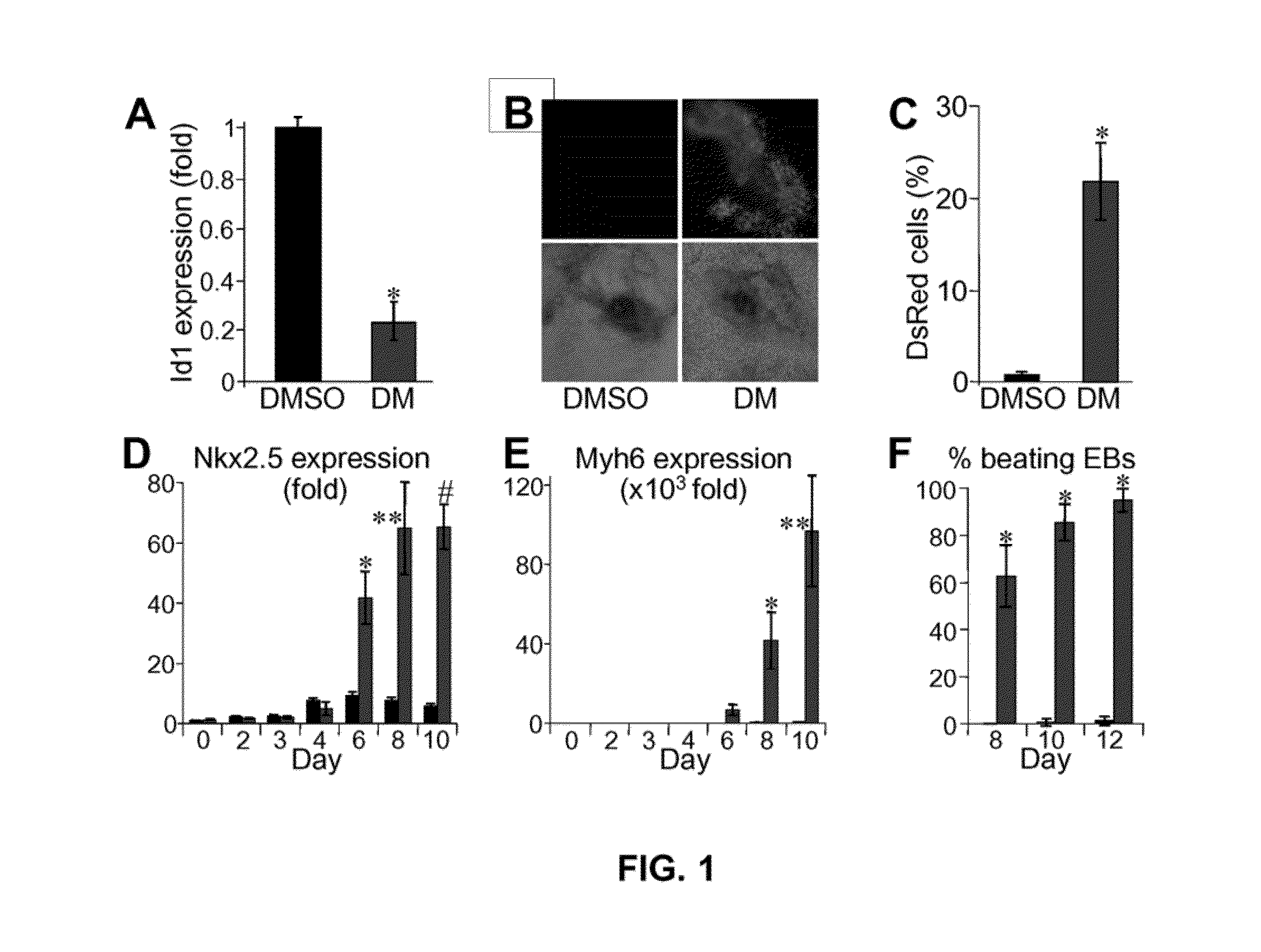
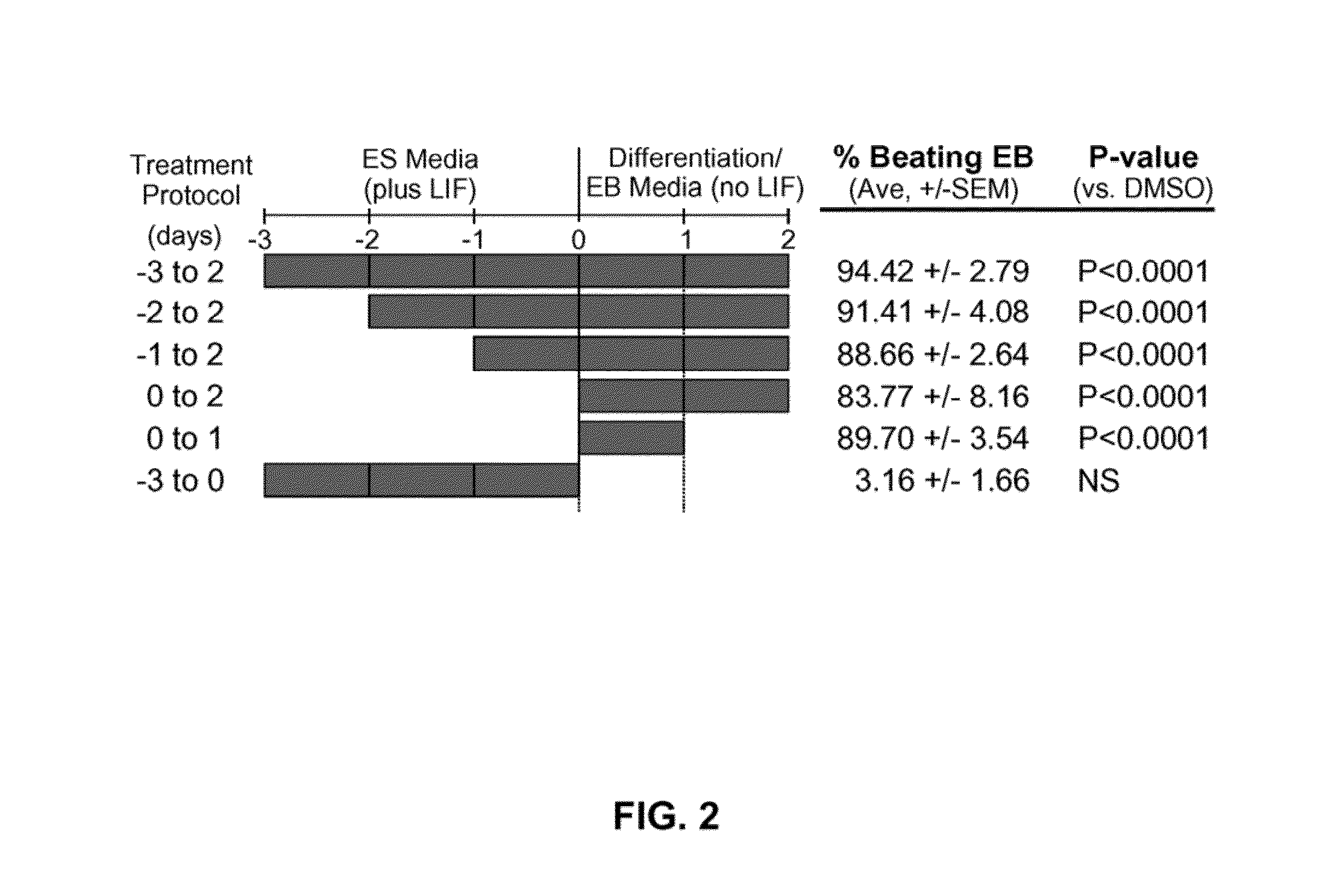
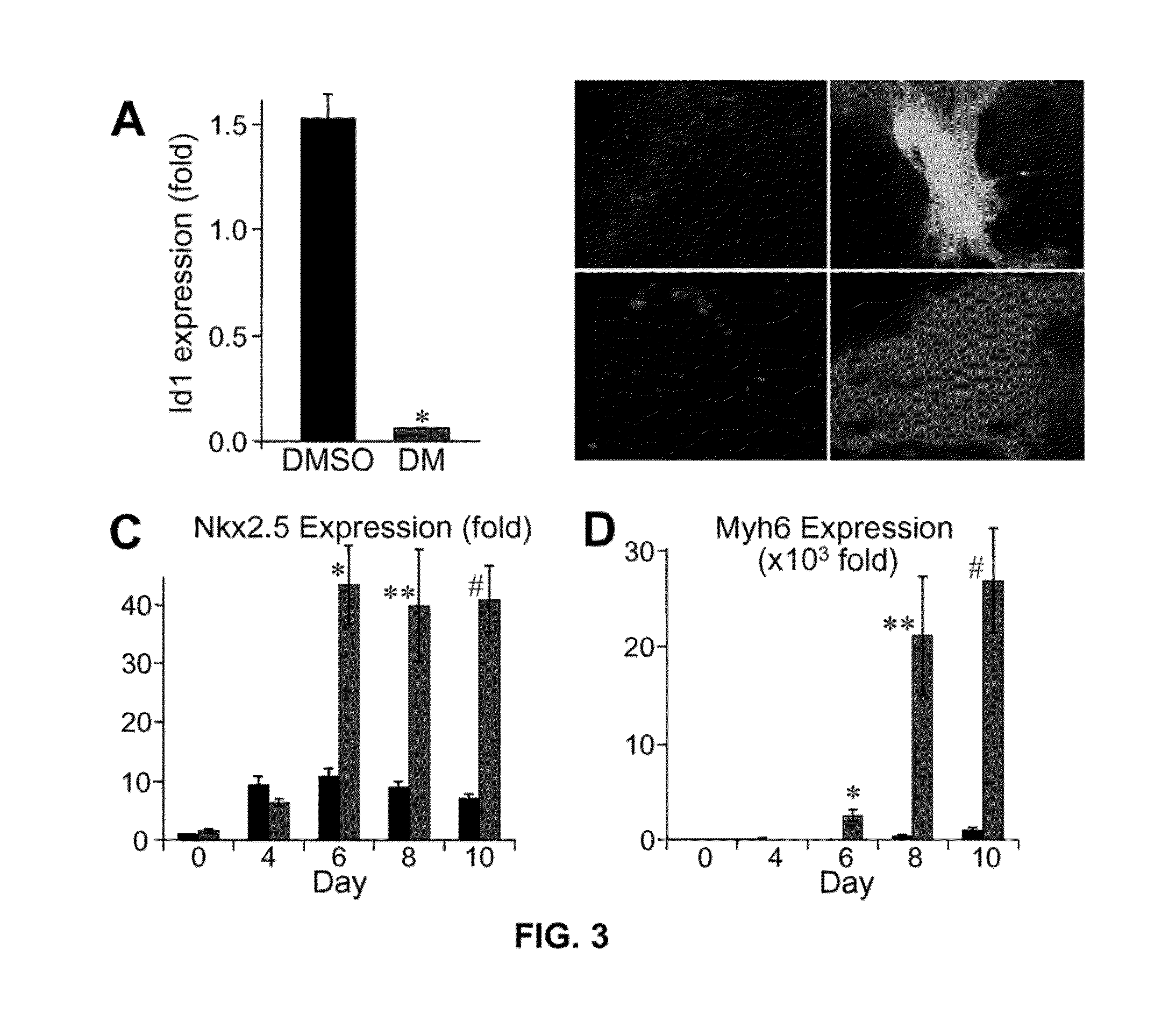
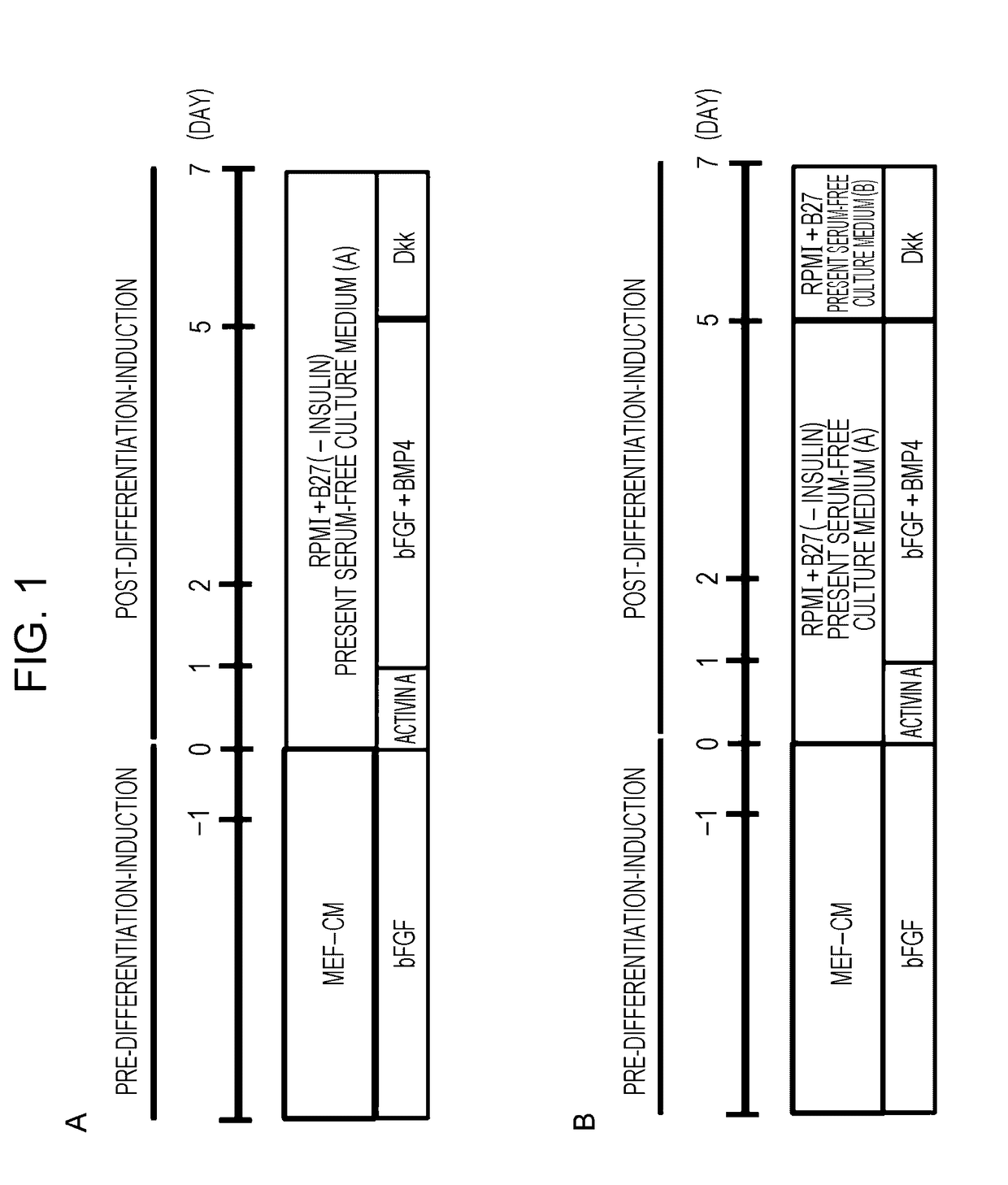
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Cardiac Progenitor Cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enriched stem cell and progenitor cell populations, and methods of producing and using such populations
InactiveUS8017389B2BiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementIschemic heartFirst myocardial infarction
The present invention provides a novel method to isolate and expand pure progenitor / stem cells from a primary tissue explant, which produces a population enriched in multipotent functional progenitor / stem cells free of contaminating fibroblasts and other cell types. Cardiac progenitor / stem cells isolated by this method maintain their self-renewal and clonogenic character in vitro and differentiate into normal cells in myocardium, including cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells, after transplantation into ischemic hearts. The present invention also includes substantially pure populations of multipotent progenitor / stem cells, e.g., cardiac progenitor / stem cells, and their use to treat and prevent diseases and injuries, including those resulting from myocardial infarction.
Owner:KECK GRADUATE INST A UNIV OF THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA
Differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to cardiac progenitor cells that promote cardiac repair
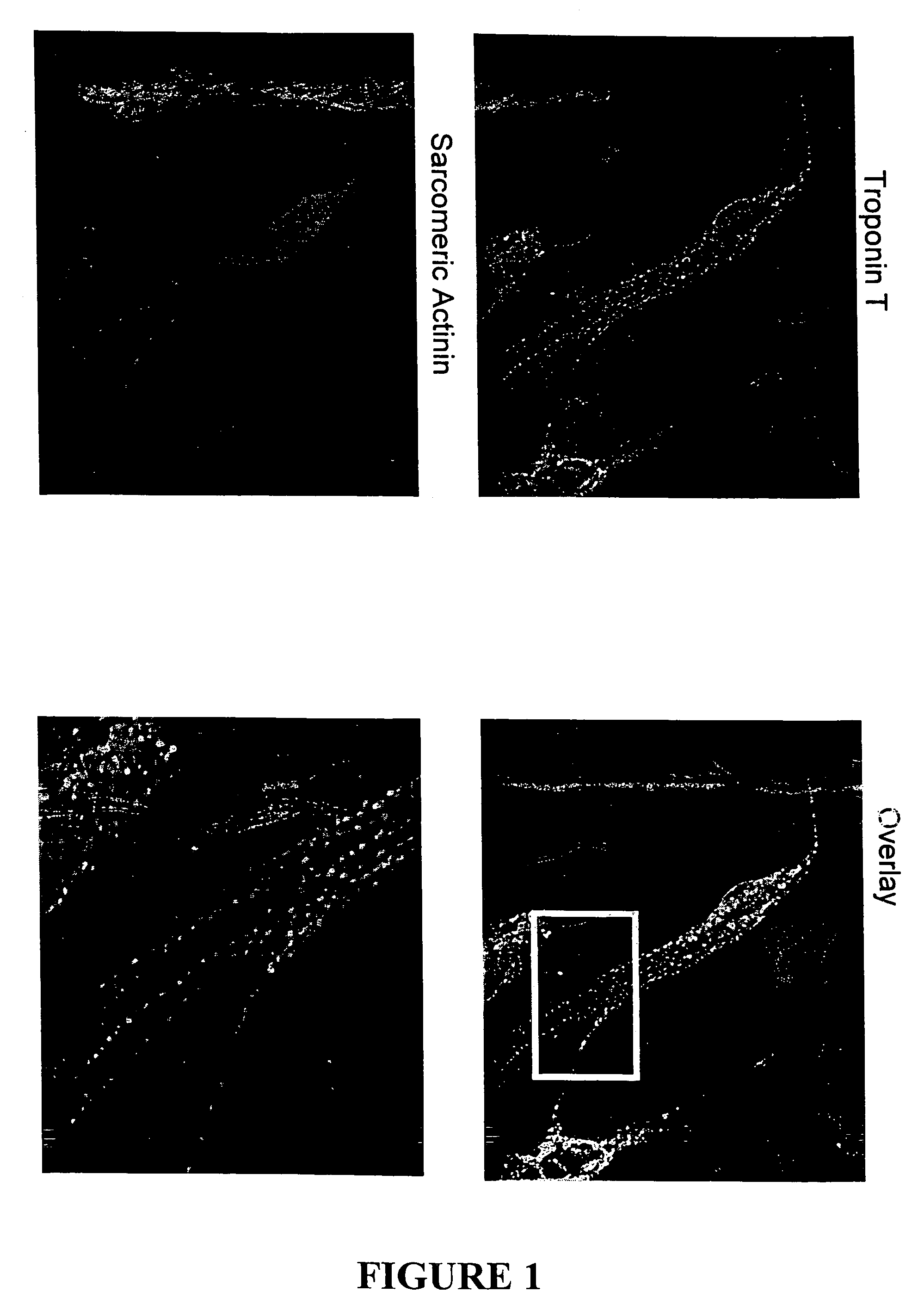
A method for treating a subject afflicted with a cardiac disorder, in vivo, comprises (i) inducing differentiation of a progenitor cell, in vitro, to a cardiogenic cell; and (ii) administering a therapeutically effective amount of the cardiogenic cell of step (i) to the subject, thereby treating the cardiac disorder in the subject. This invention further provides related articles of manufacture and methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Adult Human Cardiac-Derived Progenitor Cells
The present invention is based, in part, on the discovery that cardiac progenitor cells are present in and can be isolated from adult human heart. Accordingly, a cell of the present invention comprises a human adult cardiac-derived progenitor cell capable of differentiating into a cardiac myocyte where said cell is isolated according to the expression of specific biomarkers, identified elsewhere herein. The present invention also includes methods of use of an adult cardiac-derived progenitor cell in the treatment of heart disease.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Compounds and methods useful for directing stem cell differentiation
ActiveUS8822684B1Enhancing terminal differentiationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryBiochemistryRat heart
The presently-disclosed subject matter relates to compounds of the formula:and methods for use thereof. The presently-disclosed subject matter relates methods of selectively differentiating a stem cell, and methods of screening for compounds useful for enhancing terminal differentiation of committed cardiac progenitor cells.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Cd82-positive cardiac progenitor cells
ActiveUS20170067023A1Low rateIncrease ratingsMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsINDUCTION TREATMENTCardiac muscle cell
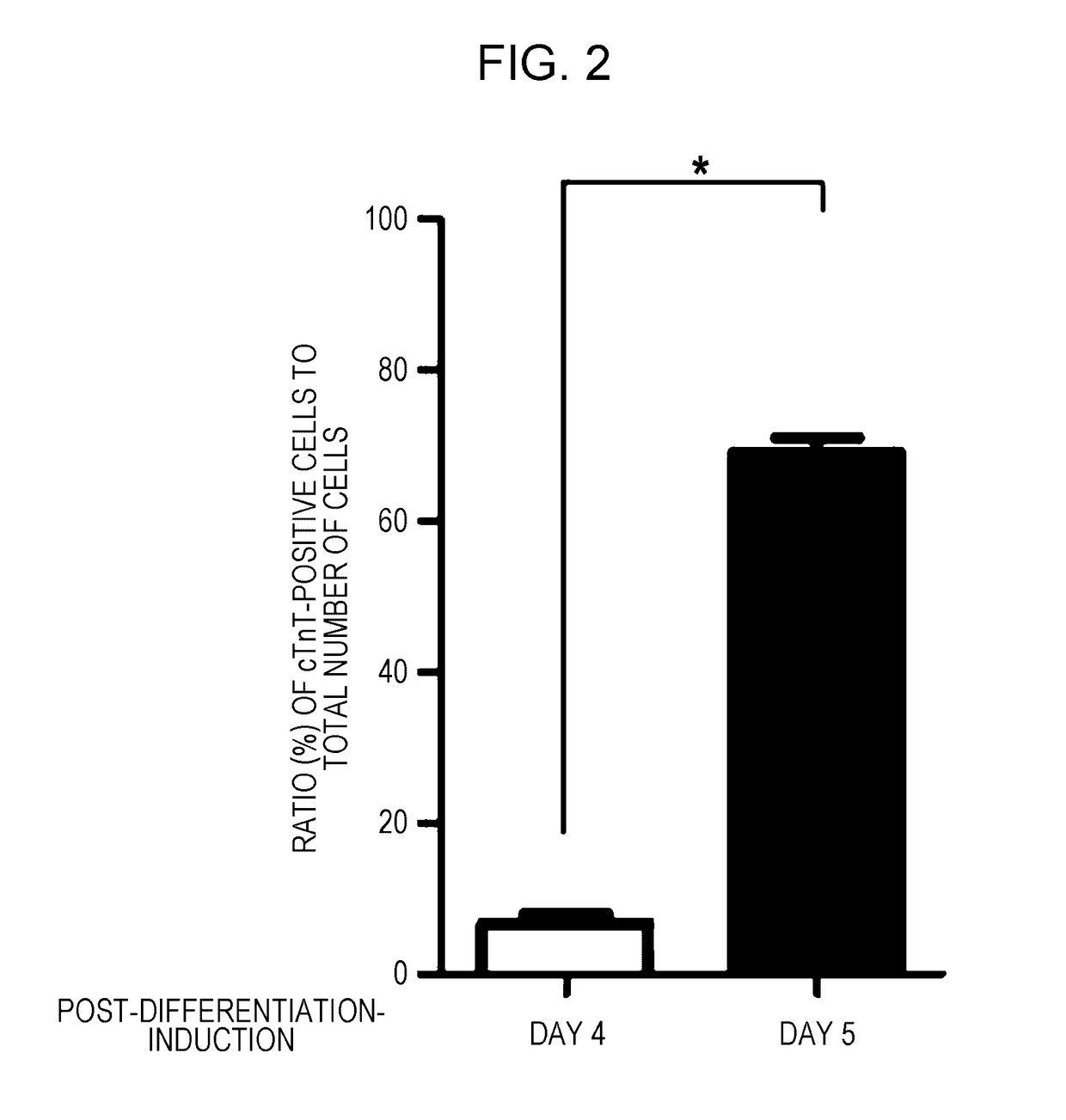
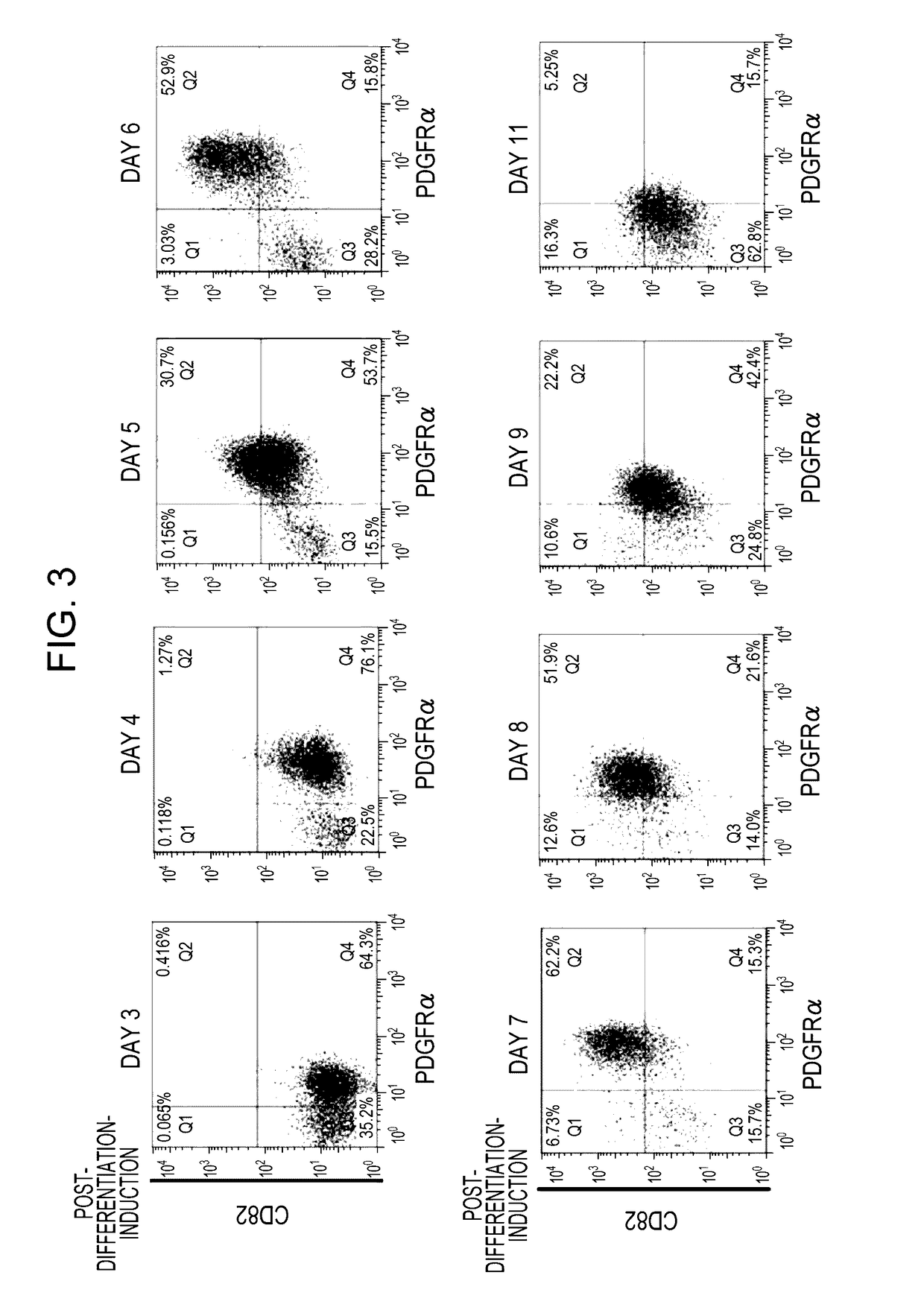
An object of the present invention is to provide a myocardial progenitor cell that is specifically induced to differentiate into a cardiomyocyte, and a method for preparing the myocardial progenitor cell. A method for preparing a CD82-positive cell includes, in sequence, a step (a) of obtaining stem cells, a step (b) of subjecting the stem cells to induction treatment of differentiation into cardiovascular cells, and a step (c) of separating, from the stem cells having been subjected to the induction treatment of differentiation in the step (b), a CD82-positive cell being negative for at least one cell surface marker selected from CD73, CD44, CD105, CD121a, CD18, and CD120a. This method enables preparation of a CD82-positive cell for use as a myocardial progenitor cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV MED PHARM COLLABORATION BUILDING
Methods of identifying small molecules for renewals, survival and migration of cardiac progenitors
InactiveUS20100261196A1Genetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysProgenitor cell
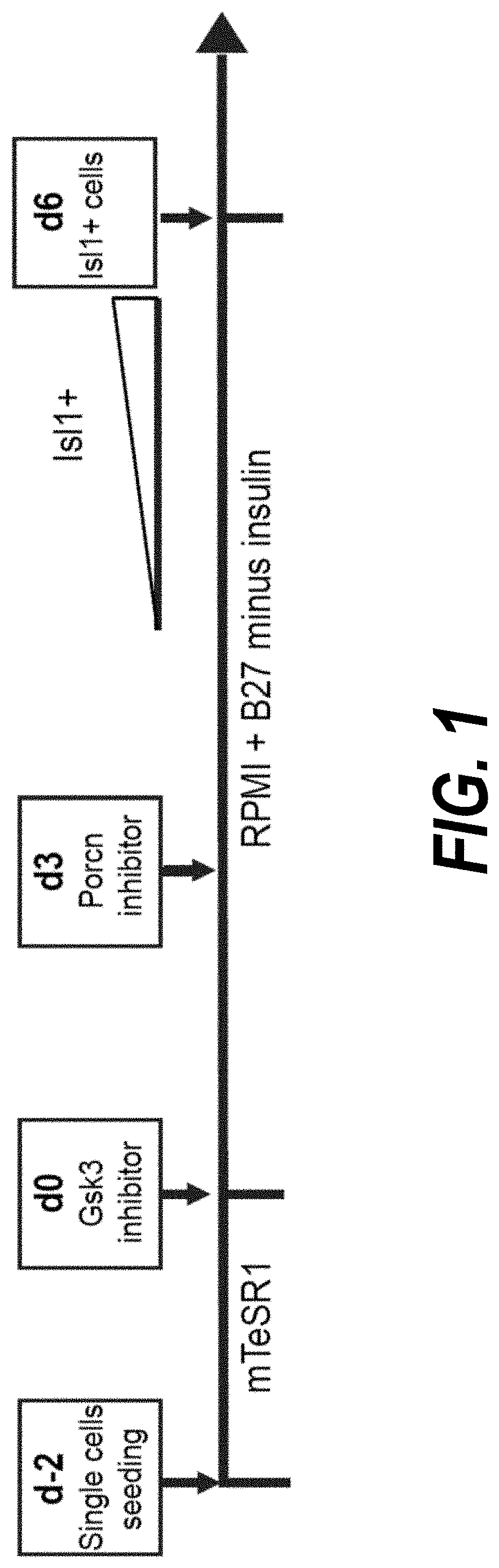
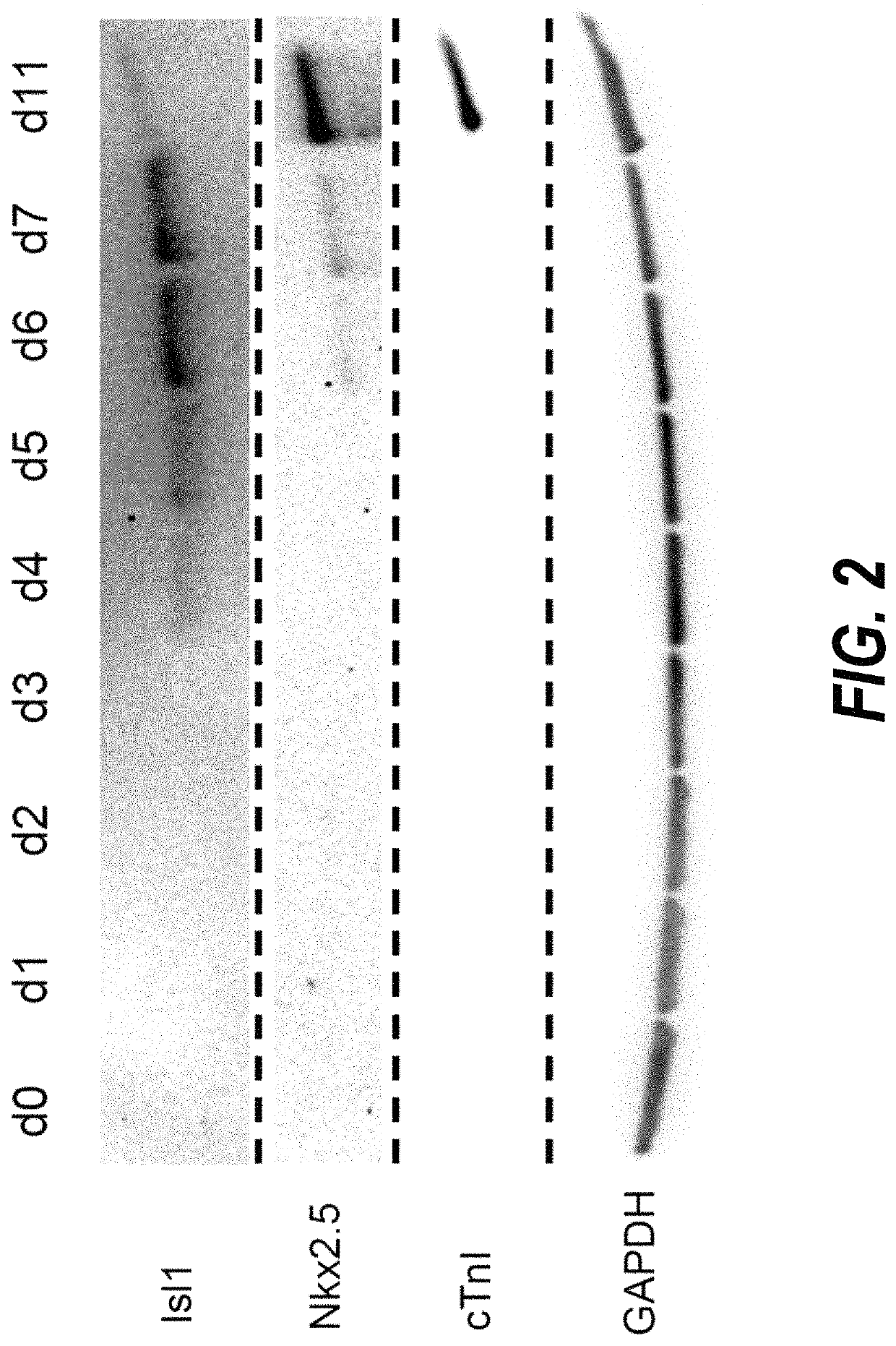
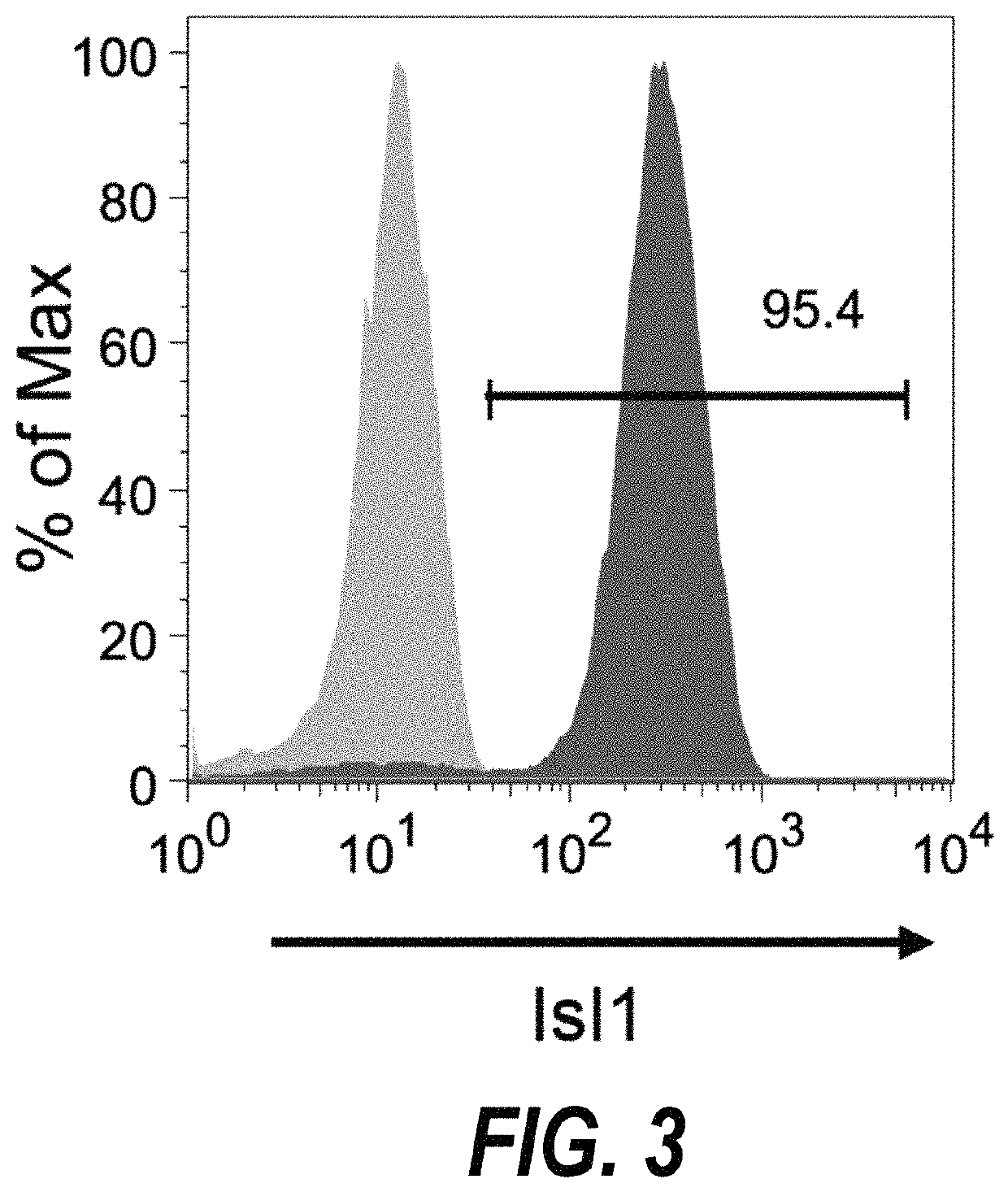
The present invention relates to a small molecule high-throughput screening assay consisting of detectably labeled cardiac progenitor cells. The invention also describes a method of identifying small molecules from the high-throughput assay affecting cardiogenesis and / or modulating cardiac progenitor cell development. Also described are methods of stimulating maturation of cardiac progenitor cells using a GSK-3β inhibitor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
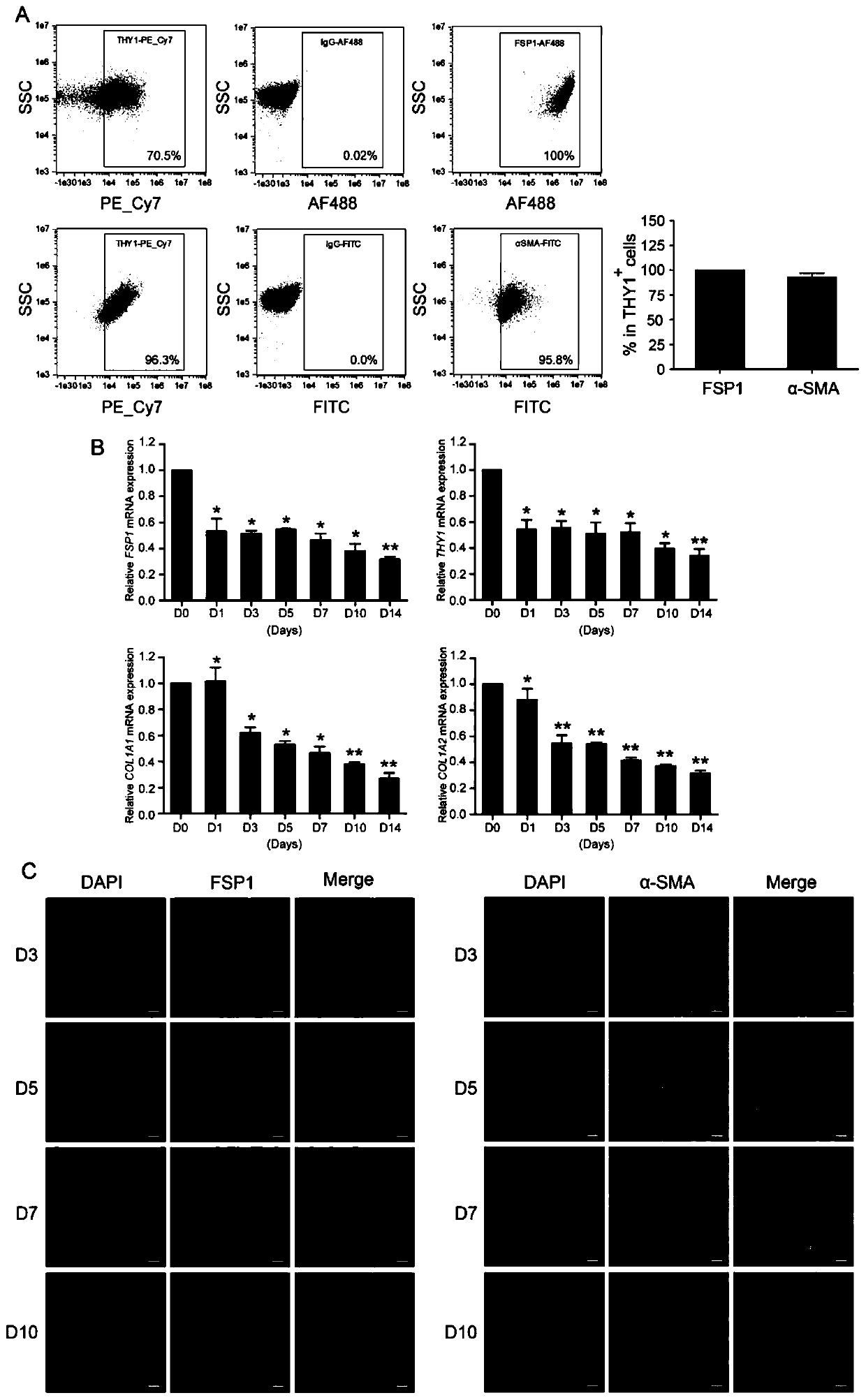
Method for the isolation of subpopulations of cardiac progenitor cells and related uses in the medical field
The present invention relates to a method for the isolation of subpopulations of cardiac progenitor cells from a heart tissue sample, the population thus obtained and the related uses in the medical field for the cell therapy or cardiac cell and / or tissue transplantation field.
Owner:奥洛克治疗有限责任公司
Methods for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
The present invention provides methods for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells (HVPs), wherein cultures of day 5-7 cardiac progenitor cells are negatively selected for one or more first markers expressed on human pluripotent stem cells, such as TRA-1-60, to thereby isolate HVPs. The methods can further include positive selection for expression of a second marker selected from the group consisting of JAG1, FZD4, LIFR, FGFR3 and TNFSF9. Large populations, including clonal populations, of isolated HVPs that are first marker negative / second marker positive are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of the HVPs for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the HVPs for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
Kit for culturing cardiac progenitor cells
ActiveCN106754671ARich sourcesDead animal preservationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCryopreservationObserved Survival
The invention provides a kit for culturing cardiac progenitor cells. A plurality of reagent bottles are arranged in the kit and contain a culture solution I, a culture solution II, a growth factor I, a growth factor II, a growth factor III, a growth factor IV, a digestive solution, a cleaning solution, a cryopreservation solution and cell seeds respectively. By the adoption of the kit, culture, amplification and cryopreservation of cardiac progenitor cells can be achieved, the problems that the culture survival rate of cardiac progenitor cells is low, culture efficiency is low, inter-batch difference is large, and cryopreservation reactivation rate is not ideal are solved, cardiac progenitor cells can be amplified in an ideal nutrient balance state without differentiation, and rich sources are provided for further experimental study and medical treatment using cardiac progenitor cells. The kit is quite suitable for cardiac progenitor cell culture.
Owner:张晓南
Differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to cardiac progenitor cells that promote cardiac repair
A method for treating a subject afflicted with a cardiac disorder, in vivo, comprises (i) inducing differentiation of a progenitor cell, in vitro, to a cardiogenic cell; and (ii) administering a therapeutically effective amount of the cardiogenic cell of step (i) to the subject, thereby treating the cardiac disorder in the subject. This invention further provides related articles of manufacture and methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
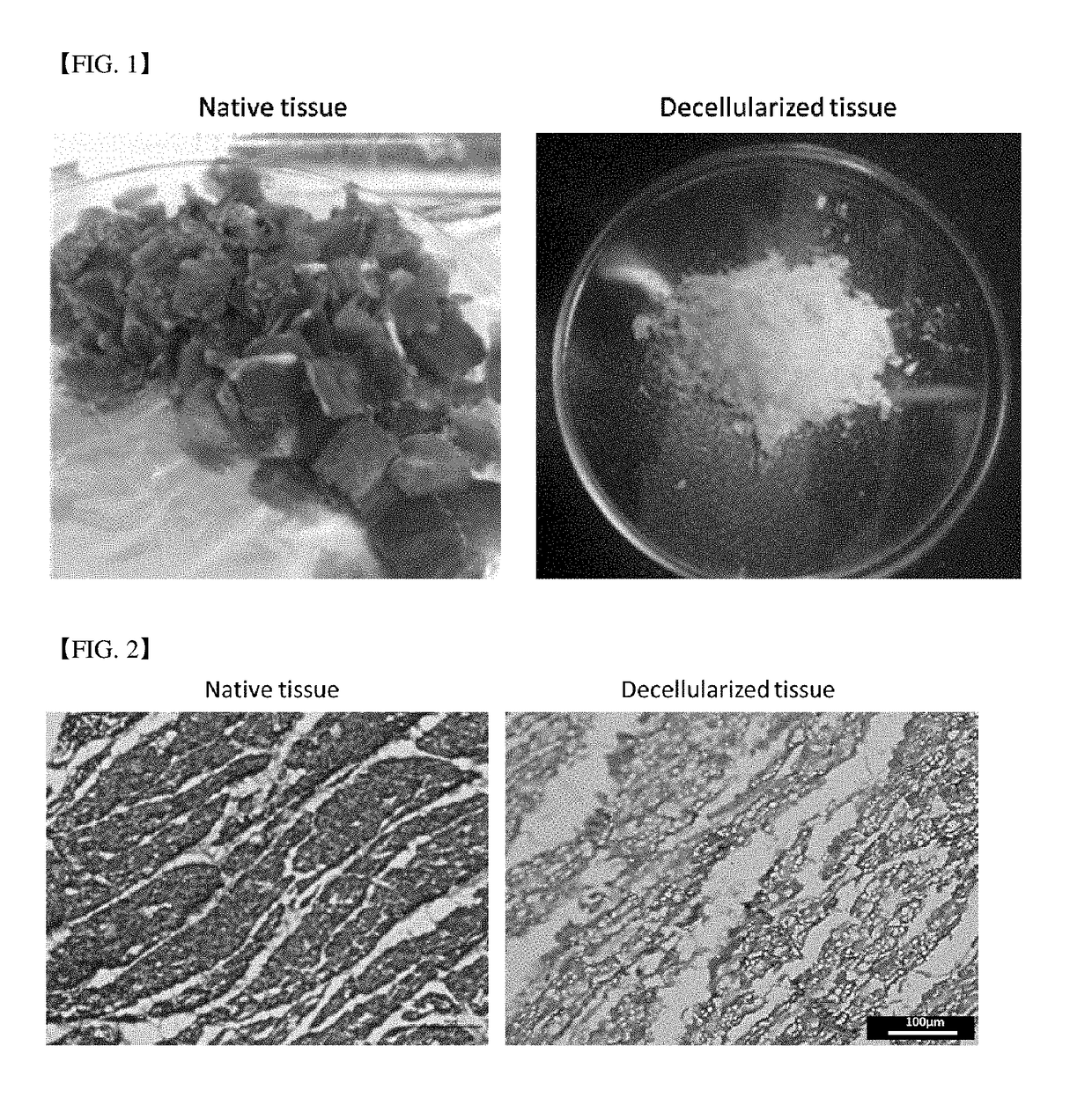
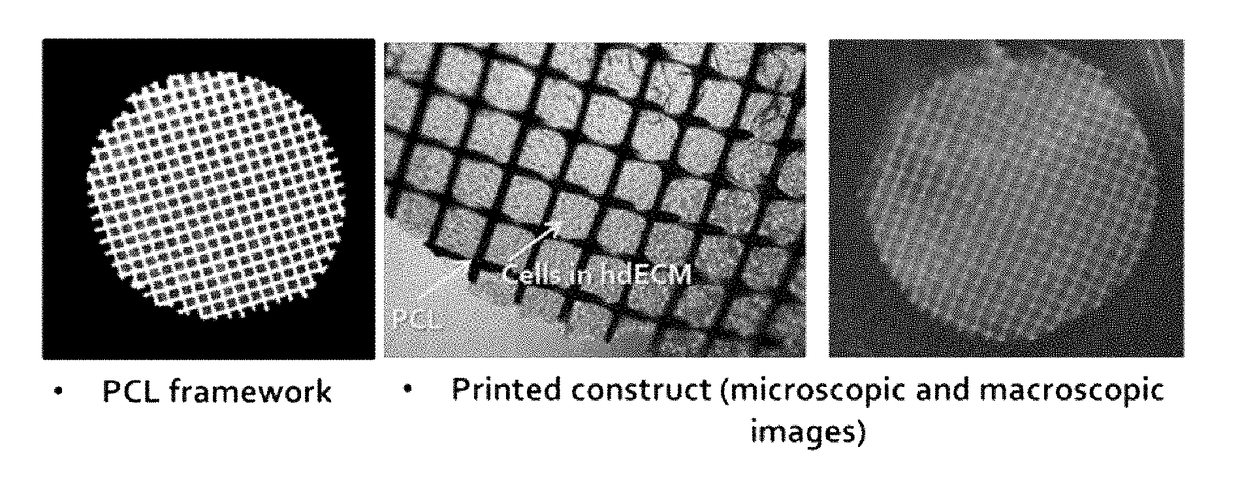
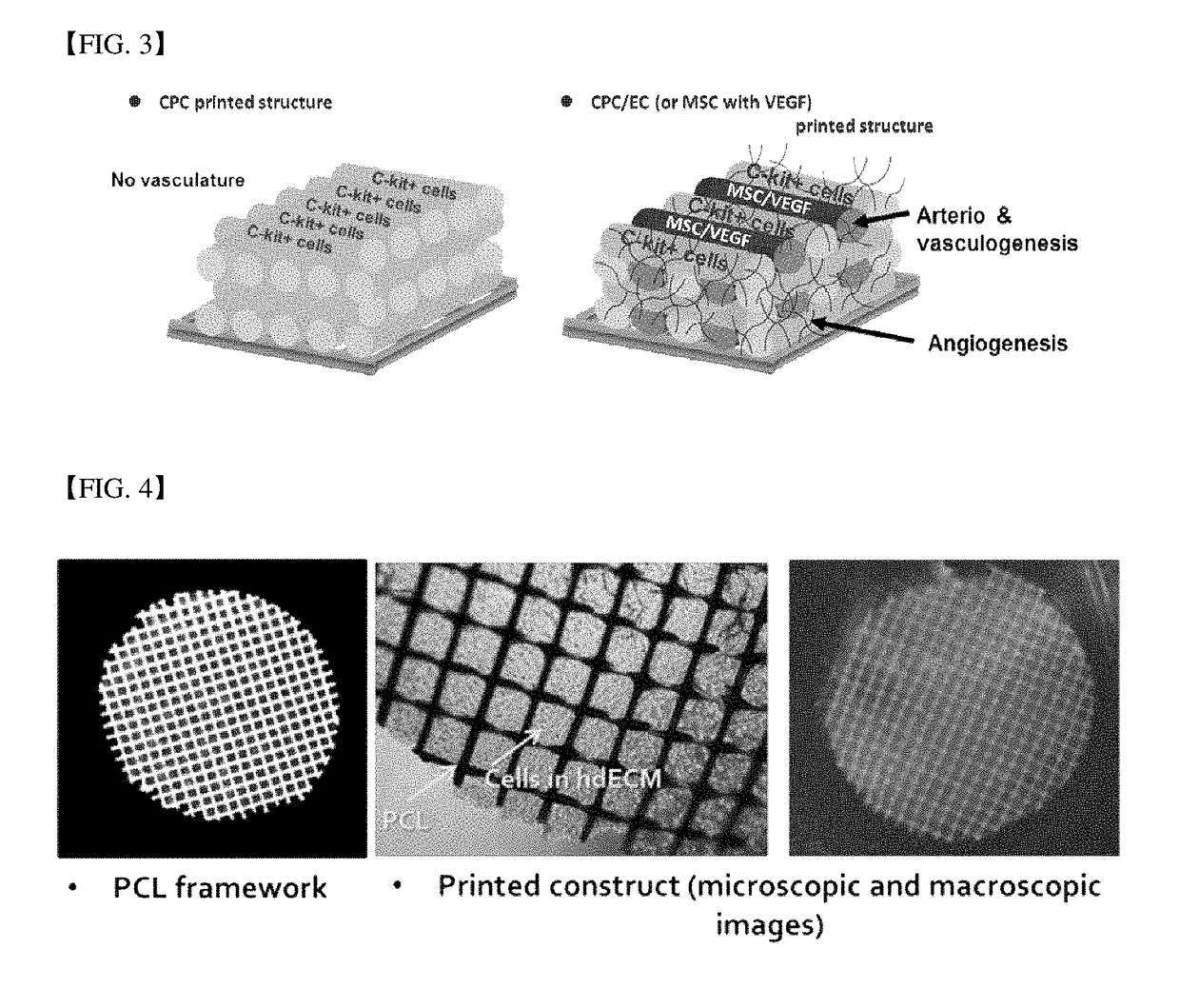
Three-dimensional structure for cardiac muscular tissue regeneration and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS20180037870A1EffectivelyImprove transmission efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusHeart valvesCell-Extracellular MatrixBlood vessel
The present invention provides a preparation method of a three-dimensional construct for regenerating a cardiac muscle tissue comprising; a step of forming a three-dimensional construct by printing and crosslinking the first bioprinting composition comprising a tissue engineering construct forming solution containing decellularized extracellular matrix and a crosslinking agent, and cardiac progenitor cells, and the second bioprinting composition comprising the tissue engineering construct forming solution, mesenchymal stem cells and a vascular endothelial growth factor, to arrange the first bioprint layer and the second bioprint layer alternately; and a step of obtaining a crosslink-gelated three-dimensional construct by thermally gelating the crosslinked three-dimensional construct, and a three-dimensional construct for regenerating a cardiac muscle tissue, and the preparation method according to the present invention not only equally positions the cardiac progenitor cells in the construct but also implements a vascular network composed of vascular cells in the construct, so that the viability of cells can be maintained for a long time and the cell transfer efficiency into the myocardium can be significantly improved.
Owner:T&R BIOFAB
Methods for reprogramming cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS10563176B2Eliminate the problemGenetically modified cellsNervous system cellsProliferative capacityCardiac Stem Cell
Owner:GENESIS TECH LTD
Novel cardiomyocyte marker
InactiveUS20140057287A1Increase chanceMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsHeart Muscle CellRat heart
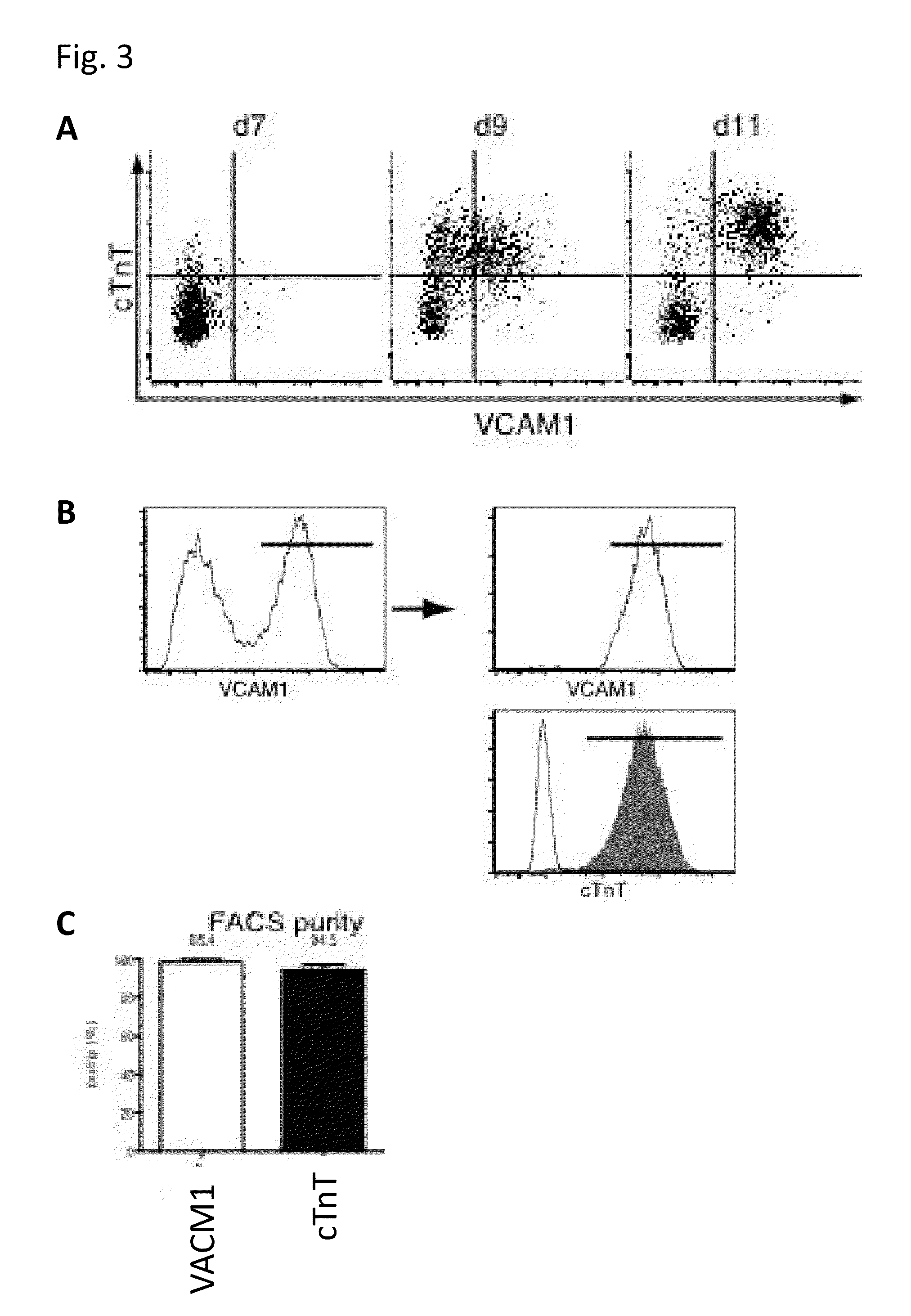
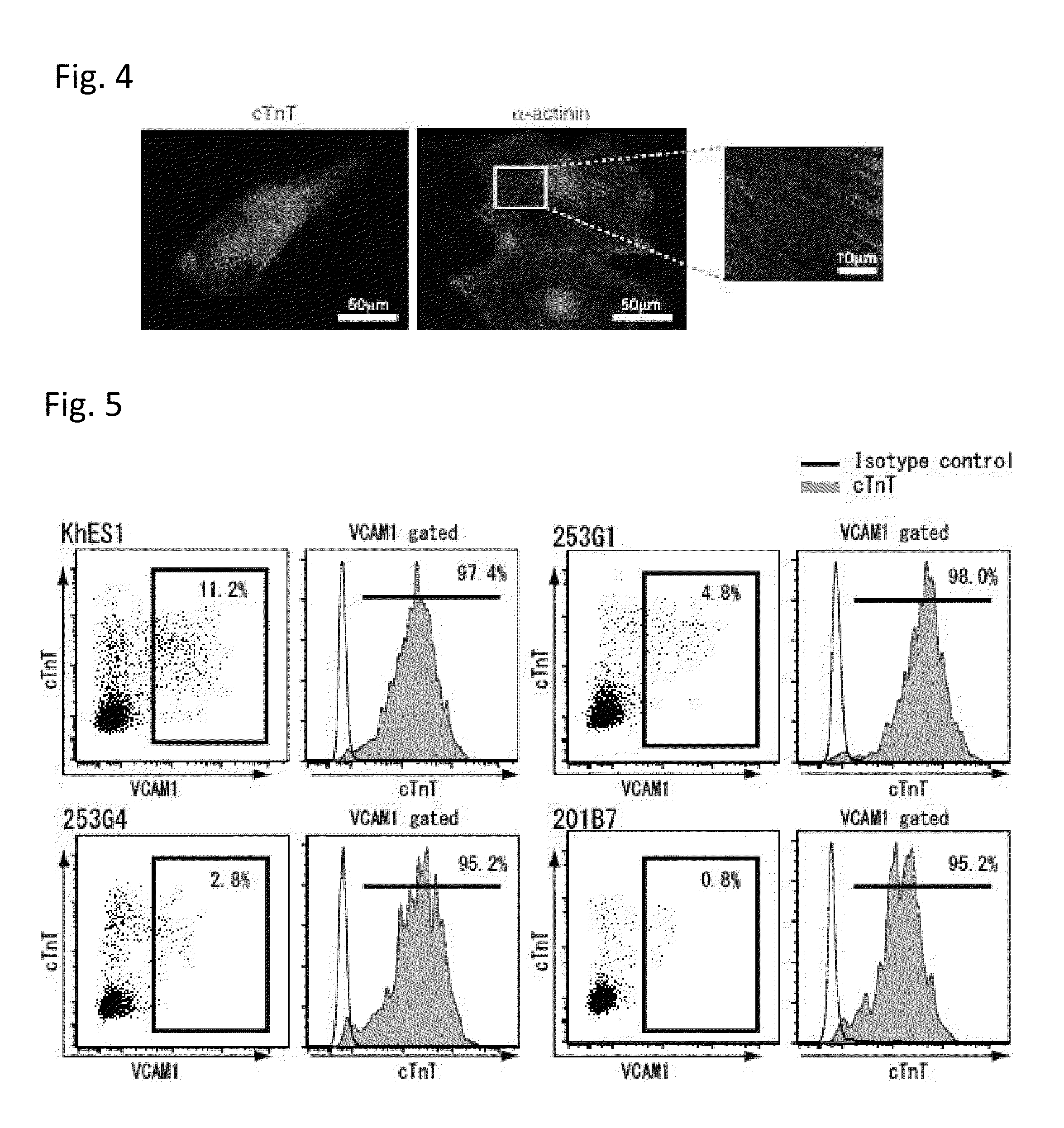
The present invention provides a method for production or detection of a cardiomyocyte(s) and / or cardiac progenitor cell(s), comprises extracting a cardiomyocyte(s) and / or cardiac progenitor cell(s) from a cell population comprising cardiomyocytes and / or cardiac progenitor cells using as an index VCAM1 positivity.
Owner:IHEART JAPAN
Three-dimensional structure for cardiac muscular tissue regeneration and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveCN107406828ARealize the microenvironmentImprove transfer efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusArtificial cell constructsCell-Extracellular MatrixBlood vessel
Owner:T&R BIOFAB
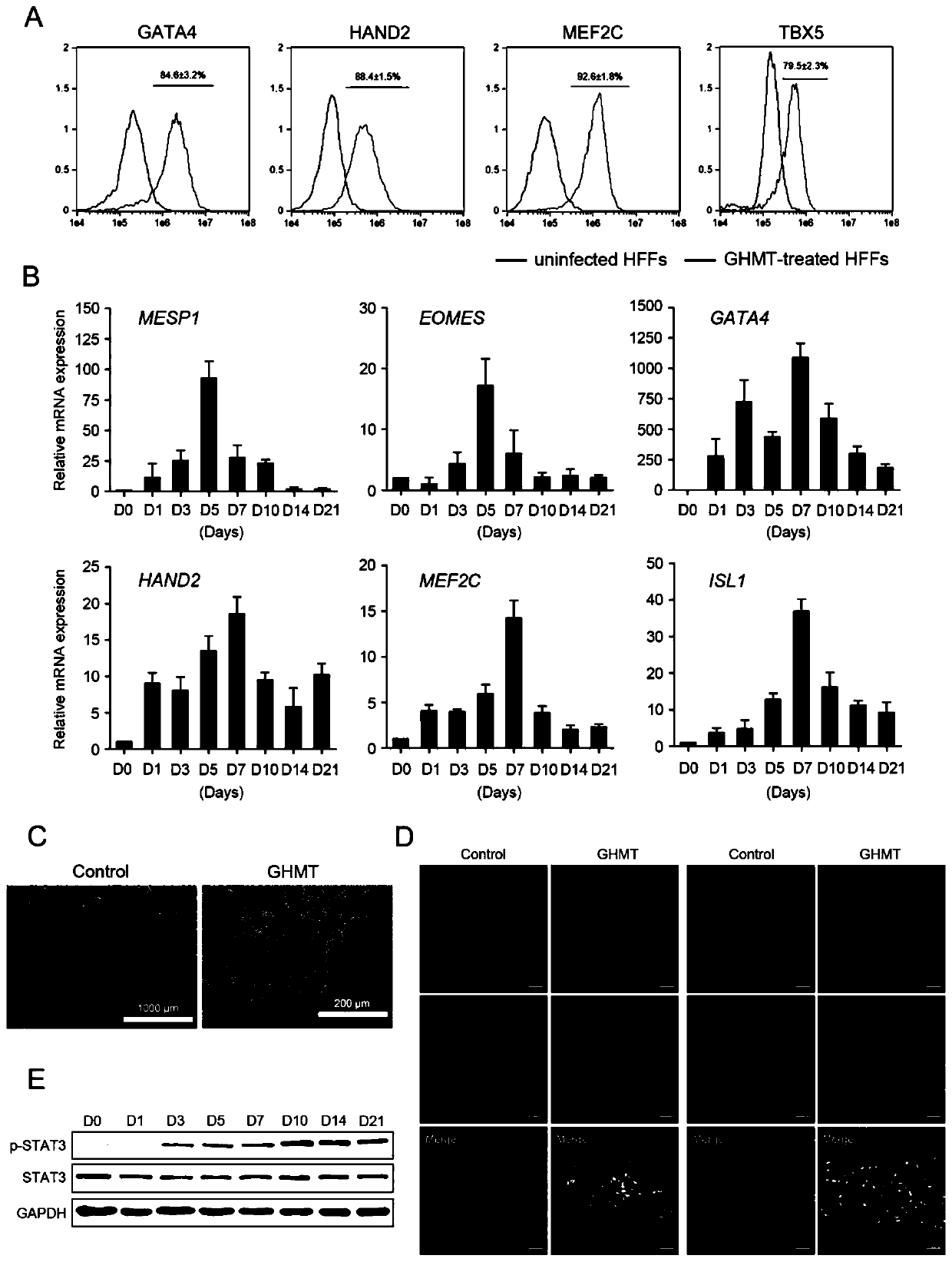
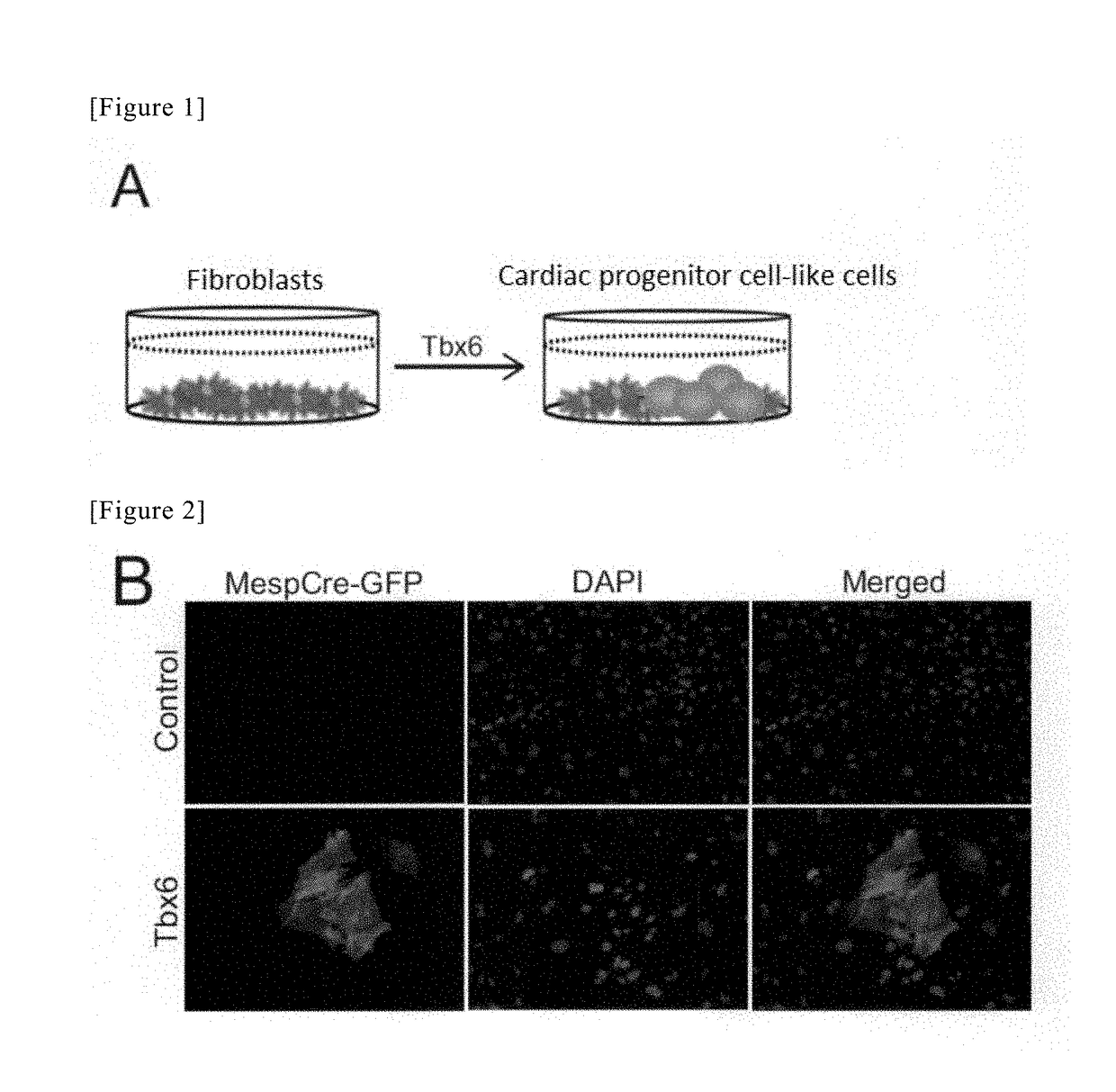
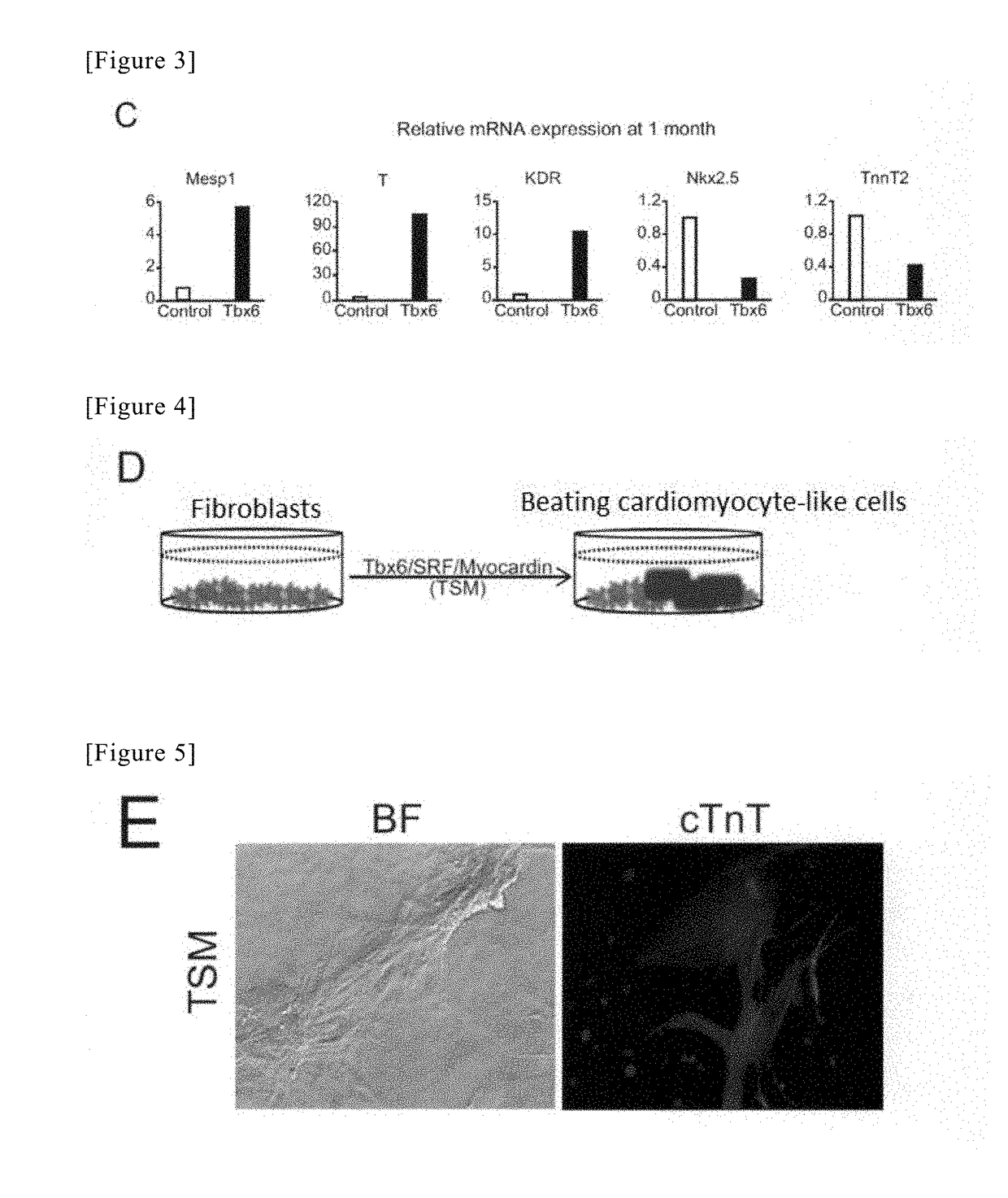
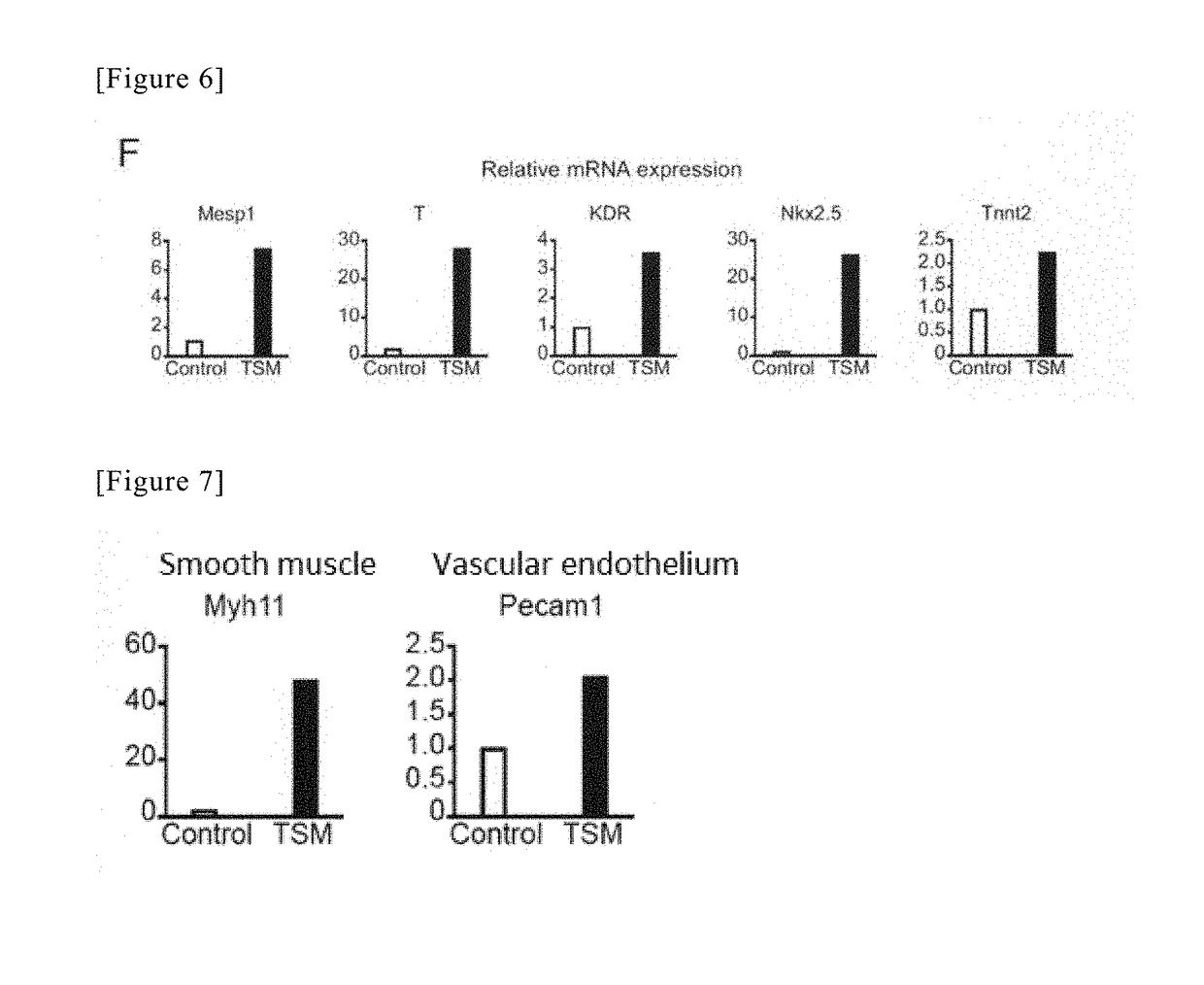
Method for directly producing cardiac precursor cell or myocardial cell from fibroblast
InactiveCN109072220APreparation method is stableCapable of proliferatingGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsMedicineCardiac muscle
The present invention provides a method for deriving a cardiac precursor cell or myocardial cell from a fibroblast. Provided is a method for producing a cardiac precursor cell that comprises introducing one myocardial reprogramming factor into a fibroblast, or a method for producing a myocardial cell that comprises introducing three myocardial reprogramming factors into a fibroblast.
Owner:UNIV OF TSUKUBA +1
Technique for heart disease external differentiation therapy by utilizing stem cells of masticatory muscles and orbicularis oculi muscles
InactiveCN102703382AArtificial cell constructsUnknown materialsCoronary artery guide catheterNon invasive
The invention belongs to the field of adult stem cells and regenerative medicine, and relates to the techniques of adult stem cell extraction, external expansion and differentiation induction as well as stem cell transplantation. The techniques are based on the theory that head and facial masticatory muscles have the same origin with cardiac progenitor cells. As shown by the analysis on the genetic expression, cardiac muscle genes Nk*2.5 and Isl1 in the masticatory muscle stem cells have expressions of different degrees. The techniques utilize that the masticatory muscle stem cells have the characteristics of the cardiac muscle stem cells, collect a masticatory muscle sample by the non-invasive biopsy method, and externally expands the masticatory muscle stem cells by the suspension culture method; and non-coding micro RNA (ribonucleic acid) is adopted to change the masticatory muscle stem cells and facilitate differentiation and purification of the masticatory muscle stem cells into the heart muscle cells. The transplantation of the purified cardiac muscle cells to a part with myocardial infarction is performed by means of the coronary artery duct injection or the cell membrane technique (the cell membrane is placed on the surface of myocardial infarction organization), so that the myocardial infarction or the ischemic heart disease can be cured.
Owner:珠海霍普金斯医药研究院股份有限公司
Method for preparing heart progenitor cells
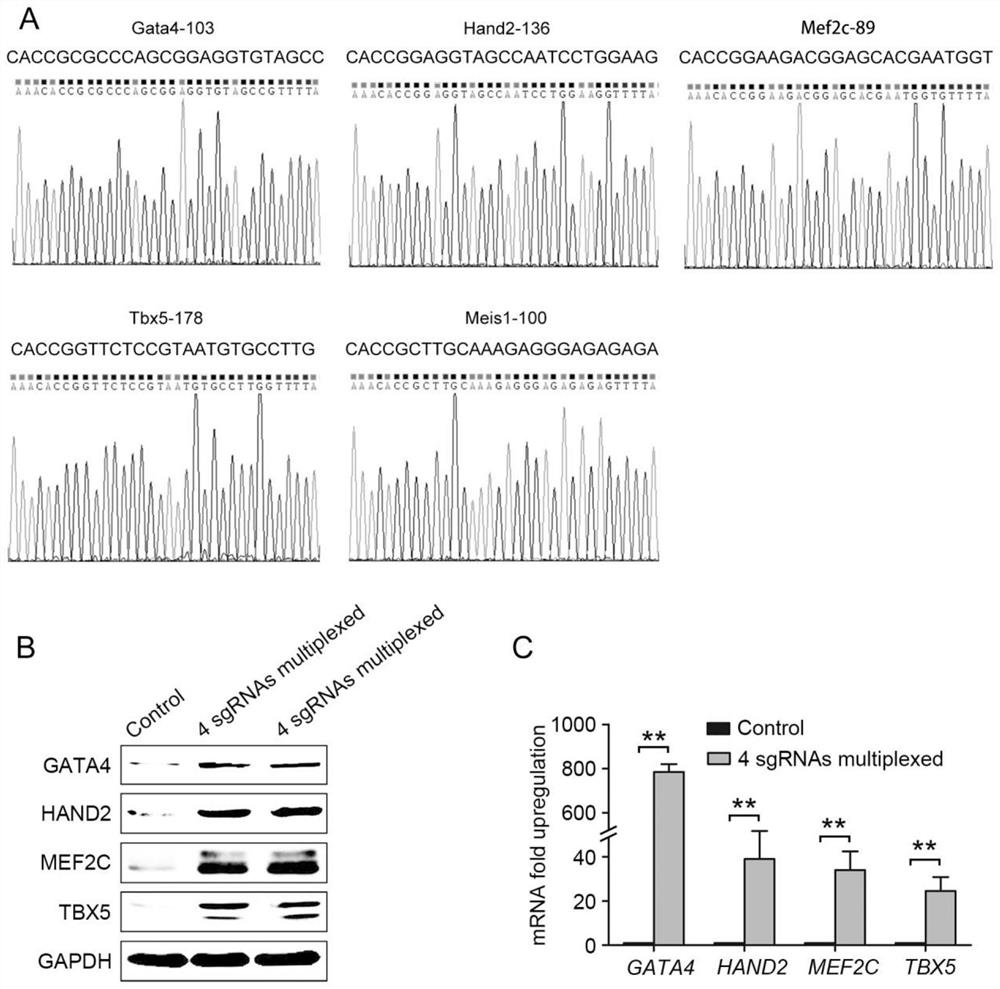
ActiveCN110760546AHigh reprogramming efficiencyInhibit synthesisHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAReprogrammingHeart development
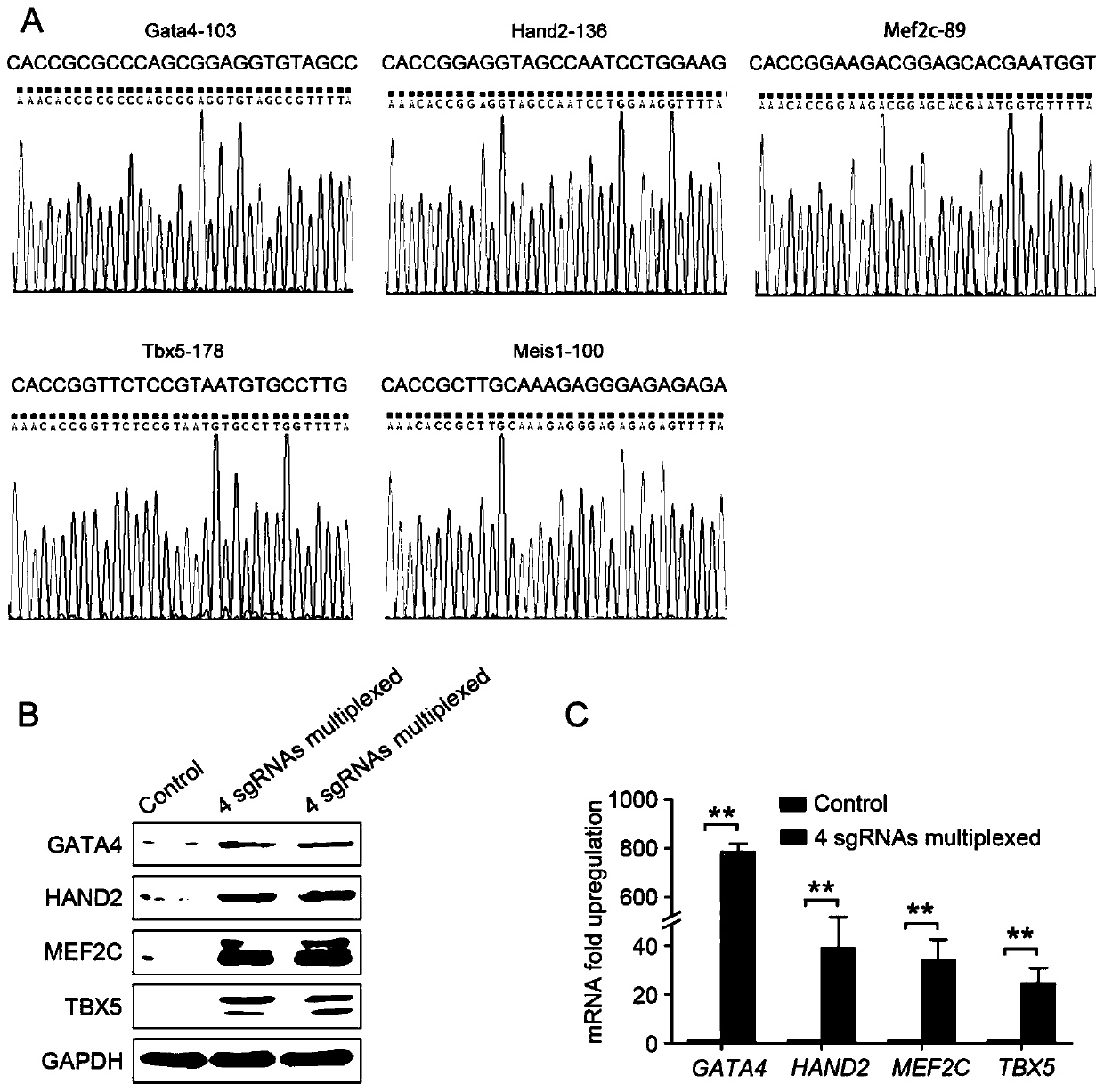
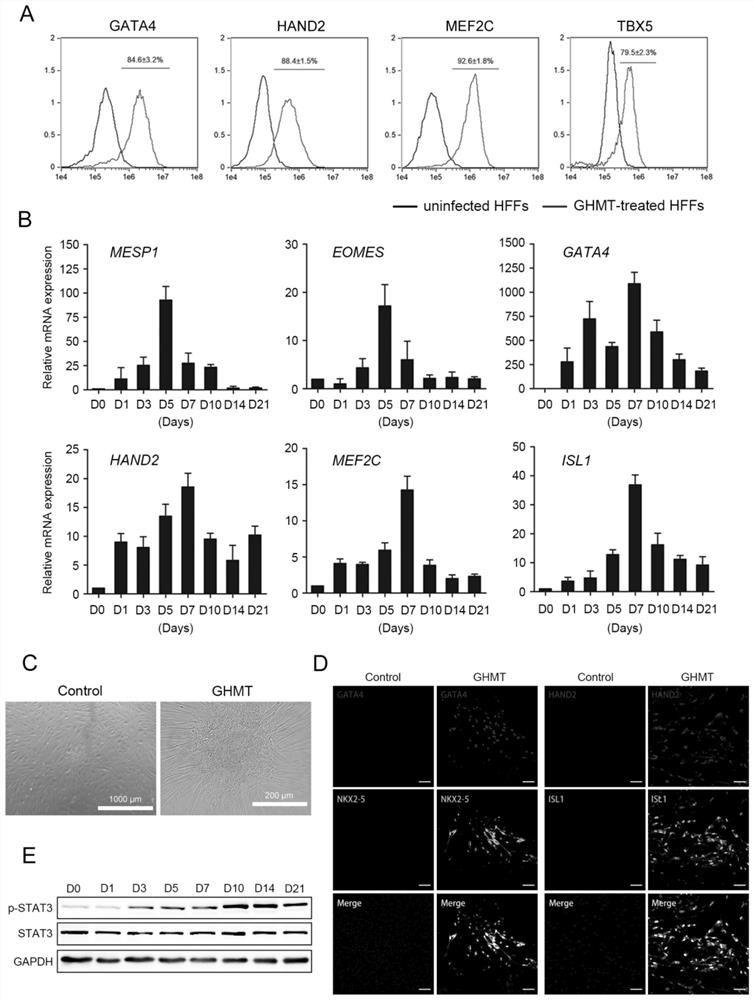
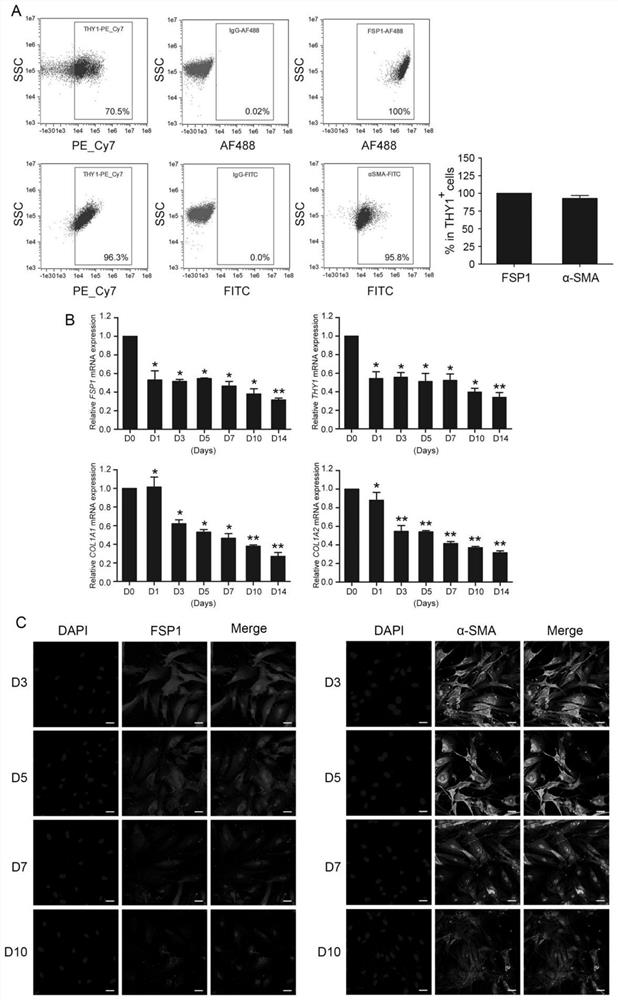
The invention provides a method for directly re-programming heart progenitor cells based on endogenous gene transcriptional activation. The method has better operation feasibility and theory creativity. For the first time, through a CRISPR / Cas9 system, endogenous heart development relevant transcription factors GATA4, HAND2, MEF2C, TBX5 and MEIS1 are activated, human foreskin fibroblasts are induced to be re-programmed into the heart progenitor cells having the potential of being disintegrated towards cardiac muscle cells, smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells, a seed cell source is provided for cardiovascular disease model construction, new medicine screening and myocardial regeneration, and besides, a novel apparent cell re-programming theory and connotation are enriched.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
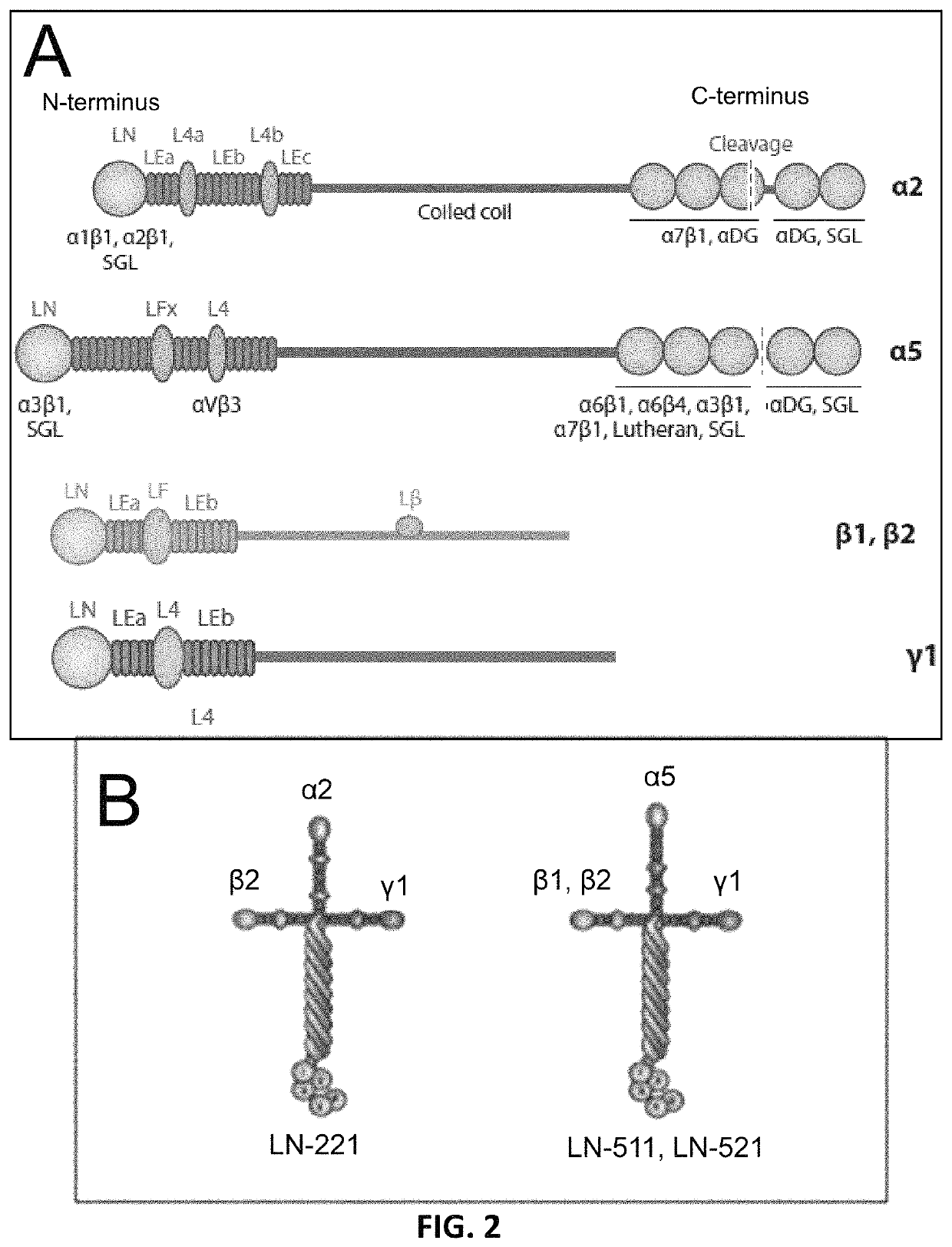
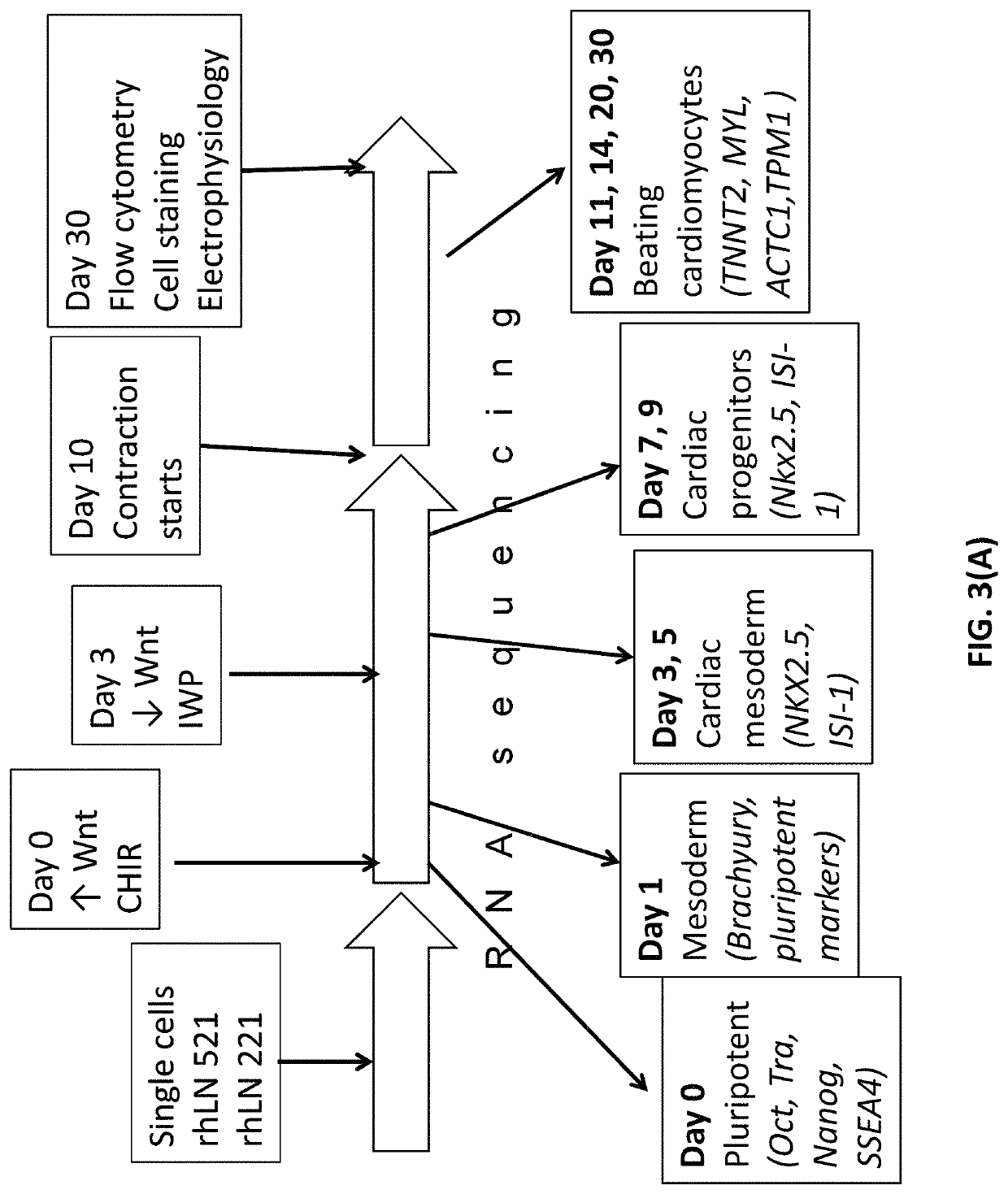
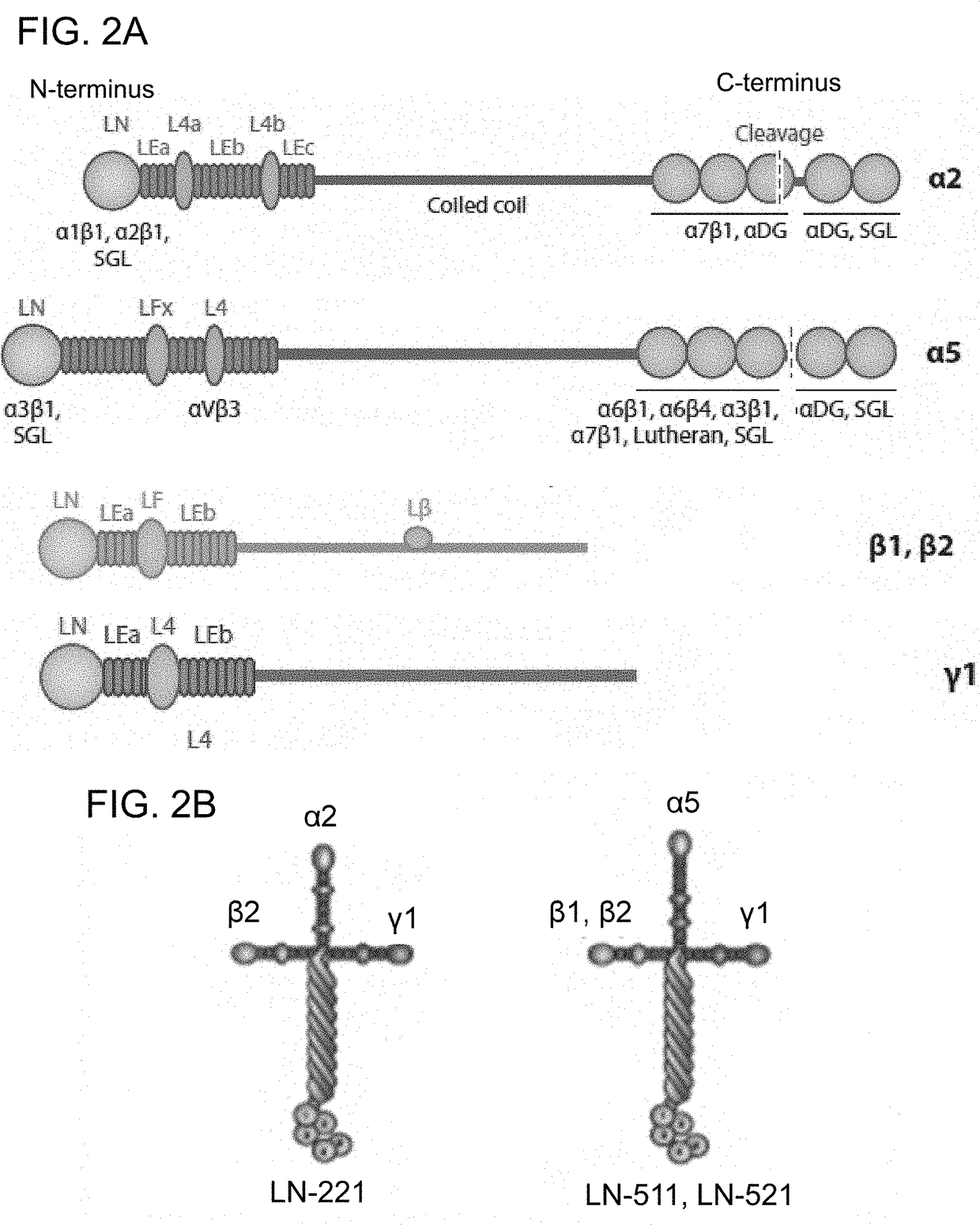
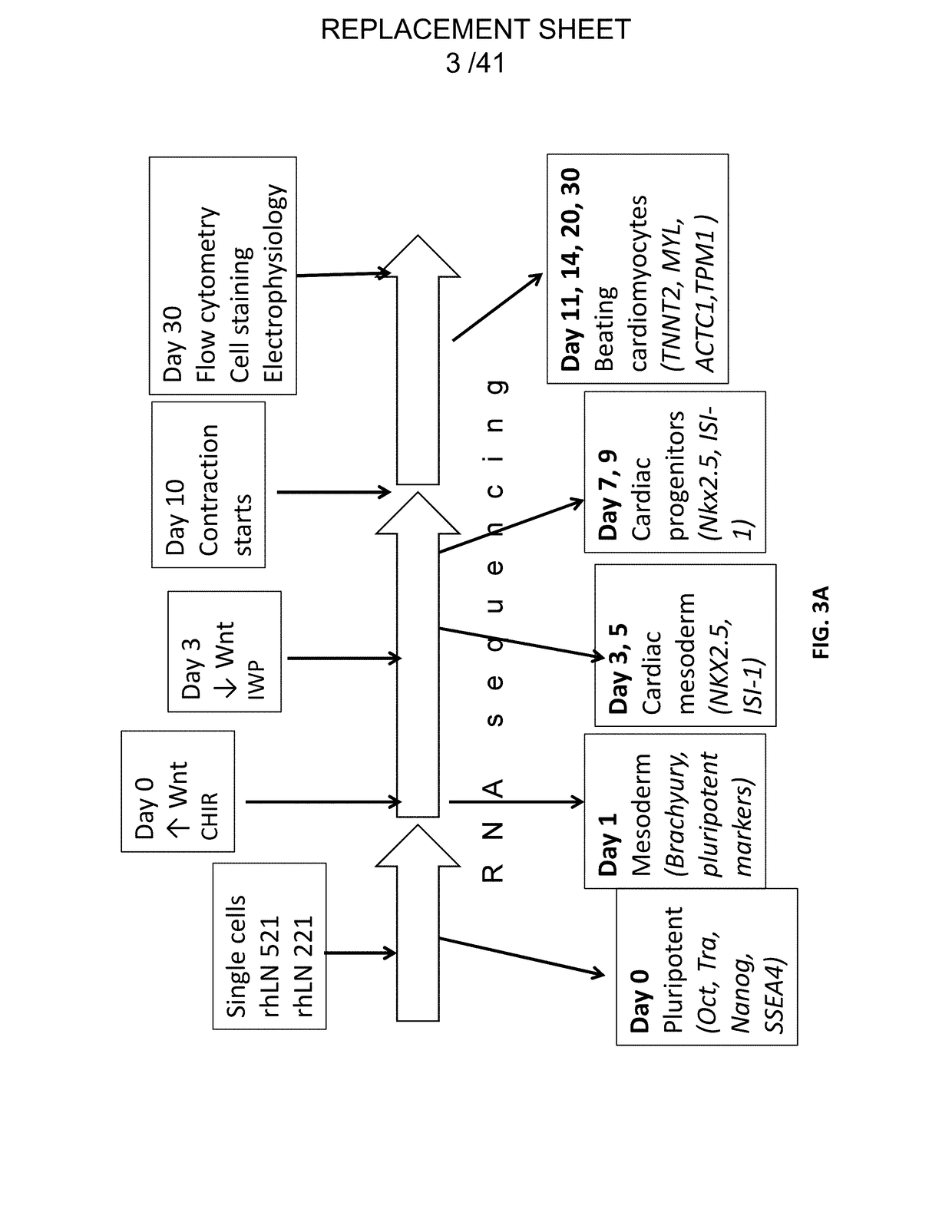
Differentiation of pluripotent stem cells and cardiac progenitor cells into striated cardiomyocyte fibers using laminins LN-511, LN-521 and LN-221
ActiveUS11001807B2Microbiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsLamininHuman myocardium
The present disclosure describes methods of differentiating cardiomyocyte progenitor cells and mature cardiomyocyte cells from pluripotent stem cells. The methods may include differentiating pluripotent stems cells on a substrate including (i) laminin-511 or 521 and (ii) laminin 221. The mature cardiomyocyte cells produced by the method may form a human heart muscle cell line for use in regenerative cardiology.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
A kit for culturing myocardial progenitor cells
ActiveCN106754671BRich sourcesDead animal preservationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsBiomedical engineeringMedical treatment
The invention provides a kit for culturing cardiac progenitor cells. A plurality of reagent bottles are arranged in the kit and contain a culture solution I, a culture solution II, a growth factor I, a growth factor II, a growth factor III, a growth factor IV, a digestive solution, a cleaning solution, a cryopreservation solution and cell seeds respectively. By the adoption of the kit, culture, amplification and cryopreservation of cardiac progenitor cells can be achieved, the problems that the culture survival rate of cardiac progenitor cells is low, culture efficiency is low, inter-batch difference is large, and cryopreservation reactivation rate is not ideal are solved, cardiac progenitor cells can be amplified in an ideal nutrient balance state without differentiation, and rich sources are provided for further experimental study and medical treatment using cardiac progenitor cells. The kit is quite suitable for cardiac progenitor cell culture.
Owner:张晓南
Method for directly producing cardiac precursor cell or myocardial cell from fibroblast
Provided is a method of inducing cardiac progenitor cells or cardiomyocytes from fibroblasts. The present invention provides a method for producing cardiac progenitor cells, comprising introducing one cardiac reprogramming factor into fibroblasts, or a method for producing cardiomyocytes, comprising introducing three cardiac reprogramming factors into fibroblasts.
Owner:UNIV OF TSUKUBA
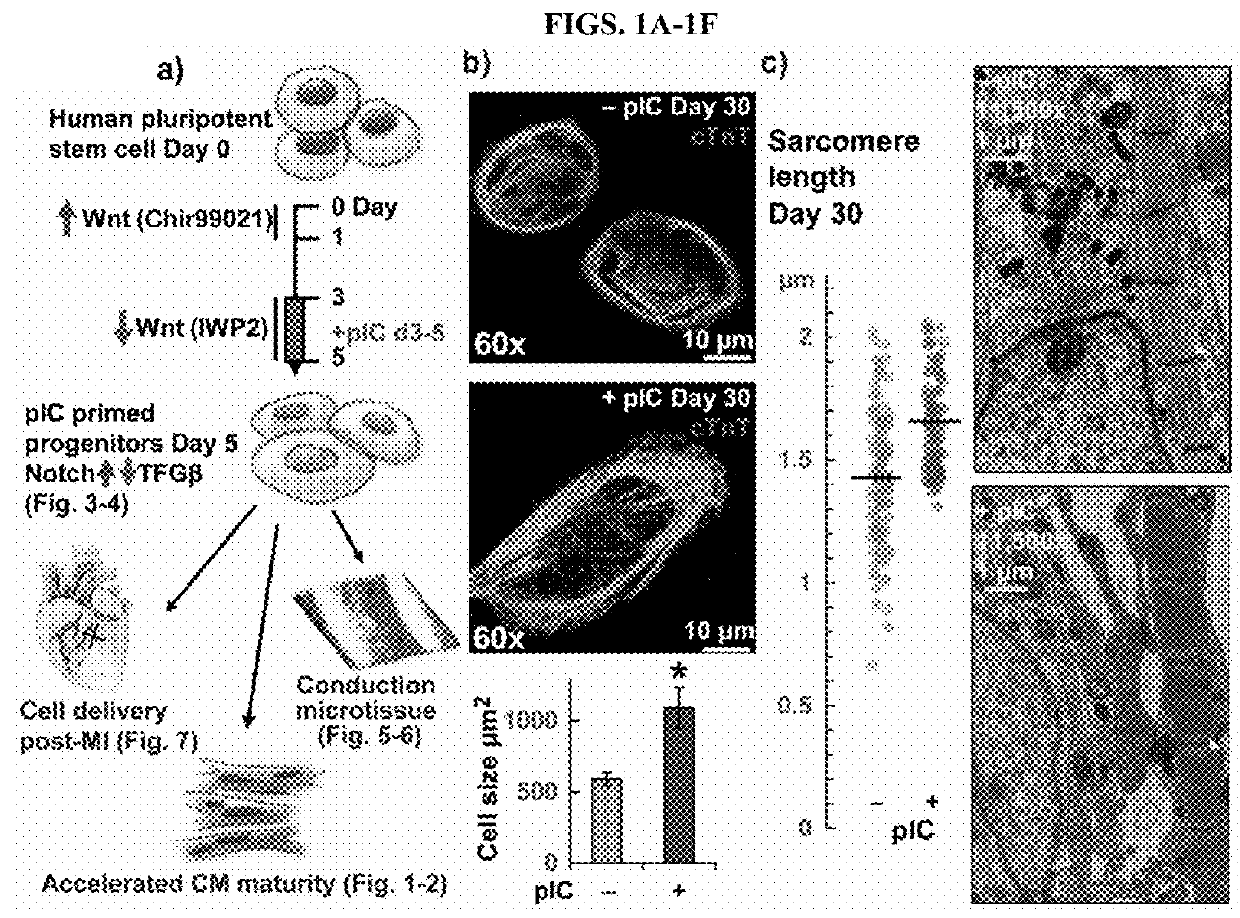
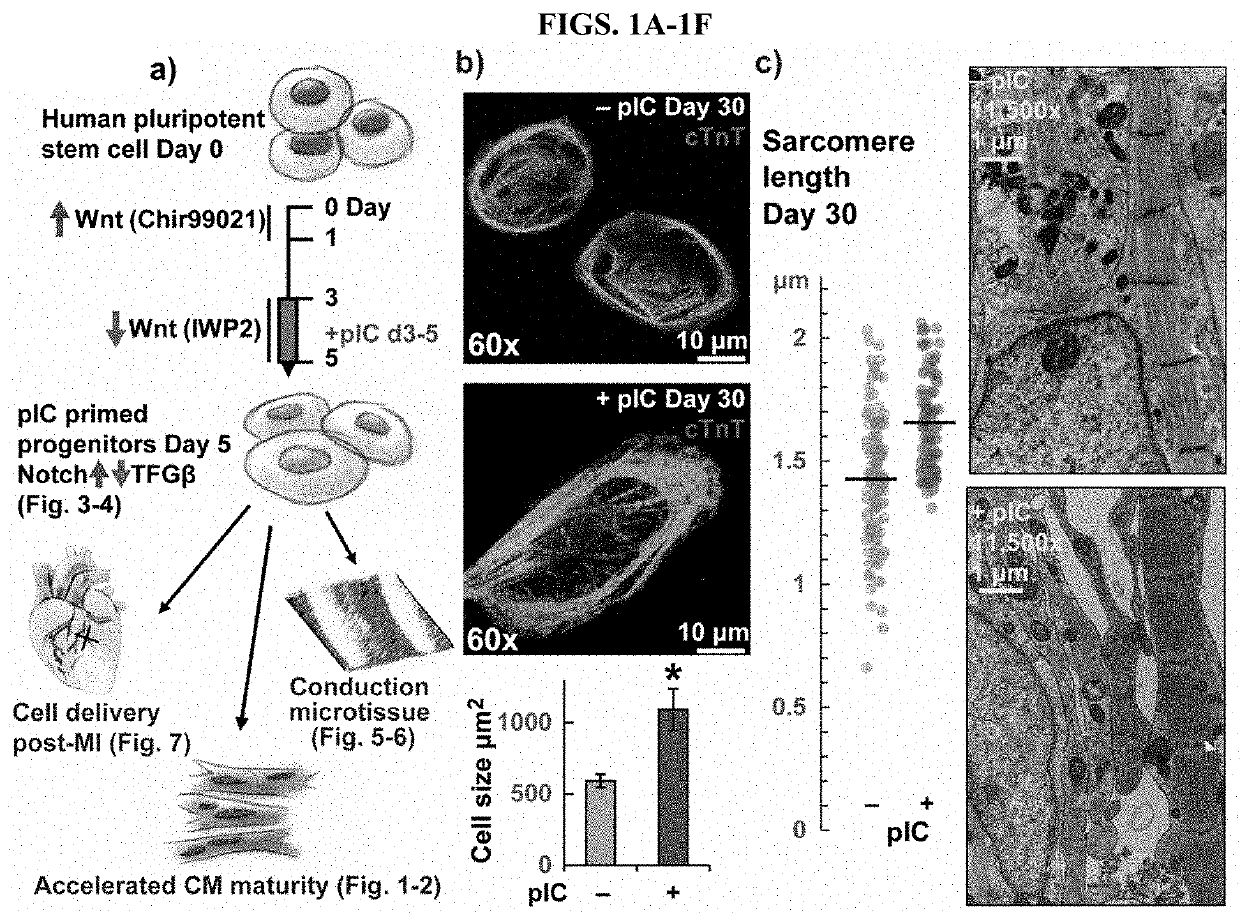
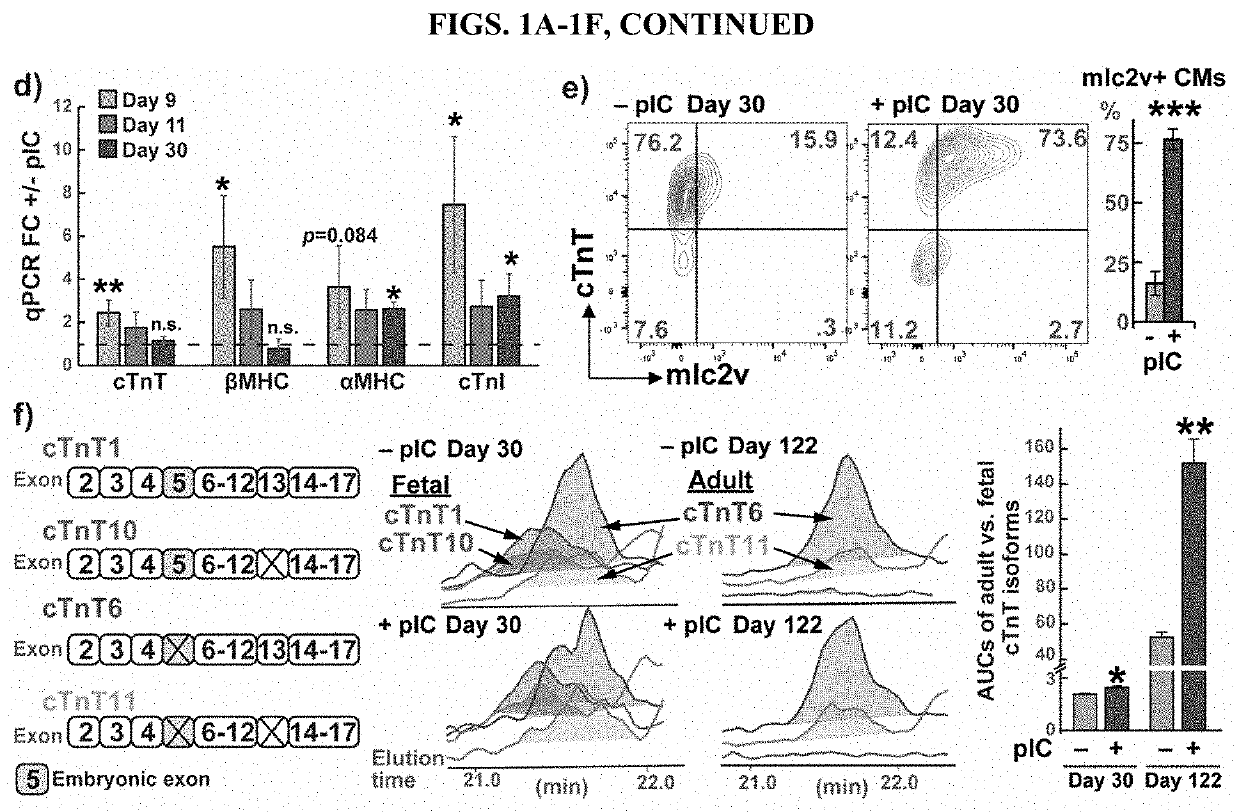
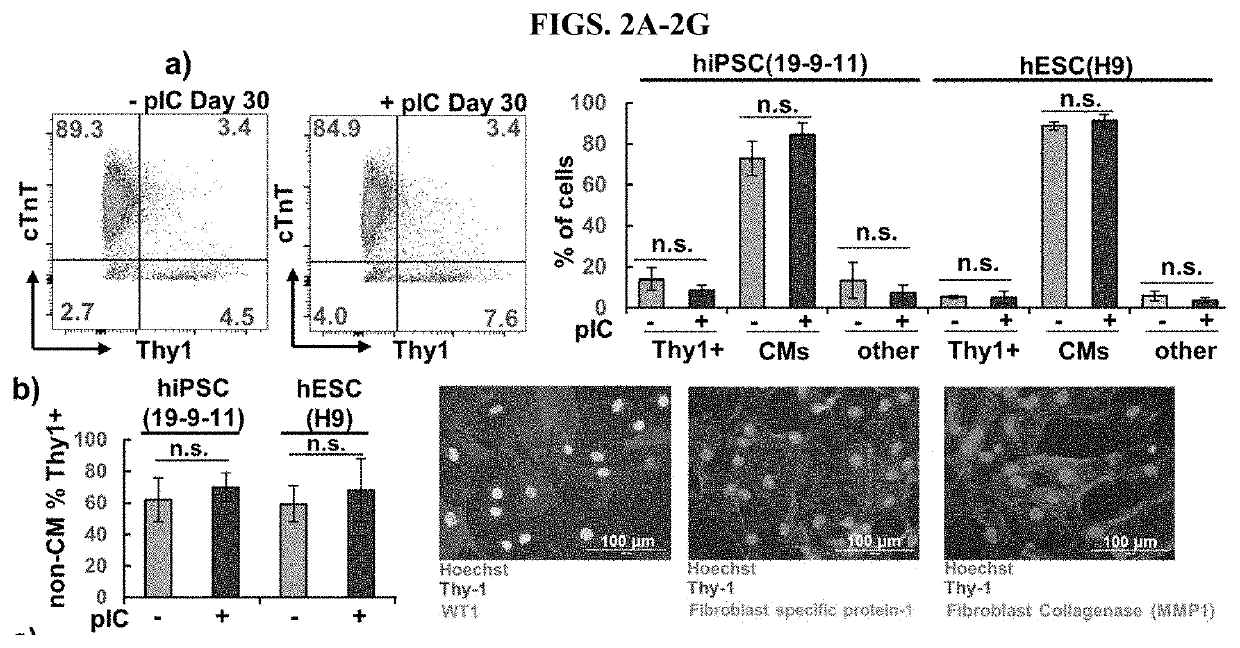
Primed Cardiac Progenitors and Methods for Making and Using Same
An improvement to the GiWi protocol for differentiating human pluripotent cells to developmentally mature cardiomyocytes includes a step of activating innate immunity in mesoderm stage cells in the in vitro differentiation culture. When the mesoderm cells, which are precursors to cardiac progenitor cells, are primed by exposure to an activator of innate immunity, a population of cardiomyocytes is generated that is more developmentally mature than is generated in the GiWi protocol without the primed step. Also provided herein are in vitro ventricular conductive microtissues and isolated, in vitro populations of ventricular conduction system-like cells and methods for making the same.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
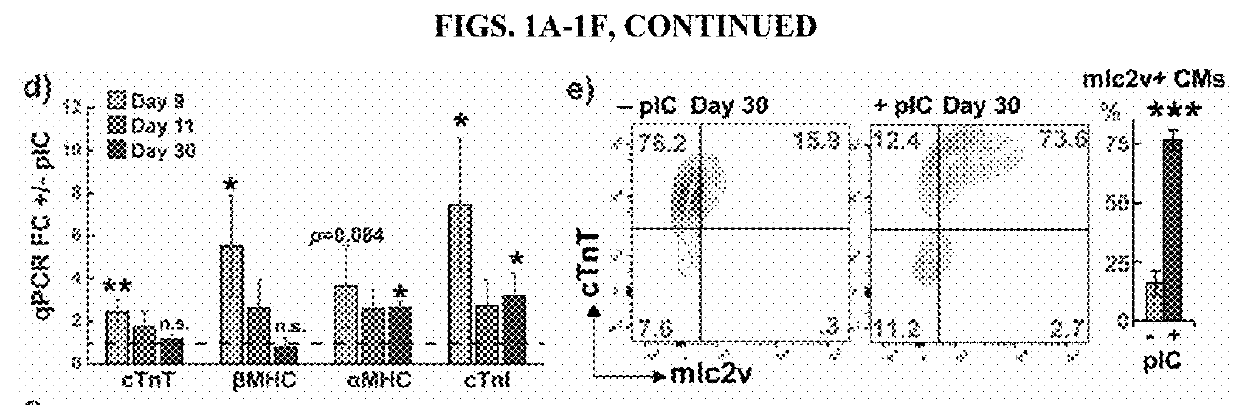
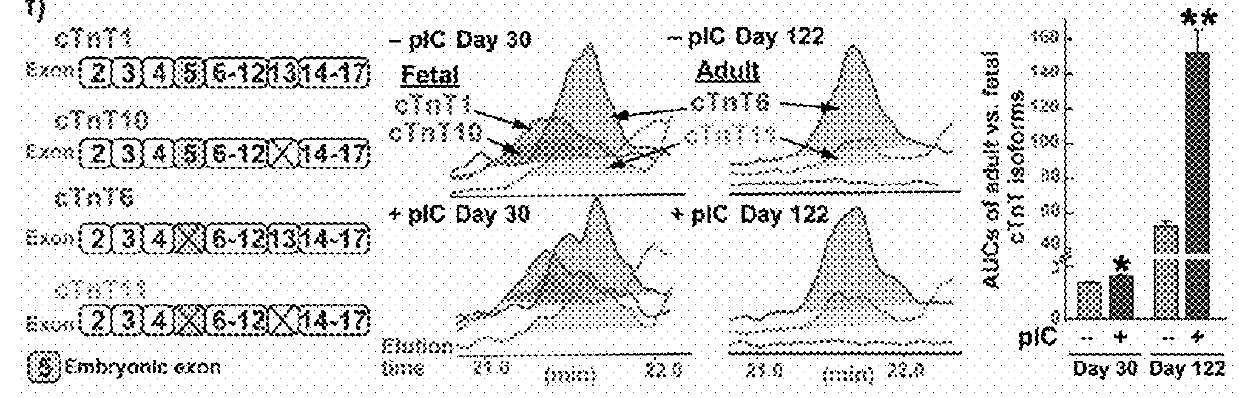
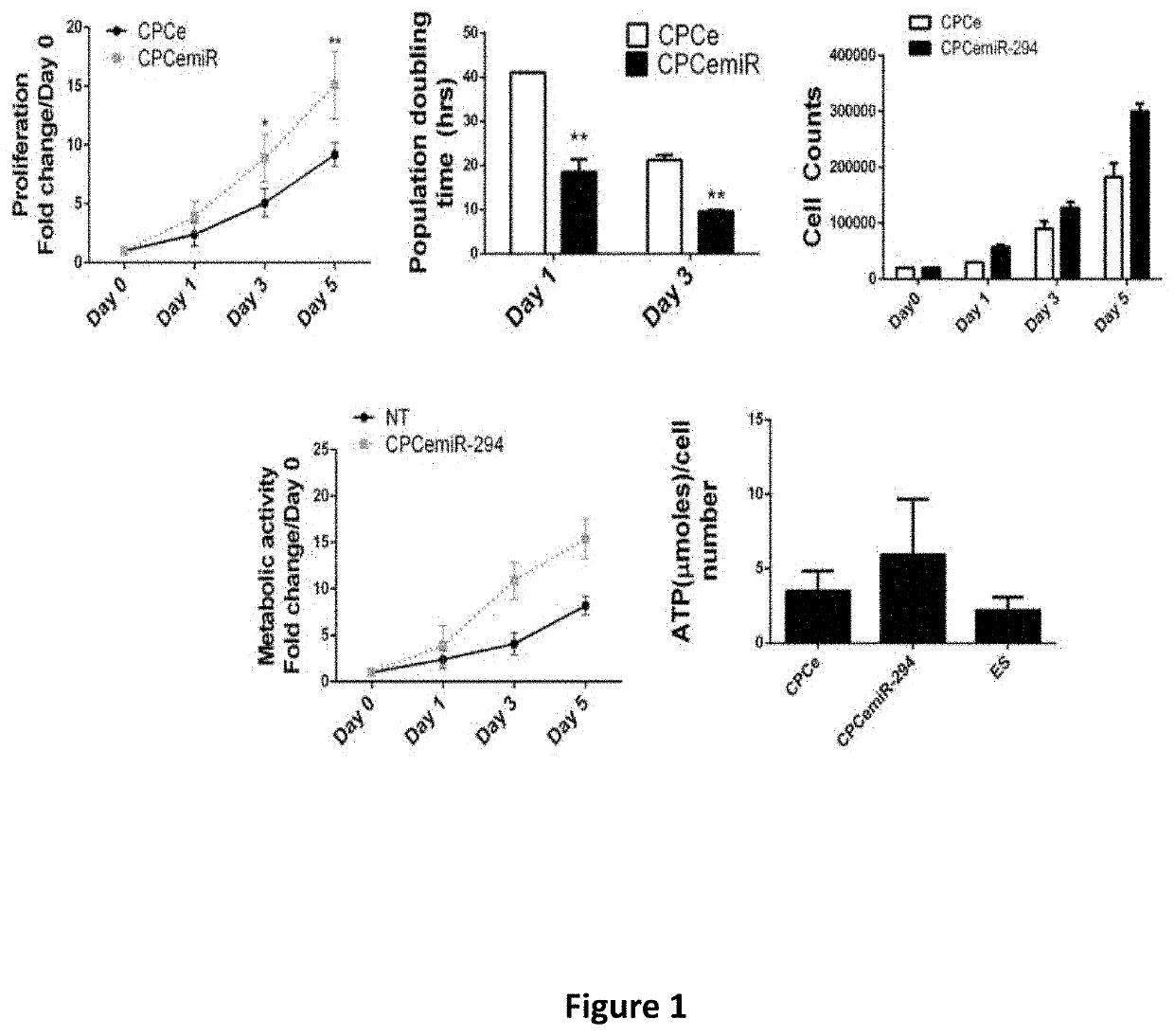
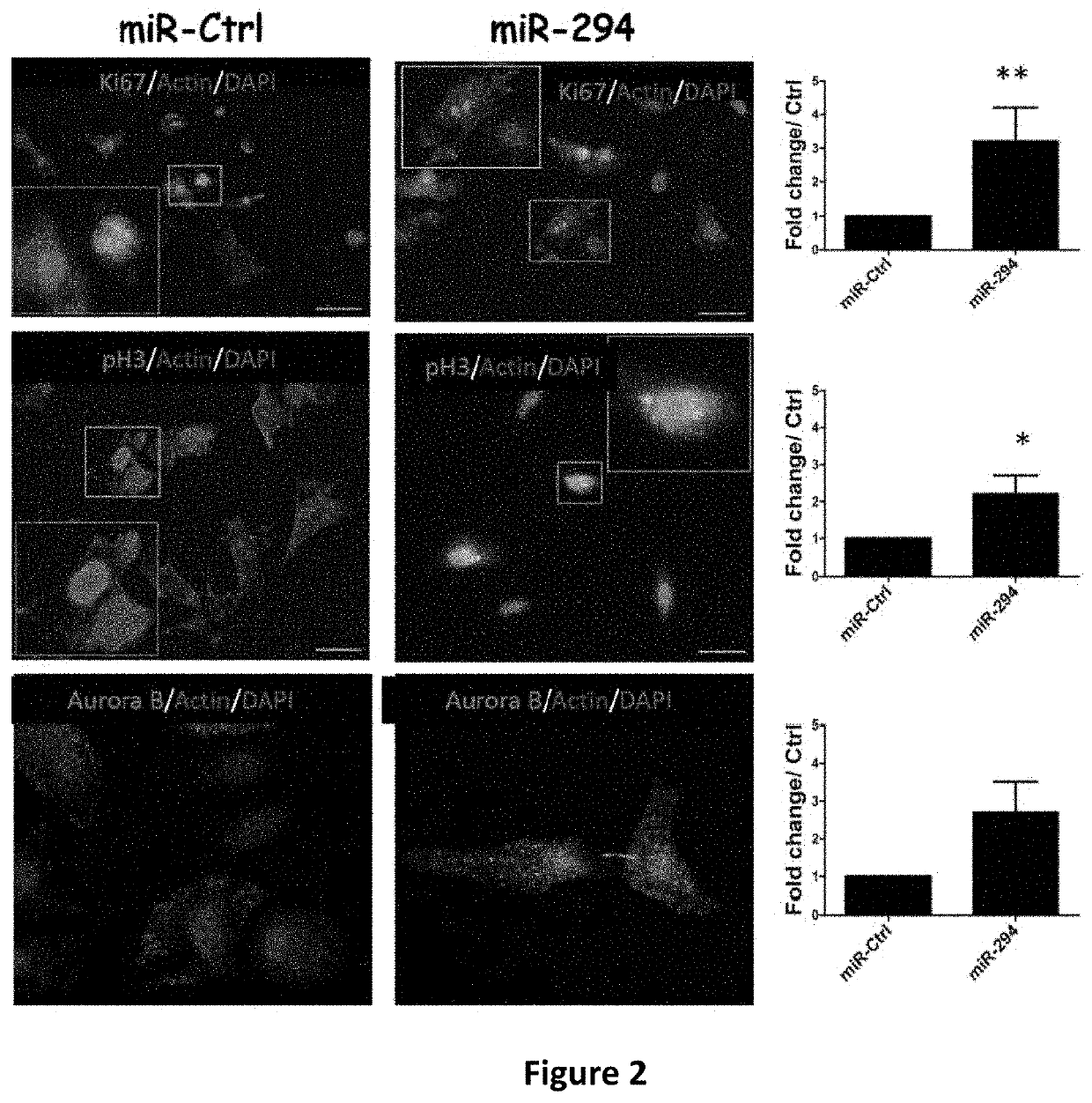
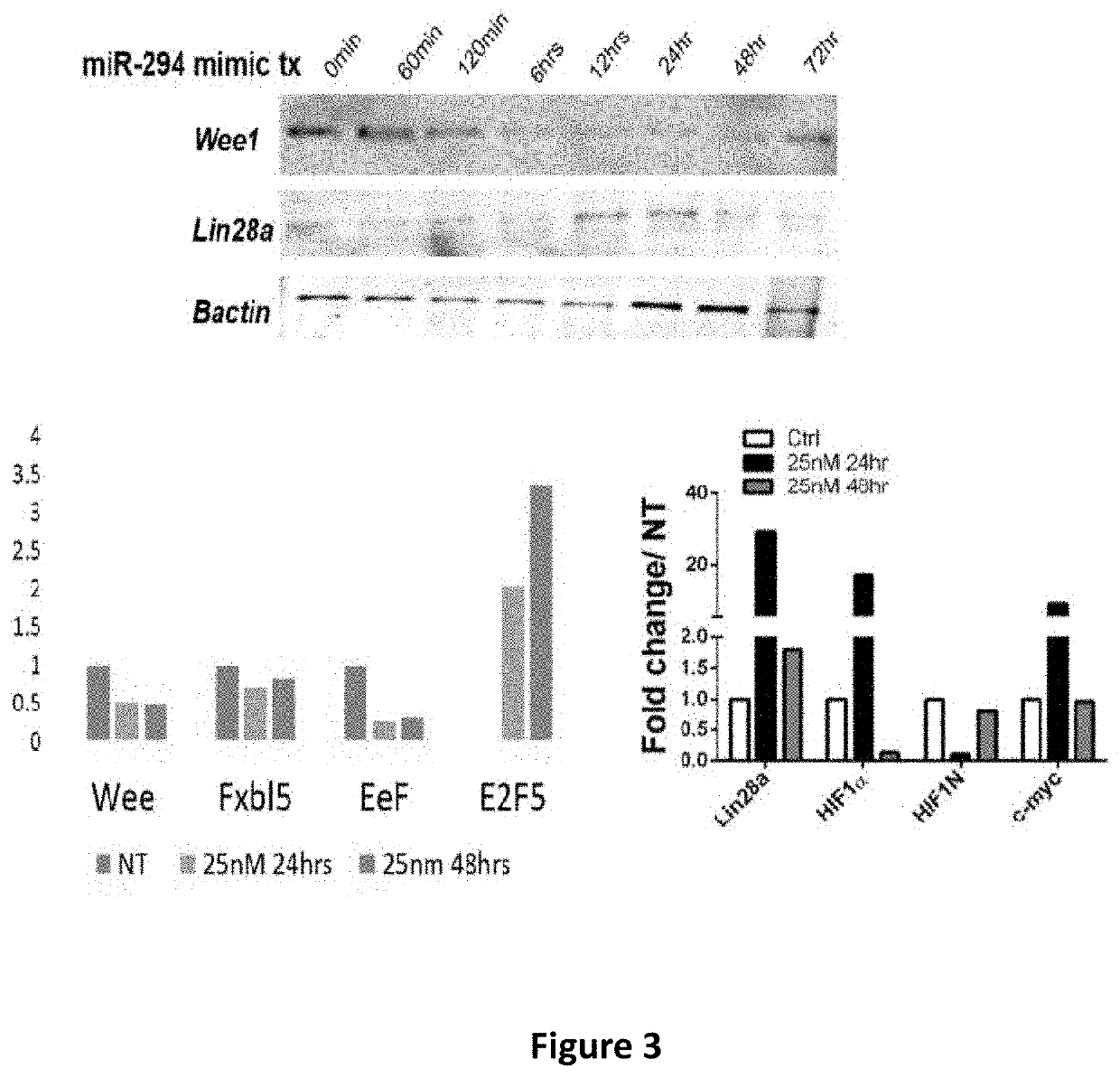
Microrna-294 and lin28a as a driver of cardiac tissue proliferation in response to pathological injury
The invention provides one or more of miR-290 family and Lin28a modified cardiac progenitor cell based therapies for the treatment of myocardial infarction. Exosomes derived from one or more of miR-290 family and Lin28a modified cardiac progenitor cells can also be used in cardiac therapy.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
Method of making cardiomyocytes from human pluripotent cells
ActiveUS11352604B2Unknown materialsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell differentationImmunoactivators
An improvement to the GiWi protocol for differentiating human pluripotent cells to developmentally mature cardiomyocytes includes a step of activating innate immunity in mesoderm stage cells in the in vitro differentiation culture. When the mesoderm cells, which are precursors to cardiac progenitor cells, are primed by exposure to an activator of innate immunity, a population of cardiomyocytes is generated that is more developmentally mature than is generated in the GiWi protocol without the primed step. Also provided herein are in vitro ventricular conductive microtissues and isolated, in vitro populations of ventricular conduction system-like cells and methods for making the same.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Differentiation of pluripotent stem cells and cardiac progenitor cells into striated cardiomyocyte fibers using laminins ln-511, ln-521 and ln-221
The present disclosure describes methods of differentiating cardiomyocyte progenitor cells and mature cardiomyocyte cells from pluripotent stem cells. The methods may include differentiating pluripotent stems cells on a substrate including (i) laminin-511 or 521 and (ii) laminin-221. The cardiomyocyte progenitor cells and mature cardiomyocyte cells produced by the methods may form a human heart muscle cell line for use in regenerative cardiology. Also described are methods of identifying functional cardiomyocyte progenitor cells and their use in therapeutic applications.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Method for preparing cardiac progenitor cells
ActiveCN110760546BHigh reprogramming efficiencyInhibit synthesisHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAReprogrammingHeart development
The invention provides a method for direct reprogramming of cardiac progenitor cells based on transcriptional activation of endogenous genes. The method has good operational feasibility and theoretical innovation. For the first time, the endogenous cardiac development-related transcription factors GATA4, HAND2, MEF2C, TBX5 and MEIS1 are activated by the CRISPR / Cas9 system to induce the reprogramming of human foreskin fibroblasts with tropism Cardiac progenitor cells with differentiation potential of cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells provide seed cell sources for the construction of cardiovascular disease models, new drug screening and myocardial regeneration, and enrich the theory and connotation of new epigenetic cell reprogramming.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
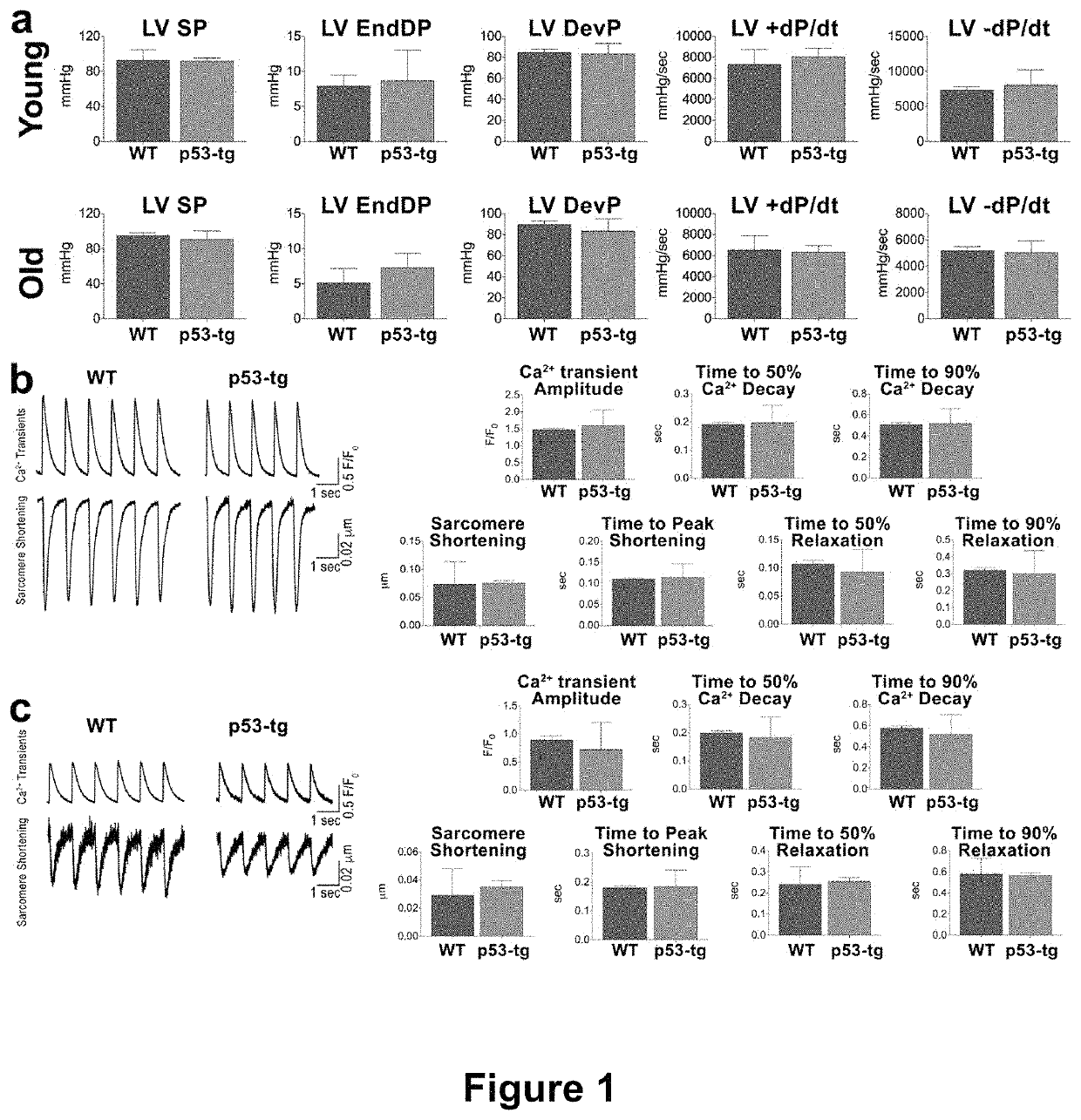
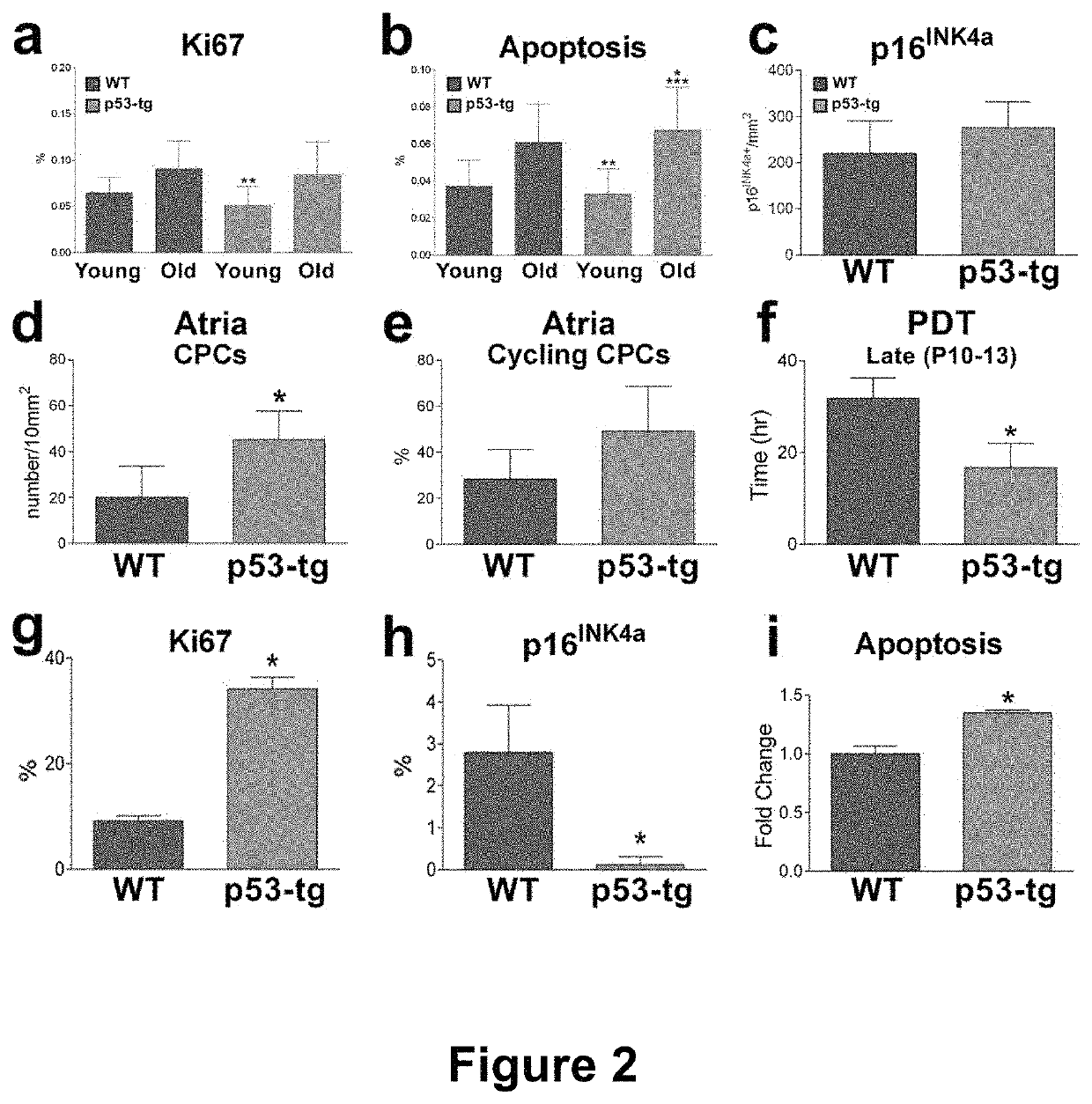
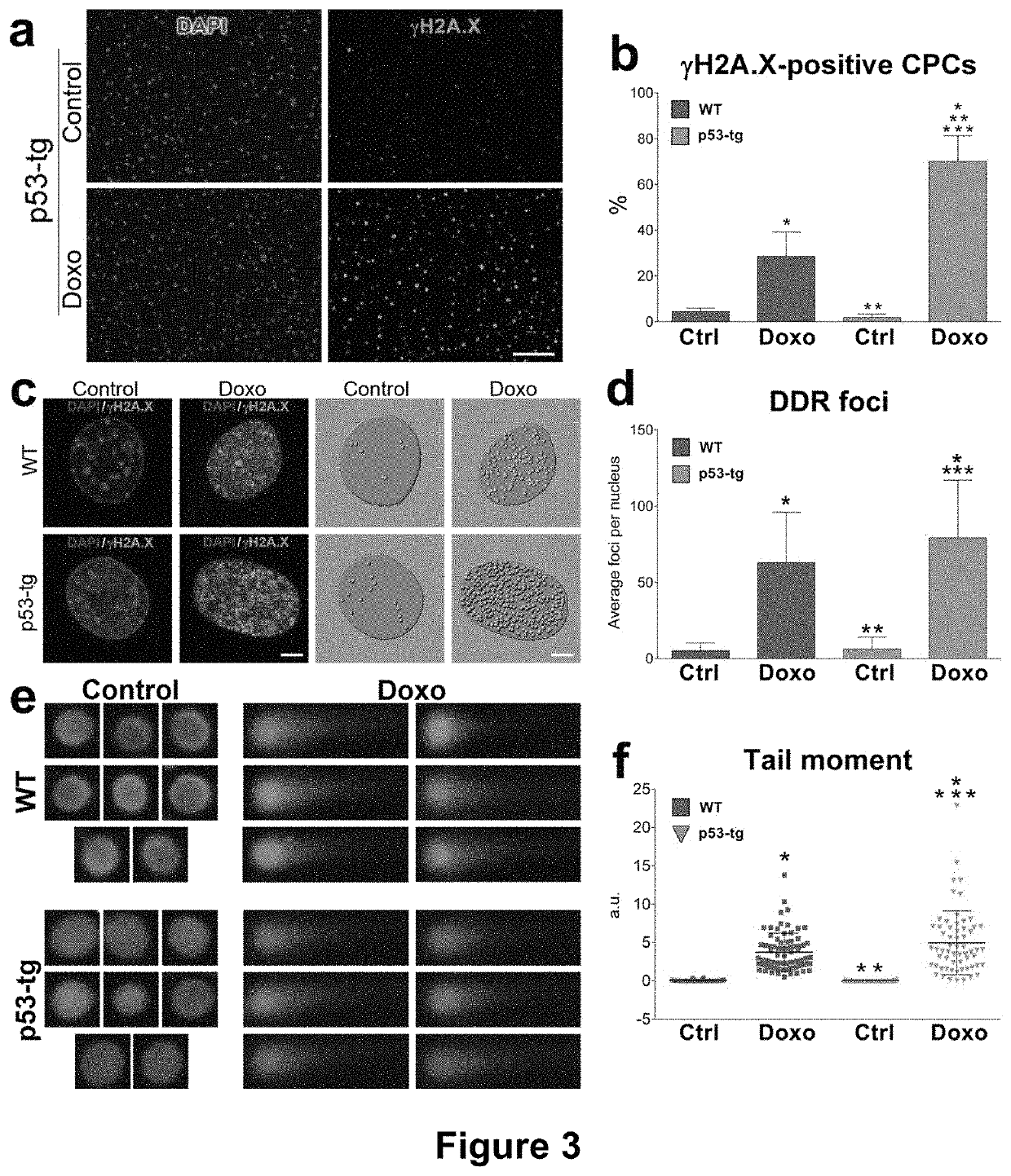
CARDIAC PROGENITOR CELLS HAVING ENHANCED p53 EXPRESSION AND USES THEREOF
Disclosed herein are compositions comprising cardiac progenitor cells that express exogenous p53 protein. Such compositions are useful for treating cardiac diseases or disorders. Also disclosed herein are methods of producing cardiac progenitor cells that express exogenous p53.
Owner:AAL SCI INC
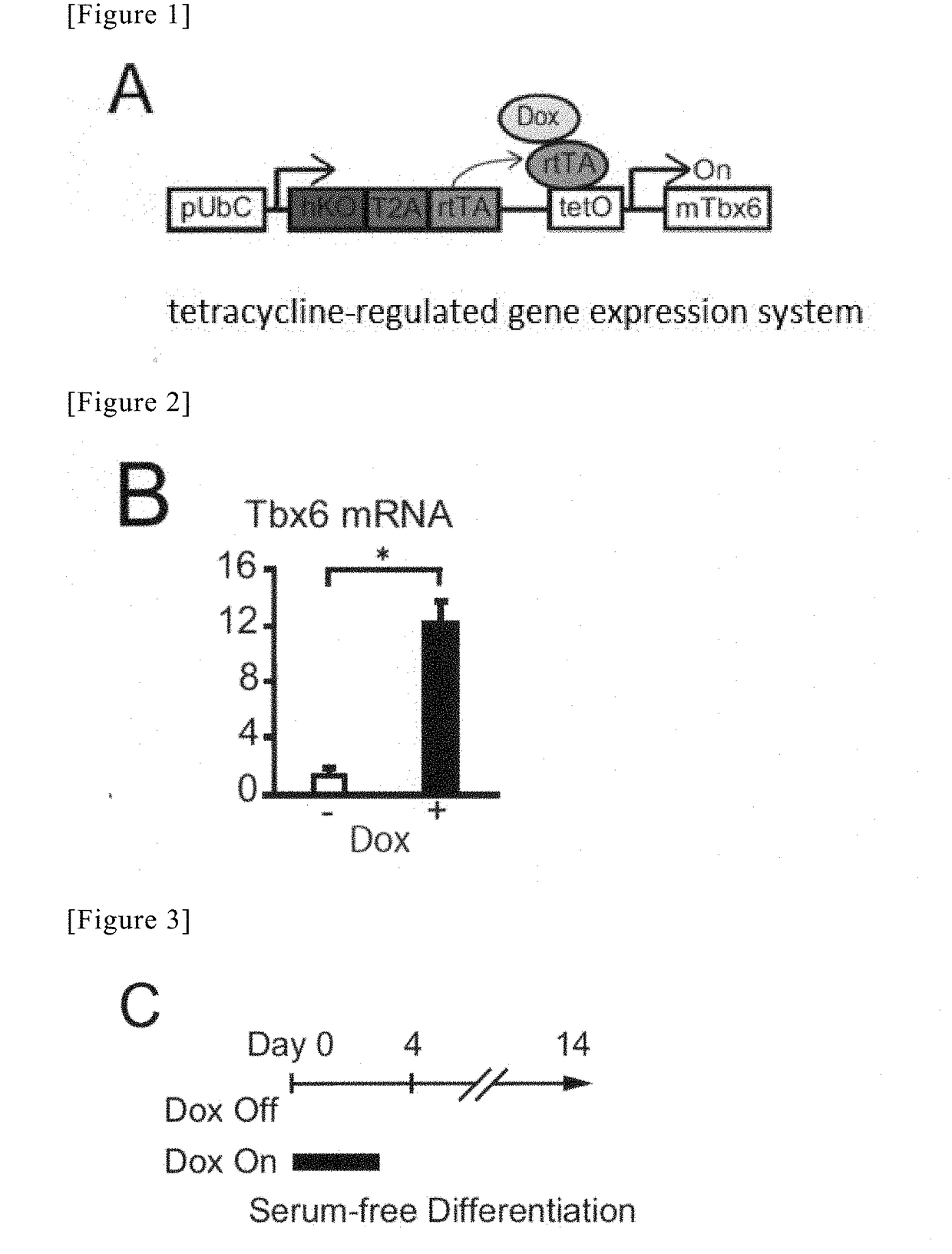
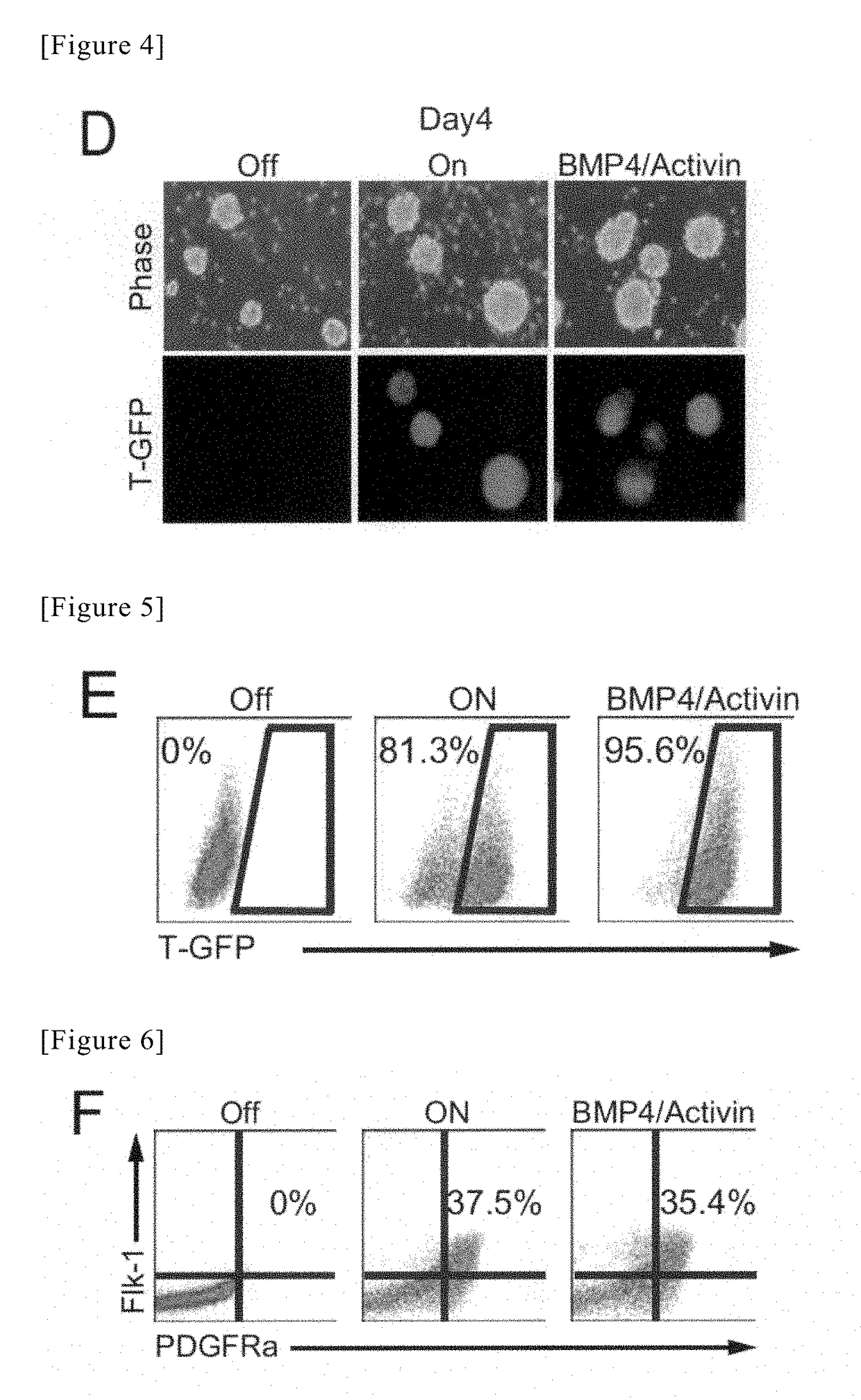
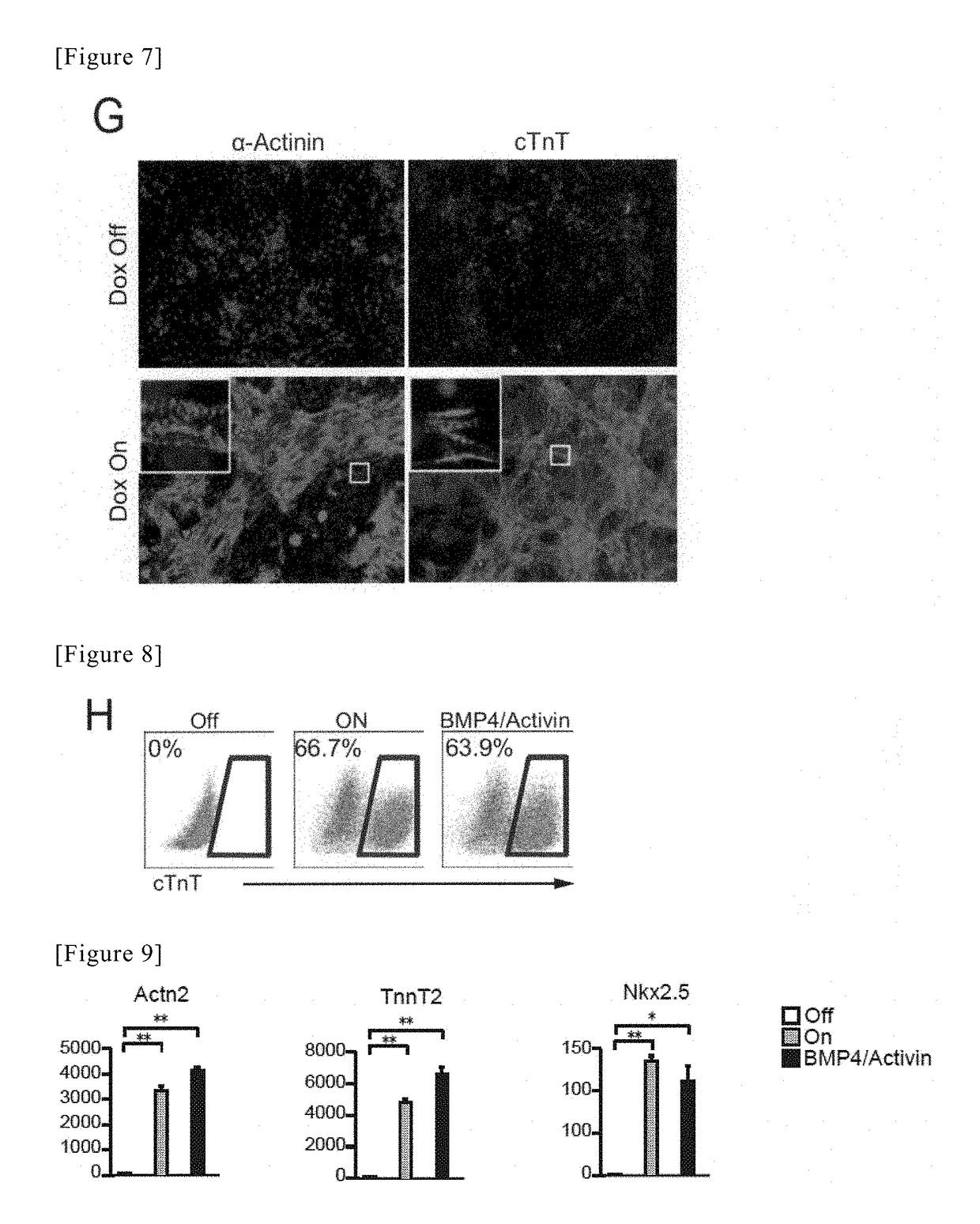
Method for producing cardiac precursor cell and myocardial cell from pluripotent stem cell
InactiveUS20190078053A1Improve efficiencyOrganic chemistryGenetically modified cellsInduced pluripotent stem cellCardiac progenitors
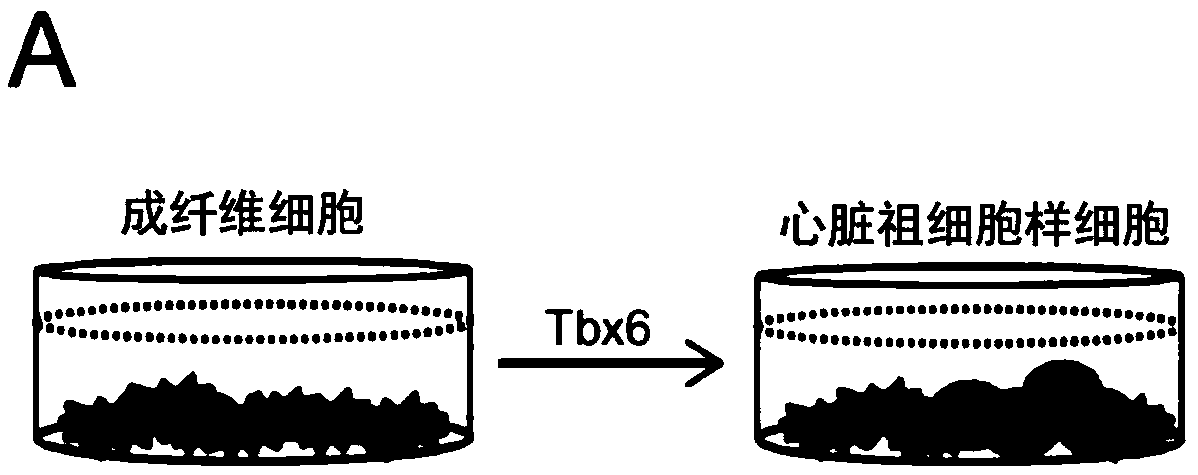
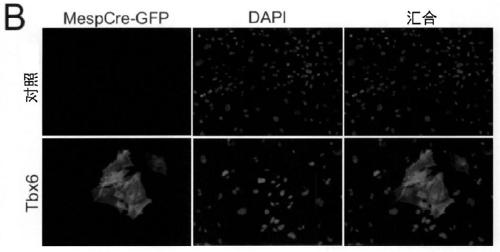
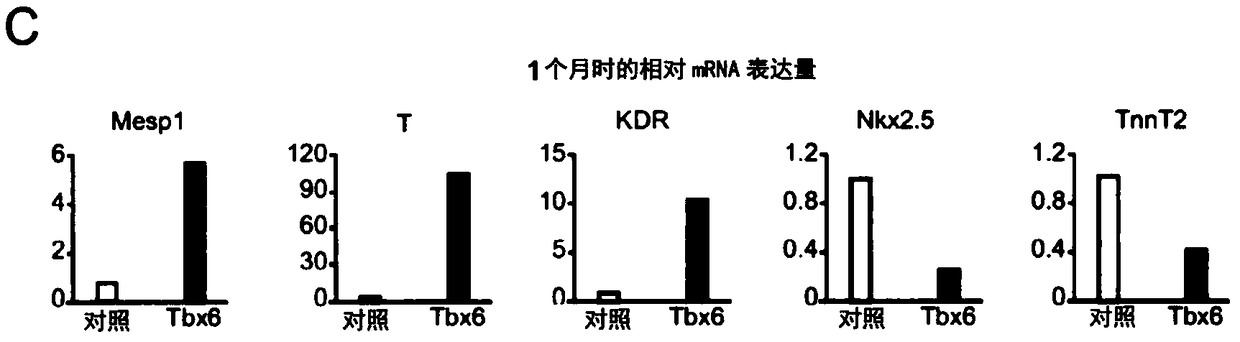
Provided is a method of inducing cardiac progenitor cells or cardiomyocytes from pluripotent stem cells.The present invention provides a method for producing cardiac progenitor cells from pluripotent stem cells, comprising expressing Tbx6 in the pluripotent stem cells. Moreover, the present invention provides a method for producing cardiomyocytes from pluripotent stem cells, comprising: a step of inducing cardiac progenitor cells from pluripotent stem cells, comprising expressing a Tbx6 gene in the pluripotent stem cells; and a step of inducing cardiomyocytes from the cardiac progenitor cells induced in the above step, comprising suppressing the expression of the Tbx6 gene.
Owner:UNIV OF TSUKUBA
Method for regulating and controlling conduction velocity of tissue-engineered conduction bundle and application
PendingCN114854693AEffective in regulating conduction velocityImprove precision controlPeptidesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHeart cellsPost transplant
The invention provides a method for regulating and controlling the conduction velocity of a tissue-engineered conduction bundle and application. By changing the cell planting density and the tissue culture period in the tissue engineering heart conduction bundle construction and culture process, it is found that the conduction speed is regulated and controlled most effectively when the planting density is 1 * 10 < 7 >-1.1 * 10 < 7 > cells / ml and the culture period is 2 weeks. On the basis of the parameters, heart cells overexpressing Tbx3 and common heart progenitor cells are jointly planted on a collagen sponge stent to construct ECT, and it is found that the effect of precise regulation and control of the conduction velocity is better through the matching of 70-80% of Tbx3 + H9C2 cells and 20-30% of Tbx3-H9C2 cells. The conduction velocity of the ECT constructed by the method is close to the in-vivo atrioventricular junction level, the key problem of realizing physiological atrioventricular electrical conduction in the process of reconstructing an atrioventricular pathway through a tissue engineering conduction bundle (ECT) is solved, namely, the problem of how to ensure atrioventricular extension after ECT transplantation is solved, and an effective method is provided for regulating and controlling the conduction velocity of the ECT.
Owner:THE NAVAL MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Composition for cell transplant, and method for cell transplant
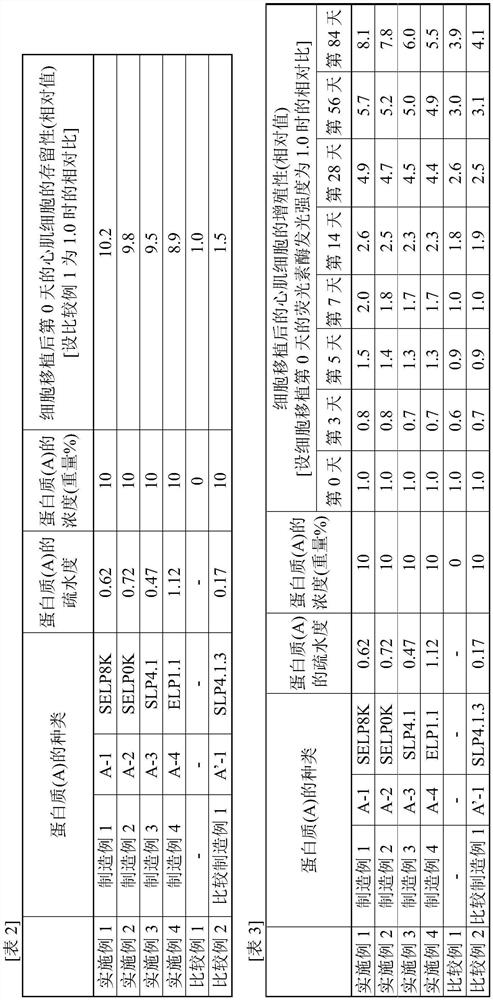
PendingCN112292157AImprove retention capacityImprove proliferative abilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticPost transplantProtein
Provided are a composition for cell transplant and a method for cell transplant that allow myocytes and / or cardiac progenitor cells to be suitably maintained in myocardial tissue and allow the survival and proliferation of transplanted cells to be improved. This composition for cell transplant comprises cells and an aqueous solution of a protein (A), and is characterized in that: the cells are myocardial cells and / or cardiac progenitor cells; protein (A) has a hydrophobicity of 0.2-1.2; the protein (A) has a polypeptide chain (Y) and / or a polypeptide chain (Y'); the total number of polypeptidechains (Y) and polypeptide chains (Y') in the protein (A) is 1-100; the polypeptide chain (Y) is an amino acid sequence (X) repeated 2-100 times, the amino acid sequence being any one of a VPGVG sequence (1) which is an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1, a GVGVP sequence (2) which is an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2, a GPP sequence, a GAP sequence, and a GAHGPAGPK sequence (3), which is an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:3; the polypeptide chain (Y') is the polypeptide chain (Y) where 0.1-5% of the amino acid residues thereof are substituted with lysine residues and / or arginine residues; and the total number of the lysine residues and arginine residues is 1-100.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Composition for cell transplant, and method for cell transplant
ActiveUS20210252074A1Easy to keepIncreased persistencePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProteinArgininic acid
Provided are a composition for cell transplant and a method for cell transplant, both of which enable a myocardial tissue to favorably retain cardiac myocytes and / or cardiac progenitors and can improve the persistence and proliferation of transplanted cells. The composition for cell transplant of the present invention is a composition for cell transplant, containing cells and an aqueous solution containing a protein (A), the cells including a cardiac myocyte and / or a cardiac progenitor, the protein (A) having a degree of hydrophobicity of 0.2 to 1.2, the protein (A) containing a polypeptide chain (Y) and / or a polypeptide chain (Y′), the protein (A) containing 1 to 100 polypeptide chains as a total of the polypeptide chain (Y) and the polypeptide chain (Y′), the polypeptide chain (Y) being a polypeptide chain having 2 to 100 continuous amino acid sequences (X), the amino acid sequence (X) having any one of a VPGVG sequence (1) corresponding to an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, a GVGVP sequence (2) corresponding to an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2, a GPP sequence, a GAP sequence, and a GAHGPAGPK sequence (3) corresponding to an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3, the polypeptide chain (Y′) being a polypeptide chain having a structure in which 0.1 to 5% amino acid residues in the polypeptide chain (Y) are replaced by a lysine residue and / or an arginine residue and including 1 to 100 residues as a total of the lysine residue and the arginine residue.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com