Patents
Literature
563 results about "Close-ended" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A closed-ended question contrasts with an open-ended question, which cannot easily be answered with specific information. Examples of close-ended questions which may elicit a "yes" or "no" response include:
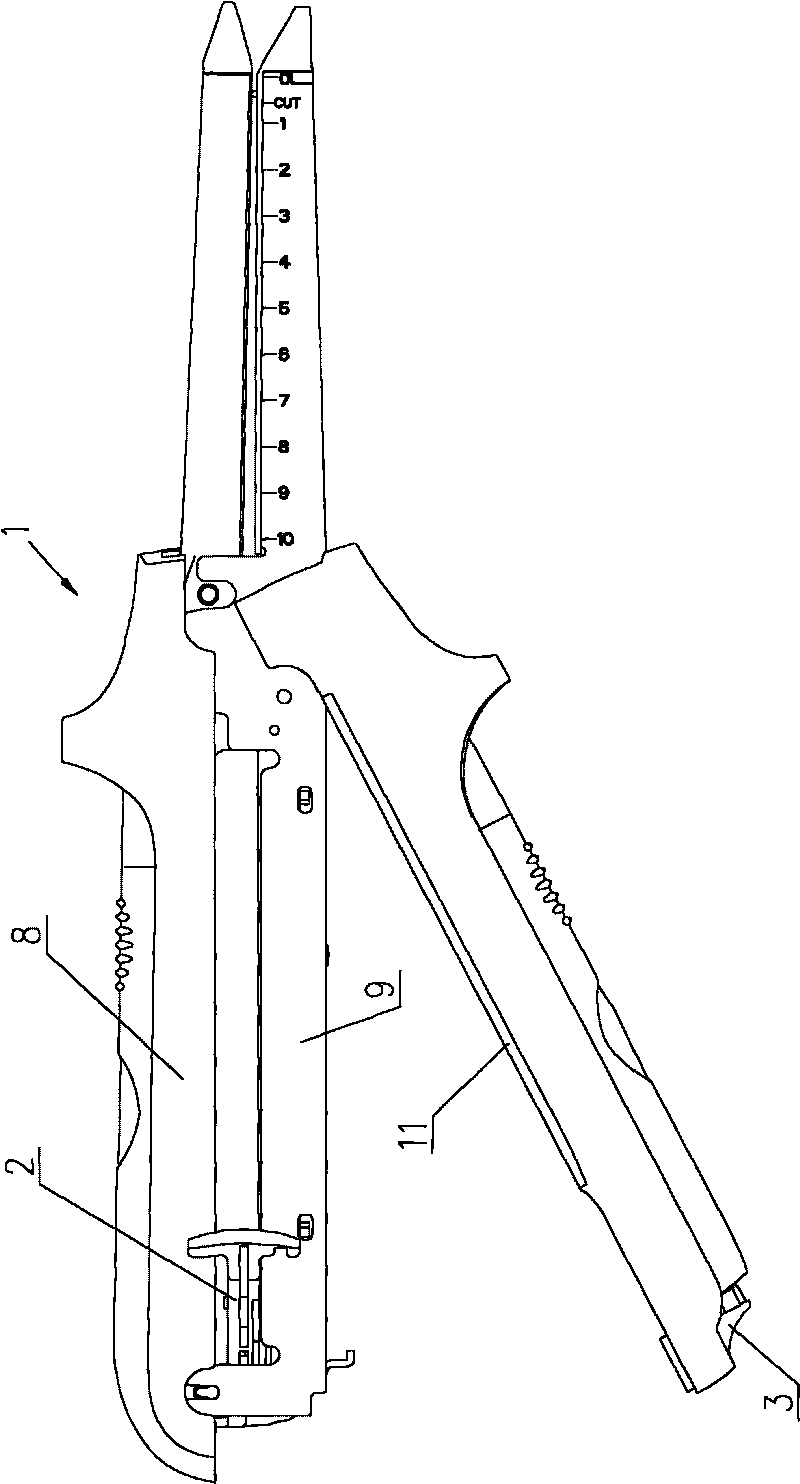
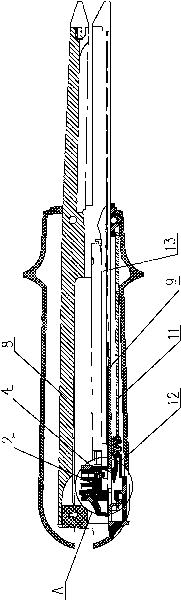
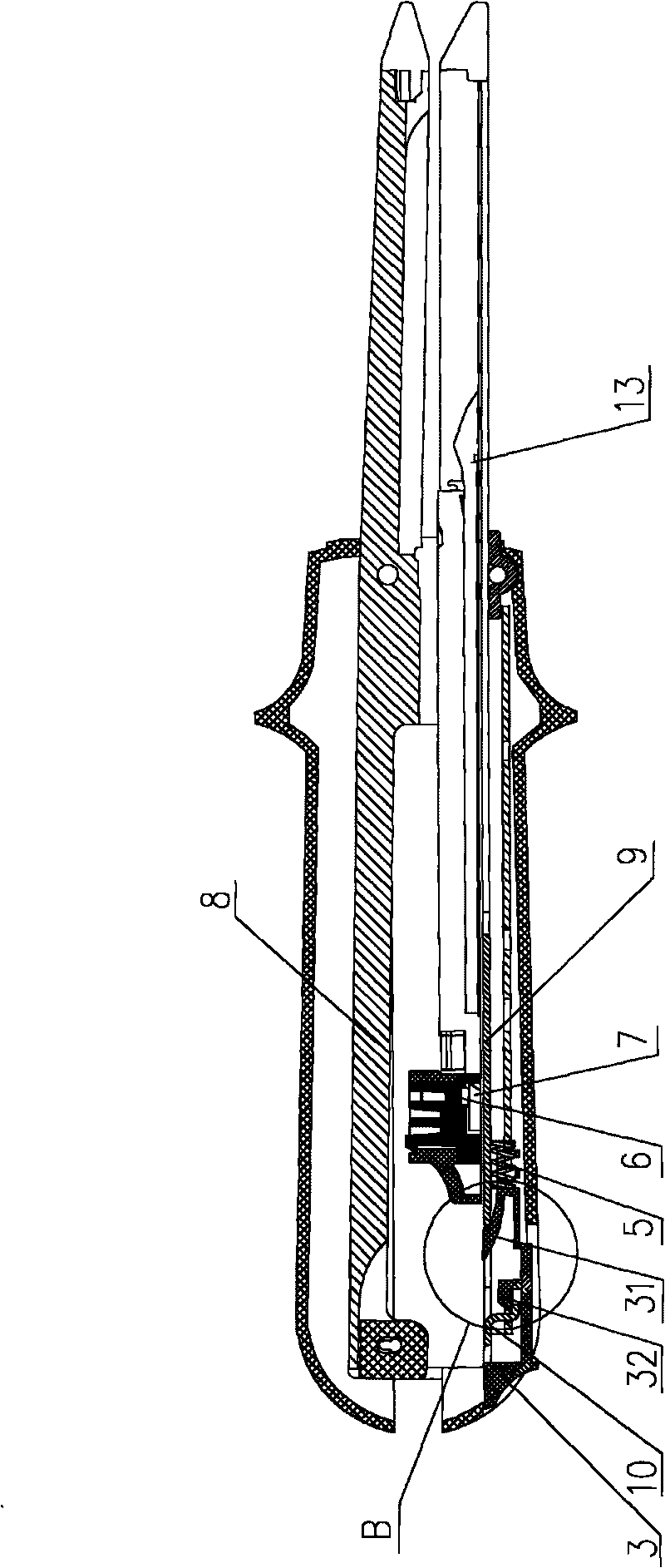
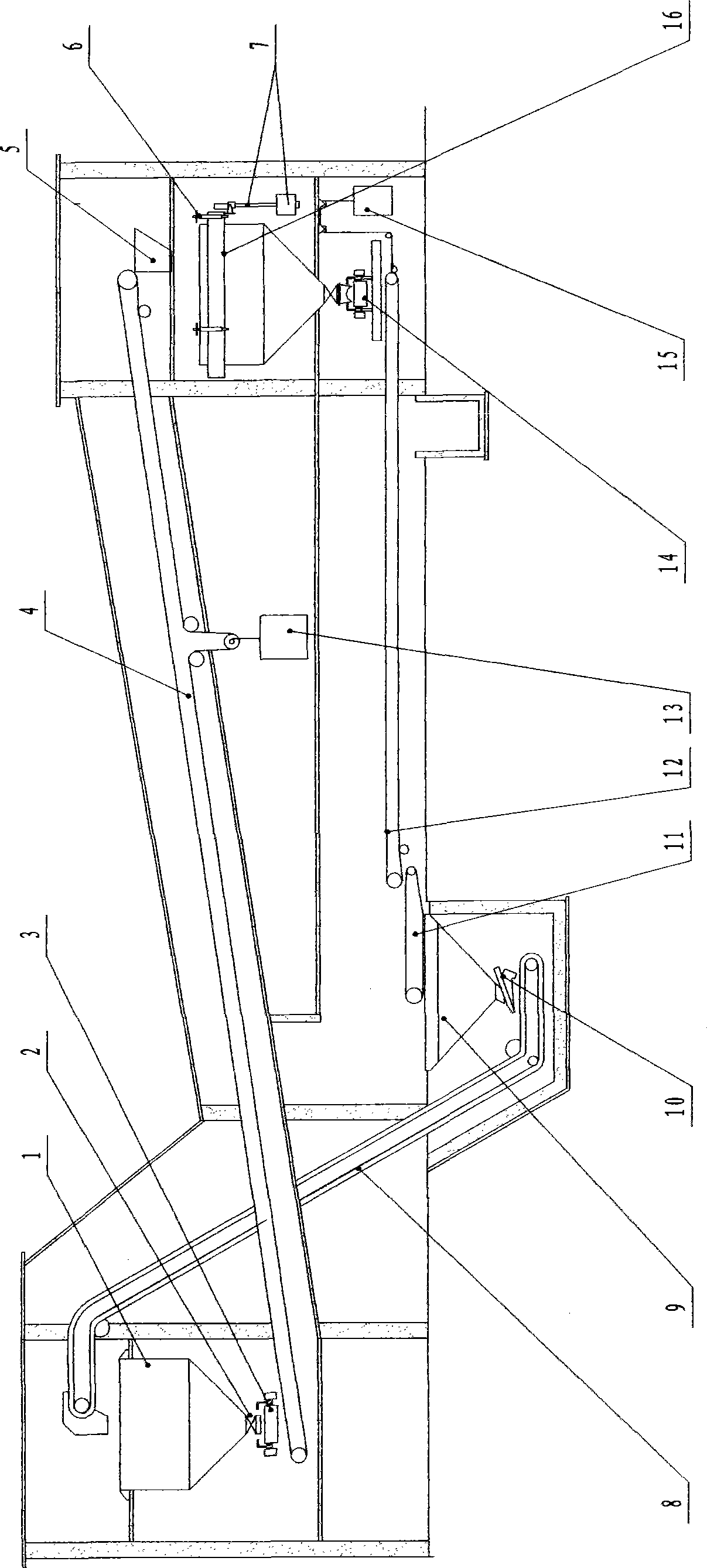
Surgical cutting and binding apparatus
The invention provides a surgical cutting and binding apparatus, comprising an upper closed forces clip, a lower closed forces clip, a closed handle, a pushing button and a releasing button. The upper and lower closed forces clips are matched and connected with a pin on one of the closed forces clips by a hook on the closed handle; the pushing button is arranged at the closer end of the apparatus and can slide relative to the closed forces clip so as to push a cutter and trigger matching pins; the releasing button is arranged at the closer end of the closed handle and opens the apparatus when being pressed; the binding apparatus comprises a locking mechanism, when the pushing button of the apparatus dose not return to the initial position, the locking mechanism enables the apparatus not to be opened. The structure of the invention can ensure that the apparatus cannot be opened accidently to cause serious results during the process of triggering, thereby further improving the safety of the apparatus.
Owner:TOUCHSTONE INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL SCIENCE CO LTD
Combustion Apparatus and Combustion Method
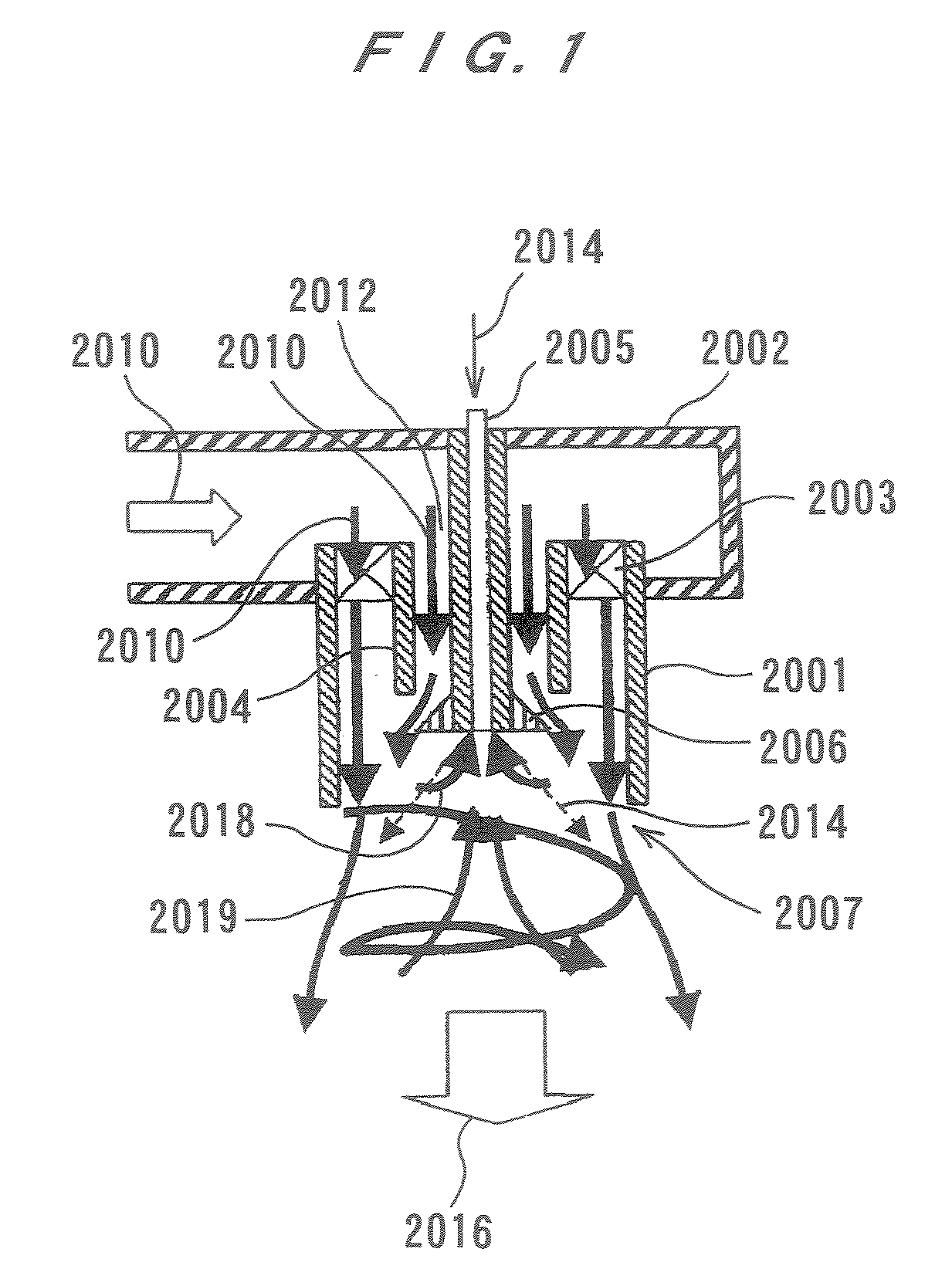
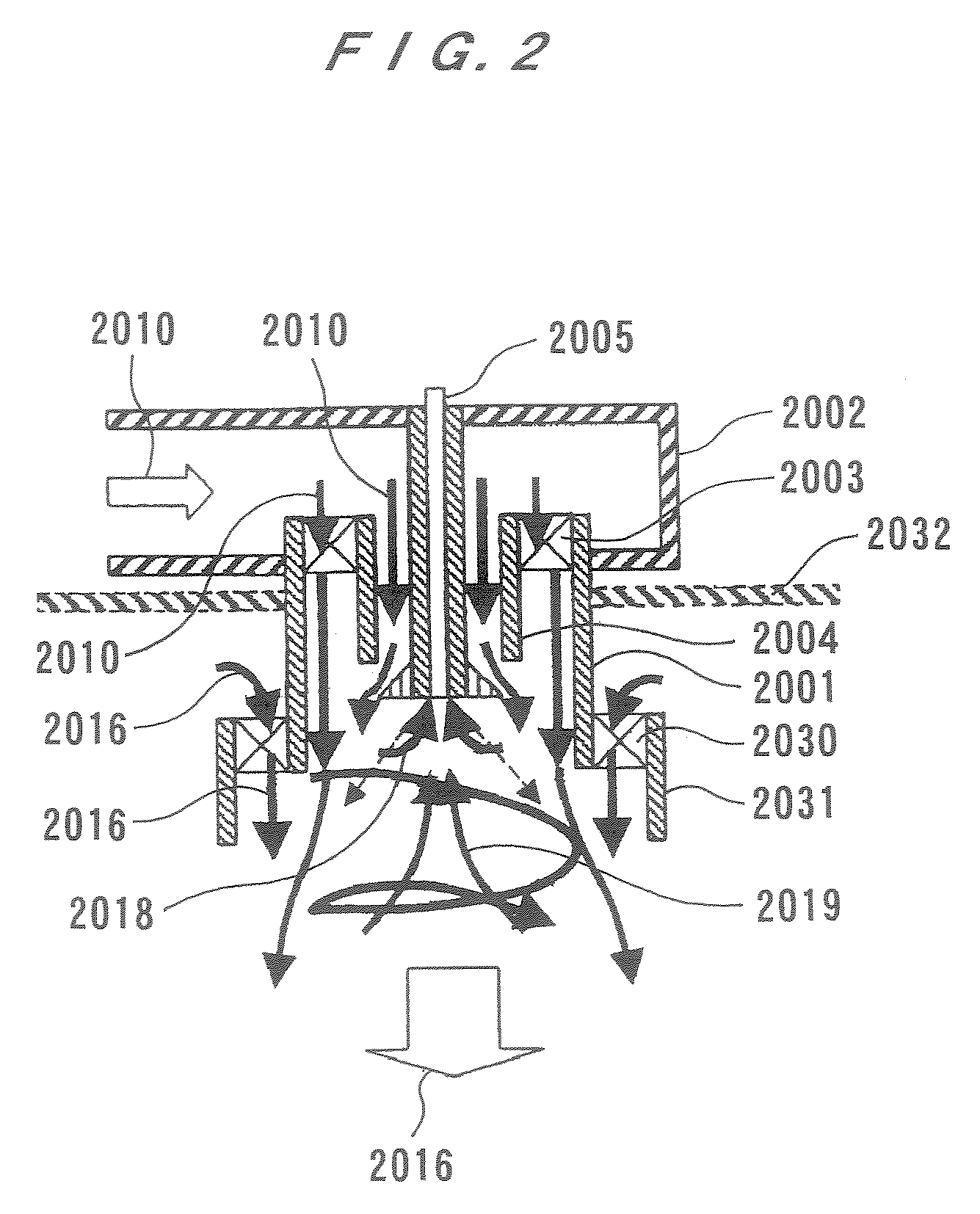
InactiveUS20070272201A1Improve stabilityMaximize the effectContinuous combustion chamberCombustion enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
A combustion apparatus according to the present invention can positively control and generate burnt gas recirculation with a simple structure. The combustion apparatus has a cylindrical container (12) having a combustion chamber, a close end (10), and an open end (26), an inflow passages (20) for supplying combustion air into the combustion chamber in the cylindrical container (12), and a fuel nozzle (18) for supplying fuel into the combustion chamber in the cylindrical container (12). A flow (28) of air is formed so as to have a velocity component in a direction of a central axis (J) from the open end (26) to the close end (10) and a velocity component to swirl in a circumferential direction of said annular container (12). Fuel is injected so as to have a velocity component in the direction of the central axis (J) from the close end (10) to the open end (26) and a velocity component directed radially outward.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Electrode assembly for nerve control
InactiveUS7844346B2Minimize cathode effectWeakening rangeSpinal electrodesEngineeringElectric current
Apparatus is provided for applying current to a nerve, including a housing, that is adapted to be placed in a vicinity of the nerve. At least one electrode is fixed to the housing such that the at least one electrode does not come in direct physical contact with the nerve, and such that the electrode surrounds greater than 180 degrees of a circumference of the nerve after the placement of the housing. Two end insulating elements are fixed to the housing. The at least one electrode is between the end insulating elements. A characteristic closest end insulating element distance to a surface of the nerve is less than 0.5 mm.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Electrode assembly for nerve control
InactiveUS20060195170A1Minimize depolarization portionAvoid adversely decreasing magnitudeSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesEngineeringElectrical current
Apparatus is provided for applying current to a nerve, including a housing, that is adapted to be placed in a vicinity of the nerve. At least one electrode is fixed to the housing such that the at least one electrode does not come in direct physical contact with the nerve, and such that the electrode surrounds greater than 180 degrees of a circumference of the nerve after the placement of the housing. Two end insulating elements are fixed to the housing. The at least one electrode is between the end insulating elements. A characteristic closest end insulating element distance to a surface of the nerve is less than 0.5 mm.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Graphite powder suitable for negative electrode material of lithium ion secondary batteries
InactiveUS6576369B1Improve discharge capacityImprove Coulombic efficiencyNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsGraphiteLithiumMicrometer
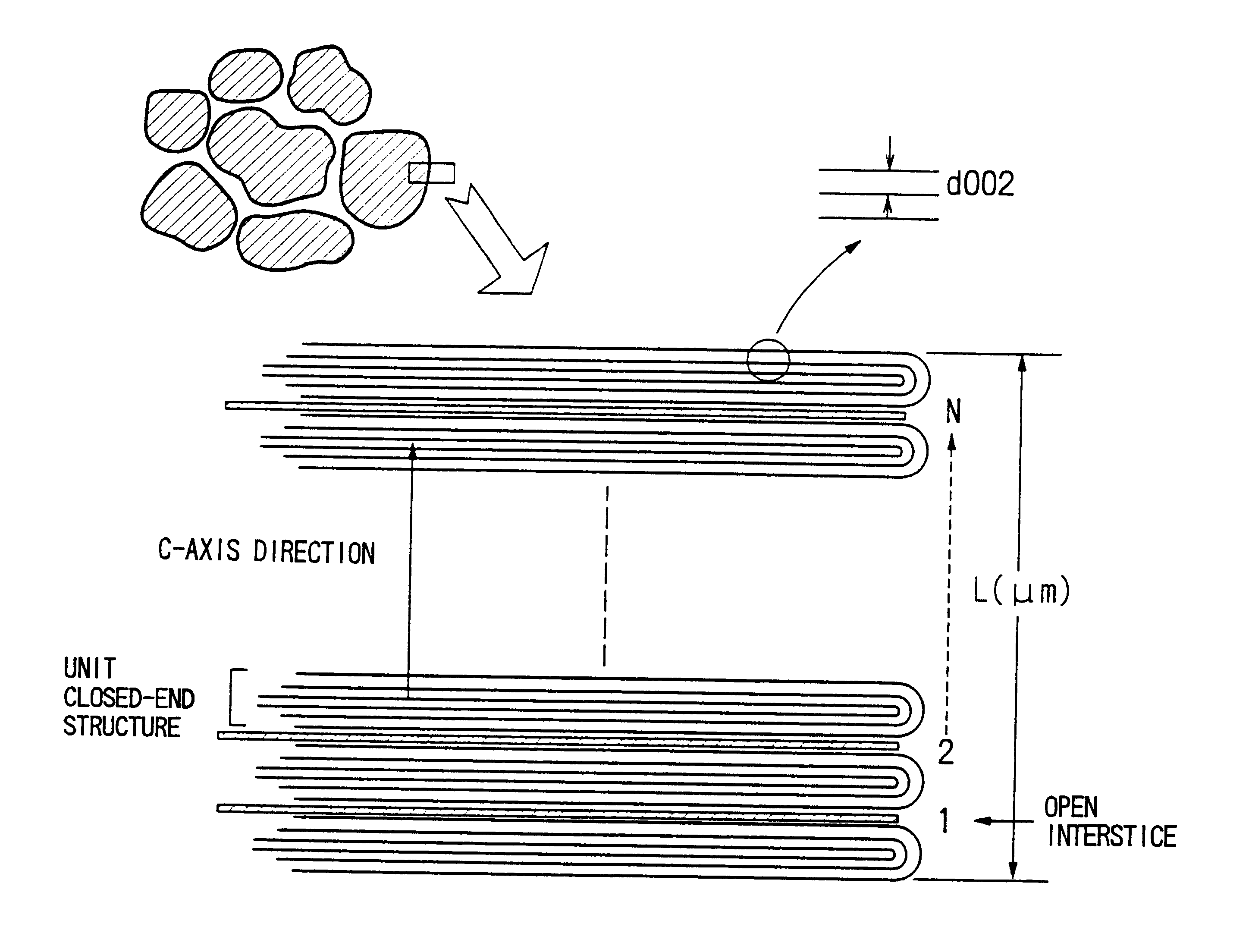
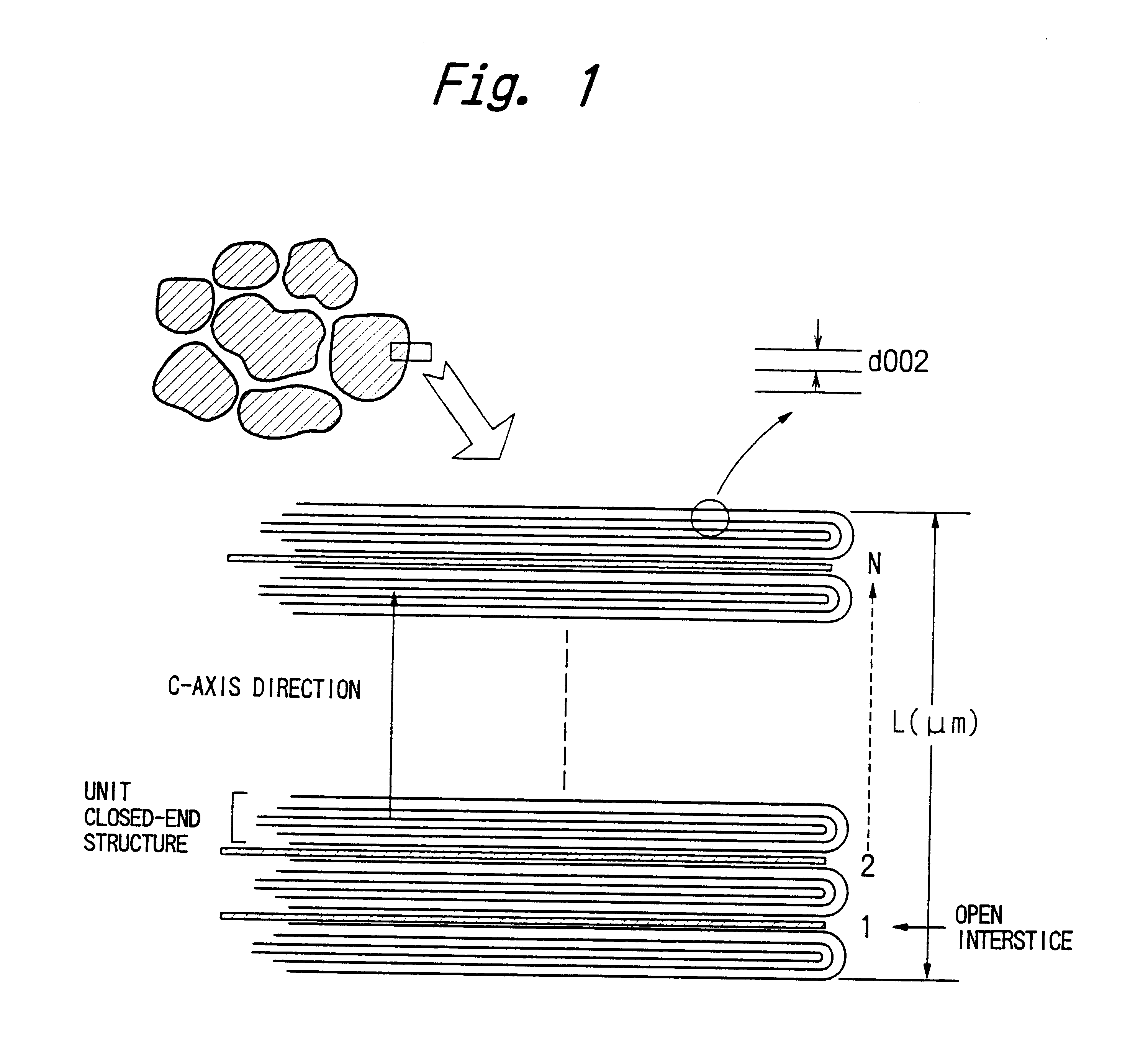
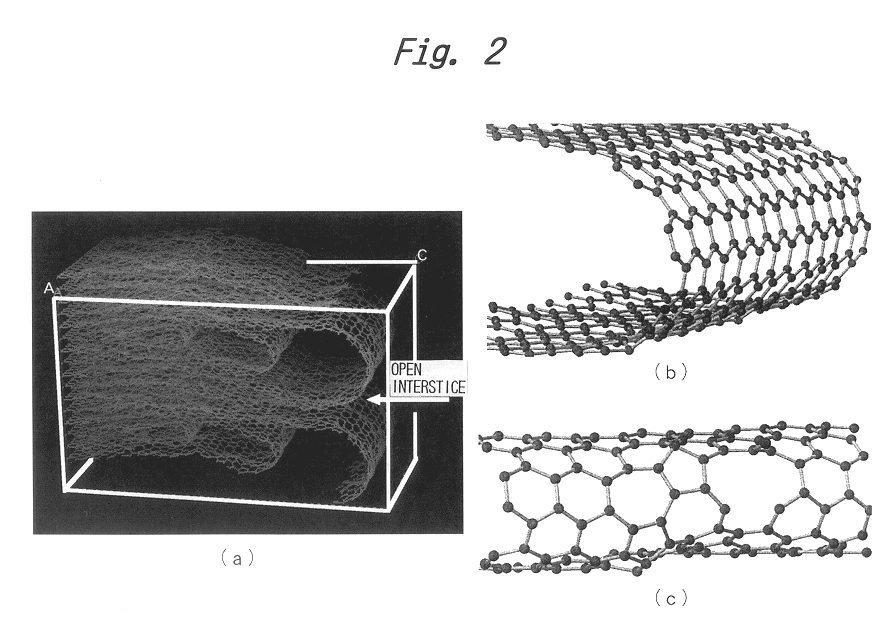
A graphite powder has surface closed-end structures in which the graphite c-plane layers of the graphite layer crystal lattices have closed-ends on the surface of the graphite powder by linking the ends of one or more pairs of the c-plane layers, leaving interstices which are open on the surface of the graphite. The number of open interstices is at least 100 and at most 1500 per micrometer in a c-axis direction of the graphite. Preferably, the graphite powder has a specific surface area of 1.0 m2 / g or less. Such a graphite powder can be prepared either by graphitizing a carbon material, which has been pulverized at a high speed under well-controlled conditions before and / or after the carbonization, or by subjecting a carbon material, which has been pulverized under well-controlled conditions before and / or after the carbonization, to graphitization and then to oxidative heat treatment at a temperature of 600-800° C. and finally to heat treatment at a temperature of 800° C. or higher in an inert gas. The graphite powder can be used to produce negative electrodes of lithium ion secondary batteries having a high discharge capacity of at least 320 mAh / g and a high charge / discharge coulombic efficiency of at least 90%.
Owner:NIPPON DENKO CO LTD +1
Foam port device having closed-end lumens
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
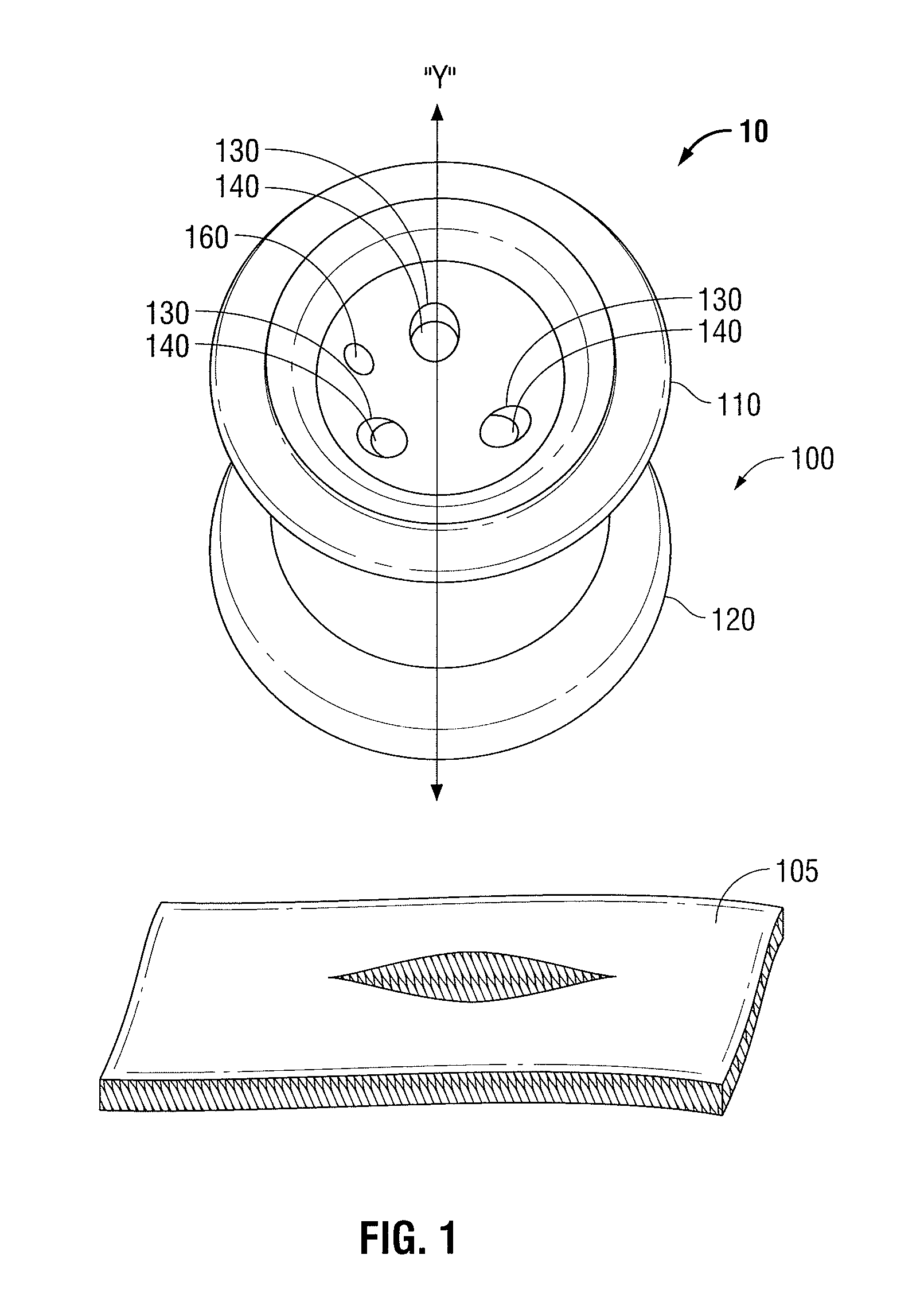
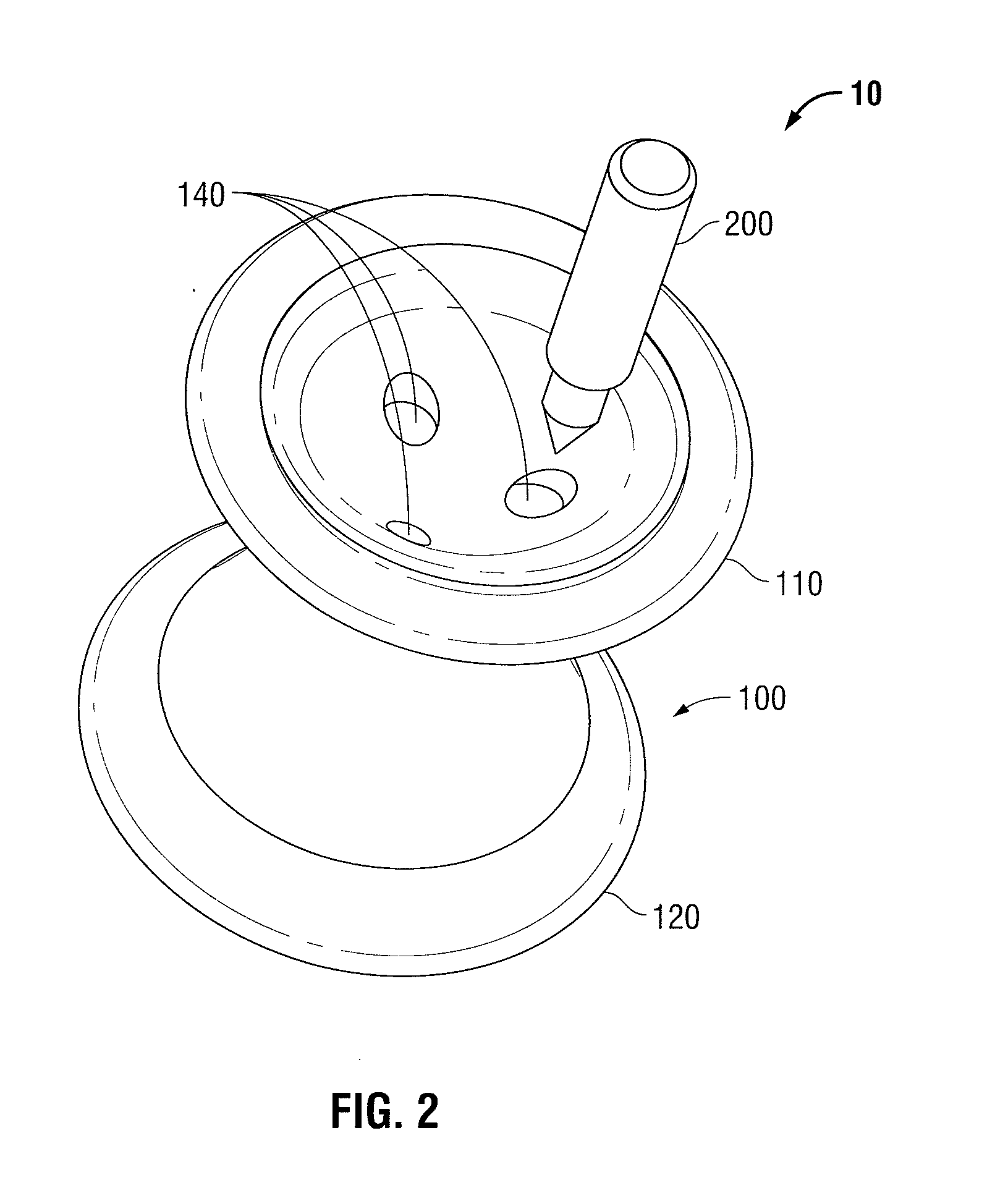
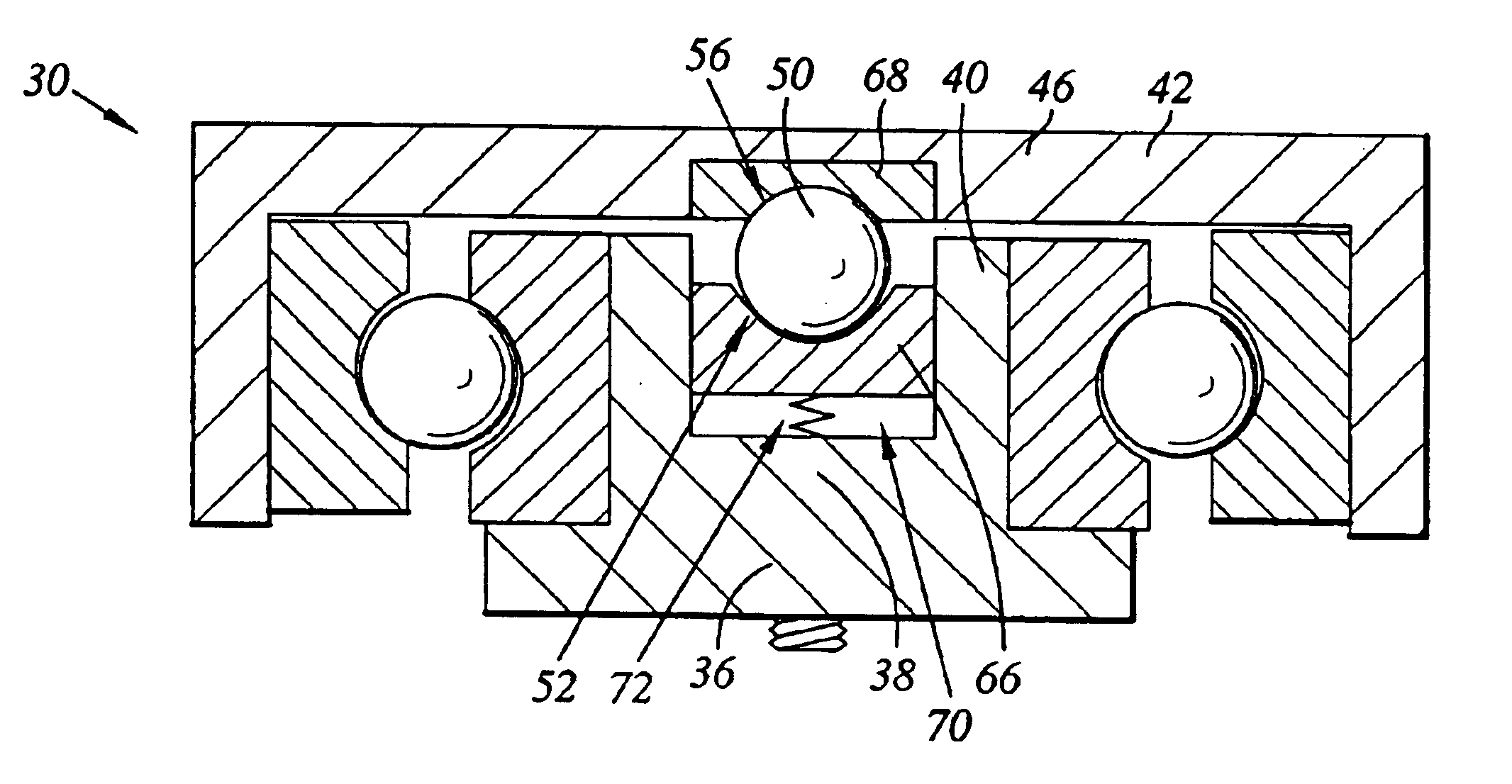
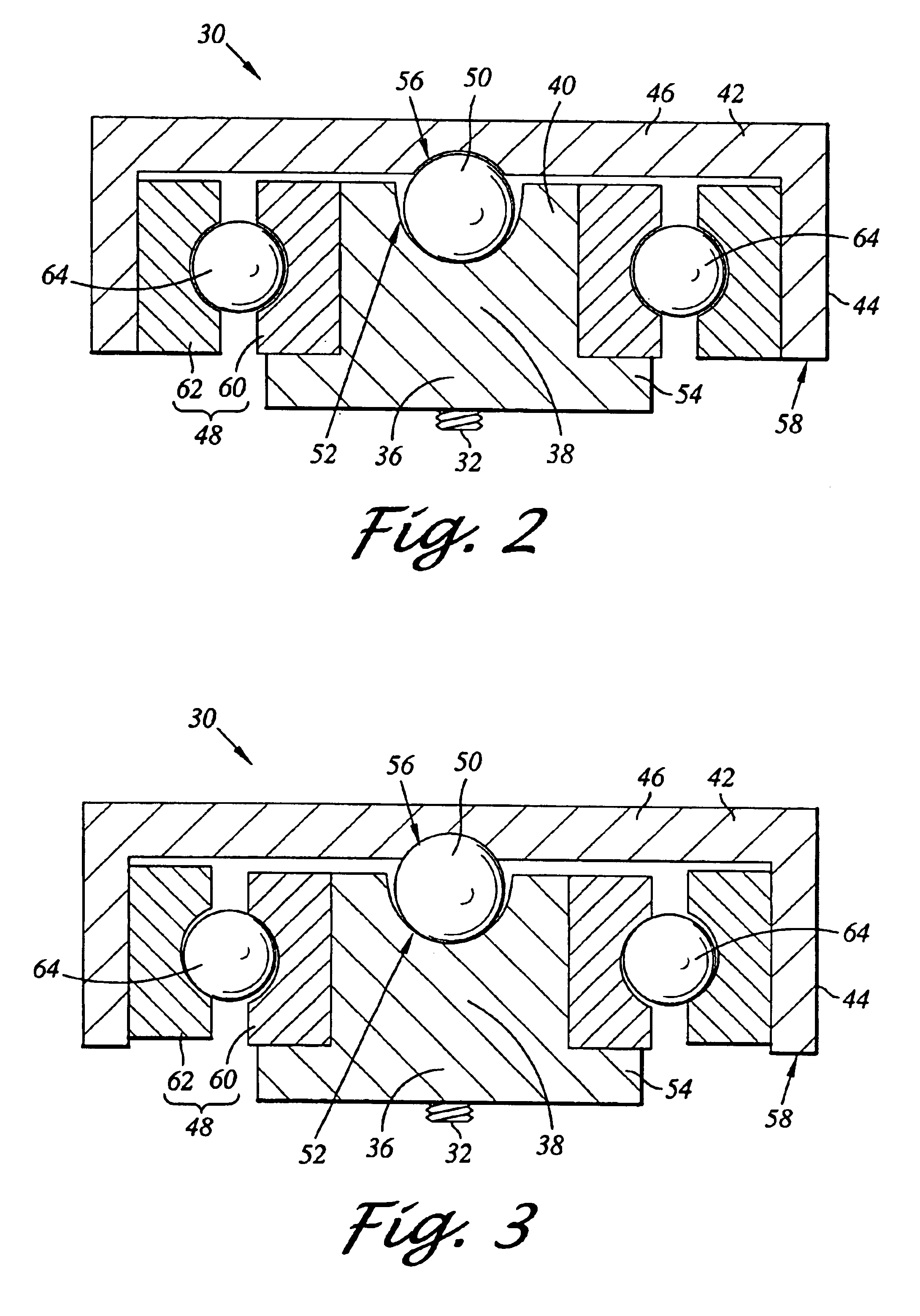
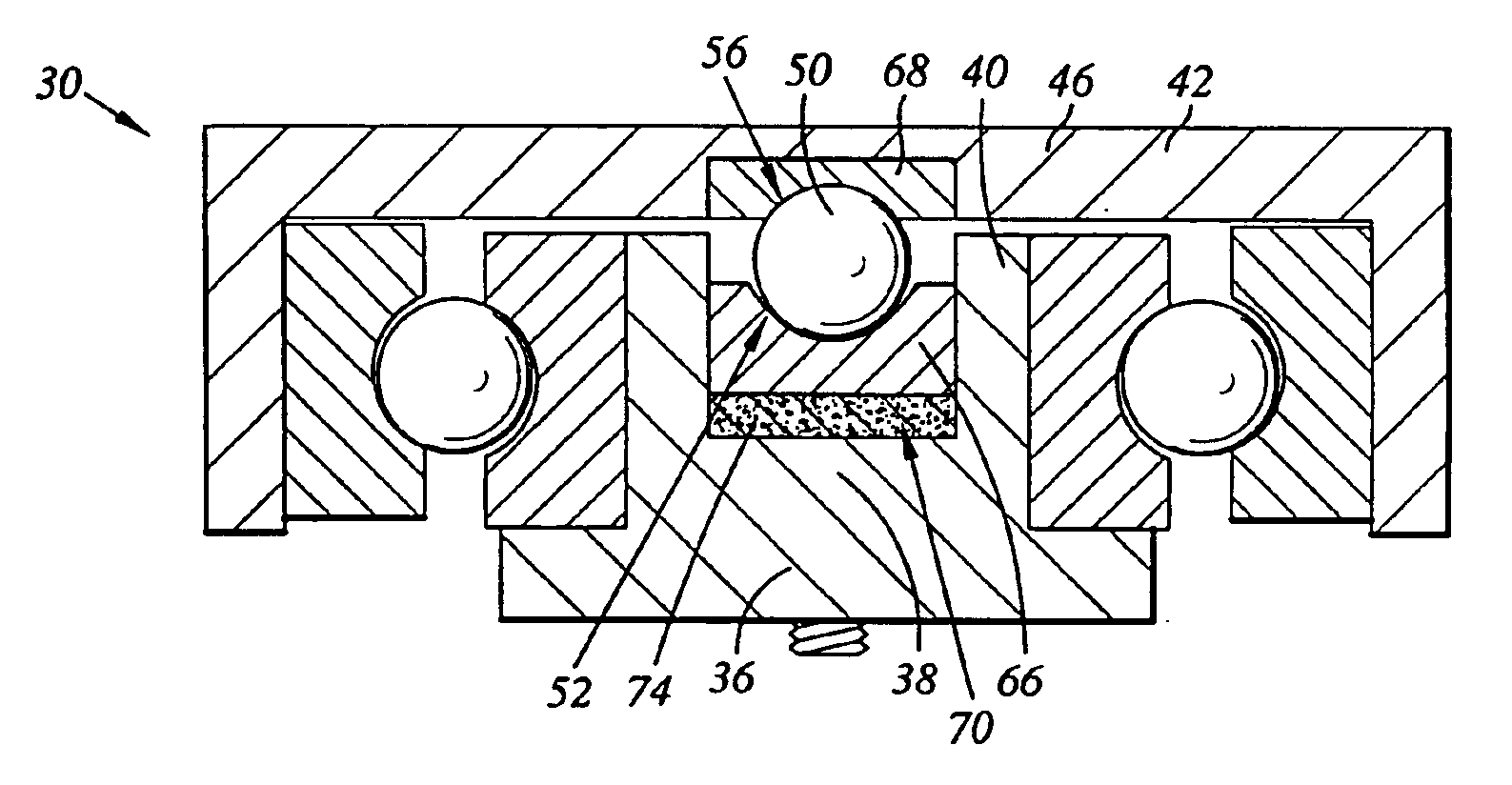
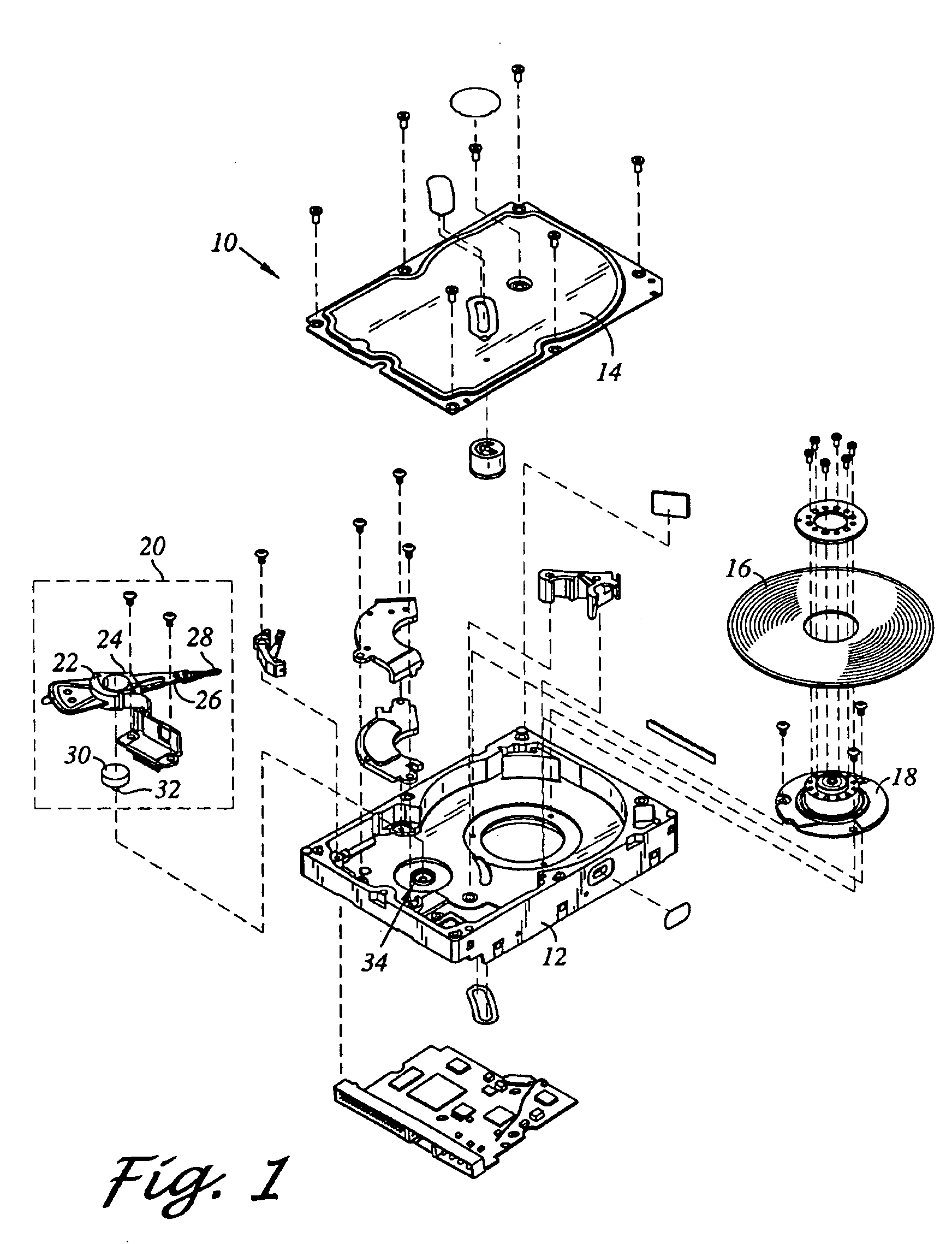
Pivot bearing cartridge including central pivot element and ball bearing set
A pivot bearing cartridge for use in a head stack assembly. The pivot bearing cartridge includes a pivot shaft including a shaft body and a shaft distal end. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a cap disposed about the pivot shaft. The cap includes a cap annular body and a cap closed end. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a ball bearing set in mechanical communication with the pivot shaft and the cap annular body. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a central pivot element disposed between and in mechanical communication with the shaft distal end and the cap closed end for facilitating rotation of the cap relative to the pivot shaft.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Pivot bearing cartridge including central pivot element and ball bearing set
A pivot bearing cartridge for use in a head stack assembly. The pivot bearing cartridge includes a pivot shaft including a shaft body and a shaft distal end. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a cap disposed about the pivot shaft. The cap includes a cap annular body and a cap closed end. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a ball bearing set in mechanical communication with the pivot shaft and the cap annular body. The pivot bearing cartridge further includes a central pivot element disposed between and in mechanical communication with the shaft distal end and the cap closed end for facilitating rotation of the cap relative to the pivot shaft.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
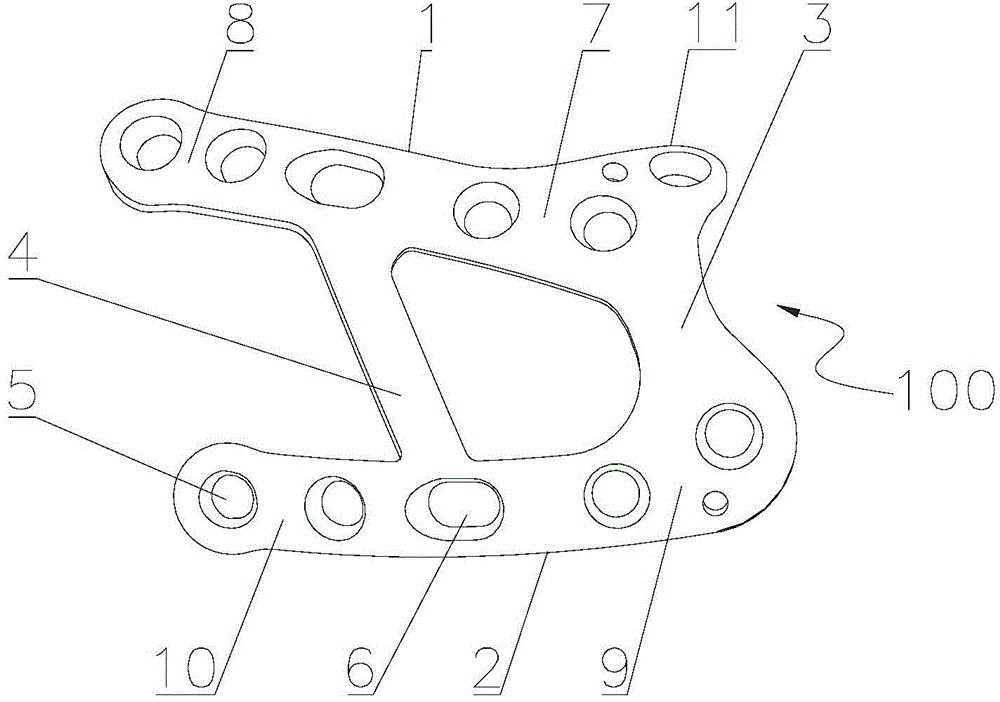
Lisfrance joint injury fusion plate
The invention relates to the field of medical devices, in particular a Lisfrance joint injury fusion plate. The fusion plate comprises a first tarsometatarsal joint plate, a second tarsometatarsal joint plate and a first transition plate for connecting the first tarsometatarsal joint plate and second tarsometatarsal joint plate; and the fusion plate provided with a plurality of fixing holes for fixing the fusion plate on a first metatarsal bone, an inner cuneiform bone, a second metatarsal bone and an intermediate cuneiform bone. The Lisfrance joint injury fusion plate has dissection-type design; in an operation, the fusion plate is not required to be pre-bent, the operation time is saved, and the bending influence on the plate strength; the close-end fixing holes of the first tarsometatarsal joint plate and the second tarsometatarsal joint plate have strong holding force for the inner cuneiform bone and the intermediate cuneiform bone; the curvature of human anatomy of Asian people is fully taken in to consideration of the design of the plates and bolts; and the fusion of multiple joint surfaces is conductive to arch anatomy reconstruction, excellent stability for joint fusion is provided, and the fixing effect of the fusion plate is further improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU WASTON MEDICAL APPLIANCE CO LTD
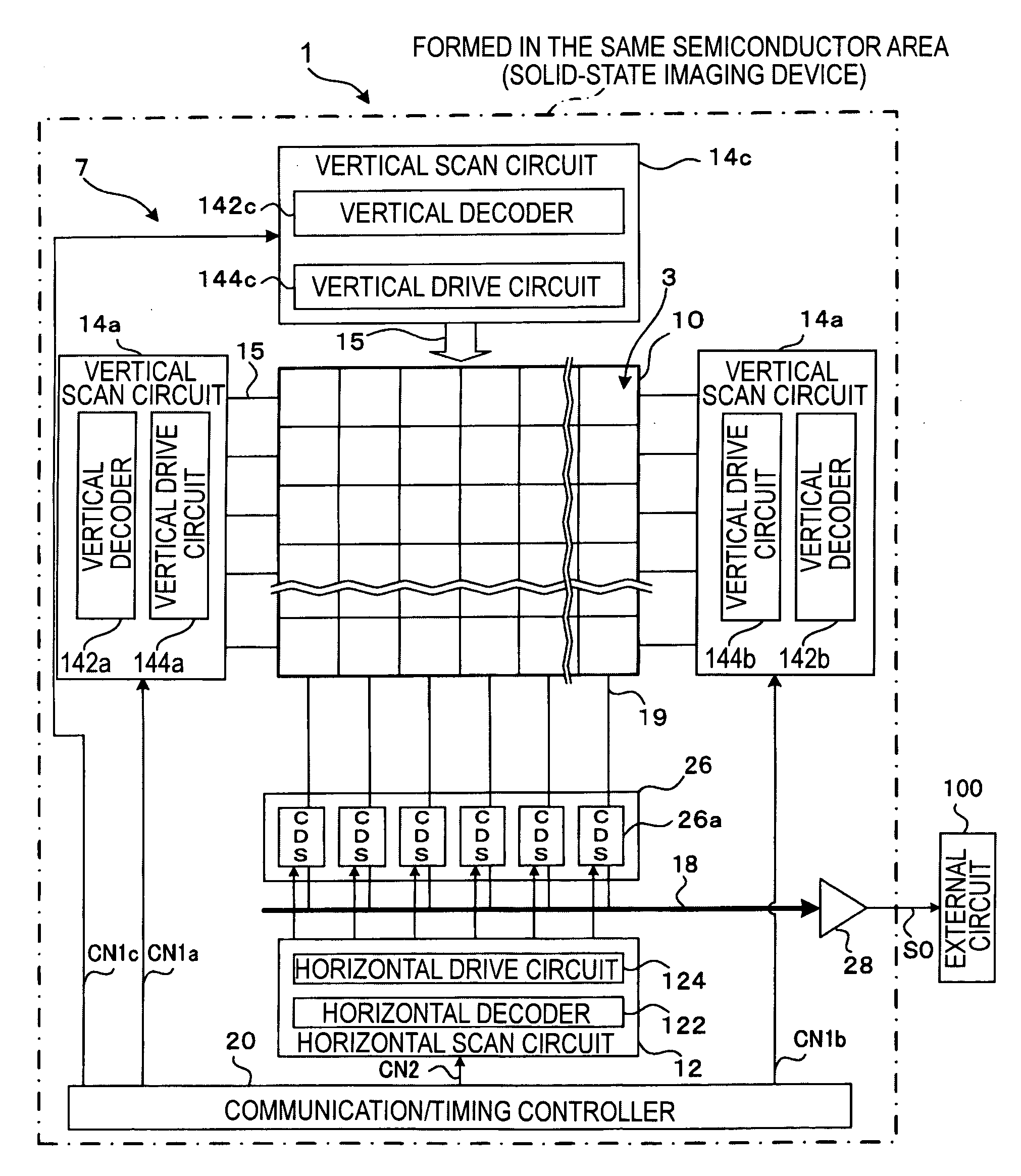
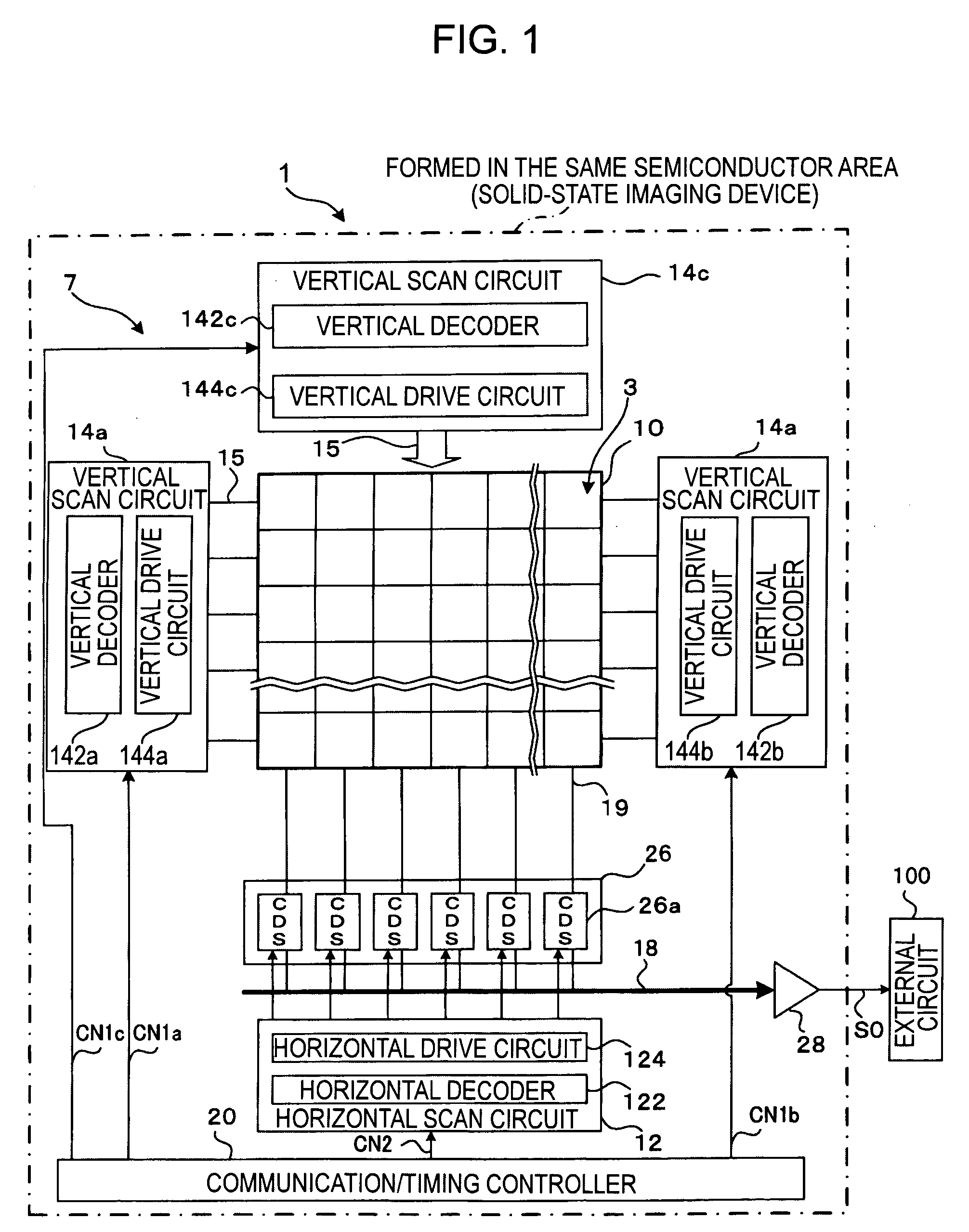
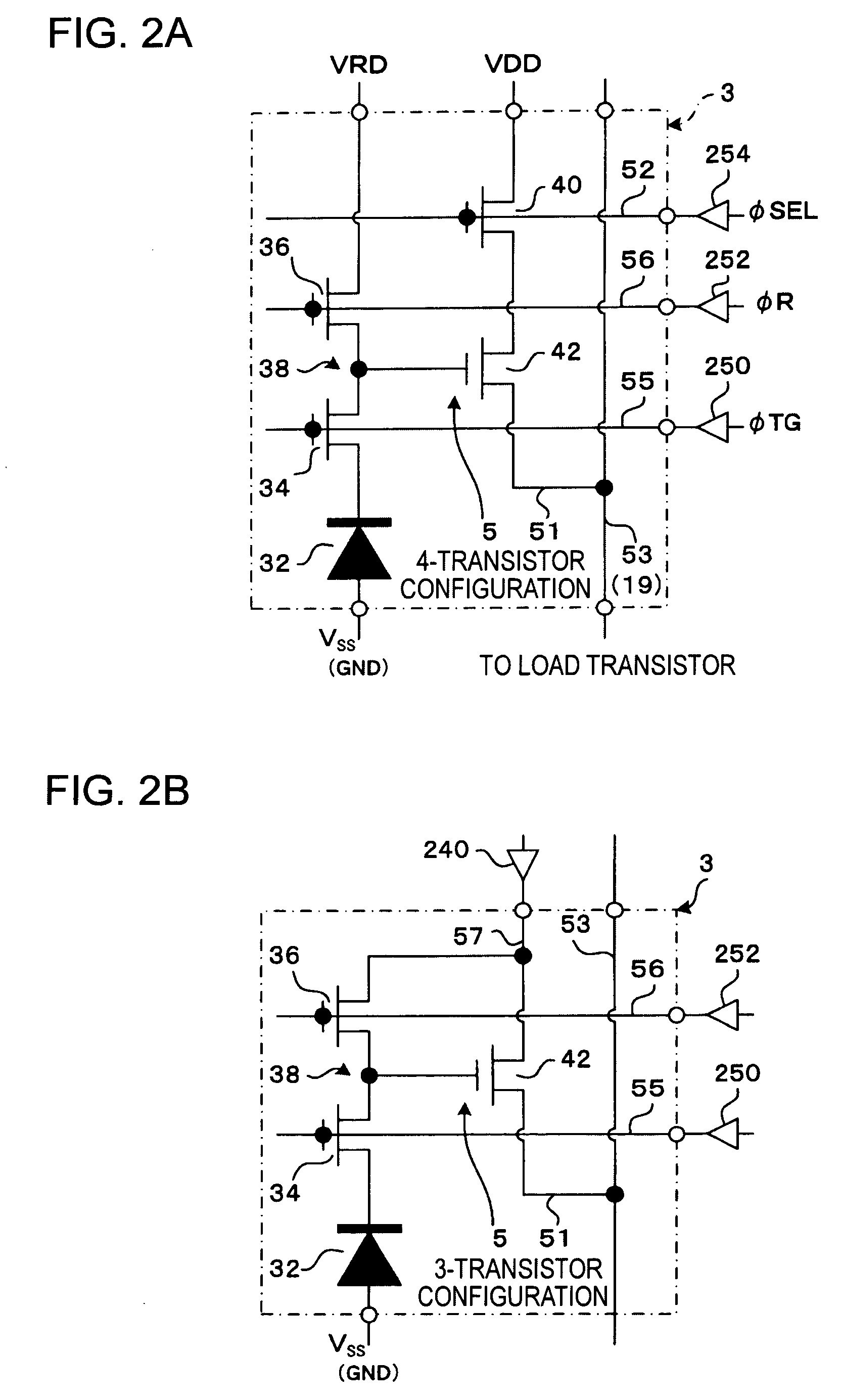
Physical information acquisition method, a physical information acquisition apparatus, and a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060001918A1Significant valueTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAcquisition apparatusDevice material
In particular for a solid-state image sensor with high resolution, a control line is not driven at any of two end points of the control line, but the control line is driven at two arbitrary dividing points on the control line. Preferably, two points on control line whose distance from a closer end of a range in which skew is to be suppressed is equal to ¼ of the total length of the range may be selected as the dividing points at which the control line is driven. In this case, the time constant at points farthest from the driving points becomes ¼ of that which occurs when the control line is driven at both end points thereof and 1 / 16 of that which occurs when the control line is driven at one end point thereof, and thus, theoretically, the skew can be reduced to ¼ or 1 / 16 of that which occurs when the control line is driven at both end points or only one end point.
Owner:SONY CORP
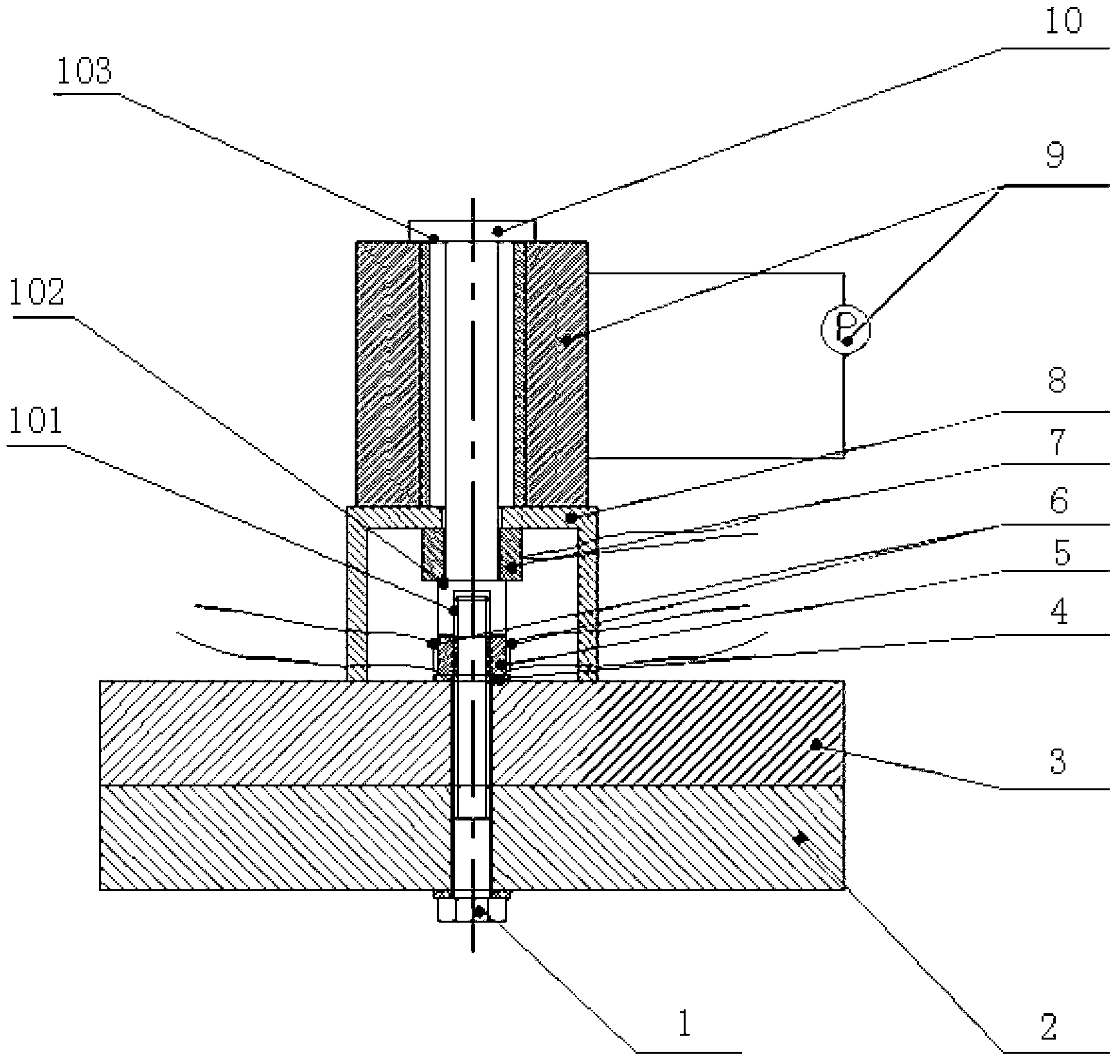
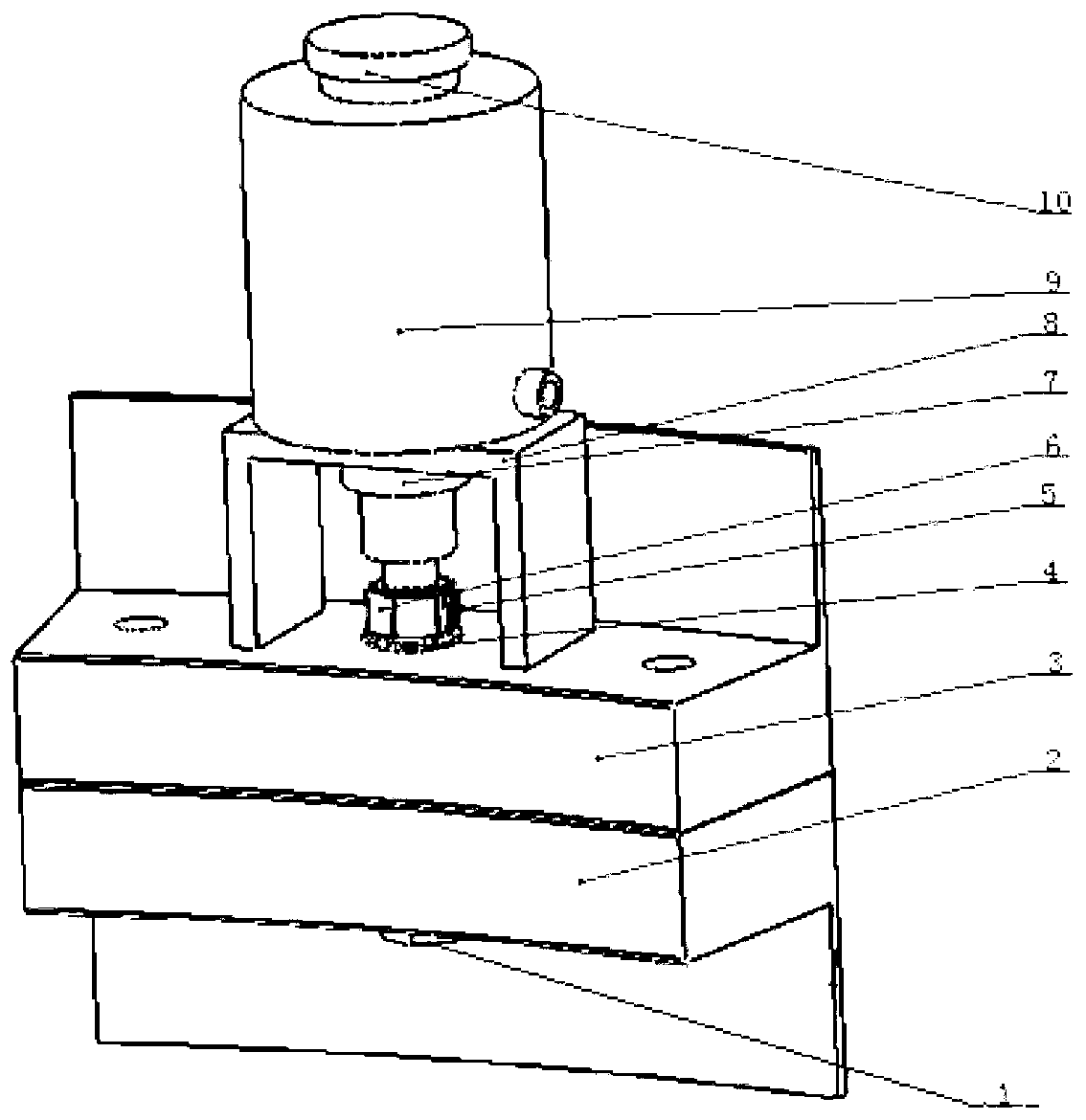
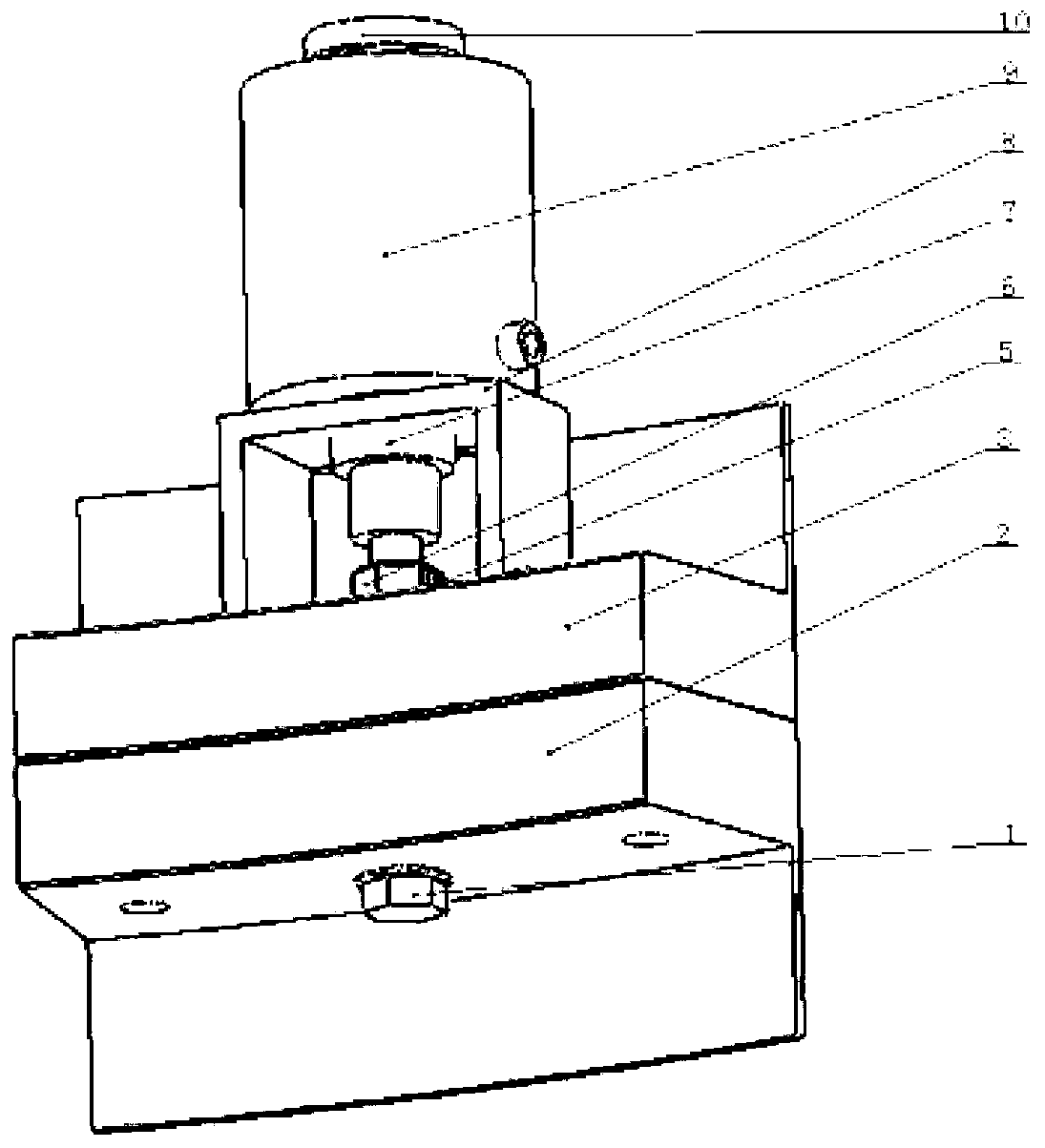
High-strength bolt axial force measuring device and measuring method
InactiveCN103245452AHigh measurement accuracyReduce adverse effectsMeasurement of torque/twisting force while tighteningMeasurement deviceProper time
The invention discloses a high-strength bolt axial force measuring device and measuring method. The measuring device comprises a pull rod, an axial force sensor, a force providing part and a support; the close end of the pull rod is provided with a connecting part for being connected with a high-strength bolt thread end, and the close and far ends of the pull rod are provided with a first match part and a second match part respectively; the first match part is in match contact with the close end face of the axial force sensor, the second match part and the far end of the force providing part act in a match mode, the far end of the support is mounted between the force providing part and the axial force sensor, and the close end of the support is used for being supported on a part connected with a high-strength bolt; and the high-strength bolt axial force measuring device also comprises a strain measuring part arranged on a nut. The measuring method comprises the steps of (1) mounting the strain measuring part on the axial outer face of the nut; 2, connecting the pull rod with the thread end of the high-strength bolt in the match mode; and 3 starting the force providing part to read the value of the axial force sensor at proper time according to the changing condition of the stain measuring part. The high-strength bolt axial force measuring device and method are accurate in measuring by directly measuring the axial force of the high-strength bolt.
Owner:LONGYUAN BEIJING WIND POWER ENG TECH
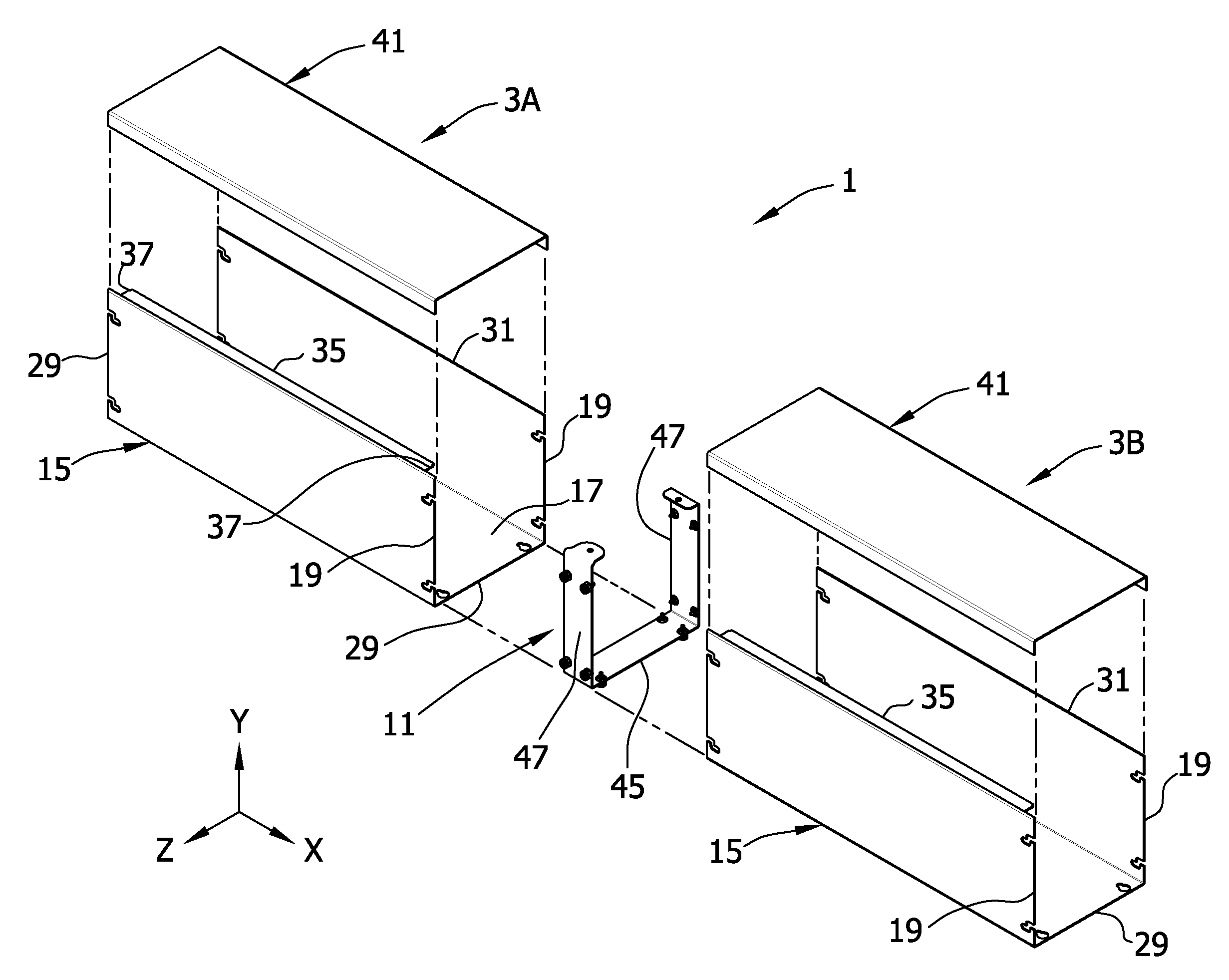
Wireway quick-connect system
A quick-connect system for connecting two or more sections of wireway in generally longitudinal alignment along an X-axis. The system involves the a series of screws in the bottom and side walls of a generally U-shaped connector receivable in corresponding slots in the bottom and side walls of the two wireway sections. In one embodiment, the bottom wall slots are closed-ended slots and the side wall slots are open-end slots extending in from respective end edges of the wireway sections. The side walls slots are configured such that they have longitudinal centerlines having X-axis and Y-axis components.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
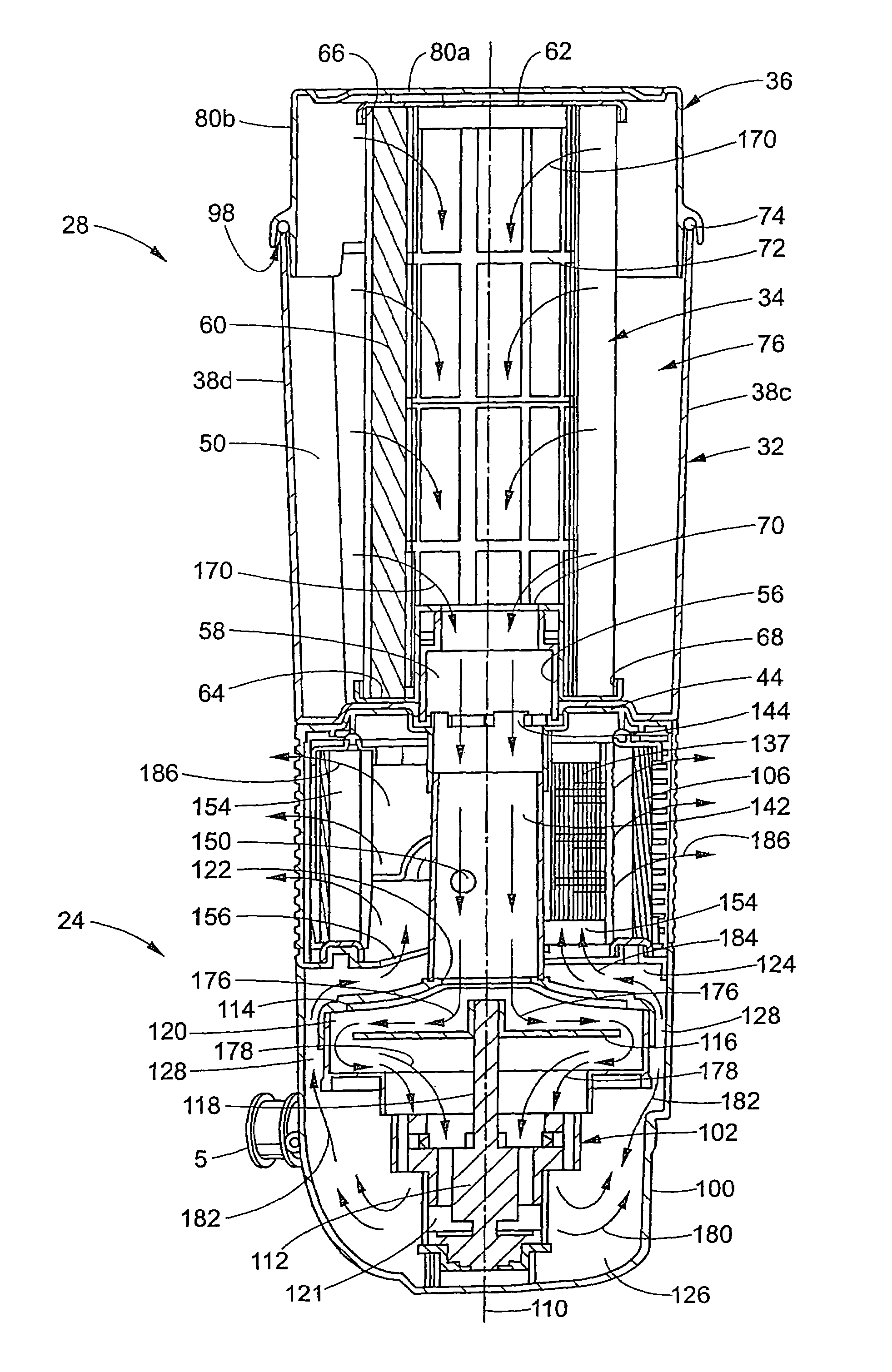
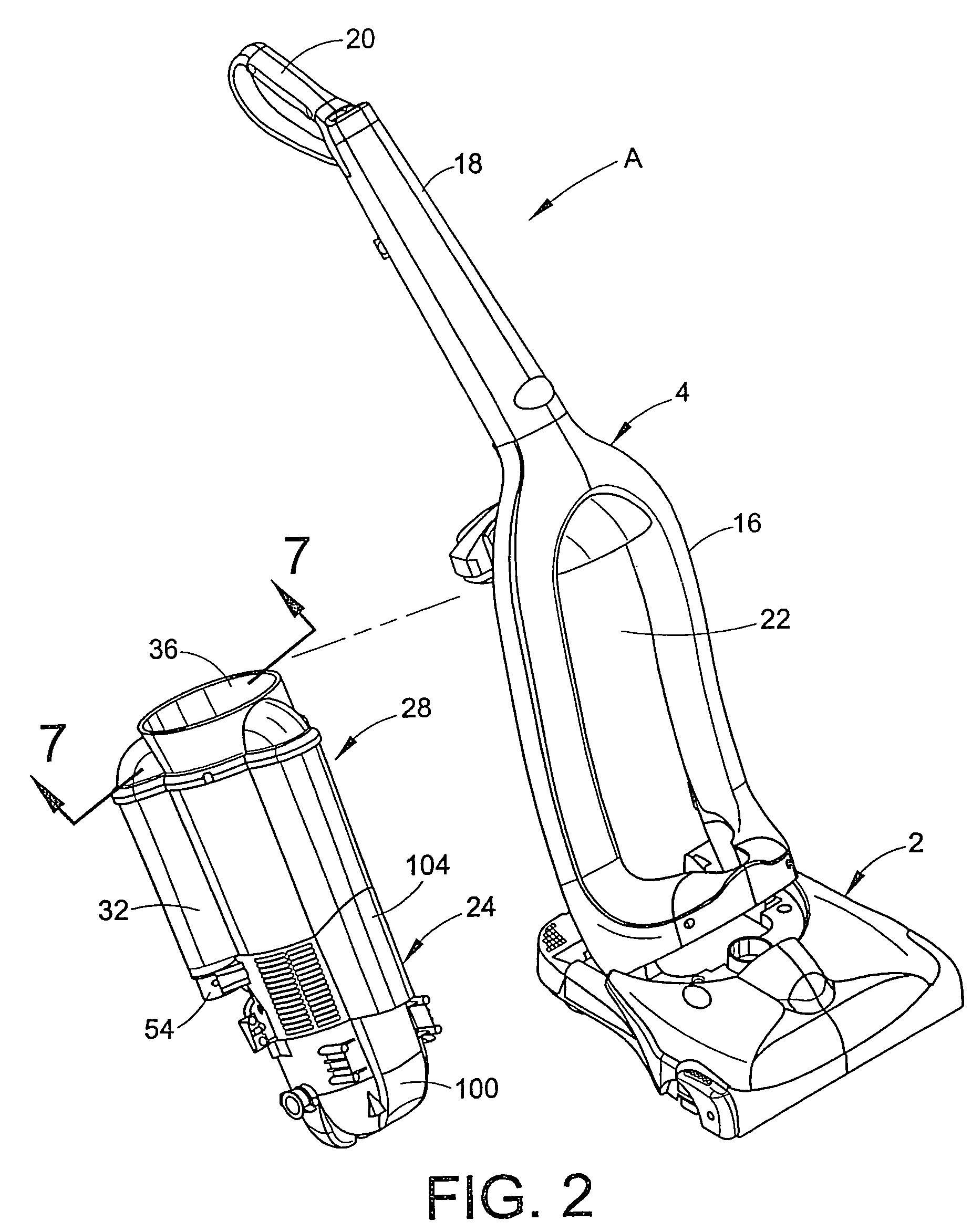
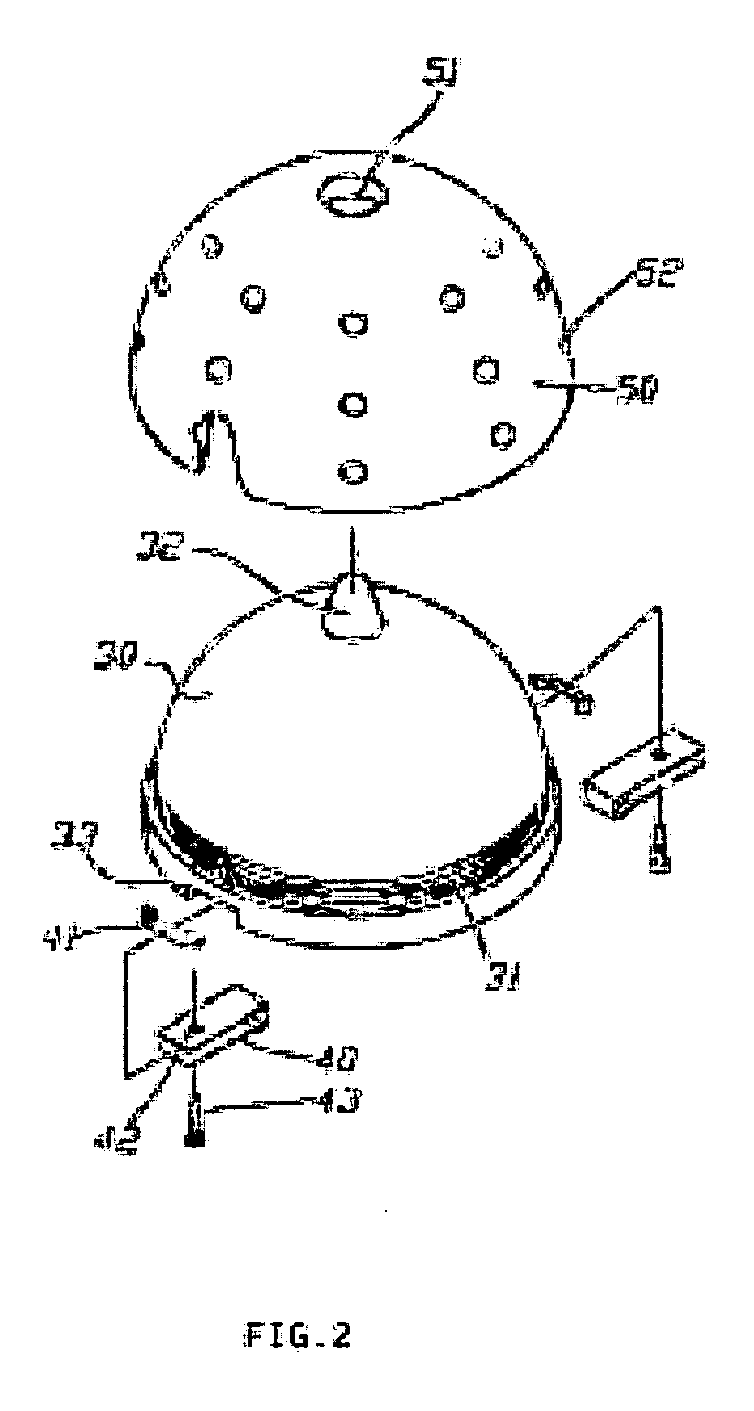
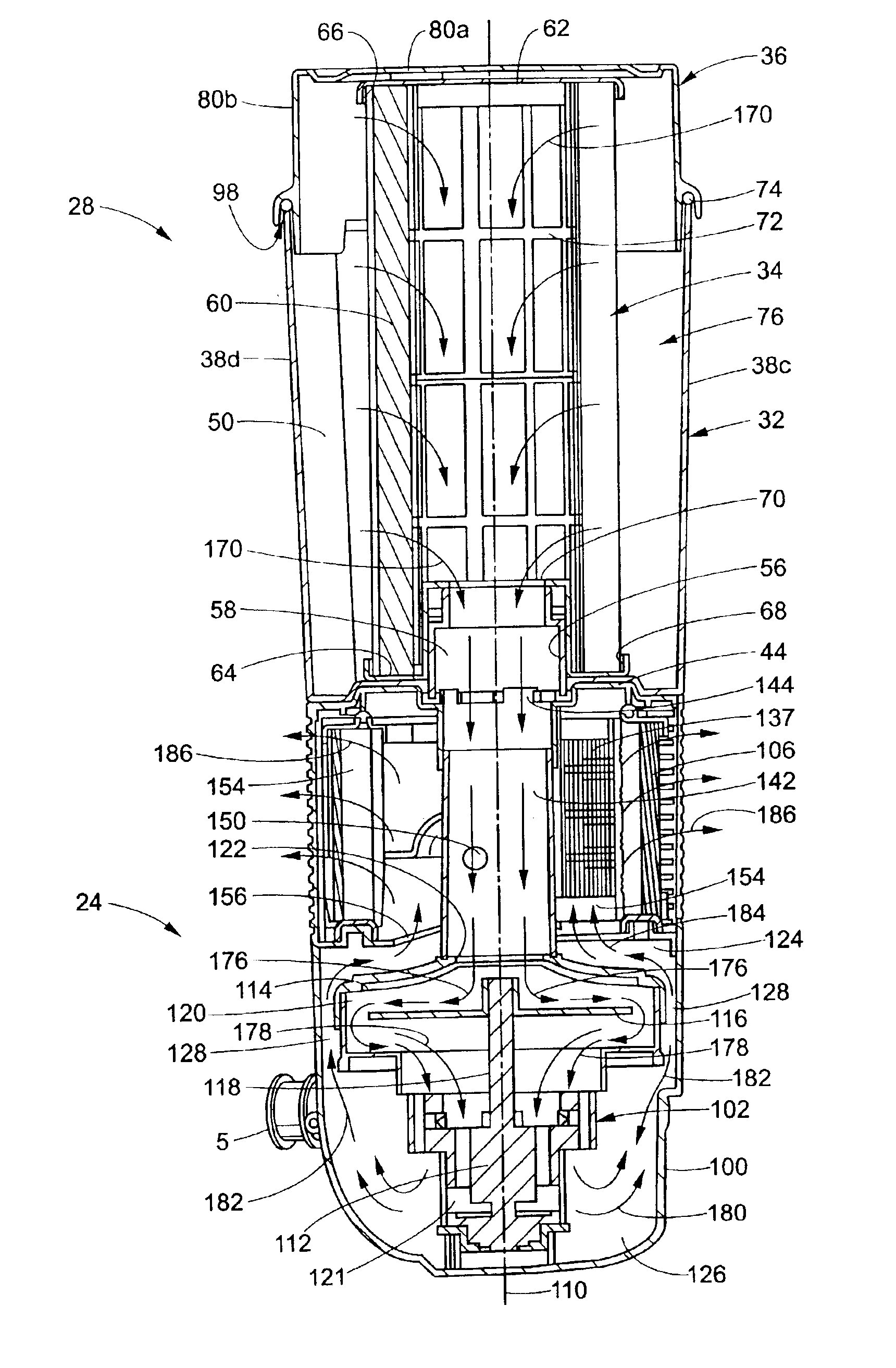
Vacuum cleaner with noise suppression features
A vacuum cleaner includes a cyclonic airflow chamber that facilitates the separation of contaminants from a suction airstream. The airflow chamber includes a chamber inlet and a chamber outlet, with the chamber inlet being fluidically connected with at least one of a suction nozzle and an above-the-floor cleaning tool. An exhaust filter housing includes a suction duct and an exhaust plenum, with the suction duct communicating with the chamber outlet. A suction source housing includes an open end communicating with the exhaust plenum and a closed end. A suction source is positioned within the suction source housing to define an annular exhaust flow passageway surrounding the suction source from the housing closed end to the housing open end. The suction source includes a suction inlet communicating with the suction duct and an exhaust outlet communicating with the housing closed end.
Owner:ROYAL APPLIANCE MFG
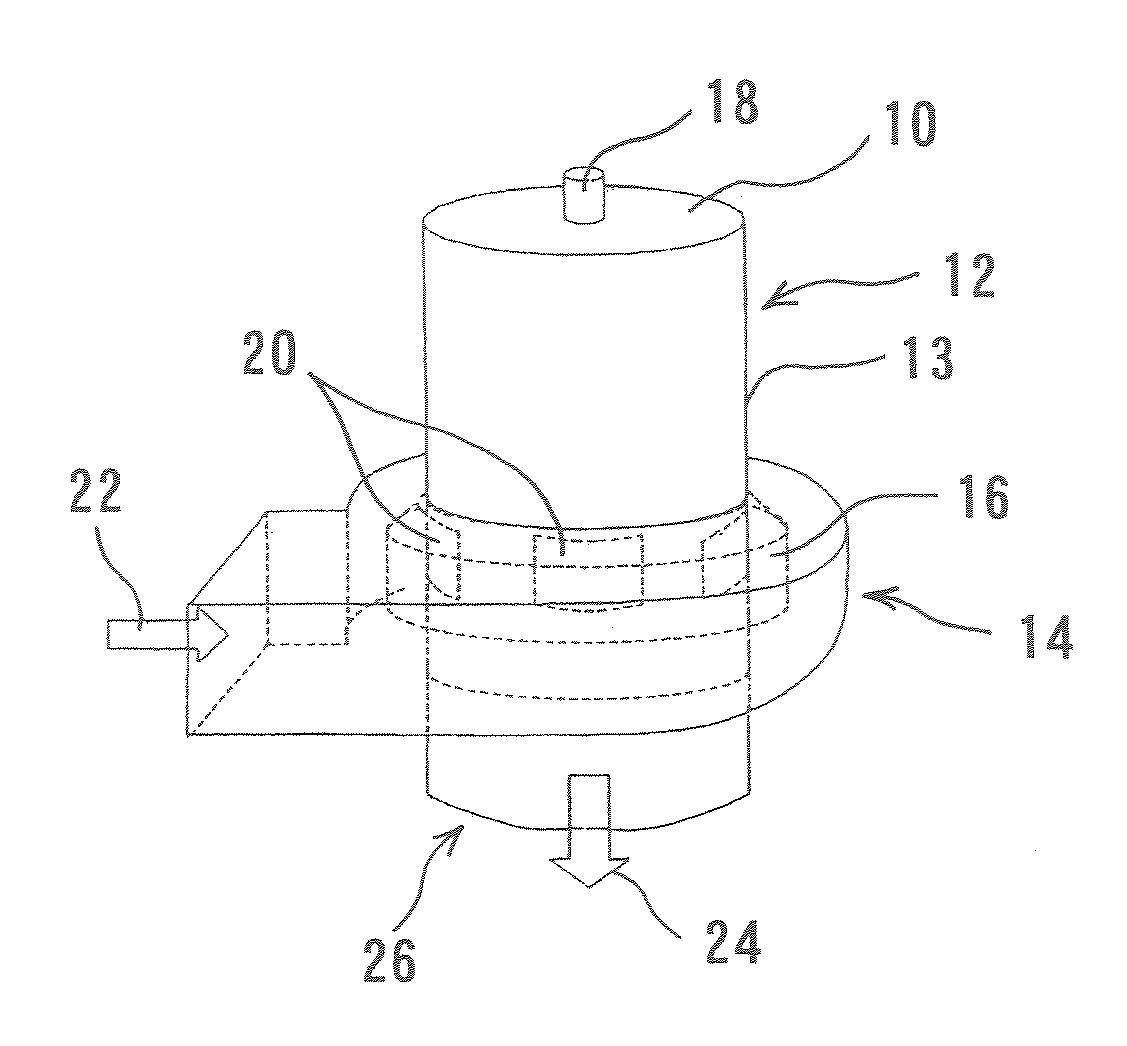
Magnifying Observation Apparatus
InactiveUS20120001069A1Increase freedomSmooth rotationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesOptical axisElectron microscope
Observation fields of an electron microscope image and an optical magnifying observation image are smoothly switched. A magnifying observation apparatus includes: a pair of end-face plates closes end faces of a body portion; an electron beam imaging device mounted on a first position of a cylindrical shaped outer surface of the body portion; an optical imaging device mounted on a second position being different from the first position in the outer surface; a rotating device that rotates the both imaging devices along the outer surface such that a distance from each of the both imaging devices to a common rotation axis of the both imaging devices is kept constant and optical axes of the both imaging devices are oriented toward the rotation axis; a specimen stage that is disposed in the chamber, and arranged to a position that is substantially the same to a height of the rotation axis.
Owner:KEYENCE
Barometric pressure microwave plasma generation device
InactiveCN101346032AReduce reflection lossPrevent leakageElectric discharge tubesPlasma techniqueEnergy couplingWaveguide
The invention relates to a normal pressure microwave plasma generating apparatus, which consists of a rectangular waveguide, a wave-transparent gas seal membrane, a waveguide changeover mechanism, a microwave resonant cavity, a closure end adjustable phase matching unit, a reactor, a flame lighter, an outer layer cooling collar and a rotating air current generating unit. The microwave transmits in the rectangular waveguide, the reactor is disposed on the geometrical center in the resonant cavity which has the air cooling collar installed outside, the flame light is disposed upon a gas reaction tube and the rotating air current generating unit, the combined type insulated high temperature resistant electrode of the flame lighter is disposed along the inner axis of the quartz tube with the end position adjustable up and down freely. The invention achieves the following advantages: adopting the rectangular waveguide and waveguide conversion can make the microwave energy gathered to process higher power; the power capacity can reach 2KW; the close end can adjust the phase matching unit to generate standing wave in the resonant cavity, ensures the microwave energy coupled to the resonant cavity, reduces microwave reflection loss and improves energy utilization efficiency.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Long excursion loudspeaker with closed magnetic circuit and ribbed robbin extending through slotted yoke
An audio loudspeaker with an internal magnet geometry motor having a slotted cylinder having closed ends, a pair of oppositely charged magnets sandwiching a top plate and disposed between the closed ends of the cylinder, and a diaphragm assembly having a bobbin with spokes which extend through the slots. Mechanically connecting to the voice coil radially through the cylinder enables the lower suspension component to be places much lower and farther from the upper suspension component, improving stability of the suspension. The closed ends of the motor provide extremely low magnetic reluctance for the magnetic circuits at the respective ends of the motor.
Owner:PLASTOFORM INDS
Hinge
InactiveUS20050034274A1Improve hingePrevent oil leakageWing fastenersDetails for portable computersEngineeringLubricant
A hinge includes a cylinder having a close end and an open end longitudinally opposite to the close end of the cylinder. A polygonal sleeve is fixedly received in the cylinder. The polygonal sleeve has multiple edges abutting against an inner periphery of the cylinder. A pivot axle is partially pivotally received in the sleeve. A sealant is mounted around the pivotally for tightly closing the open end of the cylinder to prevent the lubricant in the hinge from leaking.
Owner:WU CHING SUNG
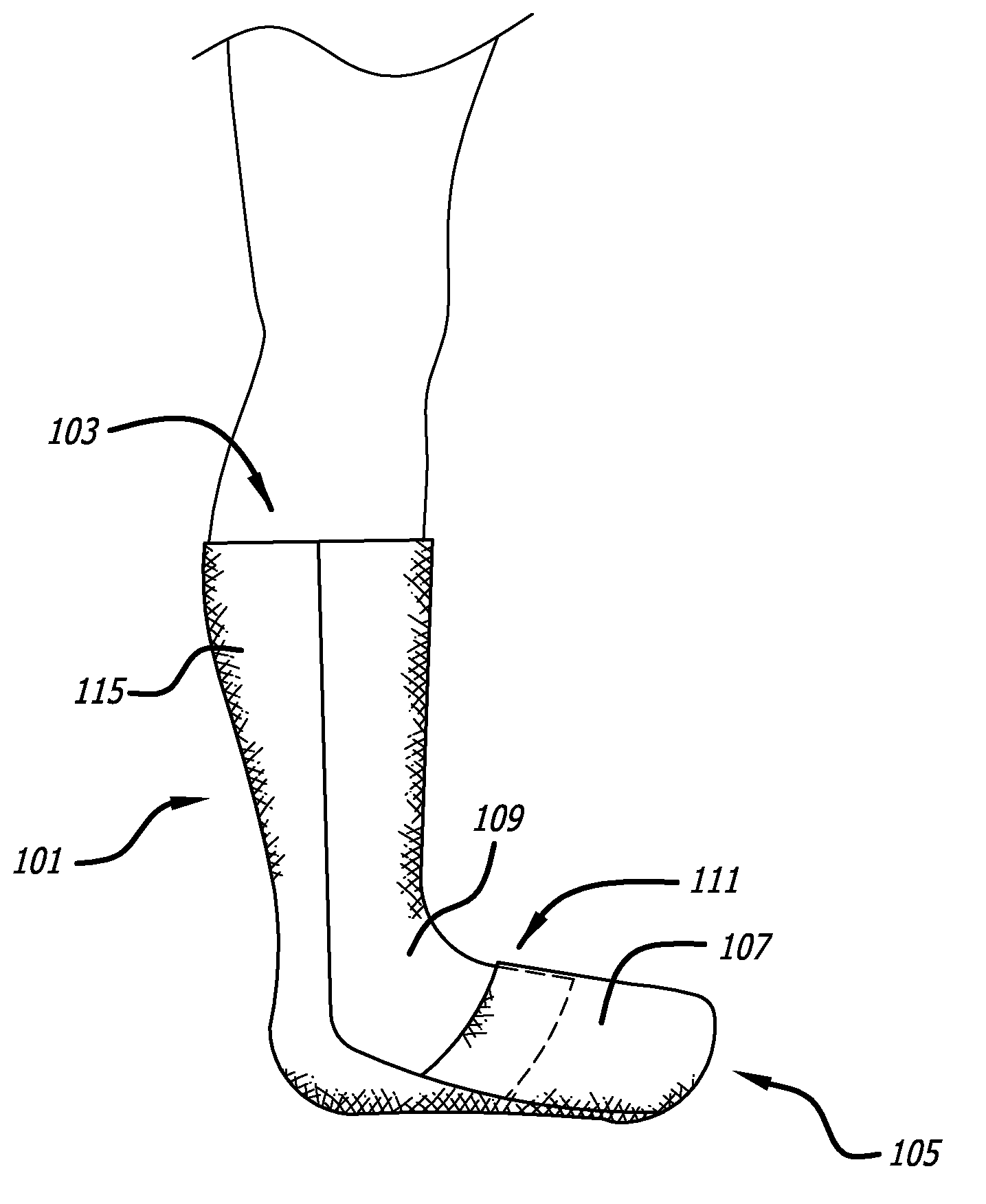
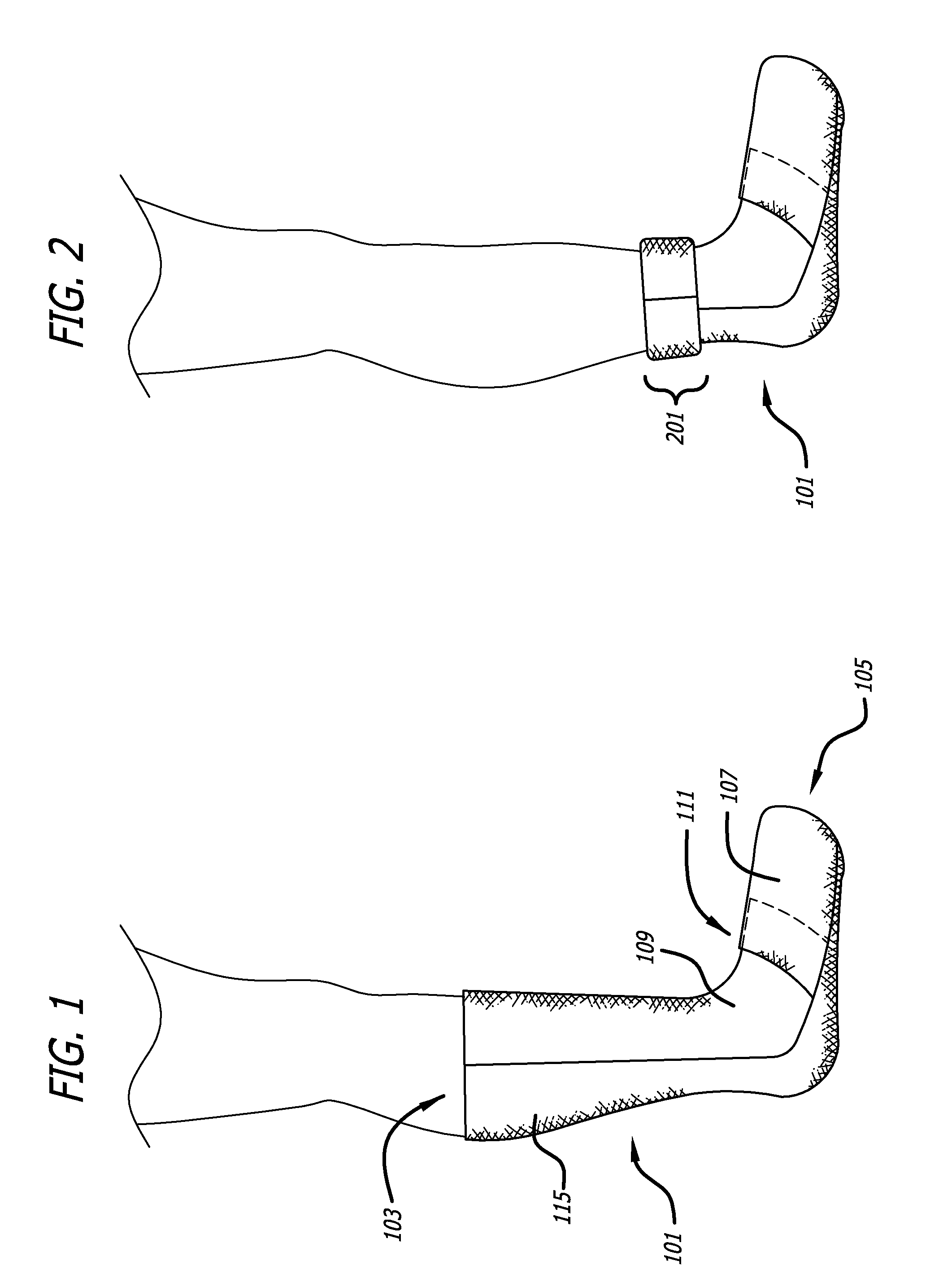
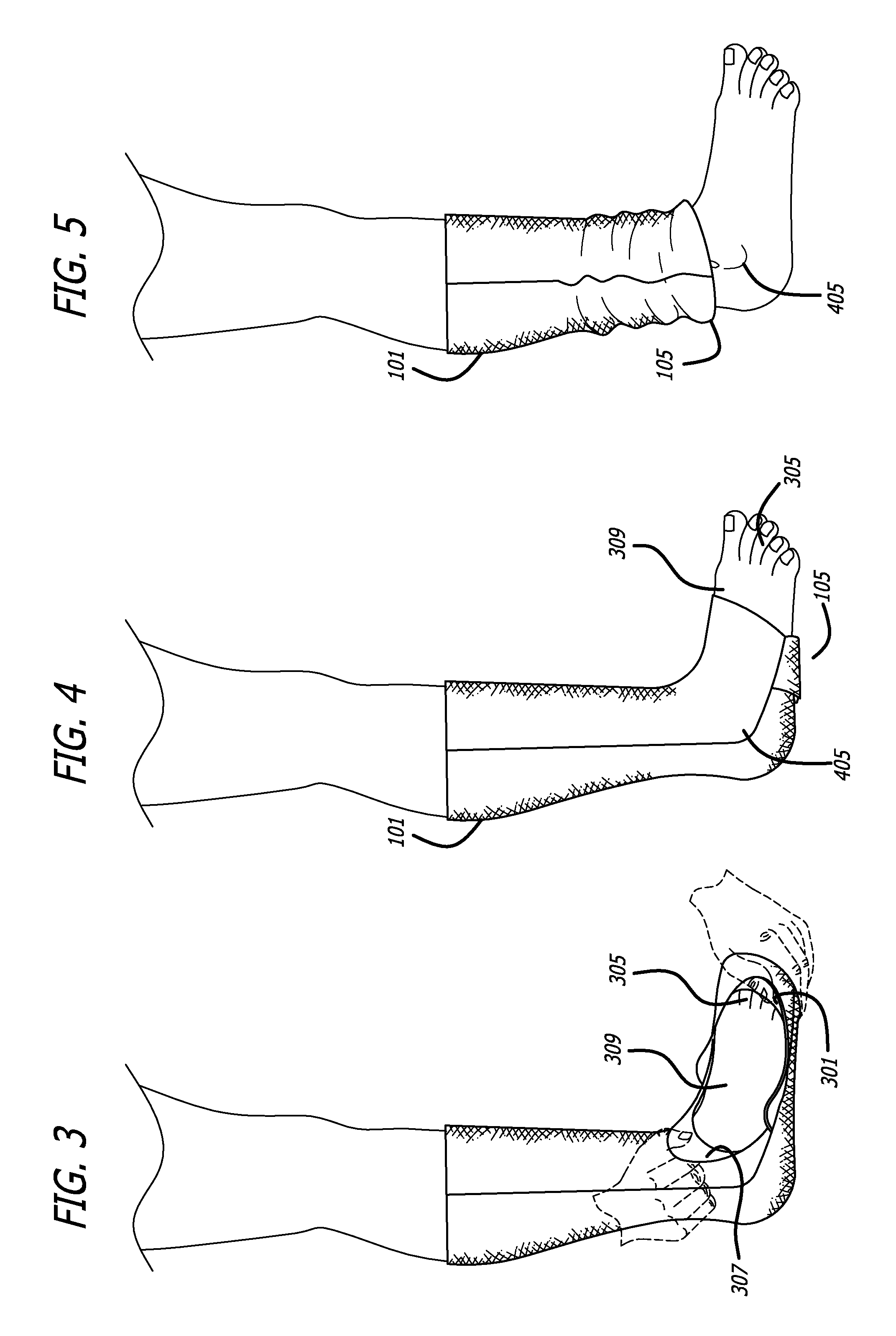
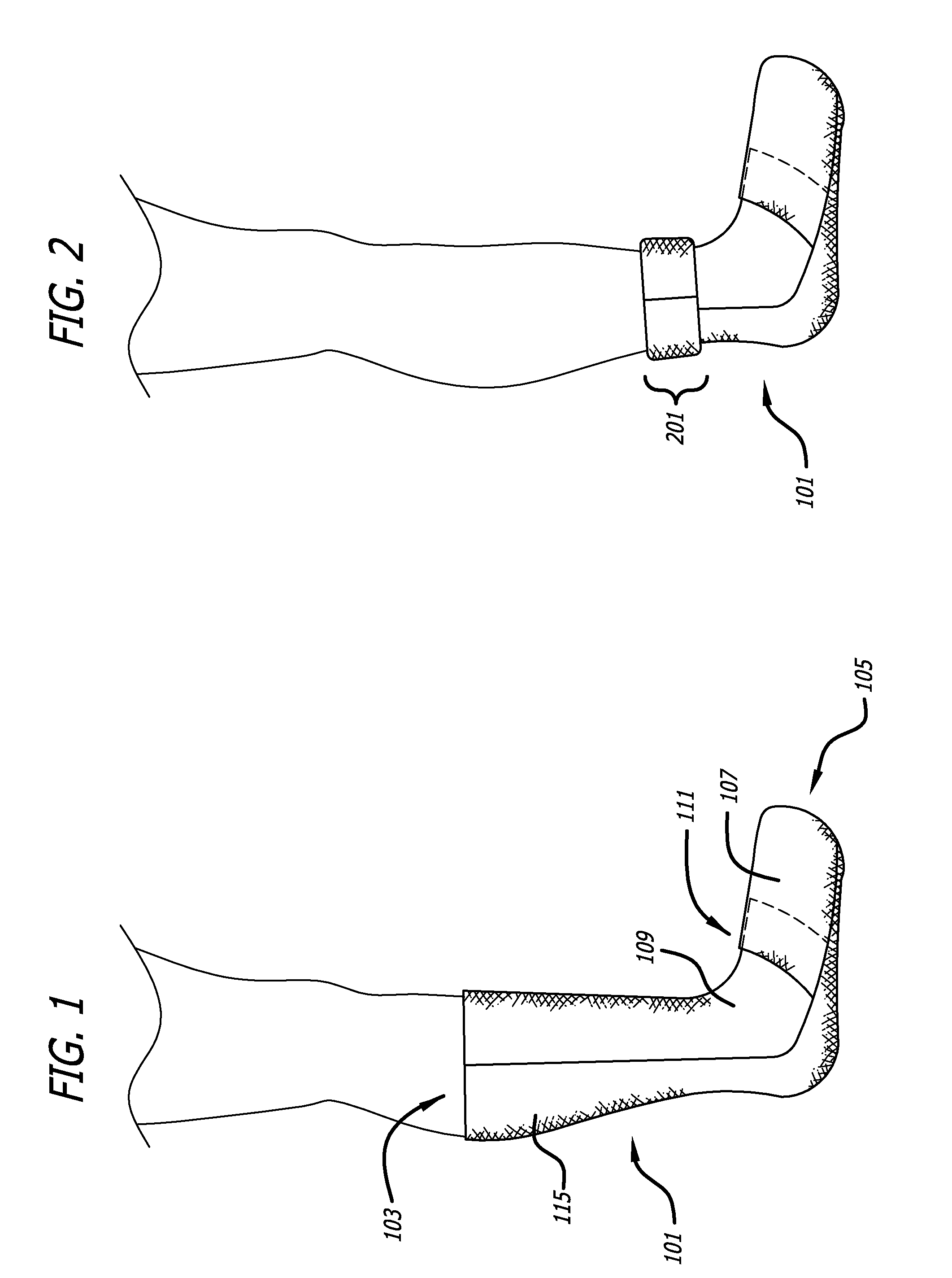
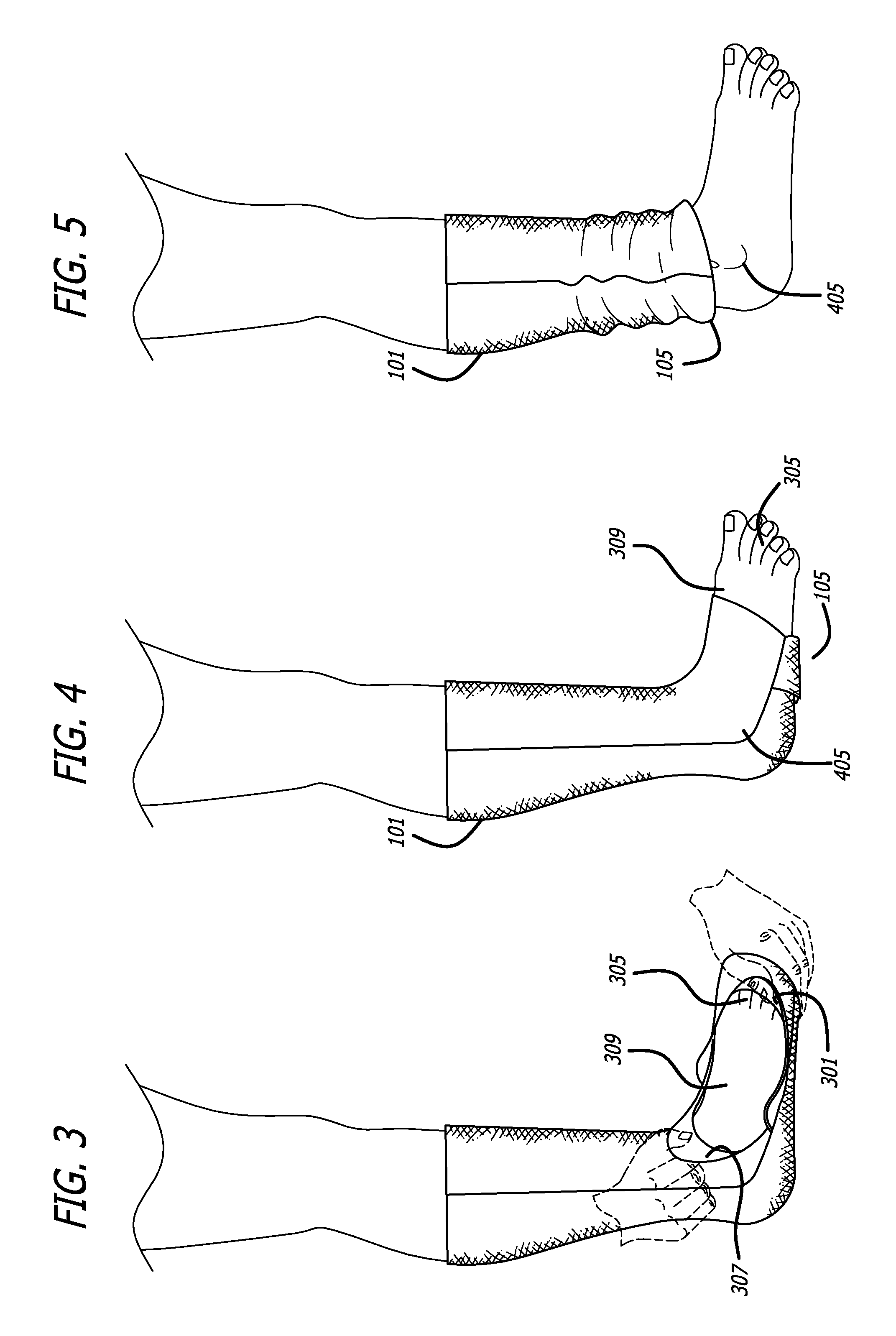
Convertible sock/slipper legwarmer
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
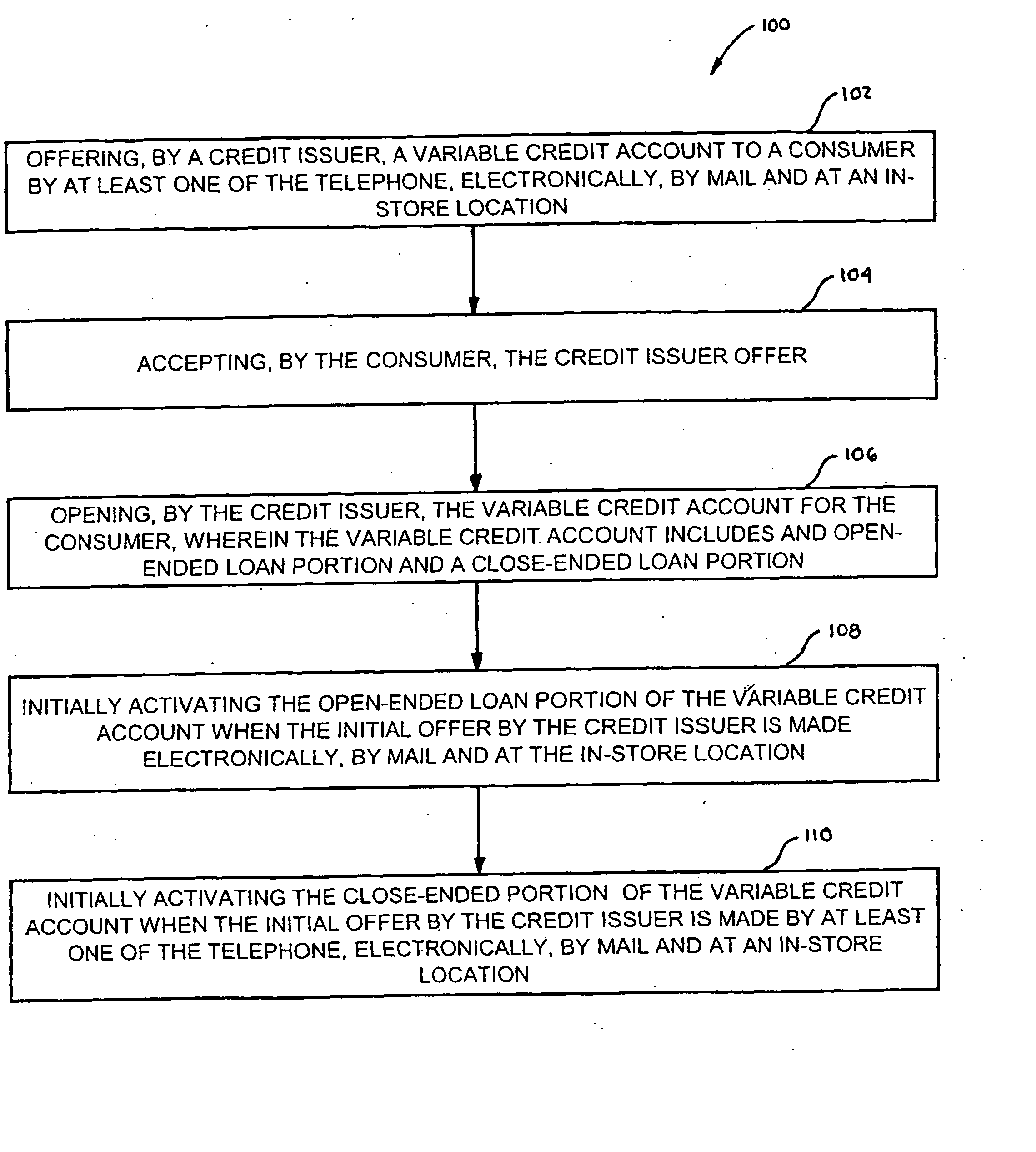
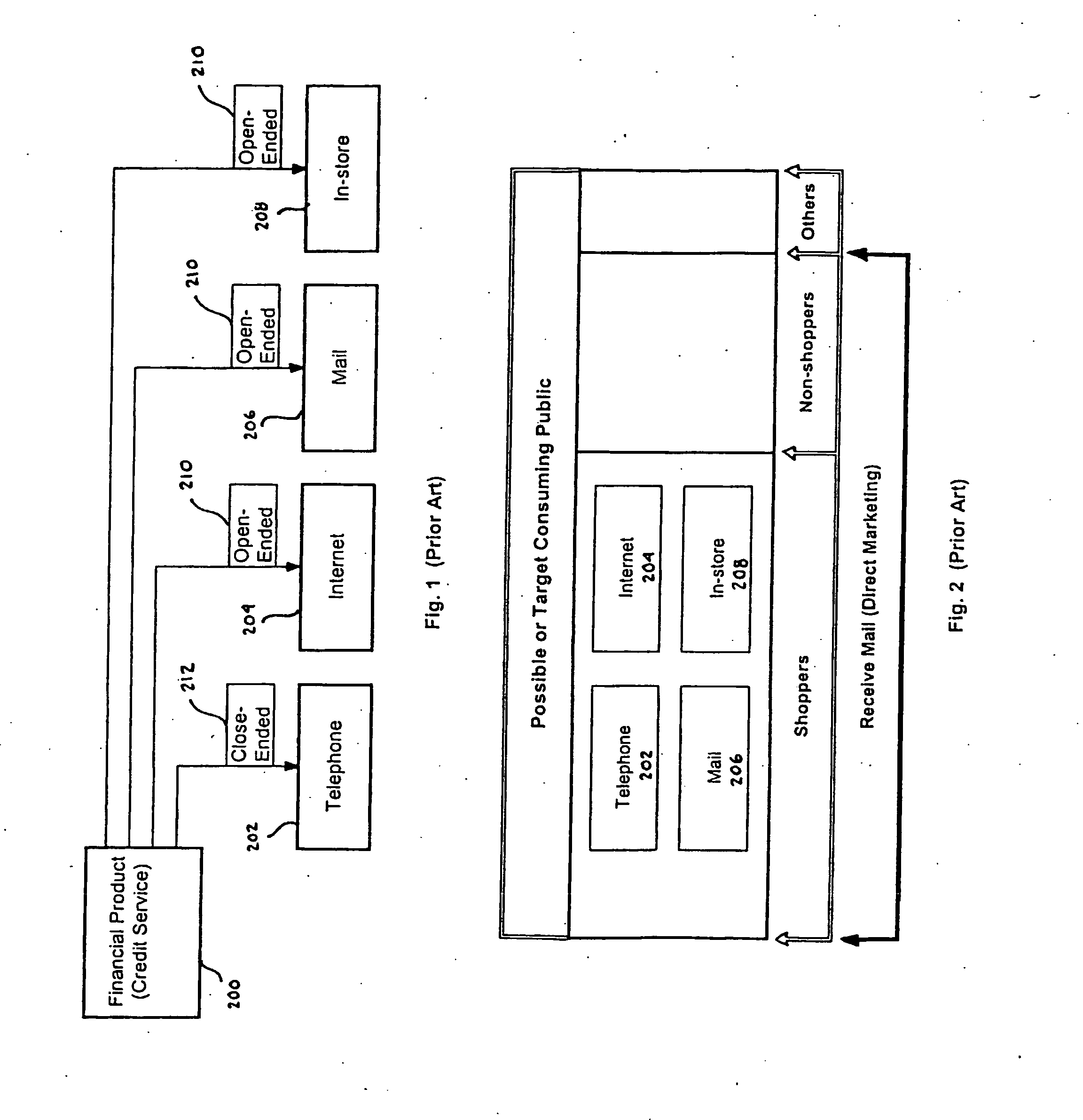
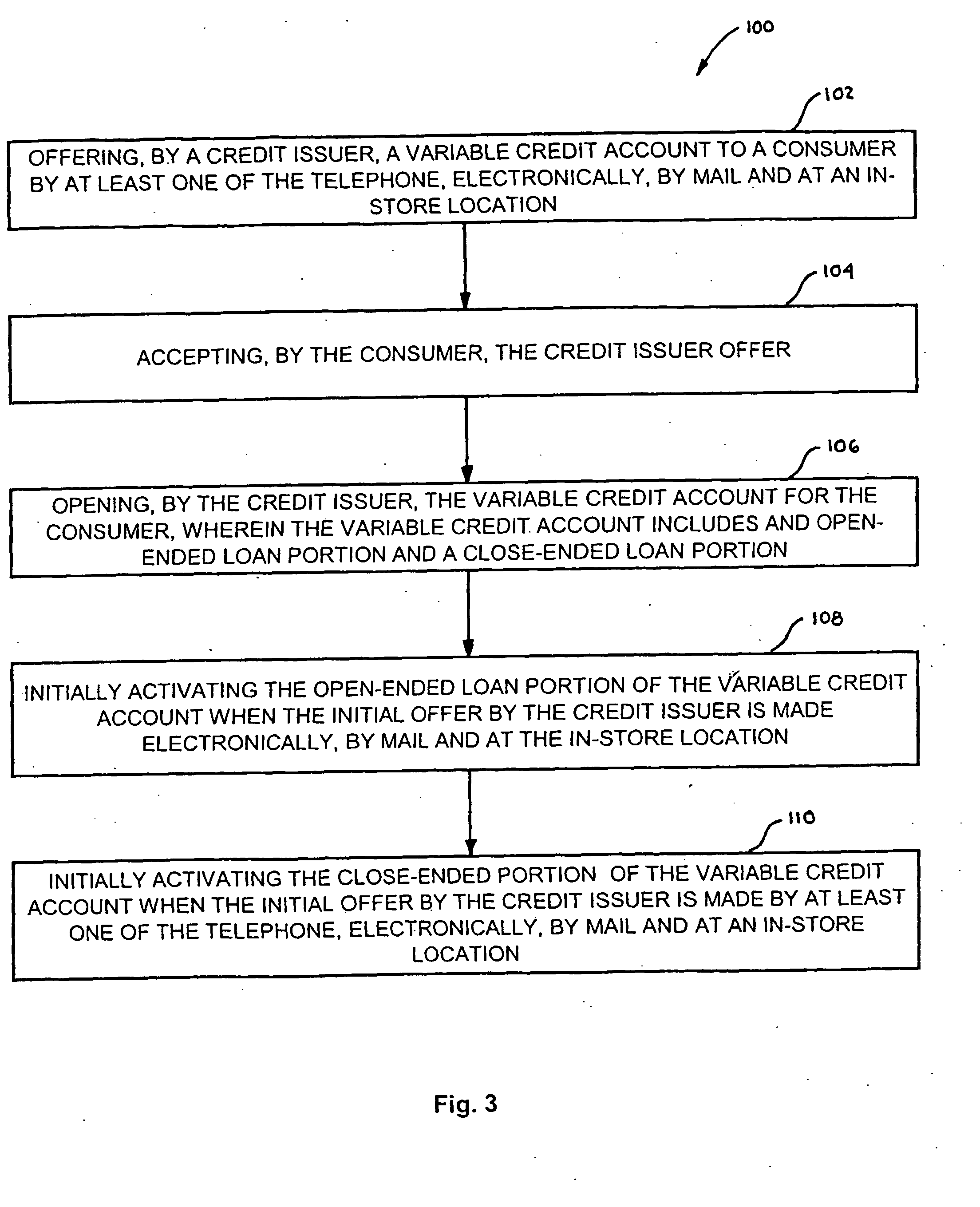
Method, System and Apparatus for Providing a Variable Credit Account to a Consumer
A method of providing a variable credit account to a consumer (12) is provided. The method includes the steps of: offering, by a credit issuer (14), a variable credit account to a consumer (12) by telephone, electronically, mail or at an in-store location; accepting, by the consumer (12), the offer; opening, by the credit issuer, the variable credit account (18) for the consumer (12), where the account includes an open-ended loan portion (22) and a close-ended loan portion (20). The method may further include the steps of initially activating the open-ended loan portion (22) when the initial offer is made electronically, by mail or at an in-store location; and initially activating a close-ended loan portion (20) of the account when the initial offer is made at any point-of-sale. A system and apparatus for providing a variable credit account to a consumer (12) is also discussed.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
Interchangeable simulated neon light tube assemblies and related accessories for use with lighting devices
InactiveUS20060250802A1Vehicle interior lightingProtective devices for lightingLight equipmentEffect light
A simulated neon light tube assembly includes an elongated tube having a light diffusing material disposed therein for simulating the appearance of neon lighting. The light tube is used in conjunction with a base portion having a light source disposed therein to provide a lighting device. The light tube assembly of the present invention is preferably closed ended, and is selectively removable from the base portion so that it can, therefore, be replaced easily with another light tube assembly. Modified retaining covers, retaining caps and mounting assemblies are also described.
Owner:HEROLD DESIGN GROUP
Inflatable head and neck support collar
A support collar having a bladder and a shell. The bladder is adapted to be inflated by a fluid. The shell is adapted to be attached to a harness. When inflated, the bladder is shaped by the shell to form an air chamber. The air chamber is characterized by a cross-section having a center of gravity and a dimension through the center of gravity. The dimension is larger at an open end than at the close end.
Owner:SIMULA
Box carrying strap assembly
InactiveUS6953214B2Easy to operateEasy to carryTravelling sacksTravelling carriersEngineeringMechanical engineering
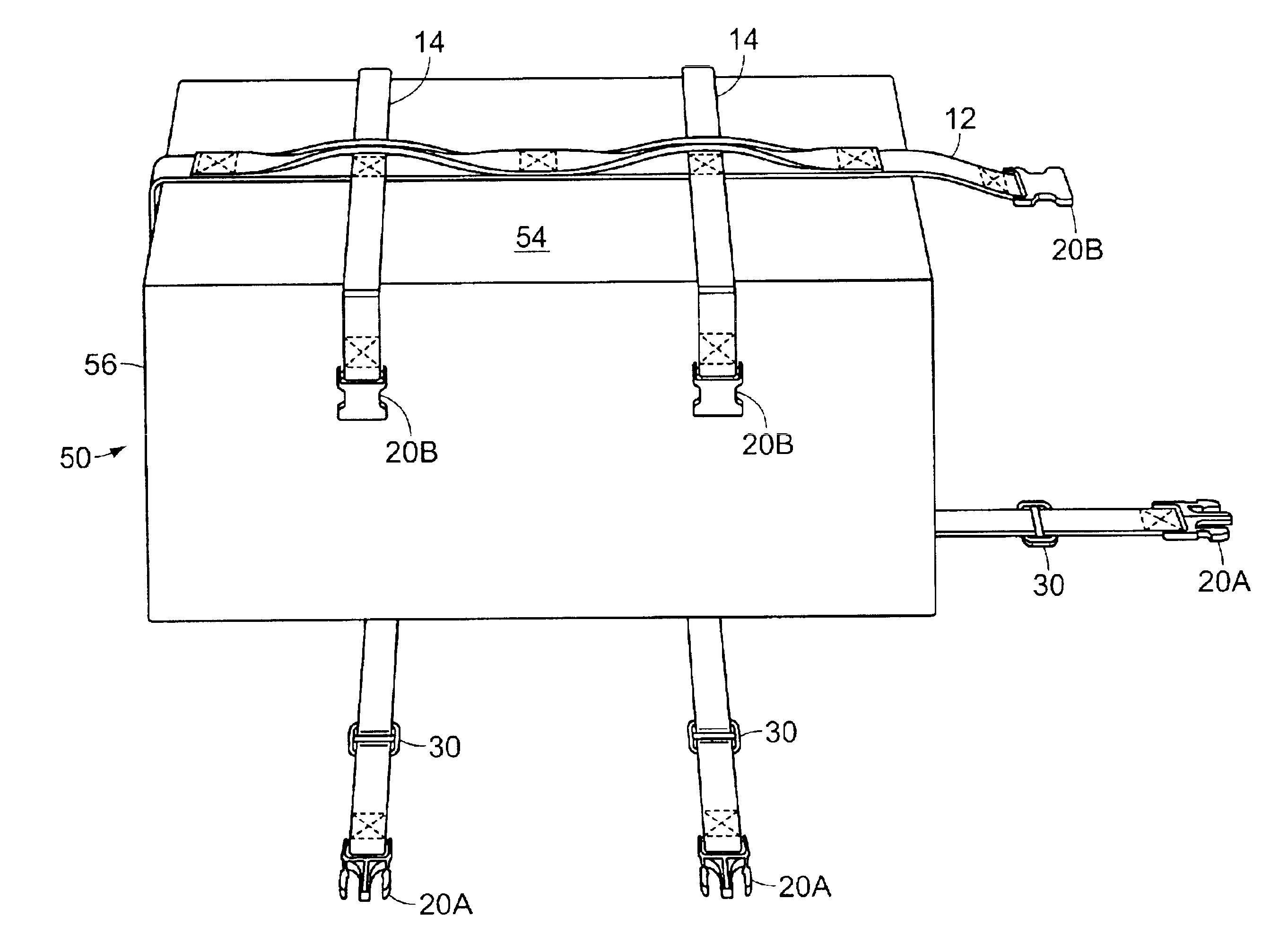
A carrying device, for carrying a box substantially in the shape of a rectangular prism, having a main strap, and a pair of transverse straps. The transverse straps extend parallel to each other, perpendicular to the main strap, cross the main strap, and are attached to the main strap at the crossings. A handle strap extends along the main strap, and is fastened to the main strap between the crossings, and between each of the crossings and the closest end of the main strap, forming handgrips at the crossings. The ends of the main strap and transverse straps have mateable buckles which allow the straps to be fastened around all sides of the box, and permit easy release.
Owner:PAZ CLARITA DELA
Nature hipbone device
InactiveUS20060178750A1Reduce frictionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsMechanical engineeringHip bone
Owner:CHIENG POONUNG
Vacuum cleaner with noise suppression features
A vacuum cleaner includes a cyclonic airflow chamber that facilitates the separation of contaminants from a suction airstream. The airflow chamber includes a chamber inlet and a chamber outlet, with the chamber inlet being fluidically connected with at least one of a suction nozzle and an above-the-floor cleaning tool. An exhaust filter housing includes a suction duct and an exhaust plenum, with the suction duct communicating with the chamber outlet. A suction source housing includes an open end communicating with the exhaust plenum and a closed end. A suction source is positioned within the suction source housing to define an annular exhaust flow passageway surrounding the suction source from the housing closed end to the housing open end. The suction source includes a suction inlet communicating with the suction duct and an exhaust outlet communicating with the housing closed end.
Owner:ROYAL APPLIANCE MFG
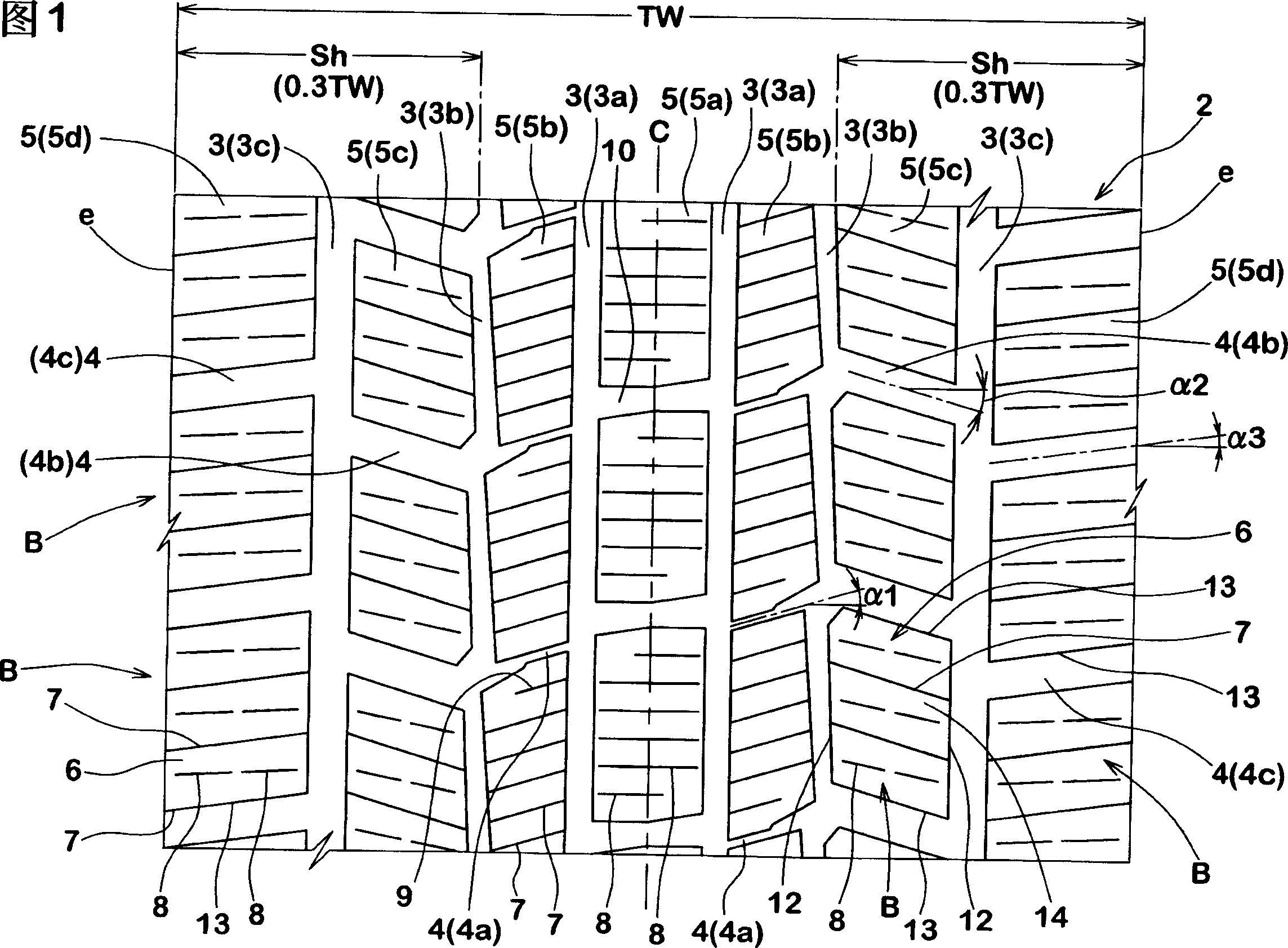
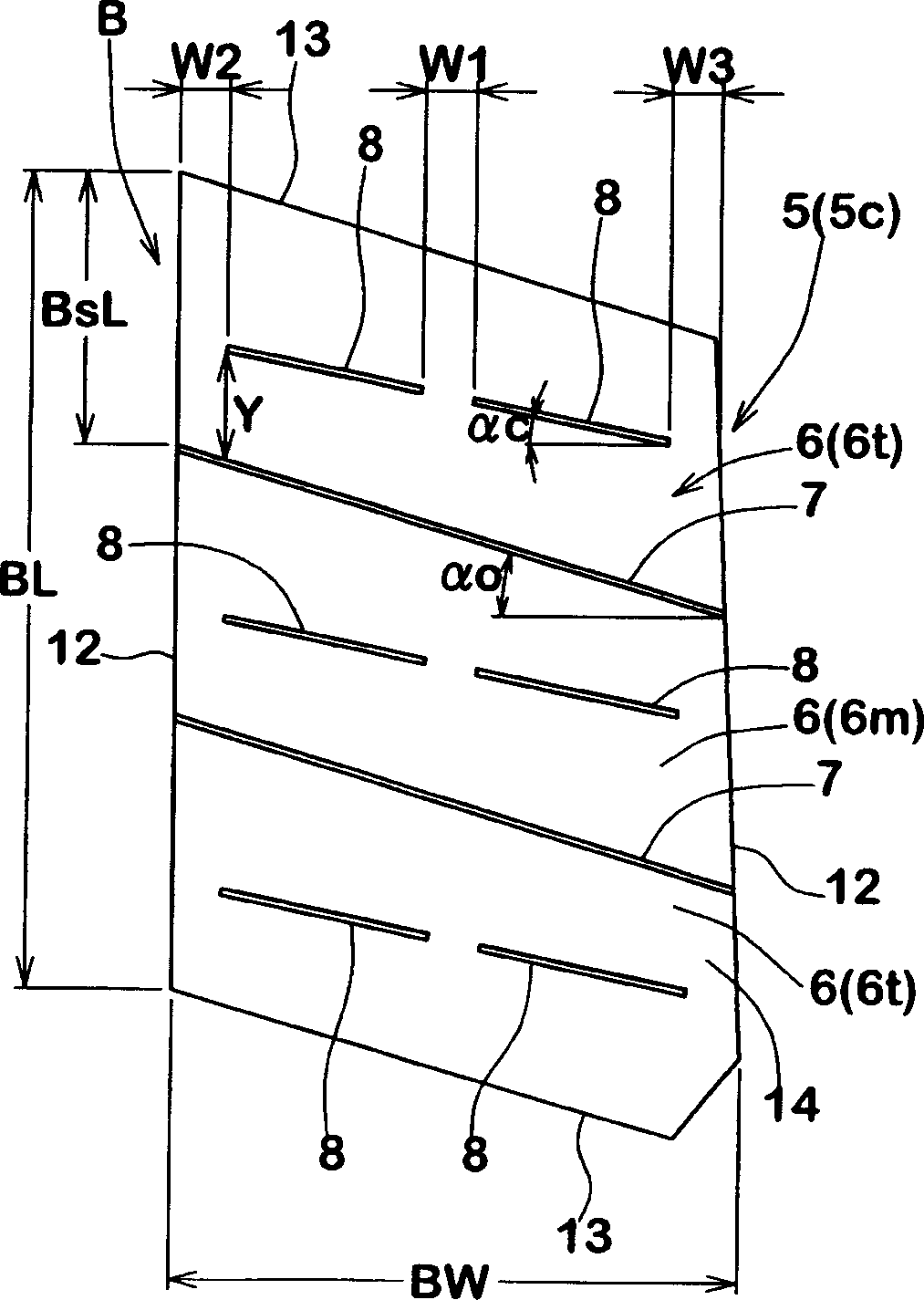
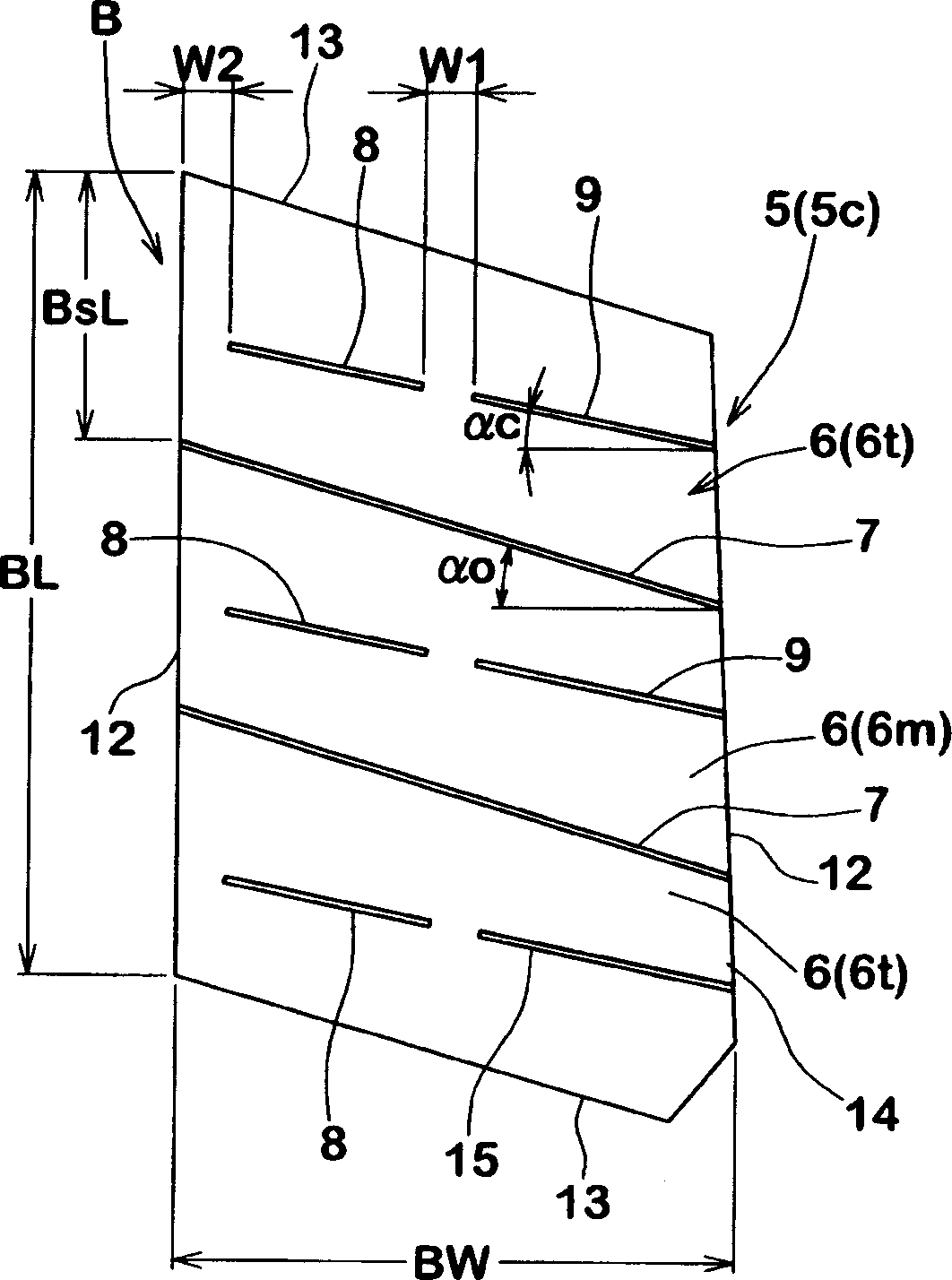
Pneumatic tire
InactiveCN1733511AReduce distortionReduce tiltTyre tread bands/patternsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Convertible Sock/Slipper Legwarmer
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
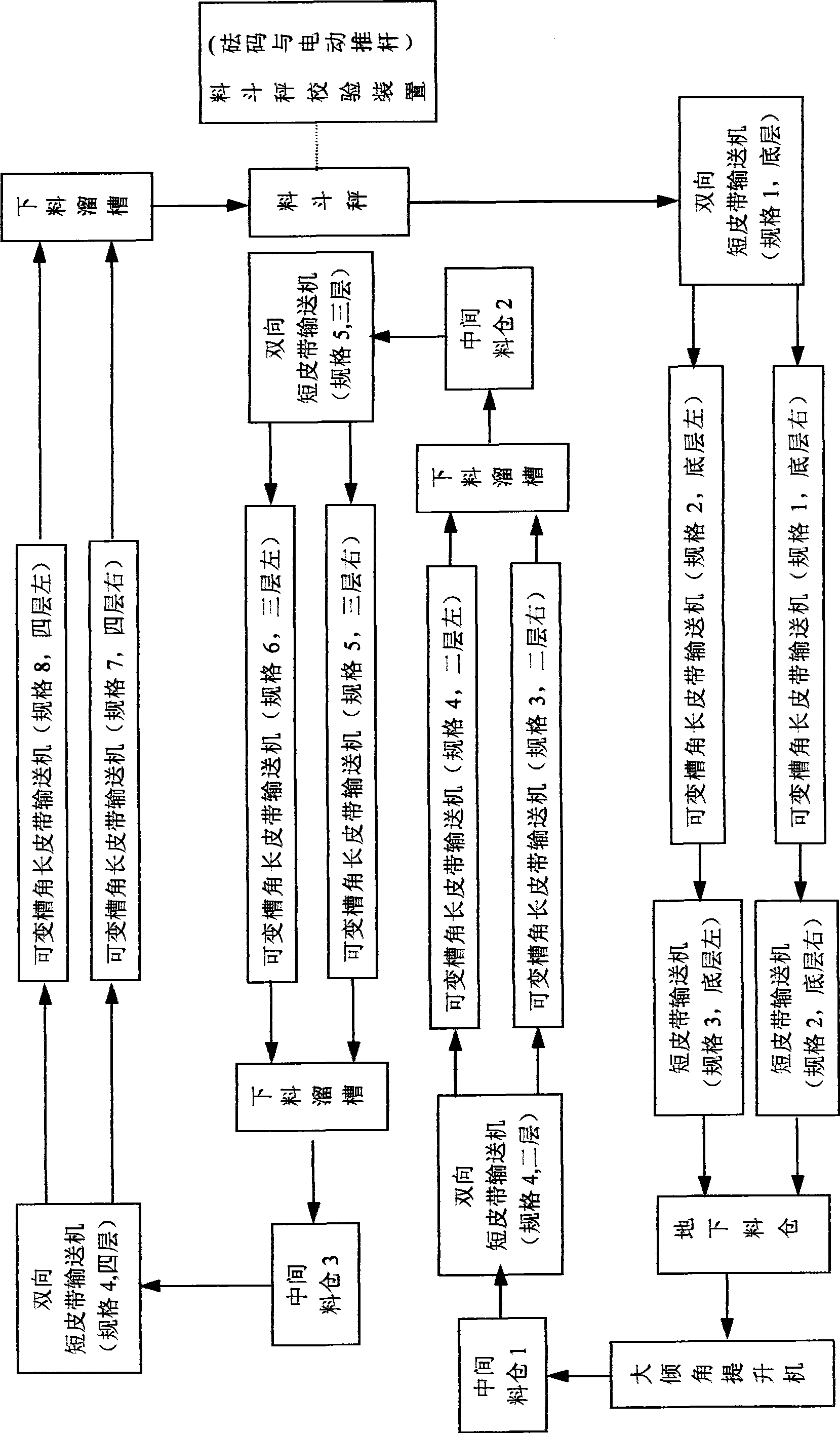
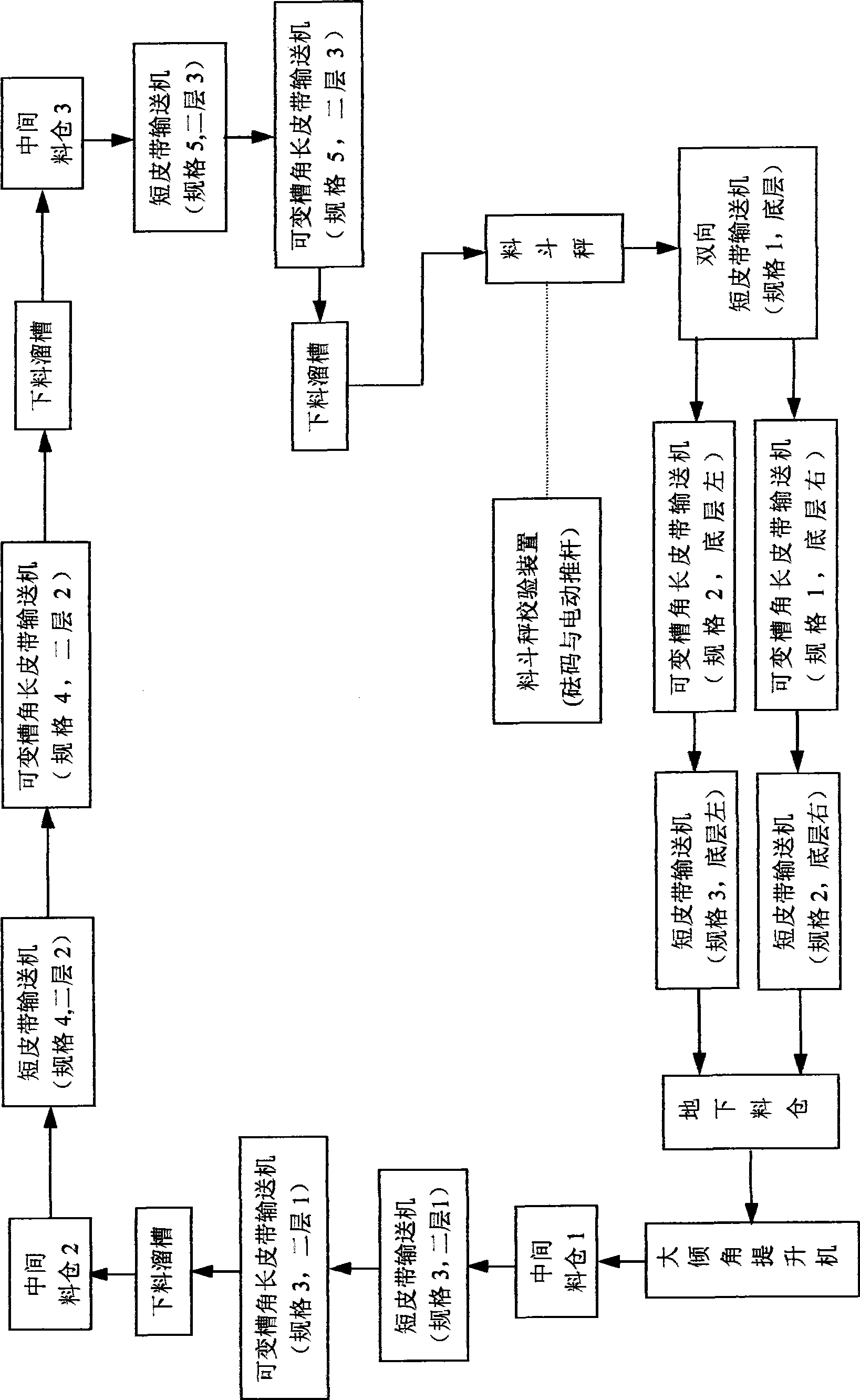
Dynamic full performance test system for multifunctional belt balance
ActiveCN101476931AExpand the belt speed coverageWeighing apparatus testing/calibrationSlope angleEngineering
The invention relates to a multifunctional belt balance dynamic overall-performance testing system with relatively less occupied area and investment, and is suitable for belt conveyors with a plurality of belt width and groove-shaped angles. The system can test both an embedded type belt balance and an integrated type belt balance, and can develop both a test project of a metering belt balance and the test project of a quantitive belt balance. The system is characterized in that a plurality of the belt conveyors with different belt width and length are mounted in different elevation by layers (at least two layers) and are close end to end; the end-to-end close part is provided with pits or feed bins which are used for continuing or caching of a tested material; at least one of the pits or feed bins is used as control weighing equipment for a high-precision hopper balance; and each conveyer can adopt a layout of a reciprocating return or annular continuous mode. Each long conveyer can be embedded with the metering belt balance to be tested with corresponding belt width; and an integrated-type quantitive belt balance to be tested can be conveniently rearranged on a short belt conveyer part. In testing, a material entering the bottom layer the pit is lifted to the feed bin of the top layer by the belt conveyor with a large slope angle and is recycled and utilized time and again.
Owner:NANJING SANAI IPC CO LTD +1
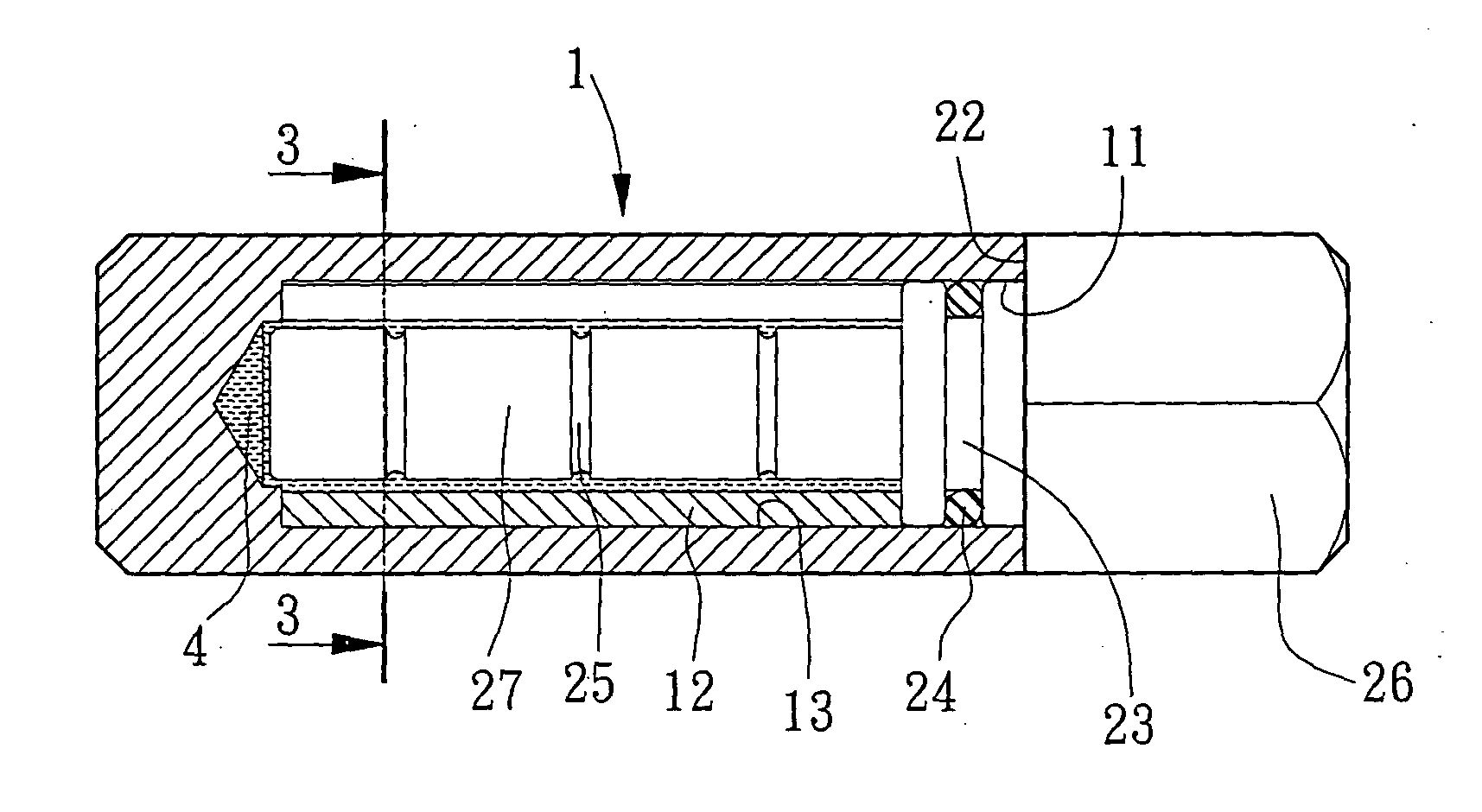
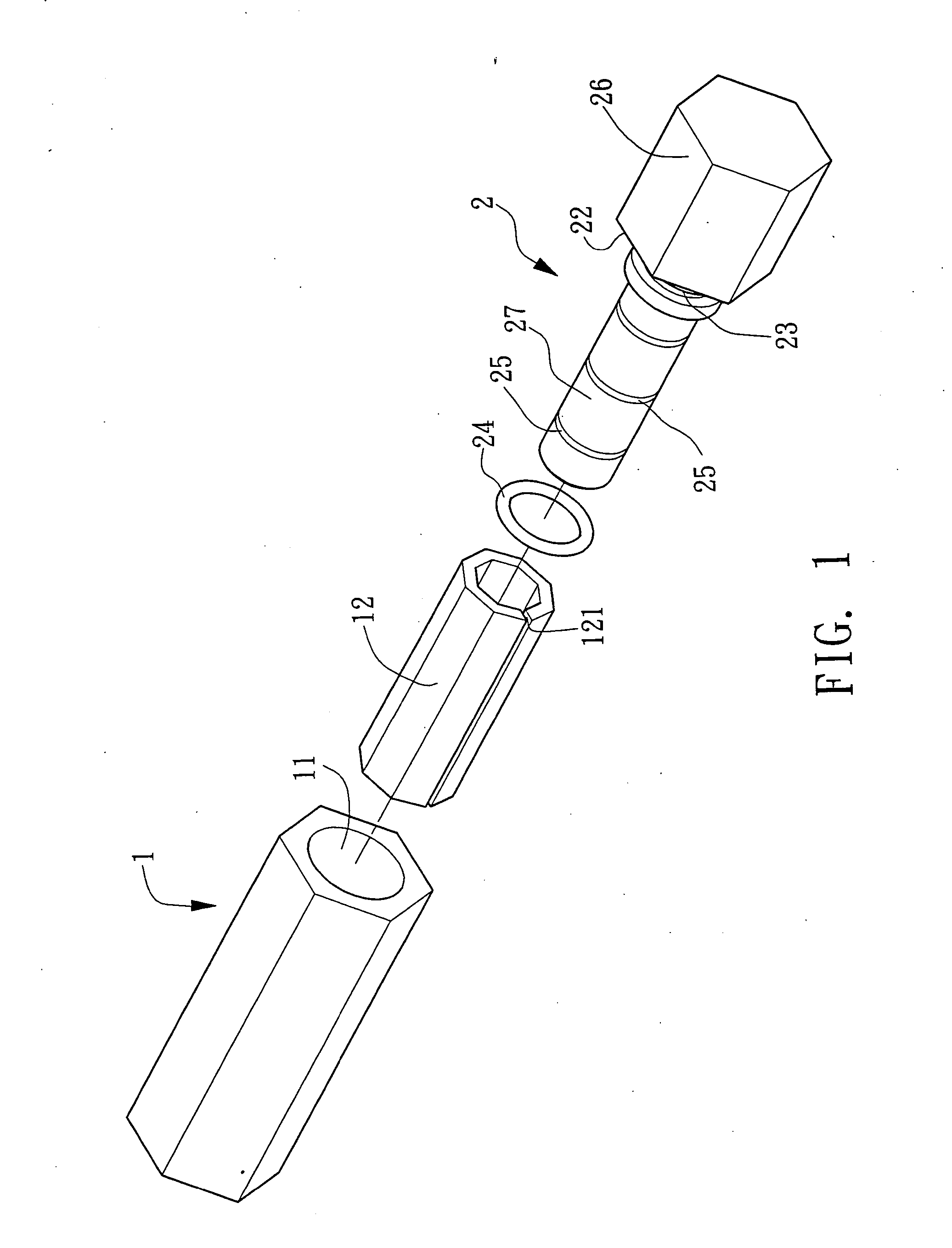
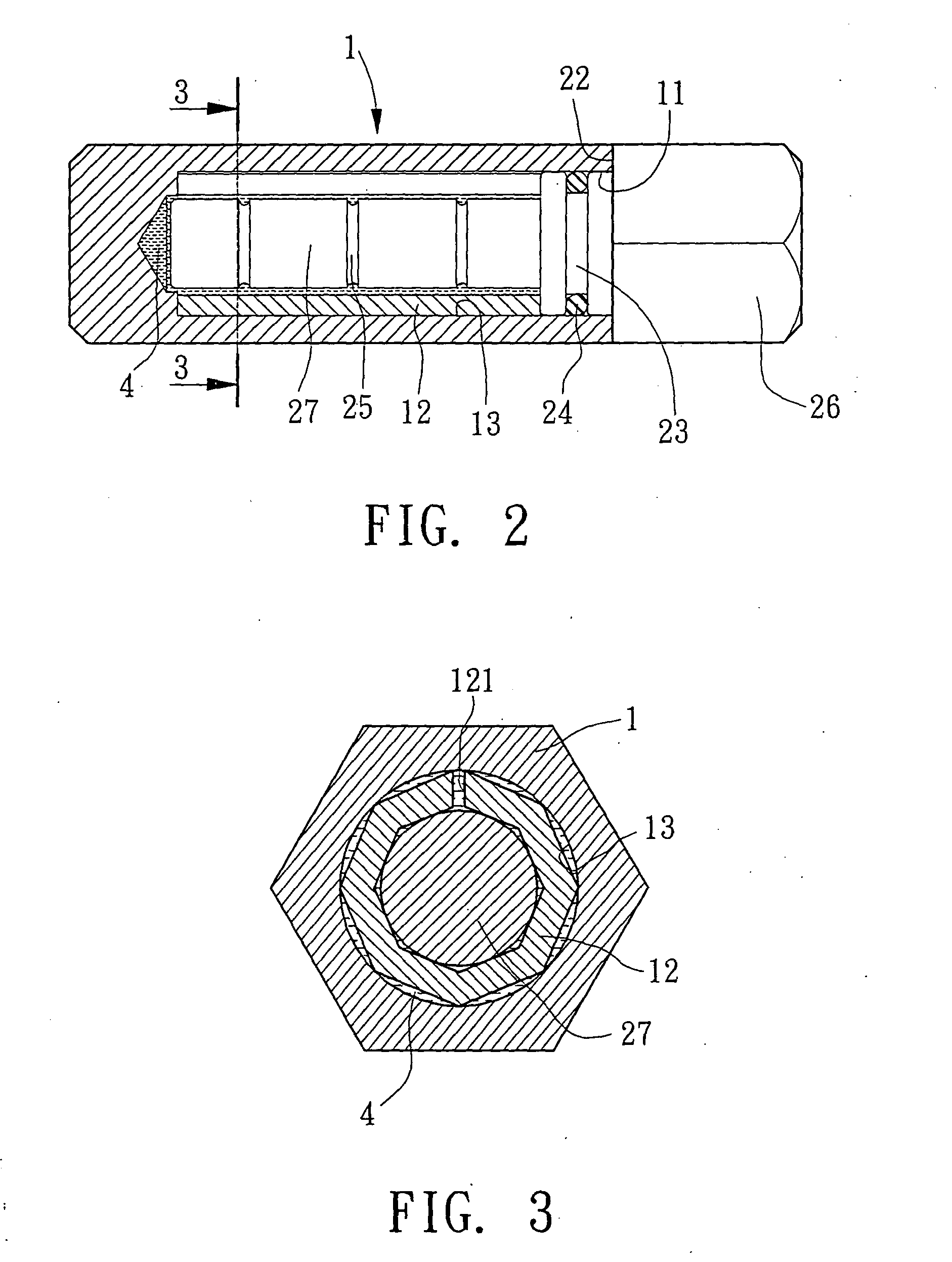
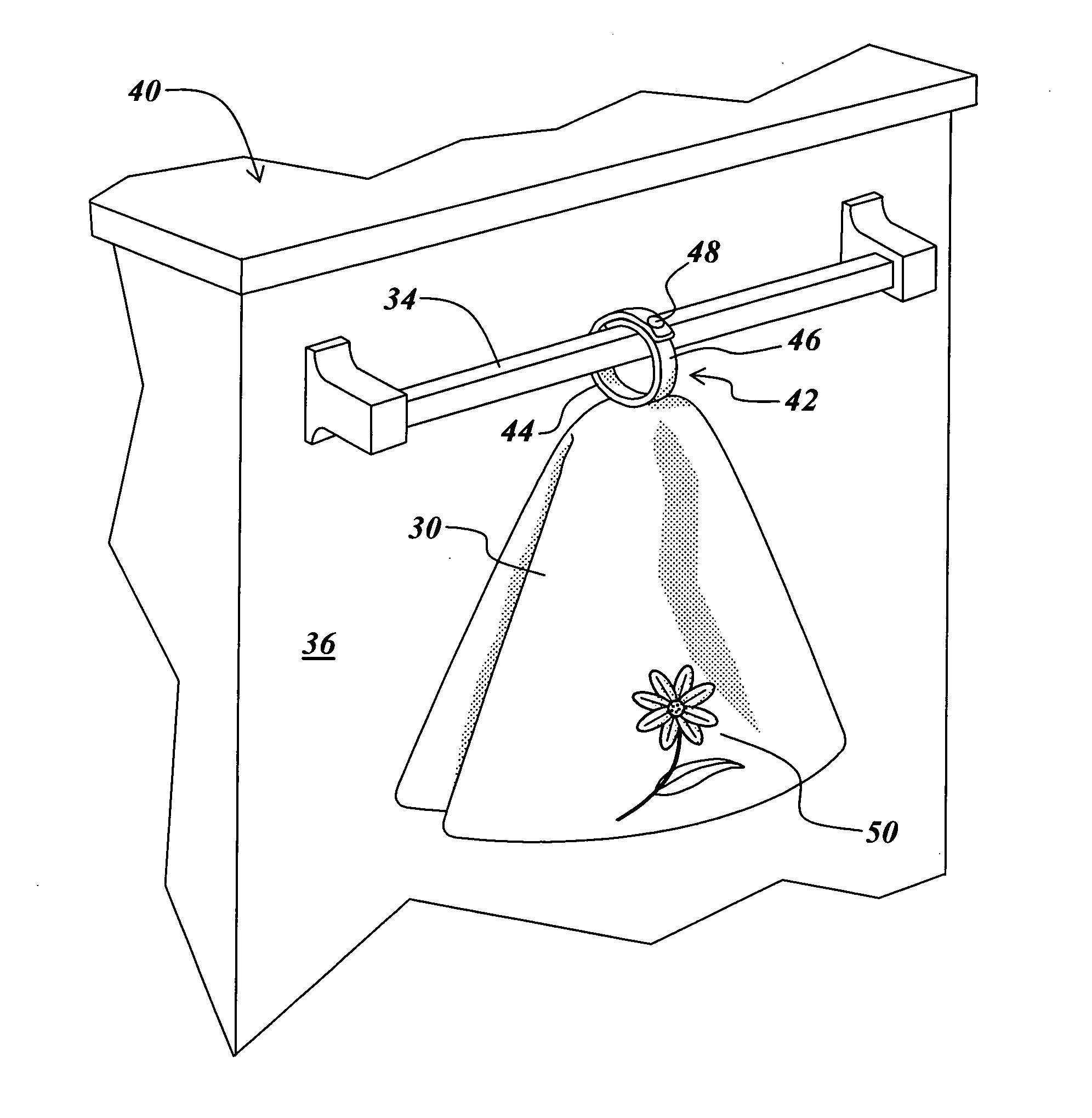
Method and apparatus for releasably attaching a towel to a close-ended rod
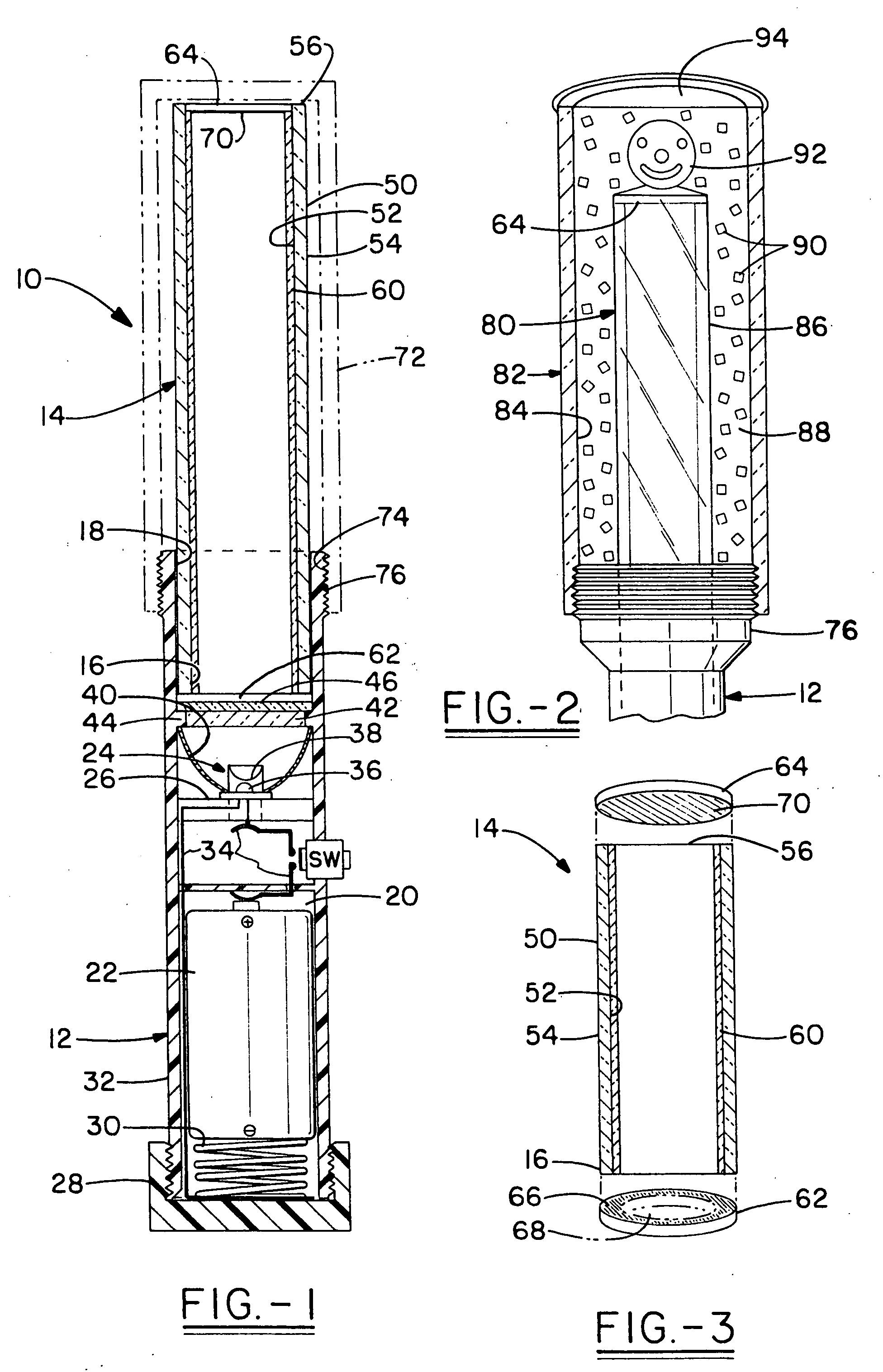
InactiveUS20090236299A1Good lookingNot look messyDomestic applicationsMechanical engineeringClose-ended
Owner:HALL SVETLANA
Illuminated handle bar grip
InactiveUS20100053984A1Easy to installEasy to replaceOptical signalLighting elementsMechanical engineeringLight emitting device
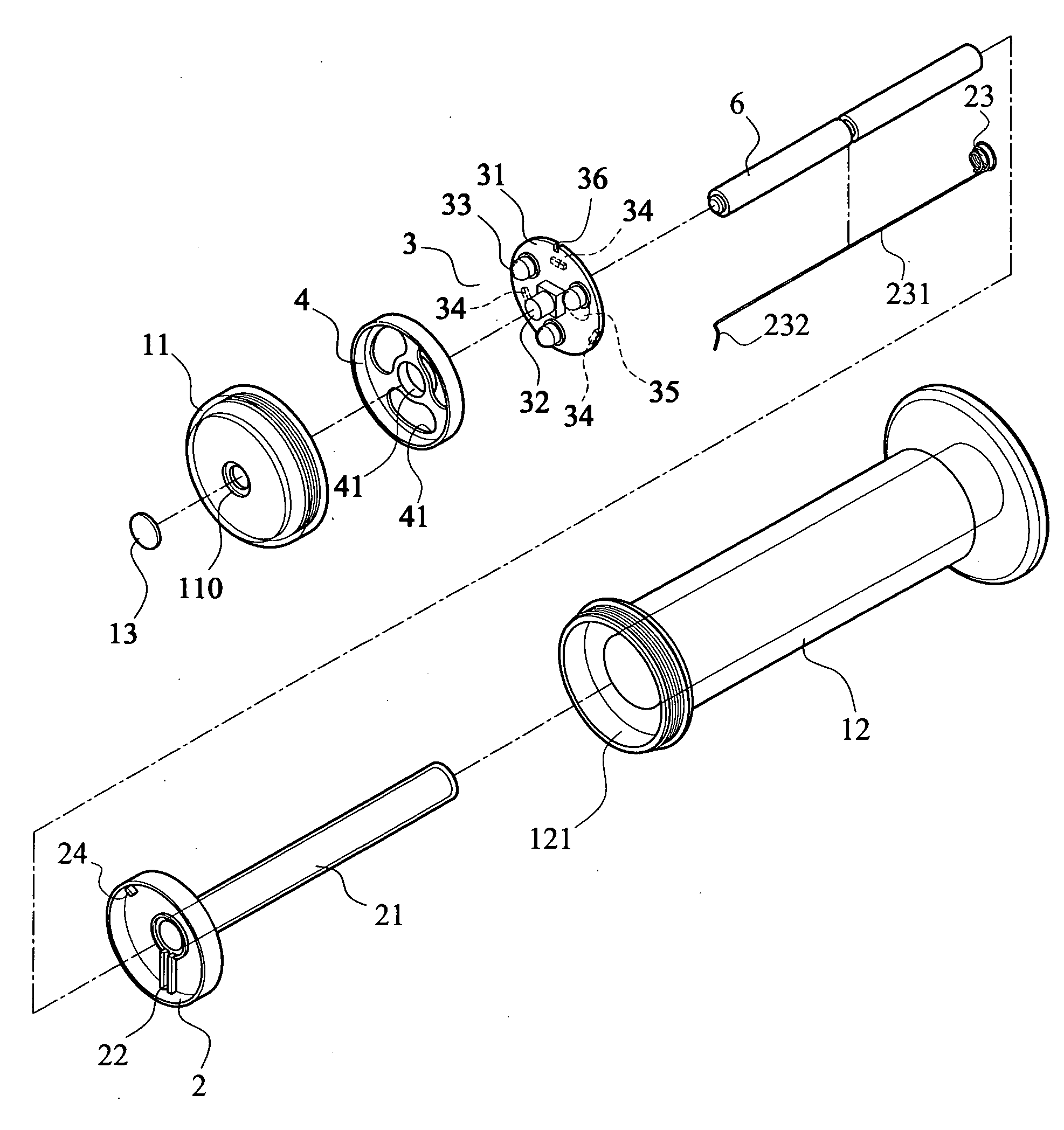
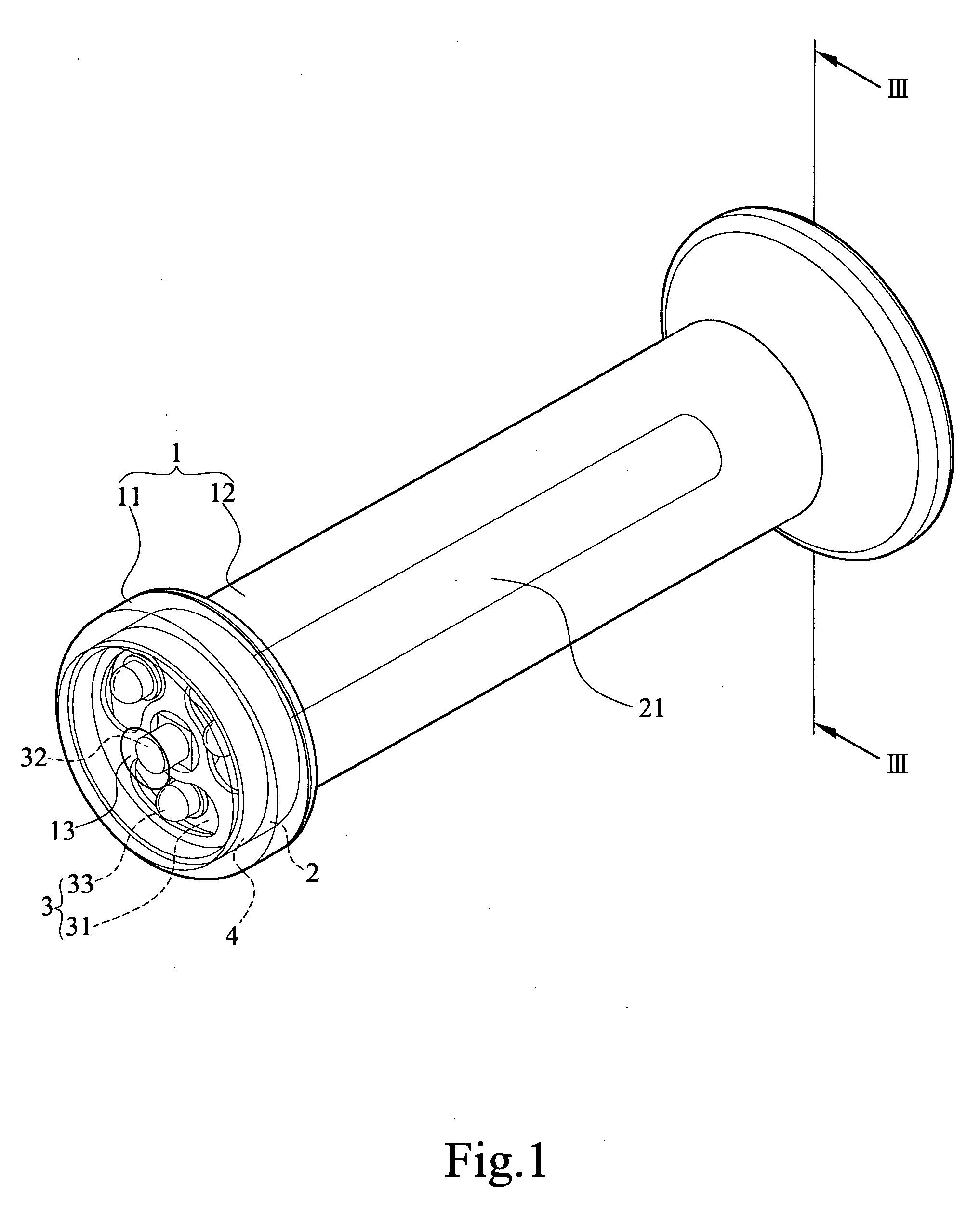
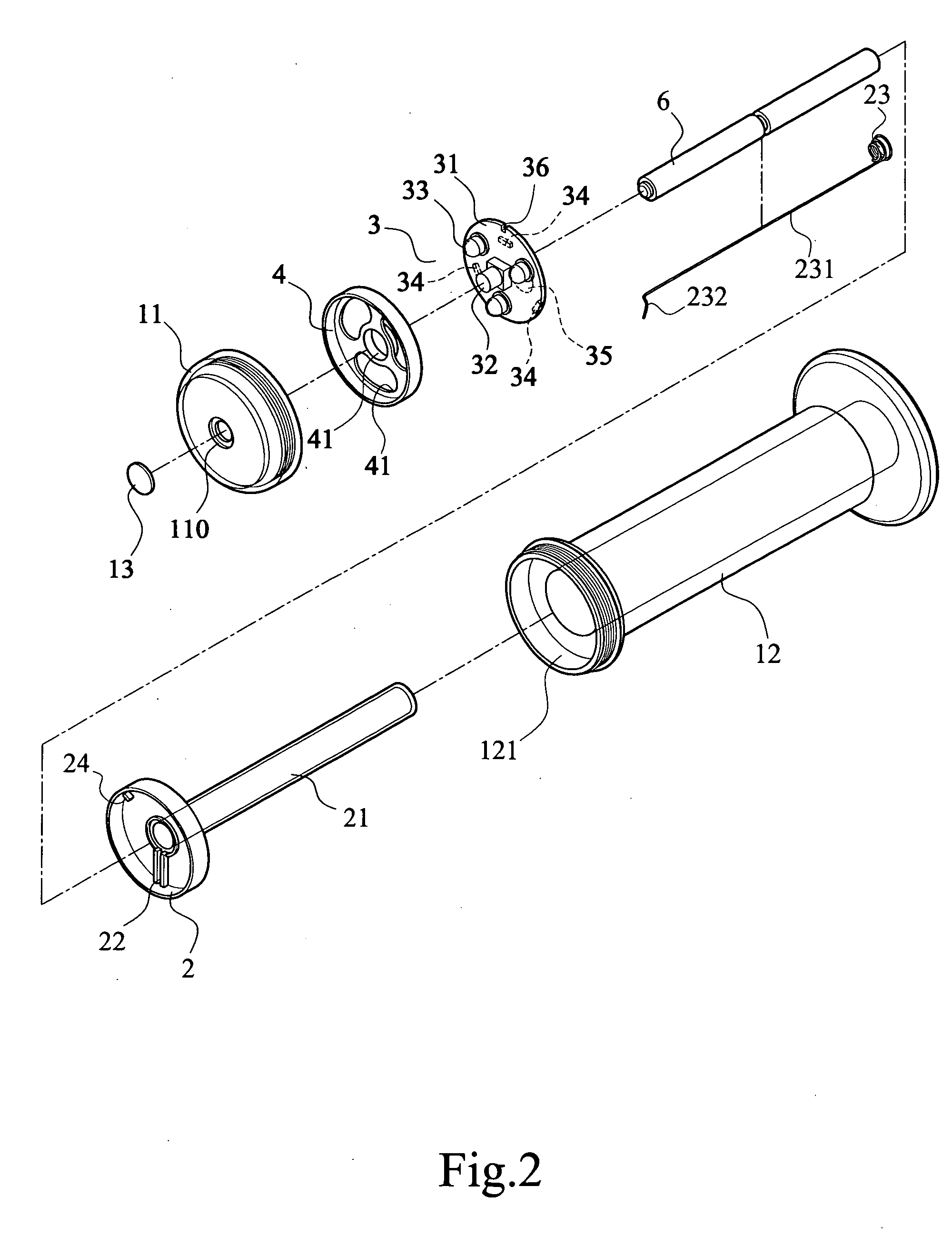
An illuminated handlebar grip (1) can be lit up thoroughly to improve two-wheeled vehicle safety comprising: a grip (12) accommodates a handlebar (9) received therein; a battery seat (2) is disposed inside the container (121) which is formed in the second close end of the grip (12), and is covered up by a cover (11) coupled to a second end of said grip (12); said battery seat (2) is extended inside the grip (12) to form a cylindrical battery chamber (21) for receiving batteries (6); a light emitting device (3) installed in the battery seat (2); and a positioning cover (4) provided between the cover (11) and PCB (31) to prevent any displacement of the PCB (31).
Owner:WANG WENG SHIH
Interchangeable simulated neon light tube assemblies and related accessories for use with lighting devices
InactiveUS20070274087A1Vehicle interior lightingProtective devices for lightingLight equipmentEffect light
A simulated neon light tube assembly includes an elongated tube having a light diffusing material disposed therein for simulating the appearance of neon lighting. The light tube is used in conjunction with a base portion having a light source disposed therein to provide a lighting device. The light tube assembly of the present invention is preferably closed ended, and is selectively removable from the base portion so that it can, therefore, be replaced easily with another light tube assembly. Modified retaining covers, retaining caps and mounting assemblies are also described.
Owner:HEROLD MICHAEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com