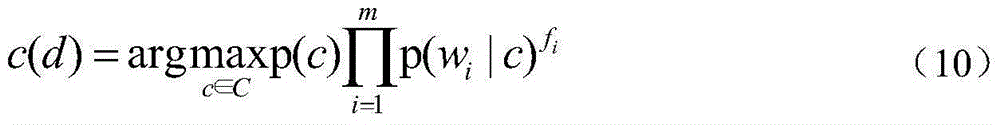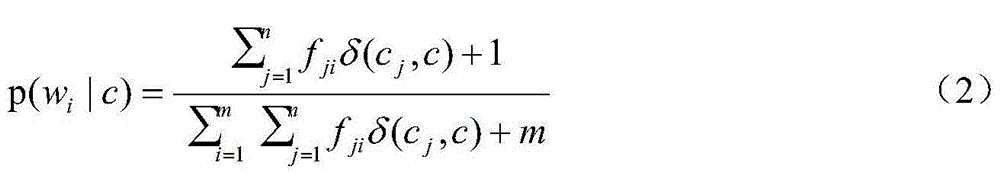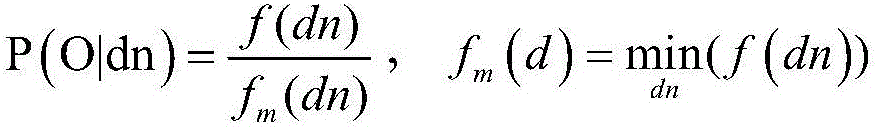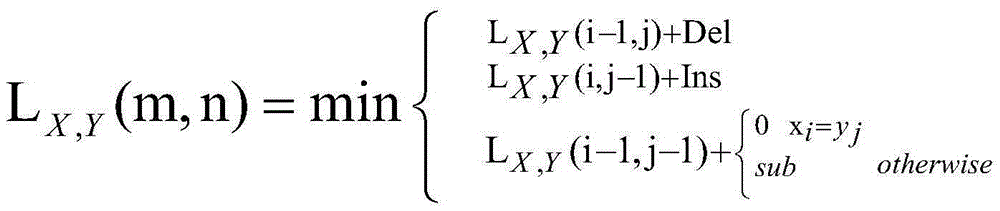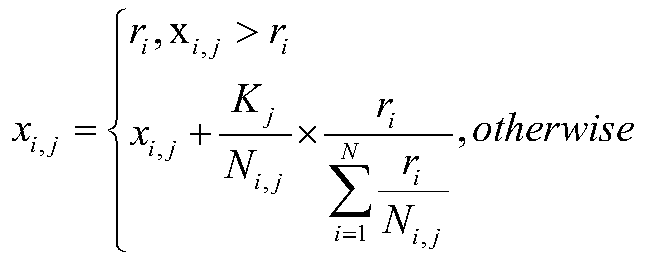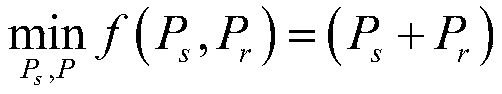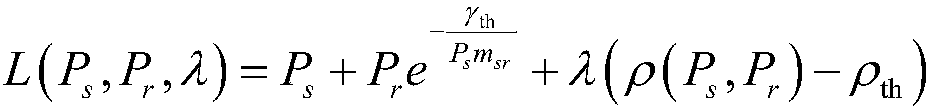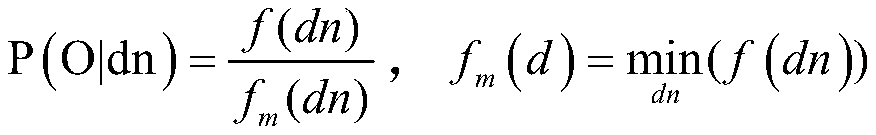Patents
Literature
31 results about "Regular conditional probability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Regular conditional probability is a concept that has developed to overcome certain difficulties in formally defining conditional probabilities for continuous probability distributions. It is defined as an alternative probability measure conditioned on a particular value of a random variable.
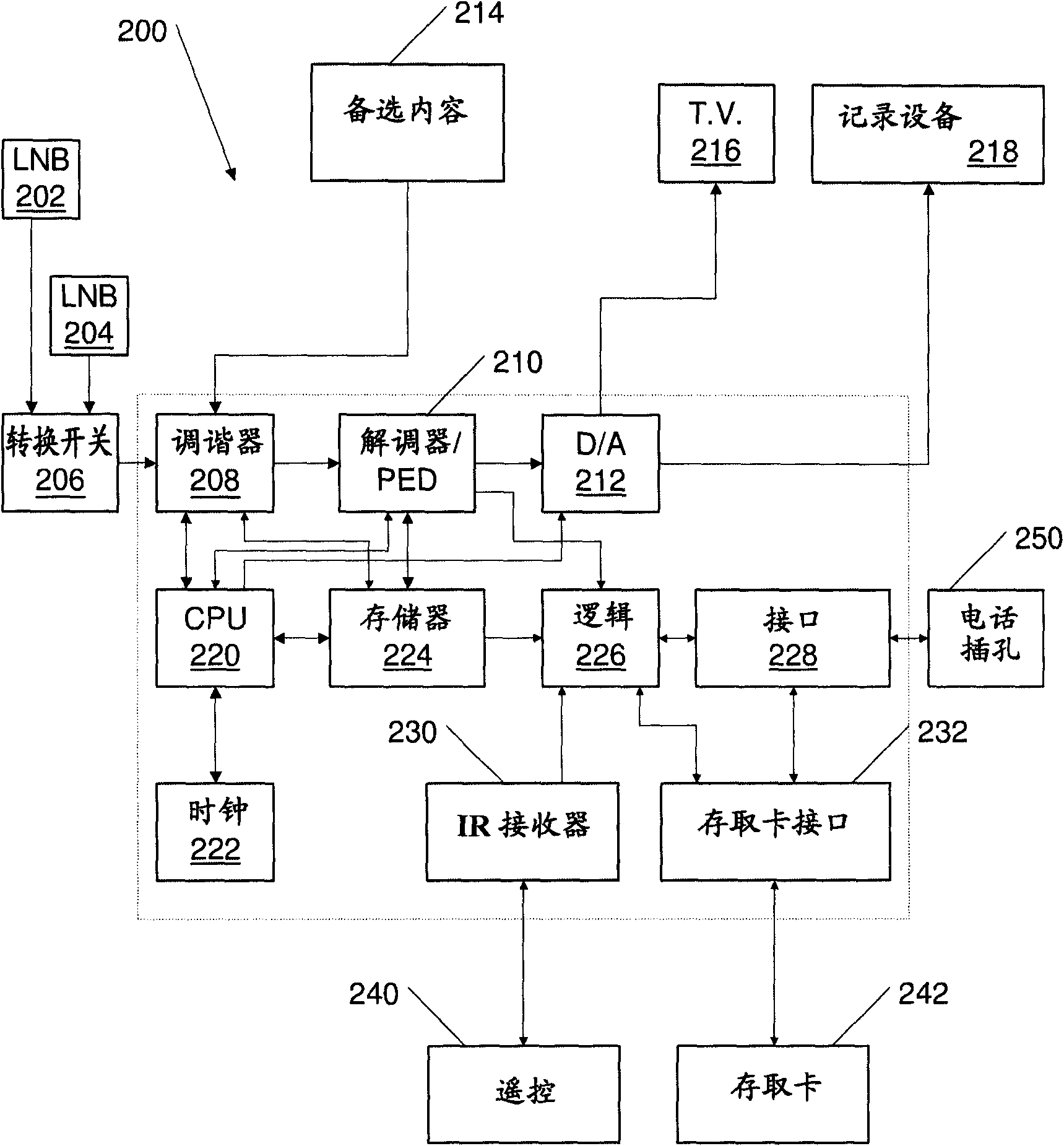
Processing associations in knowledge graphs
InactiveUS20160224637A1Web data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsRegular conditional probabilitySemantic Web
A data infrastructure for graph-based computing that combines the natural language expressiveness of the Semantic Web and the mathematical rigor of graph theory to discover meaningful associations across multiple sources towards computer-assisted serendipitous insight discovery. The process automatically integrates massive size datasets accessed using Semantic Web standards and technologies and normalizes data in graphs. The process generates a plurality of conditional probability distributions based on type-triple meta-data and triple statistics to model saliency and automatically construct and evaluate a plurality of sub-graphs based on the plurality of conditional probabilities for contextual-saliency. The process then renders a plurality of paths (i.e. sequence of associations) that model meaningful pairwise relations between objects of the normalized integrated data. The pluralities of conditional probabilities reveal and rank previously unknown associations between entities of user-interest in the knowledge graph.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
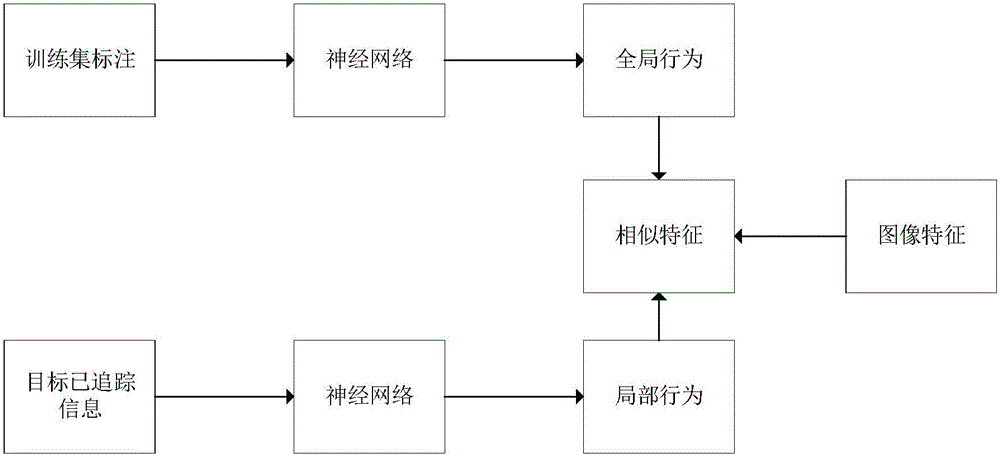
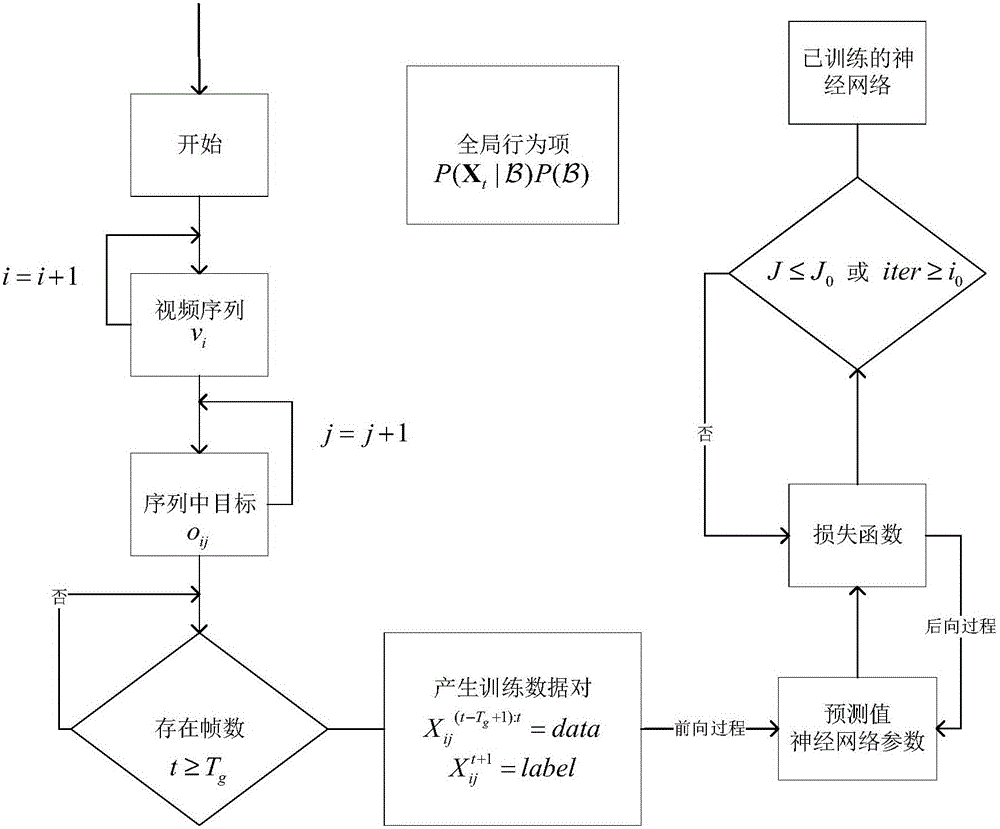
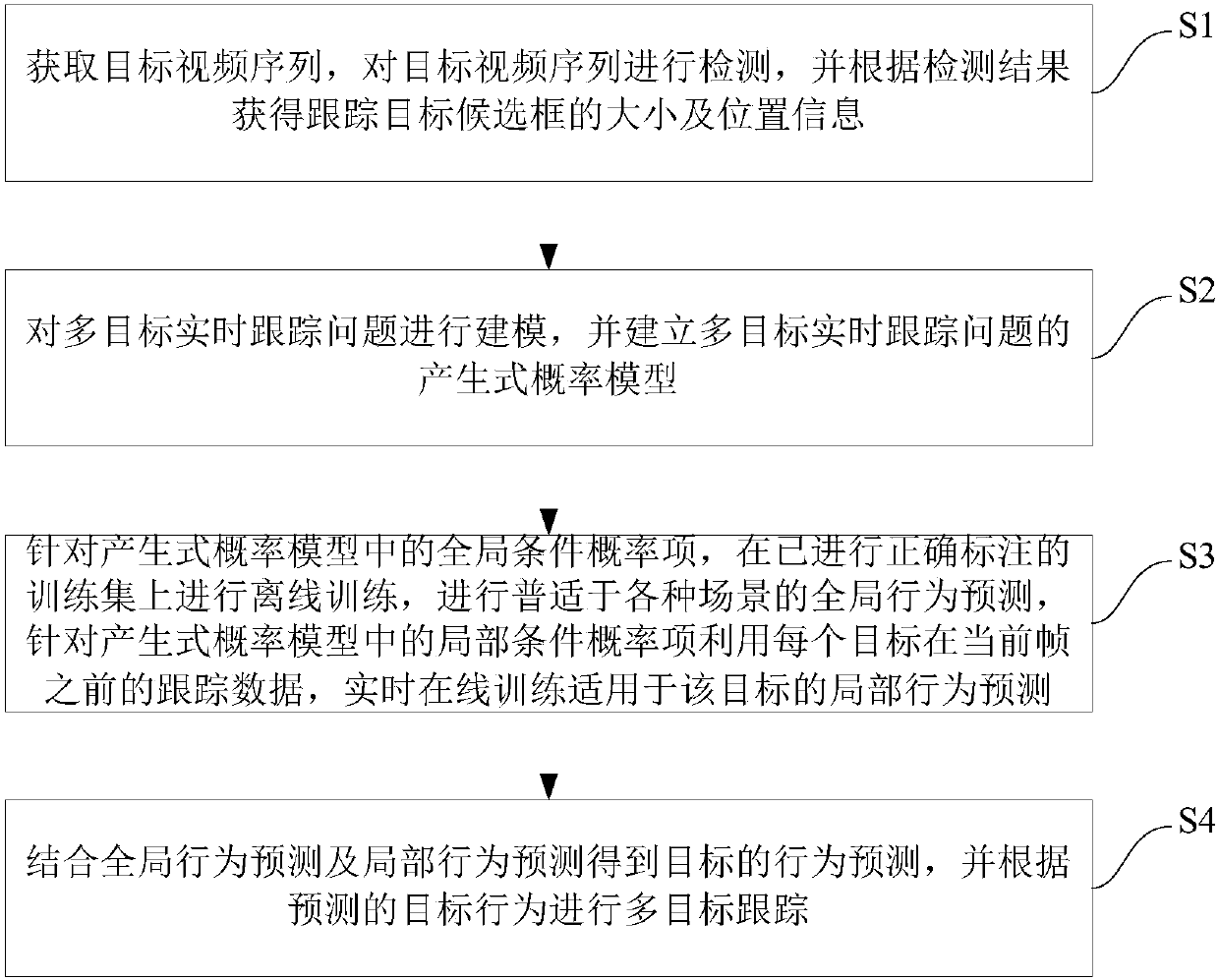
Multi-target tracking method and system based on behavior learning
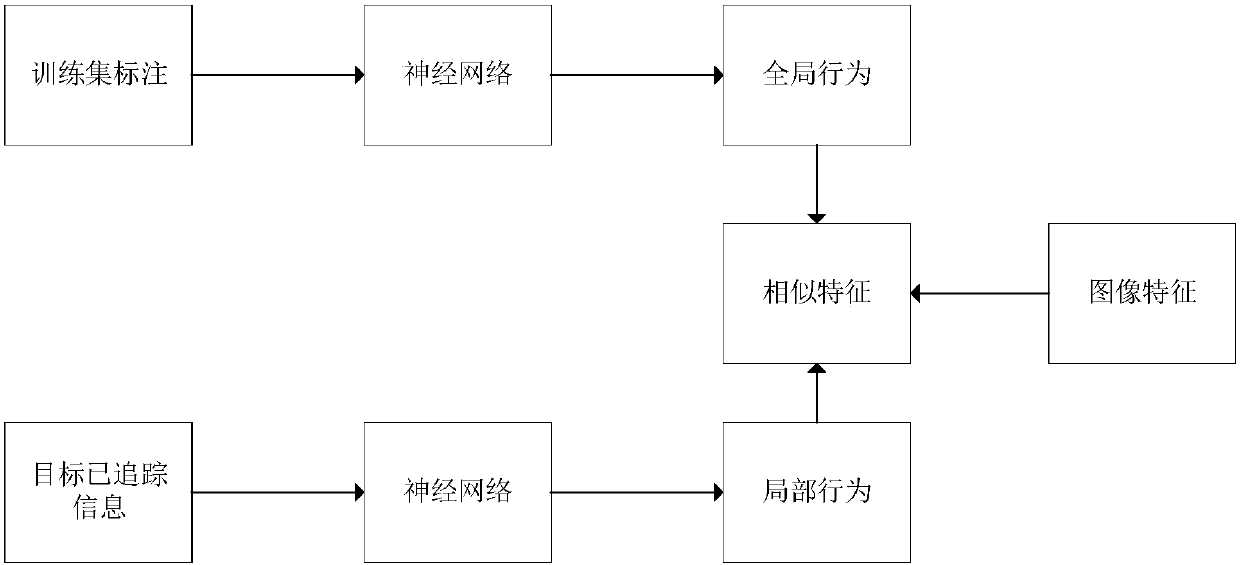
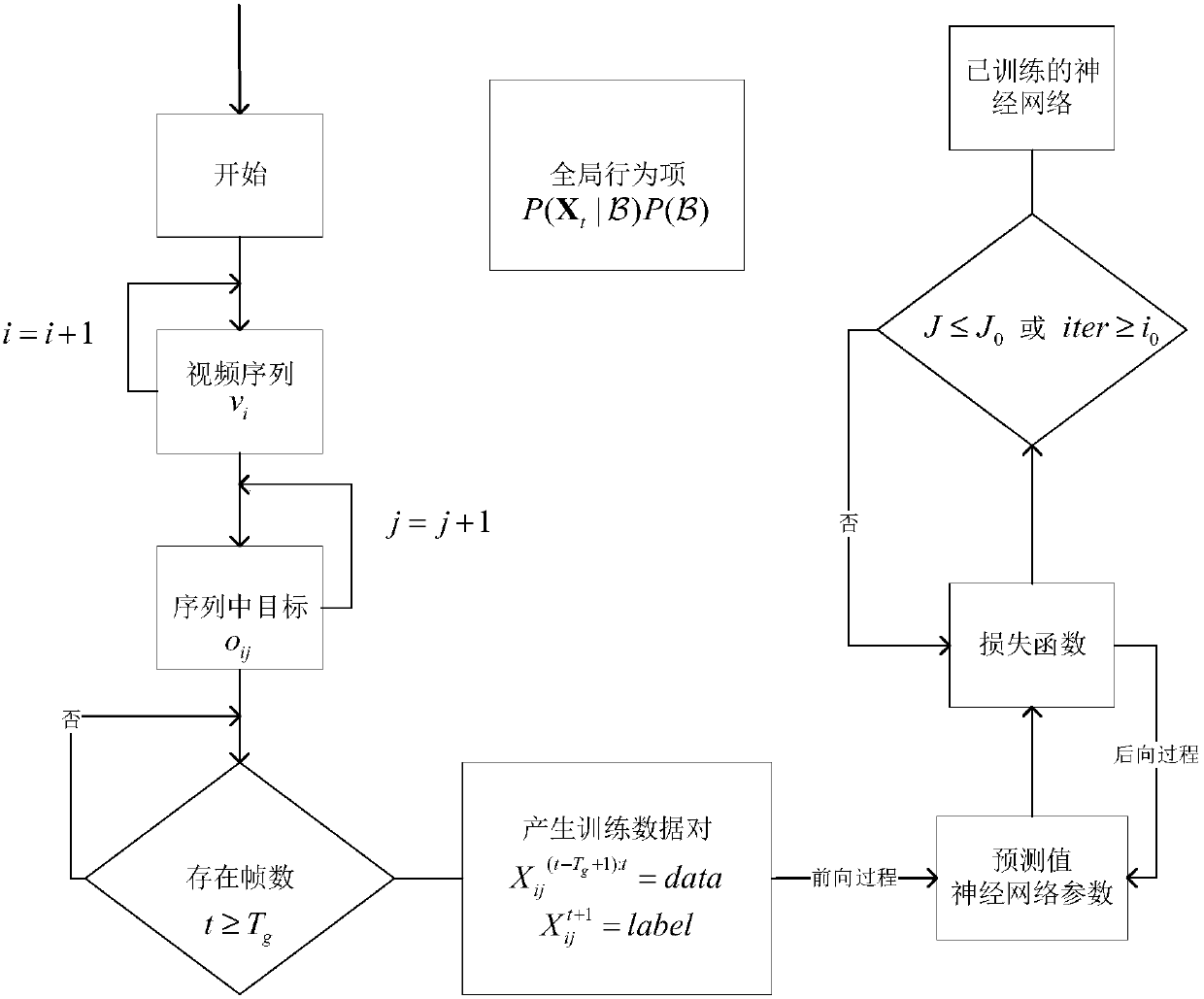
ActiveCN105957105AKeep trackReduce tracking error rateImage enhancementImage analysisProbit modelMulti target tracking
The invention provides a multi-target tracking method and system based on behavior learning. The method comprises steps of: acquiring and detecting a target video sequence, and acquiring the size and the positional information of a tracked target candidate frame depending on a detection result; modeling a multi-target real-time tracking problem and creating a production probability model of the multi-target real-time tracking problem; for the global conditional probability items in the production probability model, performing offline training on a correctly-marked training set in order to perform global behavior prediction applicable to various scenarios, and for local conditional probability items in the production probability model, on-line training local behavior prediction for each target in real time by using the tracking data of the target prior to a current frame; obtaining the behavior prediction of the target in combination with the global behavior prediction and the local behavior prediction, and tracking the multiple targets depending on the predicted target behavior. The method and the system may keep a tracking rate while tracking the multiple targets and may significantly reduce a tracking error rate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
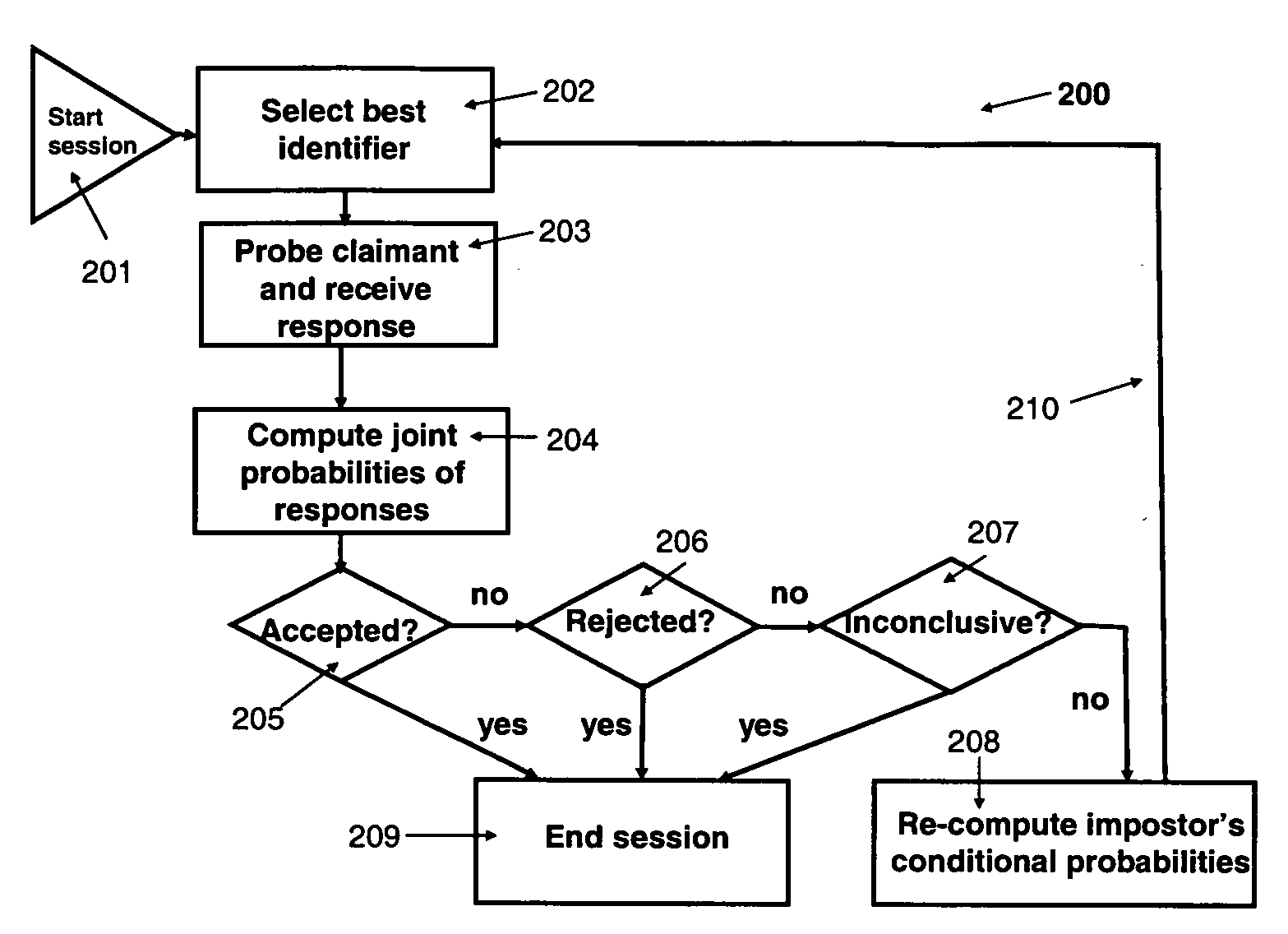
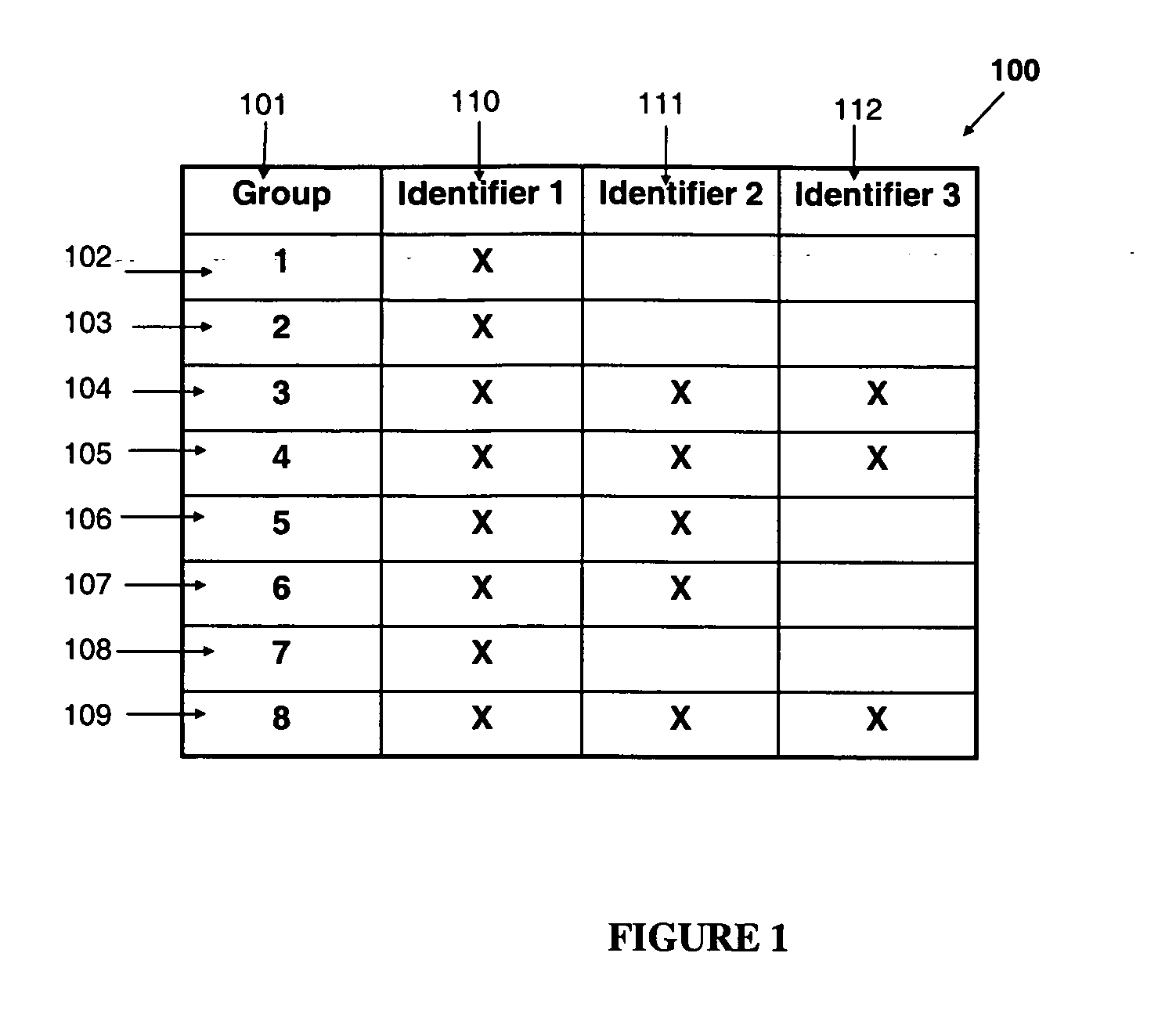
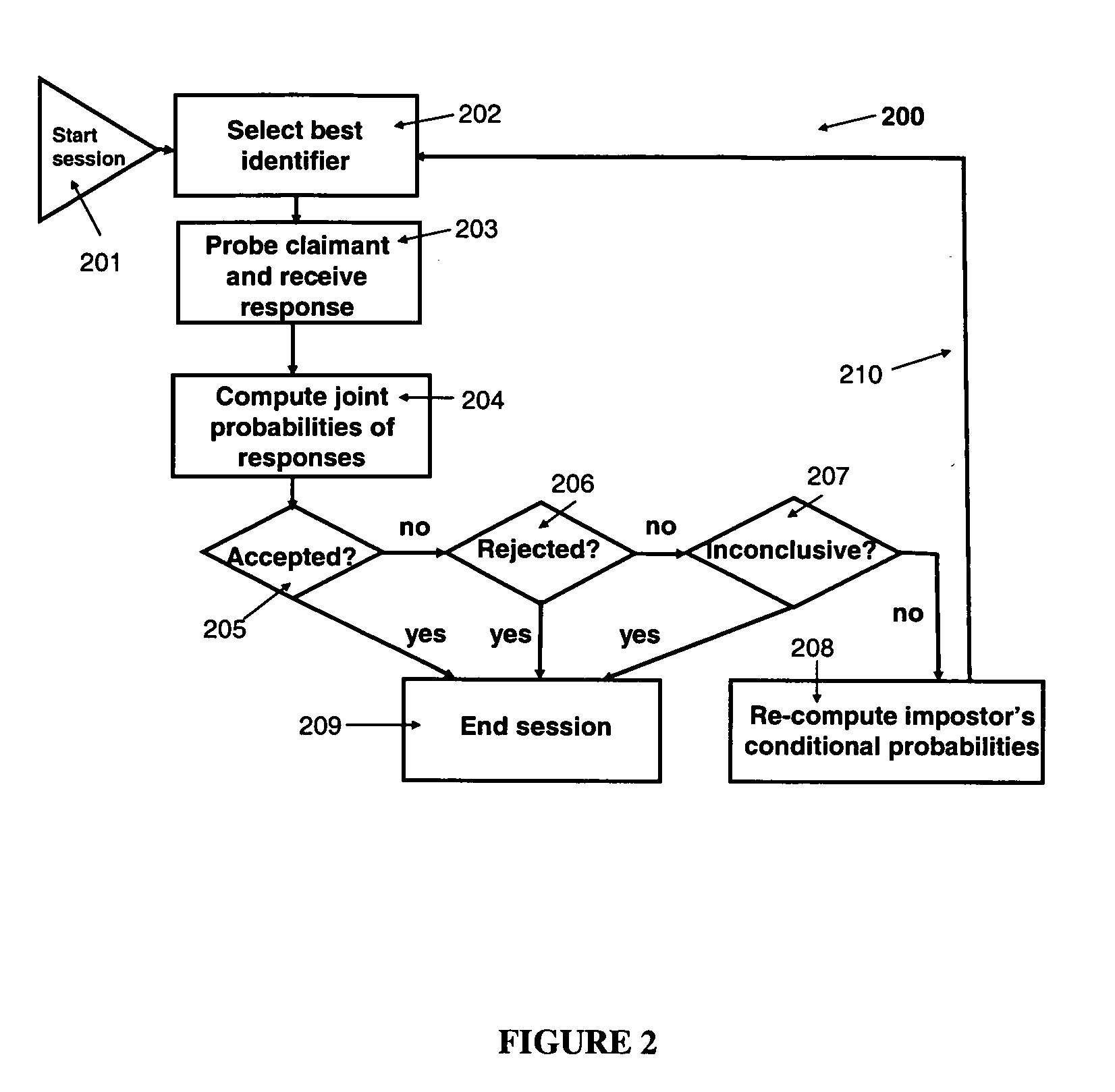
Automated adaptive method for identity verification with performance guarantees
InactiveUS20070282610A1Promote differentiationSmall proportionDigital data processing detailsSpeech analysisRegular conditional probabilityConditional probability
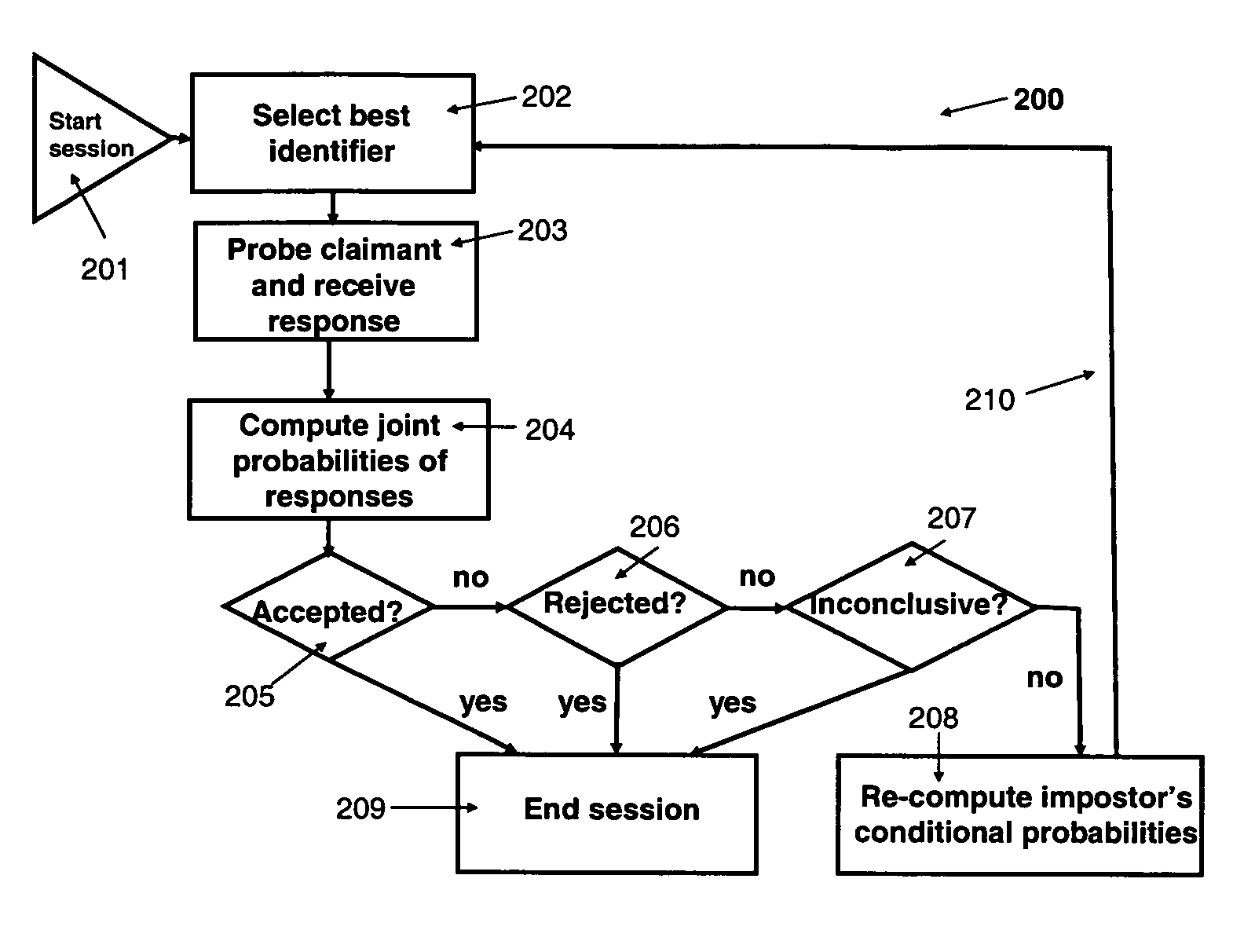
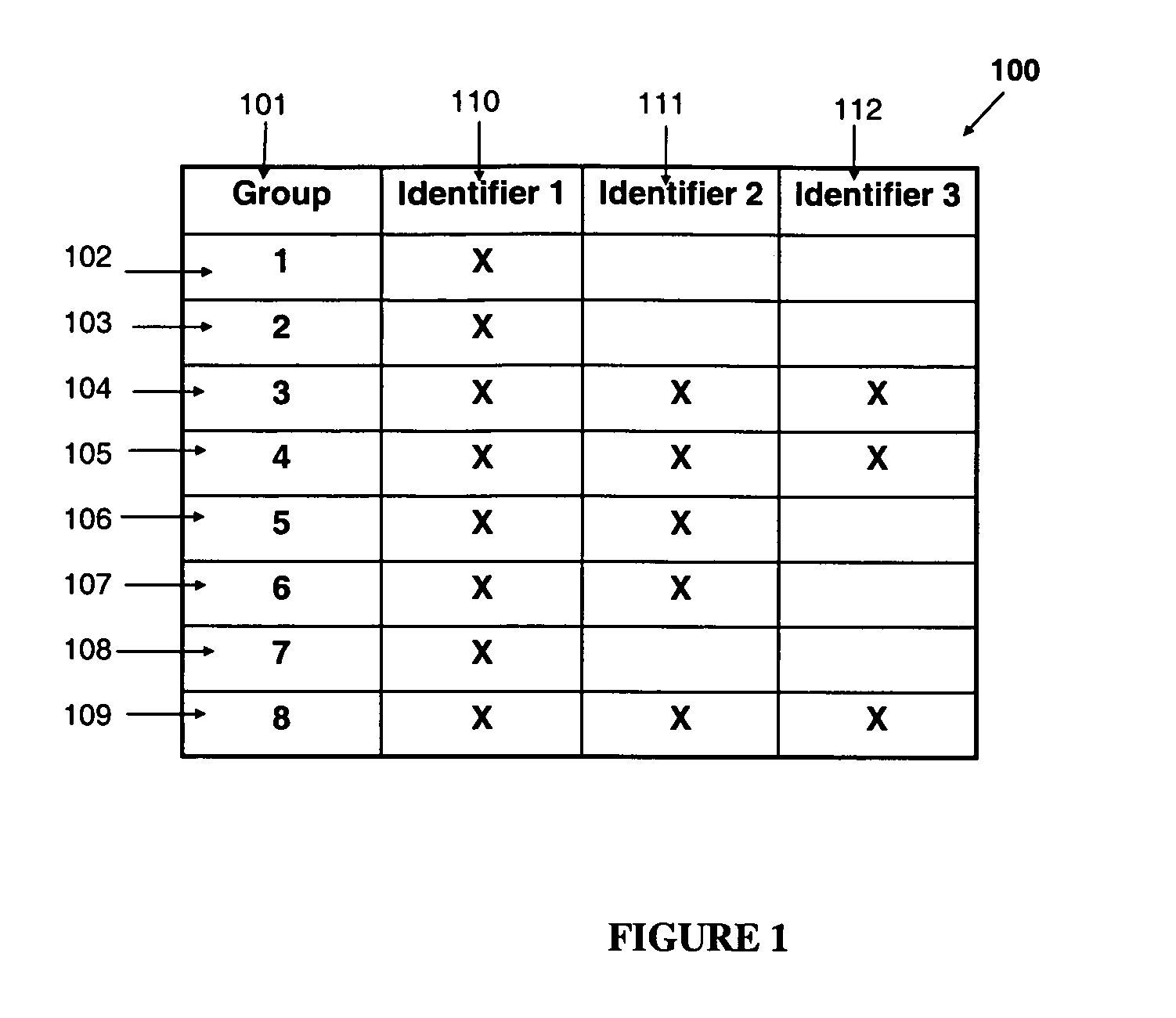
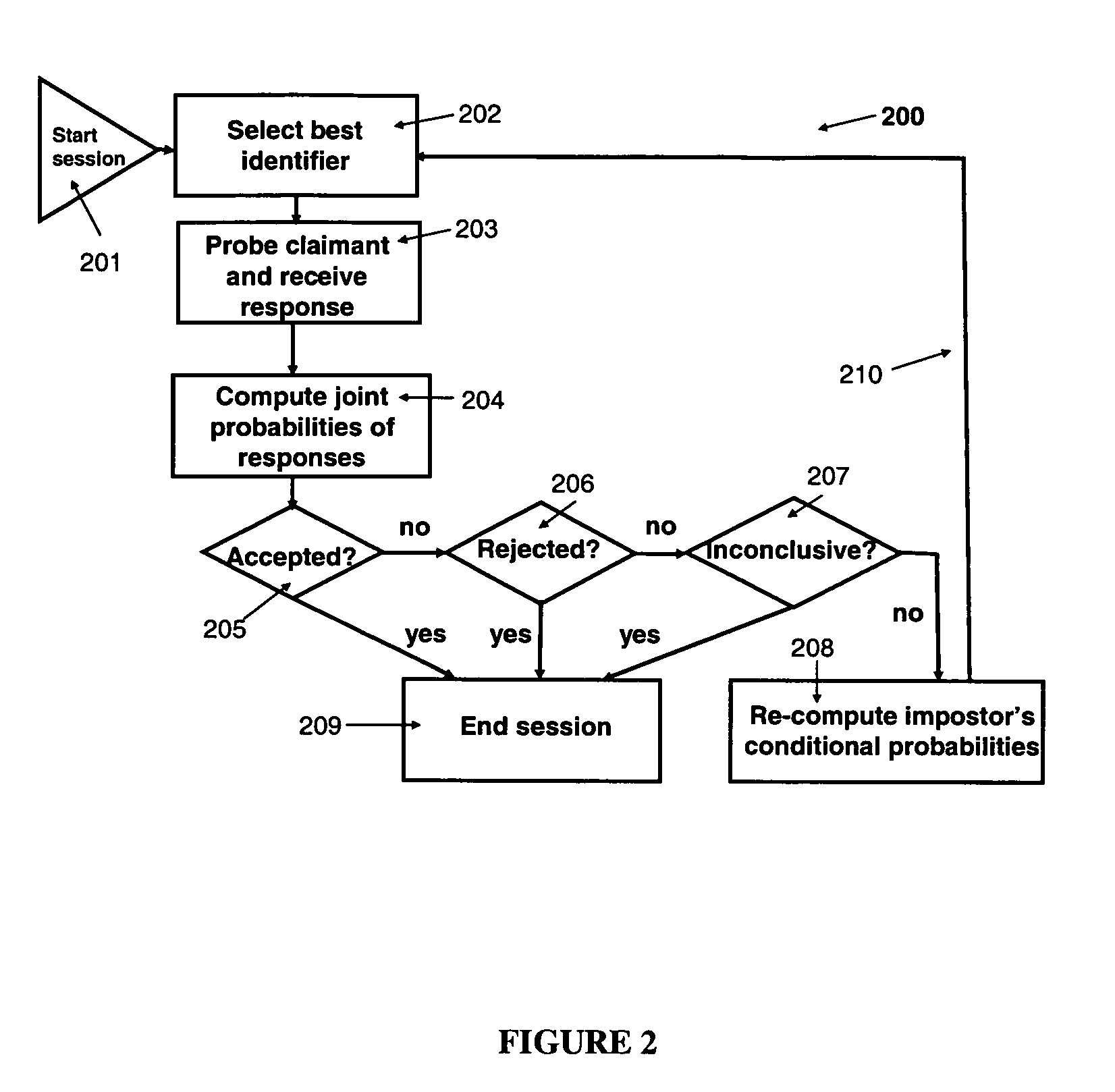
This invention provides an automated adaptive method for identity verification of claimants that attempt to get access into a resource by responding to a sequence of identifiers. The sequence has a specified maximal length and the identifiers are partitioned into multiple groups where identifiers in the same group are correlated and identifiers in different groups are not correlated. The method guarantees that an impostor will be accepted with a probability that does not exceed a specified parameter and that a legitimate claimant will be rejected with a probability that does not exceed a different specified parameter. The method also computes the probabilities that a legitimate claimant, or an impostor, will terminate an interrogation session with an inconclusive result, which would necessitate further manual interrogation. The method is adaptive as the conditional probabilities of an impostor's responses change throughout a session of interrogation.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
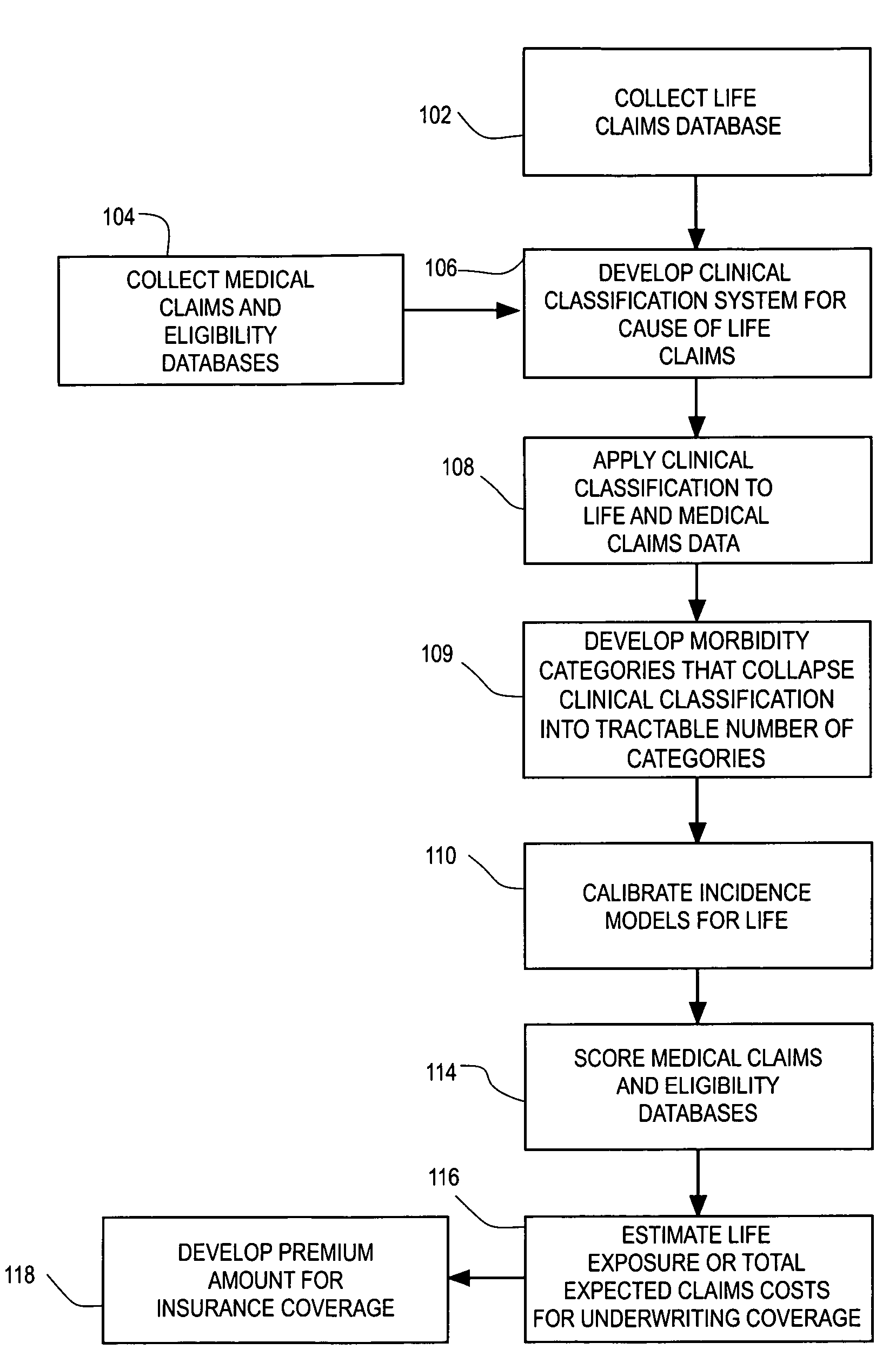
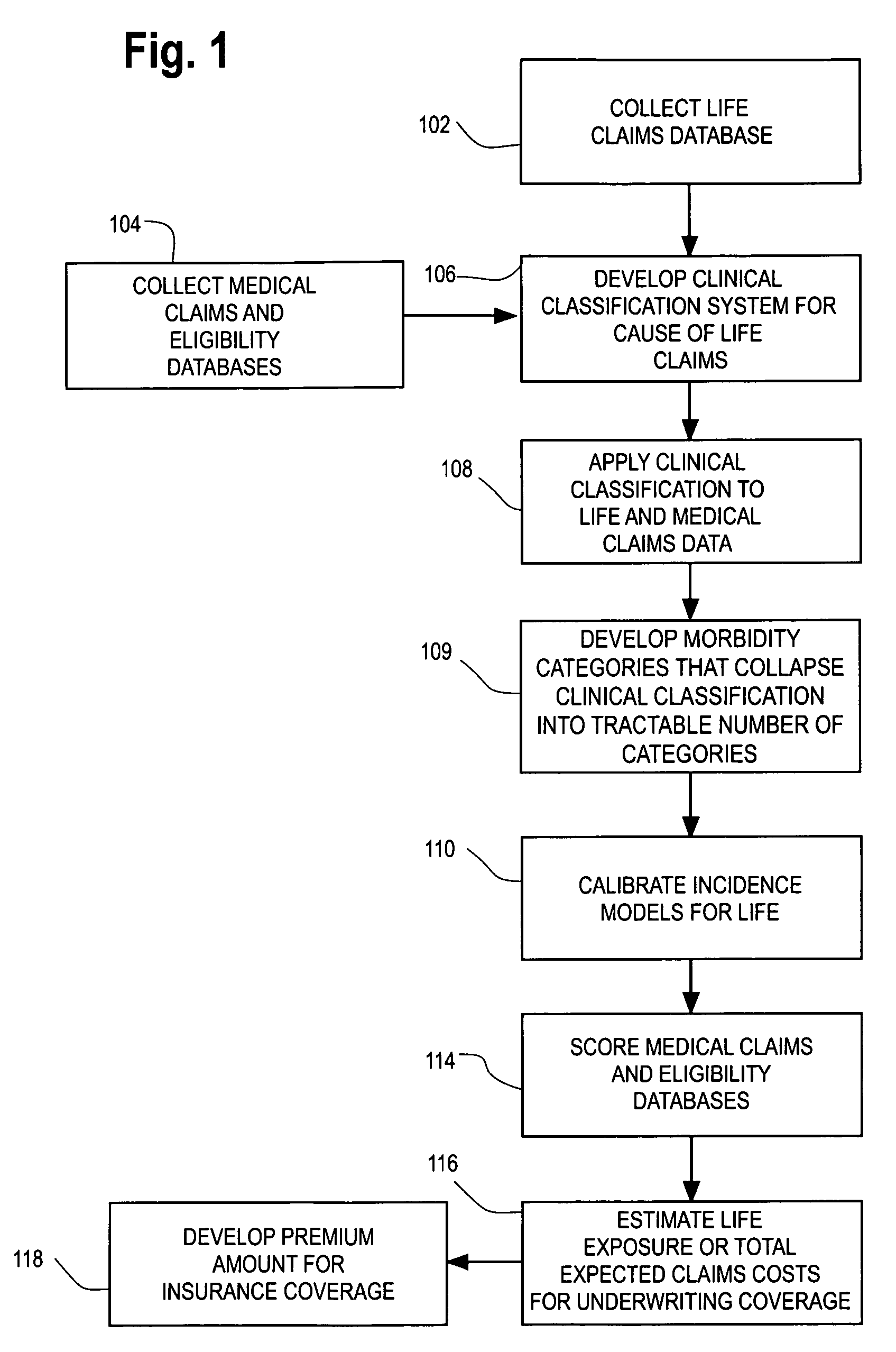
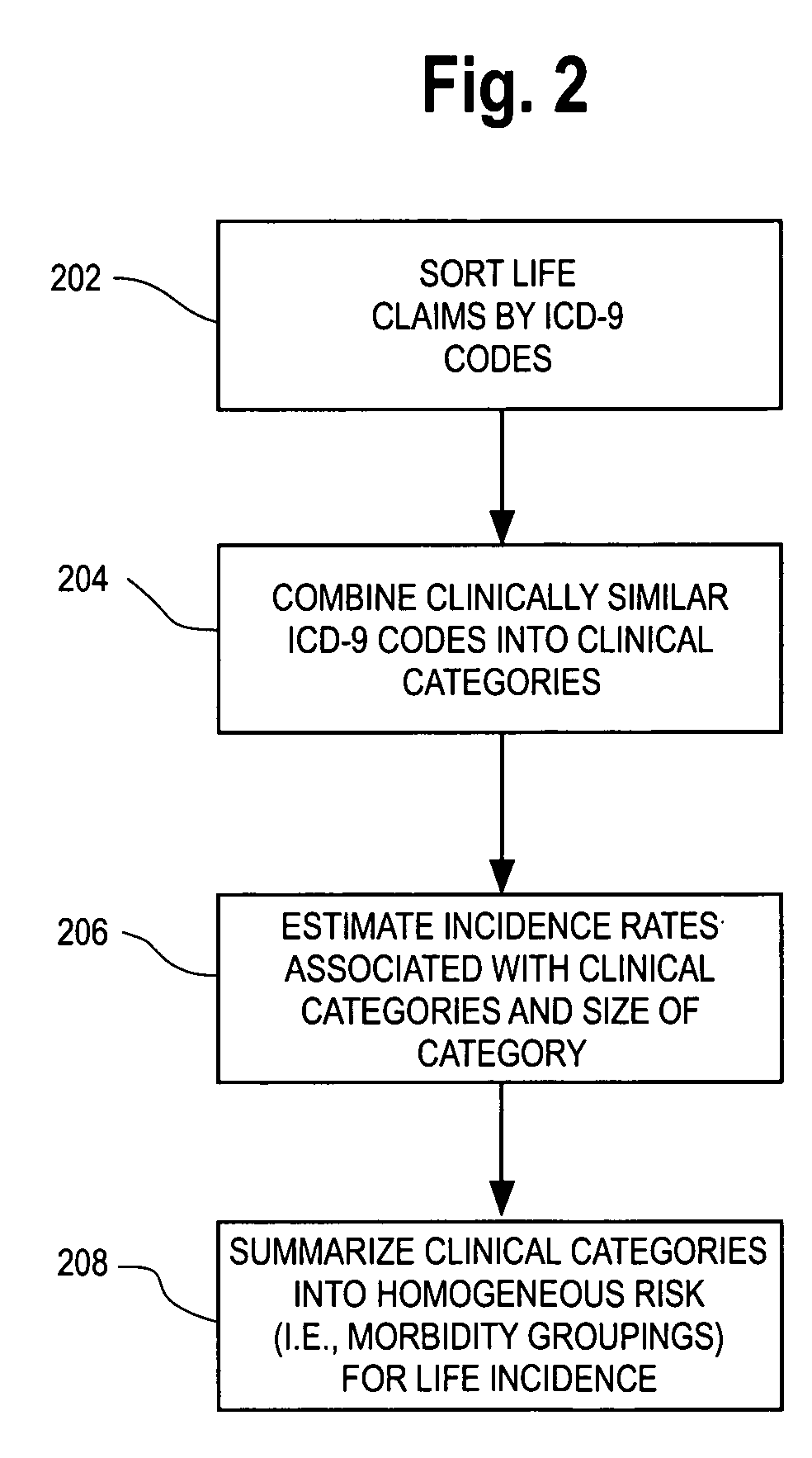
Computerized medical modeling of group life insurance using medical claims data
A method of model development for use in underwriting group life insurance for a policy period includes collecting medical claims data for the group to be underwritten, where each medical claim being related to a particular employee of the group. Morbidity categories are provided that categorize the medical claims in the medical claims data. A conditional probability model is developed and applied to the morbidity categories for each employee in the group using his medical claims, thereby calculating the expected conditional probability for each employee dying during the policy period. For each employee, an estimate of the expected life claim cost is estimated using an index of the life coverage to salary. Combining the expected conditional probability for each employee dying during the policy period with the estimate of the expected claim cost of death gives an estimate of the group's total life exposure.
Owner:TRURISK
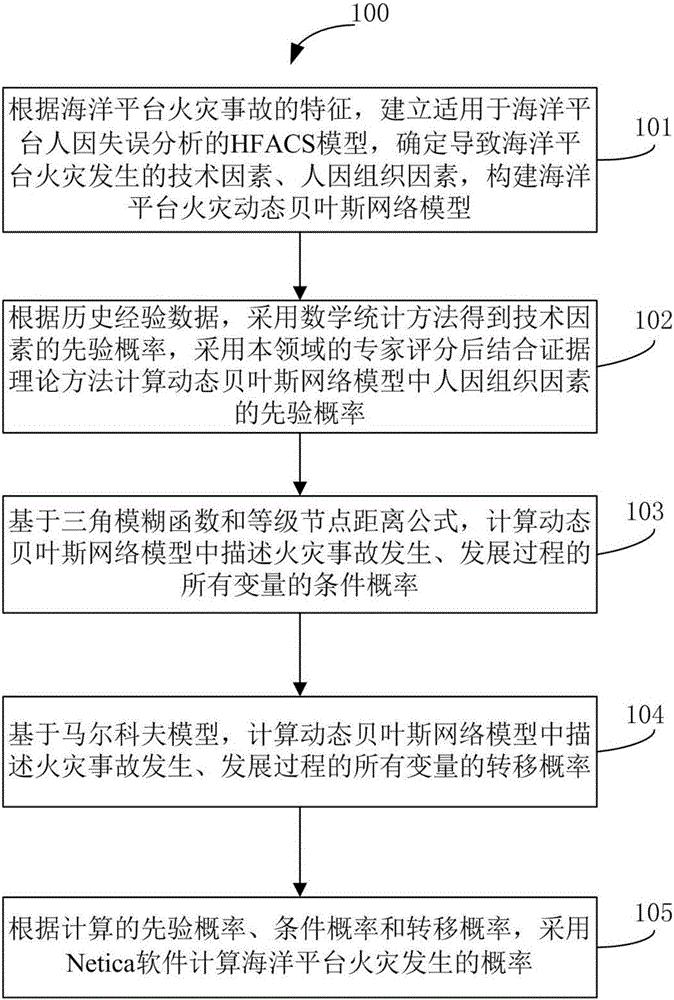
Human error and structure defect-considering ocean platform fire risk assessment method
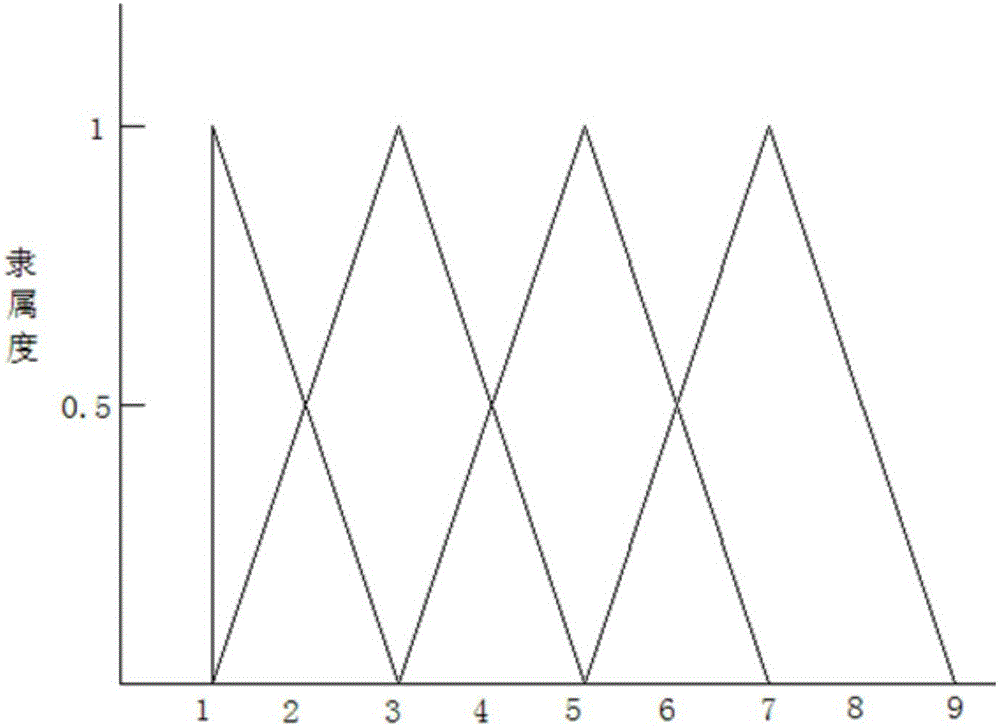
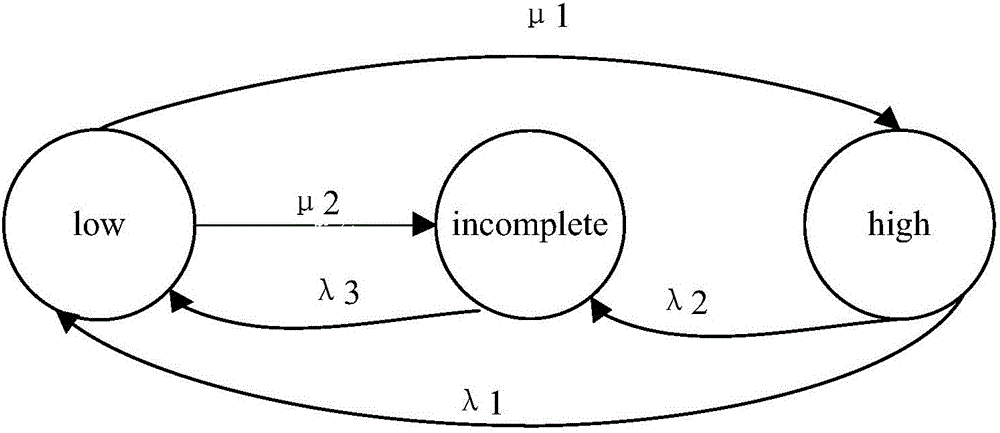
The invention discloses a human error and structure defect-considering ocean platform fire risk assessment method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing an HFACS model suitable for ocean platform human error analysis according to the features of an ocean platform fire accident, determining technical factors and human factor organizational factors of the ocean platform fire, and constructing an ocean platform fire dynamic Bayesian network model; calculating a prior probability of the human factor organizational factors in the dynamic Bayesian network model; calculating a conditional probability describing all the variables of the fire accident occurrence and development process in the dynamic Bayesian network model on the basis of a triangular fuzzy function and level node distance formula; calculating a transition probability of all the variables of the fire accident occurrence and development process in the dynamic Bayesian network model on the basis of a Markov model; and calculating an ocean platform fire occurrence probability by adoption of Netica software according to the calculated prior probability, conditional probability and transition probability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Structure extended polynomial naive Bayes text classification method
InactiveCN105045825AAvoid time-consuming structure learning phasesReduce space complexitySpecial data processing applicationsText database clustering/classificationTest documentRelationship - Father
The invention provides a structure extended polynomial naive Bayes text classification method. Firstly, a one-dependence polynomial estimator is established by using each word that occurs in a test document as a father node and then all the one-dependence polynomial estimators are subjected to weighted averaging to predict a category of the test document, wherein the weight is an information gain ratio of each word. According to the method, the structure learning phase of a Bayesian network is avoided, thereby reducing time spending brought by high dimensionality of text data; and meanwhile, the estimation process of a dual conditional probability is postponed to the classification stage, thereby ingeniously saving large space cost. According to the method, not only is classification accuracy of a polynomial naive Bayes text classifier improved, but also time spending and space cost of structure learning of the Bayesian network are avoided.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
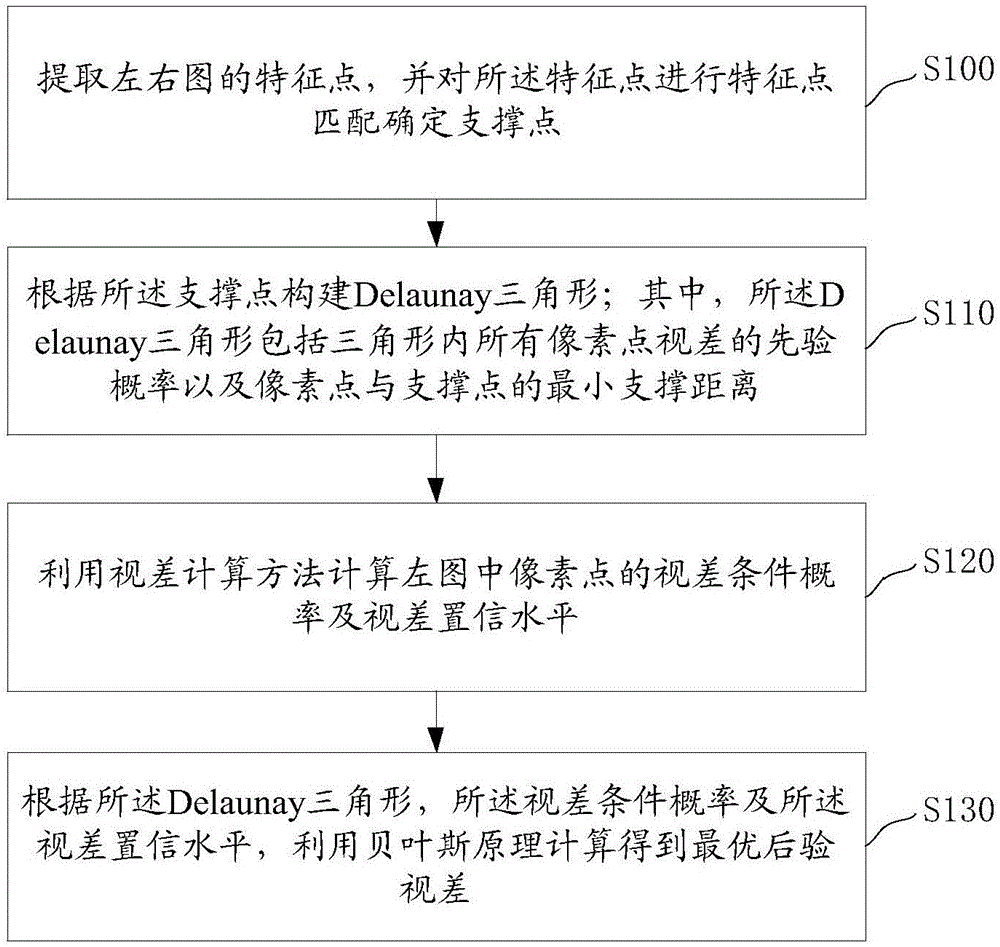
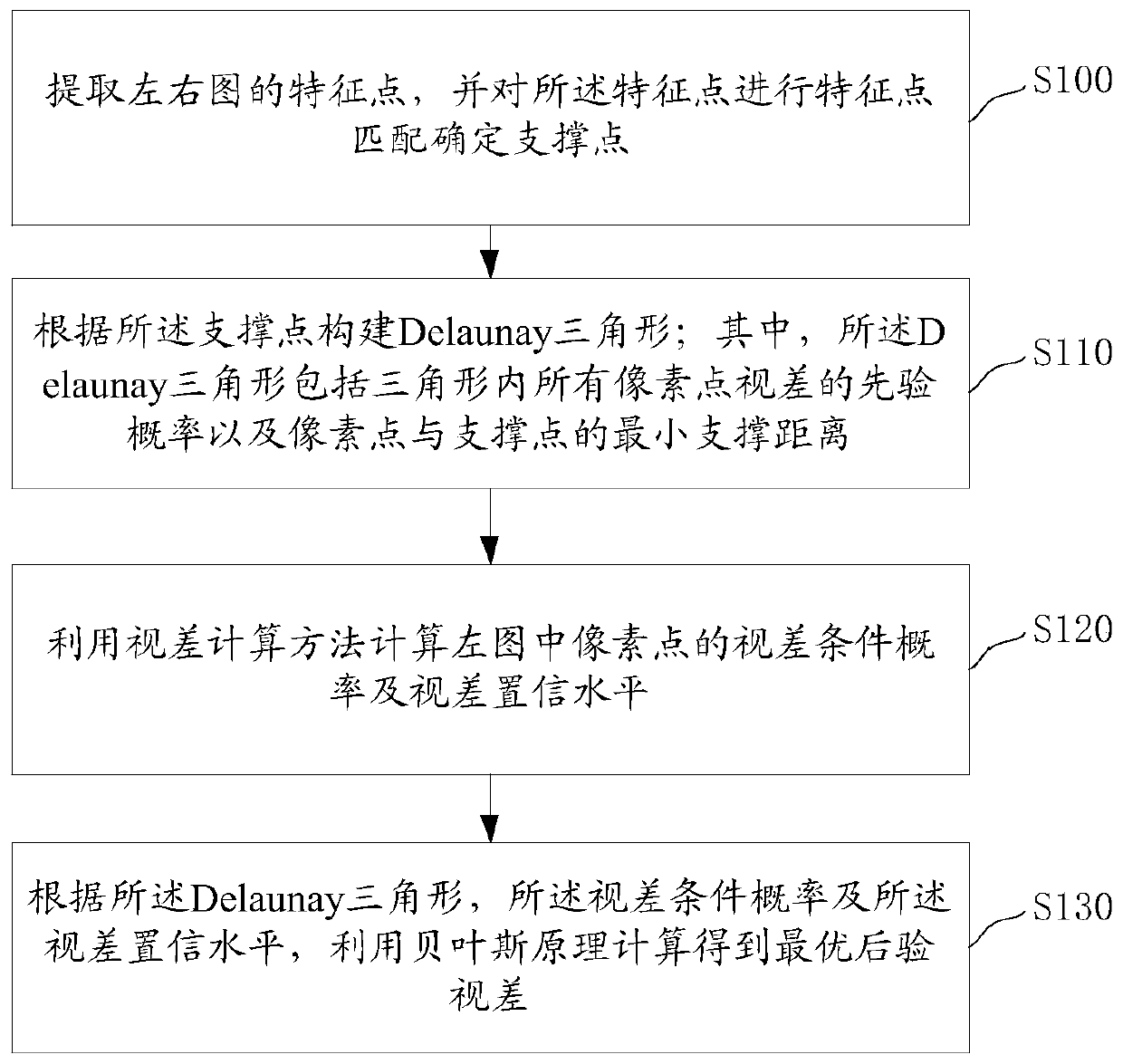
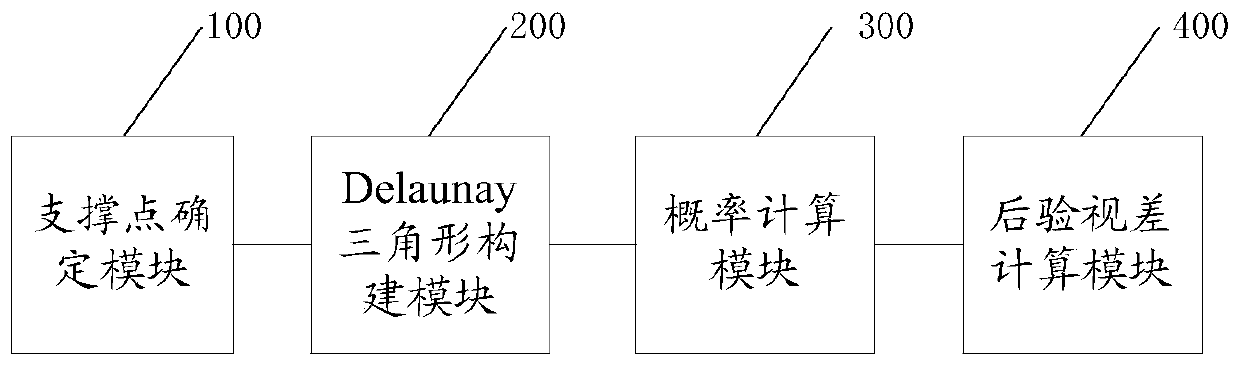
Stereo dense matching method and system
The invention discloses a stereo dense matching method, which comprises the following steps of extracting feature points of a left image and a right image and determining support points through carrying out feature point matching on the feature points; constructing a Delaunay triangle according to the support points, wherein the Delaunay triangle comprises a prior probability of disparities of all pixel points in the triangle and a minimum support distance between the pixel points and the support points; utilizing a disparity computation method to compute a disparity conditional probability and a disparity confidence level of the pixel points in the left picture; and utilizing a Bayes principle to compute an optimal posterior disparity according to the Delaunay triangle, the disparity conditional probability and the disparity confidence level. According to the method, a high-precision disparity image is obtained through rapid matching, and the method is especially suitable for a mobile platform or the application field with high real-time requirements; the invention also discloses a stereo dense matching system, which has the beneficial effects.
Owner:CHENGDU TOPPLUSVISION TECH CO LTD
Wind power weighting predication method based on conditional probability
InactiveCN103996079AAccurate predictionProof of validityForecastingPredictive methodsWeight coefficient
The invention provides a wind power short-term predication method and relates to a wind power weighting predication method based on conditional probability. The wind power weighting predication method comprises the steps of utilizing a confidence belt equivalent curve method to express an air speed-power characteristic curve of a unit; obtaining weighting coefficients at different historical moments through an actual data test to accurately predicate the air speed; obtaining the final predication power by means of a coefficient correction predication method. Effectiveness of the wind power weighting predication method based on conditional probability is proved by means of error analysis and comparison. By means of the wind power weighting predication method based on conditional probability, the accurate air speed-power characteristic curve is obtained by means of a confidence belt, and power is predicated accurately by means of the coefficient correction predication method based on actual data.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
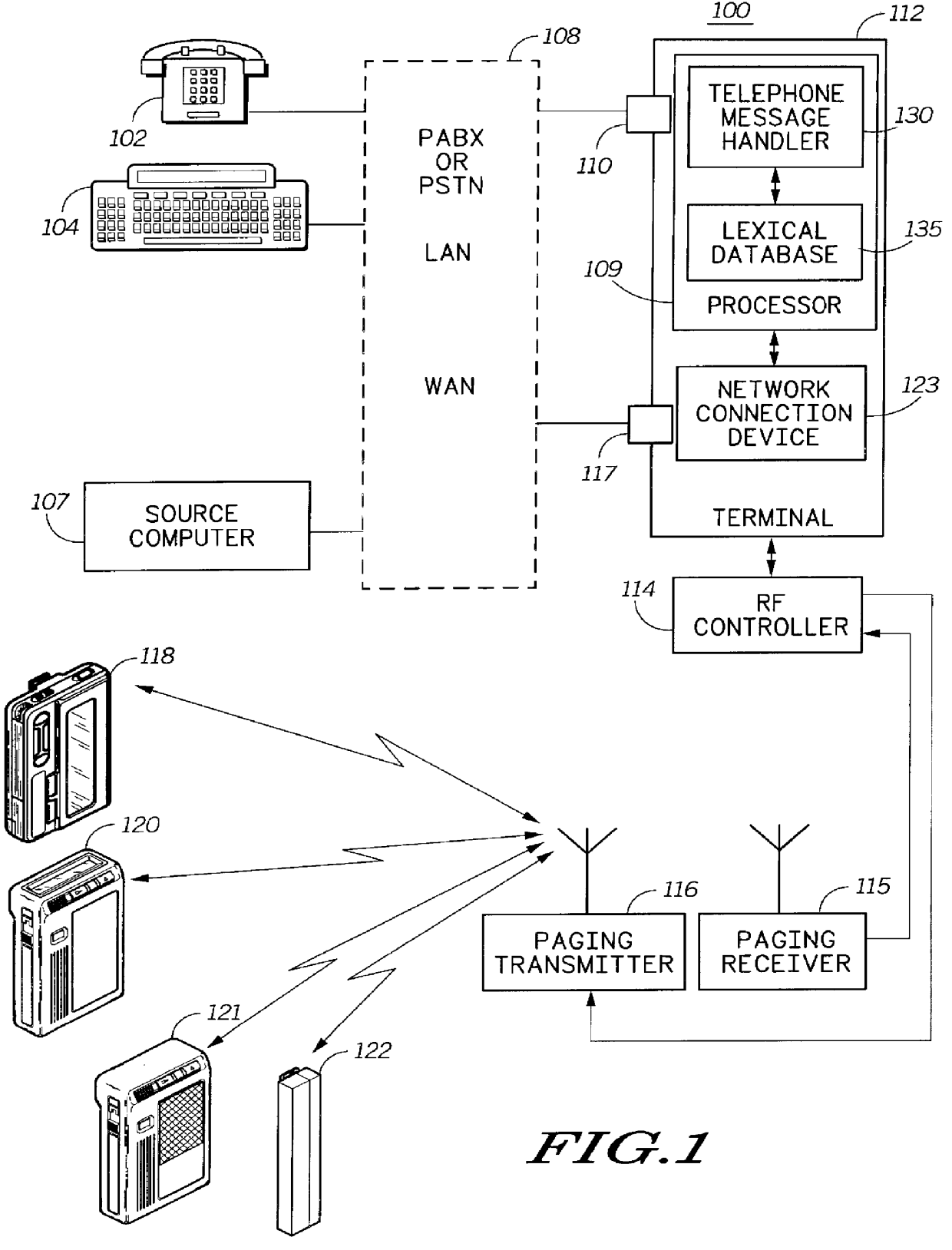
Alphanumeric message composing method using telephone keypad
InactiveUS6137867AFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelephonic communicationRegular conditional probabilityConditional probability
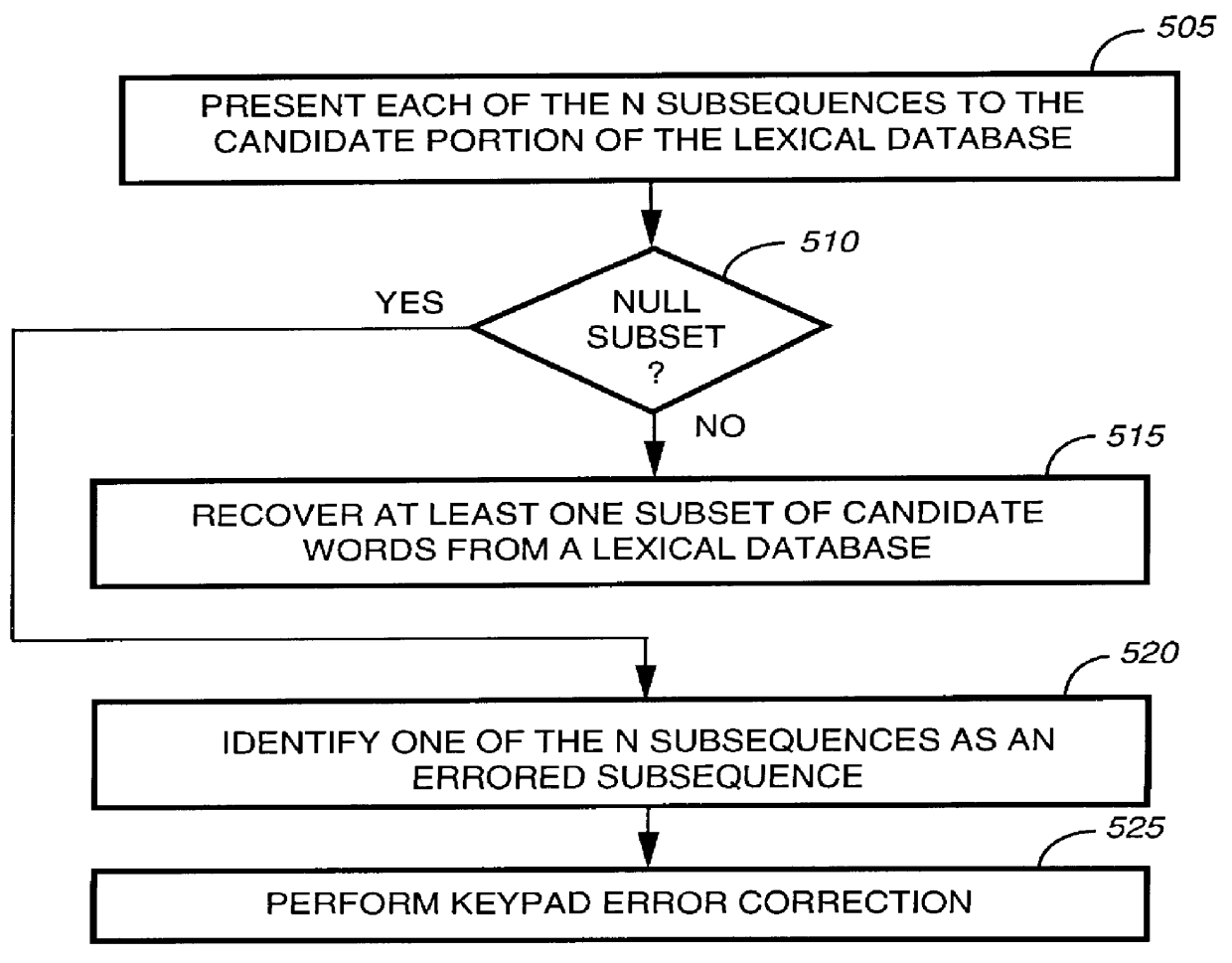
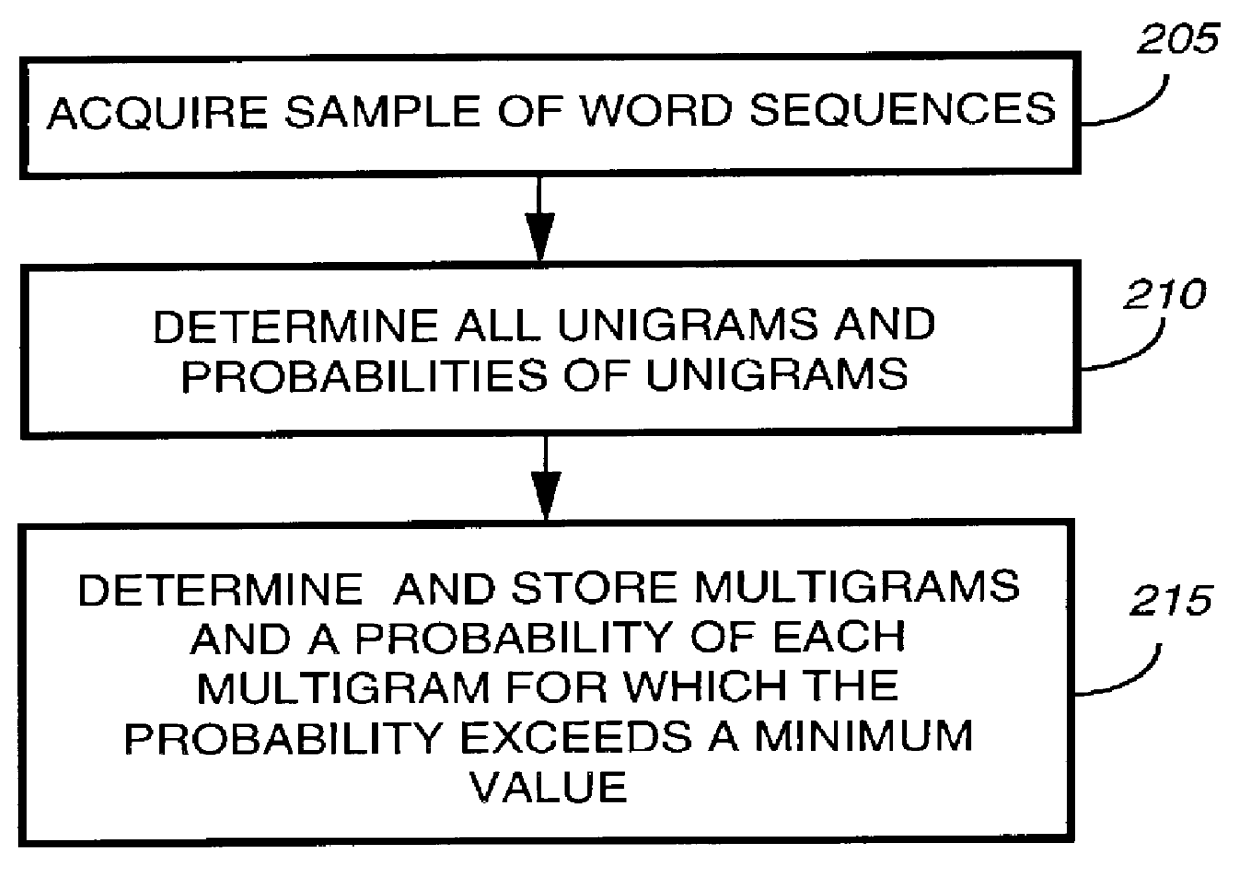
An interactive method for composing an alphanumeric message by a caller using a telephone keypad includes storing (215) a lexical database (135) from which unigram probabilities, forward conditional probabilities, and backward conditional probabilities for a plurality of words can be recovered; storing a received sequence of key codes (405) representing a sequence in which keys on a telephone style keypad are keyed; generating a word trellis including candidate words (415) derived from the sequence and the lexical database; determining a most likely phrase (420) from the candidate words, the unigram probabilities, forward conditional probabilities, and backward conditional probabilities; generating a most likely message (425) from the most likely phrase and presenting the most likely message to the caller; and confirming that the most likely message is the alphanumeric message (430).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Cerebrovascular segmentation method, system and electronic device
ActiveCN109102511AEffective candidate spaceImage enhancementImage analysisRegular conditional probabilityMaximum a posteriori estimation
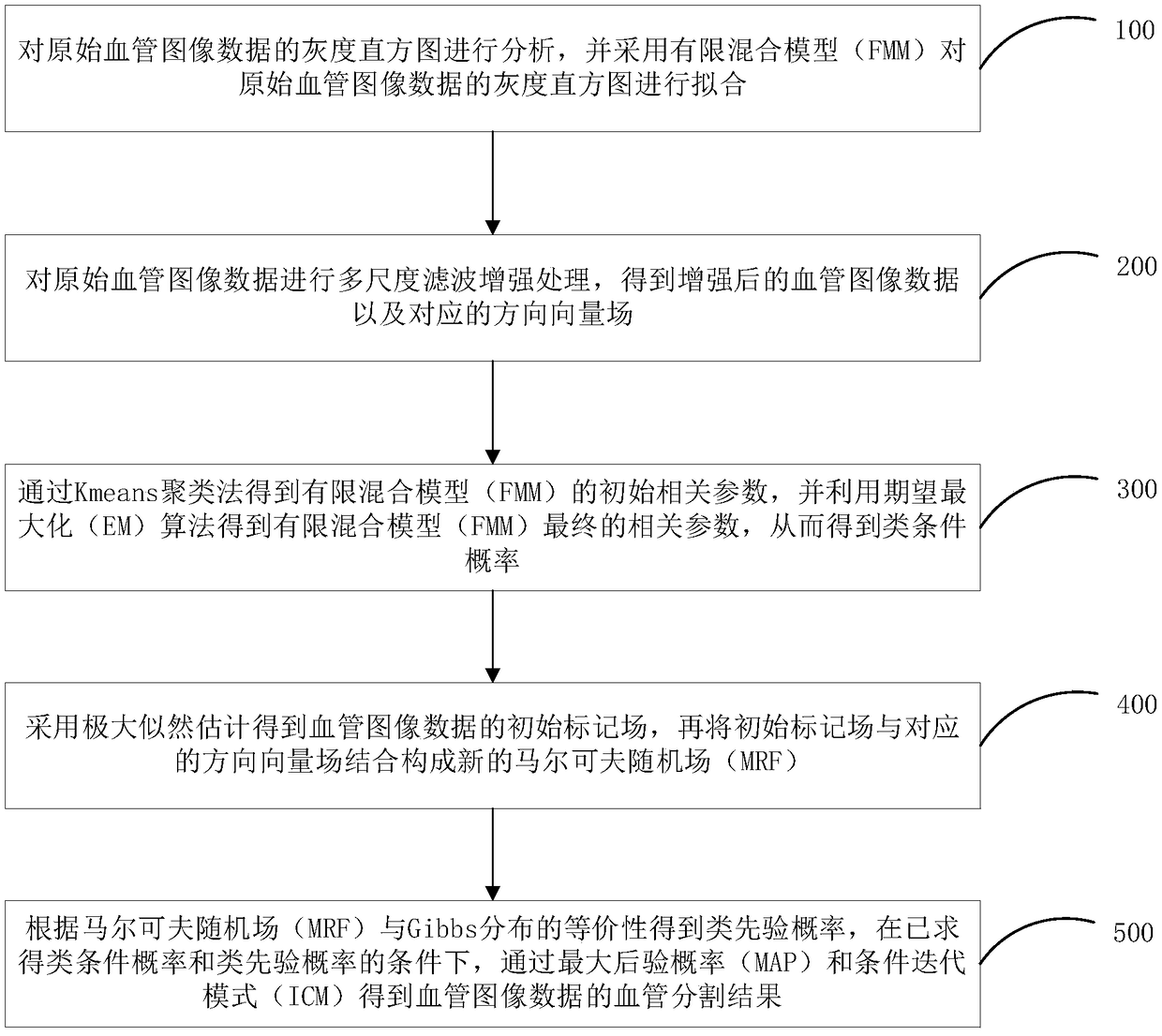
The present application relates to a cerebral vascular segmentation method, a system and an electronic device. The method comprises the following steps: the original blood vessel image data is processed by multi-scale filtering and enhancement to obtain the enhanced blood vessel image data and the corresponding direction vector field; the finite mixing model is established, and the parameters of the finite mixing model are estimated, and the class conditional probability P (y | x) is obtained; an initial marker field of the blood vessel image data is calculated and the initial marker field iscombined with a corresponding direction vector field to form a new Markov random field; according to the equivalence of Markov random field and Gibbs distribution, a priori-like probability P (x) is obtained; based on the conditional probability P (y | x) and the priori-like probability P (x), the blood vessel segmentation results of the blood vessel image data are obtained through the maximum posterior probability and the conditional iterative mode. The present application can extract more effective blood vessel candidate space, extract blood vessel structure under low contrast, and make theblood vessel network more complete.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
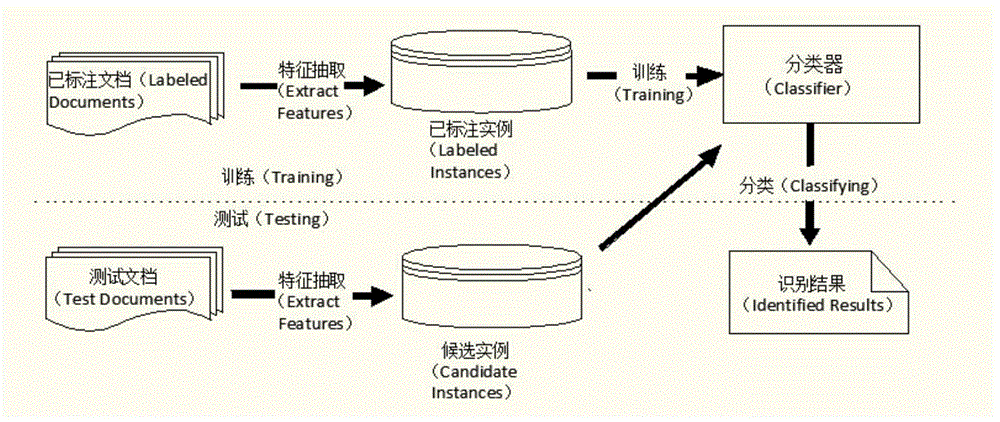
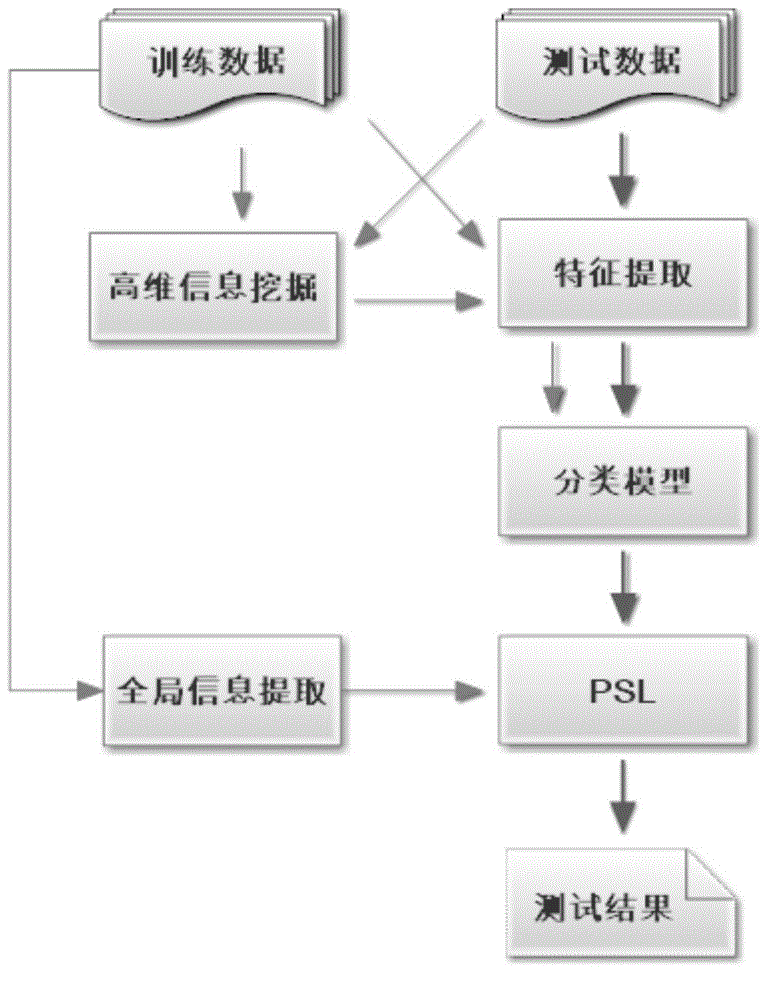
Event identification method and system based on probability soft logic PSL
ActiveCN104881399AAccurate clusteringAccurate and reliable event identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsRegular conditional probabilityConditional probability
The invention provides an event identification method and an event identification system based on probability soft logic PSL. The method comprises the following steps: calculating a conditional probability of at least a candidate and an event, and a candidate and a subject, an event and a subject appeared in at least a same file and / or a same sentence, and at least one of two different candidates or two different events; setting corresponding variables respectively for different conditional probabilities in a PSL model, designing a variable formula of the PSL model and iterating based on the variable formula of the PSL model, thereby maximizing the variables corresponding to the conditional probabilities of the candidates and the events, obtaining corresponding specific events of the candidates under the maximum conditions, and constructing an event identification model. The provided method can increase the accuracy in the event identification.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
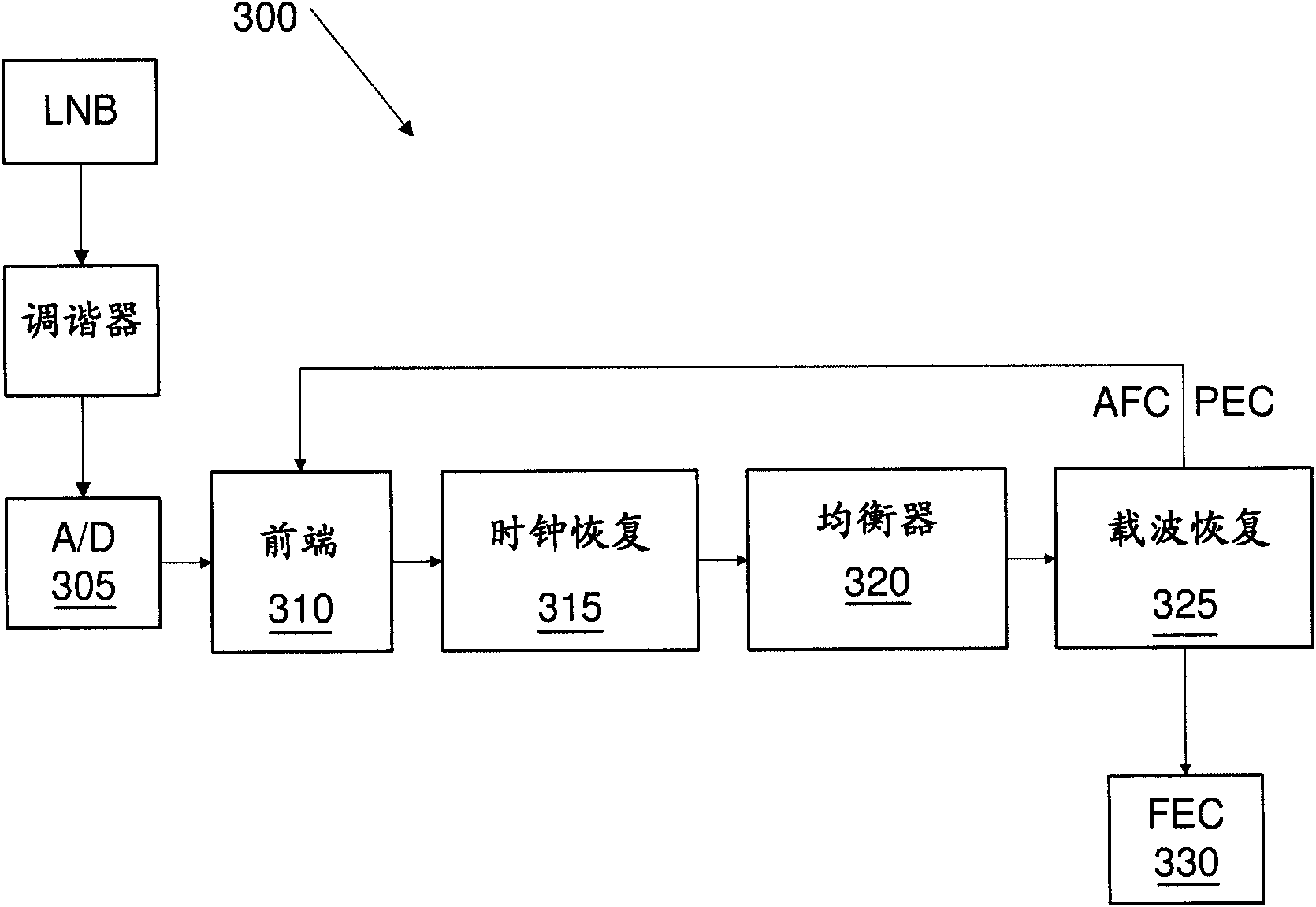
Phase error detection with conditional probabilities
InactiveCN101800717ACarrier regulationPhase-modulated carrier systemsRegular conditional probabilityConditional probability
Apparatuses, systems, and methods that employ conditional probabilities to calculate phase errors are disclosed. For a received signal, the embodiments may develop several phase error estimates relative to each point of a constellation, the number and location of points of the constellation depending on the modulation technique of the received signal. In addition to calculating the phase error estimates, the embodiments may also calculate weights, or probabilities, associated with each of the estimates. The embodiments may use the estimates and the weights to calculate a composite phase errorestimate. The composite phase error estimate may be used to correct the received signal and eliminate or reduce the impact of the phase error.
Owner:INTEL CORP
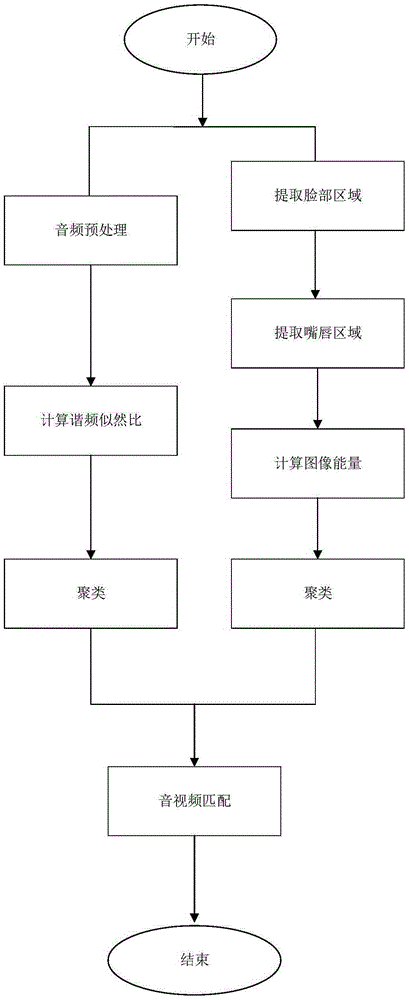
Media segment-based speaking detection method and system
ActiveCN105335755AHigh-precision detectionSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionHide markov modelRegular conditional probability
The invention provides a media segment-based speaking detection method and system. The media segment-based speaking detection method includes the following steps that: inputted media signals are divided into audio signals and video signals, and the audio signals and video signals are processed respectively, and as for the audio signals, the hidden Markov model is adopted to calculate per-second conditional probabilities based on the likelihood ratio of harmonic frequencies, and clustering is performed, and as for the video signals, a face region, a lip portion and the image energy of a lip region are extracted from each frame of image in the video signals of an inputted media file, and clustering is performed according to the image energy, and the hidden Markov model is adopted to calculate per-second conditional probabilities, and clustering is performed, and two clusters can be obtained; and clustering results of the audio signals are matched with clustering results of the video signals respectively, so that the final result of speaking detection can be obtained. According to the method and system of the invention, speaking detection is performed based on the audio and video information, and a detection rate can be improved.
Owner:博视联(苏州)信息科技有限公司
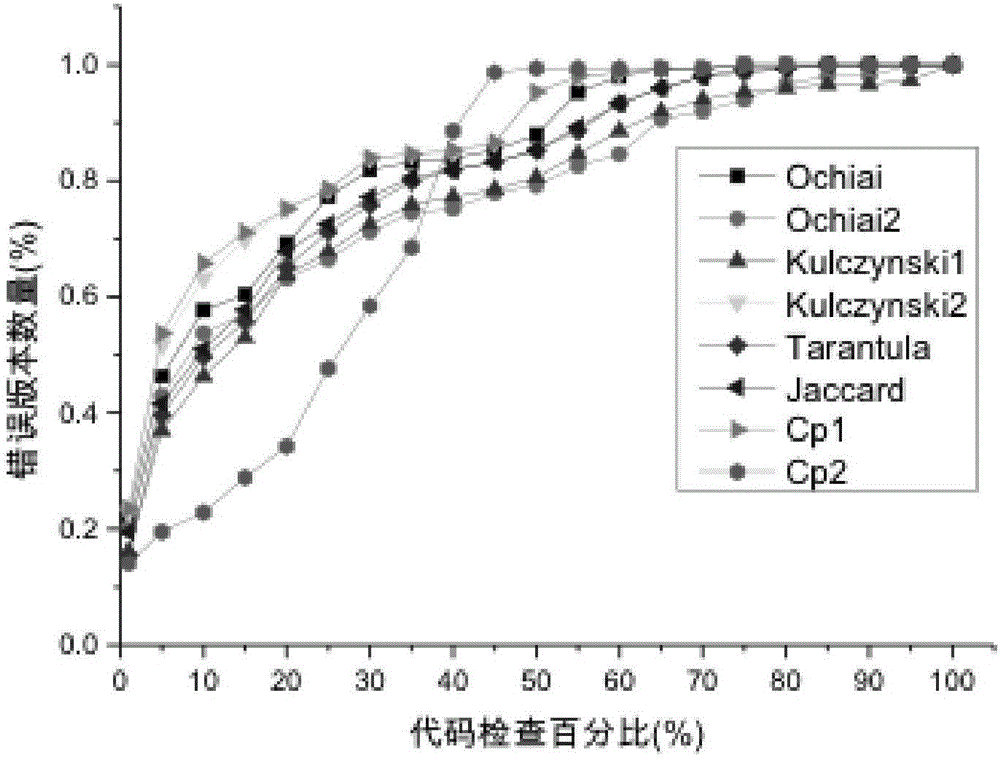
Method for program error location based on conditional probability
The invention discloses a method for program error location based on conditional probability. According to the method, by empirical research on inherent relevancy between a program frequency spectrum and execution results, conditional probability thought of statistics is introduced, and a P model for quantitative analysis on relationship strength evaluation of the program frequency spectrum and execution results is constructed. According to some classical SFL methods, a specific anomaly degree calculation formula is analyzed by means of the P model put forward, and thus essential reasons for defect location precision and efficiency difference are studied. In order to verify effectiveness of the method, in empirical research, 7 programs in a Siemens suite and a Space program are taken as standard evaluating objects, and test results indicate that compared with 13 existing classical defect location methods, the method has a better defect location effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
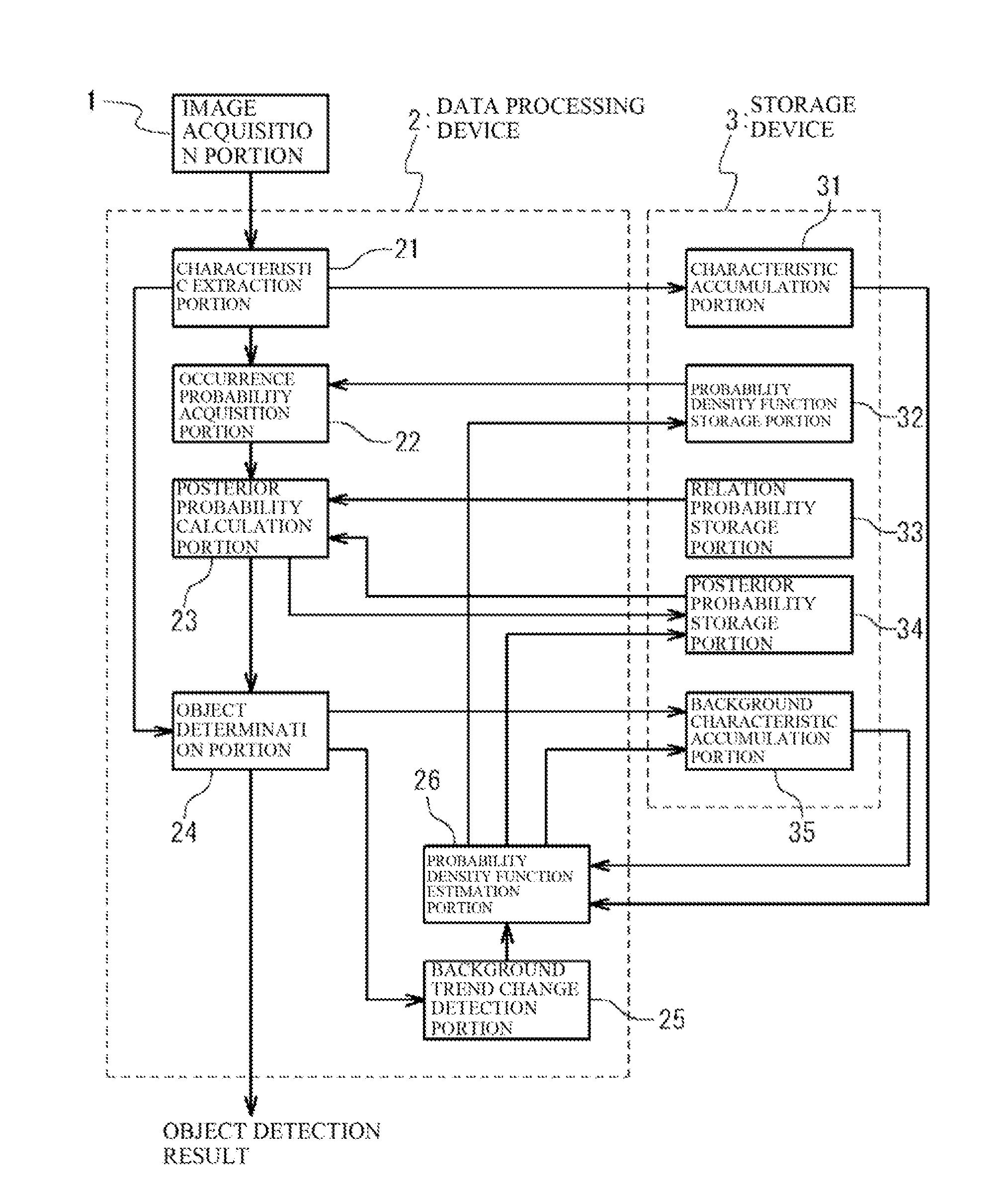
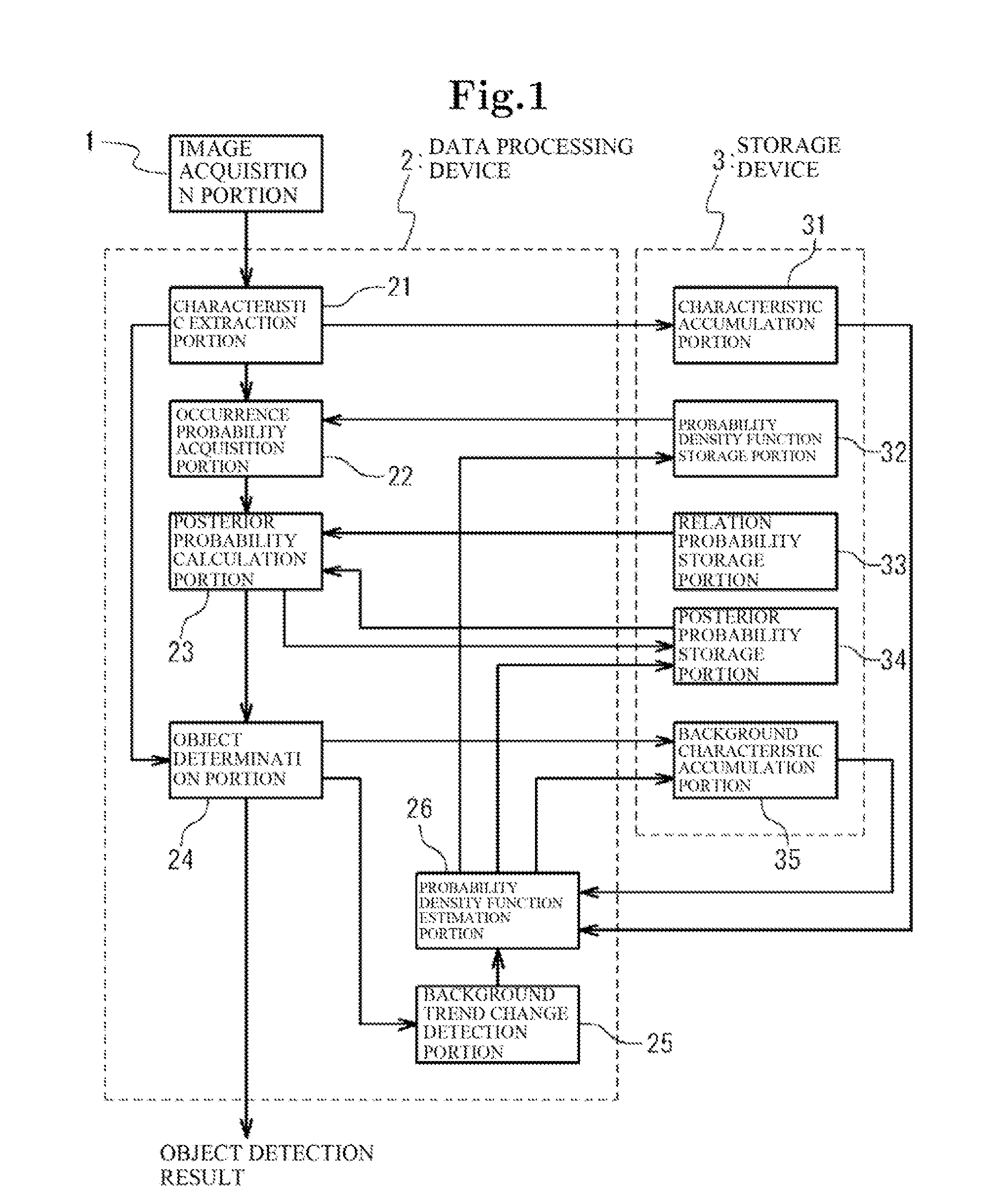
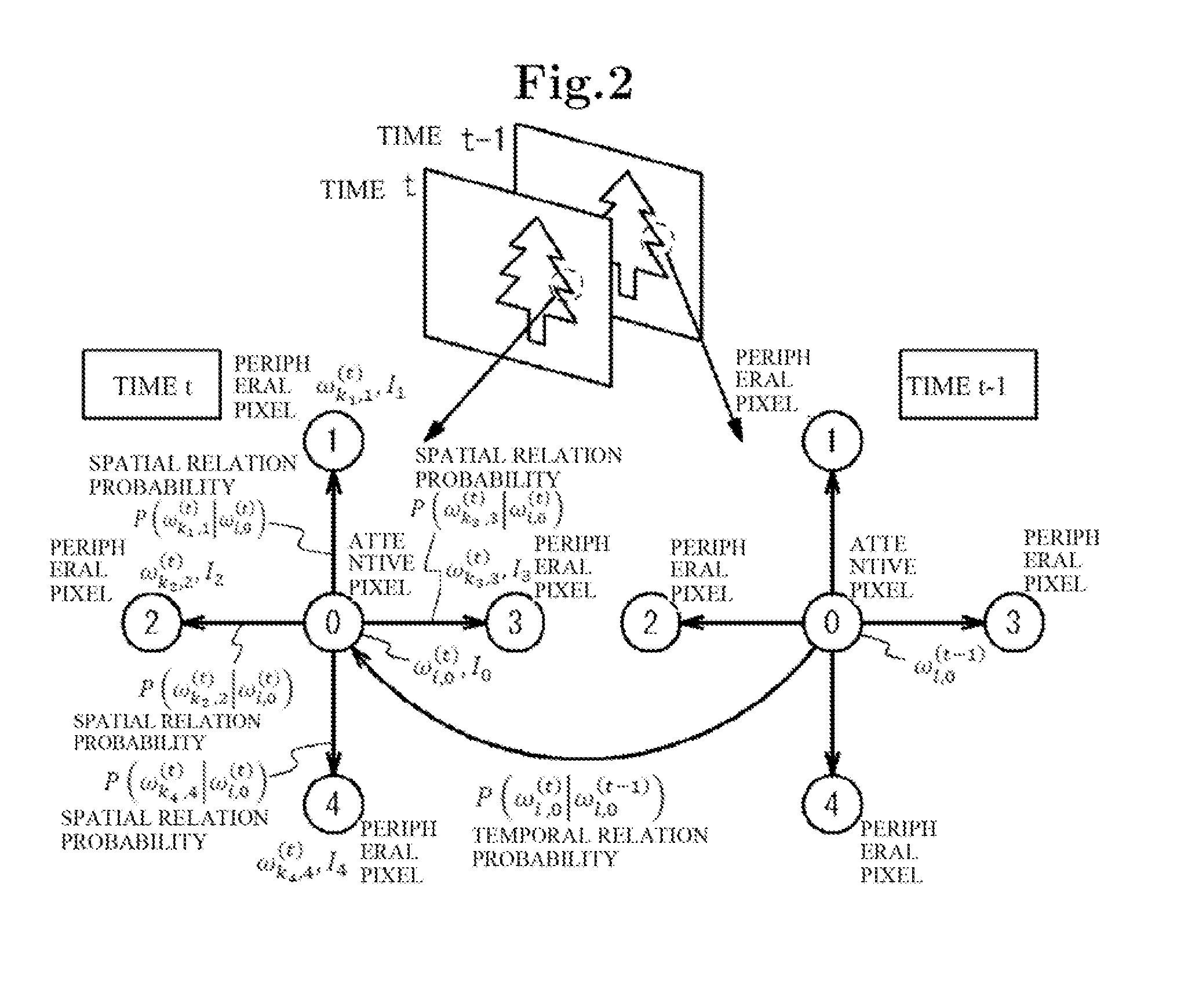
Object detection apparatus
ActiveUS8311281B2Avoid detectionAccurate detectionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionProbit modelRegular conditional probability
Owner:NEC CORP
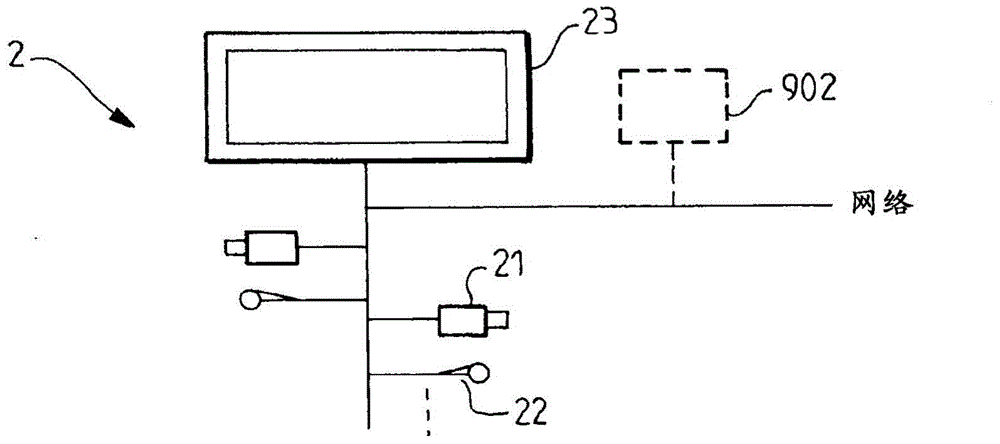
Video conference systems implementing orchestration models
InactiveCN104704813ATelevision conference systemsTwo-way working systemsHigh probabilityRegular conditional probability
A method for generating an output video stream in a video conference comprising receiving a plurality of input video streams of the video conference, Receiving a series of observation events (52, 53, 54), the observation corresponding to actions made by participants of the video conference, Providing a plurality of orchestration models each comprising a set of display states, Determining, for each of the orchestration models a probability of the series of observation events received, Selecting an orchestration model corresponding to the highest probability, Using the selected orchestration model to perform the steps of: o Selecting a display state (51, 40, 41, 42) as a candidate display state, o Determining a conditional probability of the candidate display state for the received series of observation events o Determining the candidate display state providing the highest conditional probability as an updated display state, o Generating a video stream comprising the current display state and the updated display state.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
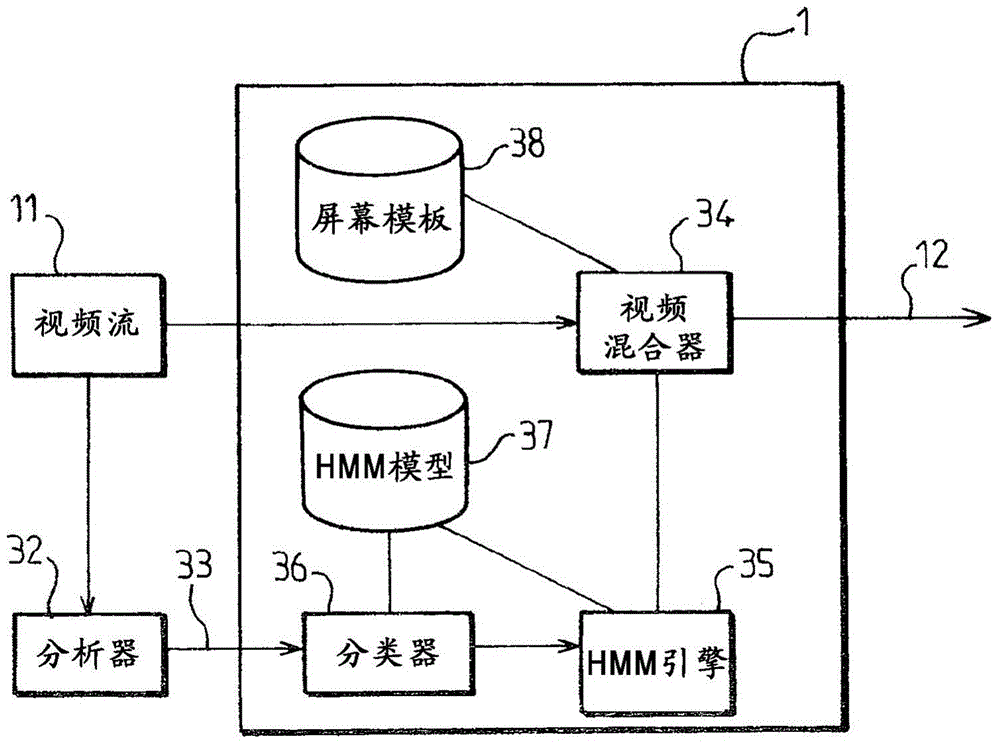
Network analysis system
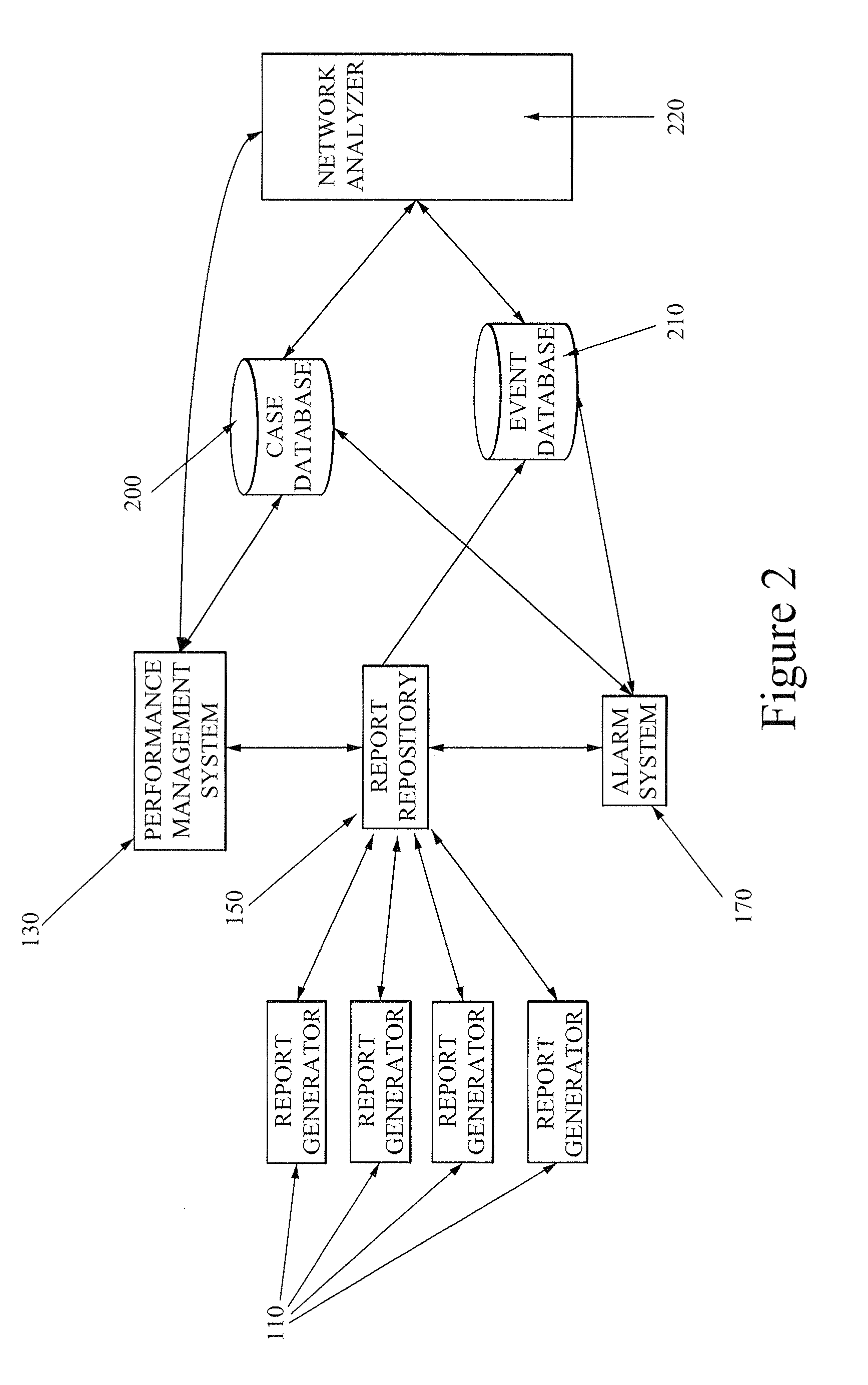
ActiveUS8918345B2Digital computer detailsData switching networksRegular conditional probabilityNetwork data
The present invention provides a method of operating a network comprising the steps of: analyzing a first datastore comprising data representing historical network performance; creating or more indices within the first datastore; creating one or more probability networks in accordance with one or more of the created indices; determining from the one or more probability networks a conditional probability associated with an alarm event; and' if the conditional probability determined is less than a threshold value, disregarding the associated alarm event; or if the conditional probability determined is greater than a threshold value, using the associated alarm event in conjunction with other historical network data to predict future alarm events.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Bayesian network-based logic alarm root analysis method and system
ActiveCN110176132AEliminate negative effectsDetect incompletenessMathematical modelsAlarmsAlarm stateRegular conditional probability
The invention discloses a Bayesian network-based logic alarm root analysis method and system, wherein an alarm state and a non-alarm state are respectively represented by binary system 1 and binary system 0. The method comprises the following steps: when the root analysis is performed online, updating the Bayesian network probability parameter set from an observation sample in a recursive mode, and estimating the probability parameter set by adopting a maximum value function; and updating the posterior probability in an online manner according to a Bayesian calculation rule and a chain rule, expressing the posterior conditional probability in a vector form and arranging the posterior conditional probability in a descending order when an alarm occurs, and determining a root cause accordingto the position of the maximum posterior probability. According to the method, the influence of random noise is reduced by a Bayesian network logic analysis method, and the correctness of root analysis is ensured; and multiple coexisting root causes can be analyzed, and the concern only for the root cause that occurs initially is avoided.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Frequency modulation capacity time-sharing optimization method based on conditional probability
ActiveCN110247406AEasy to adjustFrequency stabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionLearning machineRegular conditional probability
The invention provides a frequency modulation capacity time-sharing optimization method based on conditional probability, and belongs to the field of power system automatic power generation control of. The method comprises the steps of firstly collecting the historical data of an AGC control area, and screening a sample composed of the historical data according to an AGC assessment period; constructing and training an extreme learning machine model predicted by a net load standard deviation section to obtain a trained extreme learning machine model; in an application phase, outputting, by the trained extreme learning machine model, the net load standard deviation section predicted values corresponding to the respective time periods on a certain day in the future, and according to the screened data of each AGC assessment period, calculating frequency modulation performance standard-reaching probabilities corresponding to the up-regulation capacity and the down-regulation capacity of the prediction time period, and obtaining the up-regulation reserve capacity optimization result and the down-regulation capacity reserve capacity optimization result of this time period. The method can correct the calculation result of a frequency modulation capacity demand according to a frequency modulation score, and the obtained result can truly reflect the frequency modulation capacity demand of a power system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
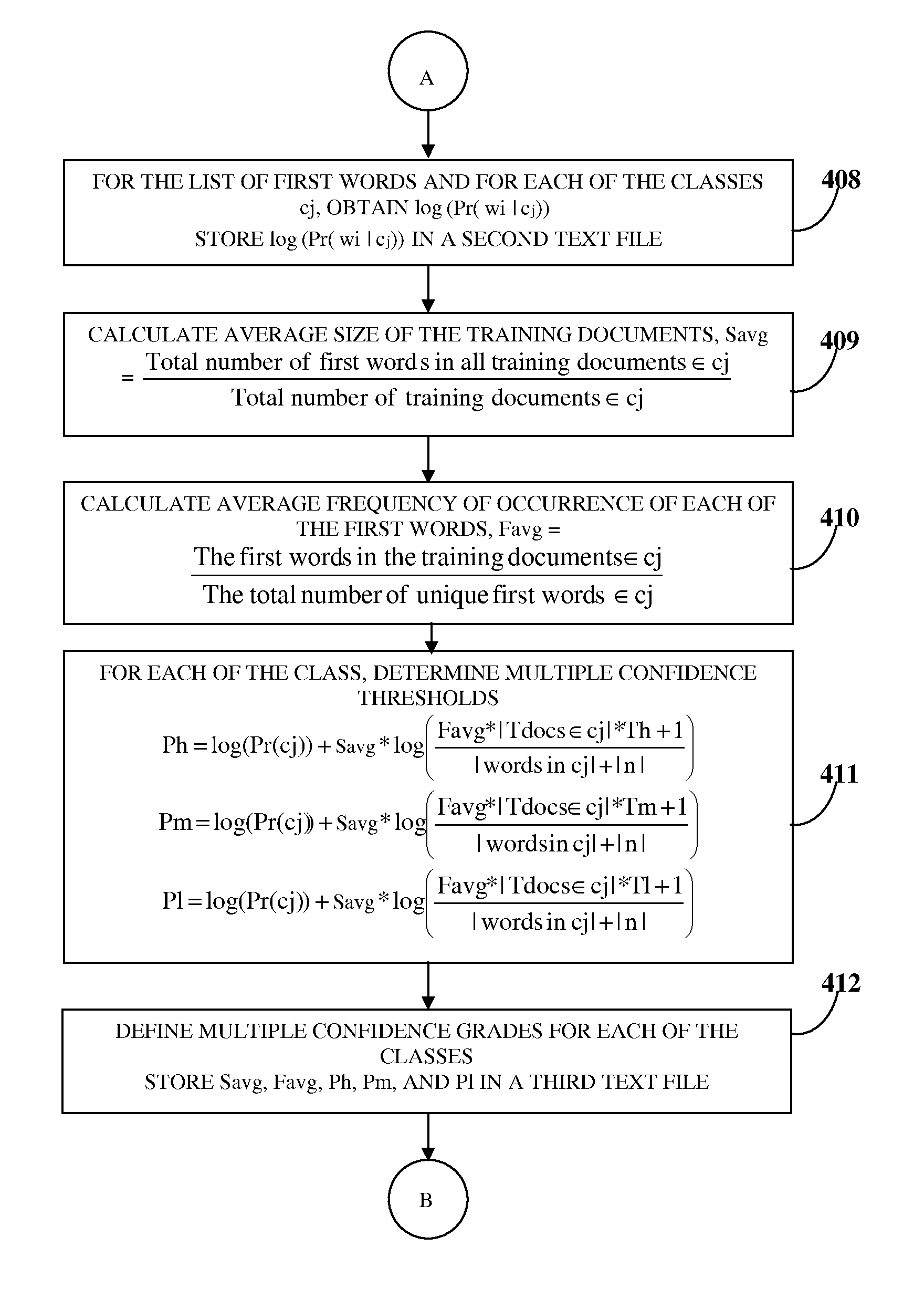
Text classification with confidence grading
InactiveUS8650136B2Digital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionText categorization
Owner:KETERA TECH INC
Intelligent prediction method for warehouse management data
InactiveCN107918809AEnsure sufficientForecastingLogisticsPredictive methodsRegular conditional probability
The invention relates to an intelligent prediction method for warehouse management data. Classification algorithm prediction is performed through a Naive Bayes theorem. A calculation formula is as follows: P(H / X)=P(X / H)P(H) / P(X), wherein P(X / H) represents an occurrence probability of an event X on the premise that an event H occurs already, and is called as a conditional probability of the event Xunder the condition that the event H occurs. A basic solving formula is as follows: P(X / H)=P(XH) / P(H). Naive Bayes classification algorithm prediction can predict a status of each material, and comprises a process of comparing a probability of borrowing the materials by teachers with a probability of not borrowing the materials by the teachers to obtain a probability of borrowing the materials next time; and the probability of borrowing each material by each teacher is predicted, so that the materials are supplemented in advance.
Owner:LIAOCHENG VOCATIONAL & TECHN COLLEGE
Phase error detection with conditional probabilities
InactiveCN101800717BCarrier regulationRadio transmissionRegular conditional probabilityConditional probability
Apparatuses, systems, and methods that employ conditional probabilities to calculate phase errors are disclosed. For a received signal, the embodiments may develop several phase error estimates relative to each point of a constellation, the number and location of points of the constellation depending on the modulation technique of the received signal. In addition to calculating the phase error estimates, the embodiments may also calculate weights, or probabilities, associated with each of the estimates. The embodiments may use the estimates and the weights to calculate a composite phase error estimate. The composite phase error estimate may be used to correct the received signal and eliminate or reduce the impact of the phase error.
Owner:INTEL CORP
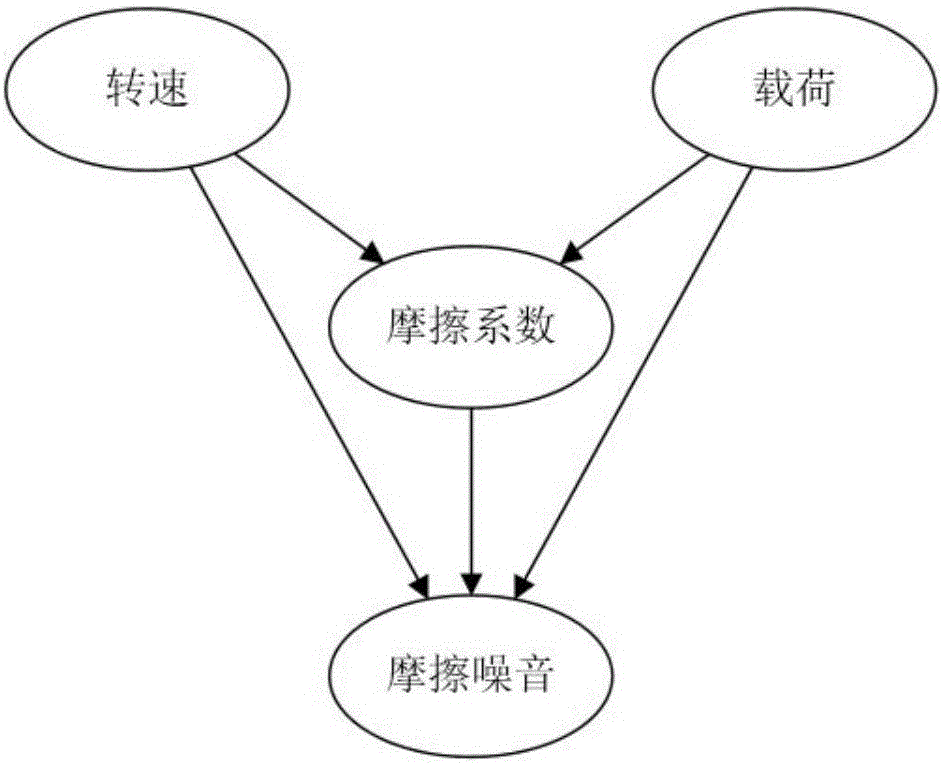
Friction noise prediction method based on Bayesian network
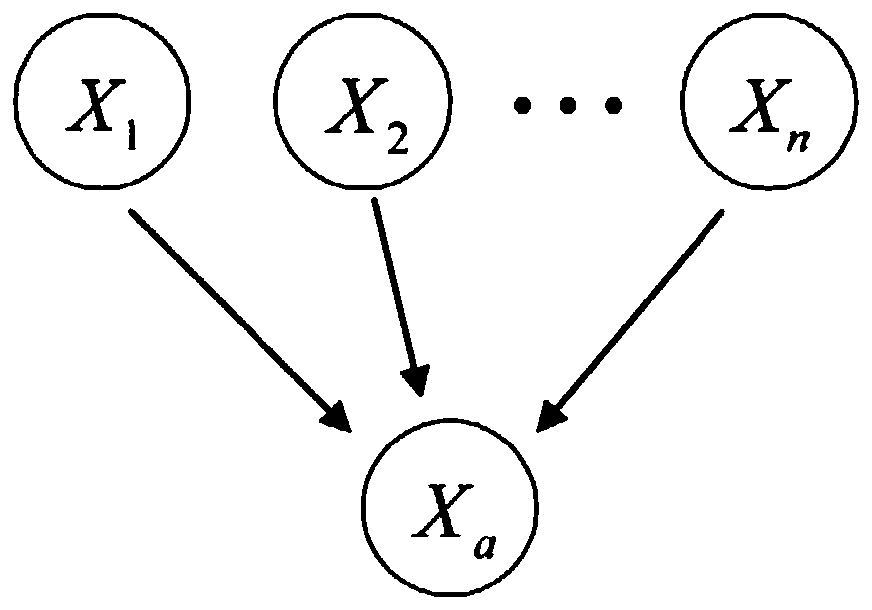
ActiveCN106407675AImprove forecast accuracyImprove reliabilityMathematical modelsSpecial data processing applicationsNODALRelationship - Father
The invention provides a friction noise prediction method based on a Bayesian network. The friction noise prediction method comprises the following steps of 1, obtaining friction noise and a data sample which is associated with the friction noise; 2, performing discretization processing on the data sample obtained in the step 1; 3, performing Bayesian network learning, and establishing a Bayesian network structure chart; 4, updating conditional probability, under a corresponding father node, of each node in the Bayesian network structure chart according to a data sample set; and 5, performing prediction on the frequency and intensity of the friction noise according to the conditional probability obtained in the step 4. The friction noise prediction based on the Bayesian network, by virtue of organic combination of a directed acyclic graph and a probability theory, intuitively expresses joint probability among random variables, so that the friction noise prediction can be carried out by only processing the measured data without considering complex appearance of a sound source and various occurrence mechanisms; and therefore, the friction noise prediction method has relatively high prediction accuracy and reliability and is quite simple, convenient and quick.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
A satellite Bayesian network health determination method based on ground test data
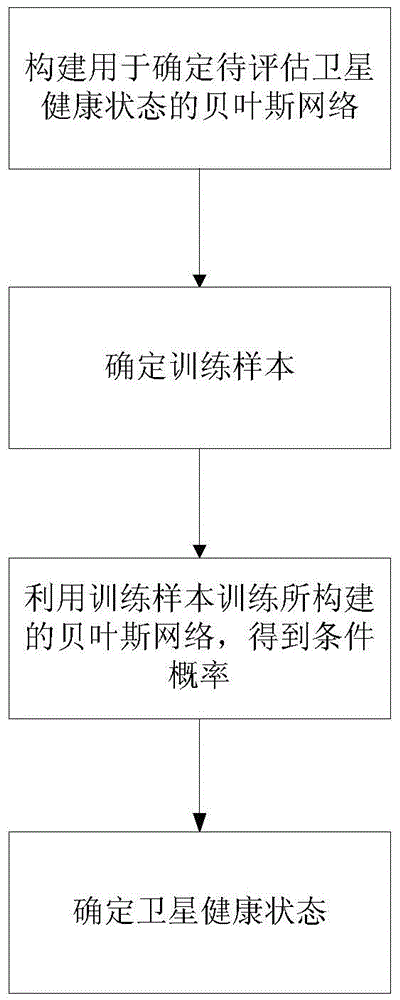
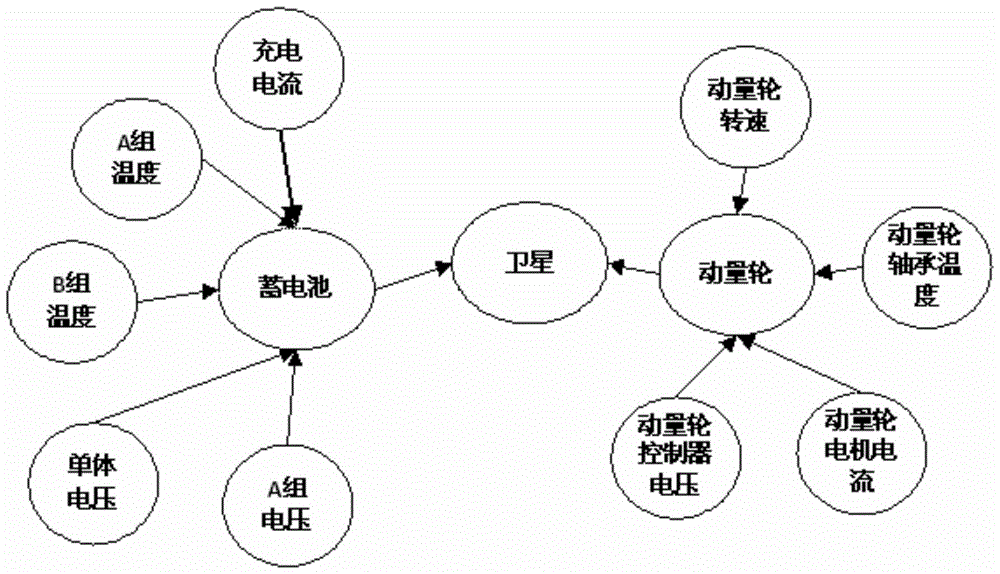
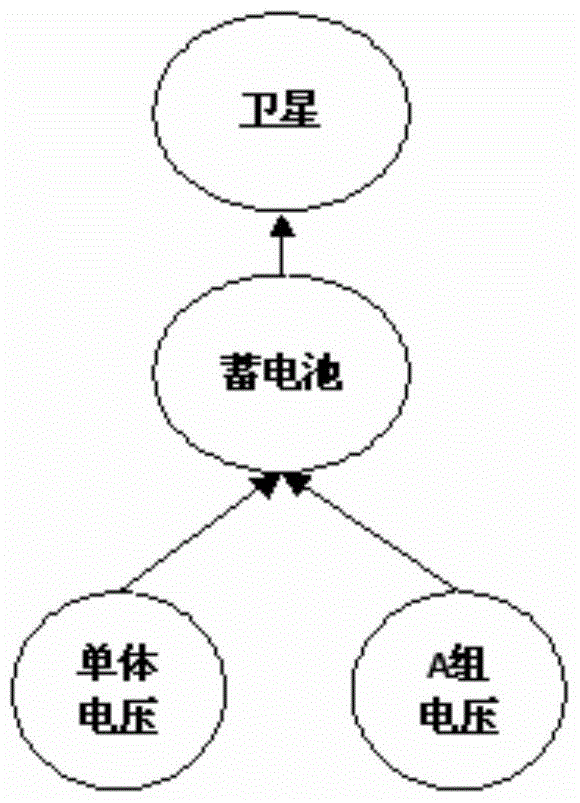
ActiveCN103678886BTrue health statusSure to achieve exactlySpecial data processing applicationsRegular conditional probabilityQuantitative determination
The invention discloses a satellite Bayesian Network health determination method based on ground test data and provides a satellite health status comprehensive and quantitative determination method based on ground test data. From the prospective of historical data, probabilities between a satellite and related parameters as well as between the satellite and onboard equipment are mined; features of data under actual conditions are fully embodied; implicit association between parameters and system health level are mined through multi-parameter conditional probabilities; the system health level is truly indicated. The health status of the satellite during a test phase can be estimated accurately, unified health level of the satellite is quantitated from multi-index telemetry parameters, and the effective method is provided for ground test and analysis of the satellite.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
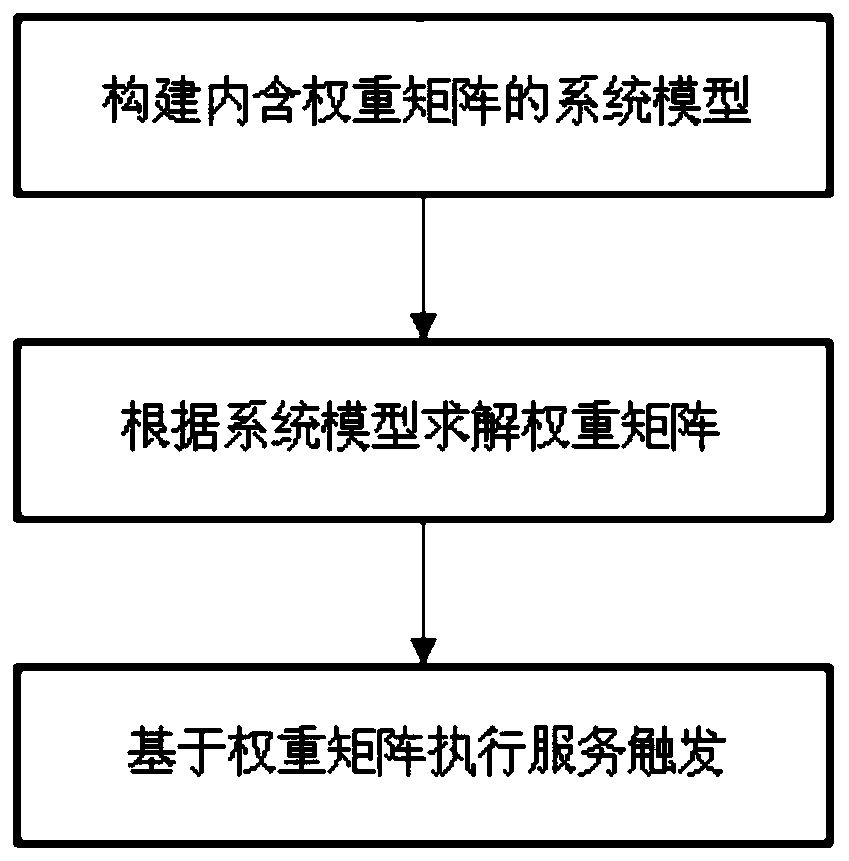
Load balancing method and system for heterogeneous multi-application server system
InactiveCN110519347ALoad balancingData switching networksApplication serverRegular conditional probability
The invention discloses a load balancing method for a heterogeneous multi-application server system. The load balancing method comprises the following steps: constructing a system model containing a weight matrix, wherein elements in the weight matrix are conditional probabilities of triggering a certain AS by a certain service; solving a weight matrix according to the system model; and executingservice triggering based on the weight matrix. The invention further discloses a corresponding system. According to the method, the weight matrix is solved through the system model, elements in the weight matrix are conditional probabilities for triggering the AS, service triggering is executed based on the weight matrix, and load balancing of the system is achieved.
Owner:NARI INFORMATION & COMM TECH +2
MAC layer cooperative power allocation method
The invention discloses an MAC layer cooperative power allocation method, belonging to the field of MAC layer cooperative communication. In the case that the conditional probability is limited, the scheme of the invention performs optimized allocation on the transmission power of a source node and a relay node, and the power consumption of the system can be further reduced. From the perspective ofthe quality of network services, that is, when the outage probability is limited, an optimal total power allocation scheme is provided in consideration of the cooperation failure in actual cooperation, that is, in the case that no suitable relay node exists. The scheme of the invention is beneficial to extending the lifetime of the nodes on the basis of ensuring the required QoS.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Automated adaptive method for identity verification with performance guarantees
InactiveUS7730520B2Digital data processing detailsSpeech analysisRegular conditional probabilityConditional probability
This invention provides an automated adaptive method for identity verification of claimants that attempt to get access into a resource by responding to a sequence of identifiers. The sequence has a specified maximal length and the identifiers are partitioned into multiple groups where identifiers in the same group are correlated and identifiers in different groups are not correlated. The method guarantees that an impostor will be accepted with a probability that does not exceed a specified parameter and that a legitimate claimant will be rejected with a probability that does not exceed a different specified parameter. The method also computes the probabilities that a legitimate claimant, or an impostor, will terminate an interrogation session with an inconclusive result, which would necessitate further manual interrogation. The method is adaptive as the conditional probabilities of an impostor's responses change throughout a session of interrogation.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
A stereo matching method and system
The invention discloses a stereo matching method, which includes: extracting feature points of the left and right images, and performing feature point matching on the feature points to determine the support points; constructing a Delaunay triangle according to the support points; wherein, the Delaunay triangle includes the disparity of all pixel points in the triangle Prior probability and the minimum support distance between pixels and support points; use the disparity calculation method to calculate the disparity conditional probability and disparity confidence level of the pixels in the left image; according to the Delaunay triangle, disparity conditional probability and disparity confidence level, use Bayesian principle The optimal posterior disparity is obtained through calculation; the method realizes rapid matching to obtain a high-precision disparity map, and is especially suitable for mobile platforms or application fields with high real-time requirements; the invention also discloses a stereo matching system, which has the above beneficial effects.
Owner:CHENGDU TOPPLUSVISION TECH CO LTD
Multi-target tracking method and system based on behavior learning
The invention provides a multi-target tracking method and system based on behavior learning. The method comprises steps of: acquiring and detecting a target video sequence, and acquiring the size and the positional information of a tracked target candidate frame depending on a detection result; modeling a multi-target real-time tracking problem and creating a production probability model of the multi-target real-time tracking problem; for the global conditional probability items in the production probability model, performing offline training on a correctly-marked training set in order to perform global behavior prediction applicable to various scenarios, and for local conditional probability items in the production probability model, on-line training local behavior prediction for each target in real time by using the tracking data of the target prior to a current frame; obtaining the behavior prediction of the target in combination with the global behavior prediction and the local behavior prediction, and tracking the multiple targets depending on the predicted target behavior. The method and the system may keep a tracking rate while tracking the multiple targets and may significantly reduce a tracking error rate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
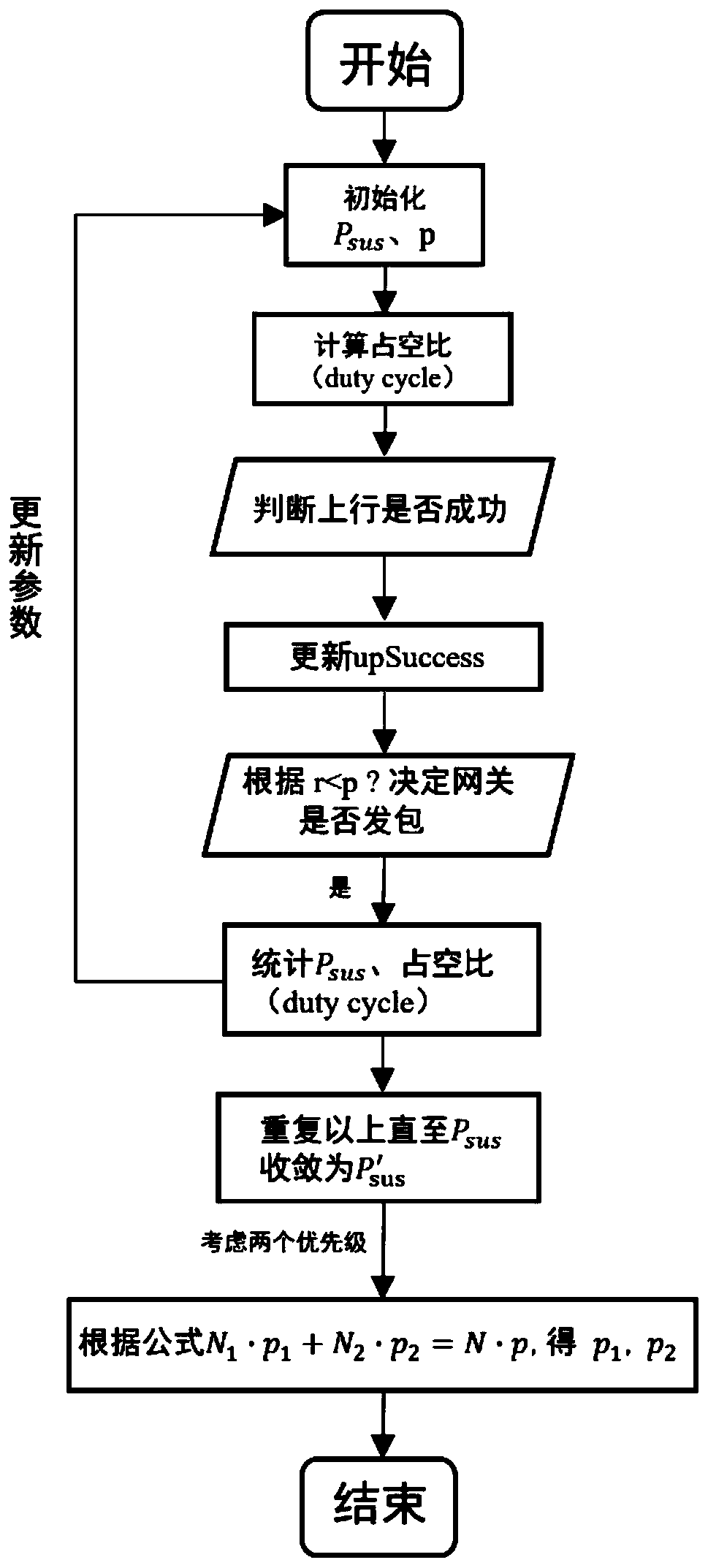
Method for realizing LoRa gateway downlink specific duty ratio based on conditional probability
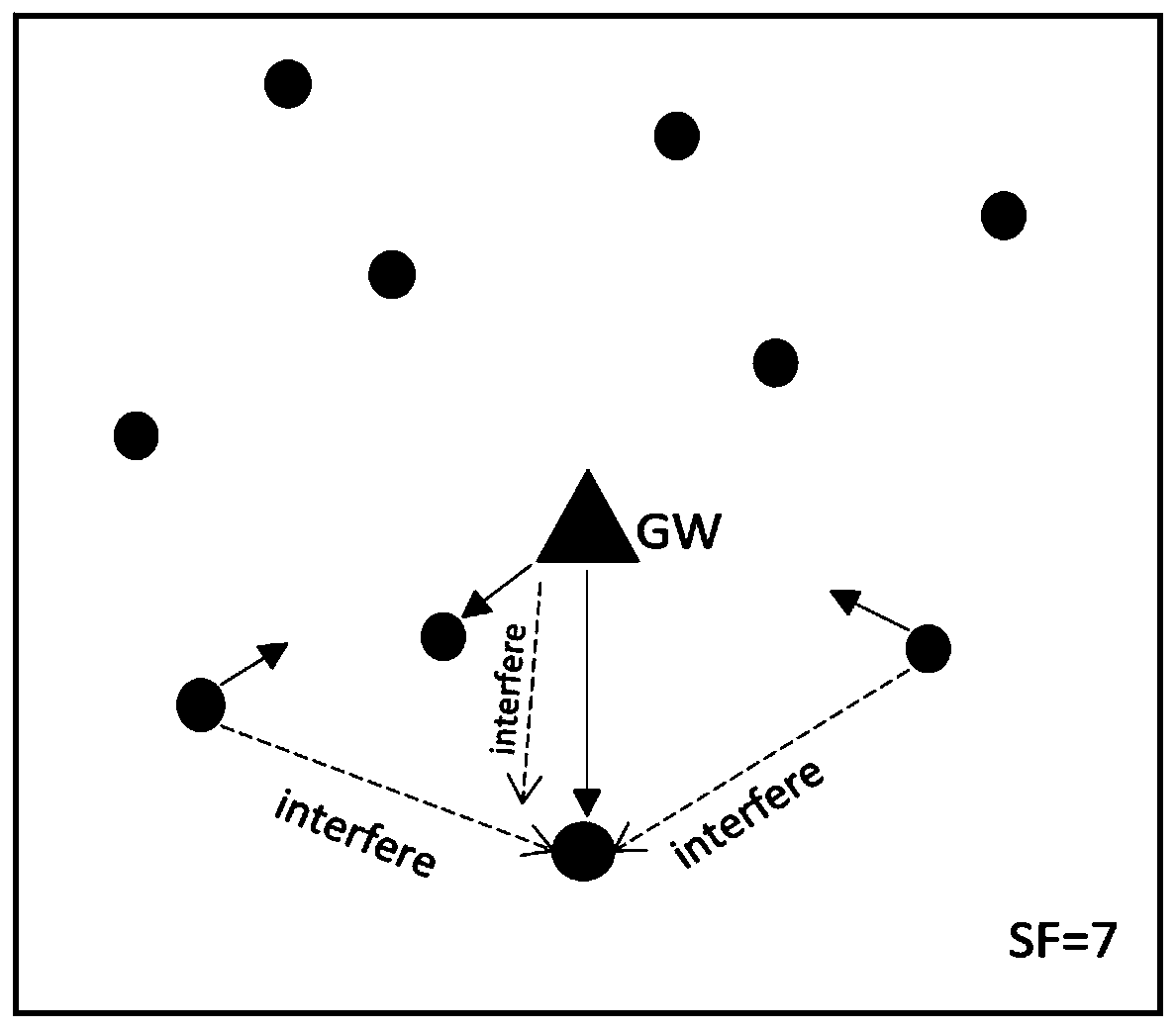
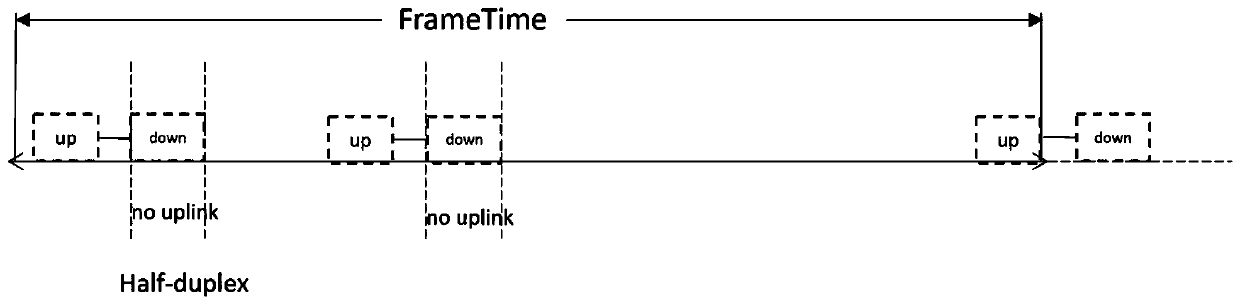
ActiveCN110392384ASolving Complex Coupling ProblemsMeet duty cycle requirementsHigh level techniquesMachine-to-machine/machine-type communication serviceRegular conditional probabilityThe Internet
The invention discloses a method for realizing a specific downlink duty ratio of a LoRa gateway based on conditional probability, and relates to LoRa of a low-power wide area network of the Internet of Things. The method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining a saturation duty ratio according to initialization parameters; 2) judging whether the terminal actual uplink is successful or not, andif so, adding 1 to the uplink count; 3) judging whether the downlink of the gateway meets the probability p or not; 4) judging whether the gateway downlink is successful or not; 5) updating an uplinksuccess probability Psus and a duty ratio according to an actual system simulation result, and adjusting a probability p to obtain a desired duty ratio requirement; (6) repeating the steps (1)-(5) until the Psus converges to a certain stable value Ps'us; and (7) if the priority is not considered, determining that the probability p obtained in the step (6) is the final downlink transmission probability of the gateway, and if the priority is considered, obtaining data from terminals with different priorities in combination with the priority relationship of the users and the number of the users,and obtaining the conditional probability of downlink transmission of the gateway to each group of users, namely, obtaining the final downlink transmission probability of the gateway of each terminal.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com