Patents
Literature
41 results about "Built in self repair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
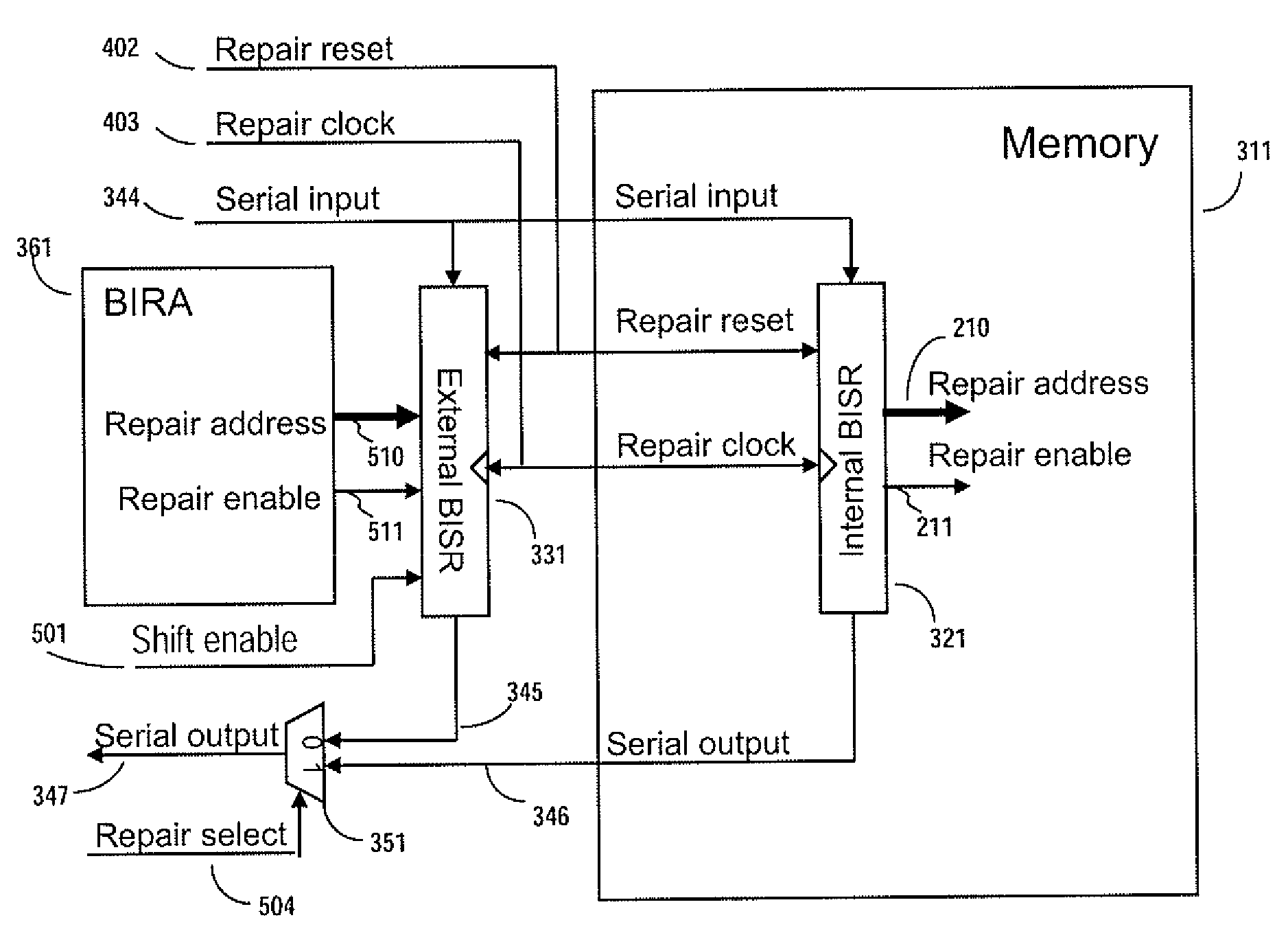
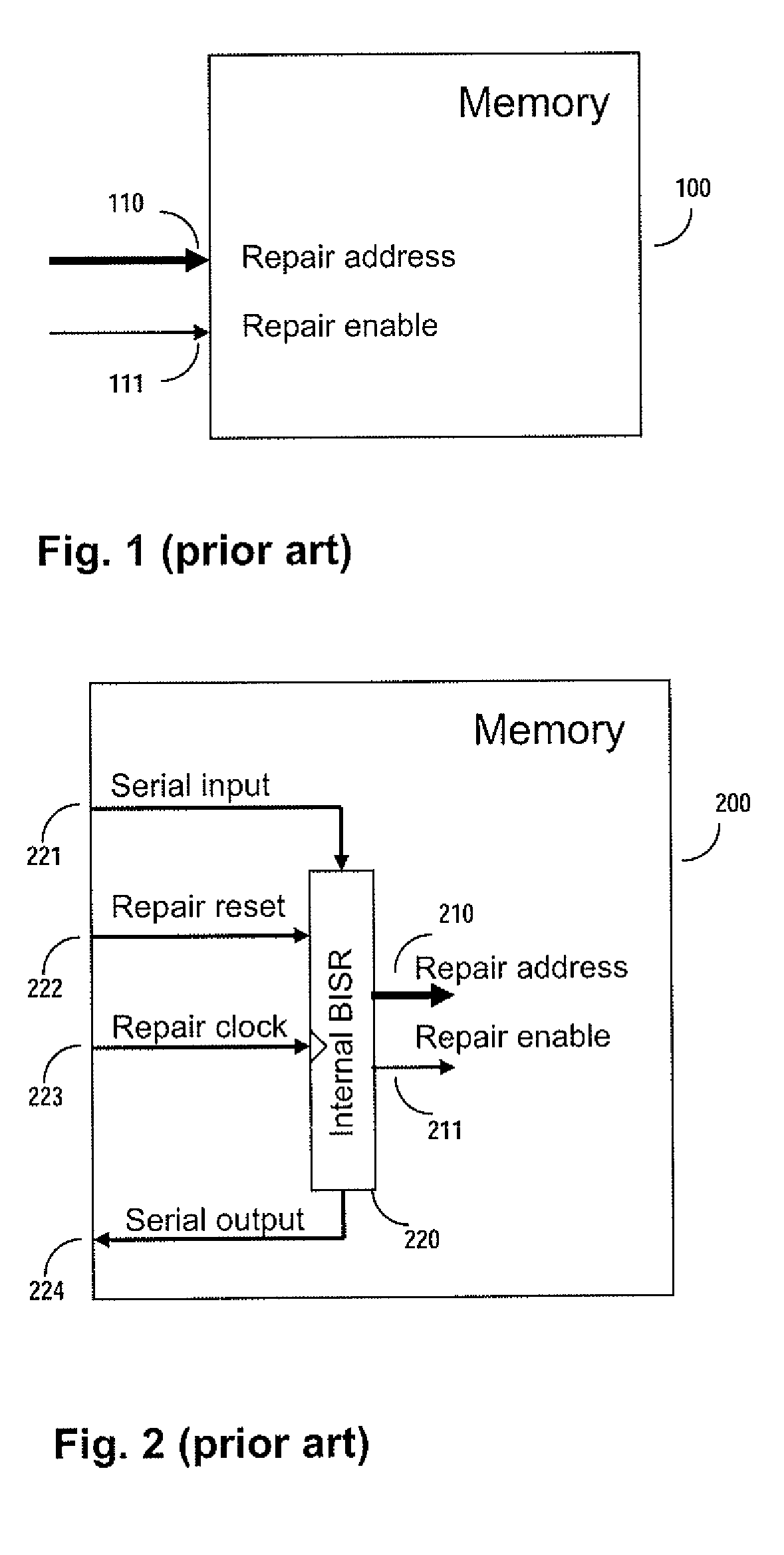
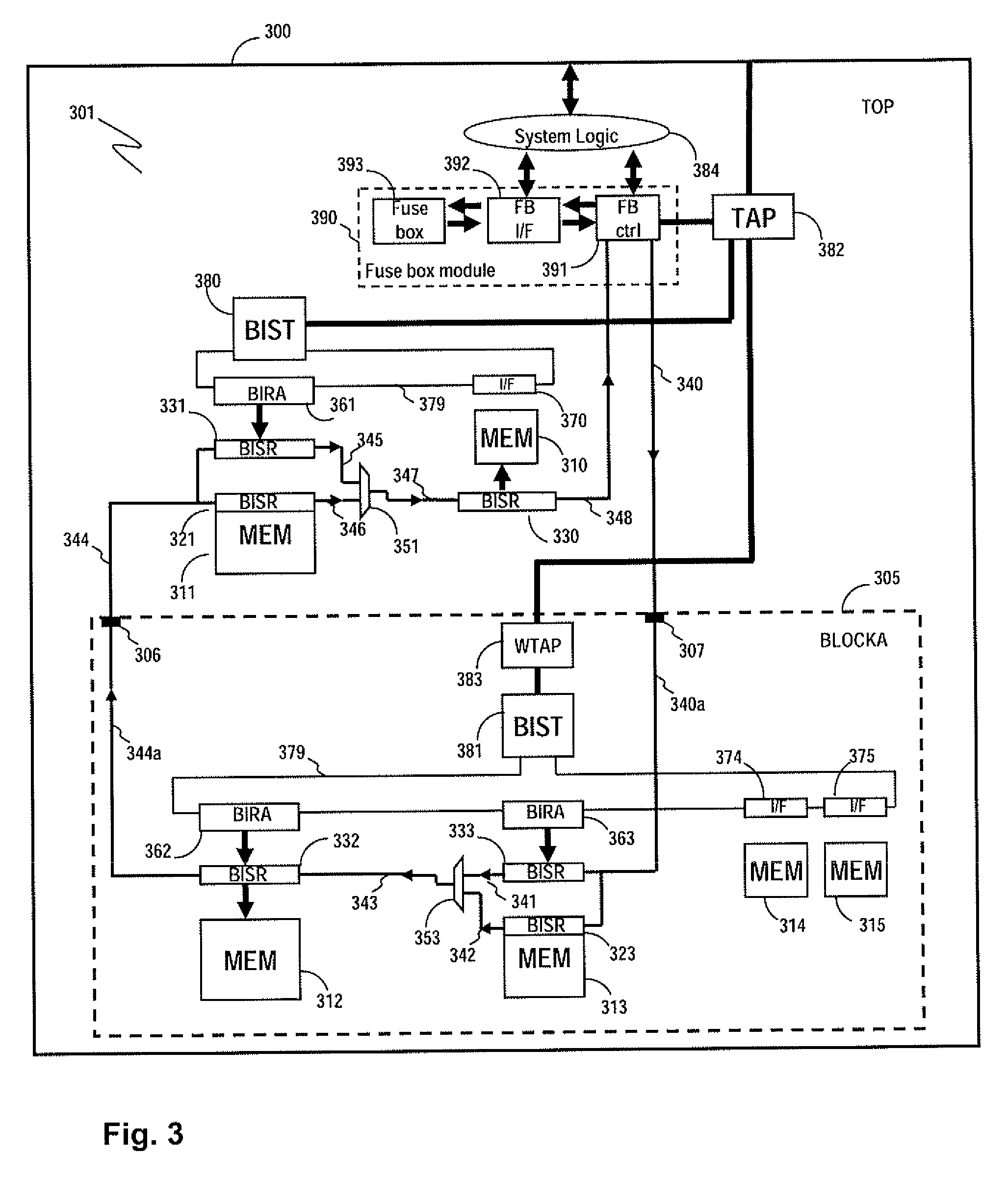
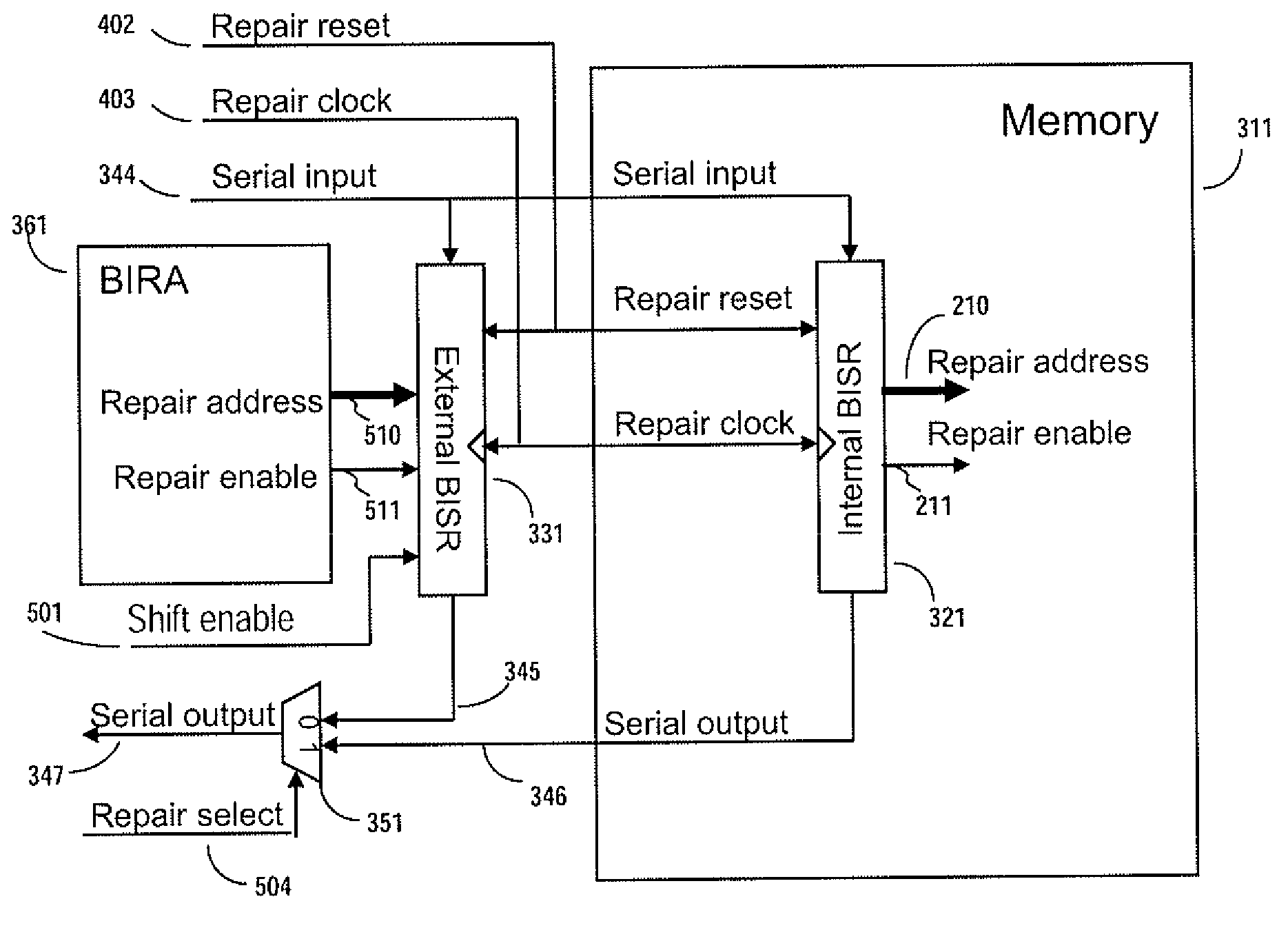
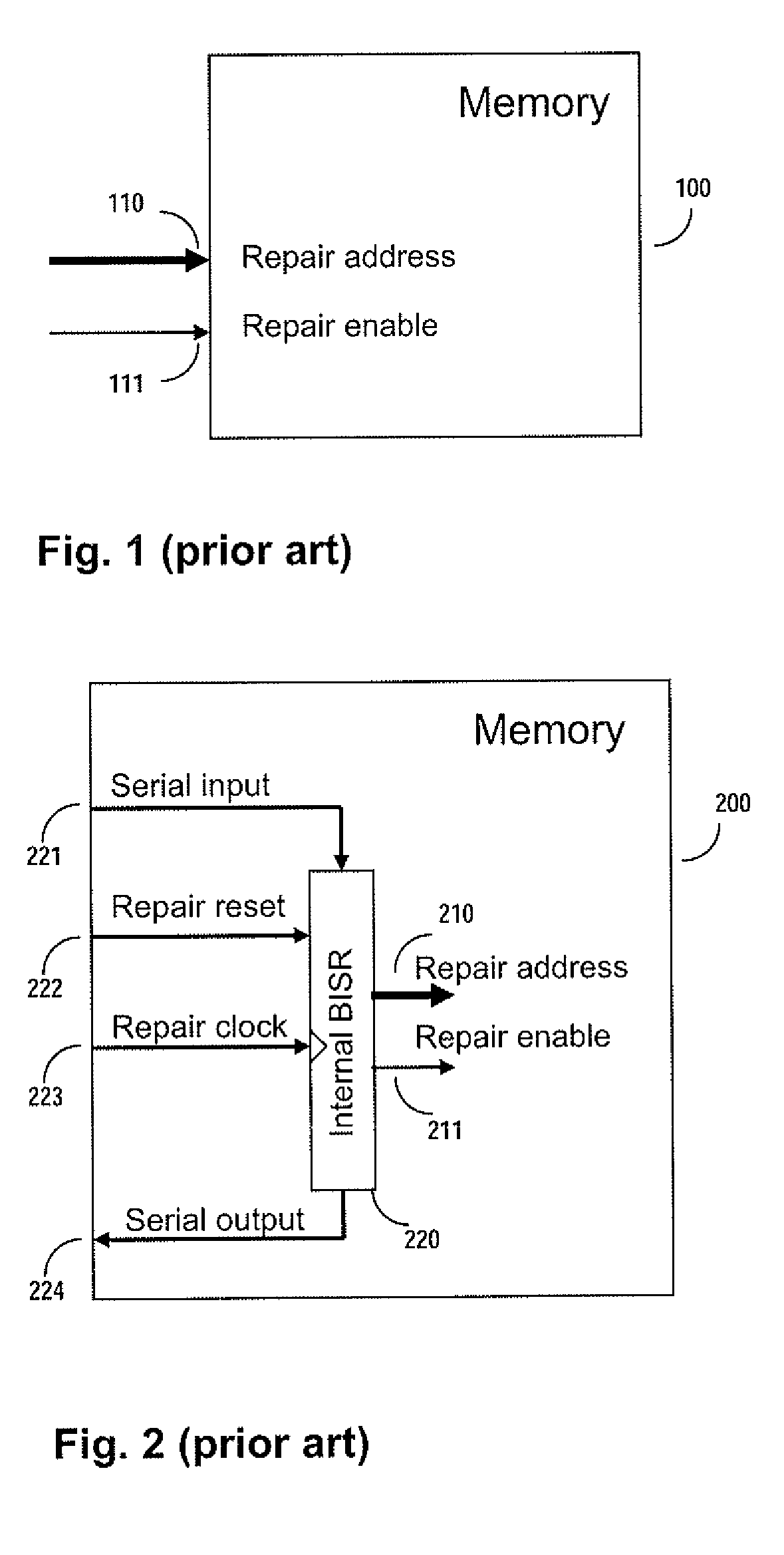
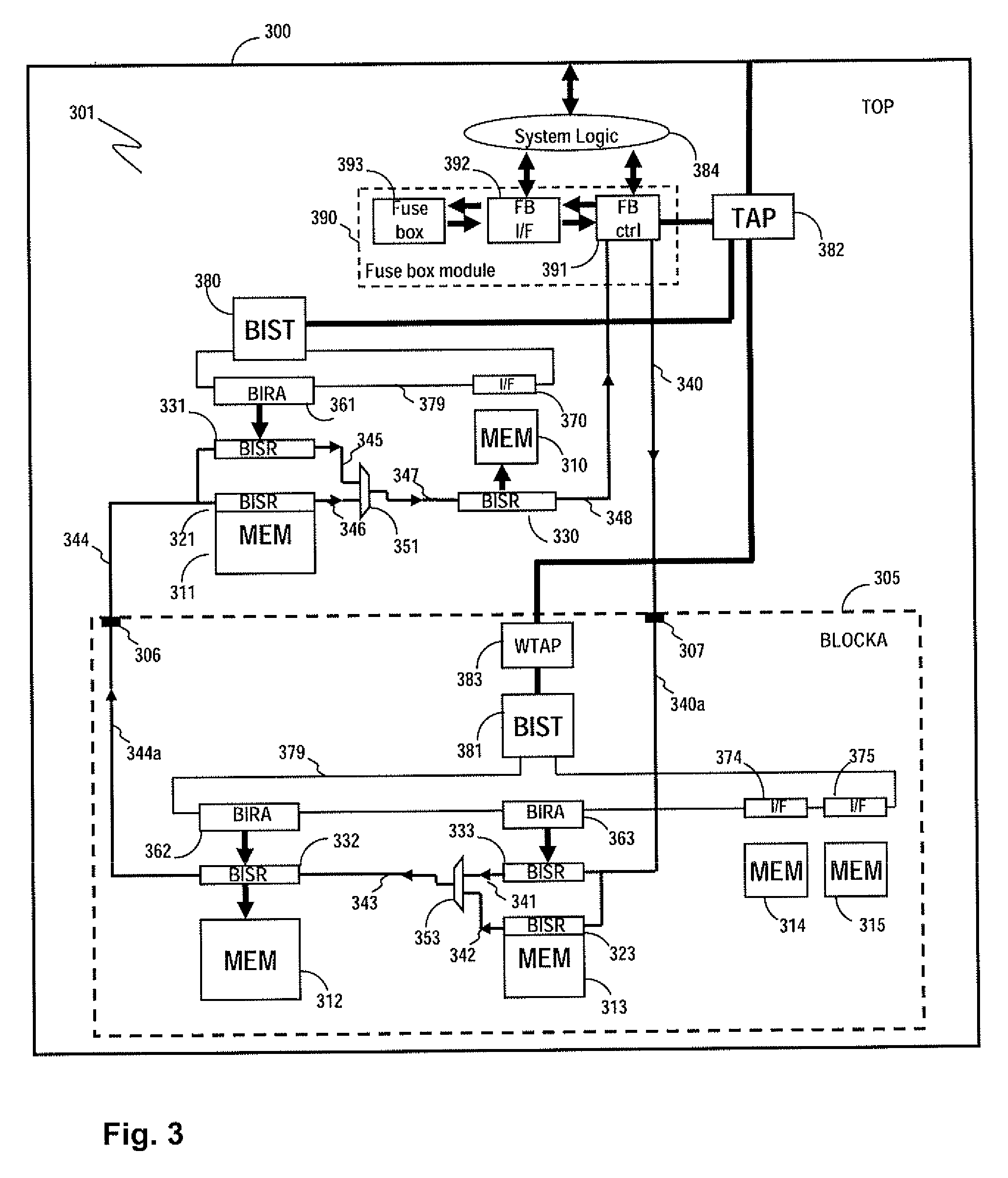
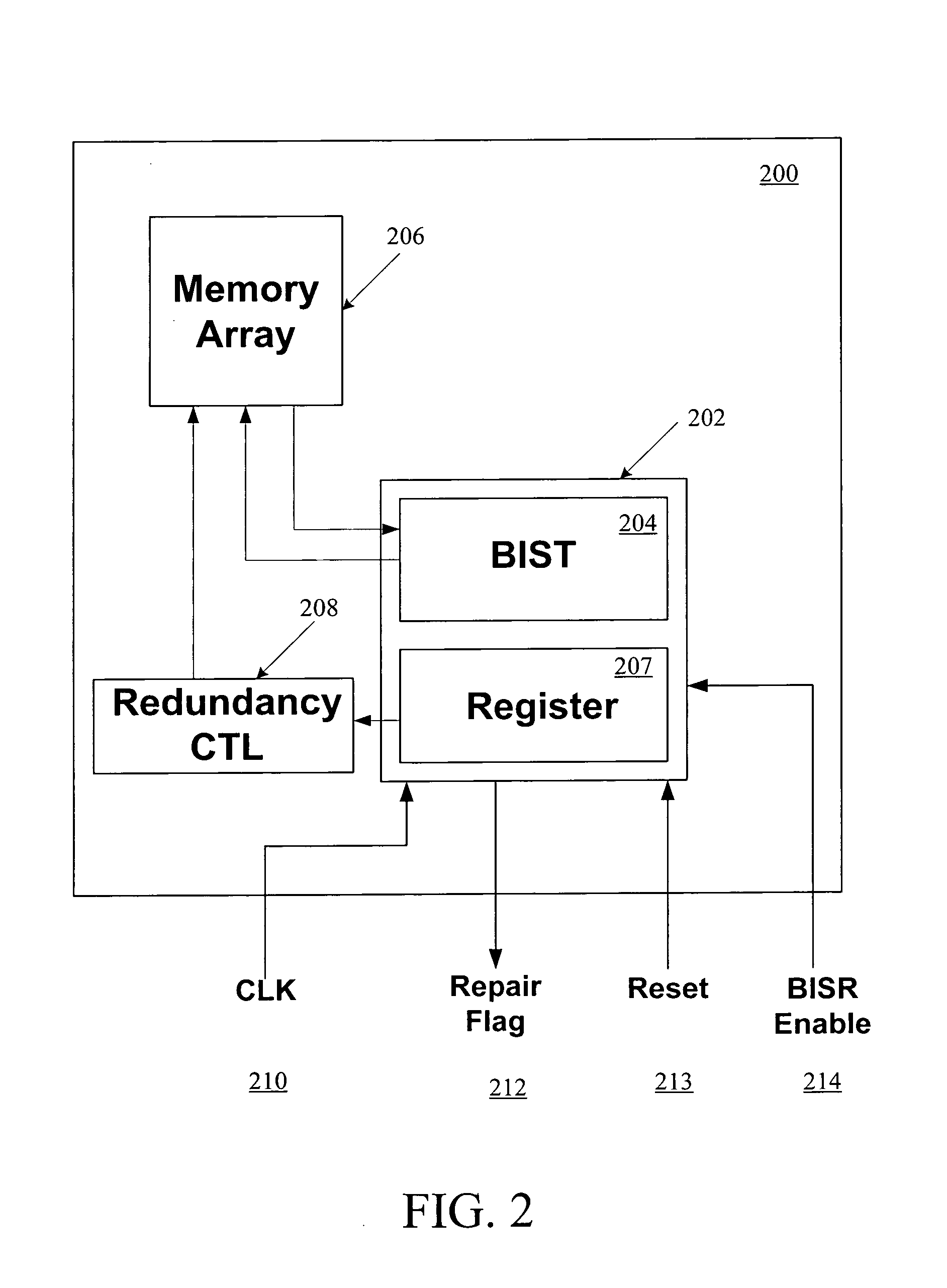
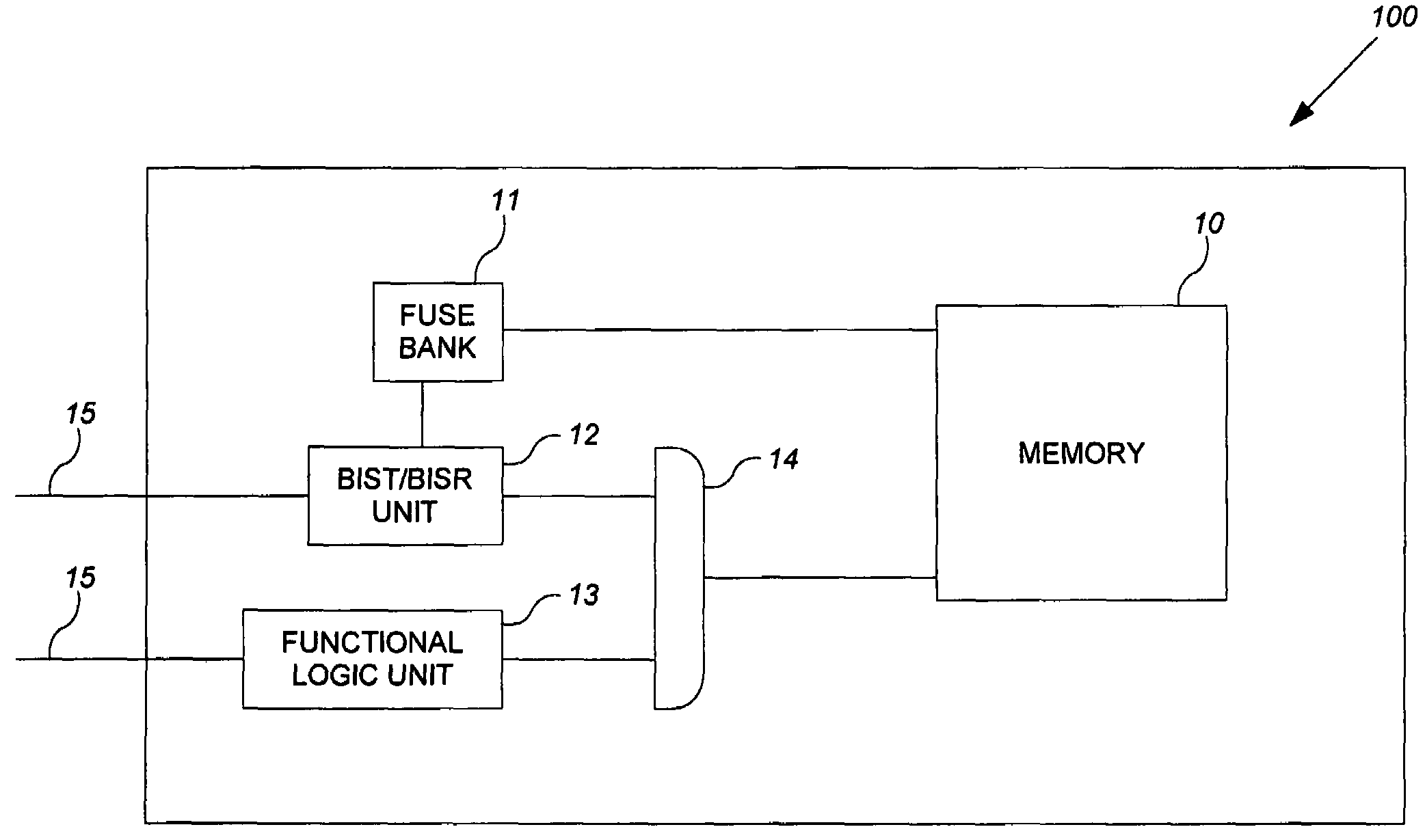
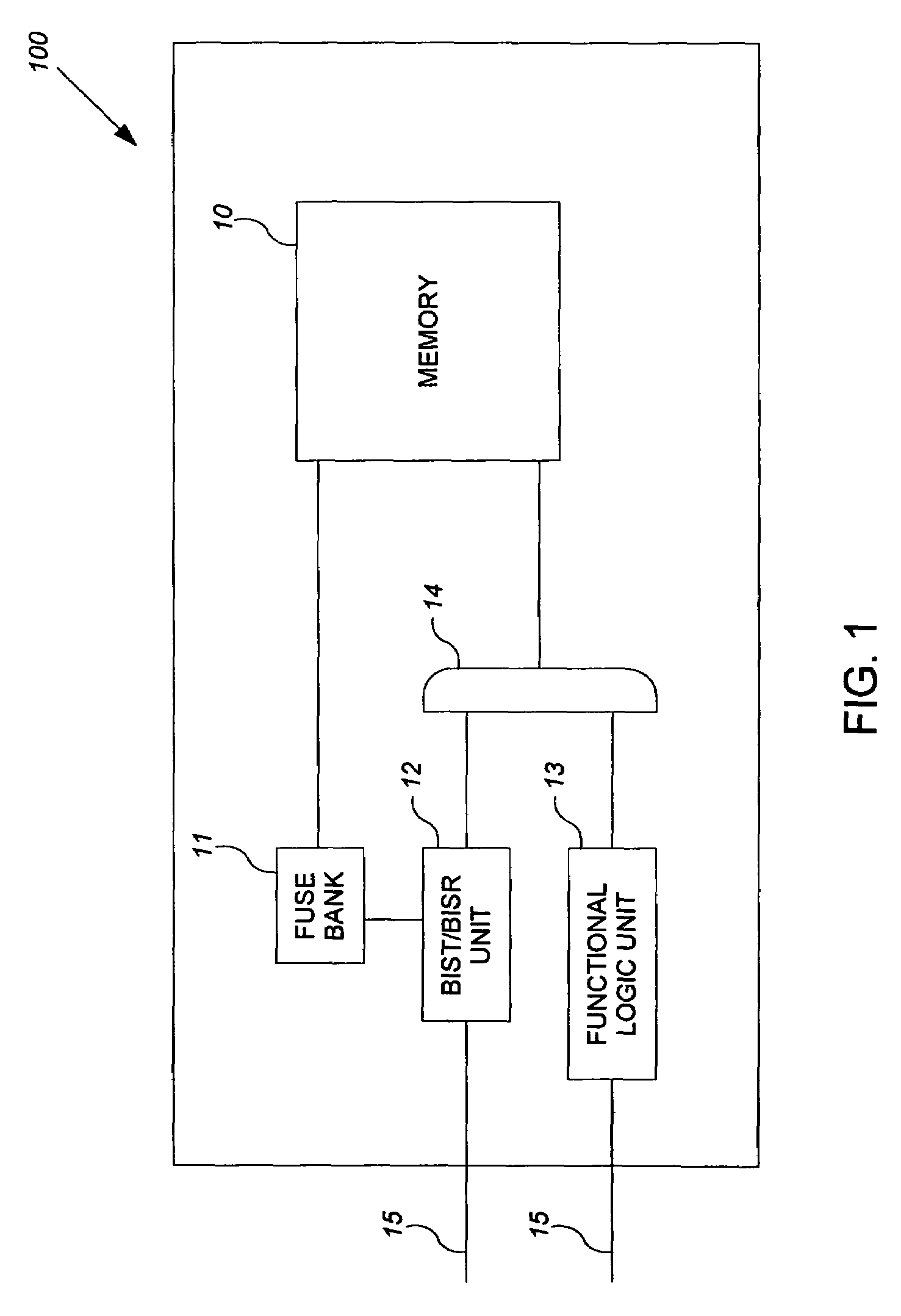
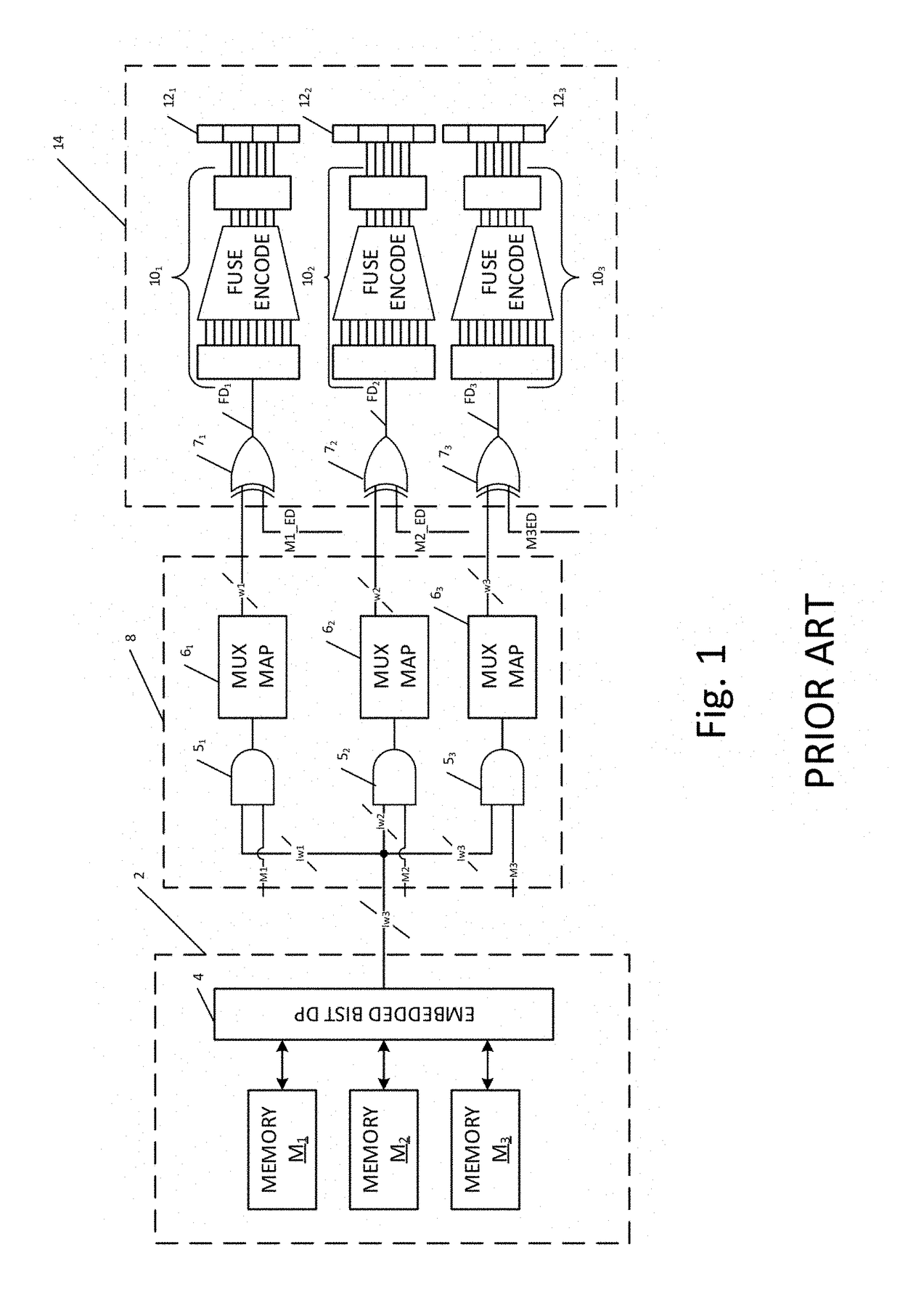
Method and apparatus for storing and distributing memory repair information
ActiveUS7757135B2Easy to integrateConvenient to accommodateElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionDistributed memoryProcessor register
A system for repairing embedded memories on an integrated circuit includes an external Built-In Self-repair Register (BISR) associated with every reparable memory. Each BISR is serially configured in a daisy chain with a fuse box controller. The controller determines the daisy chain length upon power up. The controller may perform a corresponding number of shift operations to move repair data between BISRs and a fuse box. Memories can have a parallel or serial repair interface. The BISRs may have a repair analysis facility into which fuse data may be dumped and uploaded to the fuse box or downloaded to repair the memory. Pre-designed circuit blocks provide daisy chain inputs and access ports to effect the system or to bypass the circuit block.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
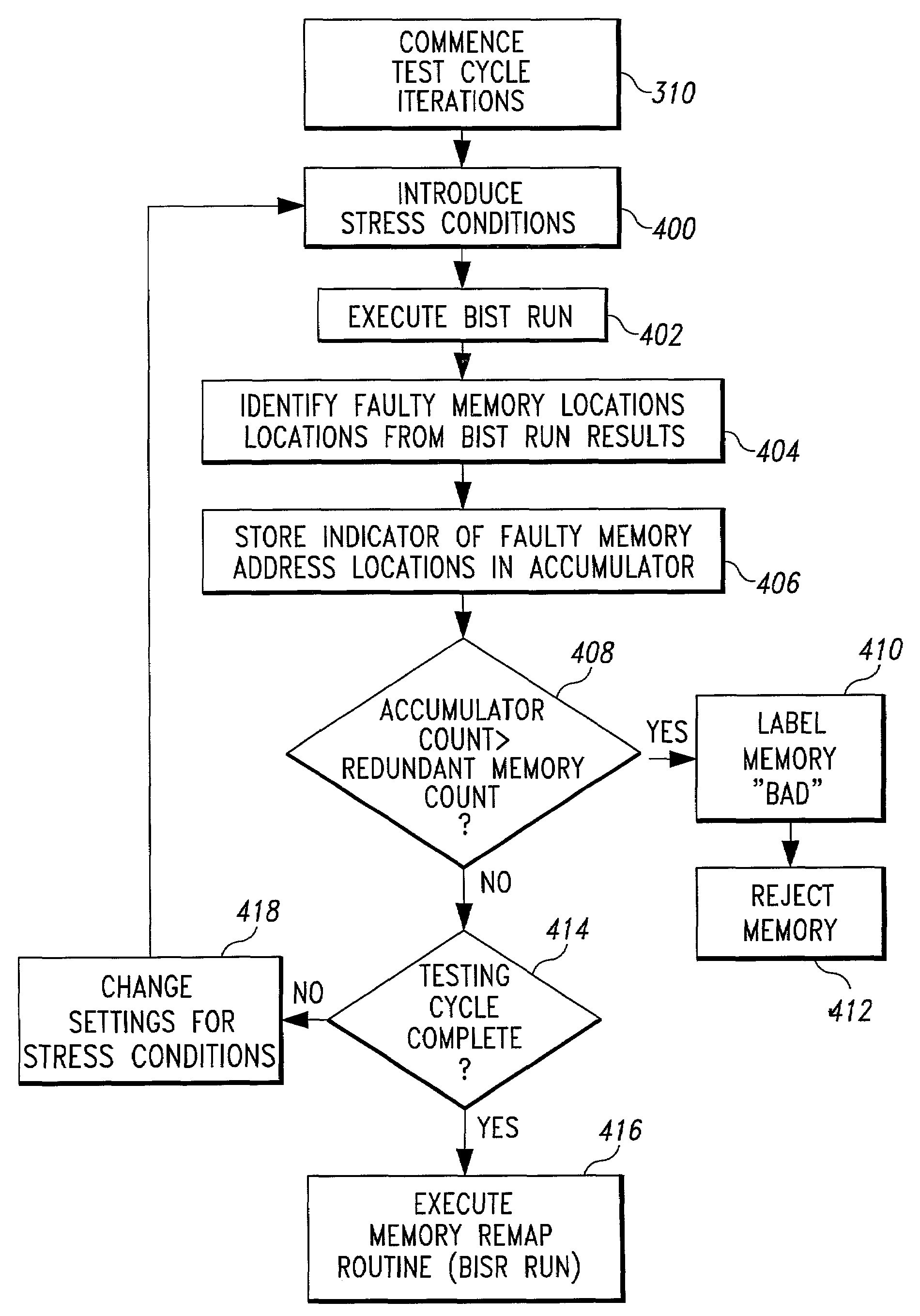
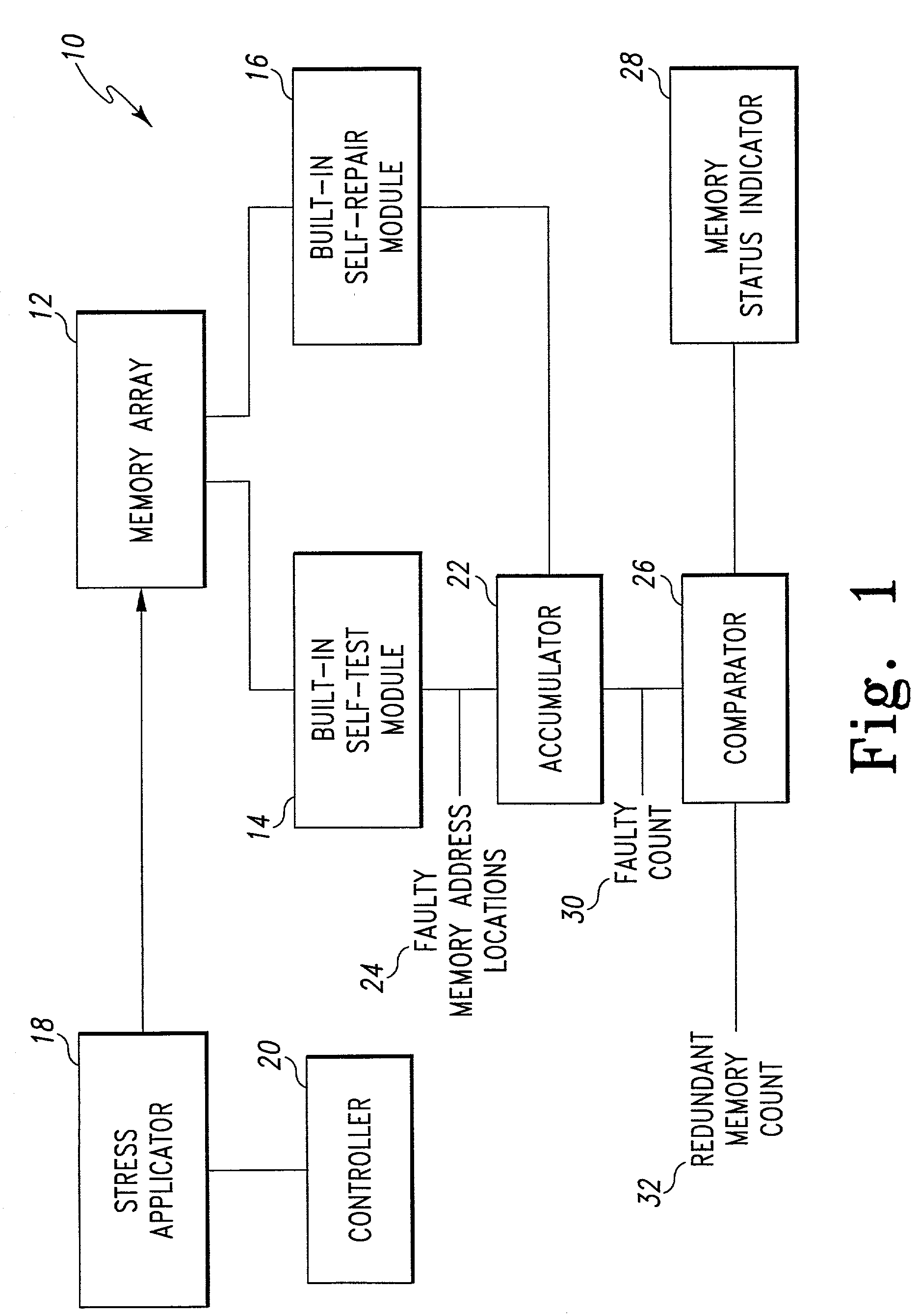
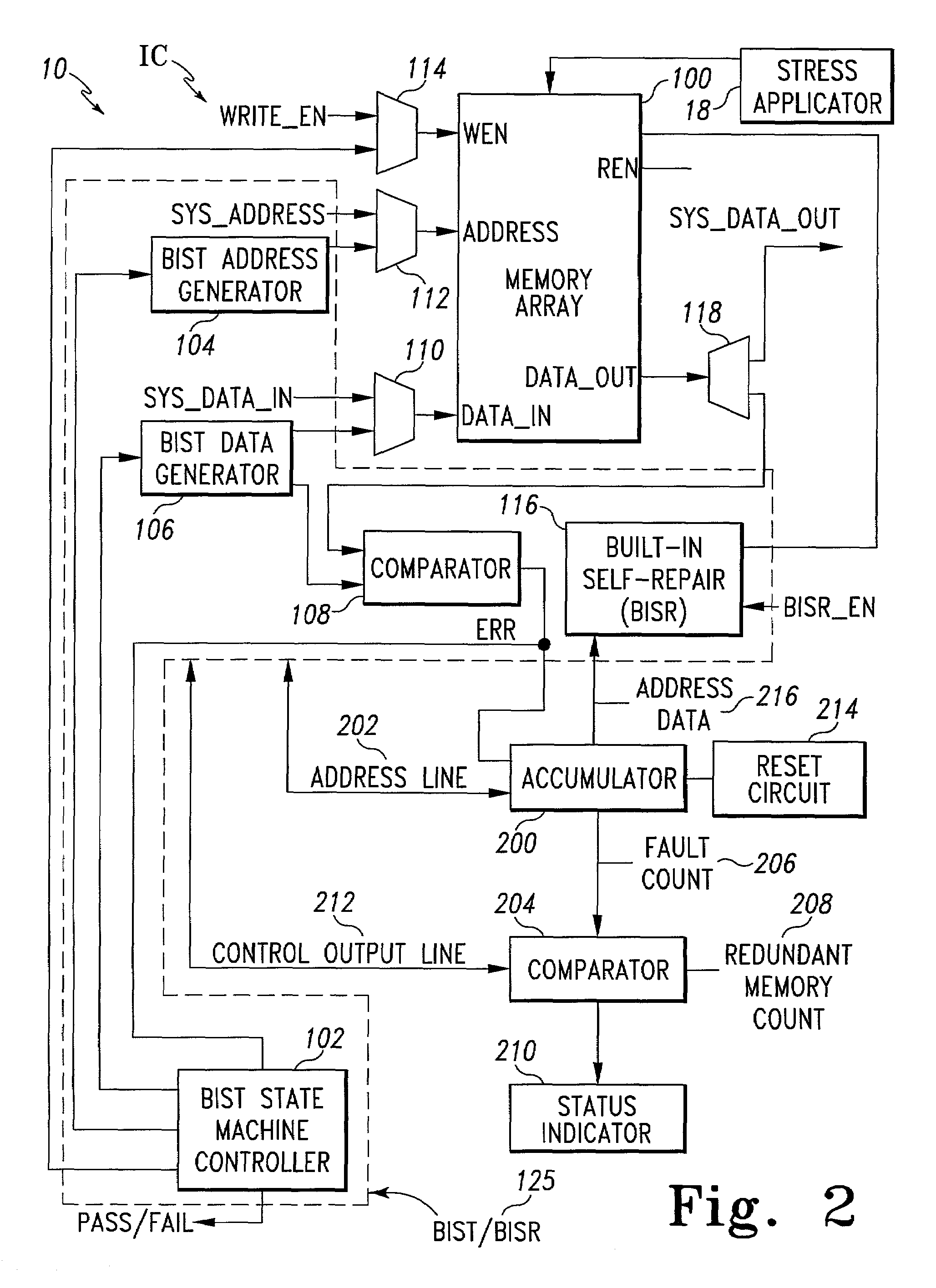
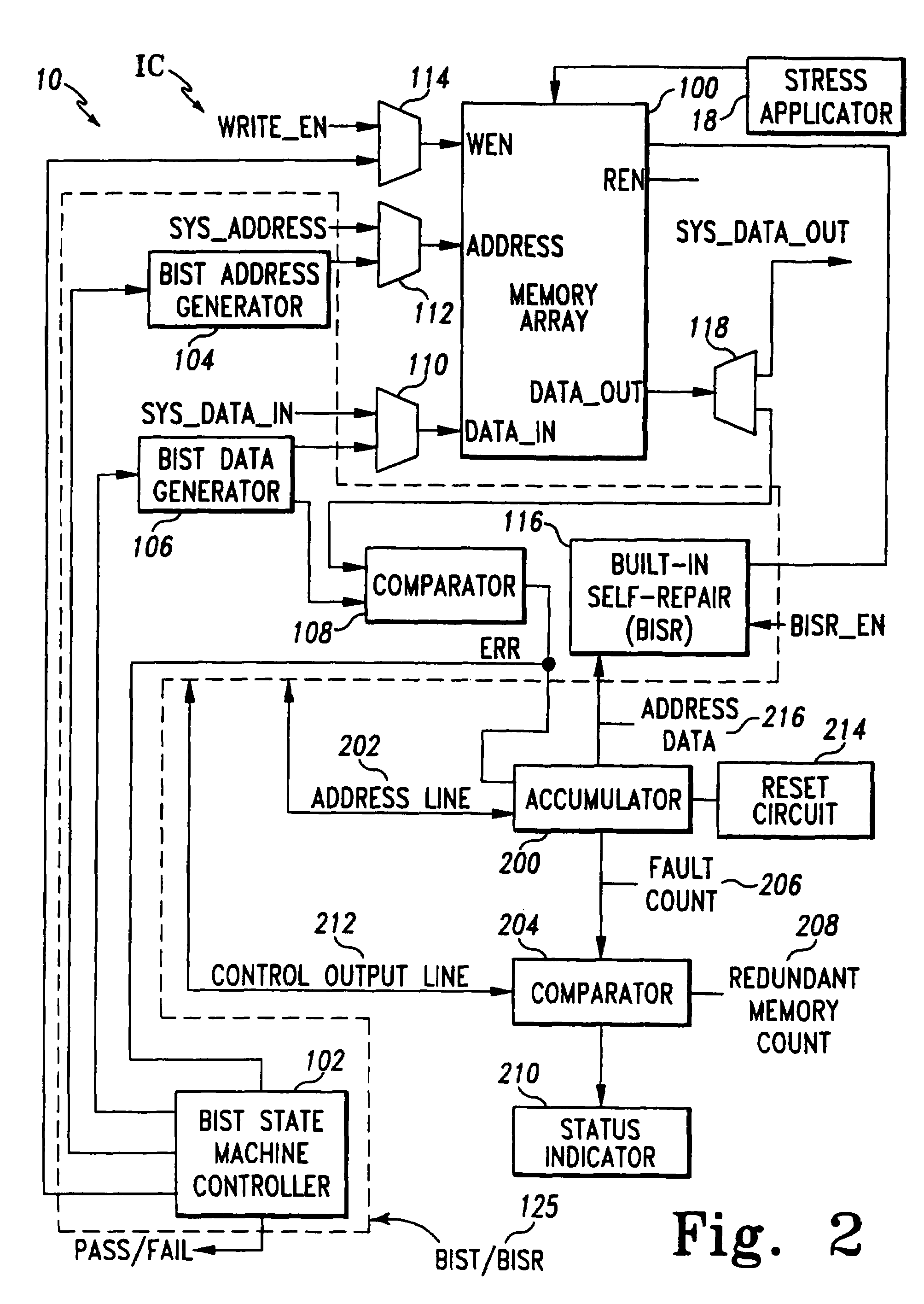
Method and system for performing built-in self-test routines using an accumulator to store fault information
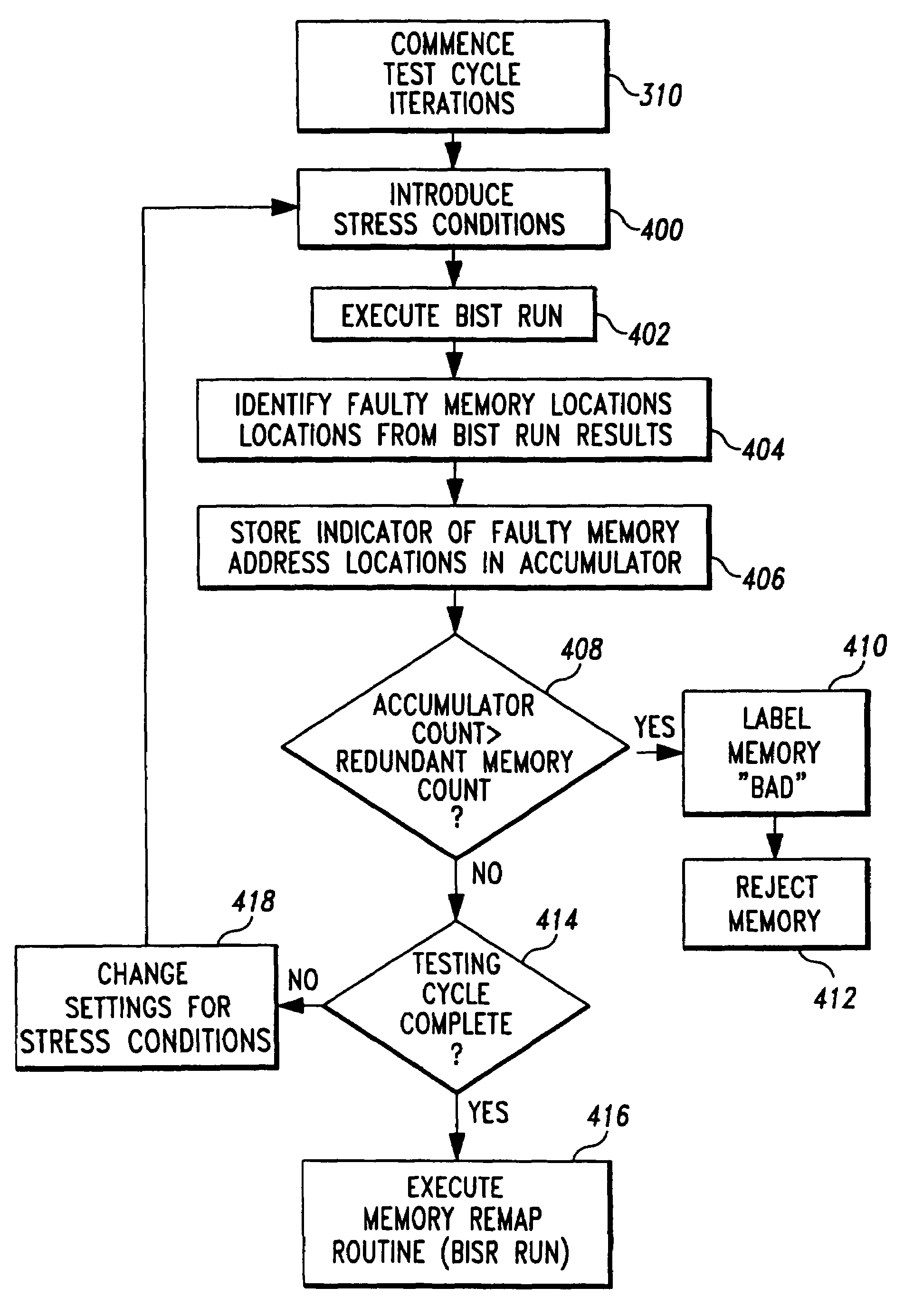
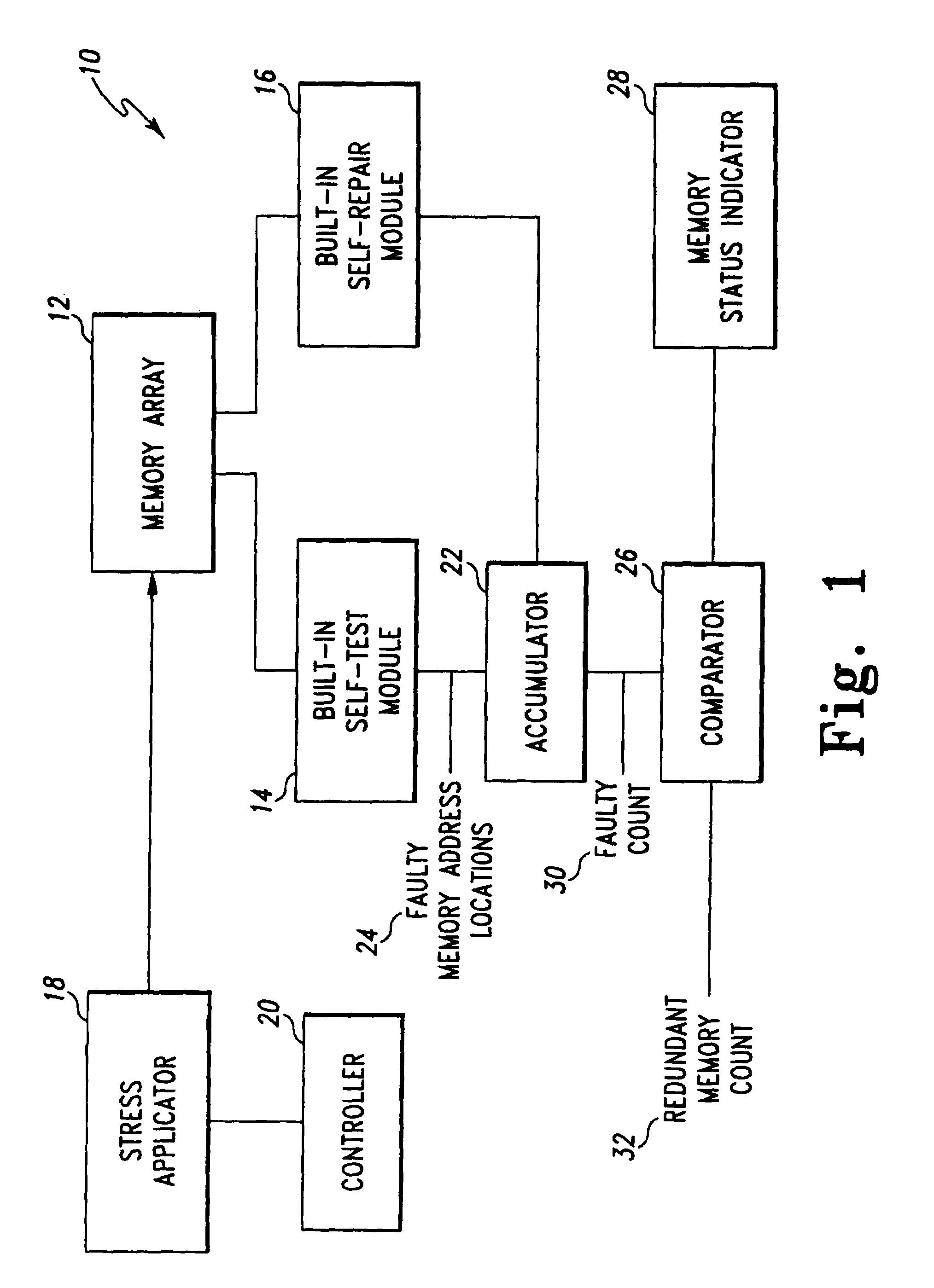
InactiveUS7260758B1Increase productionCharacteristic defectElectronic circuit testingStatic storageMemory addressStress conditions
A test system includes a built-in self-test (BIST) circuit and a stress applicator for use in analyzing a memory array. The stress applicator applies a selective set of stress factors to the memory array, such as temperature and voltage conditions. The BIST circuit executes a test routine on the memory array to detect the presence of any faulty memory address locations that may arise under the prevailing stress condition. A full testing cycle involves iterative repetition of the functions performed by the stress applicator and BIST circuit, with variations in the stress factors across the testing iterations. An accumulator cumulatively stores the fault information generated by the BIST circuit during each testing iteration. Following completion of the testing cycle, a repair operation is performed by a built-in self-repair (BISR) circuit to remap the faulty memory address locations indicated by the accumulator to redundant memory address locations.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Programmable memory built in self repair circuit
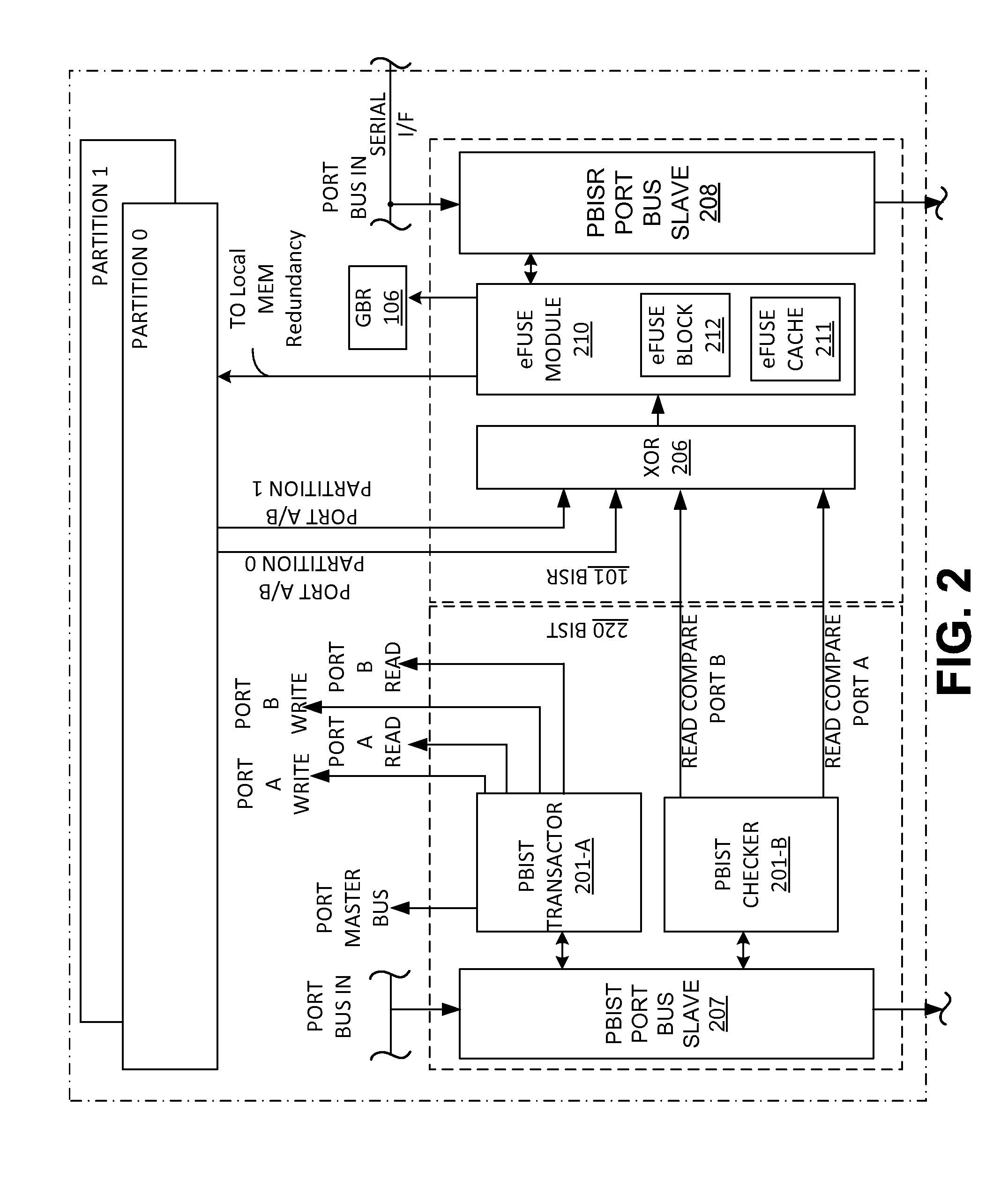
An integrated circuit chip comprising at least one programmable built-in self-repair (PBISR) for repairing memory is described. The PBISR comprises an interface that receives signals external to the integrated chip. The PBISR further includes a port slave module that programs MBISR registers, program and instruction memory. The PBISR further comprises a programmable transaction engine and a programmable checker. Further, the MBISR comprises an eFUSE cache that implements logic to denote defective elements.
Owner:MOSYS INC
Method and apparatus for storing and distributing memory repair information
ActiveUS20080065929A1Easy to integrateConvenient to accommodateElectronic circuit testingStatic storageDistributed memoryControl signal
A system for repairing embedded memories on an integrated circuit is disclosed. The system comprises an external Built-In Self-repair Register (BISR) associated with every reparable memory on the circuit. Each BISR is configured to accept a serial input from a daisy chain connection and to generate a serial output to a daisy chain connection, so that a plurality of BISRs are connected in a daisy chain with a fuse box controller. The fuse box controller has no information as to the number, configuration or size of the embedded memories, but determines, upon power up, the length of the daisy chain. With this information, the fuse box controller may perform a corresponding number of serial shift operations to move repair data to and from the BISRs and into and out of a fuse box associated with the controller. Memories having a parallel repair interface are supported by a parallel address bus and enable control signal on the BISR, while those having a serial repair interface are supported by a parallel daisy chain path that may be selectively cycled to shift the contents of the BISR to an internal serial register in the memory. Preferably, each of the BISRs has an associated repair analysis facility having a parallel address bus and enable control signal by which fuse data may be dumped in parallel into the BISR and from there, either uploaded to the fuse box through the controller or downloaded into the memory to effect repairs. Advantageously, pre-designed circuit blocks may provide daisy chain inputs and access ports to effect the inventive system therealong or to permit the circuit block to be bypassed for testing purposes.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
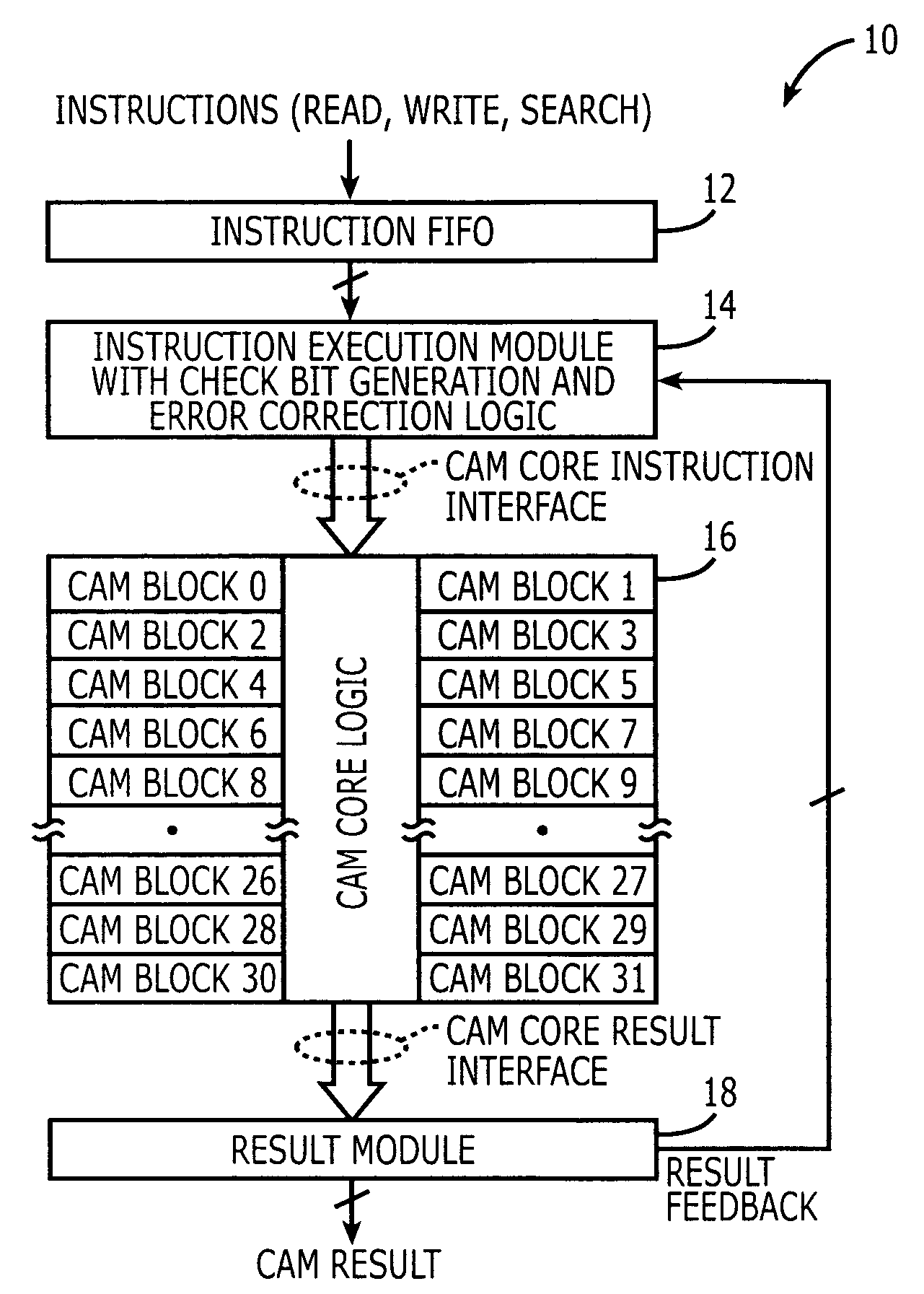
Content addressable memory (CAM) devices that support background BIST and BISR operations and methods of operating same
Search engine devices include a content addressable memory (CAM) core having a plurality of CAM array blocks therein and a control circuit. The control circuit, which is electrically coupled to the plurality of CAM array blocks, is configured to perform built-in self repair (BISR) of hard memory defects and / or compare logic defects in the plurality of CAM array blocks concurrently with operations to search entries in the plurality of CAM array blocks.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for assured built in self repair of memories
InactiveUS6973605B1Increase pressureReducing pulse widthElectronic circuit testingStatic storageMemory addressProcessor register
Owner:ARM INC
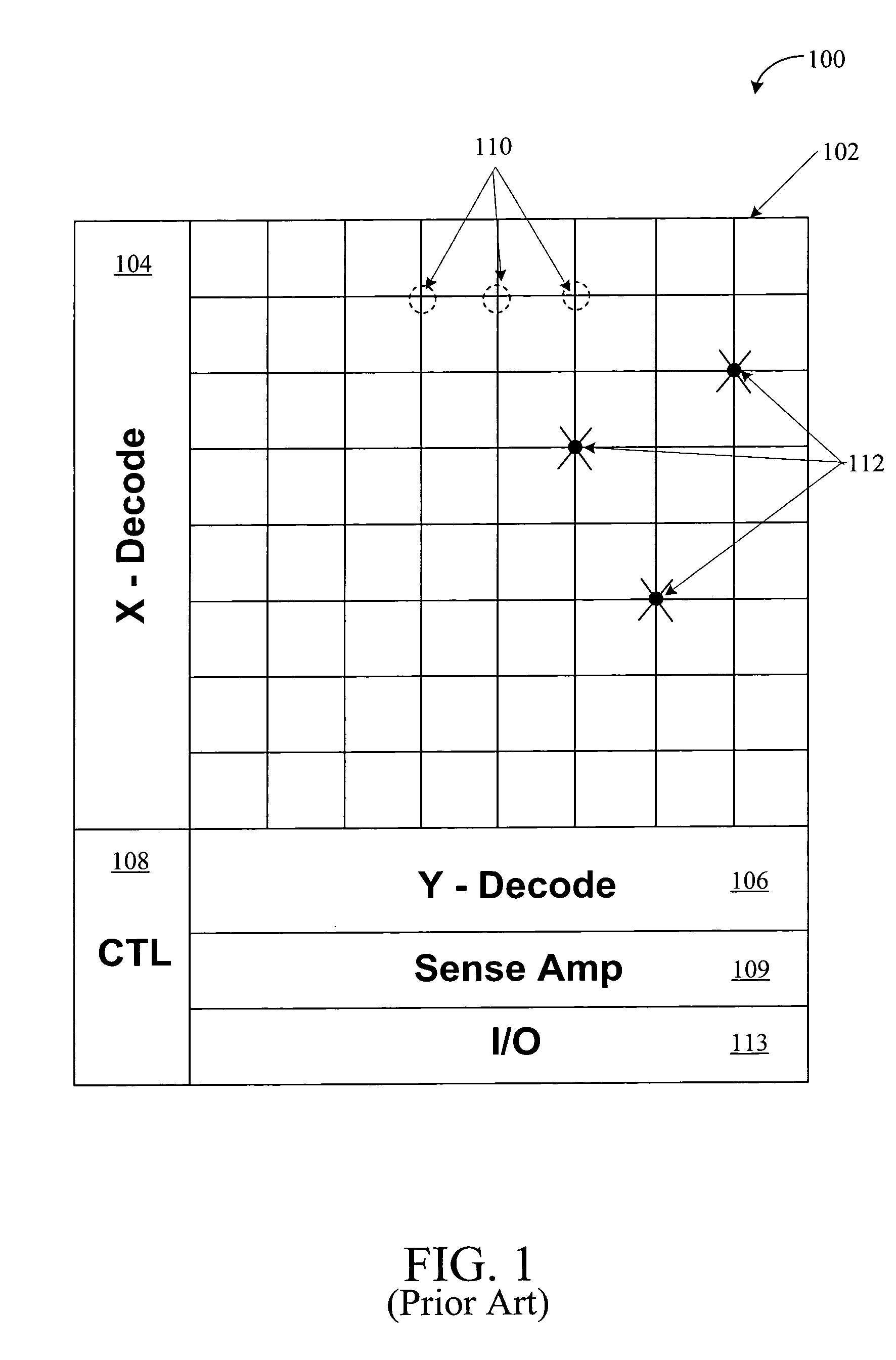
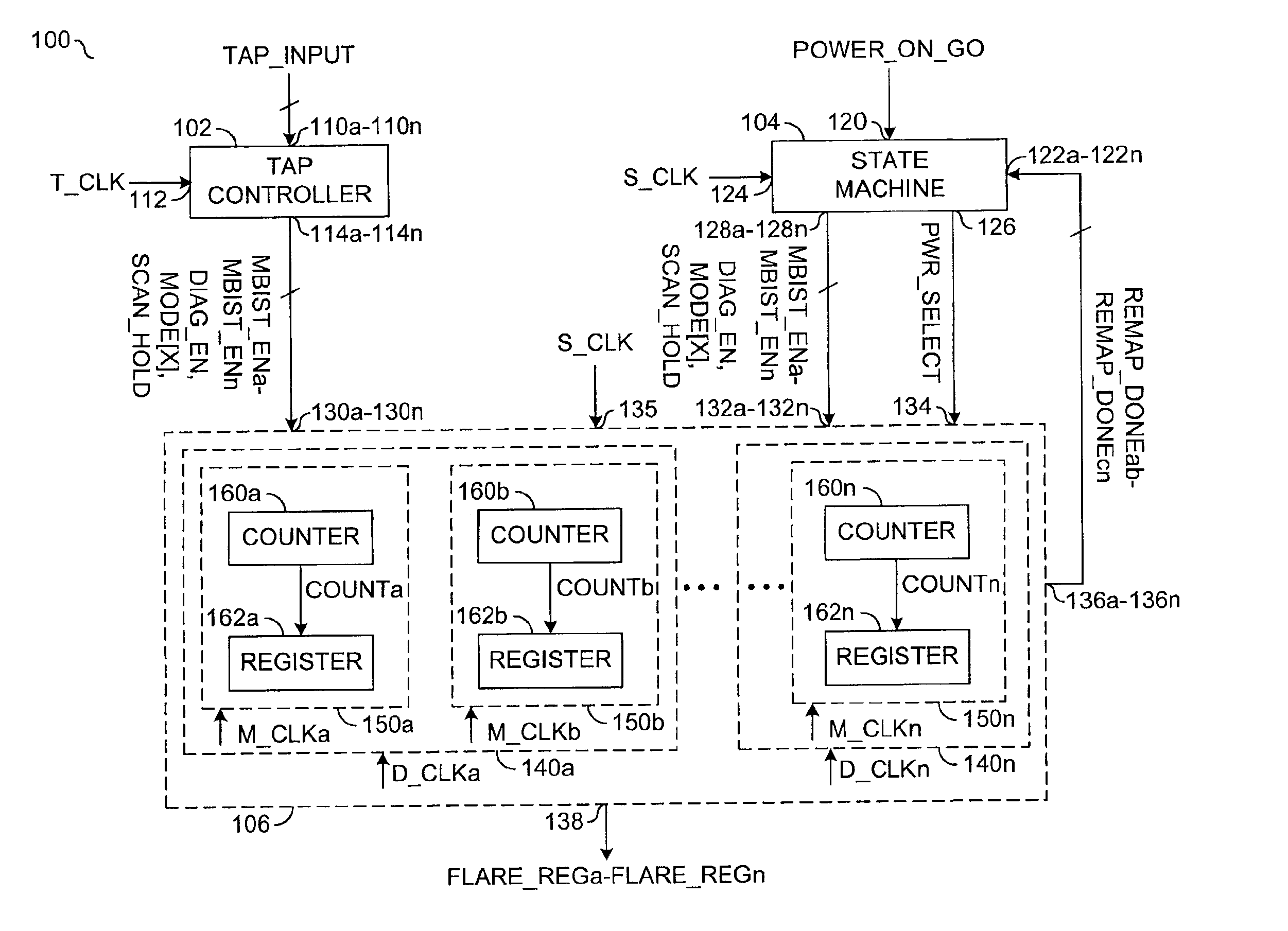
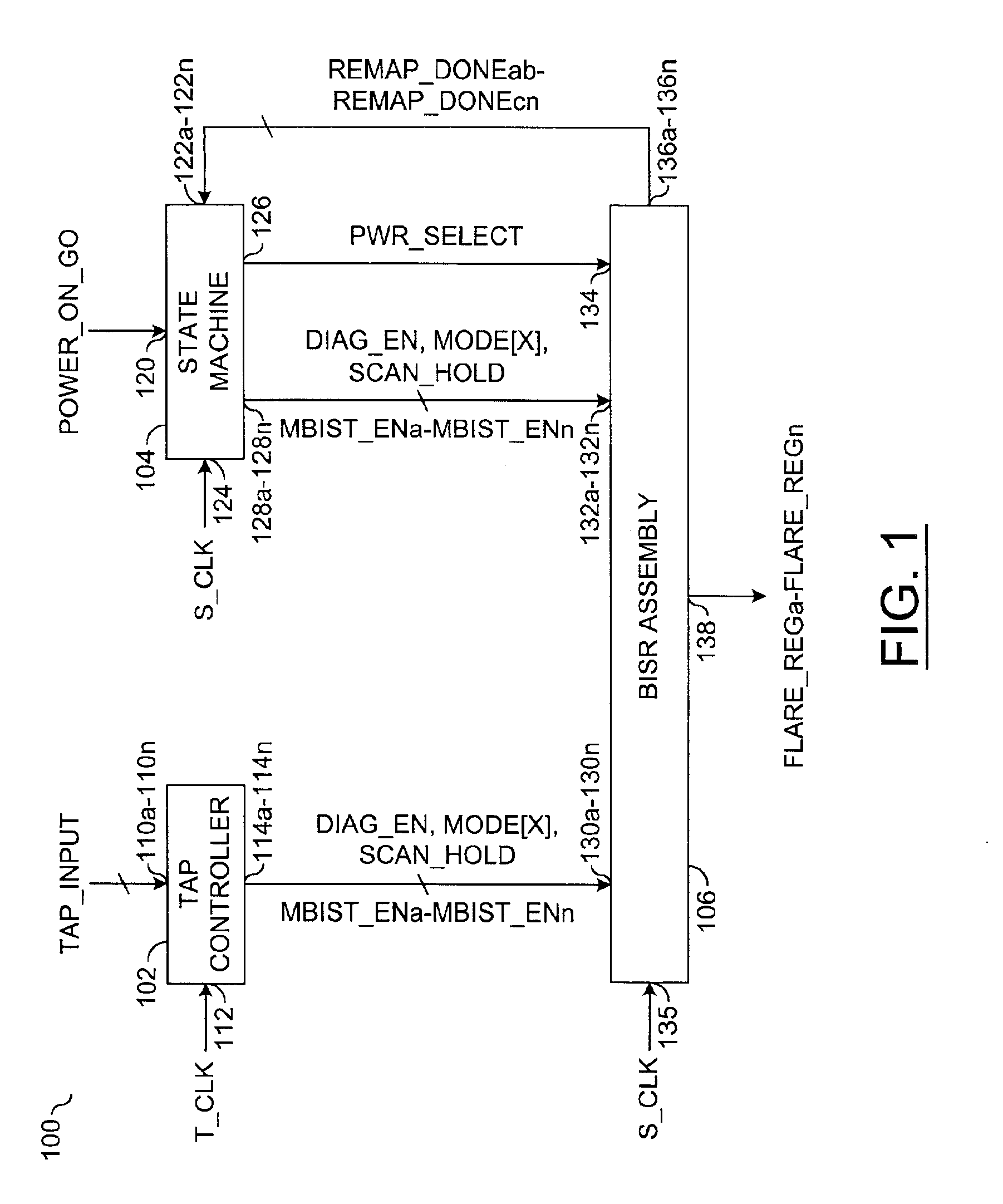
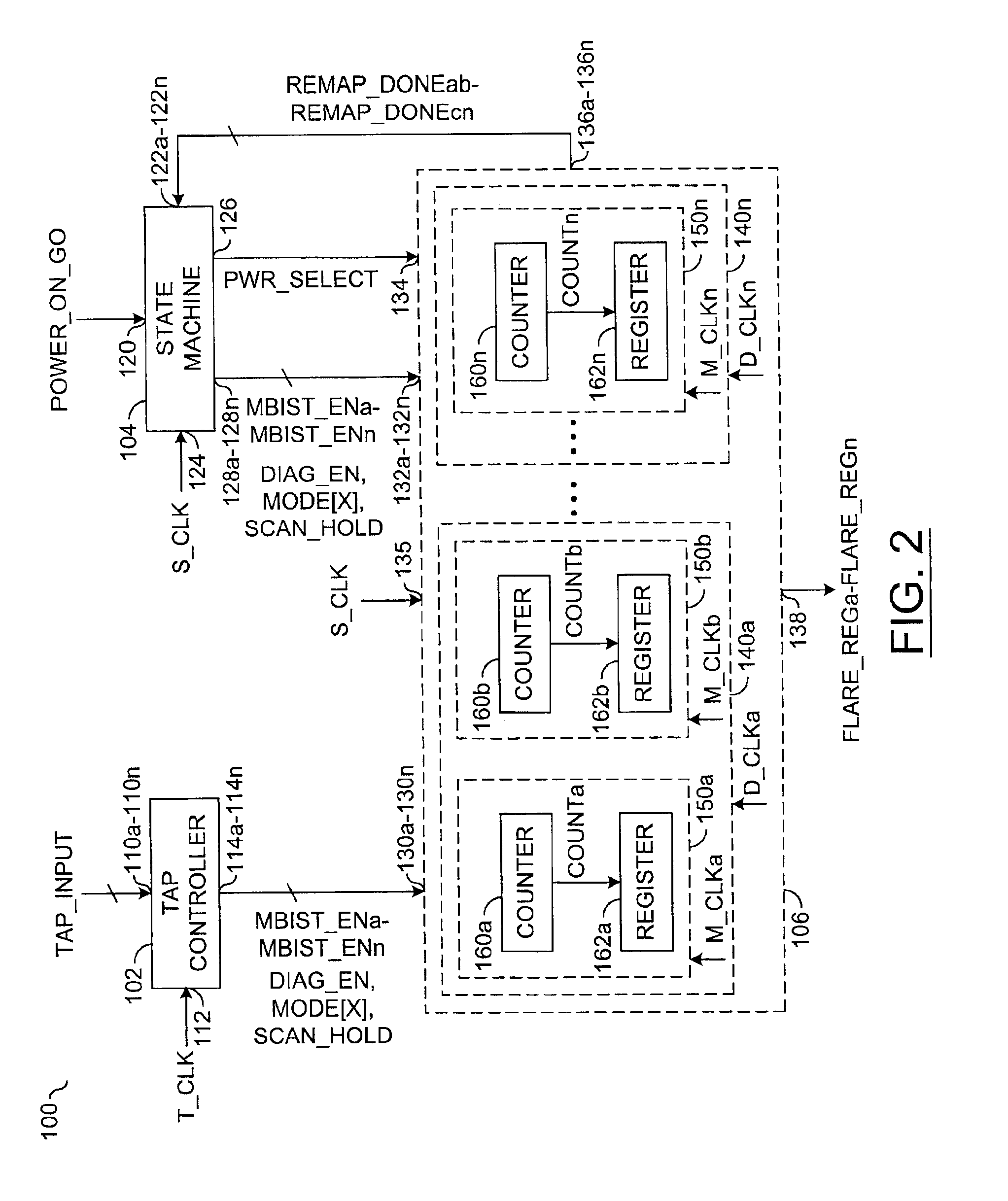
Power-on state machine implementation with a counter to control the scan for products with hard-BISR memories
InactiveUS6871297B2Eliminate user calculationReduce prototype development timeElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionControl signalOperation mode
An apparatus comprising a controller circuit and a BISR assembly circuit. The controller circuit may be configured to present one or more control signals. The control signals may be configured to control one or more built-in self-test (BIST) and built-in self-repair (BISR) modes of operation. The BISR assembly circuit generally comprises one or more memory blocks each comprising a counter configured to generate a clock cycle count value in response to a repair solution during the BIST and BISR operations. The memory blocks may be remapped in response to the count values during one or more of the BISR operations.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method for testing semiconductor devices having built-in self repair (BISR) memory
A method for testing semiconductor devices advantageously increases manufacturing yields. The method includes generating memory repair data for a wafer die by writing at least one predetermined digital bit pattern into a memory on the wafer die, reading the at least one predetermined digital bit pattern back out of the memory, comparing the at least one predetermined digital bit pattern read out from the memory against the at least one predetermined digital bit pattern written into the memory, and storing results of the comparison as the memory repair data. The writing and reading are performed a plurality of times, each time with a different voltage and clock frequency combination being applied to the wafer die. The memory repair data is programmed into the wafer die, and the wafer die is assembled into a packaged semiconductor device. The packaged semiconductor device is tested by causing the memory repair data programmed within the packaged semiconductor device to be transferred into the memory a plurality of times, each time with a different voltage and clock frequency combination being applied to the packaged semiconductor device.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Memory built-in self repair (MBISR) circuits/devices and method for repairing a memory comprising a memory built-in self repair (MBISR) structure
InactiveUS7627792B2OptimizationImprove performanceError detection/correctionDigital storageComputer scienceStorage cell
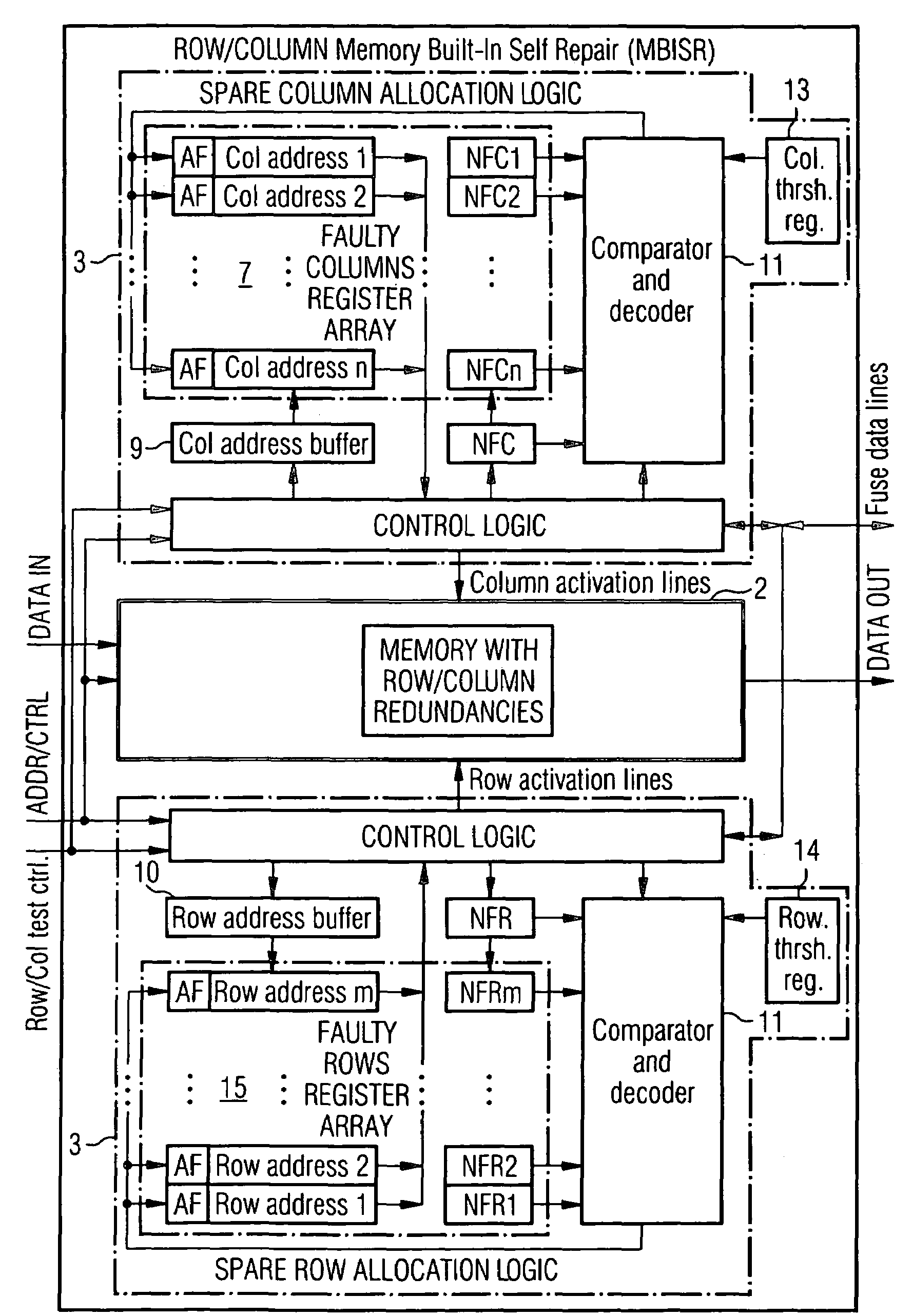
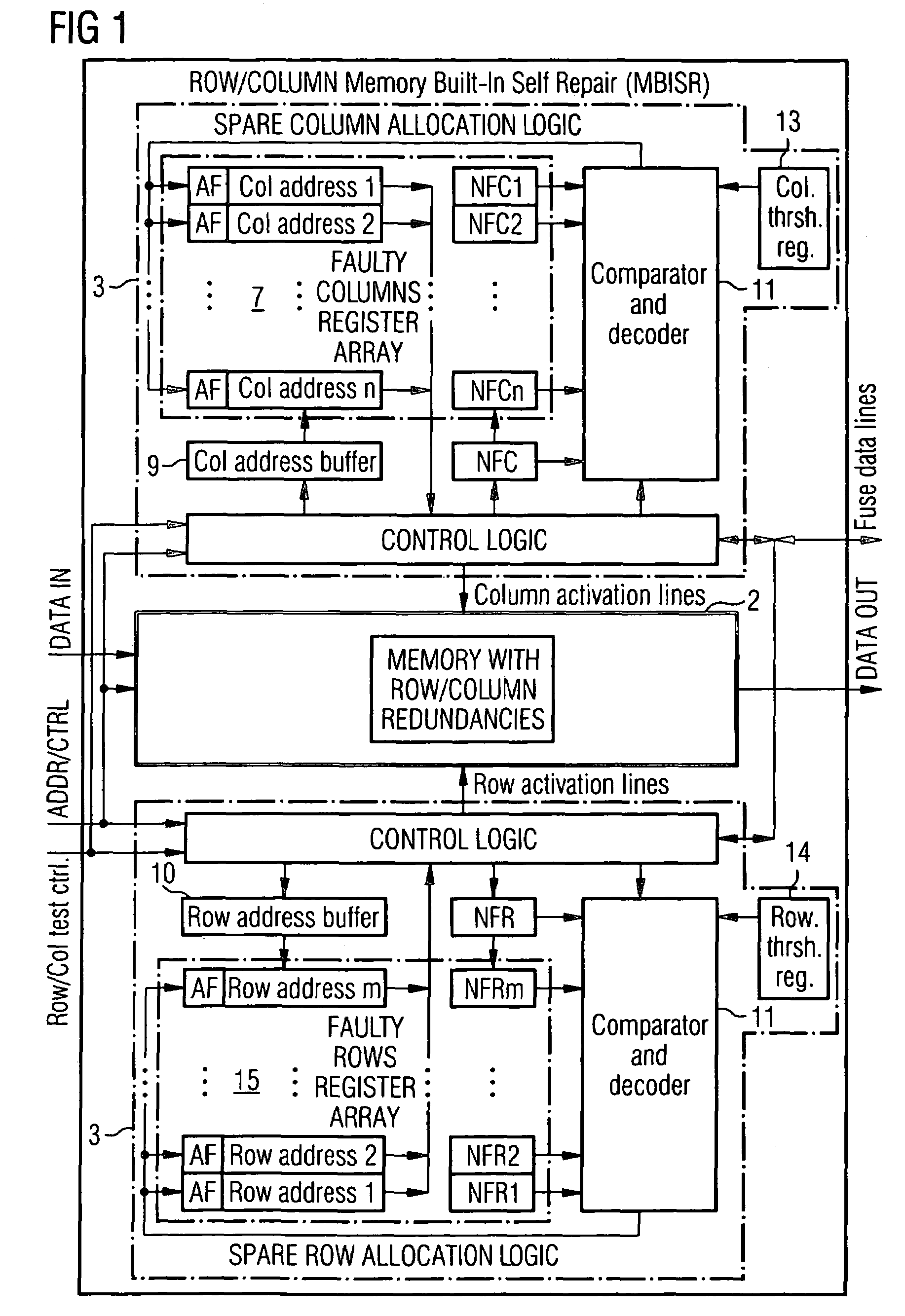
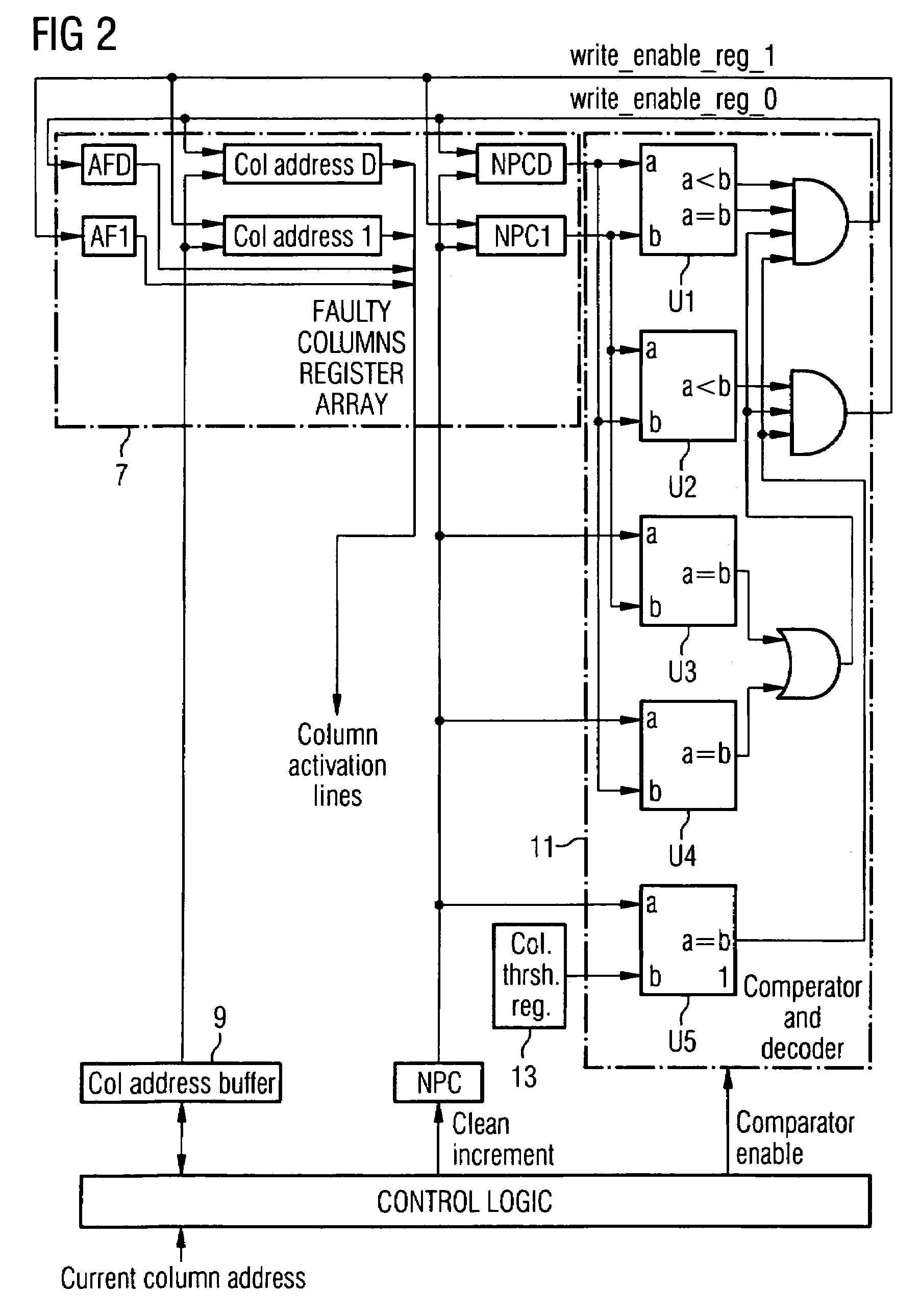
A method for repairing a memory comprising a Memory Built-In Self Repair (MBISR) structure comprises the steps of detection of defective storage cells, and redundancy allocation. The redundancy allocation step is carried out in such a way that it combines a row and / or column oriented redundancy repair approach with a word oriented redundancy repair approach. A Memory Built-In Self Repair (MBISR) device comprises at least one memory (2) with row and / or column redundancy, at least one row and / or column Memory Built-In Self Repair (MBISR) circuit (3), and a word redundancy block (4). Furthermore, a distributed MBISR structure as well as dedicated Column / Row MBISR circuits (3) are provided.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
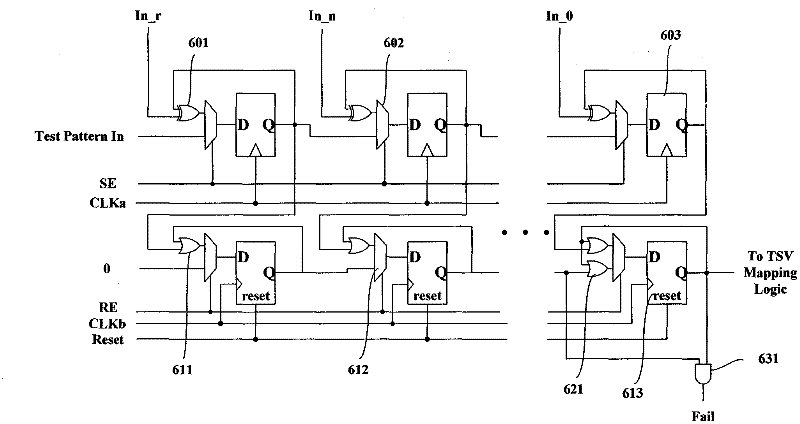
Built-in self test and built-in self-repairing technology of TSV (Through Silicon Via) interconnection of 3D chip
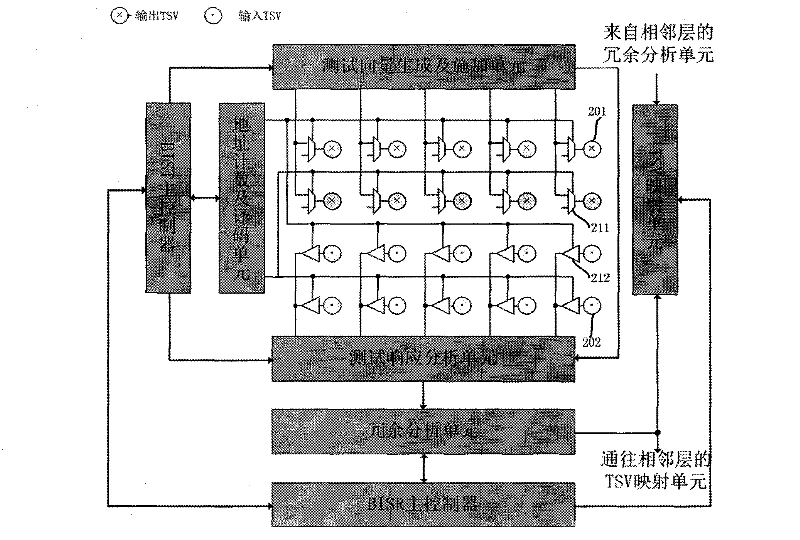
InactiveCN102655101AReduce dependenceIncrease costSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingPower-on resetElectricity
The invention relates to a built-in self test and built-in self-repairing technology of TSV (Through Silicon Via) interconnection of a 3D chip. The technology comprises the following steps: at the chip-designing stage, corresponding built-in self test and built-in self-repairing circuits are inserted, and a redundant TSV channel is designed; after power-on reset of the 3D chip, the built-in self test circuit starts to work, carries out grouped test on TSVs, generates corresponding TSV configuration information according to a test result, and then calls the built-in self-repairing circuit for configuration of a TSV mapping circuit, and simultaneously, the test of next group of TSVs is started; after the test and the configuration on all the TSVs, the circuits can enter normal working. The technology has the advantages that the difficulty of the TSV interconnection in the traditional 3D chip can be solved, the strategy can be replaced by redundancy, and the finished-product rate of the 3D chip is increased; the dependency of the 3D chip test on ATE (Automatic Test Equipment) is reduced, so that the test cost of the 3D chip is reduced; and due to independency from the specific chip function, the technology can be widely applied to the 3D chip based on the TSVs and has stronger practicability.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method and system for performing built-in-self-test routines using an accumulator to store fault information
A test system includes a built-in self-test (BIST) circuit and a stress applicator for use in analyzing a memory array. The stress applicator applies a selective set of stress factors to the memory array, such as temperature and voltage conditions. The BIST circuit executes a test routine on the memory array to detect the presence of any faulty memory address locations that may arise under the prevailing stress condition. A full testing cycle involves iterative repetition of the functions performed by the stress applicator and BIST circuit, with variations in the stress factors across the testing iterations. An accumulator cumulatively stores the fault information generated by the BIST circuit during each testing iteration. Following completion of the testing cycle, a repair operation is performed by a built-in self-repair (BISR) circuit to remap the faulty memory address locations indicated by the accumulator to redundant memory address locations.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
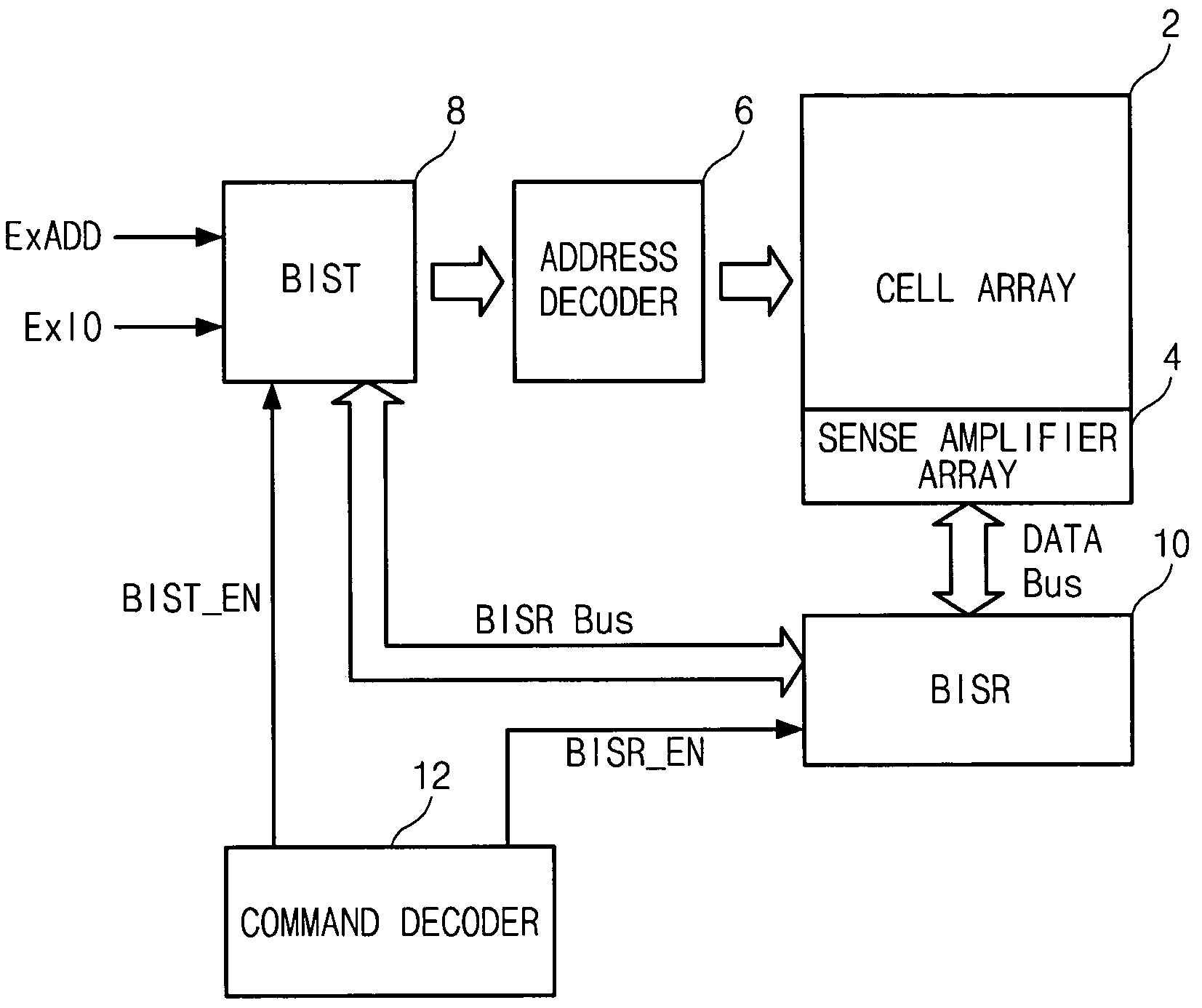
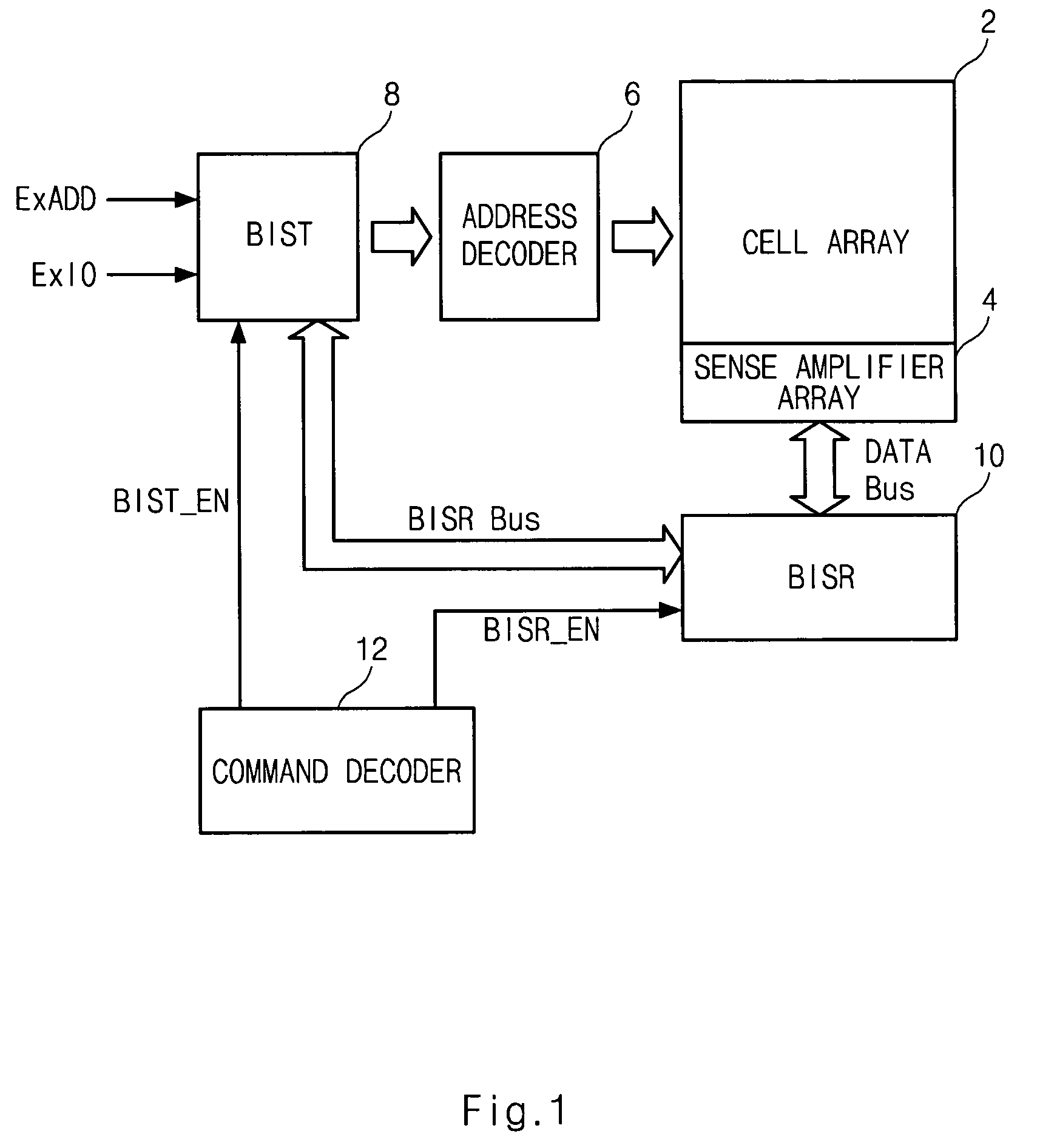
Semiconductor memory device having a test control circuit
A semiconductor memory device having a test control circuit includes a cell array, a BIST (built-in self test) circuit adapted and configured to perform a BIST operation on the cell array, a BISR (built-in self repair) circuit adapted and configured to perform a BISR operation on the cell array, and a command decoder adapted and configured to generate a first control signal for selecting a BIST operation by the BIST circuit or a test by an external tester and a second control signal for controlling a BISR operation by the BISR circuit. As a result, a test by an external tester, a BIST (built-in self test) and a BISR (built-in self repair) are individually performed in response to an additional command signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
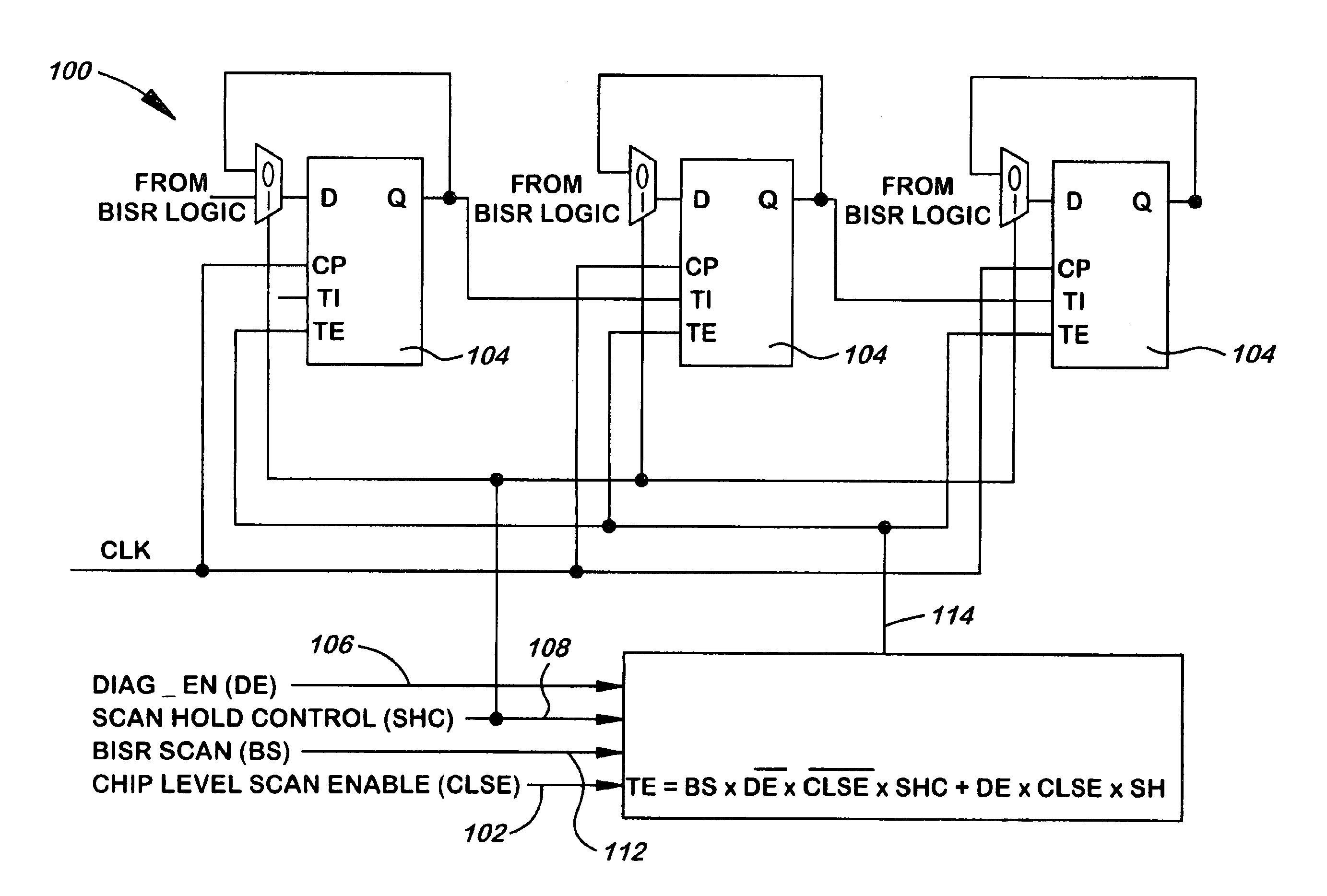
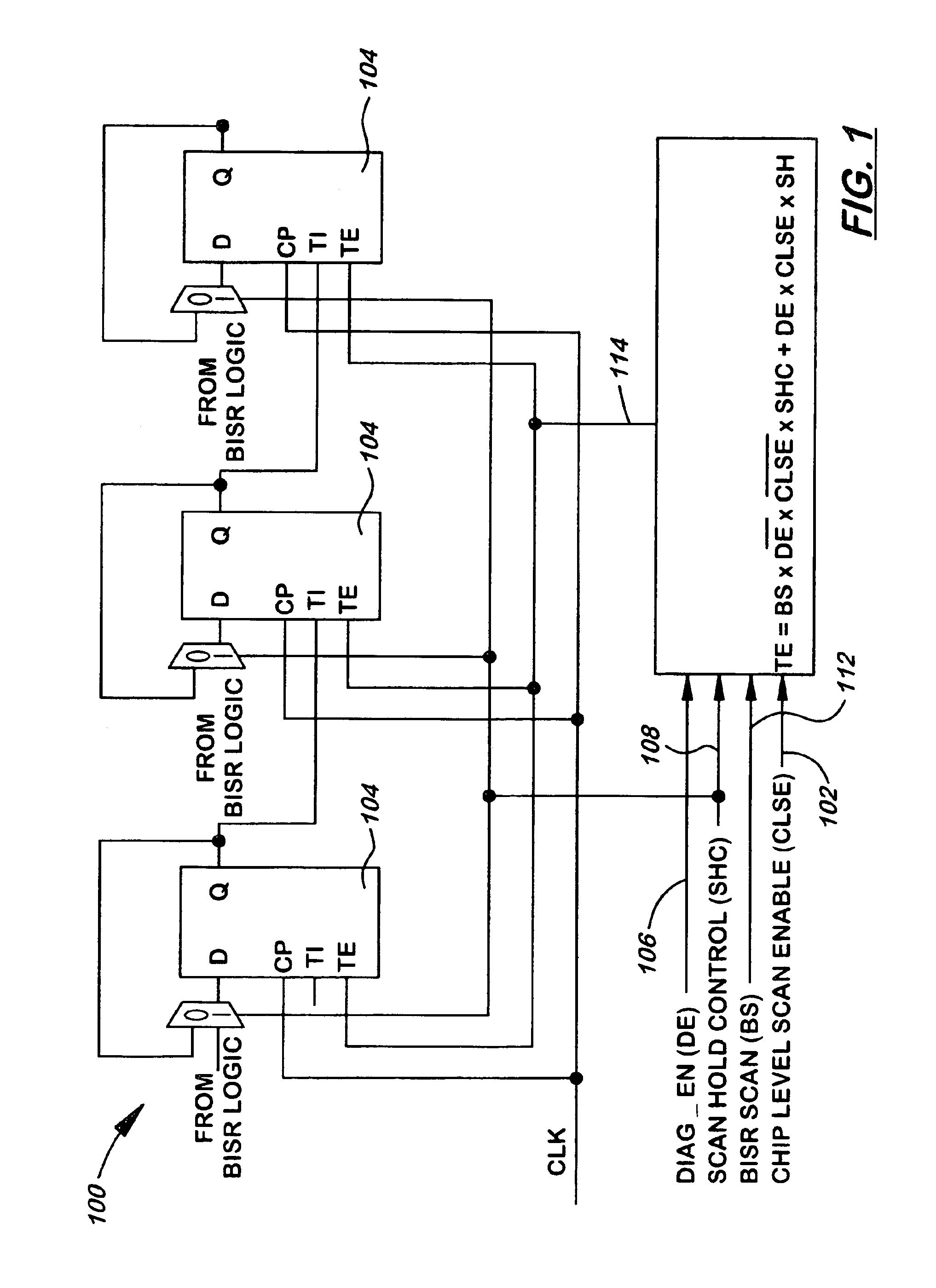
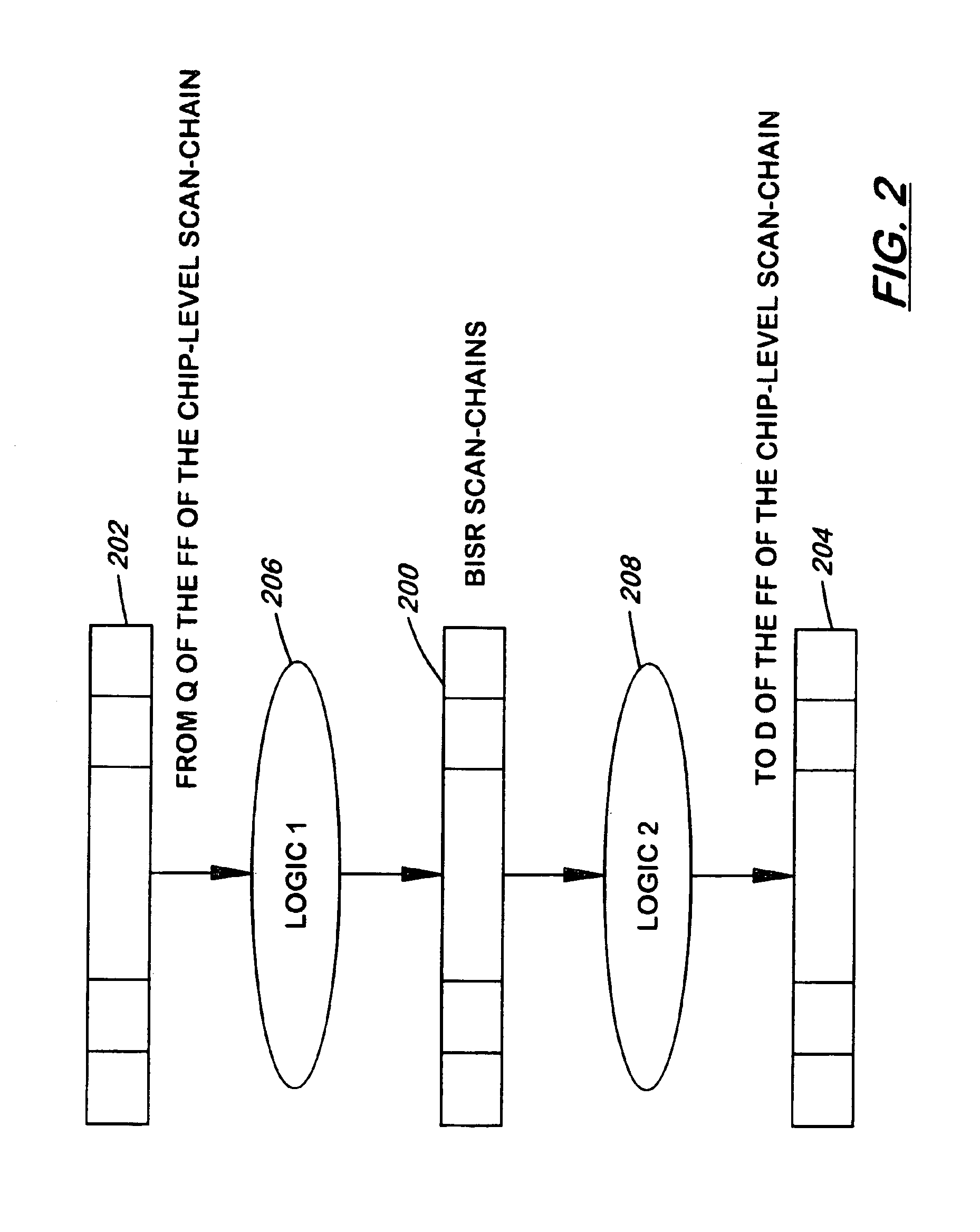
Scan method for built-in-self-repair (BISR)
A system and method for protecting the values stored in a BISR repair block and, optionally, debugging the BISR repair logic without altering normal test flow is implemented by a circuit including a plurality of soft latches within the BISR repair block, the soft latches being coupled together to form a BISR scan chain for holding BISR repair information. A chip level scan enable signal and a scan hold control signal cooperate to control connection of the BISR scan chain to other scan chains during a scan test, so that the BSR repair information is held within the soft latches. A diagnose enable signal cooperating with the chip level scan enable signal and the scan hold control signal for enabling debugging of logic connecting the BISR scan chains.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
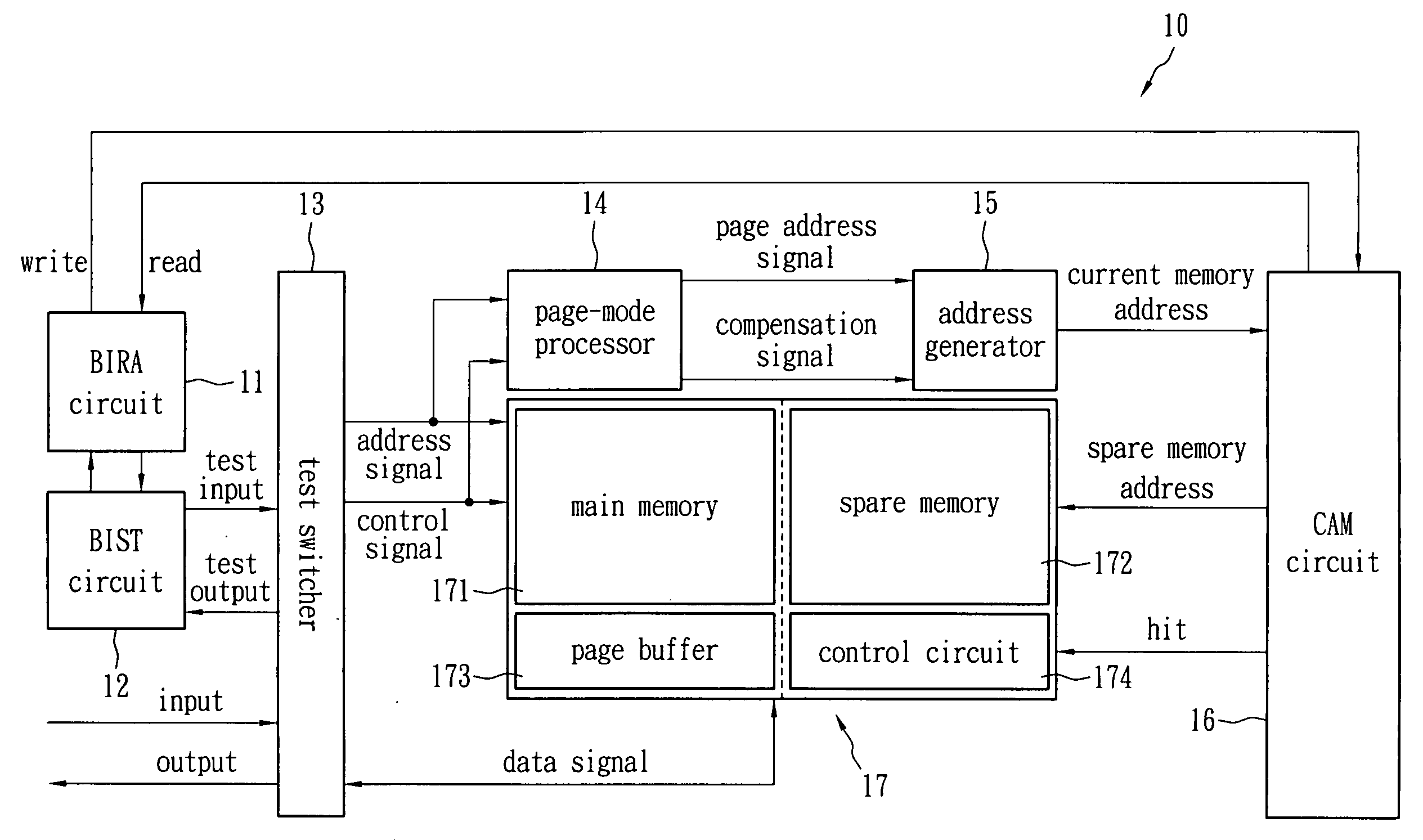
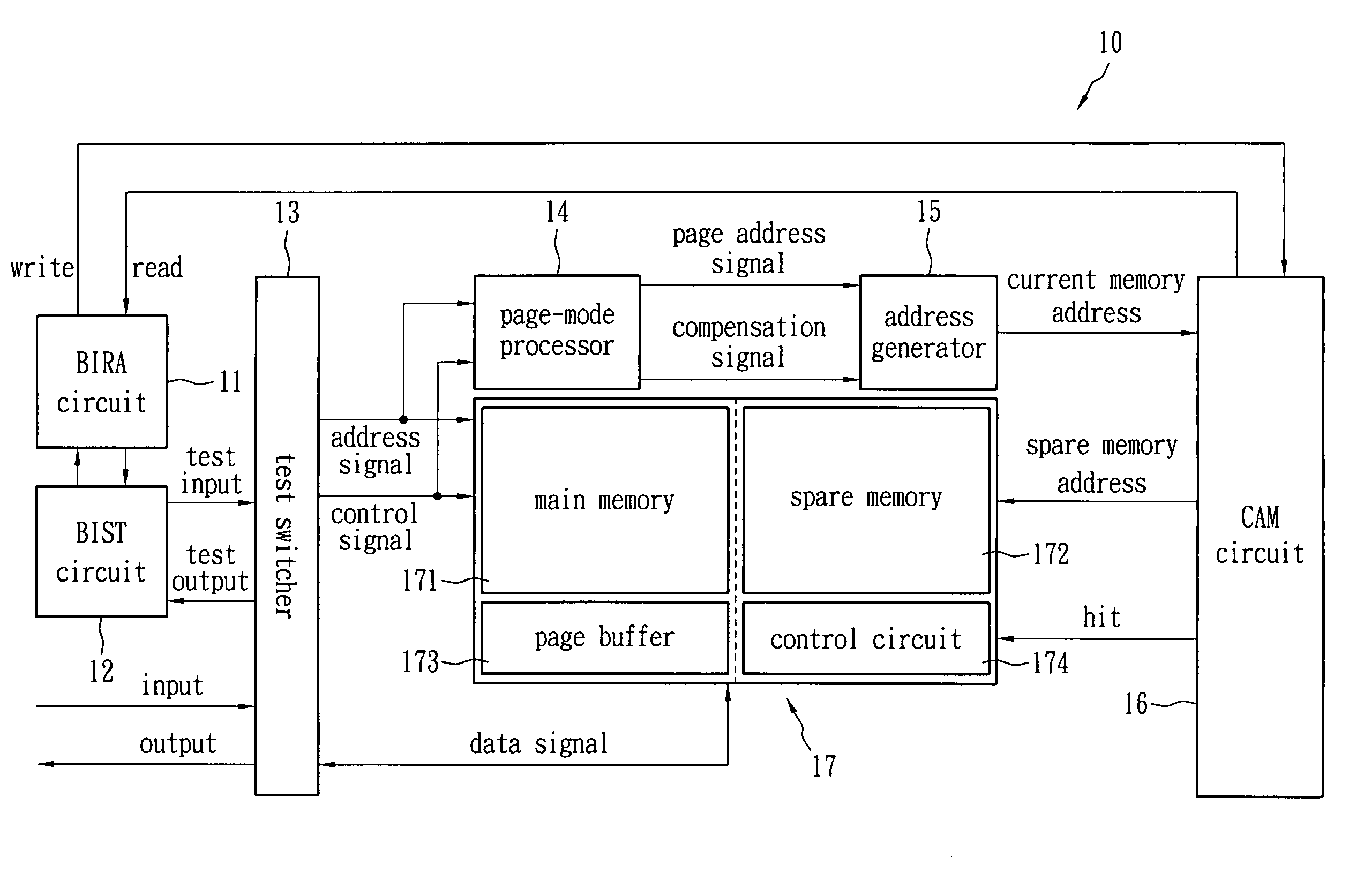
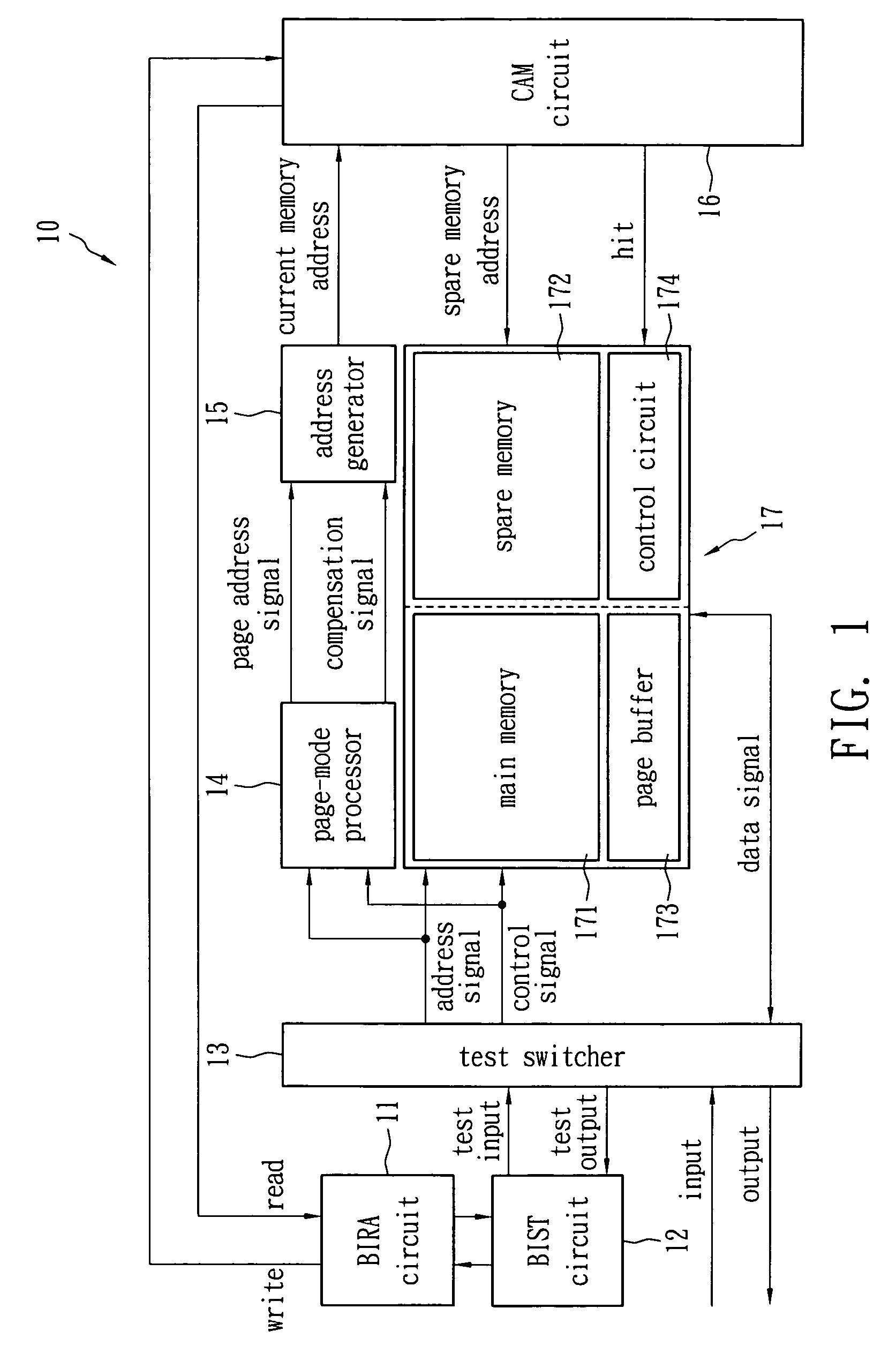
Built-in self-repair method for NAND flash memory and system thereof
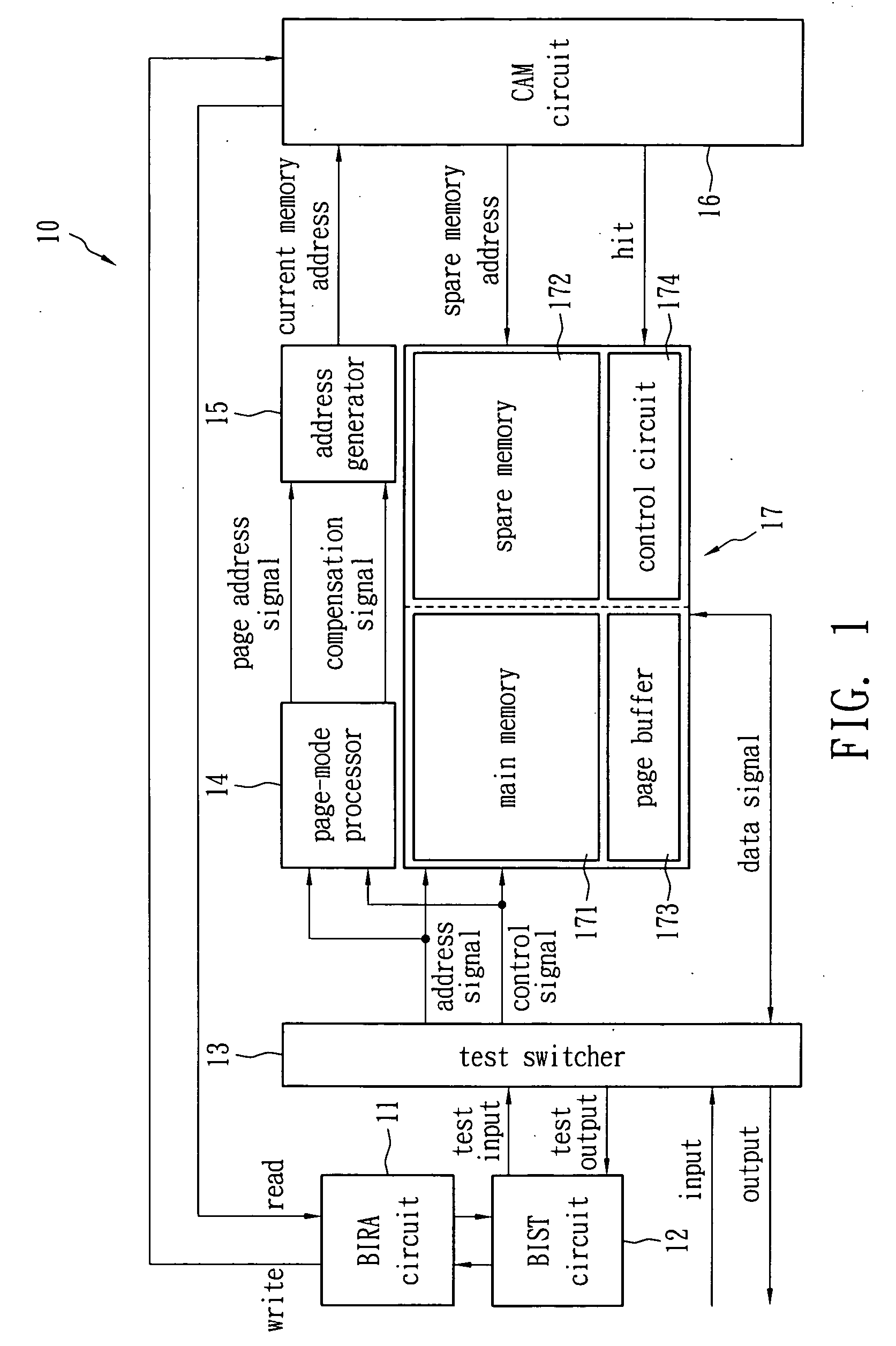
A built-in self-test system applied to NAND flash memory comprises a built-in self-test circuit, a built-in redundancy-analysis circuit, a content addressable memory, a spare memory, a page-mode processor and an address generator. The built-in self-test circuit is configured to test for defective data in a NAND flash memory. The built-in redundancy-analysis circuit is connected to the built-in self-test circuit. The content addressable memory is connected to the built-in redundancy-analysis circuit for storing the address of the defective data. The spare memory is electrically connected to the content addressable memory. The page-mode processor is configured to generate a page address signal and a compensation signal according to an address signal of the NAND flash memory. The address generator is configured to generate a current address signal according to the page address signal and compensation signal to the content addressable memory.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
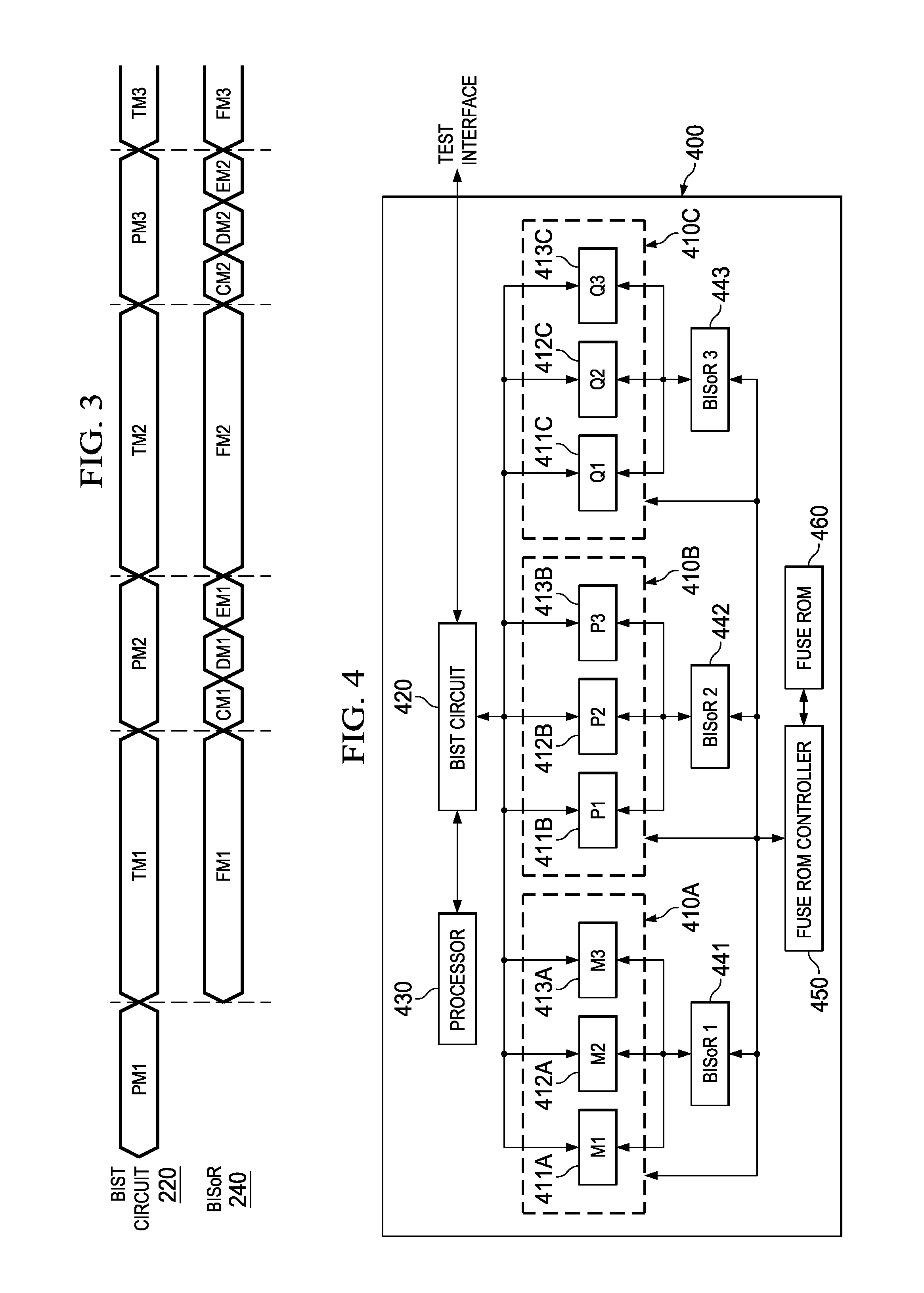
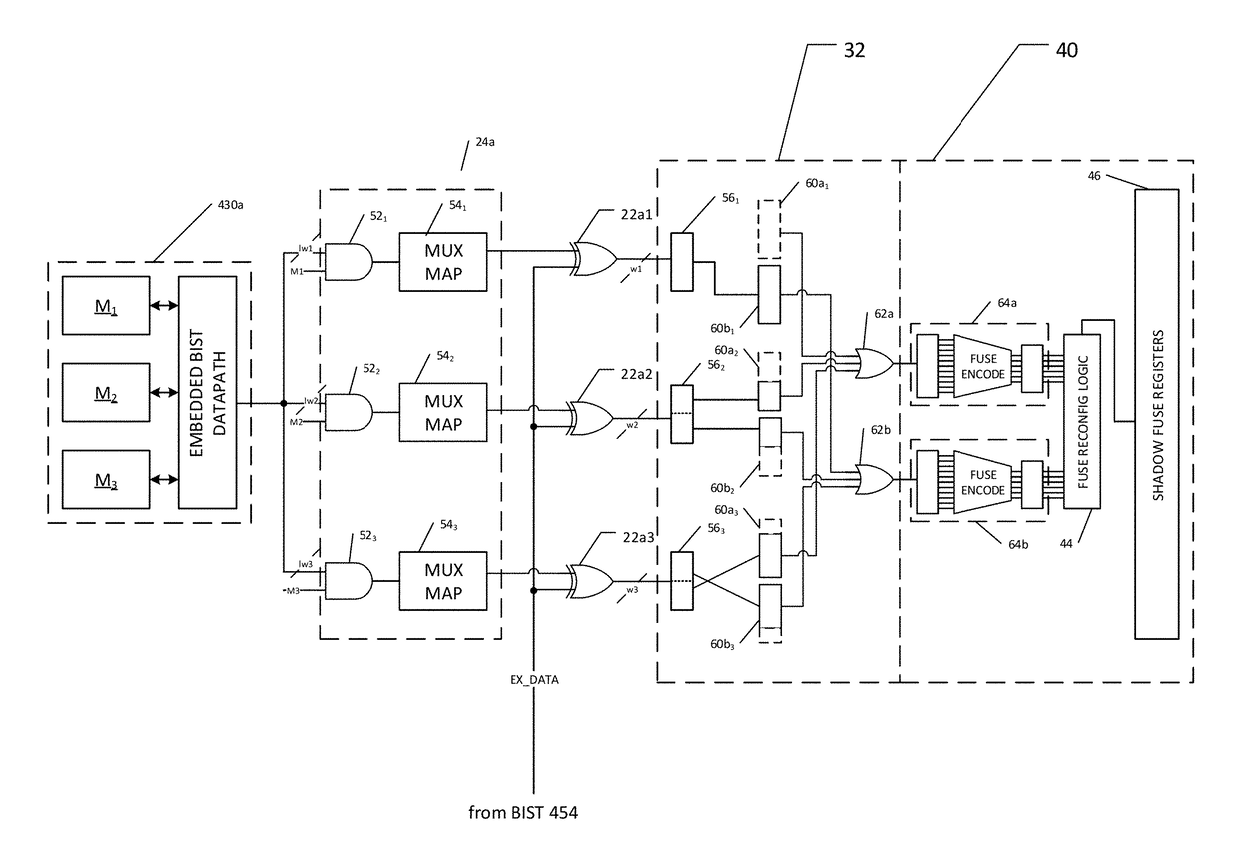
Centralized Built-In Soft-Repair Architecture for Integrated Circuits With Embedded Memories
ActiveUS20170184662A1Efficient implementationShorten test timeElectronic circuit testingStatic storageEmbedded memoryIntegrated circuit
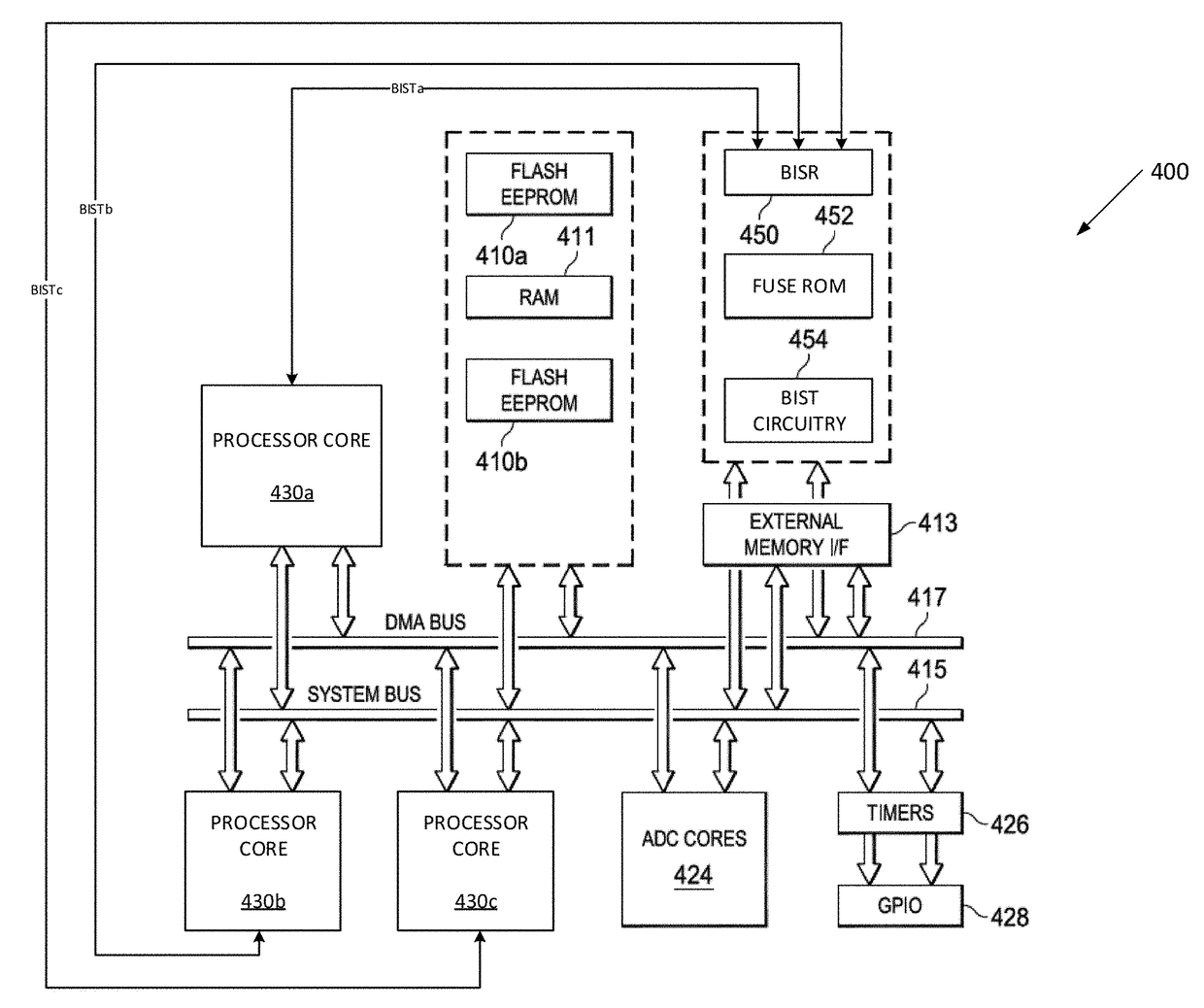
A large-scale integrated circuit with built-in self-repair (BISR) circuitry for enabling redundancy repair for embedded memories in each of a plurality of processor cores with embedded built-in self-test (BIST) circuitry. The BISR circuitry receives and decodes BIST data from the embedded memories into fail signature data in a physical-aware form on which repair analysis can be performed. The fail signature data is reformatted into a unified repair format, such that a fuse encoder circuit can be used to encode fuse patterns in that unified repair format for a repair entity for each of the embedded memories. The fuse patterns are reconfigured into the appropriate order for storing in shadow fuse registers associated with the specific embedded memories.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
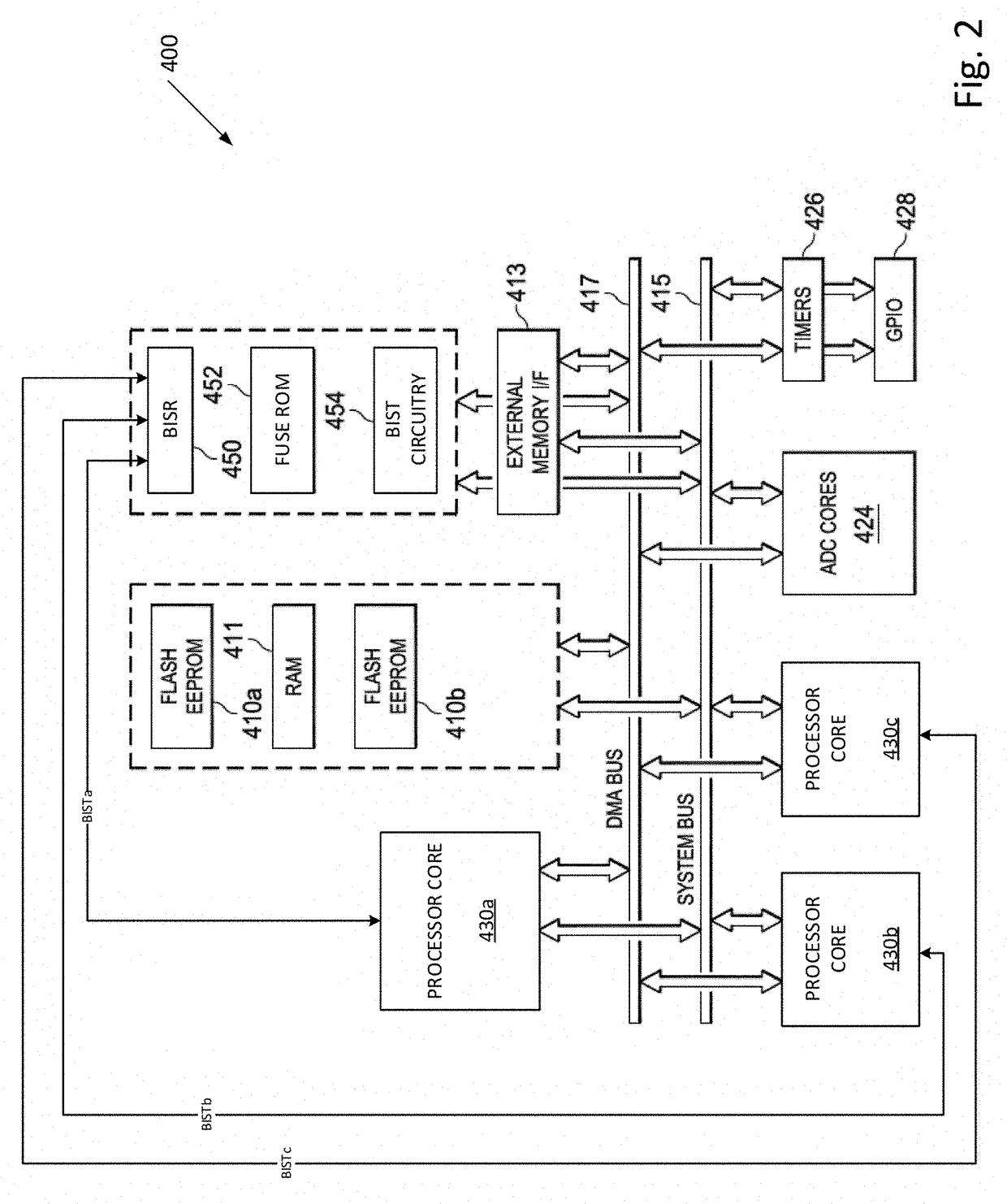
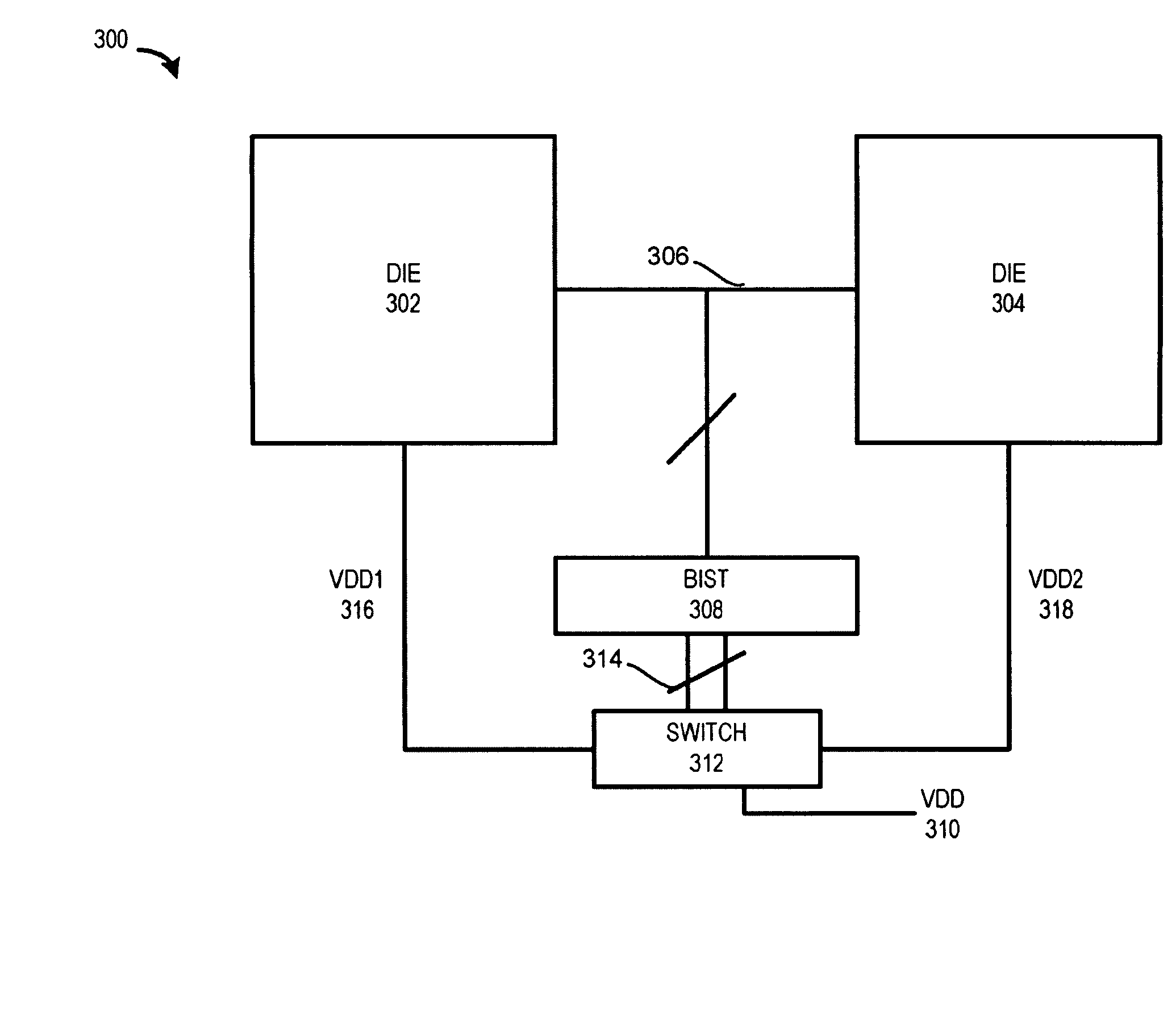
Built-in-self-repair arrangement for a single multiple-integrated circuit package and methods thereof
InactiveUS8055966B1Electronic circuit testingPower supply testingElectronic componentIntegrated circuit
A multiple integrated circuit arrangement within a single package is provided. The multiple integrated circuit arrangement includes a set of electronic components, which includes at least a set of dies. The first die of the set of dies is coupled to a first electronic component of the set of electronic components, wherein the first electronic component is not the first die. The arrangement includes a built-in-self-test (BIST) arrangement, which is at least partly encapsulated within the single package, wherein the BIST arrangement is configured for at least testing the first die of the set of dies. The arrangement also includes a built-in-self-repair (BISR) arrangement, which is at least partly encapsulated within the single package, wherein the BISR arrangement is configured for at least repairing the multiple integrated circuit arrangement.
Owner:WI2WI
Testing method and test apparatus in semiconductor apparatus
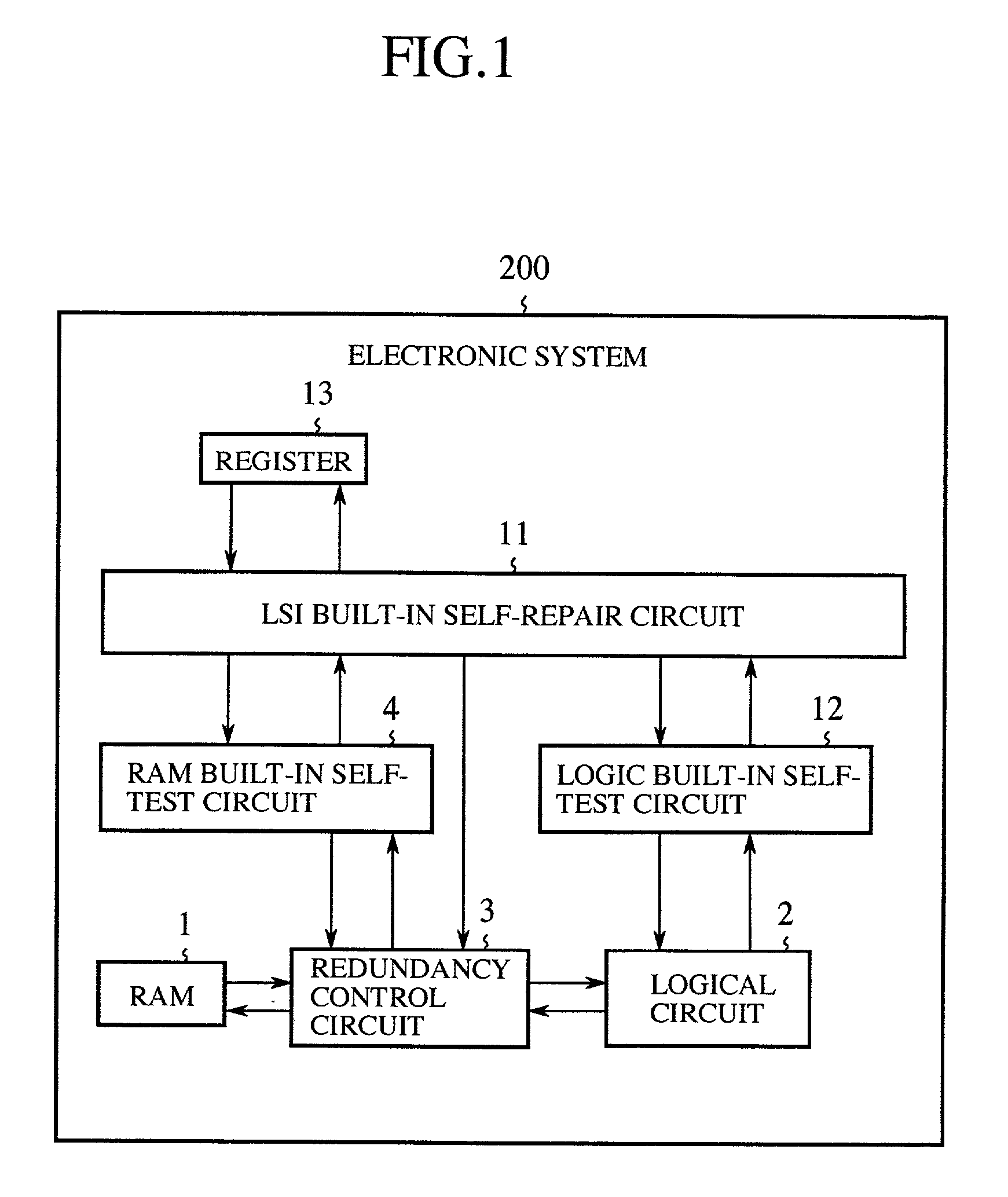
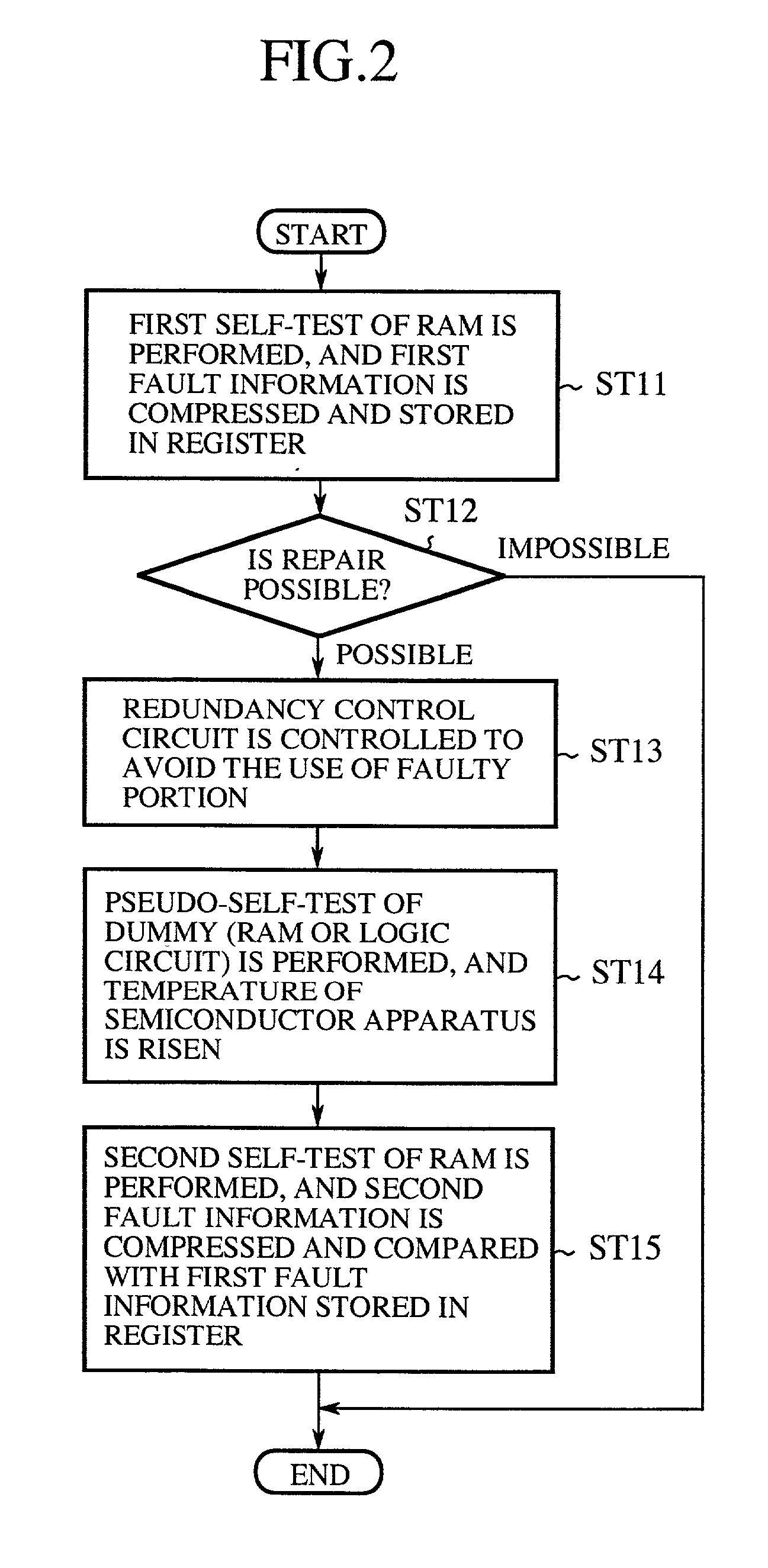
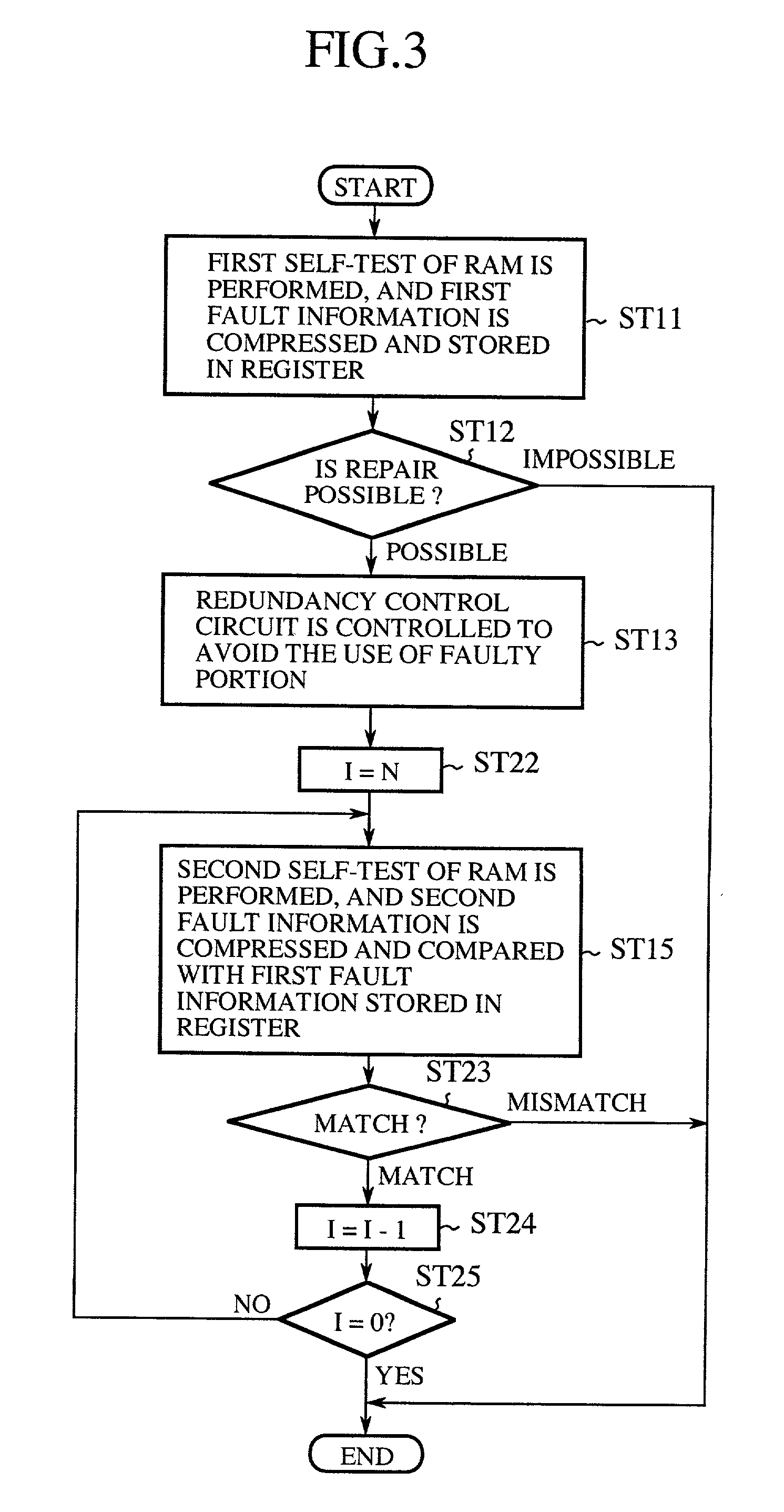
In a self-repairing operation, a first self-test of a RAM is performed at a first temperature to obtain a first RAM test result, a RAM built-in self-test circuit judges according to the first RAM test result that a faulty portion exists in the RAM, an LSI built-in self-repair circuit judges that the repair of the faulty portion of the RAM is possible, the LSI built-in self-repair circuit controls a redundancy control circuit to avoid the use of the faulty portion of the RAM in a normal operation, the temperature of the RAM is risen by operating the RAM or a logical circuit in a pseudo-self-test to change the first temperature to a second temperature, a second self-test of the RAM is performed at the second temperature to obtain a second RAM test result, and the LSI built-in self-repair circuit confirms that the repair of the faulty portion of the RAM is possible at each of the first and second temperatures by comparing the second RAM test result with the first RAM test result. Therefore, the reliability of the test of the RAM for the test condition change can be improved, and a correct operation of the RAM can be guaranteed at the first and second temperatures after a self-repair of the RAM.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
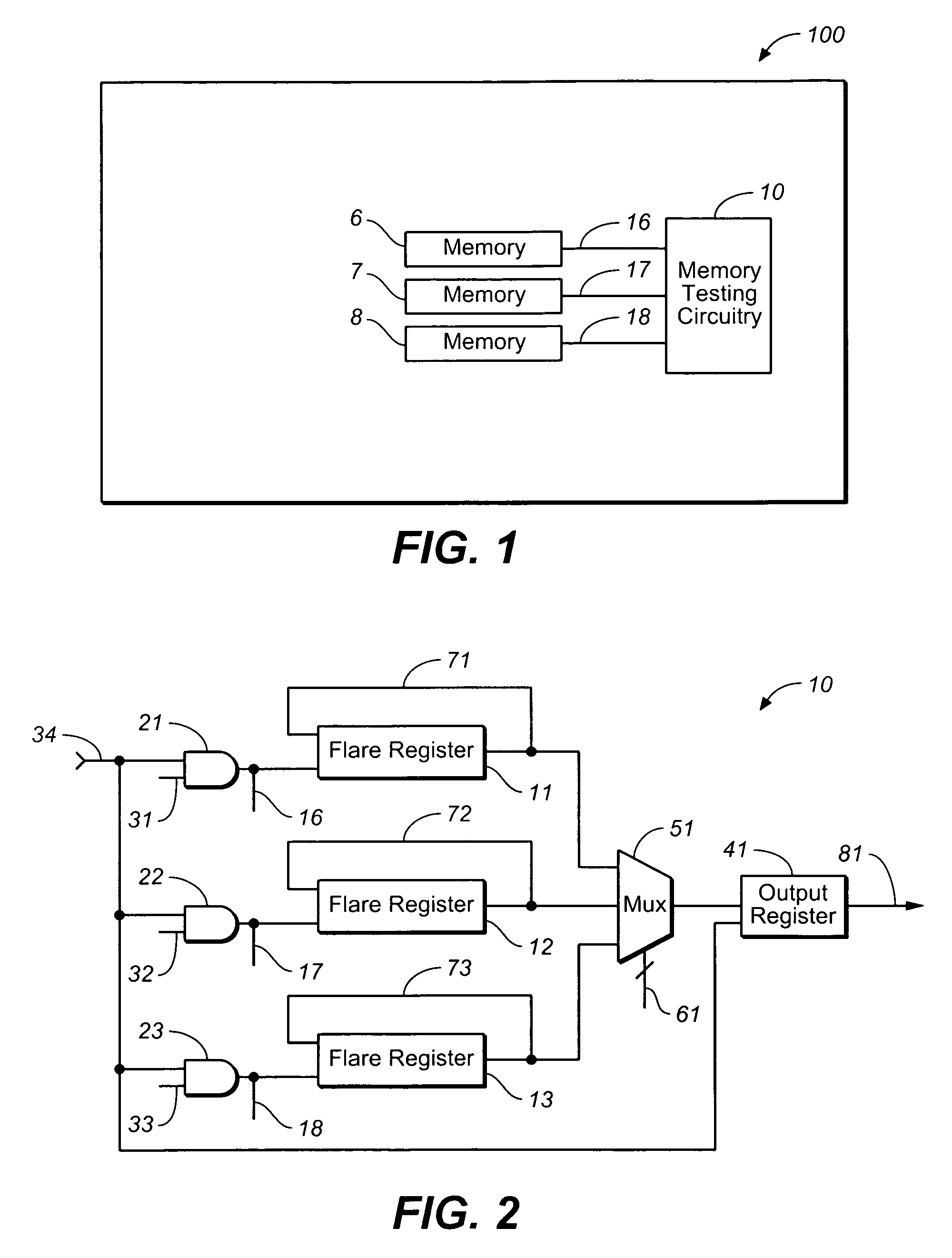
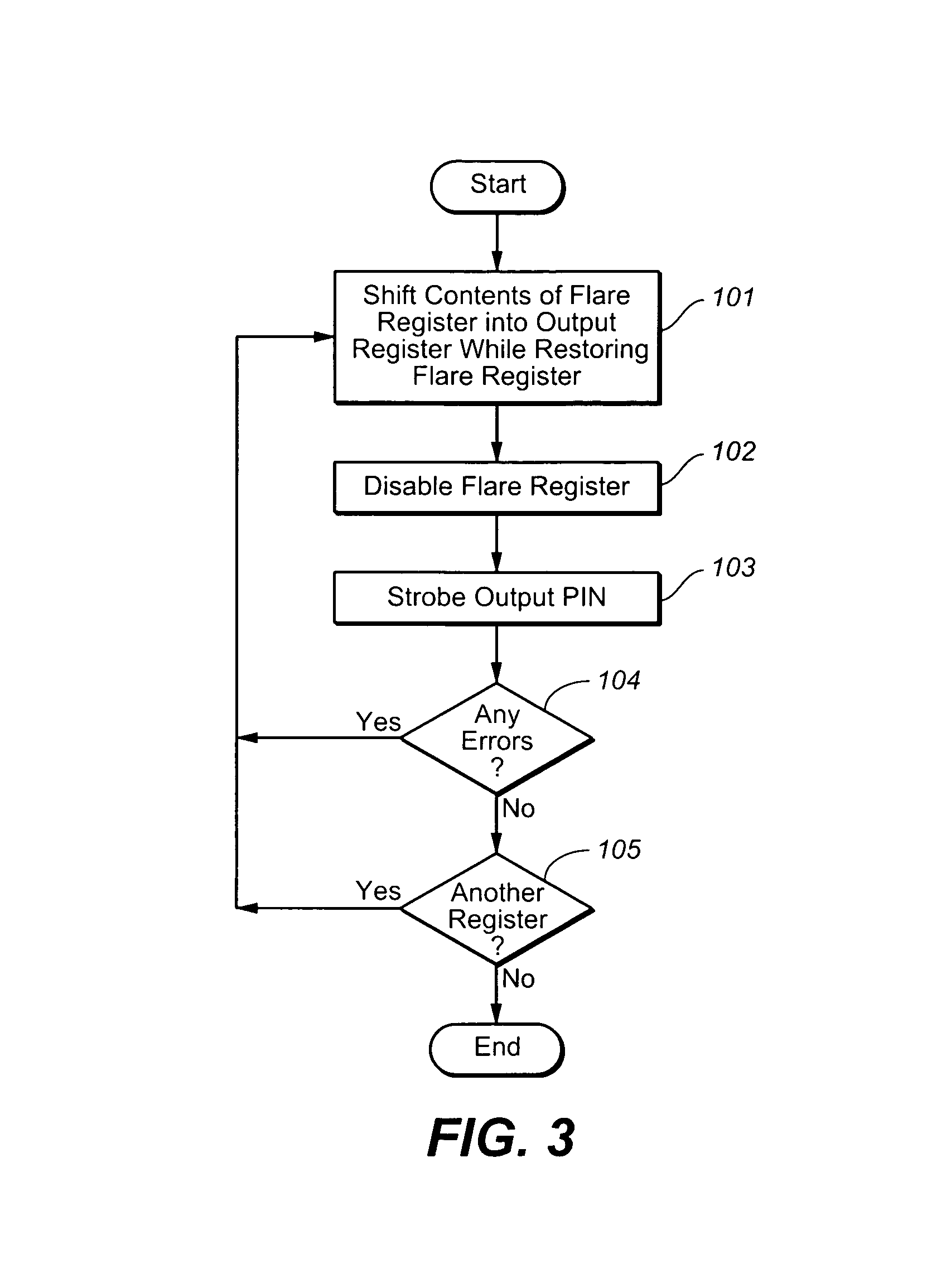
Testing implementation suitable for built-in self-repair (BISR) memories
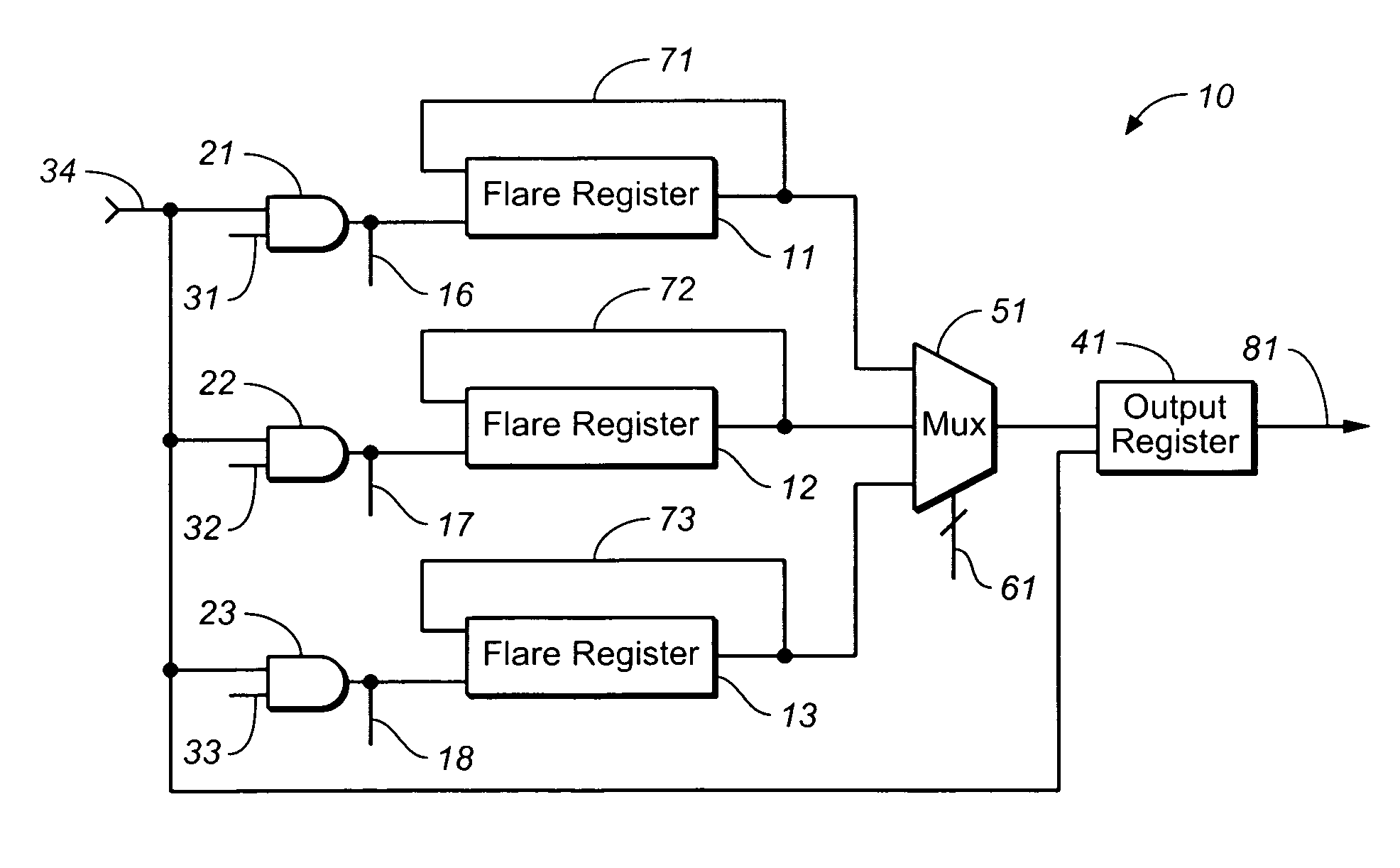
InactiveUS7185243B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesSpray nozzlesShift registerDigital data
A semiconductor memory testing implementation suitable for build-in self repair (BISR) memories provides, in one embodiment, a memory testing circuit configuration including an output register for receiving digital data. A plurality of shift registers serially output the digital data to be received by the output register. Each one of the plurality of shift registers includes a feedback path for enabling the digital data output by a corresponding one of the plurality of shift registers to be input back into the corresponding shift register in a same sequence as the digital data is output from the corresponding shift register.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Built-in self-repair method for NAND flash memory and system thereof
A built-in self-test system applied to NAND flash memory comprises a built-in self-test circuit, a built-in redundancy-analysis circuit, a content addressable memory, a spare memory, a page-mode processor and an address generator. The built-in self-test circuit is configured to test for defective data in a NAND flash memory. The built-in redundancy-analysis circuit is connected to the built-in self-test circuit. The content addressable memory is connected to the built-in redundancy-analysis circuit for storing the address of the defective data. The spare memory is electrically connected to the content addressable memory. The page-mode processor is configured to generate a page address signal and a compensation signal according to an address signal of the NAND flash memory. The address generator is configured to generate a current address signal according to the page address signal and compensation signal to the content addressable memory.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Memory built-in self-repair system and method based on Hash table
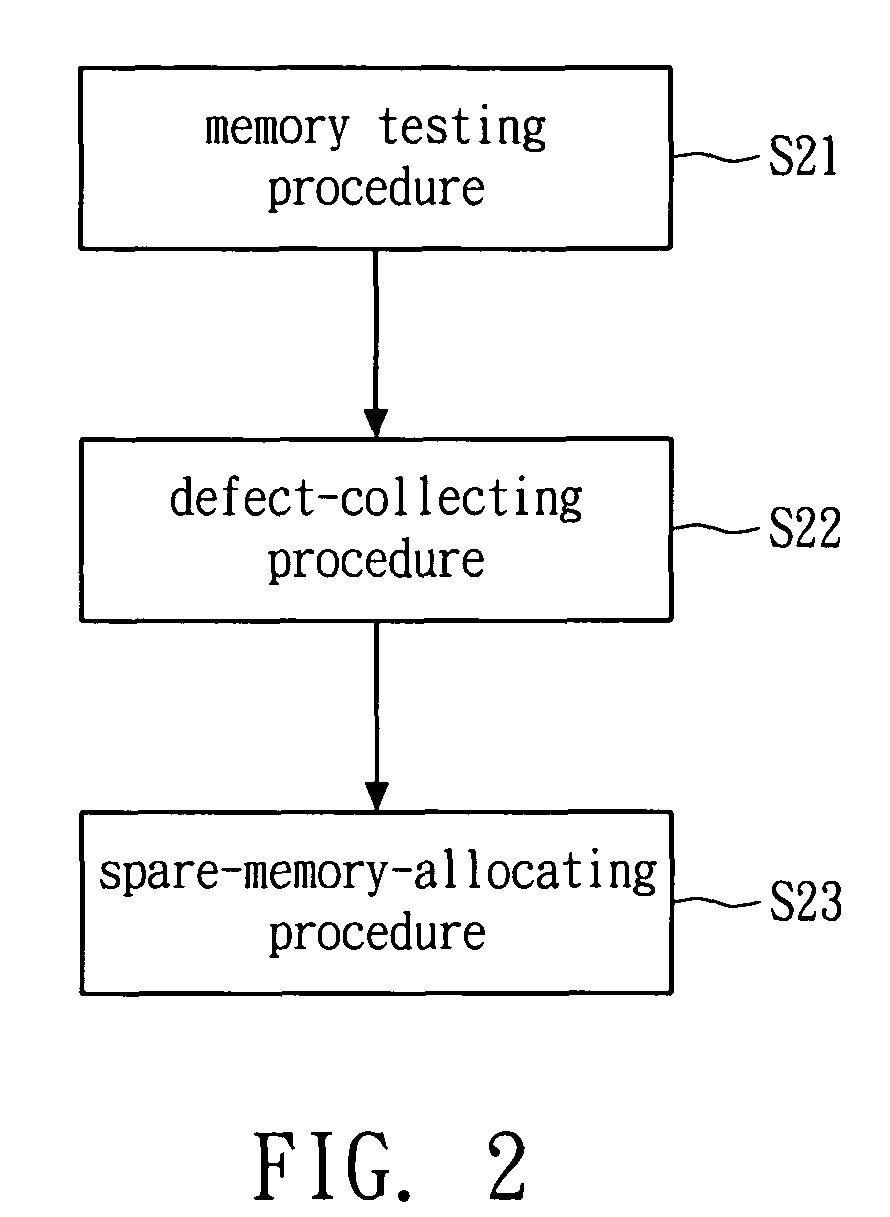
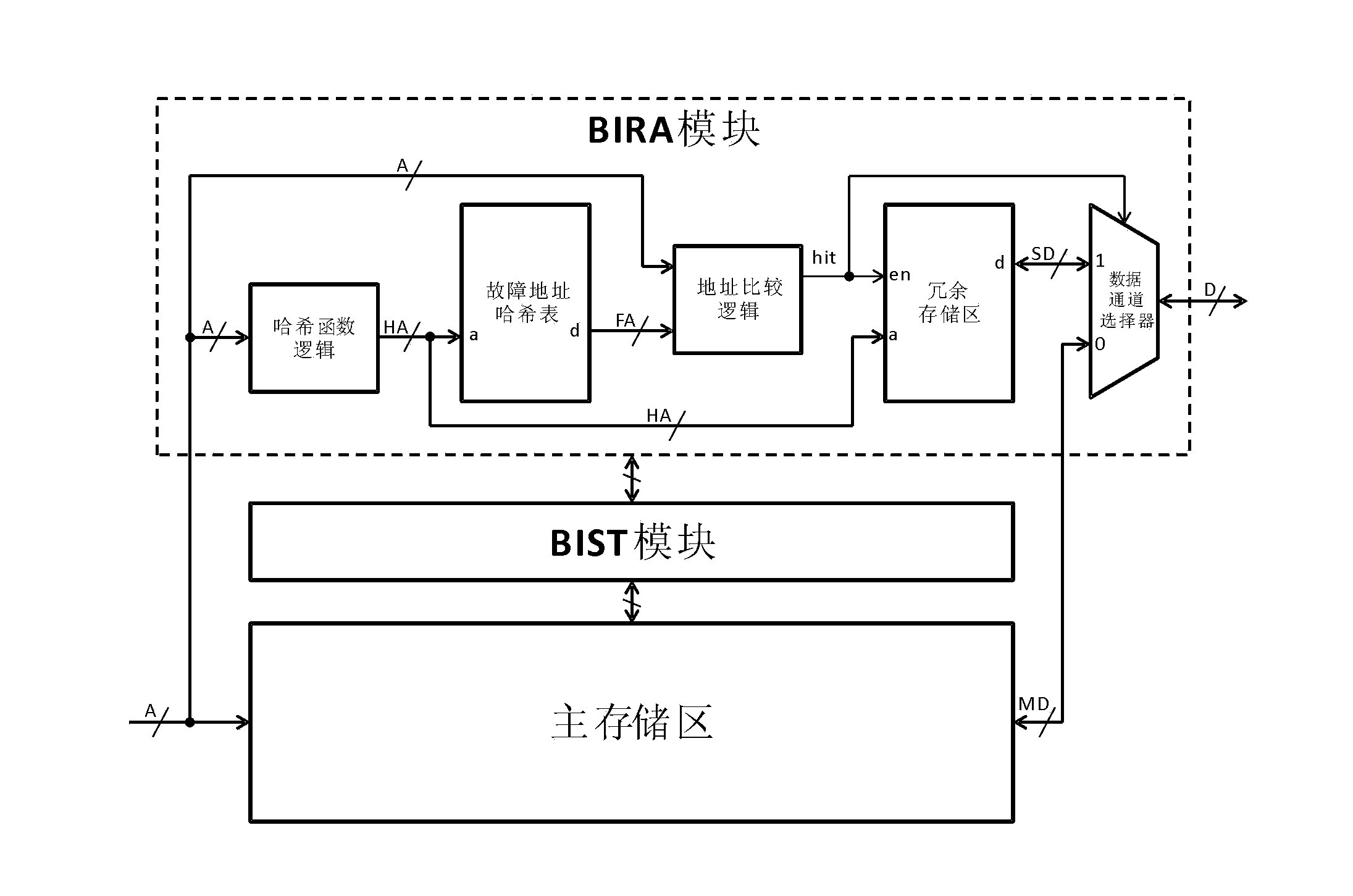
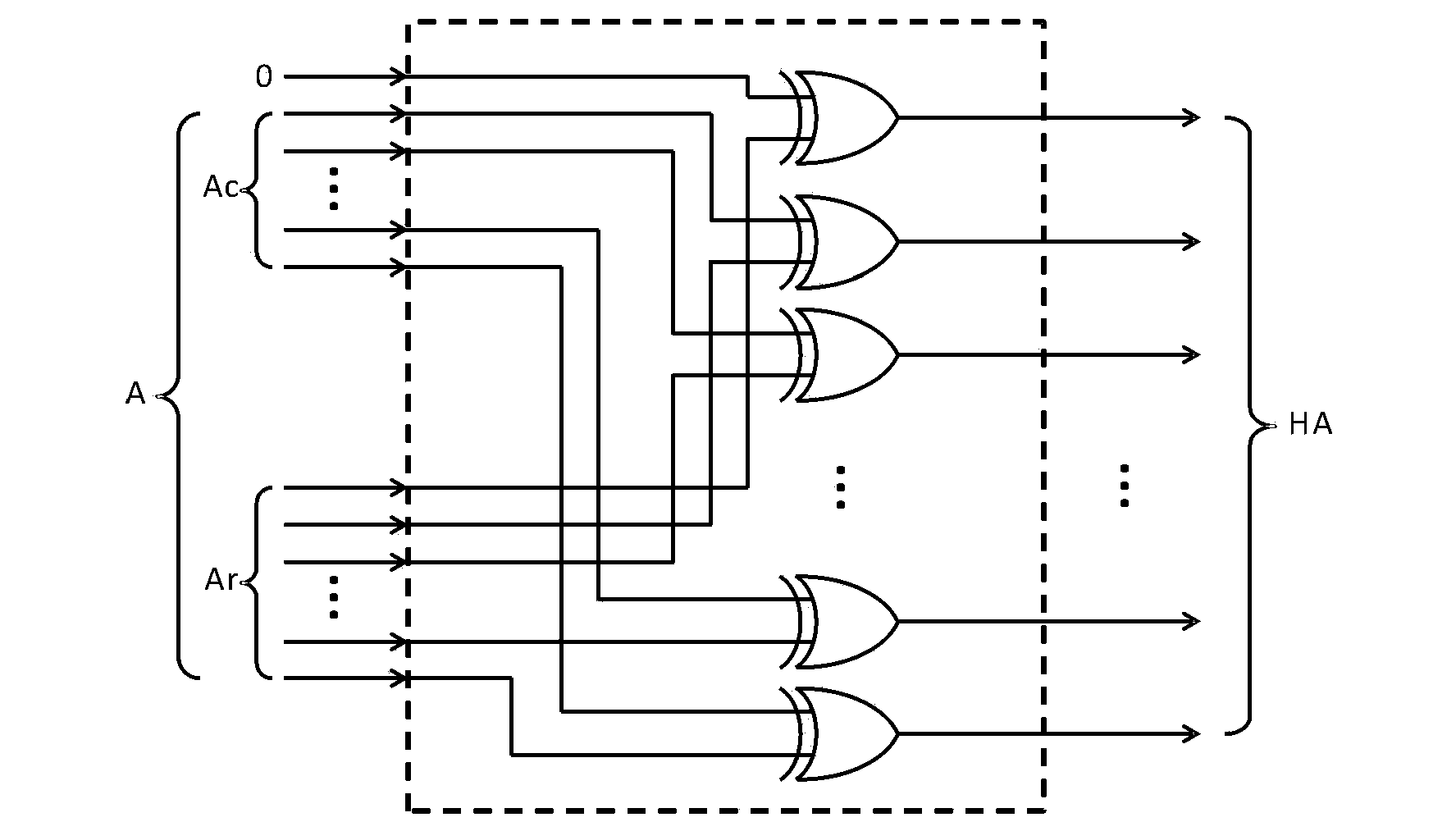
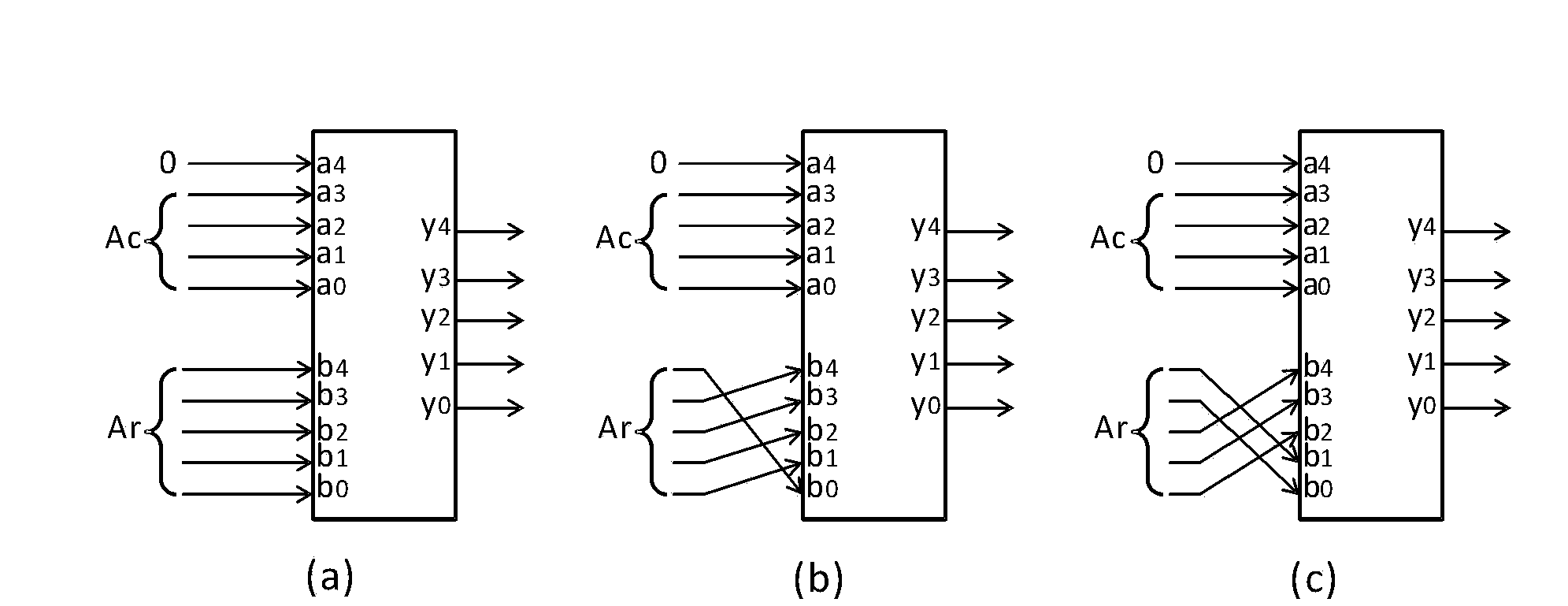
ActiveCN103390430APerformance impactAvoid comparisonStatic storageLow power dissipationMultiple fault
The invention discloses a memory built-in self-repair (MBISR) system based on Hash table. The system comprises a built-in self-test (BIST) module and a built-in redundancy analysis (BIRA) module. The BIST module is used for carrying out tests on the memory, and temporarily stores tested fault addresses in the BIST module and outputs the fault addresses to the BIRA module; and the BIRA module is used for determining whether an access address is a fault address, and distributing redundancy resource to the fault address and carries out remapping on the fault address, thereby completing repair of the memory. The invention also discloses a memory built-in self-repair method based on Hash table. The invention has high address comparison efficiency, fundamentally solves the disadvantages of a traditional memory built-in self-repair method, such as low search address comparison efficiency and incapability to genuinely repair memory with multiple faults, and has the advantages of small land occupation and low power dissipation.
Owner:锐立平芯微电子(广州)有限责任公司
Stacked chip module with integrated circuit chips having integratable and reconfigurable built-in self-maintenance blocks
ActiveUS20140110710A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSelf maintenanceComputer module
Disclosed is a stacked chip module incorporating a stack of integrated circuit (IC) chips having integratable and automatically reconfigurable built-in self-maintenance blocks (i.e., built-in self-test (BIST) circuits or built-in self-repair (BISR) circuits). Integration of the built-in self-maintenance blocks between the IC chips in the stack allows for servicing (e.g., self-testing or self-repairing) of functional blocks at the module-level. Automatic reconfiguration of the built-in self-maintenance blocks further allows for functional blocks on any of the IC chips in the stack to be serviced at the module-level even when one or more controllers associated with a given built-in self-maintenance block on a given IC chip has been determined to be defective (e.g., during previous wafer-level servicing). Also disclosed is a method of manufacturing and servicing such a stacked chip module.
Owner:IBM CORP
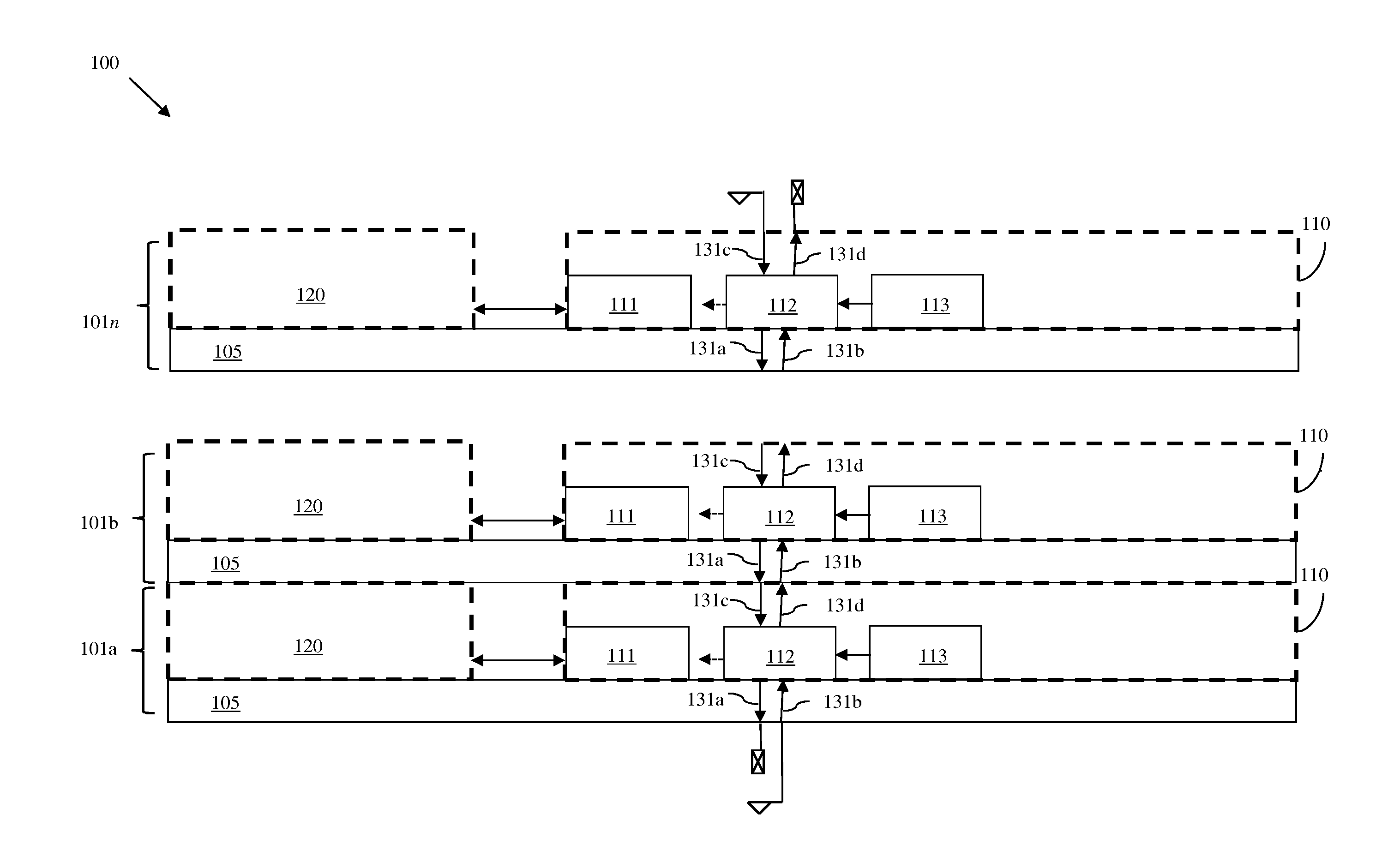
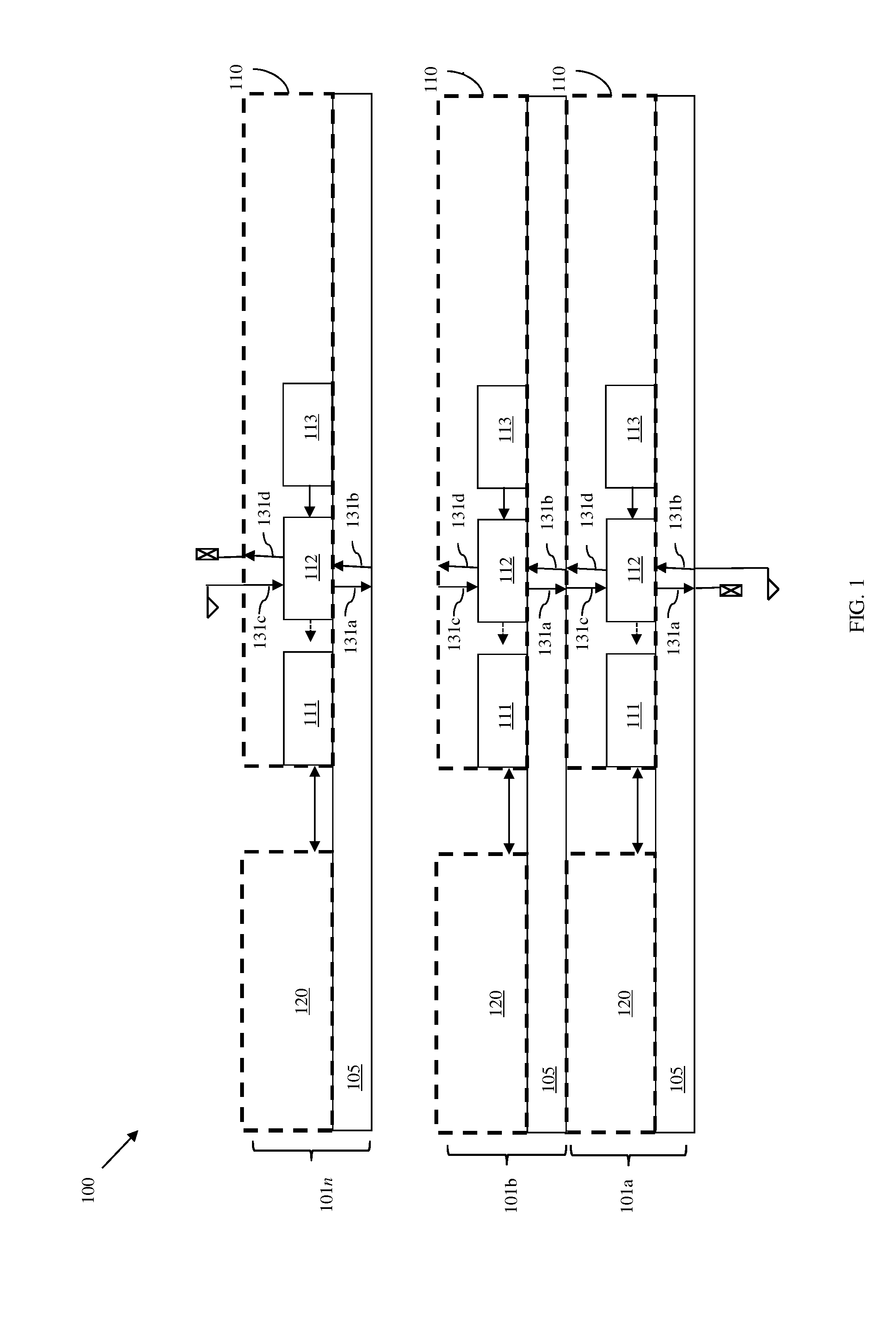
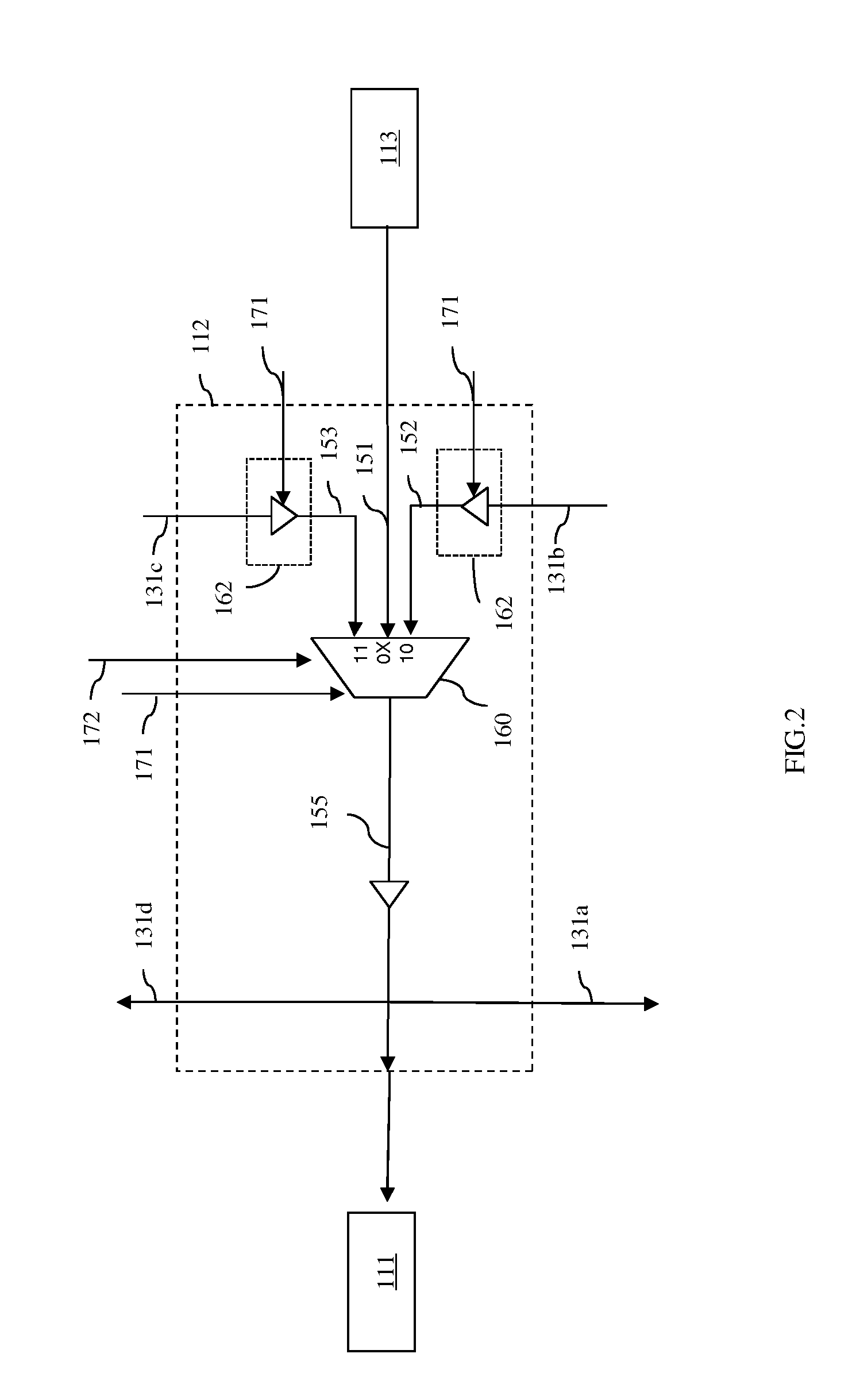
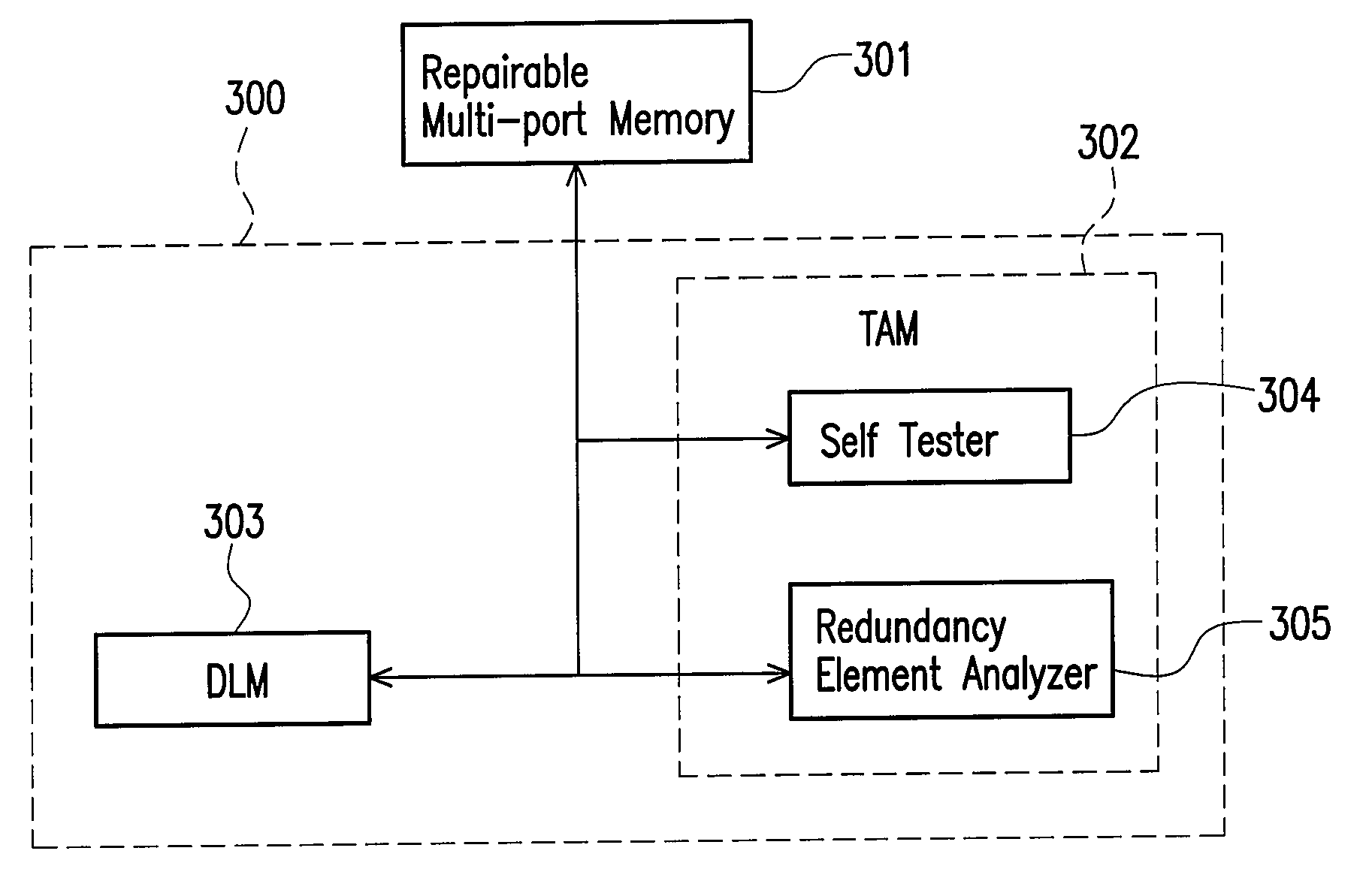
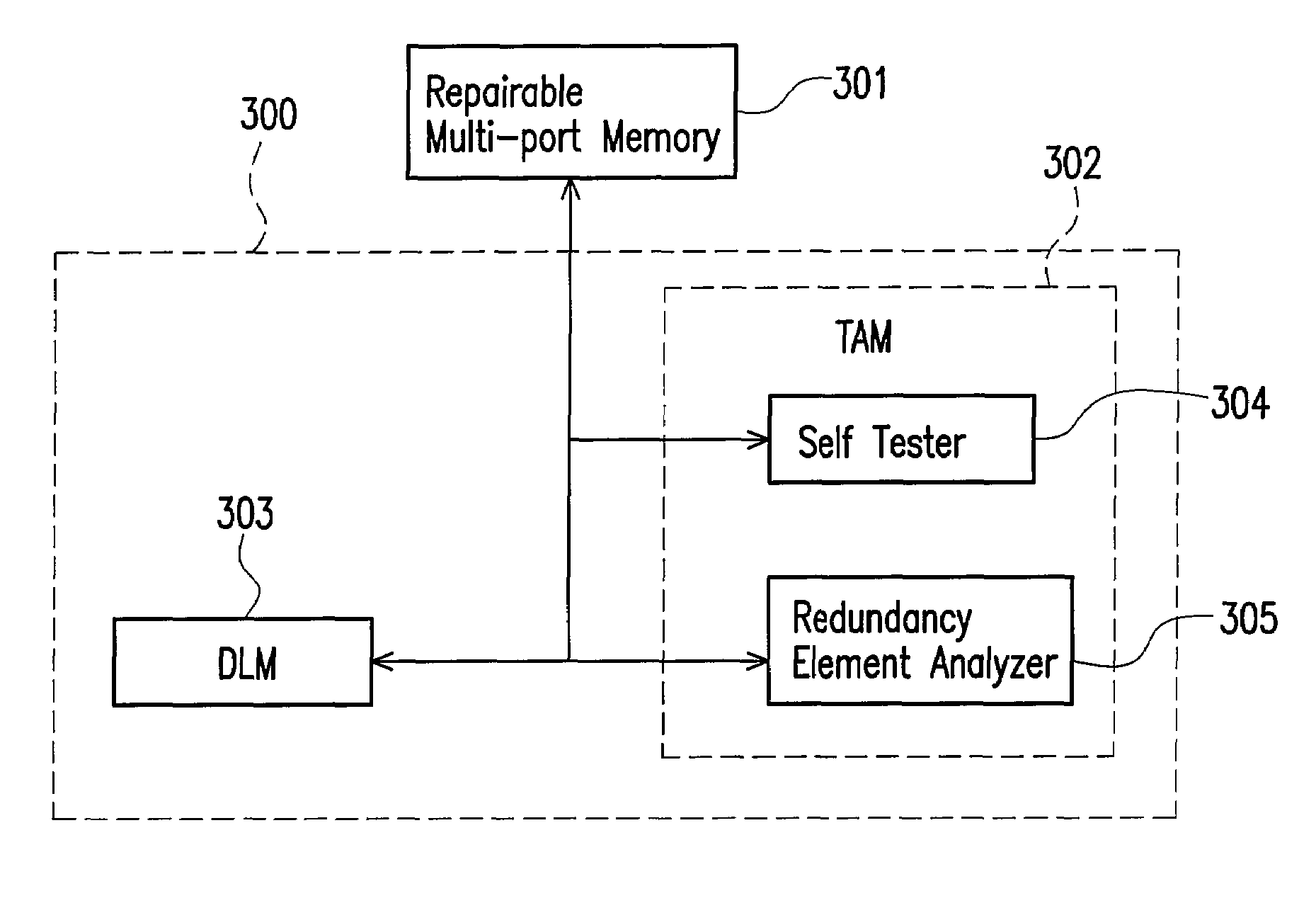
Built-in self repair circuit for a multi-port memory and method thereof
InactiveUS20090097342A1Avoid wastingImprove production yieldElectronic circuit testingDigital storageMulti portLocation determination
A built-in self repair (BISR) circuit for a multi-port memory and a method thereof are provided. The circuit includes a test-and-analysis module (TAM) and a defect locating module (DLM) coupled to the TAM. The TAM tests a repairable multi-port memory to generate a fault location and determines whether the test generates a port-specific fault candidate according to the fault location. If a port-specific fault candidate is generated, the DLM generates a defect location based on the fault location and provides the defect location to the TAM so that the TAM can determine how to repair the repairable multi-port memory according to the defect location. If no port-specific fault candidate is generated in the test, the TAM determines how to repair the repairable multi-port memory according to the fault location.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
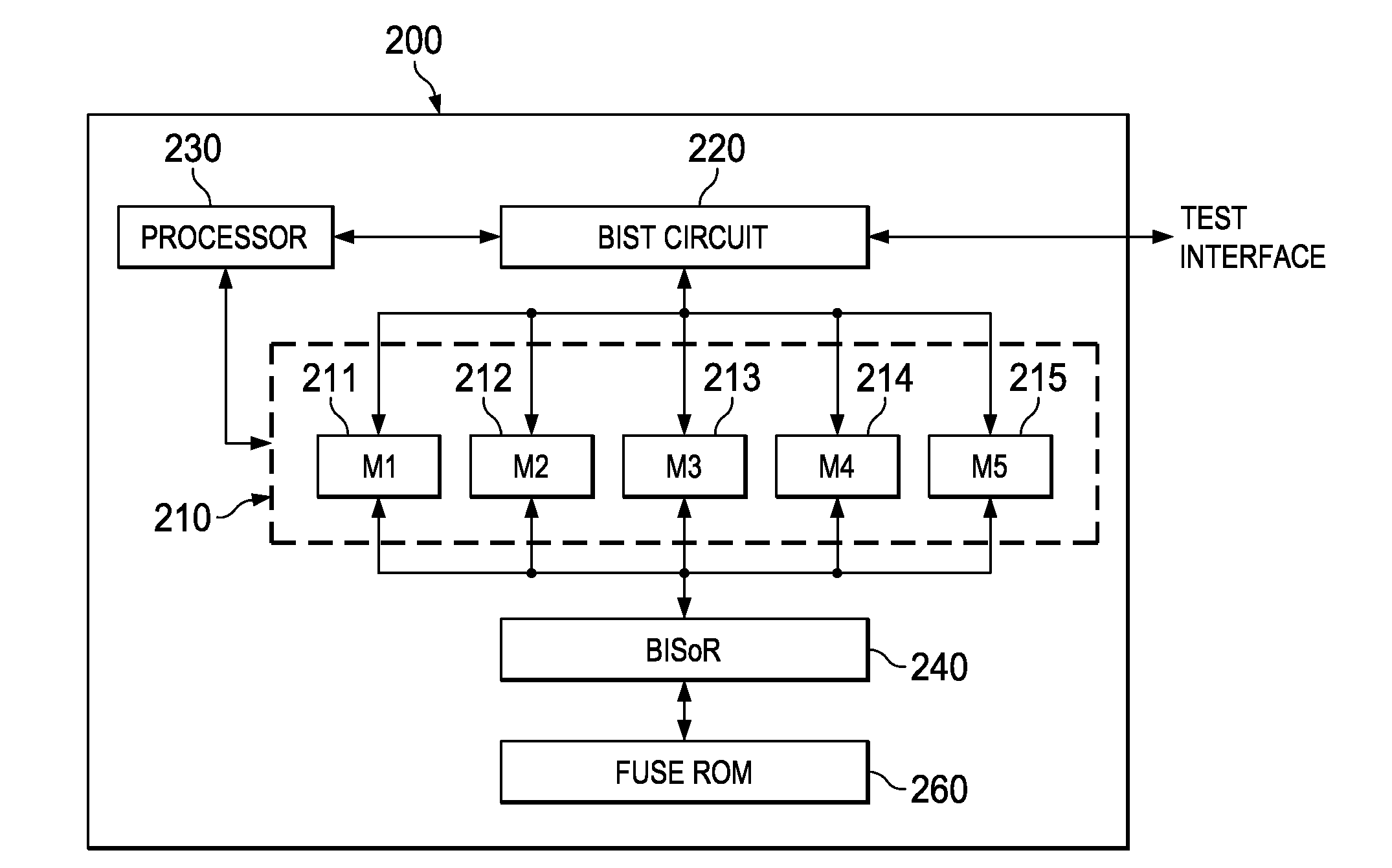
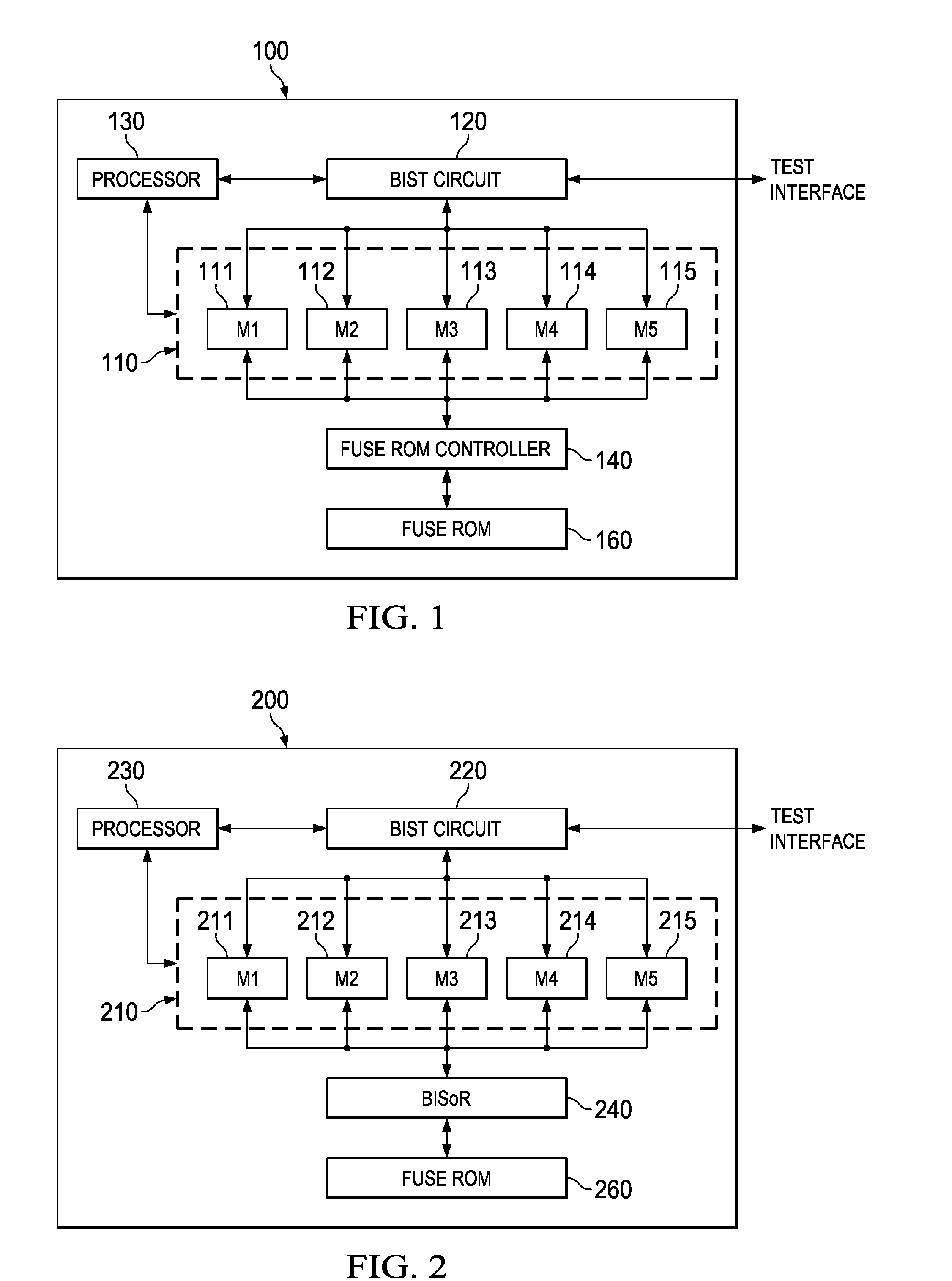
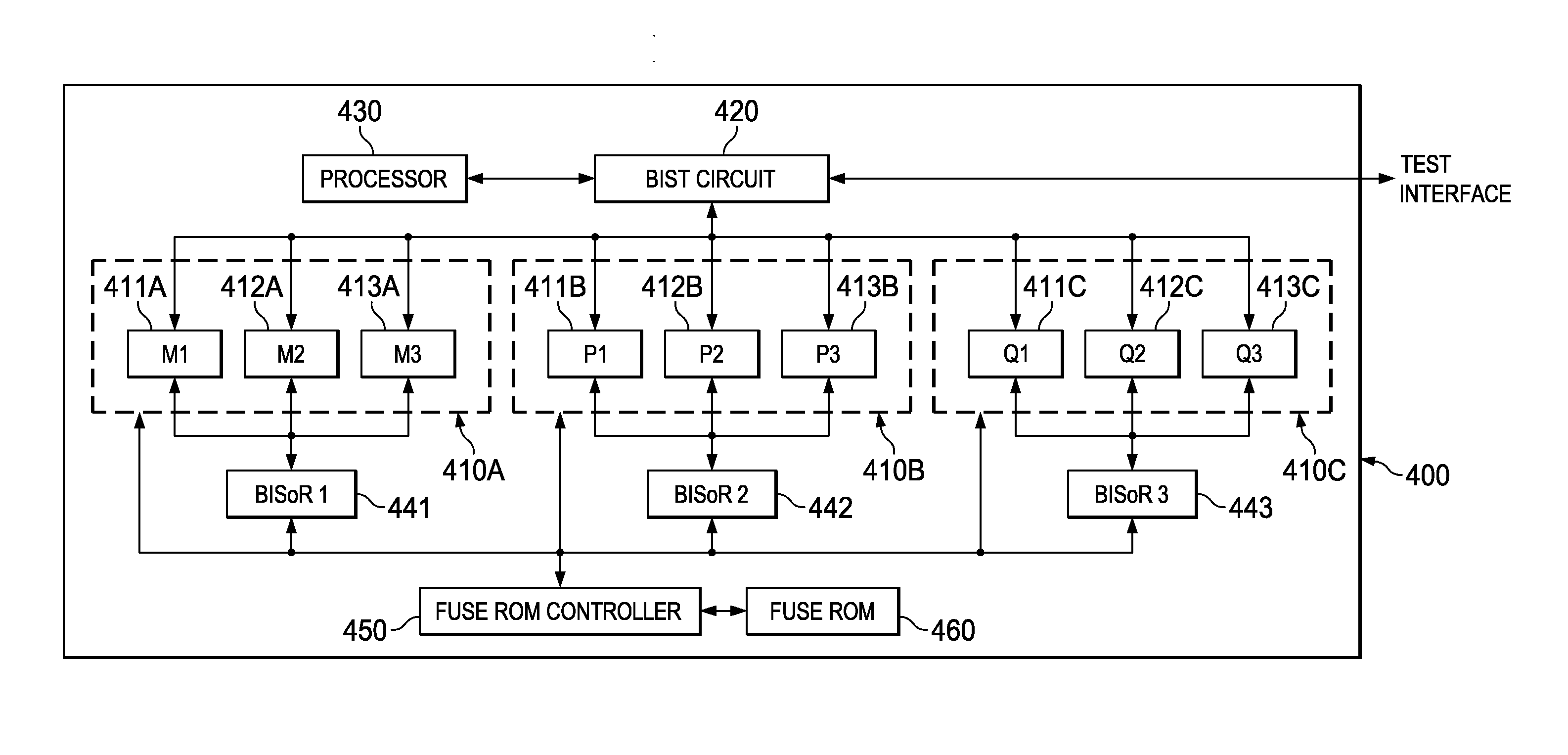
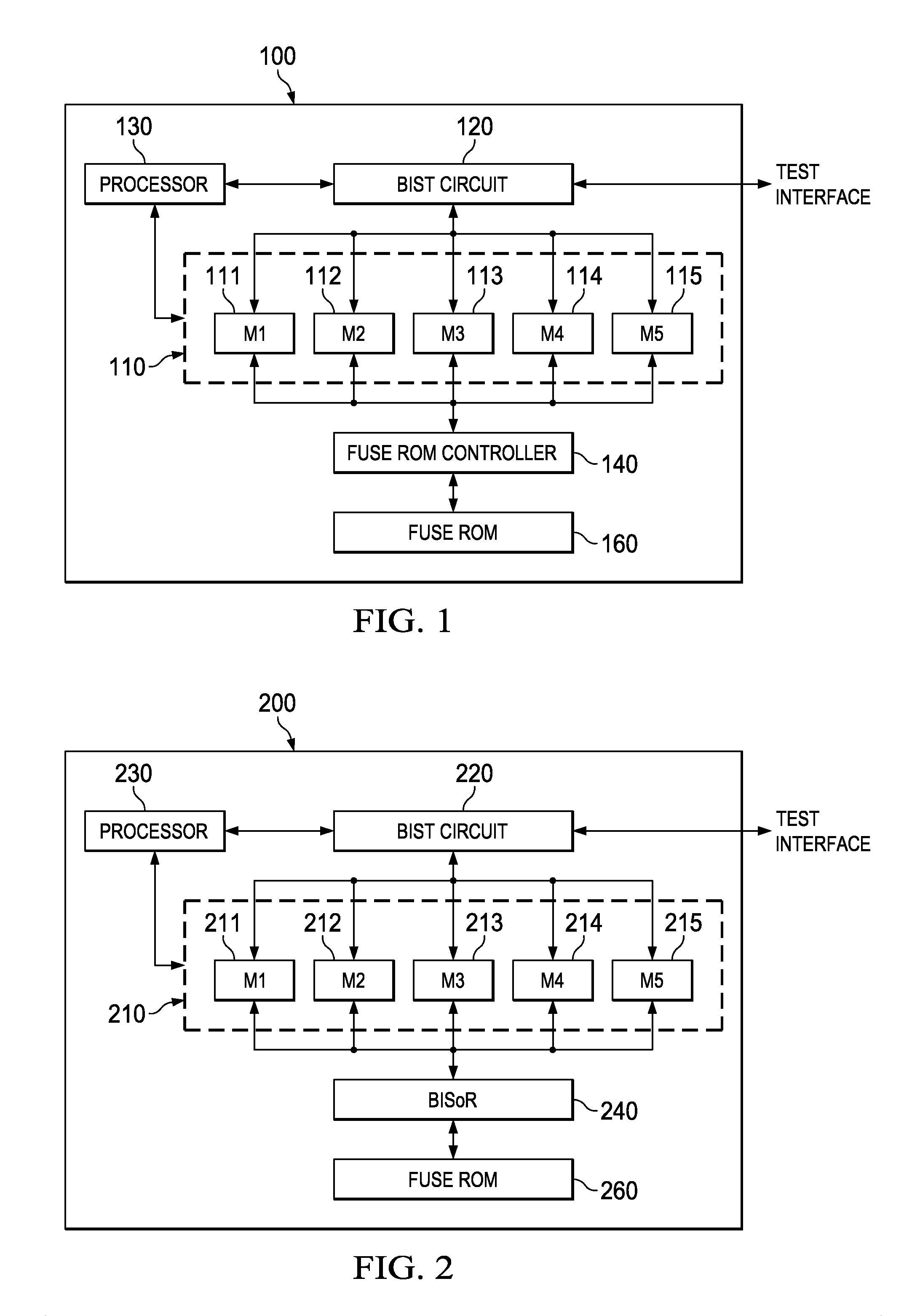
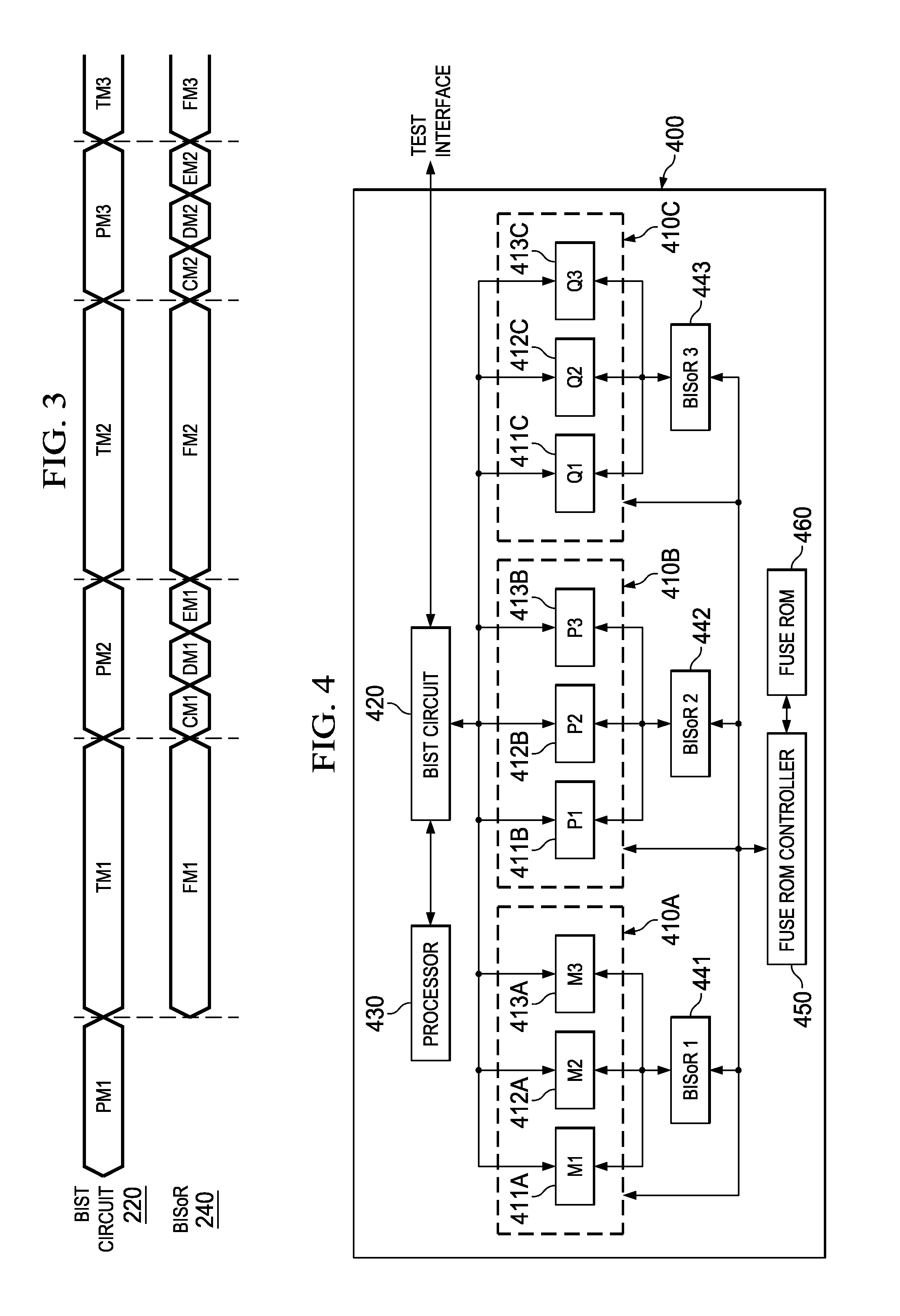
Hierarchical, Distributed Built-in Self-Repair Solution
A built-in self-test (BIST) circuit to test one or more memory blocks on an integrated circuit. The one or more memory blocks further includes a first memory block and a second memory block A built-in soft-repair controller (BISoR) is provided to soft repair the one or more memory blocks. The BIST circuit in conjunction with the BISoR is configured to test and soft repair the first memory block before performing test and soft repair of the second memory block.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Centralized built-in soft-repair architecture for integrated circuits with embedded memories
ActiveUS10134483B2Efficient implementationShorten test timeElectronic circuit testingStatic storageEmbedded memoryIntegrated circuit
A large-scale integrated circuit with built-in self-repair (BISR) circuitry for enabling redundancy repair for embedded memories in each of a plurality of processor cores with embedded built-in self-test (BIST) circuitry. The BISR circuitry receives and decodes BIST data from the embedded memories into fail signature data in a physical-aware form on which repair analysis can be performed. The fail signature data is reformatted into a unified repair format, such that a fuse encoder circuit can be used to encode fuse patterns in that unified repair format for a repair entity for each of the embedded memories. The fuse patterns are reconfigured into the appropriate order for storing in shadow fuse registers associated with the specific embedded memories.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Built-in self repair for an integrated circuit
InactiveUS20040070418A1Reliability increasing modificationsRead-only memoriesHemt circuitsSecondary circuit
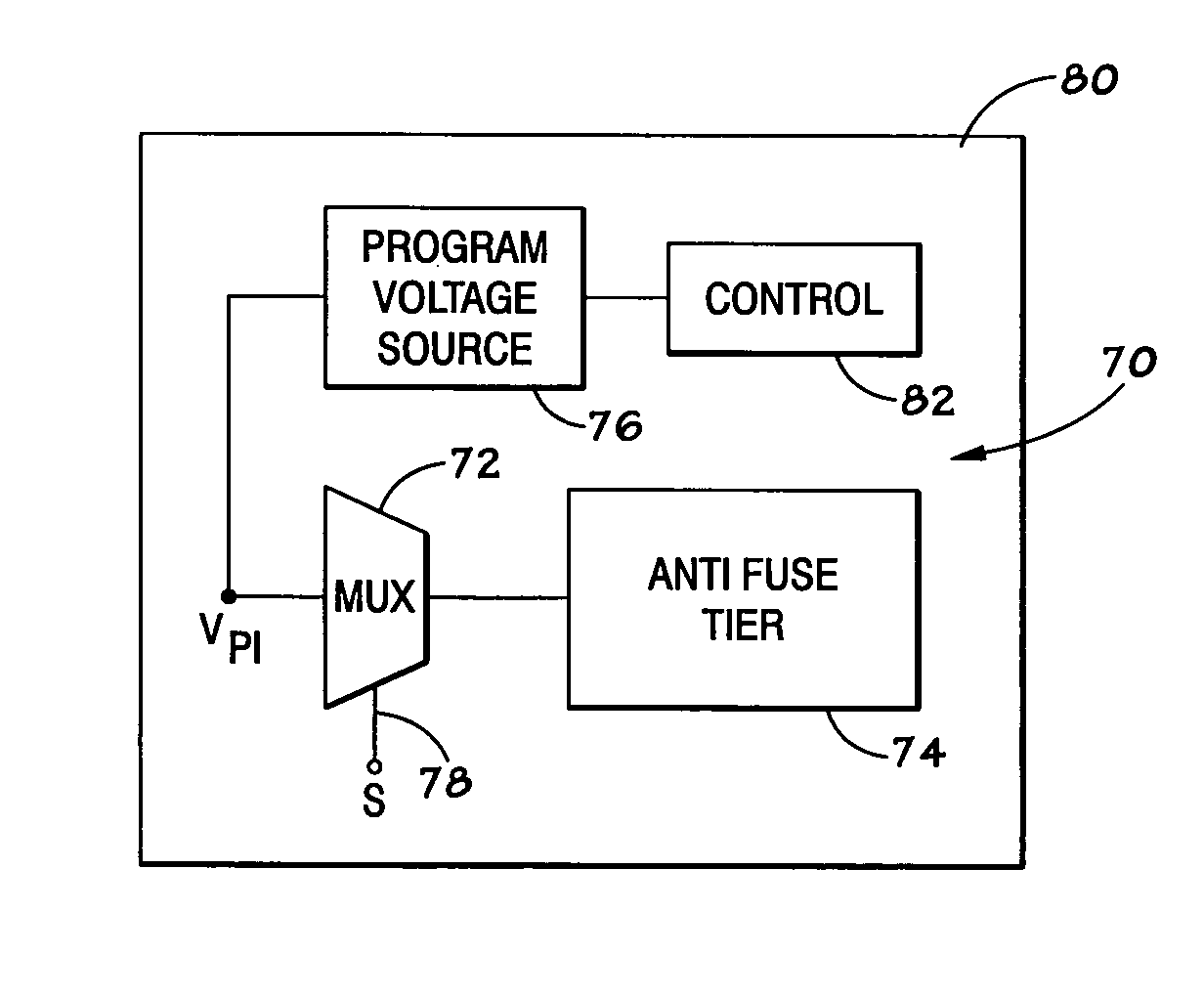
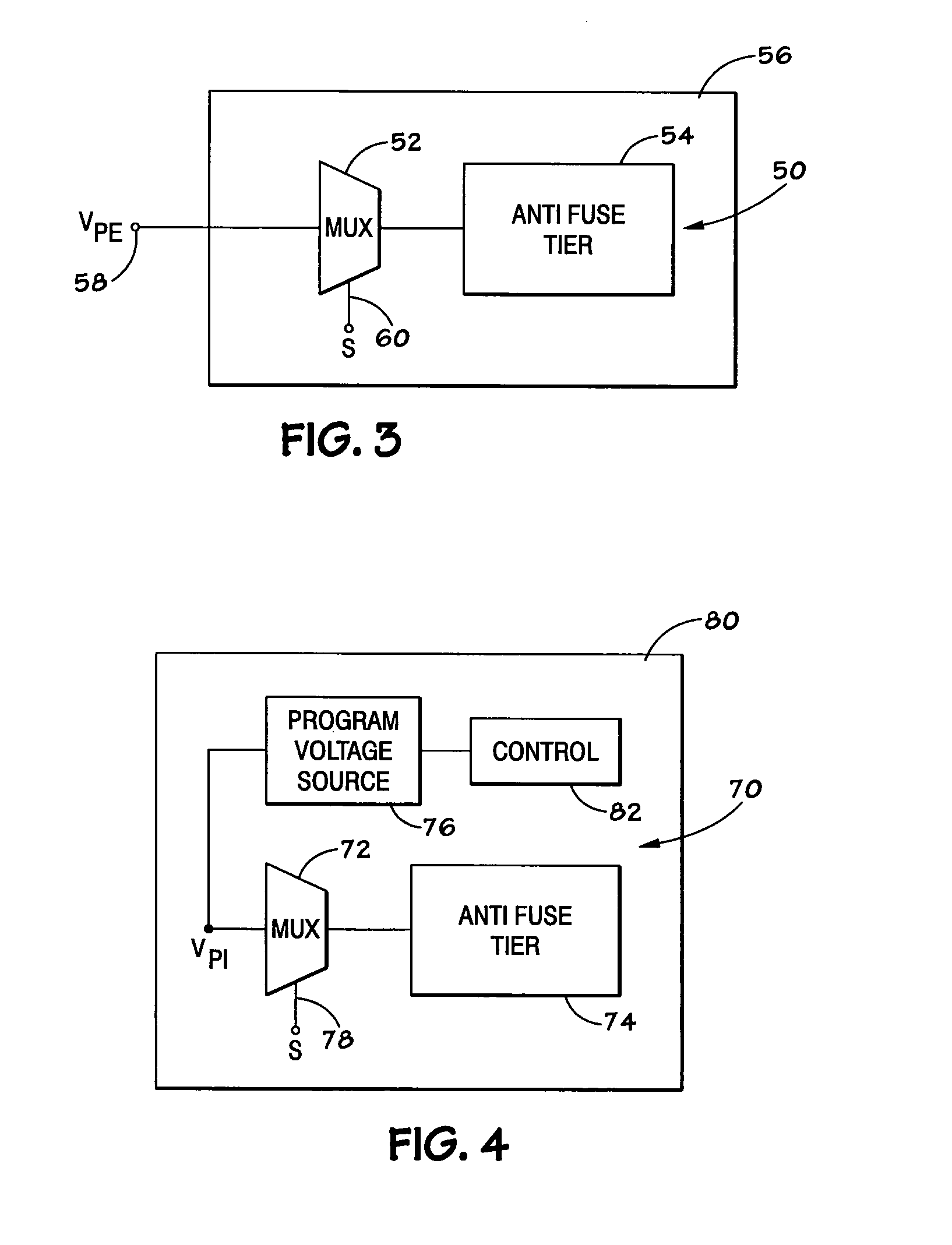
An integrated circuit, such as a memory device, includes a built-in repair circuit. The repair circuit includes an on-chip source that produces a programming signal of sufficient duration and magnitude to program a programmable element that normally isolates a secondary circuit, such as redundant circuitry, from the remainder of the circuits on the device. Once programmed, the redundant circuitry may take the place of failed circuitry, and thus repair the device.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
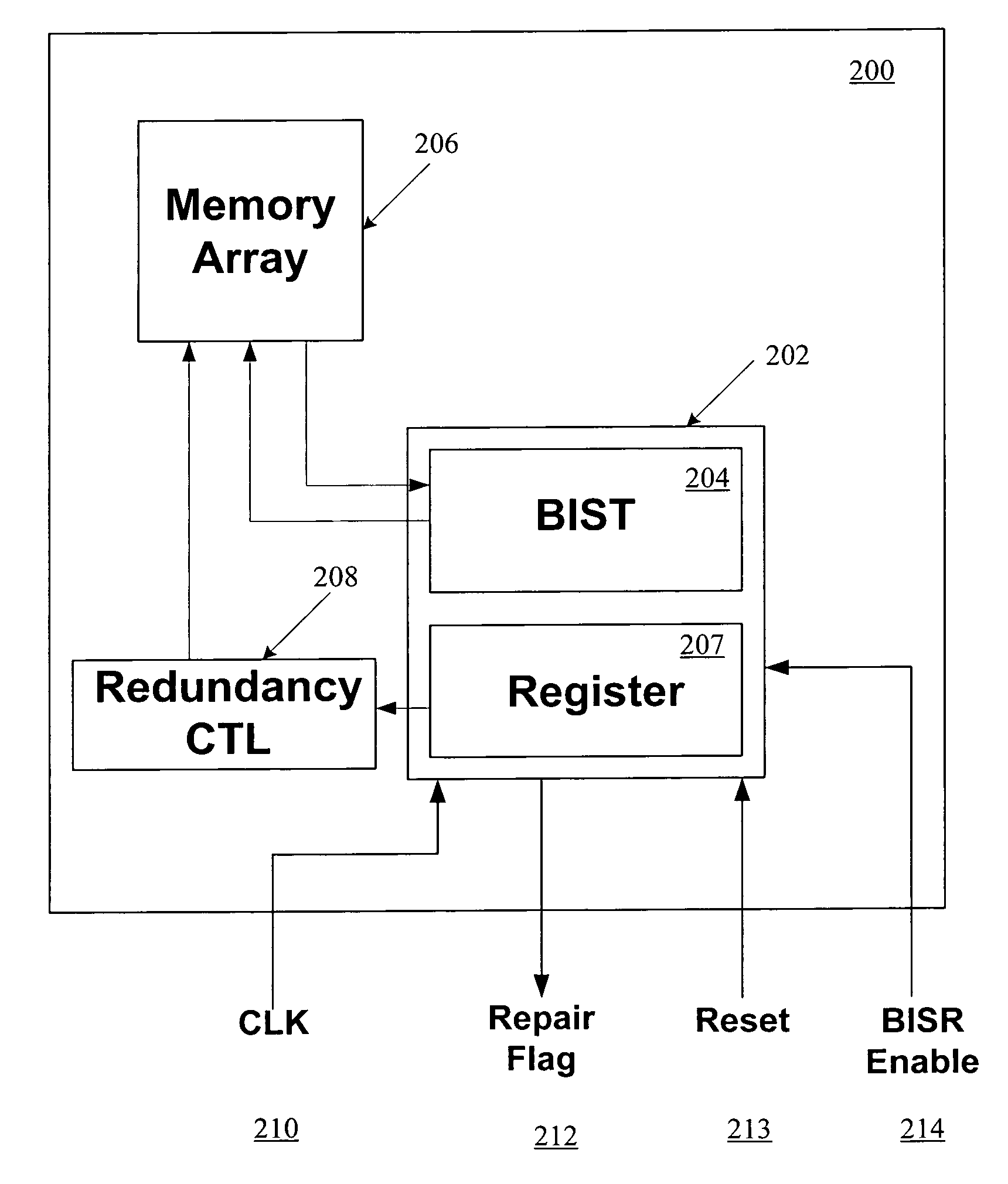
Method and system for improving reliability of memory device
A system for improving reliability of a memory device includes one or more memory banks, each of which has one or more regular memory cell rows and one or more redundant memory cell rows. At least one built-in-self-test (BIST) unit is coupled to the memory banks for testing the redundant memory cell rows to determine their respective quality standards, and testing the regular memory cell rows to identify the regular memory cell row that fails to pass a predetermined quality standard. At least one built-in-self-repair (BISR) unit is coupled to the BIST unit for replacing the failed regular memory cell row with the redundant memory cell row having a quality standard equal to or higher than the predetermined quality standard. The BIST unit repeatedly tests the regular memory cell rows a number of times, with each time applying a different quality standard.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Redundant fault-tolerant built-in self-repairing method suitable for static stage random access memory
InactiveCN103077749AAddresses defects that cannot be properly fixedStatic storageStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
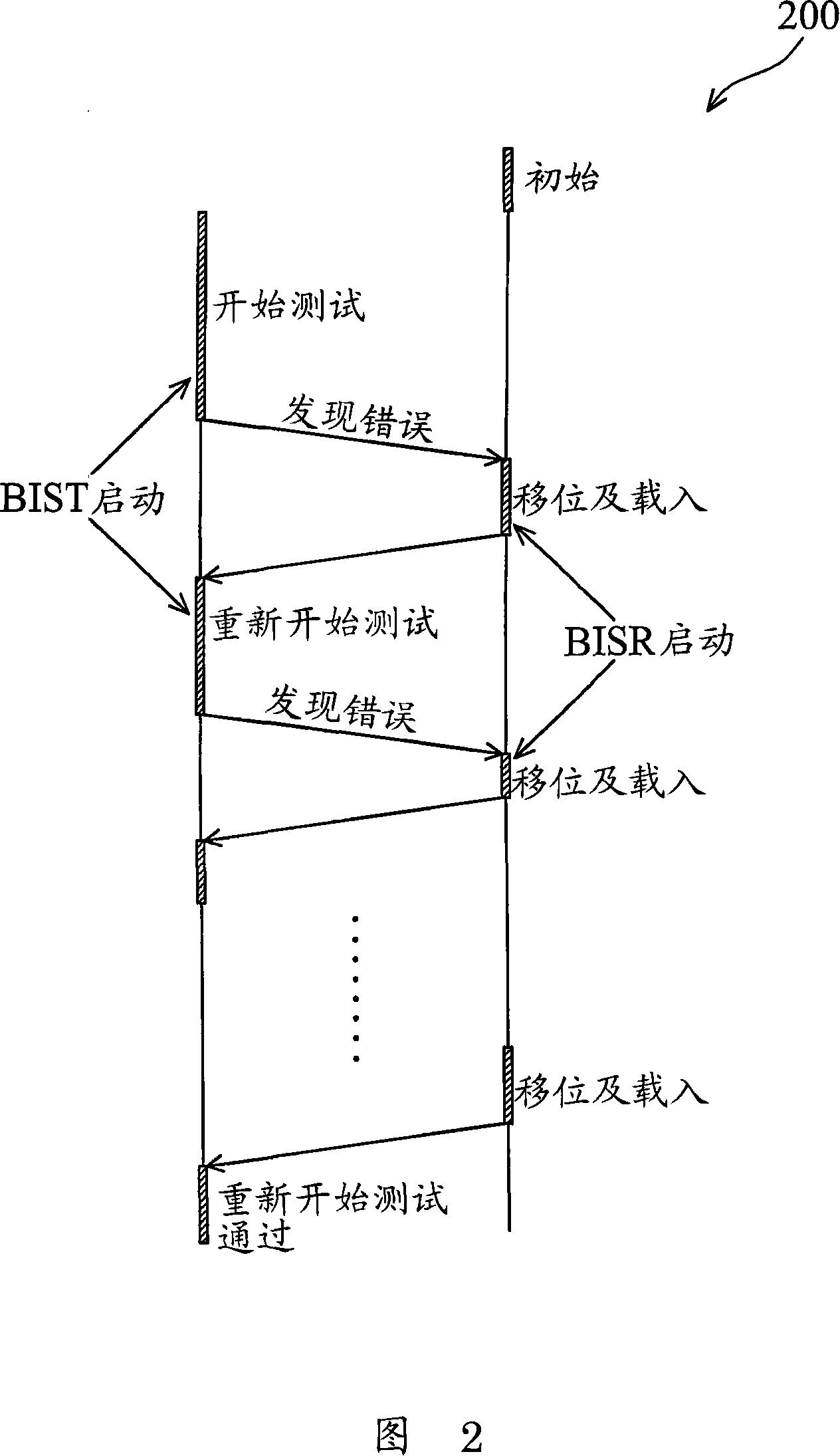
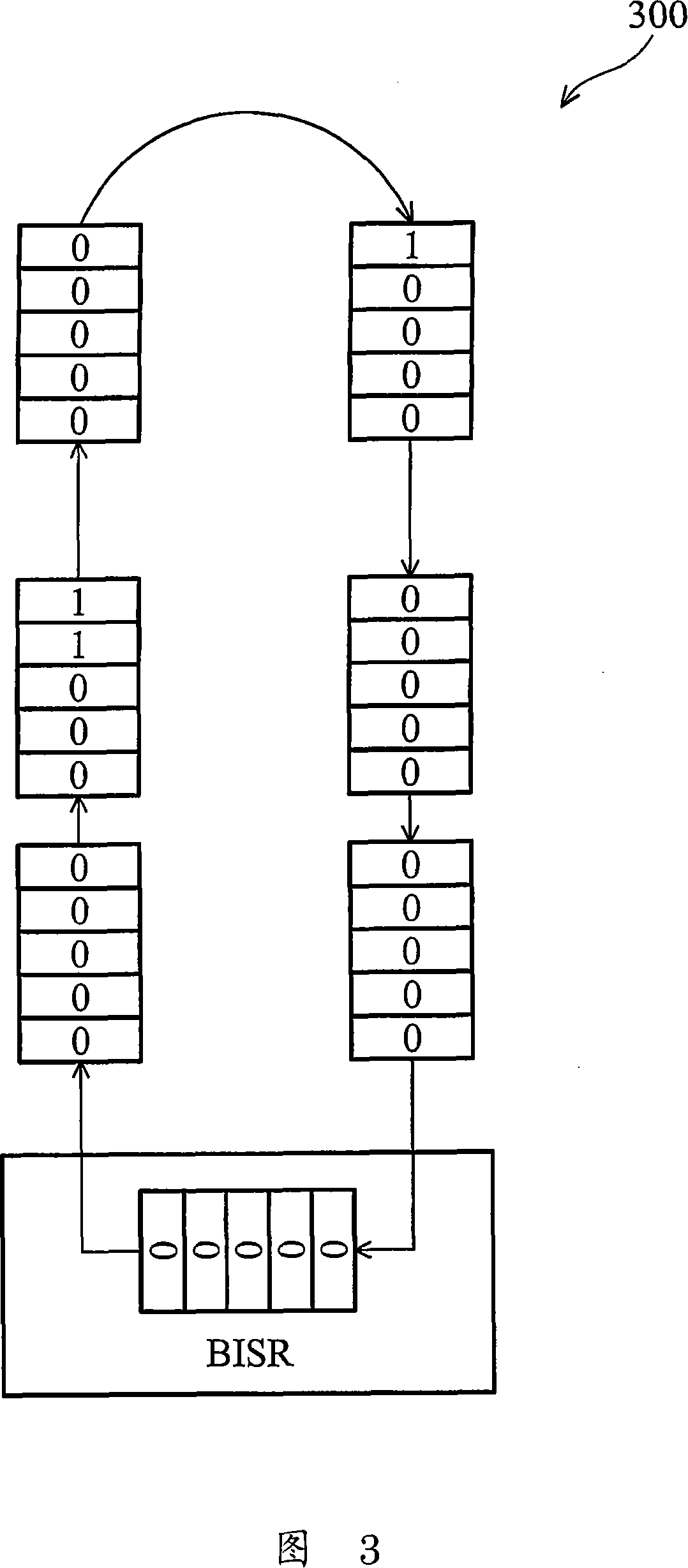
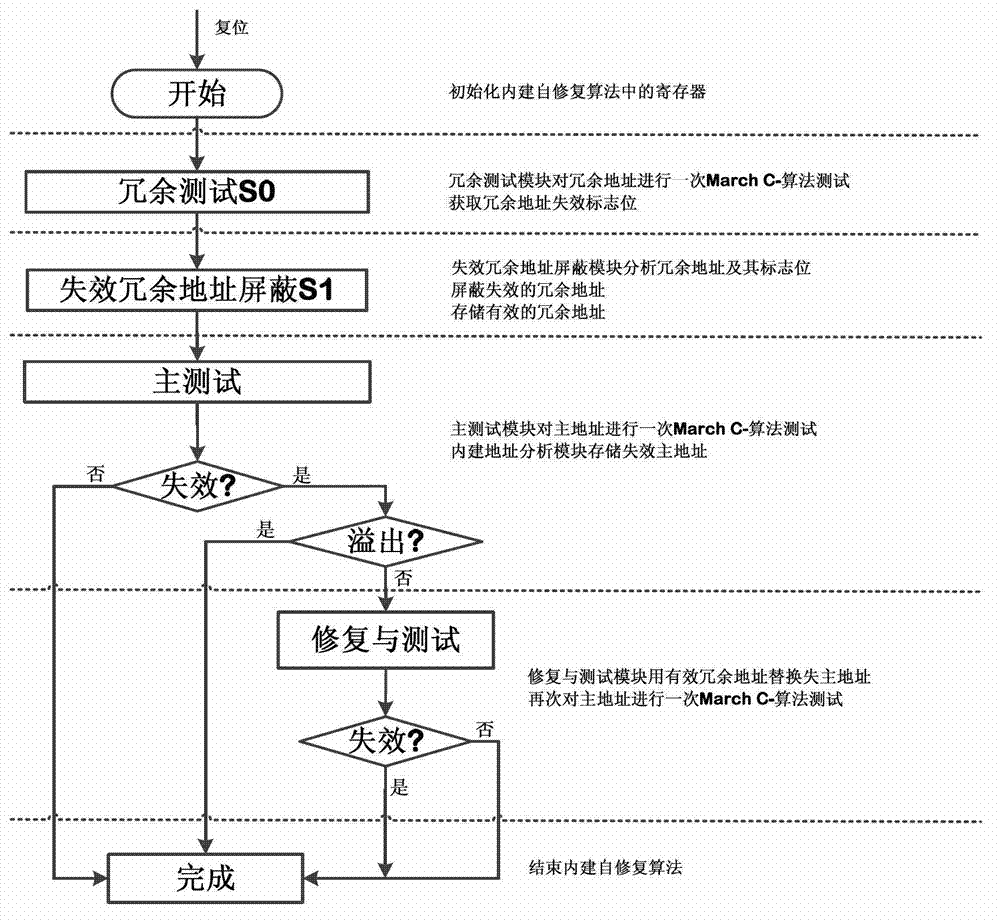
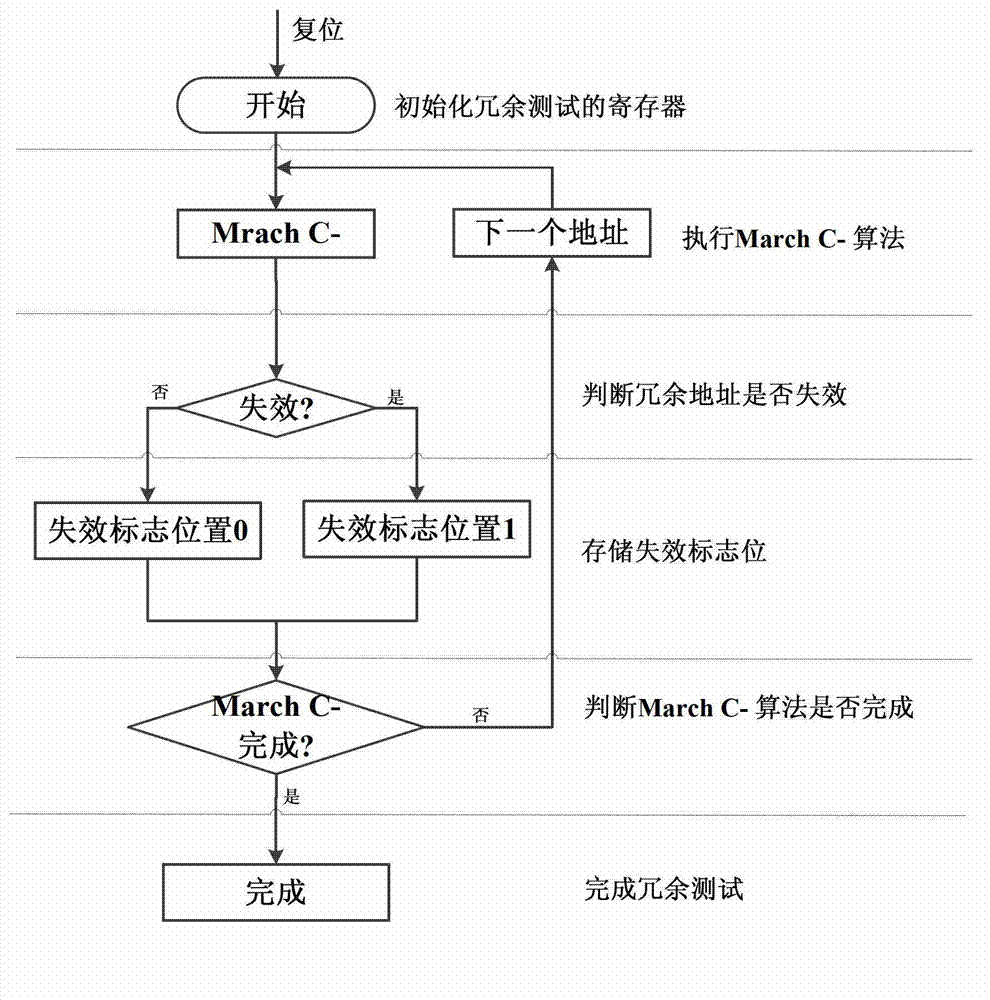
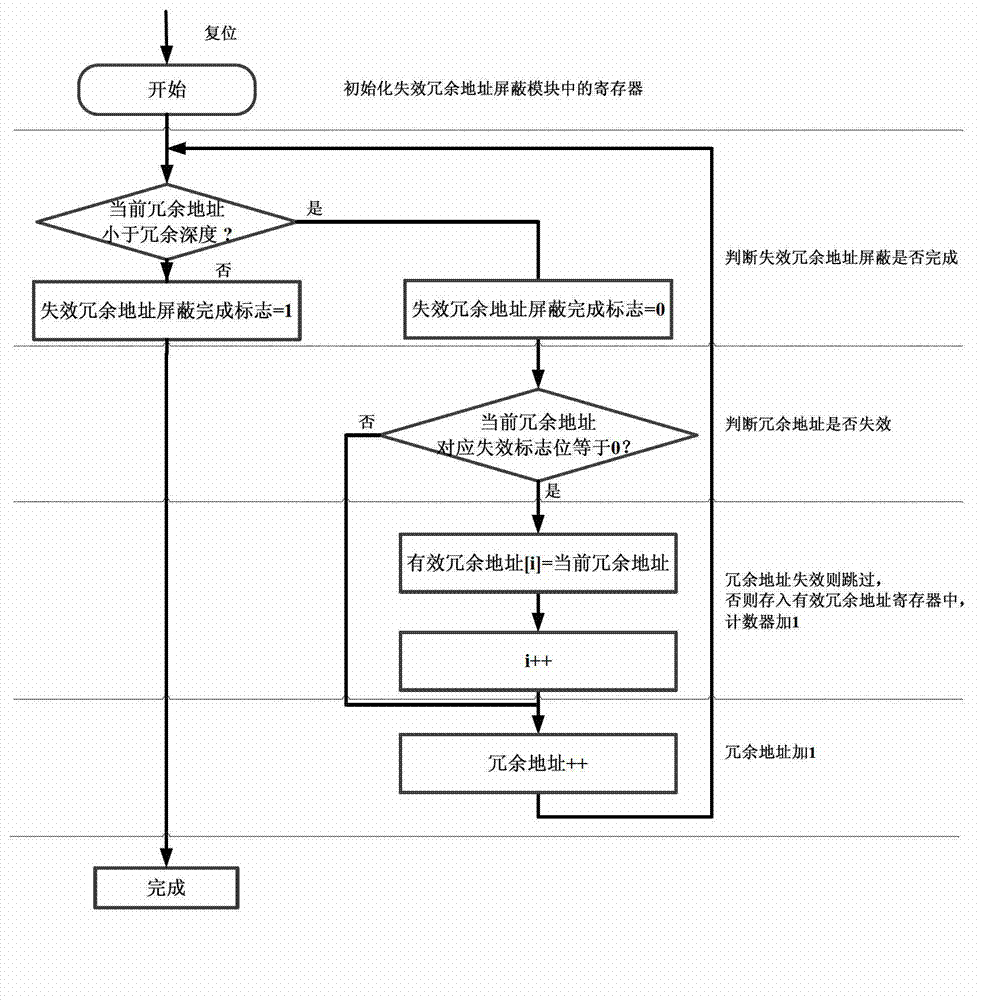
The invention provides a redundant fault-tolerant built-in self-repairing method suitable for static stage random access memory, the method provides an improvement to traditional built-in self-repairing arithmetic, a redundant test module and a lapse redundant address screening module are added, and the defect that in the traditional built-in self-repairing arithmetic, when the redundant address lapses, the reparation cannot be rightly performed is solved. Firstly, redundant test module tests the redundant address, if the tested redundant address is invalid, the invalidation flag bit is 1 and the acquiescence is 0. When the redundant test finishes; and every redundant address gets the invalidation flag bit. At the moment, an invalid redundant address screening module works and analyzes the redundant addresses; if the redundant address invalidation flag bit is 0, the redundant address is write in an effective redundant address register, otherwise, the redundant address is screened and not to be written. Through the screening of the invalid redundant addresses, all replaced redundant addresses are guaranteed to be valid when the self-repairing addresses are replaced.
Owner:XI AN UNIIC SEMICON CO LTD
Stacked chip module with integrated circuit chips having integratable and reconfigurable built-in self-maintenance blocks
ActiveUS8853847B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSelf maintenanceComputer module
Disclosed is a stacked chip module incorporating a stack of integrated circuit (IC) chips having integratable and automatically reconfigurable built-in self-maintenance blocks (i.e., built-in self-test (BIST) circuits or built-in self-repair (BISR) circuits). Integration of the built-in self-maintenance blocks between the IC chips in the stack allows for servicing (e.g., self-testing or self-repairing) of functional blocks at the module-level. Automatic reconfiguration of the built-in self-maintenance blocks further allows for functional blocks on any of the IC chips in the stack to be serviced at the module-level even when one or more controllers associated with a given built-in self-maintenance block on a given IC chip has been determined to be defective (e.g., during previous wafer-level servicing). Also disclosed is a method of manufacturing and servicing such a stacked chip module.
Owner:IBM CORP
Built-in self repair circuit for a multi-port memory and method thereof
InactiveUS7596728B2Avoid wastingImprove production yieldElectronic circuit testingDigital storageMulti portLocation determination
A built-in self repair (BISR) circuit for a multi-port memory and a method thereof are provided. The circuit includes a test-and-analysis module (TAM) and a defect locating module (DLM) coupled to the TAM. The TAM tests a repairable multi-port memory to generate a fault location and determines whether the test generates a port-specific fault candidate according to the fault location. If a port-specific fault candidate is generated, the DLM generates a defect location based on the fault location and provides the defect location to the TAM so that the TAM can determine how to repair the repairable multi-port memory according to the defect location. If no port-specific fault candidate is generated in the test, the TAM determines how to repair the repairable multi-port memory according to the fault location.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
Hierarchical, distributed built-in self-repair solution
A built-in self-test (BIST) circuit to test one or more memory blocks on an integrated circuit. The one or more memory blocks further includes a first memory block and a second memory block A built-in soft-repair controller (BISoR) is provided to soft repair the one or more memory blocks. The BIST circuit in conjunction with the BISoR is configured to test and soft repair the first memory block before performing test and soft repair of the second memory block.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com