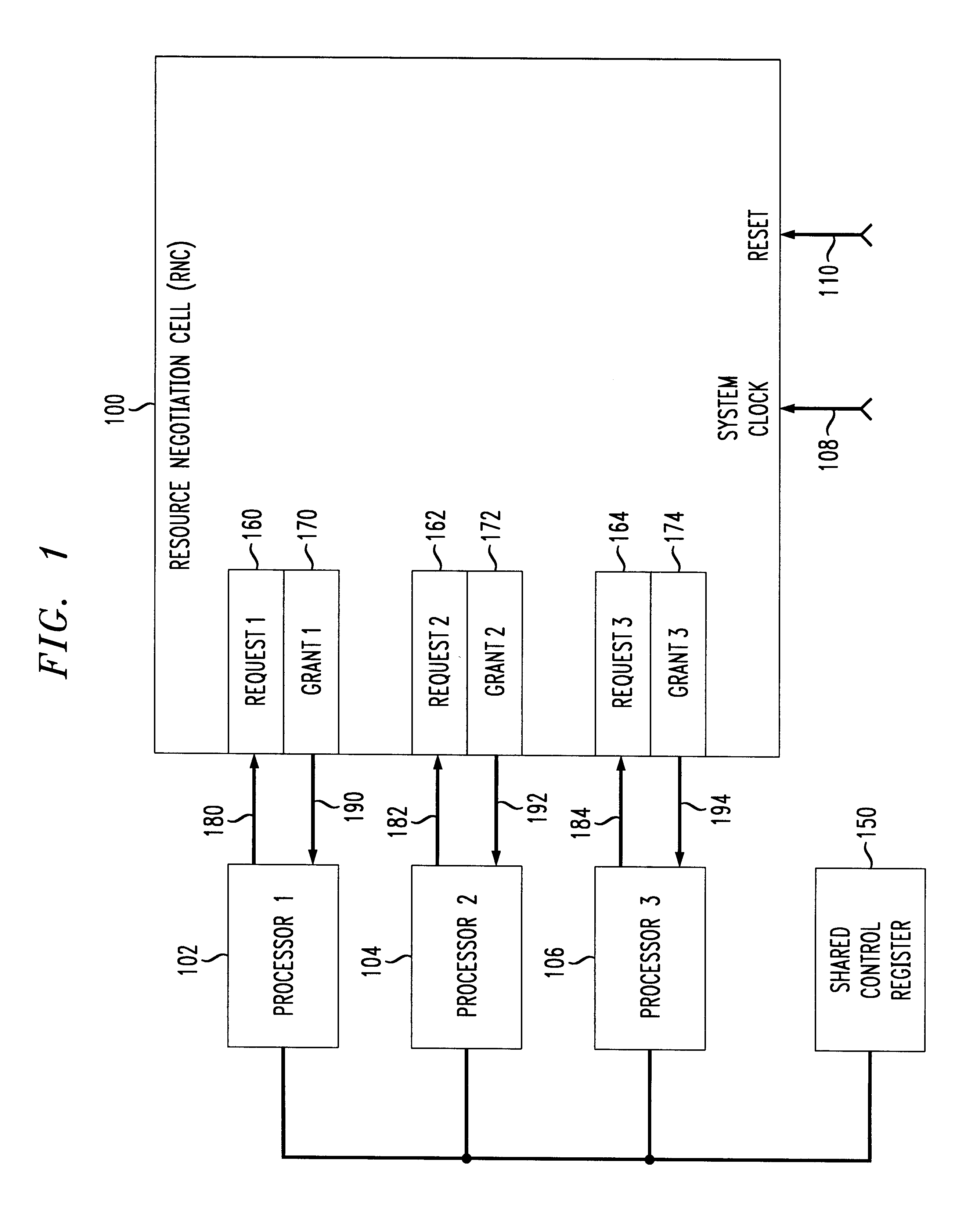
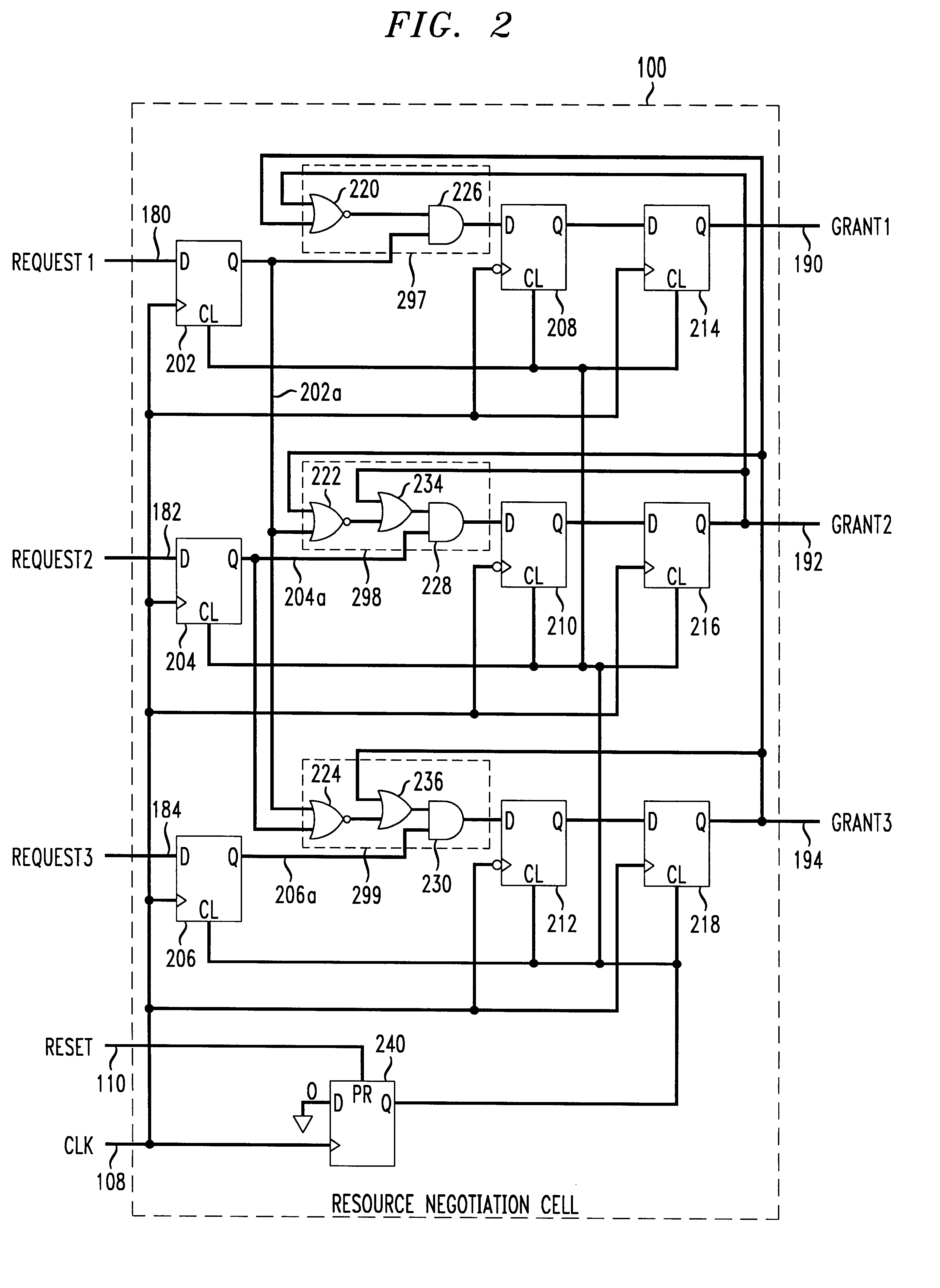
A resource negotiation technique and apparatus which streamlines arbitration for access to a shared resource by centralizing arbitration for groups of shared resources such as control registers into an access register. An accessing agent first writes a request to an appropriate bit of a resource negotiation register (RNR), and then reads back a grant status. If the request for access to the shared resource is not successful in the first attempt, the requesting processor may continuously read the grant status until it is successful. Alternatively, the resource negotiation register may cause an interrupt in the requesting processor upon grant of access to the shared resource. A logic level indicating that access is denied generally indicates that another processor in the multi-processor system is currently granted access to the corresponding shared resource. Once the processor requesting permission for writing to the shared resource has been granted permission, that winning processor is expected to complete its access to the shared resource, and then indicate back to the shared resource negotiator that access is no longer required, e.g., by clearing the corresponding request bit.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
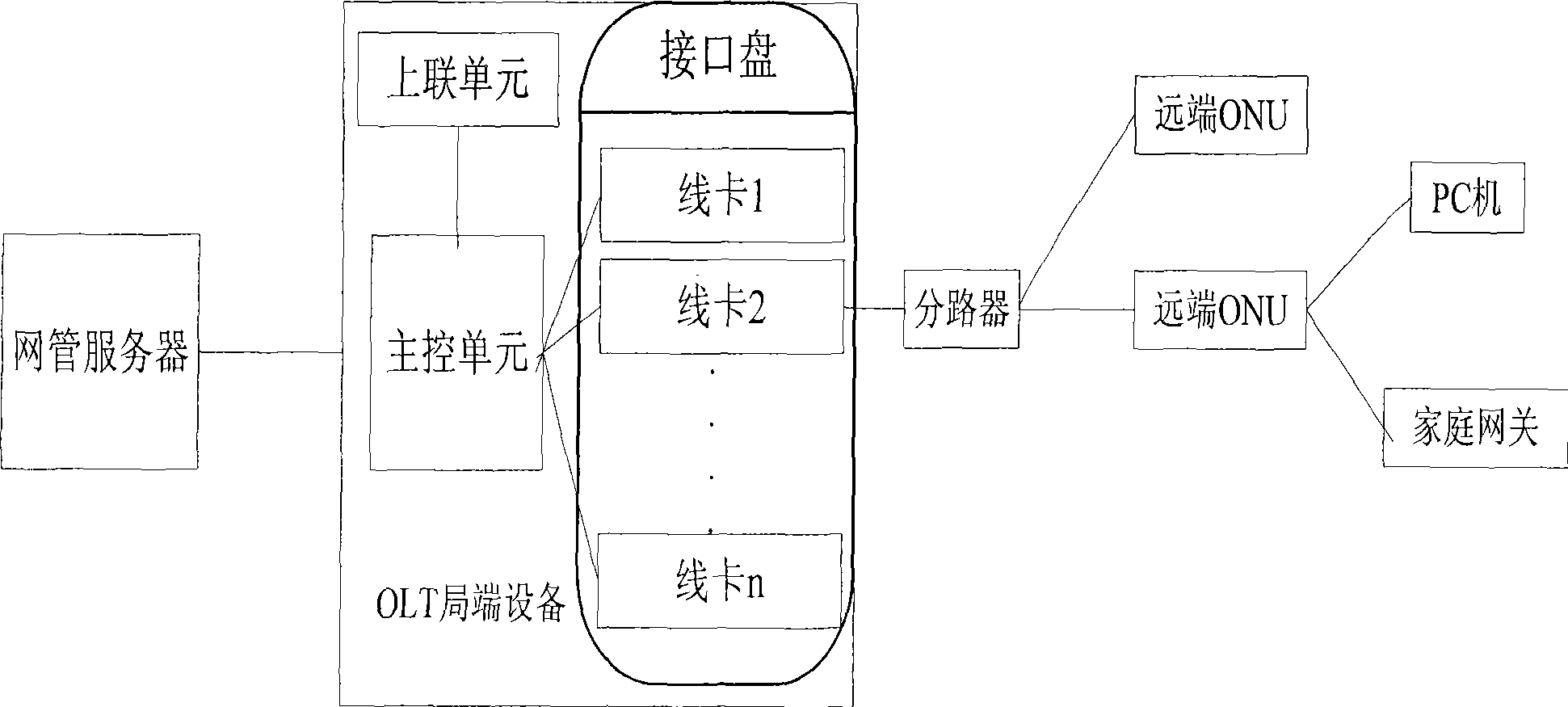
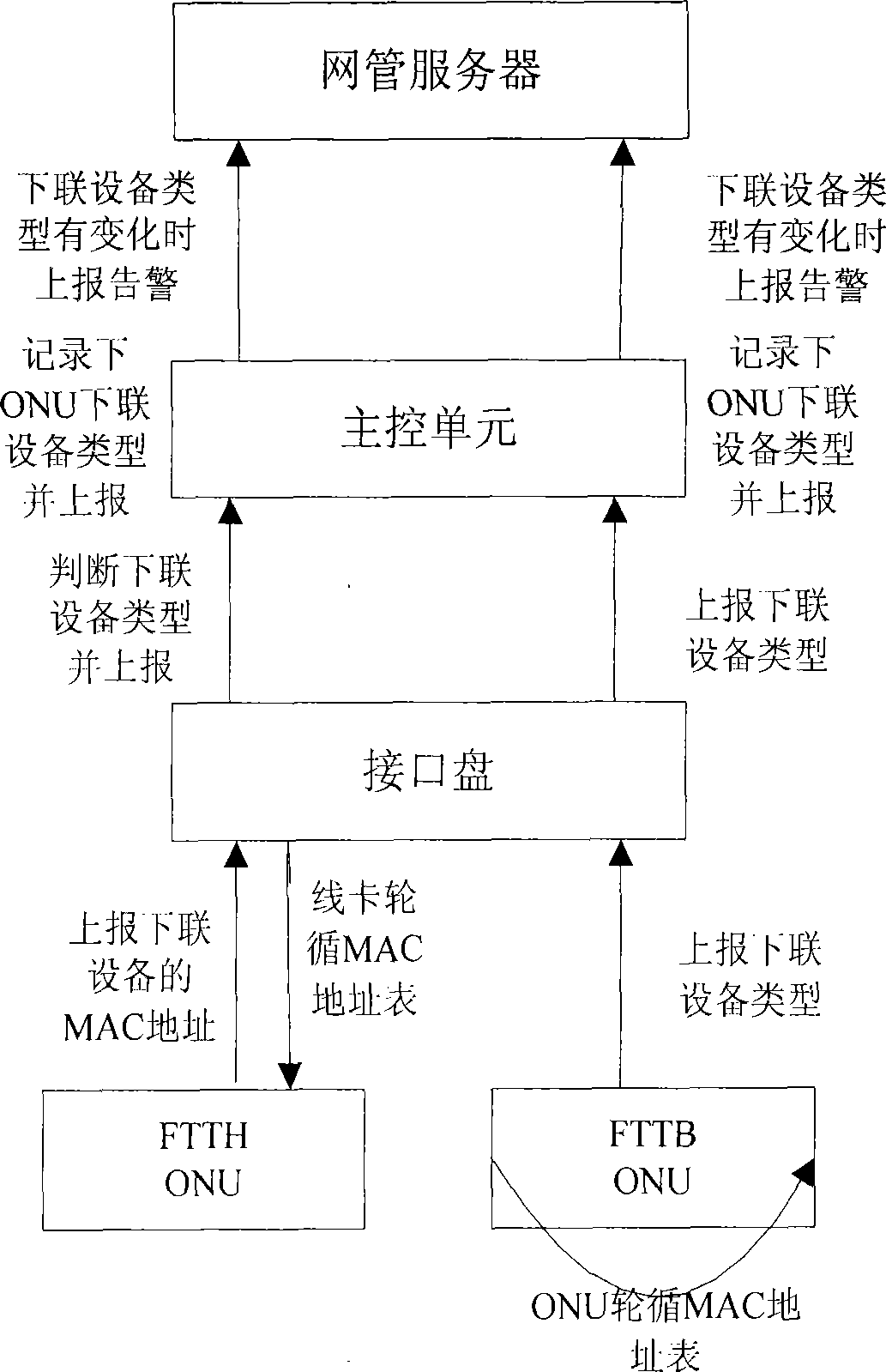
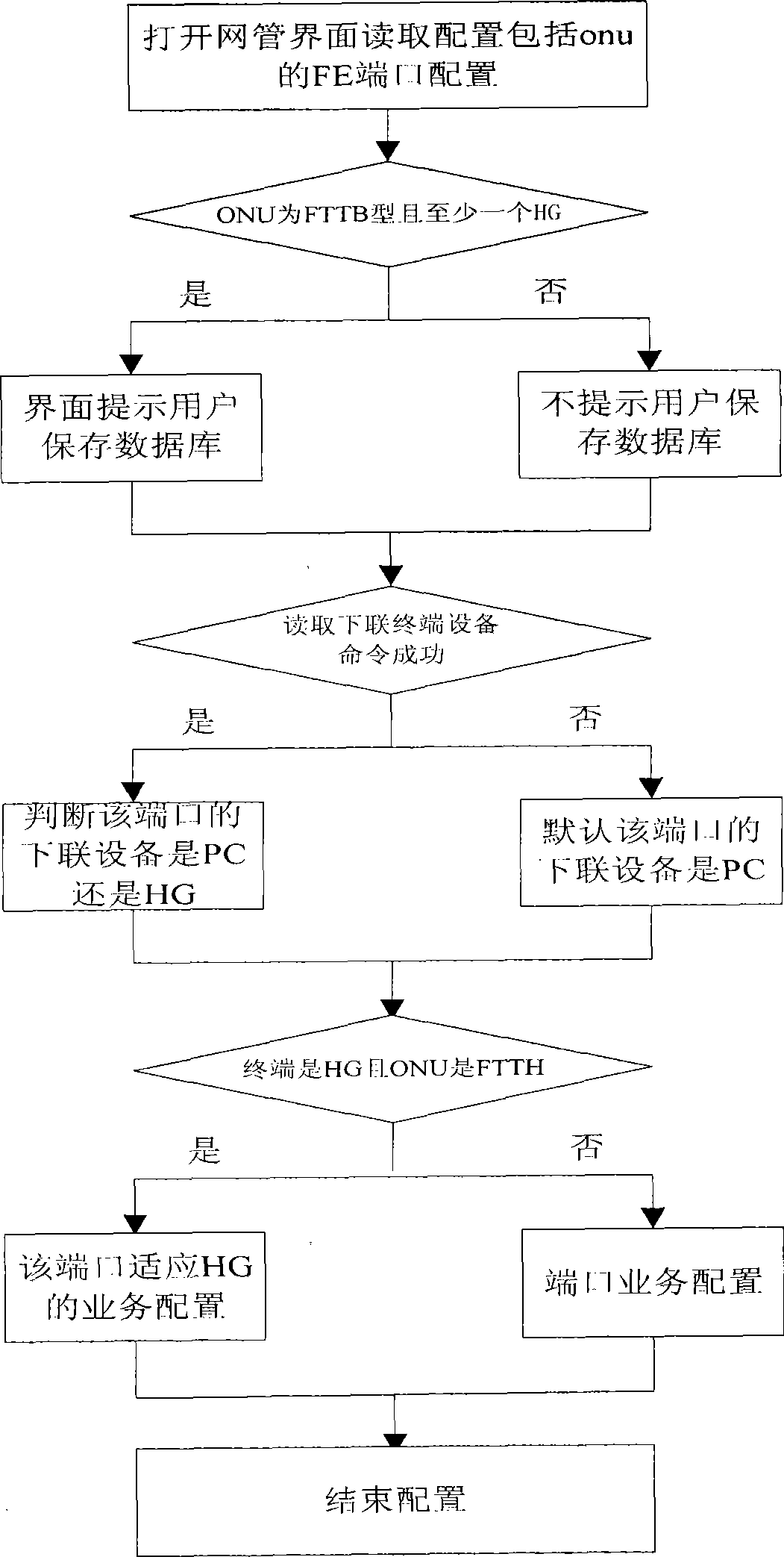
Method for identifying remote ONU down-linked terminal equipment in PON system automatically
InactiveCN101534460AImplement auto-discoveryRealize managementMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionTerminal equipmentNetwork management
The invention discloses a method for identifying remote ONU down-linked terminal equipment in PON system automatically which includes steps as follows: S1, forward planning MAC address range of a home gateway in the down-linked terminal equipment; S2. ONU accessing register to OLT automatically and obtaining authorization; S3. PON access disc obtaining MAC address of ONU end down-linked equipment, and judging the end down-linked equipment whether being home gateway or PC according with the address whether falling into the MAC address range forward planned in step S1, then reporting the down-linked equipment type to a main control unit; S4. the main control unit reporting the down-linked equipment type to a network management center. The method is uses as an important component part for processing uniform management to PON system resource which can realize finding and identifying the remote ONU down-linked equipment automatically, accordingly, realize management thereof.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for providing cooperative fault recovery between a processor and a service processor
A method and apparatus for providing cooperative fault recovery between an operating system and a service processor allows fault detection and recovery capability utilizing a service processor while an operating system is running on a main processor. A register is provided within the main processor component for sending information to the service processor. An attention signal is provided to the service processor to indicate that the operating system has written information to the register and is requesting the service processor's attention. A JTAG standard interface is used to access the register from the service processor and an interrupt is provided to the operating system to indicate that the service processor has written information to the register and is requesting the operating system's attention.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
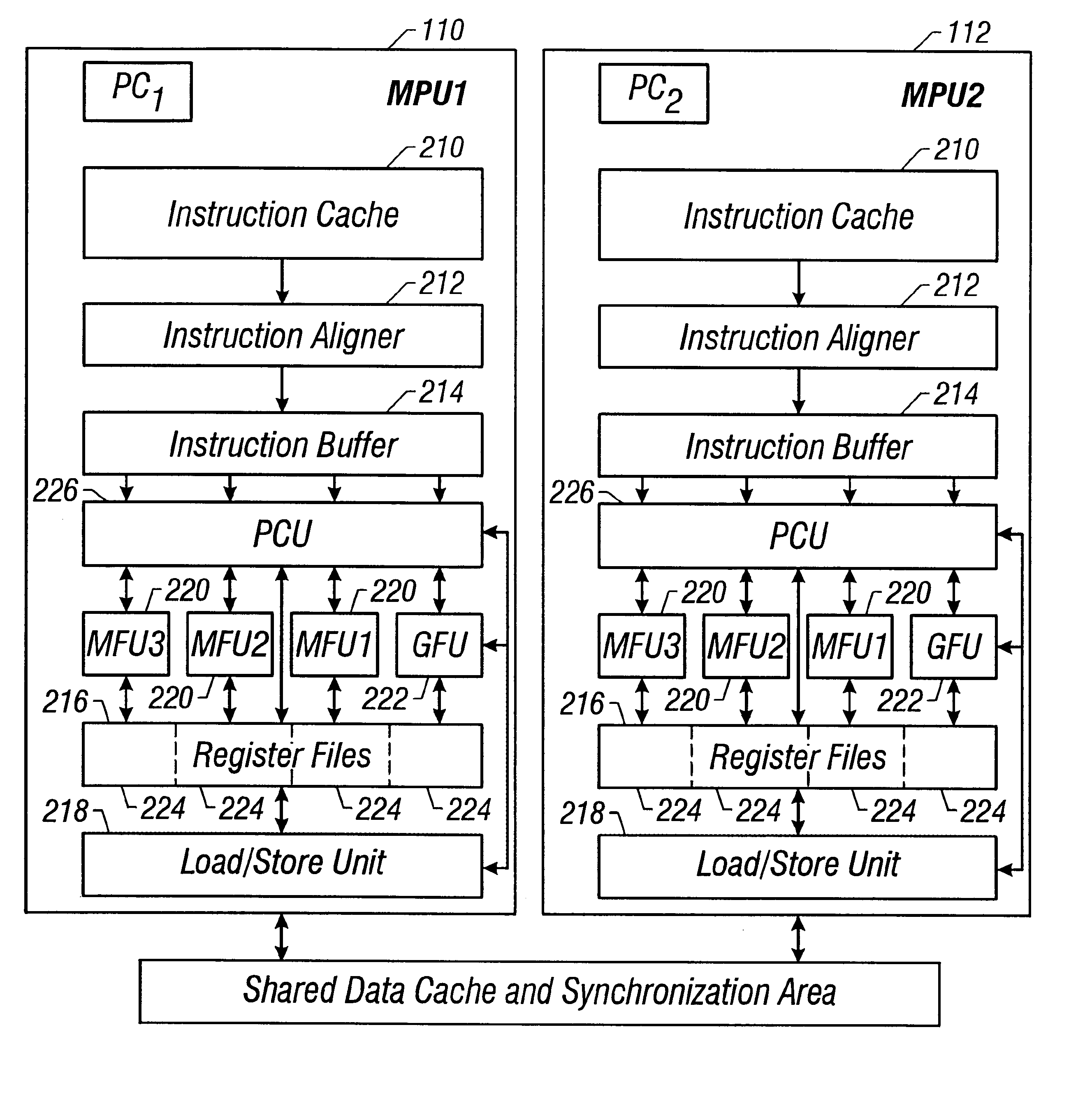
Clustered architecture in a VLIW processor
InactiveUS6615338B1Register arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessor registerBroadcasting
A Very Long Instruction Word (VLIW) processor has a clustered architecture including a plurality of independent functional units and a multi-ported register file that is divided into a plurality of separate register file segments, the register file segments being individually associated with the plurality of independent functional units. The functional units access the respective associated register file segments using read operations that are local to the functional unit / register file segment pairs. In contrast, the functional units access the register file segments using write operations that are broadcast to a plurality of register file segments. Independence between clusters is attained since the separate clustered functional unit / register file segment pairs have local (internal) bypassing that allows internal computations to proceed, but have only limited bypassing between different functional unit / register file segment pair clusters. Thus a particular functional unit / register segment pair does not bypass to all other functional unit / register segment pairs.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
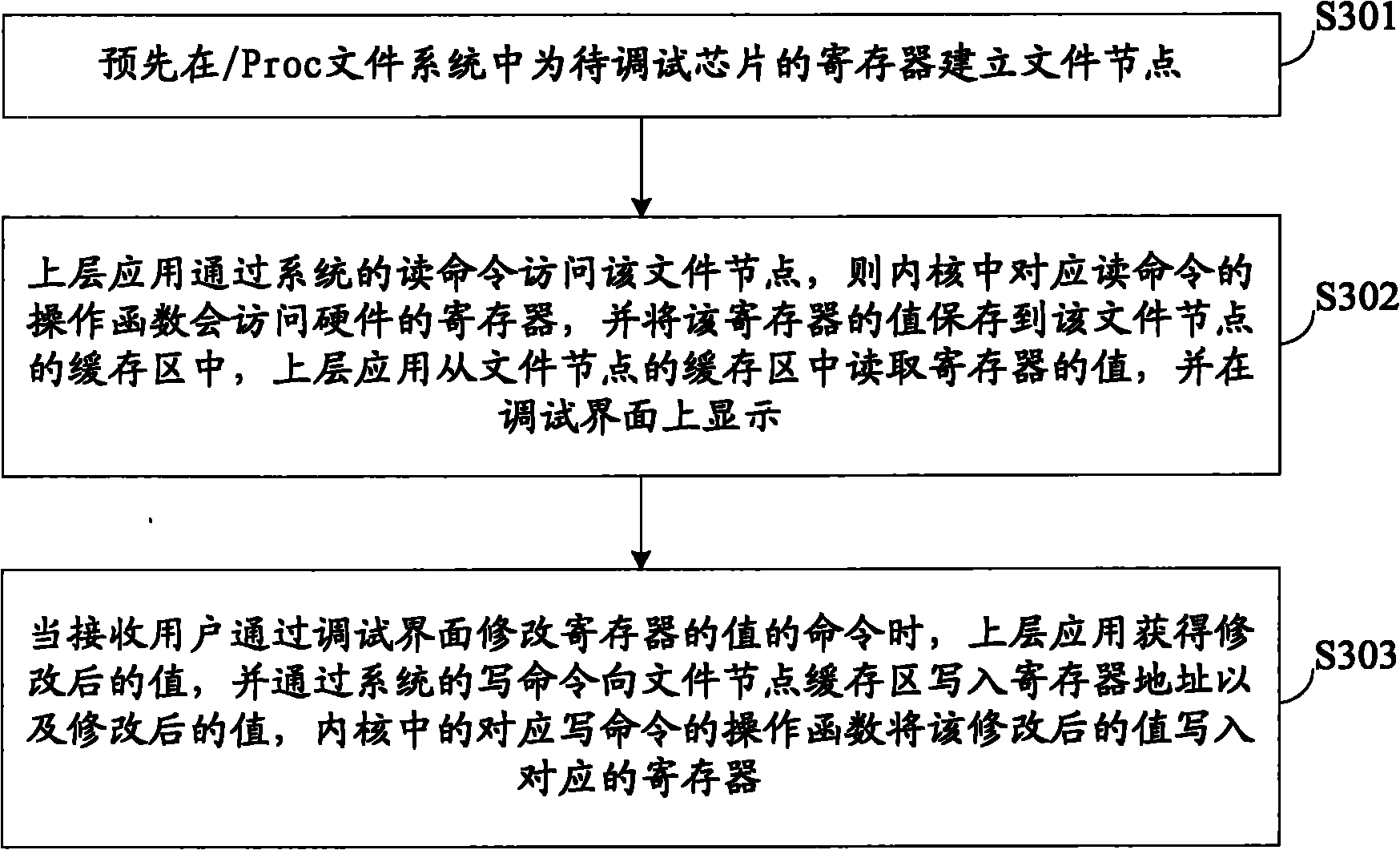
File systems accessing register dynamic collection method
InactiveCN101216850AImprove usabilityReduce sizeHardware monitoringSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemSystem testing
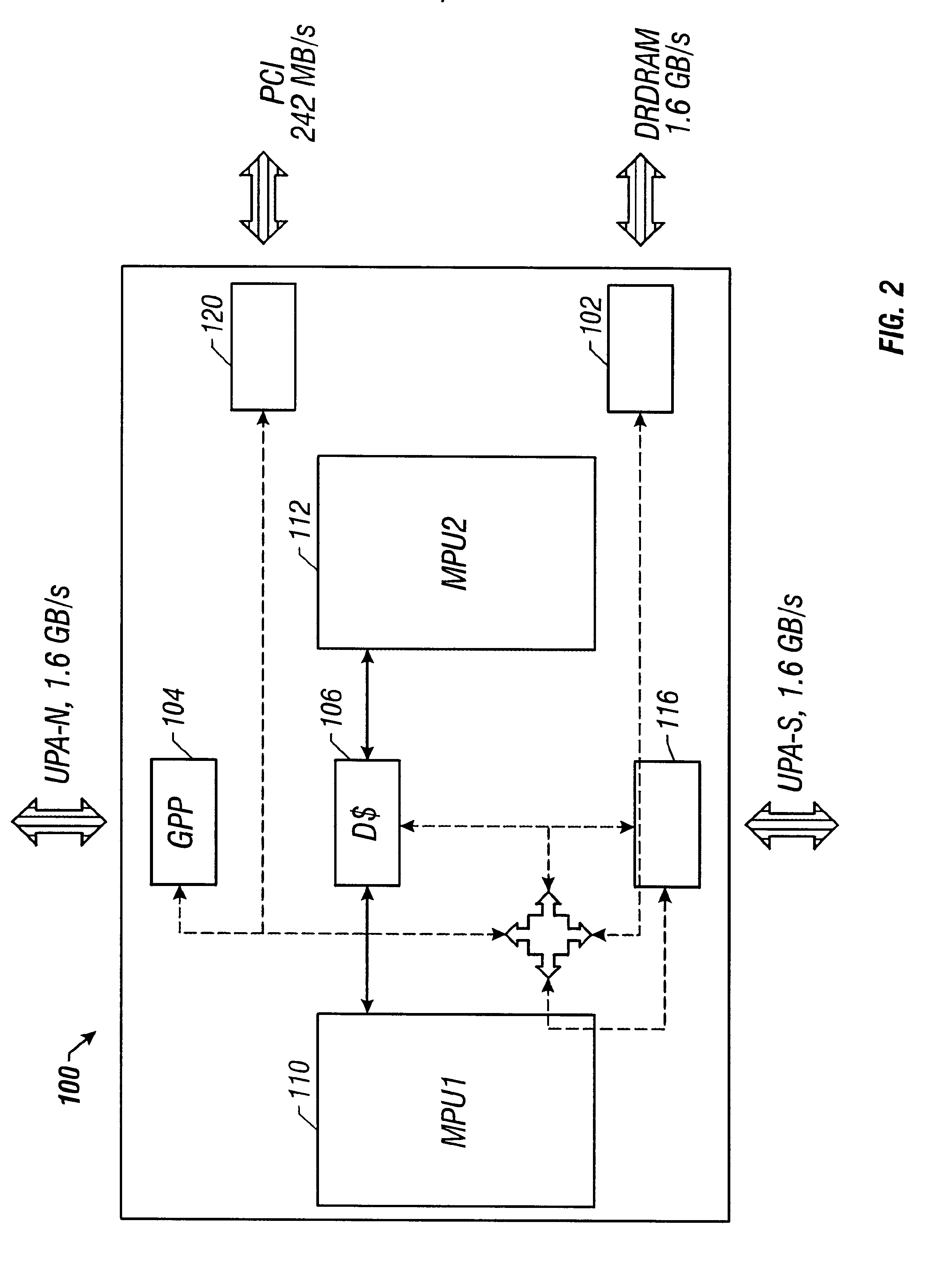
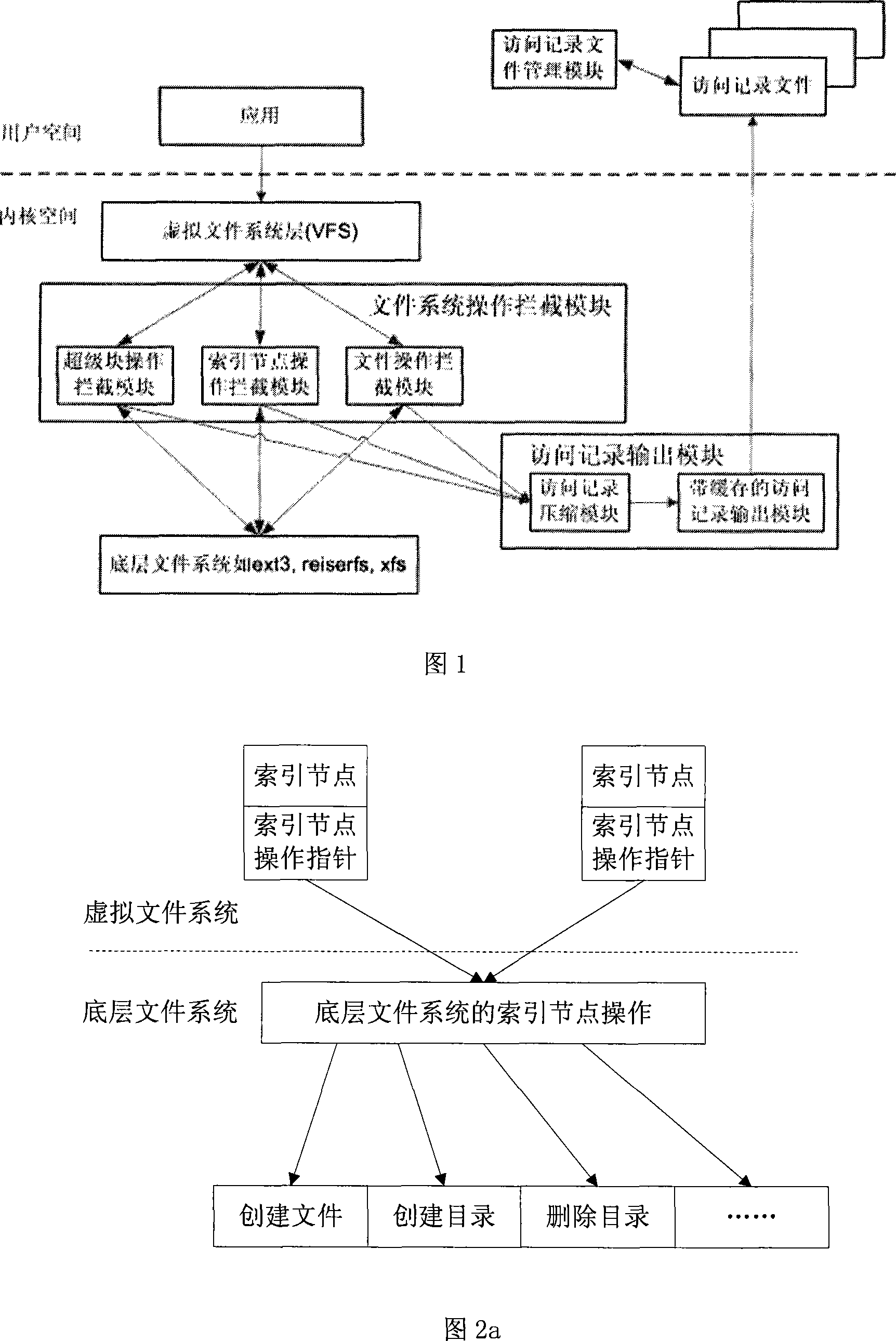
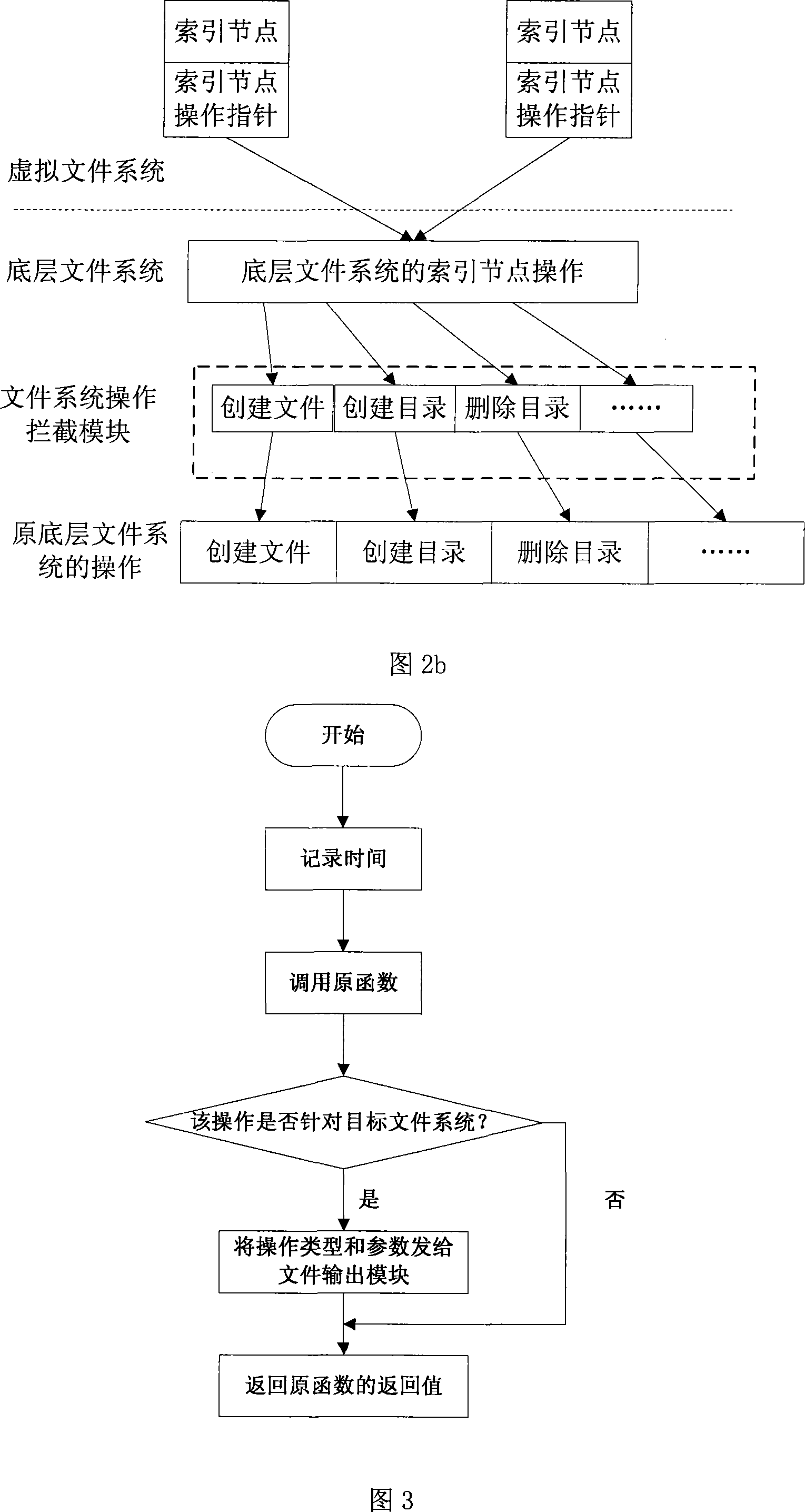
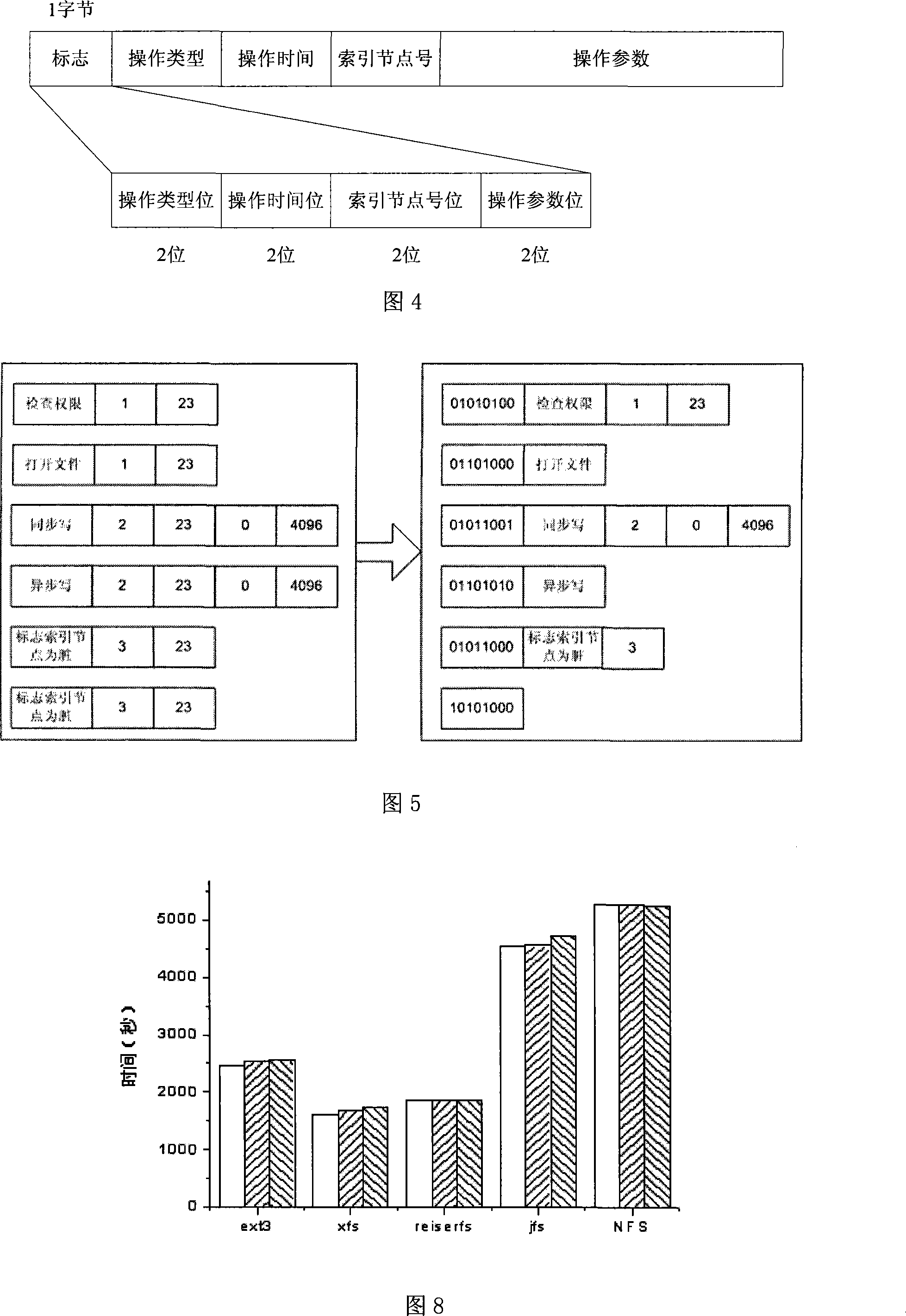
The invention discloses a dynamic acquisition method of file system access record, belonging to the field of storage system testing and performance analysis. The invention is characterized in that a kernel module can be loaded without the need of unloading the old file system, thus not needing to interrupt the working application. A file system operation interception module can dynamically intercept the underlayer file system operation by a substitution of corresponding functions in the interception module. While executing the underlayer file system operation, the functions output the operation type and parameters to an access record output module which compresses the file record and outputs a plurality of operation information at one time in a output record way of register. The access record output module controls the output file size to prevent the problems of difficult read and write and exceeding file system restriction. An access record file management module collects additional information and packages and transfers the access record according to the assignment of users, thus being convenient for users to manage. The test shows that the collection of access record has little impact on the application.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods and Apparatus to Extend Software Branch Target Hints
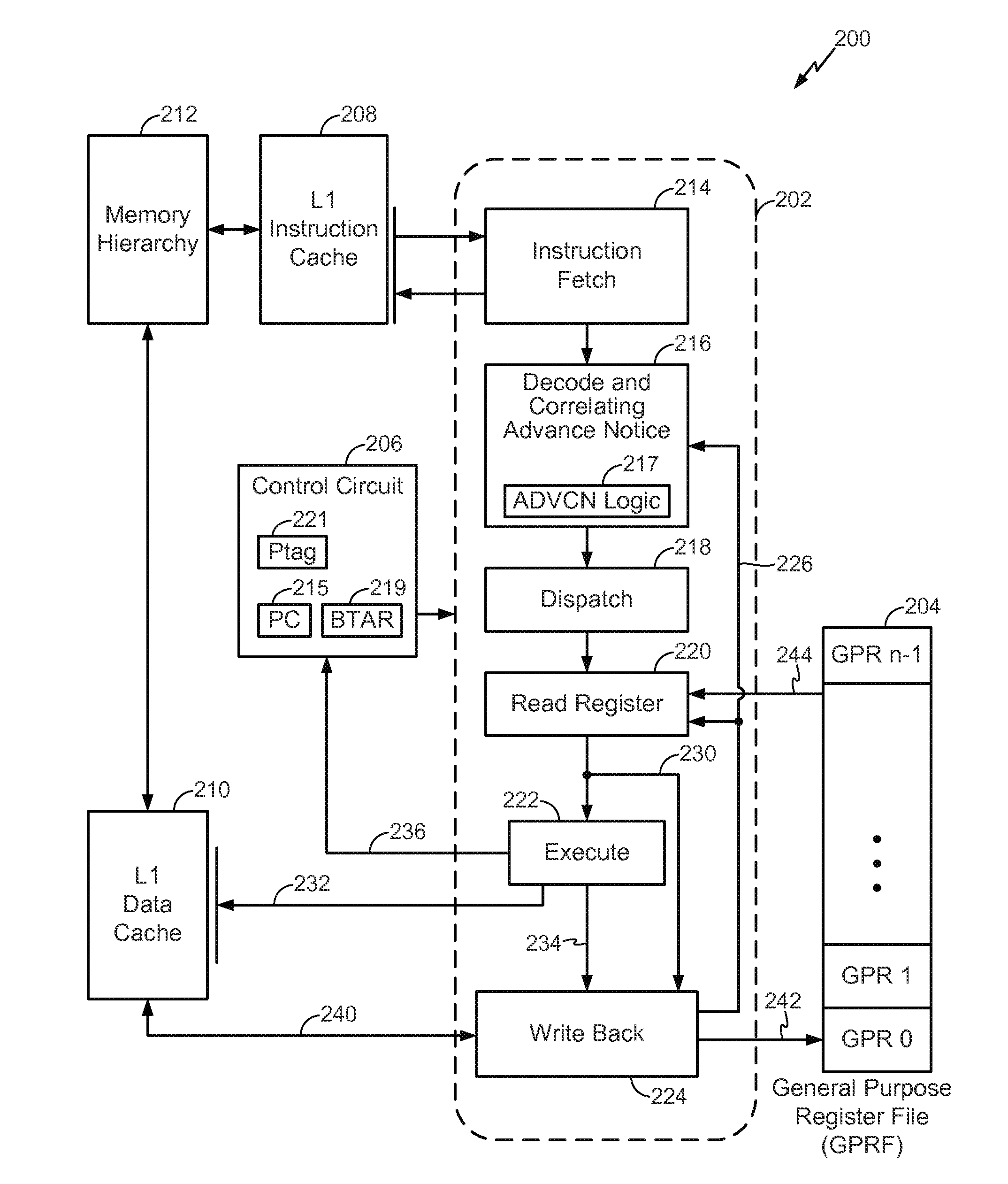
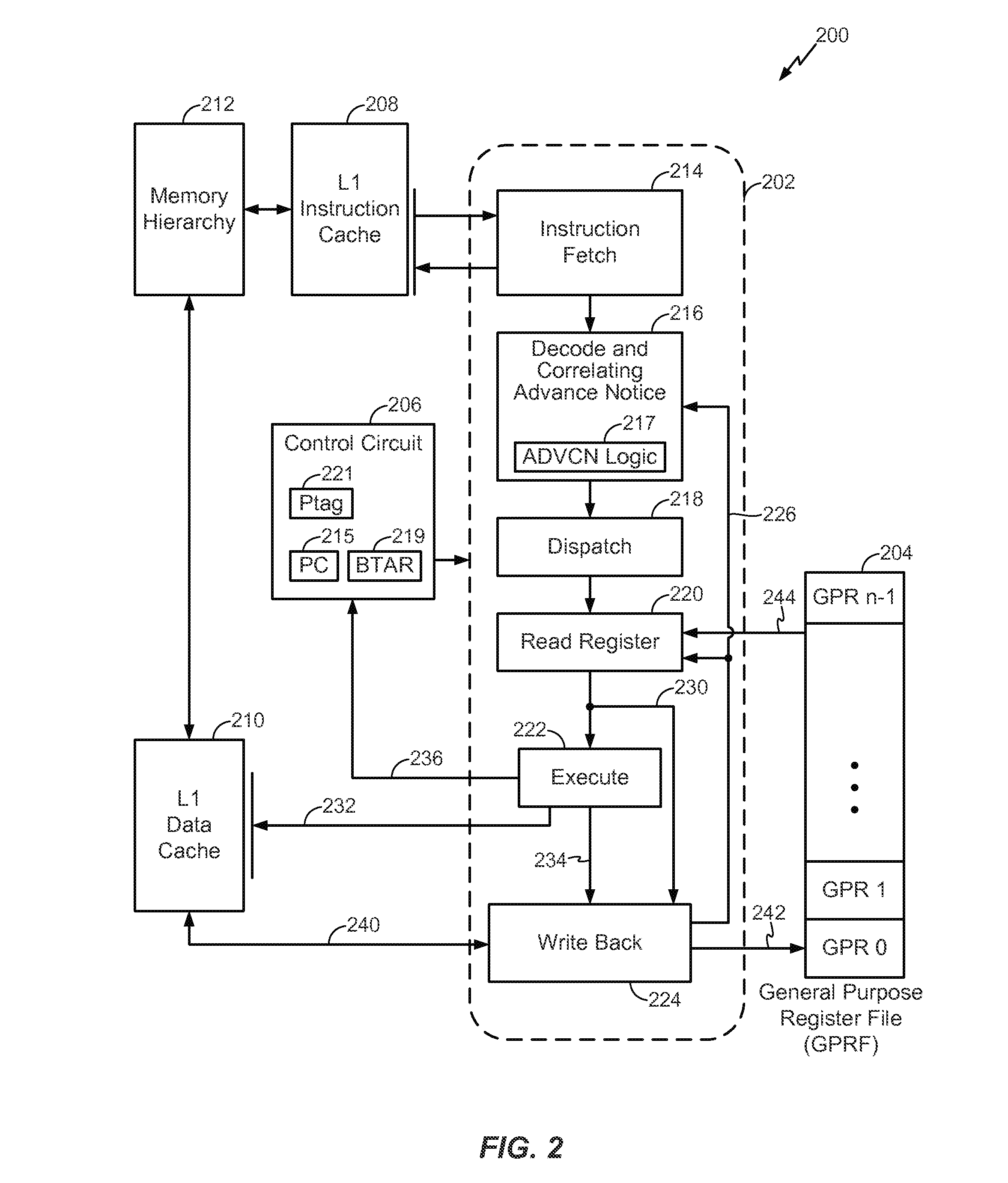
InactiveUS20130346727A1Improve performanceMinimizing mispredictions of indirect branch instructionsDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingBranch target address
Apparatus and techniques for predicting a storage address based on contents of a first program accessible register (PAR) specified in a first instruction, wherein the first PAR correlates with a target address specified by a second PAR in a second instruction. Information is speculatively fetched at the predicted storage address prior to execution of the second instruction. The first instruction is an advance correlating notification (ADVCN) instruction, the second instruction is an indirect branch instruction, and the information is a plurality of instructions beginning at the predicted storage address. The predicted storage address is a branch target address for the indirect branch instruction from which instructions are speculatively fetched. The prediction is based on contents of the first PAR specified in the ADVCN instruction. The contents of the first PAR correlate with a taken evaluation of the branch instruction.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
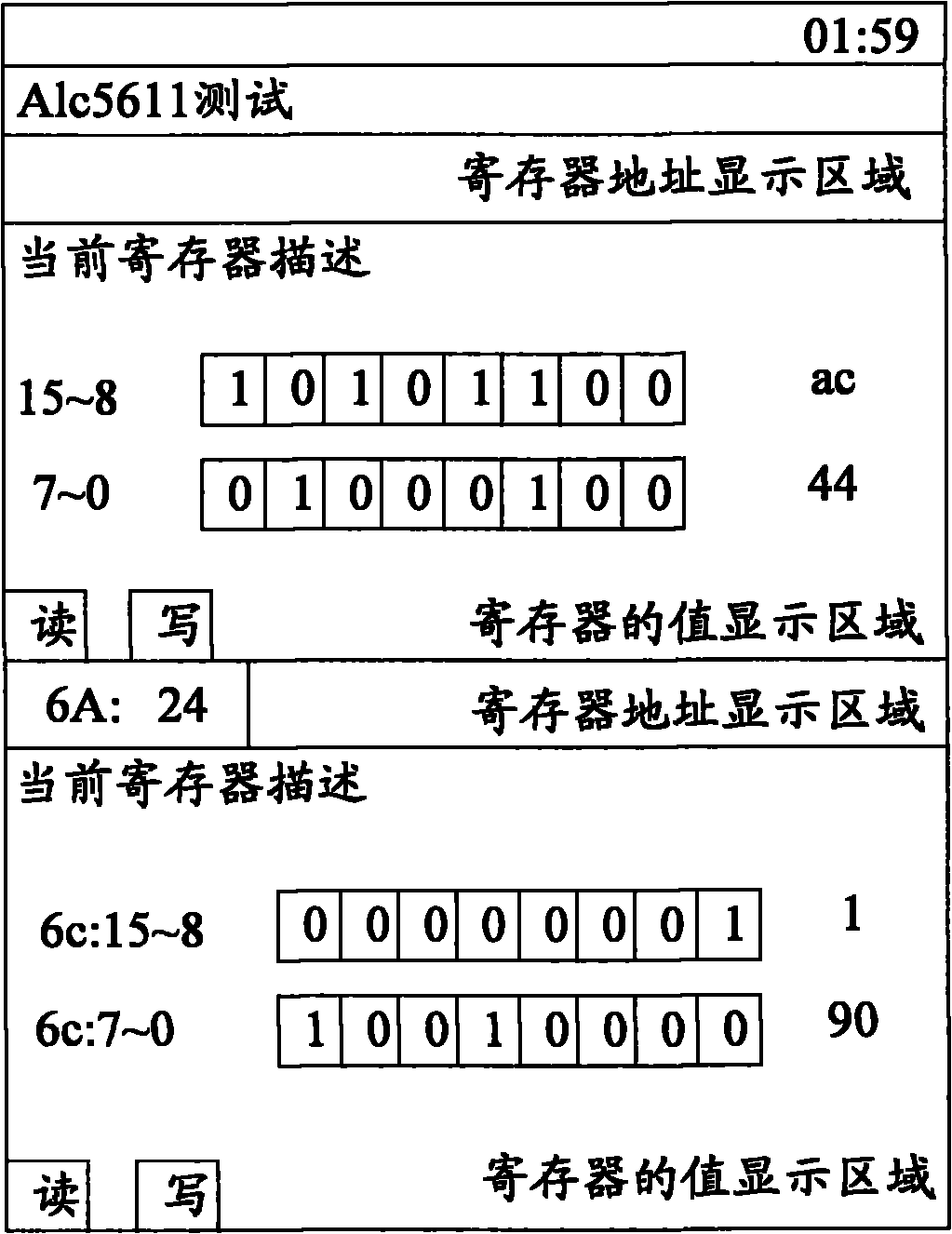
Visual terminal debugging method and device
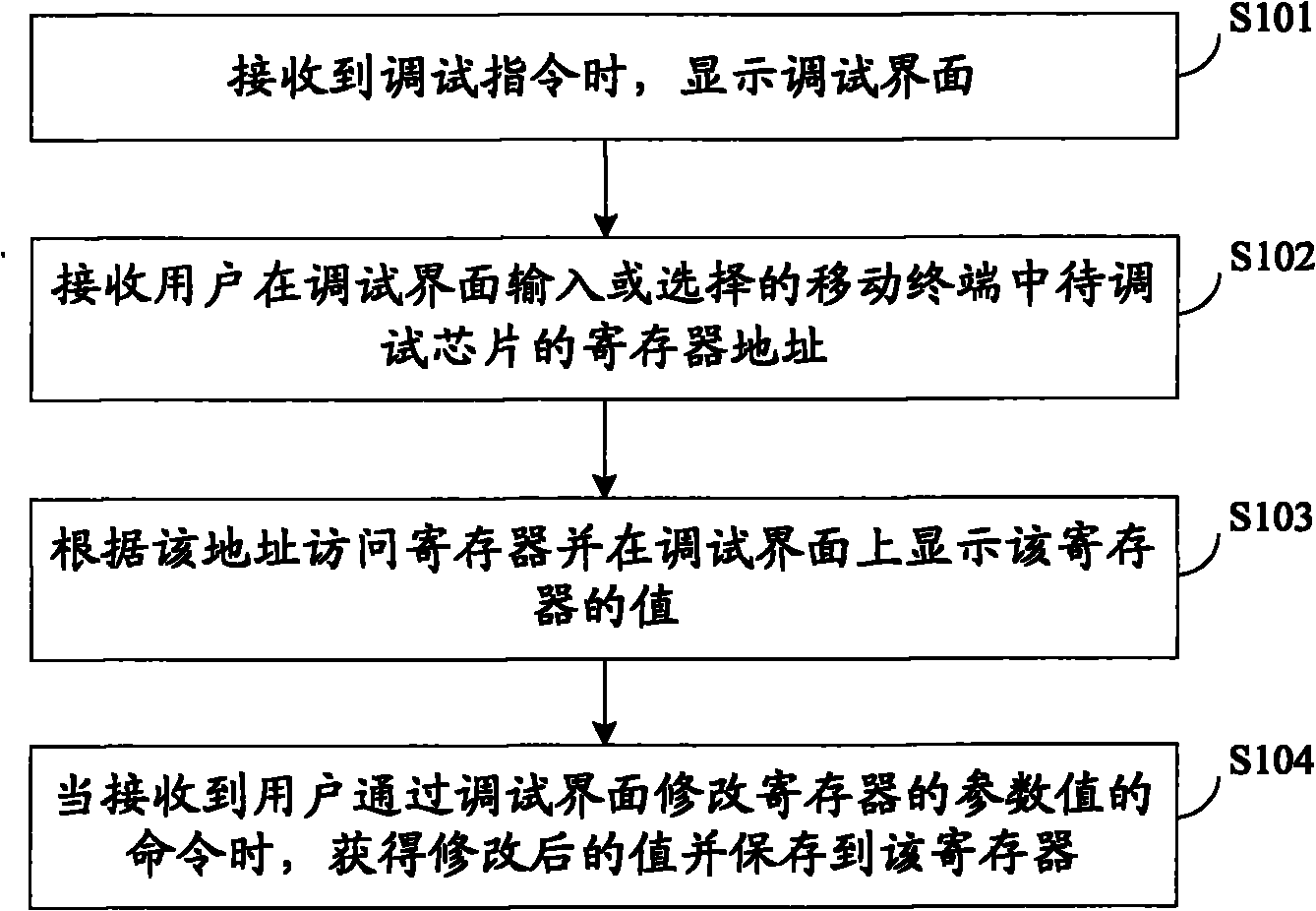
InactiveCN101938566AImprove debugging efficiencyShorten the timeSubstation equipmentProcessor registerComputer terminal
The invention discloses visual terminal debugging method and device, belonging to the field of mobile phone debugging. The efficiency of terminal debugging can be improved. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving the address of a register of a chip to be debugged in a mobile terminal inputted or selected by a user in a debugging interface, accessing the register according to the address and displaying the value of the register on the debugging interface; and when a command for modifying the value of the register through the debugging interface is received from the user, acquiring the modified value and storing the value in the register. According to the method, the value of the register of the chip to be debugged can be directly displayed on the debugging interface to be modified and the modified value of the register can be directly stored in the register. The efficiency of terminal debugging is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MOBILE COMM TECH CO LTD
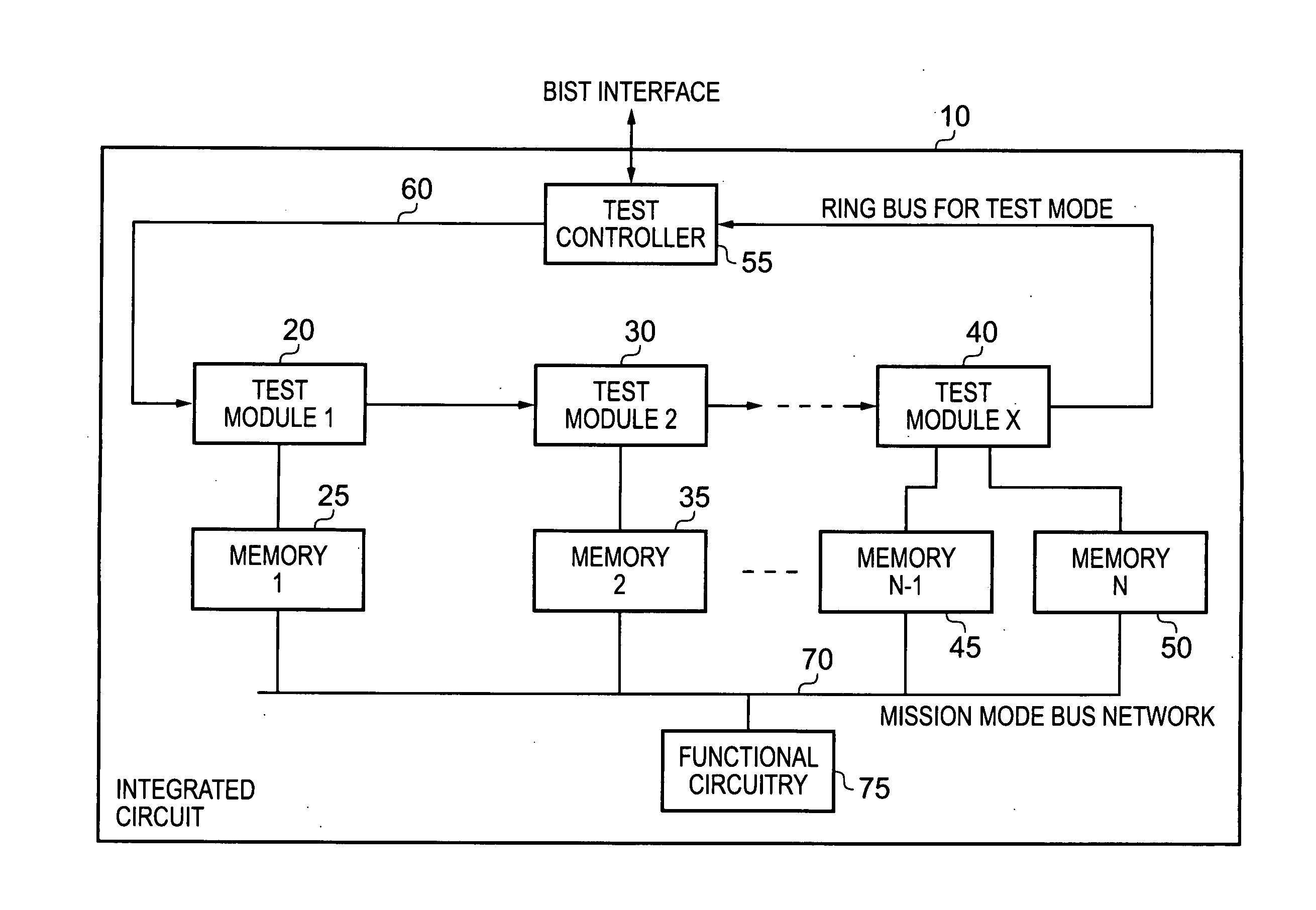
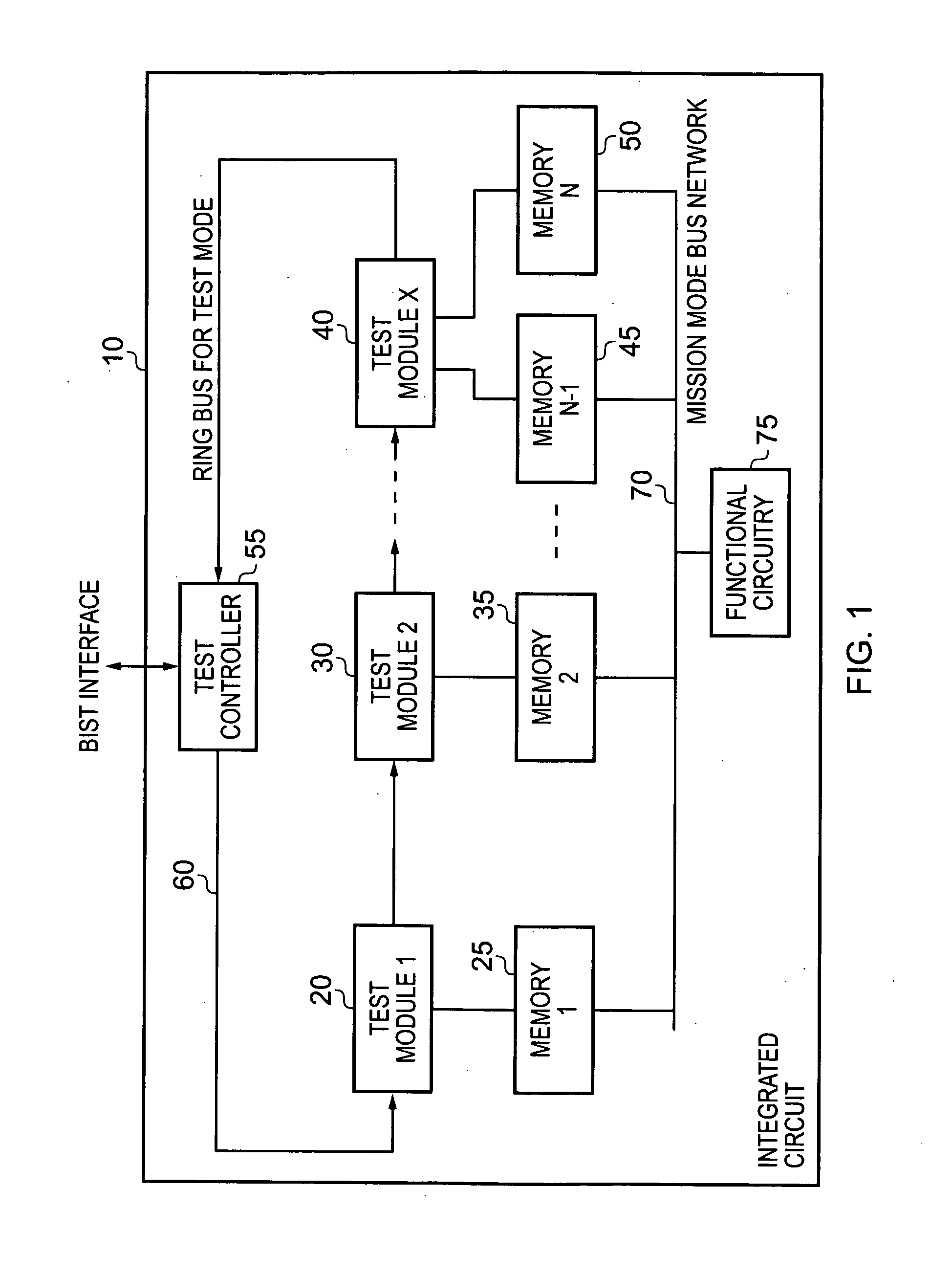
Integrated circuit and method for testing memory on the integrated circuit
ActiveUS20120204069A1Simplify the viewing processAvoid problemsError detection/correctionStatic storageProcessor registerComputer module
An integrated circuit comprises a plurality of memory units and at least one memory test module, each memory test module having at least one associated memory unit from the plurality of memory units. Each memory test module comprises a set of test registers for each associated memory unit, and a test engine configured, for each associated memory unit, to perform a test operation on that associated memory unit dependent on the status of the set of registers provided for that associated memory unit. A transaction interface of the memory test module receives a transaction specifying a register access operation, the transaction providing a first address portion having encodings allowing individual memory units to be identified and groups of memory units to be identified, and a second address portion identifying one of the test registers within the set to be an accessed register for the register access operation. Decode circuitry within each memory test module is then responsive to the transaction to selectively perform the register access operation if it is determined that the memory test module includes a set of test registers associated with a memory unit identified either individually or as part of a group by the transaction. Such an approach provides a simple programmer's view of the memory test system allowing any transaction to be targeted at an individual memory unit or at arbitrary combinations of memory units as defined by the memory groups.
Owner:ARM LTD
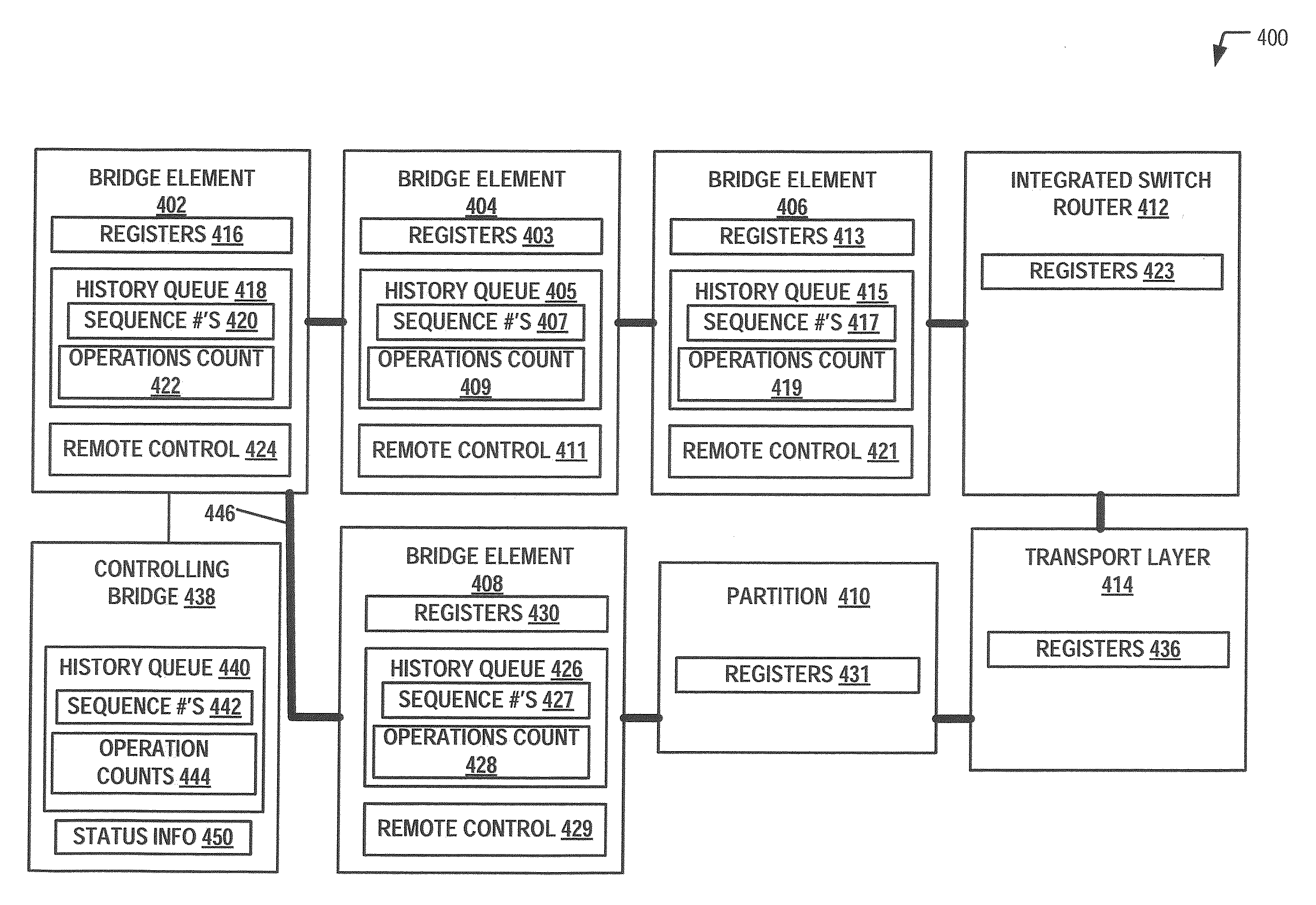
Register access in distributed virtual bridge environment
ActiveUS20120017022A1Facilitate efficient programmingReduce potential bottleneckDigital computer detailsData switching networksProcessor registerComputer science
Systems and methods to perform a register access are described. A particular method includes receiving a data frame at a bridge element of a plurality of bridge elements in communication with a plurality of server computers. The data frame may include a register access request and may be forwarded from a controlling bridge in communication with the plurality of bridge elements. A register may be accessed and execution of the register access request may be initiated in response to receiving the data frame.
Owner:IBM CORP
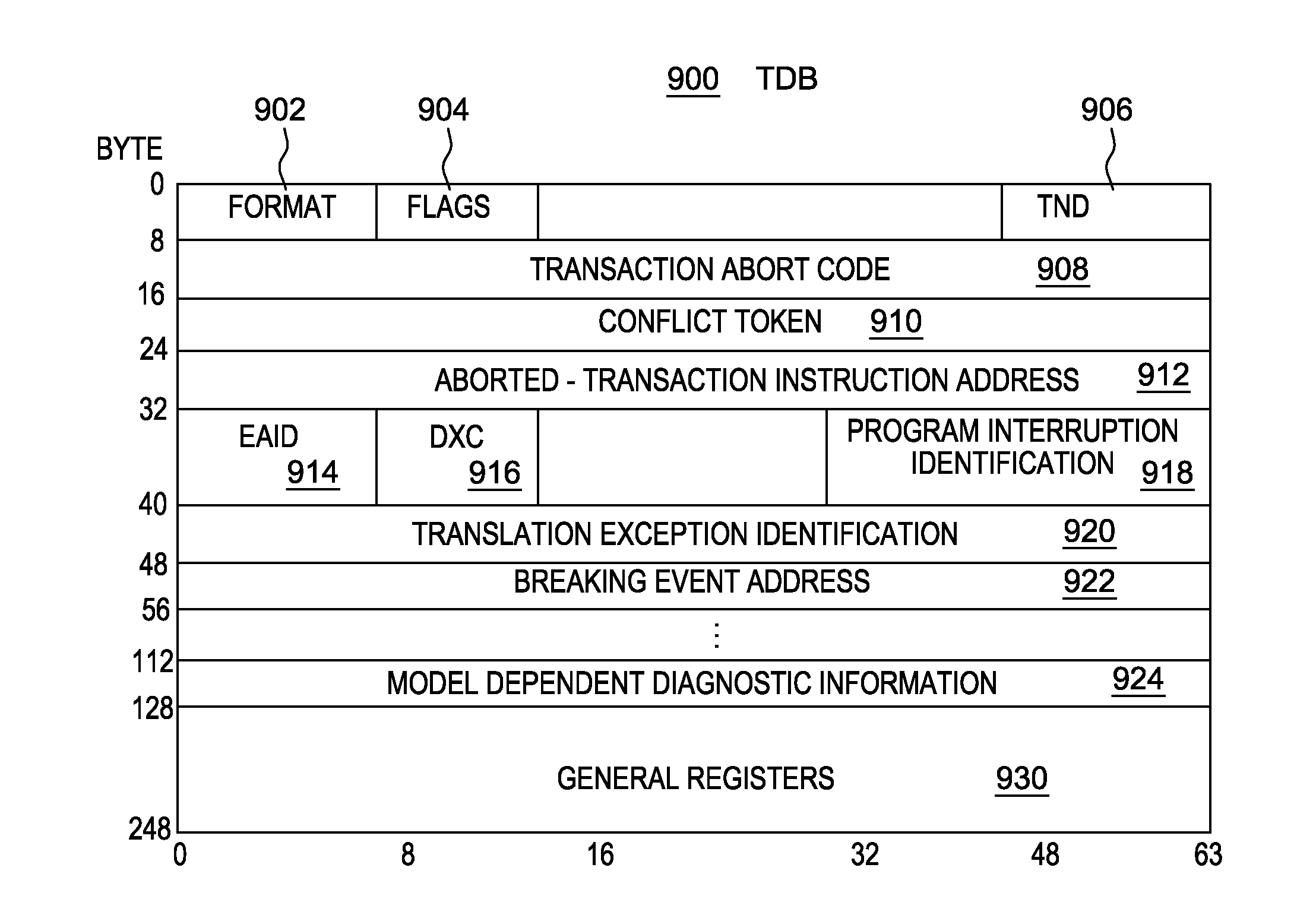
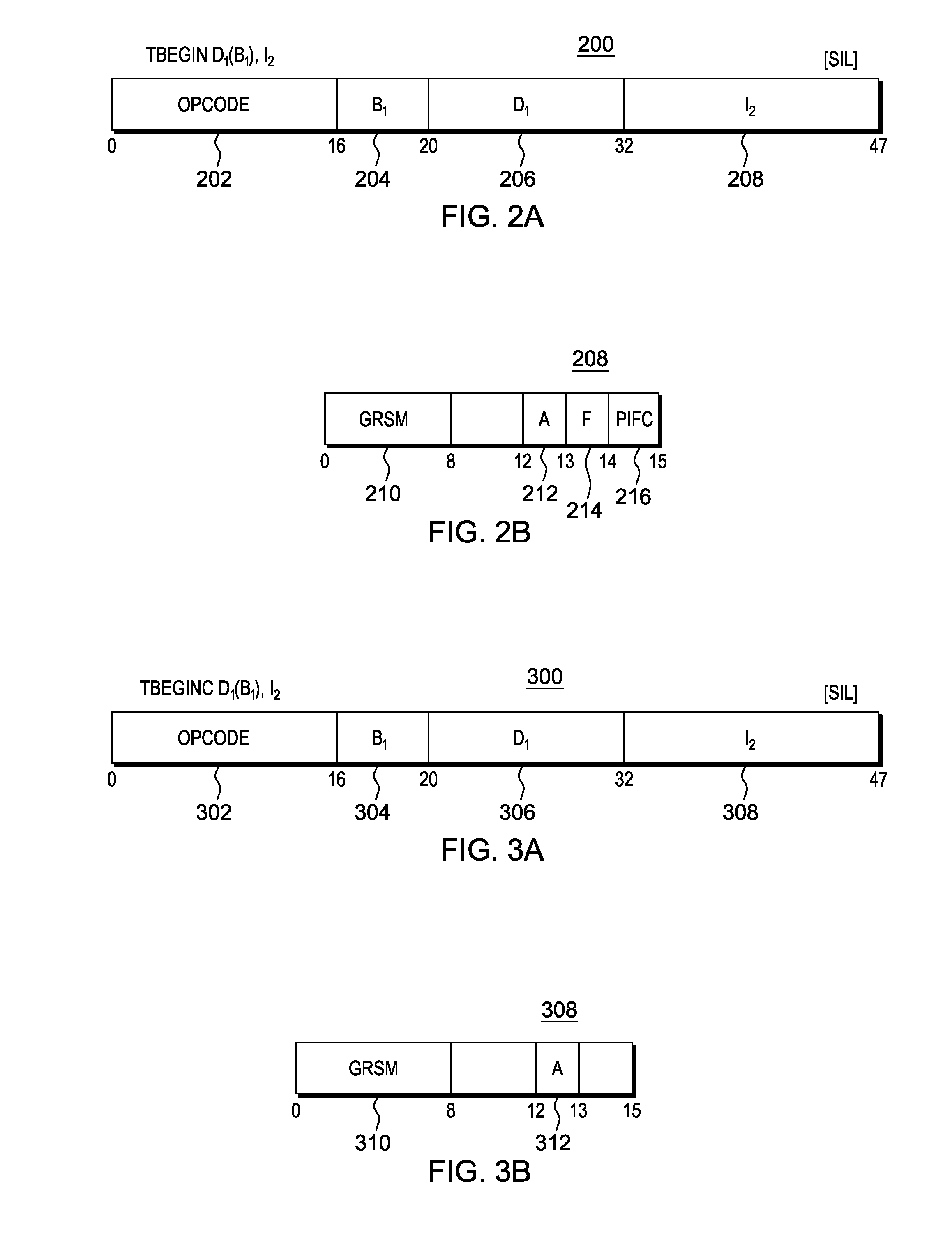
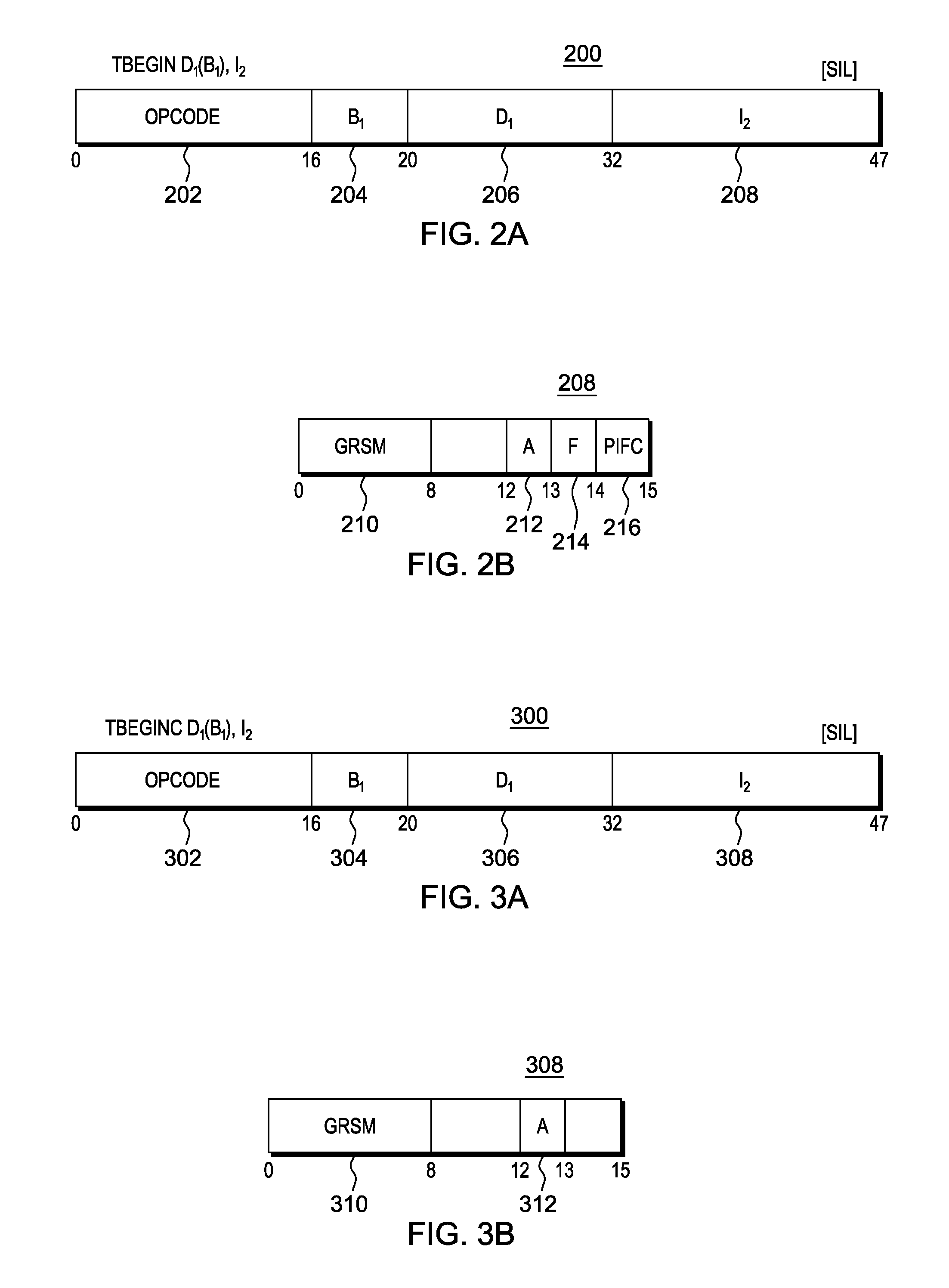
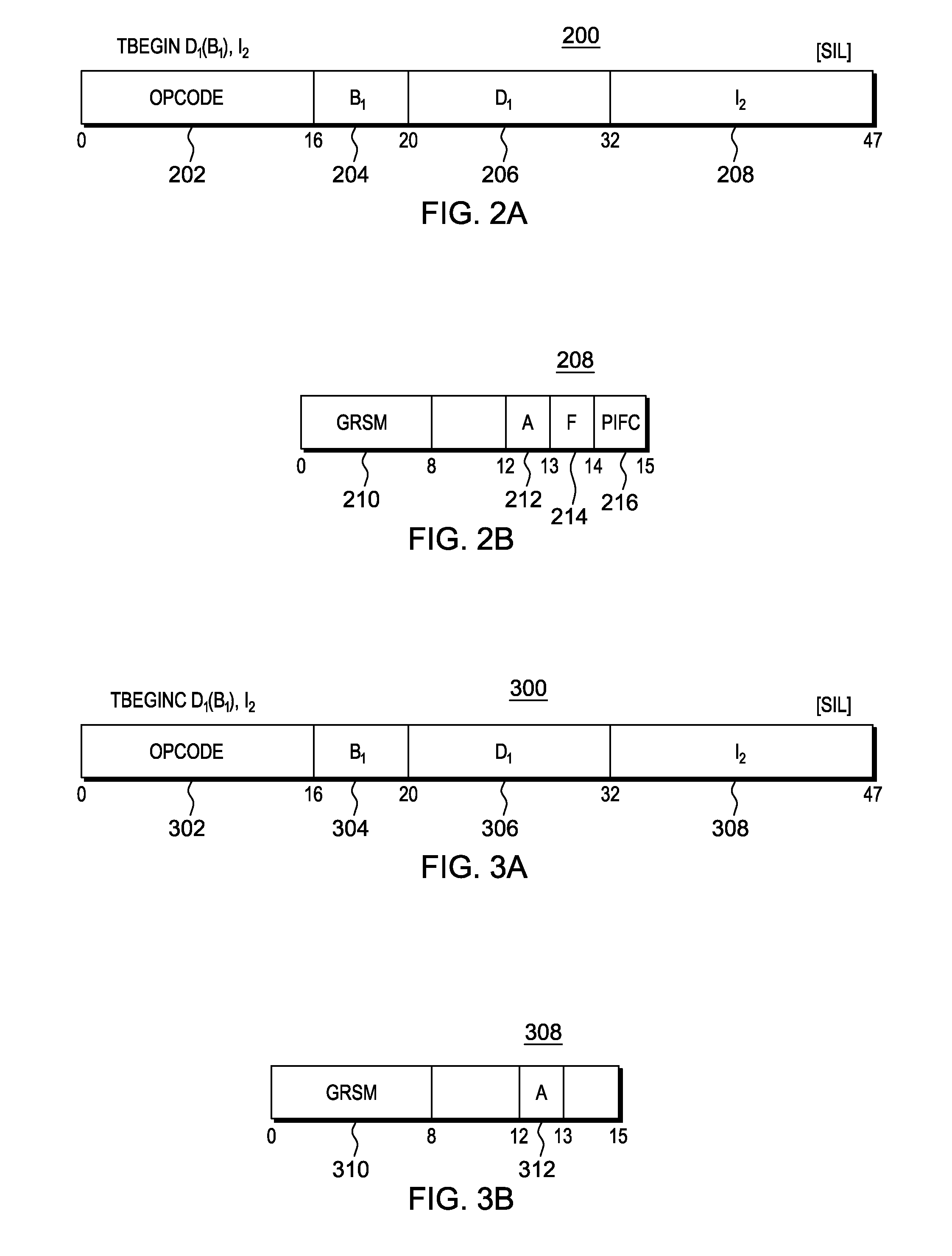
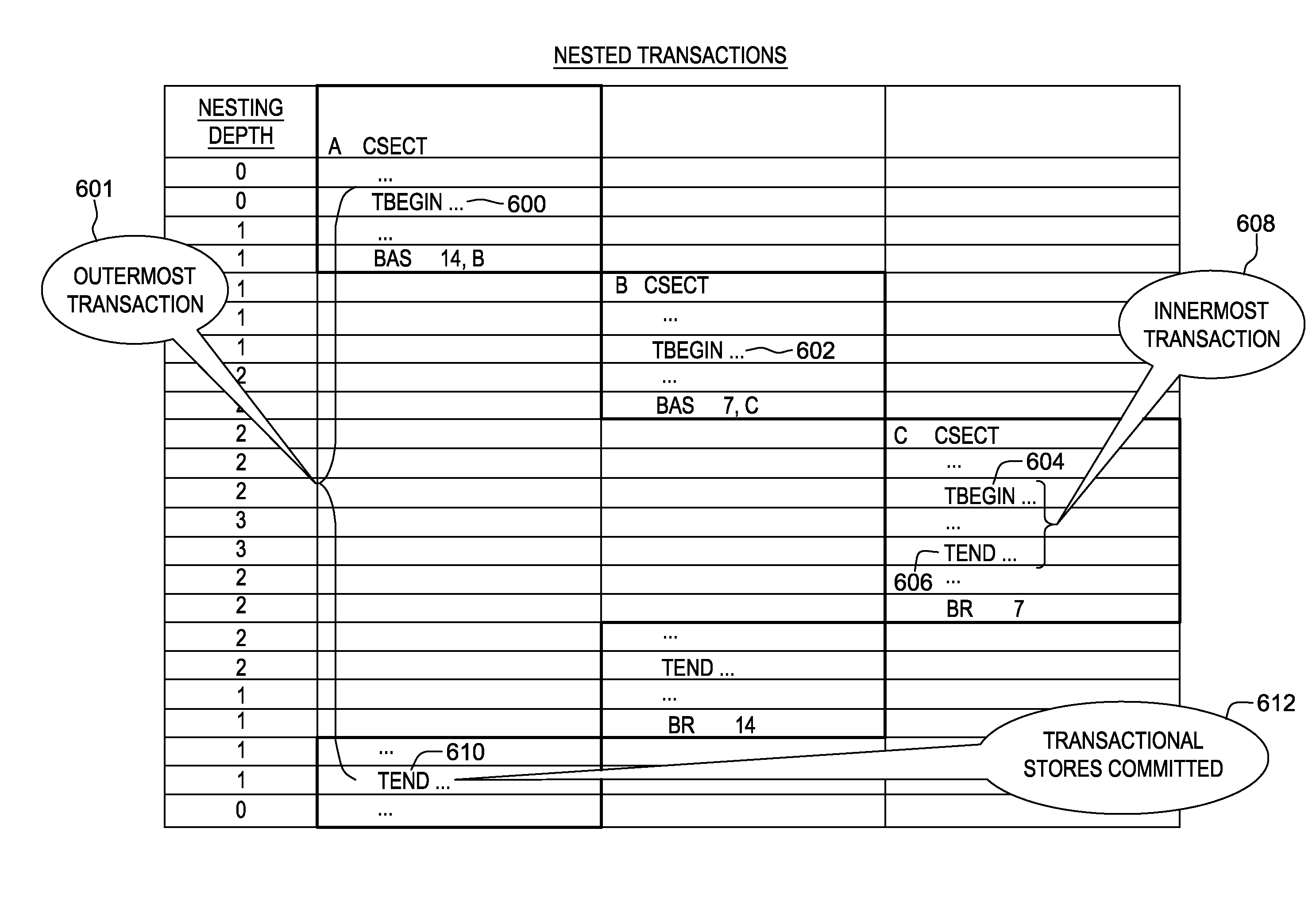
Selectively controlling instruction execution in transactional processing
ActiveUS20130339328A1Register arrangementsDigital data processing detailsProcessor registerParallel computing
Execution of instructions in a transactional environment is selectively controlled. A TRANSACTION BEGIN instruction initiates a transaction and includes controls that selectively indicate whether certain types of instructions are permitted to execute within the transaction. The controls include one or more of an allow access register modification control and an allow floating point operation control.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for using multiple working memories to improve microprocessor security
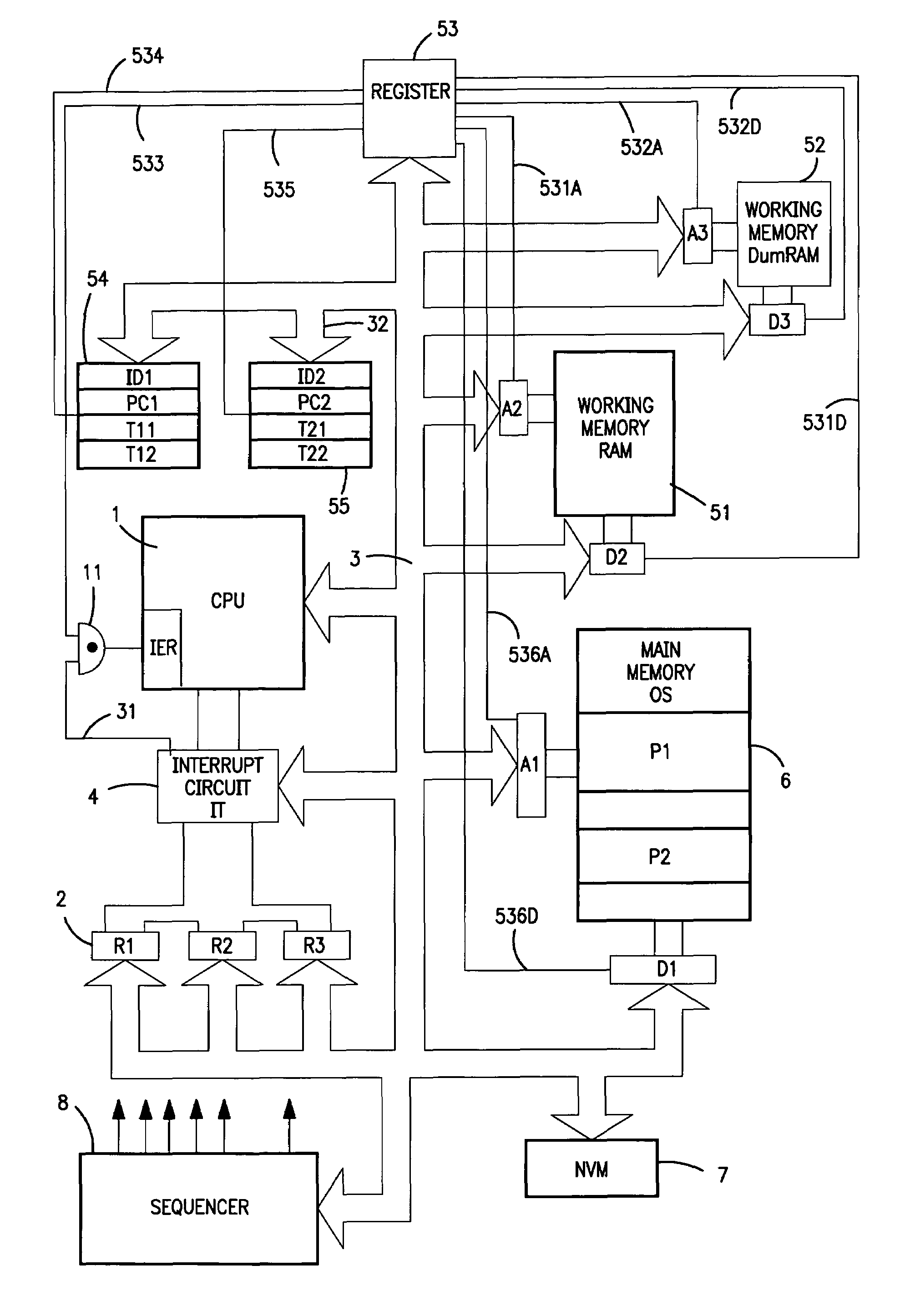
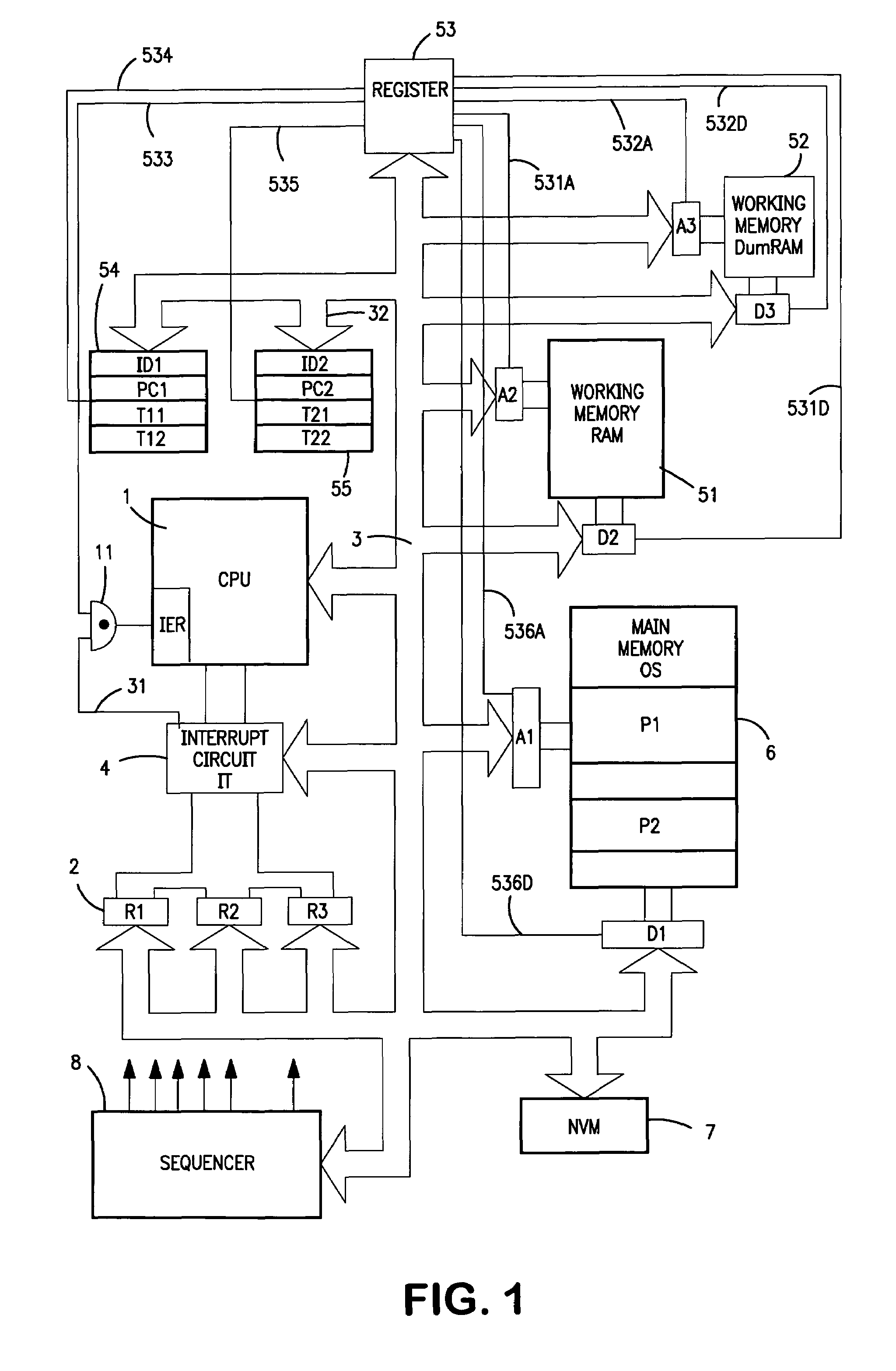
InactiveUS7036002B1Prevent illicit observationSimple design and diagnosisProgram initiation/switchingDetecting faulty computer hardwareMicrocomputerOperational system
An unpredictable microprocessor or microcomputer comprises a processor (1), a first working memory (51), a main memory (6) containing an operating system, a main program (P1) and a secondary program (P2), a second working memory (52), and switching means which, during the performance of the programs, makes it possible to switch from using one of the two working memories (51, 52) to using the other working memory, while preserving their contents. Switching means comprise at least one first block of registers (54) for storing the operating context of the programs in the main memory and a switching circuit (53) for enabling one of the working memories and the access registers (A1–a3) (d1–d3) associated with each memory (51, 52, 6) and controlled by said switching circuit (53).
Owner:CP8 TECH SA
Selectively controlling instruction execution in transactional processing
Execution of instructions in a transactional environment is selectively controlled. A TRANSACTION BEGIN instruction initiates a transaction and includes controls that selectively indicate whether certain types of instructions are permitted to execute within the transaction. The controls include one or more of an allow access register modification control and an allow floating point operation control.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Selectively controlling instruction execution in transactional processing
Execution of instructions in a transactional environment is selectively controlled. A TRANSACTION BEGIN instruction initiates a transaction and includes controls that selectively indicate whether certain types of instructions are permitted to execute within the transaction. The controls include one or more of an allow access register modification control and an allow floating point operation control.
Owner:IBM CORP
Selectively controlling instruction execution in transactional processing
Execution of instructions in a transactional environment is selectively controlled. A TRANSACTION BEGIN instruction initiates a transaction and includes controls that selectively indicate whether certain types of instructions are permitted to execute within the transaction. The controls include one or more of an allow access register modification control and an allow floating point operation control.
Owner:IBM CORP
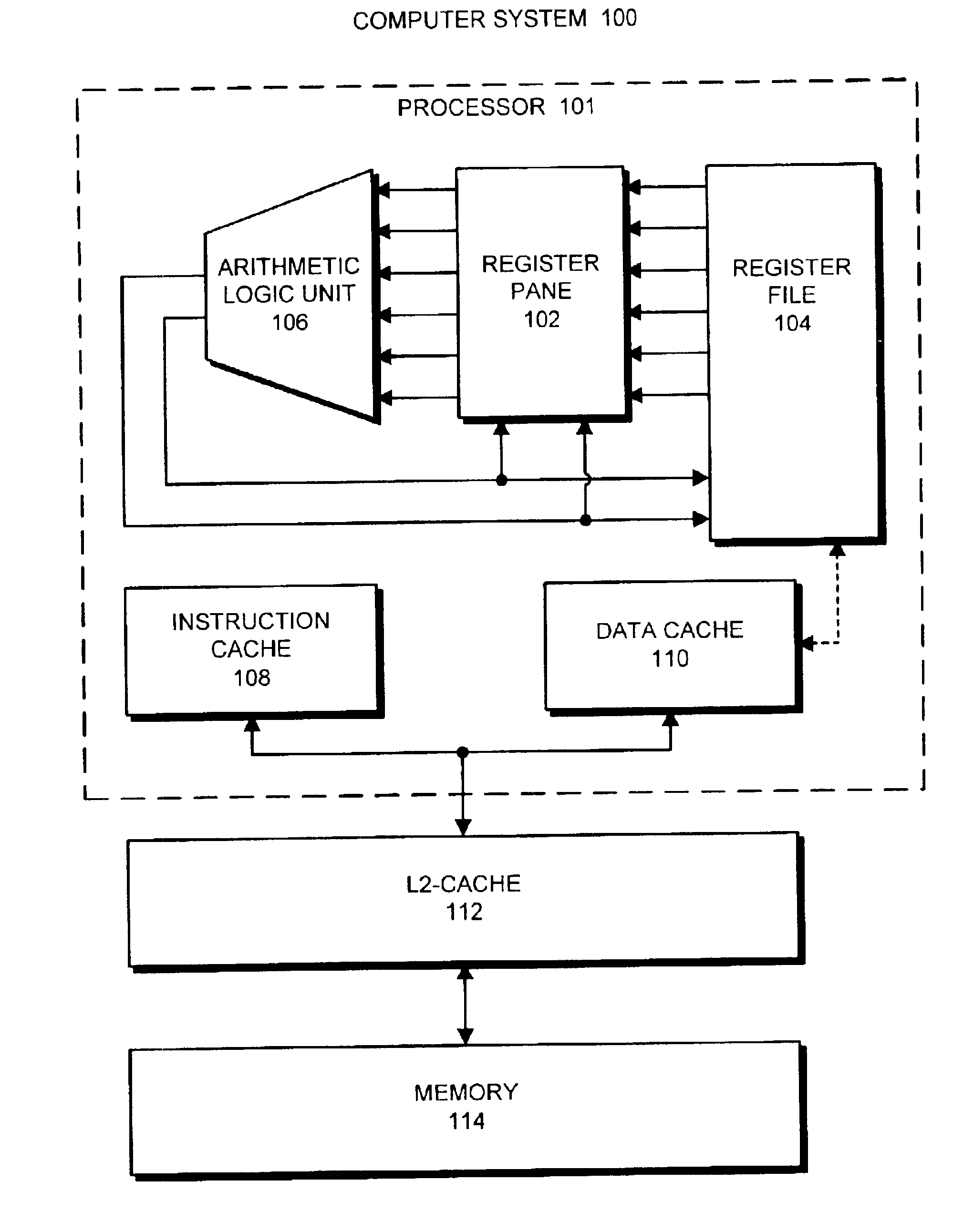
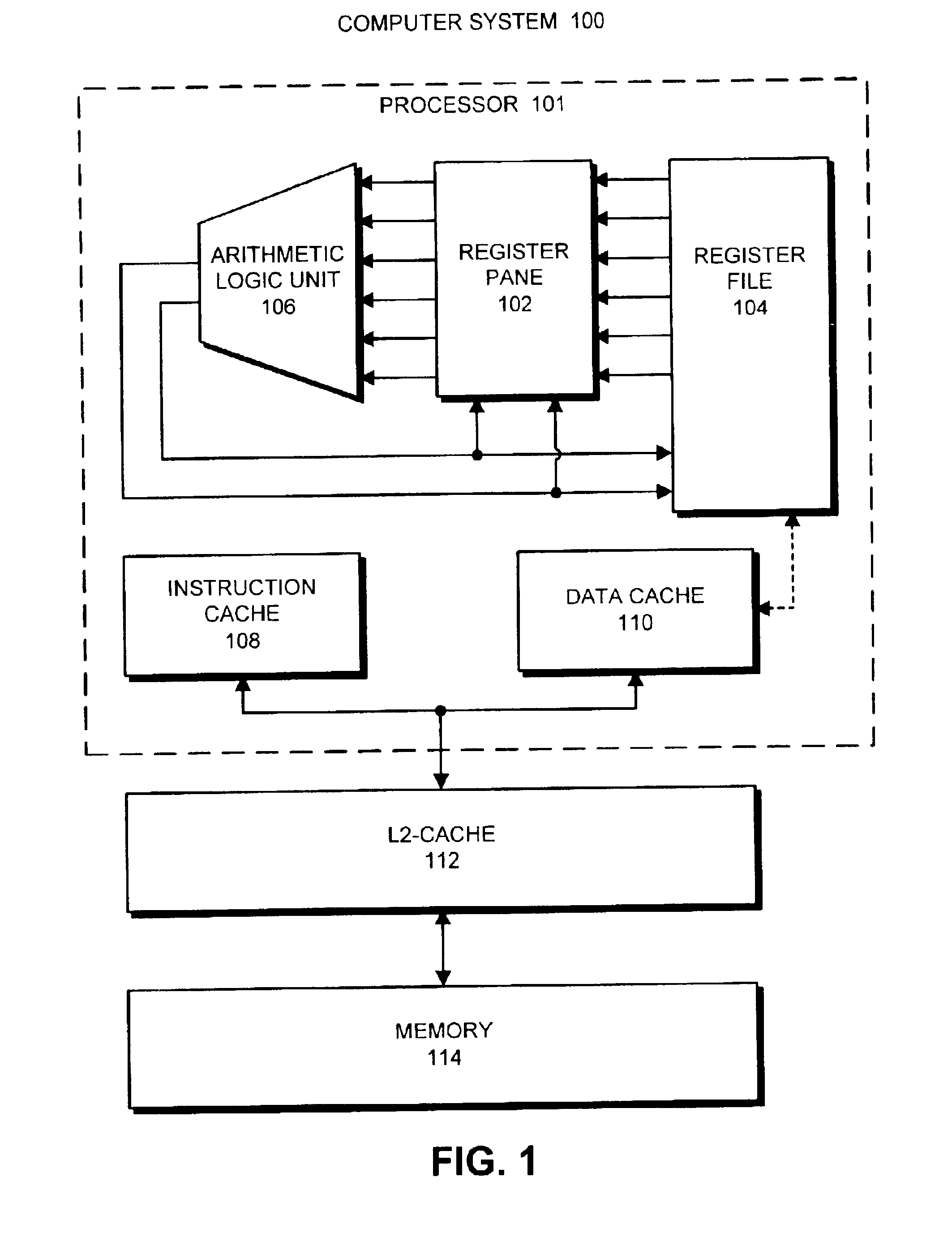
Method and apparatus for reducing register file access times in pipelined processors
ActiveUS6934830B2Shorten the timeDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionAccess timeProcessor register
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that reduces the time required to access registers from a register file within a processor. During operation, the system receives an instruction to be executed, wherein the instruction identifies at least one operand to be accessed from the register file. Next, the system looks up the operands in a register pane, wherein the register pane is smaller and faster than the register file and contains copies of a subset of registers from the register file. If the lookup is successful, the system retrieves the operands from the register pane to execute the instruction. Otherwise, if the lookup is not successful, the system retrieves the operands from the register file, and stores the operands into the register pane. This triggers the system to reissue the instruction to be executed again, so that the re-issued instruction retrieves the operands from the register pane.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
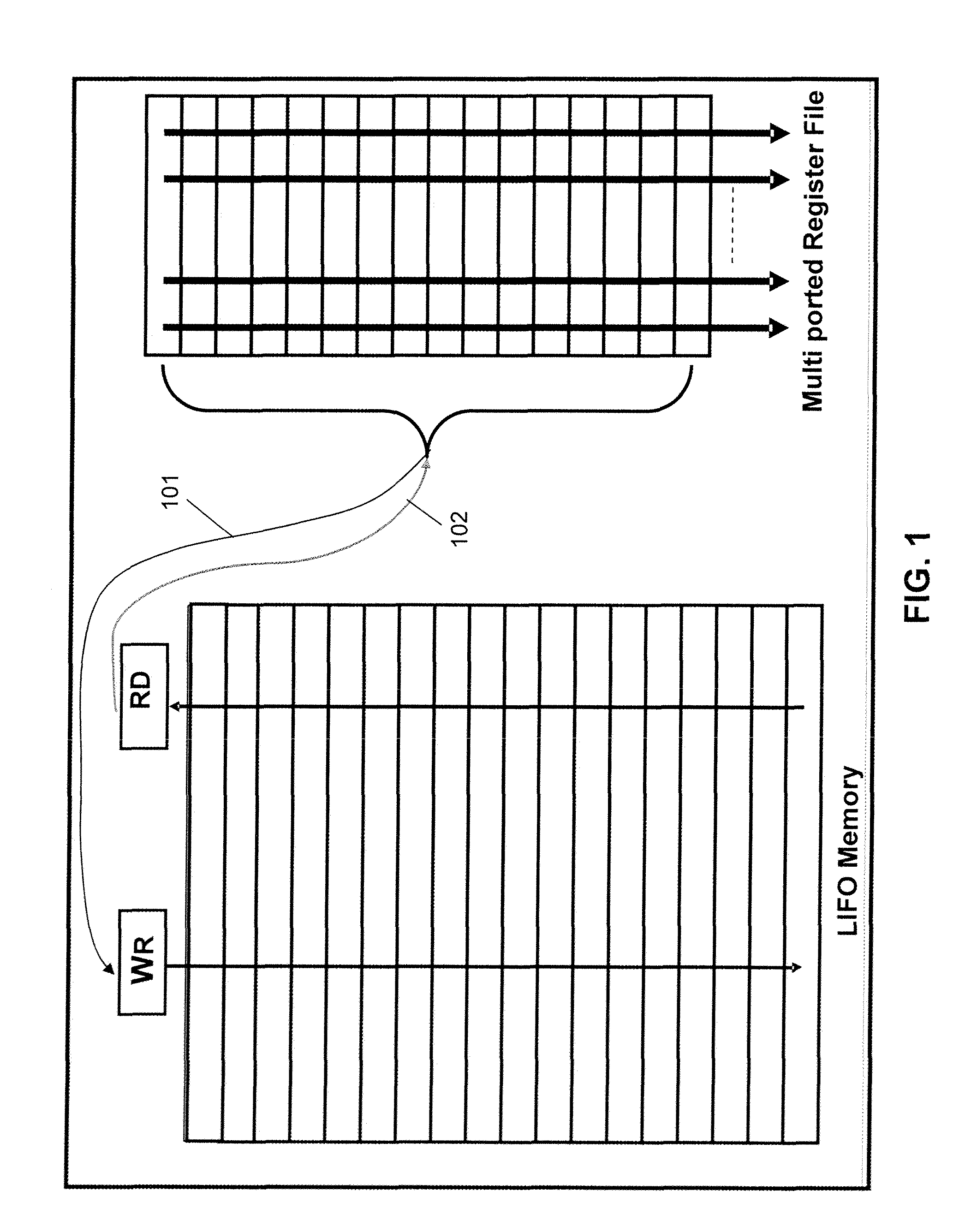
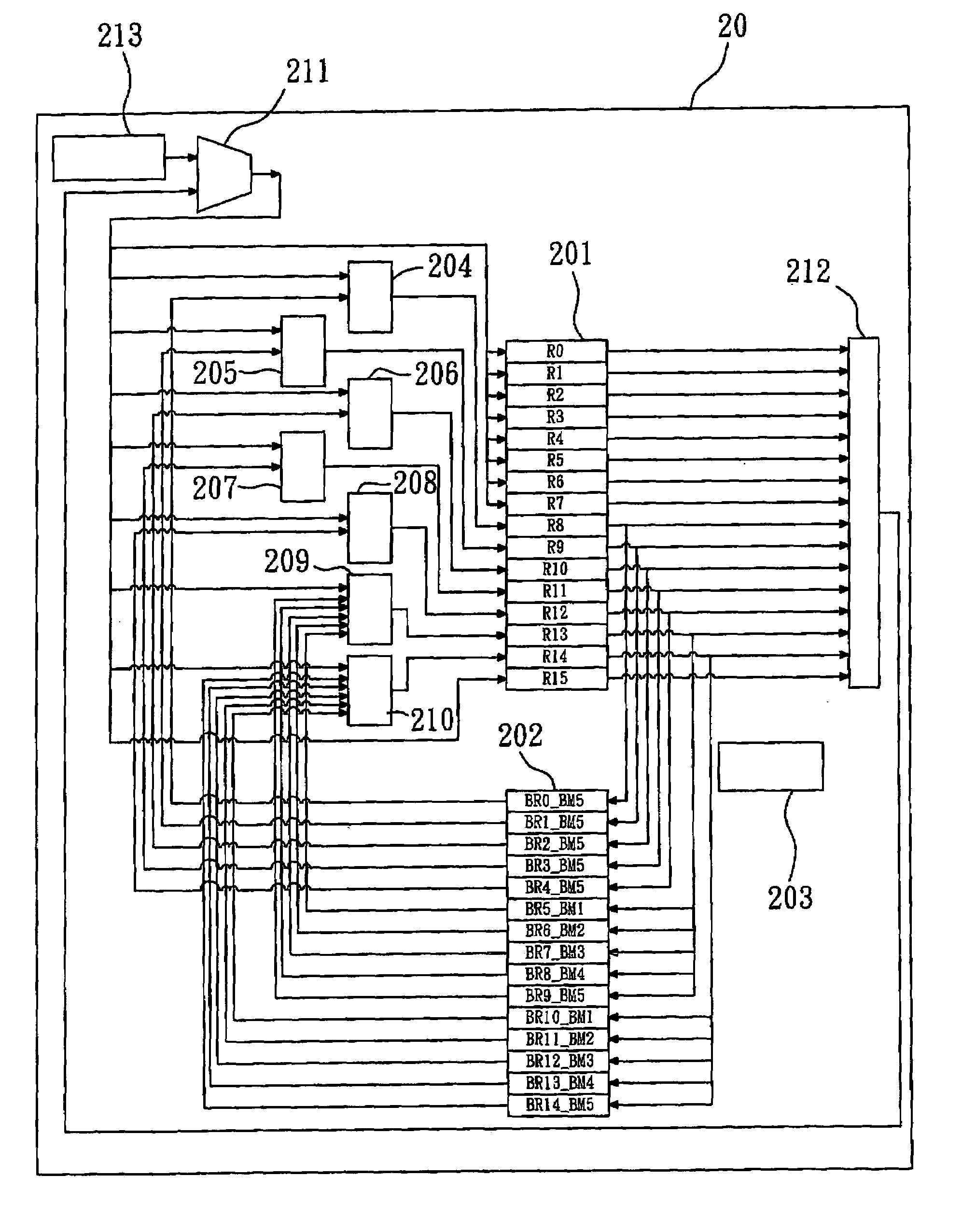
Automatic register backup/restore system and method
ActiveUS7143271B2Reduce data movementShorten access timeDigital computer detailsData acquisition and loggingProcessor registerOperation mode
Owner:NAT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
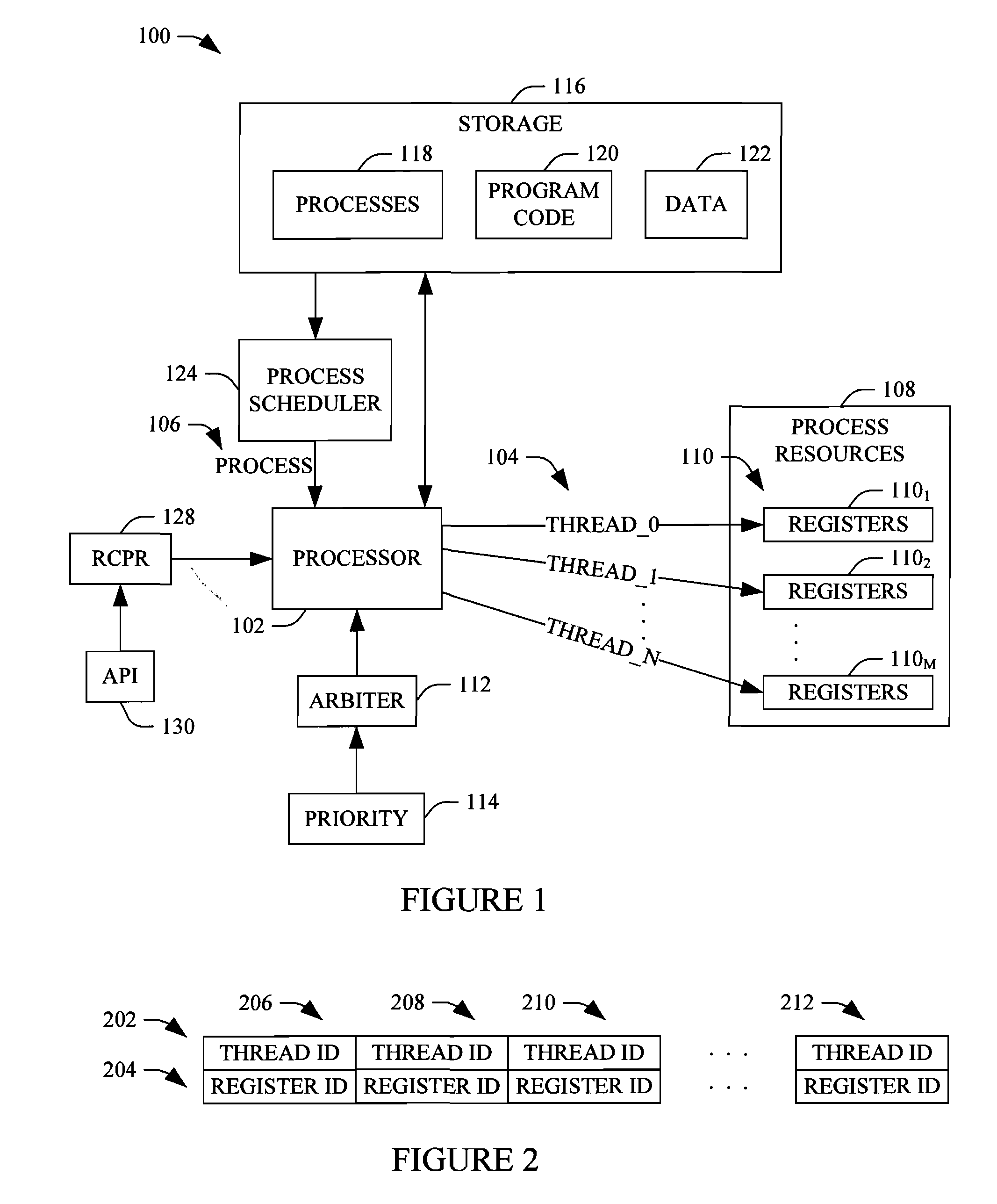
Integrated circuits with logic regions having input and output bypass paths for accessing registers
ActiveCN103577626ACAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignProcessor register
The invention relates to integrated circuits with logic regions having input and output bypass paths for accessing registers. Integrated circuits such as programmable integrated circuits may include programmable logic regions that can be configured to perform custom functions. Interconnects may be used to route signals throughout the integrated circuit. The programmable logic regions may have input selection circuitry for selecting and providing input signals from the interconnects to the programmable logic regions. The programmable logic regions may include look-up table circuitry for processing the input signals and registers for storing output signals from the look-up table circuitry. The programmable logic regions may include output selection circuitry for selecting which output signals are provided to output circuitry of the programmable logic regions. The programmable logic regions may include bypass paths that provide direct access to the registers from the interconnects by bypassing the input and output selection circuitry. Computer-aided design tools may be used to identify registers in a design that should be used for register pipelining.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
System and method for accessing registers of a hardware device in a graphical program
InactiveUS7743335B2ExecutionAvoid mistakesData processing applicationsComputer controlDrag and dropGraphics
A system and method for creating a graphical program which accesses registers of a hardware device. In one embodiment, a register access node or primitive may be included in a graphical program, such that when the graphical program is executed on the computer system, the register access node is operable to access (i.e., either read or write) registers of a hardware device in the computer system. The method may comprise first displaying a register access node in the graphical program in response to user input. For example, the user may select the register access node from a palette and drag and drop the register access node onto a window of the graphical program being created. The user may then configure the register access node to access one or more registers of a selected hardware device, e.g., by using a user interface for performing this configuration. In one embodiment, the computer may store a description of the hardware device, wherein the register access node uses the description of the hardware device to access registers of the hardware device during execution of the graphical program. In one embodiment, configuring the register access node may include displaying a list of registers or a list of fields of registers described in the description of the hardware device and receiving user input to select one or more of the registers from the list of registers. The list may also or instead comprise a list of mnemonic names of registers and / or a list of mnemonic names of fields in the registers. The user may thus configure the register access node to access selected registers described in the description of the hardware device.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Method to use an alternate I/O debug path
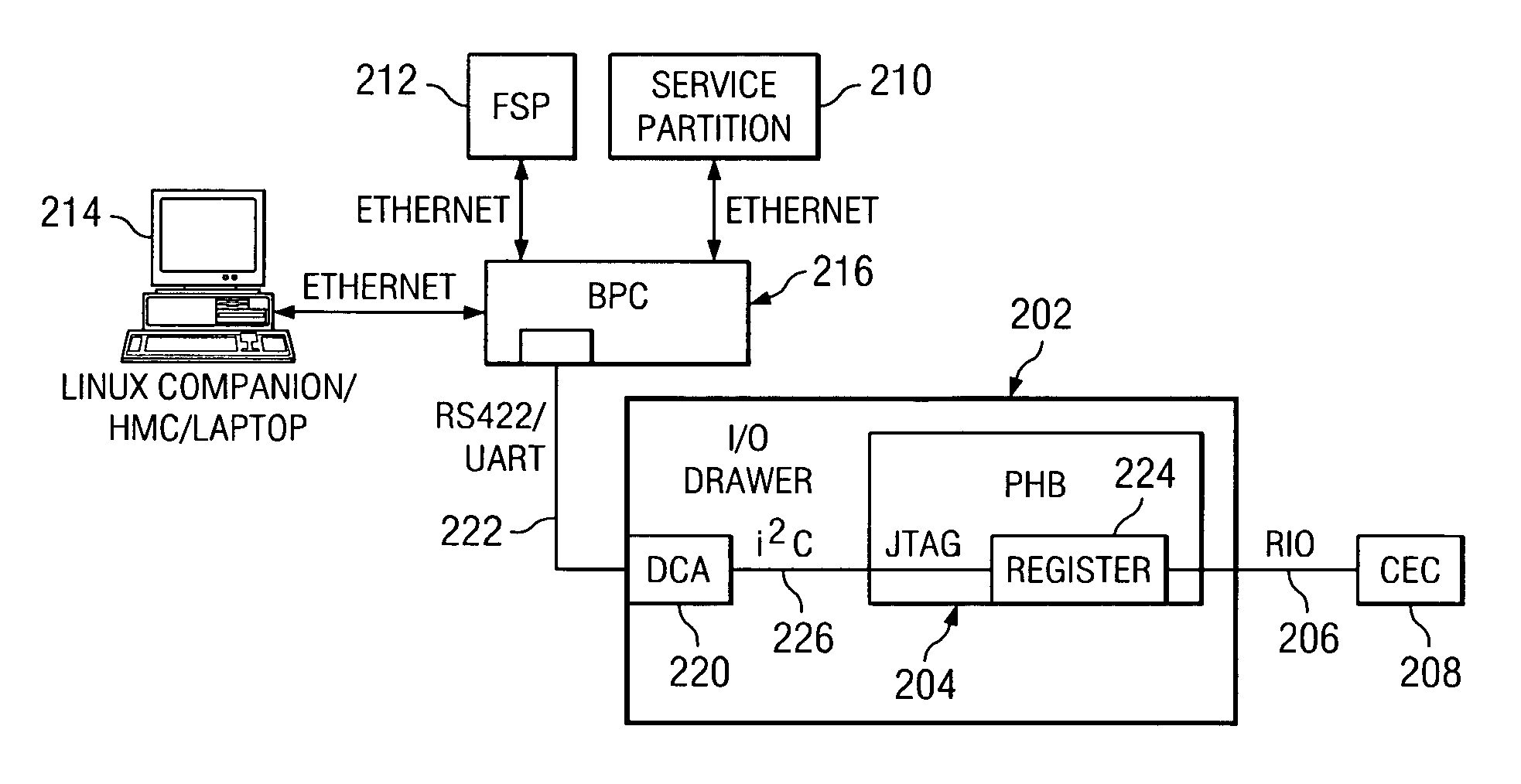
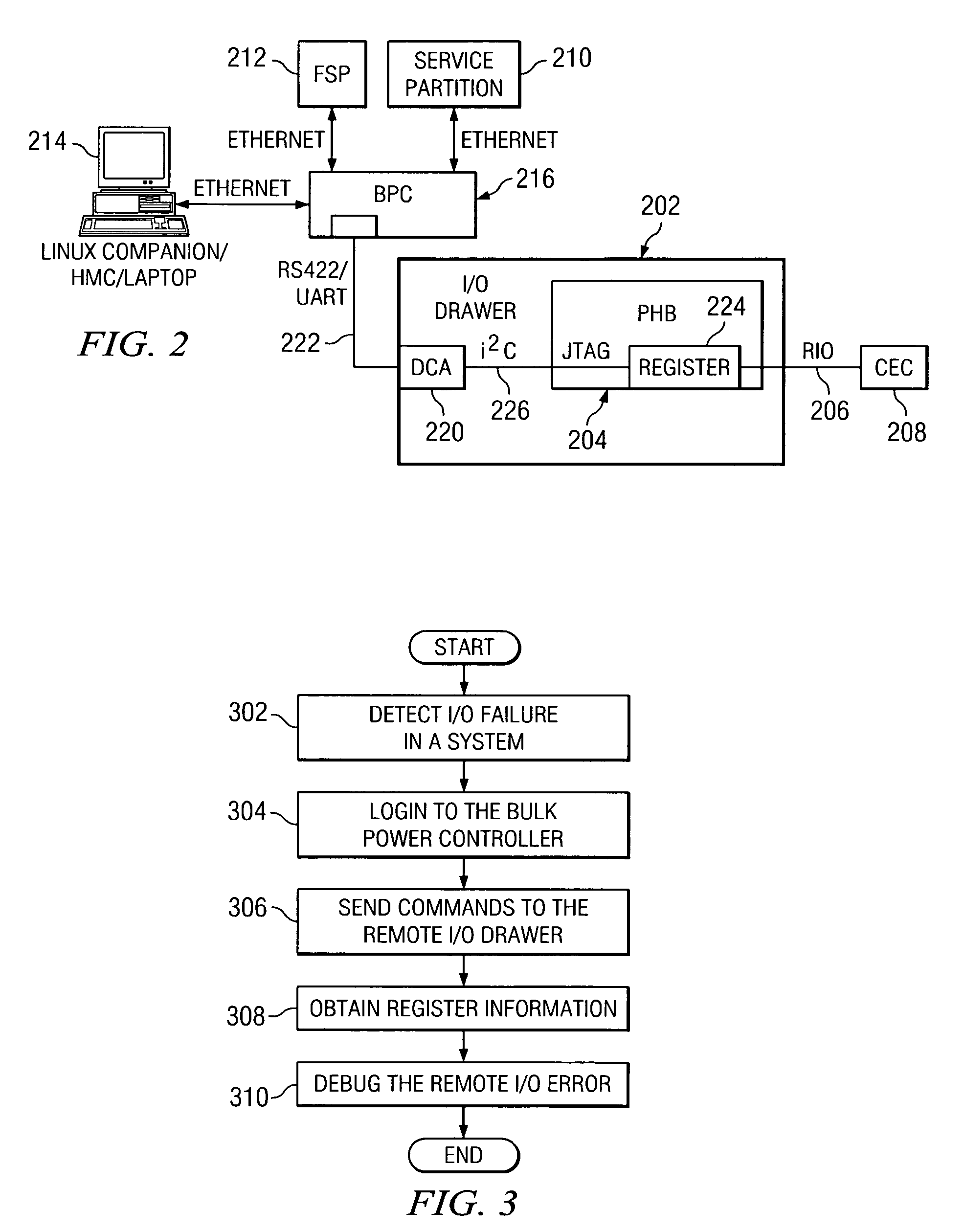
InactiveUS7290180B2Detecting faulty hardware by remote testSpecific program execution arrangementsData processing systemPower controller
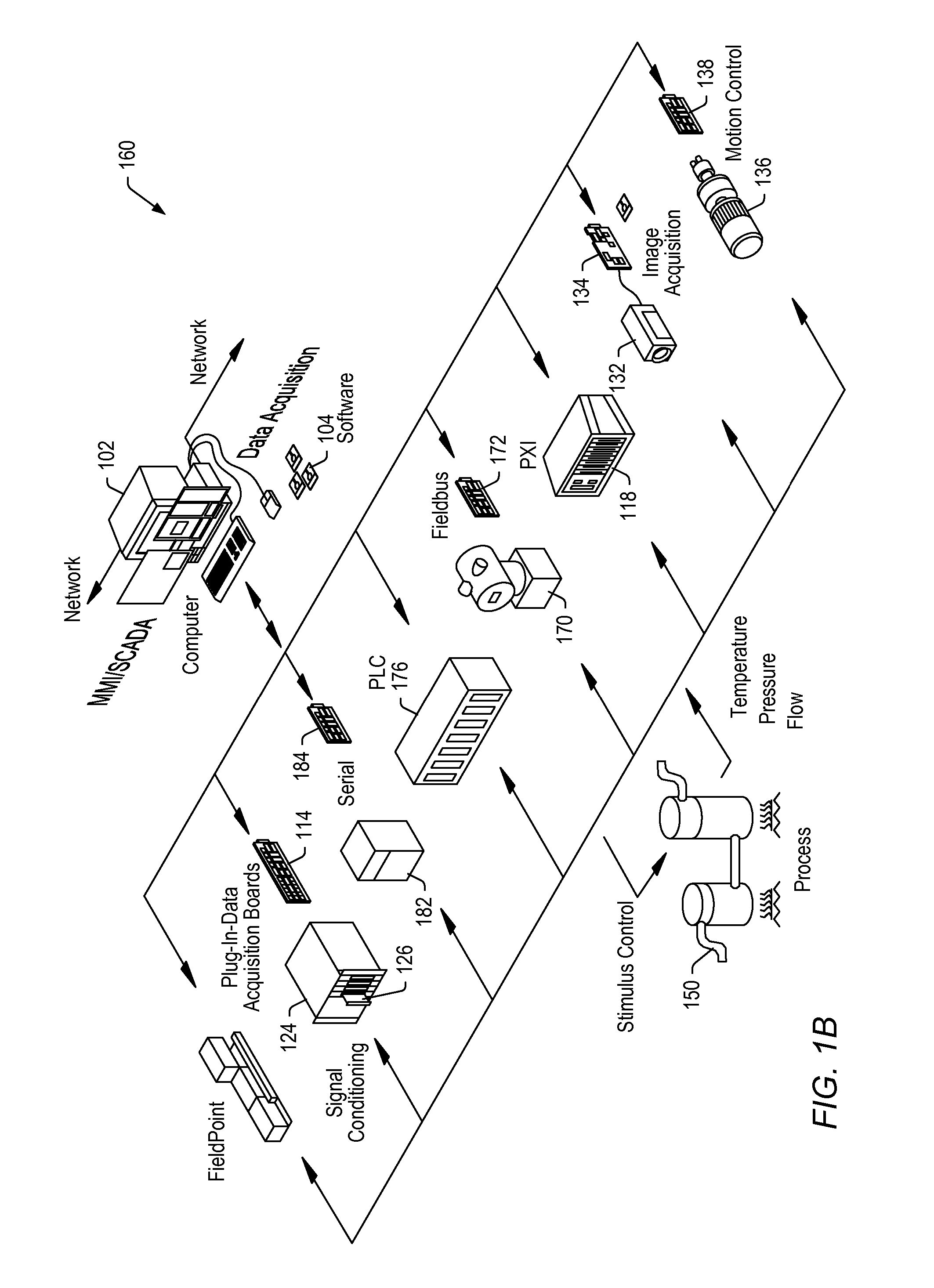
A method, system, and computer product for aiding in the debugging of an I / O failure. When an I / O failure is detected on a RIO drawer, a data processing system uses the bulk power controller to provide an alternate path, rather than using the existing RIO links, to access registers on the I / O drawers. The system logs onto the bulk power controller, which provides a communications path between the data processing system and the RIO drawer. The communications path allows the data processing system to read the chip registers on the I / O drawer. The data processing system captures I / O failure information in the I / O drawer using the communications path, wherein the I / O failure information is used to debug the I / O failure.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Multi-threaded processing
InactiveUS20090089553A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsParallel computingAccess register
A system includes a multi-threaded processor that executes an instruction of a process of an executing program. The multi-threaded processor includes at least a first and a second thread. First and second sets of source registers are respectively allocated to the first and second threads, and first and second sets of destination registers are respectively allocated to the first and second threads. A resource prefix configuration register includes mappings between each of the source and destination registers and the threads. The multi-threaded processor, during execution of the instruction by one of the first or the second threads of execution, accesses the source and destination registers based on the mapping, wherein at least one of the accessed registers is allocated to the other of the first or the second thread of execution.
Owner:IBM CORP
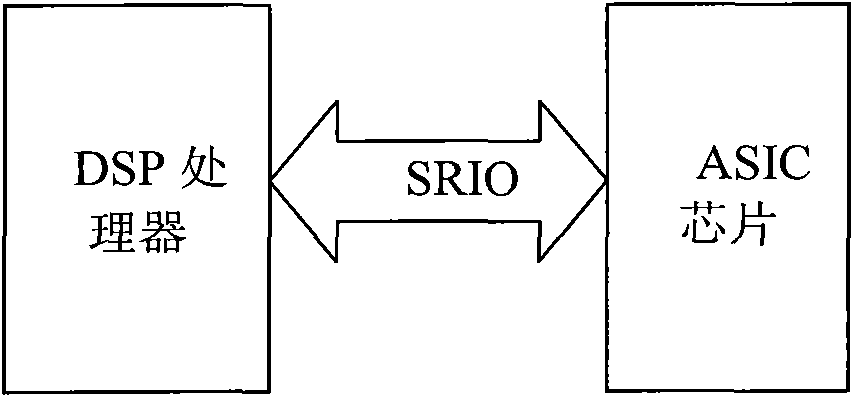
Method and device for accessing registers
InactiveCN101582058ACentralized accessImprove efficiencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWireless communicationProcessor registerComputer module
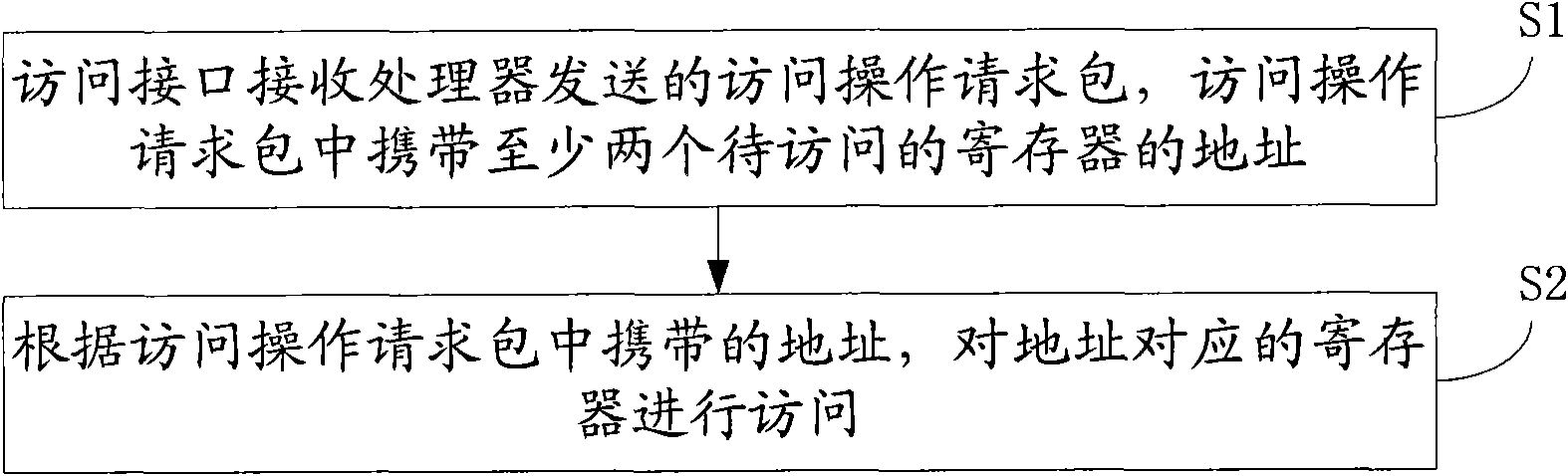
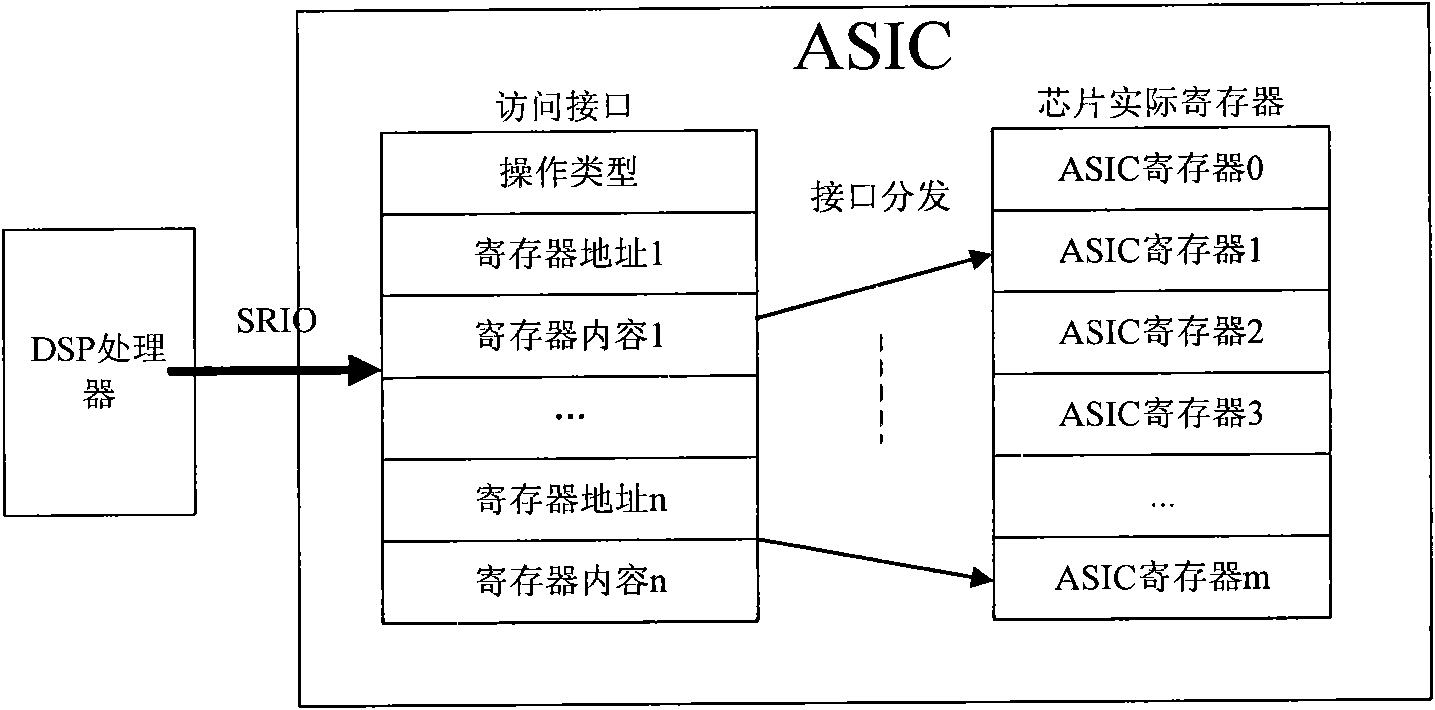
The invention discloses a method and a device for accessing registers, belonging to the communication field. The method comprises the following steps: an access interface receives an accessing operation request packet sent by a processor; the accessing operation request packet carries the addresses of at least two registers to be accessed; the registers corresponding to the addresses are accessed according to the addresses carried in the accessing operation request packet. The device comprises a receiving module and an access module. When a DSP processor accesses an ASIC chip, through the set access interface, the invention realizes concentrated access to the registers and increases the useful data load in single accessing operation, thereby effectively improving the efficiency of the SRIO interface and utilization of the transmission bandwidth.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System and method for automatically generating a hierarchical register consolidation structure
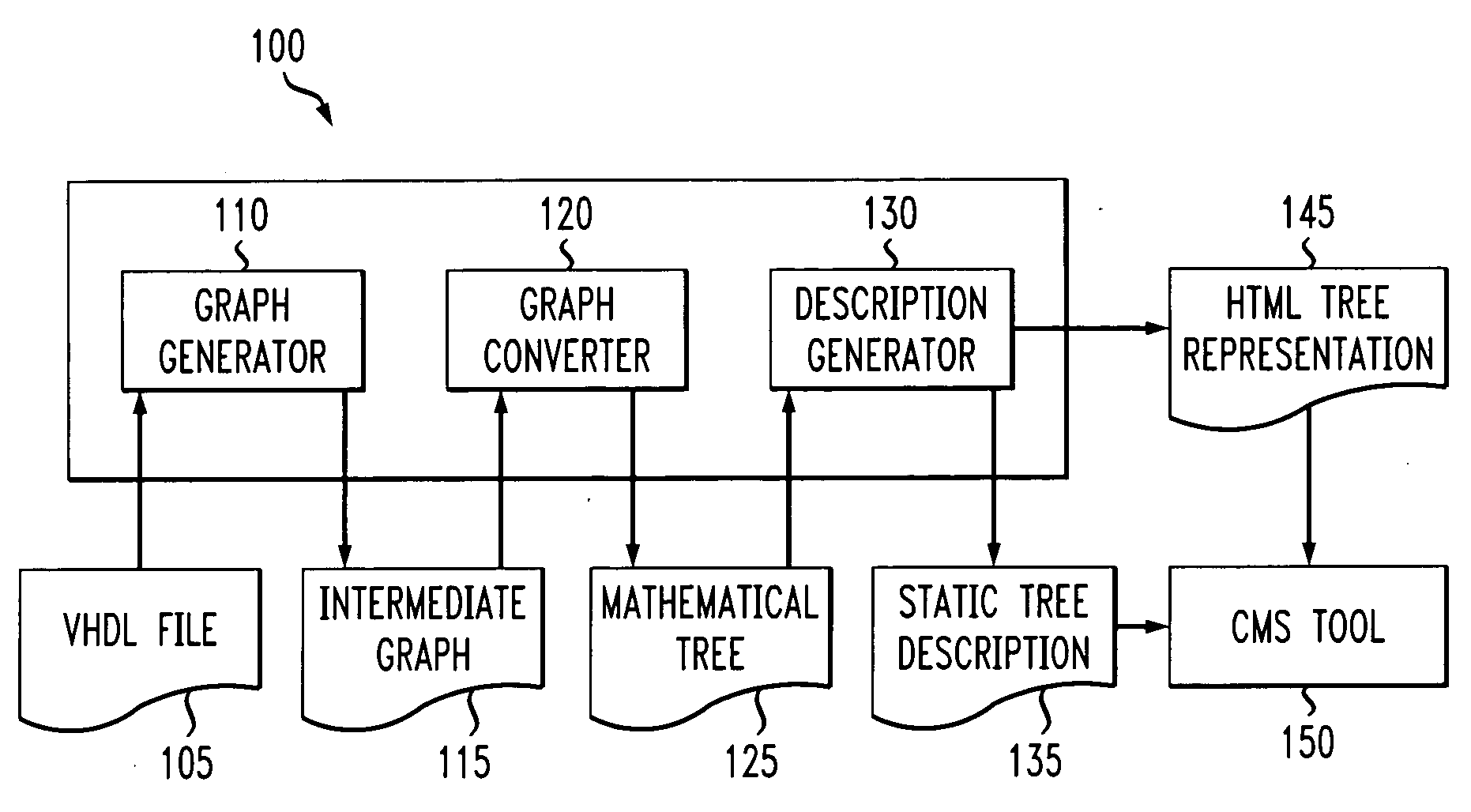
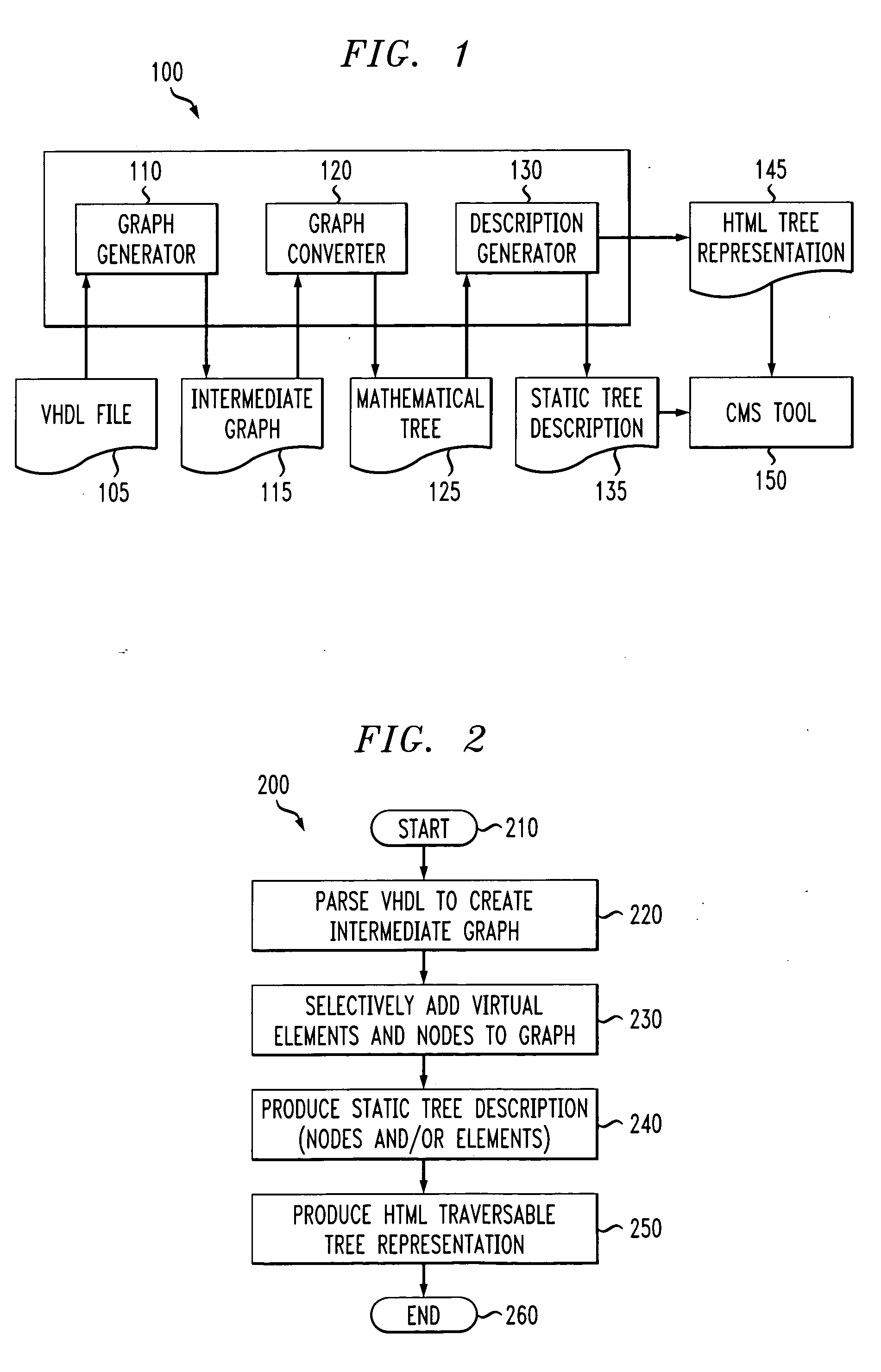
A system for, and method of, automatically generating a hierarchical register consolidation structure. In one embodiment, the system includes: (1) a graph generator that parses a High-level Design Language (HDL) file to generate an intermediate graph containing definitions of microprocessor-accessible registers, node interrelationships and summary bits and masks associated with alarm registers, (2) a graph converter, associated with the graph generator, that selectively adds virtual elements and nodes to the intermediate graph to transform the intermediate graph into a mathematical tree and (3) a description generator, associated with the graph converter, that employs the mathematical tree to generate a static tree description in a programming language suitable for use by a device-independent condition management structure.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and device for supporting vector condition memory access
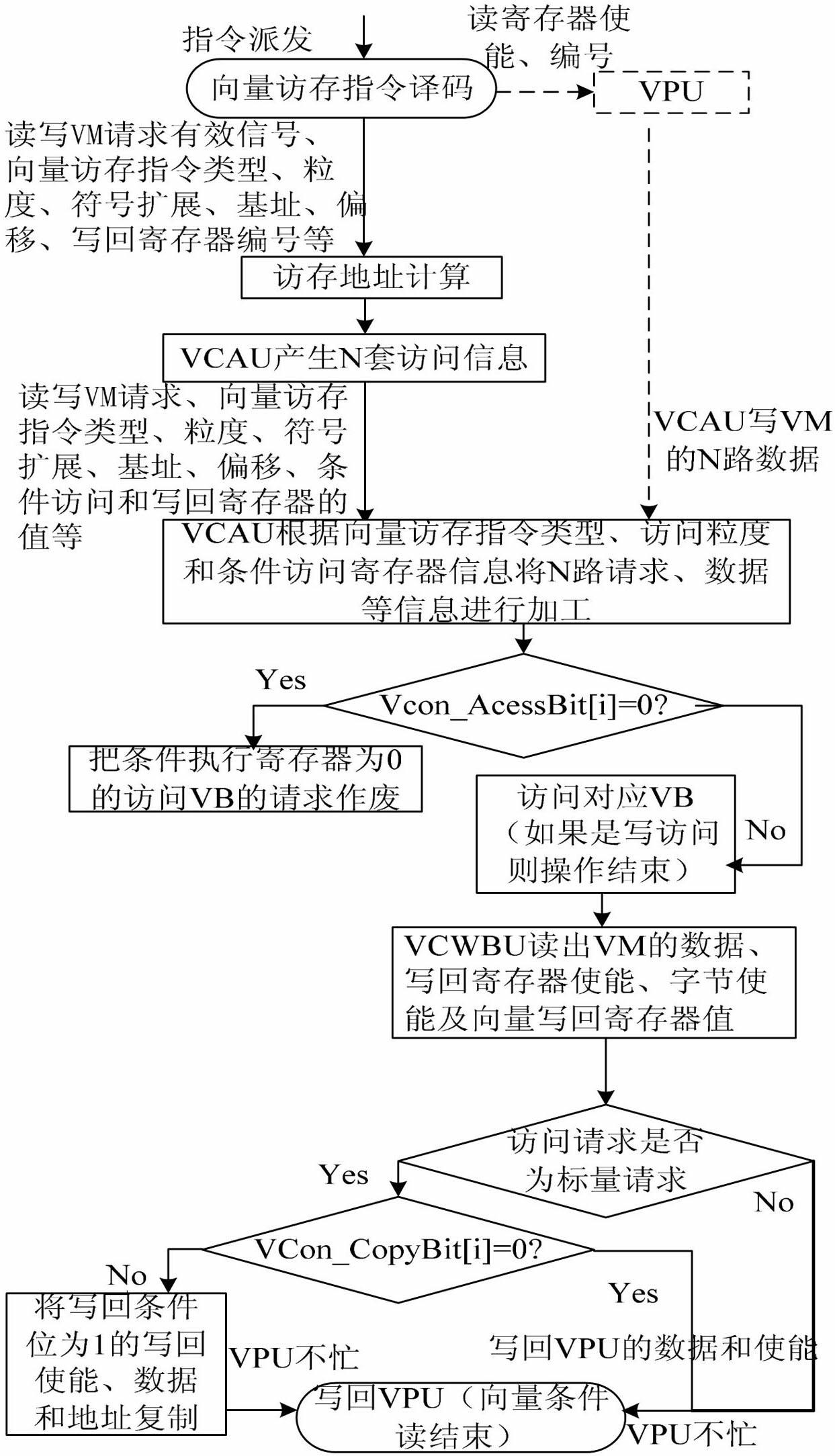
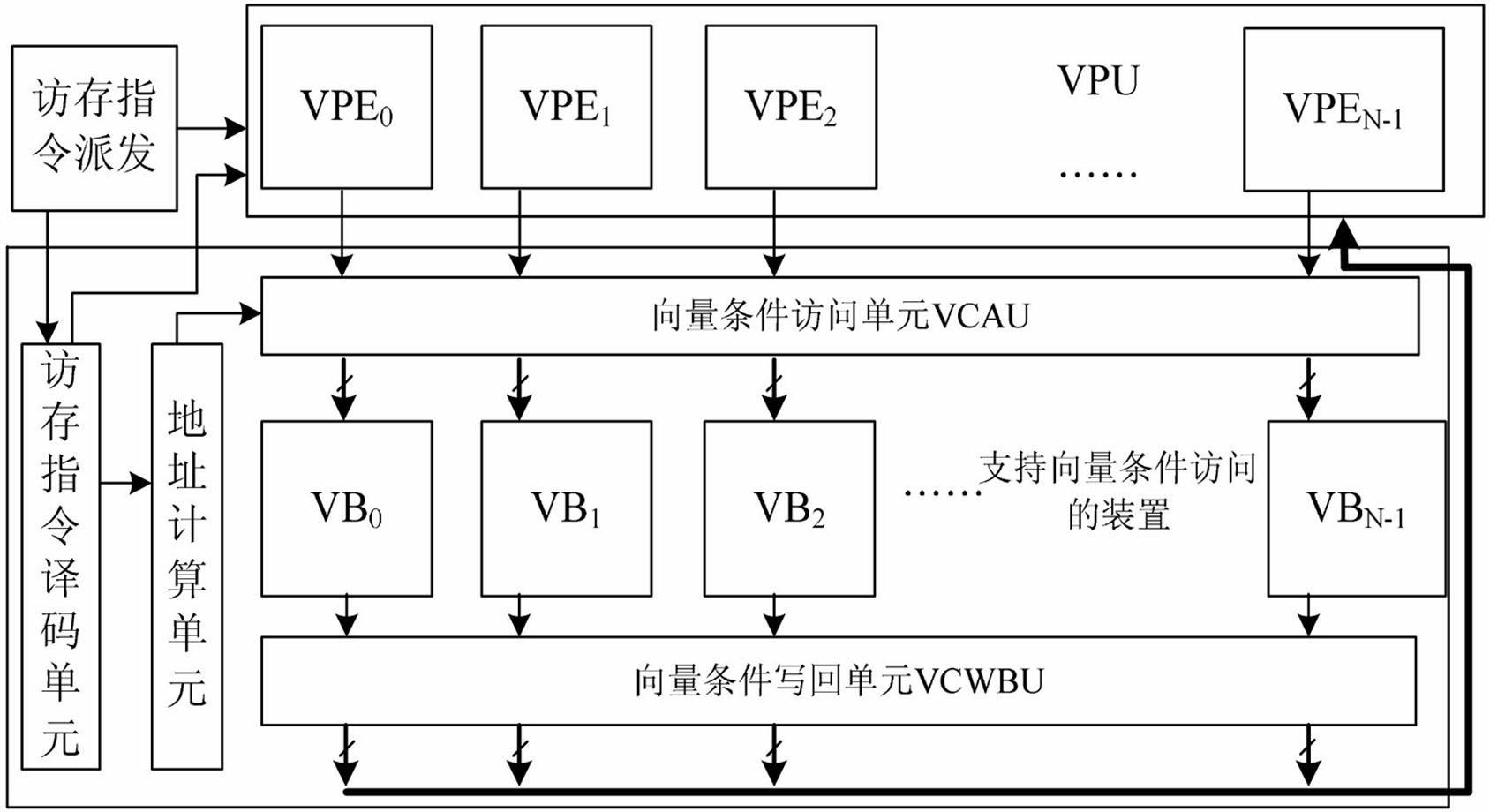
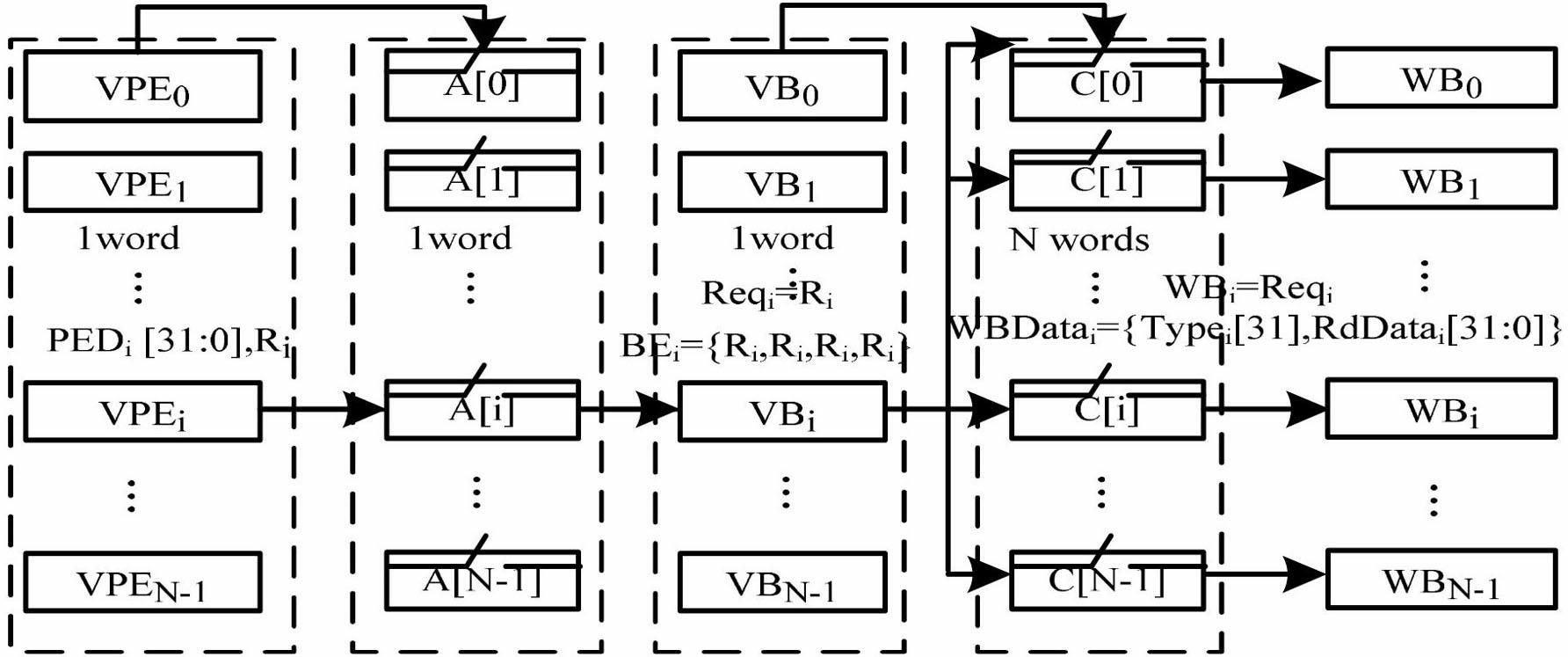
ActiveCN102629238AIncrease profitAvoid organizationConcurrent instruction executionProcessor registerParallel computing
Disclosed are a method and a device for supporting vector condition memory access. The method includes the steps that firstly, two programmable registers are set in a vector condition access unit (VCAC): an N-bit vector processing element (VPE) condition access register and an N-bit vector bank (VB) condition write back register; secondly, an instruction decoding unit receives a vector memory access instruction sent by an instruction distribution component to perform instruction decoding and decodes the memory access information in the instruction; thirdly, an address computing unit generates visiting requests (vrs) and addresses for visiting N VBs according to the memory access information and sends to the VCAU; fourthly, the VCAU subjects the all memory access information to conditional arrangement and data alignment; and fifthly the write back information of each VB access pipeline is input into a vector condition write back unit (VCWBU) for arrangement. The device comprises a vector memory (VM) which is composed of a memory access instruction decoding unit, the address computing unit, the VB, the VCAU and the VCWBU. According to the method and the device for supporting the vector condition memory access, the flexibility of memory access operation is improved, and the use ratio and memory access efficiency of the VM are effectively improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com