Patents
Literature
41results about How to "Reducing weight and cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
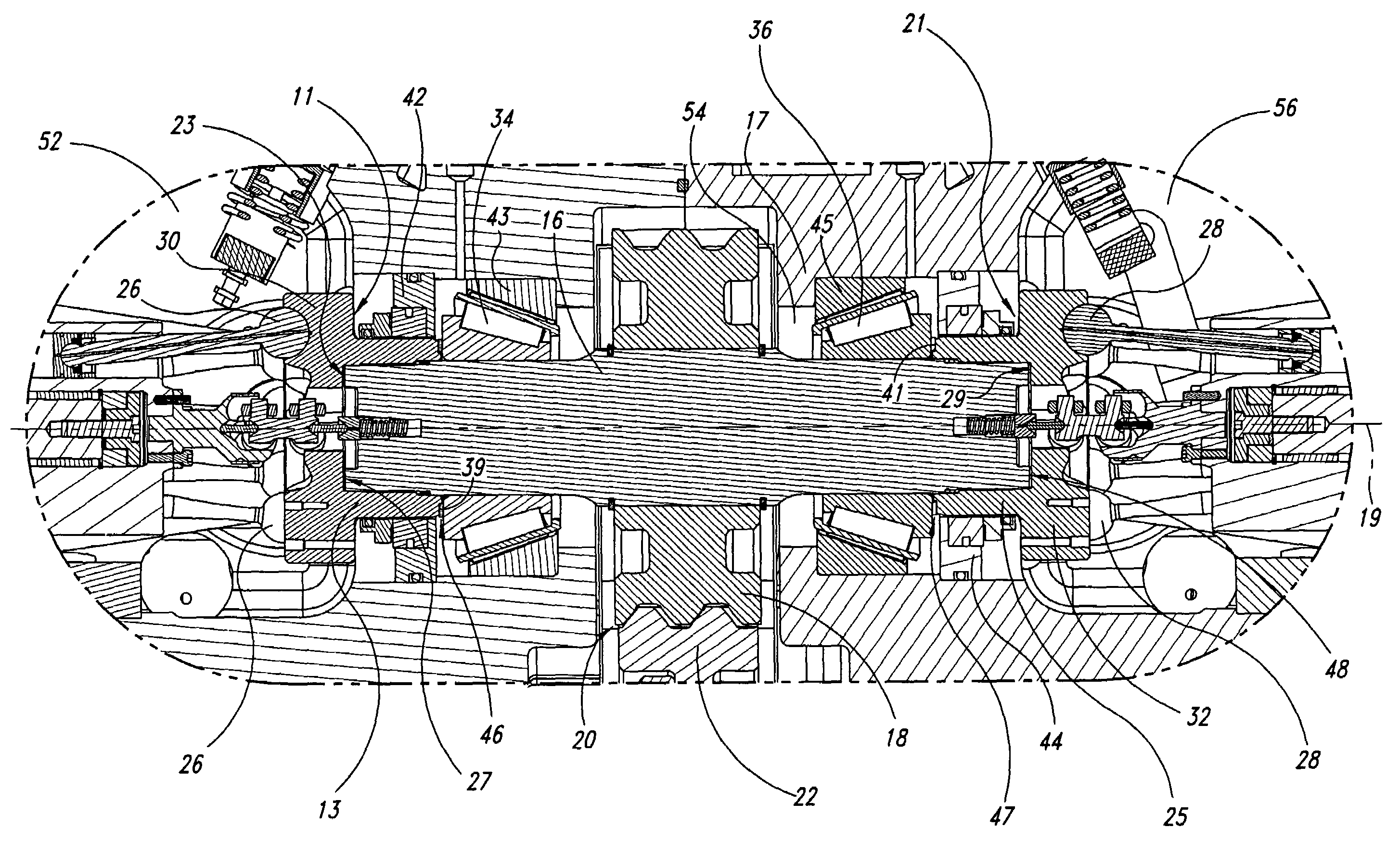
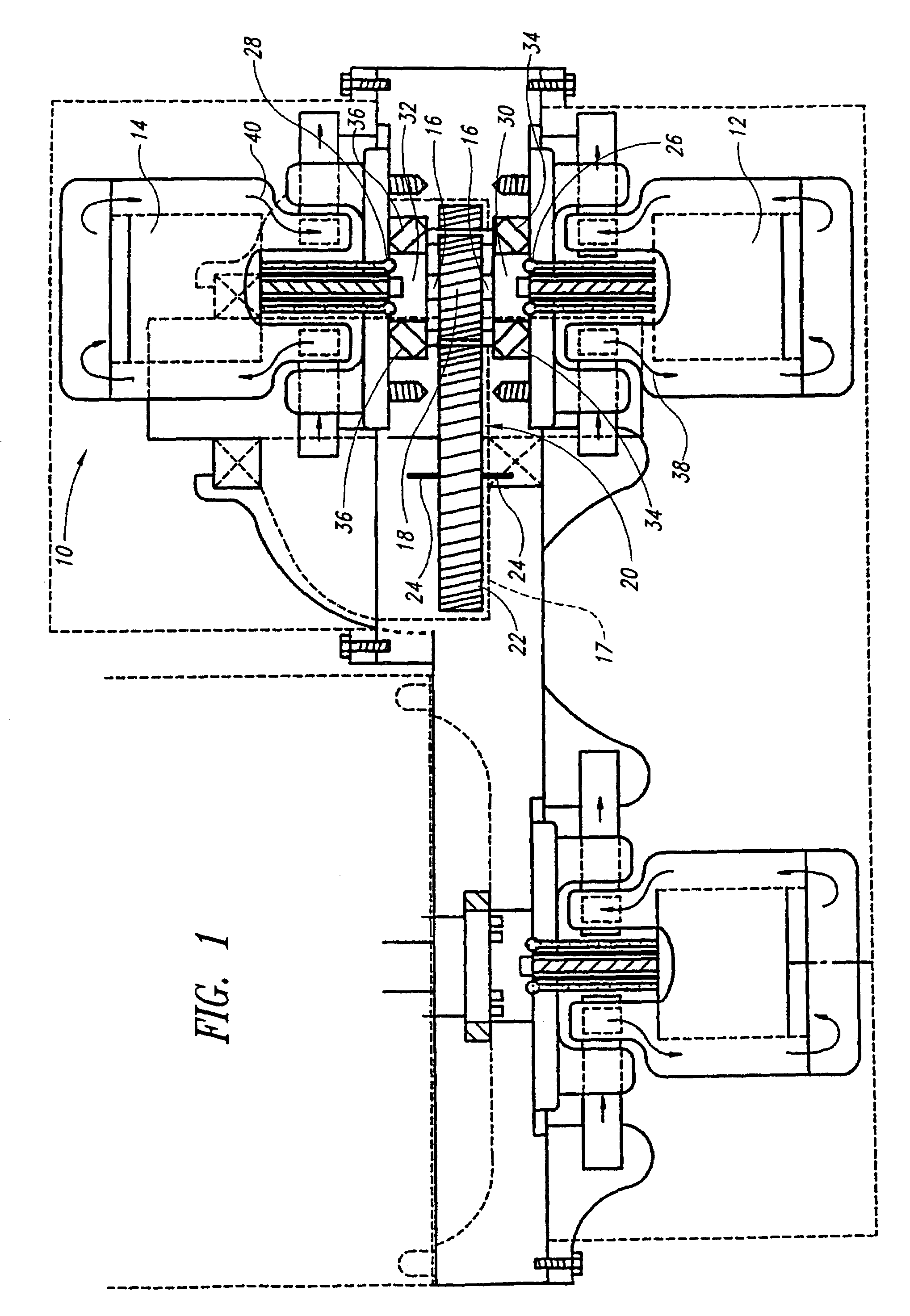
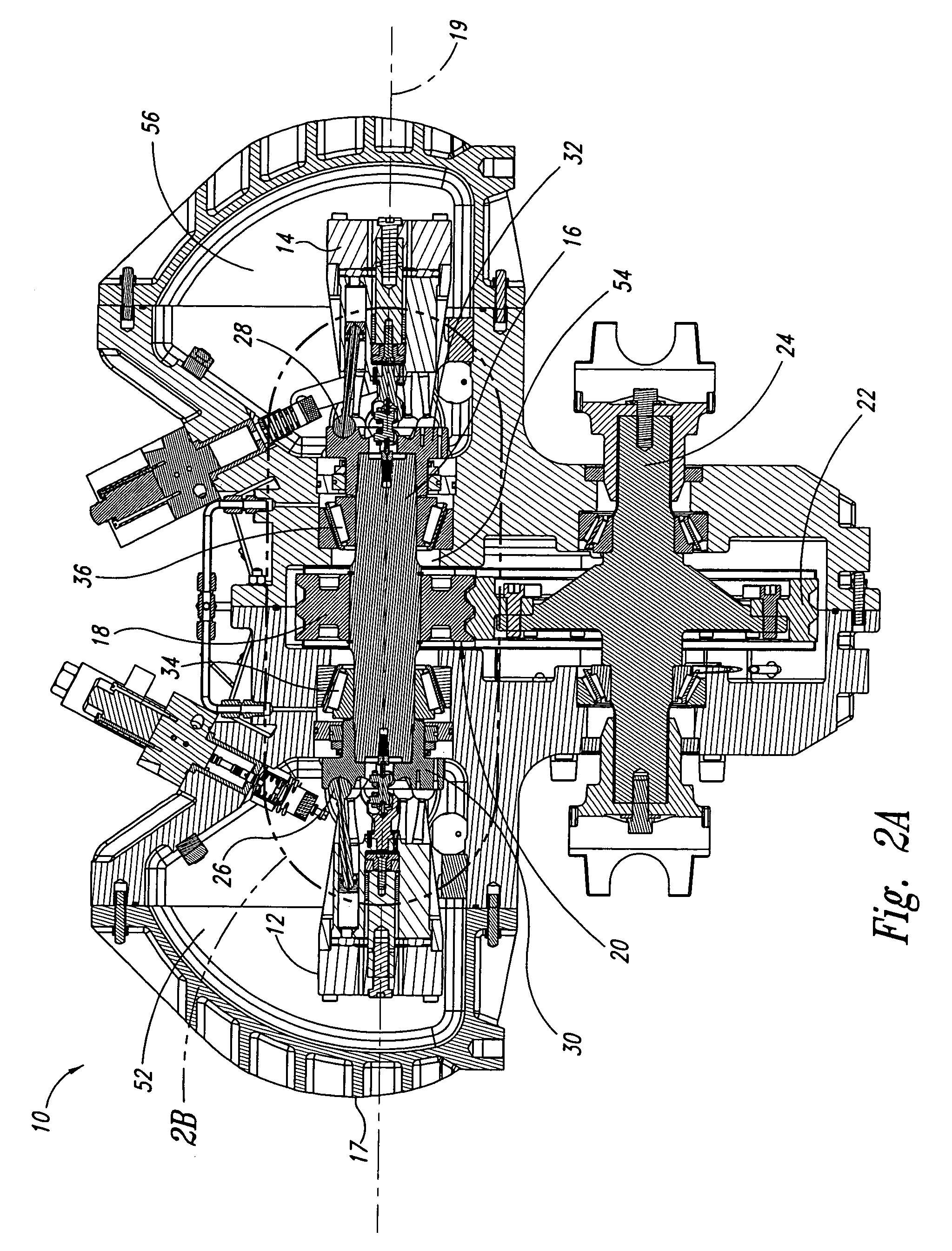
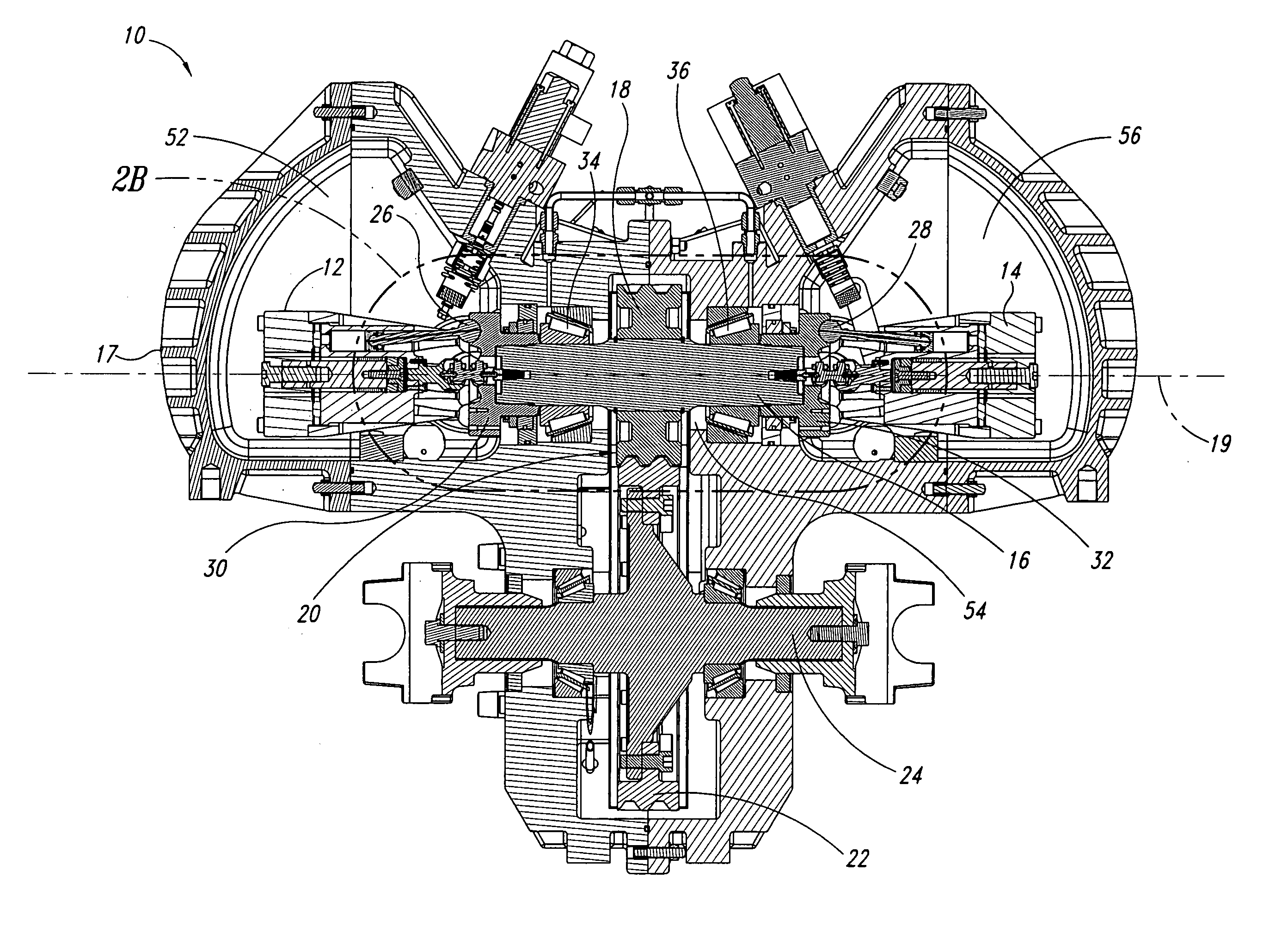
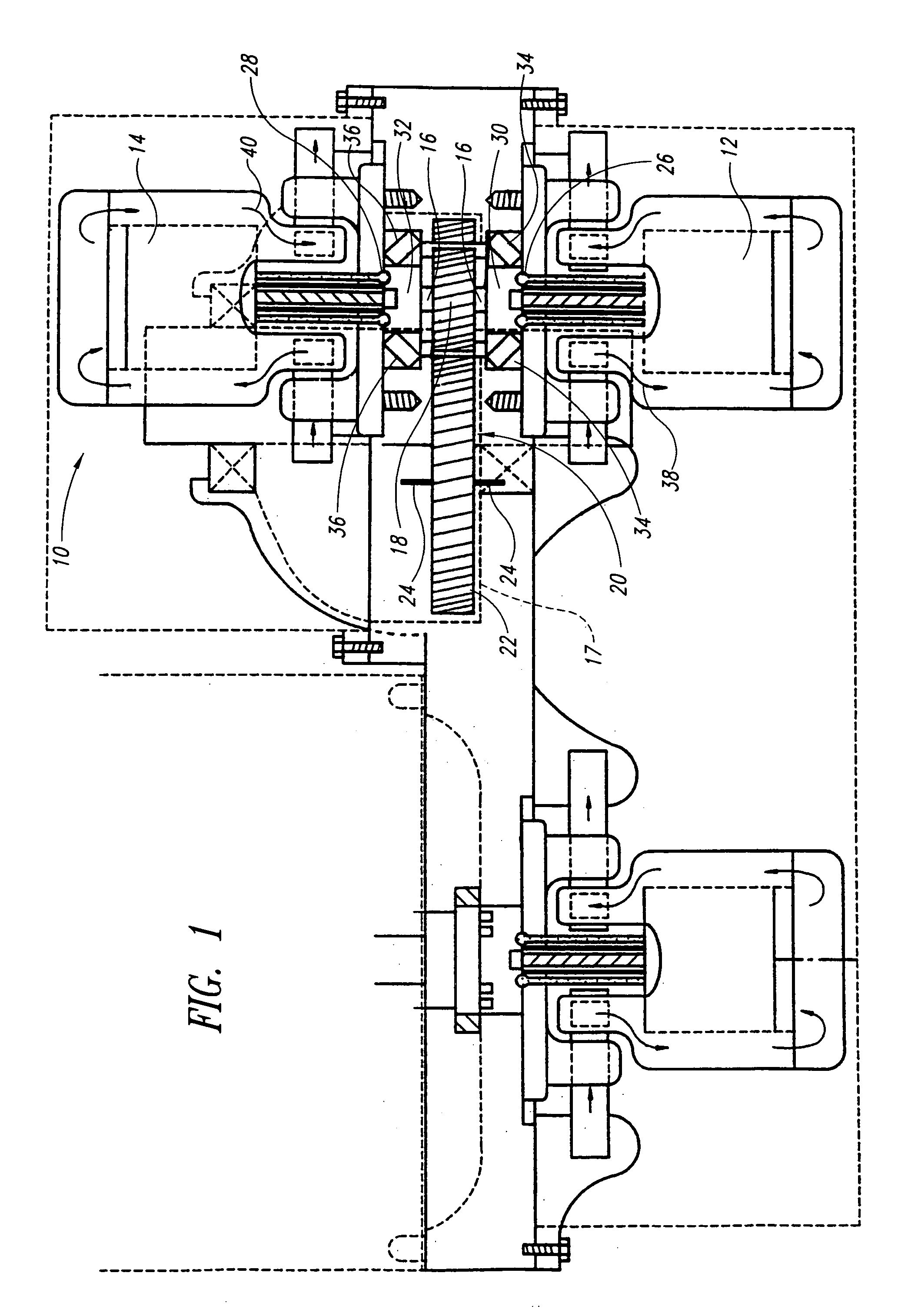
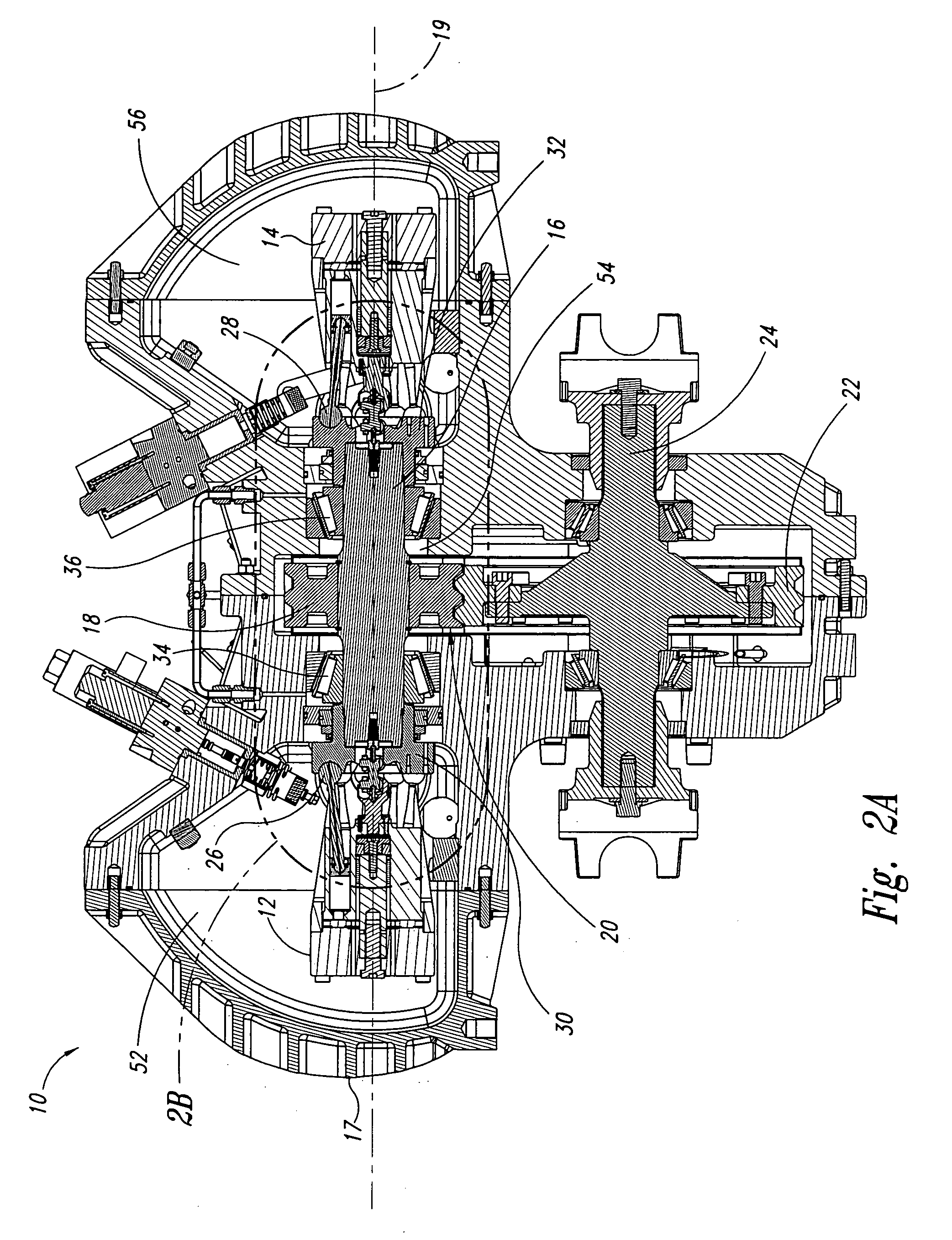
Opposing pump/motors
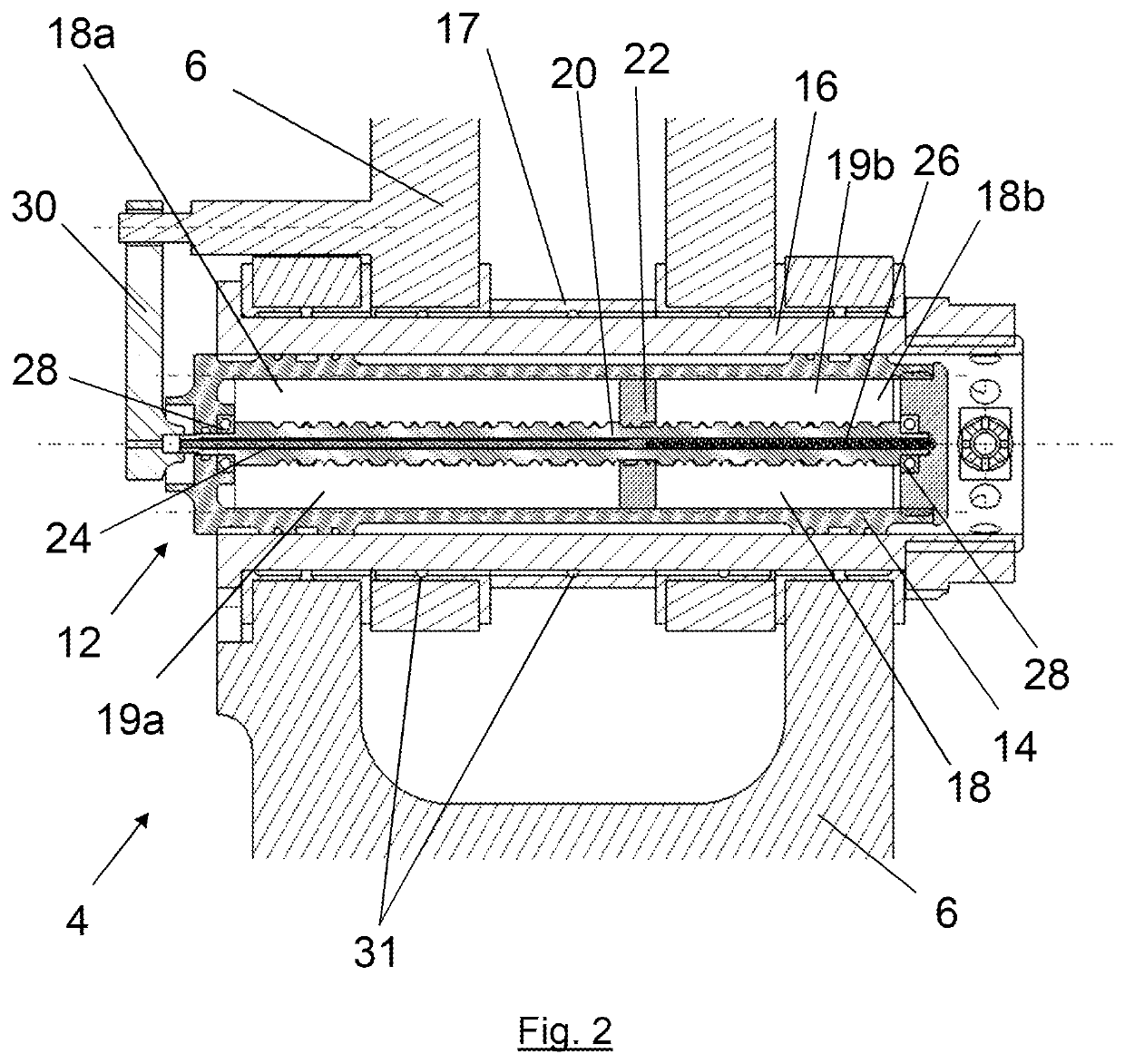
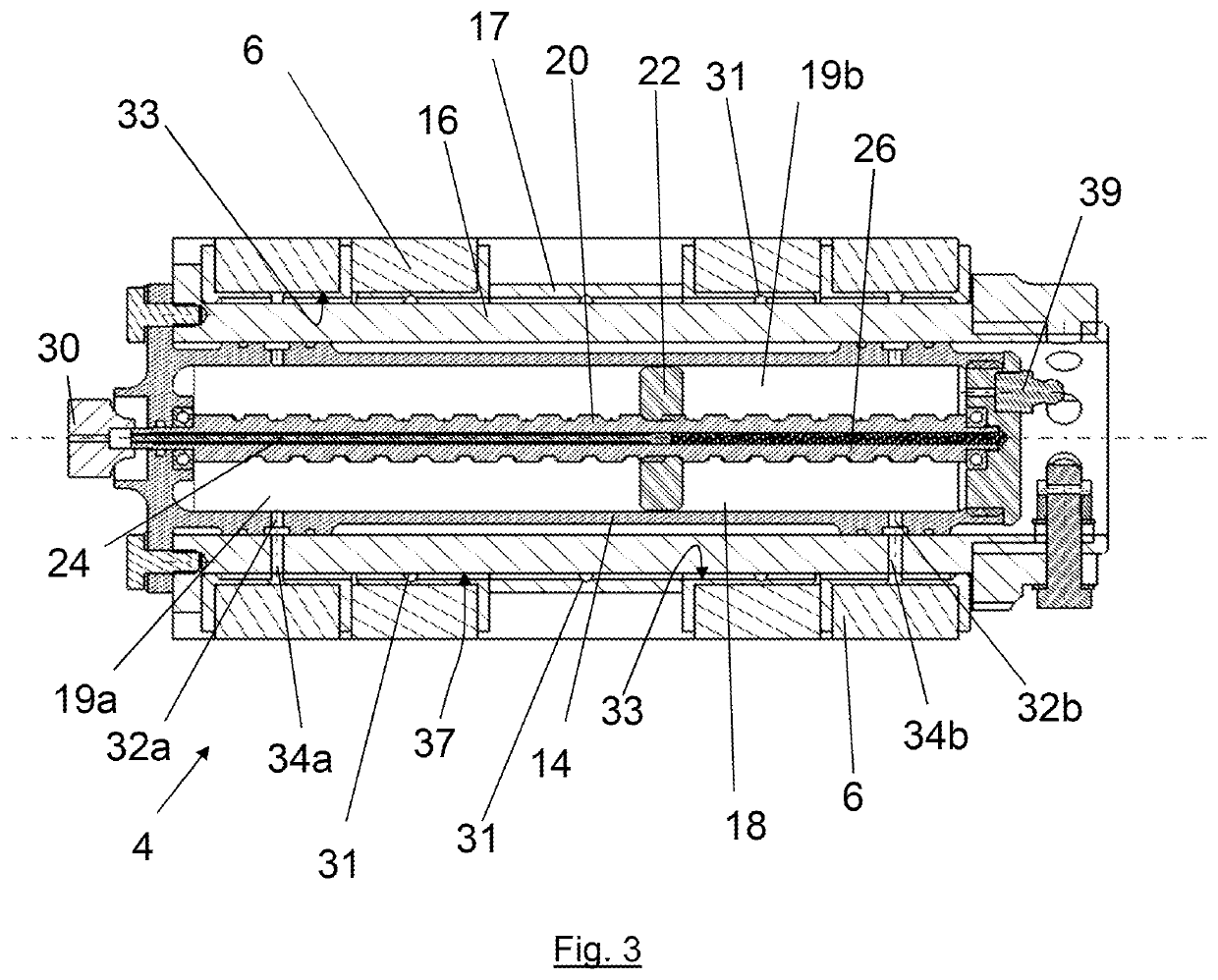
InactiveUS7374005B2Reducing weight and costSmall sizeAuxillary drivesGearing controlMotor driveEngineering
Two motors are arranged on opposing sides of a common shaft, drive plates of the pump / motors being rigidly coupled to each other, for example by being in hard contact with opposing sides of the shaft. By providing hard contact between the pump / motor drive plates and a common shaft, the drive plates and shaft act as a substantially solid element under compression, thereby substantially canceling axial loads generated by the pump / motors directly through the shaft. Residual axial loads are handled via bearings positioned on the shaft adjacent the drive plates in such a manner that the drive plates are in light contact only with the bearings. As a result, friction experienced by the bearings is substantially reduced as compared to conventional systems, thereby improving the efficiency of the system. To further reduce loads on the bearings, the pump / motors are arranged to ensure that they generate radial forces in a direction that is opposite to that of a separation force generated by a torque transferring device carried on the shaft and transmitted to the bearings. A common housing surrounding the two pump / motors, bearings and torque transferring device is divided into three regions, to segregate the bearings and torque transferring assembly from the pump / motors. In this manner, the regions containing the pump / motors are substantially filled with oil to, for example, fully lubricate the pump / motors, while the central region containing the gears and torque transferring device contains a significantly smaller volume of oil to simply splash lubricate the contents of the region, thereby reducing drag on the bearings. Control means are provided for selectively moving the two pump / motors substantially simultaneously to a selected displacement angle, using mechanical systems alone and in combination with hydraulic systems.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTRATOR OF THE U S ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY
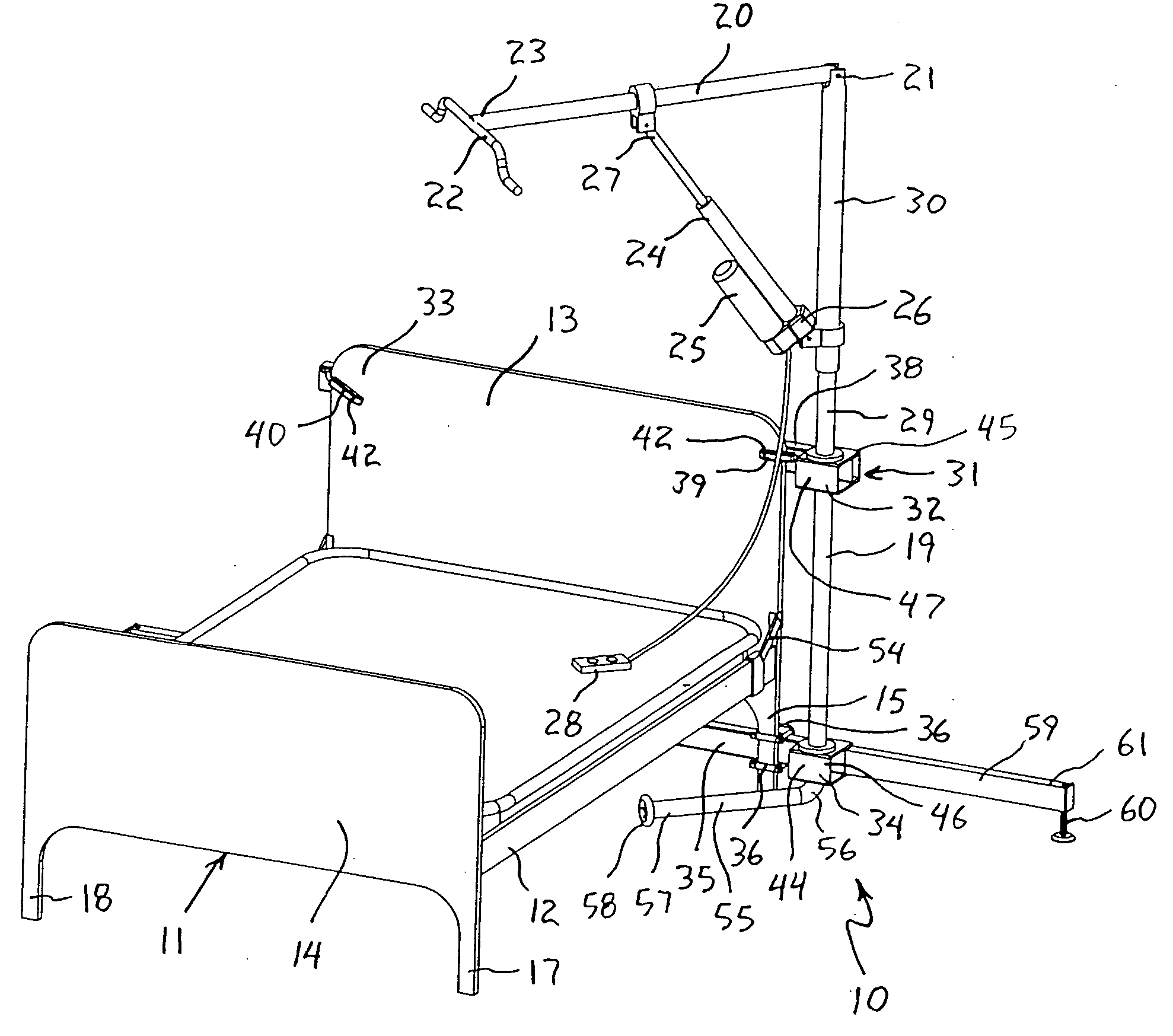
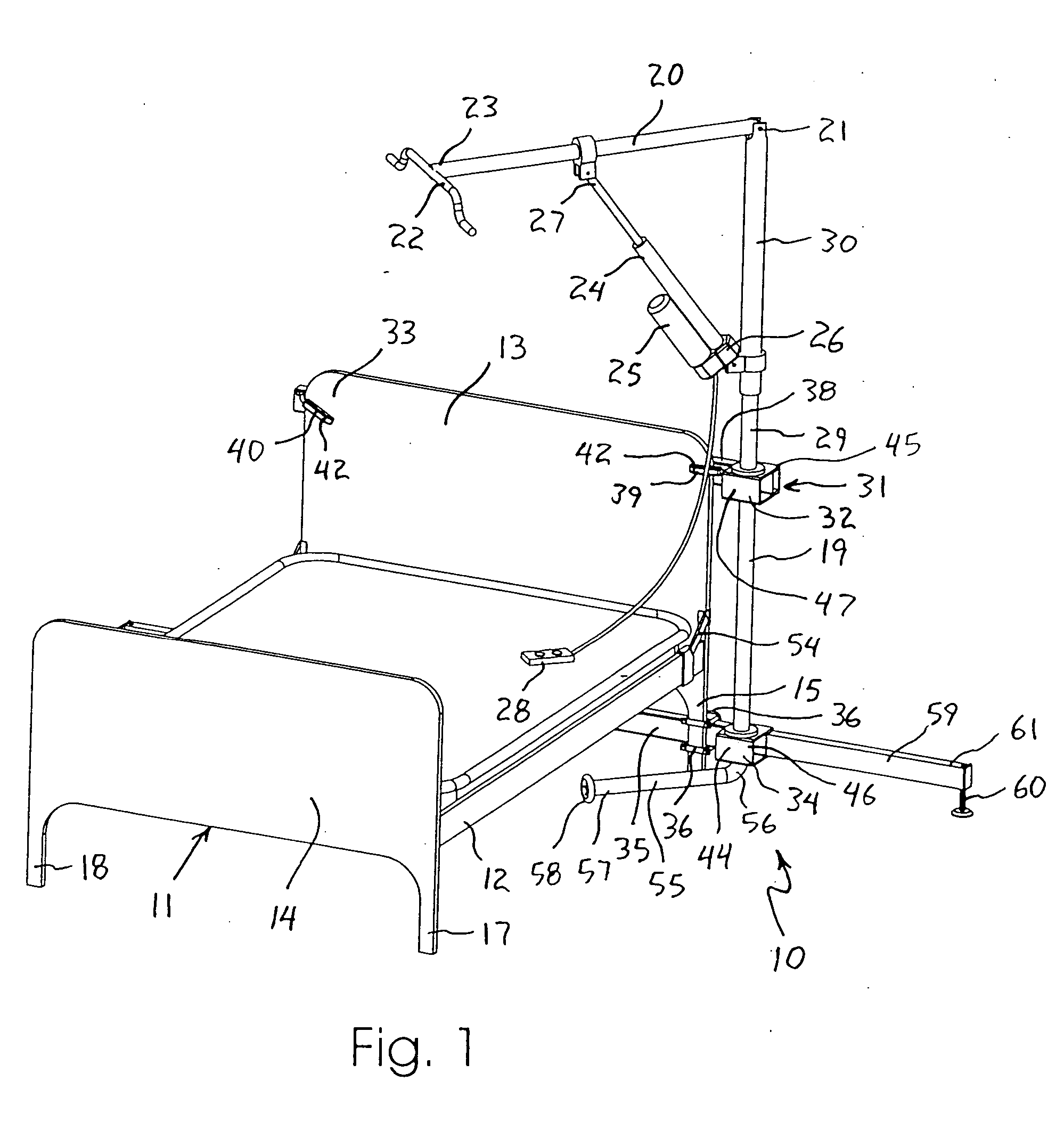
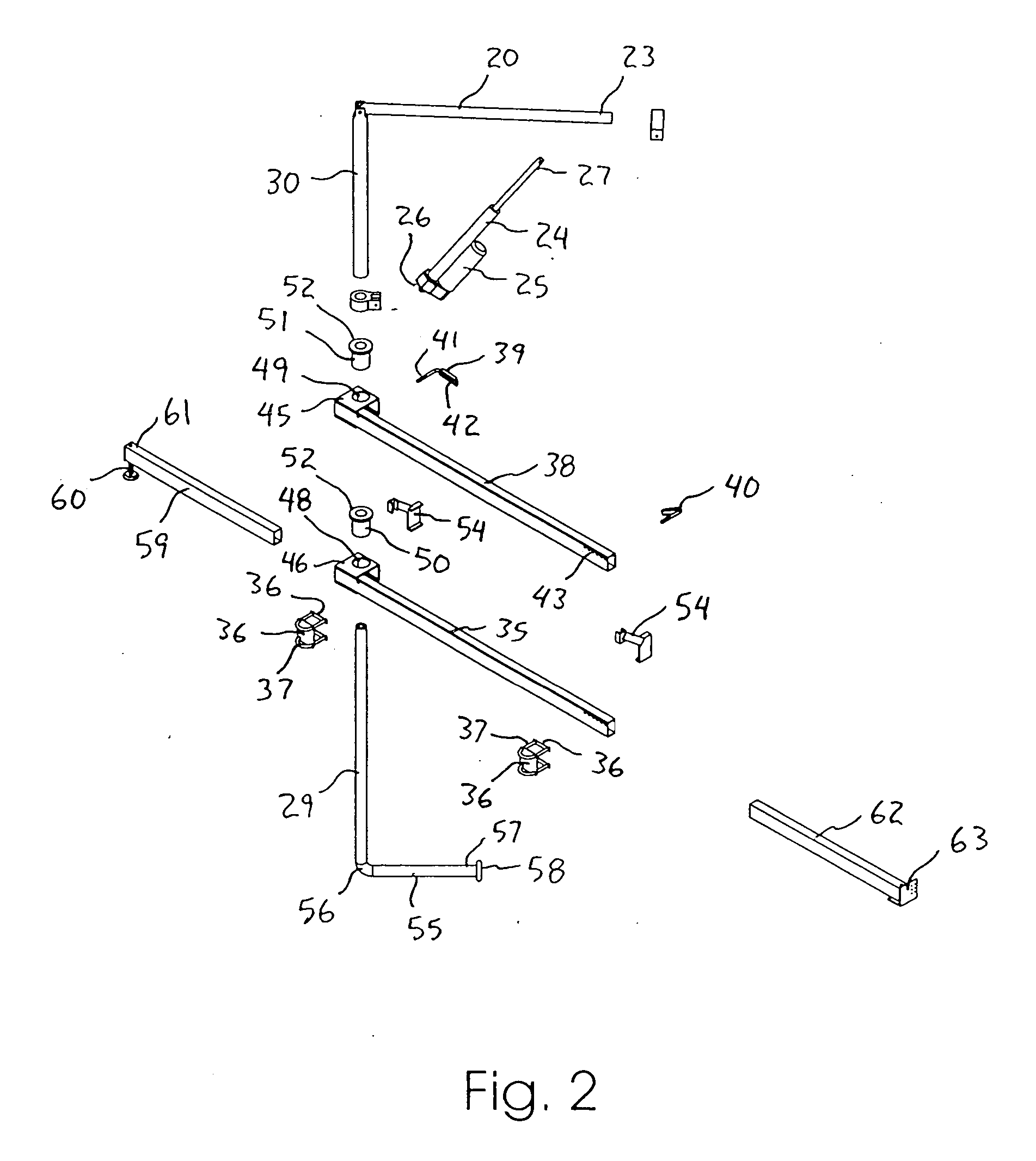
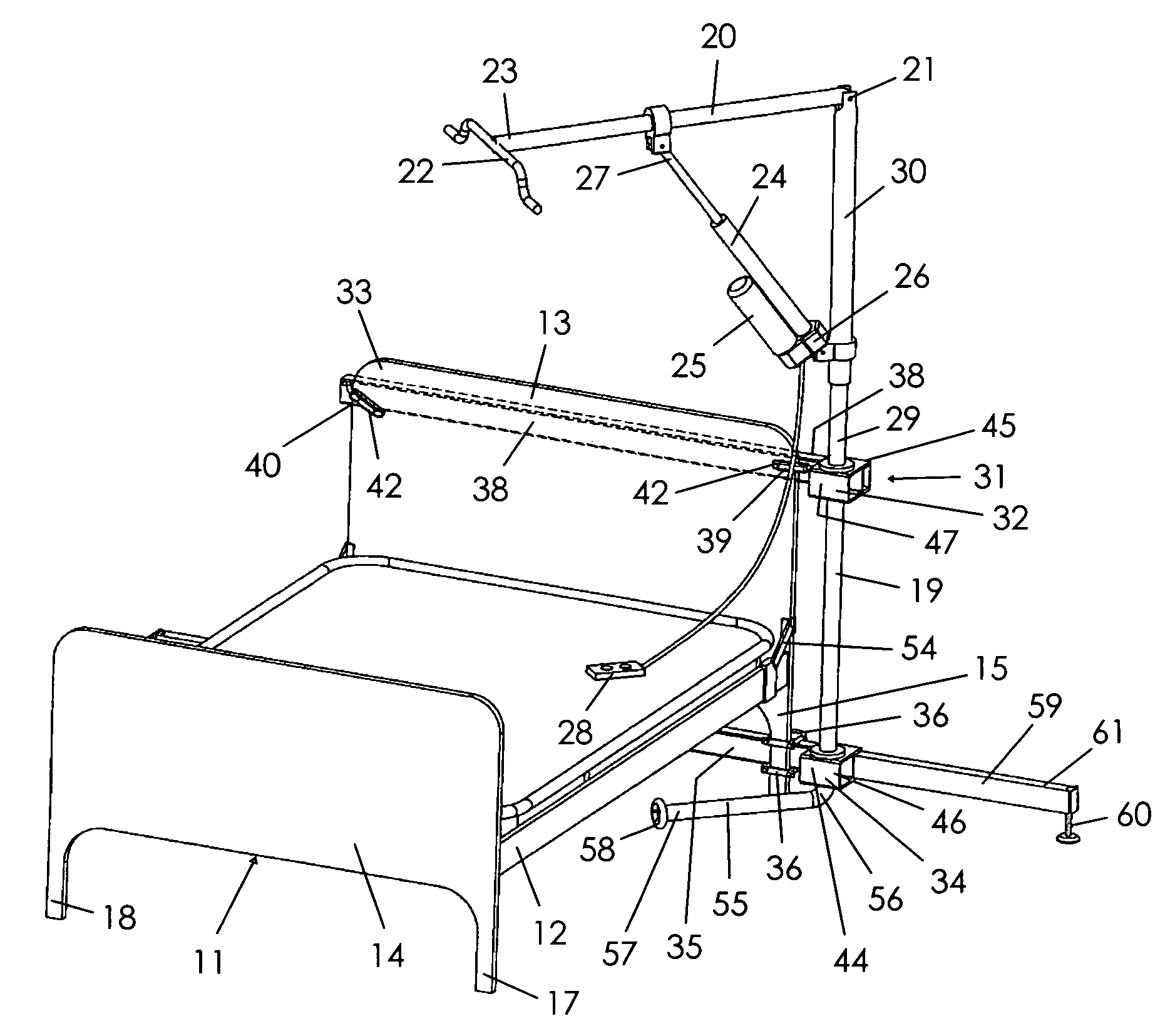
Patient lifting apparatus
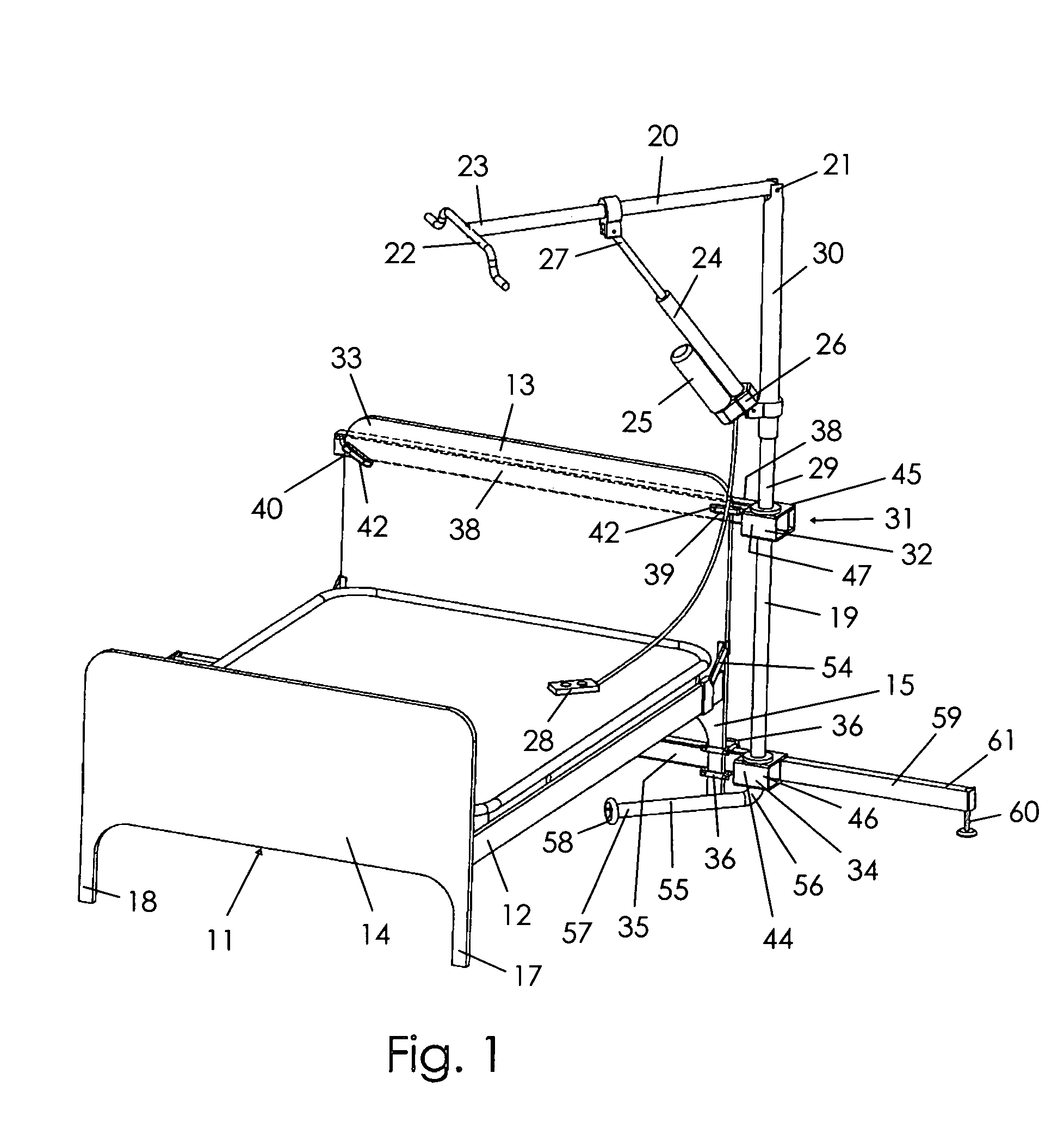
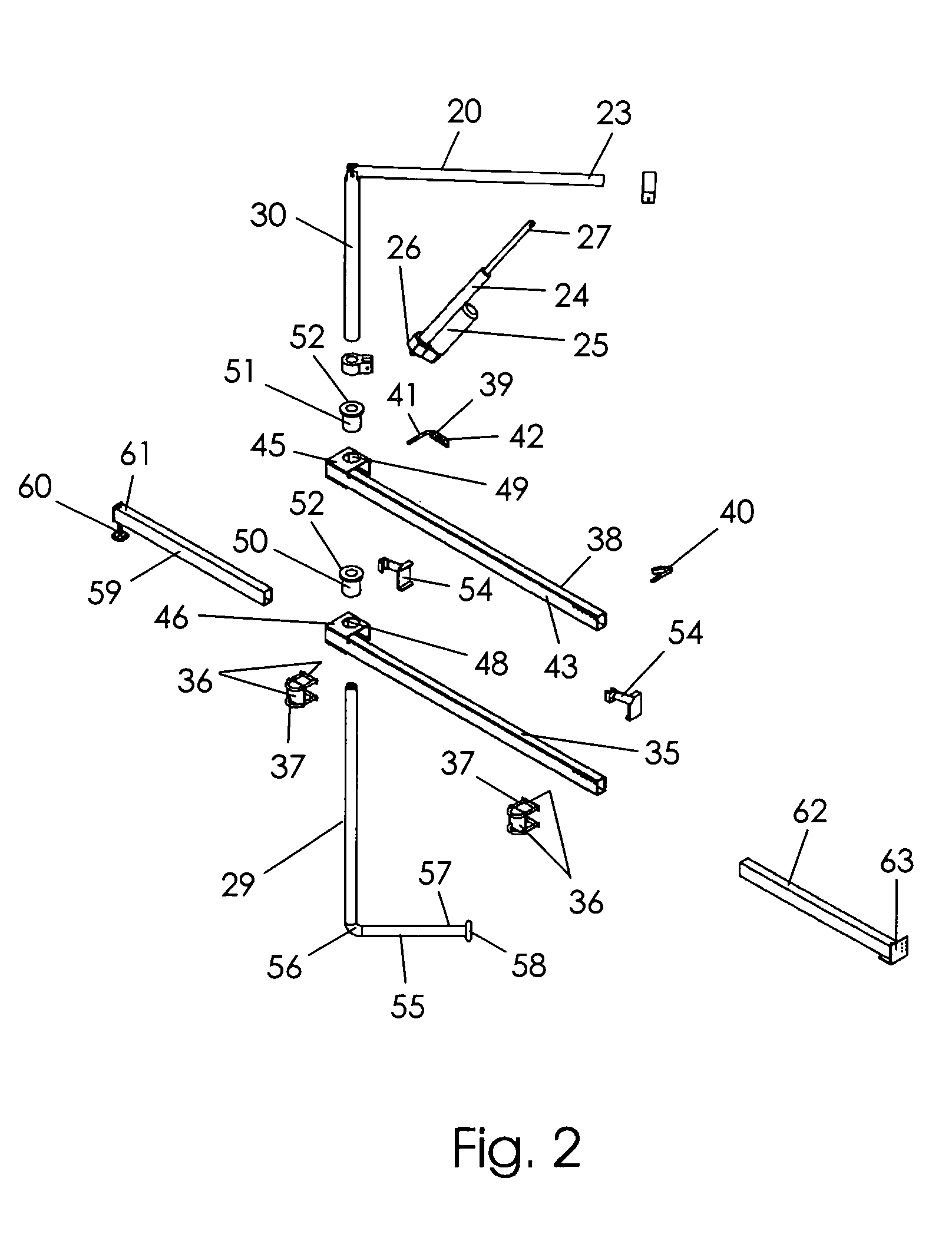
A patient lifting apparatus is provided that attaches to a bed frame having a plurality of legs and a headboard. The apparatus includes an upright member, a boom mechanically associated with the upright member, an upper support bar that extends across the bed frame and secures the upright member to each side of the headboard, and a lower support bar that extends across the bed frame and secures the upright member to the legs. The upright member is supported for rotation about a vertical axis by upper and lower bearings on the upper and lower support bars, respectively. A telescoping foot member extends from the lower support bar and is movable between a stored position and an extended position for stabilizing the lifting apparatus. A support arm extends from a lower end of the upright member and rotates along with the upright member to transfer vertical forces into the floor.
Owner:HAWK MOBILITY SYST
Fuel cell and separator for fuel cell
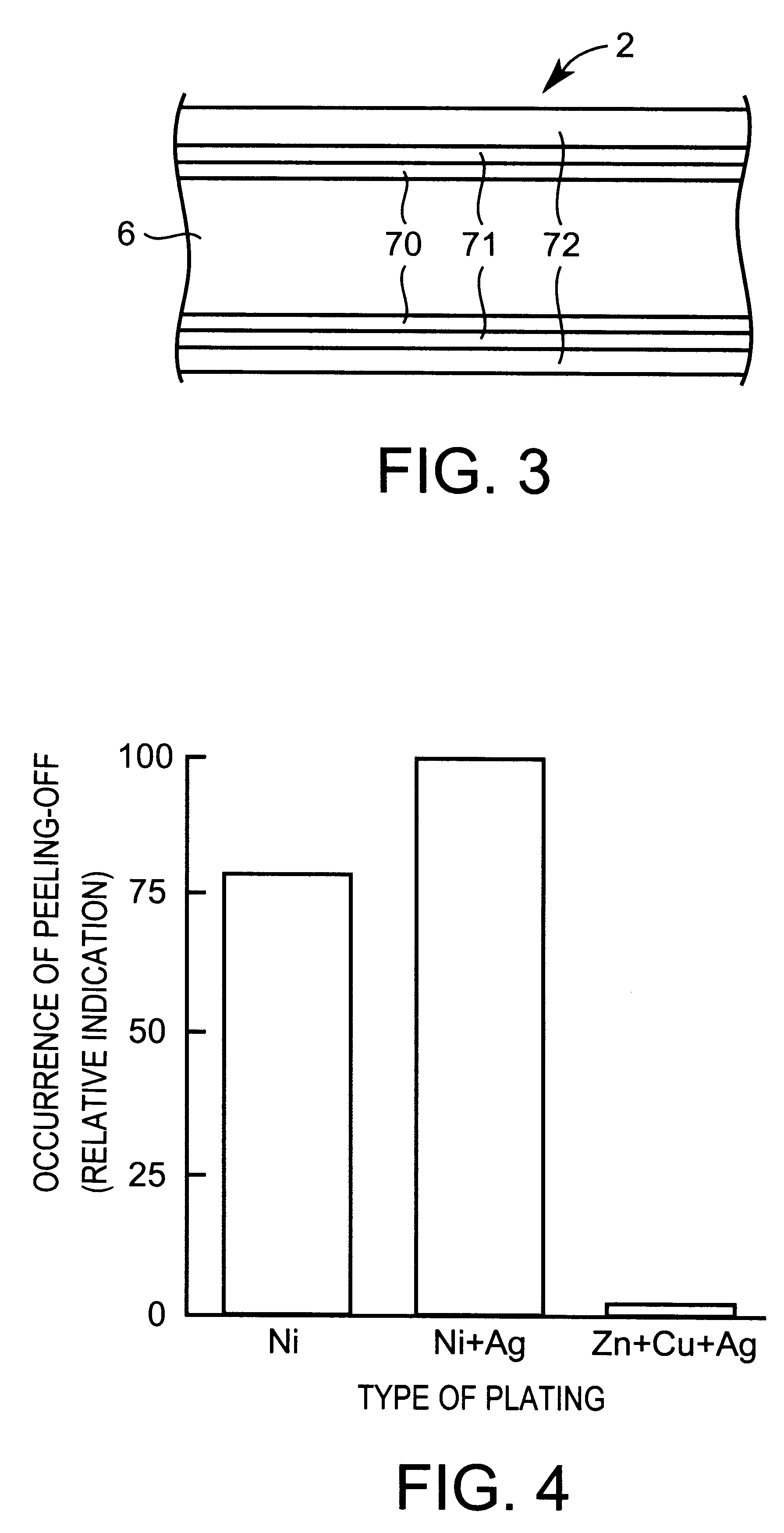
InactiveUS6403246B1Reduce weightSuppress corrosionSolid electrolytesFuel cells groupingCopper platingFuel cells
A fuel cell and a separator for same meritorious in reducing the weight and improving resistance against corrosion. In a fuel cell having a separator 2, the separator 2 includes an aluminum-based substrate 6, an intermediate plating layer layered on the aluminum-based substrate 6 and a noble metal layer 72 layered on the intermediate plating layer. The intermediate plating layer can be made up of a zinc-substitution plating layer 70 and a copper plating layer 71. The noble metal layer 72 can be a silver plating layer.
Owner:AISIN TAKAOKA CO LTD +1
Motor housing integrated-type spoke for electric bicycle, manufacturing method thereof, wheel assembly having the same and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20140077584A1Improve rigidityLow costWave amplification devicesRimsInjection mouldingElectric motor
A motor housing integrated type spoke for an electric bicycle and a manufacturing method thereof, a wheel assembly having the same, and a manufacturing method thereof, the motor housing integrated type spoke coupled to a rim and including a motor housing, which is provided at a center of the motor housing integrated-type spoke to accommodate a motor, the motor housing integrally formed with the motor housing integrated-type spoke through an injection molding.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
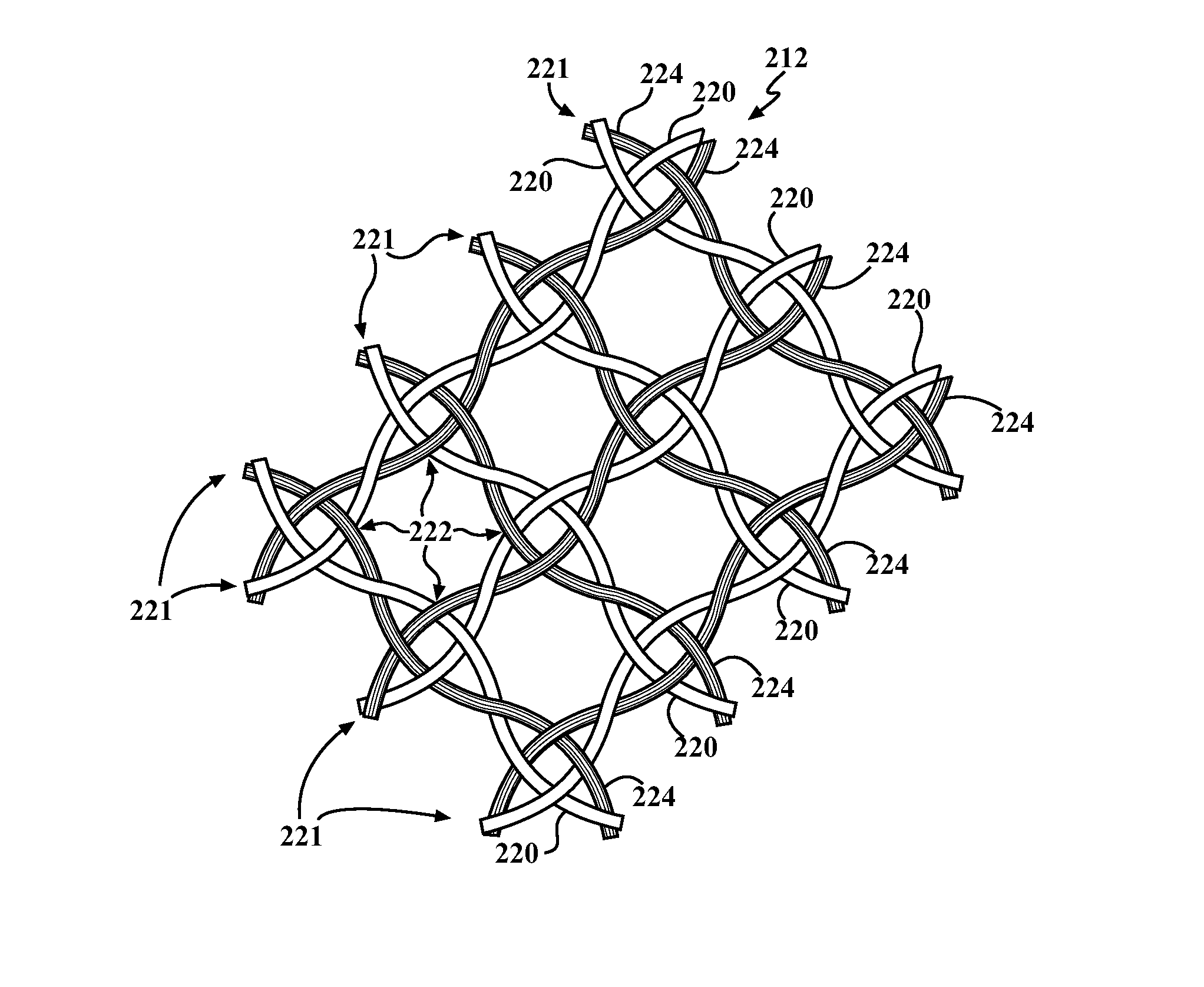
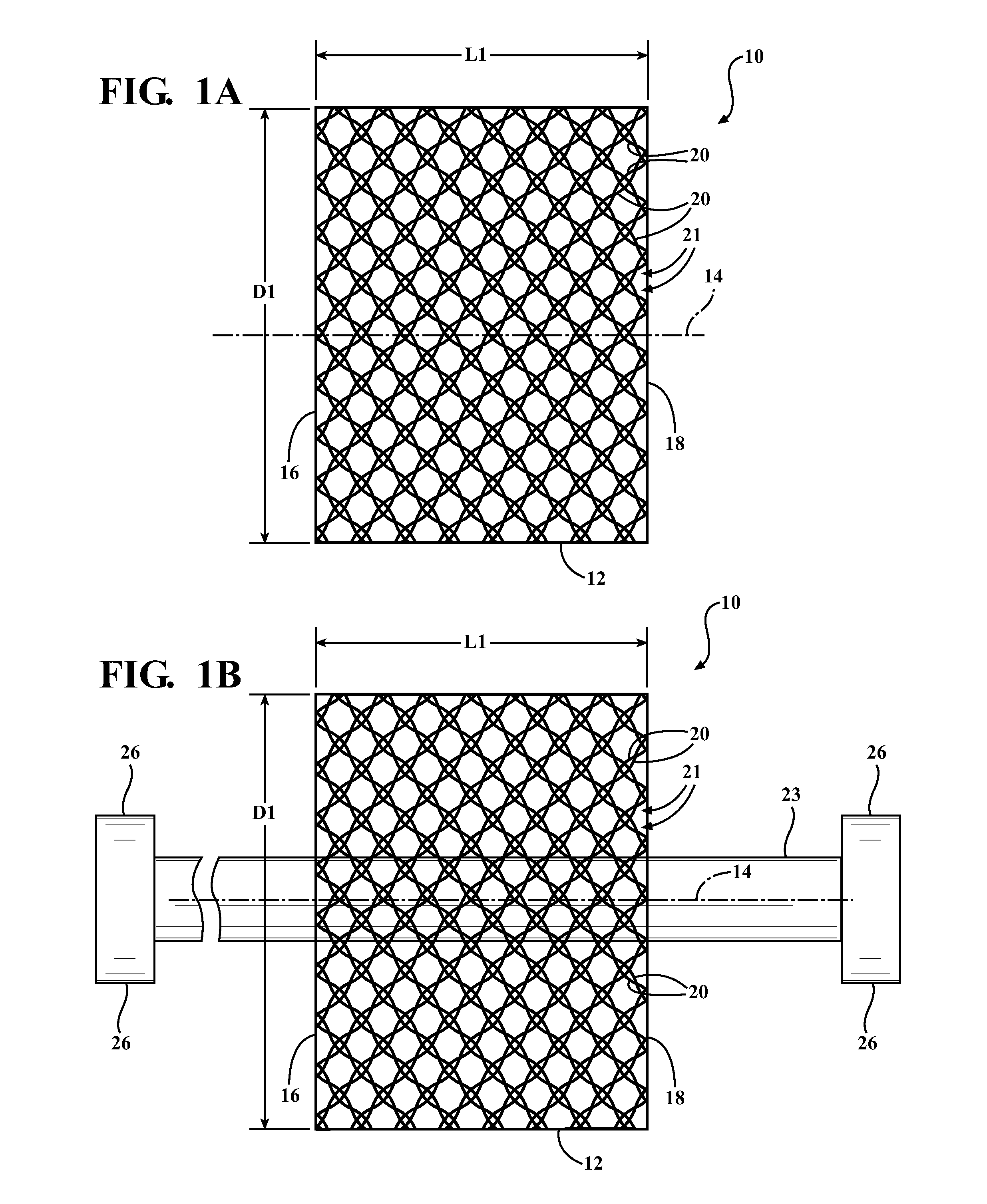
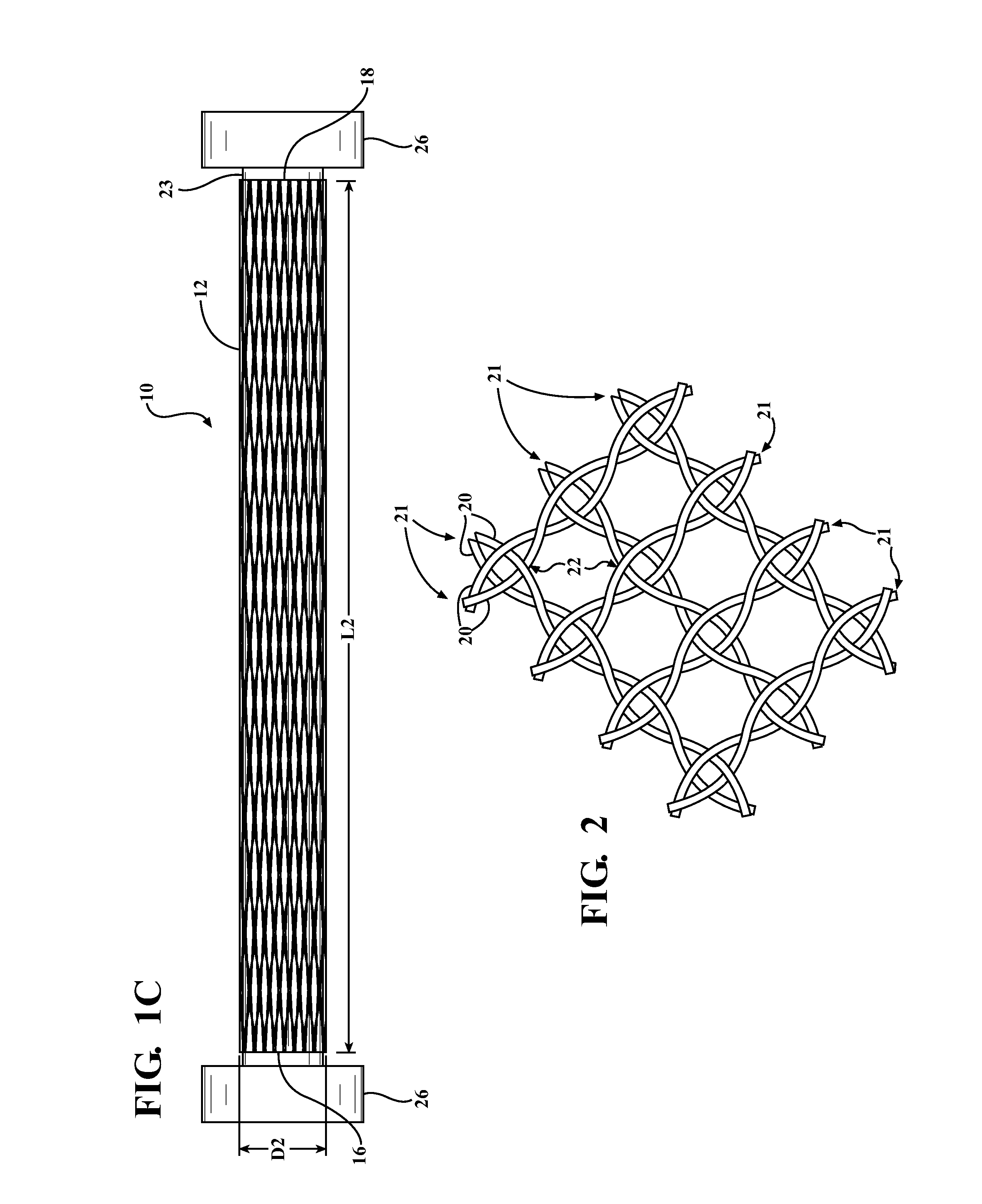
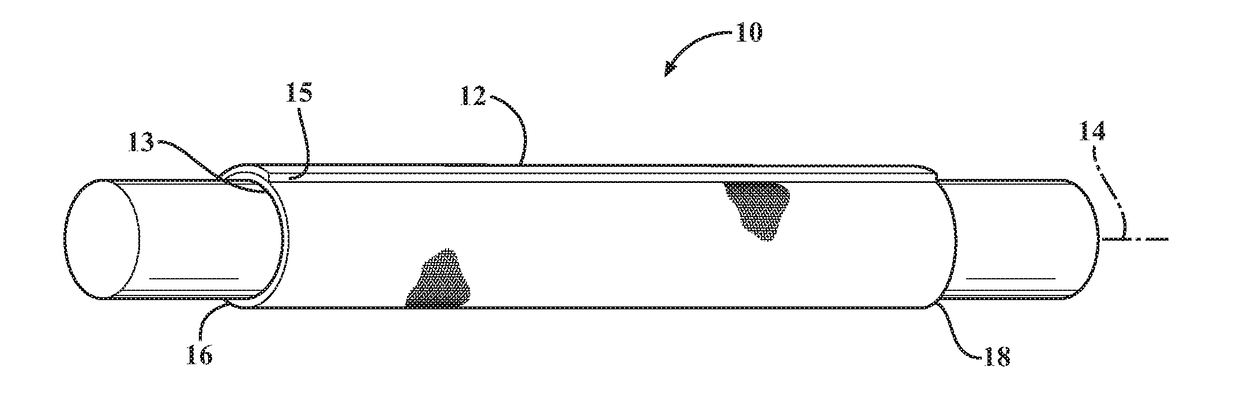
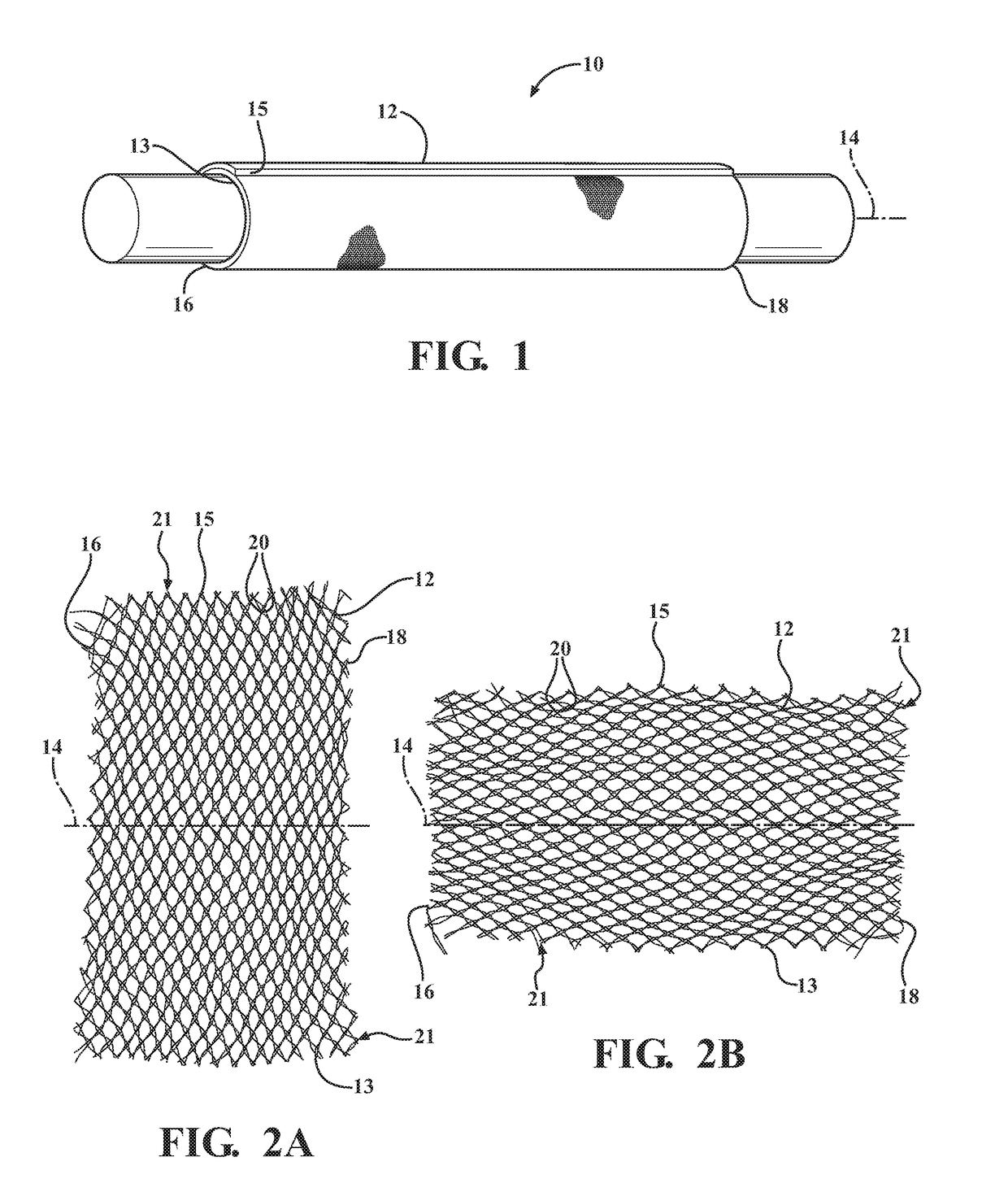
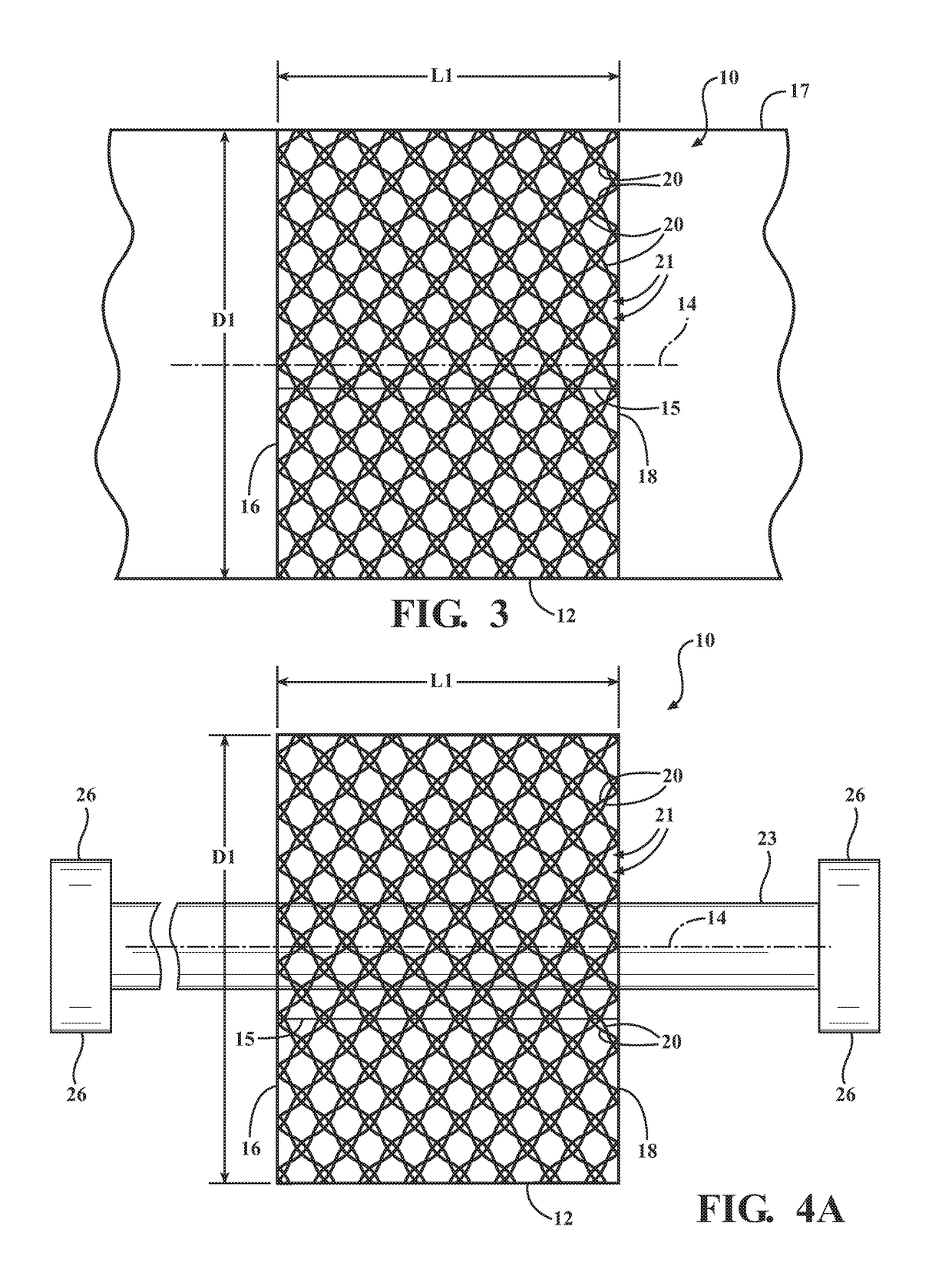
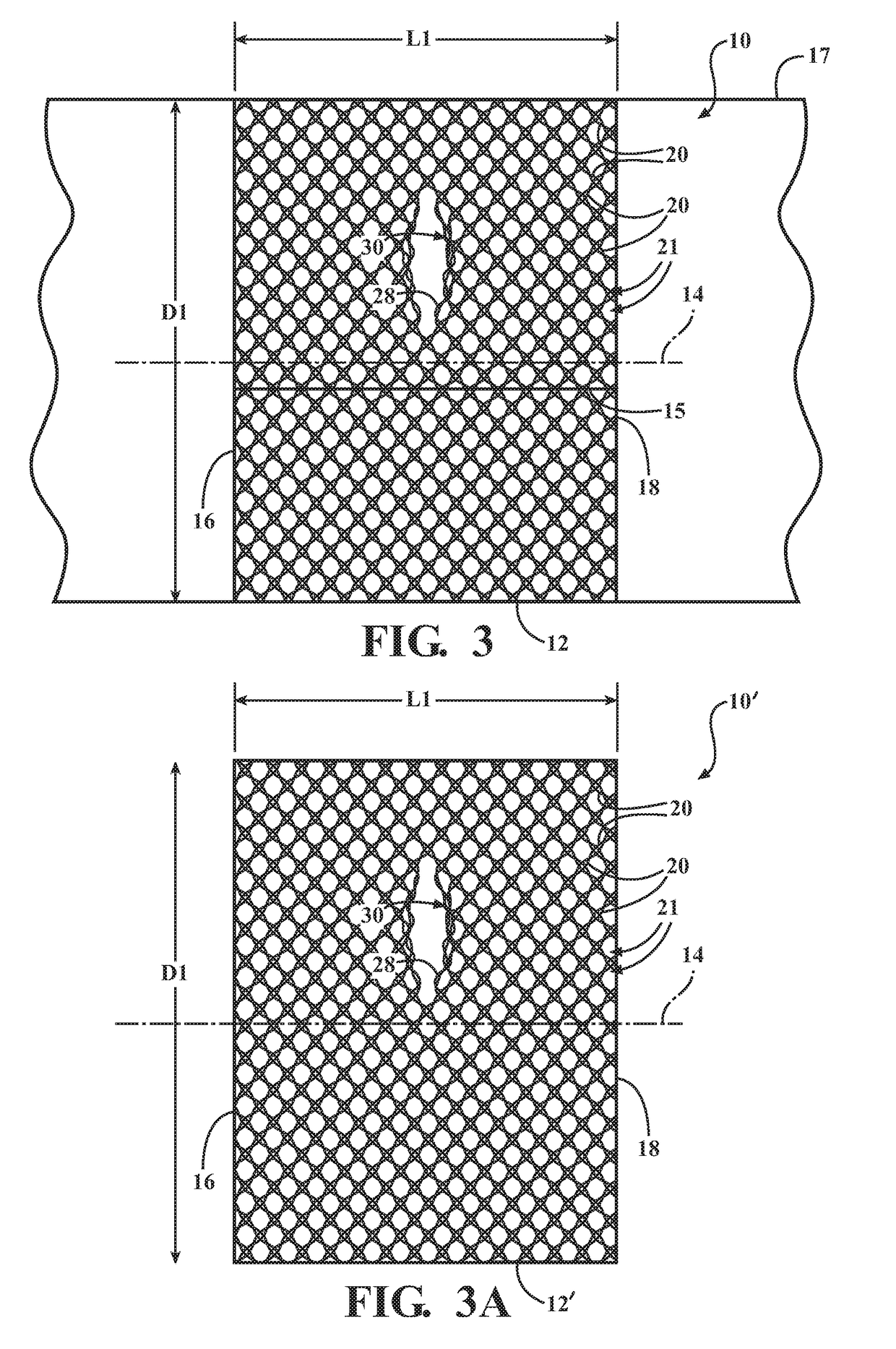
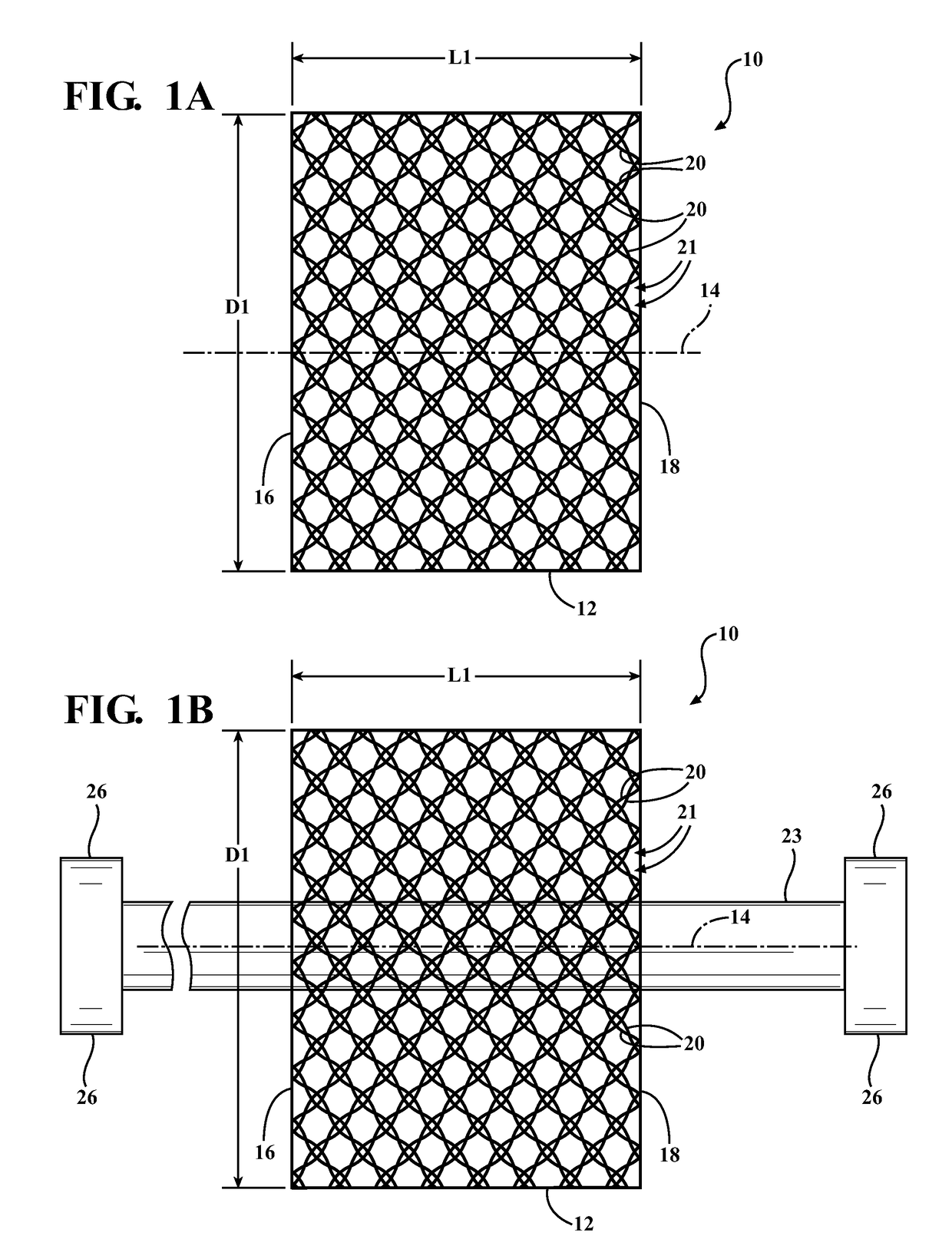
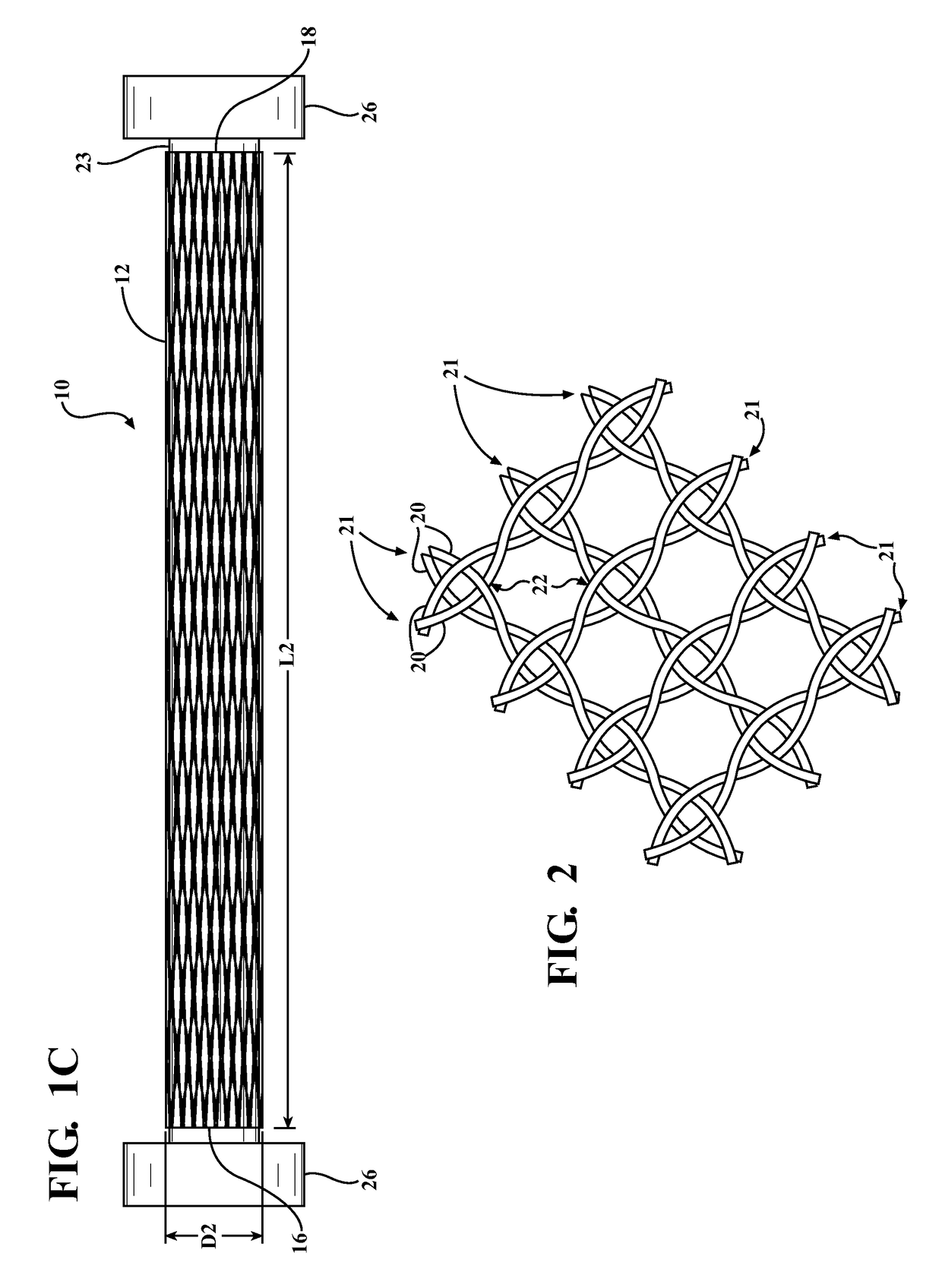
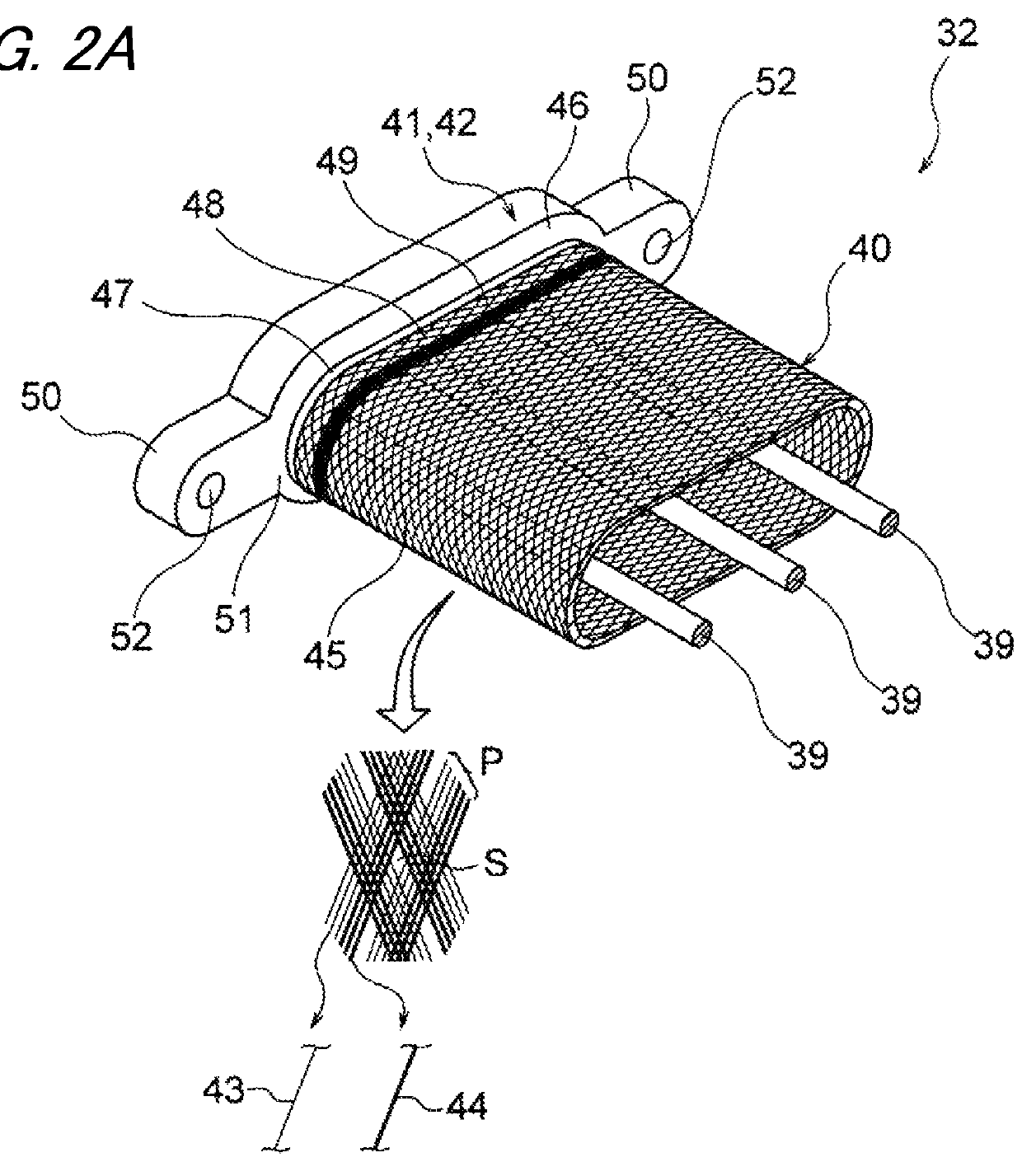
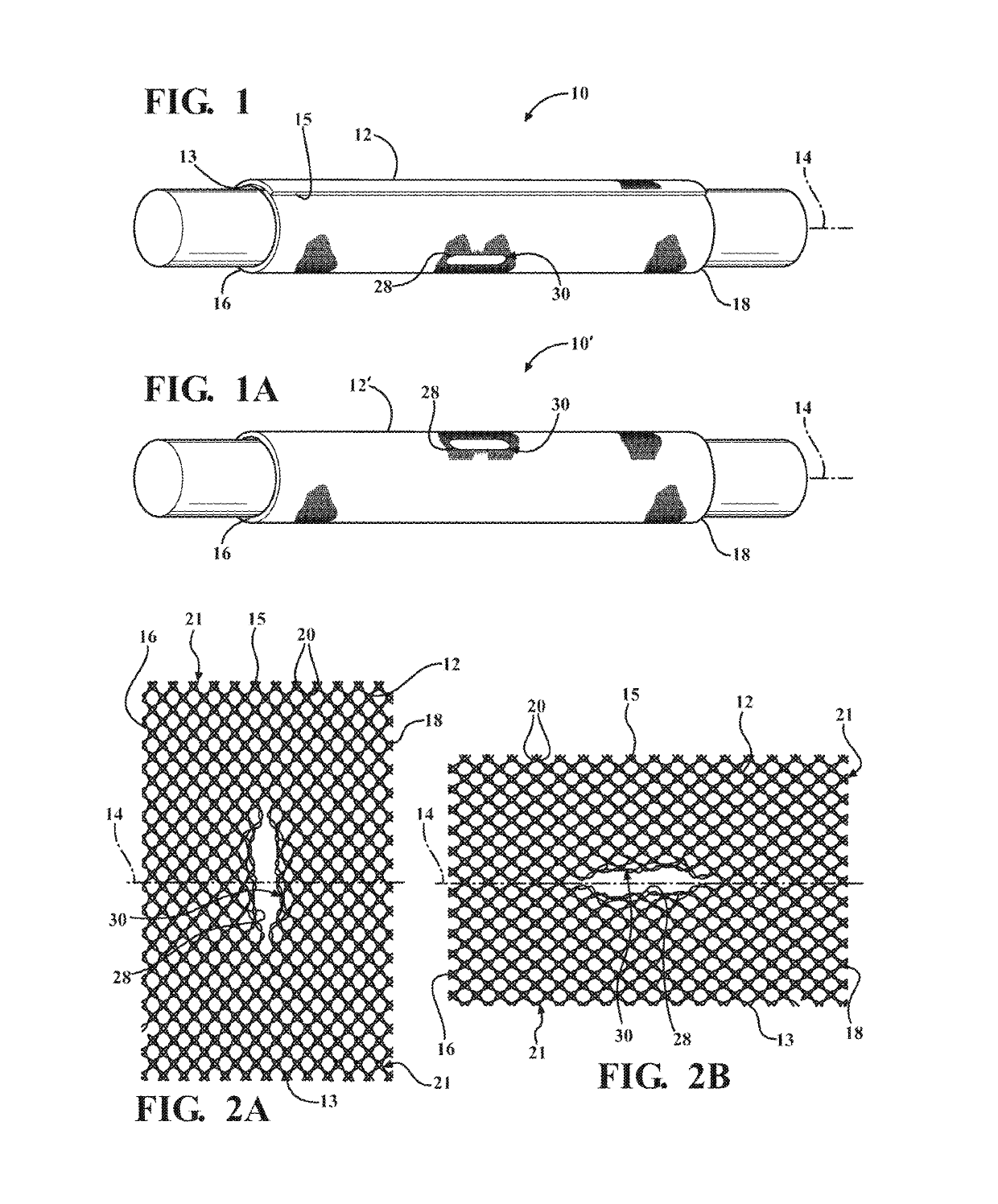
Braided textile sleeve with self-sustaining expanded and contracted states and method of construction thereof
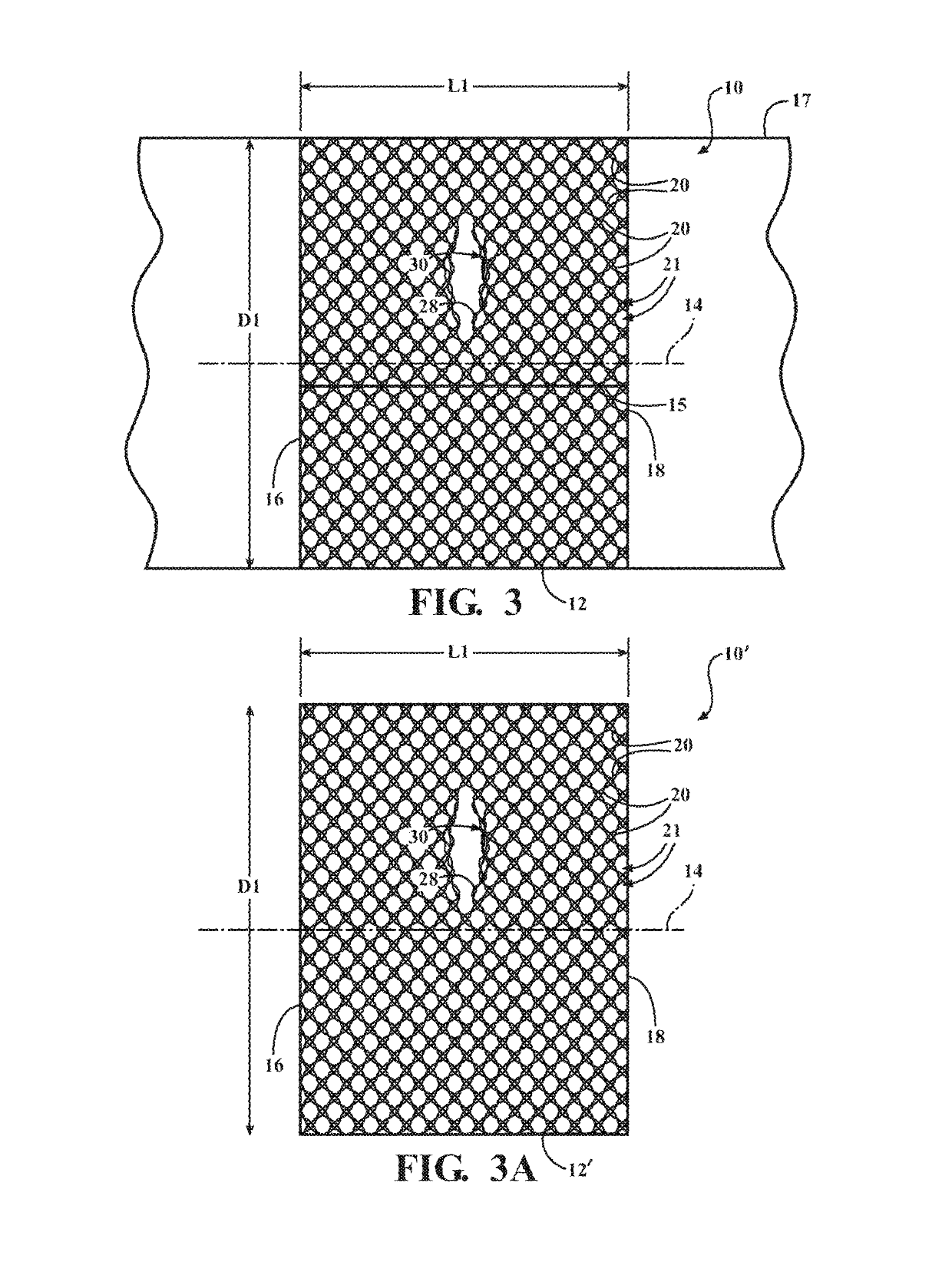
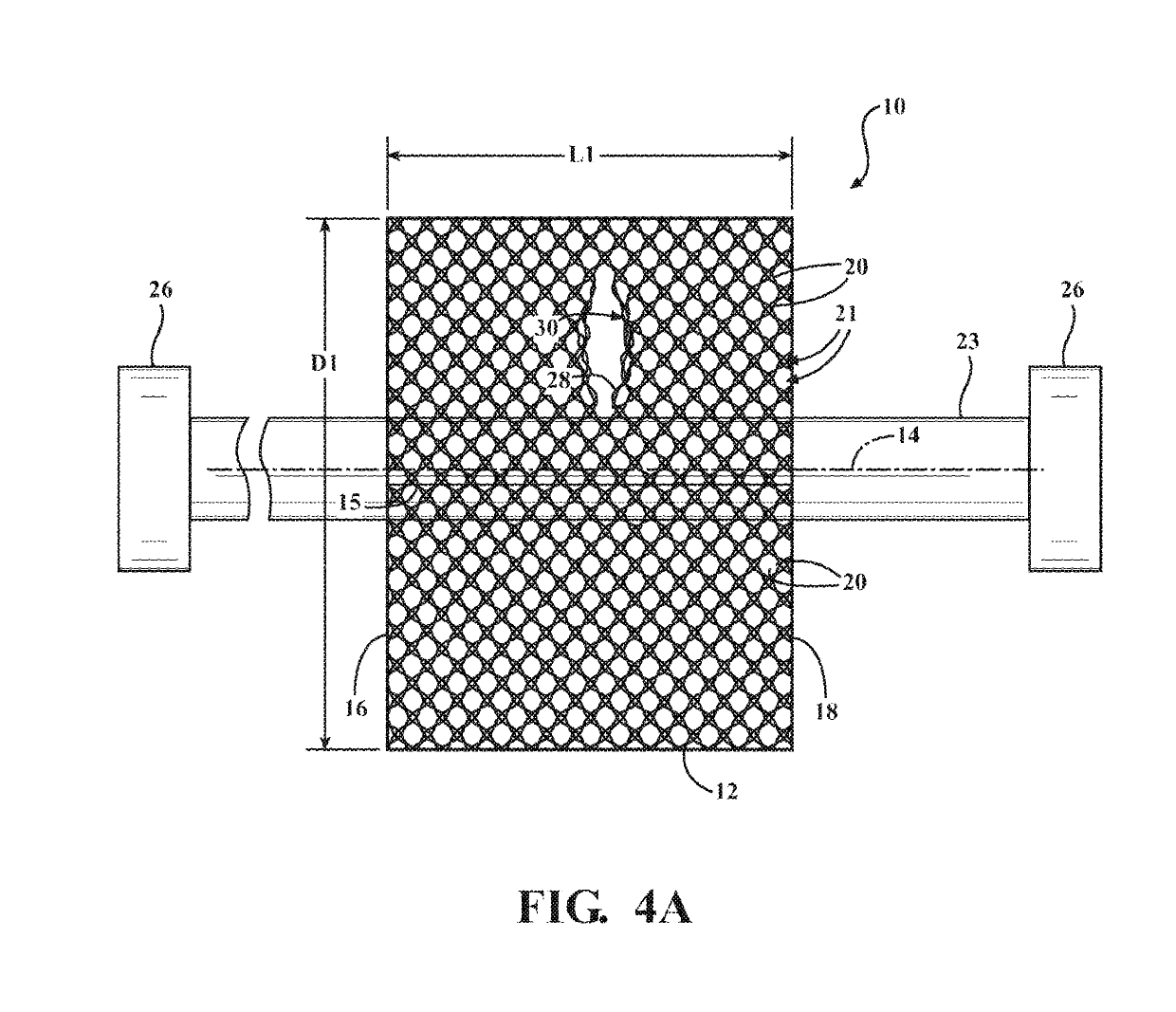
ActiveUS20160122916A1Enhance coverage protectionReducing weight and costBraidTubular articlesYarnBuilding construction
A textile sleeve and method of construction thereof is provided. The sleeve includes a braided, tubular wall extending lengthwise along a central longitudinal axis between opposite ends. The wall has a decreased length, increased cross-sectional area first state and an increased length, decreased cross-sectional area second state. Heat-set, yarns within the wall impart a bias on the wall, wherein the bias causes the wall to remain in each of the first and second states absent an externally applied force.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL POWERTAIN LLC
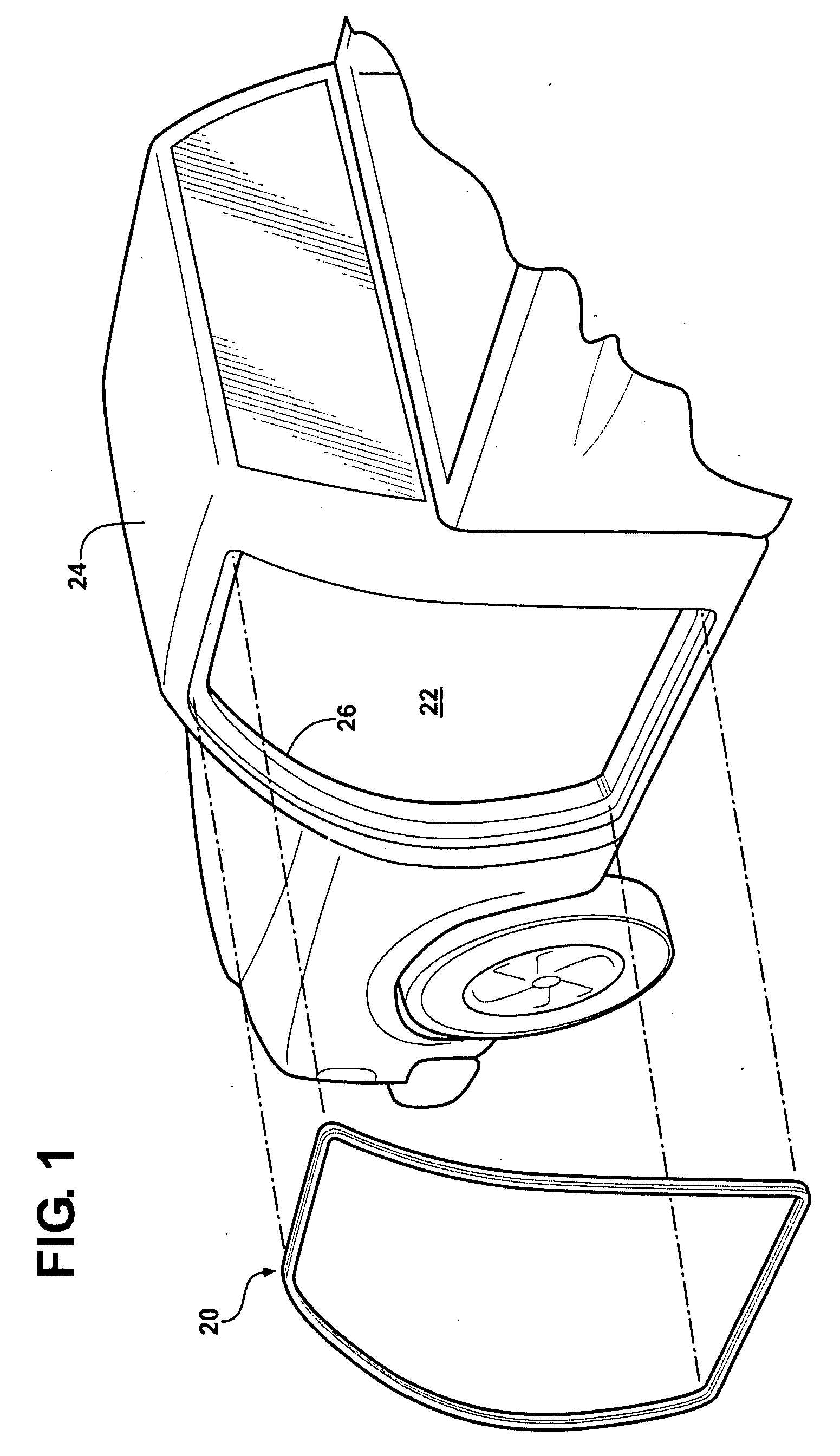
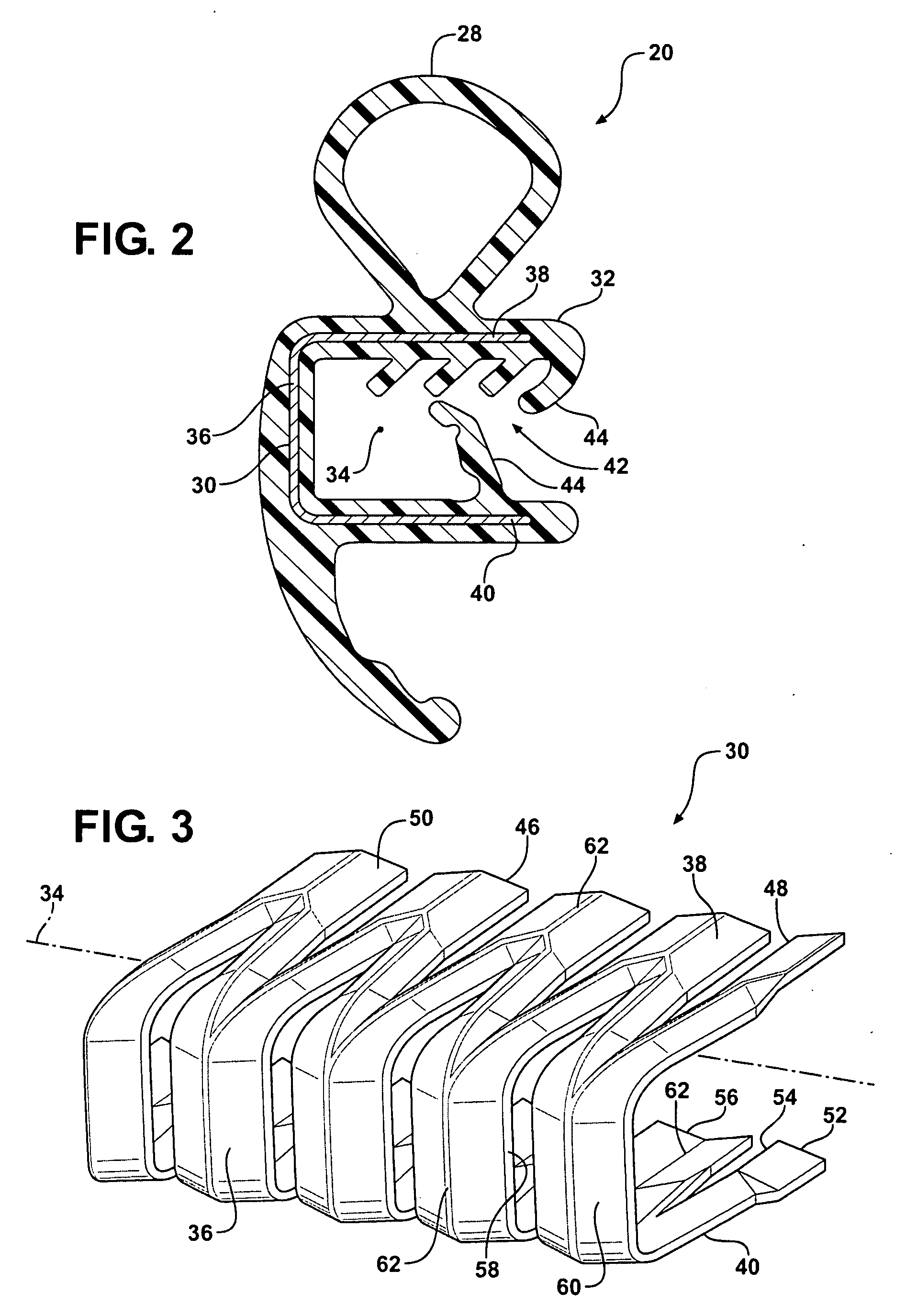
Mechanically stiffened weatherseal carrier
InactiveUS20100212230A1Reduce weightLow costLayered productsVehicle sealing arrangementsEngineeringFlange
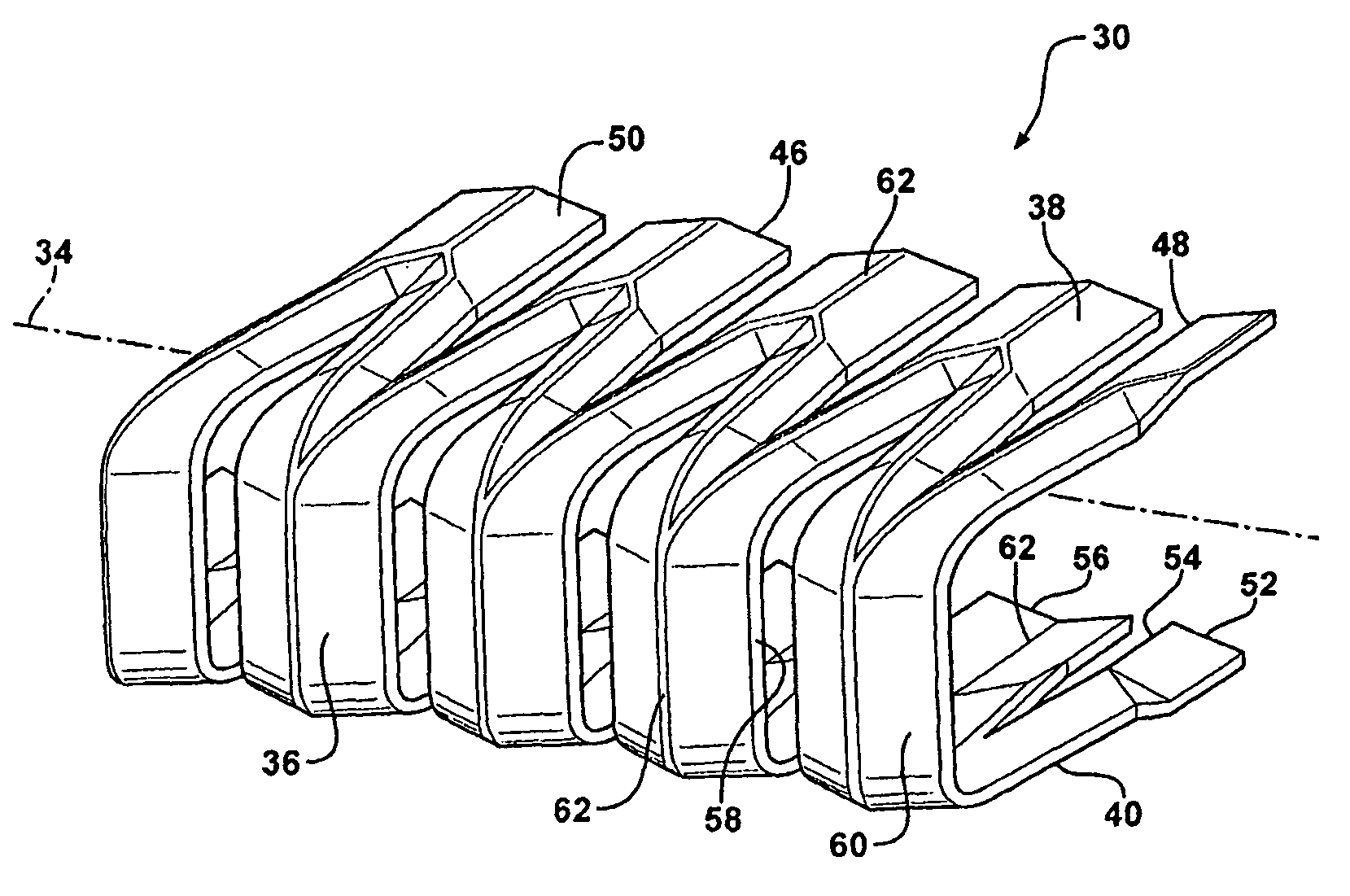
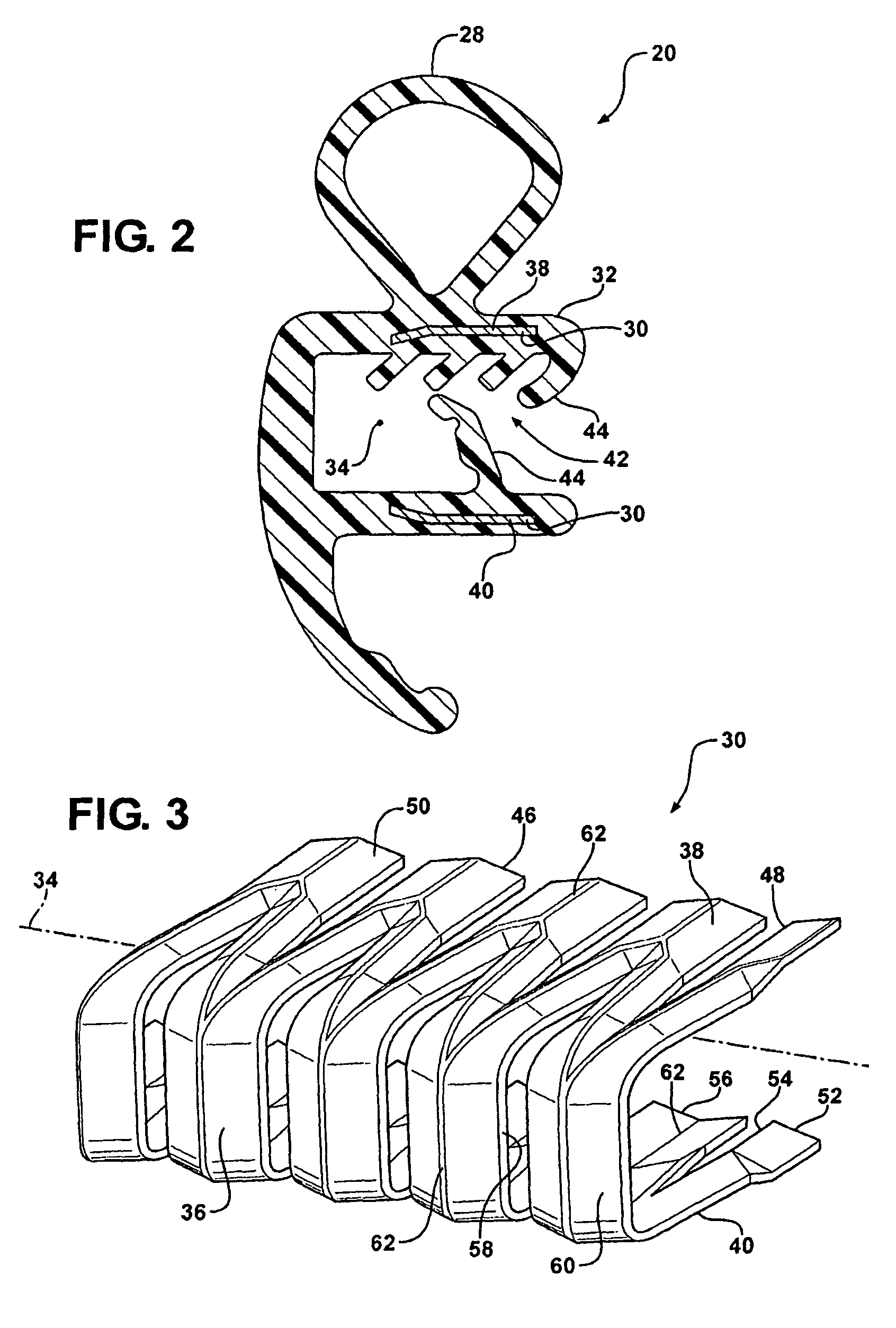
A flange mounted weatherseal includes a carrier and a flexible cover covering the carrier. The carrier includes a base portion, a first side portion and a second side portion generally parallel to the first side portion and cooperating together with the first side portion and the base portion to define a generally U-shaped channel. The first side portion defines a plurality of first fingers, the second side portion defines a plurality of second fingers opposite the first fingers along a longitudinal axis, and the base portion defines a plurality of webs offset along the longitudinal axis relative to the first fingers and the second fingers. The first fingers, the second fingers and the webs each include deformations defining a non-planar cross sectional shape along the longitudinal axis to increase the rigidity of the carrier.
Owner:HENNIGES AUTOMOTIVE SEALING SYST NORTH AMERICA
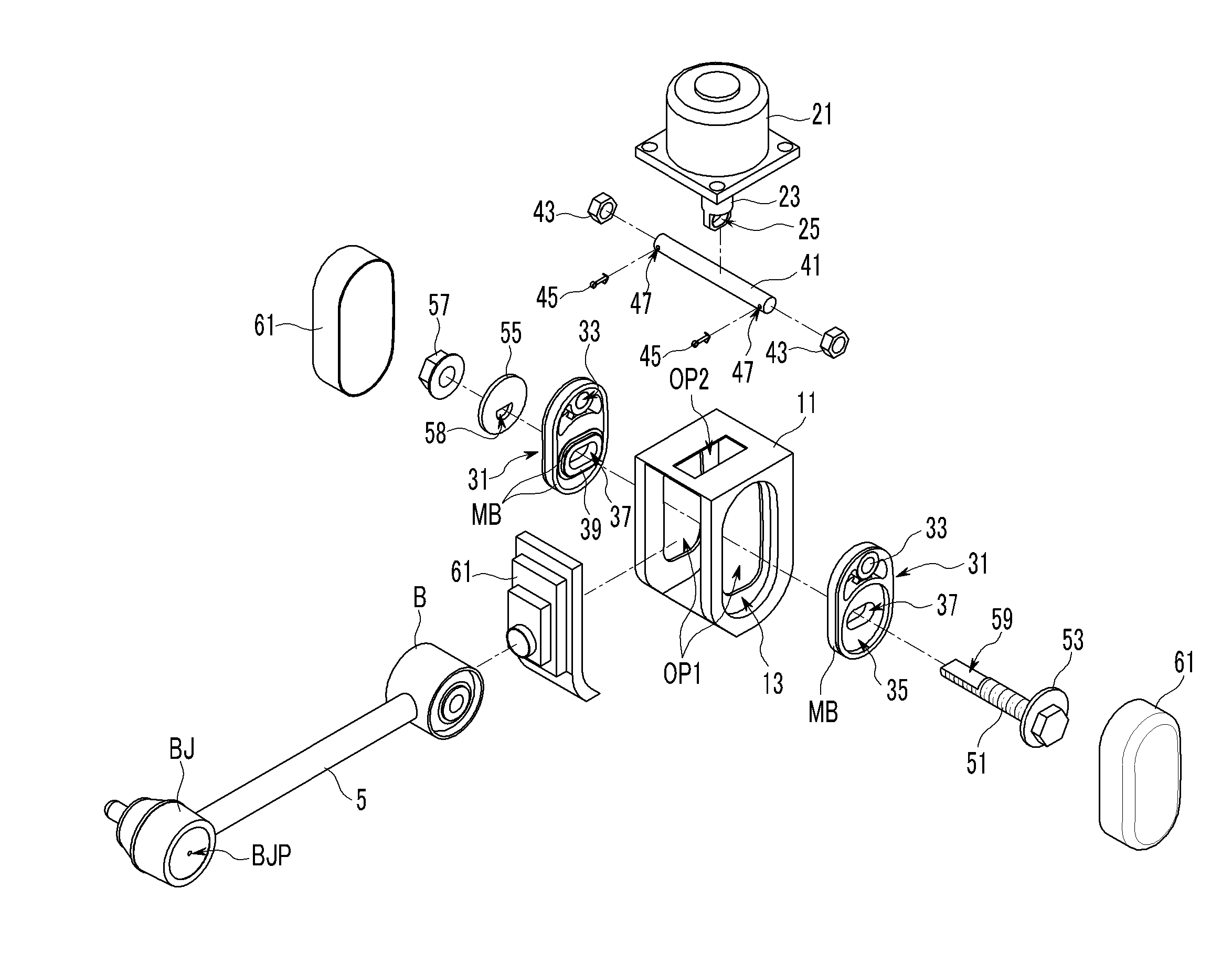
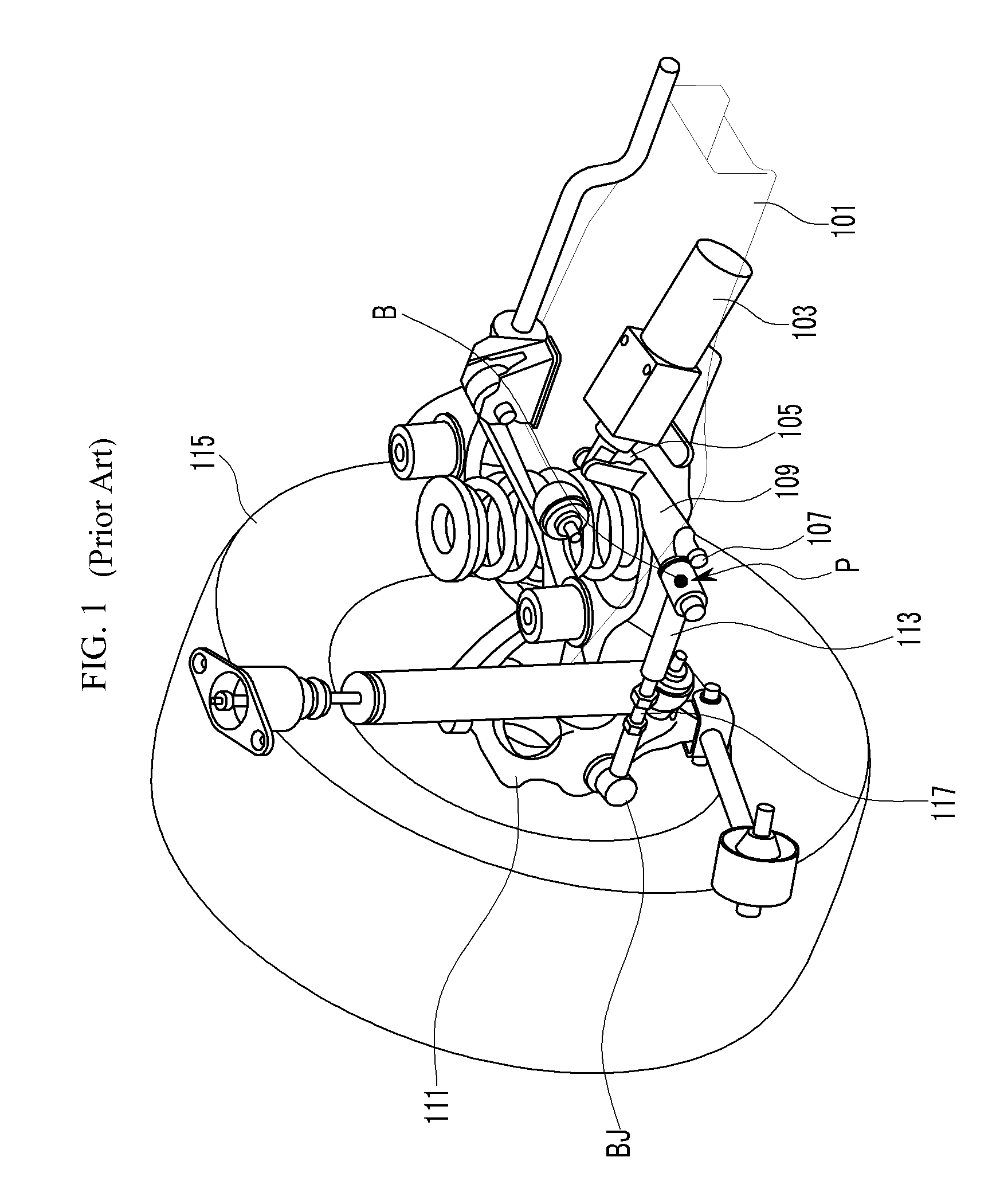
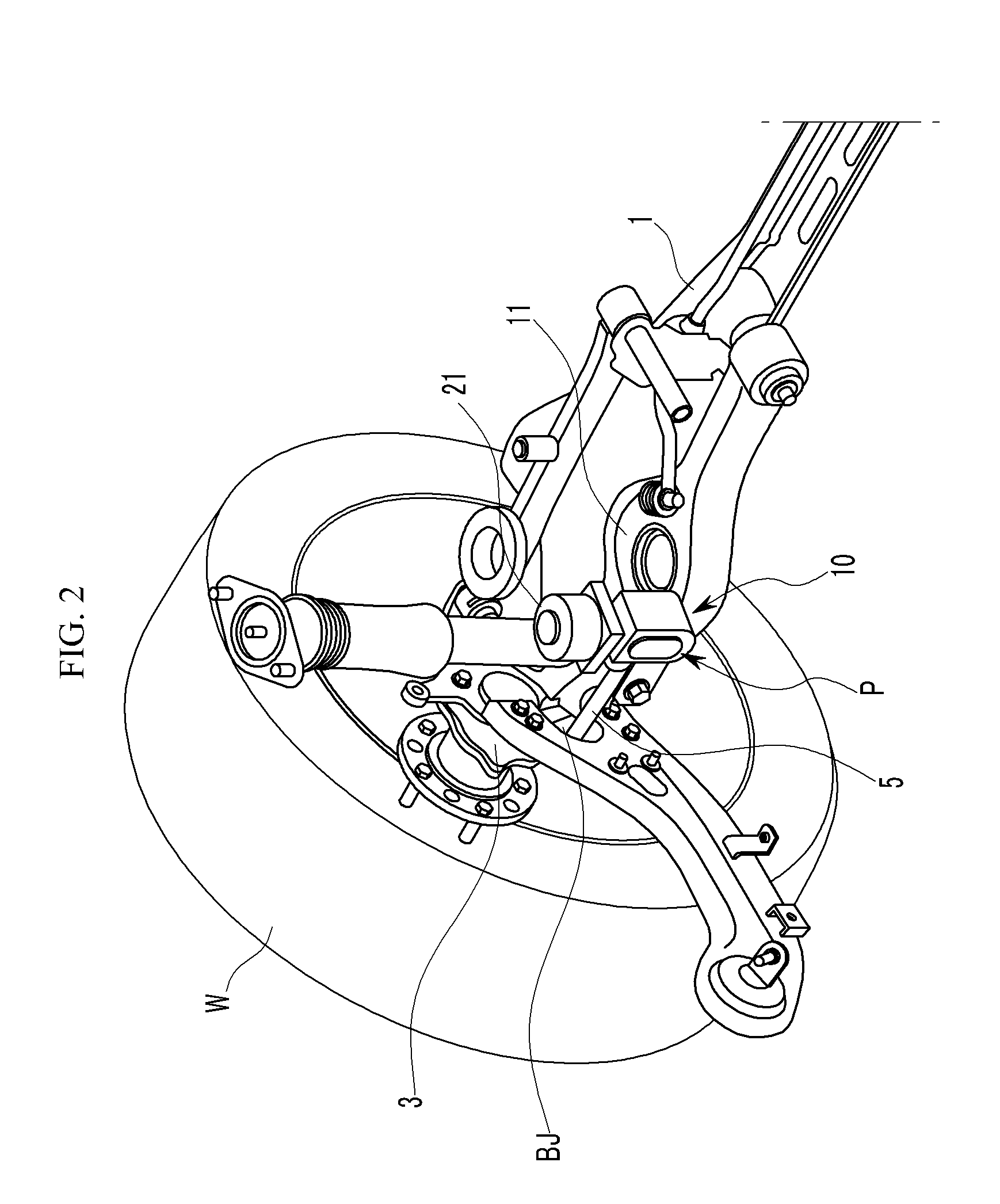
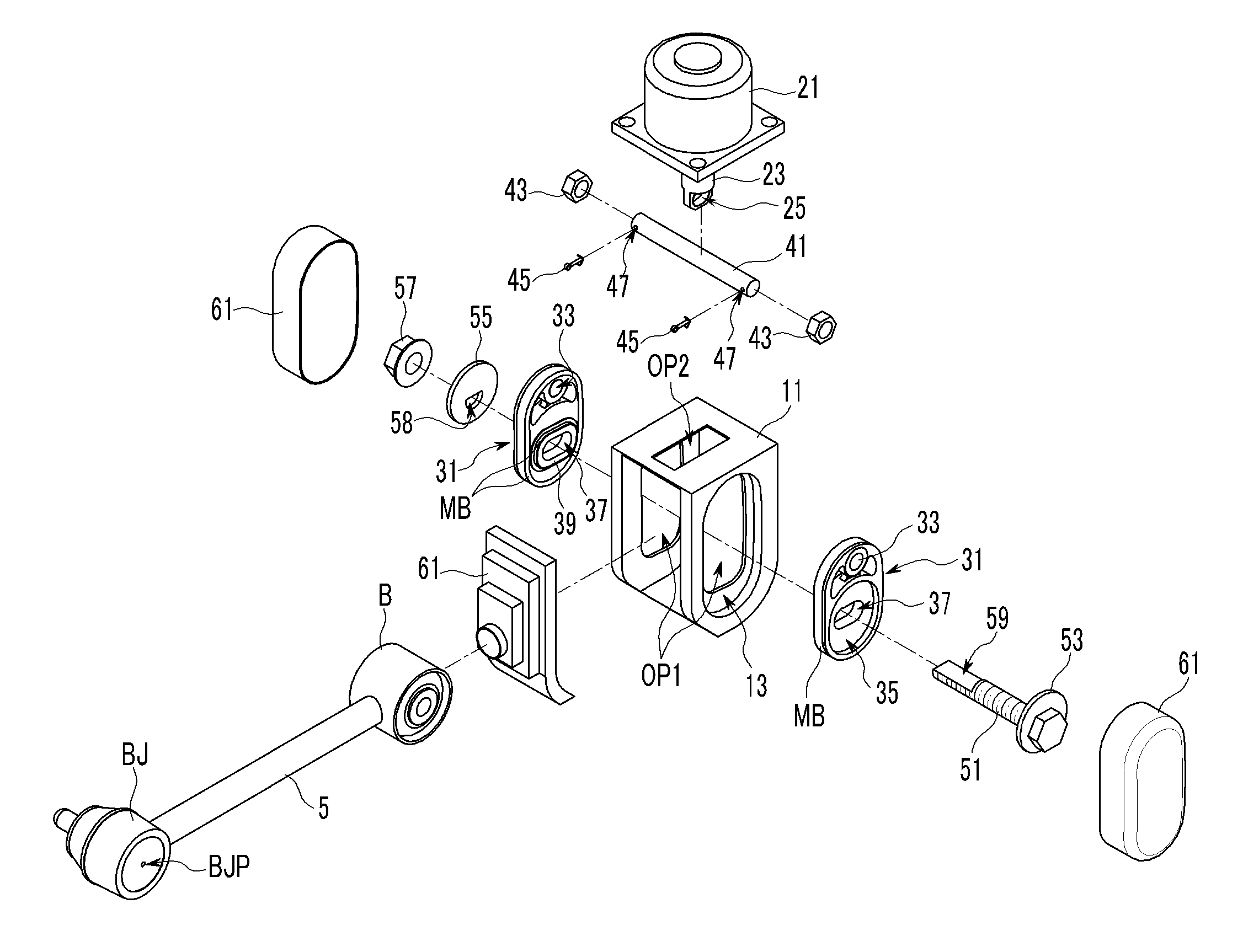
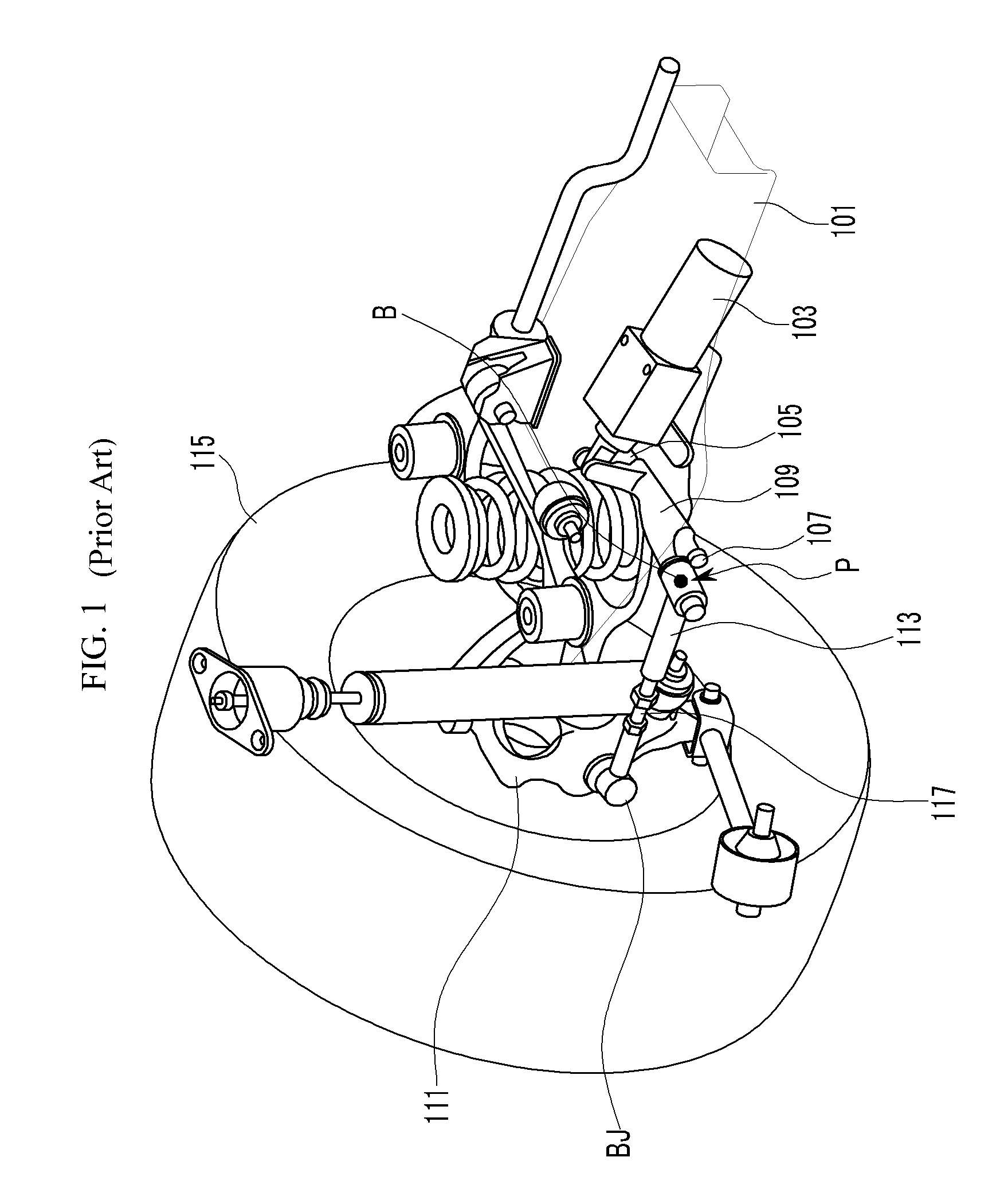
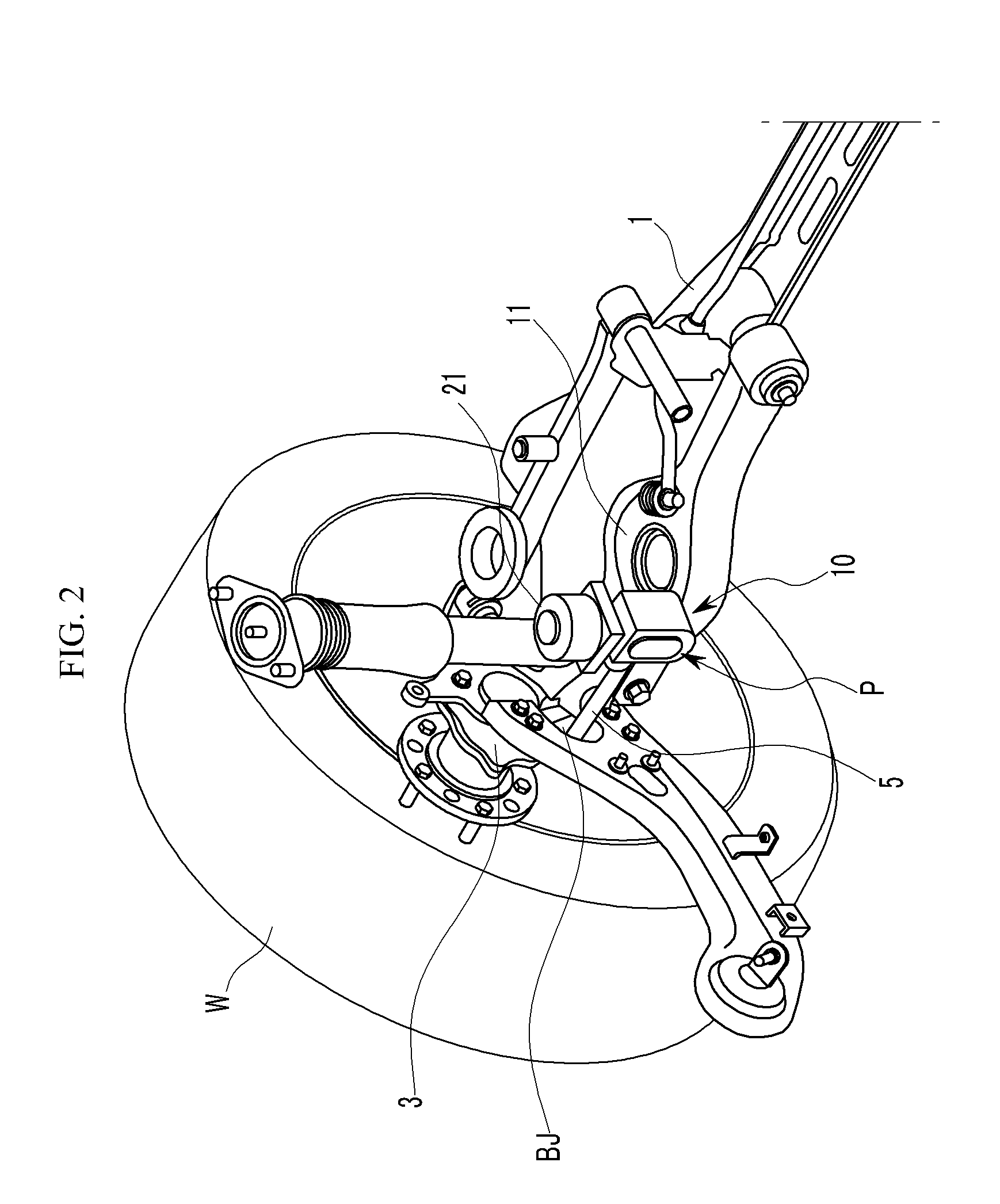
Active geometry control suspension system and actuating device driving the same
An actuating device for an active control suspension system which is provided at both ends of a sub-frame of a vehicle body and connected to one end of an assist link having the other end mounted at a knuckle and which changes a position of a mounting point of the assist link at the vehicle body, may include a member bracket fixedly mounted at each end of the sub-frame, provided with openings formed at both sides and an upper surface thereof, and formed of a pair of slide grooves having arc shape at the both ends thereof to slidably receive a pair of slide plates therein; an actuator connected to both slide plates through a pin-bolt unit; and a cam-bolt unit assembling a bush of the assist link with both slide plates and setting an initial position of the mounting point of the assist link at the vehicle body.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Self-wrapping, braided textile sleeve with self-sustaining expanded and contracted states and method of construction thereof
ActiveUS20170121868A1Enhance coverage protectionReducing weight and costOrnamental textile articlesProtective fabricsYarnArchitectural engineering
A self-wrapping protective textile sleeve and method of construction is provided. The sleeve includes a braided, tubular wall having opposite free edges extending lengthwise between opposite ends. The wall has a first state with a decreased length, increased cross-sectional area and a second state with an increased length, decreased cross-sectional area, as viewed in cross-section taken generally transversely to a central longitudinal axis. The wall further includes braided, heat-set yarns imparting a bias on the wall, wherein the bias causes the wall to self-wrap into a tubular configuration and to remain substantially in the first and second states absent some externally applied force.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL POWERTAIN LLC
Opposing pump/motors
InactiveUS20050207921A1Reduce weightLow costFlexible member pumpsGearing controlMotor driveCombined use
Two motors are arranged on opposing sides of a common shaft, drive plates of the pump / motors being rigidly coupled to each other, for example by being in hard contact with opposing sides of the shaft. By providing hard contact between the pump / motor drive plates and a common shaft, the drive plates and shaft act as a substantially solid element under compression, thereby substantially canceling axial loads generated by the pump / motors directly through the shaft. Residual axial loads are handled via bearings positioned on the shaft adjacent the drive plates in such a manner that the drive plates are in light contact only with the bearings. As a result, friction experienced by the bearings is substantially reduced as compared to conventional systems, thereby improving the efficiency of the system. To further reduce loads on the bearings, the pump / motors are arranged to ensure that they generate radial forces in a direction that is opposite to that of a separation force generated by a torque transferring device carried on the shaft and transmitted to the bearings. A common housing surrounding the two pump / motors, bearings and torque transferring device is divided into three regions, to segregate the bearings and torque transferring assembly from the pump / motors. In this manner, the regions containing the pump / motors are substantially filled with oil to, for example, fully lubricate the pump / motors, while the central region containing the gears and torque transferring device contains a significantly smaller volume of oil to simply splash lubricate the contents of the region, thereby reducing drag on the bearings. Control means are provided for selectively moving the two pump / motors substantially simultaneously to a selected displacement angle, using mechanical systems alone and in combination with hydraulic systems.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE U S ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY EPA
Patient lifting apparatus
InactiveUS6964070B2Reducing weight and costSacrificing durabilityWheelchairs/patient conveyanceNursing bedsEngineeringVertical axis
A patient lifting apparatus is provided that attaches to a bed frame having a plurality of legs and a headboard. The apparatus includes an upright member, a boom mechanically associated with the upright member, an upper support bar that extends across the bed frame and secures the upright member to each side of the headboard, and a lower support bar that extends across the bed frame and secures the upright member to the legs. The upright member is supported for rotation about a vertical axis by upper and lower bearings on the upper and lower support bars, respectively. A telescoping foot member extends from the lower support bar and is movable between a stored position and an extended position for stabilizing the lifting apparatus. A support arm extends from a lower end of the upright member and rotates along with the upright member to transfer vertical forces into the floor.
Owner:HAWK MOBILITY SYST
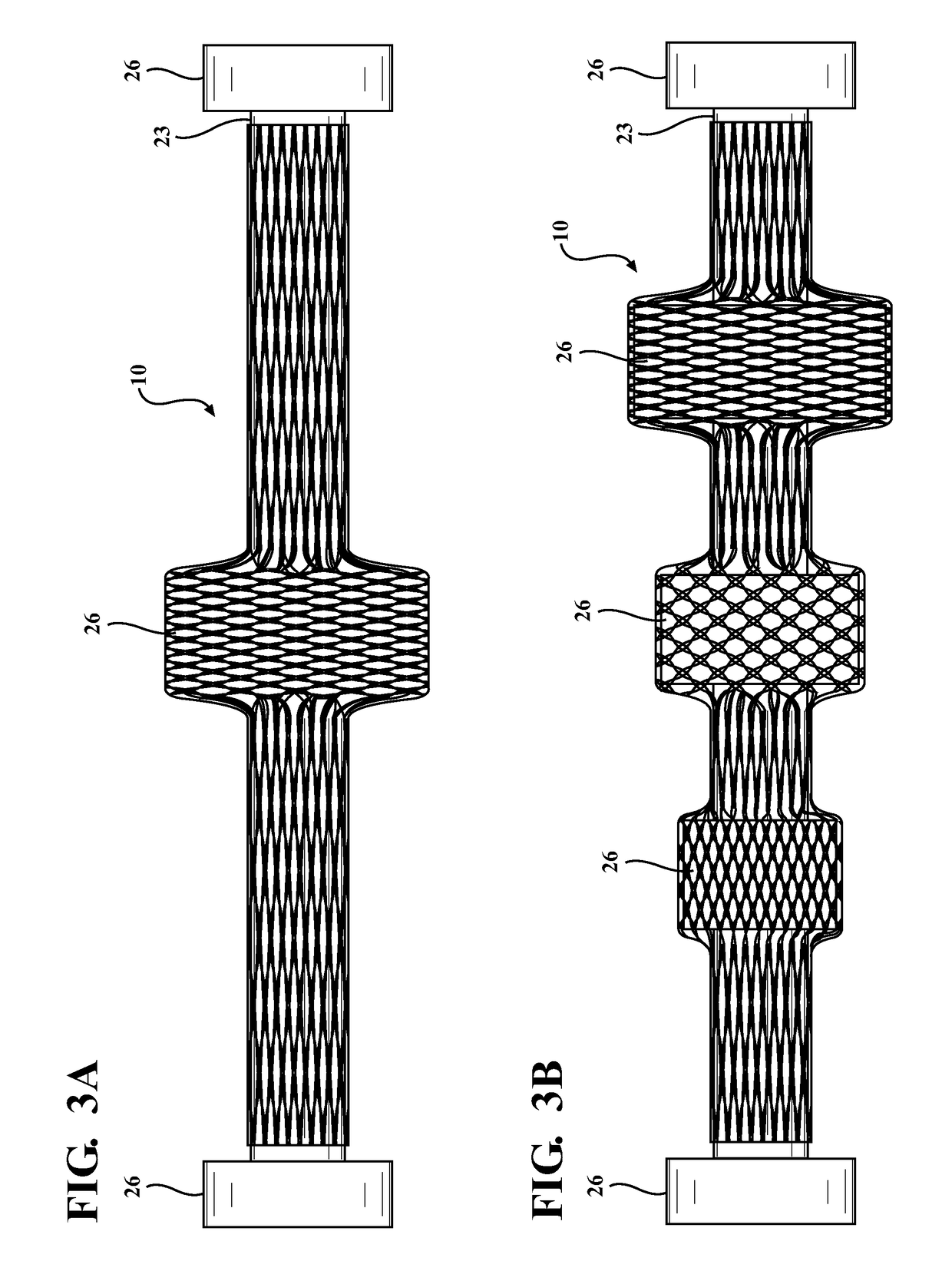
Braided textile sleeve with integrated opening and self-sustaining expanded and contracted states and method of construction thereof
ActiveUS20170121871A1Enhance coverage protectionReducing weight and costBraidVehiclesYarnEngineering
A protective textile having at least one integrated opening and method of construction thereof is provided. The sleeve includes a braided, tubular wall extending lengthwise in relation to a central longitudinal axis between opposite ends. The wall has a first state with a decreased length, increased cross-sectional area and a second state with an increased length, decreased cross-sectional area, as viewed in cross-section taken generally transversely to the central longitudinal axis. The wall further includes braided, heat-set yarns imparting a bias on the wall, wherein the bias causes the wall to remain substantially in the first and second states absent some externally applied force. The wall also includes at least one opening having a circumferentially continuous periphery bounding the opening, wherein the periphery is formed, at least in part, by braided yarns reversing direction from one S or Z helical direction to the opposite S or Z helical direction.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL POWERTAIN LLC
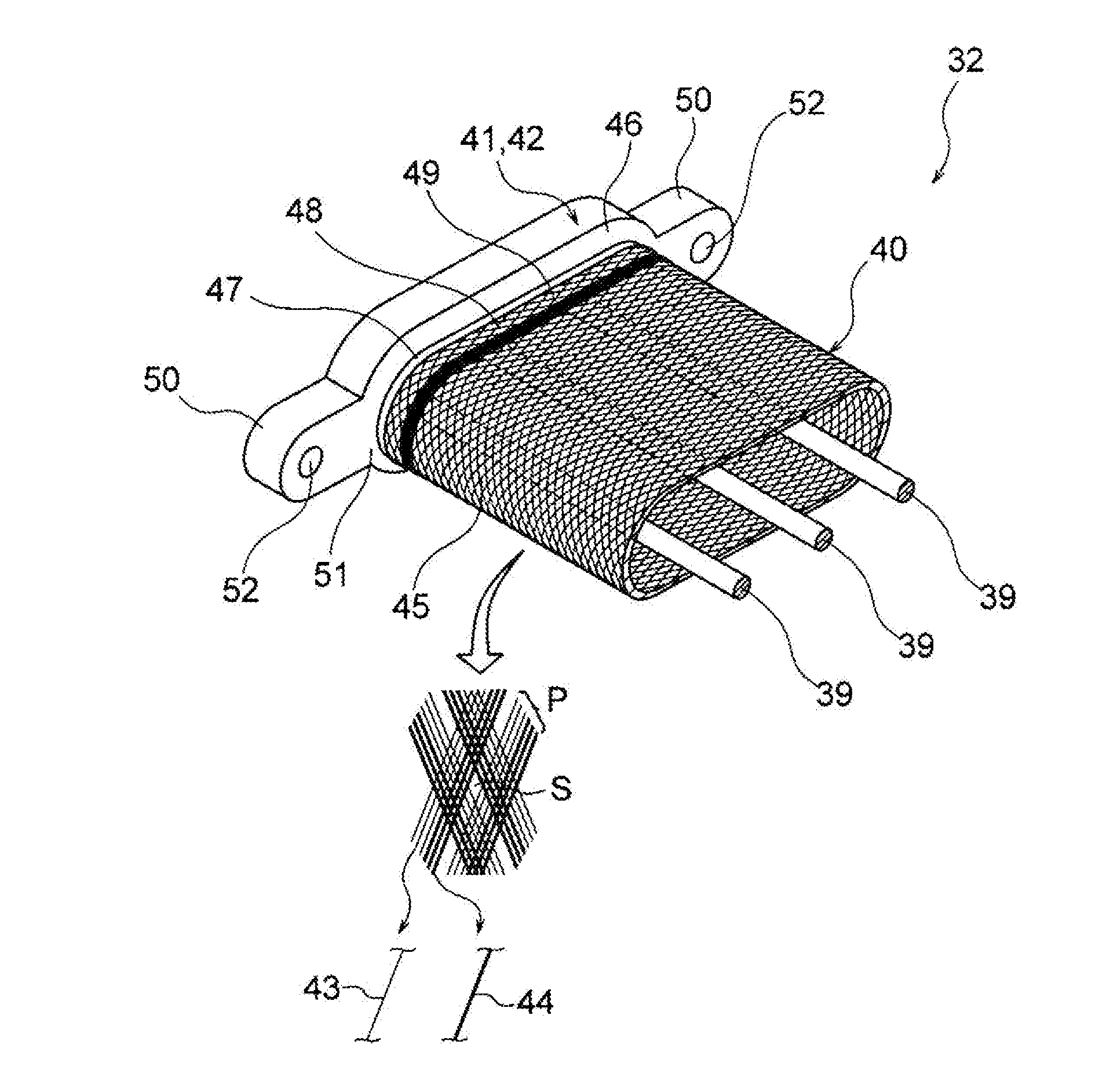
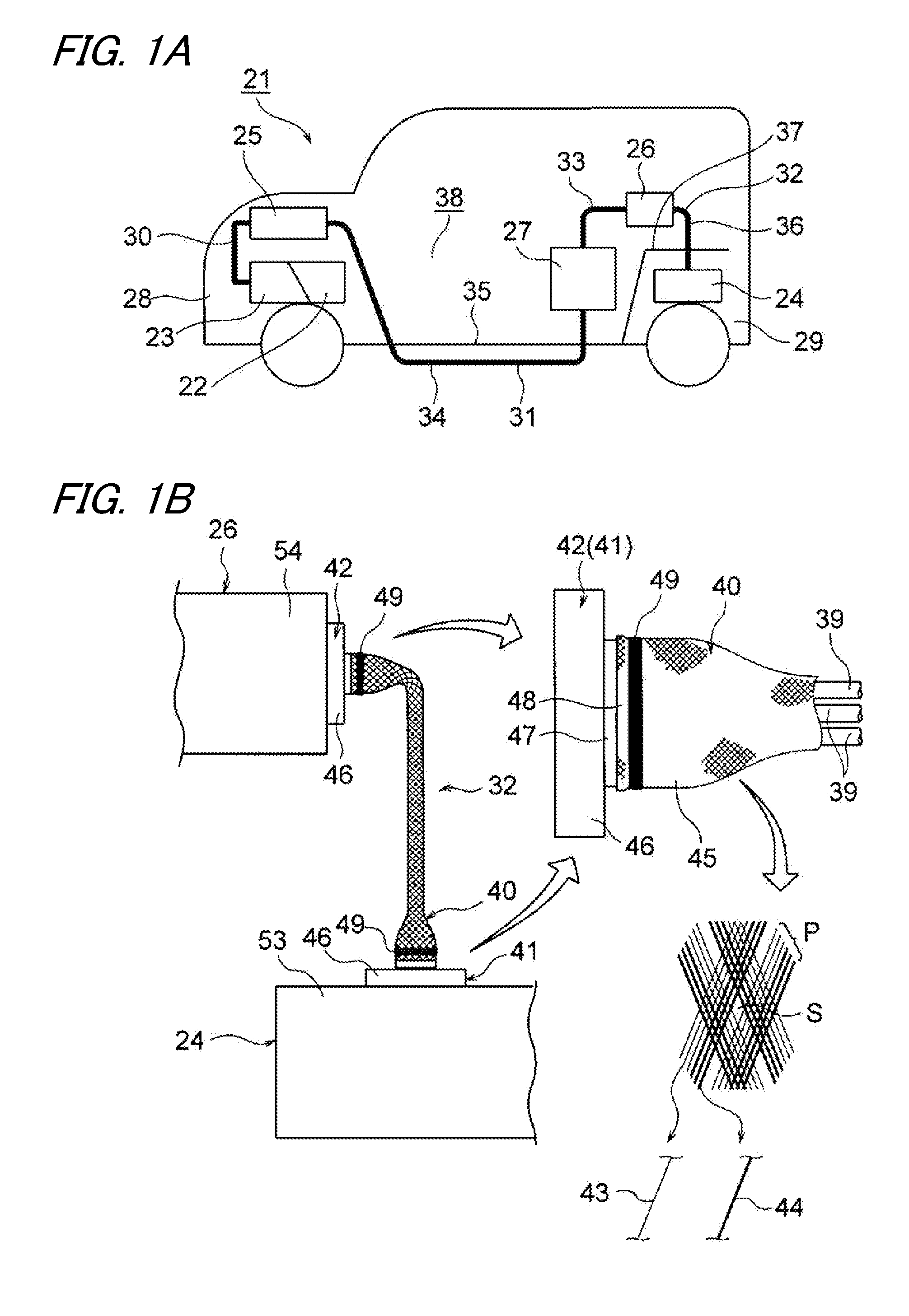
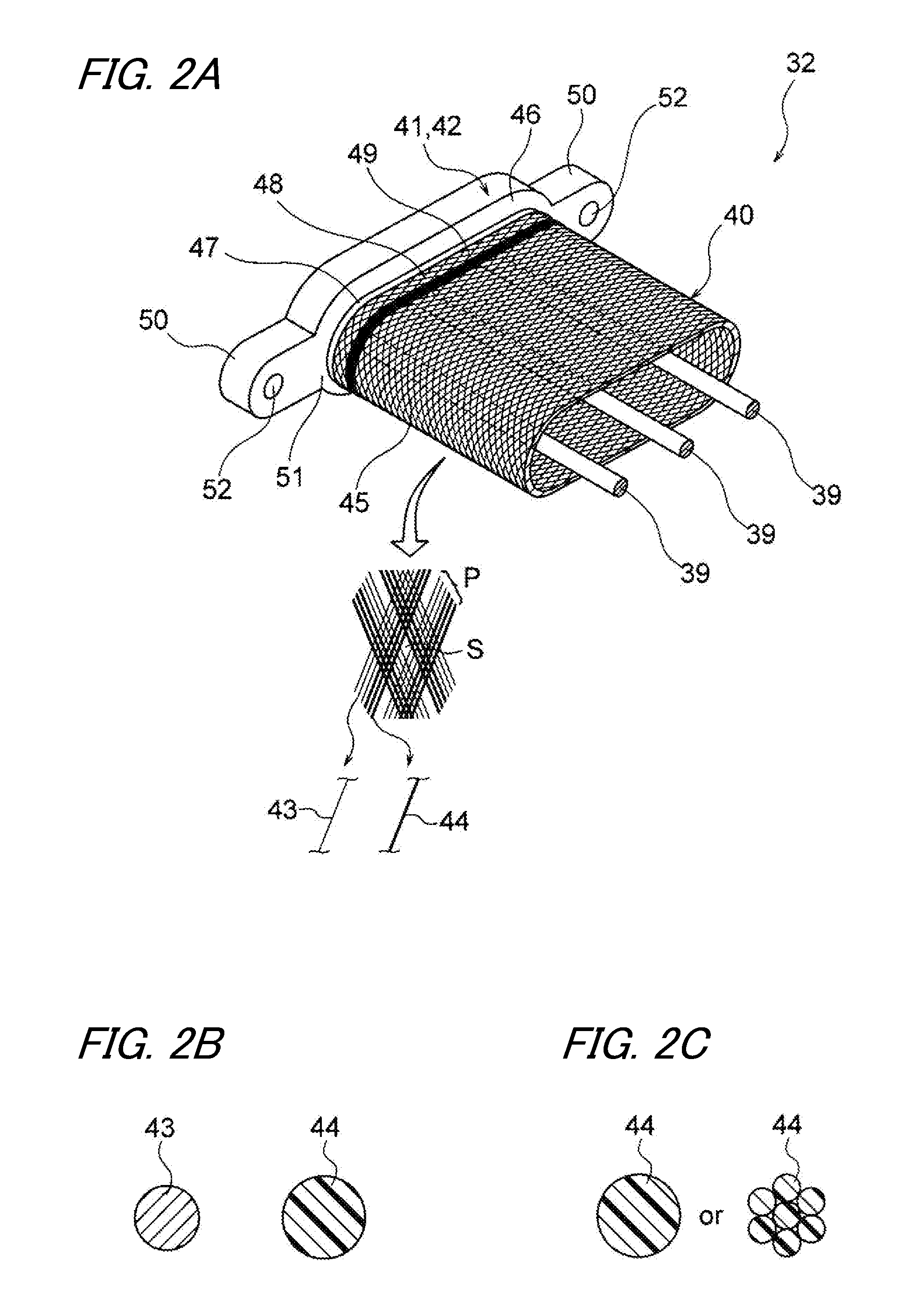
Braid and wire harness
ActiveUS20140202756A1Better braidGiving stiffnessVehicle connectorsScreening casingsElectromagnetic shieldingHybrid vehicle
A braid having a function as an exterior member as well as an electromagnetic shielding function is provided. Also, a wire harness including such a braid in a configuration is provided. A braid is used for a wire harness cabled to a hybrid vehicle. Also, the braid is formed by knitting multiple ultrathin strands in a tubular shape. The braid includes two kinds of strands, a metal strand made of metal having conductivity and a resin strand made of synthetic resin having abrasion resistance etc., and ensures abrasion resistance and impact resistance by the portion made of the resin strand while performing an electromagnetic shielding function by the portion made of the metal strand.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Active geometry control suspension system and actuating device driving the same
ActiveUS8226091B2Reducing weight and costIncreased durabilitySteering linkagesNutsEngineeringSlide plate
An actuating device for an active control suspension system which is provided at both ends of a sub-frame of a vehicle body and connected to one end of an assist link having the other end mounted at a knuckle and which changes a position of a mounting point of the assist link at the vehicle body, may include a member bracket fixedly mounted at each end of the sub-frame, provided with openings formed at both sides and an upper surface thereof, and formed of a pair of slide grooves having arc shape at the both ends thereof to slidably receive a pair of slide plates therein; an actuator connected to both slide plates through a pin-bolt unit; and a cam-bolt unit assembling a bush of the assist link with both slide plates and setting an initial position of the mounting point of the assist link at the vehicle body.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
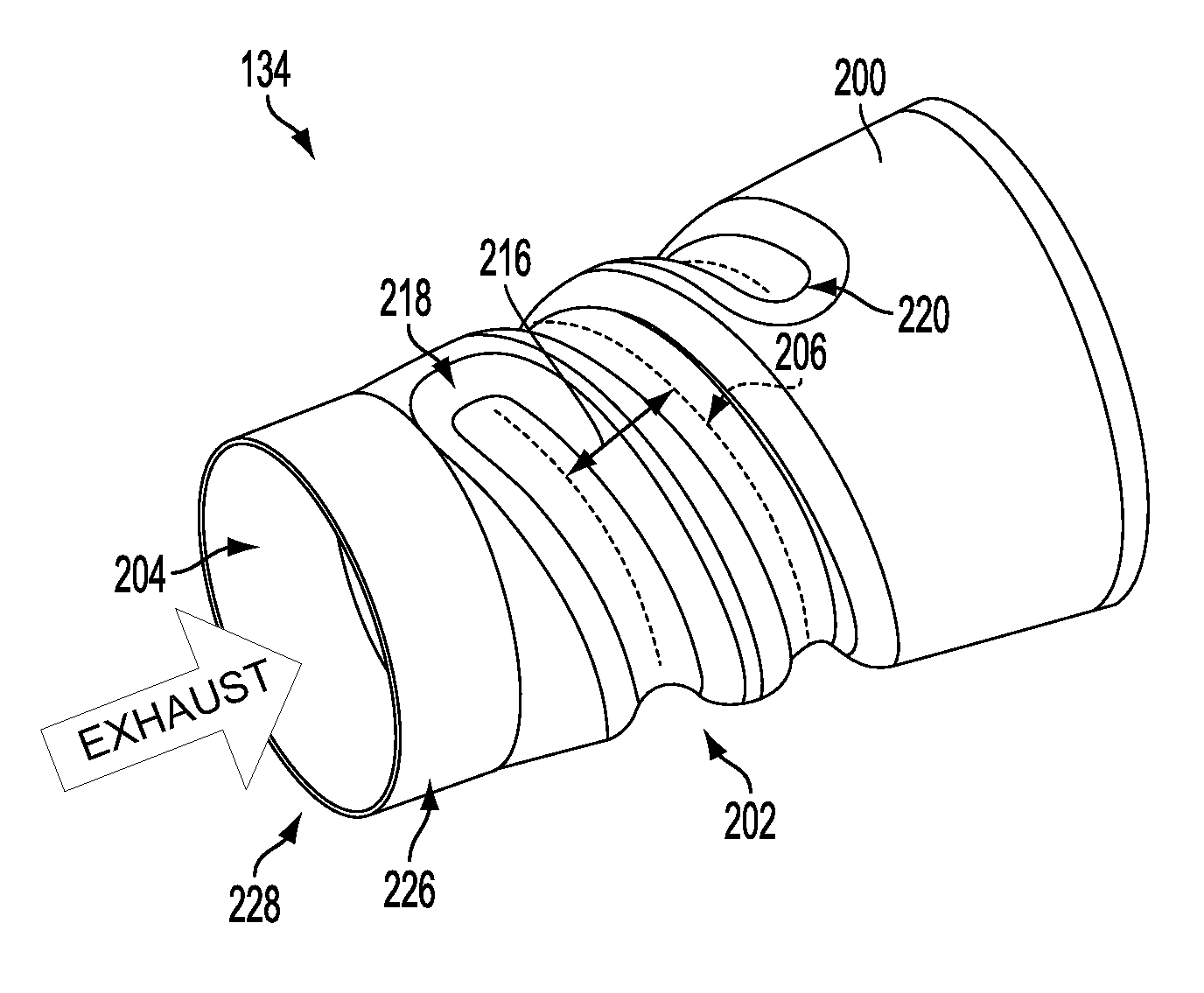
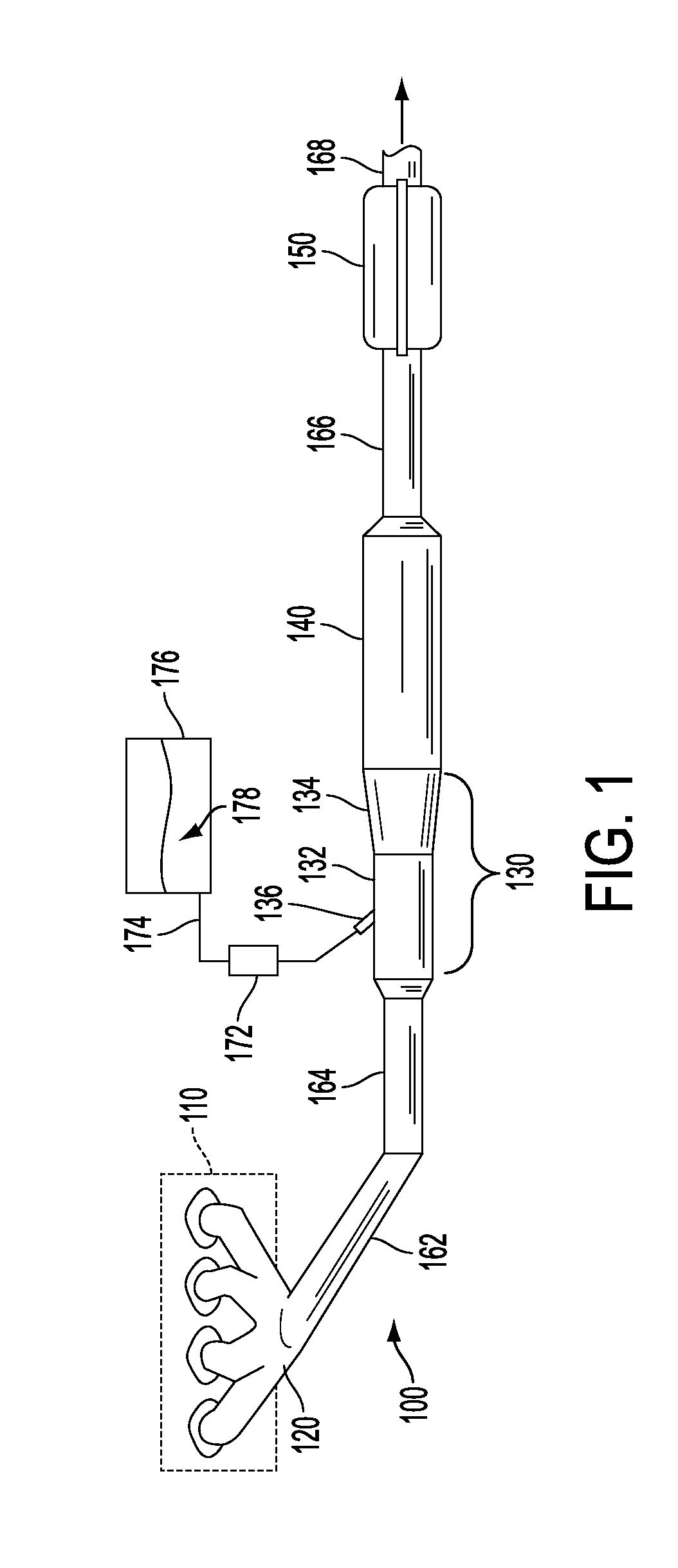
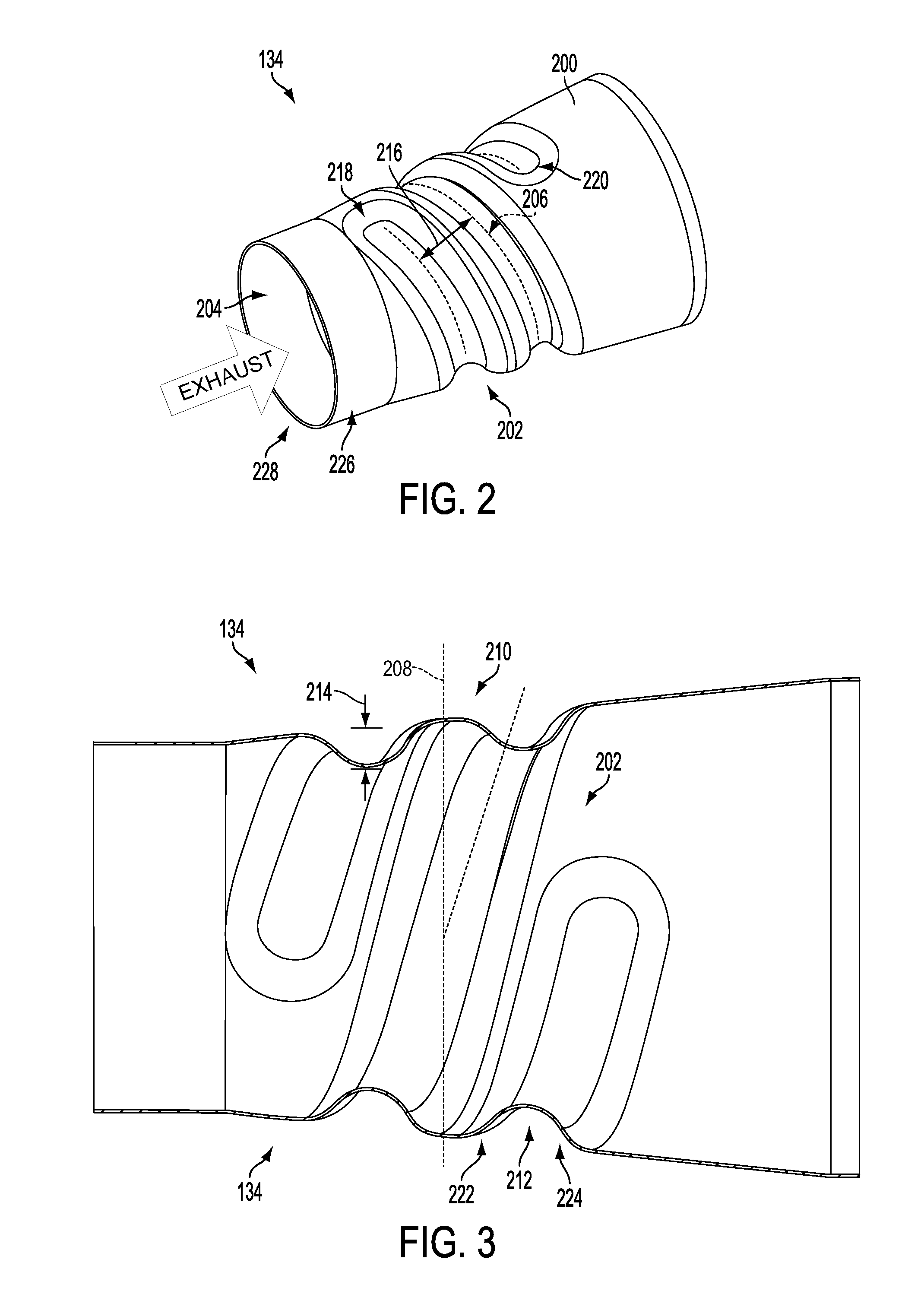
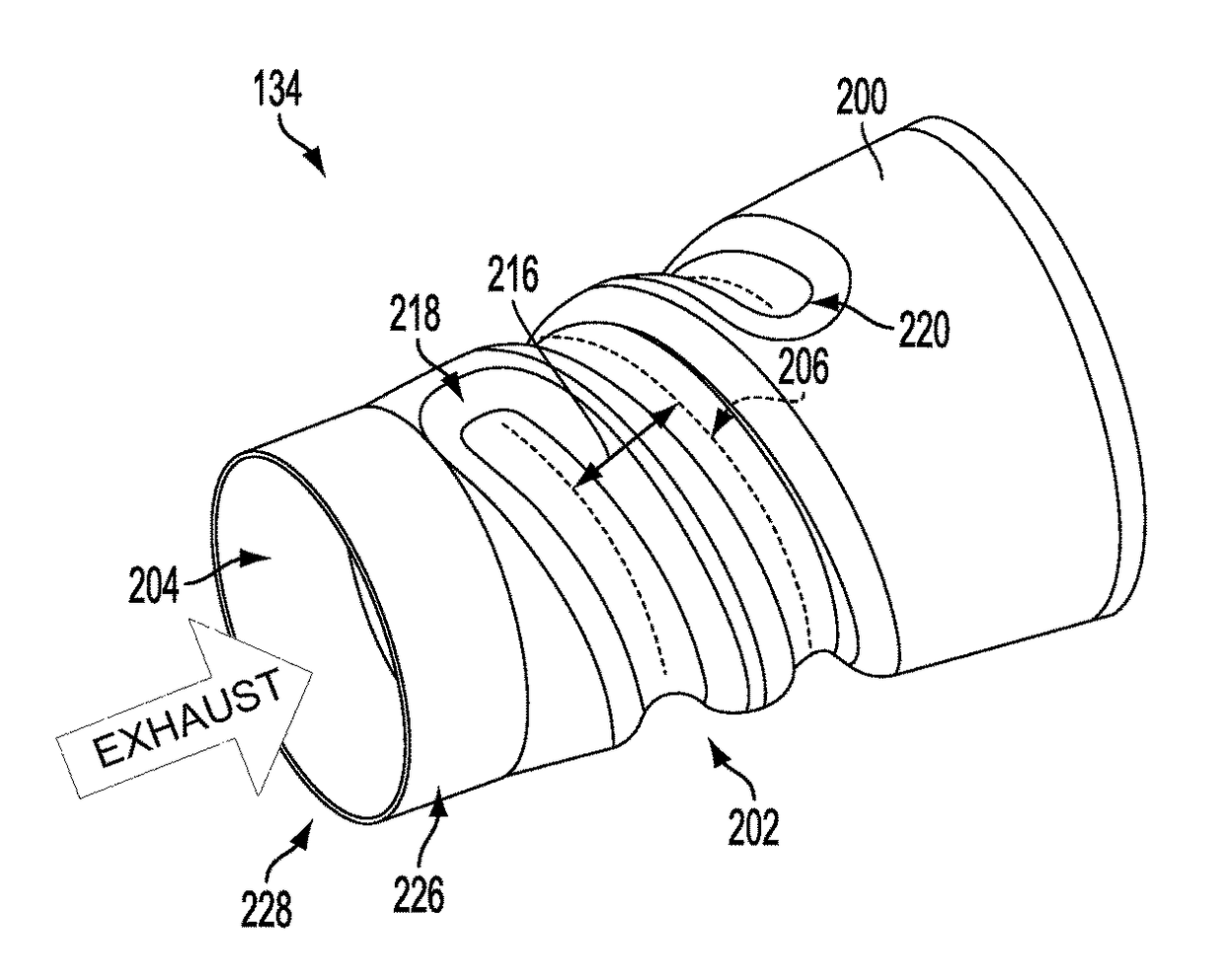
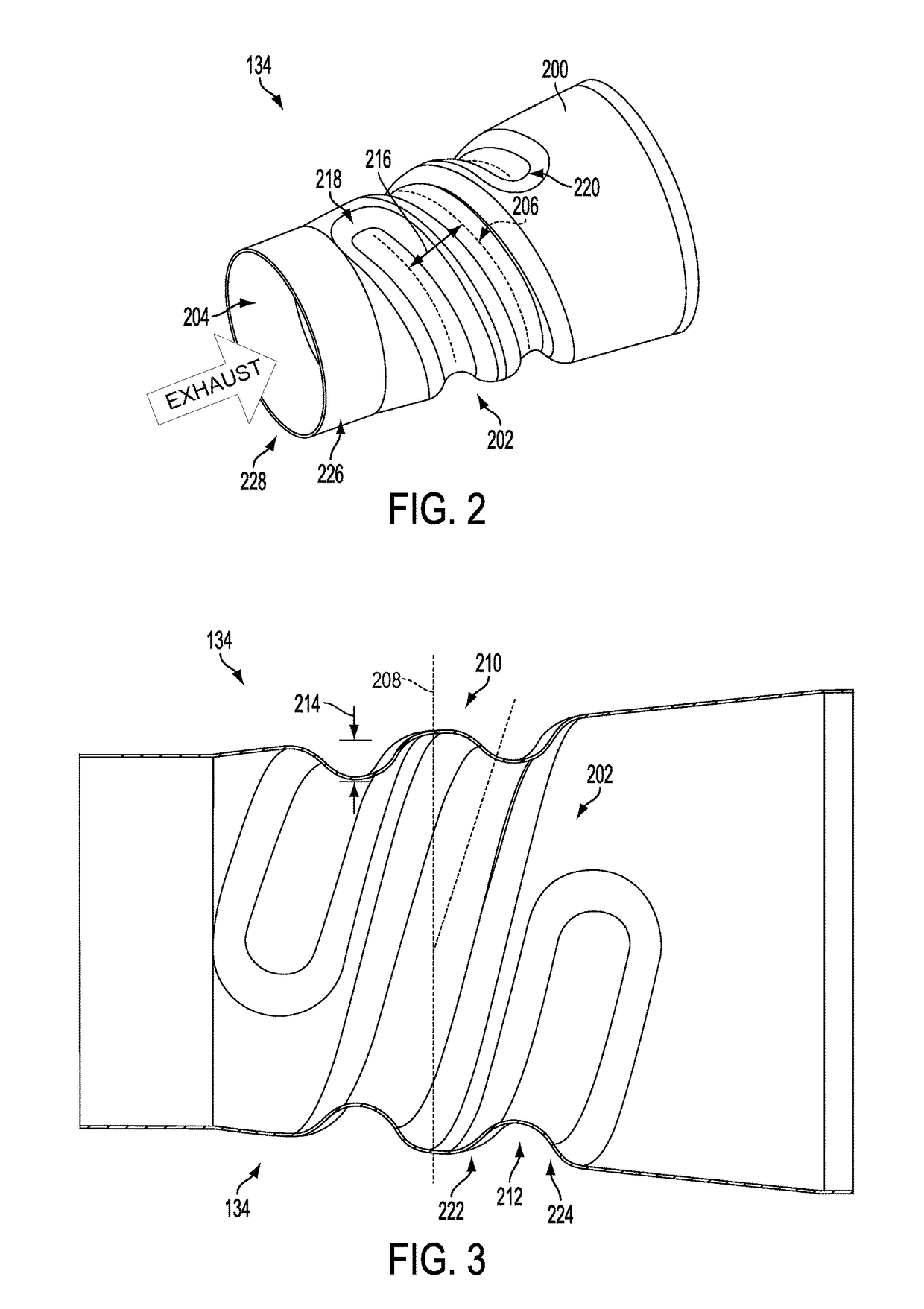
Exhaust passage
ActiveUS20120011837A1Reduce weightLow costSilencing apparatusMachines/enginesEngineeringStamping process
An exhaust system comprises a conical shell having an indentation helically traversing the exhaust passage so as to impart mixing on an engine exhaust gas flowing through an inner passage defined by the conical shell. The indentation may be formed into the conical shell via a stamping process.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
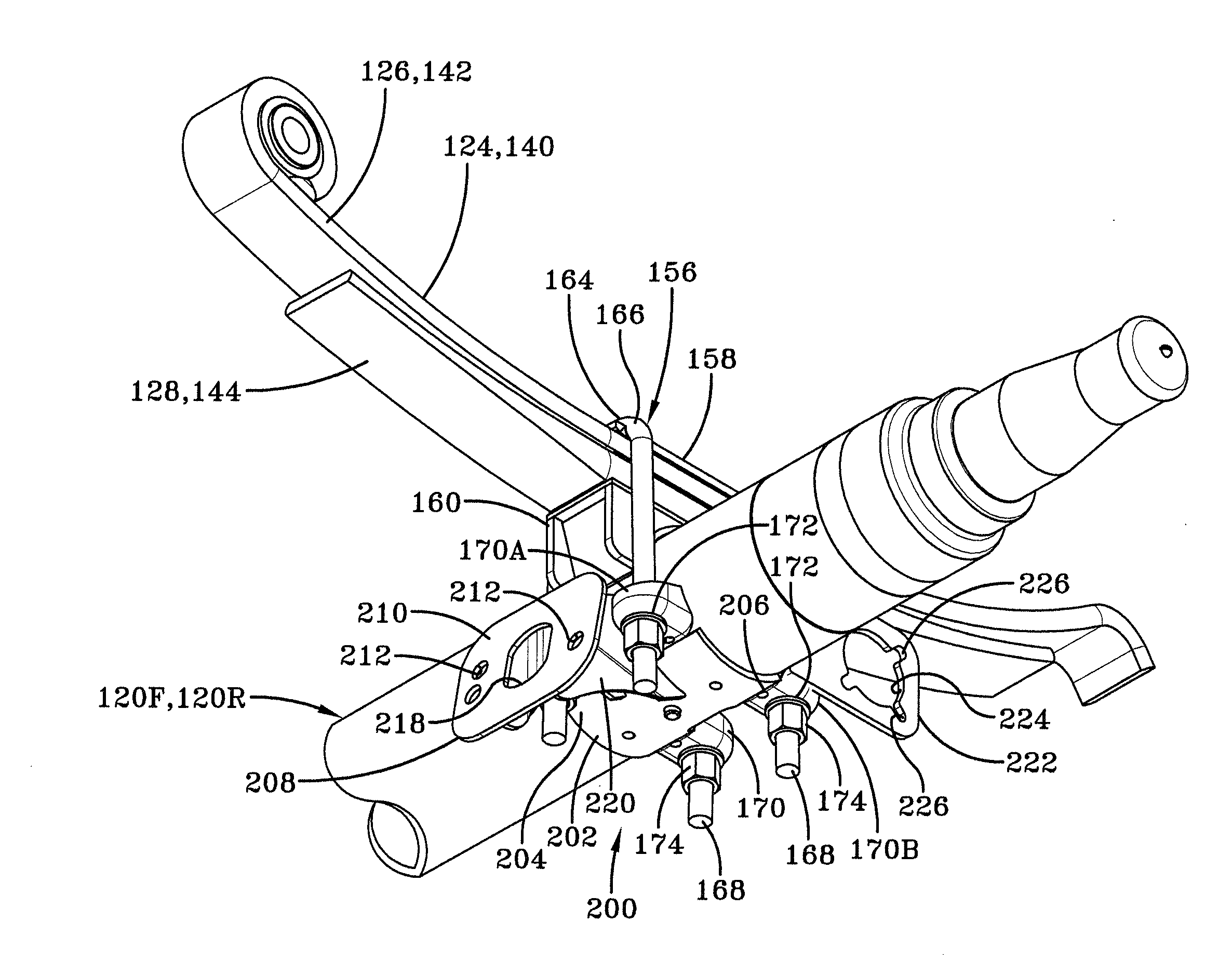
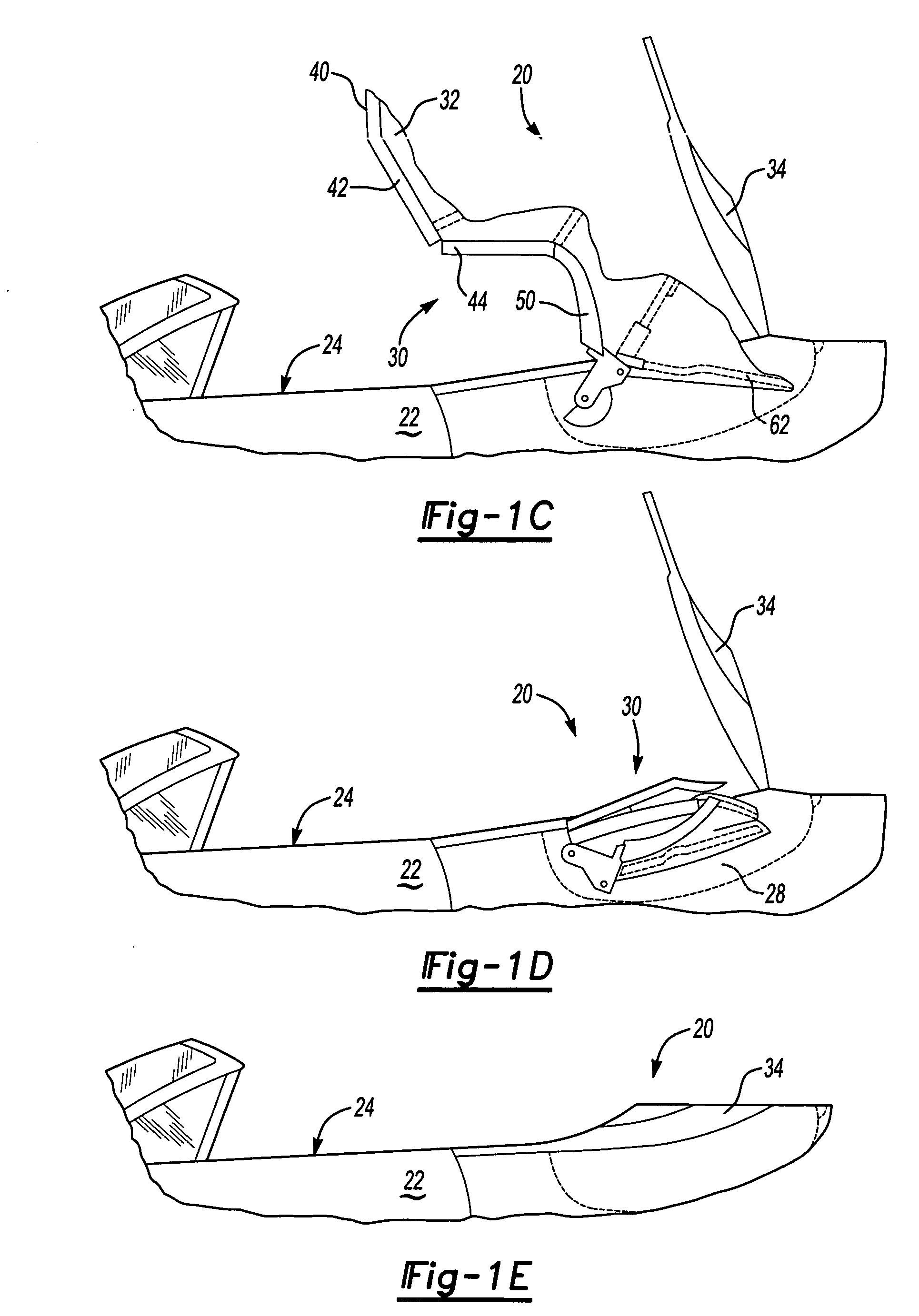
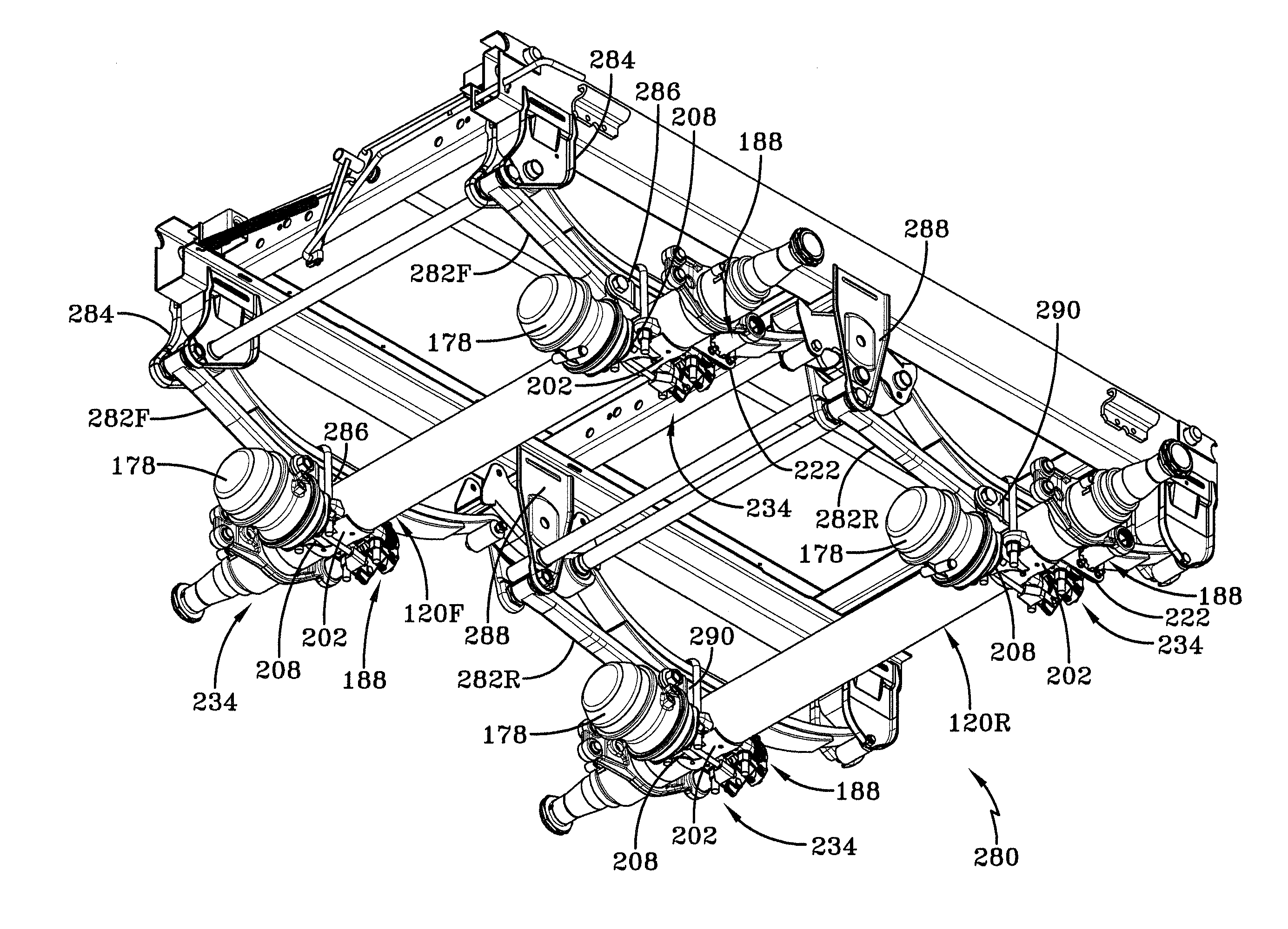
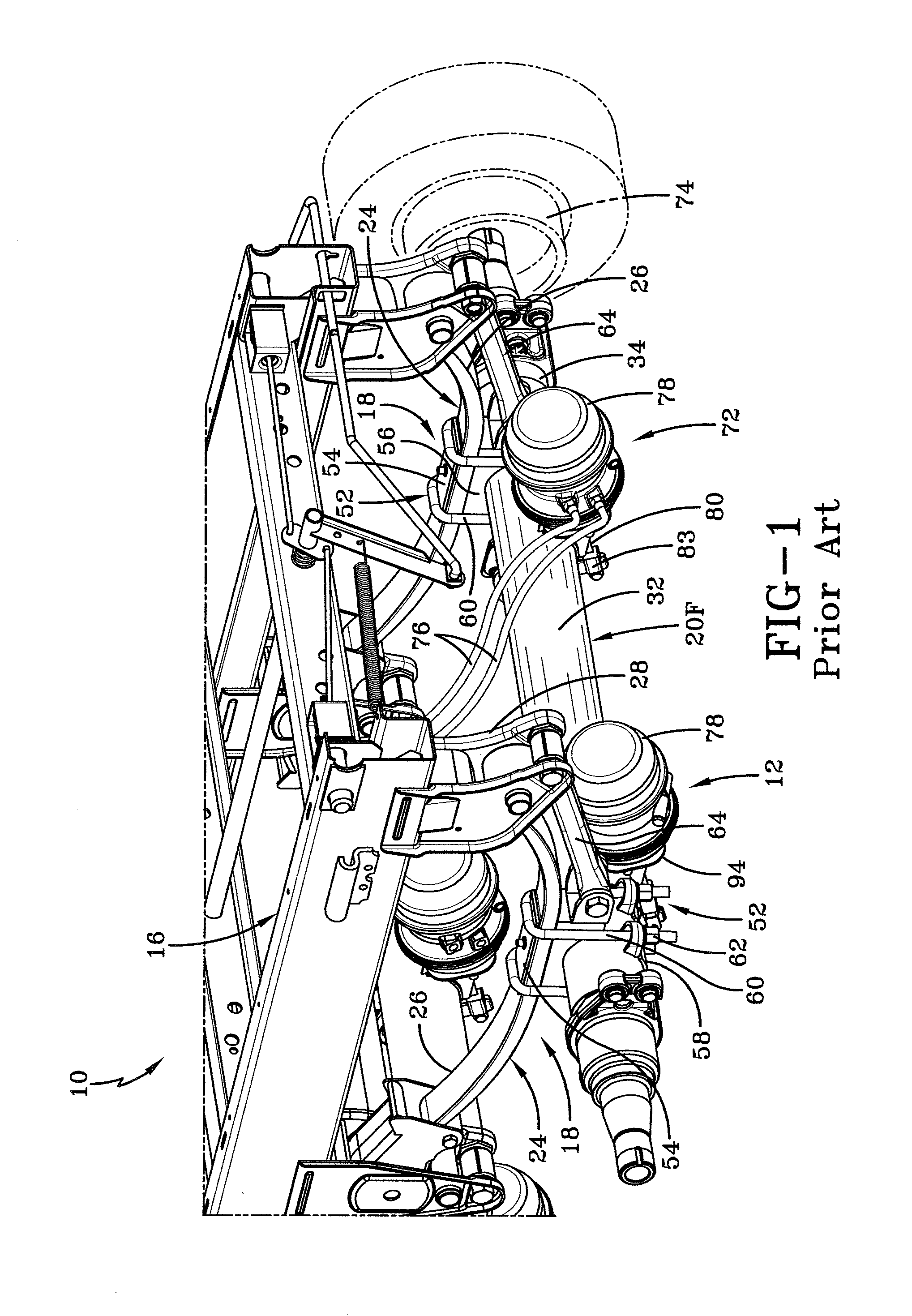
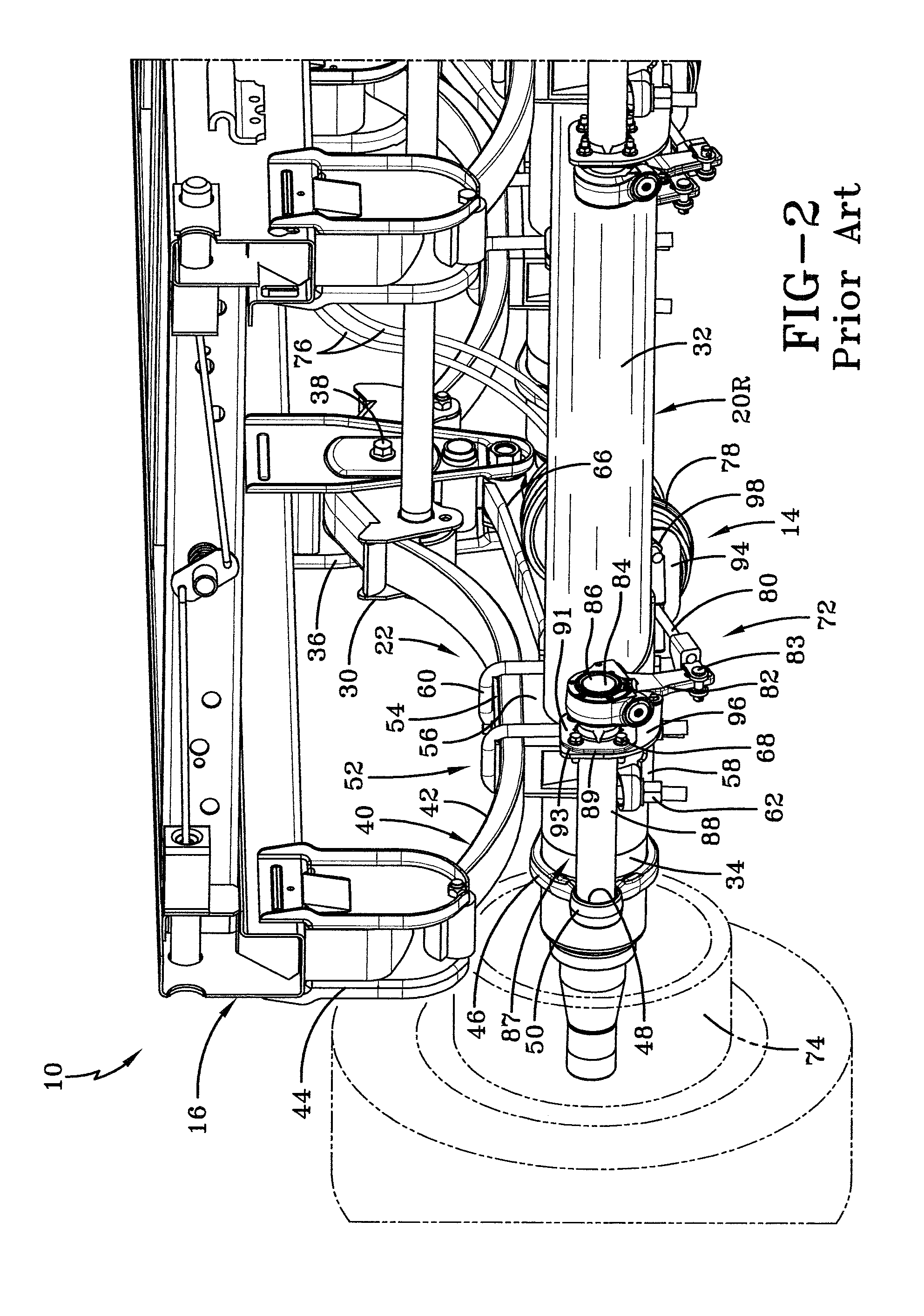
Integrated brake component mounting bracket
ActiveUS20140117176A1Reducing weight and costBraking element arrangementsFurniture partsEngineeringCam
An integrated brake component mounting bracket for a mechanical spring axle / suspension system of a heavy-duty vehicle includes an axle seat that is disposed on and is rigidly connected to an axle of the vehicle. An air chamber mounting bracket is rigidly connected to the axle seat, and a cam shaft assembly mounting bracket is rigidly connected to the axle seat. A brake air chamber of a brake system is attached to the air chamber mounting bracket, and a cam shaft assembly of the brake system is mounted to the cam shaft assembly mounting bracket. The integrated brake component mounting bracket thus provides mounting of the brake air chamber and the cam shaft assembly on the axle seat, which reduces the number of components that are welded to the axle and enables the use of a thinner-wall axle, desirably reducing the weight and cost associated with the axle / suspension system.
Owner:HENDRICKSON USA L L C
Braided textile sleeve with self-sustaining expanded and contracted states and method of construction thereof
ActiveUS10167581B2Reducing weight and costExpand coverageBraidTubular articlesYarnBuilding construction
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL POWERTAIN LLC
Mechanically stiffened weatherseal carrier
InactiveUS8205390B2Reducing weight and costSame rigidityLayered productsSealing arrangementsFlangeSecond finger
A flange mounted weatherseal includes a carrier and a flexible cover covering the carrier. The carrier includes a base portion, a first side portion and a second side portion generally parallel to the first side portion and cooperating together with the first side portion and the base portion to define a generally U-shaped channel. The first side portion defines a plurality of first fingers, the second side portion defines a plurality of second fingers opposite the first fingers along a longitudinal axis, and the base portion defines a plurality of webs offset along the longitudinal axis relative to the first fingers and the second fingers. The first fingers, the second fingers and the webs each include deformations defining a non-planar cross sectional shape along the longitudinal axis to increase the rigidity of the carrier.
Owner:HENNIGES AUTOMOTIVE SEALING SYST NORTH AMERICA
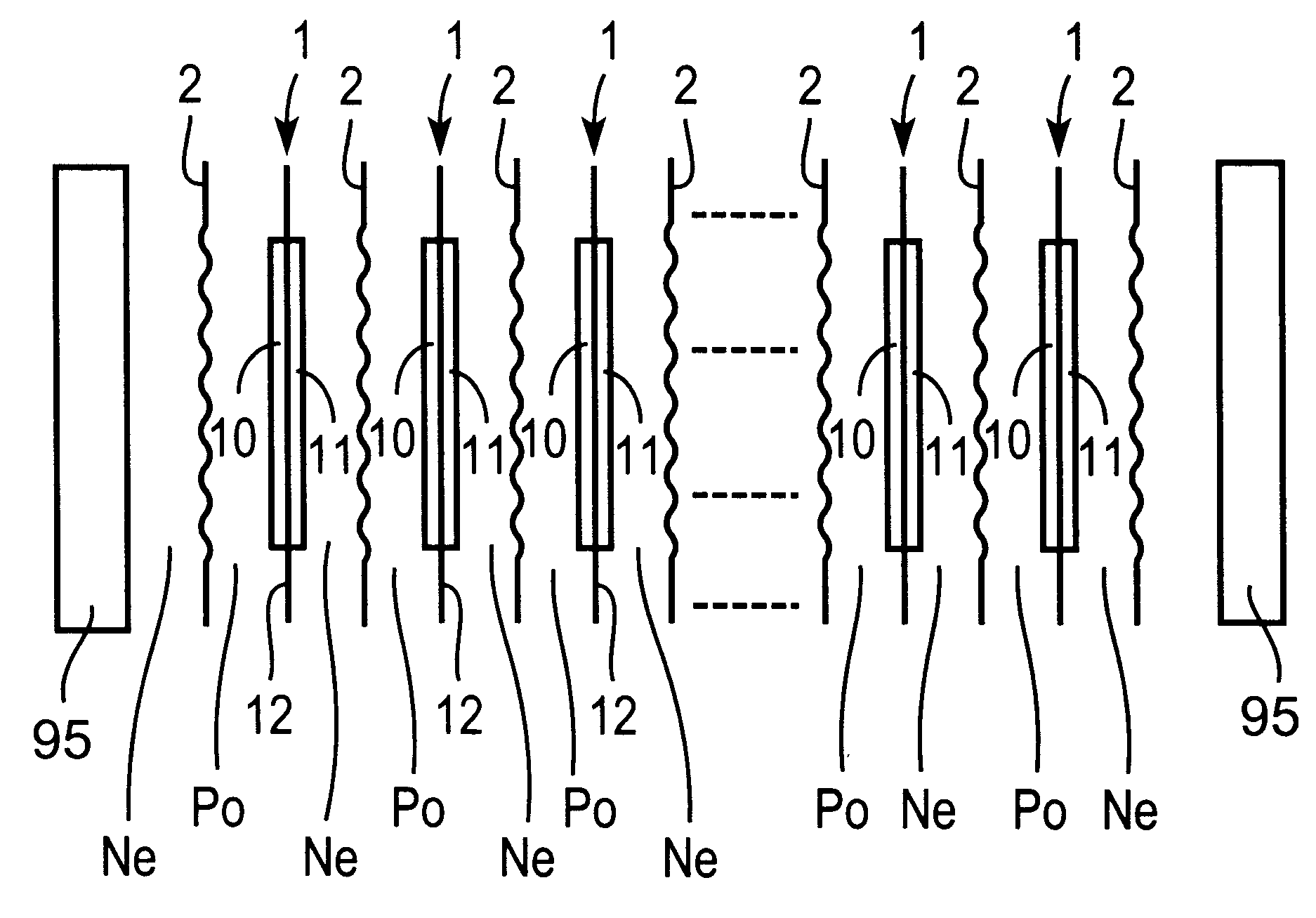
Liquid crystal cell substrate, liquid crystal cell, liquid crystal panel, and liquid crystal display
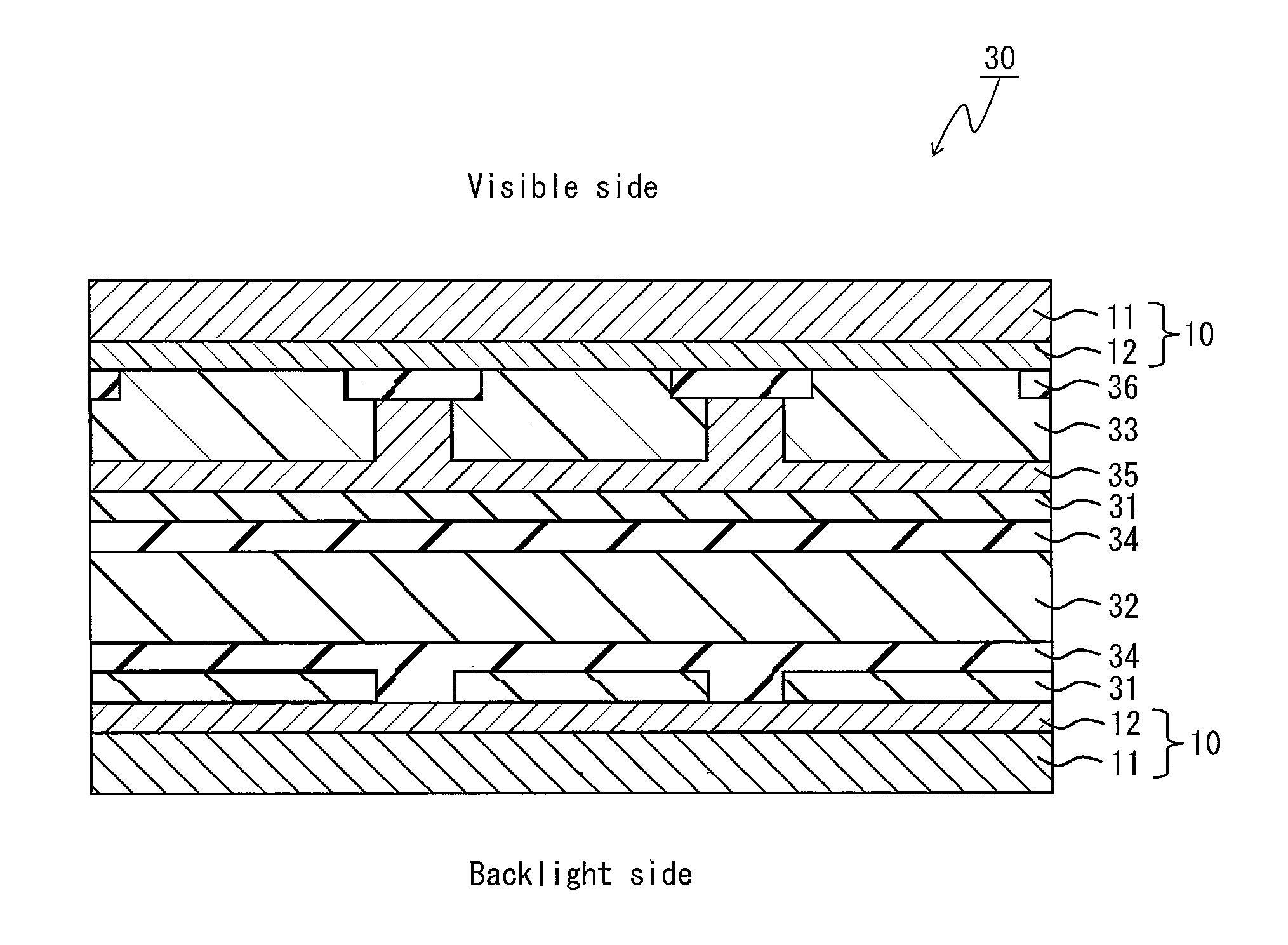
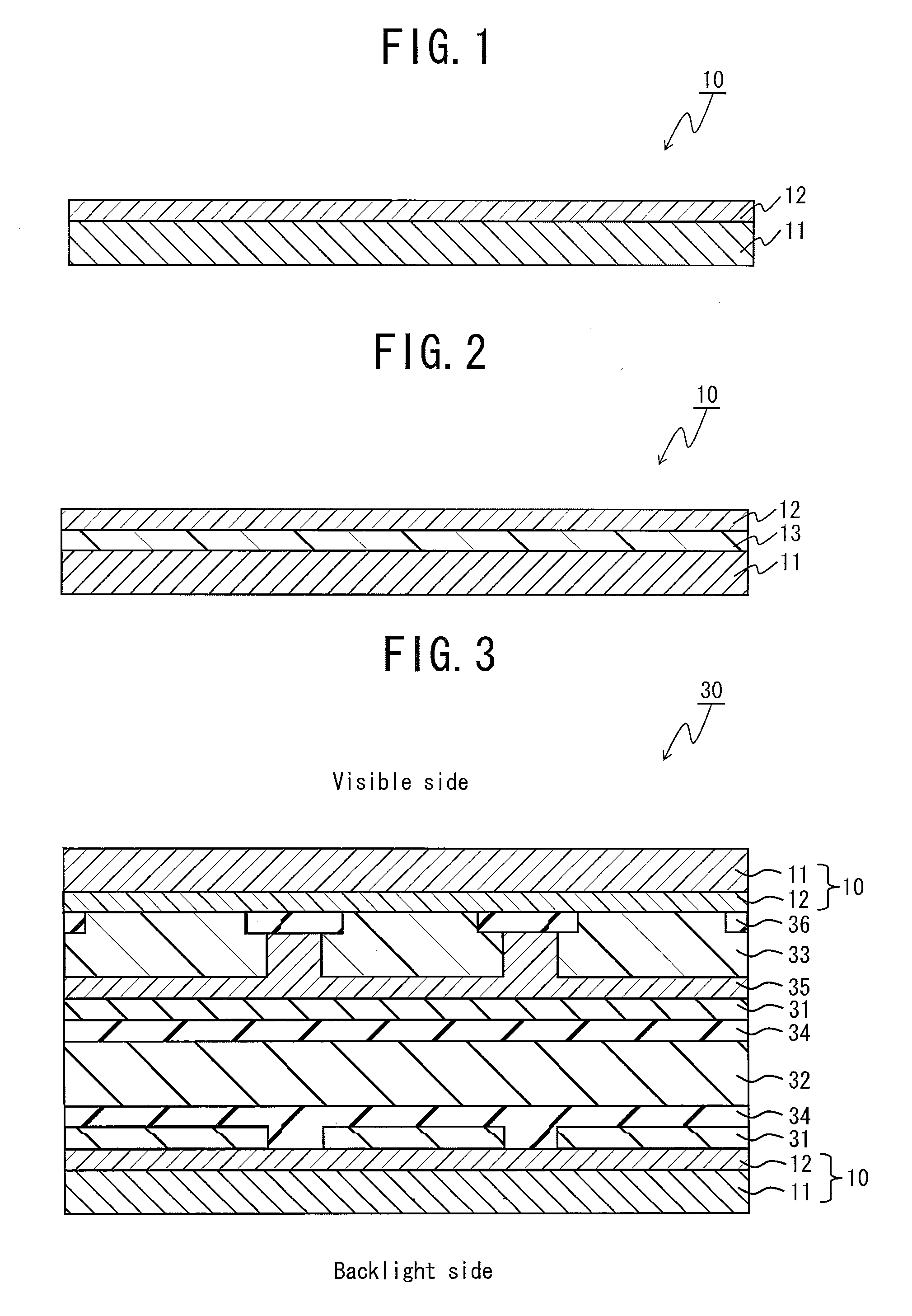
The present invention provides a liquid crystal cell substrate, a liquid crystal panel, and a liquid crystal display whose thicknesses and weights can be reduced and optical characteristics at the time of producing them are easily controlled. The liquid crystal cell substrate 10 of the present invention is a liquid crystal cell substrate including a resin substrate 11 and an optical compensation layer 12, and the optical compensation layer 12 is laminated on the resin substrate 11. The optical compensation layer 12 has a refractive index distribution satisfying nx≧ny>nz, and the optical compensation layer 12 is formed by applying a material for forming an optical compensation layer to the resin substrate 11 or a base substrate that is different from the resin substrate 11.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
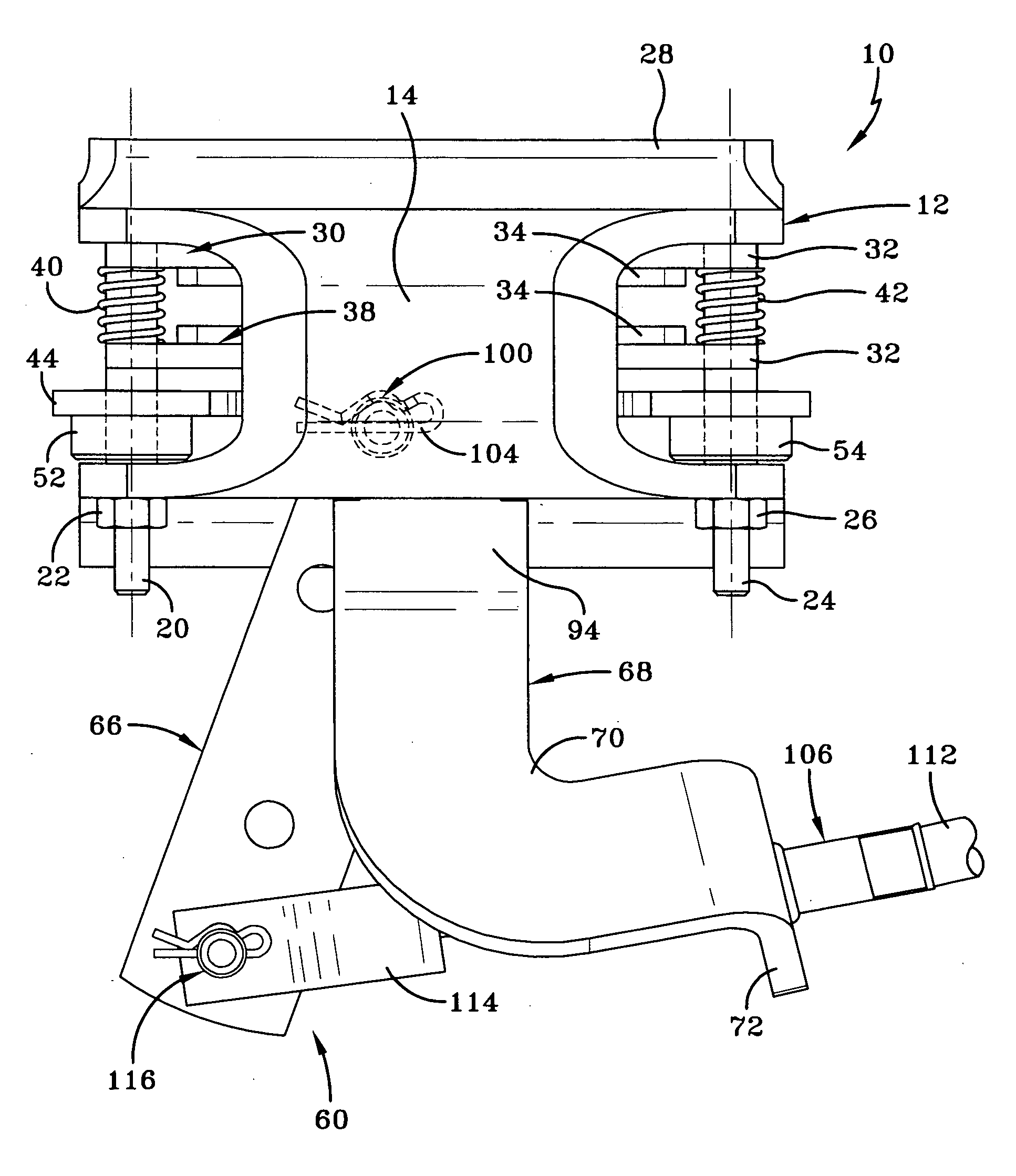
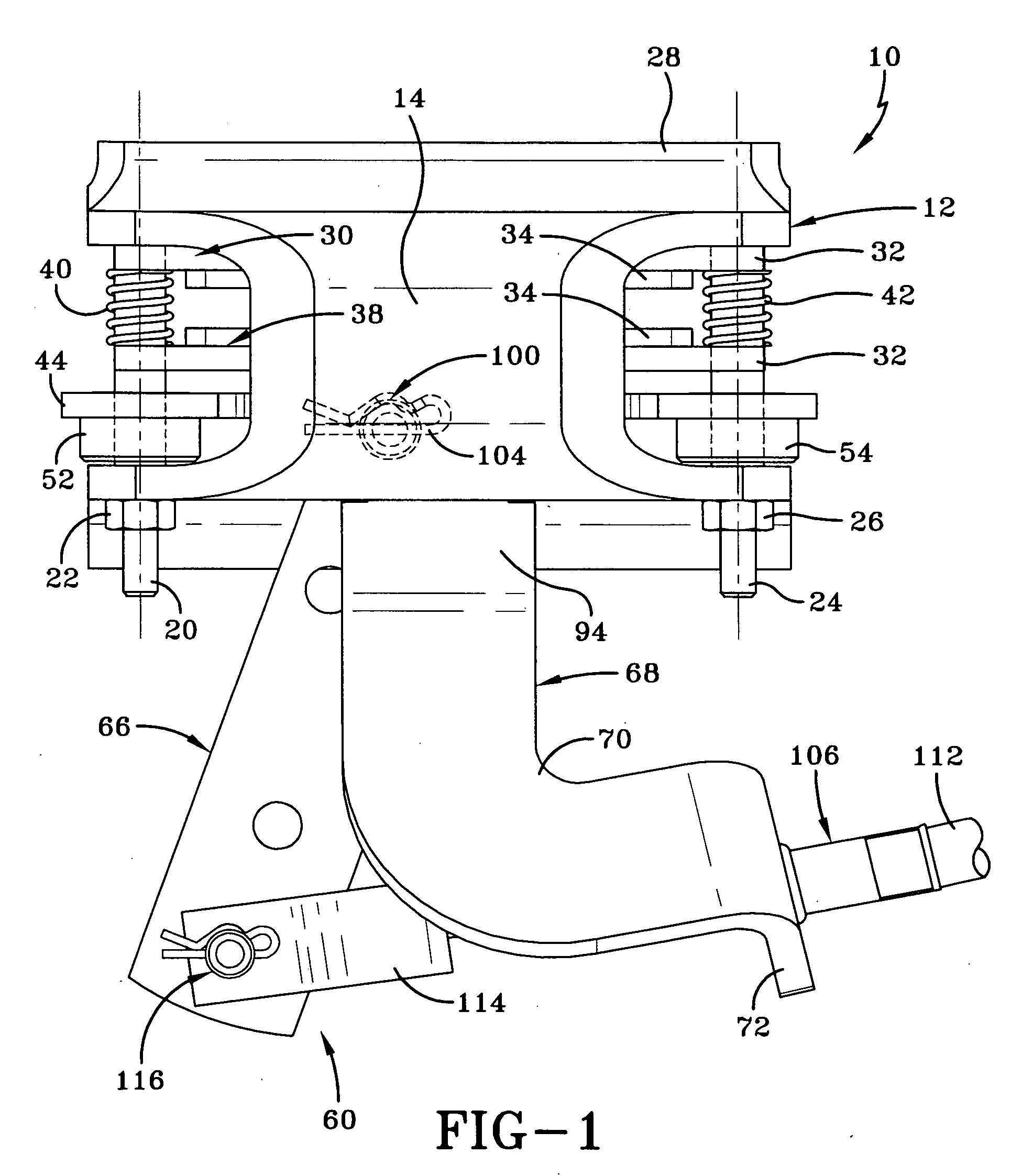
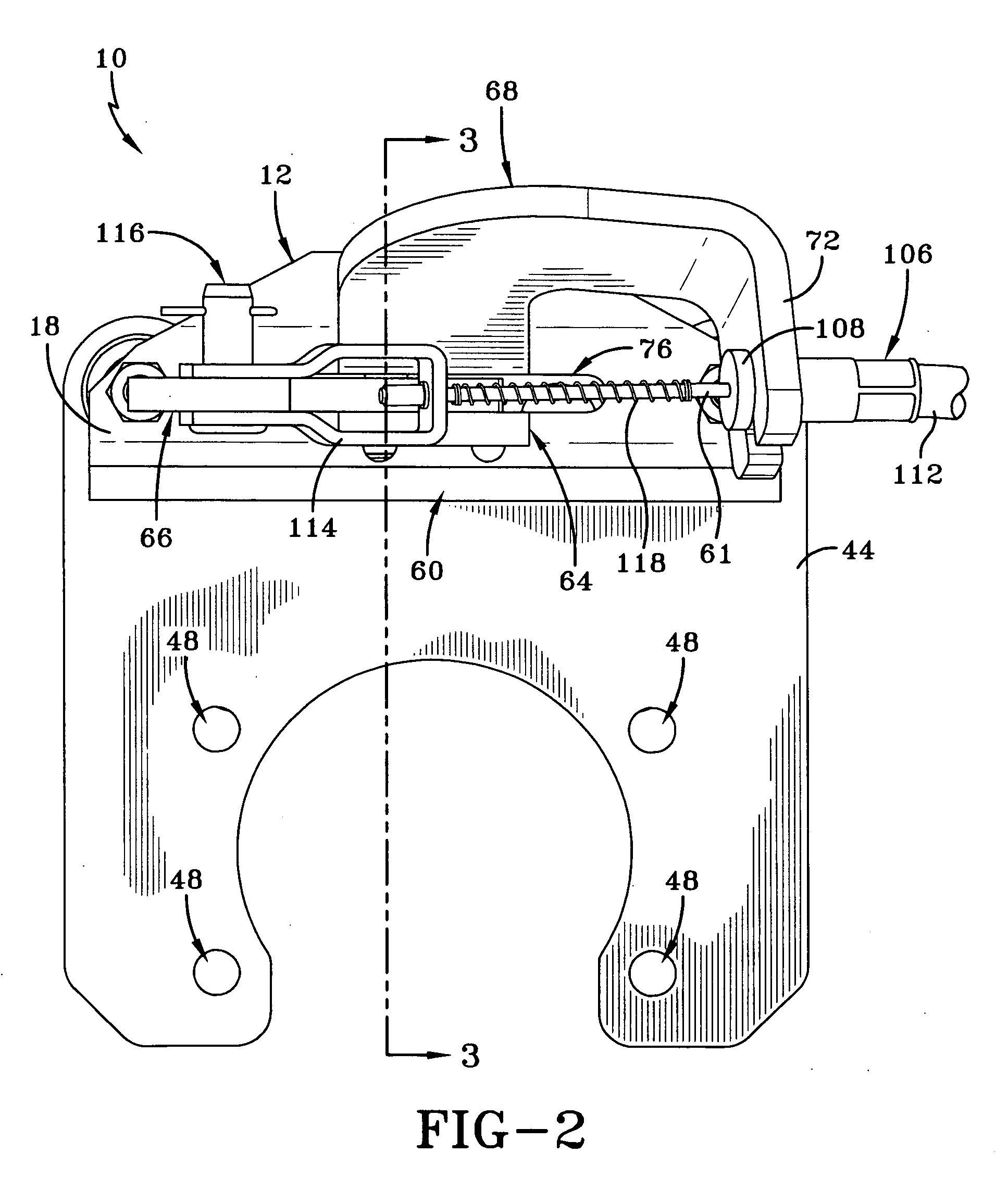
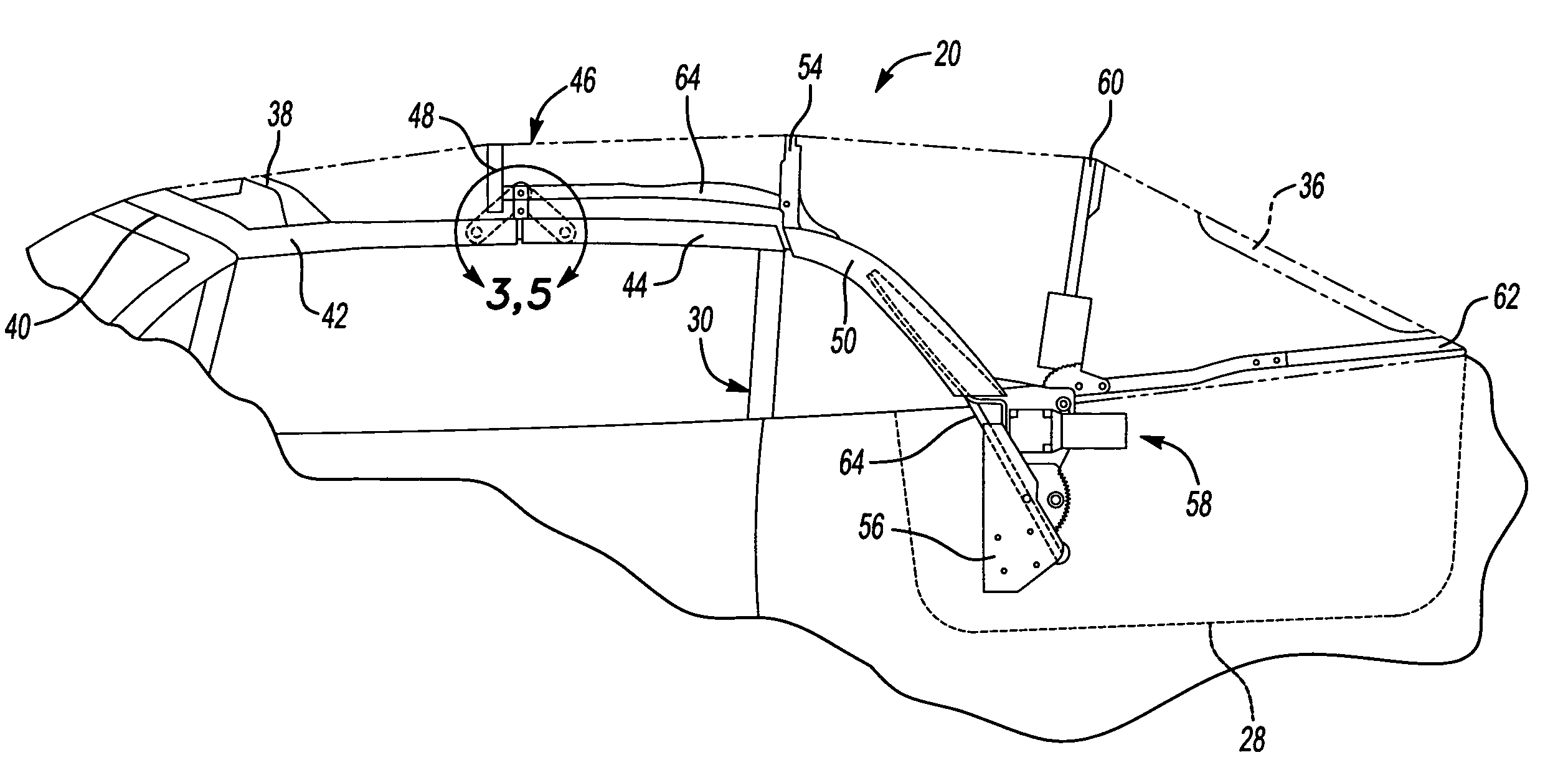
Polymeric roof rail
InactiveUS20050242614A1Improved strength to weight functionalityEasy to manufactureEngine sealsSuperstructure subunitsEngineeringMechanical engineering
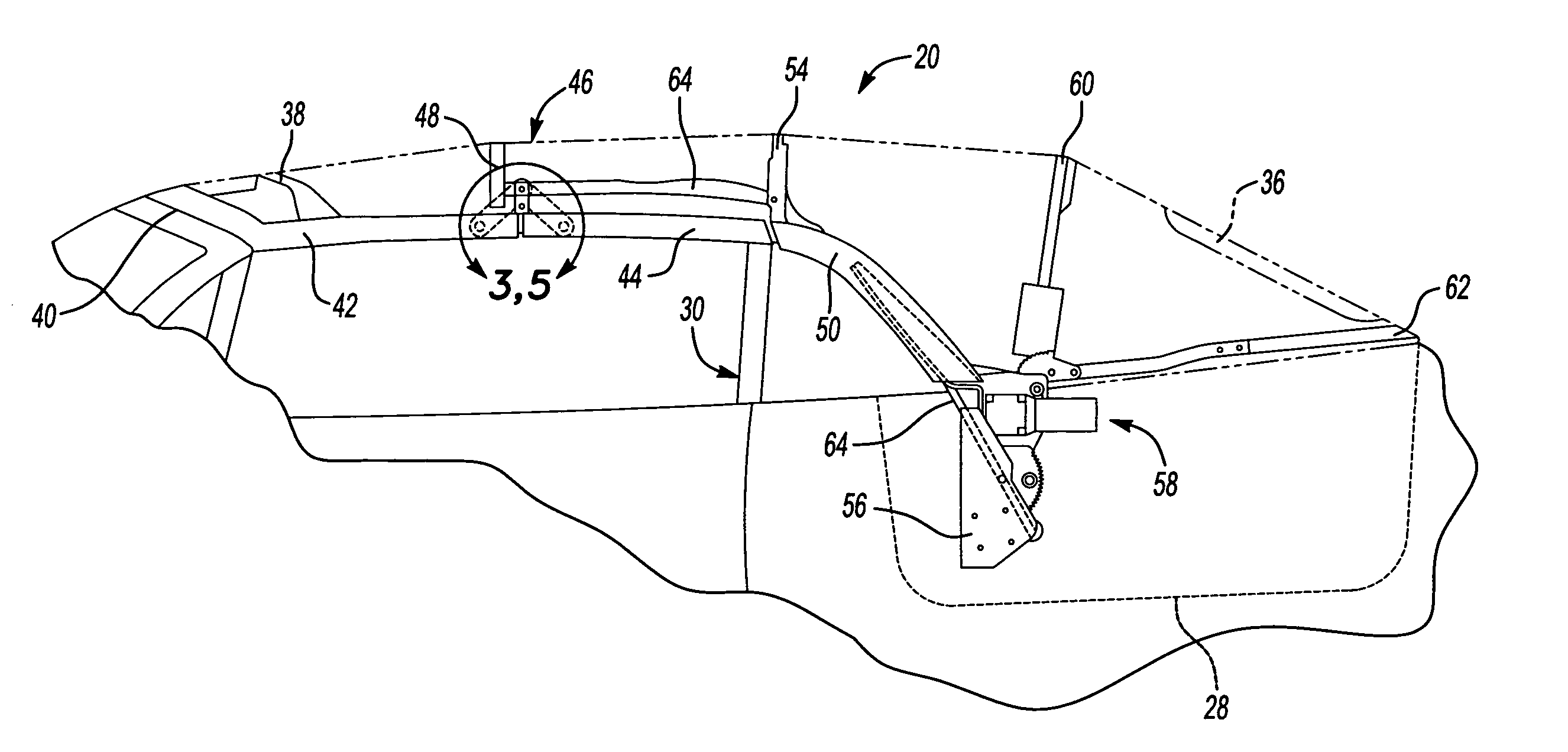
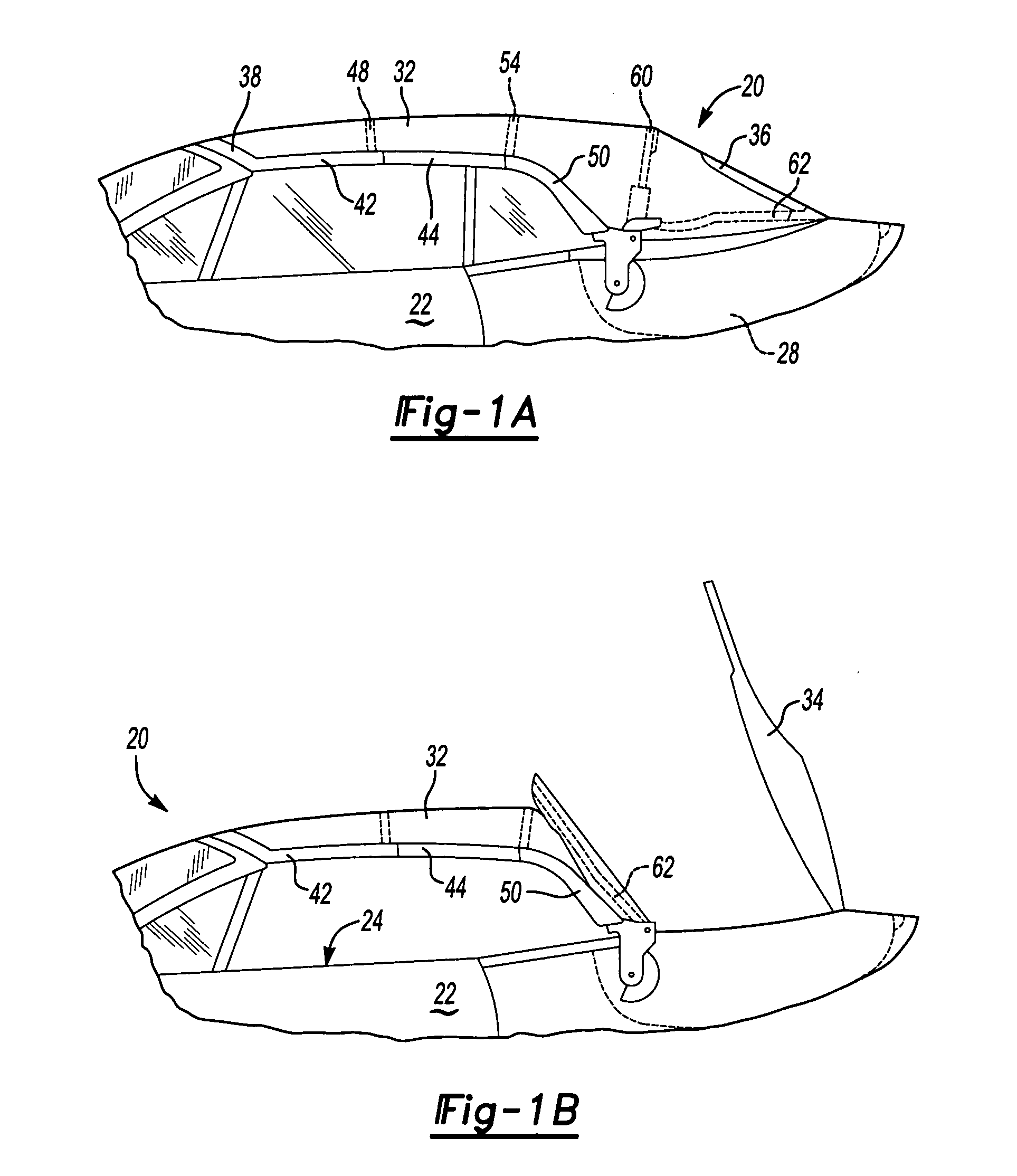
A convertible roof system uses composite roof rail(s). The composite roof rail can have portions that are made of differing materials. The composite roof rail can use universal connecting pieces for the ends of the roof rail. Adjacent composite roof rails can be formed about a connector that couples the adjacent roof rails together.
Owner:SPECIALTY VEHICLE ACQUISITION
Integrated brake component mounting bracket
An integrated brake component mounting bracket for a mechanical spring axle / suspension system of a heavy-duty vehicle includes an axle seat that is disposed on and is rigidly connected to an axle of the vehicle. An air chamber mounting bracket is rigidly connected to the axle seat, and a cam shaft assembly mounting bracket is rigidly connected to the axle seat. A brake air chamber of a brake system is attached to the air chamber mounting bracket, and a cam shaft assembly of the brake system is mounted to the cam shaft assembly mounting bracket. The integrated brake component mounting bracket thus provides mounting of the brake air chamber and the cam shaft assembly on the axle seat, which reduces the number of components that are welded to the axle and enables the use of a thinner-wall axle, desirably reducing the weight and cost associated with the axle / suspension system.
Owner:HENDRICKSON USA L L C
Caliper brake
InactiveUS20100187048A1Reduce in quantityShort response timeBraking action transmissionShaft for linear movementEngineeringCalipers
A caliper brake including a housing, an opening in the housing, and an actuating assembly received in the opening. The actuating assembly includes an actuating lever having a cam surface and a pivot aperture, a cable bracket having a cable retaining flange, a pivot aperture, and a retaining portion, and a pin received through said pivot apertures to rotatably secure the actuating lever to the cable bracket. The retaining portion of the cable bracket acts to secure the actuating assembly in the opening of the housing without the need for mechanical fasteners. A pivot plate may also be provided, the pivot plate having a pivot aperture and a retaining portion, and is positioned on one side of the actuation lever opposite the cable bracket. A cable housing is received in a bore through the cable retaining flange, and an actuation cable is slidably positioned therein and secured at one end to the actuation lever. When the cable is moved, the actuation lever pivots relative to the cable bracket to actuate the brake.
Owner:LAMBERT BRAKE
Polymeric roof rail
InactiveUS7111892B2Easy to manufactureImprove contourEngine sealsSuperstructure subunitsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A convertible roof system uses composite roof rail(s). The composite roof rail can have portions that are made of differing materials. The composite roof rail can use universal connecting pieces for the ends of the roof rail. Adjacent composite roof rails can be formed about a connector that couples the adjacent roof rails together.
Owner:SPECIALTY VEHICLE ACQUISITION
Braid and wire harness
ActiveUS9386733B2Increase the number ofWeight increaseVehicle connectorsScreening casingsElectromagnetic shieldingEngineering
A braid having a function as an exterior member as well as an electromagnetic shielding function is provided. Also, a wire harness including such a braid in a configuration is provided. A braid is used for a wire harness cabled to a hybrid vehicle. Also, the braid is formed by knitting multiple ultrathin strands in a tubular shape. The braid includes two kinds of strands, a metal strand made of metal having conductivity and a resin strand made of synthetic resin having abrasion resistance etc., and ensures abrasion resistance and impact resistance by the portion made of the resin strand while performing an electromagnetic shielding function by the portion made of the metal strand.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Landing gear joint lubrication
PendingUS20210261241A1Optimize allocationReduce the possibilityBearing repair/replacementShaft repair/replacementReciprocating motionClassical mechanics
A pin assembly for insertion into a pin joint of an aircraft landing gear is disclosed. The pin assembly includes a reservoir for storing a lubricating agent and a piston mounted for reciprocal movement within the reservoir, the piston dividing the reservoir into a first chamber and a second chamber. A bi-directional flow path between the first and second chambers via the surface to be lubricated is provided by means of a first bi-directional flow path between the first chamber and the exterior of the pin assembly and a second bi-directional flow path between the second chamber and the exterior of the pin assembly. A pin assembly including an indicator system, and a pin insert in the form of a replaceable cartridge is also disclosed along with associated methods.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Transport roller, transport device and printing apparatus
ActiveUS20100315474A1Avoid soilFavorable transport capabilityShaft and bearingsPortable power-driven toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
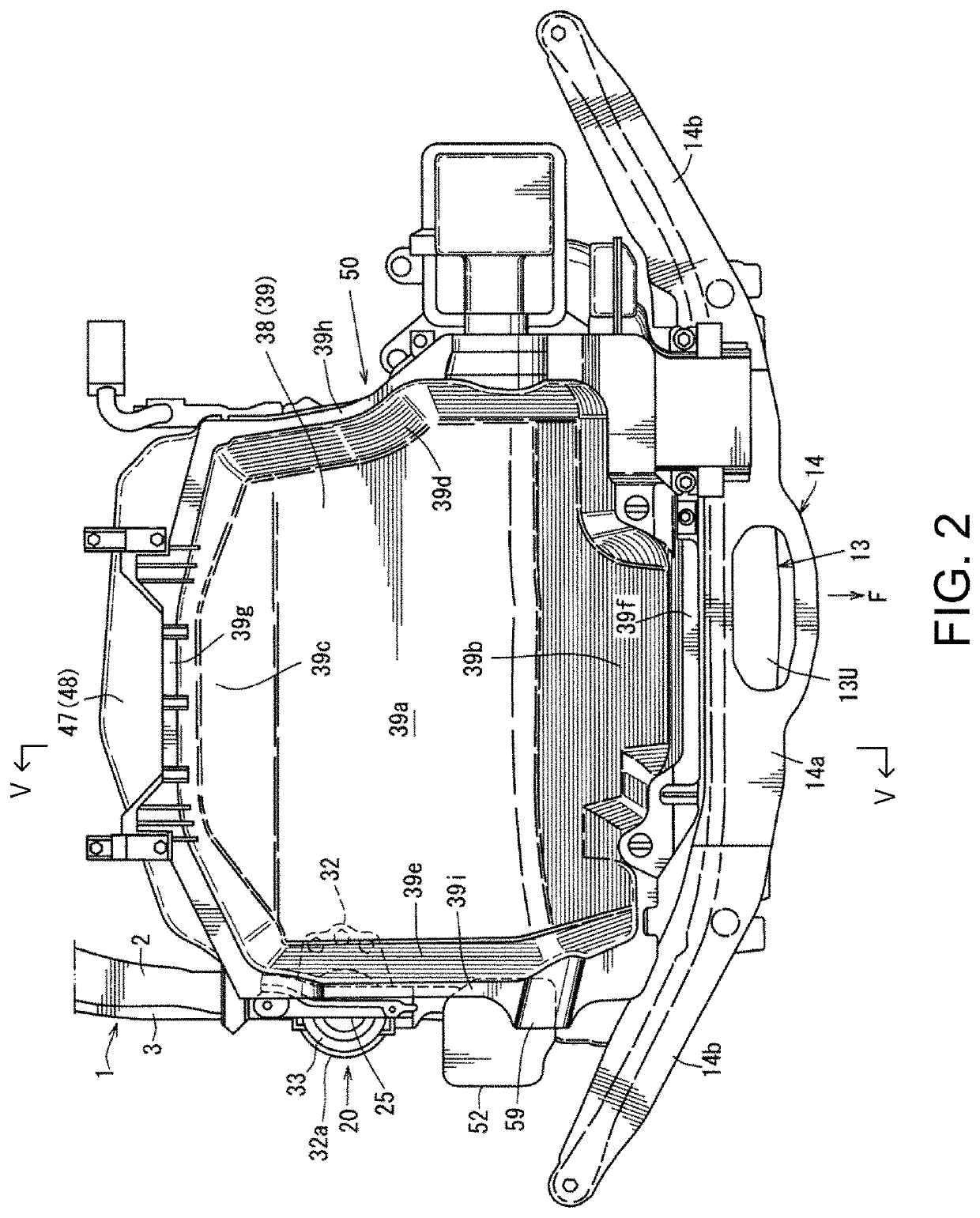
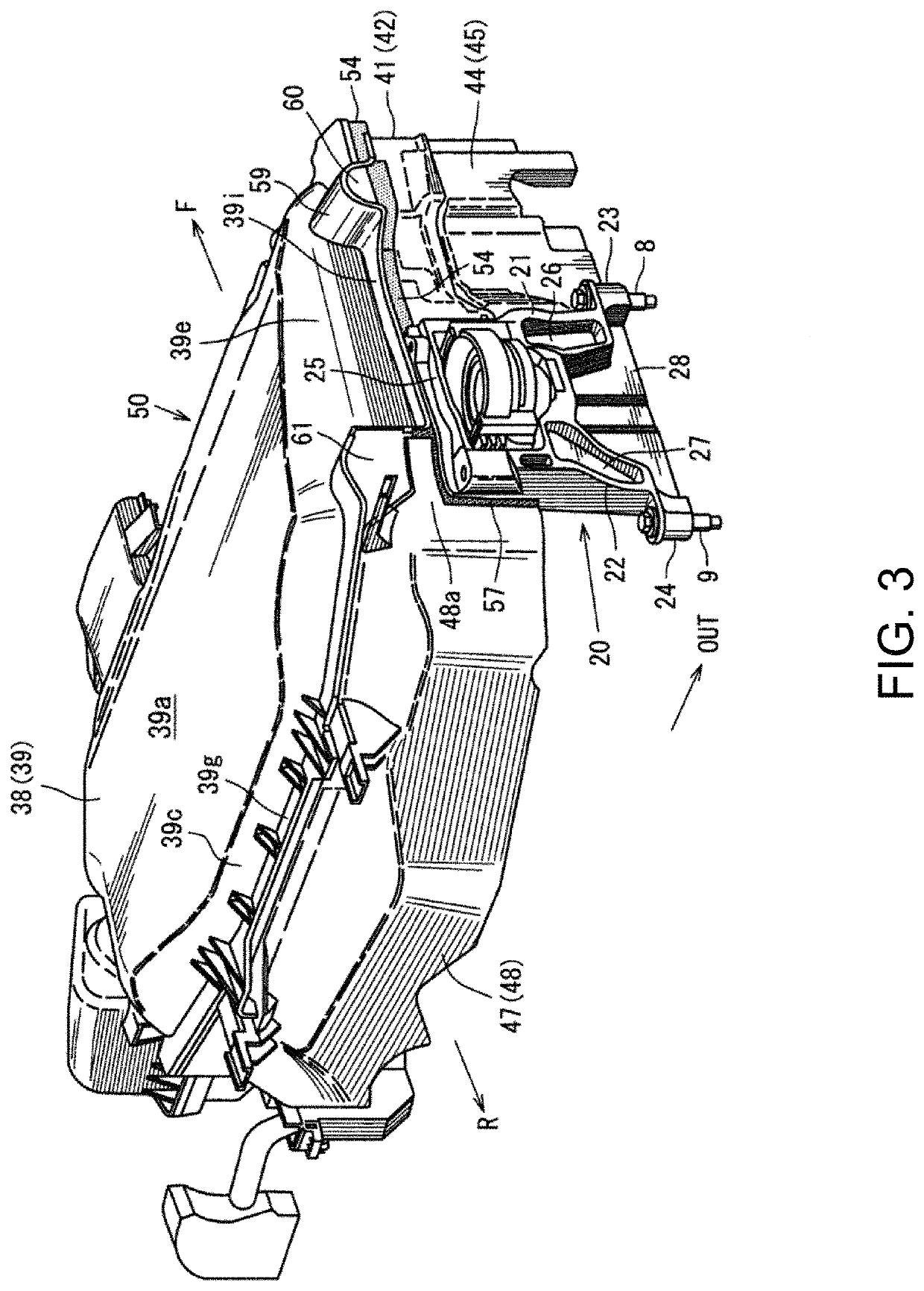
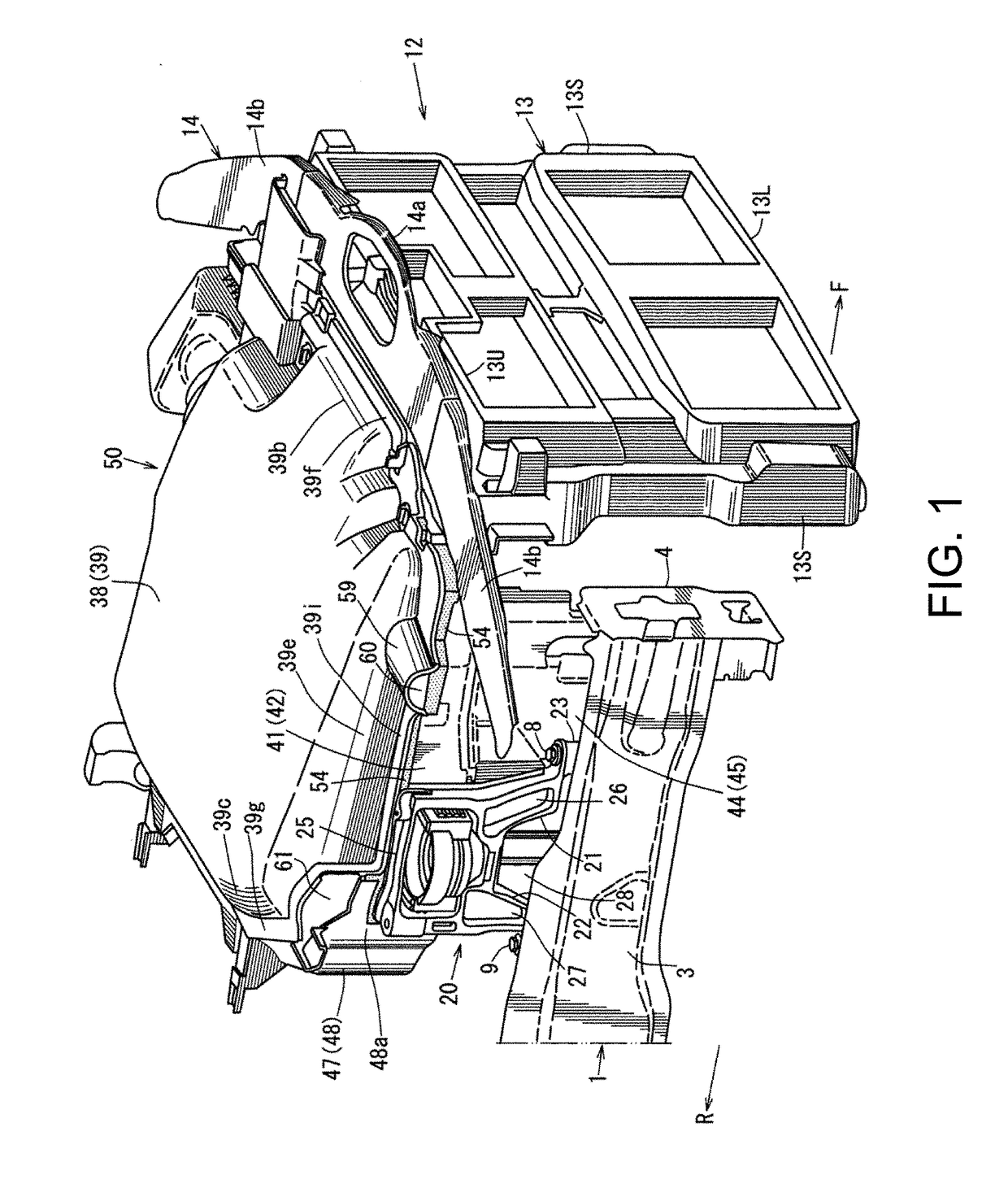
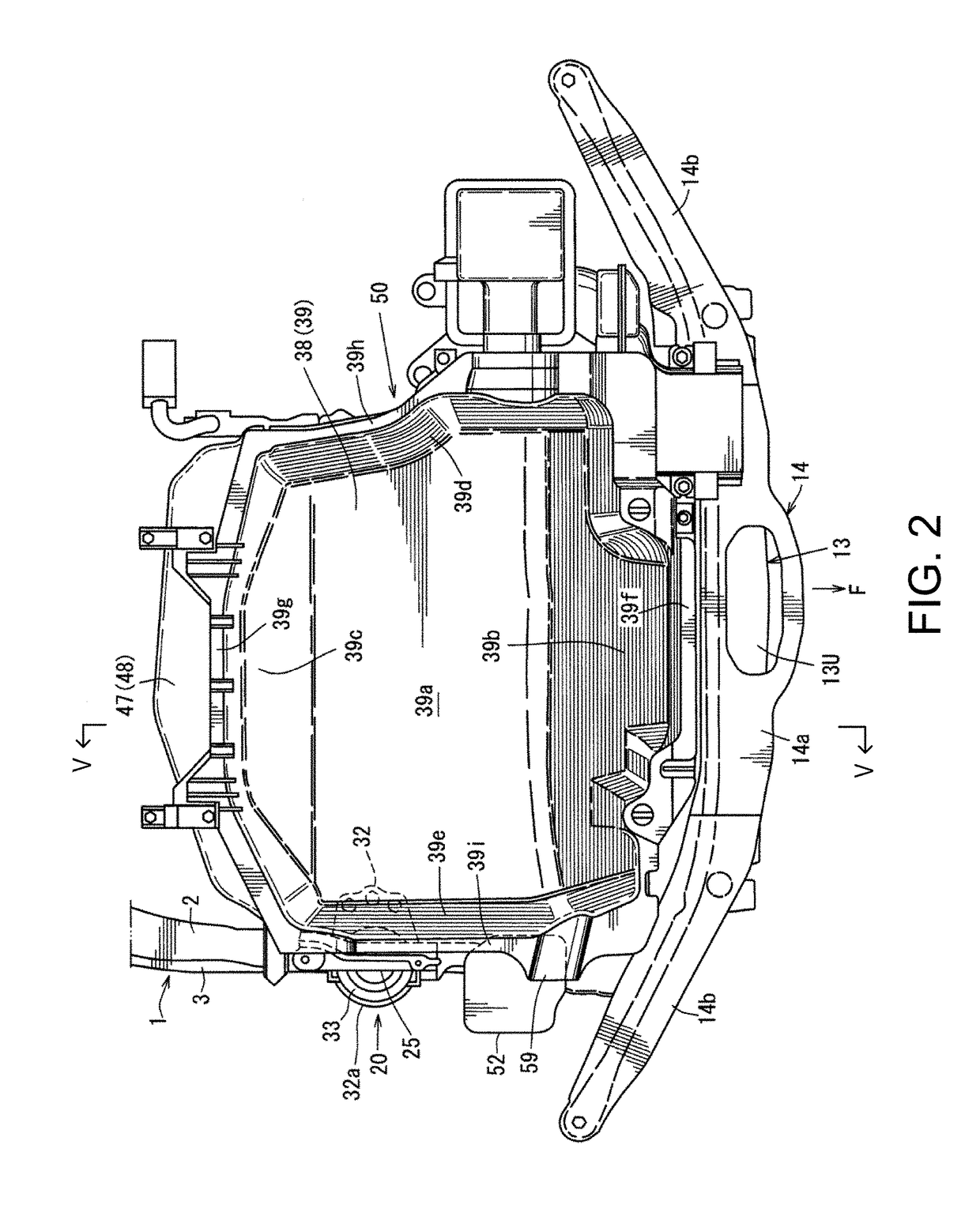
Engine heat retention structure
ActiveUS10688844B2Reduce weight and costReducing weight and costAir-treating devicesVehicle heating/cooling devicesMarine engineeringEngine mount
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Engine heat retention structure
ActiveUS20190061460A1Spacing lossReduce heat lossAir-treating devicesVehicle heating/cooling devicesEngine mountAutomotive engineering
A vehicle is provided, which includes an engine bay having an upper wall, side walls, a front wall, and a rear wall, an engine disposed inside the engine bay, and a dedicated heat retention member provided inside the engine bay, the dedicated heat retention member comprising an upper lid part covering the engine from above to be openable and closable, and side-wall parts covering a side of the engine. A portion of the side-wall parts is comprised of an engine mount bracket configured to support mounts of the engine, instead of the dedicated heat retention member.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Exhaust passage
ActiveUS9605577B2Reducing weight and costPromote atomizationSilencing apparatusMachines/enginesStamping processMechanical engineering
An exhaust system comprises a conical shell having an indentation traversing the exhaust passage in a coiled path so as to impart mixing on an engine exhaust gas flowing through an inner passage defined by the conical shell. The indentation may be formed into the conical shell via a stamping process.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
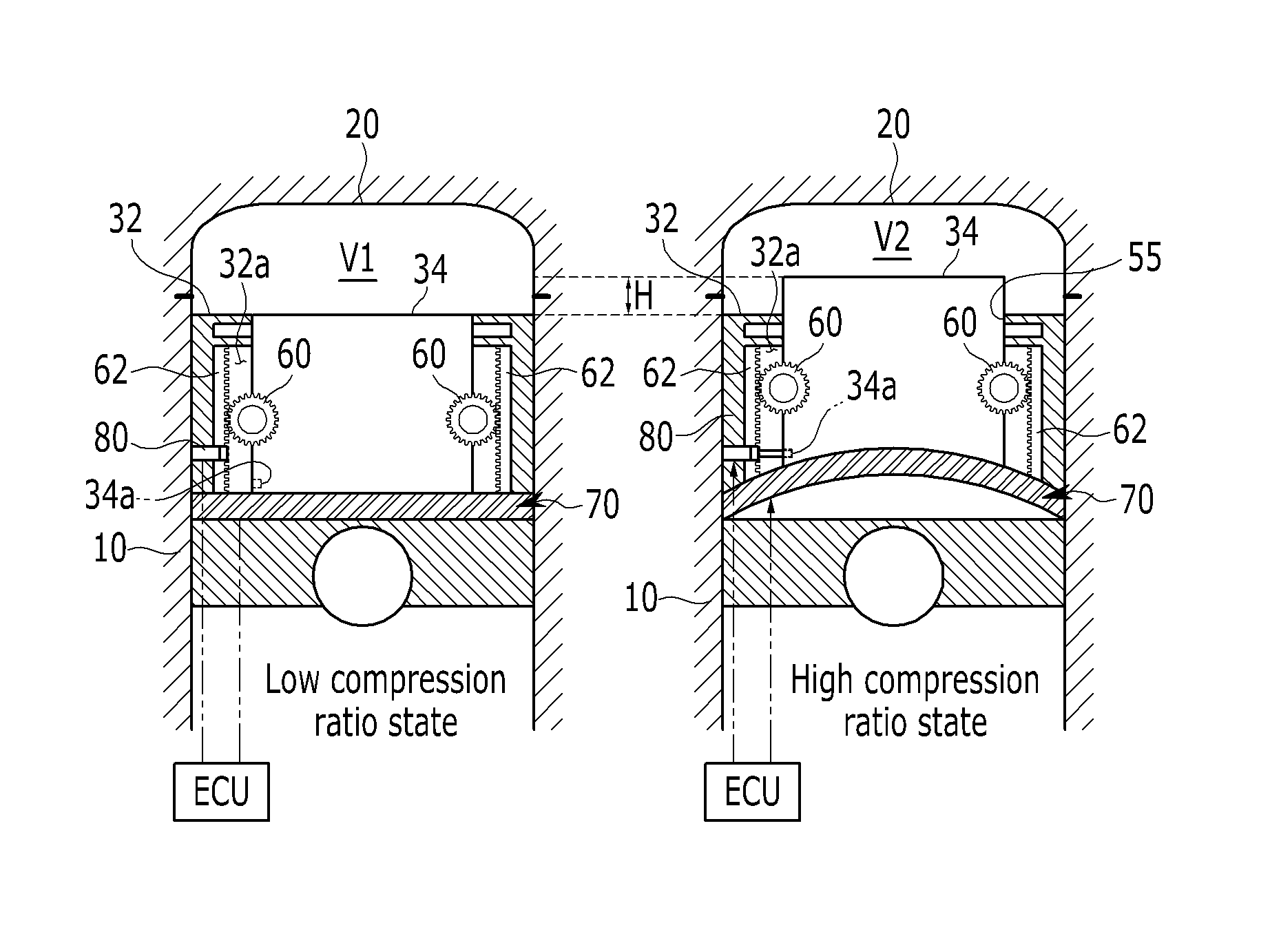
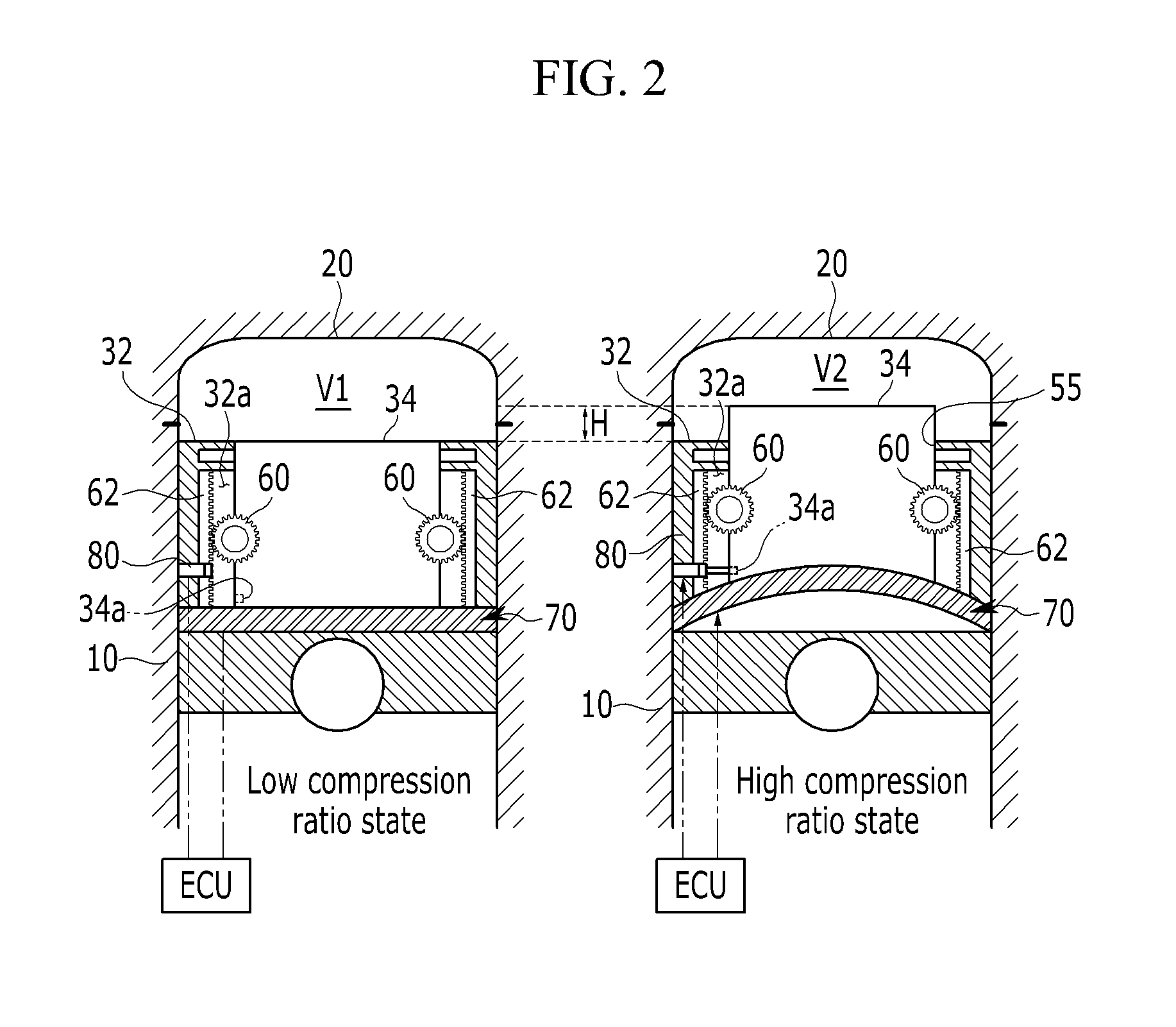
Variable compression ratio device and internal combustion engine including the same
ActiveUS20140238355A1Reduce weightLow costCombustion enginesEngine controllersEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A variable compression ratio device may include a piston assembly having double pistons of which the volume may be varied, a lifter relatively moving one piston of the double pistons with respect to the other piston of the double pistons, a guide unit engaged with the piston assembly and guiding a movement of the one piston with respect to the other piston, and a locking unit selectively coupling the one piston to the other piston.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Braided textile sleeve with integrated opening and self-sustaining expanded and contracted states and method of construction thereof
A protective textile having at least one integrated opening and method of construction thereof is provided. The sleeve includes a braided, tubular wall extending lengthwise in relation to a central longitudinal axis between opposite ends. The wall has a first state with a decreased length, increased cross-sectional area and a second state with an increased length, decreased cross-sectional area, as viewed in cross-section taken generally transversely to the central longitudinal axis. The wall further includes braided, heat-set yarns imparting a bias on the wall, wherein the bias causes the wall to remain substantially in the first and second states absent some externally applied force. The wall also includes at least one opening having a circumferentially continuous periphery bounding the opening, wherein the periphery is formed, at least in part, by braided yarns reversing direction from one S or Z helical direction to the opposite S or Z helical direction.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL POWERTAIN LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com