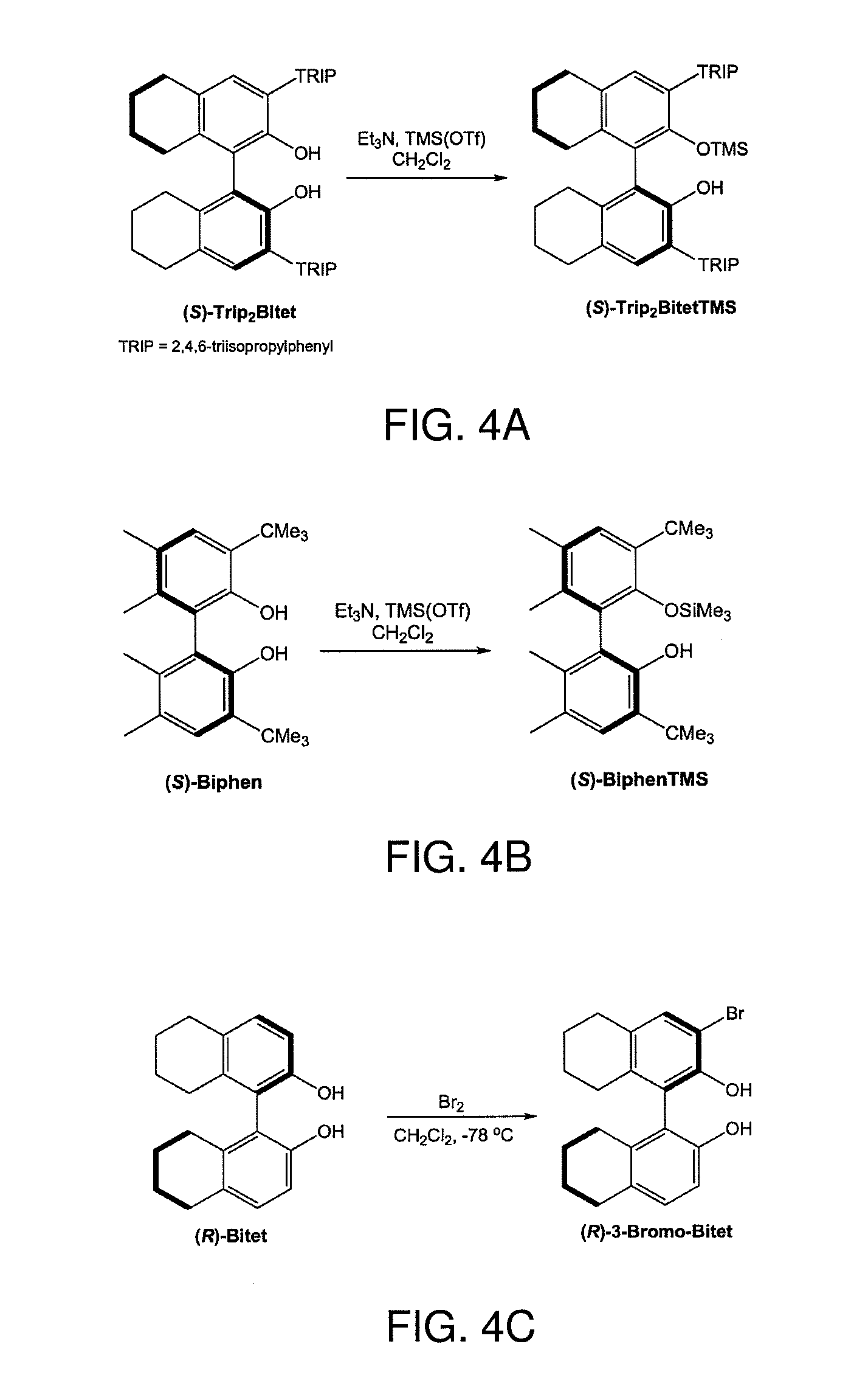
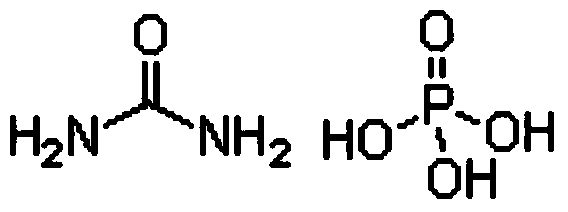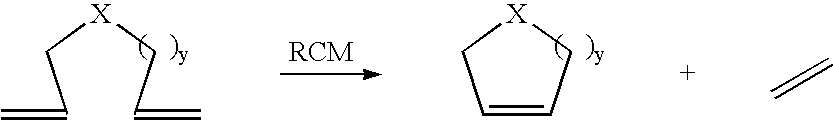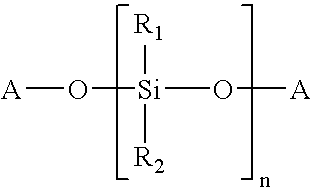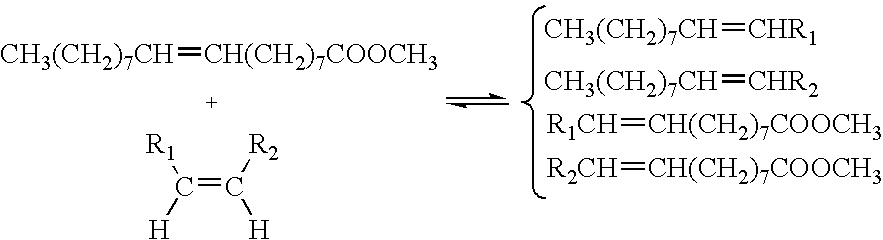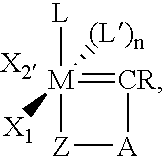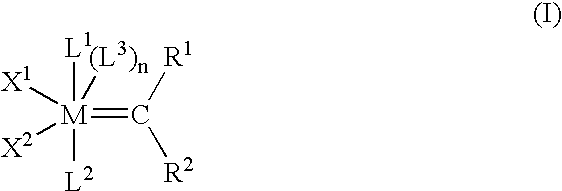Patents
Literature
571 results about "Salt metathesis reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
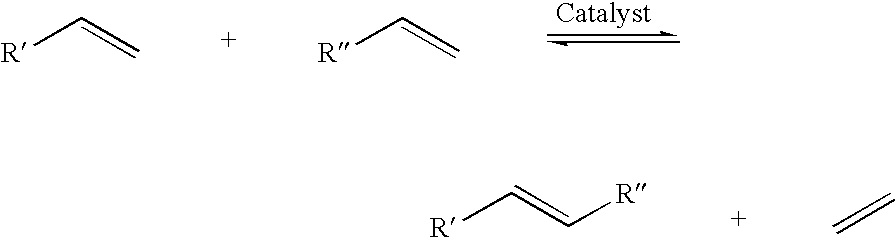
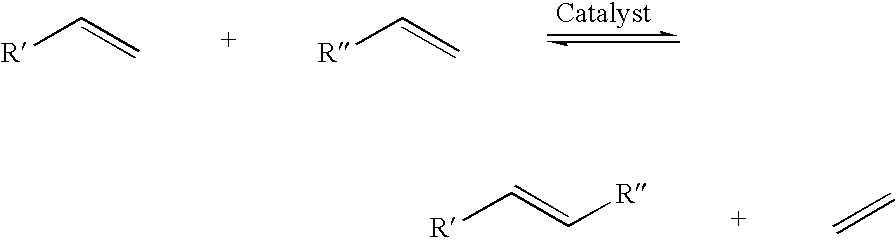
A salt metathesis reaction, sometimes called a double replacement reaction, double displacement reaction, is a chemical process involving the exchange of bonds between two non-reacting chemical species which results in the creation of products with similar or identical bonding affiliations.
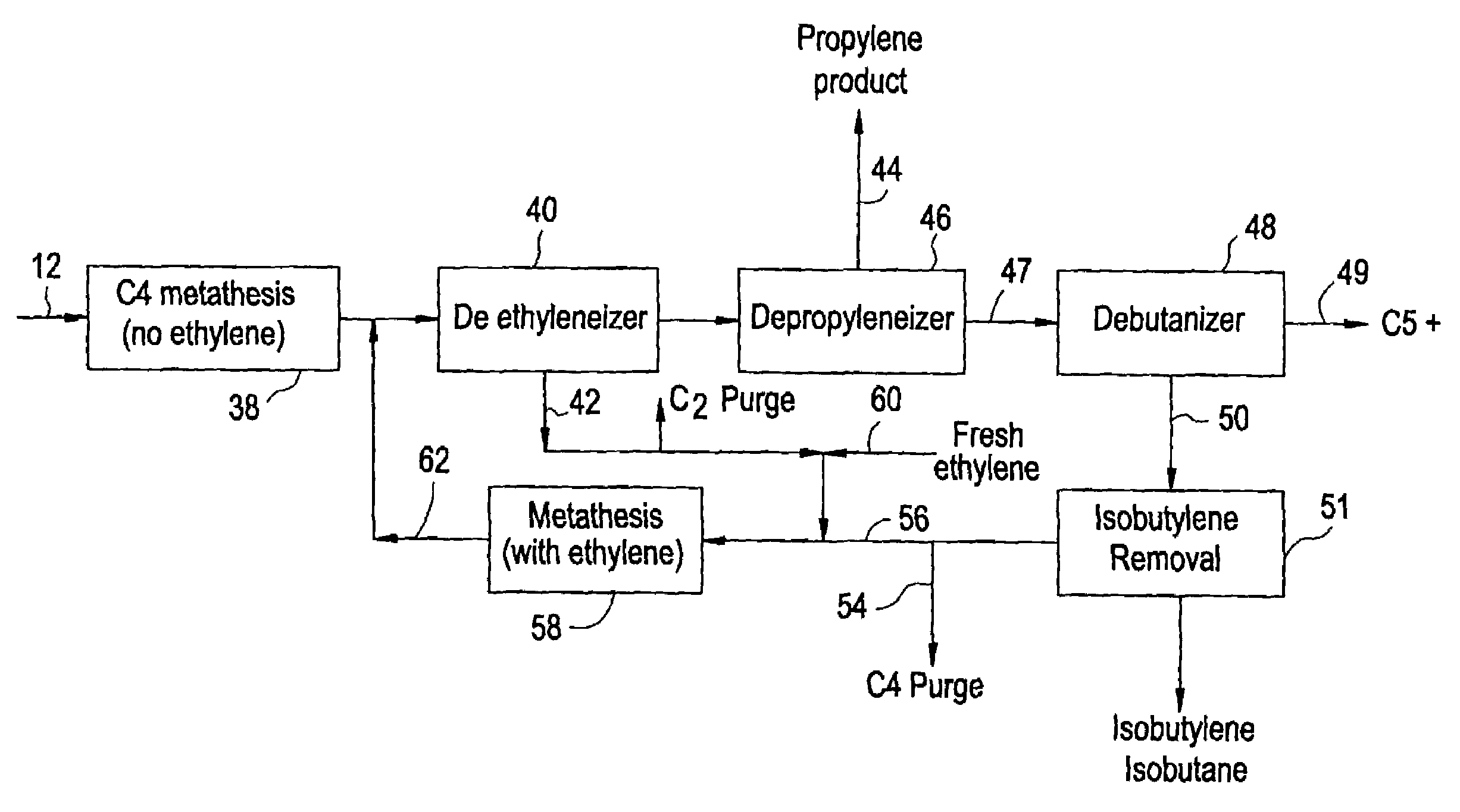
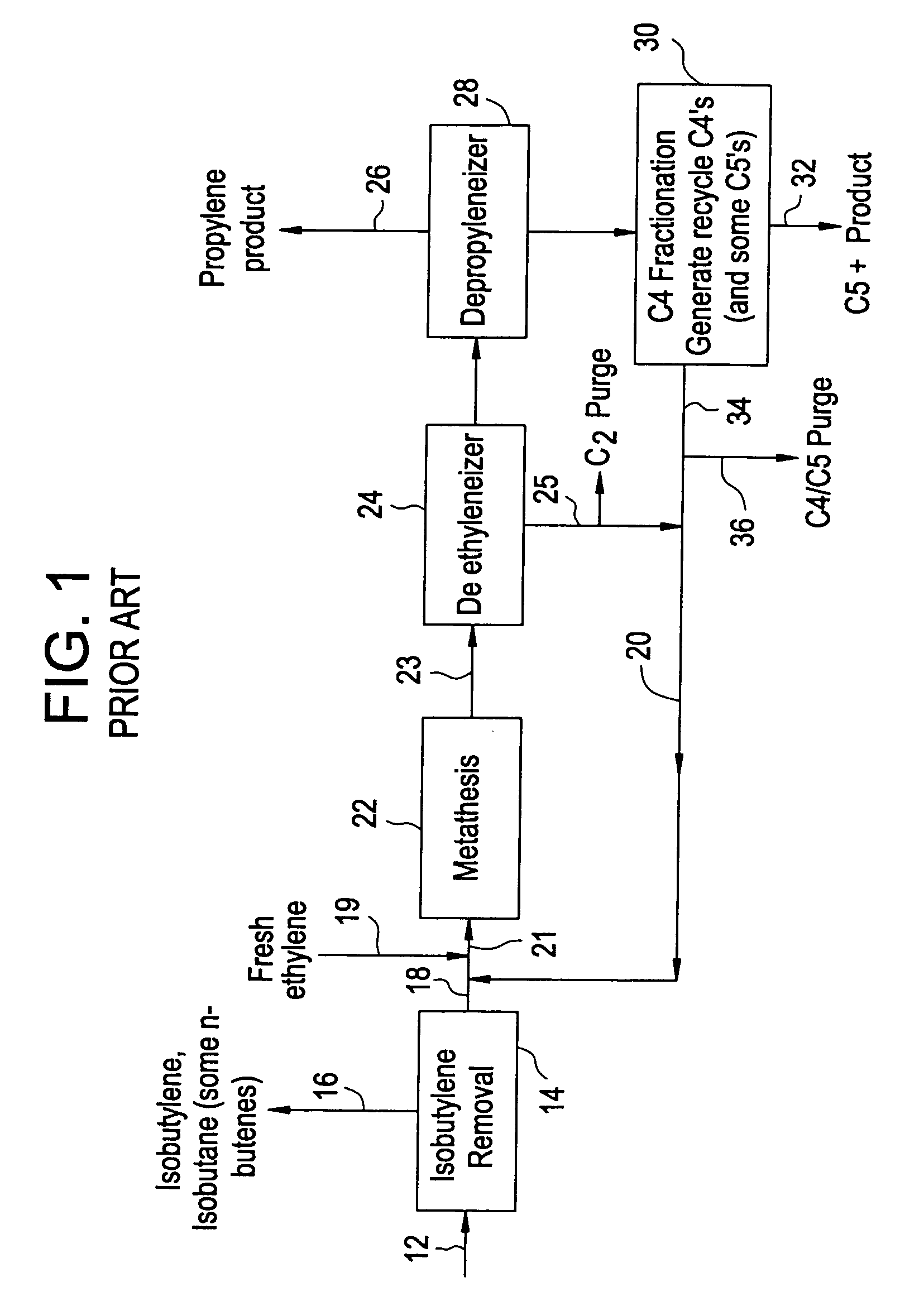
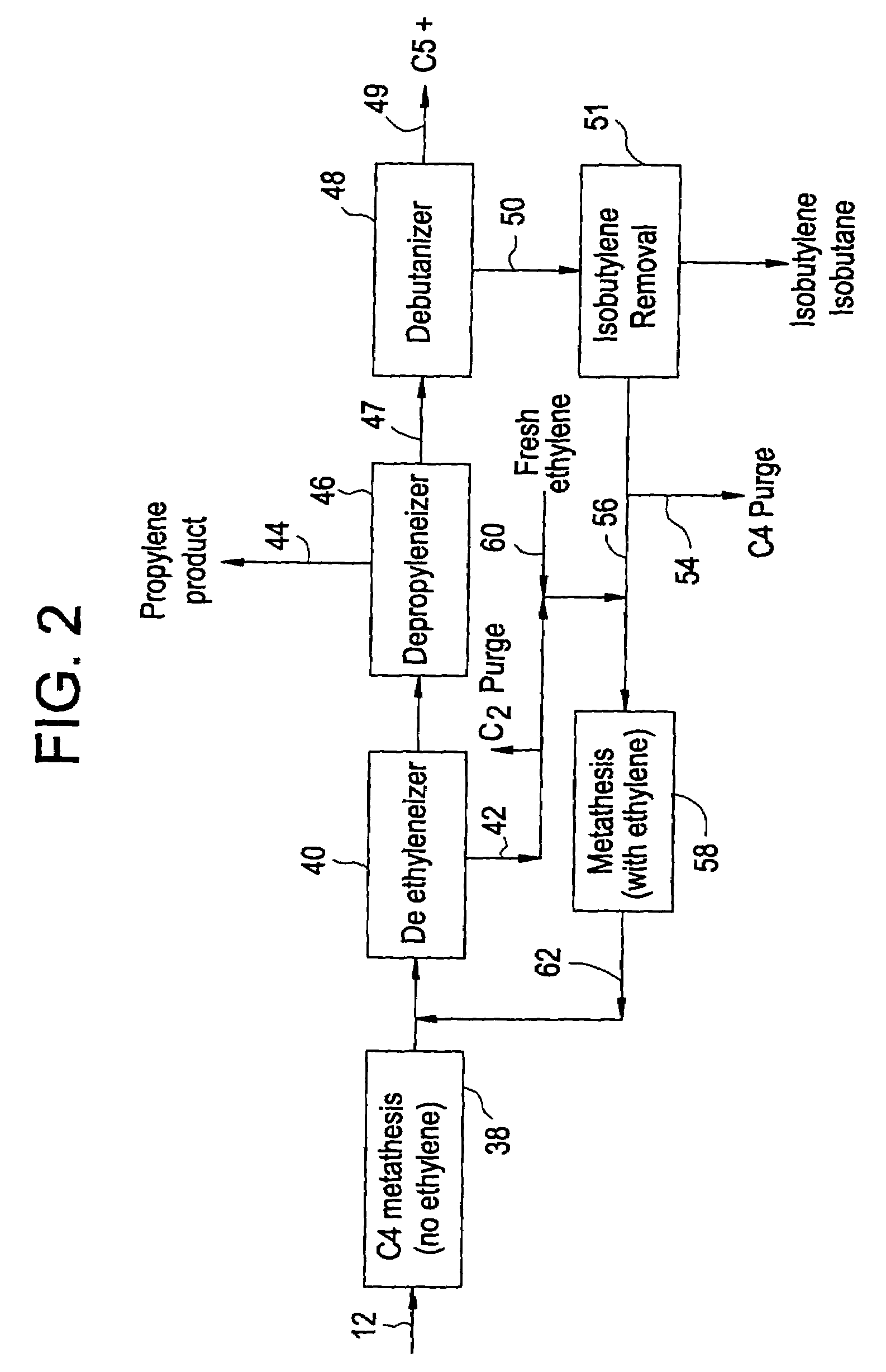
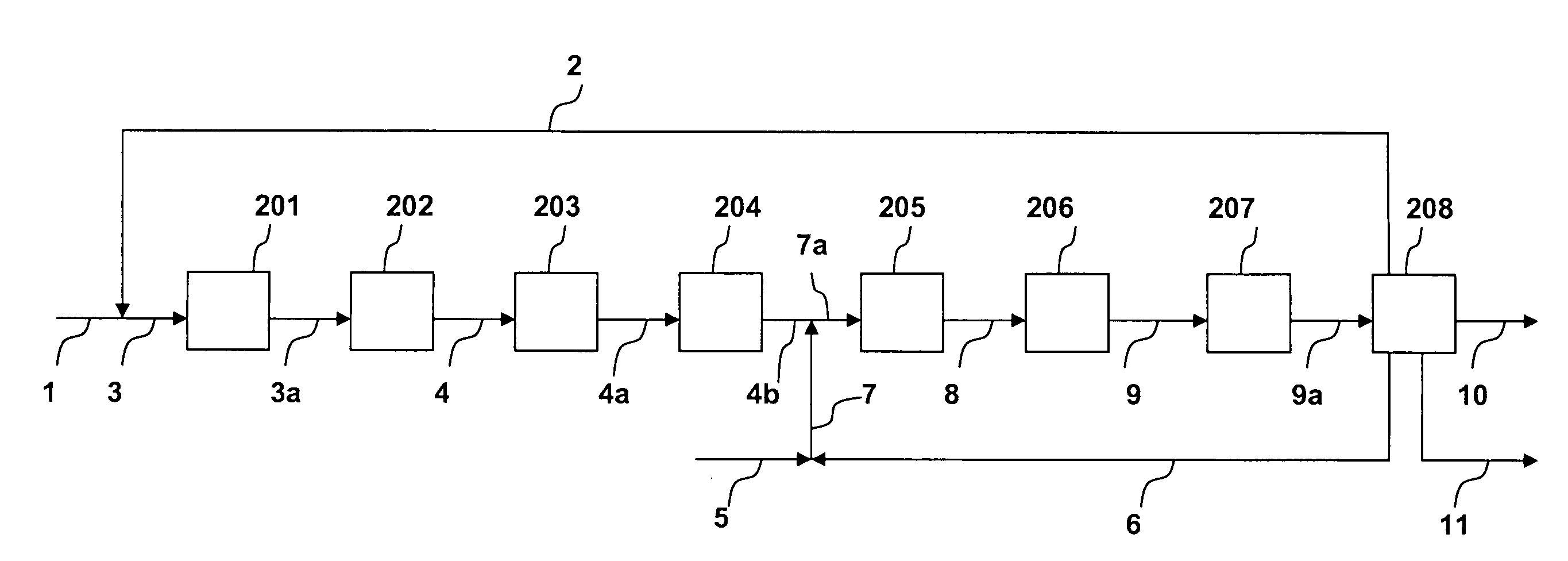
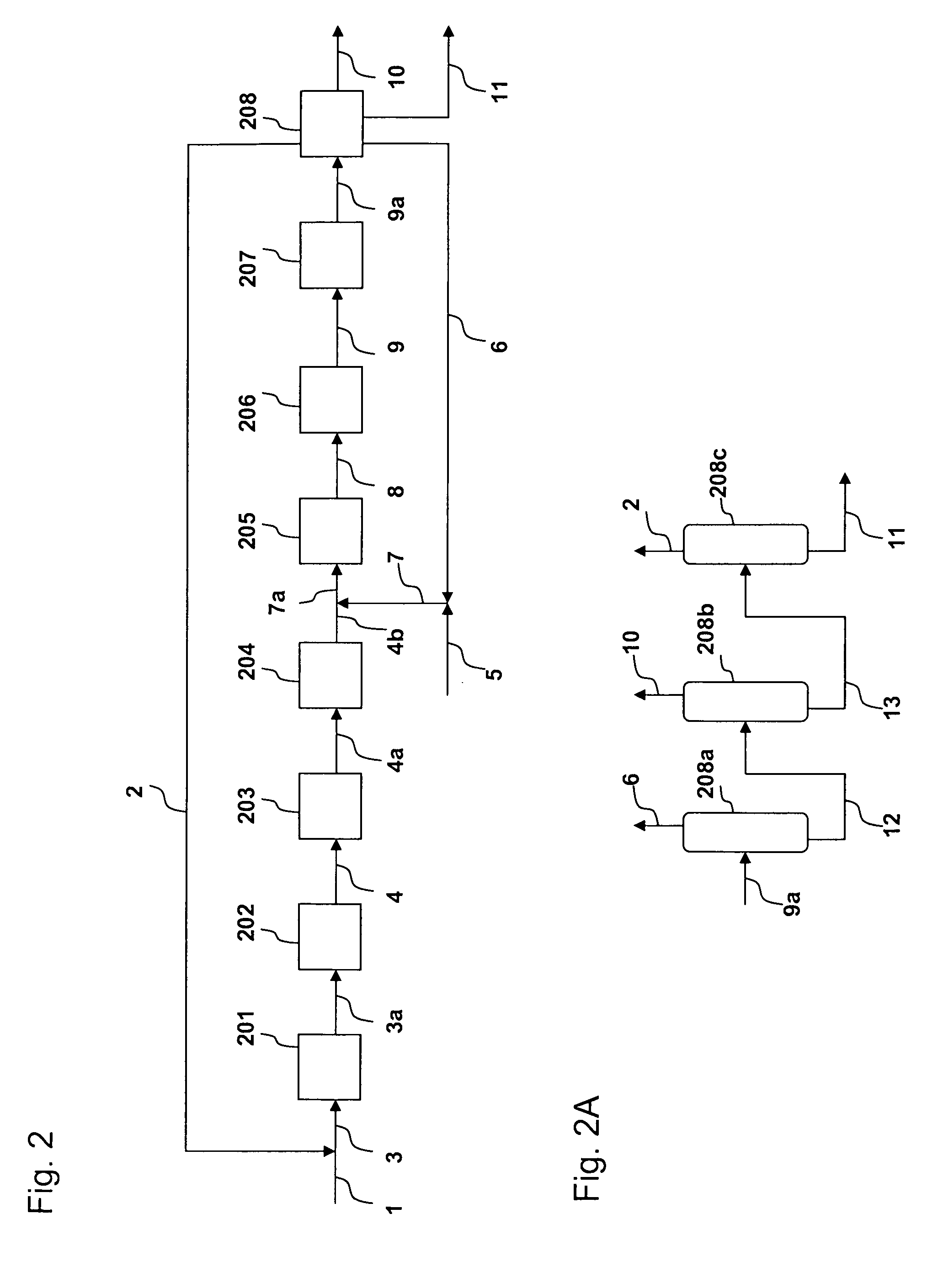
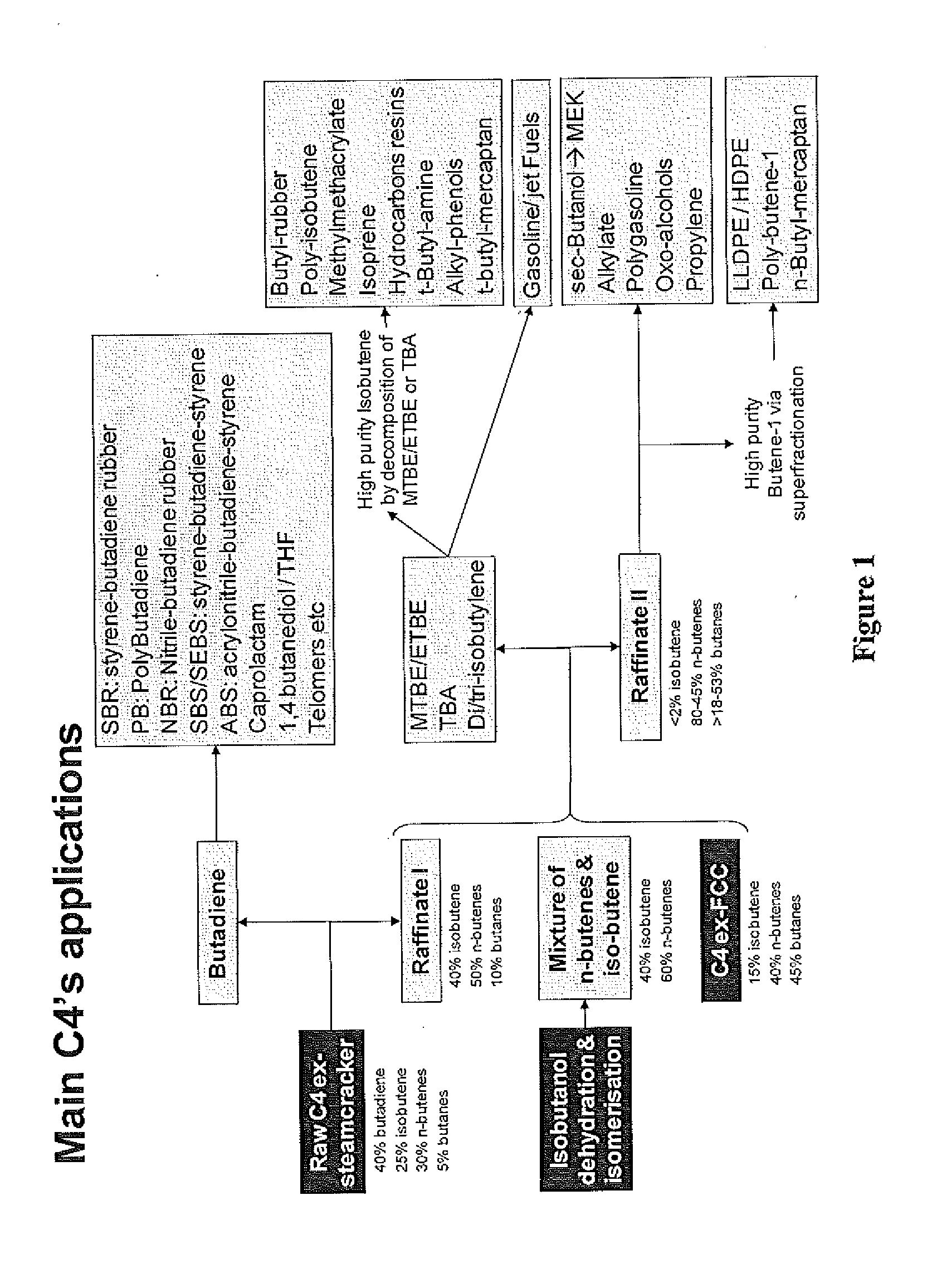
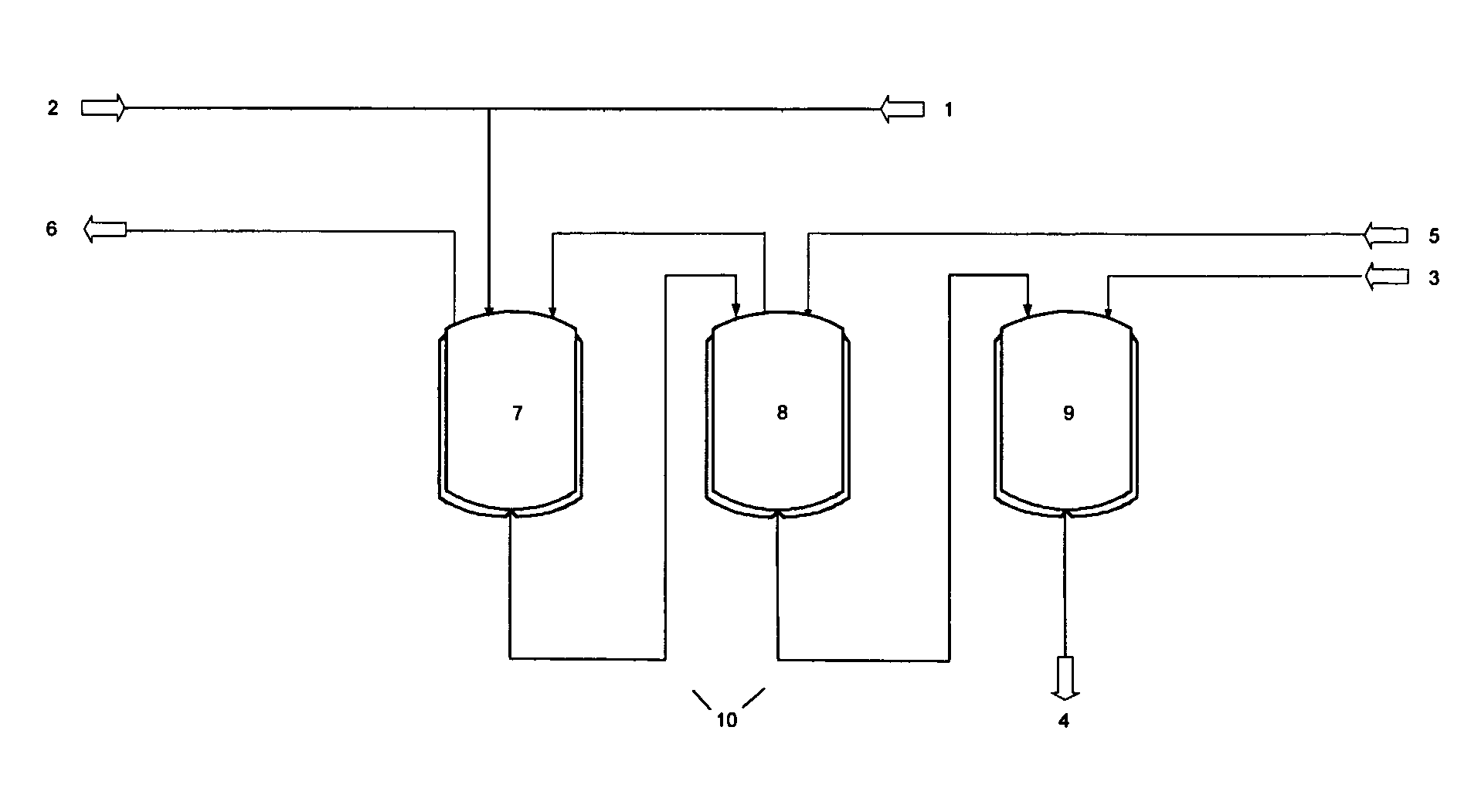
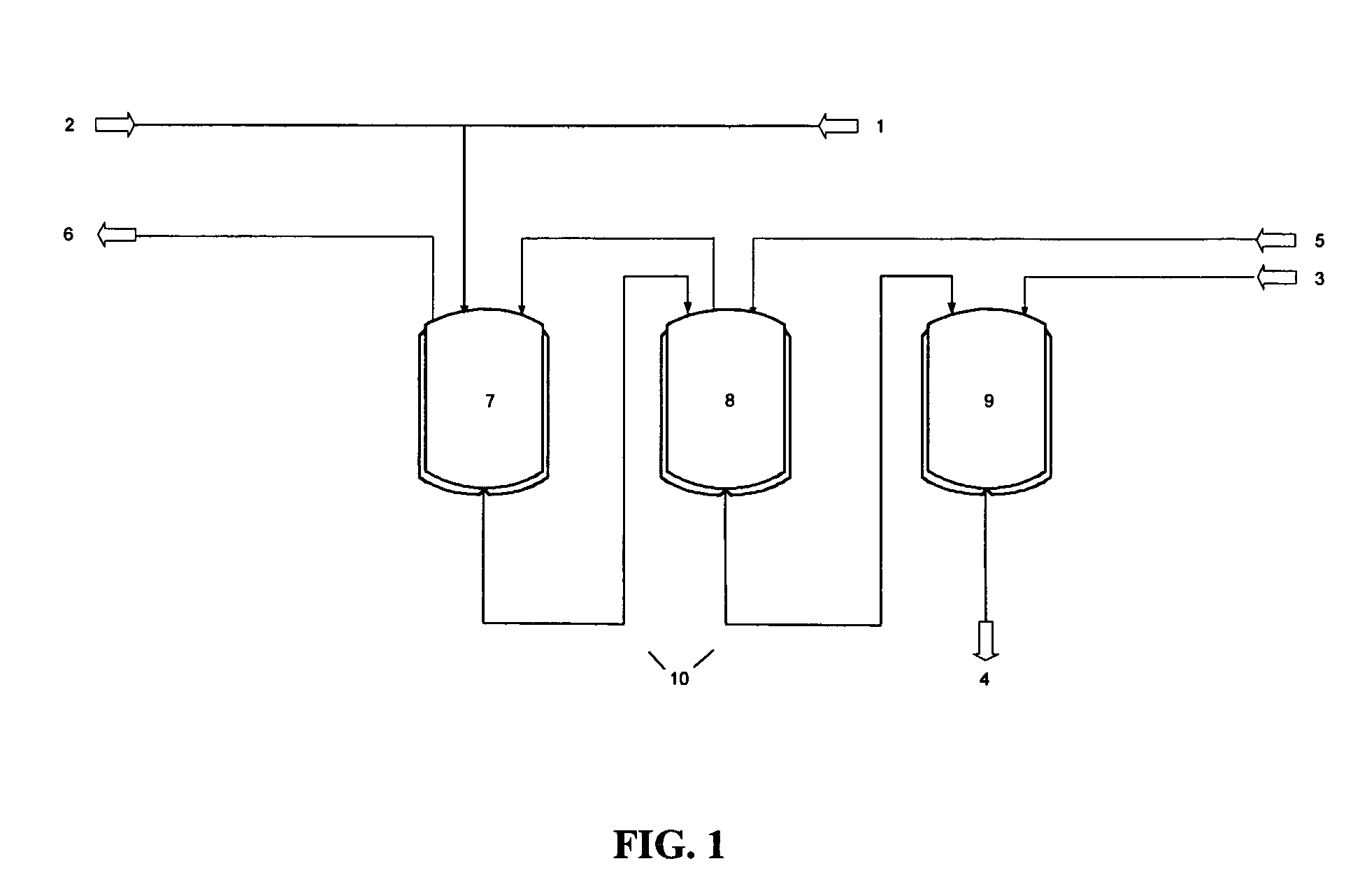
Processing C4 olefin streams for the maximum production of propylene
ActiveUS7214841B2Maximize productionImprove the level ofChemical industryCatalystsCatalytic distillation2-Butene
In order to maximize the production of propylene when the external supply of ethylene is limited, the C4 cut from a hydrocarbon cracking process is first subjected to autometathesis prior to any isobutylene removal and without any ethylene addition. This favors the reactions which produce propylene and pentenes. The ethylene and propylene produced are then removed leaving a stream of the C4's and heavier components. The C5 and heavier components are then removed leaving a mixture of 1-butene, 2-butene, isobutylene, and iso- and normal butanes. The isobutylene is next removed preferably by a catalytic distillation hydroisomerization de-isobutyleneizer. The isobutylene-free C4 stream is then mixed with the product ethylene removed from the autometathesis product together with any fresh external ethylene needed and subjected to conventional metathesis producing additional propylene.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Chelating carbene ligand precursors and their use in the synthesis of metathesis catalysts
InactiveUS7026495B1High yieldImprove isolationRuthenium organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHigh concentrationCarbene
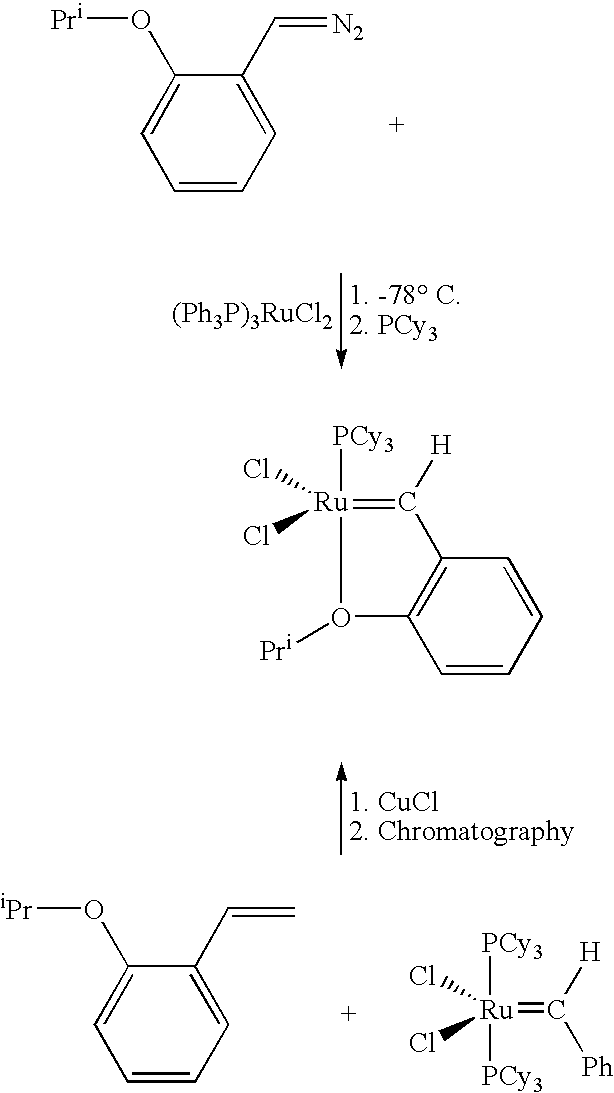
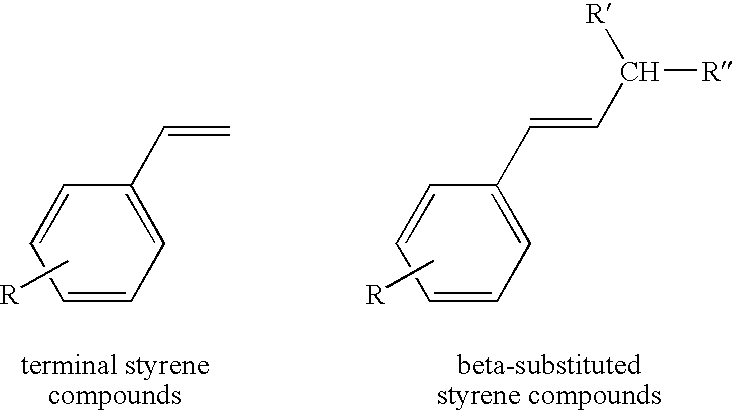
Chelating ligand precursors for the preparation of olefin metathesis catalysts are disclosed. The resulting catalysts are air stable monomeric species capable of promoting various metathesis reactions efficiently, which can be recovered from the reaction mixture and reused. Internal olefin compounds, specifically beta-substituted styrenes, are used as ligand precursors. Compared to terminal olefin compounds such as unsubstituted styrenes, the beta-substituted styrenes are easier and less costly to prepare, and more stable since they are less prone to spontaneous polymerization. Methods of preparing chelating-carbene metathesis catalysts without the use of CuCl are disclosed. This eliminates the need for CuCl by replacing it with organic acids, mineral acids, mild oxidants or even water, resulting in high yields of Hoveyda-type metathesis catalysts. The invention provides an efficient method for preparing chelating-carbene metathesis catalysts by reacting a suitable ruthenium complex in high concentrations of the ligand precursors followed by crystallization from an organic solvent.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Use of a phosphorus containing ligand and a cyclic organic ligand in a transition metal compound
ActiveUS7671224B2Ruthenium organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemical compoundDouble bond
According to the present invention there is provided a compound in the form of a transition metal compound including a transition metal, a phosphorus containing ligand, and a cyclic organic ligand. The phosphorus containing ligand is a heterocyclic organic compound with a ligating phosphorus atom which ligates with the transition metal, and which ligating phosphorus atom is an atom in the heterocyclic ring structure of the heterocyclic organic compound. The cyclic organic ligand is a cyclic organic compound with a ligating carbon atom in the cyclic ring structure of the cyclic organic compound which ligates with the transition metal by means of a double bound. The invention also relates to a method preparing such a compound and a metathesis reaction wherein such a compound is used as a catalyst.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
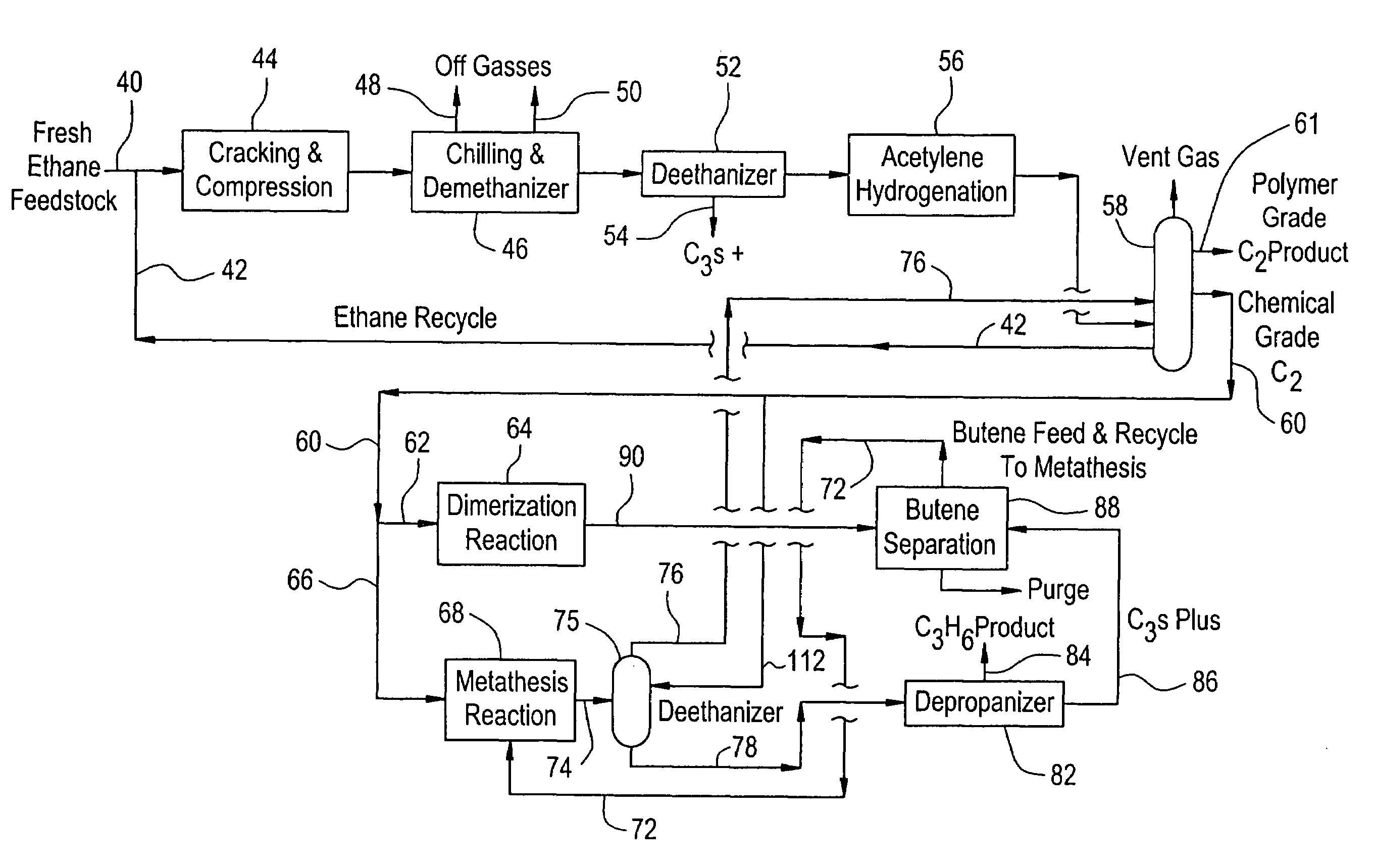
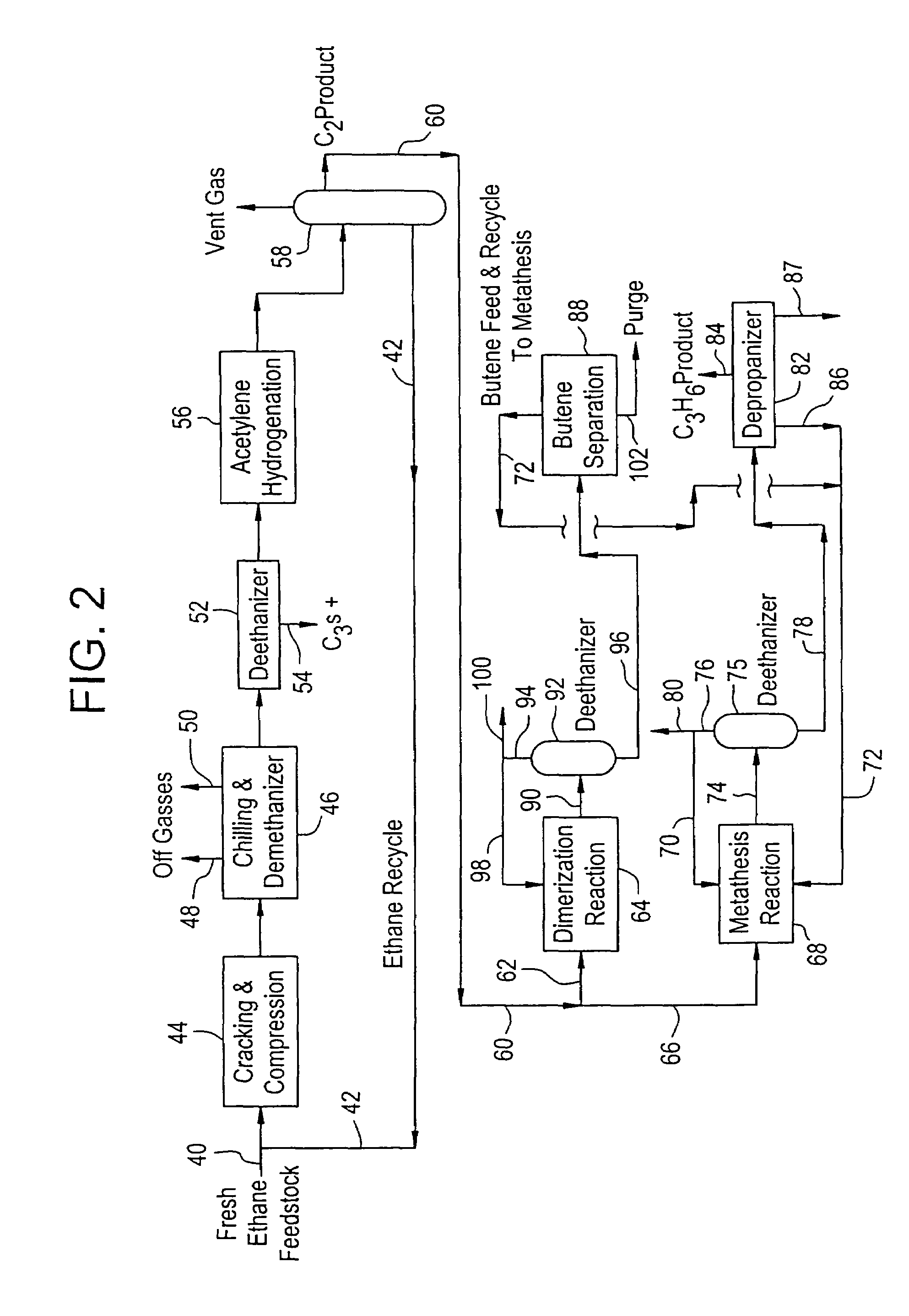
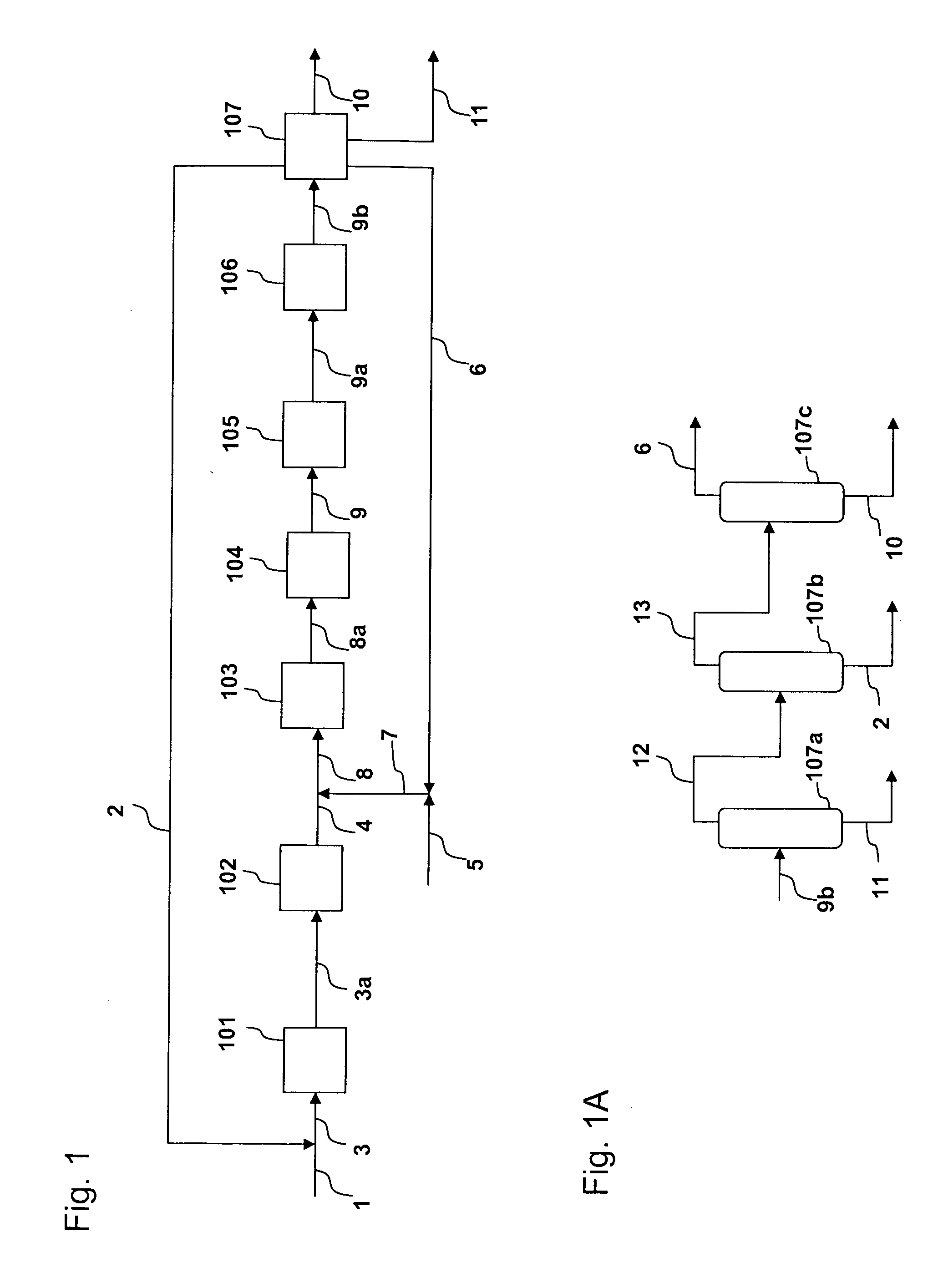
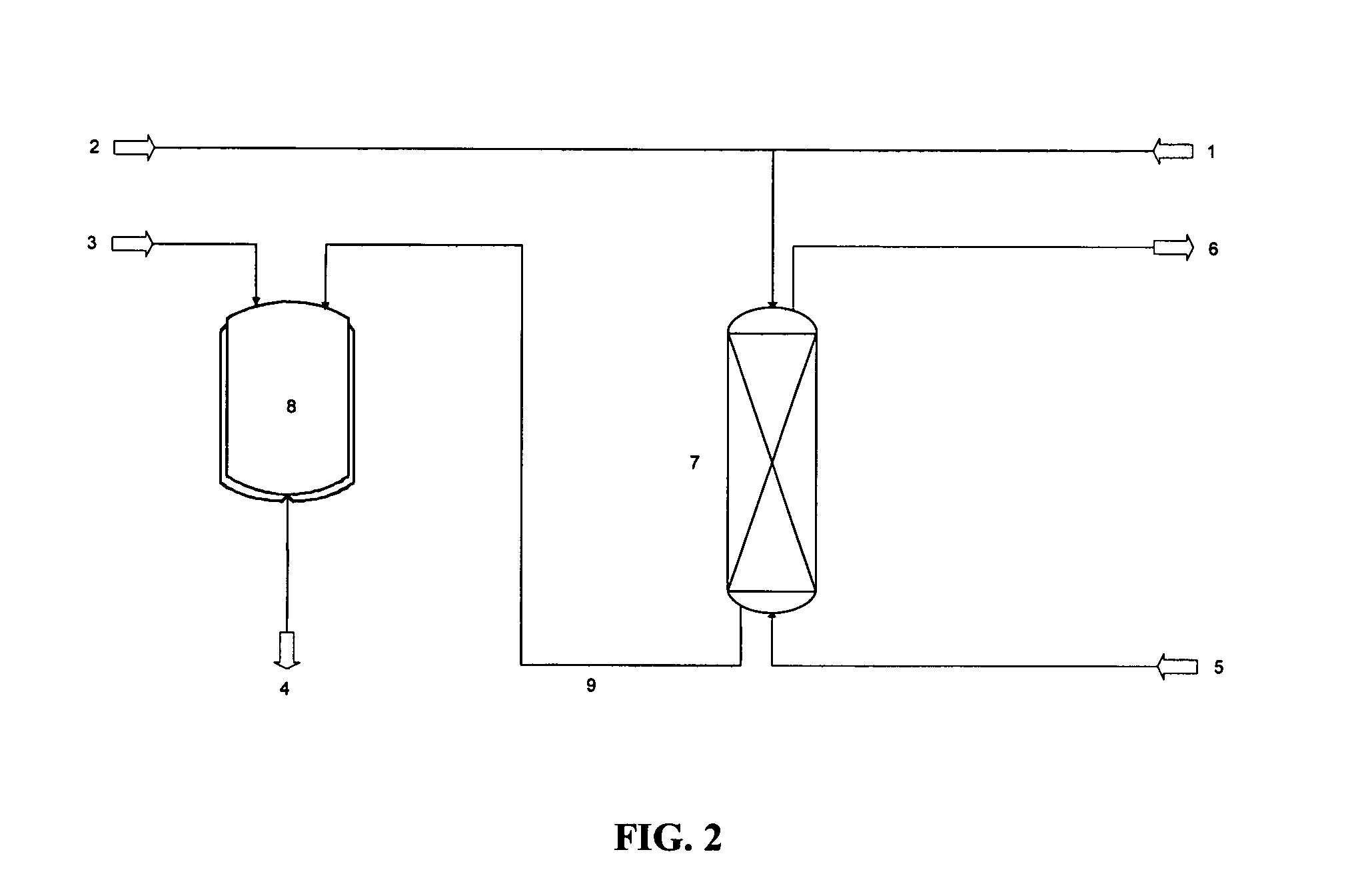
Production of propylene from steam cracking of hydrocarbons, particularly ethane
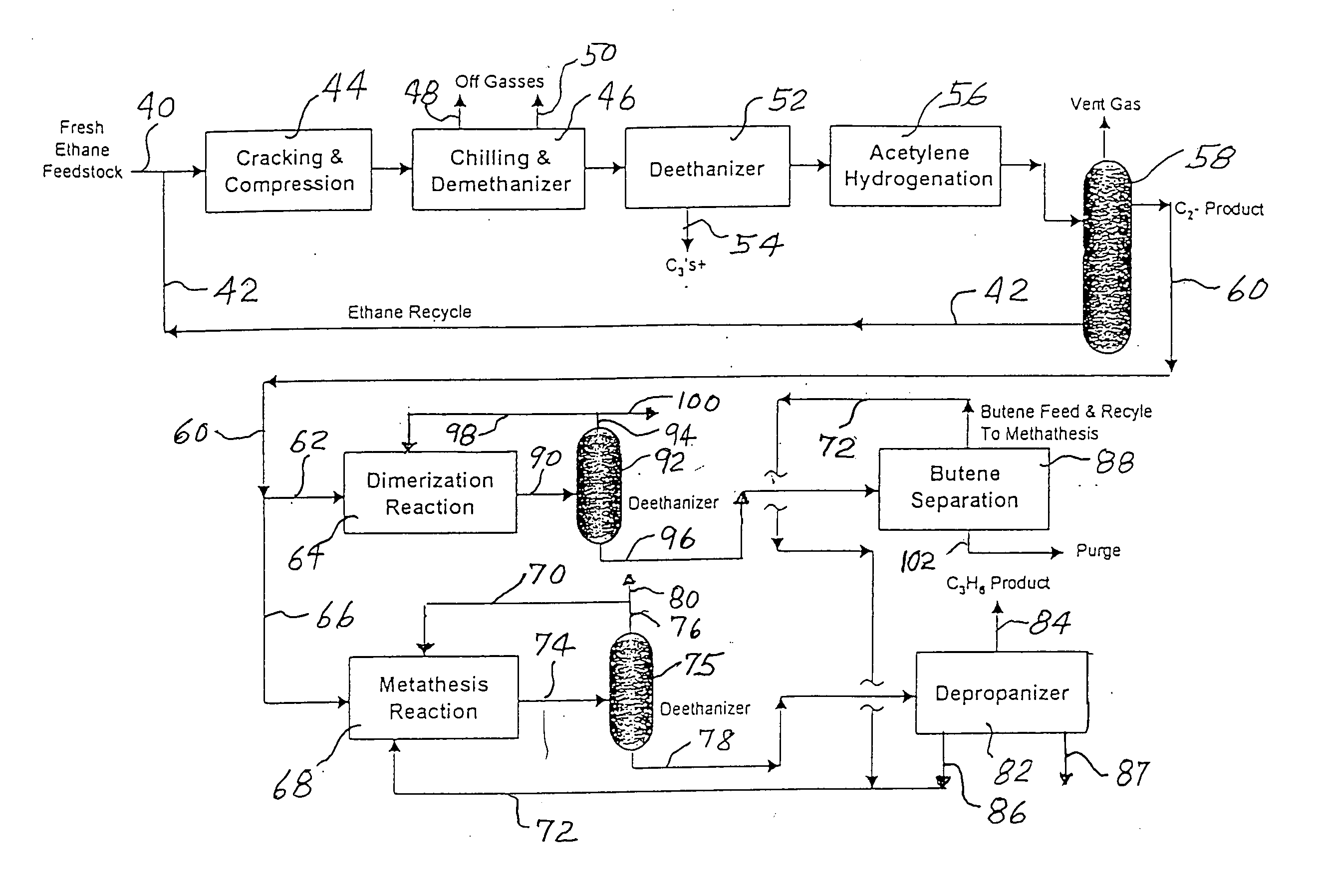
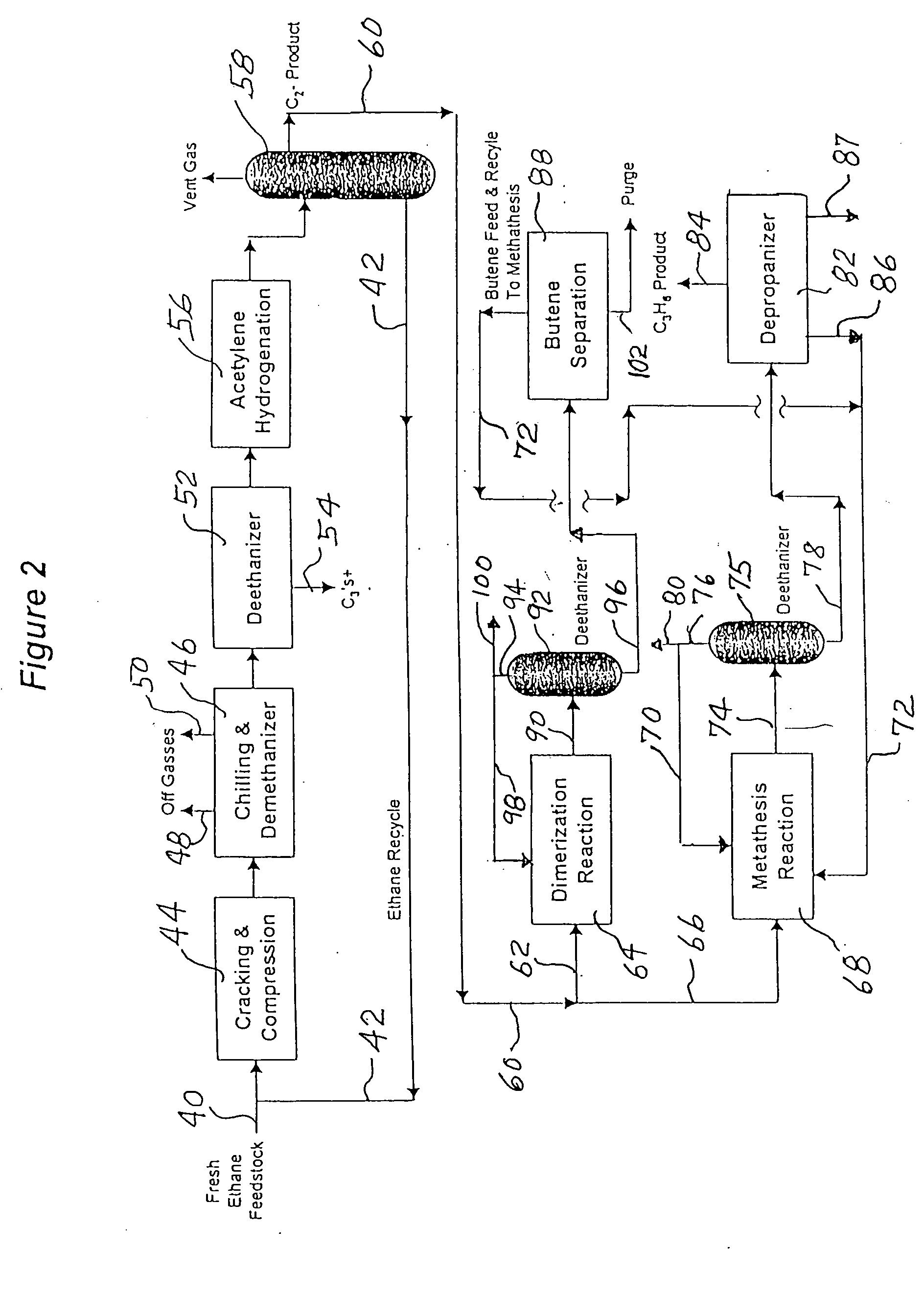
ActiveUS7223895B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionButenePolymer science
An ethane or other hydrocarbon feedstock is steam cracked to produce an ethylene stream which is processed in an ethylene plant recovery section to separate an ethane recycle and a polymer grade or chemical grade ethylene product stream. A portion of the ethylene product stream may then be reacted by dimerization to produce a butene stream. These formed butenes and / or butenes recovered from other sources and another portion of the ethylene product stream are reacted by metathesis to produce a propylene stream which is deethanized and separated from heavier hydrocarbons to produce the propylene product. The butene product stream may also be deethanized and is separated from heavier hydrocarbons. The overhead from the metathesis section deethanizer may be recycled to the ethylene plant recovery section. The reflux for the metathesis section deethanizer may be generated from the overhead or may be a portion of the ethylene product stream.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Olefin Functionalization By Metathesis Reaction
This invention relates to a process to functionalize propylene co-oligomer comprising contacting an alkene metathesis catalyst with a heteroatom containing alkene, and a propylene a co-oligomer having an Mn of 300 to 30,000 g / mol comprising 10 to 90 mol % propylene and 10 to 90 mol % of ethylene, wherein the oligomer has at least X % allyl chain ends, where: 1) X=(−0.94 (mol % ethylene incorporated)+100), when 10 to 60 mol % ethylene is present in the co-oligomer, and 2) X=45, when greater than 60 and less than 70 mol % ethylene is present in the co-oligomer, and 3) X=(1.83*(mol % ethylene incorporated)−83), when 70 to 90 mol % ethylene is present in the co-oligomer. This invention also relates to a process to functionalize propylene homo-oligomer comprising contacting an alkene metathesis catalyst with a heteroatom containing alkene, and a propylene homo-oligomer, comprising propylene, wherein the oligomer has: at least 93% allyl chain ends, an Mn of about 500 to about 20,000 g / mol, an isobutyl chain end to allylic vinyl group ratio of 0.8:1 to 1.2:1.0, and less than 100 ppm aluminum.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
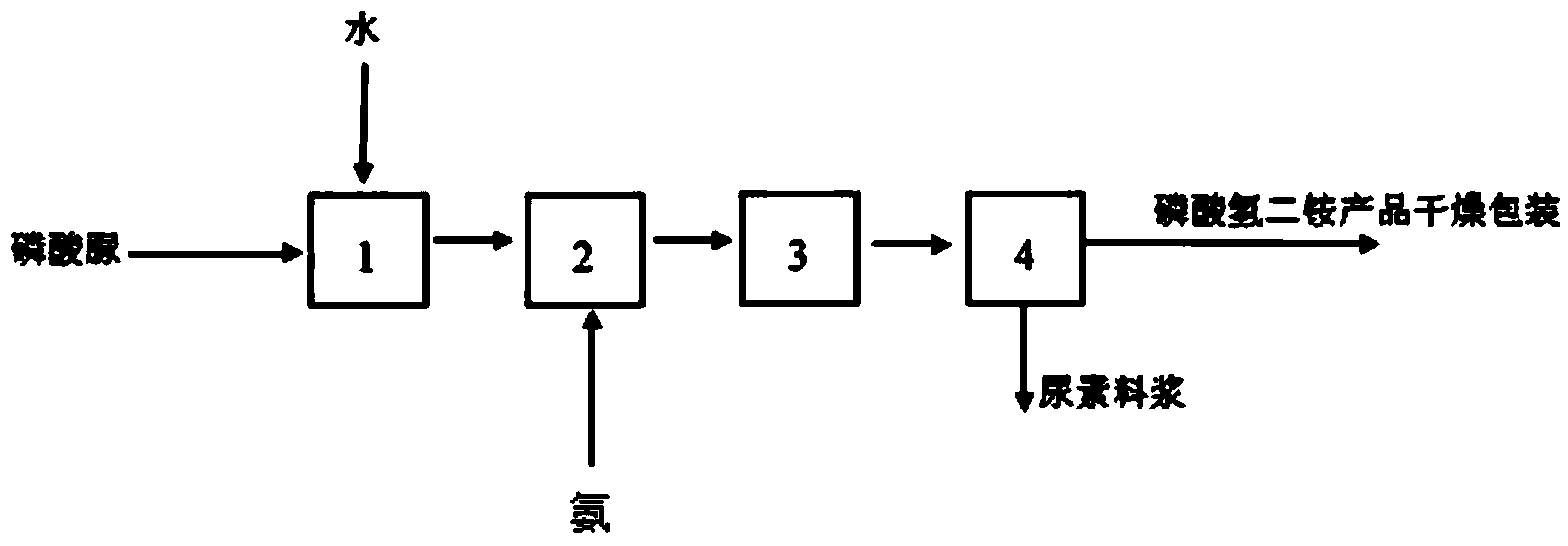
Production method for monoammonium phosphate
InactiveCN104016323AReduce energy consumptionReduce manufacturing costPhosphatesWater insolubleDecomposition
The invention relates to the technical field of chemical engineering, and particularly relates to a production method for monoammonium phosphate. A monoammonium phosphate product is prepared by directly subjecting high pure urea phosphate and ammonia to a double decomposition reaction and reacting for 20-60 min with stirring by controlling a reaction temperature at 40-80 DEG C and a pH value at a reaction endpoint being 4.2-4.6, and through the steps of cooling for crystallization; separating by centrifugation and drying. Measurements of physical and chemical indexes of the produced product show that the physical and chemical indexes of the produced monoammonium phosphate product meet an industrial first level standard. Specifically, the total nutrient content of monoammonium phosphate is higher than 73%; the content of total nitrogen is 12.01-12.23%; the content of phosphorus pentoxide is 61.05-61.25%; the content of moisture is 0.35-0.52%; a pH value is 4.2-4.6; the content of water insoluble materials is 0.090-0.096%; and the content of fluoride is 0.15-0.19%.
Owner:GUIYANG KAILIN FERTILIZER CO LTD
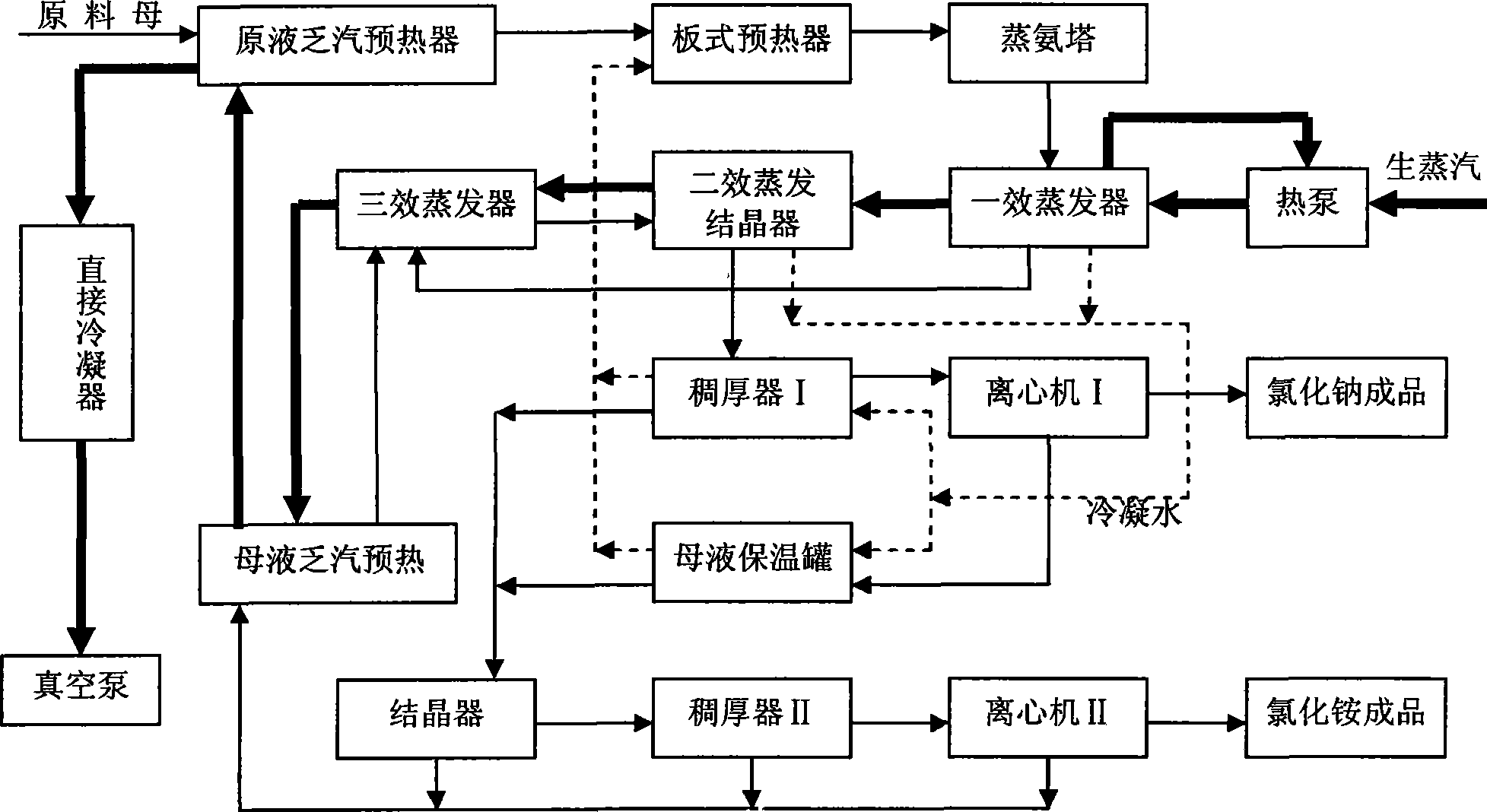
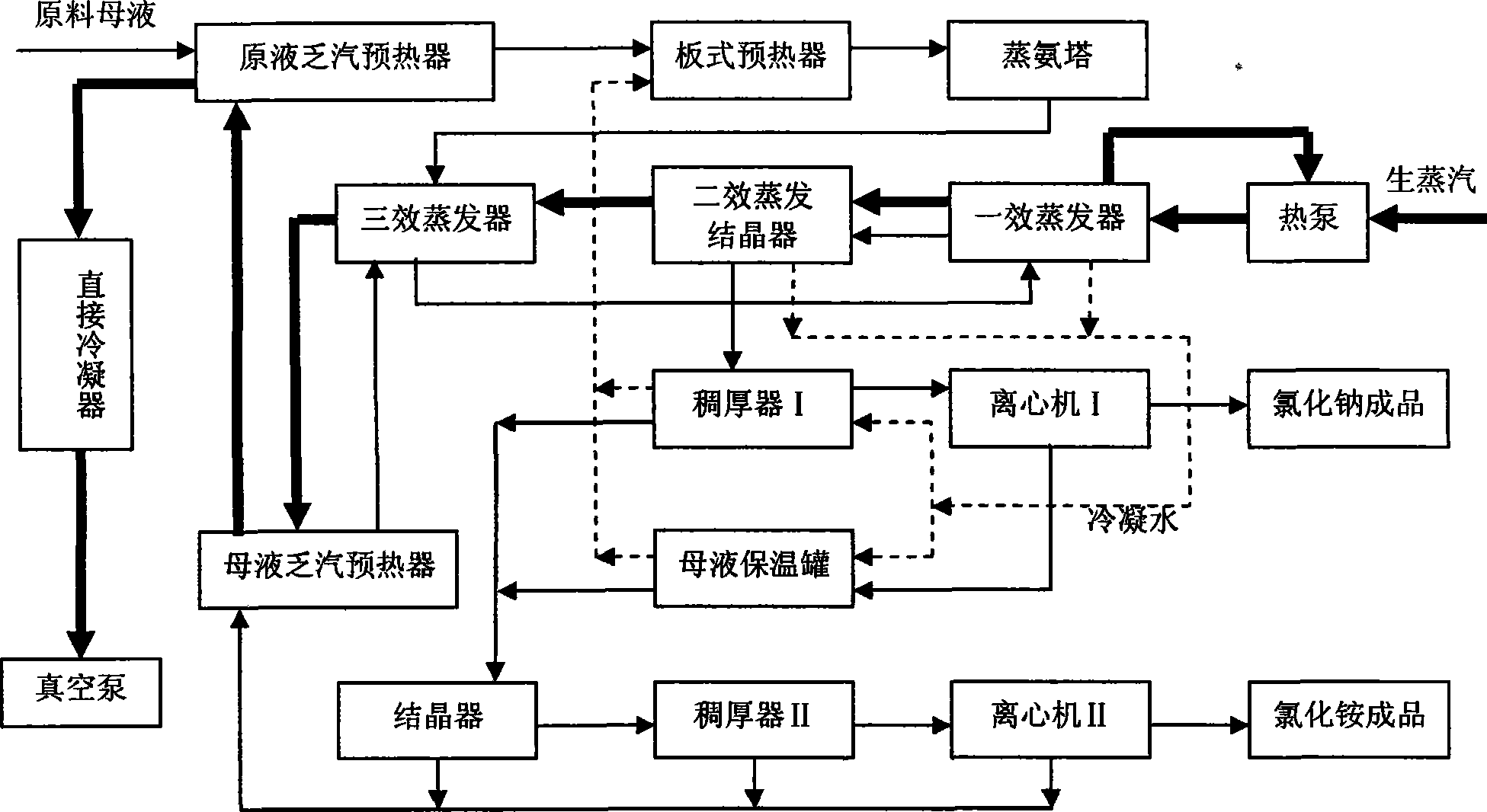
Process method for recovering ammonium chloride and sodium chloride from waste water containing ammonium chloride and sodium chloride
InactiveCN101544437AFully recycleReduce energy consumptionEnergy inputSolution crystallizationSodium bicarbonateDecomposition
The invention relates to a process method for recovering ammonium chloride and sodium chloride from waste water containing the ammonium chloride and the sodium chloride, which produces the ammonium chloride and the sodium chloride by using mother solution which is generated in a process for producing sodium bicarbonate by natural bittern double decomposition reaction and contains the ammonium chloride and the sodium chloride as raw materials. The method adopts ammonium still, evaporation, crystallization and separation process to treat, wherein the evaporation adopts multiple-effect, a heat pump and a vacuum evaporation process, and selects a falling film evaporator and a forced circulation type evaporator to perform triple-effect mixed-flow procedure, so that sodium chloride is crystallized and separated in the evaporation; and the ammonium chloride is crystallized and separated by cooling after the evaporation. The method effectively reduces the operation temperature of the equipment, can repeatedly use secondary steam and condensed water, reduces erosion of the ammonium chloride solution to the equipment, saves the energy, reduces the cost, improves the production efficiency, and reduces environmental pollution.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH +1
Production of propylene from steam cracking of hydrocarbons, particularly ethane
ActiveUS20050107650A1Improved and economical methodThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionButenePolymer science
An ethane or other hydrocarbon feedstock is steam cracked to produce an ethylene stream which is processed in an ethylene plant recovery section to separate an ethane recycle and a polymer grade or chemical grade ethylene product stream. A portion of the ethylene product stream may then be reacted by dimerization to produce a butene stream. These formed butenes and / or butenes recovered from other sources and another portion of the ethylene product stream are reacted by metathesis to produce a propylene stream which is deethanized and separated from heavier hydrocarbons to produce the propylene product. The butene product stream may also be deethanized and is separated from heavier hydrocarbons. The overhead from the metathesis section deethanizer may be recycled to the ethylene plant recovery section. The reflux for the metathesis section deethanizer may be generated from the overhead or may be a portion of the ethylene product stream.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Metal complexes useful in metathesis and other reactions
This invention provides metal complexes being useful as catalyst components in metathesis reactions and in reactions involving the transfer of an atom or group to an ethylenically or acetylenically unsaturated compound or another reactive substrate and, with respect to a sub-class thereof, for the polymerisation of α-olefins and optionally conjugated dienes, with high activity at moderate tempera-tures. It also provides methods for obtaining polymers with very narrow molecular weight distribution by means of a living reaction. It also provides methods for making said metal complexes and novel intermediates involved in such methods. It further provides derivatives of said metal complexes which are suitable for covalent bonding to a carrier, the product of such covalent bonding being useful as a supported catalyst for heterogeneous catalytic reactions. It also provides a direct one-step synthesis of pyrrole, furan and thiophene compounds from diallyl compounds.
Owner:RIMTEC CORP
Highly z-selective olefins metathesis
ActiveUS20110077421A1Organic chemistry methodsCarboxylic acid esters preparationOrganic chemistryOlefin metathesis
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Method of Producing Propylene Containing Biomass-Origin Carbon
InactiveUS20080312485A1Quality improvementSwitch-over frequencyMolecular sieve catalystsBiofuelsButeneDecomposition
Ethanol obtained from ordinary biomass resources contains many impurities other than water and these impurities themselves or their decomposition products contaminate ethylene when the ethylene is produced by a dehydration reaction, whereby the activity of metathesis catalyst is adversely affected. A method for producing propylene of the present invention is characterized in that the ethanol obtained from biomass is converted to ethylene by a dehydration reaction, the ethylene is separated from the generated water, the separated ethylene is purified by adsorption in an adsorption tower filled with an adsorbent, and then a metathesis reaction is carried out along with a raw material containing n-butene. With the present invention, propylene having biomass-derived carbon and reduced-environmental burden can be efficiently produced without lowering the catalysis activity.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Contact metathesis polymerization
InactiveUS6962729B2Contributes to manufacturing flexibilityAdhesive processesSpecial tyresOrganic chemistrySubstrate surface
Owner:LORD CORP
Ruthenium metathesis catalyst and method for producing olefin reaction product by metathesis reaction using the same
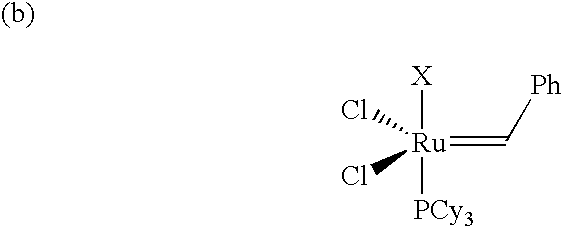
InactiveUS6175047B1Easy to prepareHigh catalytic activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsCarbon–carbon bondReducing agent
The invention has an object of safely and simply preparing a large amount of a ruthenium metathesis catalyst, which is used as a catalyst for a carbon-carbon bond formation using, particularly, a metathesis reaction. The metathesis catalyst has the following complex composition (A) or (B). The composition (A) includes RuX12(arene)(PR1R2R3) and R4CHX22, R5C=CH or R4CHX2 and a reducing agent, wherein X1 and X2 respectively are a halogen atom; arene is a hydrocarbon having a benzene ring; R1, R2 and R3, which may be the same or different, respectively are an alkyl group having 1-8 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 3-8 carbon atoms or an optionally substituted aryl group, wherein the substituent group is an alkyl group having 1-8 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1-8 carbon atoms, an alkylamino group having 1-8 carbon atoms or a halogen atom; R4 is an alkyl group which has 1-8 carbon atoms and may have an ether bond or an ester bond, an optionally subsituted aryl group, wherein the substituent group is a halogen atom or a hydroxyl group; or cycloalkyl group having 3-8 carbon atoms; and R5 is an optionally substituted alkyl group which has 1-8 carbon atoms and may have an ether bond or an ester bond, wherein the substituent group is a halogen atom or a hydroxyl group, an aryl group or a cycloalkyl group having 3-8 carbon atoms. The composition B includes [RuX12(arene)]2, PR1R2R3, R5C=CH or R4CHX2 and a reducing agent, wherein X1, arene, R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are the same as defined above.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
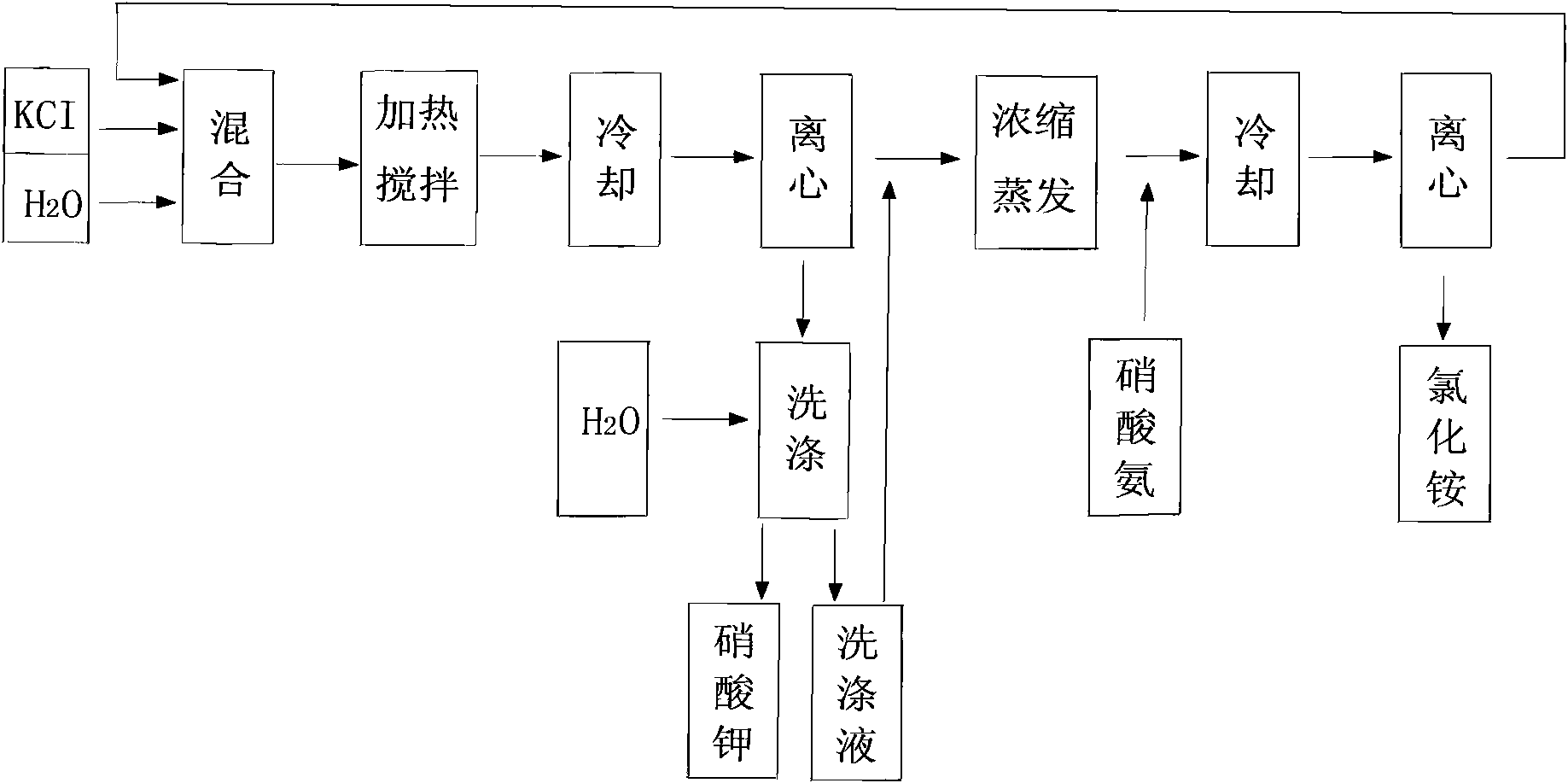
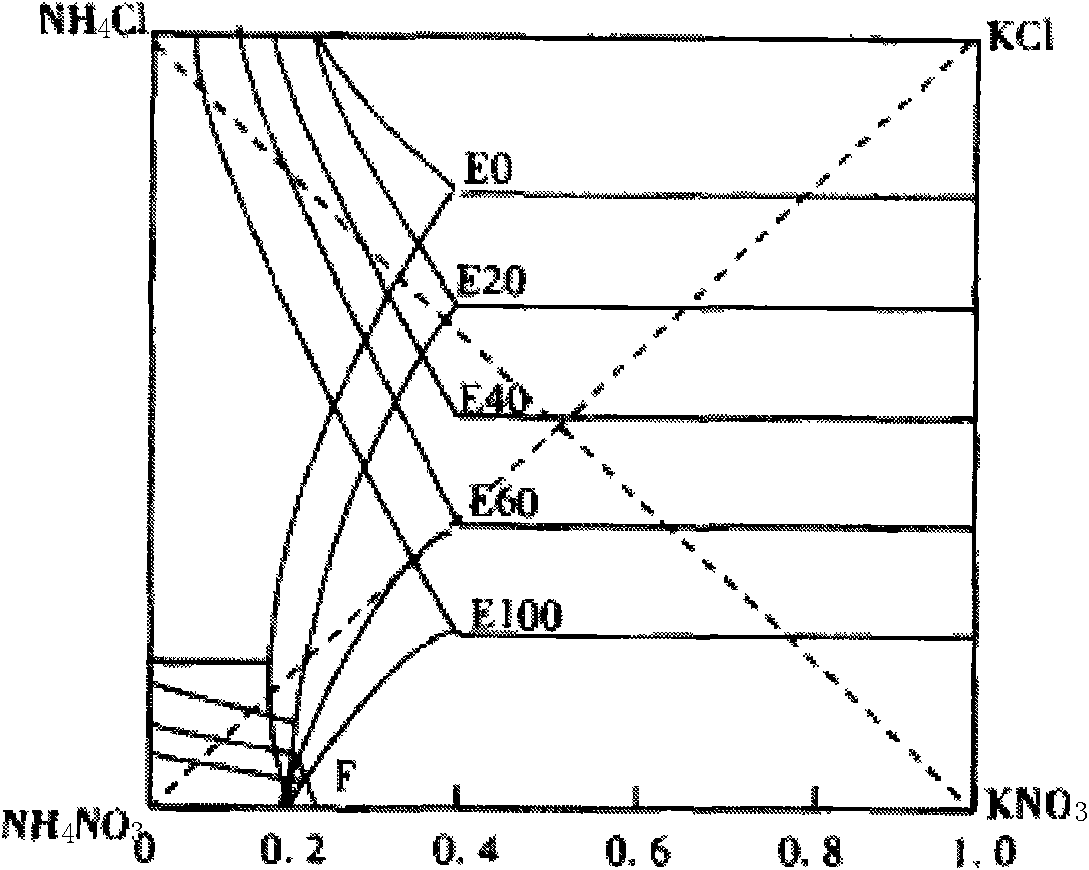
Method for preparing potassium nitrate and ammonium chloride employing double decomposition reaction
InactiveCN101628723ACreate pollutionRealize the concentrated evaporation processAlkali metal nitrate preparationAmmonium halidesDecompositionIon exchange
A method for preparing potassium nitrate and ammonium chloride employing double decomposition reaction comprises the following steps: dissolving ammonium nitrate and potassium chloride in water according to a defined ratio at 110 DEG C, continuously adding potassium chloride and water, heating while stirring to ensure that potassium nitrate is in supersaturation state, after stopping heating, cooling the solution in a vacuum cooling crystallizer to 36-40 DEG C to separate potassium nitrate crystal, placing the potassium nitrate crystal in a centrifugal machine with a filter cloth lining to obtain coarse potassium nitrate, then washing the potassium nitrate with cold water, drying to obtain the finished potassium nitrate; in addition, adding ammonium nitrate in mother solution I and cleaning solution to adjust solution concentration so that ammonium chloride can reach supersaturation state, using a vacuum concentration device to perform negative pressure evaporation, separating and precipitating ammonium chloride by centrifuging and obtaining a solid ammonium chloride product, wherein, when dissolving ammonium nitrate and potassium chloride, the ratio of ammonium ion to chlorine ion is 1:2 and when using the centrifugal machine to obtain the coarse potassium nitrate, the separated mother solution is another mother solution I sharing the same saturation point of potassium nitrate and ammonium chloride. The solution of feed liquid circular reaction overcomes the defects of the prior art that the price of potassium nitrate used in reaction is high, the resource of potassium nitrate is in short supply and the cost of devices used in ion-exchange method is high, thus being applicable to the production of potassium nitrate.
Owner:湖南丹化农资有限公司
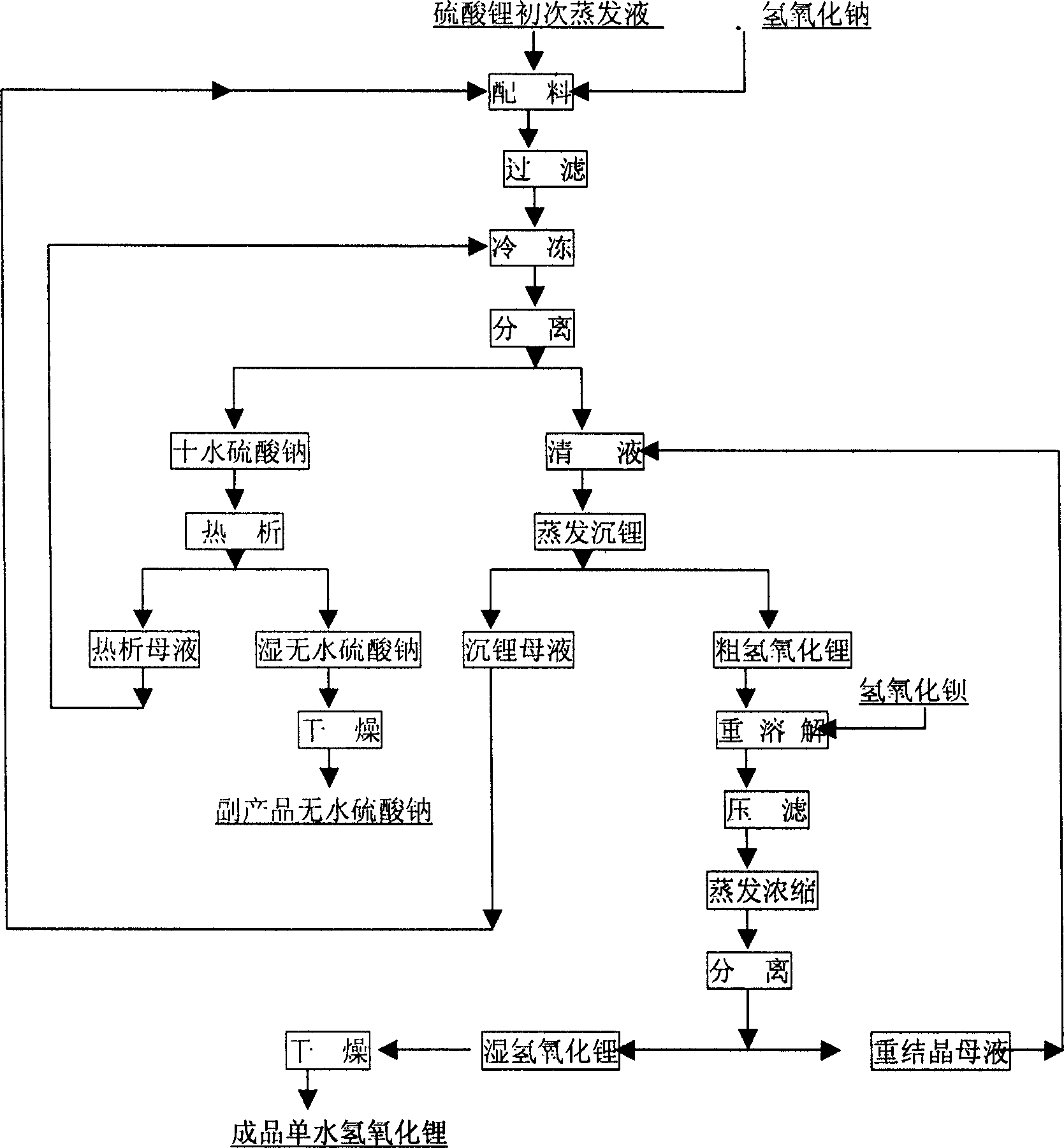
Production process of lithium hydroxide monohydrate
InactiveCN1486931AShort process routeHigh yieldSulfate/bisulfate preparationLithium oxides/hydroxidesSolubilityStrontium hydroxide octahydrate
In the production process of lithium hydroxide monohydrate, lithium sulfate solution and caustic soda are made to produce metathetic reaction to form mixture solution of sodium sulfate and lithium hydroxide, and sodium sulfate and lithium hydroxide monohydrate are then separated by means of the obvious difference in low temperature solubility. The production process includes the following steps: adding sodium hydroxide into lithium sulfate solution obtained through serial production steps to obtain mixture solution of sodium sulfate and lithium hydroxide; cooling to minus 10 deg.c to 5 deg.c for the crystallization and separation of sodium sulfate; heating to concentrate the separated clear liquid; crystallization and separation to obtain coarse lithium hydroxide monohydrate product; water dissolving coarse lithium hydroxide monohydrate, adding barium hydroxide to form insoluble barium sulfate, filtering, concentrating filtrate, crystallizing to separate wet lithium hydroxide monohydrate; and drying.
Owner:JIANGSU RONGHUI GENERAL LITHIUM IND CO LTD
Process of Producing Olefins
InactiveUS20100145126A1Low reaction temperatureBig advantageCatalystsHydrocarbon preparation catalystsRheniumAlkaline earth metal
A process of producing olefins by a metathesis reaction in a practical low temperature range by improving the reactivity of the catalyst is provided.The process of producing olefins according to the present invention allows a metathesis reaction of olefins, which uses a catalyst containing metal elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, rhenium or the like, to proceed at an industrially sufficient reaction rate in a practical low temperature range, by using a compound containing at least one metal element selected from the metals of Group Ia (alkali metals), Group IIa (alkaline earth metals), Group IIb and Group IIIa as co-catalyst and allowing hydrogen gas to co-exist with the reaction raw material.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Contact metathesis polymerization
InactiveUS6960272B1Contributes to manufacturing flexibilityAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentTyresSubstrate surfacePolymerization
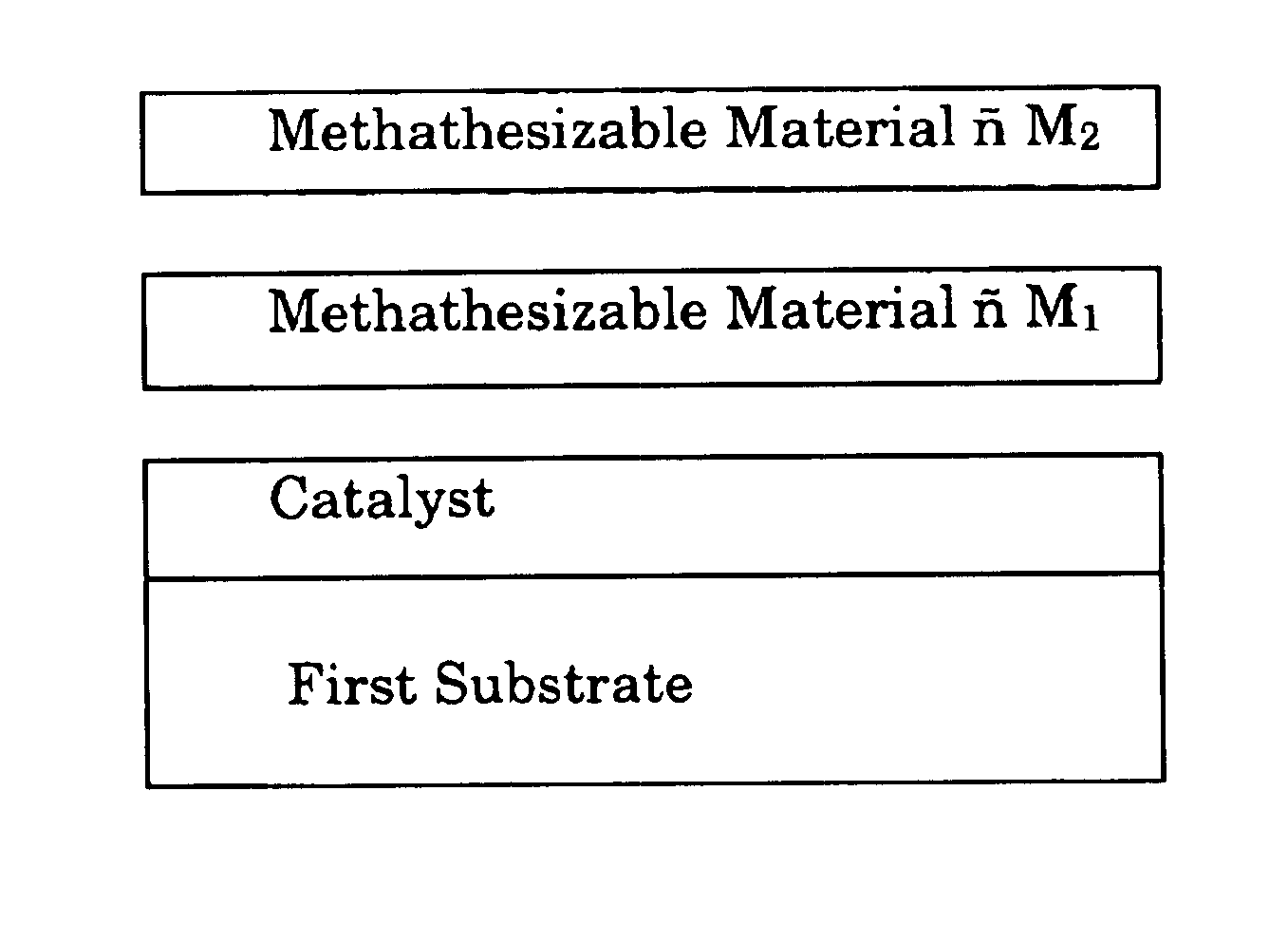
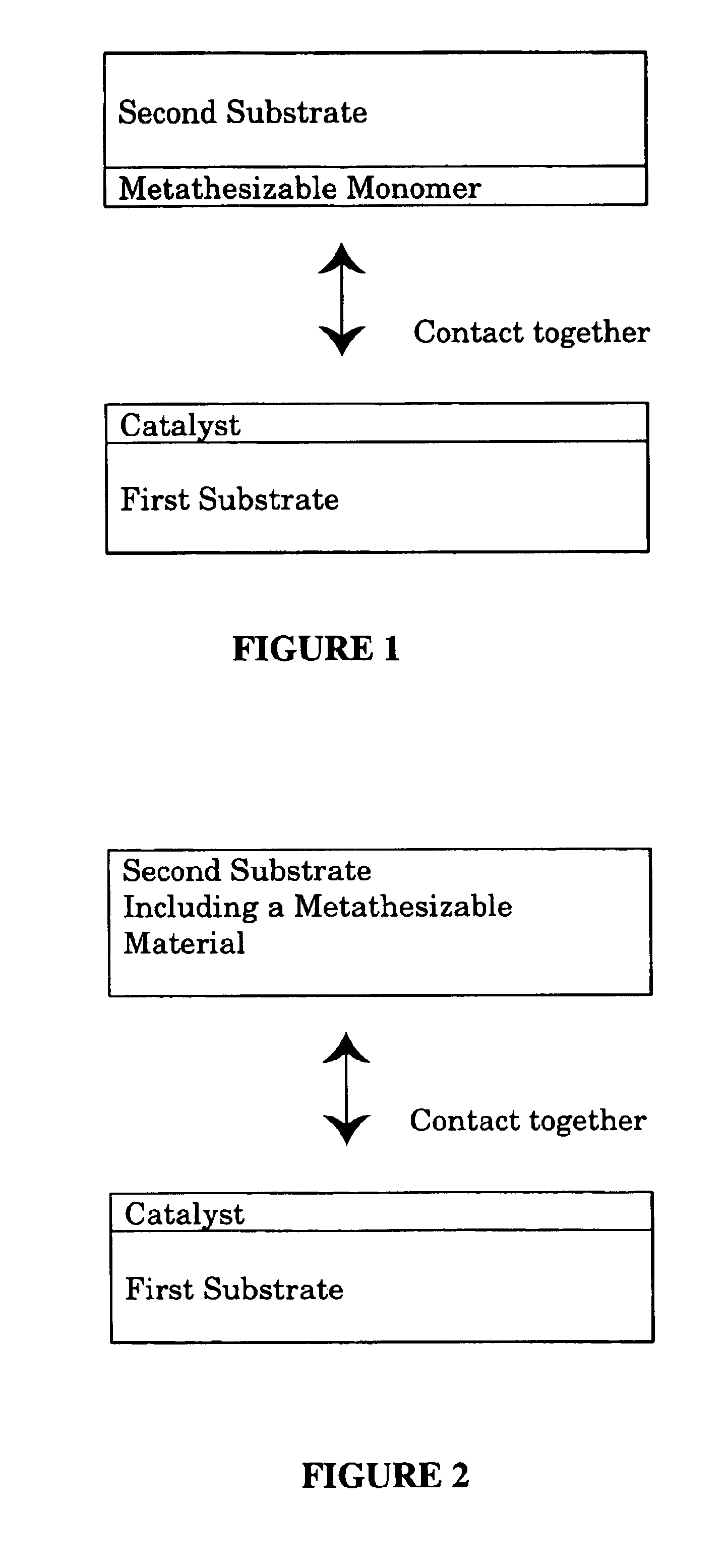
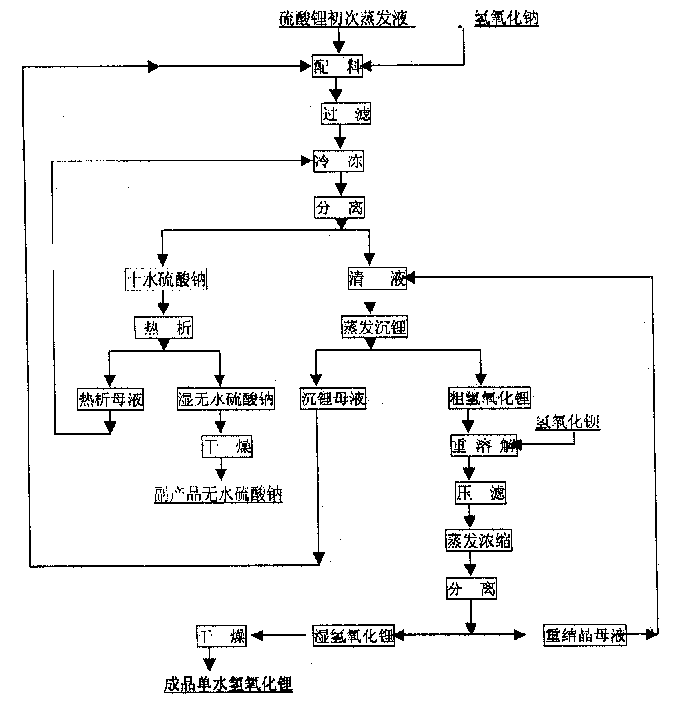
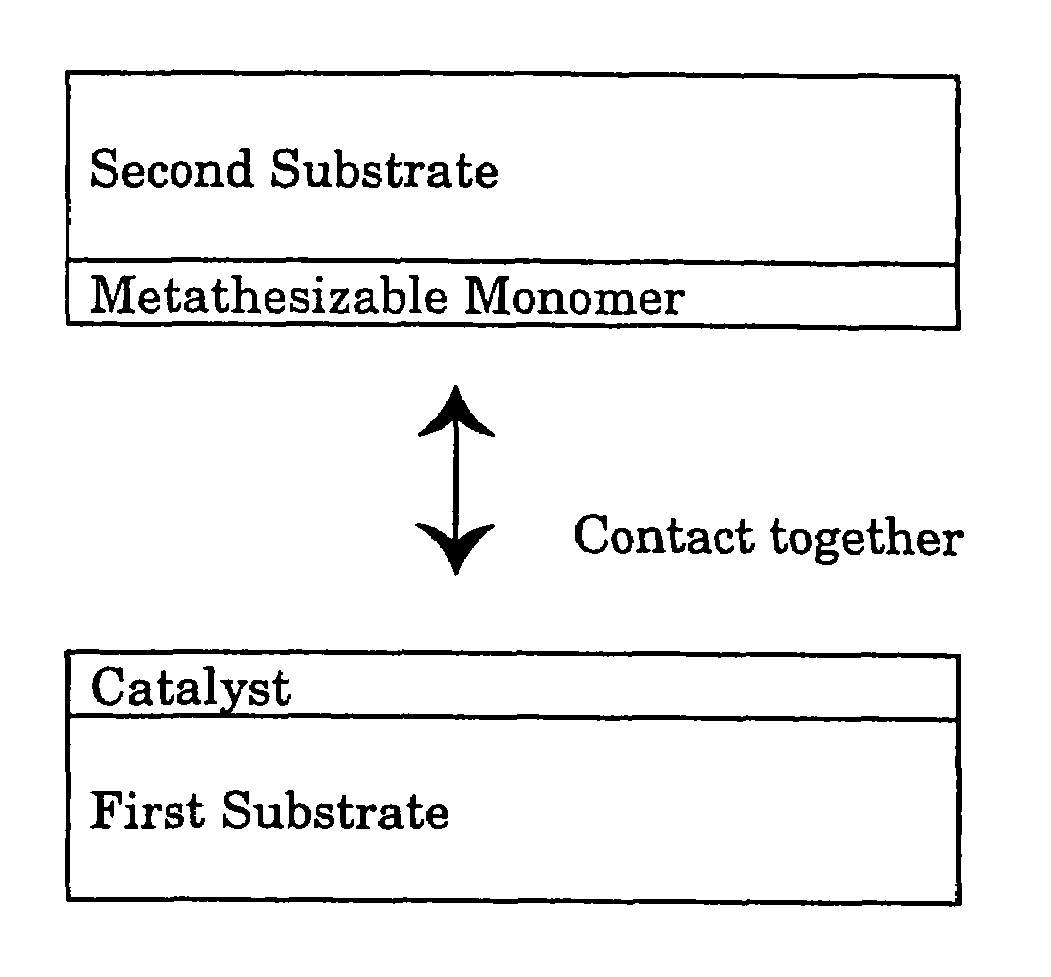
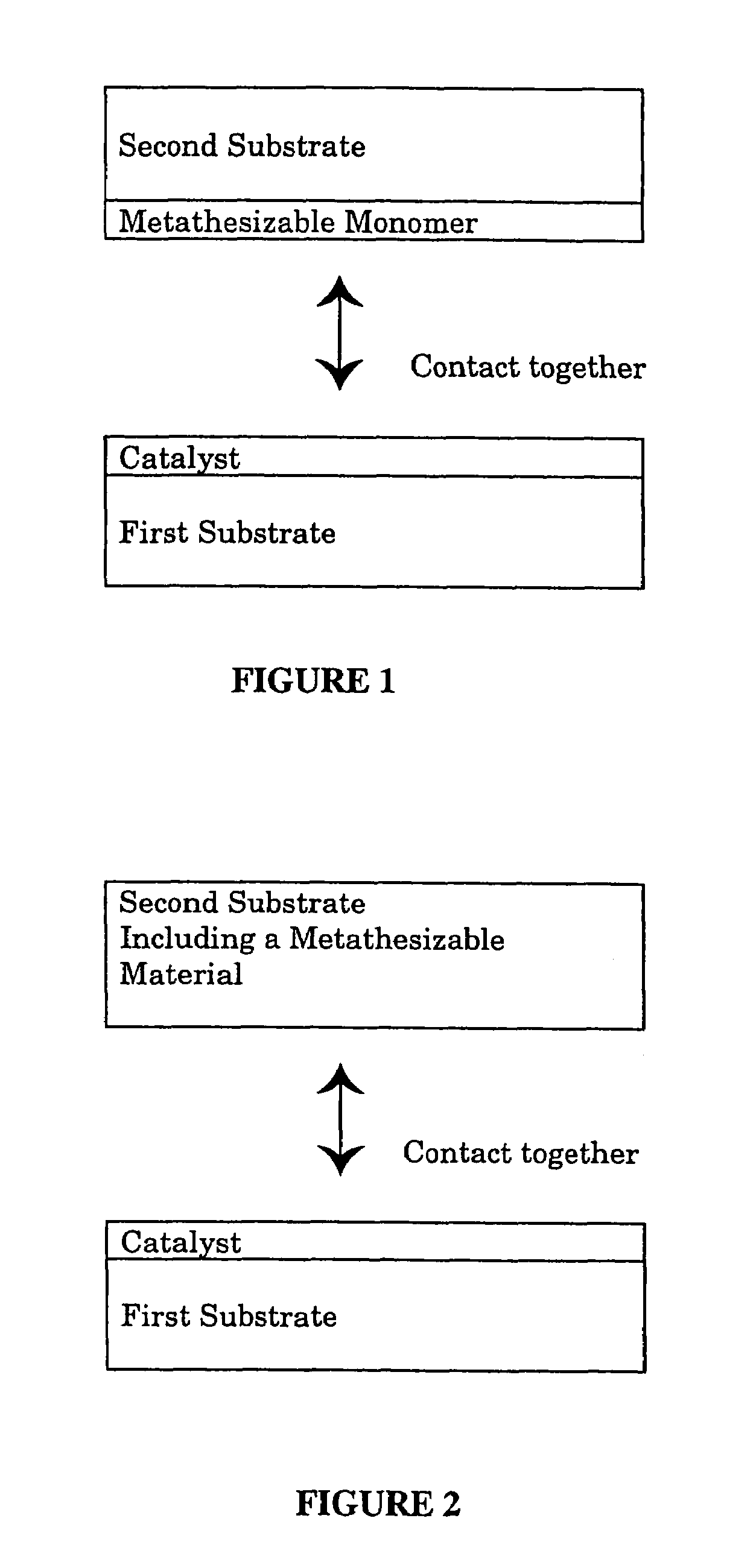
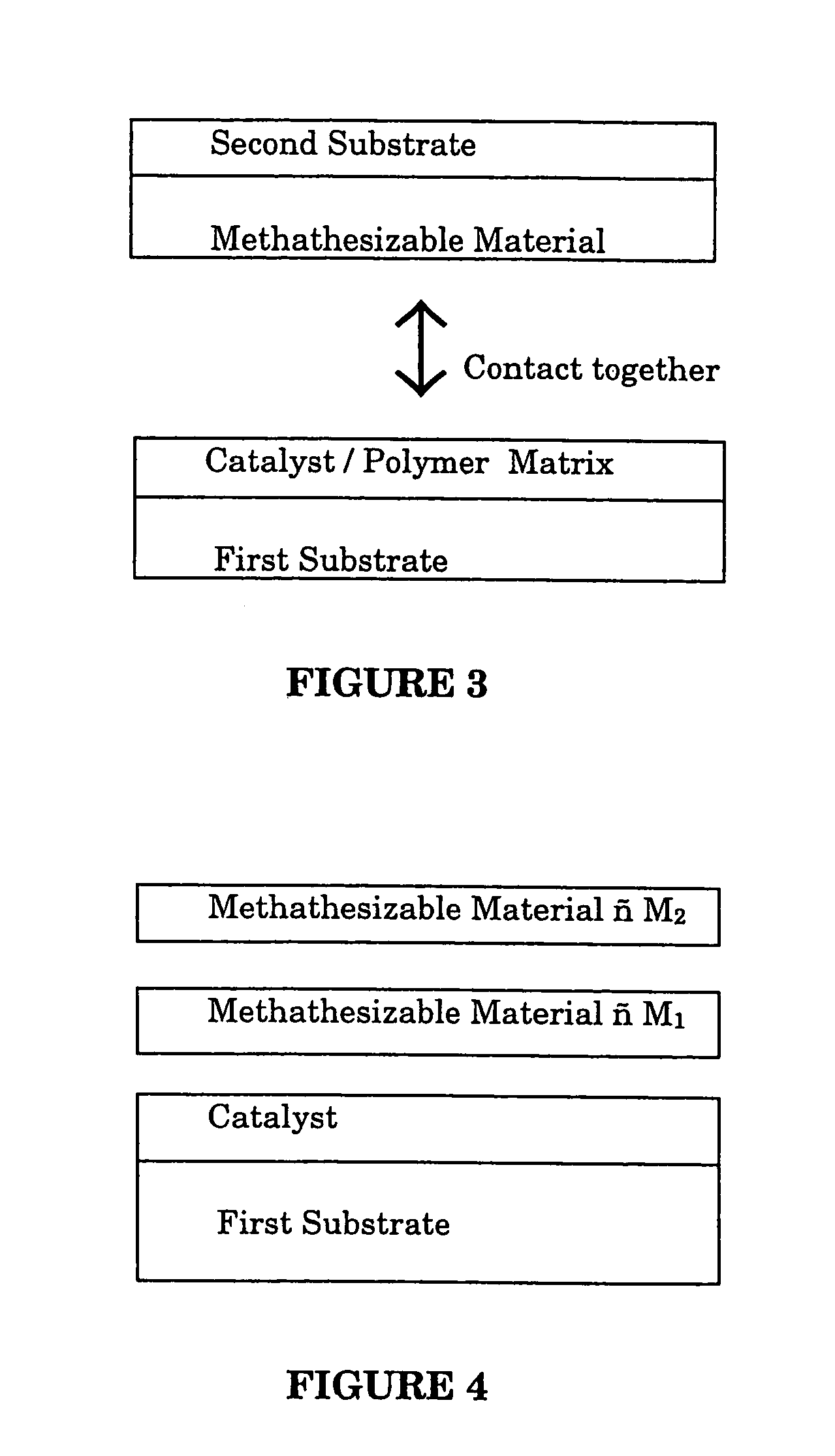
A method for bonding a material to a first substrate surface that includes providing a catalyst at the first substrate surface and then contacting that surface with a material that undergoes a metathesis reaction to bond the material to the first substrate surface. There are two embodiments of this method—a coating process and an adhesive process. In the coating embodiment, the metathesizable material is contacted with the catalyst on the substrate surface so that it undergoes metathesis polymerization to form the coating. The adhesive process includes (a) providing a catalyst at the first substrate surface, (b) providing a metathesizable material between the first substrate surface and the second substrate surface, and (c) contacting the catalyst on the first substrate surface with the metathesizable material so that the metathesizable material undergoes a metathesis reaction and bonds the first substrate surface to the second substrate surface.
Owner:LORD CORP
Use of a Phosphorus Containing Ligand and a Cyclic Organic Ligand in a Transition Metal Compound
ActiveUS20080221345A1Ruthenium organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDouble bondOrganic compound
According to the present invention there is provided a compound in the form of a transition metal compound including a transition metal, a phosphorus containing ligand, and a cyclic organic ligand. The phosphorus containing ligand is a heterocyclic organic compound with a ligating phosphorus atom which ligates with the transition metal, and which ligating phosphorus atom is an atom in the heterocyclic ring structure of the heterocyclic organic compound. The cyclic organic ligand is a cyclic organic compound with a ligating carbon atom in the cyclic ring structure of the cyclic organic compound which ligates with the transition metal by means of a double bound. The invention also relates to a method preparing such a compound and a metathesis reaction wherein such a compound is used as a catalyst.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Composition curable by metathesis reaction
InactiveUS6844409B2Increase alkalinityImpression capsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsEndcappingOligomer
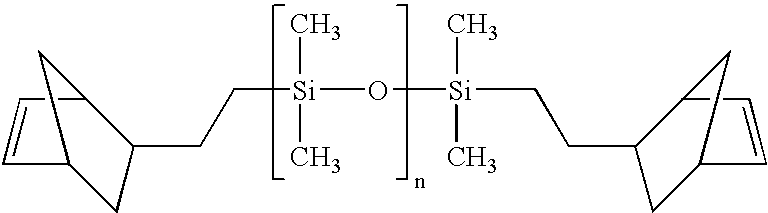
A composition curable by a metathesis reaction and comprising an olefin-containing resin system and metathesis catalyst. The resin system comprises siloxane-based oligomers or polymers end-capped and / or tethered with olefin functional groups that are capable of undergoing a metathesis reaction. The composition also includes a ruthenium carbene complex catalyst, whereby the catalyst initiates the metathesis reaction of the composition. The oligomer or polymer may be, for example, one or a combination of a telechelic polydimethylsiloxane end-capped with norbornenylethyl groups, a polydimethylsiloxane tethered and end-capped with norbornenylethyl groups, a tri-functional polydimethylsiloxane end-capped with norbornenylethyl groups, or a quadri-functional polydimethylsiloxane end-capped with norbornenylethyl groups. The catalyst may be, for example, a ruthenium carbene complex, such as 1,3-bis-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-2-(imidazolidinylidene) dichloro(o-isopropoxyphenylmethylene) ruthenium.
Owner:THE KERR
Propylene production
ActiveUS20100168487A1Save energySave equipmentHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by metathesis reactionIsomerizationEthylene
A propylene production process is disclosed. The process comprises (a) reacting a feed stream comprising isobutene in the presence of a skeletal isomerization catalyst to obtain an isomerized stream comprising C4 olefins; and (b) reacting the isomerized stream with ethylene in the presence of a metathesis catalyst to form a metathesis product stream comprising propylene, C4 olefins, and C5+ olefins. The metathesis reaction pressure is equal to or lower than that of the skeletal isomerization.
Owner:LYONDELL CHEM TECH LP
Olefin functionalization by metathesis reaction
This invention relates to a process to functionalize propylene co-oligomer comprising contacting an alkene metathesis catalyst with a heteroatom containing alkene, and a propylene a co-oligomer having an Mn of 300 to 30,000 g / mol comprising 10 to 90 mol % propylene and 10 to 90 mol % of ethylene, wherein the oligomer has at least X % allyl chain ends, where: 1) X=(−0.94 (mol % ethylene incorporated)+100), when 10 to 60 mol % ethylene is present in the co-oligomer, and 2) X=45, when greater than 60 and less than 70 mol % ethylene is present in the co-oligomer, and 3) X=(1.83*(mol % ethylene incorporated)−83), when 70 to 90 mol % ethylene is present in the co-oligomer. This invention also relates to a process to functionalize propylene homo-oligomer comprising contacting an alkene metathesis catalyst with a heteroatom containing alkene, and a propylene homo-oligomer, comprising propylene, wherein the oligomer has: at least 93% allyl chain ends, an Mn of about 500 to about 20,000 g / mol, an isobutyl chain end to allylic vinyl group ratio of 0.8:1 to 1.2:1.0, and less than 100 ppm aluminum.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Ruthenium metathesis catalyst and method for producing olefin reaction product by metathesis reaction using the same
InactiveUS6313365B1Easy to prepareHigh catalytic activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsCarbon–carbon bondReducing agent
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
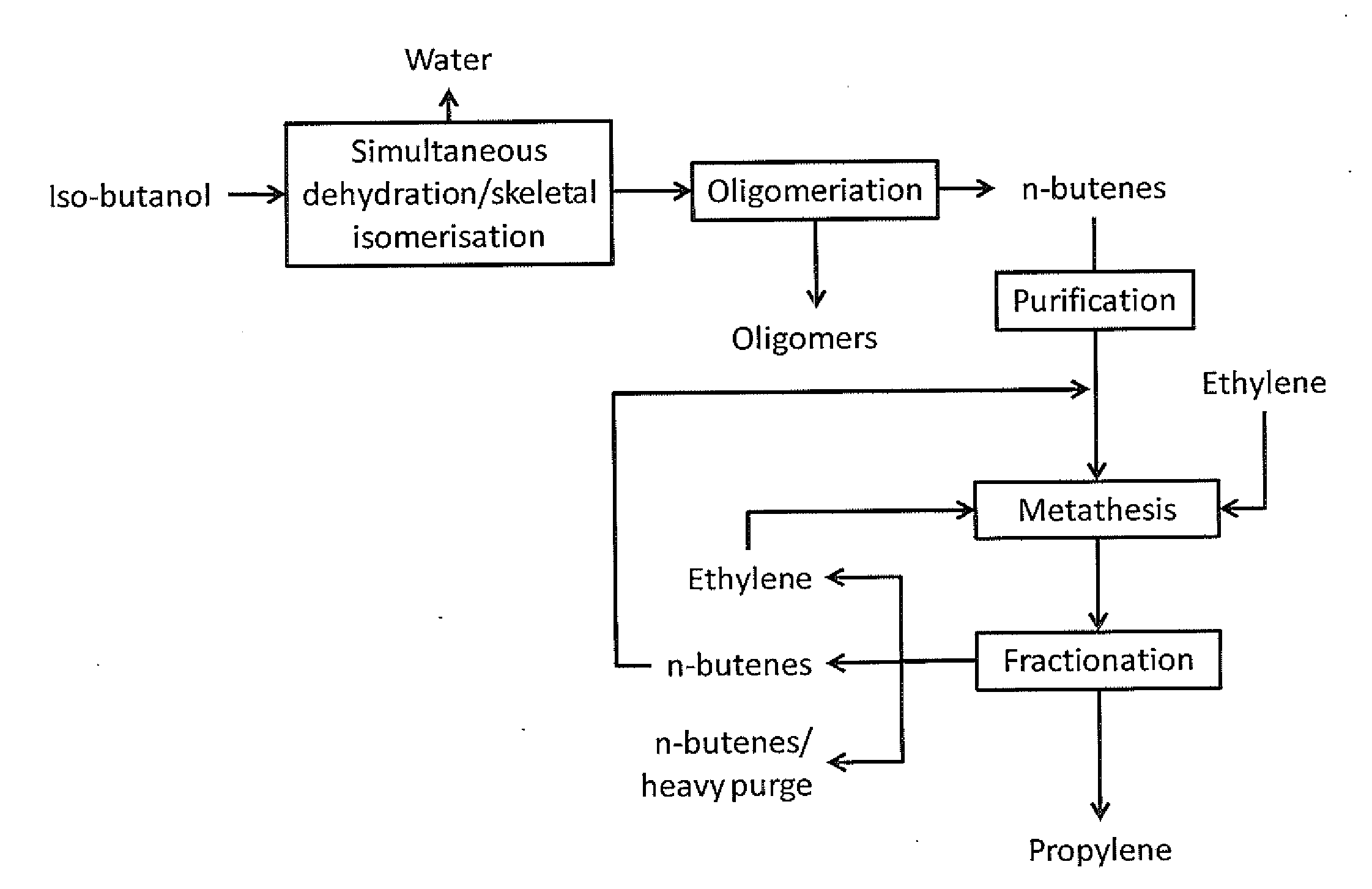
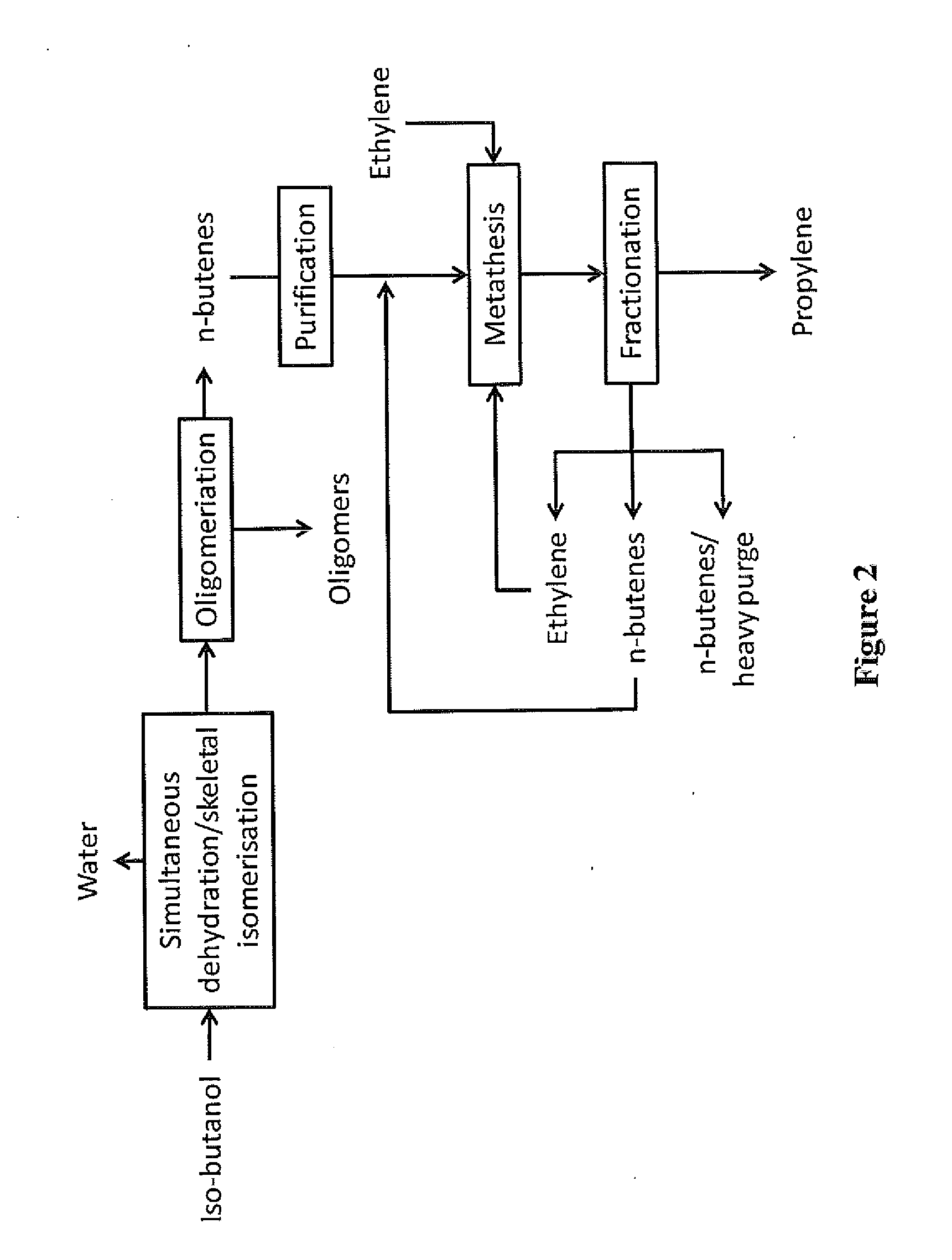
Production of propylene via simultaneous dehydration and skeletal isomerisation of isobutanol on acid catalysts followed by metathesis
ActiveUS20130245348A1High yieldCapital investment can be minimizedMolecular sieve catalystHydrocarbon purification/separationButeneIsobutanol
The present invention relates to a process for the production of propylene in which in a first step isobutanol is subjected to a simultaneous dehydration and skeletal isomerisation to make substantially corresponding olefins, having the same number of carbons and consisting essentially of a mixture of n-butenes and iso-butene and in a second step n-butenes are subjected to methathesis, said process comprising:a) introducing in a reactor a stream (A) comprising isobutanol, optionally water, optionally an inert component,b) contacting said stream with a catalyst in said reactor at conditions effective to dehydrate and skeletal isomerase at least a portion of the isobutanol to make a mixture of n-butenes and iso-butene,c) recovering from said reactor a stream (B), removing water, the inert component if any and unconverted isobutanol if any to get a mixture of n-butenes and iso-butene,d) fractionating said mixture to produce a n-butenes stream (N) and to remove the essential part of isobutene optionally recycled with stream (A) to the dehydration / isomerization reactor of step b),e) sending the stream (N) to a methathesis reactor and contacting stream (N) with a catalyst in said methathesis reactor, optionally in the presence of ethylene, at conditions effective to produce propylene,f) recovering from said methathesis reactor a stream (P) comprising essentially propylene, unreacted n-butenes, heavies, optionally unreacted ethylene,g) fractionating stream (P) to recover propylene and optionally recycling unreacted n-butenes and unreacted ethylene to the methathesis reactor.
Owner:TOTAL RES & TECH FELUY
Process for continuous ruthenium-catalysed metathesis
InactiveUS7838711B2Less fluctuationReduce riskHydrocarbon by isomerisationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSalt metathesis reactionChemistry
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
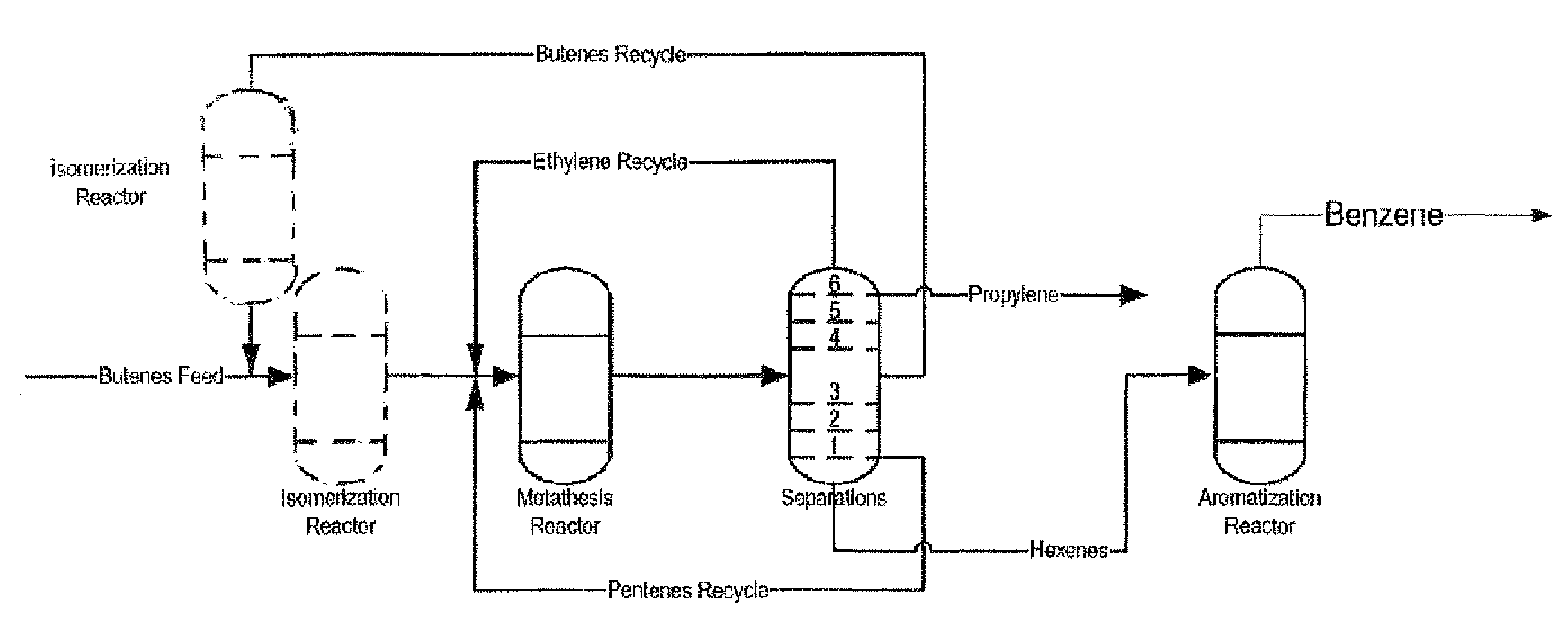
Process for producing propylene and aromatics from butenes by metathesis and aromatization
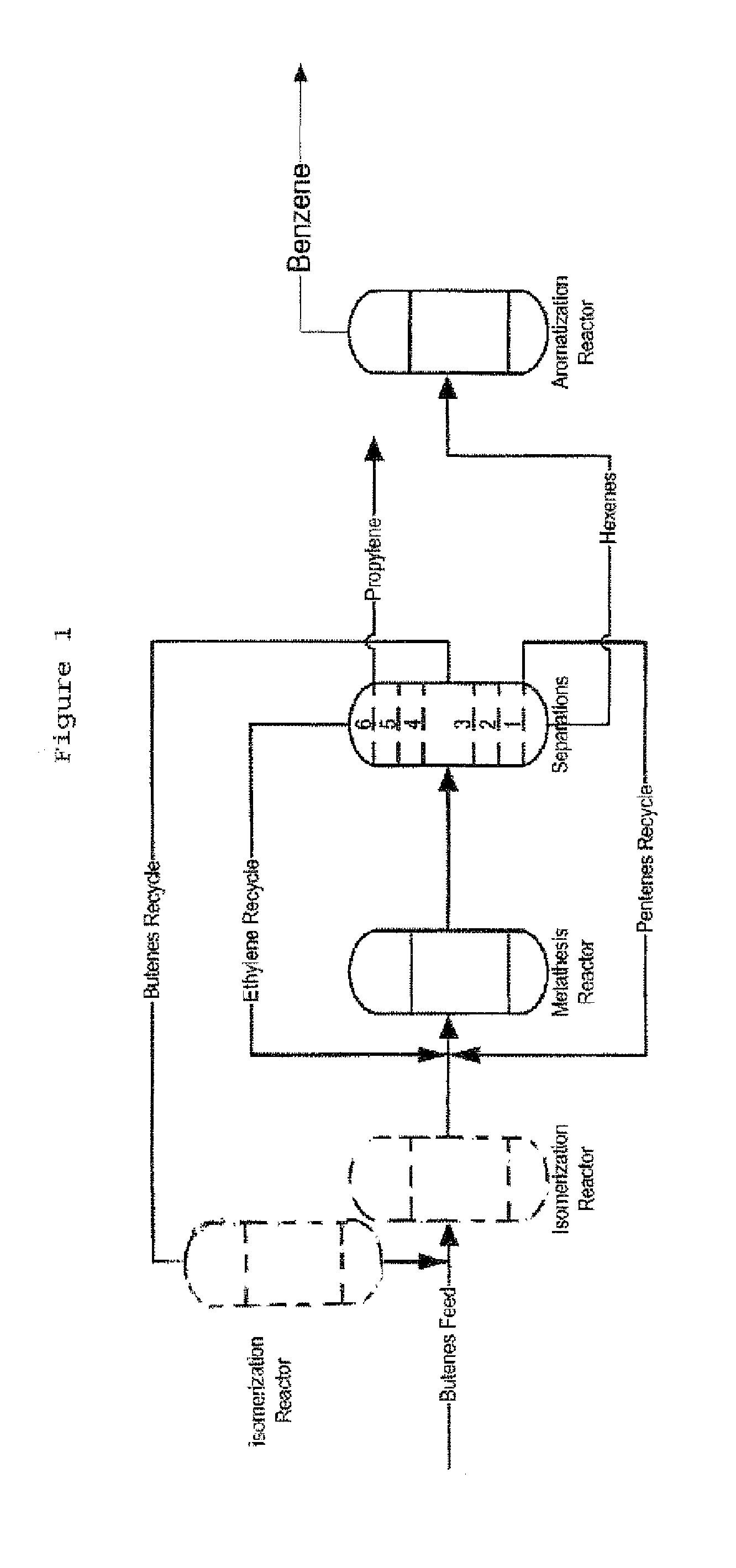
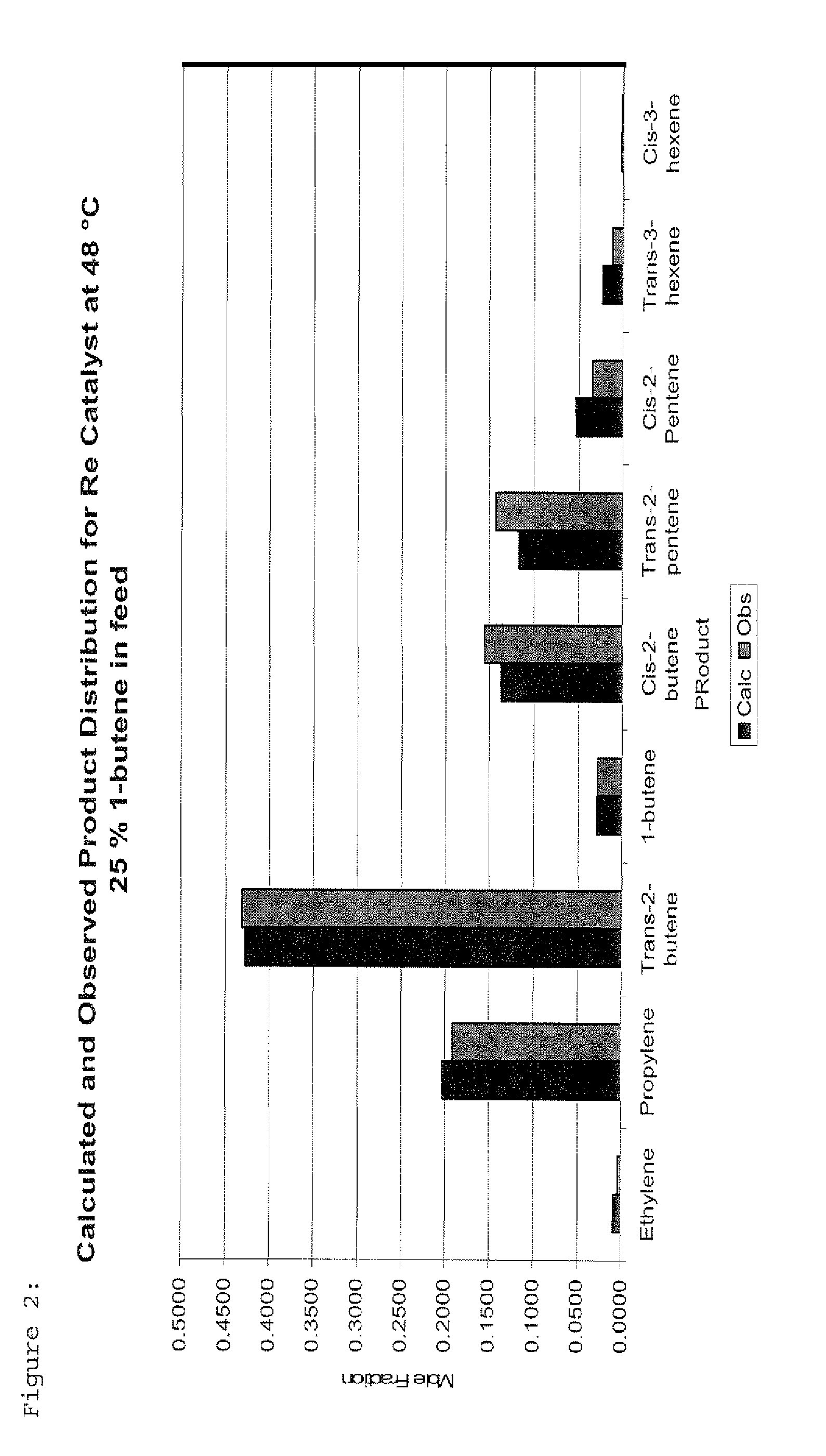
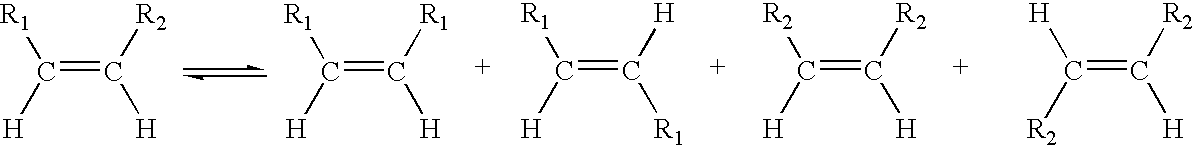
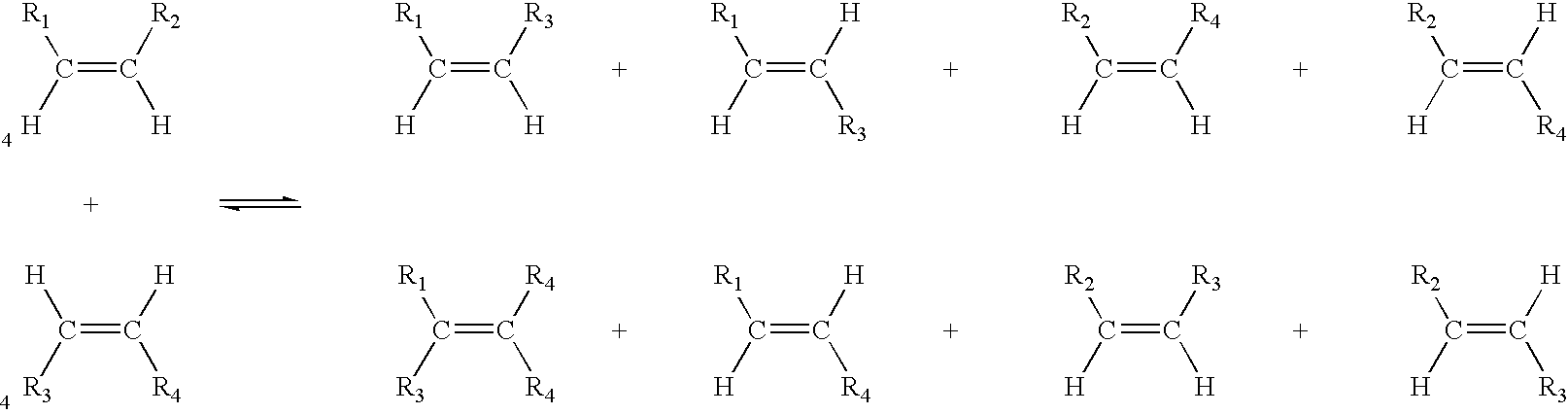
The invention is for a process for producing propylene and hexene (along with ethylene, pentenes, product butenes, heptenes and octenes) by metathesis from butenes (iso-, 1- and cis and trans 2-) and pentenes and then aromatizing the hexenes (along with higher olefins, such as heptenes and octenes) to benzene (along with toluene, xylenes, ethylbenzene and styrene). Since the desired products of the metathesis reaction are propylene and hexene, the feed to the metathesis reaction has a molar ratio for 1-butene:2-butene which favors production of propylene and 3-hexene with the concentration of hexenes and higher olefins in the metathesis product being up to 30 mole %. An isomerization reactor may be used to obtain the desired molar ratio of 1-butene:2-butene for the feed composition into the metathesis reactor. After the metathesis reaction, of hexene and higher olefins are separated for aromatization to benzene and other aromatics.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
Process for co-producing olefins and esters by ethenolysis of unsaturated fats in non-aqueous ionic liquids
InactiveUS7678932B2Fatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationGlycerol ester of wood rosinGlycerol
A process is described in which an unsaturated fat is reacted with ethylene in a metathesis reaction in the presence of at least one non-aqueous ionic liquid to produce both an olefinic fraction and a composition of monoalcohol or polyol esters.Particular application to an oleic sunflower seed oil, an oleic rapeseed oil or to a mixture of monoalcohol esters of said oils, the process producing both an olefinic fraction and a monoalcohol or glycerol esters composition generally having more than half of its chains constituted by unsaturated C10 chains.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Olefin production process
InactiveUS8299313B2Improve thermal stabilityShorten regeneration timeHydrocarbon by isomerisationOrganic chemistry methodsRheniumIsomerization
A process is provided which is capable of producing olefins stably and efficiently by a metathesis reaction of identical or different olefins while preventing the lowering in metathesis catalyst activity due to trace impurities such as heteroatom-containing compounds that are contained in a starting olefin.The olefin production process includes supplying a starting olefin containing more than 0 ppm by weight to not more than 10 ppm by weight of one or more kinds of heteroatom-containing compounds to a reactor that contains a metathesis catalyst and an isomerization catalyst, the metathesis catalyst including at least one metal element selected from the group consisting of tungsten, molybdenum and rhenium, the isomerization catalyst including calcined hydrotalcite or yttrium oxide, and performing a metathesis reaction of identical or different olefins.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Sulphur-containing metathesis catalysts
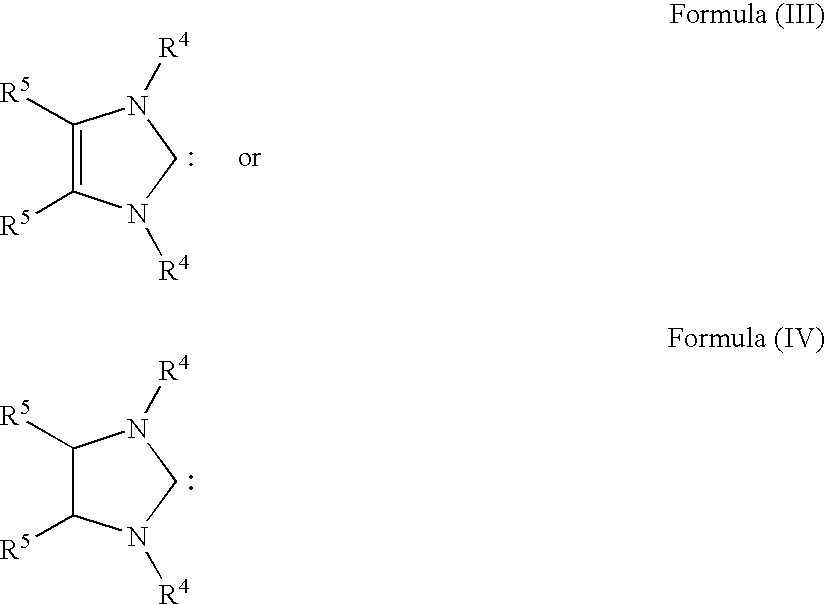
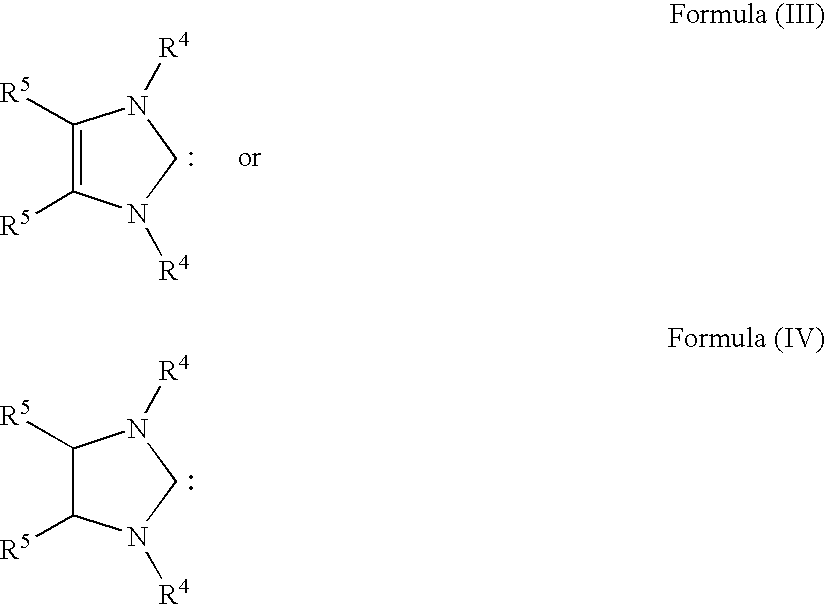
InactiveUS20080275247A1Reduced activityRapid rise in activityRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationSalt metathesis reactionTransition metal
The present invention relates to novel transition metal complexes of the formula (I)to a process for preparing these transition metal complexes and to the use of the transition metal complexes as catalysts in metathesis reactions.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method for producing sulfuric acid utilizing phosphogypsum slag
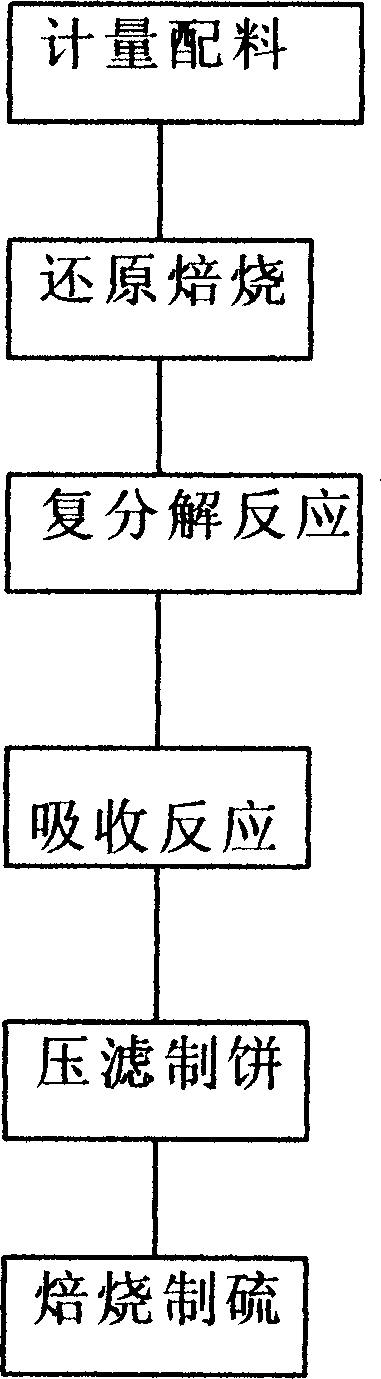
InactiveCN1775660ASolve pollutionSignificant environmental protection social benefitsSulfur compoundsSlagDecomposition
The invention is a method for making vitriol using phosphorus plaster with respect to the three-waste problem caused by the phosphorus plaster waste residues, in turn mixing, reductively baking, making double decomposition reaction, making absorption reaction, press filtering to make filter cake and baking to make sulfur, recovering and extracting sulfur ore resources from the phosphorus plaster waste residues to replace the sulfurous iron ore to act as raw material to produce vitriol product, achieving the purpose of turning waste into wealth. The invention solves the pollution problem of waste residues of puzzling long-time and restricting the development of phosphorus chemical industrial enterprises of our country. And the invention can largely reduce the production cost and has completely remarkable social and economic benefits.
Owner:四川省犍为明丰化工有限公司
Cross-metathesis of olefins directly substituted with an electron-withdrawing group using transition metal carbene catalysts
ActiveUS7598330B2Without efficiencyWithout selectivityCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationElectron donorAlkene
The invention pertains to the use of Group 8 transition metal alkylidene complexes as catalysts for olefin cross-metathesis reactions. In particular, ruthenium and osmium alkylidene complexes substituted with an N-heterocyclic carbene ligand and at least one electron donor ligand in the form of a heterocyclic group are used to catalyze cross-metathesis reactions to provide a olefin products that are directly substituted with an electron-withdrawing group.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com