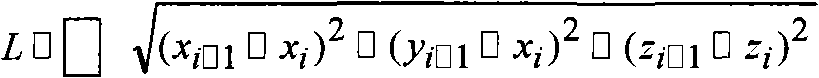Patents
Literature
45 results about "Computed tomography angiography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
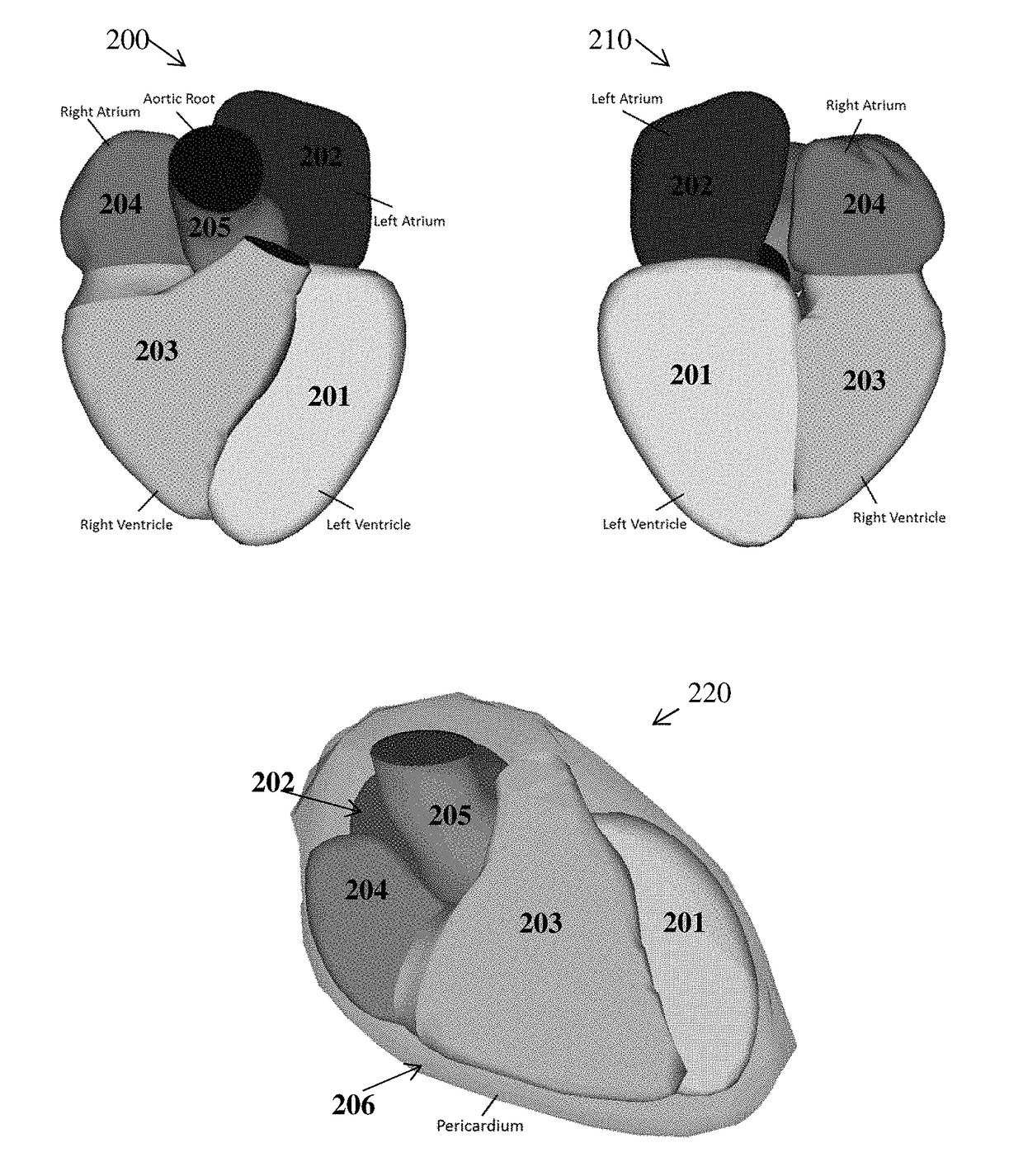
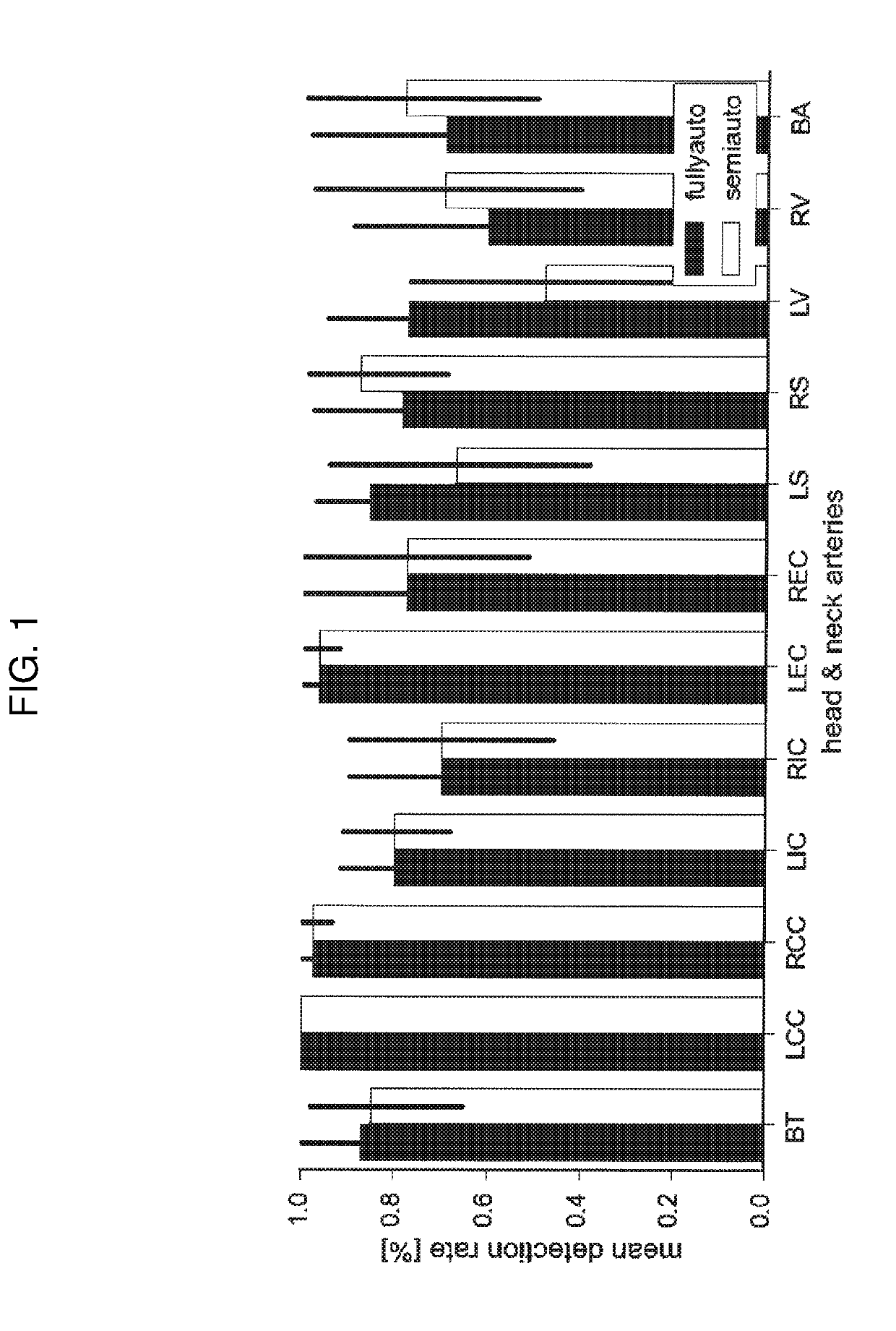
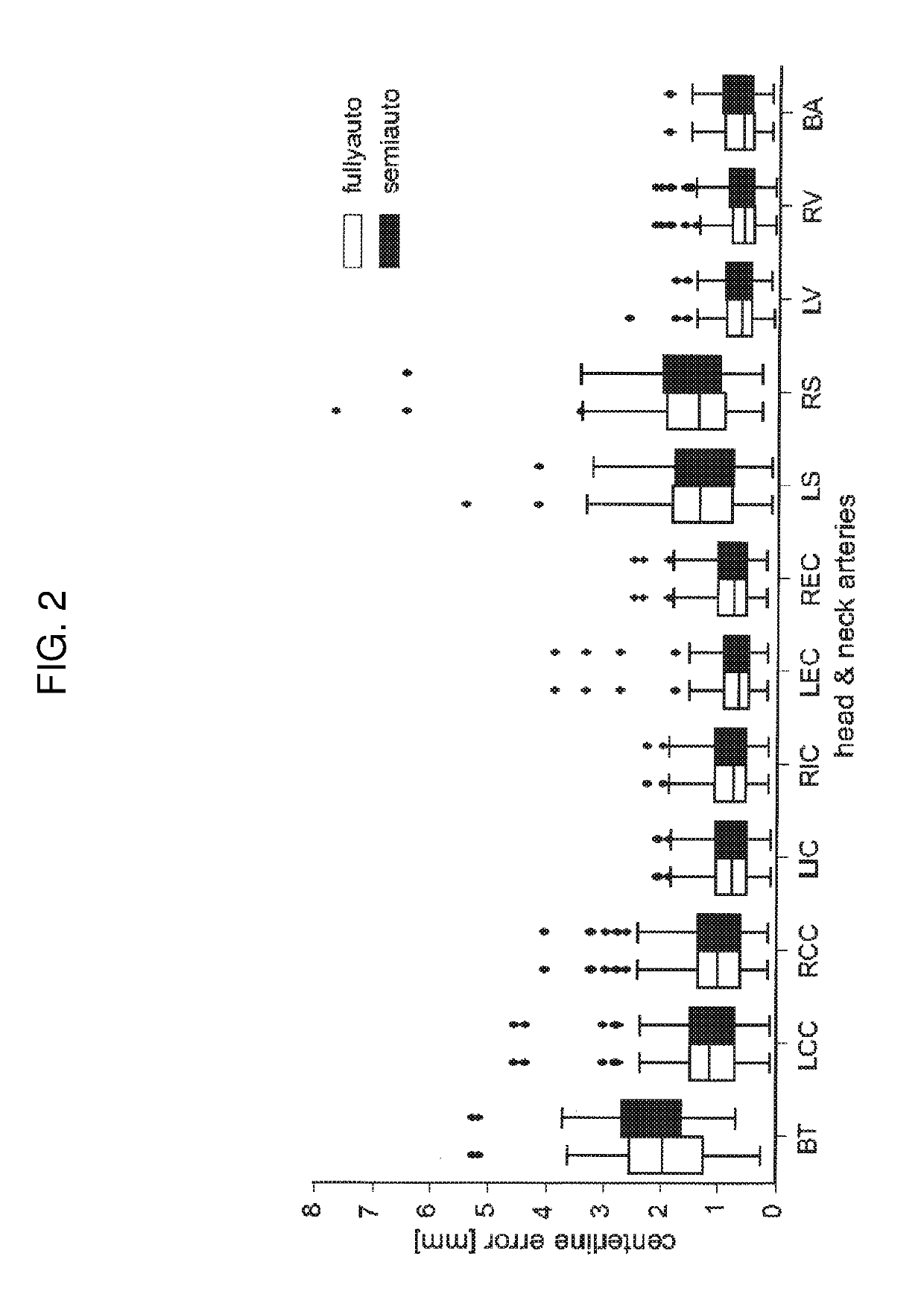
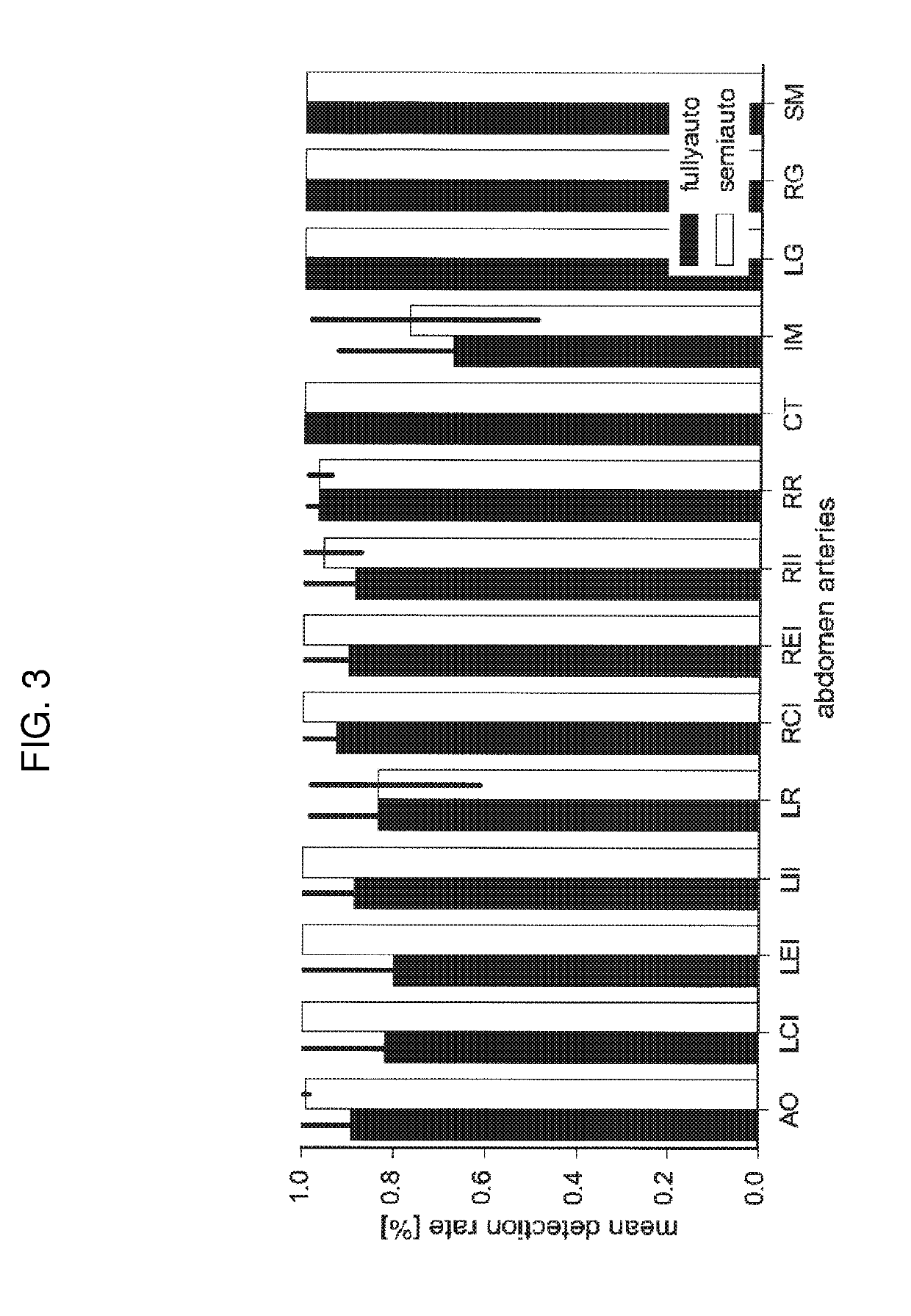
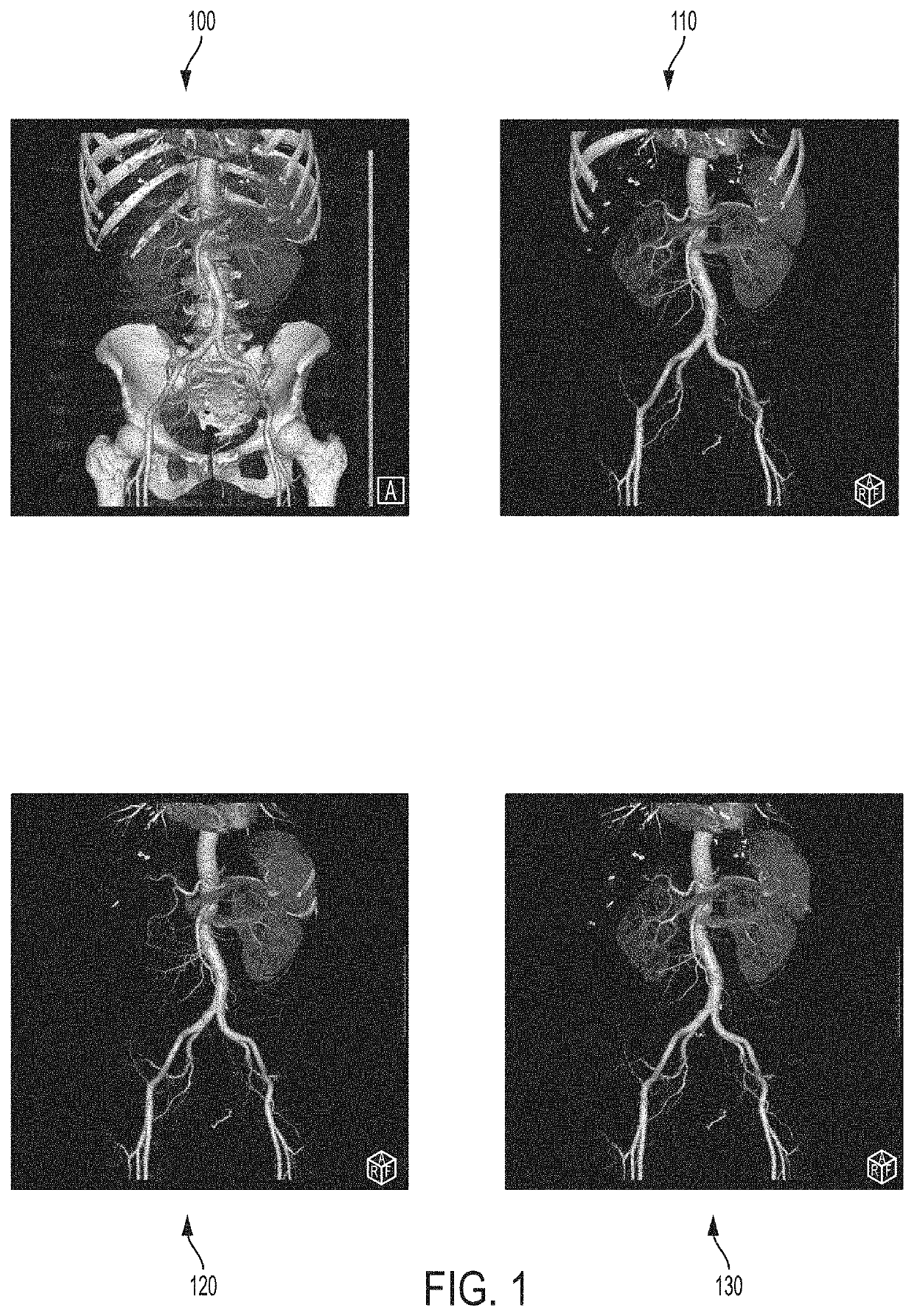
Computed tomography angiography (also called CT angiography or CTA) is a computed tomography technique used to visualize arterial and venous vessels throughout the body. Using contrast injected into the blood vessels, images are created to look for blockages, aneurysms (dilations of walls), dissections (tearing of walls), and stenosis (narrowing of vessel). CTA can be used to visualize the vessels of the heart, the aorta and other large blood vessels, the lungs, the kidneys, the head and neck, and the arms and legs.
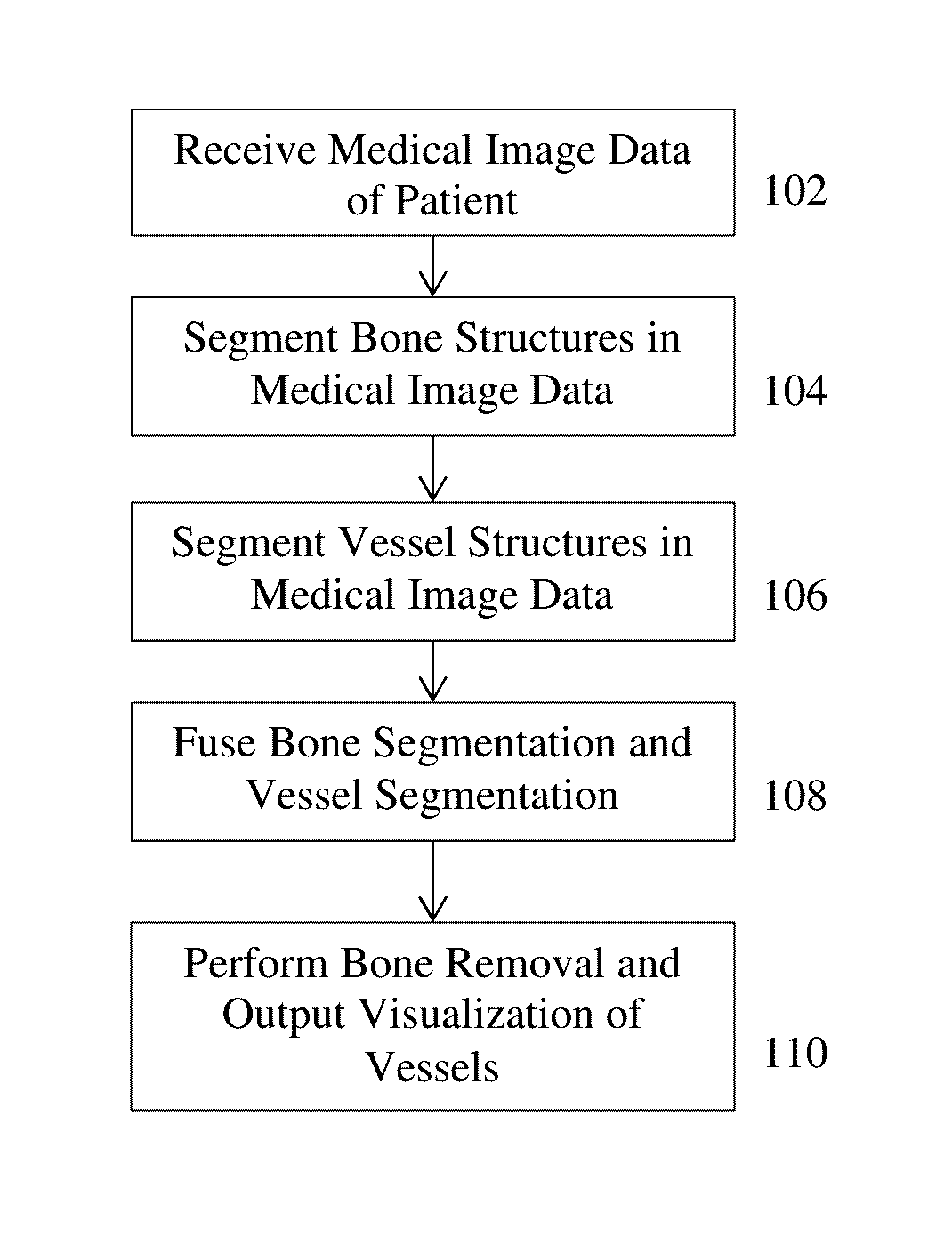
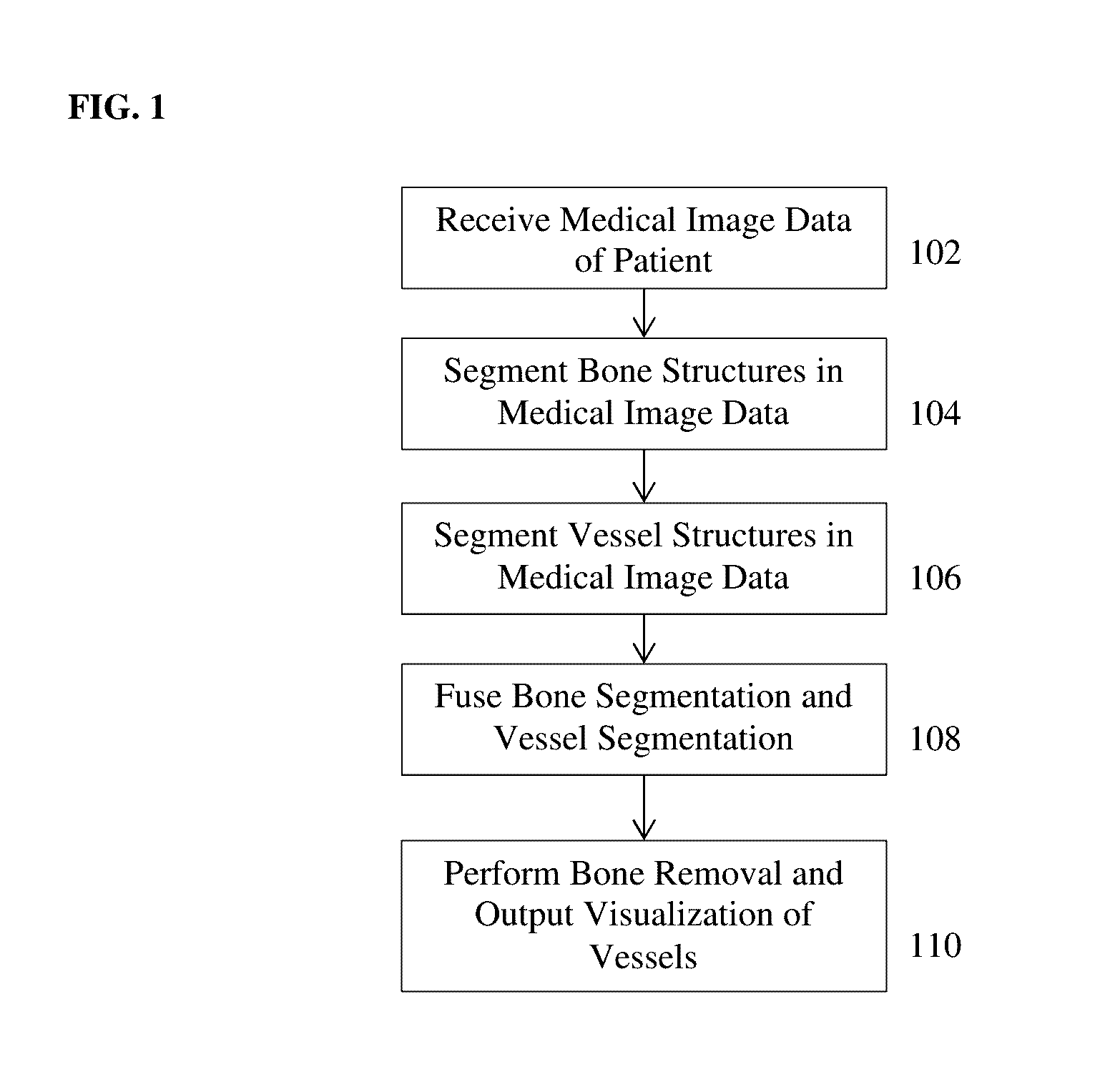
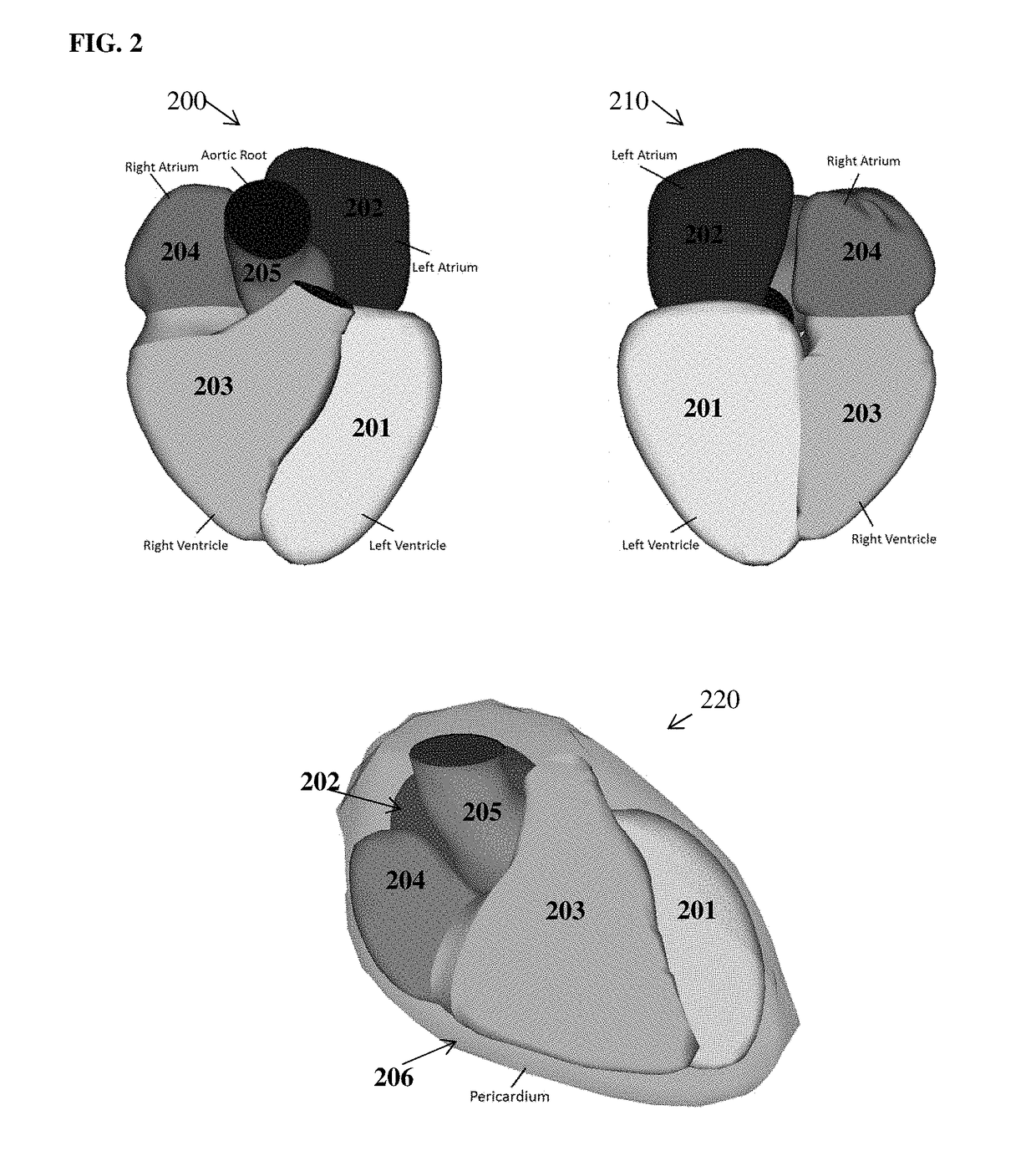
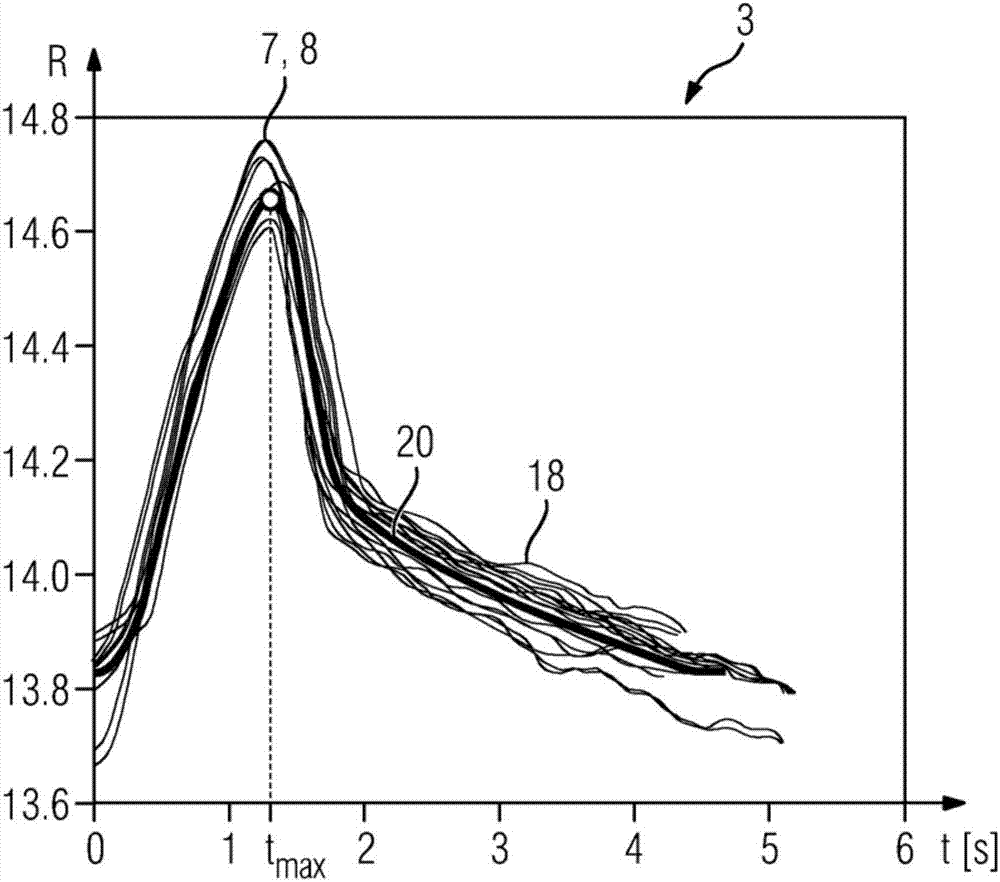
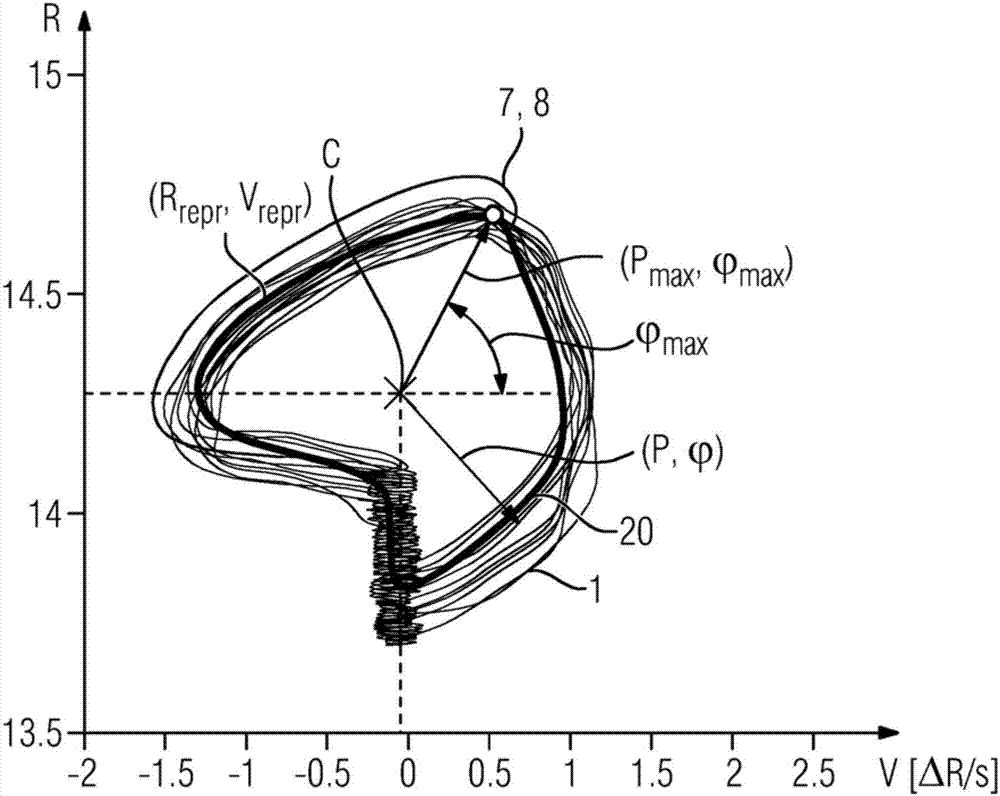
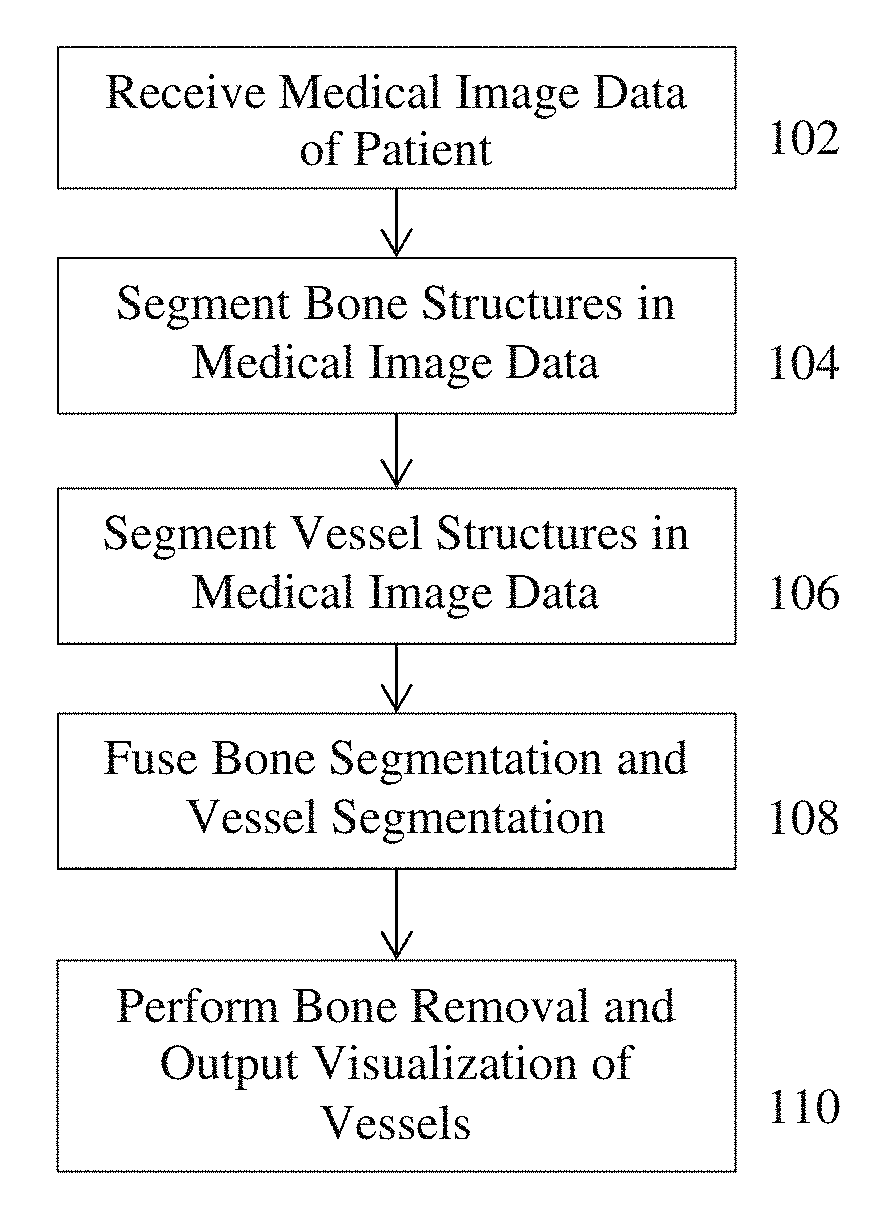
Method and System for Whole Body Bone Removal and Vascular Visualization in Medical Image Data
A method and apparatus for whole body bone removal and vasculature visualization in medical image data, such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans, is disclosed. Bone structures are segmented in the a 3D medical image, resulting in a bone mask of the 3D medical image. Vessel structures are segmented in the 3D medical image, resulting in a vessel mask of the 3D medical image. The bone mask and the vessel mask are refined by fusing information from the bone mask and the vessel mask. Bone voxels are removed from the 3D medical image using the refined bone mask, in order to generate a visualization of the vessel structures in the 3D medical image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
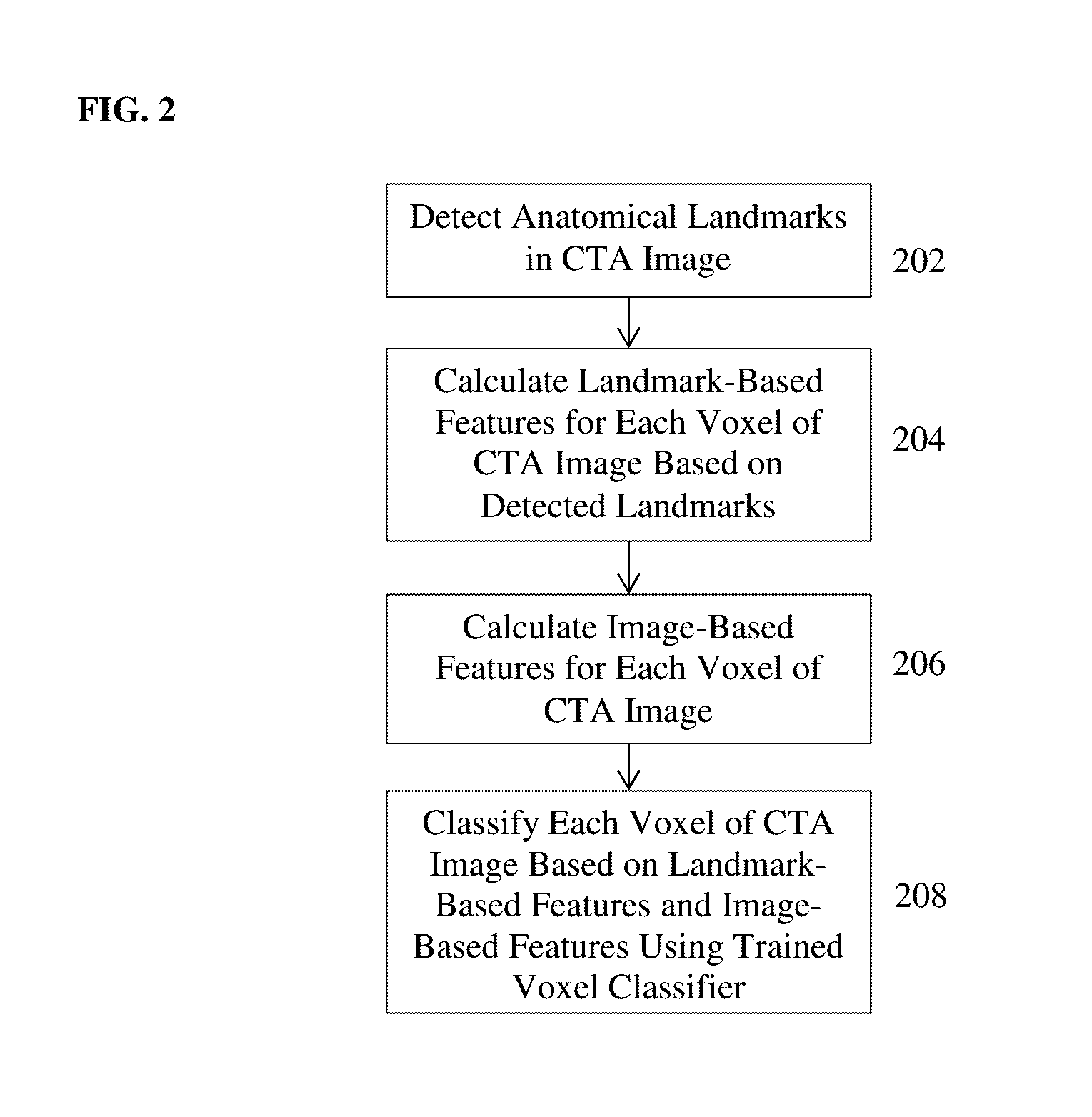
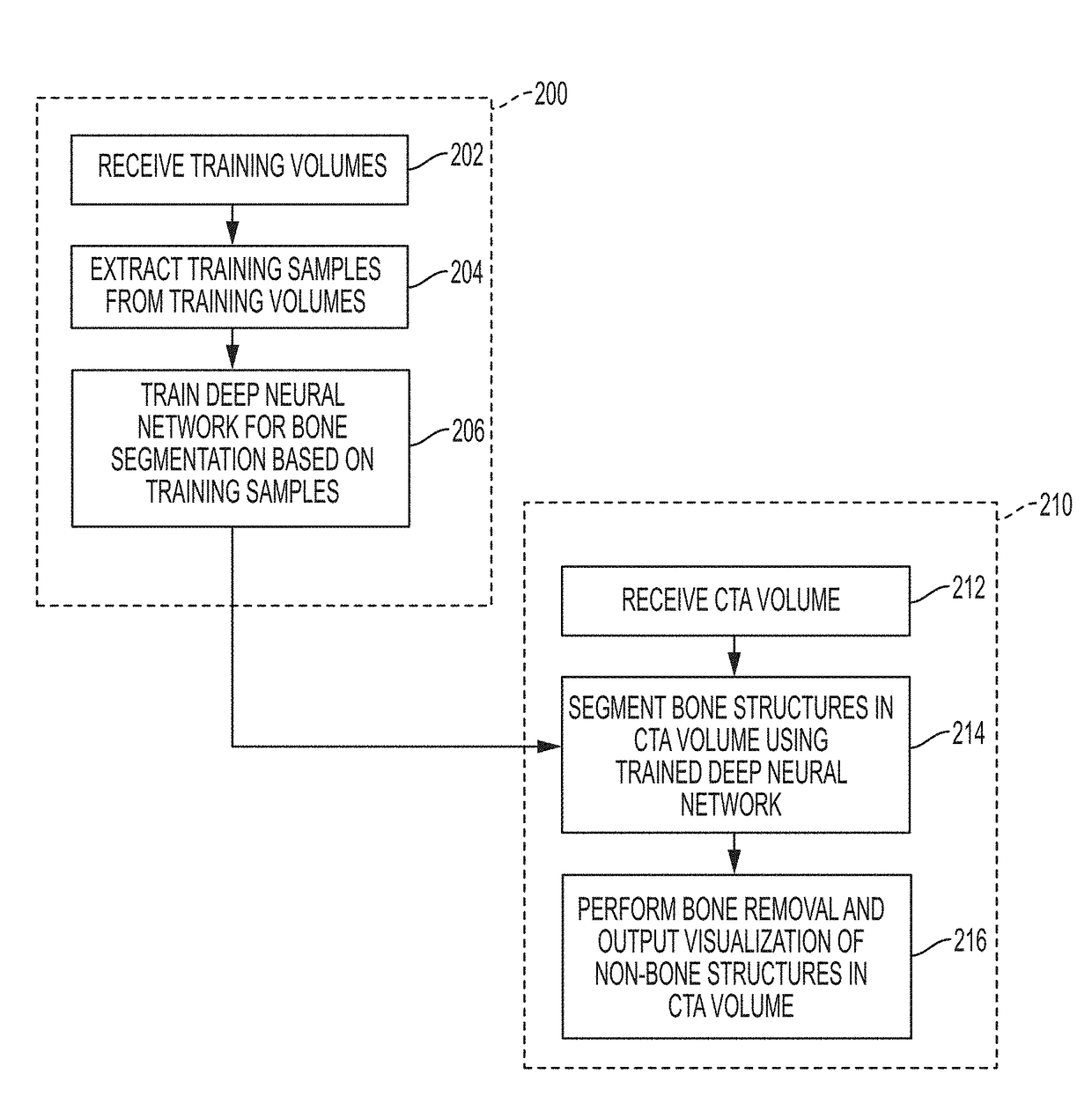
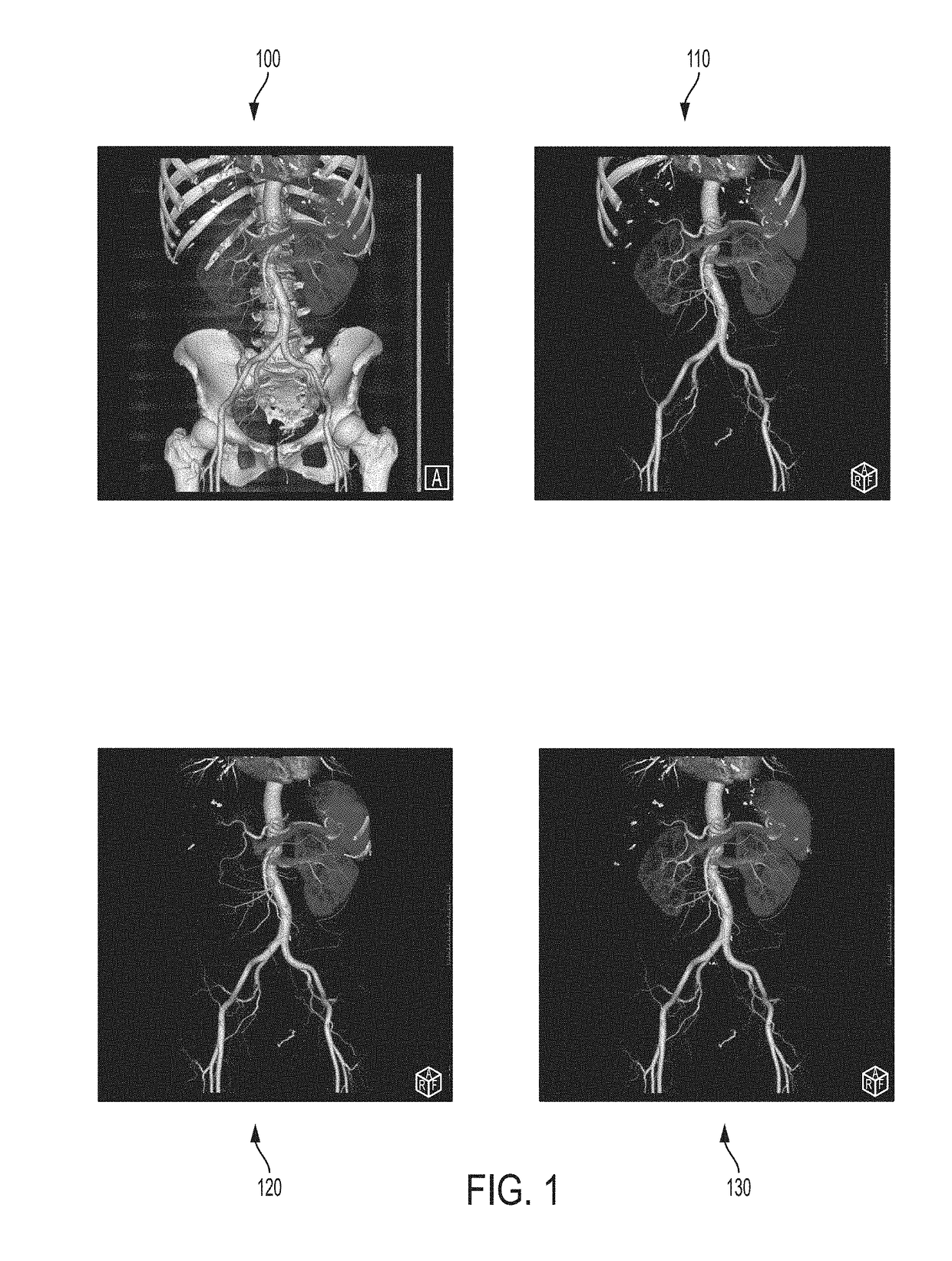
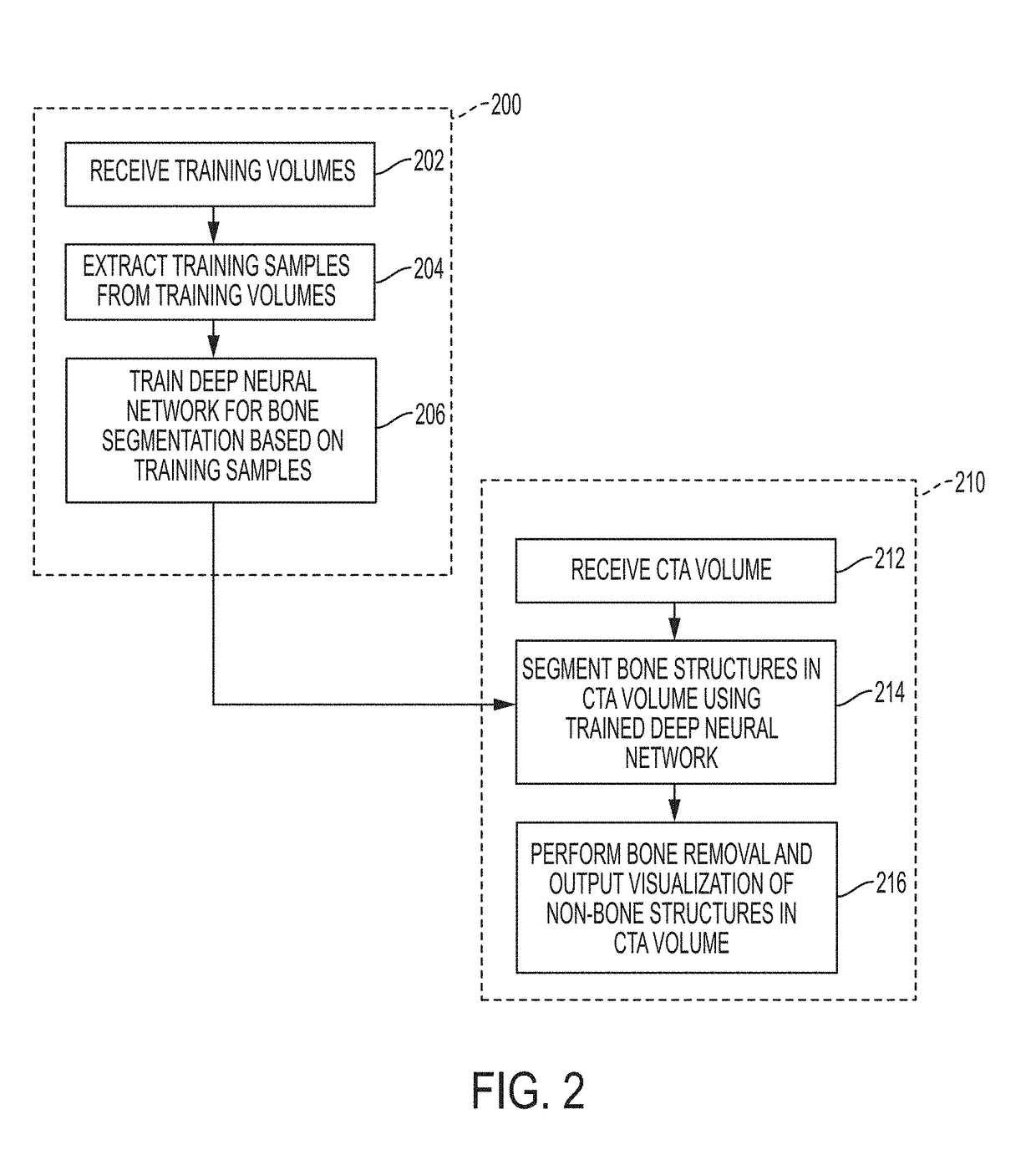
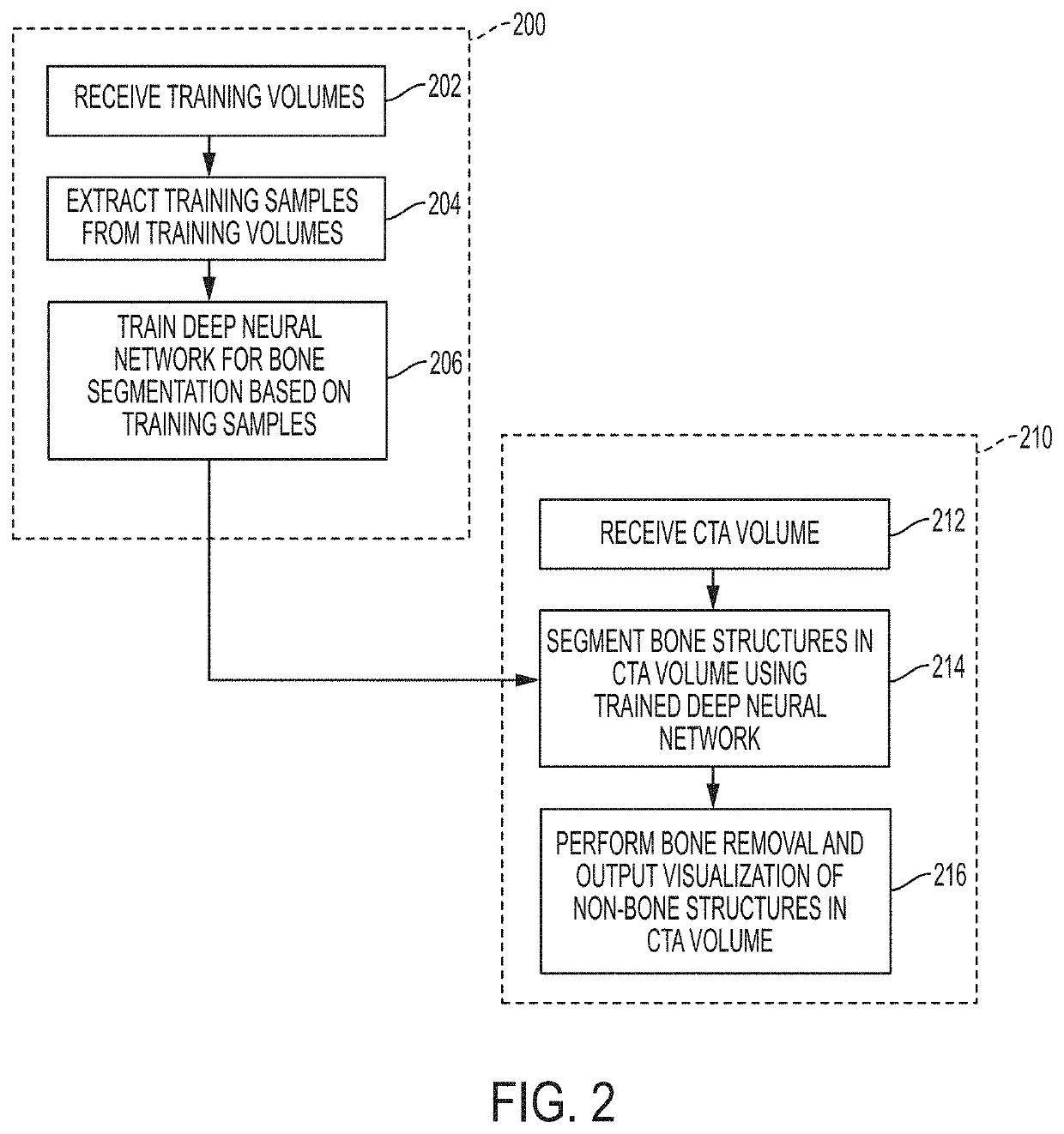
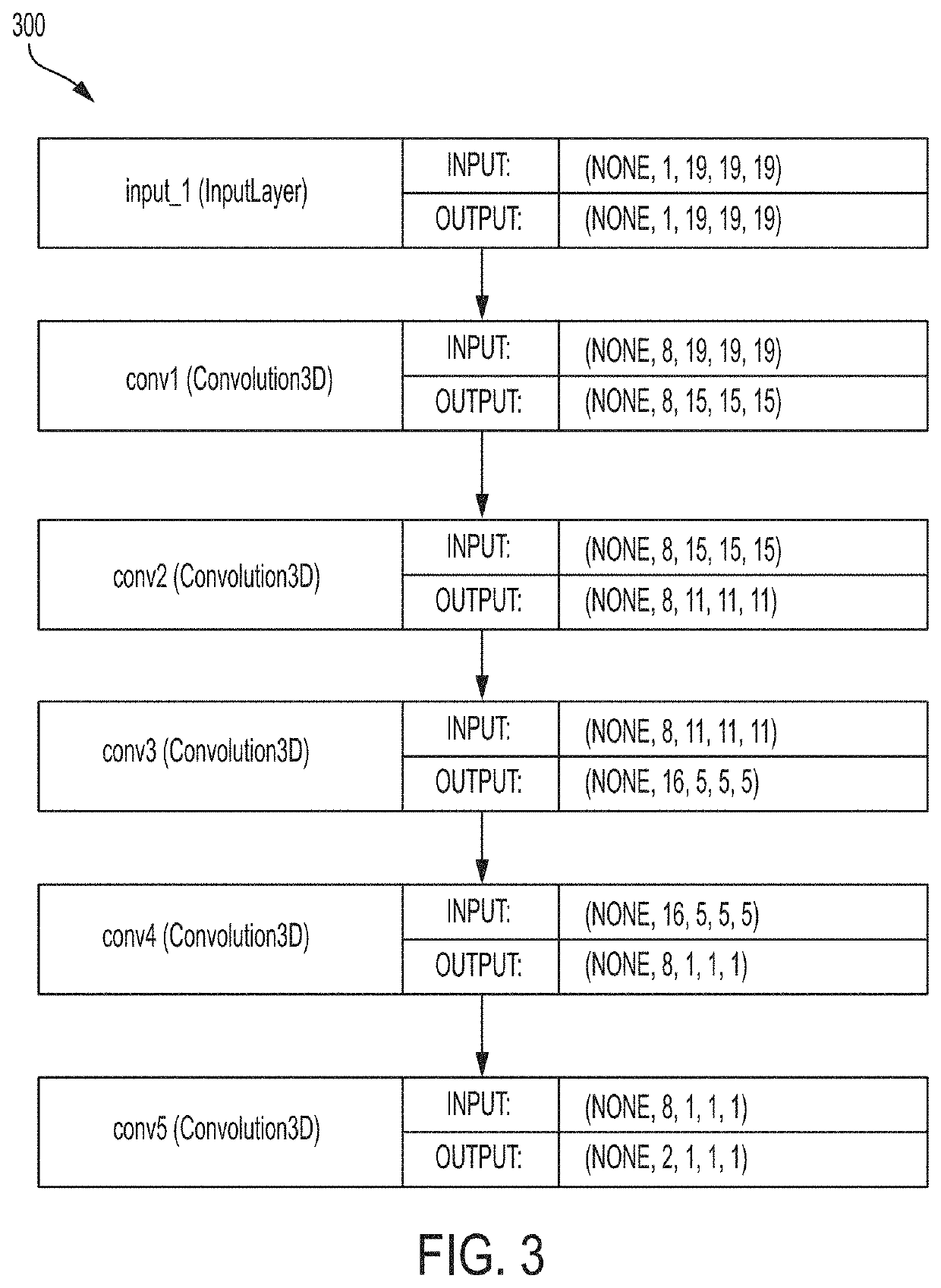
Deep Learning Based Bone Removal in Computed Tomography Angiography
A method and apparatus for deep learning based automatic bone removal in medical images, such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) volumes, is disclosed. Bone structures are segmented in a 3D medical image of a patient by classifying voxels of the 3D medical image as bone or non-bone voxels using a deep neural network trained for bone segmentation. A 3D visualization of non-bone structures in the 3D medical image is generated by removing voxels classified as bone voxels from a 3D visualization of the 3D medical image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Time resolved computed tomography angiography
InactiveUS6983182B2Reducing invasivenessLess discomfortCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsData setImage resolution
A contrast enhanced dynamic study of a subject is performed with a CT system. A series of undersampled image data sets are acquired during the study with successive data sets acquired at interleaved projection angles. More fully sampled image data sets are formed by transforming the x-ray attenuation projection data to k-space and then sharing peripheral k-space data between undersampled k-space data sets. Artifacts due to undersampling are thus reduced without significantly affecting the time resolution of a series of reconstructed images.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
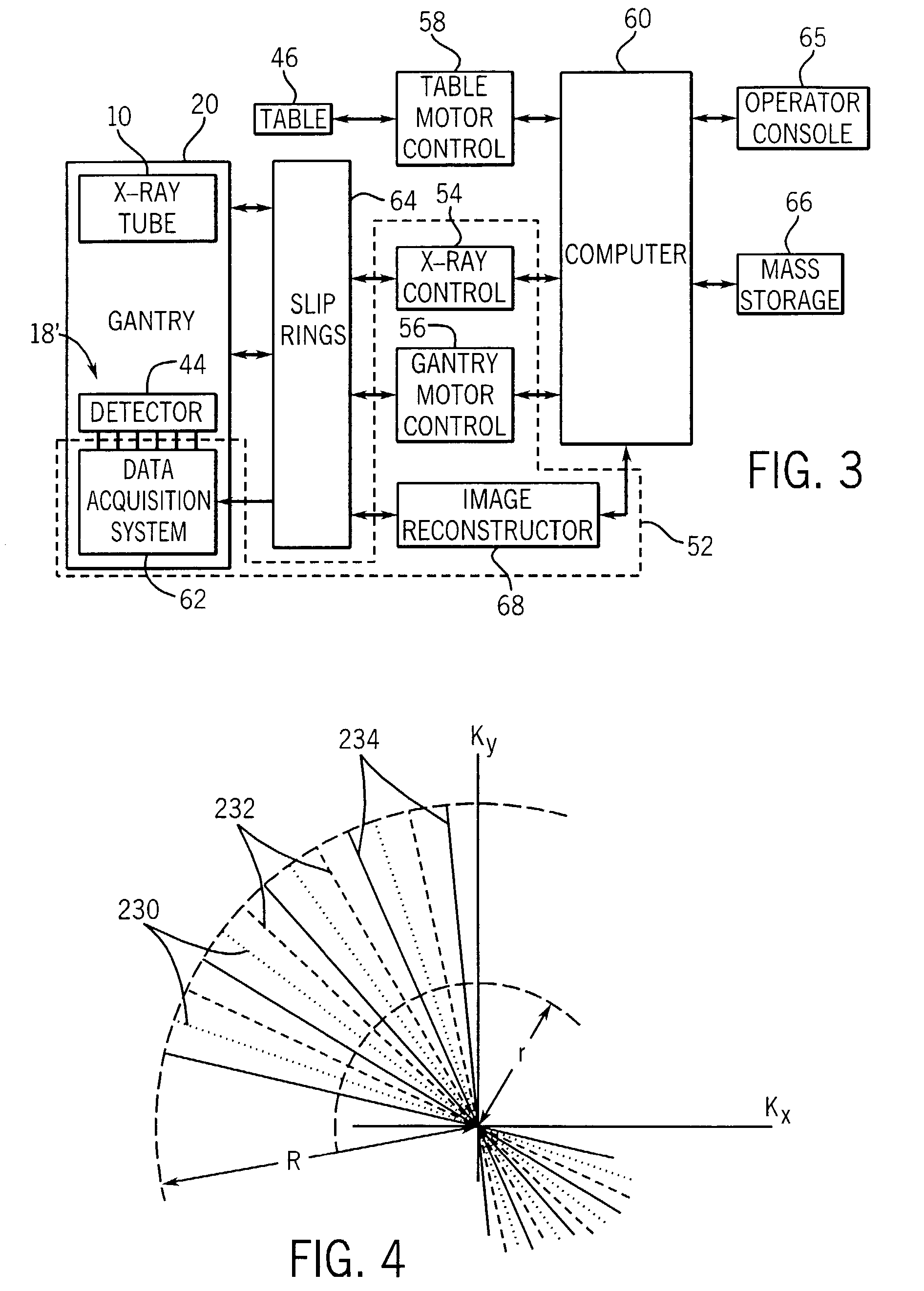
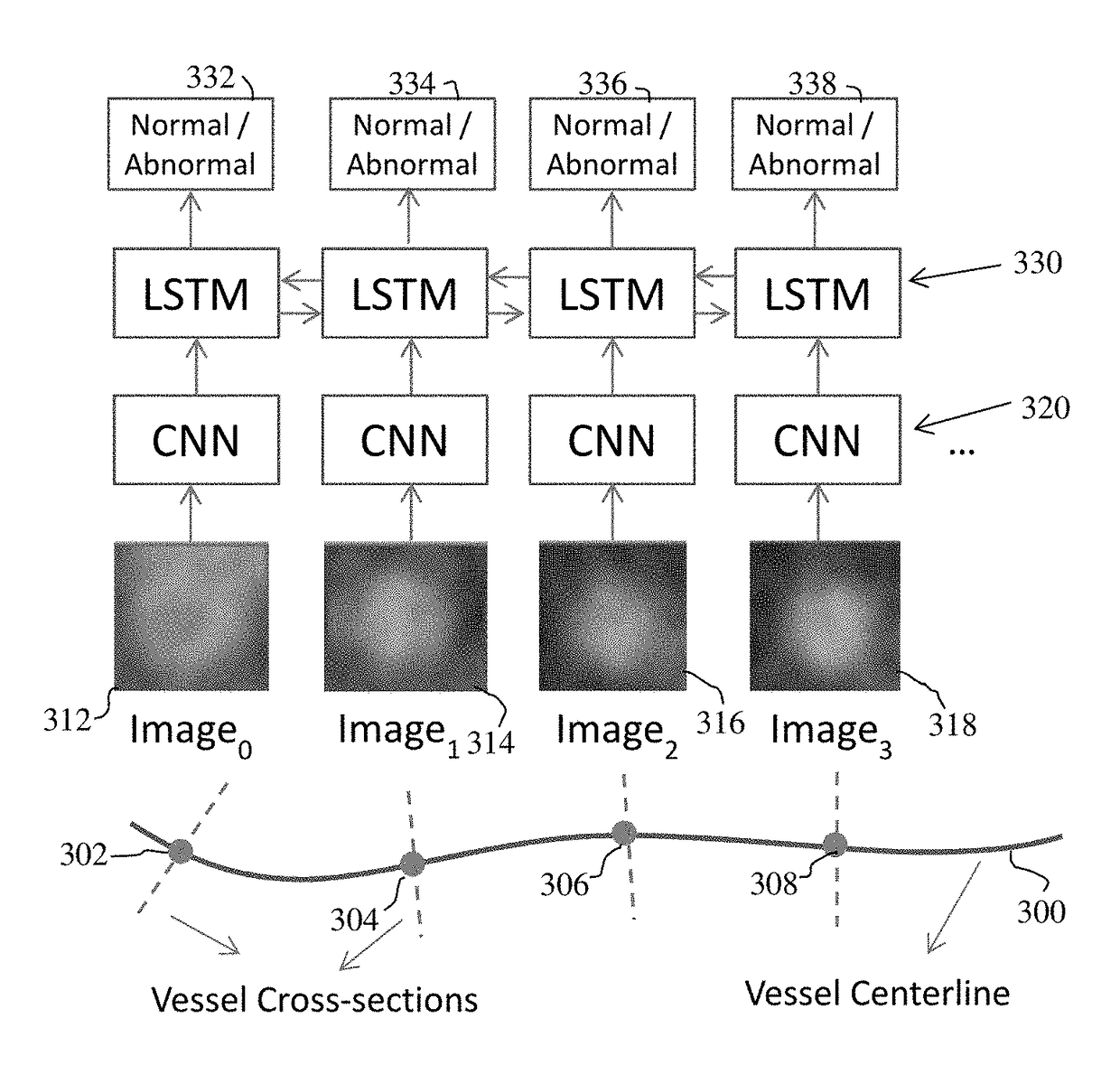
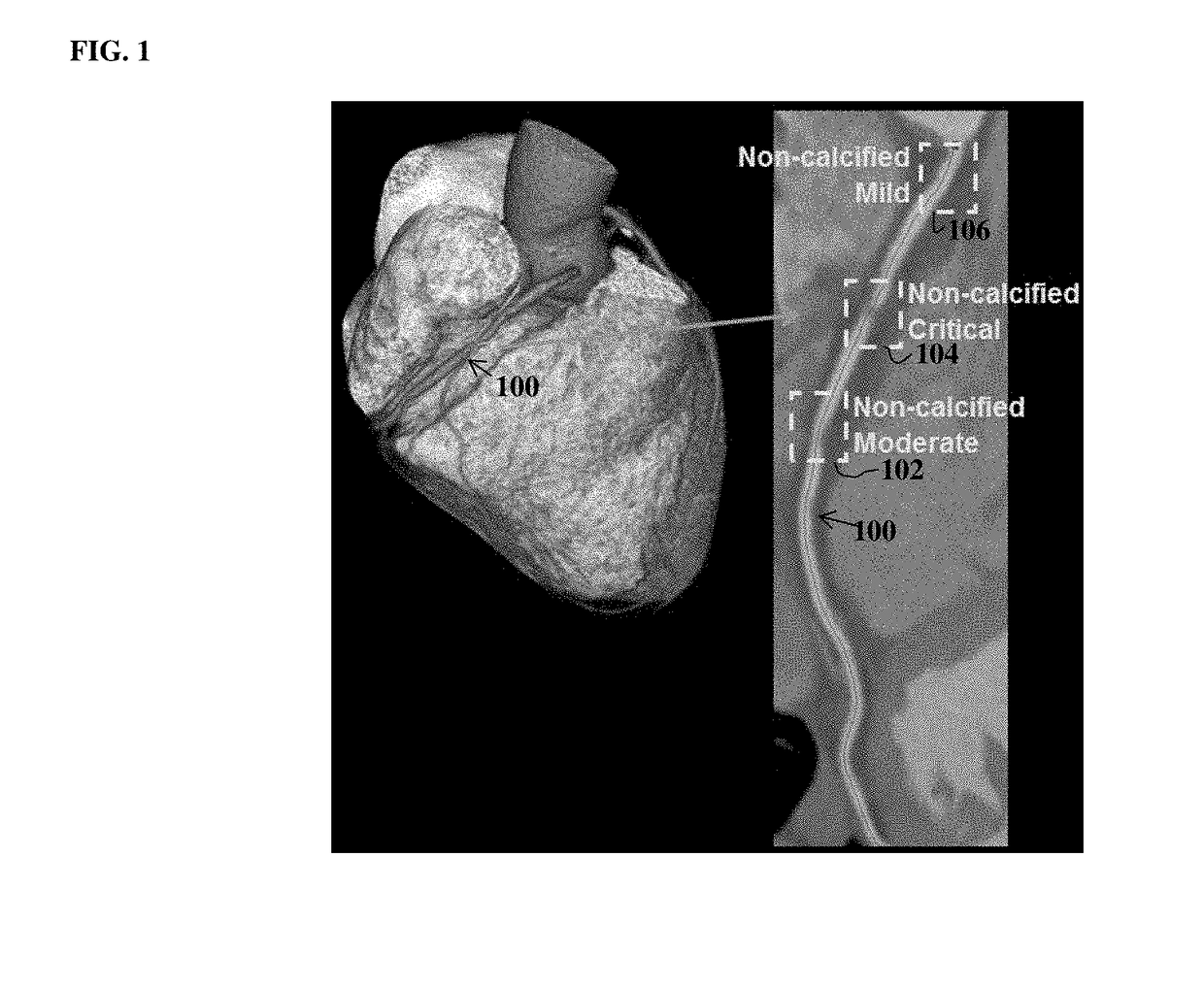
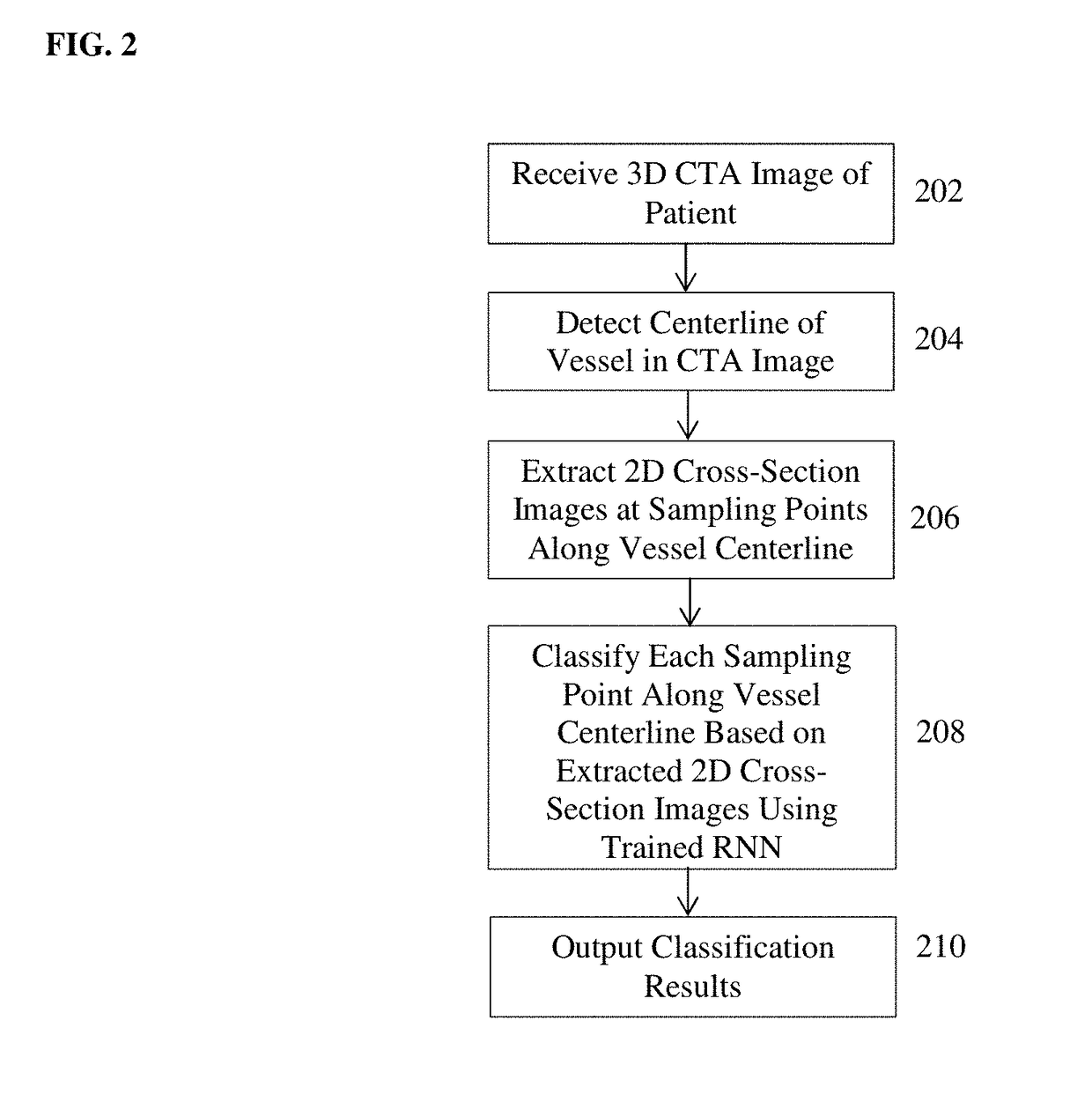
Method and System for Vascular Disease Detection Using Recurrent Neural Networks
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Blood vessel computer aided iconography evaluating system
InactiveCN101923607AEasy to importAccurate measurementSpecial data processing applications3D modellingSurface displayReconstruction method
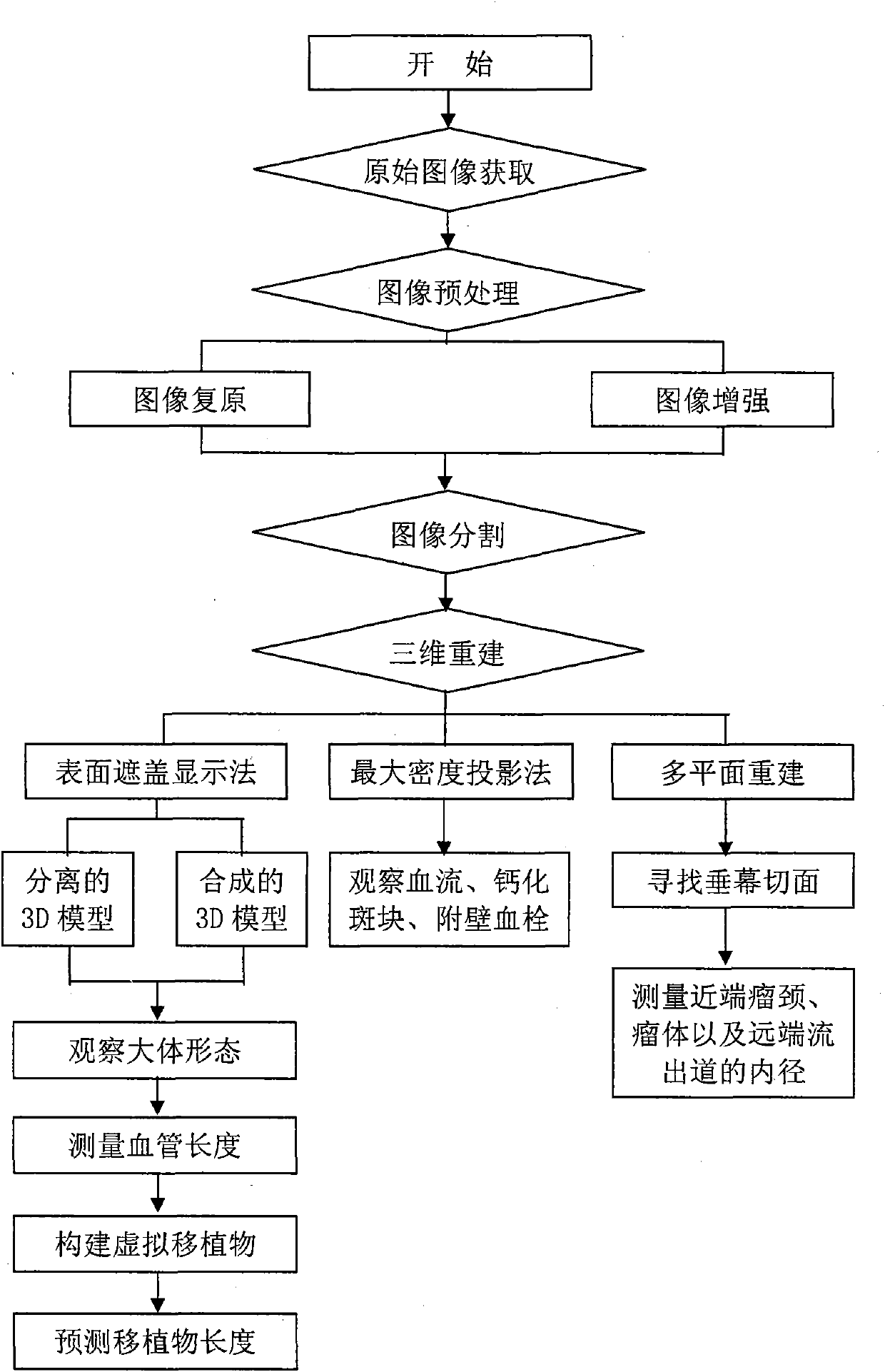
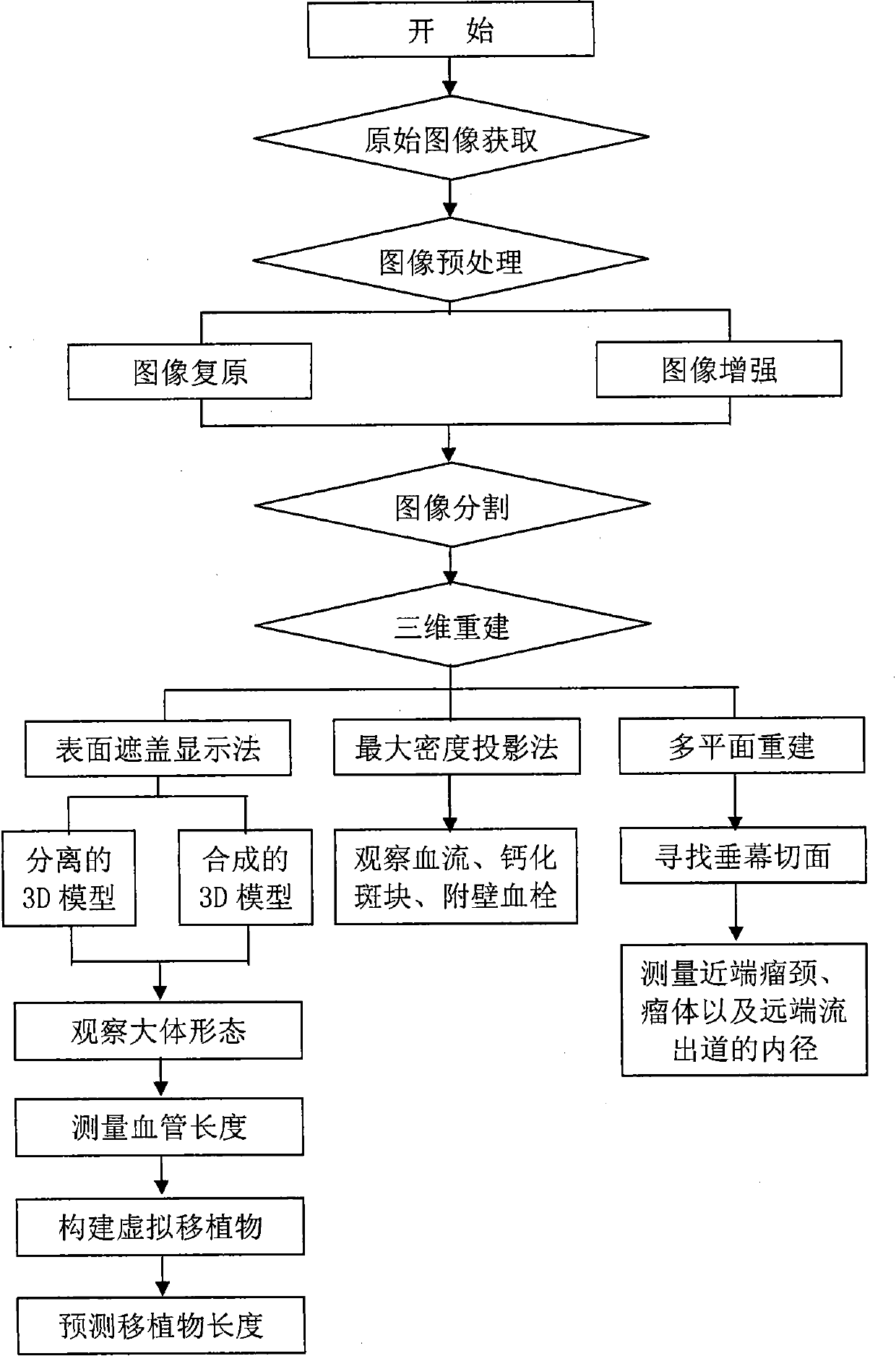
The invention relates to a blood vessel computer aided iconography evaluating system. The system comprises the following contents: (A) transmission of CTA (Computed Tomography Angiography) from a CT (Computed Tomography) working station to a PC (Personal Computer), wherein a transmission way comprises network card connection, CD burning and CT film scanning; (B) CTA three-dimensional reconstruction, wherein a three-dimensional reconstruction method comprises shaded surface display (SSD), maximum intensity projection (MIP) and multiplane reformation (MPR), obtains various real and clear three-dimensional models and images and can be used for observing a blood vessel three-dimensional space structure anytime and anywhere and lay the foundation for the three-dimensional measurement of various blood vessel geometric parameters; (C) blood vessel structure three-dimensional measurement; and (D) aneurysm endovascular graft exclusion virtual graft. The invention provides the computer aided iconography evaluating system which is suitable for people to use at random and is more accurate. In addition, the invention plays a role in blood vessel surgical scientific research, teaching, surgery training, and the like. The system realized by the invention is stable and reliable and is suitable for being popularized and used in blood vessel surgery centers of various large, medium and small hospitals.
Owner:冯睿
System, method and apparatus for small pulmonary nodule computer aided diagnosis from computed tomography scans
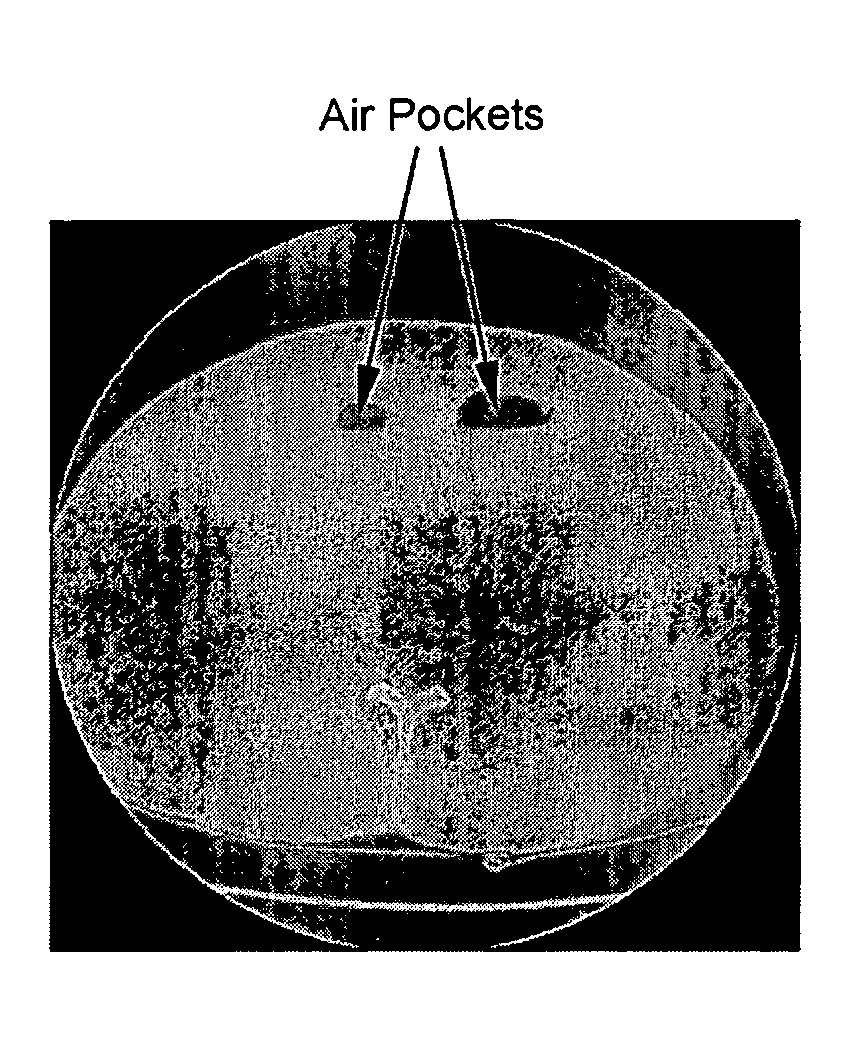
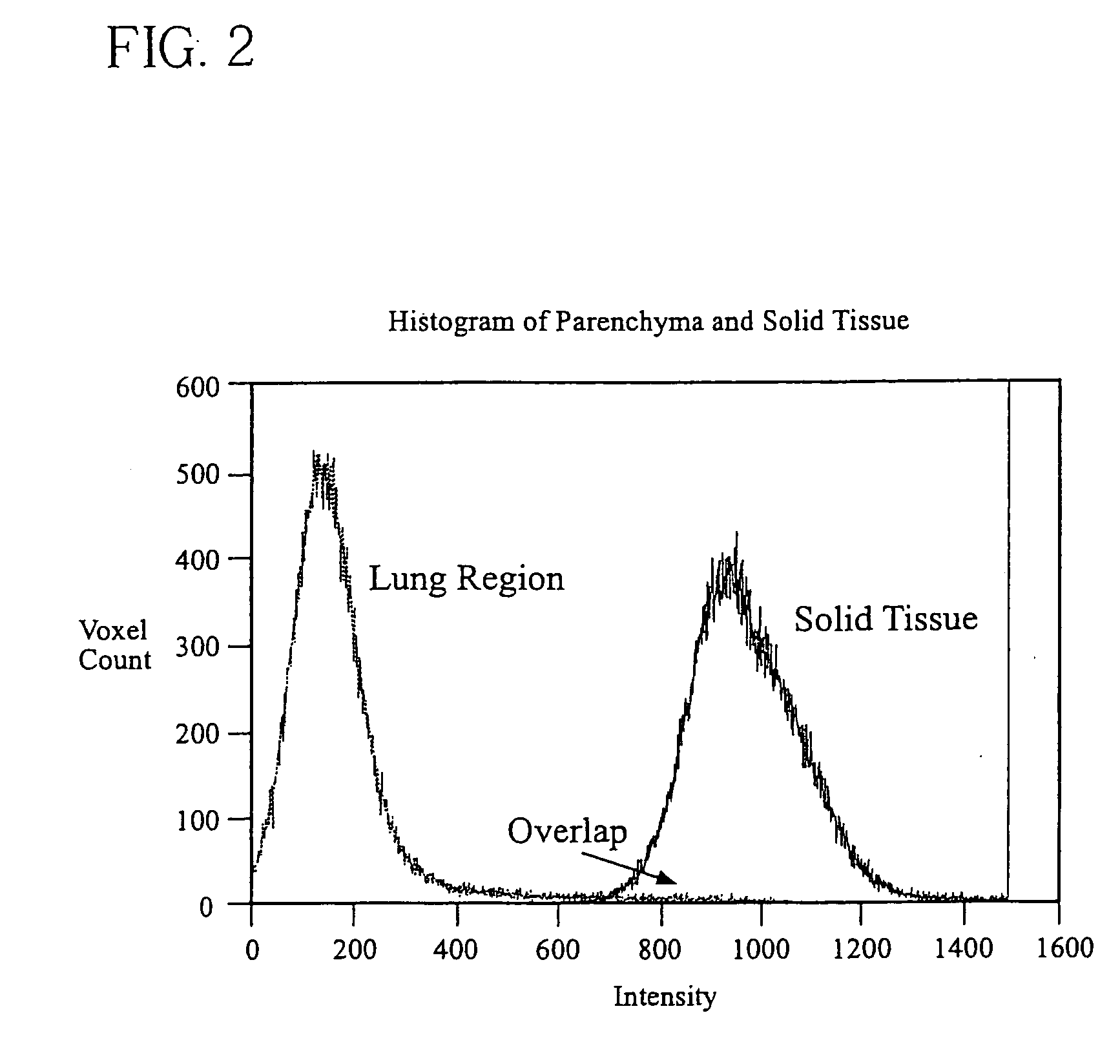
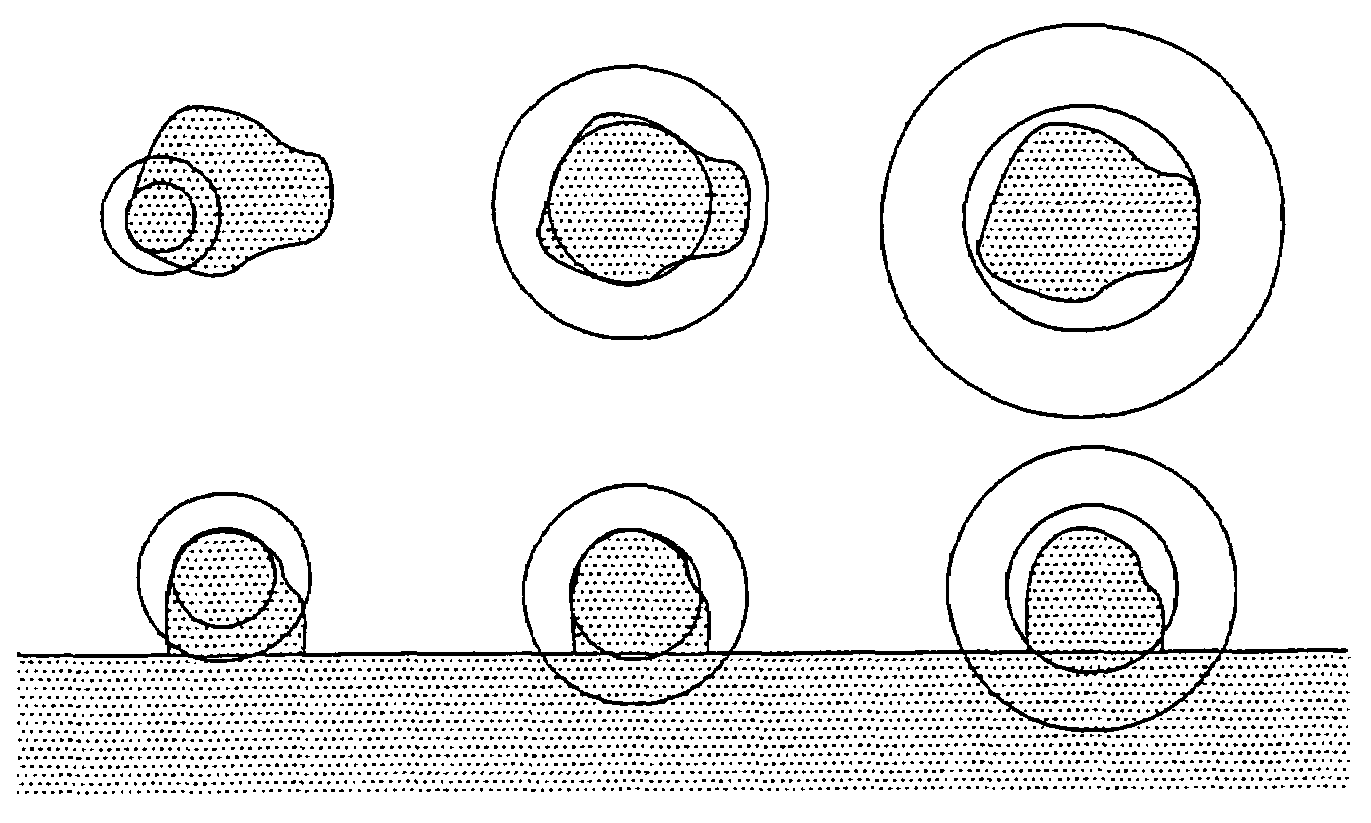
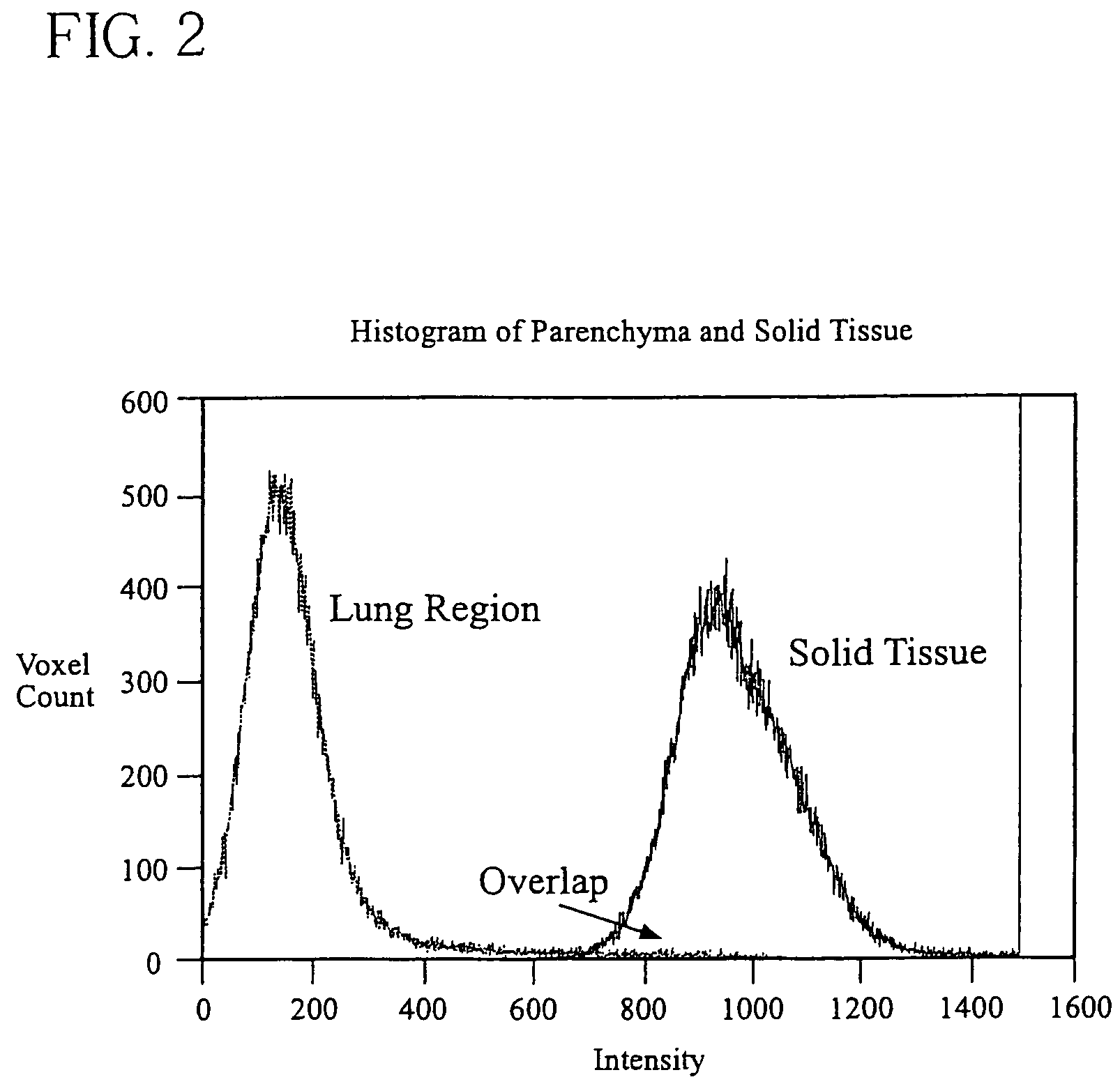
ActiveUS7499578B2Improve consistencyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleVoxel
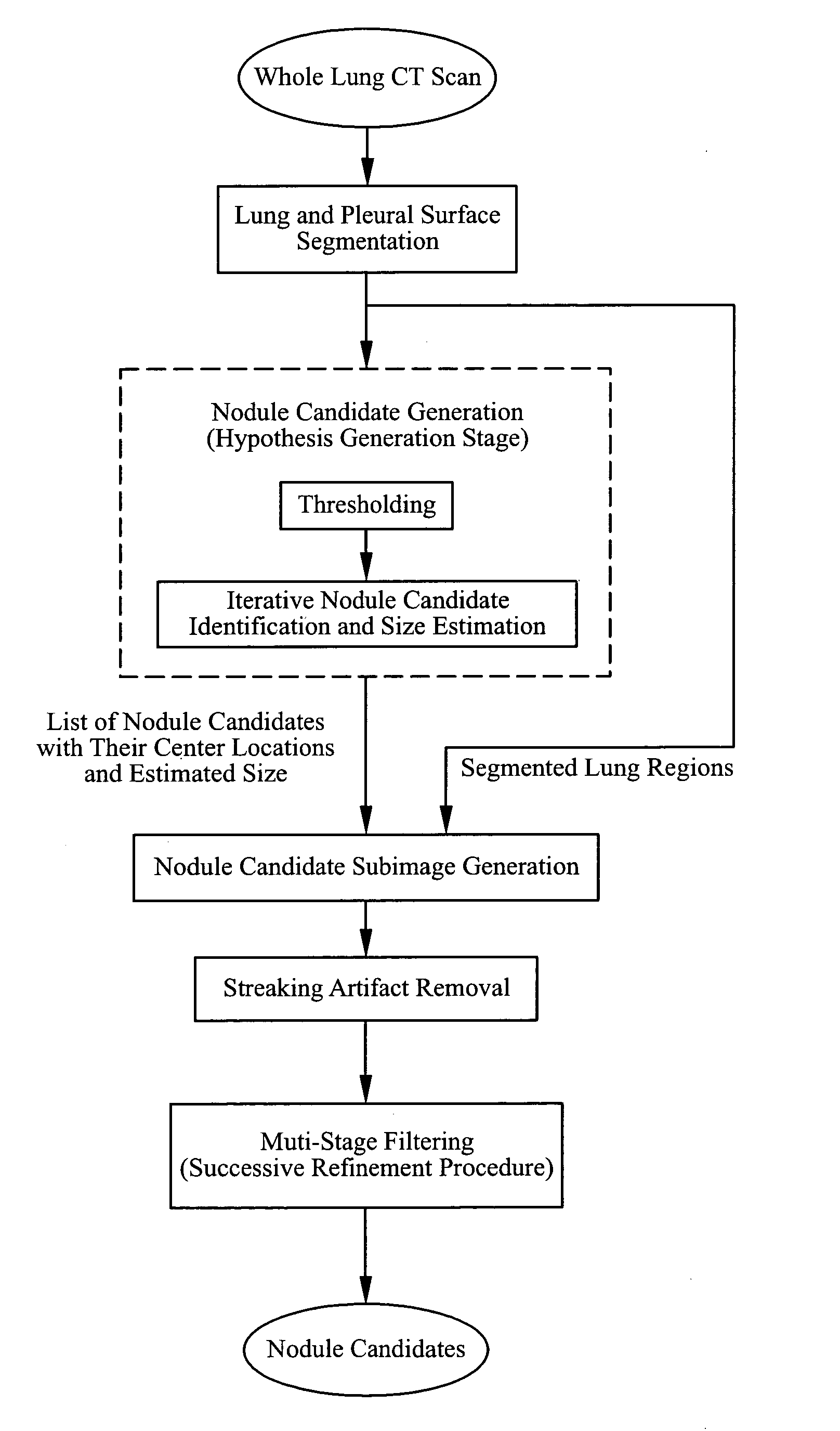
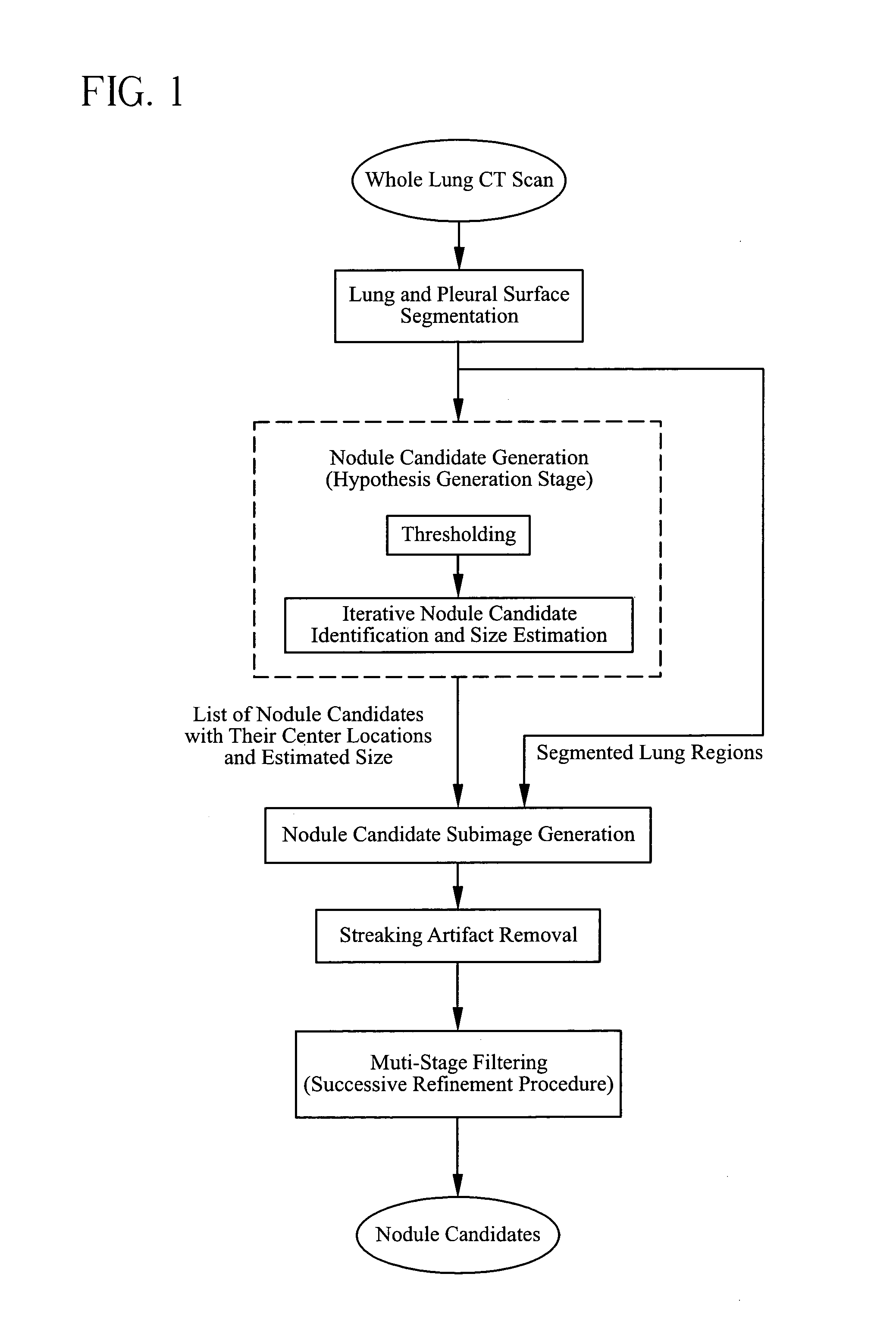
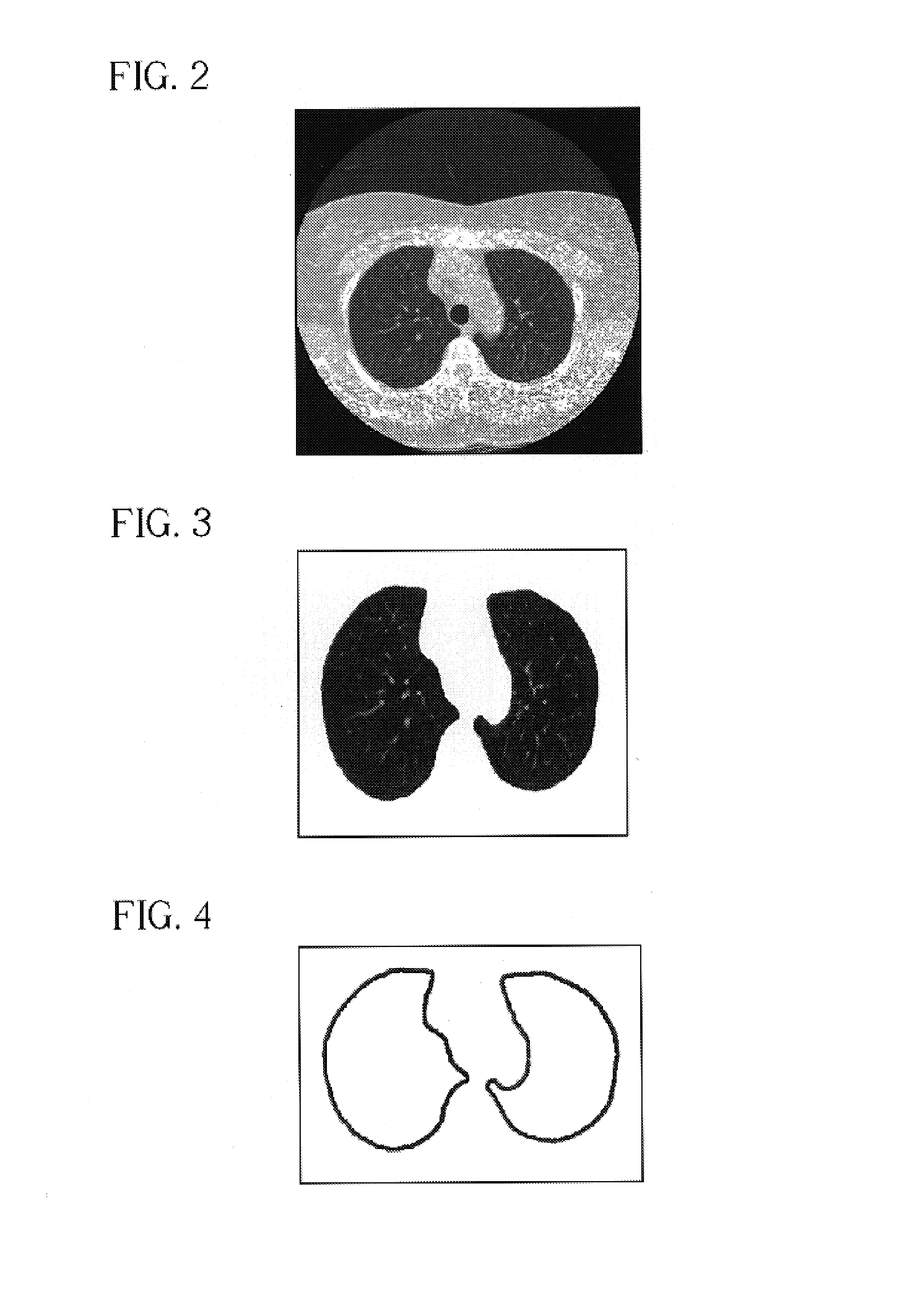
The present invention is a multi-stage detection algorithm using a successive nodule candidate refinement approach. The detection algorithm involves four major steps. First, the lung region is segmented from a whole lung CT scan. This is followed by a hypothesis generation stage in which nodule candidate locations are identified from the lung region. In the third stage, nodule candidate sub-images pass through a streaking artifact removal process. The nodule candidates are then successively refined using a sequence of filters of increasing complexity. A first filter uses attachment area information to remove vessels and large vessel bifurcation points from the nodule candidate list. A second filter removes small bifurcation points. The invention also improves the consistency of nodule segmentations. This invention uses rigid-body registration, histogram-matching, and a rule-based adjustment system to remove missegmented voxels between two segmentations of the same nodule at different times.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
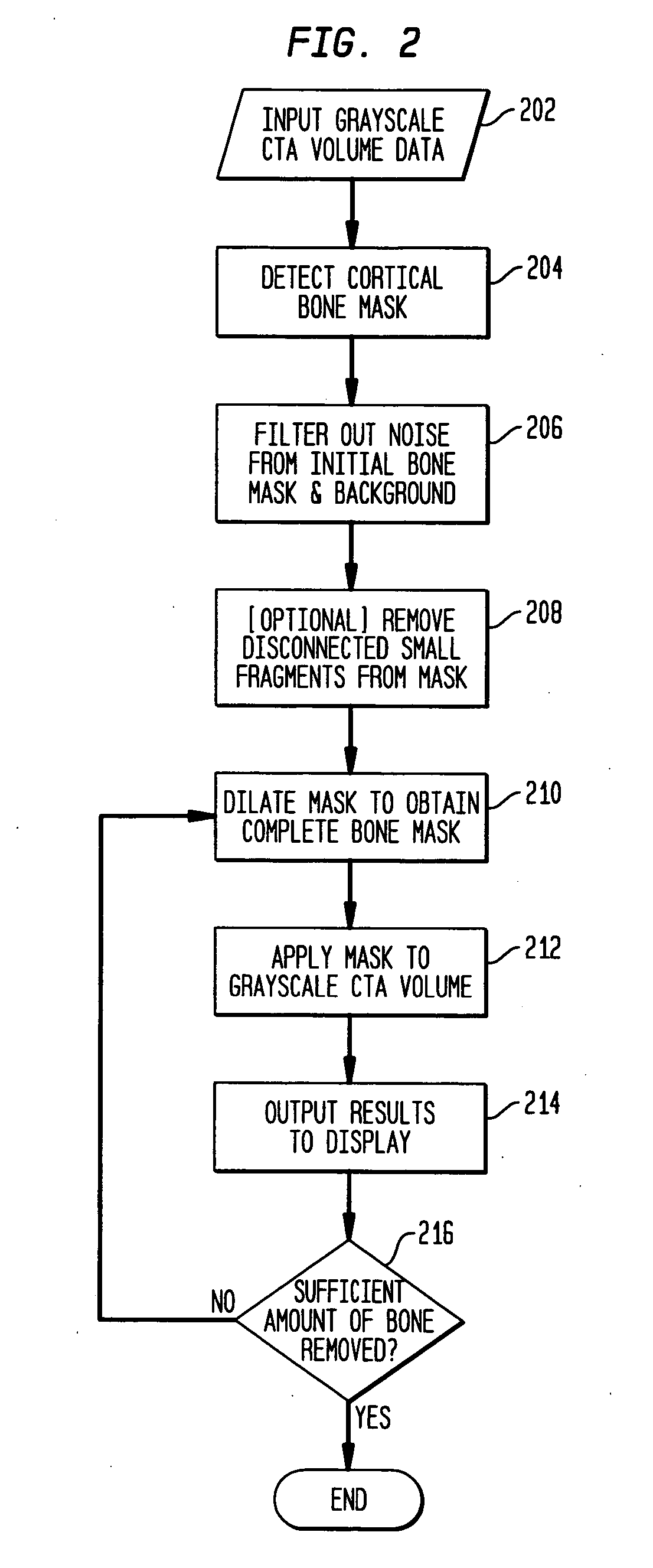
System and method for automatically segmenting bones in computed tomography angiography data
A system and method for automatically segmenting bone regions from Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) volume data is disclosed. A locally operated bone detector distinguishes between bone regions and contrast agent filled vessels. A filtering operator removes small noise from the detected bone regions. A dilator expands the filtered detected bone regions to adjacent trabecular bones. A processor applies the dilated detected bone regions to the CTA volume data. A display shows the applied CTA volume data.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Device and method for detecting blood vessel deformation area
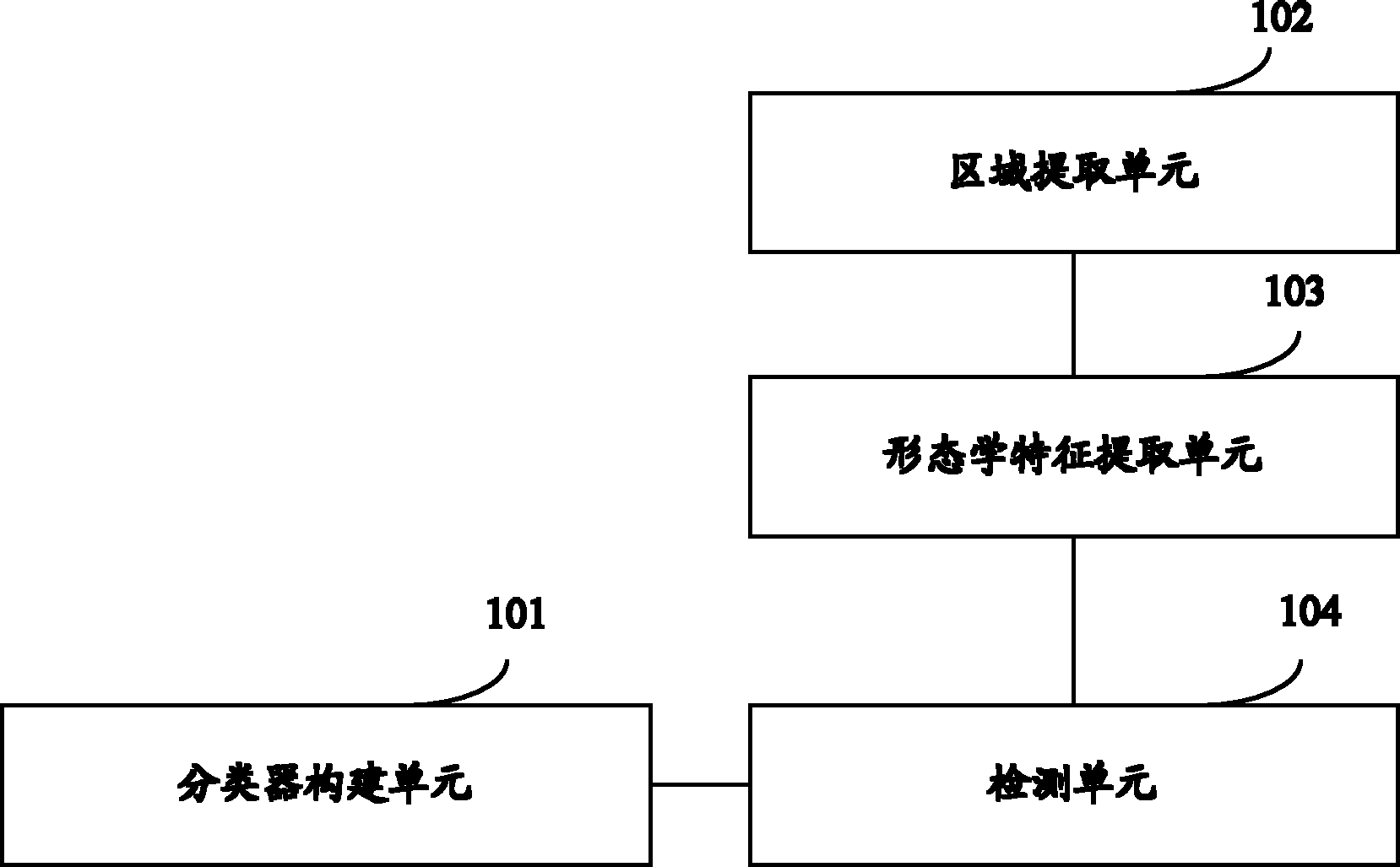
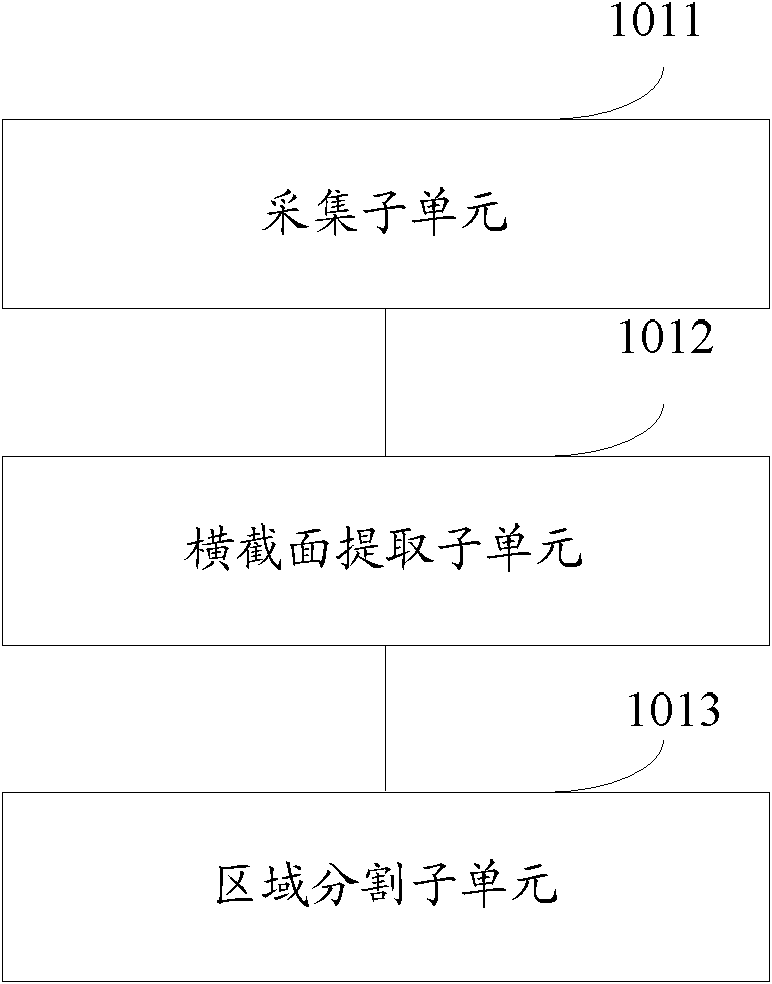
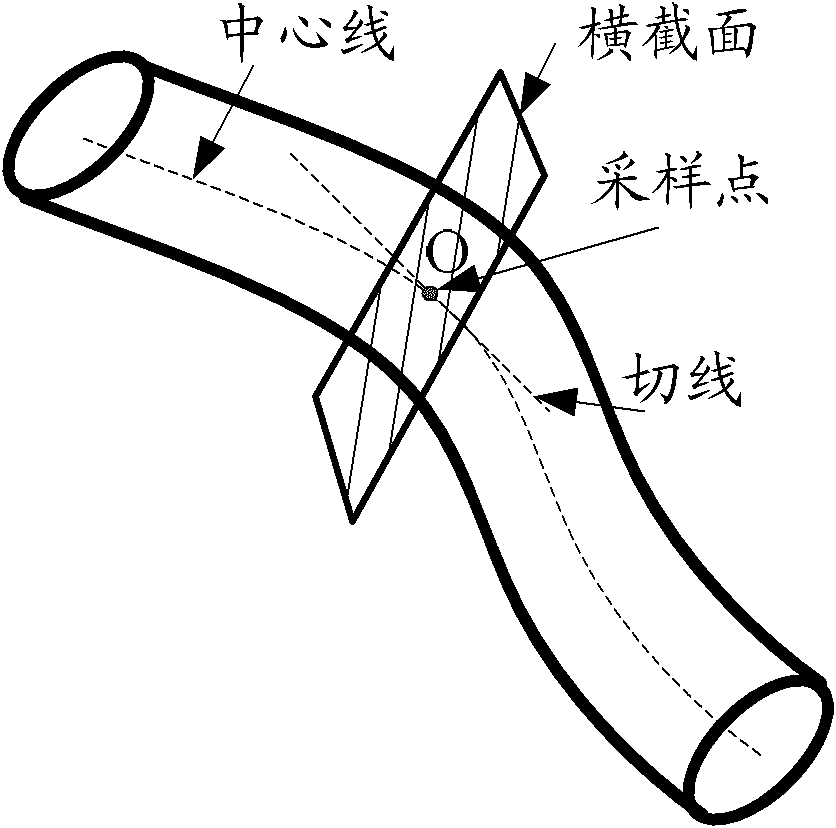
ActiveCN101996329AImprove accuracyIncreased sensitivityCharacter and pattern recognitionCharacteristic spaceComputer vision
The embodiment of the invention discloses a device and a method for detecting a blood vessel deformation area. The device comprises a classifier constructing unit, an area extracting unit, a morphological characteristic extracting unit and a detecting unit, wherein the classifier constructing unit is used for establishing a classifier according to a data classification model by taking morphological characteristics reflecting a border shape and / or an area shape in a blood vessel area as a classification basis; a characteristic space in the classifier is used for marking the presence or absence of deformation of the blood vessel area; the area extracting unit is used for extracting a blood vessel area to be detected from a blood vessel image of a computed tomography angiography (CTA); the morphological characteristic extracting unit is used for extracting morphological characteristics same as the morphological characteristics in the classifier in the blood vessel area to be detected; and the detecting unit is used for identifying the characteristic space corresponding to the extracted morphological characteristics in the classifier, and acquiring a deformation detection result of the blood vessel area to be detected according to the corresponding characteristic space. The device and the method can improve the sensitivity and the accuracy of the detection result.
Owner:SHENYANG NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
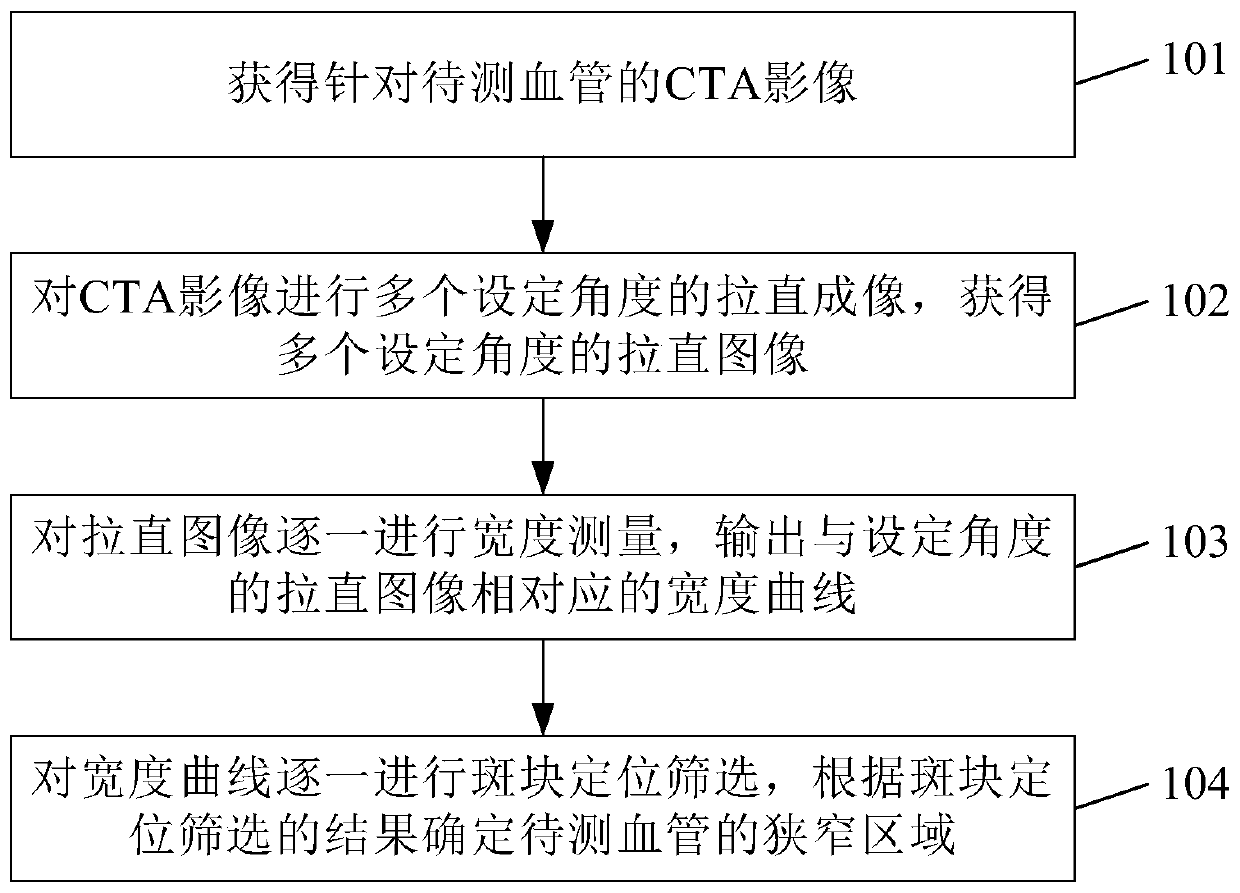
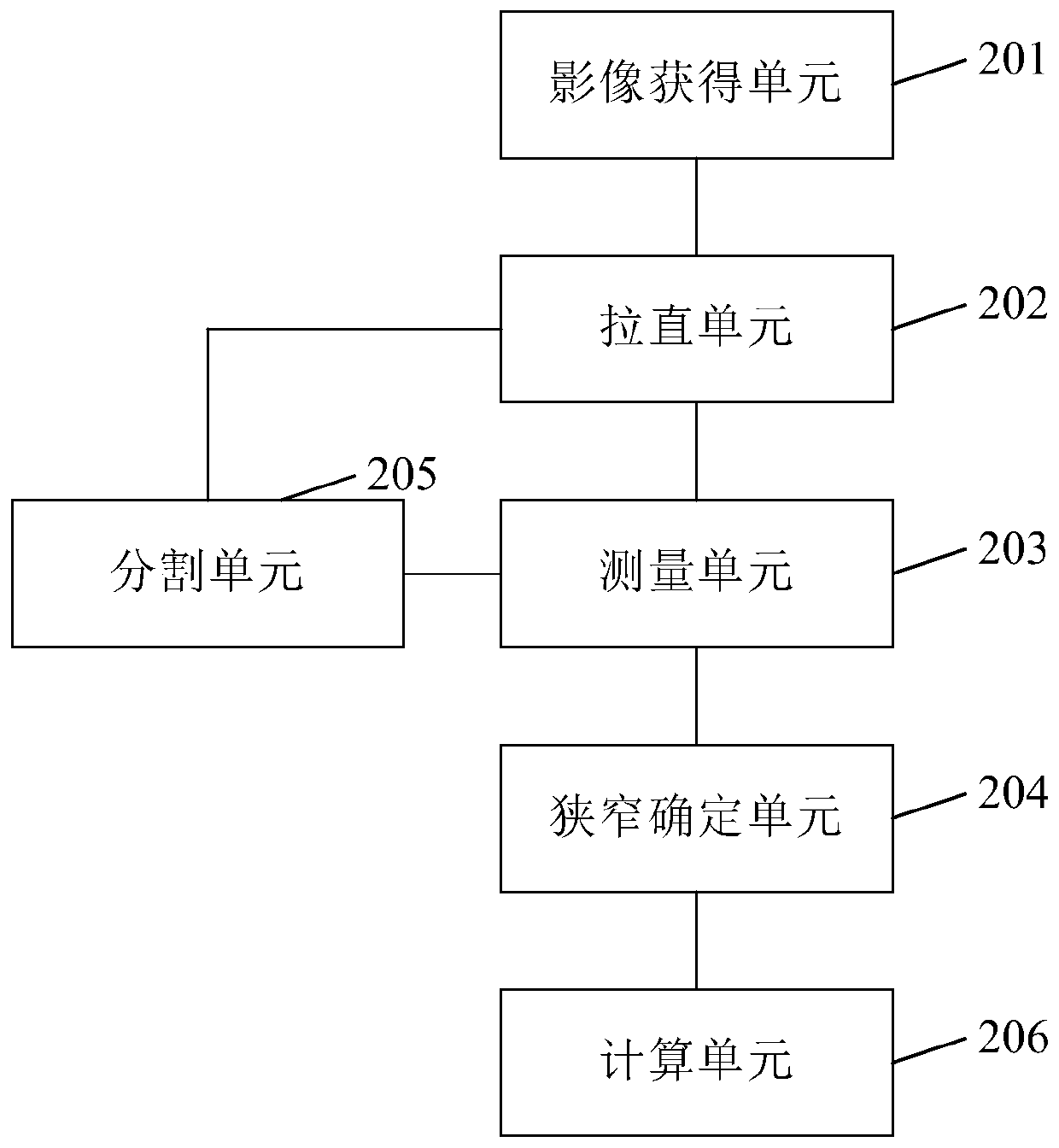
Vascular stenosis detection method and equipment
The invention discloses a vascular stenosis detection method and device. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a computed tomography angiography (CTA) image for a blood vessel to be detected; straightening and imaging the CTA image at a plurality of set angles to obtain a plurality of straightened images at a plurality of set angles; carrying out width measurement on the straightened imagesone by one, and outputting a width curve corresponding to the straightened image with the set angle; and performing plaque positioning screening on the width curve one by one, and determining a narrowarea of the blood vessel to be detected according to a plaque positioning screening result. By implementing the method and the equipment provided by the invention, the accuracy of vascular stenosis detection can be improved.
Owner:数坤(北京)网络科技股份有限公司
Method and System for Machine Learning Based Estimation of Anisotropic Vessel Orientation Tensor
A method and apparatus for machine learning based detection of vessel orientation tensors of a target vessel from a medical image is disclosed. For each of a plurality of voxels in a medical image, such as a computed tomography angiography (CTA), features are extracted from sampling patches oriented to each of a plurality of discrete orientations in the medical image. A classification score is calculated for each of the plurality of discrete orientations at each voxel based on the features extracted from the sampling patches oriented to each of the plurality of discrete orientations using a trained vessel orientation tensor classifier. A vessel orientation tensor at each voxel is calculated based on the classification scores of the plurality of discrete orientations at that voxel.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
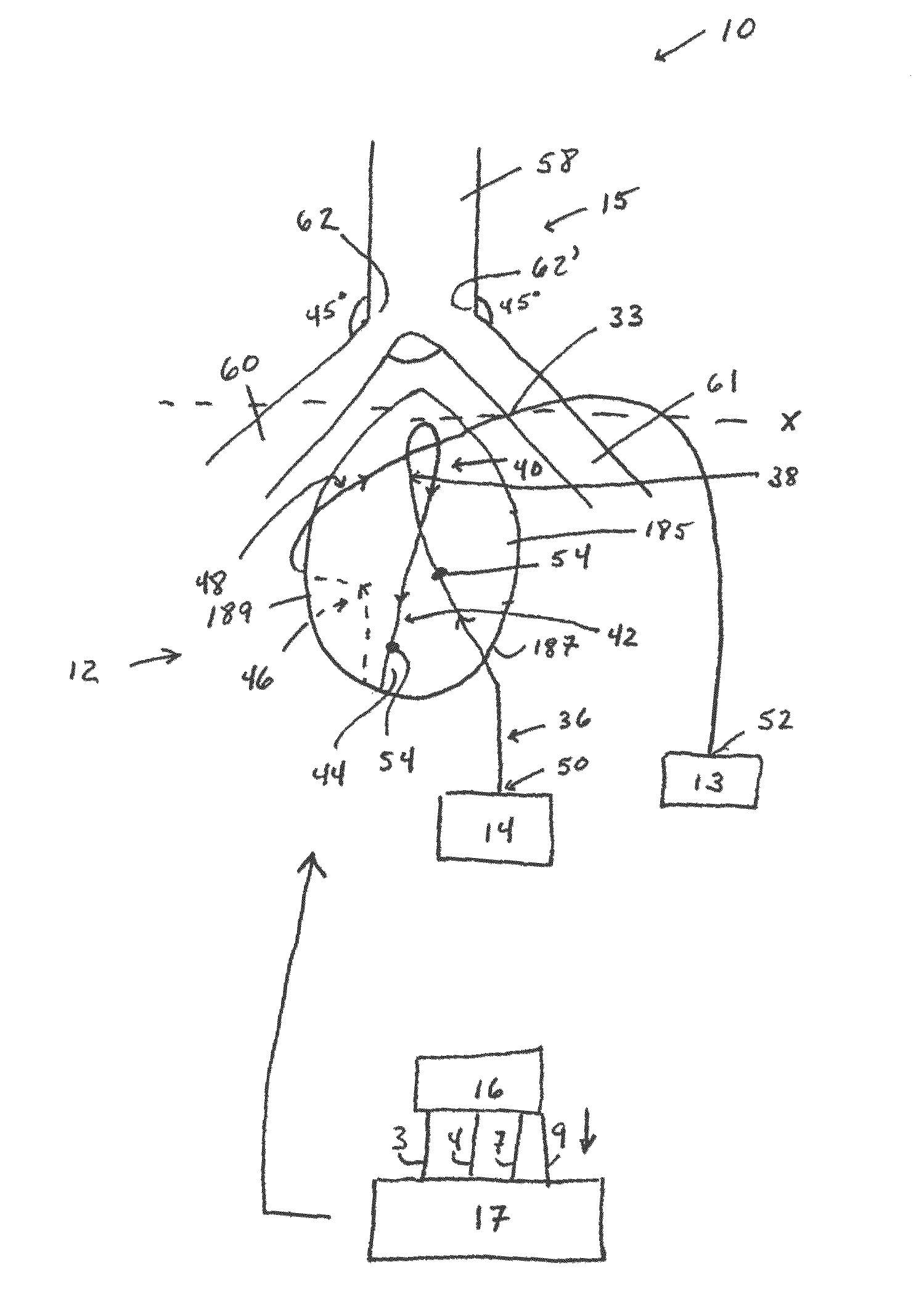
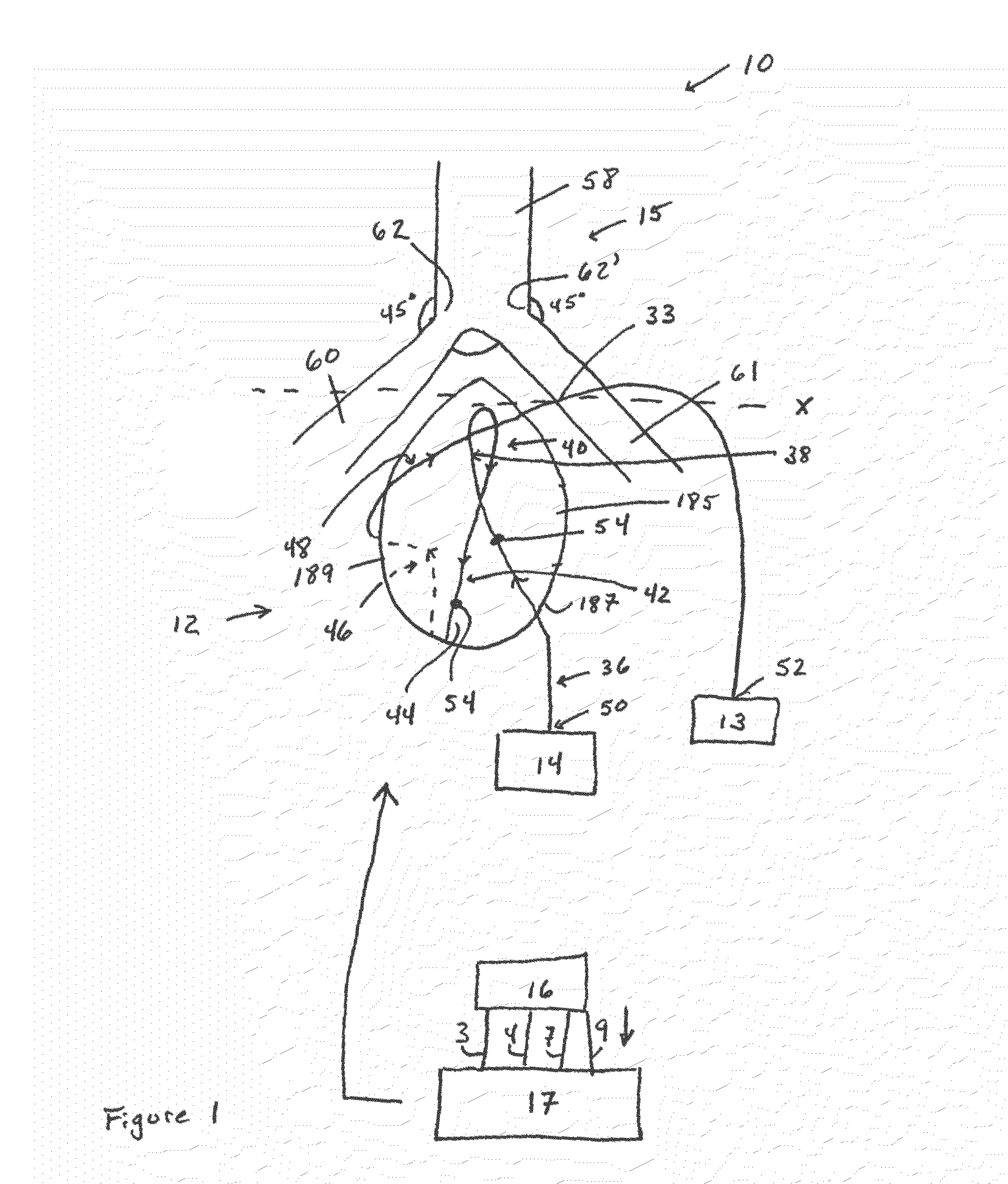
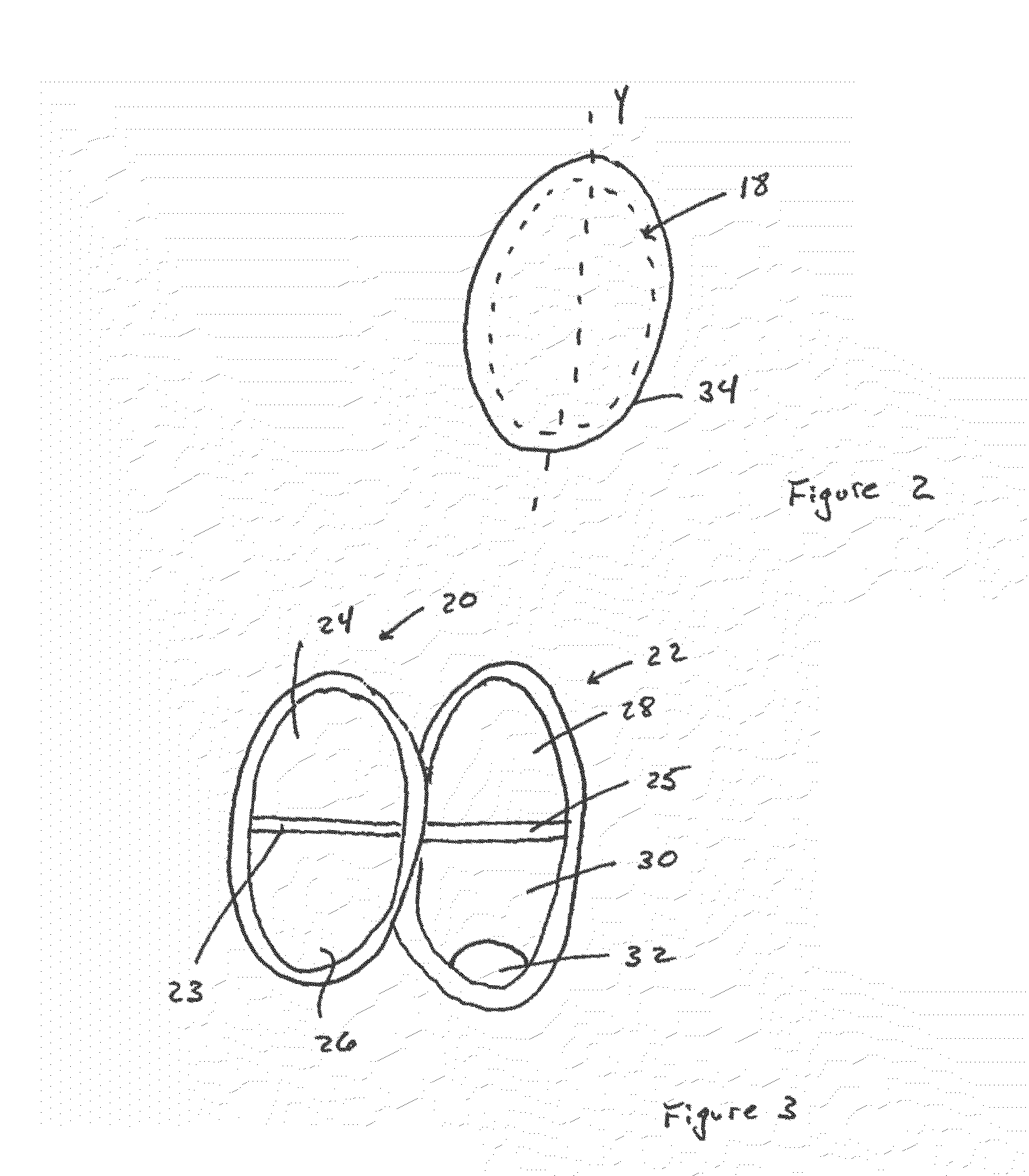
Training system for cardiac computed tomography angiography
InactiveUS8920176B1Improves preparation and practical skillPatient exposureEducational modelsProsthesisComputed tomography scannerBlood vessel
A training system comprising a phantom heart, the phantom heart comprising an exterior surface upon which a tubing is topologically arranged in a manner which mimics the placement of the distal LCx, the LAD, the PDA, and the RCA. The tubing is configured to receive a contrast agent received from a power injector. The training system further comprises an airway subsystem which is modeled to represent the trachea, the right bronchus, and the left bronchus, and which is arranged relative to the phantom heart such that a portion of the airway subsystem which approximates the position of the tracheal carina is aligned with a portion of the phantom heart that represents the ascending aorta. The training system further comprises an EKG pulse generator in electrical communication with a computed tomography scanner for purposes of conducting computed tomography angiography of the phantom heart.
Owner:YANG CLIFFORD K
System, method and apparatus for small pulmonary nodule computer aided diagnosis from computed tomography scans
InactiveUS20080187204A1Narrow down the search spaceImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleFeature extraction
The present invention is directed to diagnostic imaging of small pulmonary nodules. There are two main stages in the evaluation of pulmonary nodules from Computed Tomography (CT) scans: detection, in which the locations of possible nodules are identified, and characterization, in which a nodule is represented by measured features that may be used to evaluate the probability that the nodule is cancer. Currently, the most useful prediction feature is growth rate, which requires the comparison of size estimates from two CT scans recorded at different times. The present invention includes methods for detection and feature extraction for size characterization. The invention focuses the analysis of small pulmonary nodules that are less than 1 centimeter in size, but is also suitable for larger nodules as well.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
System, method and apparatus for small pulmonary nodule computer aided diagnosis from computed tomography scans
InactiveUS7660451B2Narrow down the search spaceImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleFeature extraction
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
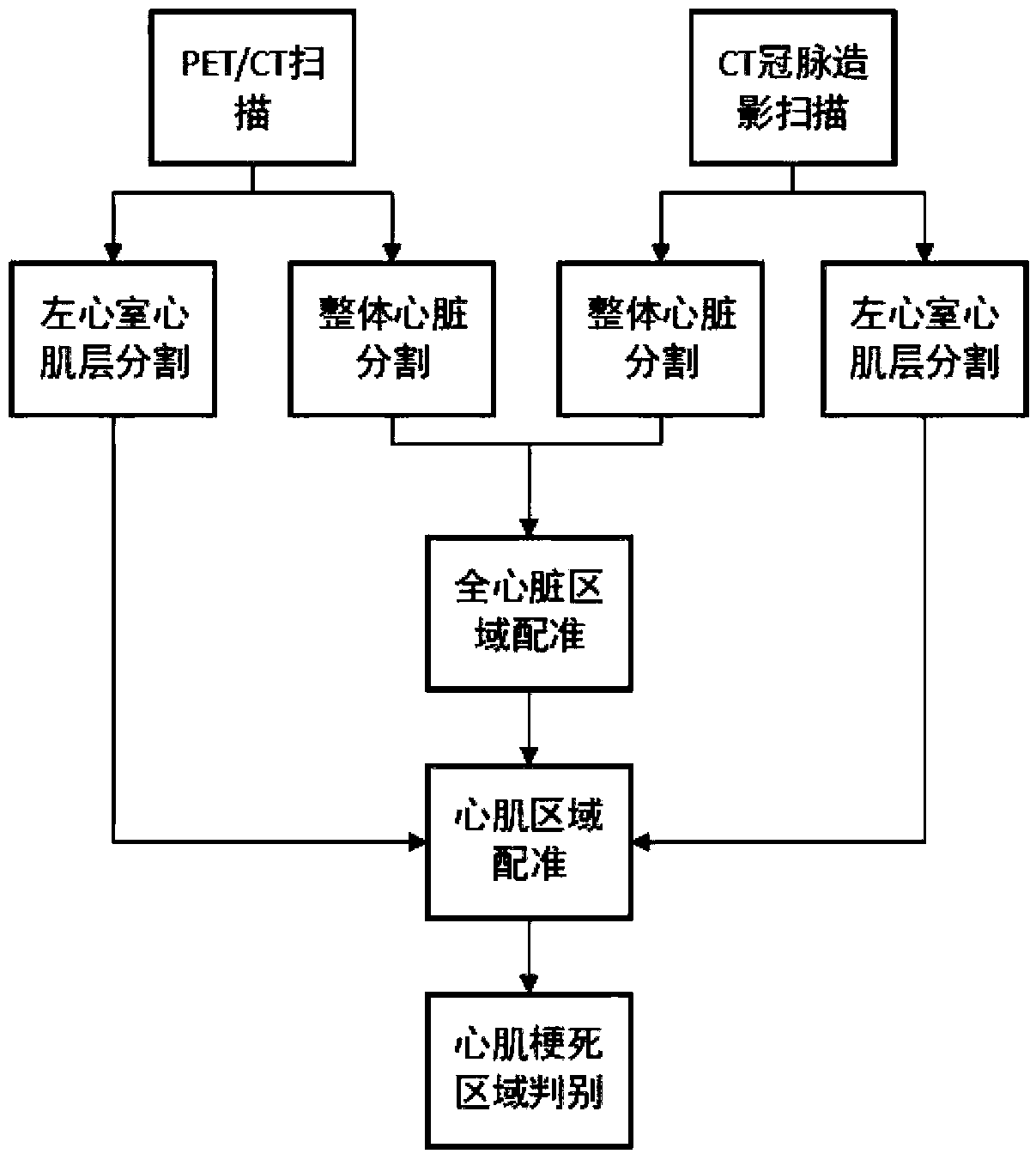
Method for quantitatively evaluating myocardial infarction on basis of nuclide image and CT (computed tomography) coronary angiography fusion
InactiveCN109498046AAvoid interferenceImprove registration efficiencyComputerised tomographsTomographyLeft ventricular sizeCompanion animal
The invention belongs to the field of medical image processing, and discloses a method and a system for quantitatively evaluating myocardial infarction on the basis of nuclide image and CT (computed tomography) coronary angiography fusion. The method includes acquiring heart PET (positron emission tomography) / CT and CTA (computed tomography angiography) data; carrying out three-dimensional DCT (discrete cosine transformation) frequency-domain interpolation on PET / CT images; acquiring heart regions in the PET / CT images and CTA images by the aid of multi-spectrum segmentation processes; acquiring left ventricular cardiac muscle regions in PET images by the aid of threshold processes; manually segmenting left ventricular cardiac muscle regions in the CTA images layer by layer; registering images; classifying pixel points according to the locations of pixel points on the registered images and tracer uptake values; inversely transforming infarction regions into original CTA spaces and dividing the volumes of left ventricular cardiac muscles from the volumes of the transformed infarction regions; three-dimensionally displaying fused images in volume rendering manners. The method and thesystem have the advantages that integral registration procedures can be fully automated, the method and the system are good in objectivity, intuitive results can be obtained, and analysis can be facilitated for clinical doctors.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
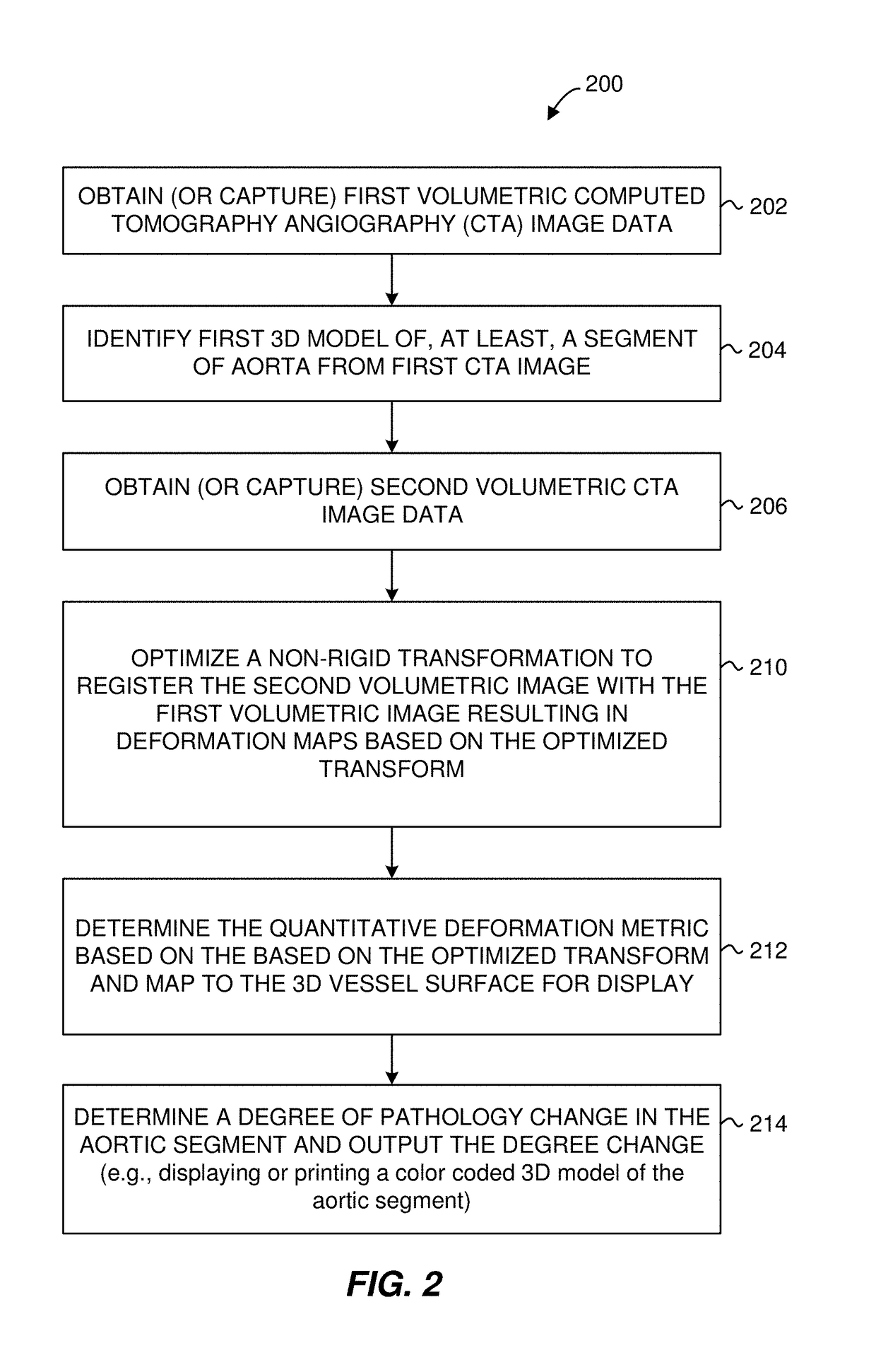
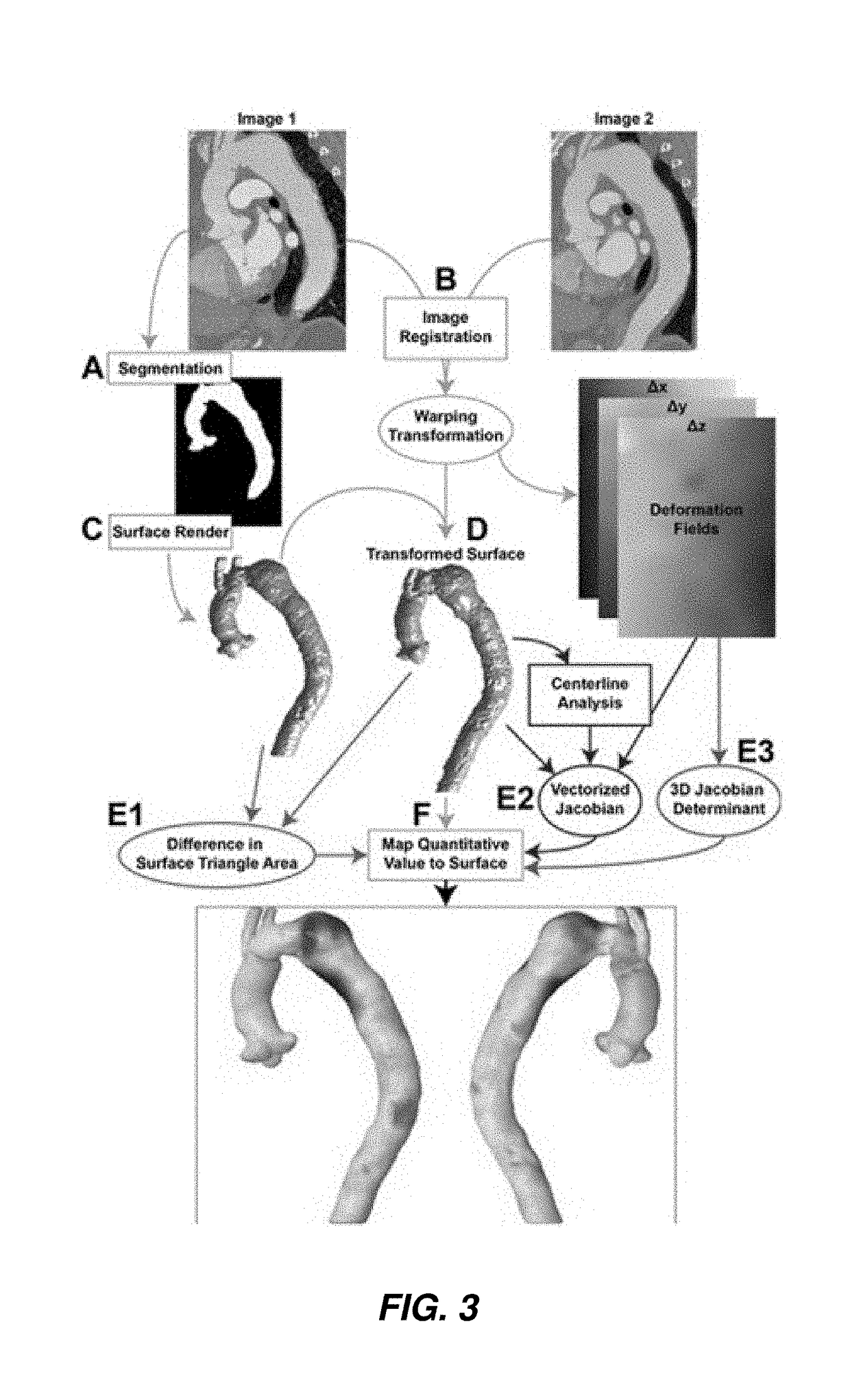
Techniques of deformation analysis for quantification of vascular enlargement
Thoracic aortic aneurysm is a common and lethal disease that requires regular imaging surveillance to determine timing of surgical repair and prevent major complications such as rupture. Current cross-sectional imaging surveillance techniques, largely based on computed tomography angiography (CTA) or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), are focused on measurement of maximal aortic diameter, although this approach is limited to fixed anatomic positions and is prone to significant measurement error. The present techniques demonstrate novel approaches (generally termed herein “Vascular Deformation Mapping (VDM)”) for assessing changes in aortic dimensions. The present techniques quantify three-dimensional changes in the anatomic dimensions of a vessel through a process that involves non-rigid co-registration of serial imaging data and quantification of vascular deformation on a 3D surface model using some derivation of the spatial deformations resulting from the optimized spatial transform.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
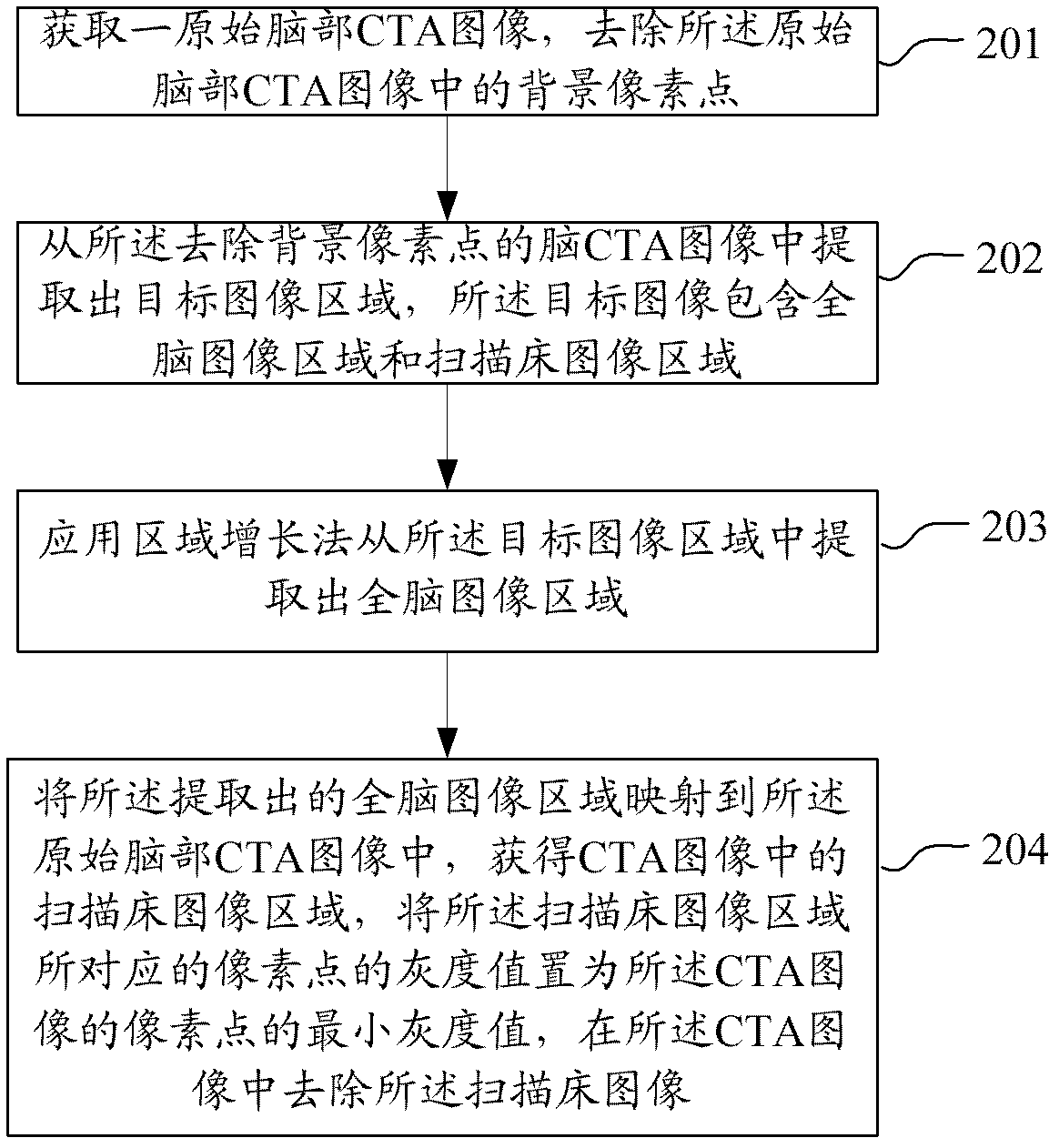
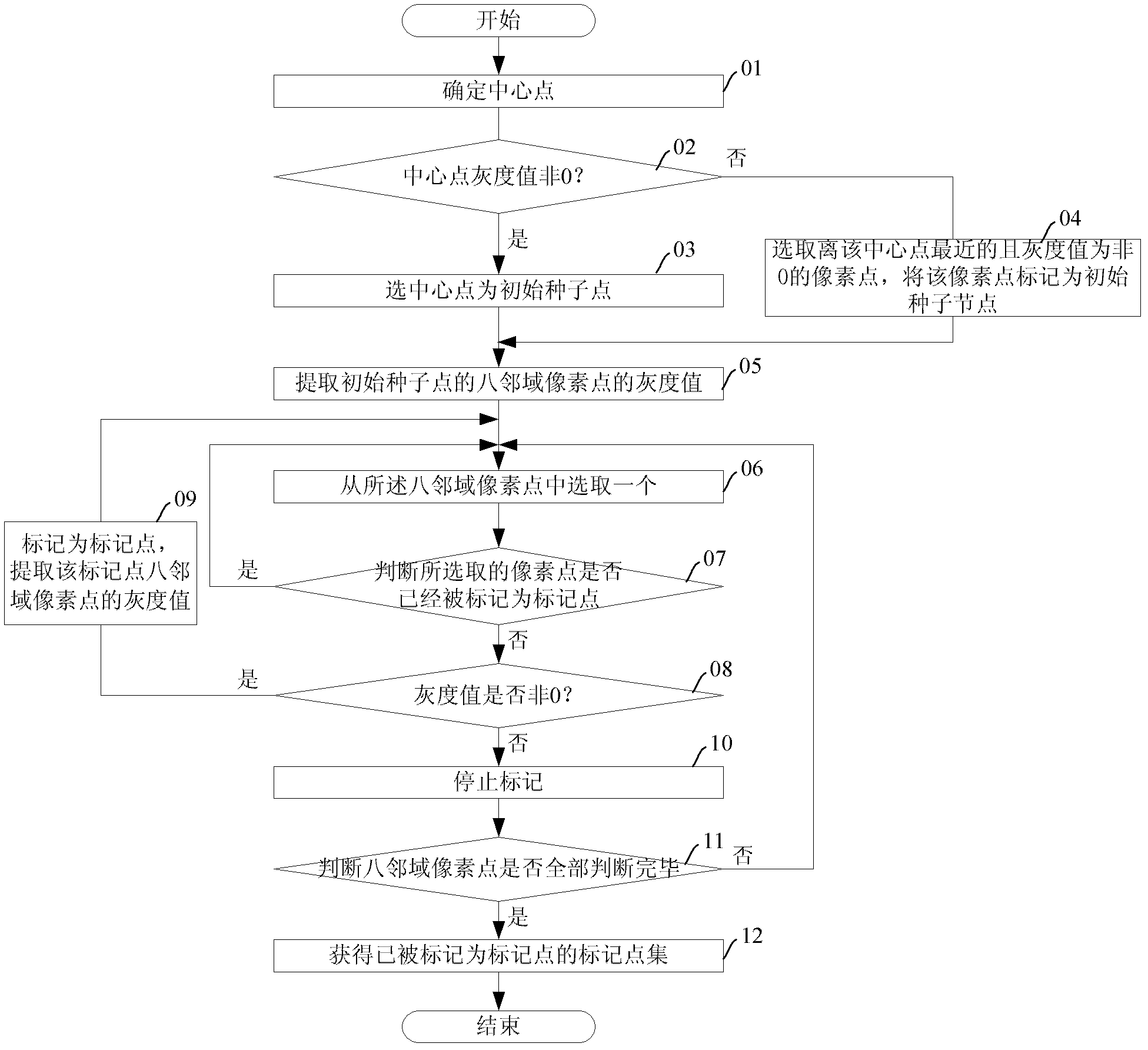
Method and device for removing scanning table from CTA (Computed Tomography Angiography) image
InactiveCN102324090AAvoid problems with partial bed imagesAccurate observationImage enhancementForeign matterBlood vessel
The application discloses a method and device for removing a scanning table from a CTA (Computed Tomography Angiography) image. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a brain CTA image, and removing background pixel points in the CTA image; extracting a whole-brain image from the brain CTA image with the background pixel points being removed; finding a pixel point corresponding to a scanning table image from the whole-brain image by using a region growing algorithm, setting the gray value of the pixel point corresponding to the scanning table image to be zero, and removing the scanning table image. By using the method and device for removing the scanning table from the CTA image, the scanning table image can be completely removed, therefore, the problem that partial scanning table image is still remained after the CTA image is subjected to subtraction operation is avoided, in addition, the problem of a table image with high brightness in a three-dimensional visualized reconstruction result is avoided, clear and foreign-matter-free brain image data is provided for three-dimensional reconstruction of brain vessels, and more accuracy and efficiency in observing the vessels is realized. In addition, the arithmetic speed is high and the time is short.
Owner:NEUSOFT CORP
Method for extracting cardiovascular vessels from CTA images, device, apparatus and storage medium
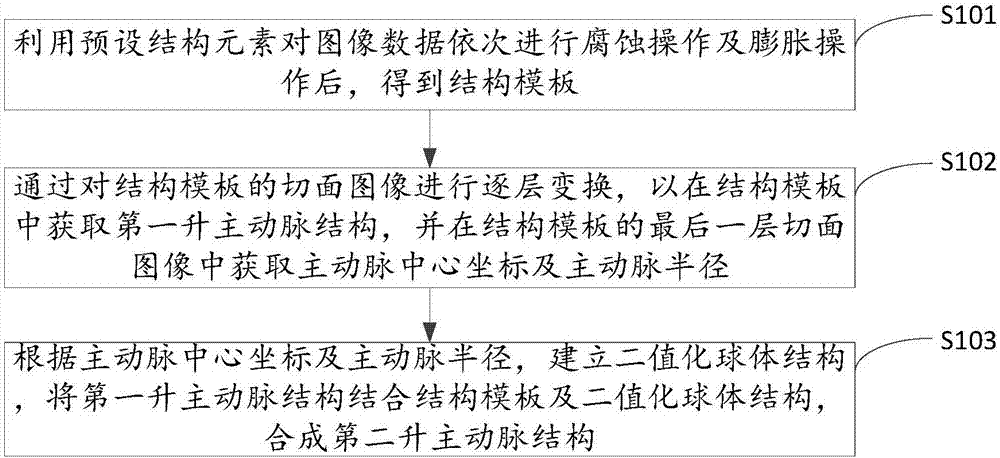
ActiveCN107451995AAccurate visualization of structuresAccurate Visualization of MorphologyImage enhancementImage analysisAortic sinusImaging data
The invention belongs to the medical image processing technical field and provides a method for extracting cardiovascular vessels from CTA (computed tomography angiography) images, a device for extracting cardiovascular vessels from CTA images, an apparatus for extracting cardiovascular vessels from CTA images and a storage medium. The method includes the following steps that: etching operation and expansion operation are sequentially performed on image data by using preset structural elements, so that a structural template is obtained; layer-by-layer transformation is performed on the sectional images of the structural template, so that a first ascending aorta structure in the structural template can be obtained, aorta center coordinates and an aorta radius are obtained from the last sectional image layer of the structural template; and a binary sphere structure is built according to the aorta center coordinates and the aorta radius, and the first ascending aorta structure is combined with the structural template and the binary sphere structure, so that a second ascending aorta structure can be obtained through combination. With the method, device, apparatus and storage medium of the invention adopted, ascending aortas and the shapes of aortic sinuses at the roots of the ascending aortas can be extracted, and therefore, the structures and shapes of the aortas can be accurately visualized, and the solving level and capability of medical image research on clinical problems can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
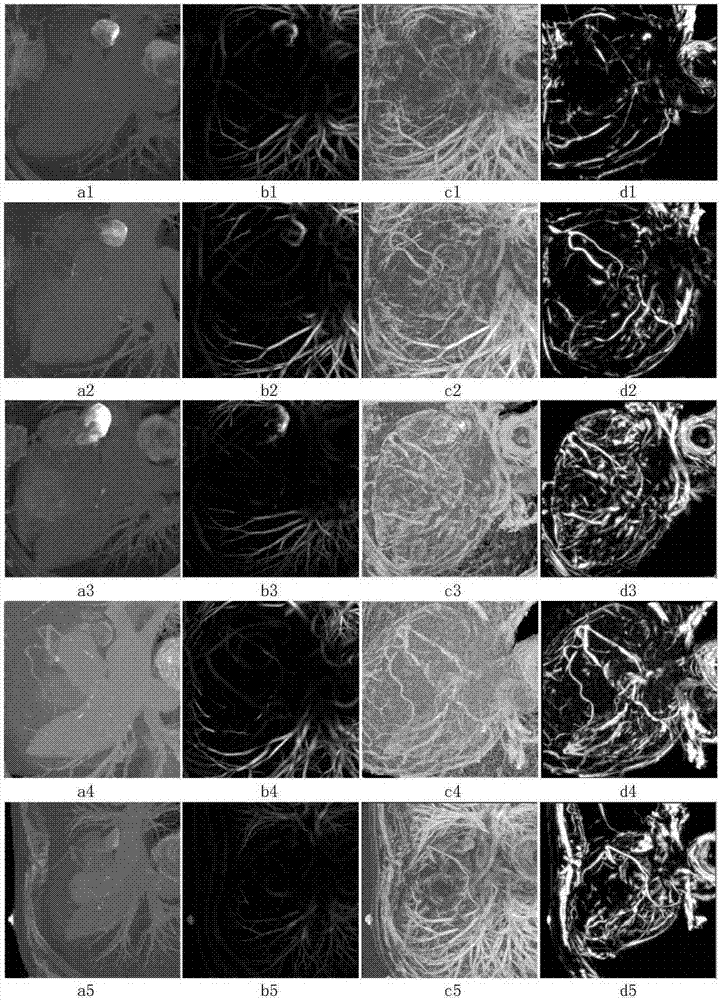
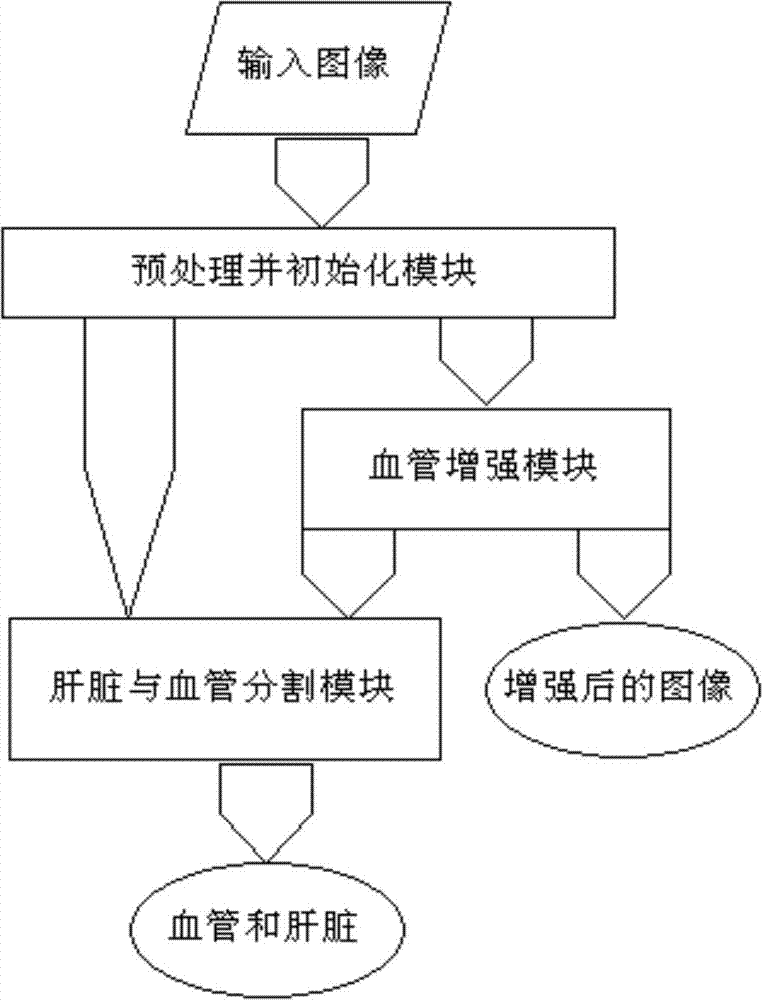
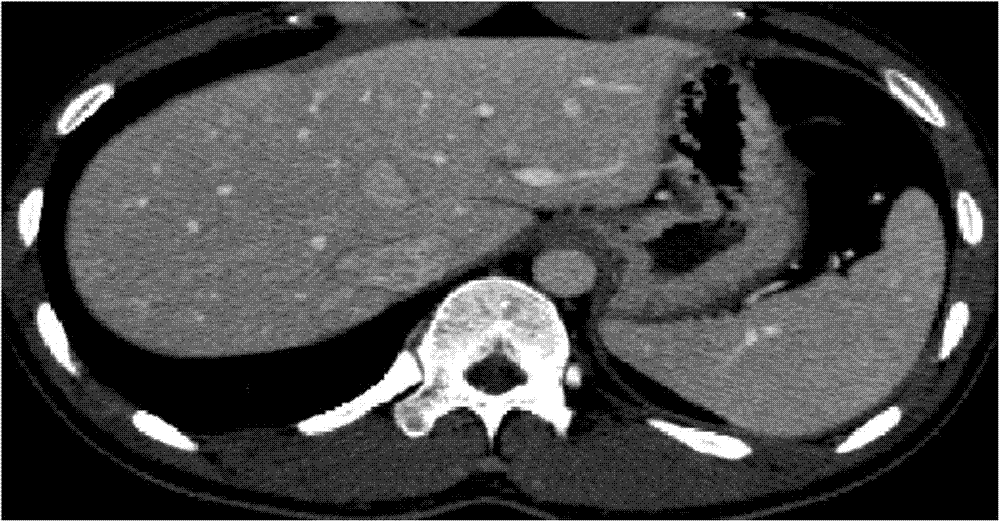
Method for simultaneously segmenting liver and blood vessel in CTA (computed tomography angiography) image
ActiveCN103700068AEasy to distinguishPrevent oversegmentationImage enhancementComputerised tomographsImaging processingGray level
The invention relates to medical image processing, and aims to provide a method for simultaneously segmenting liver and a blood vessel in a CTA (computed tomography angiography) image. The method comprises the following steps of (1) performing model initialization; (2) optimizing a new variational energy model, and simultaneously segmenting the liver and the blood vessel; (3) performing post-processing to obtain a liver contour and a blood vessel contour respectively. According to the method for simultaneously segmenting the liver and the blood vessel, the adverse impact of weak boundaries, noise and the like can be effectively overcome; particularly, due to the introduction of gray level distribution information of local neighborhoods, the liver can be well distinguished from adjacent organs or soft tissues, and the phenomenon of over-segmentation can be effectively prevented.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DE IMAGE SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Rapid algebraic reconstruction technique applied to computed tomography imaging
InactiveCN105590332AReduce storageShorten convergence timeReconstruction from projectionImage generationComputed tomographyAlgorithm convergence
The invention provides a rapid algebraic reconstruction technique (ART) applied to computed tomography (CT) imaging, belonging to the technical field of biomedical imaging, nondestructive test, etc. Based on traditional ART, the rapid ART of the invention randomly selects partial hyperplane, and performs further acceleration adjustment operation on the projection solution vector obtained through the traditional ART on the partial hyperplane, thereby allowing the solution vector after adjustment and update to be optimal on the connection line between an original solution vector and the hyperplane solution vector of last iteration. According to the rapid ART, a different hyperplane projection sequence can be employed for each iteration. A random projection sequence of each iteration allows higher efficiency under various conditions. Compared with the traditional ART, the rapid ART substantially increases an algorithm convergence speed, and can be applied to rapid CT image reconstruction under incomplete projection conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
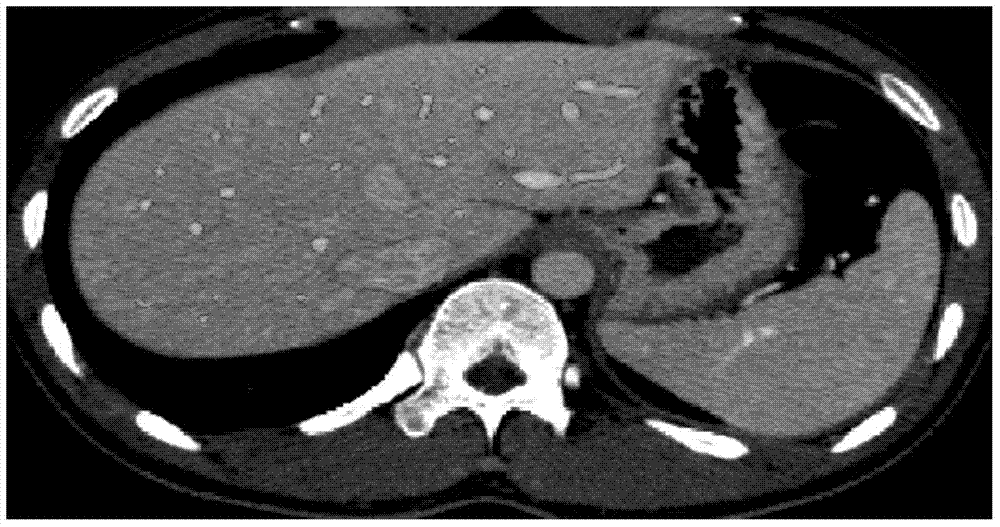
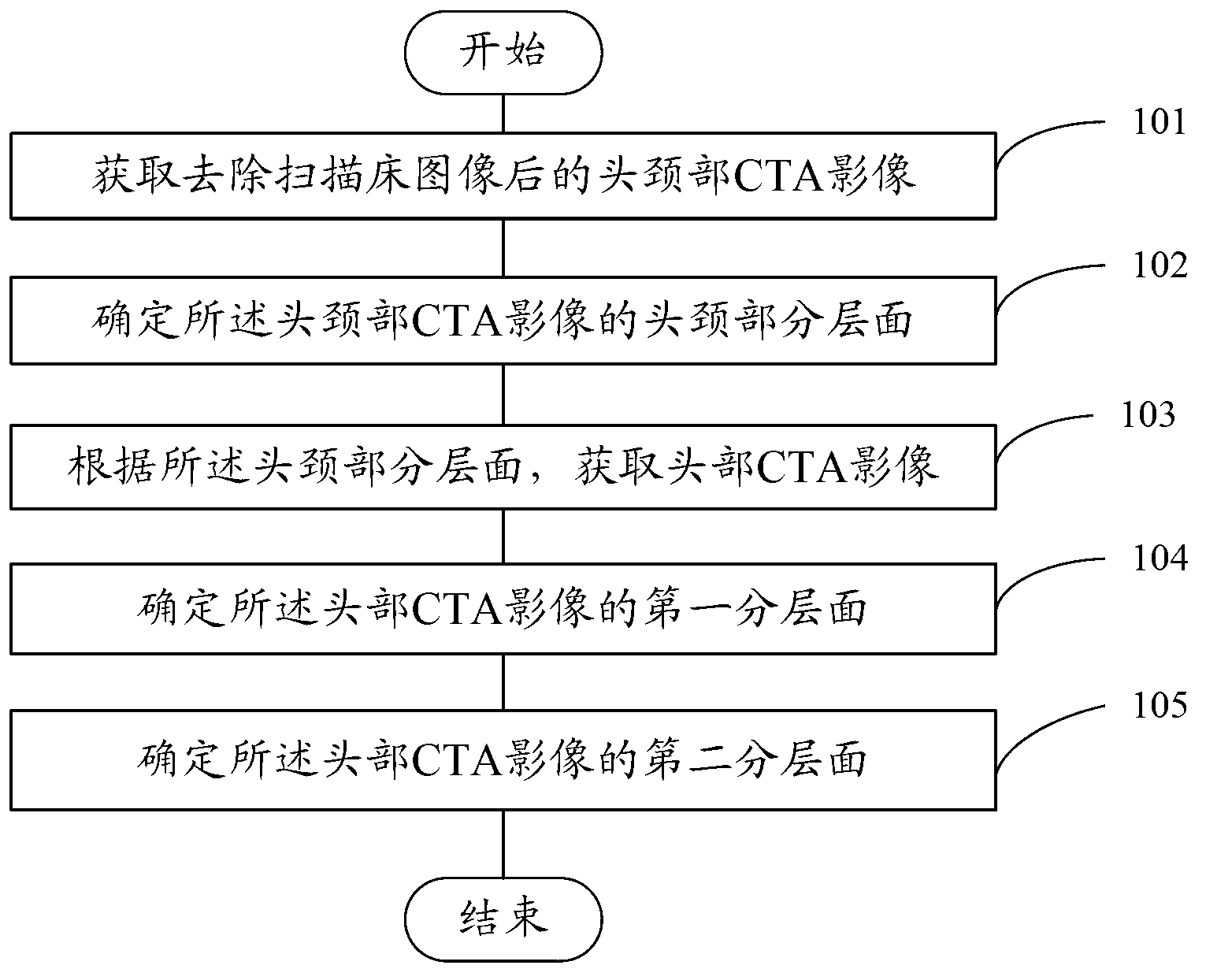
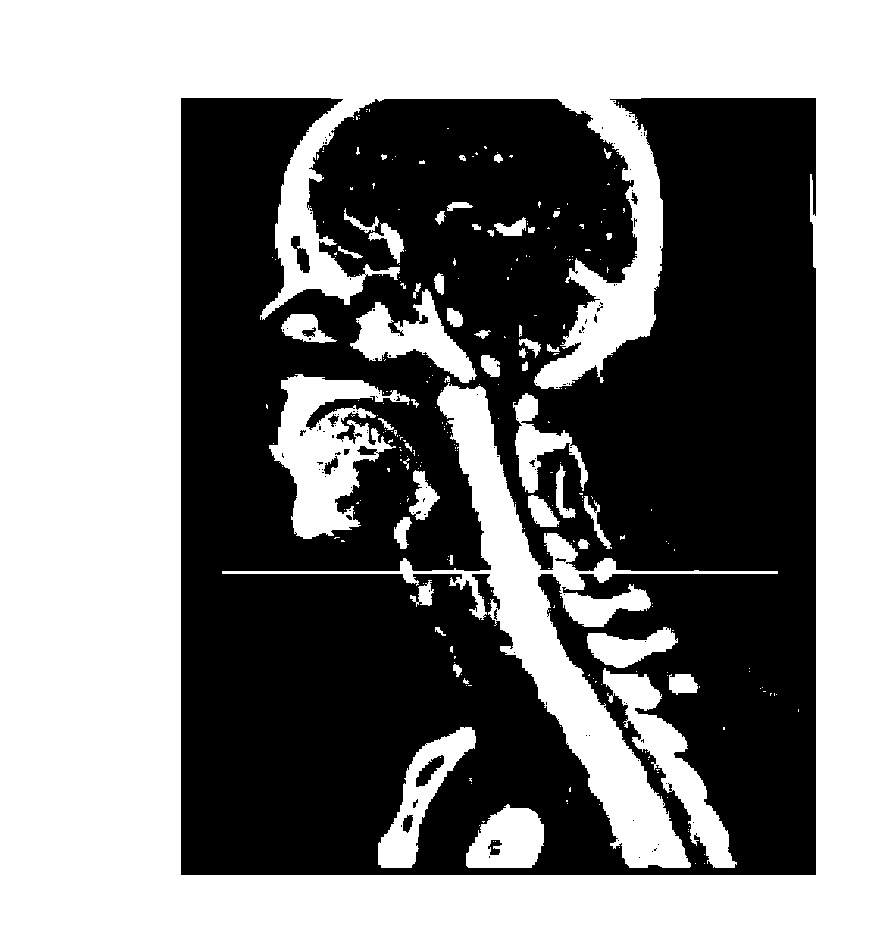
Head and neck CTA (computed tomography angiography) image layering method and device
ActiveCN103020968AImprove separation efficiencyImage analysisComputerised tomographsComputing tomographyHead and neck
An embodiment of the invention discloses head and neck CTA (computed tomography angiography) image layering method and device. The method includes: acquiring a head and neck CTA image with a scanning table image removed; determining a head and neck partition of the head and neck CTA image; acquiring a head CTA image according to the head and neck partition; determining a first partition of the head CTA image, and determining a second partition of the head CTA image. Before vessel separation, the head and neck CTA image are layered in advance according to the structural features of head and neck, and accordingly efficiency of separating vessels in the head and neck CTA image is improved.
Owner:NEUSOFT CORP
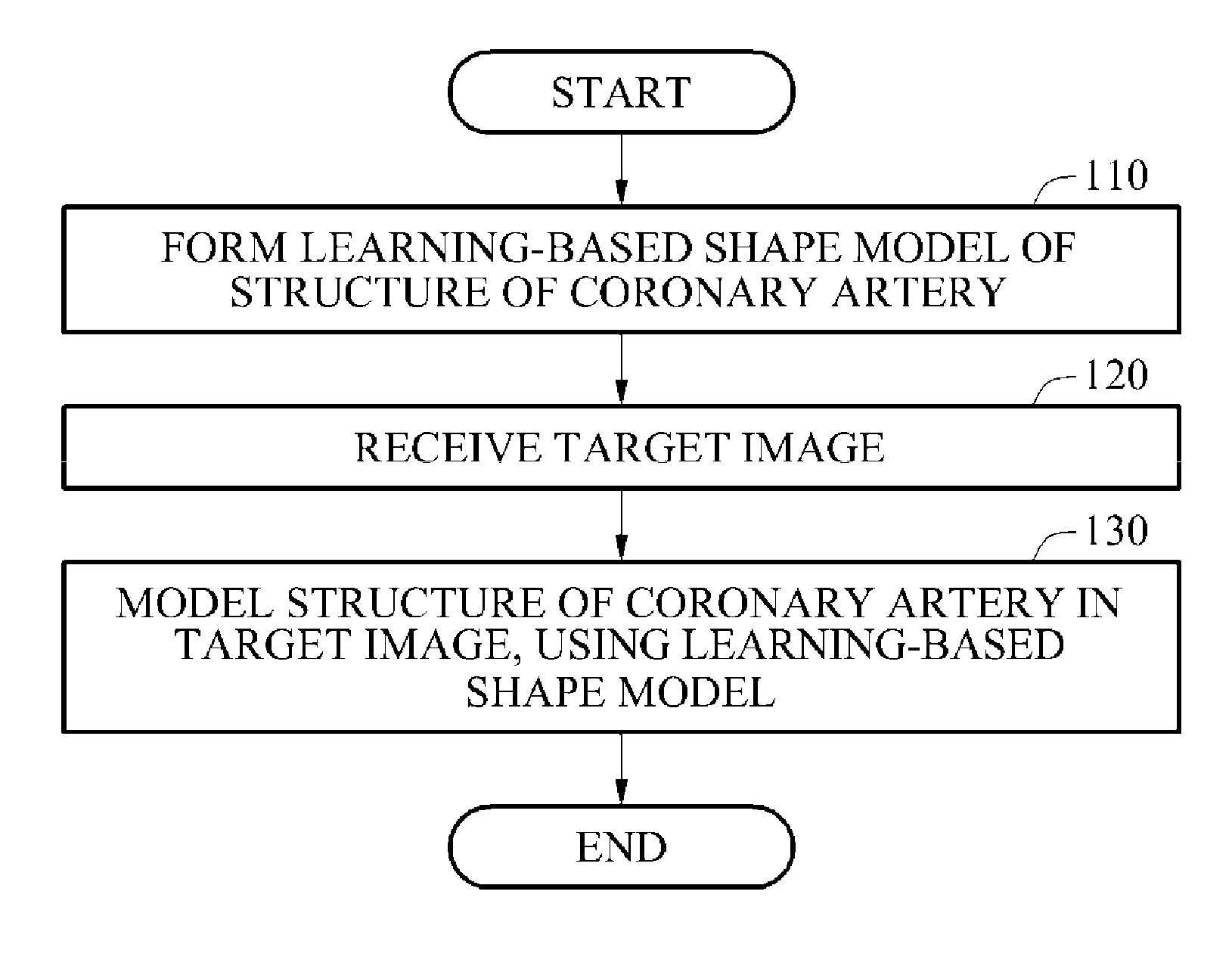
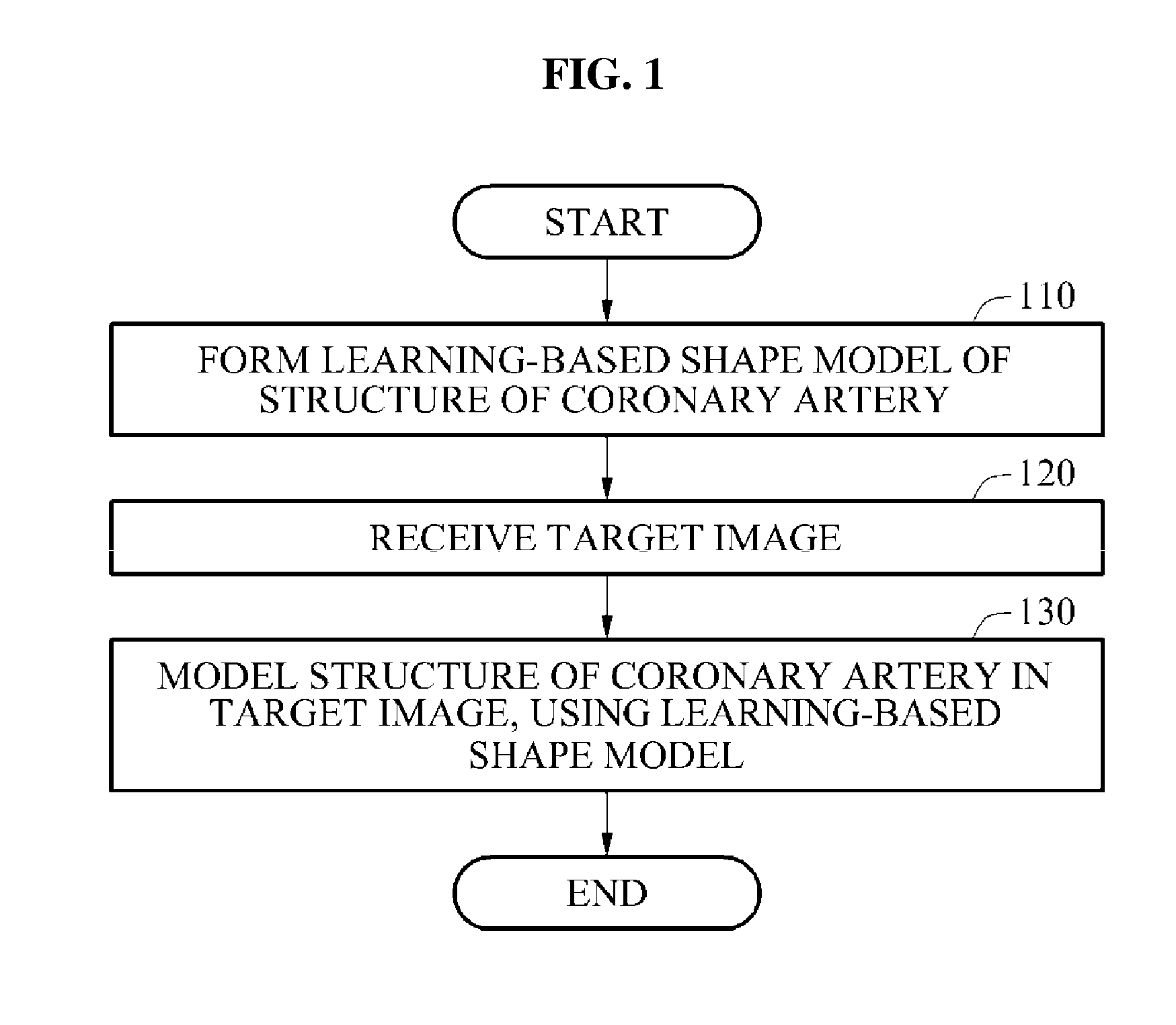
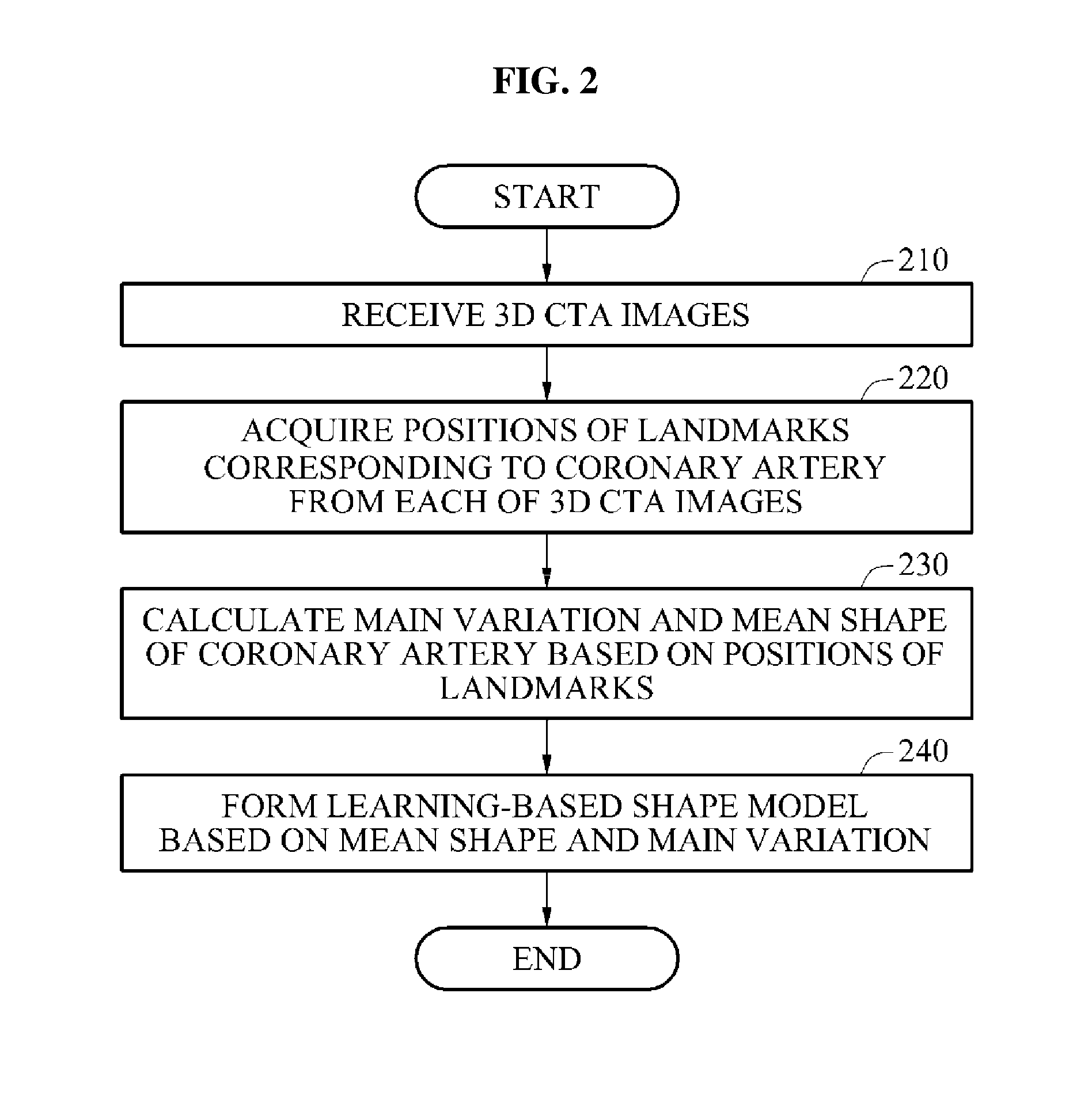
Methods of and apparatuses for modeling structures of coronary arteries from three-dimensional (3D) computed tomography angiography (CTA) images
ActiveUS20160155234A1Assist in treatmentImage enhancementImage analysisLearning basedCoronary artery structure
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
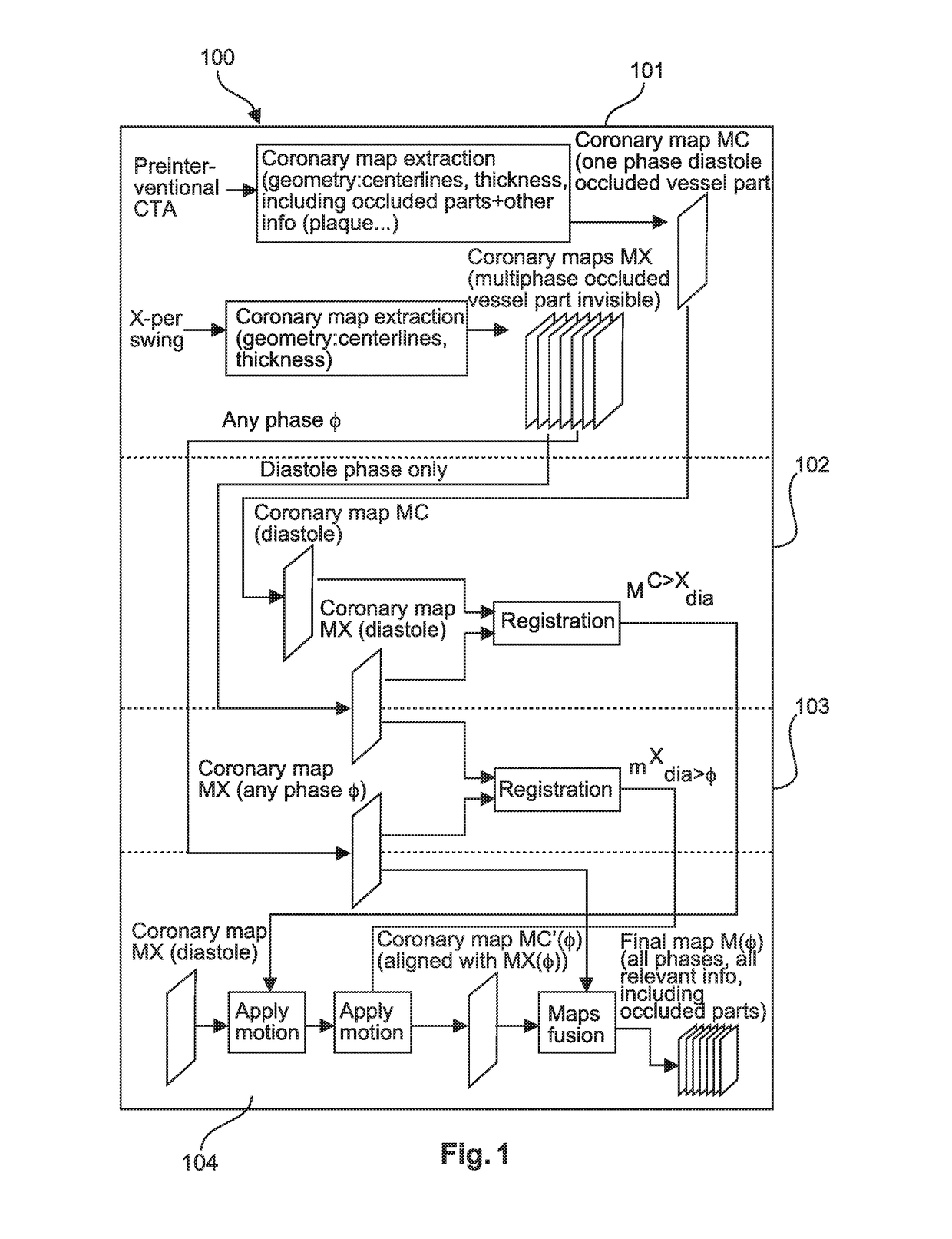
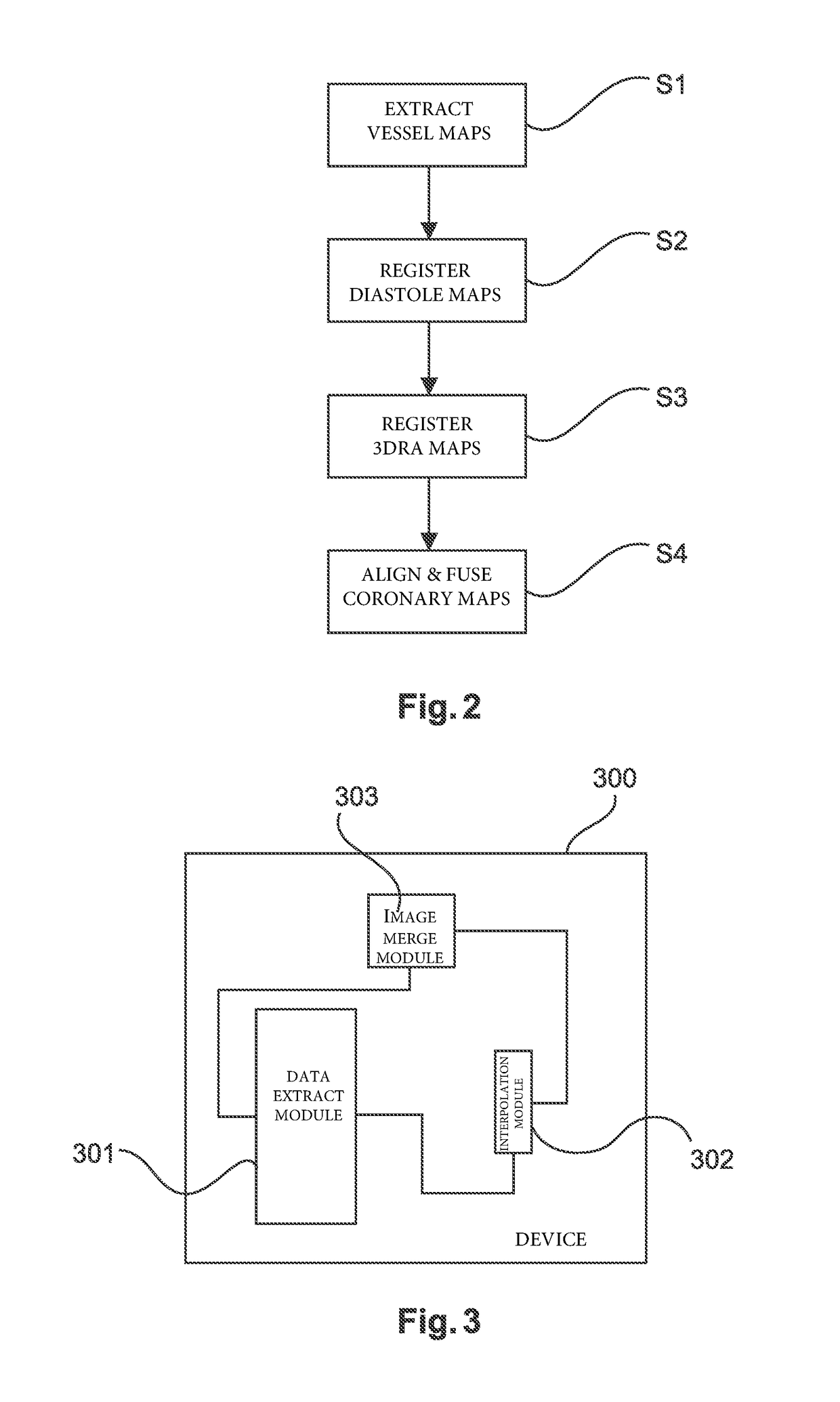
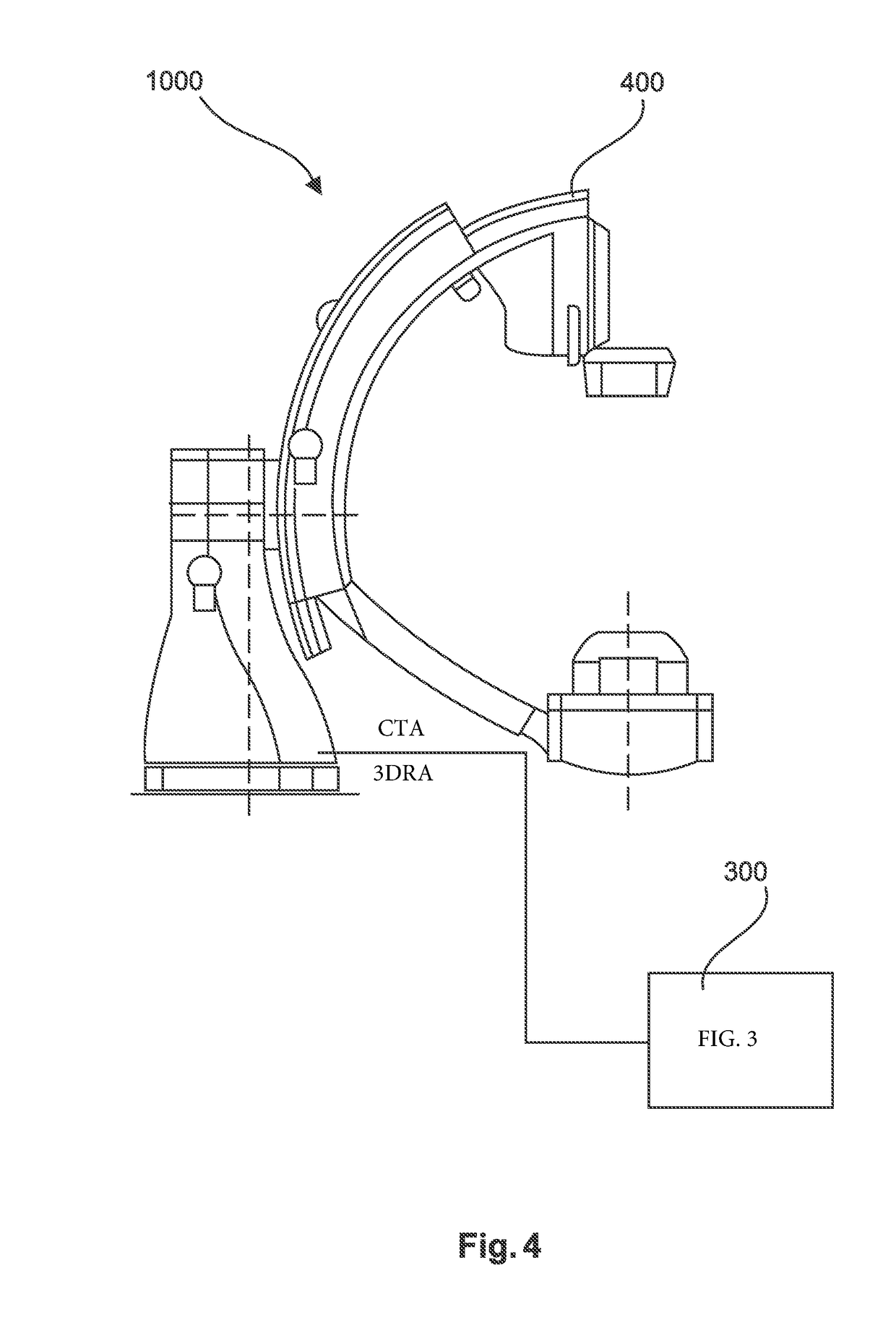
Device and method for medical imaging of coronary vessels
ActiveUS20190051002A1Image enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional rotational angiographyCardiac phase
The present invention relates to a method and a device for medical imaging of coronary vessels, the device comprising: a data extracting module configured to extract a first vessel map from computed tomography angiography data covering at least one reference cardiac phase and a set of second vessel maps from three-dimensional rotational angiography data covering at least one cardiac cycle; an interpolation module configured to generate a series of warped versions of the first vessel map aligned with the set of second vessel maps, the series starting at the at least one reference cardiac phase; and a merging module configured to merge the series and the set of second vessel maps at the different phases in order to generate a final imaging map of the coronary vessels.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
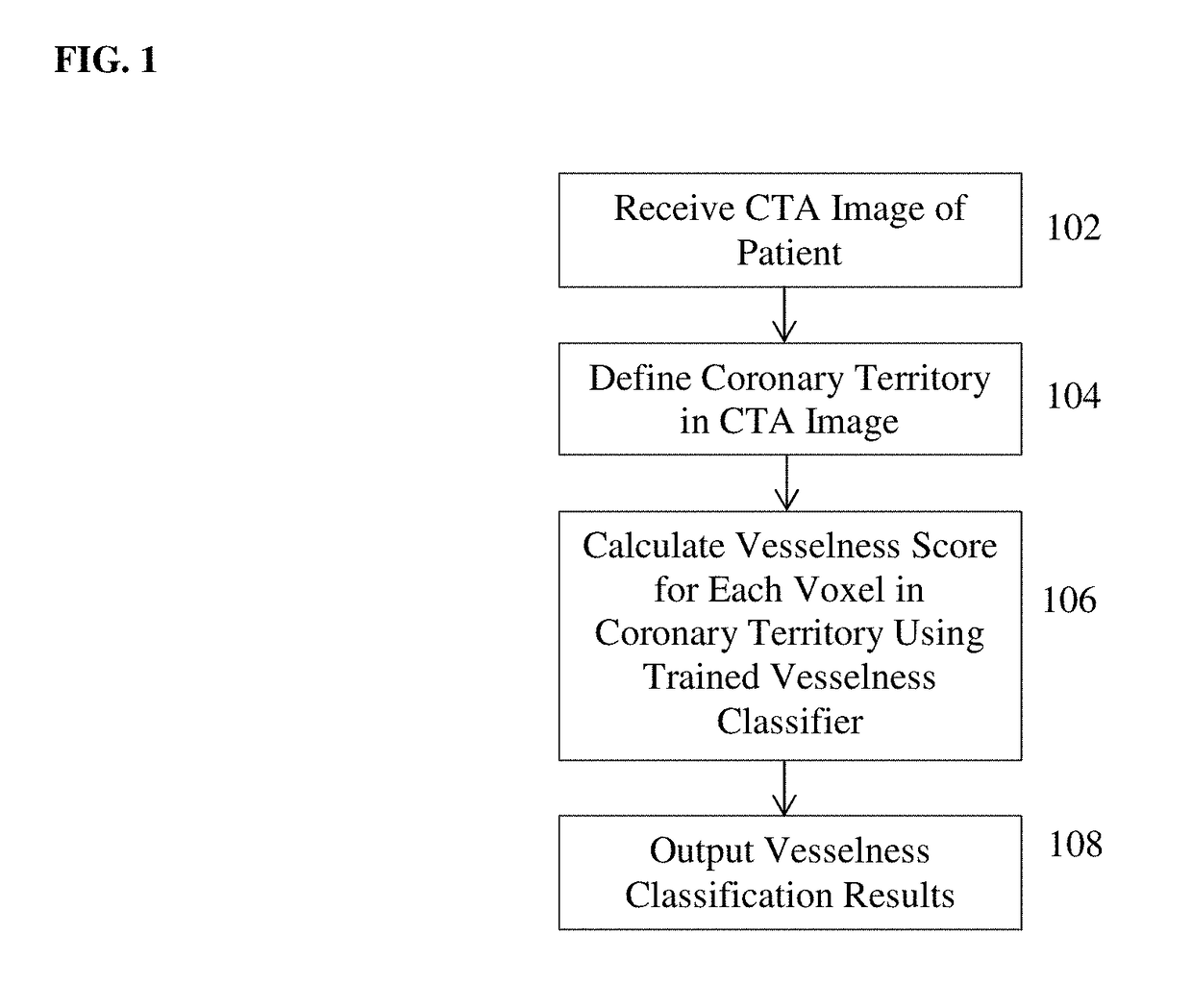
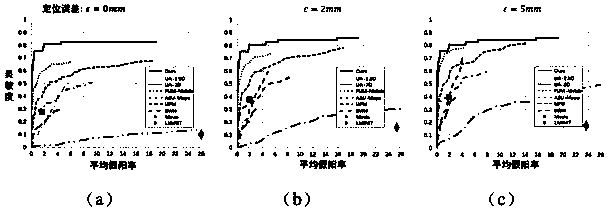
Method for automatically detecting systemic arteries in arbitrary field-of-view computed tomography angiography (CTA)
A method and system for automatically detecting systemic arteries in arbitrary field-of-view computed tomography angiography (CTA) includes fully-automatically analyzing a medical image represented by a digital image representation.
Owner:AGFA GEVAERT AG +1
Pulmonary embolism detection system based on convolutional neural network
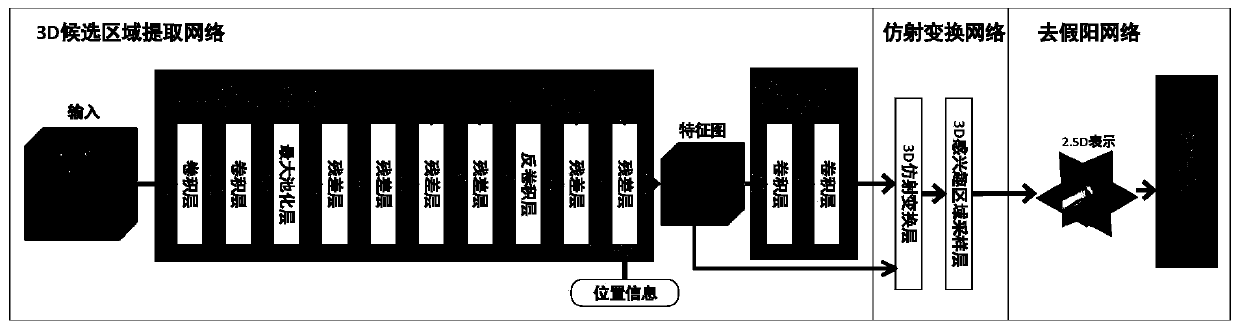
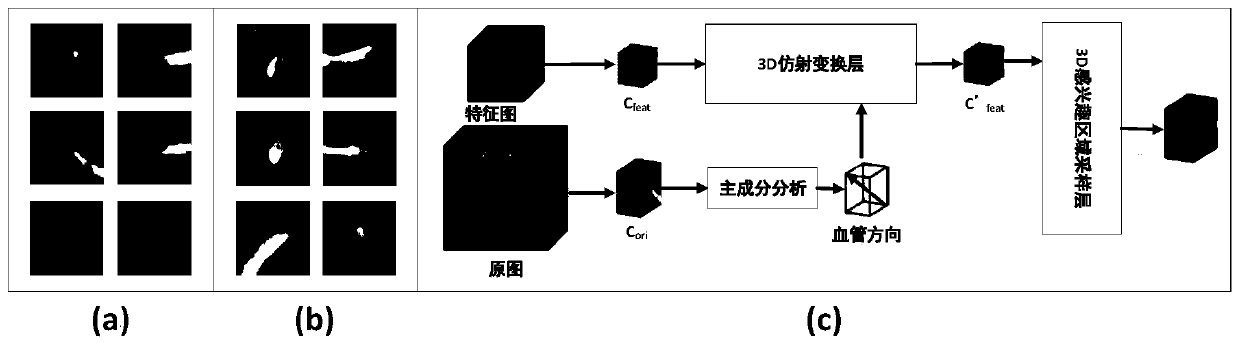
ActiveCN110717916AAvoid error accumulationReduce the effect of volume effectImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithm3d image
The invention discloses a pulmonary embolism detection system based on a convolutional neural network. The system comprises: a candidate region extraction network, which is a full convolutional network using automatic encoding and decoding with jump connection, performing candidate region extraction on a computed tomography angiography image to be detected, and obtaining a plurality of false positive candidate regions with different sizes; a 3D affine transformation network, used for generating cubes with aligned blood vessels and fixed sizes from a plurality of false positive candidate areaswith different sizes and taking out three orthogonal layers of the cubes; and a false positive prediction screening network, used for inputting the three orthogonal layers into a 2D classification network containing two full connection layers to carry out false positive prediction screening. The method can solve the problem of error accumulation. 3D image features with higher discriminability canbe automatically extracted, the influence of the volume effect is reduced, and the method does not depend on the experience of researchers. The accuracy is improved while the recall rate is ensured.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-pressure injection system used for computed tomography angiography
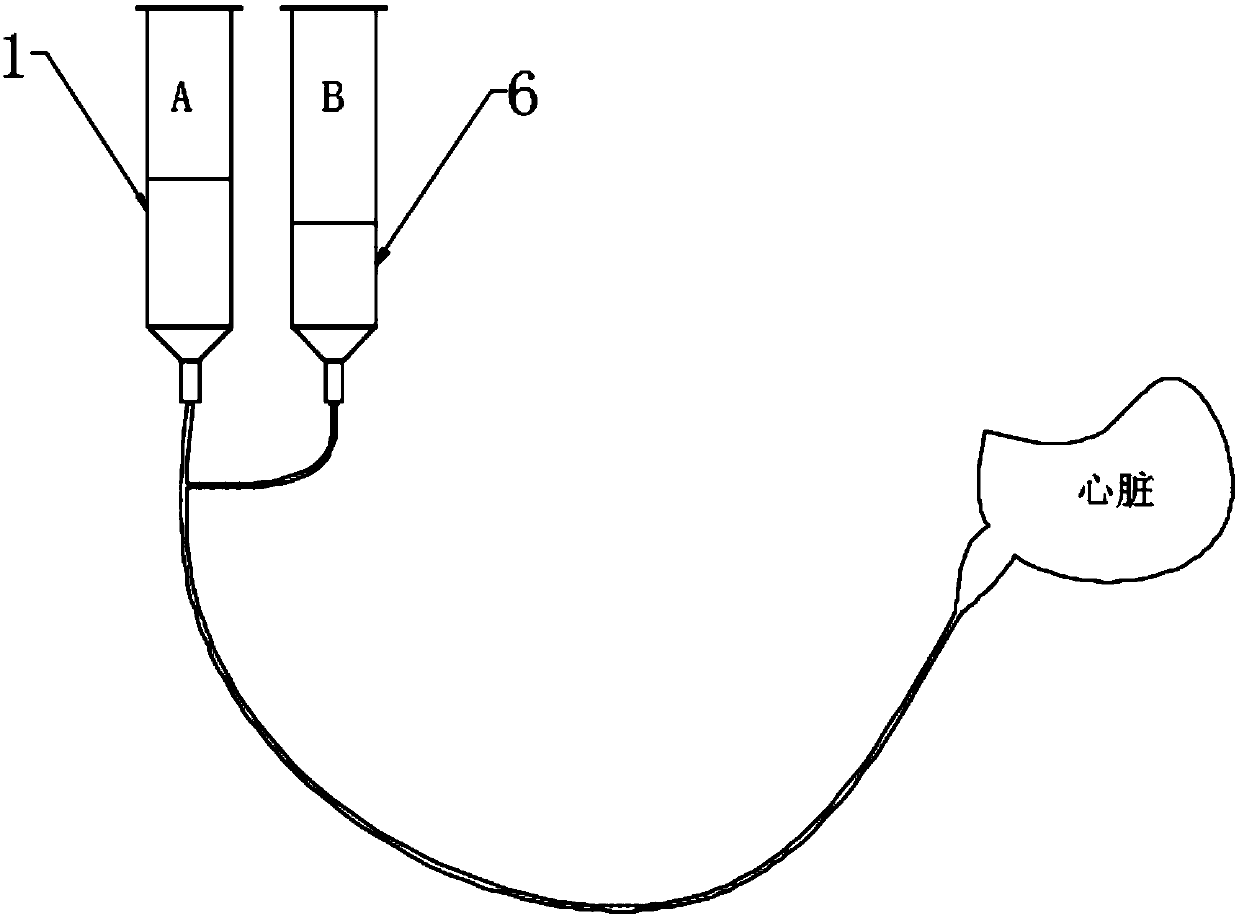
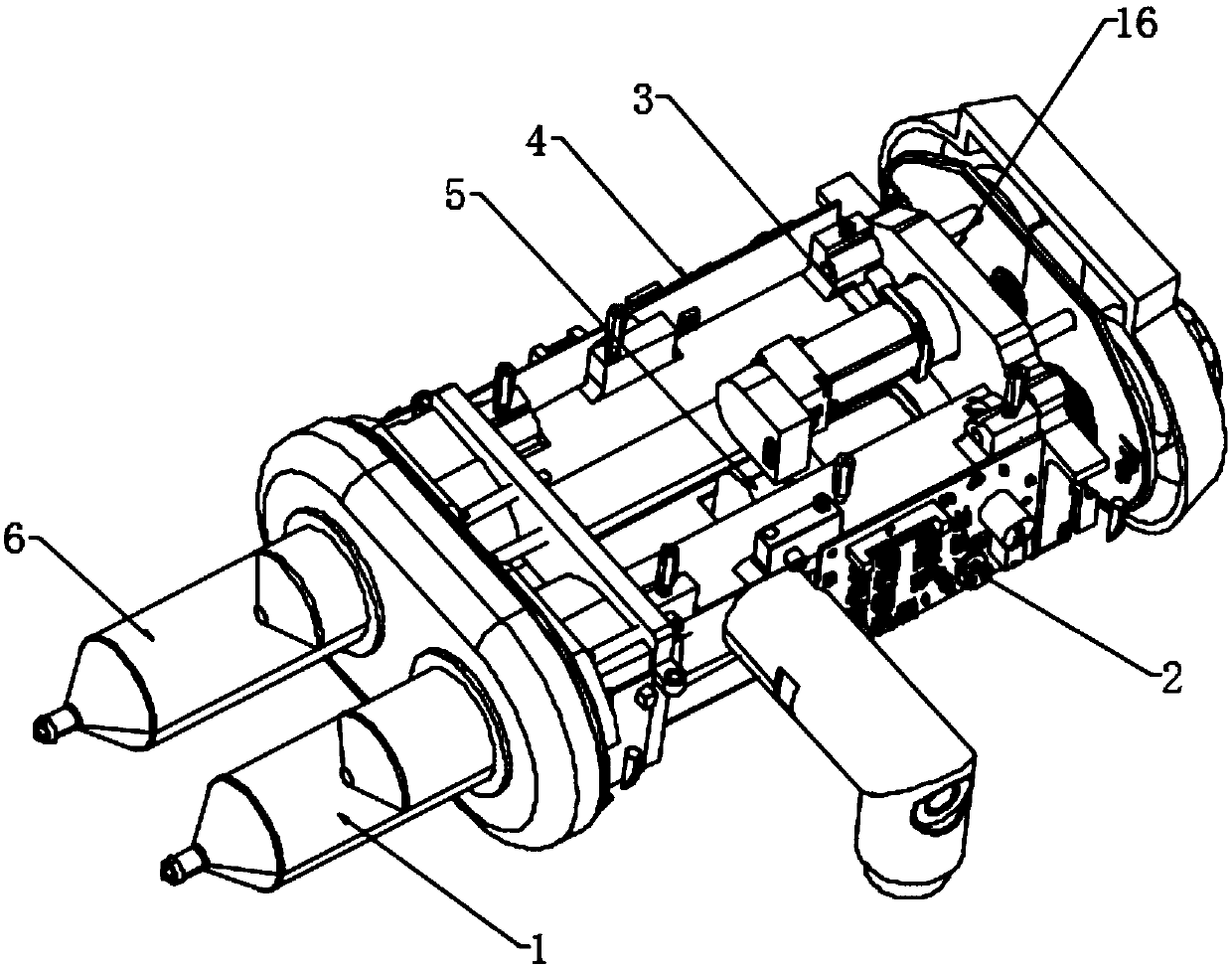
InactiveCN109602970AEnough attenuationReduce artifactsMedical devicesPressure infusionUltrasound attenuationDual injection
The invention discloses a high-pressure injection system used for computed tomography angiography, relates to the technical field of therapeutic equipment, and is mainly for solving the problem that scanned images include many has more artifacts which affect the accuracy of the diagnosis. The high-pressure injection system includes a first injection syringe, a second injection syringe and a mounting frame body used for mounting the first injection syringe and the second injection syringe, the heads of the first injection syringe and the second injection syringe are connected to the heart through the same catheter, the first injection syringe and the second injection syringe are fixed at one end of the mounting frame body, and the mounting frame body is provided with a power assembly for driving the first injection syringe and the second injection syringe. Compared with single-syringe contrast agent injection, the simultaneous injection of the dual injection syringes of the invention can minimize artifacts with appropriate contrast attenuation level while performing CT scanning so as to obtain high-quality images.
Owner:NANJING JUSHA DISPLAY TECH +1
Method for automatically detecting systemic arteries in arbitrary field-of-view computed tomography angiography (CTA)
InactiveCN109478327AImprove accuracyAchieve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisHelical computed tomographyDigital image
Owner:T2PHARMA GMBH +1
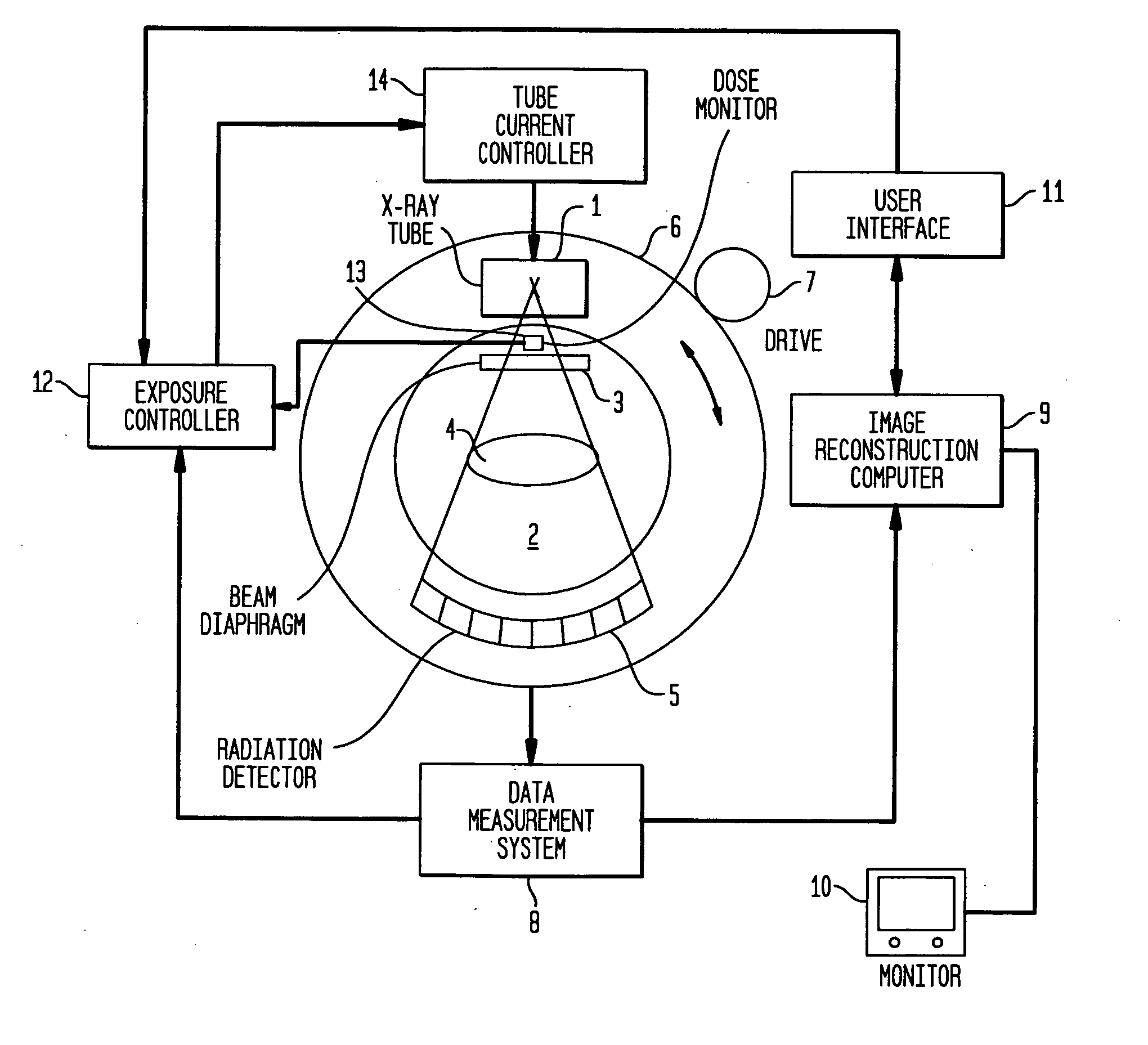
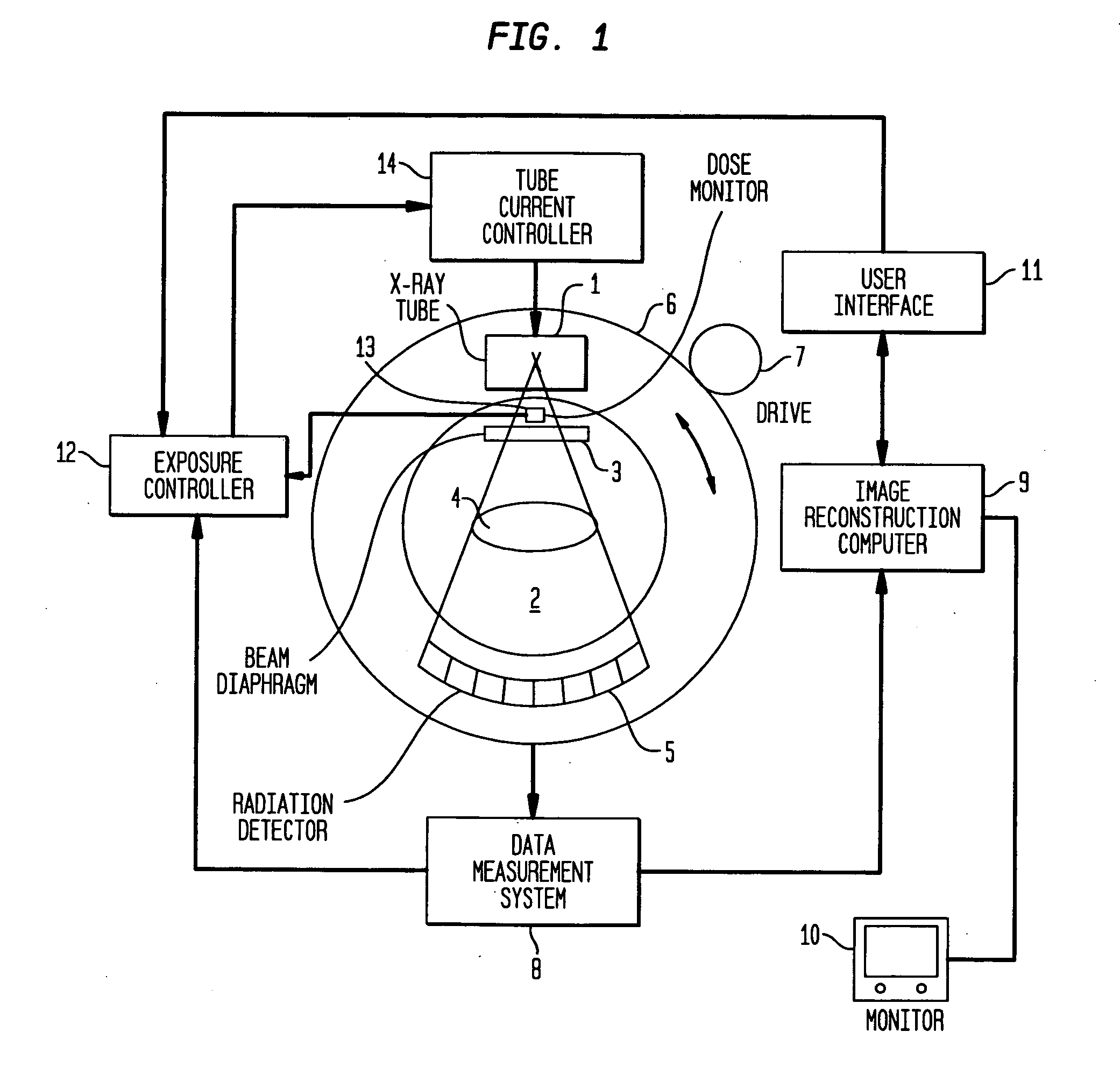
Method for respiration-correlated computed tomography imaging
In a method and apparatus for respiration-correlated computed tomography imaging, a patient-specific breathing curve is recorded and is evaluated online, and a CT scan, providing a number of raw images of a region of interest of a patient, is controlled synchronously with the patient-specific breathing curve according to the results of the online evaluation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for whole body bone removal and vascular visualization in medical image data
A method and apparatus for whole body bone removal and vasculature visualization in medical image data, such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans, is disclosed. Bone structures are segmented in the a 3D medical image, resulting in a bone mask of the 3D medical image. Vessel structures are segmented in the 3D medical image, resulting in a vessel mask of the 3D medical image. The bone mask and the vessel mask are refined by fusing information from the bone mask and the vessel mask. Bone voxels are removed from the 3D medical image using the refined bone mask, in order to generate a visualization of the vessel structures in the 3D medical image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Deep learning based bone removal in computed tomography angiography
A method and apparatus for deep learning based automatic bone removal in medical images, such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) volumes, is disclosed. Bone structures are segmented in a 3D medical image of a patient by classifying voxels of the 3D medical image as bone or non-bone voxels using a deep neural network trained for bone segmentation. A 3D visualization of non-bone structures in the 3D medical image is generated by removing voxels classified as bone voxels from a 3D visualization of the 3D medical image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Coronary artery projection image generation method and device and computer readable medium
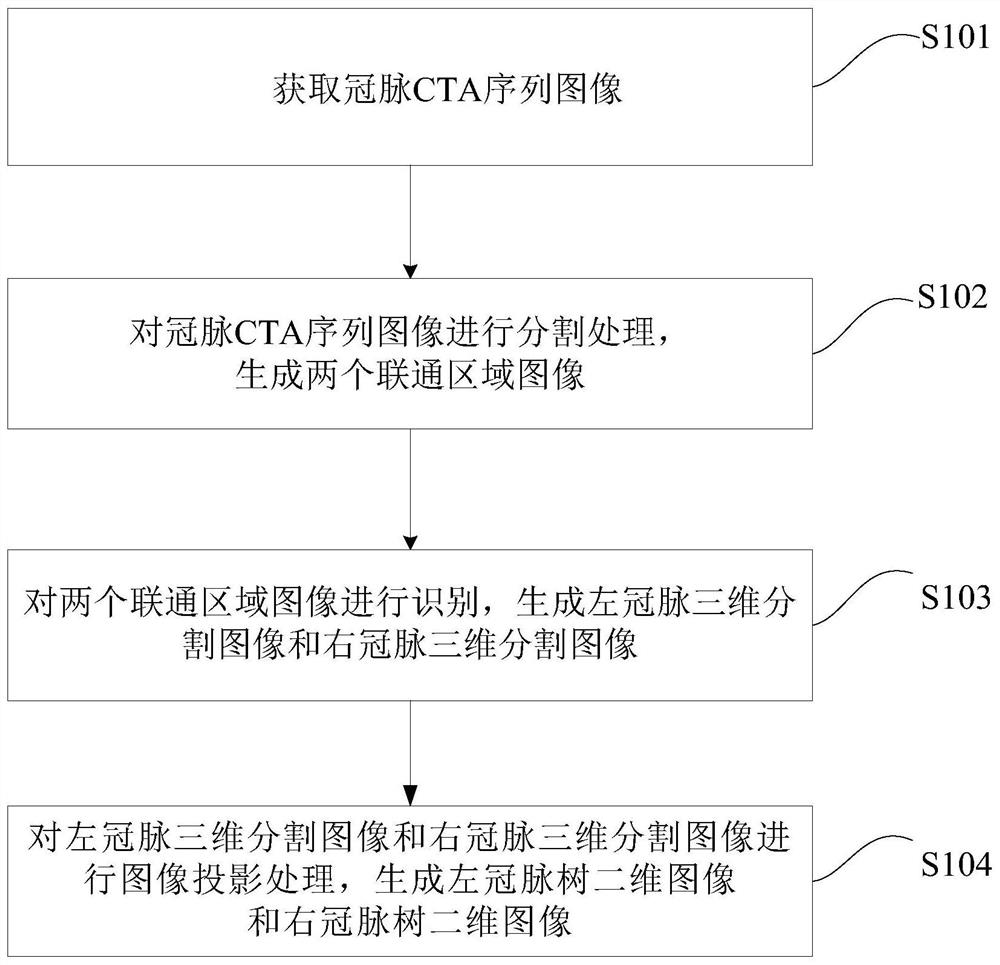
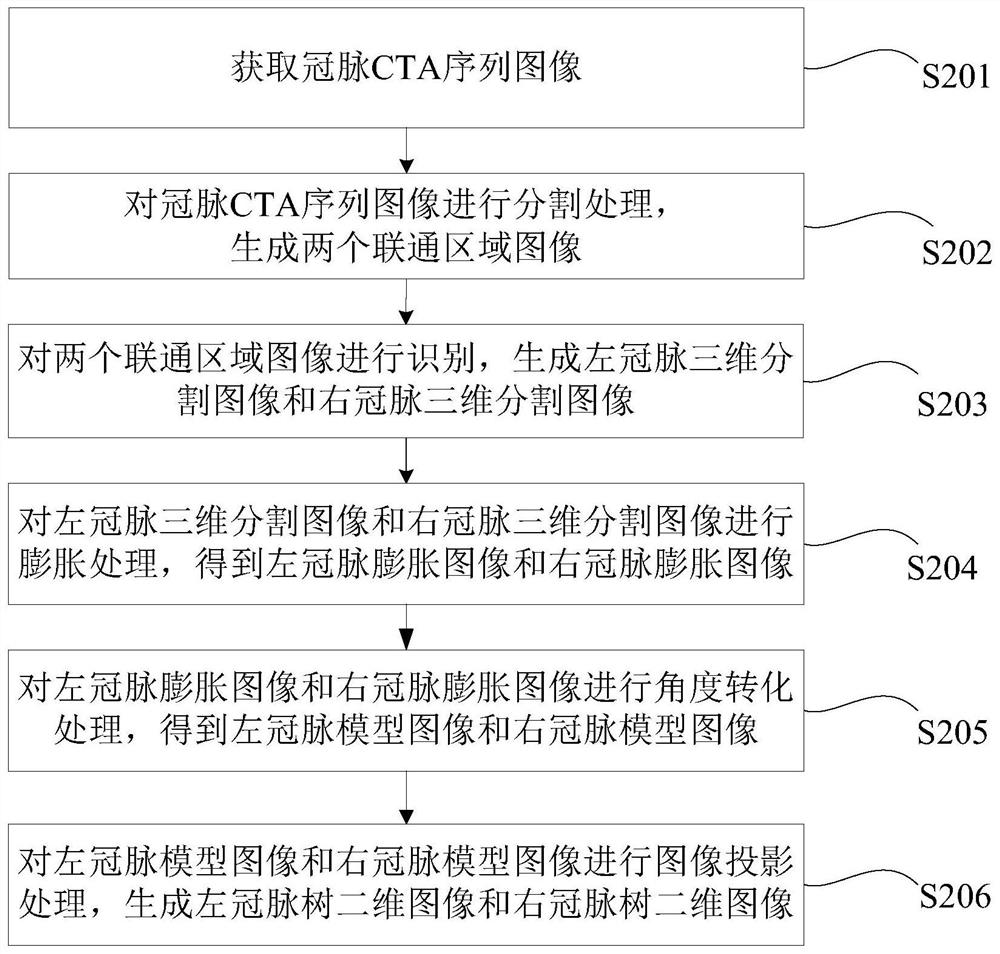
ActiveCN111627023AEliminate distractionsEasy to observeImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesProjection image
The invention discloses a coronary artery projection image generation method and device and a computer readable medium. One embodiment of the method comprises the following steps: acquiring a coronaryartery computed tomography angiography (CTA) sequence image; carrying out segmentation processing on the coronary artery CTA sequence image to generate two connected region images; identifying the two connected region images to generate a left coronary artery three-dimensional segmentation image and a right coronary artery three-dimensional segmentation image; and performing image projection processing on the left coronary artery three-dimensional segmented image and the right coronary artery three-dimensional segmented image to generate a left coronary artery tree two-dimensional image and aright coronary artery tree two-dimensional image. According to the invention, the left coronary artery CTA sequence image can be processed by the artificial intelligence model to generate the left coronary artery three-dimensional segmentation image and the right coronary artery three-dimensional segmentation image; therefore, maximum density projection is generated for the left coronary artery tree and the right coronary artery tree, interference of other tissues or blood vessel branches on coronary arteries is eliminated, and doctors can observe related problems of disease diagnosis such asblood vessel bifurcation, calcification or stenosis.
Owner:数坤(上海)医疗科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com