Patents
Literature
33 results about "Index-matching material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In optics, an index-matching material is a substance, usually a liquid, cement (adhesive), or gel, which has an index of refraction that closely approximates that of another object (such as a lens, material, fiber-optic, etc.).
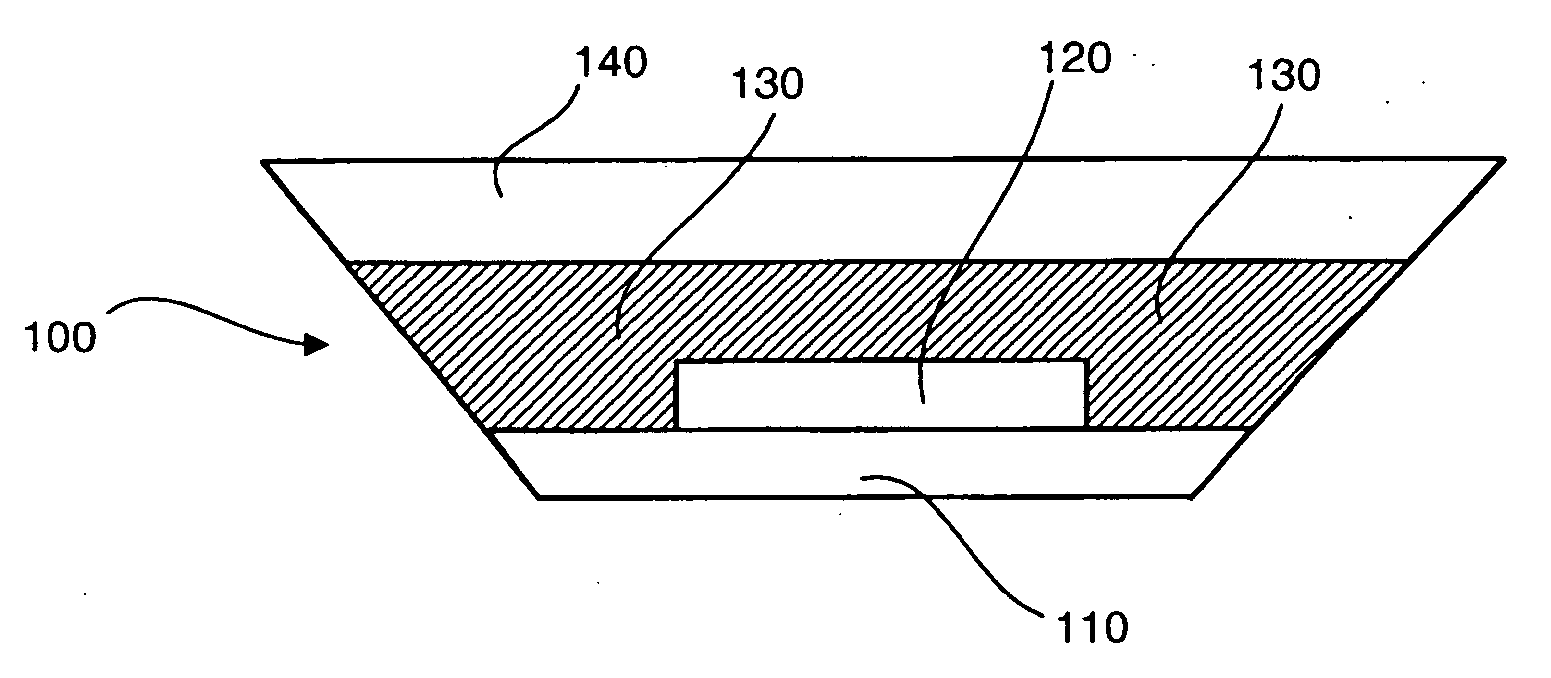
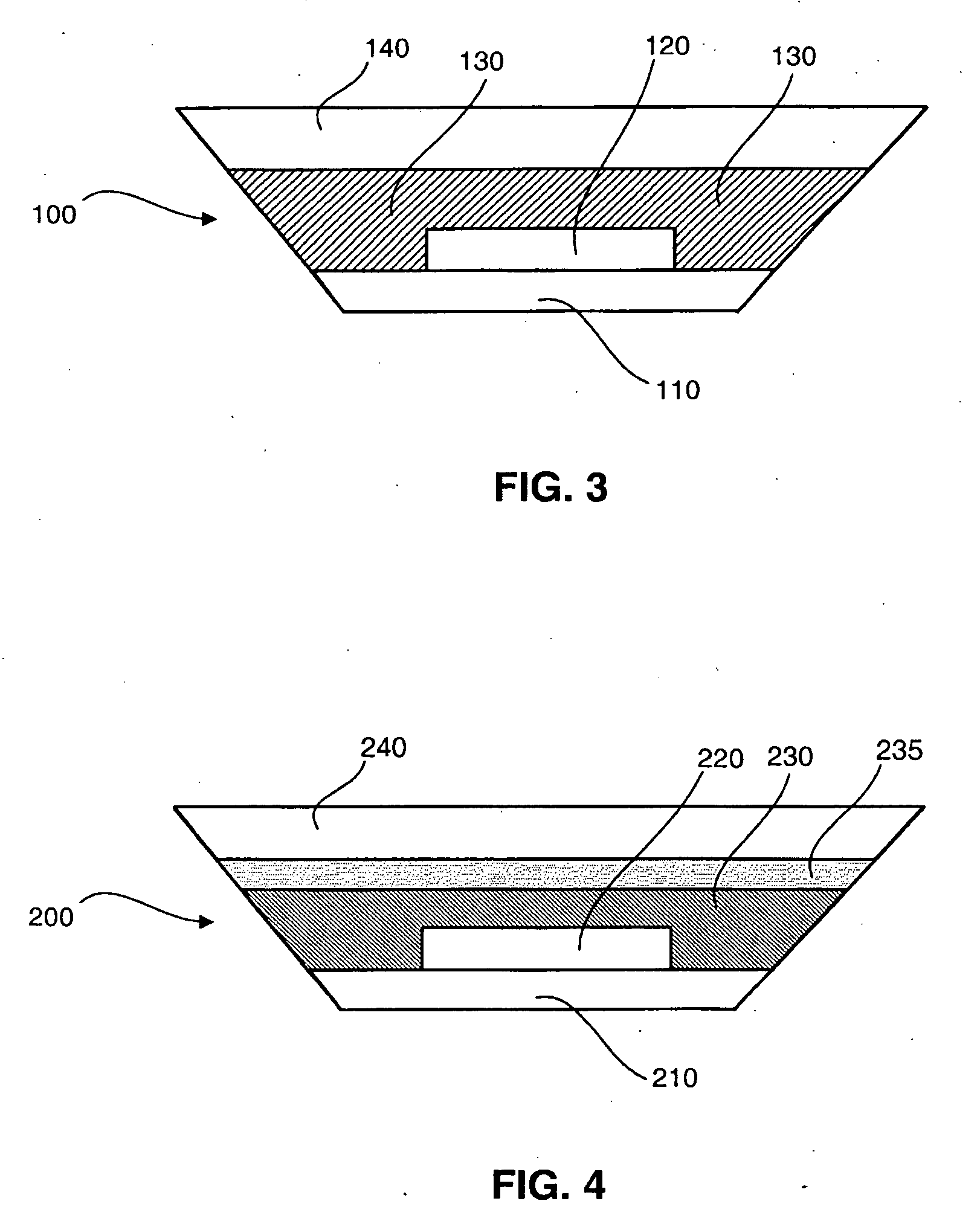
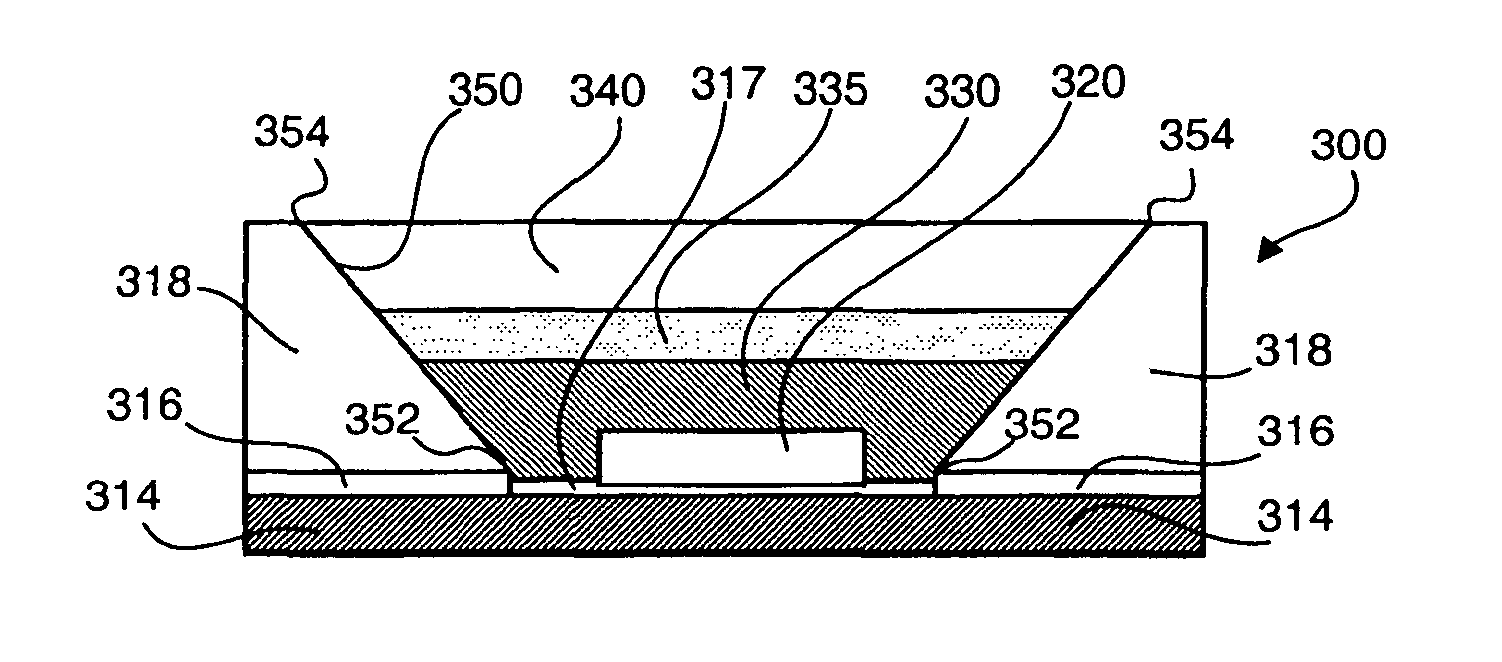
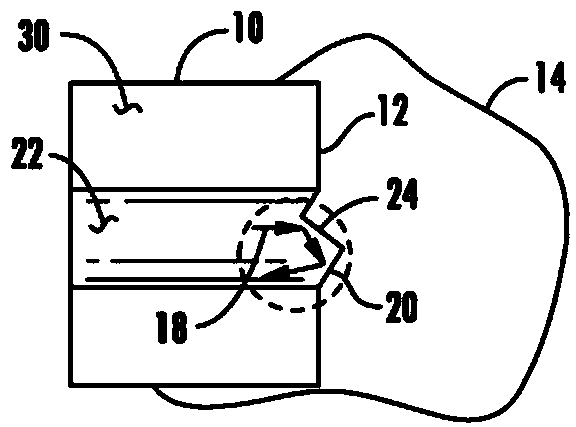
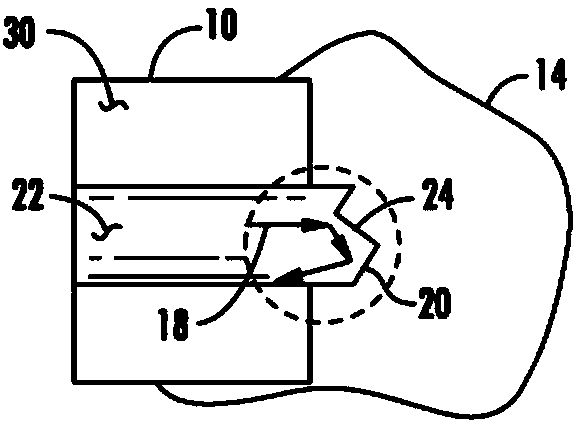
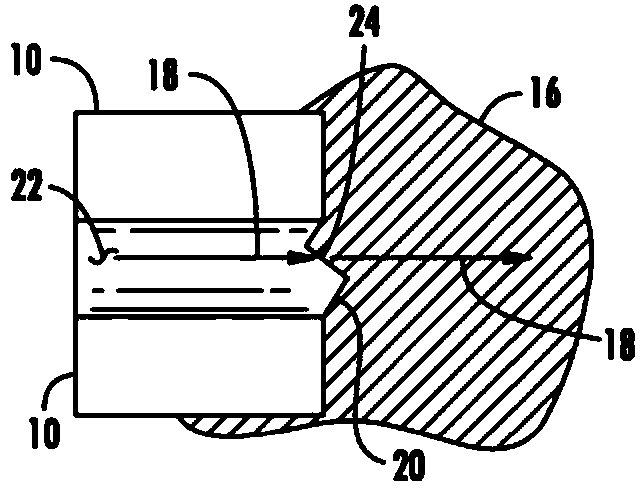
Light emitting device with a thermal insulating and refractive index matching material
ActiveUS20060091788A1Reduce heat transferPrevent thermal degradationDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsThermal insulationPhosphor
A light emitting device has a light emitting diode (LED) encapsulated by an encapsulant member. The encapsulant member includes a luminescent material, such as a phosphor, and a thermal insulating material. The thermal insulating material effectively insulates the luminescent material from the heat generated by the LED. A thermal conducting material is desirably placed in thermal contact with a back side of the LED to assist heat dissipation. The encapsulant member may be formed in two separate layers with the luminescent material forming a luminescent layer, and the thermal insulating material forming a thermal insulation layer disposed between the luminescent layer and the LED.
Owner:LED ENGIN
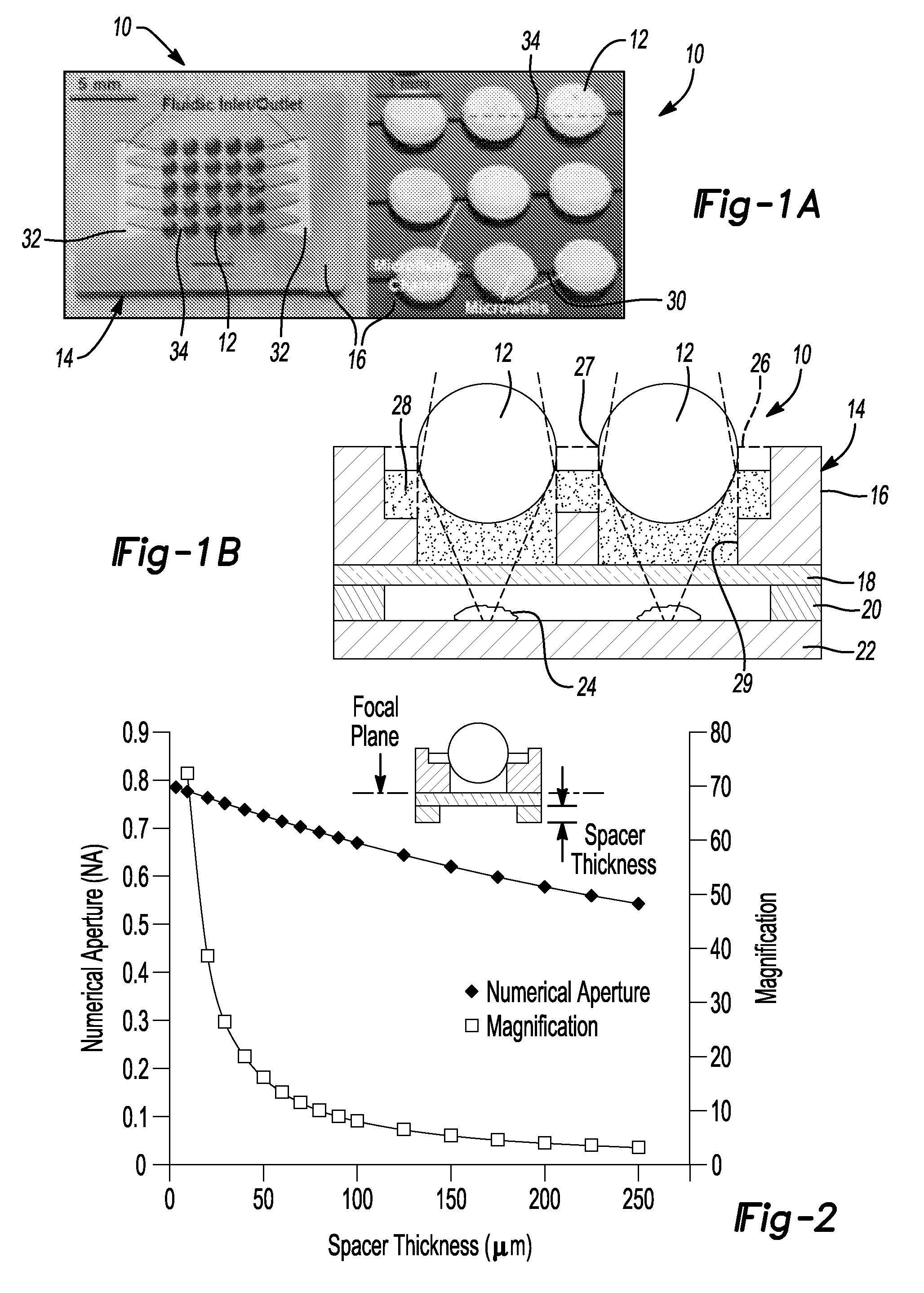
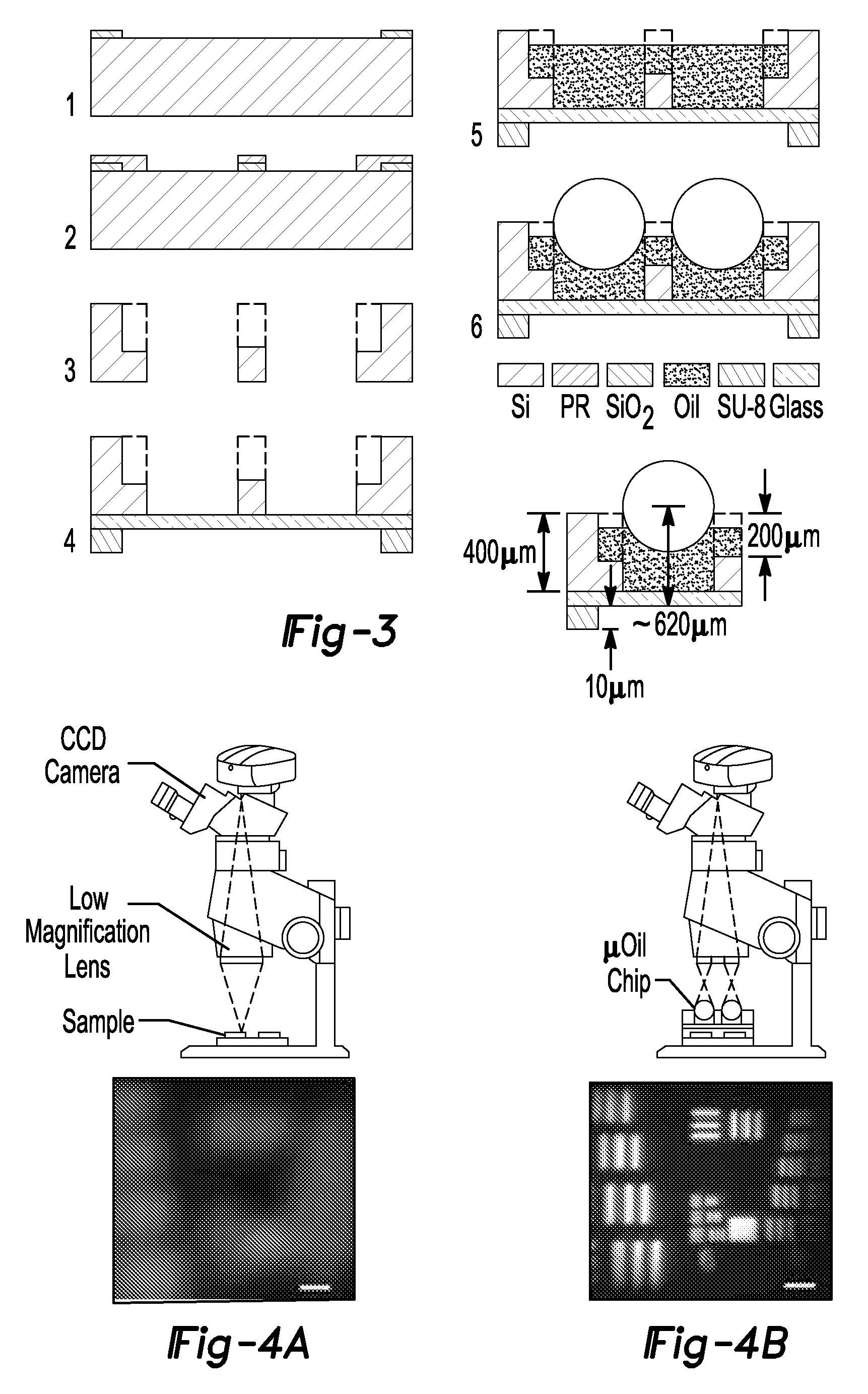
Compact lens system and array
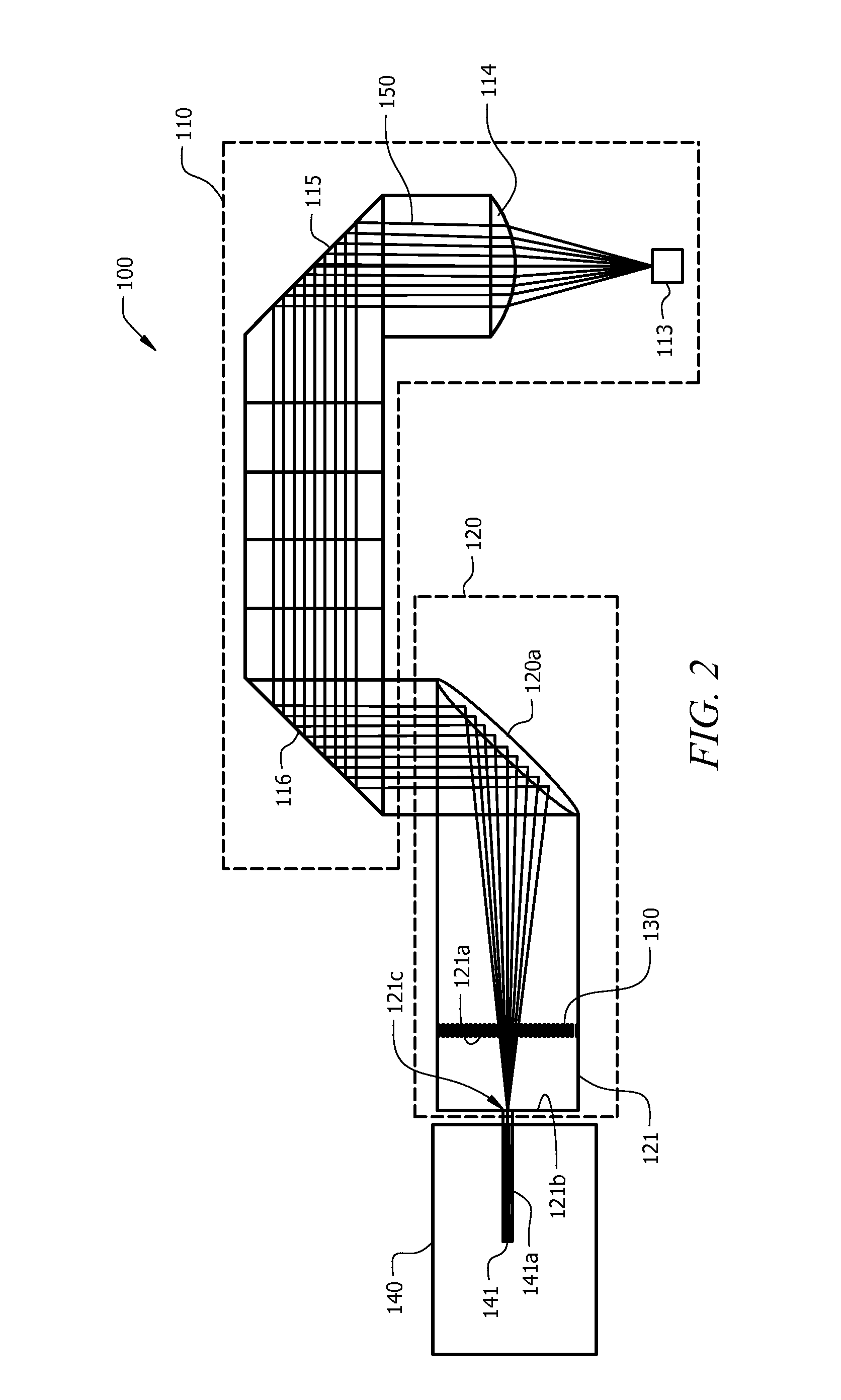
ActiveUS9304280B2Improve scalabilityHigh refractive indexMicroscopesIndividual particle analysisCamera lensIndex-matching material
A compact lens system for imaging a sample comprising a substrate having a well formed therein. Index matching material is disposed in the well and a lens member is further disposed in the well in optical contact with the index matching material disposed in the well. A spacer member extends from at least one of the substrate and the lower transparent member to define a spacing from a focal point of the lens member, wherein the lens member and index matching material cooperate to image a sample disposed below the lower transparent member.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Optical coupling system for use in an optical communications module, an optical communications module that incorporates the optical coupling system, and a method
An optical communications module is provided with an optical coupling system that includes a reflective and focusing (RAF) lens and an index-matching material that together allow air gaps along the optical pathway, which are typically associated with the use of refractive optical elements used in known optical communications modules, to be eliminated. Eliminating these air gaps allows Fresnel reflection along the optical pathway to be eliminated, or at least greatly reduced. Eliminating or reducing Fresnel reflection reduces insertion loss and optical crosstalk in the optical communications module.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
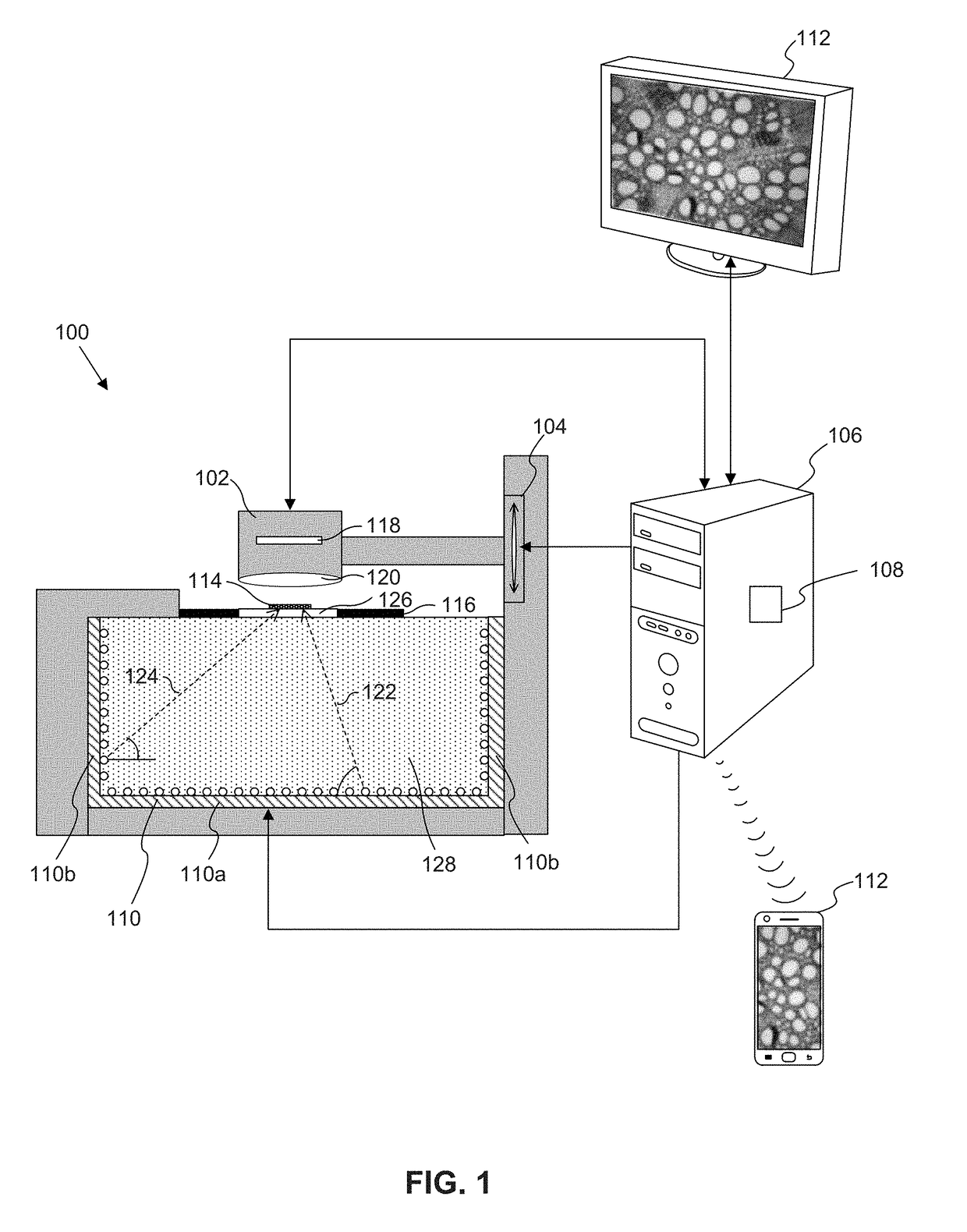
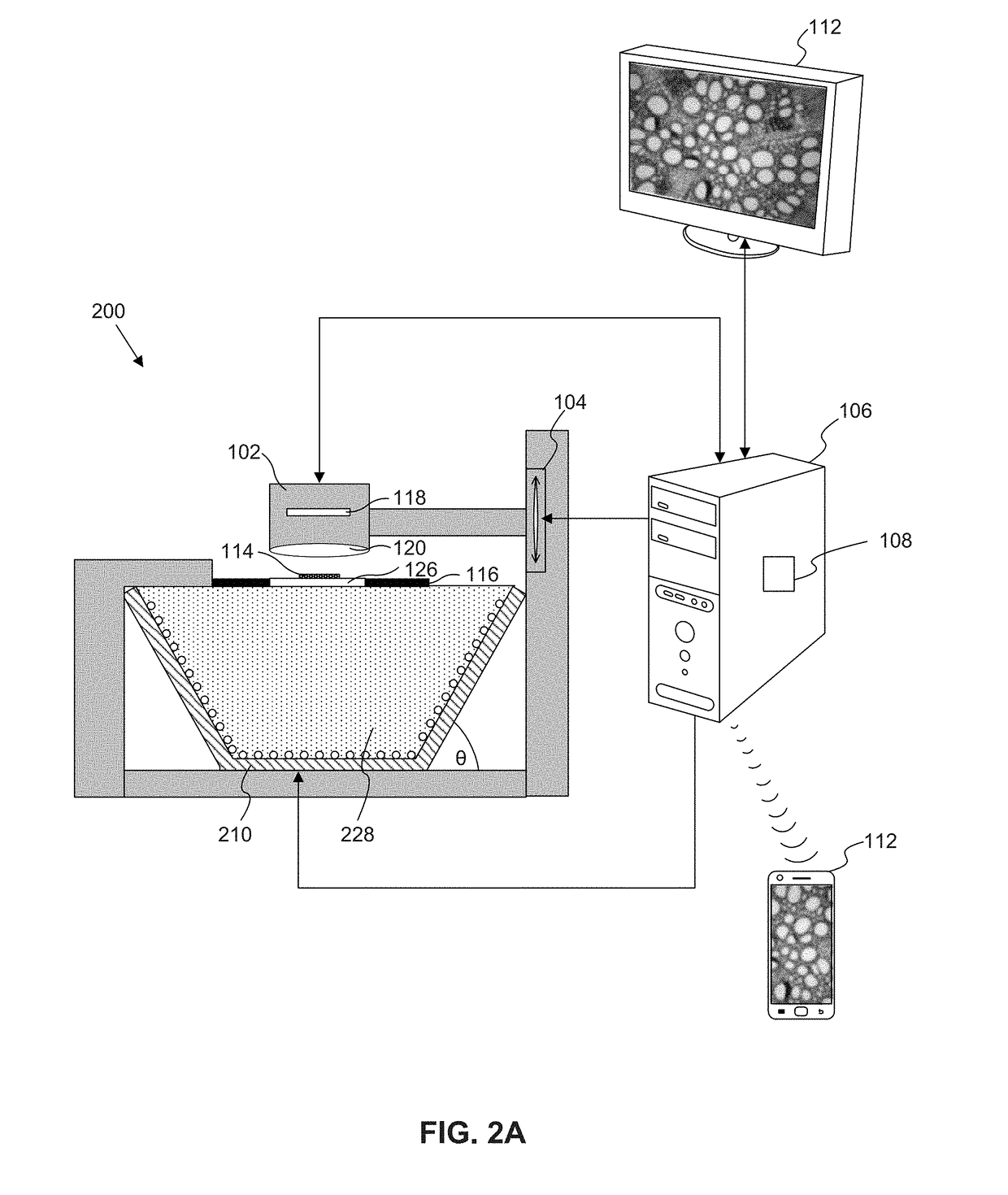
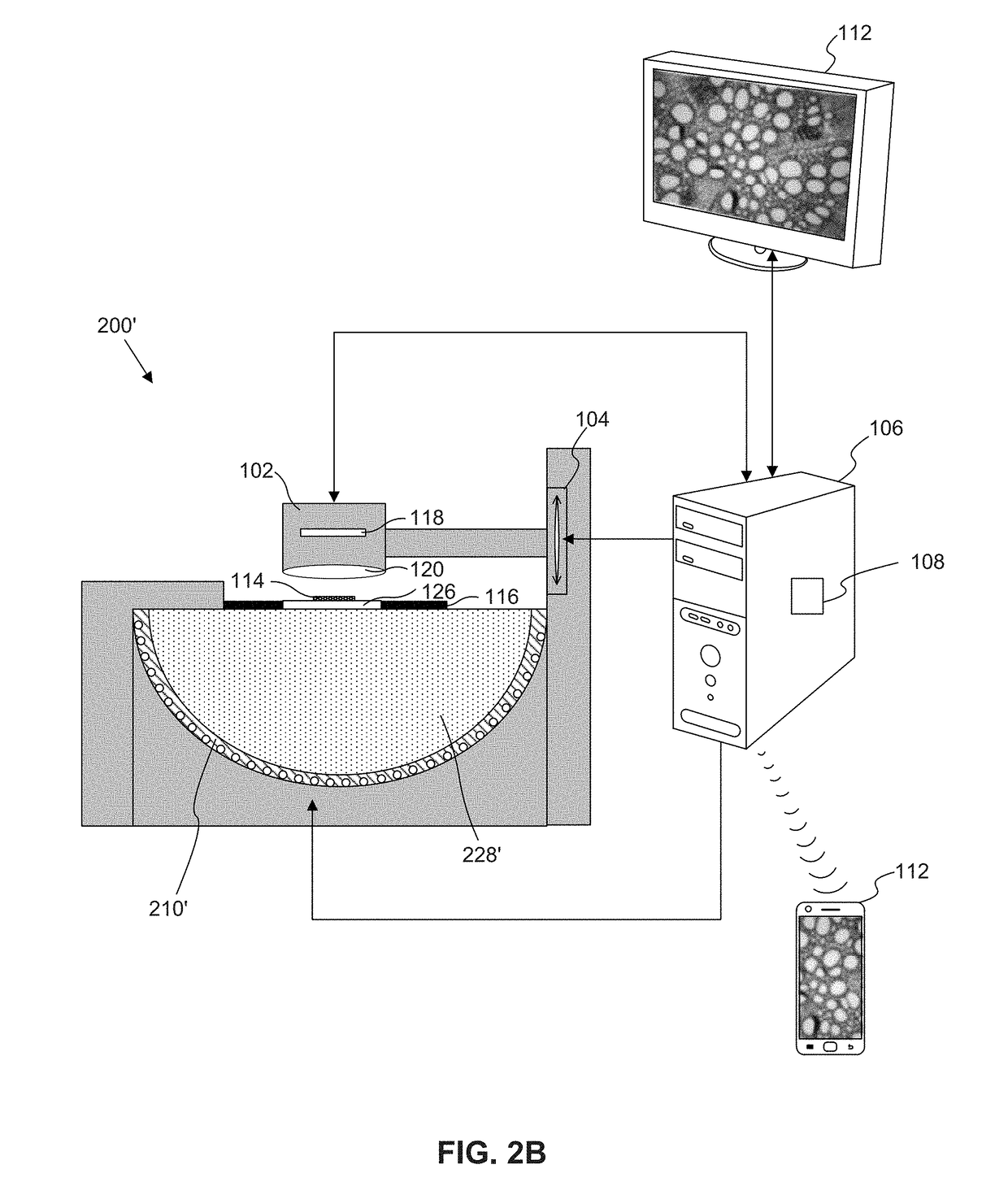
Microscope having a refractive index matching material
InactiveUS20180373016A1Geometric image transformationMicroscopesIndex-matching materialInformation capture
A microscope includes an illumination assembly configured to illuminate a sample under two or more different illumination conditions, at least one image capture device configured to capture image information associated with the sample at each of the two or more different illumination conditions, at least one processing device programmed to generate an image of the sample based on a combination of image information captured at each of the two or more different illumination conditions, and at least one refractive index matching material between the illumination assembly and the sample. The refractive index matching material is different from a medium between the at least one image capture device and the sample.
Owner:SCOPIO LABS LTD
Light emitting device with a thermal insulating and refractive index matching material
ActiveUS8134292B2Reduce heat transferPrevent thermal degradationDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsIndex-matching materialThermal insulation
A light emitting device has a light emitting diode (LED) encapsulated by an encapsulant member. The encapsulant member includes a luminescent material, such as a phosphor, and a thermal insulating material. The thermal insulating material effectively insulates the luminescent material from the heat generated by the LED. A thermal conducting material is desirably placed in thermal contact with a back side of the LED to assist heat dissipation. The encapsulant member may be formed in two separate layers with the luminescent material forming a luminescent layer, and the thermal insulating material forming a thermal insulation layer disposed between the luminescent layer and the LED.
Owner:LED ENGIN
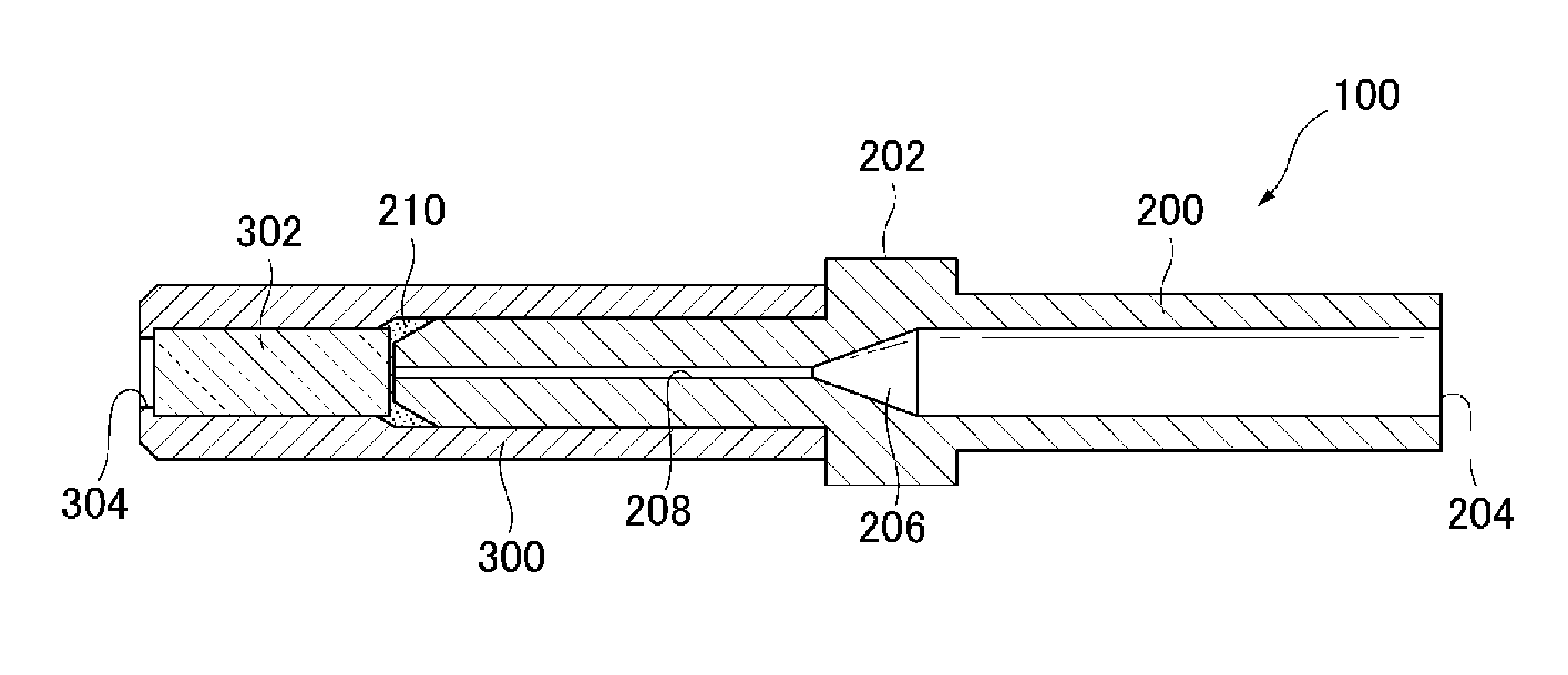
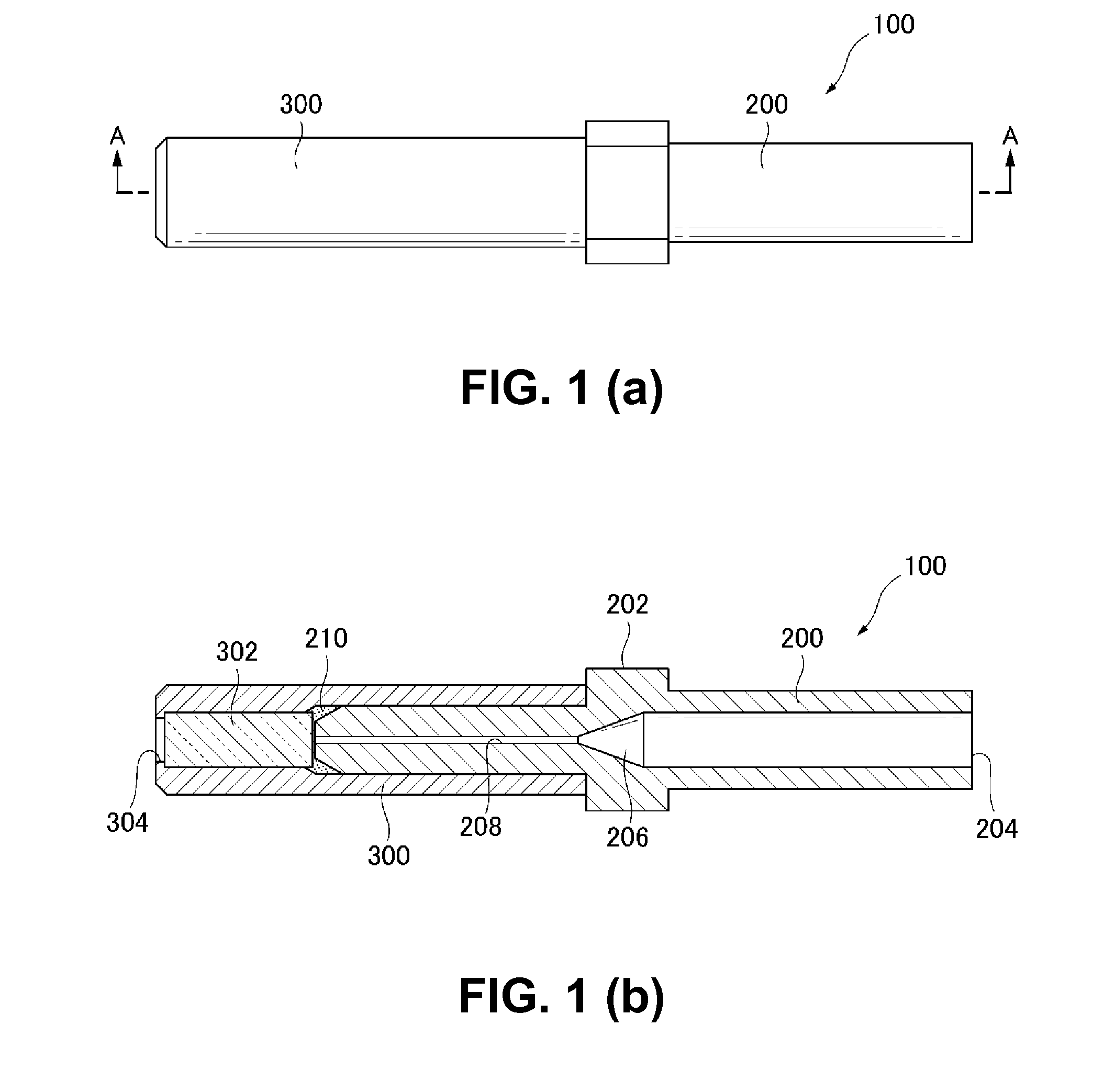
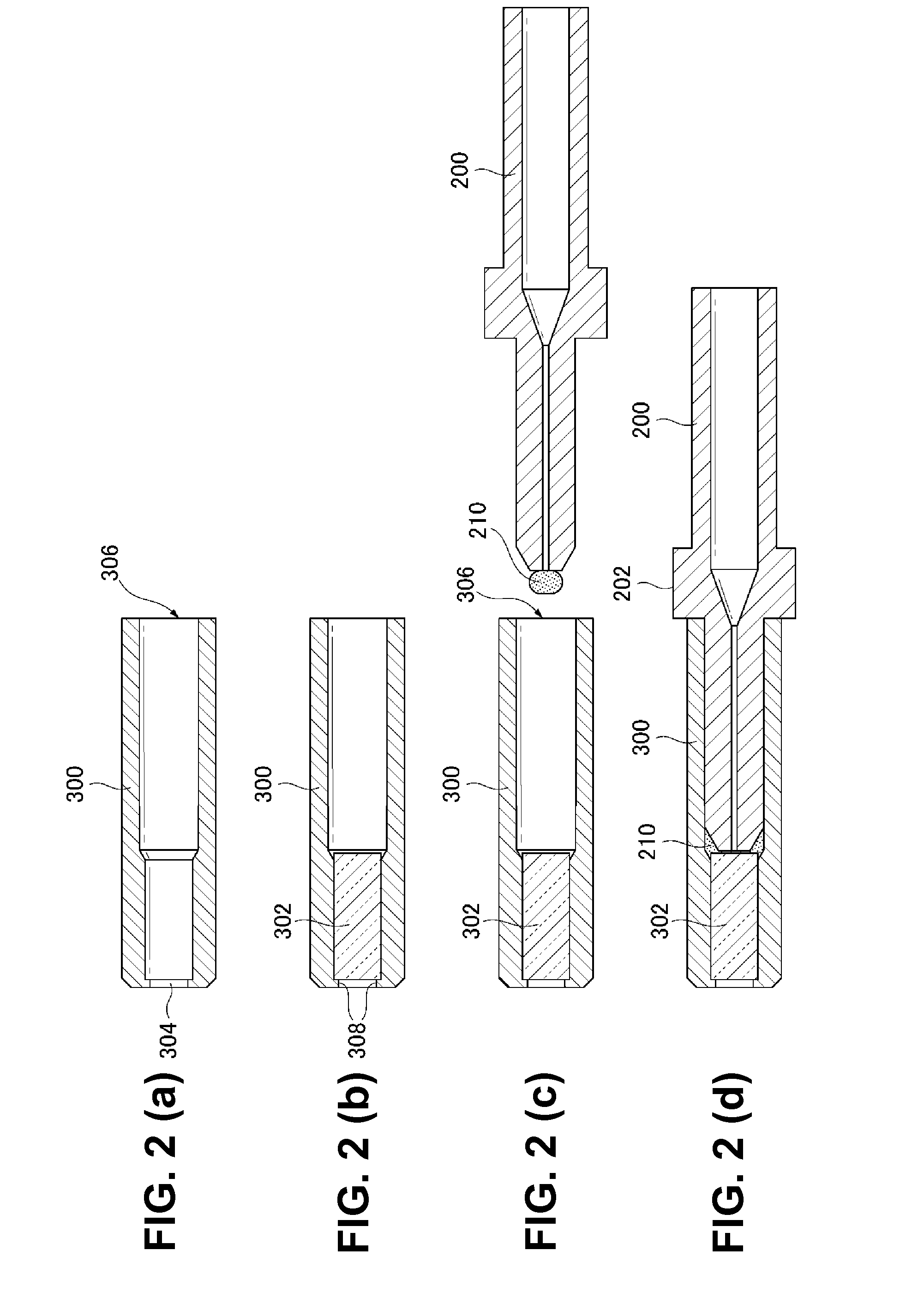
Damage resistant fiber optic connector
InactiveUS20130084042A1Coupling light guidesMetal working apparatusLeading edgeIndex-matching material
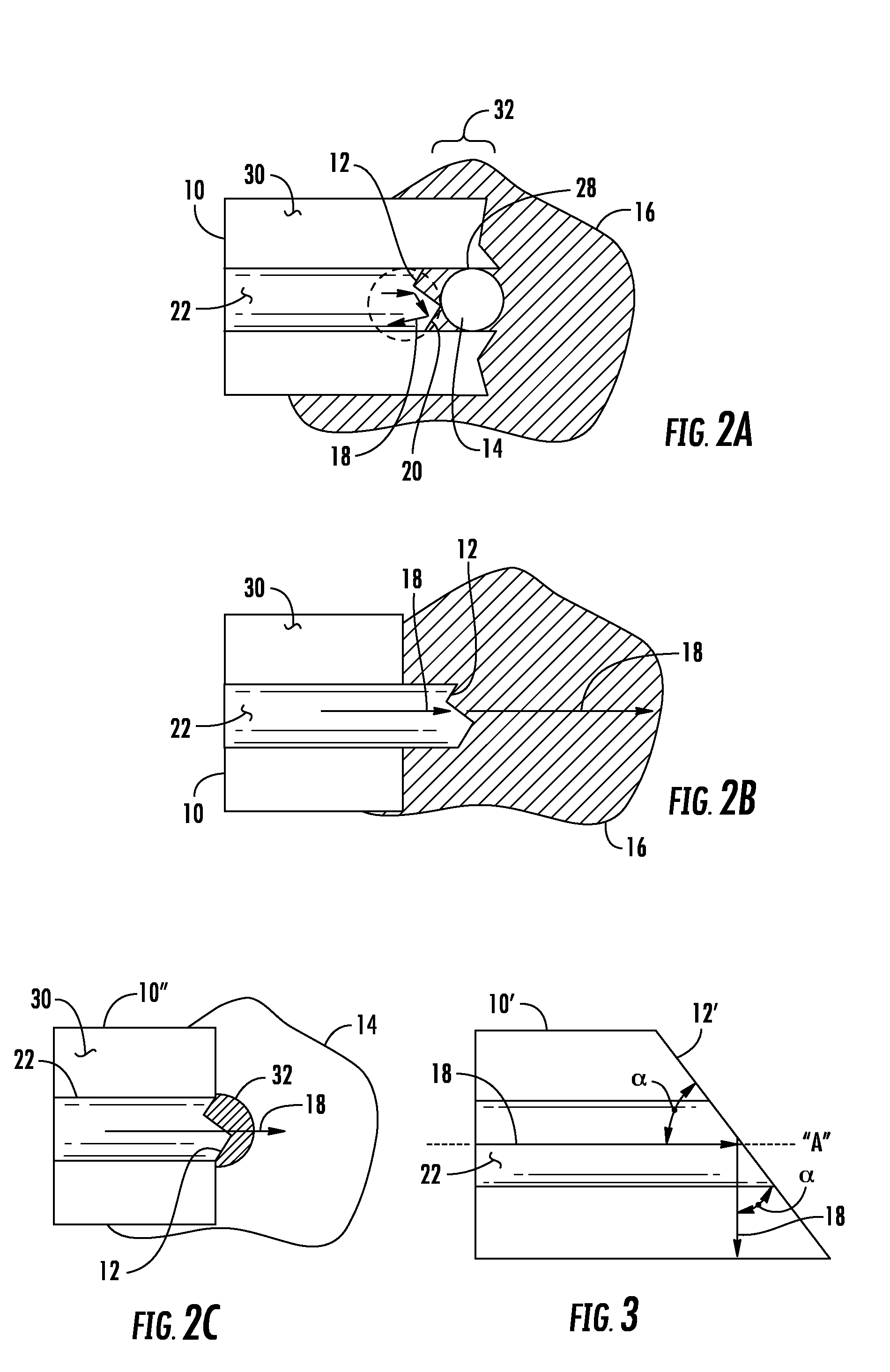
A fiber optic connector has a connector body, an elongated ferrule supported in the connector body, and a sleeve fixed on the circumference of a distal tip of the ferrule. The ferrule has an axial passage that opens on a front surface of the tip so that an endface of a fiber retained in the passage is exposed at the front surface. Further, the sleeve has a leading edge that projects a determined distance axially beyond the front surface of the tip to form a recessed region in which the exposed endface of the fiber is set back from the leading edge of the sleeve. A barrier is contained in the recessed region for protecting the fiber endface from damage by surrounding objects. The barrier may include a cured epoxy layer, a lens, or a refractive index matching material optically aligned with the fiber endface.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
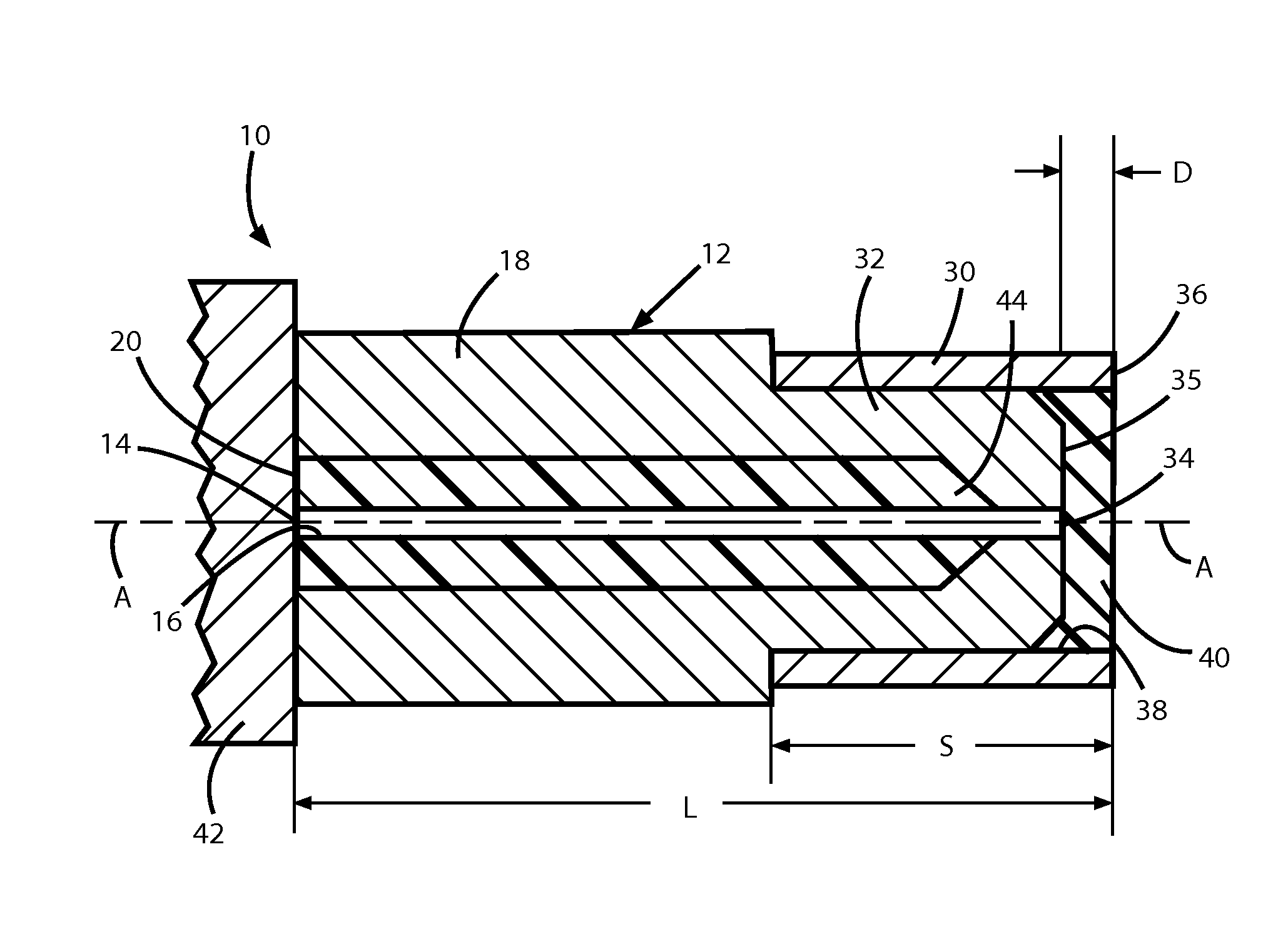
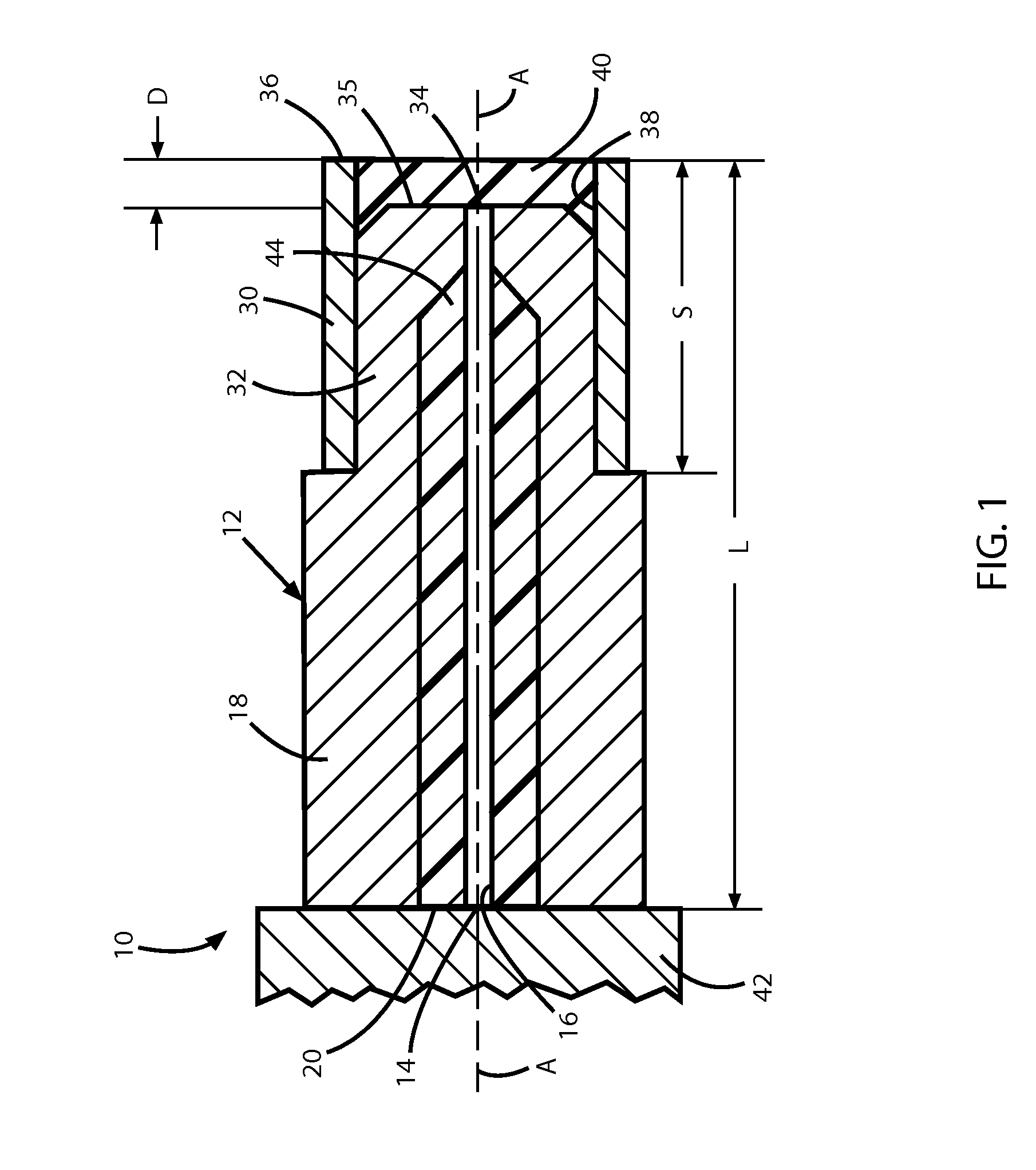
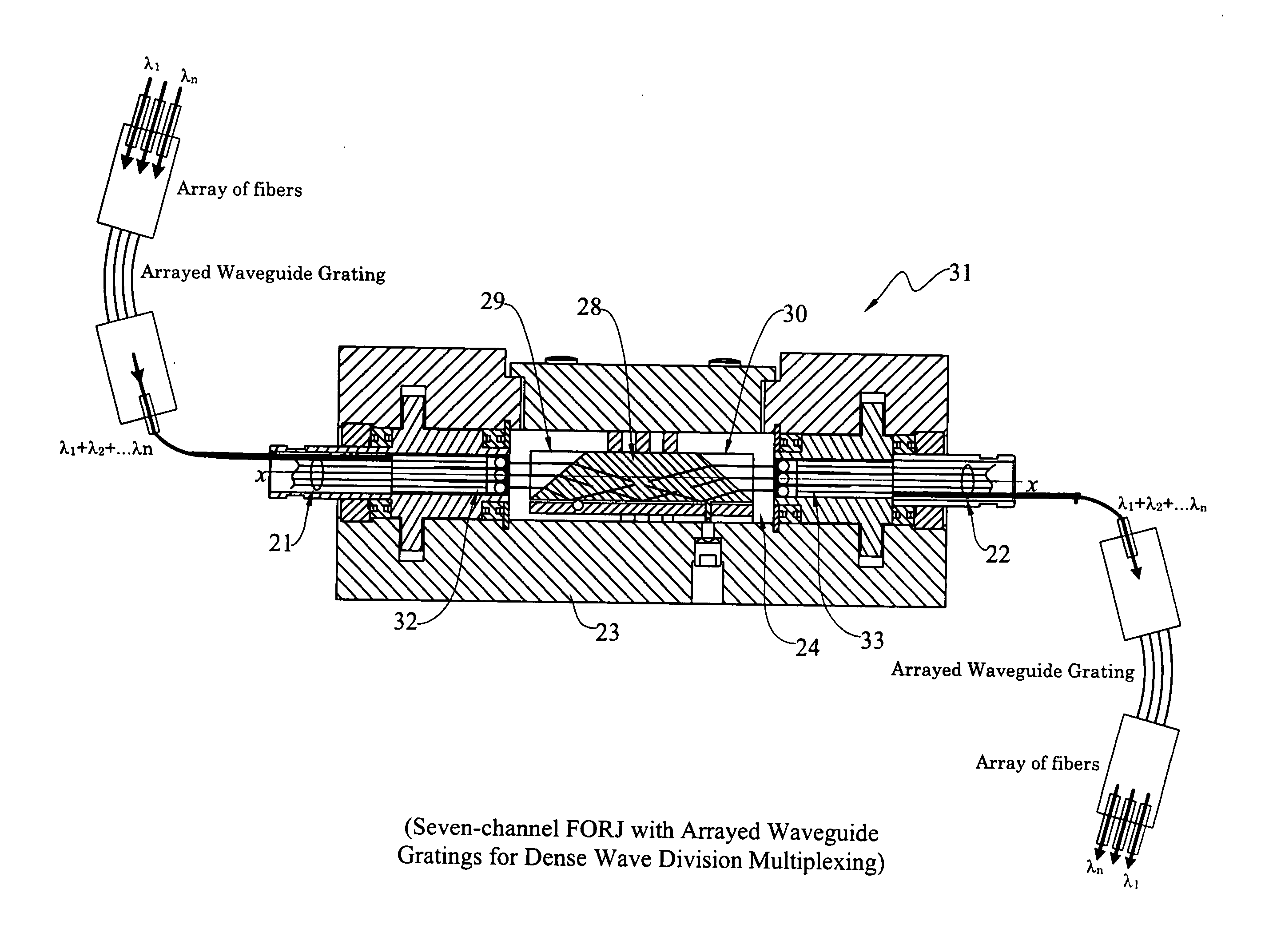
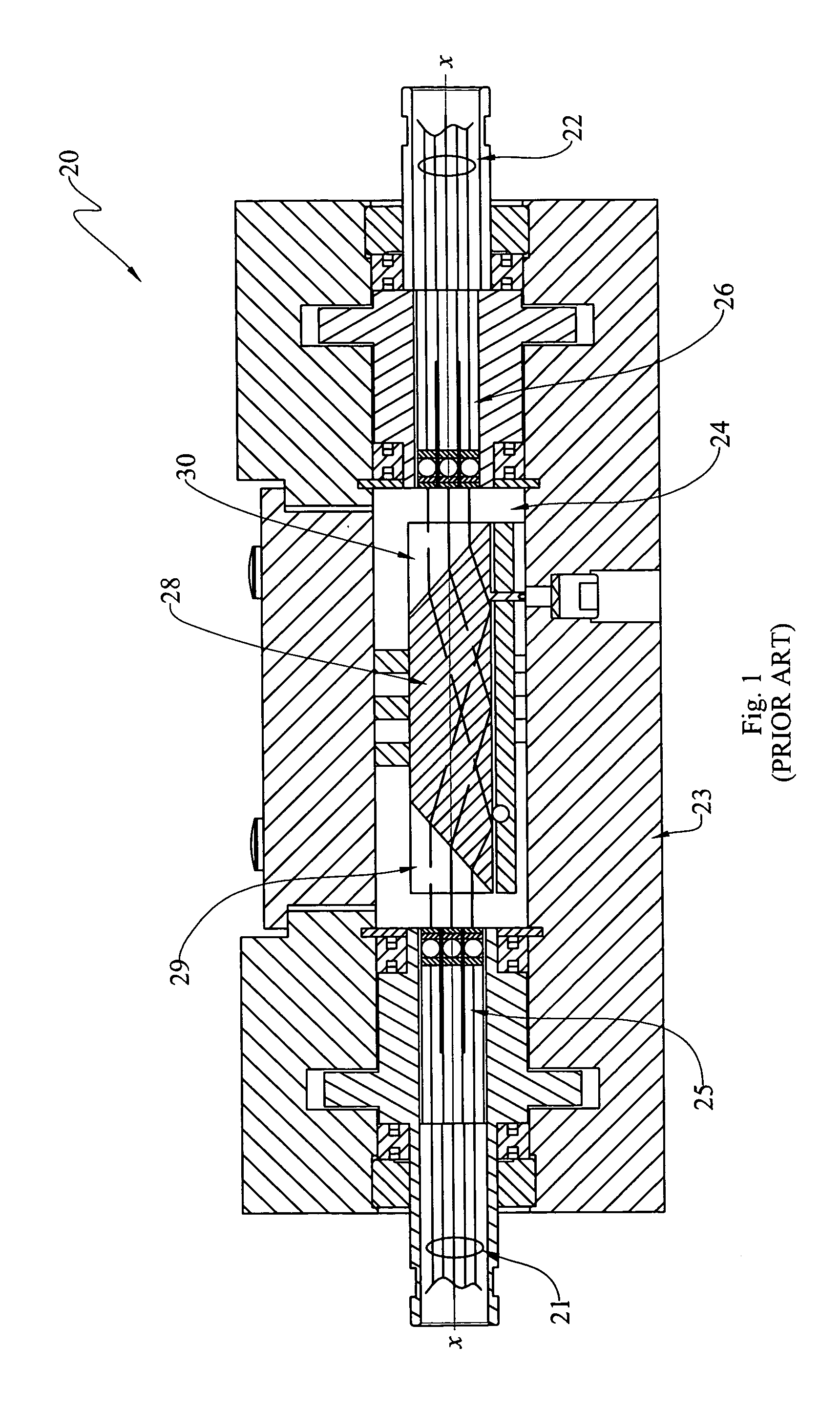
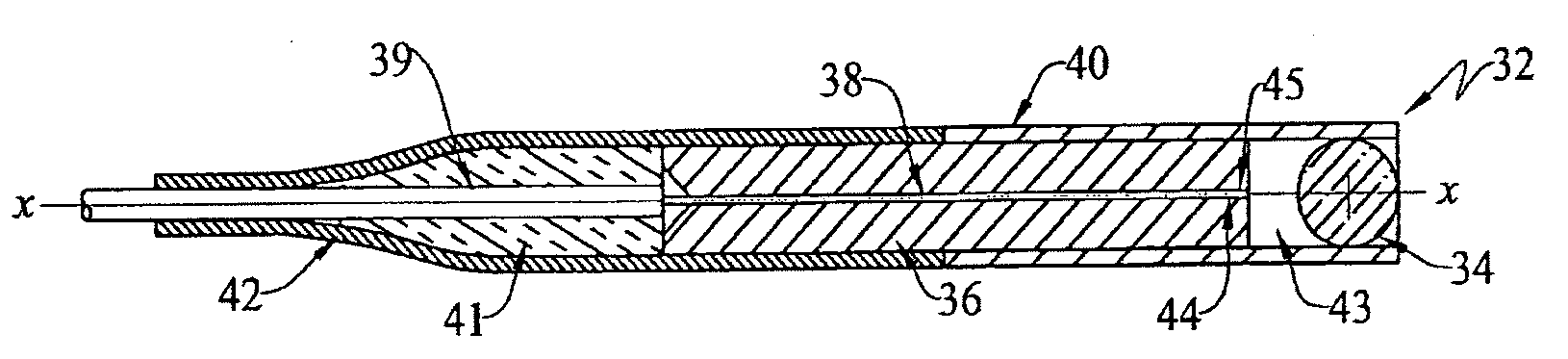
High-power collimating lens assemblies, and methods of reducing the optical power density in collimating lens assemblies
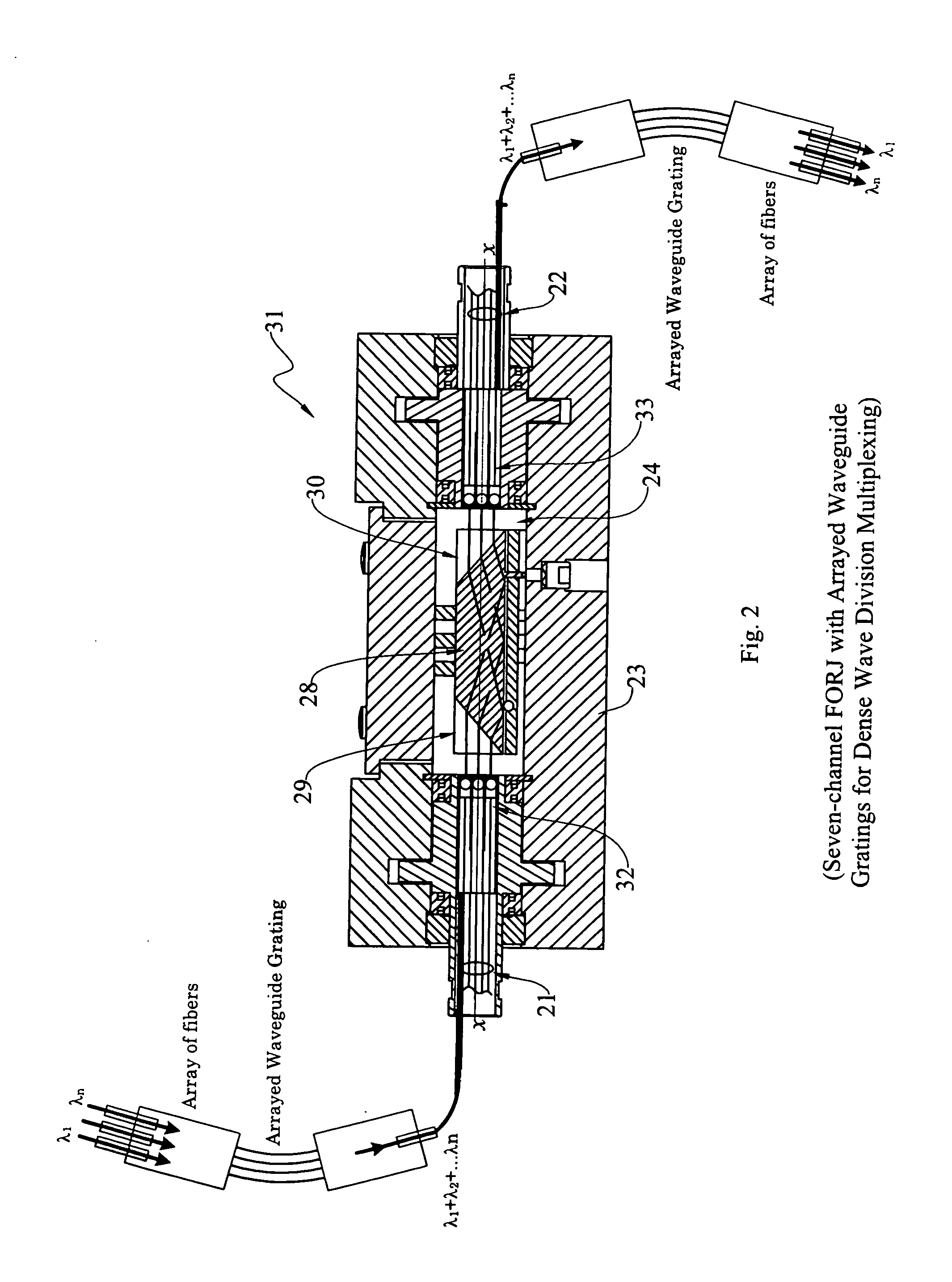
ActiveUS20110262072A1Reduce optical power densitySimple methodLine/current collector detailsCoupling light guidesEpoxyIndex-matching material
The present invention provides improved collimating lens assemblies (32), improved methods of reducing the optical power density in collimating lens assemblies, and to improved fiber optic rotary joints (31) incorporating such improved collimating lens assemblies. The improved collimating lens assembly broadly includes: a singlemode fiber (38) terminating in a distal end; a step-index multimode fiber (44) having a proximal end abutting to the singlemode fiber distal end, and having a distal end; a graded-index multimode fiber (45) having a proximal end abutting the step-index multimode fiber distal end, and having a distal end; and a collimating lens (34) longitudinally spaced from the graded-index multimode fiber distal end by an intermediate air gap (43), and operatively arranged to collimate light rays emanating from the graded-index multimode fiber distal end. The improved collimating lens assembly is characterized by the fact that there is no epoxy, silicone gel or index-matching material between the graded-index multimode fiber distal end and the collimating lens. Rather, these various elements are fusion-spliced together. The improved collimating lens assembly is capable of handling energy levels that are typically used in various wavelength division multiplexing techniques.
Owner:MOOG INC
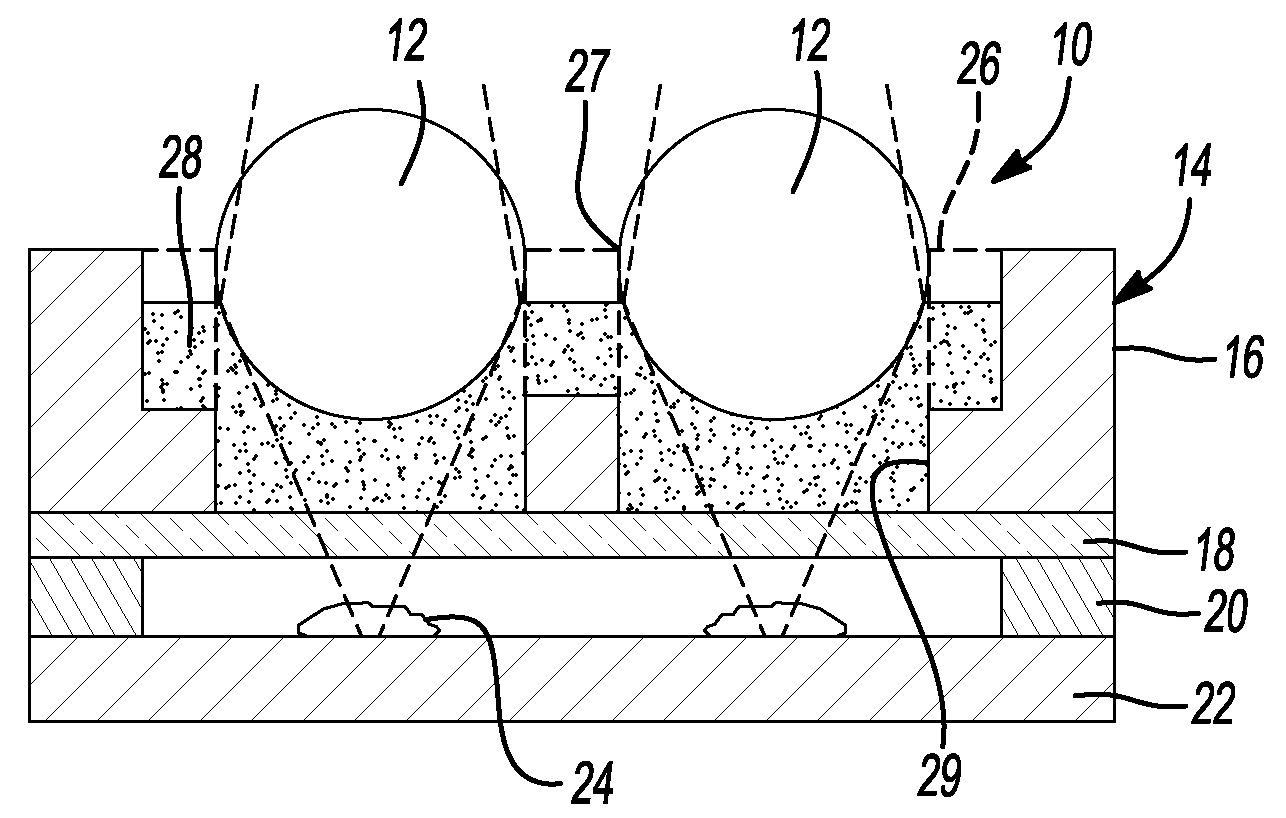
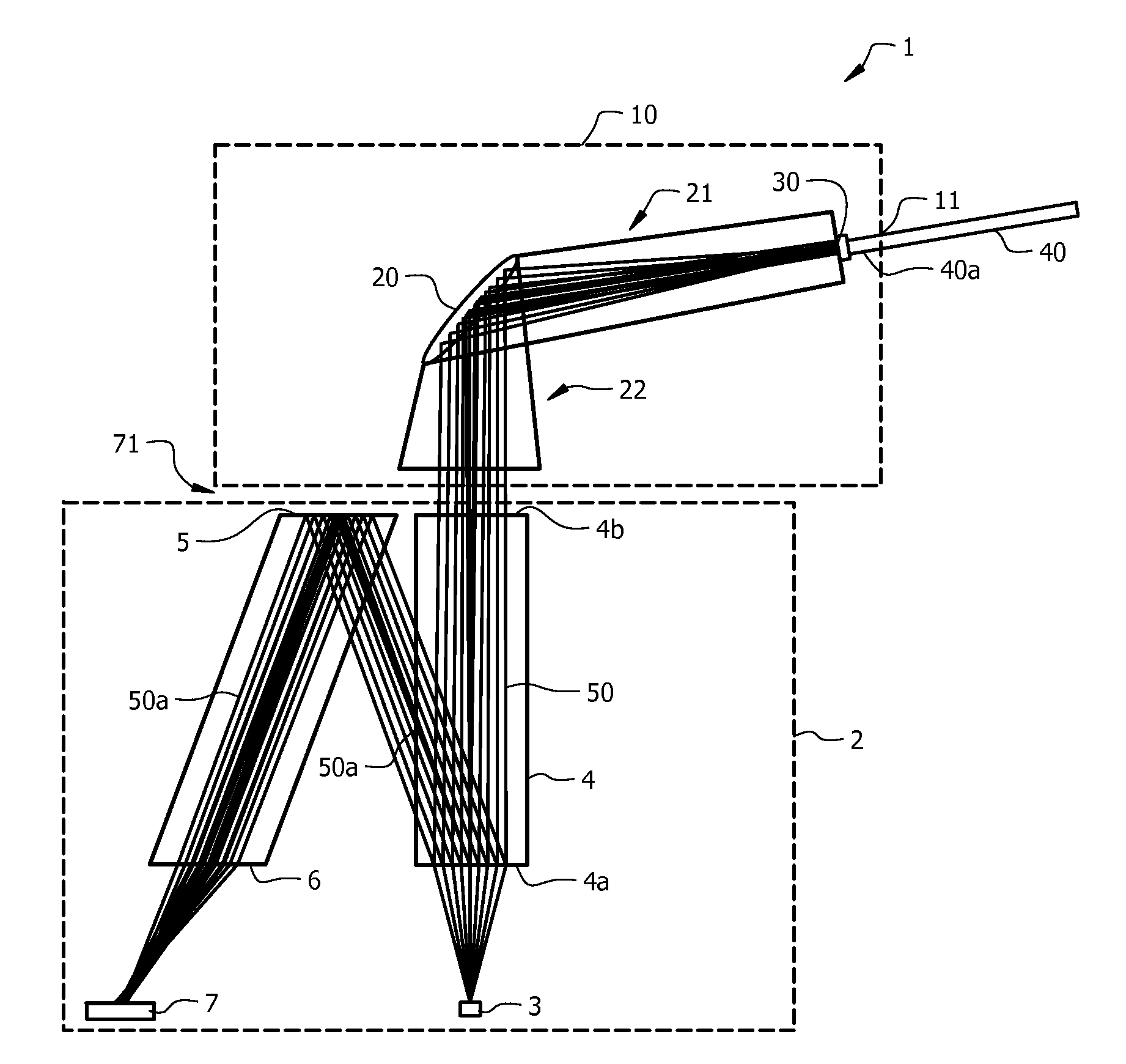
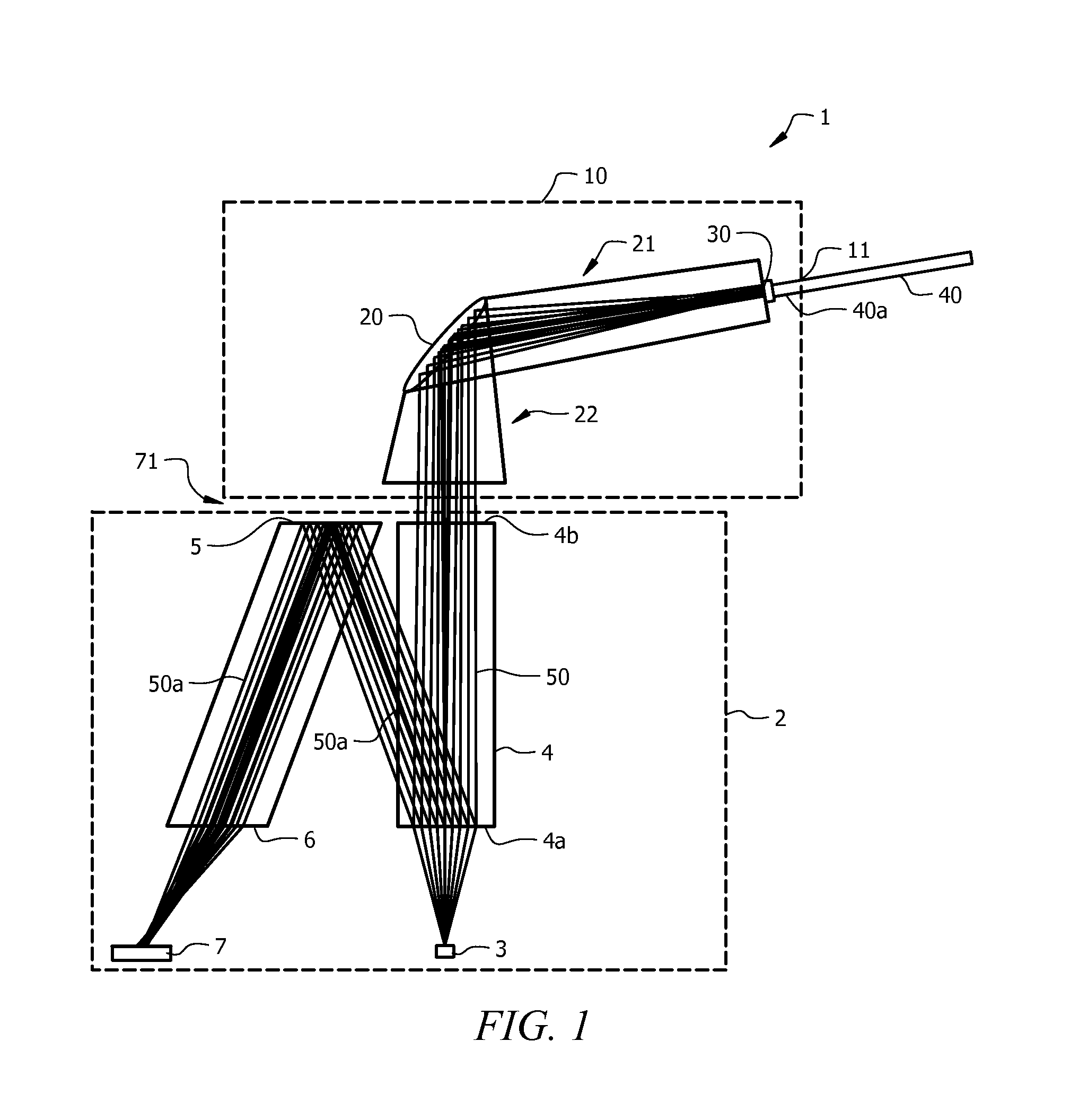
Confocal Displacement Sensor
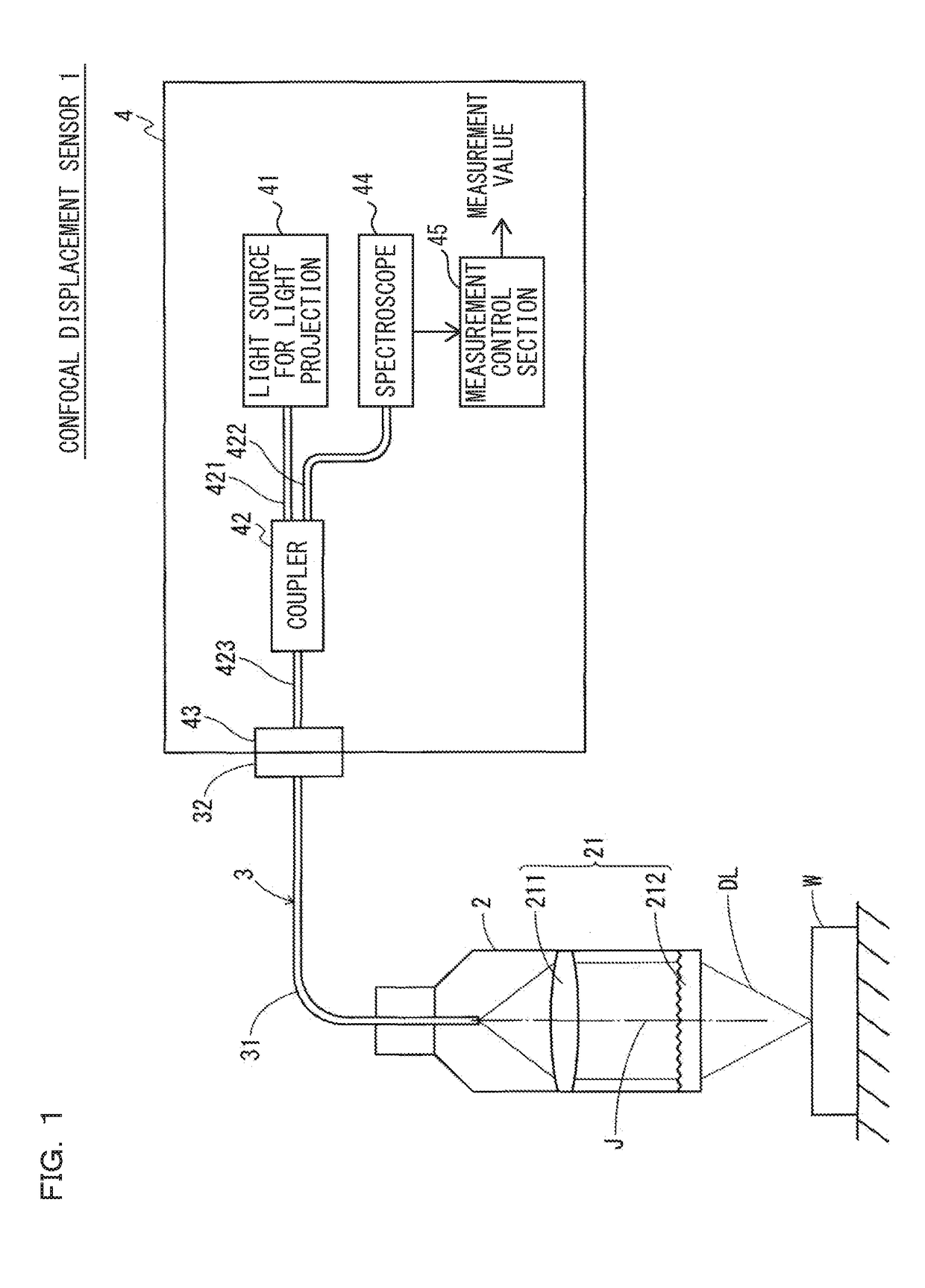
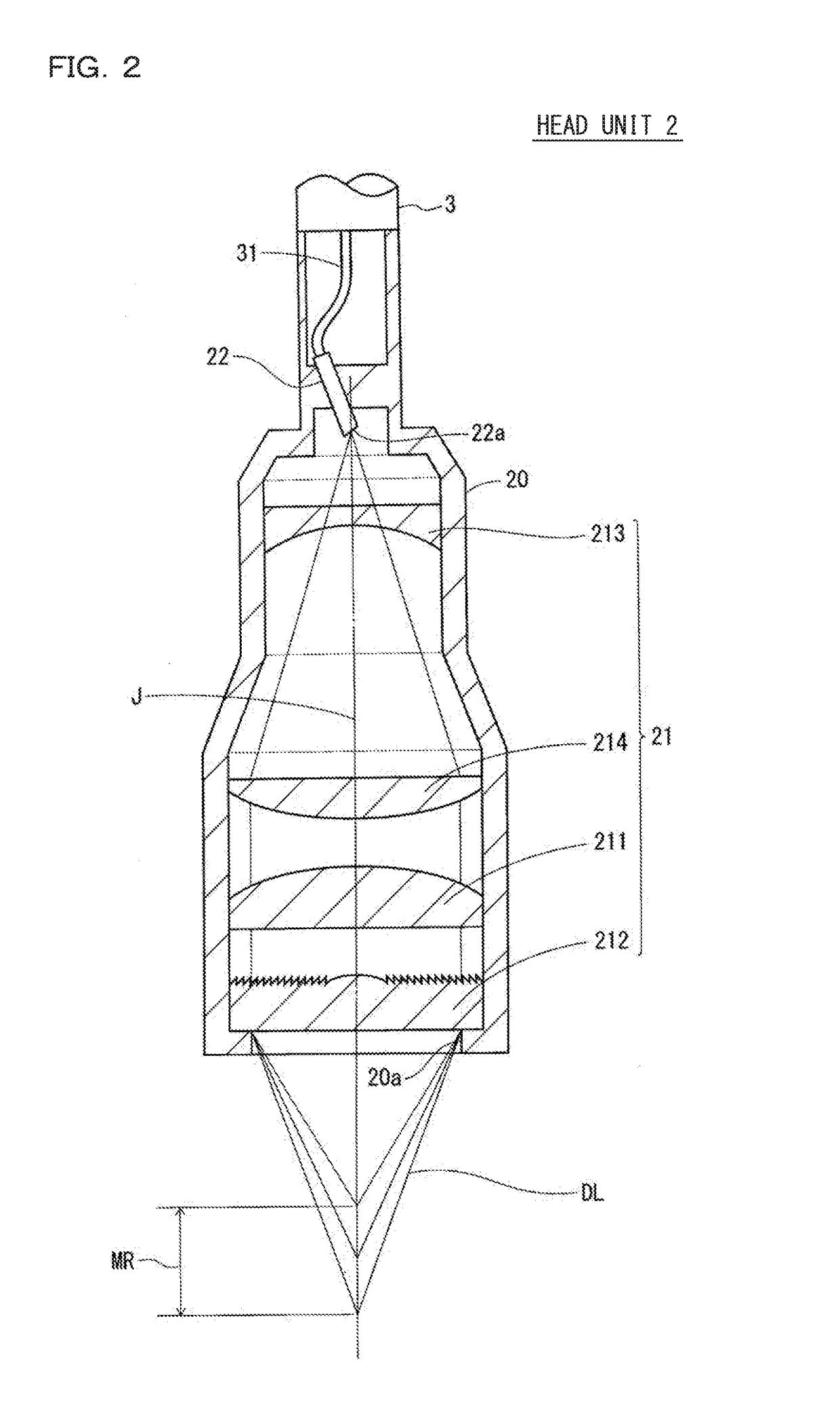
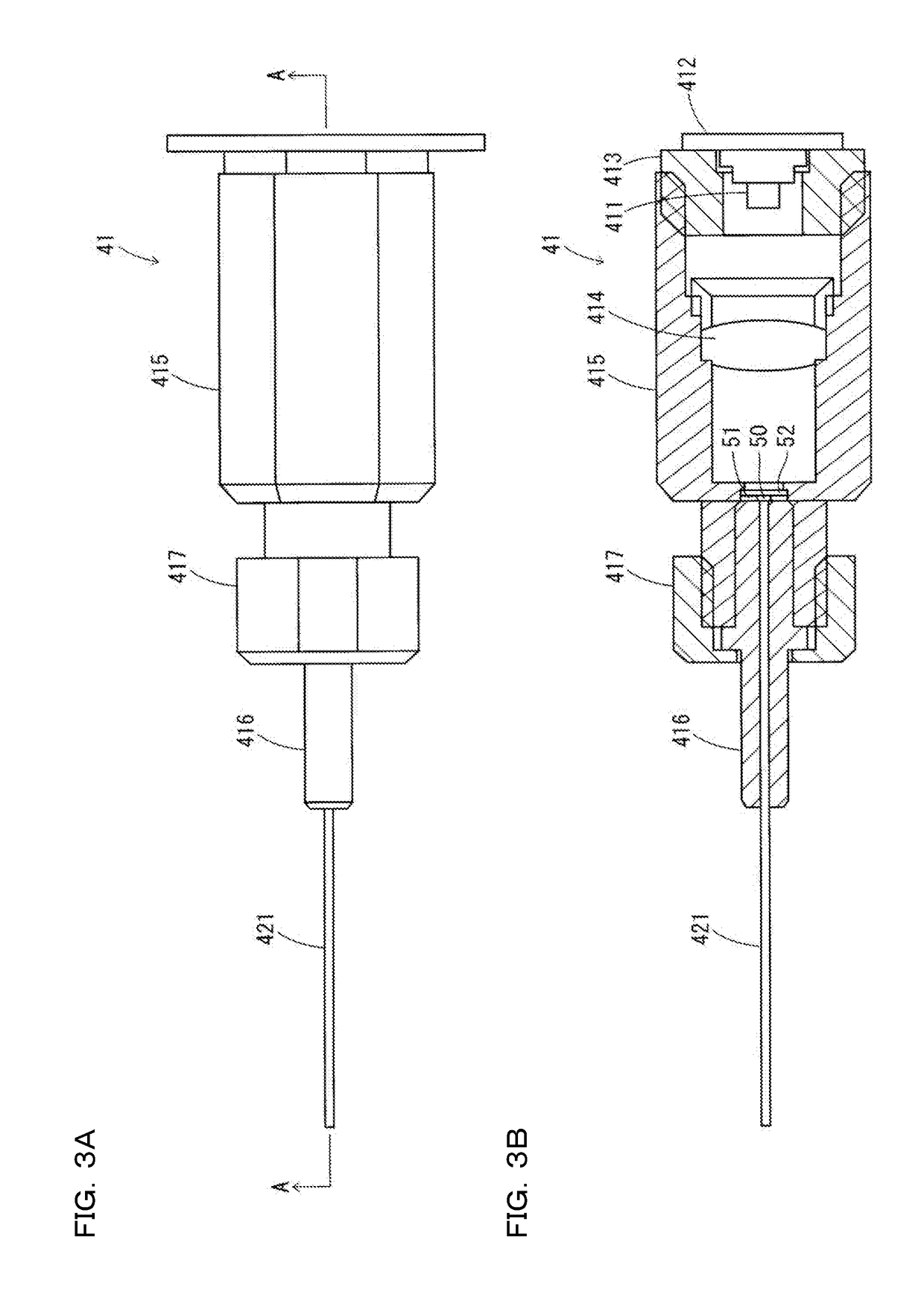
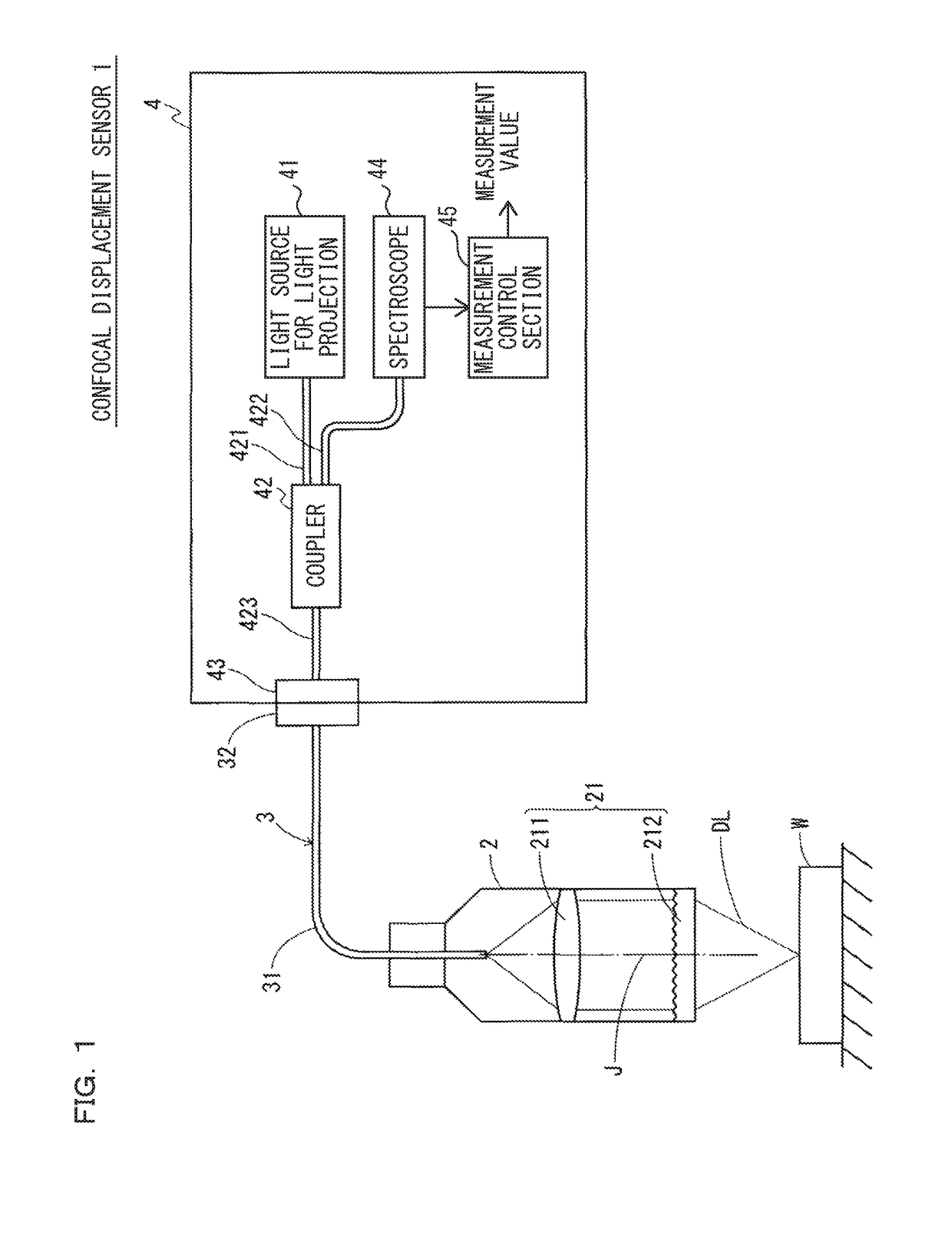
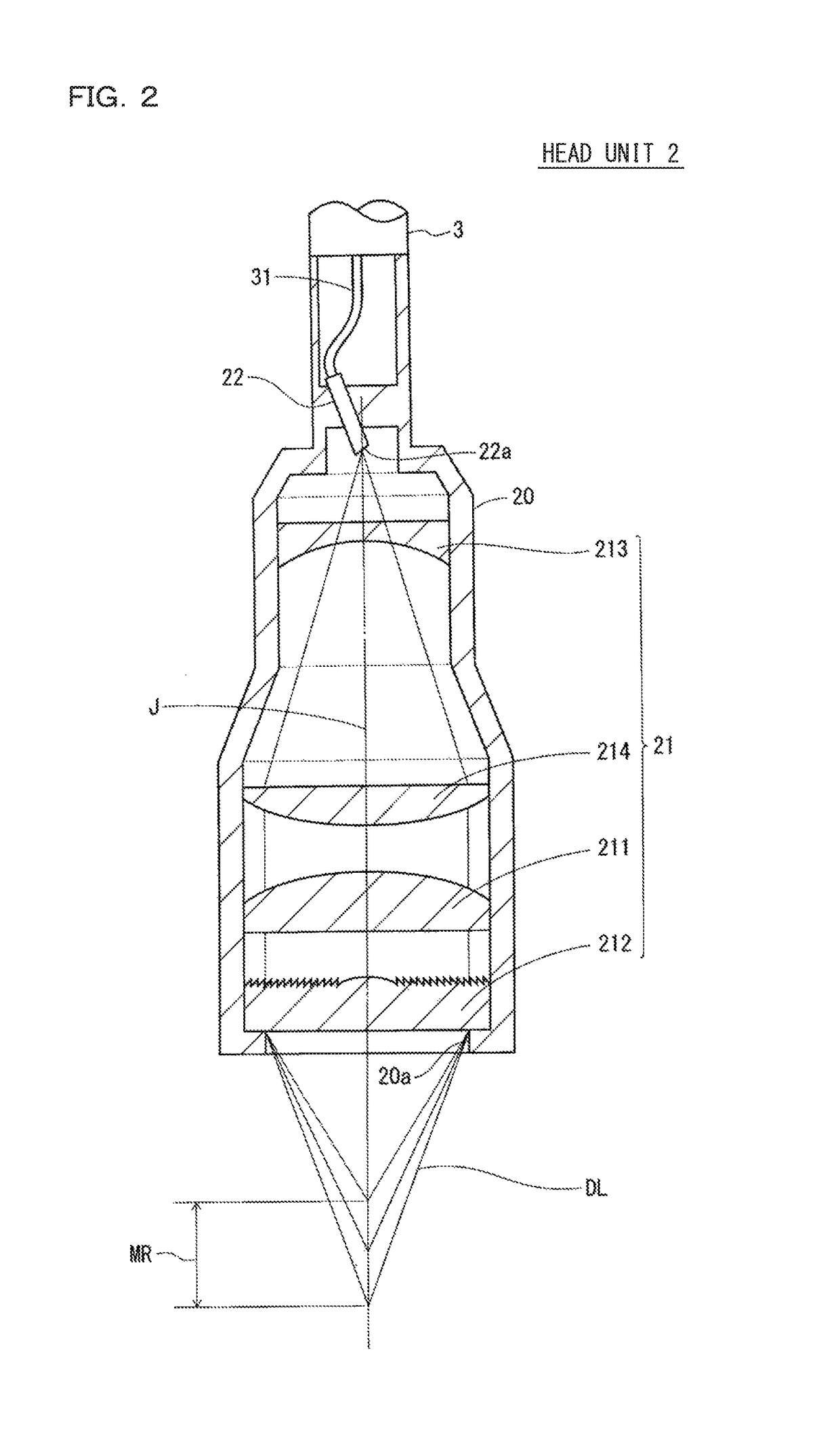
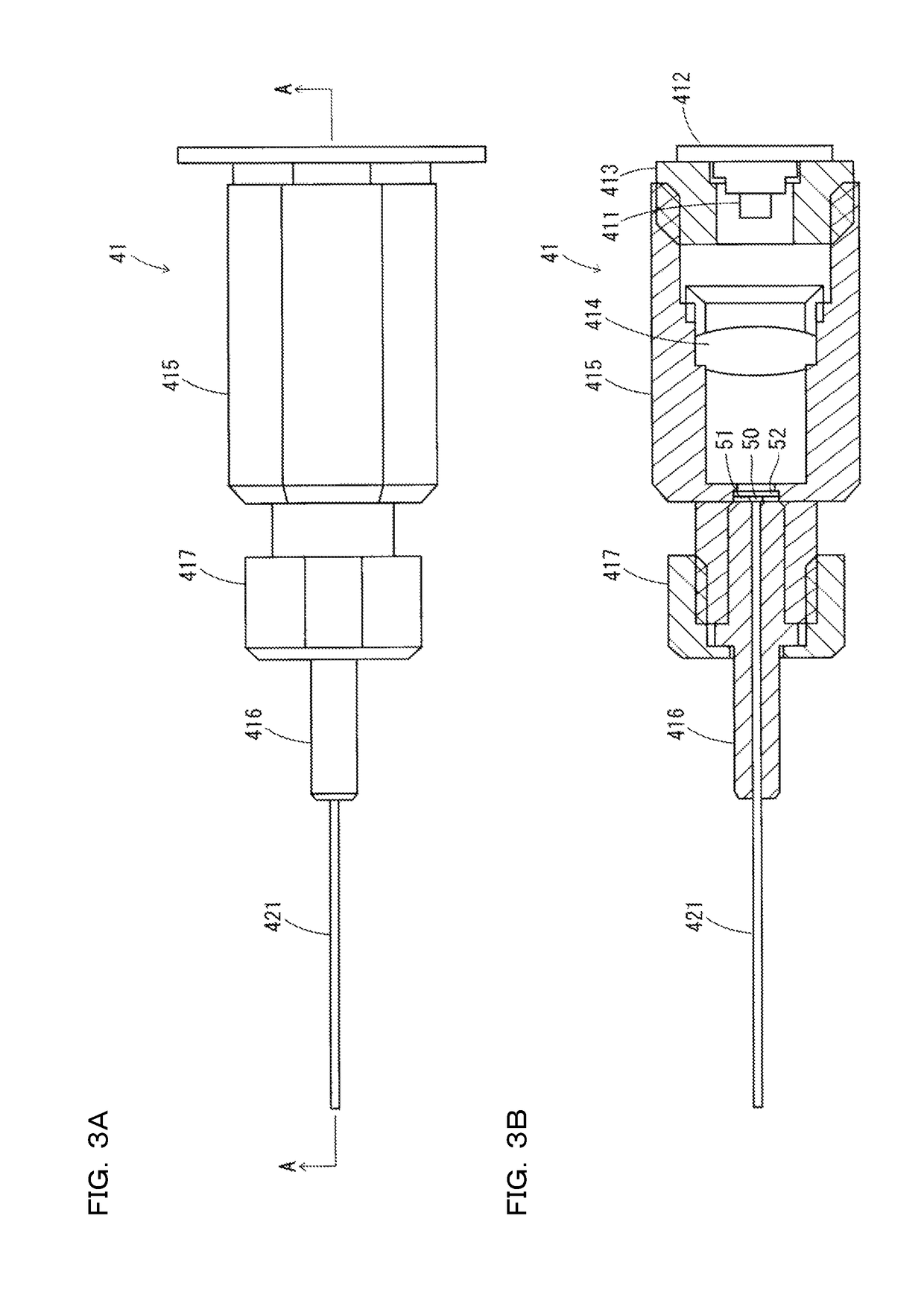
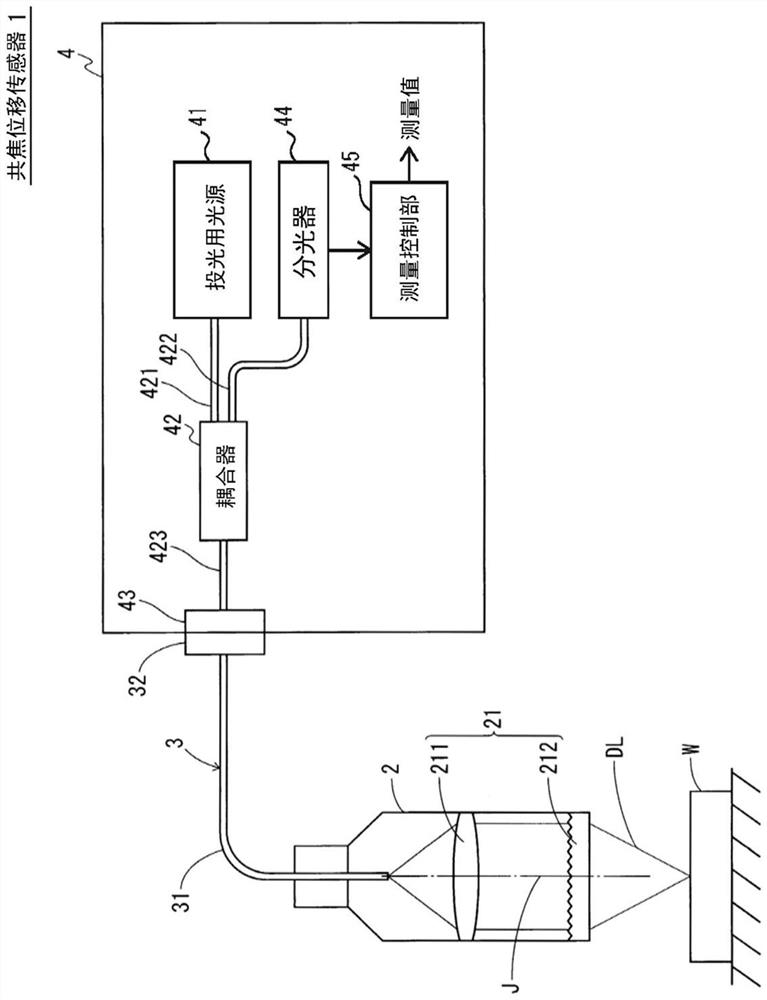
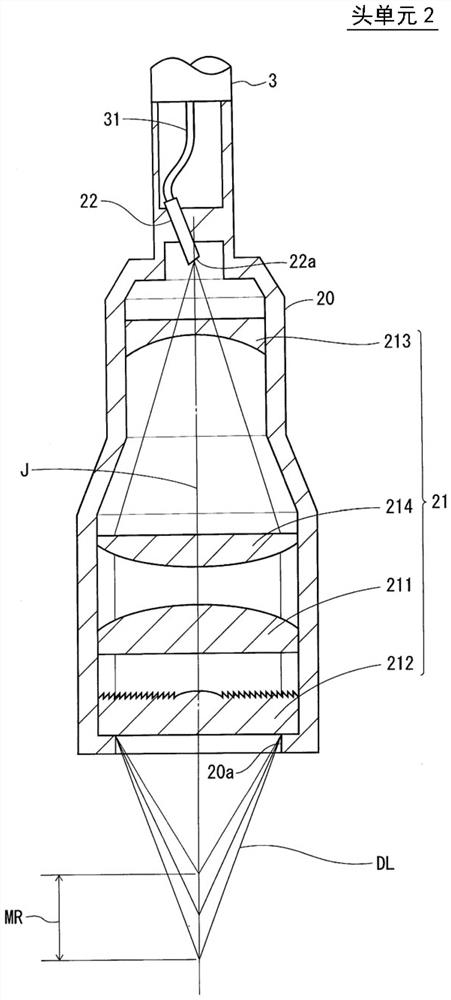
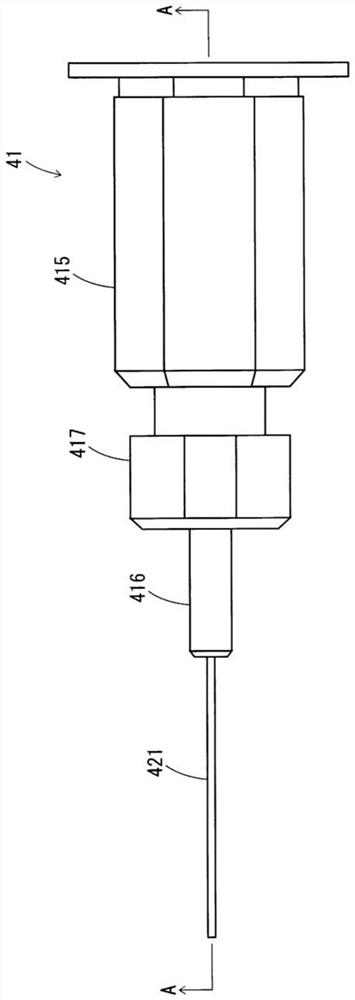
ActiveUS20180356207A1Easy to handlePrevent leakageRadiation pyrometryUsing optical meansIndex-matching materialRefractive index matching
The confocal displacement sensor includes a first optical fiber, to a first incident end of which light for light projection is input, the first optical fiber outputting the light from a first emission end, a second optical fiber, a second incident end of which is disposed to be opposed to the first emission end, the second optical fiber emitting light input via the second incident end from a second emission end, an optical member configured to cause an axial chromatic aberration on detection light emitted via the second emission end and converge the detection light toward the measurement object, a fiber connecting section configured to detachably connect the second incident end to the first emission end, and a refractive index matching material disposed between the first emission end and the second incident end.
Owner:KEYENCE
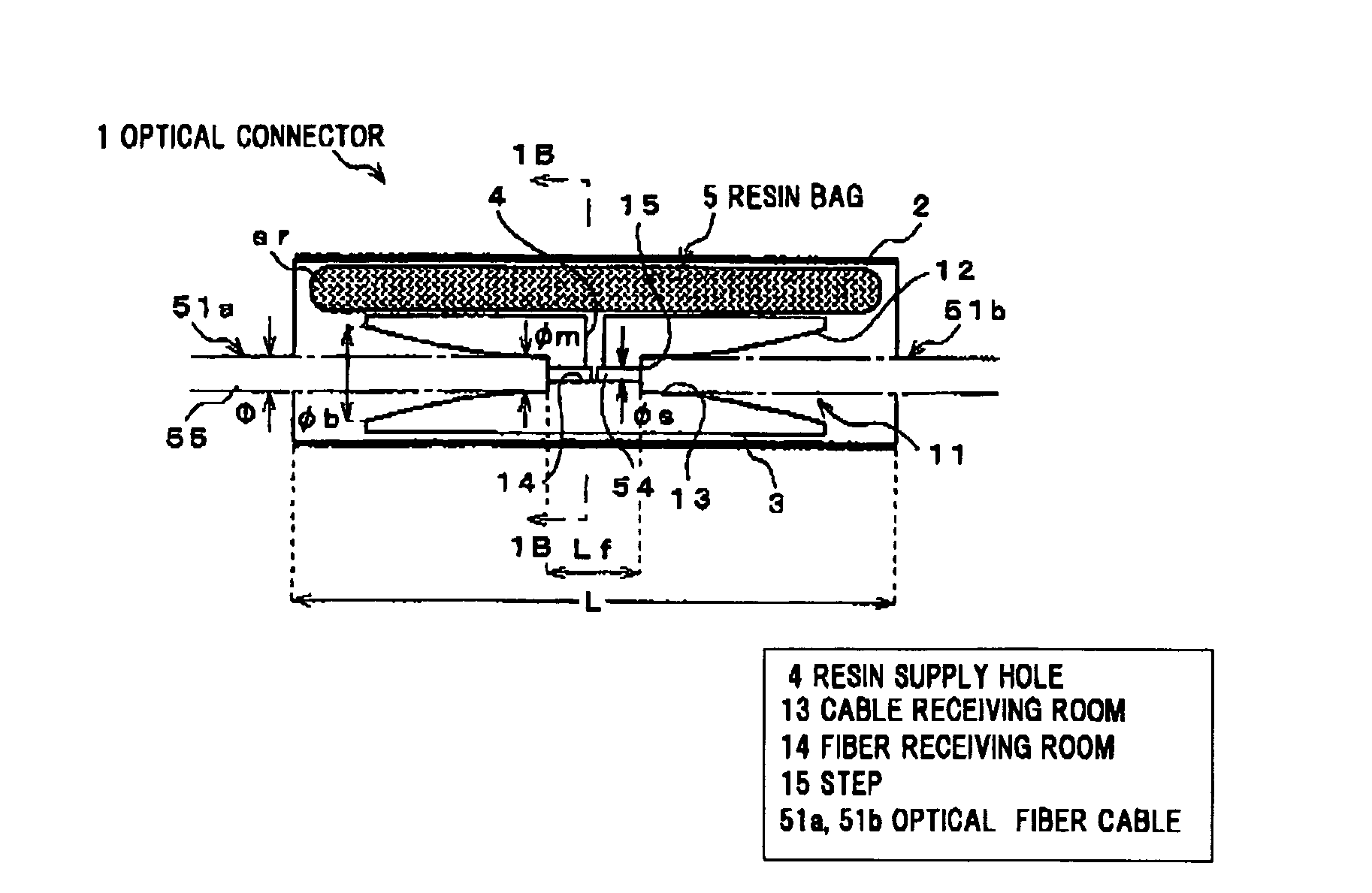
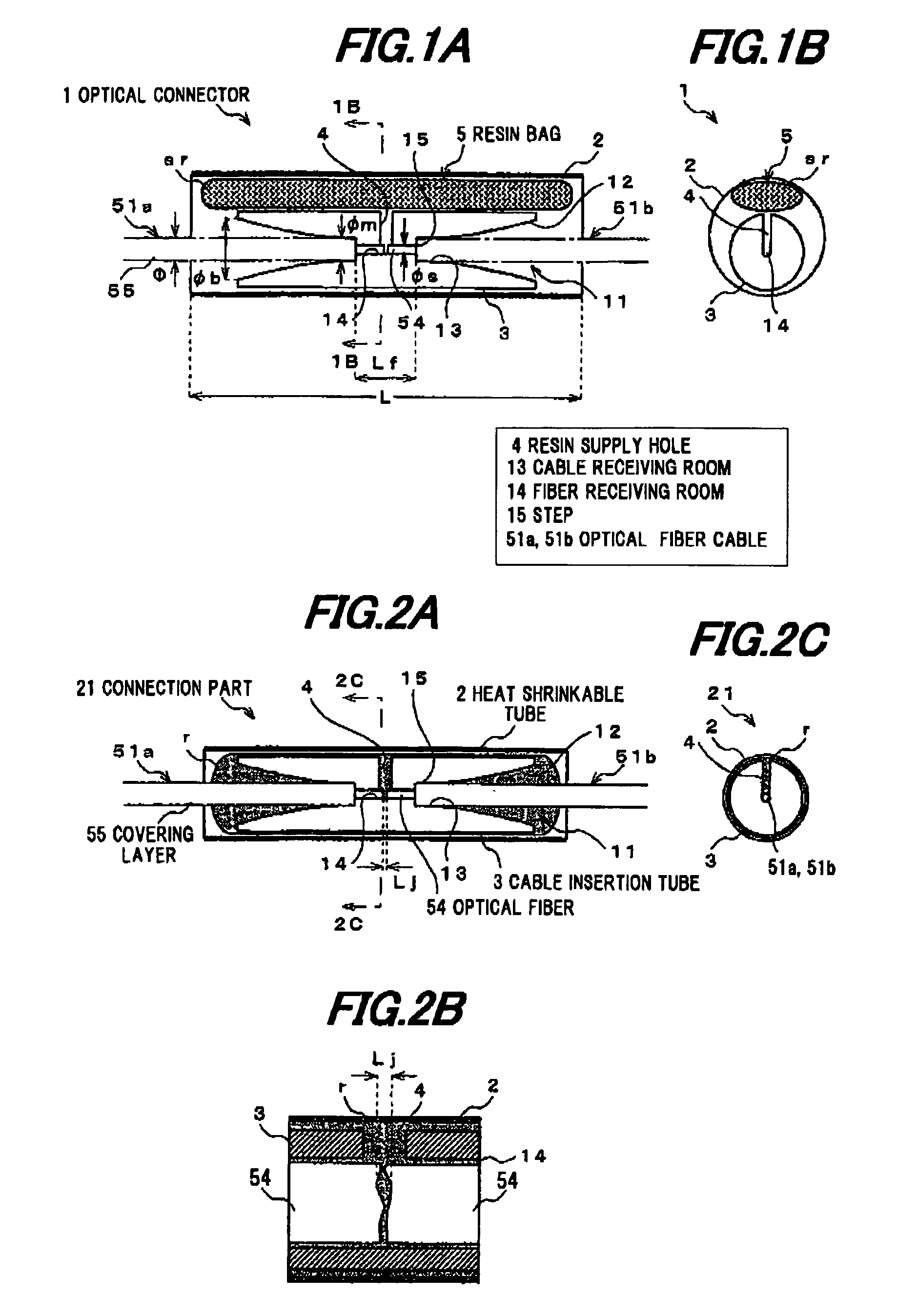
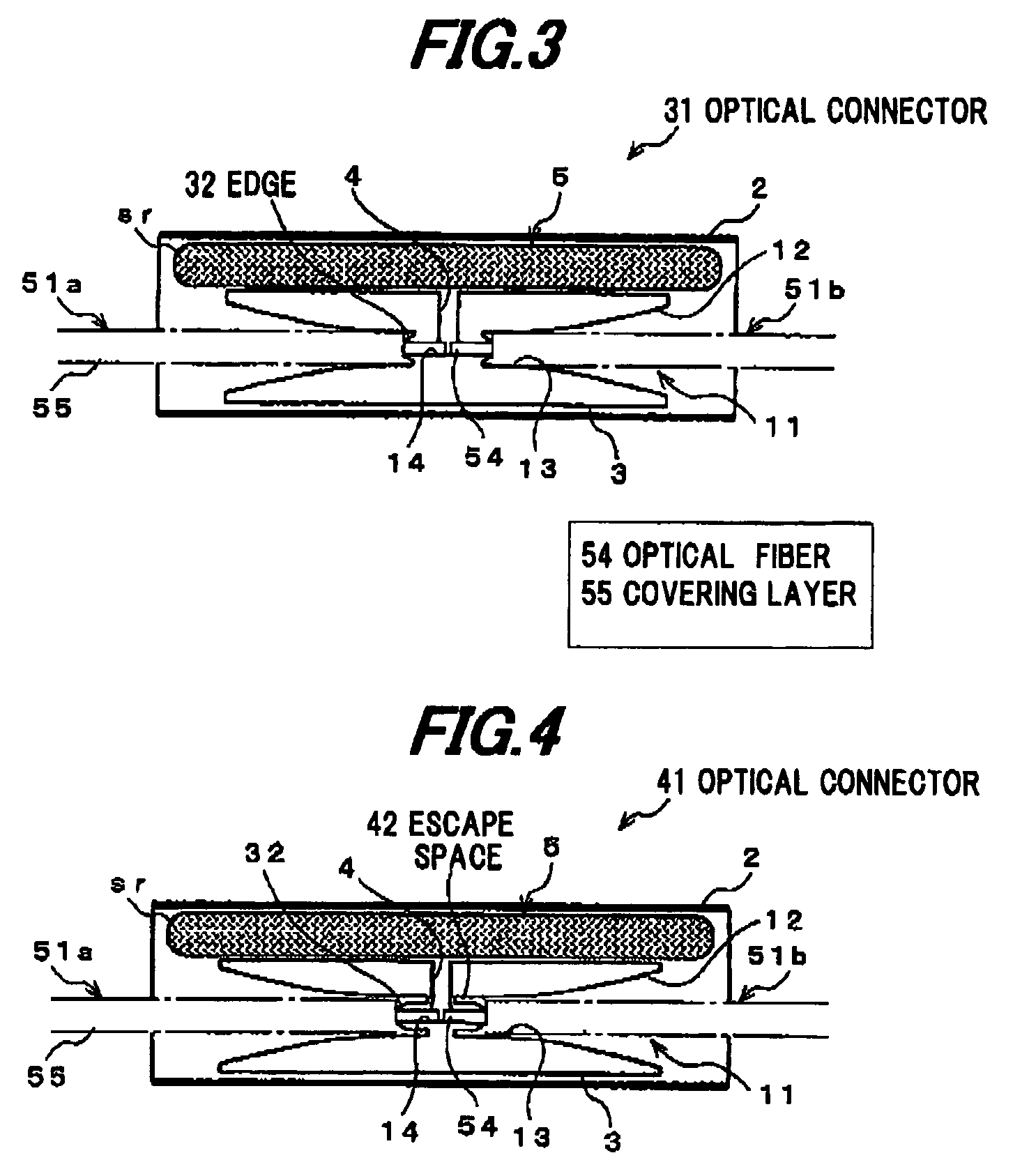
Optical connector
InactiveUS7771128B2Easy to operateEasy to optimizeGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesIndex-matching materialEngineering
In an embodiment of the invention, an optical connector for optically coupling respective end faces of two optical fiber cables including an optical fiber composed of a core and a cladding and a covering layer covering the optical fiber includes a protection sleeve, a cable insertion tube disposed in the protection sleeve for inserting thereinto and butting the respective end faces of the two optical fiber cables, an uncured refractive index matching material disposed between the protection sleeve and the cable insertion tube, and a supply hole formed in the cable insertion tube for supplying the uncured refractive index matching material to an inside of the cable insertion tube. The cable insertion tube includes a cable receiving room for receiving an end of the two optical fiber cables inserted, a fiber receiving room for receiving the optical fiber, and a covering removal member formed at a boundary of the cable receiving room and the fiber receiving room for removing the covering layer.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
Packaging for optoelectronic devices
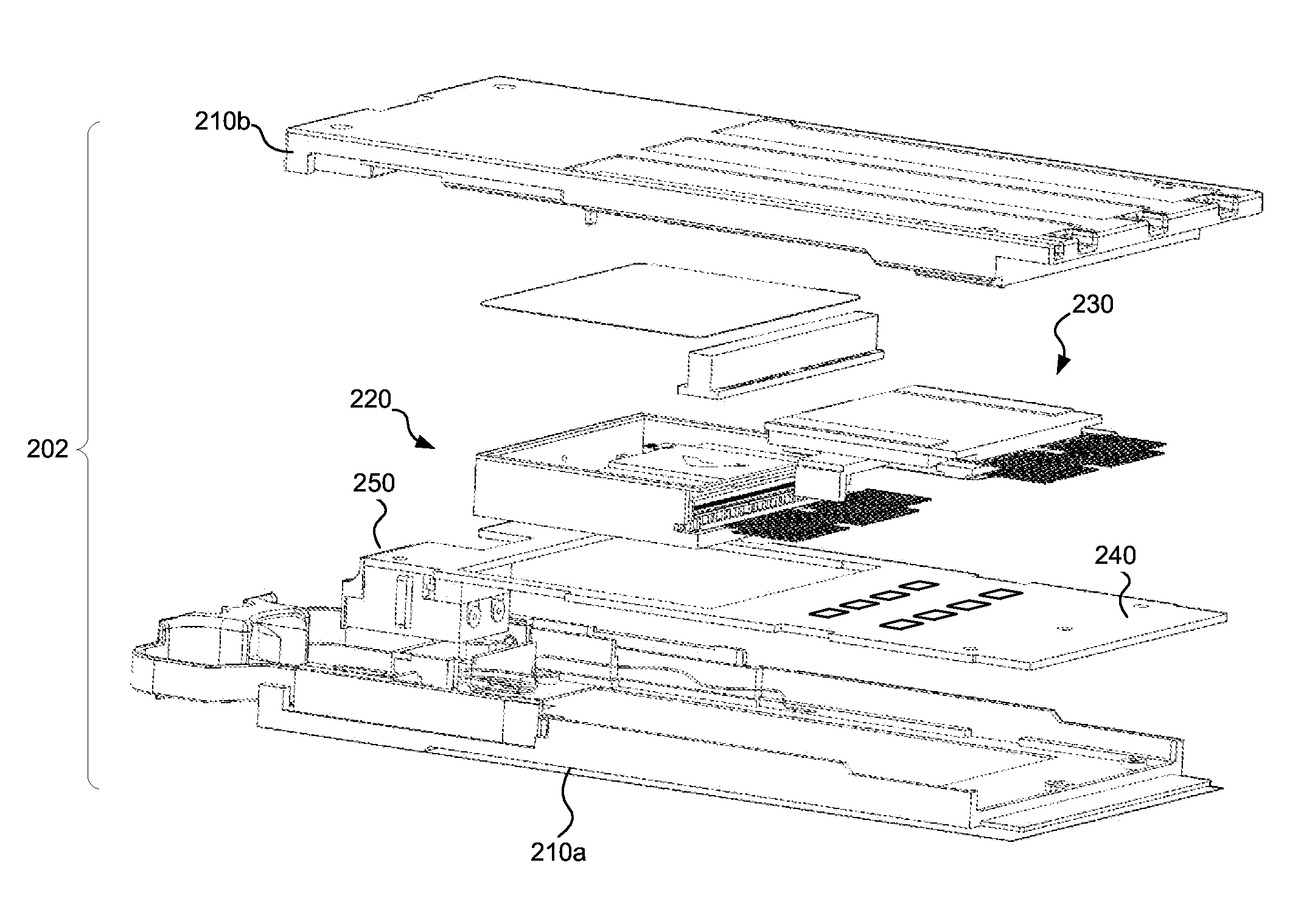
ActiveUS7091469B2Improve moisture resistanceLow costTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesIndex-matching materialRefractive index matching
An optoelectronic sensor is attached to an optically transparent substrate, such as glass, and encapsulated to form an optoelectronic device. An optical assembly can be mounted opposite the optoelectronic sensor. Filters and refractive index matching materials may be included between the optoelectronic sensor and the optically transparent substrate.
Owner:STATS CHIPPAC LTD
Packaging for optoelectronic devices
ActiveUS20050258216A1Improve moisture resistanceLow costTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesIndex-matching materialElectro-optical sensor
An optoelectronic sensor is attached to an optically transparent substrate, such as glass, and encapsulated to form an optoelectronic device. An optical assembly can be mounted opposite the optoelectronic sensor. Filters and refractive index matching materials may be included between the optoelectronic sensor and the optically transparent substrate.
Owner:STATS CHIPPAC LTD
Optical connector and method of forming plug using the optical connector
InactiveUS20140254990A1Simple configurationReduce manufacturing costCoupling light guidesMetal working apparatusIndex-matching materialEngineering
An optical fiber insertion unit includes a ferrule; a lens sleeve having a lens at a front end portion thereof and a ferrule insertion opening portion at a rear end portion thereof for inserting the ferrule; and a refractive index matching portion disposed between the ferrule and the lens sleeve. The refractive index matching portion is filled with a refractive index matching material so that the refractive index adjusting agent contacts with at least the lens.
Owner:HIROSE ELECTRIC GROUP
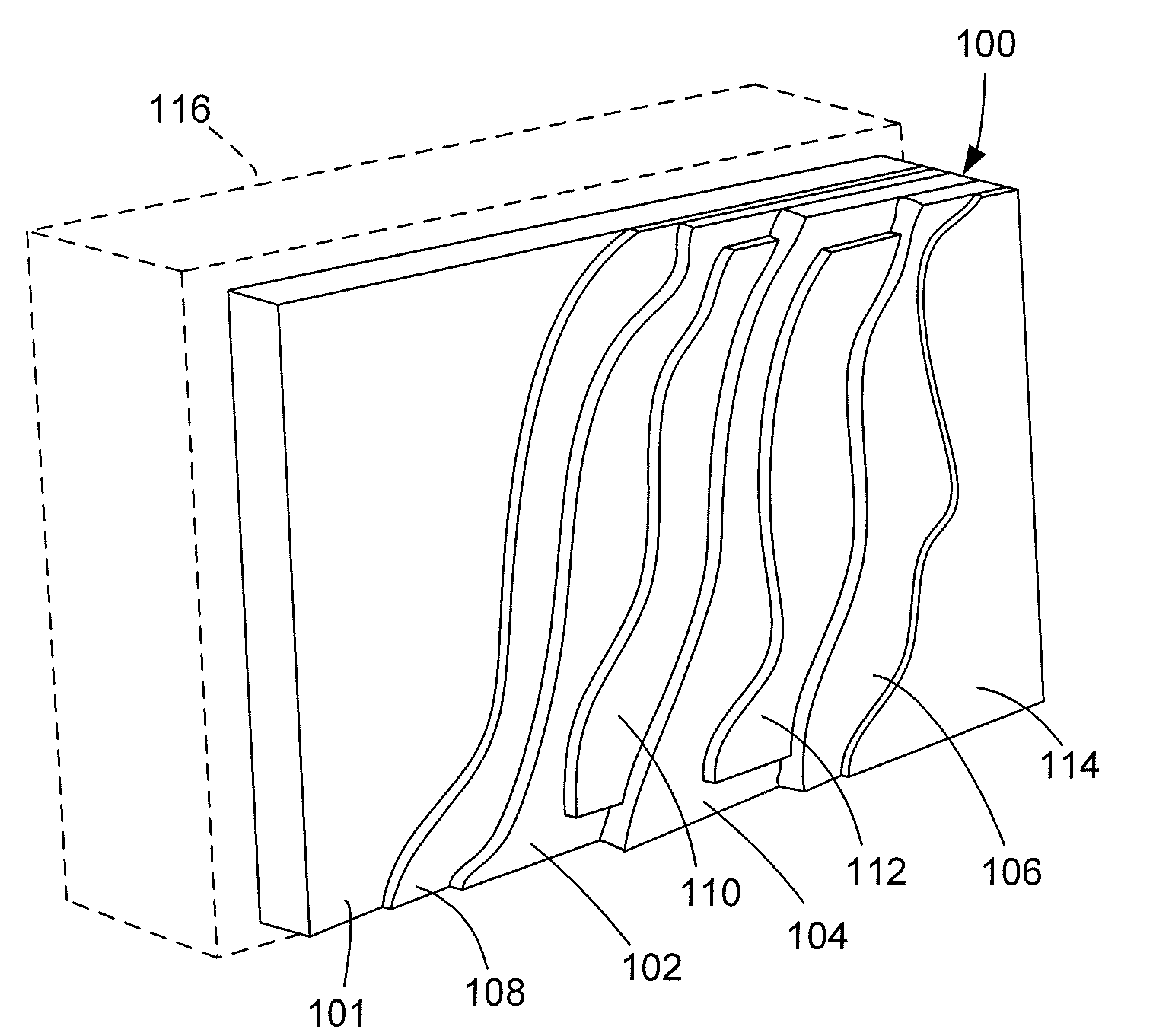
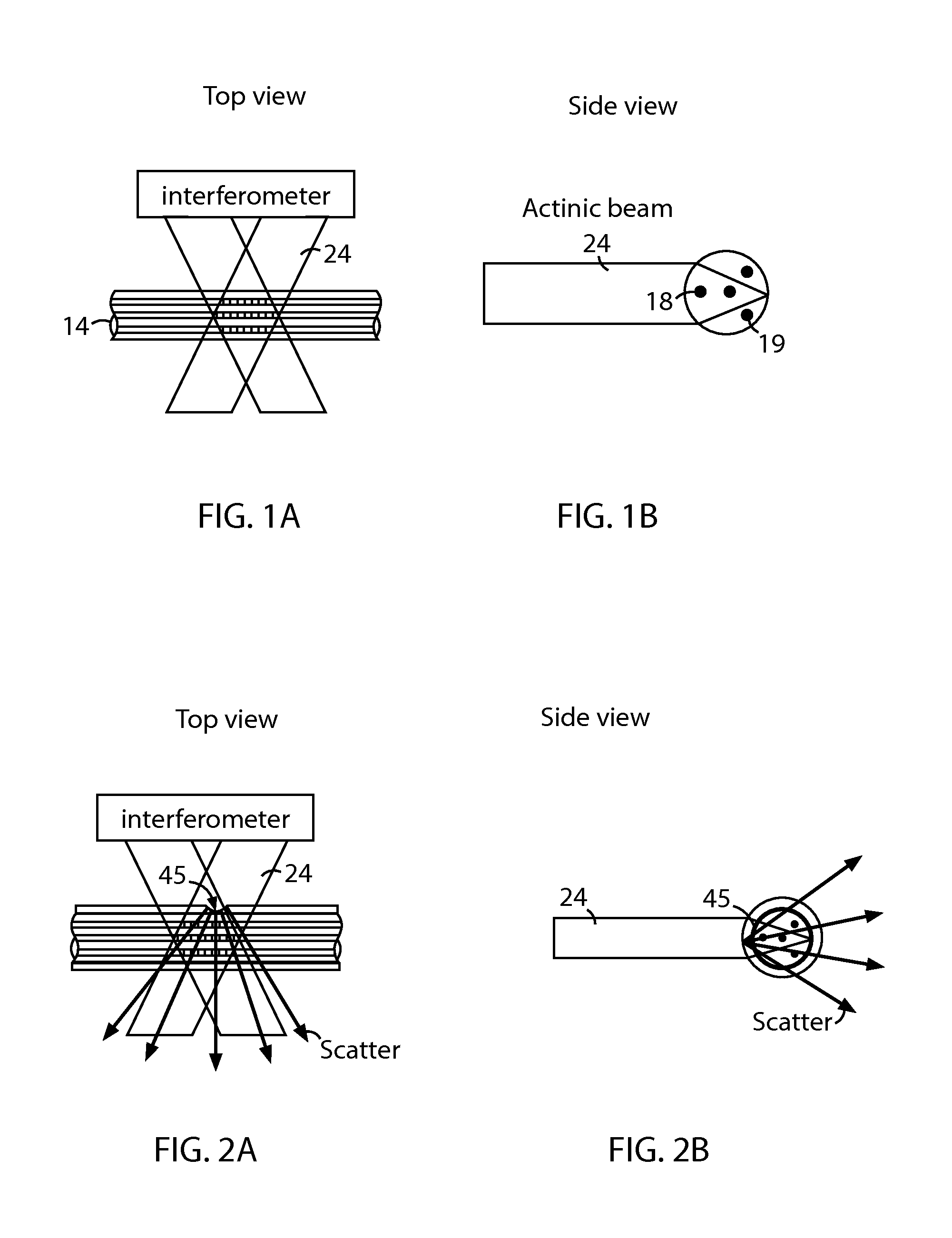
Index matched grating inscription
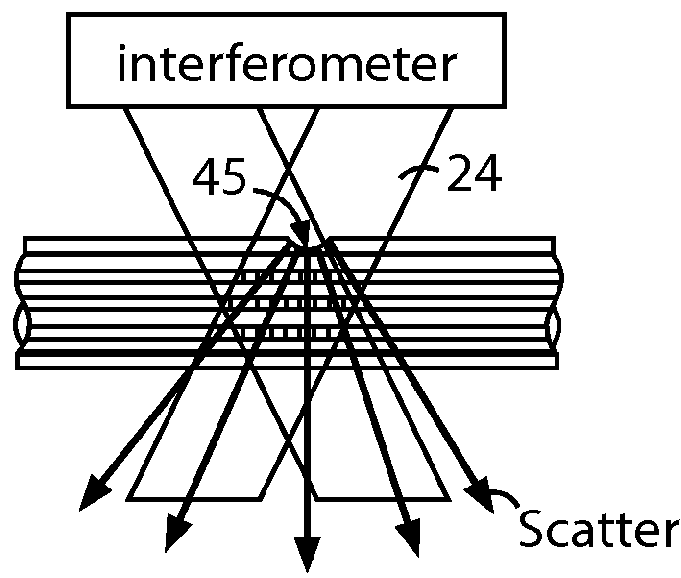
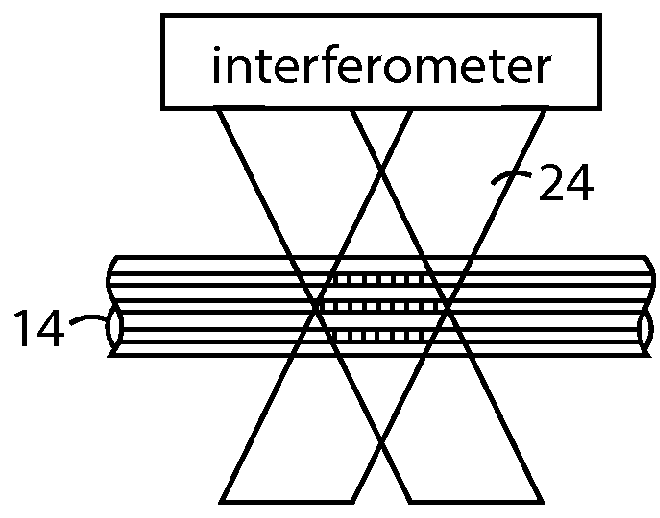
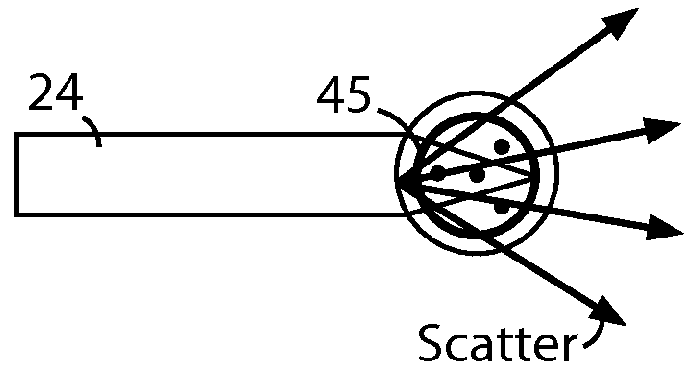
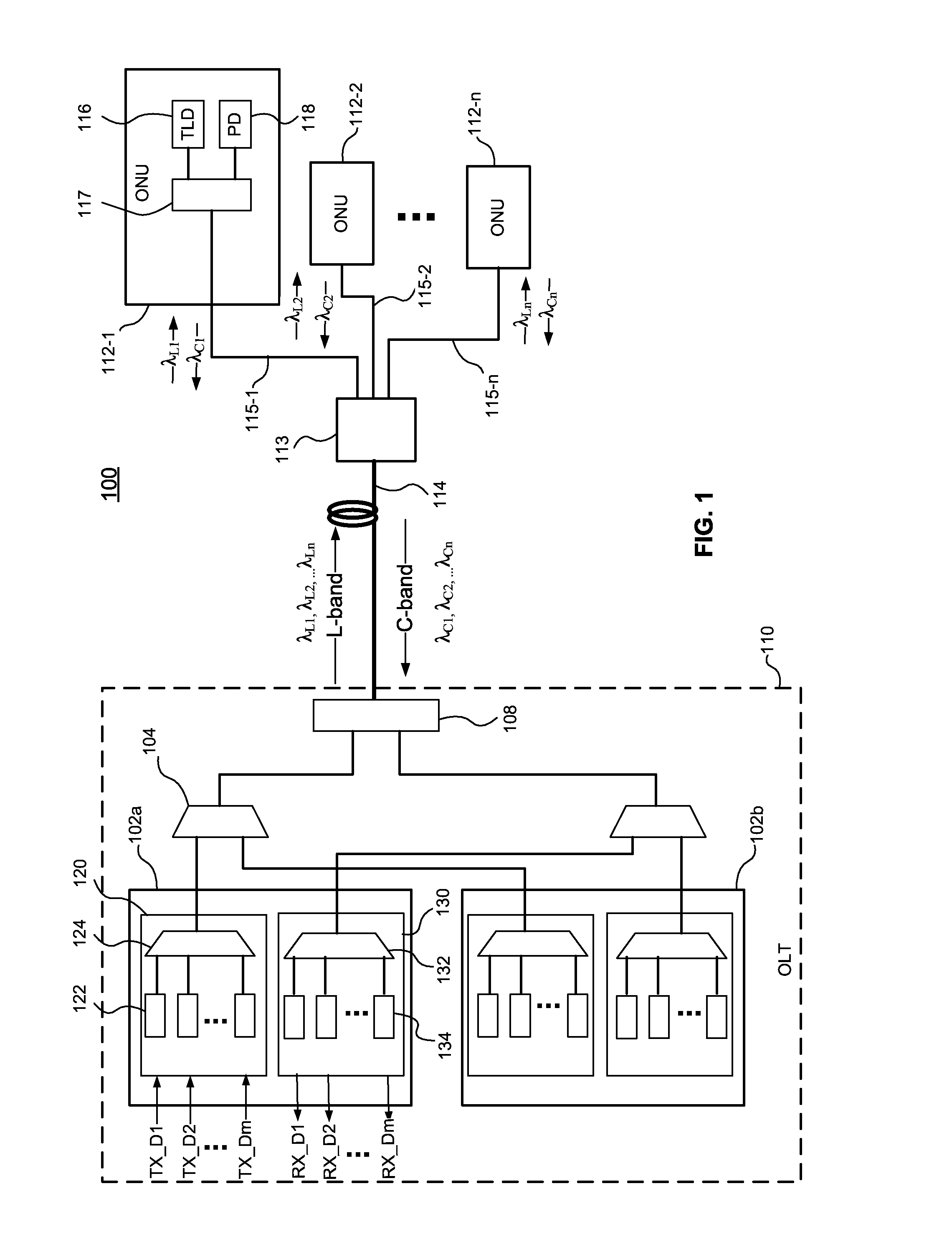
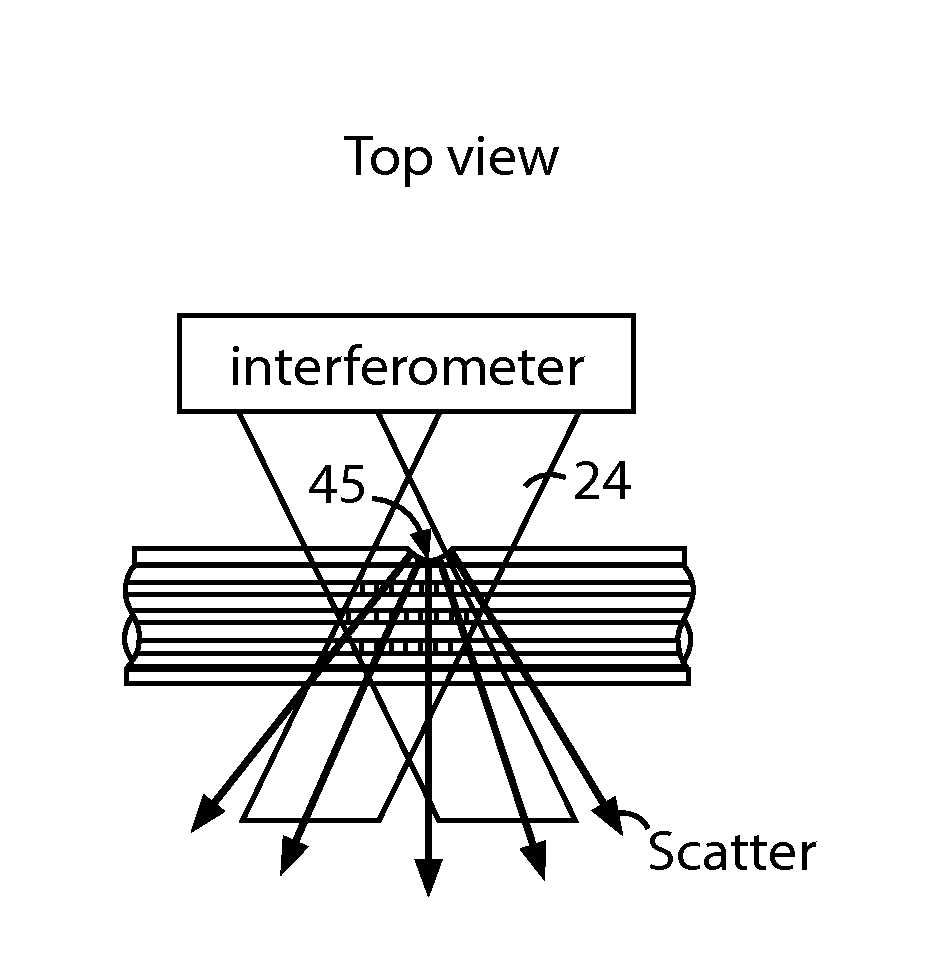
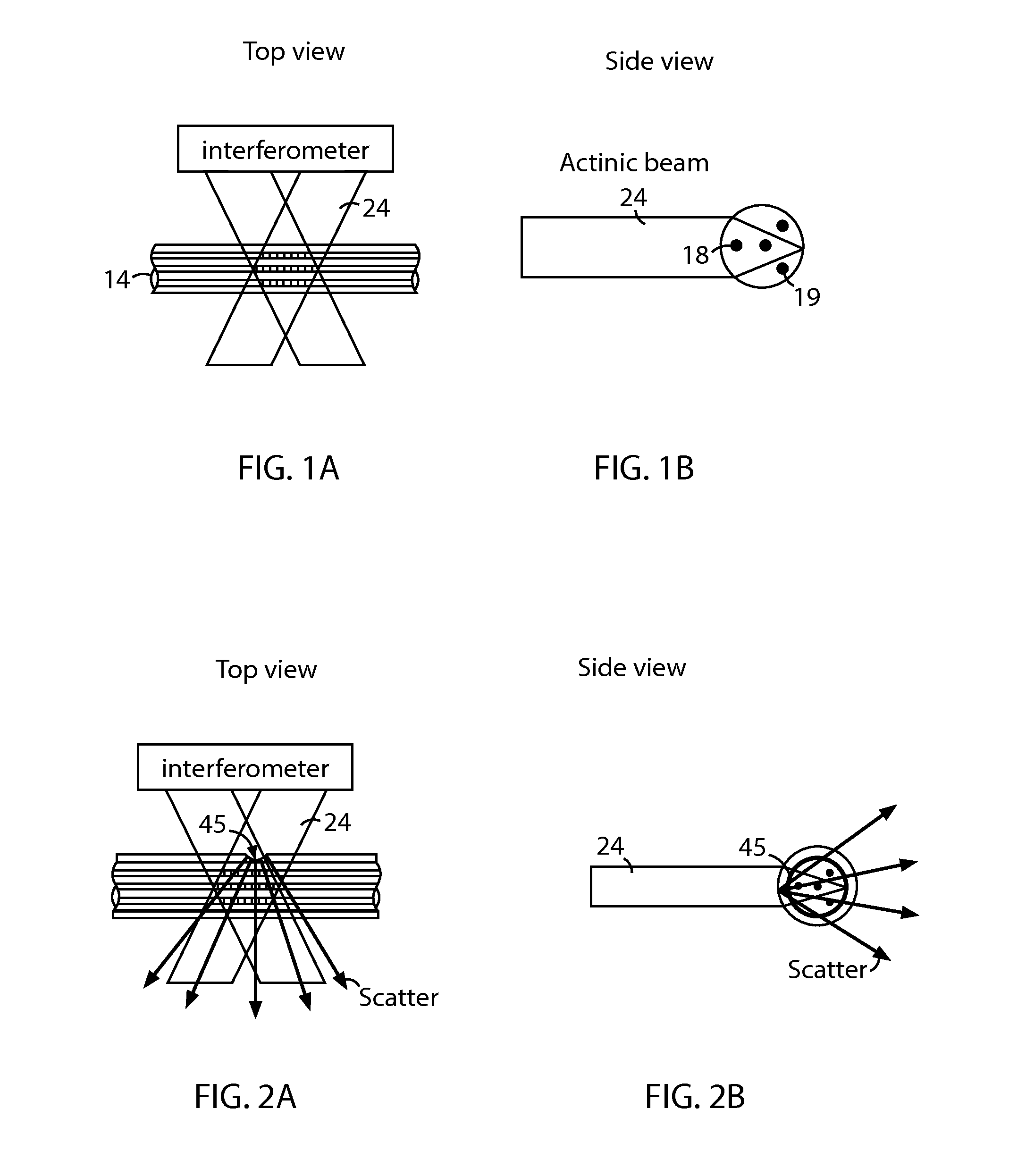
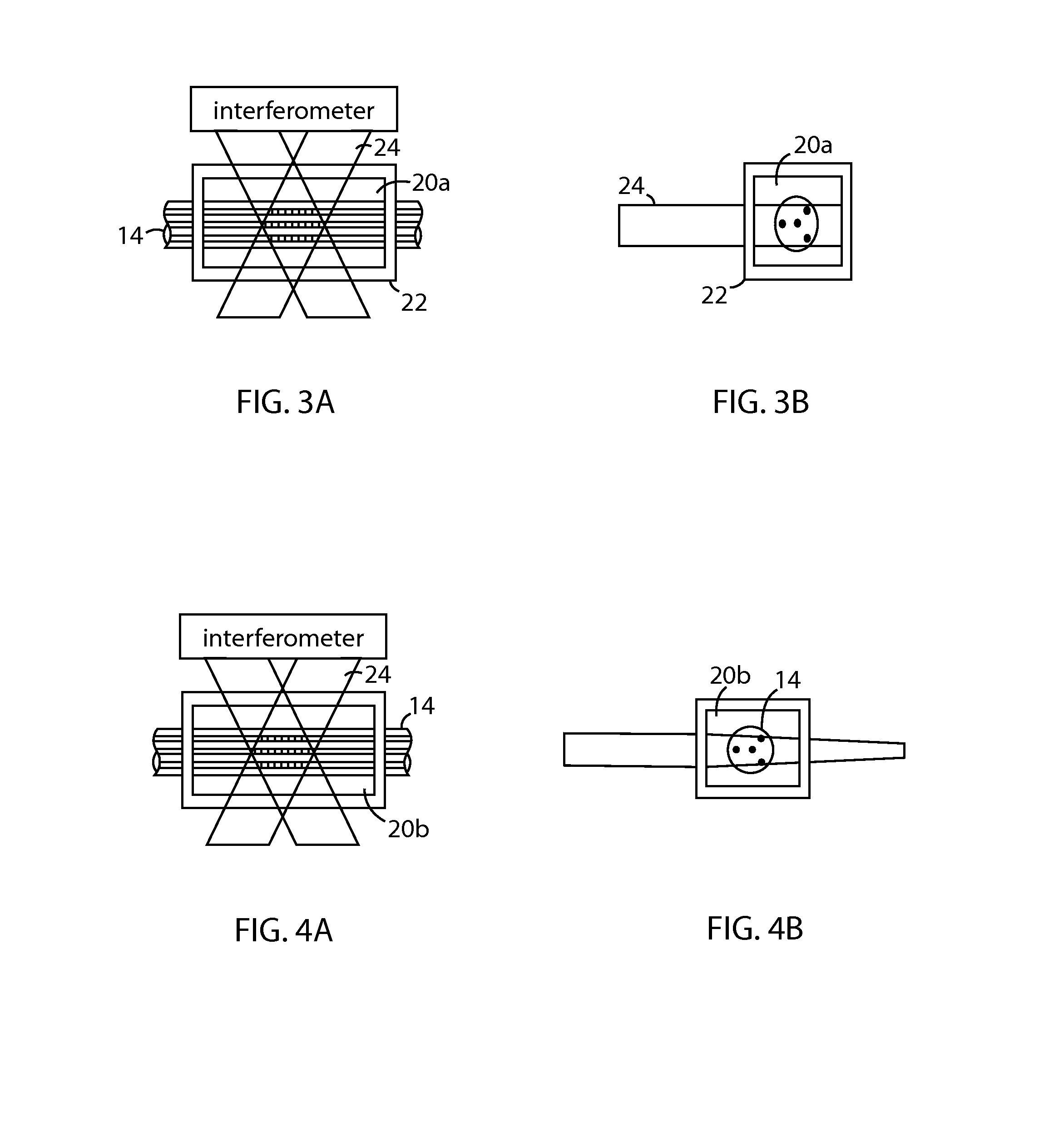
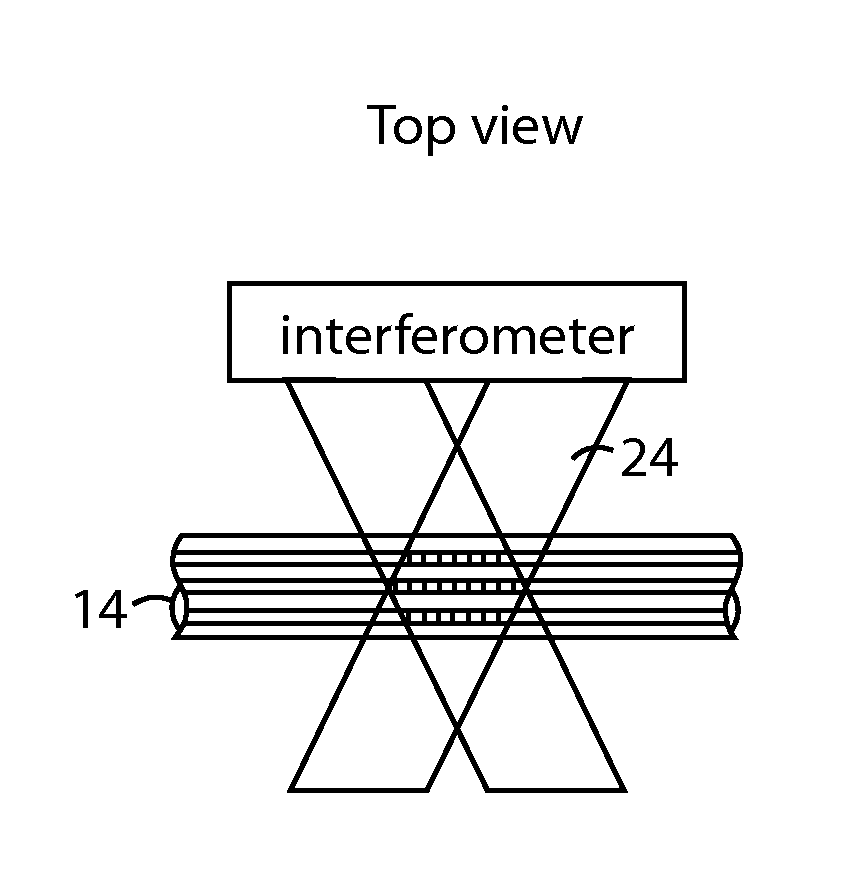
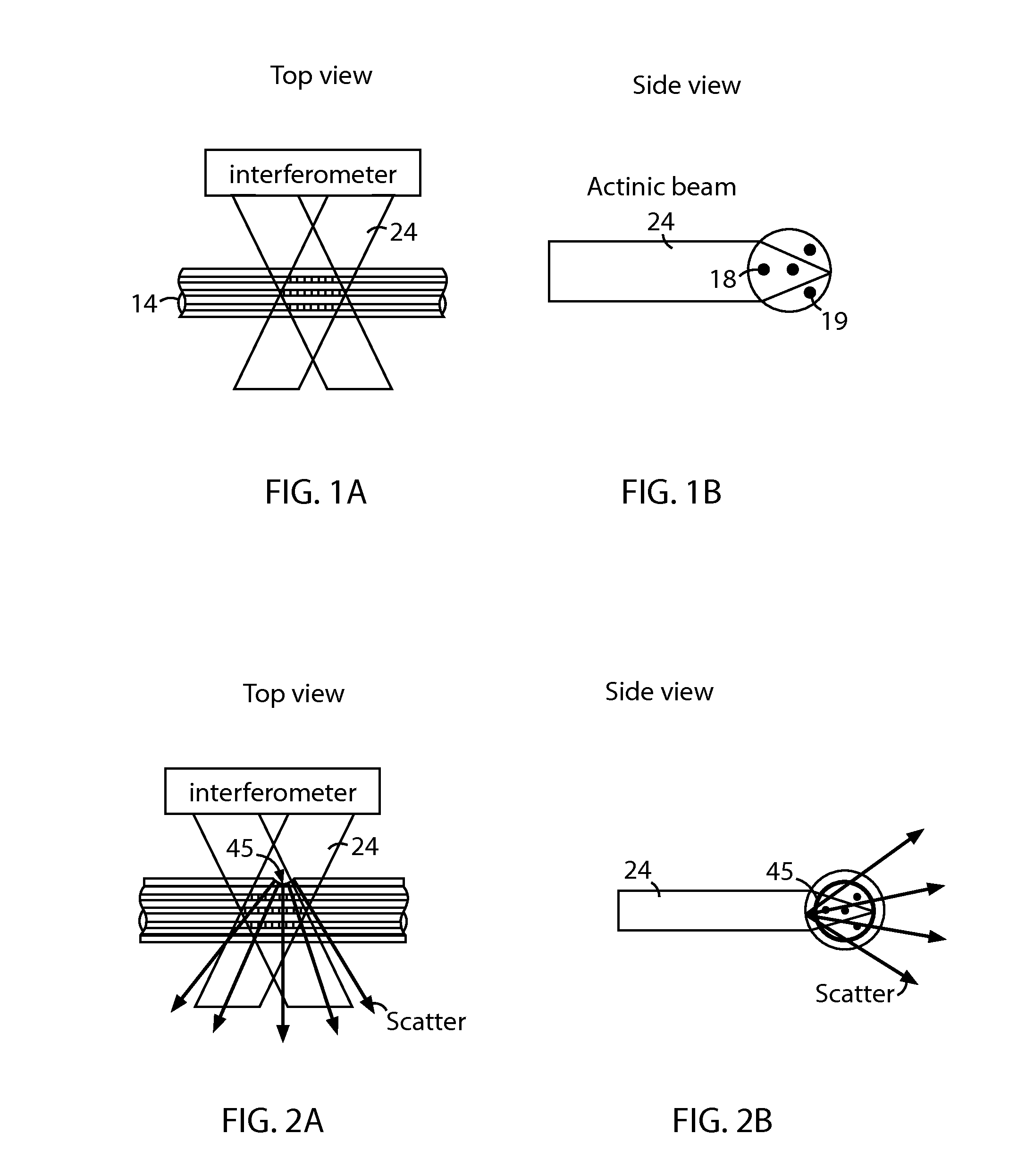
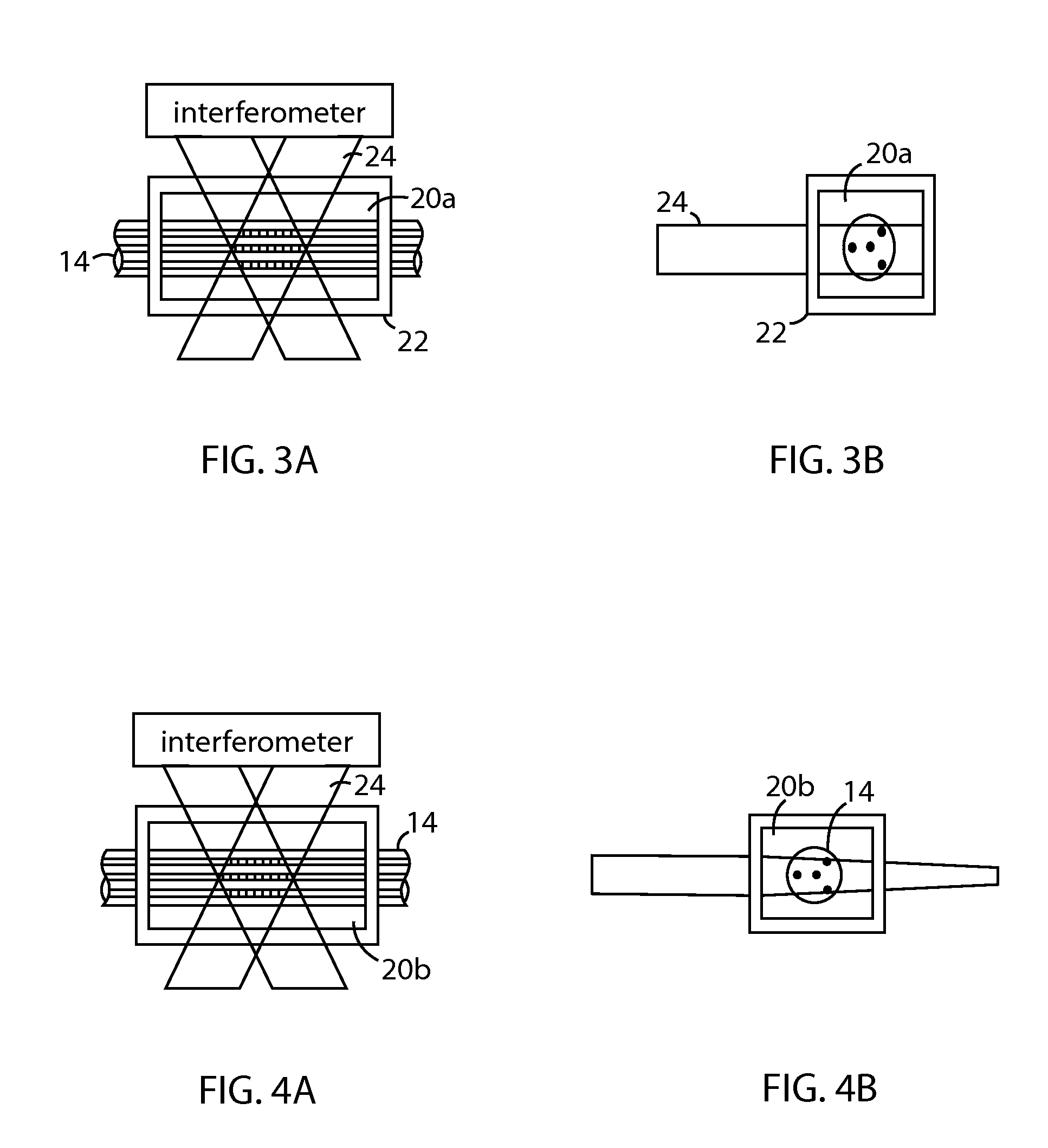
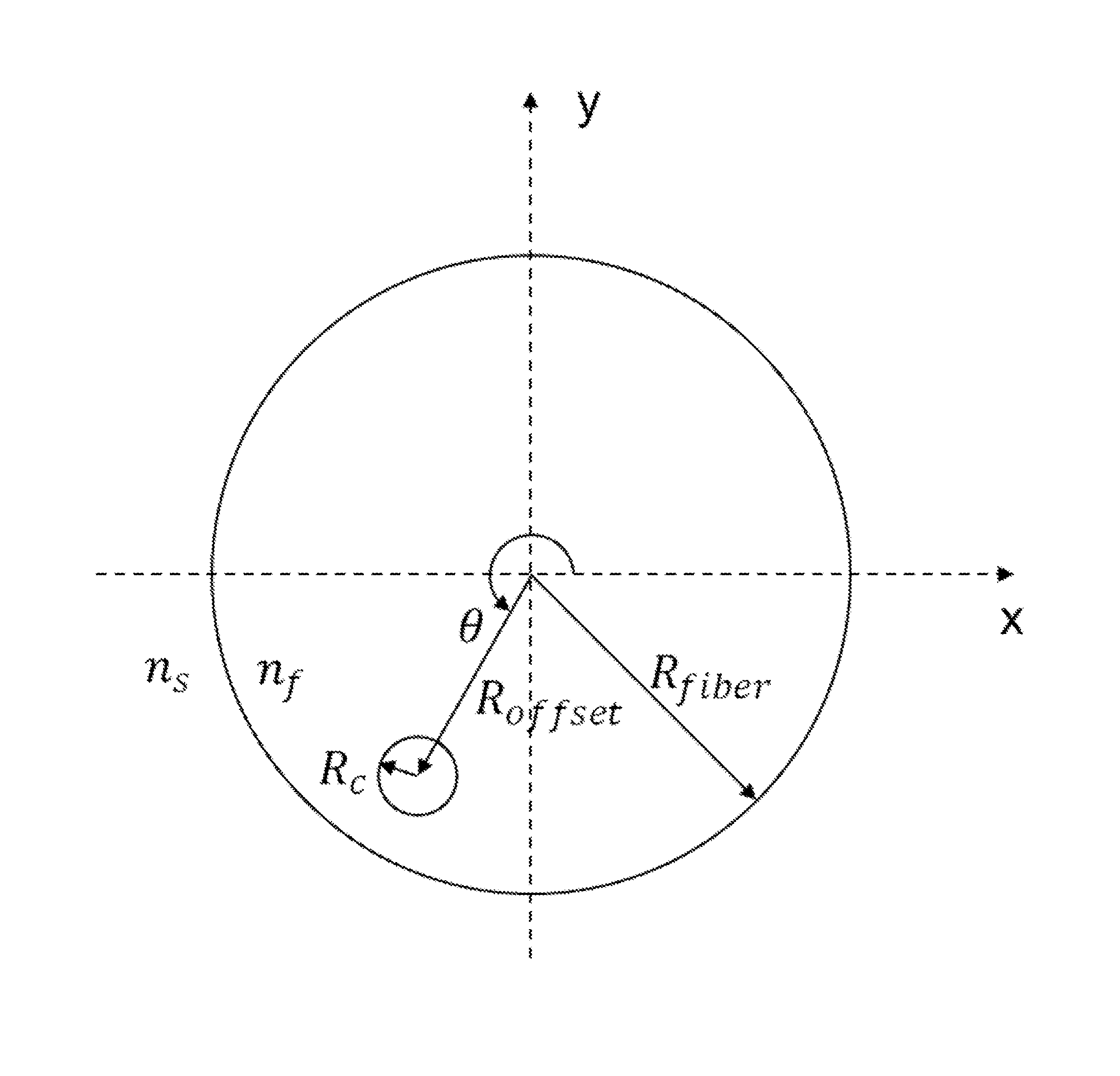
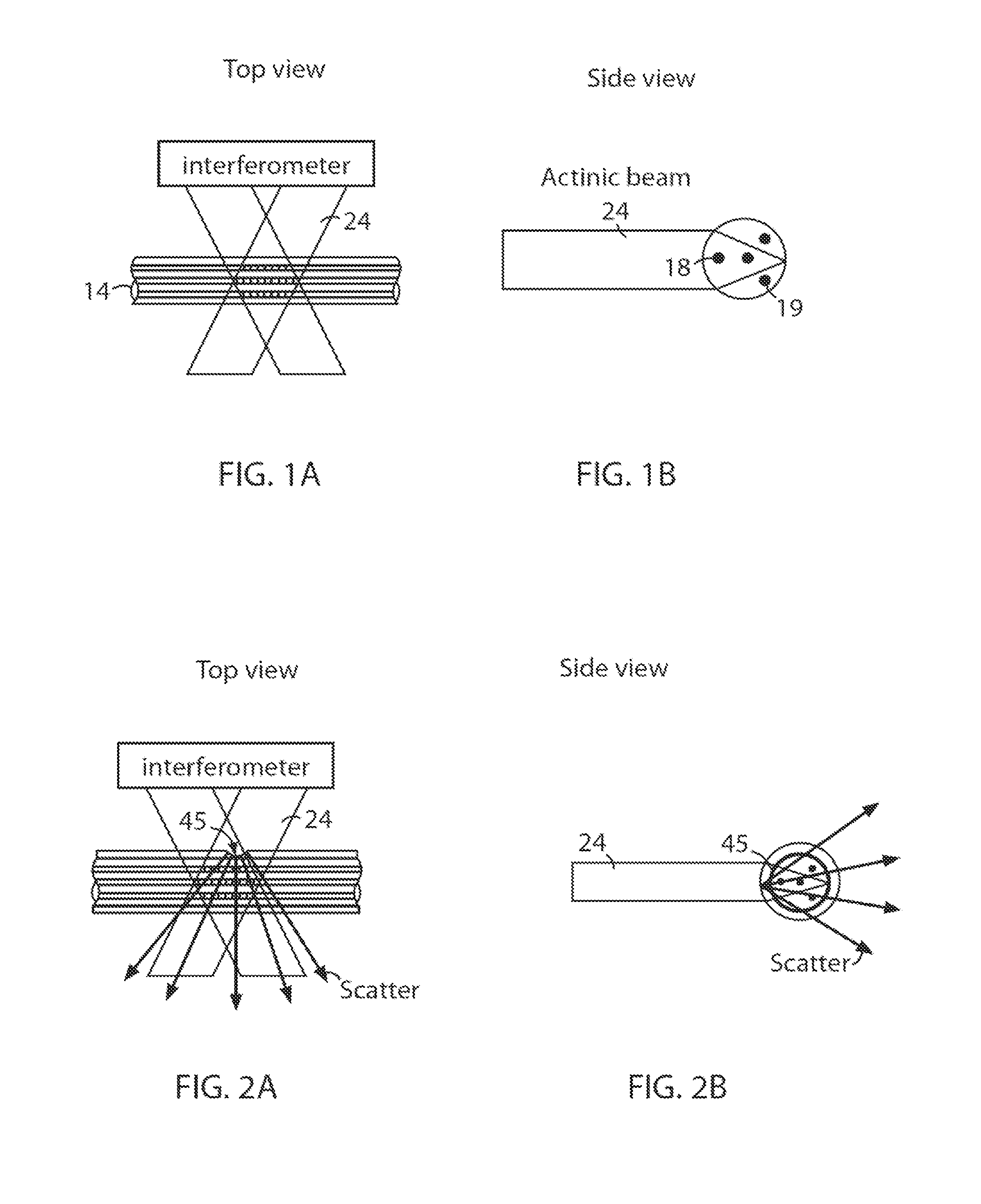
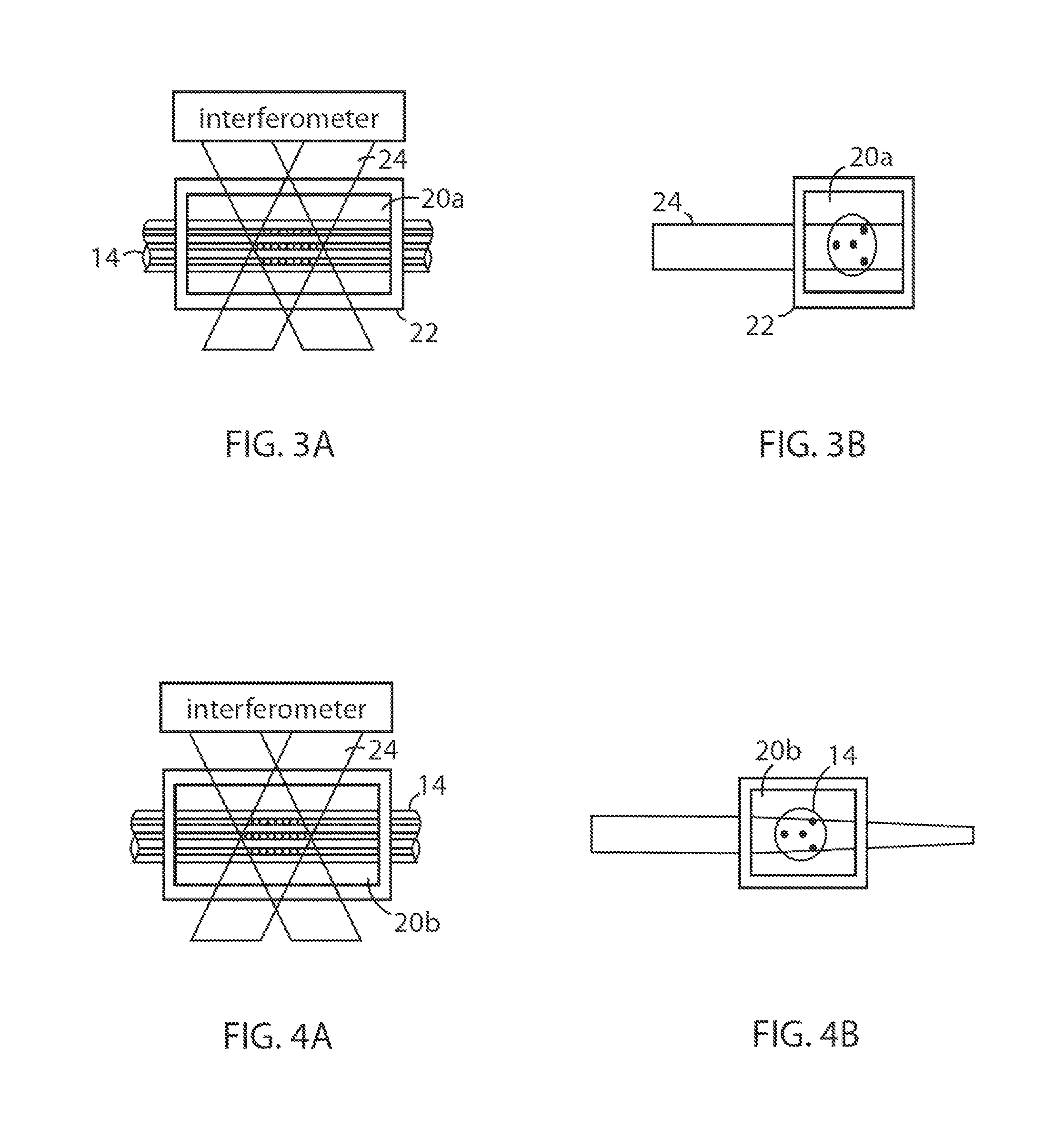
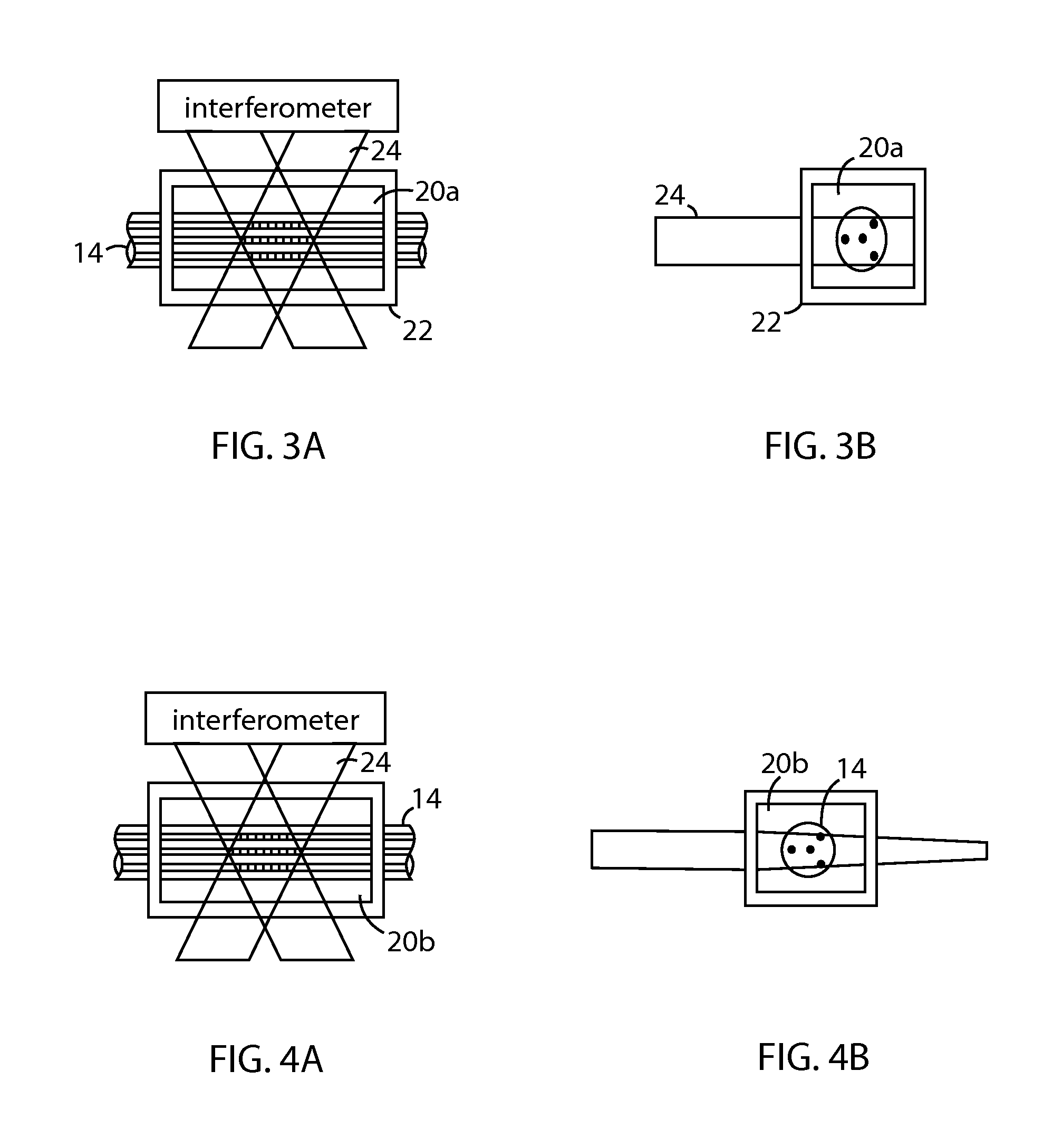
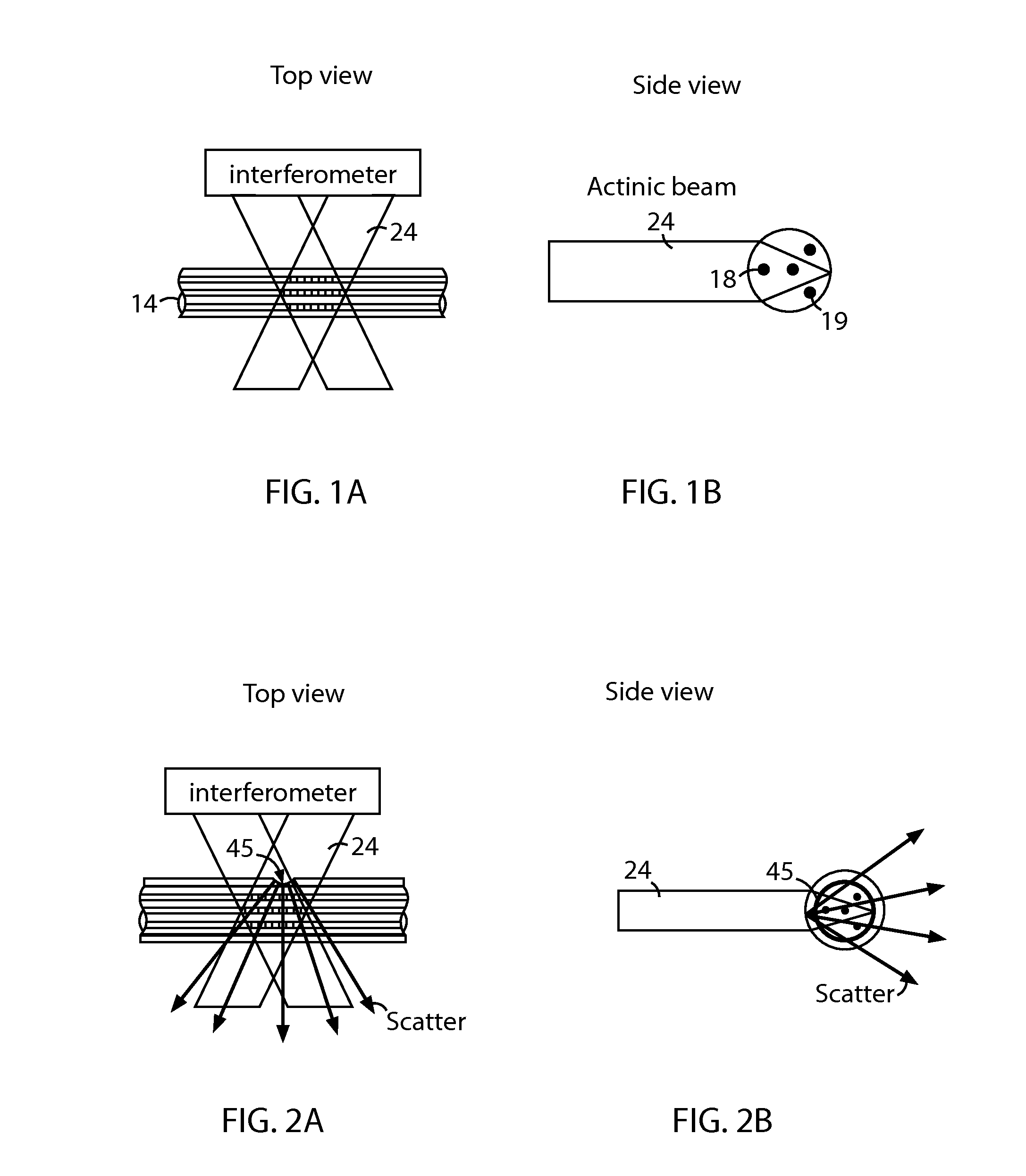
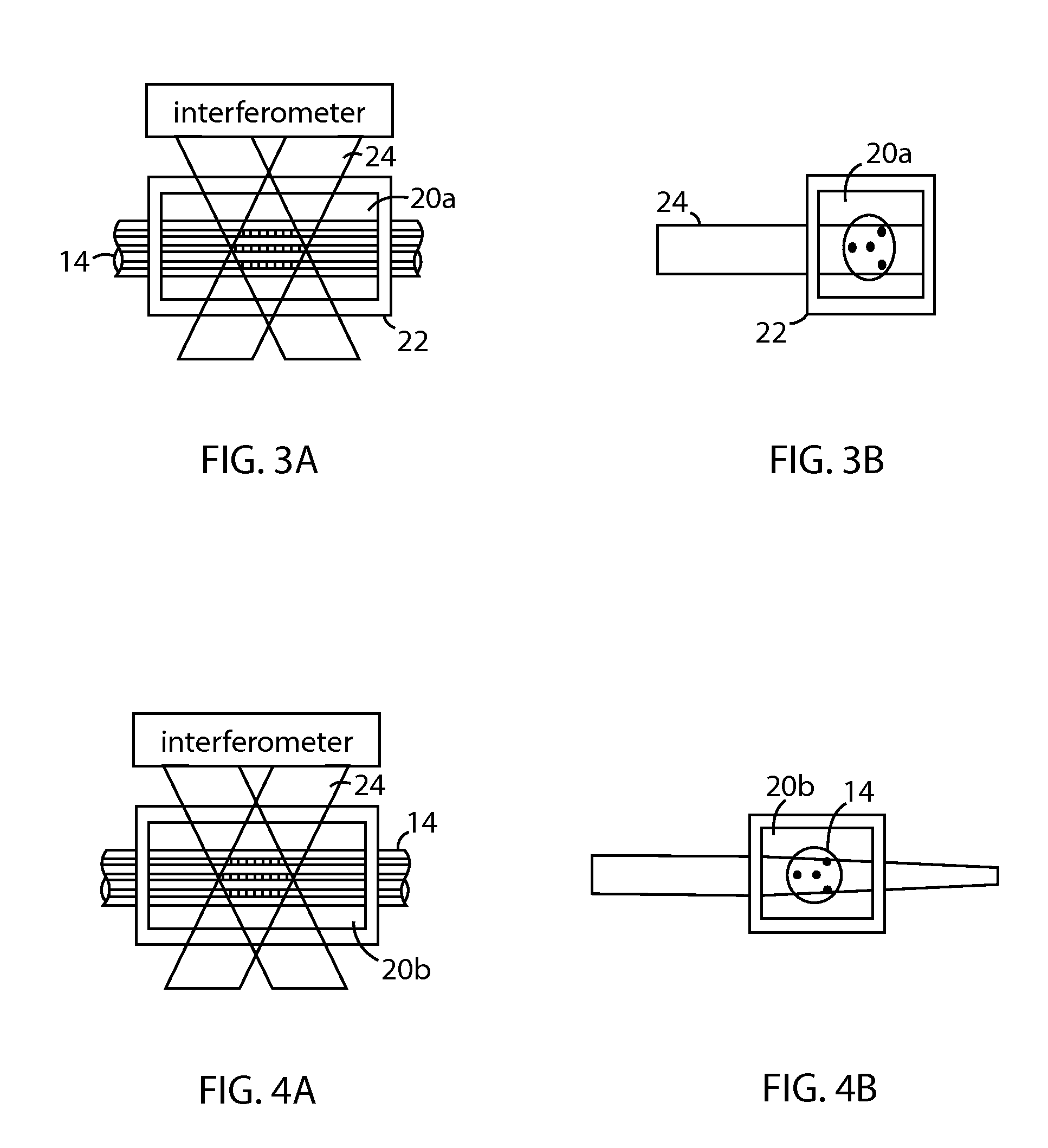
The disclosed embodiments provide systems and methods for mitigating lensing and scattering as an optical fiber is being inscribed with a grating. The disclosed systems and methods mitigate the lensing phenomenon by surrounding an optical fiber with an index-matching material that is held in a vessel with an integrated interferometer (e.g., phase mask, etc.). The index-matching material has a refractive index that is sufficient to reduce intensity variations of the actinic radiation within the optical fiber. Some embodiments of the system include different vessels for holding the index-matching material, with the vessel having an interferometer integrated into the vessel. These vessels permit the optical fiber to be surrounded by the index-matching material while the gratings are written to the optical fiber.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Coupling of photodetector array to optical demultiplexer outputs with index matched material
A system is provided for improved coupling of photodetectors to optical demultiplexer outputs, for example an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG), using a refractive index matched material. In one embodiment, the system may include an optical demultiplexer including multiple optical outputs corresponding to multiple signal channels and a photodetector array including a plurality of photodiodes aligned with the multiple optical outputs. The system may also include an epoxy disposed within a gap between each of the photodiodes and each of the corresponding optical outputs of the optical demultiplexer. The epoxy may be configured to provide an index of refraction that is matched to the optical demultiplexer.
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
Index matched grating inscription
The disclosed embodiments provide systems and methods for mitigating lensing and scattering as an optical fiber is being inscribed with a grating. The disclosed systems and methods mitigate the lensing phenomenon by surrounding an optical fiber with a liquid index-matching material that is held in a vessel. The disclosed systems also include a replenishment mechanism that replenishes the liquid index-matching material as the optical fiber is pulled through the vessel.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Method for laser interference lithography using diffraction grating
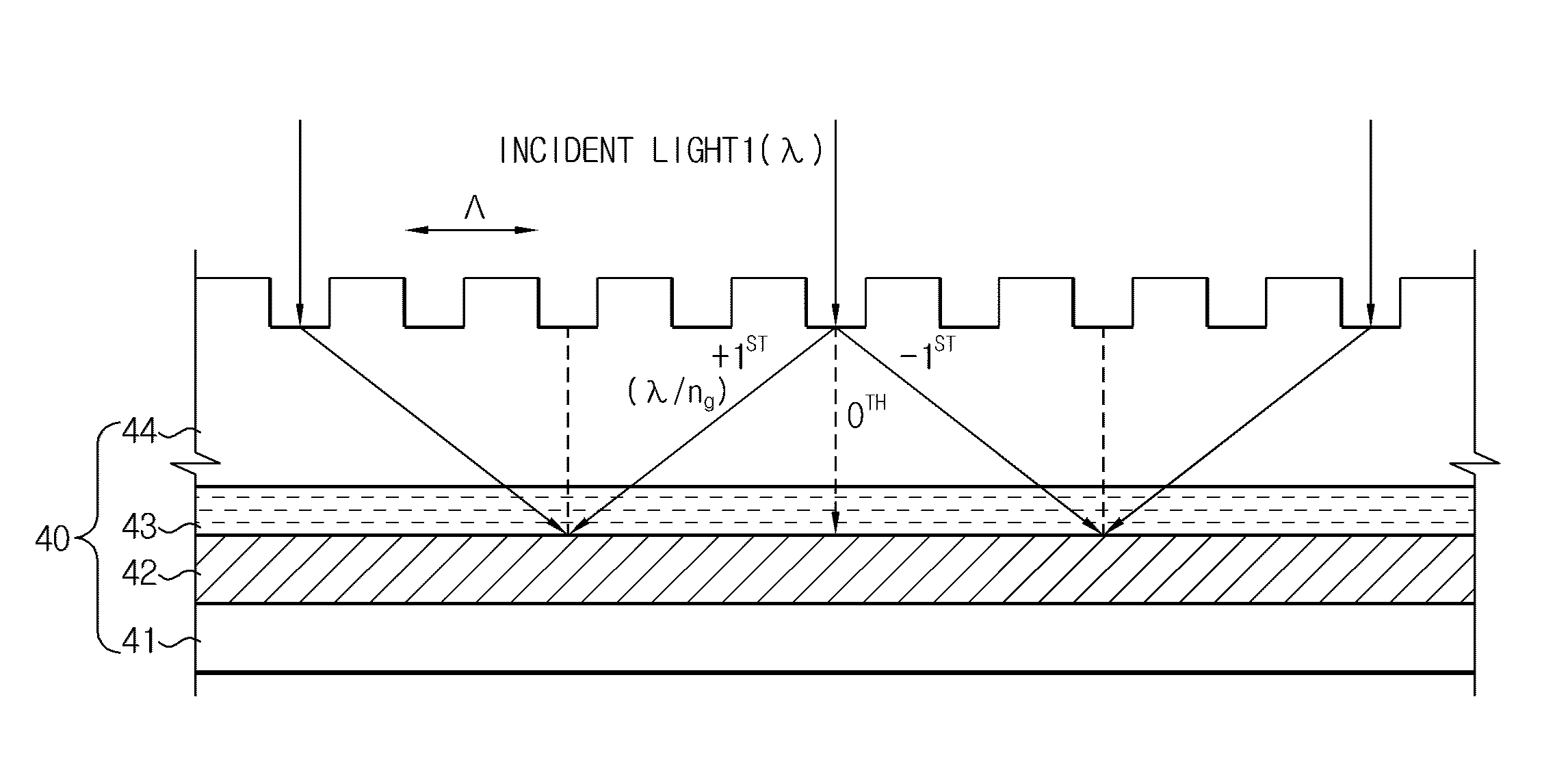
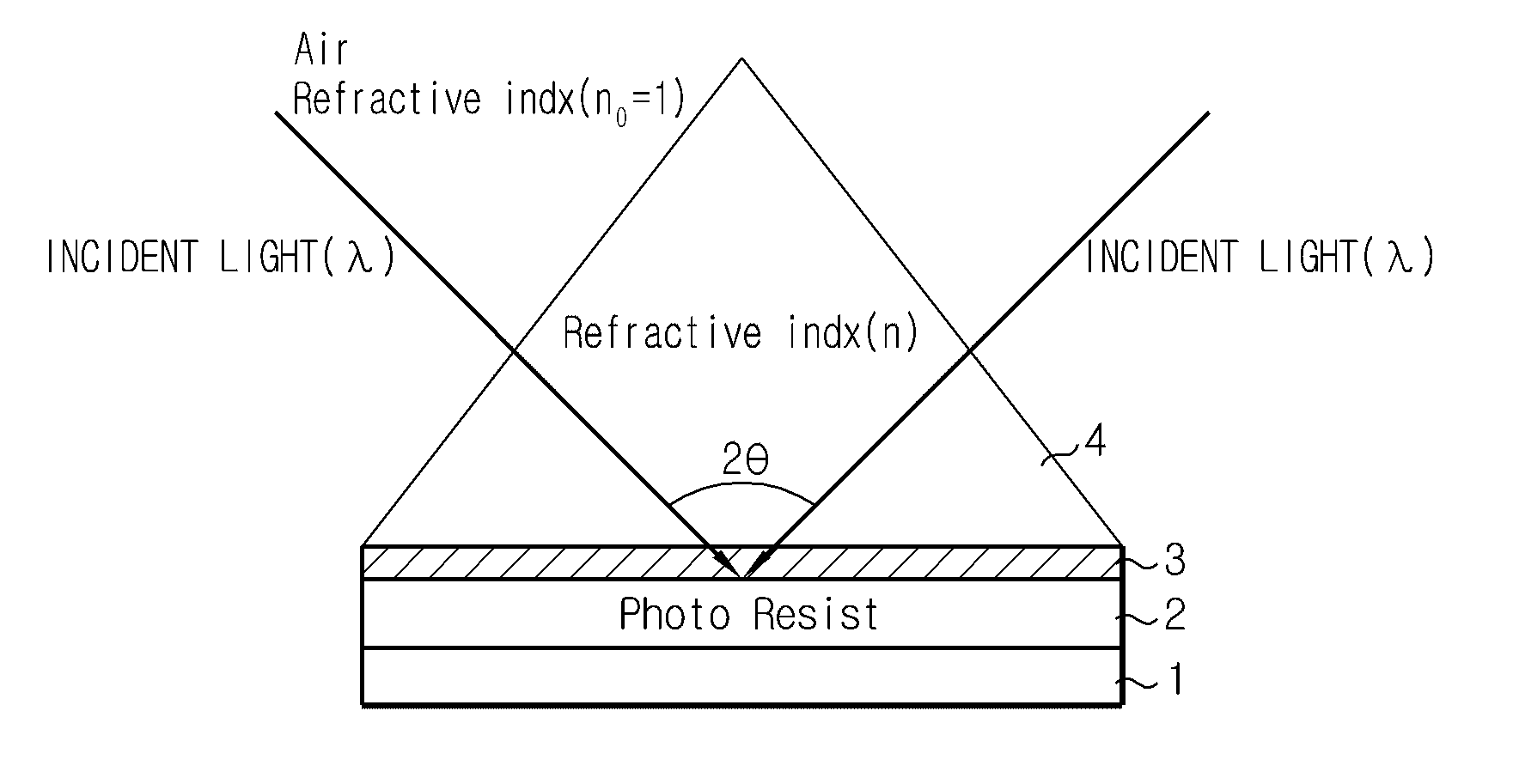
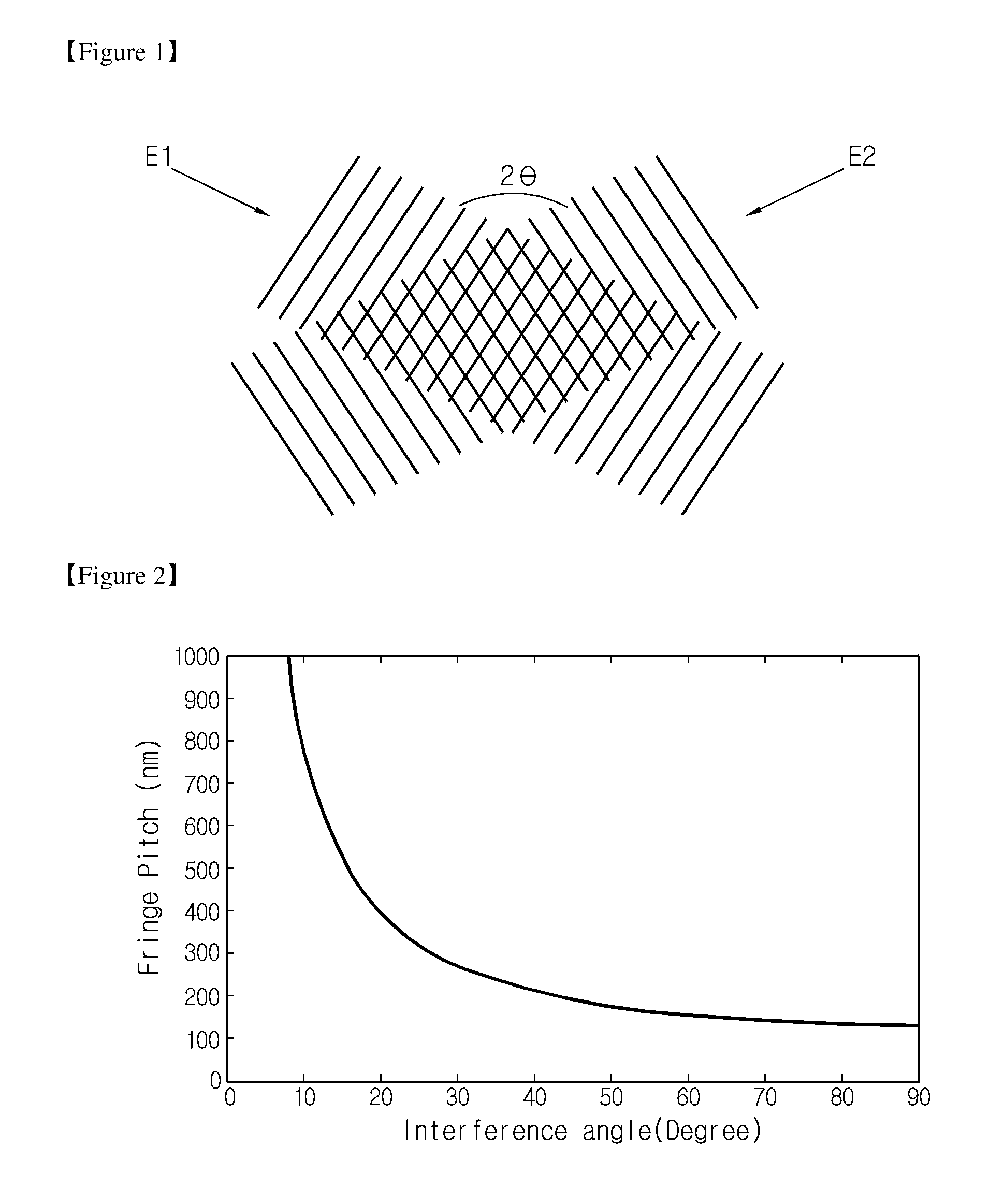
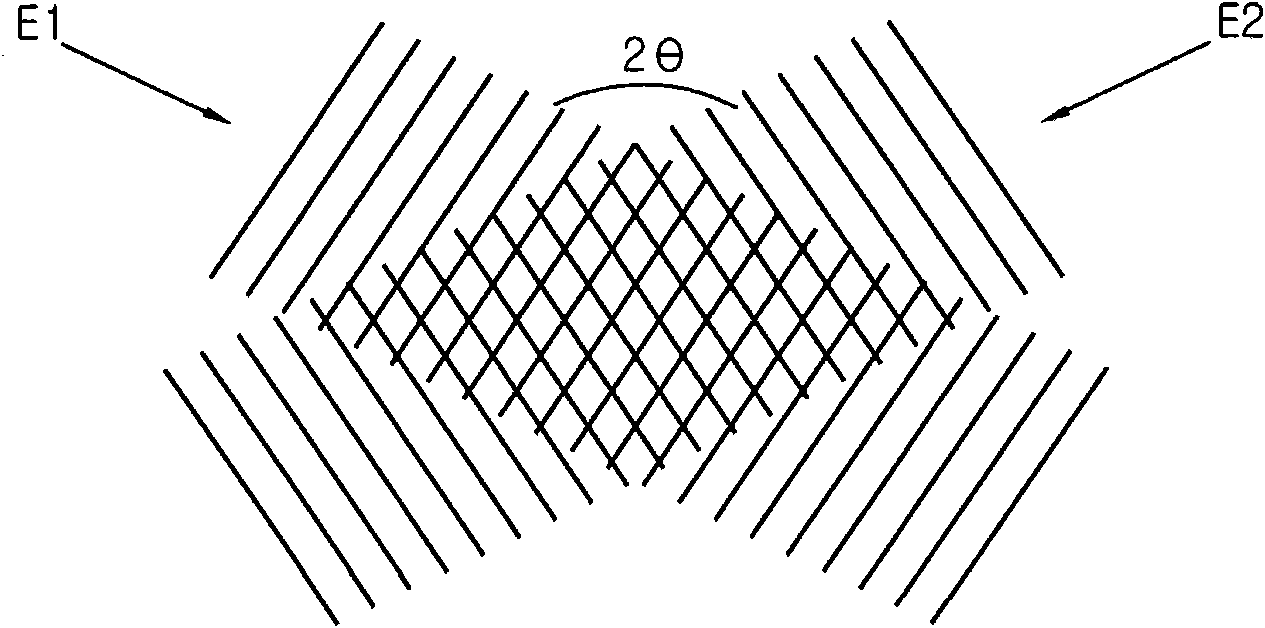
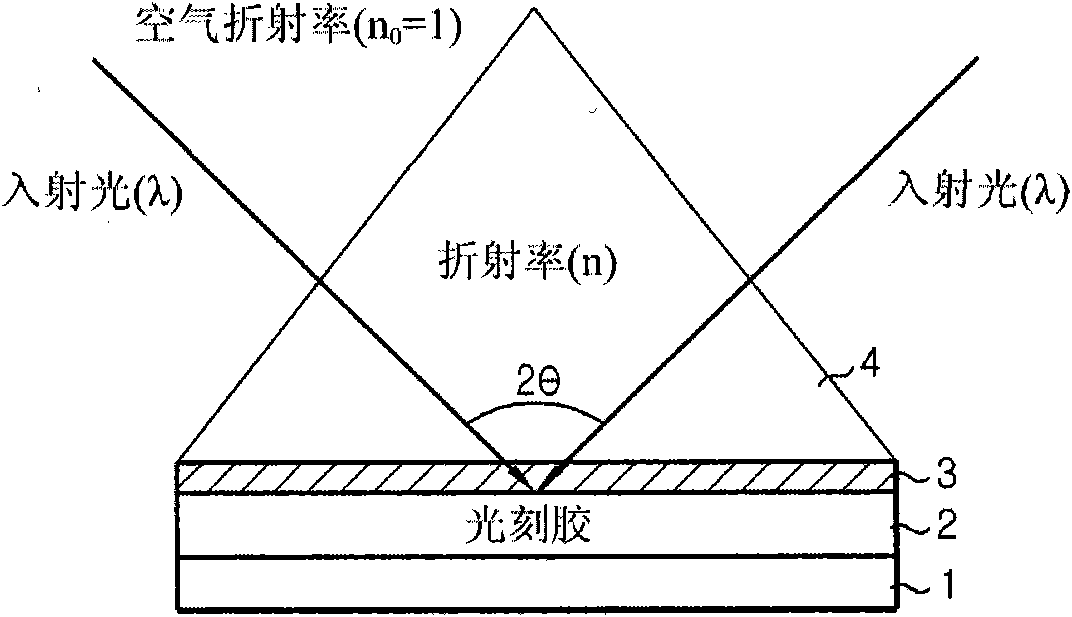
ActiveUS8399184B2High resolutionReduce coherencePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusResistIndex-matching material
A method for laser interference lithography using a diffraction grating includes (a) forming a photoresist layer on a work substrate to which a repeated fine pattern is to be formed; (b) forming a refractive index matching material layer on the photoresist layer; (c) forming on the refractive index matching material layer a diffraction grating layer having a period of diffraction grating within the range from λ / ng to λ / n0 (λ is a wavelength of laser beam, ng is a refractive index of the diffraction grating, and n0 is a refractive index in the air or in vacuum); and (d) exposing the photoresist layer by means of mutual interference of positive and negative diffracted lights with the same absolute value by inputting a laser beam perpendicularly to the diffraction grating layer. This method allows to realize an interference pattern with higher resolution and to use a laser source with lower coherence.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
High-power collimating lens assemblies, and methods of reducing the optical power density in collimating lens assemblies
ActiveUS8520990B2Weaken energyReduce optical power densityLine/current collector detailsCoupling light guidesSilicone GelsEpoxy
The present invention provides improved collimating lens assemblies (32) which include: a singlemode fiber (38) terminating in a distal end; a step-index multimode fiber (44) having a proximal end abutting to the singlemode fiber distal end, and having a distal end; a graded-index multimode fiber (45) having a proximal end abutting the step-index multimode fiber distal end, and having a distal end; and a collimating lens (34) longitudinally spaced from the graded-index multimode fiber distal end by an intermediate air gap (43), and operatively arranged to collimate light rays emanating from the graded-index multimode fiber distal end. The improved collimating lens assembly is characterized by the fact that there is no epoxy, silicone gel or index-matching material between the graded-index multimode fiber distal end and the collimating lens.
Owner:MOOG INC
Method for laser interference lithography using diffraction grating
ActiveUS20100279233A1High resolutionImprove processing conveniencePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusResistIndex-matching material
A method for laser interference lithography using a diffraction grating includes (a) forming a photoresist layer on a work substrate to which a repeated fine pattern is to be formed; (b) forming a refractive index matching material layer on the photoresist layer; (c) forming on the refractive index matching material layer a diffraction grating layer having a period of diffraction grating within the range from λ / ng to λ / n0 (λ is a wavelength of laser beam, ng is a refractive index of the diffraction grating, and n0 is a refractive index in the air or in vacuum); and (d) exposing the photoresist layer by means of mutual interference of positive and negative diffracted lights with the same absolute value by inputting a laser beam perpendicularly to the diffraction grating layer. This method allows to realize an interference pattern with higher resolution and to use a laser source with lower coherence.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Method for laser interference lithography using diffraction grating
ActiveCN101828140AHigh resolutionEnhanced process simplicityPhotomechanical apparatusOptical elementsIndex-matching materialImage resolution
A method for laser interference lithography using a diffraction grating includes (a) forming a photoresist layer on a work substrate to which a repeated fine pattern is to be formed; (b) forming a refractive index matching material layer on the photoresist layer; (c) forming on the refractive index matching material layer a diffraction grating layer having a period of diffraction grating within the range from [lambda] / ng to [lambda] / n0 ([lambda] is a wavelength of laser beam, ng is a refractive index of the diffraction grating, and n0 is a refractive index in the air or in vacuum); and (d) exposing the photoresist layer by means of mutual interference of positive and negative diffracted lights with the same absolute value by inputting a laser beam perpendicularly to the diffraction grating layer. This method allows to realize an interference pattern with higher resolution and to use a laser source with lower coherence.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Confocal displacement sensor
ActiveUS10161740B1Improve accuracyHigh measurement accuracyRadiation pyrometryUsing optical meansIndex-matching materialRefractive index matching
Owner:KEYENCE
Index matched grating inscription
ActiveUS20140232997A1Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentGratingIndex-matching material
The disclosed embodiments provide systems and methods for mitigating lensing and scattering as an optical fiber is being inscribed with a grating. The disclosed systems and methods mitigate the lensing phenomenon by surrounding an optical fiber with an index-matching material that is held in a vessel with a sealed phase mask. The sealed phase mask allows it to be in contact with a liquid index-matching material without having the liquid index-matching material seep into the grooves of the sealed phase mask. Thus, for some embodiments, the sealed phase mask may be immersed in a liquid index-matching material without adversely affecting the function of the phase mask.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Index matched grating inscription
The disclosed embodiments provide systems and methods for mitigating lensing and scattering as an optical fiber is being inscribed with a grating. The disclosed systems and methods mitigate the lensing phenomenon by surrounding an optical fiber with an index-matching material that is held in a vessel with an integrated interferometer (e.g., phase mask, etc.). The index-matching material has a refractive index that is sufficient to reduce intensity variations of the actinic radiation within the optical fiber. Some embodiments of the system include different vessels for holding the index-matching material, with the vessel having an interferometer integrated into the vessel. These vessels permit the optical fiber to be surrounded by the index-matching material while the gratings are written to the optical fiber.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Attenuated splitter module for low count output channels and related assemblies and methods
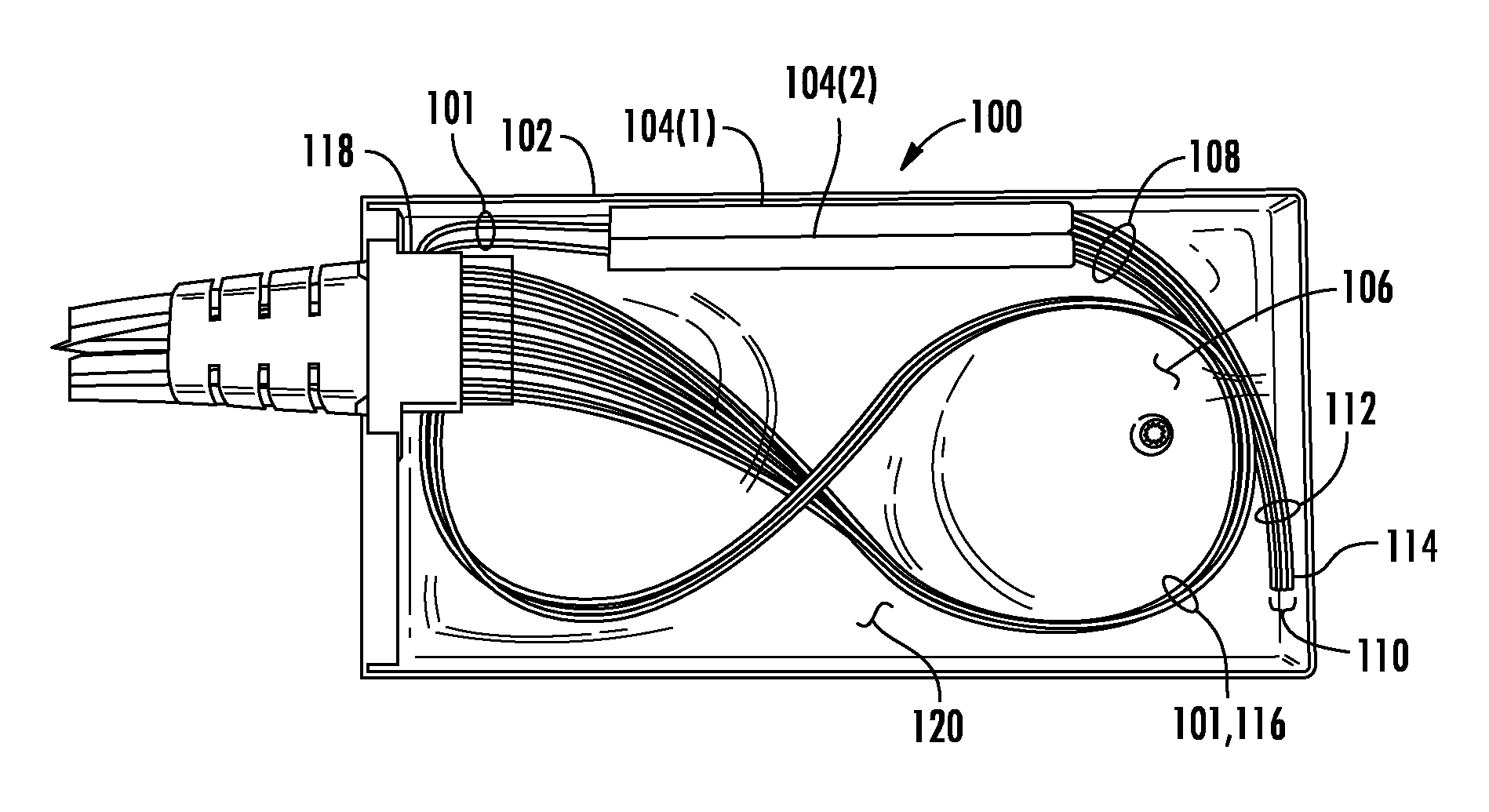
A splitter module, comprising an enclosure and a splitter device with one or more splitter legs mounted in the enclosure. Each splitter leg has an optical fiber therein extends for a certain length from the splitter. At least one of the splitter legs, and, thereby, the optical fiber, is cut. The cut may be at an angle to the longitudinal axis of optical fiber. The angle may be about 45 degrees. The coating may be stripped off such that the cut end of the optical glass fiber of the at least one output leg is exposed a certain distance. The cut end of the optical glass fiber positions in the interior of the enclosure. A glass-index-matching material, at least partially fills the interior of the enclosure such that the cut end of the optical fiber is embedded in the glass-index-matching material.
Owner:CORNING CABLE SYST LLC
Method and system for reducing fresnel depolarization to improve image contrast in a display system including multiple displays
InactiveUS20170351106A1Reduce Fresnel depolarizationImprove image contrastCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsImage contrastIndex-matching material
A multi-layered display system (e.g., a display including multiple display panels) includes at least first and second displays (e.g., display panels or display layers) arranged substantially parallel to each other in order to display three-dimensional (3D) features to a viewer(s). A refractive element is arranged on a top surface of the first display layer or between the first and second display layers. Index matching material may be provided between the first and second displays.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Attenuated splitter module for low count output channels and related assemblies and methods
InactiveCN103827710ACoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresGlass fiberIndex-matching material
A splitter module (100), comprising an enclosure and a splitter device (104(1) and 104(2) with one or more splitter legs (108) mounted in the enclosure. Each splitter leg has an optical fiber (112) therein extends for a certain length from the splitter. At least one of the splitter legs, and, thereby, the optical fiber, is cut. The cut may be at an angle to the longitudinal axis of optical fiber. The angle may be about 45 degrees. The coating may be stripped off such that the cut end of the optical glass fiber of the at least one output leg is exposed a certain distance. The cut end of the optical glass fiber positions in the interior of the enclosure. A glass-index-matching material, at least partially fills the interior of the enclosure such that the cut end of the optical fiber is embedded in the glass-index-matching material.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
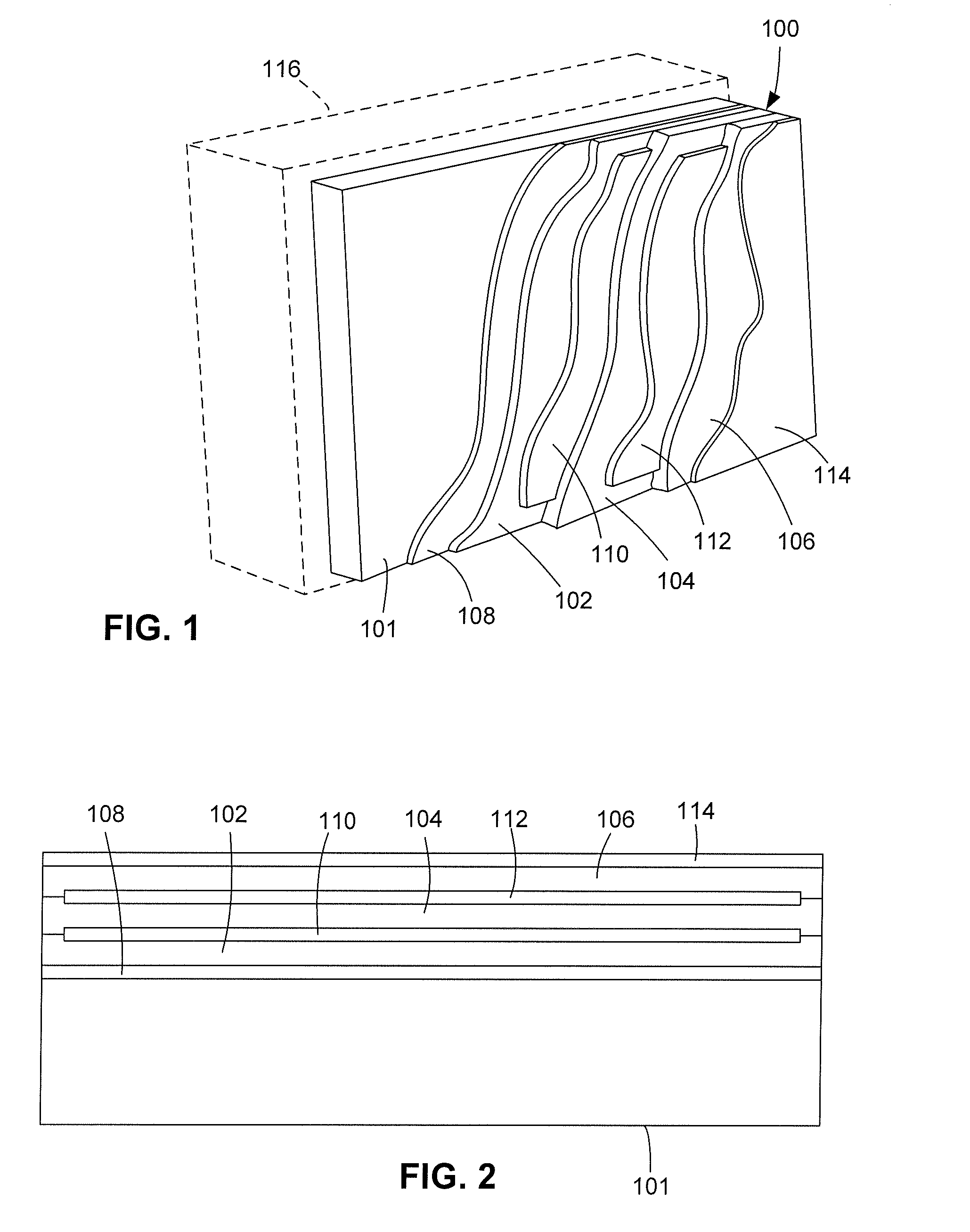
Conductive coating for reduced reflectivity on electronic displays
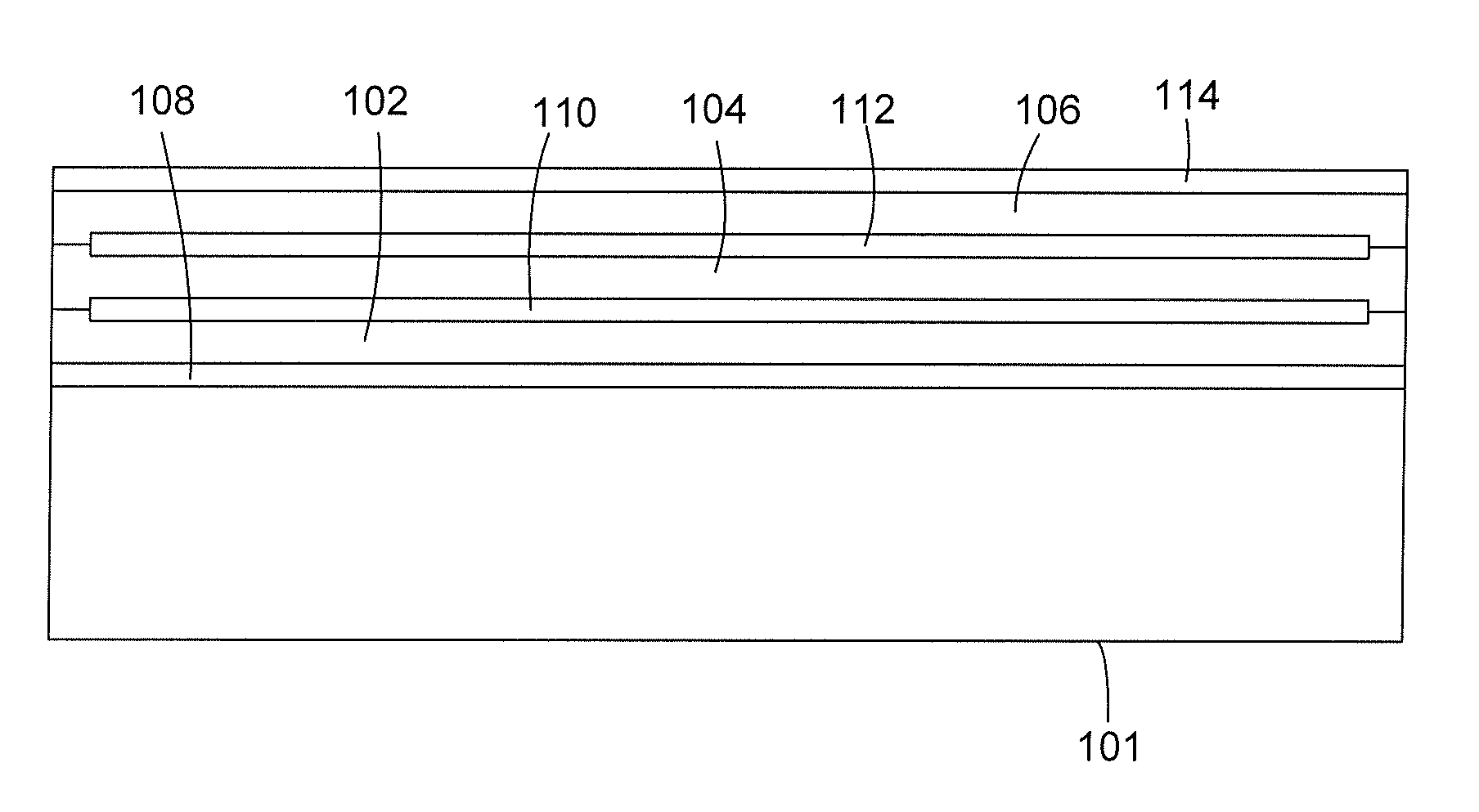
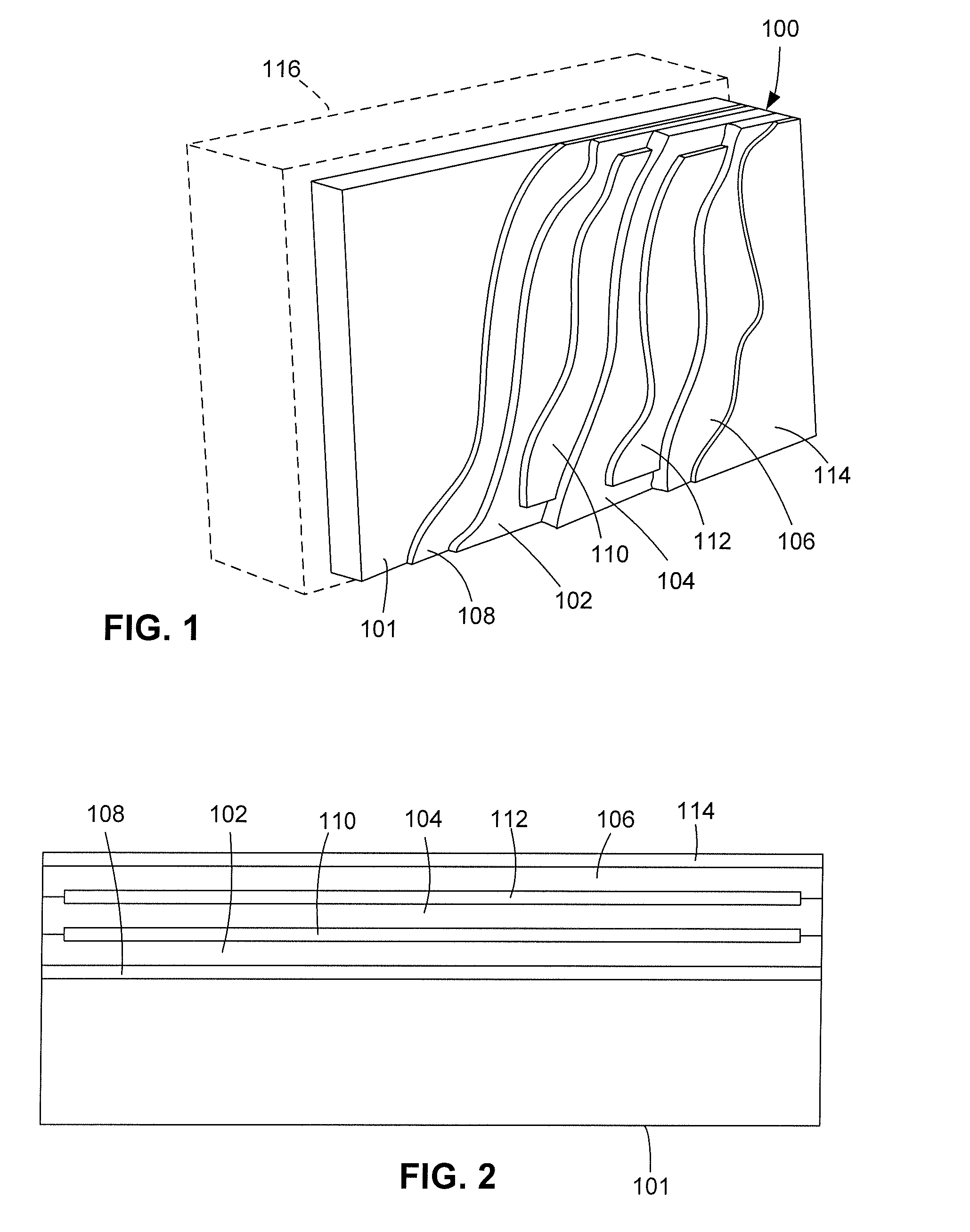
ActiveUS20080053684A1Reduce reflectivityReduce electrical conductivityMagnetic/electric field screeningFlat/ribbon cablesConductive coatingIndex-matching material
In an optical thin-film arrangement on a transparent optical substrate, such as a display screen, two or more conductive layers are stacked in an alternating fashion with one or more dielectric layers. The conductive layer can include, for example, indium-tin oxide (ITO), and the dielectric layer can include an index-matching material. The conductive layers can be in electrical contact with one another at their peripheries to provide EMI / RFI shielding. A structure having more than one conductive layer can be made to have the same net sheet resistance and thus provide the same degree of shielding as a conventional single-layer conductive coating but with lower reflectivity.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Index matched grating inscription
The disclosed embodiments provide systems and methods for mitigating lensing and scattering as an optical fiber is being inscribed with a grating. The disclosed systems and methods mitigate the lensing phenomenon by surrounding an optical fiber with a liquid index-matching material that is held in a vessel. The disclosed systems also include a replenishment mechanism that replenishes the liquid index-matching material as the optical fiber is pulled through the vessel.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Conductive coating for reduced reflectivity on electronic displays
ActiveUS7758978B2Magnetic/electric field screeningNatural mineral layered productsIndex-matching materialConductive coating
In an optical thin-film arrangement on a transparent optical substrate, such as a display screen, two or more conductive layers are stacked in an alternating fashion with one or more dielectric layers. The conductive layer can include, for example, indium-tin oxide (ITO), and the dielectric layer can include an index-matching material. The conductive layers can be in electrical contact with one another at their peripheries to provide EMI / RFI shielding. A structure having more than one conductive layer can be made to have the same net sheet resistance and thus provide the same degree of shielding as a conventional single-layer conductive coating but with lower reflectivity.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Confocal Displacement Sensor
ActiveCN109084684BHigh measurement accuracyBackground component reductionUsing optical meansSpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsIndex-matching materialReflectivity measurement
A confocal displacement sensor is provided that has improved measurement accuracy for low reflectivity measurement objects. It includes: a first optical fiber that outputs light from a first output end, and the light for projection is input to its first input end; a second optical fiber that outputs light input through a second input end from a second output end, and the second input The end is opposite to the first output end; the optical component that causes axial chromatic aberration on the detection light emitted through the second output end and converges the detection light to the measurement object; the beam splitter is used to irradiate the measurement object through the optical component Spectrum dispersion of the detection light passing through the second output port by reflection when focusing on the measurement object; measurement control section for calculating the displacement of the measurement object; detachably connecting the second input port to the first output port The optical fiber connection part used; the refractive index matching material between the first output end and the second input end. The second incident end and the first exit end are inclined at a second inclination angle smaller than the first inclination angle of the second exit end.
Owner:KEYENCE
Index matched grating inscription
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com