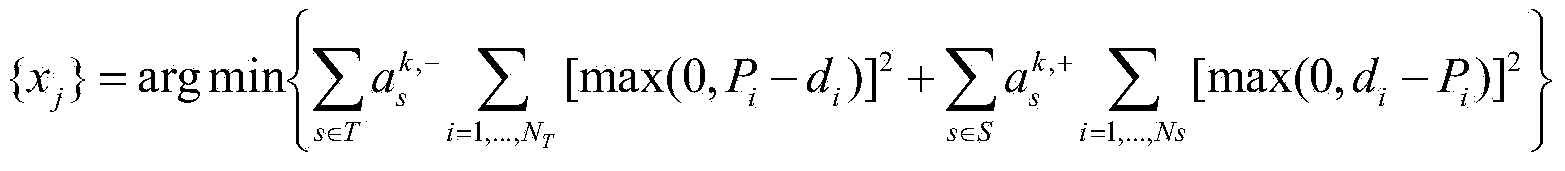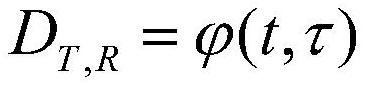Patents
Literature
31 results about "Real time dosimetry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
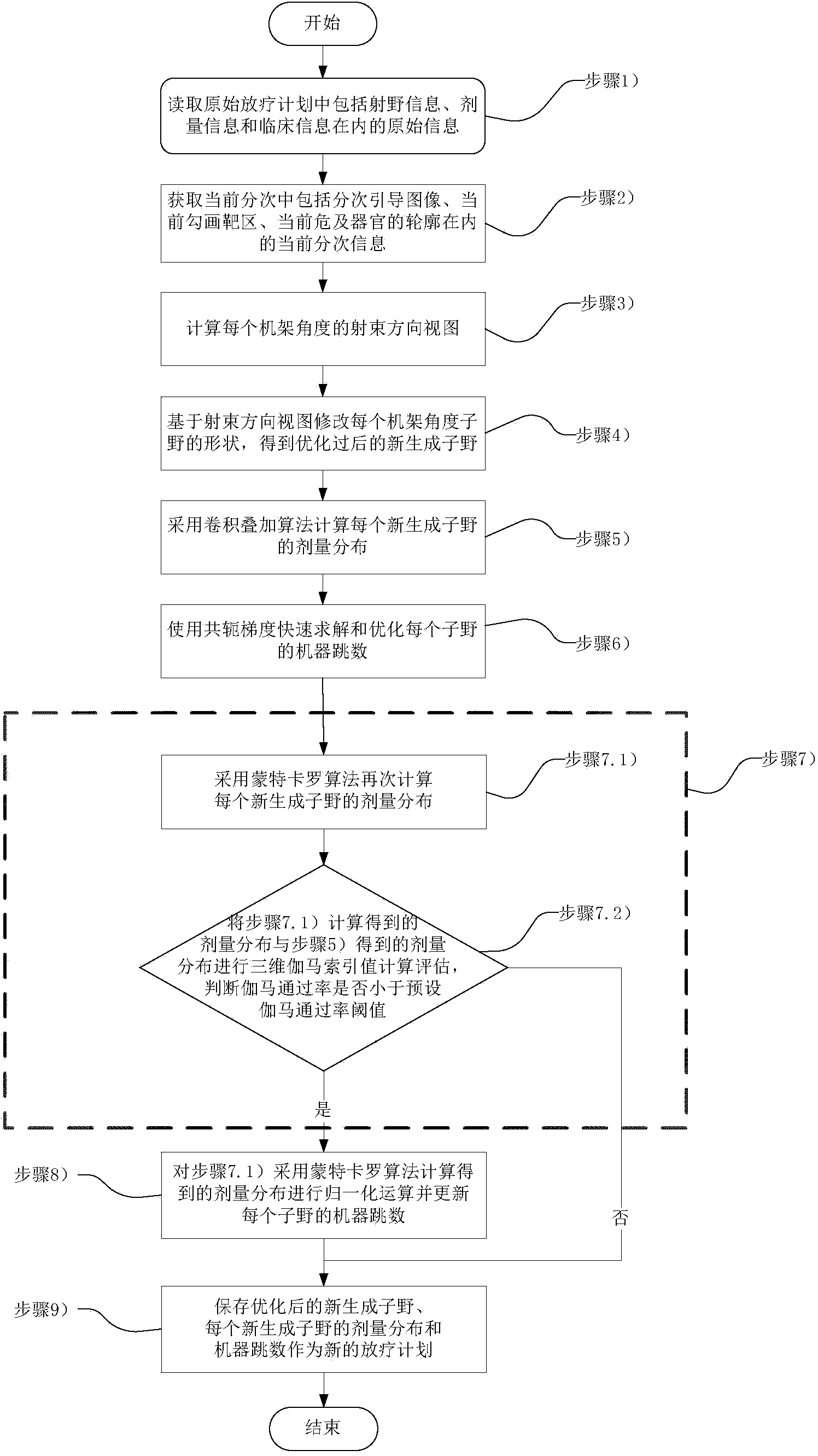
Automatic optimization method for on-line self-adaption radiotherapy plan and device
ActiveCN104338240AGuaranteed to workOnline Adaptive ImplementationRadiation therapyProgram planningAdaptive optimization
The invention discloses an automatic optimization method for an on-line self-adaption radiotherapy plan and a device. The method comprises the following steps: by reading an original radiotherapy plan and the information, such as acquired present gradation guide image and sketching target section, calculating a beam direction view of each frame angle, thereby acquiring the optimized newly generated sub-view and corresponding dose distribution, machine hop count and the like; finishing the on-line self-adaption automatic optimization of the radiotherapy plan; and meanwhile, performing secondary check on the dose distribution of the automatic radiotherapy plan through the calculation and assessment for a three-dimensional gamma index value; if failing to pass, performing normalization operation and updating the machine hop count of the new sub-view, thereby finishing the quality ensuring work. Furthermore, through the radiotherapy plan parameter transmission process check, the possibly present problem in a parameter transmitting and writing executing system is effectively avoided, and the safety monitoring is performed through real-time dosage detection during a plan executing process. The on-line self-adaption optimization of the radiotherapy plan, the quality ensuring and the full automation of parameter transmission check and real-time dosage detection are realized.
Owner:BEIJING LINKING MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
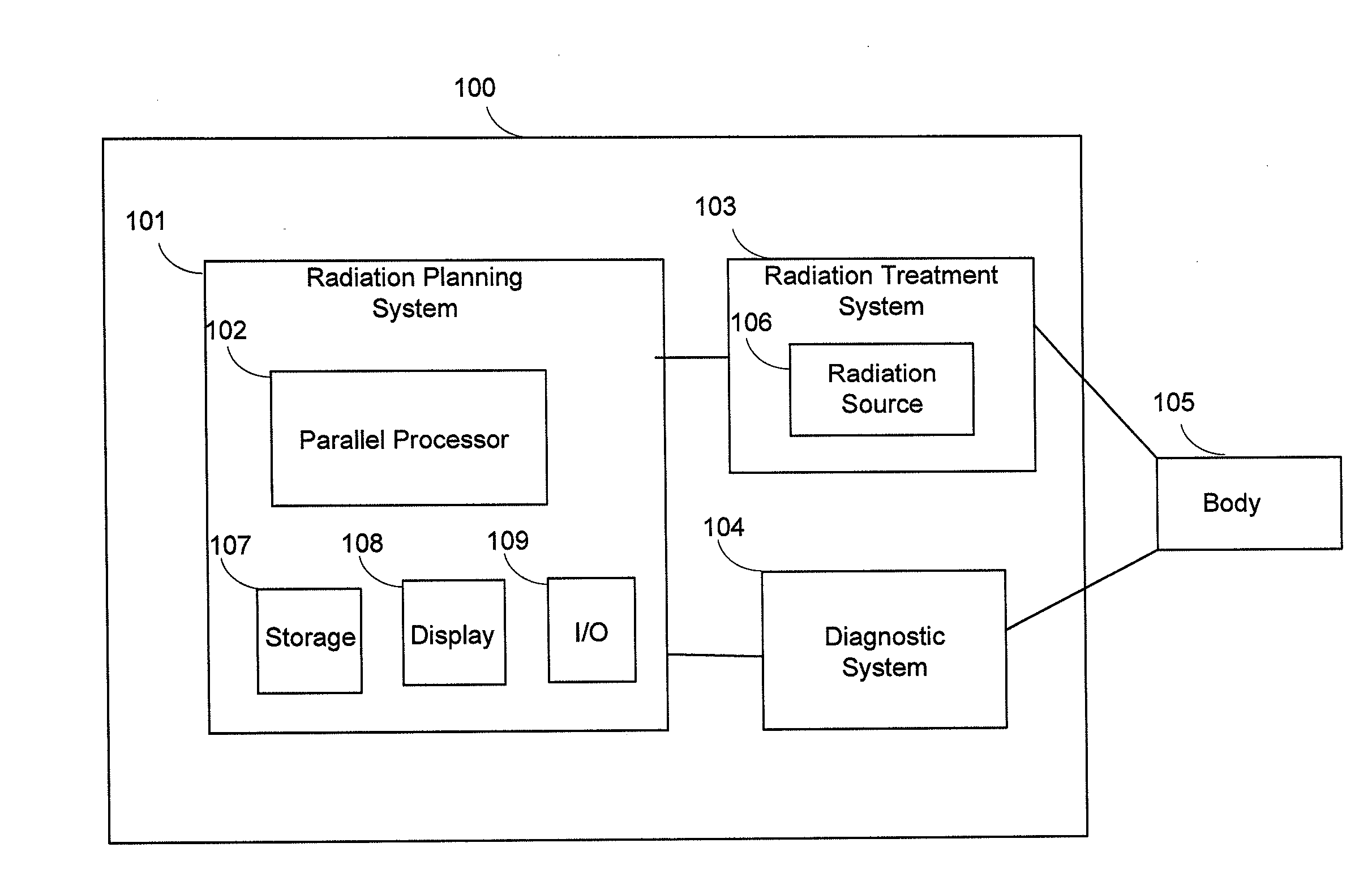
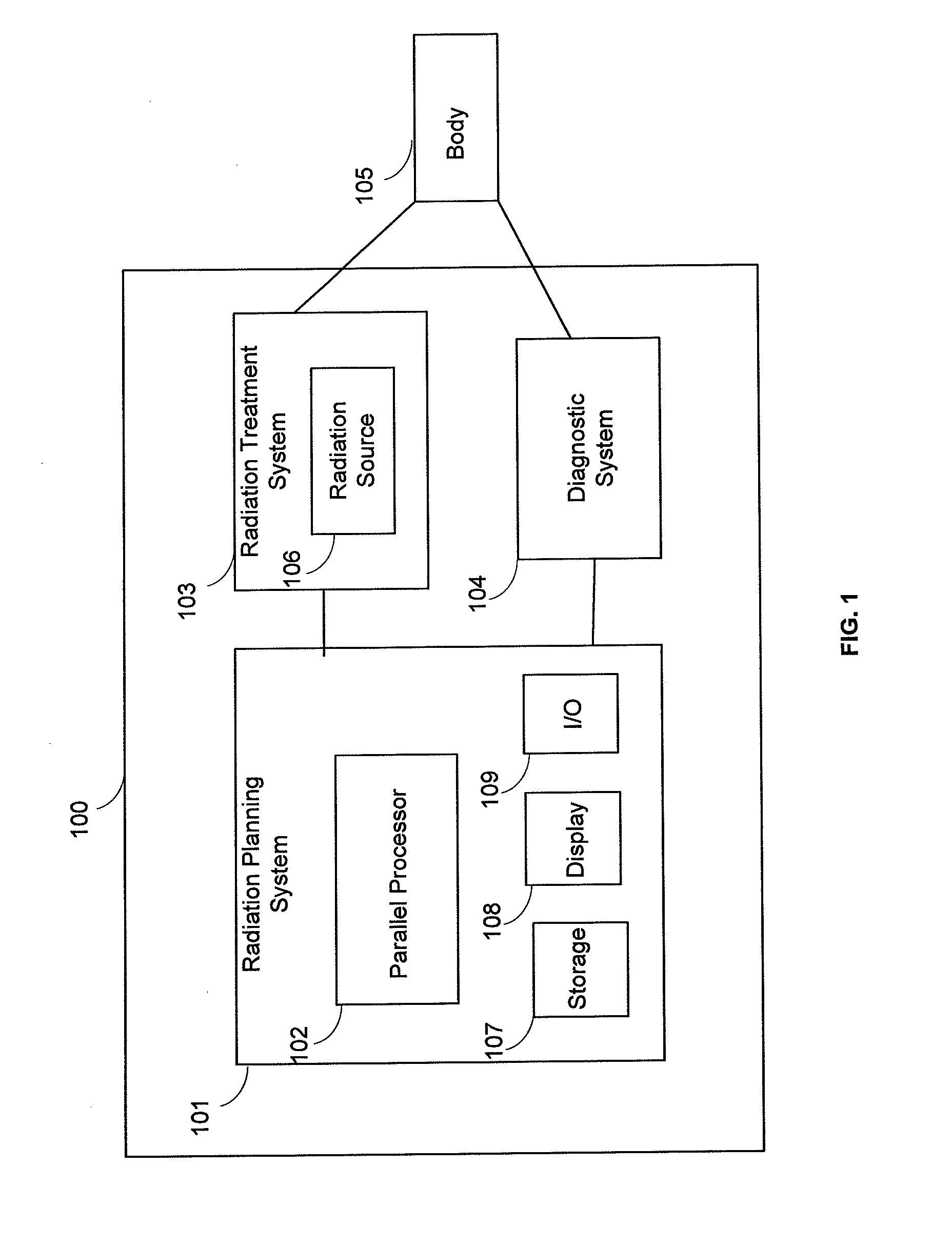
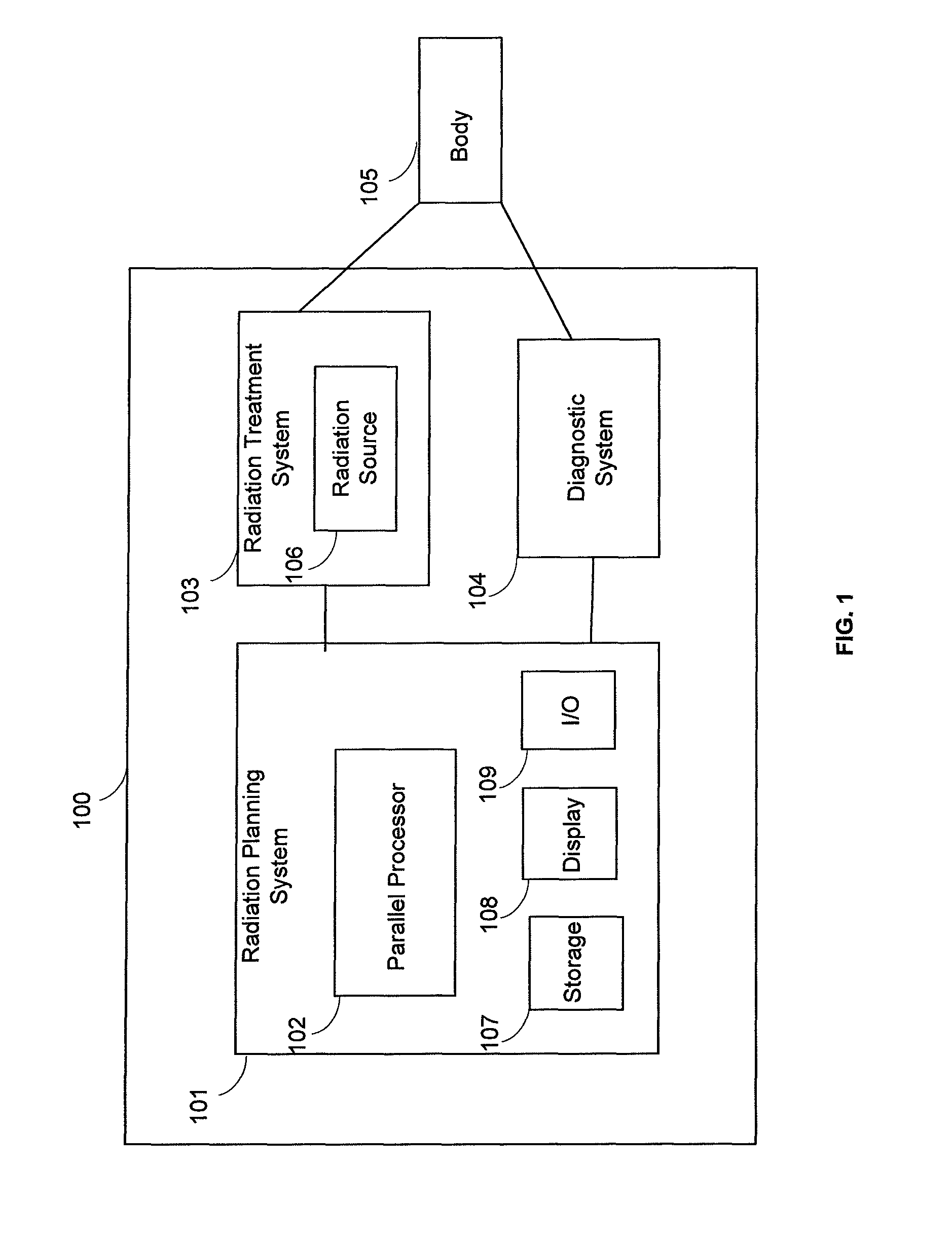
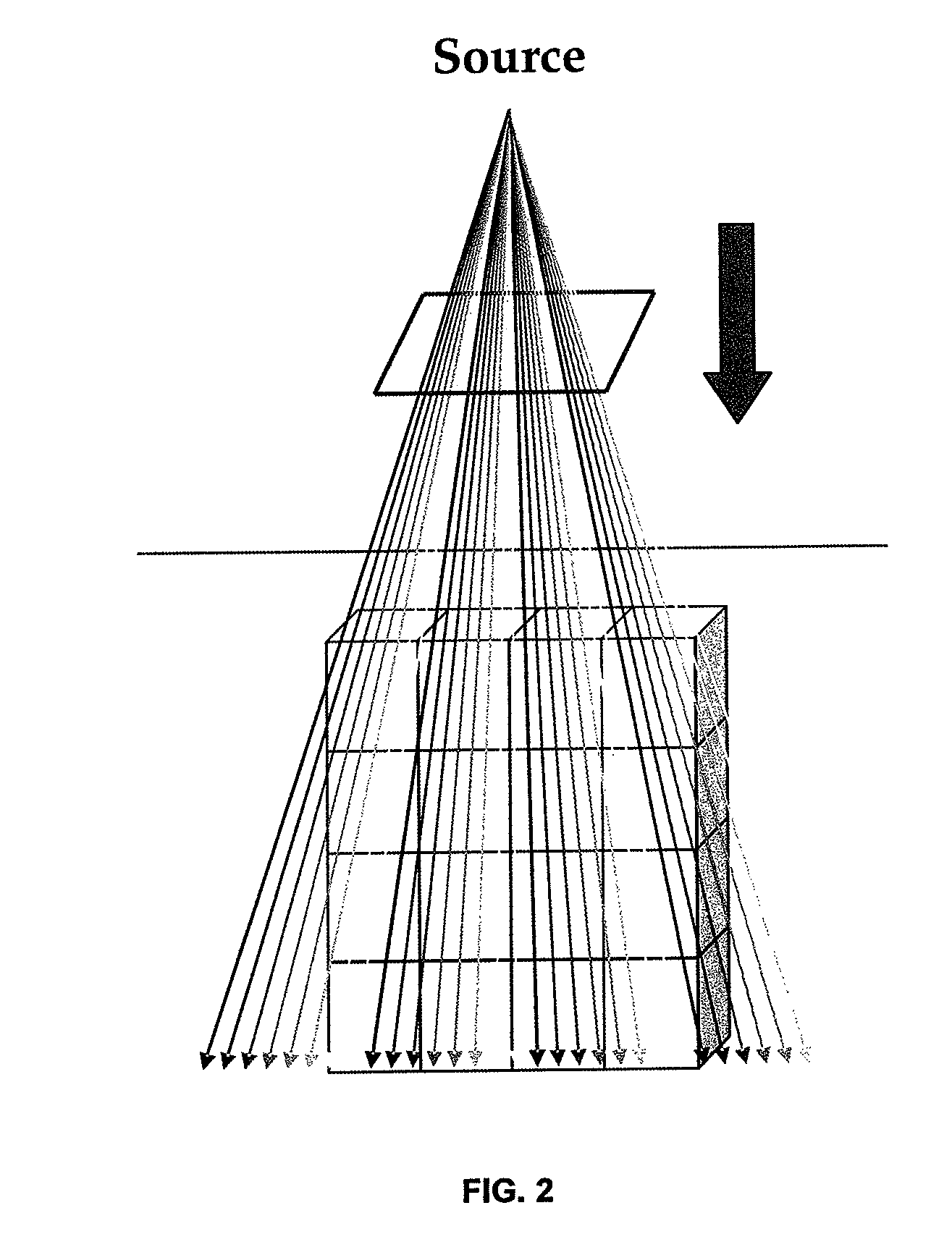
Real-time dose computation for radiation therapy using graphics processing unit acceleration of the convolution/superposition dose computation method
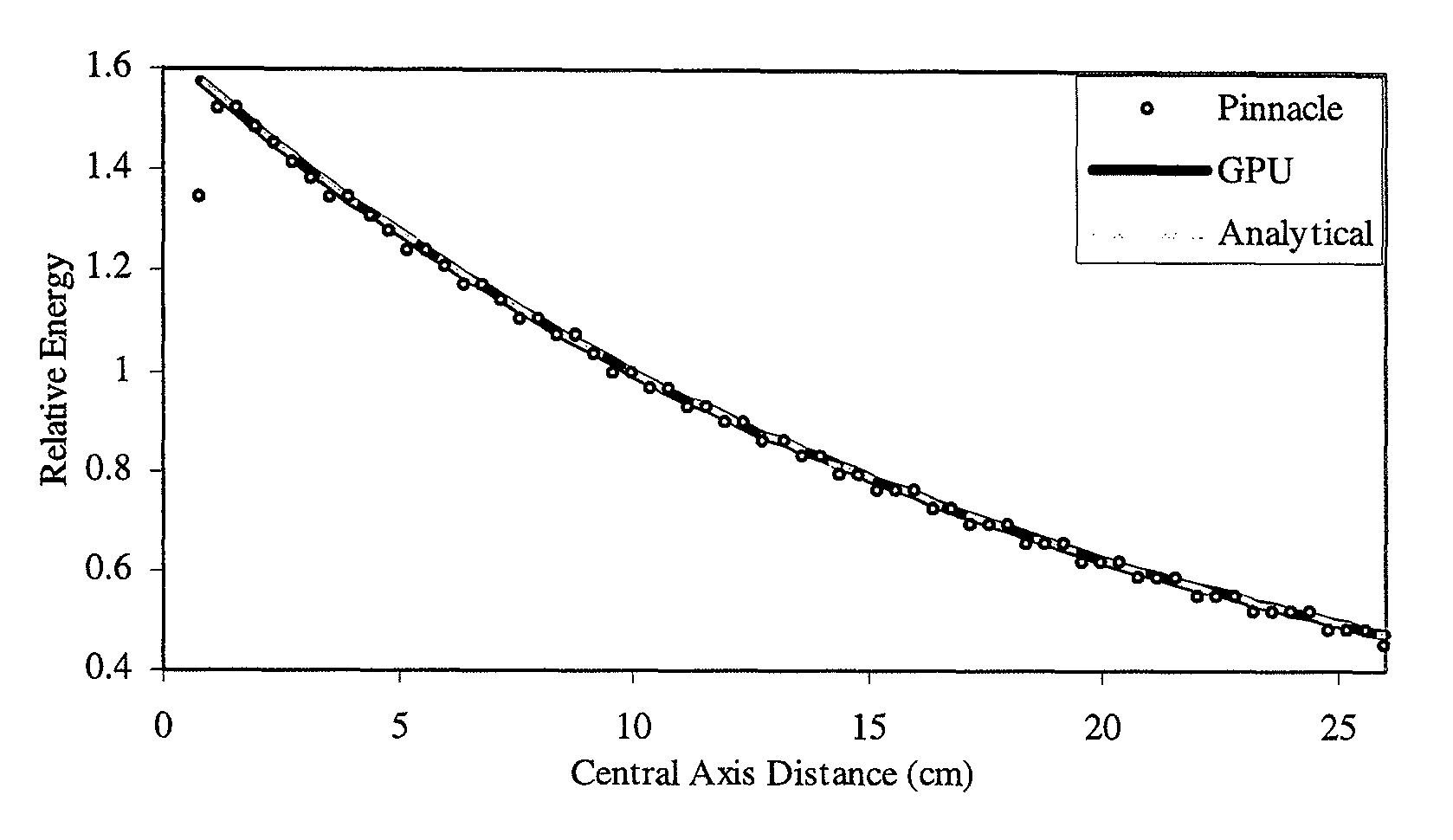
A system for radiation therapy including a radiation planning system, wherein the radiation planning system comprises a parallel processor adapted to receive input information concerning a body having an intended radiation treatment region and to output information for providing radiation treatment to the intended radiation treatment region of the body, wherein the parallel processor is adapted to perform a plurality of reverse ray tracing calculations based on the input information concerning the body in determining the output information for providing radiation treatment, each of the plurality of reverse ray tracing calculations comprising: calculating a first physical property corresponding to a first sub-region of the intended radiation treatment region of the body that is intersected by a ray traced between a source position and the intended radiation treatment region; and calculating, subsequent to the first-mentioned calculating, a second physical property corresponding to a second sub-region of the intended radiation treatment region that is intersected by the ray at a location closer to the source position than is the first sub-region.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
System and method for controlling and adjusting interstitial photodynamic light therapy parameters
ActiveUS20110034971A1Improve patient safetyAvoid damageDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsFiberOrgan at risk
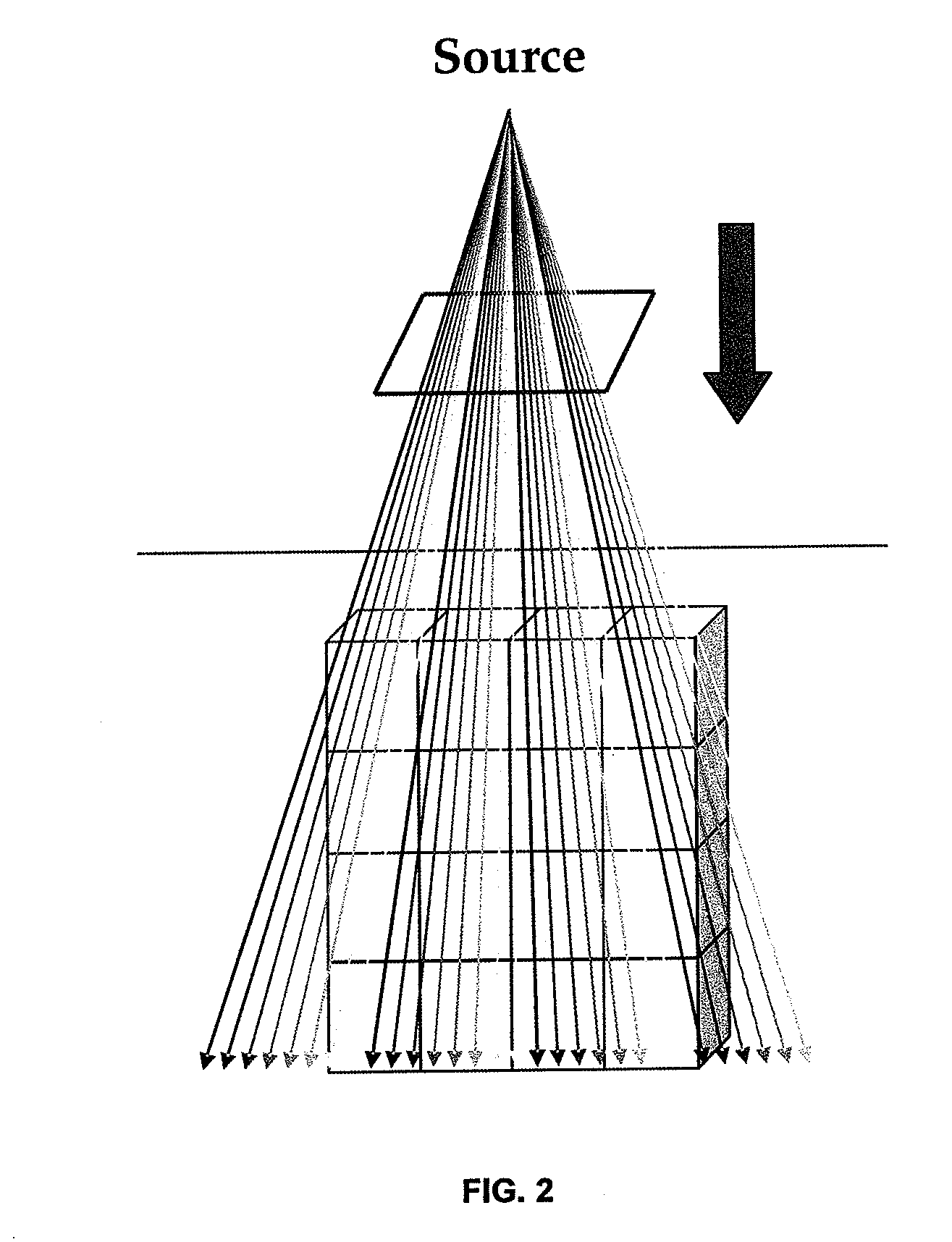
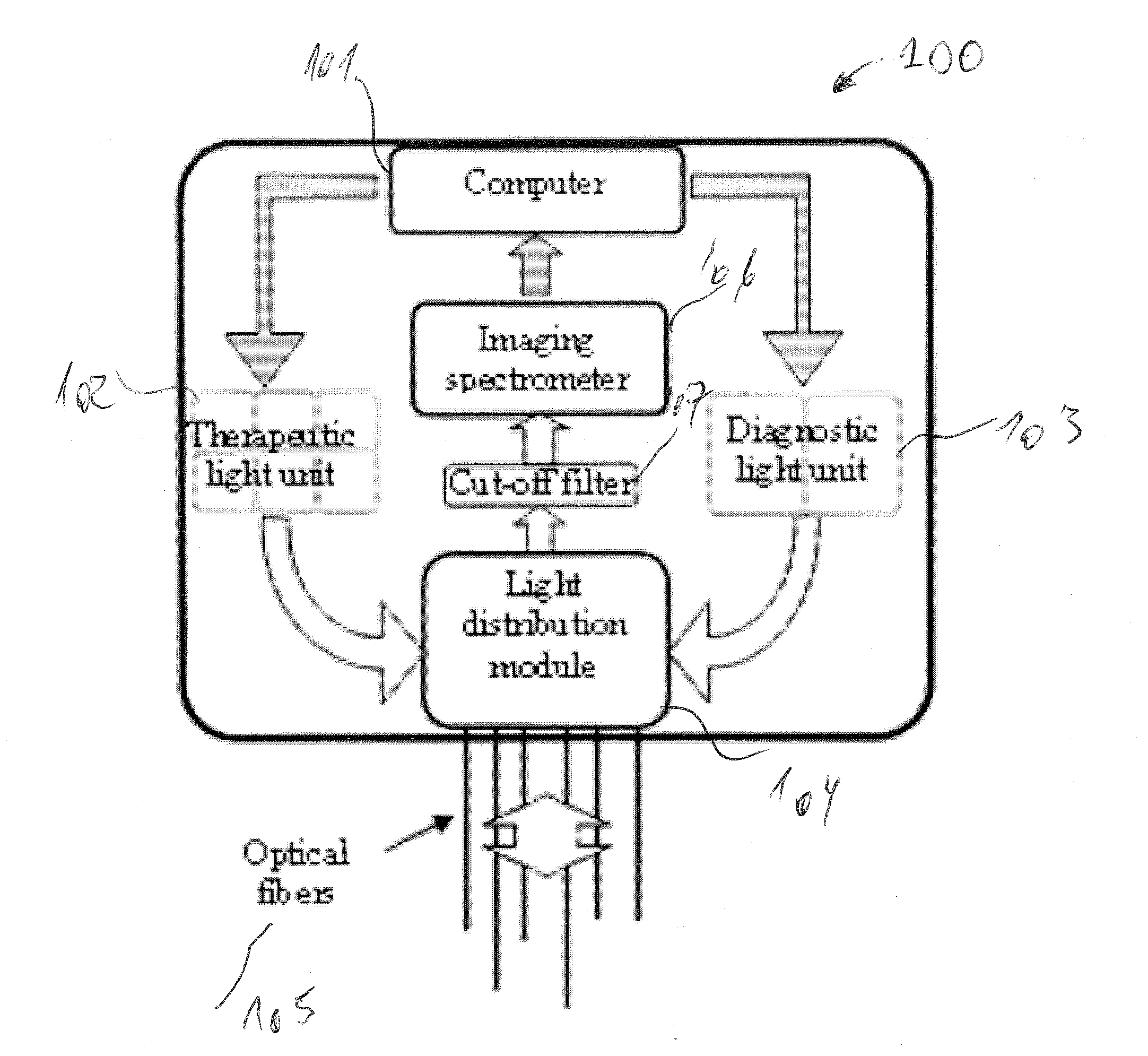
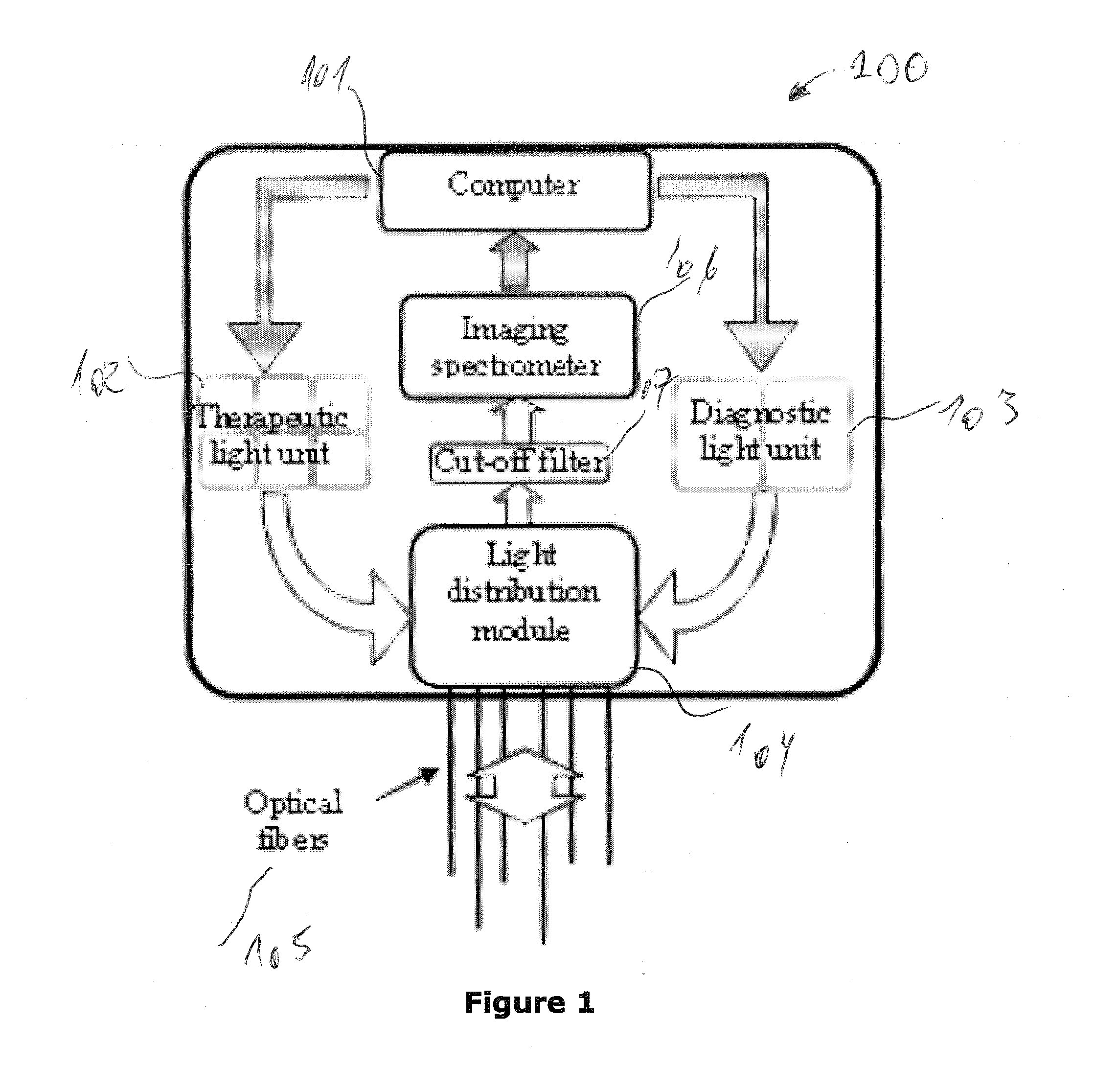
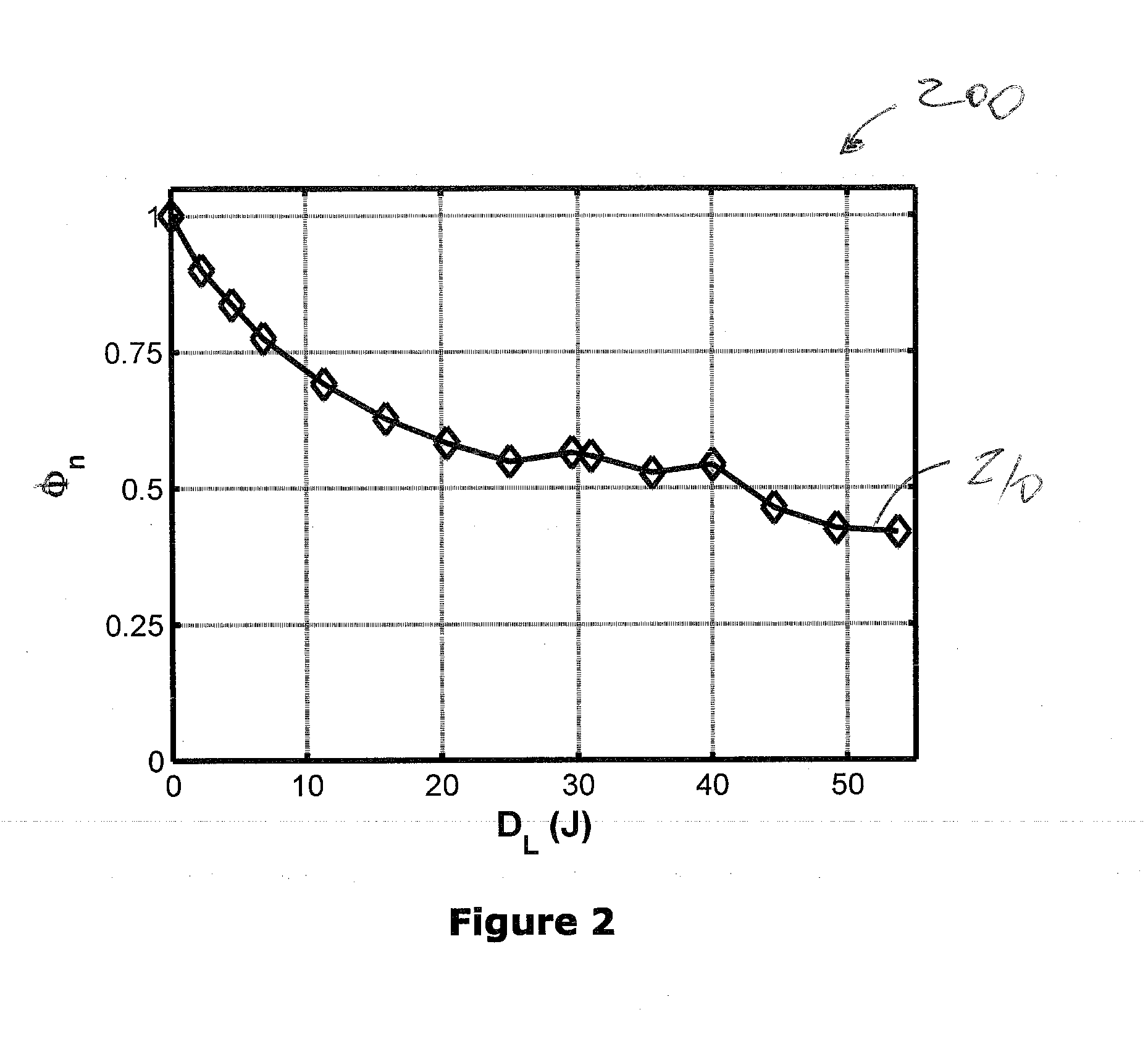
A method and system for controlling and adjusting light in interstitial photodynamic light therapy (IPDT) in a subject is disclosed. More particularly, a method for controlling the light in interstitial tumor photodynamic light therapy is described using calculation method for determination of status of tissue during the PDT treatment. The status is used in a feedback loop to control the continued PDT treatment. Methods are disclosed that constitute pre-treatment and realtime dosimetry modules for IPDT on the whole prostate glandular tissue. The method includes reconstruction of the target geometry, optimization of source fiber positions within this geometry, monitoring of the light attenuation during the treatment procedure and updating individual fiber irradiation times to take into account any variation in tissue light transmission. A control device that is arranged to restrict delivery of therapeutic light treatment at least temporary in dependence of at least one attribute of one of photodynamic treatment parameters. In comparison to no treatment feedback, a significant undertreatment of the patient as well as damage to healthy organs at risk are avoided.
Owner:SPECTRACURE
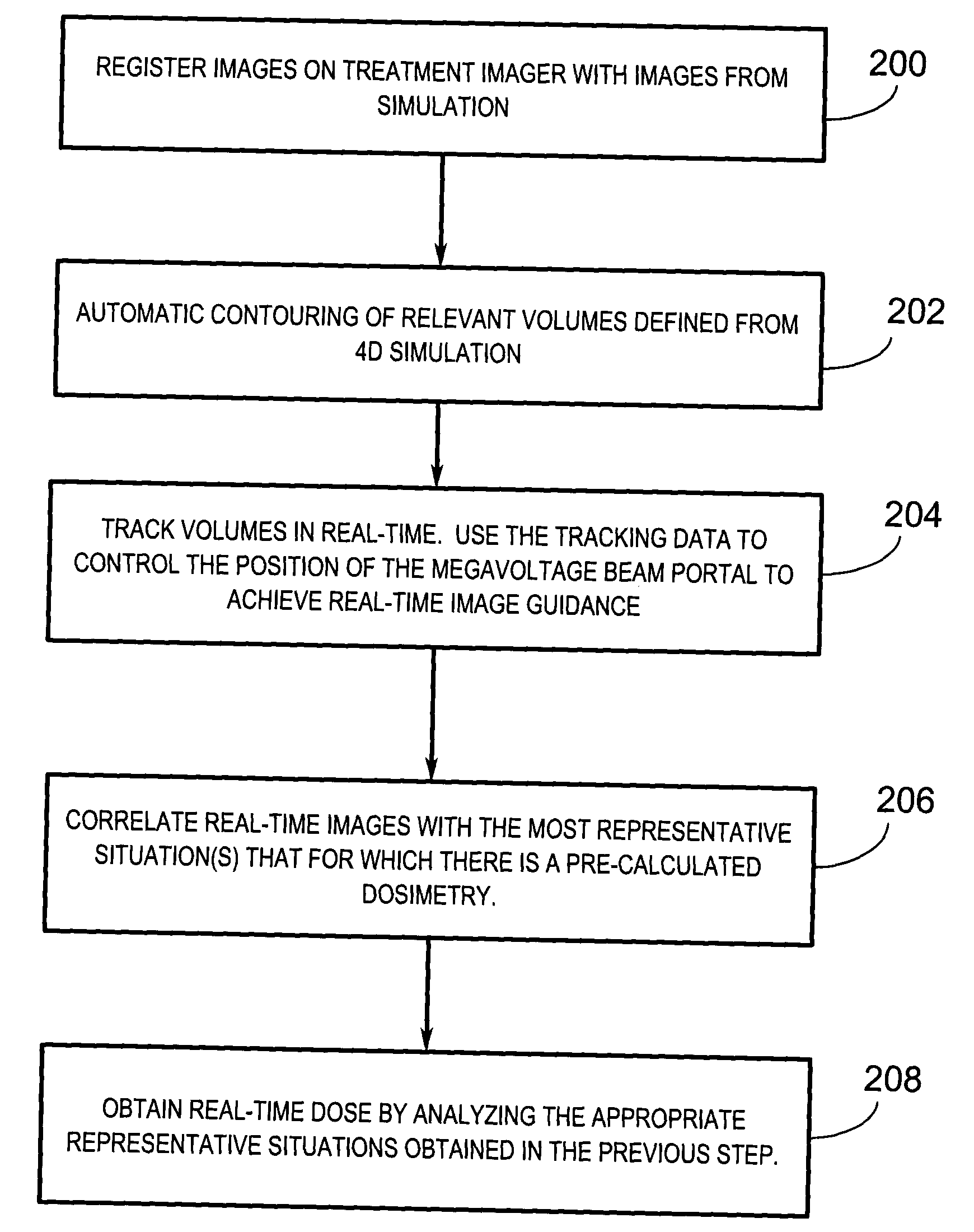
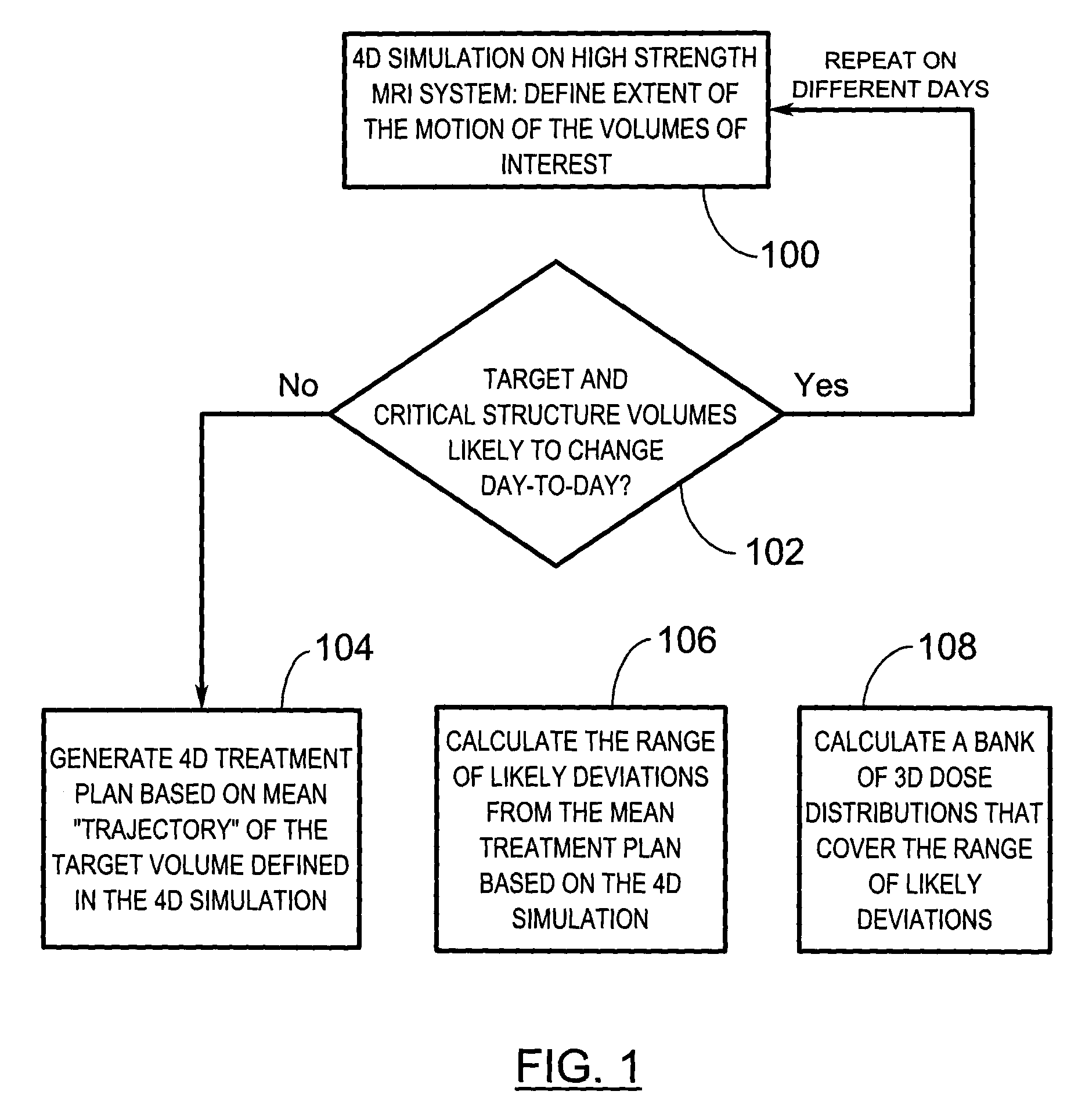
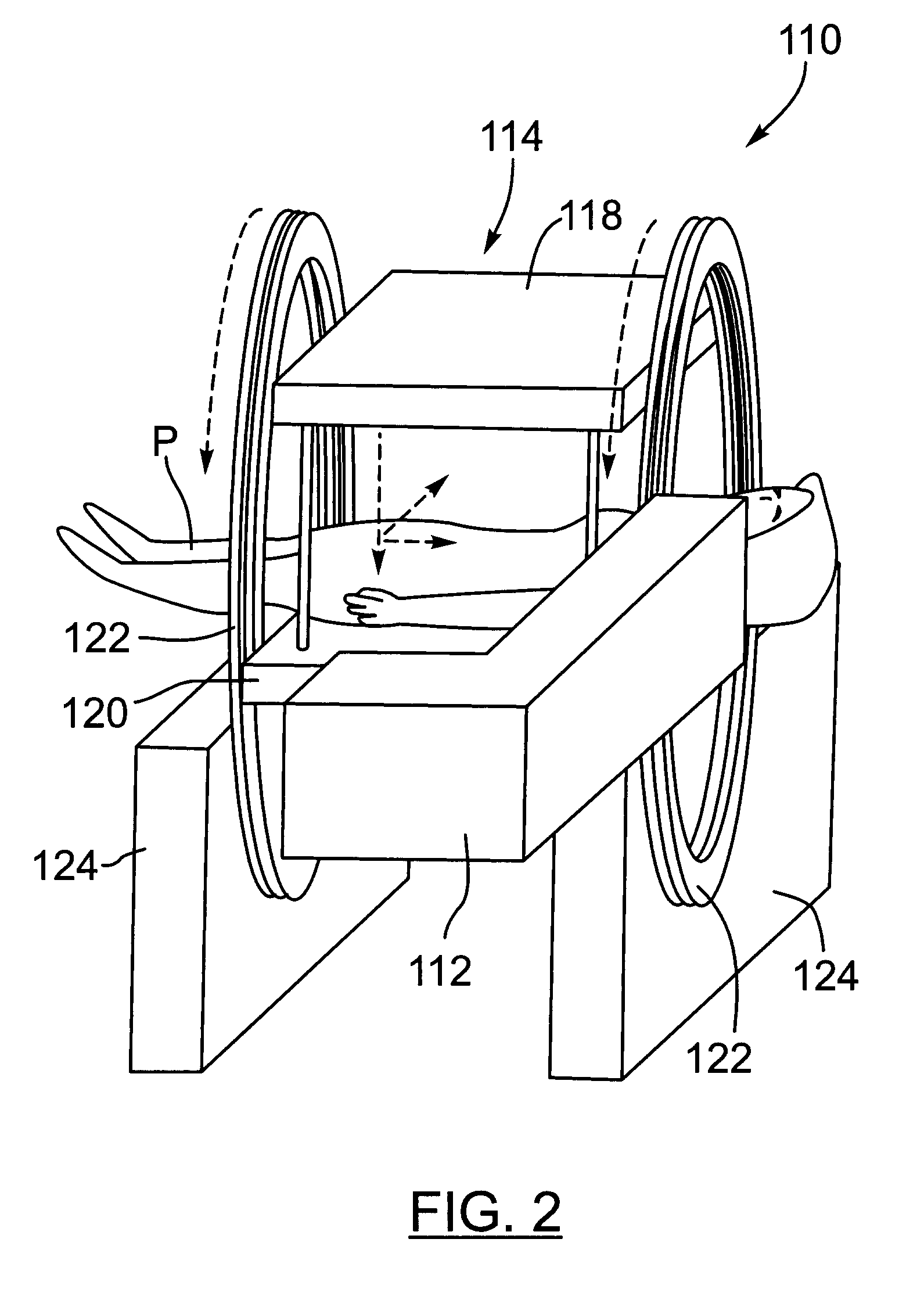
Real-time dose reconstruction using dynamic simulation and image guided adaptive radiotherapy
A radiation therapy treatment method comprises imaging a subject and simulating four-dimensional aspects of radiotherapy. A treatment plan based on the simulation is generated to permit real-time, three-dimensional dose reconstruction at the time of treatment. The simulation and treatment plan are used during treatment fractions to achieve real-time image guidance.
Owner:ALBERTA HEALTH SERVICES
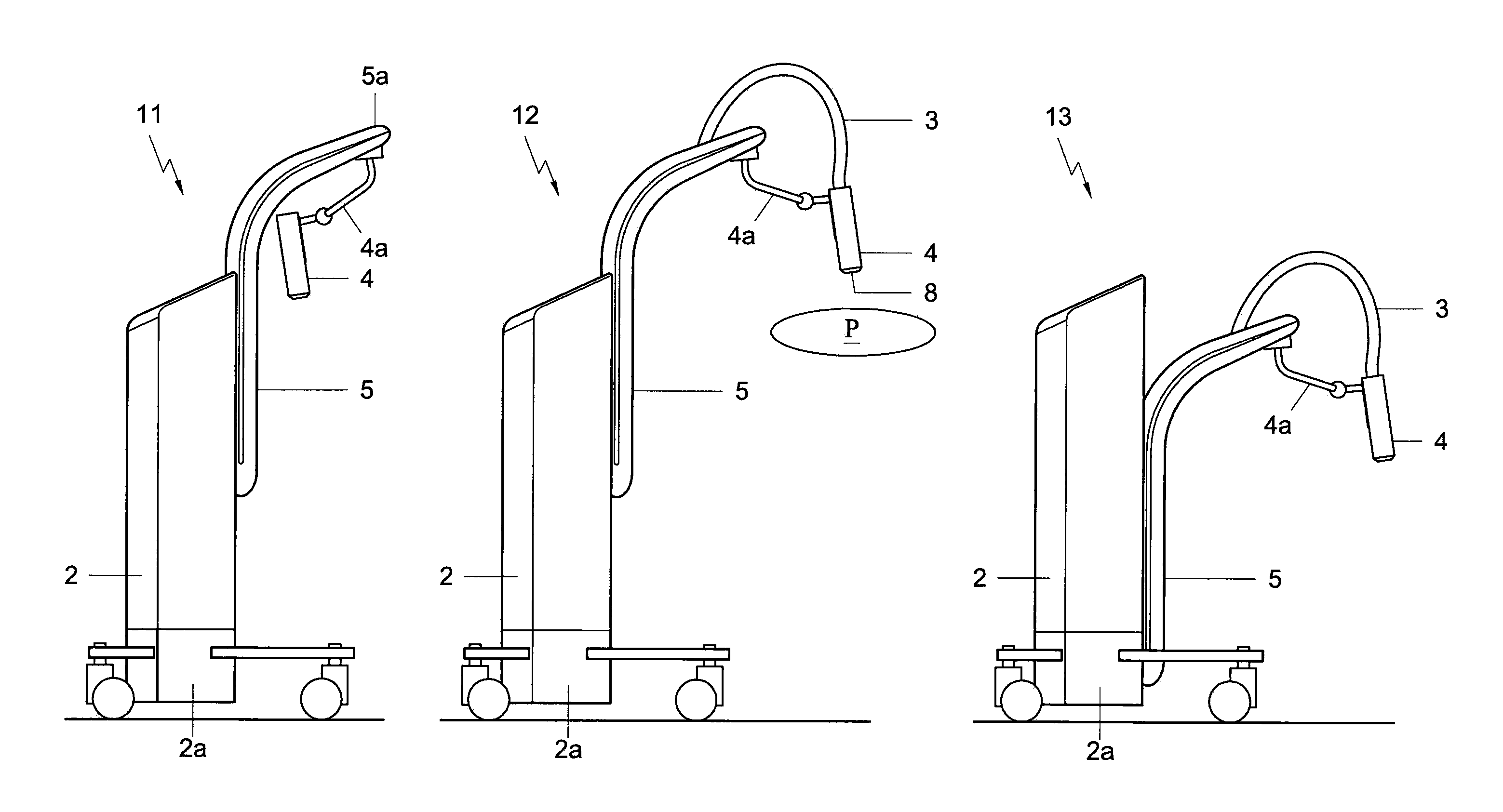
Mobile x-ray unit
ActiveUS20120163539A1Eliminating electron contaminationProtect the surfaceX-ray tube vessels/containerRadiation beam directing meansEngineeringX-ray generator
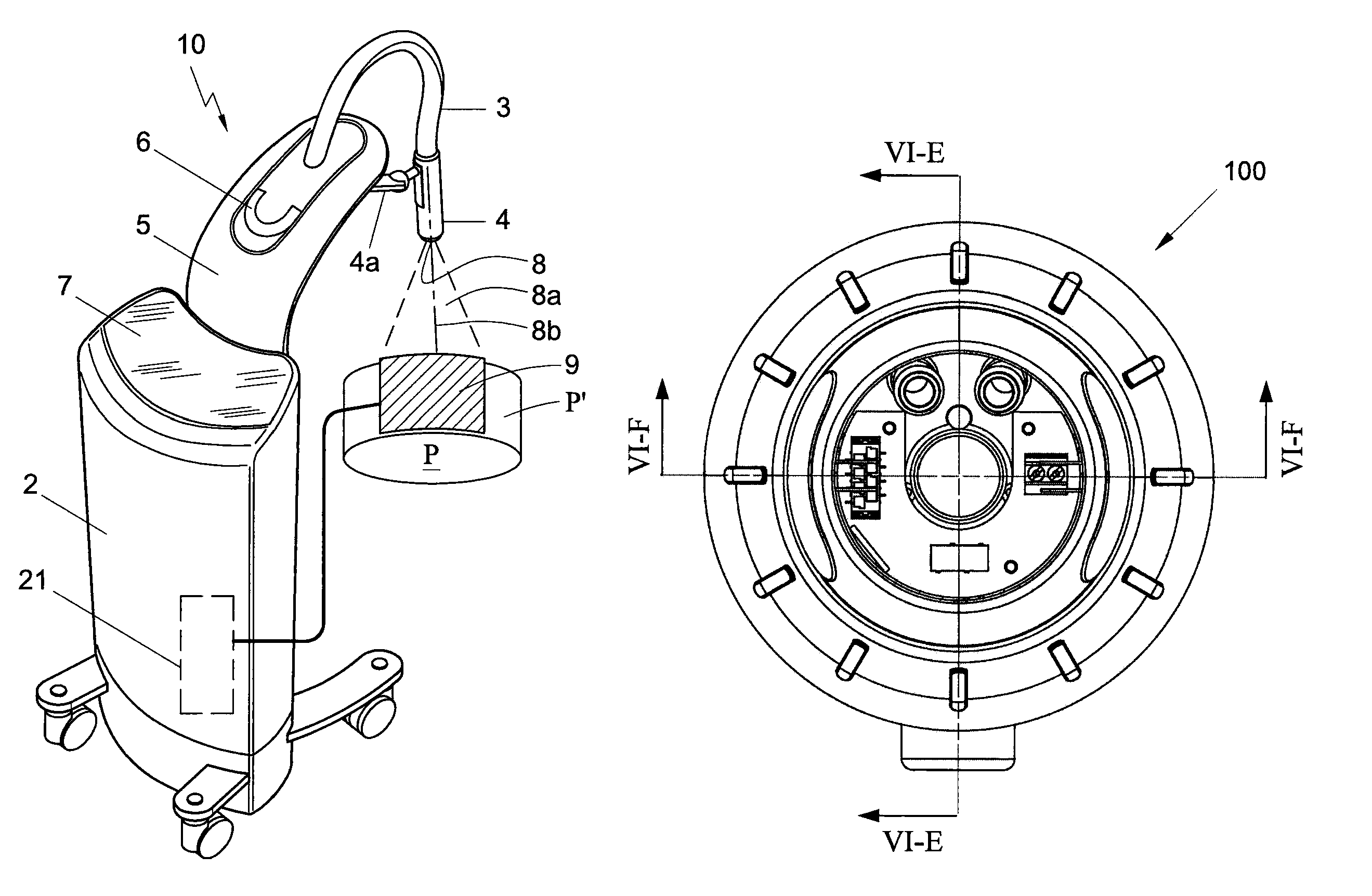
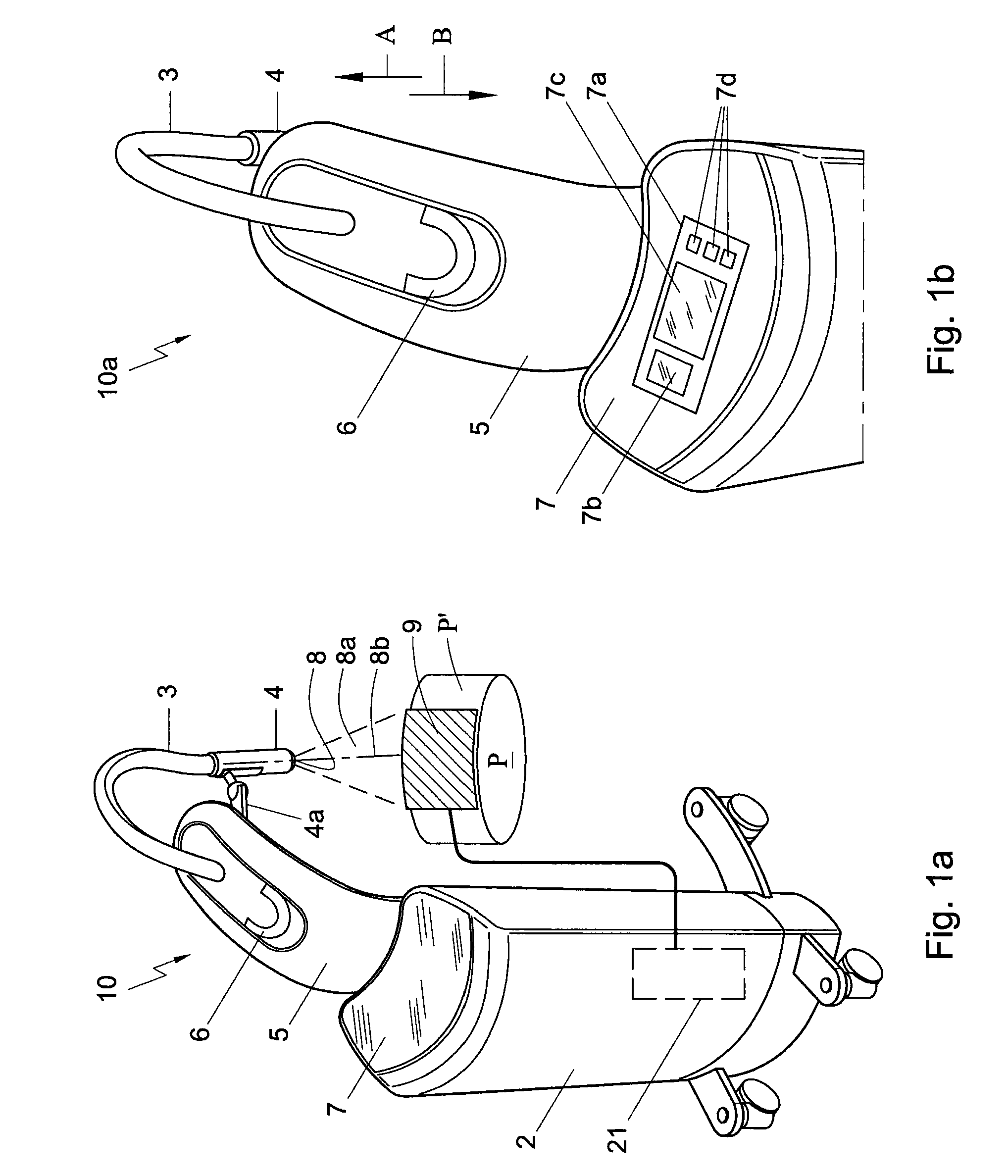
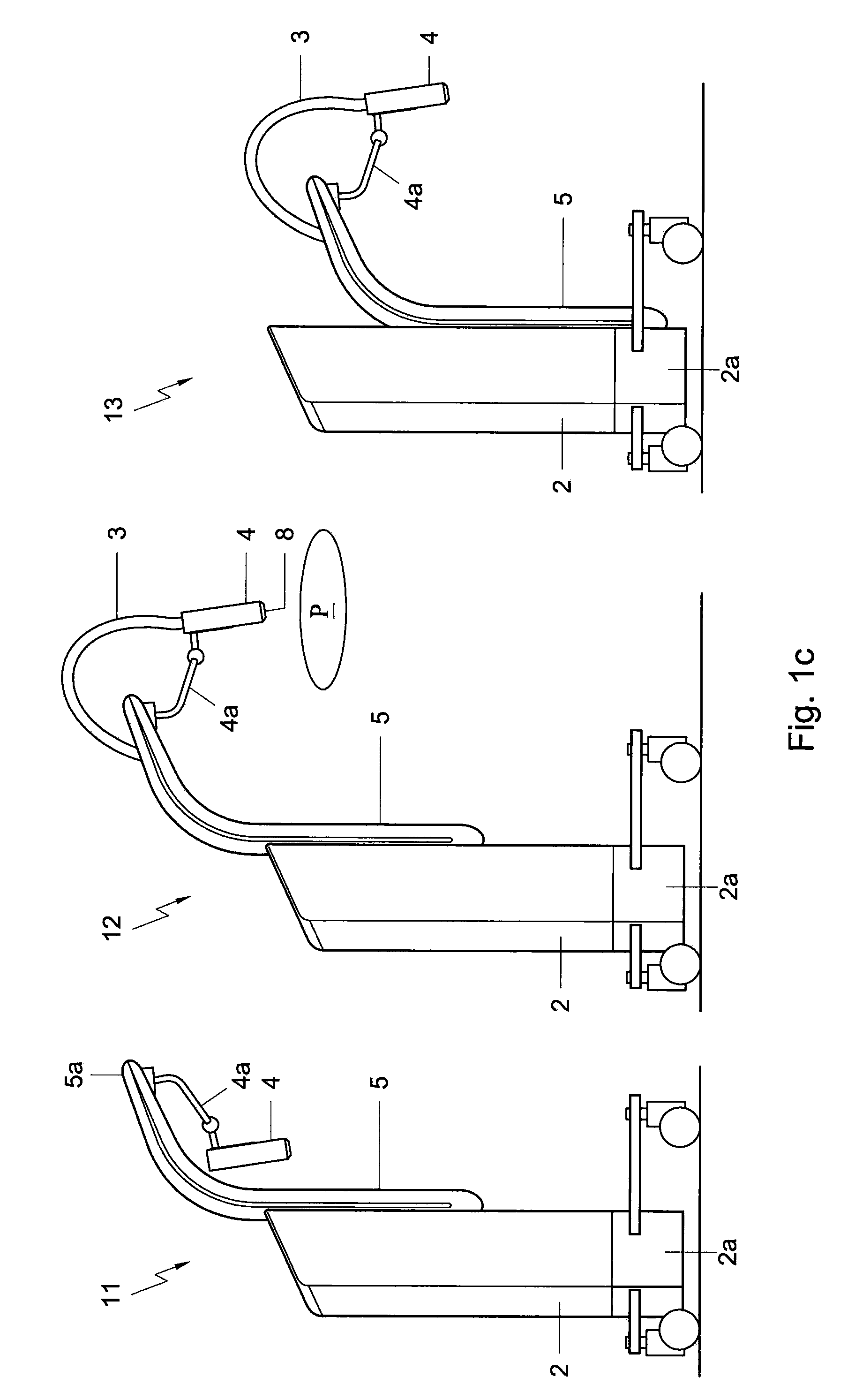
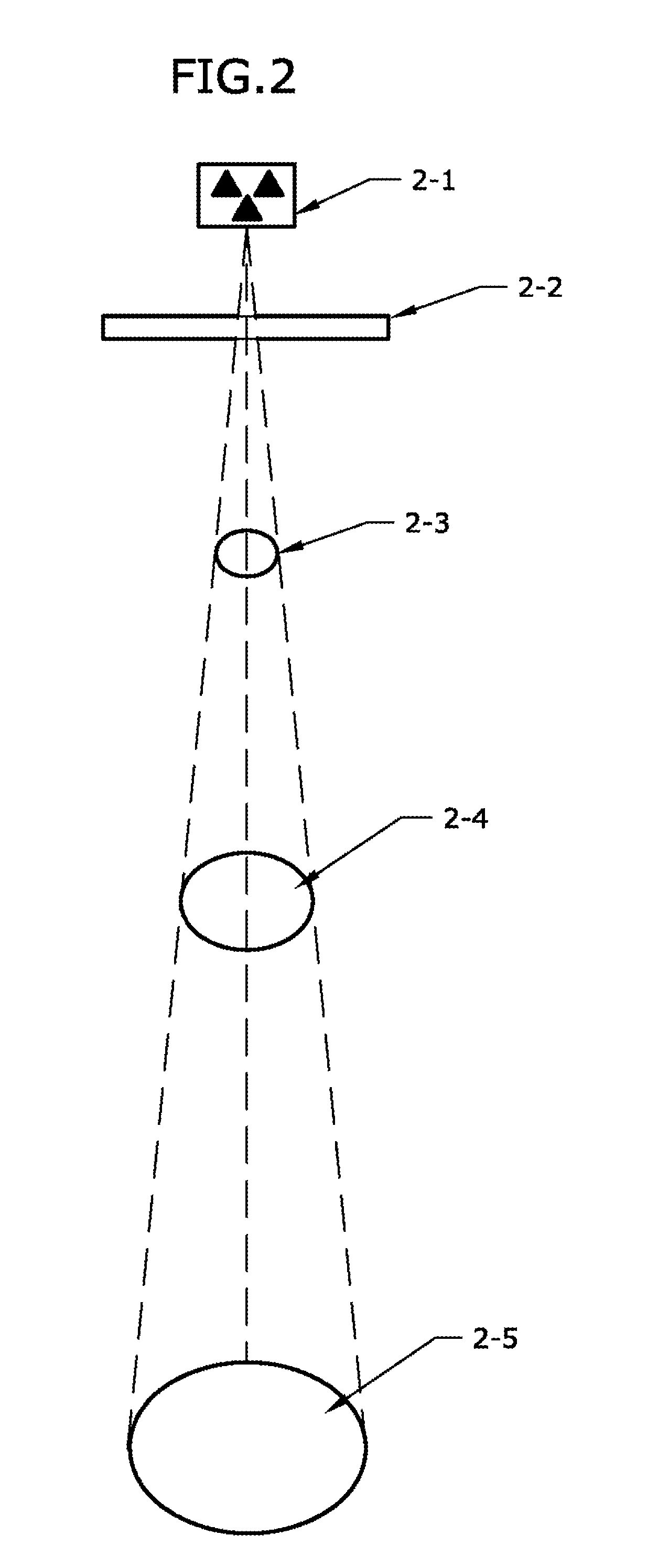
One embodiment of the present disclosure is directed to a mobile X-ray unit. The mobile X-ray unit may include a base for accommodating a control unit for controlling an X-ray applicator and a power supply for supplying power to the X-ray applicator. The mobile X-ray unit may further include an articulated arm associated with the base and coupled to the X-ray applicator. The X-ray applicator may have an X-ray tube configured to emit an X-ray beam through an exit window to irradiate an object. The mobile X-ray unit may further include a dosimetry system adapted for real time dosimetry.
Owner:NUCLETRON OPERATIONS
Real-time adaptive dose computation radiation therapy
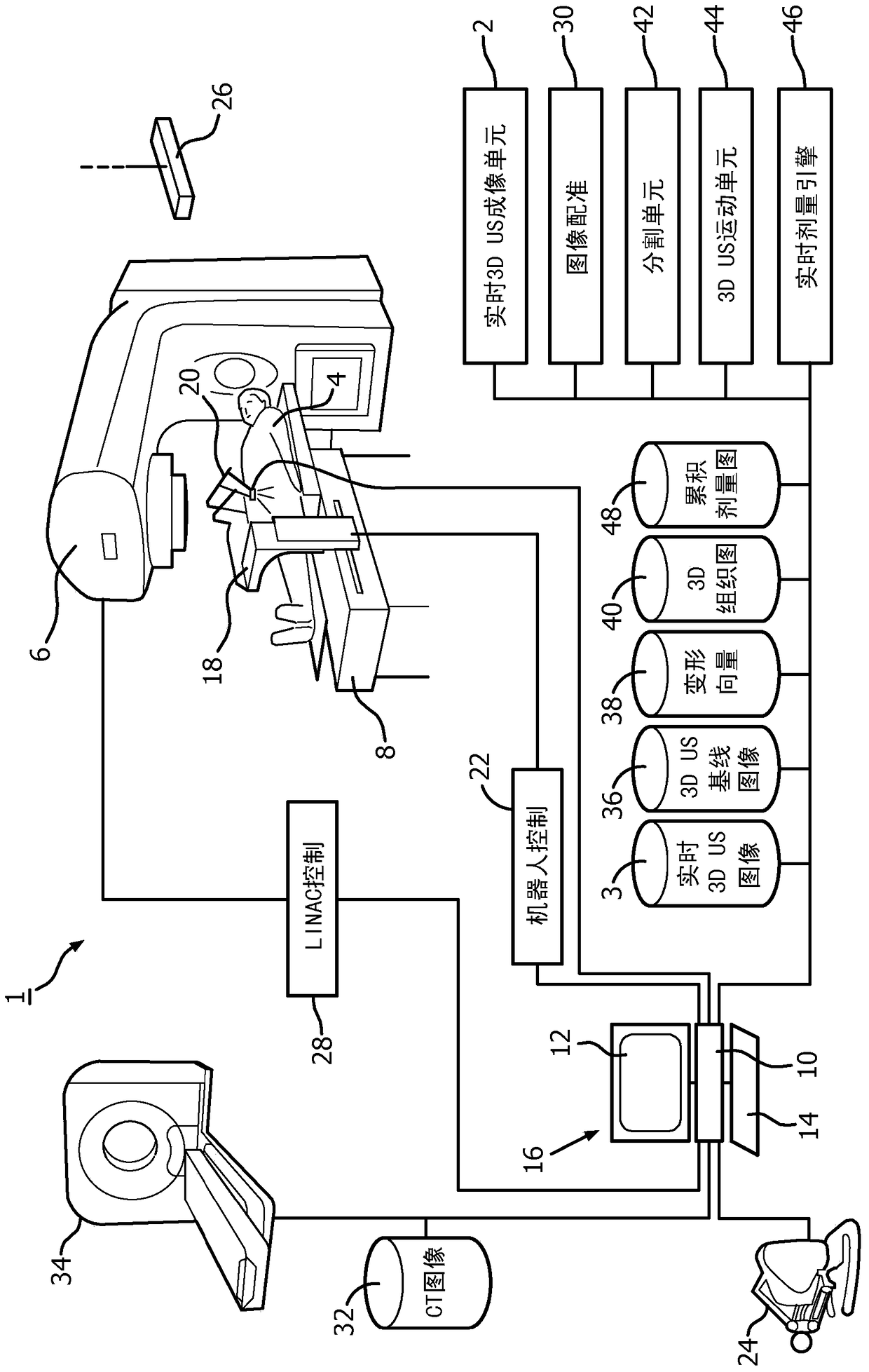
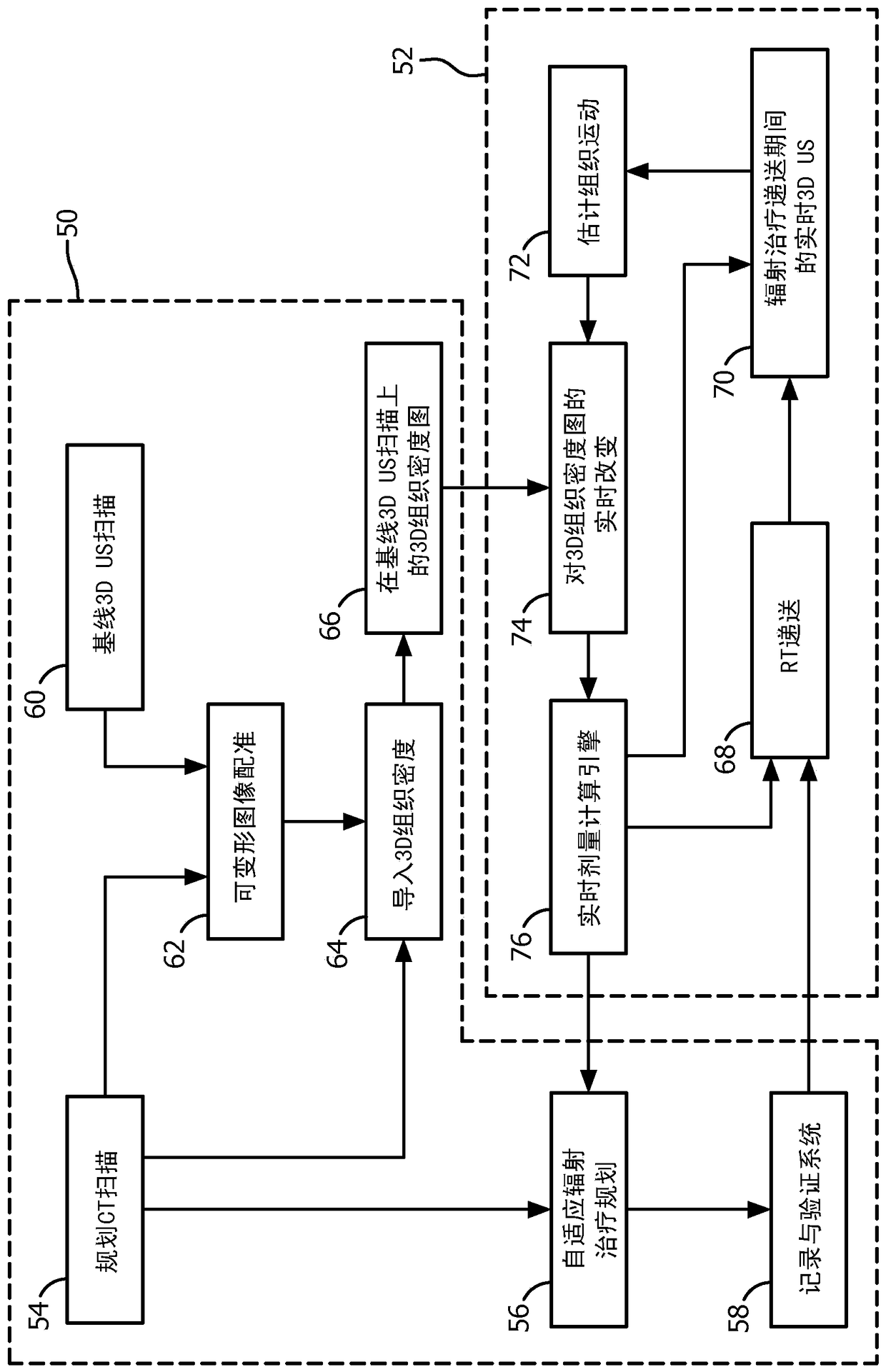
ActiveCN104884126AReal-time measurementReal-time radiation dosimetryOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsOrgan at riskRadiation therapy
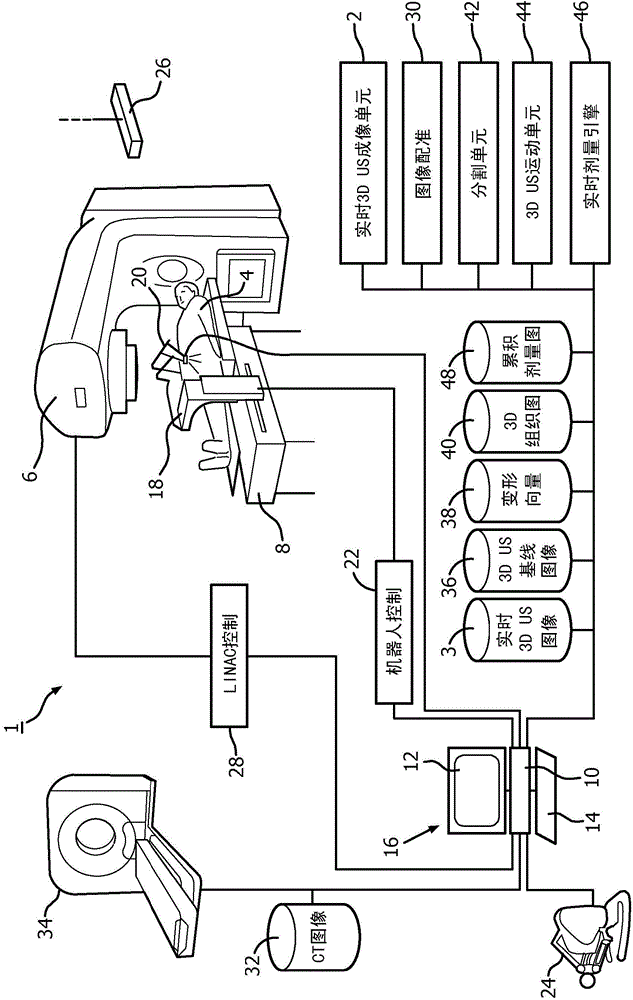
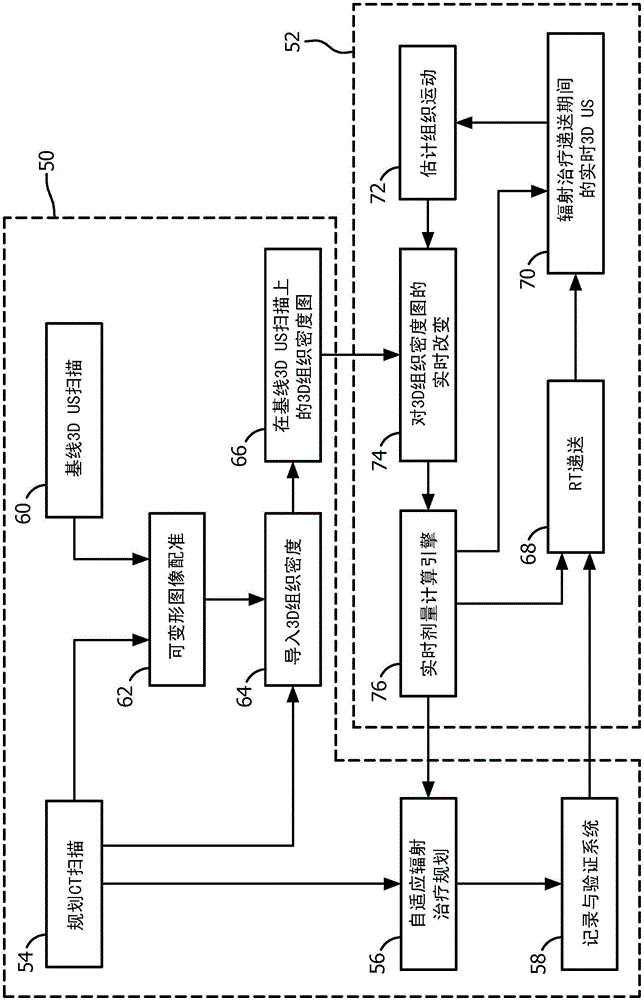
A radiation therapy system (1) includes an ultrasound (US) imaging unit (2), a registration unit (30), an US motion unit (44), and a real-time dose computation engine (46). The ultrasound (US) imaging unit (2) generates a baseline and real-time US images (3) of a subject body (4) region including a target and one or more Organs At Risk (OARs). The registration unit (30) deformably registers a planning image (32) and the baseline US image (36), and maps (66) radiation absorptive properties of tissue in the planning image (32) to the baseline US image (36). The US motion unit (44) measures motion of the target volume and OARs during radiation therapy treatment based on the real-time US images. The real-time dose computation engine (46) computes a real-time radiation dose delivered to the tissues based on the tissue radiation absorptive properties mapped from the baseline or planning images to the real-time 3D US images (3).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Energy-transfer nanocomposite materials and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20100176343A1Diagnostics using lightChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceEnergy transferDosimetry radiation
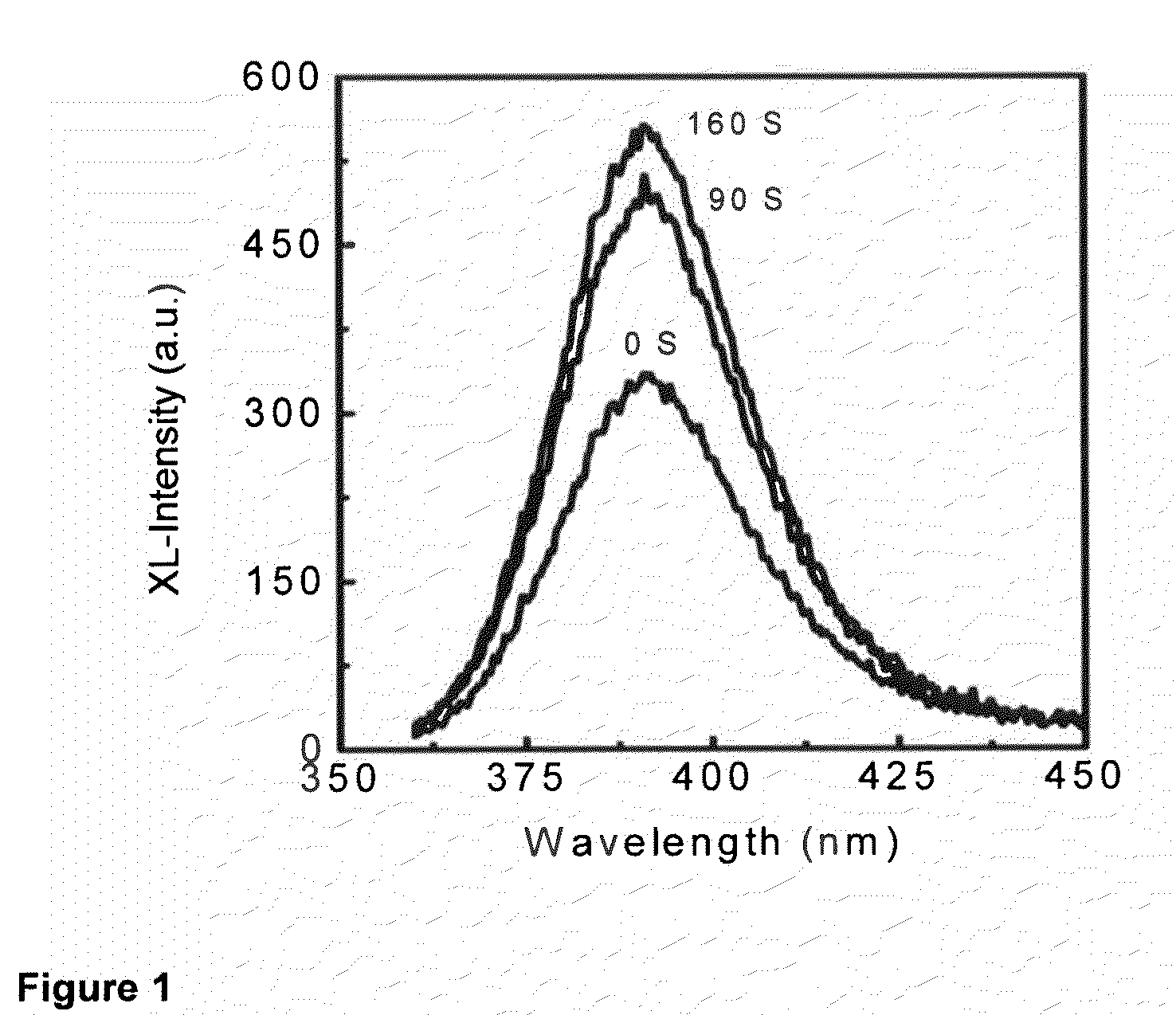
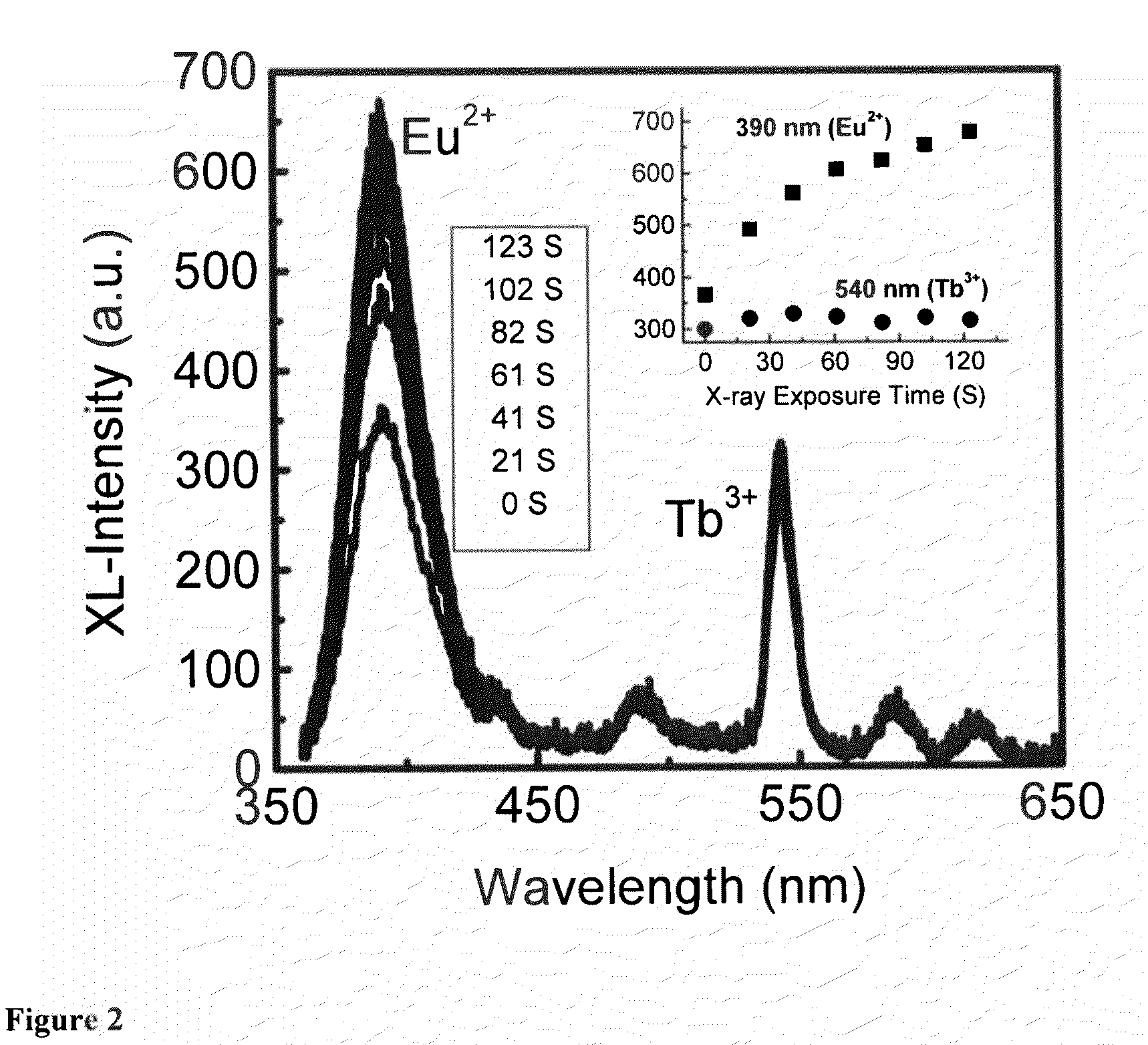
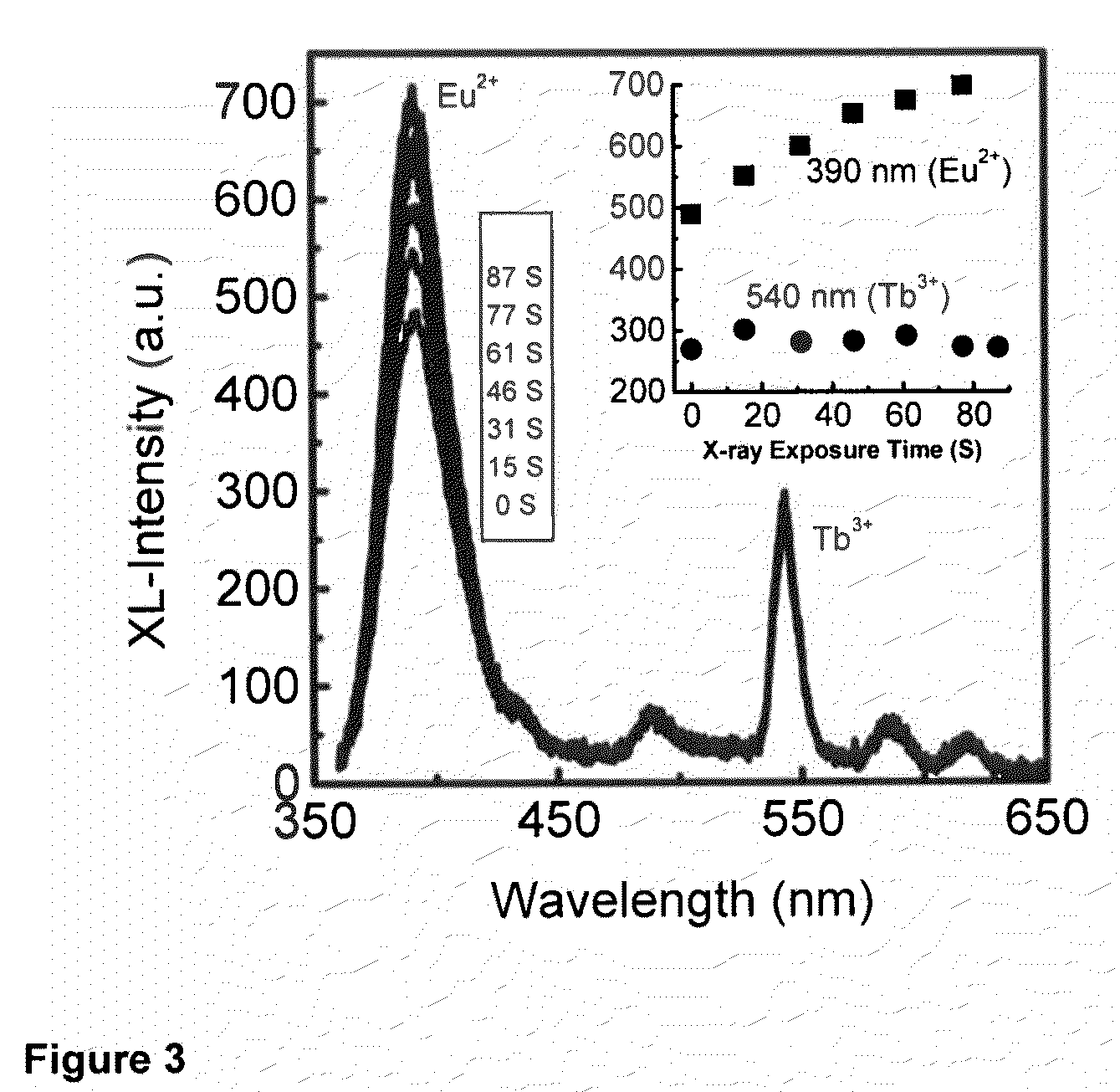
The presently claimed and disclosed inventions relate, in general, to methods of radiation dosimetry and imaging using scintillation luminescence. More particularly, materials having a scintillation luminescence response to radiation that varies with total radiation dose received can be used for dosimetry monitoring, including, but not limited to nanoparticles for in vivo, real-time dosimetry. Energy-transfer nanocomposite materials as well as methods of making and using such materials in various applications including, but not limited to, in vivo radiation dosimetry and imaging, are disclosed. More particularly, the presently claimed and disclosed inventions relate to nanoparticle scintillation luminescence particles encapsulated in hosts of the general formula BaFX and BaFX:Eu2+ where X═Cl, Br and I.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
Real-time dose computation for radiation therapy using graphics processing unit acceleration of the convolution/superposition dose computation method
A system for radiation therapy including a radiation planning system, wherein the radiation planning system comprises a parallel processor adapted to receive input information concerning a body having an intended radiation treatment region and to output information for providing radiation treatment to the intended radiation treatment region of the body, wherein the parallel processor is adapted to perform a plurality of reverse ray tracing calculations based on the input information concerning the body in determining the output information for providing radiation treatment, each of the plurality of reverse ray tracing calculations comprising: calculating a first physical property corresponding to a first sub-region of the intended radiation treatment region of the body that is intersected by a ray traced between a source position and the intended radiation treatment region; and calculating, subsequent to the first-mentioned calculating, a second physical property corresponding to a second sub-region of the intended radiation treatment region that is intersected by the ray at a location closer to the source position than is the first sub-region.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
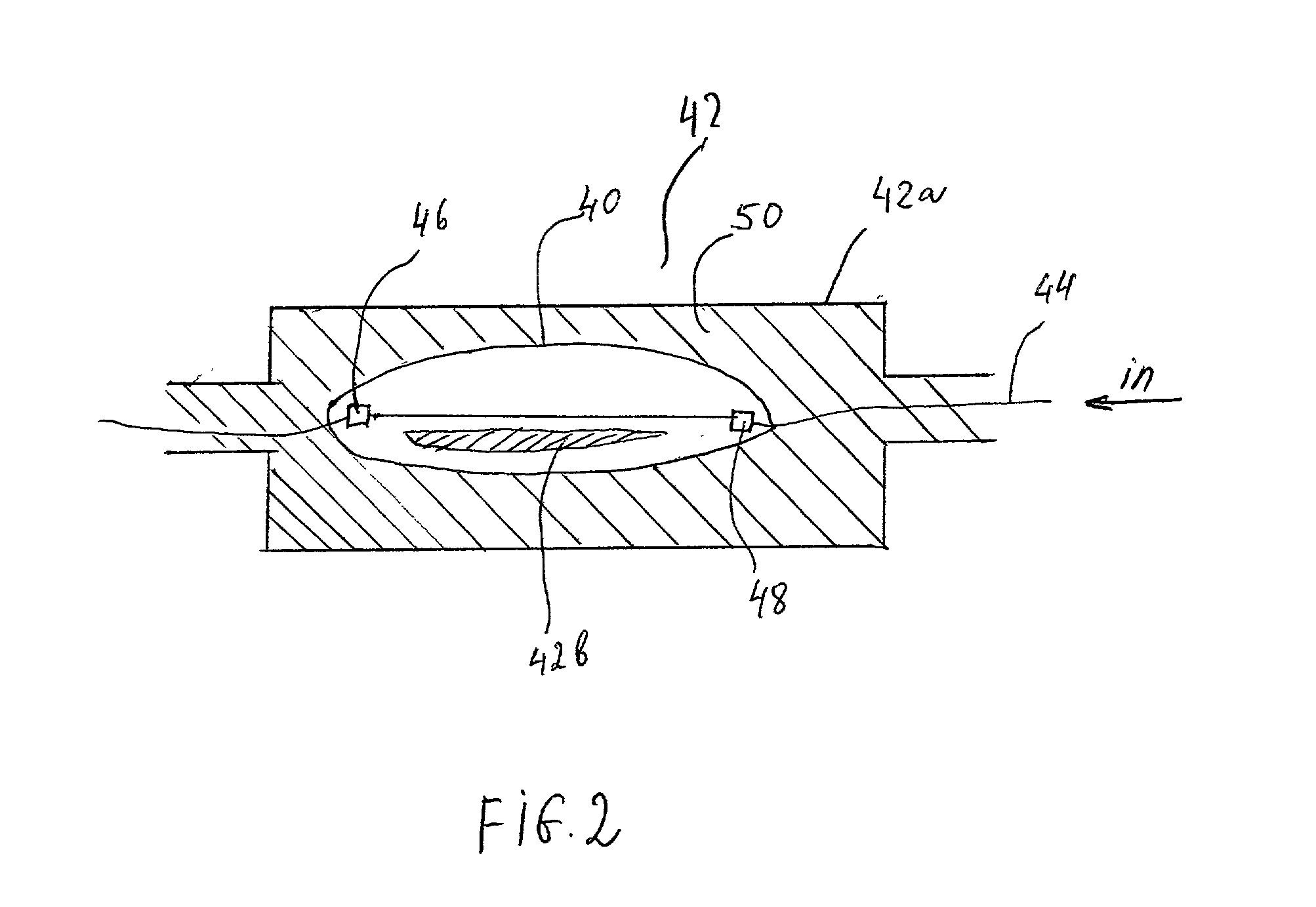
Method and apparatus for real time dosimetry
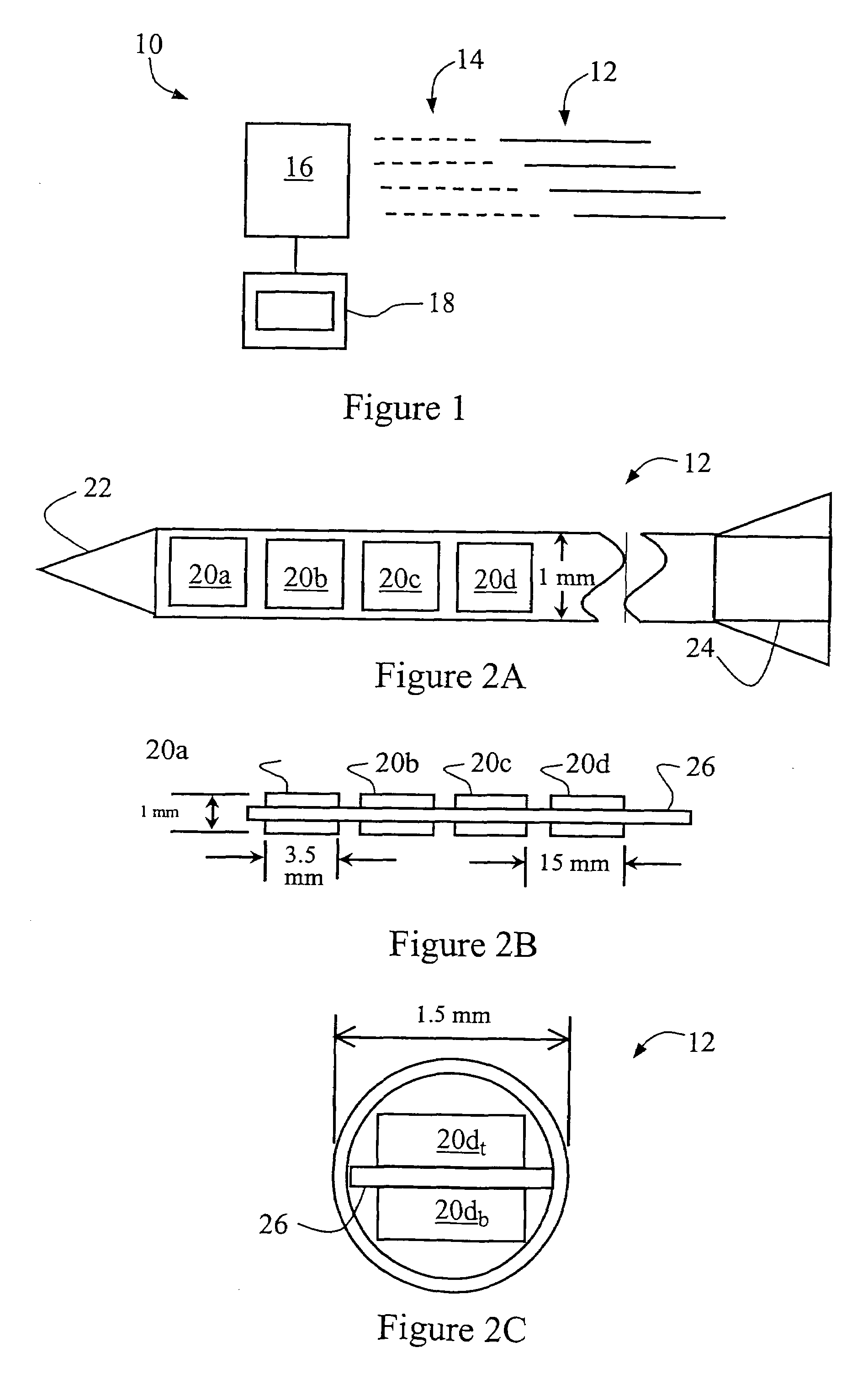
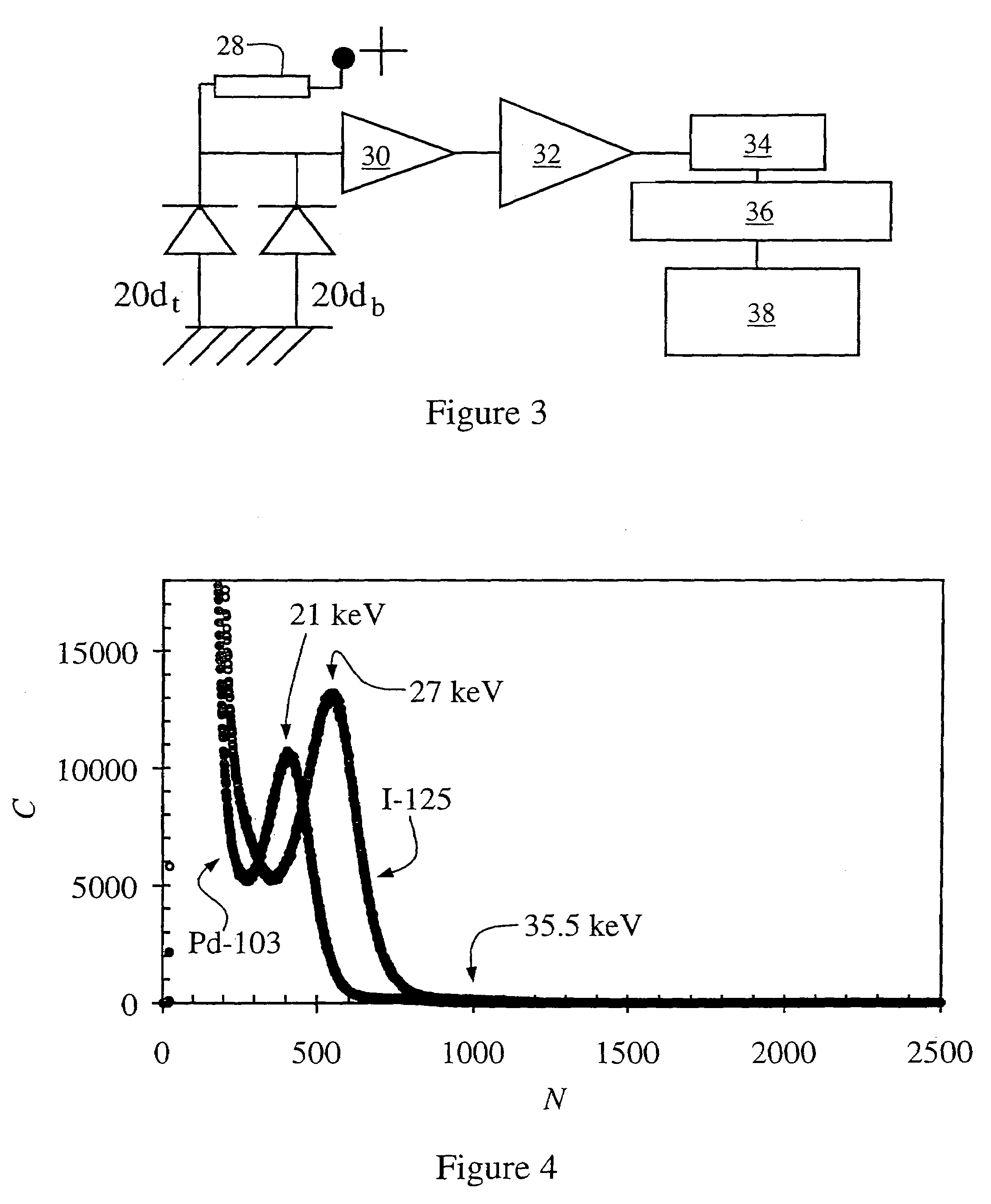
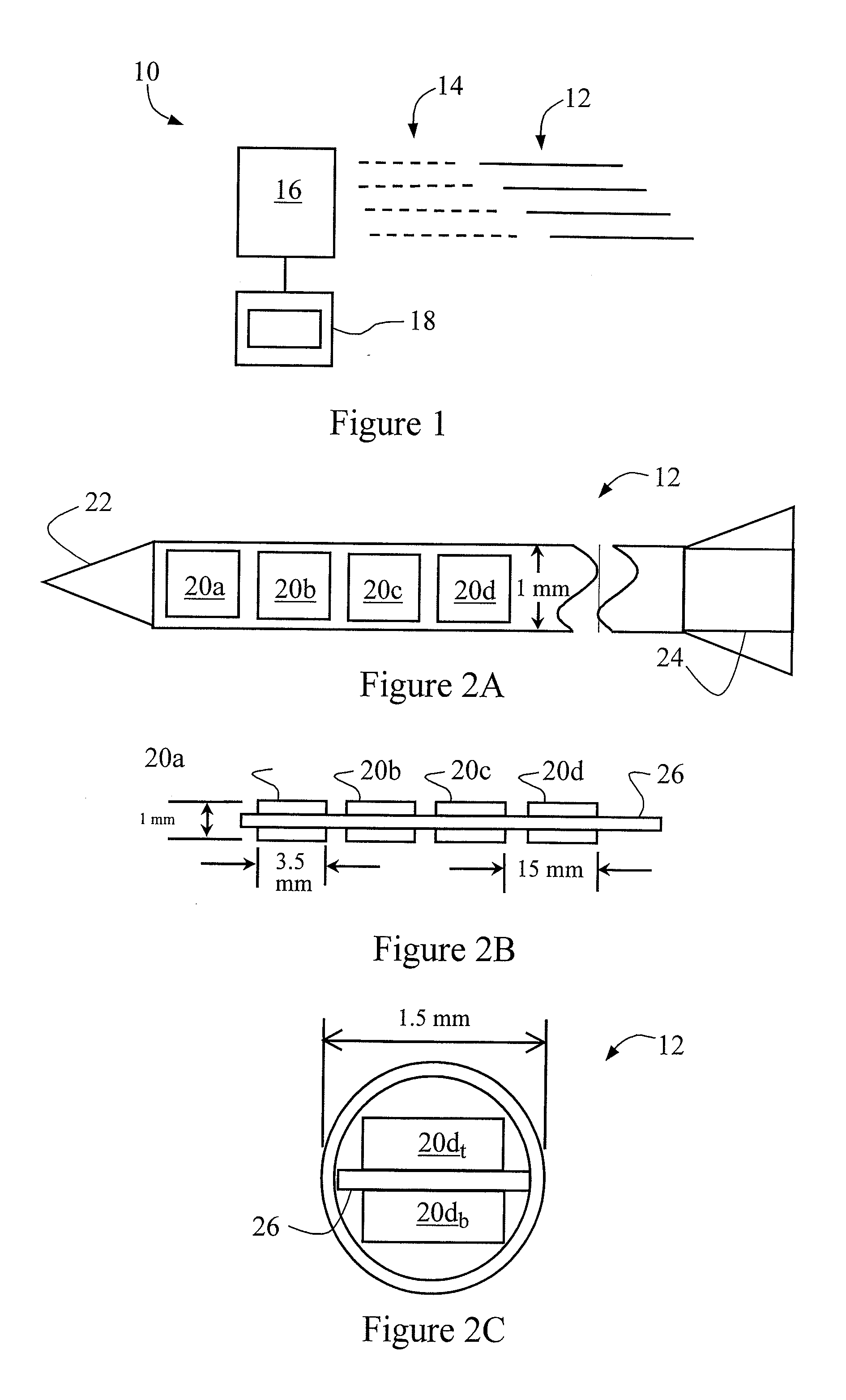
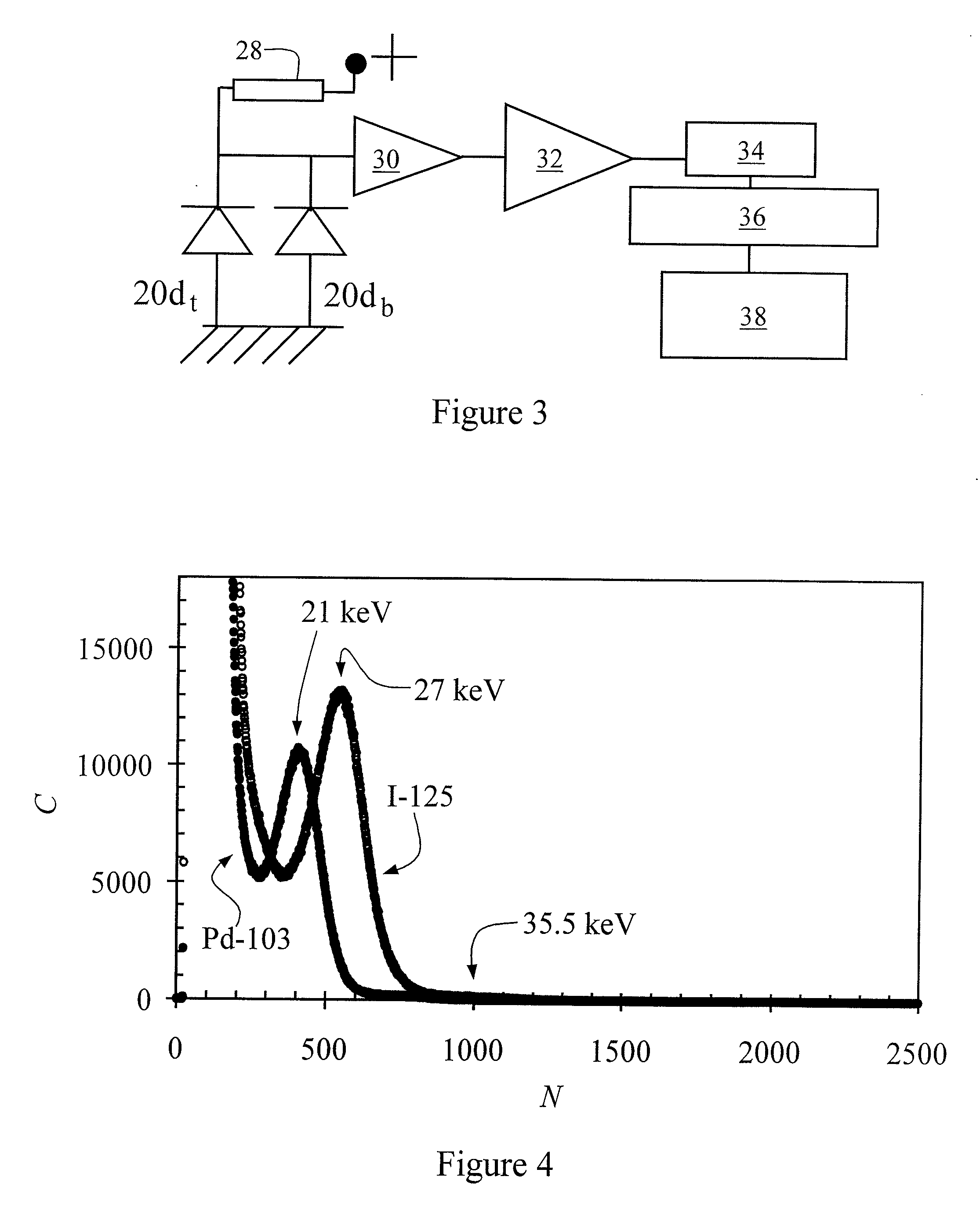
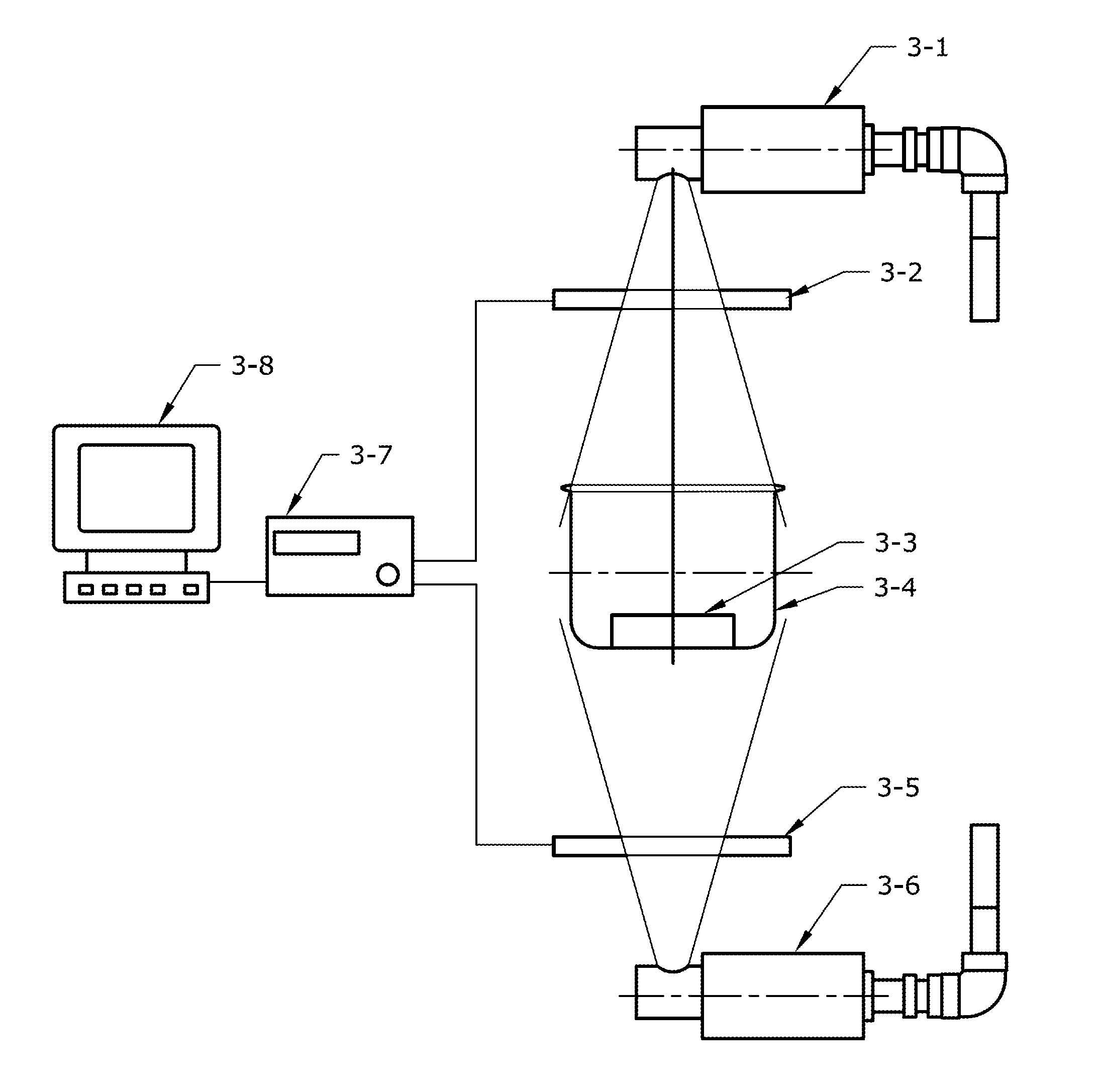
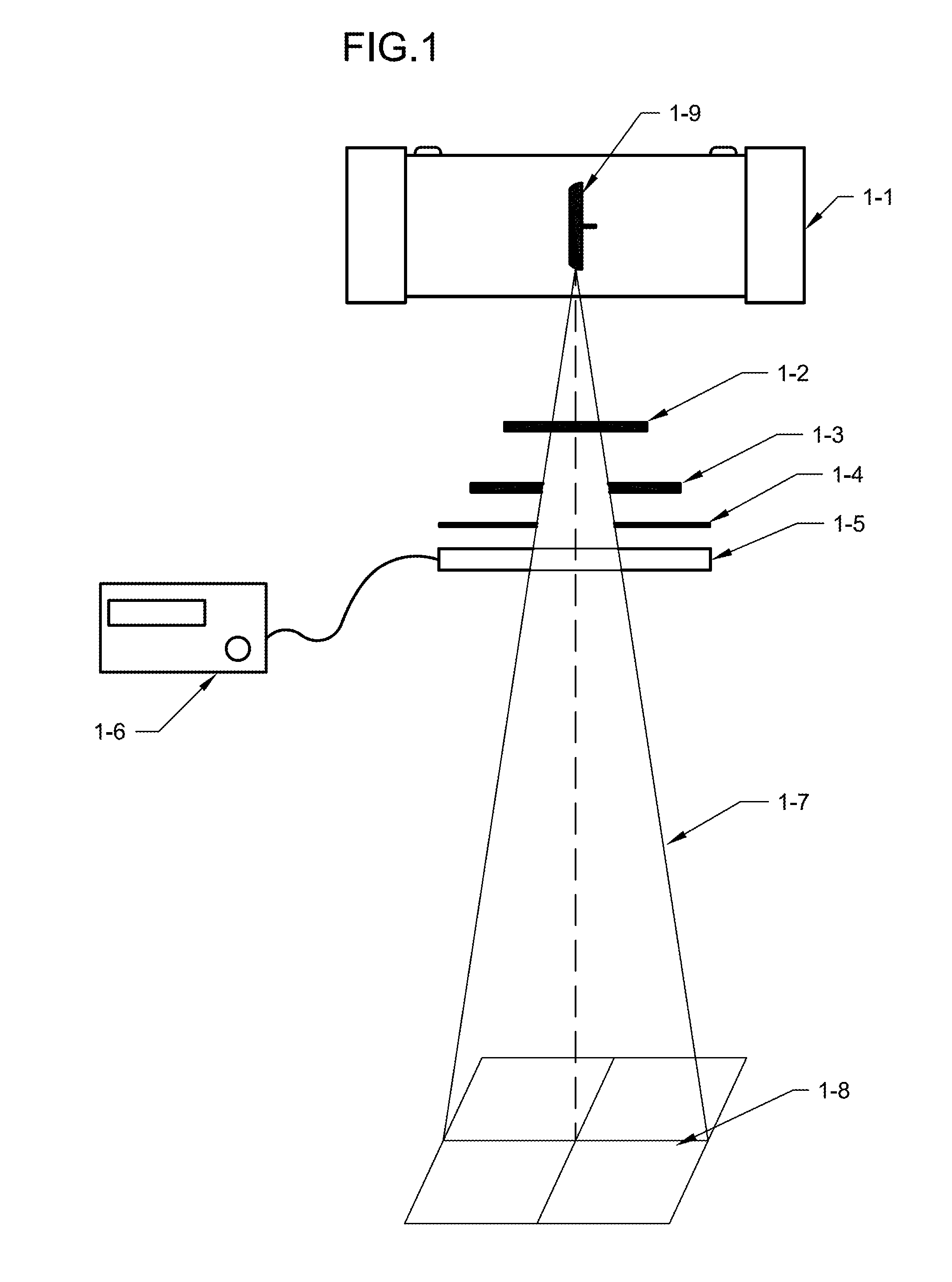
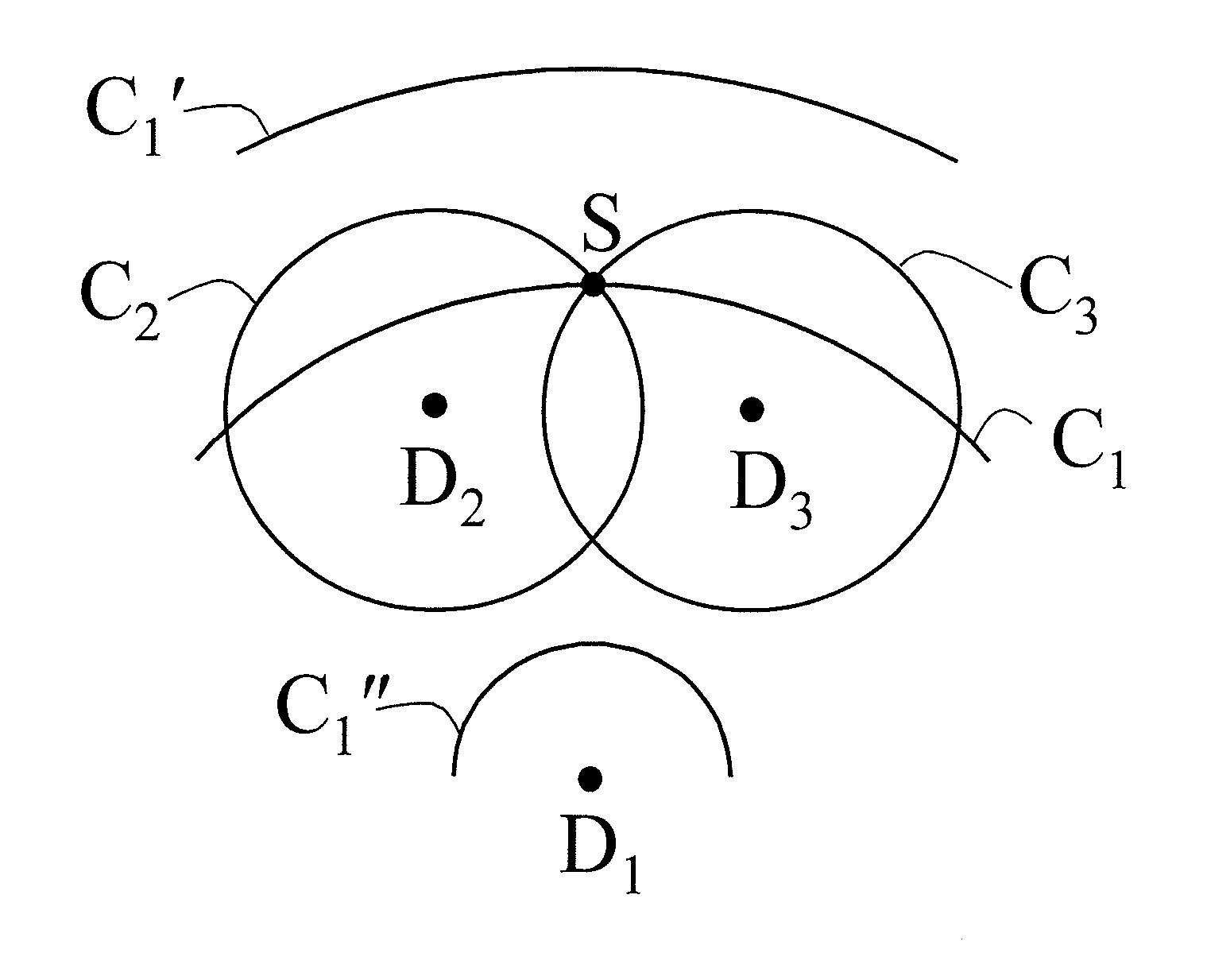
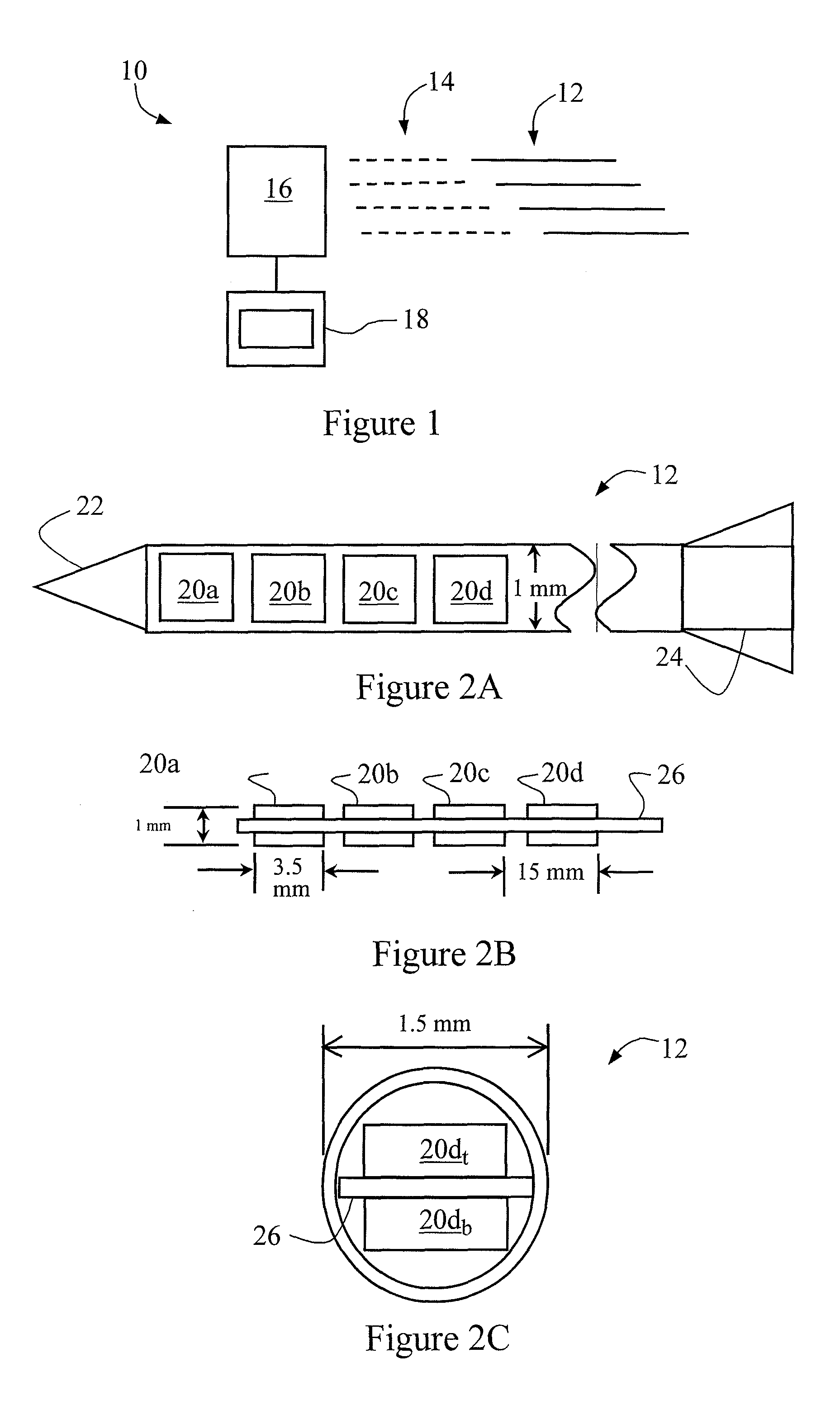
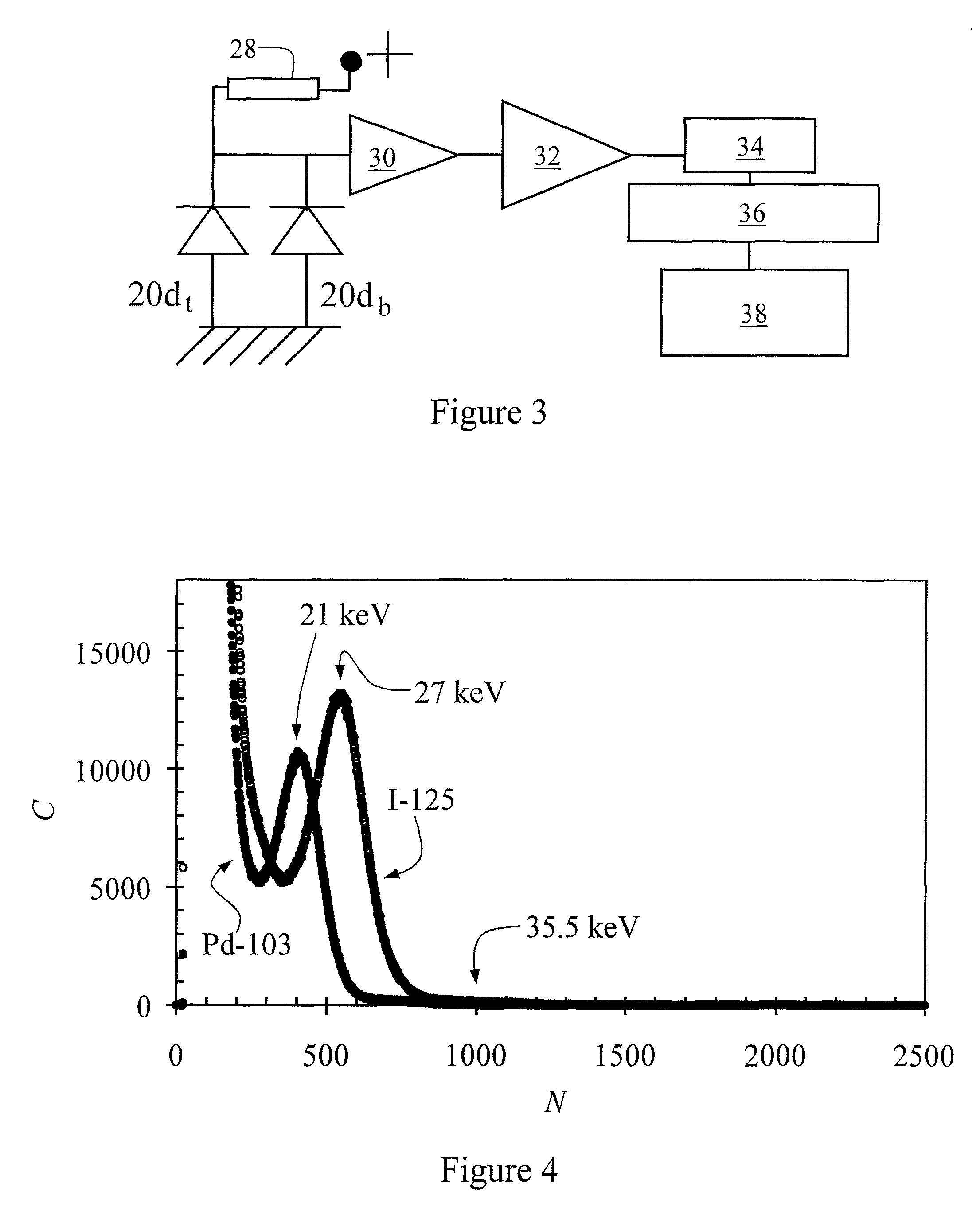
ActiveUS7361134B2The result is accurateSmall amountX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose rateLocation determination
The present invention provides a method of determining the dose rate of a radiation source including locating three or more detectors in the vicinity of said source, each for providing an output indicative of the amount of radiation received from said source and determining the location of said source from at least some of said detector outputs, wherein as many of said detector outputs is required to provide an acceptably accurate result are used in determining said location whereby the dose of radiation from said source can be determined from said determined location of said source and either a known activity of said source or a measure of the activity of said source determined by said detectors.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT +1
Mobile X-ray unit
ActiveUS8995616B2X-ray tube vessels/containerRadiation beam directing meansEngineeringX-ray generator
One embodiment of the present disclosure is directed to a mobile X-ray unit. The mobile X-ray unit may include a base for accommodating a control unit for controlling an X-ray applicator and a power supply for supplying power to the X-ray applicator. The mobile X-ray unit may further include an articulated arm associated with the base and coupled to the X-ray applicator. The X-ray applicator may have an X-ray tube configured to emit an X-ray beam through an exit window to irradiate an object. The mobile X-ray unit may further include a dosimetry system adapted for real time dosimetry.
Owner:NUCLETRON OPERATIONS
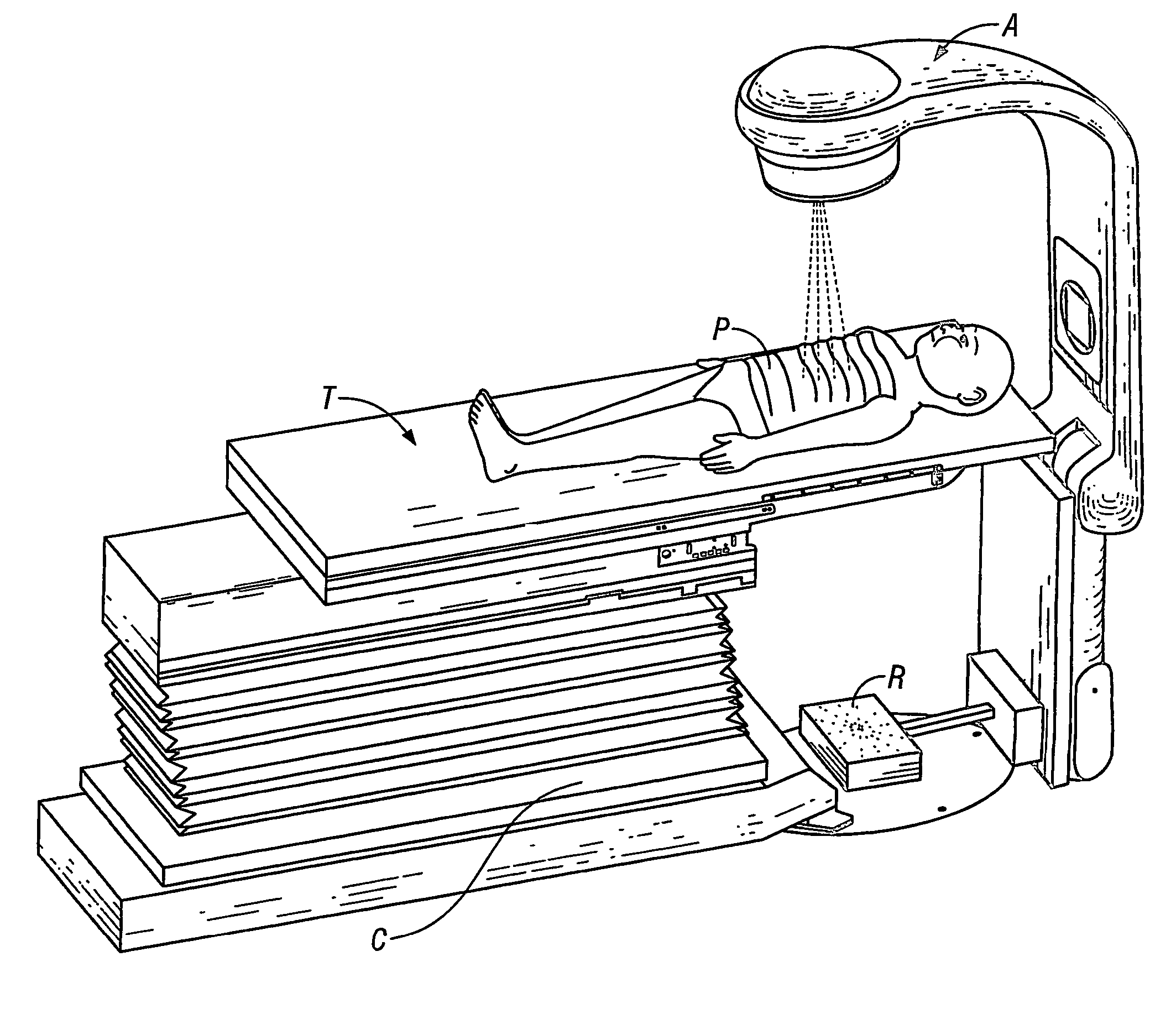
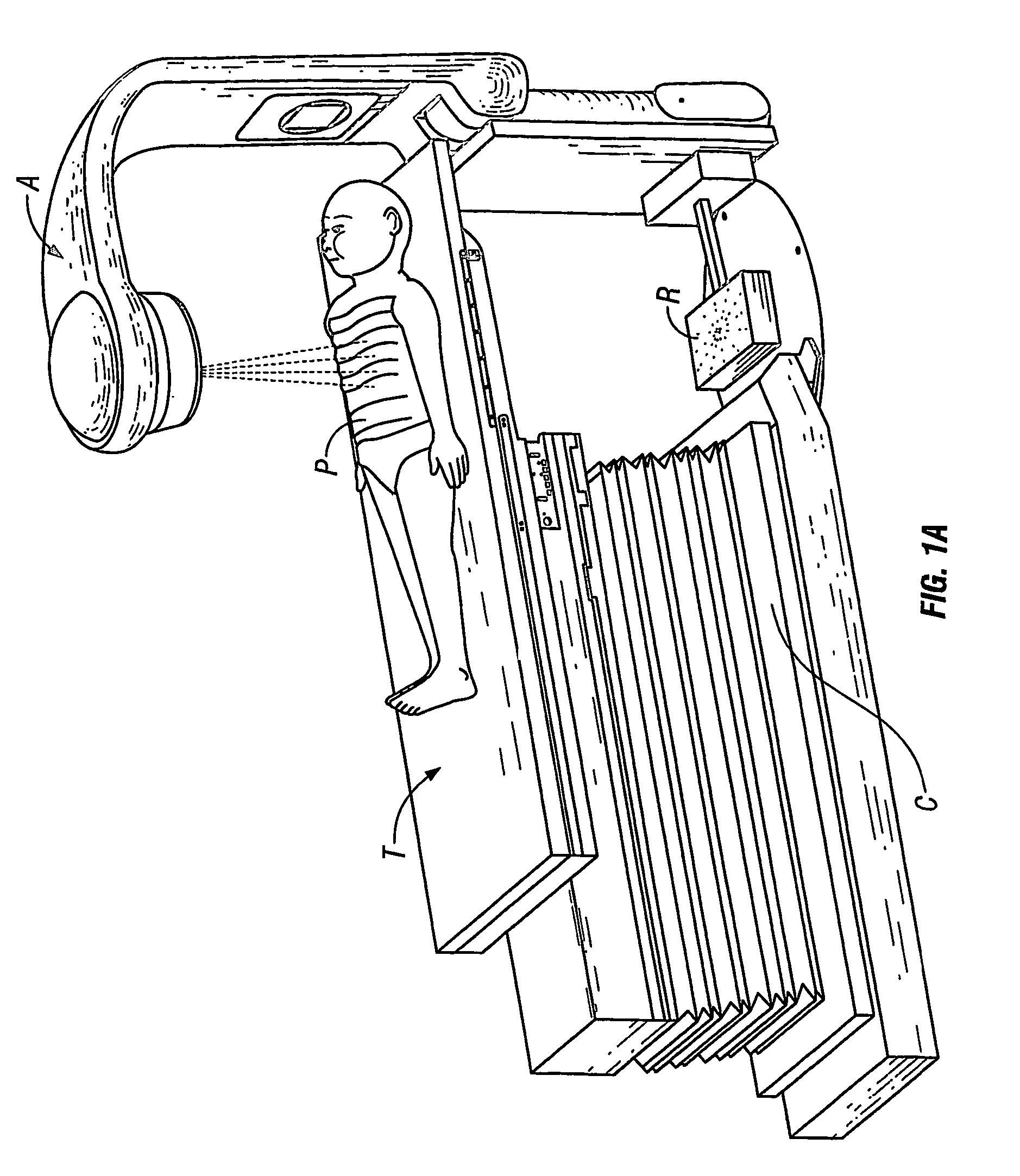
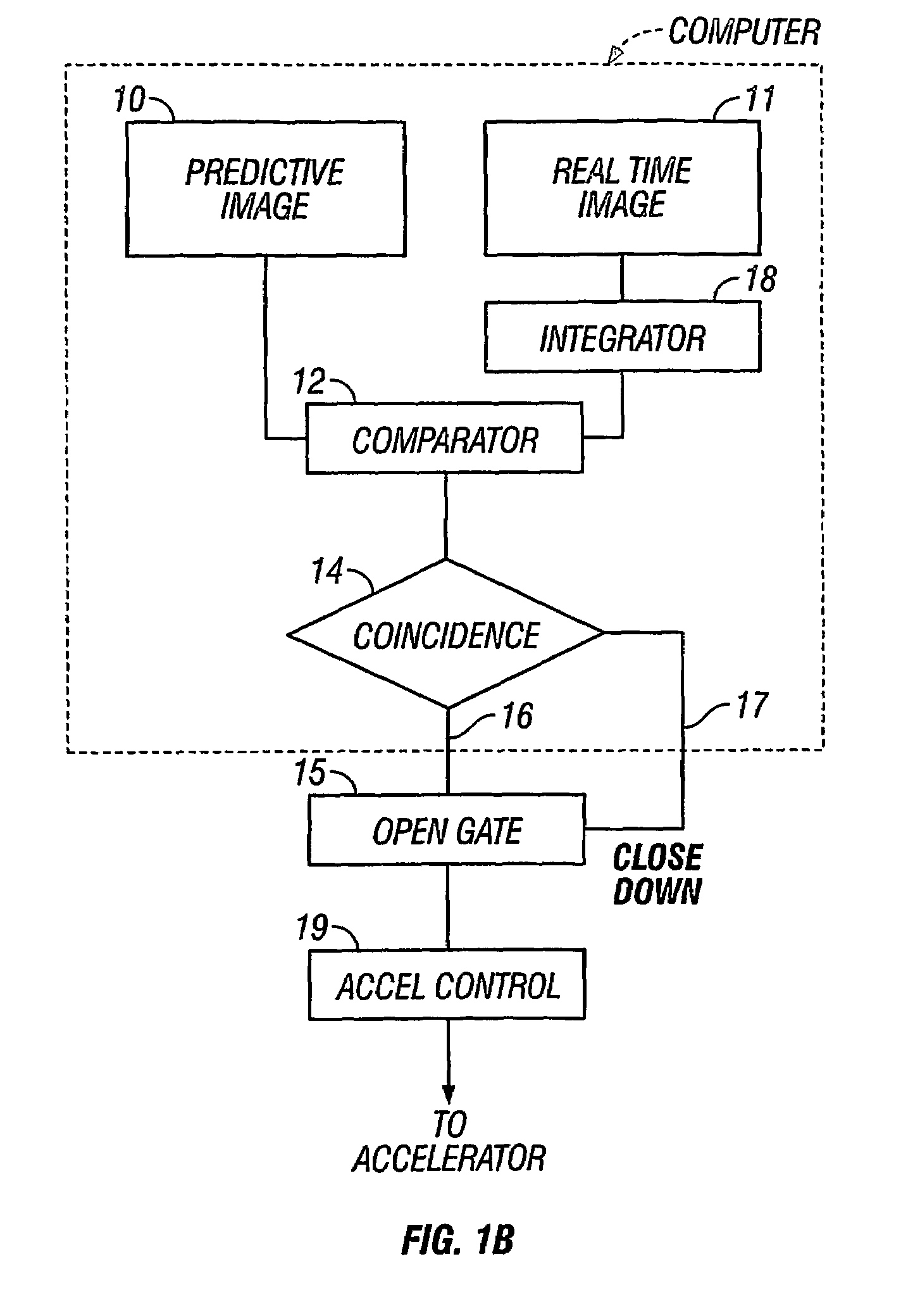
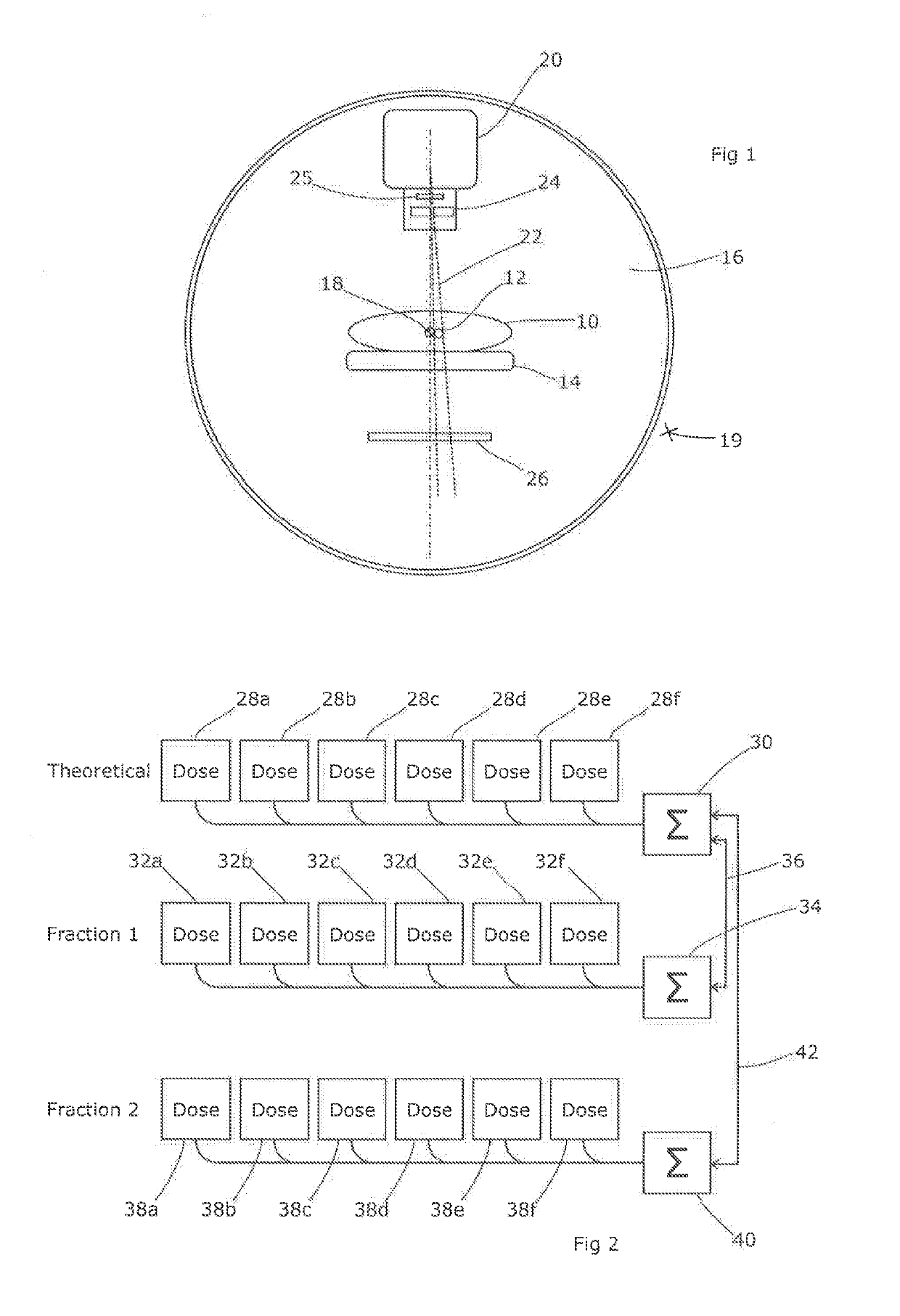
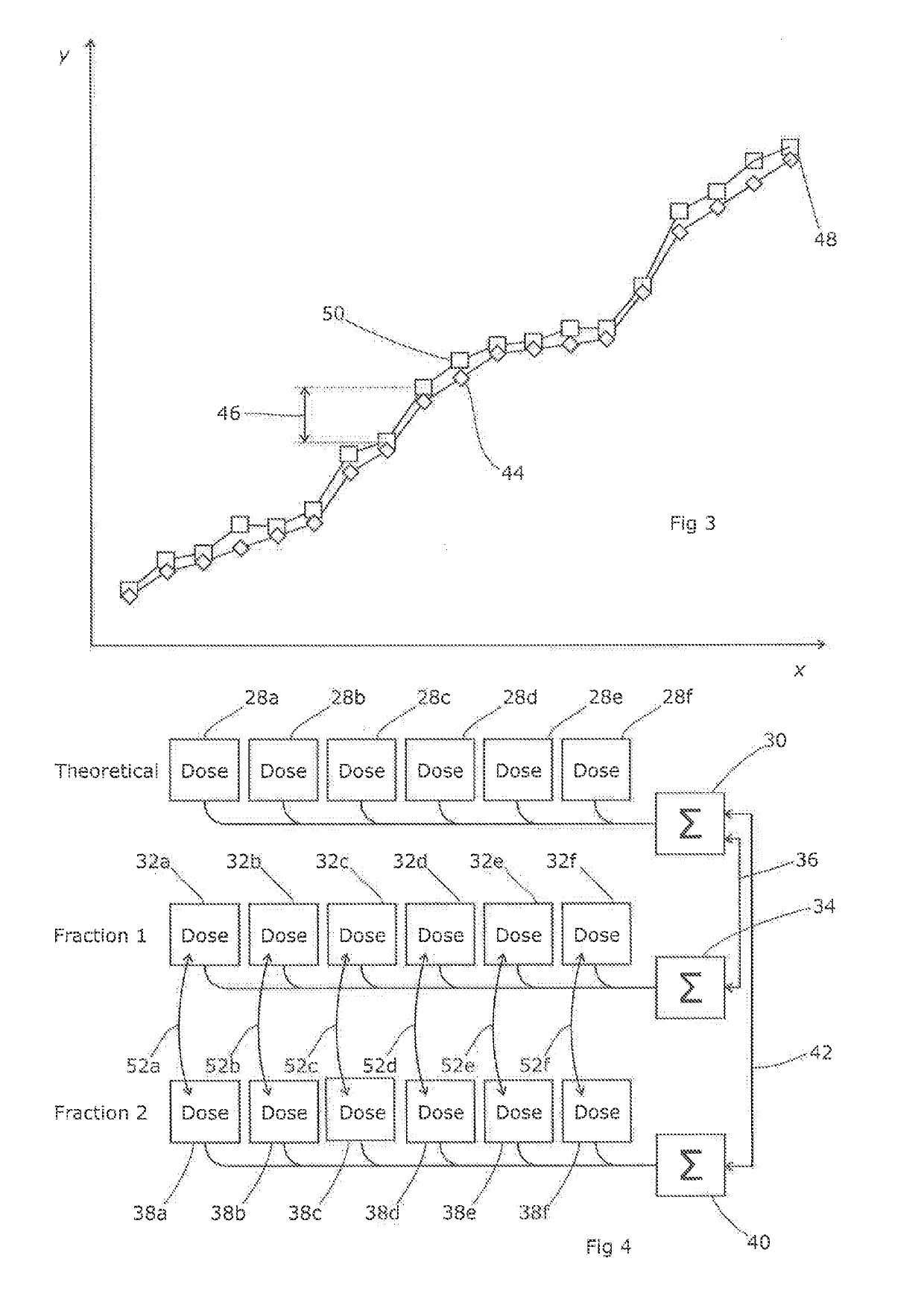
Apparatus and process for dose-guided radiotherapy
A method and an apparatus for dose-guided radiotherapy for a patient (P) having an identified radiotherapy target utilizes a radiation detecting array (R) of radiation-sensitive dosimeters for the real-time remote measurement of radiotherapy at the radiation detecting array (R). The radiation detecting array is positioned within the patient's (P) body along the treatment path before or after the identified radiotherapy target or the device may be positioned beyond the patient (P) to measure transit dose. A radiation source (A) for emitting radiation for radiotherapy along a treatment path through the patient (P) to the identified radiotherapy target is utilized. The method includes generating a predicted dose pattern of radiation at the placed radiation detecting array (R). The predicted dose pattern assumes an on-target radiation source (A) emitting the radiotherapy beam along the treatment path through the patient (P) to the identified radiotherapy target. Gating of the radiation source (A) can occur responsive to the comparing of the predicted dose pattern of radiation to the real-time dose pattern at the radiation detecting array (R). Radiation intensity can vary between low levels to a treatment level responsive to coincidence of the predicted dose pattern of radiation to the real-time dose pattern at the radiation detecting array (R).
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Method and apparatus for real time dosimetry
ActiveUS20080161632A1The result is accurateSmall amountX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose rateReal time dosimetry
A method of determining the dose rate of a radiation source includes locating three or more detectors in the vicinity of the source. Each detector provides an output indicative of the amount of radiation received from the source and determining the location of the source from at least three of the detector outputs, wherein as many of the detector outputs is required to provide an acceptably accurate result are used in determining the location. Thus, the dose of radiation from the source can be determined from the determined location of the source and either a known activity of the source or a measure of the activity of the source determined by means of the detectors.
Owner:UNIV OF WOLLONGONG
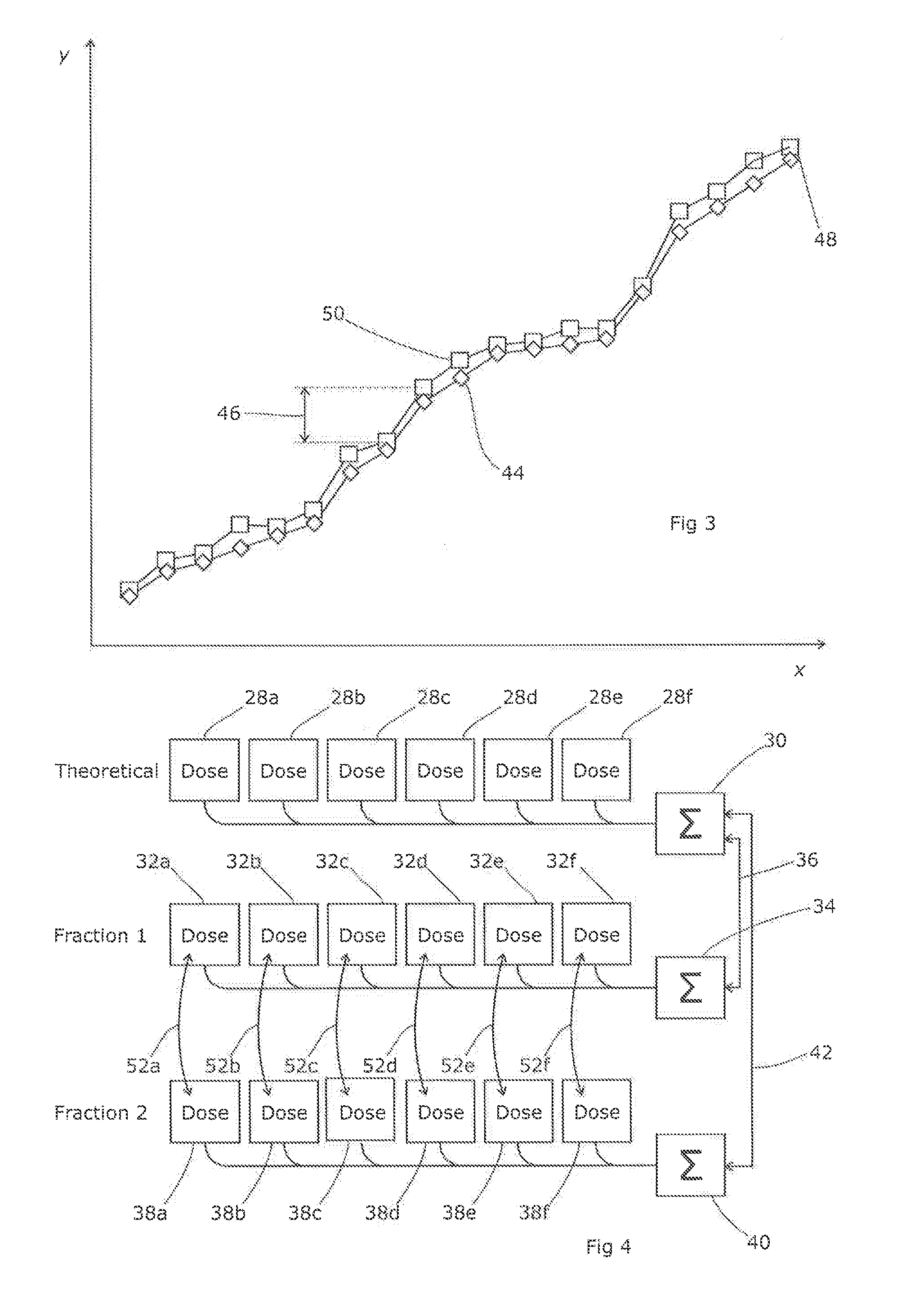
Dosimetry techniques for radiotherapy
ActiveUS20160361569A1Further precisionAccurate trackingDosimetersDiagnostic recording/measuringComparatorDosimetry
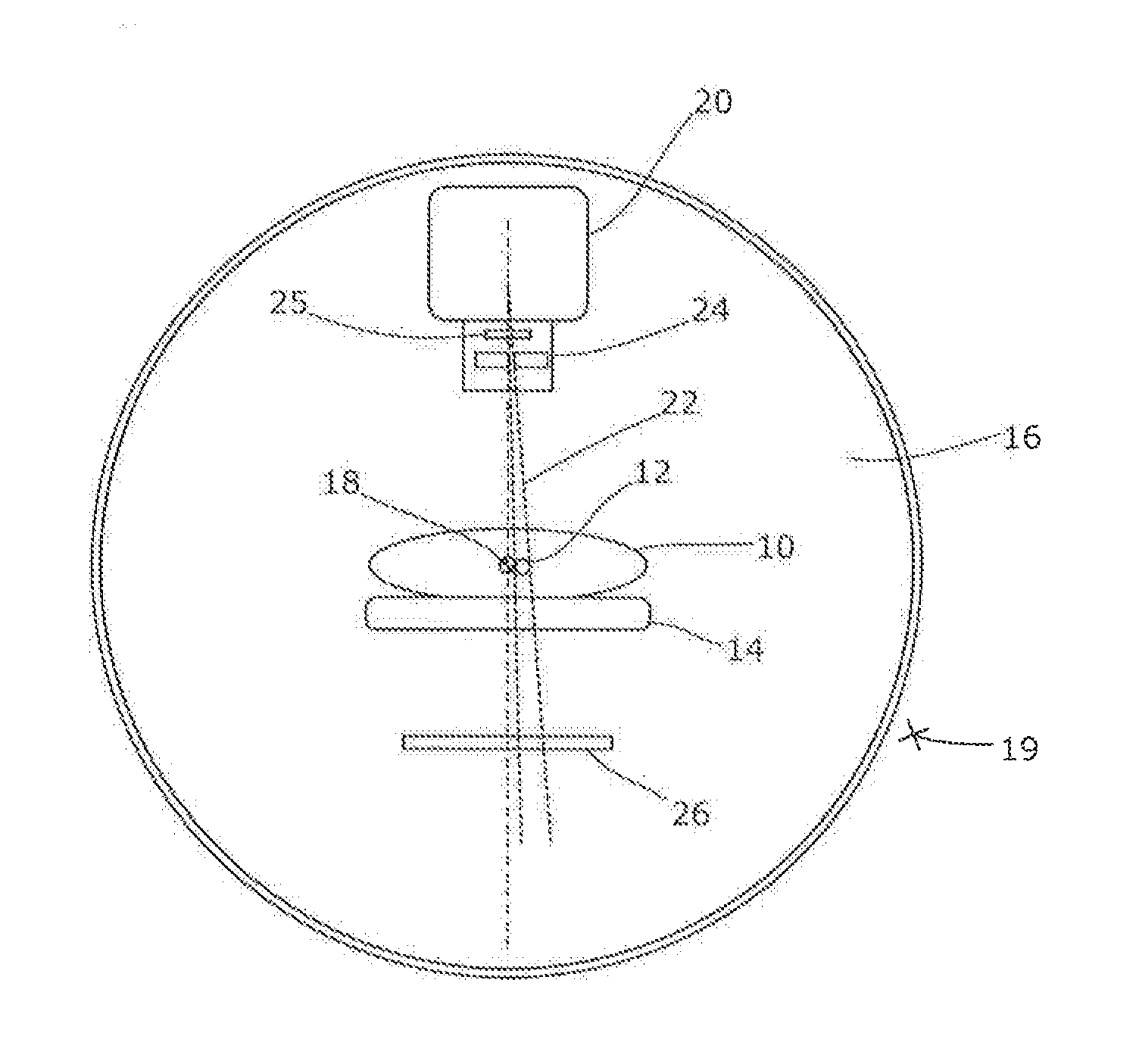
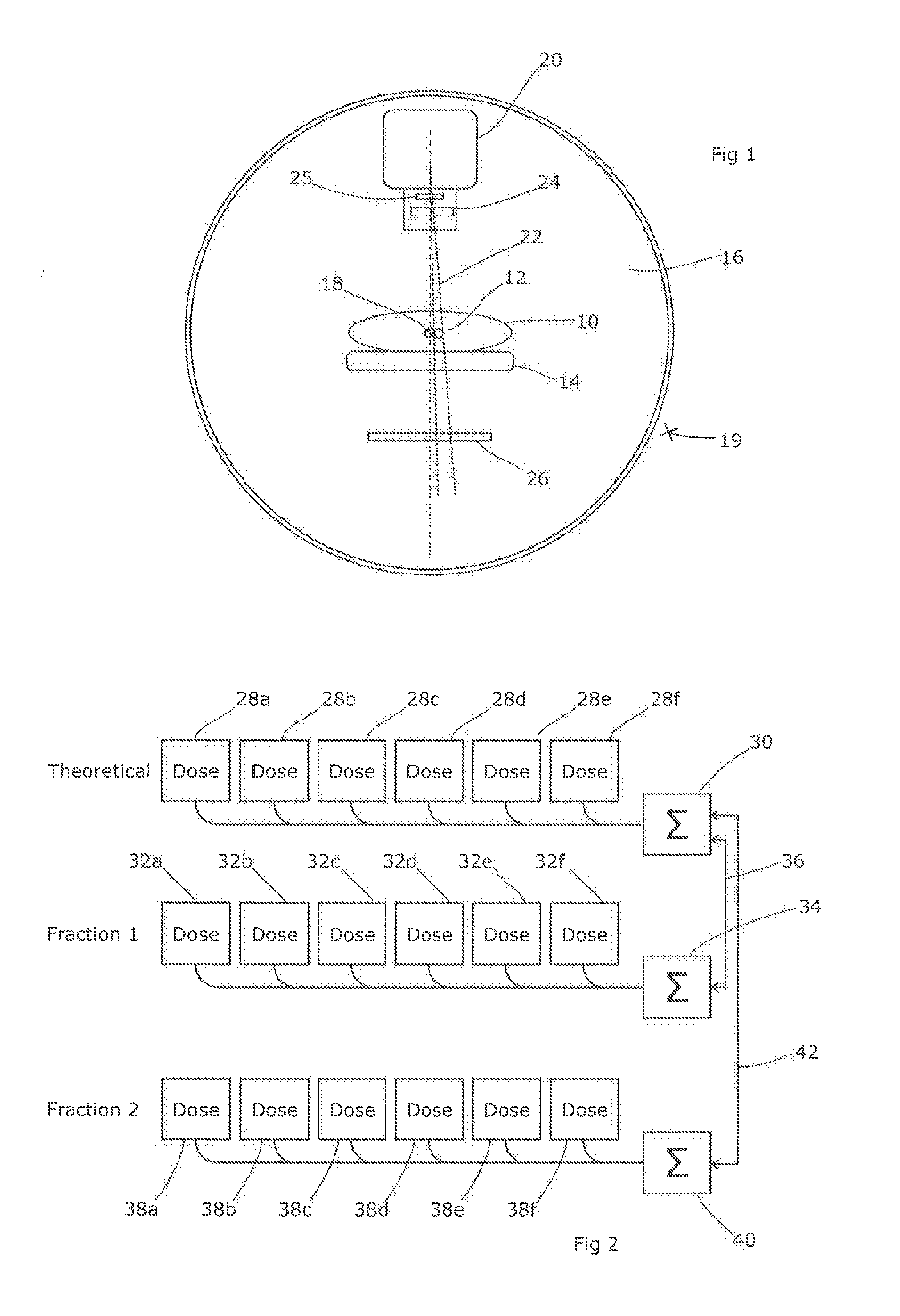
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide improved techniques for dosimetry in radiotherapy treatment. In a fractionated radiotherapy treatment, once the first fraction is complete and has been verified, data is generated which is representative of the dose development during delivery of the treatment for that patient and that treatment plan. This data can be used as a comparator for the instantaneous doses observed during subsequent fractions, allowing real-time dosimetry verification for the second and subsequent fractions after a successful first fraction.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
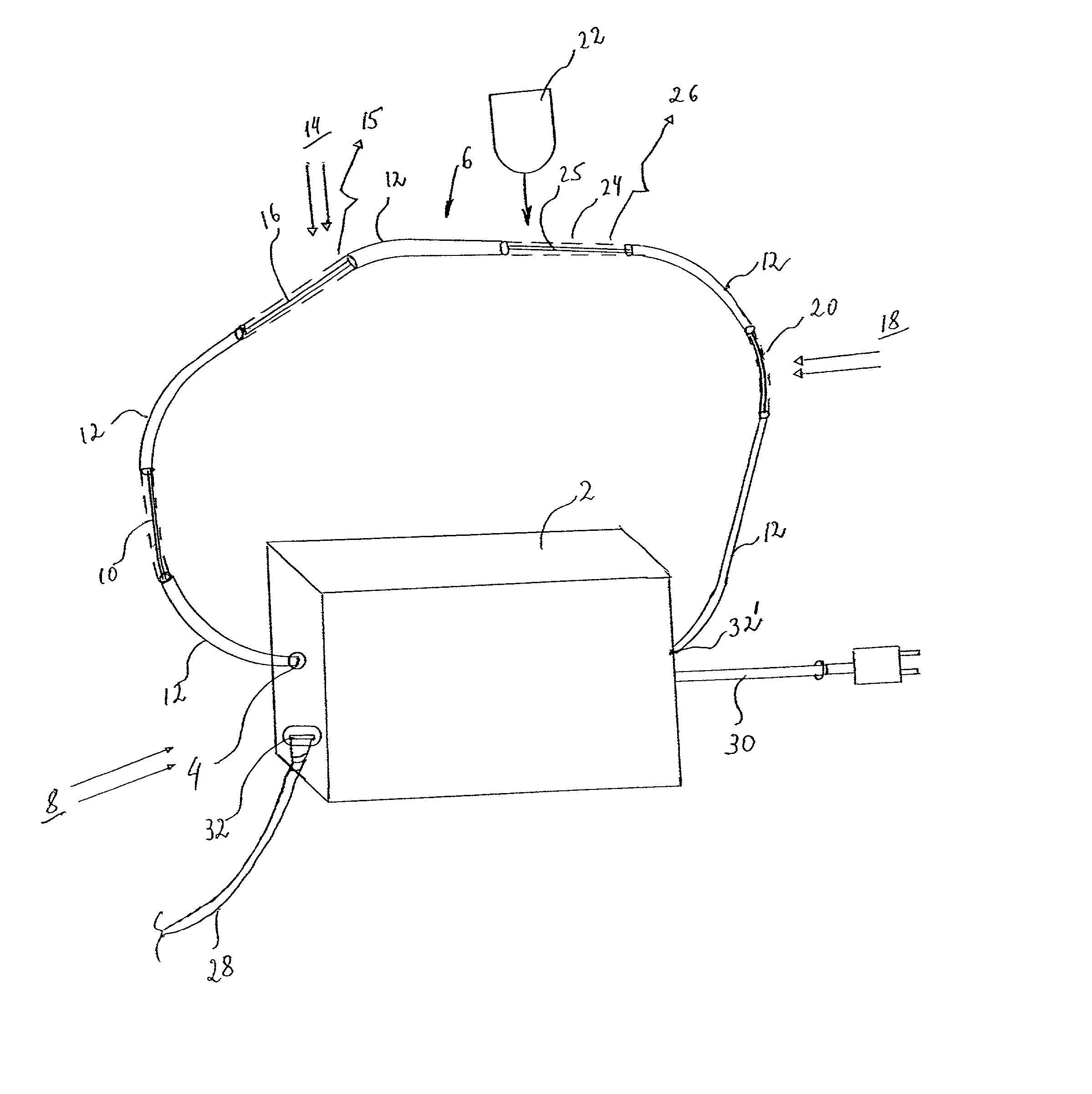
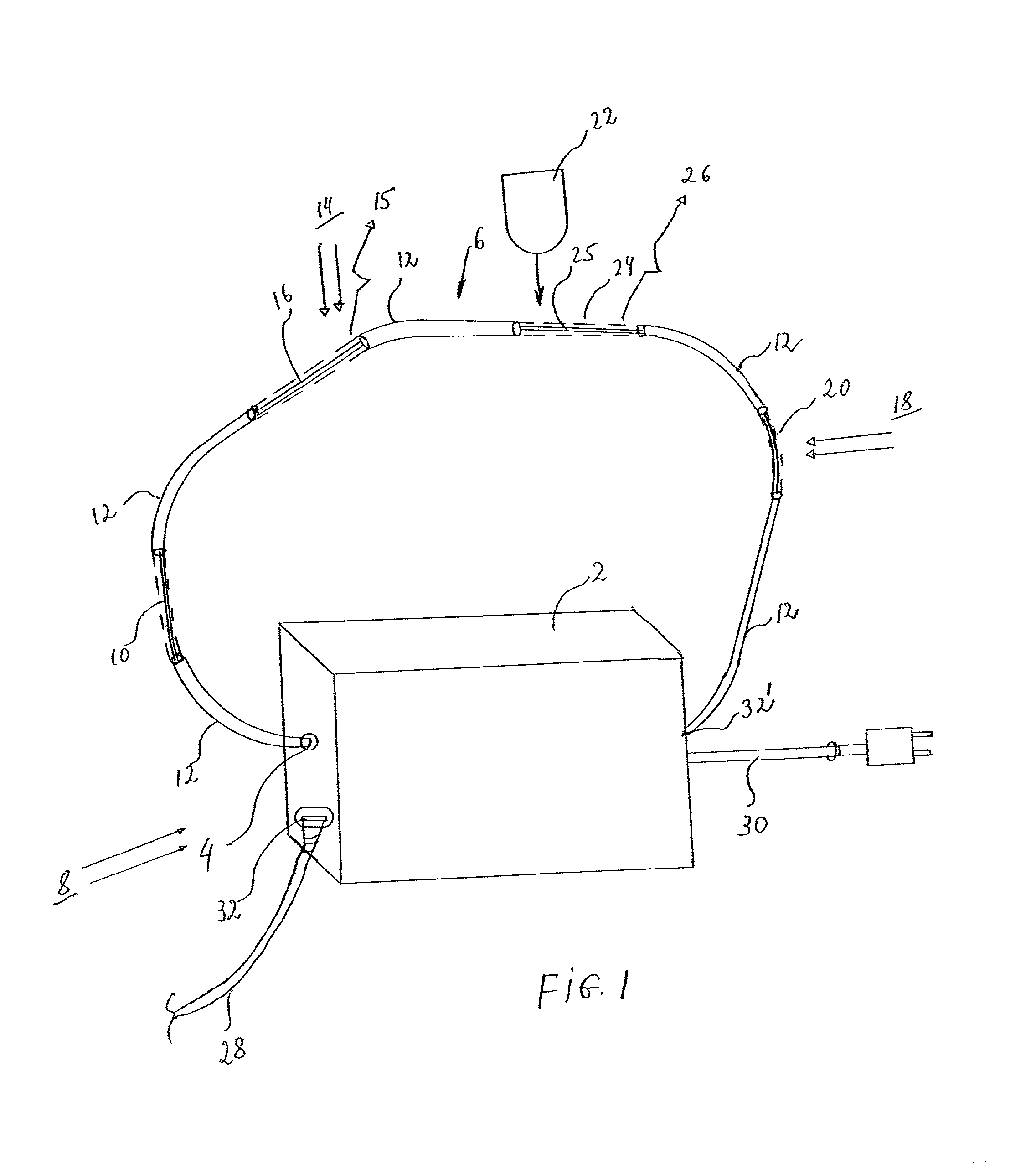
Distributed fiberoptic sensors
InactiveUS20030025072A1More shapeThin optical fiberRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDosimeterRadiation sensor
A distributed fiberoptic radiation sensor is described which may employ one or more radiation sensor elements distributed in a single optical fiber. Such optical fibers may be placed on surfaces, or even within parts, to unobtrusively measure radiation in precise and even difficult to reach locations. Different sensor elements may respond to different radiation types and wavelength ranges, with each sensor element causing a different wavelength of light to be emitted or absorbed within the fiber. By employing an appropriate combination of detection methods at the ends of the fiber, the distributed sensor may provide type and calorimetric discrimination of radiation incident on one or more distinguishable locations. The radiation information thus detected may be integrated, if desired, to obtain corresponding real-time dose information. With such integration, the device becomes a distributed real-time dosimeter. In another embodiment, the particular radiation sensors distributively employed may undergo permanent change in absorption characteristics. Such a device infers a total radiation dose over a particular period by measuring a change in optical response between the beginning and the end of the particular period.
Owner:HRL LAB
Real-Time Dosimetry System, RTDS
ActiveUS20120177184A1Increase and decrease doseAccurate measurementRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusIonization chamberElectrometer
Real-Time Dosimetry System, RTDS, is dose measurement system consisting of an ionization chamber and electrometer with the ability to measure, record, and display the high radiation doses required to meet approved standards for sterilization of medical, industrial and food products.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
Method and apparatus for real time dosimetry
InactiveUS7972259B2The result is accurateSmall amountX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose rateReal time dosimetry
A method of determining the dose rate of a radiation source includes locating three or more detectors in the vicinity of the source. Each detector provides an output indicative of the amount of radiation received from the source and determining the location of the source from at least three of the detector outputs, wherein as many of the detector outputs is required to provide an acceptably accurate result are used in determining the location. Thus, the dose of radiation from the source can be determined from the determined location of the source and either a known activity of the source or a measure of the activity of the source determined by means of the detectors.
Owner:UNIV OF WOLLONGONG
Real-time dosimetry system, RTDS
Real-Time Dosimetry System, RTDS, is dose measurement system consisting of an ionization chamber and electrometer with the ability to measure, record, and display the high radiation doses required to meet approved standards for sterilization of medical, industrial and food products.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
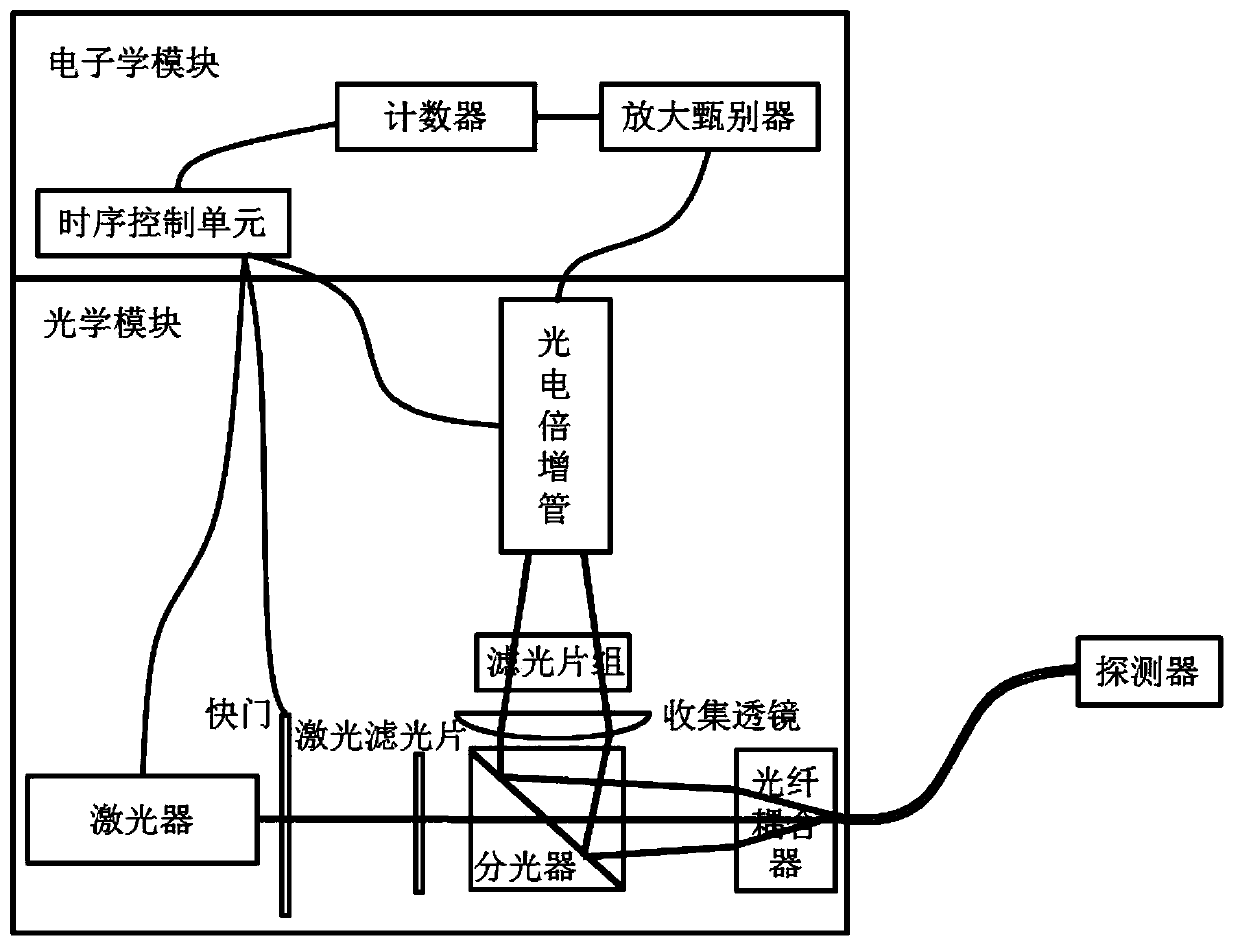
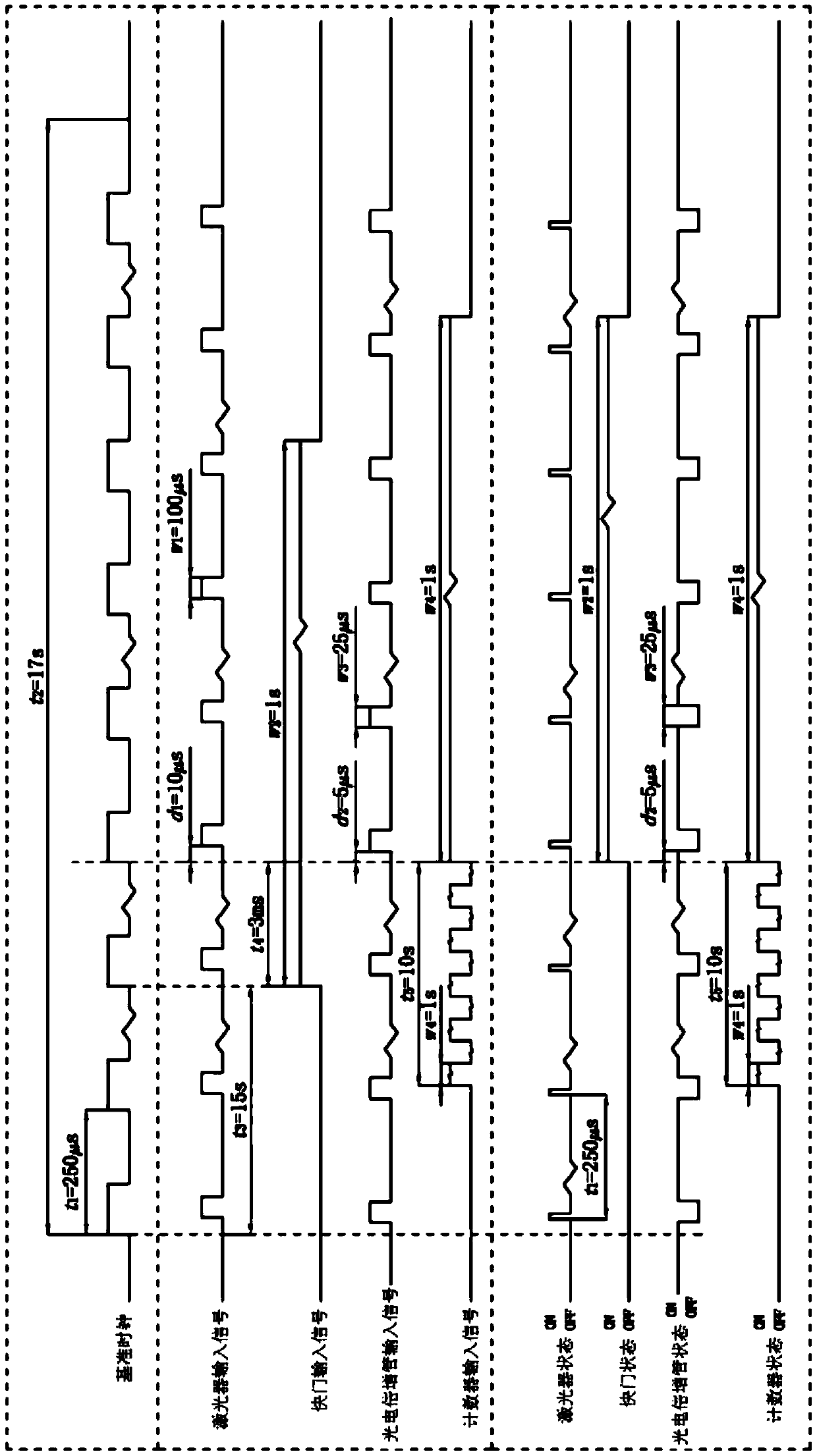
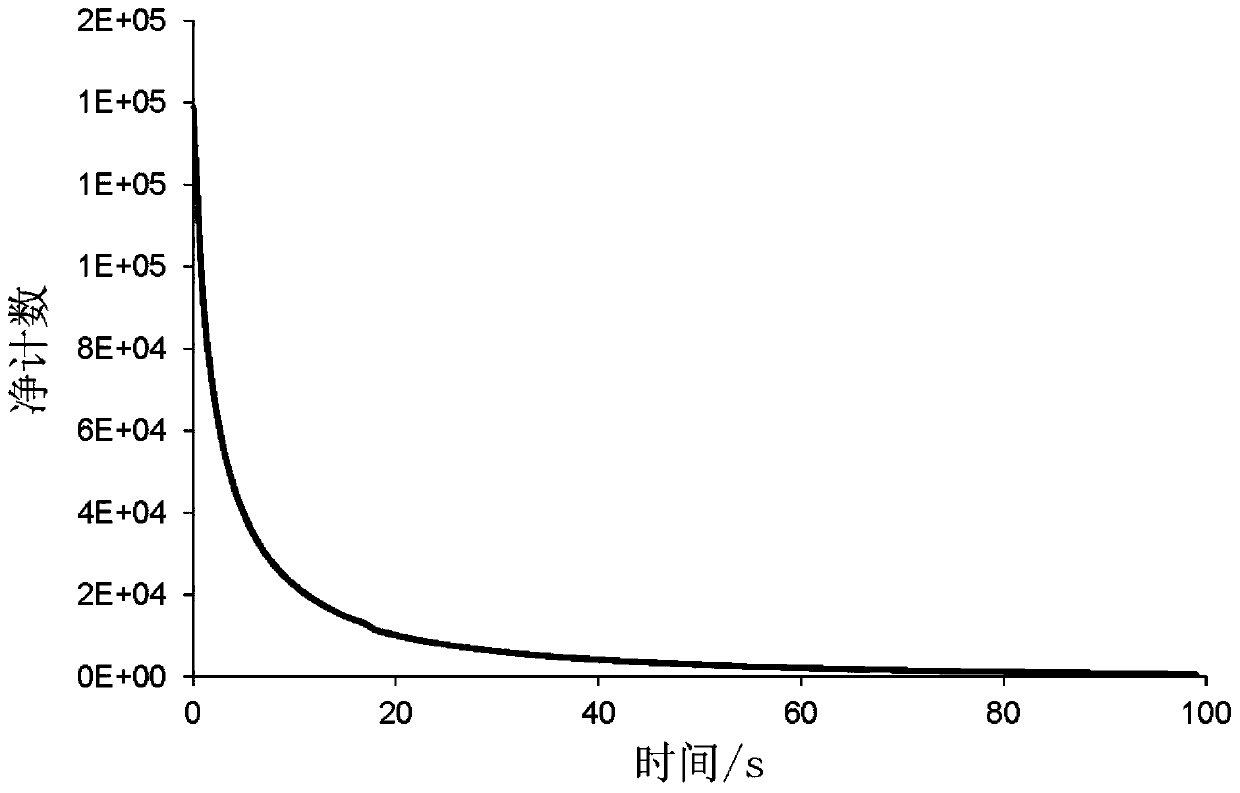
Time sequence control logic and signal processing algorithm suitable for pulsed optically stimulated luminescence technique-based quasi-real-time dose rate measuring devices
ActiveCN110376937APrecise timing controlAccurately give quasi-real-time dose rateProgramme controlComputer controlMeasurement deviceDose rate
The invention relates to the technical field of nuclear radiation detection and provides time sequence control logic and signal processing algorithm suitable for pulsed optically stimulated luminescence technique-based quasi-real-time dose rate measuring devices. The time sequence control logic provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that a same reference clock is adopted as a reference to generate input pulse signals of a laser, a shutter, a photomultiplier and a counter; and the precise time sequence control of the laser, the shutter, the photomultiplier and the counter can be realized by each pulse signal through setting the number of skipped reference pulses and the relative time delay relative to the reference clock. The signal processing algorithm provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that various dynamic and static backgrounds are considered; the relationship between cumulative dose and count value is given by linear fitting results of experimental data; the cumulative dose loss caused by each dose rate measurement is compensated; and therefore, the quasi-real-time dose rate can be accurately given.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
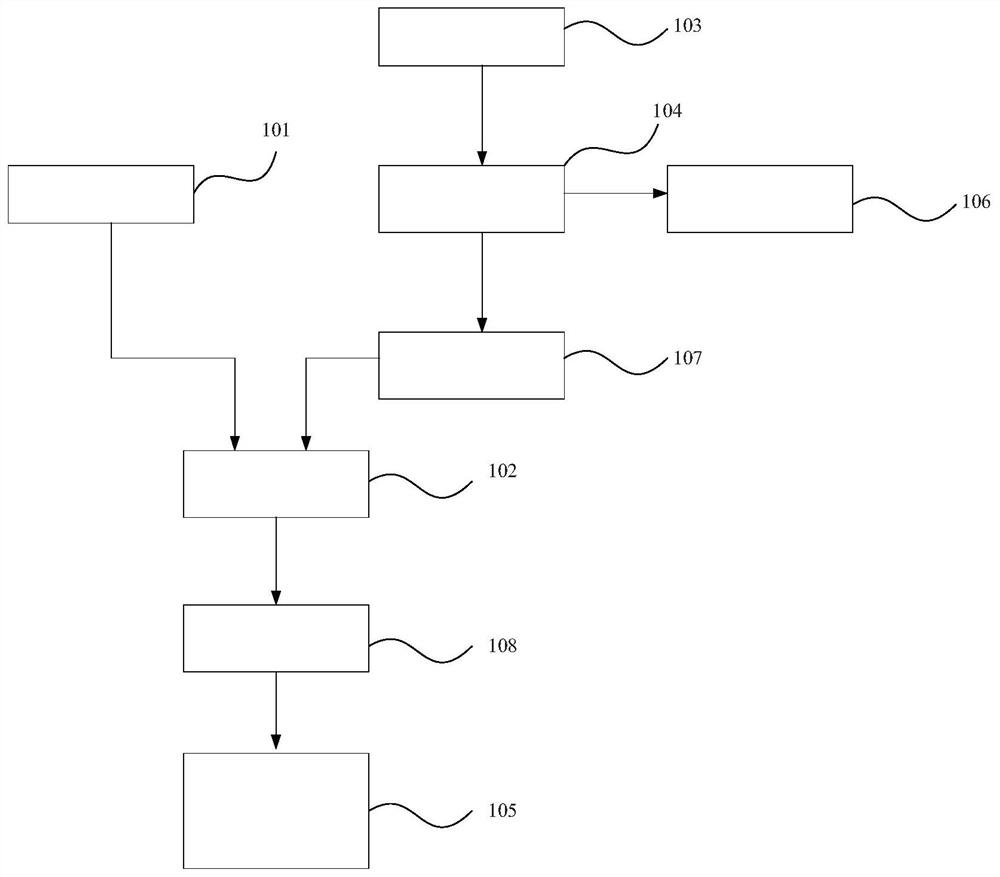
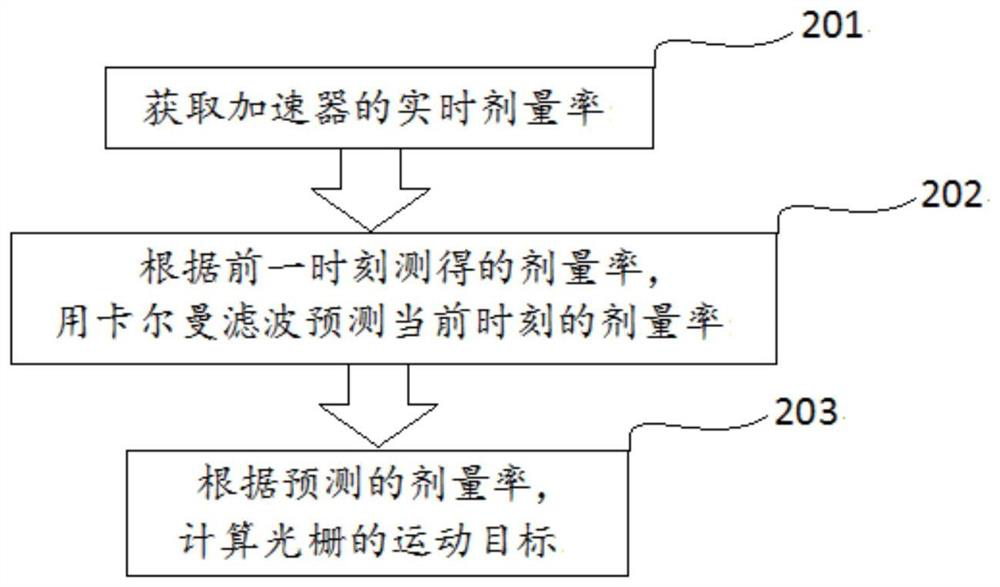
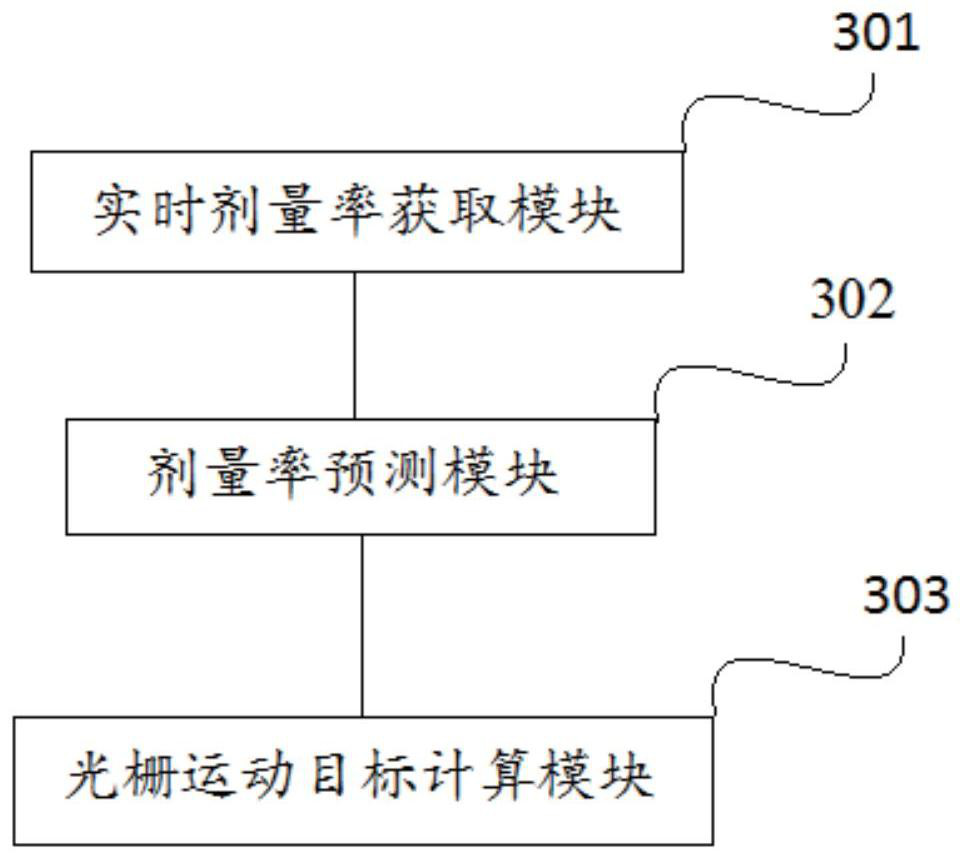
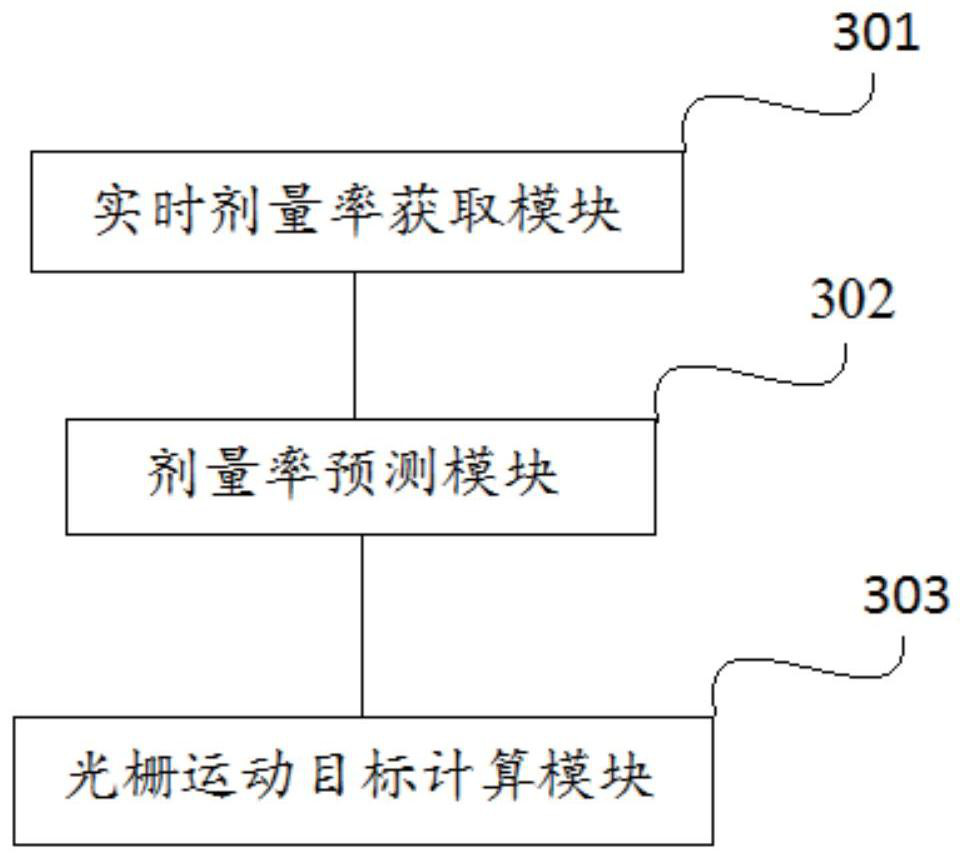
Method and device using grating servo dosage rate, and radiotherapy equipment
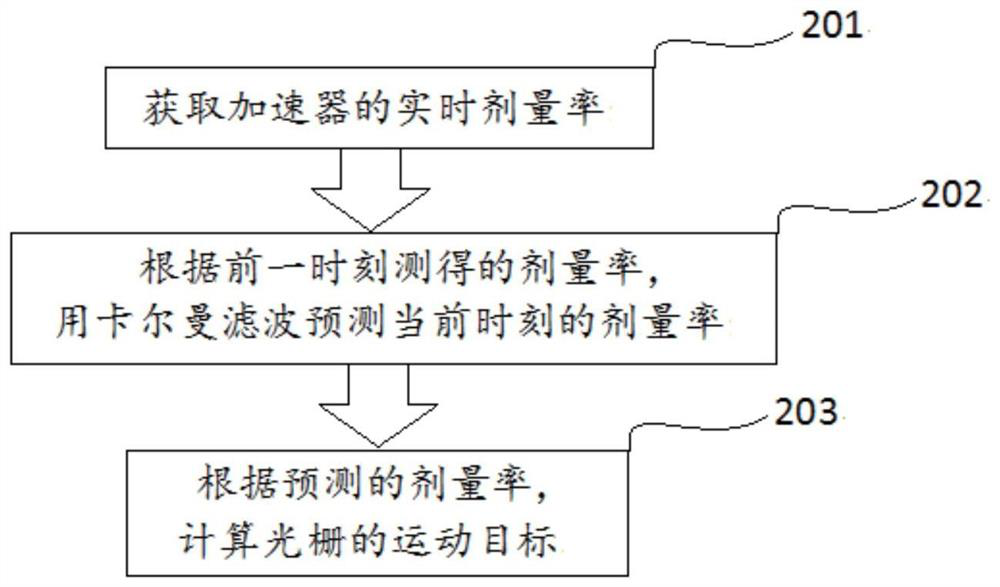
ActiveCN111773558AAccurate irradiationPrecision radiotherapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDoses rateGrating
The invention provides a method and device using grating servo dosage rate, and radiotherapy equipment, and relates to the technical field of radiotherapy. The method using grating servo dosage rate provided by the invention comprises the steps of obtaining real-time dosage rate of an accelerator; according to the dosage rate measured at the last time, predicting the dosage rate of the current time with a kalman filter; and according to the predicted dosage rate, calculating the moving target of grating. The dosage rate of the accelerator is monitored in real time, and the operating speed of the grating is adjusted according to an algorithm, so that the grating movement can serve fluctuation of the dosage rate, the dosage illumination is more pinpoint, and the effect of precise radiotherapy is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU LINATECH MEDICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
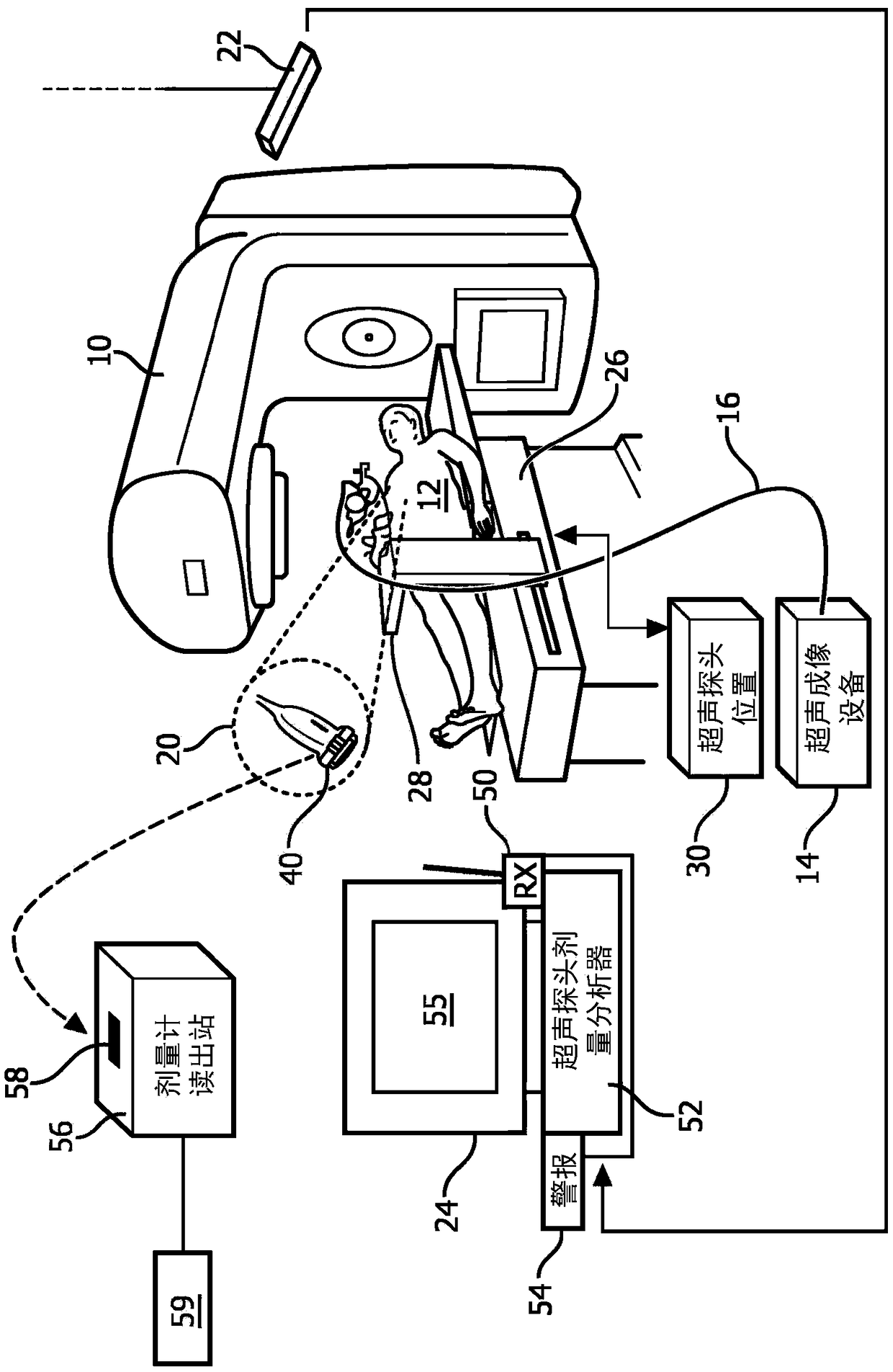
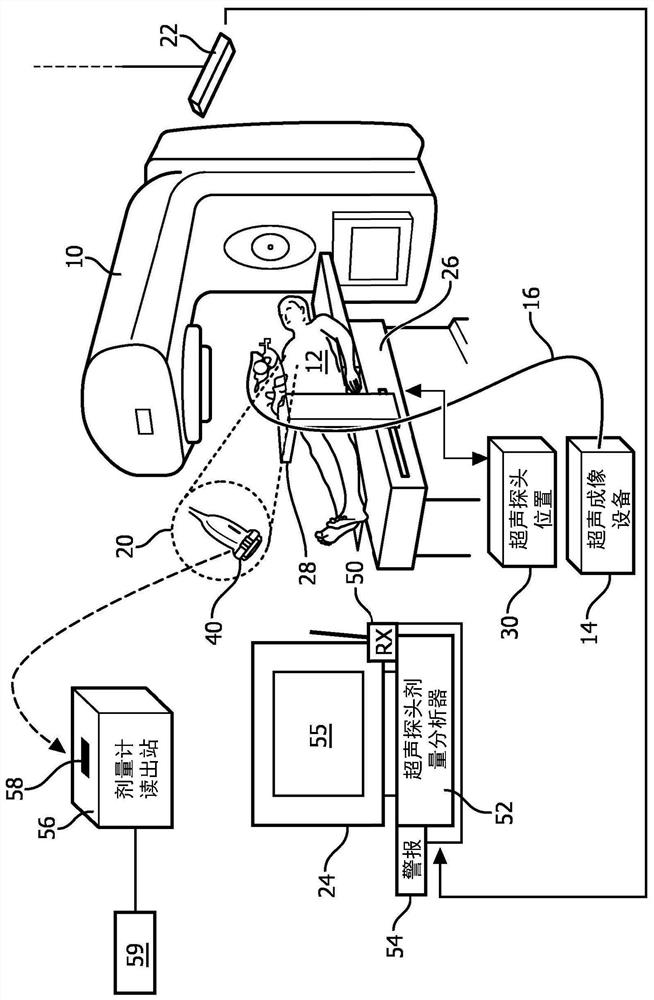
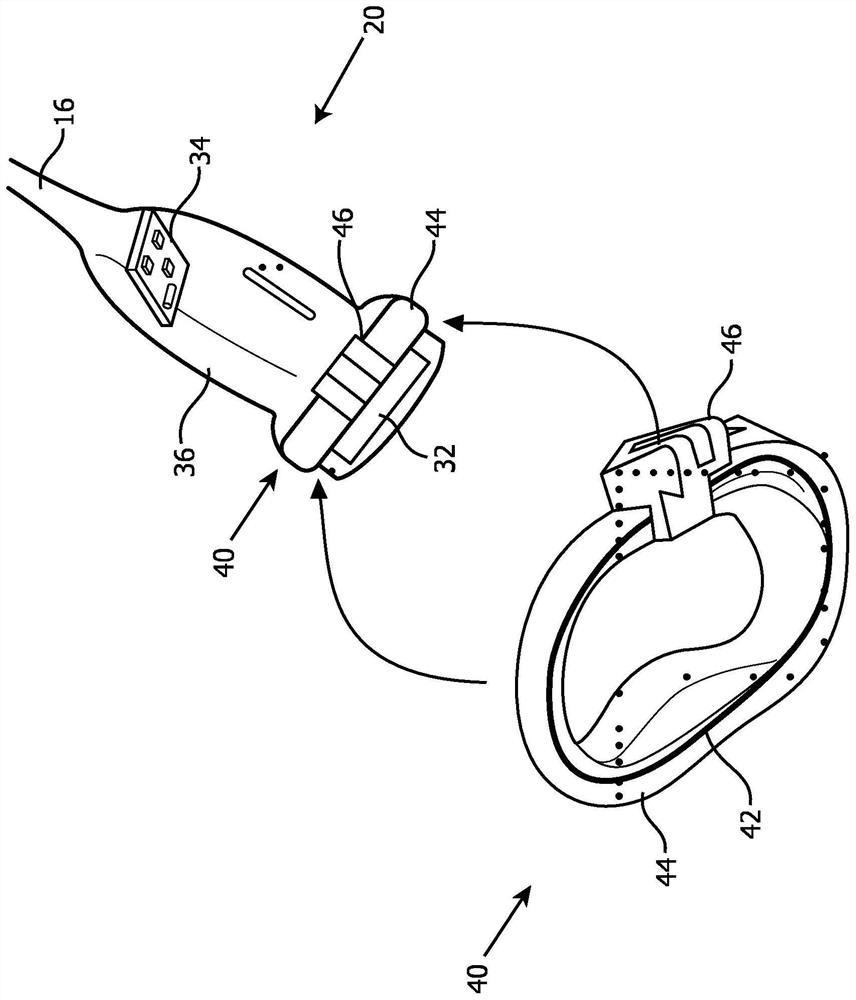
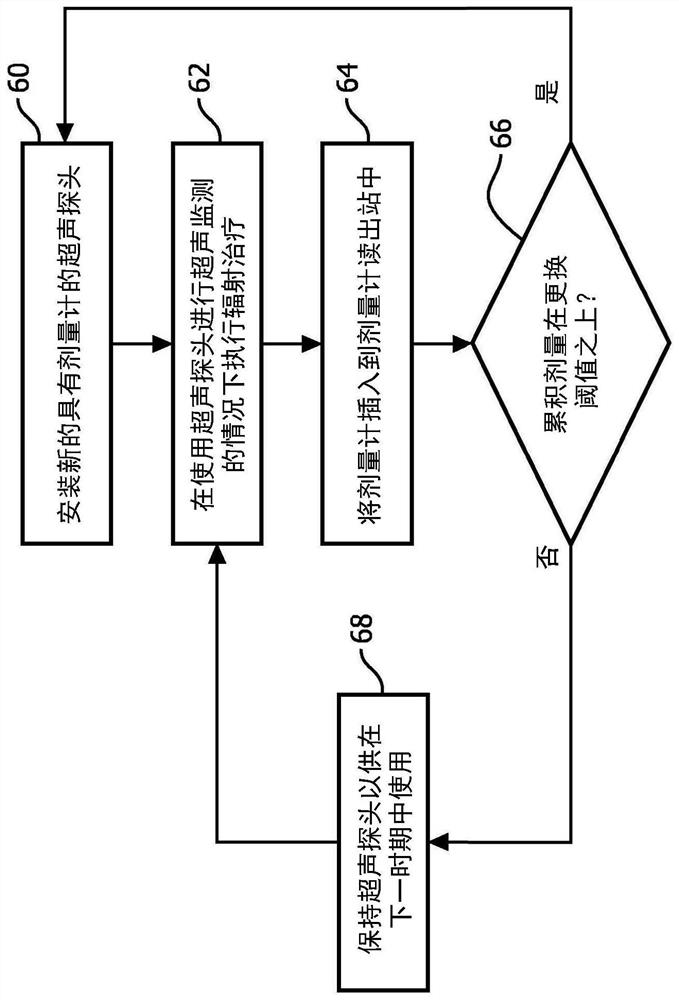
Real time dosimetry of ultrasound imaging probe
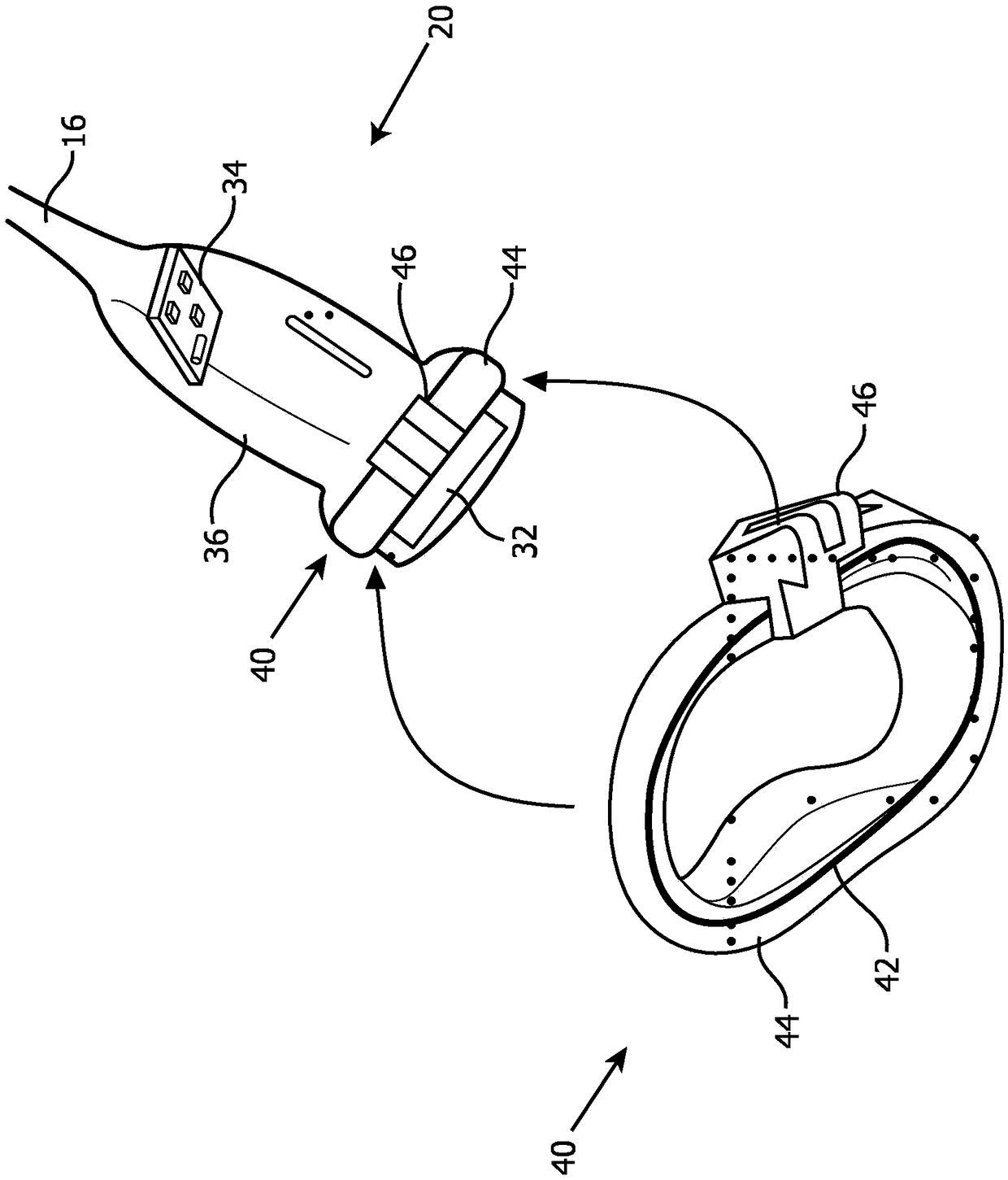
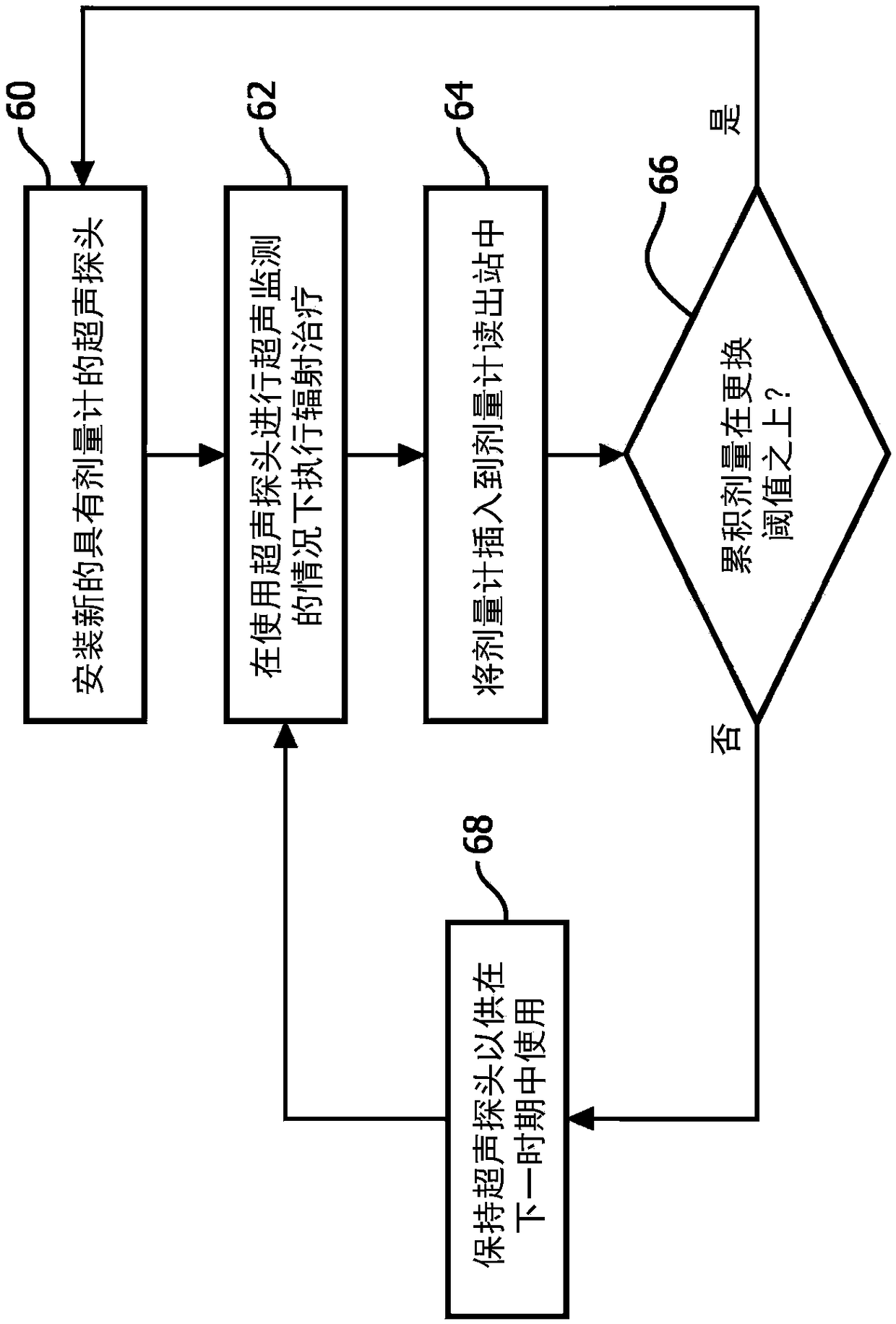
ActiveCN109414594ATimely replacementImprove quality controlUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingSonification
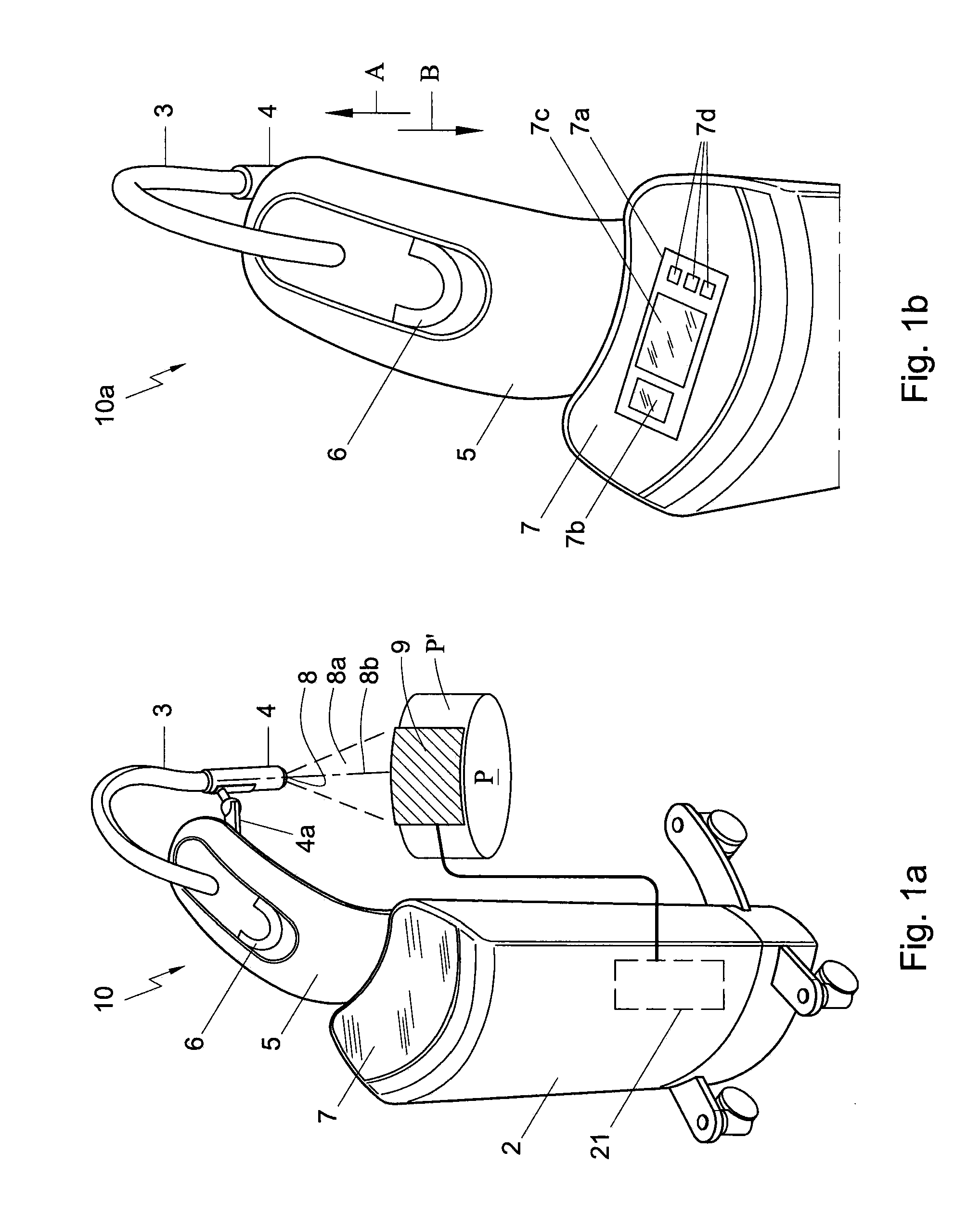
An ultrasound probe includes an ultrasound probe housing (36) and one or more ultrasound transducers (32) disposed in the ultrasound probe housing. A dosimeter (40) or ionizing radiation detector is disposed in or attached to the ultrasound probe housing. An alarm device (24, 52, 54, 56) receives radiation dose or radiation exposure data acquired by the dosimeter or ionizing radiation detector. The alarm device includes an electronic processor (24, 56) programmed to detect excessive radiation dose or radiation exposure received by the ultrasound probe based on the radiation dose or radiation exposure data acquired by the dosimeter or ionizing radiation detector, and output an alarm warning of the detection of excessive radiation dose or radiation exposure received by the ultrasound probe.In some embodiments, the dosimeter is a one-time use dosimeter that is not resettable.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method, device and radiotherapy equipment using grating servo dose rate
ActiveCN111773558BAccurate irradiationPrecision radiotherapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDoses rateNuclear medicine
The invention provides a method, device and radiotherapy equipment using grating servo dose rate, and relates to the technical field of radiotherapy. The grating servo dose rate method provided by the present invention includes: obtaining the real-time dose rate of the accelerator; using the Kalman filter to predict the dose rate at the current moment according to the dose rate measured at the previous moment; and calculating the motion of the grating according to the predicted dose rate Target. By monitoring the dose rate of the accelerator in real time, the operating speed of the grating is adjusted according to the algorithm, so that the motion of the grating can servo the fluctuation of the dose rate, making the dose irradiation more accurate and achieving the effect of precise radiotherapy.
Owner:SUZHOU LINATECH MEDICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Real-time adaptive dose calculation for radiation therapy
ActiveCN104884126BReal-time measurementReal-time radiation dosimetryOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingRadiation Dosages
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
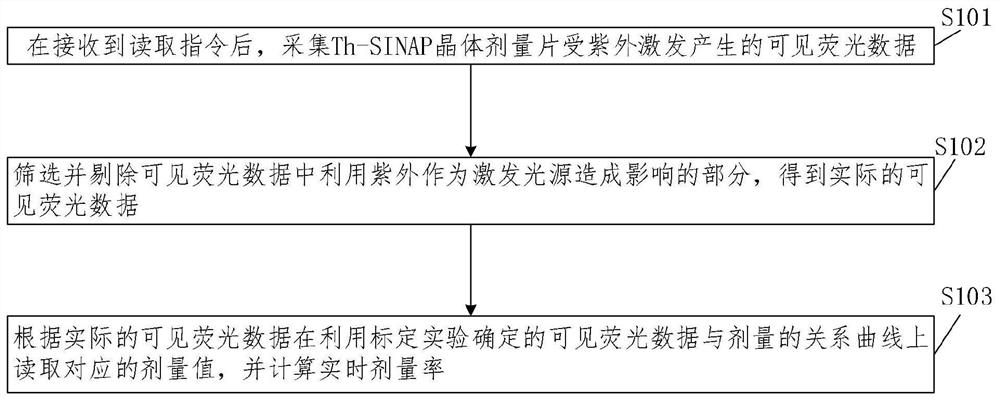
High radiation dose measurement method and system
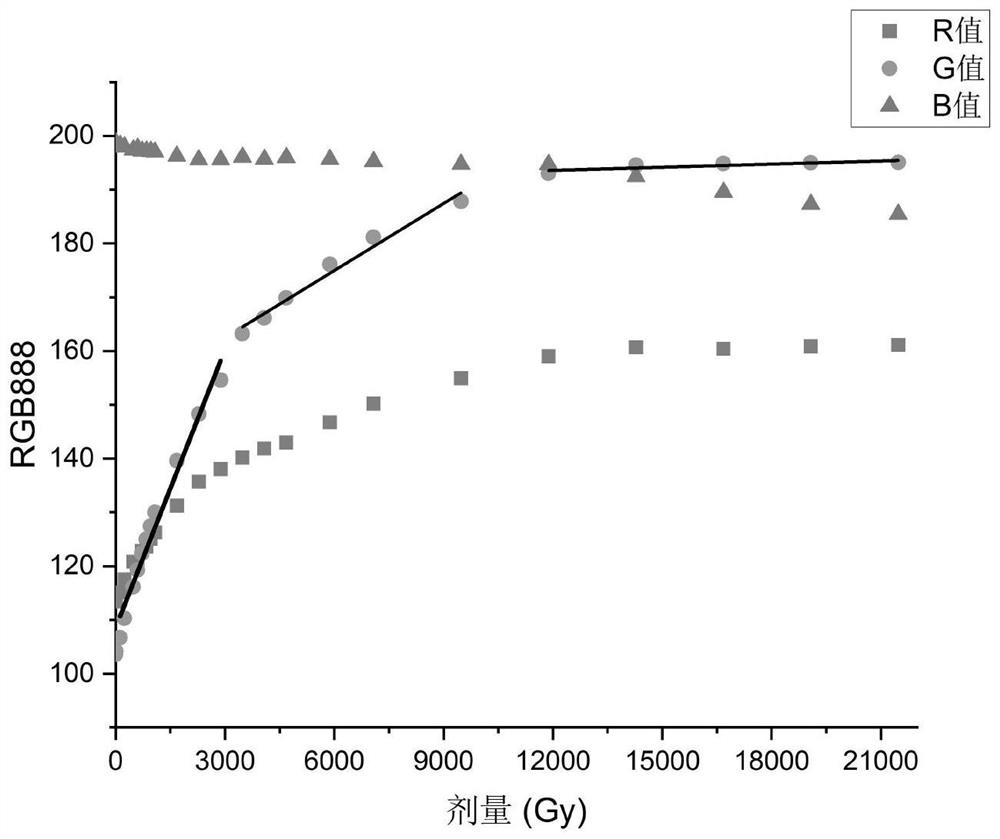
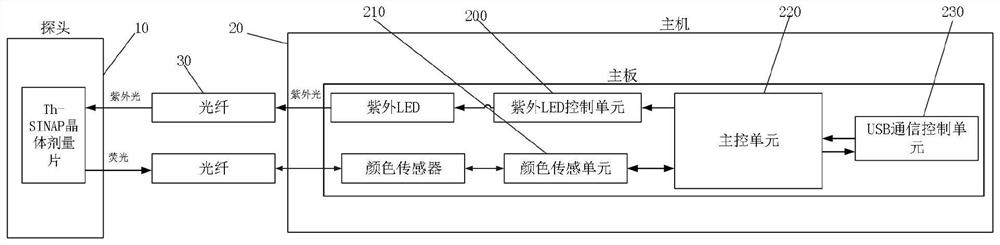
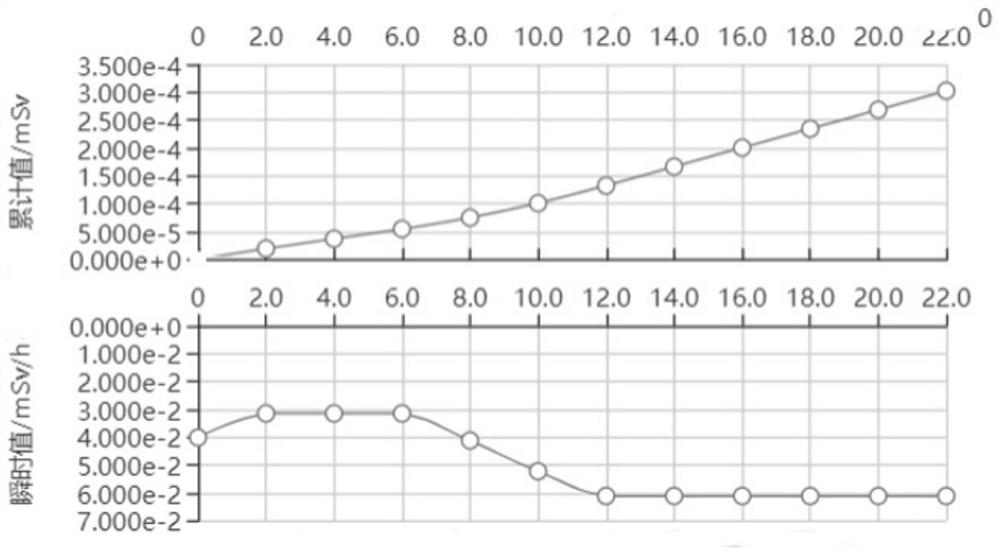
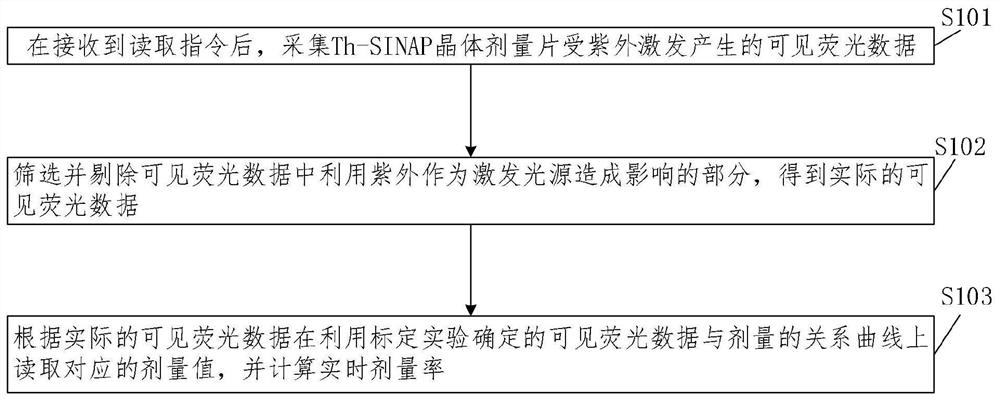
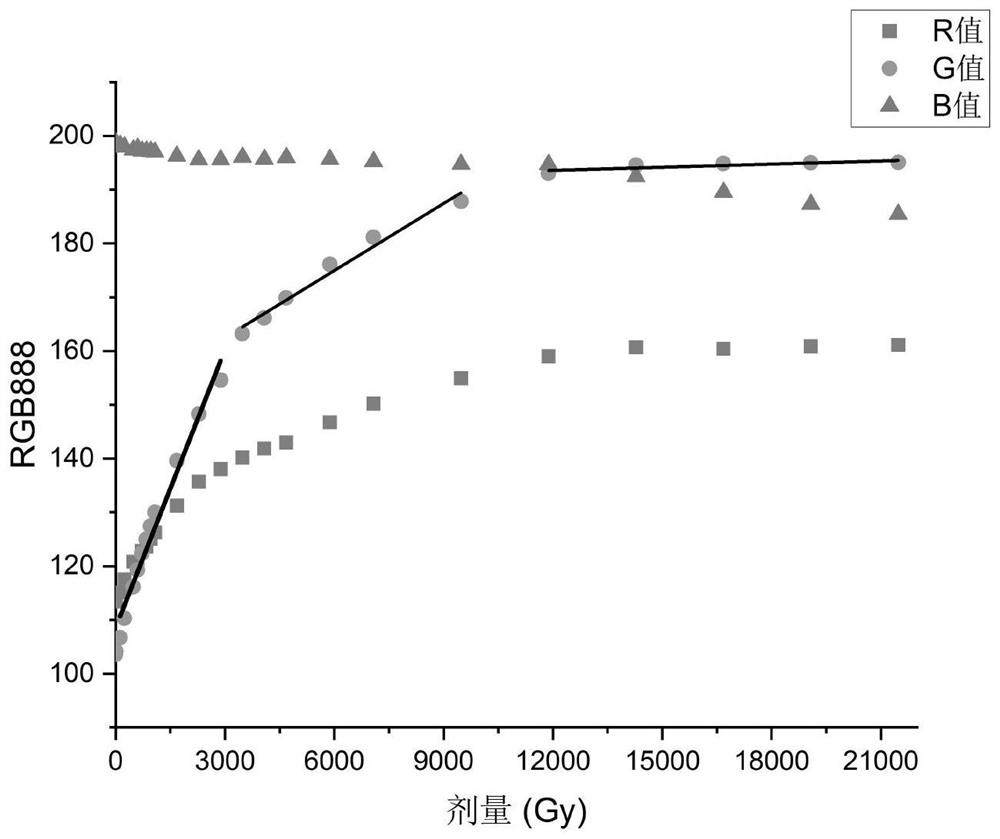
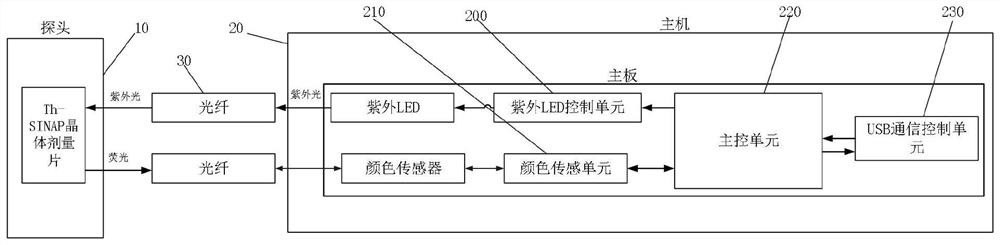
The invention relates to a high radiation dose measurement method and system, and the method comprises the steps: collecting visible fluorescence data generated by a Th-SINAP crystal dose sheet under excitation of ultraviolet after a reading instruction is received; screening and removing the part which is influenced by using ultraviolet as an excitation light source in the visible fluorescence data to obtain actual visible fluorescence data; and according to the actual visible fluorescence data, reading a corresponding dose value on the relation curve of the visible fluorescence data and the dose determined by the calibration experiment, and calculating the real-time dose rate. According to the method, ultraviolet is utilized to excite fluorescence, the radiation dose is measured by collecting the color of the fluorescence, and the part, which is influenced by utilizing the ultraviolet as an excitation light source, in visible fluorescence data is eliminated; the problems of long dose data acquisition time, complex data acquisition steps and inaccurate dose value reading when the traditional technology is used for measuring the high radiation dose (Gy / h-MGy / h magnitude) are solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dosimetry techniques for radiotherapy
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide improved techniques for dosimetry in radiotherapy treatment. In a fractionated radiotherapy treatment, once the first fraction is complete and has been verified, data is generated which is representative of the dose development during delivery of the treatment for that patient and that treatment plan. This data can be used as a comparator for the instantaneous doses observed during subsequent fractions, allowing real-time dosimetry verification for the second and subsequent fractions after a successful first fraction.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Real-time path planning method and device based on visual radiation scene
PendingCN114217342AEnsure safetyReduce psychological burdenX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCloud renderingEngineering
The invention relates to a real-time path planning method and device based on a visual radiation scene, and the method is characterized in that a dosimeter system is utilized, the dosimeter system comprises a cloud rendering server and a portable dosimeter, the cloud rendering server is used for rendering a three-dimensional scene model and storing three-dimensional scene data, and the portable dosimeter is used for storing the three-dimensional scene data; the portable dosimeter is used for responding to user requests, and the requests comprise three-dimensional scene model calling, visual radiation field calling and path planning. The path planning method comprises the following steps: calling a three-dimensional scene model stored in a cloud rendering server by using a portable dosimeter and displaying the operable three-dimensional scene model for a user; calling and outputting a visual radiation field associated with the three-dimensional scene model by using the portable dosimeter; a portable dosimeter is used for carrying out path planning request, and real-time dose and accumulated dose calculation of the human organ level is realized based on a GPU acceleration technology.
Owner:DMS CORP
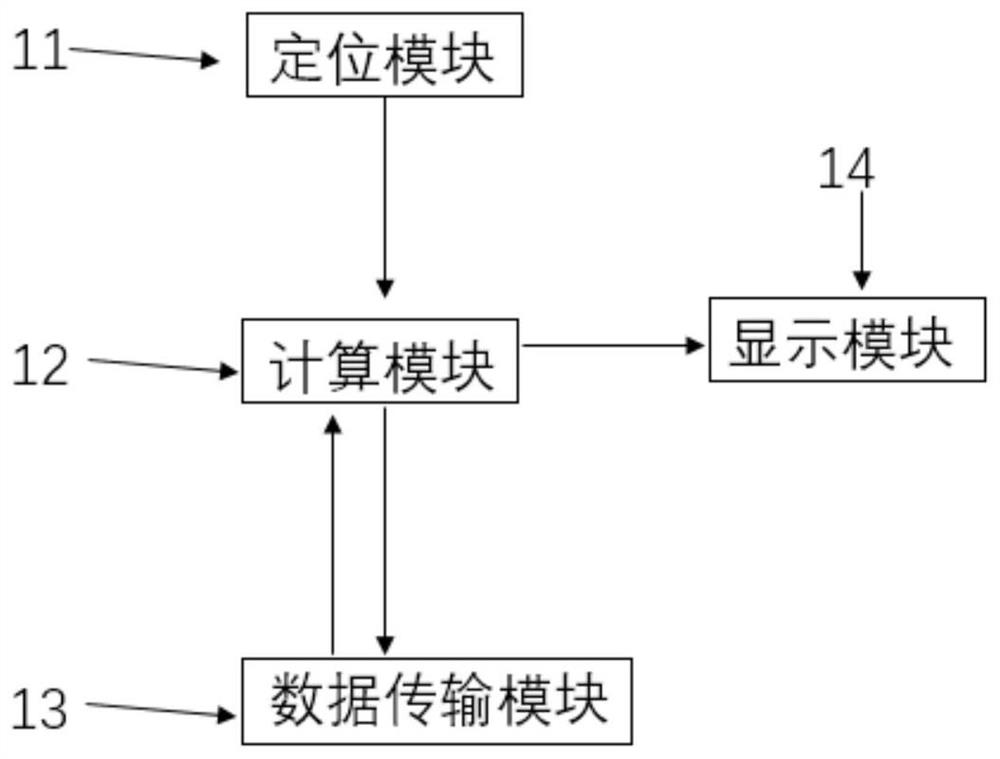
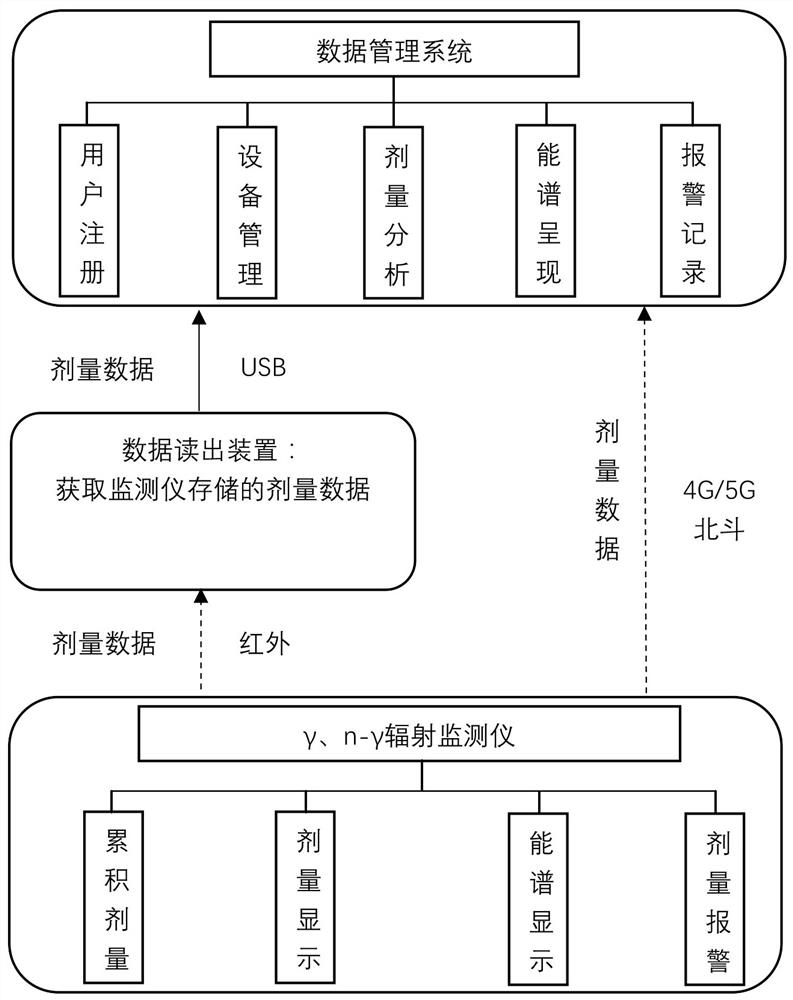
Individual dose equivalent measuring system in complex environment
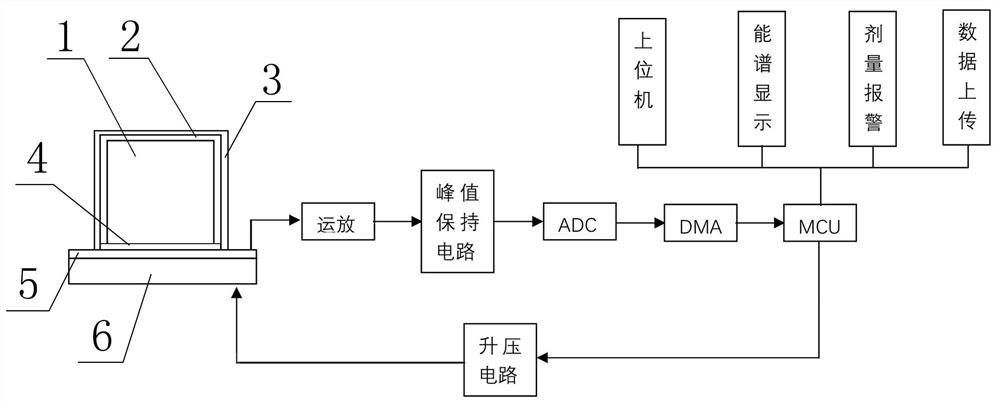
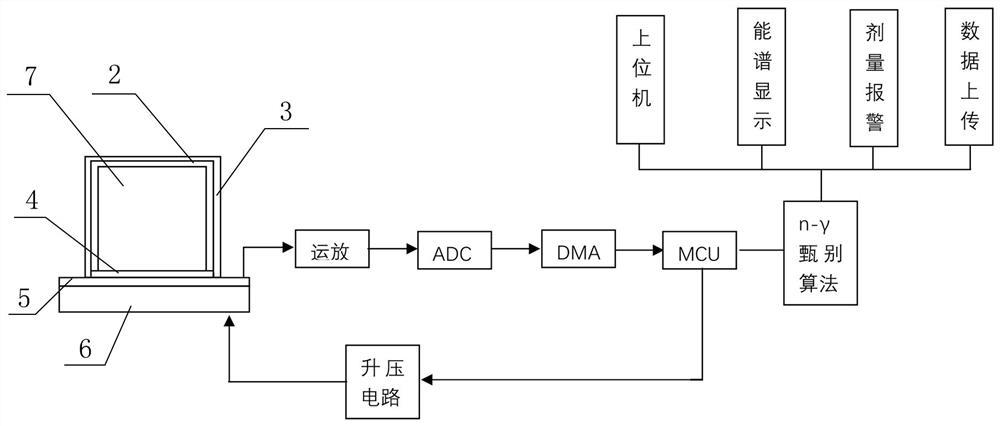
PendingCN114167473AComprehensive Security MonitoringMeasurement with semiconductor devicesDosimetersIndividual doseData management
The invention discloses a complex environment individual dose equivalent measuring system, which comprises a radiation monitor, a data reading device and a data management system, and is characterized in that the data reading device is connected with the radiation monitor and is used for acquiring dose data of the radiation monitor and uploading the dose data to the data management system; the radiation monitor comprises a gamma radiation monitor and an n-gamma radiation monitor; the data management system is used for providing user registration, equipment management, dose analysis, energy spectrum presentation and alarm recording, the system further comprises a network transmission module, the radiation monitor is connected with the data management system through the network transmission module, and the network transmission module adopts 4G / 5G and Beidou for transmission. According to the invention, comprehensive safety monitoring can be carried out on multiple aspects of radiation quantity, radionuclide type, real-time dose, dose equivalent rate and the like of individual irradiation; and when the exposure amount exceeds a threshold value, an alarm prompt is given.
Owner:成都天核科技有限公司
Nuclear facility retired human body exposure dose evaluation method
PendingCN114201878AEasy to view in real timeReduce psychological burdenDesign optimisation/simulationResourcesHuman bodyNuclear decommissioning
The invention relates to a nuclear facility decommissioning human body exposure dose evaluation method, which utilizes a dose evaluation system, and the dose evaluation system is used for evaluating the exposure dose of a human body in a nuclear facility decommissioning operation process according to a three-dimensional scene model and a radiation field model called by the dose evaluation system. The dose evaluation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: scanning position information of current equipment to obtain coordinate data of current operated equipment and operating personnel; calling the three-dimensional scene model and the radiation field model based on the coordinate data of the operated equipment; obtaining the nuclear facility disassembly and assembly information correction three-dimensional scene model and the radiation field model in the nuclear decommissioning operation process; and calculating a real-time dose and an accumulated dose received by the operator based on the corrected radiation field model.
Owner:DMS CORP
High radiation dose measurement method and system
The invention relates to a high radiation dose measurement method and system. The method comprises: after receiving a reading instruction, collecting visible fluorescence data generated by a Th-SINAP crystal dose tablet excited by ultraviolet rays; screening and eliminating visible fluorescence data by using ultraviolet rays as excitation For the part affected by the light source, the actual visible fluorescence data is obtained; according to the actual visible fluorescence data, the corresponding dose value is read on the relationship curve between the visible fluorescence data and the dose determined by the calibration experiment, and the real-time dose rate is calculated. The invention uses ultraviolet to excite fluorescence and measures the radiation dose by collecting the fluorescence color. By eliminating the part of the visible fluorescence data that is affected by using ultraviolet as the excitation light source, it solves the problem of measuring high radiation dose (Gy / h-MGy / h amount in the traditional technology) The problems of long acquisition time of dose data, complicated data acquisition steps and inaccurate reading of dose values existed in the case of high level).
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
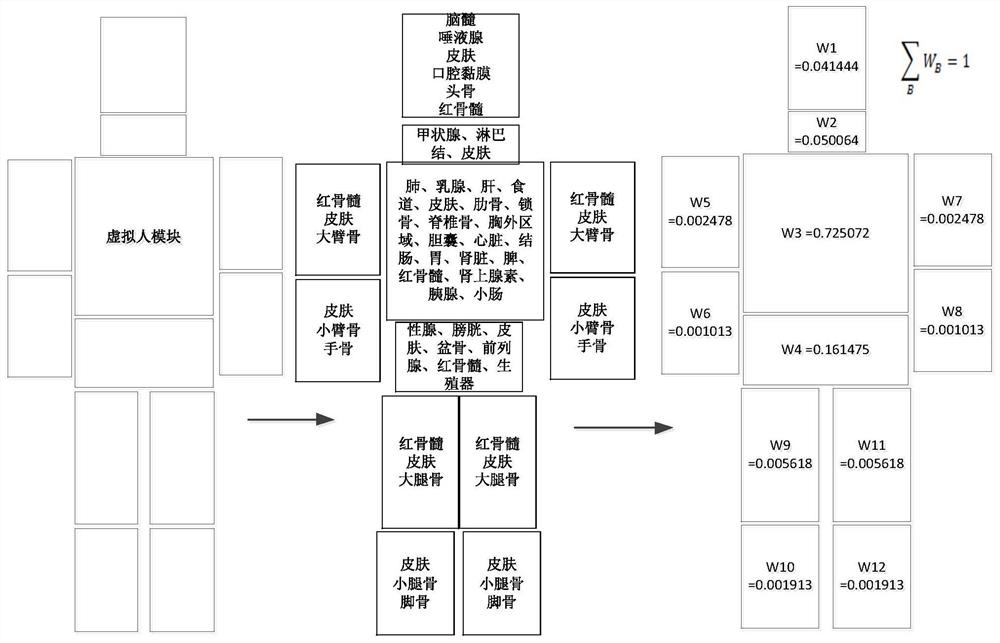
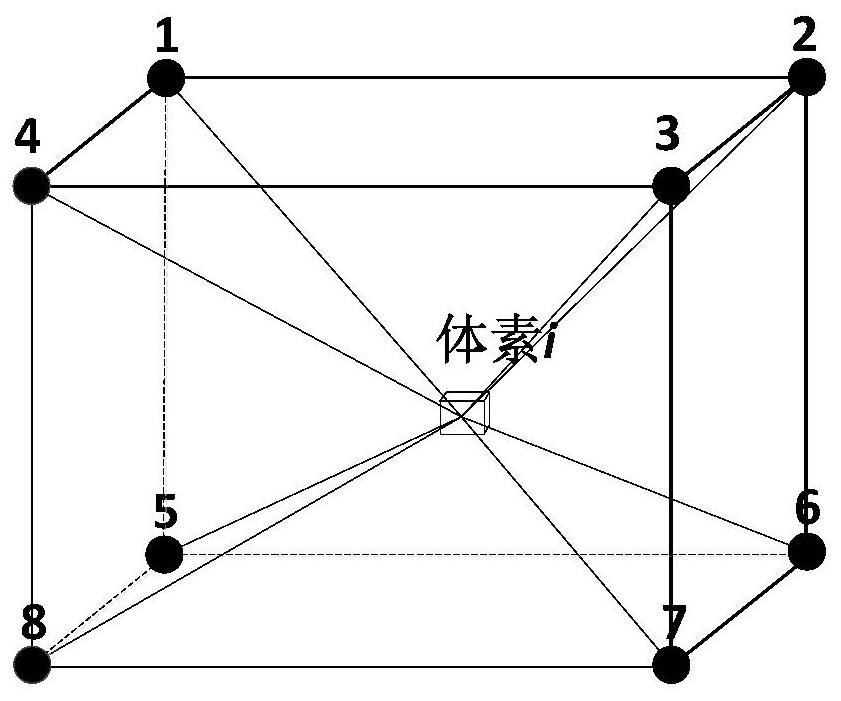
A Voxel-Based Simulation Method of Human External Exposure Dose
ActiveCN107832545BImplement voxelizationSimple stepsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman bodyVoxel
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Real-time Dosimetry with Ultrasound Imaging Probes
ActiveCN109414594BTimely replacementImprove quality controlUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingFallout exposure
An ultrasonic probe comprising: an ultrasonic probe housing (36); one or more ultrasonic transducers (32) disposed in the ultrasonic probe housing; a dosimeter (40) or an ionizing radiation detector, which disposed in or attached to the ultrasound probe housing; an alarm device (24, 52, 54, 56) that receives radiation dose collected by the dosimeter or ionizing radiation detector or radiation exposure data, the alarm device includes an electronic processor (24, 56) programmed to detect excessive radiation dose or radiation exposure received by the ultrasound probe, and outputting an alarm warning of detection of excessive radiation dose or radiation exposure received by the ultrasound probe. In some embodiments, the dosimeter is a non-resettable single-use dosimeter.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com