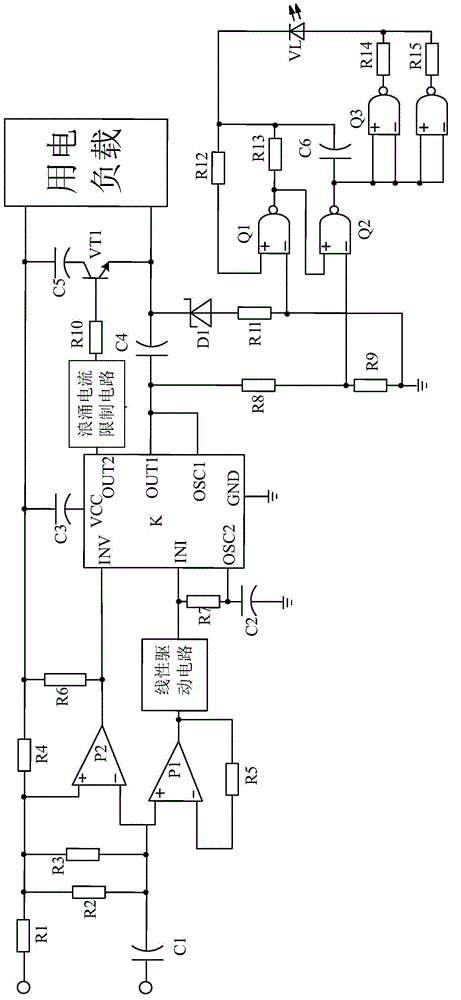
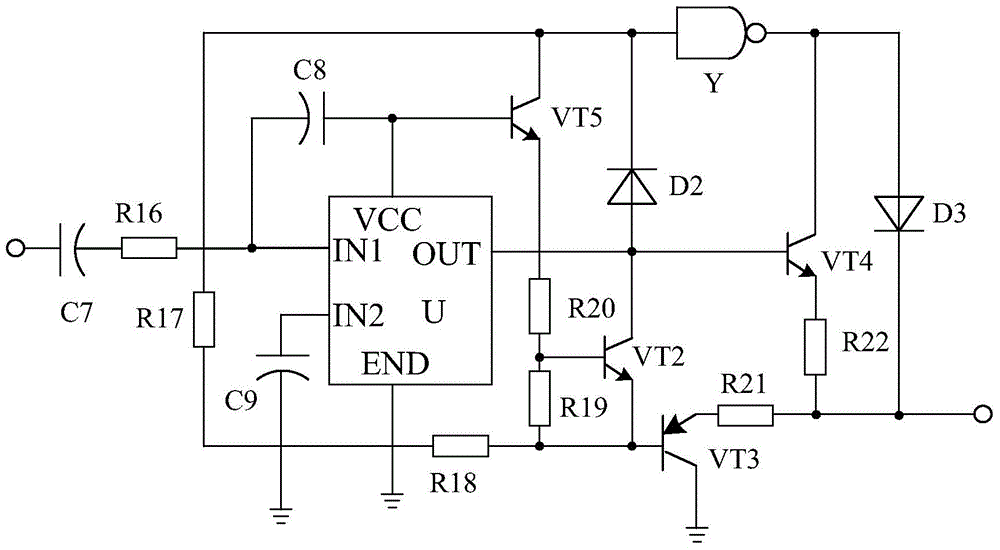
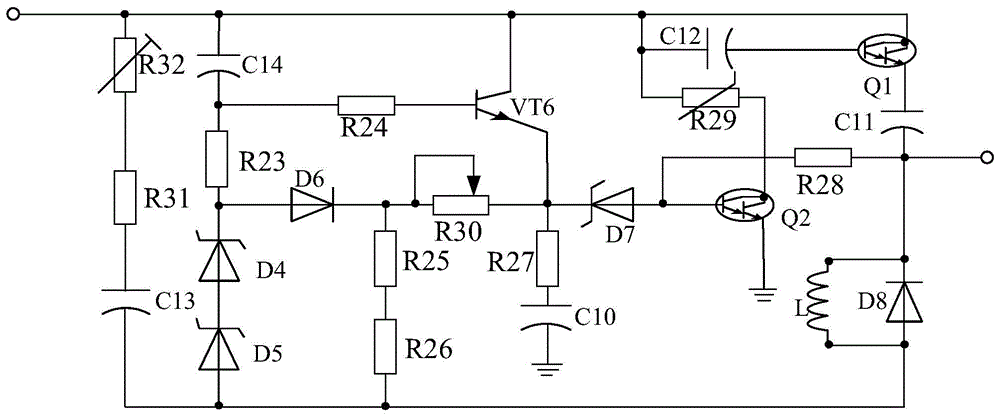
Patents
Literature
43results about How to "Current limit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
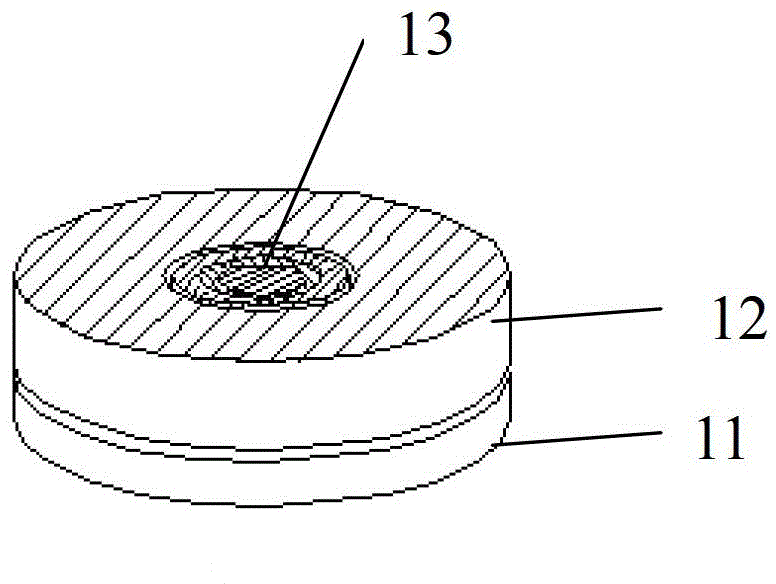
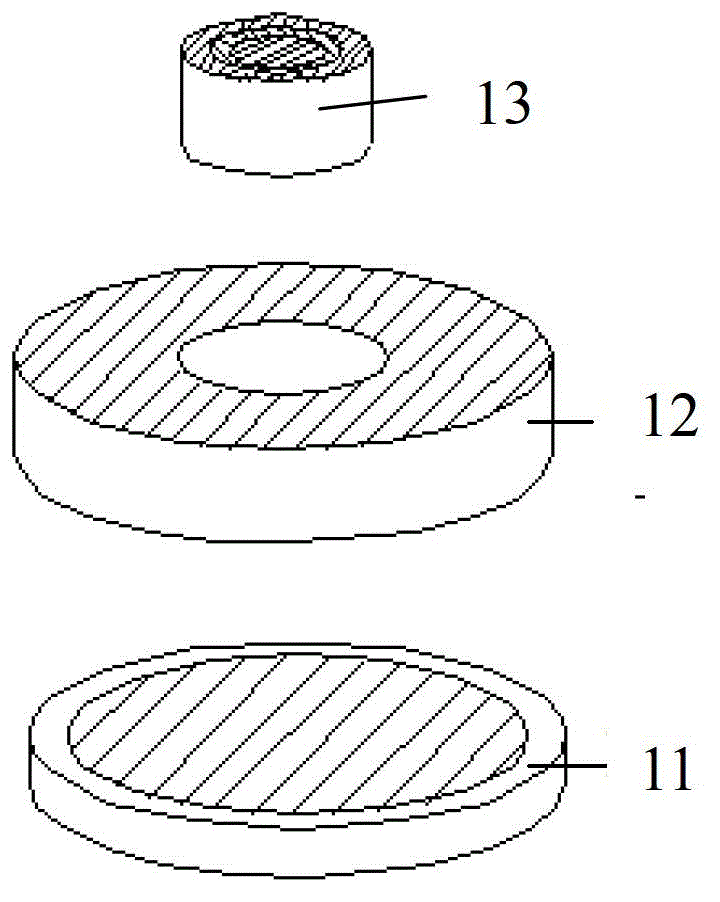
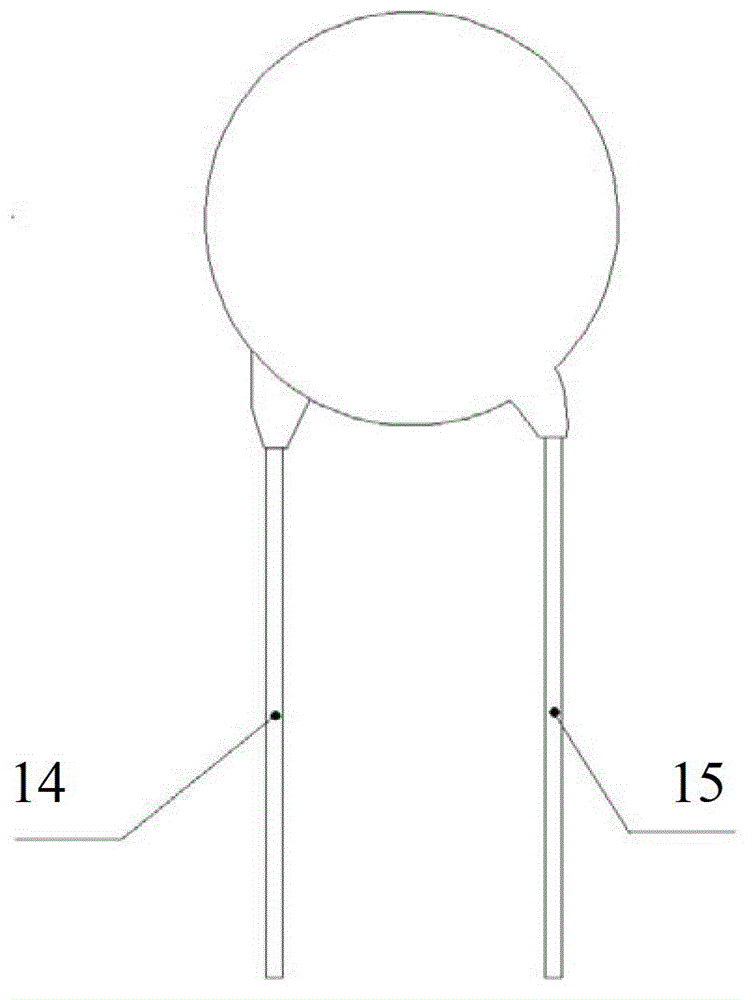
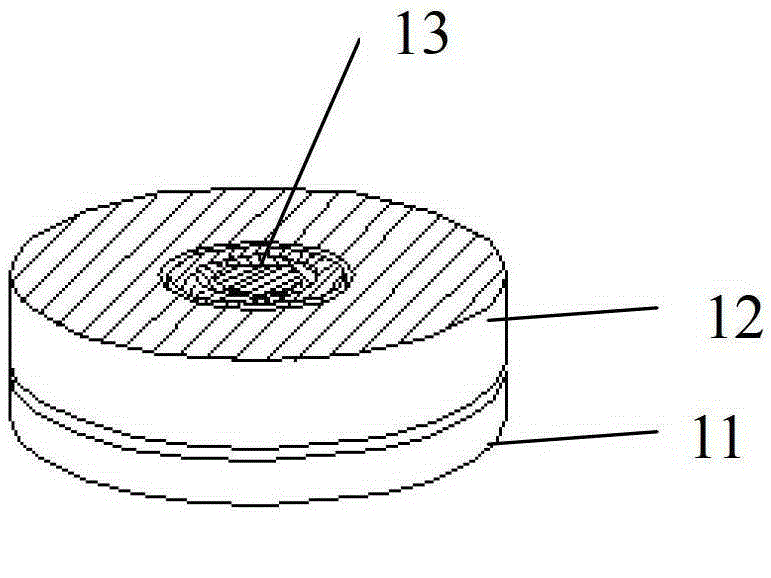
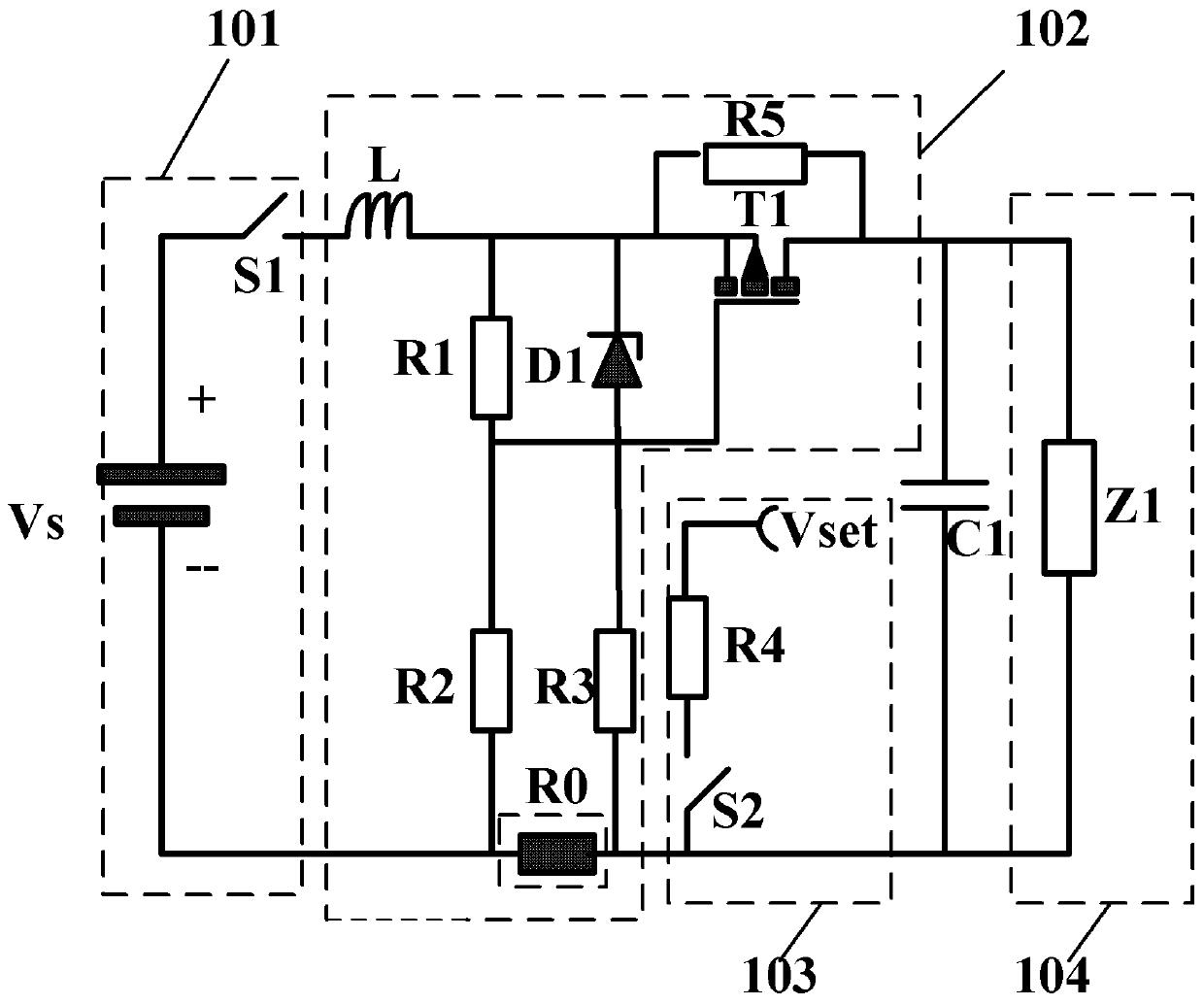
Anti-thunder overvoltage protection device
InactiveCN103346547ANormal work is not affectedCurrent limitEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentOvervoltageLightning strokes
The invention discloses an anti-thunder overvoltage protection device. The anti-thunder overvoltage protection device comprises a piezoresistor, a positive temperature coefficient thermistor and a gas discharge tube, wherein the positive temperature coefficient thermistor is connected with the gas discharge tube in parallel and then connected with the piezoresistor in series; the positive temperature coefficient thermistor and the piezoresistor form a thermal coupling relationship. The piezoresistor, the positive temperature coefficient thermistor and the gas discharge tube can be packaged into a whole, or the piezoresistor and the positive temperature coefficient thermistor are packaged into a whole, thus a packaged body is formed, and the gas discharge tube is located outside the packaged body. The anti-thunder overvoltage protection device not only can restrain operation overvoltage and fault power frequency overvoltage, but also can have the protection function of a normal voltage-sensitive element when lightning stroke pulse overvoltage occurs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +2
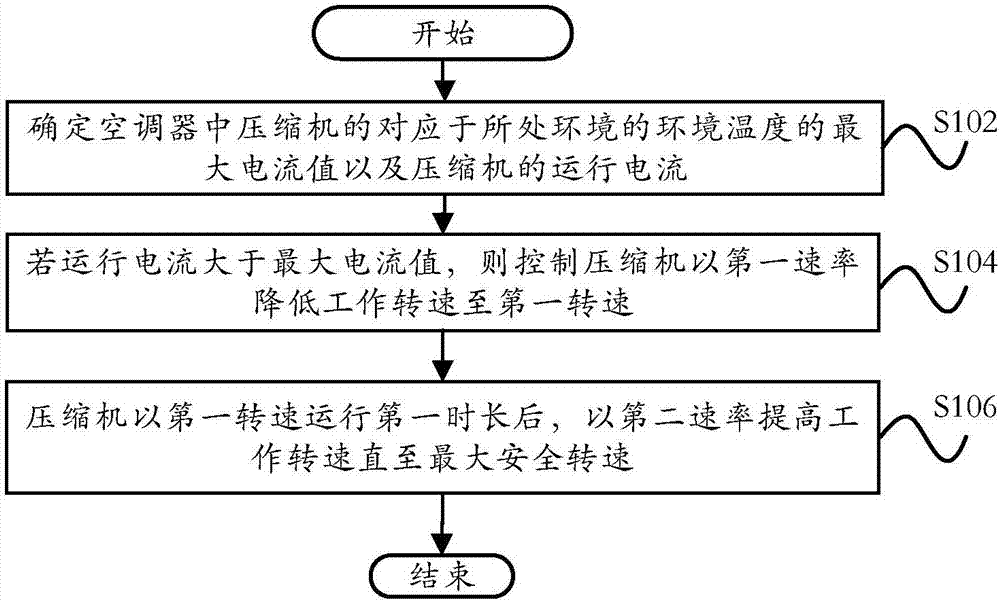
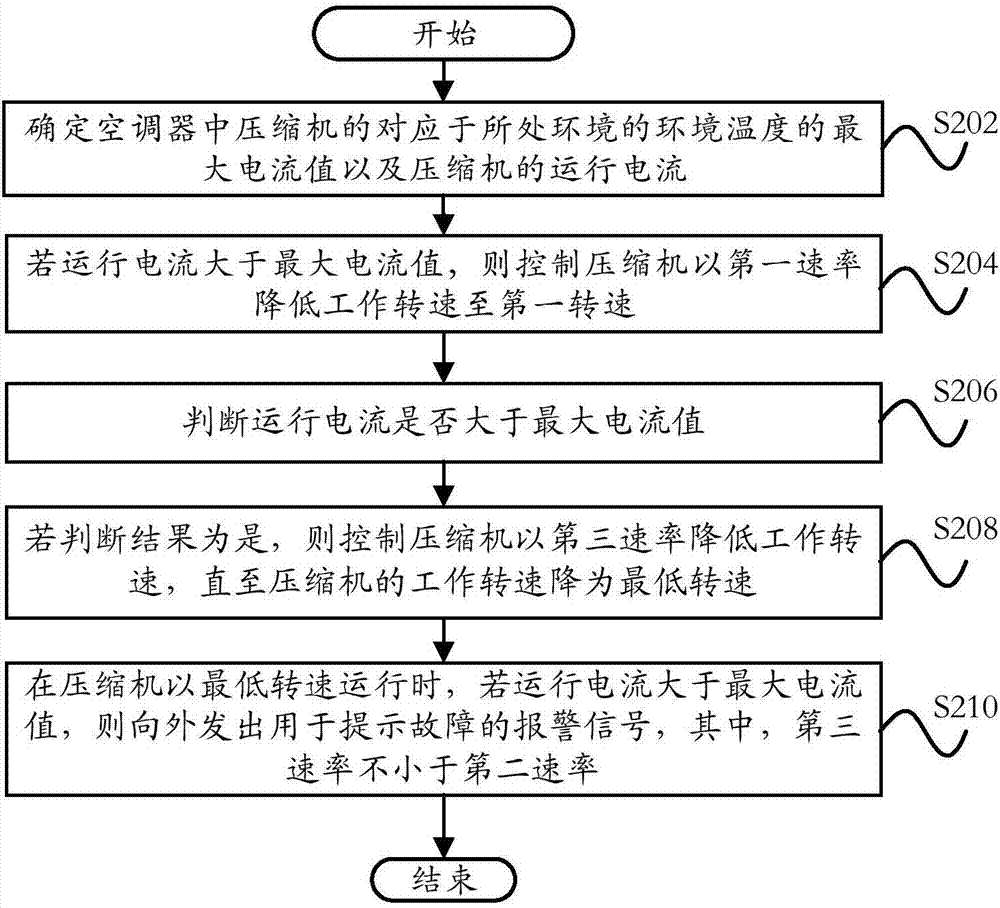
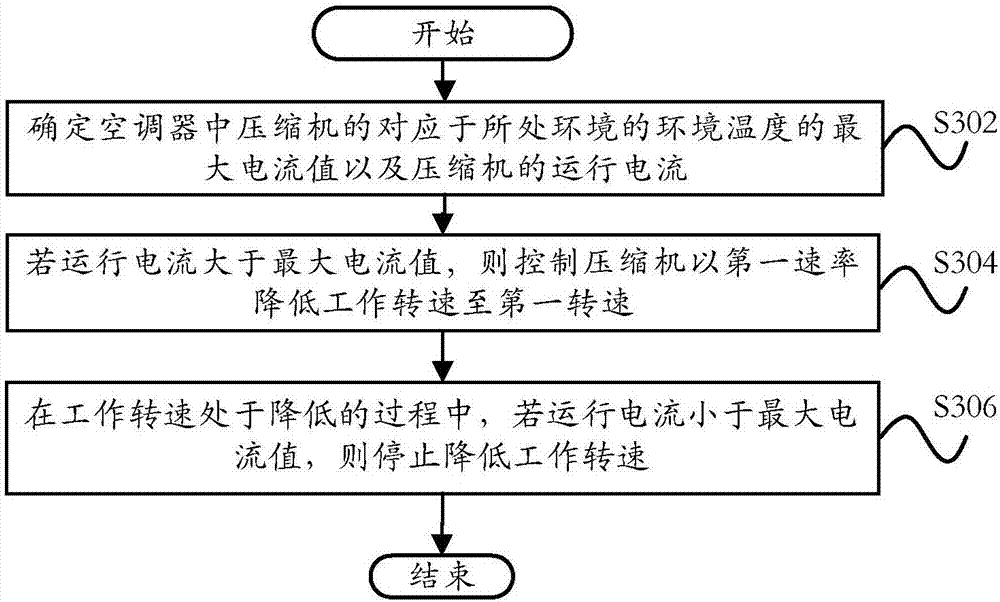
Current control method, current control system and air conditioner
ActiveCN107091516ACurrent limitAvoid damageMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsControl systemComputer module
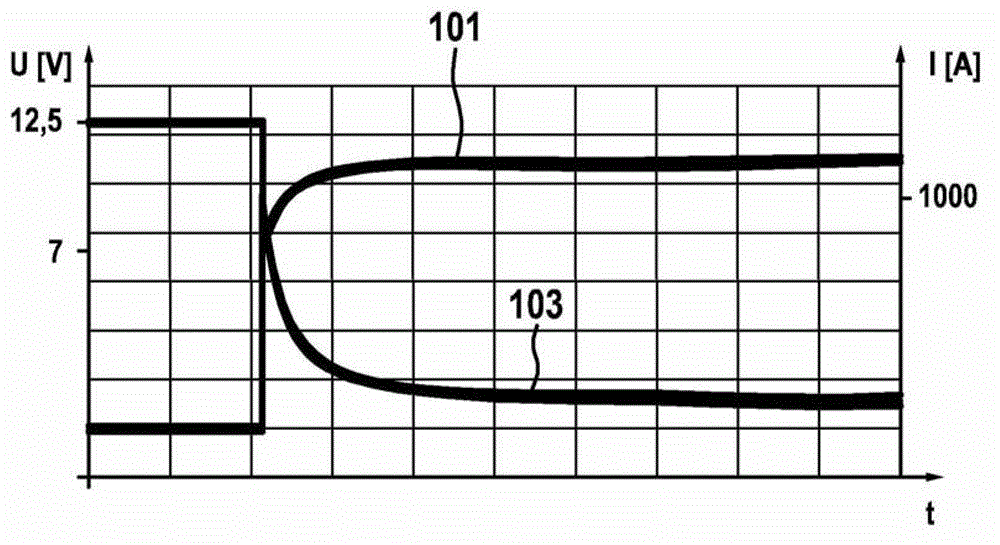
The invention provides a current control method, a current control system and an air conditioner. The current control method is used for the air conditioner and comprises the following steps: determining the maximum current value, which corresponds to the environmental temperature of an environment where the air conditioner is placed, of a compressor in the air conditioner and operation current of the compressor; if the operation current is greater than the maximum current value, controlling the working rotating speed of the compressor to be reduced to a first rotating speed at a first rate; and after the compressor operates for a first time length at the first rotating speed, increasing the working rotating speed at a second rate till the rotating speed reaches the maximum safety rotating speed. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, when the operation current detected of the compressor is greater than a safety range, the operation current of the compressor is reduced to be within the safety range; and after temperatures of a power module and an element for controlling a computer board are reduced to be within the safety range, the compressor operates at the maximum power, so that the system reliability of the air conditioner is improved, the refrigeration effect of the air conditioner is enhanced, and the user experience is increased.
Owner:GD MIDEA HEATING & VENTILATING EQUIP CO LTD +1
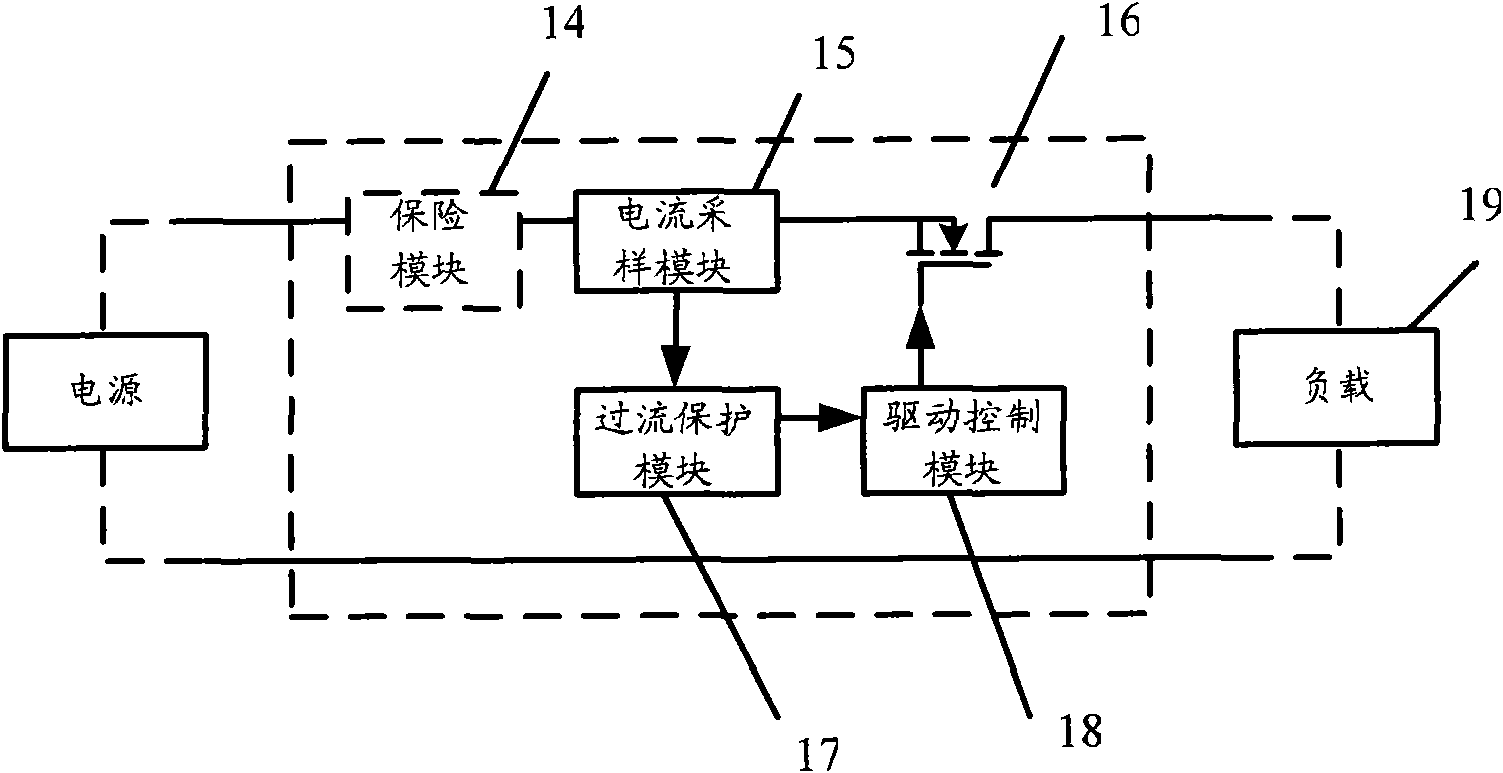
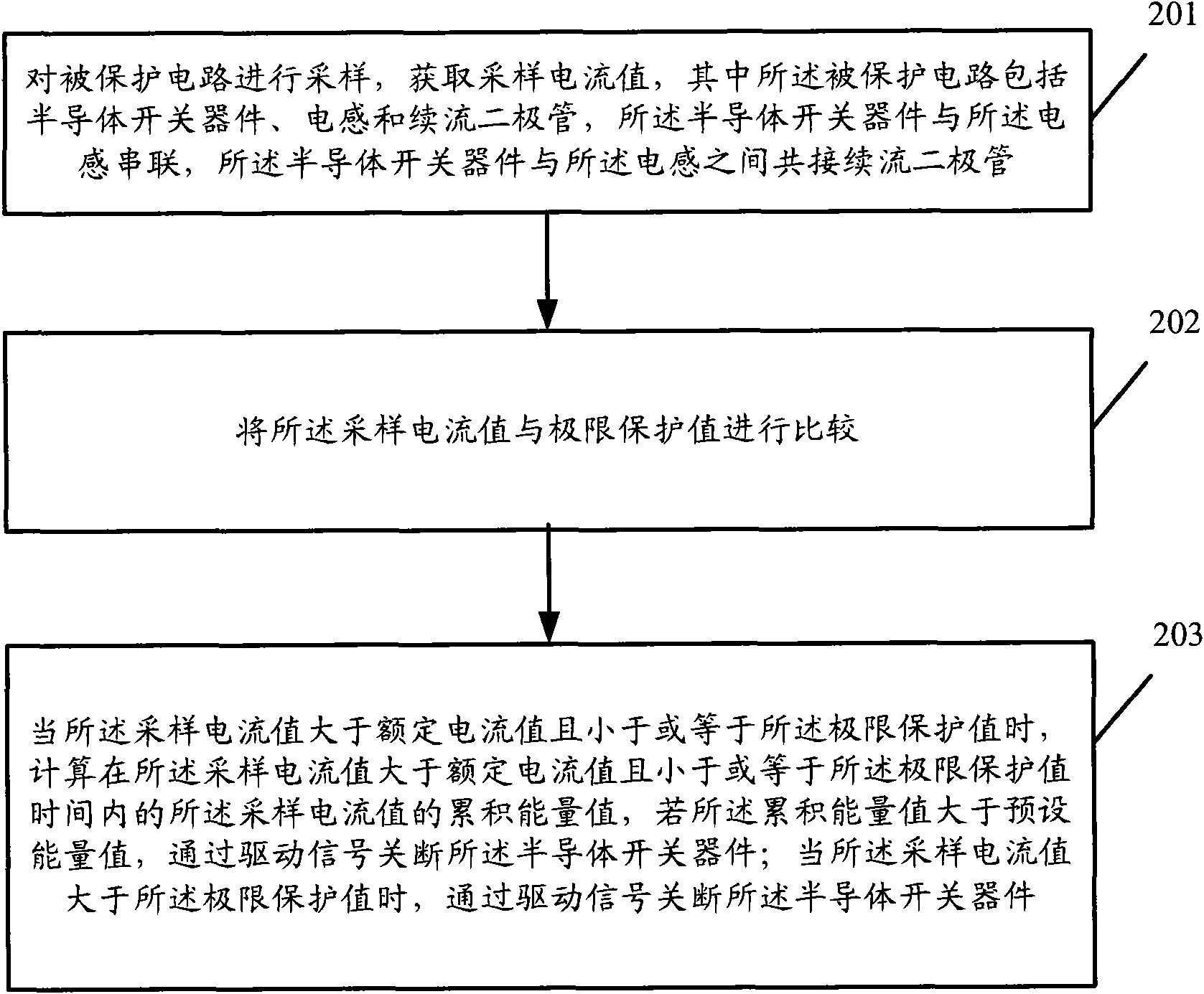
Distribution protection method and distribution protection device
ActiveCN101651336AEffective current limitCurrent limitEmergency protective circuit arrangementsInductorFlyback diode
The invention discloses a distribution protection method and a distribution protection device. The method comprises the following steps: sampling a protected circuit and acquiring a sampling current value, wherein the protected circuit comprises a semiconductor switching device, an inductor and a fly-wheel diode; the semiconductor switching device is connected in series with the inductor; and thefly-wheel diode is jointly connected between the semiconductor switching device and the inductor; comparing the sampling current value with a limit protection value; calculating a cumulative energy value of the sampling current value when the sampling current value is larger than a rated current value, but smaller than or equal to the limit protection value; switching off the semiconductor switching device by a driving signal if the cumulative energy value is larger than a preset energy value; and switching off the semiconductor switching device by the driving signal when the sampling currentvalue is larger than the limit protection value. The technical scheme improves the accuracy of overcurrent judgment and reduces the possibility of damaging semiconductor devices.
Owner:HUAWEI DIGITAL POWER TECH CO LTD
Method for operating a power converter in a soft-switching range
InactiveCN101194412ACurrent limitSmall currentDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringBridge circuit
In order to convert the first DC voltage into a second DC voltage, a first bridge circuit included in the power converter is controlled to convert the first DC voltage into a first AC voltage. This first AC voltage is transformed into a second and possibly further AC voltage. The second and possibly further AC voltages are converted into DC voltages via respective bridge circuits. In order to increase the efficiency of the power converter, the switches of the power converter are controlled to operate in soft switching. Additionally, the duty cycle of each AC voltage is controlled. In one embodiment, the half-cycle voltage-time integral of each AC voltage is controlled to be substantially equal.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
Magnetic coupling commutation type transfer circuit and use method thereof
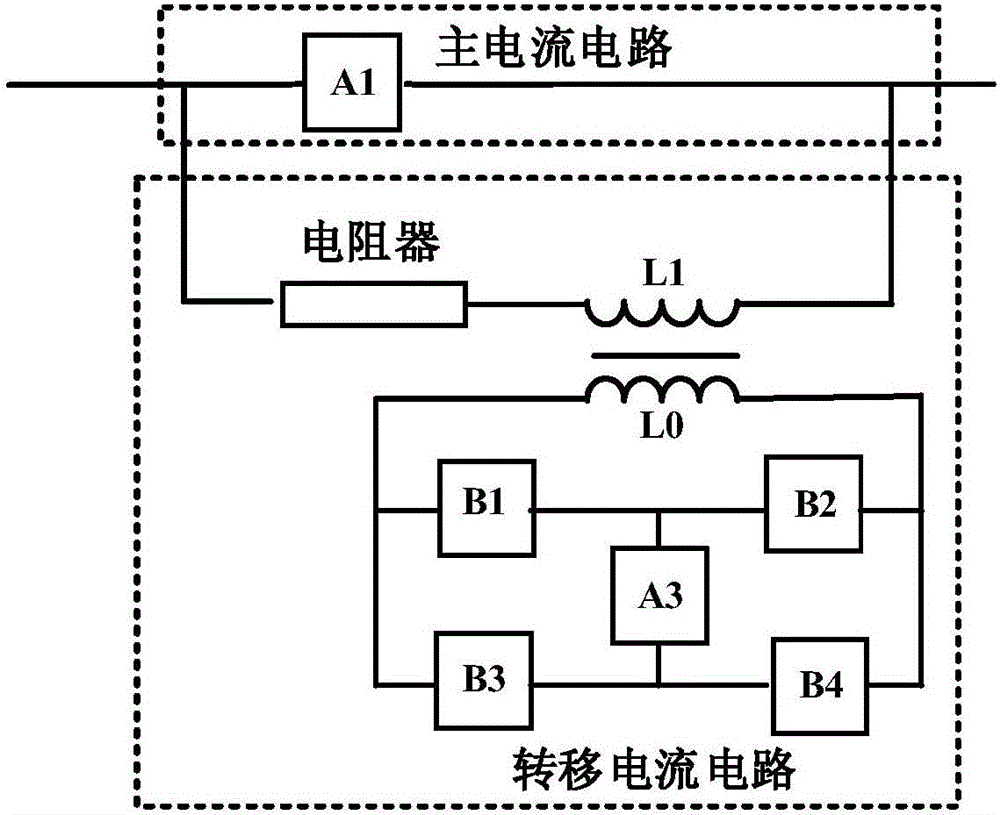
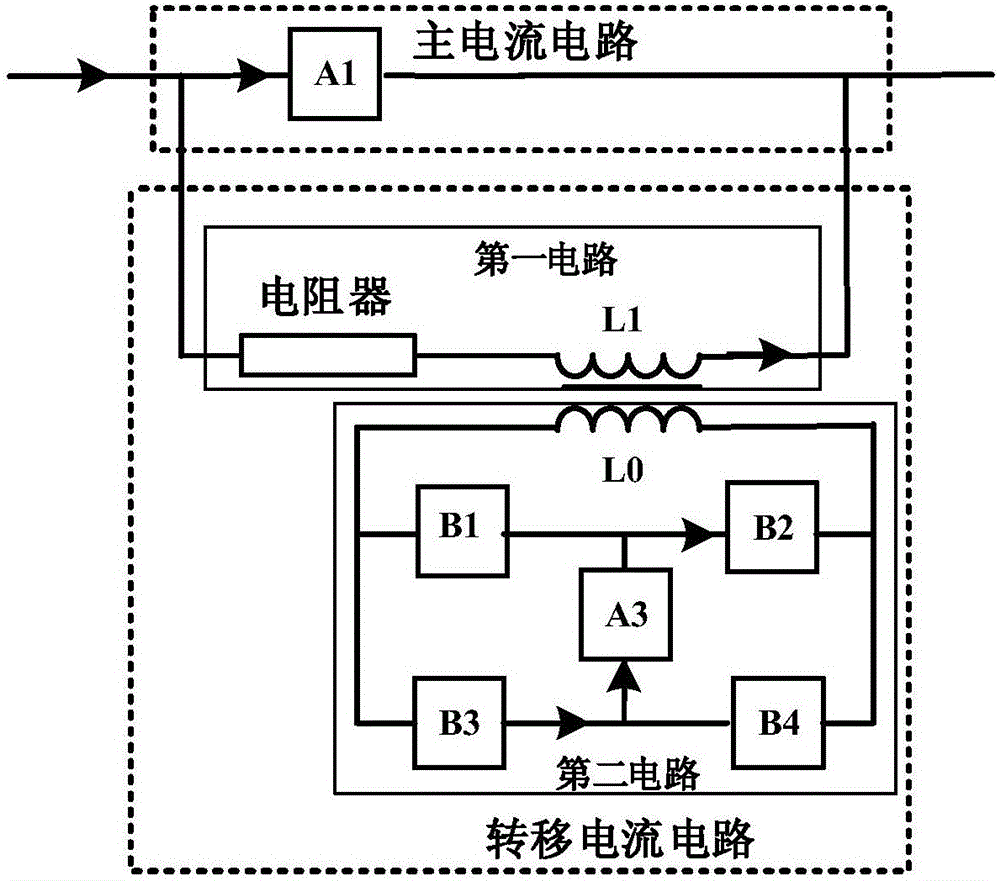
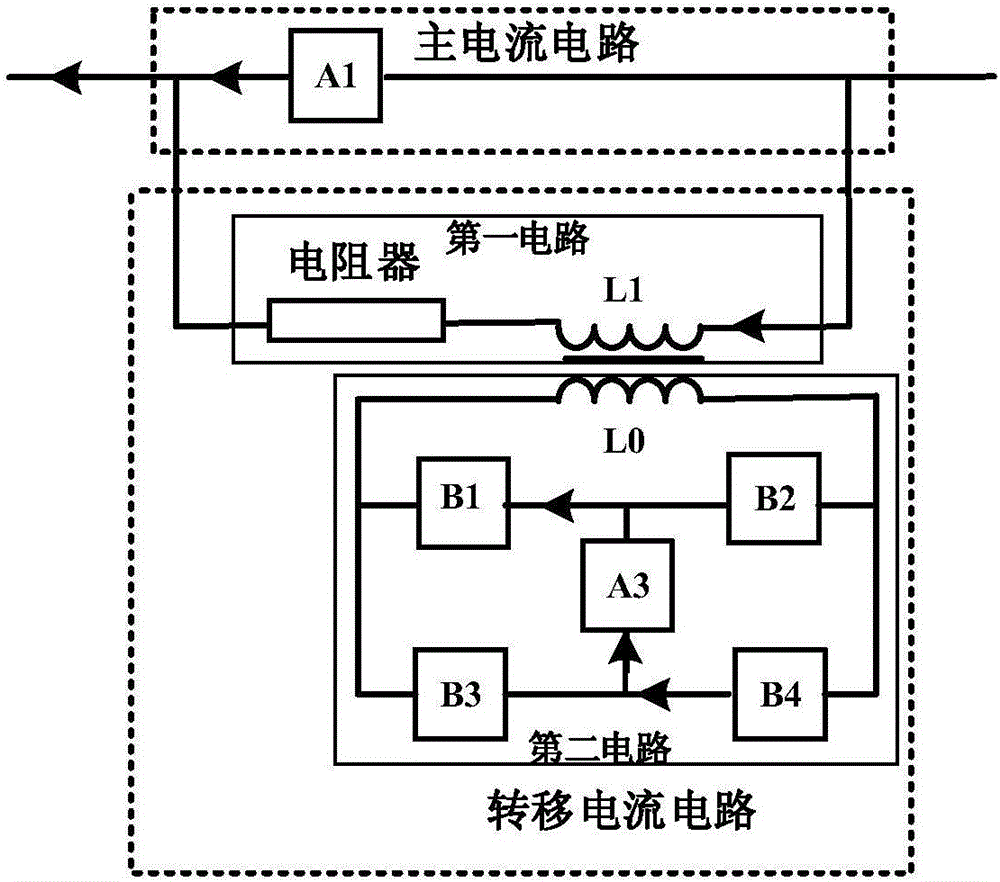
ActiveCN106356834ACurrent limitAchieve isolationDc network circuit arrangementsCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a magnetic coupling commutation type transfer circuit and a use method thereof. The magnetic coupling commutation type transfer circuit comprises a main current circuit and a transfer current circuit, wherein the main current circuit is formed by connecting a mechanical switch, a power electronic device, a current limiter, a resistor and one or more of conducting wires in series or parallel; the transfer current circuit comprises a first circuit and a second circuit; the first circuit is formed by connecting an inductor L1 at a secondary side and a resistor in series; the second circuit is formed by connecting a third circuit A3, power semiconductor devices or triggering gaps B1-B4, and an inductor L0 at a primary side in series, and the third circuit consists of a precharging capacitor or a superconduction inductor. The magnetic coupling commutation type transfer circuit has the advantages that the voltage produced by a voltage transformer is used for directly transferring current to the resistor, the process of transferring the current into the capacitor or the power electronic device is not needed, and compared with the prior art, the current limiting speed and reliability are higher; a capacitor charging unit can be isolated from a direct current system, the voltage class and size of the charging unit are obviously reduced, and the action reliability is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Starting overshoot suppression circuit used for LDO
ActiveCN109450417AAchieve inhibitionFlow load avoidanceElectronic switchingEnergy efficient computingPower flowEngineering
The invention discloses a starting overshoot suppression circuit used for an LDO. The circuit comprises a first overshoot suppression circuit connected between a power end and an output end of an error amplifier of the LDO; the first overshoot suppression circuit comprises a first switch control unit and a voltage clamp unit which are in series connection, moreover, an enabling signal of the firstswitch control unit is obtained through inverting the enabling signal of the LDO and delaying for first predetermined time, thus, within the first predetermined time of starting of the LDO, through the voltage clamp unit, grid voltage of a power tube of the LDO is clamped to a first predetermined value, and grid source voltage of the power tube is maintained at a second predetermined value, so, current output to a load by the LDO is limited. With simpler circuit design, smaller circuit area and ultralow circuit power consumption, the starting overshoot suppression circuit provided by the invention realizes suppression of overshoot generated when the LDO starts, and thus, relatively small starting overshoot is realized.
Owner:深圳芯智汇科技有限公司
Power semiconductor device for igniter
InactiveCN102185597ACurrent limitSmall currentSolid-state devicesElectronic switchingPower semiconductor deviceIgnition coil
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Current-limiting arc-extinguishing shunted exciter tripping type earthing short circuit protection device
InactiveCN101350514ARealize the protection functionAvoid shockArrangements responsive to excess currentCurrent limitingLow voltage
The present invention belongs to the technical field of protecting single-phase grounding short-circuit which results from insulation failure of single-phase and three-phase power consuming equipment in a low-voltage power network, and in particular relates to a current-limiting, arc-eliminating and excitation-dividing tripping type grounding short-circuit protection device. The technical proposal consists of a circuit breaker actuating device, a circuit breaker starting mechanism, and a short-circuit detection actuating mechanism. Because the current or voltage signals which are used for actuating the protection device is not related to the short-circuit current of the original grounding short-circuit loop, the protection device solves the problem of dependence on the fuse for the grounding short-circuit failure in the long term and the problem that the short-circuit switch with current as a parameter can not easily generate the maximum allowable temperature rise (igniting fire) in the loop wire within the protective range, and in particular in the terminal insulating wire of the power consuming equipment, so as to timely cut off the circuit.
Owner:章宏
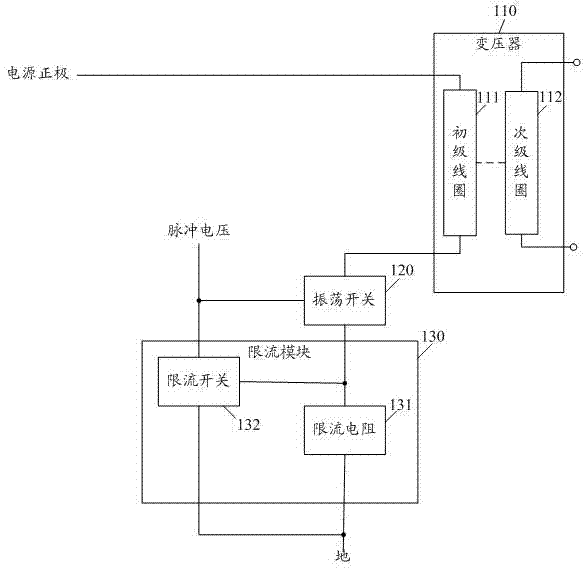
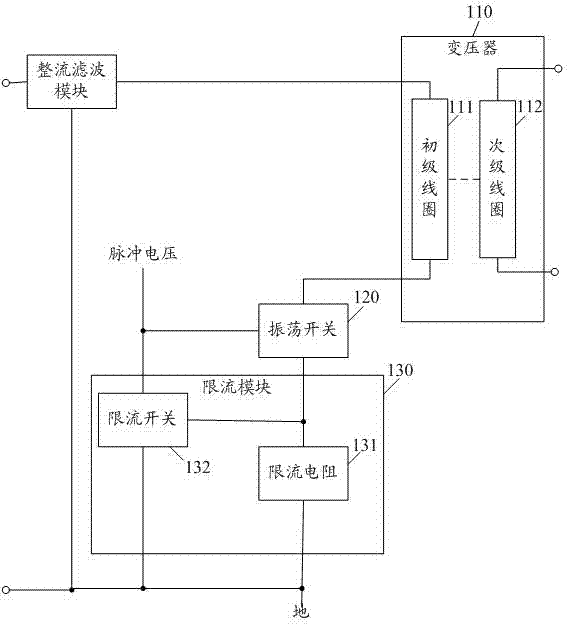
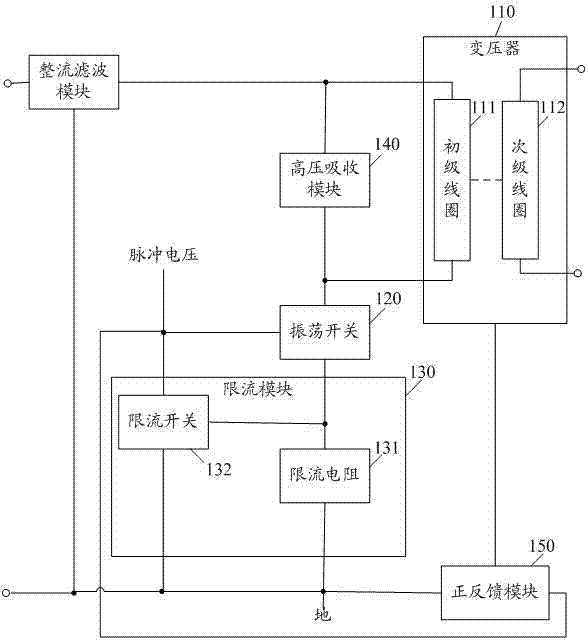
Current limiting charging circuit
InactiveCN103368243ASmall currentCurrent limitBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerPower flowCurrent limiting
The embodiment of the invention discloses a current limiting charging circuit comprising a transformer, an oscillation switch and a current limiting module. The current limiting module comprises a current limiting resistor and a current limiting switch. A primary coil of the transformer, the oscillation switch and the current limiting resistor are in series connection in order and then are connected between an anode of a power supply and the ground. A control end of the oscillation switch is communicated with pulse voltage. The current limiting switch is connected between the control end of the oscillation switch and the ground. A control end of the current limiting switch is connected with a common node of the current limiting resistor and the oscillation switch. By employing the current limiting charging circuit, the current of the charging circuit can be effectively limited, the burning of a component due to overcurrent is prevented, and the service life of the charging circuit is prolonged.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
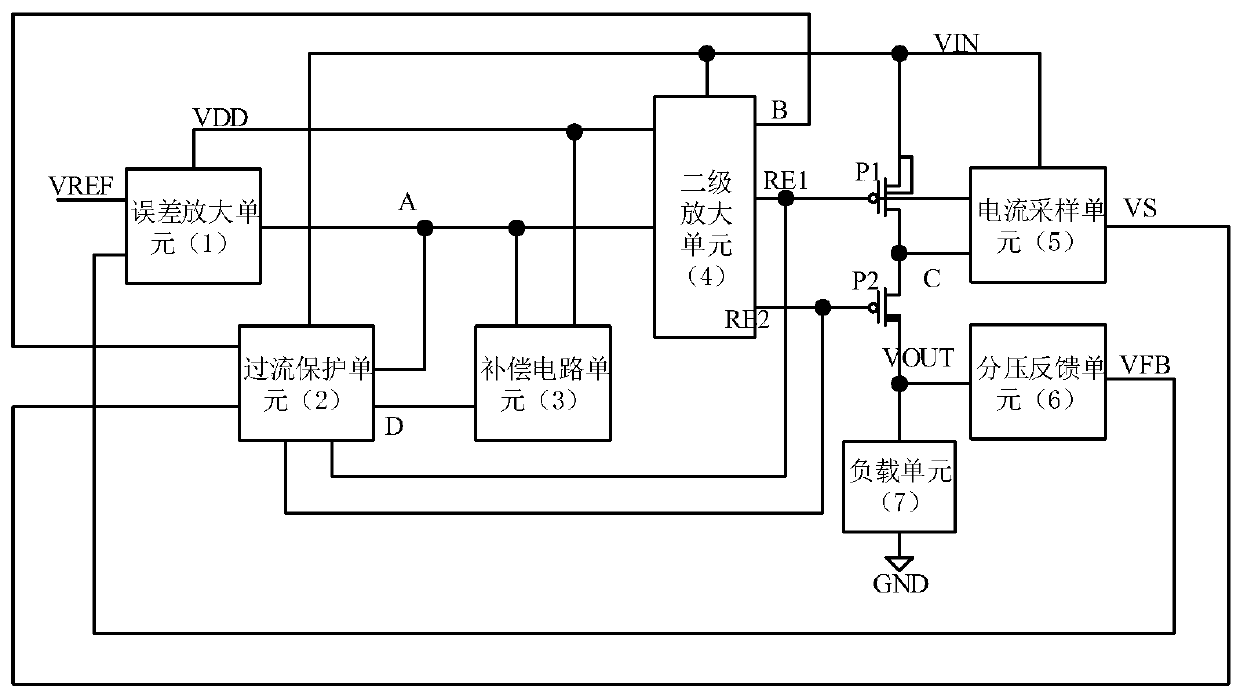
High-input-voltage double-loop stable linear voltage regulator
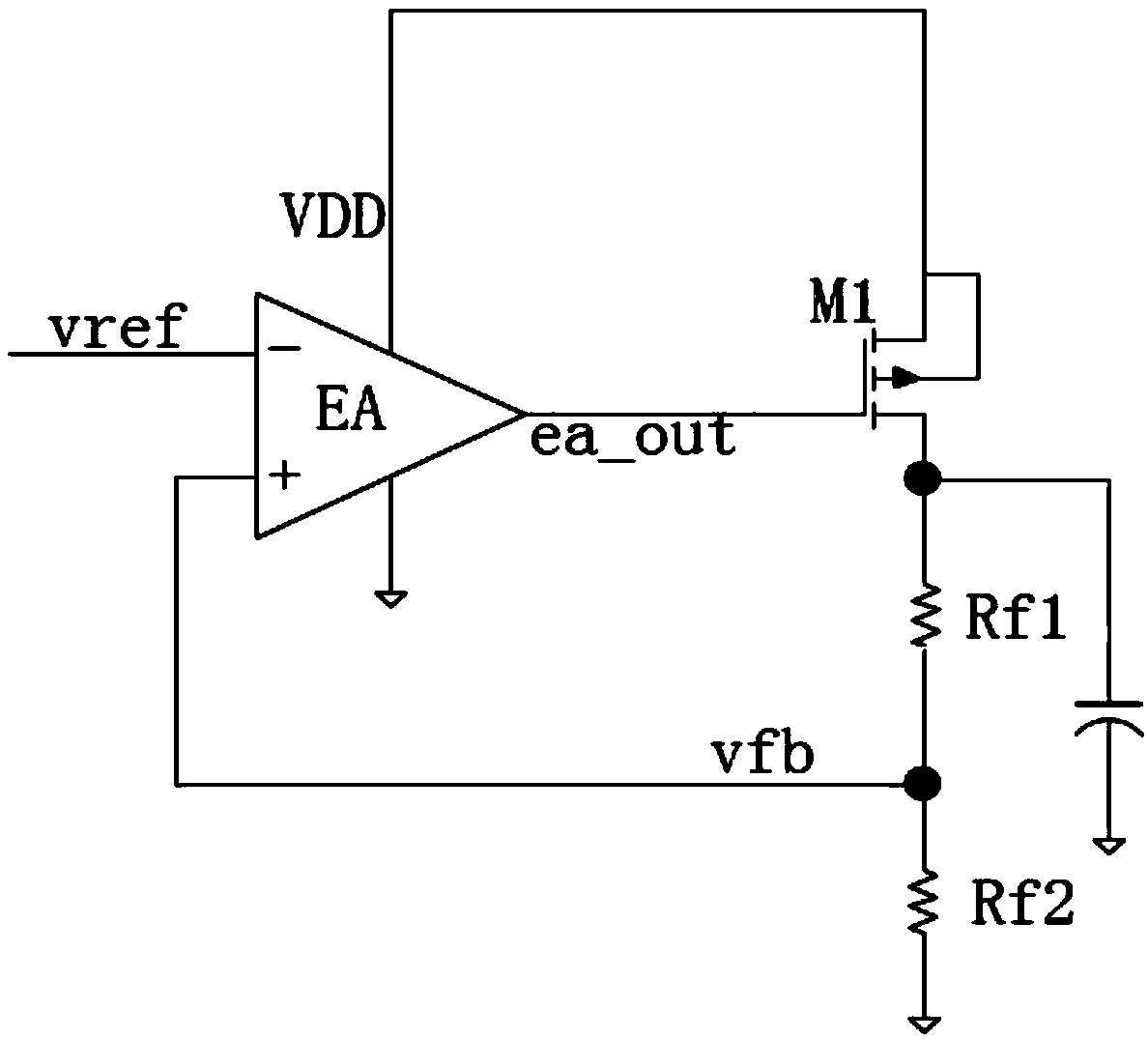
ActiveCN111190456ADoes not affect normal workDoes not affect pole-zero distributionElectric variable regulationFrequency compensationControl signal
The invention discloses a high-input-voltage double-loop stable linear voltage regulator. The linear voltage regulator comprises an error amplification unit (1), an overcurrent protection unit (2), acompensation circuit unit (3), a secondary amplification unit (4), a current sampling unit (5), a first PMOS transistor P1 and a second PMOS transistor P2. The error amplification unit (1) is used forcompleting conversion from double-end input to single-end output; the overcurrent protection unit (2) is used for realizing an over-current protection function; the compensation circuit unit (3) is used for ensuring the stability of a loop under various loads; and the secondary amplification unit (4) is used for converting the output of an error amplifier into two paths of control signals relatedto the power supply voltage. There are an error amplification unit main loop and an over-current protection loop, the two loops are both provided with frequency compensation circuits, and frequency compensation does not interfere with each other. The voltage regulator is suitable for a power supply environment with high power supply voltage and a large load change range.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
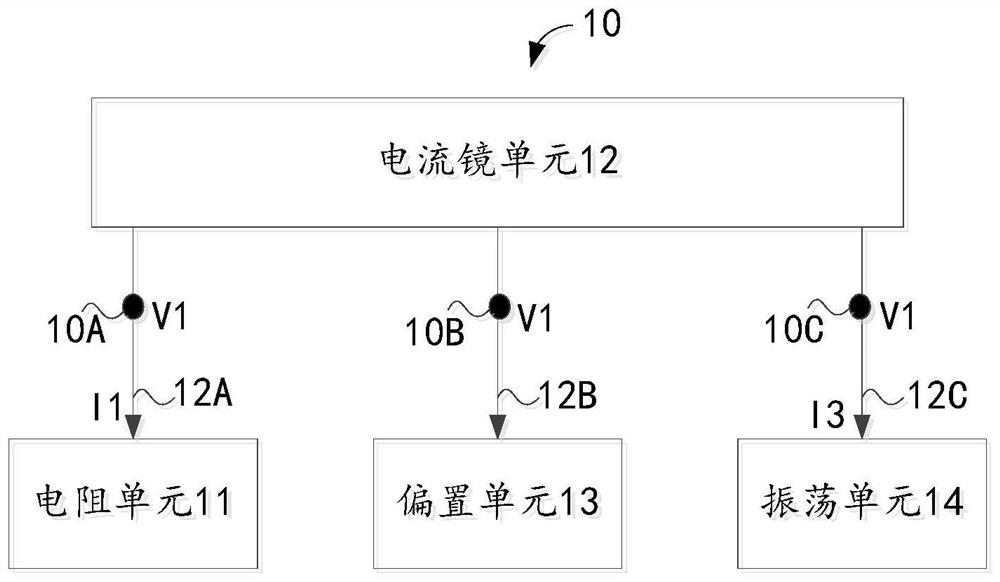
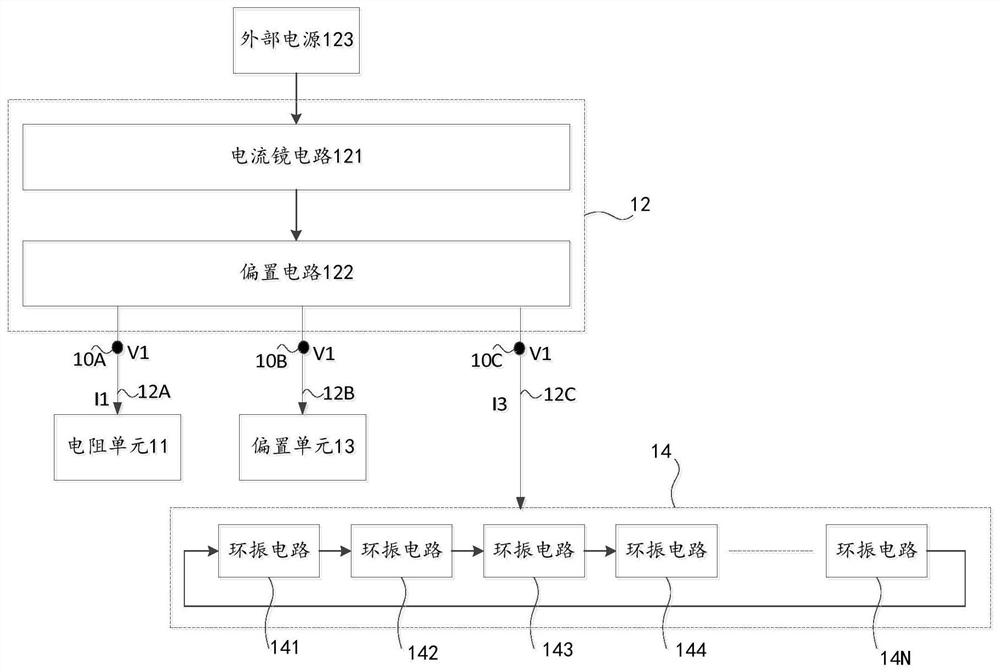
Voltage-controlled oscillator, integrated chip, and electronic device
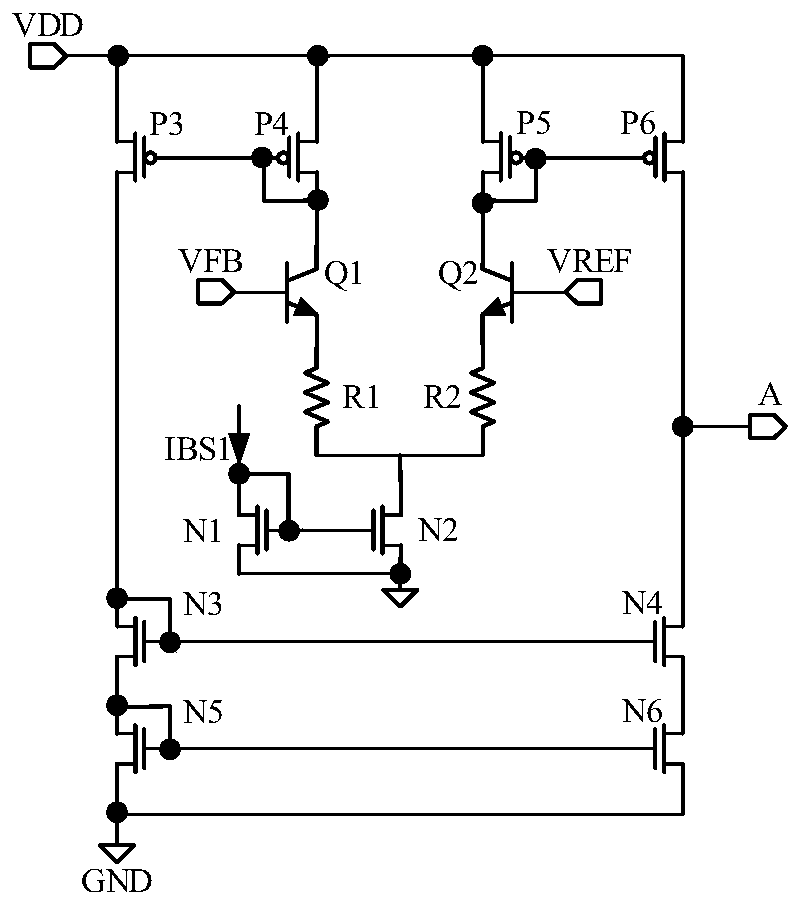
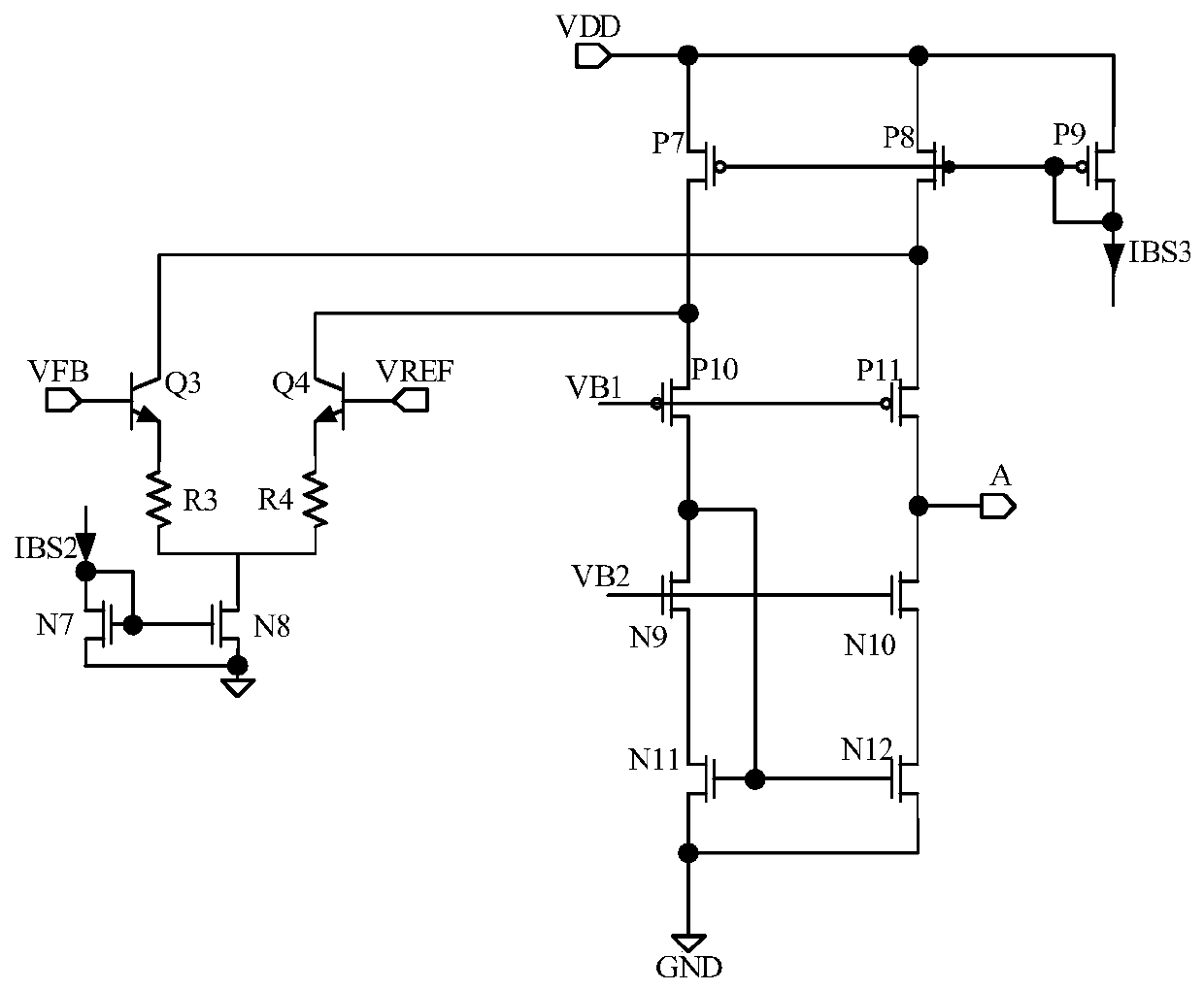
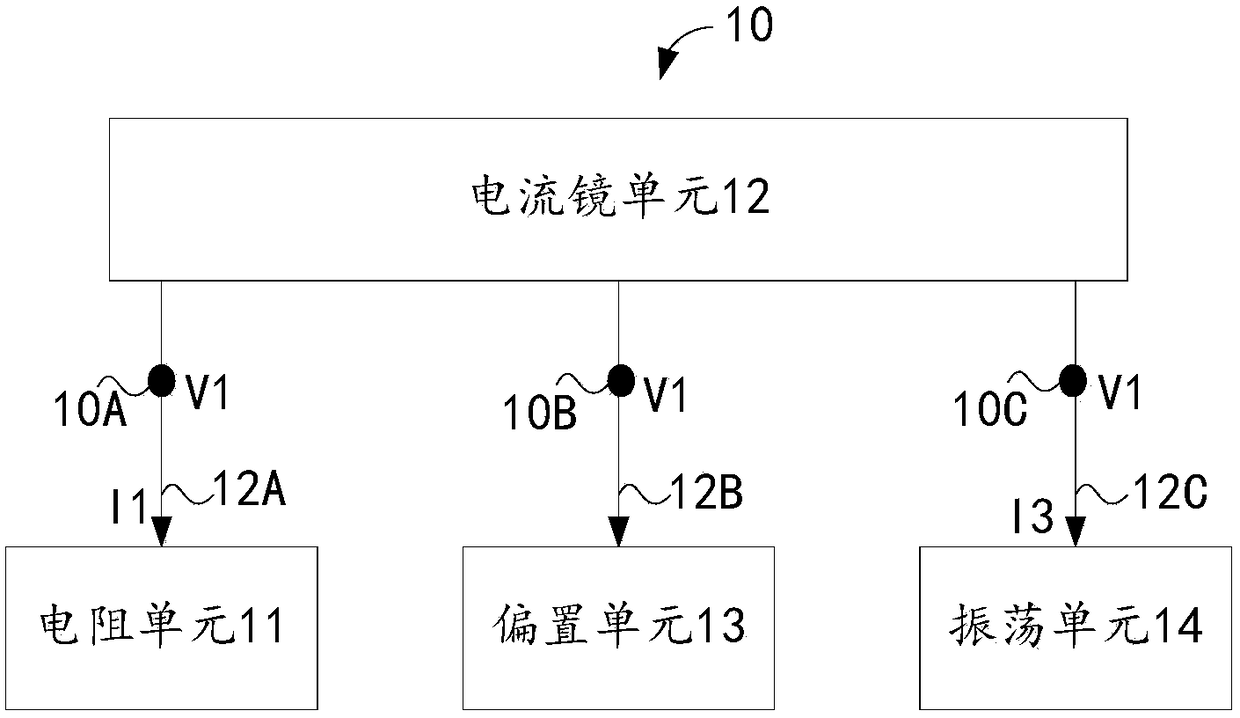
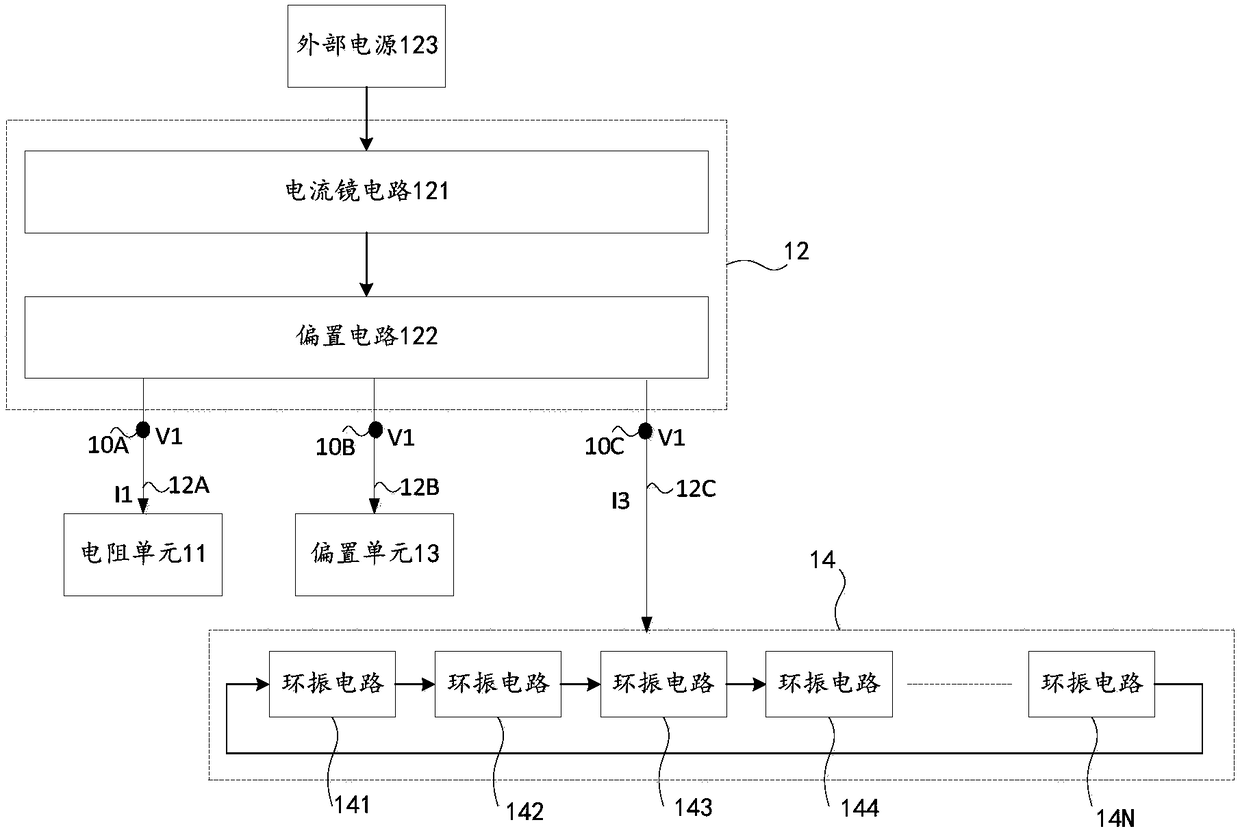
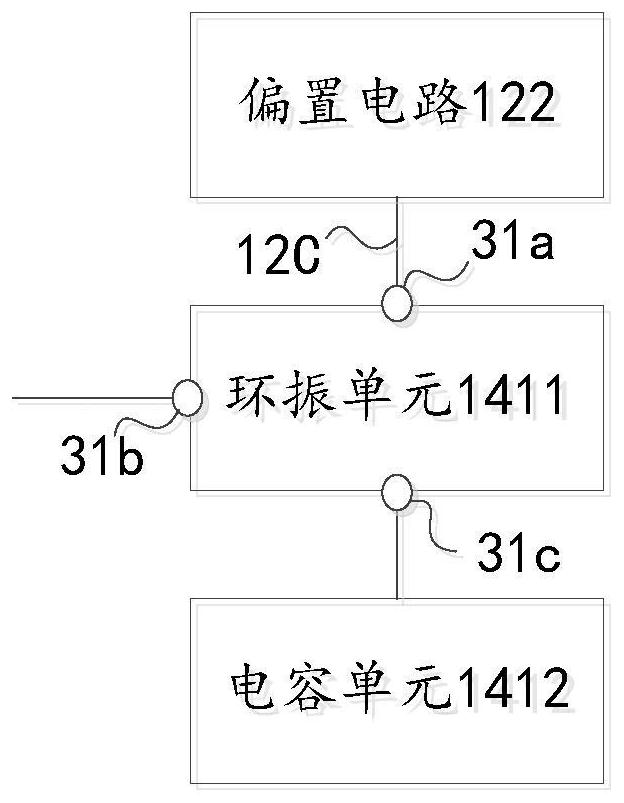
ActiveCN109286369AHigh precisionCurrent limitOscillations generatorsCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention relates to the technical field of integrated circuits, in particular, to a voltage-controlled oscillator, an integrated chip, and an electronic device. The voltage-controlled oscillatorcomprises a resistor unit, a current mirror unit, a bias unit, and an oscillating unit. The current mirror unit responds to a first bias voltage provided by the bias unit to carries out bias processing on a voltage of a first node at a first current path and a voltage of a third node at a third current path to generate a first bias voltage and is also used for responding to resistance configuration of the resistor unit and adjusting a third current flowing through the third current path, wherein the first current flowing through the first current path is equal to the third current. Therefore,with configuration of the resistance corresponding to the resistor unit, the charging and discharging time of the capacitor of the oscillating unit can be indirectly adjusted to change the oscillationperiod of the oscillating unit and thus the changed oscillation period is closer to a desired oscillation period, so that the output accuracy of the oscillation period is improved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
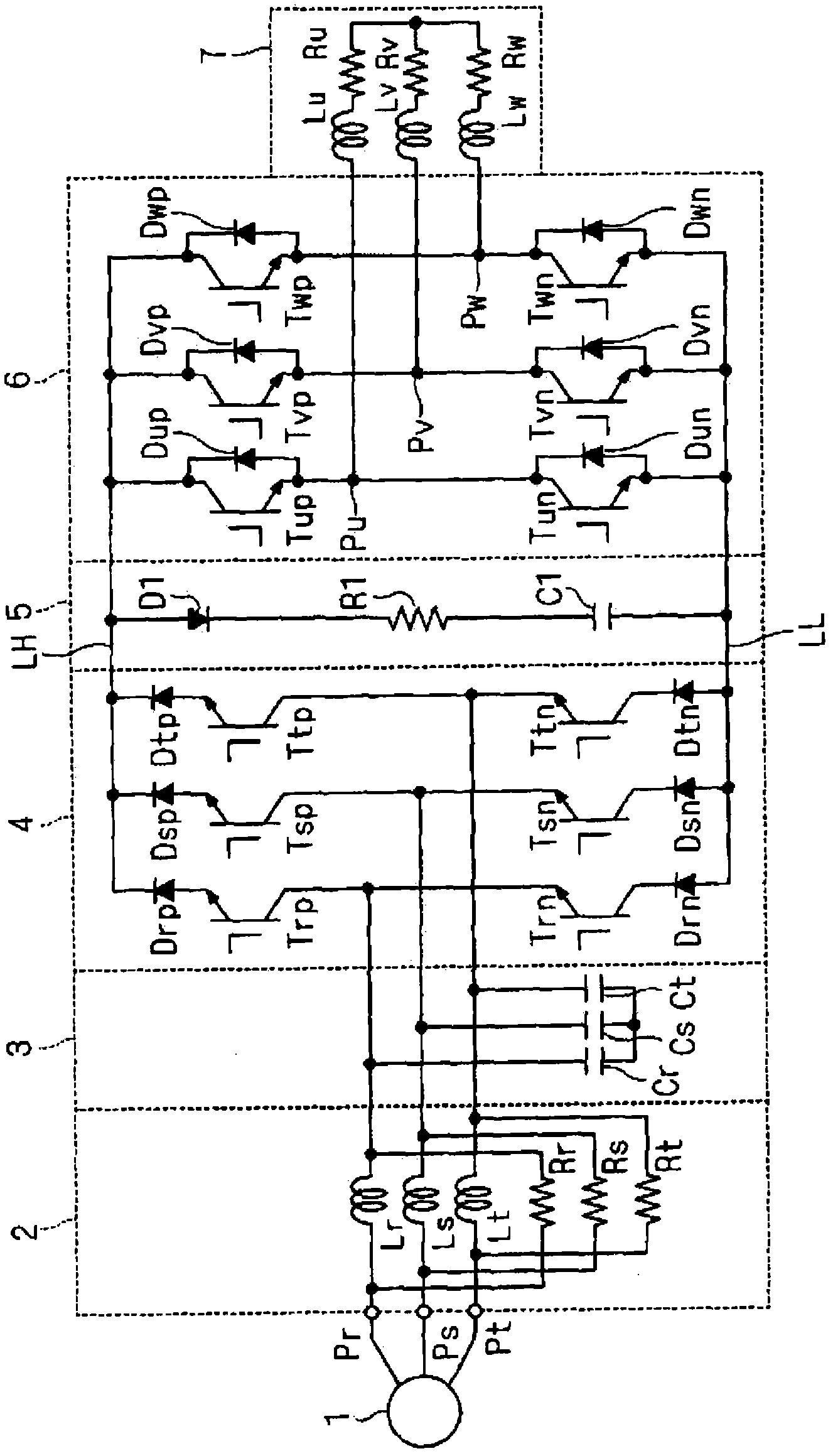
Power converter
ActiveCN102422518ACurrent limitSuppresses increasing currentAc-dc conversion without reversalAc-ac conversionElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
Provided is a power converter which suppresses a current that flows to a capacitor due to a direct current link voltage increase generated by parasitic inductance when a switching a converter is switched in the normal operation. The converter (4) has switching elements, which are connected between a plurality of input terminals (Pr, Ps, Pt) and a direct current power supply line (LH), and switching elements, which are connected between the plurality of input terminals (Pr, Ps, Pt) and a direct current power supply line (LL). A capacitor (C1), a resistor (R1), and a diode (D1) are connected to each other in series between the direct current power supply lines (LH, LL).
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
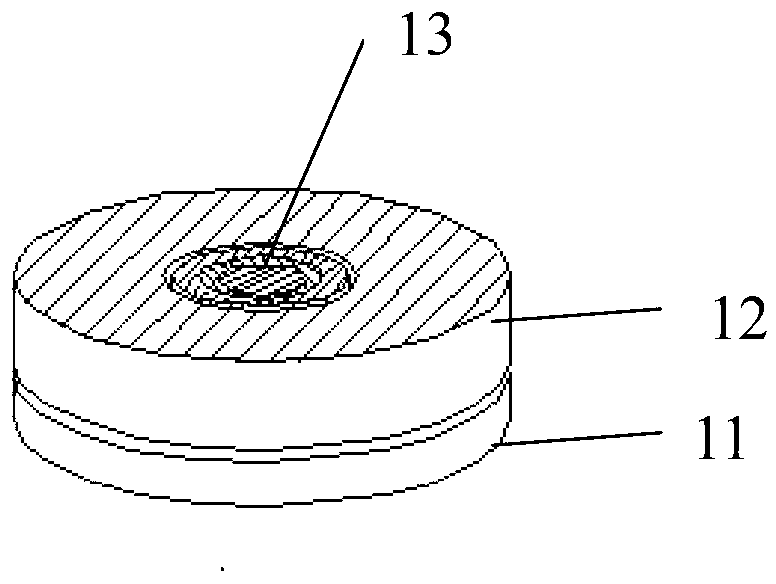
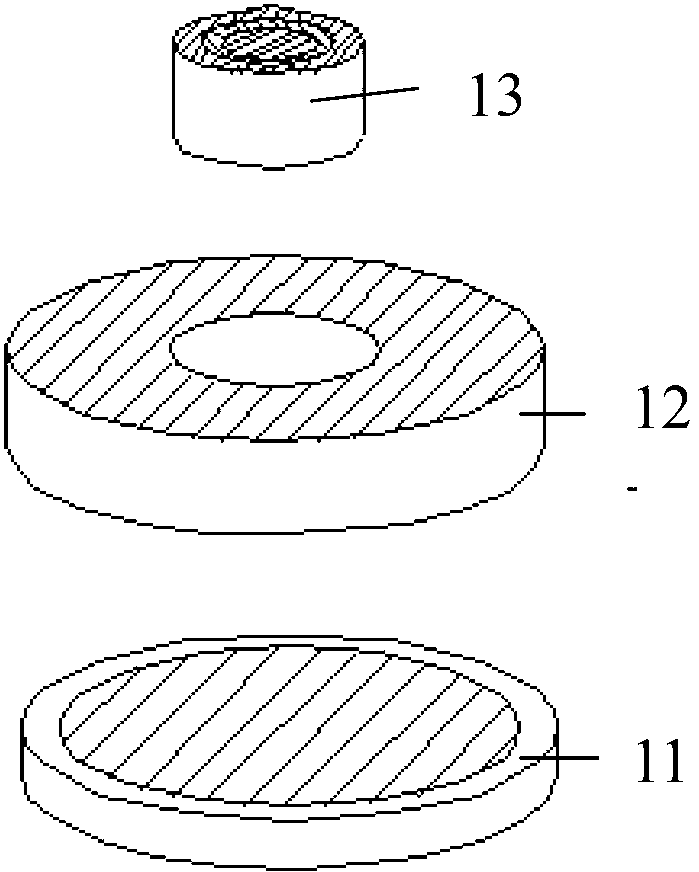
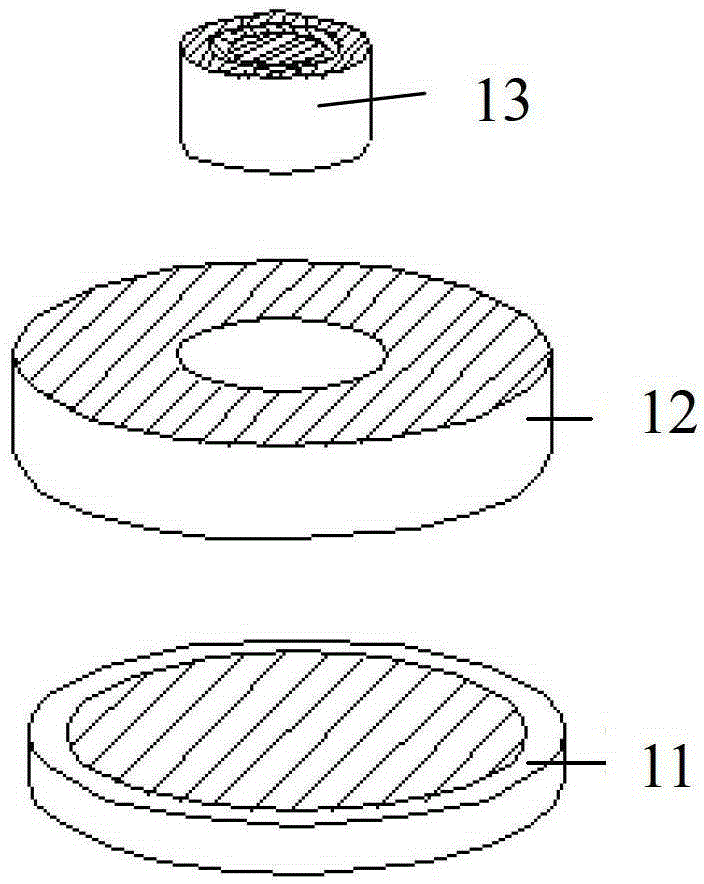
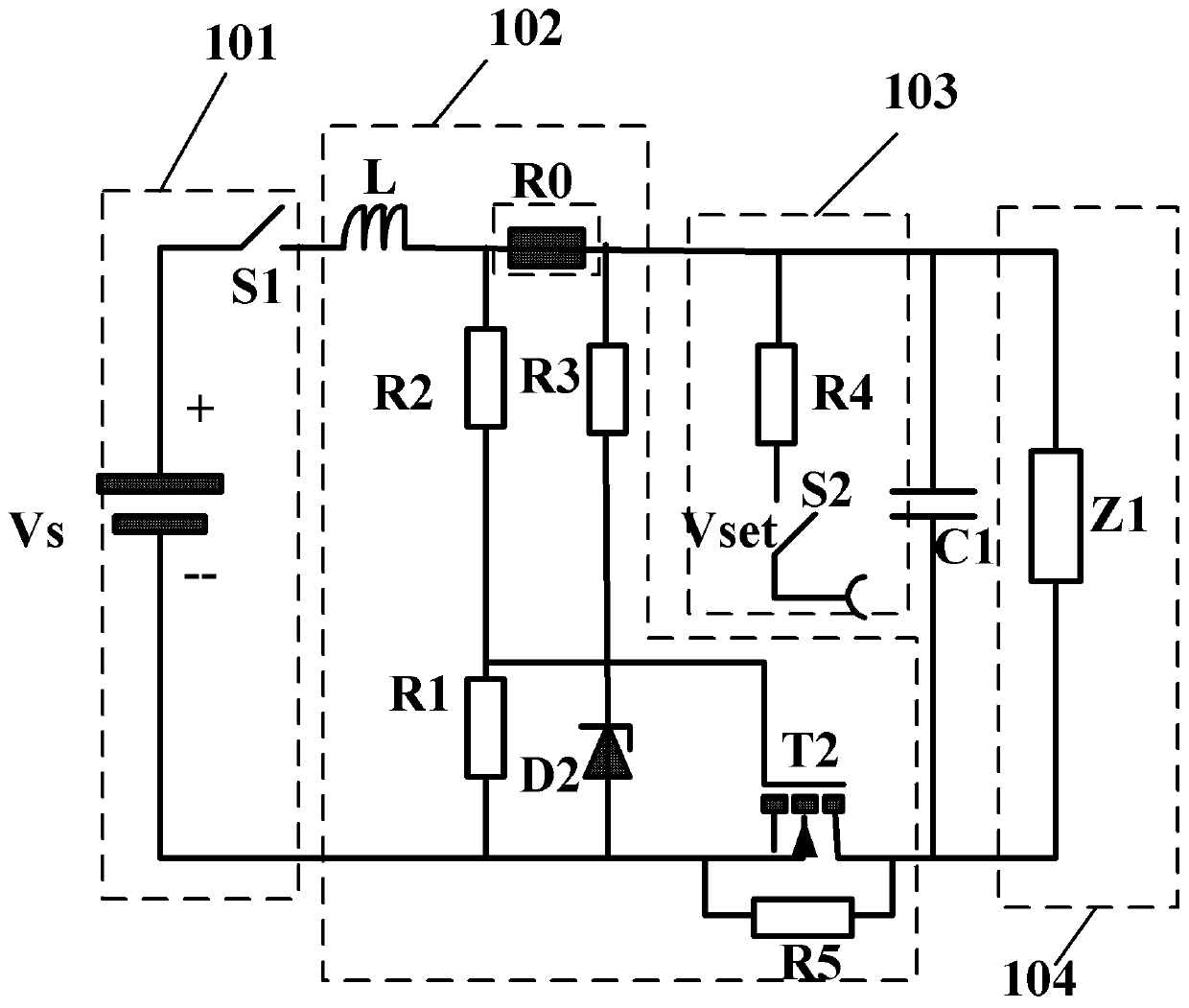
Anti-thunder overvoltage protection component
InactiveCN103337848APrevent deflagration accidentsNormal work is not affectedEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentPressure cellThermistor
The invention discloses an anti-thunder overvoltage protection component which comprises a piezoresistor disc, a positive temperature coefficient thermistor disc and a gas discharge tube, wherein the piezoresistor disc, the positive temperature coefficient thermistor disc and the gas discharge tube are integratedly packaged; the first common terminal of the positive temperature coefficient thermistor disc and the gas discharge tube is a first leading-out terminal; the second common terminal of the positive temperature coefficient thermistor disc and the gas discharge tube is connected with one end of the piezoresistor disc; the other end of the piezoresistor disc is a second leading-out terminal. The anti-thunder overvoltage protection component can restrain the switching overvoltage and fault power frequency overvoltage, and can play the protective role of a normal pressure cell in case of a thunderstrike pulse overvoltage.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +2
A lightning protection overvoltage protection device
InactiveCN103346547BNormal work is not affectedCurrent limitEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentLightning strokesEngineering
The invention discloses an anti-thunder overvoltage protection device. The anti-thunder overvoltage protection device comprises a piezoresistor, a positive temperature coefficient thermistor and a gas discharge tube, wherein the positive temperature coefficient thermistor is connected with the gas discharge tube in parallel and then connected with the piezoresistor in series; the positive temperature coefficient thermistor and the piezoresistor form a thermal coupling relationship. The piezoresistor, the positive temperature coefficient thermistor and the gas discharge tube can be packaged into a whole, or the piezoresistor and the positive temperature coefficient thermistor are packaged into a whole, thus a packaged body is formed, and the gas discharge tube is located outside the packaged body. The anti-thunder overvoltage protection device not only can restrain operation overvoltage and fault power frequency overvoltage, but also can have the protection function of a normal voltage-sensitive element when lightning stroke pulse overvoltage occurs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +2
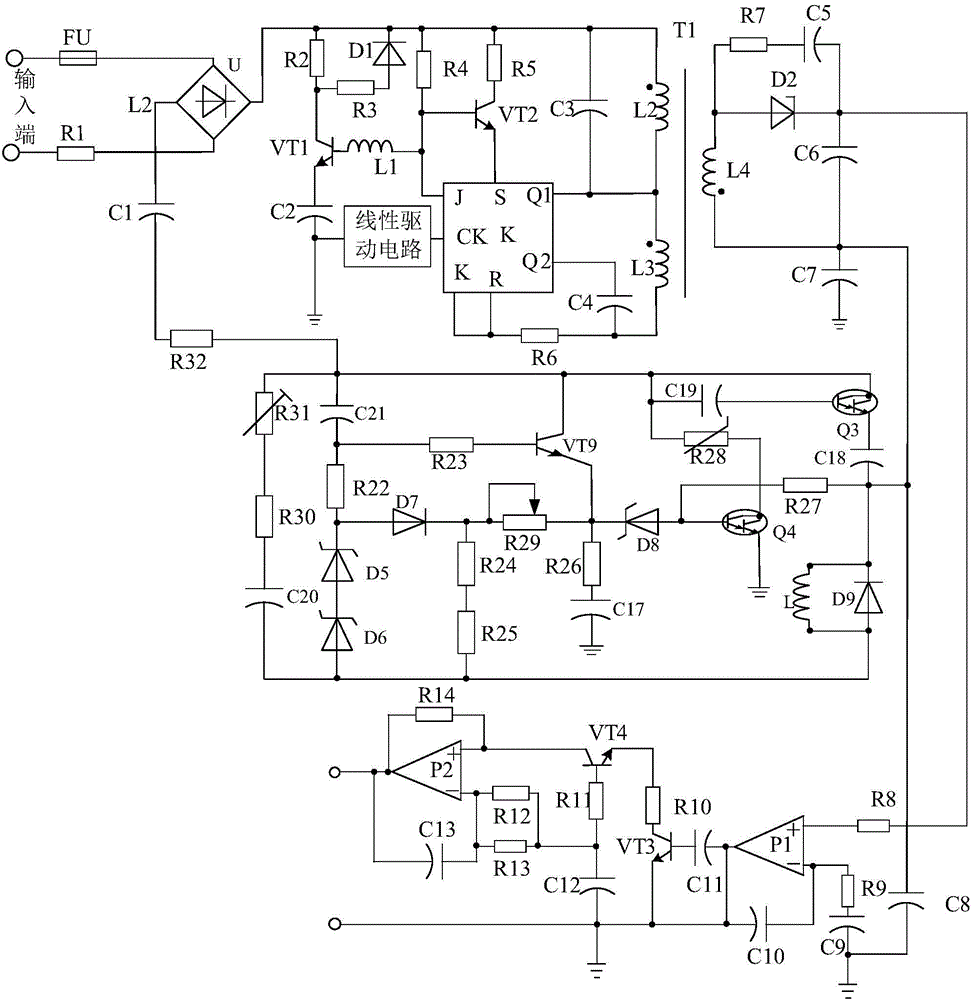
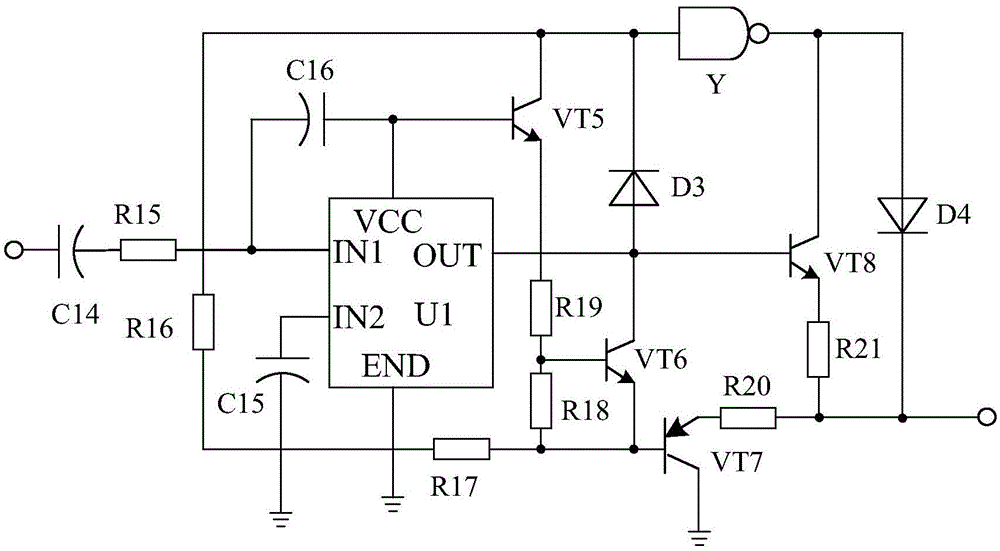
High-power trigger booster system based on surging current limitation
InactiveCN104980051ASolve the defect of excessive currentCurrent limitAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionCurrent limitingPower flow
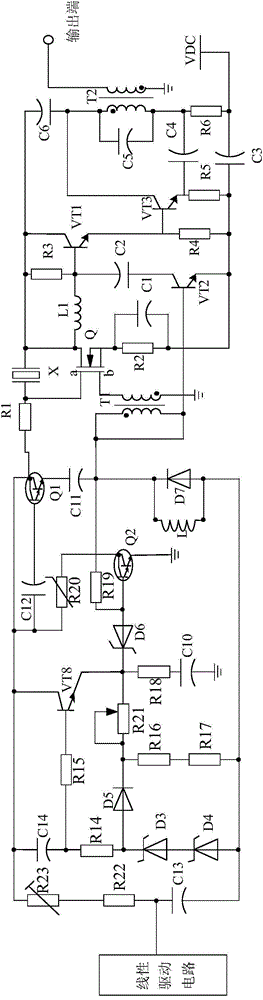
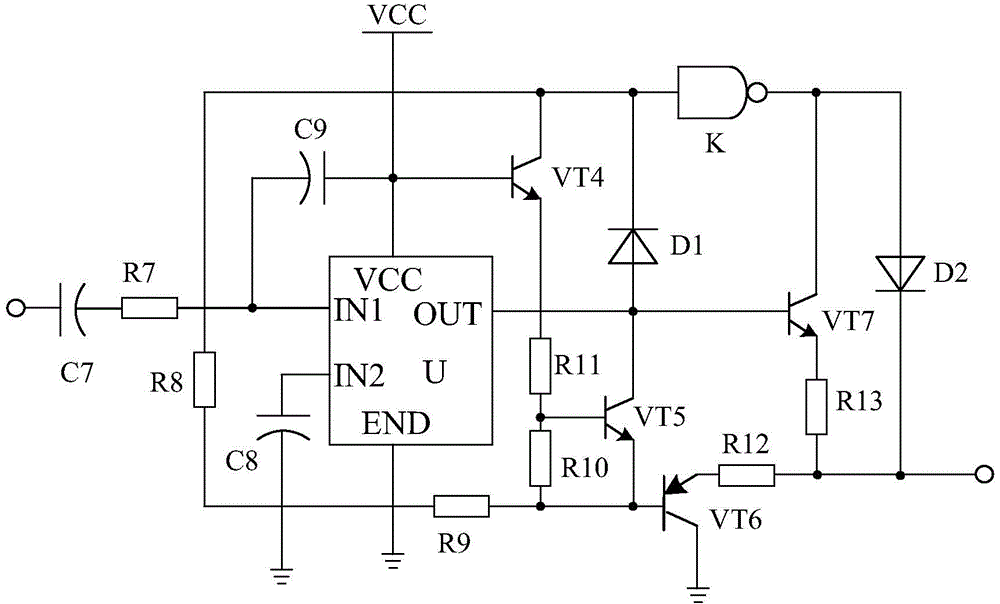
The invention discloses a high-power triggering and boosting circuit based on linear driving. The high-power triggering and boosting circuit based on linear driving is mainly composed of a rectification filter circuit, a triggering circuit connected with the rectification filter circuit, a boosting circuit connected with the triggering circuit, a two-stage low-pass filtration and amplification circuit connected with the boosting circuit. The high-power triggering and boosting circuit based on linear driving is characterized in that a linear driving circuit is arranged between the filter circuit and the triggering circuit and is composed of a driving chip U1, a triode VT5, a triode VT6, a triode VT7, a triode VT8, a capacitor C14, a resistor R16 and the like, the positive electrode of capacitor C14 is connected with the filter circuit, the negative electrode of the capacitor C14 passes through a resistor R15 and then is connected with an IN1 pin of the driving chip U1, one end of the resistor R16 is connected with the collector electrode of the triode VT5, and the other end of the resistor R16 passes through a resistor R17 and then is connected with the base electrode of the triode VT7. According to the high-power triggering and boosting circuit based on linear driving, the linear driving circuit is adopted, in this way, higher power can be output by the circuit, high stability can be maintained, and the operating requirement of high-power production equipment is met.
Owner:CHENGDU JIESHENG TECH CO LTD
Low-noise high-frequency converter based on surging current limitation
InactiveCN104980042AIncrease working frequencyMeet job needsAc-ac conversionLow noiseCurrent limiting
Owner:CHENGDU JIESHENG TECH CO LTD
Method and device for operating a starter of a vehicle
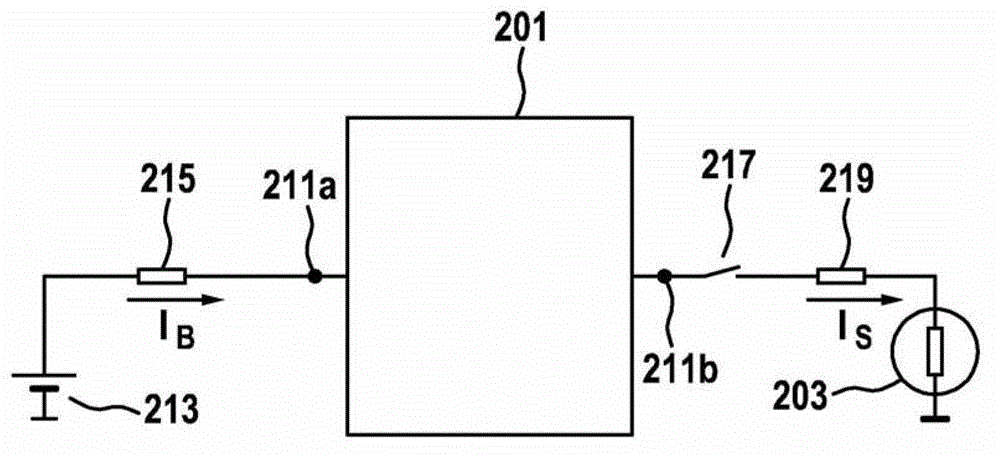
ActiveCN103069154ACurrent limitCurrent is not limitedProgramme controlComputer controlPower flowElectrical current
The invention relates to a method for operating a starter (203) of a vehicle, according to which a physical quantity is measured, characterized in that, depending on the measured physical quantity, a starter current of the starter (203) is limited or not limited, wherein, in the event that the starter current is limited, the limitation is ended after a predetermined time. The invention further relates to a device (201) for operating a starter of a vehicle and to a control program.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
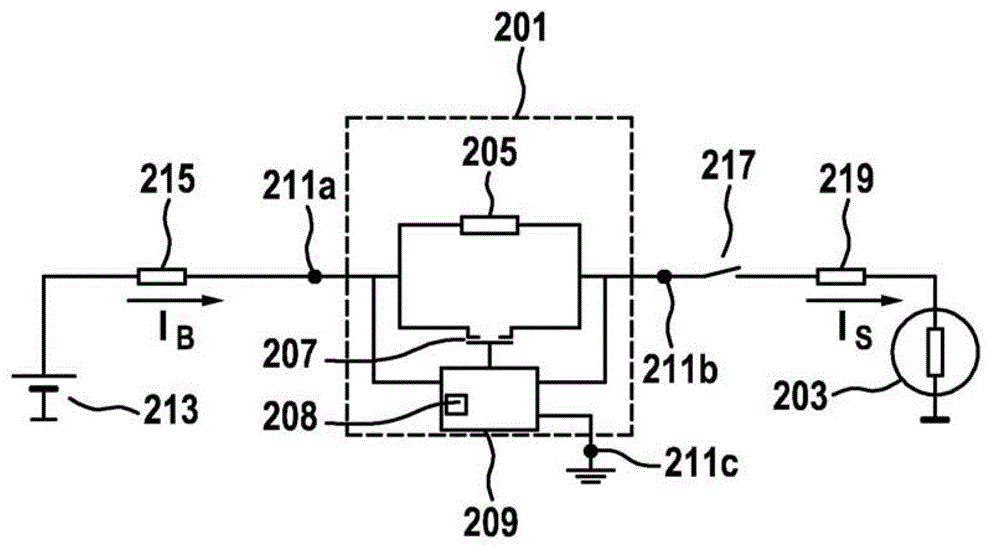
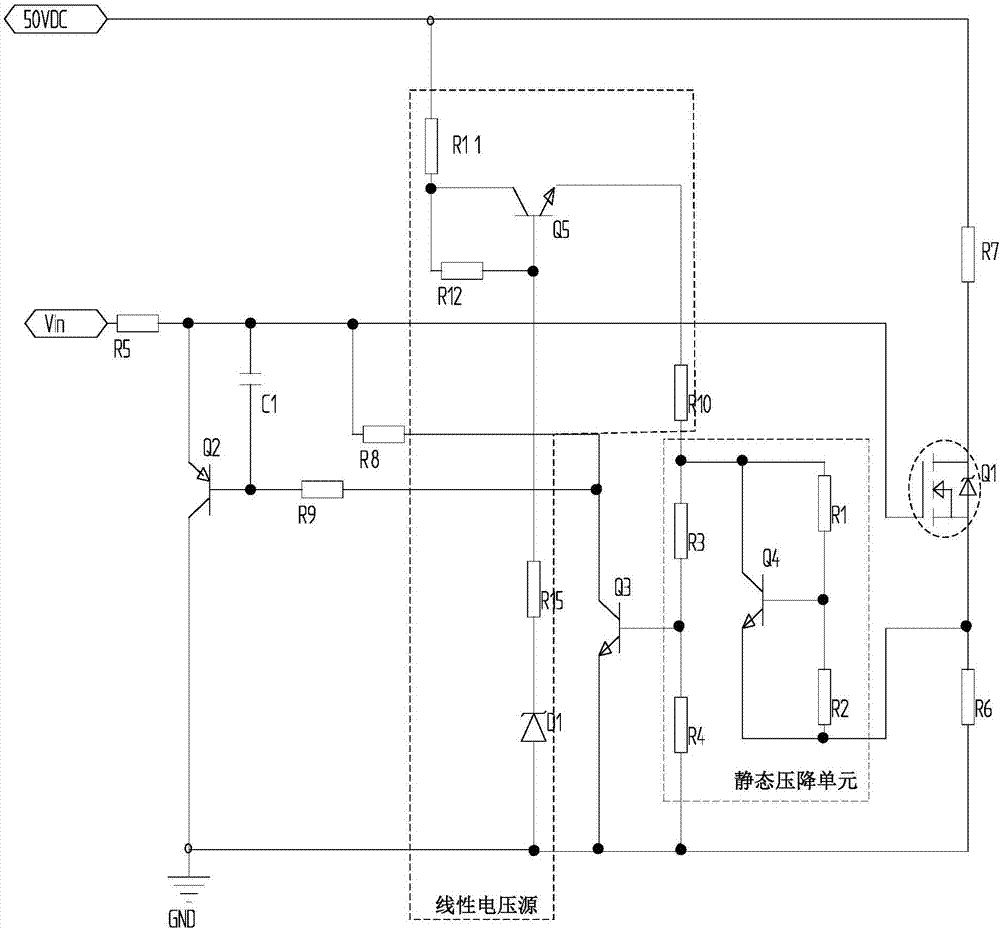
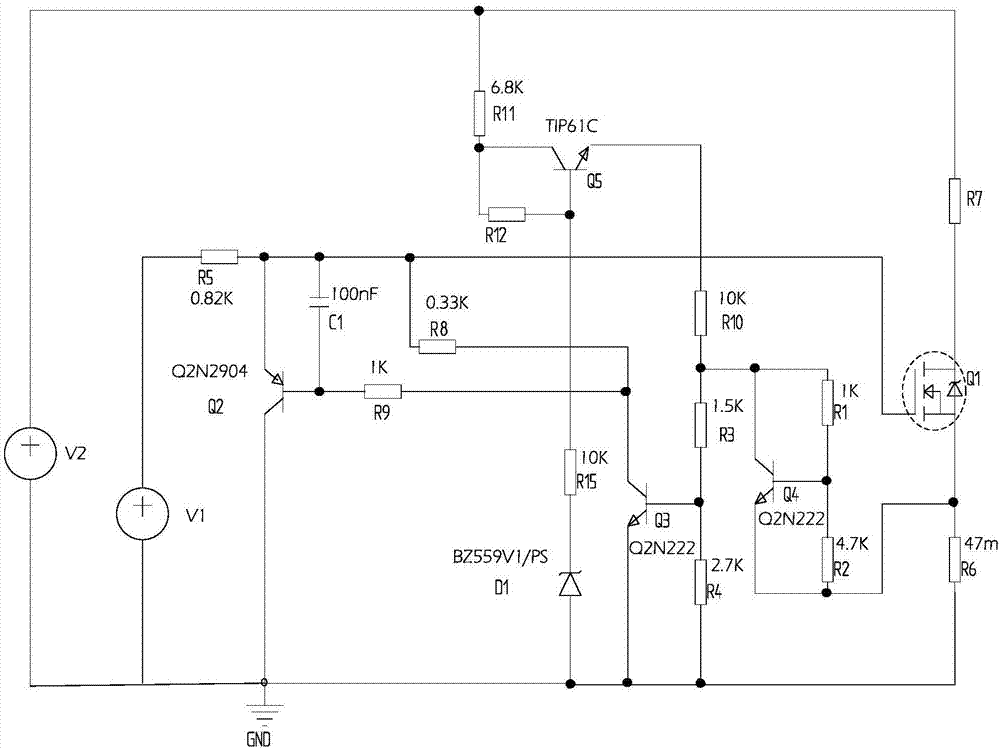
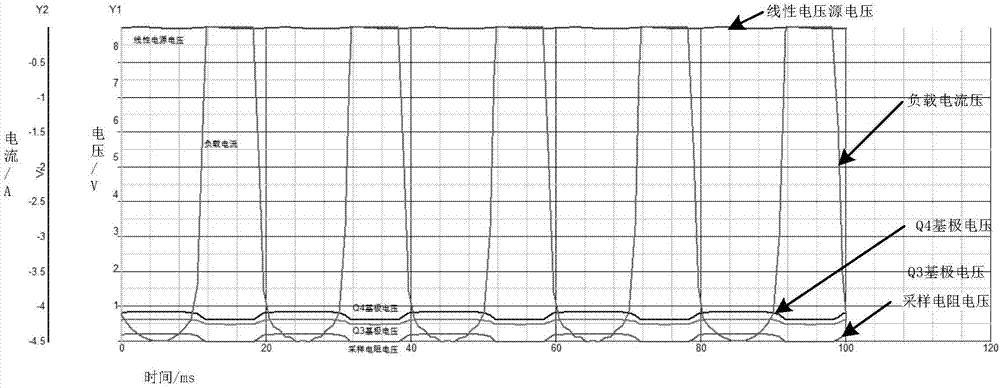
Current-limiting circuit used for MOS tube and MOS switch device
The invention discloses a current-limiting circuit used for an MOS tube and an MOS switch device. The circuit comprises a first PNP type audion, a second NPN type audion, a static voltage drop unit and a current sampling resistor, wherein the emitter of the first PNP type audion is connected with the drive signal source output end of the MOS tube, the base of the first PNP type audion is connected with the collector of the second NPN type audion, and the collector of the first PNP type audion is grounded; the base of the second NPN type audion is connected with one end of the static voltage drop unit, and the emitter of the second NPN type audion is grounded; the other end of the static voltage drop unit is connected with the end, connected with the source of the MOS tube, in the current sampling resistor, and the other end of the current sampling resistor is grounded; the drain of the MOS switch tube is connected with a load, the grid off the MOS switch tube is connected with the drive signal source output end. When the sum of voltage drop generated on the current sampling resistor and voltage of the static voltage drop unit is larger than turn-on voltage of the second NPN type audion, the second NPN type audion is switched on, then the first first PNP type audion is switched on, and G electrode drive voltage of the MOS switch tube is limited to limit currents.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Automatic emergency light system based on surge current limiting
InactiveCN105050244AHigh sensitivityCurrent limitElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesDriver circuitCurrent limiting
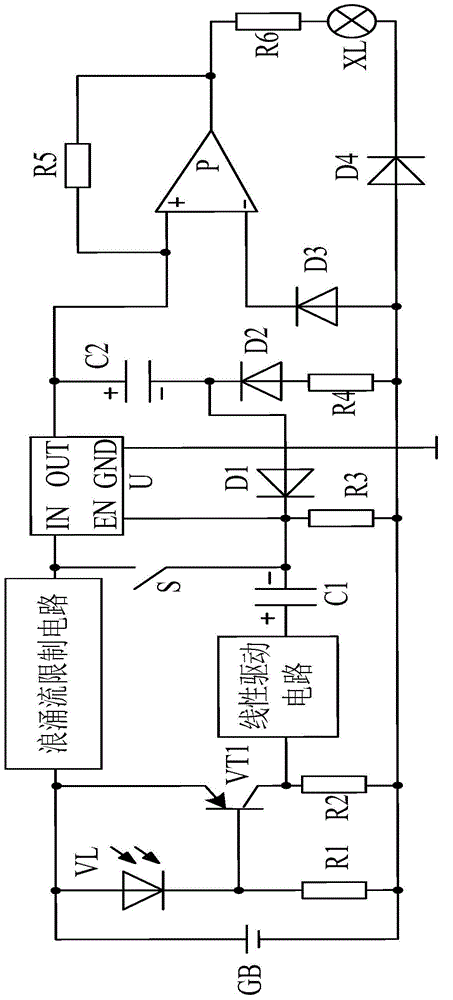
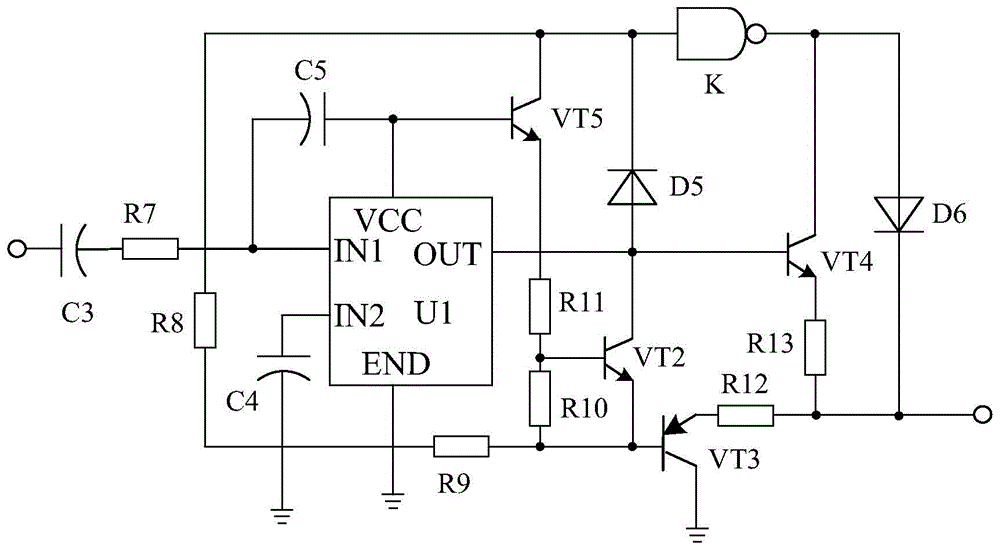
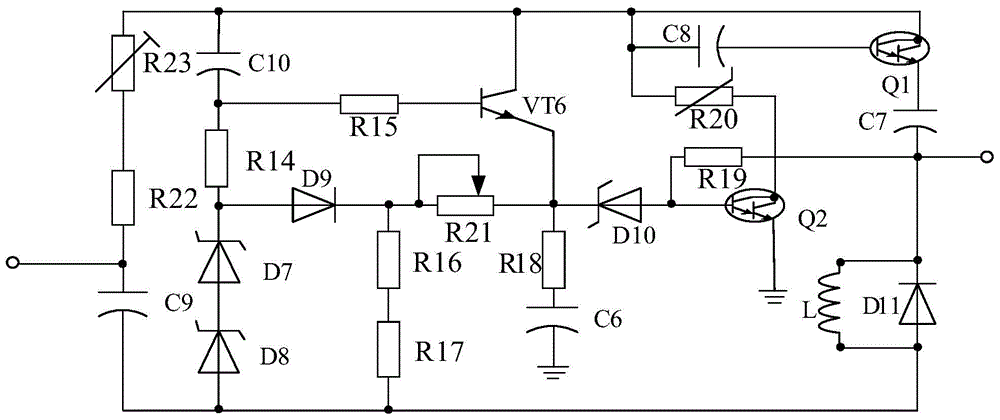
The invention discloses an automatic emergency lamp system sensitive in induction. The automatic emergency lamp system comprises an emergency lamp XL, a battery GB, a light control circuit connected with the positive pole and the negative pole of the battery GB, a switching circuit connected with the output terminal of the light control circuit, a time delay circuit connected with the output terminal of the switching circuit, and an amplifying circuit connected with the output terminal of the time delay circuit, wherein the emergency lamp XL is connected with the amplifying circuit. The automatic emergency lamp system is characterized by also comprising a linear driving circuit connected between the light control circuit and the switching circuit, wherein the linear driving circuit comprises a driving chip U1, an audion VT2, an audion VT3, an audion VT4, an audion VT5, a polar capacitor C3 and the like; the positive pole of the polar capacitor C3 is connected with the light control circuit and the negative pole of the polar capacitor C3 passes through a resistor R7 and then is connected with an IN1 pin of a driving chip U. The automatic emergency lamp system is provided with the linear driving circuit, and can improve the sensitivity of the emergency lamp.
Owner:CHENGDU JIESHENG TECH CO LTD
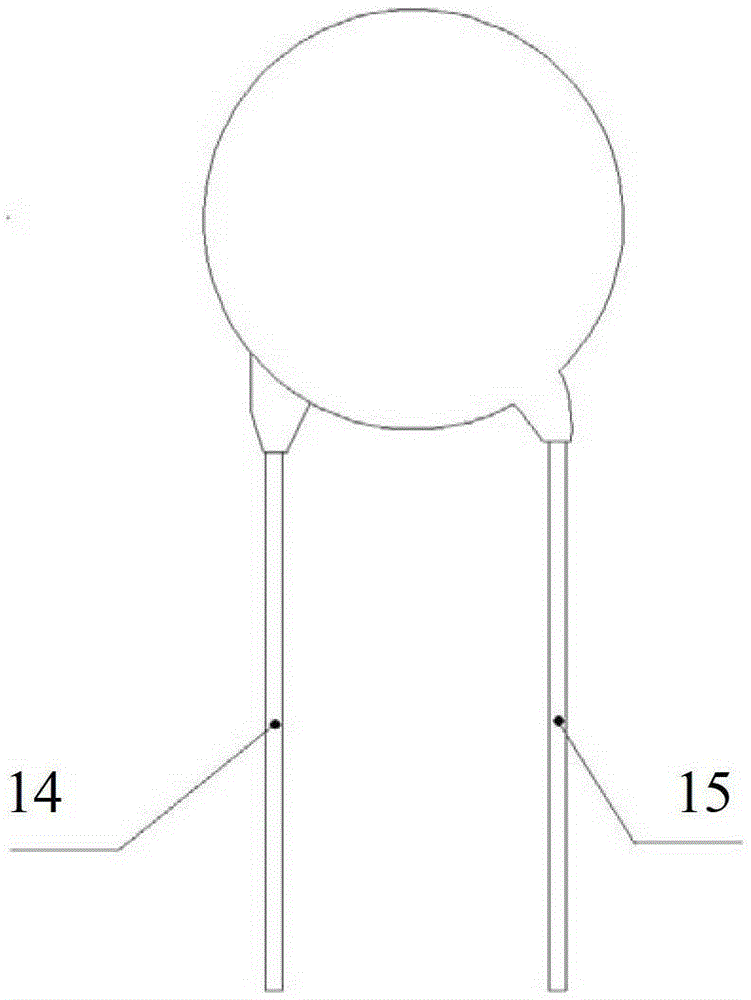
Thunder-prevention overvoltage protection device
InactiveCN103311916ANormal work is not affectedCurrent limitEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentOvervoltageLightning strokes
The invention discloses a thunder-prevention overvoltage protection device. The thunder-prevention overvoltage protection device comprises a piezoresistor sheet, a positive temperature coefficient thermistor sheet and a gas discharge tube, wherein the piezoresistor sheet and the positive temperature coefficient thermistor sheet are encapsulated integrally to form an encapsulation body. One end of the positive temperature coefficient thermistor sheet is a first leading-out end. The other end of the positive temperature coefficient thermistor sheet is connected with one end of the piezoresistor sheet to form a public end, and the public end serves as a third leading-out end. The other end of the piezoresistor sheet serves as a second leading-out end. The gas discharge tube is located outside the encapsulation body, and two ends of the gas discharge tube are connected with the first leading-out end and the third leading-out end respectively. The thunder-prevention overvoltage protection device can inhabit operation overvoltage and fault power frequency overvoltage and can play a protecting role of a normal voltage-sensitive element when lightning stroke pulse overvoltage occurs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +2
Driving circuit
InactiveCN1144368CCurrent limitElectronic switchingReliability increase in field effect transistorsDriver circuitMOSFET
The invention relates to a driving circuit comprising a driver control circuit, a first and a second driving transistor and a current limiting device. In order to limit the current flowing through the driving transistor, said current limiting device controls the voltage at the gate of said first driving transistor. A control input of the current limiting device is used to adjust the current-limitation application point to the load to be controlled by a negative feedback. According to a second embodiment, a driving circuit having one of its two transistors designed as a MOSFET and the other one as a bipolar transistor is produced in such a way that diodes of the two driving transistors block the switched-off supply voltage or transmit the voltage according to a voltage applied on the output of said driving circuit.
Owner:LANTIQ DEUT GBMH
Electric system based on surge current limiting
InactiveCN104991598ACurrent limitImprove the defect of excessive currentCurrent/voltage measurementElectric variable regulationCurrent limitingPower flow
The invention discloses an electrical system based on linear driving. The electrical system based on linear driving is mainly composed of a front-end processing circuit, an amplification circuit connected with the output end of the front-end processing circuit, a pulse rectifying circuit connected with the output end of the amplification circuit, a fine adjustment circuit connected with the pulse rectifying circuit and a warning circuit connected with the output end of the pulse rectifying circuit. The electrical system based on linear driving is characterized in that a linear driving circuit is arranged between the amplification circuit and the pulse rectifying circuit and is composed of a driving chip U, a triode VT2, a triode VT3, a triode VT4, a triode VT5, a polar capacitor C7 and the like, the positive electrode of the polar capacitor C7 is connected with the amplification circuit, and the negative electrode of the polar capacitor C7 passes through a resistor R16 and then is connected with an IN1 pin of the driving chip U. According to the electrical system based on linear driving, due to the fact that the linear driving circuit is arranged, the electrical system can be more stable.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Light-emitting diode (LED) ground lamp with self protection function
InactiveCN102410472AProtection LED Ground LightCurrent limitPoint-like light sourceLighting safety devicesEngineeringLight fixture
The invention relates to the field of light-emitting diode (LED) illuminating lamps, in particular to an LED ground lamp with a self protection function. The LED ground lamp comprises a lamp, an LED driving power supply and LED lamp beads packaged in the lamp. The LED ground lamp is characterized by also comprising at least one self-restoring fuse tube which is packaged in the lamp, forms an electric loop with the LED lamp beads and the LED driving power supply and is high in resistance when the current or the temperature is abnormal; and the plurality of LED lamp beads can be connected in series or in parallel, and can be connected in series and in parallel, or can be connected crossly. The LED ground lamp has the advantages that: when the current in a circuit is overhigh or the temperature in the LED lamp is overhigh, the resistance of the self-restoring fuse tube is very high, so the current of a main circuit or sub-circuits is limited, and the LED lamp beads of the LED ground lamp are prevented from being damaged; the operation of the LED ground lamp is kept and the LED ground lamp is effectively protected by limiting the current of a part of sub-circuits but not affecting other sub-circuits.
Owner:SUZHOU JINGLEI PHOTOELECTRIC LIGHTING TECH
Method for operating a power converter in a soft-switching range
InactiveCN101194412BCurrent limitSmall currentDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationConvertersSoft switching
For converting a first DC voltage to a second DC voltage, a first bridge circuit comprised in a power converter is controlled to convert the first DC voltage to a first AC voltage. The first AC voltage is transformed to a second and possibly further AC voltage. The second and each possibly further AC voltage is converted to a DC voltage by respective bridge circuits. To increase efficiency of the power converter switches of the power converter are controlled to operate in soft switching. Thereto a duty cycle of each AC voltage is controlled. In an embodiment, a half-cycle voltage-time integral of each AC voltage is controlled to be substantially equal.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
Converter circuit, corresponding device and method
PendingCN113497559AExtended on-timeImproved current slew rateEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionConvertersHemt circuits
The embodiment of the invention relates to a converter circuit, a corresponding device and a method. The converter circuit includes a half-bridge power circuit having first and second switches between the input node and the current node and between the current node and ground, respectively. The inductor is coupled between the current node and the output node. A logic control circuitry is configured to switch the first and second switches to a current recirculation state and a current charging state. The logic circuitry is configured to switch the switch from the current recirculation state to the current charging state as a result of the voltage indicator signal from the output voltage comparator being asserted while initiating an on-time counter signal having an expiration value, and switches the switch from the current charging state to the current recirculation state as a result of a combination of the on-time counter signal having reached its expiration value with the voltage indicator signal from the voltage comparator being de-asserted.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
A device for current limiting protection of load or output
ActiveCN104242277BHigh impedanceIncrease total resistanceEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentHigh resistanceField-effect transistor
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A voltage-controlled oscillator, integrated chip and electronic equipment
The invention relates to the technical field of integrated circuits, in particular, to a voltage-controlled oscillator, an integrated chip, and an electronic device. The voltage-controlled oscillatorcomprises a resistor unit, a current mirror unit, a bias unit, and an oscillating unit. The current mirror unit responds to a first bias voltage provided by the bias unit to carries out bias processing on a voltage of a first node at a first current path and a voltage of a third node at a third current path to generate a first bias voltage and is also used for responding to resistance configuration of the resistor unit and adjusting a third current flowing through the third current path, wherein the first current flowing through the first current path is equal to the third current. Therefore,with configuration of the resistance corresponding to the resistor unit, the charging and discharging time of the capacitor of the oscillating unit can be indirectly adjusted to change the oscillationperiod of the oscillating unit and thus the changed oscillation period is closer to a desired oscillation period, so that the output accuracy of the oscillation period is improved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Emergency lighting device
ActiveCN100576687CIncreased maintenance burdenIncrease temperatureBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerLight equipmentEffect light
An emergency lighting device comprises an illumination lamp for illuminating an area and an energy storage unit for providing electrical energy for powering the lamp. According to the invention, the energy storage unit comprises an ultra-capacitor for storing the electrical energy. As the ultra-capacitor shows hardly any deterioration over time, extensive, e.g. periodical testing of the emergency lighting device during its lifetime can be omitted. A charging arrangement for charging the ultra-capacitor in the emergency lighting device is described.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
A lightning protection overvoltage protection component
InactiveCN103337848BNormal work is not affectedCurrent limitEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentPressure cellThermistor
The invention discloses an anti-thunder overvoltage protection component which comprises a piezoresistor disc, a positive temperature coefficient thermistor disc and a gas discharge tube, wherein the piezoresistor disc, the positive temperature coefficient thermistor disc and the gas discharge tube are integratedly packaged; the first common terminal of the positive temperature coefficient thermistor disc and the gas discharge tube is a first leading-out terminal; the second common terminal of the positive temperature coefficient thermistor disc and the gas discharge tube is connected with one end of the piezoresistor disc; the other end of the piezoresistor disc is a second leading-out terminal. The anti-thunder overvoltage protection component can restrain the switching overvoltage and fault power frequency overvoltage, and can play the protective role of a normal pressure cell in case of a thunderstrike pulse overvoltage.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +2
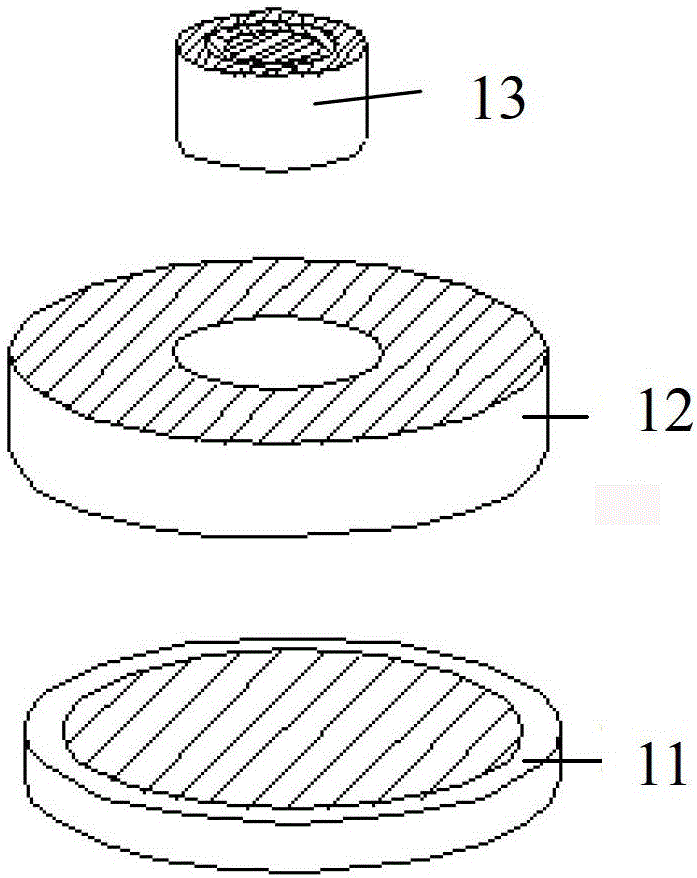
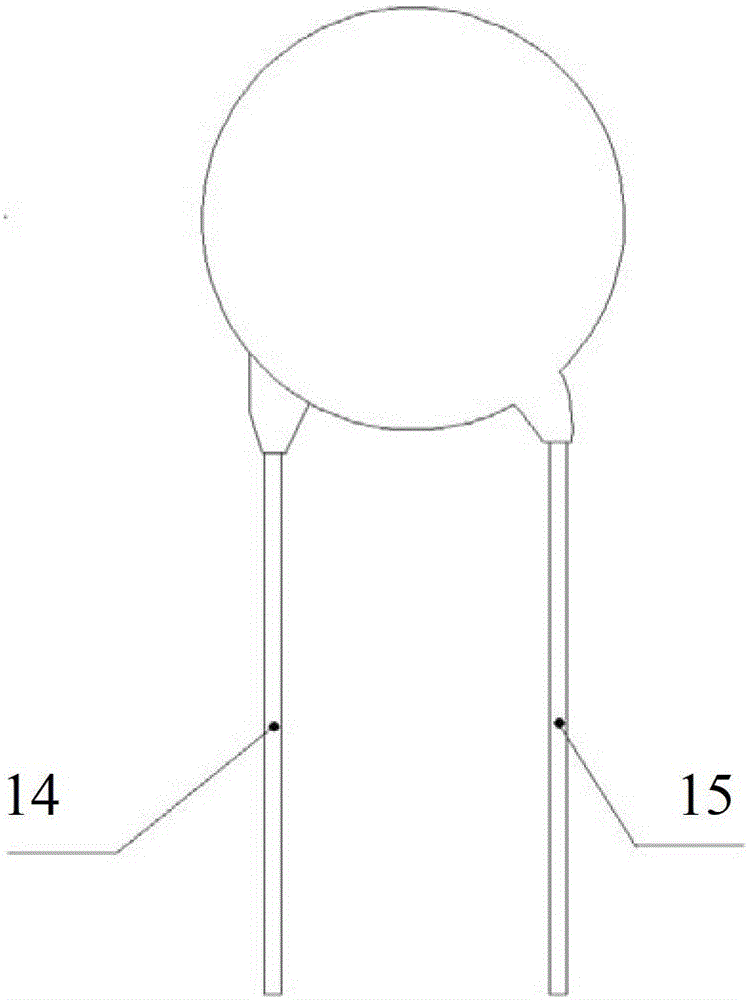
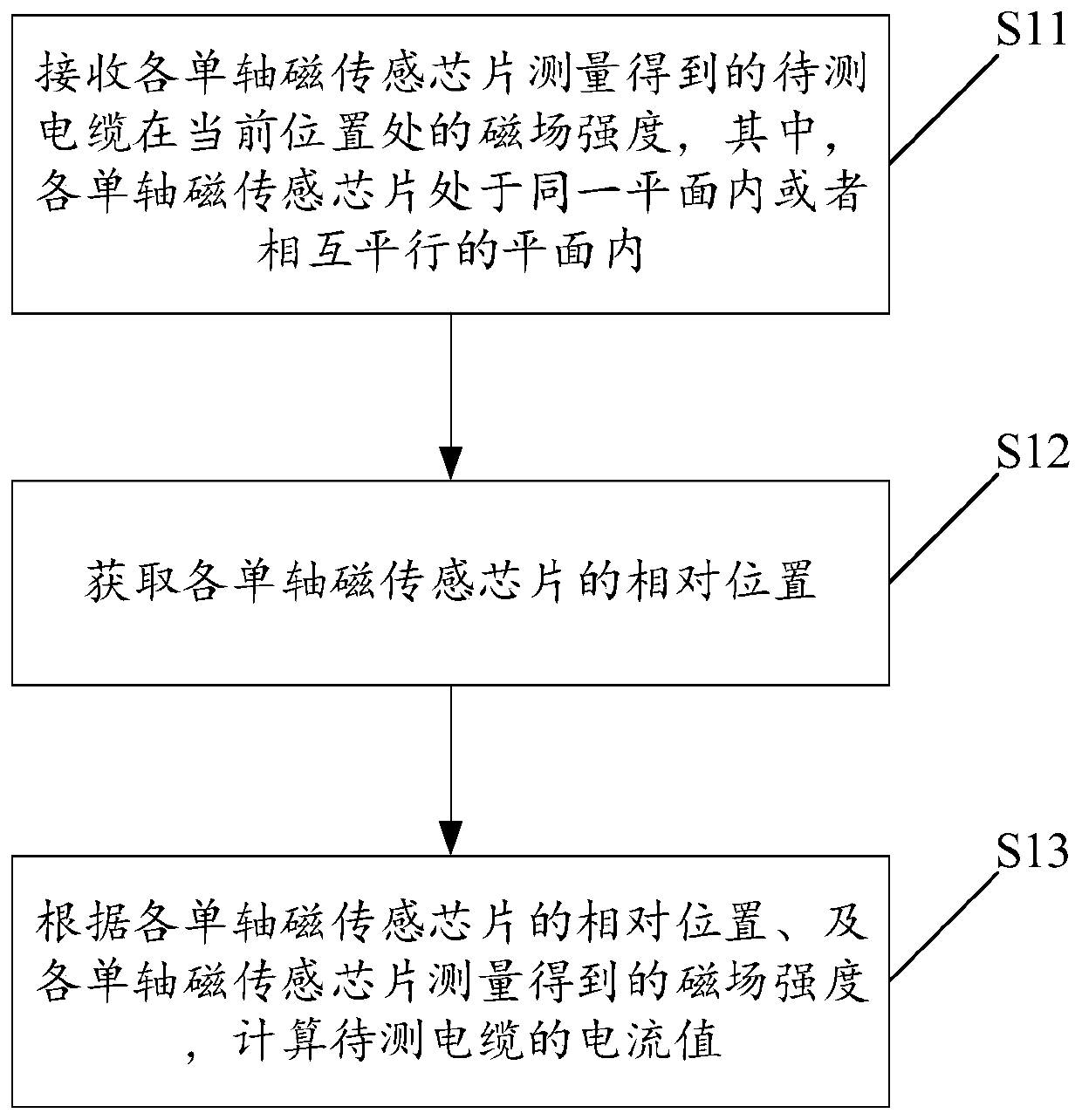
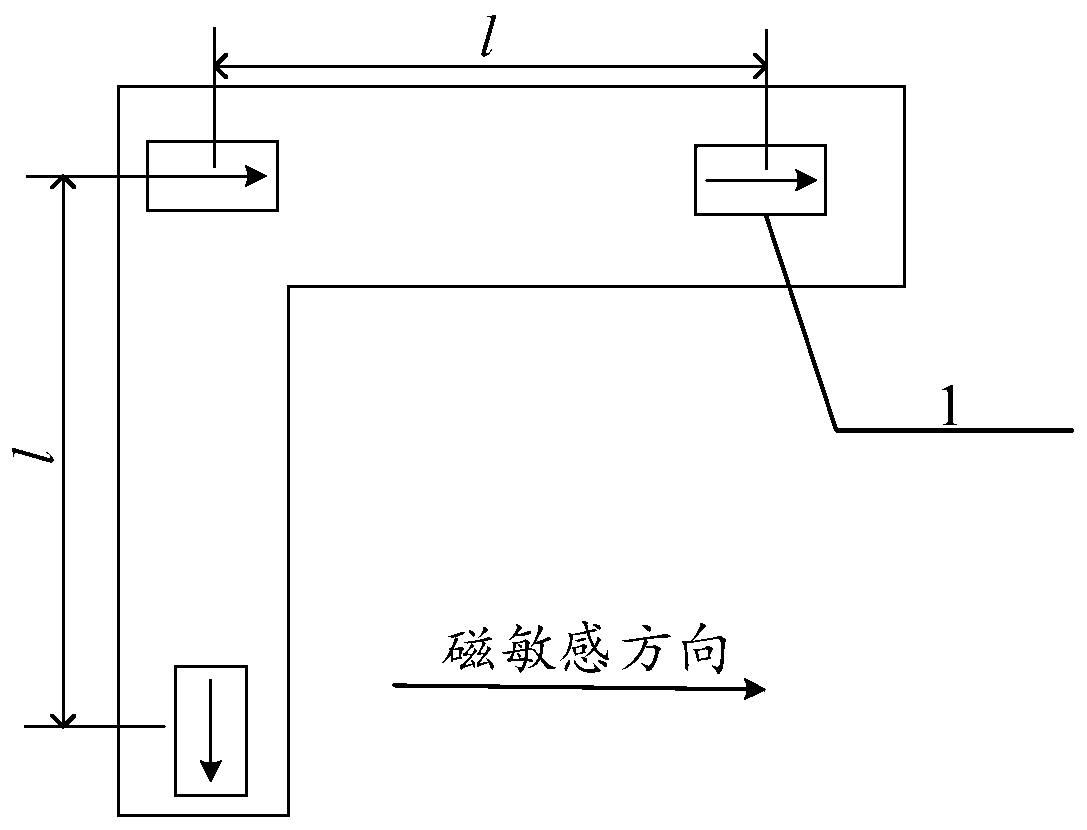
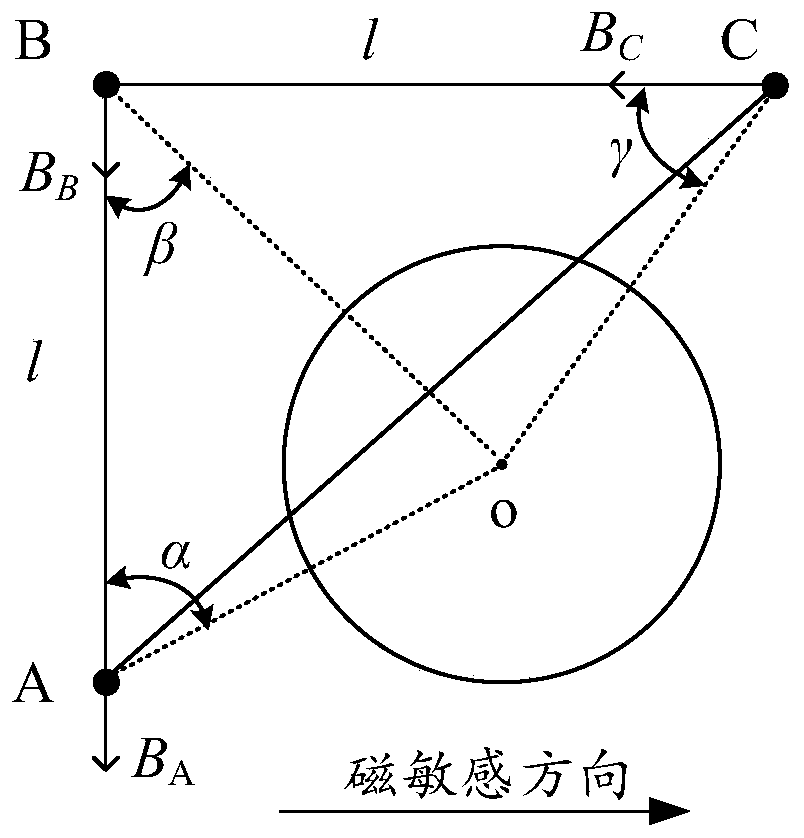
A current measurement method and device based on a uniaxial magnetic sensor chip
ActiveCN109521375BReduce complexityCurrent limitElectrodynamic magnetometersEngineeringElectric cables
The invention discloses a current measurement method and device based on single-axis magnetic sensing chips. The method comprises the steps: receiving the magnetic field intensity, measured by each single-axis magnetic sensing chip, of a to-be-measured cable at the current position, wherein the single-axis magnetic sensing chips are located in the same plane or mutually parallel planes; obtainingthe relative position of each single-axis magnetic sensing chip; and calculating the current value of the to-be-measured cable according to the relative positions of the single-axis magnetic sensing chips and the magnetic field intensity measured by the single-axis magnetic sensing chips. According to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, non-closed-loop measurement can be realized by utilizing the single-axis magnetic sensing chips, so that the cumbersome degree of current measurement can be reduced, and the current value of a to-be-measured cable in almost any scene can be measured, so that the current measurement is not limited by the installation scene of the to-be-measured cable.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com