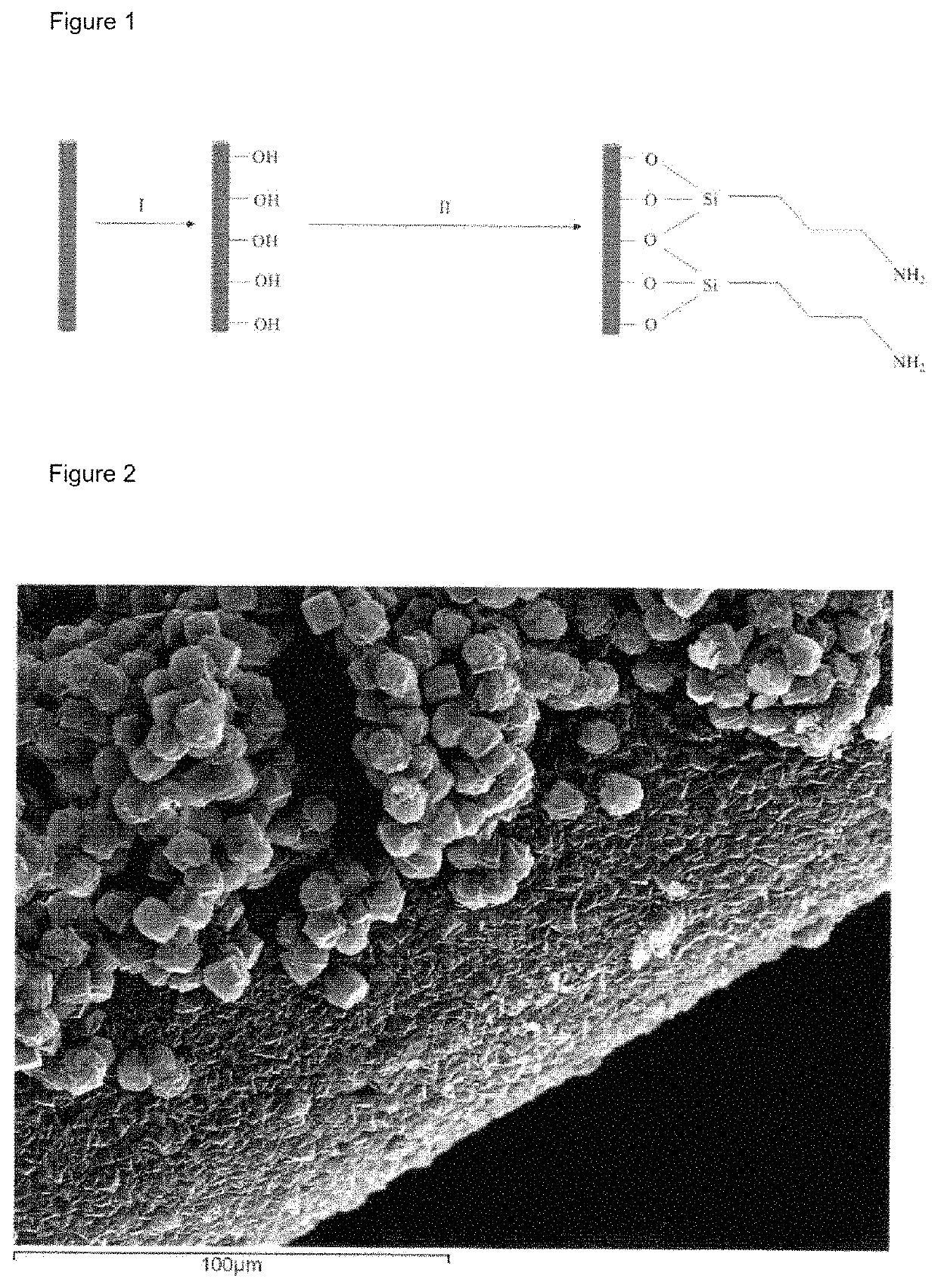
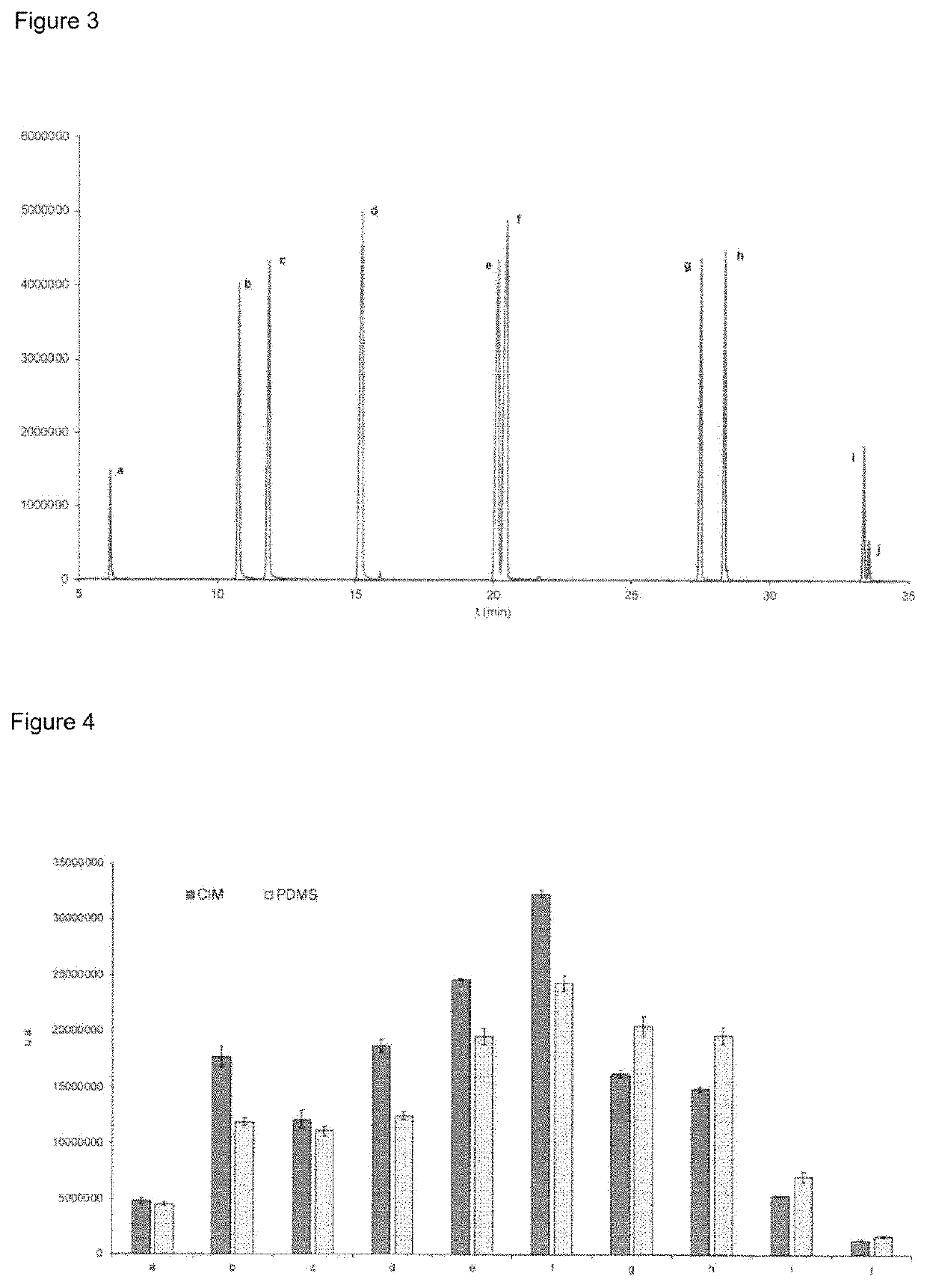
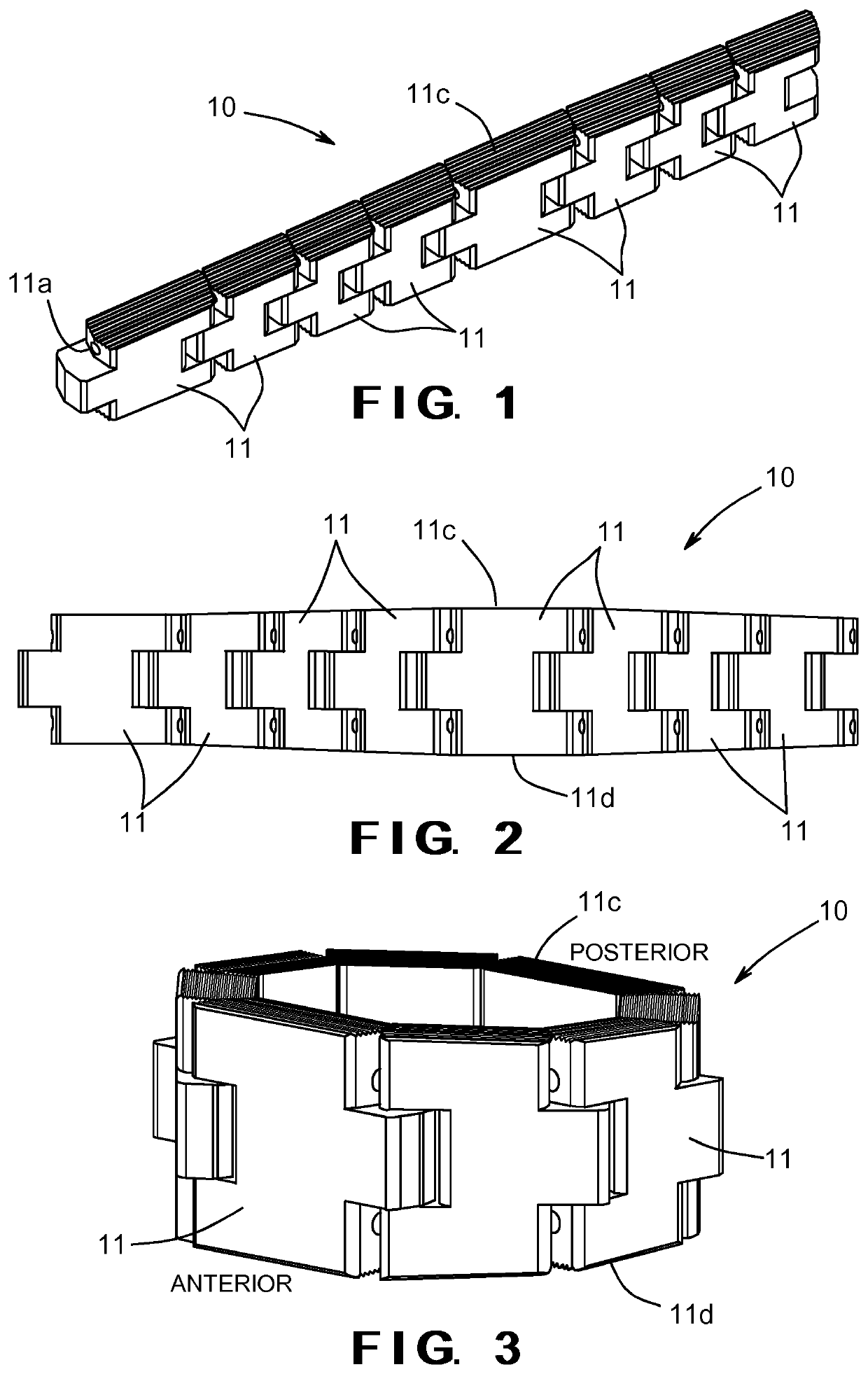
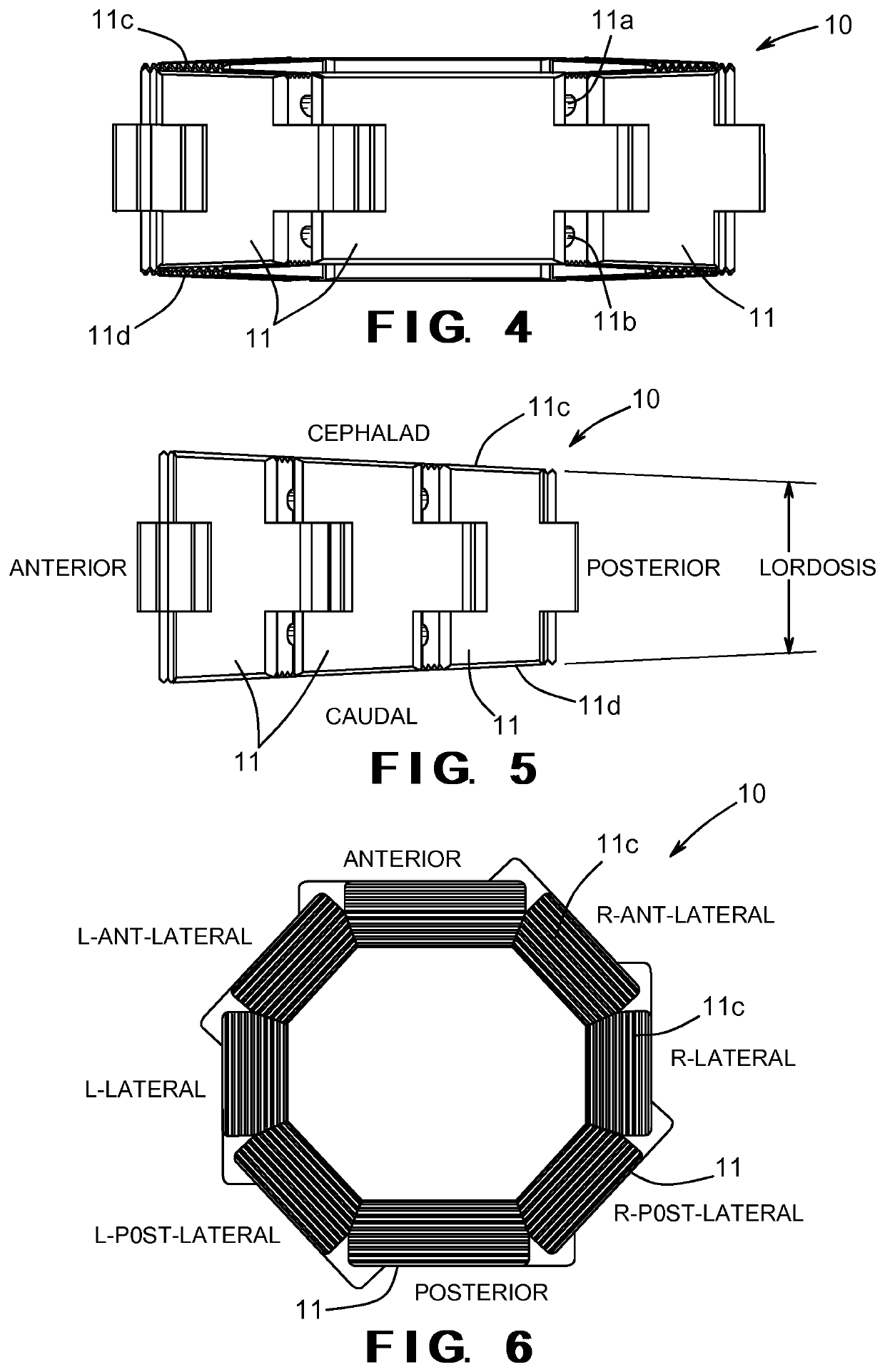
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Nitinol SE" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
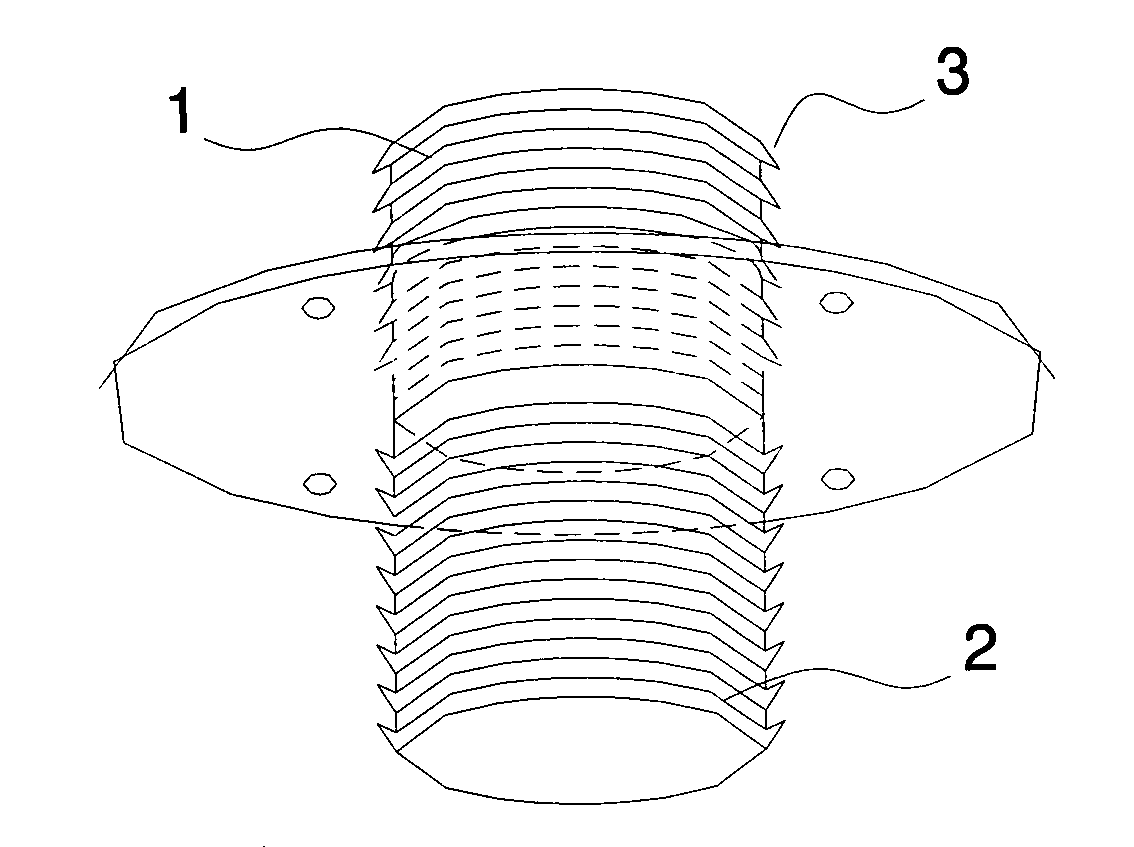
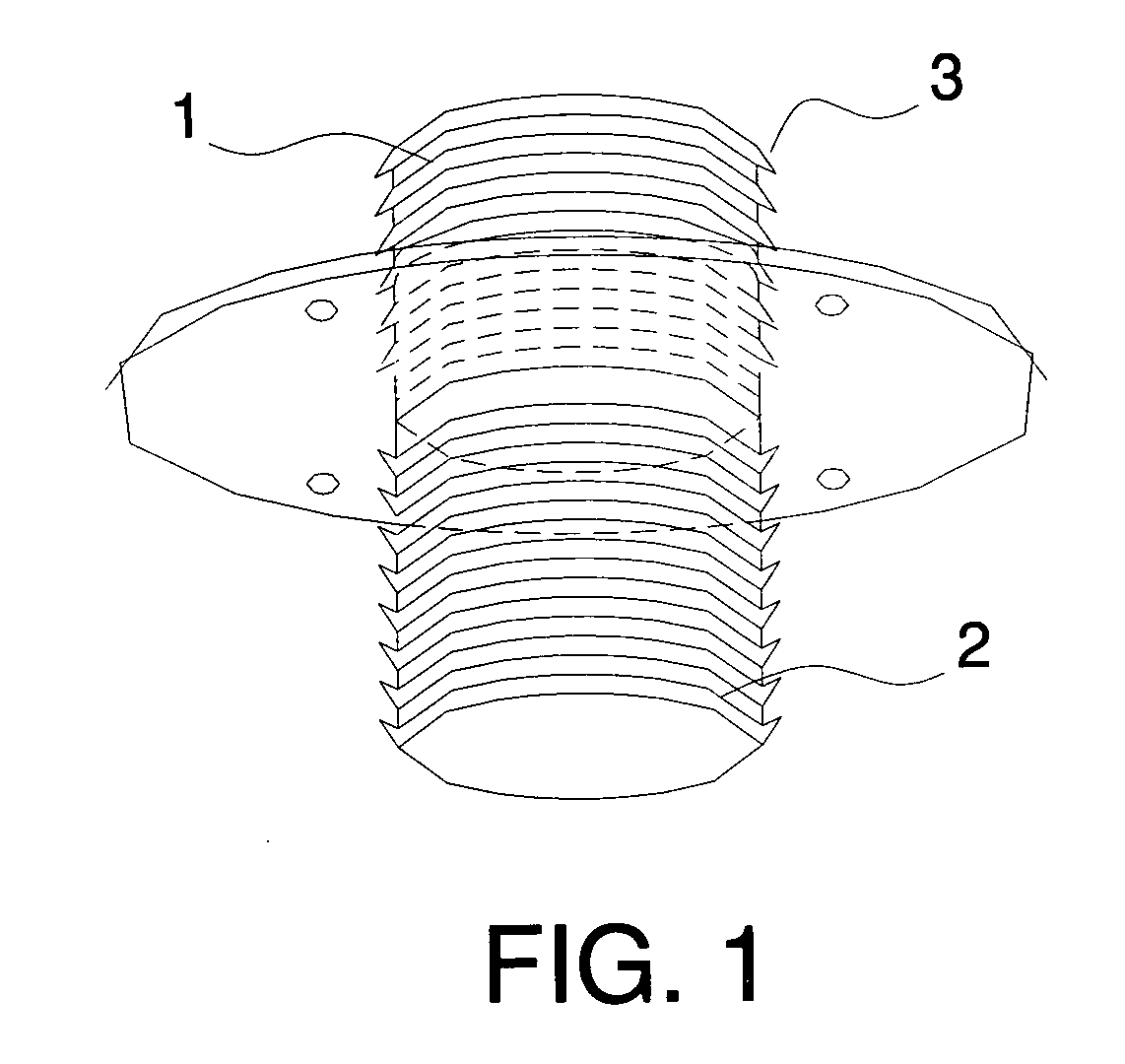
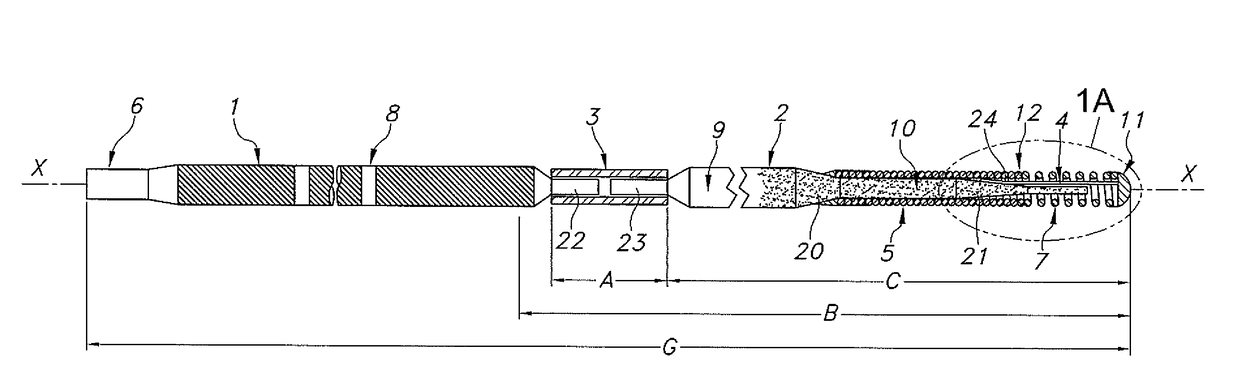
Bone anchor comprising a shape memory element and utilizing temperature transition to secure the bone anchor in bone
A bone anchor that uses temperature transition of a shape memory material to expand the anchor within a bone. Thermal transformation of the metallic crystal state (and hence the stress / strain properties) of shape memory alloy (e.g., Nitinol, NiTi) expands engagement elements within the bone to fix the bone anchor in place. Various self-locking assemblies for attached suture material to the bone anchor are also disclosed.
Owner:TORNIER INC
Tool and method for using surgical endoscope with spiral lumens
An embodiment of the present invention provides for an elongated medical device with a hypotube backbone running through the device, and a spiral lumen spiraled around the backbone along the length of the backbone. The backbone may be formed from a nitinol alloy for increased bendability without compromising axial stiffness. The device may also incorporate a jacket around the hypotube and spiral lumen formed using either melting, molding, bonding, or casting. The spiral lumen may be configured to accommodate a variety of uses, including actuation members (e.g., pull wires), tools, and means for aspiration, irrigation, image capture, and illumination. Additionally, the present invention provides a method for constructing an elongated medical device with a hypotube backbone running through the device, and a spiral lumen spiraled around the backbone along the length of the backbone.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Tool and method for using surgical endoscope with spiral lumens
An embodiment of the present invention provides for an elongated medical device with a hypotube backbone running through the device, and a spiral lumen spiraled around the backbone along the length of the backbone. The backbone may be formed from a nitinol alloy for increased bendability without compromising axial stiffness. The device may also incorporate a jacket around the hypotube and spiral lumen formed using either melting, molding, bonding, or casting. The spiral lumen may be configured to accommodate a variety of uses, including actuation members (e.g., pull wires), tools, and means for aspiration, irrigation, image capture, and illumination. Additionally, the present invention provides a method for constructing an elongated medical device with a hypotube backbone running through the device, and a spiral lumen spiraled around the backbone along the length of the backbone.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Fatigue-Resistant Nitinol Instrument
InactiveUS20120231414A1Improve the immunityFew stepsMetal-working drilling toolsFurnace typesWire rodTitanium
A fatigue-resistant Nitinol instrument has a working portion in the deformed monoclinic martensitic state and an austenite finish temperature in the range of 40° to 60° C. Because the operating environment of the instrument is about 37° C., the working portion remains in the monoclinic martensitic state during its use. The relatively high austenite finish temperature and fatigue resistance is achieved by subjecting the nickel-titanium alloy to a final thermal heat treat in a temperature range of about 410° to 440° C. while the nickel-titanium alloy is under constant strain of about 3 to 15 kg. Further, the high austenite finish temperature is achieved without subjecting the alloy to thermal cycling to produce shape memory. Additionally, there are no intermediate processing steps occurring between obtaining a finished diameter of the wire or blank through cold working and the final thermal heat treat under constant strain.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
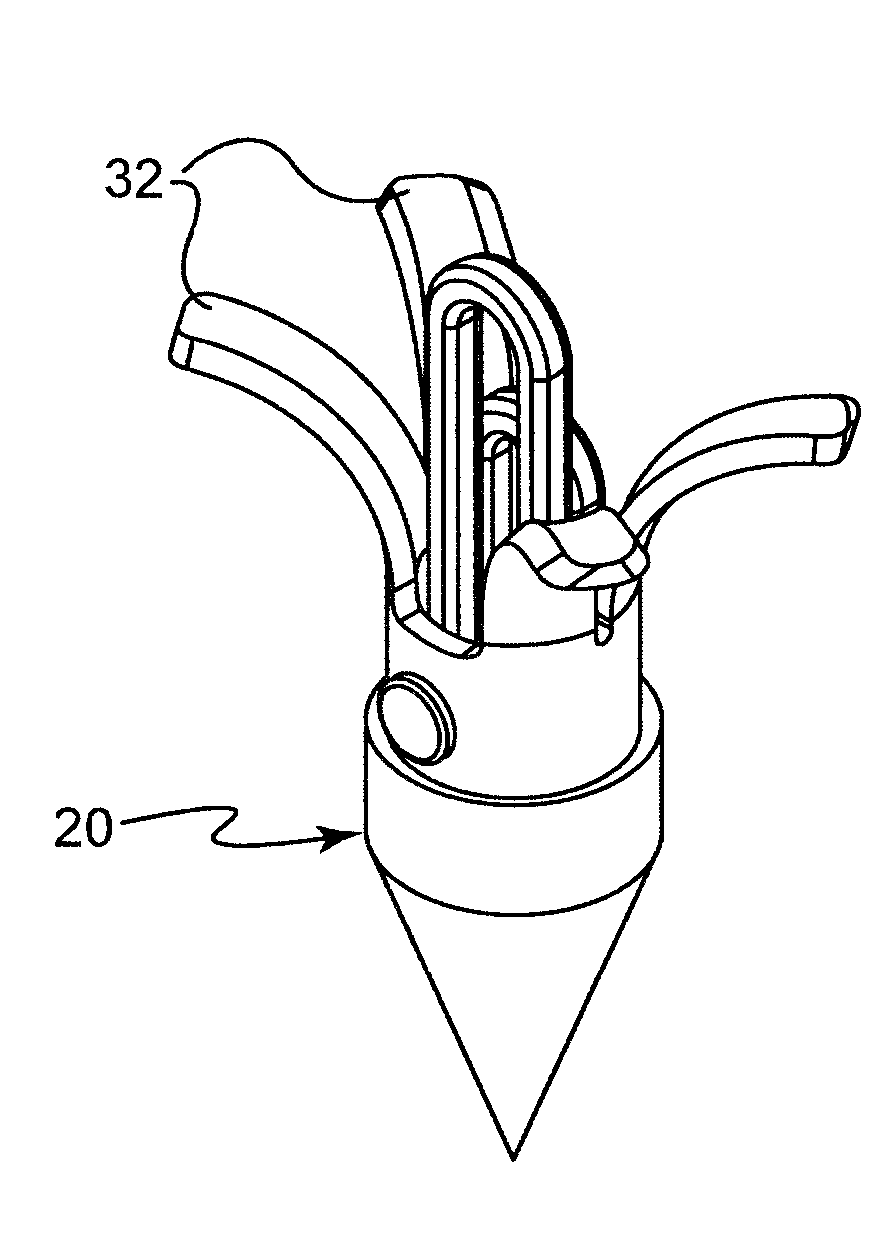
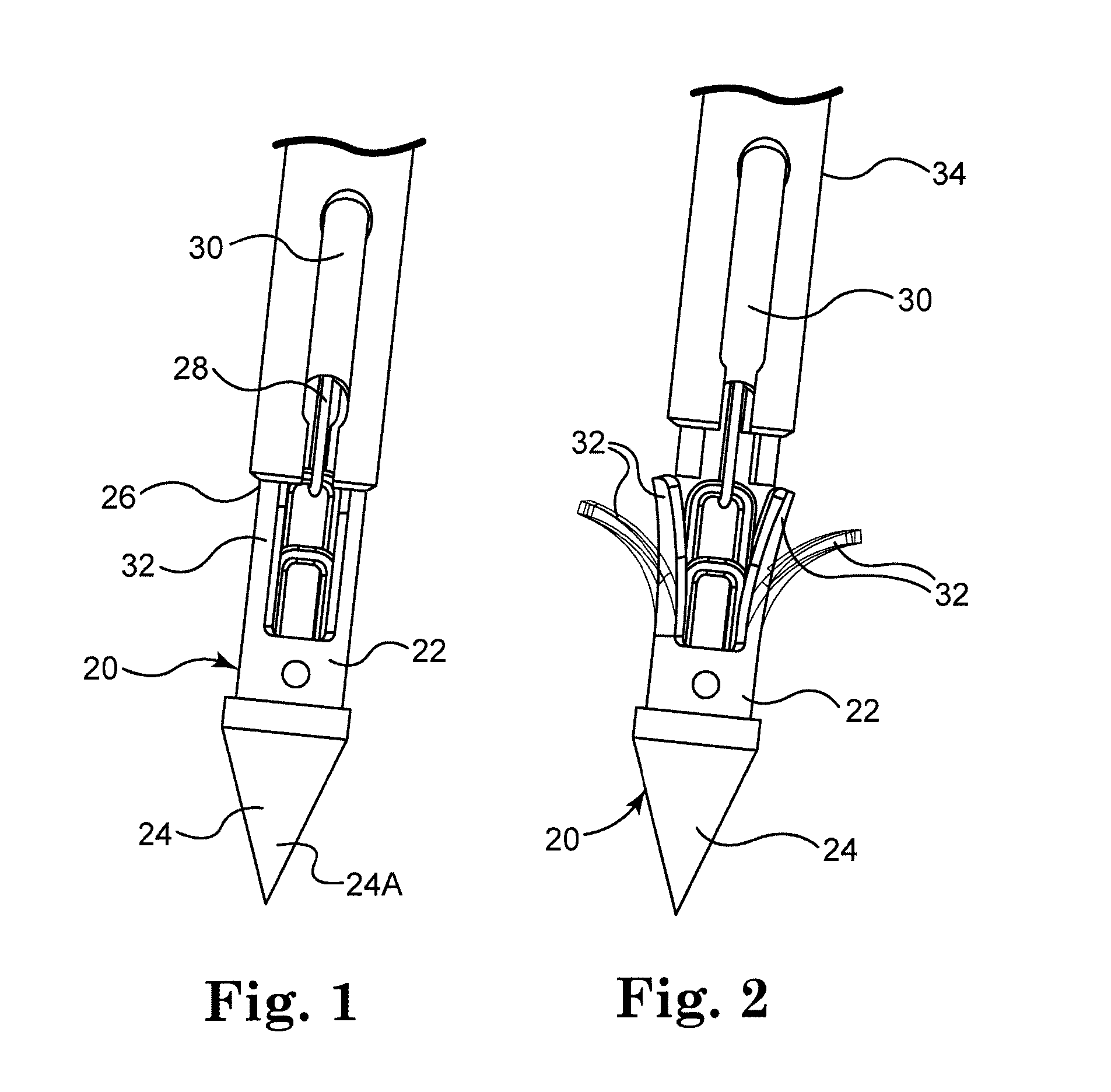
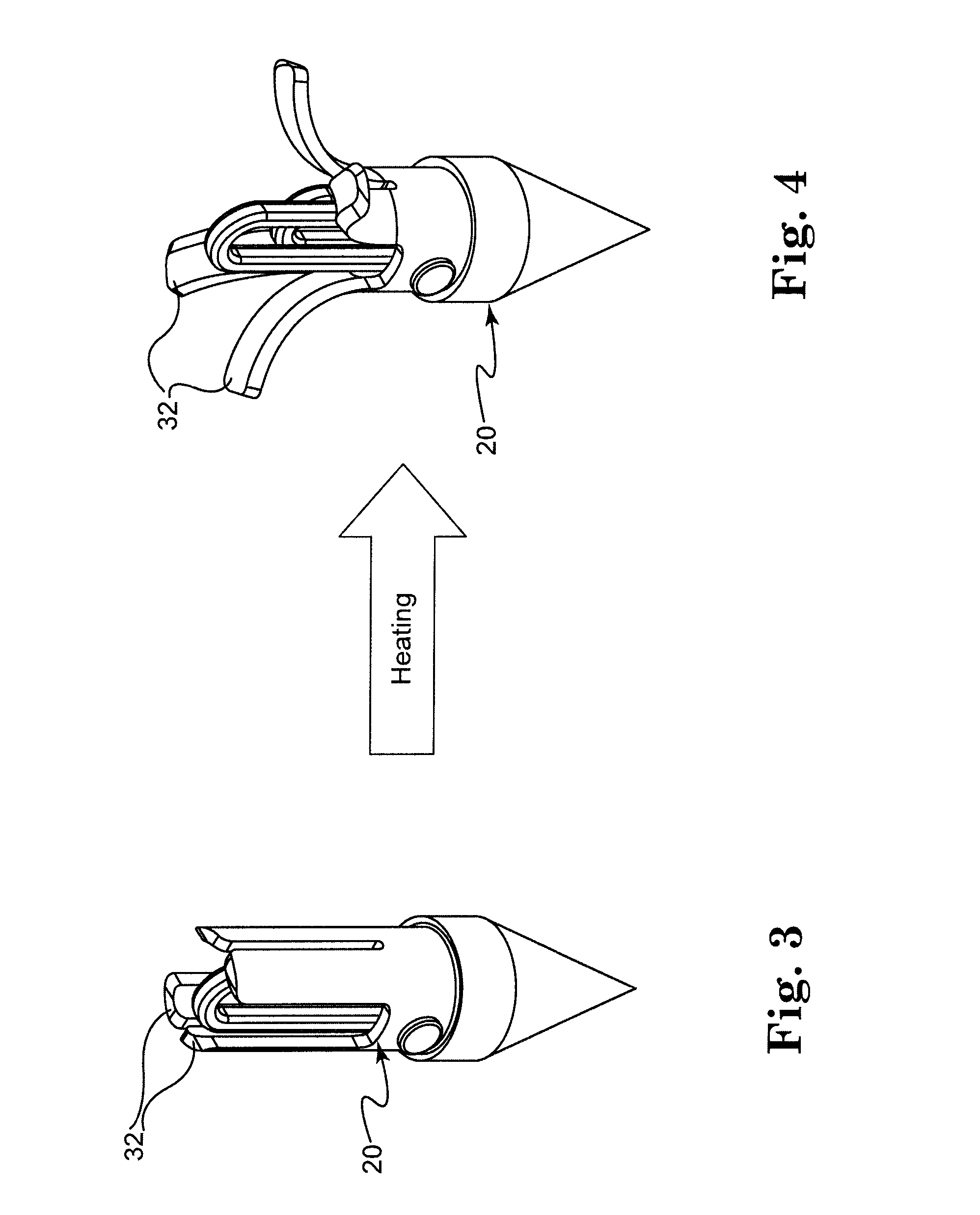
Improved tissue fixation devices
ActiveCN107666868AAvoid plastic deformationFunction increaseHeart valvesWound clampsTissue fixingSuture line
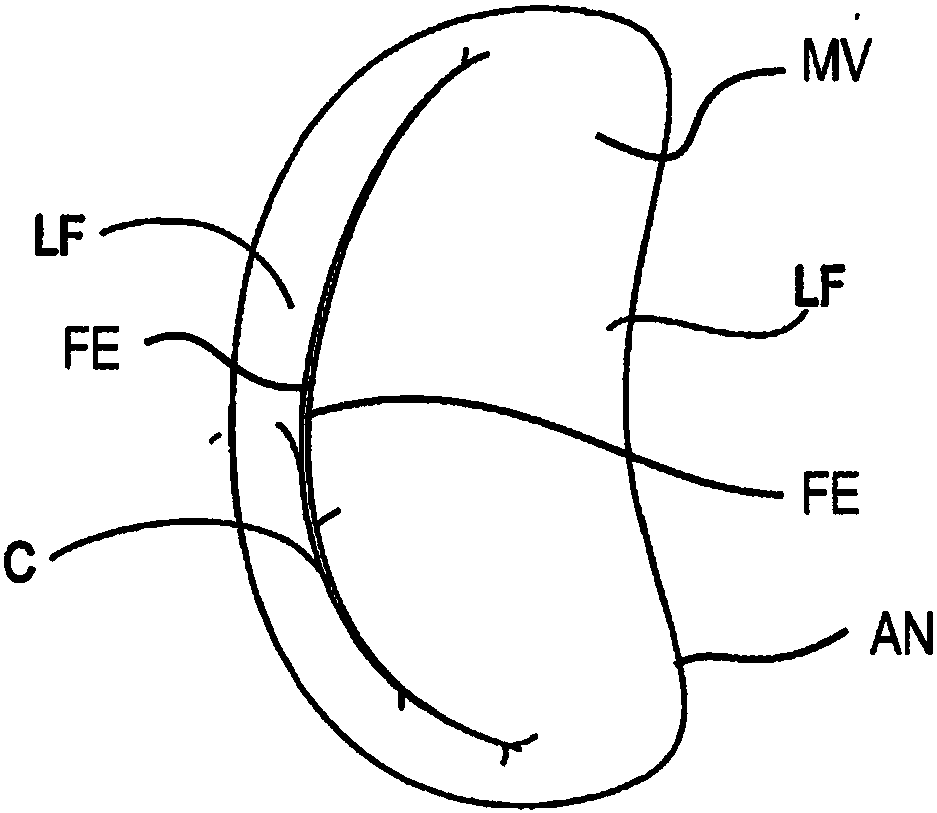
The present disclosure describes tissue gripping devices, systems, and methods for gripping mitral valve tissue during treatment of a mitral valve and while a tissue fixation device is implanted in the mitral valve. The tissue gripping device includes a flexible member and one or more tissue gripping members coupled to one or more arms of the flexible member. The flexible member is formed from a shape-memory material, such as nitinol, and the tissue gripping member(s) are formed from a material that is more rigid than the shape-memory material. The tissue gripping member(s) are attached to theflexible member by threading or looping suture lines around and / or through the tissue gripping member(s) and the flexible member and / or by applying a cover material to the tissue gripping device to hold the tissue gripping member(s) against the flexible member.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Composite medical device having a titanium or titanium based alloy section and a ferrous metal section
InactiveUS20050142377A1Welding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMaterials scienceMedical treatment
A composite medical device having a titanium, and titanium based alloy, section welded to a ferrous metal section. The weld provides supplementary filler material to alter the proportions of various elements in the weld pool to ensure a strong and reliable weld. Certain fillers, such as nickel or iron, added to the weld pool enable high quality welds to be fabricated utilizing a wide variety of fusion welding techniques between the titanium, or titanium based alloy, section and the ferrous metal section. The sections may include nickel-titanium, also known as nitinol. The sections may be in the form of wires, bars, ribbons, and sheets. The composite medical device of the present invention may include guidewires, stents, right-angle needles, suture passers, retractors, graspers, baskets, and various retrieval devices.
Owner:EDISON WELDING INSTITUTE INC
Shape memory alloy (SMA) hinge apparatus, and systems and methods employing same
ActiveUS20200108951A1Increase power generationLimited abilityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsShape-memory alloyEngineering
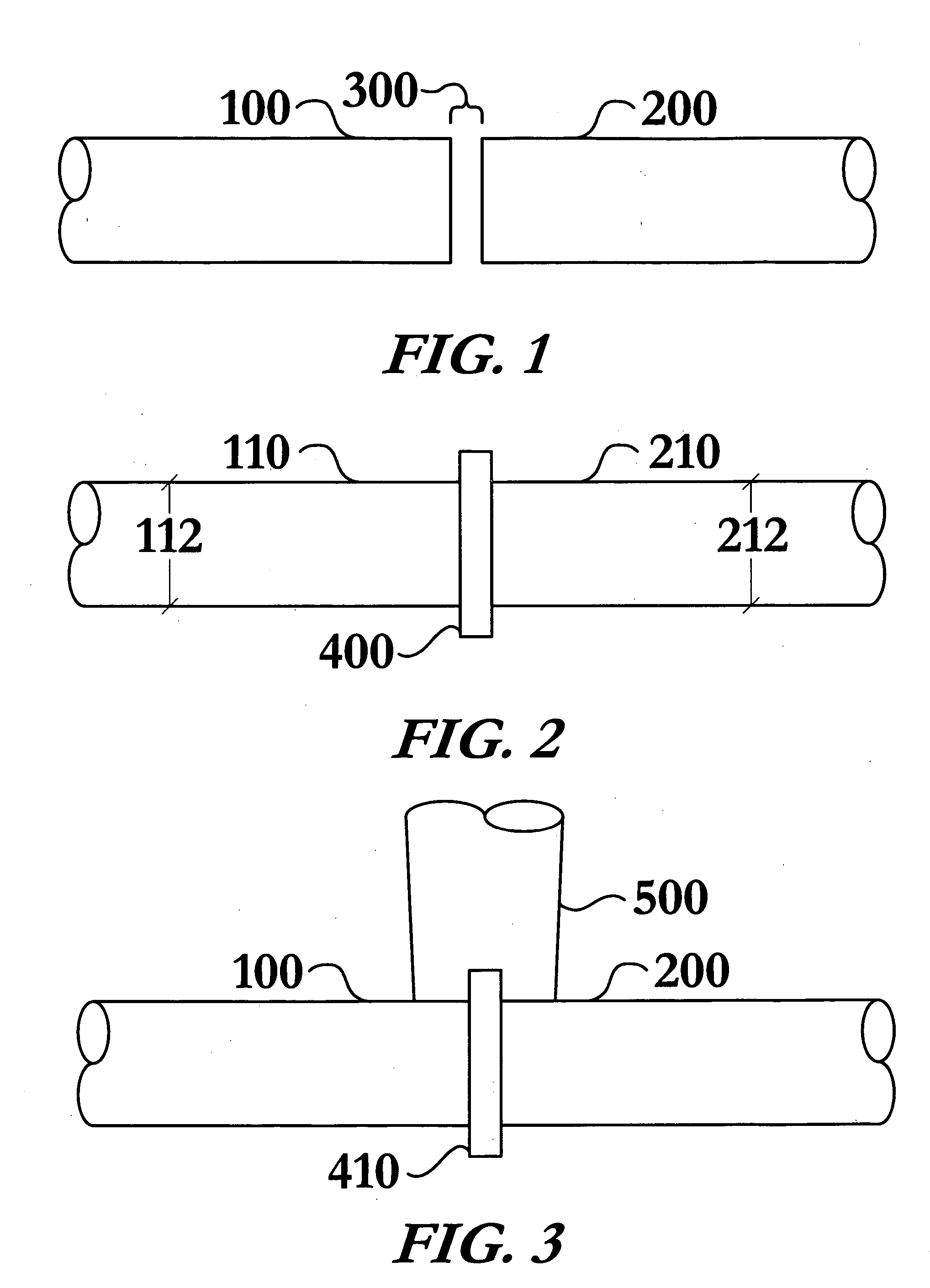
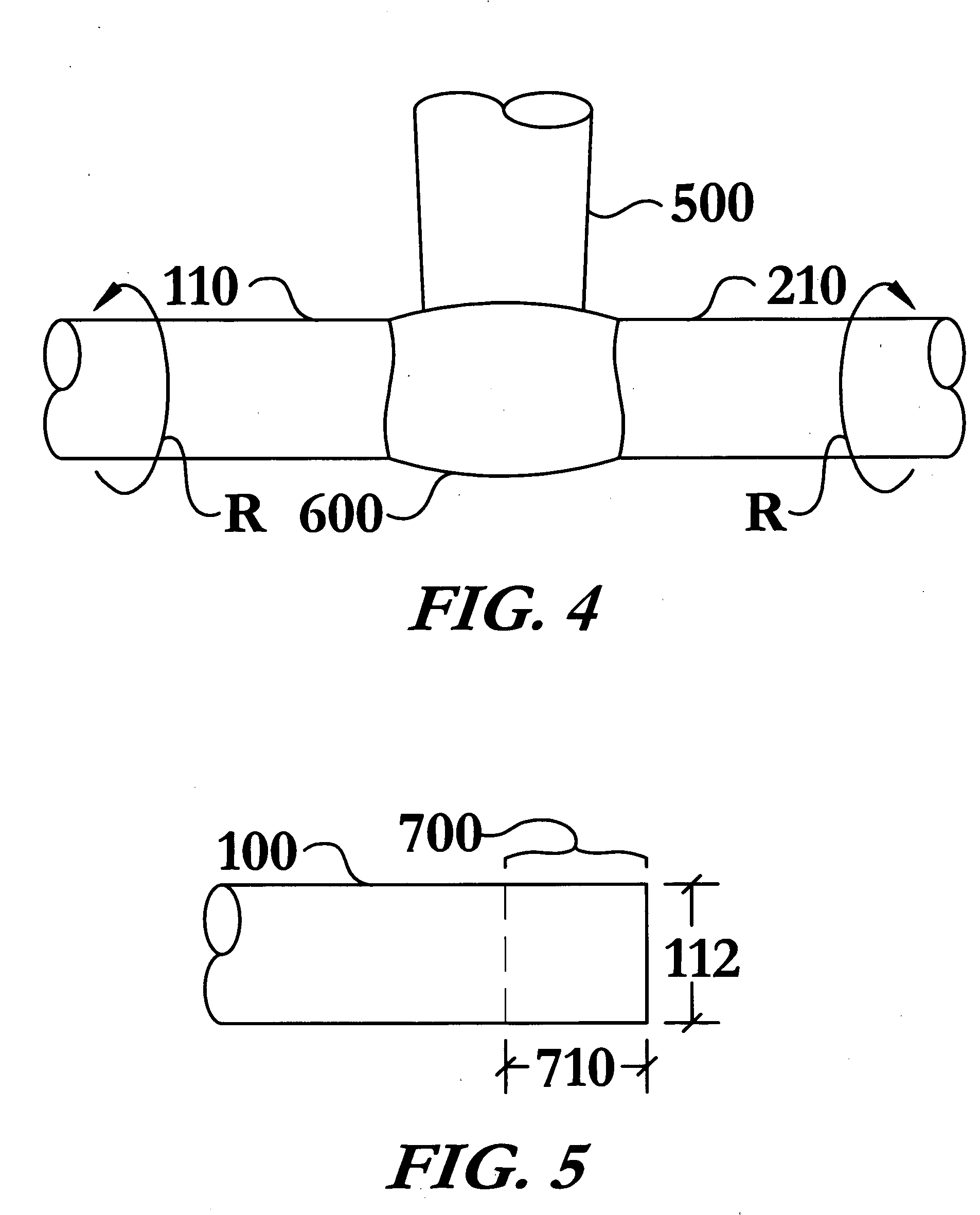
A controllable shape memory alloy (SMA) hinge apparatus comprises multiple SMA elements to effect a first angle of rotation and a second angle of rotation between a first object and a second object. In one example, respective SMA elements are independently activated by Joule heating to rotate the first object and / or the second object. SMA elements undergo a three-dimensional transformation (e.g., bending or torsion), and a pair of elements may undergo antagonistic transformations so as to provide for a multiple-use bidirectional non-continuous rotary actuator. SMA elements may be trained to achieve different angles of rotations between the objects (e.g., zero degrees and 90 degrees). SMA elements may be nitinol, and may be formed as wires, rectangular sheets, or coils. In some examples, the first object may be a spacecraft (e.g., a satellite) and the second object may be a deployable structure (e.g., a robotic appendage, a deployable solar panel, a deployable aperture, a deployable mirror, a deployable radiator, and at least one actuator to steer an antenna dish).
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
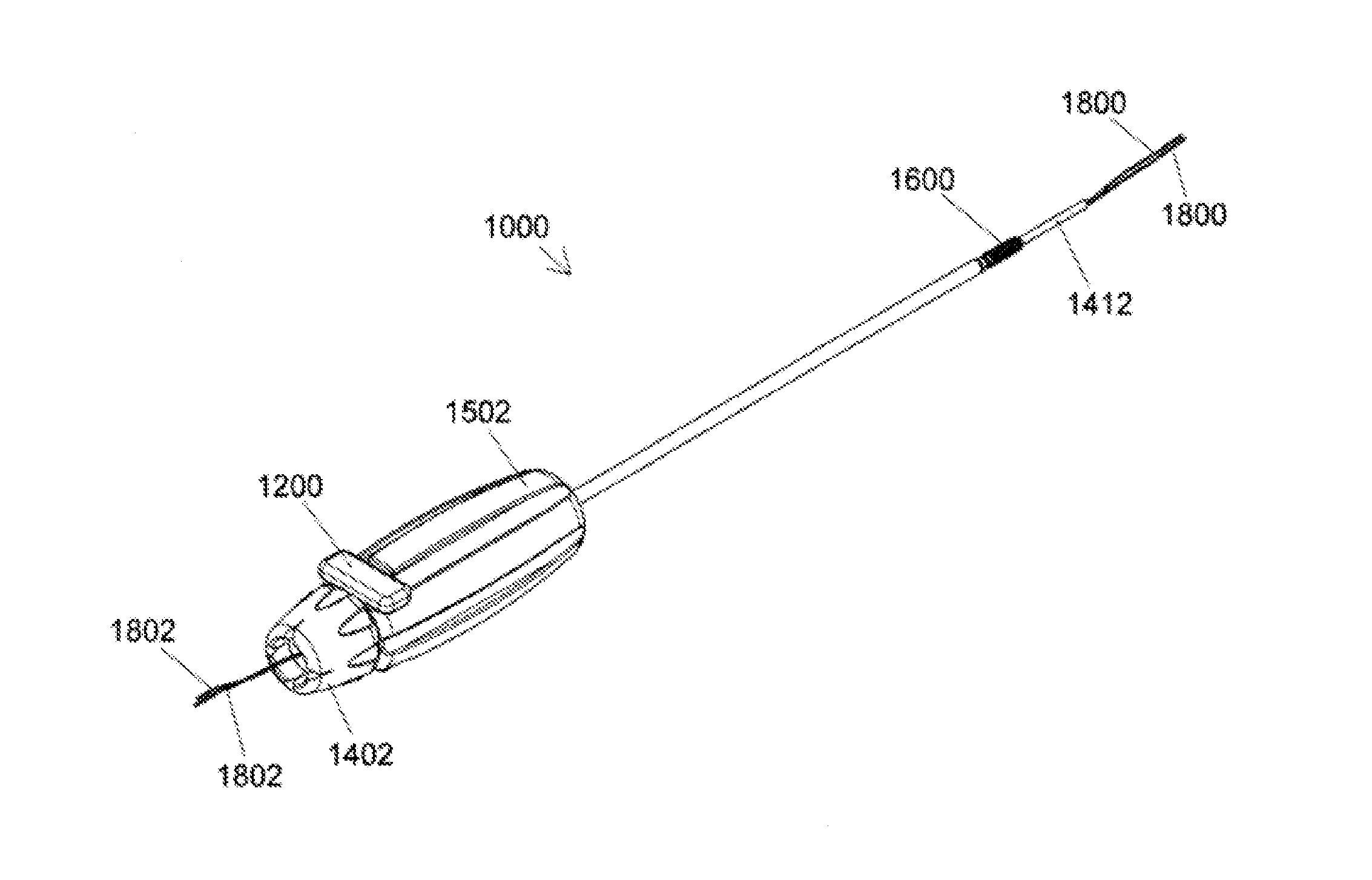
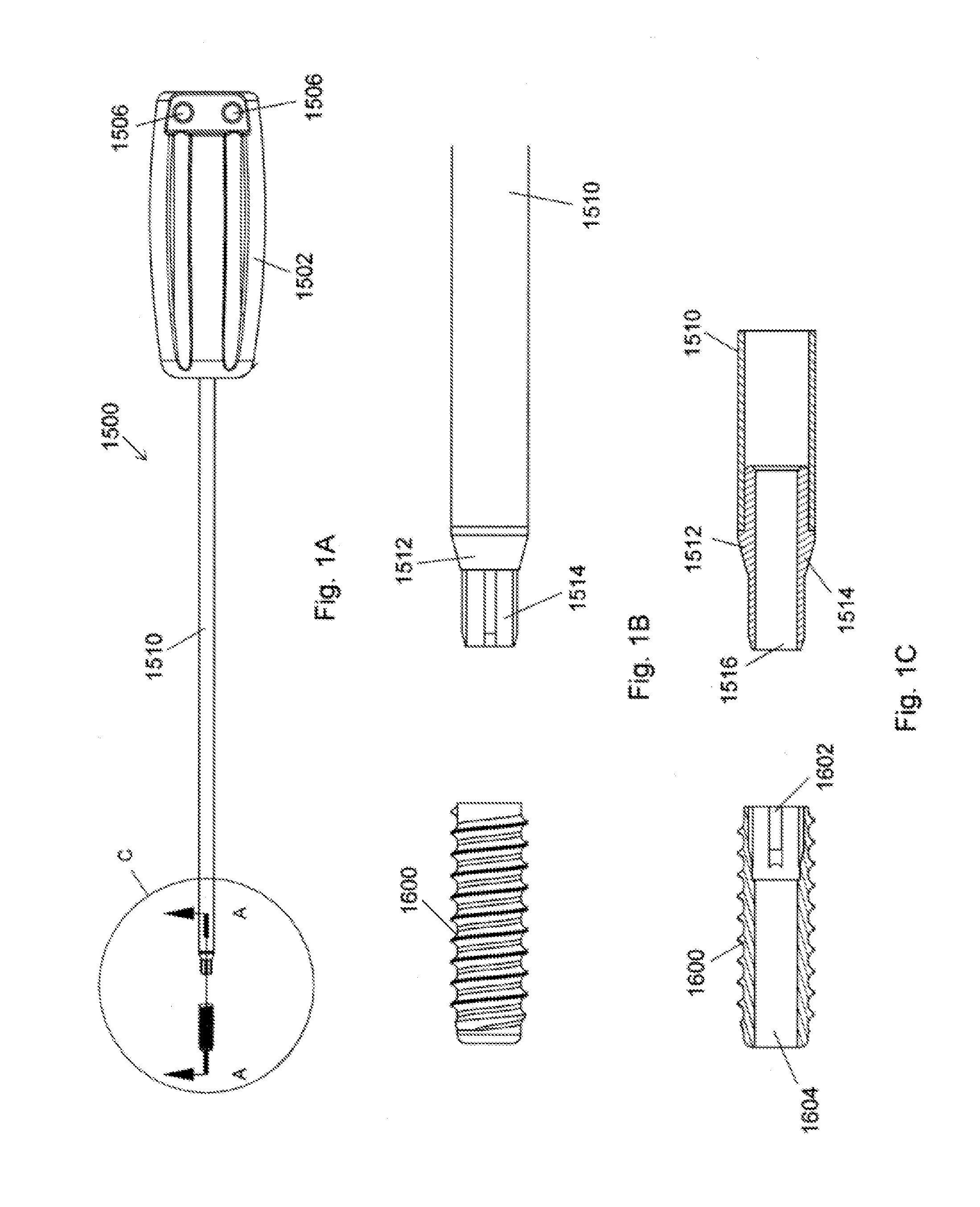
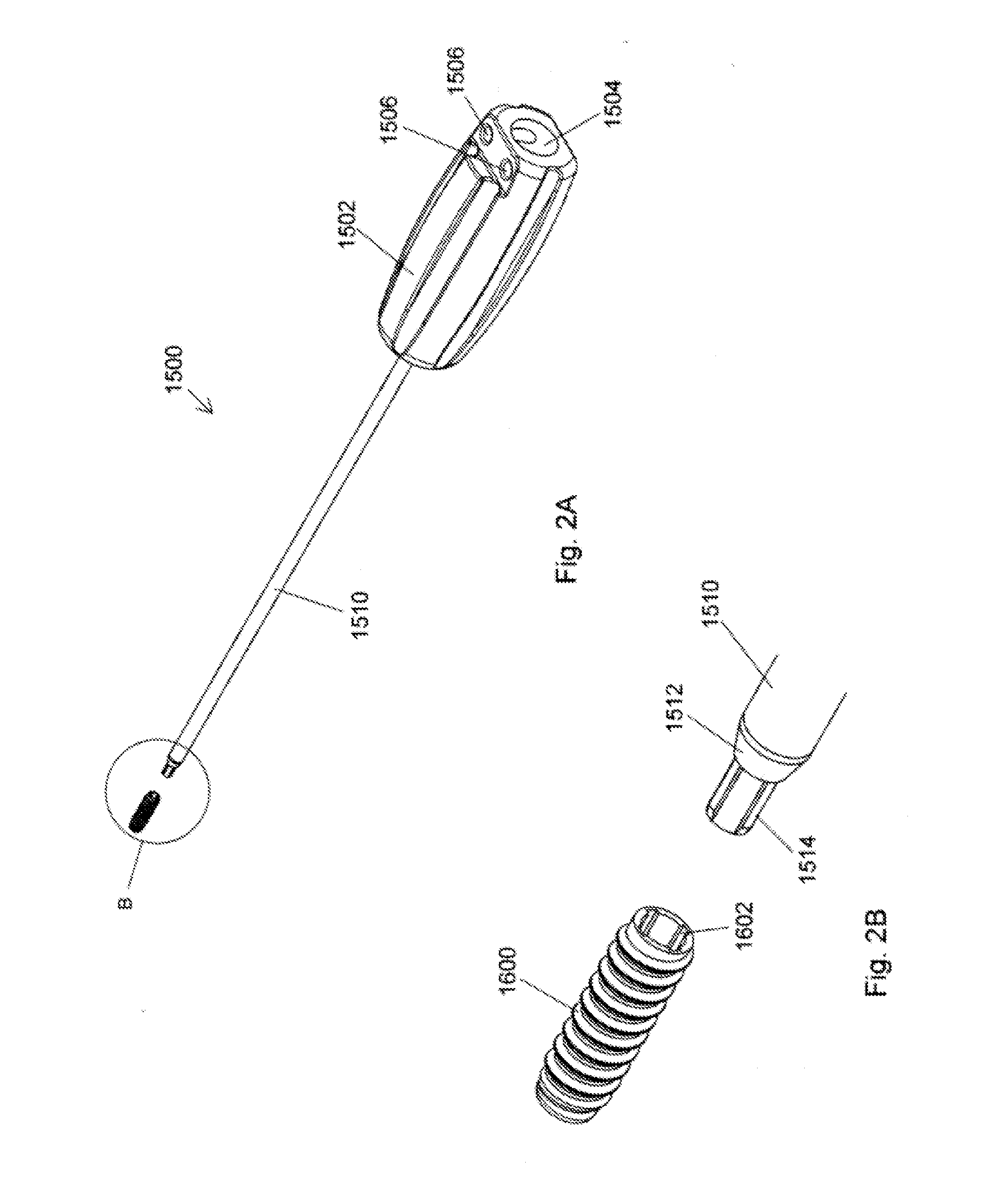
Ceramic implant placement systems and superelastic suture retention loops for use therewith
ActiveUS20170000476A1Twisting of the sutures or graft is preventedAvoid distortionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsTissue GraftingBone tissue
Described herein is a simplified placement system and method for a tissue graft anchor by which a surgeon may introduce one or more sutures into a hole in a boney tissue, apply a precise amount of tension to the sutures to advance a soft tissue graft to a desired location, and then advance the anchor into the bone, preferably while maintaining the requisite pre-determined suture tension and without introducing spin to the suture. Particularly preferred embodiments allow for the placement of small diameter knotless anchors. For example, the implant placement system may include a cannulated tensioning device having disposed therein an elongate member of a suitably elastic metallic or polymeric material, such as nitinol, that includes at its distal end a loop of material suitable for suture retention. The implant placement system may further include high tensile strength knotless anchors provided with internal drive features that coordinate with torque-transmitting features unique to the driver devices of the present invention.
Owner:TENJIN
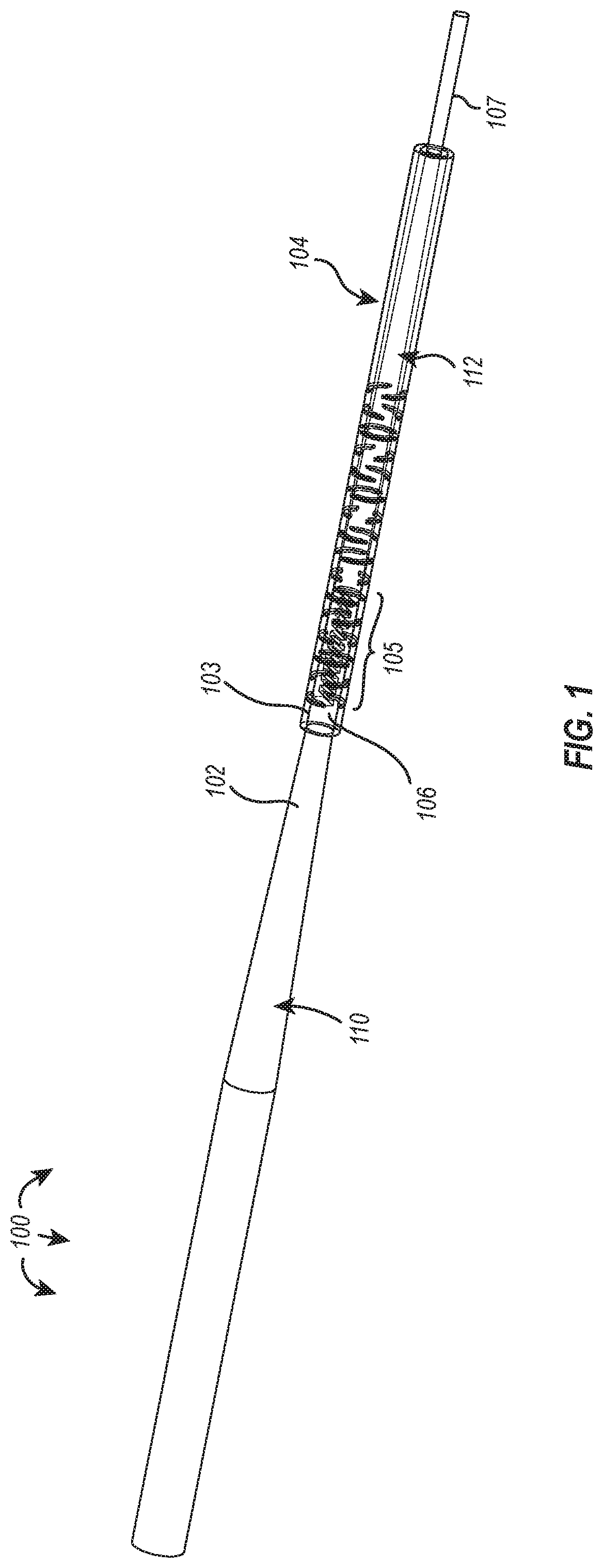
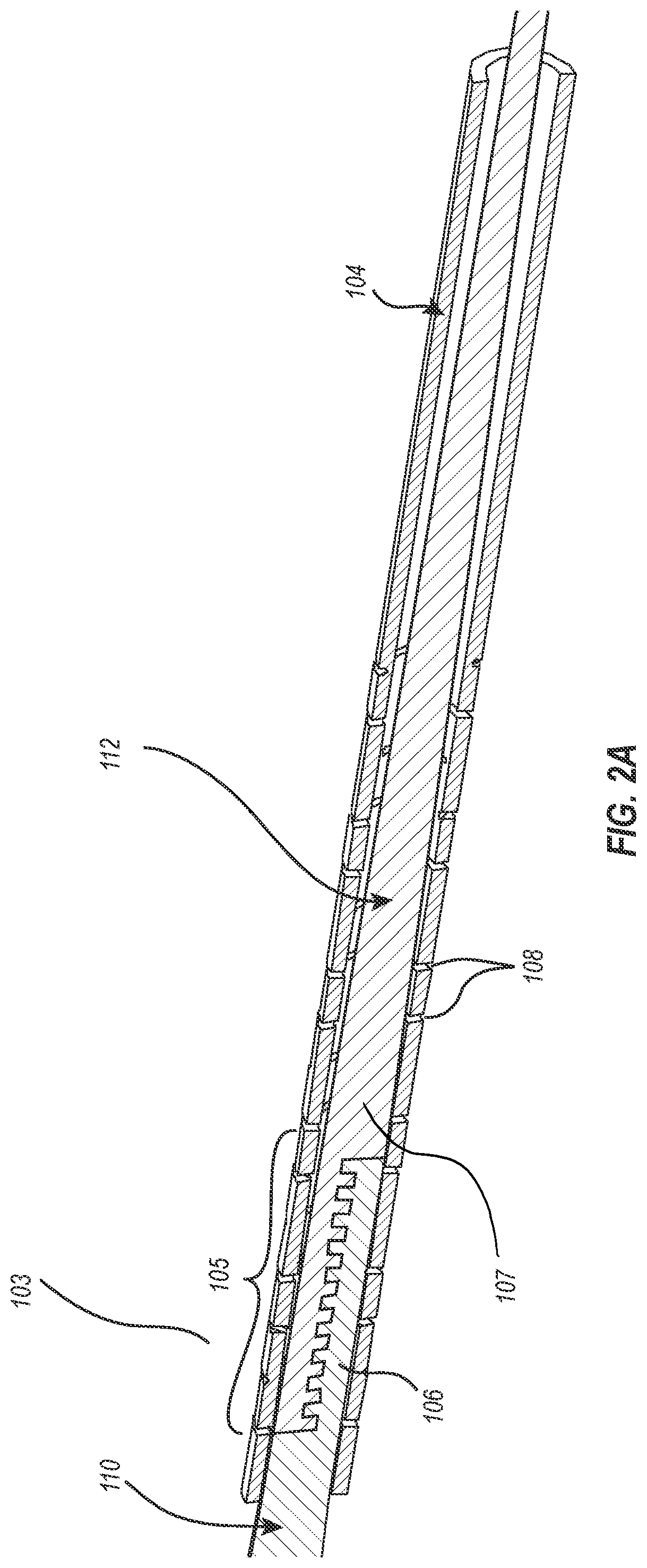
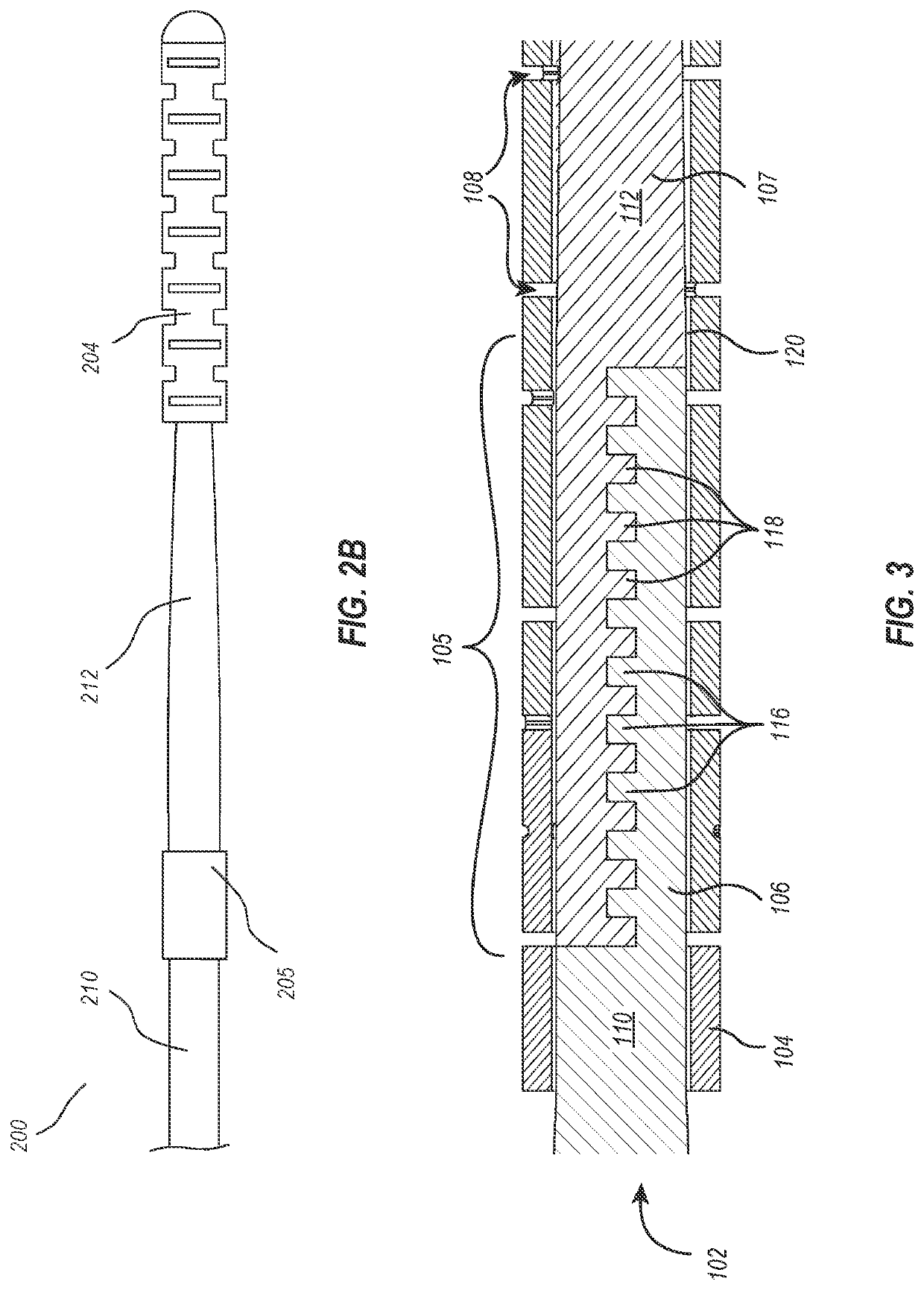
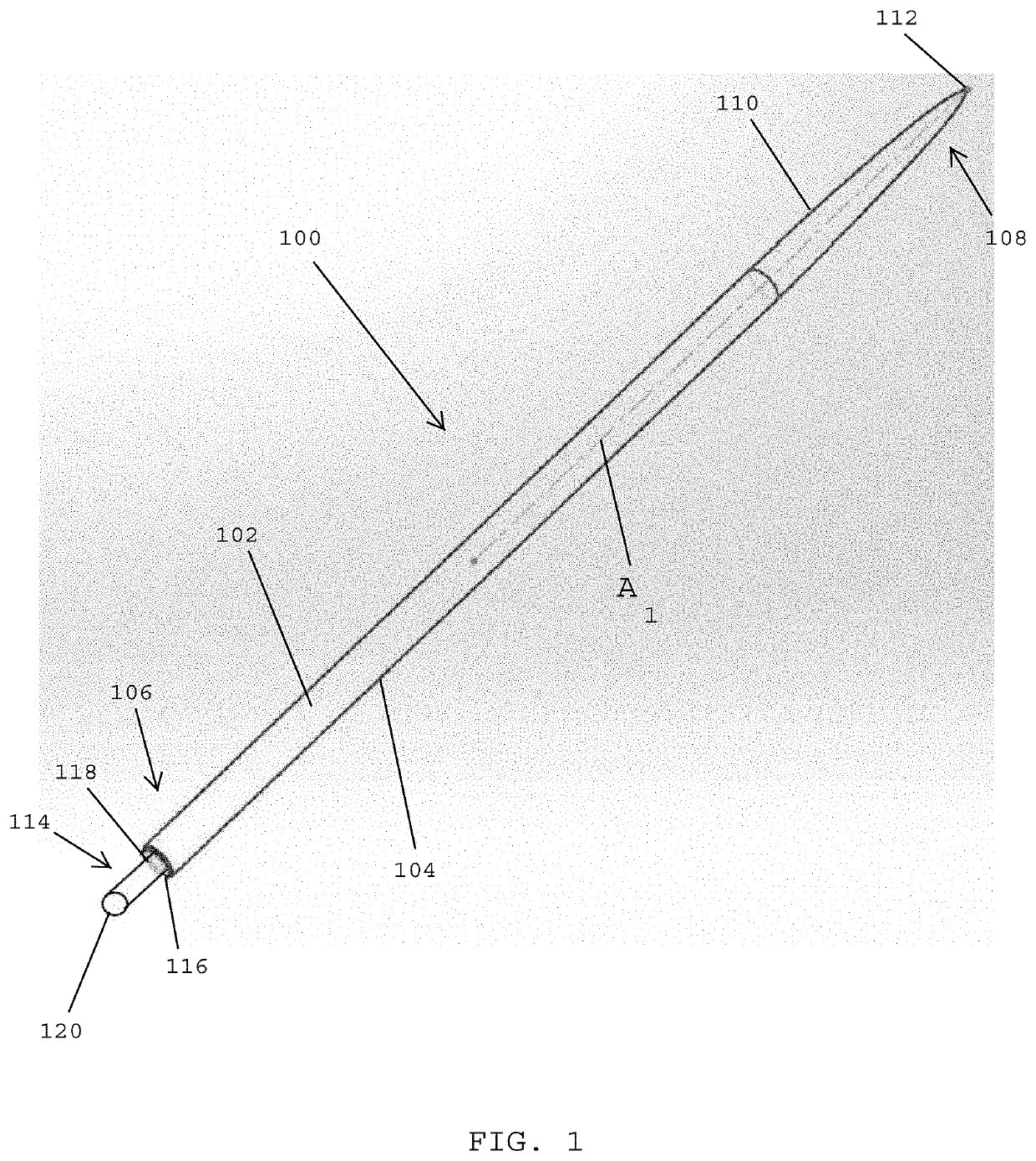
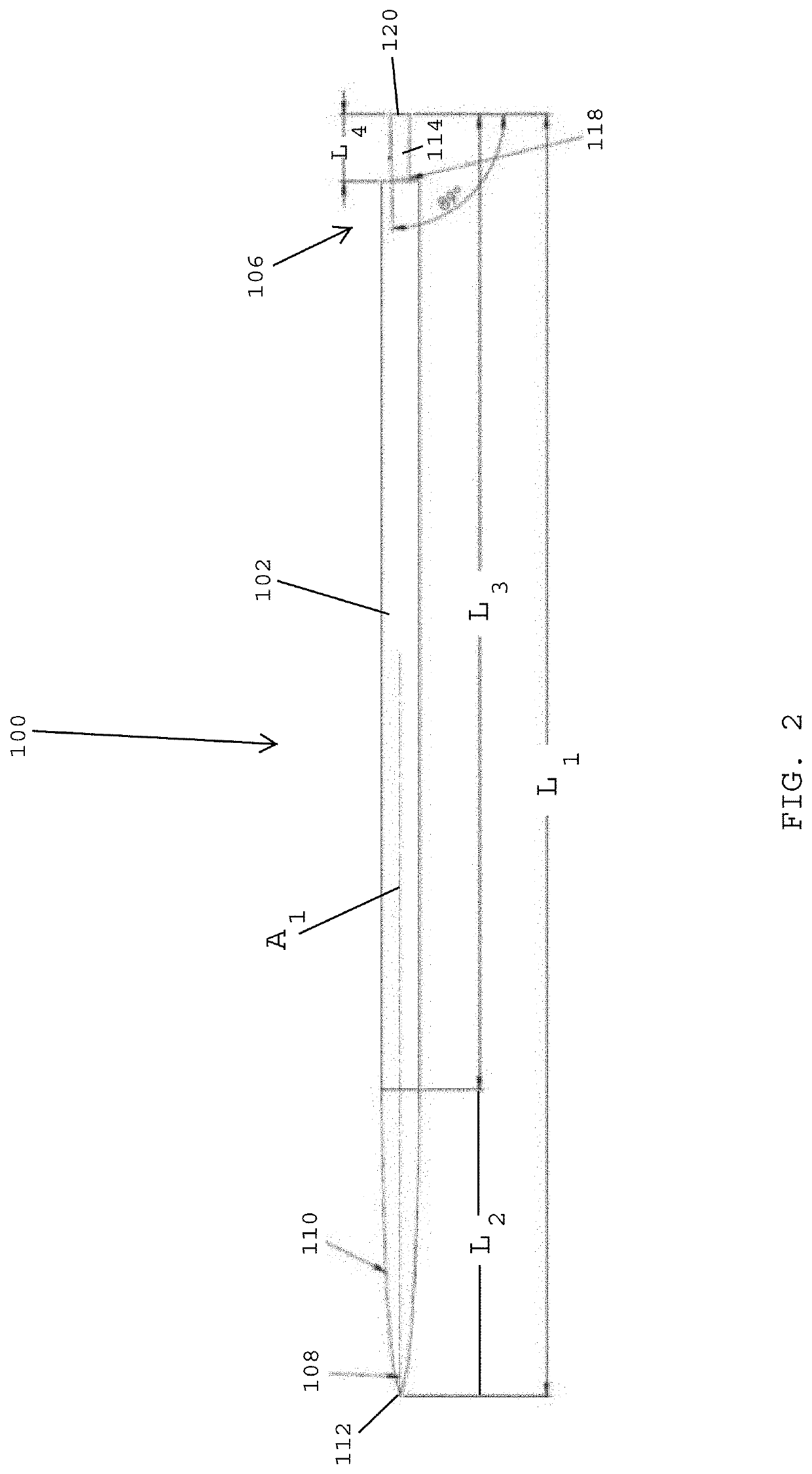
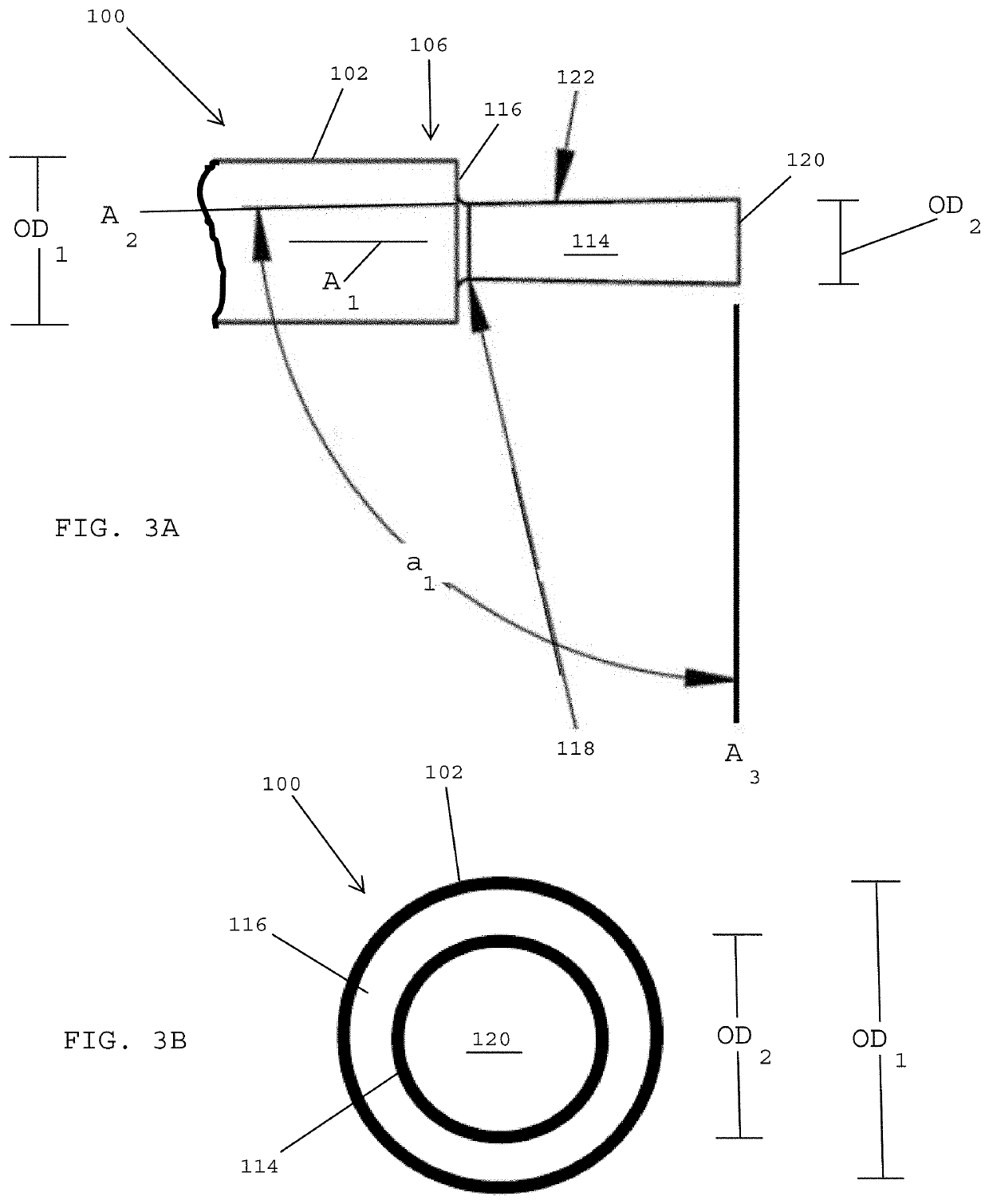
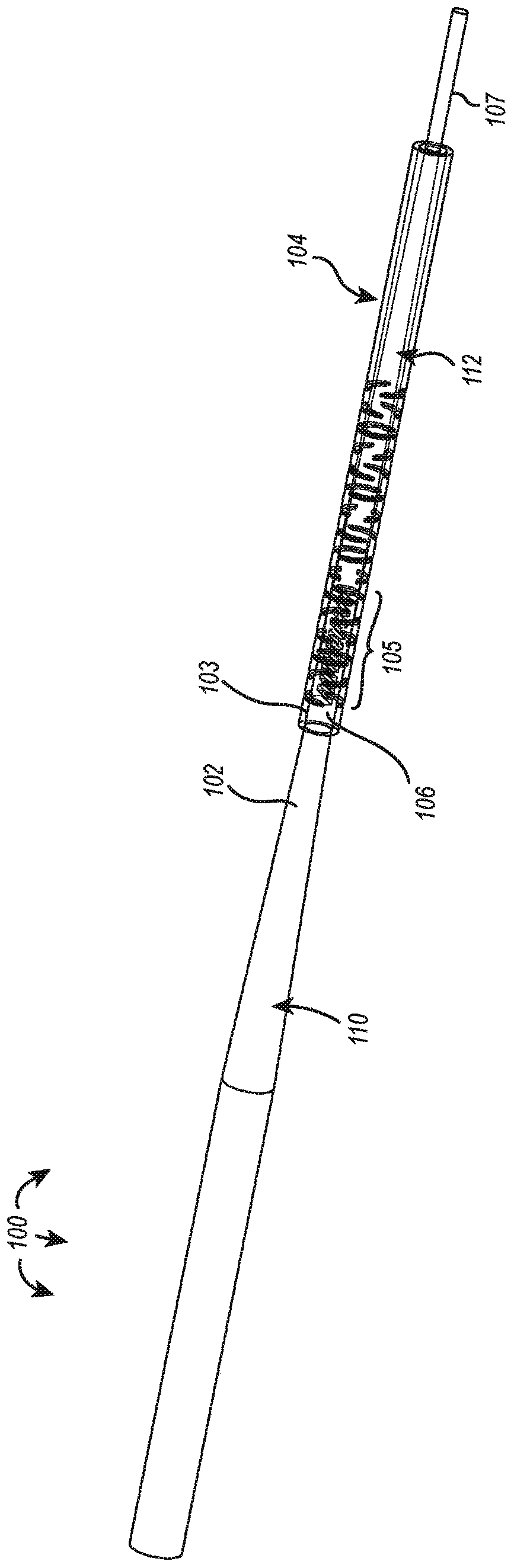
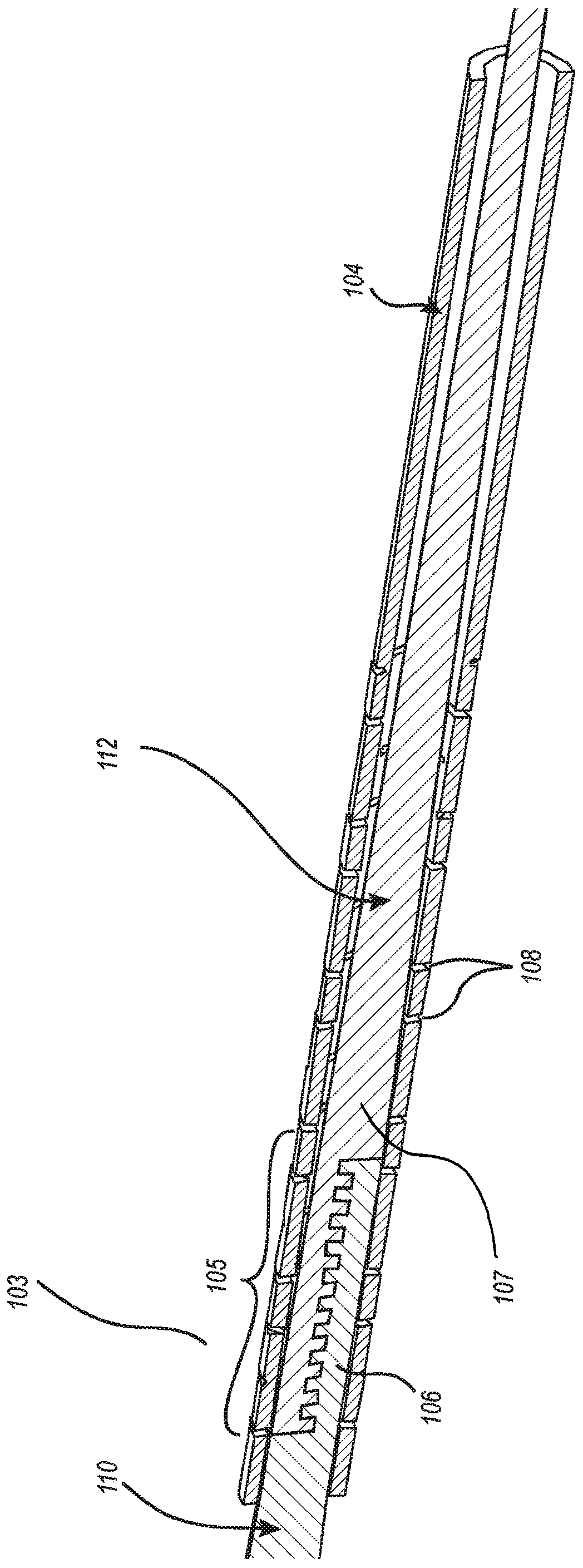
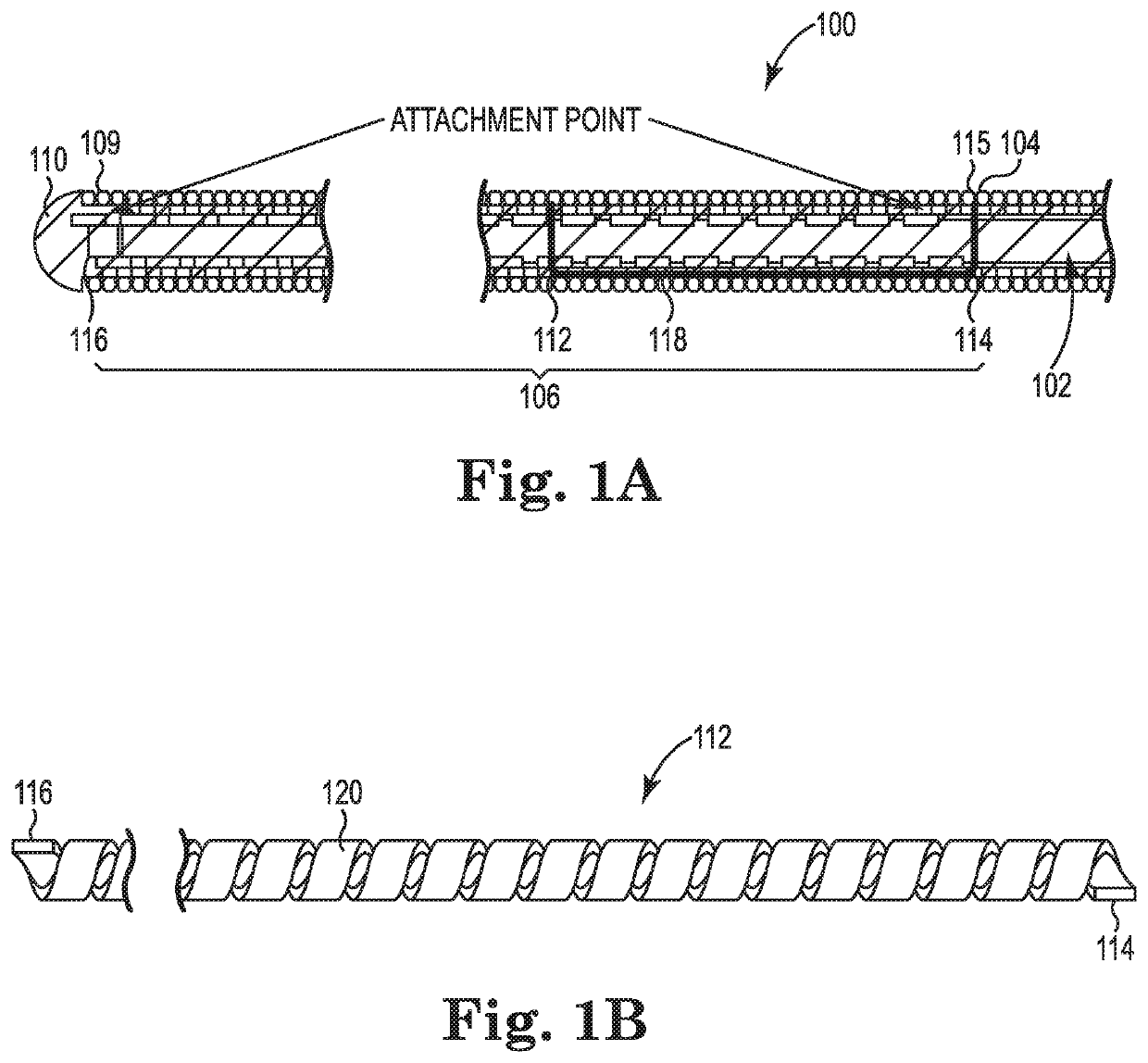
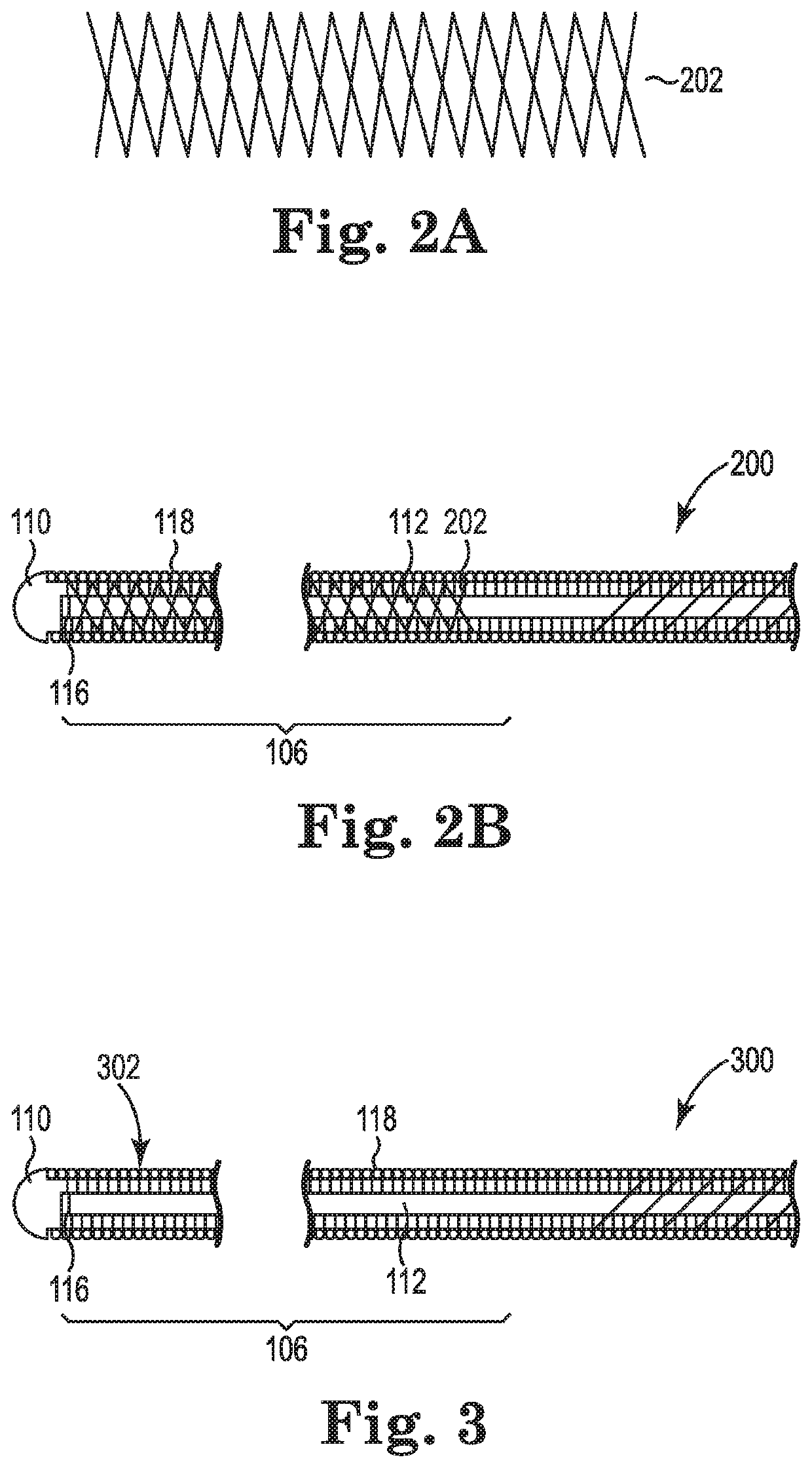
Core-wire joint with micro-fabricated medical devices
The present disclosure relates to core-wire joints for micro-fabricated medical devices, such as guidewires. A hybrid guidewire device includes a core (102) having a joint (105) between a proximal section (110) and a distal section (112) of the core and a tube structure (104) surrounding the joint. The proximal section of the core is made of or includes stainless steel and the distal section is made of or includes a superelastic material such as nitinol. Further, the terminal, distal portion of the proximal section of the core includes serrations (116), and a terminal, proximal portion of the distal section of the core includes complementary serrations (118) sized and shaped to interlock with serrations (116). The distal end of the proximal section mechanically interlocks with a proximal end the distal section to form the joint.
Owner:SCIENTIA VASCULAR INC
Fatigue-resistant Nitinol instrument
InactiveUS8714976B2Improve the immunityFew stepsMetal-working drilling toolsFurnace typesWire rodTitanium
A fatigue-resistant Nitinol instrument has a working portion in the deformed monoclinic martensitic state and an austenite finish temperature in the range of 40° to 60° C. Because the operating environment of the instrument is about 37° C., the working portion remains in the monoclinic martensitic state during its use. The relatively high austenite finish temperature and fatigue resistance is achieved by subjecting the nickel-titanium alloy to a final thermal heat treat in a temperature range of about 410° to 440° C. while the nickel-titanium alloy is under constant strain of about 3 to 15 kg. Further, the high austenite finish temperature is achieved without subjecting the alloy to thermal cycling to produce shape memory. Additionally, there are no intermediate processing steps occurring between obtaining a finished diameter of the wire or blank through cold working and the final thermal heat treat under constant strain.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
Fatigue-Resistant Nitinol Instrument
ActiveUS20140242543A1Improve the immunityFew stepsMetal-working drilling toolsWristbandsWire rodTitanium
A fatigue-resistant Nitinol instrument has a working portion in the deformed monoclinic martensitic state and an austenite finish temperature in the range of 40° to 60° C. Because the operating environment of the instrument is about 37° C., the working portion remains in the monoclinic martensitic state during its use. The relatively high austenite finish temperature and fatigue resistance is achieved by subjecting the nickel-titanium alloy to a final thermal heat treat in a temperature range of about 410° to 440° C. while the nickel-titanium alloy is under constant strain of about 3 to 15 kg. Further, the high austenite finish temperature is achieved without subjecting the alloy to thermal cycling to produce shape memory. Additionally, there are no intermediate processing steps occurring between obtaining a finished diameter of the wire or blank through cold working and the final thermal heat treat under constant strain.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
Prosthesis for anastomosis
InactiveUS20100082048A1Quick clampingEliminate contactSuture equipmentsBlood vesselsSide to side anastomosisDistal anastomosis
Prosthetic devices are provided that are used in end-to-side, end-to-end and side-to-side anastomosis without clamping and sutureless, without clamping and with suture, with clamping and sutureless, and / or with clamping and with suture, where the graft is inserted under the light of prosthesis or in at least one of the intraluminal portions of the prosthesis tubular member. The prosthesis can be produced in varied shapes and sizes to accommodate varied sizes and types of grafts, and also can be formed by two halves that can be joined by pressure, bolts or by a rocker portion, and can be made of any proper material for surgical use, such as titanium, stainless steel, nitinol, pyrolitic carbon, silicon, biodegradable materials, or any other biocompatible and inert materials.
Owner:GRANJA FILHO LUIZ GONZAGA
Variable stiffness guidewire
InactiveUS20180256860A1Distally-decreasing stiffnessFacilitate entryGuide wiresVariable stiffnessEngineering
The core element for a guidewire comprises a proximal stainless steel portion and a distal nitinol portion. The distal nitinol portion comprises a proximal segment of an at least partially linear elastic nitinol and a distal segment of a super elastic nitinol. The proximal end of a first spring coil contacts the super elastic nitinol with the first spring coil distal end being proximal the distal end of the distal segment of the super elastic nitinol. A second spring coil has a proximal portion that contacts the first spring coil distal end at a spring coil connection. Further, the second spring coil extends distally to an atraumatic tip. Extending radially from a longitudinal axis of the core wire, the first and second spring coils are spaced from and circumferentially unsupported by the distal nitinol core portion at the spring coil connection.
Owner:LAKE REGION MFG
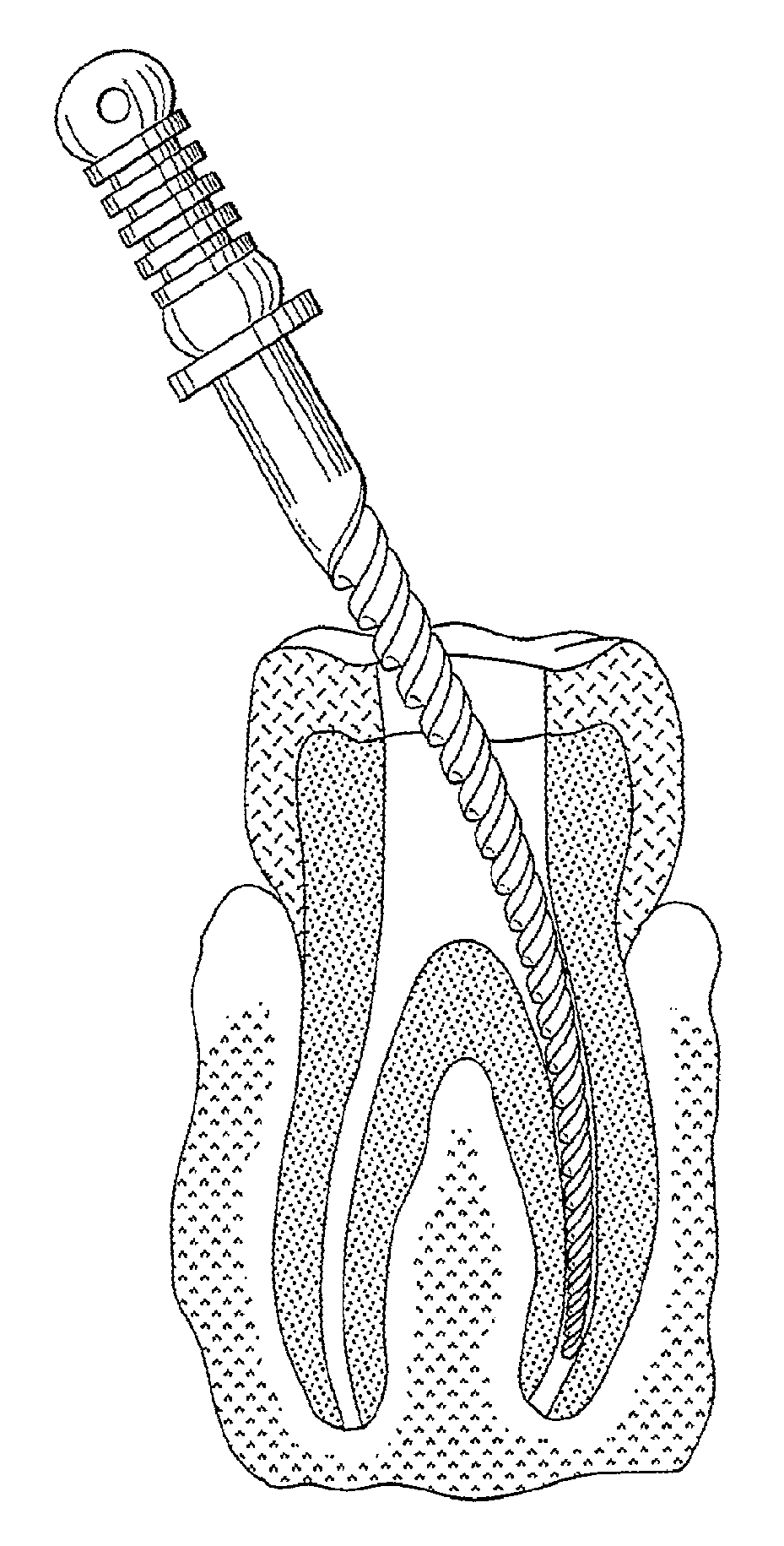
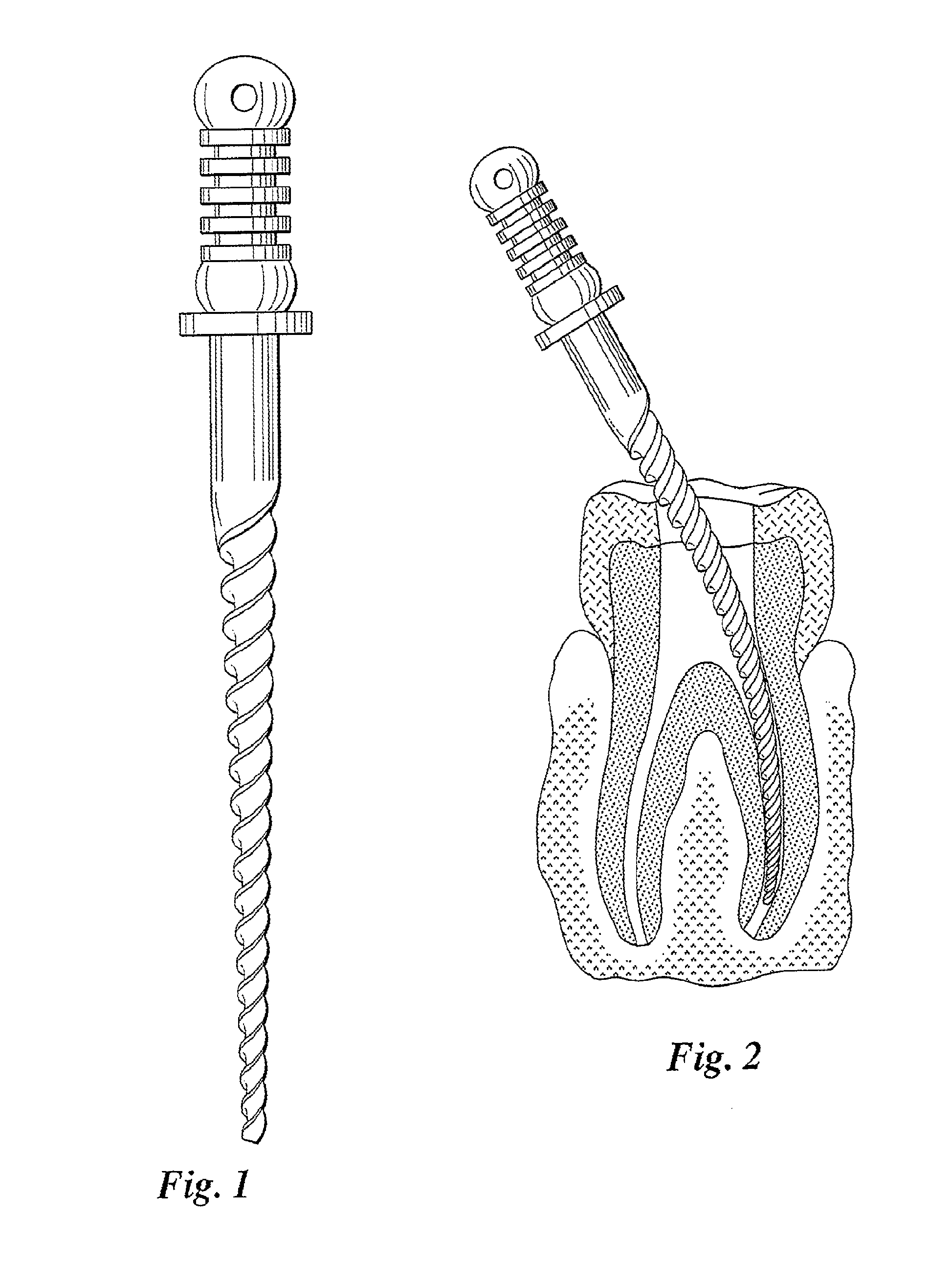
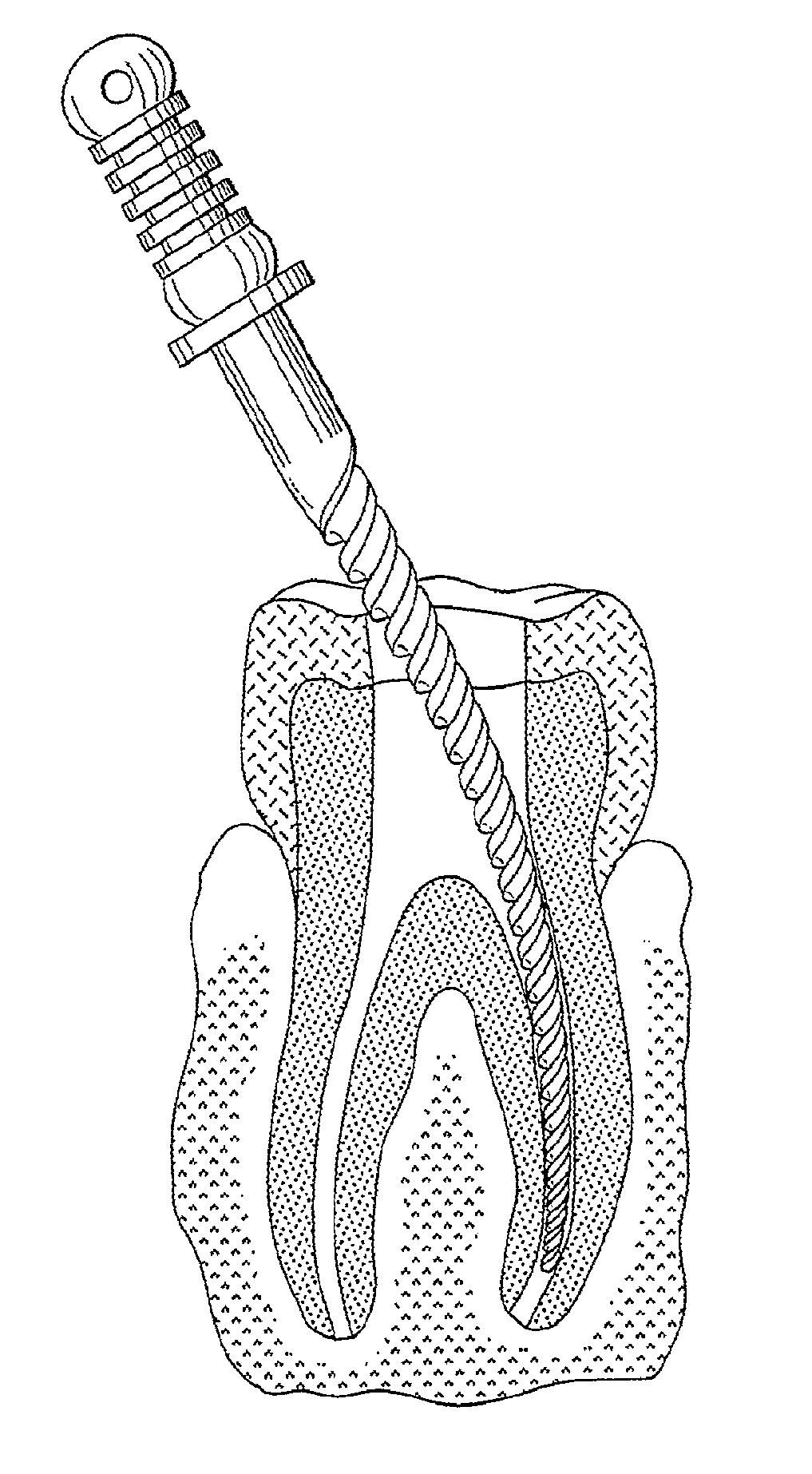
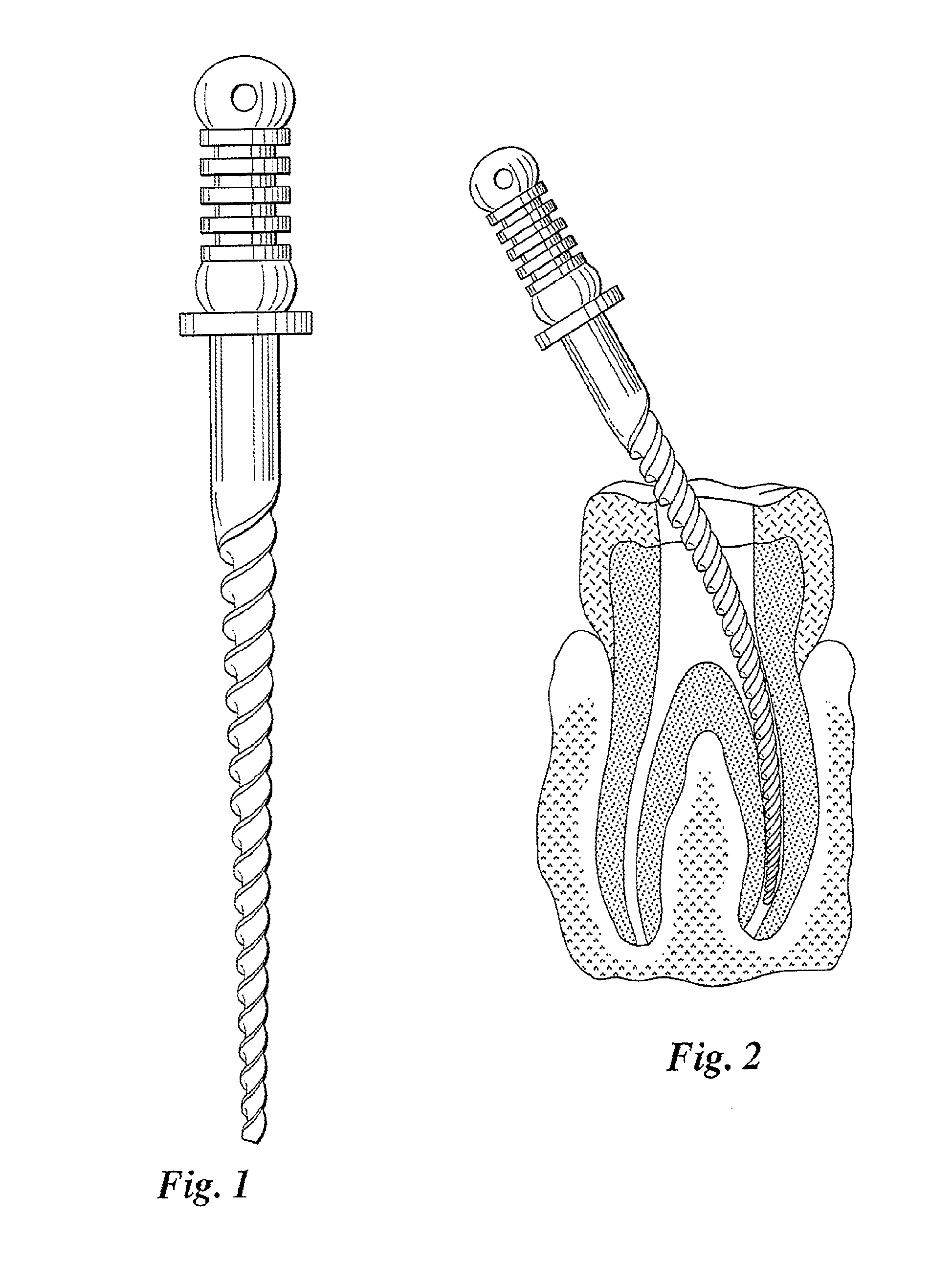
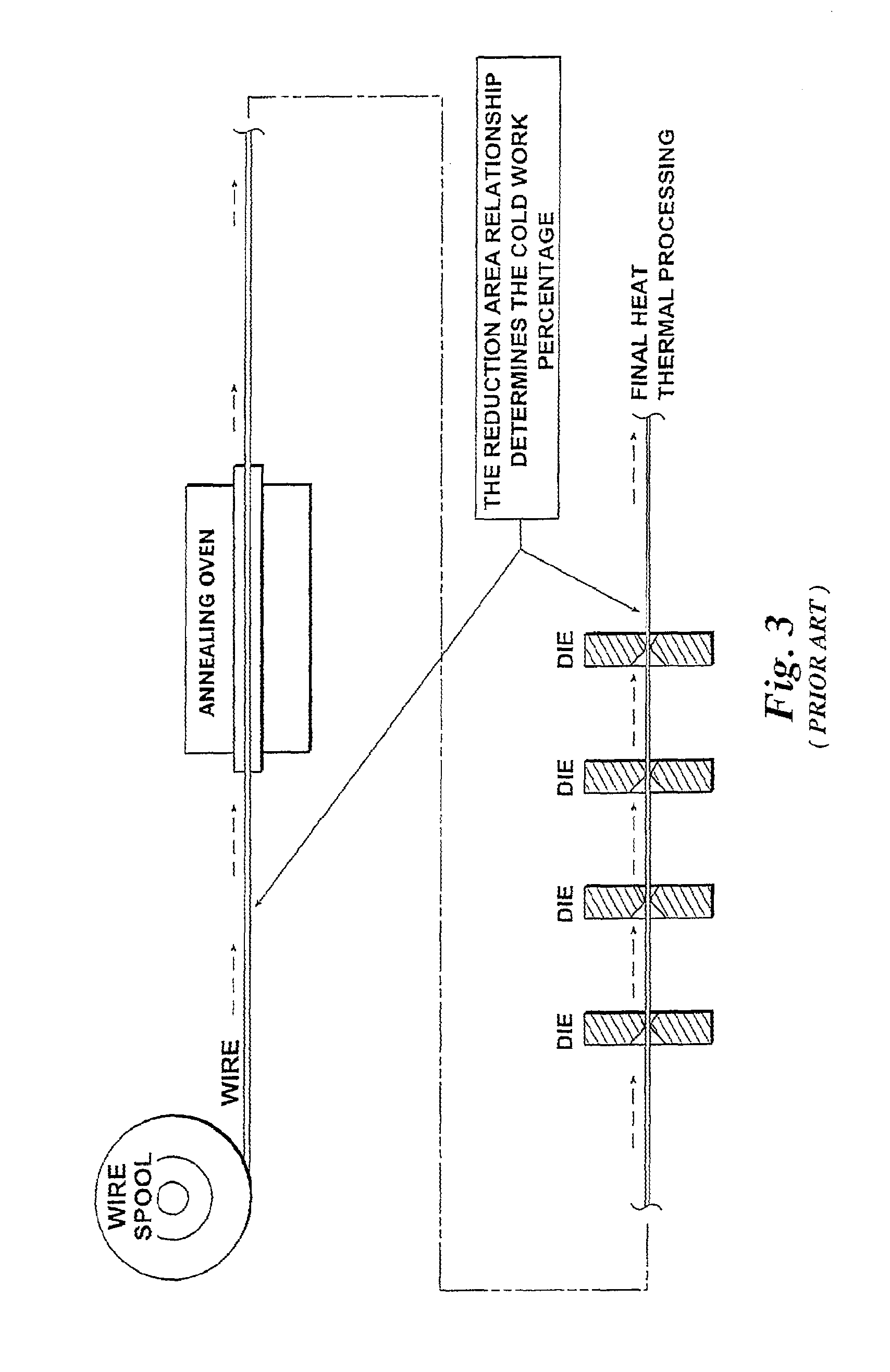
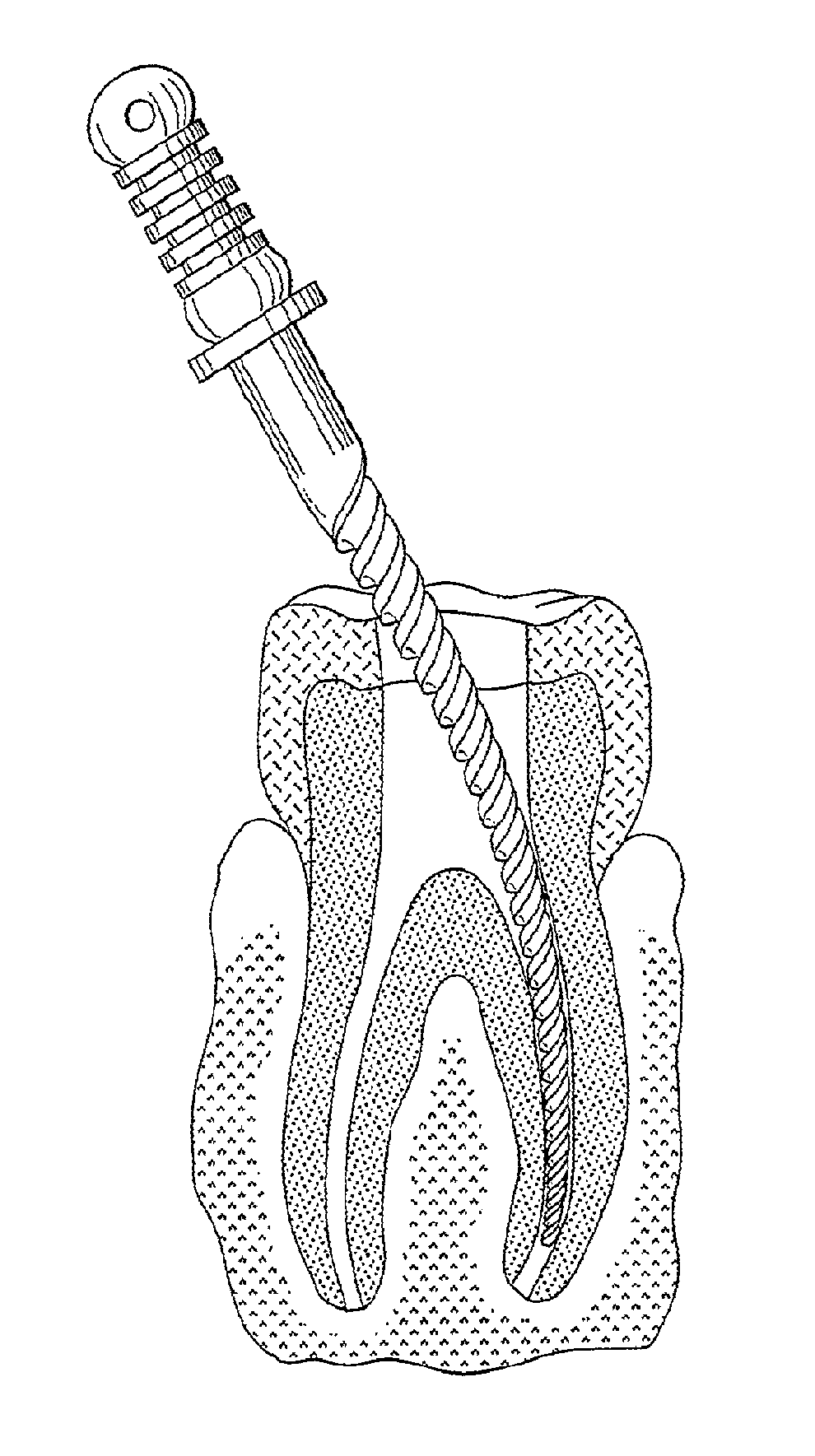
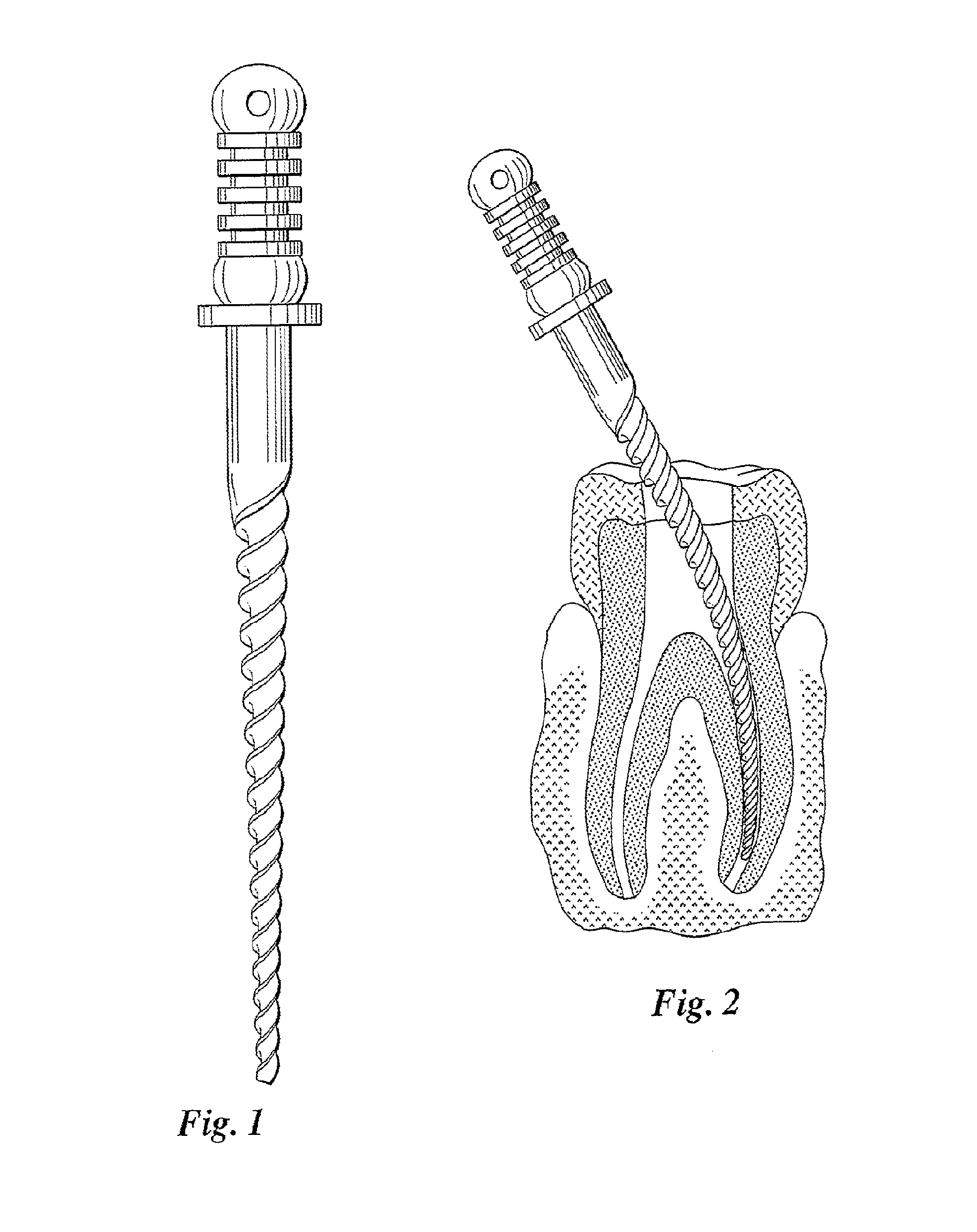
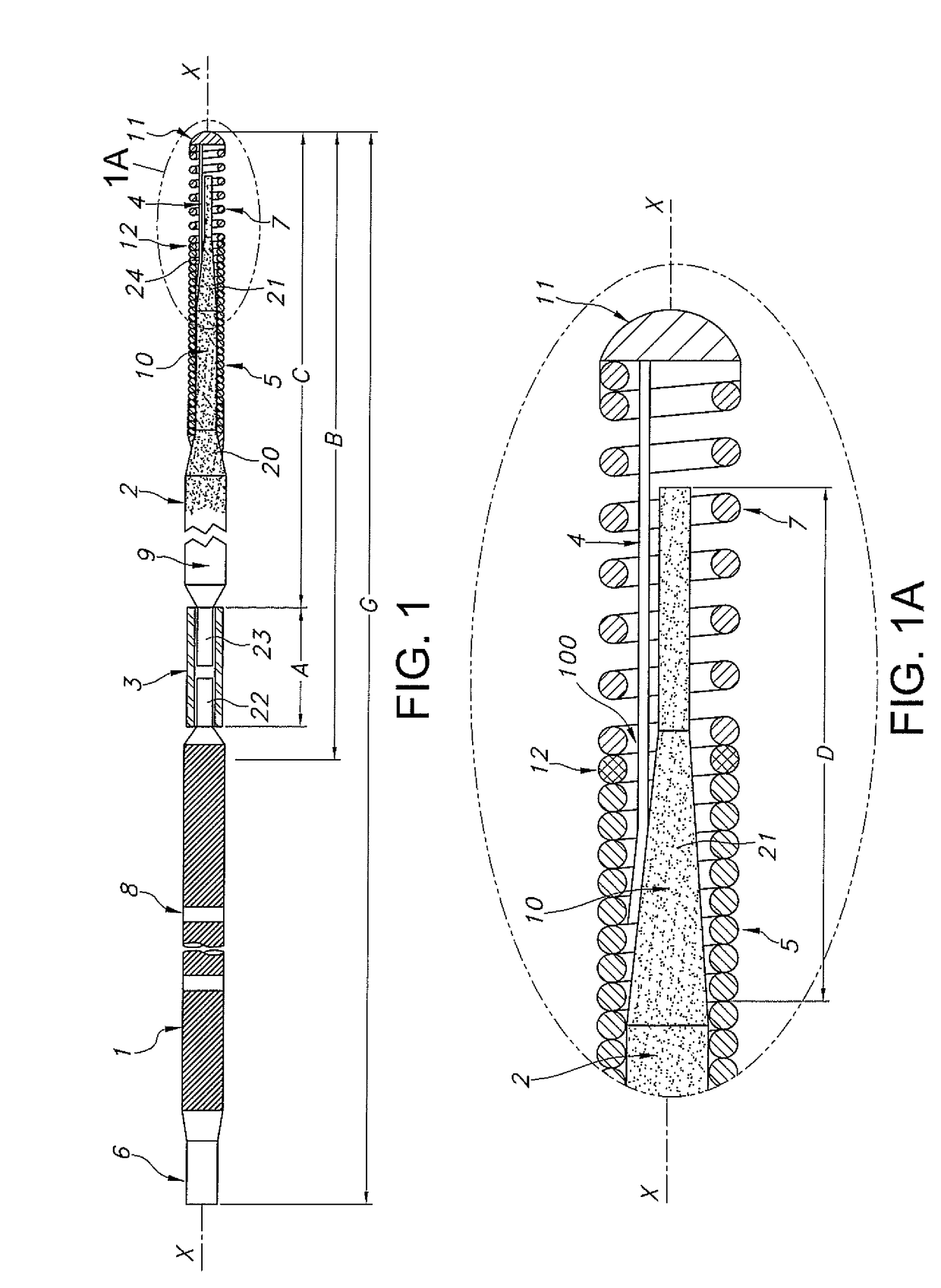
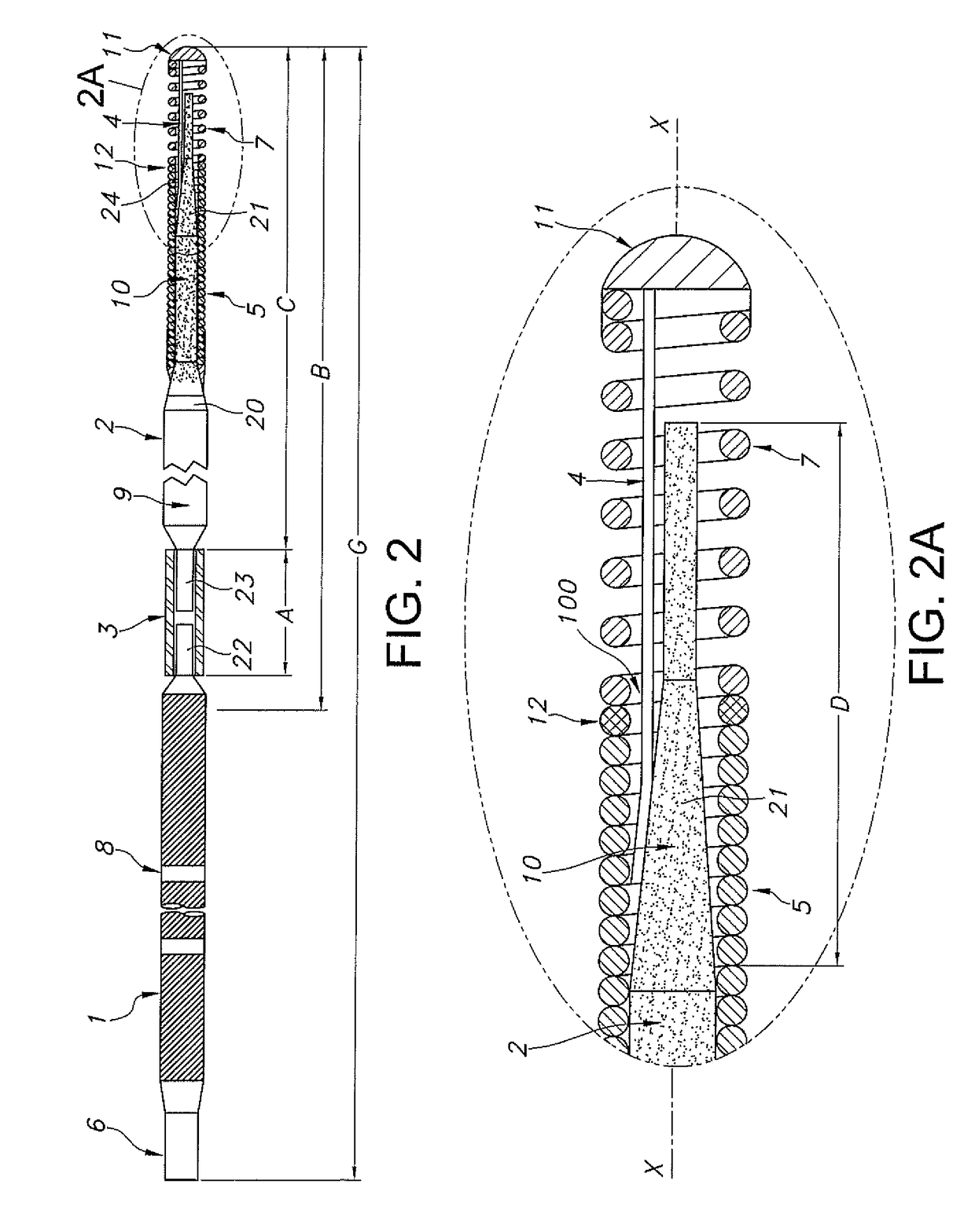
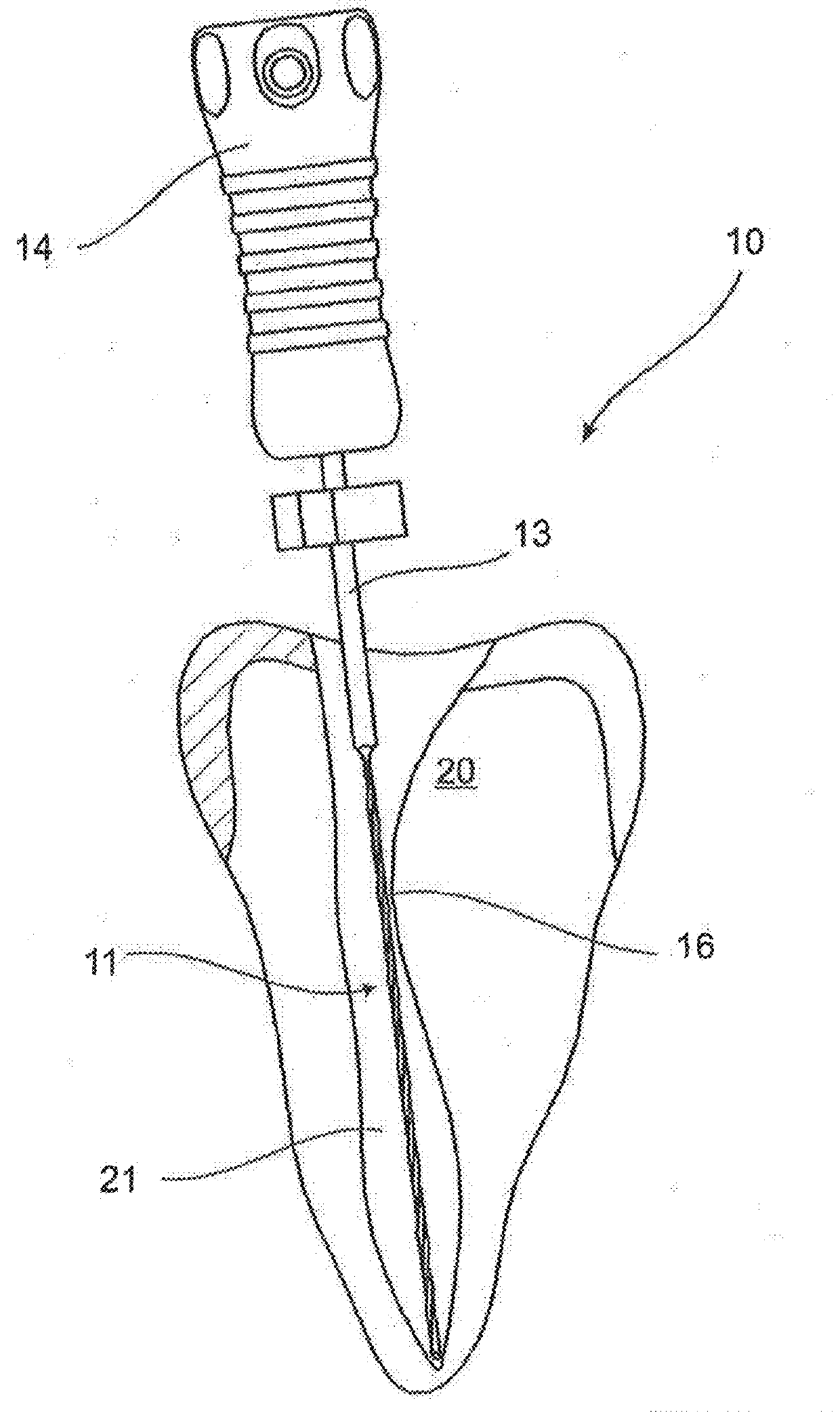
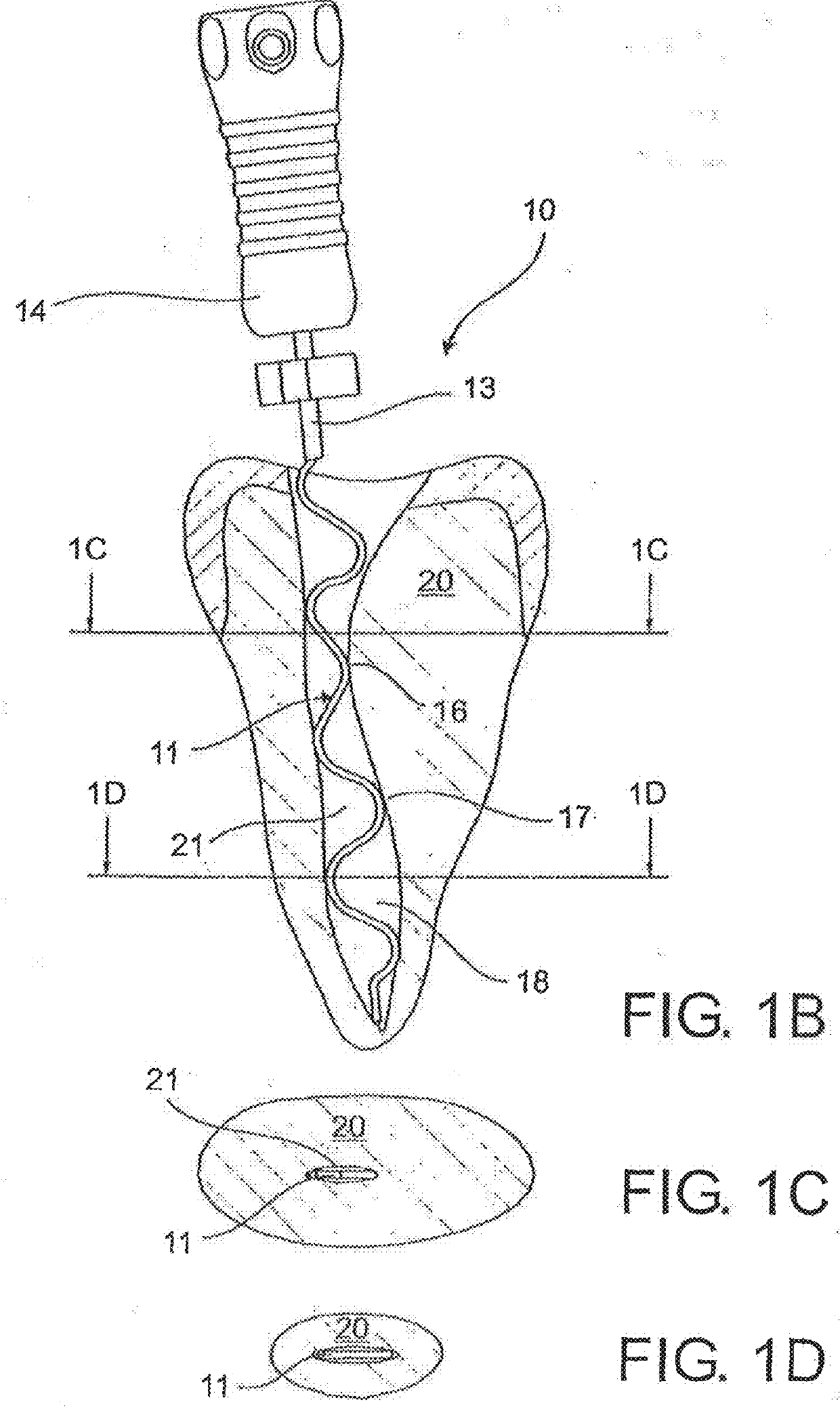
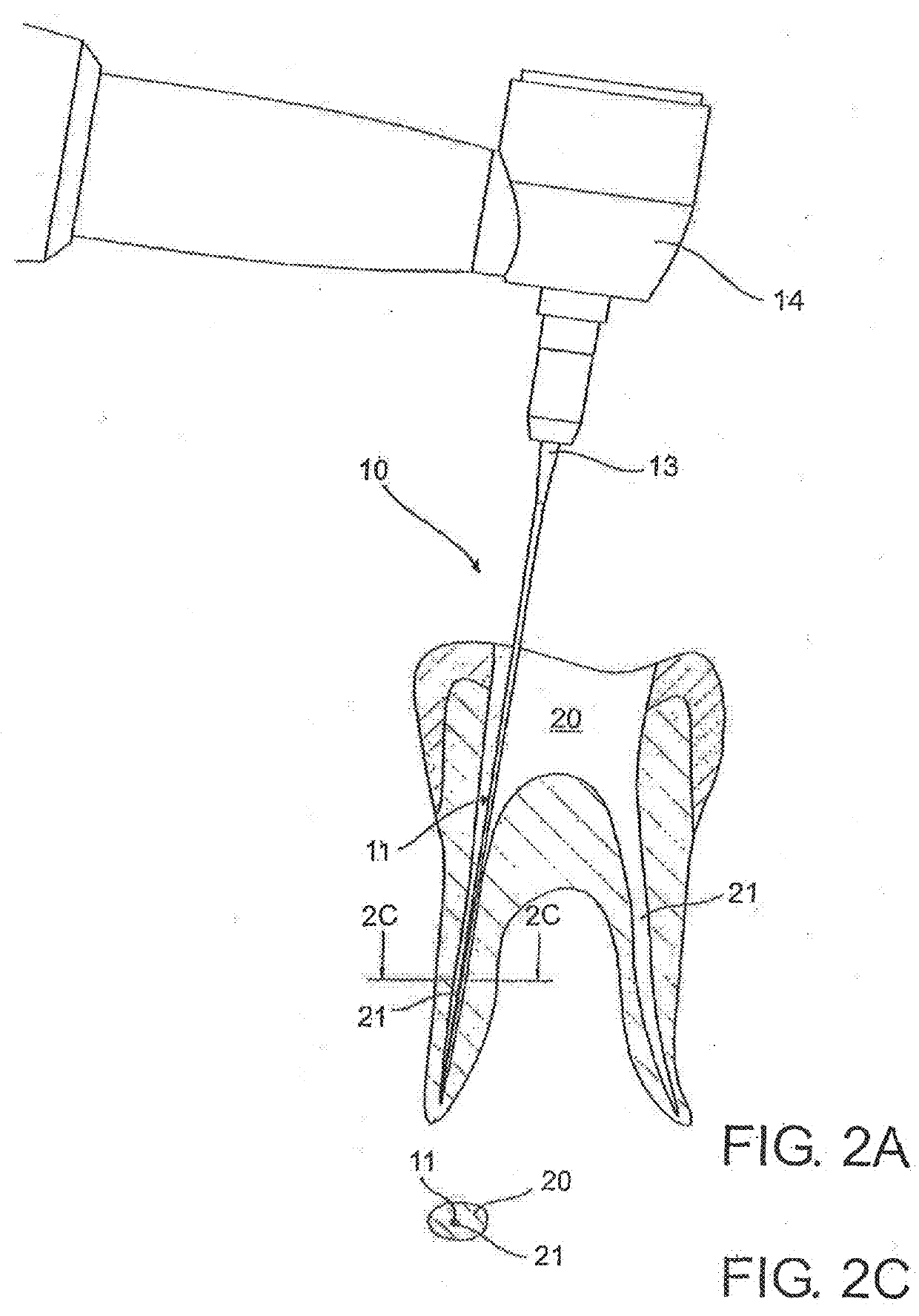
Endodontic instrument for drilling the root canals of a tooth
A method of forming a dental tool or instrument having a memorized shape. The method comprises selecting a nitinol wire having an initial transition temperature below room temperature; grinding the nitinol wire to form the dental tool or instrument so as to have a shank, located adjacent a first end, and a working area, with at least one cutting edge, located adjacent an opposite second leading end; molding the working area into a molded shape having at least one protrusion formed therein; heating the dental tool or instrument to both: a) alter the initial transition temperature of the dental tool or instrument to a final transition temperature, and b) memorize the Molded shape including the at least one protrusion so that the dental tool or instrument will automatically return to the molded shape having the at least one protrusion when at a temperature at or above the final transition temperature.
Owner:FKG DENTAIRE SARL
Working wire for a biological sensor
A working wire for a biological sensor is disclosed. The working wire includes a substrate comprising cobalt-chromium (Co—Cr) alloy or Nitinol alloy, a platinum layer comprising platinum on the substrate, and a membrane layer comprising a biological membrane applied over the platinum layer.
Owner:ZENSE LIFE INC
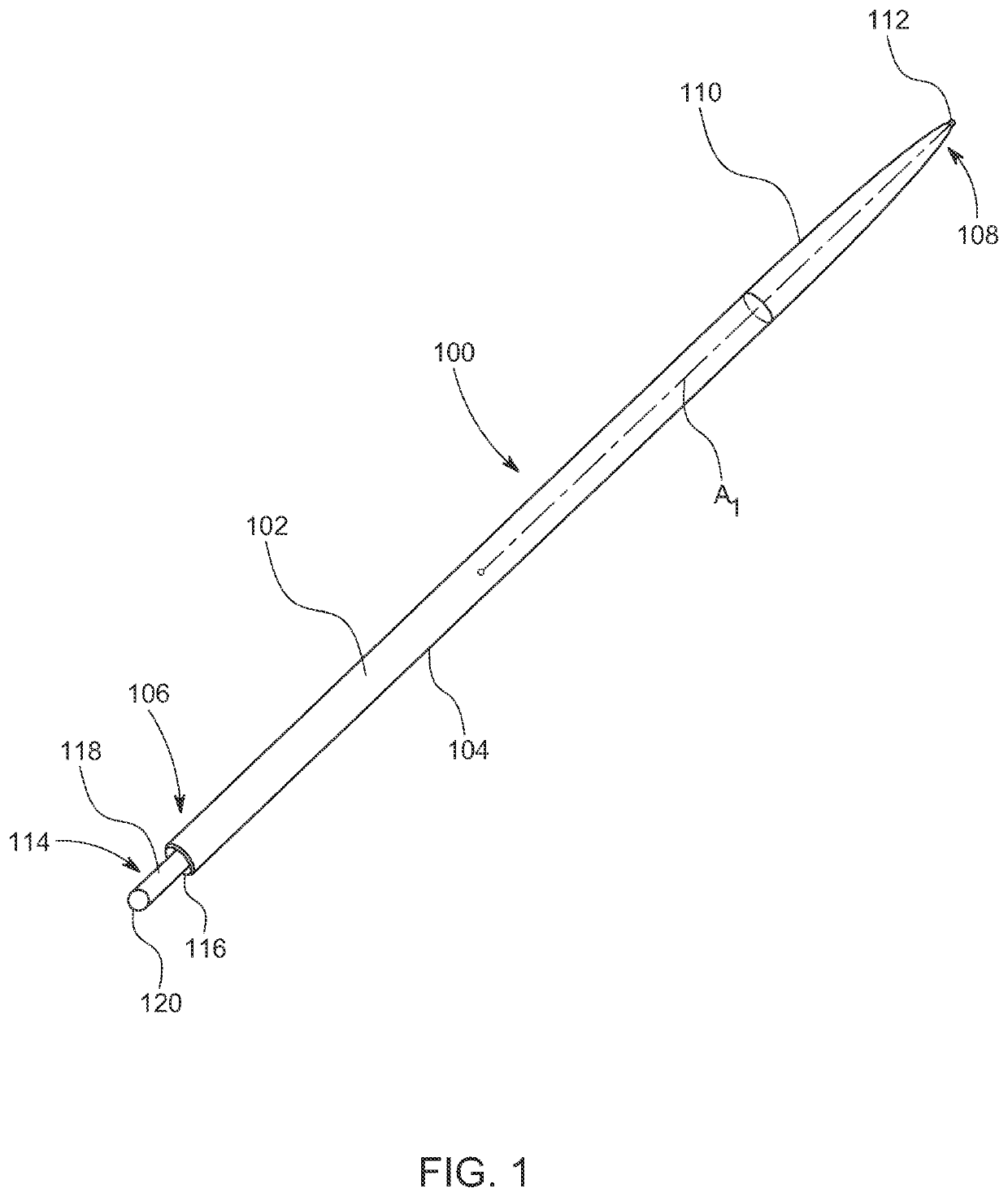
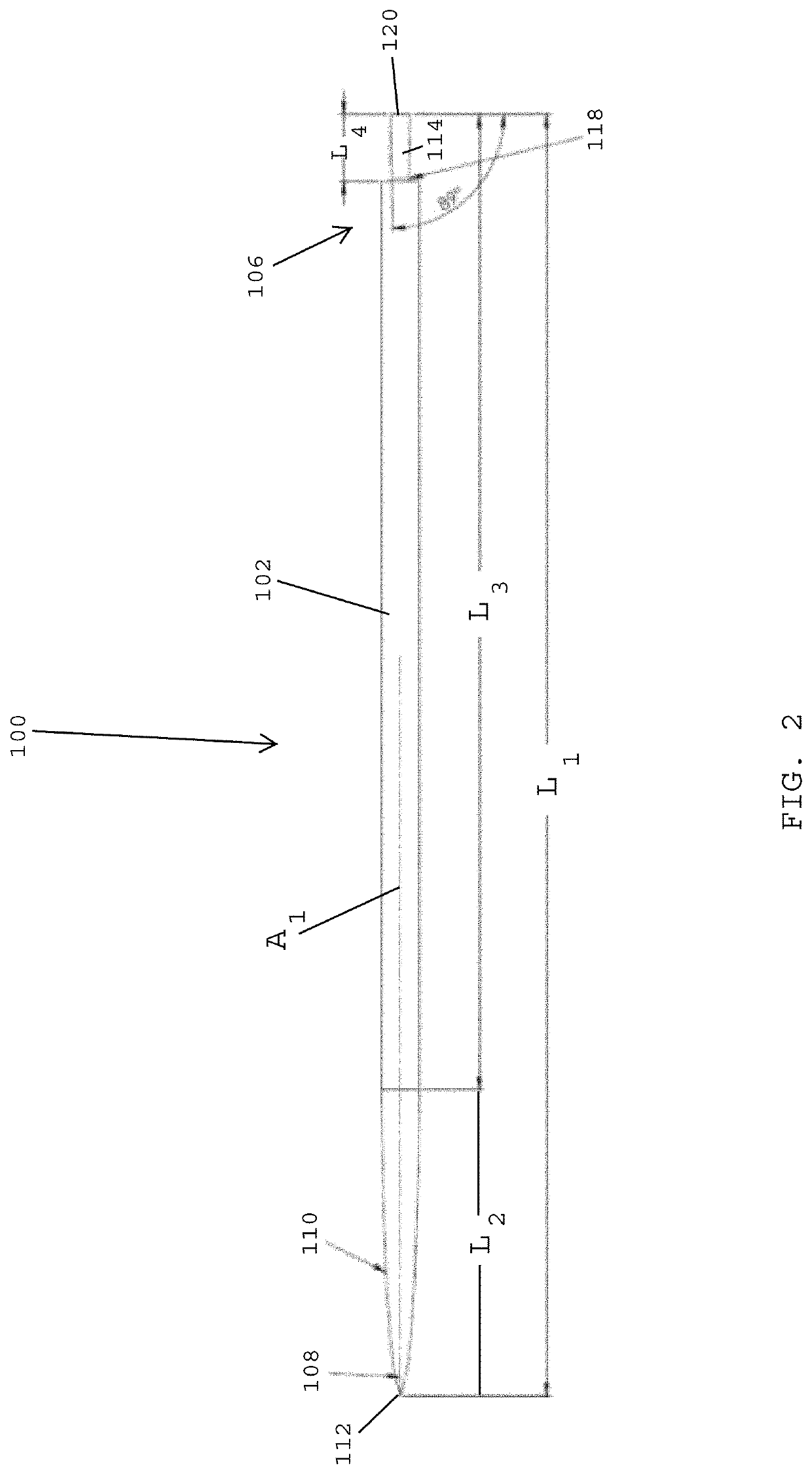
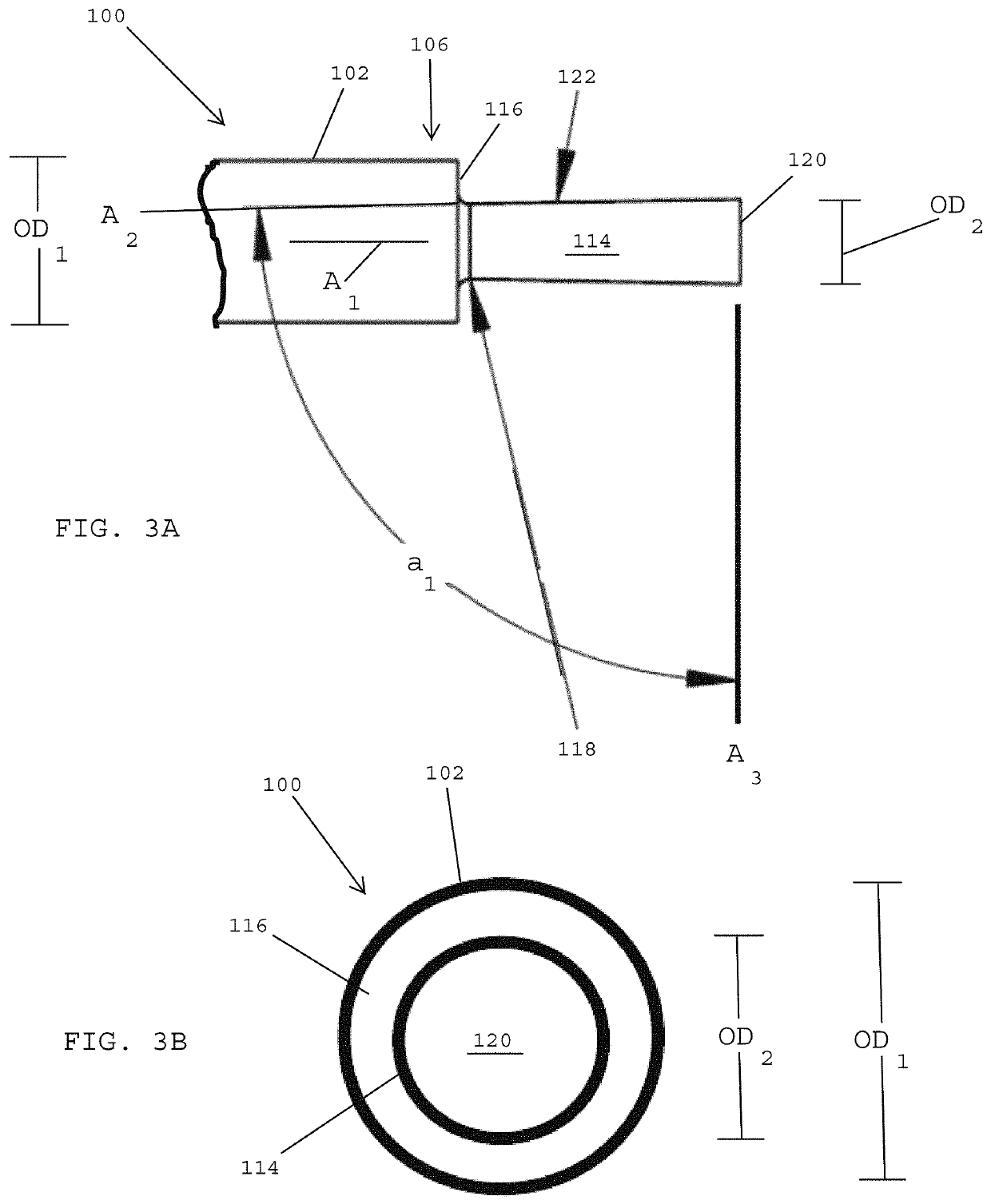
Systems, devices and methods for securing sutures to surgical needles made of superelastic materials
ActiveUS20200268375A1Easy to transportSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSurgeryBiomedical engineering
A needle and suture assembly includes a needle made of a superelastic alloy, such as Nitinol, including an elongated body having a proximal end and a distal end with a sharpened tip, a suture having a free end juxtaposed with the proximal end of the elongated body of the needle, and a connector disposed between the needle and the suture. The connector includes a first end attached to the proximal end of the elongated body of the needle and a second end attached to the free end of the suture. The connector is made of a material, such as stainless steel, having less elasticity and greater plasticity than the superelastic alloy of the needle.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Hybrid shape memory effect elements for facile integration to structures
ActiveUS10543533B2Thin material handlingMetal layered productsSelf-propagating high-temperature synthesisMetallurgy
There is disclosed a method for chemically bonding TiNi materials to Nitinol constructs, comprising placing a Nitinol construct within a mold and packing a powder combination comprising Ti powder and Ni powder, and powder comprised of zero or more of the elements Cu, Hf, Zr, Pt, Pd, Au, Cd, Ag, Nb, Ta, O, N, B, and H, into the mold. The method further includes initiating a process of self-propagating high temperature synthesis of the powder combination within the mold to create a chemical bond between the Nitinol construct and a resulting TiNi foam to thereby create a Nitinol and TiNi assembly.
Owner:SHAPE CHANGE TECH
Metal plate with one-way shape memory effect
A metal plate contains a shape memory alloy (e.g., a nitinol alloy) capable of exhibiting the one-way memory effect.
Owner:CLEVELAND STATE UNIVERSITY
Core-wire joint with micro-fabricated medical devices
The present disclosure relates to core-wire joints for micro-fabricated medical devices, such as guidewires. A hybrid guidewire device includes a core (102) having a joint (105) between a proximal section (110) and a distal section (112) of the core and a tube structure (104) surrounding the joint. The proximal section of the core is made of or includes stainless steel and the distal section is made of or includes a superelastic material such as nitinol. Further, the terminal, distal portion of the proximal section of the core includes serrations (116), and a terminal, proximal portion of thedistal section of the core includes complementary serrations (118) sized and shaped to interlock with serrations (116). The distal end of the proximal section mechanically interlocks with a proximal end of the distal section to form the joint.
Owner:SCIENTIA VASCULAR INC
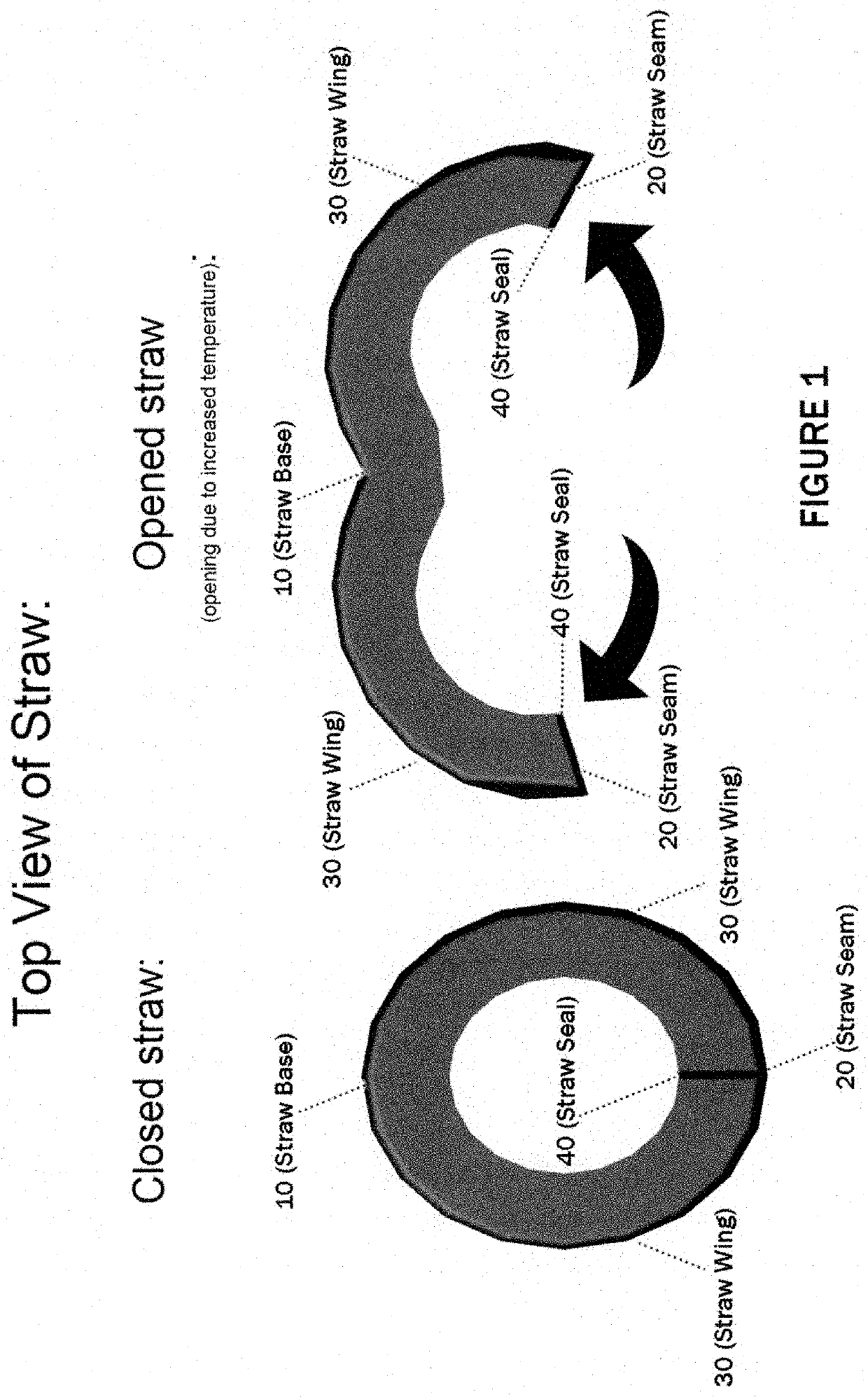
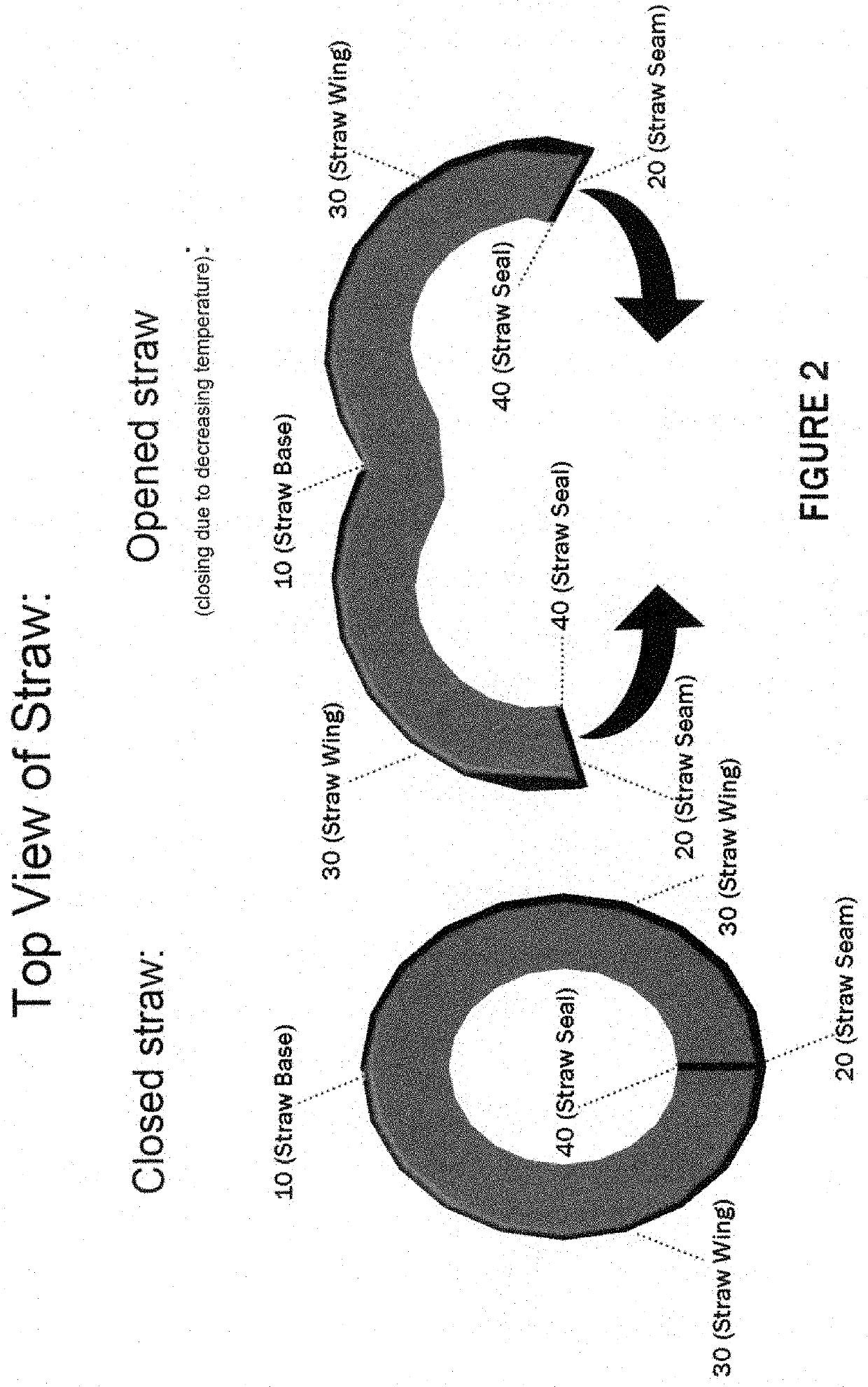
Temperature activated unfolding structure for drinking straws and other enclosed containers
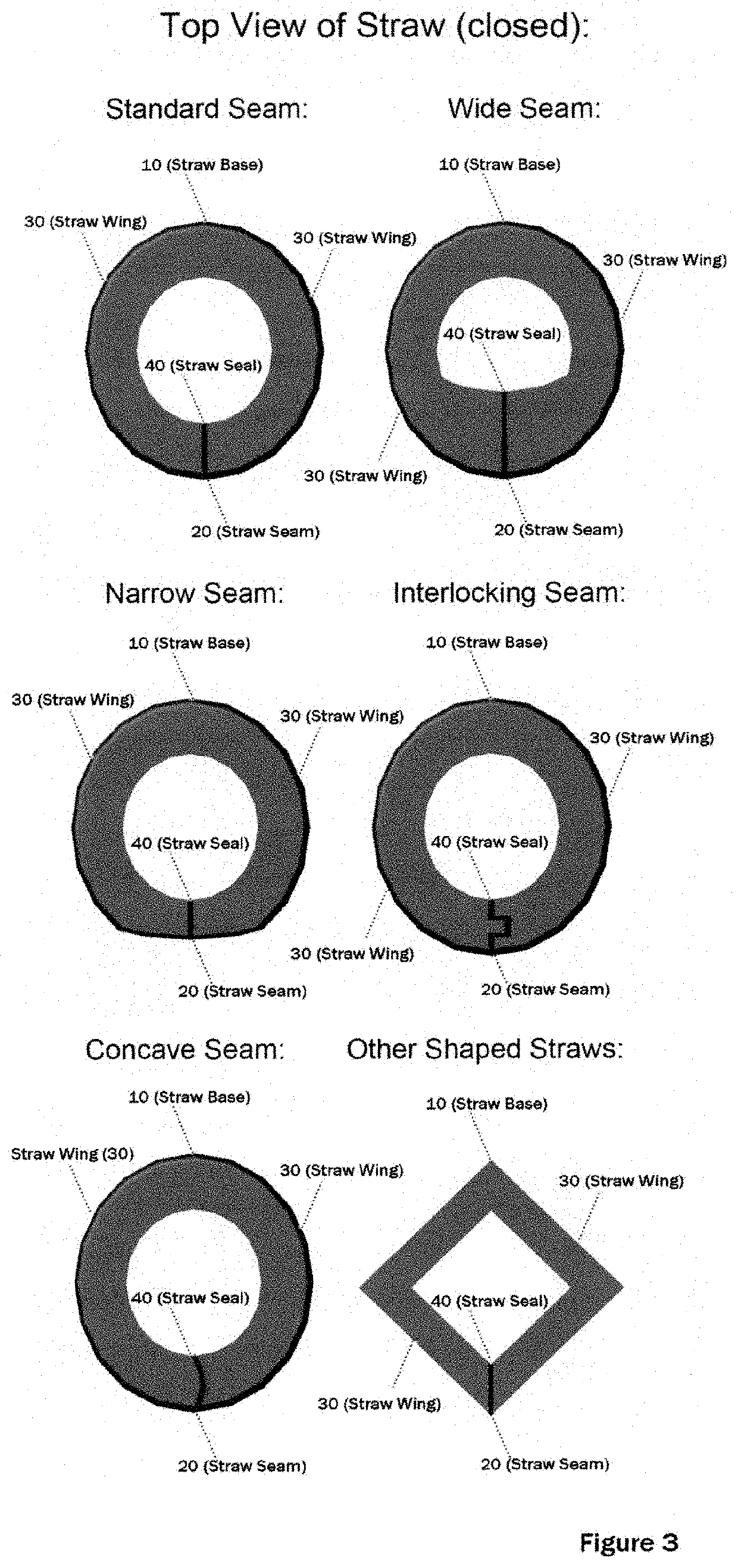
InactiveUS20220073234A1Promote sheddingMachines/enginesContainer/bottle contructionDrinking strawMechanical engineering
A machine for opening drinking straws and / or other enclosed containers using temperature changes. In the drinking straw variety, the straw is made in part or in full by Nitinol (also known as nickel titanium), Shape Memory Material, or similar such material that allows for the change in the straw's shape (known as the parent phase) in the elevated temperature of a dishwashing machine or similar machine using the Nitinol's or Shape Memory Material's reversible solid-state phase change (known as a martensitic transformation). When the straw is returned to room temperature, the straw closes to its original shape (known as its daughter phase) allowing it to be used as a standard straw. The container variety uses the same method but adapts it for container shapes. This phase change allows for lodged materials in the straw and / or container to be easily dislodged by the object opening in the dishwasher.
Owner:HALE III RICHARD THOMAS
Method For Making A Guidewire From A Drawn-Filled Tube Of A Stainless Steel Sheath Jacketing A Nitinol Core Wire
PendingUS20210379341A1Lacking pushabilityLess supportingGuide wiresMedical devicesWire rodSS - Stainless steel
A guidewire made from a drawn-filled tube composite wire is described. The composite wire has a stainless steel outer sheath jacketing a nitinol core wire. The drawn-filled tube composite wire is ground at its distal end to expose the nitinol core, which has superelastic and kink resistant properties that are desirable for the distal end of a guidewire. The proximal end of the drawn-filled tube is not ground or if ground, the outer sheath of stainless steel is not removed to an extent sufficient to expose the nitinol core.
Owner:LAKE REGION MEDICAL INC
Stationary phase for solid-phase microextraction device
ActiveUS11433372B1Synthetic is simpleImprove efficiencyOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationMetal-organic frameworkTitanium alloy
Owner:UNIV DE LA LAGUNA - OTRI
Expandable inter-vertebral cage and method of installing same
ActiveUS10828171B2Facilitate proper securingSmall shapeJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral spacesShape-memory alloy
An intervertebral cage includes a plurality of segments that are connected together by one or more members formed from a shape memory alloy material such that the segments are automatically moved from an initial orientation before implantation / insertion in an intervertebral space to an expanded orientation after implantation / insertion in the intervertebral space. Each of the plurality of segments may have a plurality of passageways or recesses formed therethrough, and wherein a wire formed from a shape memory alloy material extends through each of the plurality of passageways or recesses. The member may be formed from a shape memory alloy material that demonstrates shape memory effects and superelasticity properties, such as nitinol.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Annuloplasty device and methods
ActiveUS10980635B2Improve sealingReduce the overall diameterBalloon catheterAnnuloplasty ringsNitinol stentBiomedical engineering
An annuloplasty device formed from a Nitinol stent frame that expands into contact with the annulus above the native leaflets. A torus balloon activates barbs along the perimeter to fasten the stent frame to the annulus. A cinch ring is placed under tension to reduce the perimeter of the stent frame. The cinch ring and torus balloon are implanted along with the stent frame.
Owner:DRASLER WILLIAM JOSEPH +1
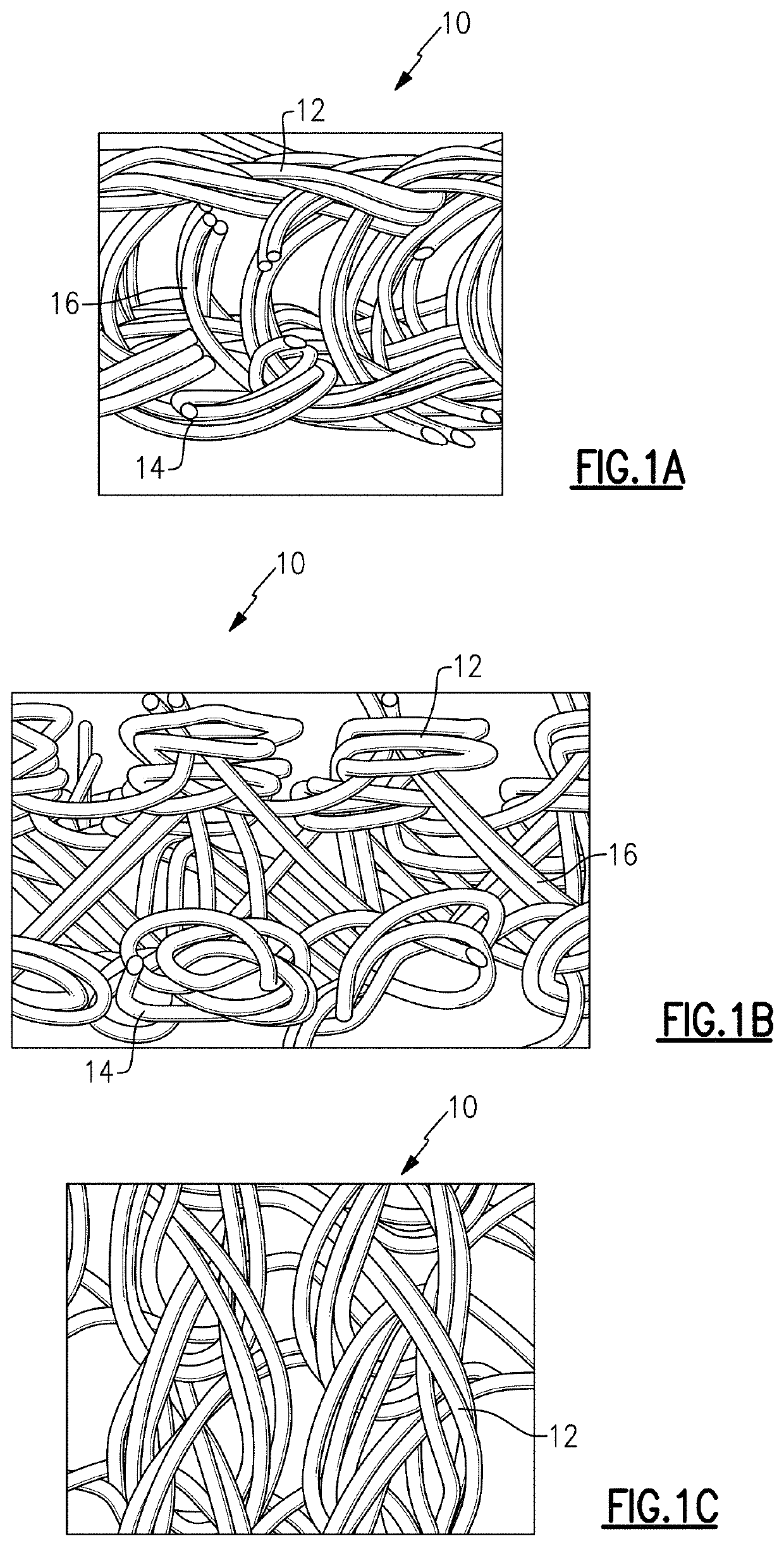
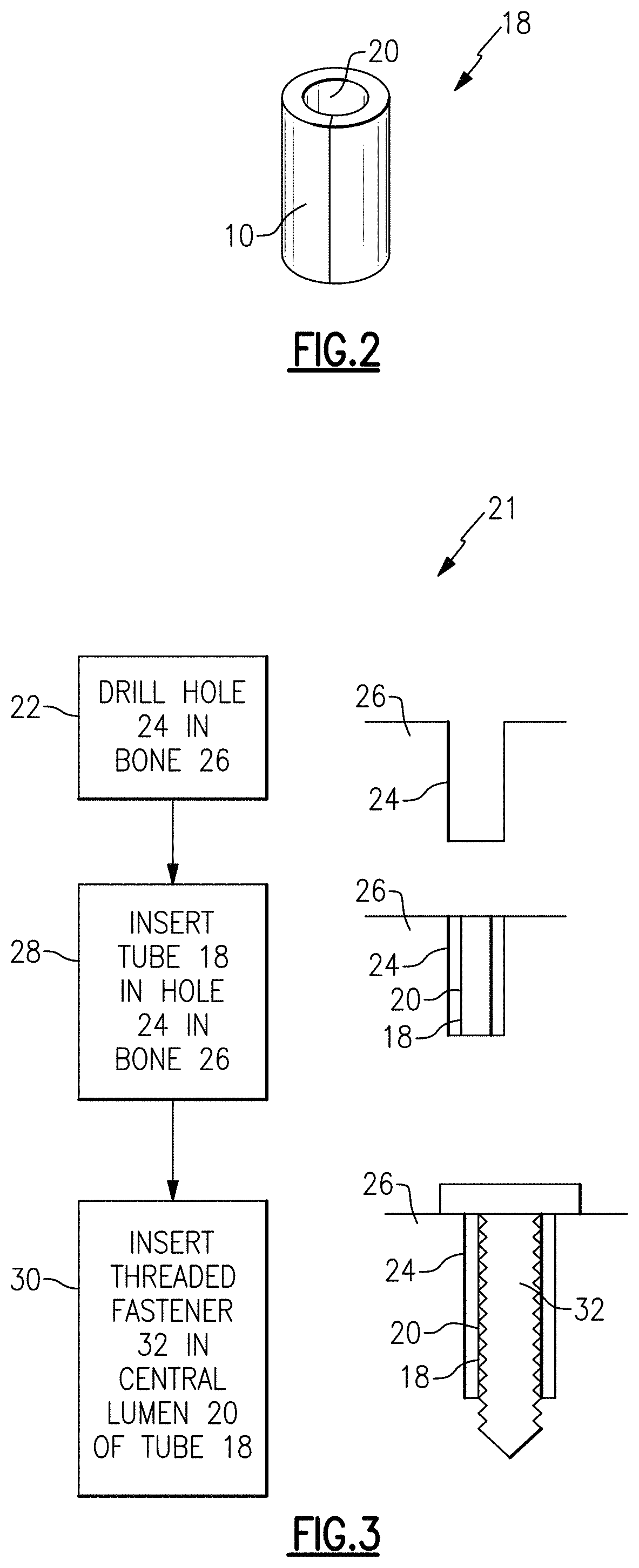
Three dimensional spacer fabric to increase the holding power of screws
ActiveUS10524837B2Improve pullout forceInternal osteosythesisProsthesisOsteoporotic boneBone quality
Owner:ARTHREX
Improved tissue fixation device
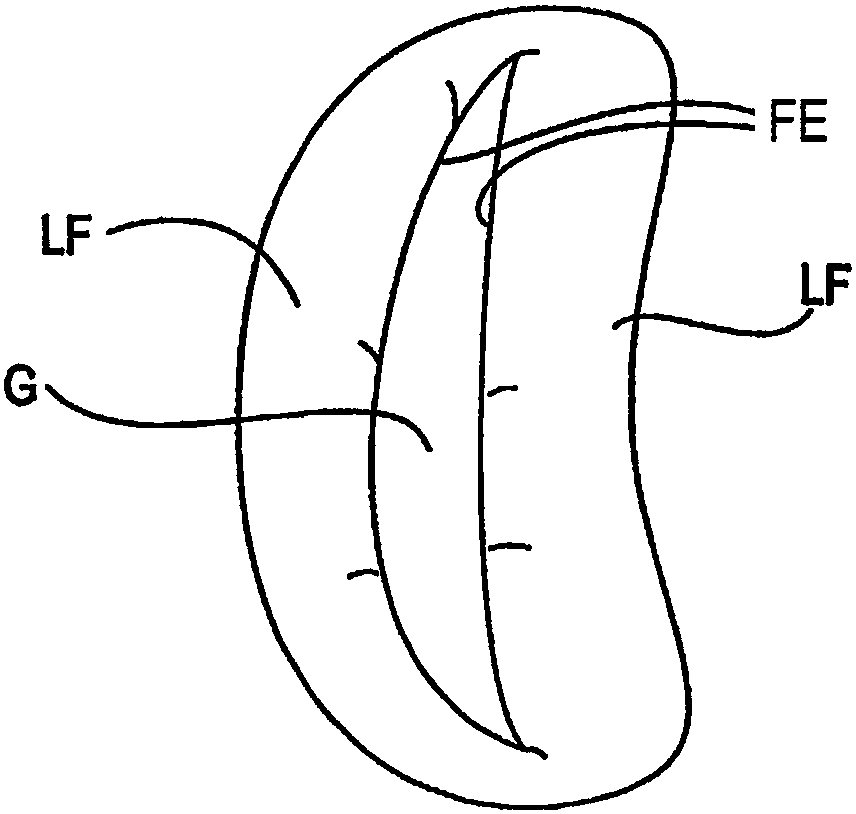
The present disclosure describes tissue grasping devices, systems, and methods for grasping mitral valve tissue during treatment of the mitral valve and when implanting a tissue fixation device into the mitral valve. The tissue grasping device includes a flexible member and one or more tissue grasping members coupled to one or more arms of the flexible member. The flexible member is formed from a shape memory material, such as Nitinol, and the tissue grasping member is formed from a material that is harder than the shape memory material. The tissue grasping member is secured by threading or looping suture around and / or through the tissue grasping member and the flexible member and / or by applying a covering material to the tissue grasping device to hold the tissue grasping member against the flexible member. Attached to the flexible member.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Apparatuses and methods for endoscopic tool joints
Embodiments of the present disclosure are directed to apparatuses, devices, and methods for secure connections between tubular structures. In one implementation, a first tube constructed of nitinol may have windows formed on an end thereof. A second tube constructed of stainless steel tube may be inserted within the first tube, and the windows may be filled with adhesive or solder. The adhesive or solder may bond with the first tube, forming connection pins which secure the tubes together. In some embodiments, the connected tubes may form an endoscopic needle. The nitinol portion of the needle may be sufficiently flexible for positioning within the bending section of an endoscope without deformation. The stainless steel portion of the needle may render the needle significantly less expensive than prior needles constructed solely of nitinol.
Owner:HOYA CORP
System for securing a clock movement in a watch case
PendingCN109782567AClockwork casesShock protection arrangementShape-memory alloyStructural engineering
The system (10) for fixing a timepiece movement (2) to a watch case (30) element (3) comprises at least one clamp (1), in particular at least two clamps, preferably three clamps or four clamps, whichis intended to come into contact firstly with the movement and secondly with the watch case element, the at least one clamp being made of a superelastic alloy and / or of a shape memory alloy, particularly of a nickel-titanium alloy such as Nitinol.
Owner:ROLEX SA
Systems, devices and methods for securing sutures to surgical needles made of superelastic materials
ActiveUS11272923B2Easy to transportSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesBiomedical engineeringMaterials science
A needle and suture assembly includes a needle made of a superelastic alloy, such as Nitinol, including an elongated body having a proximal end and a distal end with a sharpened tip, a suture having a free end juxtaposed with the proximal end of the elongated body of the needle, and a connector disposed between the needle and the suture. The connector includes a first end attached to the proximal end of the elongated body of the needle and a second end attached to the free end of the suture. The connector is made of a material, such as stainless steel, having less elasticity and greater plasticity than the superelastic alloy of the needle.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Reformable guidewire tip
ActiveUS10806905B2Reduce riskIncrease resistanceGuide wiresMedical devicesHigh speed rotational atherectomyEngineering
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com