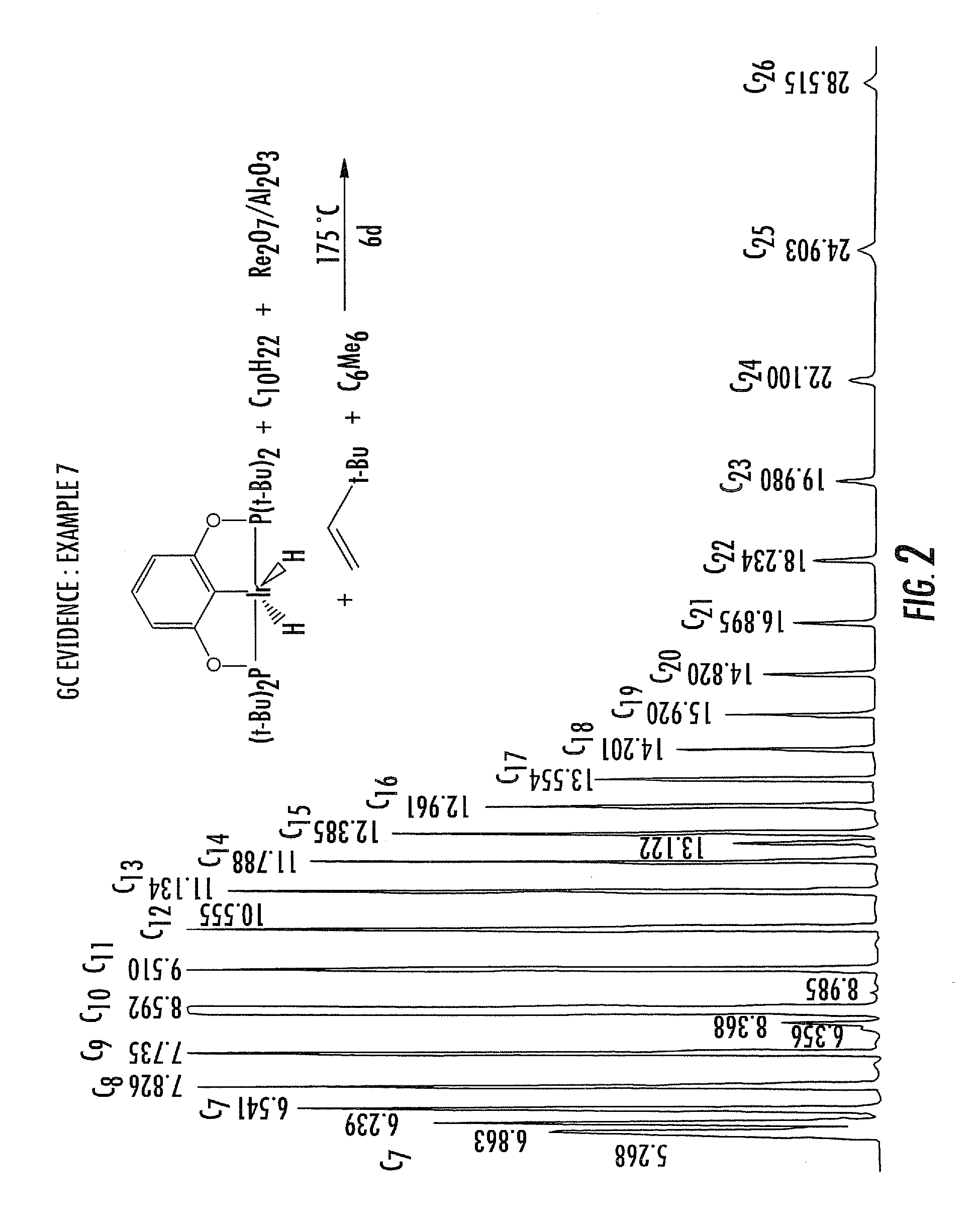
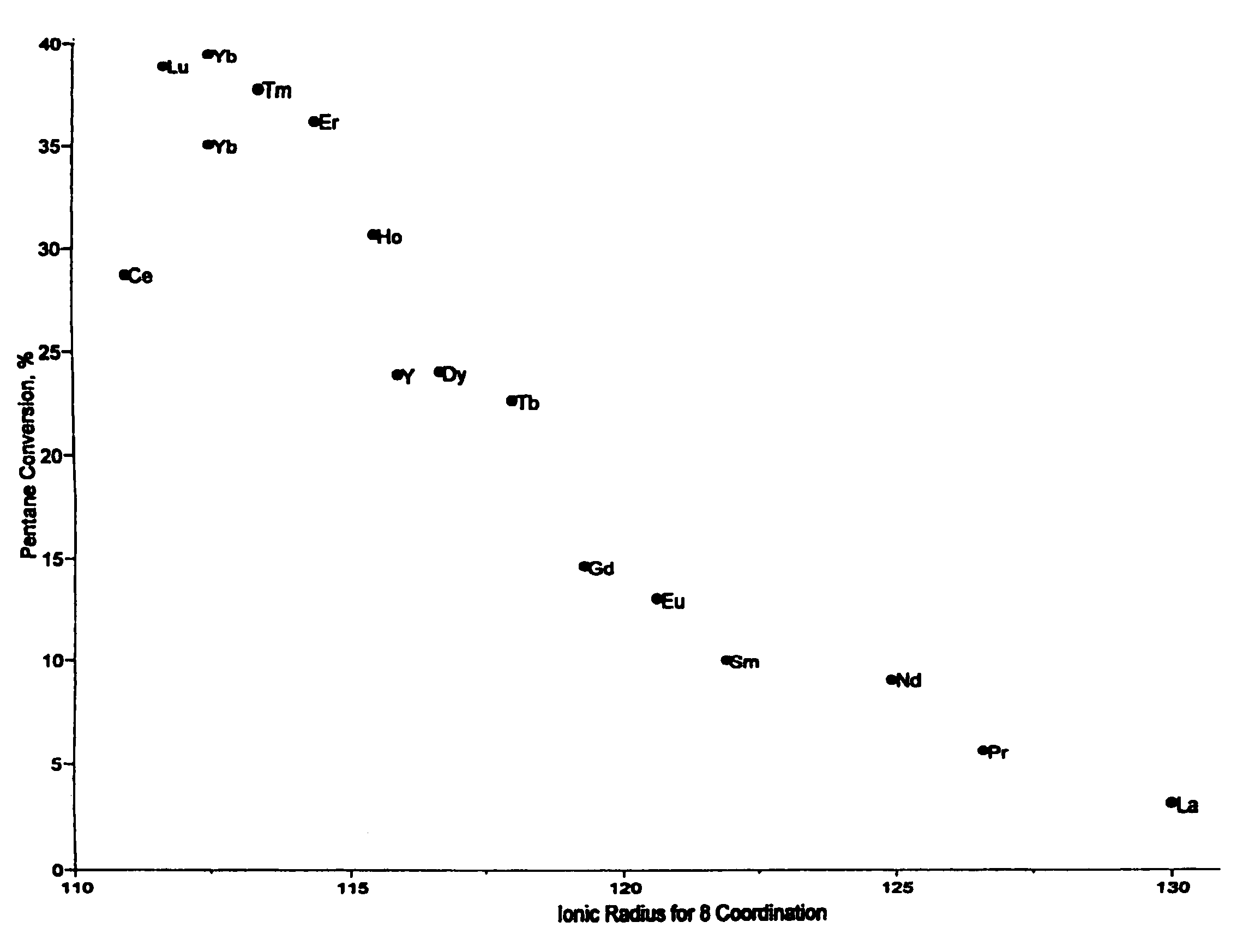
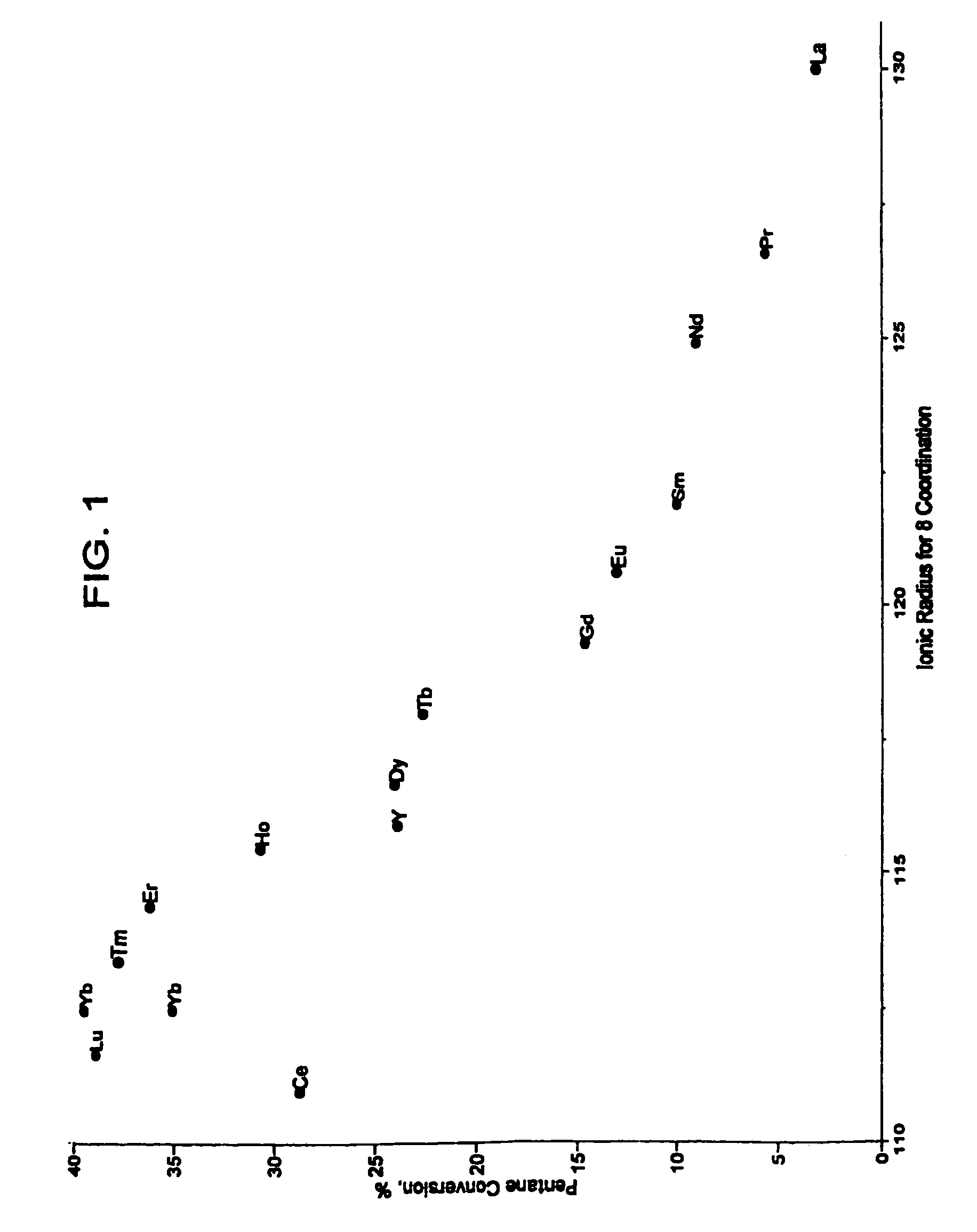
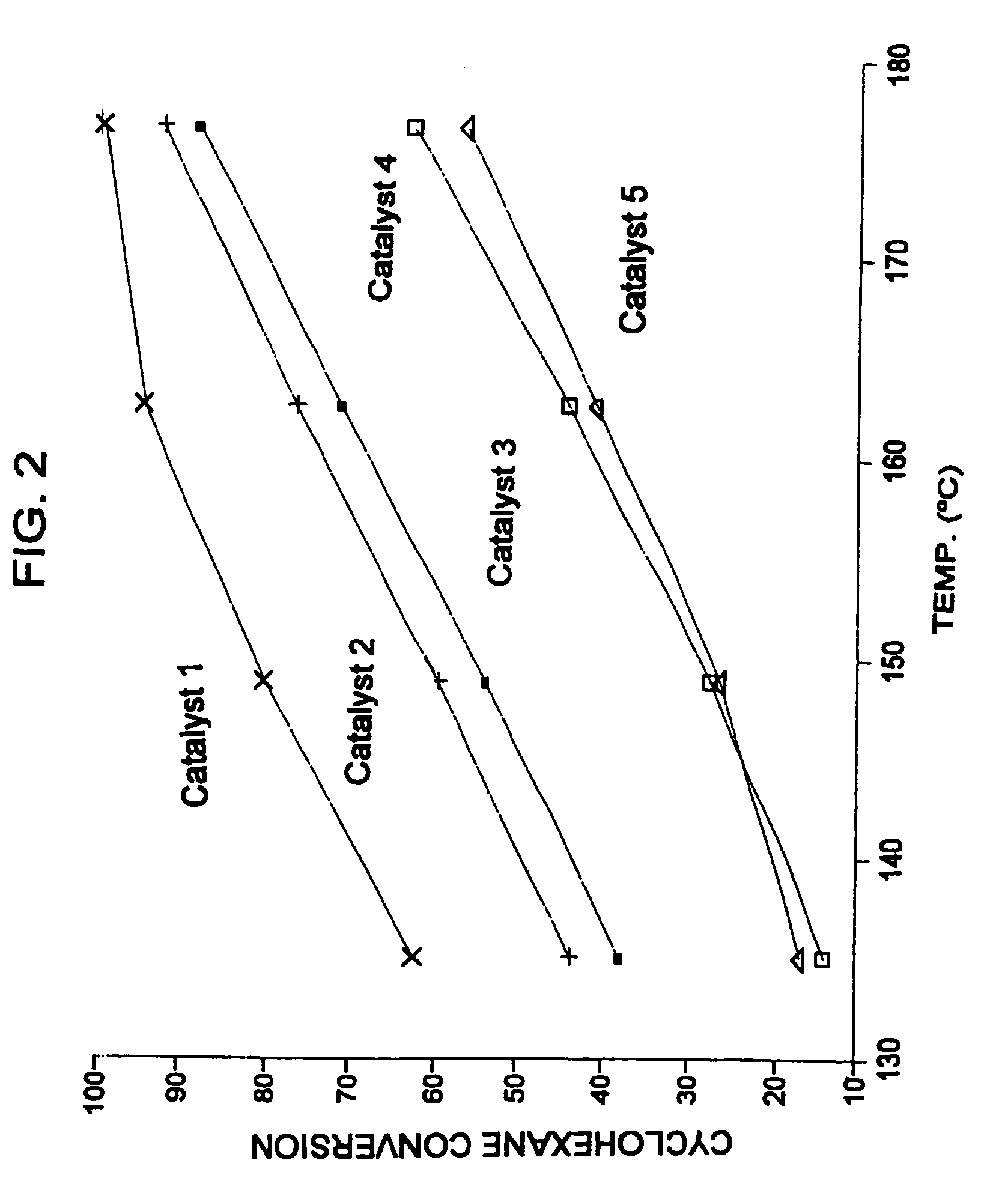
Patents
Literature
58results about "Hydrocarbon by saturated bond conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solid-acid isomerization catalyst and process
ActiveUS7041866B1Improve performanceImprove stabilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingAlkaneSulfation
A catalyst and process is disclosed to selectively upgrade a paraffinic feedstock to obtain an isoparaffin-rich product for blending into gasoline. The catalyst comprises a support of a sulfated oxide or hydroxide of a Group IVB (IUPAC 4) metal, a first component comprising at least one Group III A (IUPAC 13) component, and at least one platinum-group metal component which is preferably platinum.
Owner:UOP LLC
Isomerization catalyst and processes
InactiveUS6977322B2Improve performanceImprove stabilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingAlkaneIsomerization
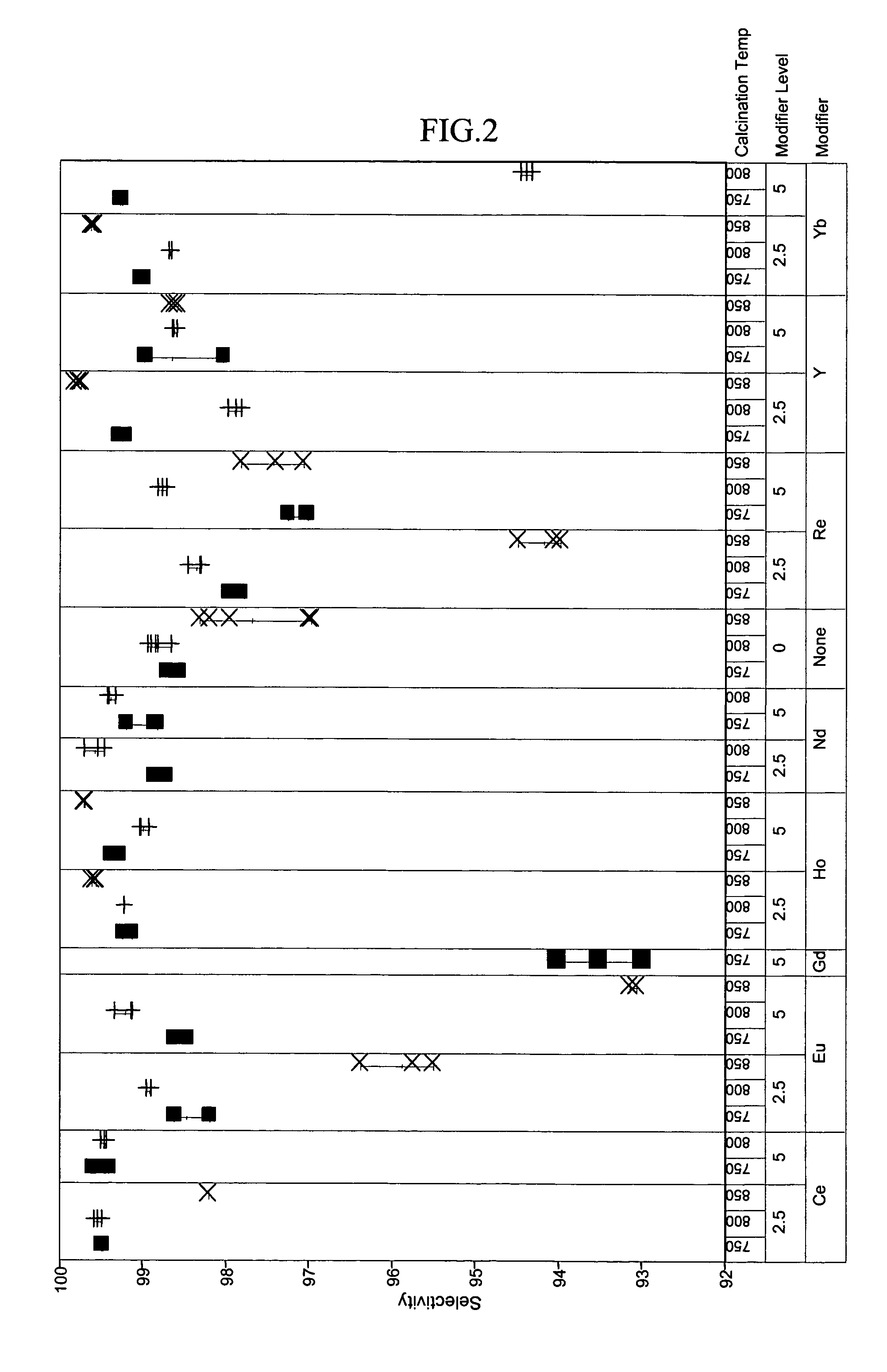
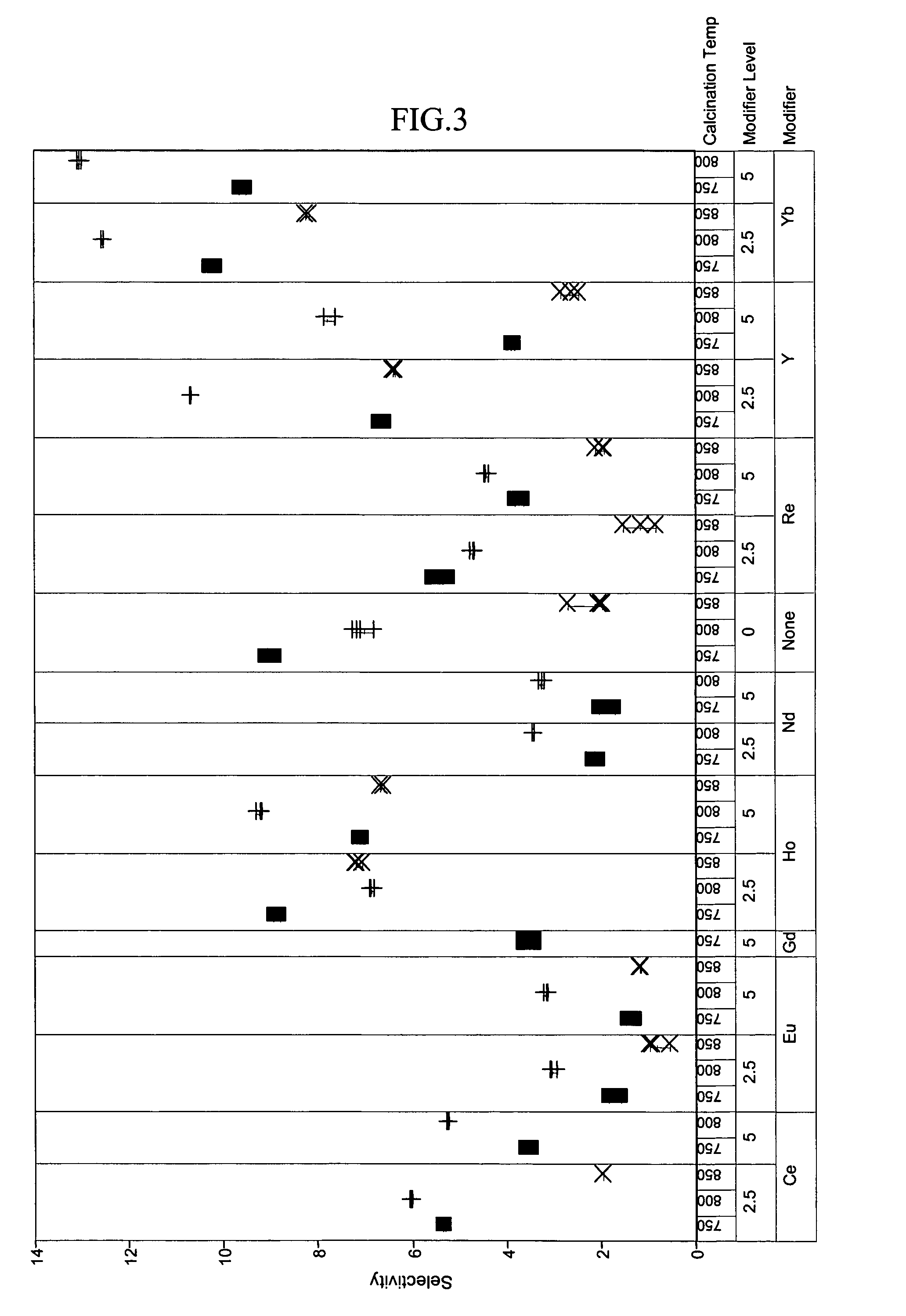
A catalyst and process is disclosed to selectively upgrade a paraffinic feedstock to obtain an isoparaffin-rich product for blending into gasoline. The catalyst comprises a support of a tungstated oxide or hydroxide of a Group IVB (IUPAC 4) metal, a first component of at least one lanthanide element, yttrium or mixtures thereof, which is preferably ytterbium or holmium, and at least one platinum-group metal component which is preferably platinum.
Owner:UOP LLC
Hydrocarbon conversion processes using non-zeolitic molecular sieve catalysts
Hydrocarbon or oxygenate conversion process in which a feedstock is contacted with a non zeolitic molecular sieve which has been treated to remove most, if not all, of the halogen contained in the catalyst. The halogen may be removed by one of several methods. One method includes heating the catalyst in a low moisture environment, followed by contacting the heated catalyst with air and / or steam. Another method includes steam-treating the catalyst at a temperature from 400° C. to 1000° C. The hydrocarbon or oxygenate conversion processes include the conversion of oxygenates to olefins, the conversion of oxygenates and ammonia to alkylamines, the conversion of oxygenates and aromatic compounds to alkylated aromatic compounds, cracking and dewaxing.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for continuous ruthenium-catalysed metathesis
InactiveUS20060009667A1Less fluctuationReduce riskHydrocarbon by isomerisationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemistryRuthenium catalyst
The invention relates to a process for carrying out metathesis reactions, wherein the process is carried out continuously and a ruthenium-containing catalyst is used.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Supported iridium catalysts
A method of converting at least one first alkane to a mixture of at least one low molecular weight alkane (optionally also including additional lower and / or higher molecular weight alkanes) and at least one high molecular weight alkane, comprises: reacting a first alkane in the presence of dual catalyst system comprising a first catalyst (i.e., a hydrogen transfer catalyst) and a second catalyst (i.e., a metathesis catalyst) to produce a mixture of low and high molecular weight alkanes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
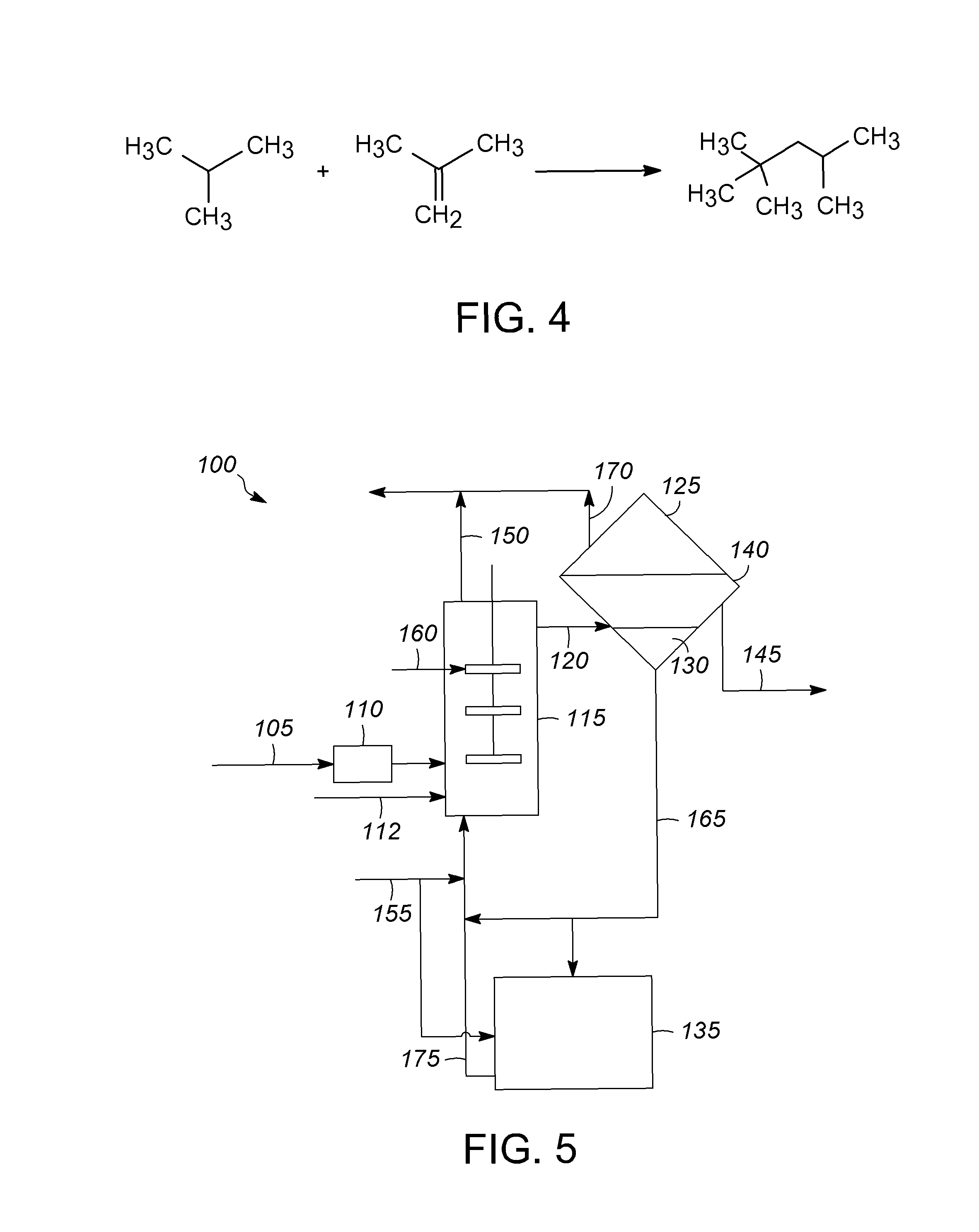
Supported ionic liquid and the use thereof in the disproportionation of isopentane
InactiveUS20050033102A1Increased product formationIncreased formationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalysts2-methylbutaneAlkane
A catalyst system containing an ionic liquid dispersed on a support having an average pore diameter greater than about 225 Å is disclosed. The catalyst system is employed in a process to disproportionate a C5 paraffin.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
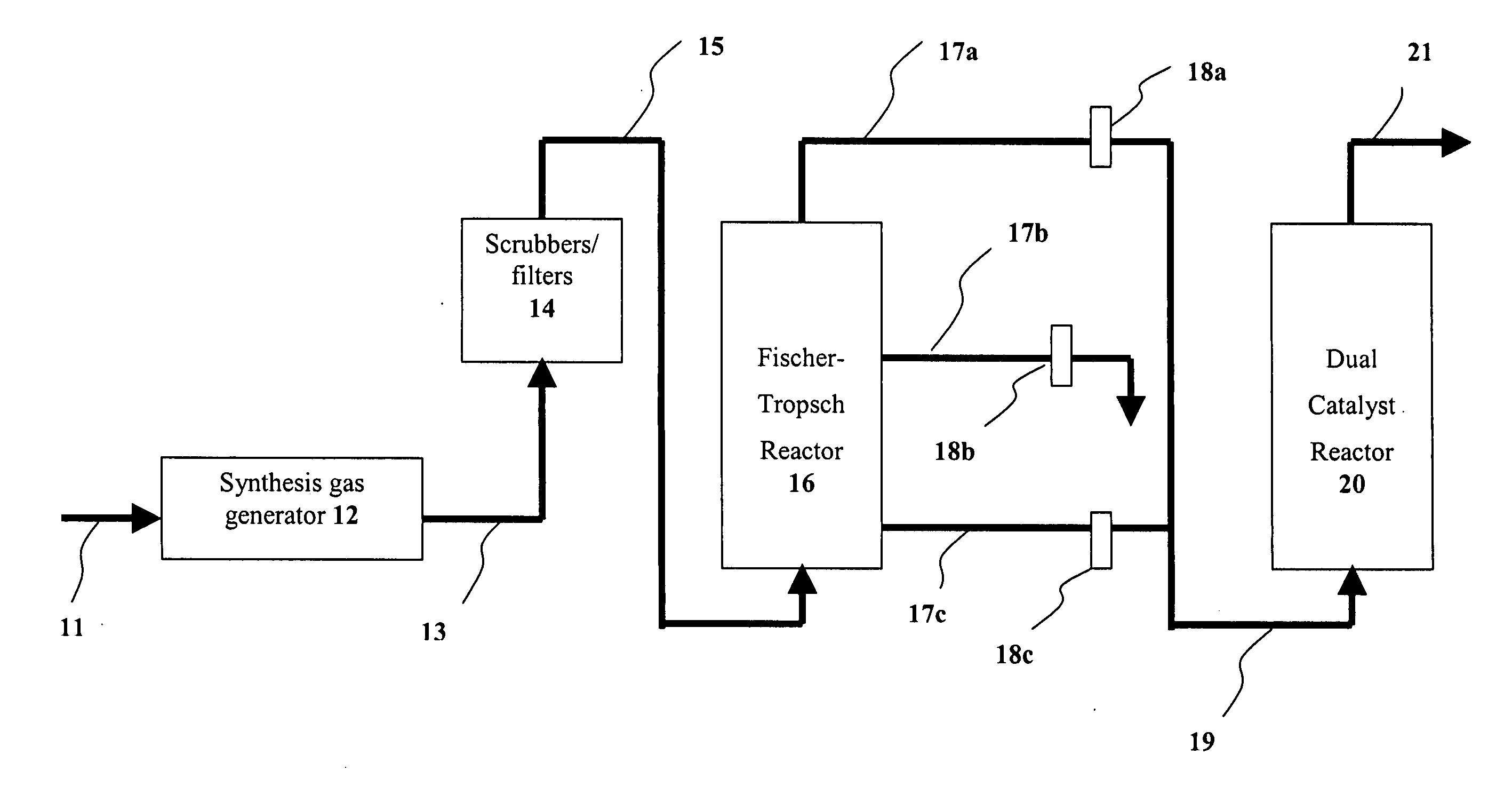
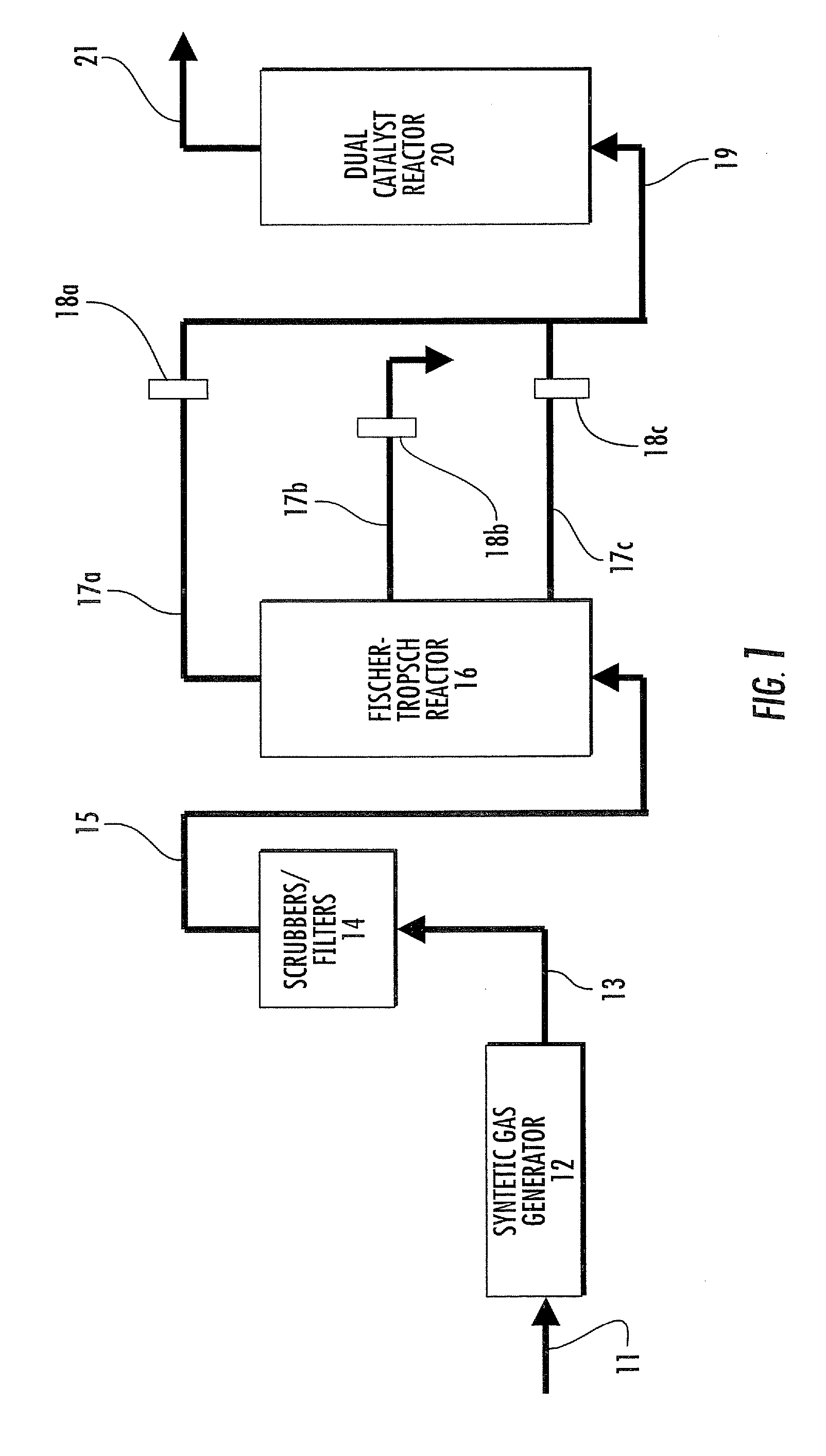
System and process for production of liquid product from light gas
InactiveUS20090001316A1Increase ratingsLow costTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersLiquid productHydrogen
A method for producing a product comprising at least one selected from C2+ hydrocarbons, oxygenates, and combinations thereof from light gas comprising one or more of carbon dioxide, methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, and methanol by forming a dispersion of light gas in a liquid feed, wherein the dispersion is formed at least in part with high shear forces and wherein at least one of the liquid feed and the light gas is a hydrogen source. A system for carrying out the method is also presented.
Owner:HRD CORP
Process for continuous ruthenium-catalysed metathesis
InactiveUS7838711B2Less fluctuationReduce riskHydrocarbon by isomerisationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSalt metathesis reactionChemistry
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Solid acid catalyst and method of using same
A catalyst composition includes an oxygen compound of an element selected from Group IVB or Group IVA of the Periodic Table of the Elements; an oxygen compound of an element selected from Group VIB or Group VIA of the Periodic Table of the Elements; and at least about 1% by weight based upon total catalyst weight of fumed silica particles. The catalyst composition is advantageously employed in hydrocarbon conversion processes such as isomerization.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Method of starting up a reaction system
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Dual catalyst system for alkane metathesis
InactiveUS7902417B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsAlkanePtru catalyst
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
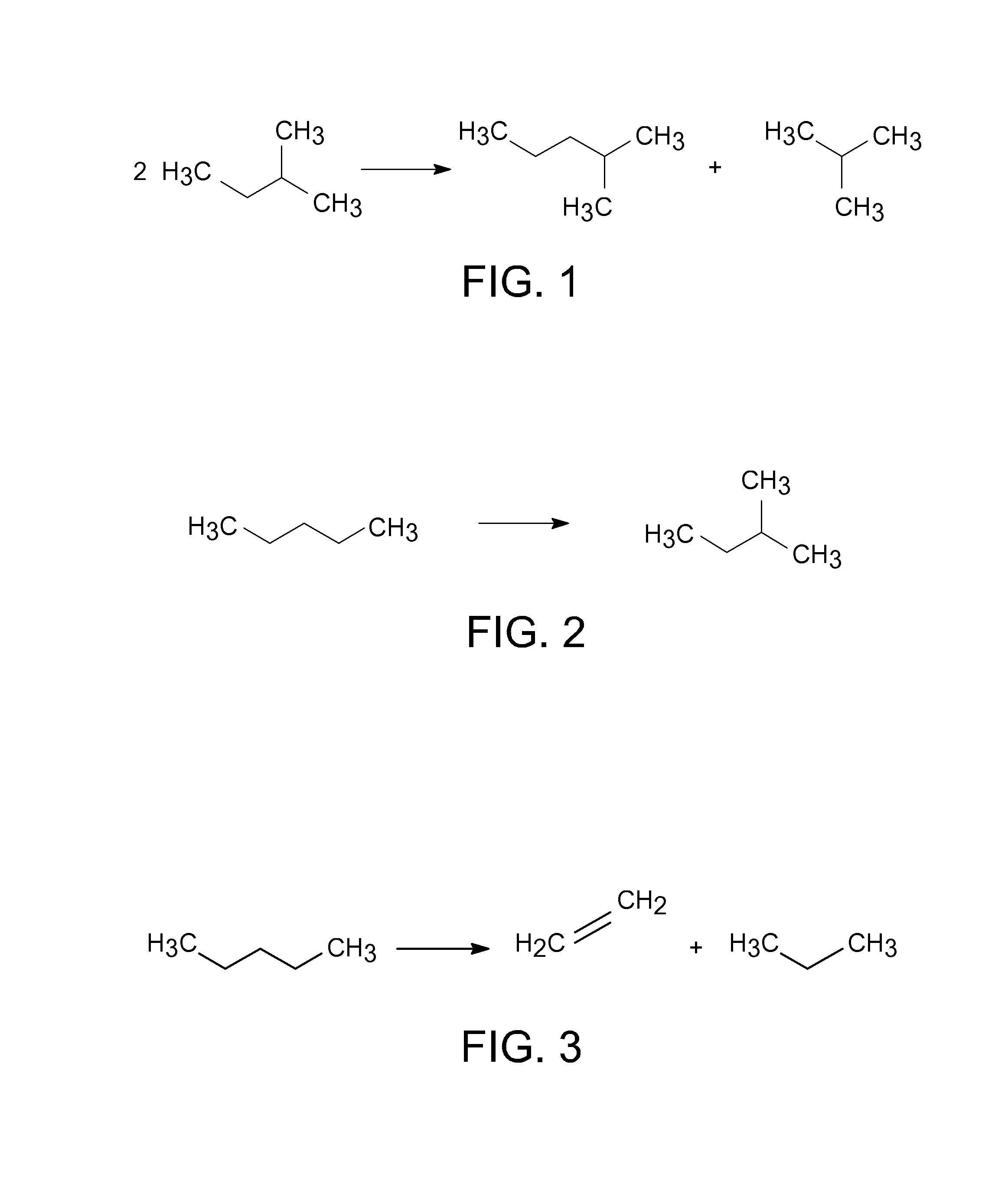
Disproportionation of isopentane
A process for disproportionating isopentane into isomers of hexane and butane that utilizes a fixed bed reactor employing a catalyst composition comprising aluminum halide. The process additionally includes a product separation zone which can be configured to recover and return at least a portion of the isopentane product stream to the inlet of the disproportionation reactor.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Dual catalyst system for alkane metathesis
InactiveUS20070060781A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsAlkaneOrganic chemistry
A method of converting at least one first alkane to a mixture of at least one low molecular weight alkane (optionally also including additional lower and / or higher molecular weight alkanes) and at least one high molecular weight alkane, comprising: reacting a first alkane in the presence of dual catalyst system comprising a first catalyst (i.e., a hydrogen transfer catalyst and preferably an iridium pincer complex catalyst) and a second catalyst (i.e., a metathesis catalyst) to produce a mixture of low and high molecular weight alkanes.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
High-activity isomerization catalyst and process
InactiveUS7015175B2Improve performanceImprove stabilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingAlkaneIsomerization
A catalyst and process is disclosed to selectively upgrade a paraffinic feedstock to obtain an isoparaffin-rich product for blending into gasoline. The catalyst comprises a support of a sulfated oxide or hydroxide of a Group IVB (IUPAC 4) metal, a first component of at least one lanthanide element or yttrium component, which is preferably ytterbium, and at least one platinum-group metal component which is preferably platinum and a refractory-oxide binder having at least one platinum-group metal component dispersed thereon.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for increasing yield of ethylene and propylene
ActiveCN101239868AReduce partial pressureHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystEthyleneDimethyl ether
The invention relates to a method for improving yield of ethylene and propylene, which solves the problem of low yield of ethylene and propylene during lower olefins preparing process from conversion of methanol and dimethyl ether. The invention uses at least one of methanol and dimethyl ether and C4 hydrocarbon as materials, the materials enter into a reaction region from a distributor at the bottom of a fluidization bed reactor or from at least a position axially separated along the reaction region, and contact and react with a catalyst to generate an effluent containing ethylene, propylene and C4 hydrocarbon, the effluent is separated to obtain ethylene, propylene and C4 hydrocarbon; wherein, the C4 hydrocarbon material is from fresh mixed C4 hydrocarbon or mixed C4 hydrocarbon obtained by separation or mixtures thereof. In this way, the invention sloves the problem well, and is useful in industrial production of ethylene and propylene.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Implants for administering substances and methods of producing implants
InactiveUS20110052659A1BiocideHydrocarbon active ingredientsAdministered substanceSubcutaneous implantation
A porous silicon implant impregnated with a beneficial substance, such as a micromineral required for healthy physiology, is implanted subcutaneously and is entirely corroded away over the following months / year to release the micromineral in a controlled manner. In a second embodiment the implant may have a large number of holes which contain beneficial substance and which are closed by bio-errordable doors of different thickness so as to stagger the release of the beneficial substance over time as the doors are breached.
Owner:SEC OF STATE OF DEFENCE THE DEFENCE EVALUATION & RES AGENCY +1
Inorganic mesoporous solids, a process for their preparation and their use, notably as catalysts and adsorbents
InactiveUS20040035751A1Hydrocarbon by isomerisationIon-exchanger regenerationInorganic particleSorbent
The present invention relates to new mesoporous inorganic solids in the form of primary and / or secondary inorganic particles of D10>=1 mum and D50>=3 mum, preferably from D10>=2 mum and D50>=10 mum the size of which can go up to 10 mm, wherein the microporous volume (pores of size less than or equal to 2 mum) represents at most 10% of the total porous volume up to 300 nm. These solids can advantageously be used as catalytic component supports in polymerization reactions, as reaction catalysts in the refining and petrochemical fields, as adsorbents for separating the components of a gaseous or liquid mixture consisting of at least 2 different compounds and as chromatography column packing supports.
Owner:CECA SA
Hydrocarbon transformations using carbocatalysts
InactiveUS20140275684A1Broad synthetic utilityEfficient and cheapMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsChemical transformationHydrocarbon
Owner:MOSELEY SAMUEL G +8
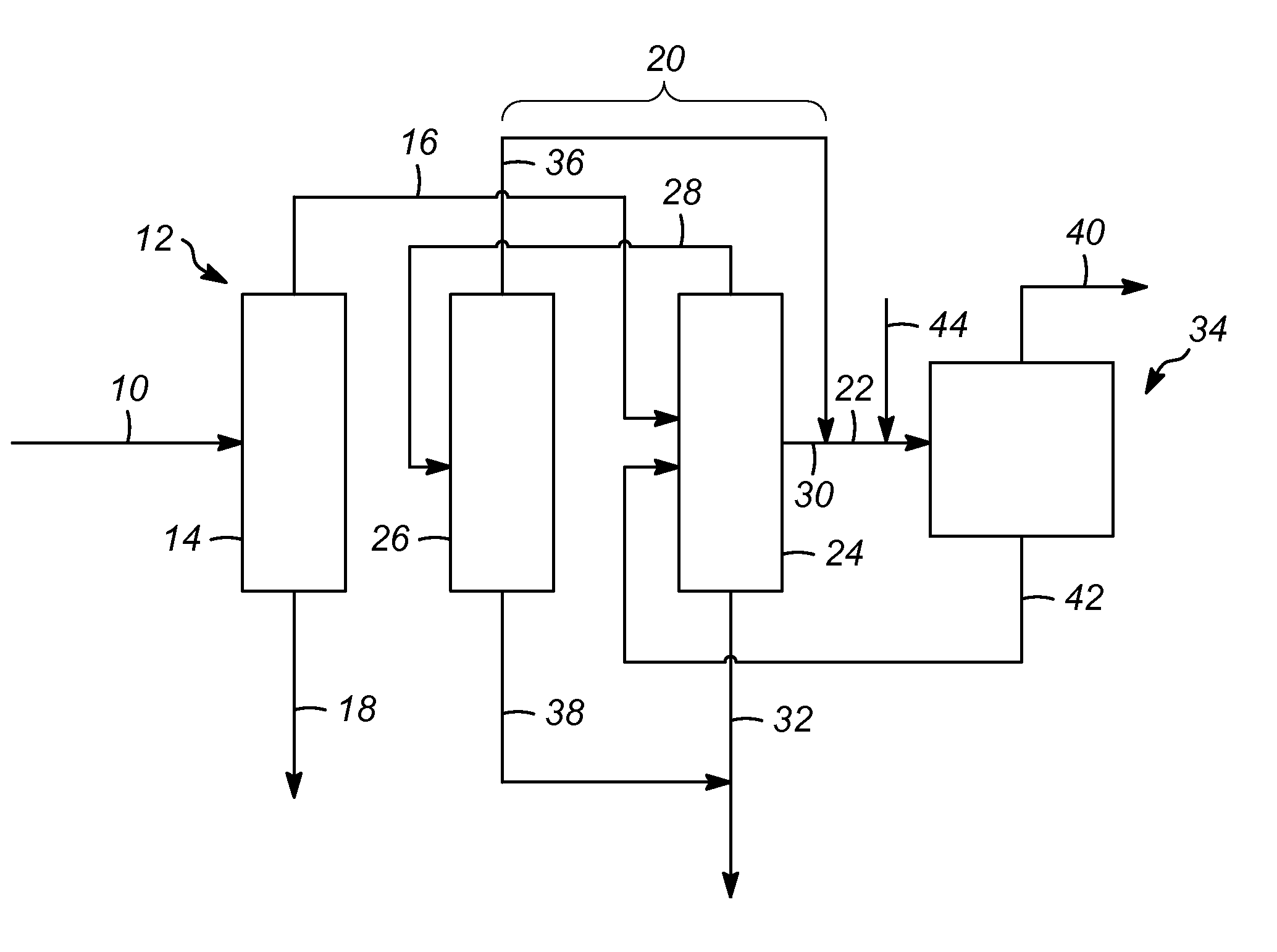
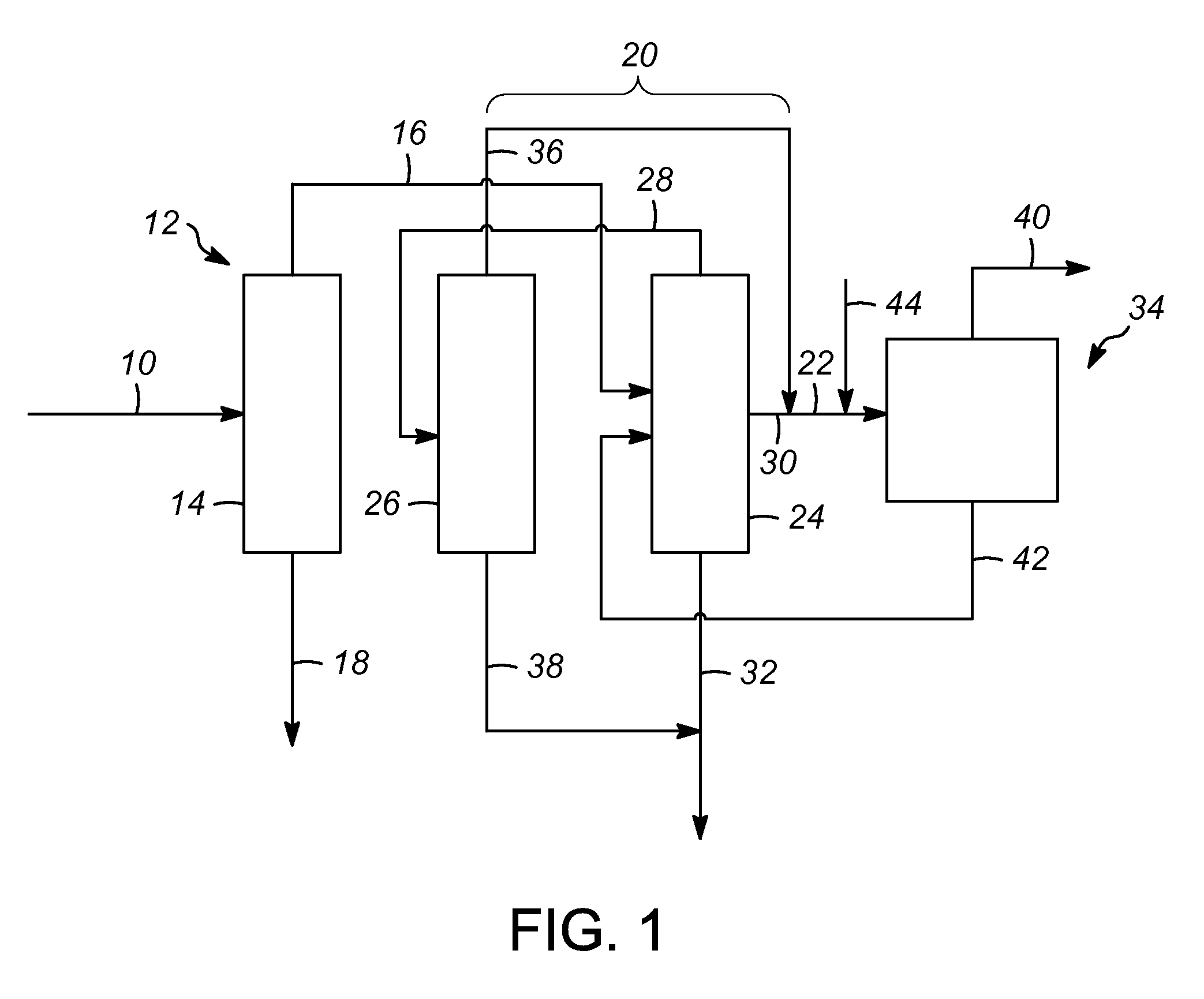
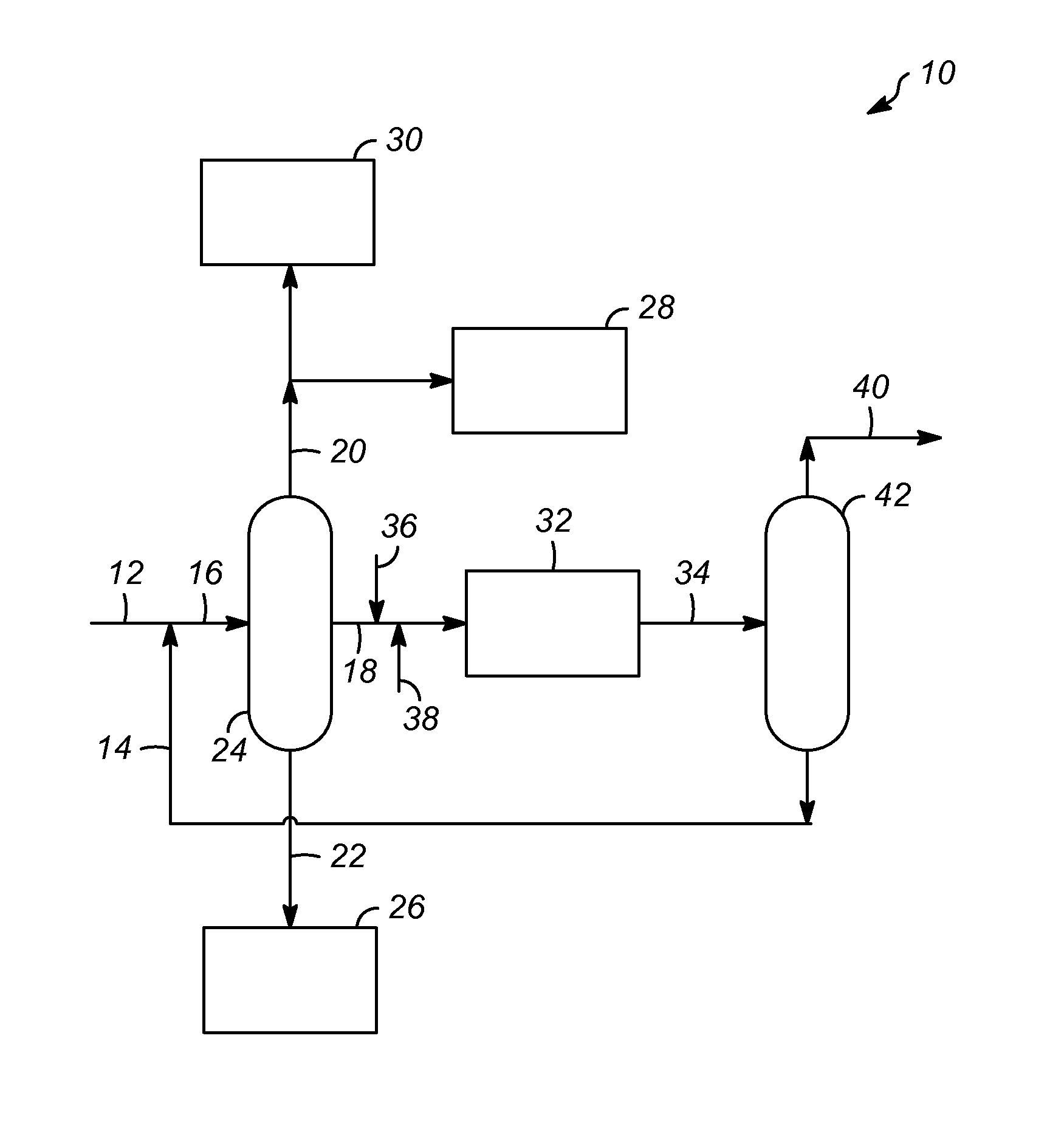
Process for increasing the yield of an isomerization zone
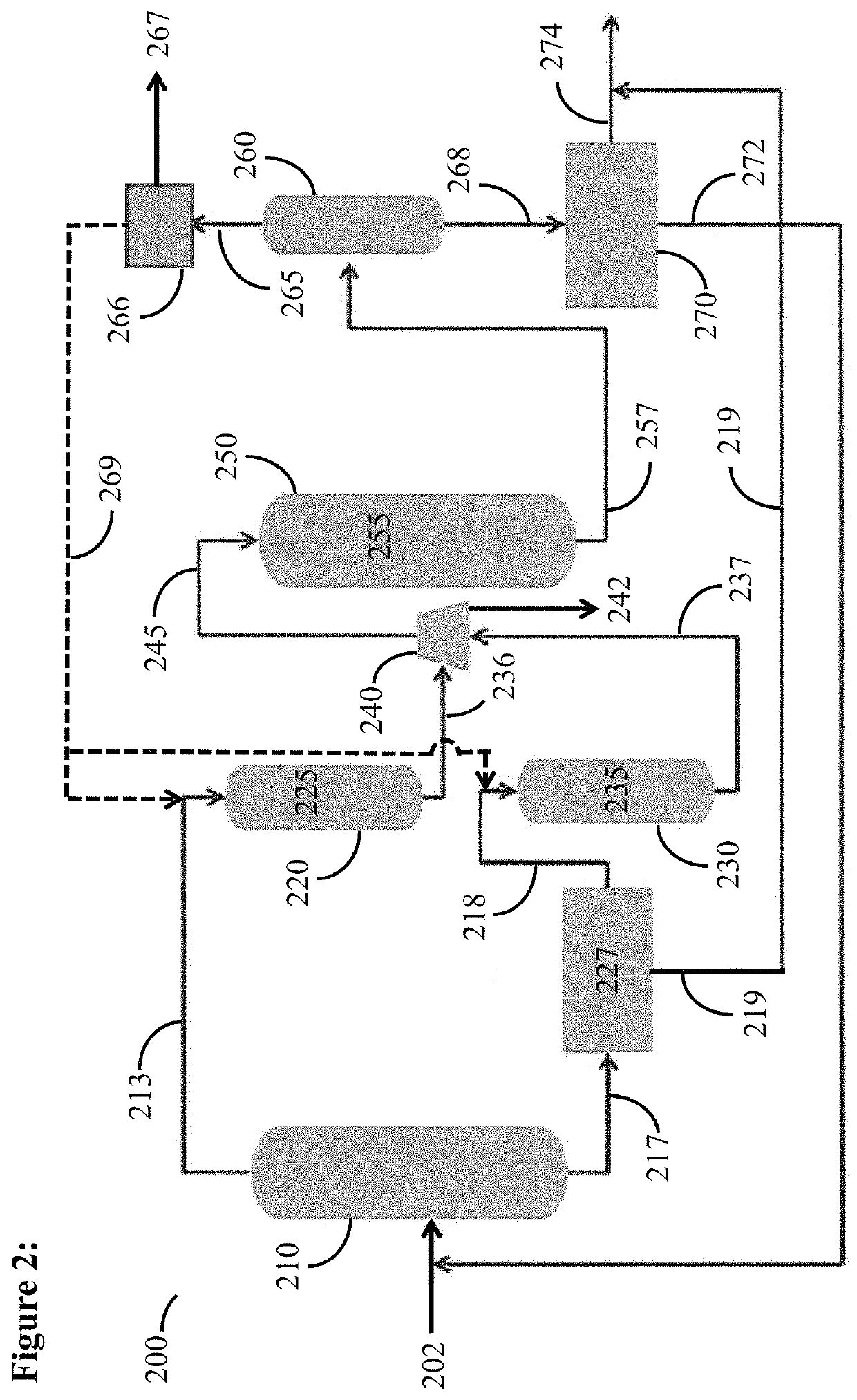
ActiveUS9302958B2Raise the ratioSpeed up the conversion processHydrocarbon by isomerisationDistillation purification/separationIsomerizationHydrogen
A process for increasing a yield of an isomerization zone by removing at least a portion of the C6 cyclic hydrocarbons from a stream prior to it being passed into the isomerization zone. Additionally, disproportionation reaction selectivity is also increased, producing valuable C3 hydrocarbons and C4 hydrocarbons. Also, a higher ring opening conversion of C5 cyclic hydrocarbons is observed. The isomerization zone may have an average operating temperature of at least 176° C. and an outlet molar ratio of hydrogen to hydrocarbon feed in the isomerization zone is less than about 0.2.
Owner:UOP LLC
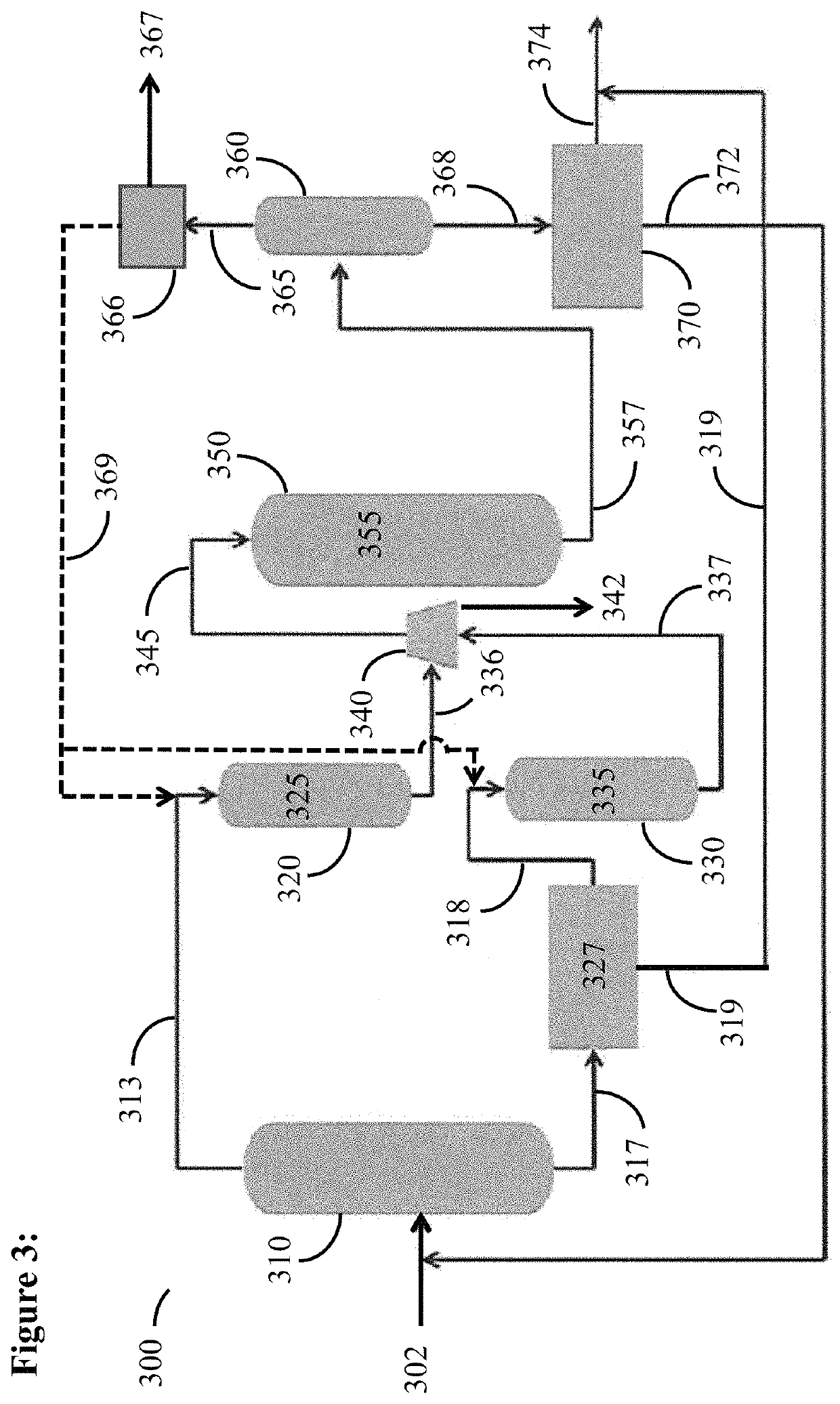
Process for producing a feed stream for a steam cracker
ActiveUS9302960B2Speed up the conversion processThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbon by isomerisationIsomerizationChloride
A process for producing a feed for a stream cracker. At least a portion of the C6 cyclic hydrocarbons are removed from a stream prior to it being passed into an isomerization zone. Disproportionation reaction selectivity is increased, producing valuable C3 hydrocarbons and C4 hydrocarbons. Also, a higher ring opening conversion of C5 cyclic hydrocarbons is observed. The yield may be adjusted by controlling an amount of C6 cyclic hydrocarbons passed to the isomerization zone. The catalyst in the isomerization zone is free of chloride, and the streams including effluent from the isomerization zone may be passed to a steam cracker without requiring chloride removal.
Owner:UOP LLC
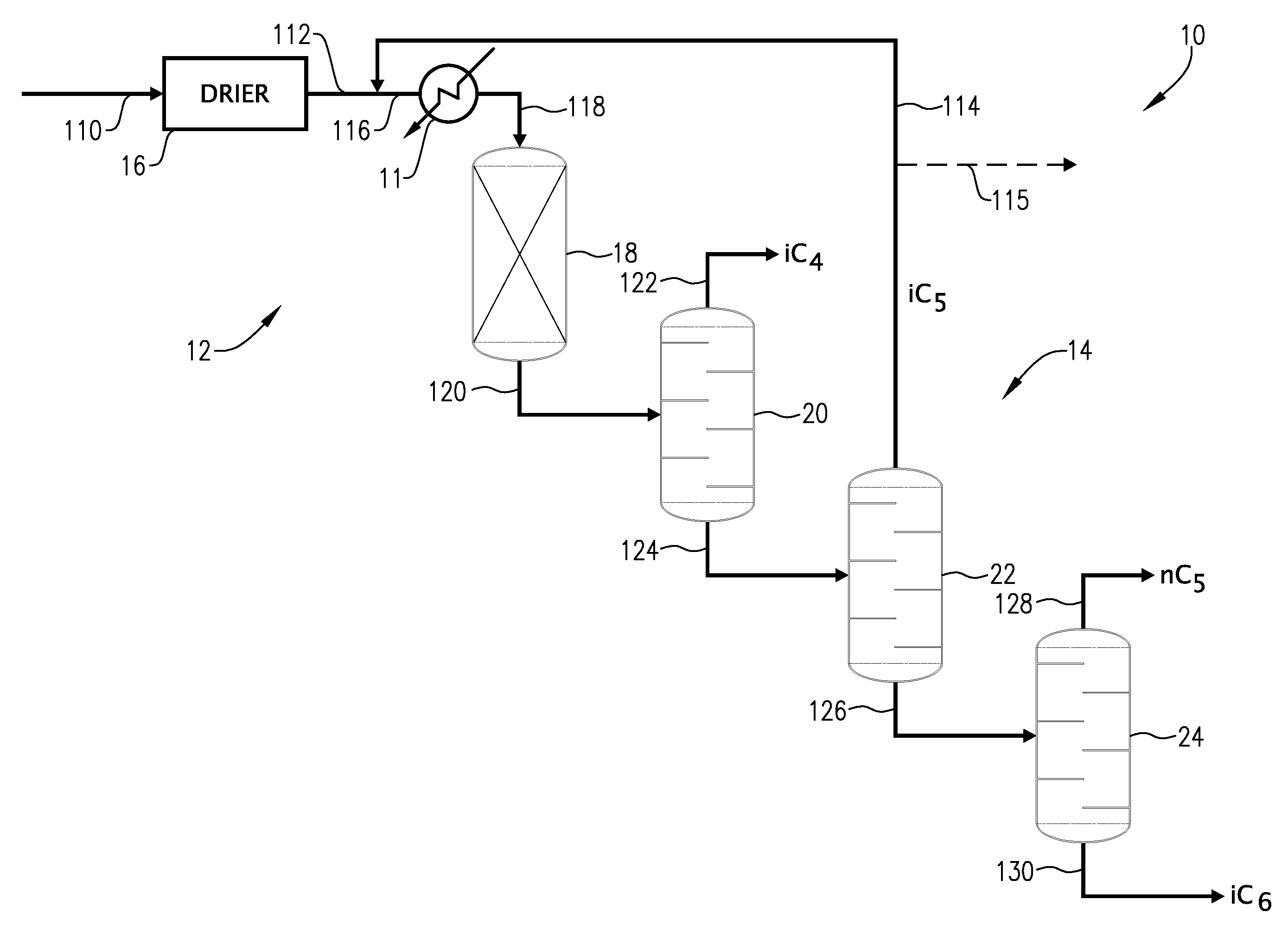
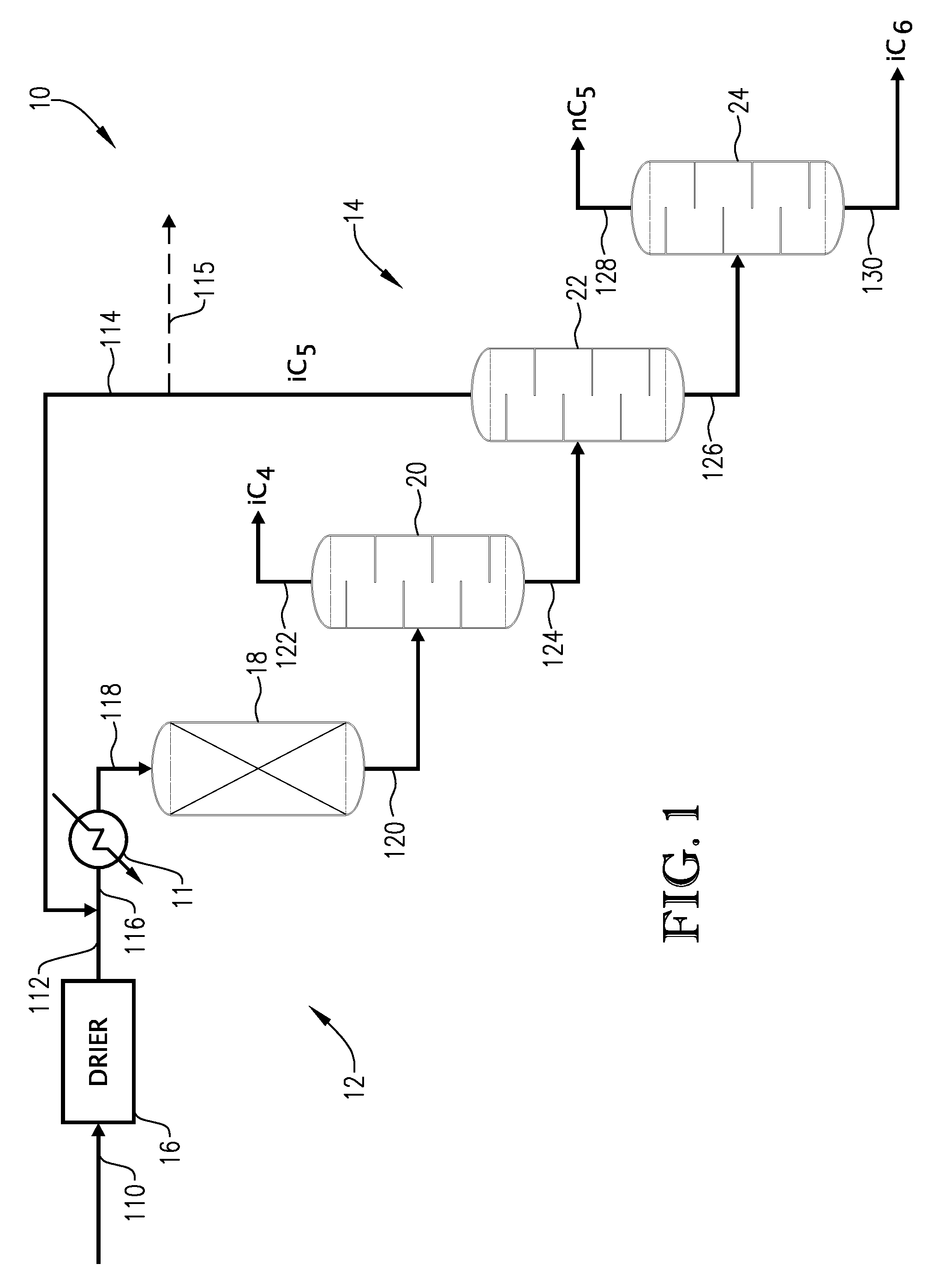
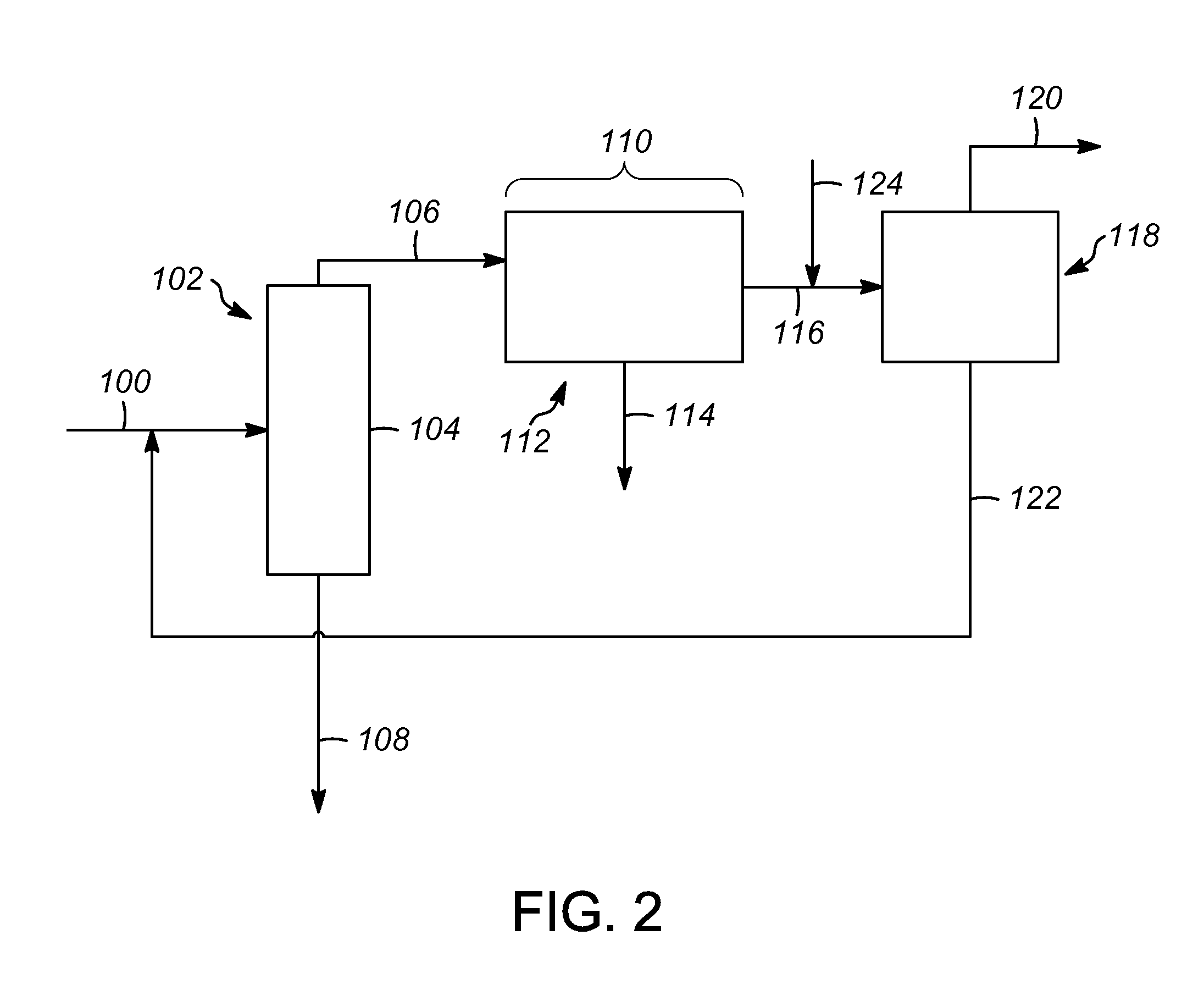
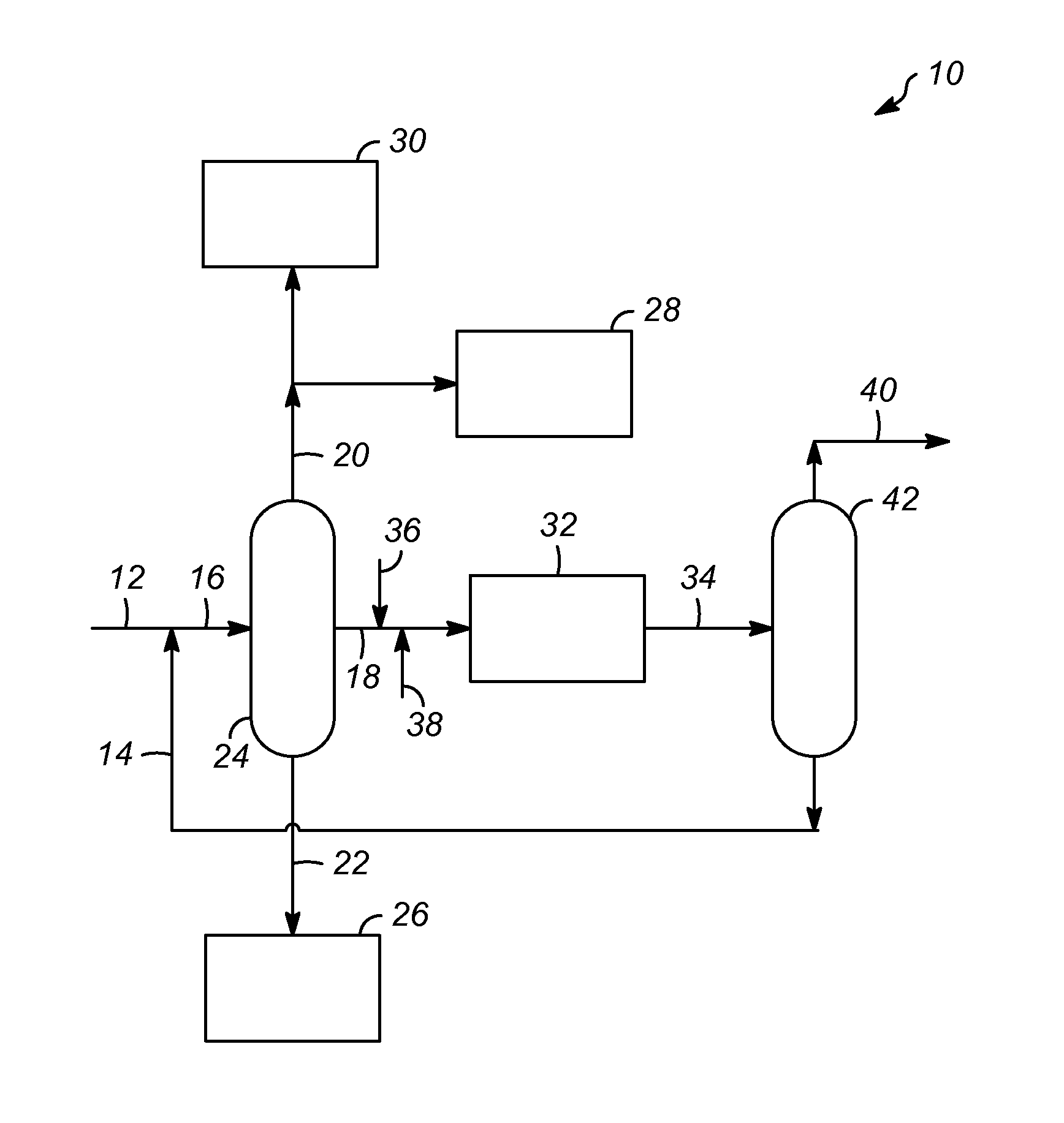
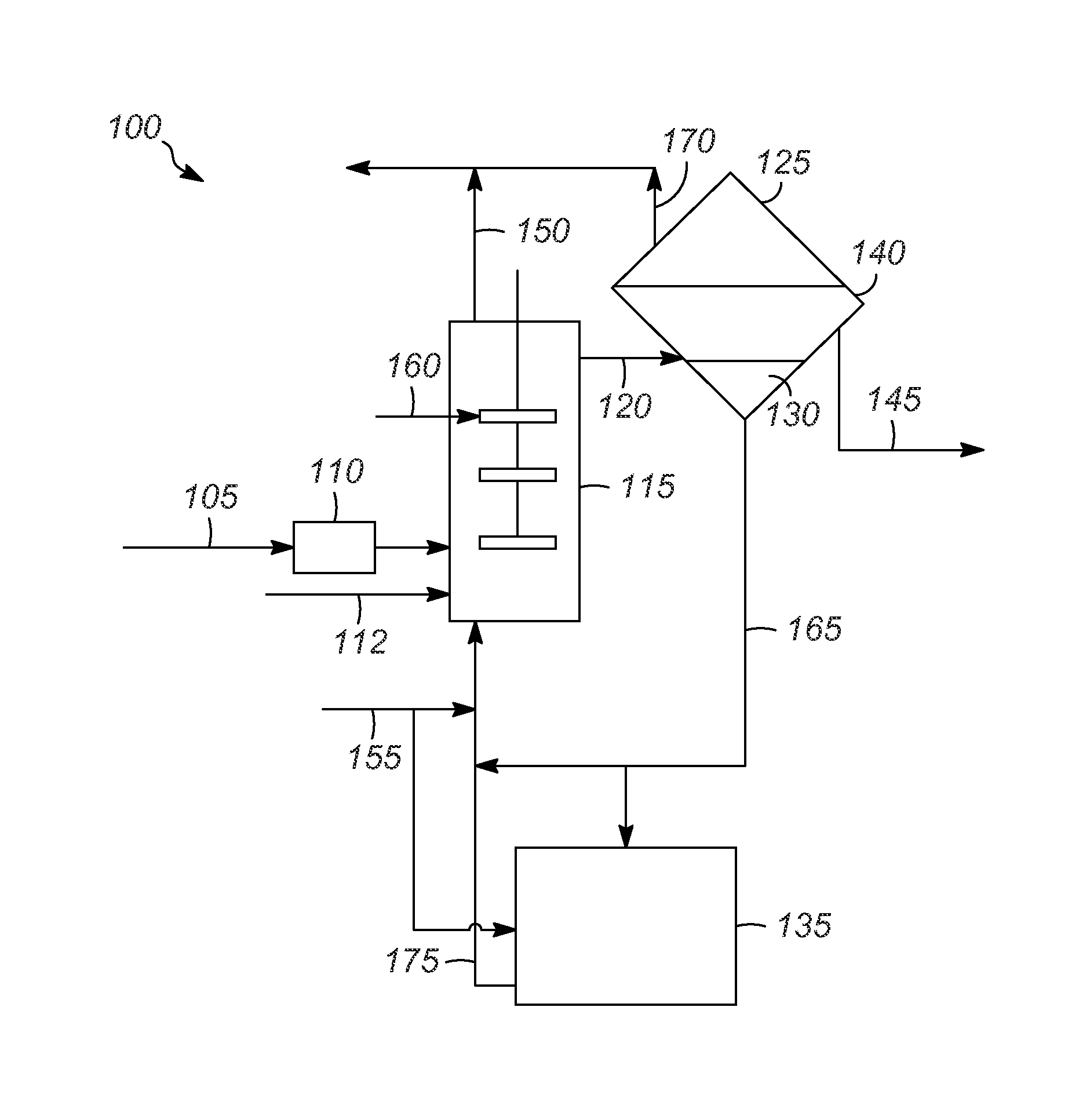
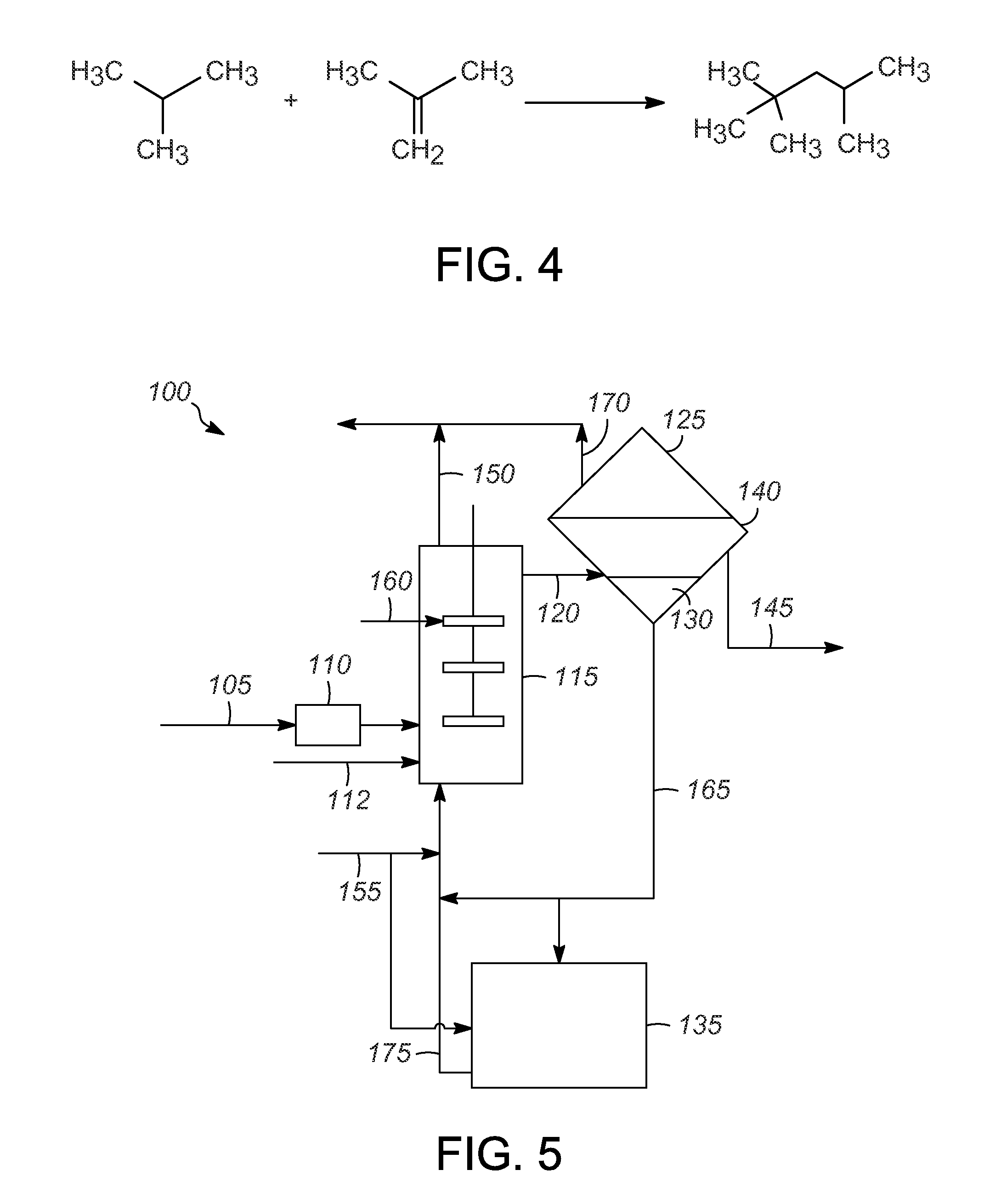
Hydrocarbon processing apparatuses and processes for producing n-pentane and isobutane
Hydrocarbon processing apparatuses and processes for producing n-pentane and isobutane are provided herein. In an embodiment, a process for producing n-pentane and isobutane includes providing a hydrocarbon feed stream that includes C4 and C5 hydrocarbons. A recycle stream that includes C4+ hydrocarbons and the hydrocarbon feed stream is combined to produce a combined feed stream. The combined feed stream is separated to produce an iC4 product stream, an nC5+ product stream, and an iC5 / nC4 feed stream. The iC5 / nC4 feed stream is simultaneously disproportionated and isomerized in an isomerization zone to produce an intermediate stream that includes C3-C6 hydrocarbons. The C3-C6 hydrocarbons in the intermediate stream are separated to produce a C3− stream and the recycle stream that includes C4+ hydrocarbons.
Owner:UOP LLC
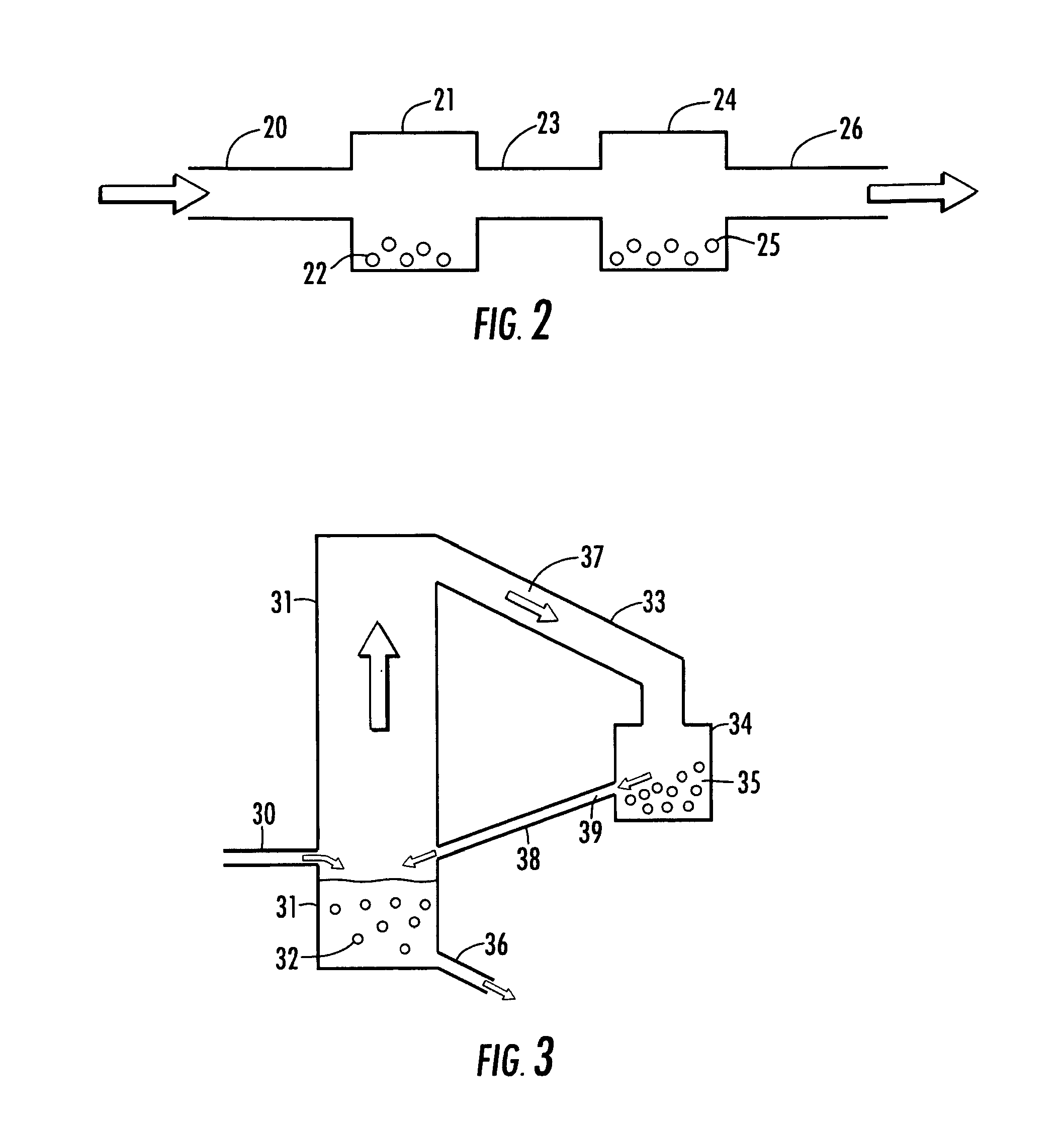
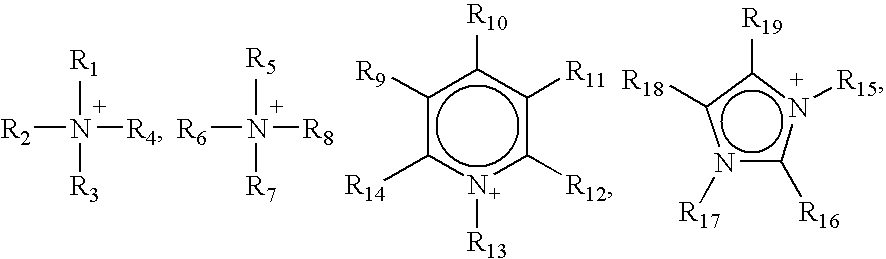
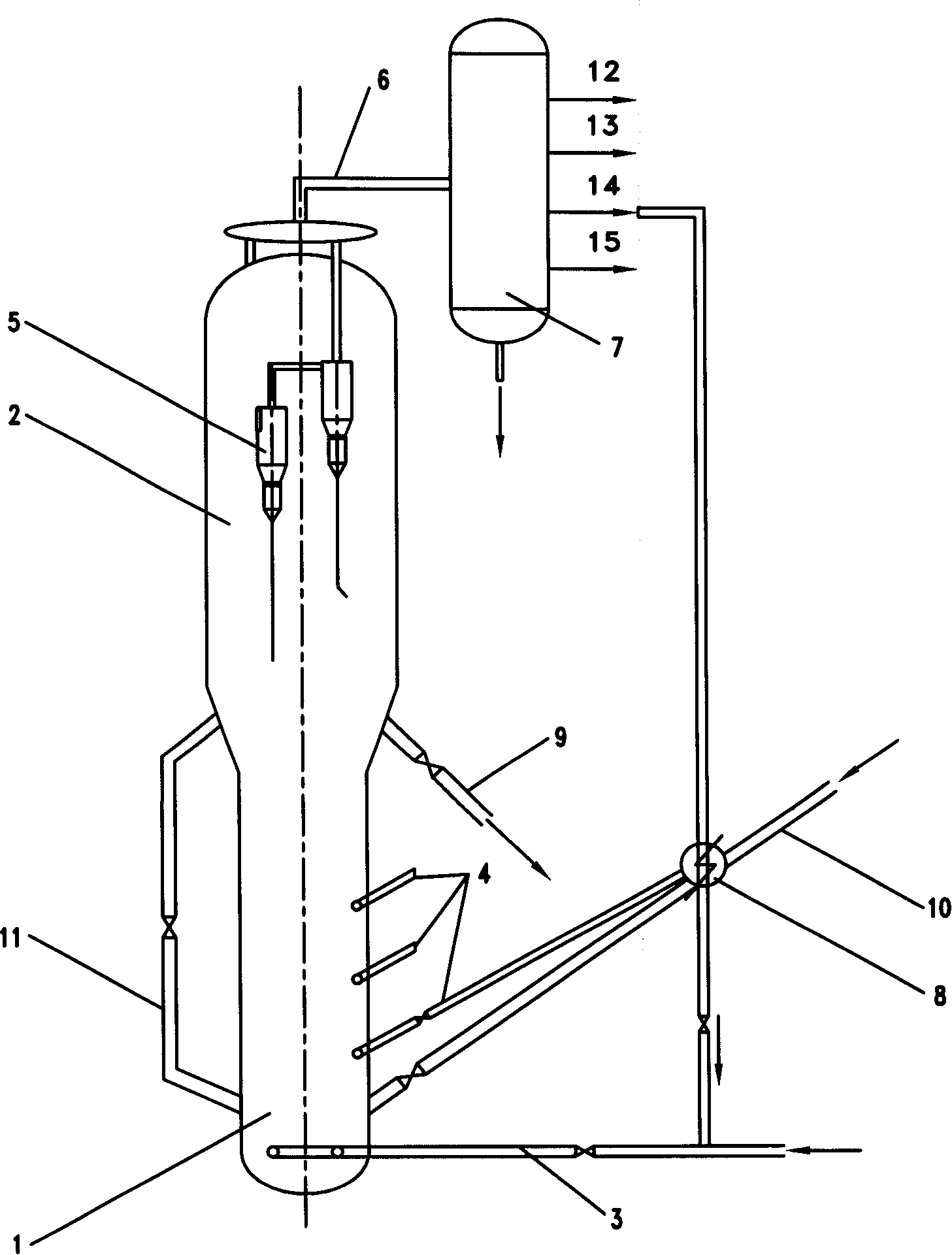
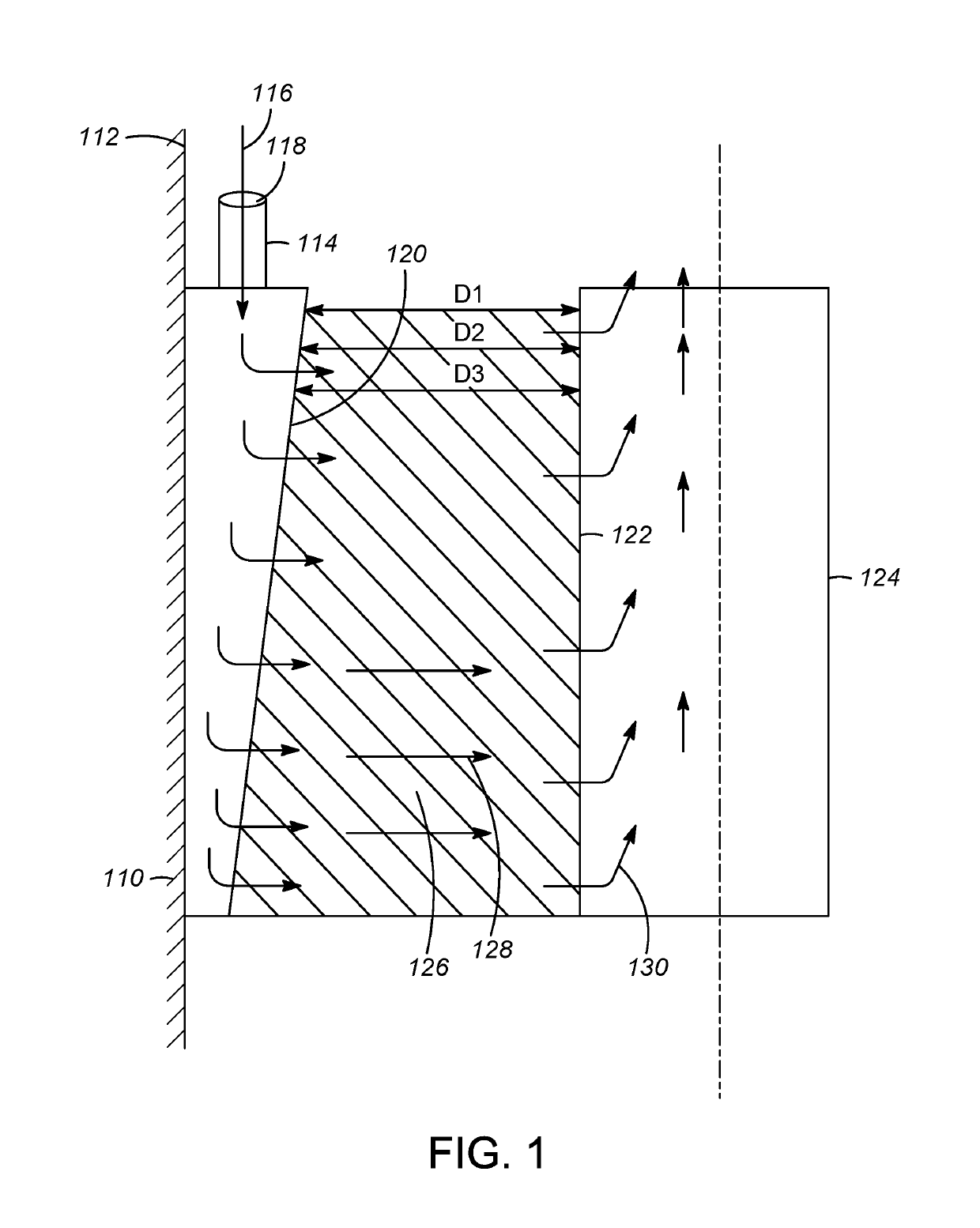
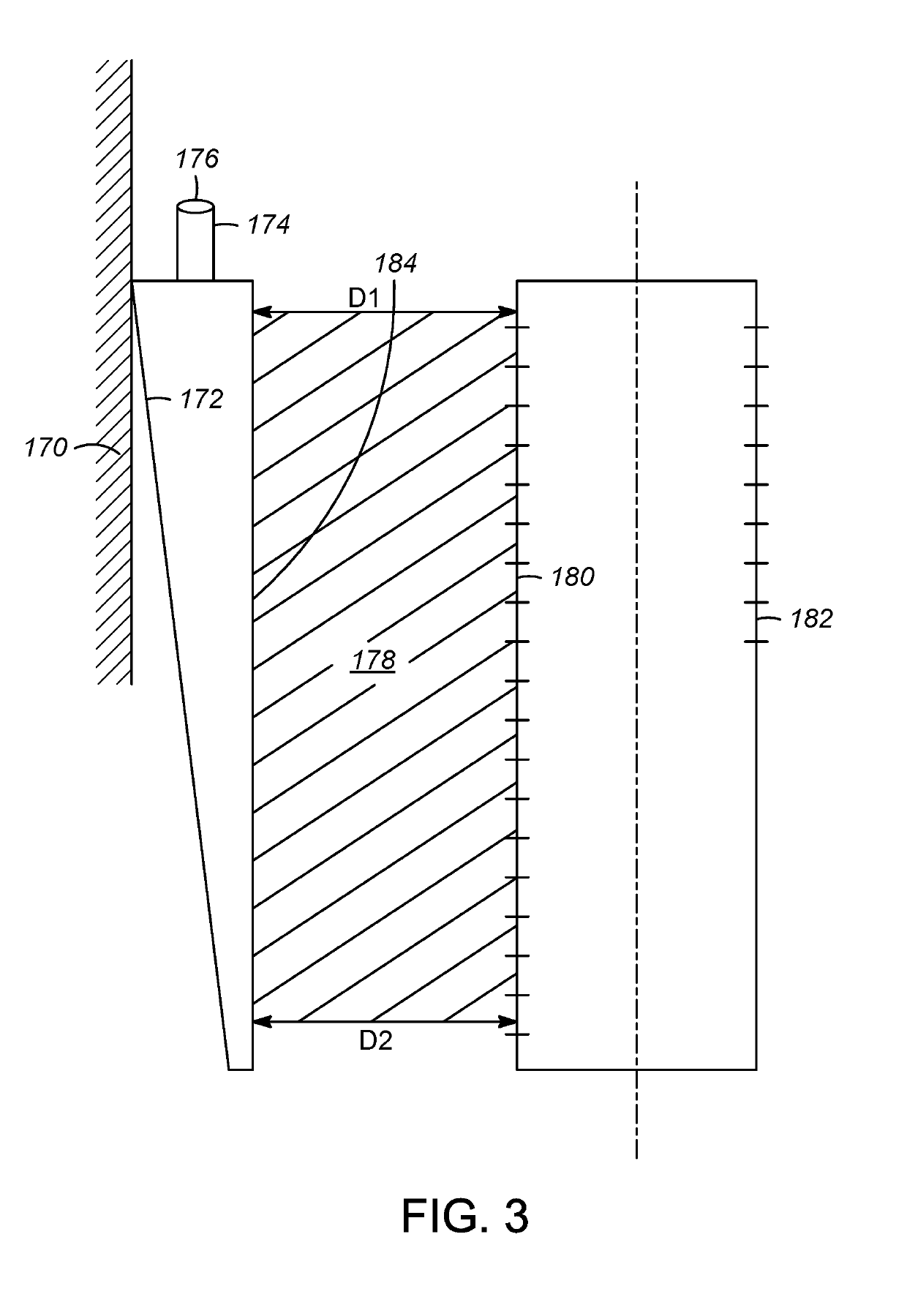
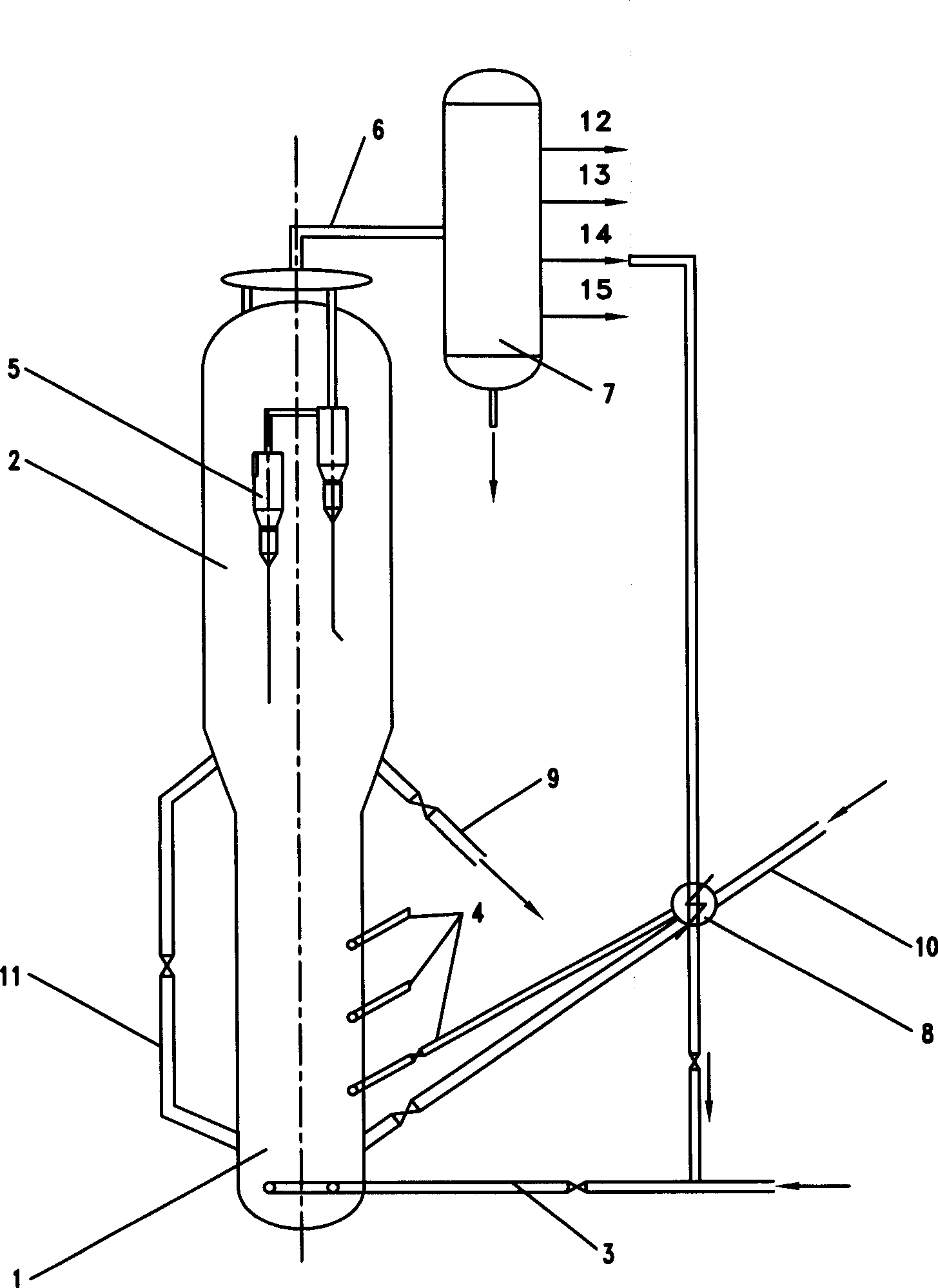
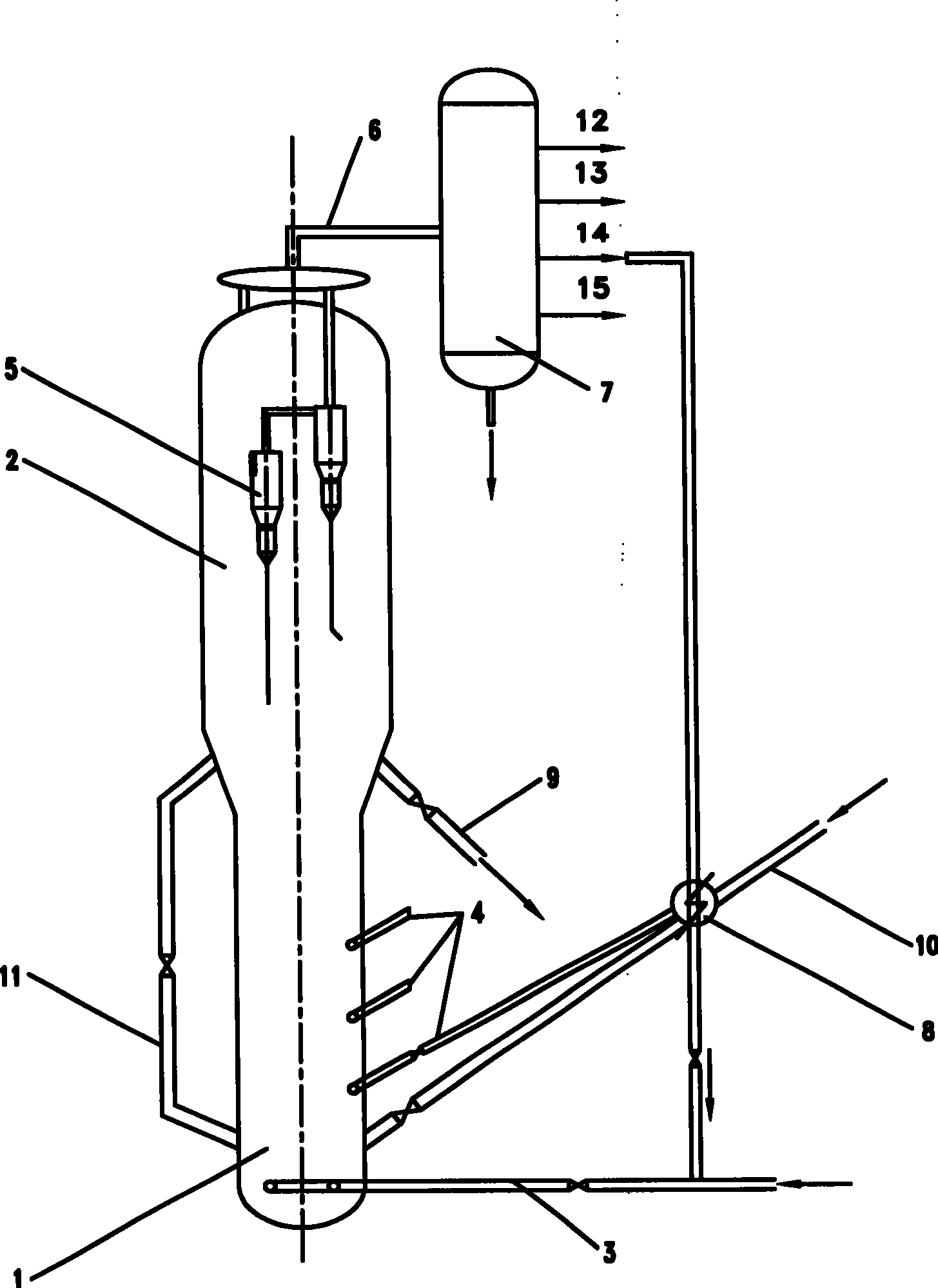
Tapered conduits for reactors
ActiveUS10384181B2Dispersed particle separationHydrocarbon by saturated bond conversionBiomedical engineeringAirflow
An apparatus is provided for directing a fluid in a radial reactor comprising: a vertically elongated conduit comprising a front face comprising a surface comprising apertures, two side faces, and a rear face and two ends, wherein an end of the front face and an end of the rear face are a distance D1 apart and wherein a second opposite end of the front face and a second corresponding end of the rear face are a distance D2 apart wherein D1 is greater than D2 and wherein a riser are connected to a top surface of said vertically elongated conduit to allow a gas stream to flow through the riser to the vertically elongated conduit.
Owner:UOP LLC
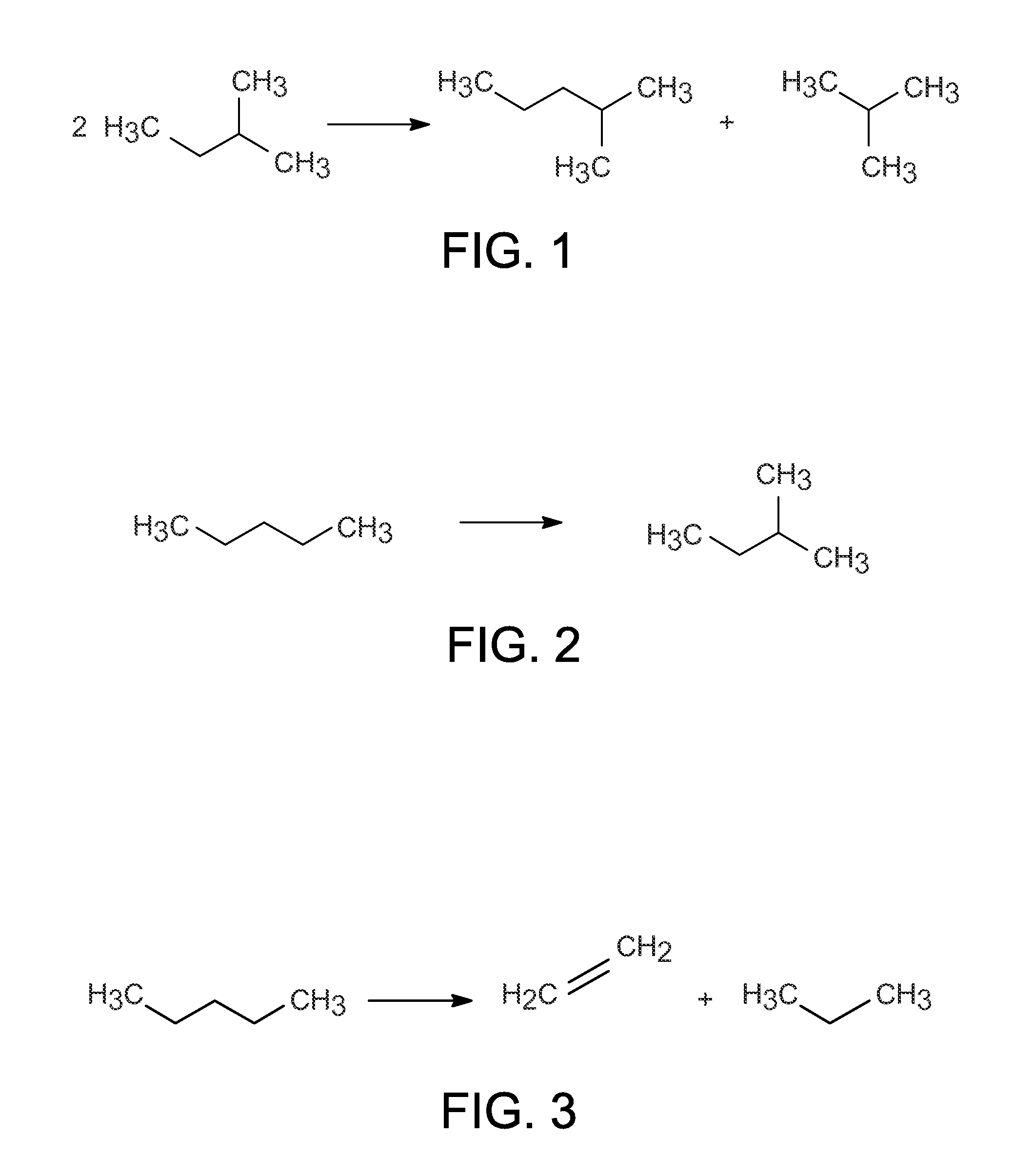
Disproportionation of hydrocarbons using solid acid catalysts
A hydrocarbon disproportionation process is described. The process includes contacting a hydrocarbon feed in a disproportionation reaction zone with a disproportionation catalyst in the presence of hydrogen and an added chloride promoter under disproportionation conditions including to obtain disproportionation products, wherein the disproportionation catalyst comprises a solid catalyst comprising a refractory inorganic oxide having a metal halide dispersed thereon.
Owner:UOP LLC
Catalytic isomerization of heptane using ionic liquids
Processes for the disproportionation and isomerization of a C7 hydrocarbon feed using a liquid catalyst comprising an ionic liquid and a carbocation promoter are described. The ionic liquid is unsupported, and the reactions occur at temperatures below about 200° C.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for increasing yield of ethylene and propylene
ActiveCN101239868BReduce partial pressureHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystDimethyl etherEthylene
The invention relates to a method for improving yield of ethylene and propylene, which solves the problem of low yield of ethylene and propylene during lower olefins preparing process from conversion of methanol and dimethyl ether. The invention uses at least one of methanol and dimethyl ether and C4 hydrocarbon as materials, the materials enter into a reaction region from a distributor at the bottom of a fluidization bed reactor or from at least a position axially separated along the reaction region, and contact and react with a catalyst to generate an effluent containing ethylene, propylene and C4 hydrocarbon, the effluent is separated to obtain ethylene, propylene and C4 hydrocarbon; wherein, the C4 hydrocarbon material is from fresh mixed C4 hydrocarbon or mixed C4 hydrocarbon obtained by separation or mixtures thereof. In this way, the invention solves the problem well, and is useful in industrial production of ethylene and propylene.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
High metal content molecular sieves and their manufacture
InactiveCN101952200AMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by saturated bond conversionMolecular sieveStructure type
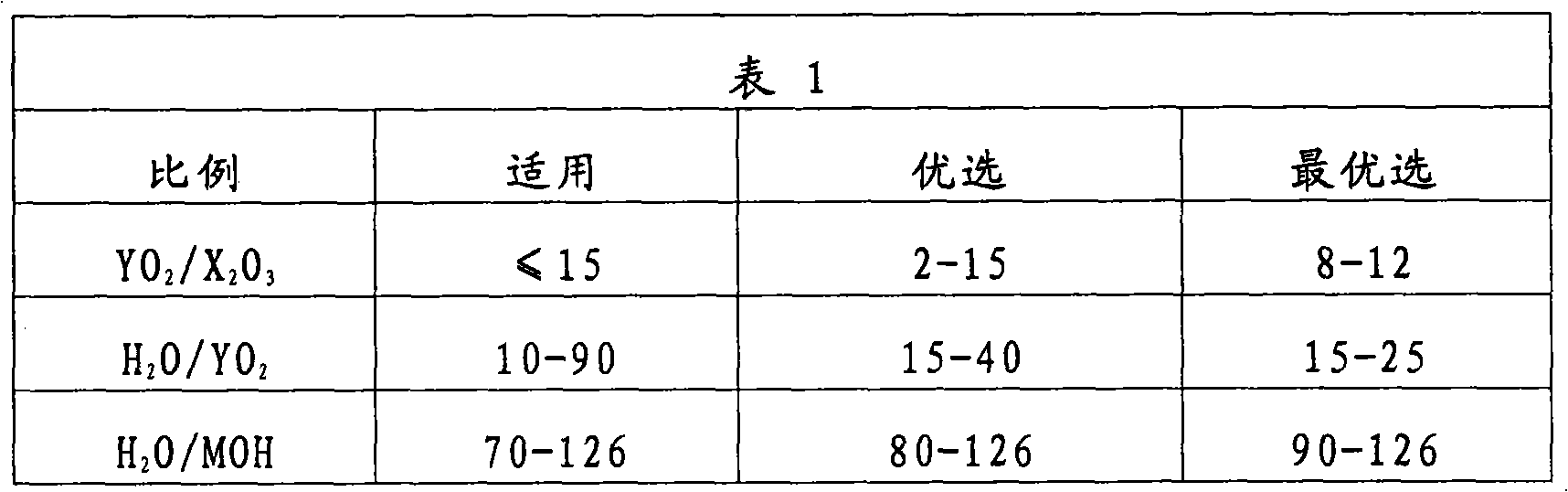
A process for manufacturing a synthetic porous crystalline molecular sieve requires an aqueous reaction mixture comprising a source of X2O3 (X is a trivalent element), a source of YO2 (Y is a tetravalent element) and a source of MOH (M is an alkali metal). The H2O / MOH molar ratio is within the range of 70 to 126 and the source Of X2O3 and YO2 is an amorphous material containing both X2O3 and YO2 and having YO2 / X2O3 molar ratio of 15 or less. The molecular sieve products are useful as catalysts and / or absorbents. Such molecular sieves having MFI structure type, TON structure type or the structure type of zeolite beta and a composition involving the molar relationship (n) YO2:X2O3 wherein n is from 2 to less than 15 are novel compositions of matter.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Catalytic reverse disproportionation of paraffins using ionic liquids
A reverse disproportionation reaction of two hydrocarbon feeds allows production of a reaction mixture containing products with intermediate carbon numbers. The amount of at least one of the products with intermediate carbon numbers is equal to or greater than the amount formed from disproportionation of the hydrocarbon alone. A reverse disproportionation reaction mixture is also described.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method of starting up a reaction system
ActiveUS7259287B2Hydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingMolecular sieveComputational chemistry
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Catalytic activation and alkylation of isopentane-enriched mixtures
ActiveUS10815438B2Increase productionReduce productionHydrocarbon by dehydrogenationCatalytic crackingAlkanePtru catalyst
The present disclosure relates generally to processes and systems for producing liquid transportation fuels by converting a feed stream that comprises both isopentane and n-pentane, and optionally, some C6+ hydrocarbons. Isopentane and smaller hydrocarbons are separated to form a first fraction while n-pentane and larger components of the feed stock form a second fraction. Each fraction is then catalytically-activated in a separate reaction zone with a separate catalyst, where the conditions maintained in each zone maximize the conversion of each fraction to olefins and aromatics, while minimizing the production of C1-C4 light paraffins. In certain embodiments, the first fraction is activated at a lower temperature than the second fraction. Certain embodiments additionally comprise mixing at least a portion of the two effluents and contacting with an alkylation catalyst to provide enhanced yields of mono-alkylated aromatics that are suitable for use as a blend component of liquid transportation fuels or other value-added chemical products.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Process for increasing the yield of an isomerization zone fractionation
ActiveUS9302956B2Speed up the conversion processIncrease productionHydrocarbon by isomerisationDistillation purification/separationIsomerizationFractionation
A process for increasing a yield of an isomerization zone by removing at least a portion of the C6 cyclic hydrocarbons from a stream prior to it being passed into the isomerization zone. Additionally, disproportionation reactions occur producing valuable C3 hydrocarbons and C4 hydrocarbons. Also, a higher ring opening conversion of C5 cyclic hydrocarbons is observed.
Owner:UOP LLC
Popular searches
Hydrocarbon by polyaryl split-off Hydrocarbon by hydrogenation Catalytic naphtha reforming Treatment with hydrotreatment processes Hydrocarbon from saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon addition Hydrocarbon by polyarylsubstituted aliphatic compound split-off Refining to eliminate hetero atoms Hydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon addition Hydrocarbon oil cracking Hydrocarbons
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com