Patents
Literature
48 results about "Computer Grid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Grid computing is the collection of computer resources from multiple places to reach a common goal. The grid can be thought of as a distributed system with non-interactive workloads that involve a large number of files.
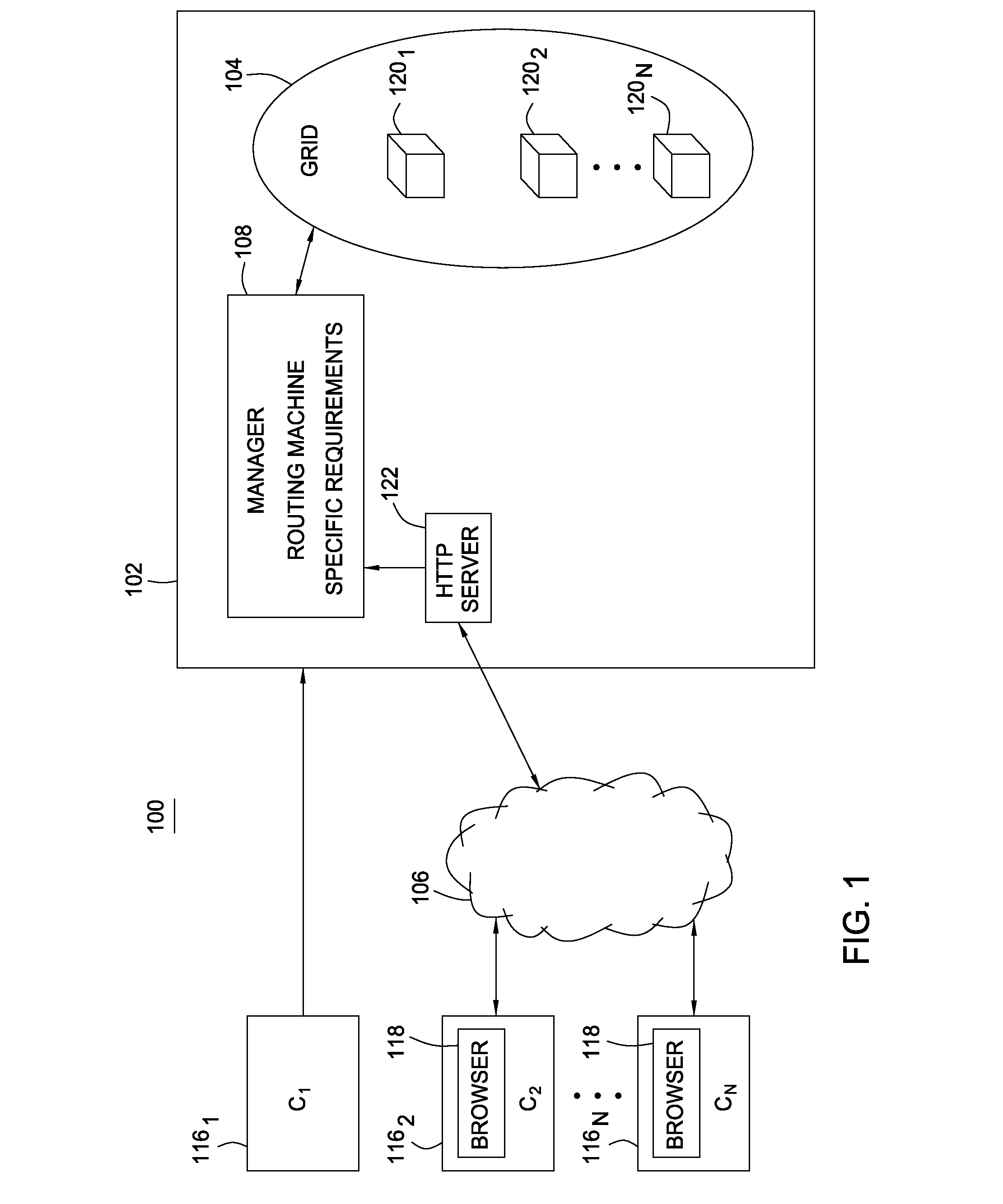
Power on demand tiered response time pricing
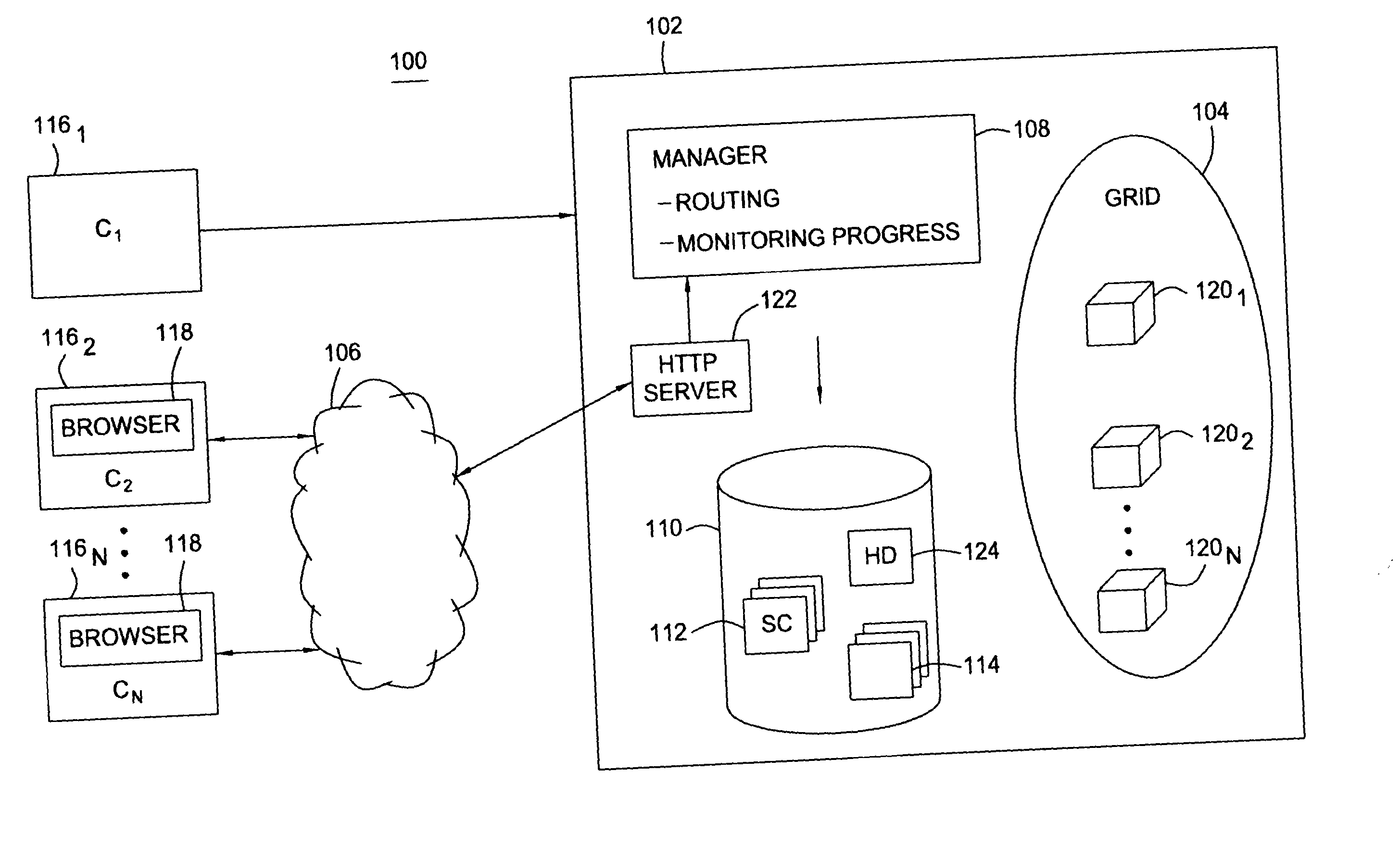
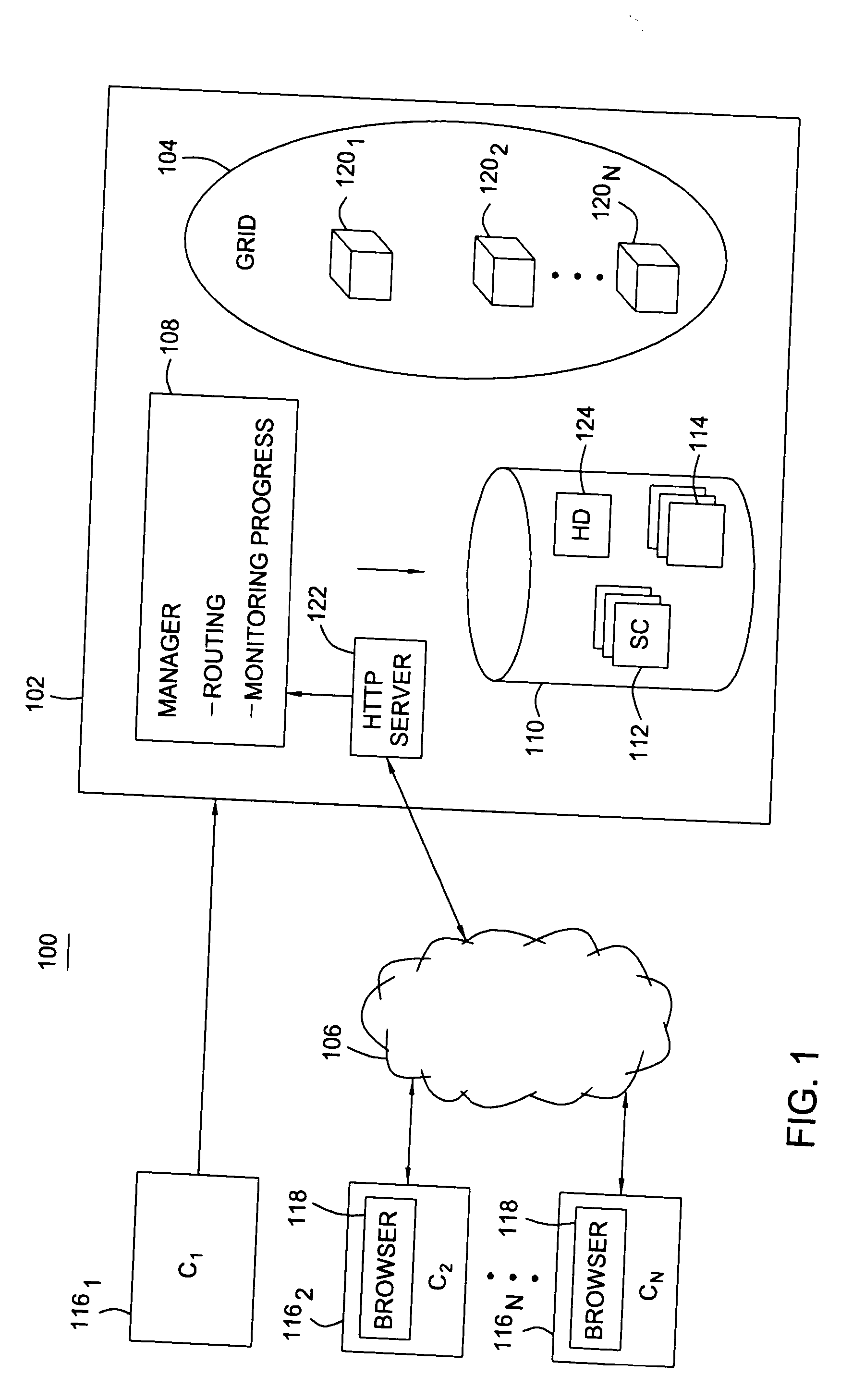
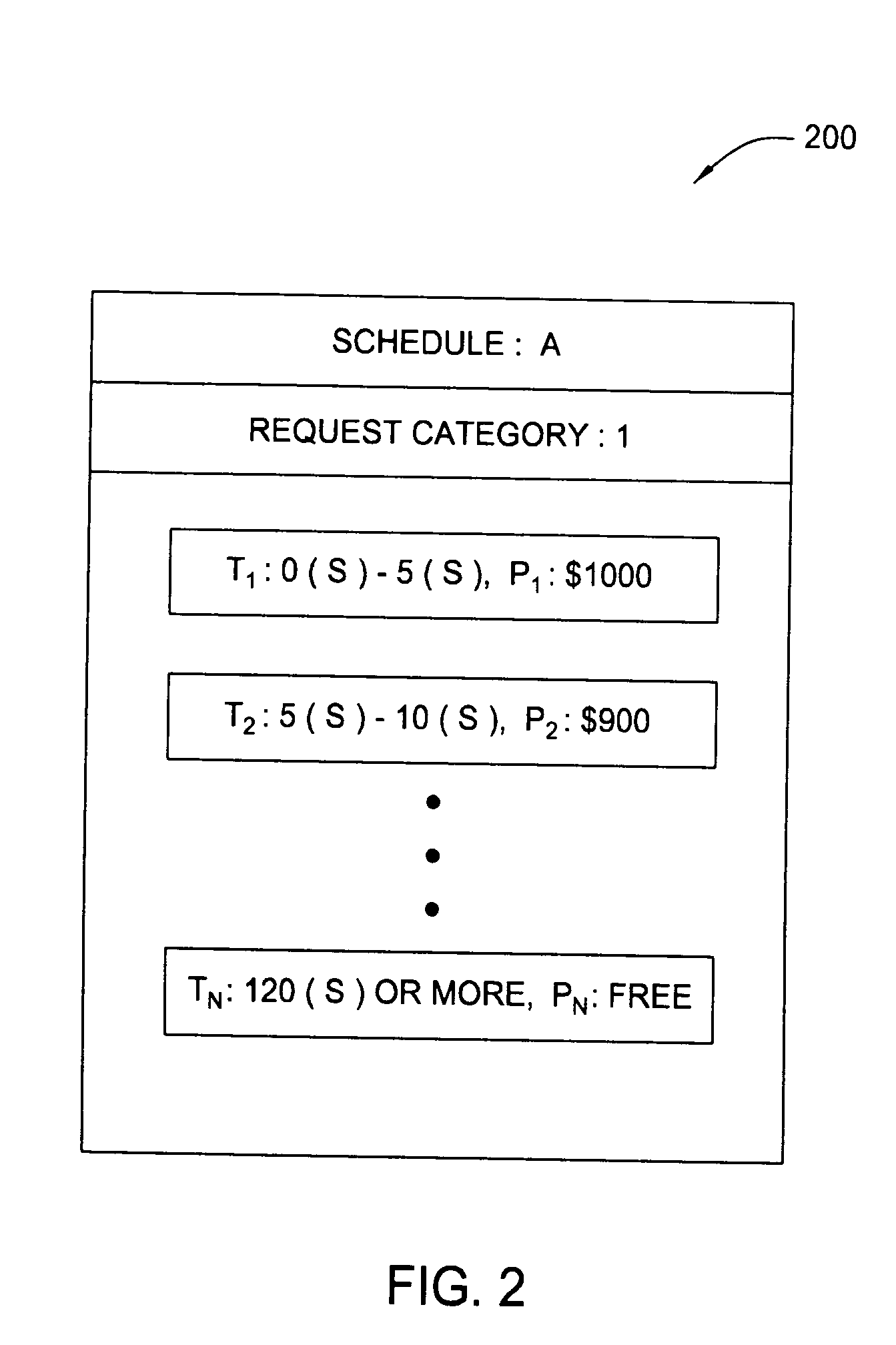
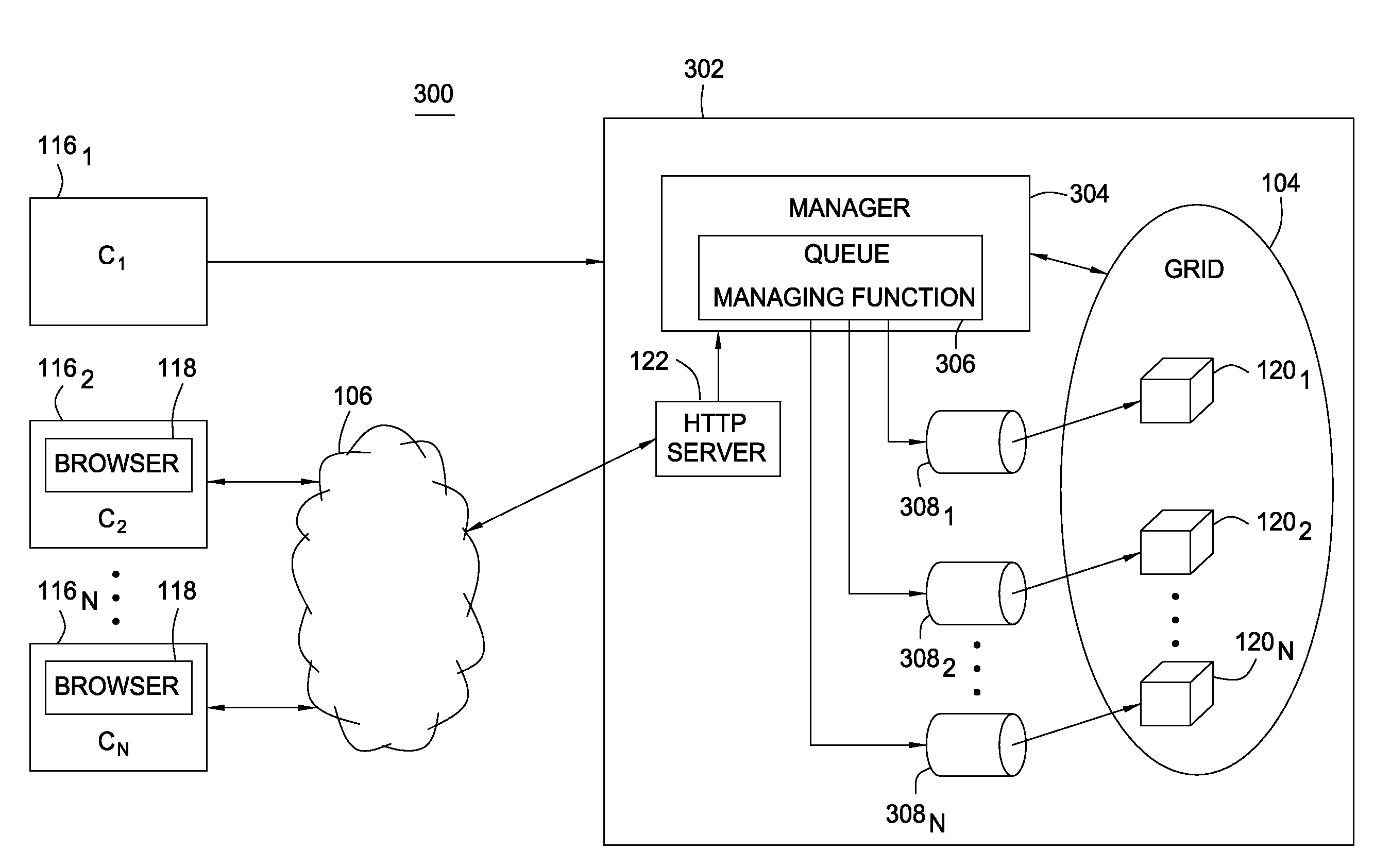
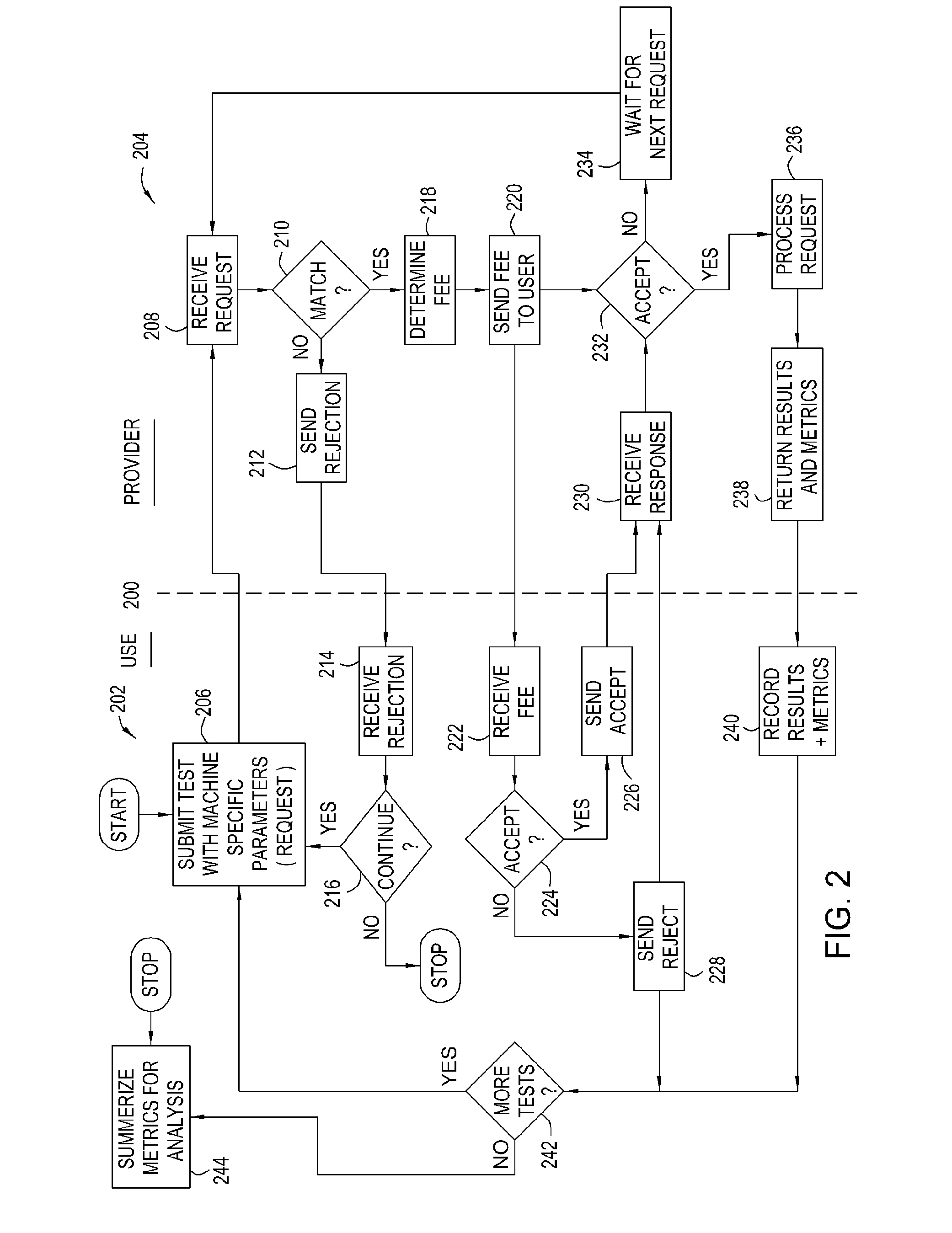
Methods, articles of manufacture, and systems for determining a fee to be charged for requests processed in a grid computing environment based. In one embodiment the fee may be determined based on the time it takes to process a request and / or pricing schedules that may vary depending on a variety of pricing criteria. In another embodiment, a completion time criterion that defines a maximum acceptable time to complete a request may be specified. If the amount of time needed to perform the request is less than the maximum acceptable time specified, returning the results may be delayed to avoid providing services valued in excess of what the customer has paid for.
Owner:EBAY INC
System and method for providing identification and search information
InactiveUS20050131894A1Special data processing applicationsWeb data retrieval using information identifiersPopulation statisticsApplication software
A system and method for identifying an entity. In one embodiment, the system and process defines the person by assigning a distinct code for each person's information such as demographic information, personal information and traits. The identification information may be incorporated into one or more web pages associates with the person to facilitate searching by others using an Internet search engine, or grid computing application, a peer-to-peer / file-sharing network.
Owner:VUONG CHAU MINH
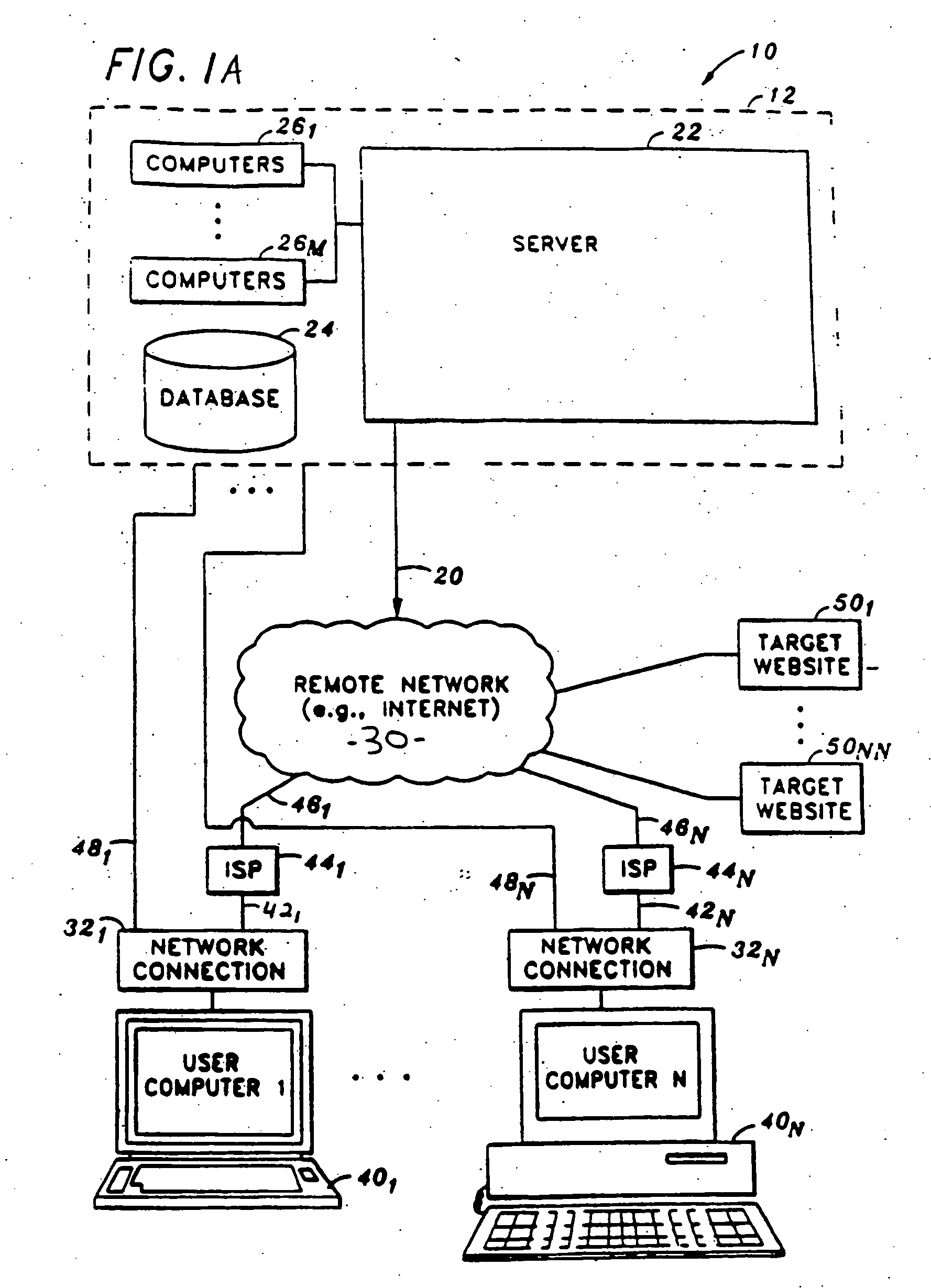
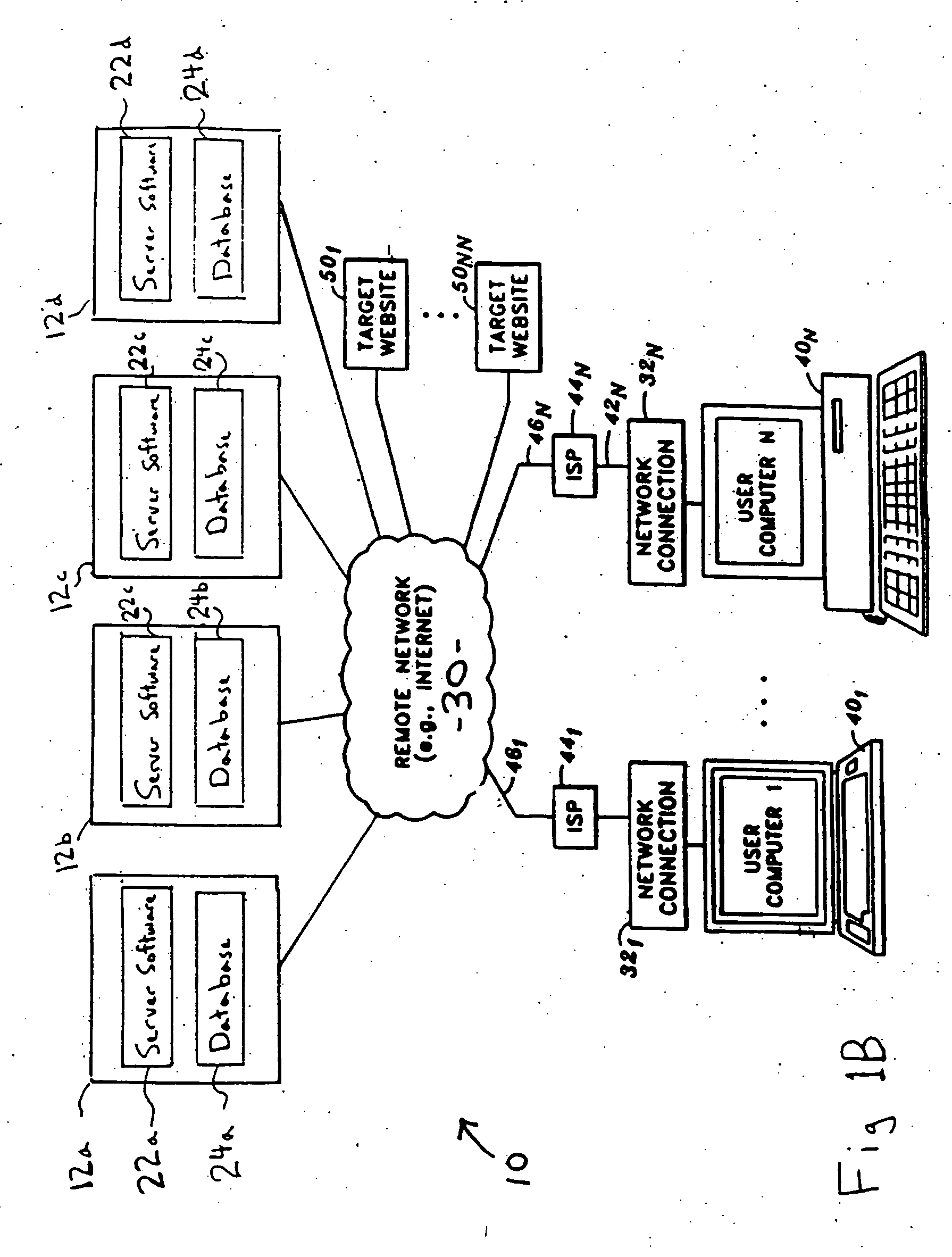
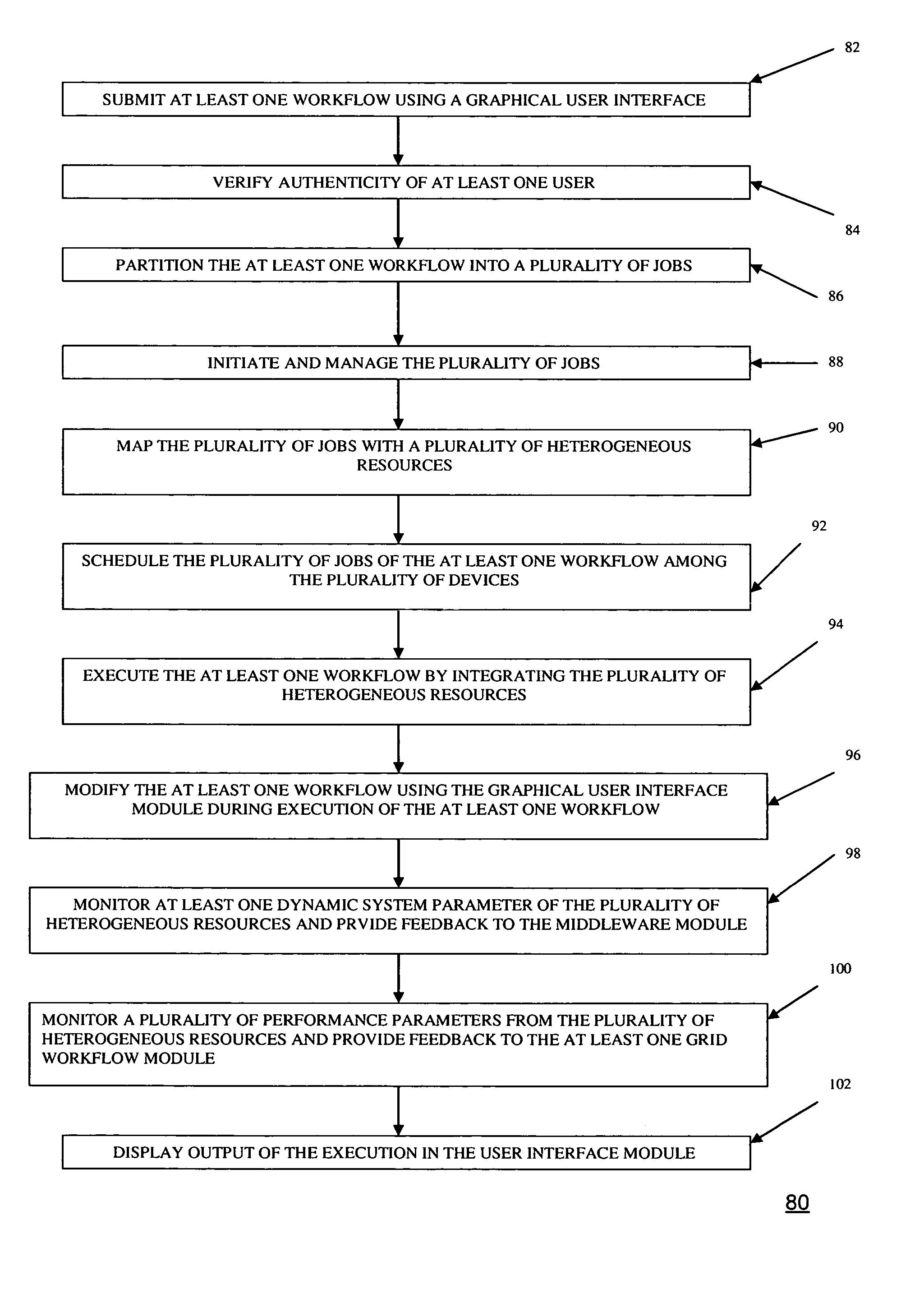
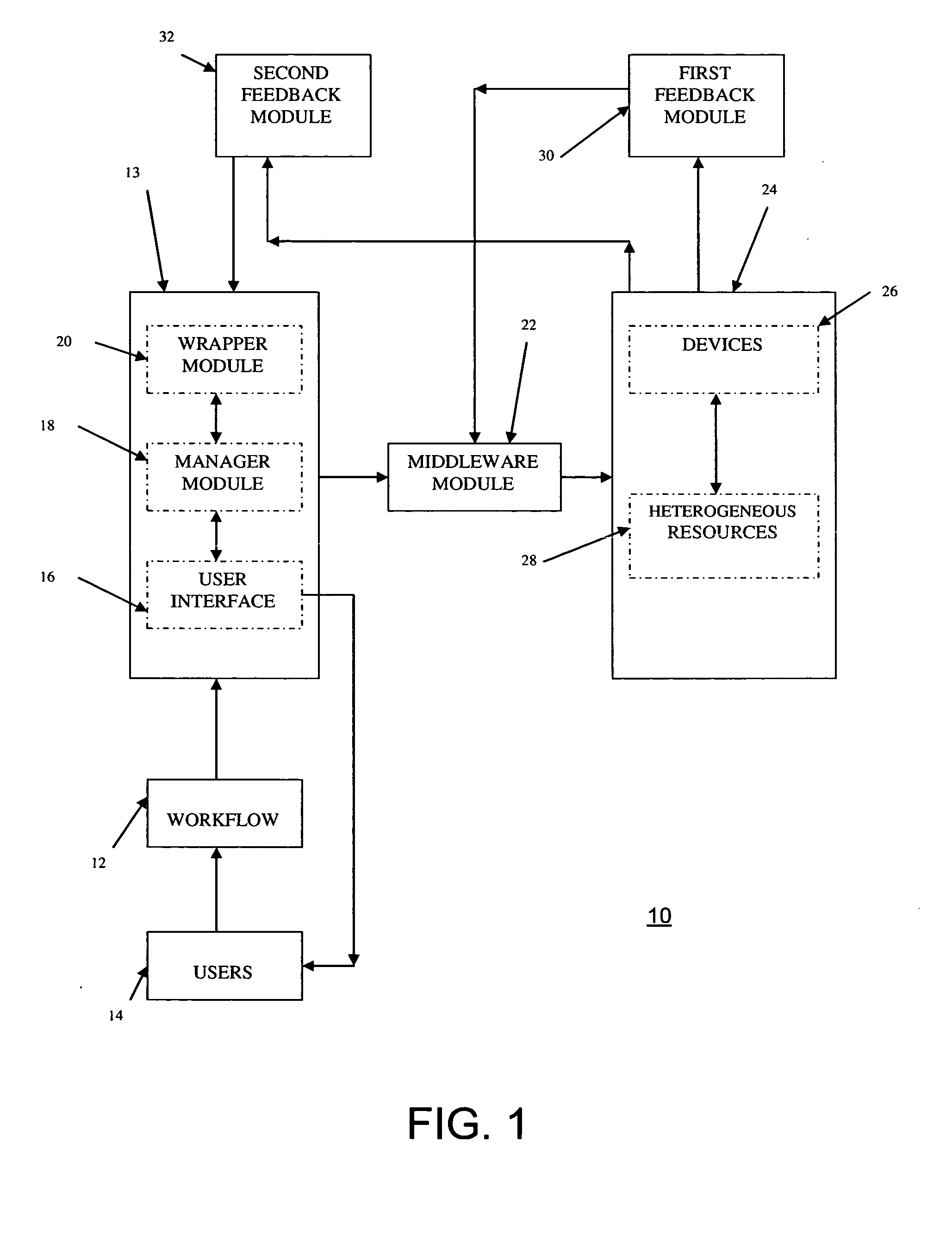
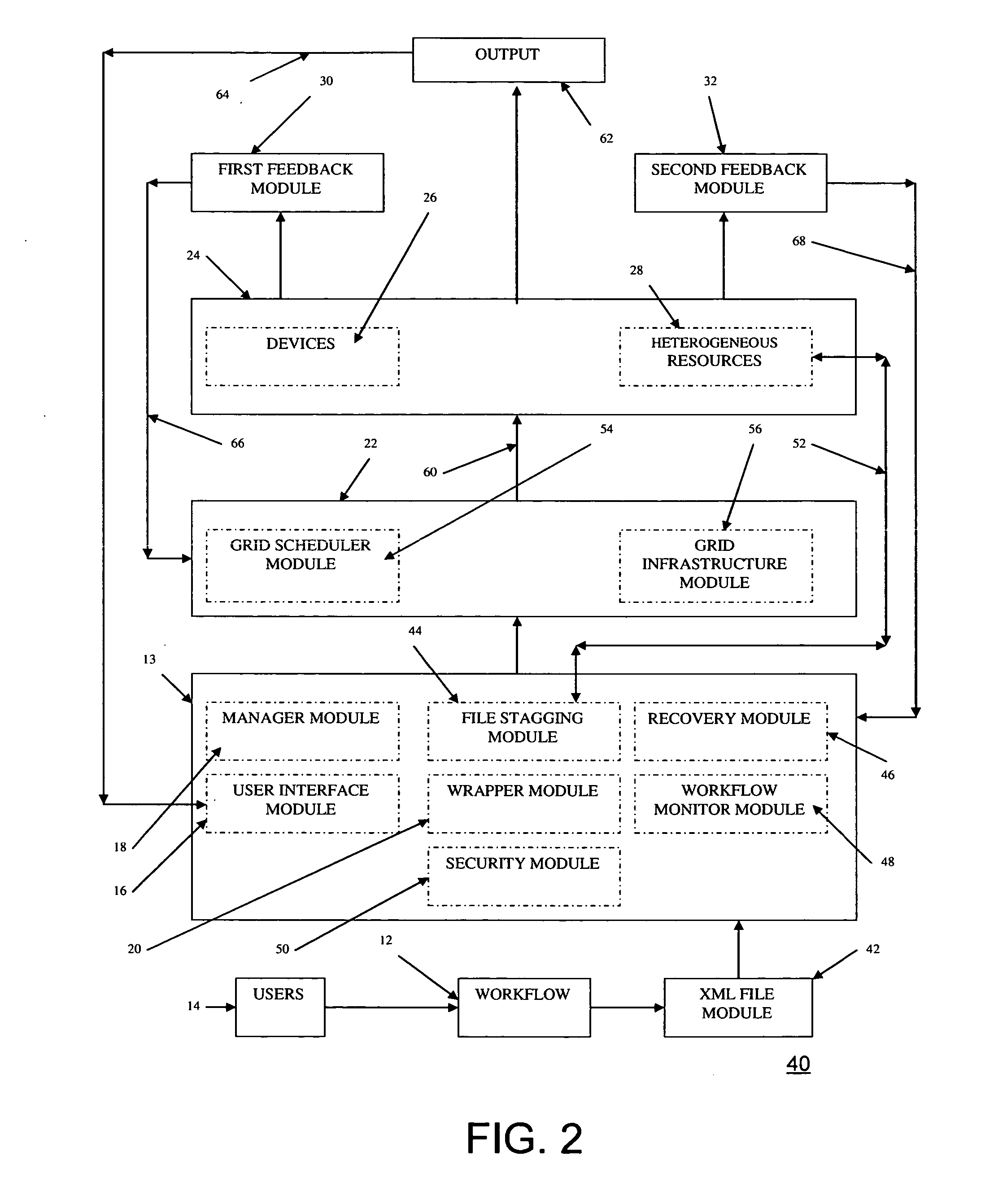
Grid computing systems and methods thereof
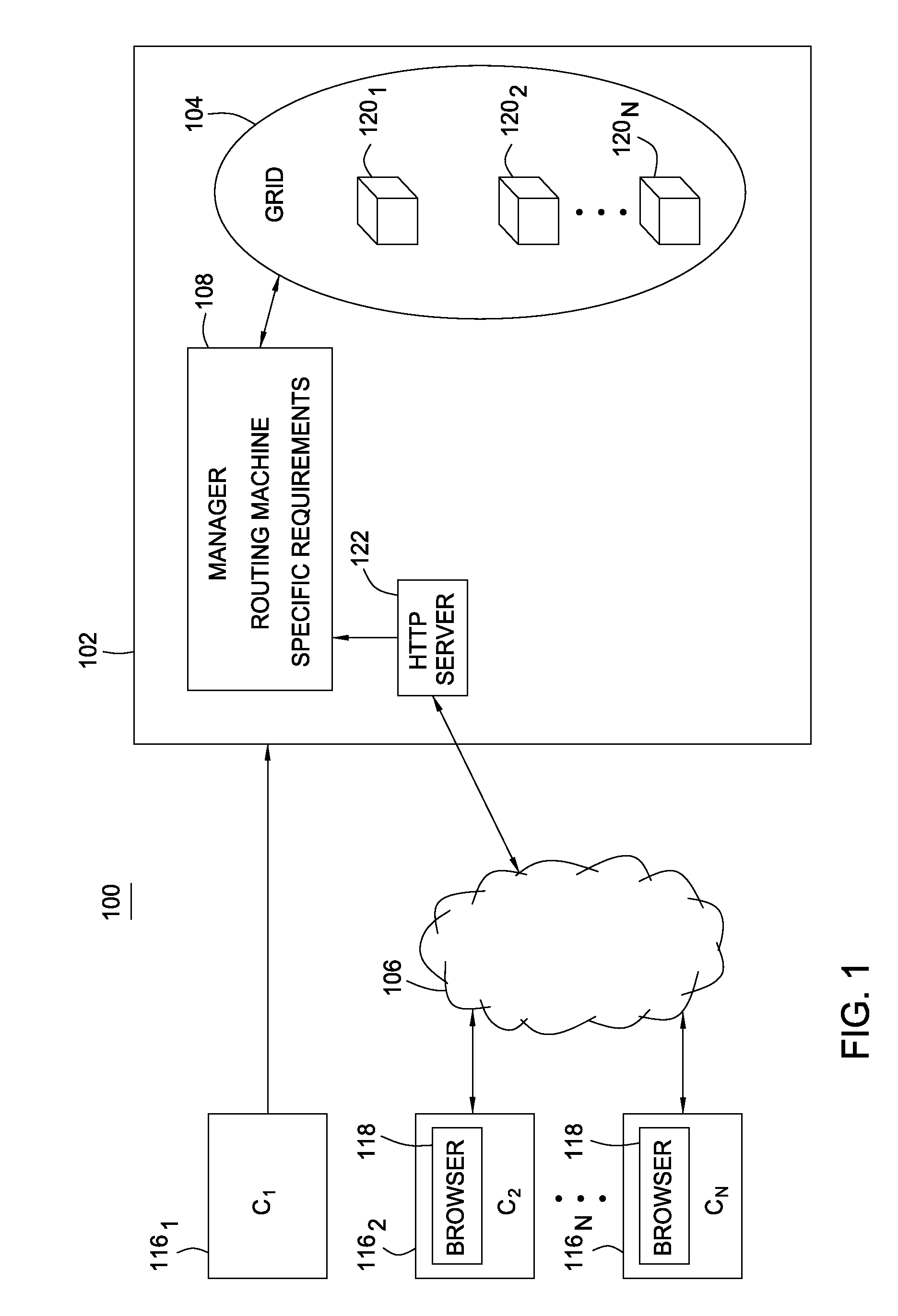
A grid computing system, method, and computer program product, adapted to execute at least one workflow having a set of predefined operating parameters and including an execution module comprising a plurality of devices having a plurality of heterogeneous resources, wherein the plurality of devices is adapted to execute the at least one job by integrating the plurality of heterogeneous resources. The system further includes at least one grid workflow module. The grid workflow module includes a graphical user interface to provide at least one user to initiate and manage the at least one workflow based on the set of predefined operating parameters and the plurality of heterogeneous resources. Furthermore, the grid workflow module includes a manager module adapted to partition the at least one workflow into multiple jobs prior to the execution of the at least one workflow.
Owner:INFOSYS TECH LTD (IN)
Methods and systems for technology analysis and mapping
InactiveUS20050192968A1Automatically analyzedPatent retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
Systems and methods for cladistics-based content searching, analysis, and / or diagrammatic representation of results in graphical user interface format for viewing by at least one user on a grid computing network, in particular for technology and patent-related content stored in at least one database.
Owner:SPORE
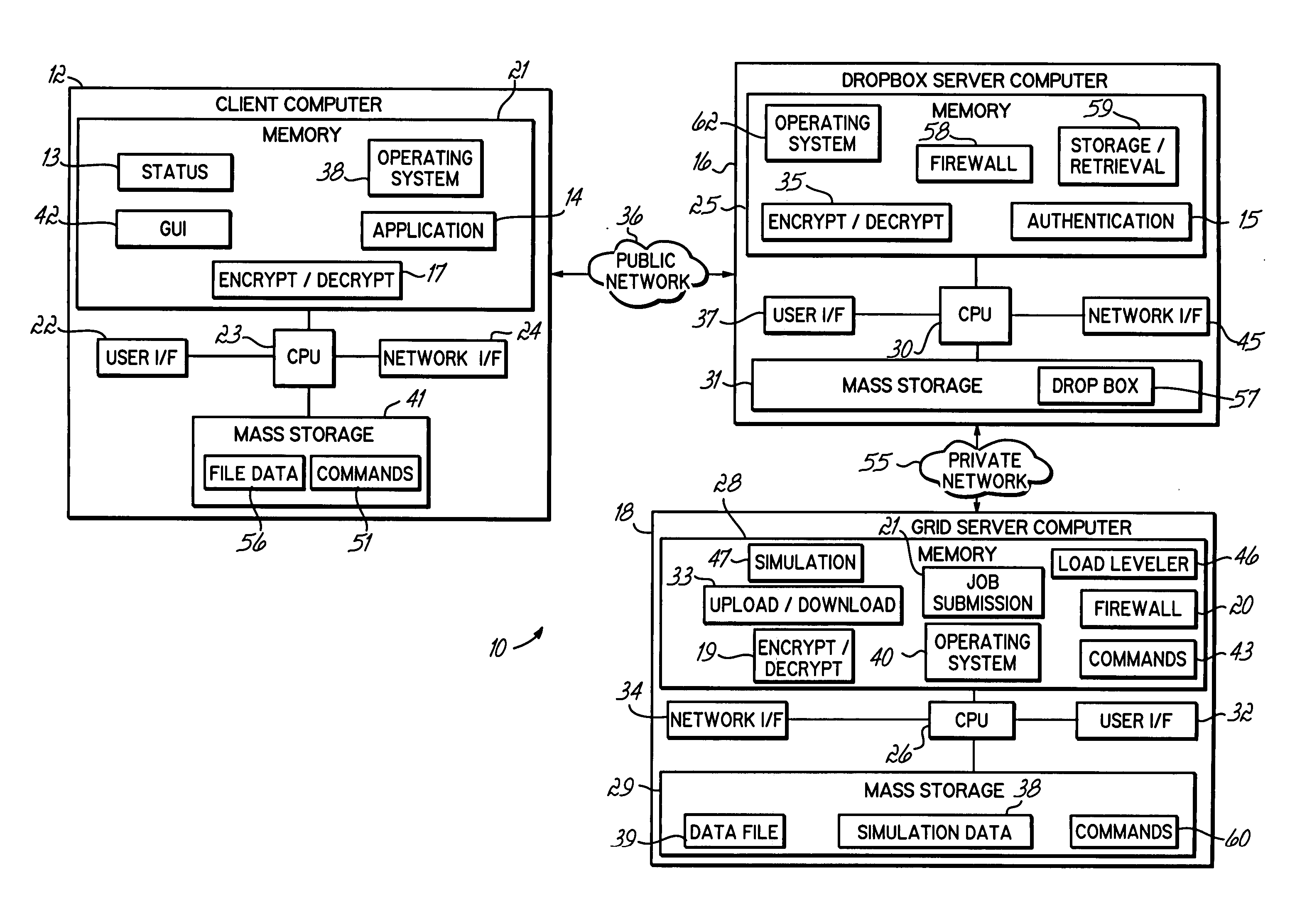
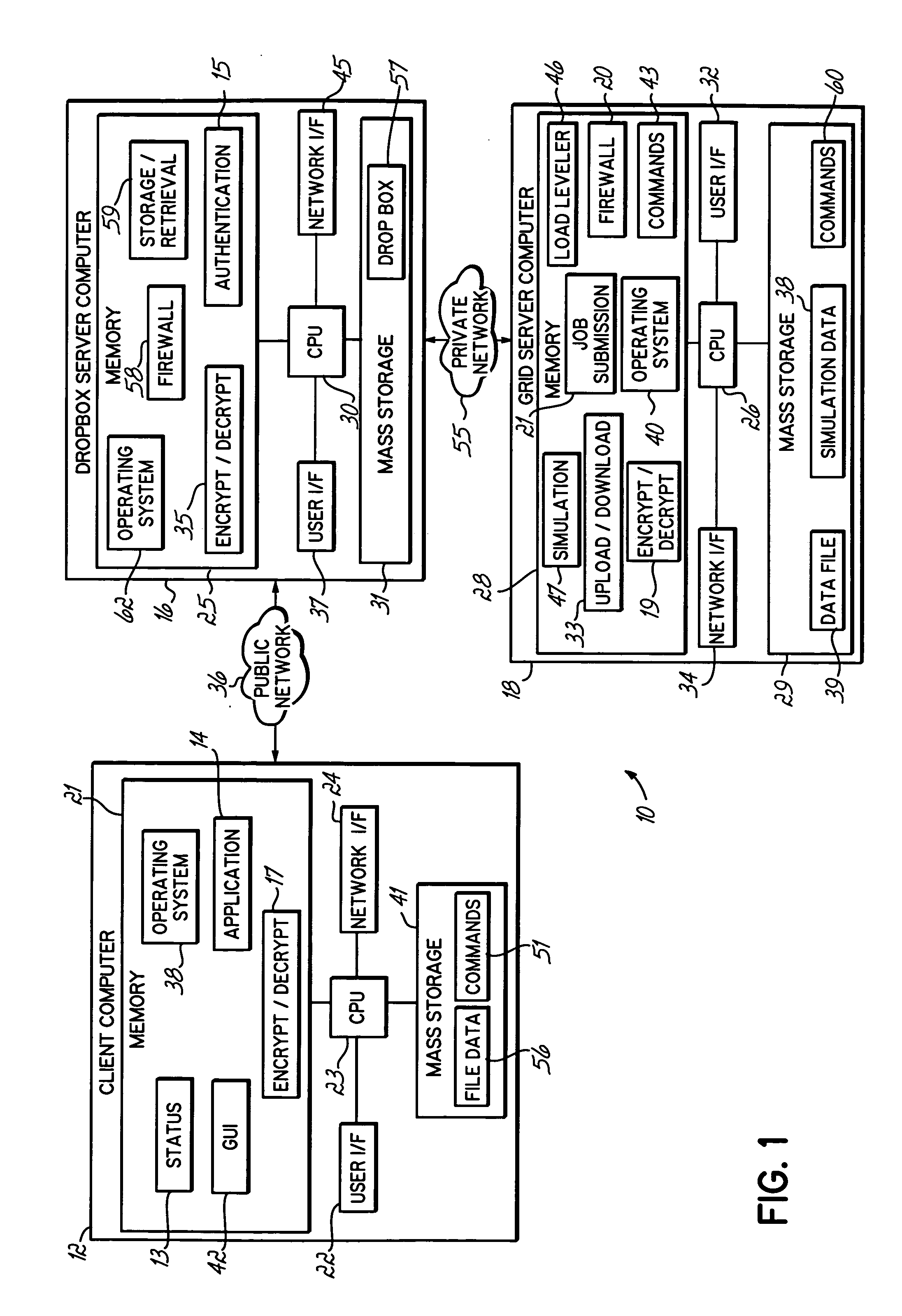
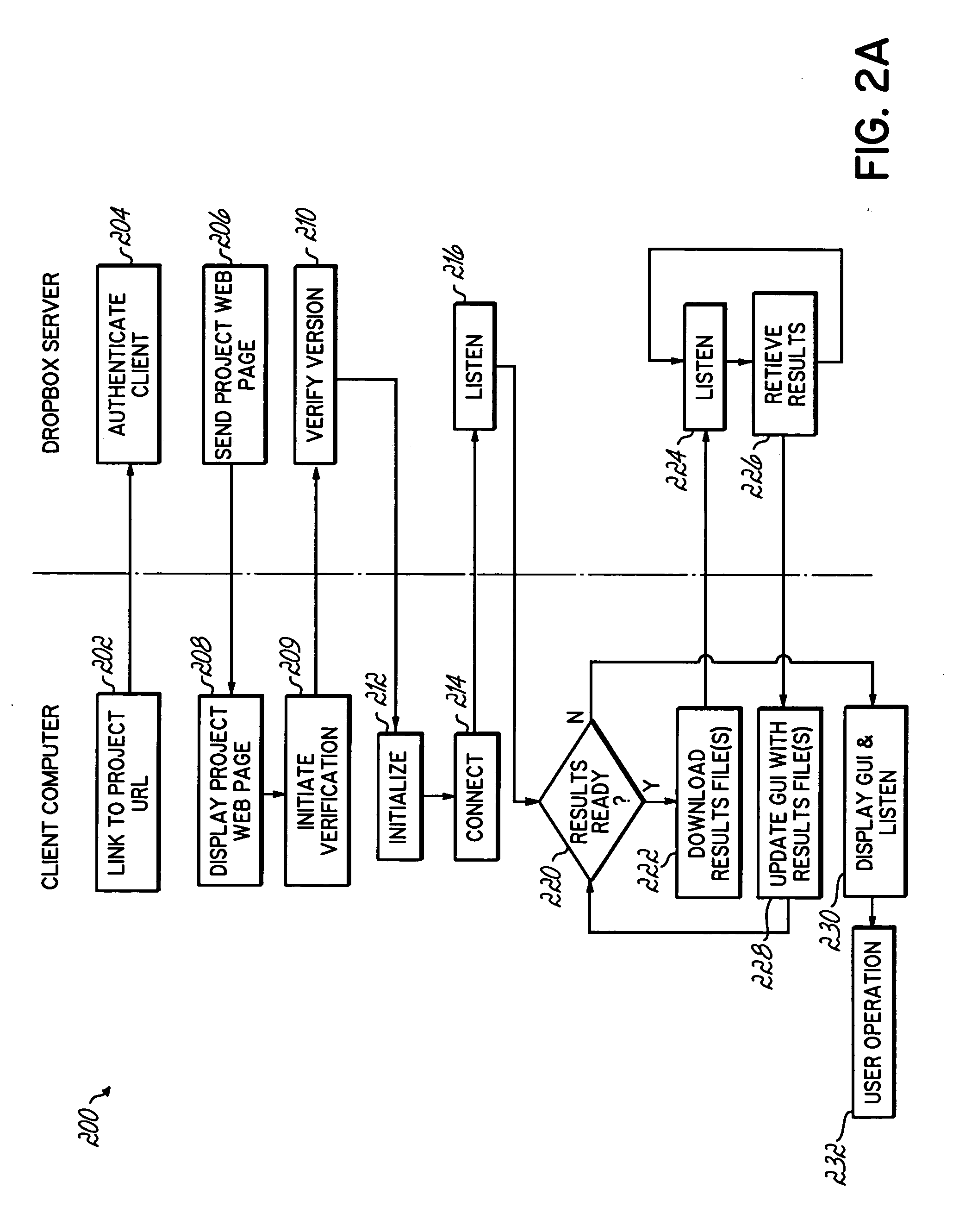
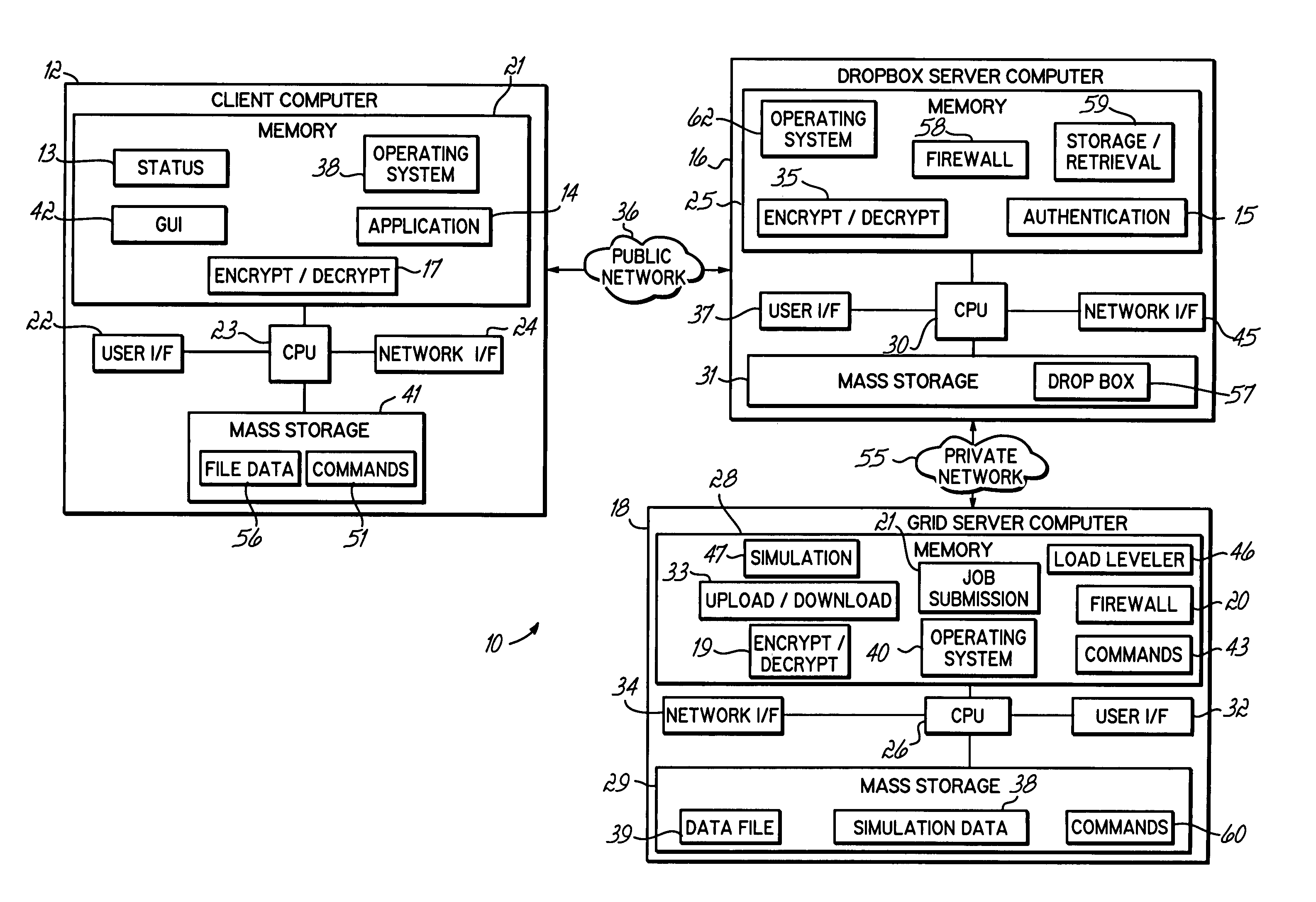
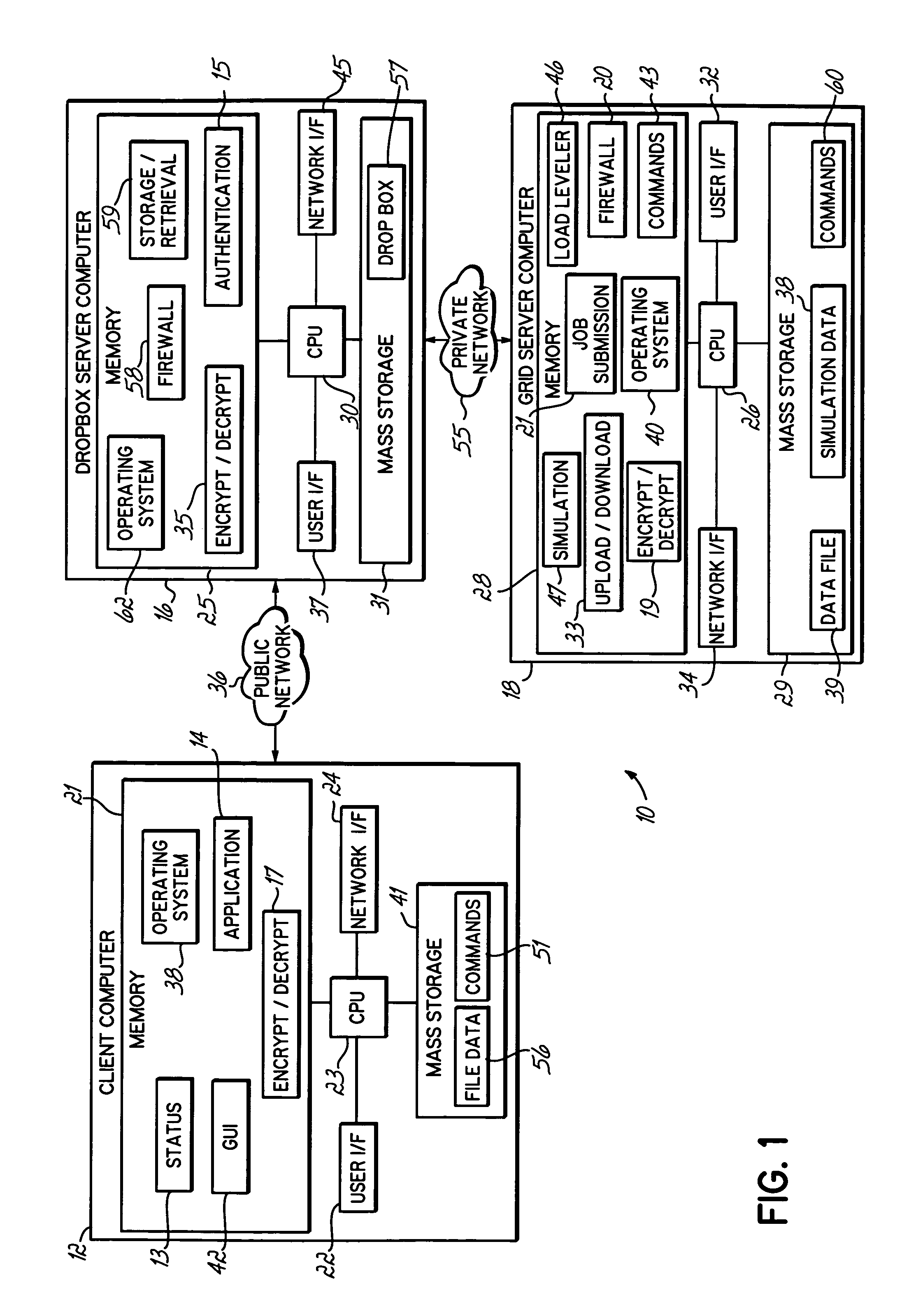
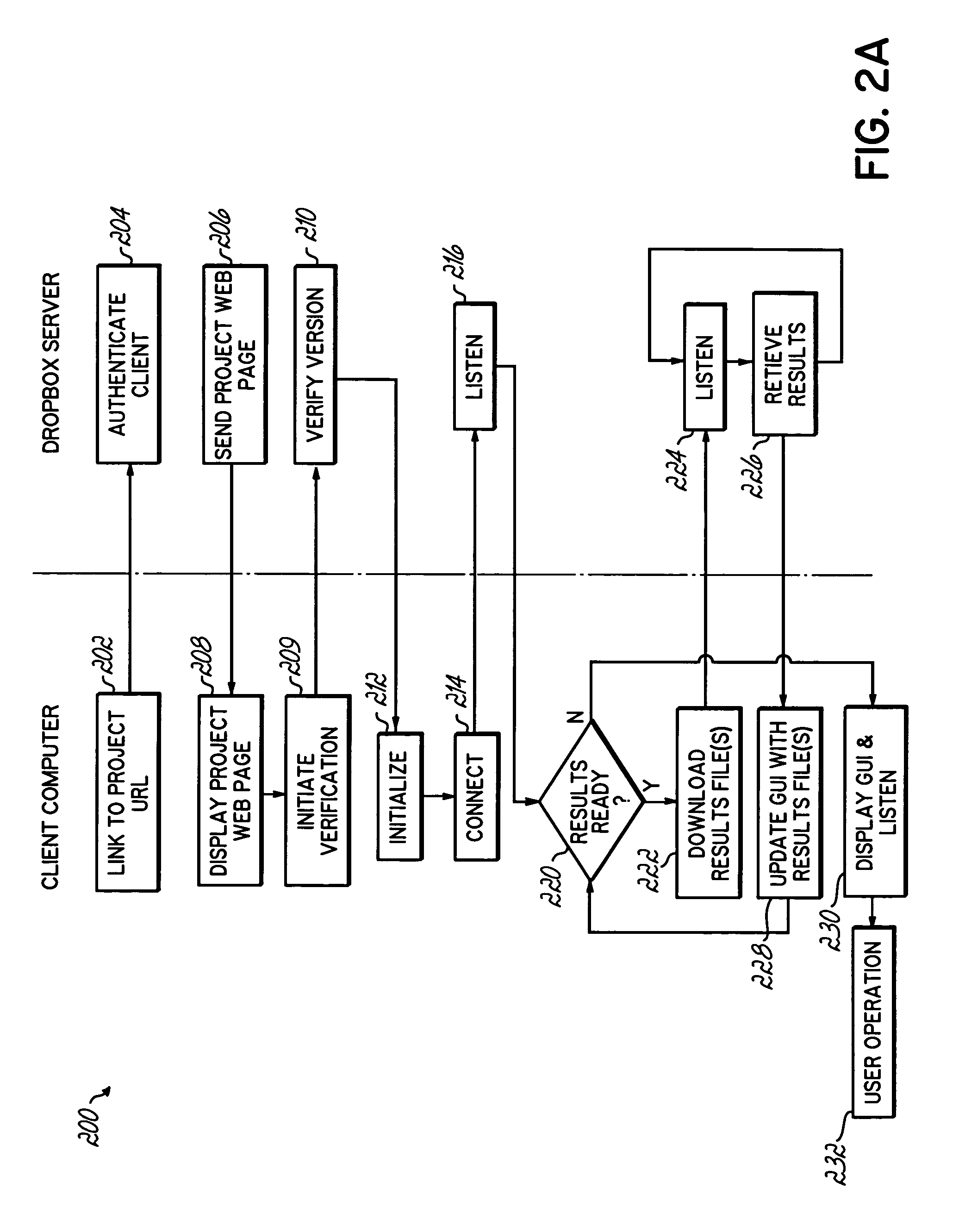
Computer grid access management system
InactiveUS20050246547A1Promotes great processing speedImprove efficiencyComputer security arrangementsSecret communicationComputer GridClient-side
An apparatus, program product and method for managing access to a remote computing grid that is not normally accessible to a client. A client computer may communicate with the computing grid via a dropbox configured to receive and distribute data between the client computer and the grid. The connection may remain open while multiple commands are thus communicated to the computing grid, and the identity of the client submitting the commands may be authenticated.
Owner:AIRBNB
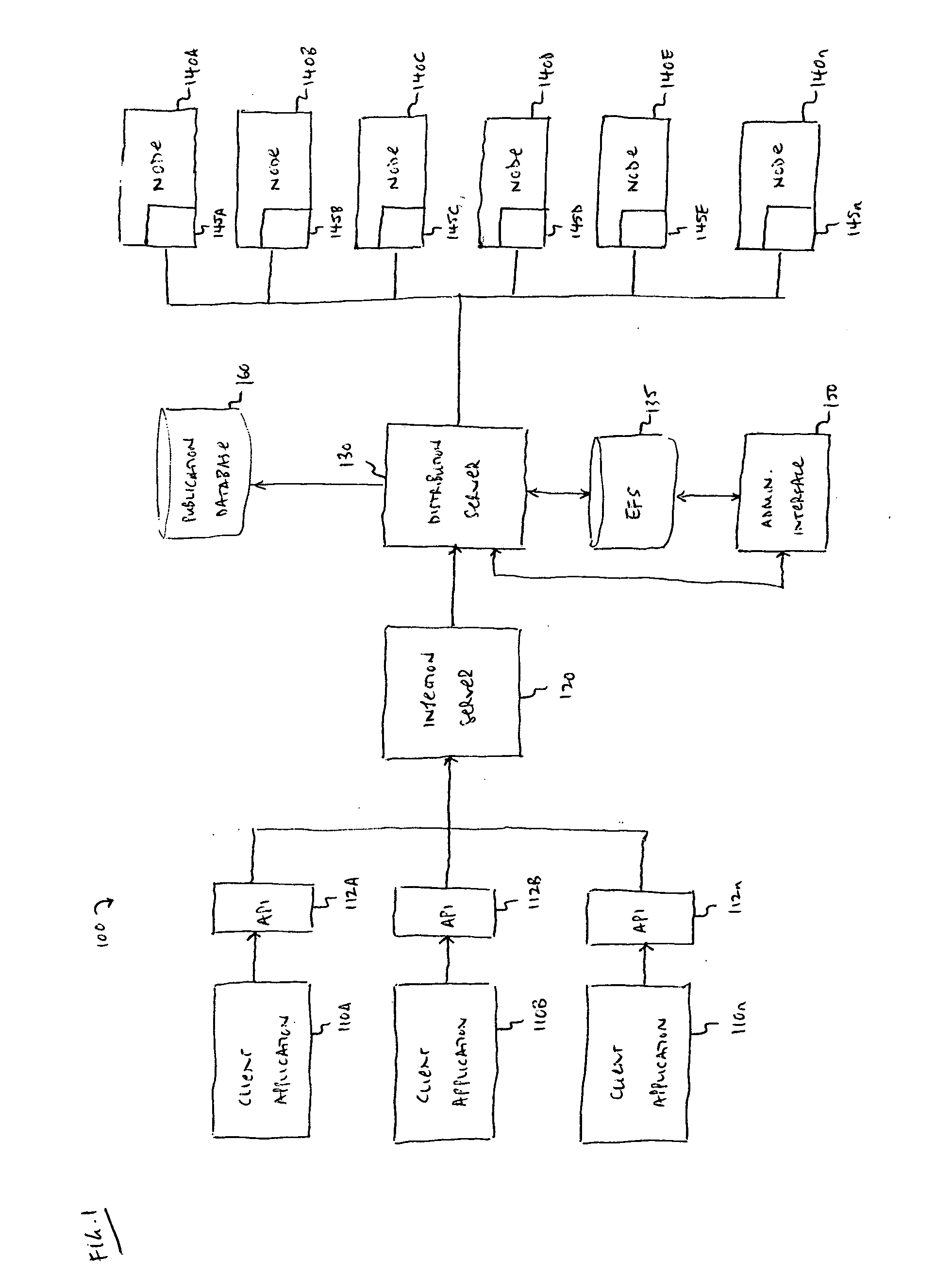
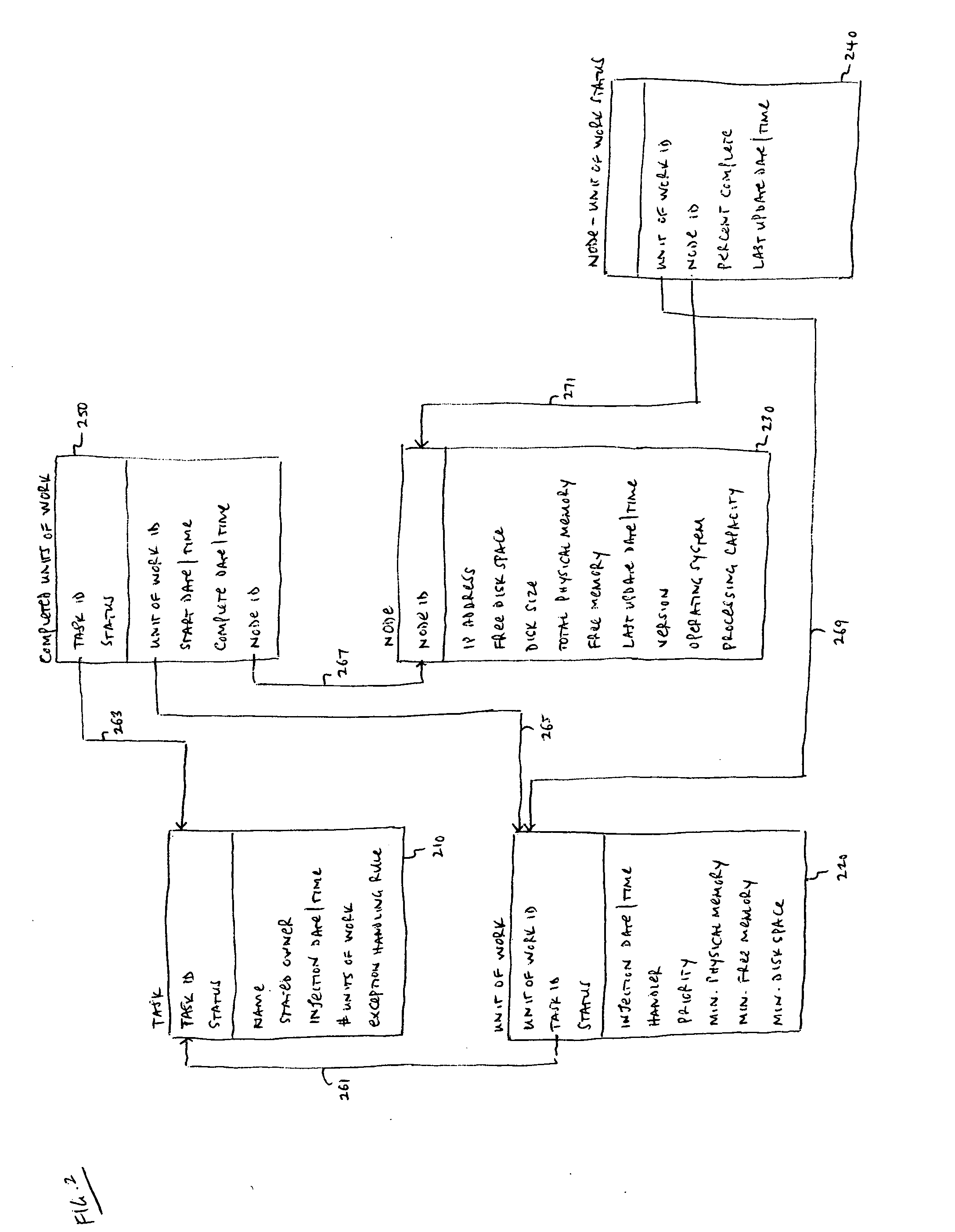
Method and apparatus for processing of heterogeneous units of work
InactiveUS20070106773A1Improve abilitiesDigital computer detailsProgram controlInternet trafficComputer Grid
Methods and apparatus are provided which may be employed to perform speech recognition processing on a grid computing system. In some embodiments, the grid computing system includes a server system which receives processing tasks from one or more client applications, divides the processing tasks into units of work, and assigns the units of work to one or more of the nodes. Dividing a processing task into units of work may involve dividing audio input data into segments defined by natural speech boundaries. A mathematical representation may be created for each segment prior to its distribution on the grid to minimize network traffic. A node in the system may perform heterogeneous units of work concurrently, such as by isolating the execution of each unit of work in an application domain.
Owner:CALLMINER INC
Computer grid access management system
InactiveUS7523317B2Improve efficiencyIncrease speedComputer security arrangementsSecret communicationComputer GridClient-side
An apparatus, program product and method for managing access to a remote computing grid that is not normally accessible to a client. A client computer may communicate with the computing grid via a dropbox configured to receive and distribute data between the client computer and the grid. The connection may remain open while multiple commands are thus communicated to the computing grid, and the identity of the client submitting the commands may be authenticated.
Owner:AIRBNB
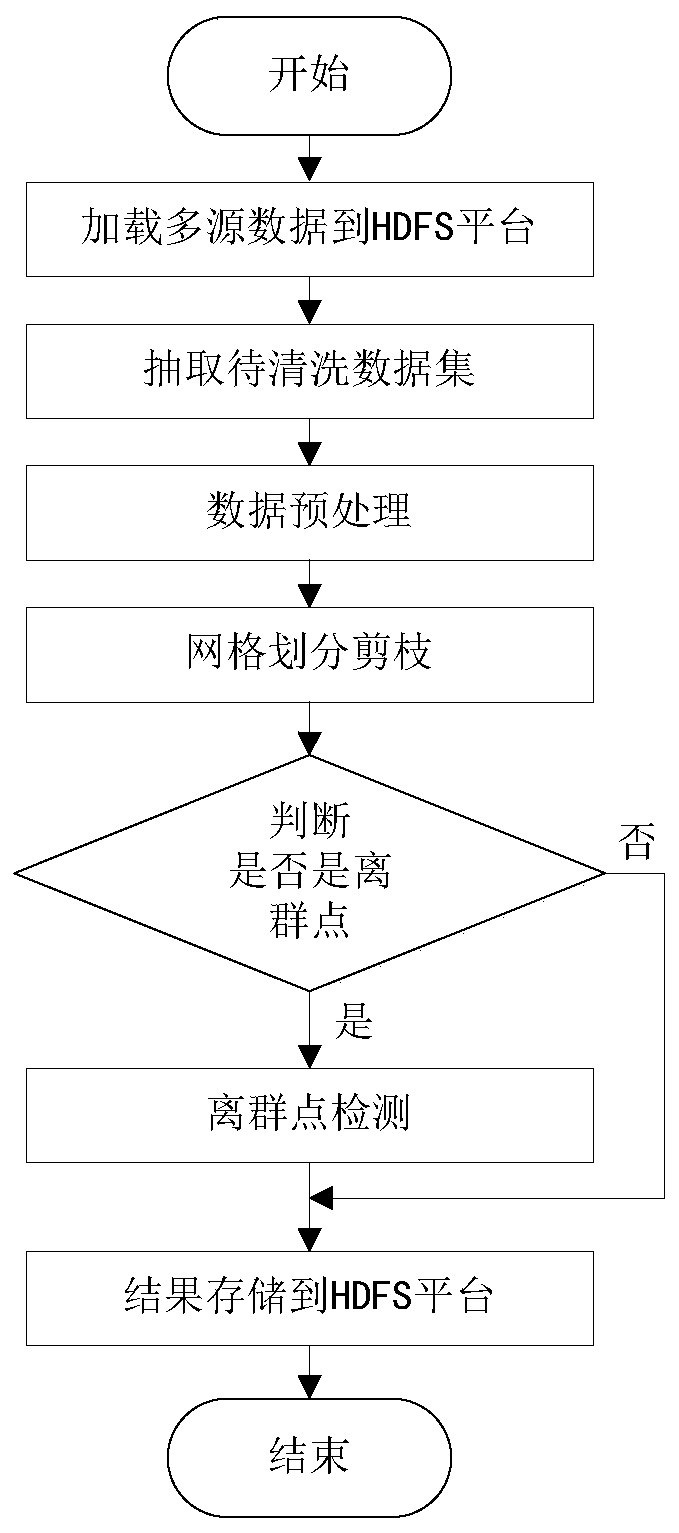
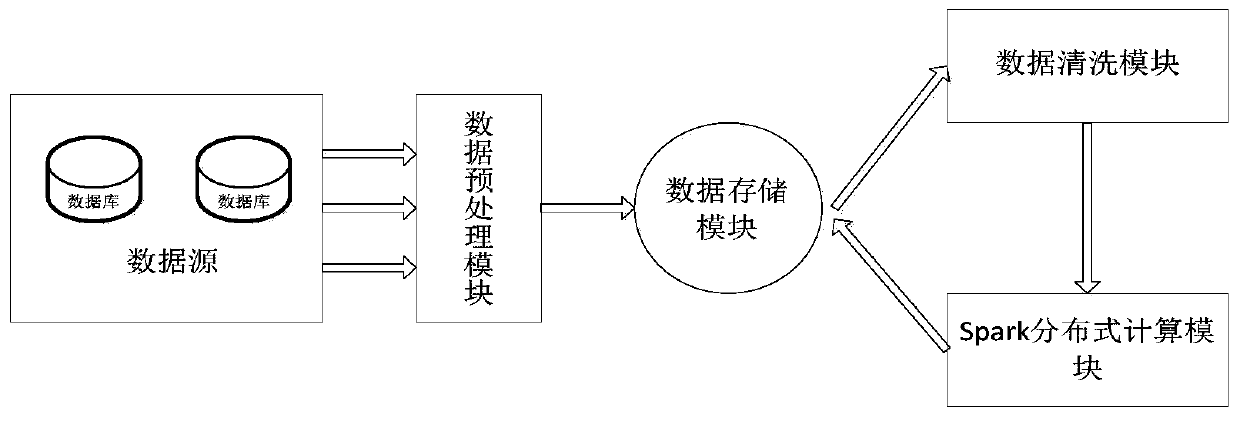
LOF outlier detection method and system based on grid pruning
PendingCN110471946AReduce complexityReduce the probability of accidental deletionDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsGrid densityData set
The invention relates to an LOF outlier detection method and an LOF outlier detection system based on grid pruning. The method comprises the steps that S1, reading and preprocessing a data set; S2, performing equidistant division on the data set, calculating a boundary range of each grid, and numbering the grids; S3, comparing each data object in the data set with the boundary range of the grid tofind the grid to which the data object belongs; S4, calculating the grid density and the clustering radius of each grid, and determining a grid density threshold value and a clustering radius threshold value; S5, pruning the grids; S6: carrying out outlier detection. The device comprises a data preprocessing module, a data storage module, a data cleaning module and a Spark distributed computing module. According to the method, the problem of poor practicability caused by relatively high time and space complexity when an existing LOF outlier detection method is used for processing real-time large-scale high-dimensional data objects is solved. The high efficiency and the practicability of a calculation process are improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
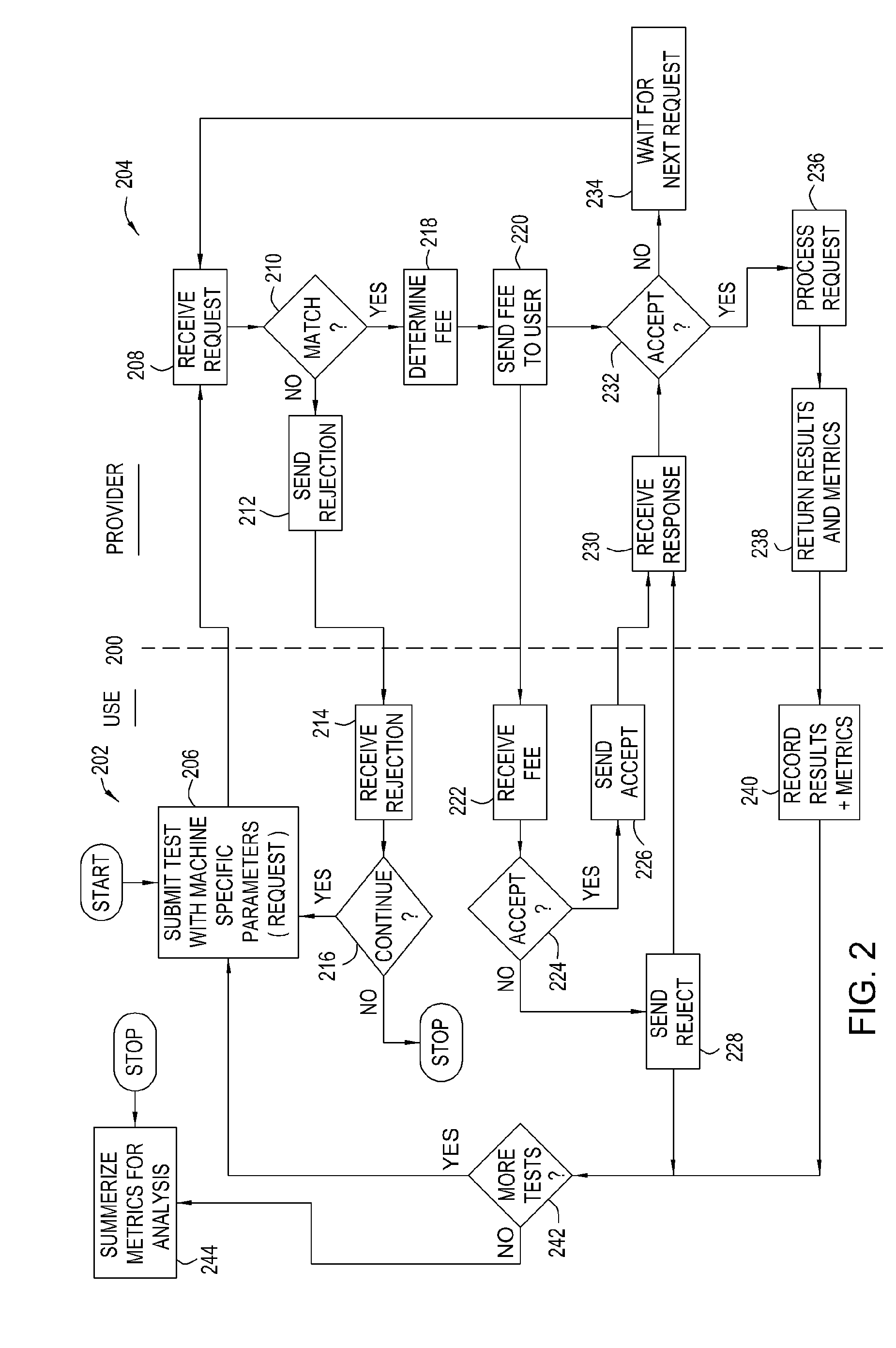
Request type grid computing
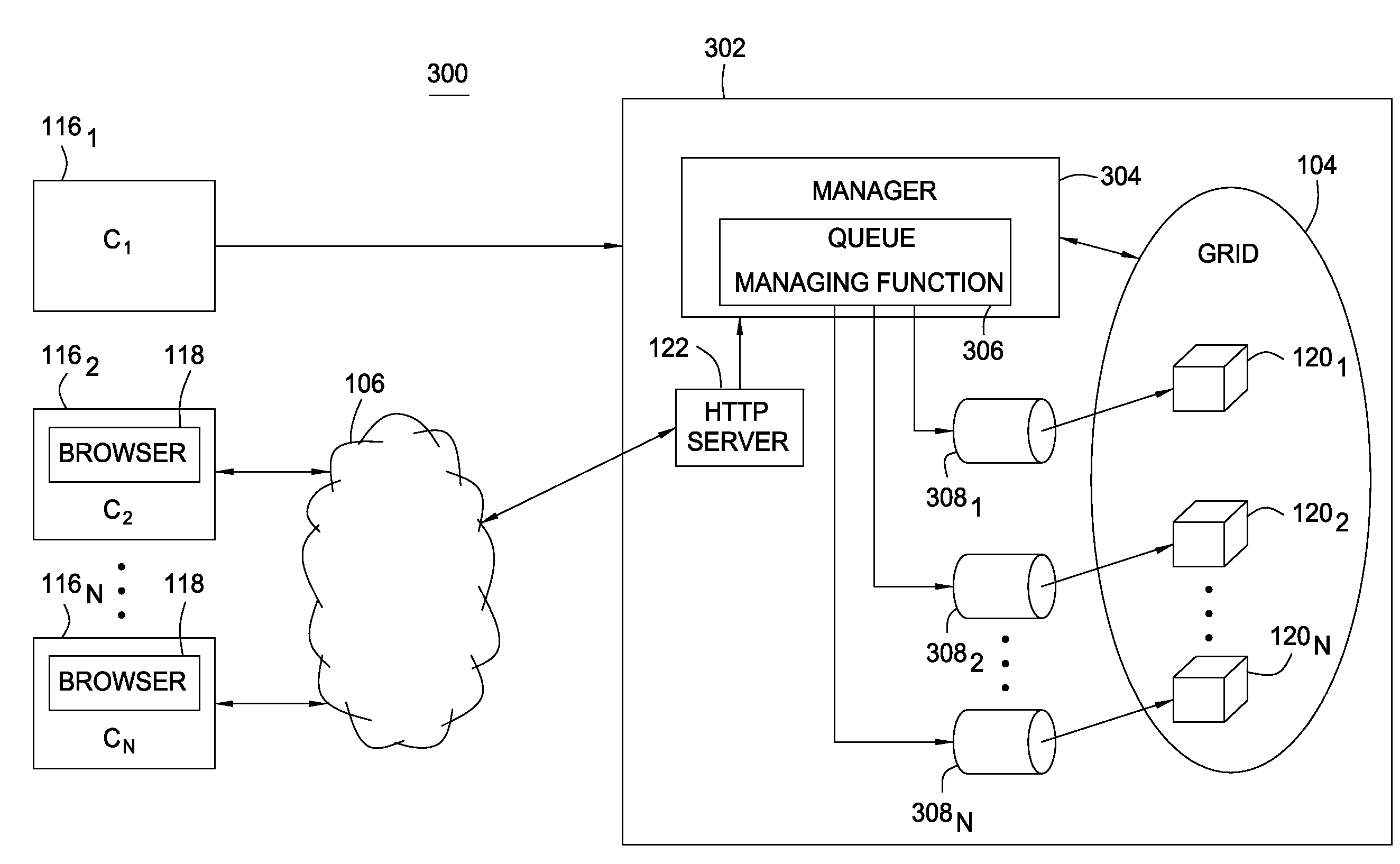
Methods, articles of manufacture, and systems for providing access to a grid computing environment. In one environment, requests include resource specific criteria used to identify a particular grid resource to perform the request. In another embodiment, a request includes a queue criterion used to identify one of a plurality of queues on which the request is placed.
Owner:RED HAT
Request type grid computing
Methods, articles of manufacture, and systems for providing access to a grid computing environment. In one environment, requests include resource specific criteria used to identify a particular grid resource to perform the request. In another embodiment, a request includes a queue criterion used to identify one of a plurality of queues on which the request is placed.
Owner:RED HAT
Self-powered, self-propelled computer grid with loop topology
InactiveUS20190219026A1Efficient HarvestingWind motor controlAuxillariesEnergy harvesterComputer Grid
An energy-harvesting compute grid includes computing assemblies that cooperate with mobile energy harvesters configured to be deployed on a body of water. The plurality of energy harvesters are positioned on and move adjacent to an upper surface of a body of water, and the locations of the energy harvesters can be monitored and controlled. The wide-spread gathering by the harvesters of environmental data within that geospatial area permits the forecasting of environmental factors, the discovery of advantageous energy-harvesting opportunities, the observation and tracking of hazardous objects and conditions, the efficient distribution of data and / or tasks to and between the harvesters included in the compute grid, the efficient execution of logistical operations to support, upgrade, maintain, and repair the cluster, and the opportunity to execute data-gathering across an area much larger than that afforded by an individual harvester (e.g., radio astronomy, 3D tracking of and recording of the communication patterns of marine mammals, etc.). The computational tasks can be shared and distributed among a compute grid implemented in part by a collection of individual floating self-propelled energy harvesters thereby providing many benefits related to cost and efficiency that are unavailable to relatively isolated energy harvesters, and likewise unavailable to terrestrial compute grids of the prior art.
Owner:LONE GULL HLDG LTD
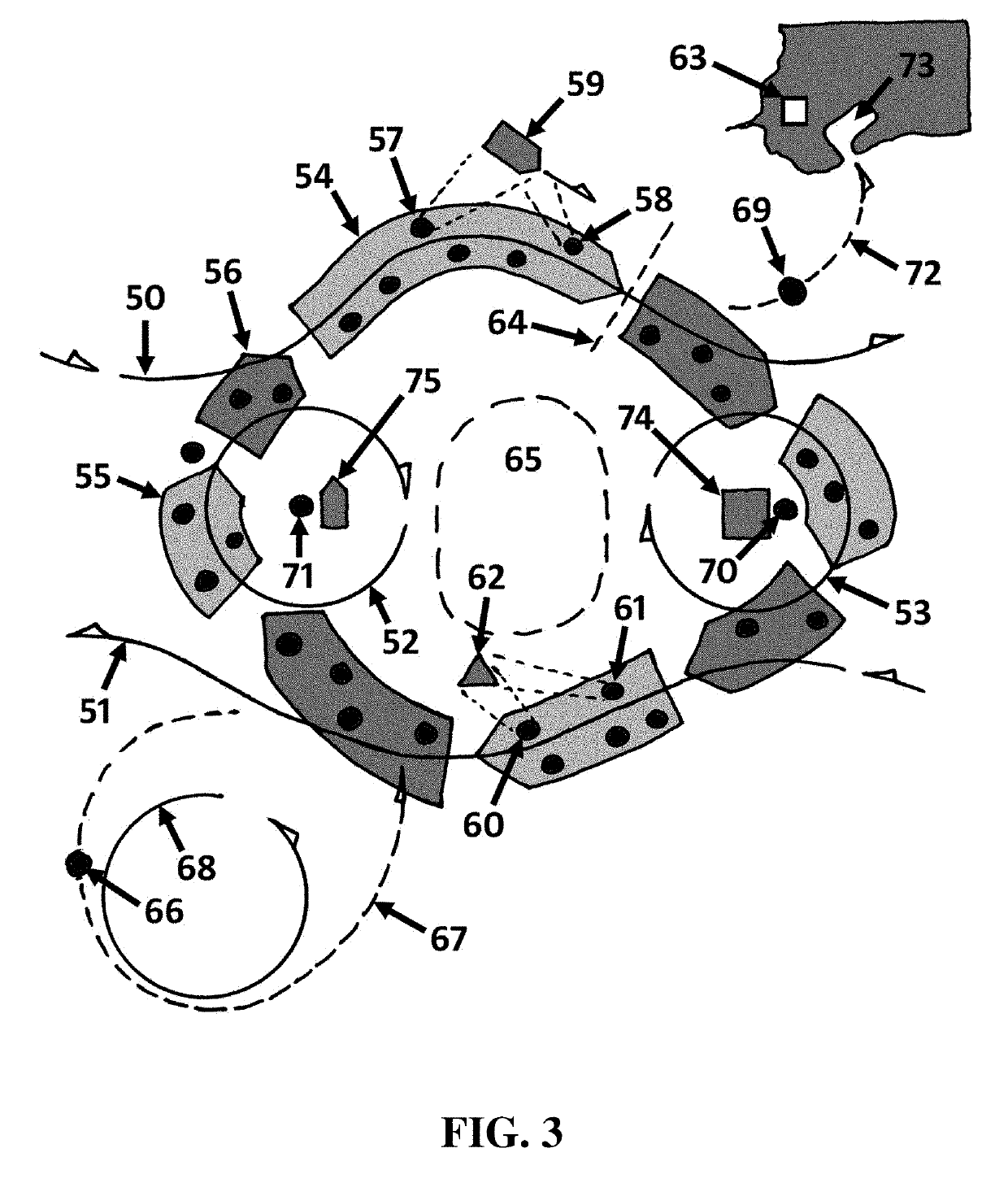
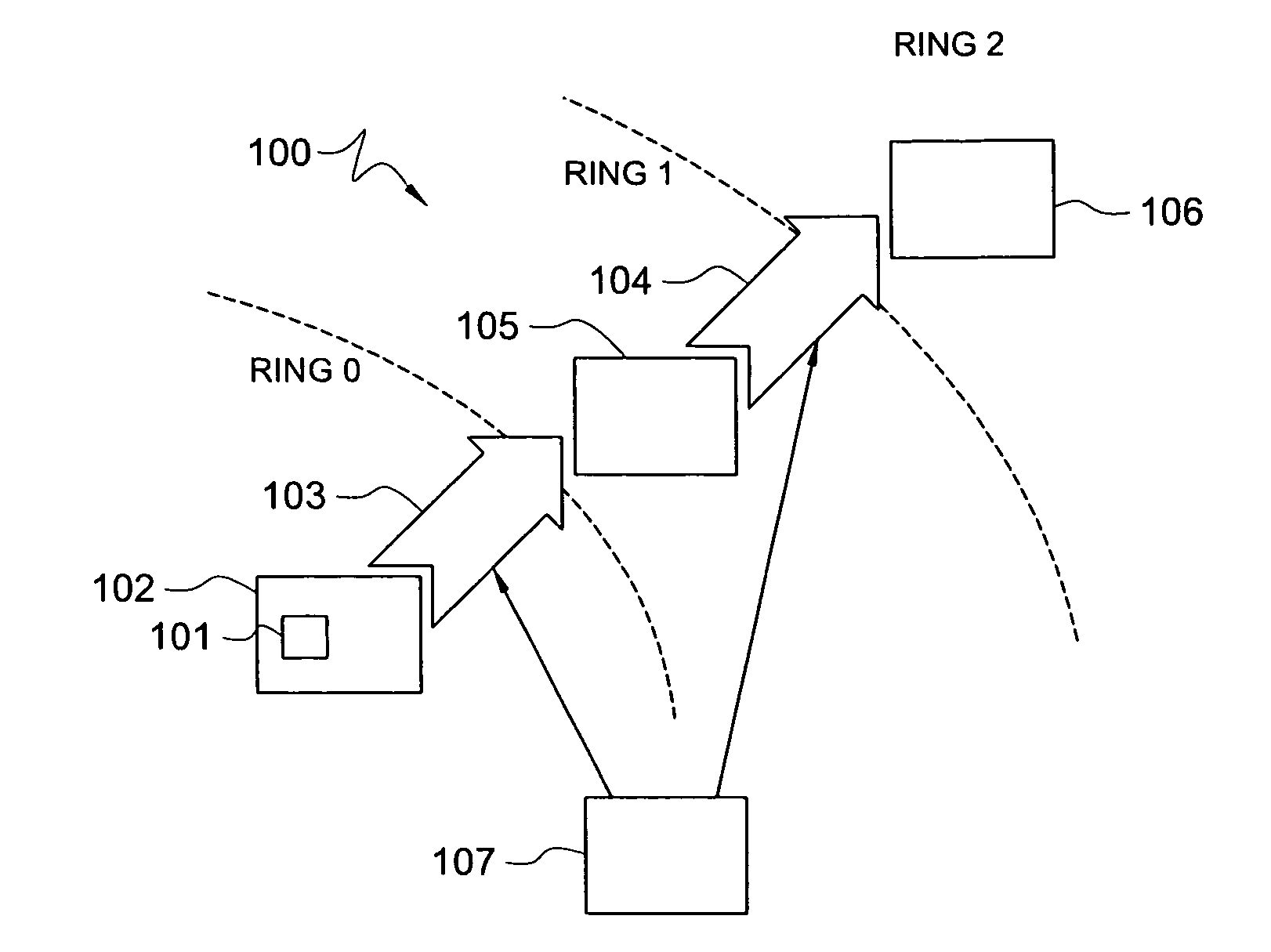
Federation of grids using rings of trust
A system for sharing computer resources comprises a node in a first computer grid, and one or more processing units adapted to instantiate an information path from said node to computing resources of a plurality of other grids, said information path configured as hierarchical rings of trust such that each grid of said plurality of other grids is assigned to one of a plurality of hierarchical trust levels.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Arc rail armrest positioning line laying and template construction method
ActiveCN105544990APrecise positioningShorten the installation periodBuilding material handlingStairway-like structuresArchitectural engineeringComputer Grid
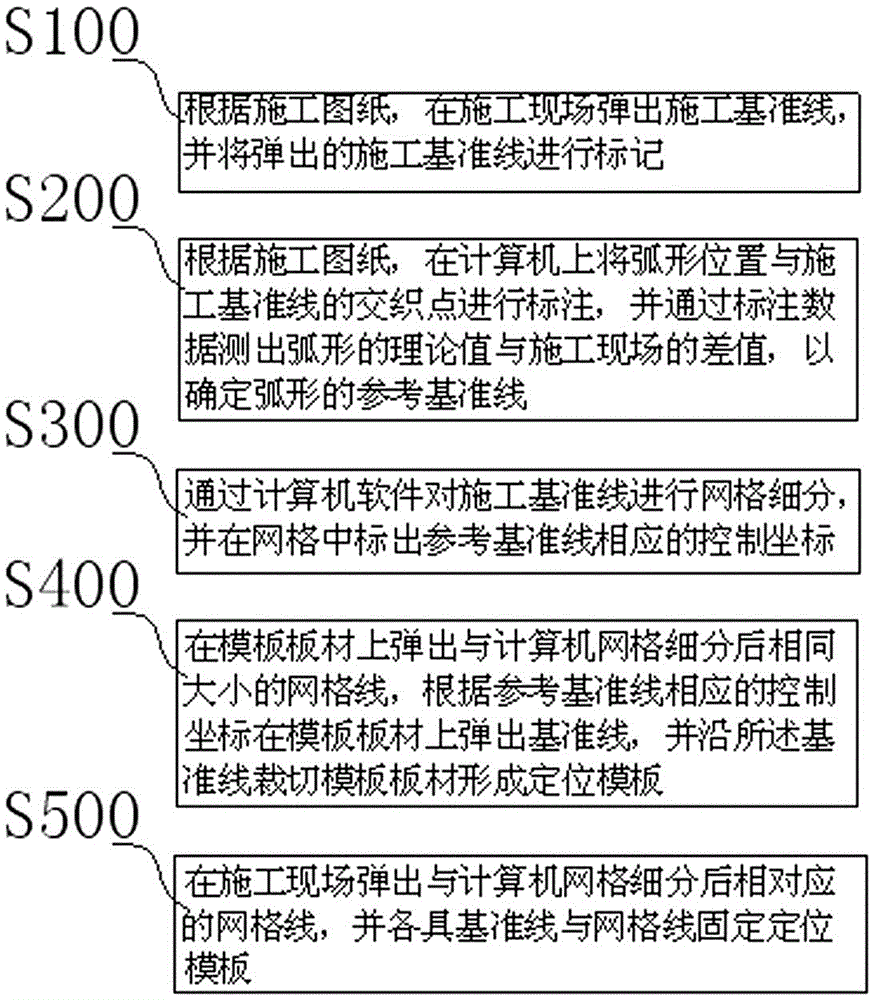
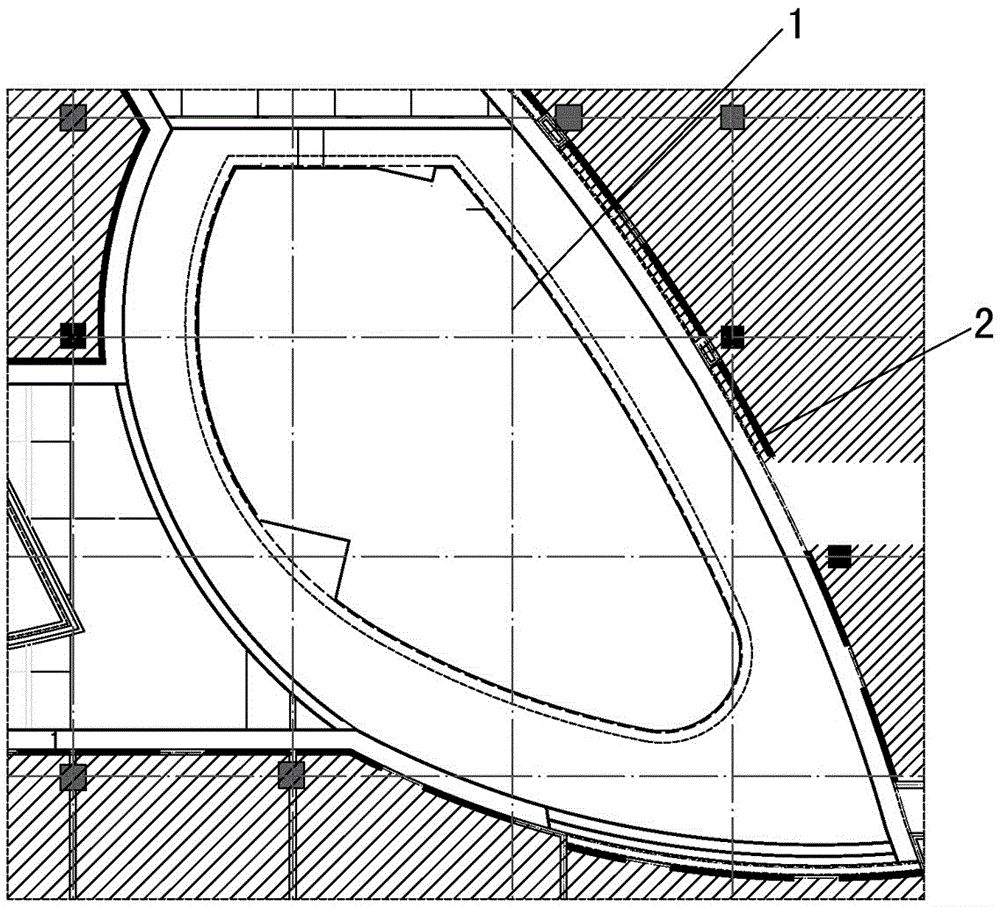
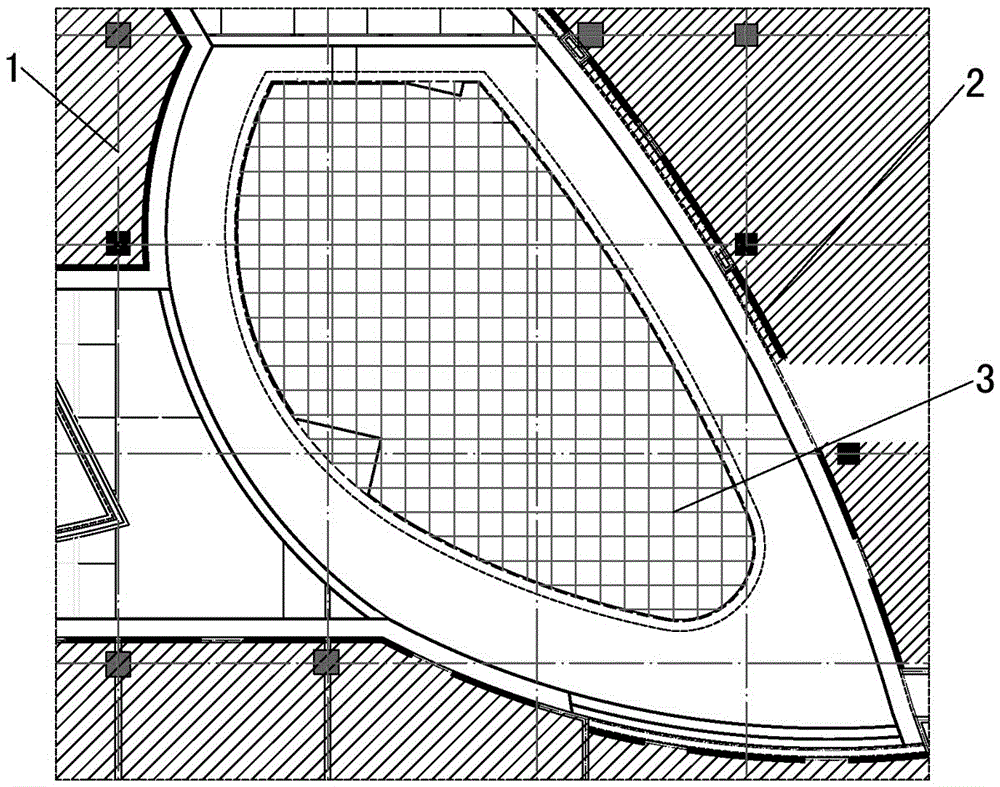
The invention provides an arc rail armrest positioning line laying method comprising the following steps: S100, popping a construction reference line in construction field, and marking the popped construction reference line; S200, marking an interlacing point between the arc position and the construction reference line on a computer, and using marking data to measure difference value between arc theoretical value and construction field value, thus determining an arc reference base line; S300, carrying out grid segmentation for the construction reference line, and marking control coordinates corresponding to the reference base line in the grid; S400, popping a datum line on a template panel according to the control coordinates corresponding to the reference base line, and cutting the template panel along the datum line so as to form a positioning template; S500, popping grid lines corresponding to computer grid segmentation in the construction field, and fixing the positioning template according to the datum line and the grid lines. The method is wide in applicability, high in construction efficiency, and can ensure construction precision.
Owner:CHINA CONSTR FIRST BUREAU GRP INTERIOR FITOUT ENG +1
Information service construction system and construction method
InactiveCN1790261AEasy to operateSimplify the development processTransmissionSpecific program execution arrangementsService developmentRelevant information
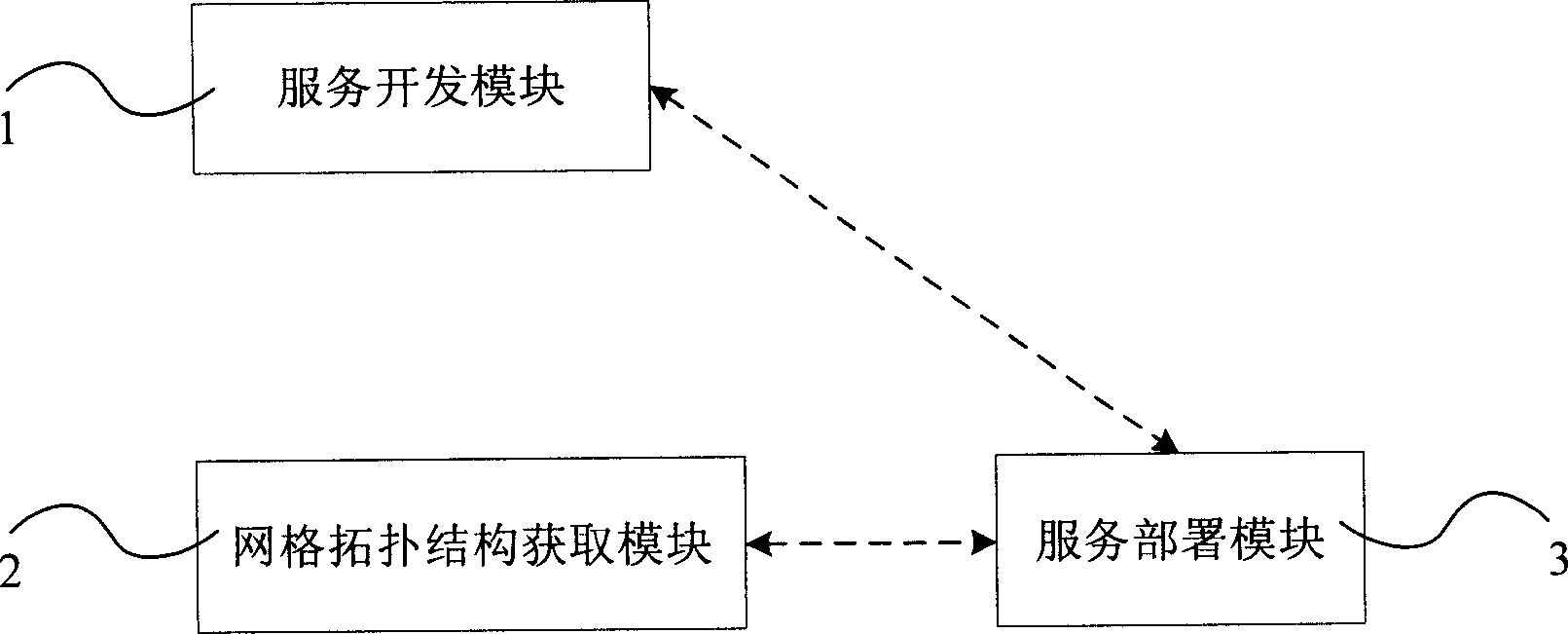
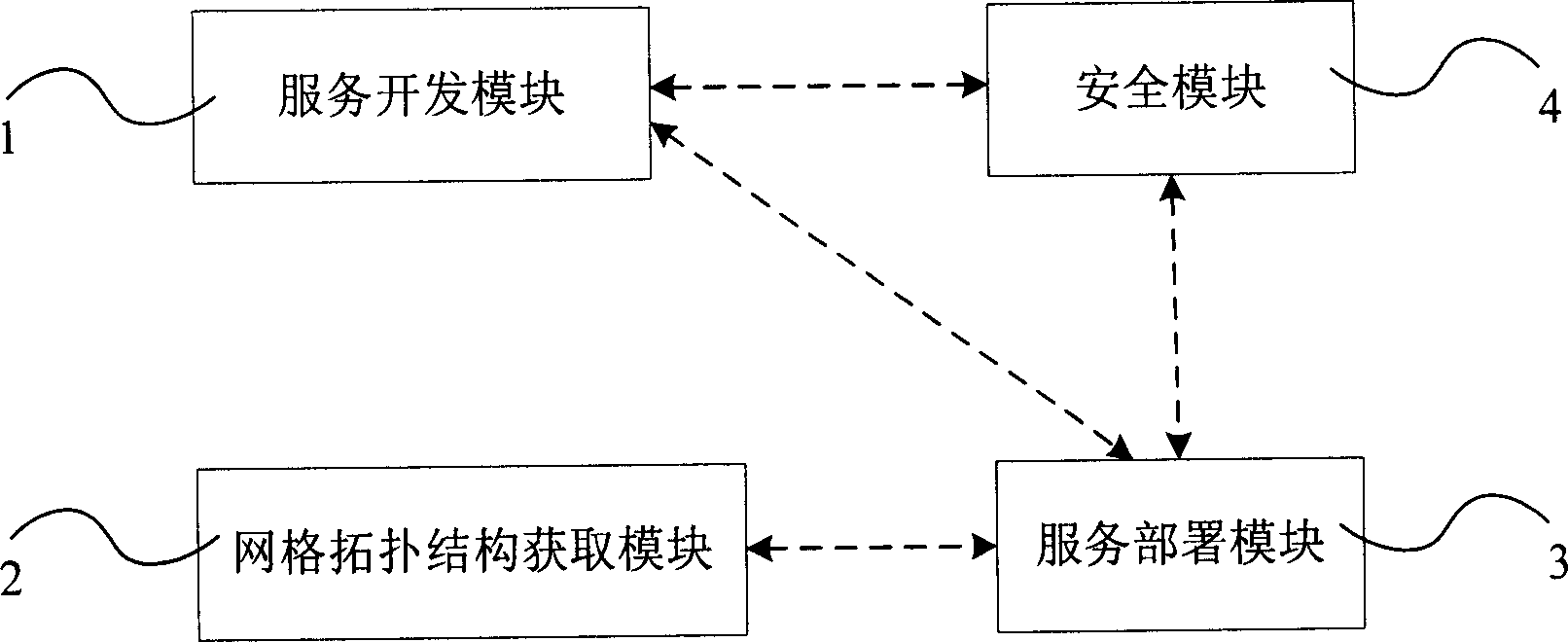
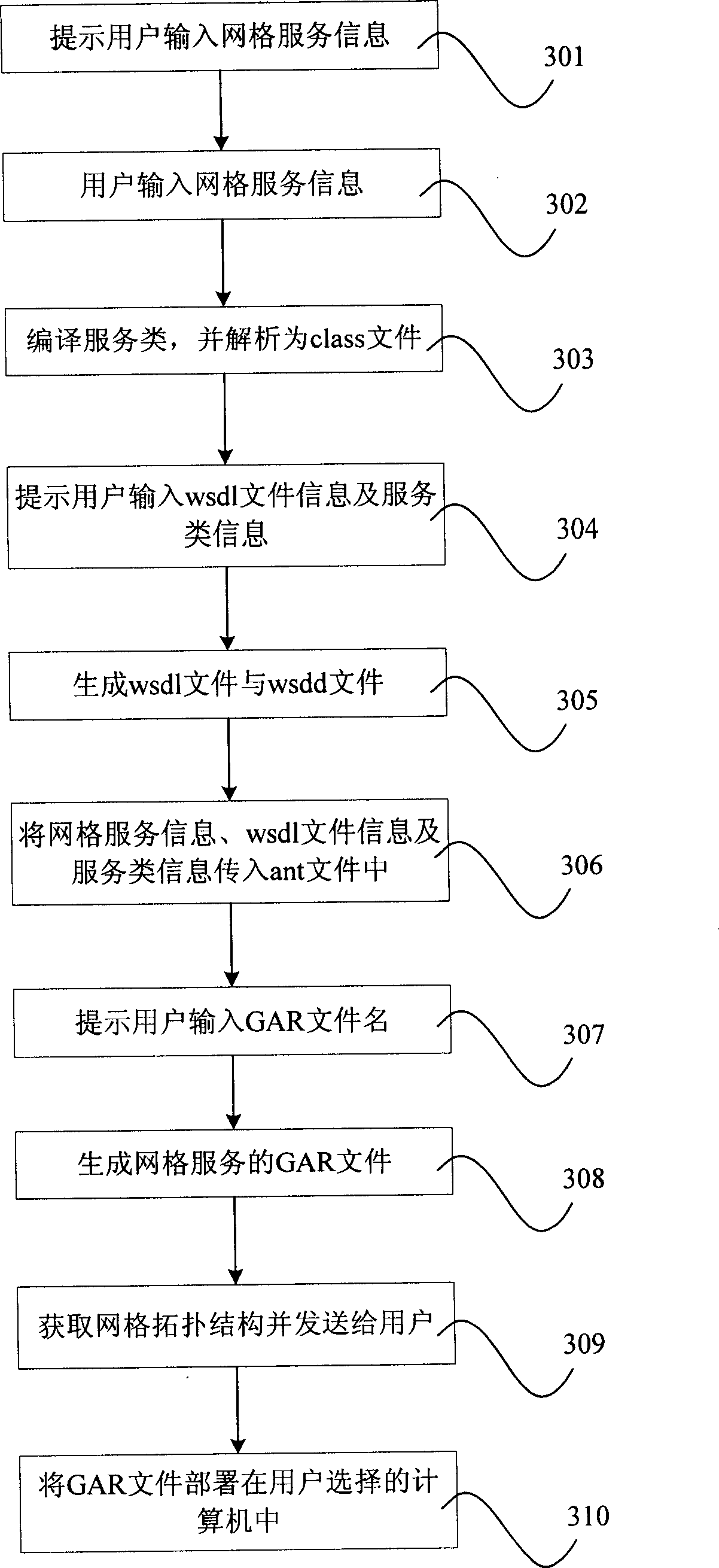
The invention discloses an information service system development establishing device and method, which comprises the following parts: grid service development mode, grid topological structure obtaining mode and service deploy mode, wherein the service deploy mode connects the grid service development mode and grid topological structure obtaining mode simultaneously; the grid service development mode prompts the relative information of built grid service, which generates the GAR file for user to input information; the network topological structure obtaining mode obtains the grid topological structure of grid service and each computer information in the grid for user; the GAR file of service deploy mode is allocated in the computer grid. The invention can establish and allocate the grid service automatically, which simplifies the development flow path of operational and network service.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Constant mean curvature hook face construction method based on normal mean
InactiveCN108053484AAdaptableEfficientComplex mathematical operations3D modellingPartition of unityAlgorithm
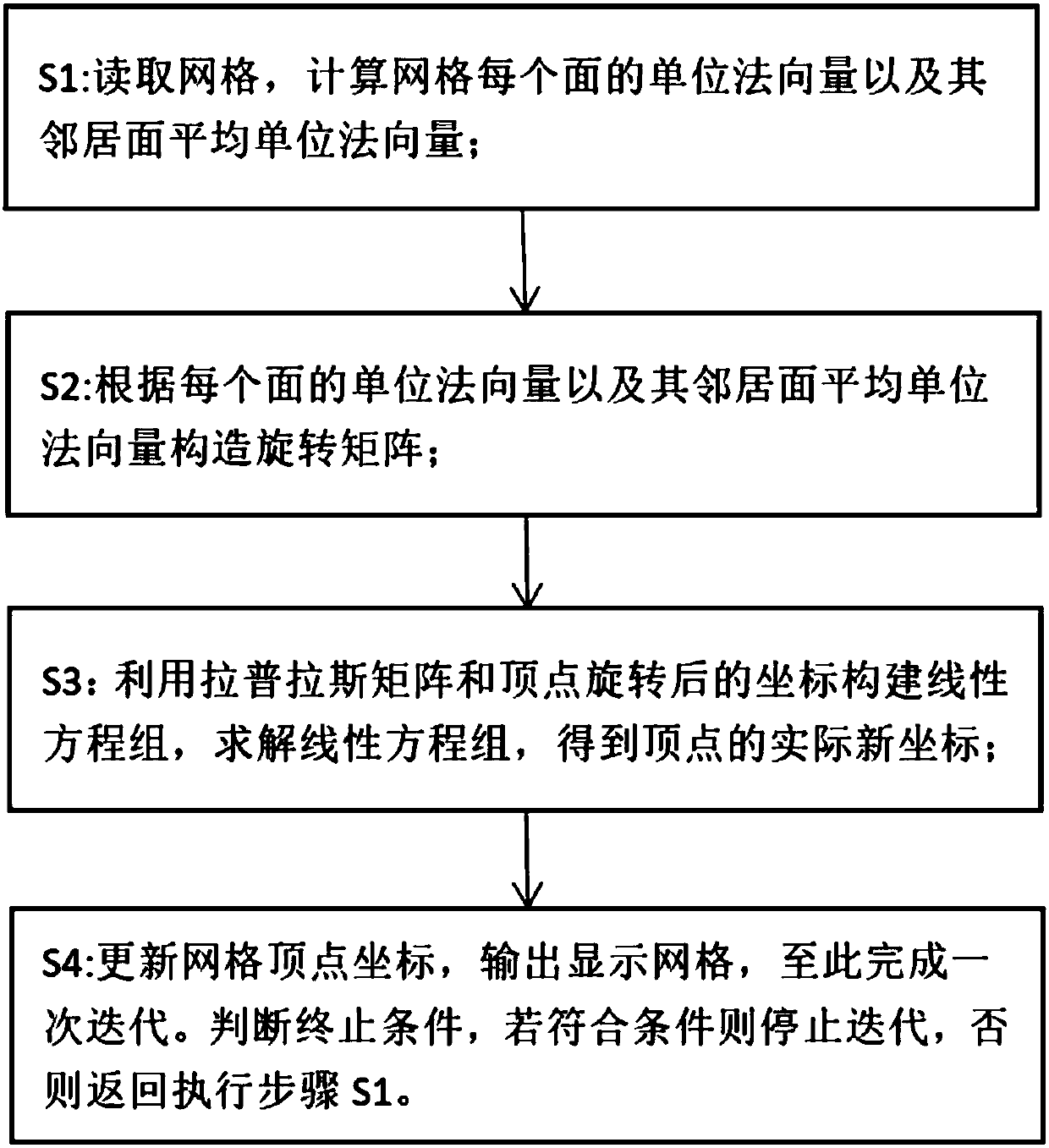
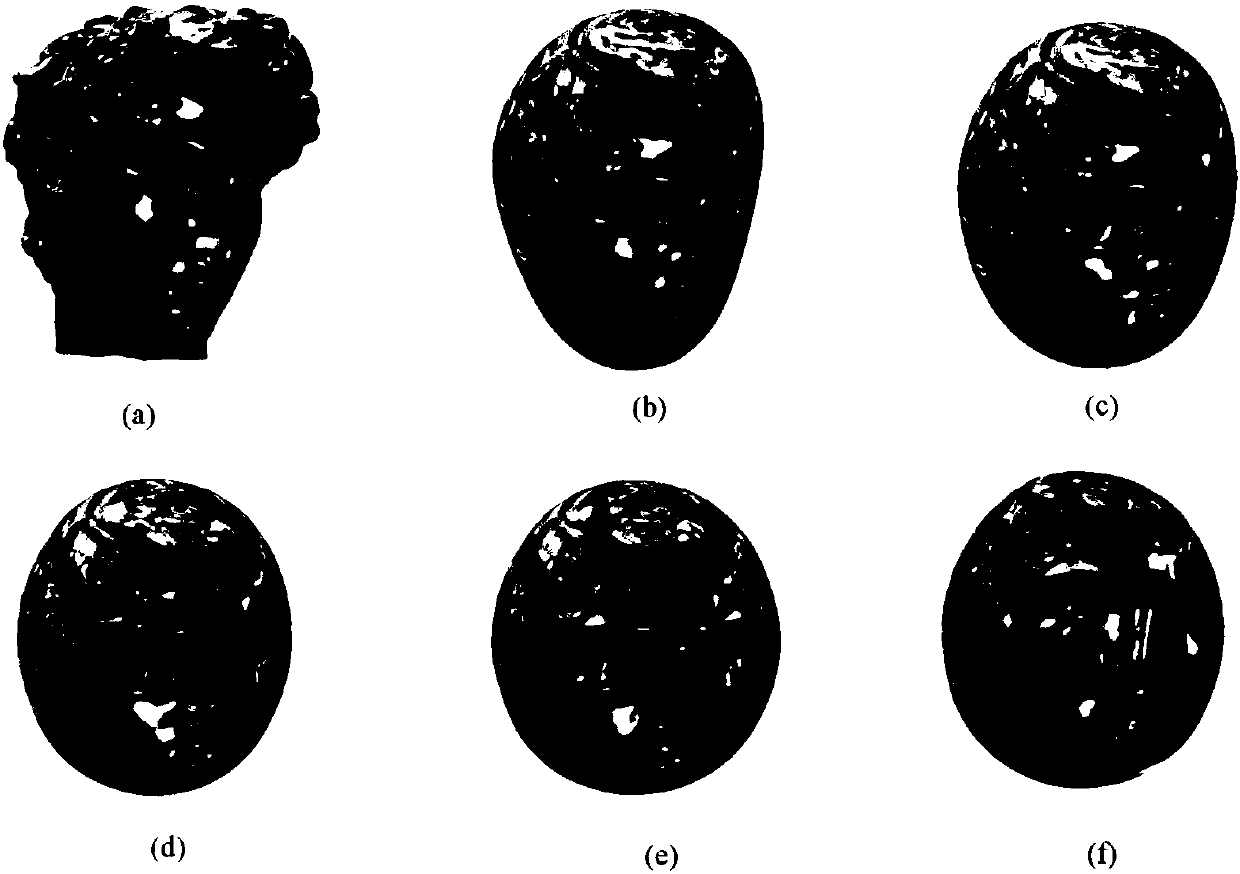
The invention discloses a constant mean curvature hook face construction method based on a normal mean. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, reading a grid, and calculating the unitnormal vector of each surface of the grid and the average unit normal vector of a neighbor surface; then, according to the unit normal vector of each surface and the average unit normal vector of theneighbor surface, constructing a rotation matrix; then, calculating the Laplacian matrix of the vertex of the grid, utilizing the rotation matrix to calculate a coordinate matrix after the vertex ofthe grid rotates, and utilizing the Laplacian matrix and the coordinate after the vertex of the grid rotates to solve a linear equation set to obtain the practical new coordinate of the vertex; finally, updating a grid vertex coordinate, and outputting a display grid so as to finish one-time iteration; and judging a termination condition, stopping iteration if a condition is conformed to obtain afinal output model, and otherwise, and taking a current output grid as input to return to execute the first step. The method exhibits good robustness and adaptation and high efficiency, and the problem of poor adaption, low efficiency and surface patch overturning in a current constant mean curvature hook face construction method can be effectively solved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Self-powered, self-propelled computer grid with loop topology
PendingUS20200318602A1Efficient HarvestingWind motor controlWaterways transportEnvironmental resource managementEnergy harvester
An energy-harvesting compute grid includes computing assemblies that cooperate with mobile energy harvesters configured to be deployed on a body of water. The plurality of energy harvesters are positioned on and move adjacent to an upper surface of a body of water, and the locations of the energy harvesters can be monitored and controlled. The wide-spread gathering by the harvesters of environmental data within that geospatial area permits the forecasting of environmental factors, the discovery of advantageous energy-harvesting opportunities, the observation and tracking of hazardous objects and conditions, the efficient distribution of data and / or tasks to and between the harvesters included in the compute grid, the efficient execution of logistical operations to support, upgrade, maintain, and repair the cluster, and the opportunity to execute data-gathering across an area much larger than that afforded by an individual harvester (e.g., radio astronomy, 3D tracking of and recording of the communication patterns of marine mammals, etc.). The computational tasks can be shared and distributed among a compute grid implemented in part by a collection of individual floating self-propelled energy harvesters thereby providing many benefits related to cost and efficiency that are unavailable to relatively isolated energy harvesters, and likewise unavailable to terrestrial compute grids of the prior art.
Owner:LONE GULL HLDG LTD
Point accumulation method and device applied to maps
ActiveCN108509532AAccurately reflectAvoid influenceArtificial lifeSpecial data processing applicationsComputational scienceAlgorithm
The invention discloses a point accumulation method and device applied to maps. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a honeycomb unit grid which covers a map; calculating a numberof point elements and an intensity of the point elements in each honeycomb unit of the honeycomb unit grid, wherein the point elements are point elements on the map; sorting the honeycomb units in the honeycomb unit grid according to the number of the point elements and the intensity of the point elements so as to obtain a sorted honeycomb unit sorting list; and clustering each honeycomb unit ofthe honeycomb unit grid on the basis of the honeycomb unit sorting list so as to obtain one or more honeycomb unit clusters, wherein a coordinate of each honeycomb unit cluster is formed by centroidsof all the point elements in the honeycomb unit cluster. According to the method and device, original point positions can be reflected more accurately, influences, on point accumulation results, of iteration sequences are avoided, local updating and aggregation of point elements are supported, and the effect of the point accumulation method can be enhanced by sufficiently utilizing a distributed parallel calculation technology.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAHUA TECH CO LTD
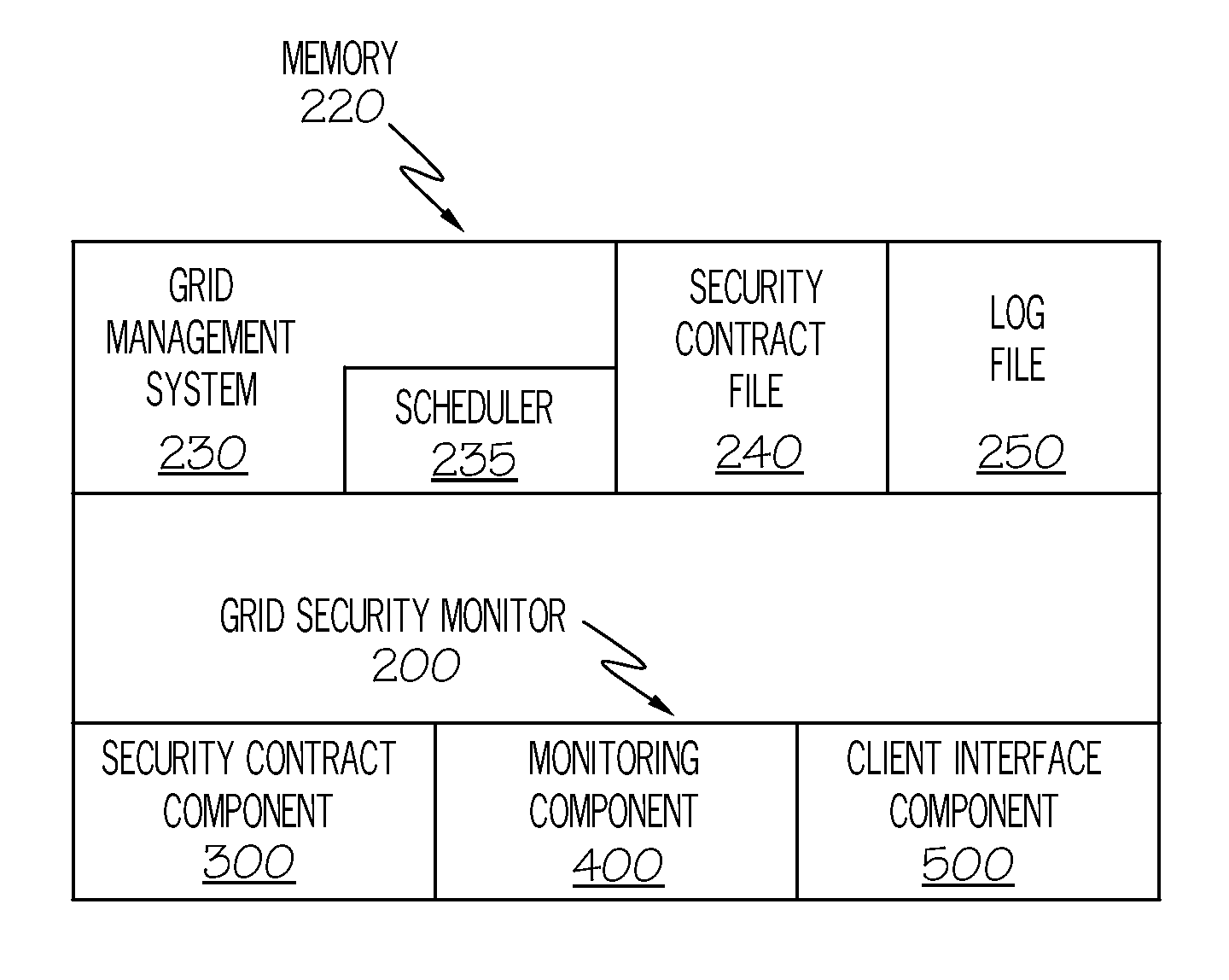
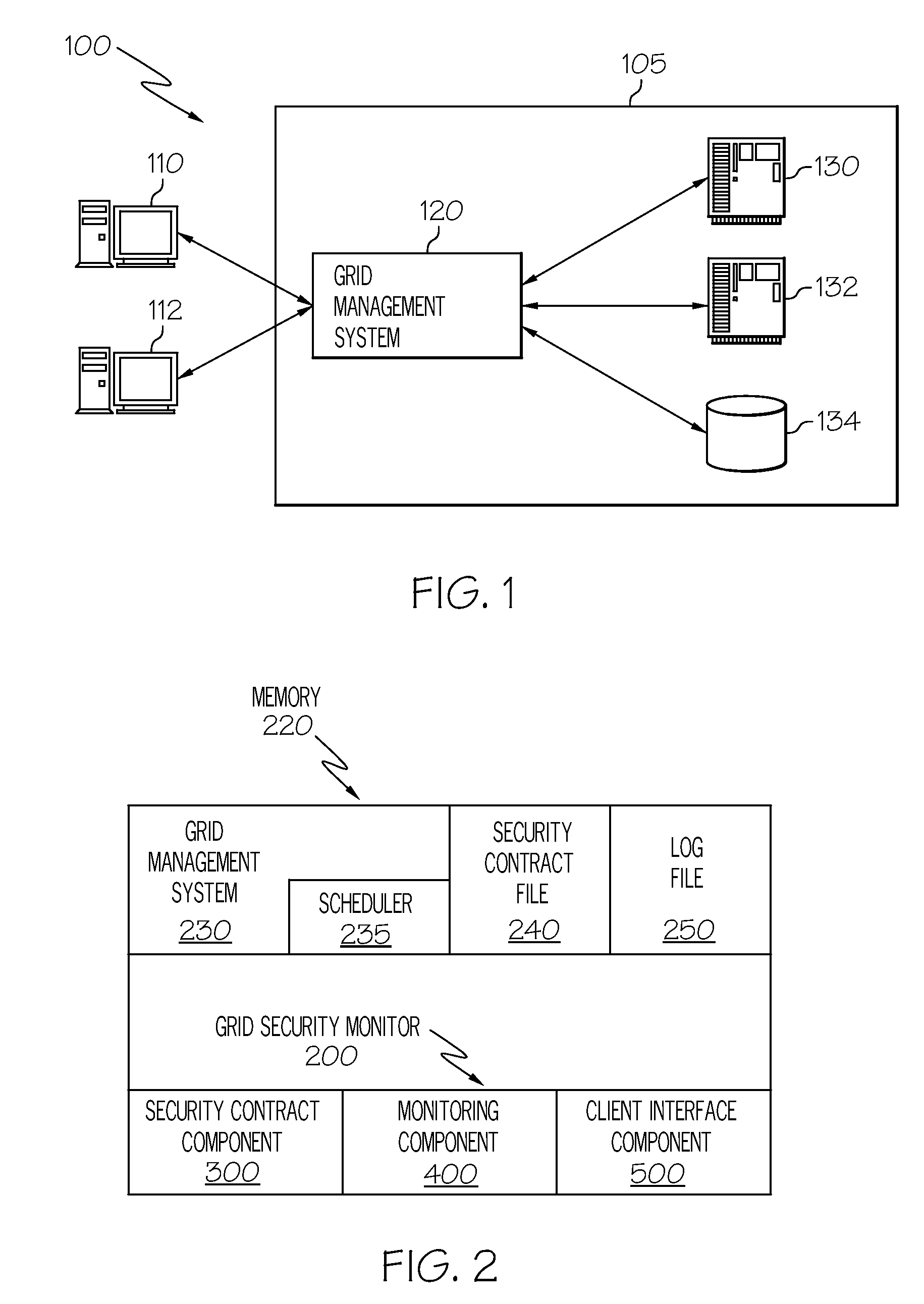
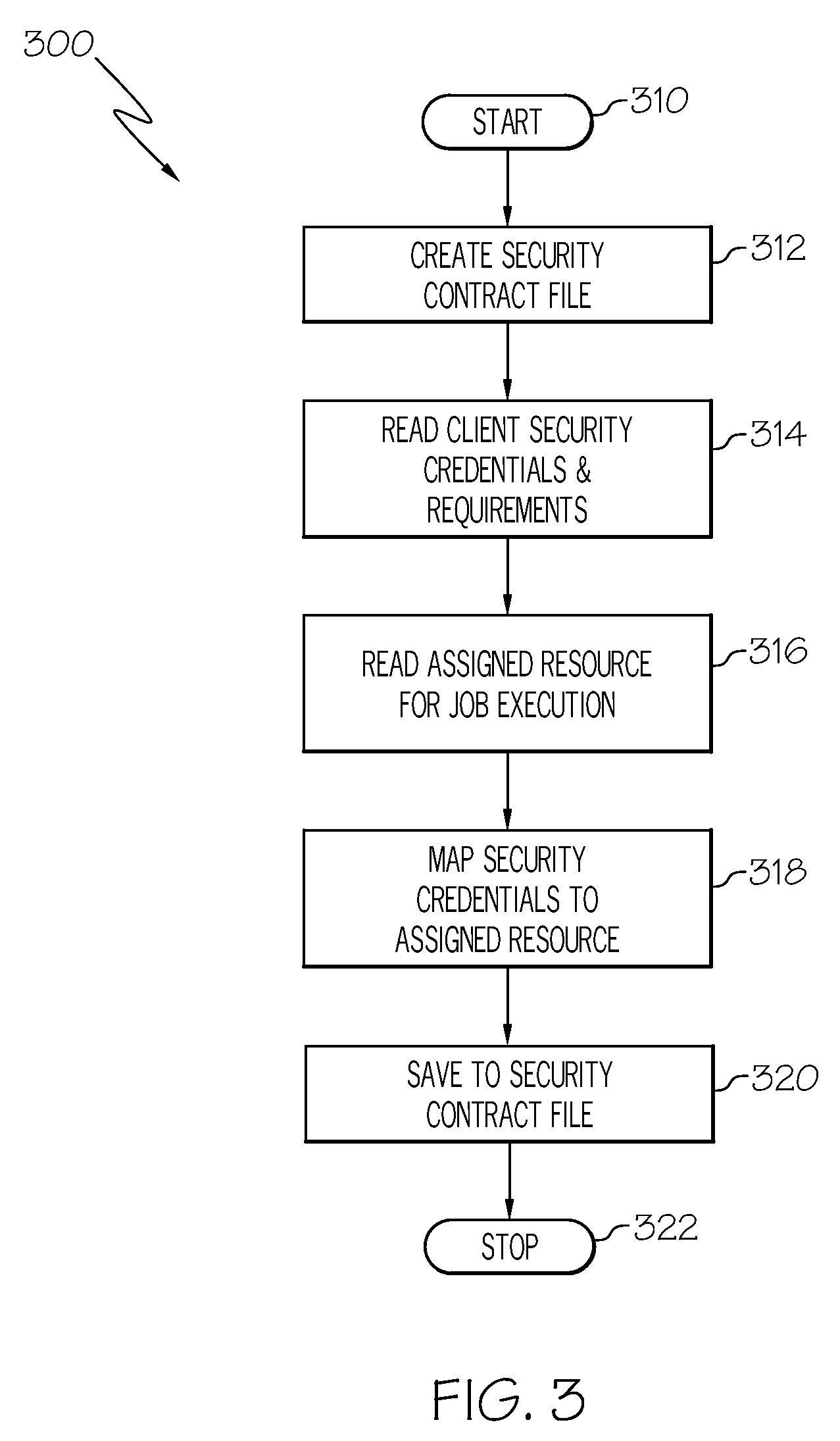
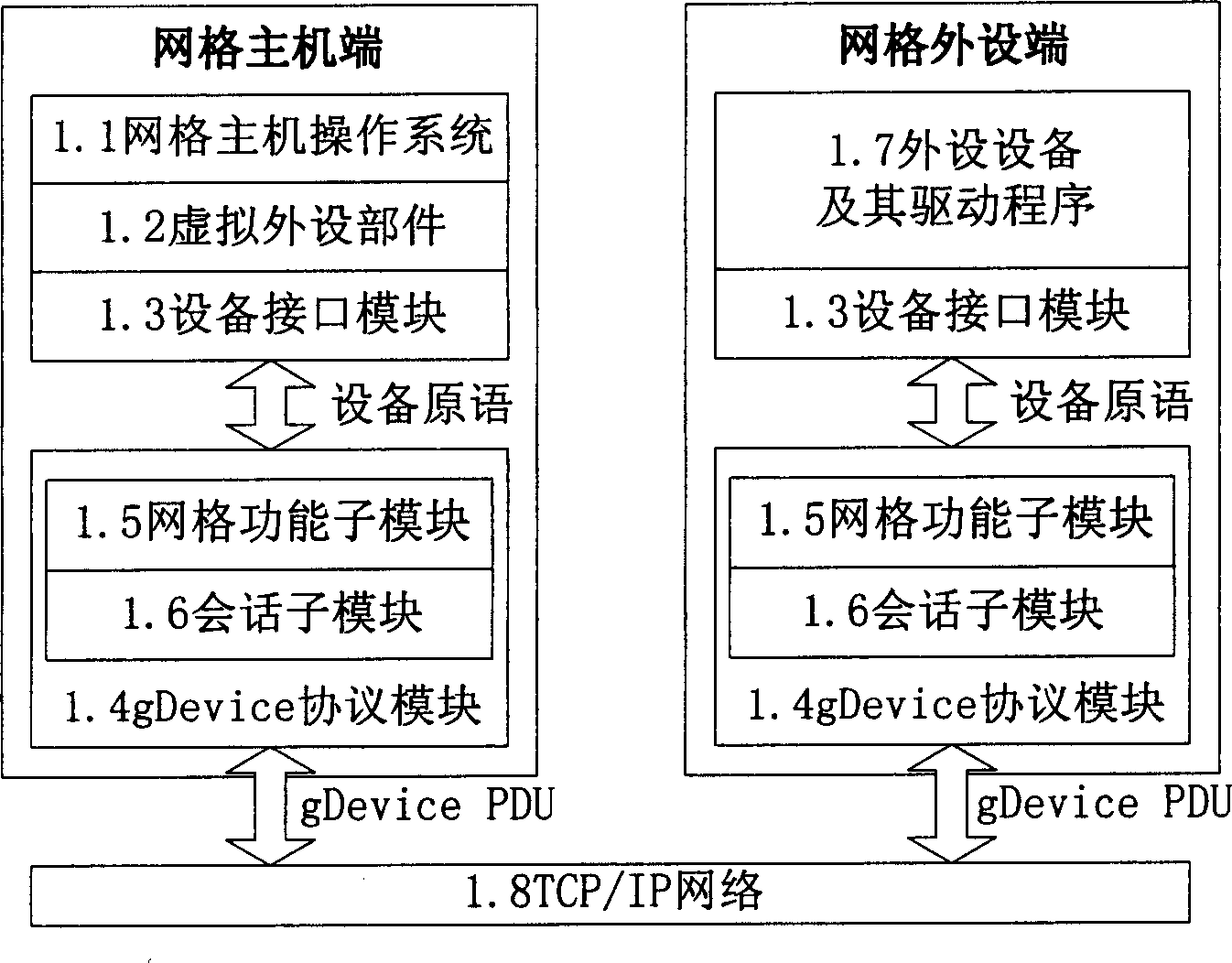
Tracking the security enforcement in a grid system
The “Grid Security Monitor” tracks the security status of resources in a grid computer system. When a client submits a job to the grid scheduler, the Grid Security Monitor creates a security contract. The security contract comprises all the security credentials needed to access the resource executing the job, as well as privacy and security requirements. The Grid Security Monitor compares the security status of the resource to the requirements of the security contract. If the security status of the resource changes or violates the security contract, then the Grid Security Monitor notifies the client. The Grid Security Monitor has a user interface that allows the client to perform a manual security validation by asking the grid management system to verify the security status of the resource.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Computer peripheral unit part connection system and method based on grid computer system
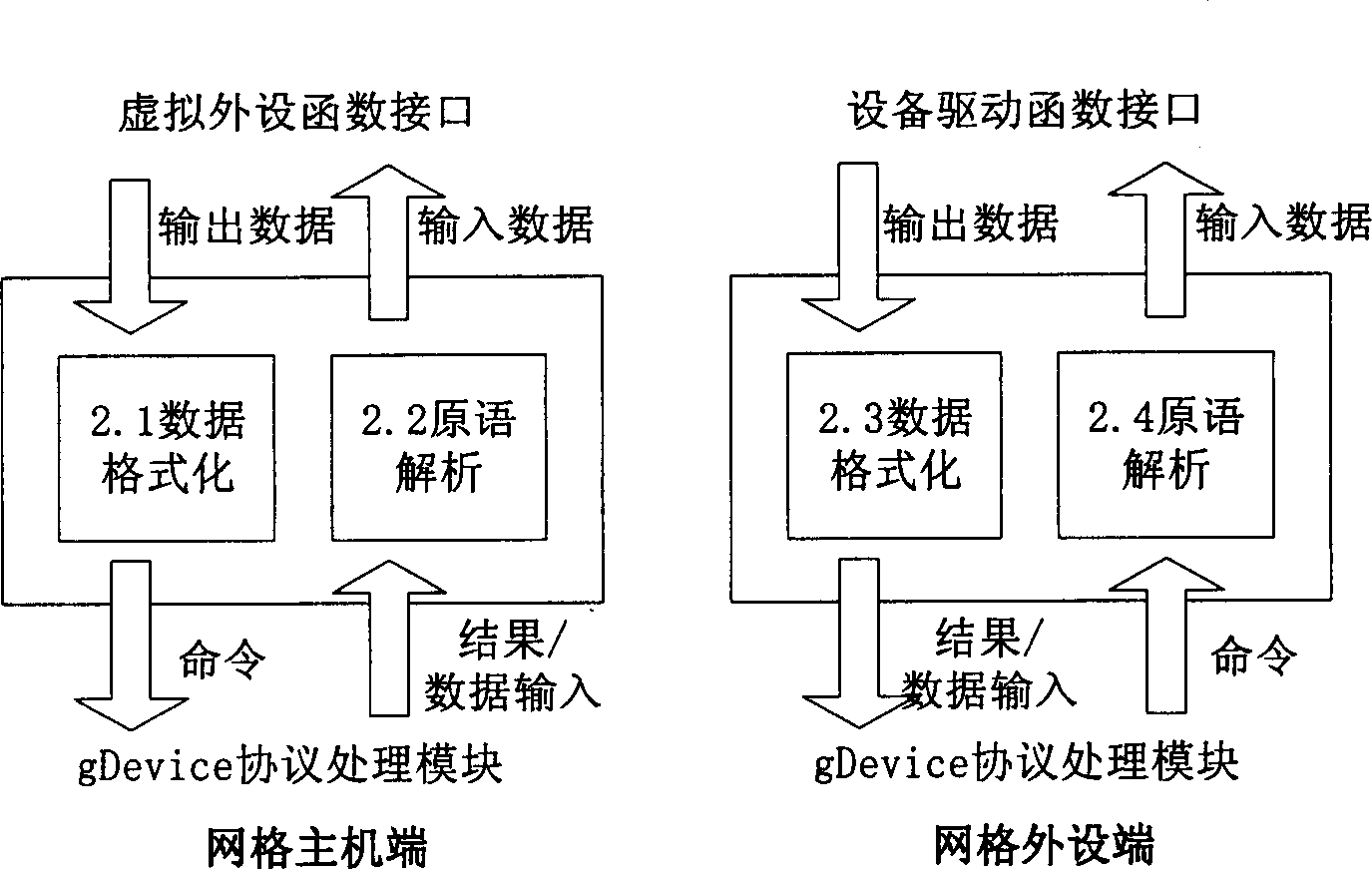
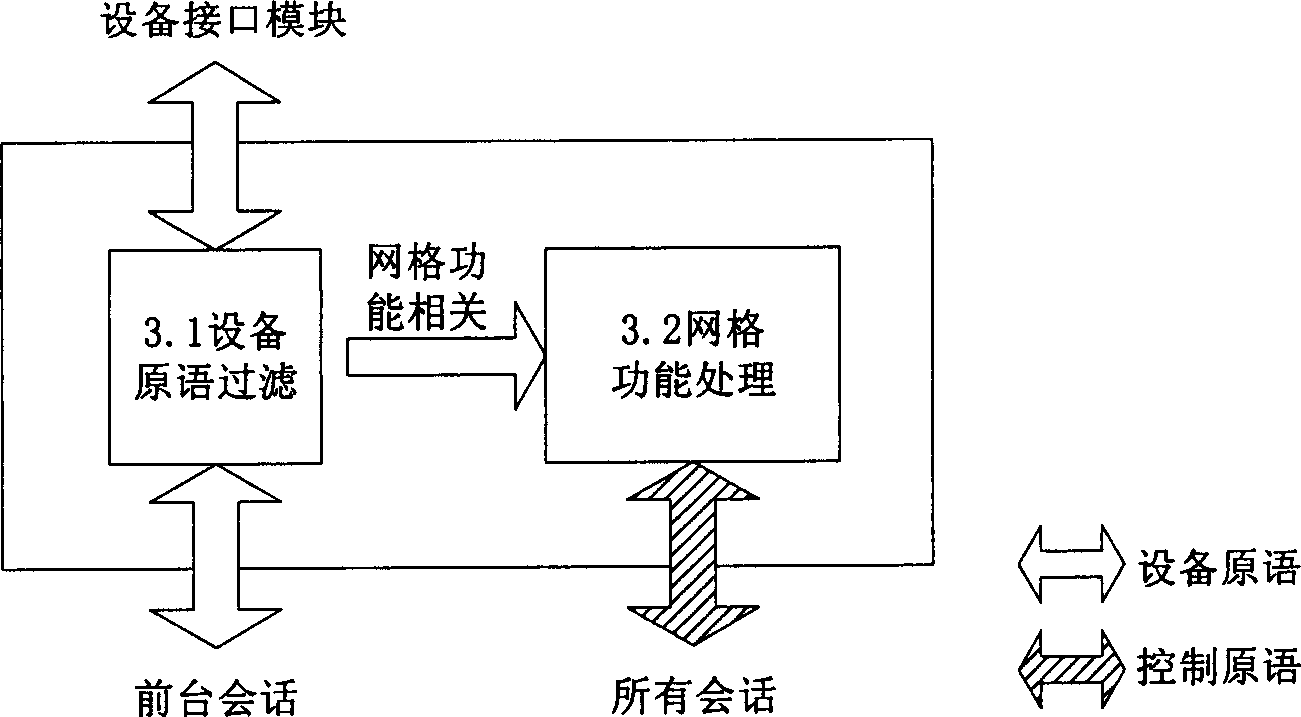
ActiveCN1777187AReduce correlationStateless implementationTransmissionElectric digital data processingAsynchronous communicationComputer module
The invention solves issue of network remote interconnection between grid host and grid peripheral equipment in grid computer system. Being built on TCP / IP network, the system is in layered structured modules, sets down device interface and gDevice protocol process including two main functional modules: sub module of grid function and session sub module, and defines message transmission or interactive format including device primitive, control primitive, gDevice PDU etc. Based on the said mechanism of message transmission, the invention implements connection between grid host and grid peripheral equipment. Virtual device mode is adopted in the system so as to realize remote transparent access from host to grid peripheral equipment. Specific techniques including standardization of interface and message transmission format, and asynchronous communication mechanism support loosely coupled characters of grid computer system.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rotor-sliding bearing system lubrication basin dynamic grid parallel computing method
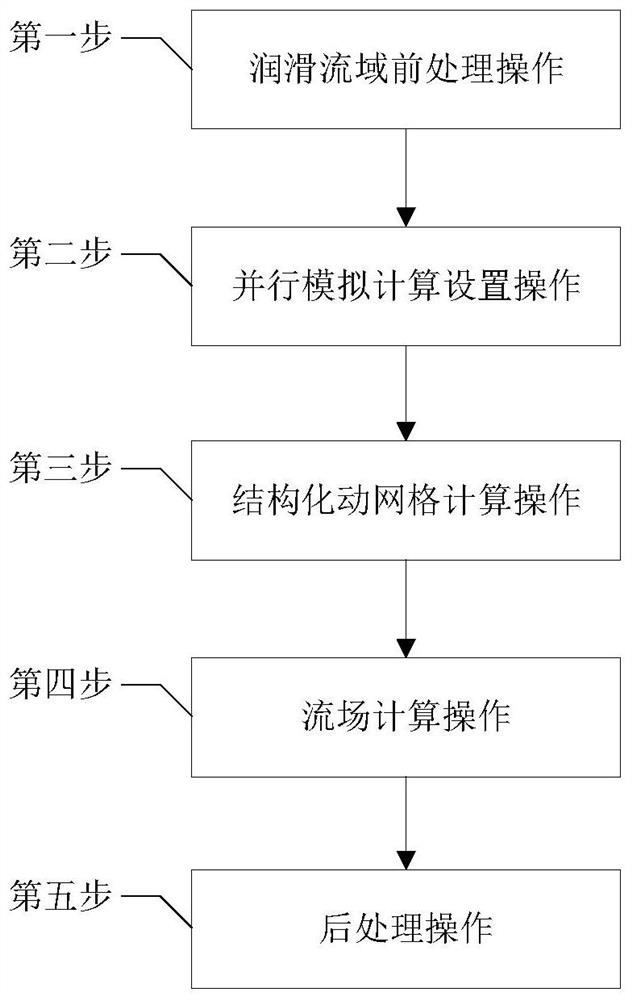
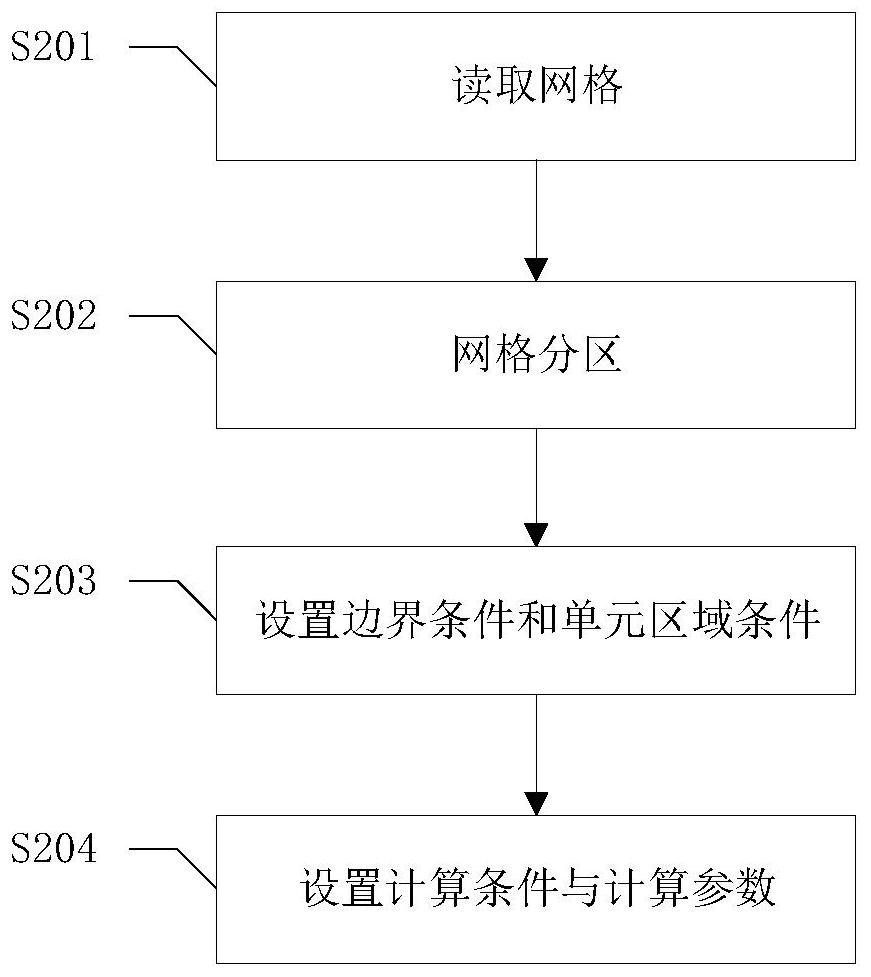
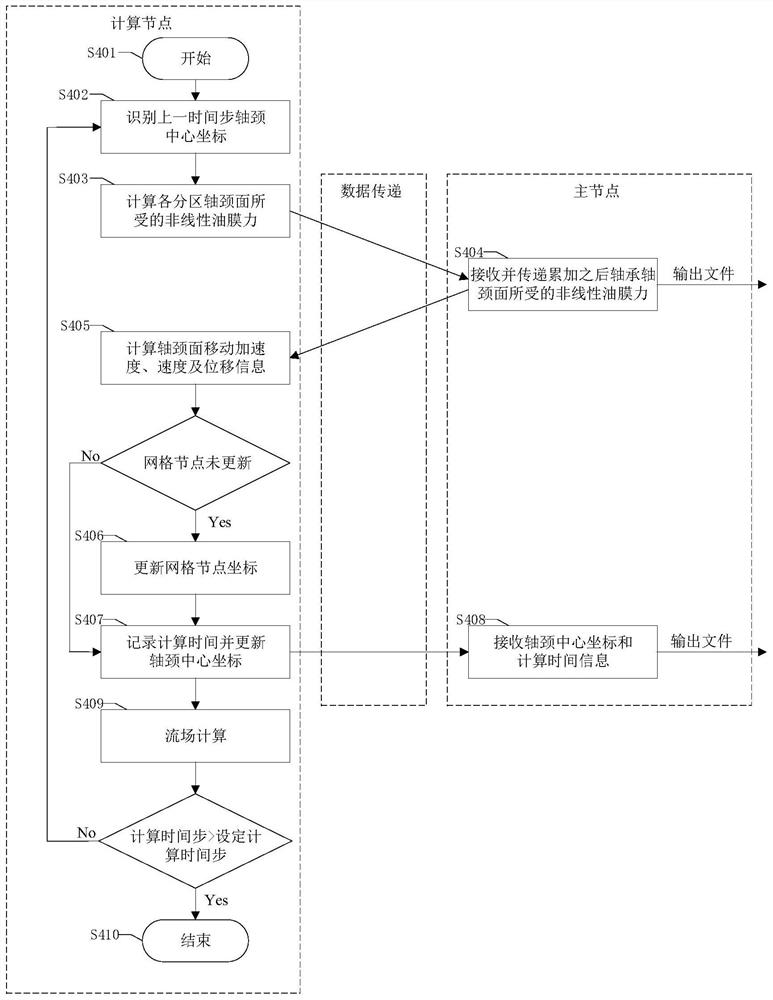
ActiveCN112949112ASolve problems that cannot be applied to parallel computing environmentsAccurate and Efficient SimulationHydro energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationConcurrent computationAnalogue computation
The invention discloses a rotor-sliding bearing system lubrication basin dynamic grid parallel calculation method. The method comprises the steps of lubrication basin pretreatment operation, parallel simulation calculation setting operation, structured dynamic grid calculation operation, flow field calculation operation and post-treatment operation. According to the rotor-sliding bearing system lubrication basin dynamic grid parallel computing method, multi-core parallel simulation of a lubrication basin of a high-speed rotor-sliding bearing system based on a structured dynamic grid is achieved in a parallel computing environment; the problem that an original dynamic grid program cannot be suitable for a parallel environment due to lack of data transmission, summarization and export functions in the parallel computing environment is solved, accurate and efficient simulation of the rotor axis track in the rotor-sliding bearing system is achieved, and the defect that an existing computing method is low in simulation efficiency is overcome. The calculation efficiency can be improved while the calculation precision is ensured, and the stability of the high-speed rotor-bearing system is predicted.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
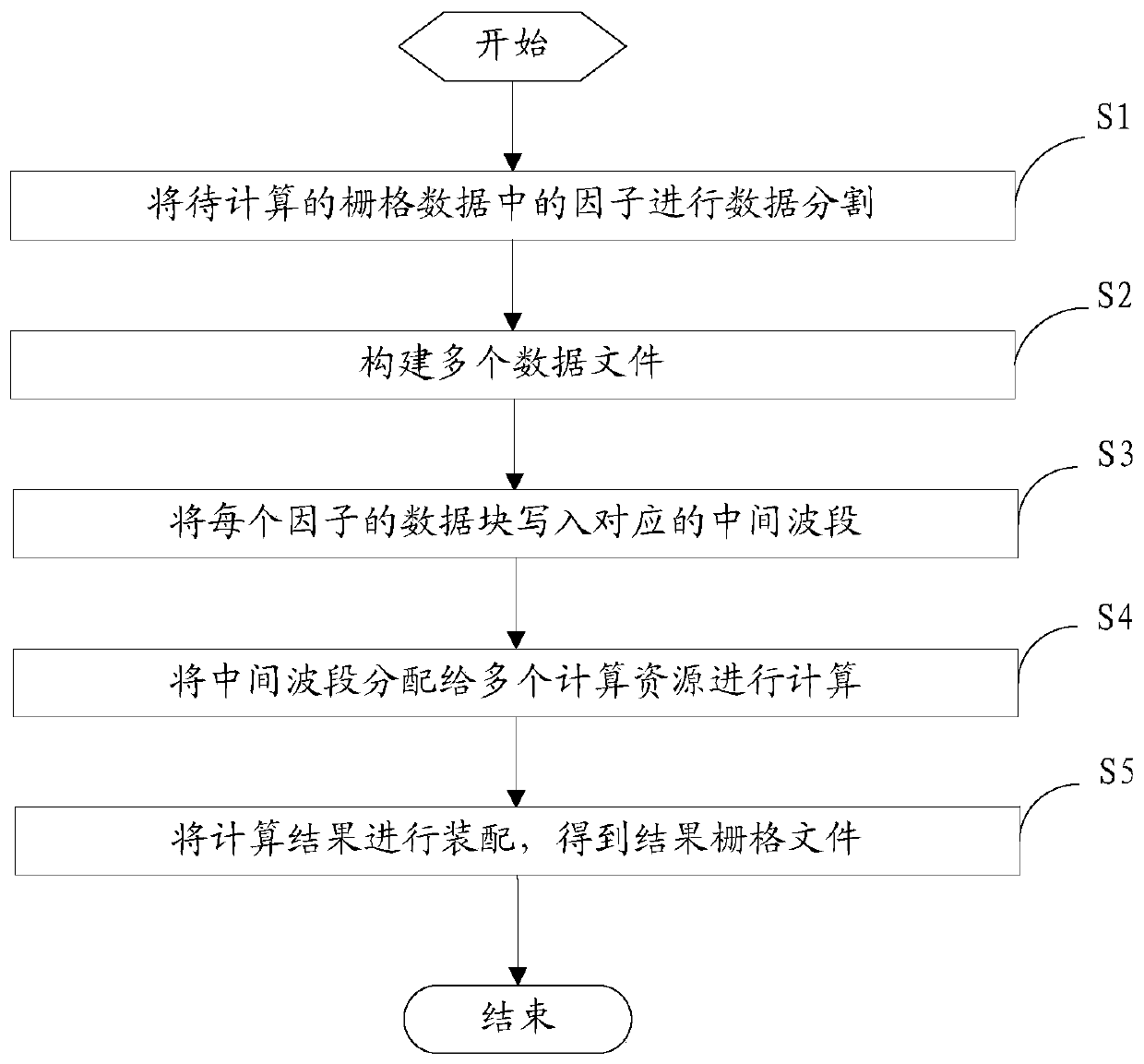
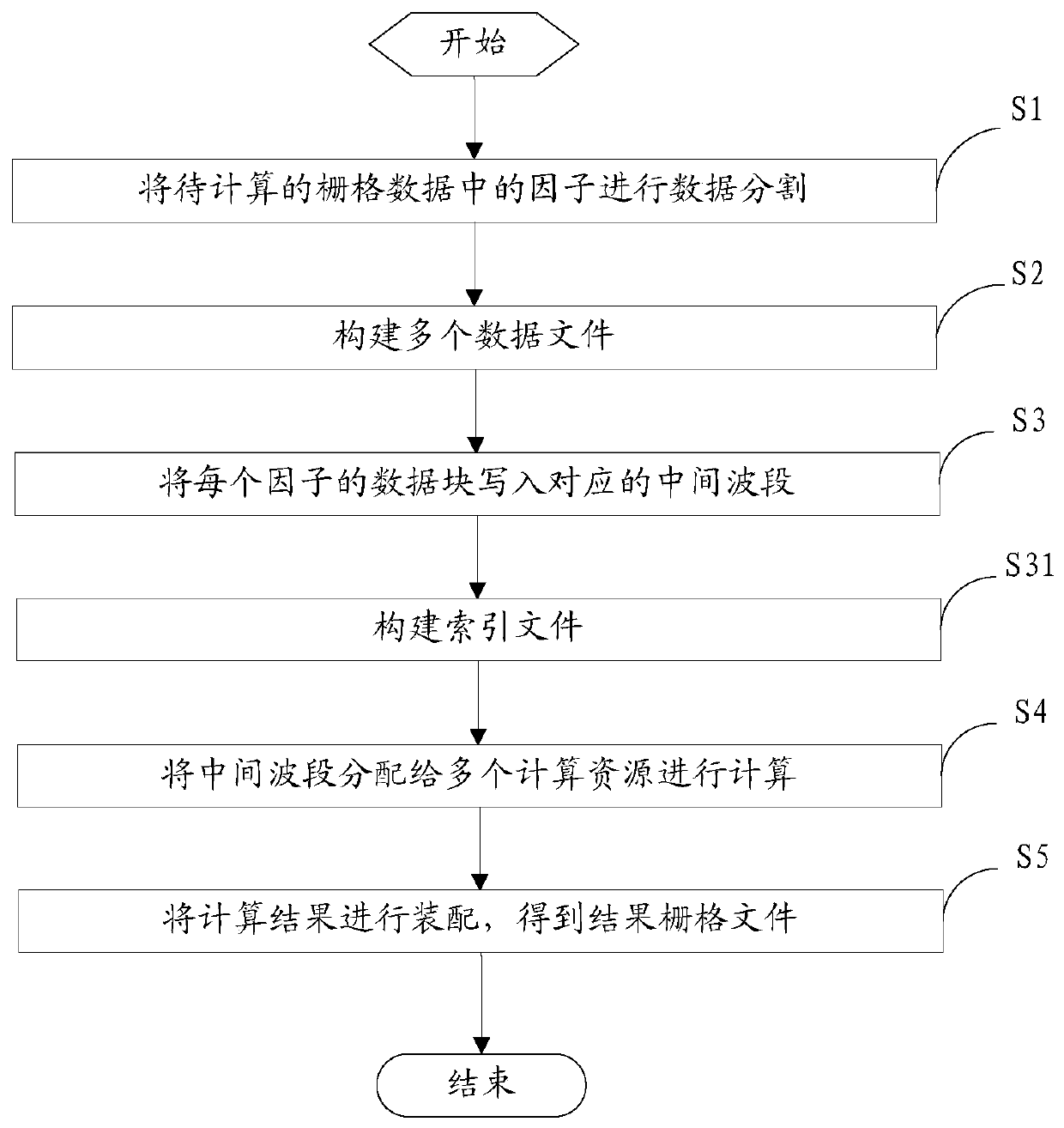
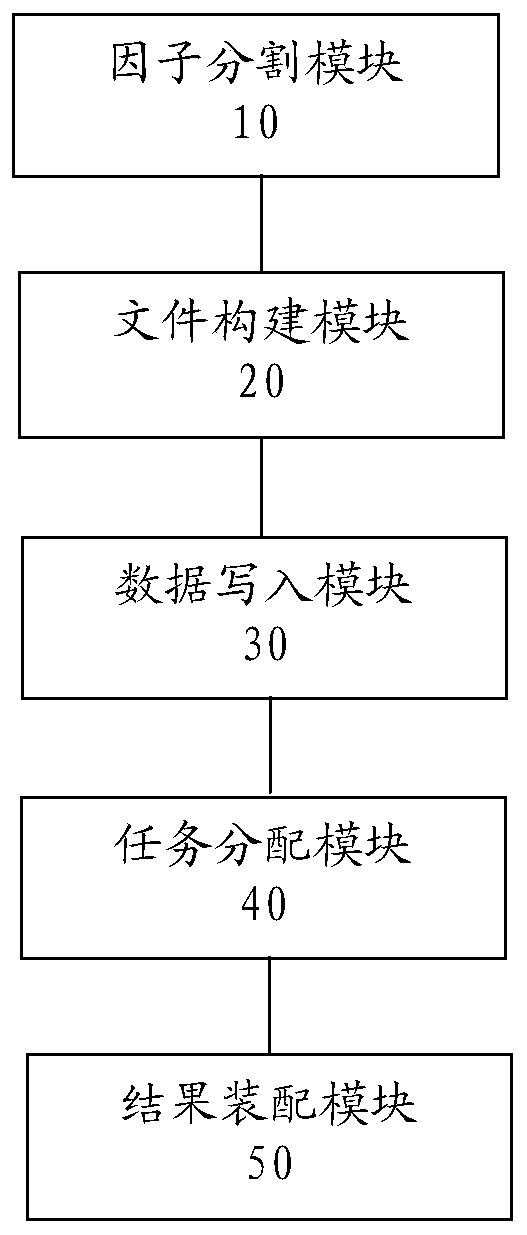
A data processing method and device for raster data
ActiveCN109829078AImprove computing efficiencySolve processing problemsResource allocationOther databases indexingComputational scienceParallel computing
The embodiment of the invention provides a data processing method and device for raster data, and the method specifically comprises the steps: carrying out the segmentation of each factor in raster data to be calculated, and obtaining a preset number of data blocks; Constructing a plurality of data files of which the number is the same as that of the data blocks, each data file comprising a plurality of intermediate wavebands, and the number of the intermediate wavebands being the same as that of the factors; Writing each data block of each factor into the intermediate wave band at the corresponding position of each data file; Allocating a plurality of intermediate wavebands containing the data blocks to a plurality of computing resources for computing to obtain a plurality of computing results; And assembling all calculation results to obtain final result grid data. The task is segmented by using the wave band, and the segmented task can be allocated to a plurality of computing resources for computing, so that the computing efficiency can be improved, and the problem that the result is difficult to compute during large-range grid computing is solved.
Owner:BEIJING DATUM TECH DEV +1
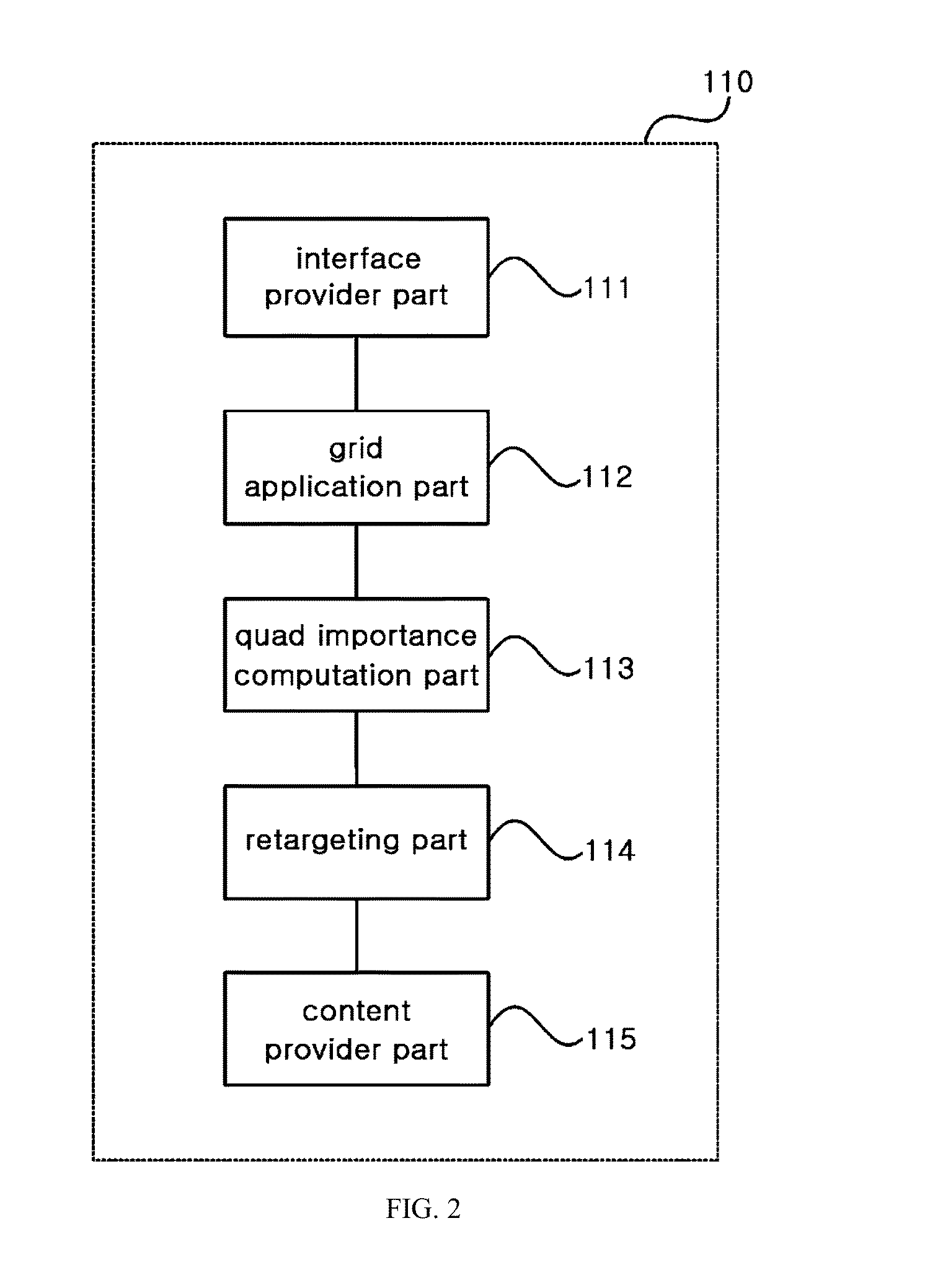
Content retargeting method and apparatus
ActiveUS20150348230A1Minimize distortionReduce complexityImage enhancementImage analysisComputer GridEngineering
A content retargeting method and apparatus are disclosed. An embodiment of the invention provides a content retargeting method that includes: dividing an original content into a grid having M rows×N columns of quads; computing degrees of importance of the divided quads; and scaling the quads based on the computed degrees of importance, the quads axis-aligned by rows or columns.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Microprocessor Including a Model of an Enterprise
ActiveUS20180349101A1Improve performanceImprove securityComputer security arrangementsPower supply for data processingParallel computingComputational model
The present innovative solution introduces two designs of hardware / software units. The first one is a single computational model based on understanding and running a Domain Overlay Model, and providing the appropriate infrastructure in the form of a single board computing device or a single chip computing device. The second one, introduces a computer grid that is a grid of single units designed for distributed Domain Overlay Models, providing the appropriate security and performance. The Overlay Model Computational Unit is a secure, high performance, standalone core for mobile device. The Grid of Overlay Computation Units is preferred for componentized processing of enterprise models which is important when the sense of an enterprise may involve many enterprises and when software design and implementation cannot wait for a central stakeholder like an enterprise or several enterprises to control the development and implementation. With the advent of IoT and ecosystems in the cyber sphere independent development and implementation is inevitable.
Owner:LYRAS DIMITRIS
Grid computing on radiology network
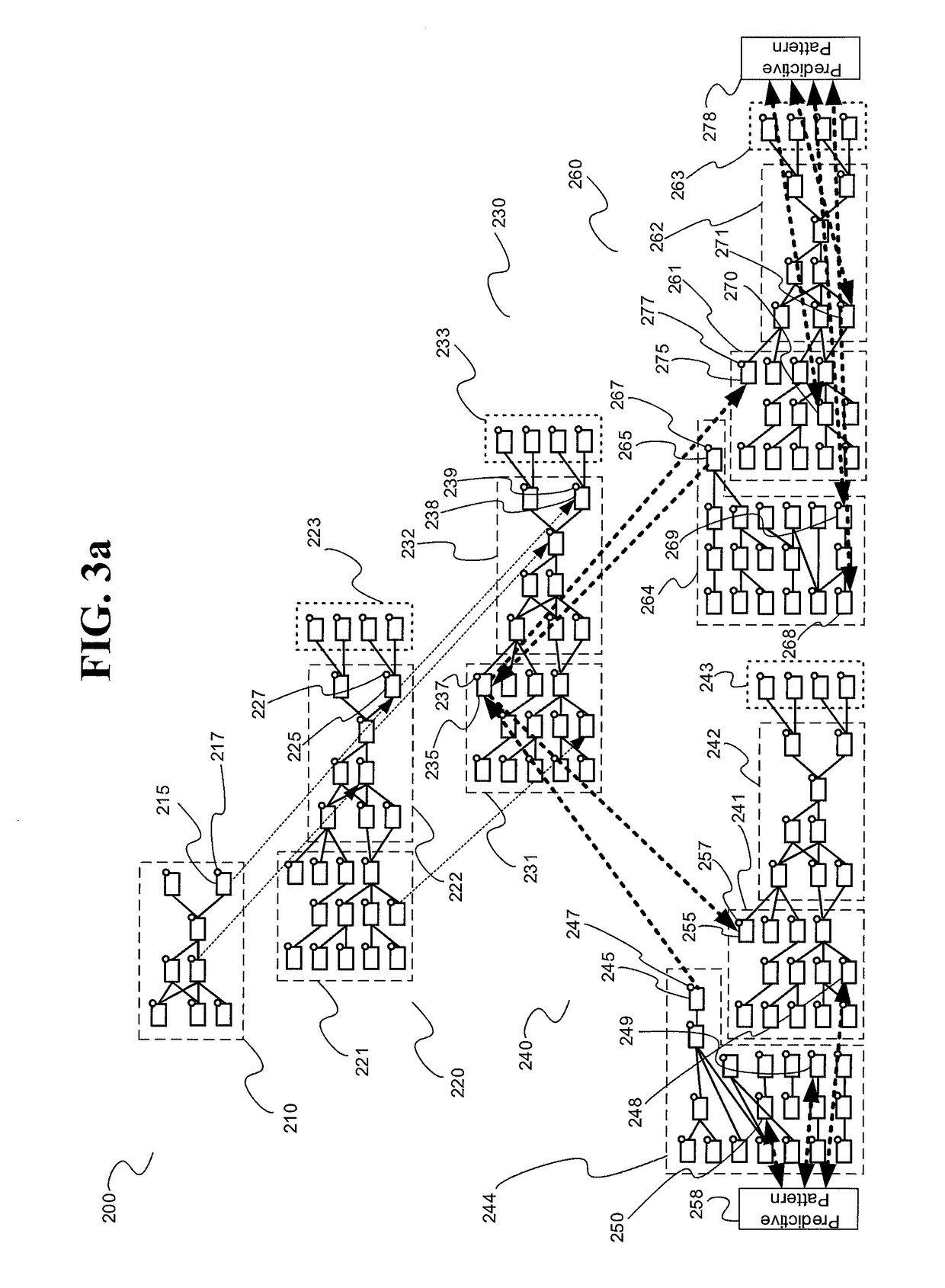
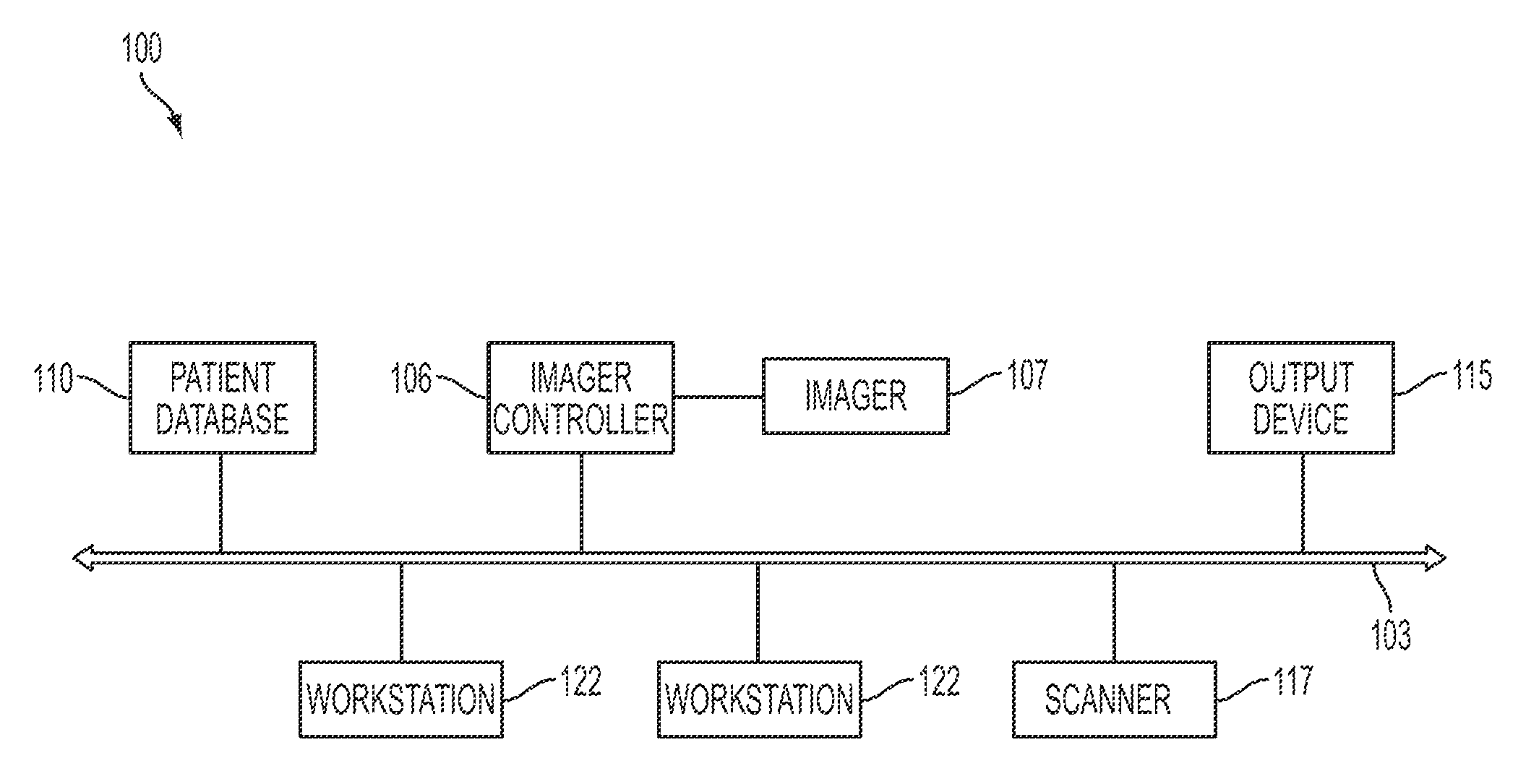
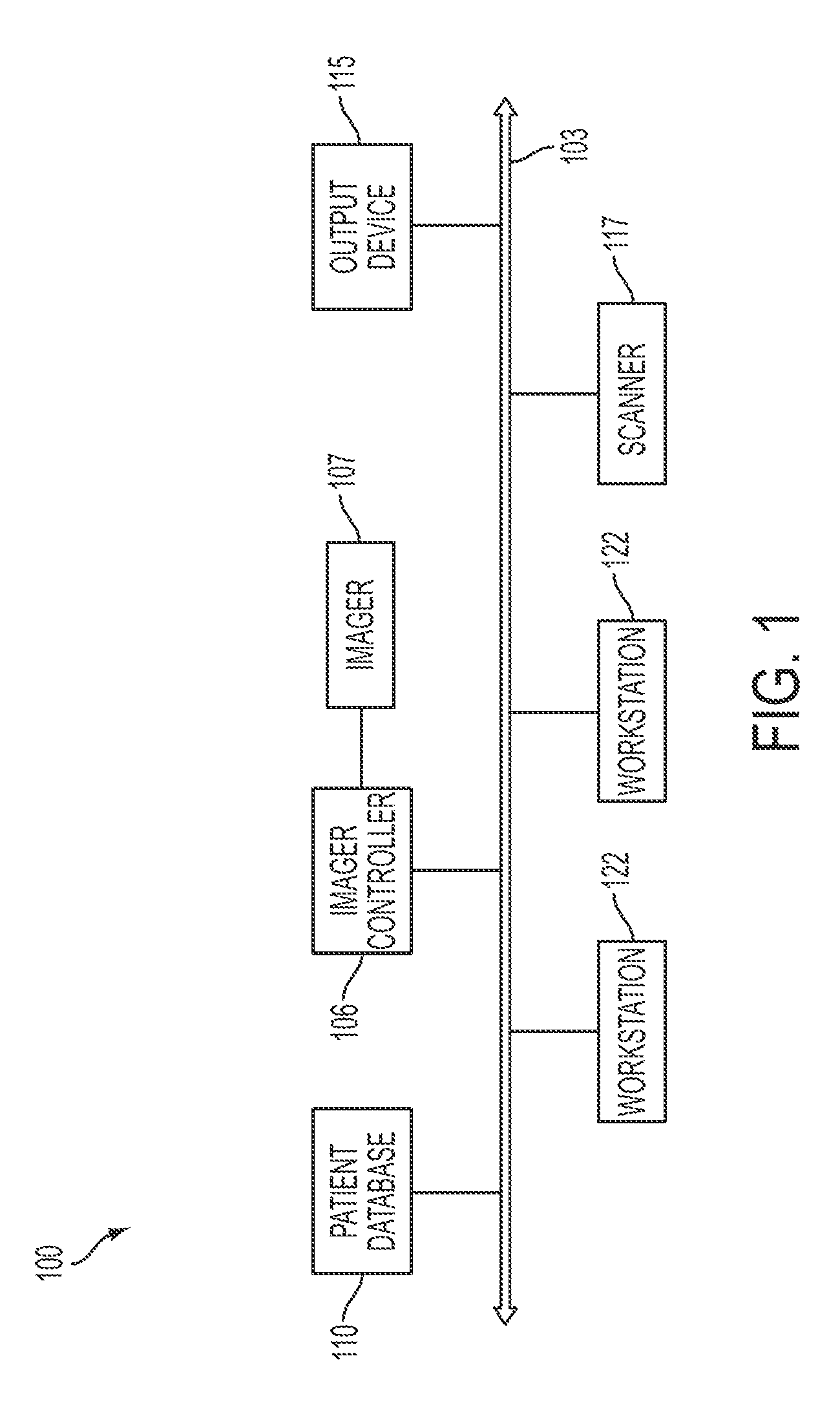
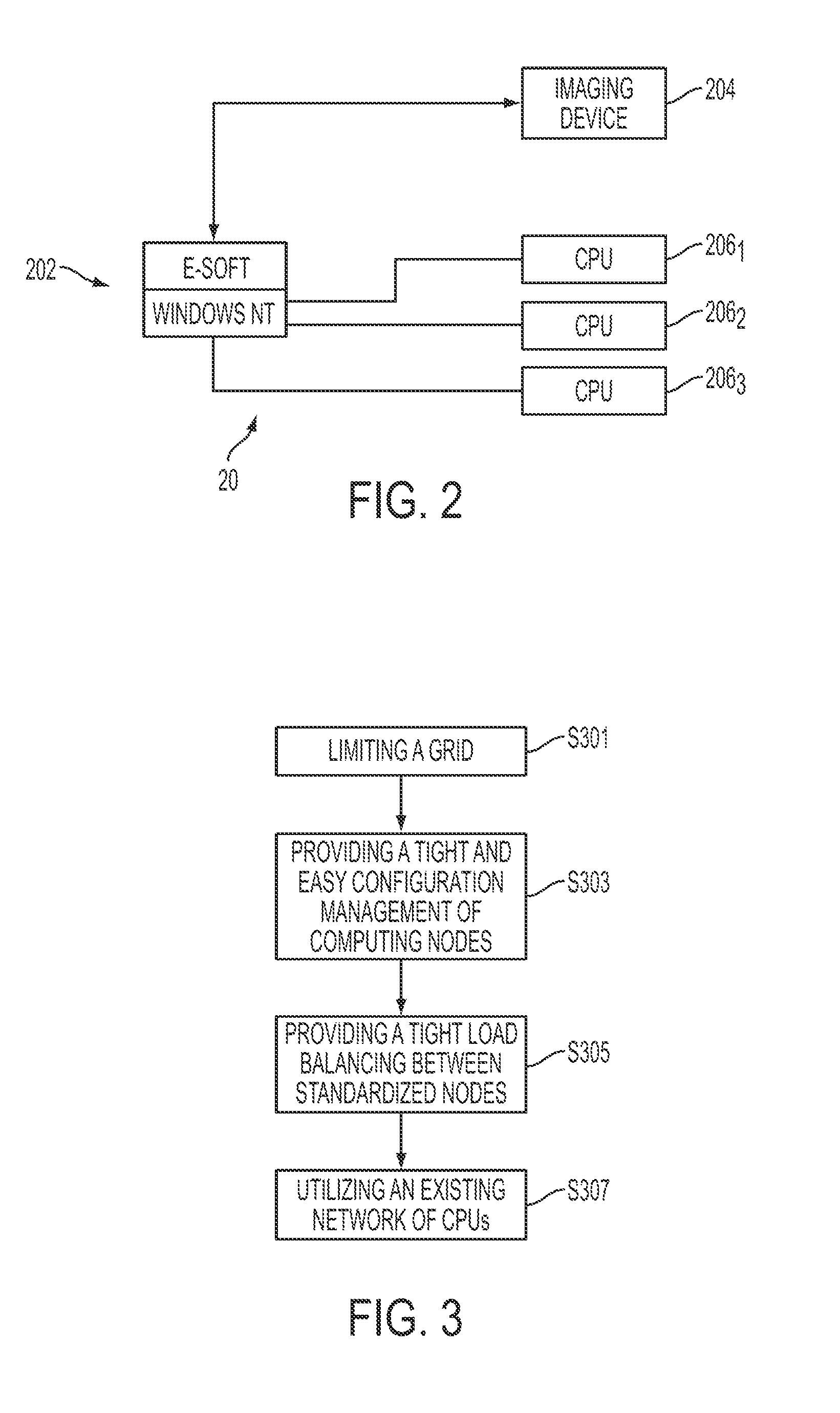
ActiveUS8818066B2Improve performanceIncrease powerDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setComputer Grid
A grid computing system and method is provided for medical data processing. The grid computing system comprises a software infrastructure, and an imaging device capable of interfacing with the software infrastructure over a distributed electronic network. Also included is a plurality of CPUs capable of interfacing with the software infrastructure over the network. The performance of the plurality of CPUs is dependent on balancing load. A large medical dataset is split onto several processing nodes of the plurality of CPUs, respectively, such that performance and power is increased. In the grid computing method, a grid is limited to a nuclear medicine or radiology network. A tight and easy configuration management of computing nodes, and a tight load balancing between standardized nodes are provided. An existing network of CPUs is utilized, such that the greatest benefit is provided at the lowest cost.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Scheduling method of grid resources of multi-Qos
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
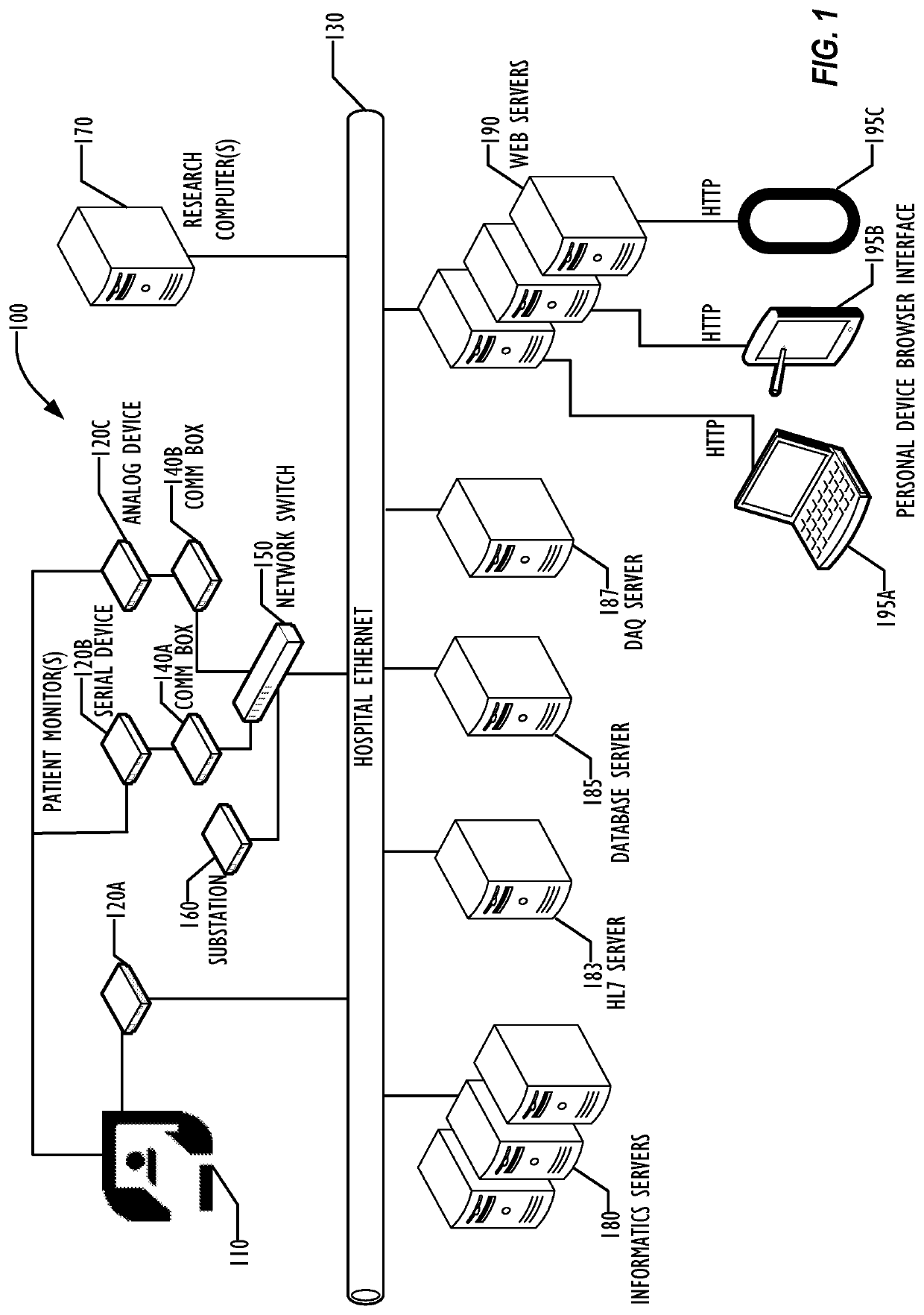
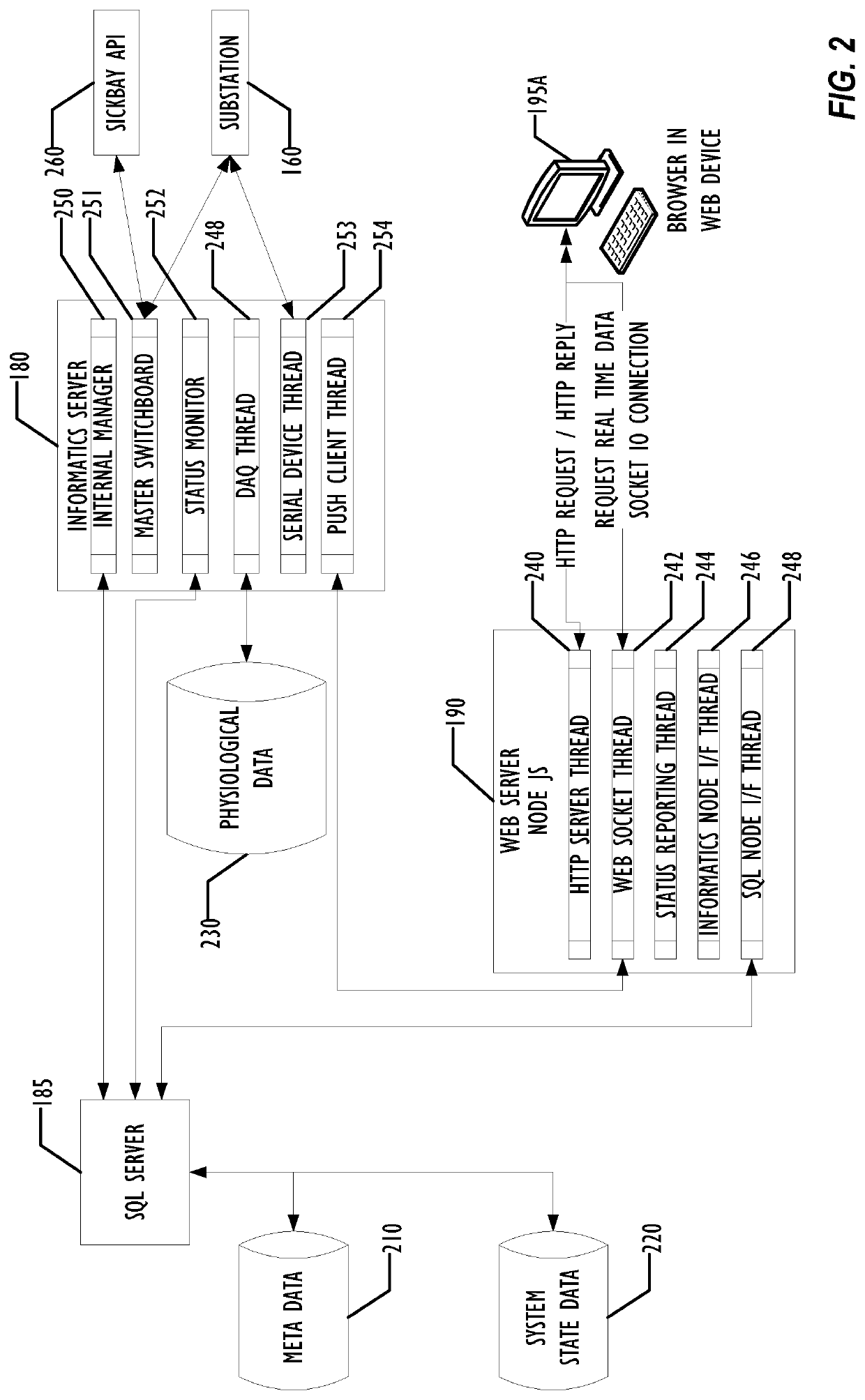
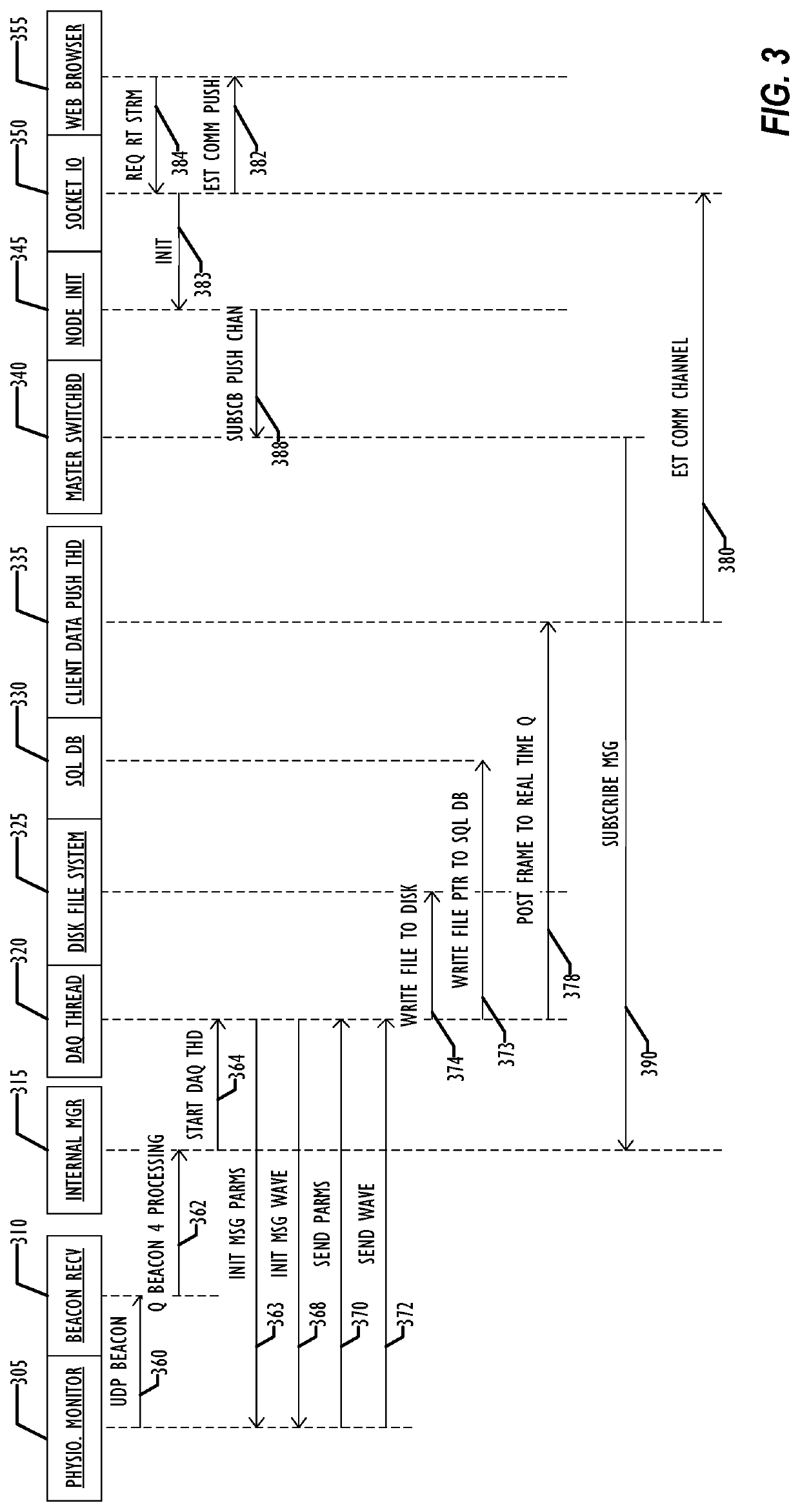
Distributed grid-computing platform for collecting, archiving, and processing arbitrary data in a healthcare environment
A set of software programs runs in a parallel configuration on local hospital servers. The software gathers all the data directed to it from a hospital patient's data sources (including, but not limited to, data formats from patient monitor devices, HL7 feeds, and other hospital data systems). Data can be time-synchronized, transformed, and routed from both currently networked device and non-networked devices. The data is made available for redisplay and analysis to system users and program agents.
Owner:MEDICAL INFORMATICS
Semantic vision SLAM method based on probabilistic grid filtering
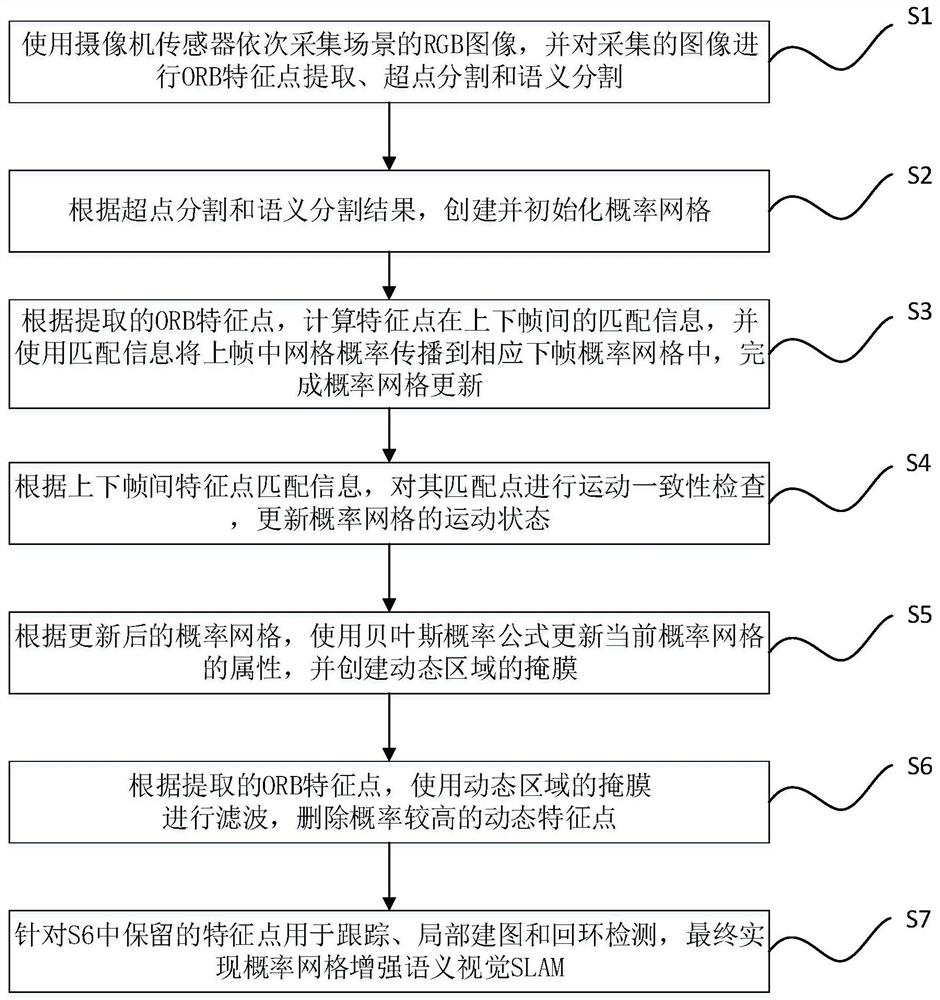
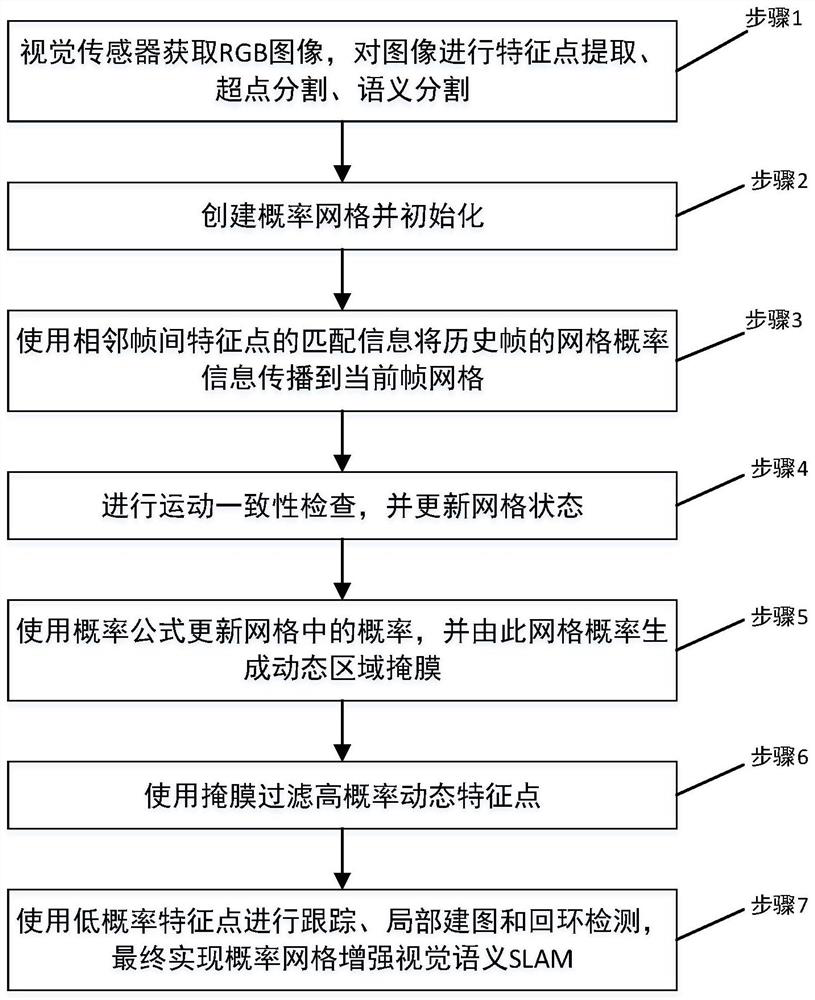
InactiveCN112465858AReliable Dynamic CharacteristicsPrecise positioningImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionRgb image
The invention discloses a semantic vision SLAM method based on probability grid filtering, and the method comprises the steps: sequentially collecting RGB images of a scene through a camera sensor, and carrying out the ORB feature point extraction, super-point segmentation and semantic segmentation on the collected images; creating and initializing a probability grid; calculating matching information of the feature points between an upper frame and a lower frame, and using the matching information to propagate the probability of the grids in the upper frame to the probability grids of the corresponding lower frame to complete probability grid updating; performing motion consistency check on the matching points, and updating the motion state of the probability grid; updating the attribute of the current probability grid by using a Bayesian probability formula according to the updated probability grid, and creating a mask of a dynamic region; according to the extracted ORB feature points, performing filtering by using a mask of a dynamic region, and detecting the dynamic feature points with relatively high probability; and using the reserved feature points for tracking, local mappingand loopback detection, and finally realizing probability grid enhanced semantic vision SLAM.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Grid simulation platform and grid simulation method
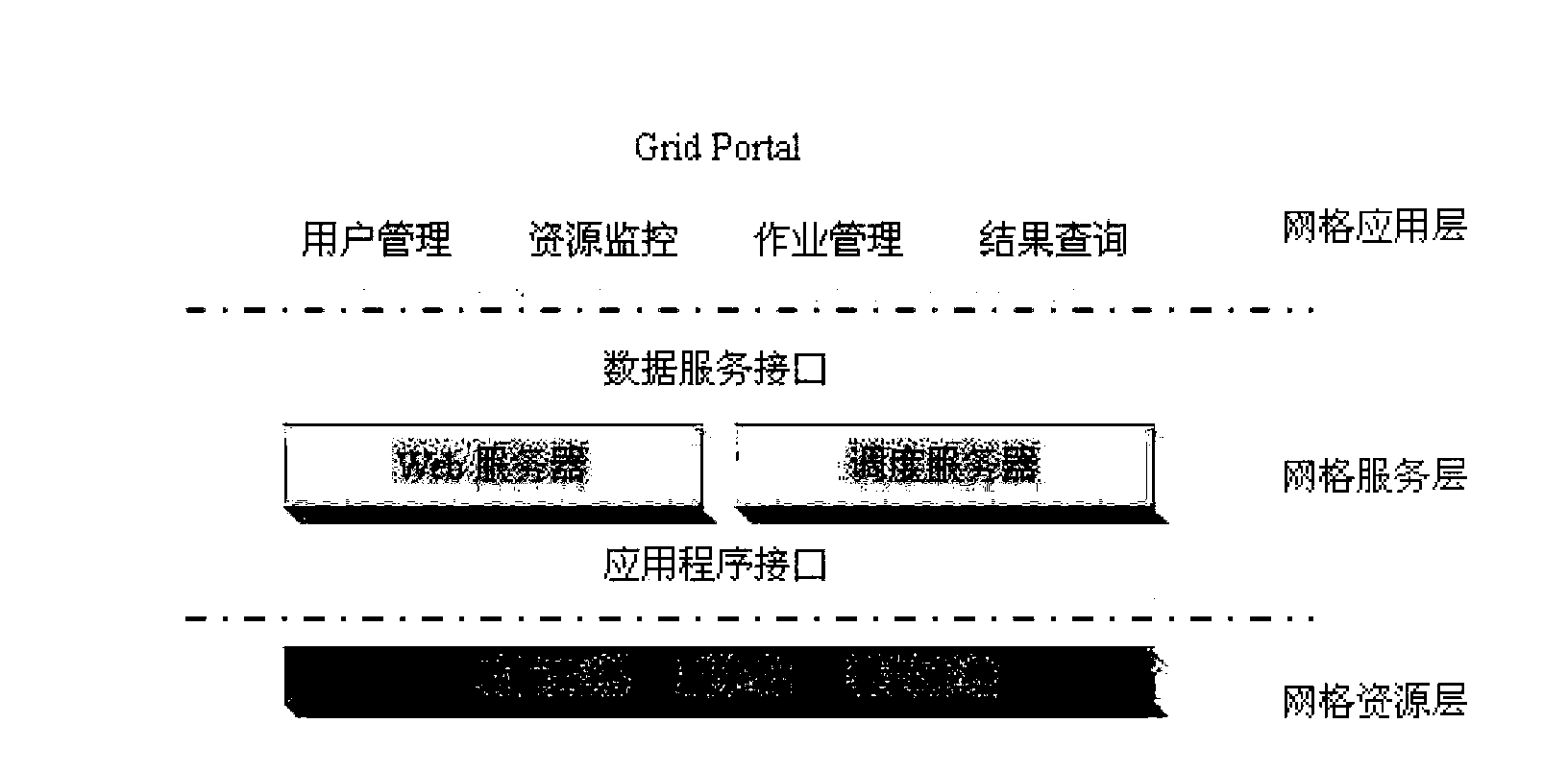
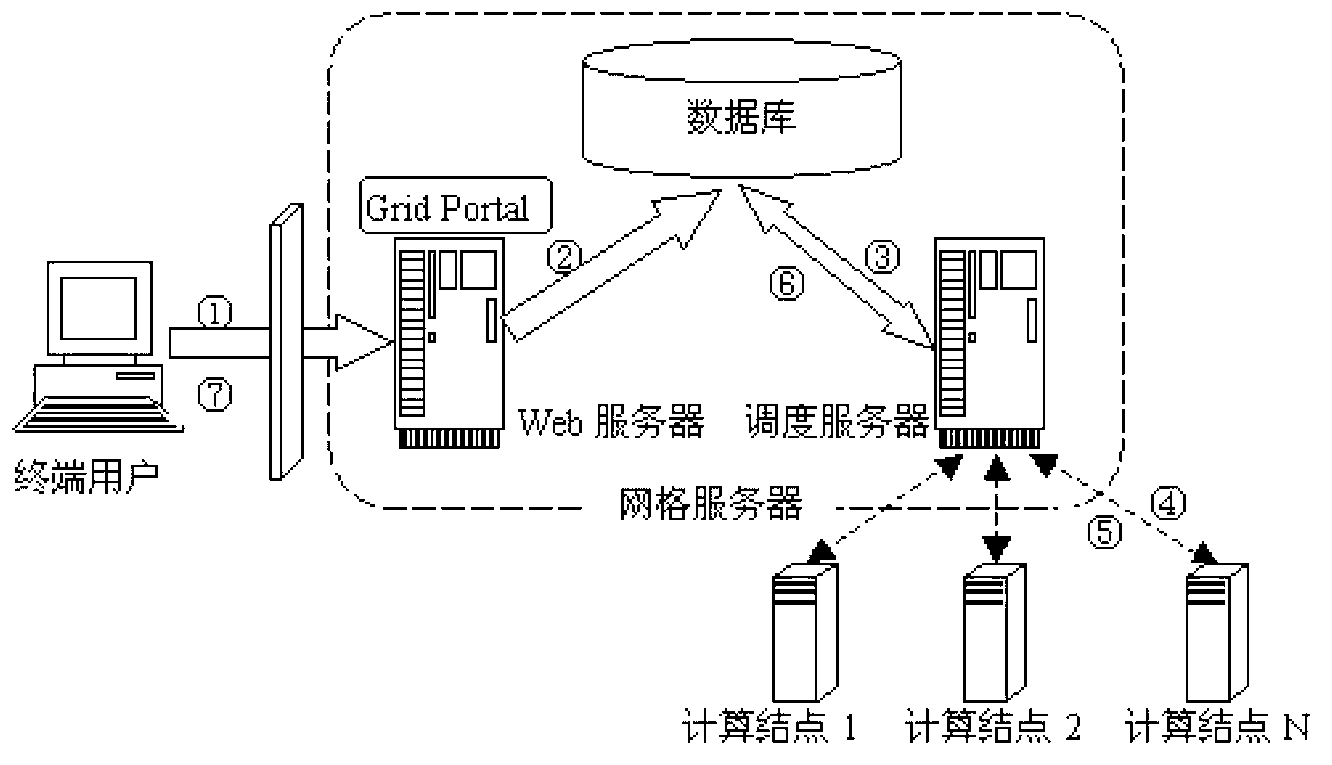
ActiveCN103020197AImprove or expand efficiencyIncrease or expand utilizationTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsResource utilizationWeb service
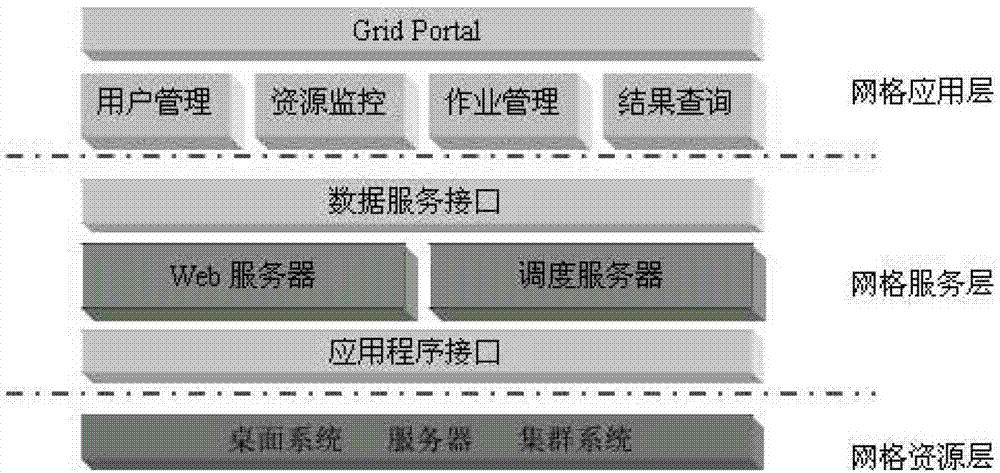
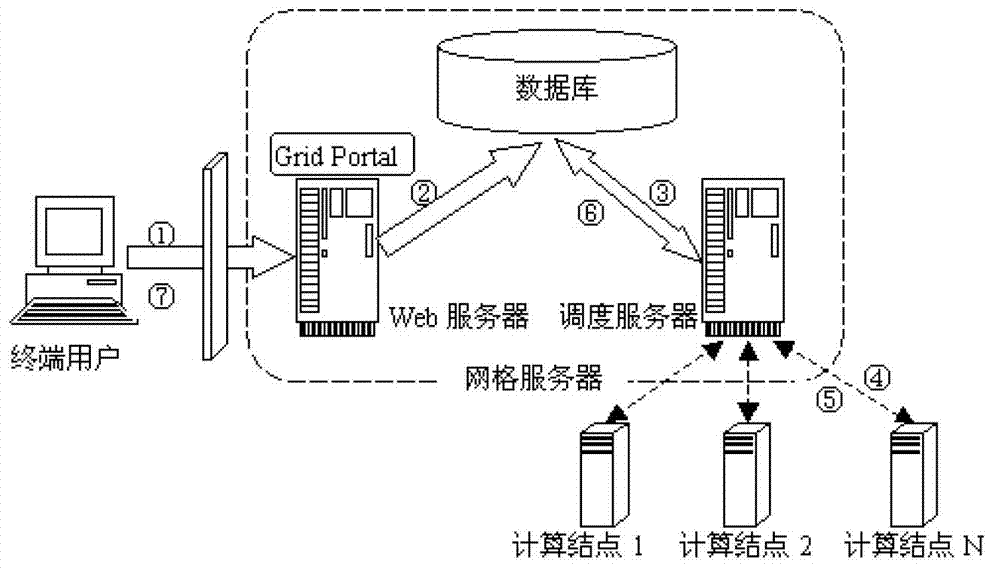
The invention discloses a grid simulation platform, which comprises a terminal user, a grid server and computing nodes. After the terminal user logs onto a grid portal through a browser, grid services, such as job submission, information inquiry and the like, can be used. The grid server comprises a Web server, a dispatch server and a database. The grid computing nodes comprise all personal computers (PC) and cluster systems participating in computing. The invention also provides a corresponding grid simulation method. According to the grid simulation platform and the grid simulation method disclosed by the invention, computing of population fitness values is reasonably parallelized, and therefore, resource sharing of distributed desktop systems and cluster systems is realized, the problem that product development and production are influenced due to the fact that a single enterprise resource is insufficient at present is solved, the resource utilization rate is effectively improved, and a large number of funds are saved for enterprises.
Owner:WUXI VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE
Multi-robot continuous monitoring method and non-temporary computer readable storage medium
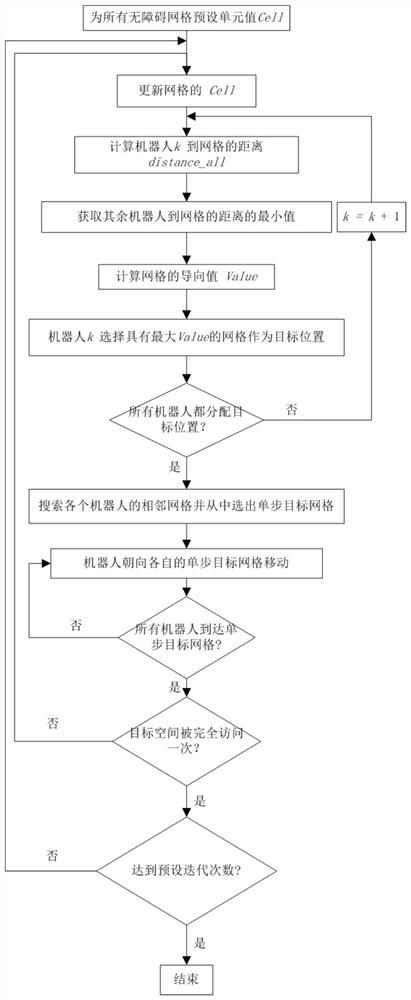
PendingCN114859891AHigh frequencyImprove adaptabilityTotal factory controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimulationComputer Grid
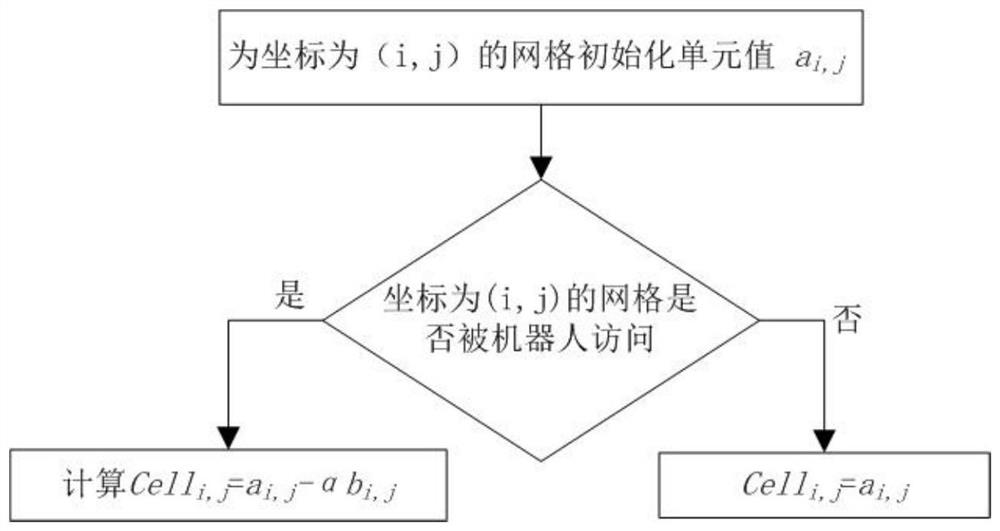
The invention discloses a multi-robot continuous monitoring method and a non-temporary computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: S1, initializing; s2, the guiding value Value of each robot is calculated; s3, acquiring a coordinate corresponding to the maximum guide value Value of each robot, and adding the coordinate as a global target position into the set optcount; s4, searching the adjacent grids of the current position carpos of each robot, and removing the grids occupied by the obstacles; s5, the distance between the adjacent grids and the corresponding global target position is calculated, and the adjacent grid with the minimum distance to the target position is selected as the single-step target position to which the robot moves at the speed Vel; and S6, judging whether each robot arrives at the single-step target position in the step S5 or not, if so, updating the current position carpos of the robot, setting the unit value of the grid corresponding to the current position carpos to be 0, and increasing delta t to the unit values of the other grids. According to the multi-robot continuous monitoring method, partition does not need to be considered, and adaptability is good.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Grid simulation platform and grid simulation method
ActiveCN103020197BMeet needsSolve the shortageTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsResource utilizationWeb service
The invention discloses a grid simulation platform, which comprises a terminal user, a grid server and computing nodes. After the terminal user logs onto a grid portal through a browser, grid services, such as job submission, information inquiry and the like, can be used. The grid server comprises a Web server, a dispatch server and a database. The grid computing nodes comprise all personal computers (PC) and cluster systems participating in computing. The invention also provides a corresponding grid simulation method. According to the grid simulation platform and the grid simulation method disclosed by the invention, computing of population fitness values is reasonably parallelized, and therefore, resource sharing of distributed desktop systems and cluster systems is realized, the problem that product development and production are influenced due to the fact that a single enterprise resource is insufficient at present is solved, the resource utilization rate is effectively improved, and a large number of funds are saved for enterprises.
Owner:WUXI VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com