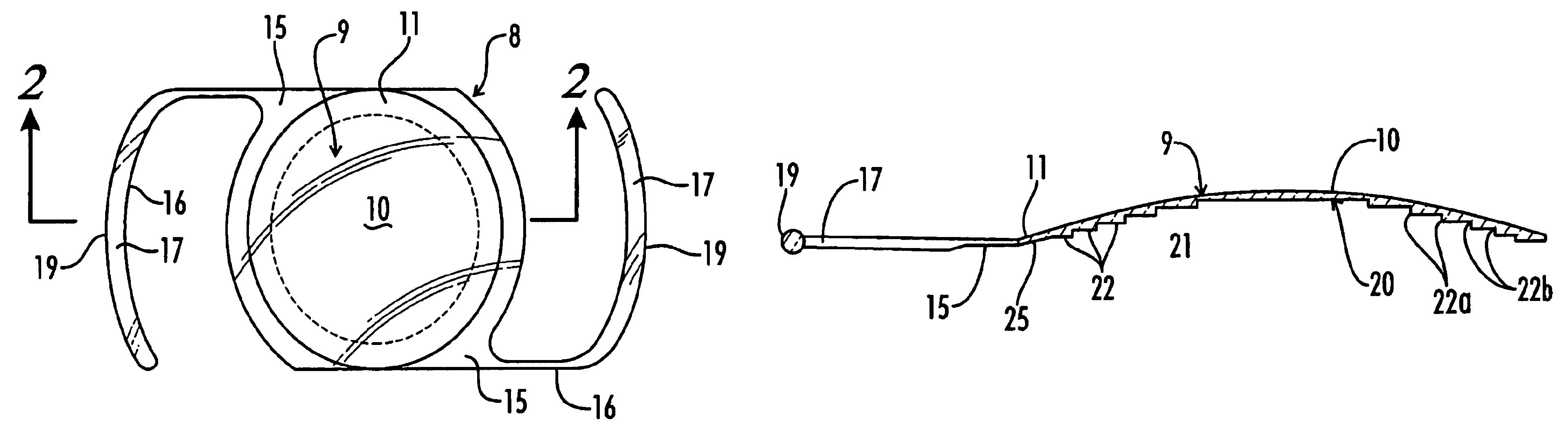
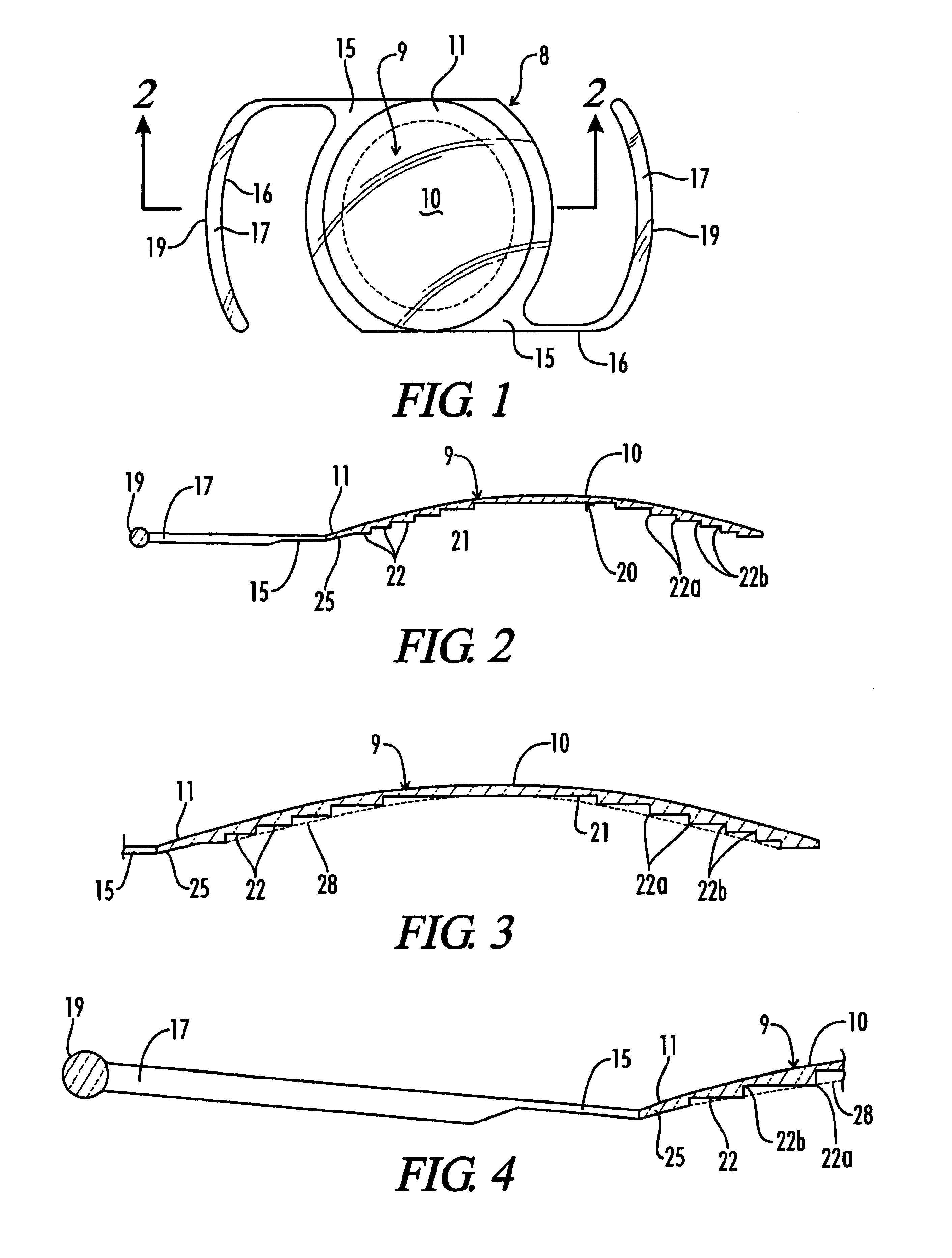
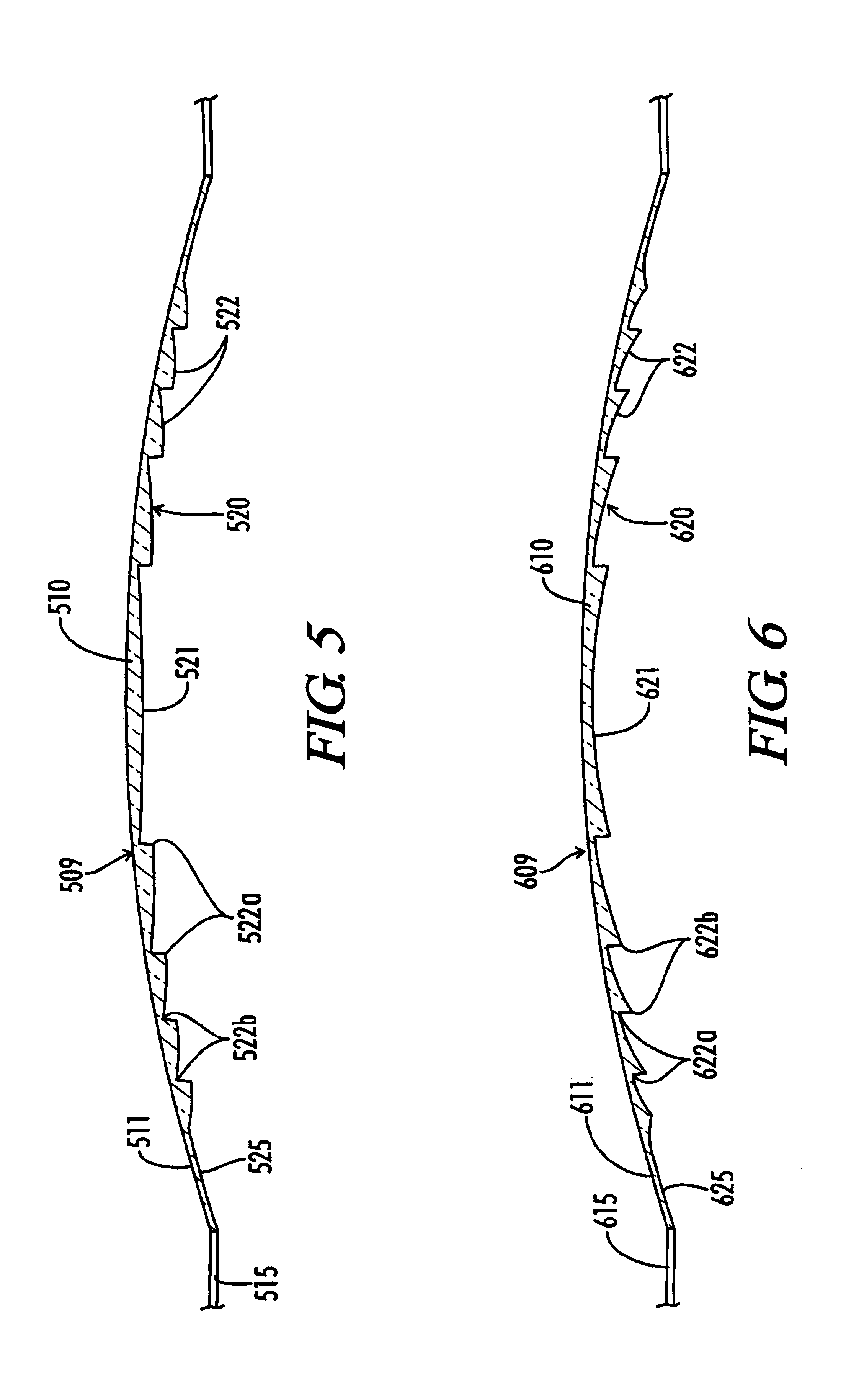
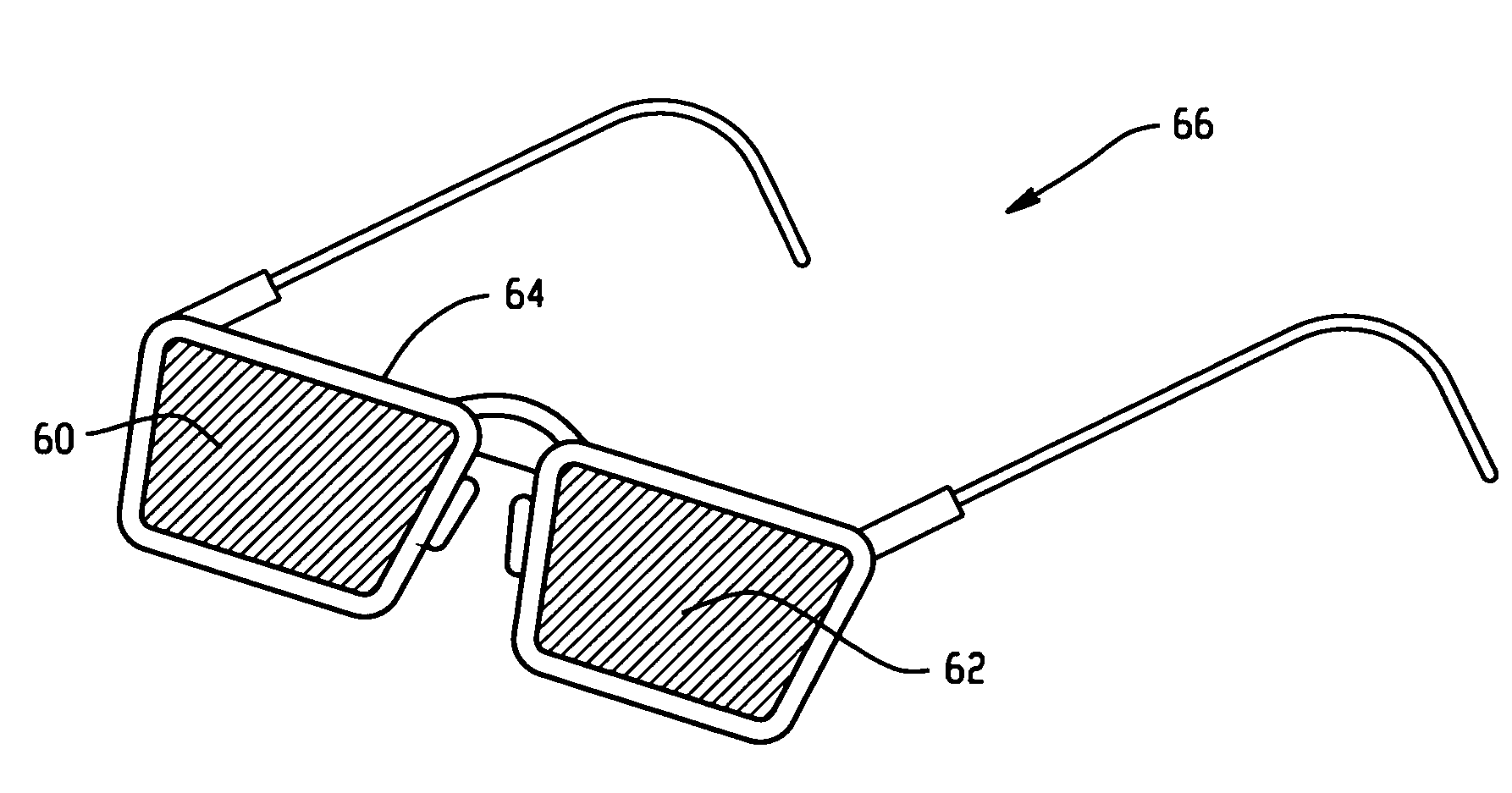
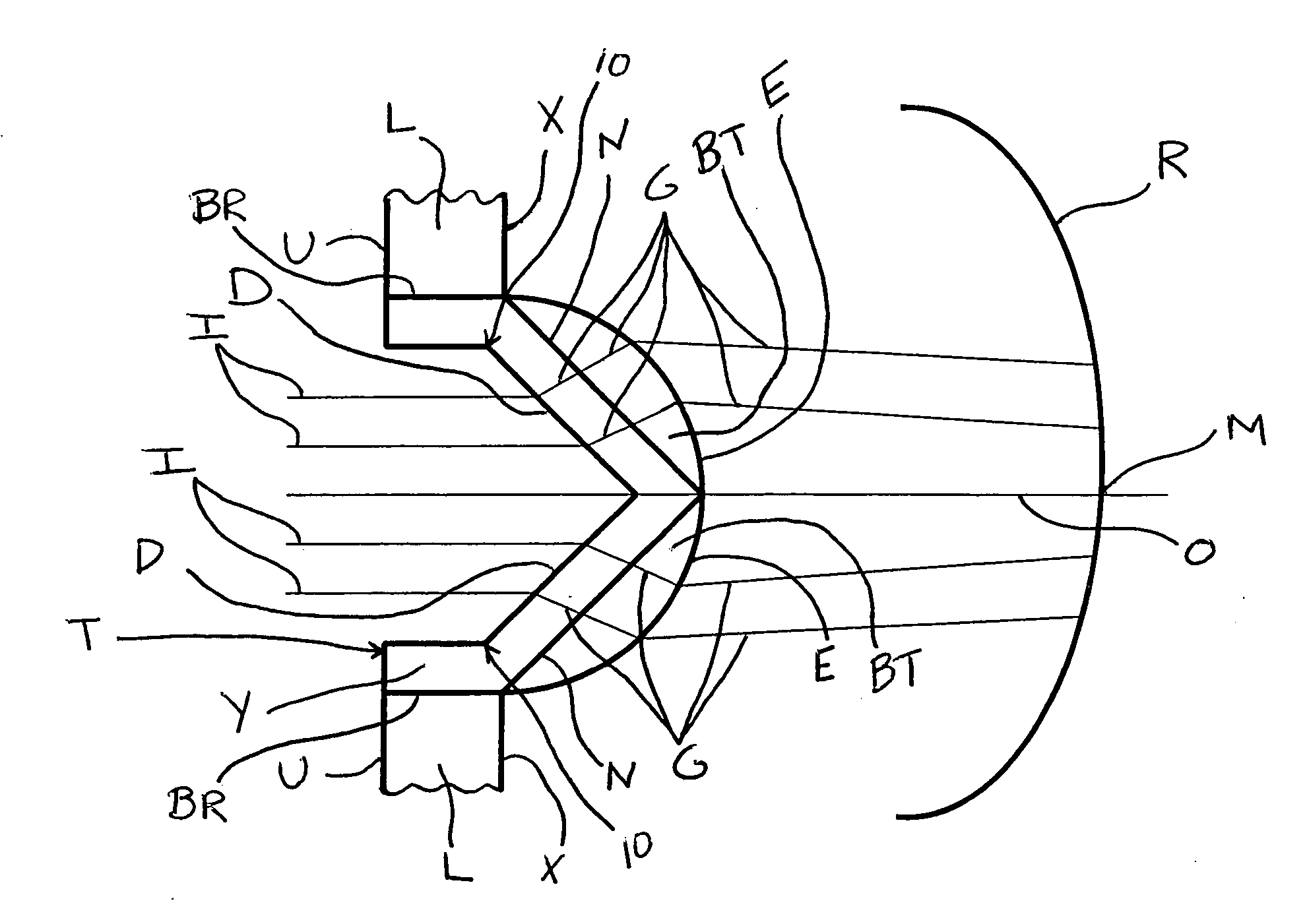
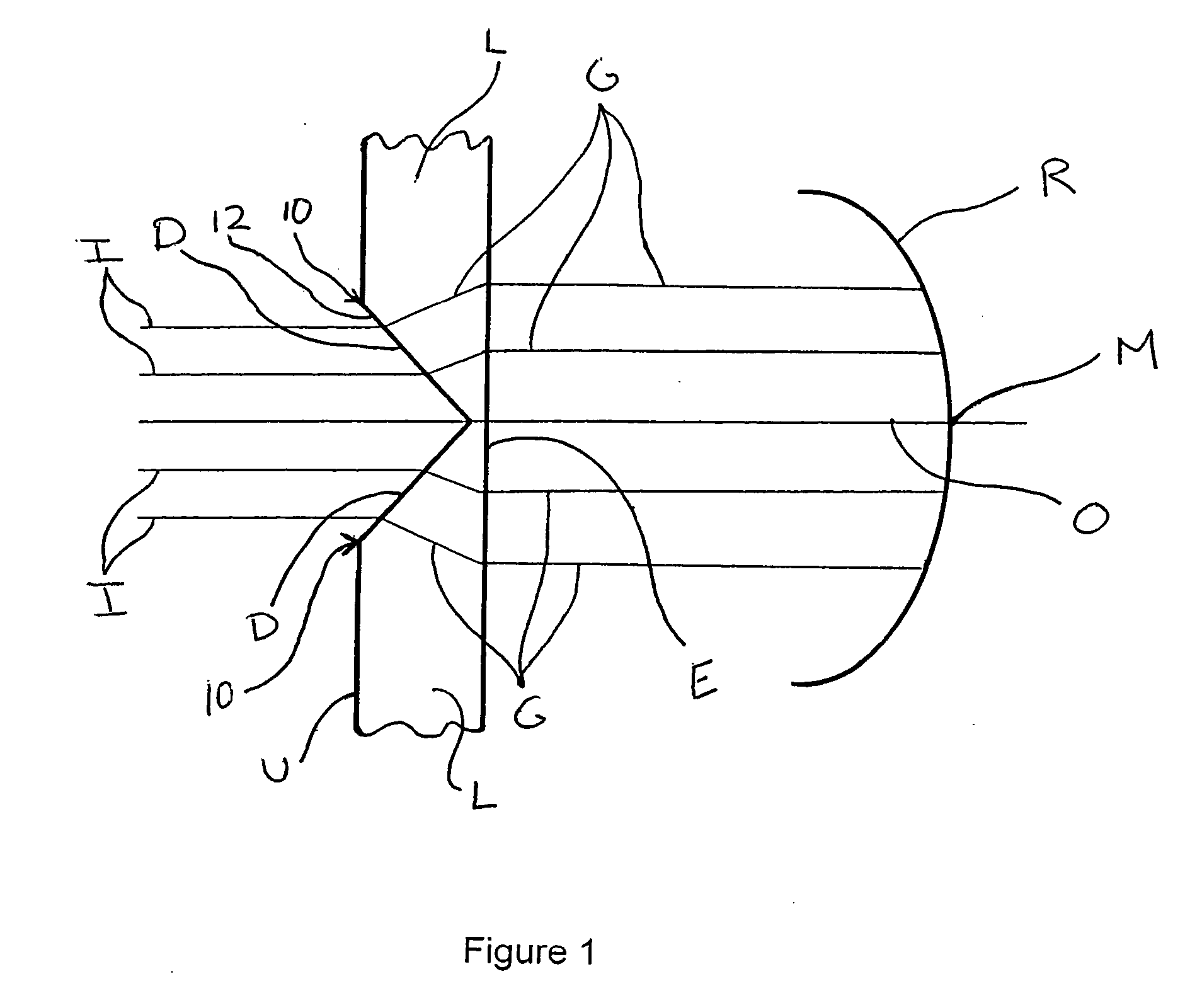
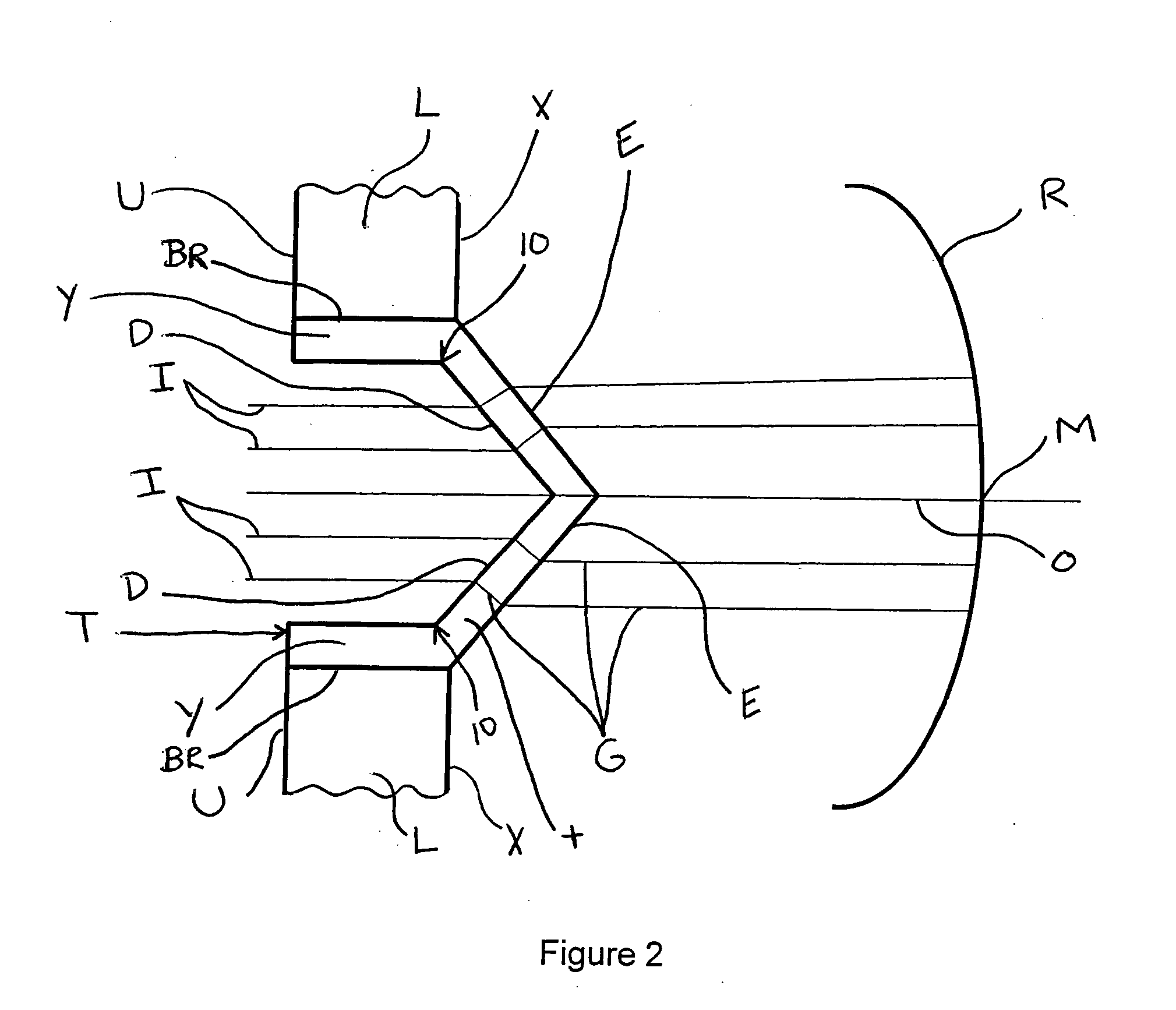
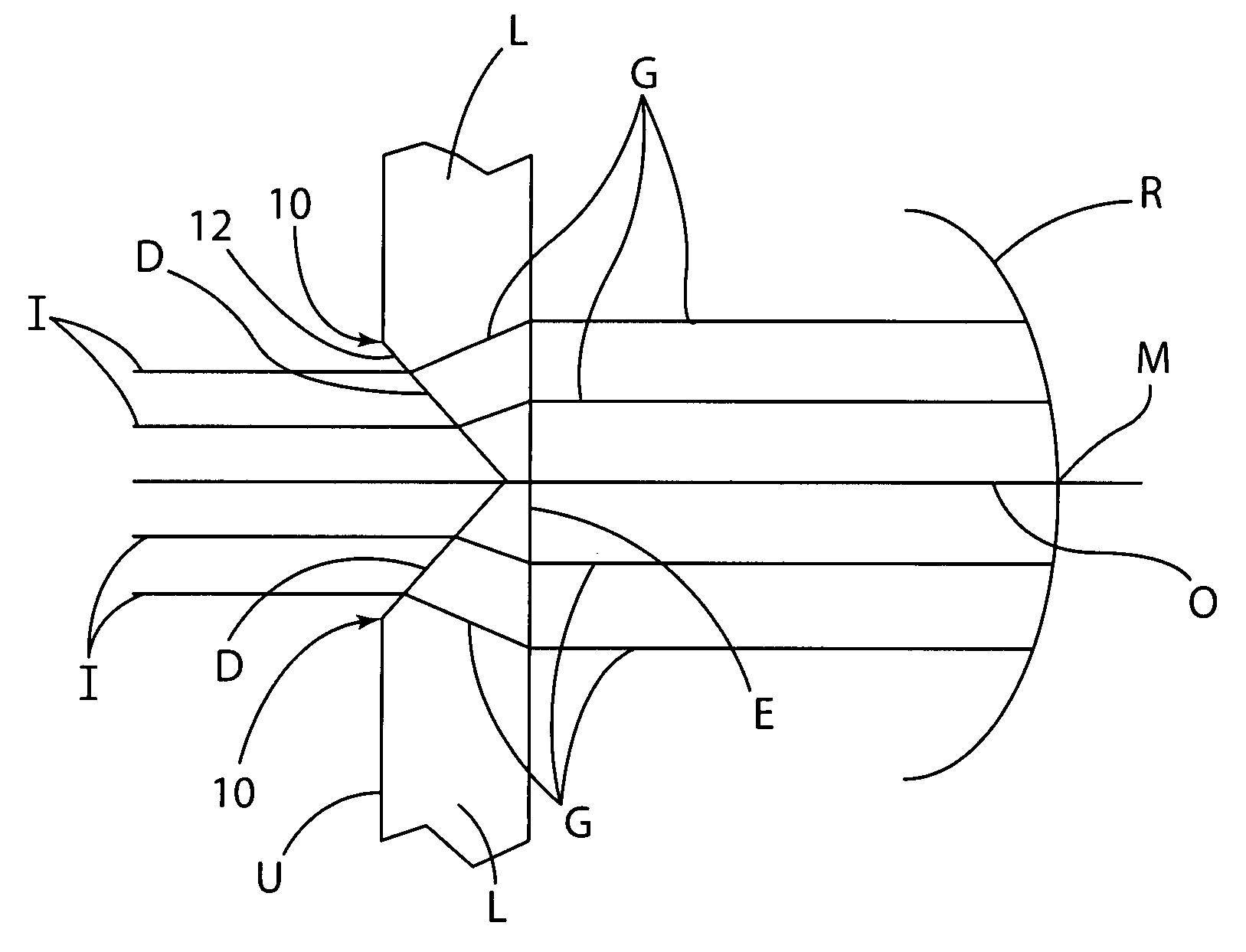
Patents
Literature
129 results about "Corrective lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
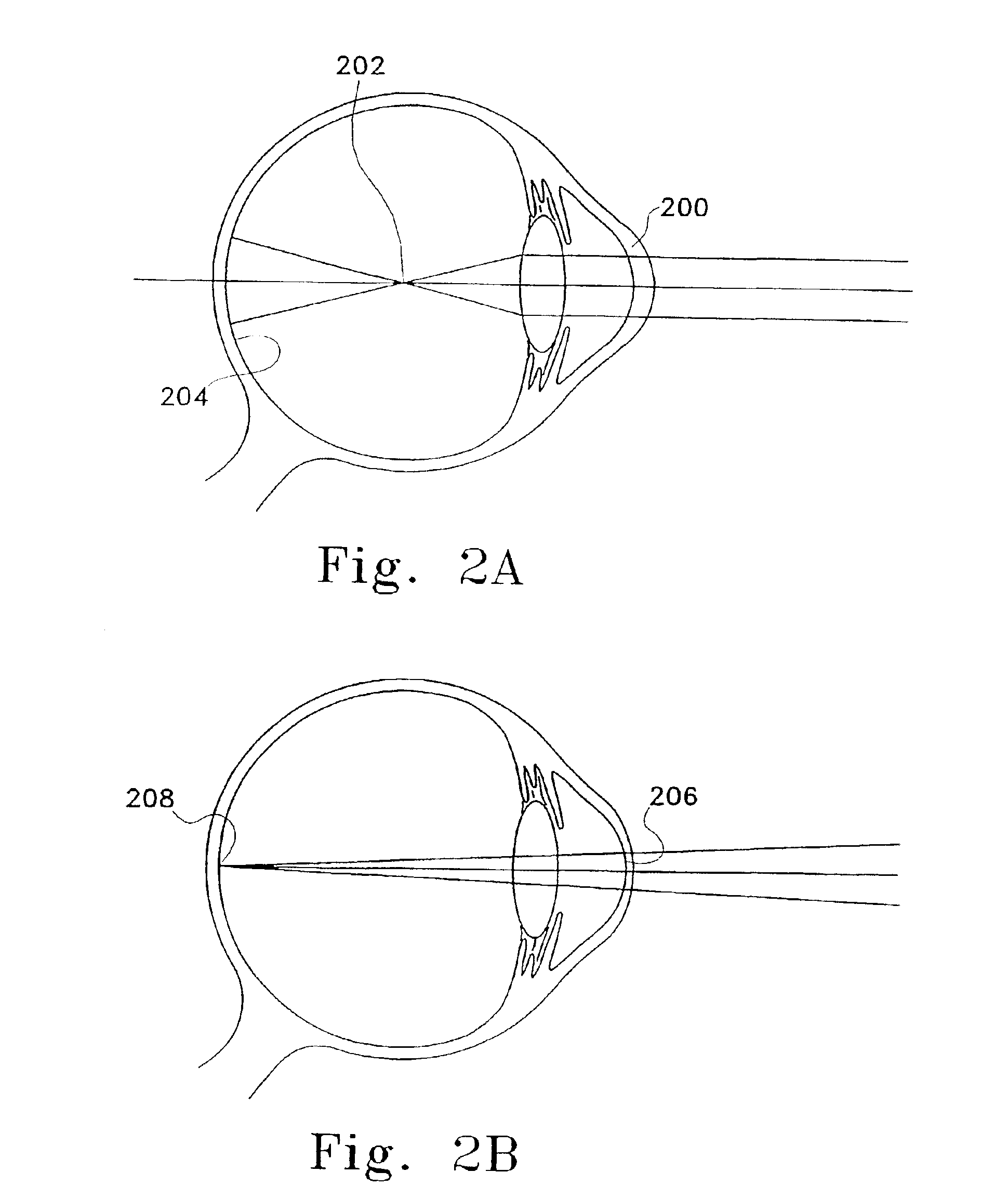
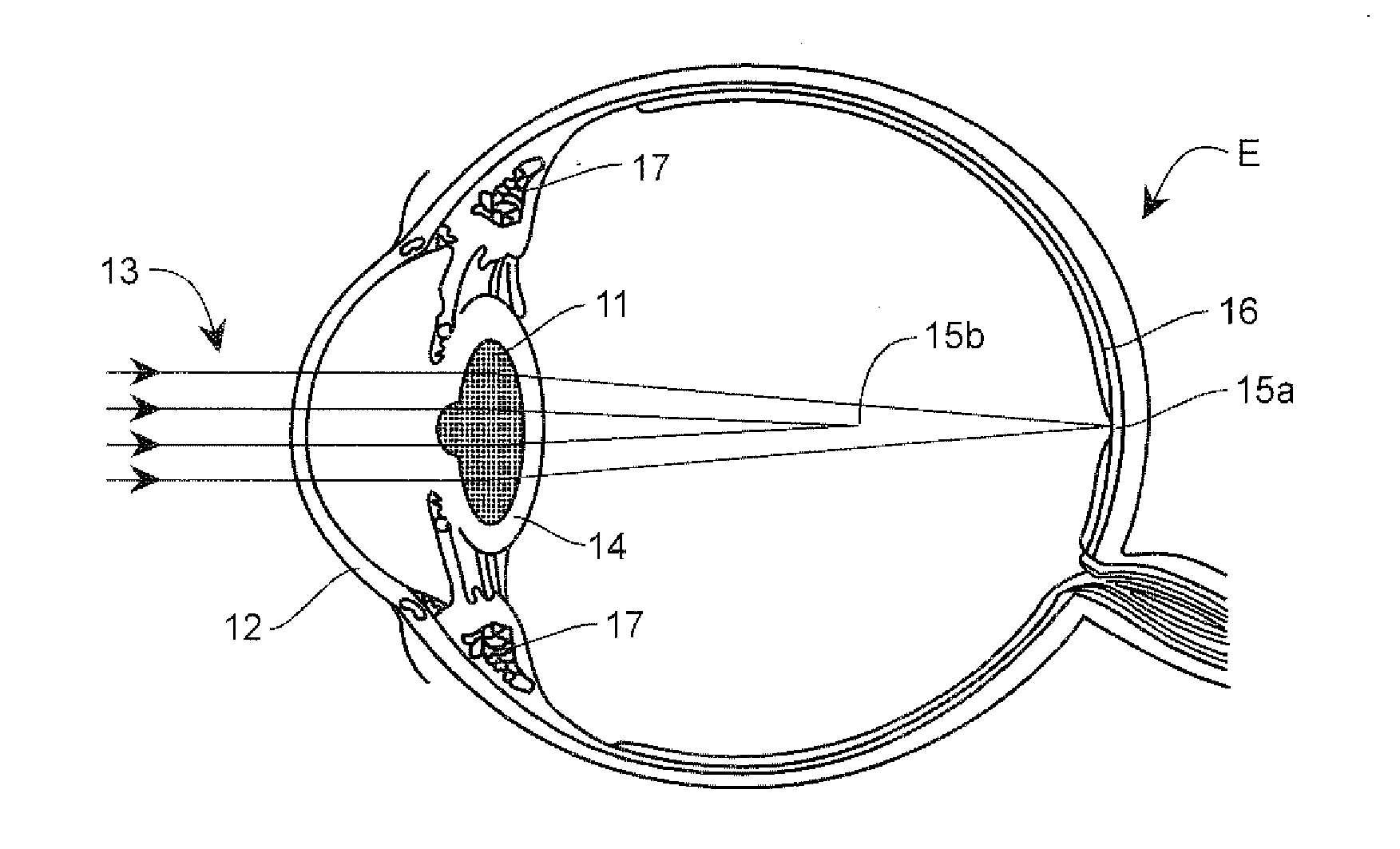
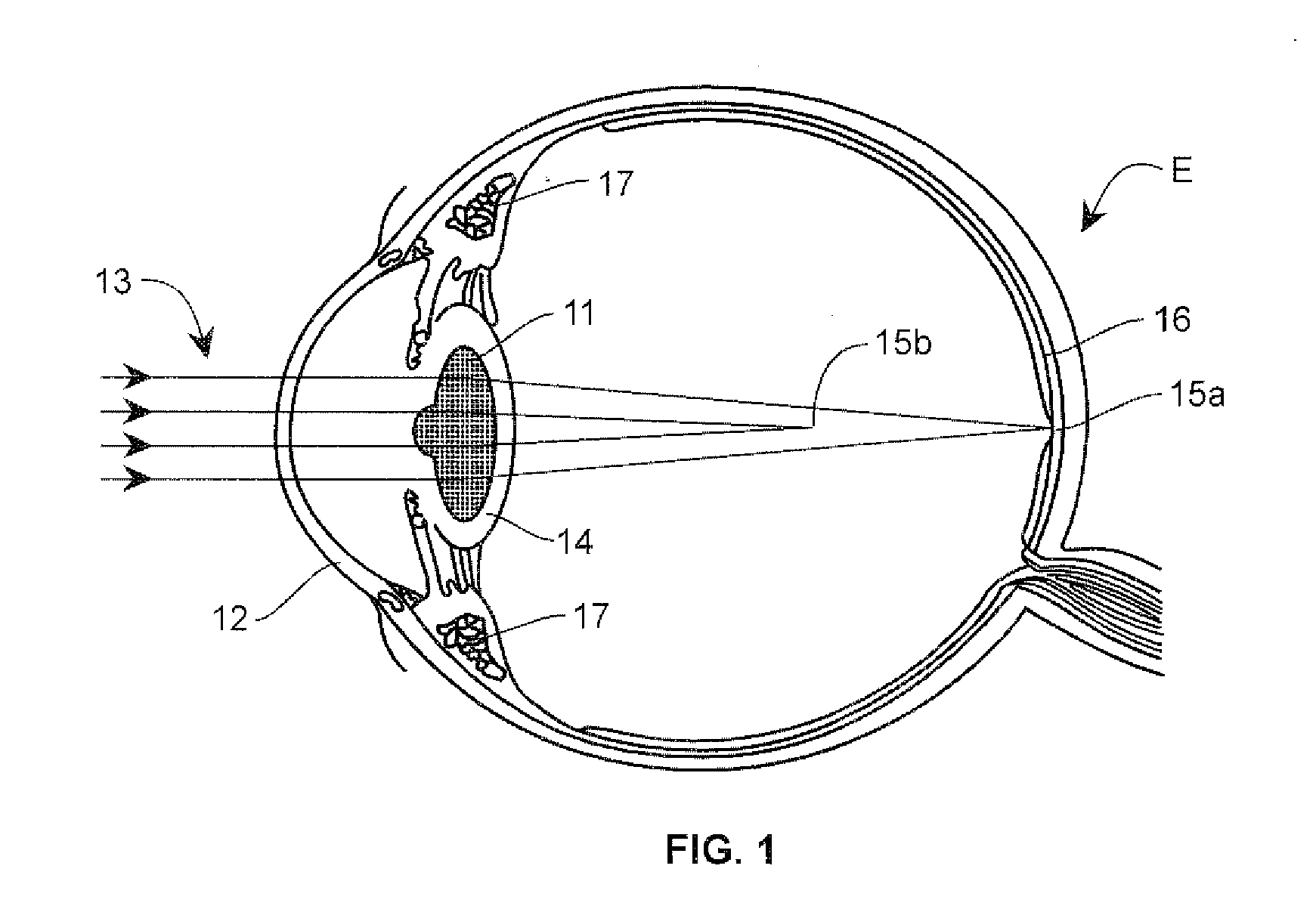
A corrective lens is a lens typically worn in front of the eye to improve vision. The most common use is to treat refractive errors: myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Glasses or "spectacles" are worn on the face a short distance in front of the eye. Contact lenses are worn directly on the surface of the eye. Intraocular lenses are surgically implanted most commonly after cataract removal, but can be used for purely refractive purposes.
Refractive corrective lens (RCL)
InactiveUS20060116765A1Corrected visionReduce pressureOptical articlesIntraocular lensCorrective contact lensCorrective lens
Owner:BLAKE LARRY W +3
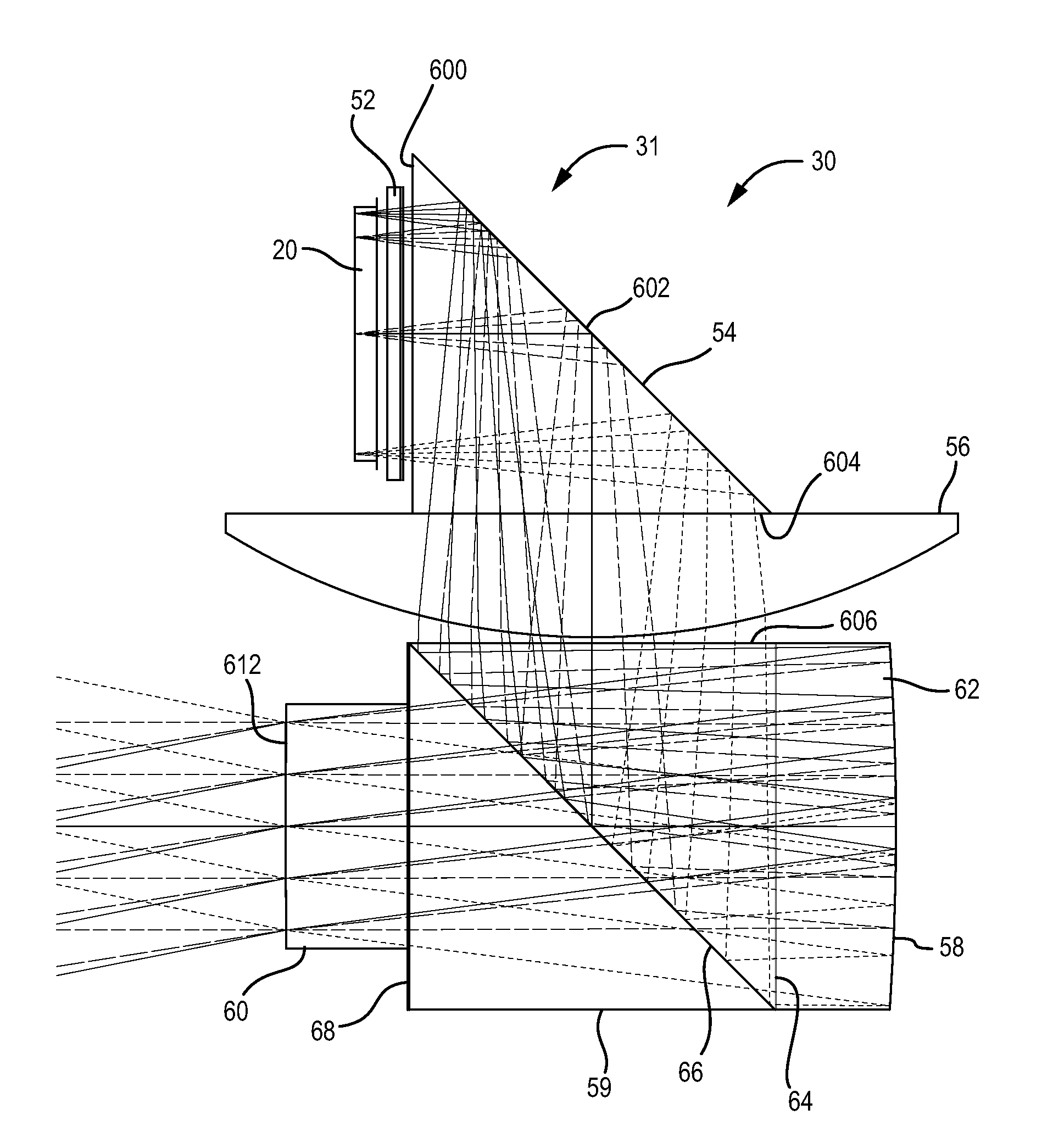
System for and method of catadioptric collimation in a compact head up display (HUD)
A head up display can use a catadioptric collimating system. The head up display includes an image source. The head up display also includes a collimating mirror, and a polarizing beam splitter. The light from the image source enters the beam splitter and is reflected toward the collimating mirror. The light striking the collimating mirror is reflected through the beam splitter toward a combiner. A corrective lens can be disposed after the beam splitter.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Method of lifting an epithelial layer and placing a corrective lens beneath it
This relates to a lens made of donor corneal tissue suitable for use as a contact lens or an implanted lens, to a method of preparing that lens, and to a technique of placing the lens on the eye. The lens is made of donor corneal tissue that is acellularized by removing native epithelium and keratocytes. These cells optionally are replaced with human epithelium and keratocytes to form a lens that has a structural anatomy similar to human cornea. The ocular lens may be used to correct conditions such as astigmatism, myopia, aphakia, and presbyopia.
Owner:TISSUE ENG REFRACTION
Acoustic touch apparatus
ActiveUS8823685B2Digital data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingCorrective contact lensTransducer
Acoustic touch apparatus comprising a substrate having first and second surfaces capable of propagating surface acoustic waves, the second surface comprising a touch region and the first and second surfaces coupled via a rounded connecting surface; at least one acoustic wave transducer on the first surface; and at least one reflective array on the first surface. The transducer is capable of transmitting or receiving waves to and from the reflective array. The substrate and reflective array can acoustically couple waves between the first and second surfaces. The substrate has a border region on the first surface adapted to hide the transducer and reflective array and preclude distortion of waves propagating over a window in the border region. The border region may have a border layer except at the window and a corrective lens is used proximate the window, or the border region comprises discolored glass except at the window.
Owner:ELO TOUCH SOLUTIONS INC
Deformable intraocular corrective lens
InactiveUS6921415B2Common problemStable positionEye surgeryIntraocular lensPhakic iolCorrective lens
A deformable, artificial intraocular contact lens for implantation into the human eye to correct normal-vision problems. The lens may be positioned posteriorly from the iris, resting against the anterior surface of the posterior capsule's natural lens. Alternatively, the lens may be positioned in the anterior chamber of the eye. The implanted lens works in conjunction with the cornea and natural lens to provide proper vision, as a substitute for regular contact lens, spectacles, and radial keratotomy. The lens may be designed from a rigid or semi-rigid material. Due to the thinness of the structure, the lens may be rolled and inserted into the eye, minimizing both the length of the corneal incision and the stretching of the cornea.
Owner:THINOPTX
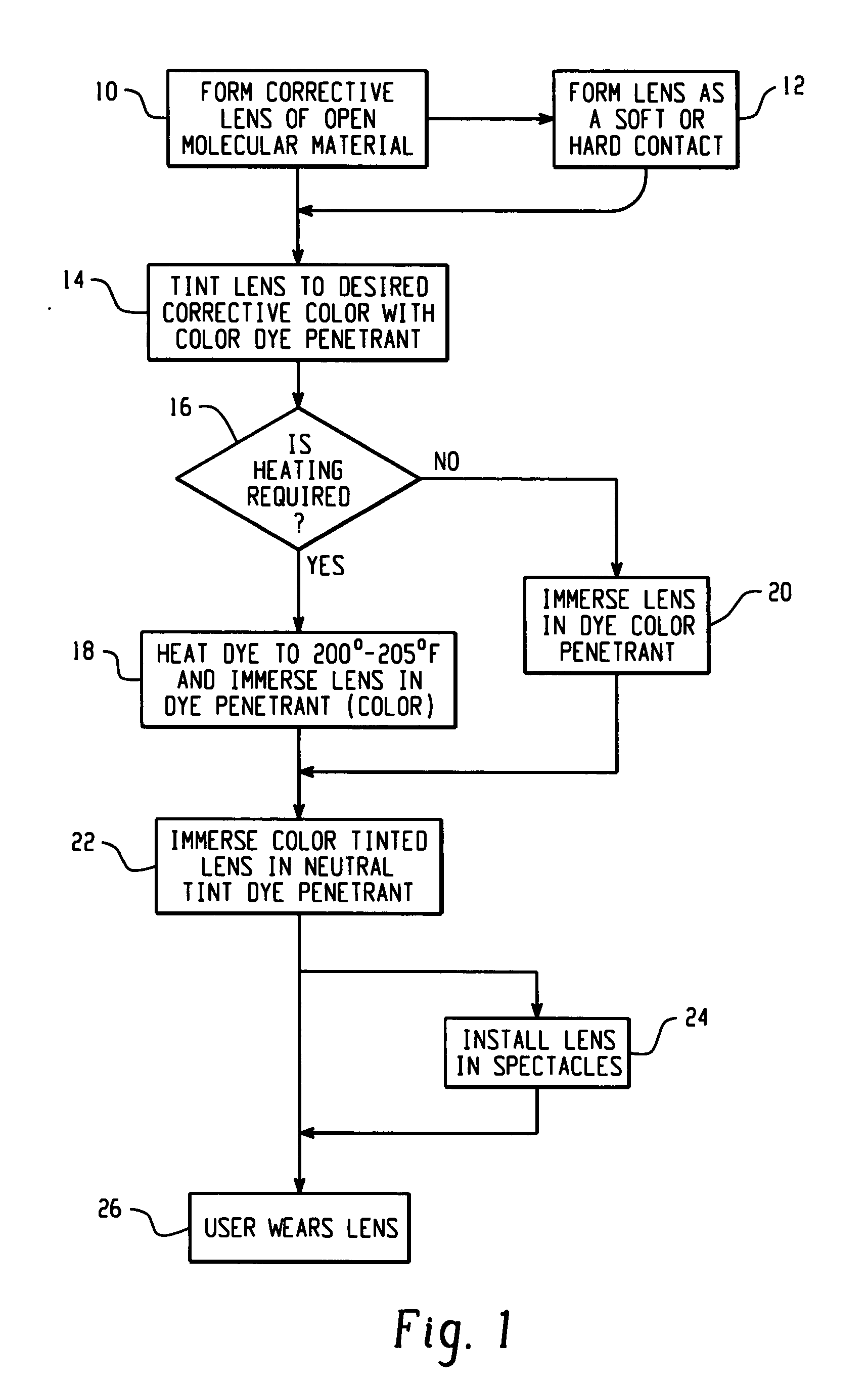
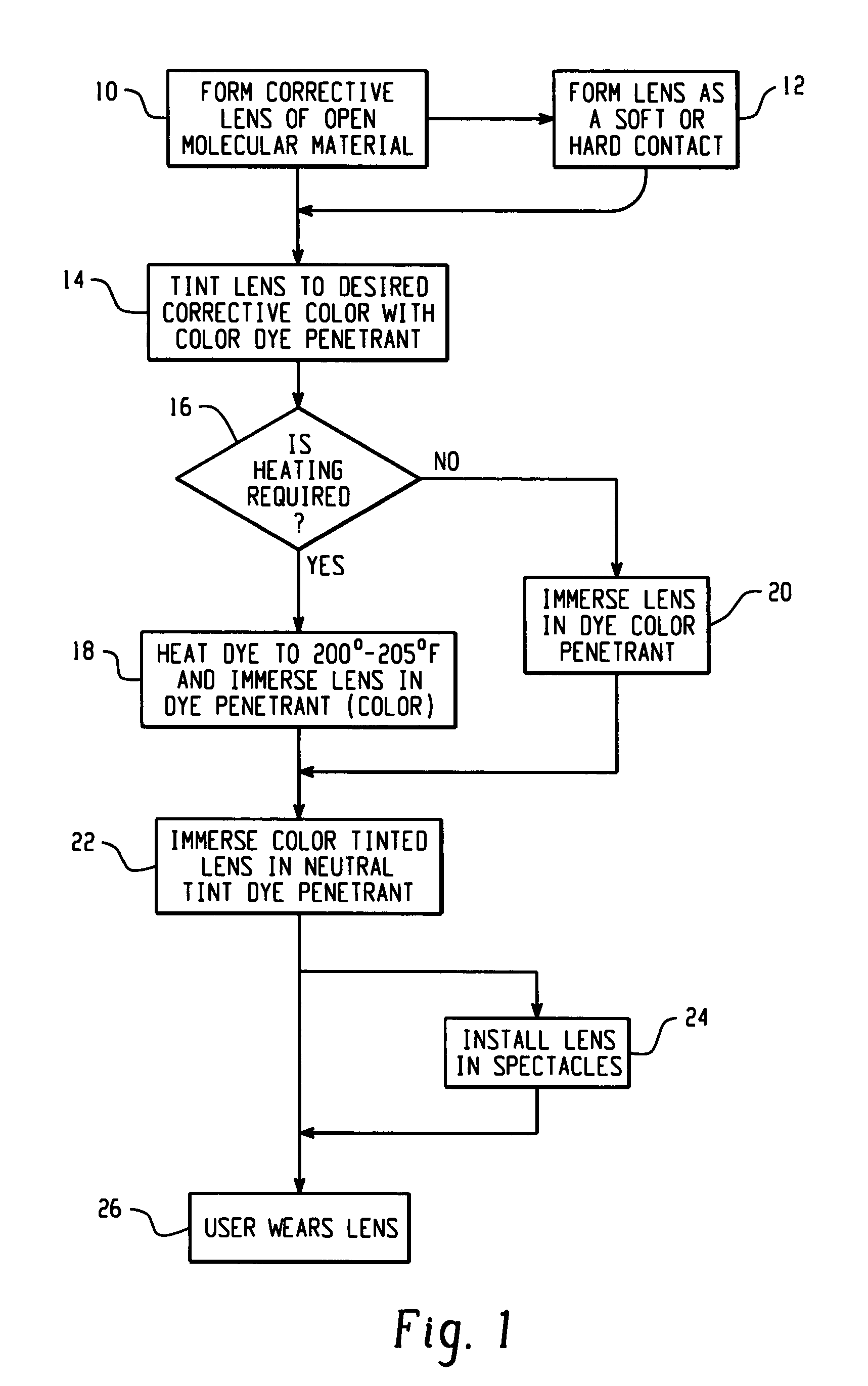
Tinted lens and method of making same
A lens and a method of making lenses suitable for color blindness correction are disclosed. The corrective lens may be formed of an optically transparent base material, which is tinted to the desired color for correction by immersion in a colorant dye. The color tinted lens is then tinted by a neutral tint dye to render the lens observable as a regular corrective lens. If desired, the dyes may be heated during immersion.
Owner:CHROMAGEN VISION
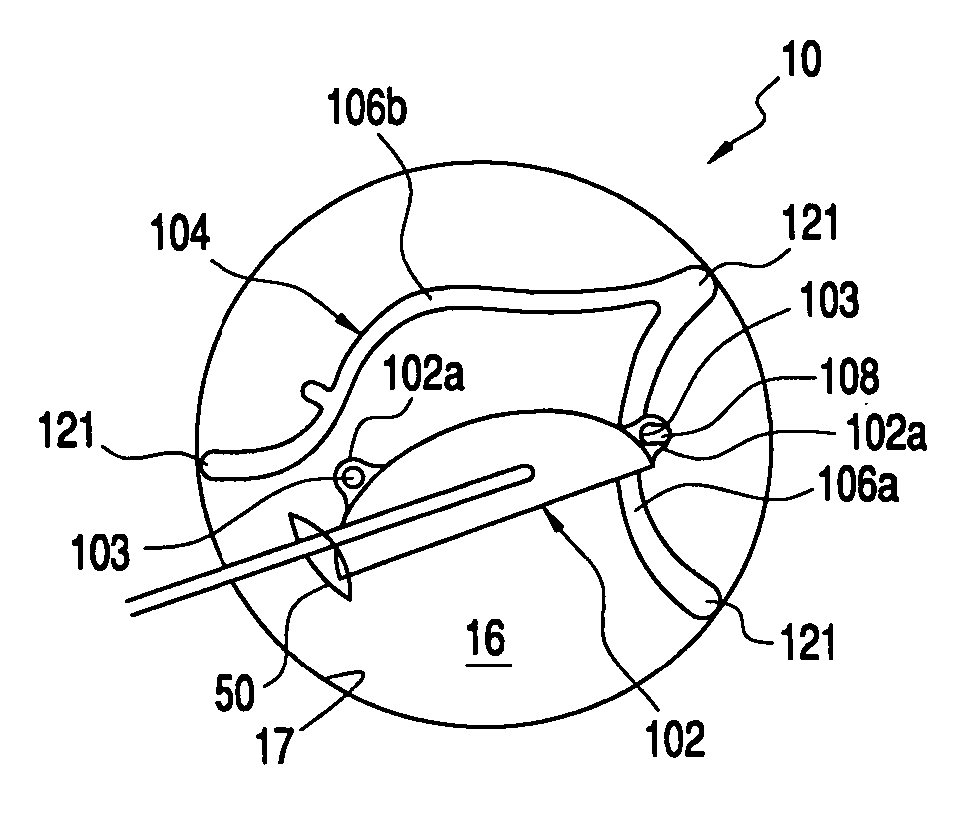
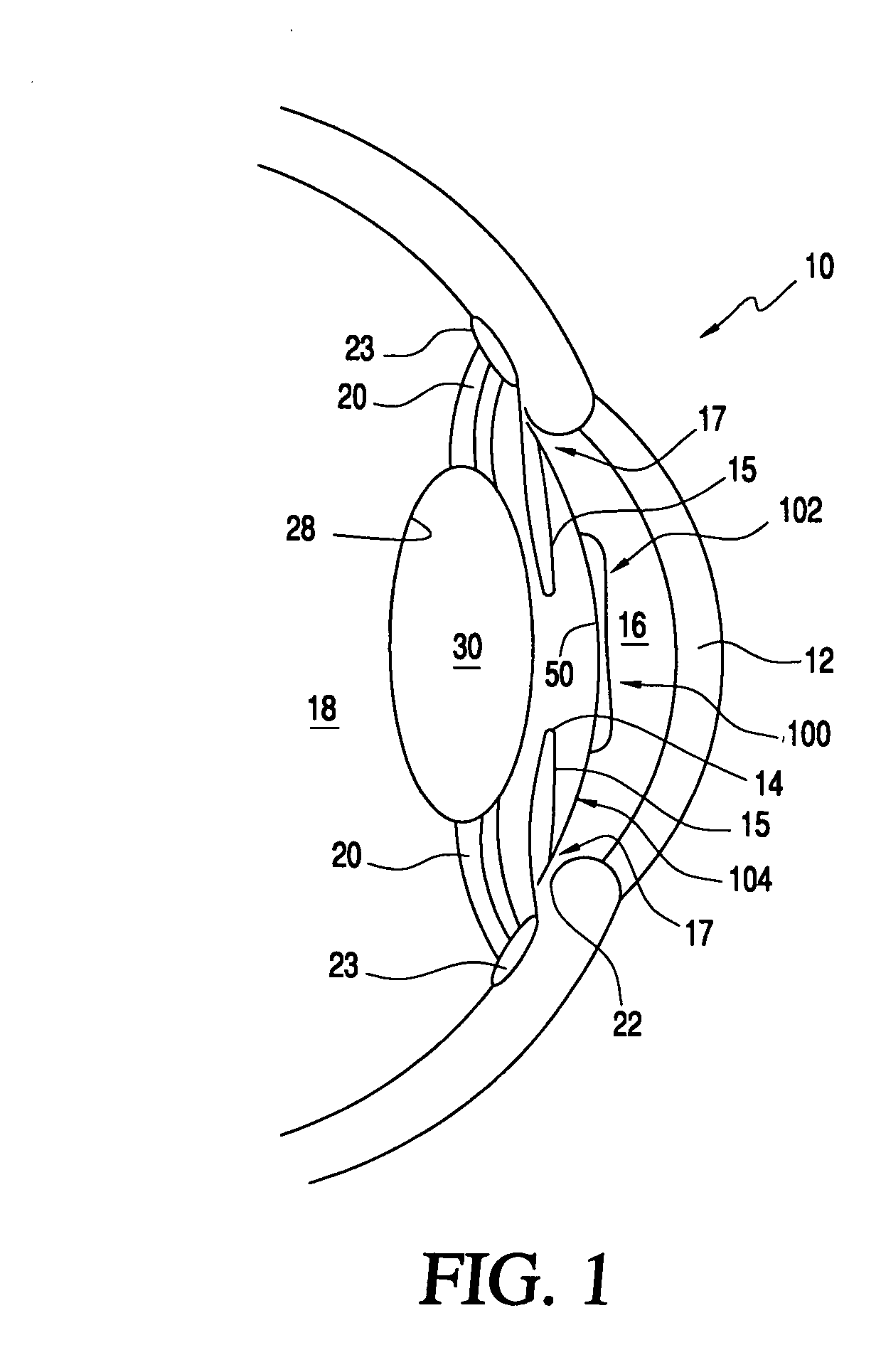
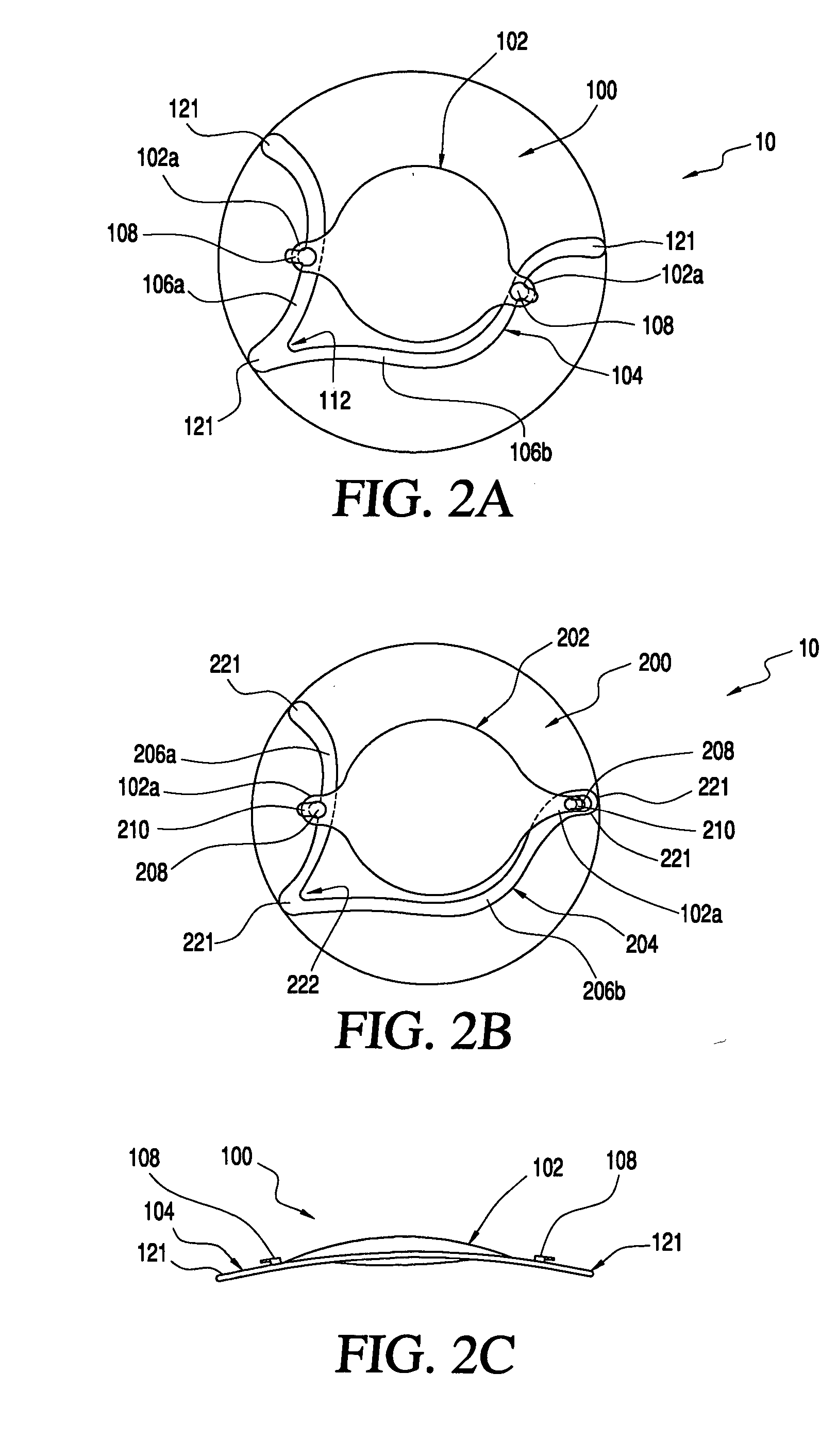
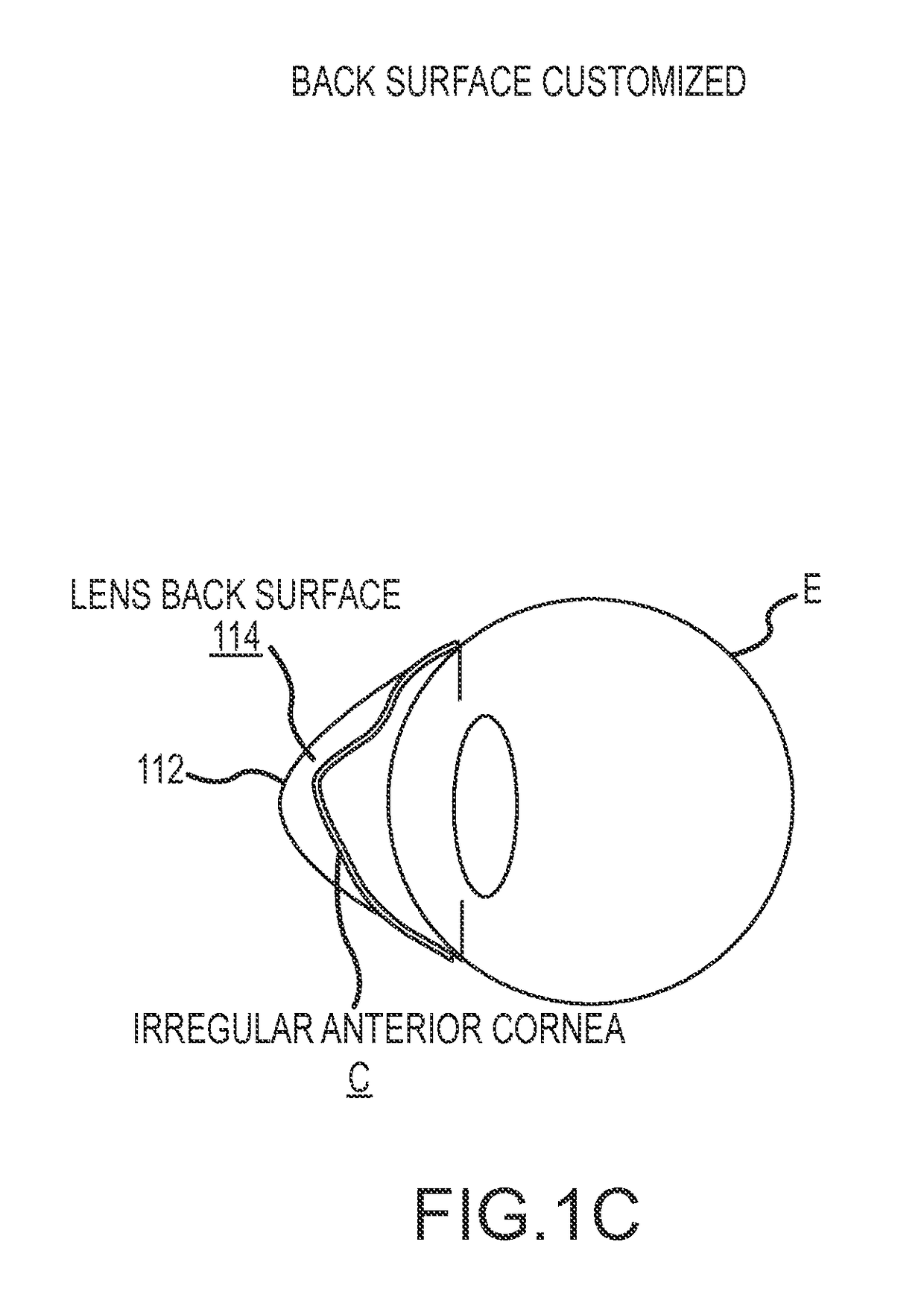
Corrective lens for corneal reshaping and method of determining the design of the corrective lens
InactiveUS20050213030A1Improve deficiency in eyesightSpectales/gogglesEye treatmentCorneal surfaceEyelid
The present invention includes corrective lenses for reshaping the cornea of an eye to improve vision, and methods of designing such corrective lenses. In accordance with various embodiments, the corrective lenses include a central portion, a periphery portion, and a junction region joining the central portion and the periphery portion comprised of a semi-rigid and / or flexible material. The corrective lenses are designed such that localized forces (e.g., lid forces and / or fluid forces in the eye) act on the corrective lenses to draw the periphery portion of a corrective lens to the corneal surface, which causes the junction region and / or central portion to apply pressure on the cornea to change the shape of the cornea. Because different individuals may require a different adjustment to their corneas to correct their particular problem, a corrective lens in accordance with the present invention may be specially designed to reshape the cornea of each user according to his / her particular needs.
Owner:PARAGON VISION SCI INC
Automated image scaling
InactiveUS6922494B1Accurate scaleSpectales/gogglesCharacter and pattern recognitionCorrective contact lensImage manipulation
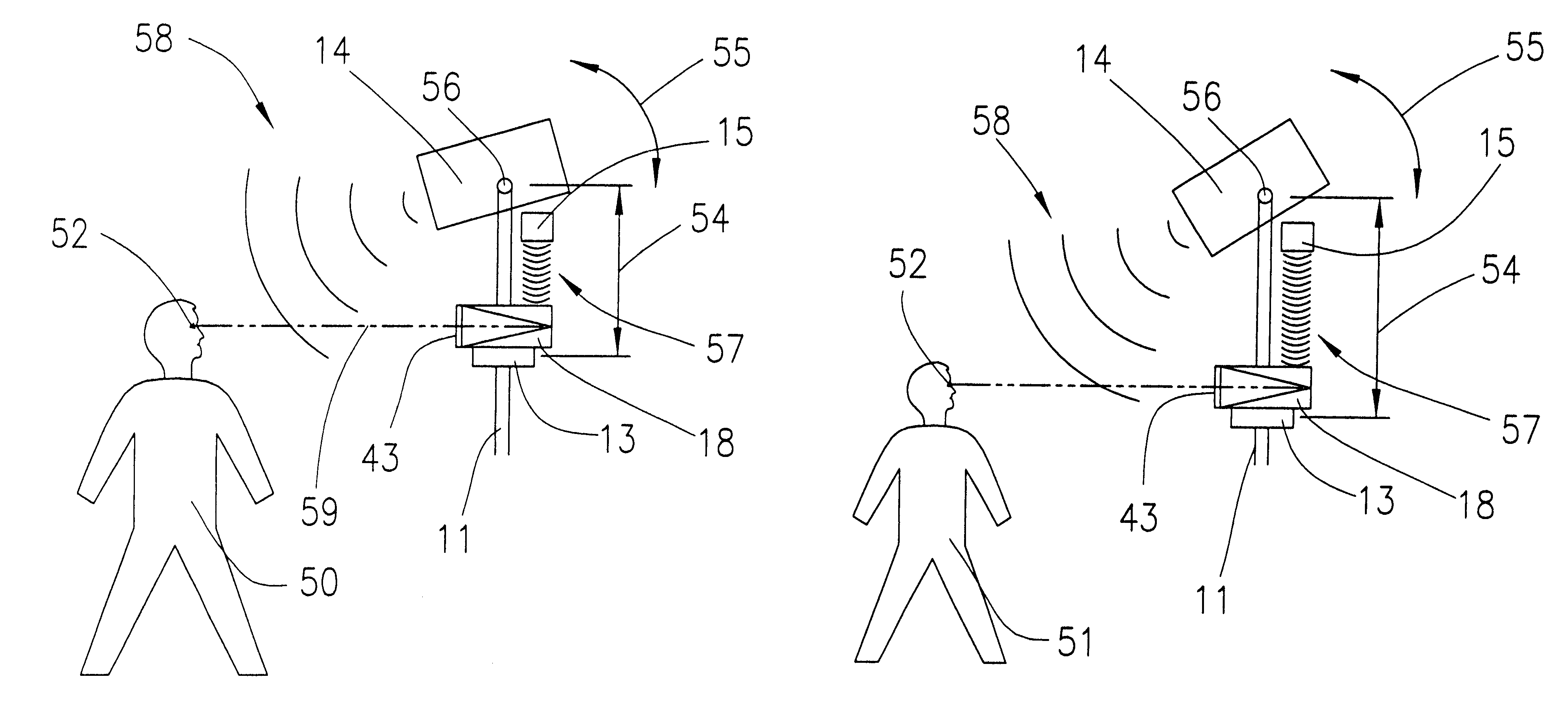
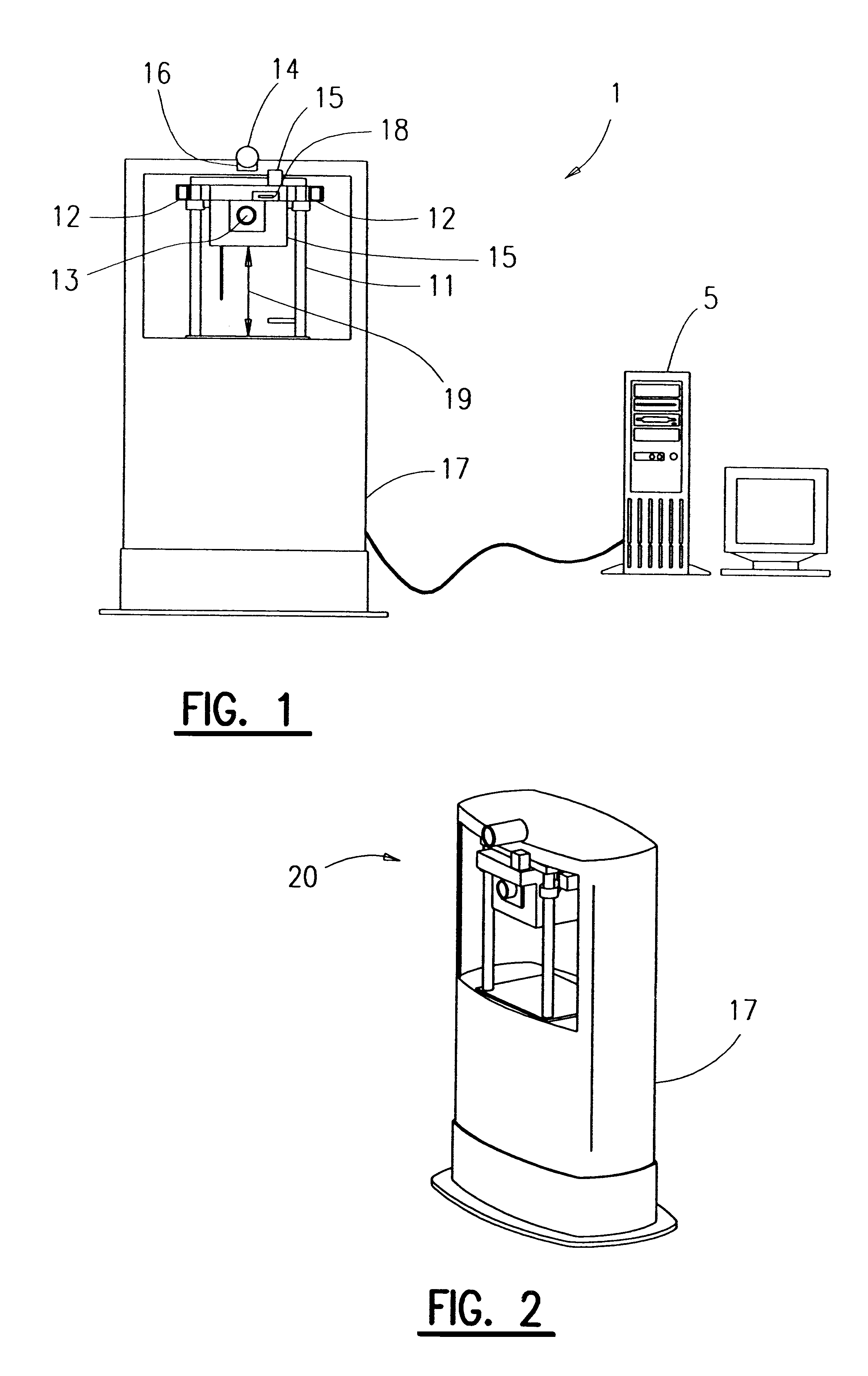
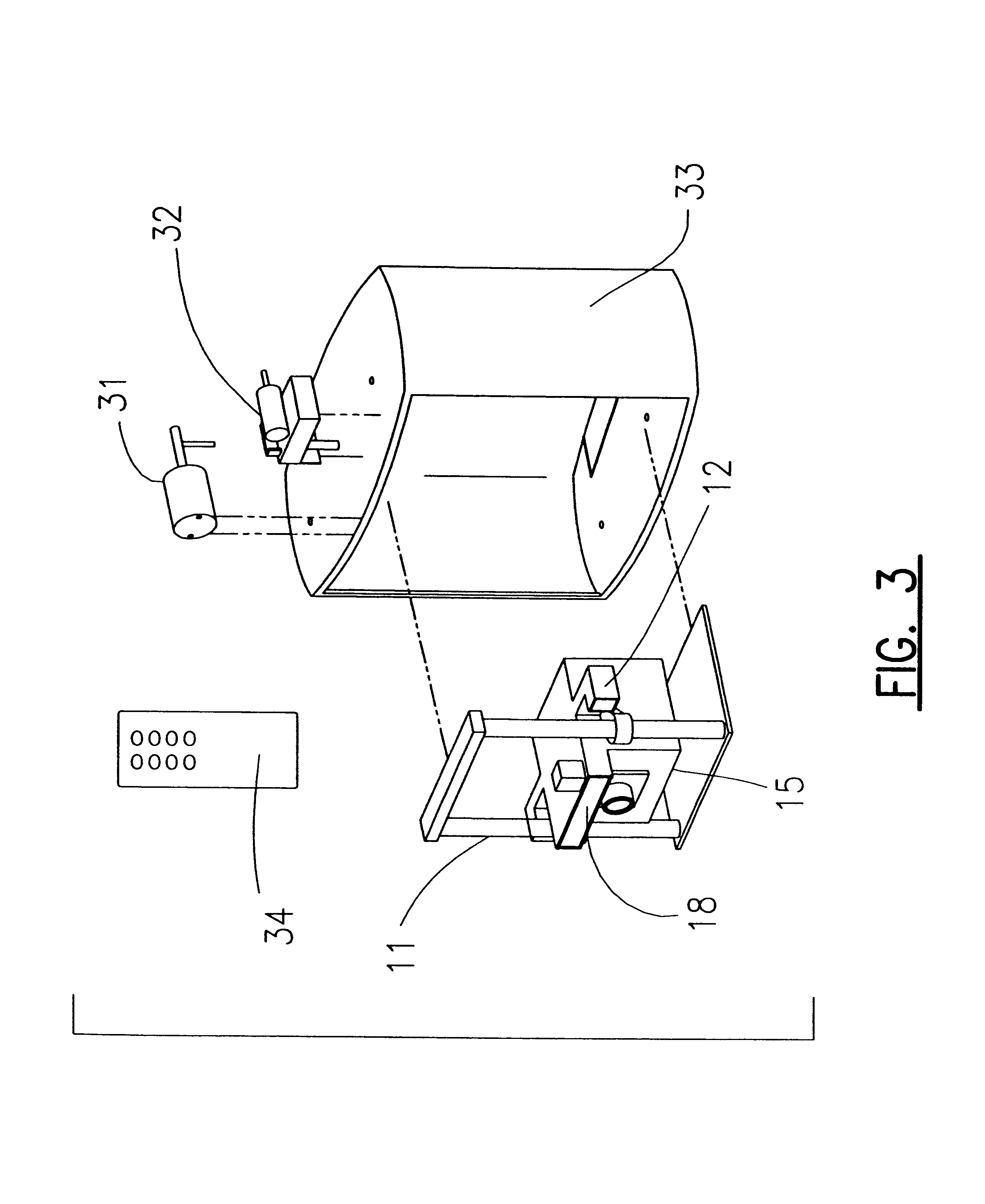
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for capturing an image of a persons head, or other object, positioned in front of a camera and accurately scaling the head based on the distance of the head from the camera. A sonar system is used determine the distance of the object to the camera. The sonar system can include a first sonar device which is operated to measure the distance of the object to a predetermined point and a second sonar device which is used to measure the distance of the camera to the predetermined point. A calculation of the distance from the object to the camera is based upon the sonar measurements. The image created by the camera can be scaled according to the distance of the object to the camera as determined with the sonar. An image created by the camera can be displayed on a screen of a computer associated with the imaging system. Software on the computer can transpose an image of an eyeglass frame over the image of a face, wherein the image of the face was captured by the camera. Measurements relating to proper sizing of an eyeglass or other corrective lens can be performed on the computer screen. Other observations and image manipulations can also be made including skin tone, facial features, head shape and size, application of cosmetics, proposed surgery, and many other uses.
Owner:FCPR CDC INNOVATION 2000 +1
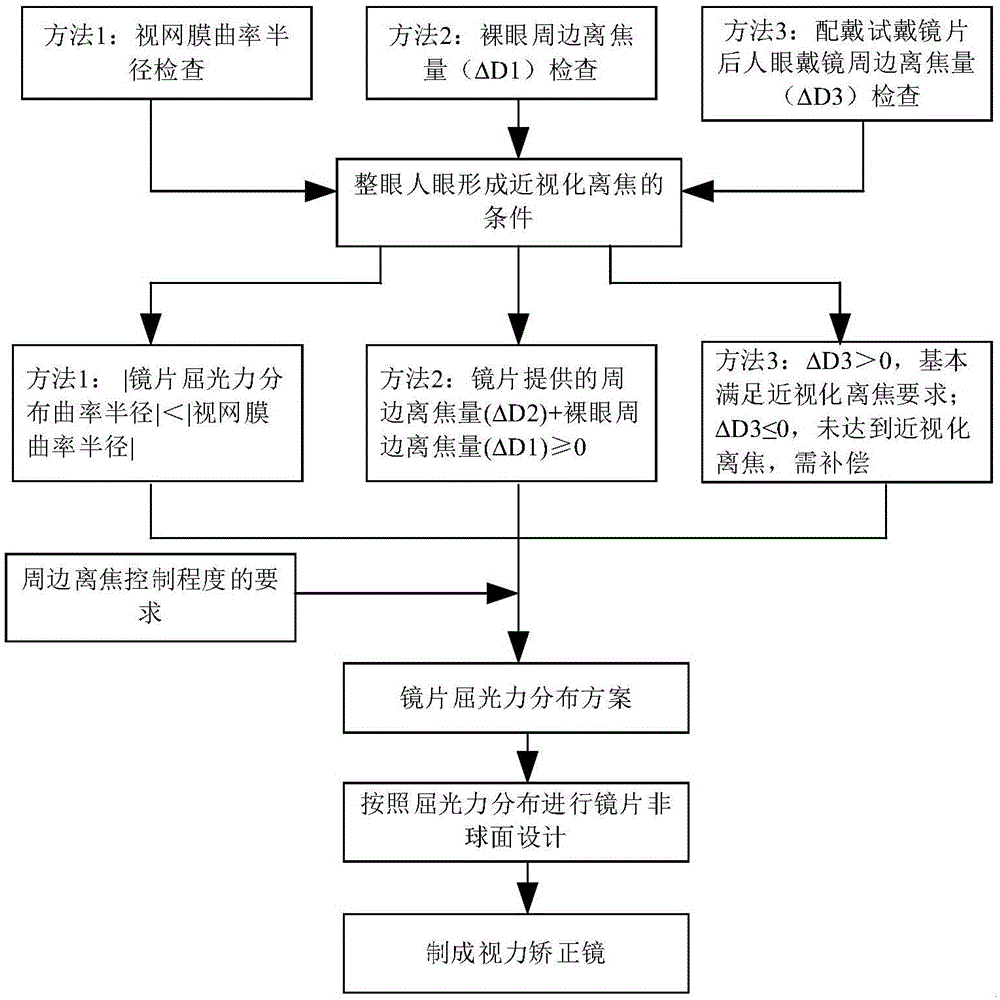
Preparation method for aspherical vision correction lens with controllable peripheral defocus
The invention relates to a preparation method for an aspherical vision correction lens with controllable peripheral defocus. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) through the checking of human eye retina shape or human naked eye peripheral defocusing amount or human eye glasses-wearing peripheral defocusing amount, calculating and judging the conditions needed by forming myopization defocus of the human eye; (2) according to the conditions obtained by the myopization defocus, forming a distribution solution of refractive power of the vision correction lens changed along with the pore diameter; (3) according to the distribution solution of the refractive power of the vision correction lens, making the vision correction lens, so the refractive power distribution in the peripheral area of the whole eye refractive power formed on the retina is greater than that in the center area after the refractive power of the vision correction lens is attached to the human eye, and forming the myopization defocus before falling on the retina; using an aspheric surface to control the surface shape and curvature radius of an optic zone of the vision correction lens, so that the vision correction lens is evenly changed in the aperture direction according to the stated refractive power peripheral defocusing amount, the refractive power is increased along with the increase of the aperture, so the degree-controllable myopization defocus is provided to the human eye.
Owner:EYEBRIGHT MEDICAL TECH BEIJING
Tinted lens and method of making same
A lens and a method of making lenses suitable for color blindness correction are disclosed. The corrective lens may be formed of an optically transparent base material, which is tinted to the desired color for correction by immersion in a colorant dye. The color tinted lens is then tinted by a neutral tint dye to render the lens observable as a regular corrective lens. If desired, the dyes may be heated during immersion.
Owner:CHROMAGEN VISION
Image stabilization control circuit
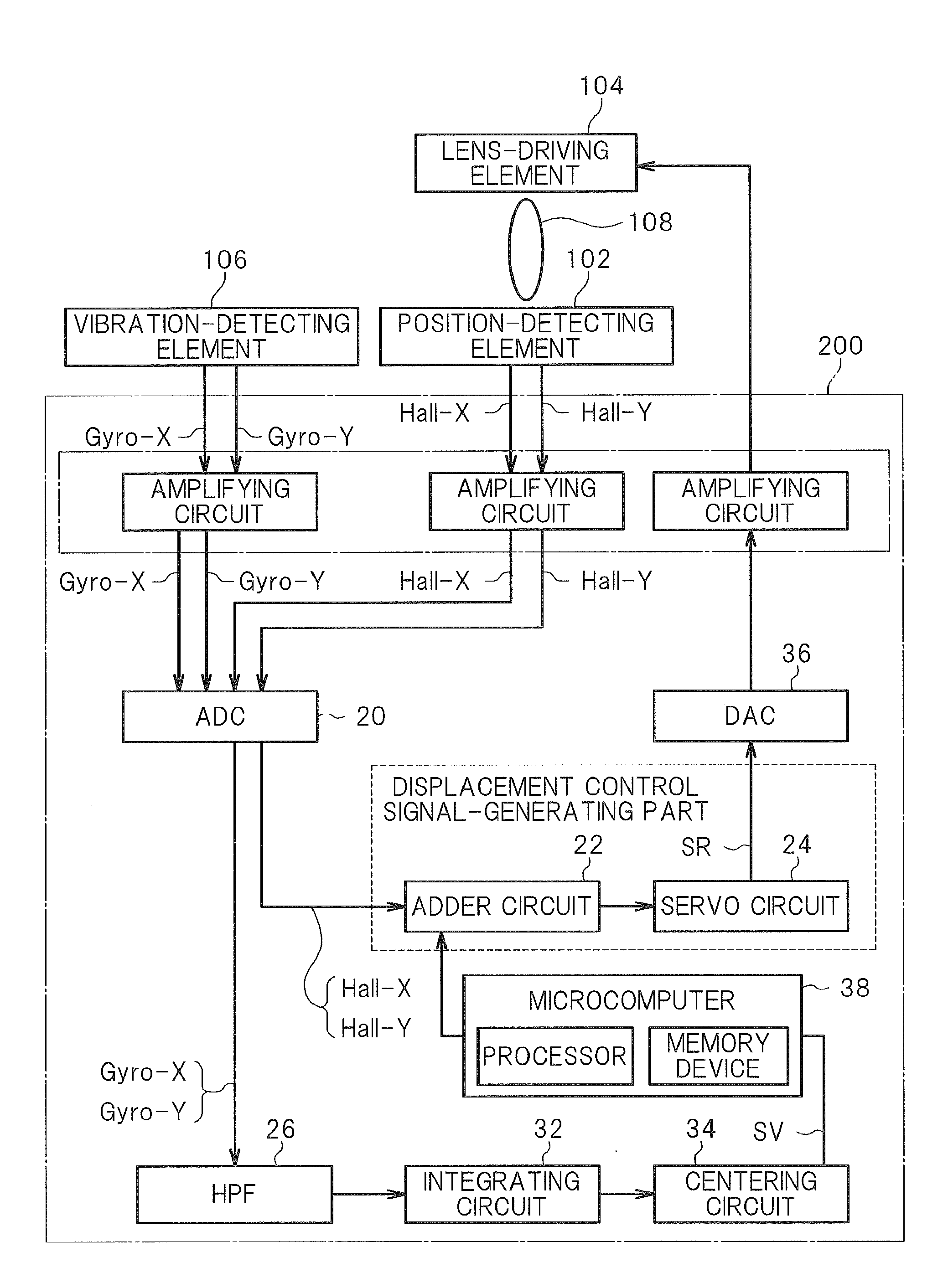
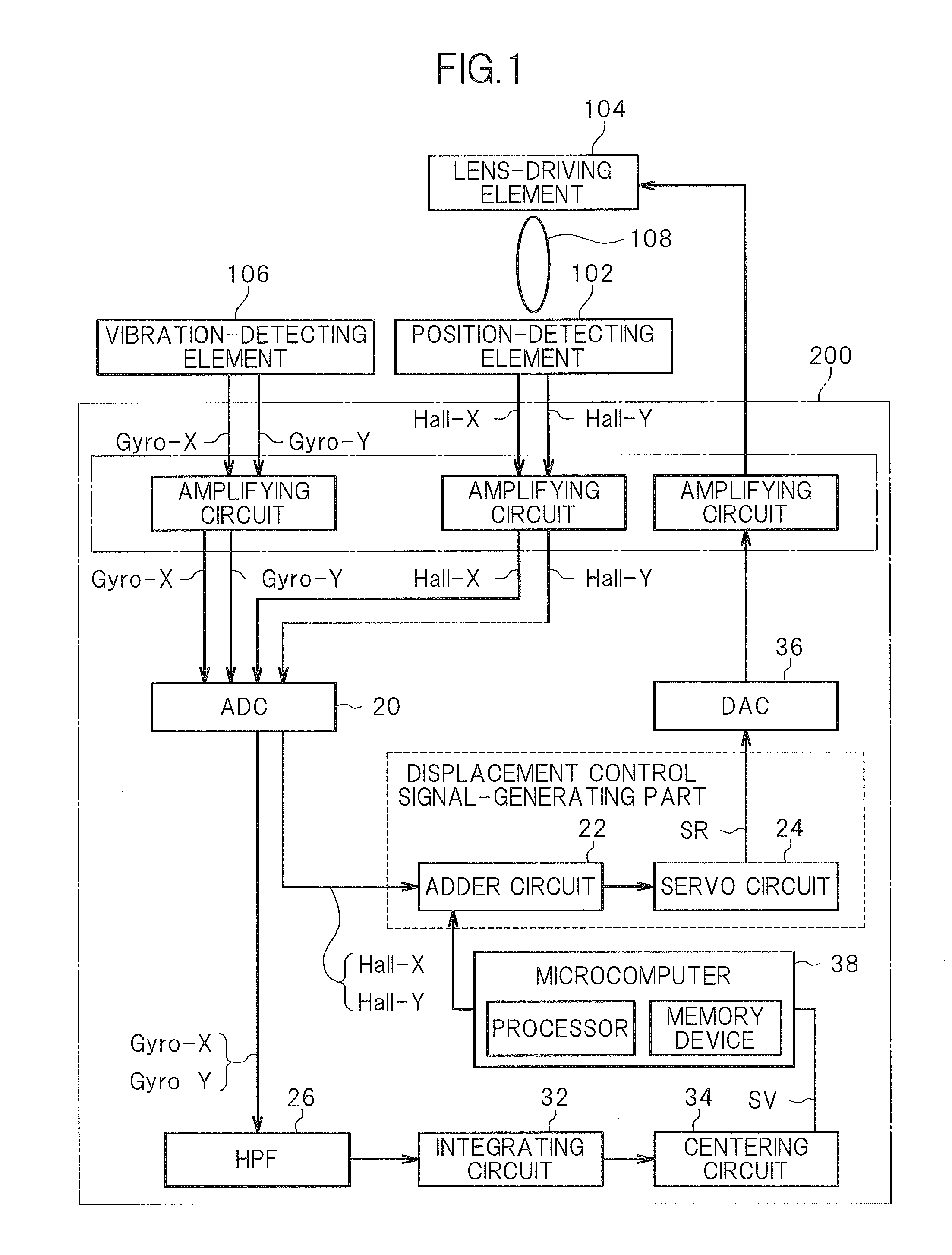
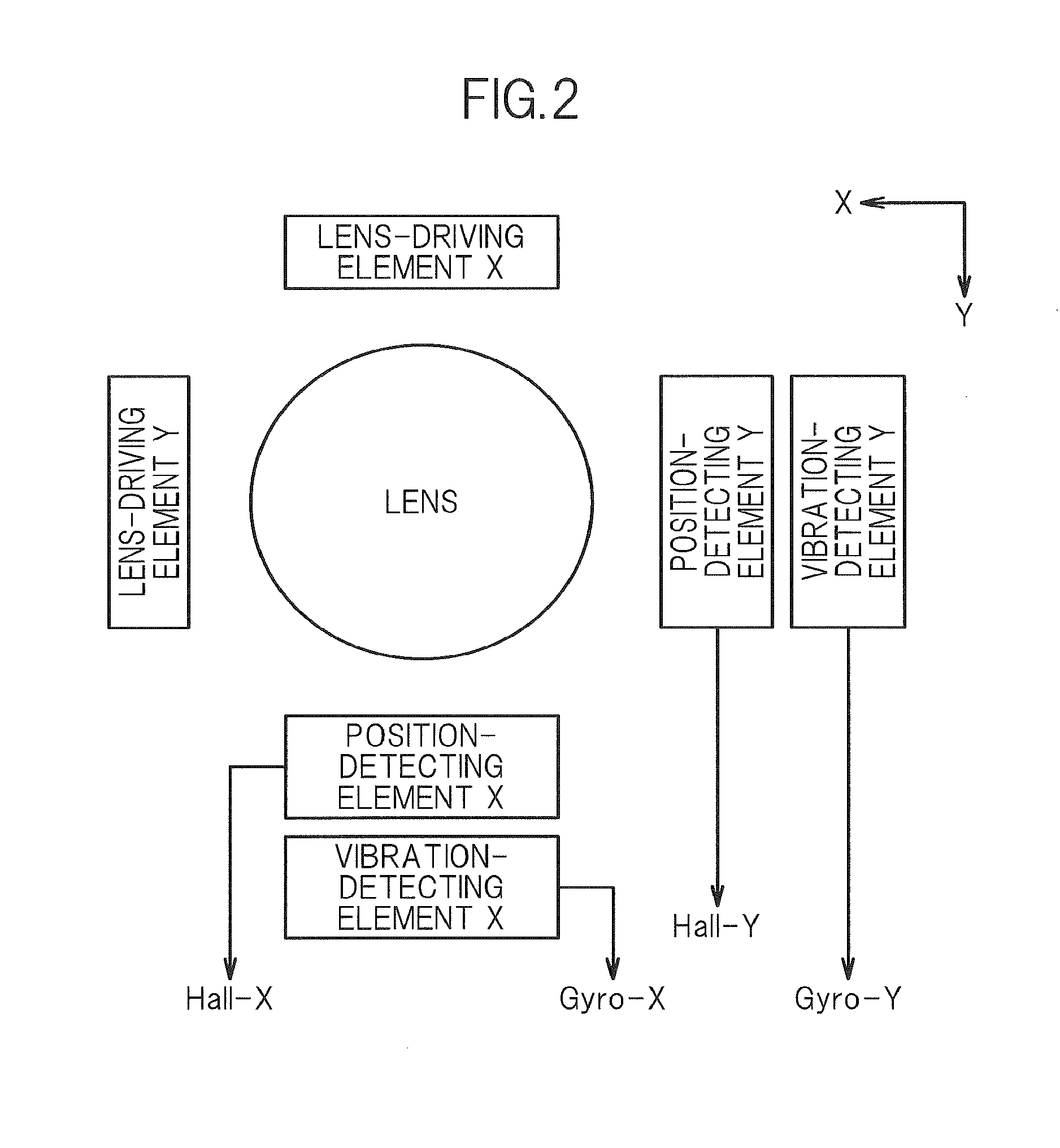
The accuracy of servo control of a corrective lens in an image stabilization control circuit is prevented from decreasing due to non-linear characteristics of a position-detecting element. A signal representing a component of vibration of an image pickup apparatus is generated based on an angular velocity signal from a vibration-detecting element. A microcomputer corrects the vibration component signal according to a predetermined correction function and generates a target position signal representing a target position of the lens. A position-detection signal based on an output from the position-detecting element is compared with the target position signal, and the position of the lens is servo-controlled. The correction function is set so that the characteristics of variation of the target position signal relative to the target position will be the same as the characteristics of variation of the position-detection signal relative to the actual position of the lens.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Multiple-feed electromagnetic signal receiving apparatus
This invention discloses a novel design for receiving electromagnetic signals broadcasted from at least two of satellite clusters and collected by a single dish antenna. At least two signal feeds are used to feed the signals to a processing circuit. The processing circuit performs signal selection, amplification, and frequency conversion. Corrective lens are used to ensure uniform wavefront of the electromagnetic signals received by the signal feeds located farther away from the focal point of the dish antenna. A convenient adjustment device is provided for adjustment of the relative positions of the signals feeds to the dish antenna.
Owner:ACER INC
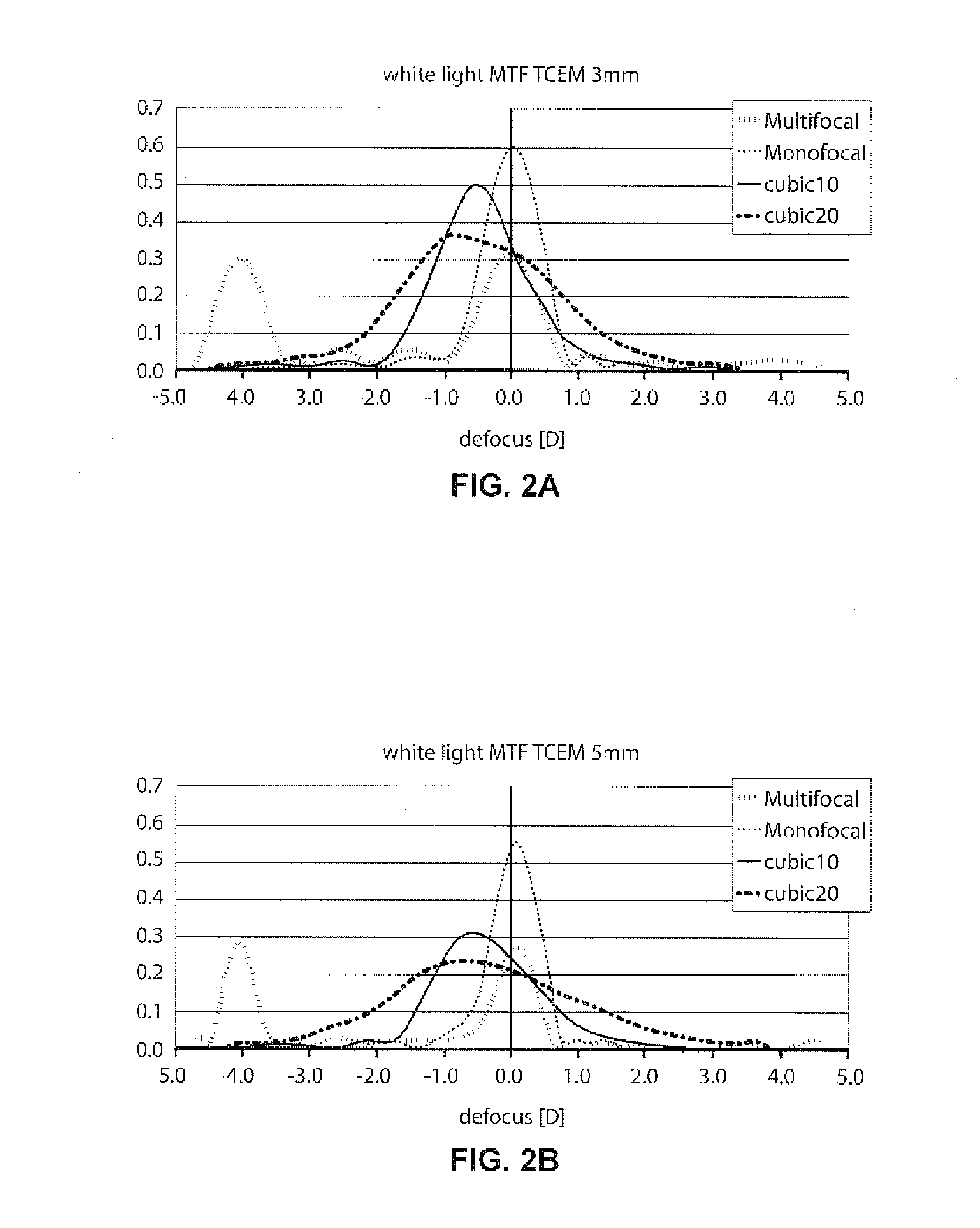
Lens providing extended depth of focus and method relating to same
ActiveUS20140257480A1Increase depth of focusSuppresses the distinct bifocalityIntraocular lensOptical partsCamera lensCorrective contact lens
Ophthalmic lenses providing an extended depth of focus include anterior and posterior faces, wherein at least part of the anterior or posterior face has a curvature based upon the summation of a cubic and / or pentic phase profile, and methods relating to same. The ophthalmic lens may be a contact lens, an intraocular lens (IOL), or other corrective lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
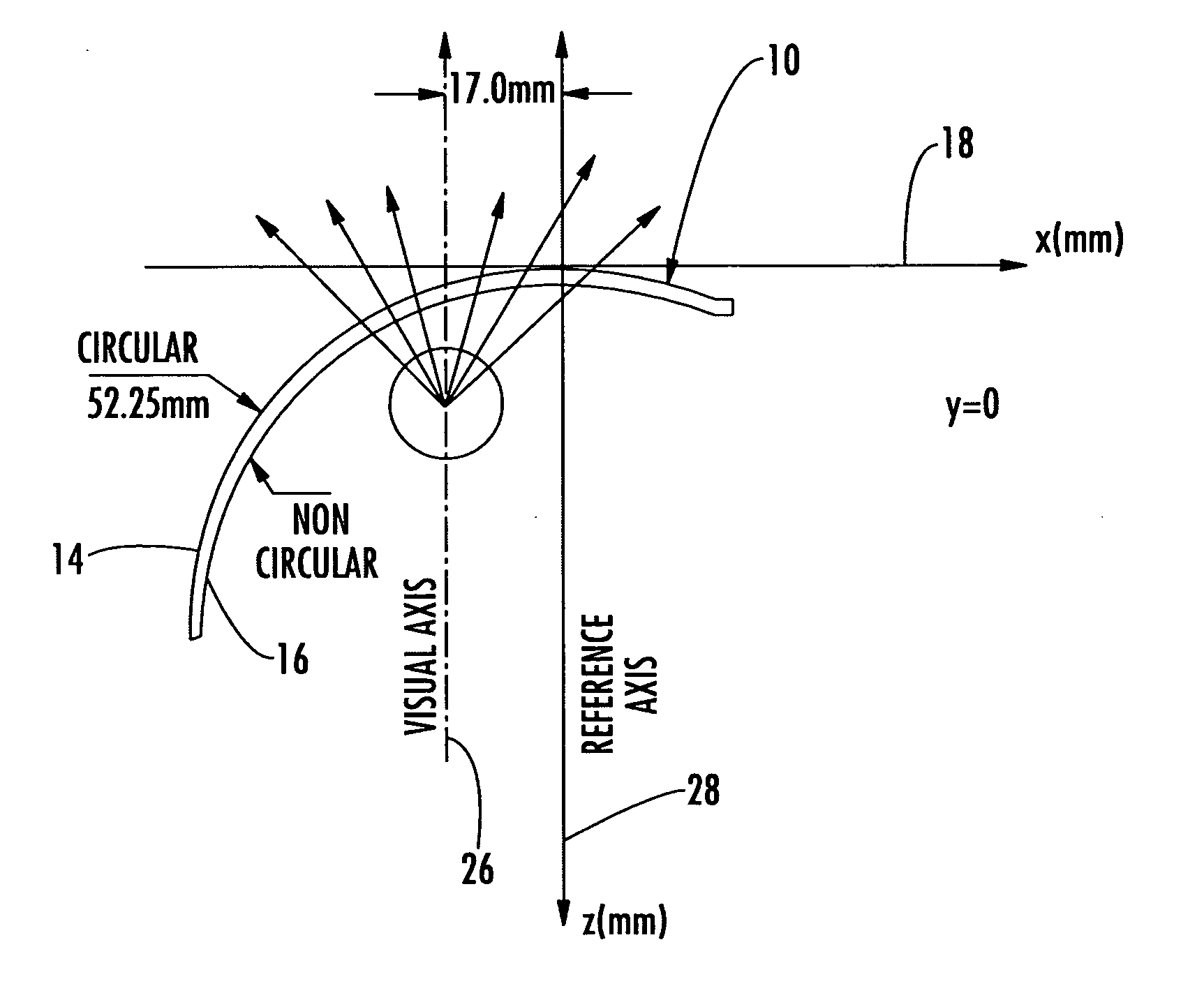
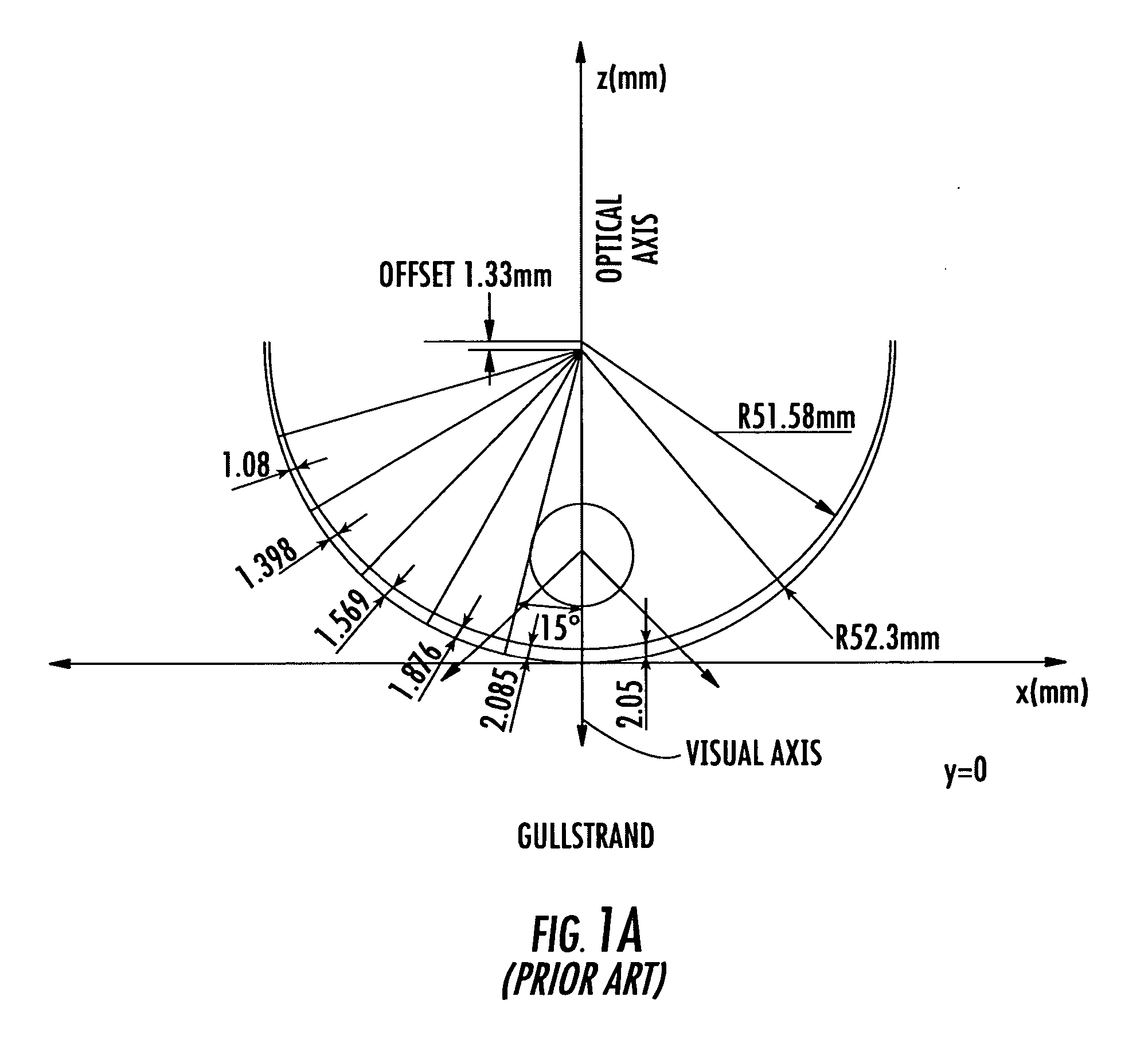
Non-corrective lenses with improved peripheral vision
InactiveUS20060098161A1Improve eyesightImprove deviationEye diagnosticsNon-optical partsCorrective contact lensConvex side
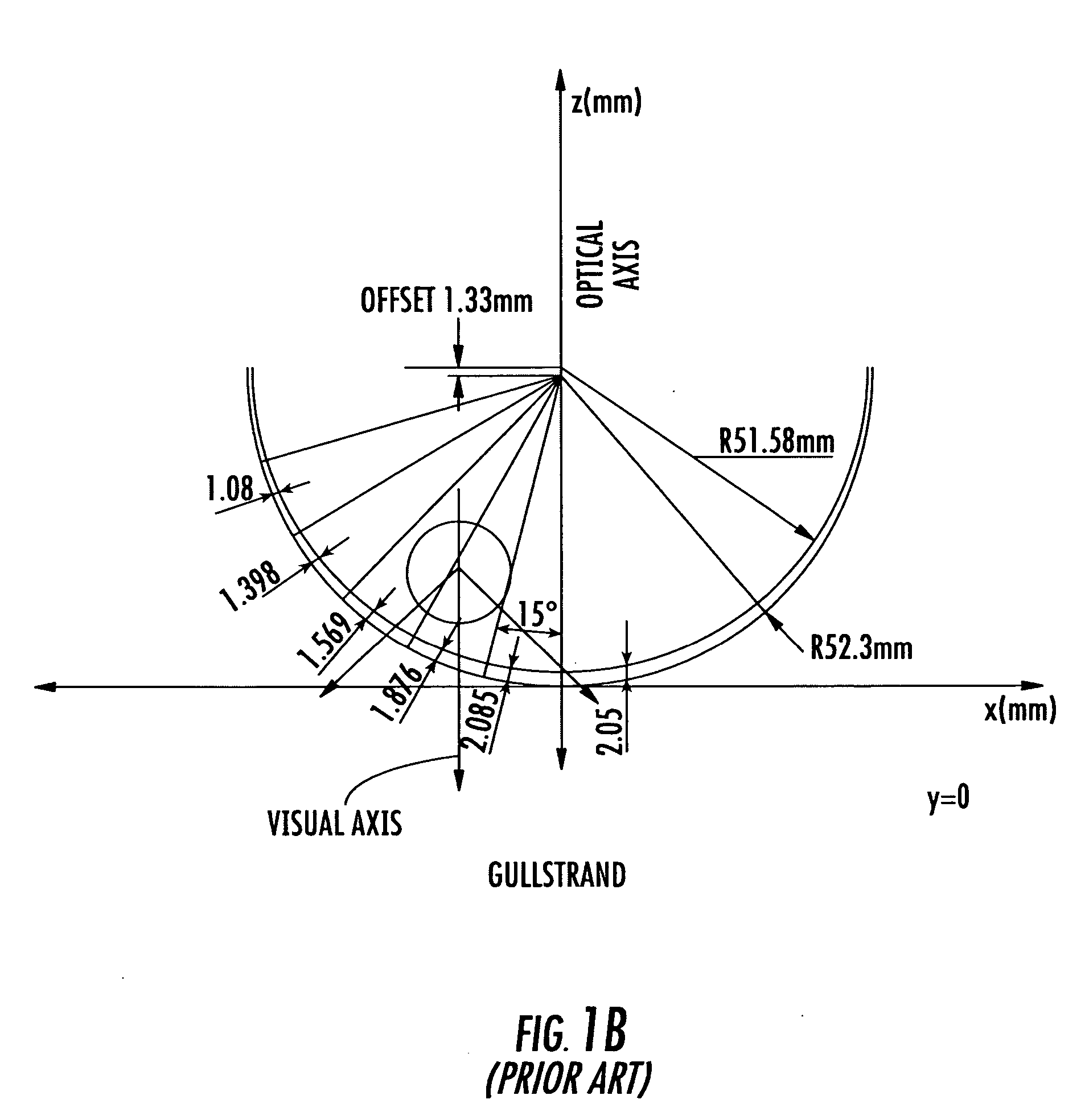
A method for modifying the shape of a spheric or toric non-corrective lens blank such that astigmatic and peripheral defects are reduced. The outer convex and inner concave sides of the lens are initially designed according to the Gullstrand Formula. Thereafter, a visual axis of the lens is defined relative to a reference axis of the lens blank. In the preferred toric lens, the visual axis of the lens is offset from the reference axis. Once the visual axis is defined, the inner concave surface of the lens is modified so as to improve optical quality in a visual center surrounding the visual axis.
Owner:HONEYWELL SAFETY PROD USA INC
Surface CMOS image sensor camera shooting module
ActiveCN104270555ASmall sizeFew lensesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensImaging quality
The invention discloses a surface CMOS image sensor camera shooting module. According to the surface CMOS image sensor camera shooting module, a double-Gauss lens without a spherical aberration corrective lens is adopted to serve as a main lens, the face, opposite to the face facing the main lens, of a sensor is designed to be a concave surface and correspond to the main lens, and the two ends of each optical fiber connected with a color filter in a coupling mode are connected with a photo diode and the main lens in a coupling mode to transmit the incident light, so that the incident light led out from the main lens can enter all the optical fibers in a divergent mode and arrive at the corresponding photo diodes after being restored by the corresponding color filters, reflection and crosstalk among pixels of the incident light can be eliminated effectively, the light sensitivity is improved, and the size of the module is contracted while the whole image quality is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT +1
Lens barrel
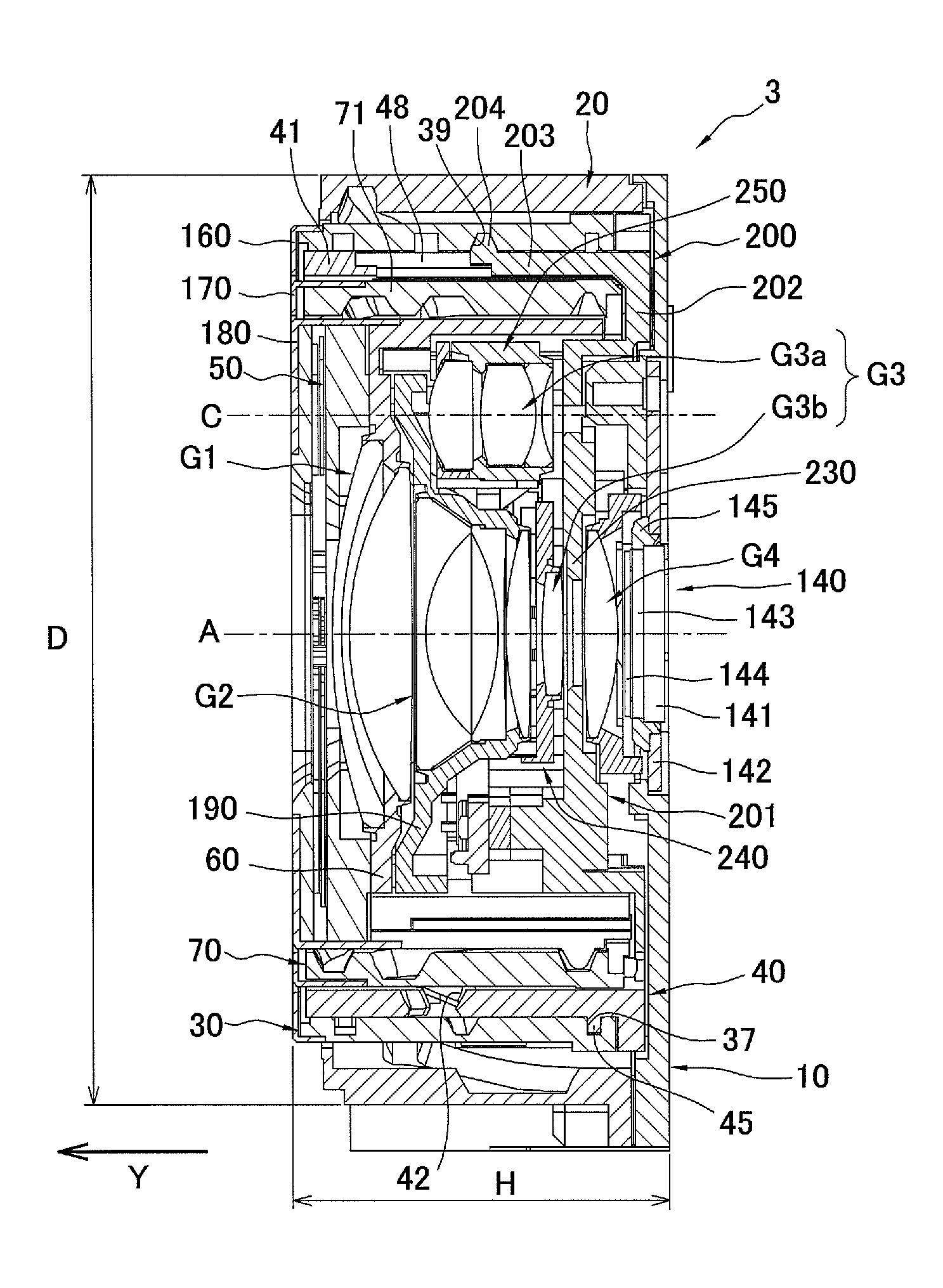
A lens barrel which includes an optical system, a support mechanism, a drive correcting mechanism, a retractable lens frame, and a drive retracting mechanism. The optical system includes a corrective lens group and a retractable lens group. The support mechanism movably supports the corrective lens group in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the optical system. The drive correcting mechanism is configured to drives the support mechanism so that the corrective lens group moves in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of the optical system. The retractable lens frame retractably supports the retractable lens group to a first position in which the optical axis of the retractable lens group is offset from the optical axis of the optical system. The drive retracting mechanism is configured to drive the retractable lens frame so that the retractable lens group retracts to the first position.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
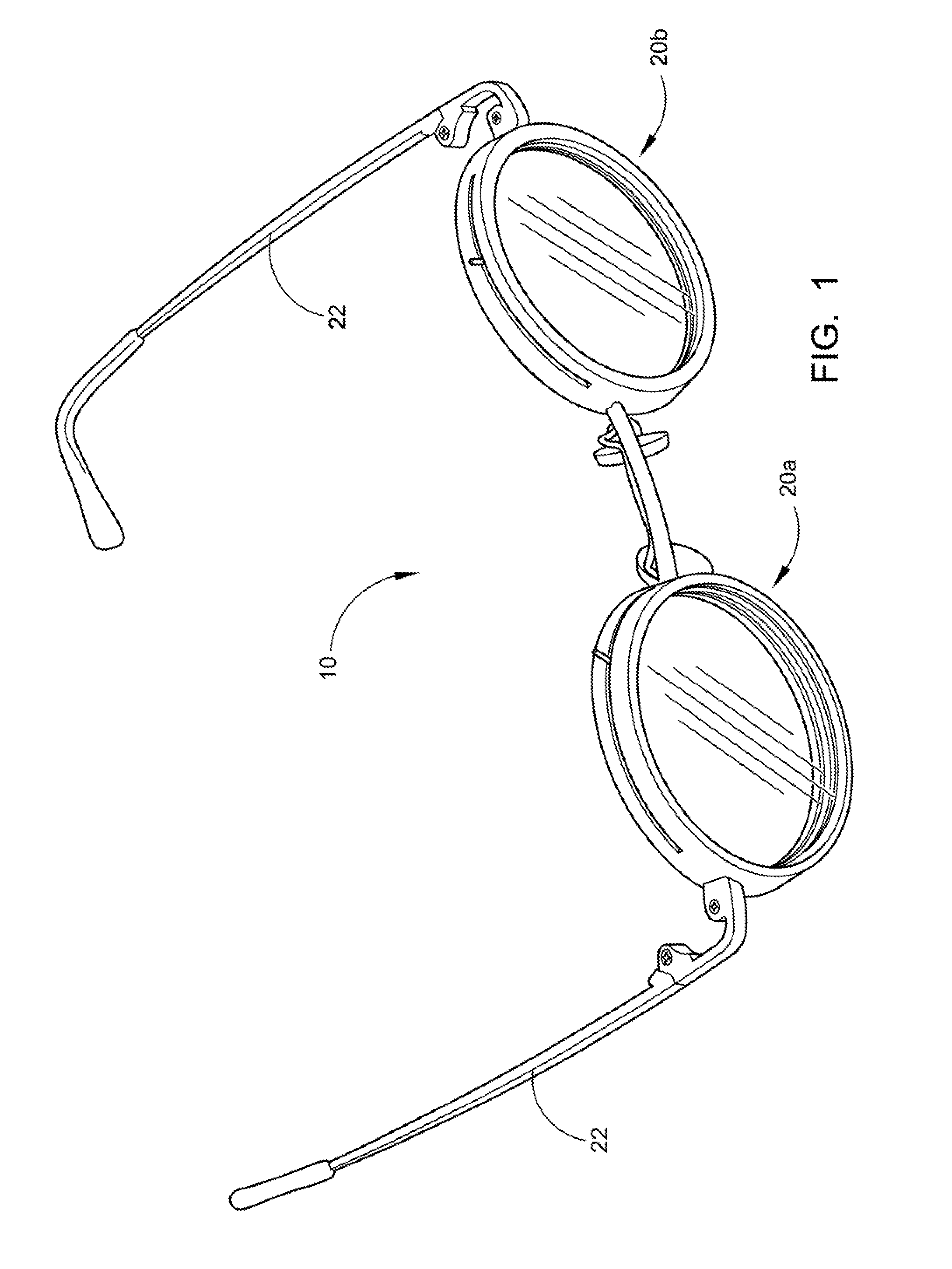
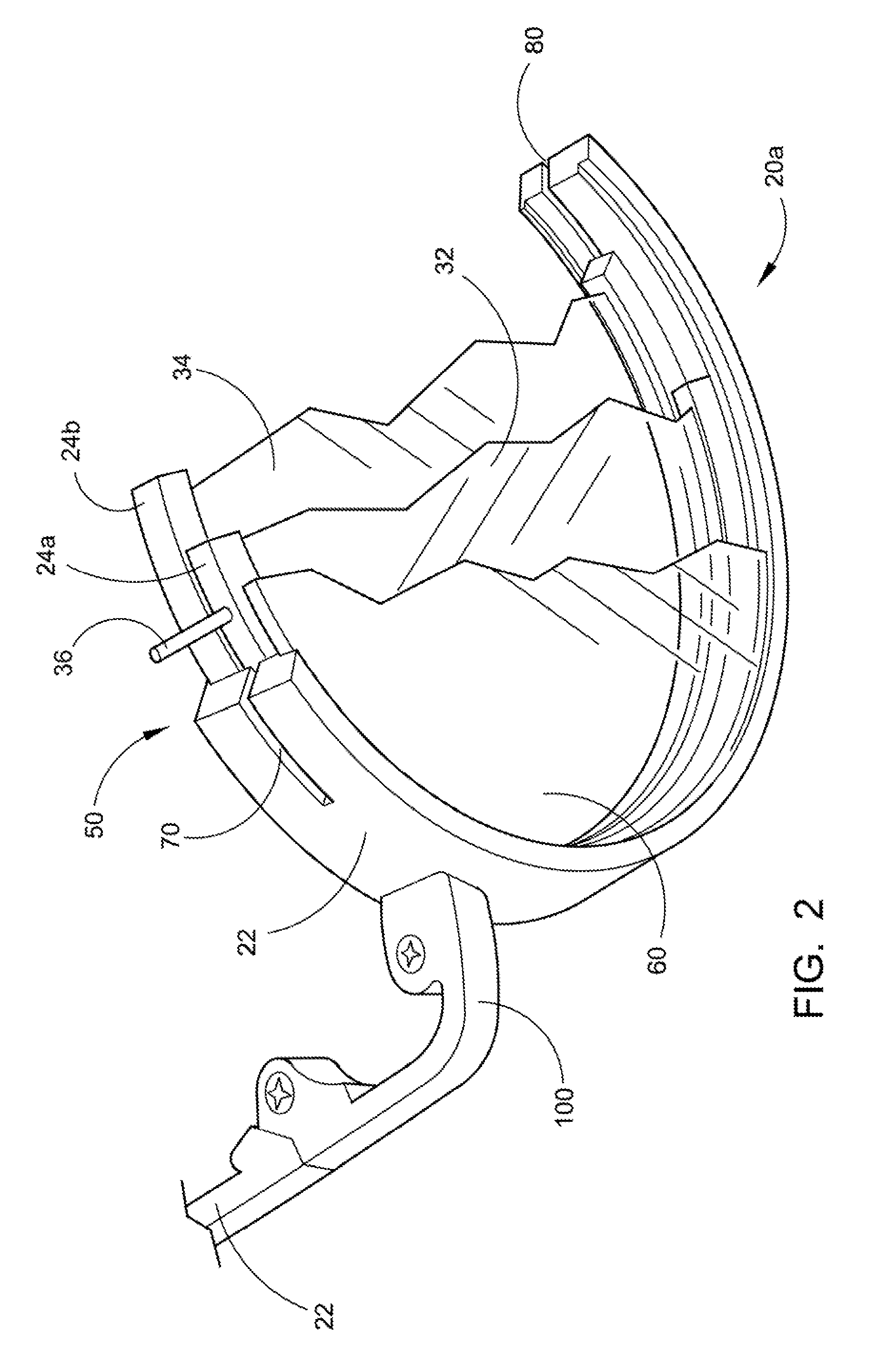
Variable prism eyeglasses
InactiveUS20110194071A1Improve eyesightReduce manufacturing costSpectales/gogglesOptical partsCorrective contact lensPrism
The present invention is directed to an eyeglass device that has manually variable prisms to correct strabismus; that is, double vision. The variable prism eyeglasses consist of an eyeglass frame that holds two primary rings in position and provides baseline reference points for alignment. Prism lenses and corrective lenses fit inside the primary rings and allow the two prism lenses of each primary ring to rotate independently and to hold the corrective lens fixed in place relative to the primary rings. Detent channels on the upper surface and lower surface of the primary rings are the means by which the prisms are adjusted. Each prism lens is moved and positioned via a prism lens pin located in the base of each prism lens. The prism lens pins fit into the detents in the detent channels of the primary ring. The detent selected determines the amount of corrective power the prisms will produce.
Owner:CRONIN JOHN V +1
Method for determining corneal characteristics used in the design of a lens for corneal reshaping
The present invention provides methods for measuring corneal characteristics and distortions to determine one or more appropriate designs for one or more corrective lenses used to reshape the cornea of an eye. The method includes measuring and / or mapping the topology of the cornea, identifying a desired new shape for the cornea, comparing the current shape of the cornea to the desired shape, and configuring one or more corrective lenses to apply force to the cornea to change its shape. The process of measuring and / or mapping, comparing, and configuring may be repeated until the cornea takes on the desired shape.
Owner:PARAGON VISION SCI INC
Eyewear with pinhole aperture and lens
InactiveUS7914144B2Improving or enhancing one's visual acuityReduce widthOptical partsLens assembliesCamera lensCorrective contact lens
Eyewear is equipped with at least one lens and at least one pinhole aperture. Lenses and apertures may be used in place of or in combination with one another, and may be disposed in or on full frame, half frame, wire frame or rimless eyeglasses. The lens may be a corrective lens. Pinhole apertures may have a diameter no greater than about 3 mm, and a diameter / thickness ratio is no less than about 66.7%.
Owner:SHUSTER GARY STEPHEN
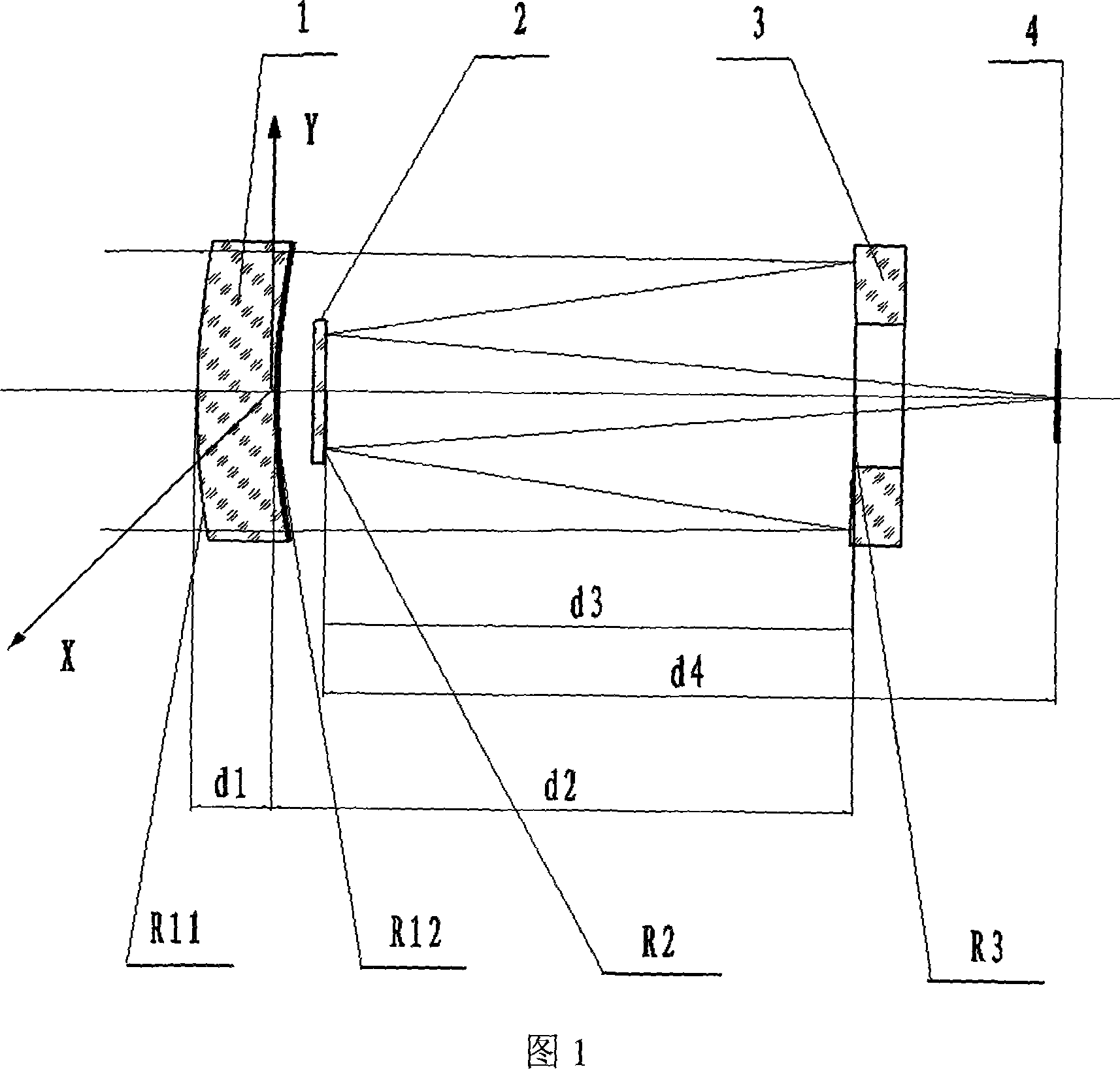
Refraction-diffraction mixed telescope optical system
InactiveCN101211006AReduce difficultyReduce manufacturing costOptical elementsCorrective contact lensLight beam
The invention discloses an optical system for a refractive / diffractive telescope, mainly applying in the astronomical observation, imaging of objectives at long distance, etc. The optical system comprises a corrective lens, a primary reflector and a sub-reflector in the sequence from object space to image space. The corrective lens of optical element in front of the system is a binary diffractive lens of optical element. Light beam from the object space passes through the corrective lens of the binary diffractive element, and irradiates on the primary reflector, and then is reflected to the sub-reflector by the primary reflector, finally finishes imaging after being reflected to the imaging plane by the sub-reflector and. Both the primary and the sub-reflector of the optical system adopt spherical reflectors. The processing, inspection and assembly of the reflectors become much easier, obviously reducing the manufacturing cost and improving the processing efficiency. The binary diffractive corrective lens can be produced in batch through the molding of optical plastics, which can further reduce the manufacturing cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wraparound Corrective Lens
InactiveUS20110134388A1Improve eyesightReadily manufactured and dispensedEye diagnosticsOptical partsCorrective contact lensLens plate
A corrective wraparound lens is provided for a wearer where the wraparound lens has a non-corrective lens element and a corrective lens element where the curvature of the non-corrective lens element is different from the curvature of the corrective lens element. Such lens has the ability to correct the defect in eyesight while capable of contouring to the face of the wearer thus able to protect the face of the wearer. In addition, a method to correct defect in eye is provided using a corrective wraparound lens for a wearer comprising a non-corrective lens element and a corrective lens element wherein a first curvature of said non-corrective lens element is different than a second curvature of said corrective lens element.
Owner:HSU ROGER WEN YI
Acoustic Touch Apparatus
ActiveUS20130093731A1Digital data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingCorrective contact lensTransducer
Acoustic touch apparatus comprising a substrate having first and second surfaces capable of propagating surface acoustic waves, the second surface comprising a touch region and the first and second surfaces coupled via a rounded connecting surface; at least one acoustic wave transducer on the first surface; and at least one reflective array on the first surface. The transducer is capable of transmitting or receiving waves to and from the reflective array. The substrate and reflective array can acoustically couple waves between the first and second surfaces. The substrate has a border region on the first surface adapted to hide the transducer and reflective array and preclude distortion of waves propagating over a window in the border region. The border region may have a borderlayer except at the window and a corrective lens is used proximate the window, or the border region comprises discolored glass except at the window.
Owner:ELO TOUCH SOLUTIONS INC
Method and device for estimating the optical power of corrective lenses in a pair of eyeglasses worn by a spectator
This invention relates to a method for estimating the optical power of corrective lenses in a pair a eyeglasses worn by a spectator, characterized in that it comprises the following steps: - acquire two consecutive images of this spectator's face located in front of a means for acquiring these two images, one of these images being acquired with eyeglasses and the other without, - calibrate one of the two acquired images with respect to the other, - identify the position of the iris of each eye in each image, - evaluate the size magnification or size reduction of each imaged iris, and - estimate the optical power of the corrective lenses based on the evaluated magnification or reduction.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
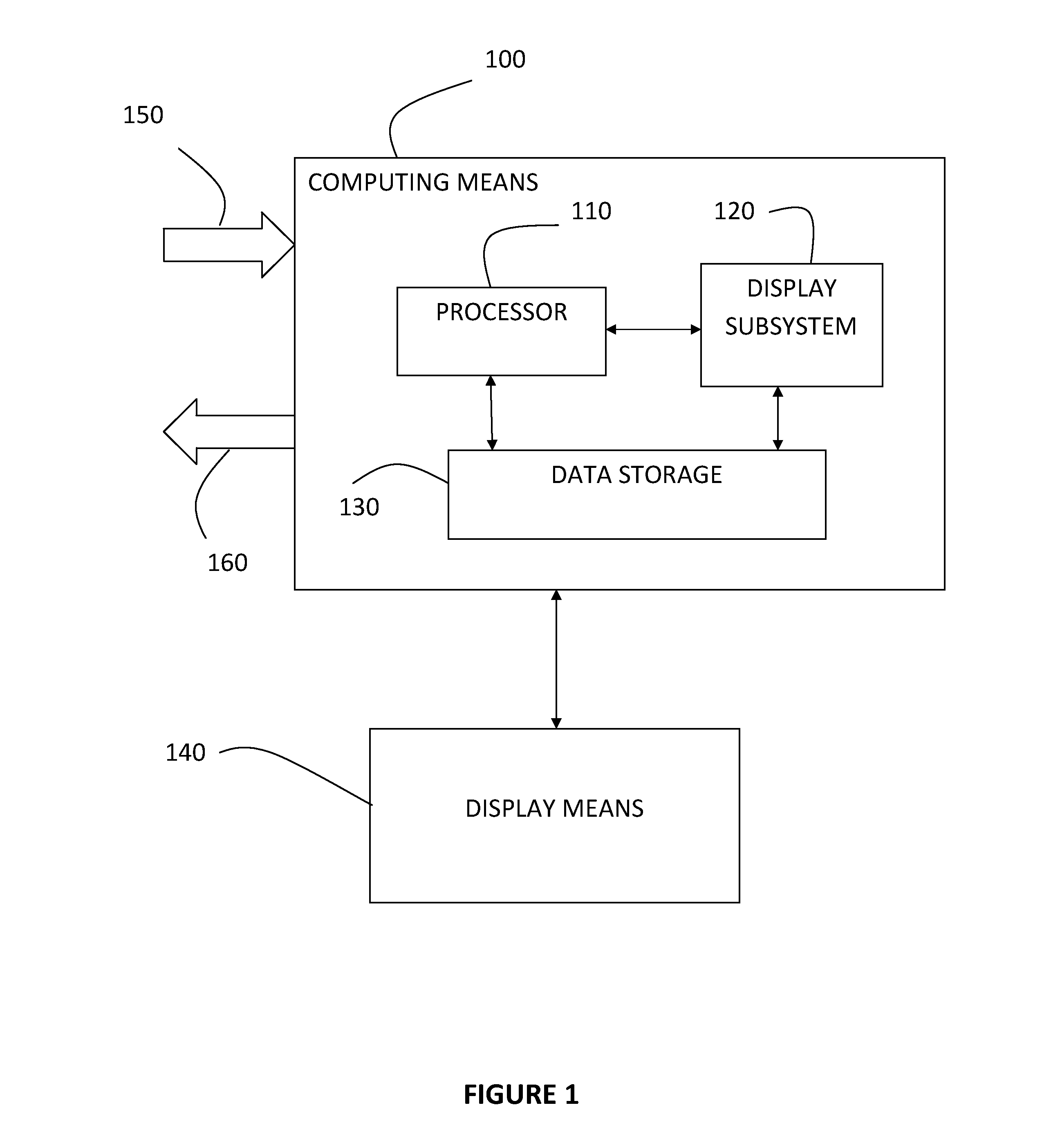
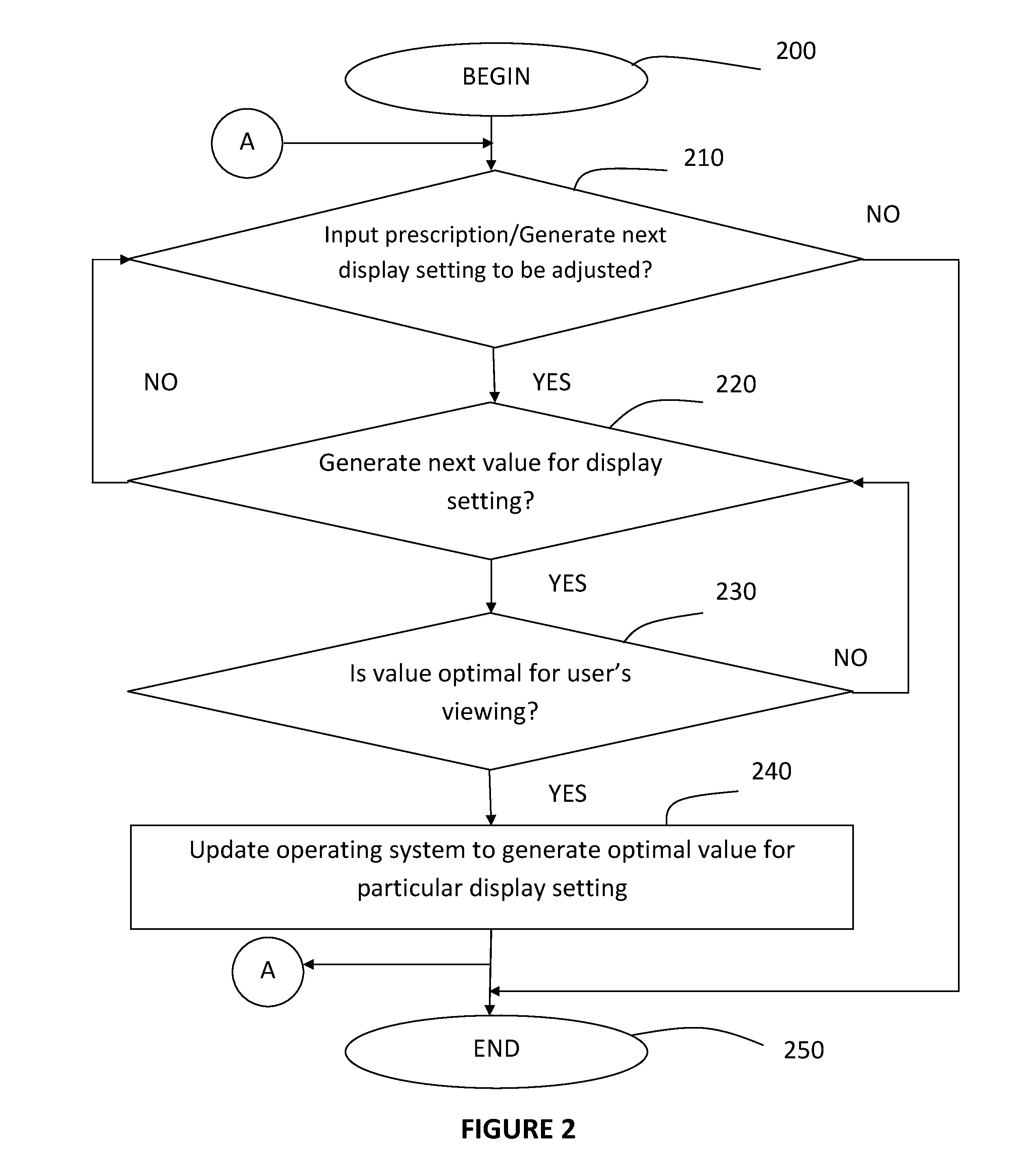
Method and system for adjusting a display to account for the users' corrective lenses or preferred display settings
InactiveUS20130127821A1Increase valueEasy to watch2D-image generationCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
A system and method for adjusting display settings to allow a user that requires prescriptive eyewear to view images on the display without the eyewear. The user provides input on which value for each display setting is optimal for the user's viewing experience. Once the optimal values are determined, the present invention adjusts the settings of the display means. The user is then able to view the text or images without wearing his / her prescriptive eyewear. The present invention optimally manipulates at least one of the following settings to achieve this aim: brightness, contrast, clock / phase, sharpness, colour, resolution, aspect ratio, gamma setting, and any other settings of the display means that are available to adjust the display so that a user may view the image to his or her satisfaction. The display means may be a monitor, or any other means that displays text or images.
Owner:LEWIS JEFFREY PHILLIP +1
Eyewear with pinhole aperture and lens
InactiveUS20080273164A1Improve eyesightReduce widthOptical partsLens assembliesCorrective contact lensEyewear
Eyewear is equipped with at least one lens and at least one pinhole aperture. Lenses and apertures may be used in place of or in combination with one another, and may be disposed in or on full frame, half frame, wire frame or rimless eyeglasses. The lens may be a corrective lens. Pinhole apertures may have a diameter no greater than about 3 mm, and a diameter / thickness ratio is no less than about 66.7%.
Owner:SHUSTER GARY STEPHEN
Method of producing a corrective spectacle lens and lens blank used for same
InactiveUS20050213032A1Reduce formationPrecise processingSpectales/gogglesOptical articlesPlastic polymerCorrective lens
The method of the invention for manufacturing a correctable lens for glasses from an injectable thermo-plastic polymer material, or other moldable polymer, consists in: molding a glass blank (2) provided with the contour of the corrective lens; assembling the lens blank with a peripheral piece (3) having the same internal radius of curvature as that of the glass blank (2), so as to compose a lens blank (1); grinding and polishing the internal face of the lens blank (1) to obtain the desired ocular correction; separating the glass blank (2) from the lens blank to obtain the corrective lens ready for assembly with the frame.
Owner:THOMAS SA +1
Vision enhancing device
A vision enhancing device for a person having macular degeneration of the retina, comprises a lens and a light diverging surface on the lens that symmetrically diverges away from the eye at an angle relative to an optic axis to redirect incident light away from the optic axis outwardly toward an un-diseased region of the retina. The light diverging surface can be a smooth surface, which can be a continuous curved surface, and can be a diverging conical surface. The lens can be an eyeglass lens, contact lens, intraocular lens, telescopic lens, correction lens, or magnification lens. A light diverging insert having a conical surface and, optionally, an end surface can be used in a lens for redirecting light to the un-diseased region of the retina.
Owner:STC UNM
Vision enhancing device
A vision enhancing device for a person having macular degeneration of the retina, comprises a lens and a light diverging surface on the lens that symmetrically diverges away from the eye at an angle relative to an optic axis to redirect incident light away from the optic axis outwardly toward an un-diseased region of the retina. The light diverging surface can be a smooth surface, which can be a continuous curved surface, and can be a diverging conical surface. The lens can be an eyeglass lens, contact lens, intraocular lens, telescopic lens, correction lens, or magnification lens. A light diverging insert having a conical surface and, optionally, an end surface can be used in a lens for redirecting light to the un-diseased region of the retina.
Owner:STC UNM
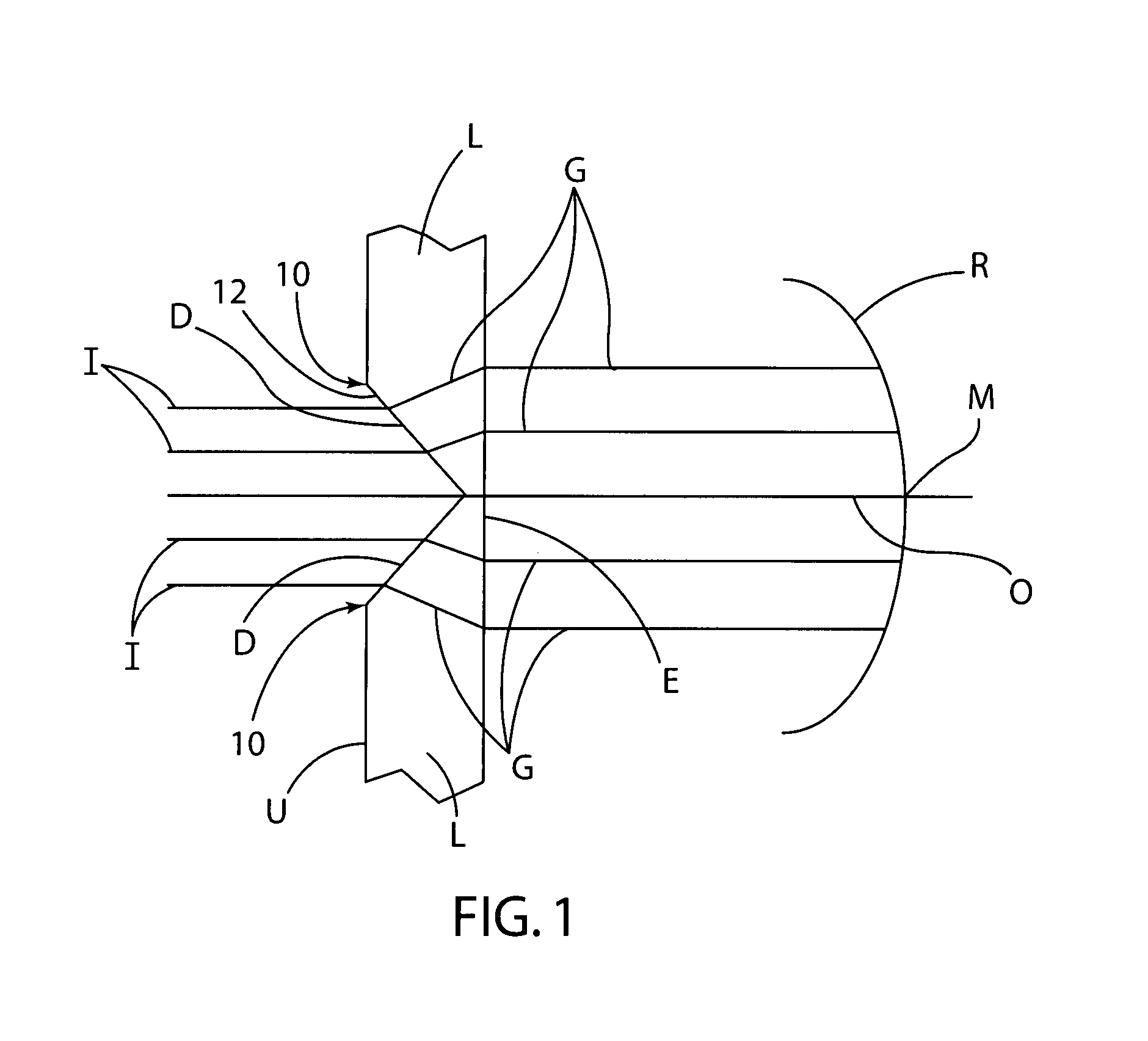
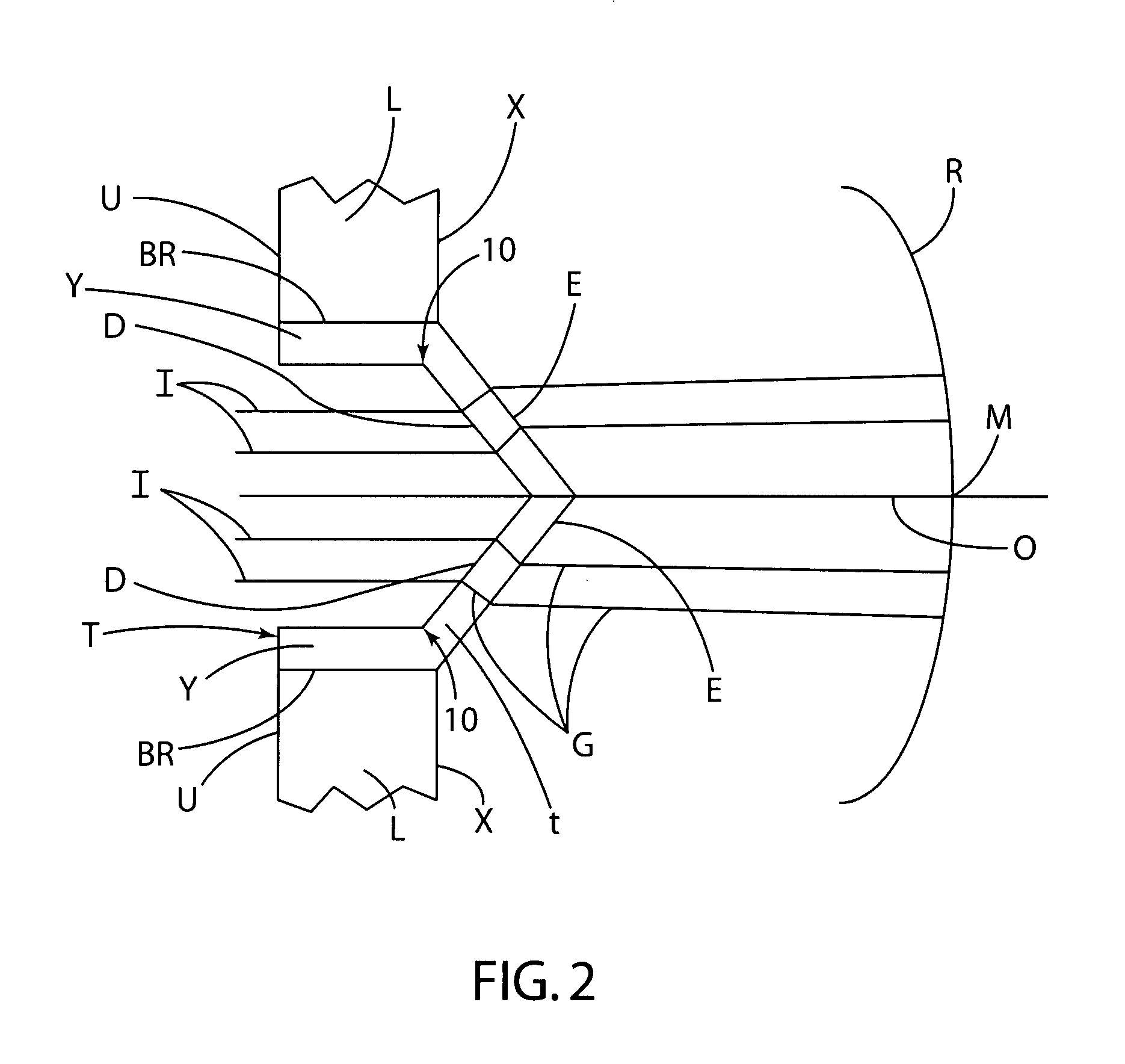
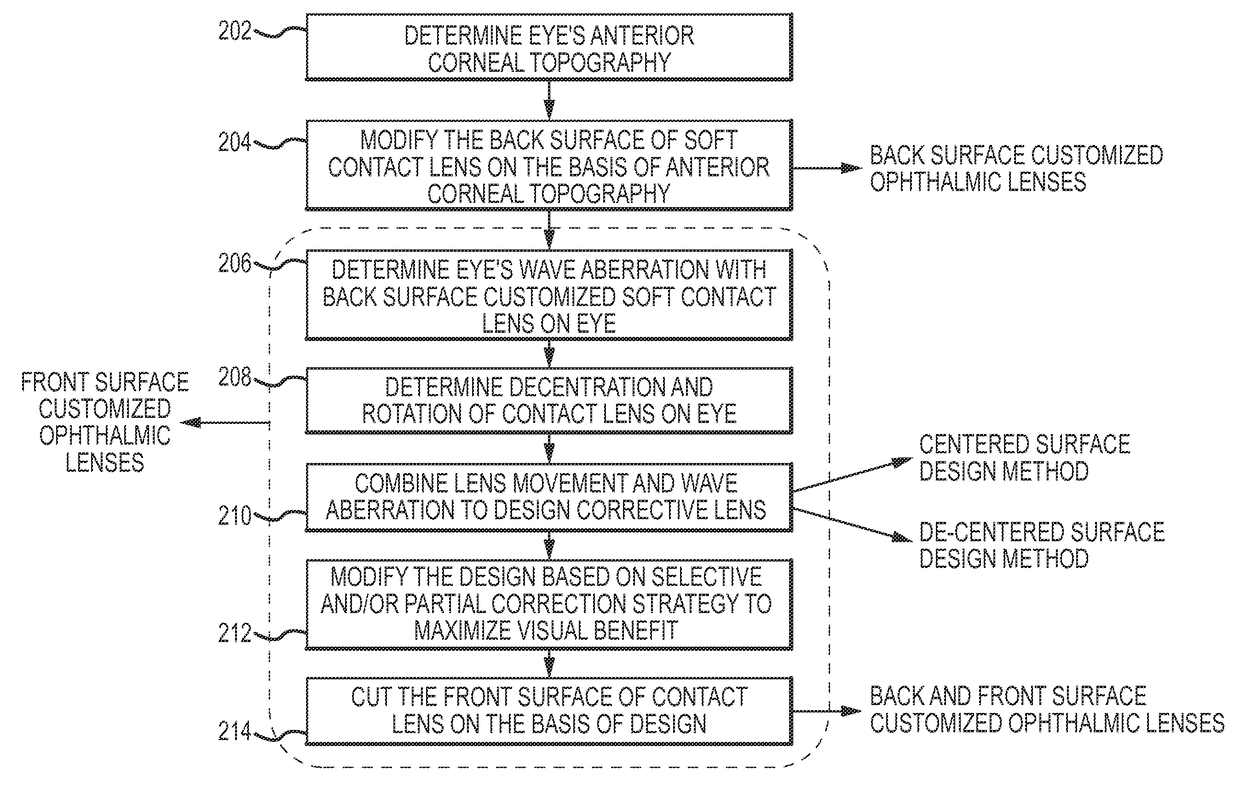
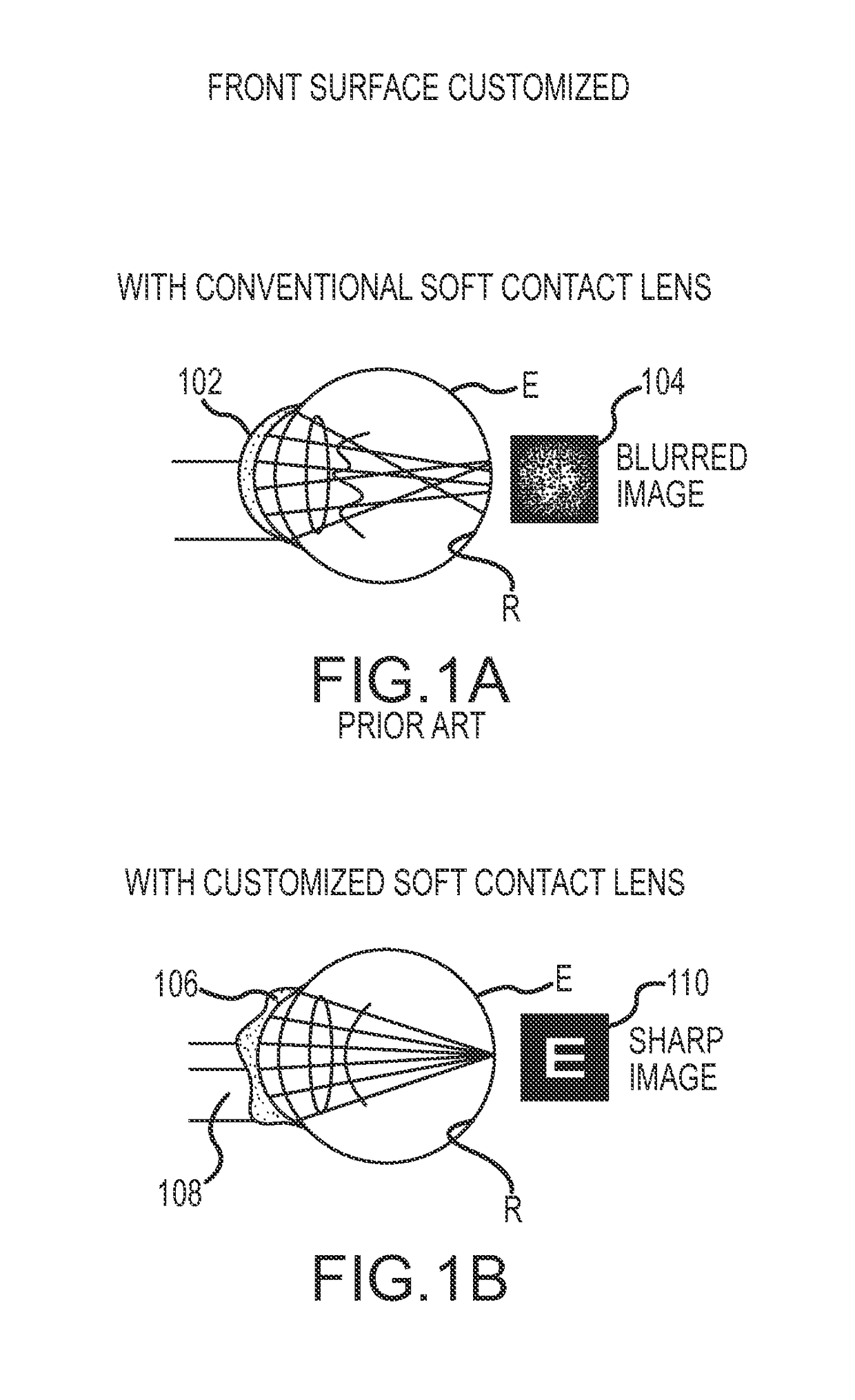
System and method for designing wavefront-guided ophthalmic lenses
The design of a corrective lens combines the measured aberration with decentration and rotation of the lens to design customized optical surface profiles to reliably achieve vision correction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
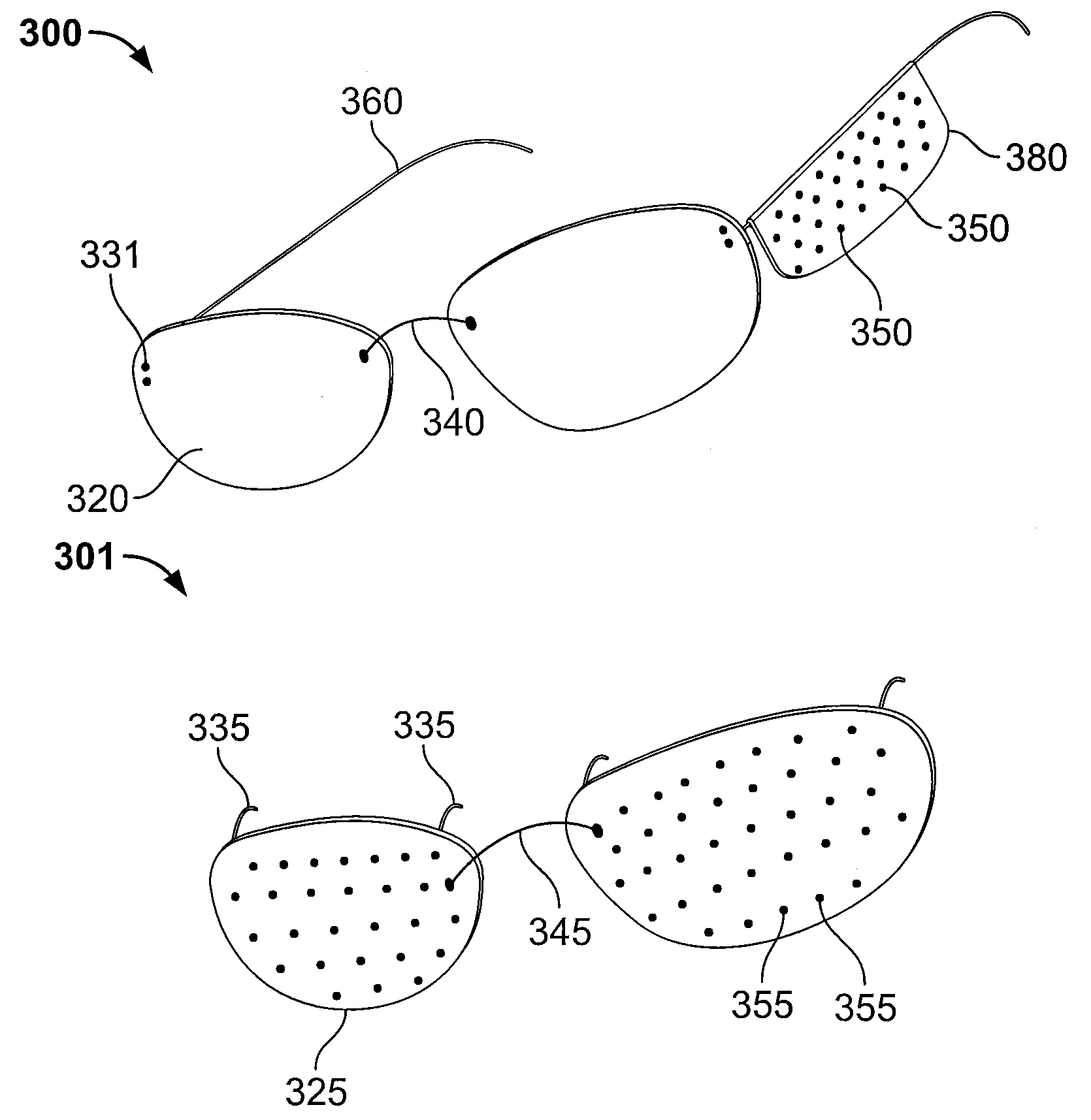
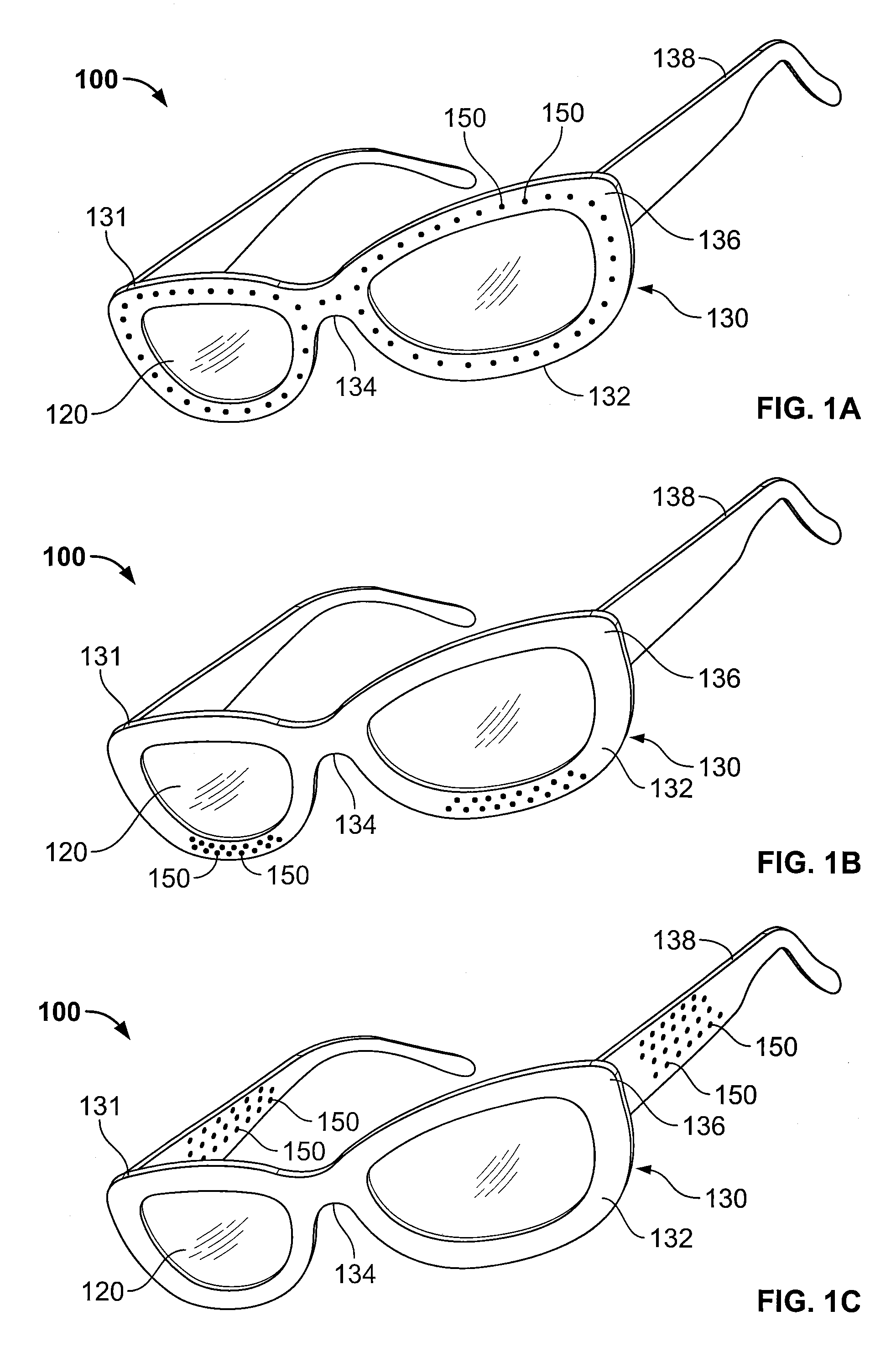
Peripheral vision reflector
An improved low vision device for macular degeneration victims comprising any one of the following elements; (1) two reflecting elements permanently affixed to the frame, (2) reflecting elements mounted to the frame along their outer edges, (3) a single unified lower reflecting element or frame, (4) a corrective lens pivotally attached to a reflecting element in such a way that it may be removed or rotated away, (5) a shield covering the frame that blocks ancillary light from entering the eye, (6) a shield attached to a reflecting element that blocks light from entering the eye between the upper and lower reflecting elements, and (7) a handheld design featuring two reflecting elements for use with only one eye.
Owner:THIR PETER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com