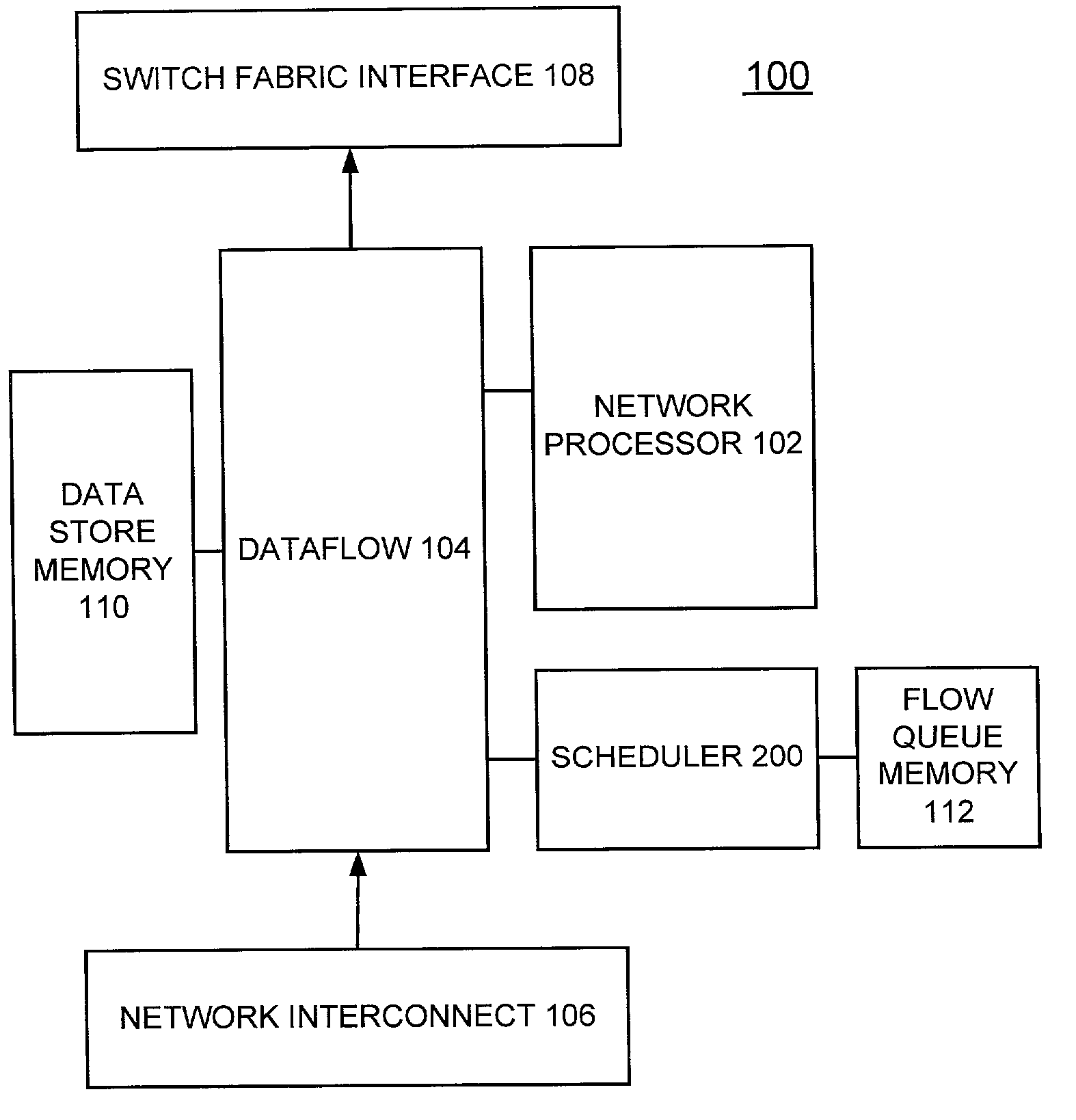
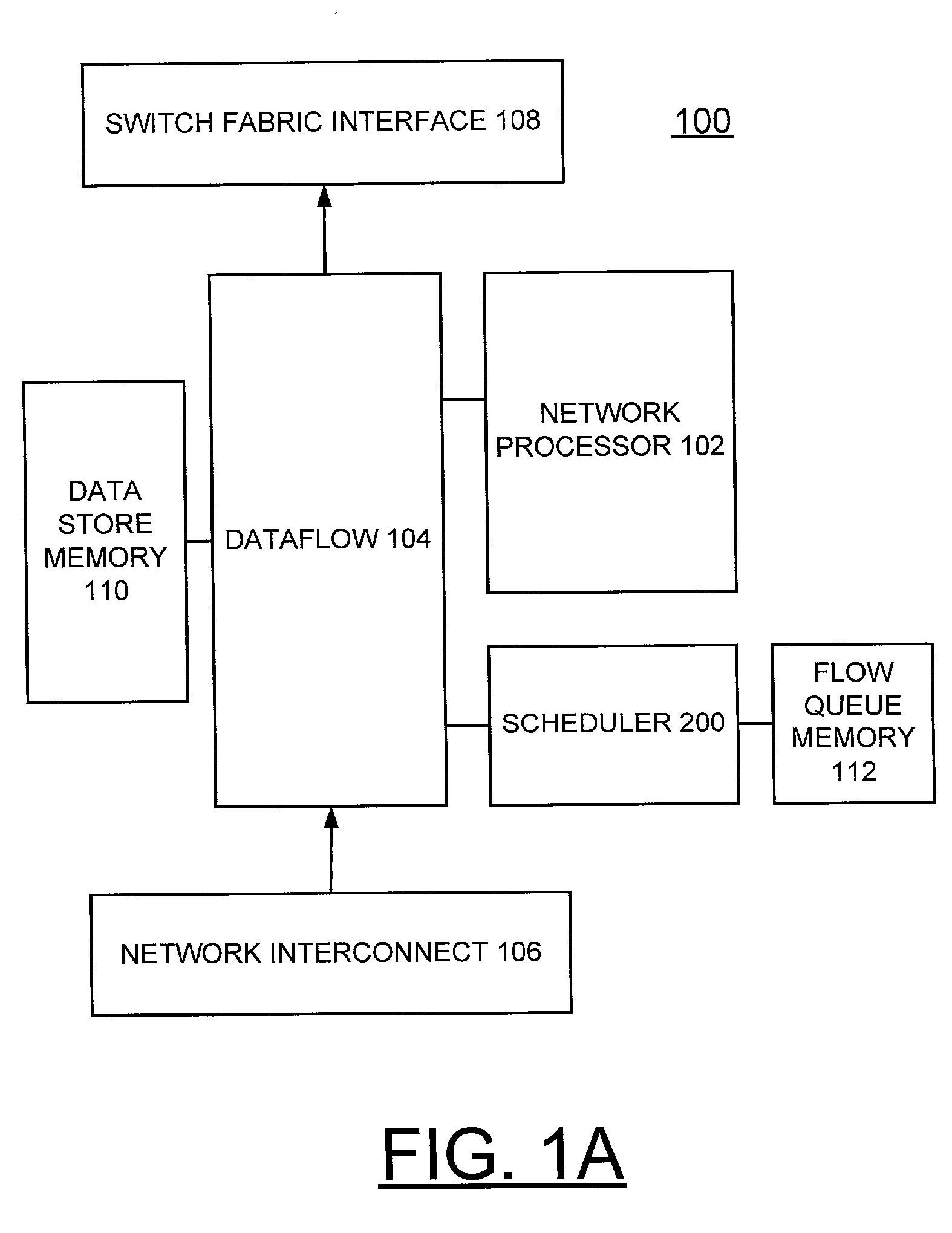
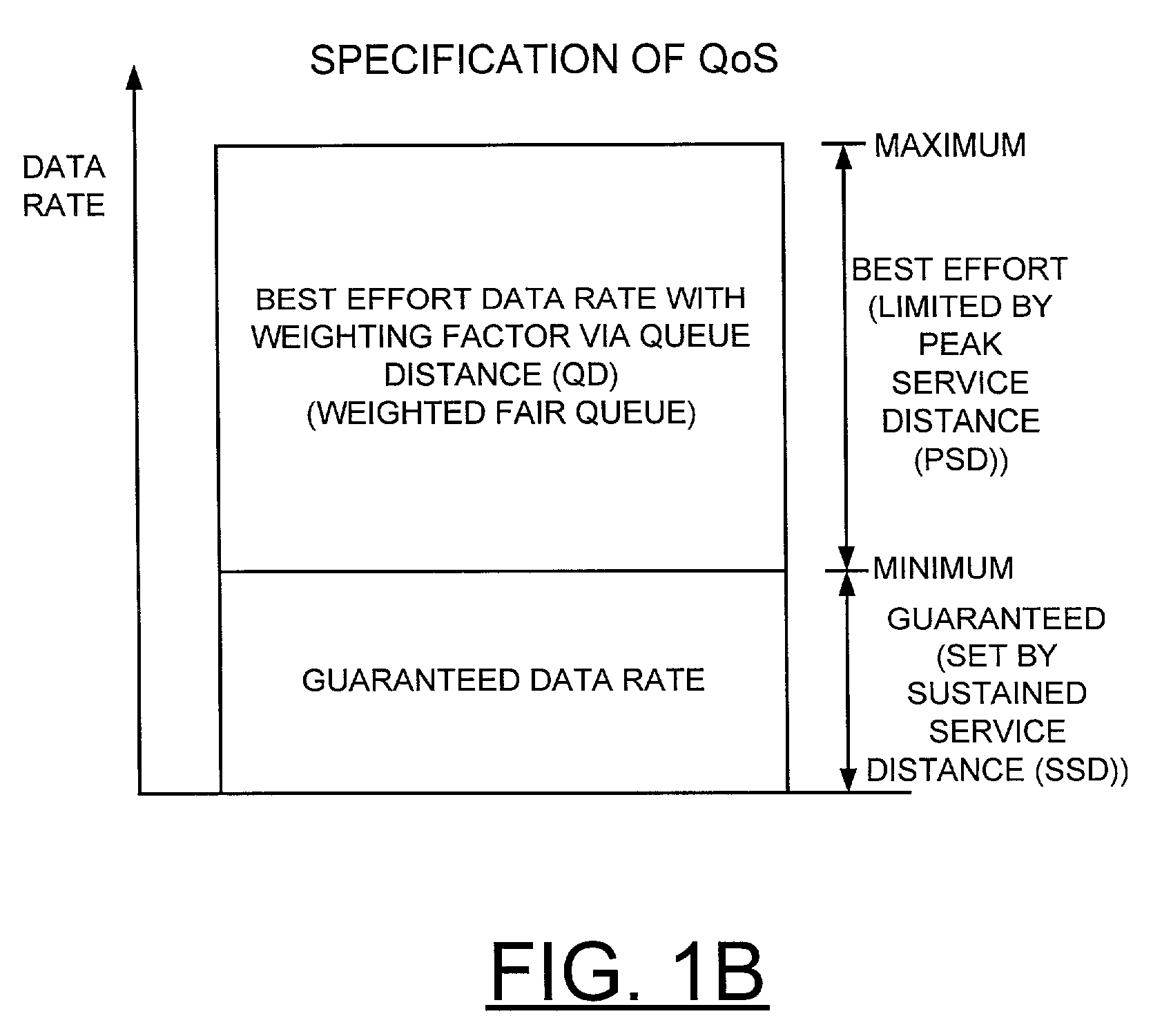
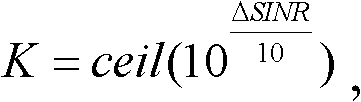Patents
Literature
79 results about "Qos scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
System and Methods for Distributed Medium Access Control and QOS Scheduling in Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks
ActiveUS20100246549A1Wireless commuication servicesData switching networksClear to sendChannel parameter
A communication device and method are provided for communicating with a receiving device over a channel within a mobile ad-hoc network. The receiving device includes a clear-to-send (CTS) packet generating portion that can generate and a CTS packet based on a parameter of the channel and that can transmit the CTS packet over the channel. The communication device includes a transmitter portion, a receiver portion and a management portion. The transmitter portion can transmit information into the channel. The receiver portion can receive information from the channel. The management portion includes a request-to-send (RTS) packet generating portion, a CTS packet receiving portion, a threshold database, a comparator and an RES packet generating portion. The management portion is in communication with the transmitter portion and the receiver portion. The RTS packet generating portion can generate a RTS packet and can provide the RTS packet to the transmitter portion. The transmitter portion can transmit the RTS packet to the receiving device by way of the channel. The receiver portion can receive the CTS packet from the receiving device by way of the channel and can provide the CTS packet to the CTS packet receiving portion. The threshold database can store a threshold value for the parameter of the channel and can provide the threshold value to the comparator. The CTS packet receiving portion can provide channel parameter information, to the comparator, based on the CTS packet. The comparator can compare the threshold value and the channel parameter information and can generate an instruction signal based on the comparison. The RES packet generating portion can generate an RES packet based on the instruction signal and can provide the RES packet to the transmitter portion.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
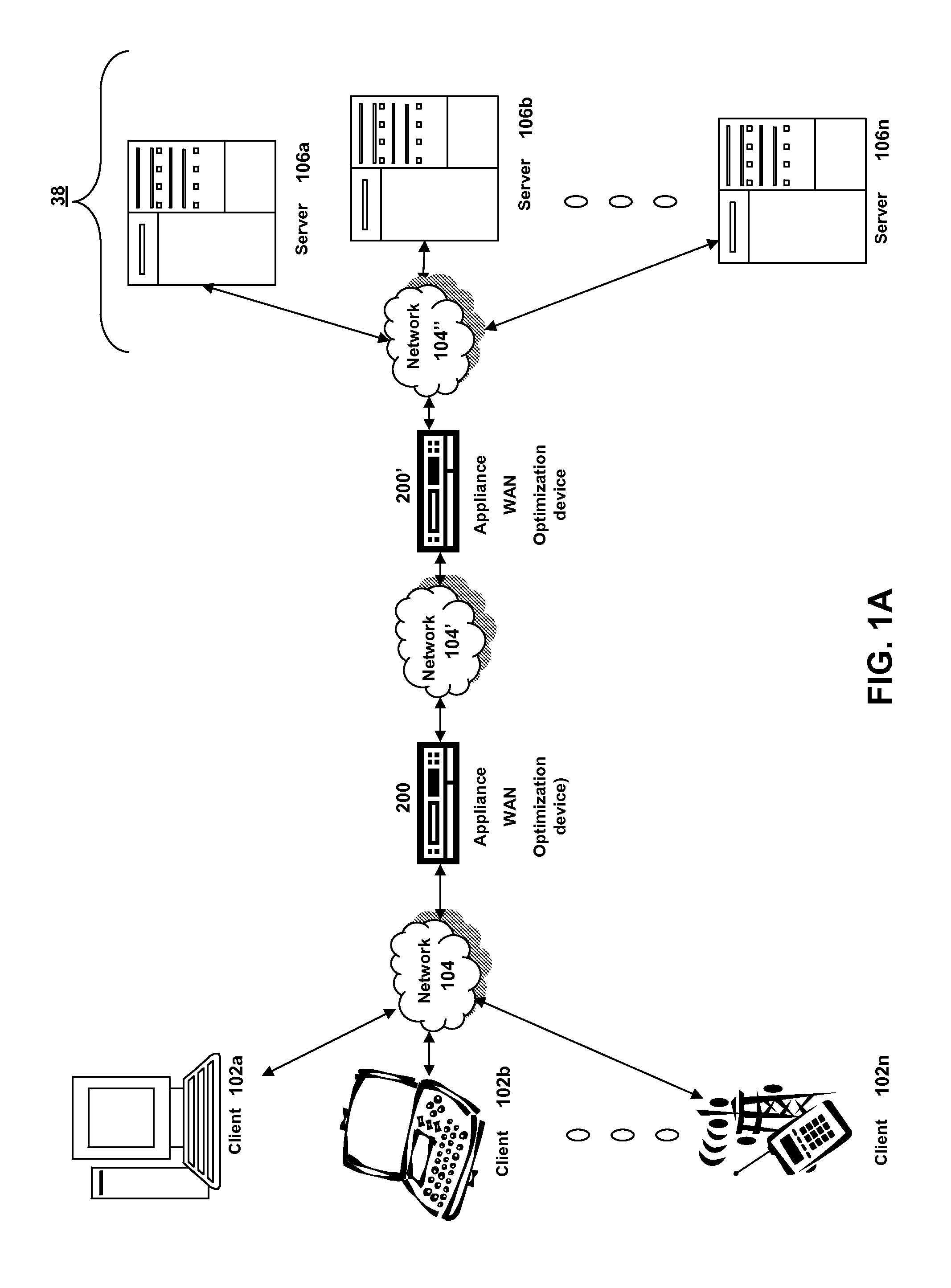
Systems and methods for providing quality of service via a flow controlled tunnel
ActiveUS20120078994A1Improve balanceEasily prioritizedTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityVoice over IP
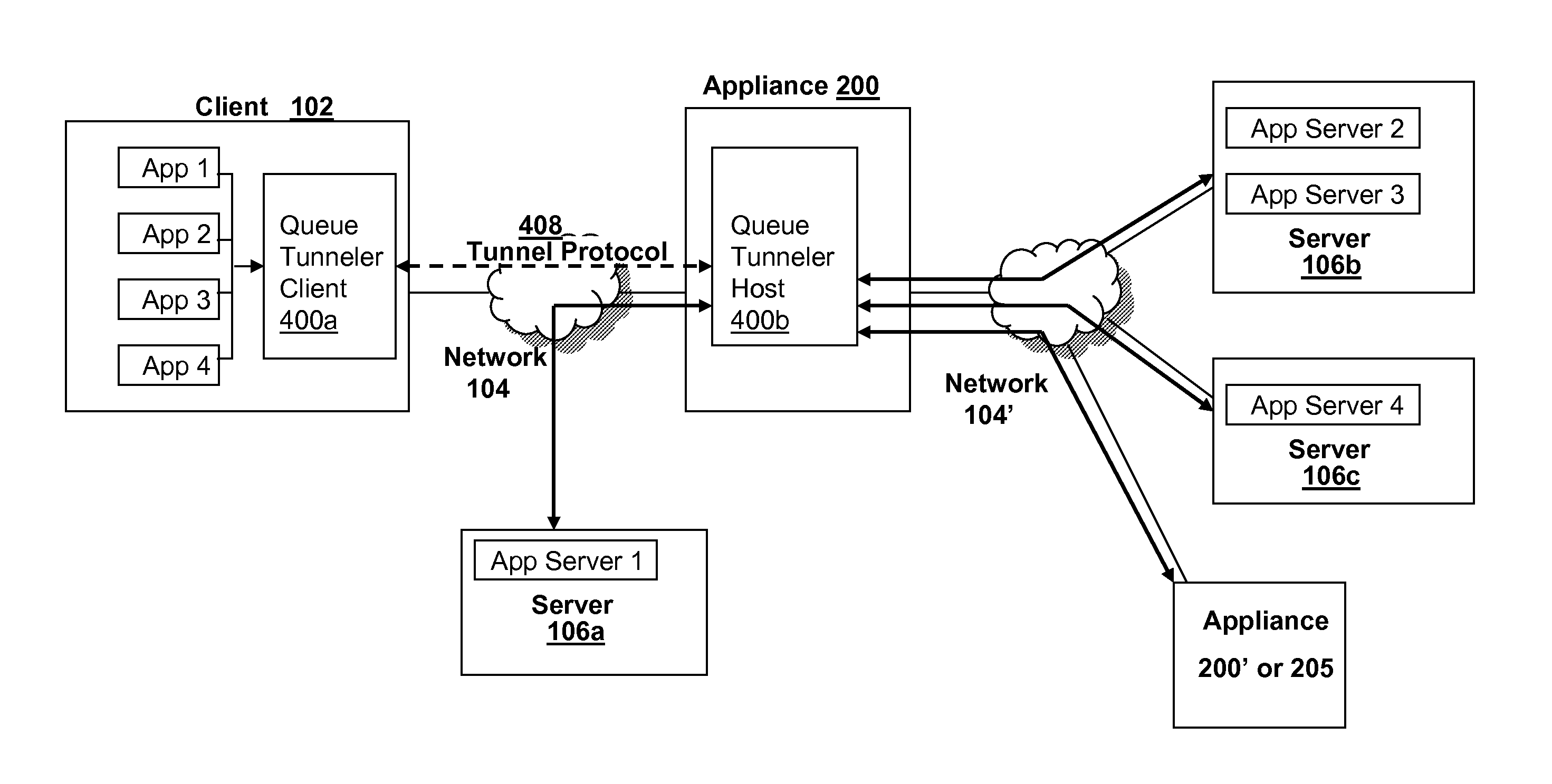
The present invention is directed towards systems and methods for providing Quality of Service (QoS) via a flow controlled tunnel. Traffic from a plurality of applications may be directed into a single connection or flow-controlled tunnel and QoS policies may be applied across the plurality of applications without configuration of individual link speeds, enabling QoS scheduling to dynamically adjust traffic transmission and reception rates to ensure priority management of applications regardless of a final endpoint of the application communications. Accordingly, traffic of different types, including VPN, HTTP, Voice-over-IP (VoIP), remote desktop protocol traffic, or other traffic may be easily balanced and prioritized. In many embodiments, the tunnel may be transparent to applications, such that without any application configuration, application traffic may still be prioritized by QoS requirements.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
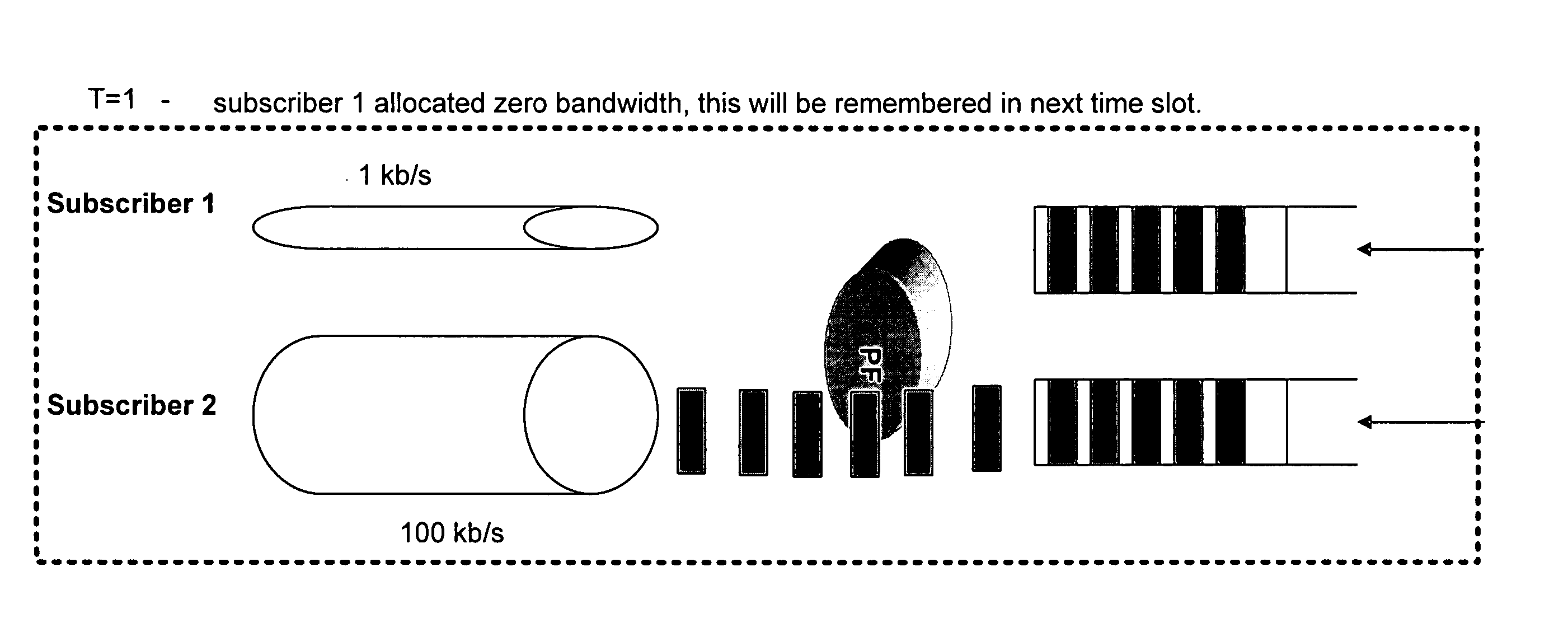
Integrated packet latency aware QoS scheduling using proportional fairness and weighted fair queuing for wireless integrated multimedia packet services
ActiveUS20070041364A1Network traffic/resource managementIn VoIP networksPacket communicationPacket scheduling
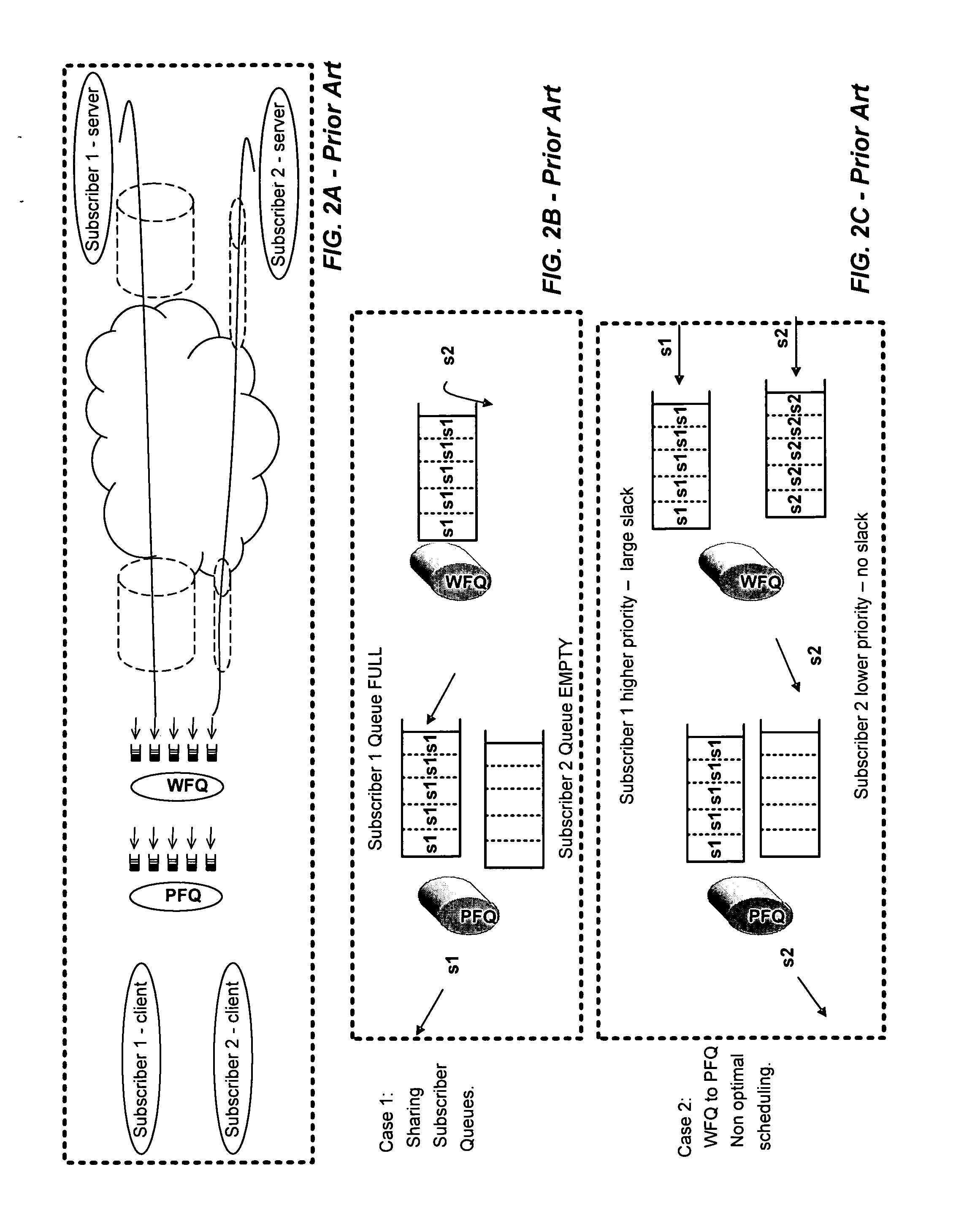
Packet communication networks for transmission to wireless subscriber devices utilize both wireline and wireless packet routing components. The routing elements of these two different types often implement different packet scheduling algorithms, typically a form of Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) in the wireline portion of the network and Proportional Fairness (PF) queuing in the wireless domain. To improve resource allocation and thus end to end quality of service for time sensitive communications, such as integrated multimedia services, the present disclosure suggests adding the notion of slack time into either one or both of the packet scheduling algorithms. By modifying one or more of these algorithms, e.g. to reorder or shuffle packets based on slack times, global optimal resource allocations are possible, at least in certain cases.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC
Systems and methods for providing quality of service via a flow controlled tunnel
ActiveUS8433783B2Easily balanced and prioritizedTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityVoice over IP
The present invention is directed towards systems and methods for providing Quality of Service (QoS) via a flow controlled tunnel. Traffic from a plurality of applications may be directed into a single connection or flow-controlled tunnel and QoS policies may be applied across the plurality of applications without configuration of individual link speeds, enabling QoS scheduling to dynamically adjust traffic transmission and reception rates to ensure priority management of applications regardless of a final endpoint of the application communications. Accordingly, traffic of different types, including VPN, HTTP, Voice-over-IP (VoIP), remote desktop protocol traffic, or other traffic may be easily balanced and prioritized. In many embodiments, the tunnel may be transparent to applications, such that without any application configuration, application traffic may still be prioritized by QoS requirements.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Packet flow control method and device
InactiveUS7039013B2Reduces packet-dropsImproves overall packet-throughputError preventionTransmission systemsData connectionTraffic capacity
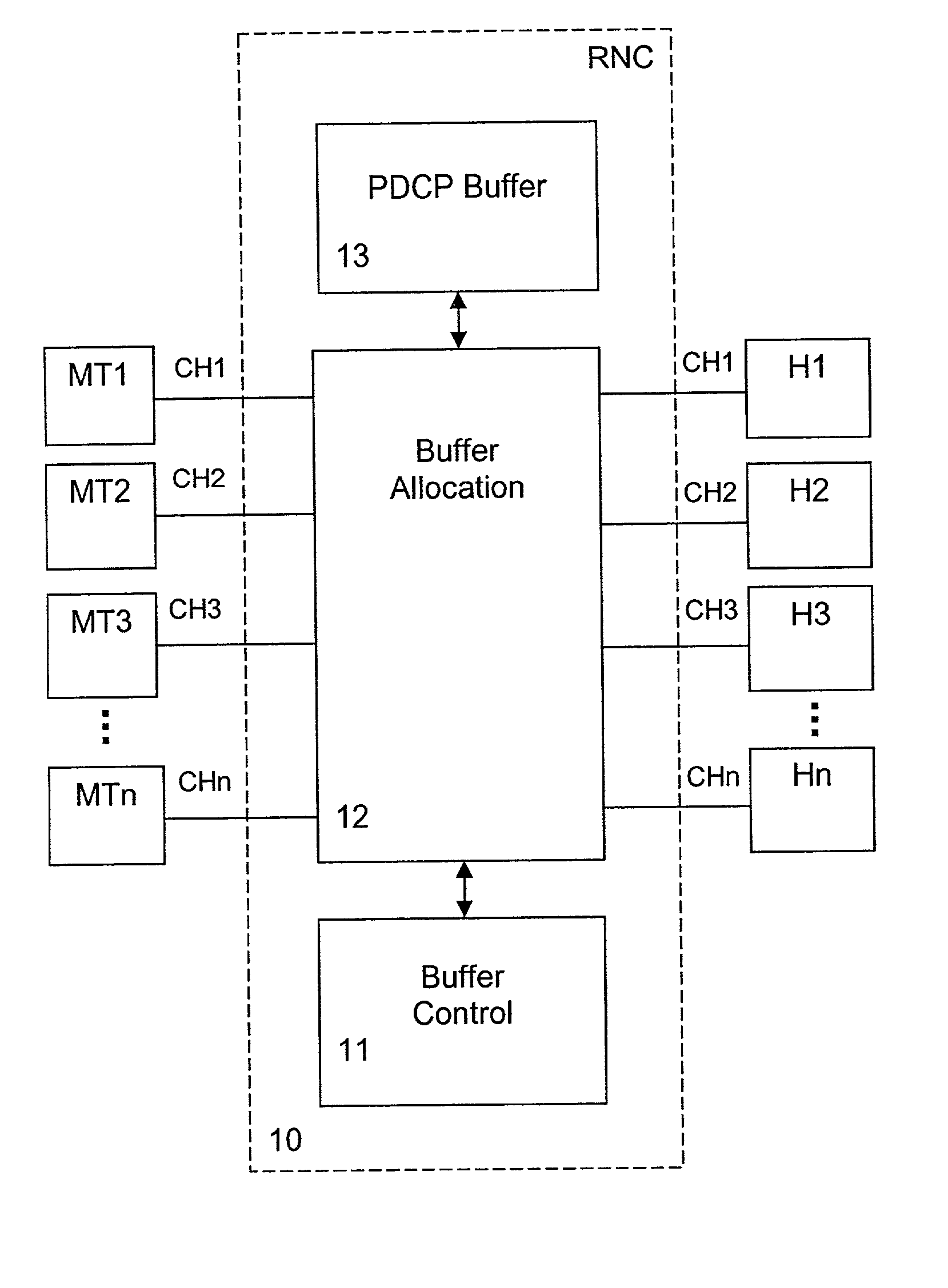
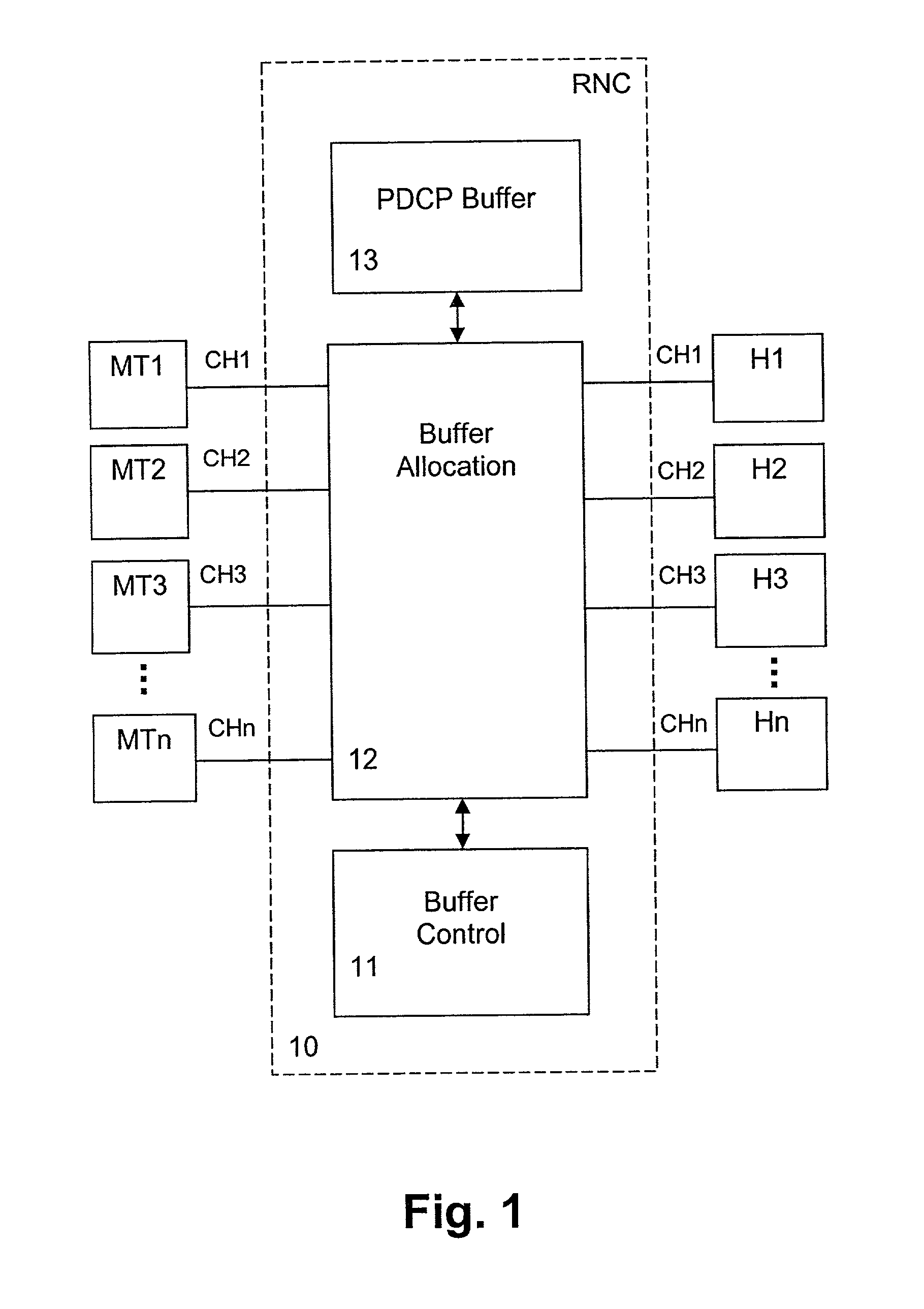
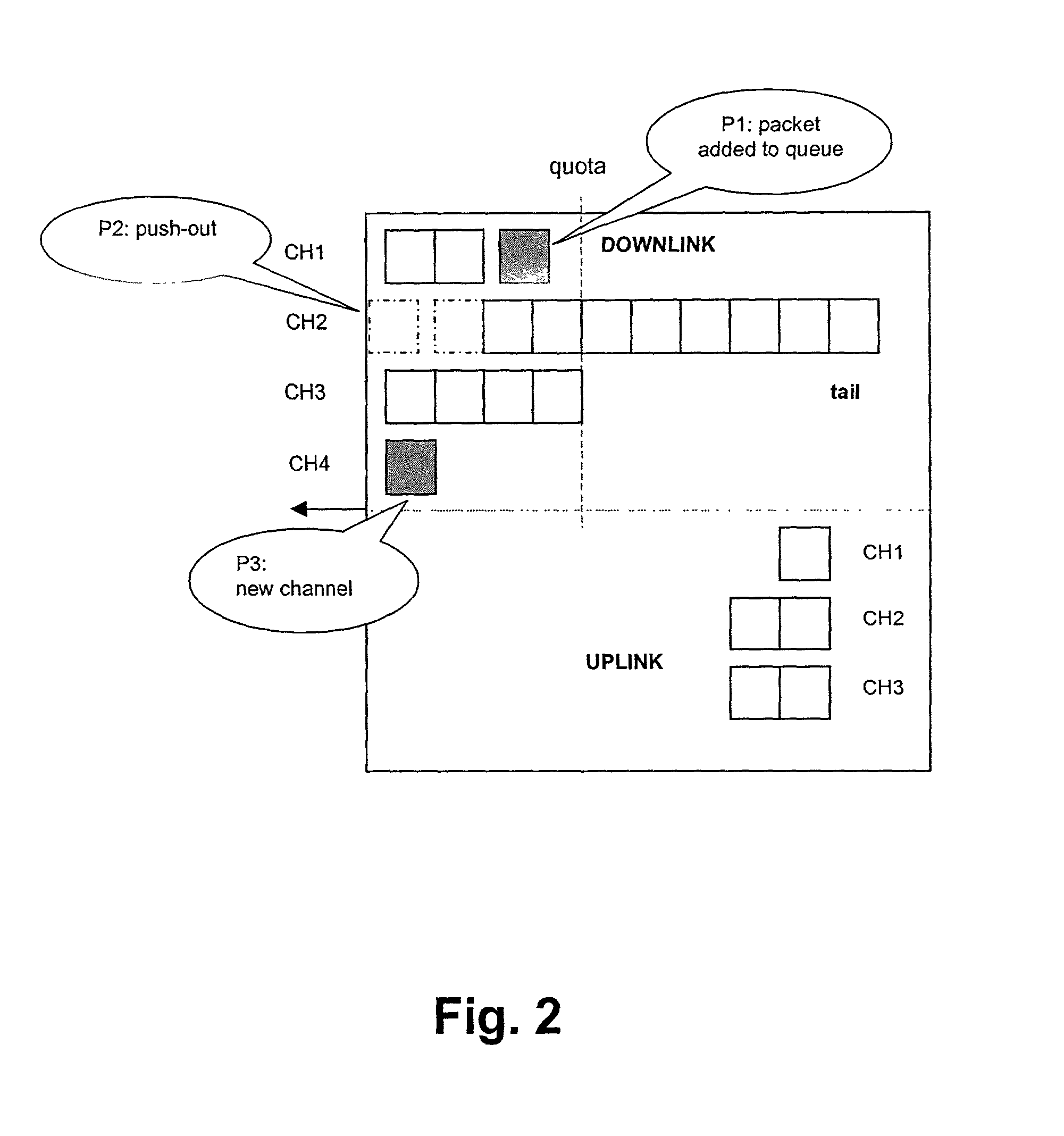
The present invention relates to a method and network node for controlling packet flow in a buffer means (13; 14) of a network node of a data network, wherein a nominal capacity is assigned to each data flow, and an additional or free capacity is shifted from a first flow portion to a second flow portion when a new data packet of said second flow portion has been received and said nominal capacity has been exceeded. The nominal capacity may be an upper buffer memory limit used for controlling queuing of data packets in a buffer memory (13) of said buffer means, wherein the memory space of the buffer memory (13) is shared between a plurality of channels allocated to respective packet data connections. Then, the free capacity corresponds to a memory space shifted from a first channel to a second channel, when a new data packet of the second channel has been received and not enough memory space is available for the second channel. Thus, a dynamic buffer-sharing mechanism is provided which reduces the number of packet drops in the buffer memory (13) during congestion and improves network throughput. Alternatively, the nominal capacity may be a nominal flow rate at which data flow traffic is guaranteed in a QoS scheduling algorithm. Then, a residual rate corresponding to the difference between the nominal flow rate and an instantaneous traffic is shifted between flow portions of a buffer means controlled by the scheduling algorithm to maximize total system throughput.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
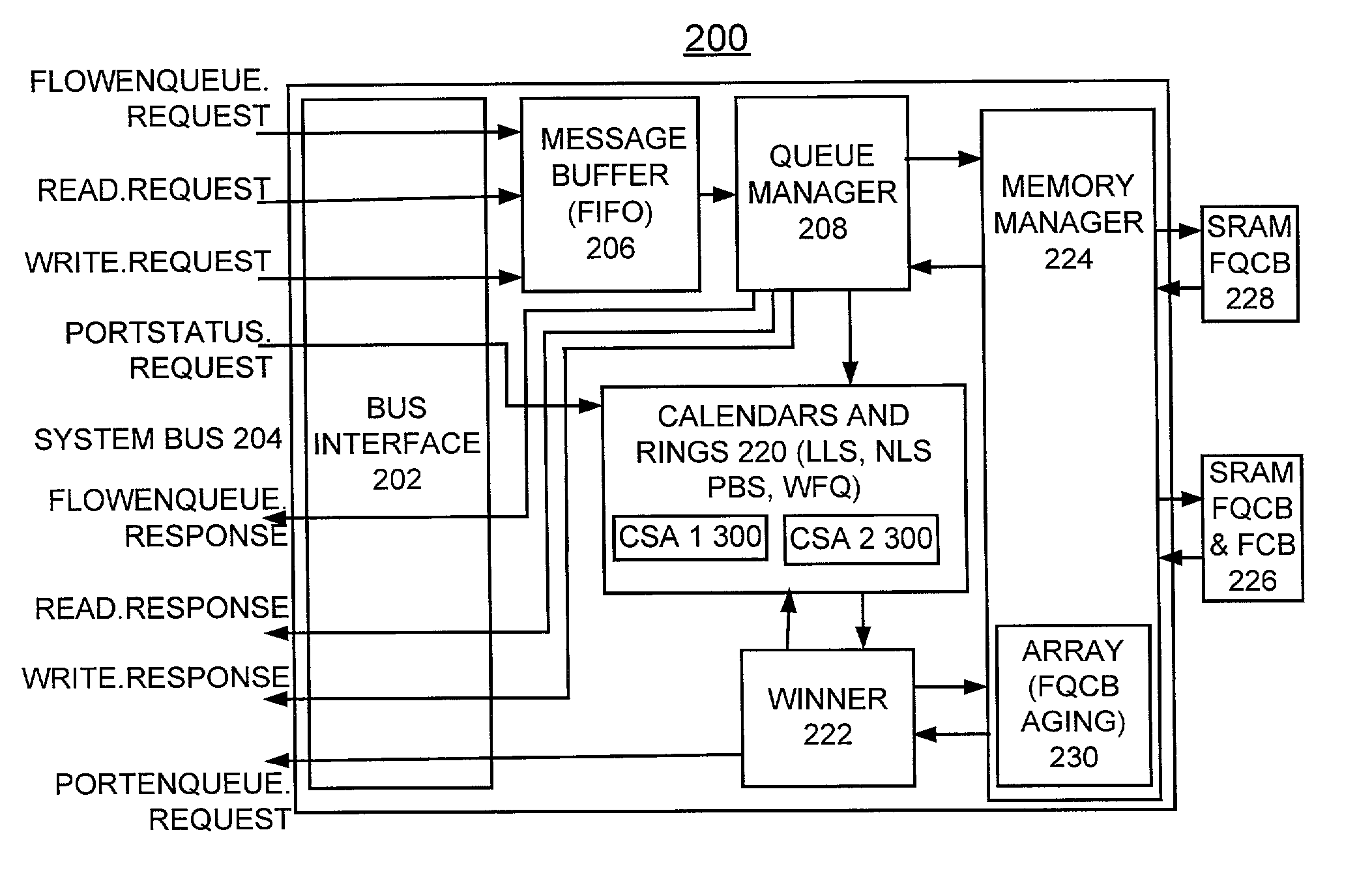
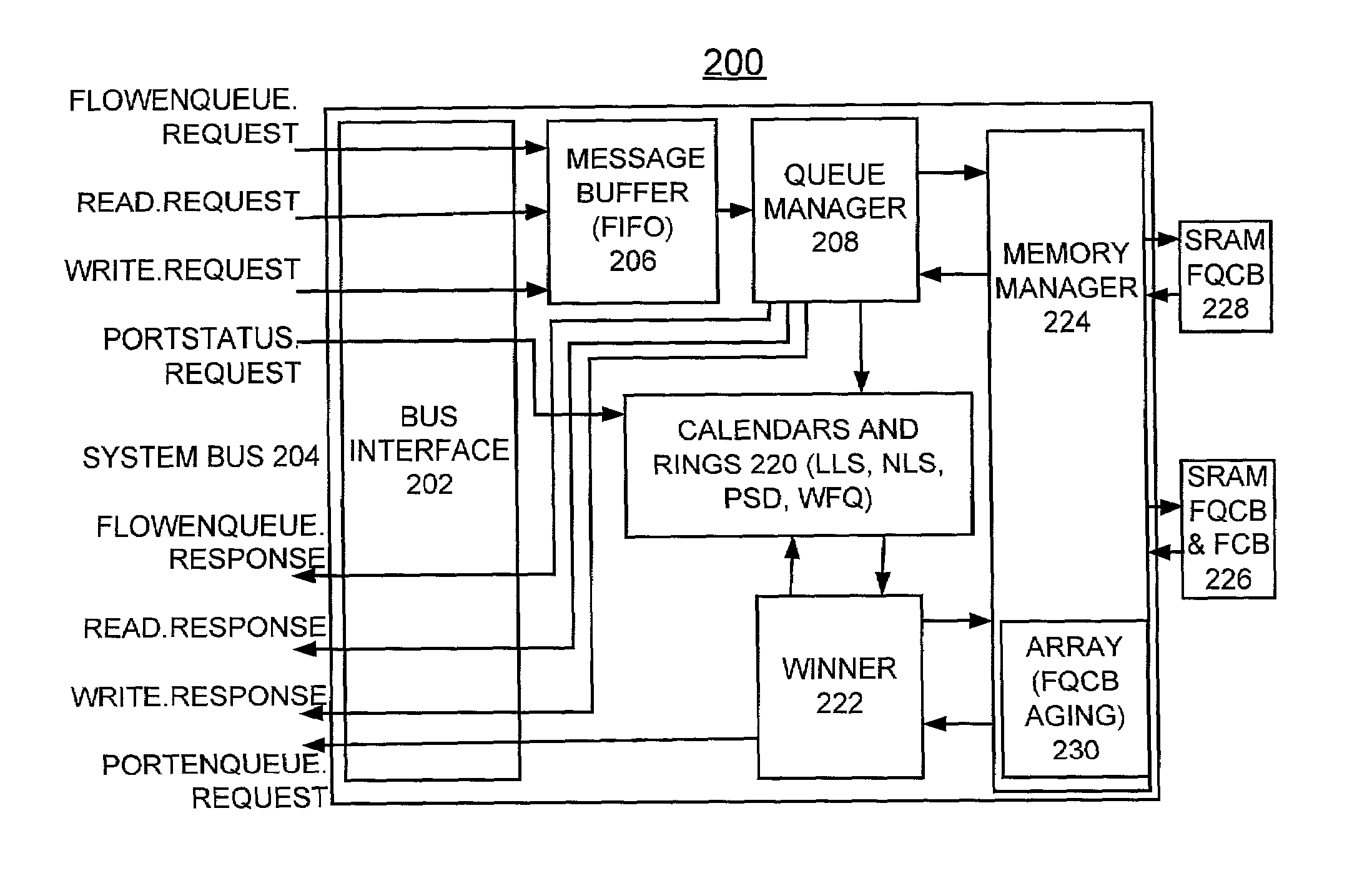
QoS scheduler and method for implementing quality of service with cached status array
InactiveUS7046676B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsArray data structureImage resolution
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
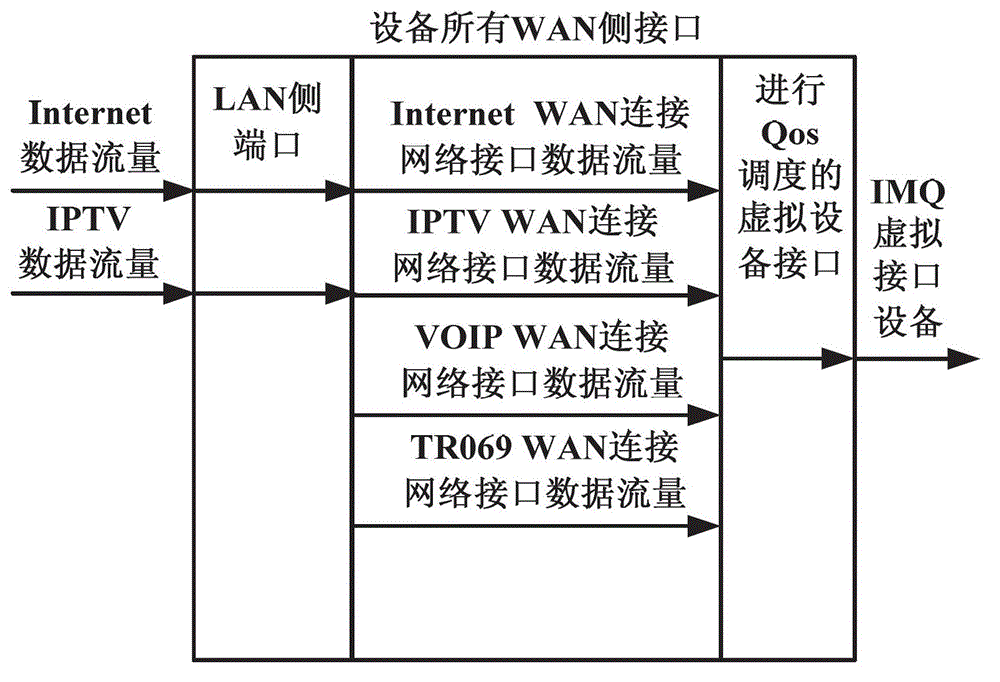
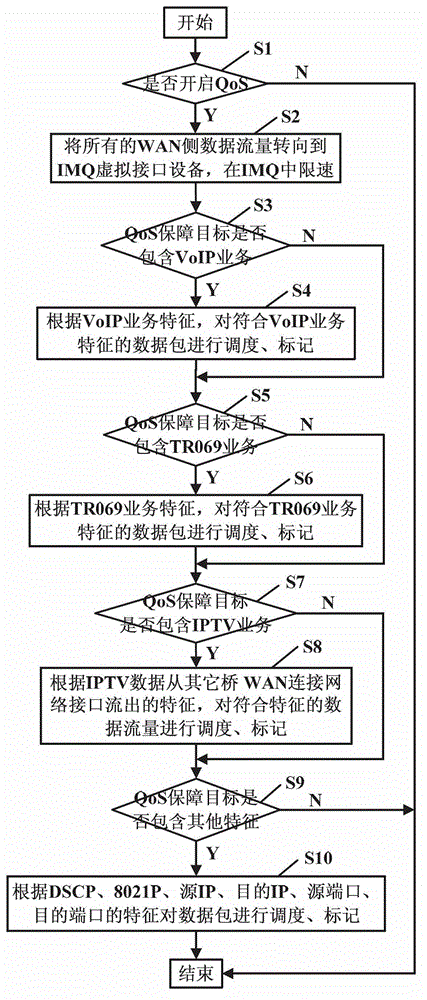
Linux software based uplink QoS scheduling method and device
ActiveCN102916901ANo change in flowImplement flow controlData switching networksTraffic capacityGNU/Linux
The invention discloses a Linux software based uplink QoS (Quality of Service) scheduling method and device, and relates to the field of IP network data transmission. The method comprises the following steps: clustering uplink data of residential gateway equipment to IMQ virtual interface equipment for speed limiting, wherein the flow control and scheduling of data packets are realized, and at the same time, the flow direction of data in the residential gateway is not changed; identifying the characteristics of the data packets at the IMQ virtual interface equipment of an uplink data exit of the residential gateway equipment, placing the data packets in different priority queues according to the corresponding relation of the data packet characteristics and the priority queues; and processing the data packets in the corresponding queue according to an absolute priority strategy by using the priority queues, so as to realize the priority guarantee during data packet forwarding process. According to the method and device based on the Linux software, not only the functions of classifying, scheduling and marking the data packets are realized, but also the uplink QoS scheduling in the residential gateway equipment based on the Linux inner core is realized. In addition, the hardware cost is reduced, and the market competitiveness is improved.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
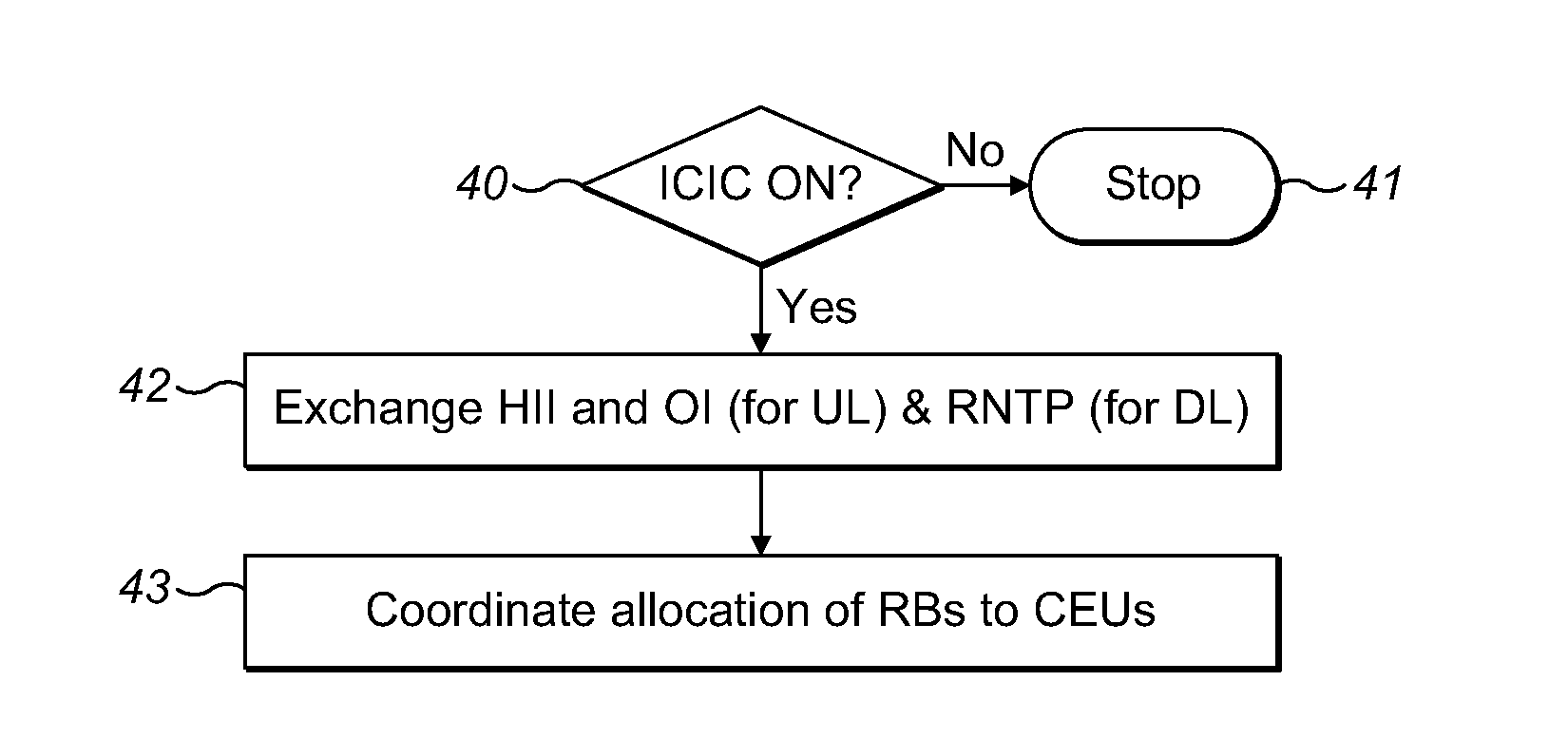
COORDINATION AND QoS SCHEDULING
ActiveUS20140073342A1Quality assuranceRaise priorityWireless communicationTelecommunications networkResource block
A scheduler for a cellular telecommunications network is provided having a first base station corresponding to a first cell and serving a cell area, the scheduler being adapted to: identify mobile devices located at the edge of the cell area; obtain resource usage information of mobile devices located at the edge of neighbouring cell areas; and, allocate resource blocks for data transmission based on the location of the mobile devices and the received resource usage information, wherein those data transmissions with a high priority indication and which are for mobile devices located at the edge of the cell area are allocated with a higher priority than those data transmissions with a high priority indication and which are for mobile devices not located at the edge of the cell area. An associated method and computer readable storage medium are also provided.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
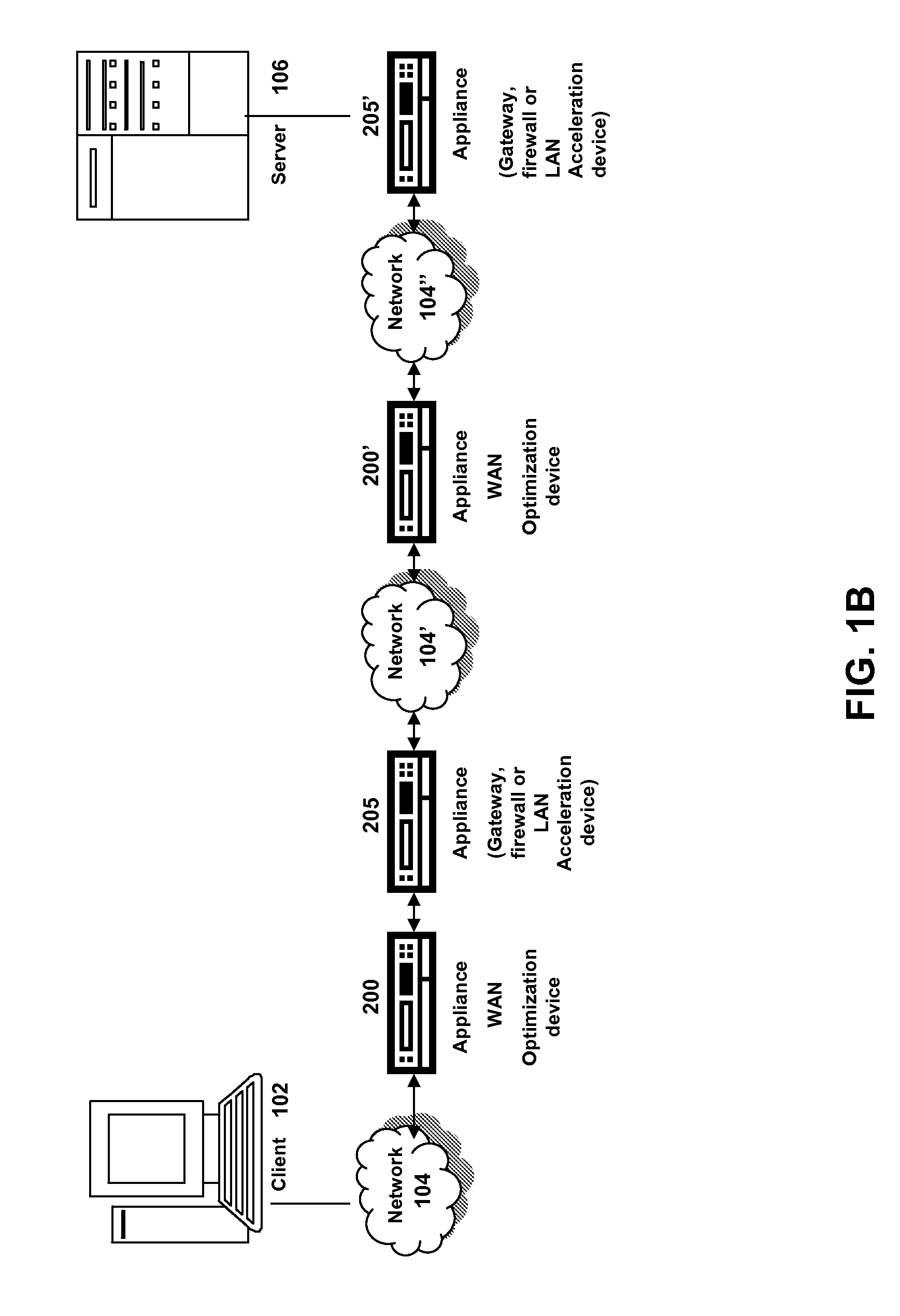
Method and device for enhancing service quality in wireless local area network
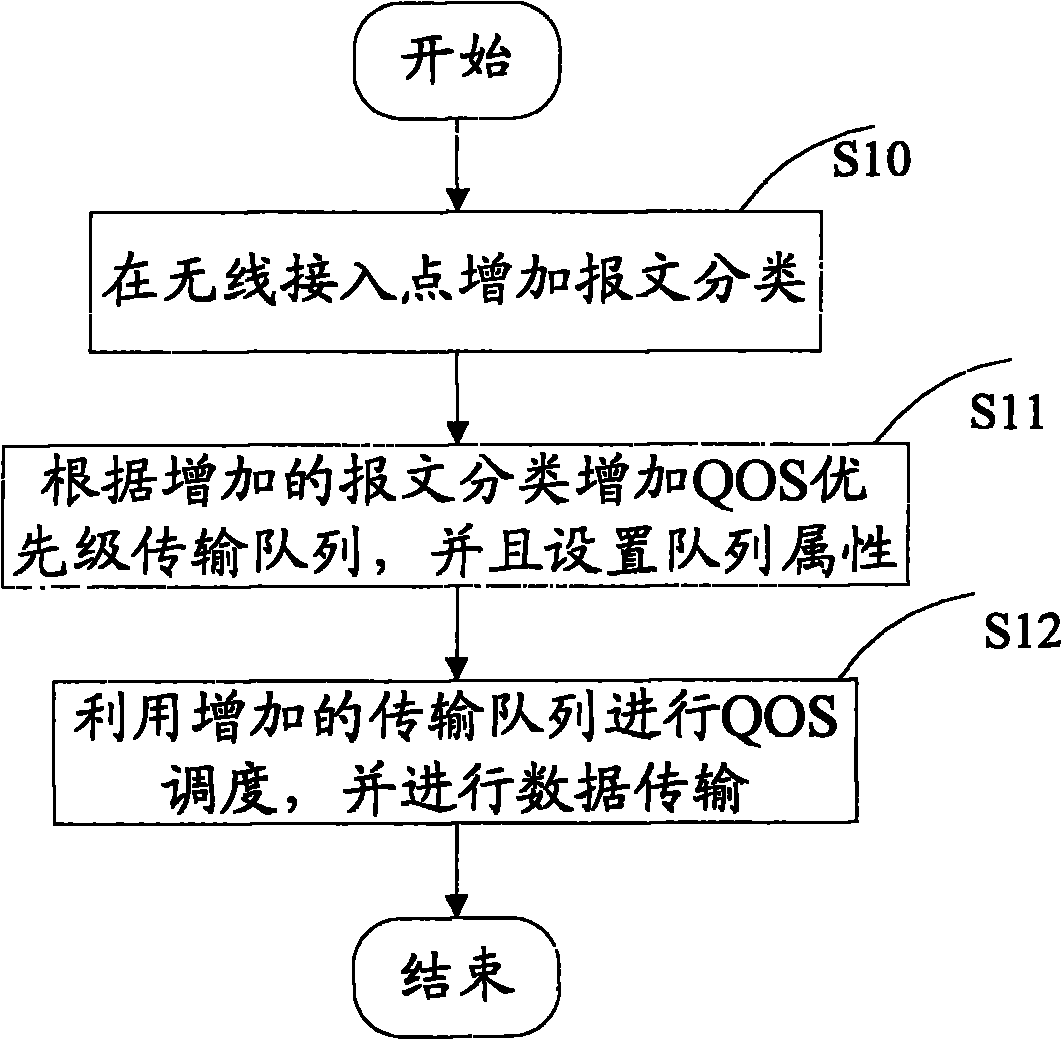
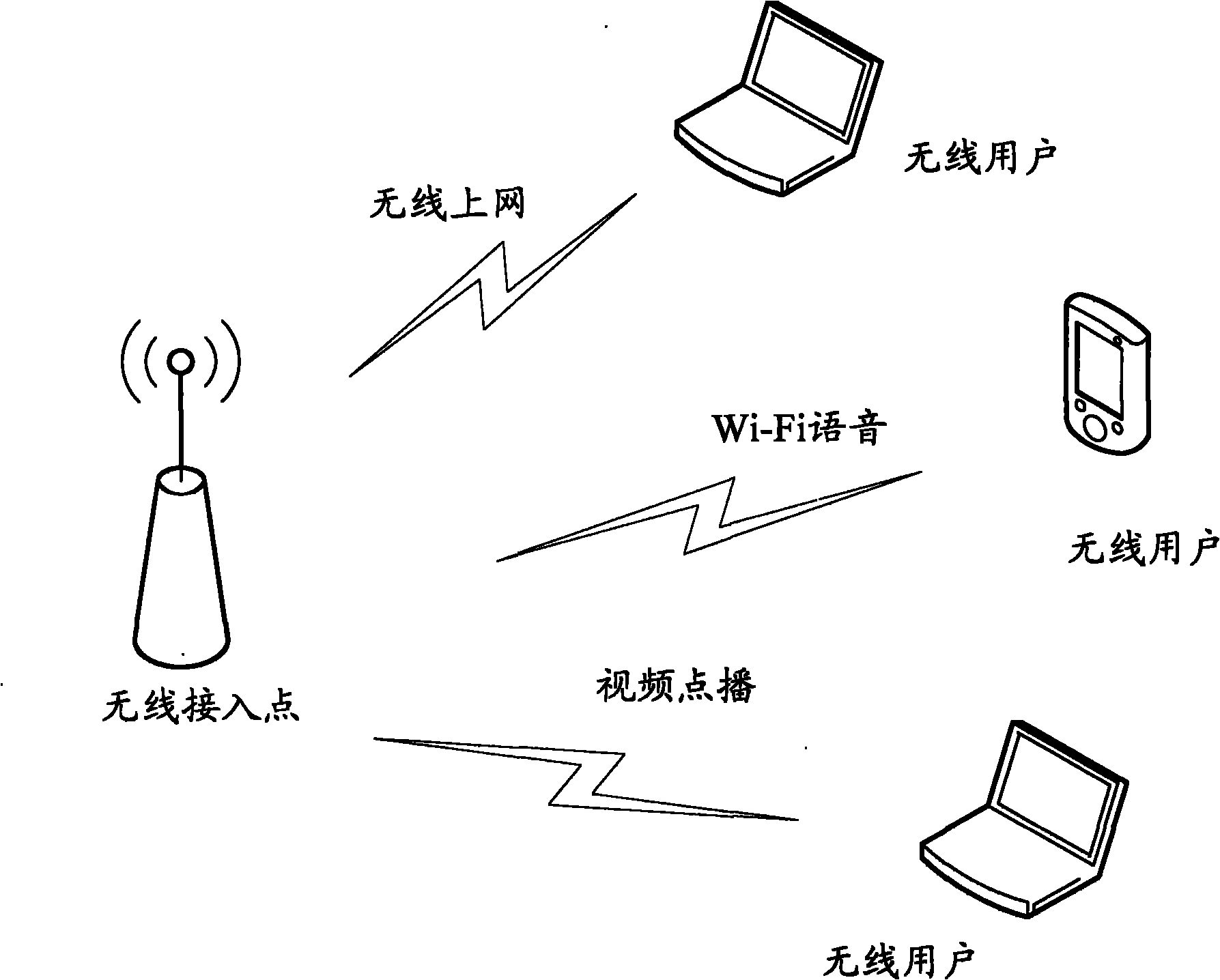
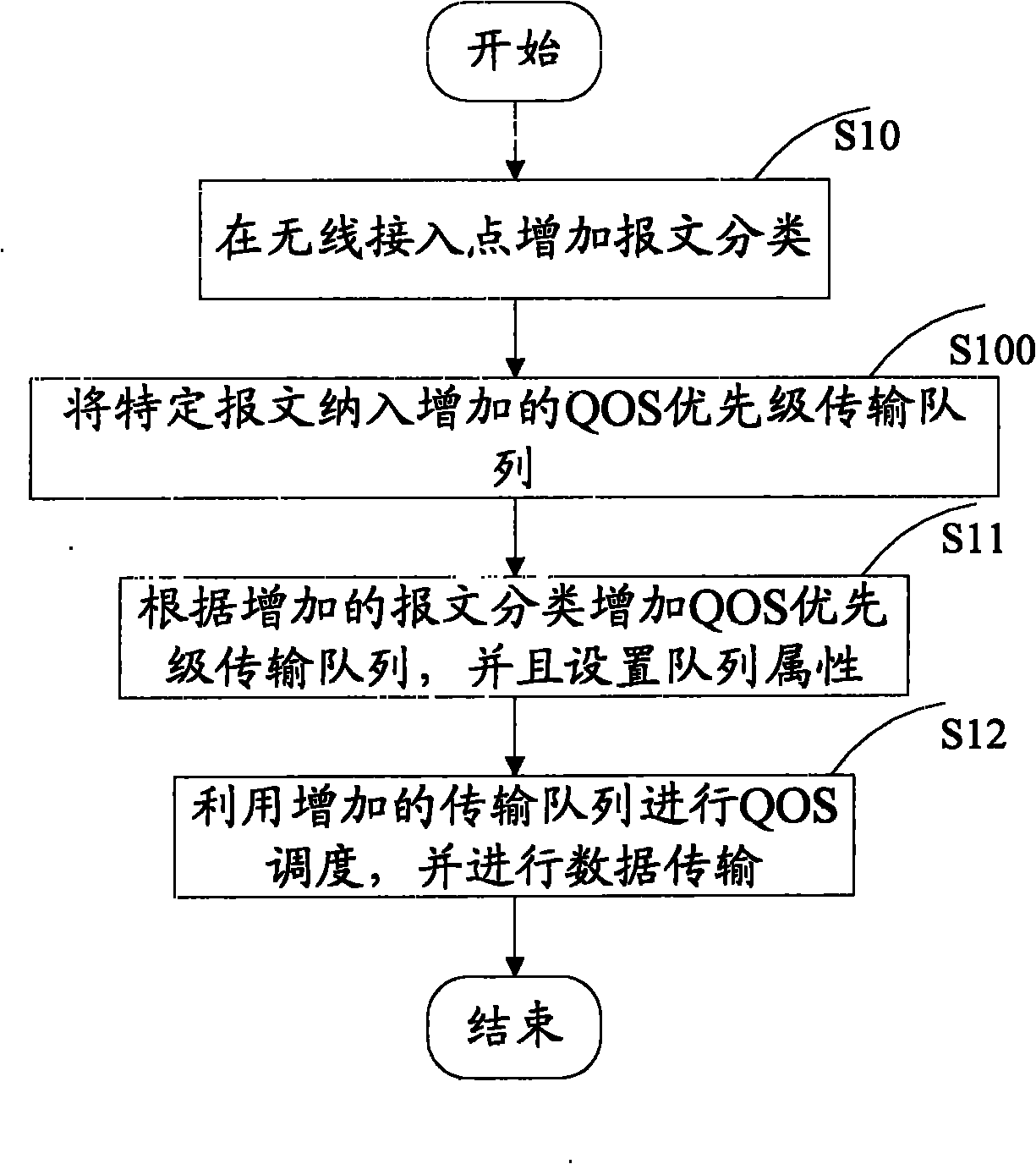
InactiveCN101784082AGuarantee normal developmentImprove experienceNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesData transmissionEnhanced service
The invention discloses a method and a device for enhancing service quality in a wireless local area network. The method for enhancing the service quality in the wireless local area network comprises the following steps: adding packet classification to a wireless access point; adding a QOS priority level transmission queue according to the added packet classification and setting a queue property; and performing QOS dispatching by using the added transmission queue and performing data transmission. The device for enhancing the service quality in the wireless local area network can ensure that a wireless full service is normally performed according to the requirement of a user by strategies of expanding the packet classification in EDCA QOS, correspondingly adding a wireless priority level queue, intelligently dropping a packet and the like, so that the service quality is enhanced to improve user experience.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and device for data relay transmission in wireless relay network
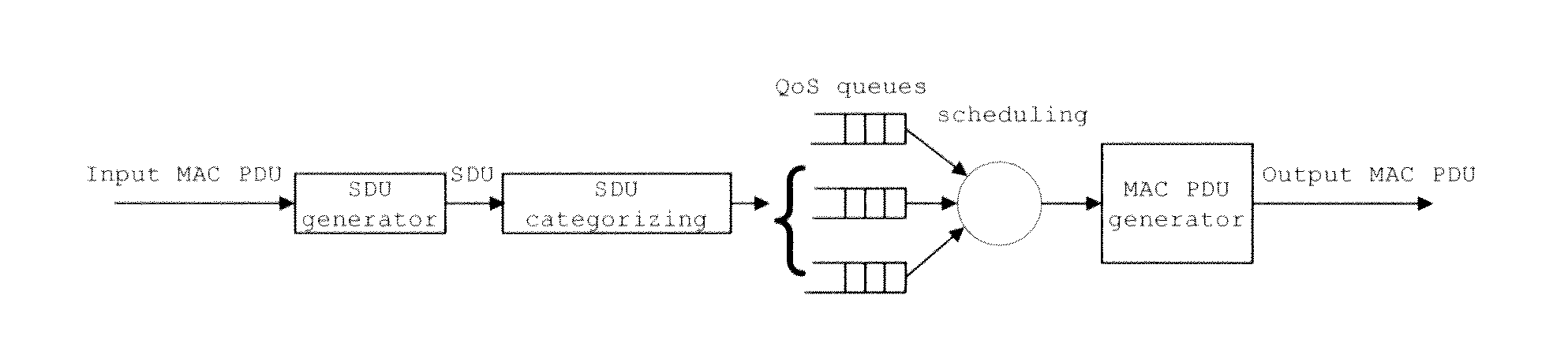
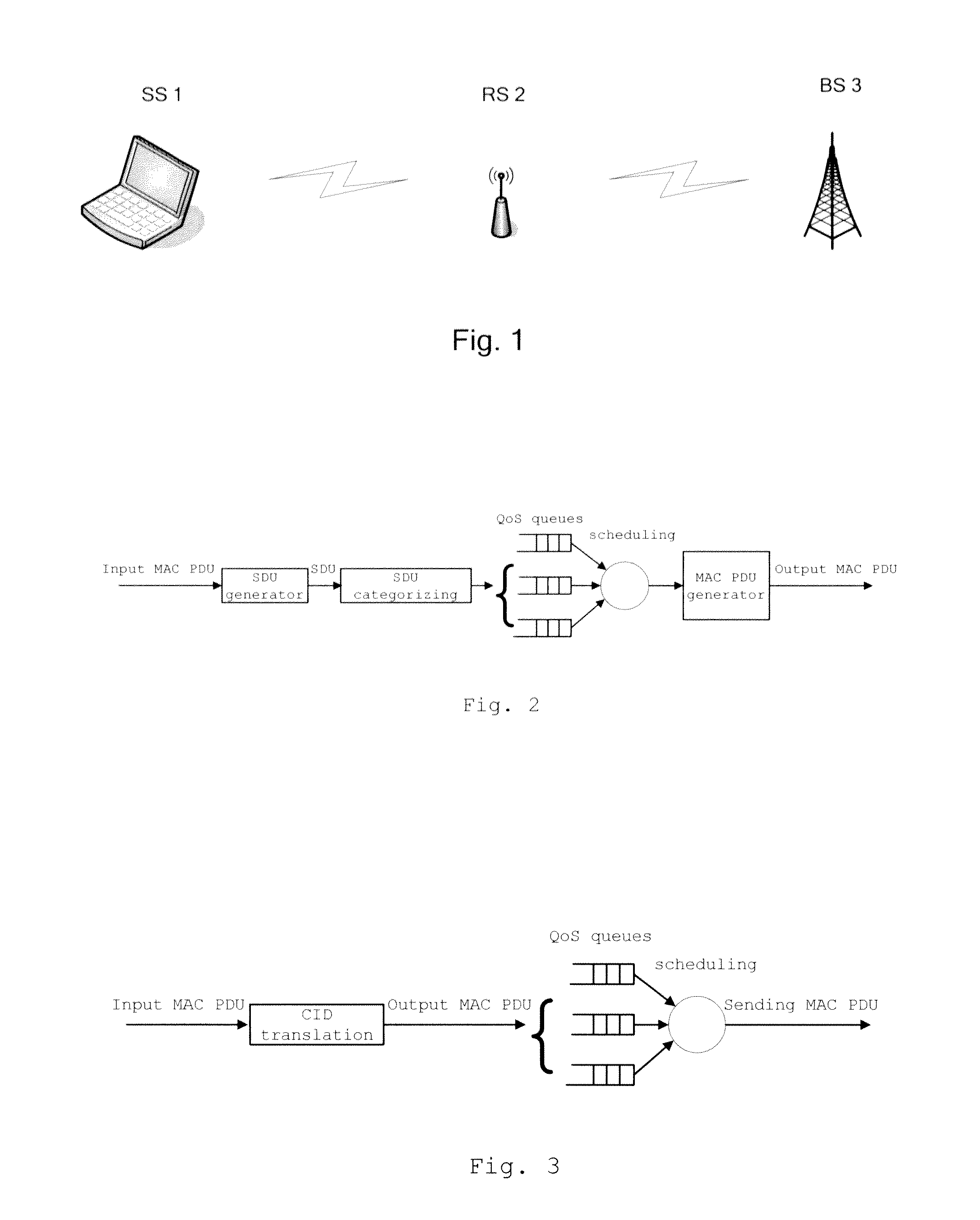
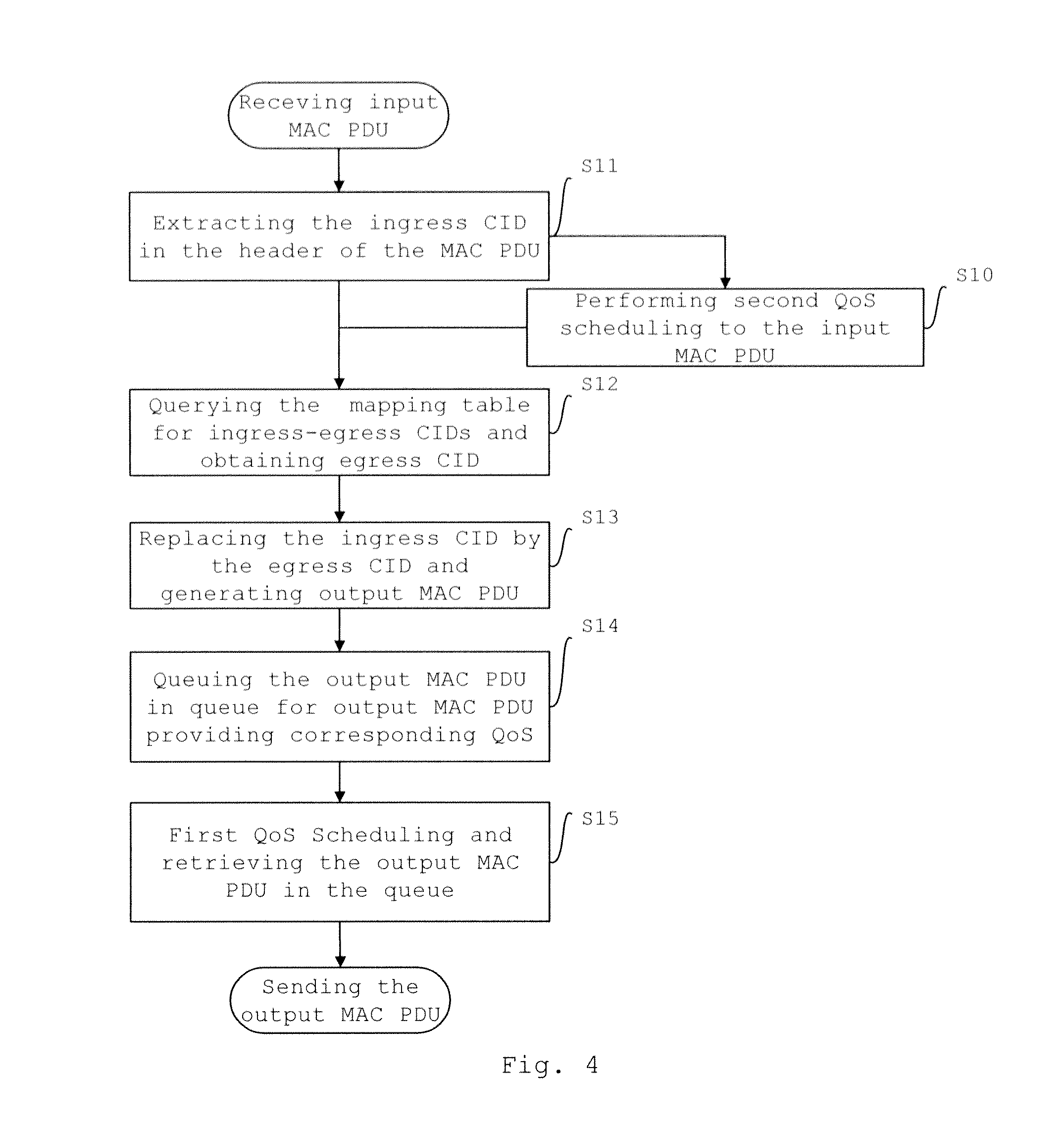
ActiveUS20100309792A1Improve QoS service performanceCancels the waiting latencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless relay networkWaiting time
A method and a device for data relay transmission in a wireless relay communication network are provided, in which, the relay station directly obtains corresponding egress CID related information based on input MAC PDUs, then generates output MAC PDUs including the egress CID related information, and at last, according to the egress CID related information, performs QoS scheduling for the output MAC PDUs, so as to output them in an sequence of QoS. The invention omits the steps of de-cascading, de-segmenting or de-capsulating the MAC PDUs in order to obtain MAC SDUs, and the steps of scheduling by category, cascading, segmenting, and encapsulating the MAC SDUs in order to re-generate the MAC PDUs in the prior art, and the invention simplifies the data processing procedure and achieves the goal of decreasing the relay latency. Preferably, before the relay station generates the output MAC PDUs based on the input MAC PDUs, it can also schedule the input MAC PDUs based on the ingress CID information therein, so as to further improve the QoS service performance.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Service forwarding and priority mapping method for China-data over cable system interface specification (C-DOCSIS) system
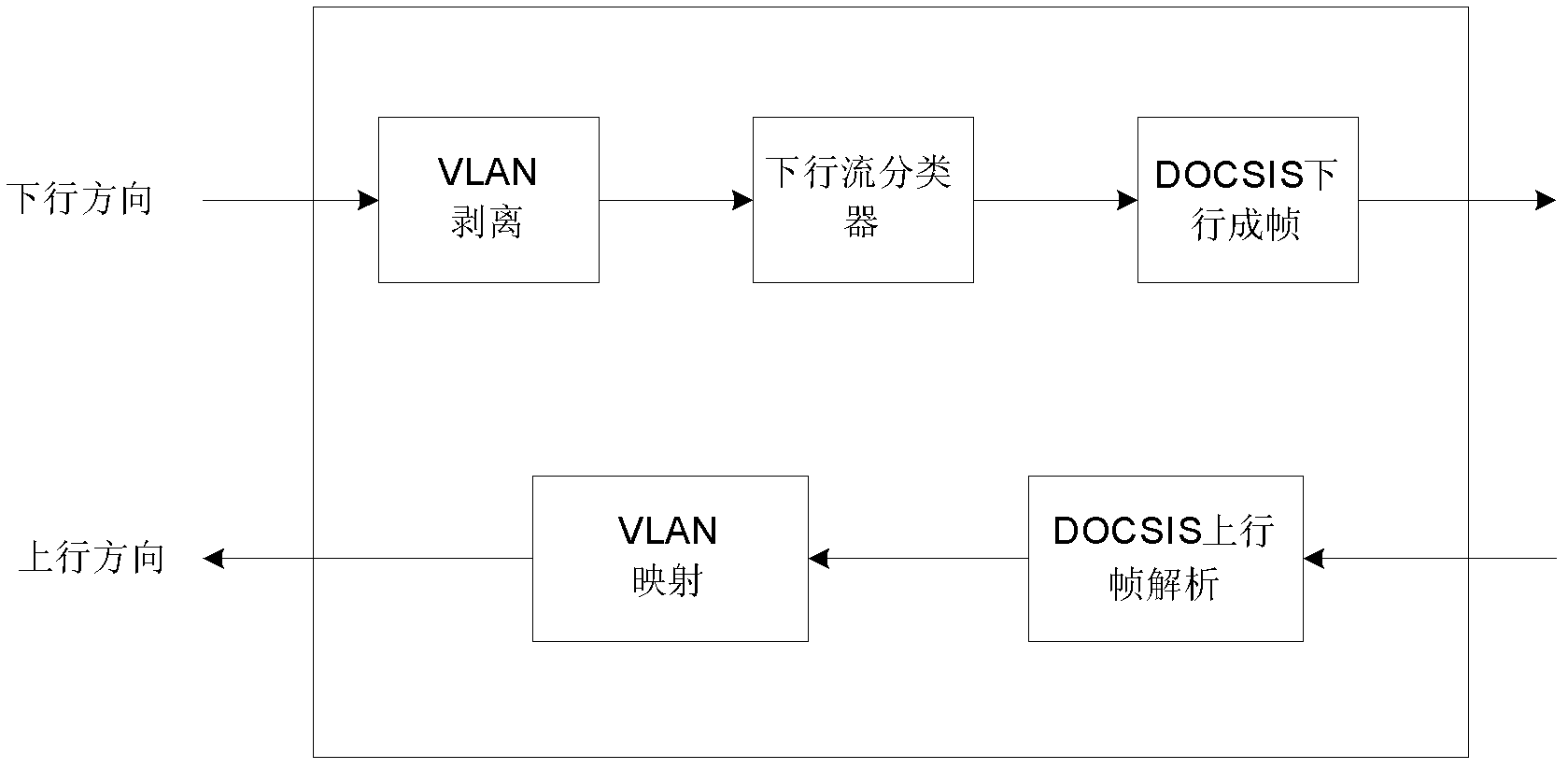
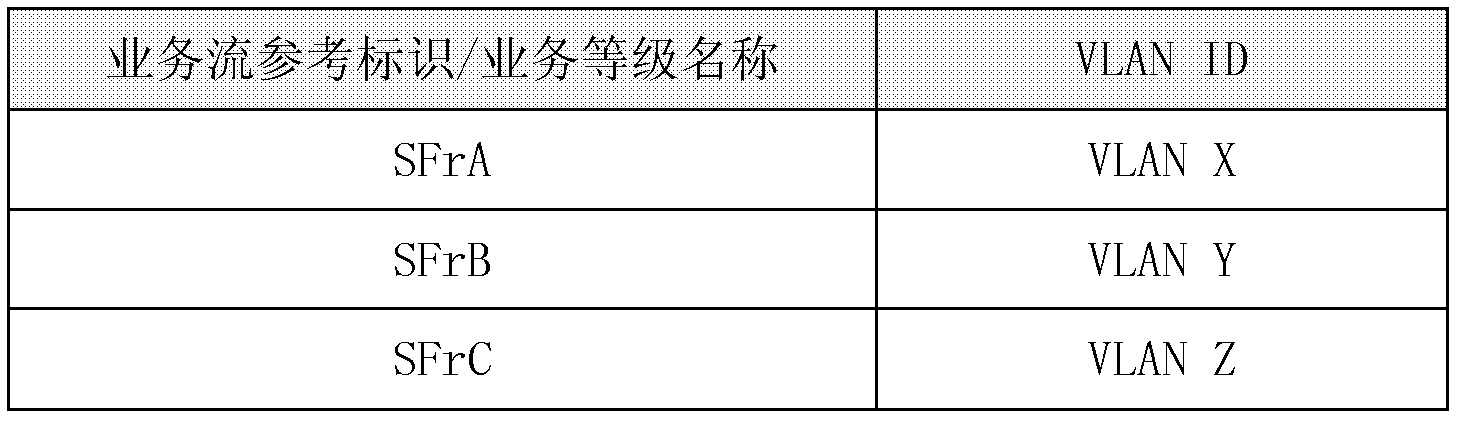
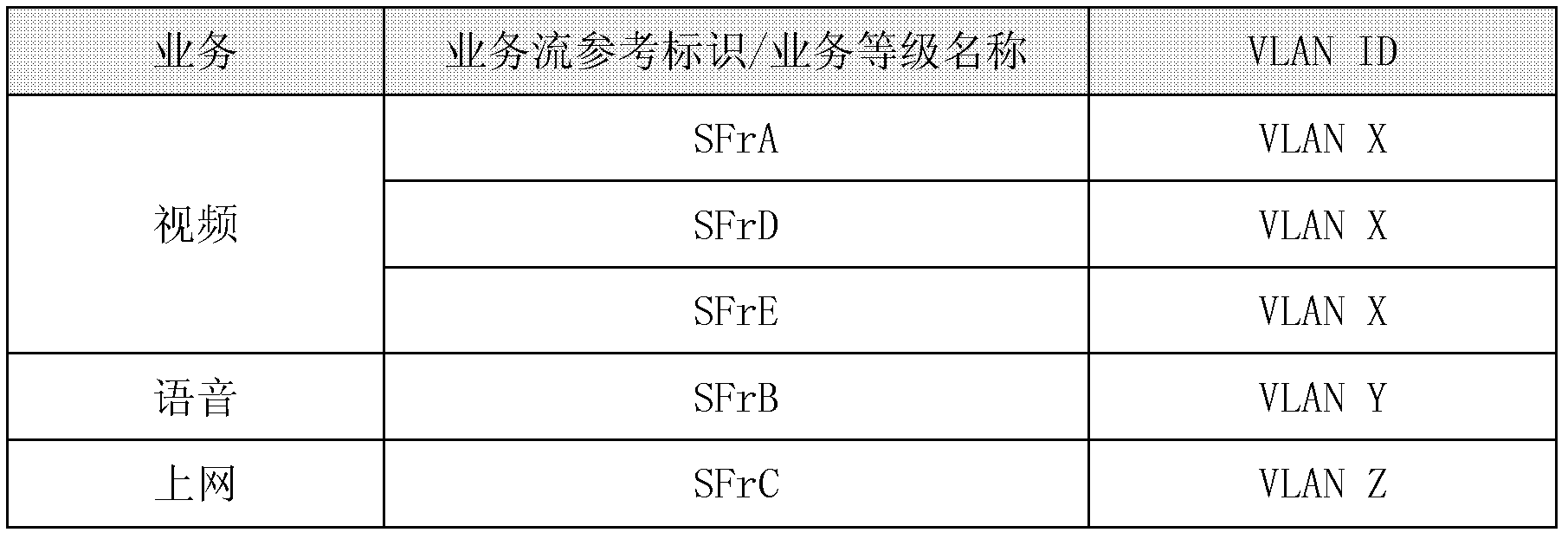
InactiveCN102546118AAchieve deliveryError preventionNetworks interconnectionData streamUplink transmission
The invention discloses a service forwarding and priority mapping method for a China-data over cable system interface specification (C-DOCSIS) system. The method comprises the following steps that: in an uplink direction, a C-DOCSIS head end resolves received C-DOCSIS frames; the C-DOCSIS head end converts the data payload of the C-DOCSIS frames into a standard Ethernet frame structure according to the control field of C-DOCSIS frame headers and performs uplink transmission on the frames, wherein the C-DOCSIS head end performs virtual local area network (VLAN) information mapping on the C-DOCSIS frames when performing standard Ethernet frame structure conversion, and the VLAN information mapping comprises VLAN identity (VLAN ID) mapping and VLAN priority mapping; in a downlink direction, the C-DOCSIS head end performs VLAN TAG information stripping on received Ethernet frames; and the C-DOCSIS head end performs data flow feature matching on the Ethernet frames, performs frame classification, quality of service (QoS) scheduling and forwarding on the Ethernet frames according to matched data flow features, the Ethernet frames are encapsulated into C-DOCSIS data frames, and the C-DOCSIS head end performs downlink transmission on the C-DOCSIS data frames. By the method, delivery of service identification and service priority is realized, and service identification information and service priority information can be reserved when the C-DOCSIS head end bridges a C-DOCSIS and a gathering network.
Owner:国家广播电影电视总局广播电视规划院 +2
QoS scheduler and method for implementing quality of service with cached status array
InactiveUS20030081544A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsArray data structureImage resolution
A QoS scheduler, scheduling method, and computer program product are provided for implementing Quality-of-Service (QoS) scheduling with a cached status array. A plurality of calendars are provided for scheduling the flows. An active flow indicator is stored for each calendar entry in a calendar status array (CSA). A cache copy subset of the active flow indicators from the calendar status array (CSA) is stored in a cache. The calendar status array (CSA) is updated based upon a predefined calendar range and resolution. The cache copy subset of the active flow indicators from the calendar status array (CSA) is used to determine a given calendar for servicing. The subset of the active flow indicators from the calendar status array (CSA) is used to increment a current pointer (CP) by an identified number of positions up to a current time (CT) value, where the identified number of positions is equal to a variable number of inactive flow indicators up to the current time (CT) value and the identified number of positions has a maximum value equal to a number of entries in the cache.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for multiuser QOS dispatching
InactiveCN1949748ASolve resource problemsTroubleshoot configuration issuesData switching networksDistributed computingSoftware
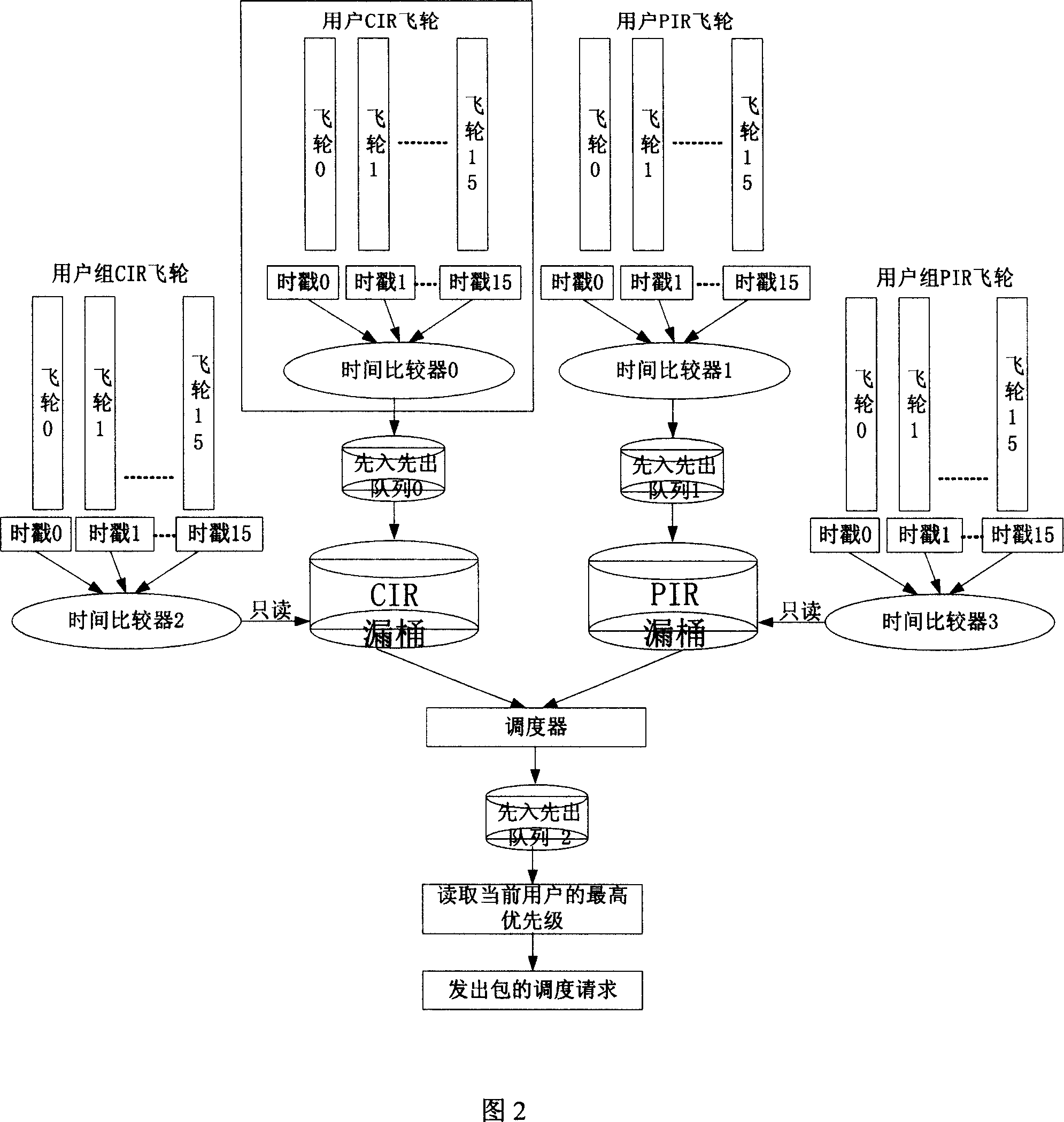
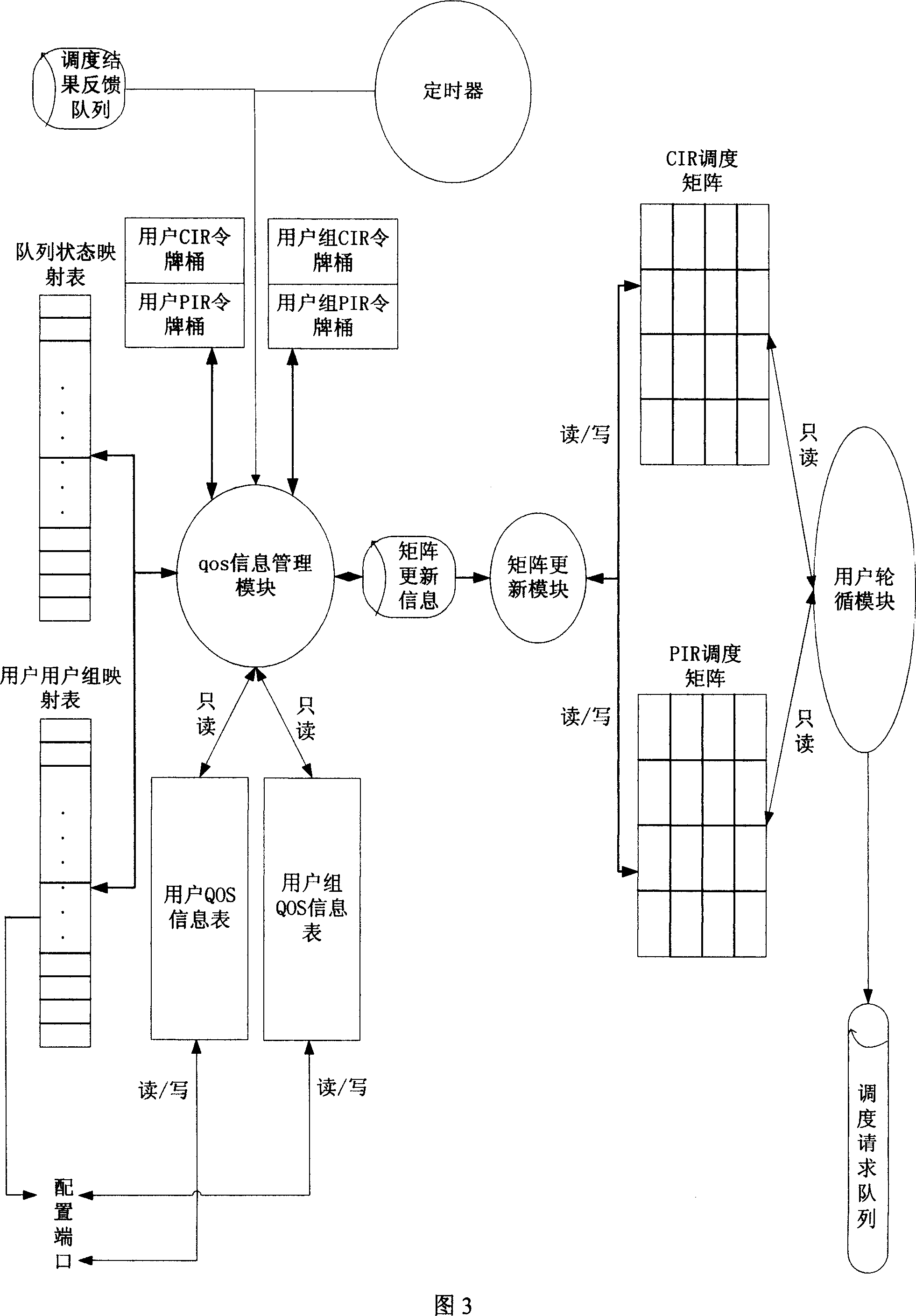
The invention discloses a method and device for making QOS scheduling for multiple users, belonging to communication technical field. And the invention advances a method for implementing MDRR algorithm by token bucket and finally implementing users'QOS scheduling, comprising the concrete steps of: according to the configured QOS informatiojn table, regularly refreshing token number in token bucket; finding the to-be-scheduled user number in scheduling matrix in round robin mode; according to the user number, sending out scheduling request; obtaining the previous scheduling result feedback, and executing the scheduling request. And the invention also provides a device for implementing QOS scheduling for multiple users, comprising configuration module, token bucket refreshing module, scheduling matrix updating module, round robin module, scheduling request sending module and token removing module.
Owner:BEIJING HUAWEI DIGITAL TECH
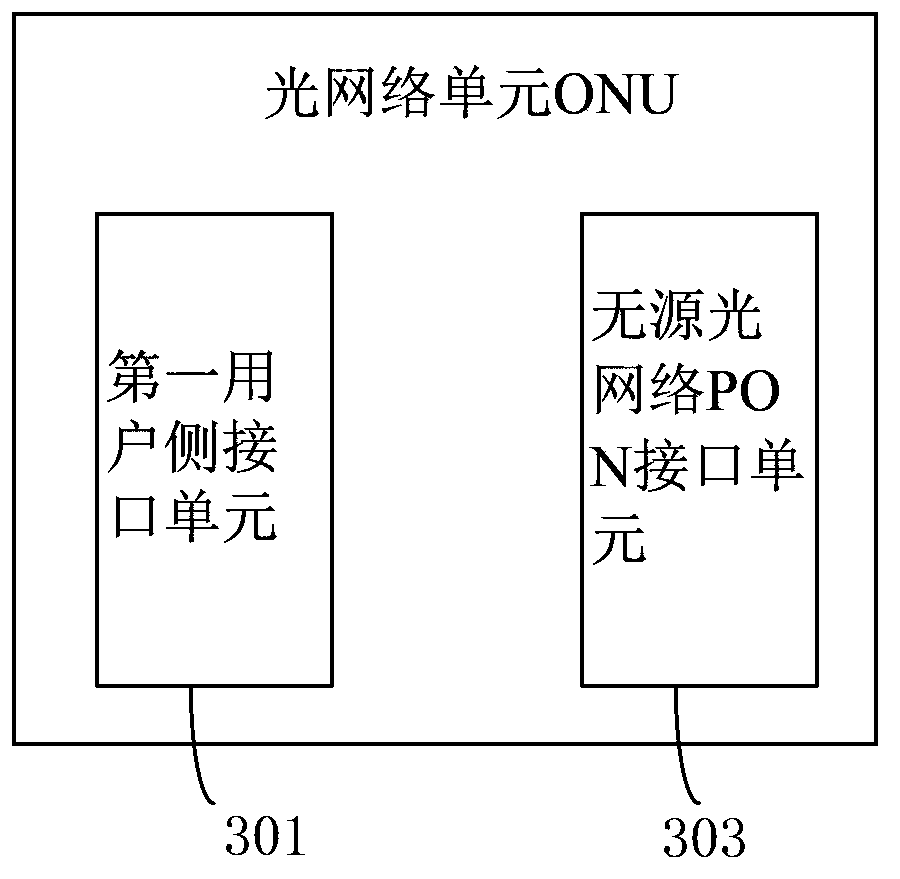
ONU, OLT and information transmission method
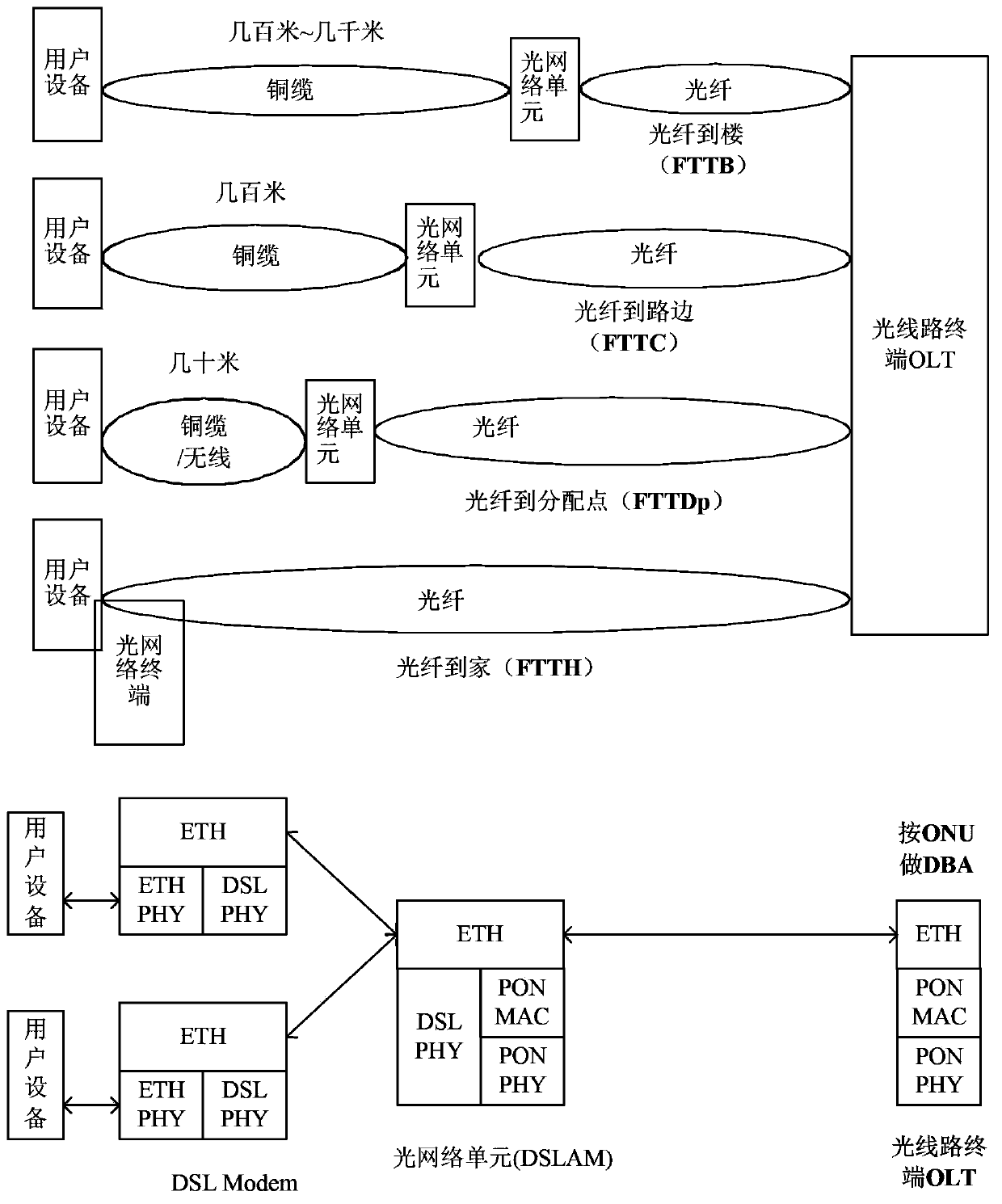
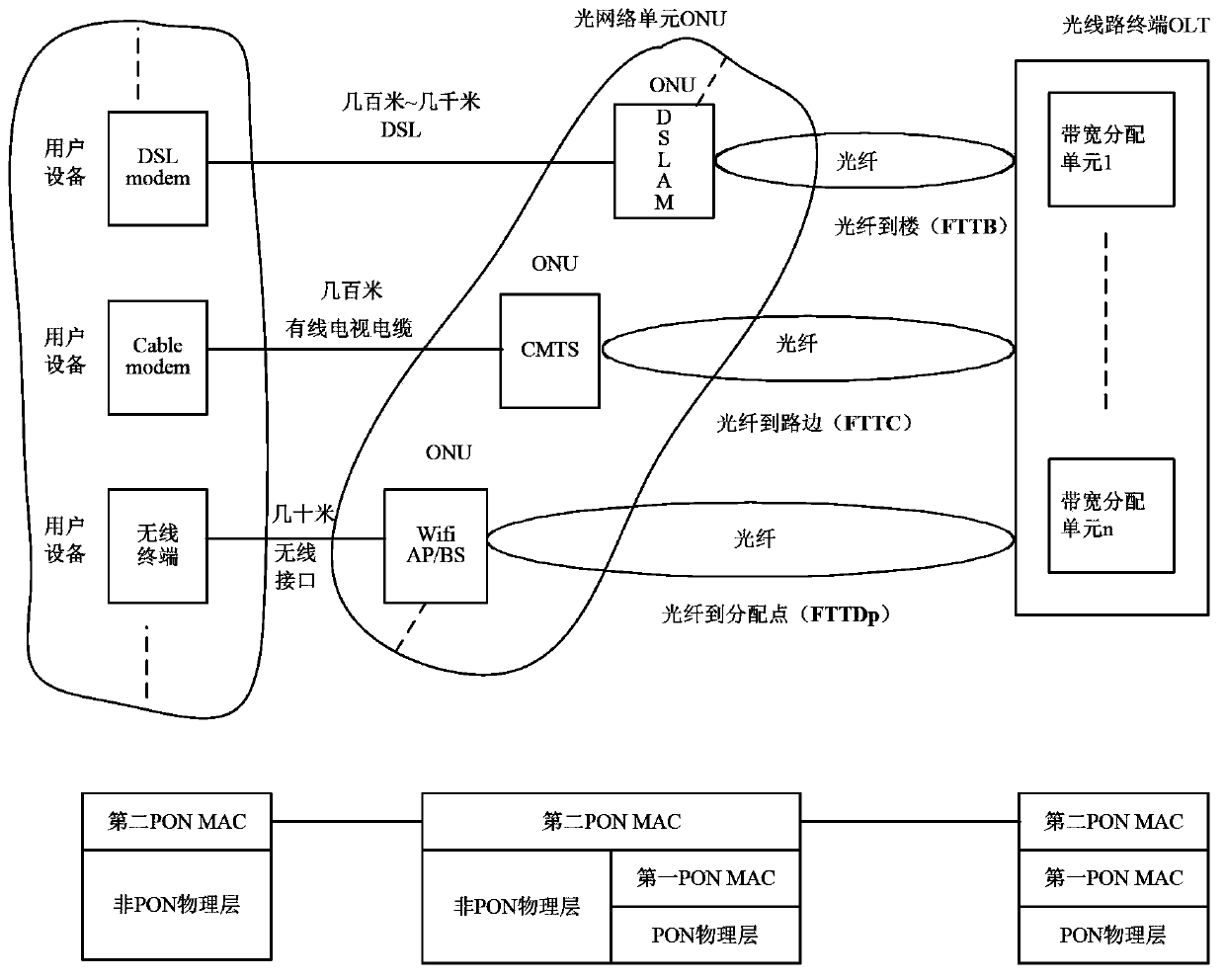
ActiveCN104243092AEnsure functionMake sure user devices are functionalMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionComputer hardwareInformation transmission
The invention discloses an ONU, an OLT and an information transmission method, and belongs to the field of network communication. The ONU comprises a user side interface unit and a PON interface unit. The PON interface unit is used for receiving a first PON physical layer frame from the OLT and removing a first PON physical layer frame header and a first PON MAC frame header in the first PON physical layer frame so as to obtain a first frame. The first user side interface unit is used for packaging a first non-PON physical layer frame header on a second frame obtained by the first user side interface unit so as to obtain a first non-PON physical layer frame and sending the first non-PON physical layer frame to user equipment, wherein the second frame is the first frame or a frame obtained based on the first frame. In the data transmission process, QoS scheduling is not needed, an expensive queue scheduling memorizer is omitted, and therefore cost is reduced.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
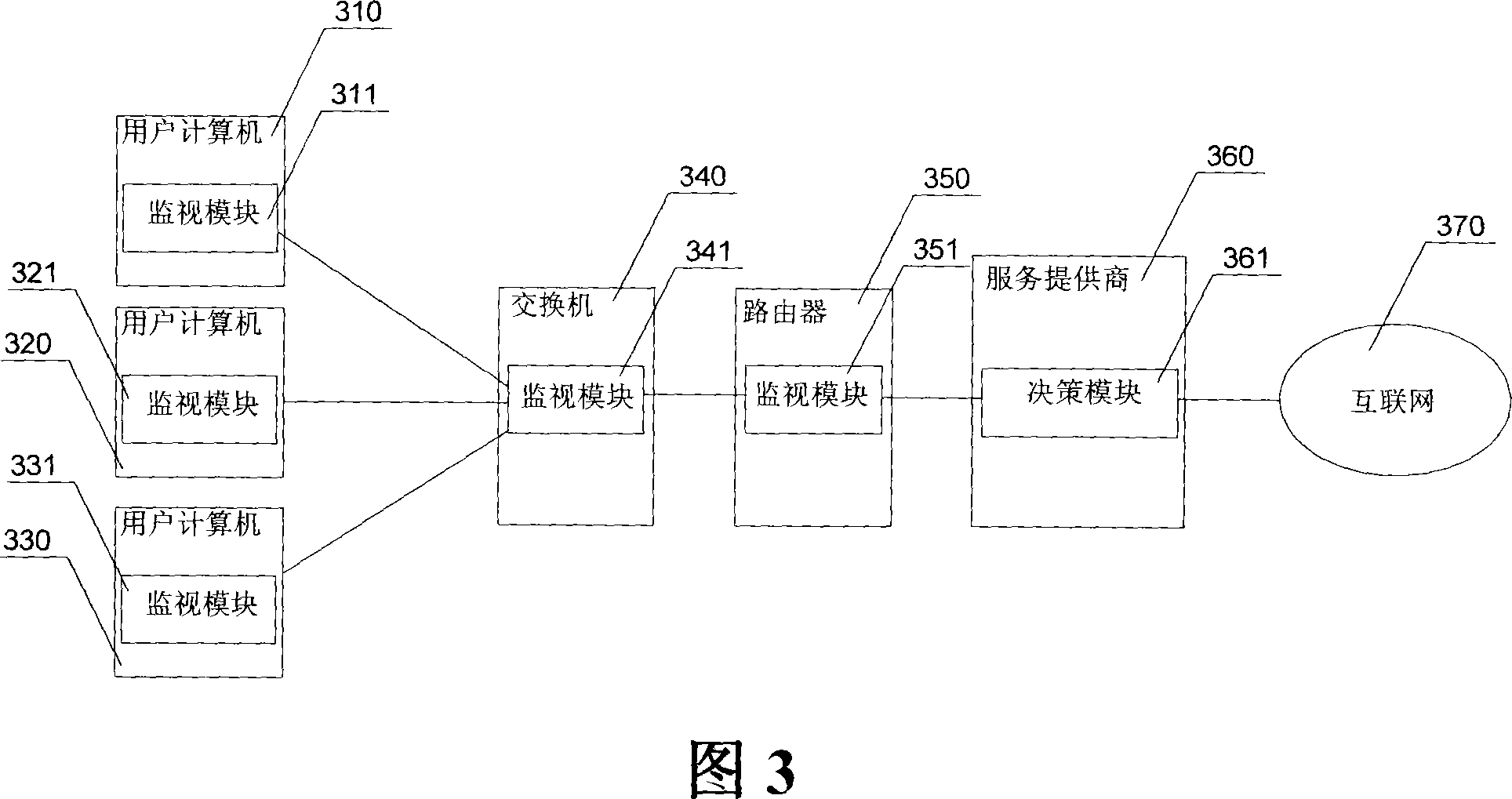
Dynamic multilevel service quality assurance dispatching system and method
ActiveCN101060434AReasonable distributionAccurate guarantee of service qualityData switching networksThe InternetNetwork topology
The provided dynamic hierarchical QoS guarantee scheduling system comprises: a user computer, an exchange, a router, an ISP terminal, and the internet, wherein the PC reports network topology message to the ISP terminal, a monitor module in PC / exchange / router collects QoS message, and a decision module in ISP regulating H-QoS scheduling according to collected message. This invention collects network topology and QoS message real-time to regulate H-QoS scheduling strategy for precise allocation.
Owner:ZTE CORP
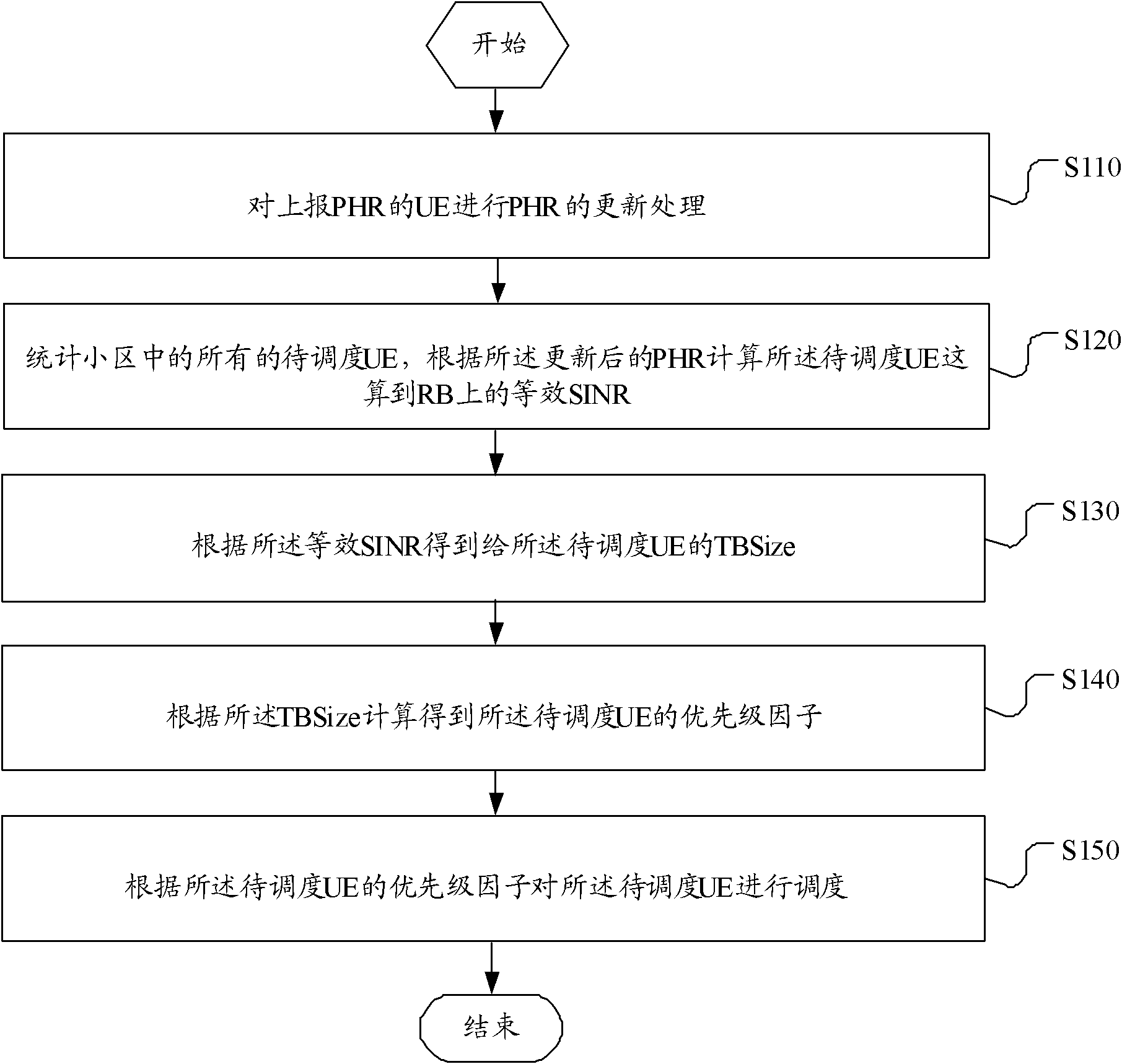
Method for carrying out QoS scheduling according to PHR and server
ActiveCN102595516AImprove throughputReasonable QoS priority calculationPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Resource block
The invention relates to a method for carrying out QoS scheduling according to PHR and a server. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out updating processing of the PHR on user equipment (UE) which reports the power head room (PHR); counting all UE to be scheduled in a cell, and according to updated PHR, calculating an equivalent signal to noise ratio (SINR) when converting the UE to be scheduled into a single resource block (RB); according to the equivalent SINR, obtaining a data packet size TBSize of the UE to be scheduled; according to the TBSize, calculating a priority factor of the UE to be scheduled; scheduling the UE to be scheduled according to the priority factor of the UE to be scheduled. According to the method for carrying out the QoS scheduling according to the PHR and the server, priority ordering is carried out through the power head room of the UE, thus uplink QoS priority calculation is more reasonable, throughput of a system cell is raised, and the stability of a system is raised.
Owner:ZTE CORP
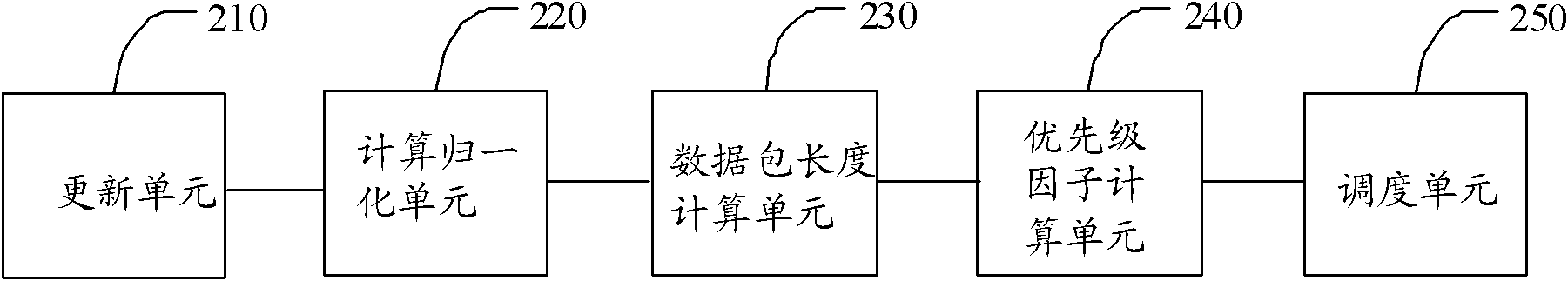
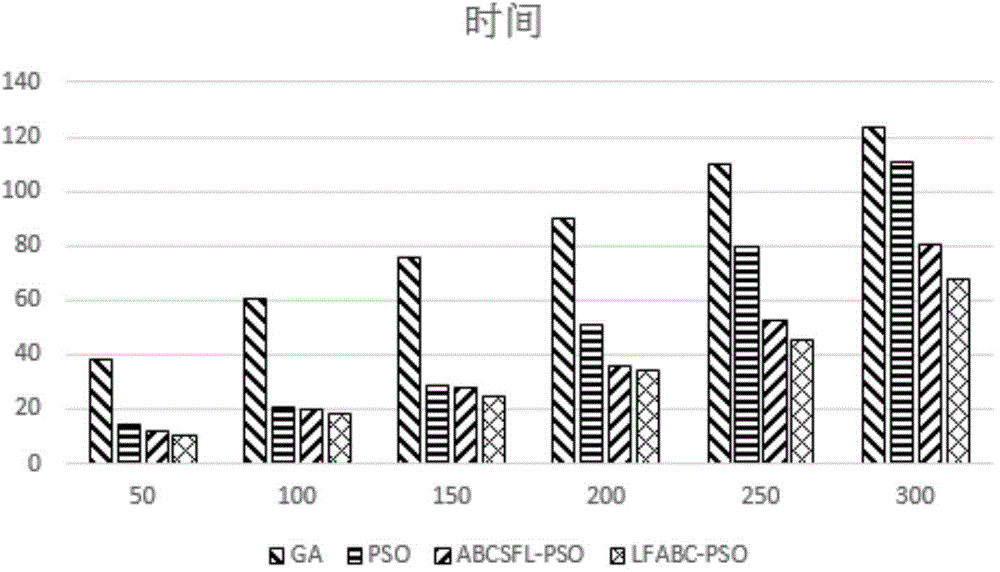
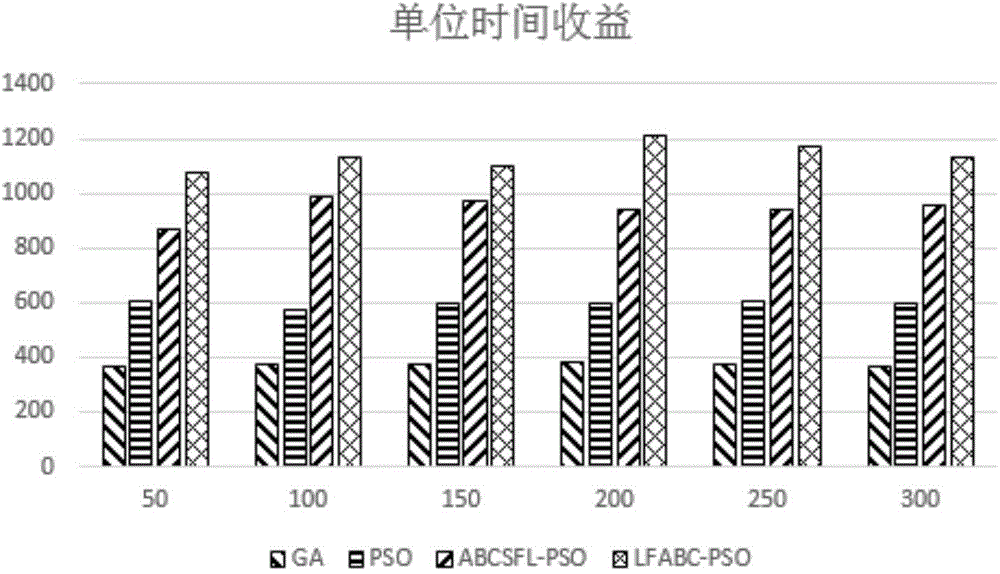
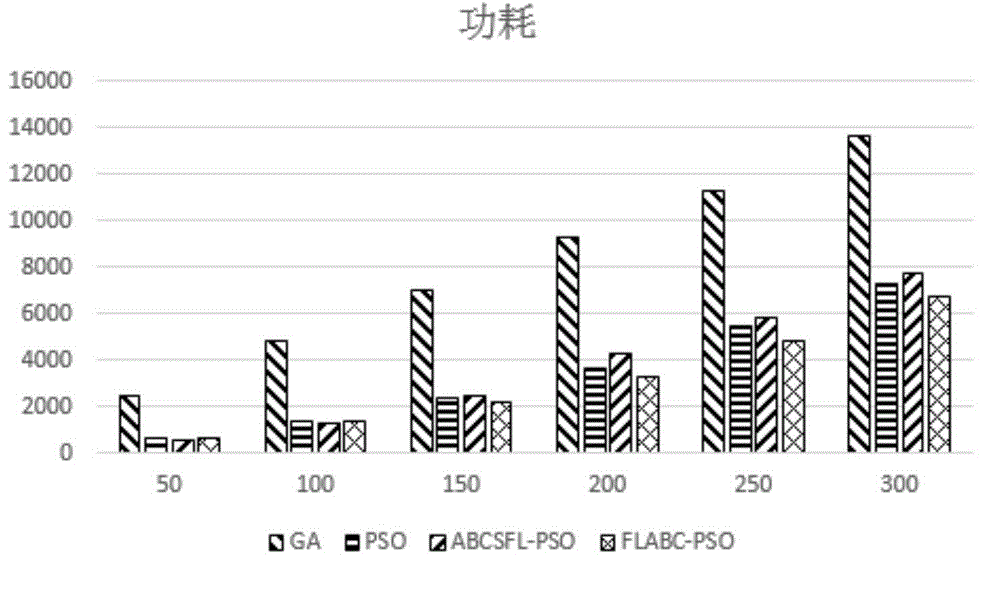
Cloud computing task scheduling method of artificial bee colony particle swarm algorithm based on Levy flight
The invention discloses a cloud computing task scheduling model based on service revenue and power dissipation and a cloud computing task scheduling method of an artificial bee colony particle swarm algorithm based on Levy flight. A multi-QoS scheduling model with introduced processor power dissipation and task scheduling revenue is provided for achieving a green cloud computing thinking. The artificial bee colony particle swarm algorithm based on Levy flight is provided for achieving multi-QoS cloud computing task scheduling. An artificial bee colony local search strategy is introduced in the particle swarm algorithm to improve the local search precision of the algorithm. Levy operation is conducted on the global optimum to avoid local optimum, and therefore the convergence precision is improved. The method can effectively increase the revenue of the cloud computing task scheduling, and can shorten user waiting time and can reduce processor power dissipation.
Owner:杭州远创新智信息技术有限公司
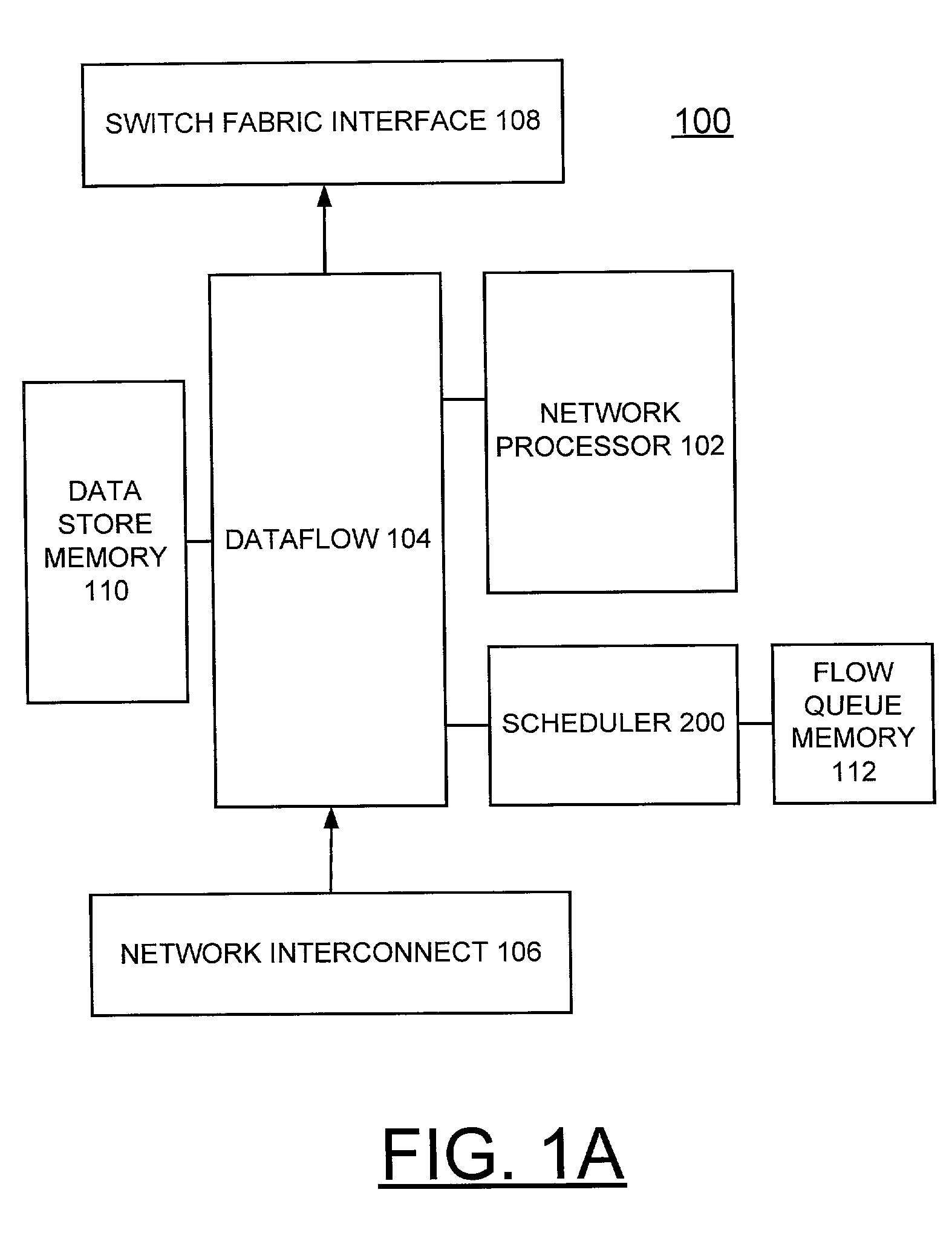
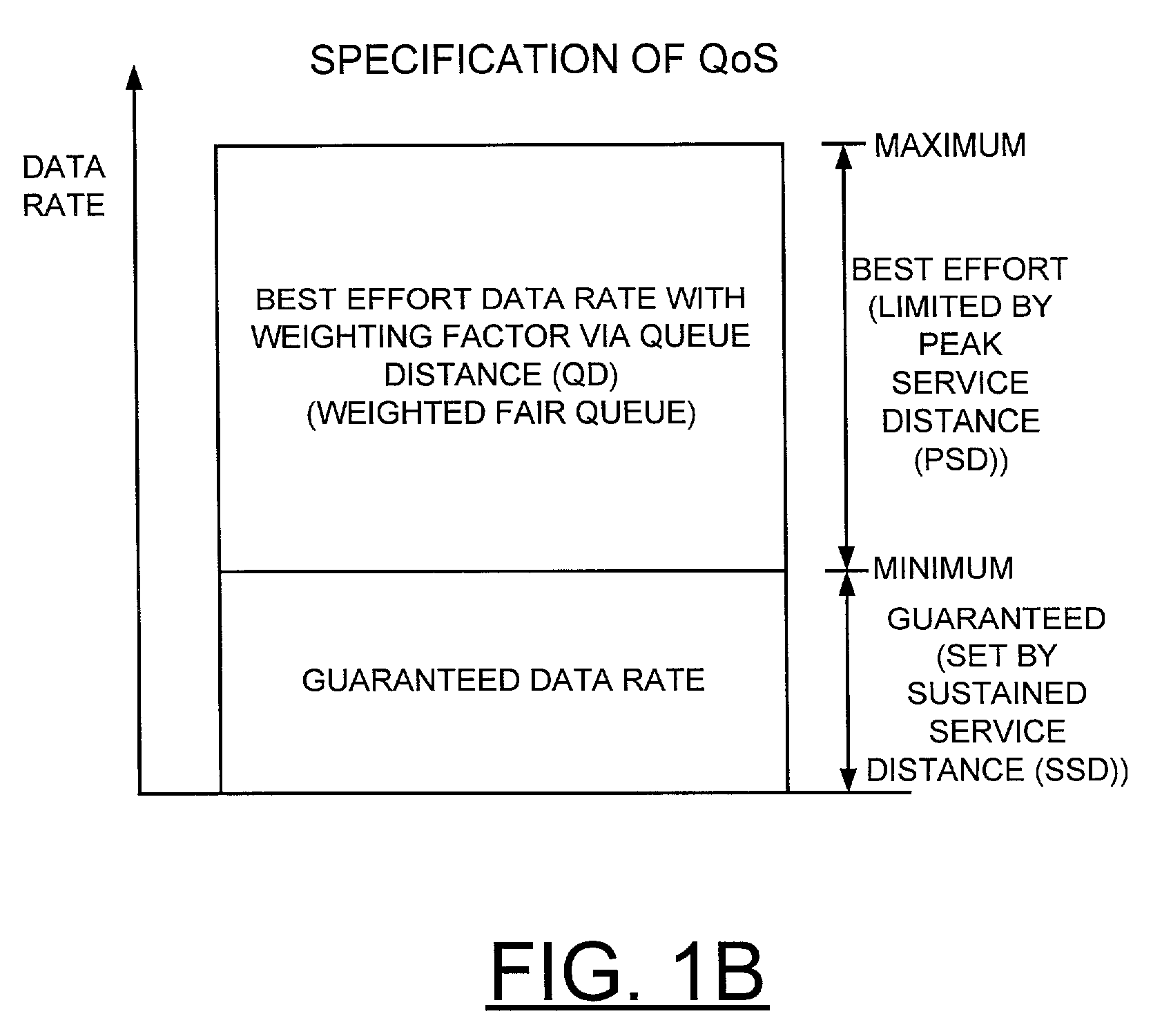
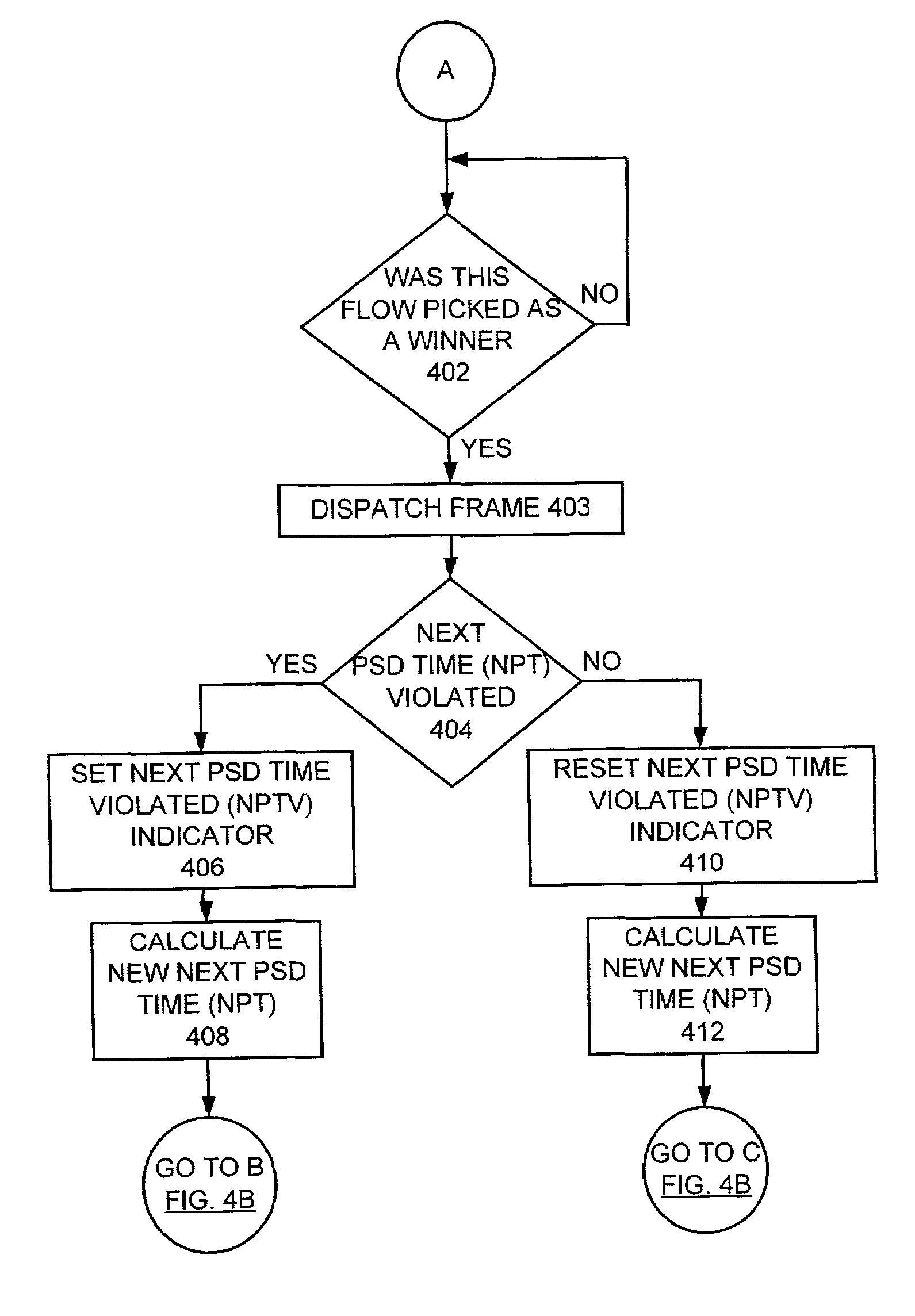
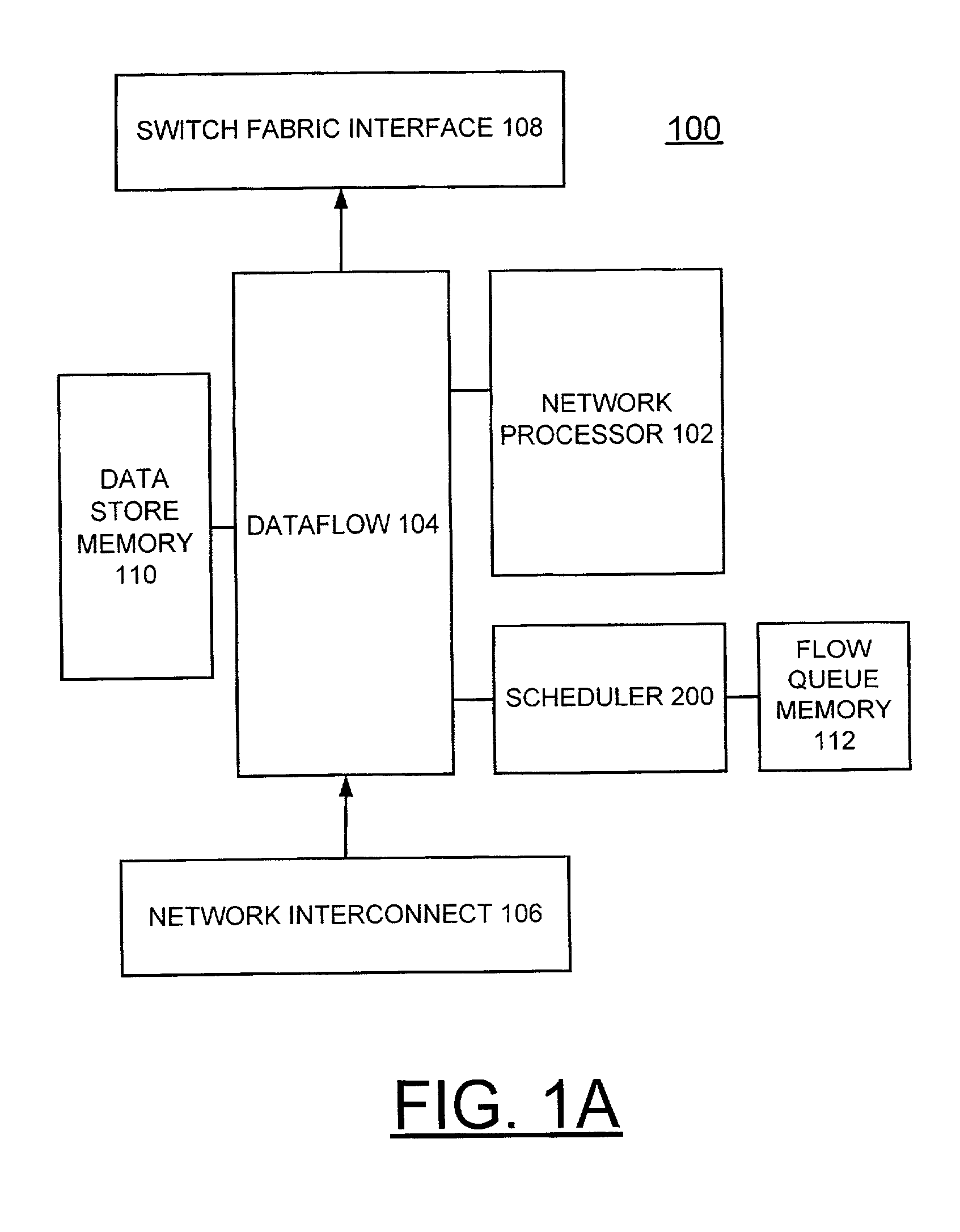
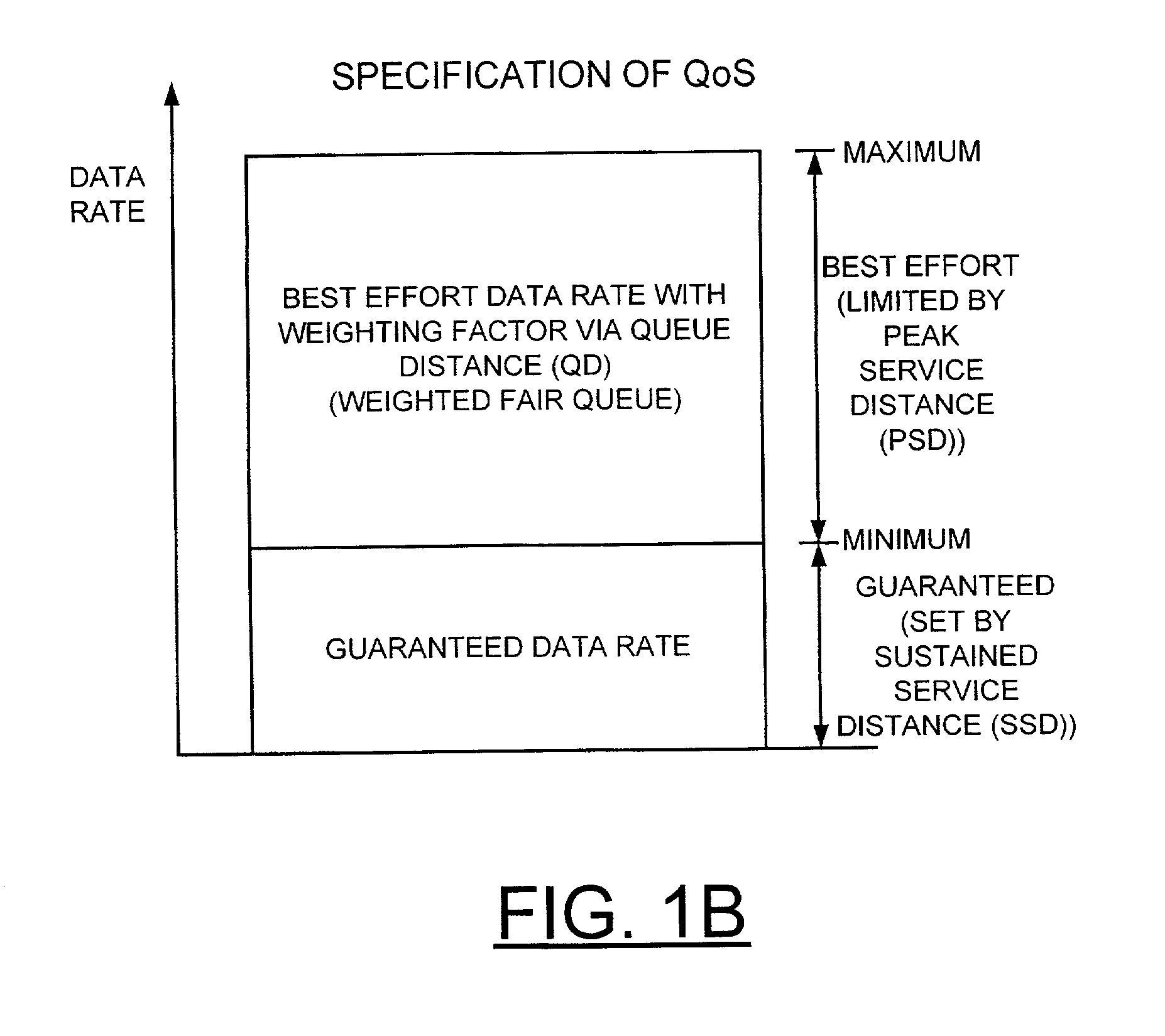
QoS scheduler and method for implementing peak service distance using next peak service time violated indication
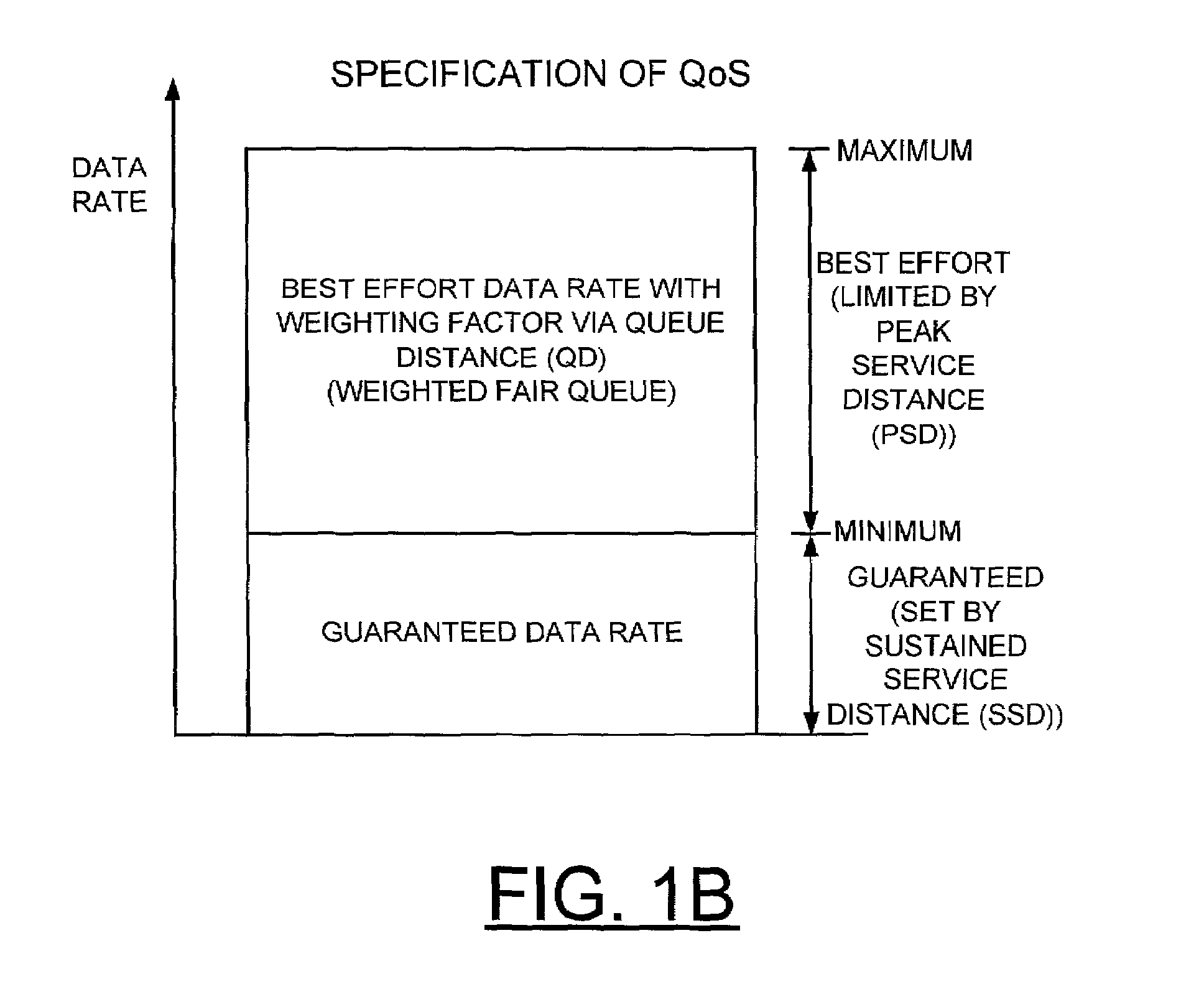
InactiveUS6973036B2Overcome disadvantagesError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPeak value
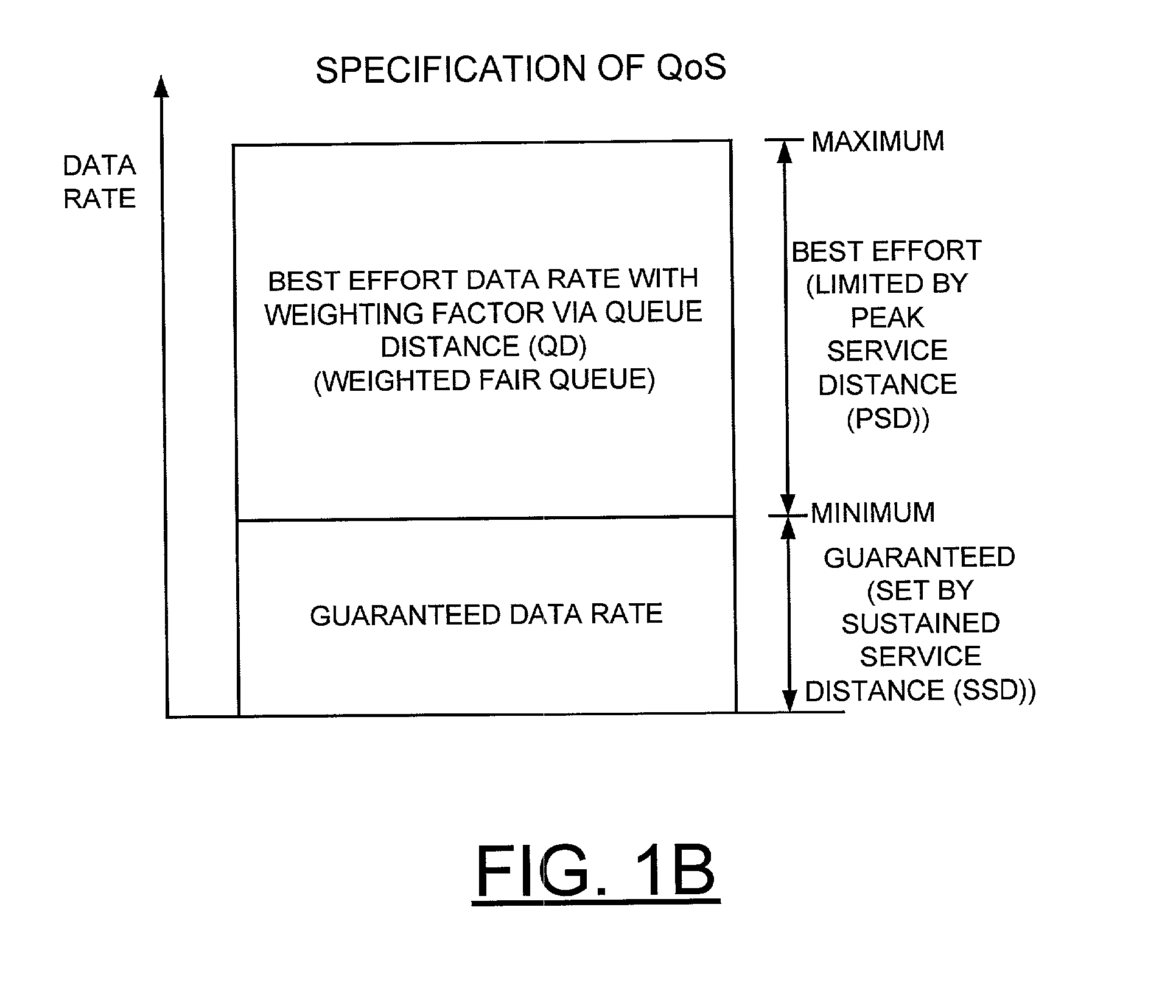
A scheduler and scheduling method implement peak service distance using a next peak service time violated (NPTV) indication. A flow scheduled on a best effort or weighted fair queue (WFQ) is identified for servicing and a frame is dispatching from the identified flow. A next PSD time (NPT) being violated is checked for the flow. Responsive to identifying the next PSD time (NPT) being violated for the identified flow, a NPTV indicator is set. Alternatively, responsive to identifying the next PSD time (NPT) not being violated for the identified flow, the NPTV indicator is reset. A next PSD time (NPT) value is calculated for the flow. Checking for more frames to be dispatched from the flow is performed. Responsive to identifying no more frames to be dispatched from the flow, the NPTV indicator is utilized to identify a calendar for attaching the flow upon a new frame arrival for the flow. If the NPTV indicator is not set when the flow goes empty, upon a new frame arrival for the flow, the flow is attached to a weighted fair queue (WFQ) ring using a queue distance calculation. If the NPTV indicator is set when the flow goes empty, upon a new frame arrival for the flow, then it is determined if the next PSD time (NPT) value for the flow has been passed. If the next PSD time (NPT) value has been passed, then the flow is attached to the weighted fair queue (WFQ) ring using the queue distance calculation. If the next PSD time (NPT) value has not been passed, then the flow is attached to a peak bandwidth service (PBS) calendar using the next PSD time (NPT) value.
Owner:IBM CORP
HQoS control method, RSG and HQoS control system
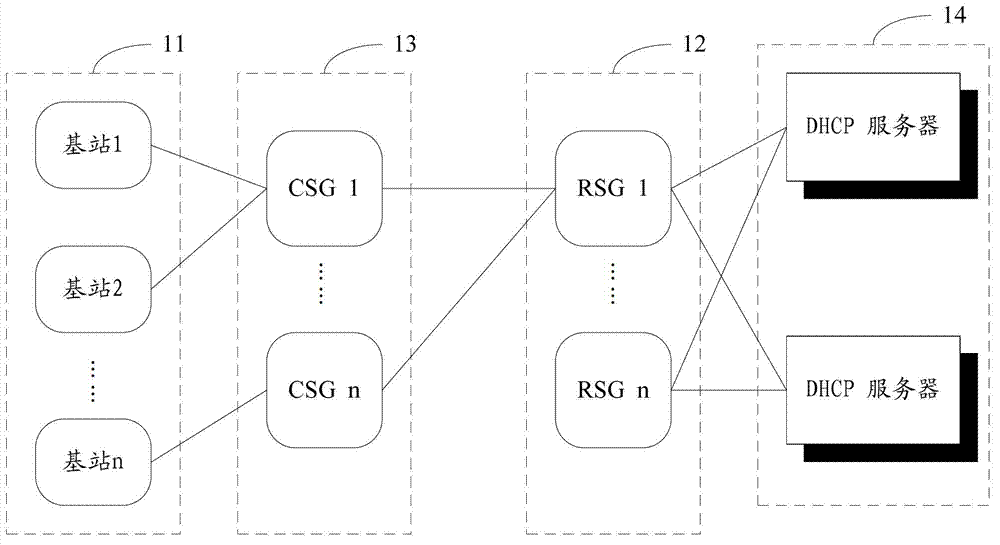
ActiveCN103249091AMitigate the risk of concentrationEnsure safe crossingNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksControl systemIp address
The invention is applicable to the field of communication and provides an HQoS (Hierarchical Quality of Service) control method, an RSG (Radio Network Controller Site Gateway) and an HQoS control system, wherein the RSG is connected with a plurality of CSGs (Content Service Gateway), each CSG in the CSGs is connected with a plurality of base stations, and the RSG is used for configuring bandwidth limitation parameters for each CSG in the CSGs; the RSG is used for creating different AAA regions for network segments with different IP addresses, and configuring QoS (Quality of Service) scheduling parameterS in each AAA region; the RSG determines the bandwidth limitation parameters of the CSG connected with a first base station, and determines the QoS scheduling parameters of the first base station; and the configuration parameters are used for indicating SSG connected with the first base station and also used for indicating the AAA region corresponding to the first base station. According to the invention, the risks of over concentration of base station gateways can be reduced greatly, and that service message traverses a secondary pipeline of a fixed network operator safely can be ensured effectively.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
QoS scheduler and method for implementing quality of service anticipating the end of a chain of flows
InactiveUS6982986B2Overcome disadvantagesTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDistributed computingStreamflow
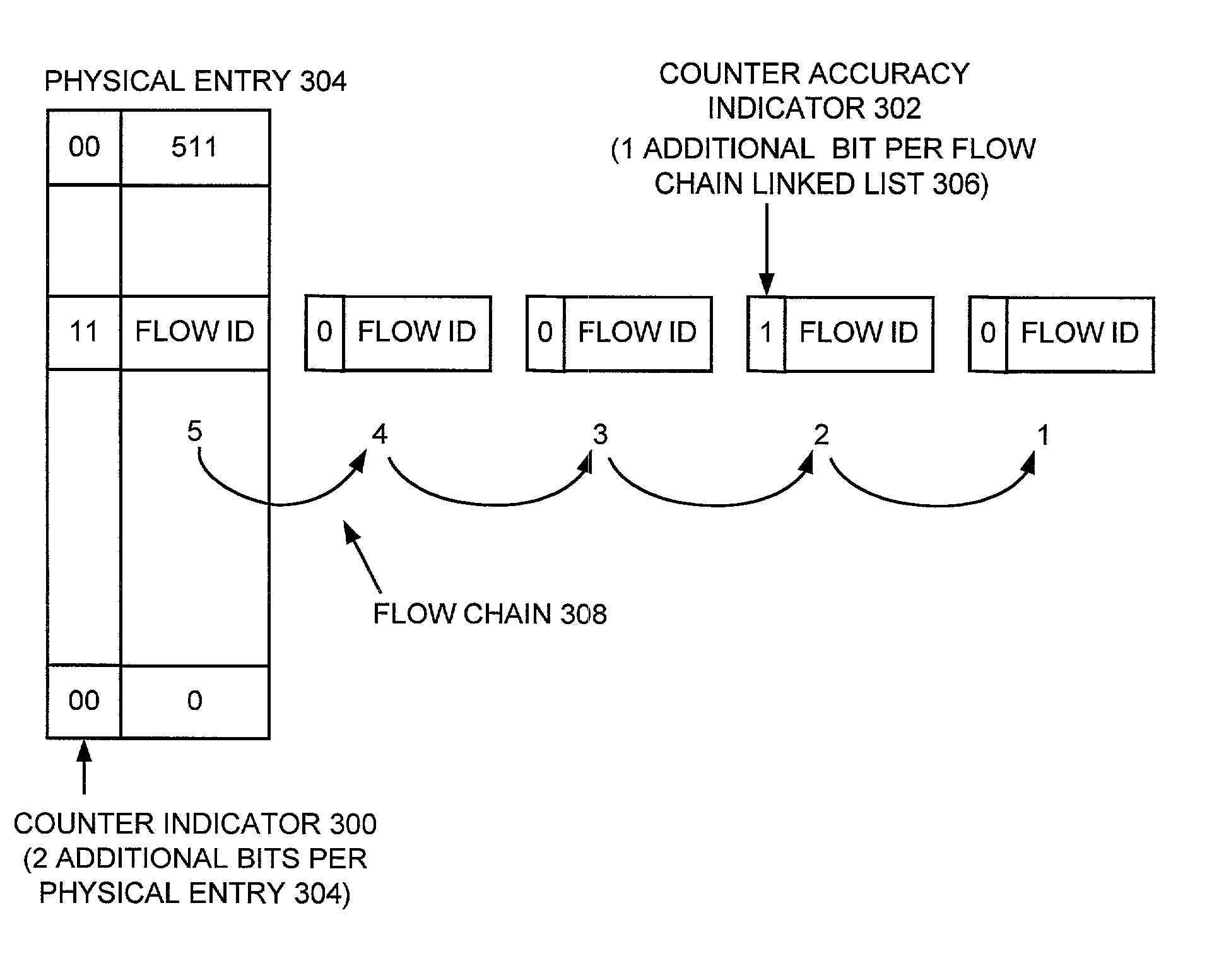
A QoS scheduler, scheduling method, and computer program product are provided for implementing Quality-of-Service (QoS) scheduling with detecting and anticipating the end of a chain of flows. A first indicator is provided for indicating a number of flows being chained to a physical entry. A second indicator is provided for indicating when the first indicator has saturated. The second indicator is set active for a flow whose chaining causes the first indicator to saturate. During de-chaining of the flows from the physical entry, the second indicator is used to determine when the first indicator becomes accurate to begin decrementing the first indicator. The first indicator is decremented for detecting the end of the chain of flows. Responsive to the first indicator being not saturated, the first indicator is used for anticipating the end of a chain of flows. The first indicator and the second indicator include a predefined number of bits or n-bits. The first indicator includes n−1 bits stored in a physical entry and the second indicator includes 1-bit stored in a chained link list.
Owner:IBM CORP
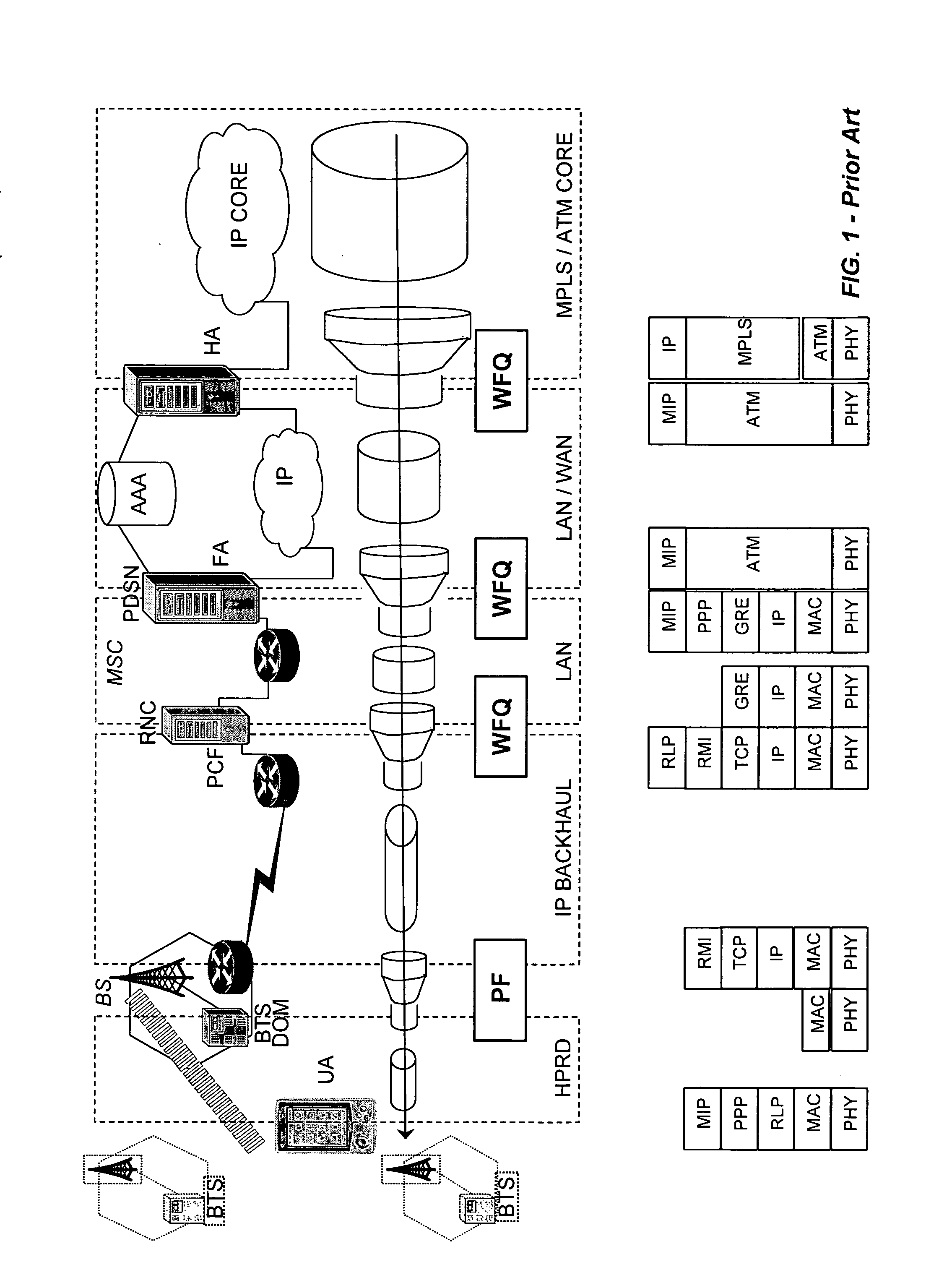
Method and system for enhanced packet transmission in cellular networks
InactiveUS7075911B2Improve approachAvoid problemsNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationData streamComputer science
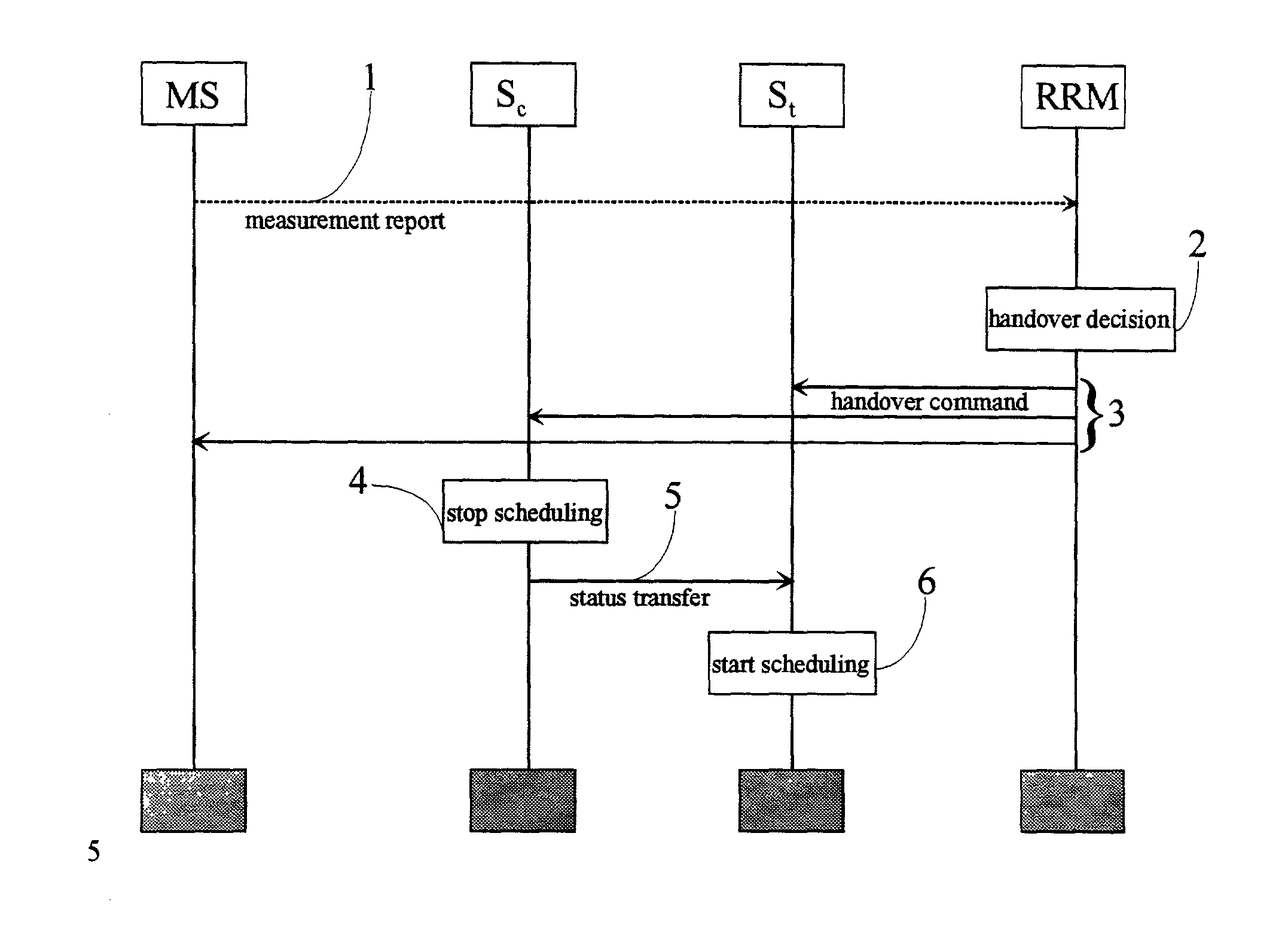
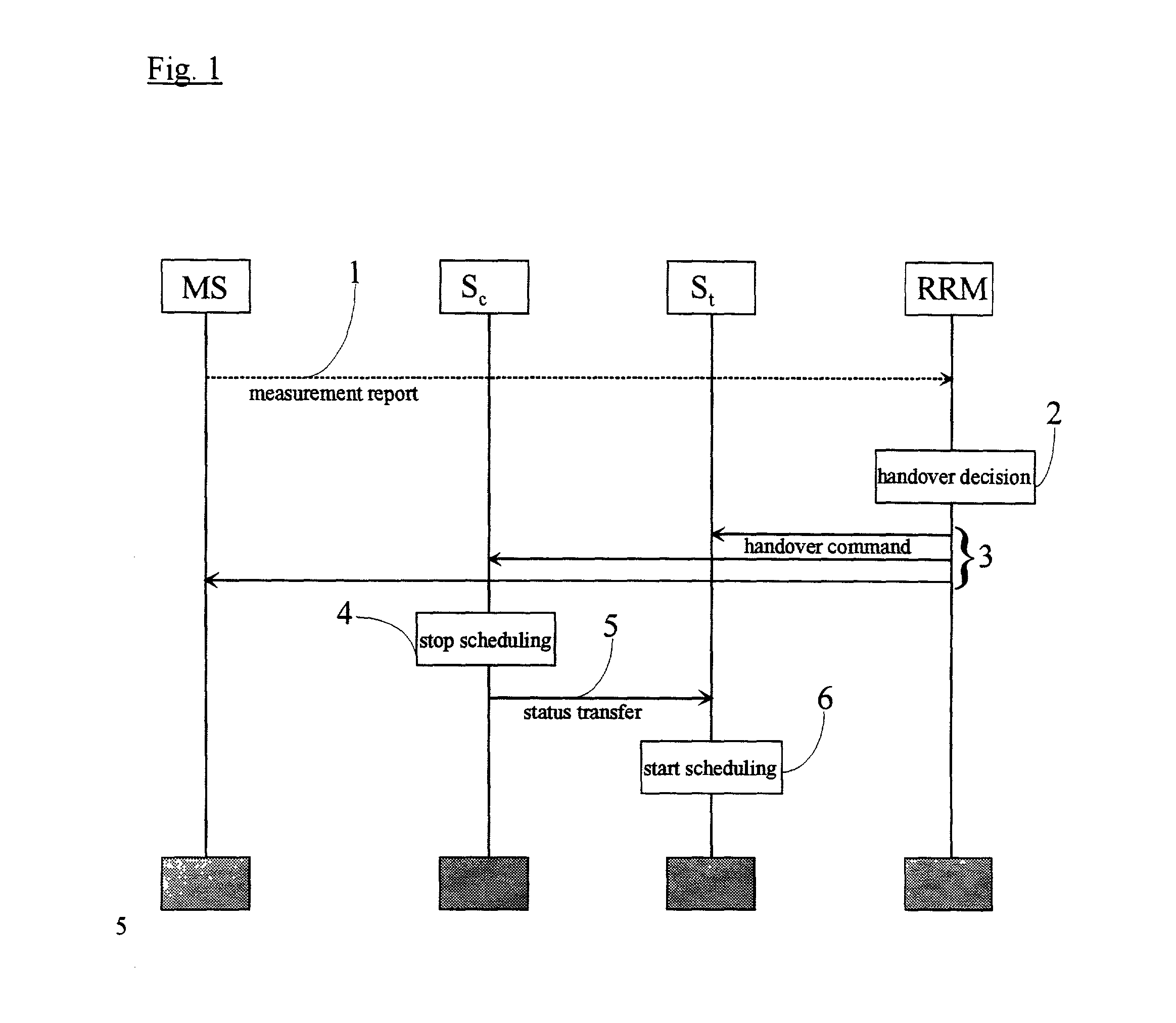
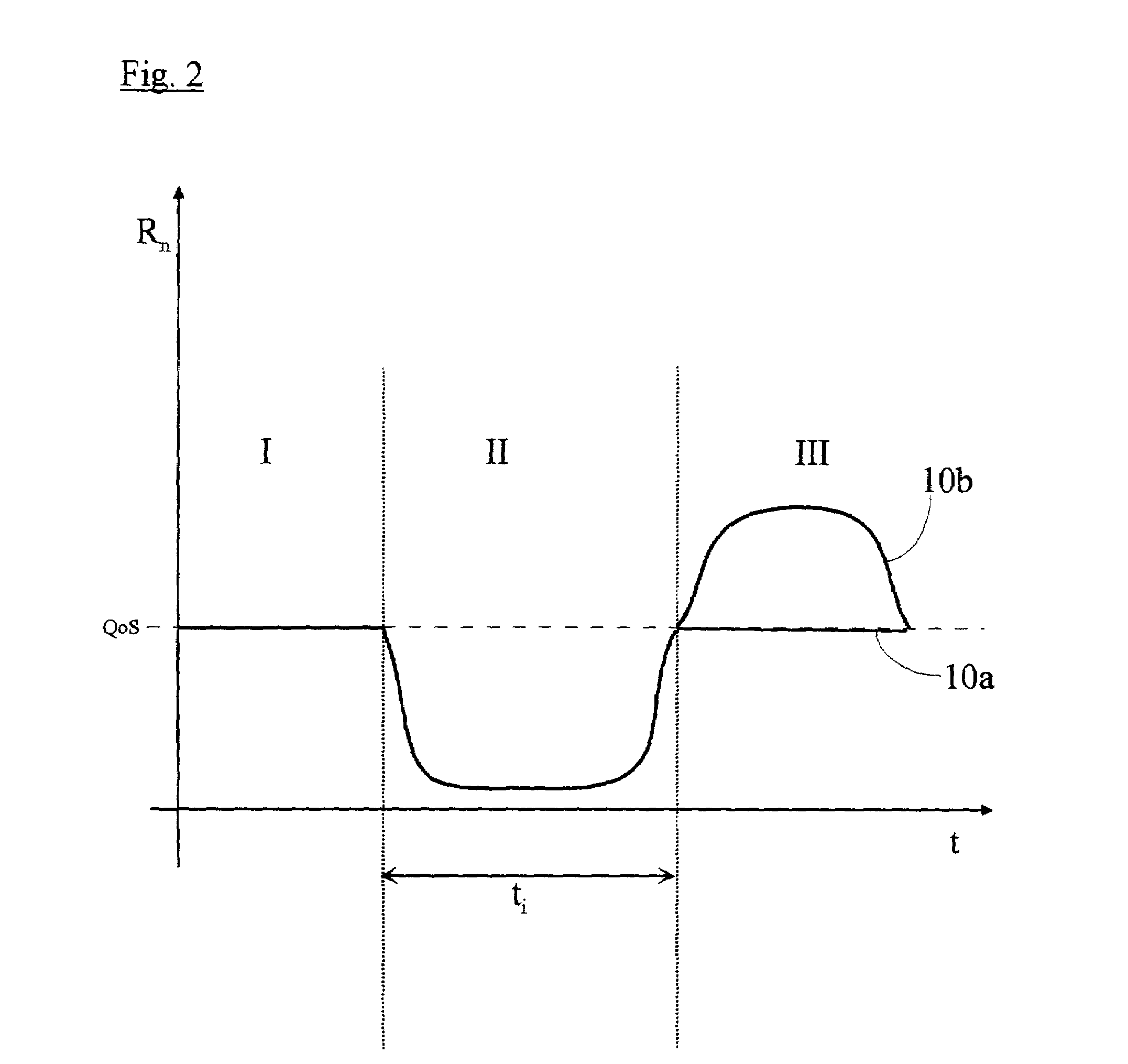
QoS scheduling is used for handling multiple data flows in packet switched cellular systems, especially in a packet switched mobile telecommunication system, wherein the scheduling mechanism of a specific cell is coupled with the scheduling mechanism of at least one second cell, in particular by transferring data between the specific cell and at least one second cell comprising a status information concerning data flow within the specific cell.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Message forwarding method, data processing method, device and network system
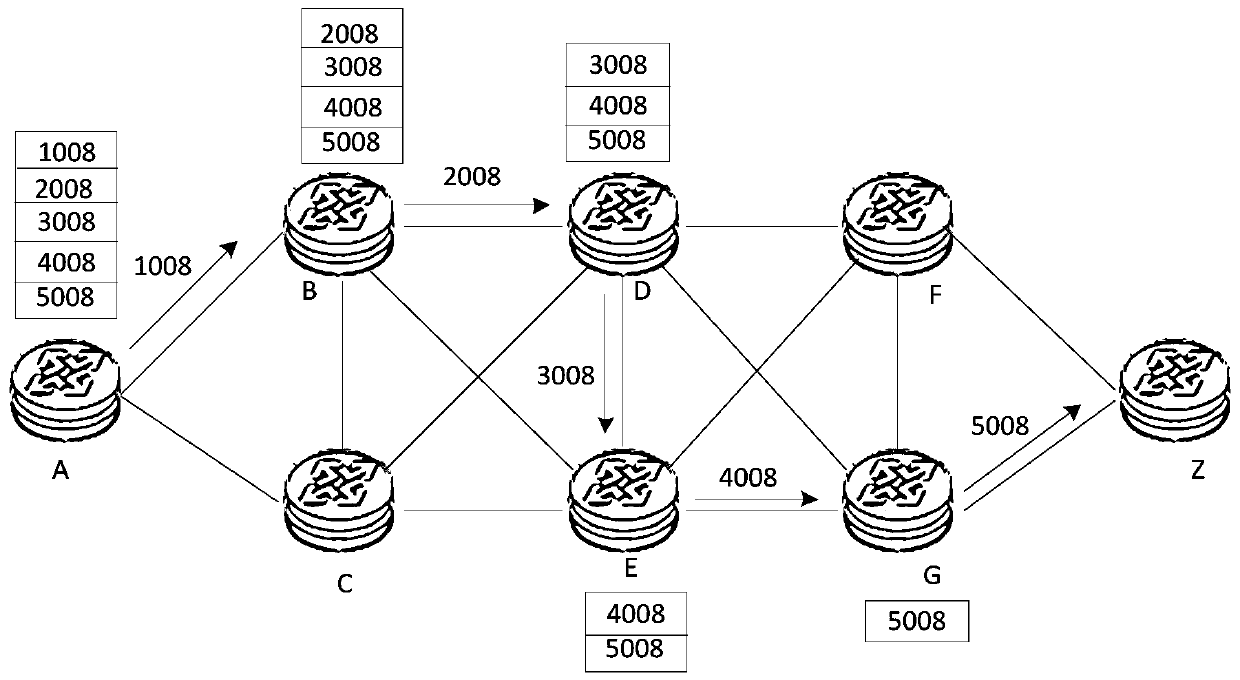
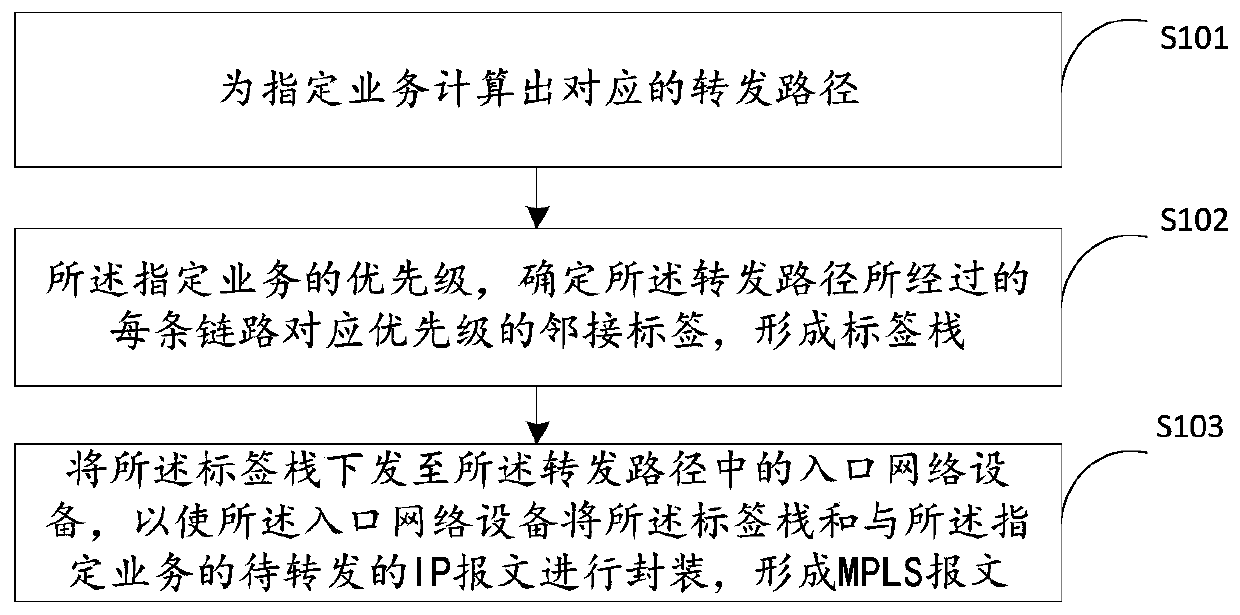
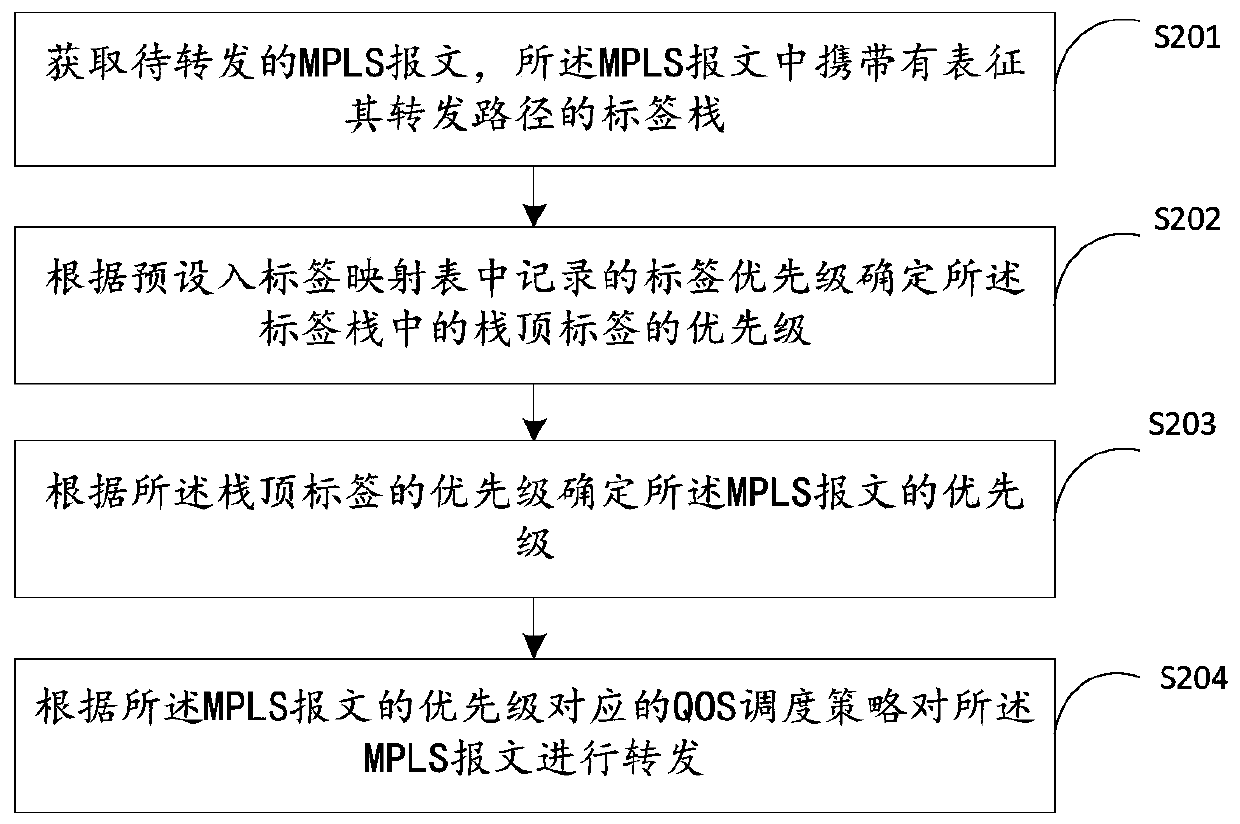
ActiveCN110351188AImplement Differentiated ServicesDiffServ RichData switching networksDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
The invention discloses a message forwarding method and device, a data processing method and device and a network system, and belongs to the technical field of data communication. The message forwarding method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-forwarded MPLS message, wherein the MPLS message carries a label stack representing a forwarding path of the MPLS message; determining the priority of a stack top label in the label stack according to the label priority recorded in a preset label mapping table; determining the priority of the MPLS message according to the priority of the stack toplabel; and scheduling the MPLS message according to the QOS scheduling strategy corresponding to the priority of the MPLS message. Priorities of labels are set in advance, therefore, when the message is forwarded, the priority of the MPLS message can be determined by determining the priority of the stack top label in the label stack, differentiated services are realized, and richer and finer differentiated services can be provided under the conditions of not changing the original MPLS processing logic and not increasing the system processing overhead.
Owner:MAIPU COMM TECH CO LTD
Method for providing QoS service for virtual special net user
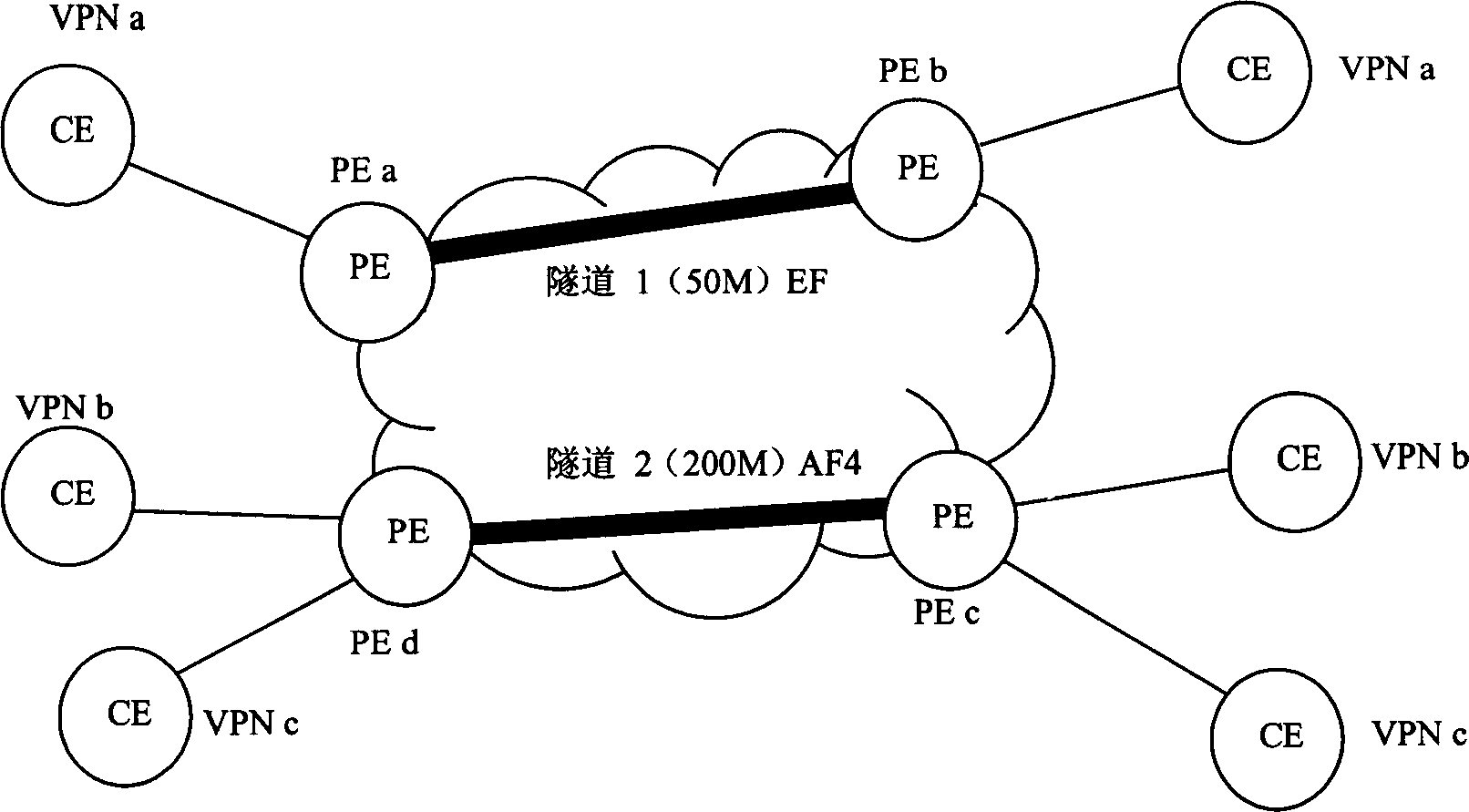
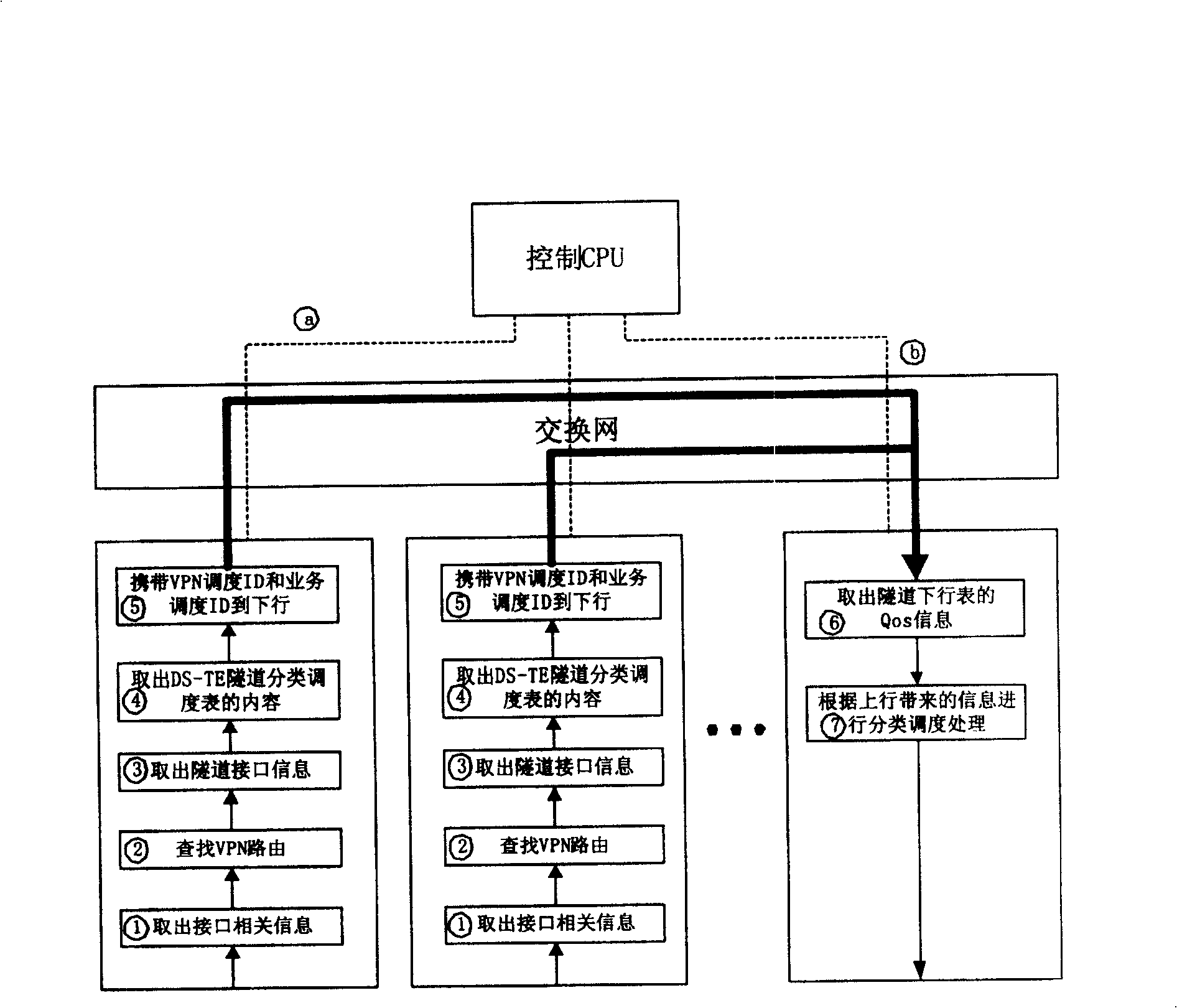
InactiveCN1859294AFine-grained divisionNetworks interconnectionDistributed computingValue-added service
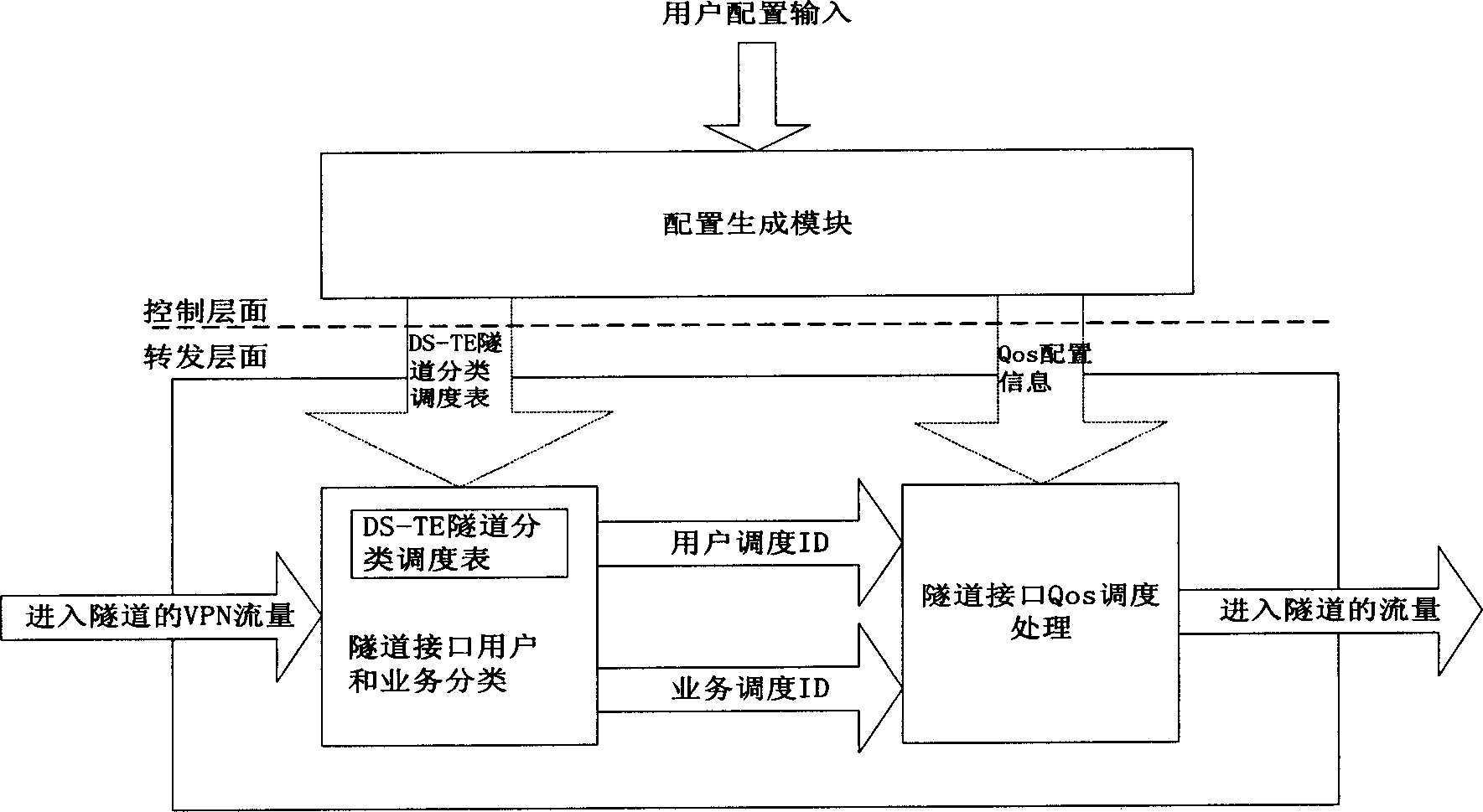
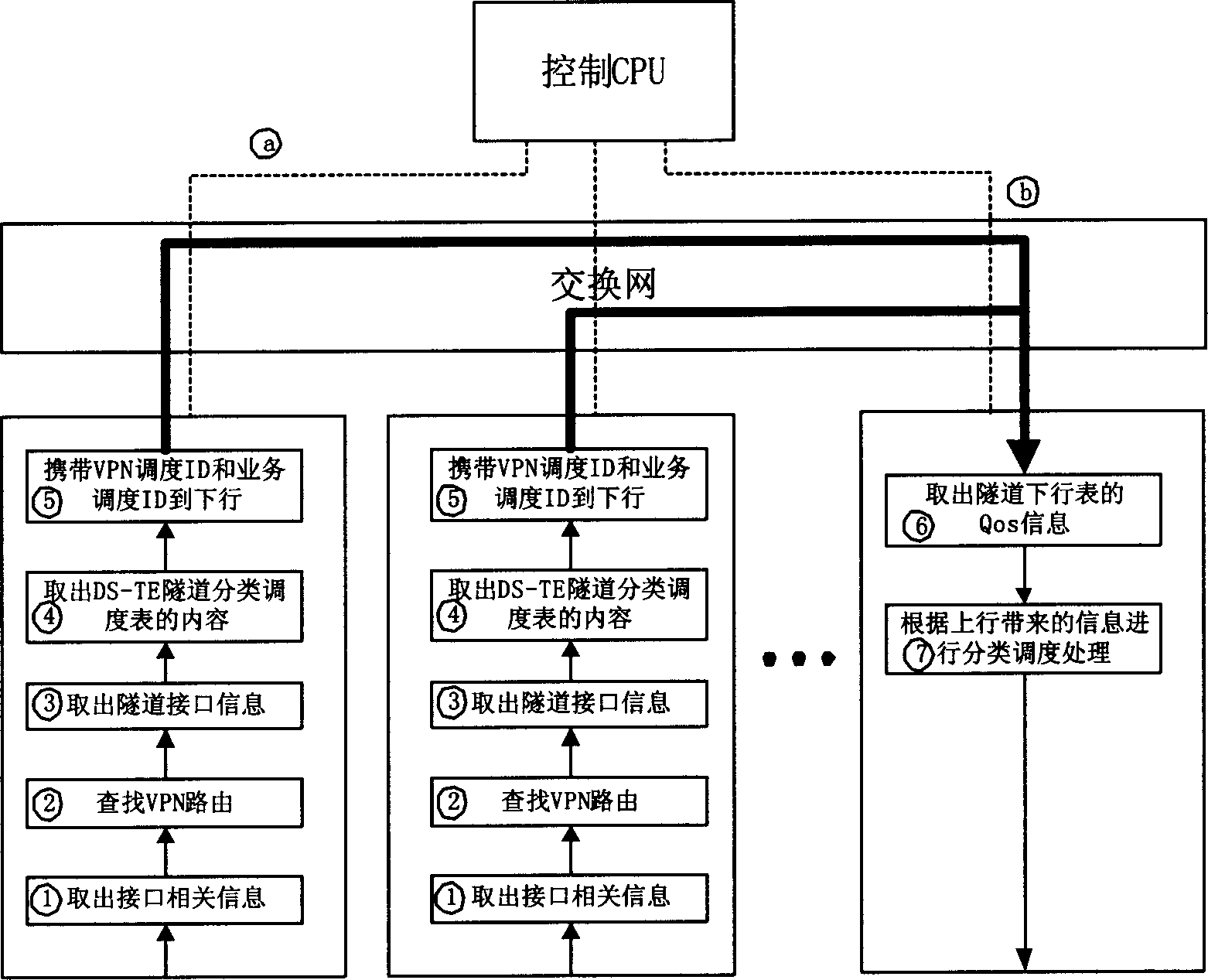
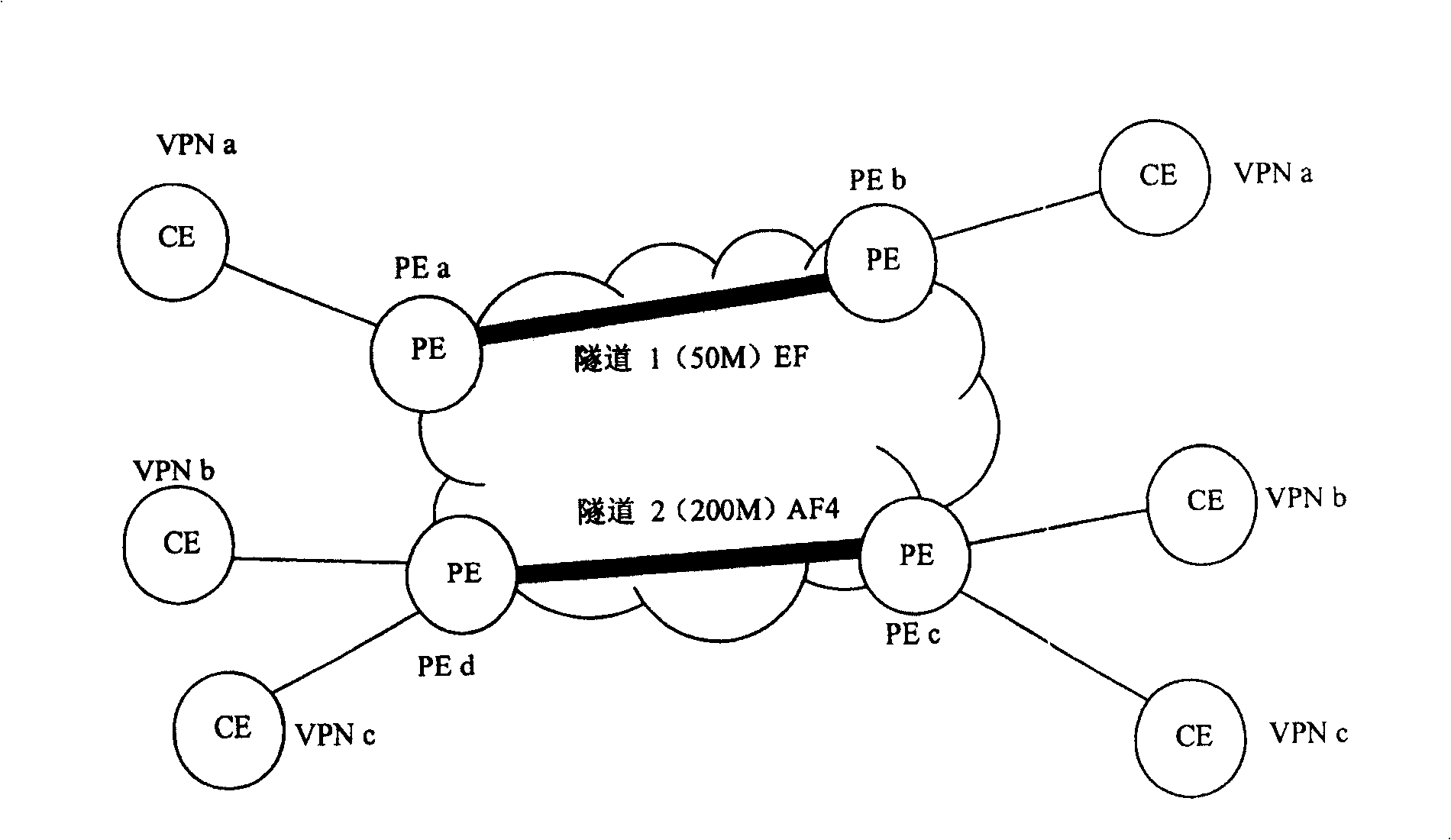
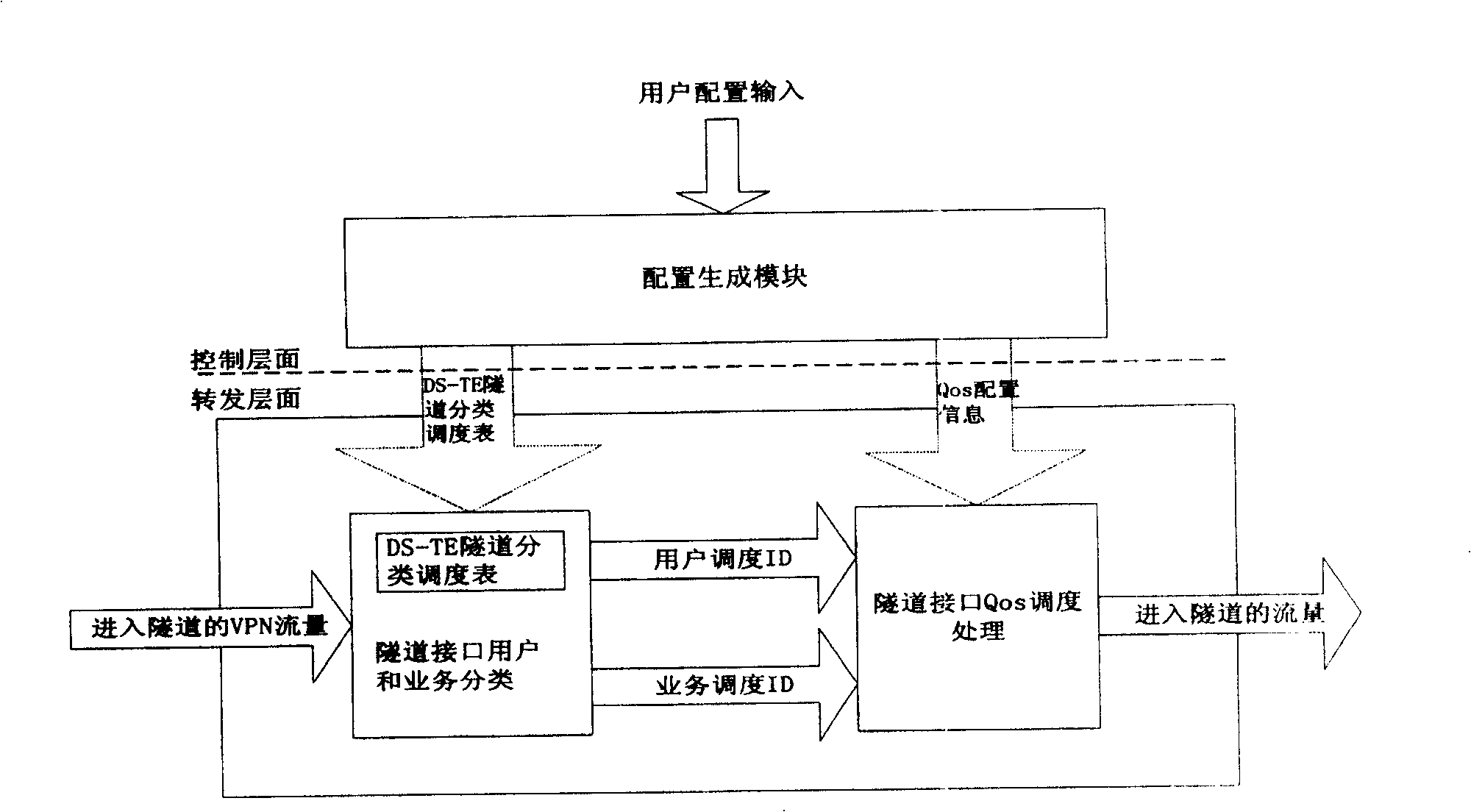
The present invention discloses a method providing QoS ministrant to virtual special network user, capable of providing multi-user multiple service difference service to virtual special network VPN. Said method includes based on user scheduling ID, DSCP or 8021. P value and service scheduling ID to construct DS-TE tunnel classified schedule table, querying DS-TE tunnel classified schedule table, if configured multi-user scheduling and / or multiple service scheduling, obtaining user scheduling ID and / or service scheduling ID; according to said user scheduling ID and / or service scheduling ID, tunnel interface QoS scheduling process, providing QoS service.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for providing QoS service for virtual special net user
InactiveCN100450093CMeticulously dividedNetworks interconnectionDistributed computingValue-added service
The present invention discloses a method providing QoS ministrant to virtual special network user, capable of providing multi-user multiple service difference service to virtual special network VPN. Said method includes based on user scheduling ID, DSCP or 8021. P value and service scheduling ID to construct DS-TE tunnel classified schedule table, querying DS-TE tunnel classified schedule table, if configured multi-user scheduling and / or multiple service scheduling, obtaining user scheduling ID and / or service scheduling ID; according to said user scheduling ID and / or service scheduling ID, tunnel interface QoS scheduling process, providing QoS service.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Wireless communication method and system
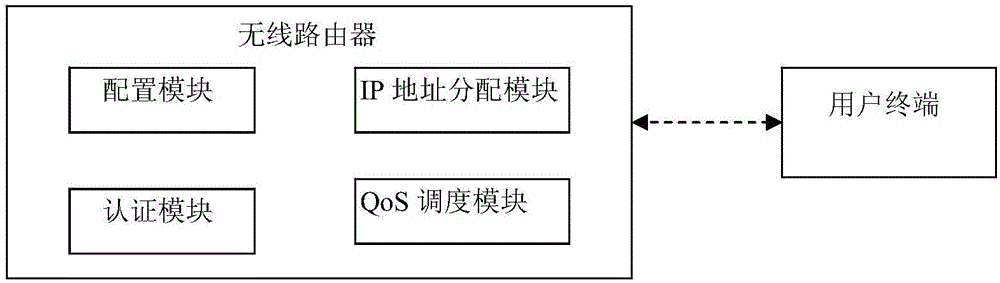
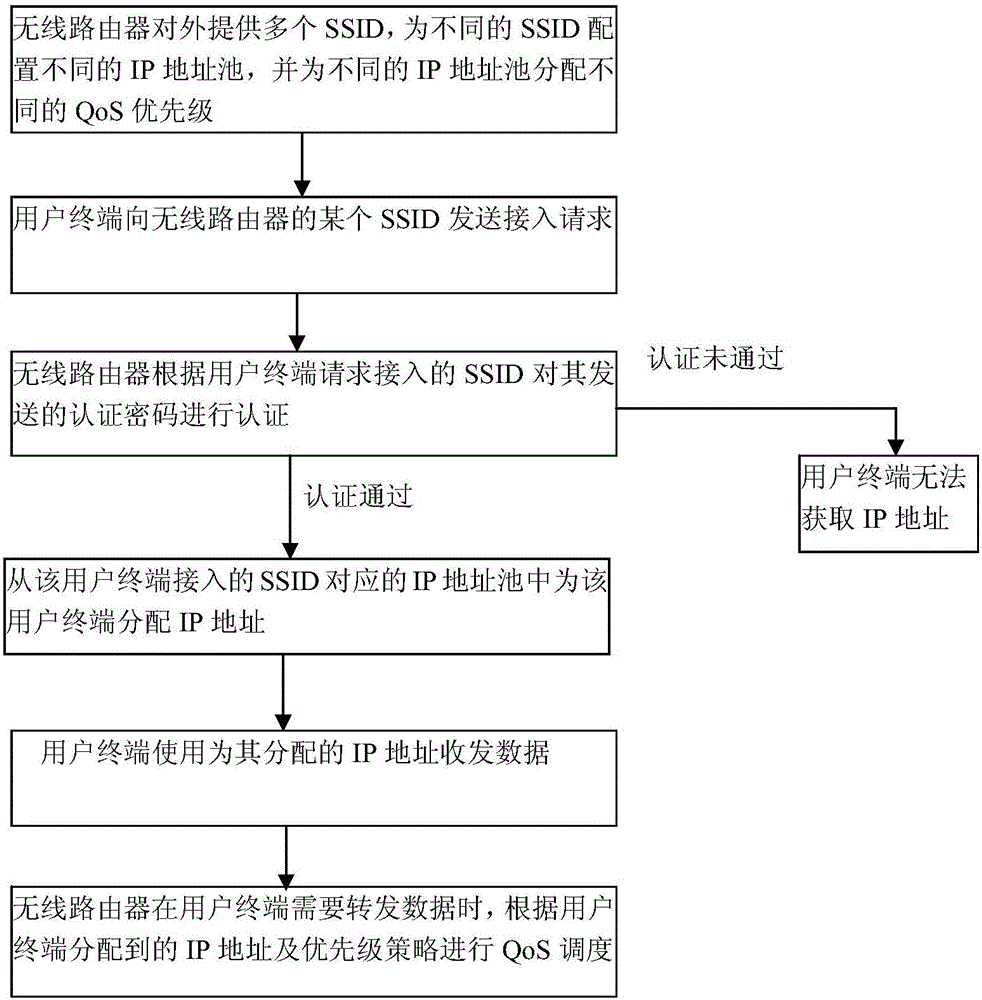
InactiveCN106792679AMinor architectural changesRealize differentiated servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionWireless routerPassword
The invention relates to a wireless communication technology, and discloses a wireless communication method and system. Under the condition of network link congestion, the method and the system ensure that the data traffic of an important user is preferentially forwarded. The method comprises the steps of a, a wireless router providing a plurality of SSIDs (Service Set Identifiers) to the outside, configuring different IP address pools for different SSIDs, and allocating different QoS (Quality of Service) priorities for different IP address pools; b, a user terminal sending an access request to a certain SSID of the wireless router; c, the wireless router authenticating an authentication password sent by the user terminal according to the SSID requested to access by the user terminal, and allocating an IP address to the user terminal from the IP address pool corresponding to the SSID accessed by the user terminal after the authentication passes; d, the user terminal using the IP address allocated to the user terminal; d, the user terminal transceiving data by using the IP address allocated to the user terminal; and e, when the user terminal needs to forward data, the wireless router performing QoS scheduling according to the IP address allocated to the user terminal and the priority strategy.
Owner:MAIPU COMM TECH CO LTD
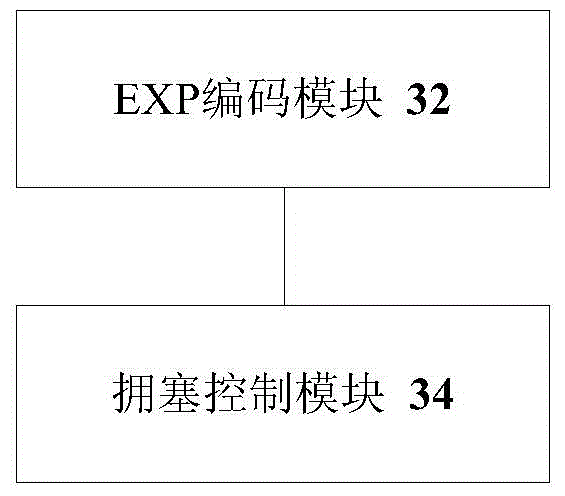
External layer label coding method, traffic congestion control method and device
The invention discloses an external layer label coding method, a traffic congestion control method and a traffic congestion control device. The external layer label coding method comprises the steps that a PE head node codes an EXP field of an external layer label of a message according to a service type of an incoming node PHB and message color information of the message, wherein the EXP field comprises a first field for identifying the service type of the message and a second field for identifying whether the message entering a virtual link of the PE head node is a virtual private network service message in a committed bandwidth, so that a P node can map PHB according to the EXP field, conducts congestion management control of each tunnel and each queue and conducts second-level QOS dispatching management conditionally, thereby solving the problem in the related technology that end-to-end QoS control cannot be achieved since the P node cannot analyze VPN information under the condition of multi-VPN service multiplexing tunnels in an E-LSP-based MPLS network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
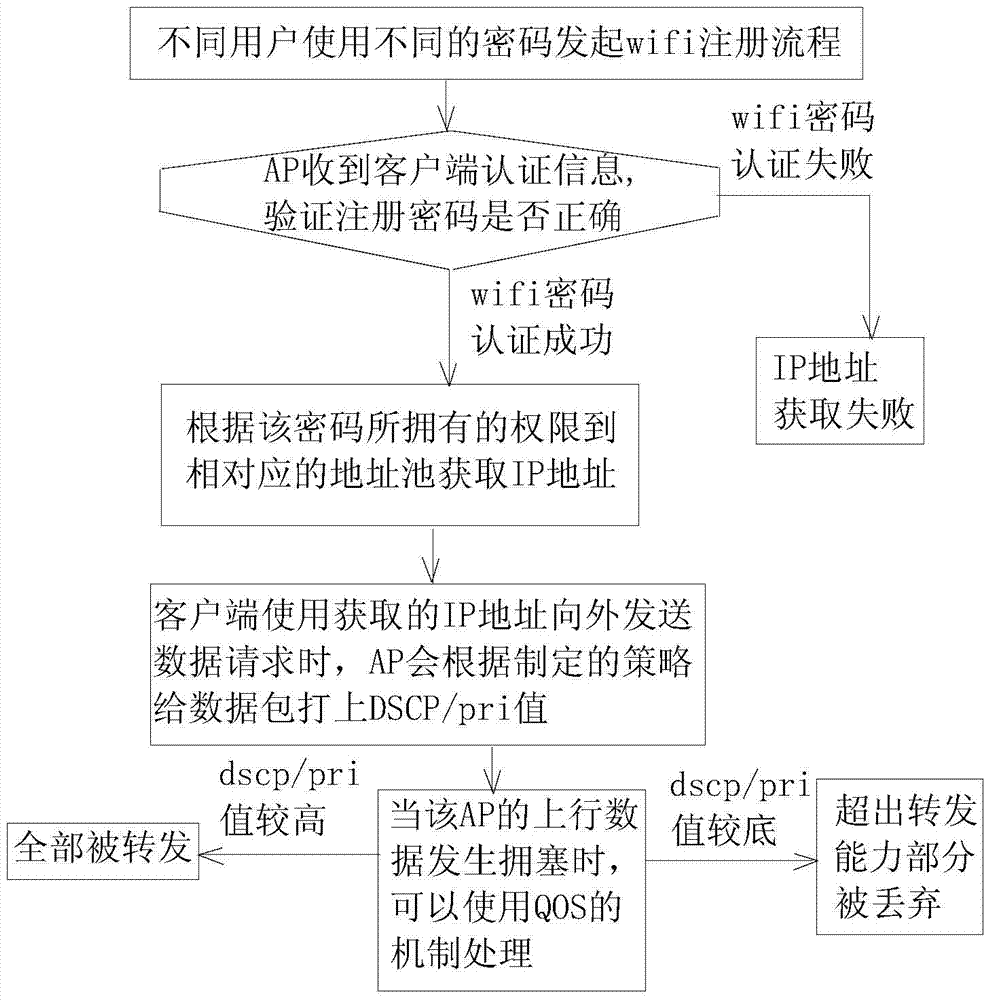
QoS (Quality of Service) scheduling method based on WIFI (Wireless Fidelity) password of AP (Access Point) router
InactiveCN103701713ASolve congestionGuaranteed service qualityData switching networksCode pointDifferentiated service
The invention relates to a QoS (Quality of Service) scheduling method based on a WIFI (Wireless Fidelity) password of an AP (Access Point) router. With the development of the science, the technology and the network, equipment capable of using the network is not limited to computers. The method provided by the invention comprises the steps that a user initiates registration to a WIFI network during connection, the WIFI network prompts the user to input a WIFI registration password, an AP receives client authentication information to verify whether the registration password is correct or not, the AP goes to a corresponding address pool to obtain an IP (Internet Protocol) address according to authority owned by the correct registration password of a client, the AP attaches a DSCP (Differentiated Service Code Point) / priority value to a data packet according to formulated policies when the client uses the IP address allocated by the AP to outwards transmit a data request, and a QoS mechanism is used for processing when the uplink data of the AP encounters congestion. The QoS scheduling method based on the WIFI password of the AP router is used for dividing service classes based on the WIFI password of the AP router.
Owner:TAICANG T&W ELECTRONICS CO LTD
QoS scheduler and method for implementing quality of service with aging time stamps
InactiveUS7103051B2Avoid disadvantagesHybrid switching systemsData switching by path configurationAccess timeFlow time
A scheduler, scheduling method, and computer program product are provided for implementing Quality-of-Service (QoS) scheduling of a plurality of flows with aging time stamps. Subsets of time stamp data stored in a time stamp aging memory array are sequentially accessed. Each time stamp data subset contains time stamp data for a subplurality of flows. Guaranteed aging processing steps are performed for each flow utilizing the time stamp data subsets to identify and mark invalid calendar next time values. When a new frame arrival for an empty flow is identified, flow queue control block (FQCB) time stamp data and the flow time stamp data in the time stamp aging memory array are accessed. Based on the calendar to which the new frame is directed or the target calendar for the new frame, the target calendar next time valid bit of the time stamp aging memory array data is checked. When the target calendar next time valid bit is on, a target calendar next time value from the flow queue control block (FQCB) time stamp data is compared with a current time. When the target calendar next time is less than the current time, the target calendar next time valid bit is turned off to mark the target calendar next time as invalid. The guaranteed aging processing steps for each flow in the time stamp data subset includes checking a selection indicator of the time stamp aging memory array data for the flow to identify a calendar. Responsive to the selection indicator value, a calendar valid bit is checked. When the calendar valid bit is on, a calendar next time is compared with a current time. When the calendar next time is less than the current time, the calendar valid bit is turned off to mark the calendar next time as invalid. Invalid time stamp values are identified for all scheduler calendars.
Owner:IBM CORP
Sorting method of Qos scheduling
ActiveCN101848500ARaise priorityMaximize capacityNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemComputer science
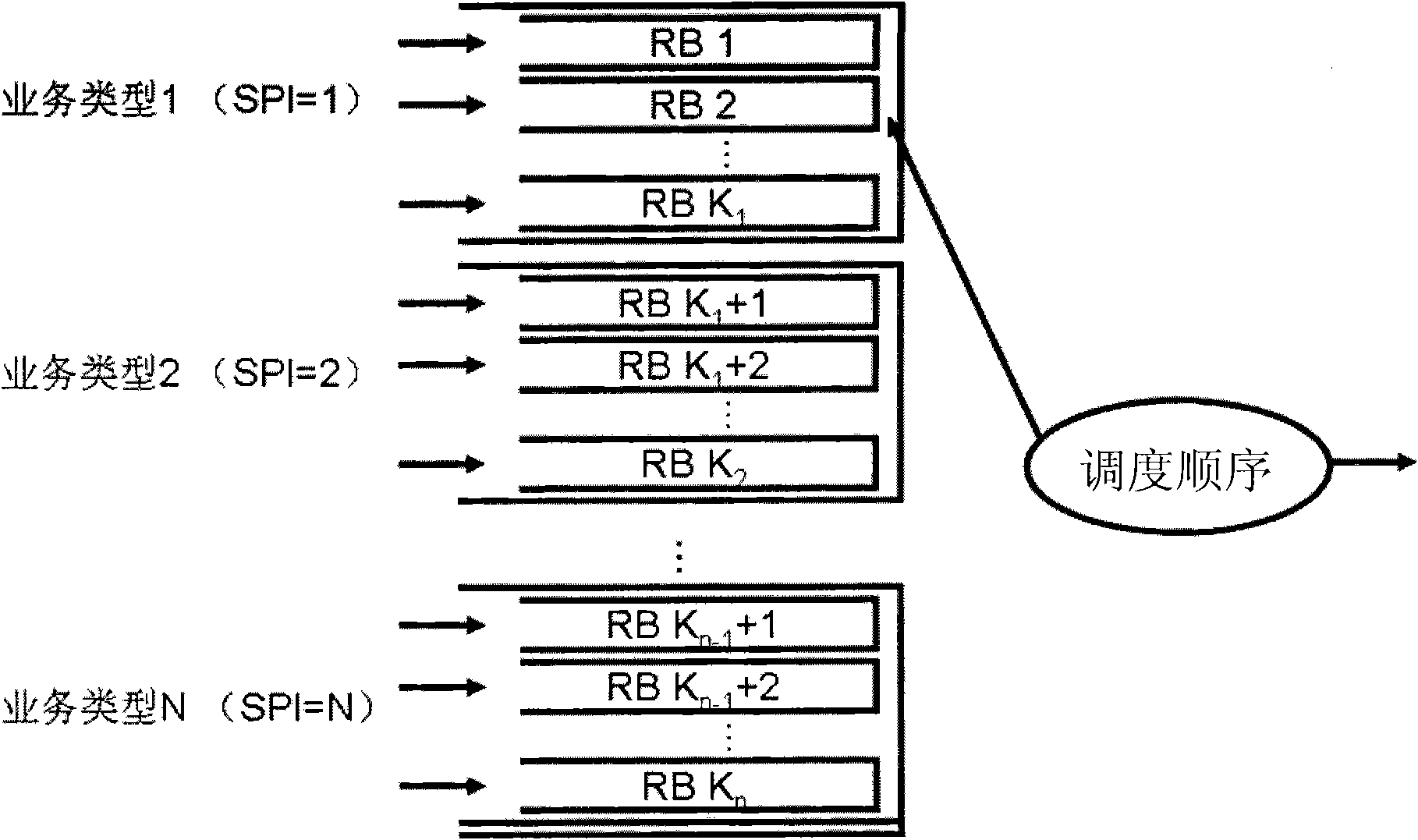
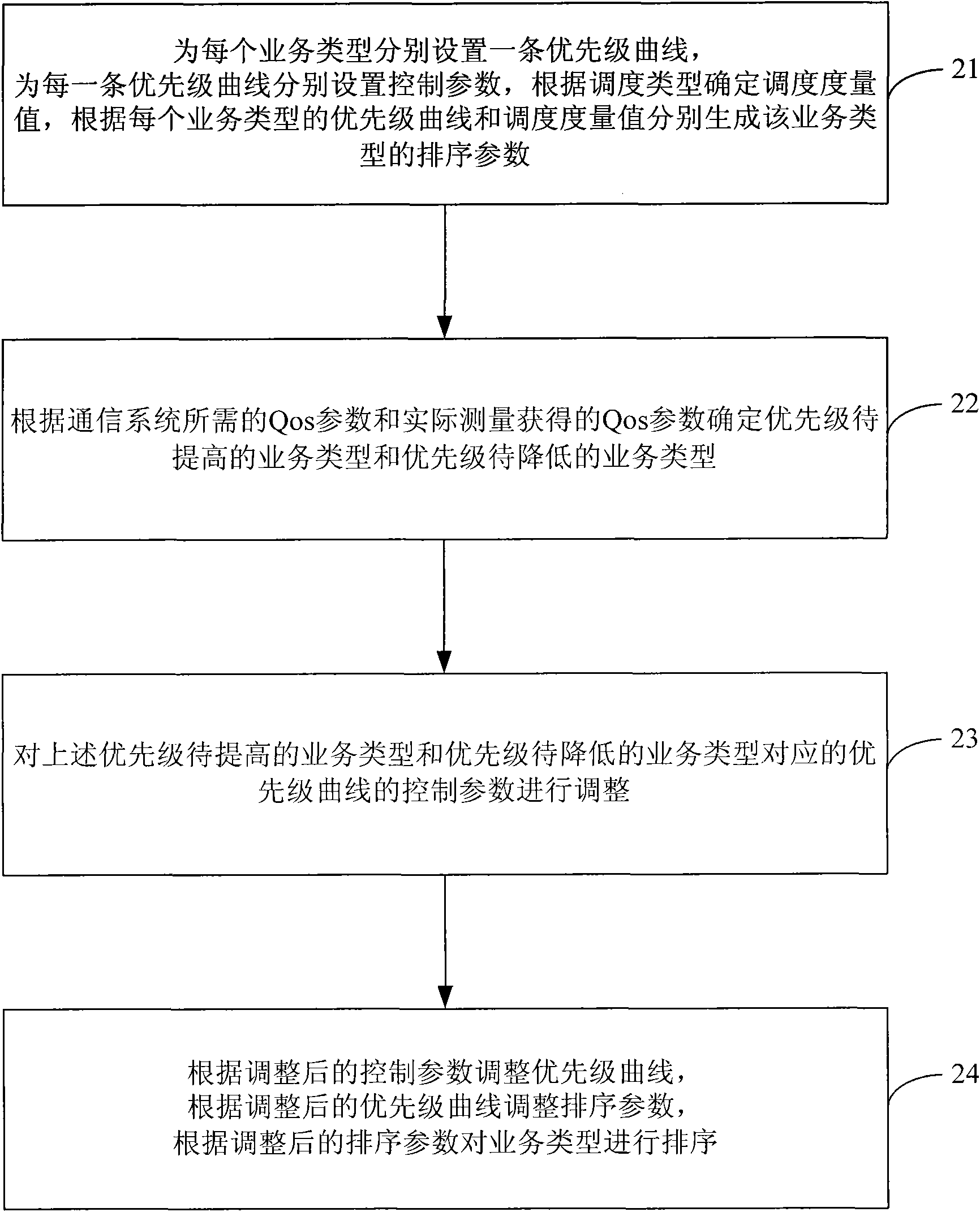
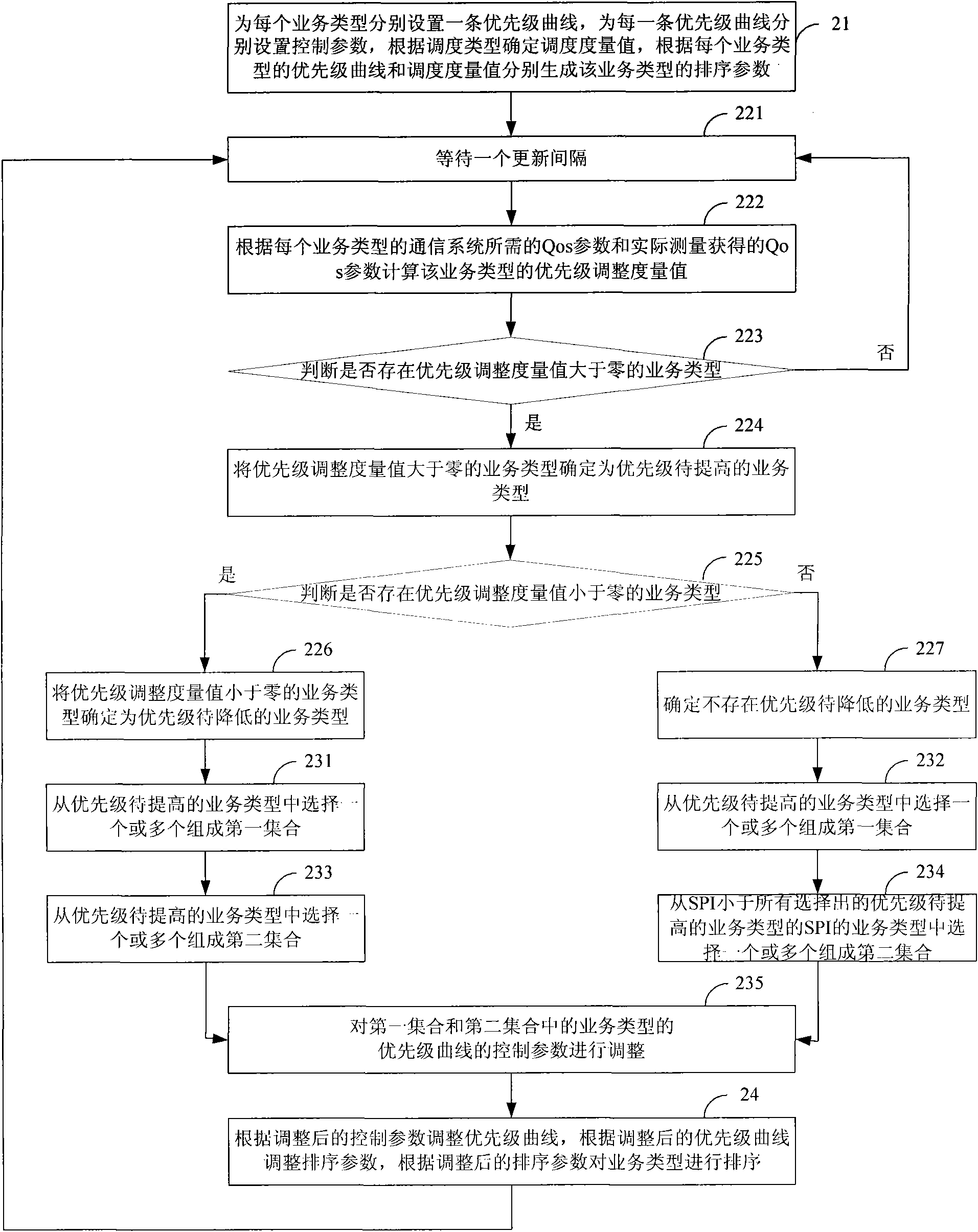
The present invention discloses a sorting method of Qos scheduling, which comprises the following steps: respectively setting a priority curve for each business type, and respectively setting a control parameter for each priority curve; generating sorting parameters according to the priority curve of each business type and a scheduling metric value, and determining the business type the priority of which needs to be increased and the business type the priority of which needs to be decreased according to the Qos parameters needed by a communication system and Qos parameters obtained by actual measurement, and adjusting the control parameters of the priority curves; adjusting the priority curves according to the adjusted control parameters, and adjusting the sorting parameters according to the adjusted priority curves; and sorting for queues of all business types according to the adjusted sorting parameters. The sorting method can maximize the capacity of the system under the condition of meeting the Qos requirements of the business types, and ensures the Qos requirements of the business type with high priority when the load of the system is excess.
Owner:北京万海云科技有限公司
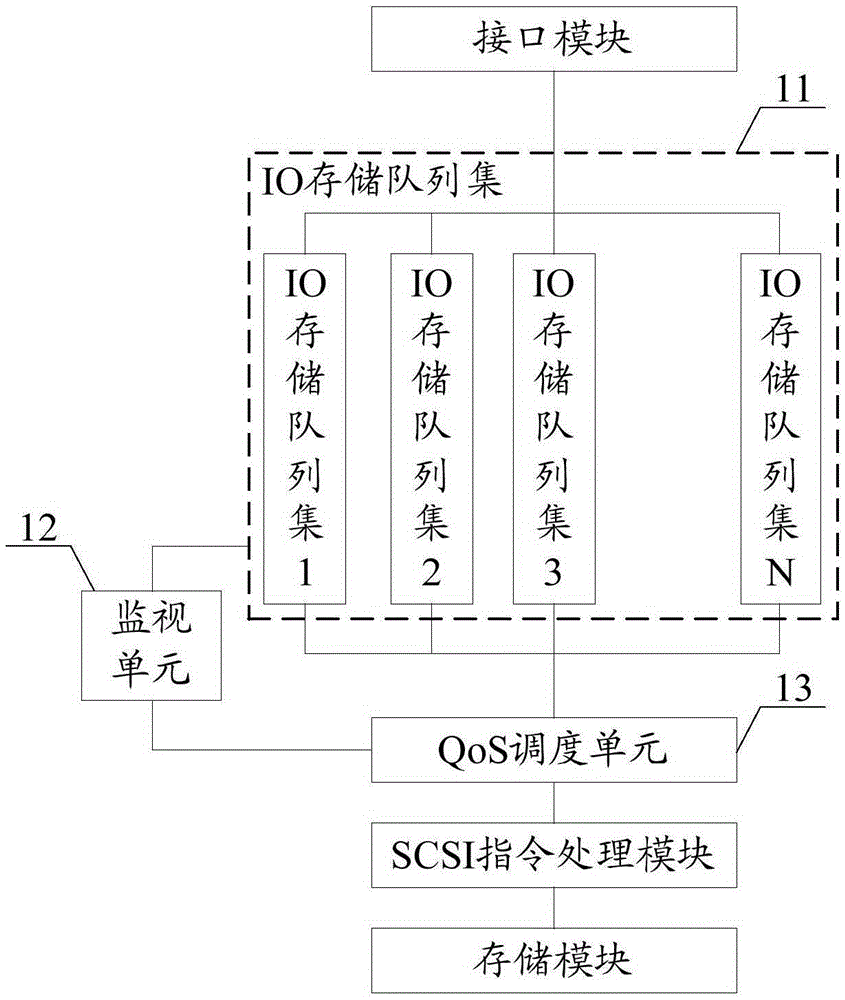
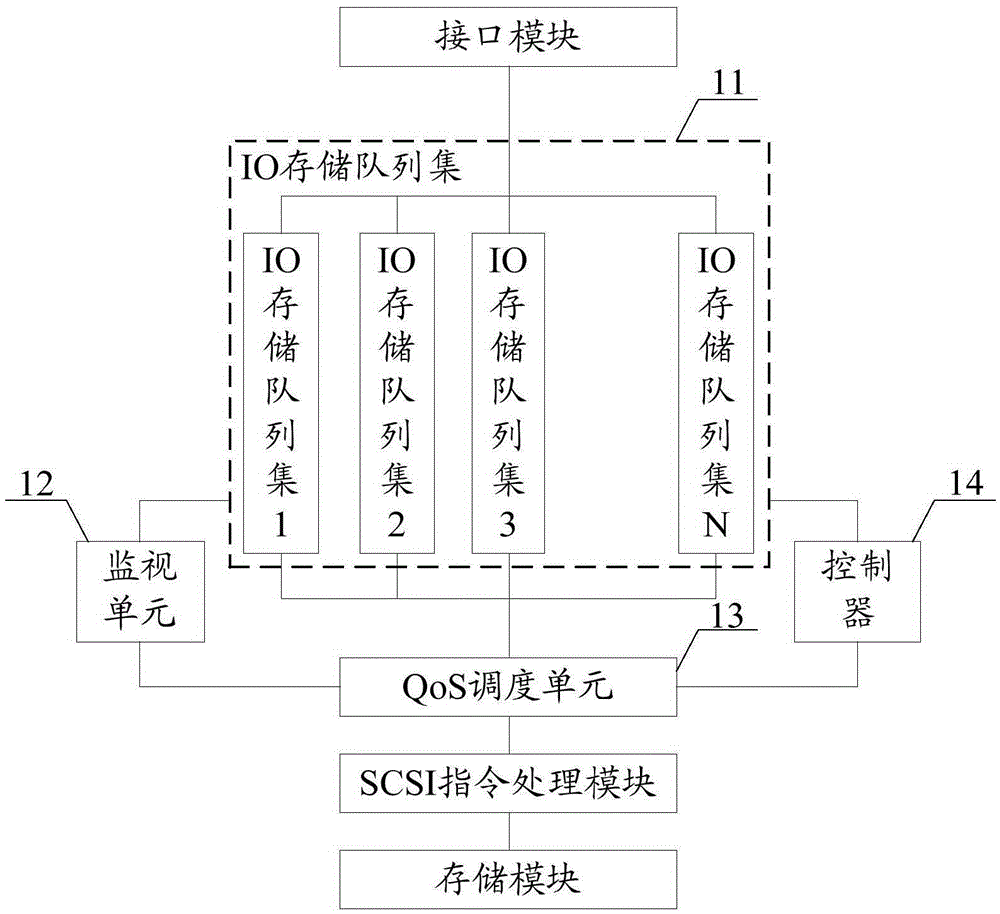
QoS scheduler and scheduling method for SCSI target device
The invention discloses a QoS scheduler and a scheduling method for an SCSI target device. The QoS scheduler comprises an IO storage queue set, a monitoring unit and a QoS scheduling unit, wherein the IO storage queue set comprises N IO storage queues, the IO storage queues and servers are in one-to-one correspondence, each storage queue stores IO data sent by the corresponding server, the monitoring unit adjusts scheduling priority of each IO storage queue in the IO storage queue set to acquire corresponding QoS scheduling strategy, so IO data stored in each IO storage queue can be sequentially processed according to the QoS scheduling strategies, natural competition among the servers for system processing capability resources can be avoided, and a confusion situation of an original IO request processing process is eliminated.
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com