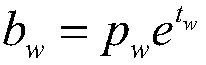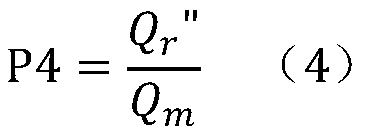Patents
Literature
31 results about "Entry rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Entry rate. Entry rate is a digital analytics performance indicator determined by taking the number of visits involving more than one page (entering visits) and dividing it by the total number of visits.
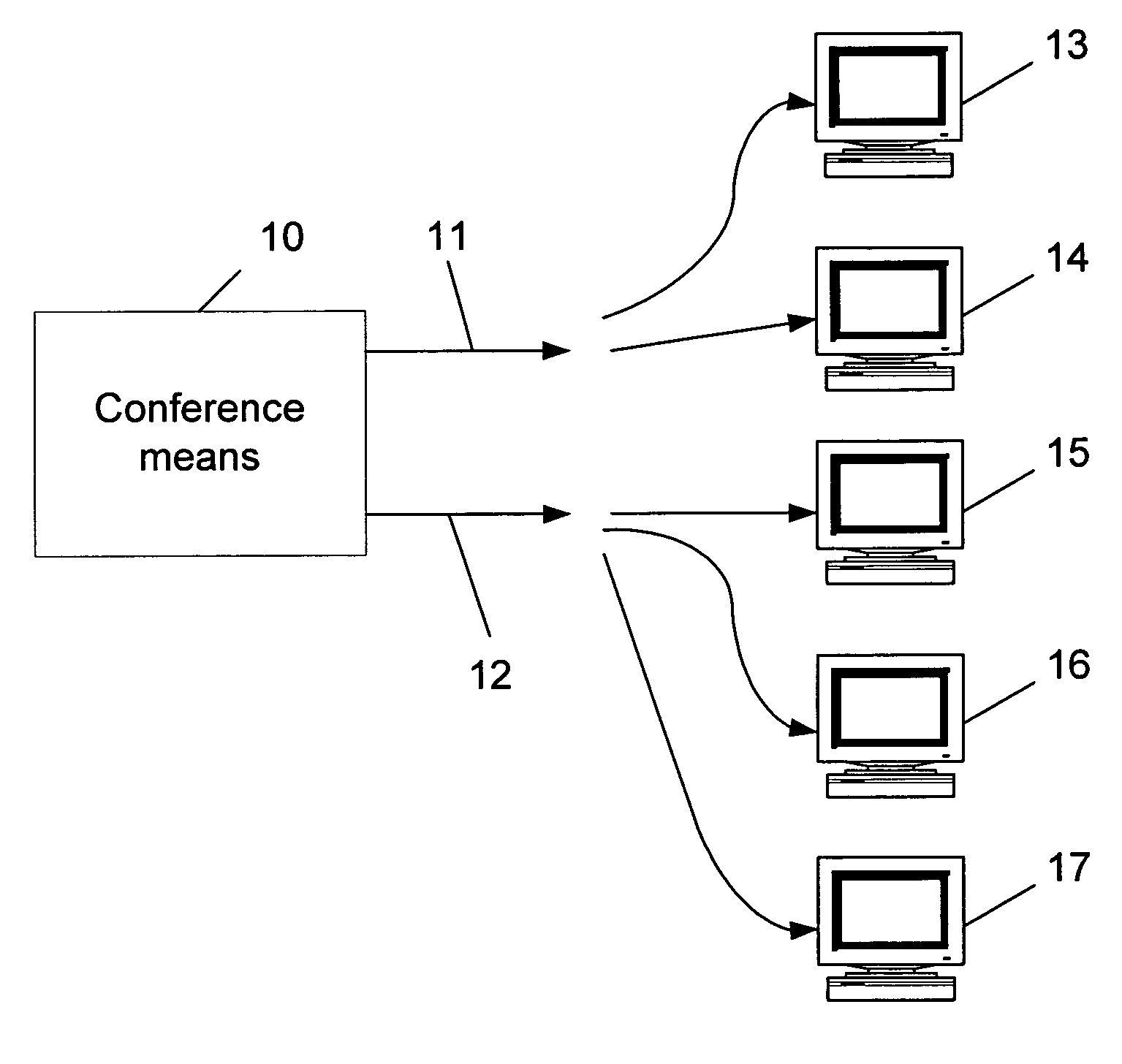
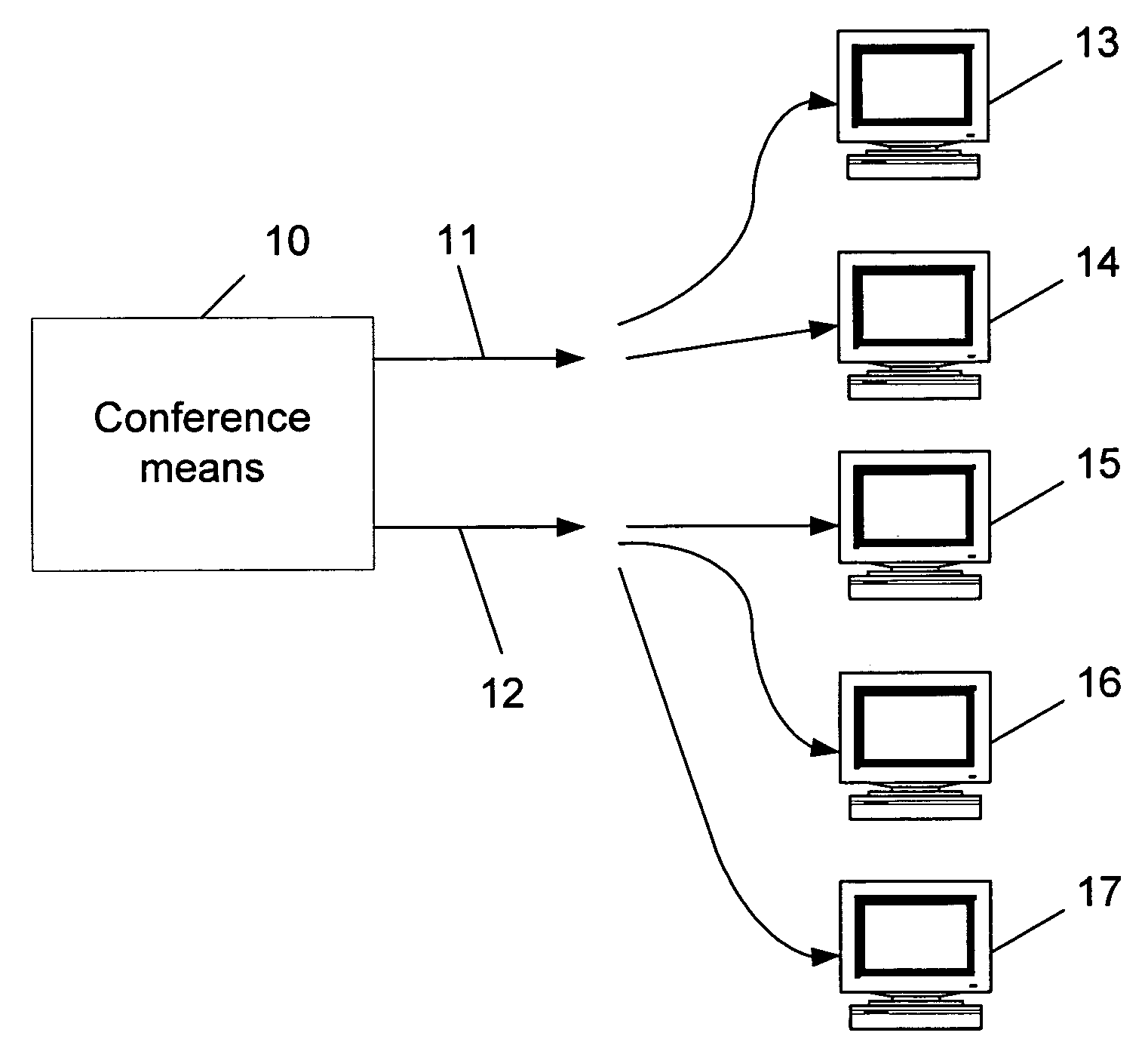
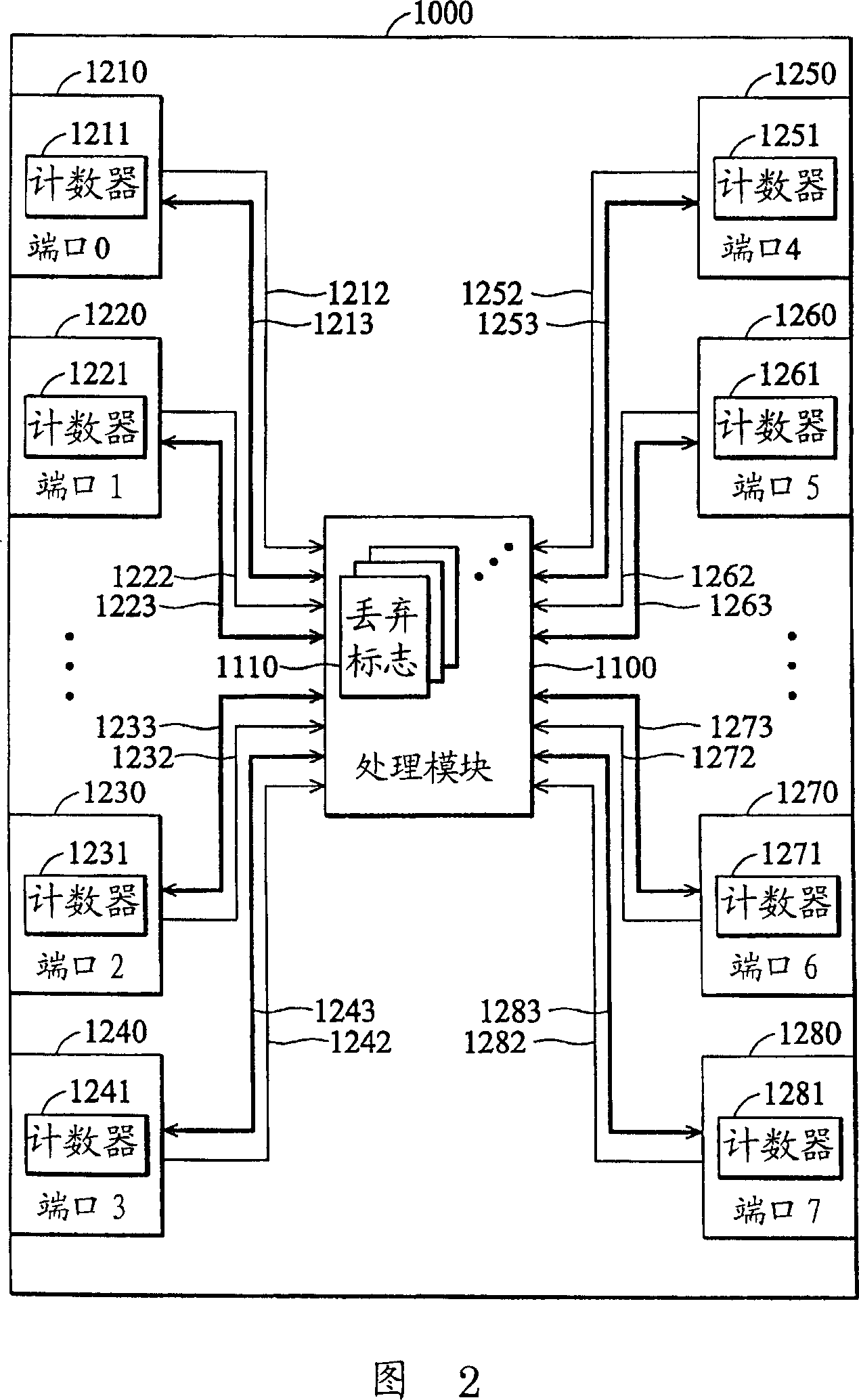
Method for dynamically optimizing bandwidth allocation in variable bitrate (multi-rate) conferences
ActiveUS7492731B2Reduce rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationHigh rateVideo rate
Method for dynamically optimizing bandwidth allocation in a variable bitrate conference environment. Conference means with two or more outputs are provided, where each one can output data at different rates, in order to support two or more endpoints which may have different media rates. Two or more endpoints are connected to these conference means for participating in the conference. Whenever more than one video rate is used by participants during the conference, each set of output rates is selected from all possible combinations of output rates in the conference means, wherein the lowest output rate in each selected set is the entry rate of the endpoint joining the conference at the lowest rate. A Quality Drop Coefficient (QDC) for each endpoint that joins the conference is determined for each selected set, wherein the QDC is computed according to the endpoint entry rate and the highest rate, among the output rates of each selected set, that is lower or equal to said endpoints' entry rate. A Quality Drop Value (QDV) is calculated for each of the selected sets, wherein, preferably, the set of output rates with the lowest QDV is determined as the optimal video rate set to select. The video rate of all the endpoints having a video rate above the highest optimal video rate is reduced to the highest optimal video rate, if required, and the video rate of other endpoints having video rate between two consecutive levels of optimal video rates is reduced to the lowest level among said levels. Whenever a change occurs in either the amount of participating endpoints in the conference or in the declared bit rate capability of the participating endpoints, the video rates of all the outputs are recalculated.
Owner:AVAYA INC
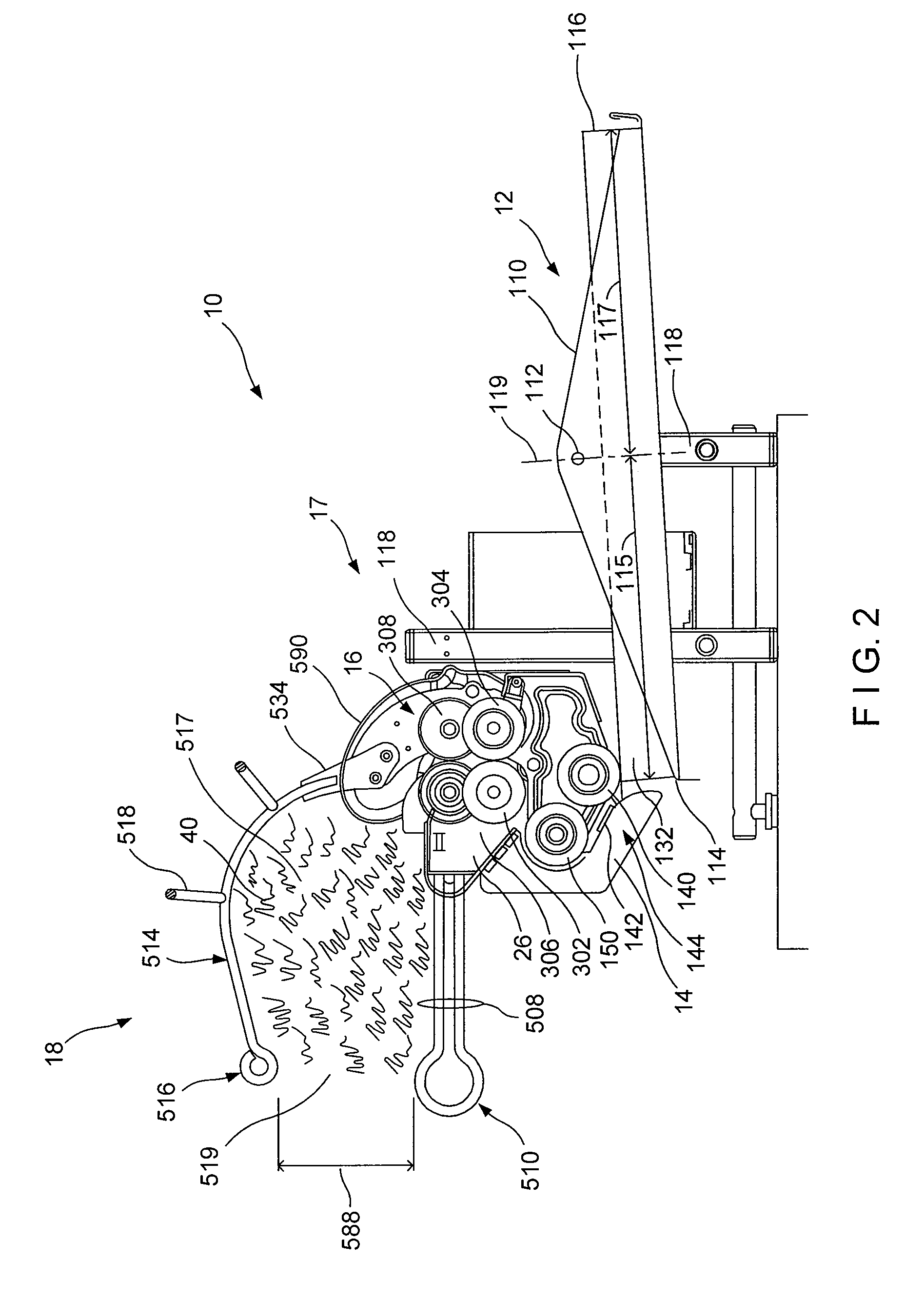
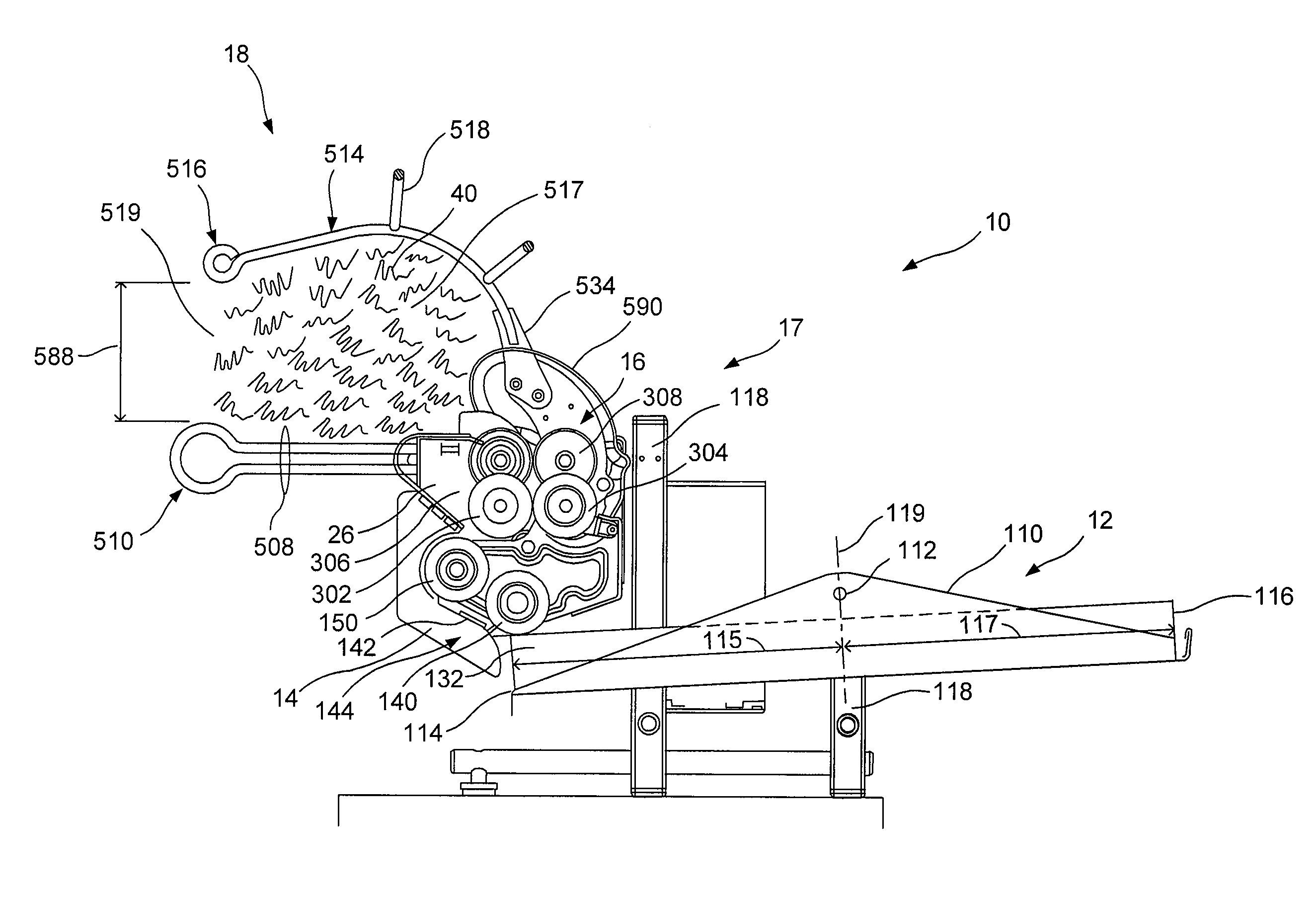
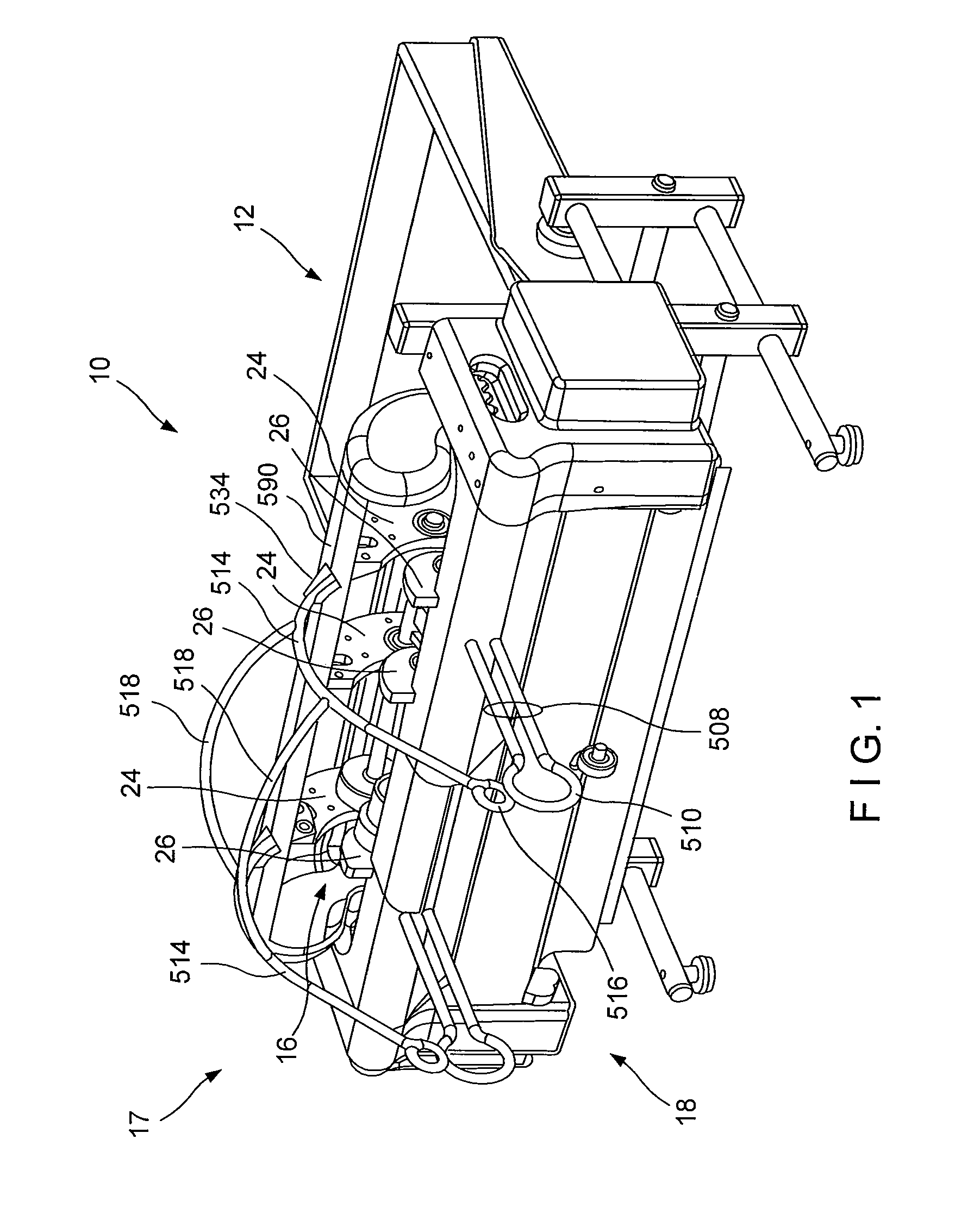
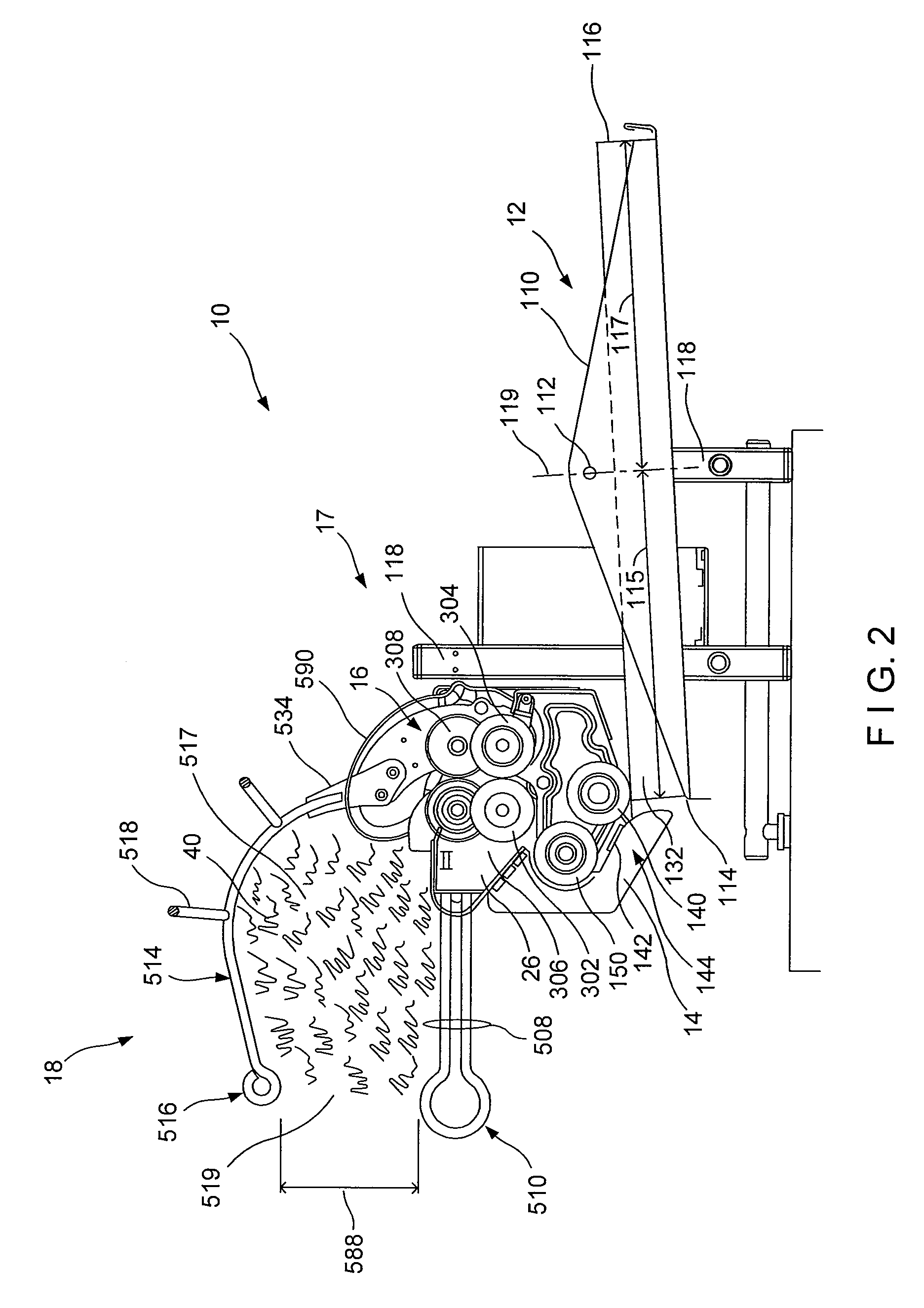
Crumpling mechanism for creating dunnage
A dunnage crumpling apparatus is provided having first and second entry-side crumpling members and first and second exit-side crumpling members. The first and second entry-side crumpling members define an entry therebetween. The first and second exit-side crumpling members define an exit therebetween that is disposed along the longitudinal path downstream of the entry. A crumpling zone being defined between the entry and exit. The first entry-side crumpling member is configured for moving at an first rate and is associated with the second entry-side crumpling member for moving sheet material through the entry in a first direction along a longitudinal path at an entry rate. The first exit-side crumpling member is configured for moving at an second rate and is associated with the second exit-side crumpling member for moving the sheet material through the exit in the first direction along the path at a exit rate that is slower than the entry rate to crumple the sheet material for producing dunnage. The entry and exit-side crumpling members are displaced laterally along the path with respect to each other to cause shearing of the sheet within the crumpling zone.
Owner:PREGIS INNOVATIVE PACKAGING
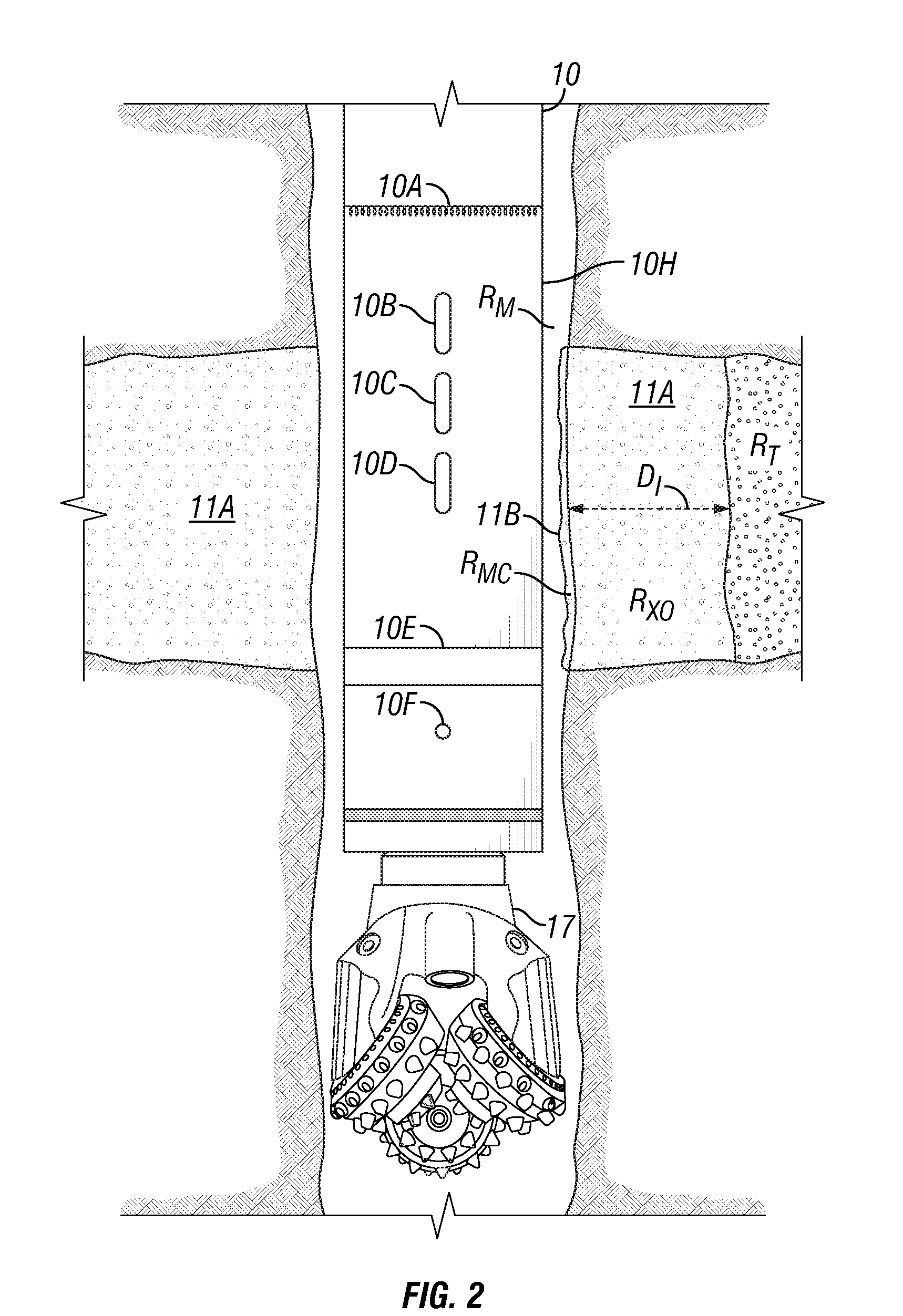
Method for estimating formation permeability using time lapse measurements
A method for determining permeability of a subsurface formation includes measuring a parameter related to fluid content of the formation at a first time from within a wellbore penetrating the formation. A rate of entry of fluid from the wellbore into the formation is determined from the measurement of the parameter made at the first time. The permeability is determined from the rate of entry.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
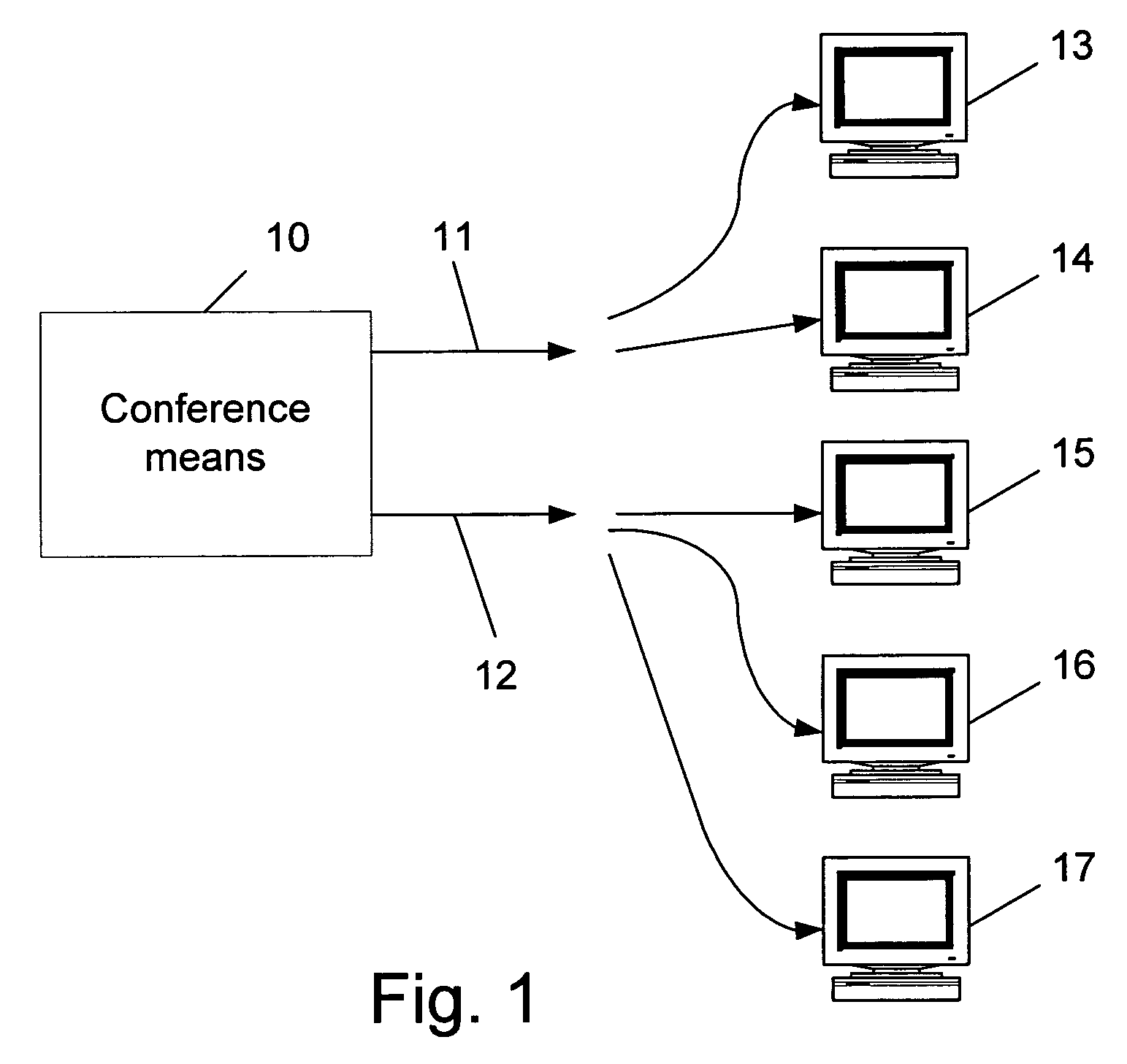
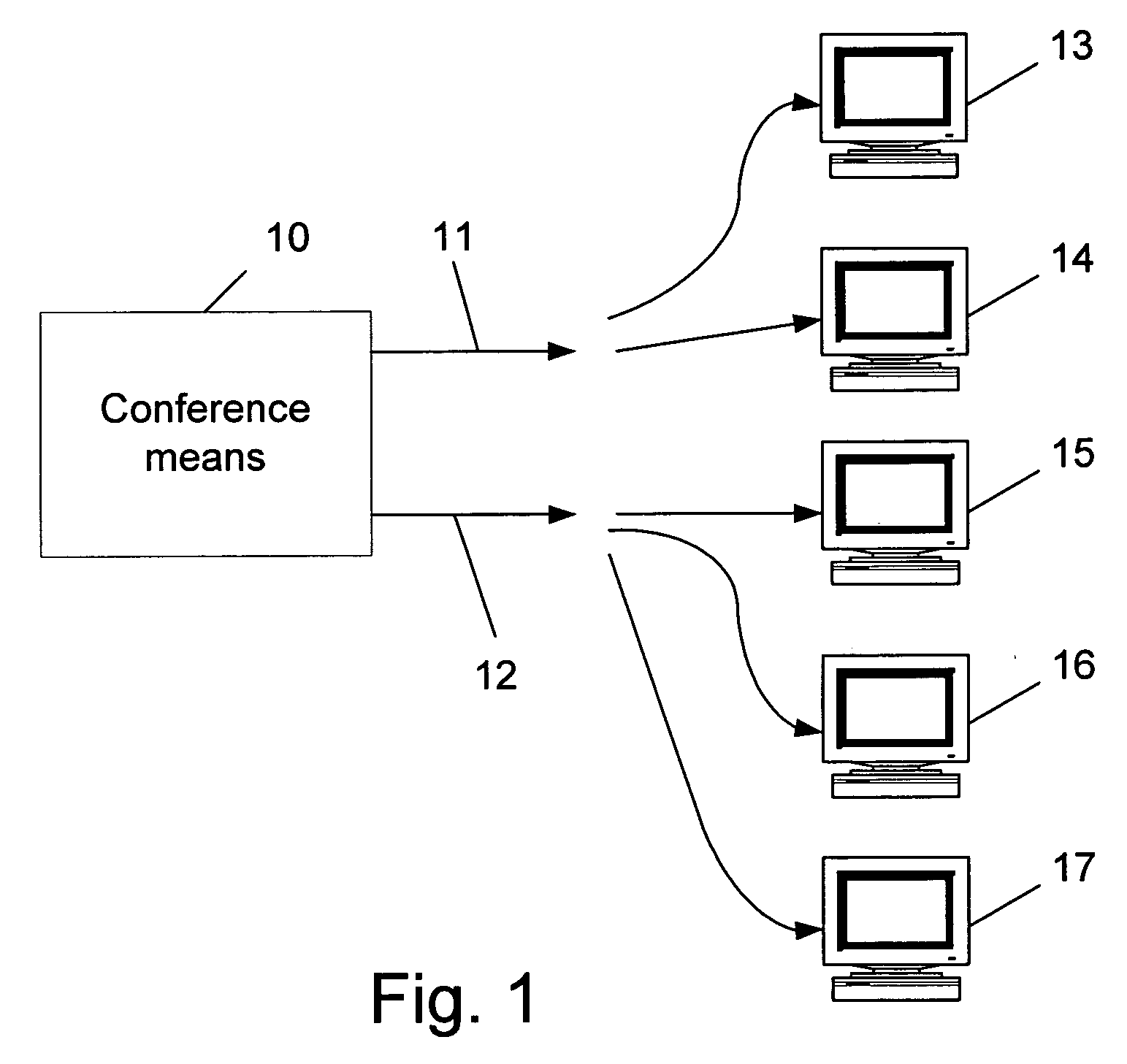
Method for dynamically optimizing bandwidth allocation in variable bitrate (multi-rate) conferences
ActiveUS20060067251A1Reduce rateSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsHigh rateVideo rate
Method for dynamically optimizing bandwidth allocation in a variable bitrate conference environment. Conference means with two or more outputs are provided, where each one can output data at different rates, in order to support two or more endpoints which may have different media rates. Two or more endpoints are connected to these conference means for participating in the conference. Whenever more than one video rate is used by participants during the conference, each set of output rates is selected from all possible combinations of output rates in the conference means, wherein the lowest output rate in each selected set is the entry rate of the endpoint joining the conference at the lowest rate. A Quality Drop Coefficient (QDC) for each endpoint that joins the conference is determined for each selected set, wherein the QDC is computed according to the endpoint entry rate and the highest rate, among the output rates of each selected set, that is lower or equal to said endpoints' entry rate. A Quality Drop Value (QDV) is calculated for each of the selected sets, wherein, preferably, the set of output rates with the lowest QDV is determined as the optimal video rate set to select. The video rate of all the endpoints having a video rate above the highest optimal video rate is reduced to the highest optimal video rate, if required, and the video rate of other endpoints having video rate between two consecutive levels of optimal video rates is reduced to the lowest level among said levels. Whenever a change occurs in either the amount of participating endpoints in the conference or in the declared bit rate capability of the participating endpoints, the video rates of all the outputs are recalculated.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Crumpling mechanism for creating dunnage
A dunnage crumpling apparatus is provided having first and second entry-side crumpling members and first and second exit-side crumpling members. The first and second entry-side crumpling members define an entry therebetween. The first and second exit-side crumpling members define an exit therebetween that is disposed along the longitudinal path downstream of the entry. A crumpling zone being defined between the entry and exit. The first entry-side crumpling member is configured for moving at an first rate and is associated with the second entry-side crumpling member for moving sheet material through the entry in a first direction along a longitudinal path at an entry rate. The first exit-side crumpling member is configured for moving at an second rate and is associated with the second exit-side crumpling member for moving the sheet material through the exit in the first direction along the path at a exit rate that is slower than the entry rate to crumple the sheet material for producing dunnage. The entry and exit-side crumpling members are displaced laterally along the path with respect to each other to cause shearing of the sheet within the crumpling zone.
Owner:PREGIS INNOVATIVE PACKAGING
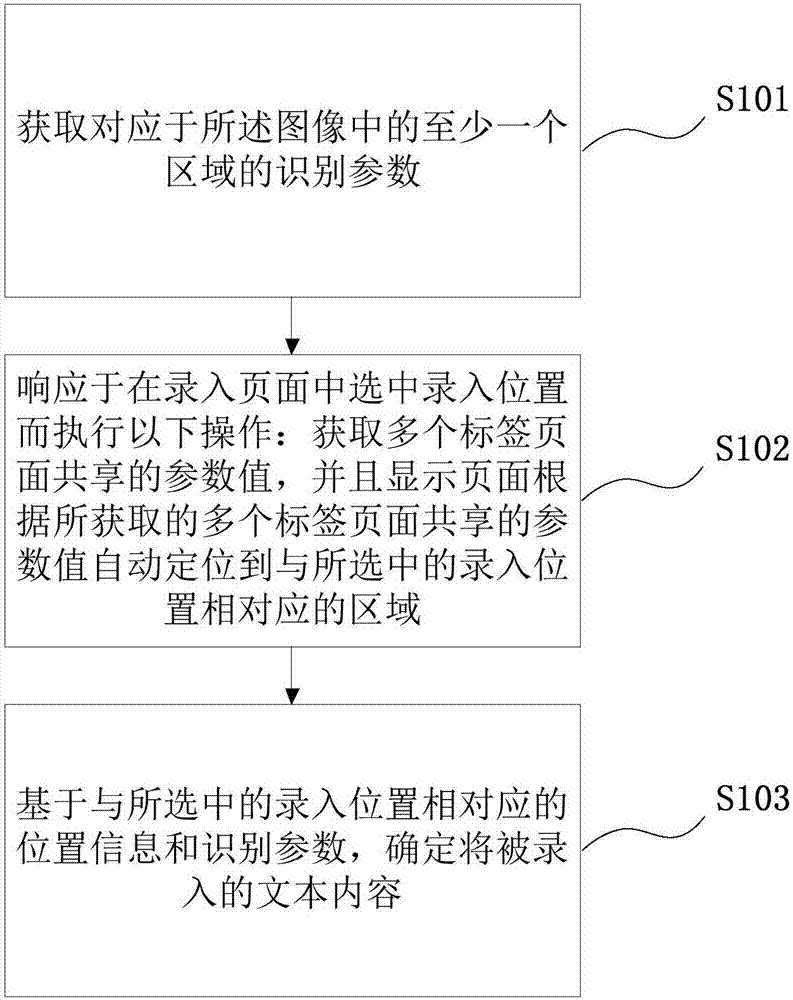
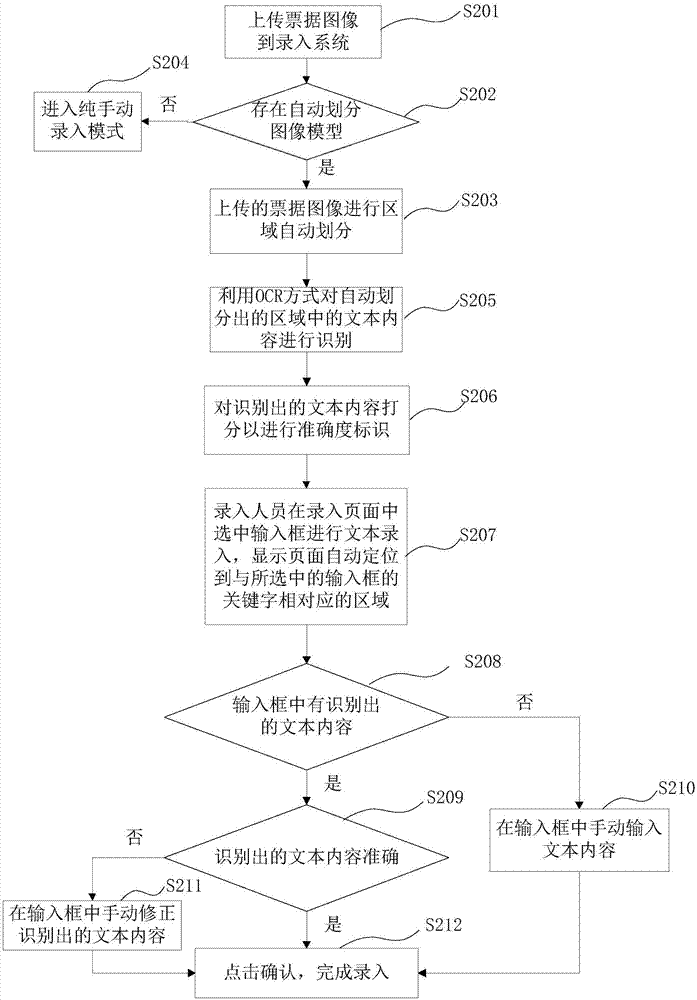
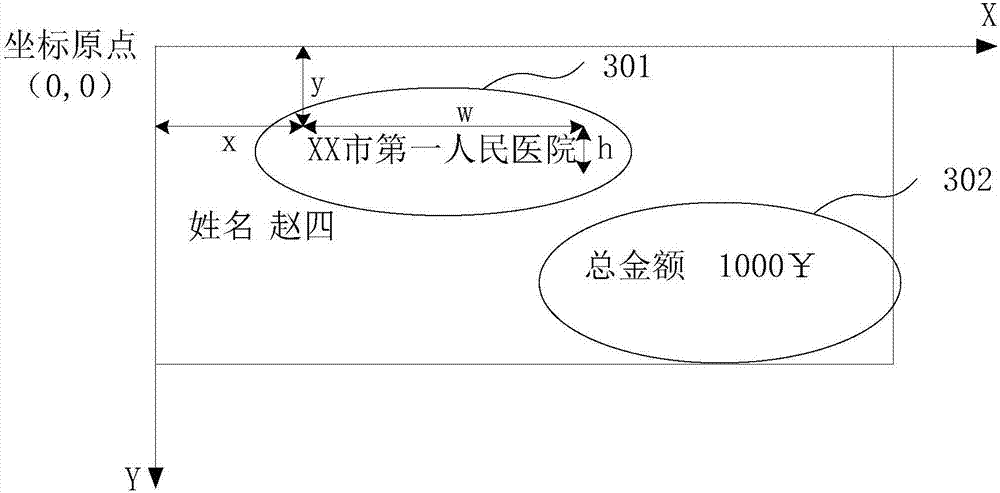
Image-based text entry method
The invention provides an image-based text entry method. The method comprises the steps of acquiring an identification parameter corresponding to at least one region in an image, wherein the identification parameter comprises text content identified from the at least one region and position information related to the at least one region; in response to selection of an entry position in an entry page, executing the following operations: acquiring a parameter shared by multiple tab pages, and displaying a region that is corresponding to the selected entry position and automatically located by the page according to the acquired parameter shared by multiple tab pages, wherein the parameter shared by multiple tab pages comprises position information corresponding to the selected entry position;and determining to-be-entered text content according to position information corresponding to the selected entry position and the identification parameter.
Owner:ZHONGAN INFORMATION TECH SERVICES CO LTD
Crumpling mechanism for creating dunnage
A dunnage crumpling apparatus is provided having first and second entry-side crumpling members and first and second exit-side crumpling members. The first and second entry-side crumpling members define an entry therebetween. The first and second exit-side crumpling members define an exit therebetween that is disposed along the longitudinal path downstream of the entry. A crumpling zone being defined between the entry and exit. The first entry-side crumpling member is configured for moving at an first rate and is associated with the second entry-side crumpling member for moving sheet material through the entry in a first direction along a longitudinal path at an entry rate. The first exit-side crumpling member is configured for moving at an second rate and is associated with the second exit-side crumpling member for moving the sheet material through the exit in the first direction along the path at a exit rate that is slower than the entry rate to crumple the sheet material for producing dunnage. The entry and exit-side crumpling members are displaced laterally along the path with respect to each other to cause shearing of the sheet within the crumpling zone.
Owner:PREGIS INNOVATIVE PACKAGING
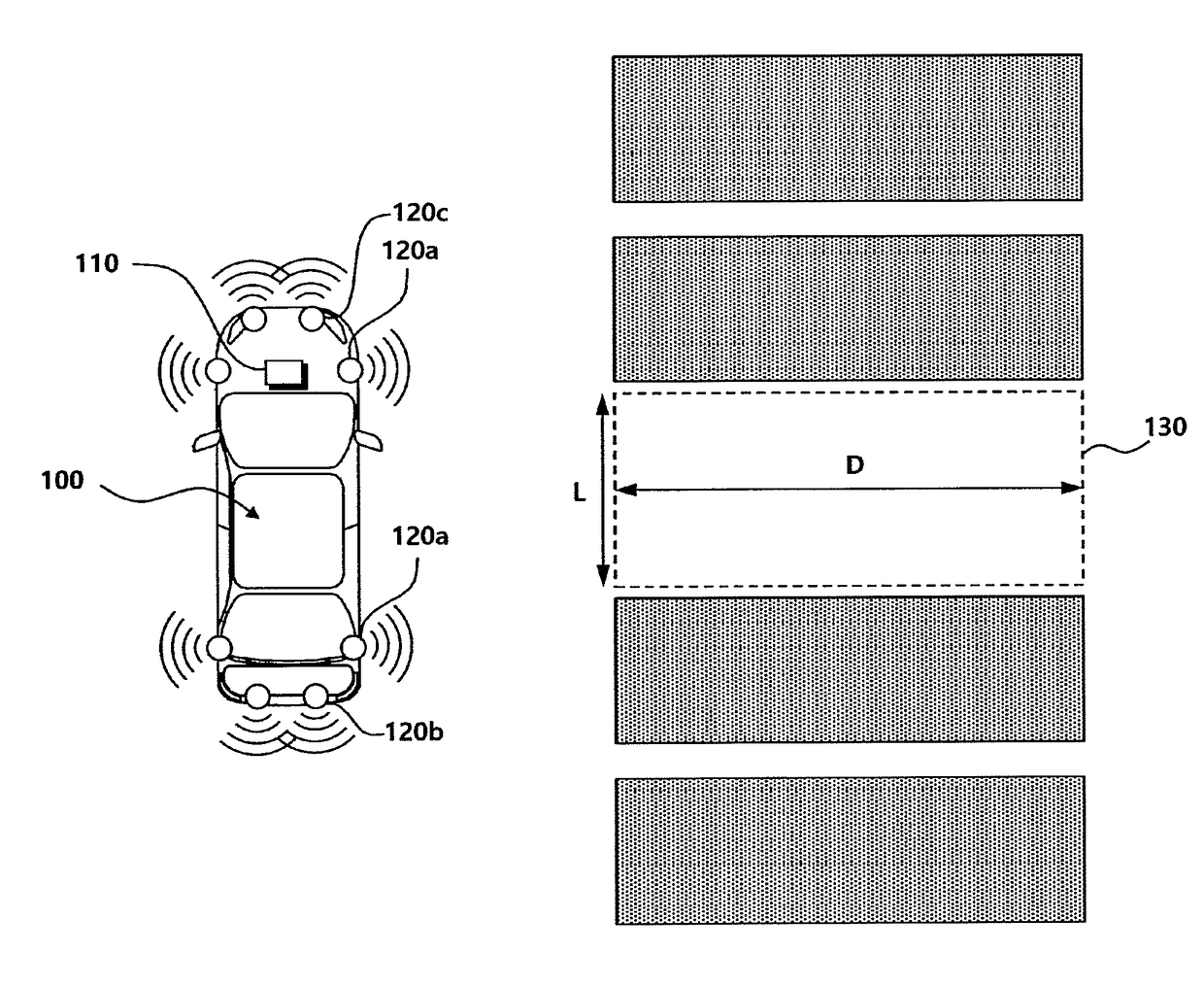
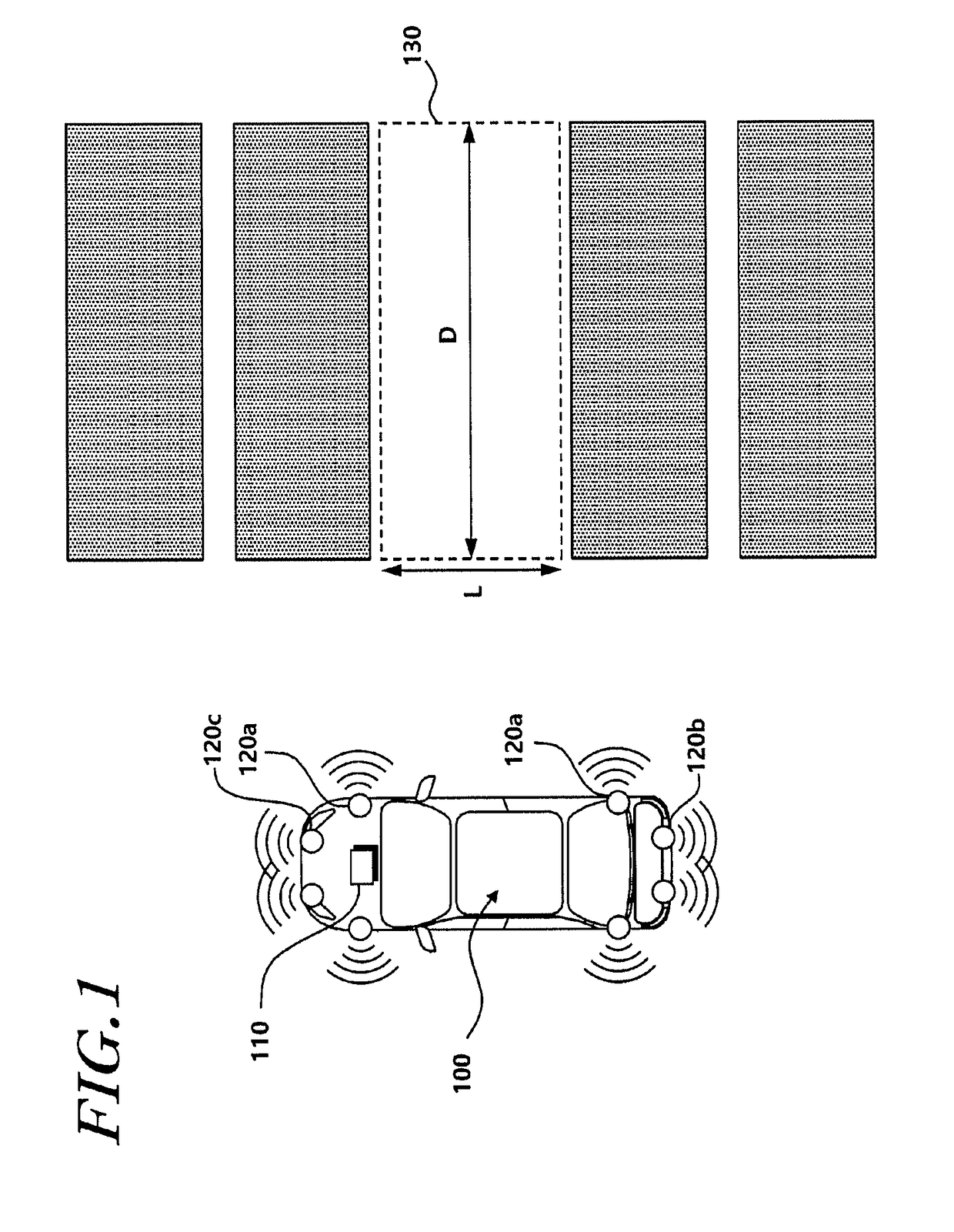
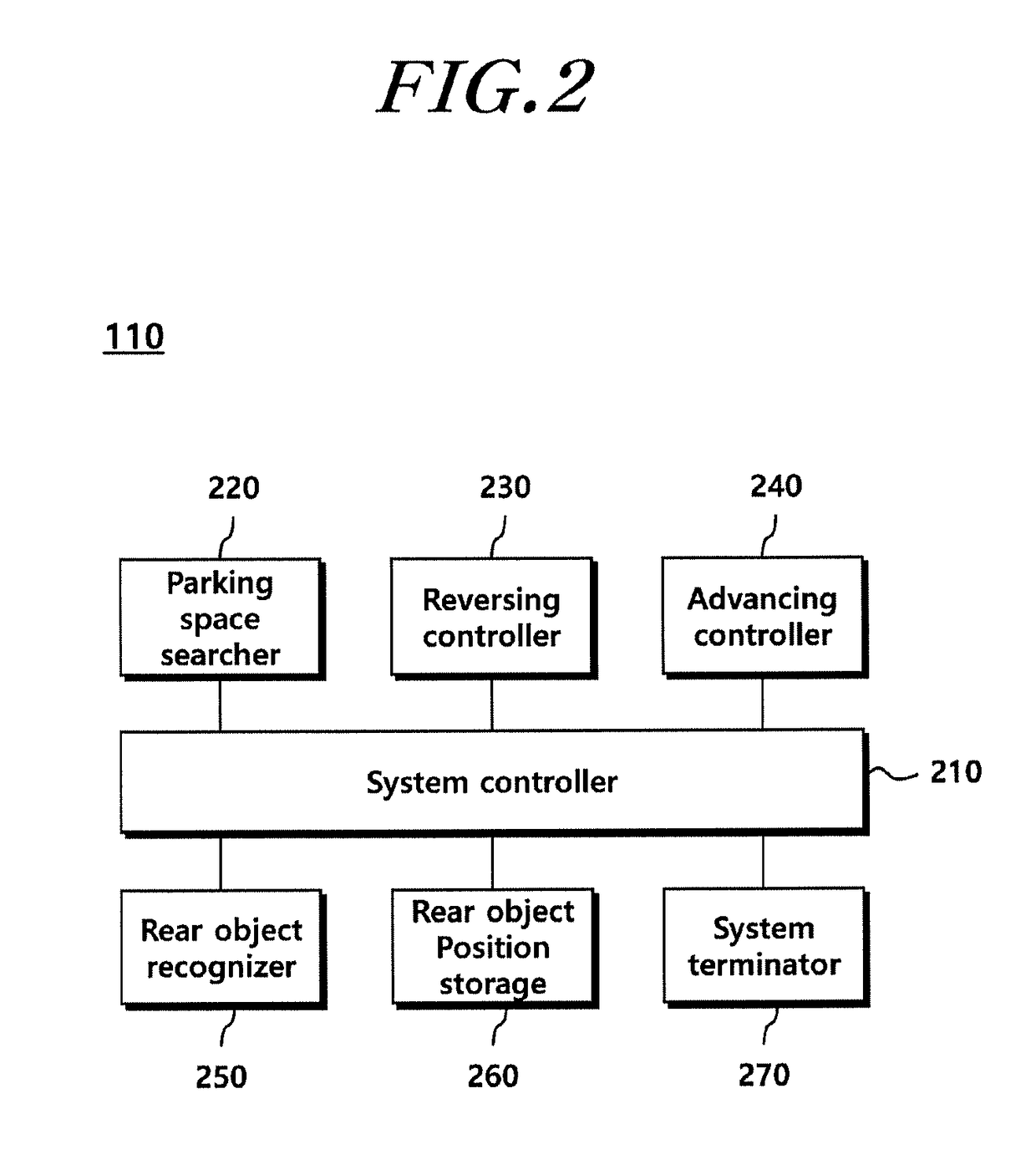
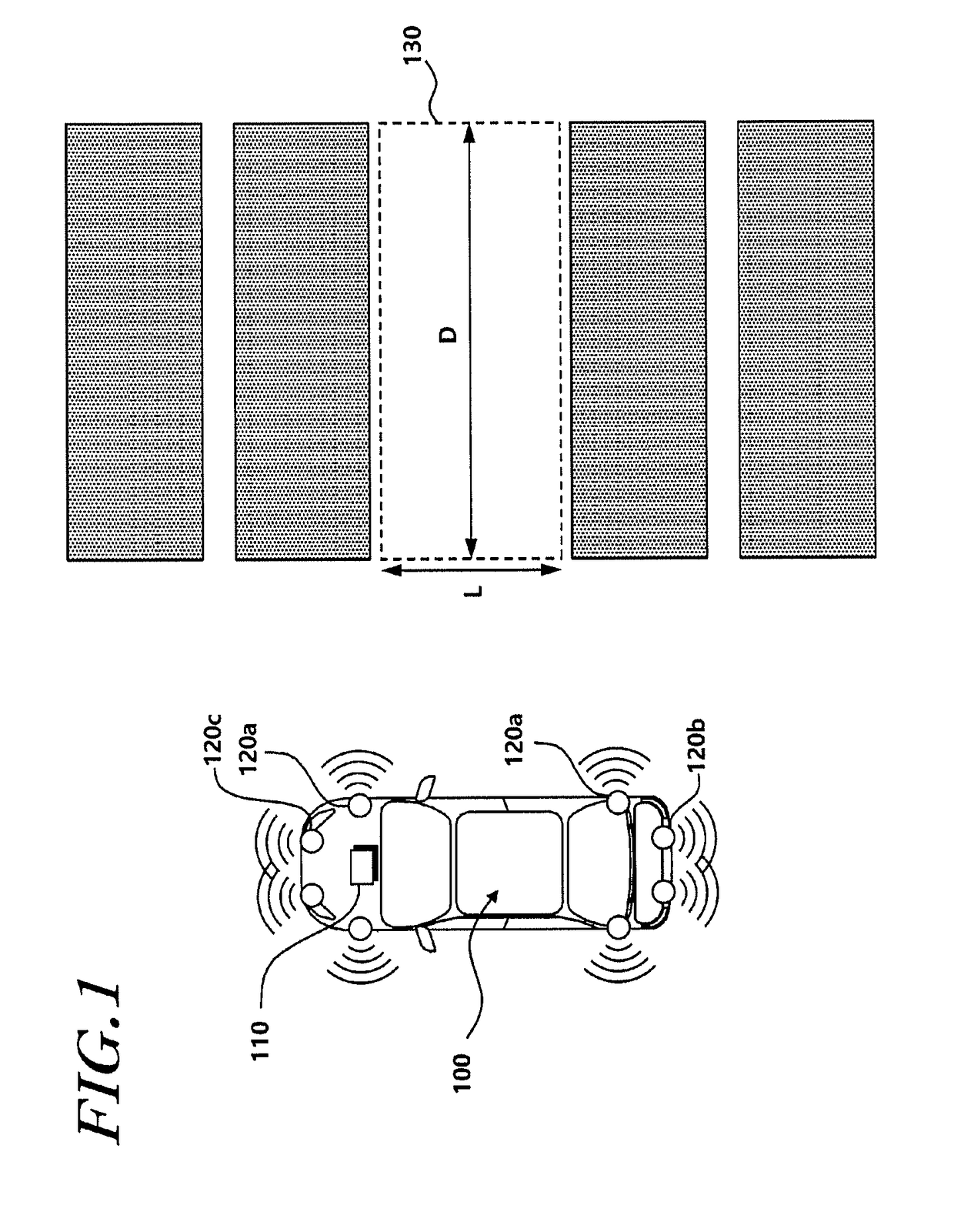
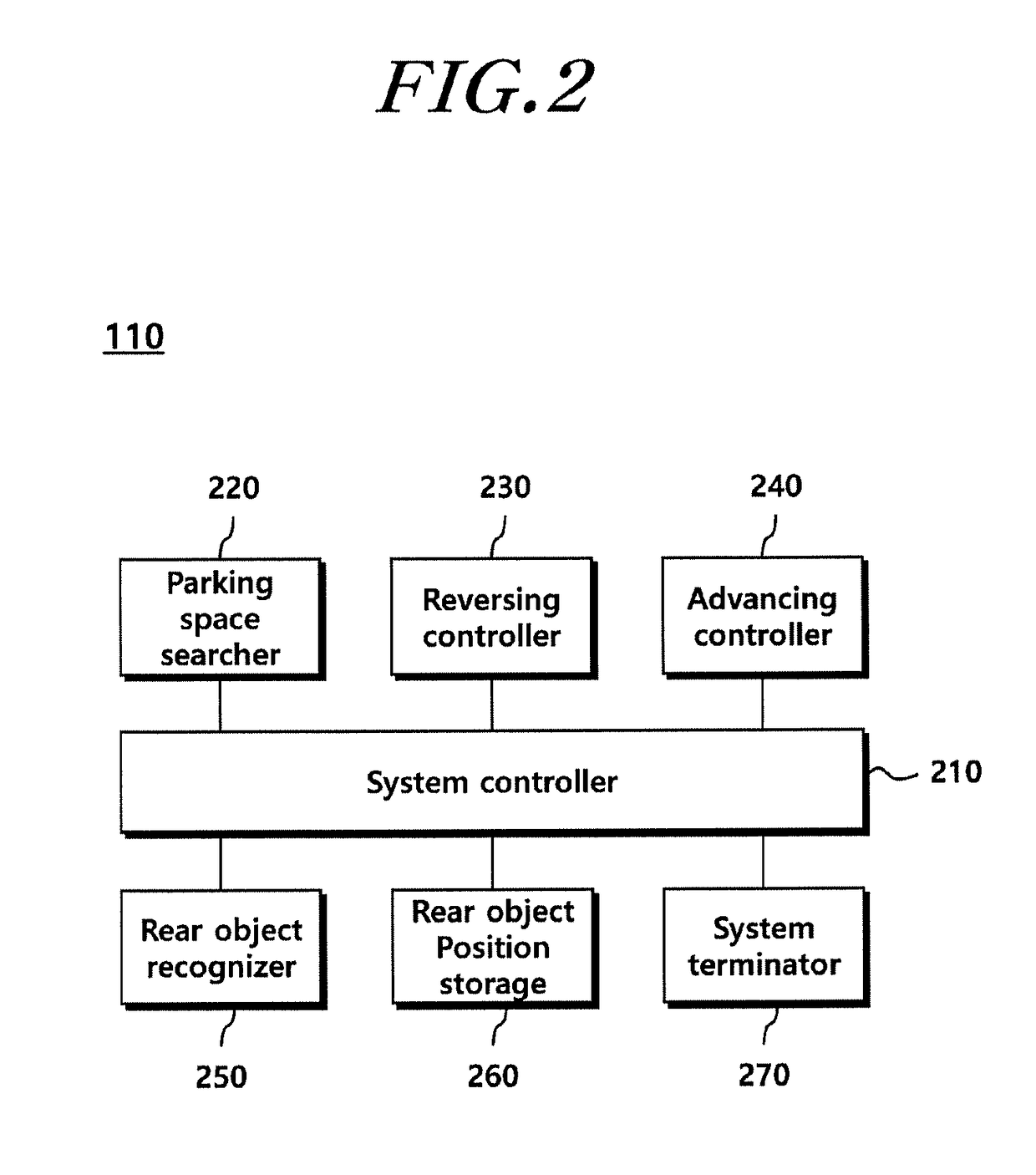
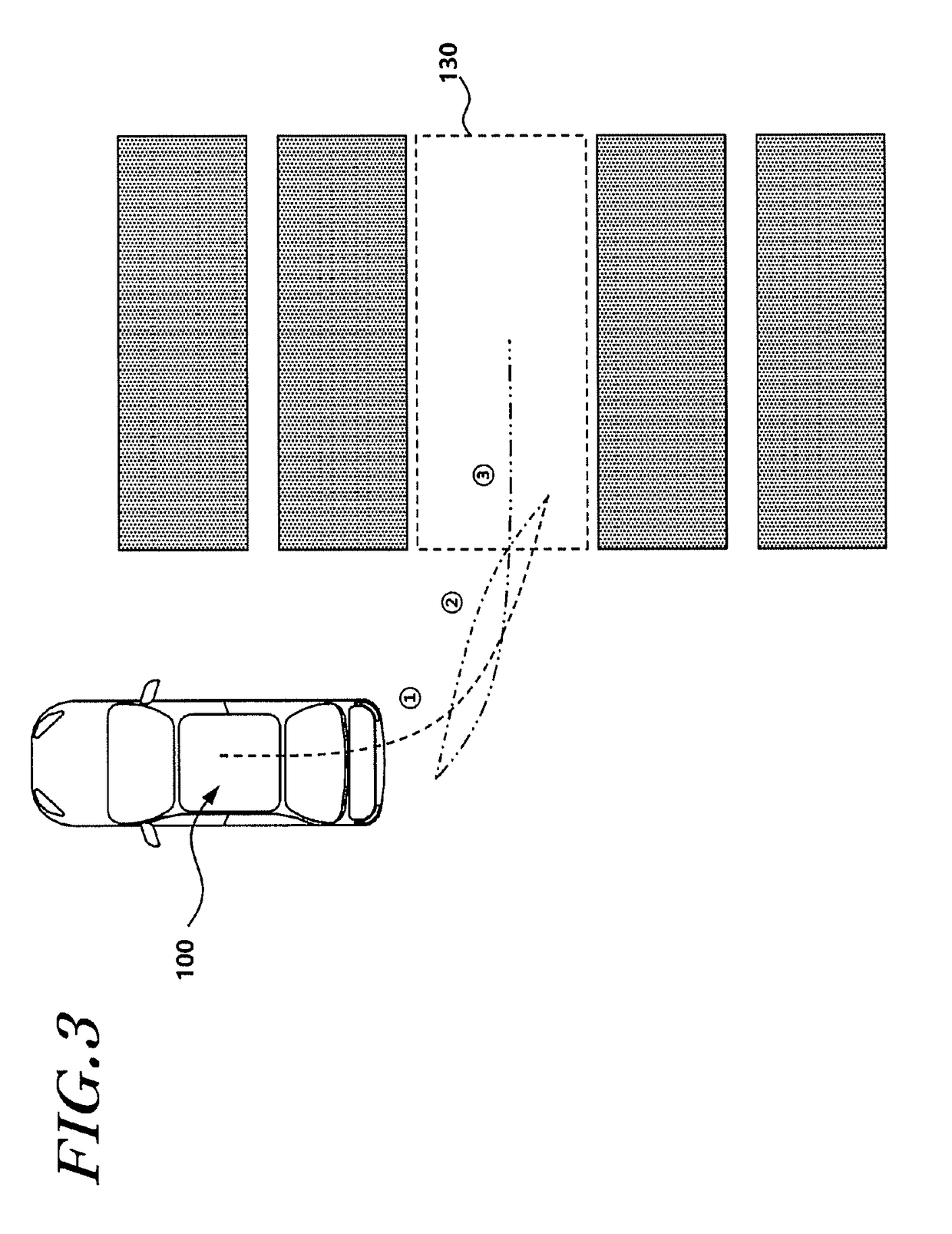
Parking assist system and method
The present disclosure provides a parking assist system including: a rear object recognizer that recognizes a rear object existing behind a vehicle through rear sensors; a reversing controller that controls the vehicle to reverse until an entry rate to the parking space becomes a first reference value or more, and ends reversing control when a distance between the vehicle and the rear object becomes less than a second reference value; a rear object position storage that stores position information of the rear object and increases a count when the reversing control is ended on the basis of the distance between the vehicle and the rear object; and a system terminator that ends parking control when the position information of the rear object before and after the count is increased is substantially the same.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
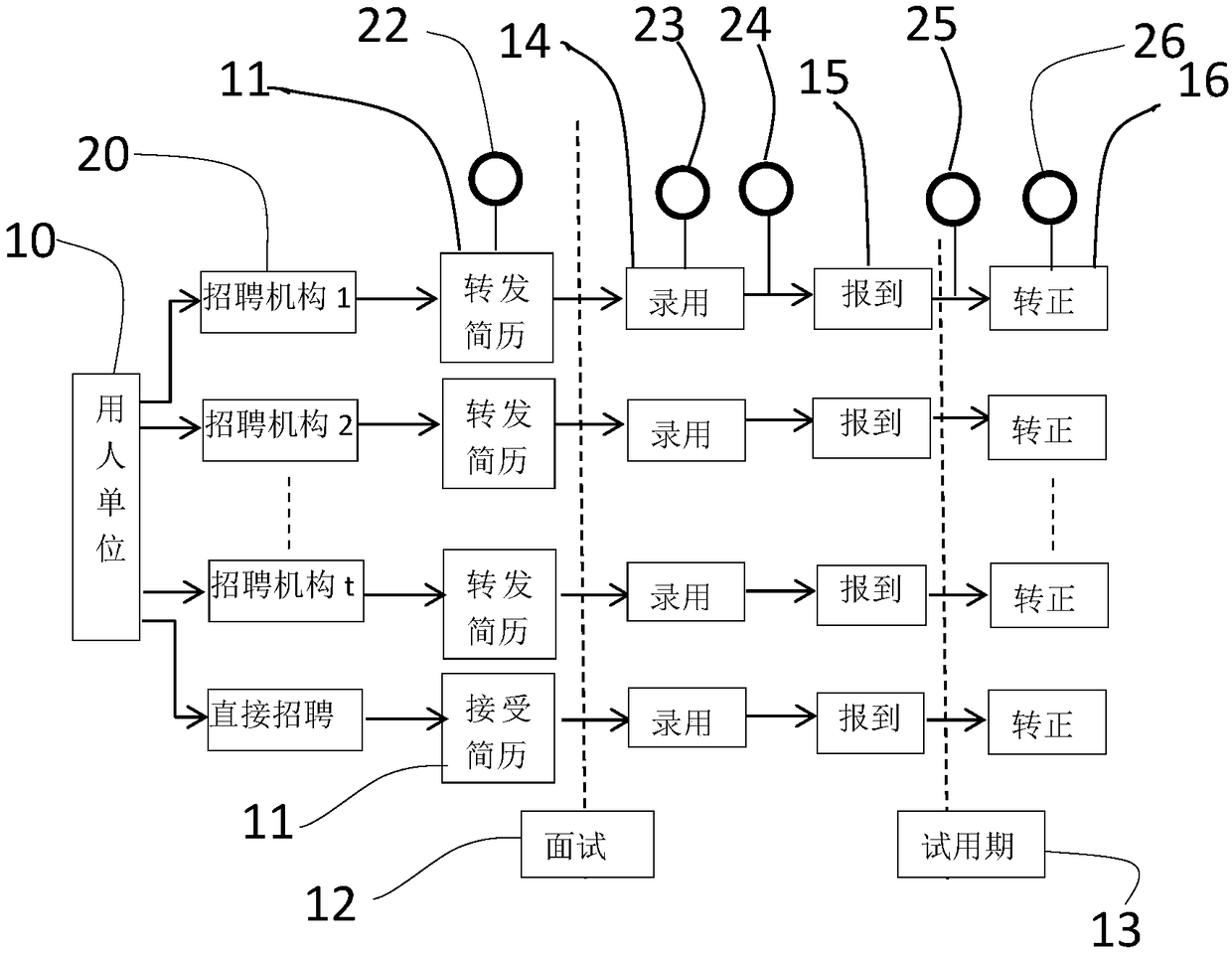
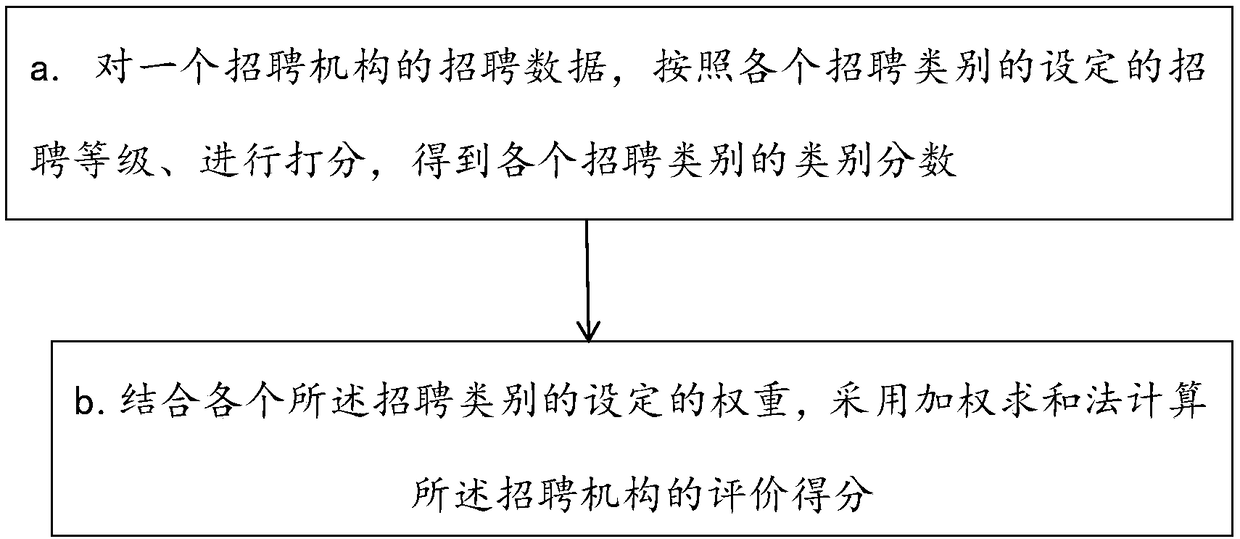
A method and system for quantitatively evaluating the recruitment capability of a recruitment agency
PendingCN109003004AReduce labor costsImprove recruitment efficiencyOffice automationResourcesPass rateEvaluation system
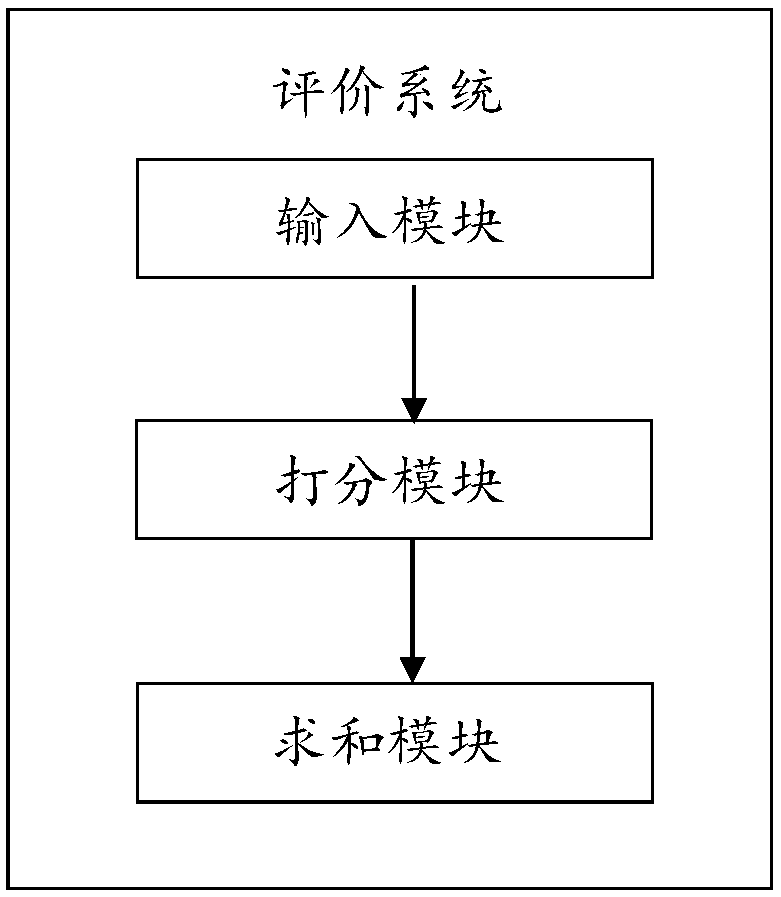
The present application discloses a method and system for quantitatively evaluating the recruitment capability of a recruitment agency. The evaluation method scores recruitment data of a recruitment agency according to a set recruitment grade of each recruitment category, and calculates an evaluation score of the recruitment agency according to the set weight of each recruitment category. The recruitment category at least comprises the number of resumes of candidates recommended by the recruitment agency, the pass rate of interviews, the abandonment rate, the turnover rate during the probationperiod, and the recommended entry rate of the regular employees in the total number of employees. The evaluation system implements the evaluation method by setting corresponding modules. By using theevaluation score of the application, the employer can conveniently compare the recruitment ability of each recruitment agency horizontally, and determine and select the recruitment agency with the best performance in the future recruitment, so as to improve the recruitment efficiency, save the recruitment-related expenses and save the employment cost of the enterprise.
Owner:上海态特网络科技有限公司
Store entry rate statistical method based on yolo and centroid tracking
InactiveCN109658128ASolve the accuracy problemSolve real-timeMarket predictionsImage analysisPattern recognitionVisual perception
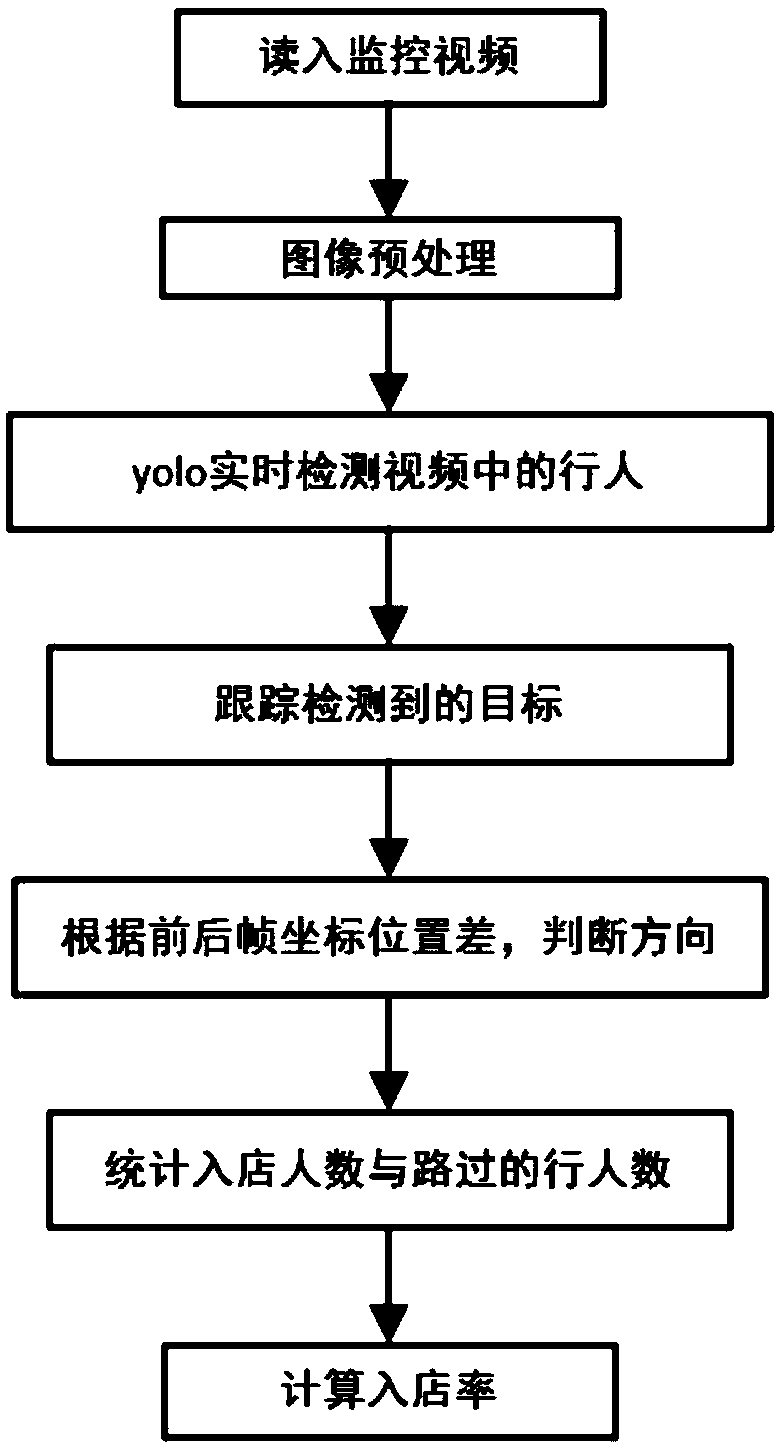
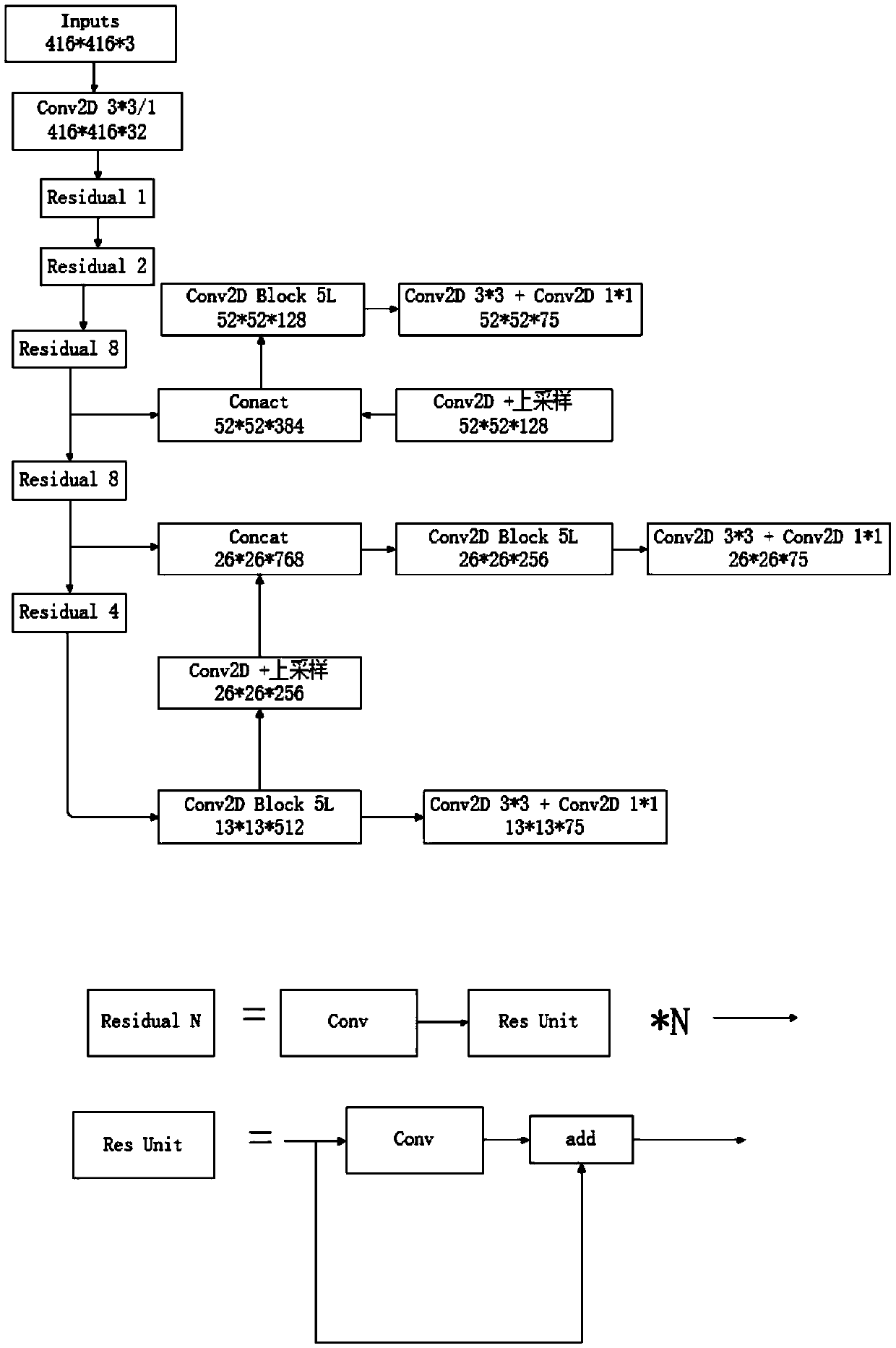
The invention discloses a store entry rate statistical method based on yolo and centroid tracking, and relates to the field of monitoring video, deep learning, computer vision and pedestrian detection, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the real-time detection of a picture in a monitoring video through a yolo target detection model; Therefore, obtaining the target category and the corresponding target position in each frame of image data, screening out the category belonging to a person, and the centroid position of the target is stored. And tracking the target through a centroidtracking algorithm, keeping the unique distribution of the target ID, calculating the target motion direction through the upper and lower frames of the video, and counting the number of people entering the store and passing through the store to obtain the store-in and store-out rate. The invention provides a store entry rate statistical method based on yolo and centroid tracking, and the method is simple in algorithm, is beneficial to software realization, and achieves the statistics of the movement direction of pedestrians through target detection and a centroid tracking algorithm.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
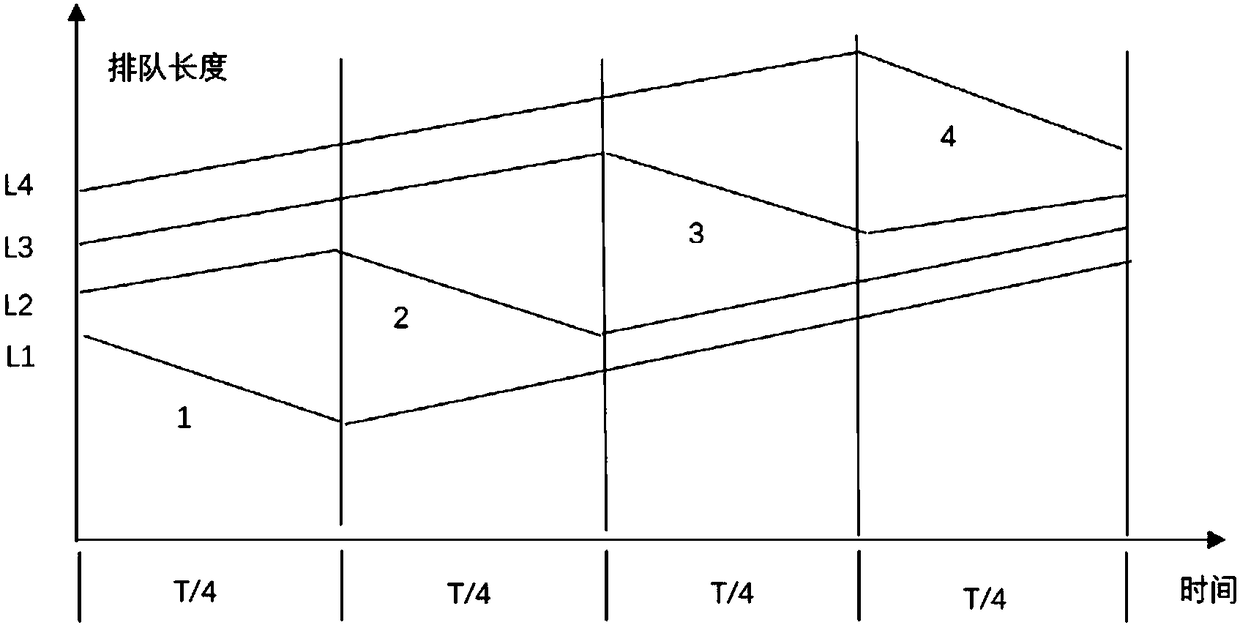
Single-intersection signal timing method based on cooperative game theory cost distribution method
ActiveCN108364483AReduce delayImprove adaptabilityControlling traffic signalsFuzzy logic based systemsCost distributionSimulation
The invention relates to a single-intersection signal timing method based on a cooperative game theory cost distribution method, and the method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: 1), carrying out the modeling analysis of a single intersection through employing a cost distribution model in the cooperative game theory, and obtaining a single-intersection signal timingmodel which comprises a cost feature function and a cost distribution function; 2), obtaining the calculation parameters of all phases of the single intersection through a vehicle-road cooperation system, wherein the calculation parameters comprise the queuing length of each phase in a former period, the vehicle entry rate and leaving rate of a current period, and a total signal lamp period of the intersection; 3), calculating and obtaining the green-light distributed time duration of each phase according to the obtained calculation parameters of each phase of the intersection and the signaltiming model. The method can be widely used in the field of signal timing of the single intersection.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
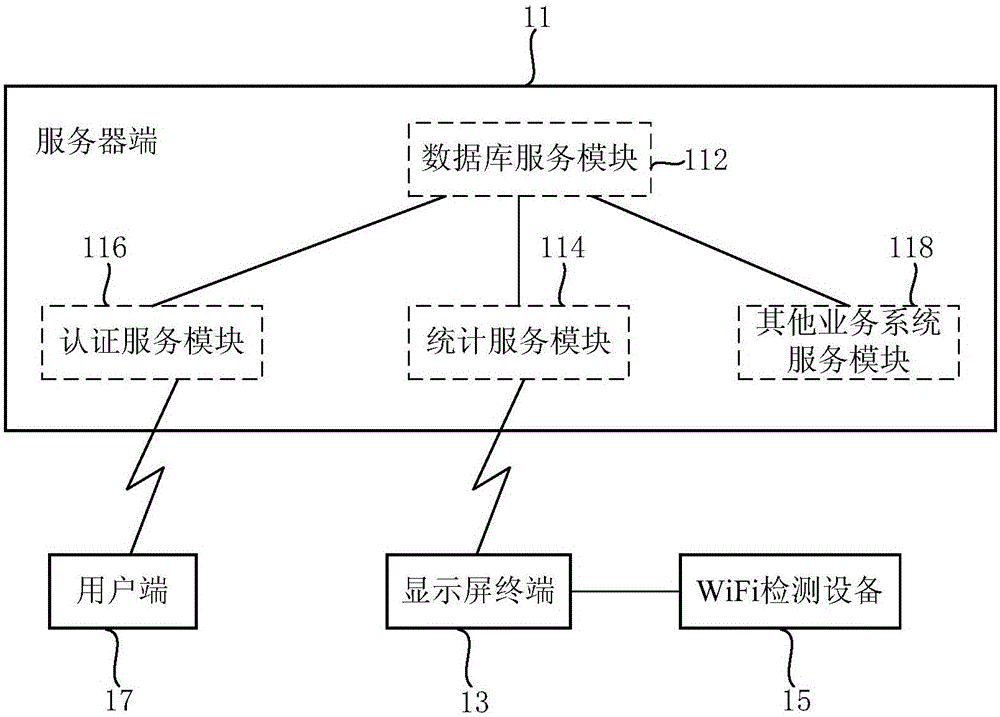
Display screen attention statistic method and system
ActiveCN105117767AImprove discriminationStatistically accurateCounting objects with random distributionMarketingEntry timeComputer terminal
The invention relates to a display screen attention statistic method and a system. The method comprises the following steps of (a) detecting an unique identification code of each mobile terminal whose WiFi is in an open state in a coverage area of WiFi detection equipment, entry time and departure time, wherein the WiFi detection equipment is arranged near a target display screen; (b) carrying out association storage on the entry time, the departure time and the unique identification code; (c) according to a difference of the departure time and the entry time, calculating standing time of each mobile terminal in the coverage area of the WiFi detection equipment and carrying out association storage on the standing time and the unique identification code of the mobile terminal; and (d) calculating the number of the associated unique identification codes when the standing time is greater than a standing time threshold in preset time so as to obtain a quantity of crowds who pay attention to the target display screen. By using the method and the system, a visitor flow rate and an attention degree of the display screen can be accurately calculated; each display screen can be distinguished and data sensitivity is high.
Owner:XIAN NOVASTAR TECH
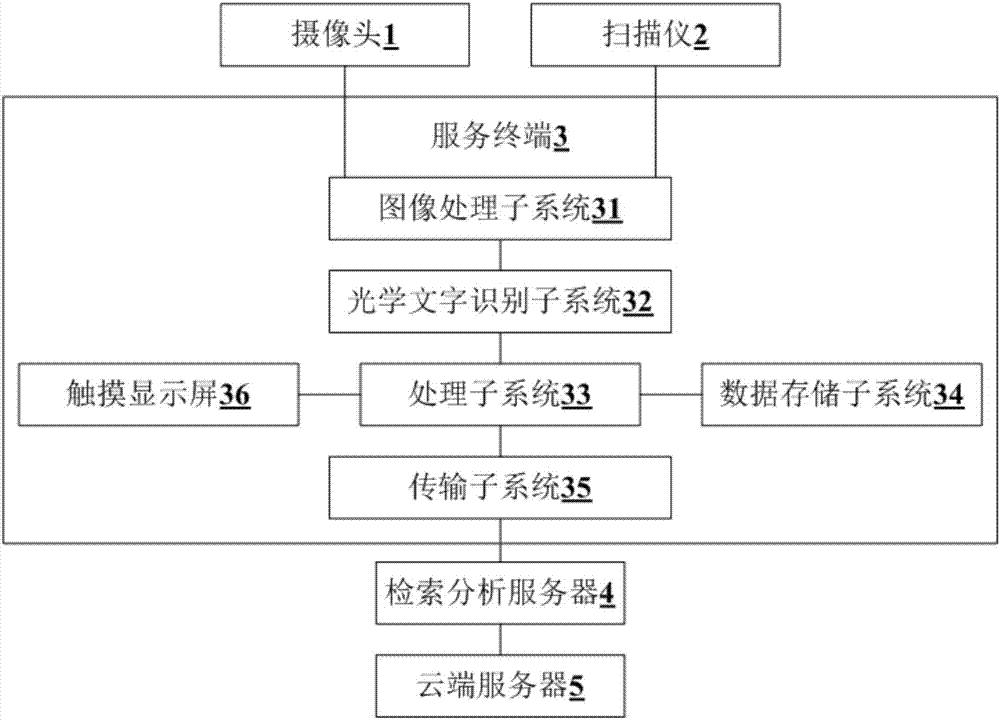
System and method of information retrieval classification based on cloud computing
PendingCN107122498ASpeed up the entry processAccelerate entry rateVectoral format still image dataSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingImaging processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of Internet, and provides a system and method of information retrieval classification based on cloud computing. The system comprises a camera, a scanner, a service terminal, a retrieval analysis server and a cloud server. The service terminal comprises an image processing subsystem, an optical character recognition subsystem, an information processing subsystem, a data storage subsystem, a transmission subsystem and a touch display screen; the image processing subsystem, the optical character recognition subsystem, the information processing subsystem and the data storage subsystem are connected sequentially; the information processing subsystem is connected with the transmission subsystem and the touch display screen respectively; the camera and the scanner are connected with the image processing subsystem; the transmission subsystem, the retrieval analysis server and the cloud server are sequentially connected. The system and method of information retrieval classification based on the cloud computing can speed up the information entry rate and improve the retrieval efficiency of scientific literatures.
Owner:黑龙江省科学技术情报研究院
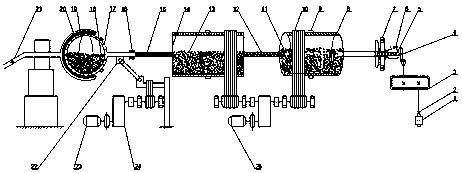
Special-shaped barrel combined continuous ball mill
The invention relates to the technical field of ball mills, in particular to a special-shaped barrel combined continuous ball mill. The special-shaped barrel combined continuous ball mill comprises afirst motor; the first motor is connected with a first speed reducer through a coupling; the first speed reducer is connected with a spiral feeding device through an open bevel gear; the spiral feeding device is connected with a cylindrical smashing bin through a feeding end cover; a smashing bin grinder is arranged in the cylindrical smashing bin; the cylindrical smashing bin is connected with acoarse grinding bin through a first filter screen, and the cross section of the coarse grinding bin is regularly octagonal; and the cylindrical smashing bin and the coarse grinding bin are connected through a second motor through a belt. The special-shaped barrel combined continuous ball mill has the beneficial effects that the coarse grinding bin is of a regular octagon barrel structure, and thecross section of the coarse grinding bin is regularly octagonal instead of being round, so that the phenomenon of rotation is relieved to a certain extent and the grinding effect is greatly improved;and the first filter screen can prevent the smashing bin grinder and unground materials from entering the coarse grinding bin and can control the entry rate of ground materials into the coarse grinding bin.
Owner:JINGDEZHEN CERAMIC INSTITUTE
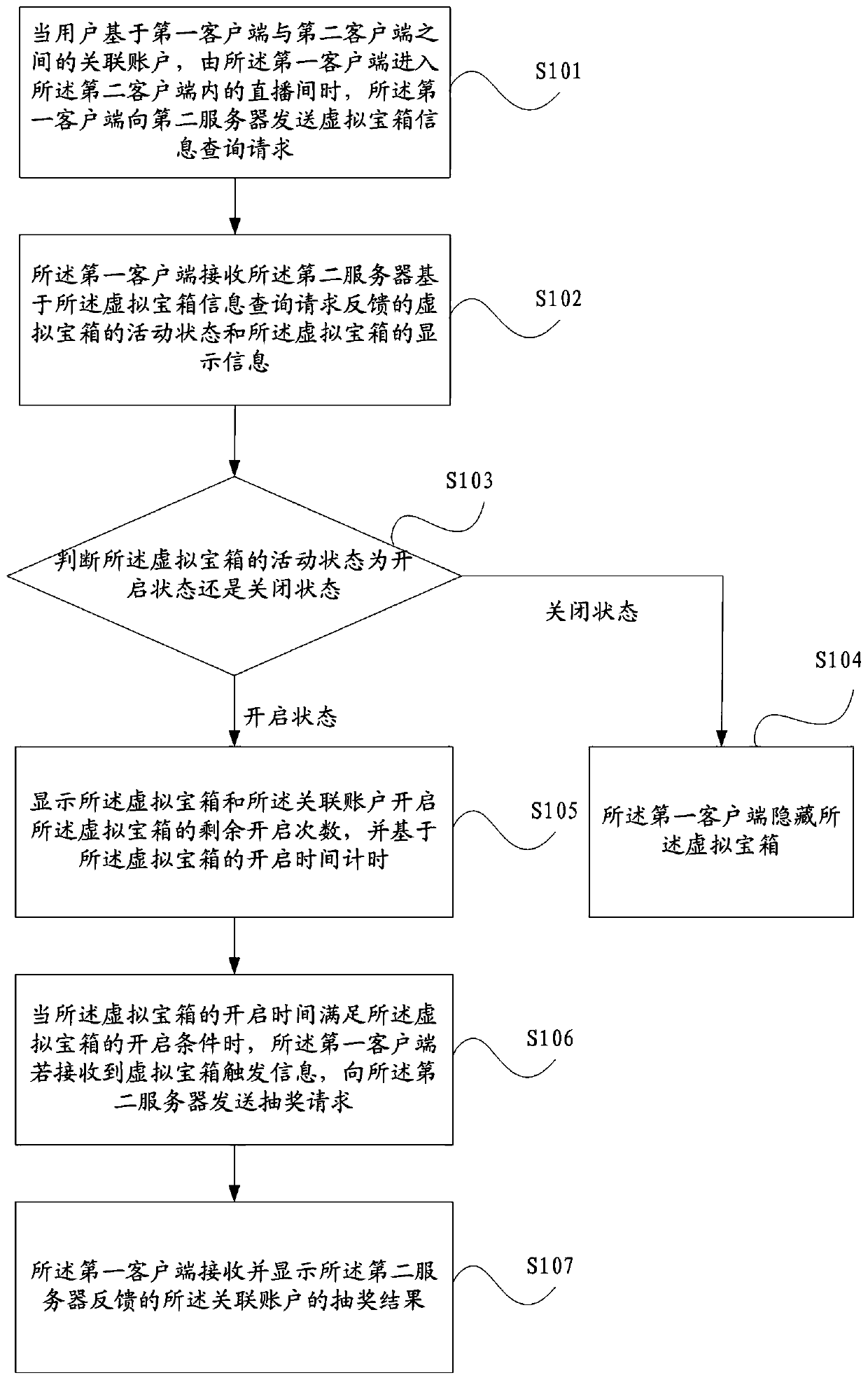
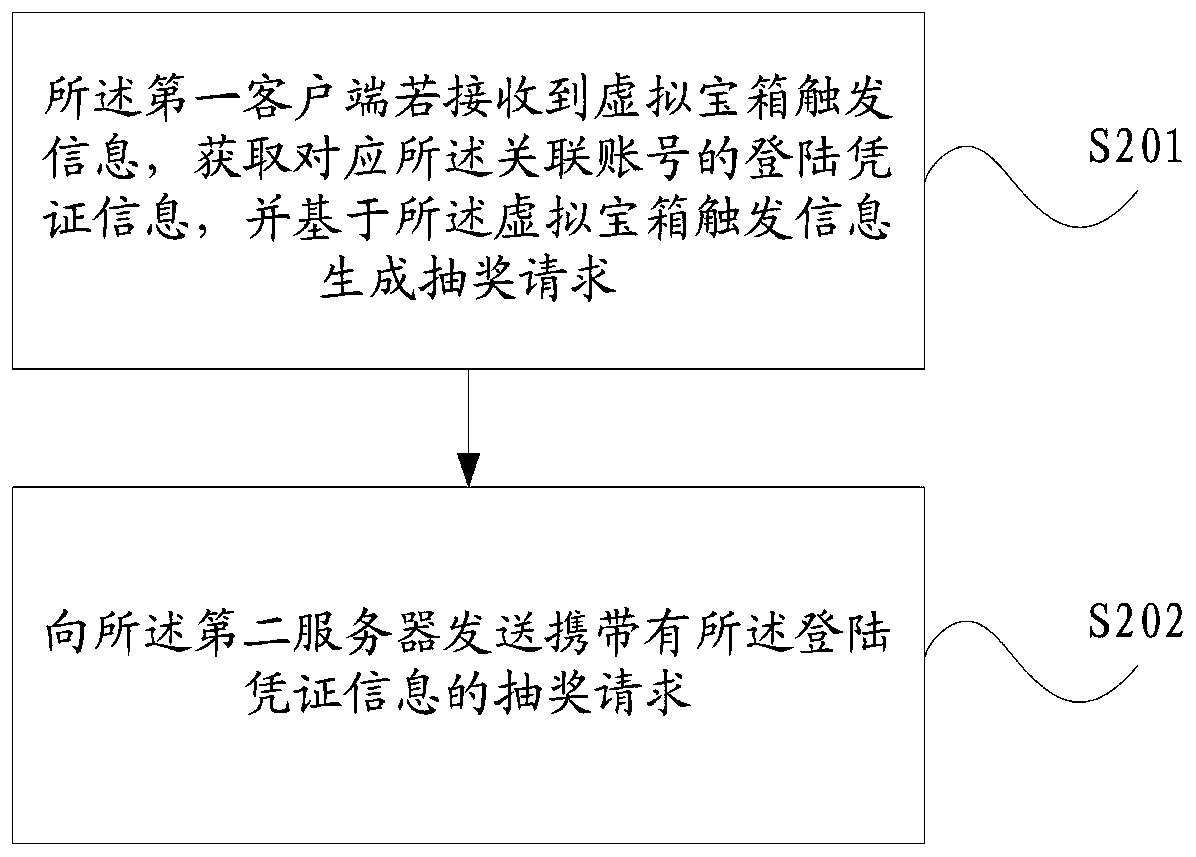
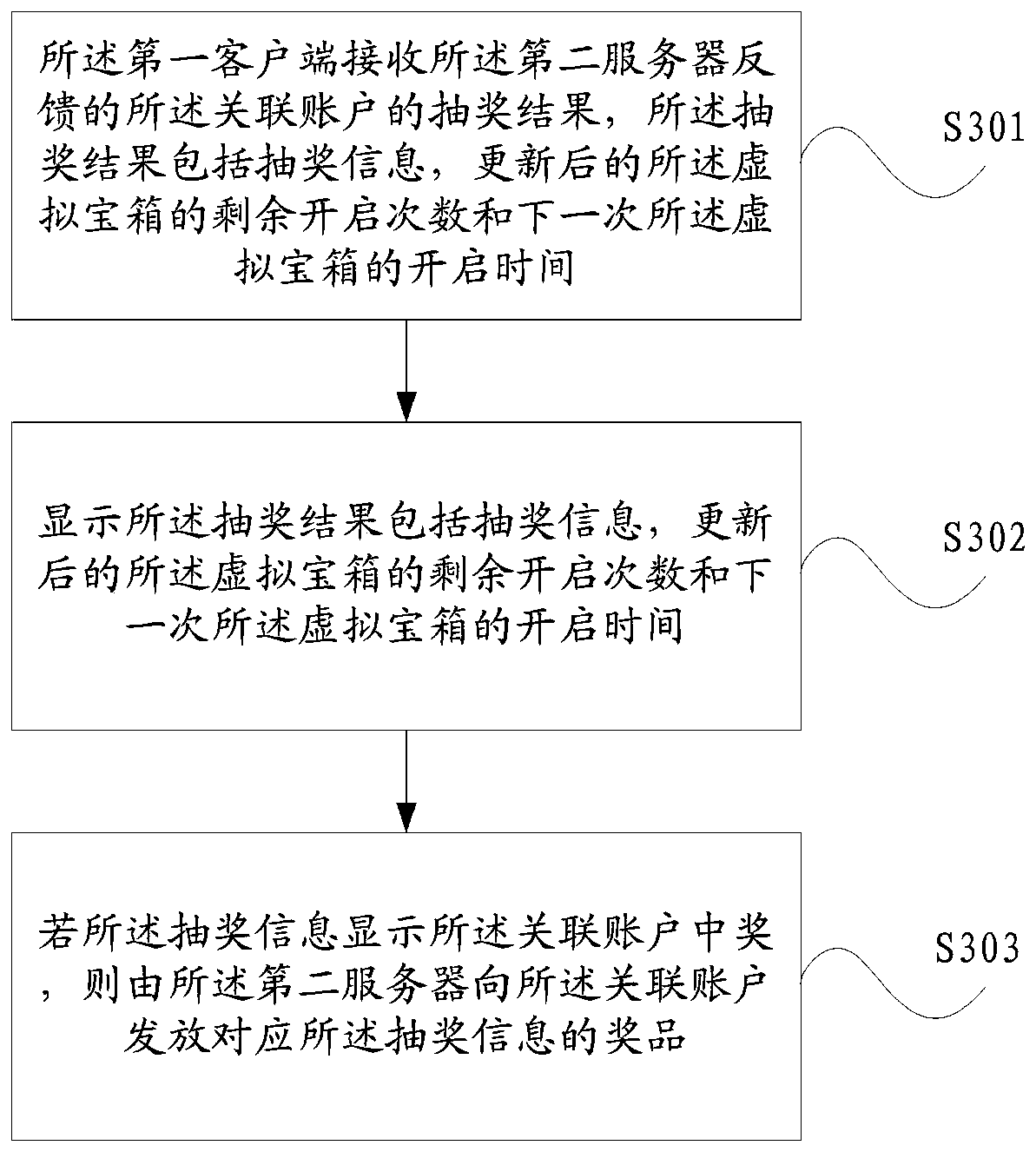
Virtual treasure box processing method, client and server
ActiveCN110087138AIncrease entry rateImprove retentionSelective content distributionClient-sideEntry rate
The invention discloses a virtual treasure box processing method, a client and a server. When a user enters a live broadcast room in a second client from a first client based on an associated accountbetween the first client and the second client, the first client sends a virtual treasure box information query request to a second server, the first client receives the activity state of the virtualtreasure box and the display information of the virtual treasure box fed back by the second server based on the virtual treasure box information query request, and when the opening time of the virtualtreasure box meets the opening condition of the virtual treasure box, the first client sends a lottery drawing request to the second server if receiving the virtual treasure box triggering information, and the first client receives and displays a lottery drawing result of the associated account fed back by the second server. According to the above method, the first client receives and displays the lottery drawing result obtained by the associated account fed back by the second server, so that the user corresponding to the associated account obtains the virtual treasure box, and the entry rateand retention rate of the user in the live broadcast room are improved.
Owner:广州方硅信息技术有限公司
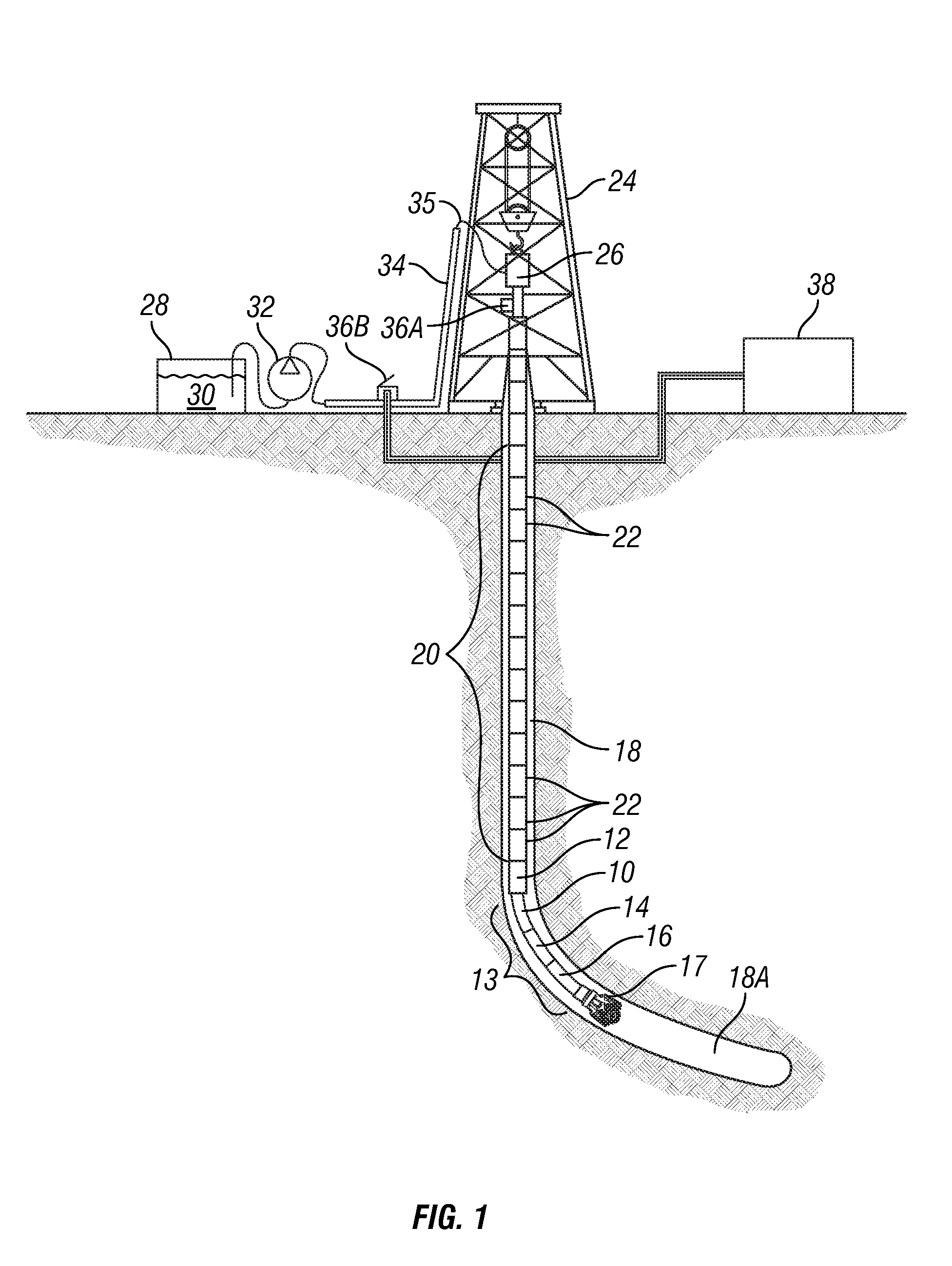
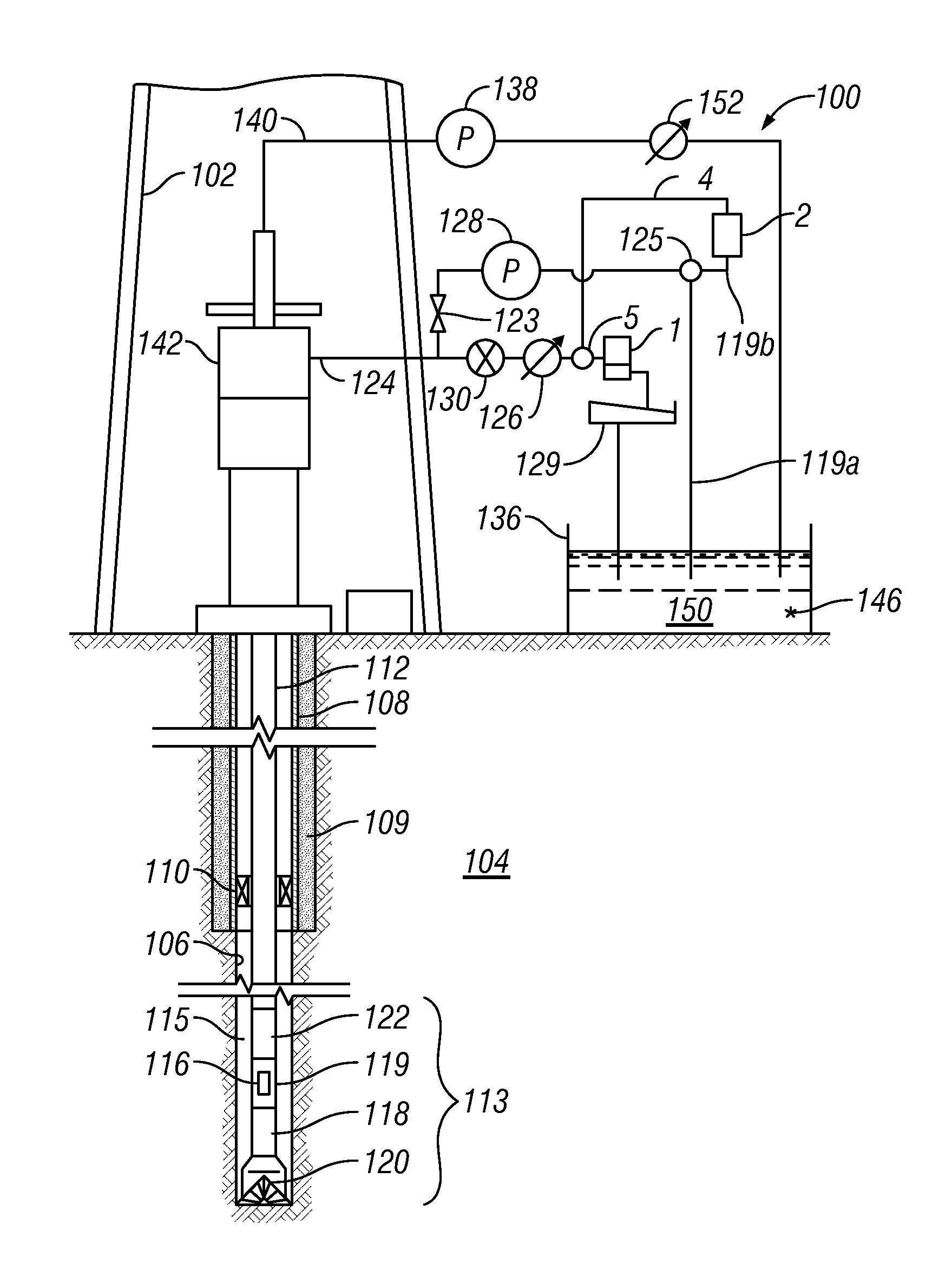
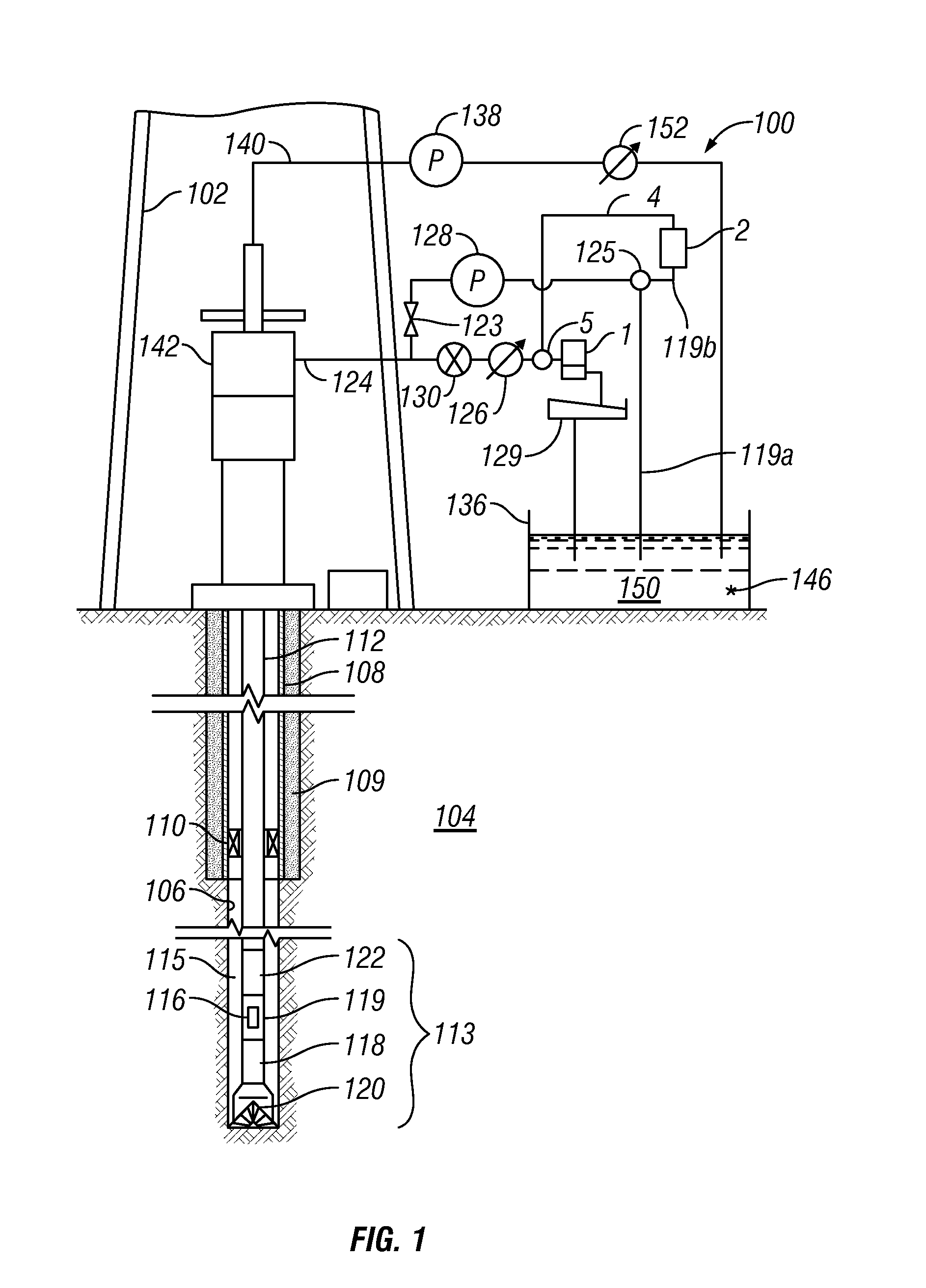
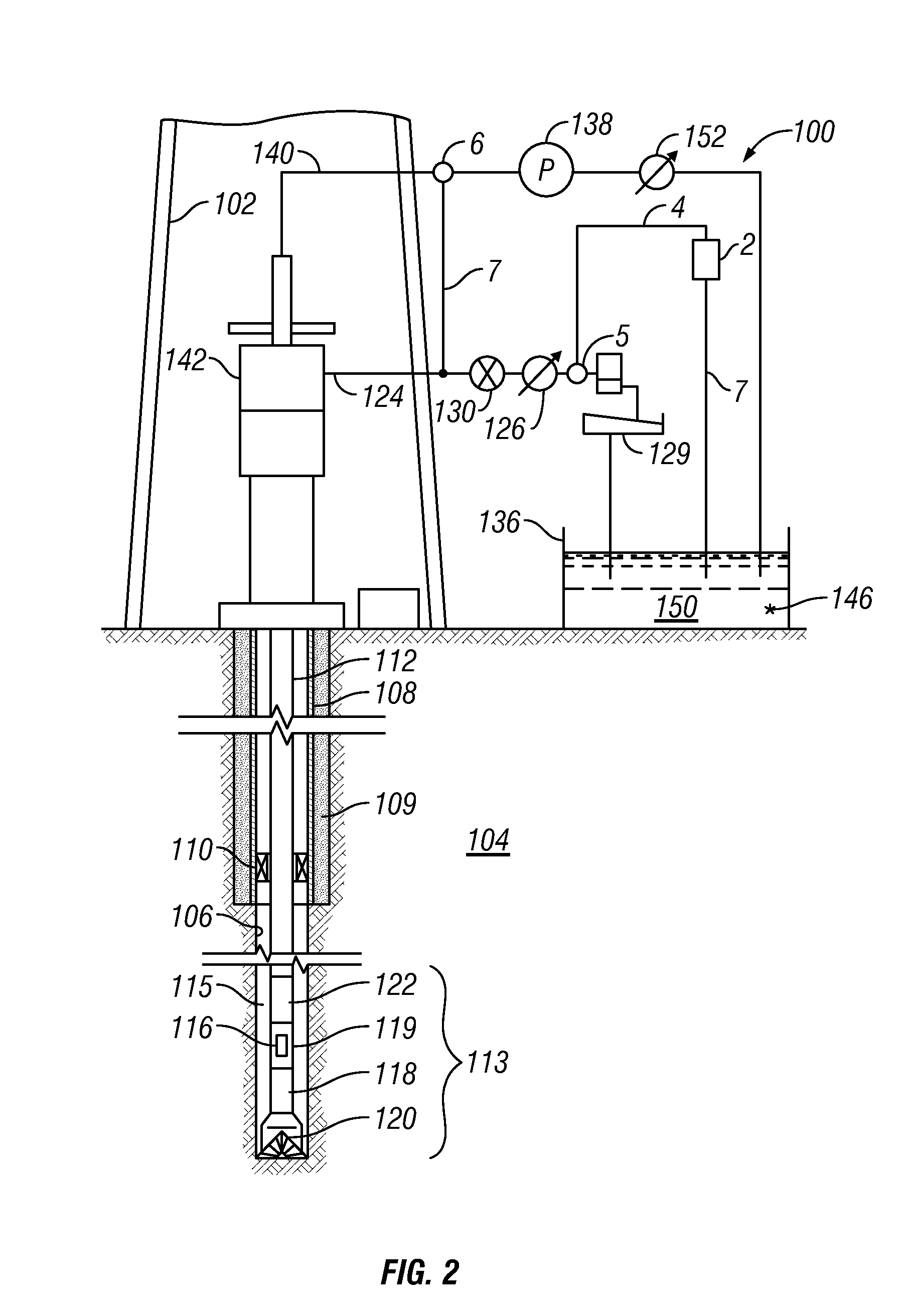
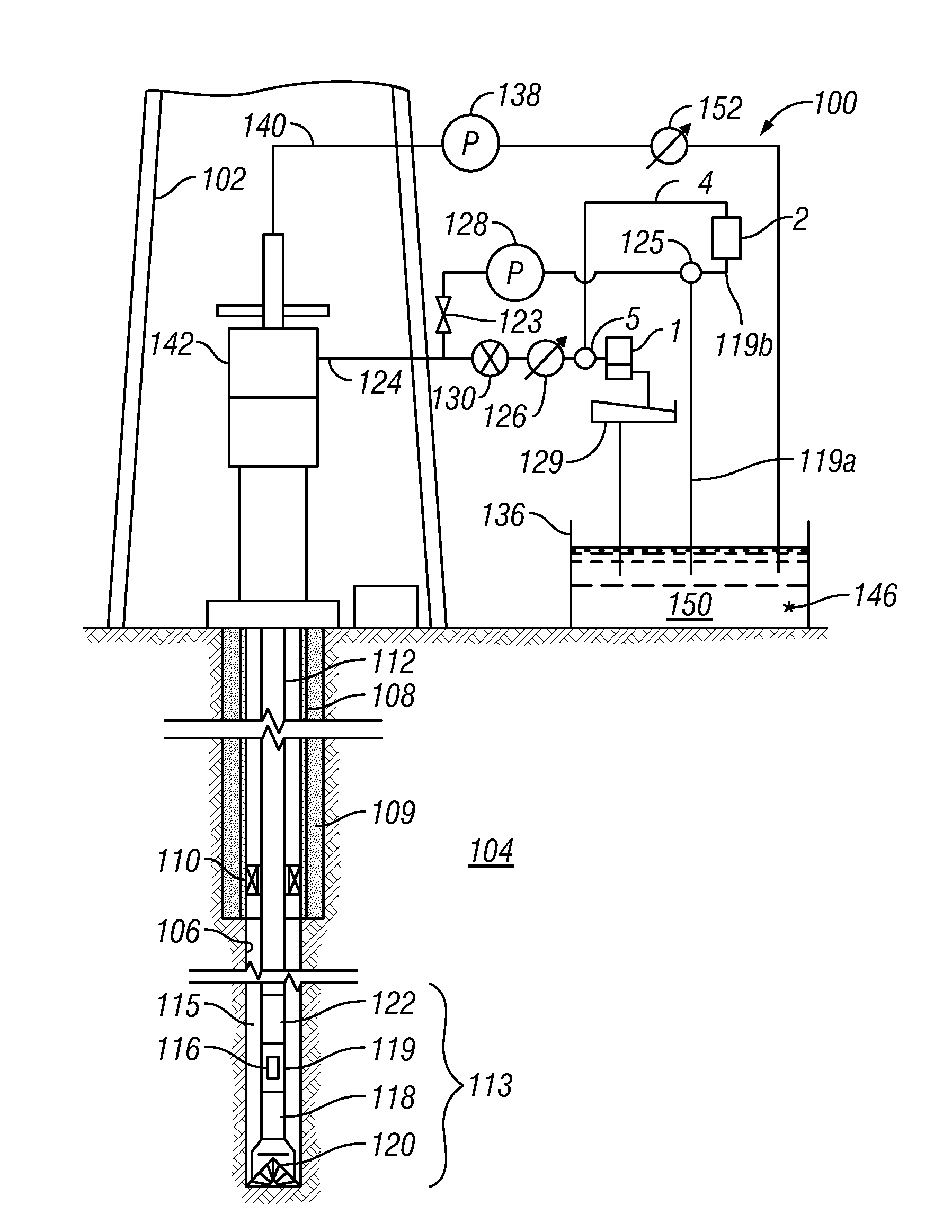
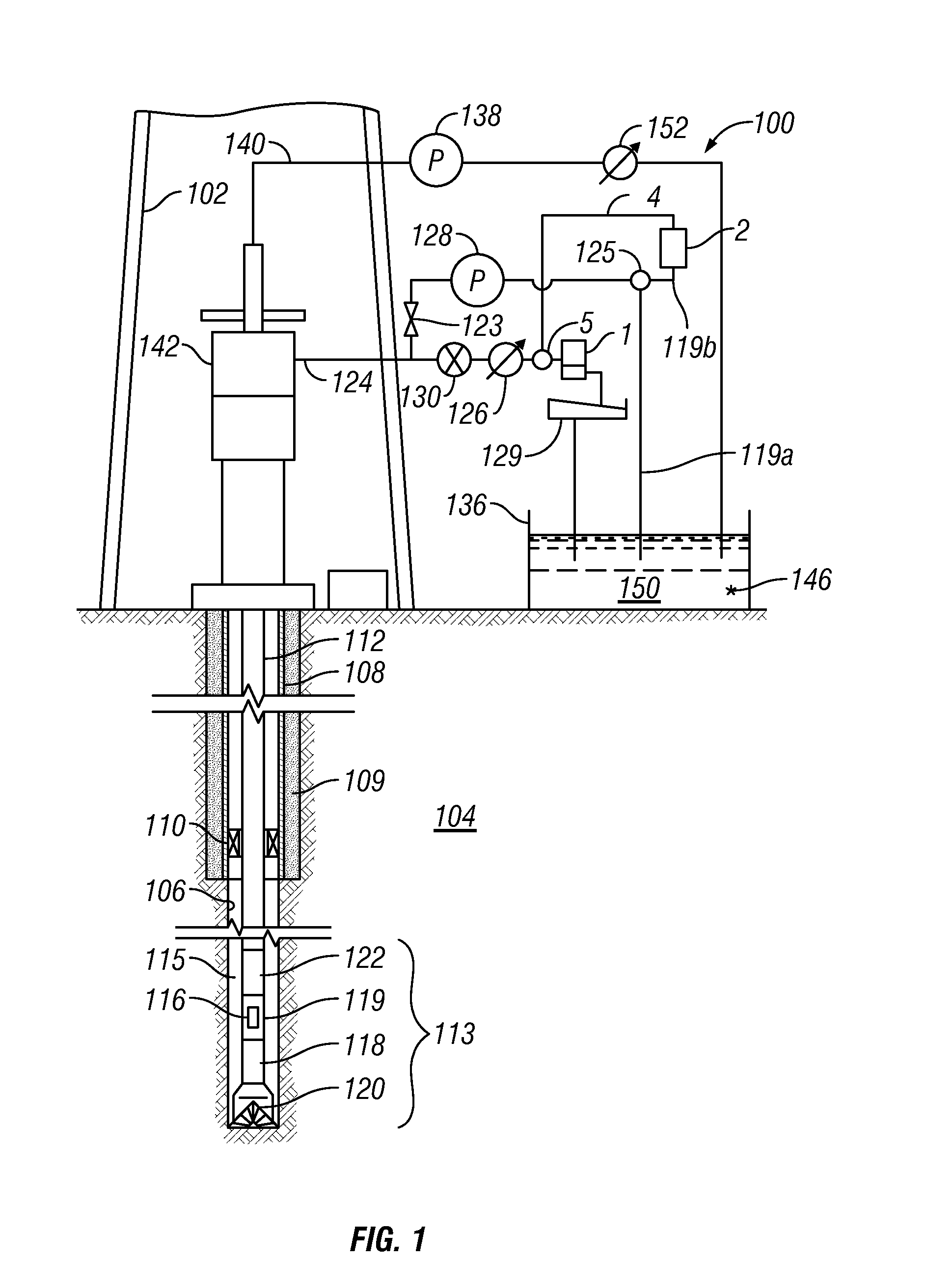
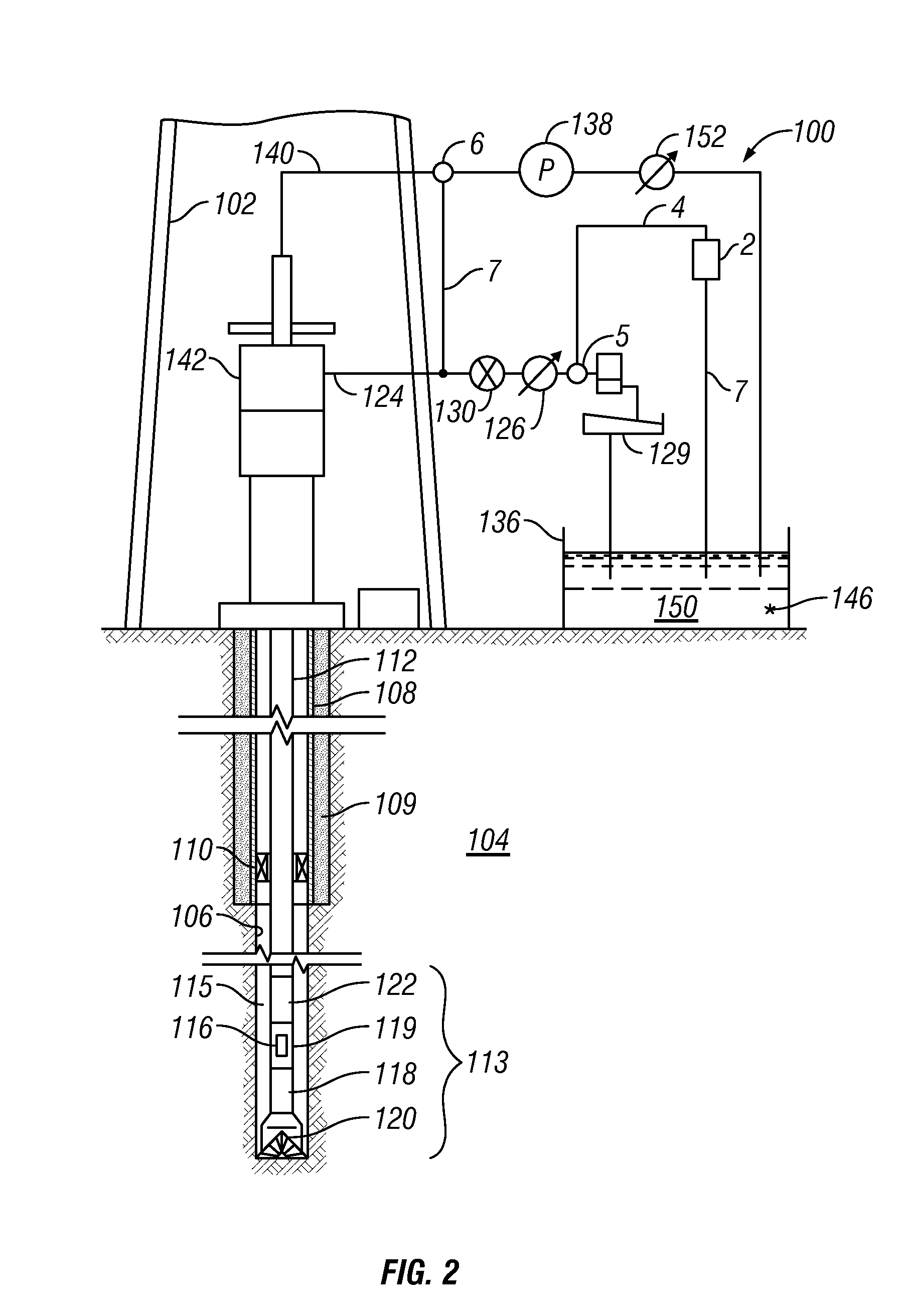
Method for drilling through nuisance hydrocarbon bearing formations
A method for controlling entry of hydrocarbon into a wellbore from a subsurface formation includes determining whether hydrocarbon is entering the wellbore. Whether a rate of hydrocarbon entry into the wellbore is slowing is then determined Control of discharge from the wellbore is then switched from maintaining a selected wellbore pressure to controlling a rate of discharge of fluid from the wellbore to be substantially constant if the hydrocarbon entry rate is slowing. Control of discharge from the wellbore is returned to maintaining the selected wellbore pressure when the hydrocarbon stops entering the wellbore.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
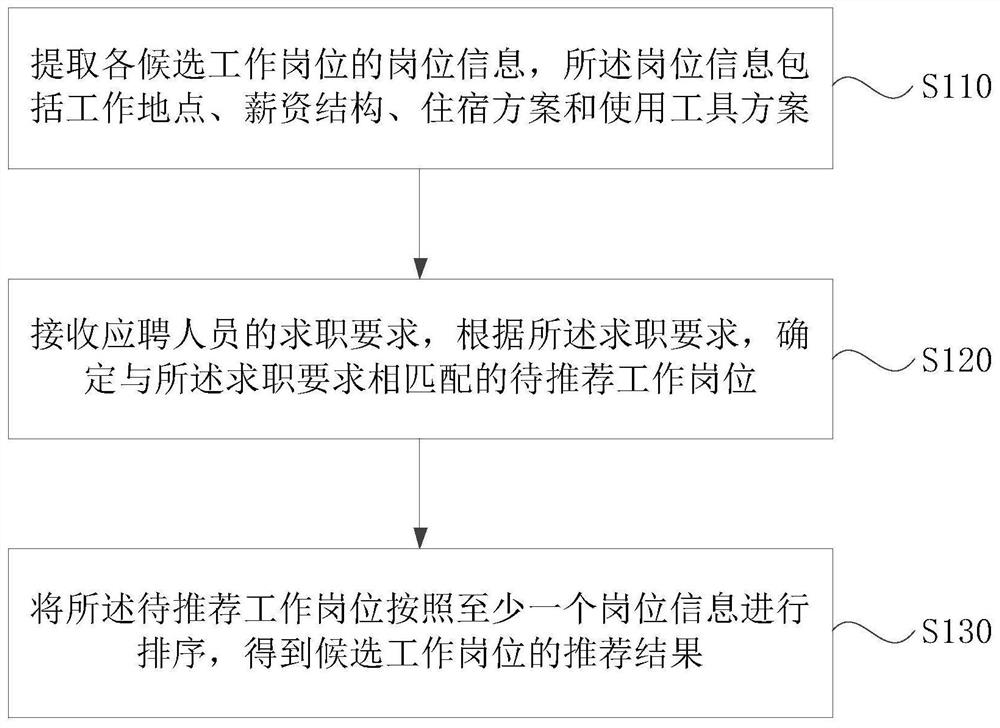
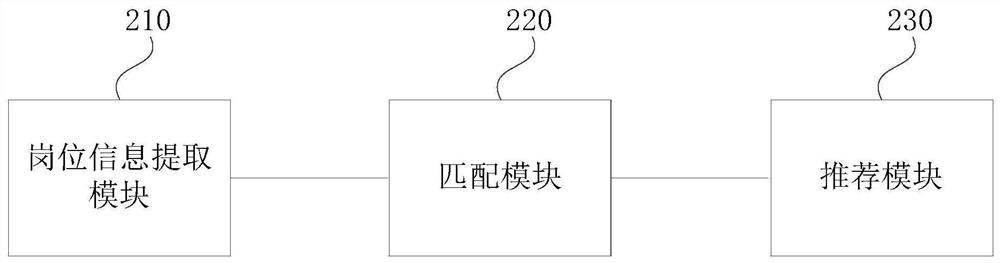
Applicant and working post matching method and device, medium and electronic equipment
PendingCN112801512AImprove matching resultsImprove job entry ratesOffice automationResourcesMatching methodsComputer science
The embodiment of the invention discloses an applicant and working post matching method and device, a medium and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: extracting post information of each candidate working post, wherein the post information comprises a working place, a salary structure, an accommodation scheme and a tool use scheme; receiving a job hunting requirement of an applicant, and determining a to-be-recommended working post matched with the job hunting requirement according to the job hunting requirement; and sorting the to-be-recommended working posts according to at least one post information to obtain a recommendation result of the candidate working posts. According to the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, the post information of the candidate working posts can be extracted and matched, and the candidate working posts are arranged according to a certain sequence, so that the applicant can preferentially know the post information which is most matched with the applicant, the matching result of the applicant and the working posts is improved, and the employment entry rate and the stability are improved.
Owner:好活(昆山)网络科技有限公司
Broadcast storm control system and method
InactiveCN1968207AAvoid Situations That Stop DeliveryData switching networksElectric digital data processingBroadcast packetControl system
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Crumpling mechanism for creating dunnage
A dunnage crumpling apparatus is provided having first and second entry-side crumpling members and first and second exit-side crumpling members. The first and second entry-side crumpling members define an entry therebetween. The first and second exit-side crumpling members define an exit therebetween that is disposed along the longitudinal path downstream of the entry. A crumpling zone being defined between the entry and exit. The first entry-side crumpling member is configured for moving at an first rate and is associated with the second entry-side crumpling member for moving sheet material through the entry in a first direction along a longitudinal path at an entry rate. The first exit-side crumpling member is configured for moving at an second rate and is associated with the second exit-side crumpling member for moving the sheet material through the exit in the first direction along the path at a exit rate that is slower than the entry rate to crumple the sheet material for producing dunnage. The entry and exit-side crumpling members are displaced laterally along the path with respect to each other to cause shearing of the sheet within the crumpling zone.
Owner:PREGIS INNOVATIVE PACKAGING
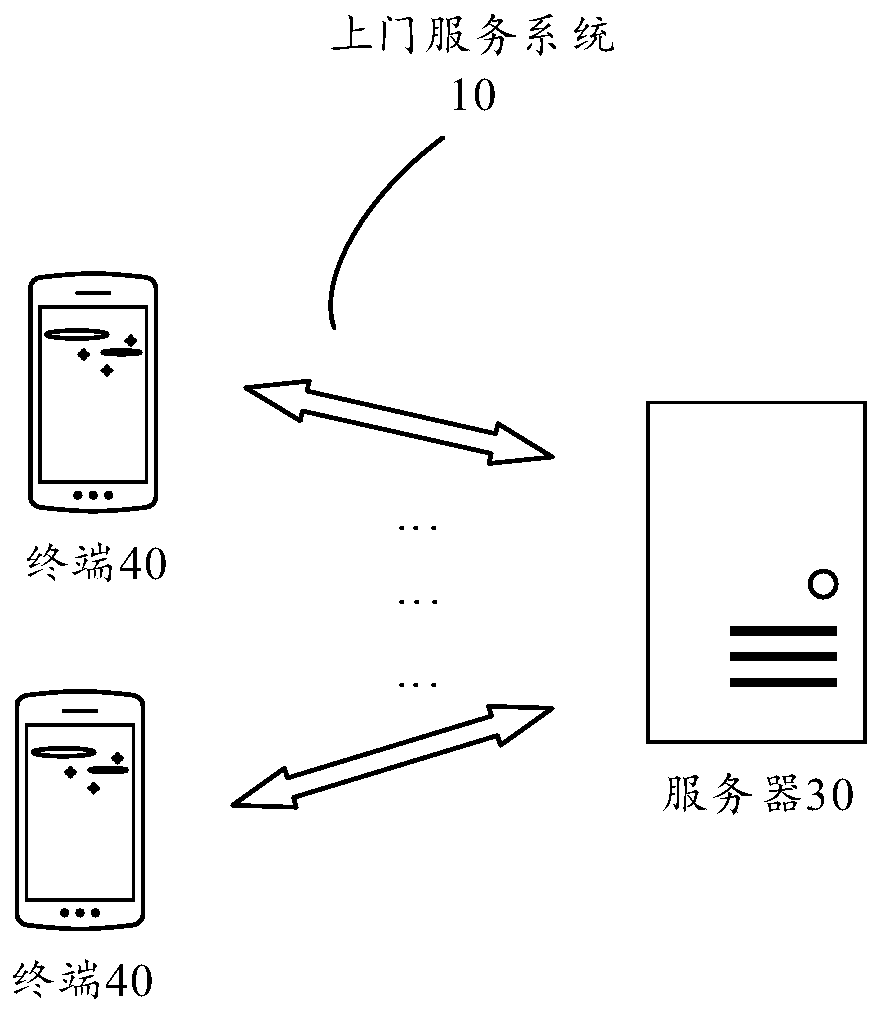
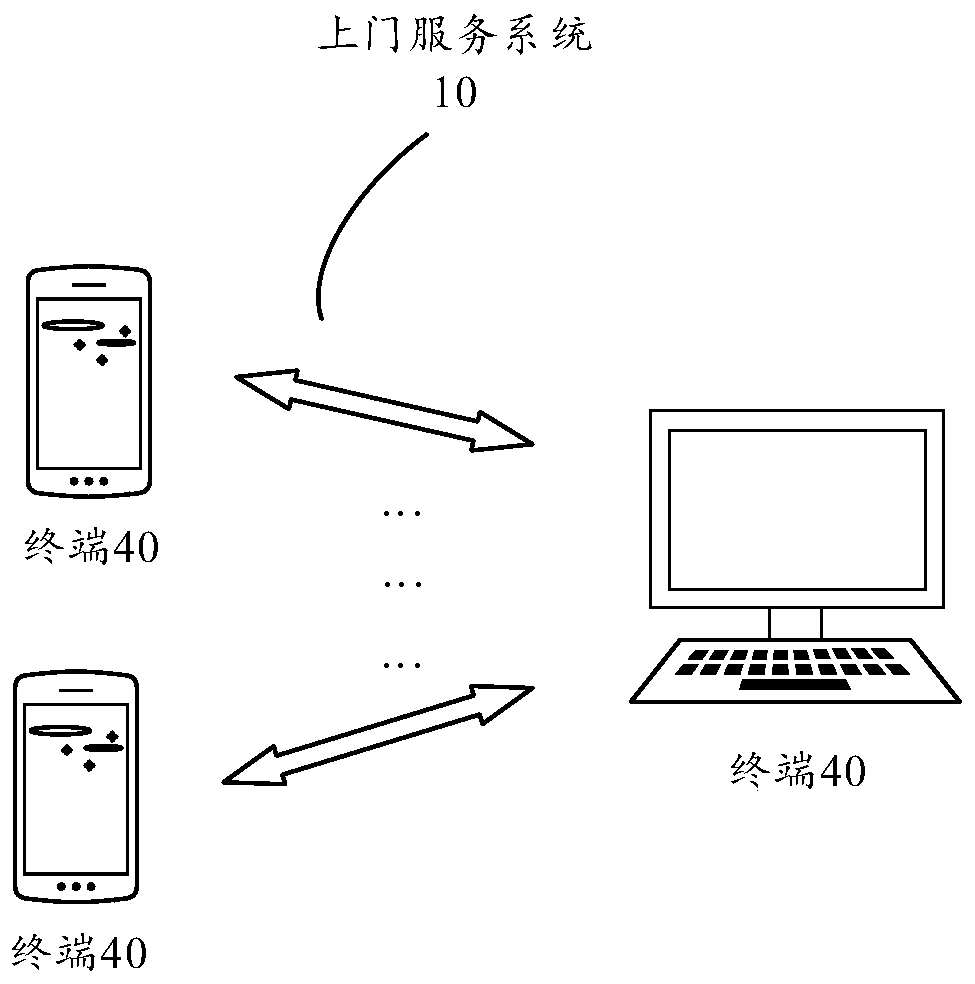
Door-to-door service method and device, storage medium and electronic device
InactiveCN109934365AAvoid the problem of not being able to complete the serviceImprove the efficiency of door-to-door serviceReservationsResourcesUser needsResidence
The embodiment of the invention provides a door-to-door service method and device, an electronic device and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining the residence position of auser needing door-to-door service in a user list, and obtaining the current position of the user; determining a target user of which the distance between the current position of the user and the residence position is within a preset distance from the user list; and sending prompt information used for prompting that the door-to-door service is about to be carried out to the target user, and sendingindication information used for indicating that the door-to-door service is about to be carried out to the target user to the service personnel. The residence position and the current position of theuser needing door-to-door service in the user list are acquired, and whether the distance between the residence position and the current position is within the preset distance or not is judged, so that whether the user needing door-to-door service can open the door for the service personnel or not in the current time period and receive the door-to-door service of the service personnel can be known. Therefore, the scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention can simply and efficiently improve the home-entry rate of the service personnel in door-to-door service.
Owner:李超杰
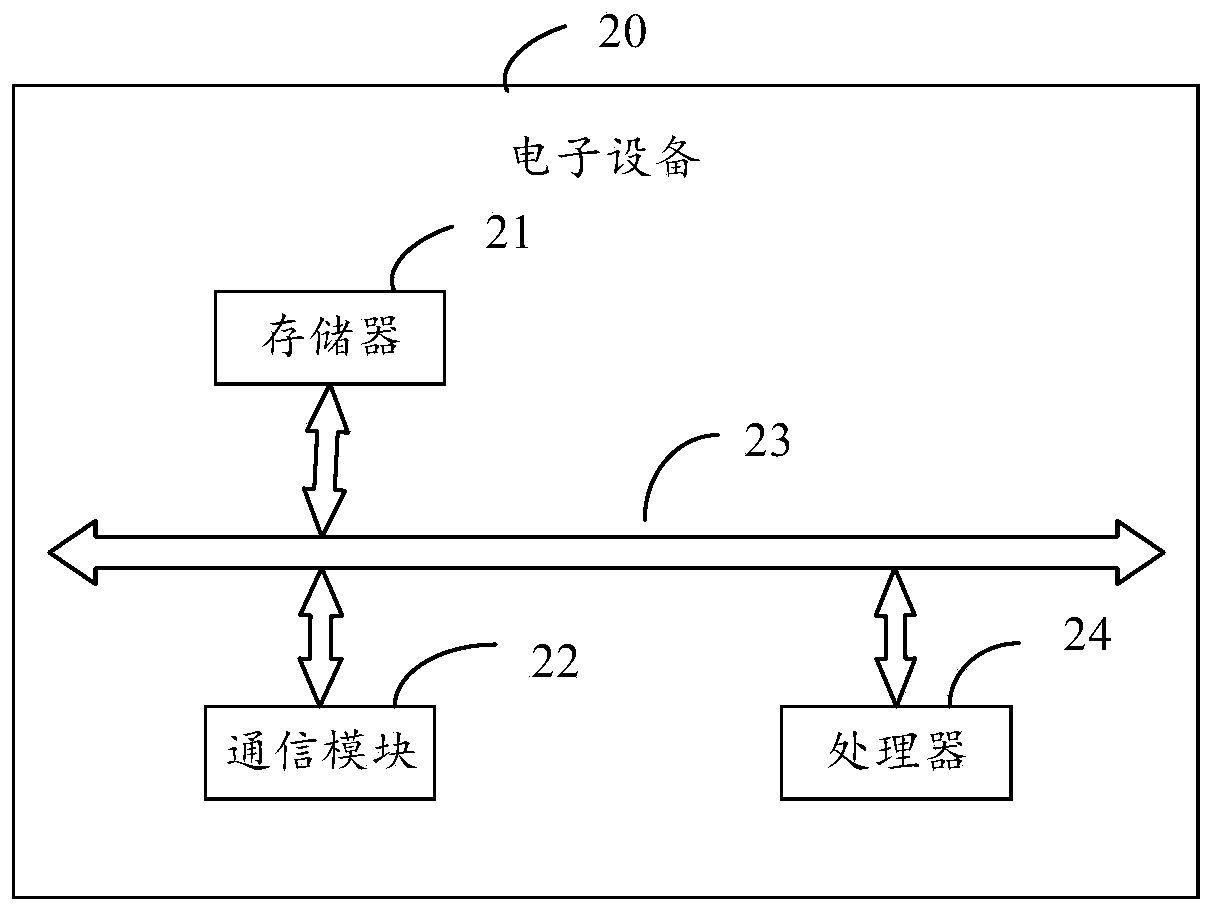
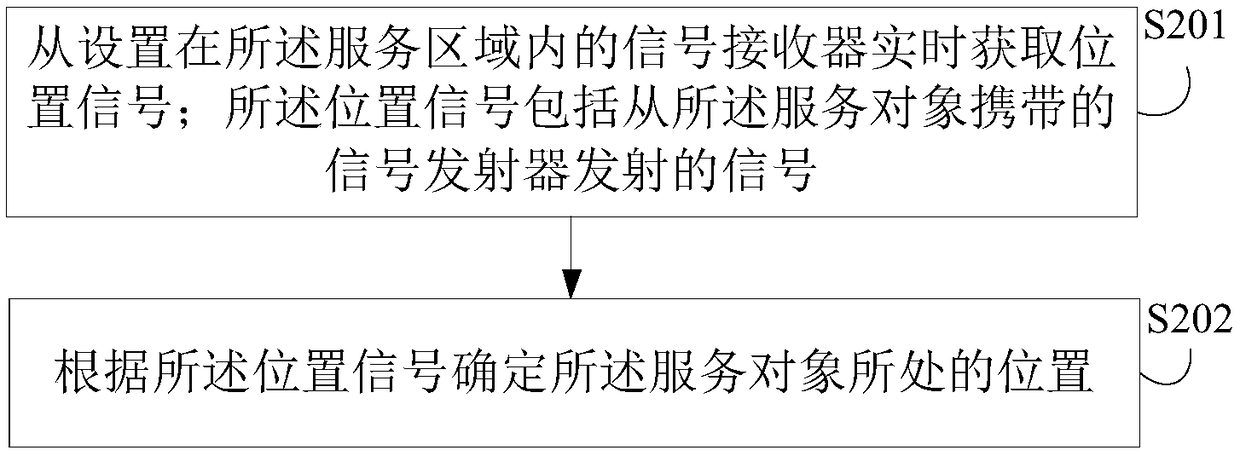
Object property determining method and device, interception policy adjustment method and device, and electronic device
PendingCN108668225AImprove accuracyImprove objectivityAssess restrictionLocation information based serviceElectronOperations research
Embodiments of the invention disclose an object property determining method and device, an interception policy adjustment method and device, and an electronic device. The method comprises the steps ofdetecting a position of a serving object through a signal detection device; according to the position of the serving object, determining a first entry rate of a served object when the serving objectis in a service area, and a second entry rate of the served object when the serving object is out of the service area; and according to the first entry rate and the second entry rate, determining success rate indicating that the serving object intercepts the served object. Through adoption of the method, the position of the serving object can be identified by the signal detection device, the entryrates of the served object can be detected when the serving object in different positions, and then the interception success rate of the serving object is determined, so that the accuracy rate is high, further, the interception success rate is calculated according to data detected by the signal detection device, the result is objective, and the property of the serving object is reflected more accurately and objectively.
Owner:北京天正聚合科技有限公司 +1
Method for drilling through nuisance hydrocarbon bearing formations
A method for controlling entry of hydrocarbon into a wellbore from a subsurface formation includes determining whether hydrocarbon is entering the wellbore. Whether a rate of hydrocarbon entry into the wellbore is slowing is then determined Control of discharge from the wellbore is then switched from maintaining a selected wellbore pressure to controlling a rate of discharge of fluid from the wellbore to be substantially constant if the hydrocarbon entry rate is slowing. Control of discharge from the wellbore is returned to maintaining the selected wellbore pressure when the hydrocarbon stops entering the wellbore.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
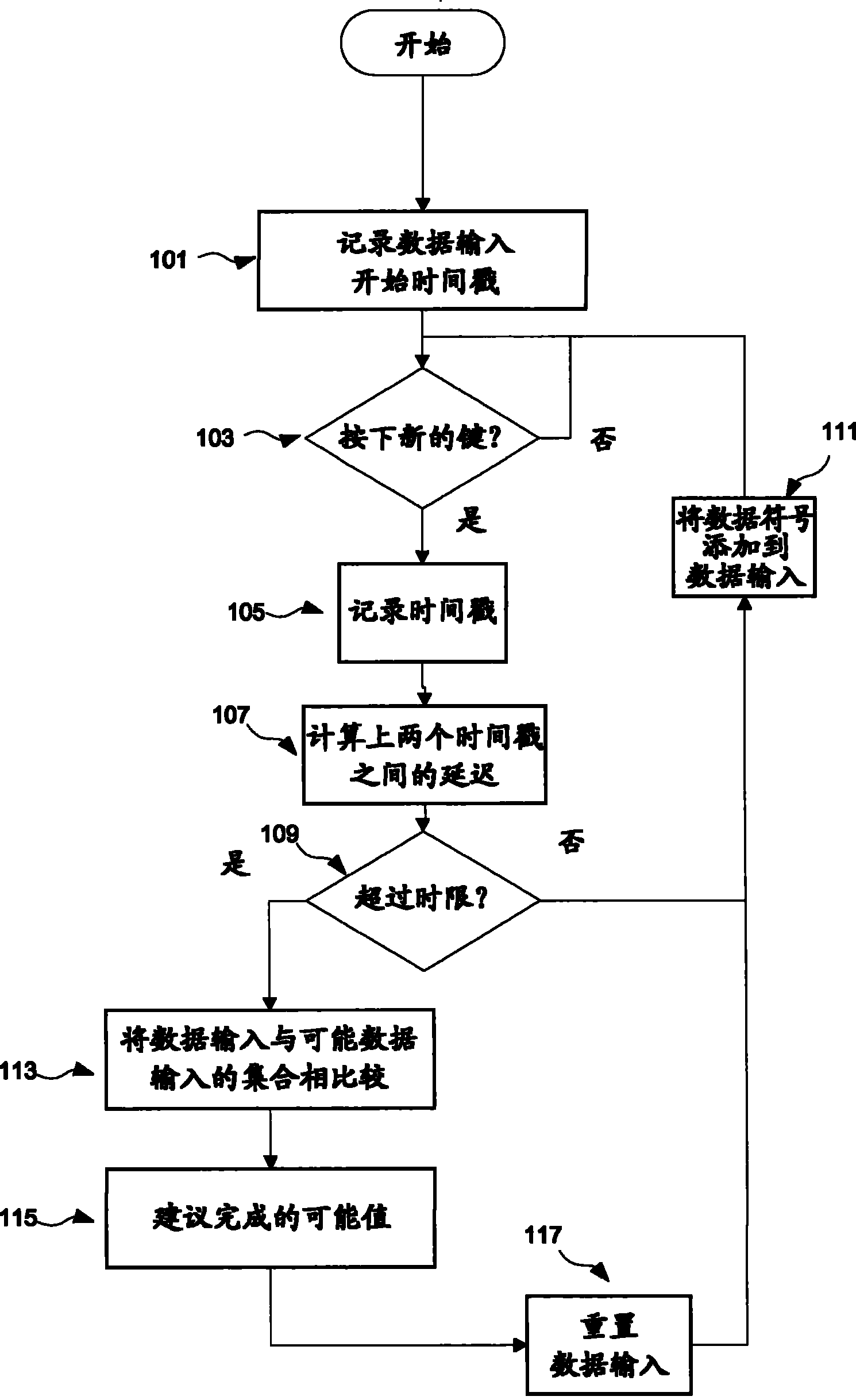
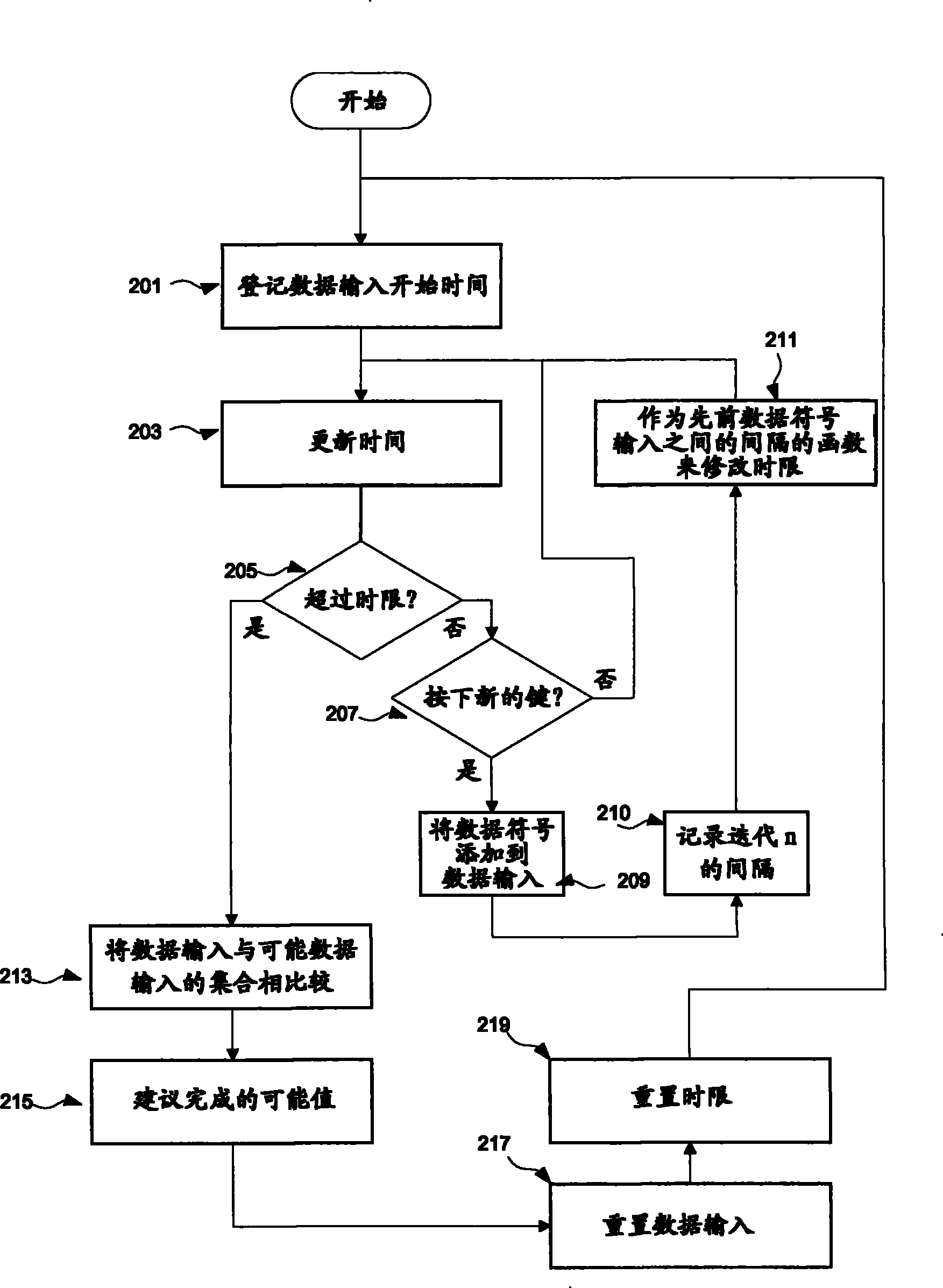
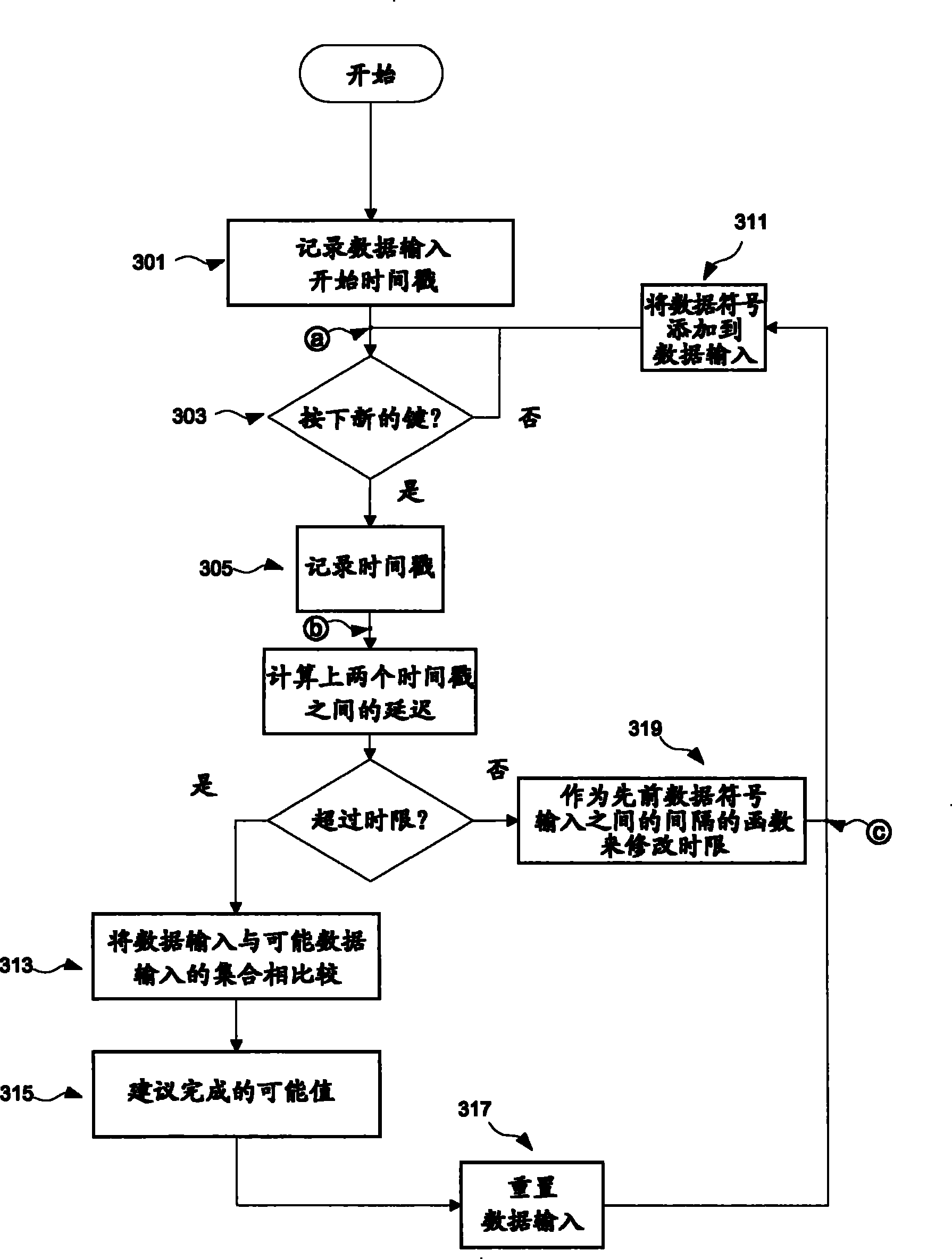
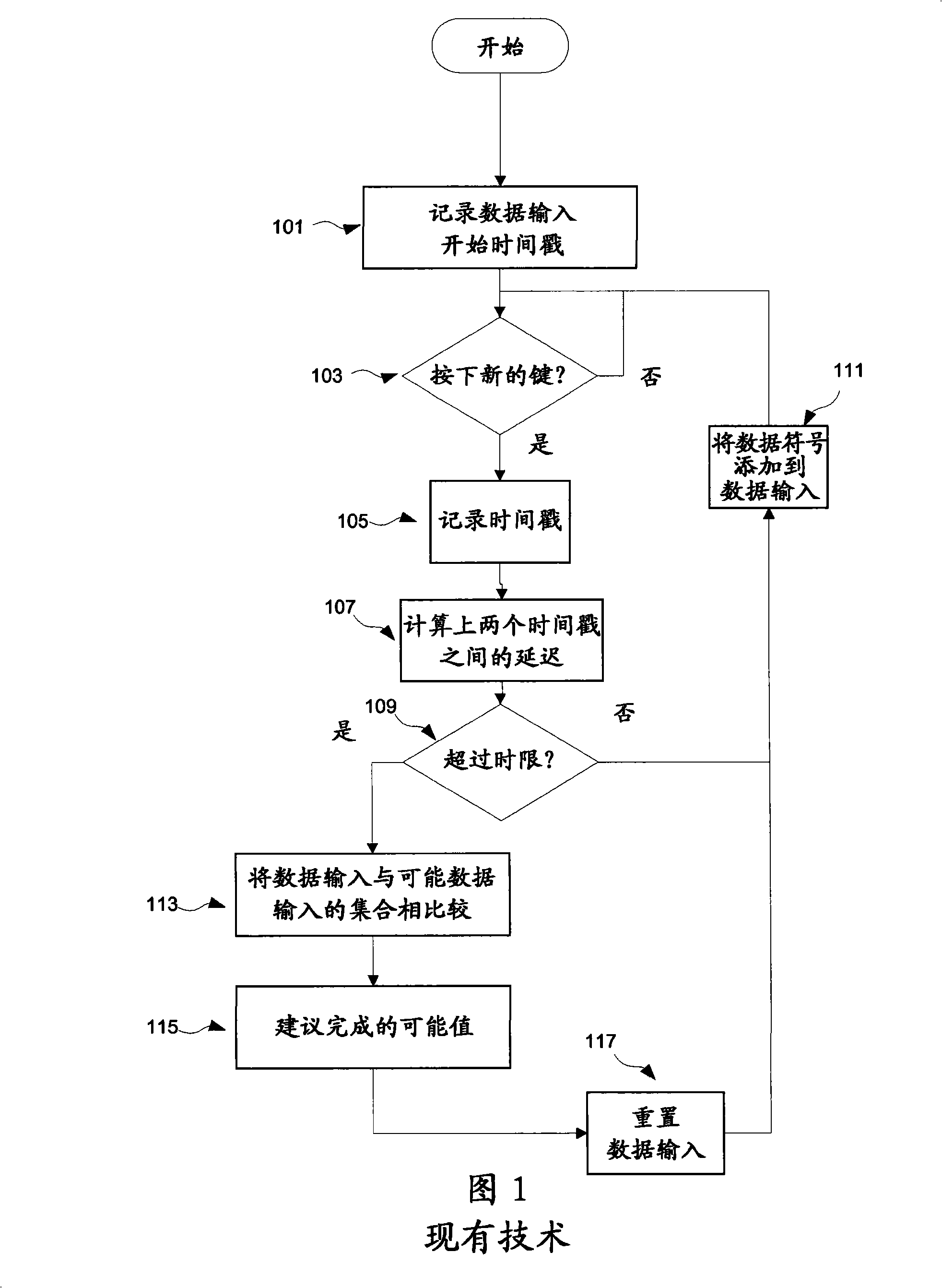
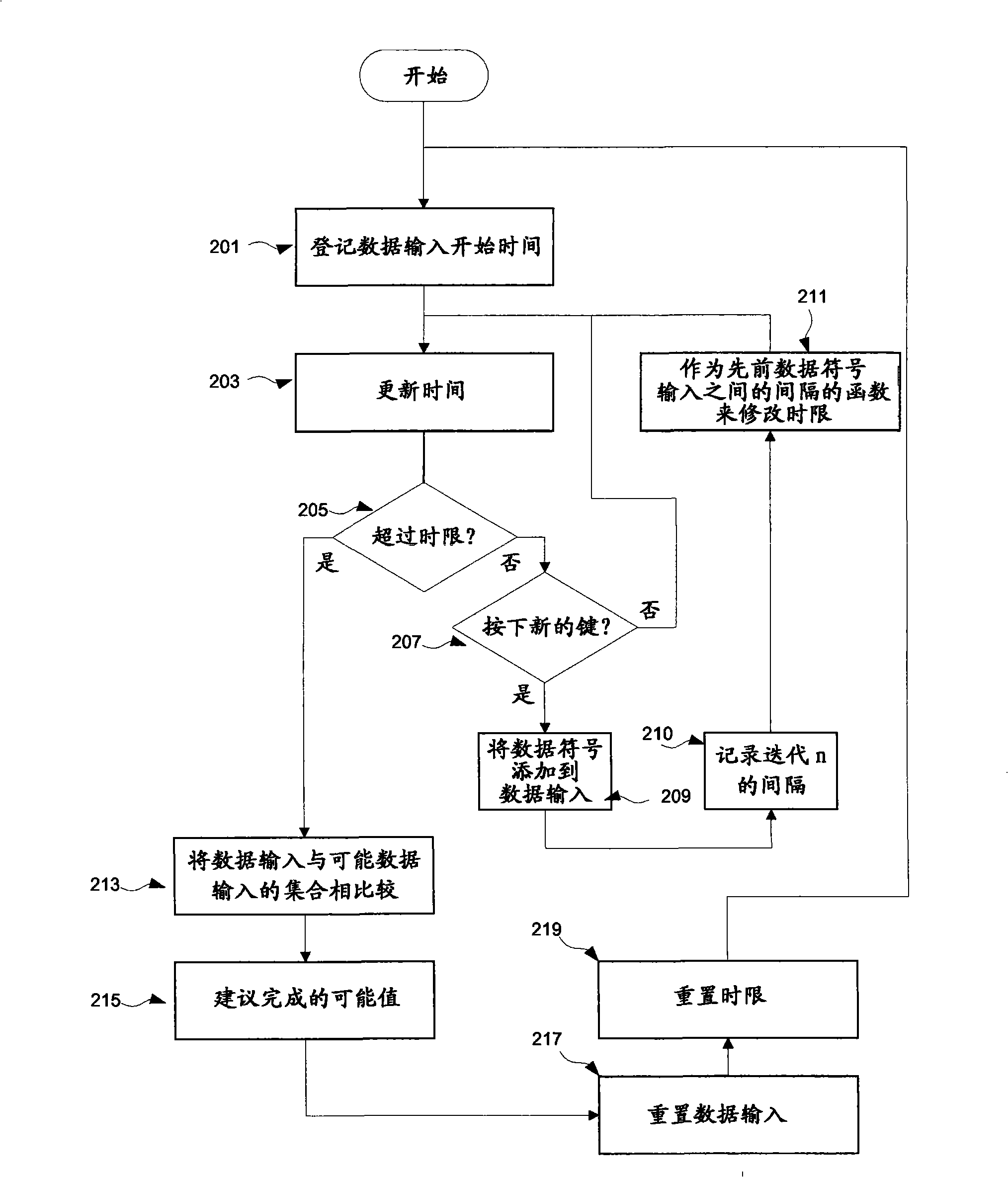
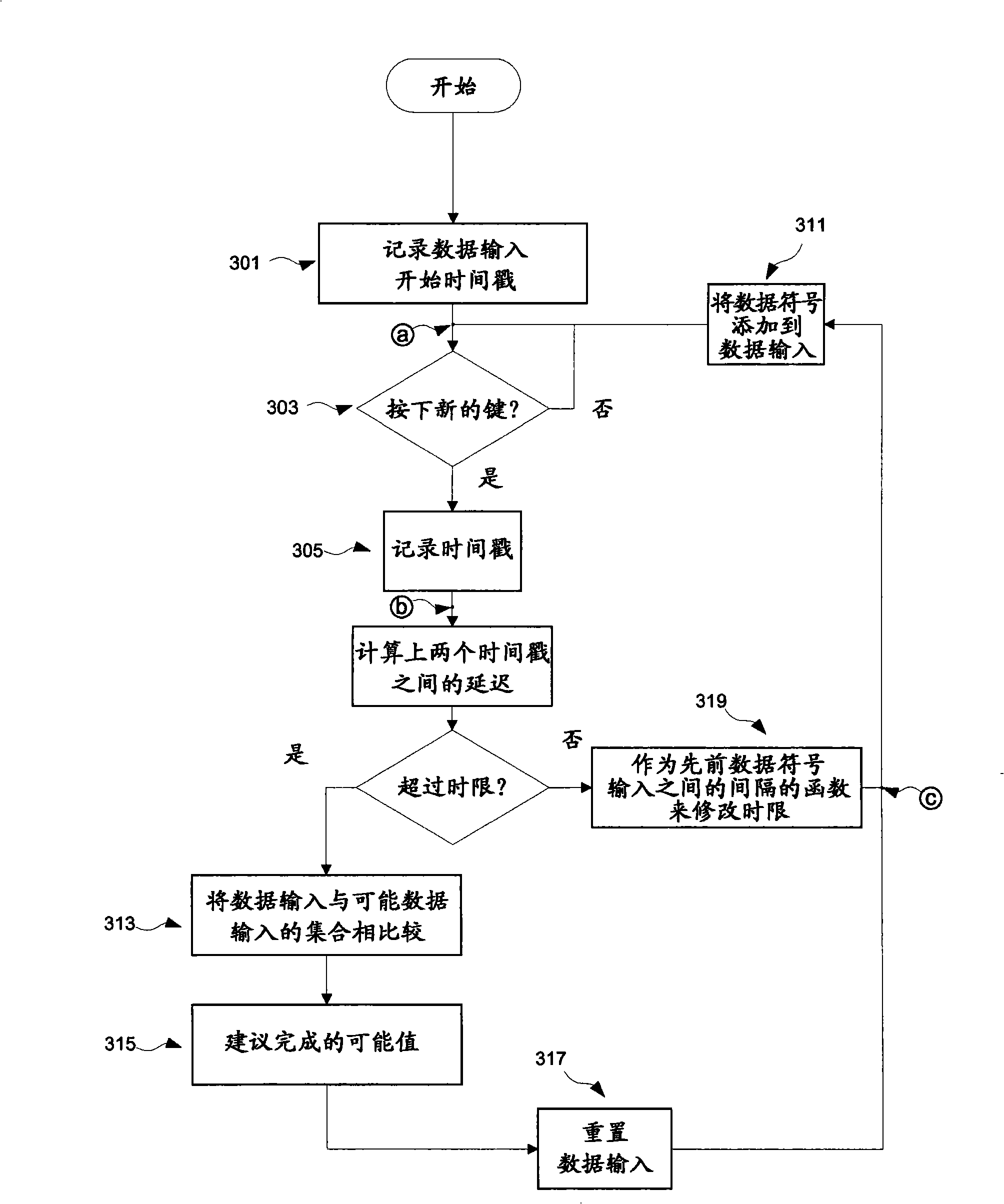
Autocompletion method and system
ActiveCN101317147BNatural language data processingInput/output processes for data processingTime limitEngineering
Provided is an implementation of an auto-completion or auto-correction mechanism where a dictionary of entry list look-up is triggered by the expiry of a time limit between data entry events such as key-press events, where the value of the time limit is dynamically determined as a function of the entry rate. The time limit may be calculated for example on the basis of an average entry rate, and may include an extra margin value. The occurrence of look up triggering will therefore tend to be optimised to the present user's data entry rate.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Manipulator for laying soldering terminals of diodes
ActiveCN104384656AHigh penetration rateImprove efficiencyMetal working apparatusSolder feeding devicesEngineeringSoldering
The invention discloses a manipulator for laying soldering terminals of diodes, which comprises a support and a hollow sealed magazine, wherein the magazine is arranged on the support and is transversely extended out, a certain number of soldering terminals are loaded in the magazine, moreover, the manipulator is also provided with a soldering terminal plate which can be transversely extended and retracted relative to the magazine, up to 2000 pits are formed in the soldering terminal plate, the soldering terminal plate is also provided with a pipeline which communicates with each pit and is connected with a vacuumizer, and a motor is also arranged on one transverse end of the magazine, and can drive the magazine to transversely revolve clockwise and counterclockwise. The manipulator utilizes the simple cooperation between the motor, the magazine and the soldering terminal plate to automatically lay the soldering terminals in the magazine into the soldering terminal plate, thus realizing the mechanization of soldering terminal laying, greatly increasing efficiency and saving manpower. The usage of the manipulator can greatly increase the entry rate of the soldering terminals into the soldering terminal plate to more than 99.7 percent and decrease the repetitive entry rate to less than 0.1 percent, manpower is replaced, working efficiency is greatly increased, and meanwhile, the defect rate is remarkably decreased.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
A manipulator for laying diode solder sheet
ActiveCN104384656BHigh penetration rateImprove efficiencyMetal working apparatusSolder feeding devicesEngineeringSoldering
The invention discloses a manipulator for laying soldering terminals of diodes, which comprises a support and a hollow sealed magazine, wherein the magazine is arranged on the support and is transversely extended out, a certain number of soldering terminals are loaded in the magazine, moreover, the manipulator is also provided with a soldering terminal plate which can be transversely extended and retracted relative to the magazine, up to 2000 pits are formed in the soldering terminal plate, the soldering terminal plate is also provided with a pipeline which communicates with each pit and is connected with a vacuumizer, and a motor is also arranged on one transverse end of the magazine, and can drive the magazine to transversely revolve clockwise and counterclockwise. The manipulator utilizes the simple cooperation between the motor, the magazine and the soldering terminal plate to automatically lay the soldering terminals in the magazine into the soldering terminal plate, thus realizing the mechanization of soldering terminal laying, greatly increasing efficiency and saving manpower. The usage of the manipulator can greatly increase the entry rate of the soldering terminals into the soldering terminal plate to more than 99.7 percent and decrease the repetitive entry rate to less than 0.1 percent, manpower is replaced, working efficiency is greatly increased, and meanwhile, the defect rate is remarkably decreased.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
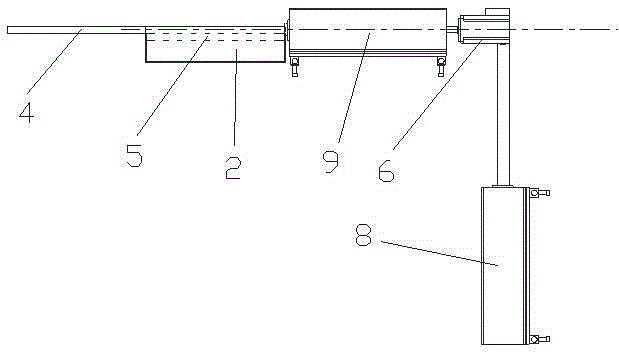
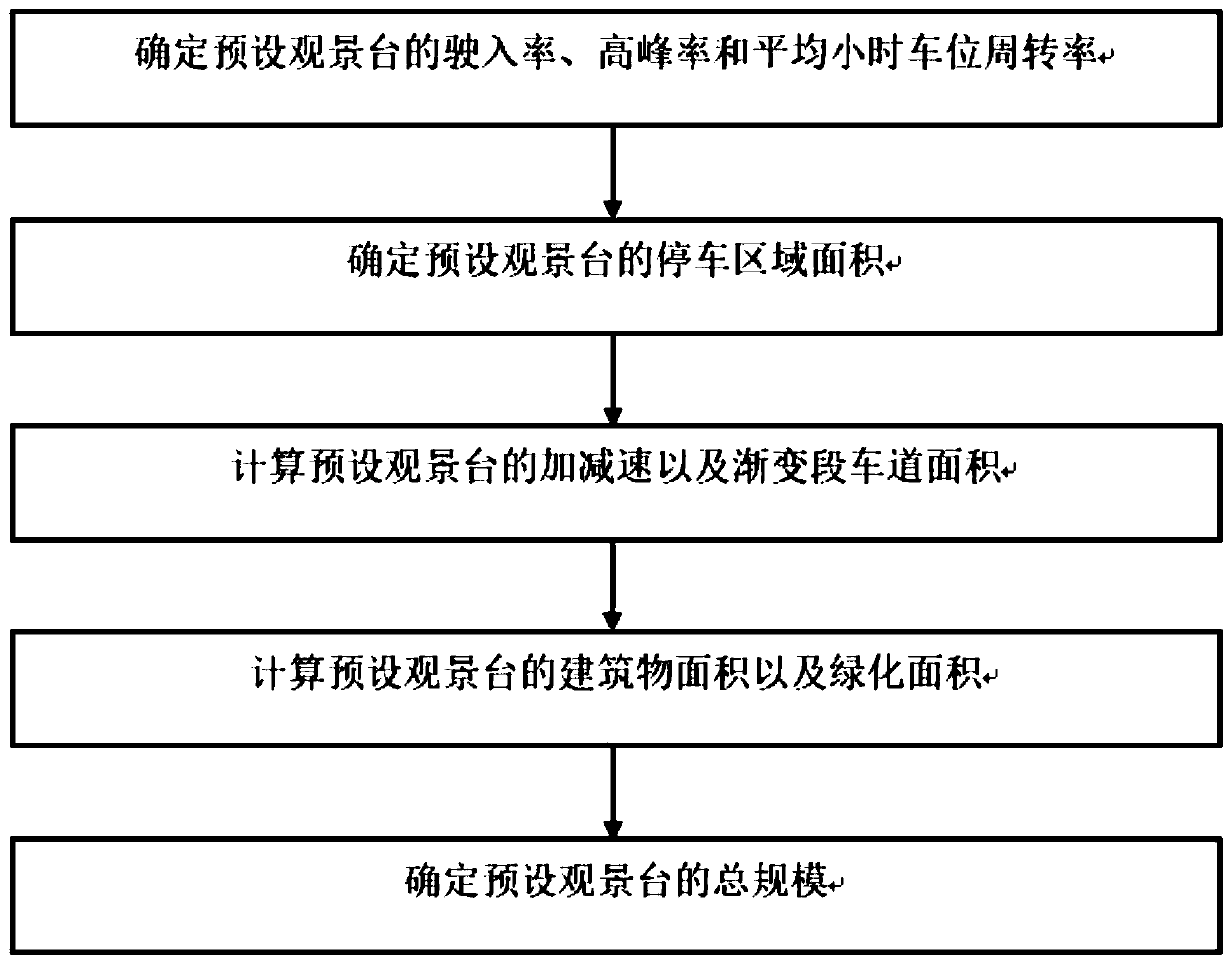
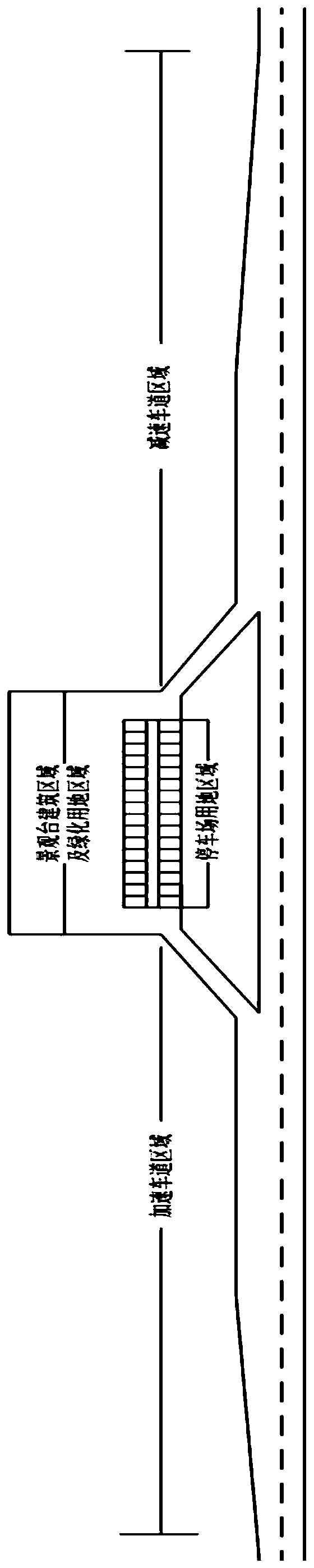
Arterial highway viewing platform land scale planning method
The invention discloses an arterial highway viewing platform land scale planning method, and belongs to the field of traffic engineering. The method solves the problem of lack of research on the scaleof the viewing platform of the arterial highway at present. The method comprises: using the beautiful scenery area along the arterial highway as a viewing platform layout object; investigating the entry rate, the peak rate and the turnover rate of the preset viewing platform to determine the scale of the parking area; calculating the corresponding acceleration and deceleration lane scale according to the highway design grade; and finally, determining a preset viewing platform building area and a greening area according to the occupied area of the common trunk road service facility, so as to determine the preset landscape platform scale according to the size of the landscape platform, so that land resources can be effectively utilized, self-driving tourists can experience a more comfortable viewing effect. A research method for the scale of the landscape platform of the arterial road is provided, and the defects in the prior art are overcome. The method can be applied to scale planningof the arterial highway viewing platform.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Autocompletion method and system
ActiveCN101317147ANatural language data processingInput/output processes for data processingTime limitIndustrial engineering
Provided is an implementation of an auto-completion or auto-correction mechanism where a dictionary of entry list look-up is triggered by the expiry of a time limit between data entry events such as key-press events, where the value of the time limit is dynamically determined as a function of the entry rate. The time limit may be calculated for example on the basis of an average entry rate, and may include an extra margin value. The occurrence of look up triggering will therefore tend to be optimised to the present user's data entry rate.
Owner:IBM CORP
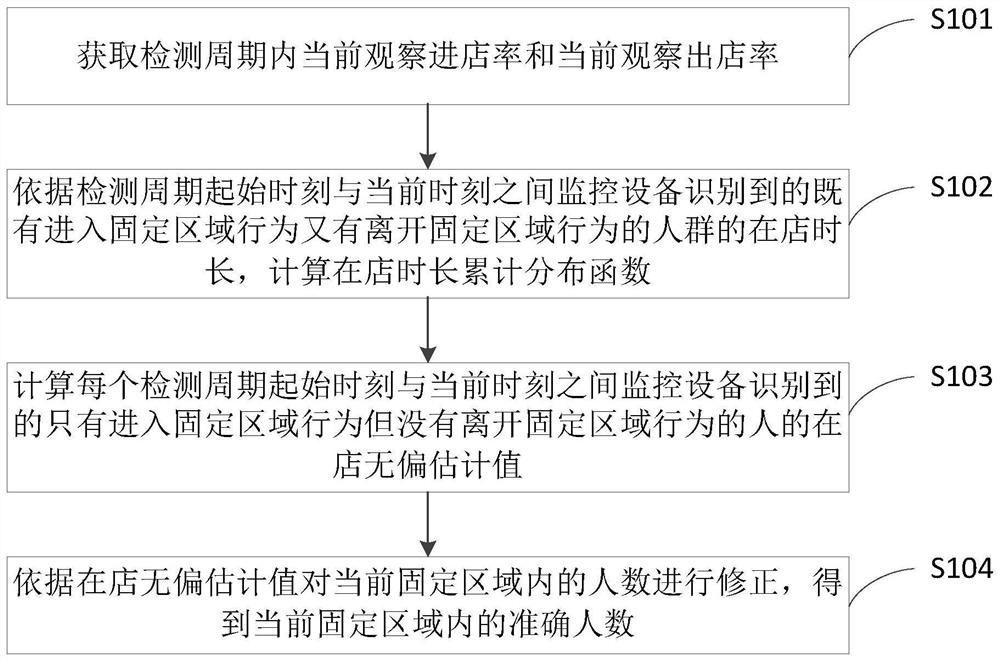
A method and device for detecting the number of people in a fixed area
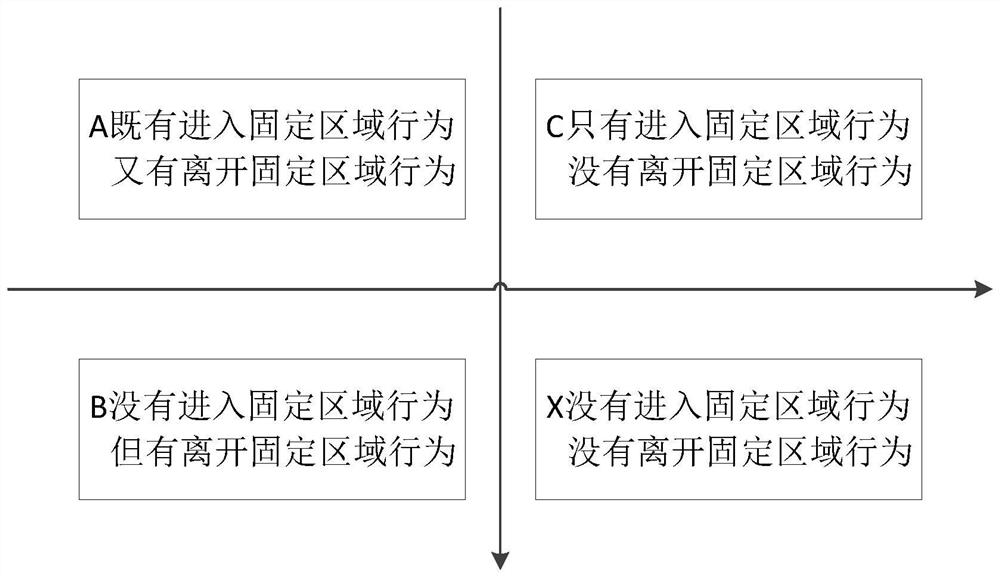
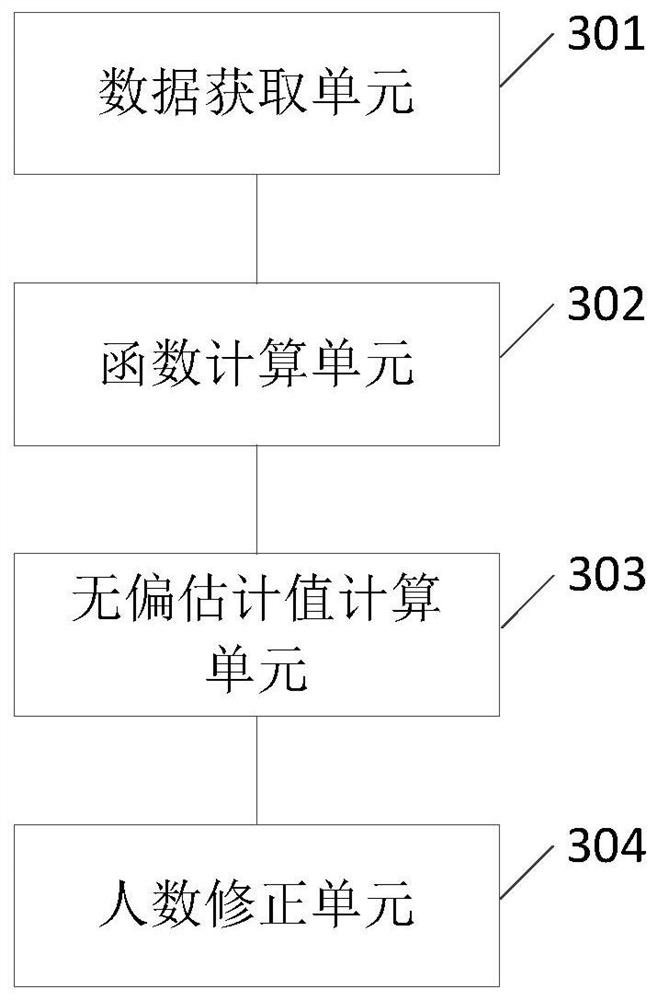
ActiveCN110826482BImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMonitor equipmentOperations research
The present invention provides a method and device for detecting people in a fixed area, wherein the method includes: obtaining the current observed store entry rate and the current observed store exit rate in the detection period; Calculate the length of time in the store for the people who have both the behavior of entering the fixed area and the behavior of leaving the fixed area, and calculate the cumulative distribution function of the length of time in the store; calculate the time between the start of each detection cycle and the current time. The monitoring equipment recognizes only entering the fixed area The unbiased estimate of the people who act but did not leave the fixed area; the number of people in the current fixed area is corrected according to the unbiased estimate of the store, and the accurate number of people in the current fixed area is obtained, which improves the detection of the number of people in the fixed area. 's accuracy.
Owner:北京爱笔科技有限公司
Vehicle-mounted equipment and method for updating vocabulary
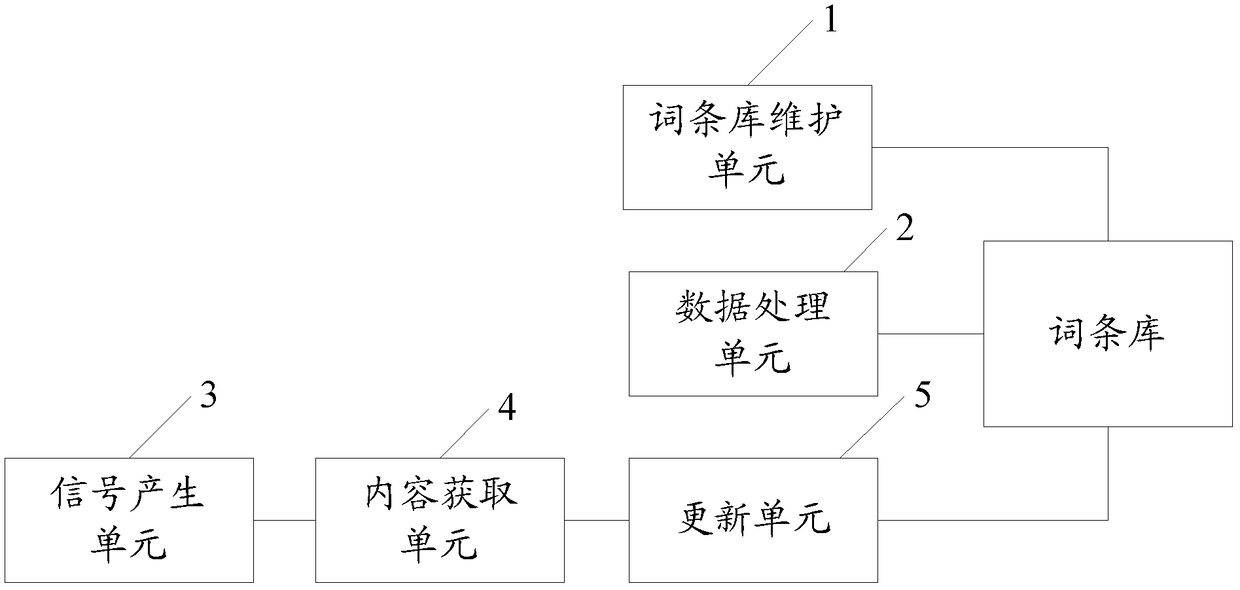
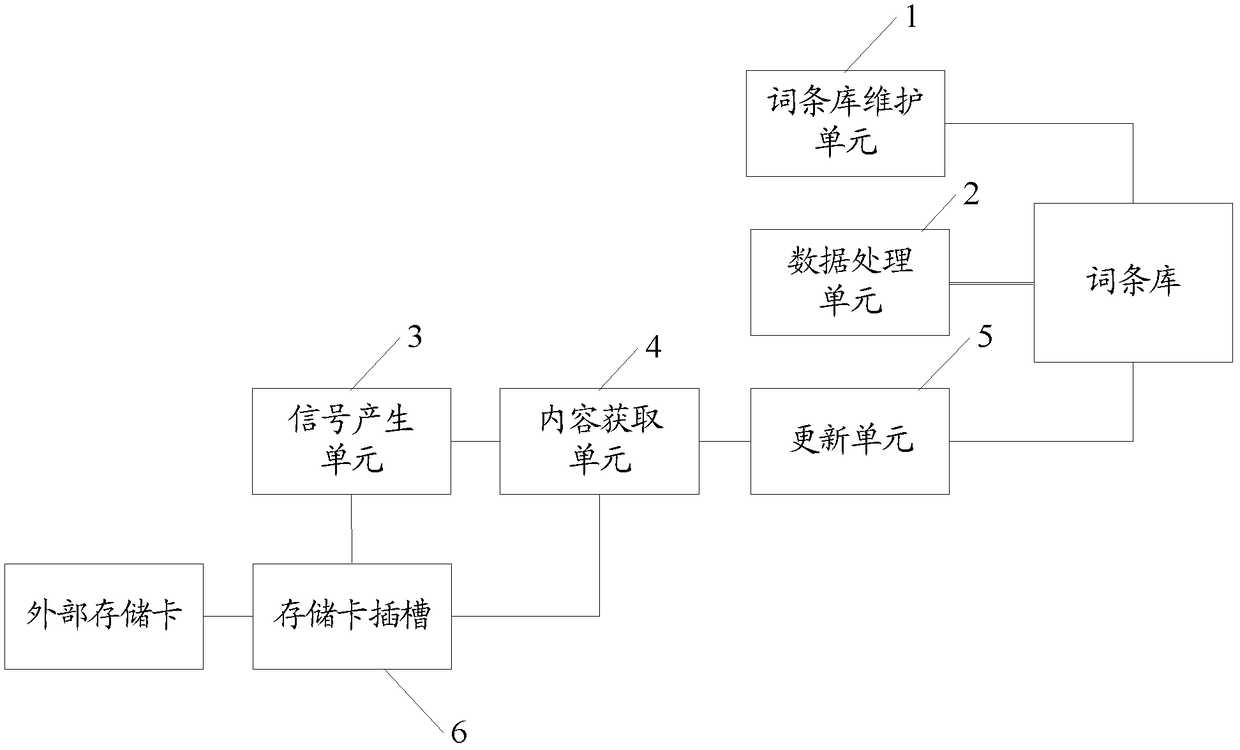
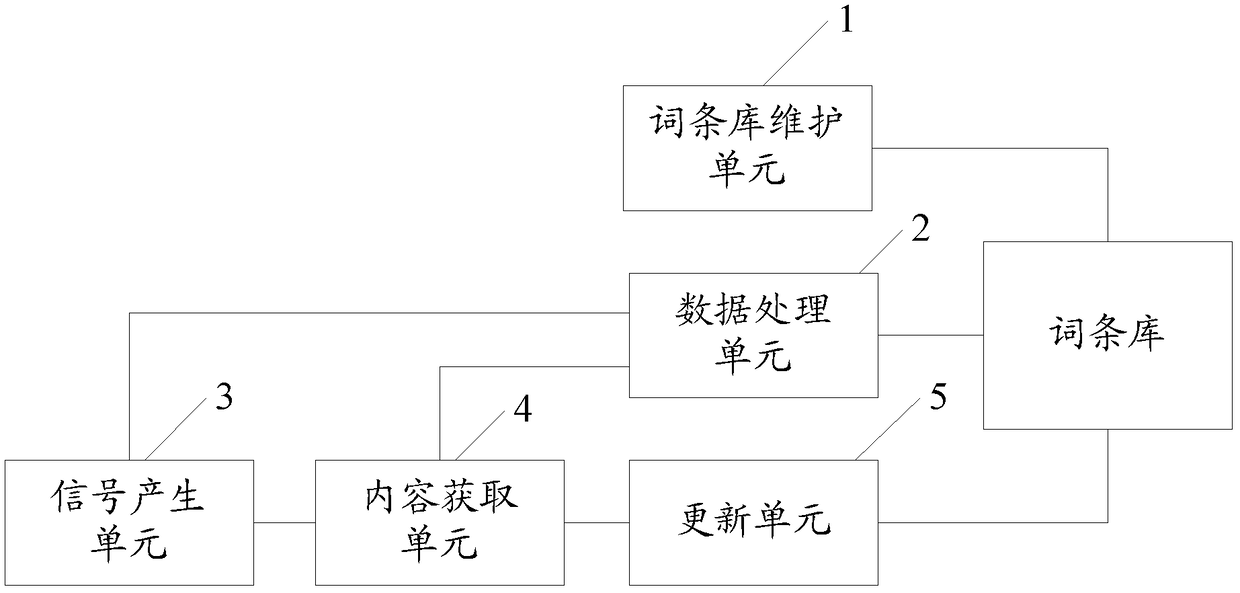
ActiveCN103164478BMeet the ever-increasing demand for termsImprove operational efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsOn boardEmbedded system
The invention provides on-board equipment and an entry base update method. The on-board equipment comprises an entry base maintenance unit which is suitable for maintaining music entry data in an entry base needed when the on-board equipment operates, a data processing unit which is suitable for processing the music entry data in the operation process of the on-board equipment, a signal generating unit which is suitable for generating a triggering signal which is used for instructing the update of the music entry data, a content acquiring unit which is suitable for reading new music data used for updating the new entry data based on the triggering signal, and an updating unit which is suitable for using the new music data to update the music entry data. According to the on-board equipment and the entry base update method, an entry base can be updated automatically, and thus the increasing entry demands of users are met.
Owner:SHANGHAI PATEO ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURING CO LTD
Parking assist system and method
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com