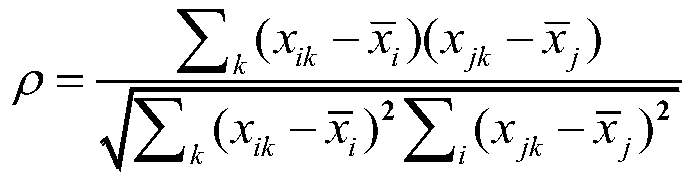Patents
Literature
37 results about "Semi automatic segmentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semi-automatic segmentation algorithm for pet oncology images
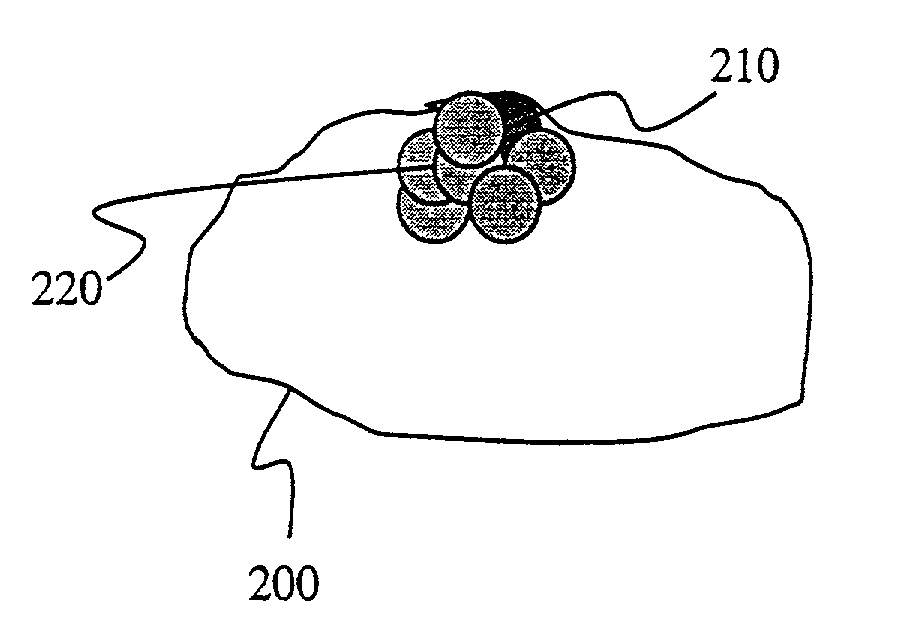
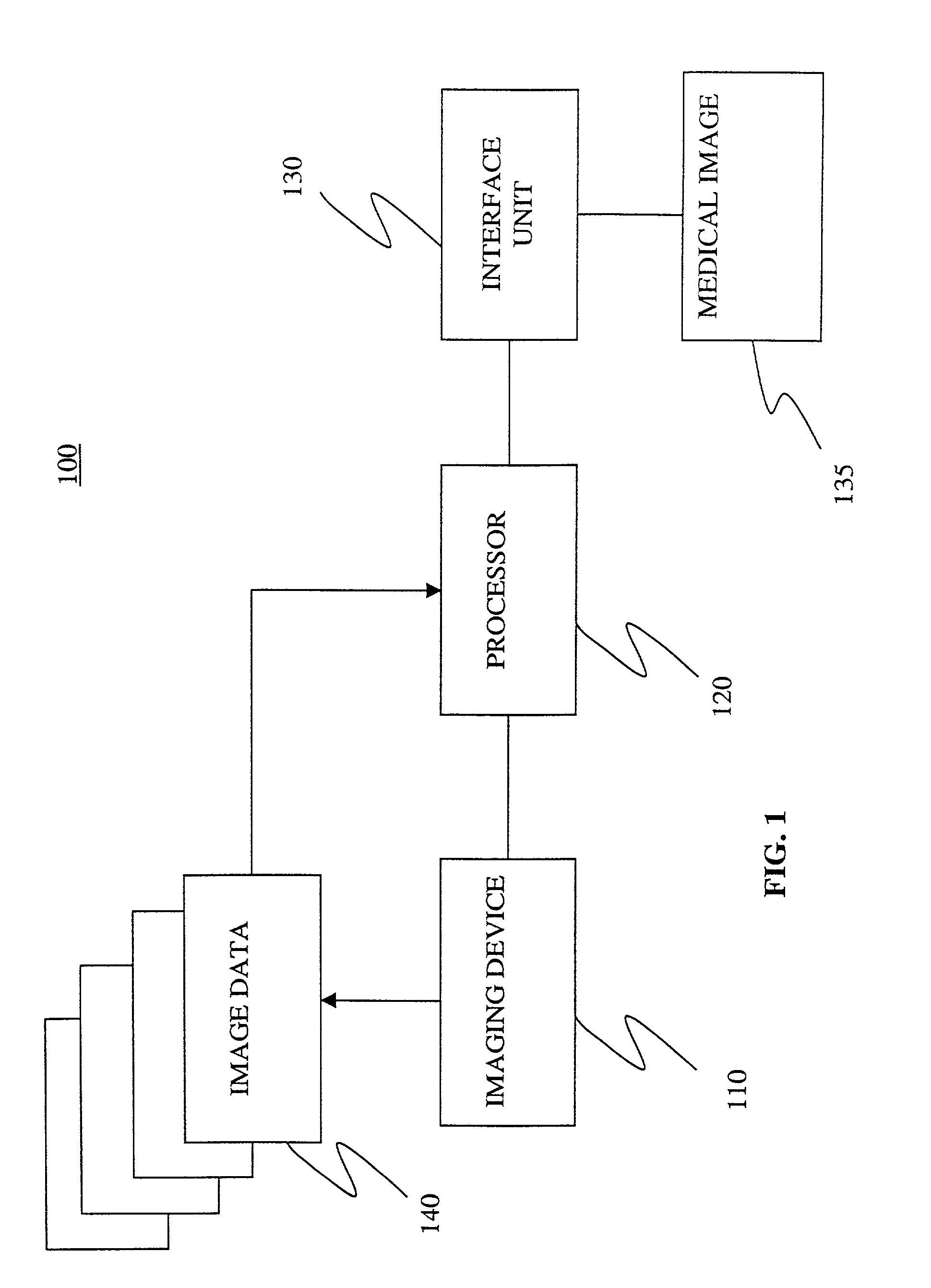
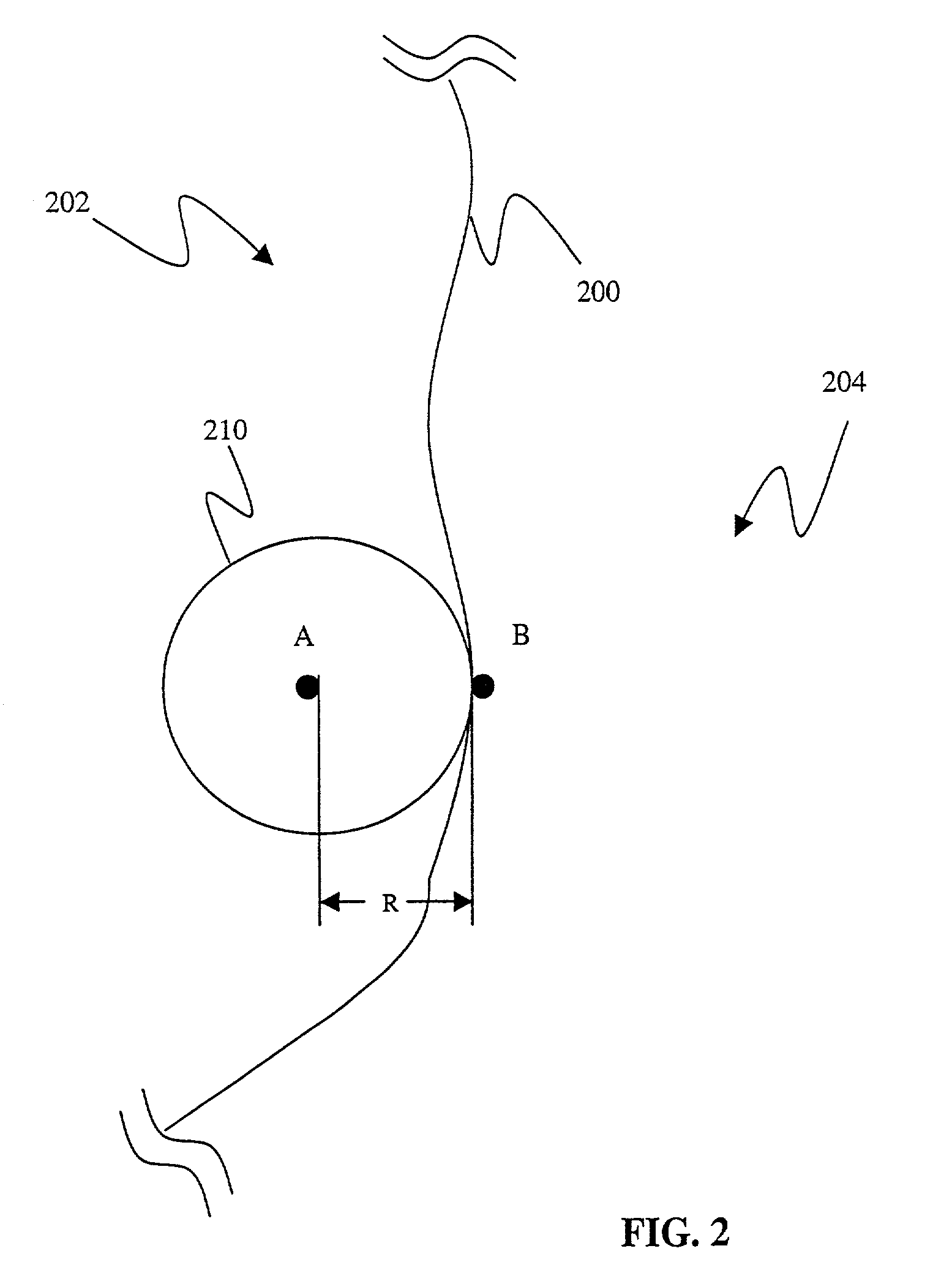
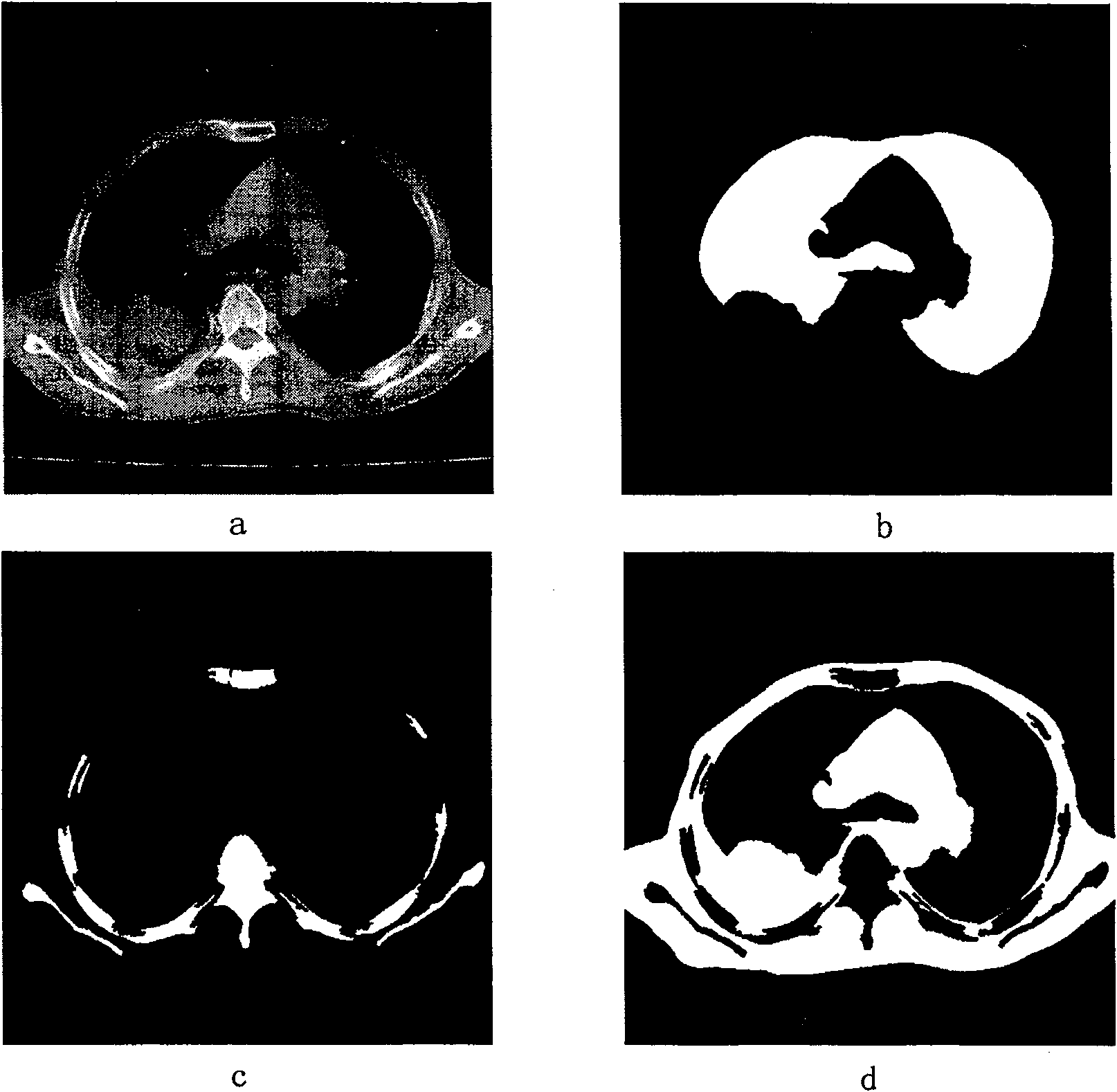
An apparatus and method for segmenting three-dimensional (3D) medical images containing a region of interest is provided that identifies a first set of seed points within the region of interest and a second set of seed points outside the region of interest. A first sphere is constructed within the region of interest. Voxels contained within the medical image are classified using a spatial constrained fuzzy clustering algorithm. A plurality of second spheres is generated. Ones of the plurality of second spheres are accepted that satisfy the homogeneity function threshold as defined by the spatial constricted fuzzy clustering algorithm. A three-dimensional area is grown that defines the region of interest. The region of interest defined by the three-dimensional area is displayed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
A semi-automatic sequential image segmentation method and system
InactiveCN102289811ASegmentation is fast and accurateImage analysisPattern recognitionSemi automatic
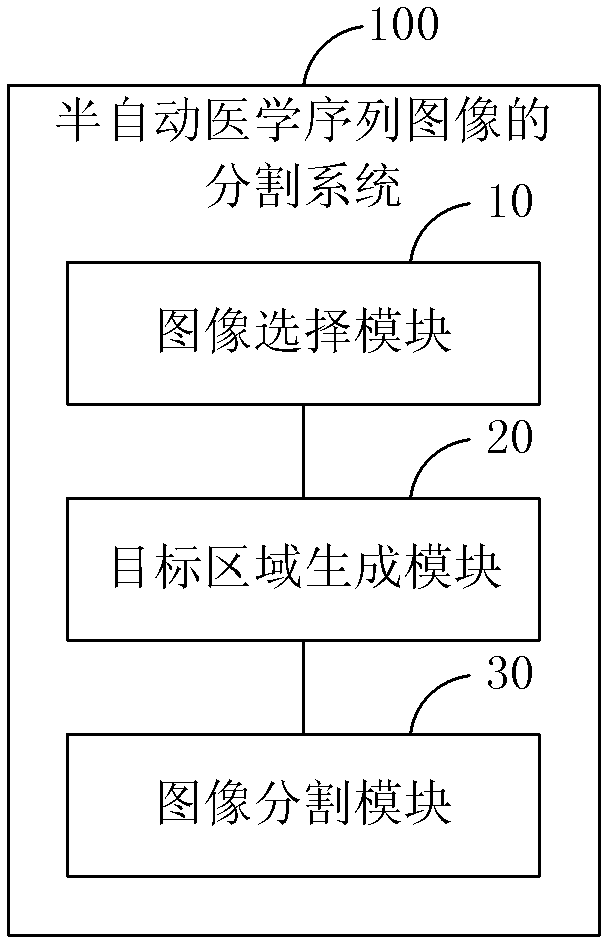
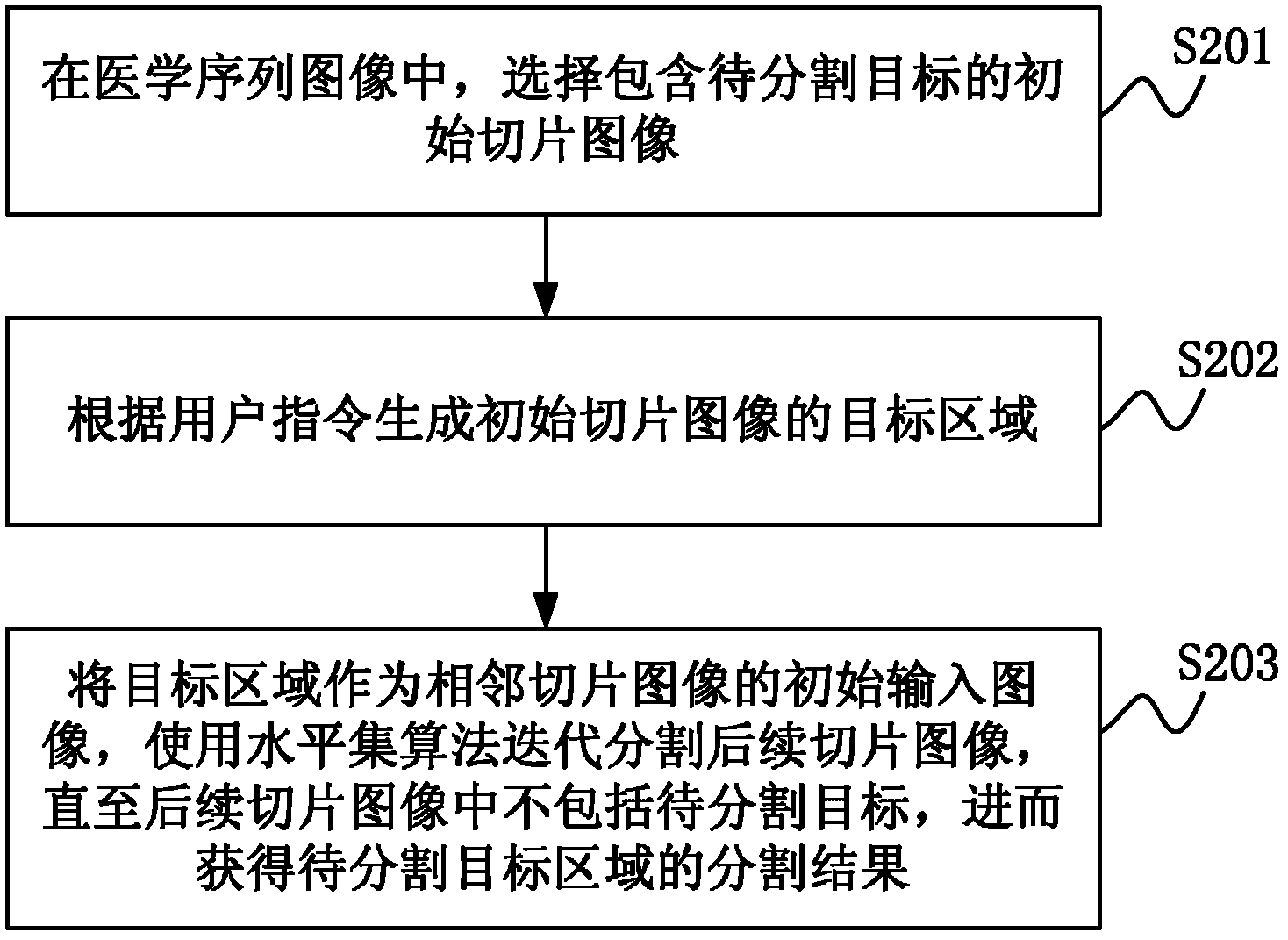
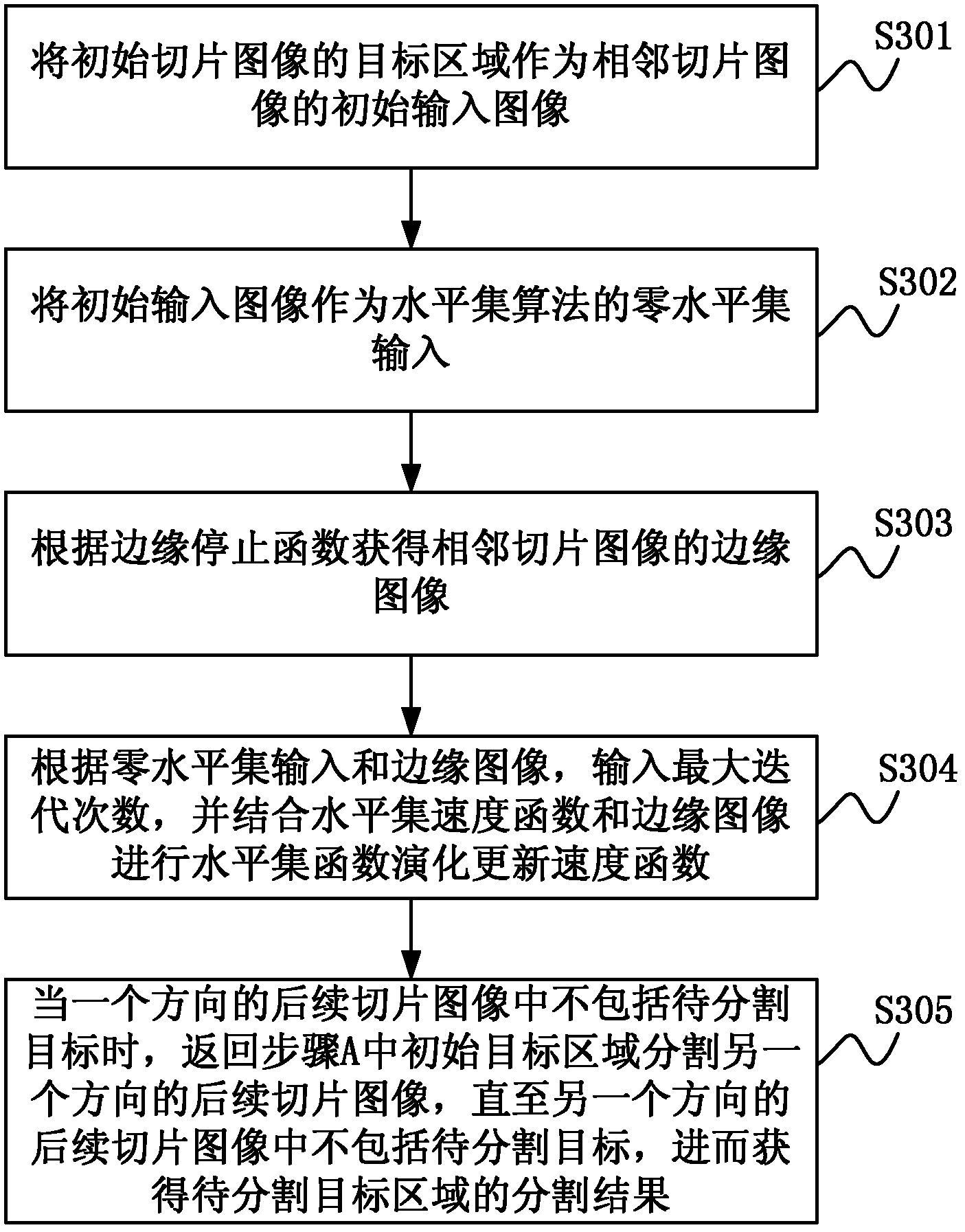
The invention discloses a semi-automatic medical sequence image segmentation method and system. The segmentation method includes the steps of: selecting an initial slice image containing a target to be segmented in the medical sequence image; generating the initial slice image according to user instructions. Target area: using the target area as the initial input image of the adjacent slice image, using the level set algorithm to iteratively segment the subsequent slice image until the subsequent slice image does not include the target to be segmented, and then obtain the segmentation result of the target area to be segmented . Thereby, the present invention can quickly and accurately segment the target region to be segmented in the medical sequence images.
Owner:SHENZHEN YORATAL DMIT
Method and apparatus for semi-automatic segmentation technique for low-contrast tubular shaped objects
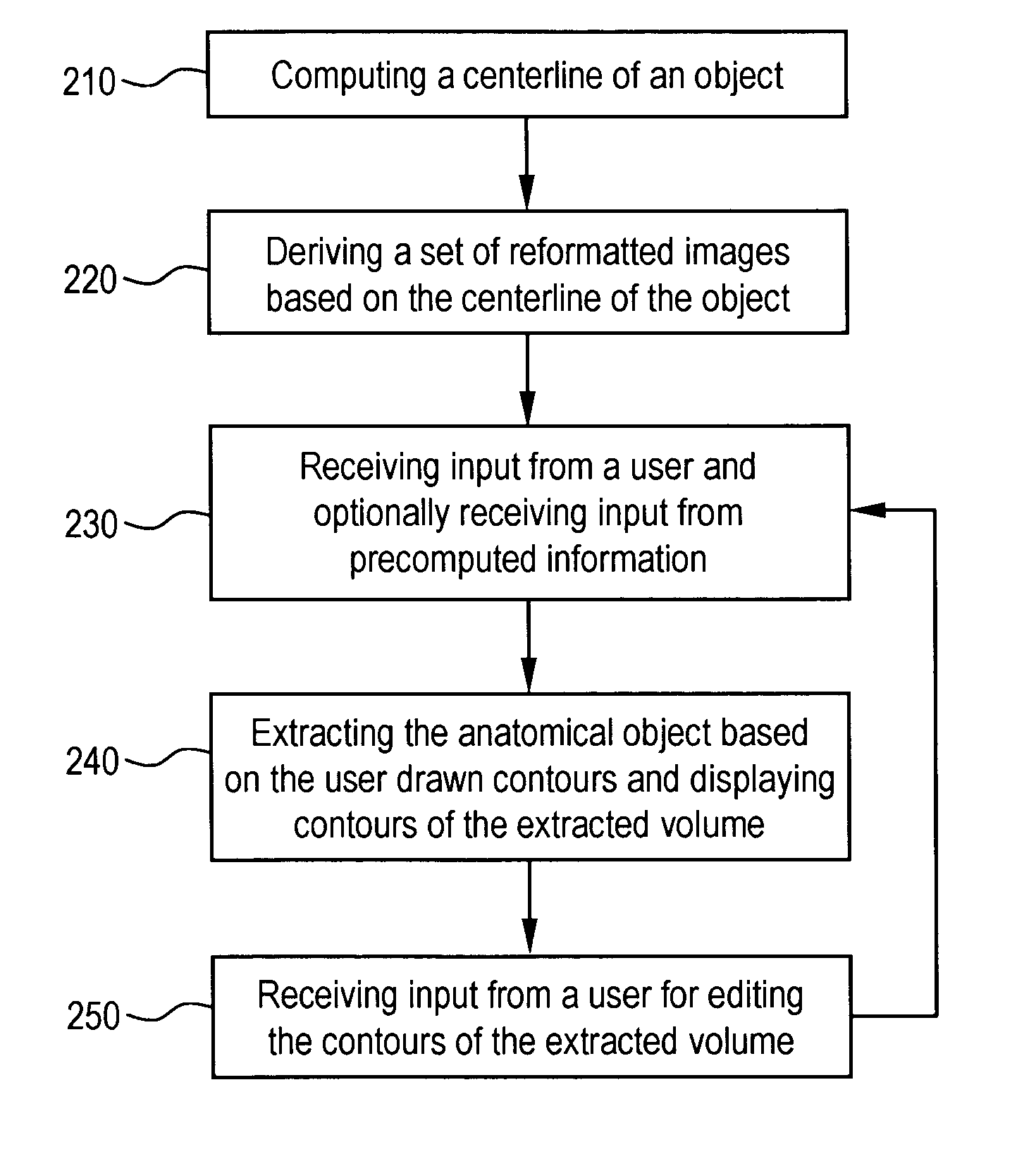
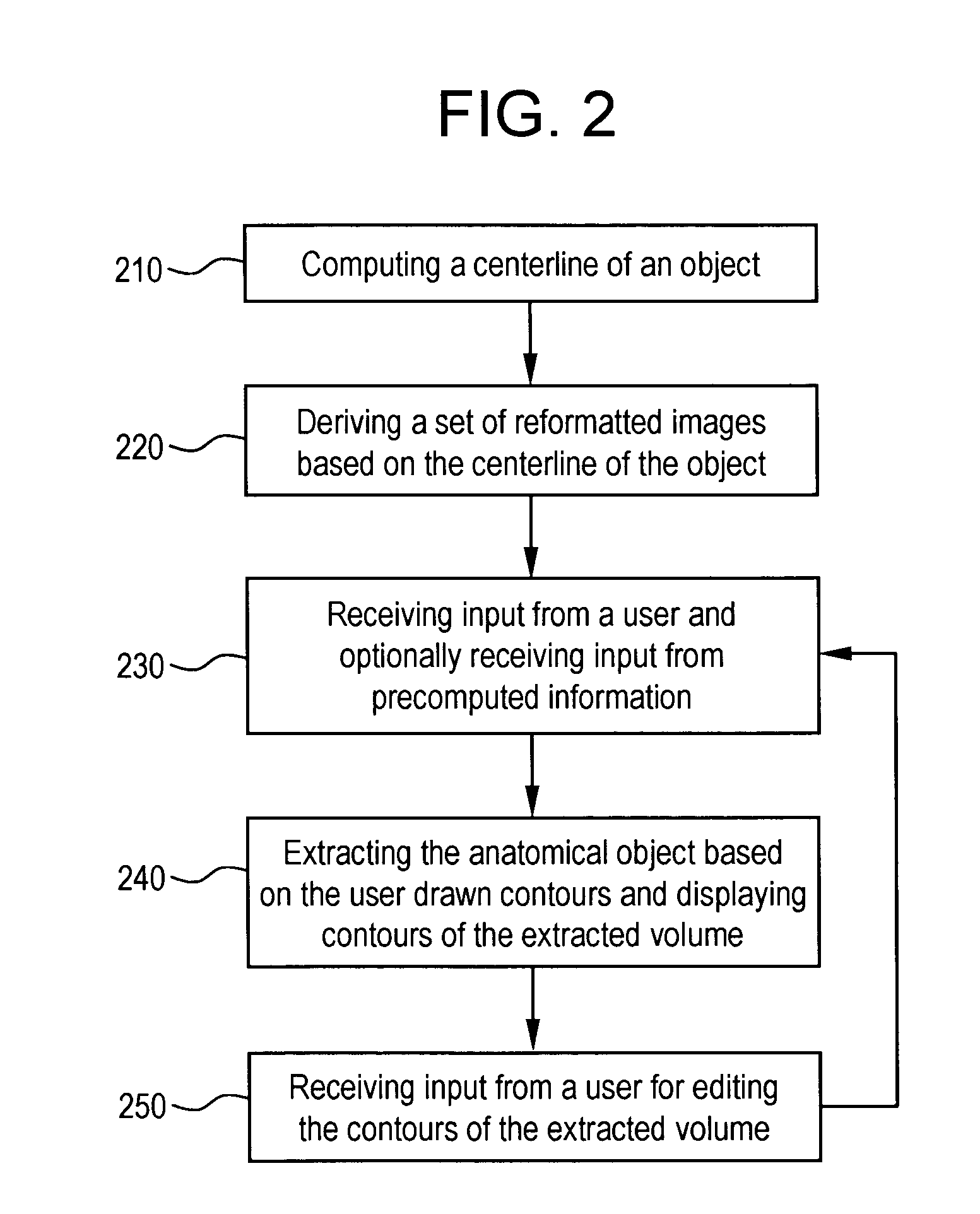
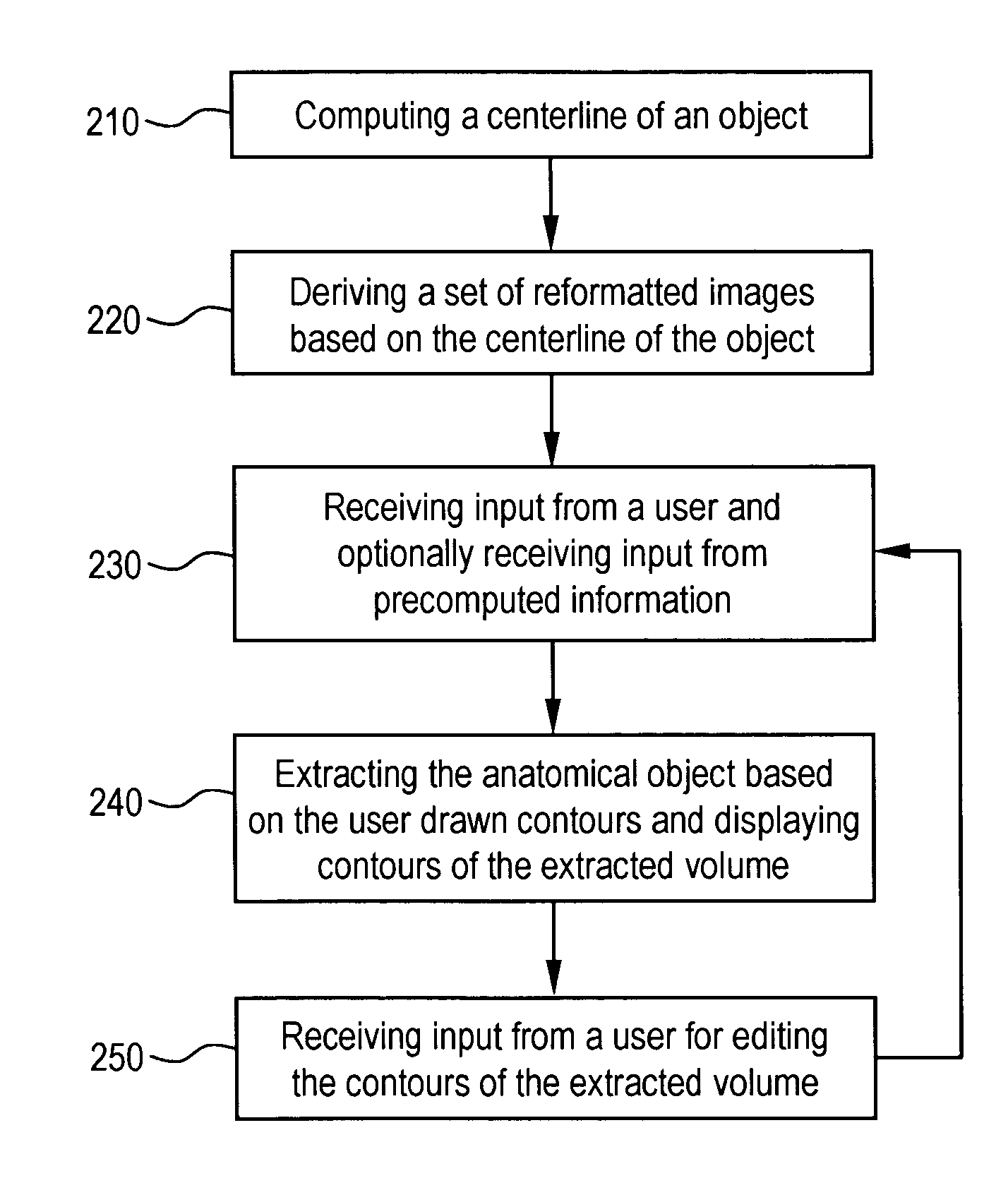
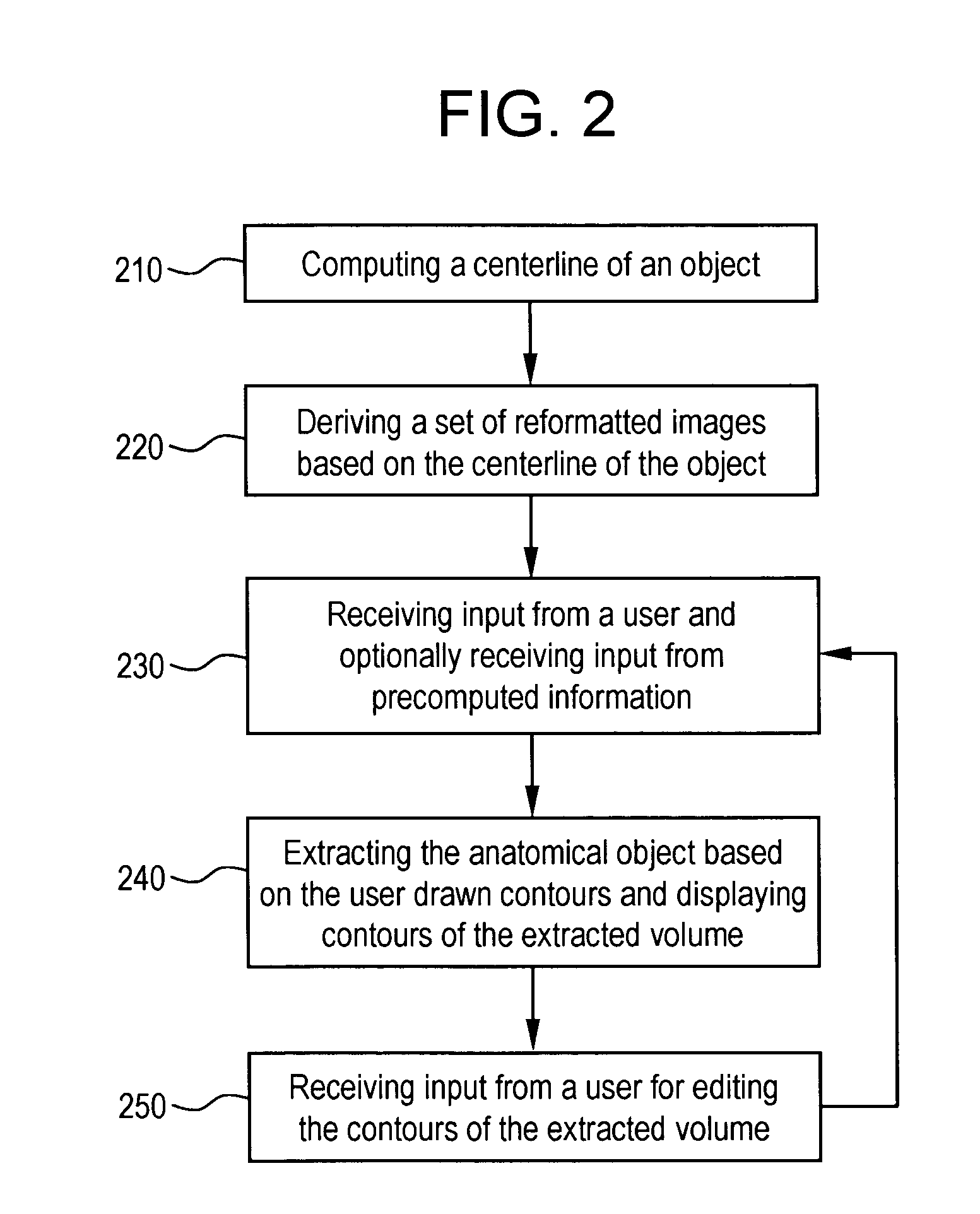
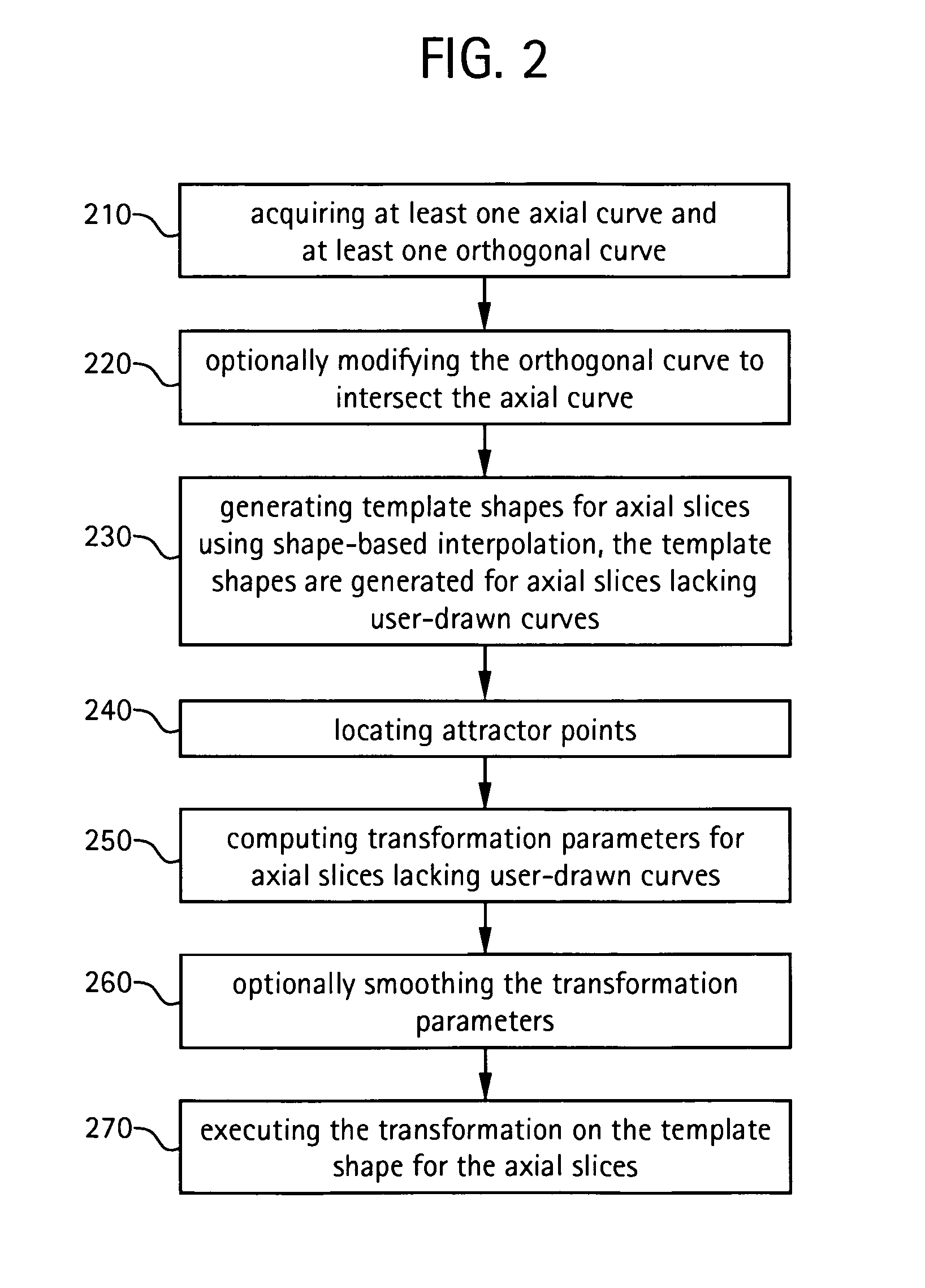
A system and method for segmenting and editing anatomical objects from medical images is disclosed. The system may be a medical diagnostic imaging system. A computer unit may execute computer software for segmenting anatomical objects from medical images. The computer software may extract an anatomical object from planar curves. The computer software may extract an anatomical object by computing the centerline of the anatomical object. A set of reformatted images may then be derived based on the centerline of the object. A user may then provide input in the form of user drawn contours on a plurality of reformatted images. In an embodiment the reformatted images may include a reformatted longitudinal view, a curved reformatted view, or a lumen view. The user drawn contours may correspond to the boundaries of the anatomical object to be segmented. The anatomical object may then be extracted based on the user drawn contours.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
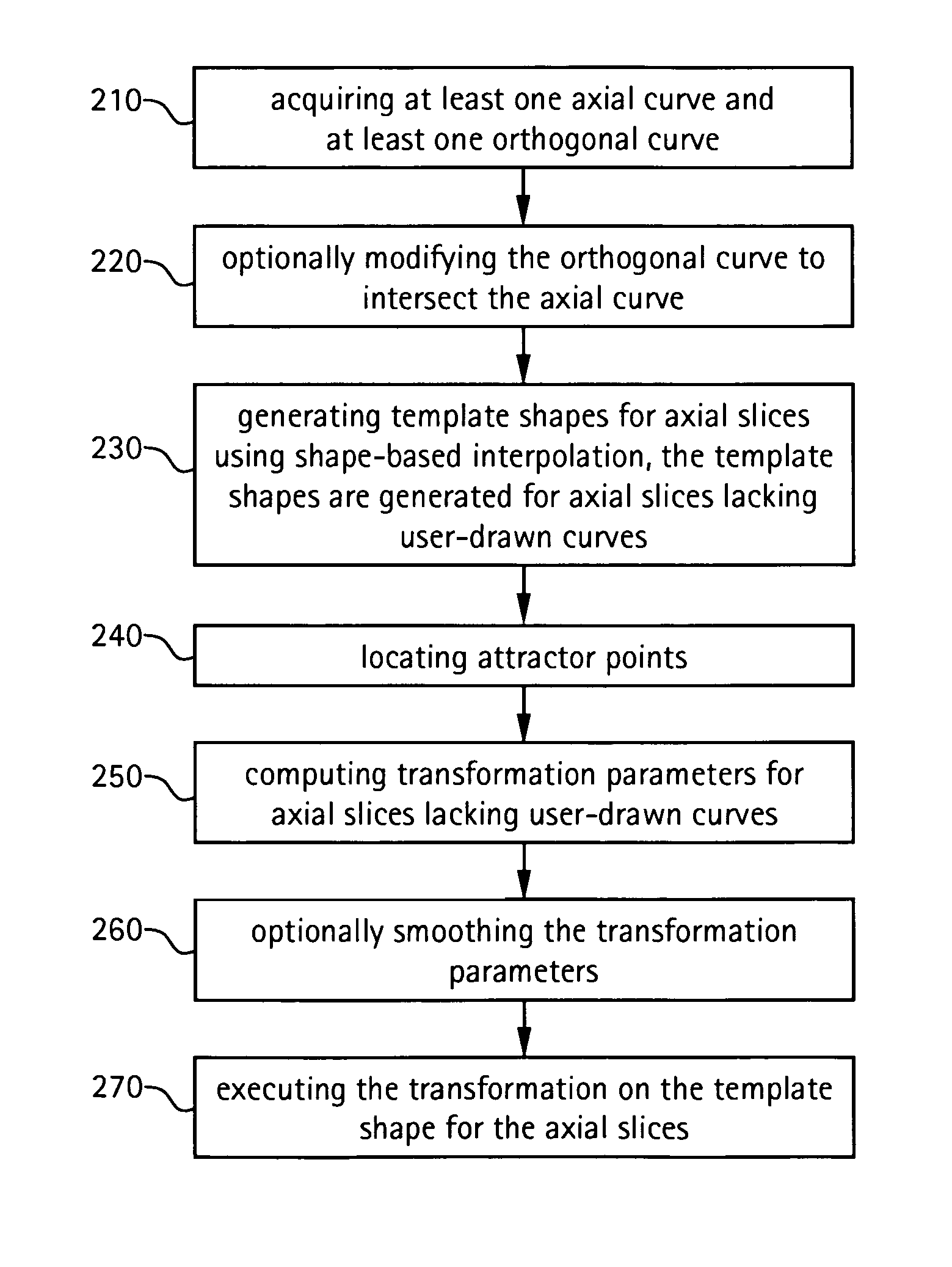
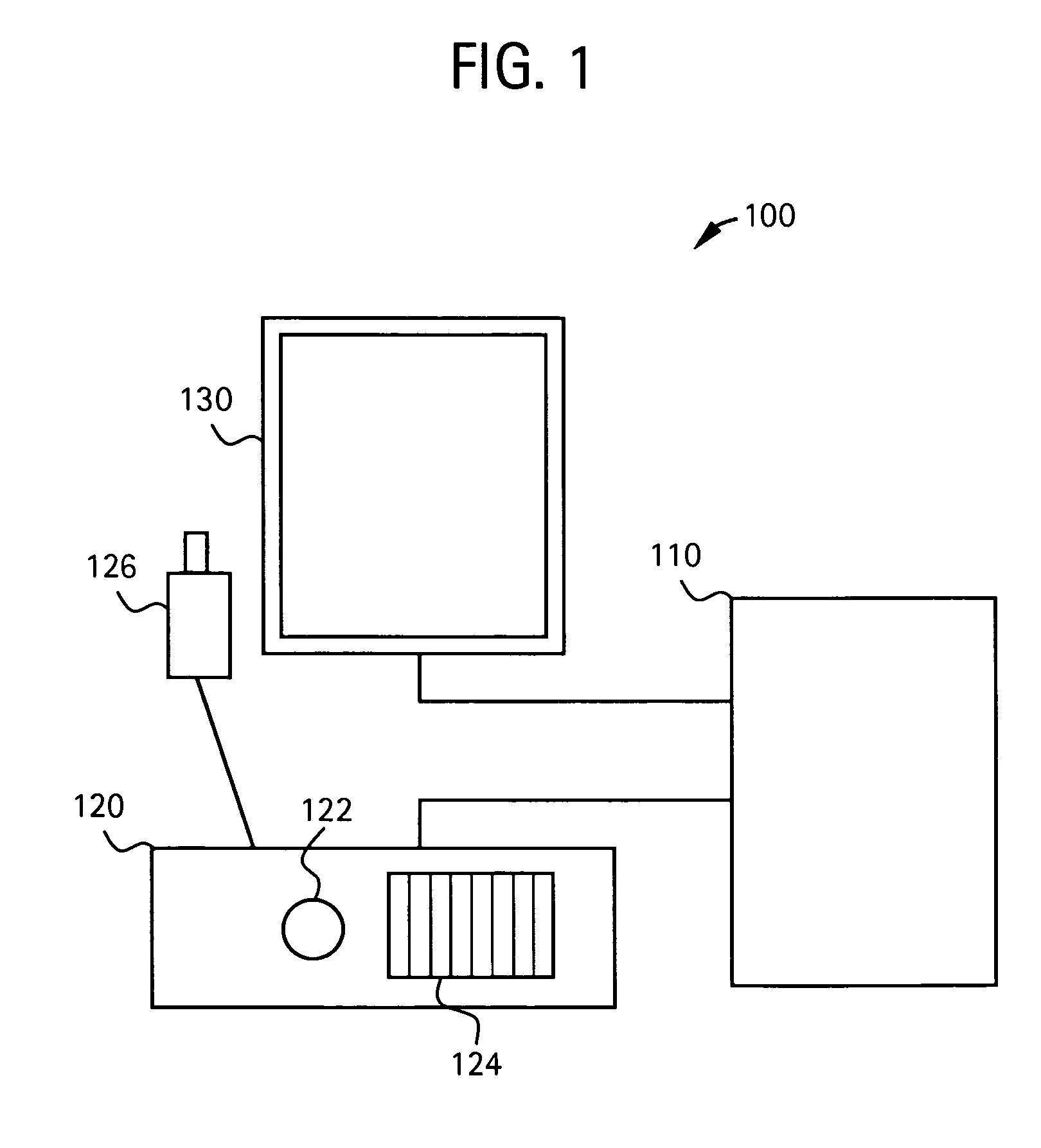
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional interactive tools for semi-automatic segmentation and editing of image objects
A system and method for segmenting and editing anatomical objects from medical images is disclosed. The system may be a medical diagnostic imaging system. A computer unit may execute computer software for segmenting anatomical objects from medical images. The computer software may extract an anatomical object from planar curves. Additionally, the computer software may correct the shape of an existing three-dimensional anatomical object from planar curves. The planar curves may be orthogonal to each other. A user may contour of an anatomical object on a plurality of slices, such as an axial slice a sagittal slice, a coronal slice, or some combination thereof. The contour may be drawn using a tracing pen on a display unit. The display unit may receive touch screen input from the tracing pen. The display unit may display the three-dimensional segmented anatomical object.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
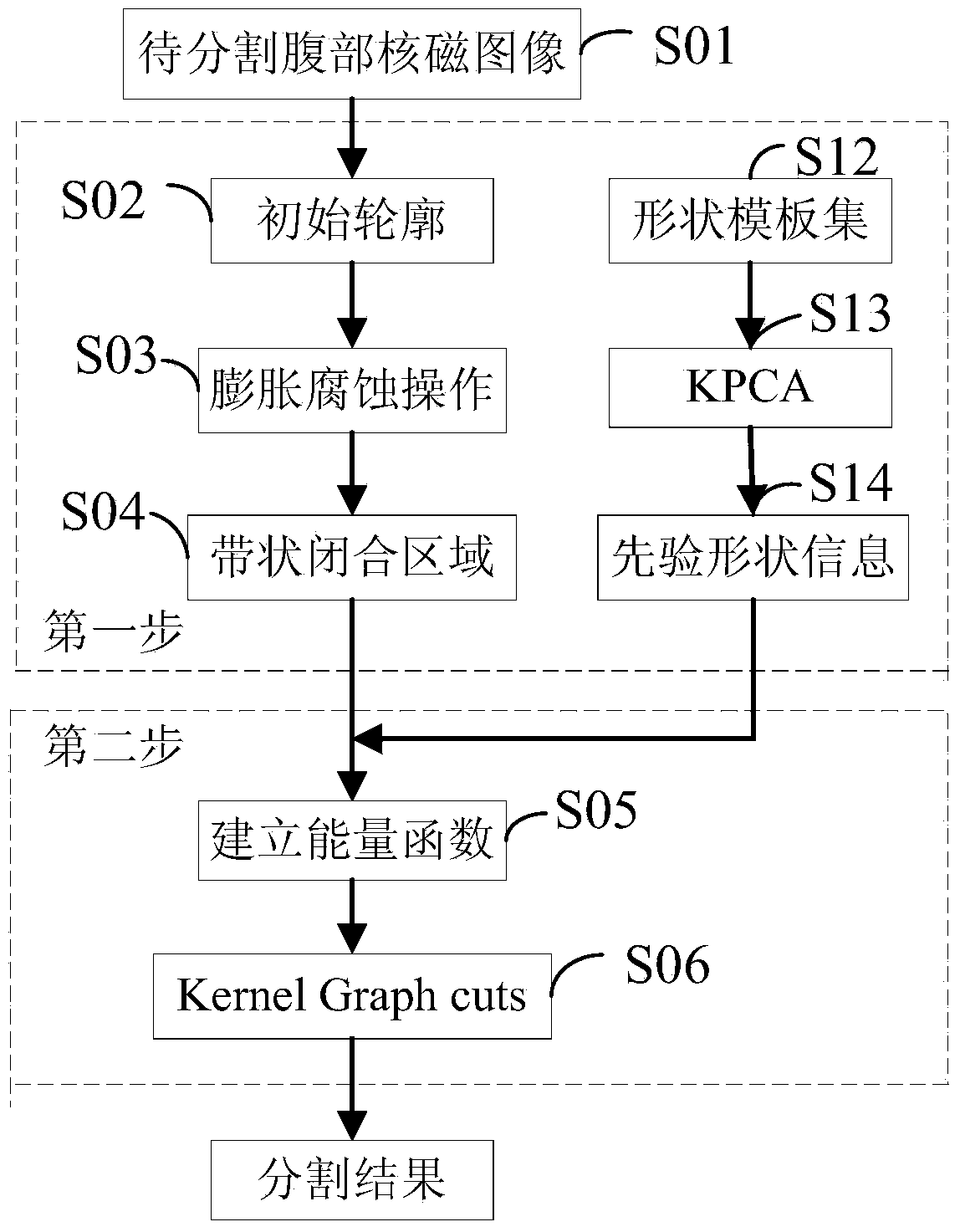
Segmentation method and system for abdomen soft tissue nuclear magnetism image
ActiveCN103473767AImprove robustnessThe segmentation result is accurateImage analysisKernel principal component analysisImage segmentation algorithm
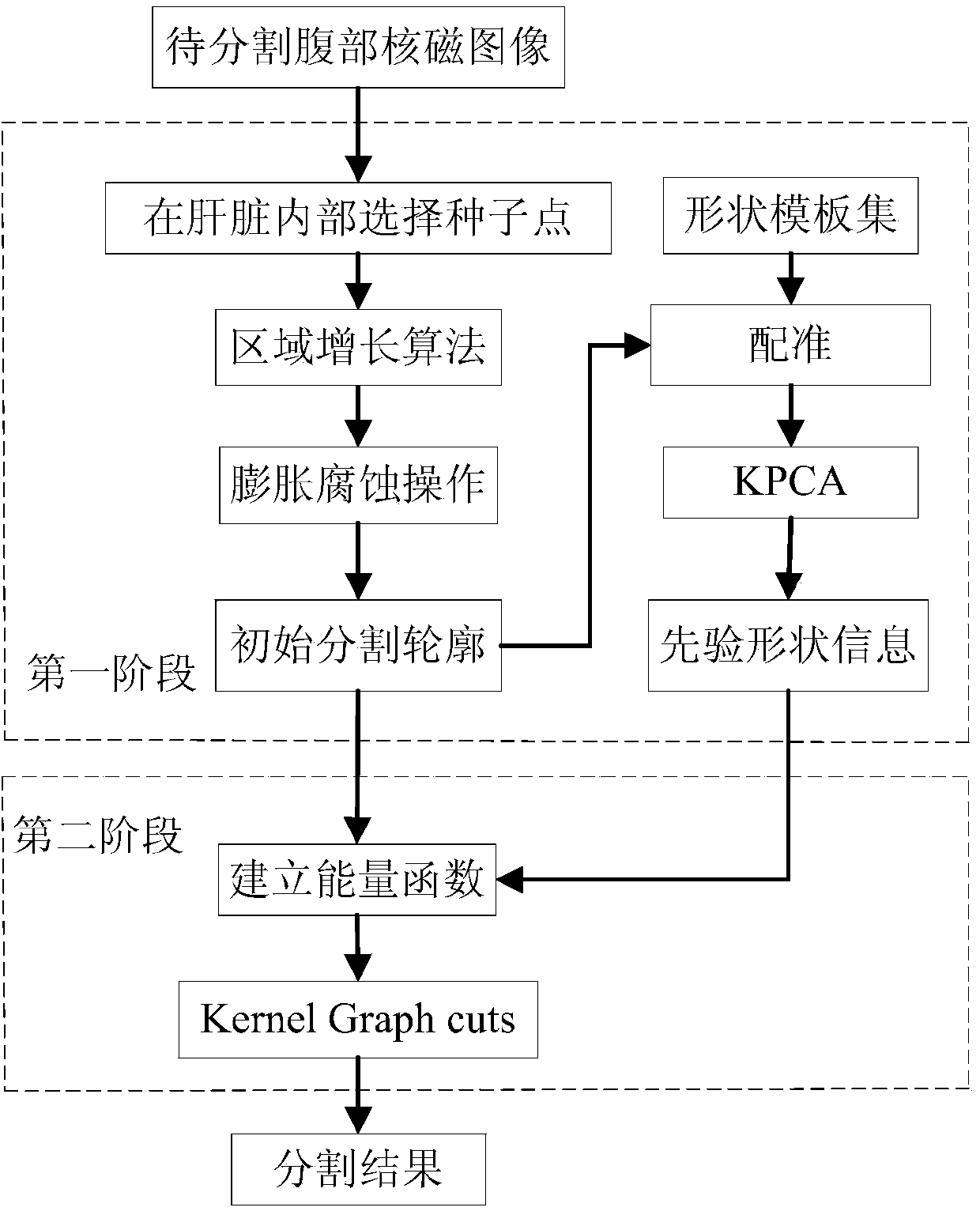
The invention discloses a segmentation method and system for an abdomen soft tissue nuclear magnetism image. The segmentation method comprises the steps that pre-segmentation is conducted on an area to be segmented through an area growing algorithm, then a morphological operator is adopted to conduct expansion and corrosion operations to carry out further processing on the pre-segmentation result, so that the pre-segmentation result forms an original segmentation outline. After rectification is conducted between a shape template set and the original segmentation outline, kernel principal component analysis is conducted, and prior shape information is obtained through a statistics model. The prior shape information is combined with data items of an energy function of a nuclear magnetism image segmentation model, and an energy function is built; a kernel graph cuts algorithm is used for carrying out segmentation on the original segmentation outline and an objective outline is obtained. The segmentation method and system can achieve semi-automatic segmentation, the system is simple, the robustness of the nuclear magnetism image segmentation algorithm is effectively improved so as to enable the segmentation result to be more accurate, and the segmentation method and system for the abdomen soft tissue nuclear magnetism image can be applied to nuclear magnetism image segmentation.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Human body thoracic and abdominal cavity CT image aorta segmentation method based on GVF Snake model
InactiveCN105976384AAvoid the disadvantages of heavy workload and long time consumptionGood repeatabilityImage enhancementImage analysisExternal energyDiffusion equation
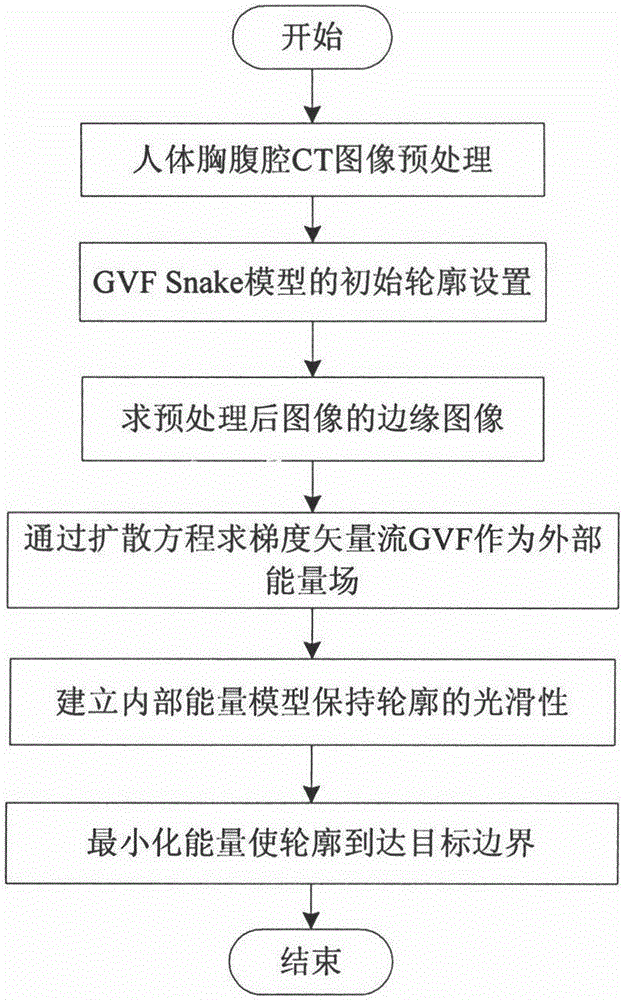
The invention discloses a human body thoracic and abdominal cavity CT image aorta segmentation method based on a GVF Snake model. The method overcomes the shortcomings of the heavy workload and long time consuming of the traditional manual and semi-automatic segmentation, the repeatability of the method is good, and the uncertainty caused by artificial segmentation is prevented. The method includes (1) reading a CT image and performing image preprocessing; (2) performing the initial profile setting of the GVF Snake model on the image obtained after the preprocessing; (3) obtaining the edge image of the image after the preprocessing; (4) obtaining gradient vector flow GVF as the external energy field by the diffusion equation based on the obtained edge image; (5) establishing an internal energy model to maintain the smoothness of the profile; and (6) constructing an energy function E by means of internal energy and external energy, obtaining the minimum value of energy E by means of iteration operation, and the target boundary of the profile can be obtained at the end. The method has important application values in the field of human body thoracic and abdominal cavity aorta interlayer segmentation diagnosis treatment.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
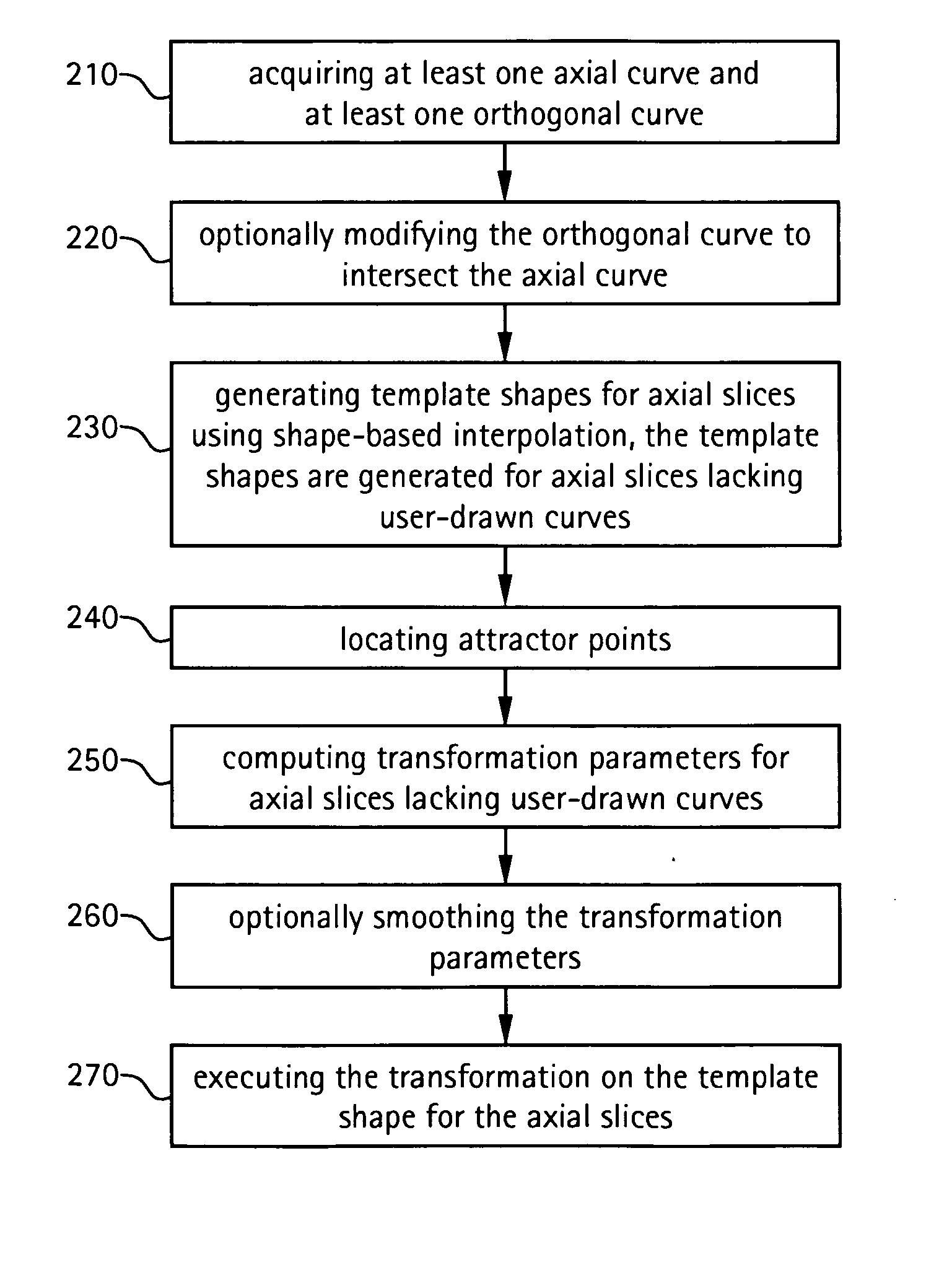
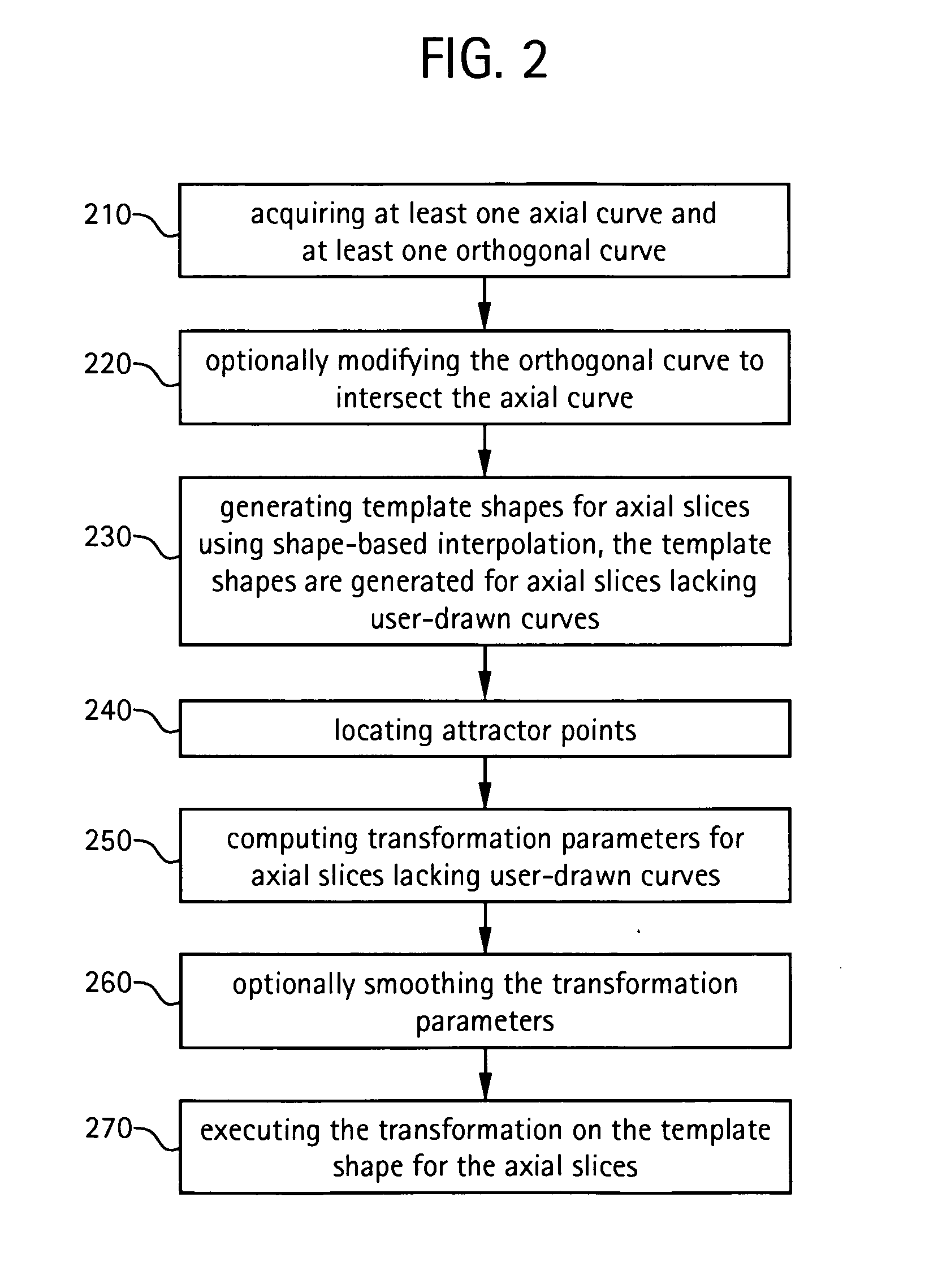
Method and apparatus for semi-automatic segmentation technique for low-contrast tubular shaped objects
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Image segmentation annotation method and device
ActiveCN110570434AImprove segmentation performanceReduce the difficulty of segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionManual annotation
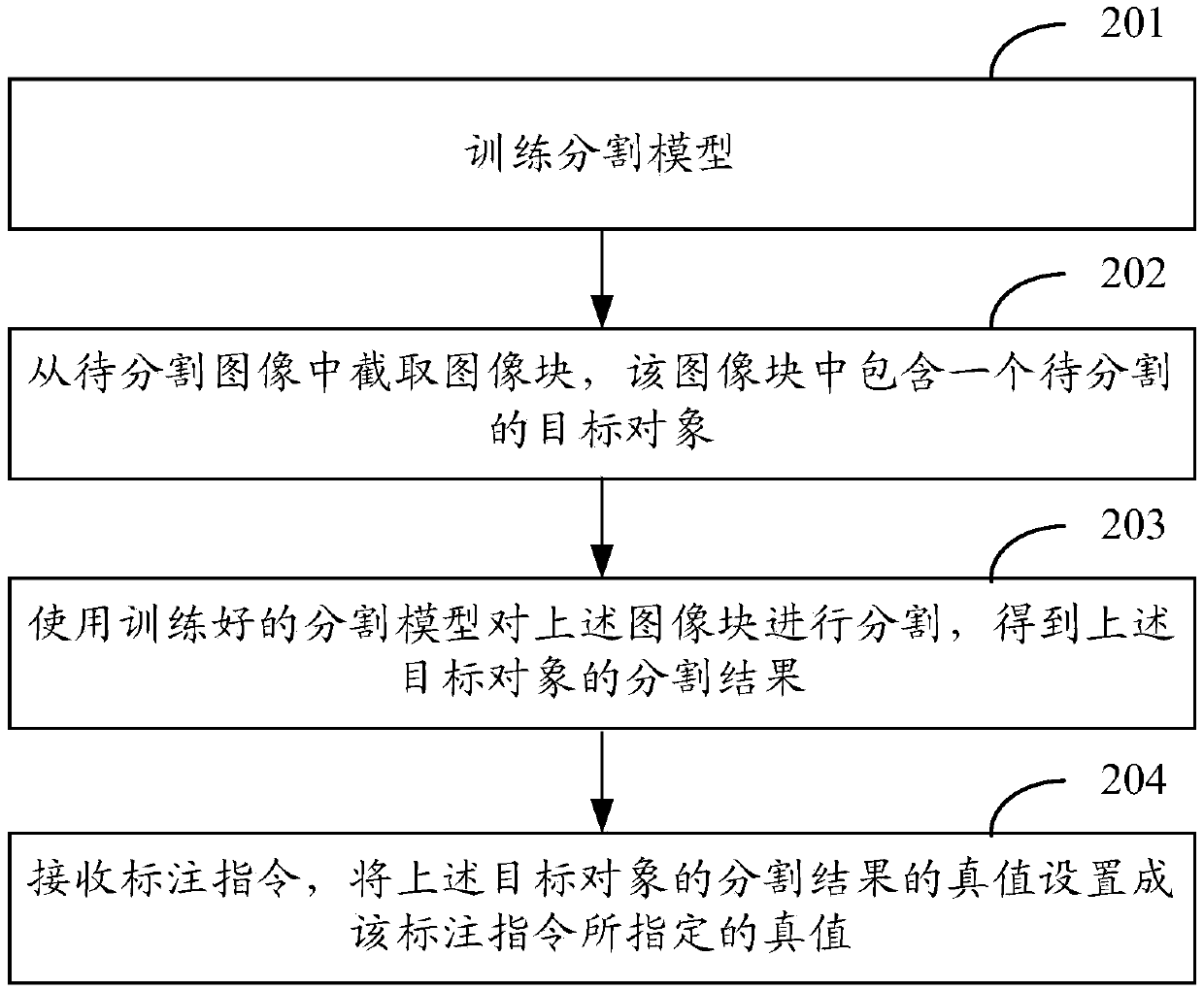
The embodiment of the invention provides an image segmentation annotation method and device, and the method comprises the steps: intercepting an image block from a to-be-segmented image, and enablingthe image block to comprise a to-be-segmented target object; segmenting the image block by using a trained segmentation model to obtain a segmentation result of the target object; wherein the segmentation model is used for predicting segmentation results of different types of objects and endowing the segmentation results of different types of objects with the same true value; and receiving an annotation instruction, and setting the true value of the segmentation result of the target object as the true value specified by the annotation instruction. The embodiment of the invention provides a semi-automatic segmentation annotation tool, and annotation time and labor cost can be reduced under the condition that the same precision as manual annotation is guaranteed.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
Liver cancer image feature extraction and pathological classification method and device based on imaging omics
ActiveCN111242174AEfficient use ofExcellent performance for distinguishing subtle differencesImage enhancementImage analysisBiopsy methodsStatistical analysis
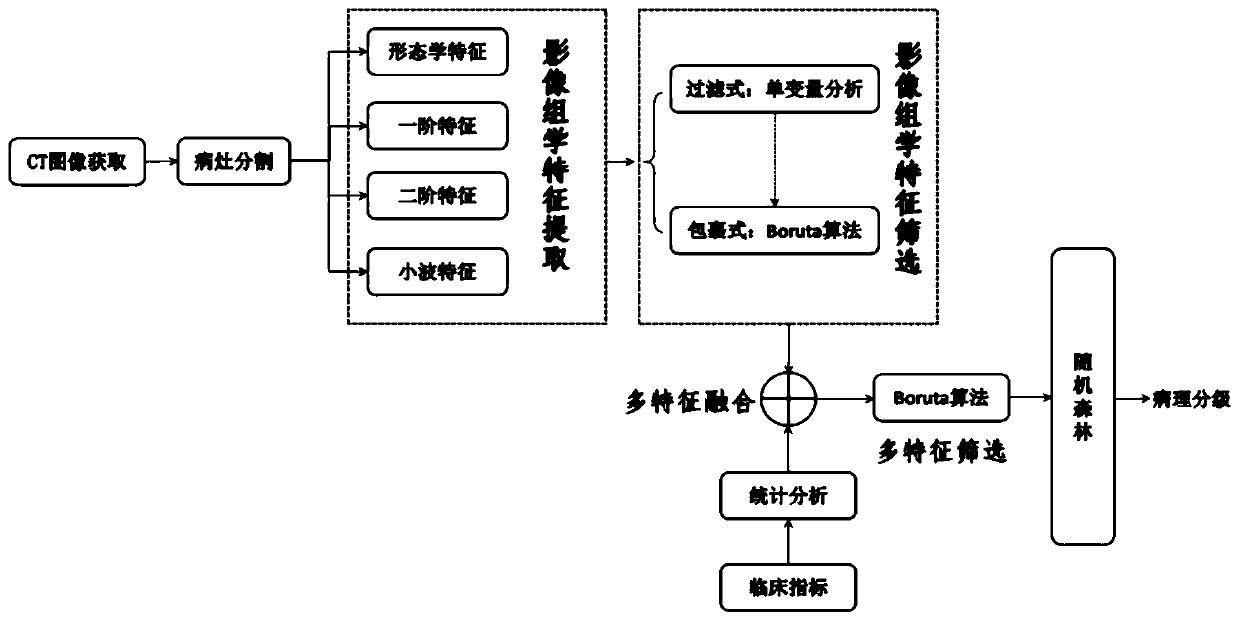
The invention discloses a liver cancer image feature extraction and pathological classification method and device based on imaging omics. The method comprises the following steps: 1) collecting a patient clinical image meeting the standard, and sketching a liver cancer lesion area of the collected image by adopting a Growcut semi-automatic segmentation method; 2) performing different levels of image omics feature extraction on the segmented lesion area; 3) feature screening: starting from a filtering method, extracting non-redundant features strongly related to the classification targets by adopting a filtering Boruta algorithm; 4) in combination with clinical indexes of the patient, filtering out significant and undifferentiated features through preliminary statistical analysis, and thenfusing the image omics features to perform next Boruta screening; and 5) training on a random forest by using the finally screened features to obtain classification labels, and completing prediction of pathological classification of liver cancer. Compared with a clinically traditional biopsy method, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of non-invasion, safety and stability,and is expected to become an effective preoperative evaluation tool for clinic.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
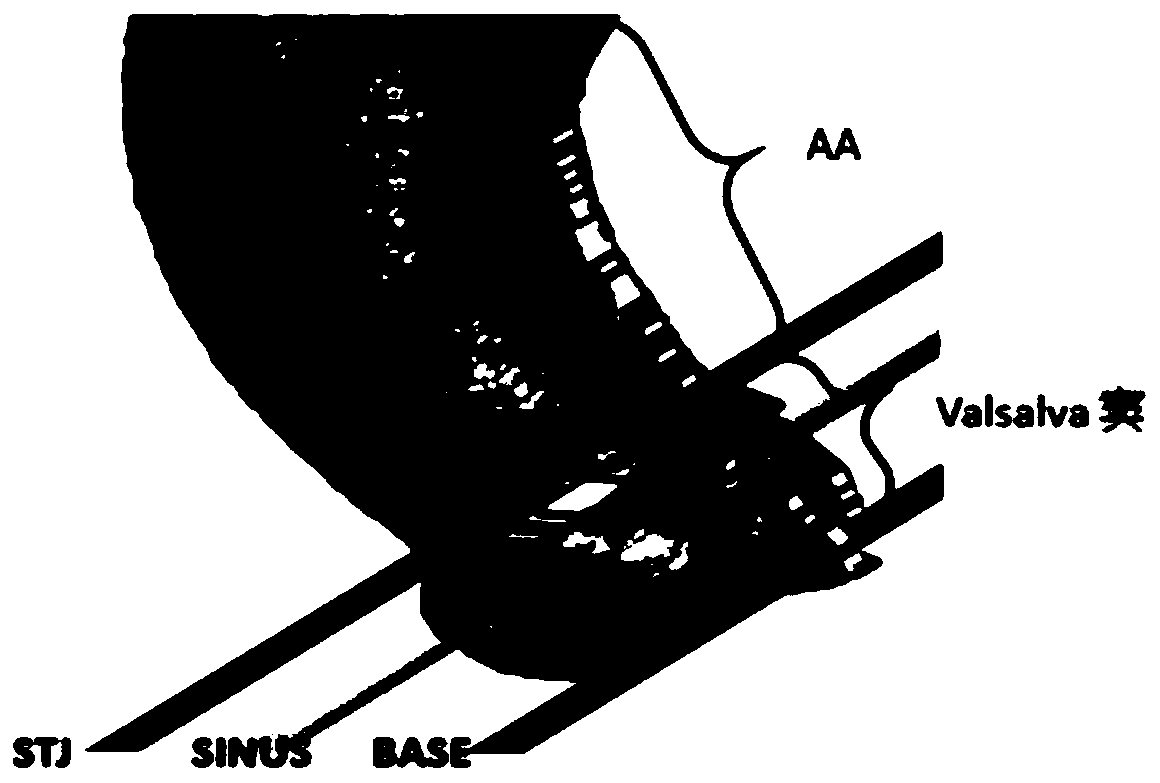
Aortic valve semi-automatic segmentation method based on CTA dynamic image
ActiveCN110570424ASolving Consistency IssuesAccurately reflectImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationFeature extraction
The invention discloses an aortic valve semi-automatic segmentation method based on a CTA dynamic image, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining CT angiography image data under electrocardio gating, carrying out the division of 20 time phases, and carrying out the following steps for an image of each time phase point: step A, segmenting Valsalva sinus according to the upper and lower boundaries of the root of an aorta; and step B, segmenting the aortic valve from the Valsalva sinus. According to the method, the feature extraction range in the CTA image is expanded, so that more completeanatomical details are presented, and the working efficiency and safety during an operation are further improved.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
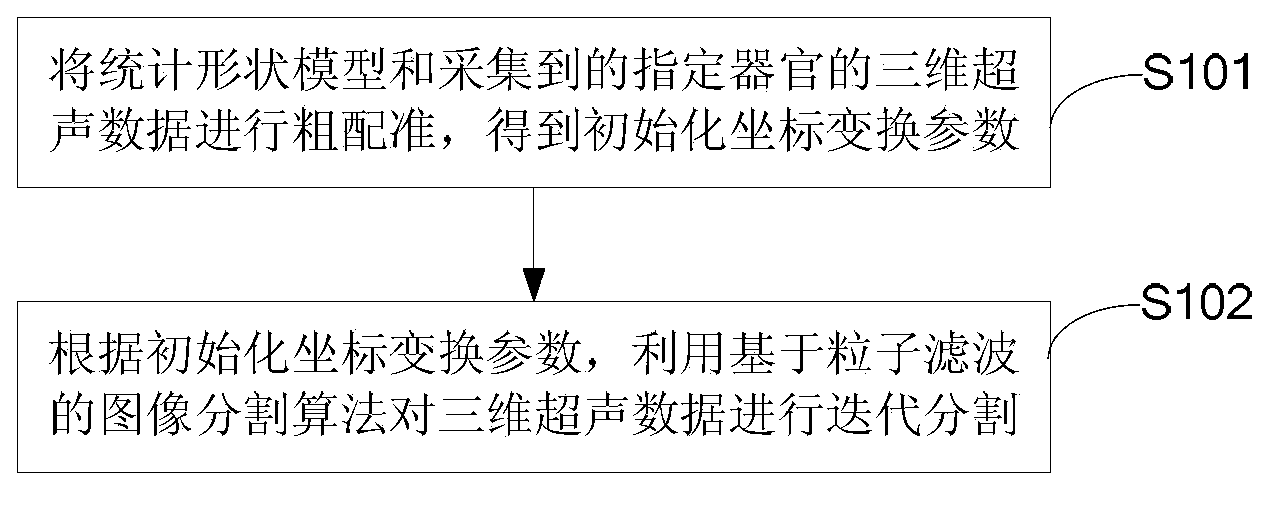
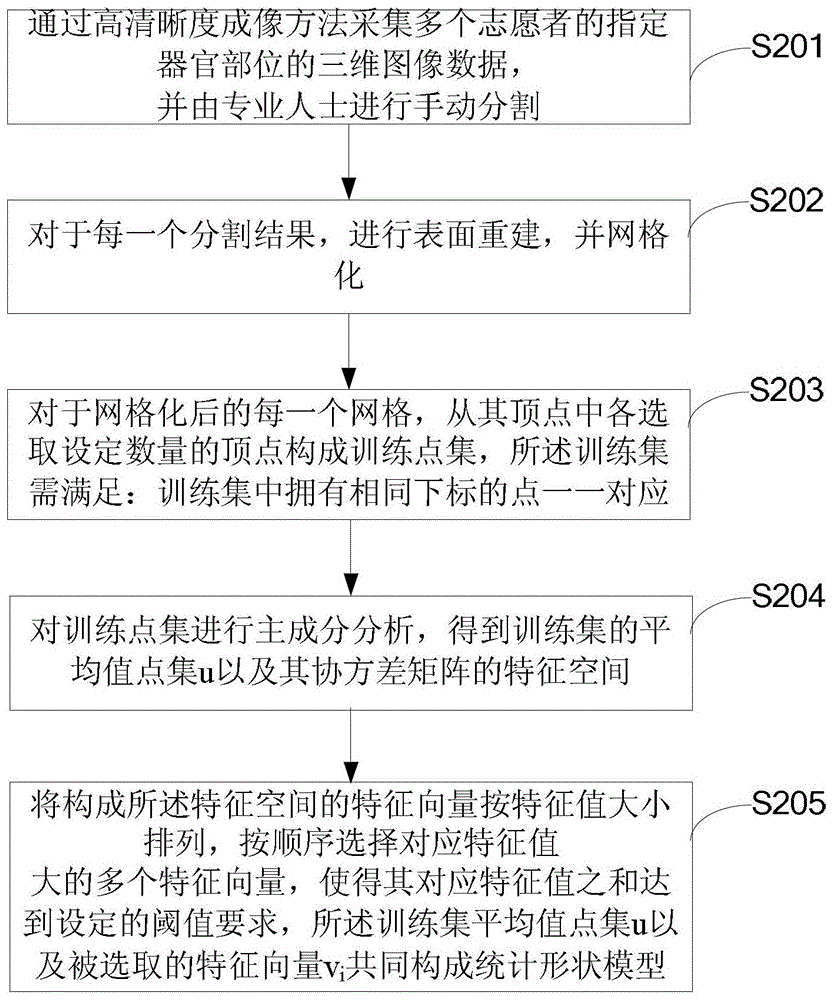
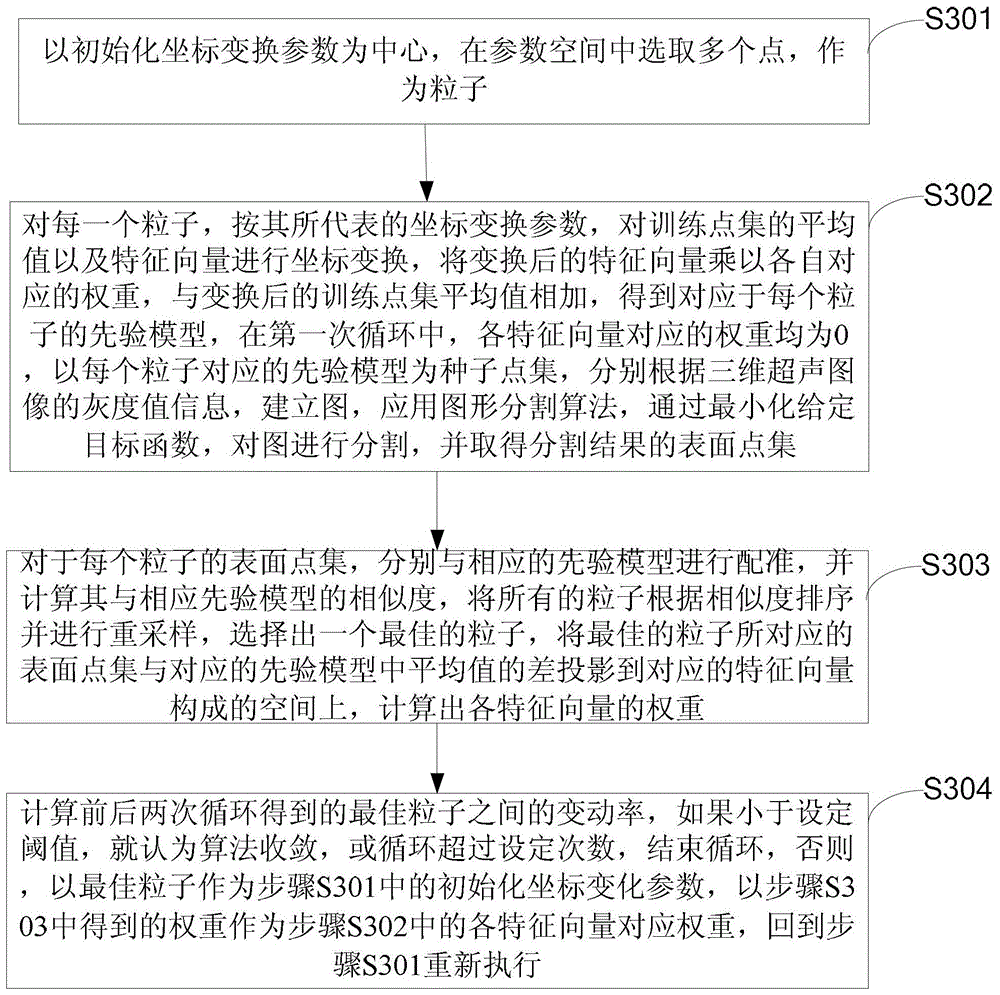
Ultrasound image segmentation method and system
ActiveCN103903255AAvoid the local minimum problemAvoid Manual SegmentationImage analysisSonificationImage segmentation algorithm
The invention is suitable for the technical field of image processing, and particularly relates to an ultrasound image segmentation method and system. The method includes the following steps that coarse registration is conducted on a statistical shape model and collected three-dimensional ultrasound data of a specified organ to obtain initialized coordinate transformation parameters; according to the initialized coordinate transformation parameters, an image segmentation algorithm based on particle filter is used for conducting iteration segmentation on the three-dimensional ultrasound data, wherein the statistical shape model is a combination of an average value obtained by training manual segmentation results of a plurality of high-definition three-dimensional data and a group of feature vectors of a representation change mode. Therefore, the problem that more artificial participation is needed in manual segmentation and semi-automatic segmentation is solved. Compared with an existing full-automatic segmentation method, the ultrasound image segmentation method and system solve the problems of low image resolution and segmentation accuracy under the image fuzzy condition.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional interactive tools for semi-automatic segmentation and editing of image objects
A system and method for segmenting and editing anatomical objects from medical images is disclosed. The system may be a medical diagnostic imaging system. A computer unit may execute computer software for segmenting anatomical objects from medical images. The computer software may extract an anatomical object from planar curves. Additionally, the computer software may correct the shape of an existing three-dimensional anatomical object from planar curves. The planar curves may be orthogonal to each other. A user may contour of an anatomical object on a plurality of slices, such as an axial slice a sagittal slice, a coronal slice, or some combination thereof. The contour may be drawn using a tracing pen on a display unit. The display unit may receive touch screen input from the tracing pen. The display unit may display the three-dimensional segmented anatomical object.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
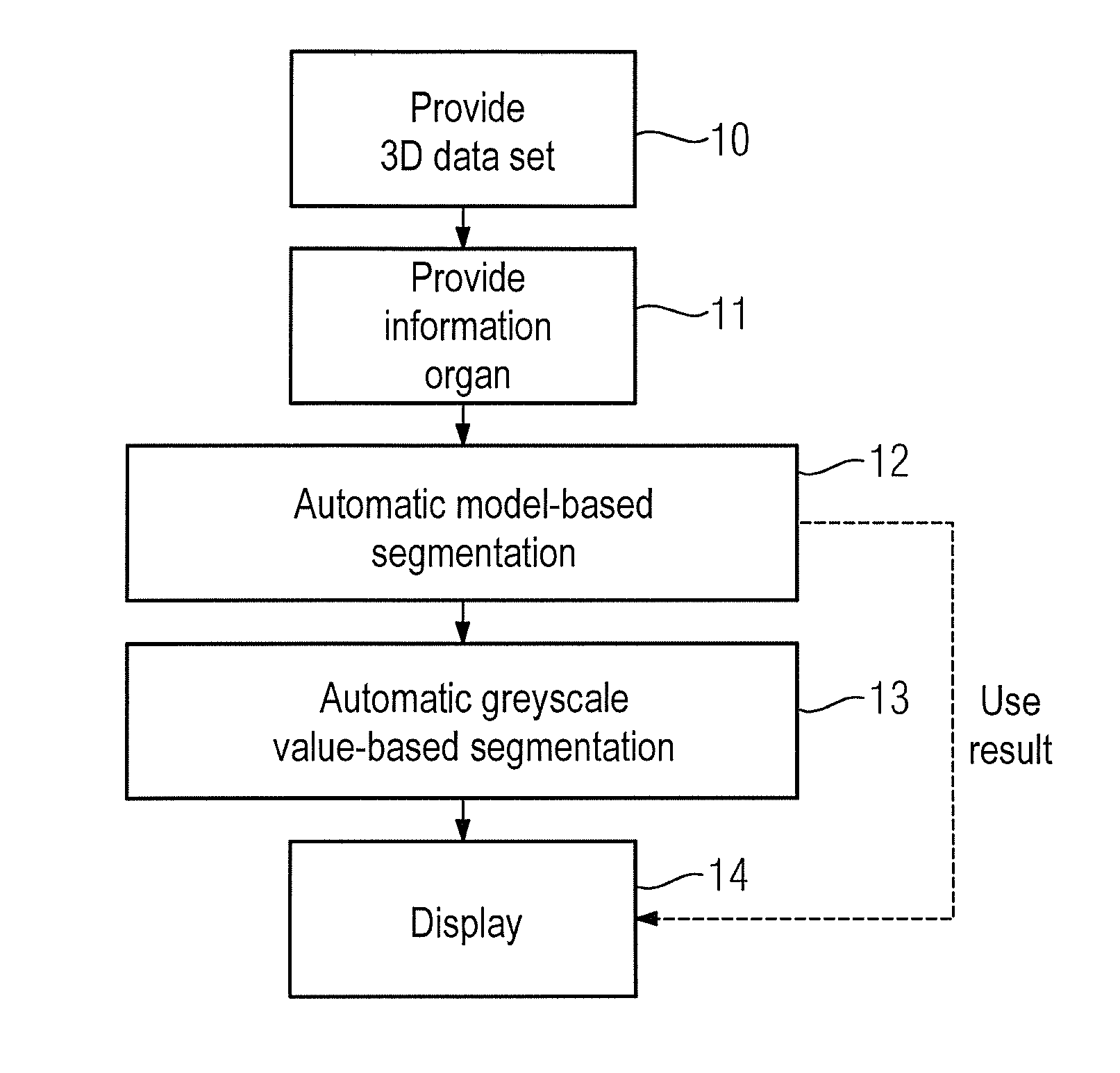
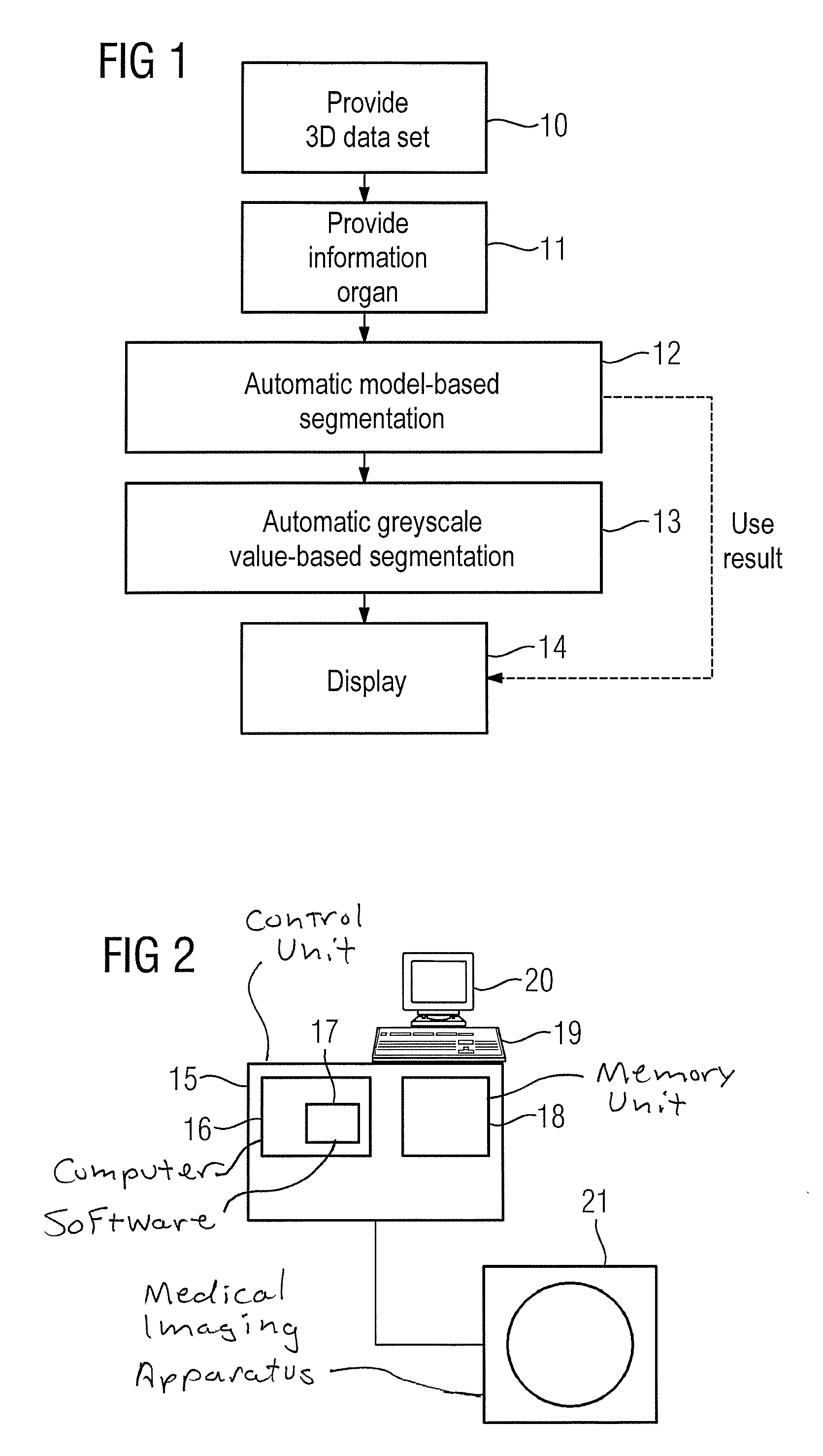
Method and device for automatic or semi-automatic segmentation of a 3D image data set
ActiveUS9384413B2Avoid disadvantagesMethod implementationImage enhancementImage analysisData set3d image
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
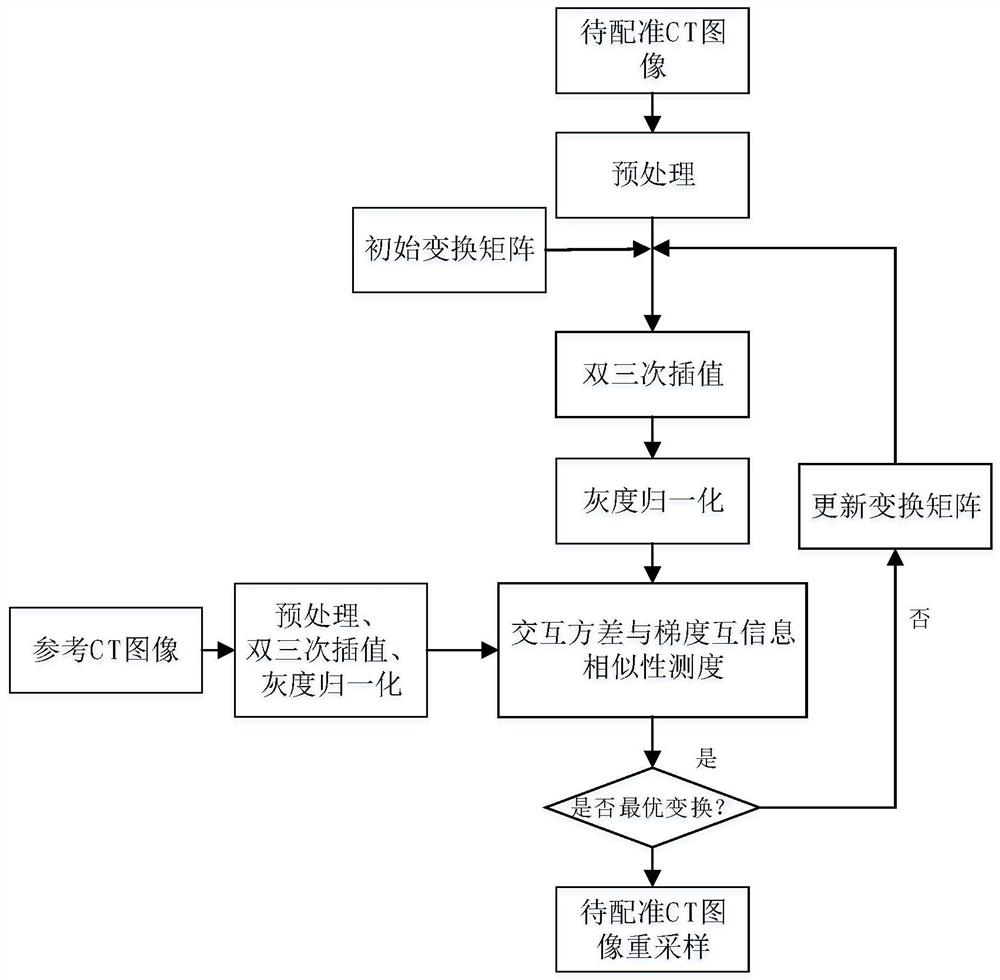
A semi-automatic segmentation sequential optimization registration method
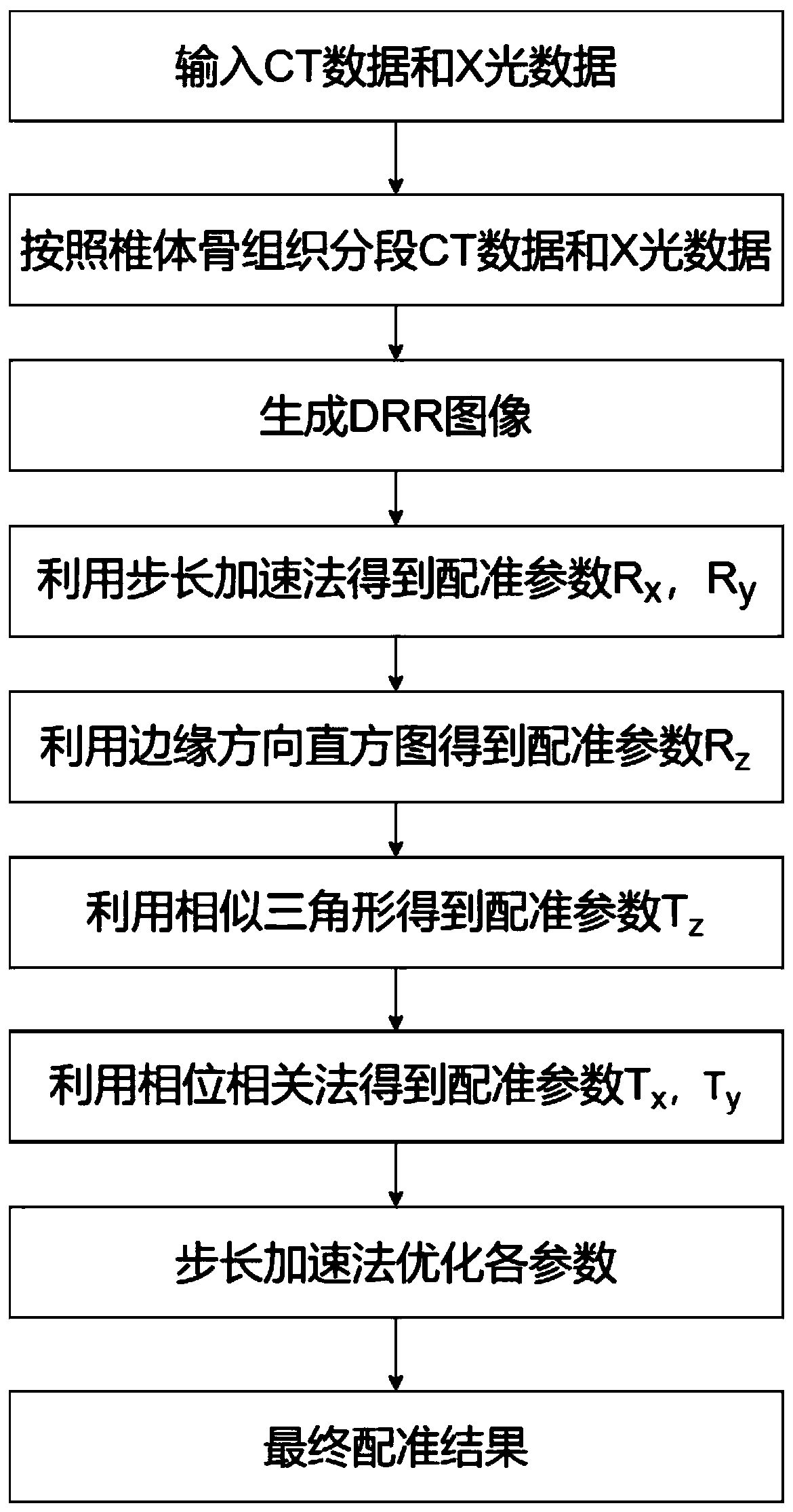
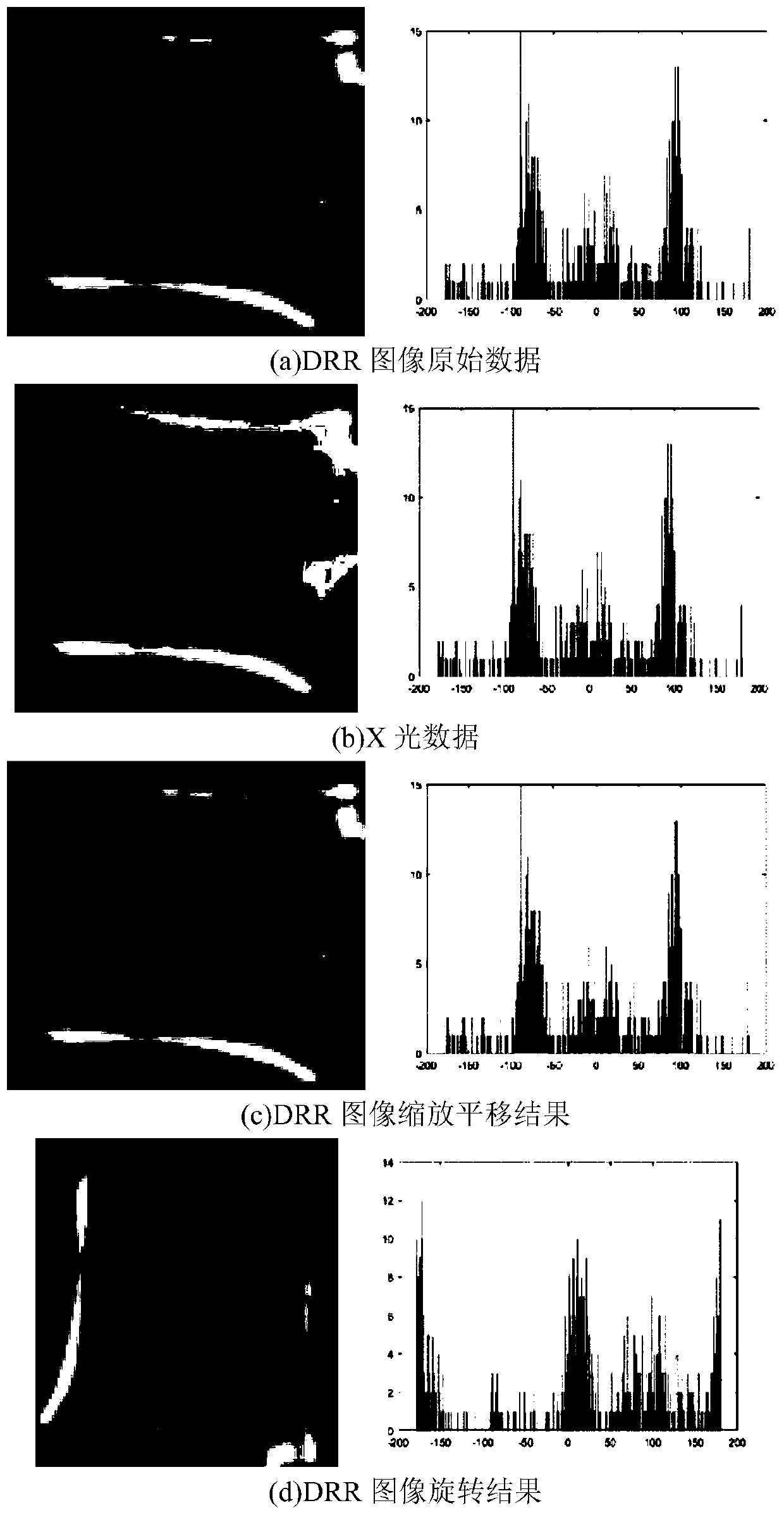
ActiveCN109767458ATo overcome the shortcomings of experimental errorOvercoming demandsImage enhancementImage analysisPlane segmentationBone tissue
The invention discloses a semi-automatic segmentation 2D-3D sequential optimization registration method. The method comprises the steps that a CT sequence containing bone tissue is traversed, corner points are extracted through a Curveur Scale (CSS) algorithm, the bone tissue range is iteratively expanded, and plane segmentation is utilized to obtain volume data of all segments; a sequential optimization registration method is adopted, the initial registration parameters are obtained in a solution space according to the sequence, and finally a step acceleration method is used in a very small range for optimization search. According to the present invention, the problems that the preoperative CT and intraoperative X-ray shooting time are different, and the bone tissues generate the relativemotion, and the registration time is increased along with the increase of the number of segments, are solved, and the time complexity is reduced to O (6n).
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
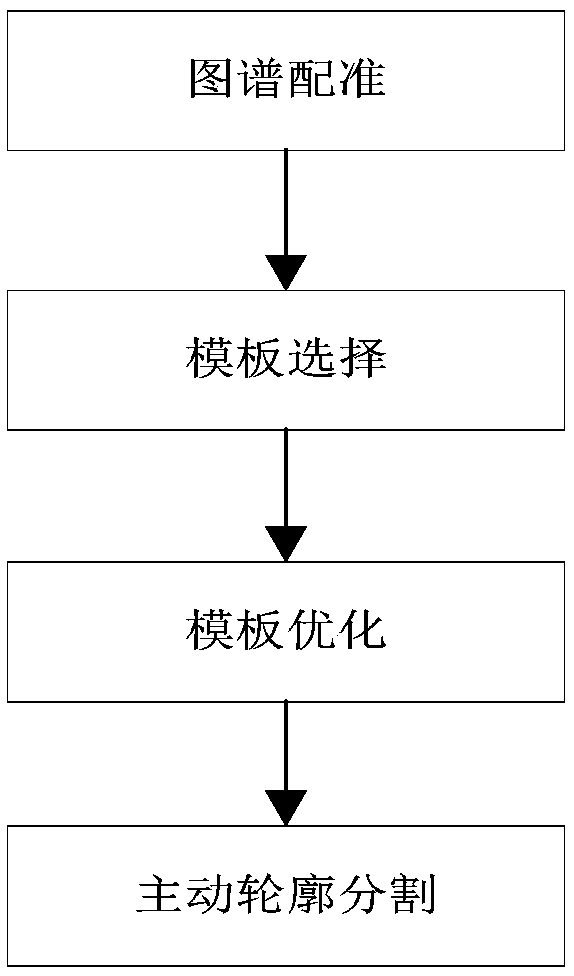
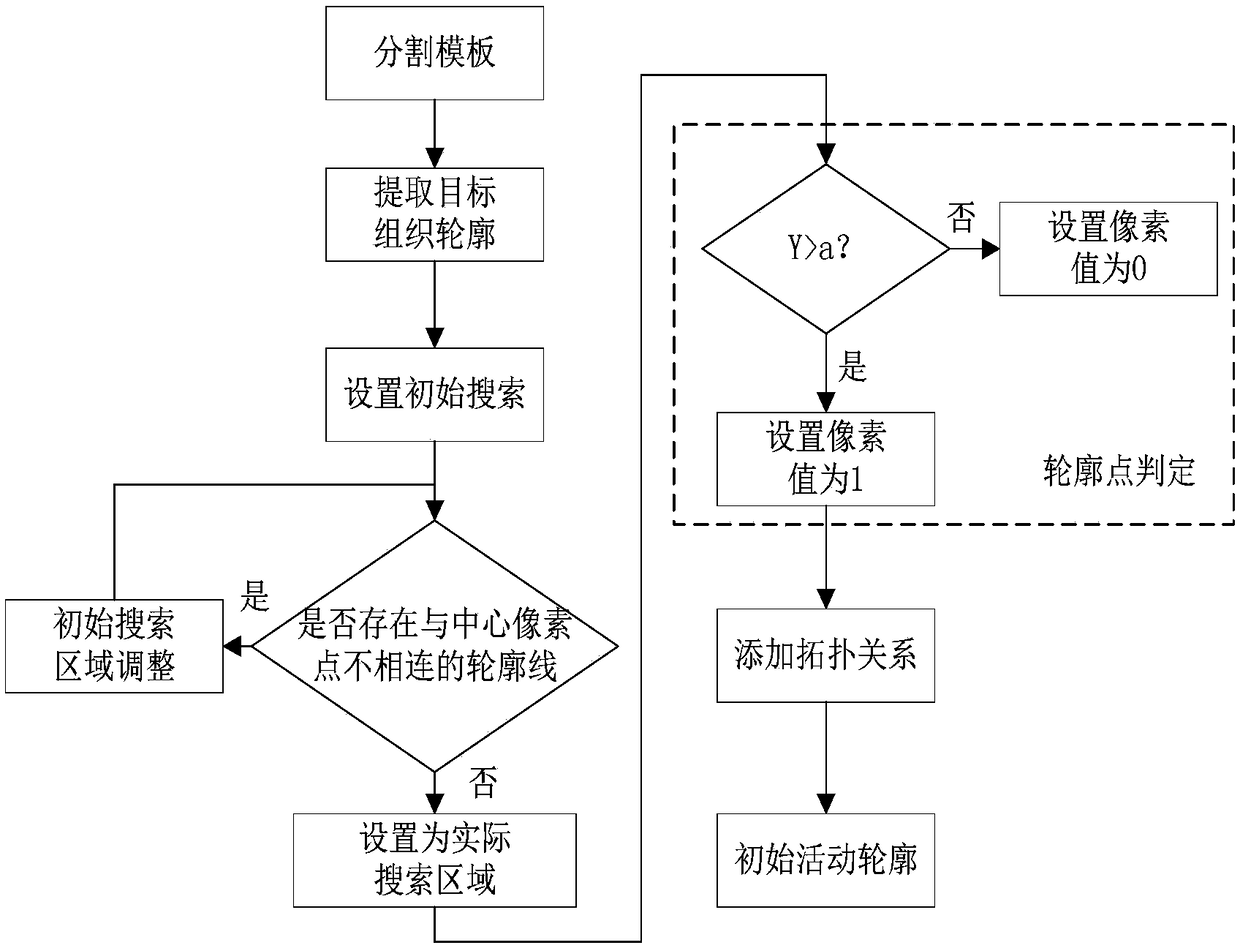
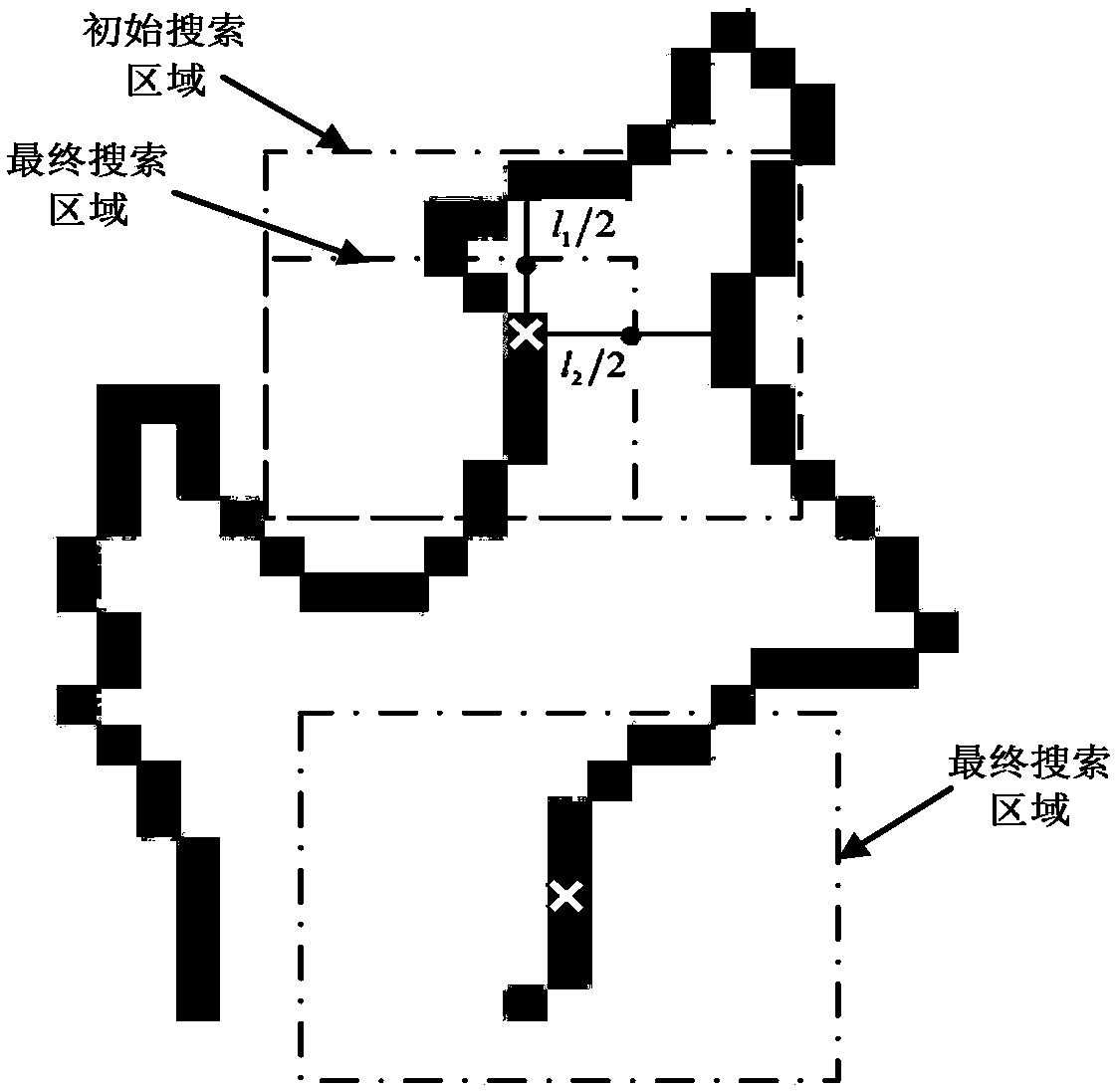
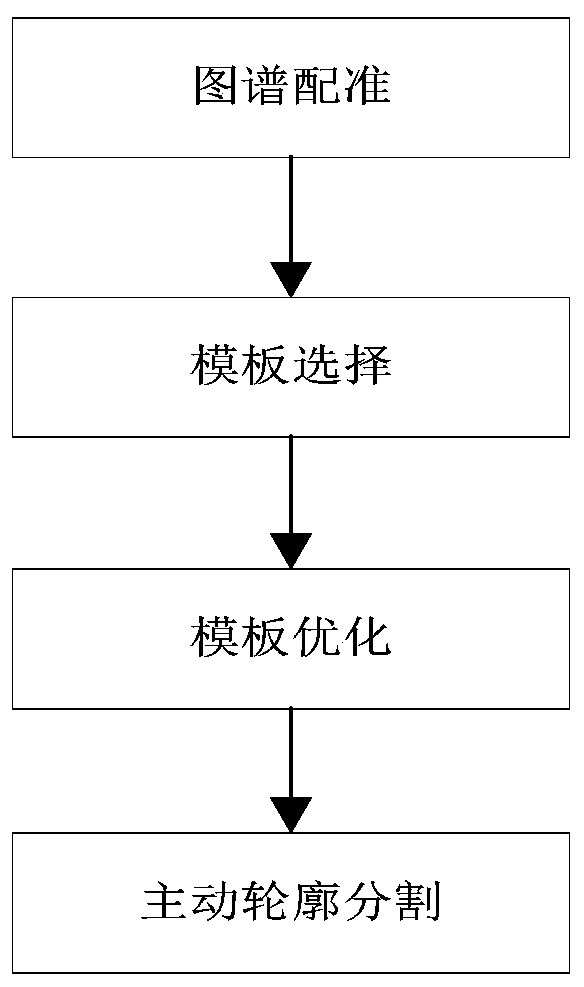
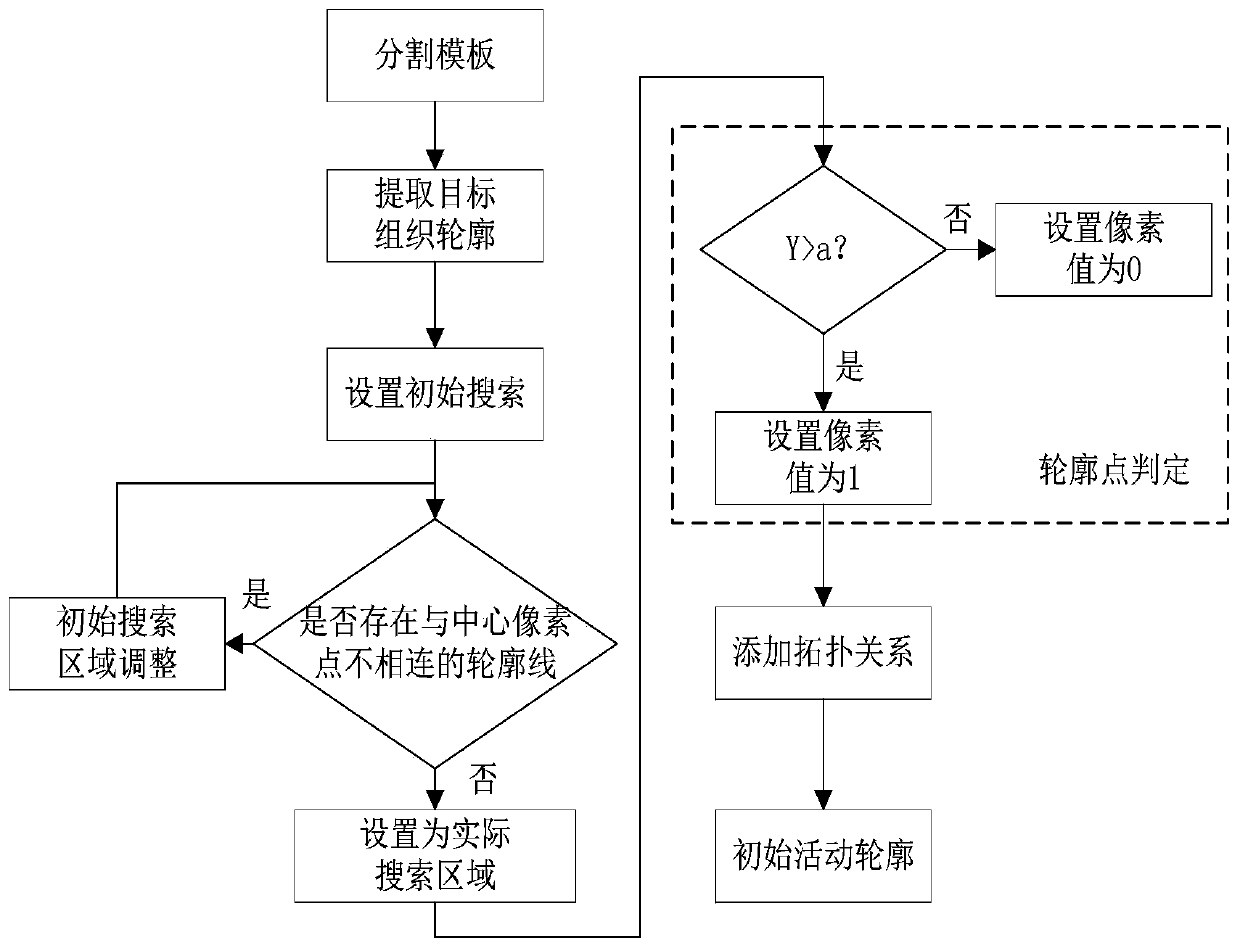
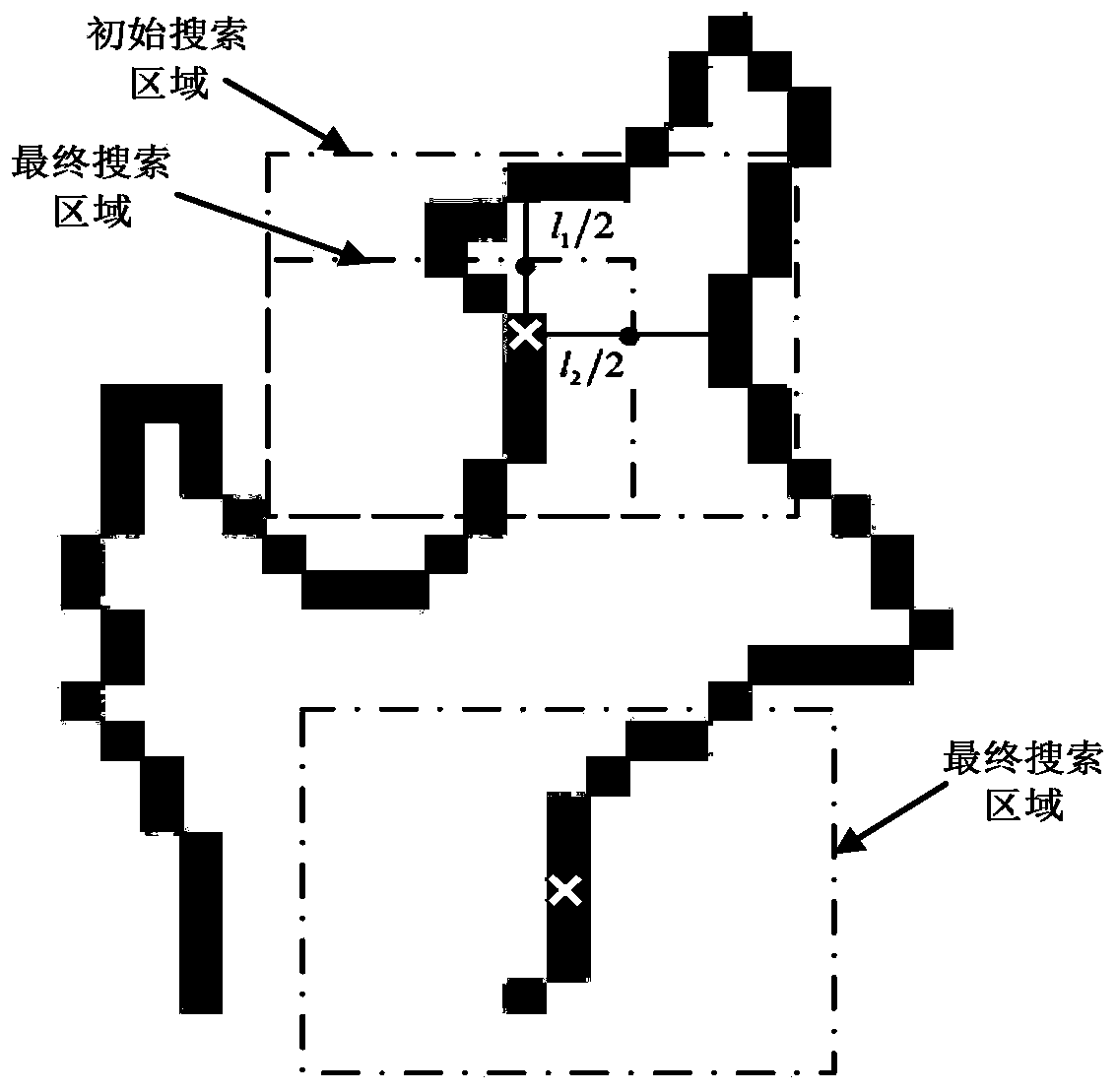
A semi-automatic brain image segmentation method
InactiveCN109509203AAvoid the influence of subjective factorsReduce mistakesImage enhancementImage analysisContour segmentationPrior information
The invention discloses a semi-automatic brain image segmentation method, in particular comprising the following steps: firstly, a map registration and a template selection method are used to obtain shape prior information of a target tissue and generate a segmentation template; Secondly, the template optimization method is used to reduce the error in the process of map registration and generate the initial active contour. Finally, the active contour model is used to segment the target tissue. The invention combines the advantages of the atlas registration method and the active contour segmentation method, and realizes the semi-automatic segmentation of the brain image. The method of the invention effectively utilizes shape prior information of the atlas, and can obtain smooth and continuous target tissue outline.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System, method and computer-accessible medium for the determination of accelerated brain atrophy and an optimal drainage site for a subdural hematoma using computed tomography
ActiveUS20190012783A1Small structureSatisfied with the resultImage enhancementMedical imagingLesionMri brain
To that end, in order to overcome some of the deficiencies presented herein above, an exemplary system, method and computer-accessible medium for determining an attribute(s) of a brain of a patient, can include, for example, receiving information obtained from a computed tomography (“CT”) scan(s) of a portion(s) of the brain, generating a CT image(s) that can be based on the information, and determining the attribute(s) of the brain based on the CT image(s) by segmenting an intracranial space (ICS) in the CT image(s). The attribute(s) can include a presence or absence of Alzheimer's disease, total volume of the ICS, brain, CSF or a lesion or the volumes of ICS, brain, CSF or lesion(s) expressed as a percentage of other volume(s). The aforementioned areas can be segmented using a combination of thresholding, morphological erosions, morphological dilations, manual segmentation or semi-automatic segmentation techniques, all of which can be parallel procedures. These attributes can be further used to determine treatment, for example, optimizing the location of the twist drill craniotomy to drain hematoma in subdural hematoma.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
OCT eye fundus image semi-automatic segmentation method and device based on curve group matching
ActiveCN108182686AAccurate and reliable extractionEffective segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSplit lines
The invention discloses an OCT eye fundus image semi-automatic segmentation method and device based on curve group matching. The method comprises: receiving and preprocessing an m-row n-column eye fundus image; determining the grayscale value vector curve of each column of the eye fundus image, calculating the descriptor of each pixel in the grayscale value vector curve, and obtaining a descriptorsub-matrix of the eye fundus image; and based on the description sub-matrix, matching every two grayscale value vector curves by using a dynamic time planning algorithm to obtain a spatial correspondence matrix between paired curved pixels; receiving a pixel manually designated by a user, searching out all pixels corresponding to the pixel according to the coordinate of the point and the spatialcorrespondence matrix, and fitting a smooth segmentation line. The technical solution of the invention ensures the segmentation accuracy of OCT eye fundus image, has strong adaptability, can segment the obvious layered structure on the retina, and can process the overlapping area at a central recess.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
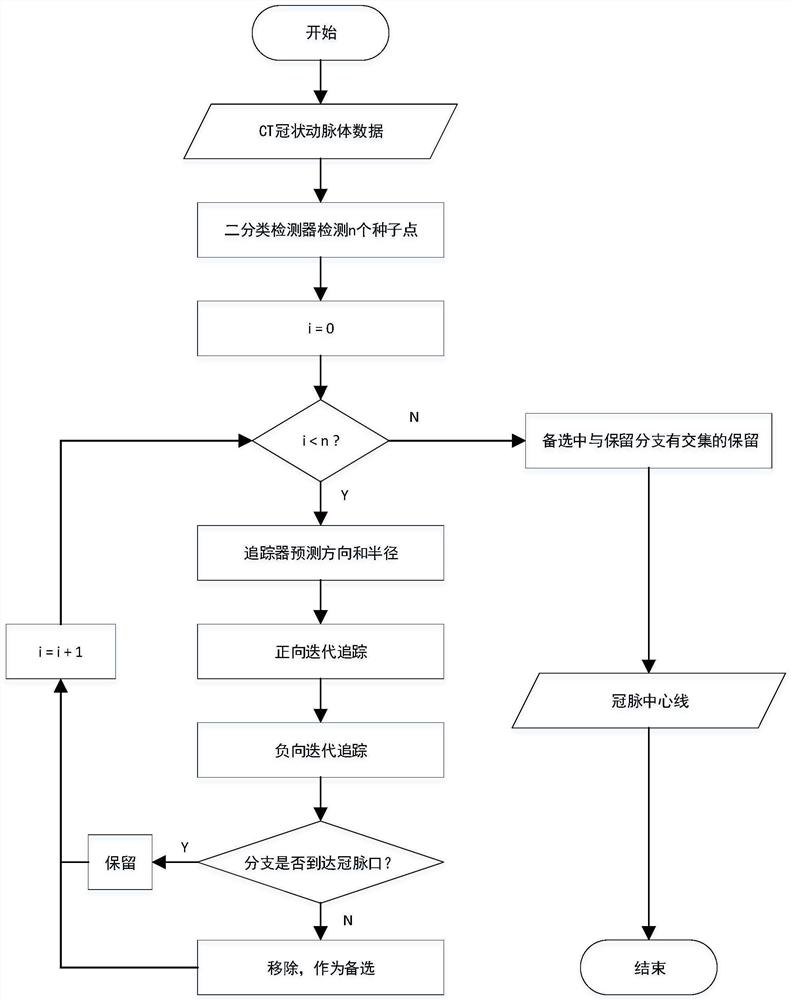
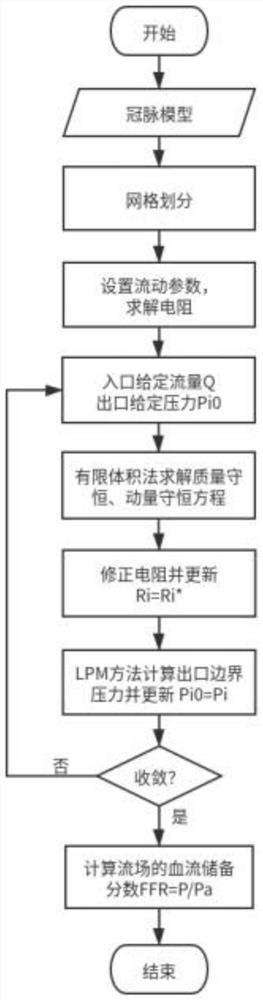
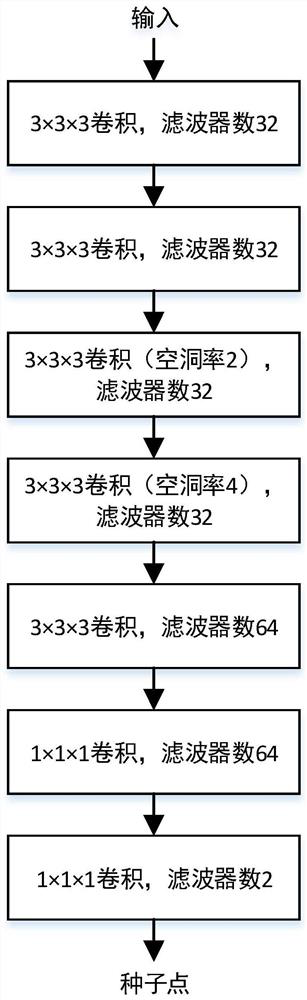
Coronary artery reconstruction and fractional flow reserve calculation method and device based on deep learning, equipment and readable storage medium
PendingCN111652881AEasy extractionImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesHematological test
The invention relates to a coronary artery reconstruction and fractional flow reserve calculation method and device based on deep learning, equipment and a readable storage medium. A coronary artery blood vessel model is automatically reconstructed through a deep learning model, and a functional parameter, namely the fractional flow reserve, is obtained by solving a hemodynamic control equation. Acoronary artery center line is automatically searched in a deep learning mode, and the coronary artery model is automatically segmented, so that the workload and the working time of manual segmentation or semi-automatic segmentation are greatly reduced. In addition, based on hemodynamic calculation of a lumped parameter model, the microcirculation resistance is coupled at the outlet boundary, sothat blood flow in coronary artery of the patient can be simulated more truly, and the fractional flow reserve can be calculated more accurately.
Owner:HANGZHOU ARTERYFLOW TECH CO LTD
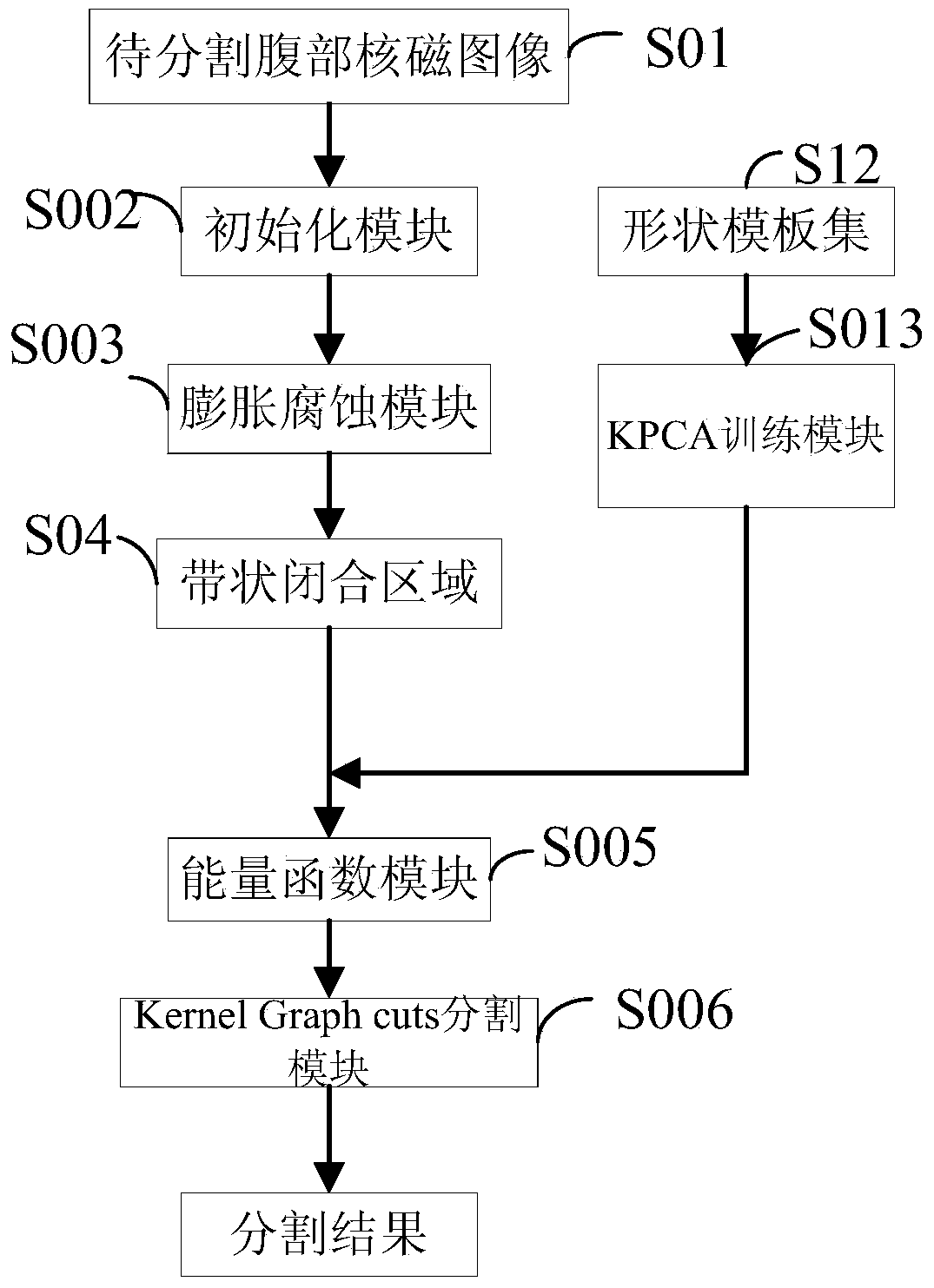
Method and device for abdomen soft tissue nuclear magnetism image segmentation
ActiveCN103473768AEasy to implementSimple Automatic SegmentationImage analysisImage segmentation algorithmBand shape
The invention discloses a method and device for abdomen soft tissue nuclear magnetism image segmentation. The method comprises the steps that an original outline is initialed near an objective outline; a morphological operator is used for carrying out expansion and corrosion operations on the original outline, and a band-shaped closed area is formed in and outside the objective outline to be segmented; KPCA training is conducted on a collected shape template and prior shape information is obtained through a statistics model; the prior shape information is combined with data items of an energy function of a nuclear magnetism image segmentation model, and an energy function is constructed; a kernel Graph cuts algorithm is used for carry out segmentation on the band-shaped closed area and an objective outline is obtained. The method and device for abdomen soft tissue nuclear magnetism image segmentation can achieve semi-automatic segmentation, the device is simple, the robustness of the nuclear magnetism image segmentation algorithm is effectively improved so as to enable the segmentation result to be more accurate, and the method and device for abdomen soft tissue nuclear magnetism image segmentation can be applied to most nuclear magnetism image segmentation.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for automatic or semi-automatic segmentation of a 3D image data set
ActiveUS20150078643A1Avoid disadvantagesMethod implementationImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationData set
In a method and apparatus for automatic or semi-automatic segmentation of a 3D image data set, acquired by a medical imaging apparatus, of an examination region that includes an organ, the 3D image data set is provided to a computer / processor, which is also provided with information with designating the type of organ imaged in the examination region. The 3D image data set is automatically segmented in the computer / processor using a model-based segmentation algorithm, wherein the designated type of organ is used as a basis of the model. The 3D data set is also automatically or semi-automatically segmented using a greyscale value-based segmentation algorithm. At least one of the segmentation results is displayed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
A semi-automatic segmentation method for sketching a regional growth lung tumor radiotherapy target region
PendingCN109767421ARobust Lesion SegmentationEfficient and accurate lesion segmentationImage analysisPulmonary tumorParenchyma
The invention provides a semi-automatic segmentation method for sketching a regional growth lung tumor radiotherapy target region, and the method specifically comprises the following steps of S1, lesion automatic initial seed point selection characterized by obtaining lesion seed points from a lung parenchyma gradient image containing lesion through the step, and obtaining a lung parenchyma CT image gradient minimum value through calculation; and S2, final lesion position refinement characterized by carrying out the refinement of the final lesion position by determining a more accurate lesionboundary definition. By using the method provided by the invention, the steady, efficient and accurate lung lesion segmentation can be automatically realized.
Owner:SHANDONG RES INST OF TUMOUR PREVENTION TREATMENT
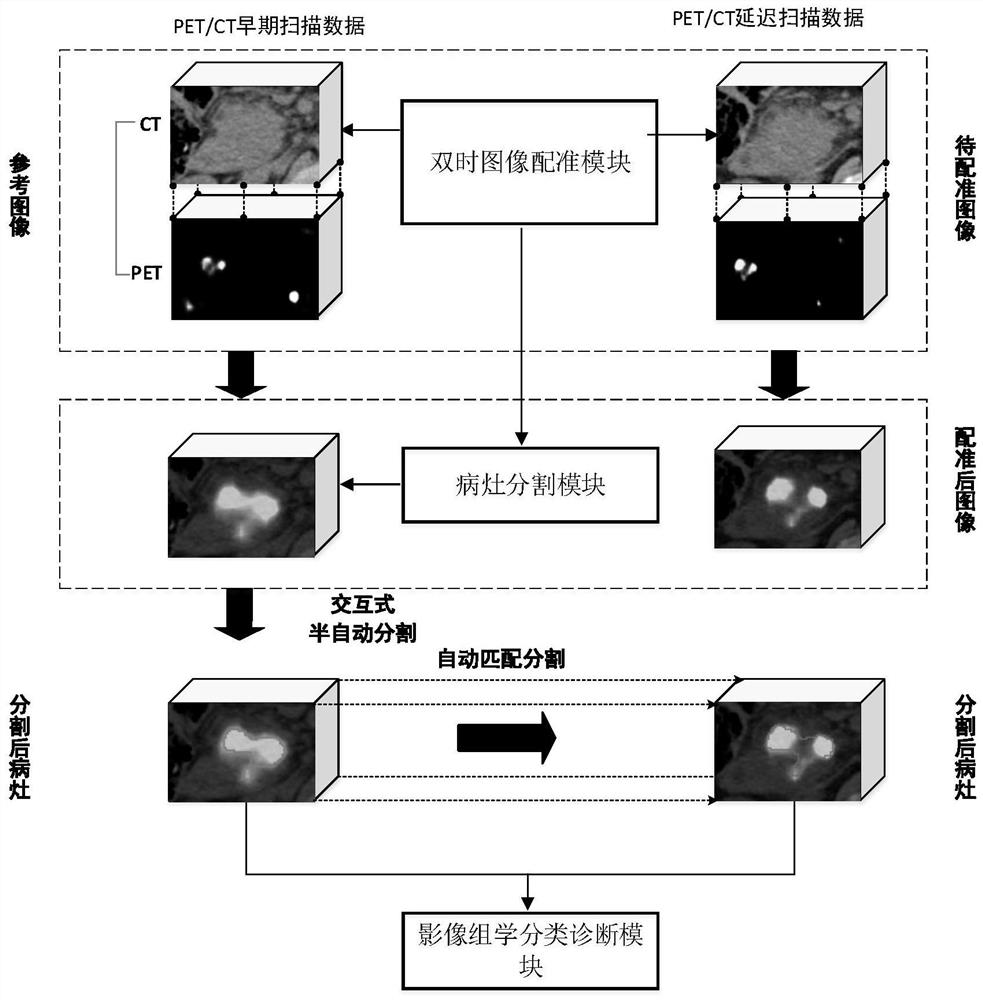
Pancreatic cancer accurate diagnosis system based on PET/CT double-time imaging
PendingCN112070809AReduce false positive rateGood precisionImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationPancreas Cancers
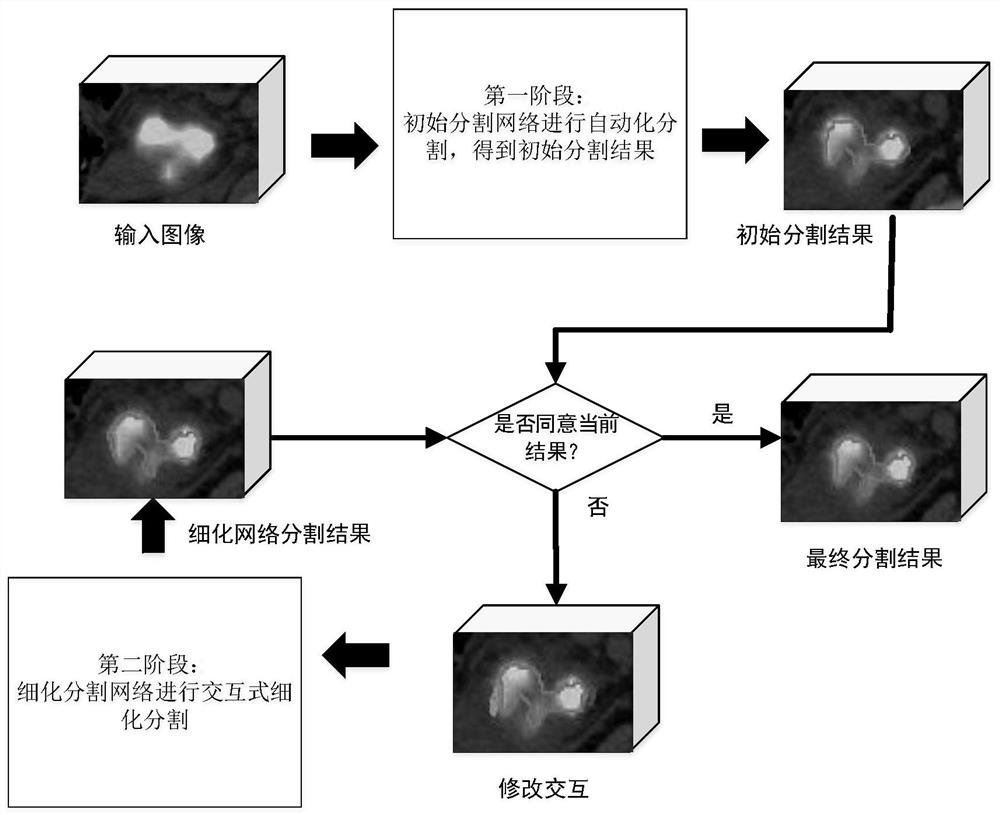
The invention discloses a pancreatic cancer accurate diagnosis system based on PET / CT double-time imaging, which comprises: a dual-time image registration module is used for registering PET / CT delayedscanning image data acquired through PET / CT image scanning with PET / CT early scanning image data; a focus segmentation module which is used for carrying out interactive semi-automatic segmentation onthe early PET image by adopting a deep interactive segmentation network model based on a convolutional neural network; and an imaging omics classification diagnosis module which is used for analyzingthe segmented PET / CT early scanning image and PET / CT delayed scanning image to obtain a diagnosis result. According to the method, the segmentation error caused by the partial volume effect of the PET image is reduced, the segmentation habit of a current clinician is automatically learned, the precision and robustness of automatic segmentation of a single CNN network are further improved, the false positive rate of pancreatic cancer diagnosis can be effectively reduced, and the system has good clinical popularization and application prospects.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A method and system for ultrasonic image segmentation
ActiveCN103903255BAvoid the local minimum problemResolve accuracyImage analysisSonificationImage segmentation algorithm
The invention is suitable for the technical field of image processing, and particularly relates to an ultrasound image segmentation method and system. The method includes the following steps that coarse registration is conducted on a statistical shape model and collected three-dimensional ultrasound data of a specified organ to obtain initialized coordinate transformation parameters; according to the initialized coordinate transformation parameters, an image segmentation algorithm based on particle filter is used for conducting iteration segmentation on the three-dimensional ultrasound data, wherein the statistical shape model is a combination of an average value obtained by training manual segmentation results of a plurality of high-definition three-dimensional data and a group of feature vectors of a representation change mode. Therefore, the problem that more artificial participation is needed in manual segmentation and semi-automatic segmentation is solved. Compared with an existing full-automatic segmentation method, the ultrasound image segmentation method and system solve the problems of low image resolution and segmentation accuracy under the image fuzzy condition.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Processing method of atherosclerotic plaque medical image
InactiveCN103164854ADraw reliableComplementary medical researchImage analysisCommercial softwareSemi automatic segmentation
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Semi-automatic partition method of lung CT image focus
InactiveCN100573581CAccurate segmentationImprove efficiencyImage enhancementComputerised tomographsSemi automaticUsability
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
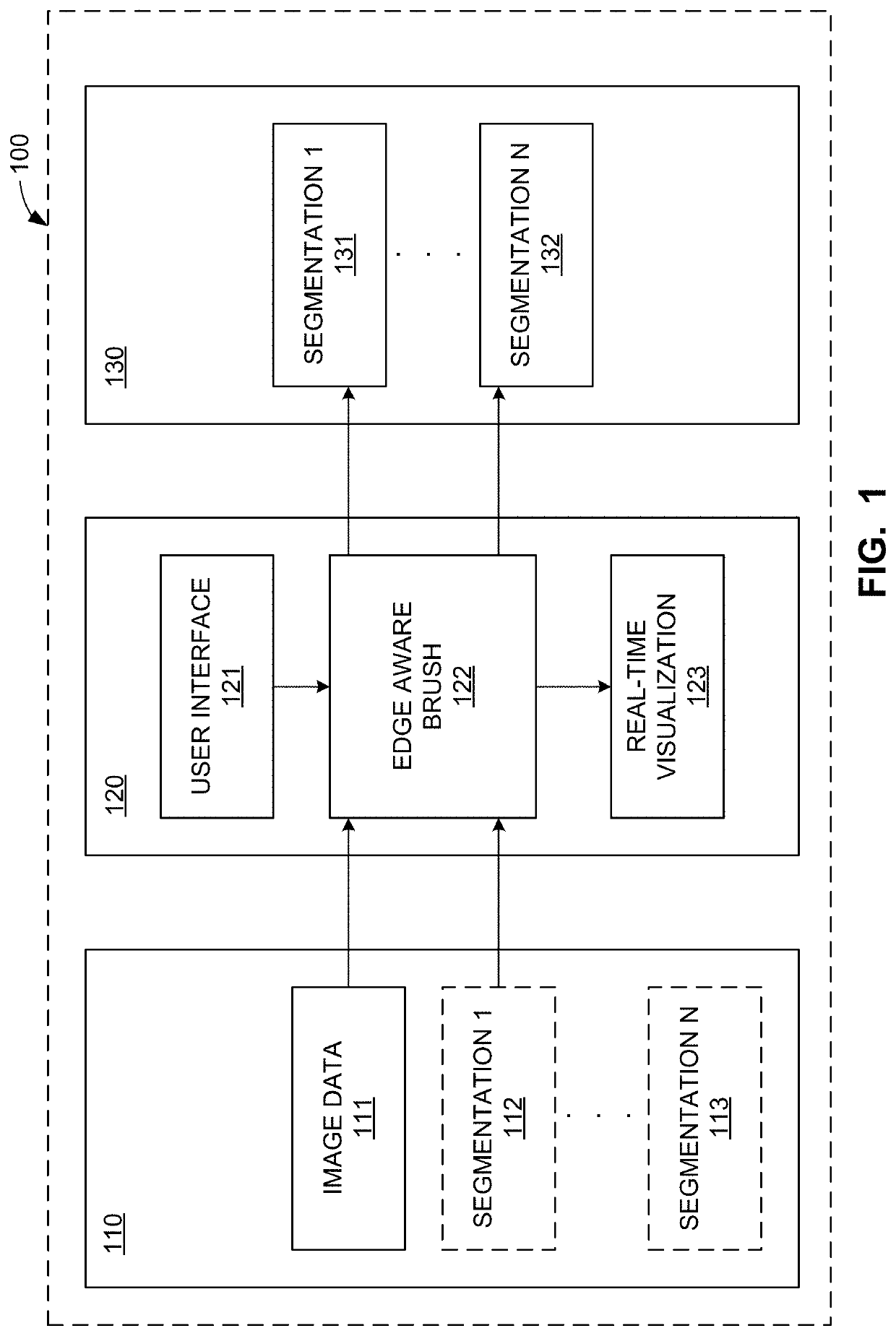
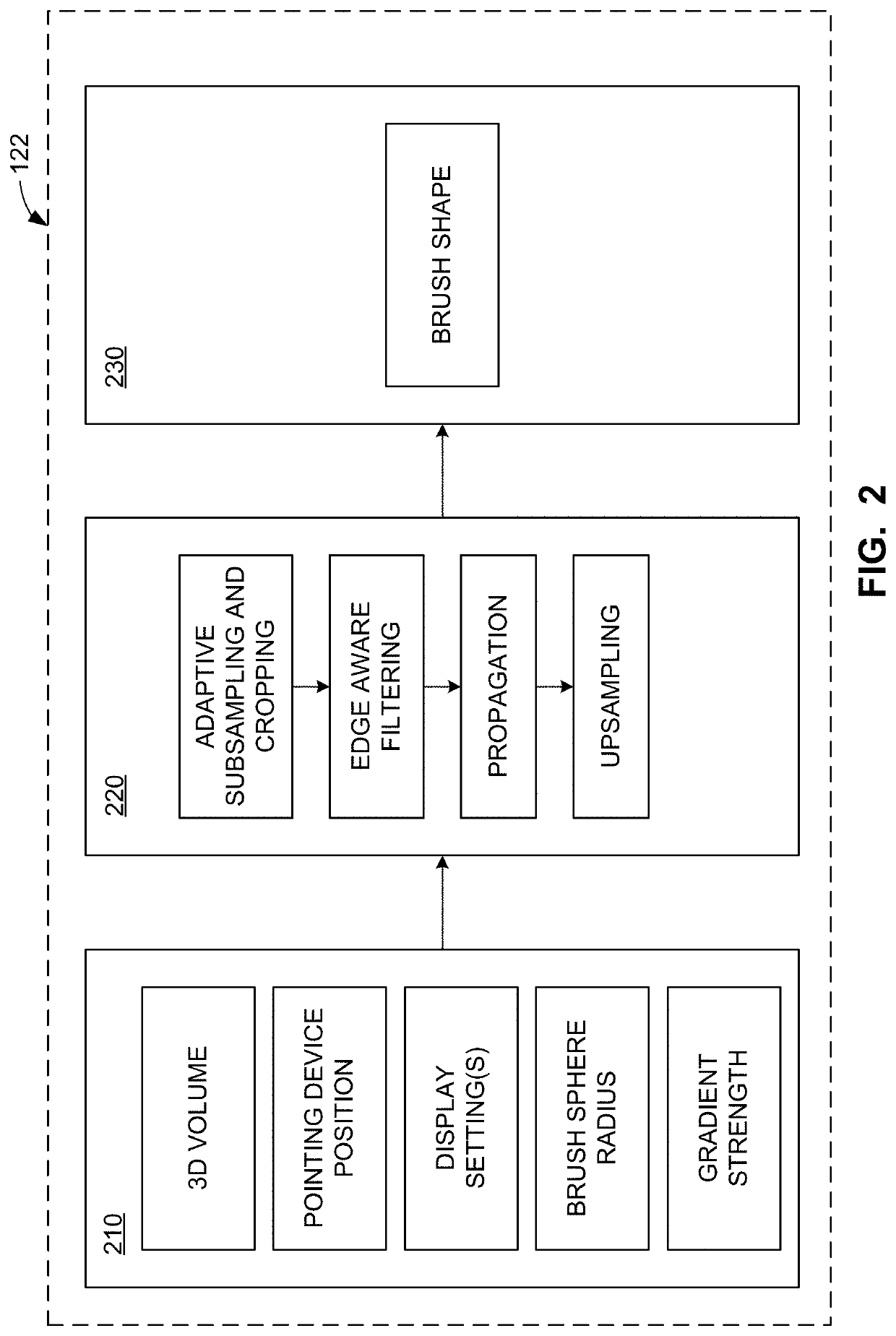
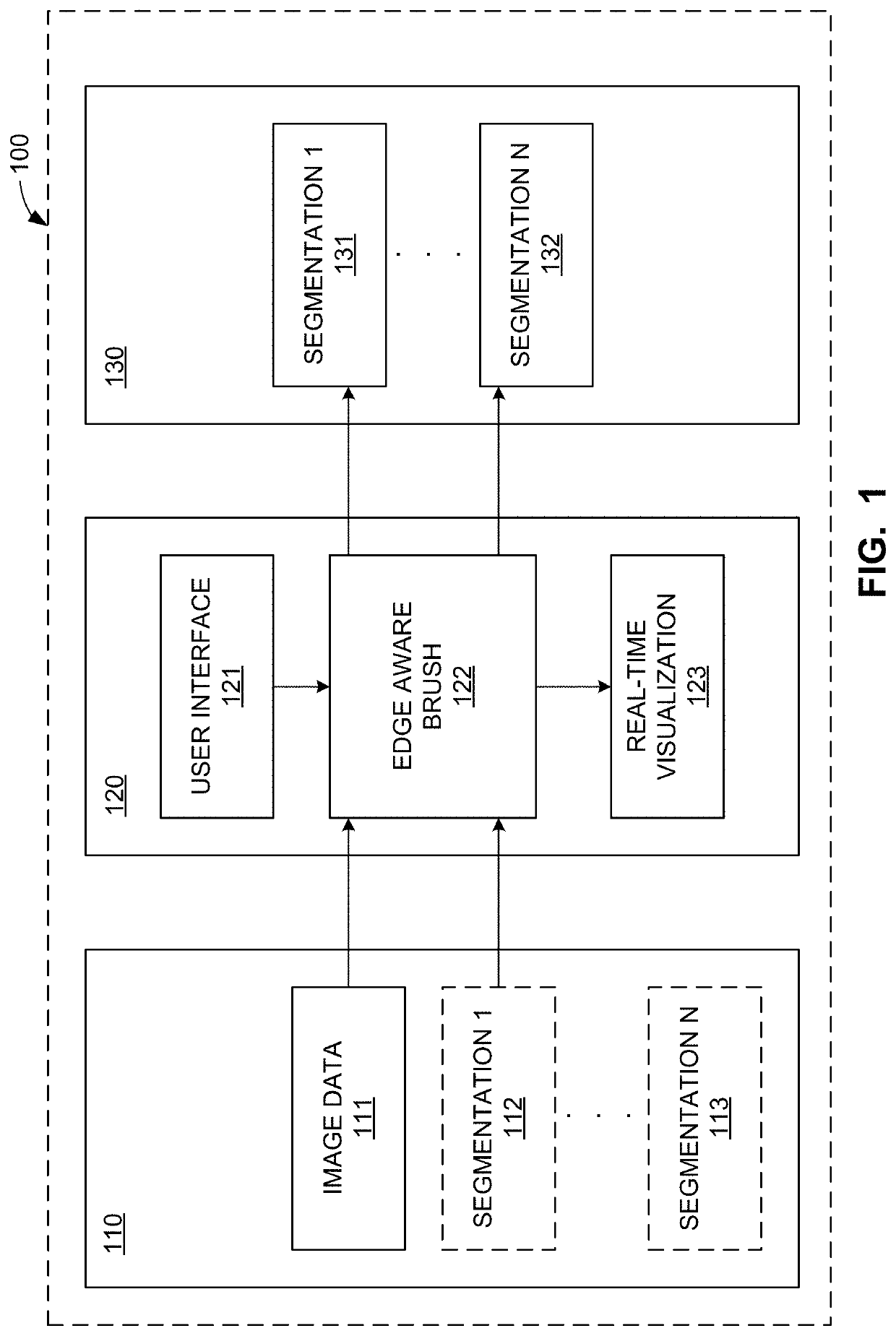
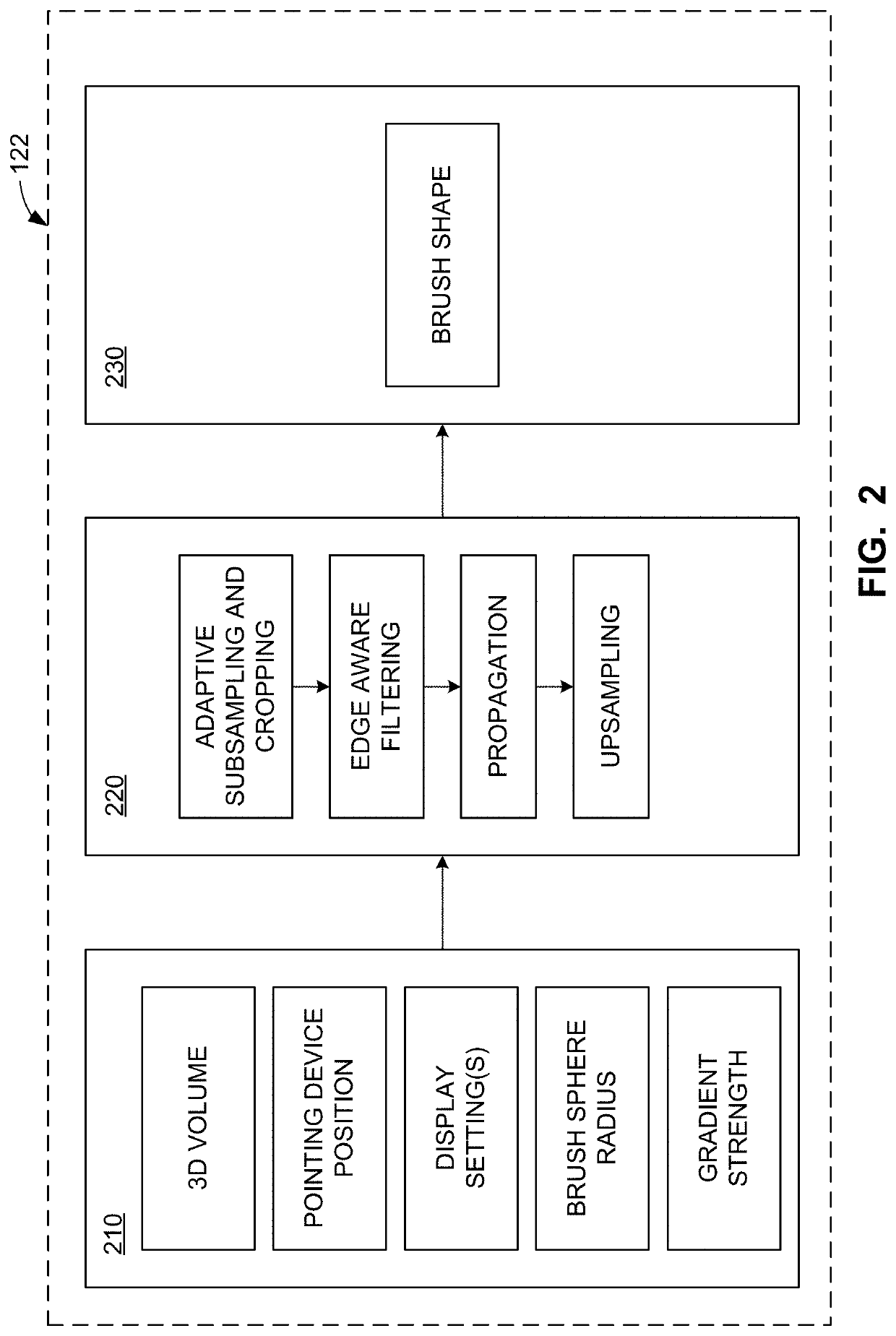
Systems and methods to semi-automatically segment a 3D medical image using a real-time edge-aware brush
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods to semi-automatically segment a 3D medical image using a real-time edge-aware brush
Apparatus, systems, and methods to generate an edge aware brush for navigation and segmentation of images via a user interface are disclosed. An example processor is to at least: construct a brush for segmentation of image data; provide an interactive representation of the brush with respect to the image data via a user interface, the interactive representation to be displayed and made available for interaction in each of a plurality of viewports provided for display of views of the image data in the user interface; enable update of the viewports based on manipulation of the representation; facilitate display of a preview of a segmentation of the image data corresponding to a location of the representation; and, when the segmentation is confirmed, facilitate generation of an output based on the segmentation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
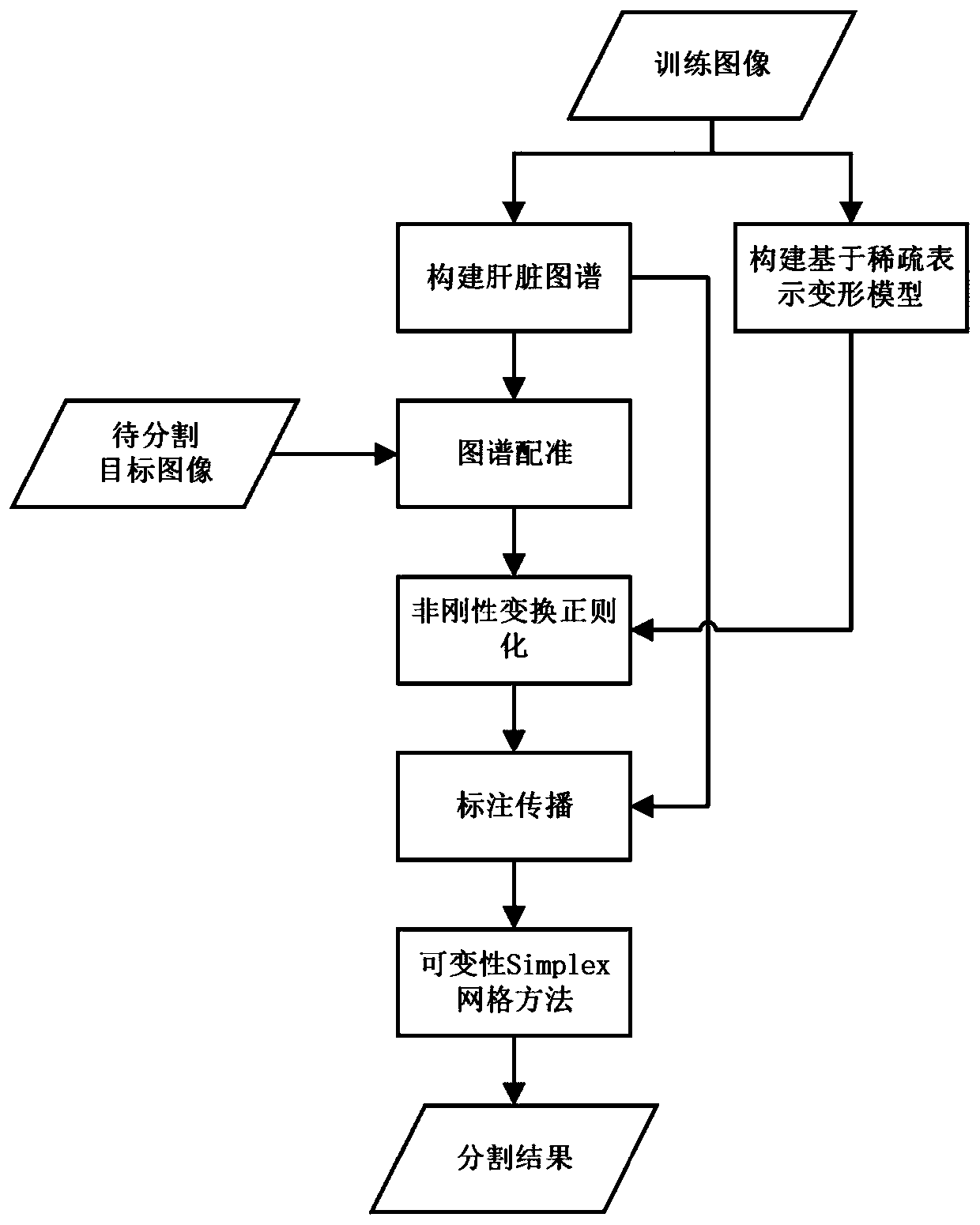
Automatic liver segmentation method based on deformation model of CT image
InactiveCN111462159AImprove robustnessVerify validityImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationRadiology
The invention discloses an automatic liver segmentation method based on a deformation model of a CT image. The method comprises the steps: 1, building a liver atlas, and representing the deformation model SRDM based on sparsity, and the liver atlas comprises a gray level image and a marking image corresponding to the gray level image; 2, performing liver map registration on a to-be-segmented target image, and constructing a non-rigid transformation model for aligning a grayscale image of the liver map to the target image; 3, regularizing the non-rigid transformation model in the step 2 by using a sparse representation deformation model SRDM; 4, propagating the labeled image of the liver map to a target image by using the regularized transformation model to obtain an initial segmentation result; and step 5, for the data with relatively large segmentation errors, carrying out fine segmentation on an initial segmentation result. Through the scheme, the segmentation precision close to thatof a semi-automatic segmentation method is obtained, and the experimental result can be repeated.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A Semi-Automatic Brain Image Segmentation Method
InactiveCN109509203BAvoid the influence of subjective factorsReduce mistakesImage enhancementImage analysisContour segmentationPrior information
The invention discloses a semi-automatic brain image segmentation method, in particular comprising the following steps: firstly, a map registration and a template selection method are used to obtain shape prior information of a target tissue and generate a segmentation template; Secondly, the template optimization method is used to reduce the error in the process of map registration and generate the initial active contour. Finally, the active contour model is used to segment the target tissue. The invention combines the advantages of the atlas registration method and the active contour segmentation method, and realizes the semi-automatic segmentation of the brain image. The method of the invention effectively utilizes shape prior information of the atlas, and can obtain smooth and continuous target tissue outline.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Pulmonary nodule interactive segmentation method based on medical image
PendingCN112581479AThe segmentation result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleAutomatic segmentation
The invention discloses a pulmonary nodule interactive segmentation method based on a medical image. The method comprises the following steps: extracting a focus area according to a real nodule and aground glass nodule, wherein the segmentation algorithm is a semi-automatic segmentation algorithm, the lung real nodule segmentation method needs artificial participation to delineate a nodule region, and the lung frosted glass nodule segmentation method is automatic segmentation; if modification is needed after segmentation is completed, selecting two-dimensional modification or three-dimensional modification according to requirements to obtain an accurate segmentation result. Therefore, the rapid segmentation of pulmonary nodules is realized for further diagnosis and analysis.
Owner:睿佳(武汉)软件科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com