Patents
Literature
30 results about "Sodium current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sodium currents are essential for the initiation and propagation of neuronal firing. Alterations of sodium currents can lead to abnormal neuronal activity, such as occurs in epilepsy. The transient voltage-gated sodium current mediates the upstroke of the action potential.
Treating neurological disorders using selective antagonists of persistent sodium current
ActiveUS20050054695A1Reducing neuronal deathReduce deathBiocideAnimal repellantsDiseaseSodium Channel Antagonists
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Treating pain using selective antagonists of persistent sodium current
The present invention provides methods of treating chronic pain in a mammal by administering to the mammal an effective amount of a selective persistent sodium channel antagonist that has at least 20-fold selectivity for persistent sodium current relative to transient sodium current.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Compositions and methods for short interfering nucleic acid inhibition of NAv1.8
InactiveUS20060199779A1Inhibition of translationInhibit expressionNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsChronic painCell membrane
The invention provides short interfering nucleic acids, either single-stranded or double-stranded, that cause RNAi-induced degradation of mRNA from the Nav1.8 sodium channel gene; to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such short interfering nucleic acids; recombinant vectors comprising such short interfering nucleic acids; a method for inhibiting translation of an mRNA; a method for inhibiting expression of a polypeptide; a method for blocking the membrane potential in a cell; a method for blocking the sodium current in a cell; and a method for inhibiting chronic pain.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP +1
Treating pain using selective antagonists of persistent sodium current
The present invention provides methods of treating chronic pain in a mammal by administering to the mammal an effective amount of a selective persistent sodium channel antagonist that has at least 20-fold selectivity for persistent sodium current relative to transient sodium current.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
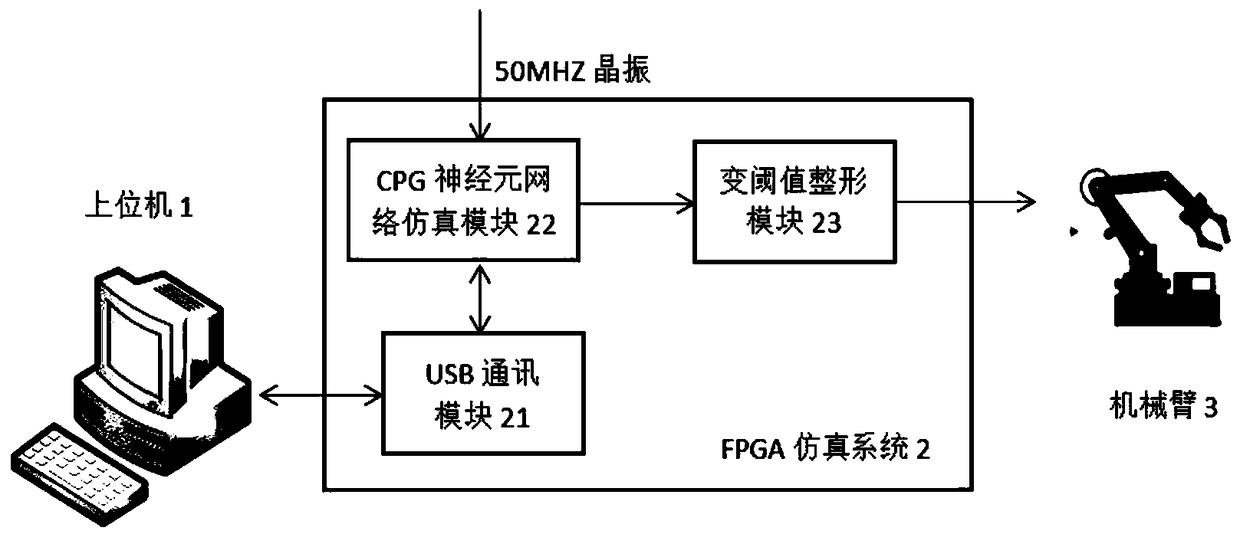
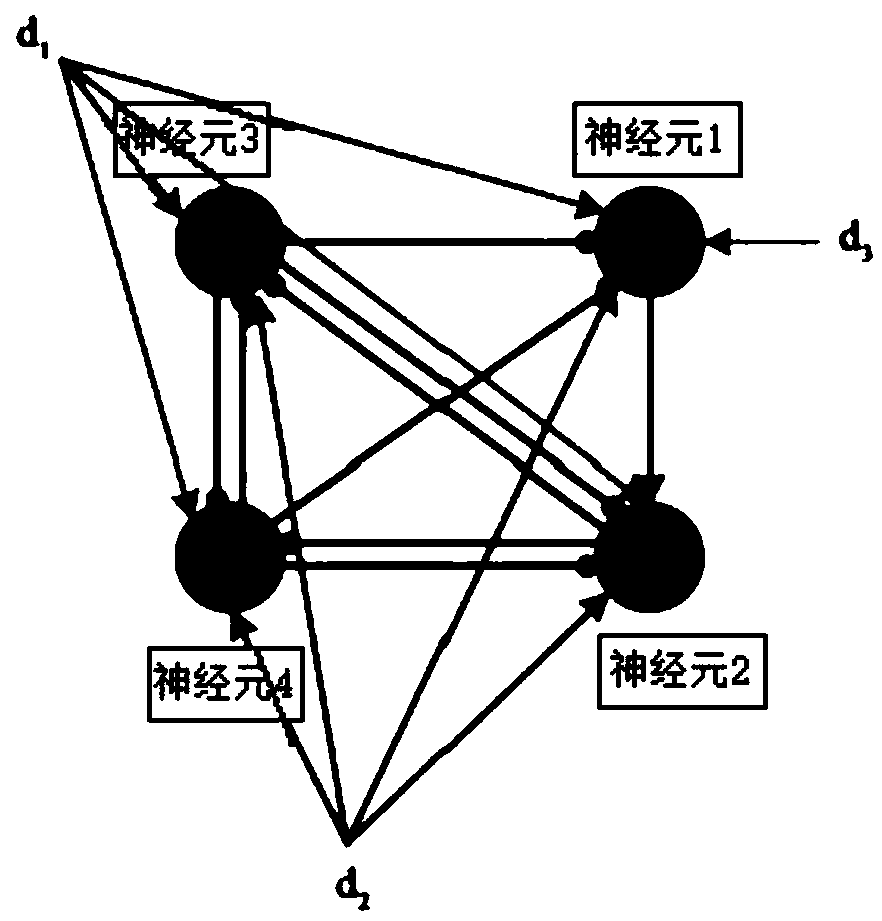
Mechanical arm movement rhythm control method based on CPG neural network
ActiveCN109352644AFast operationControl amplitudeProgramme-controlled manipulatorPhysical realisationControl signalFpga implementations
The invention relates to a mechanical arm movement rhythm control method based on a CPG neural network. The method comprises the following steps that (1) an upper computer is used for setting electricconductivity and reverse potential parameters corresponding to nerve cell continuous sodium current, potassium current and leakage current as well as an upper limit threshold value, a lower limit threshold value and a threshold value period during variable-threshold shaping, and transmitting the electric conductivity, the reverse potential parameters, the upper limit threshold value, the lower limit threshold value and the threshold value period to the FPGA through USB communication; (2) the FPGA is used for establishing a CPG neural network simulation model according to the set parameters, simulation is carried out, a discharge waveform is output in the simulation process, and the waveform is transmitted to the upper computer to be displayed; (3) the FPGA is used for achieving variable-threshold shaping, the discharge waveform output by the CPG neural network in the step 2 is set, moreover, a control signal is output to a mechanical arm so as to control and adjust the movement rhythmof the mechanical arm, and the angular displacement of a mechanical arm joint is transmitted to the upper computer to be displayed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
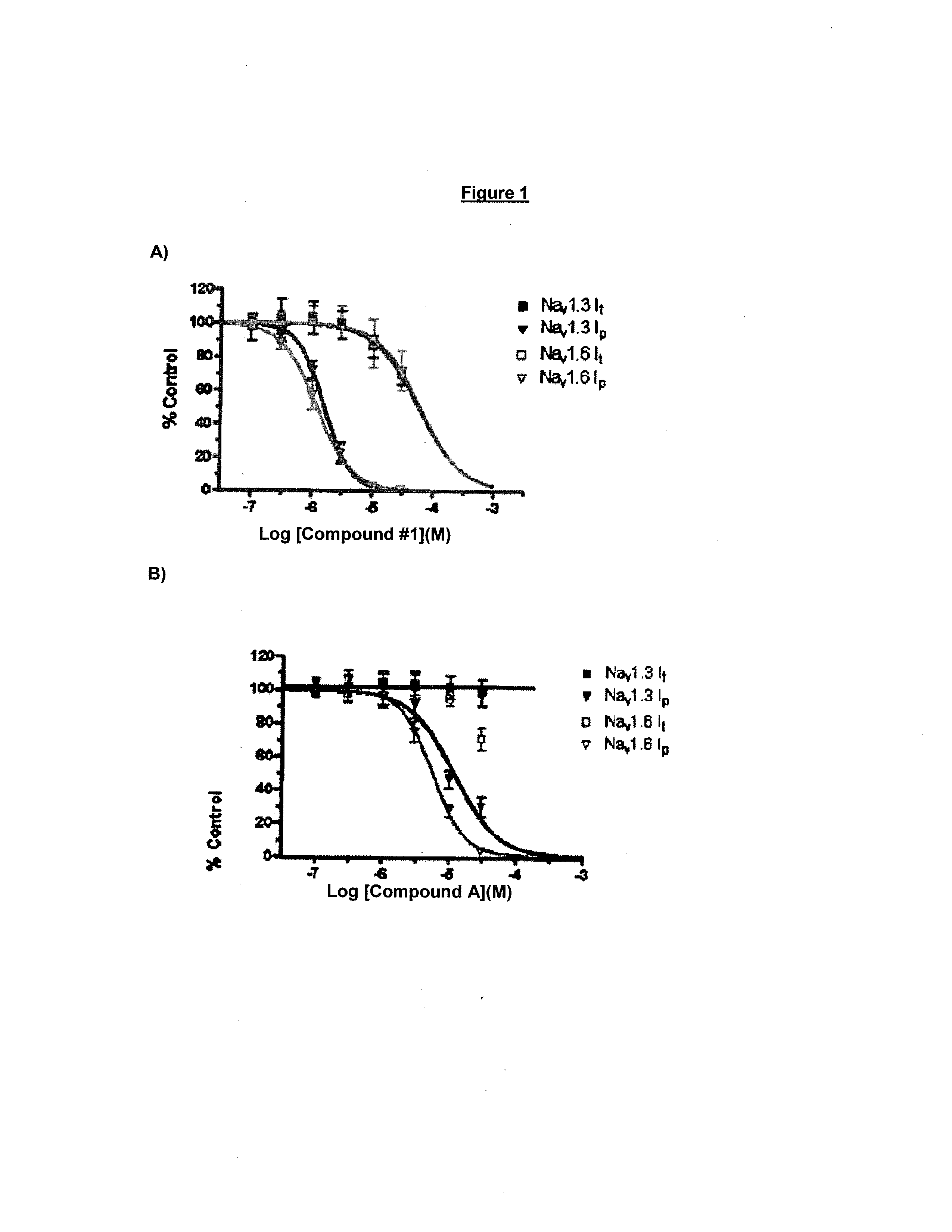
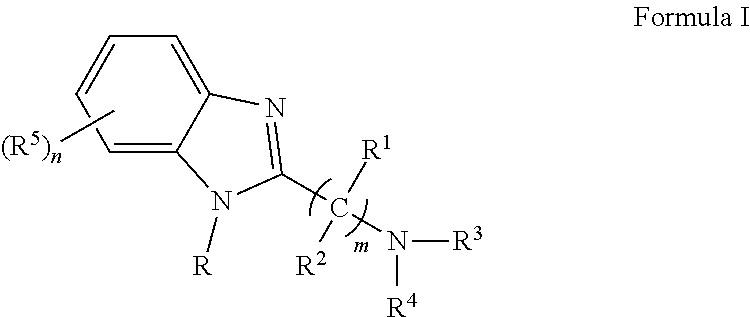
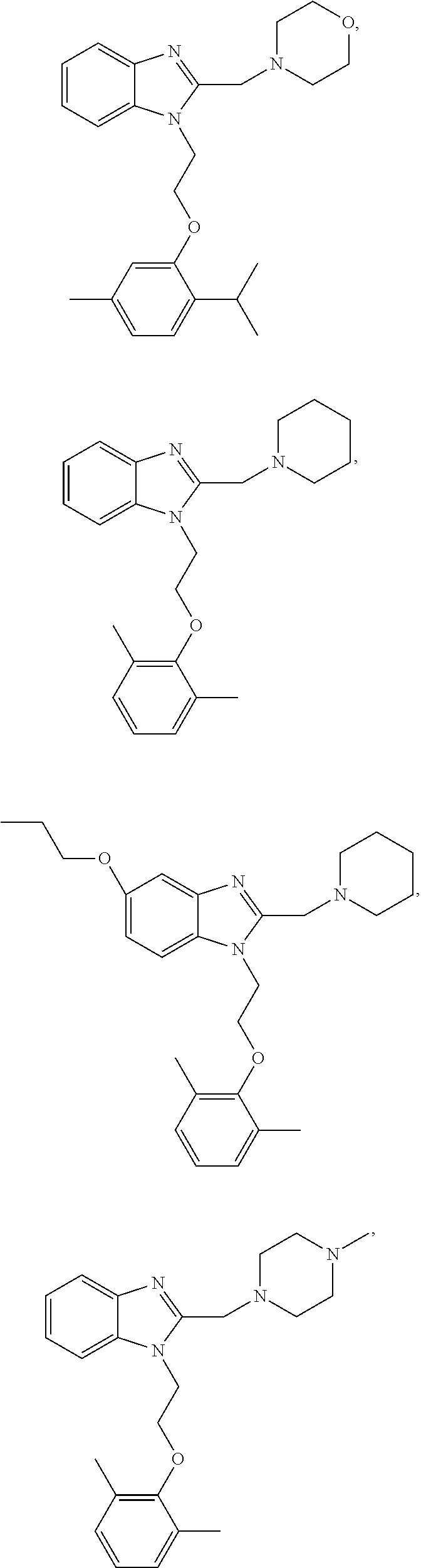
Benzimidazole derivatives as selective blockers of persistent sodium current
The present invention is directed to a compound of Formula Ior a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; wherein R, R1, R2, R3, R4, m, and n are as defined herein, to pharmaceutical compositions comprising said compound, and to methods of treating diseases or conditions mediated by elevated persistent sodium current, such as an ocular disorder, multiple sclerosis, seizure disorder, and chronic pain.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
New application of Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and guanfu base VIIII
The invention provides a preparation method of Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and applications in preparing a slow sodium-ion passage blocking agent and preparing drugs for resisting arrhythmia. Both the Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and the guanfu base I are provided to have an effect for inhibiting slow sodium current of ventricular muscles of cavies. The invention particularly relates to an application of guanfu base VIIII in preparing a drug-metabolizing enzyme inhibitor. The invention also provides an application of guanfu base VIIII in preparing a slow sodium-ion passage blocking agent.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
Novel application of Arctigenin in preparation of anti-arrhythmia medicine
InactiveCN103156842ASmall contraction forceHeart rate slowing effectOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderSide effectAntiarrhythmic effect
The invention discloses a novel application of a traditional Chinese medicine extract product-Arctigenin in preparation of anti-arrhythmia medicines. A research found that the Arctigenin has bidirectional anti-arrhythmia effect and can adjust arrhythmia caused by aconitine and ouabain. Arctigenin has an effect for reducing ventricular muscle contraction force. A pharmacological effect of the Arctigenin is bidirectional adjusted cardiac muscle cell inner calcium current, the cardiac muscle cell inner potassium current is increased, and the sodium current is inhibited. The invention shows that the Arctigenin has anti-arrhythmia effect, and especially has bidirectional adjusting on arrhythmia, the side-effect is smaller, the Arctigenin has application prospect for treating toxic arrhythmia and ischemic-reperfusion arrhythmia in aconitine and ouabain; and the Arctigenin with myocardial contractility reduction effect can be taken as an auxiliary treatment measurement for hypertensive disease.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
Application of adrenergic receptor antagonist in preparation of drug for relieving sodium current increasing caused by brain injury
The invention discloses application of an adrenergic receptor antagonist in preparation of a drug for relieving sodium current increasing caused by brain injury. After a hypoxic-ischemic brain injury mouse is injected with the adrenergic receptor antagonist, the change of a sodium channel and increasing of a current amplitude can be significantly relieved, so that the adrenergic receptor antagonist can be applied to the preparation of the drug for relieving the sodium current increasing caused by the brain injury and has a potential application prospect in the treatment field of the brain injury.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
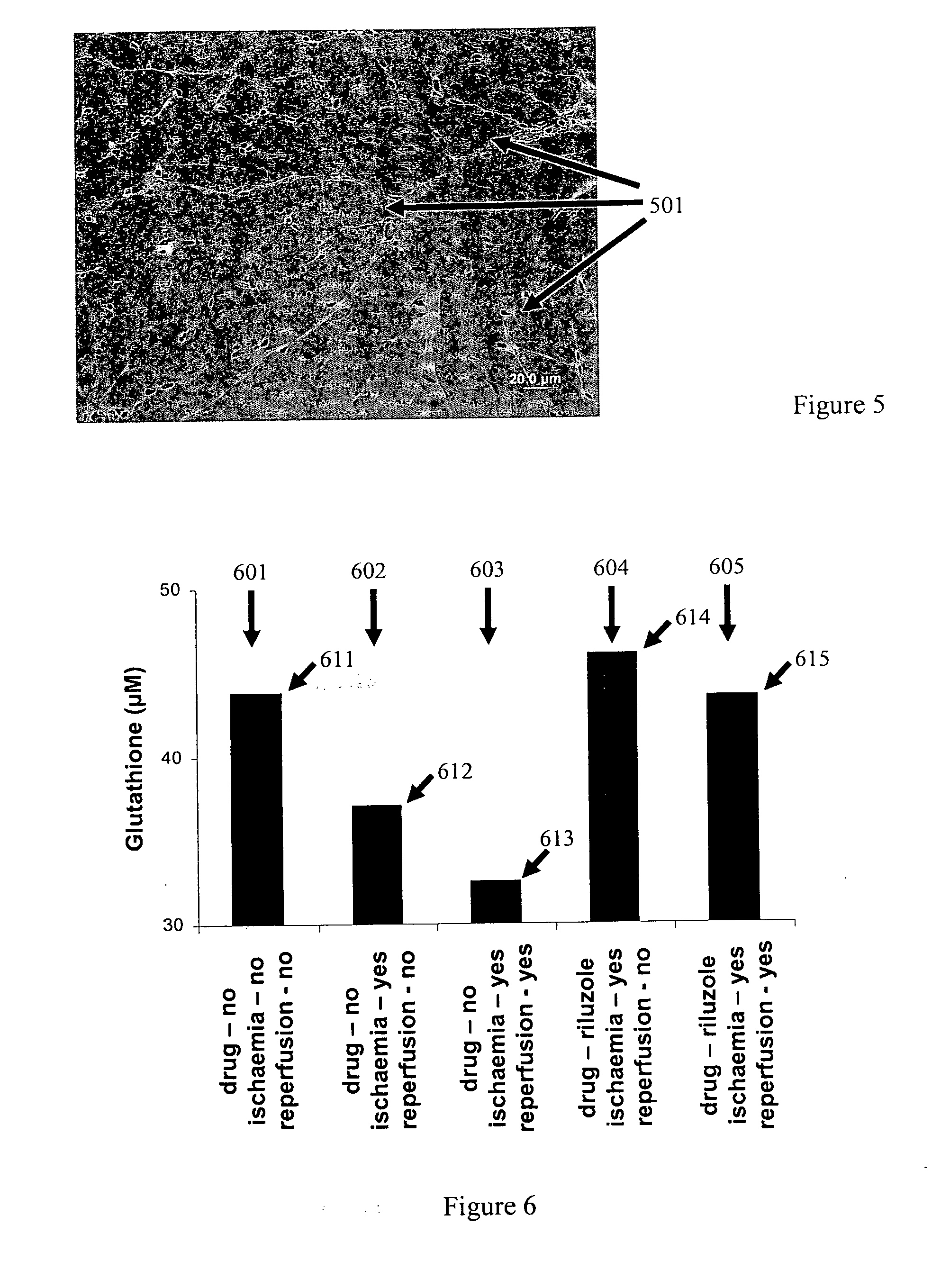
Treatment of non-neuronal and non-myocardial cell, tissue and organ damage and associated pain with persistent sodium current blockers
The present invention relates to a method for slowing the development of mammalian organ, tissue and cellular damage and death by using a persistent sodium current blocker (or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or derivative thereof). The present invention further relates to a method for preventing damage and death in mammalian organs, tissues and cells or reducing the extent of damage and death in mammalian organs, tissues and cells. In particular the invention relates to a method for the treatment, amelioration or prevention of non-neuronal and non-myocardial cell or tissue damage or death and for reducing the pain associated with non-neuronal and non-myocardial cell or tissue damage.
Owner:OZTEO
Benzimidazole derivatives as selective blockers of persistent sodium current
The present invention is directed to methods of treating diseases or conditions mediated by elevated persistent sodium channel, such as ocular disorders, pain, multiple sclerosis, and seizure disorders utilizing a compound of Formula Ior a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a pharmaceutical composition comprising said compound, wherein variables R, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, m, and n in Formula I are as defined herein.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Novel modification-specific signal Conus superfamily toxin and uses thereof
InactiveCN101307101ABiologically activeHas central analgesic effectNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPurification methodsNeural biology
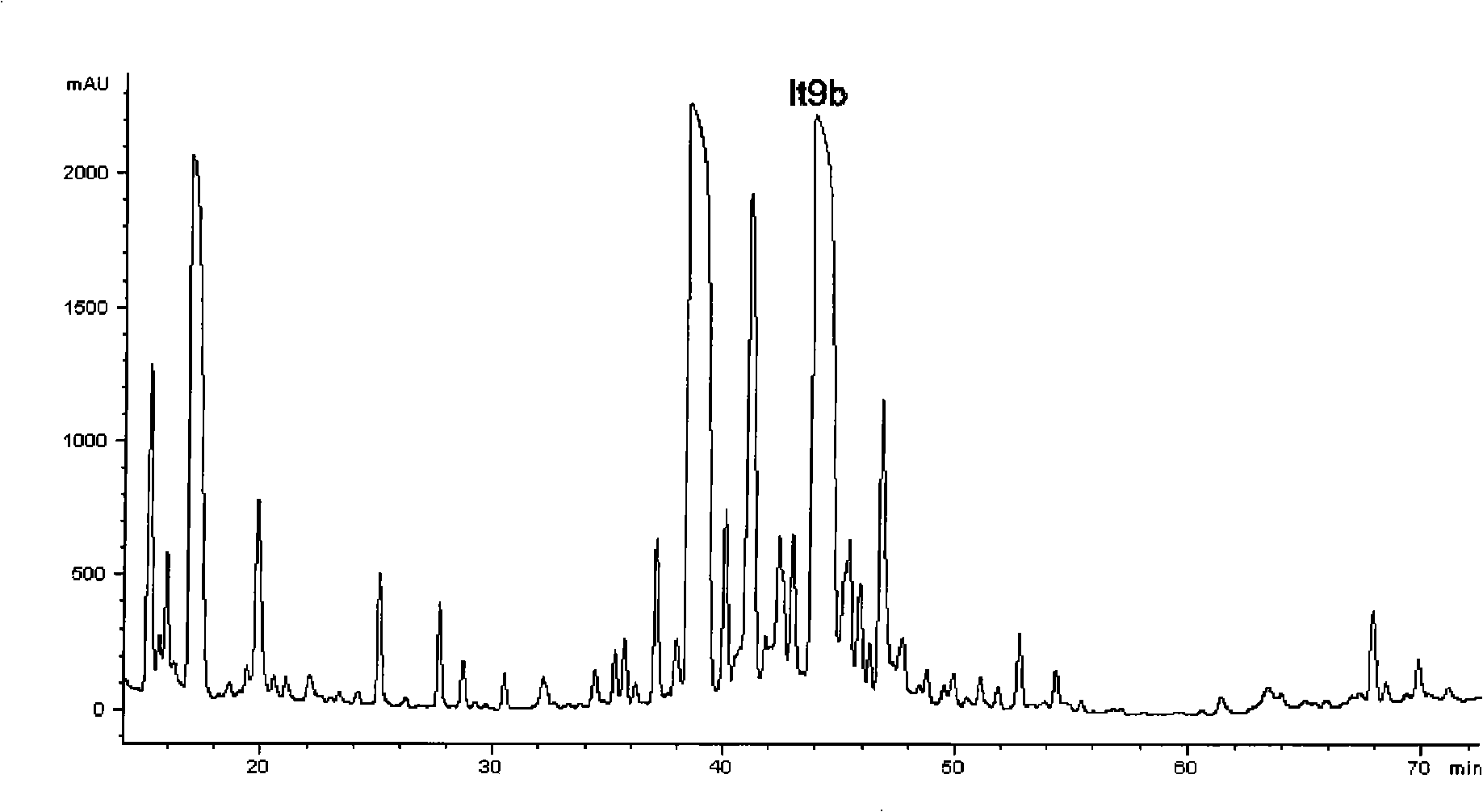
The invention relates to a novel South China Sea conus littertus Linnaeus P-superfamily toxin polypeptide sequence 1t9b with post-translational modification, and an application of the polypeptide to the neurobiological study, ionic channel study and analgesic development. The invention obtains the 1t9b from the toxic pipe of the South China Sea signal conus through a plurality of separation and purification methods, and the amino acid sequence of the 1t9b is showed by the andlt;400andgt;1 sequence in a sequence table. The conus toxin 1t9b has an obvious inhibiting action on a TTX sensitive type sodium current in a density of 500nM. A mouse hot plate experiment also discloses that the conus toxin 1t9b has a central analgesia action. Thus, the conus toxin 1t9b can serve as a probe which is applicable to the classification and determination of ion channel types and hypotypes or to the research and development of instrumental medicines and the preparation of analgesics.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani and novel use of Guanfu base I
The invention provides a preparation method of total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani as well as an application of the total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani in preparing a slow sodium ion channel blocker and an antiarrhythmic medicine. Researches show that both the total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani and Guanfu A hydrochlorate have an inhibiting effect on a slow sodium current of the ventricular muscle of a guinea pig. The invention particularly relates to an application of the Guanfu base I in preparing enzyme inhibitors for drug metabolism. The invention further provides an application of the Guanfu base A in preparing the slow sodium ion channel blocker.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
Application of sodium houttuyfonate to preparation of medicament for treating heart failure and/or arrhythmia
PendingCN108210487ALittle side effectsImprove myocardial systolic dysfunctionAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderMedicineCardiac muscle
The invention provides application of sodium houttuyfonate to preparation of a medicament for treating heart failure and / or arrhythmia. The invention also provides application of the sodium houttuyfonate to preparation of a medicament for enhancing contractile force of ventricular myocytes. The sodium houttuyfonate increases L-type calcium current (Ica.L), and can improve myocardial systolic dysfunction caused by the reduction of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca release when the heart failure is occurred. The sodium houttuyfonate blocks peak sodium current (Ina.p) and has the characteristics of class-I antiarrhythmic medicaments, and can also block late sodium current (INa.L) increased by the induction of congestin II (ATX-II) and has the potential of inhibiting the arrhythmia caused by the increment of the INa.L.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Treating neurological disorders using selective antagonists of persistent sodium current
ActiveUS20060106112A1Reduce deathBiocideKetone active ingredientsSodium Channel AntagonistsSodium current
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
New application of Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and guanfu base VIIII
The invention provides a preparation method of Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and applications in preparing a slow sodium-ion passage blocking agent and preparing drugs for resisting arrhythmia. Both the Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and the guanfu base I are provided to have an effect for inhibiting slow sodium current of ventricular muscles of cavies. The invention particularly relates to an application of guanfu base VIIII in preparing a drug-metabolizing enzyme inhibitor. The invention also provides an application of guanfu base VIIII in preparing a slow sodium-ion passage blocking agent.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
Benzimidazole derivatives as selective blockers of persistent sodium current
The present invention is directed to a compound of Formula Ior a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; wherein R, R1, R2, R3, R4, m, and n are as defined herein, to pharmaceutical compositions comprising said compound, and to methods of treating diseases or conditions mediated by elevated persistent sodium current, such as an ocular disorder, multiple sclerosis, seizure disorder, and chronic pain.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Compositions and methods for short interfering nucleic acid inhibition of Nav1.8
InactiveUS7786291B2Nervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsCell membraneSingle strand
The invention provides short interfering nucleic acids, either single-stranded or double-stranded, that cause RNAi-induced degradation of mRNA from the Nav1.8 sodium channel gene; to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such short interfering nucleic acids; recombinant vectors comprising such short interfering nucleic acids; a method for inhibiting translation of an mRNA; a method for inhibiting expression of a polypeptide; a method for blocking the membrane potential in a cell; a method for blocking the sodium current in a cell; and a method for inhibiting chronic pain.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP +1
New Application of Total Alkaloids of Guanbaifu and Guanfu Nonin
The invention provides a preparation method of total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani as well as an application of the total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani in preparing a slow sodium ion channel blocker and an antiarrhythmic medicine. Researches show that both the total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani and Guanfu A hydrochlorate have an inhibiting effect on a slow sodium current of the ventricular muscle of a guinea pig. The invention particularly relates to an application of the Guanfu base I in preparing enzyme inhibitors for drug metabolism. The invention further provides an application of the Guanfu base A in preparing the slow sodium ion channel blocker.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
Treating neurological disorders using selective antagonists of persistent sodium current
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Applications of icariin in preparation of medicines treating arrhythmia
InactiveCN106902130AProlong and increase the occurrence time of induced arrhythmiaExtend and increase timeOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderLeft ventricular sizeVentricular tachycardia
The invention belongs to the technical field of icariin applications, and discloses applications of icariin in preparation of medicines treating arrhythmia. According to a technical scheme, the medicines are capsules, micro-capsules, lipidosomes, granules, injections, tablets or oral liquids. Beneficial effects of the applications are that the icariin can prolong occurrence time (a time threshold) and increase the using amount (a dosage threshold) for arrhythmia induced by aconitine under a whole (living body) condition, and the icariin can effectively reduce the occurrence rates of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation which are induced by the aconitine and the death rate of New Zealand big-ear rabbits. The icariin can retard instantaneous sodium current (I<NaT>), late sodium current (I<NaL>) and L-type calcium current (I<CaL>) and plays a role of an arrhythmia preventing medicine. The icariin has no obvious effects on inward rectifier potassium current (I<K1>) of left-ventricular muscle (LVM), rapid delayed rectifier potassium current (I<Kr>), instantaneous outward potassium current (I<to>) of left atrial muscle (LAM) and ultra-rapidly activated delayed rectifier potassium current (I<Kur>), thus improving medication safety.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel application of Arctigenin in preparation of anti-arrhythmia medicine
InactiveCN103156842BSmall contraction forceHeart rate slowing effectOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderSide effectAntiarrhythmic effect
The invention discloses a novel application of a traditional Chinese medicine extract product-Arctigenin in preparation of anti-arrhythmia medicines. A research found that the Arctigenin has bidirectional anti-arrhythmia effect and can adjust arrhythmia caused by aconitine and ouabain. Arctigenin has an effect for reducing ventricular muscle contraction force. A pharmacological effect of the Arctigenin is bidirectional adjusted cardiac muscle cell inner calcium current, the cardiac muscle cell inner potassium current is increased, and the sodium current is inhibited. The invention shows that the Arctigenin has anti-arrhythmia effect, and especially has bidirectional adjusting on arrhythmia, the side-effect is smaller, the Arctigenin has application prospect for treating toxic arrhythmia and ischemic-reperfusion arrhythmia in aconitine and ouabain; and the Arctigenin with myocardial contractility reduction effect can be taken as an auxiliary treatment measurement for hypertensive disease.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
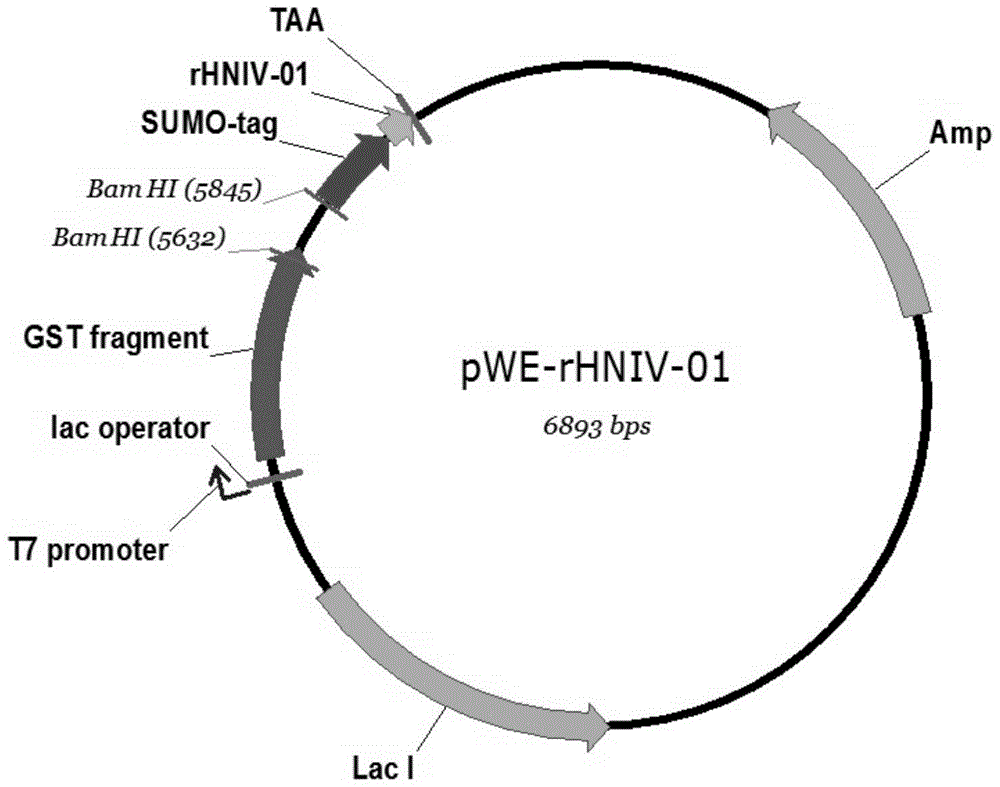
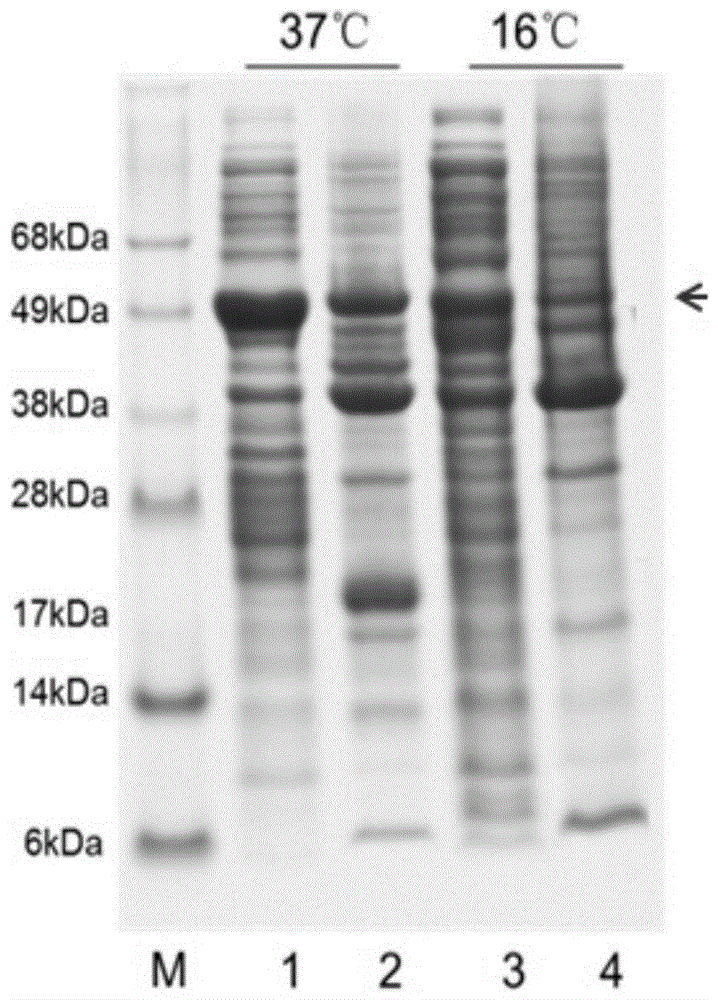
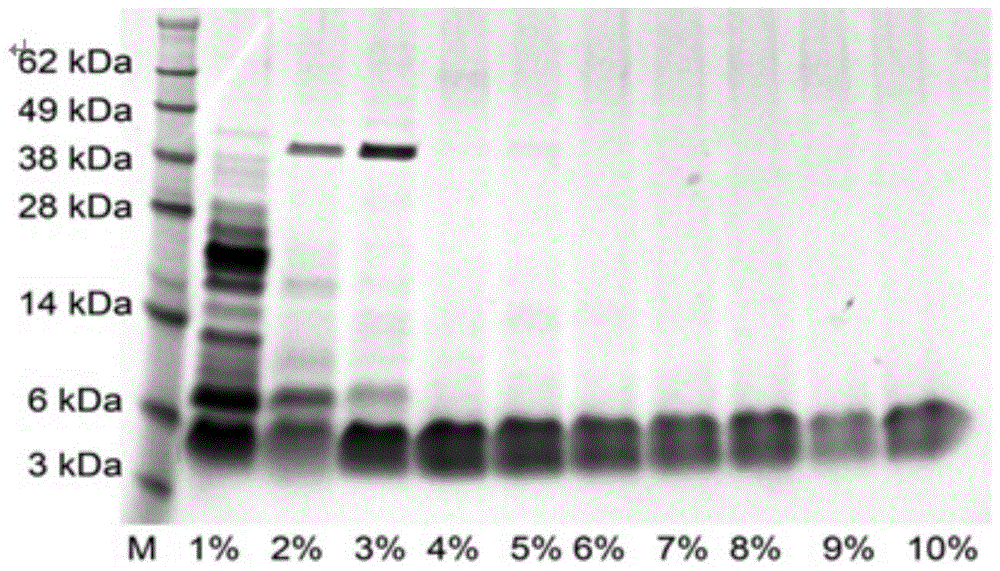
Expression vector of Hainan toxin-iv analog rhniv-01 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104099362BEfficient separationIncrease resistanceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDrug biological activityAmino acid
The invention provides an expression vector and a preparation method thereof, and high-purity recombinant HNTX (Hainantoxin)-IV analogue rHNIV-01 with biological activity can be rapidly prepared by the expression vector. Compared with natural HNTX-IV, an amino acid sequence of rHNIV-01 is almost the same as that of natural HNTX-IV, and only the C terminal of rHNIV-01 is not subjected to amidation modification. The method does not adopt conventional affinity chromatography for purifying fusion protein, protein kinase is directly added in a cell lysis product for cutting, then a cutting product rHNIV-01 is directly subjected to selective active extraction with a TCA (trichloroacetic acid) extraction method, and finally, RP-HPLC (reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography) is adopted for purification. With the adoption of the method, 3 mg / L high-purity rHNIV-01 can be obtained stably; and purified rHNIV-01 can selectively inhibit TTX-S (tetrodotoxin-sensitive) sodium current on DRG (dorsal root ganglia) cells of a rat.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Application of Adrenergic Receptor Antagonist in the Preparation of Drugs for Alleviating Increased Sodium Current Caused by Brain Injury
The invention discloses application of an adrenergic receptor antagonist in preparation of a drug for relieving sodium current increasing caused by brain injury. After a hypoxic-ischemic brain injury mouse is injected with the adrenergic receptor antagonist, the change of a sodium channel and increasing of a current amplitude can be significantly relieved, so that the adrenergic receptor antagonist can be applied to the preparation of the drug for relieving the sodium current increasing caused by the brain injury and has a potential application prospect in the treatment field of the brain injury.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
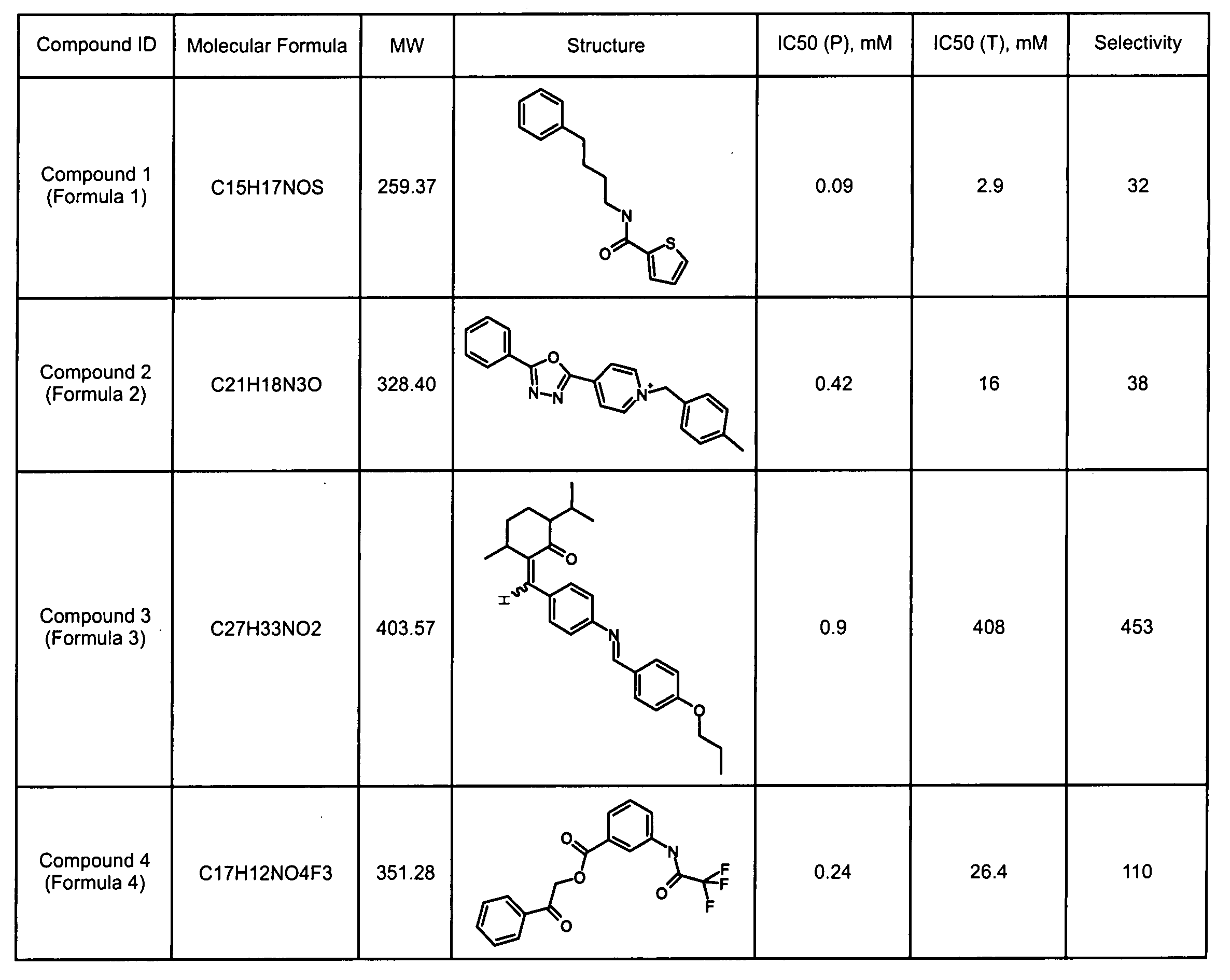
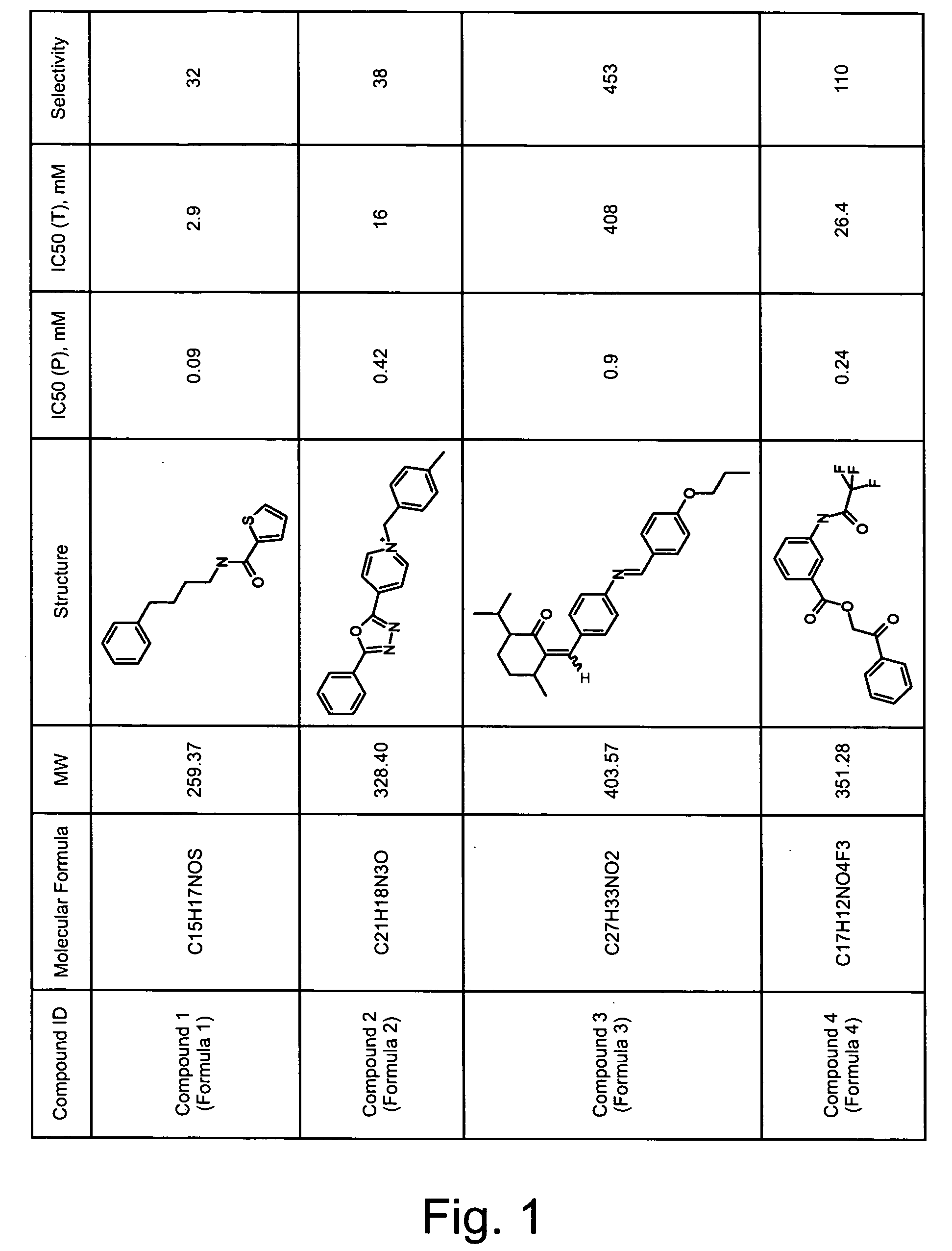
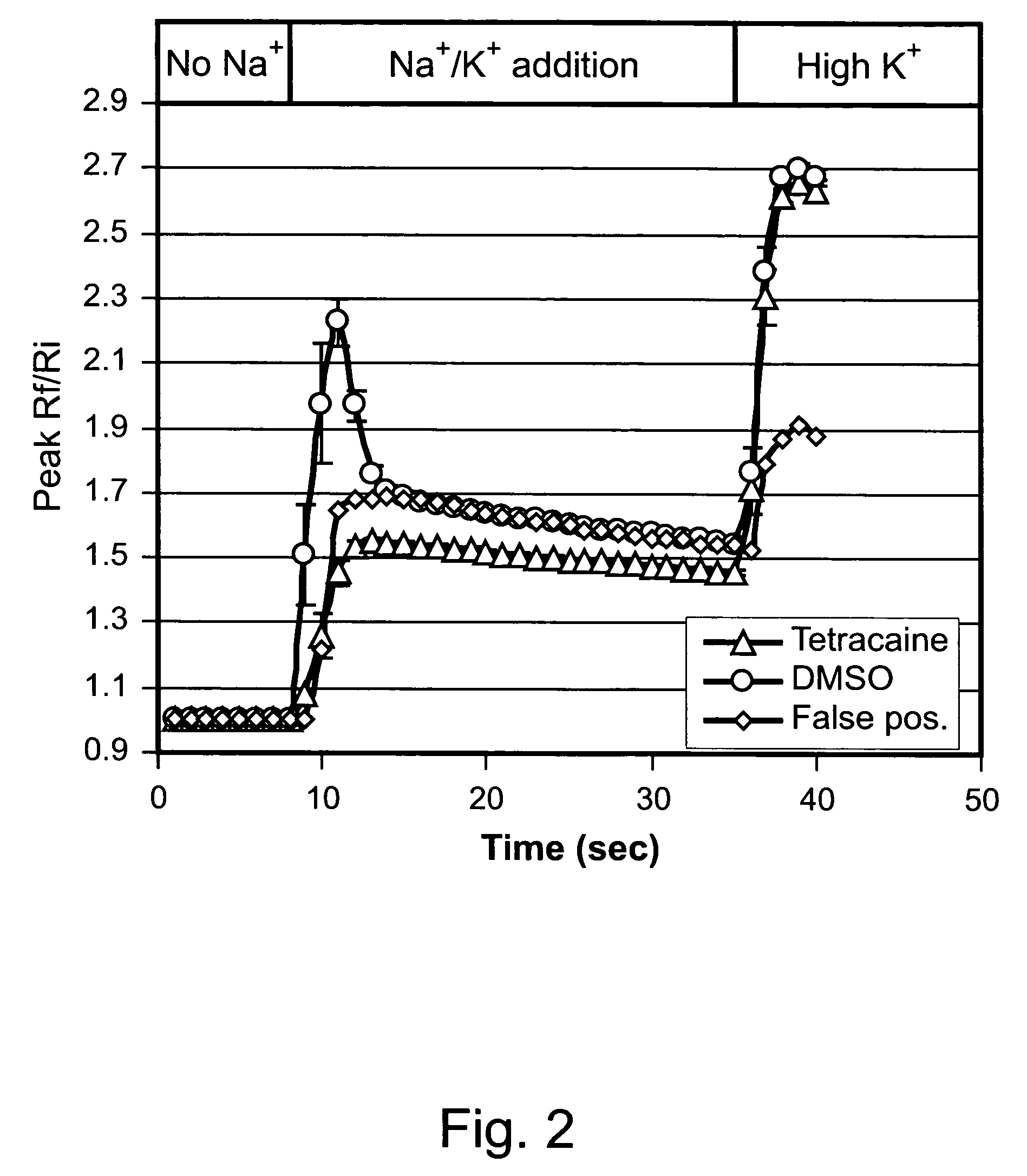
Application of 3-phenylfuran substituted 2-phenyl-4H-benzo[1,3]oxazine derivative
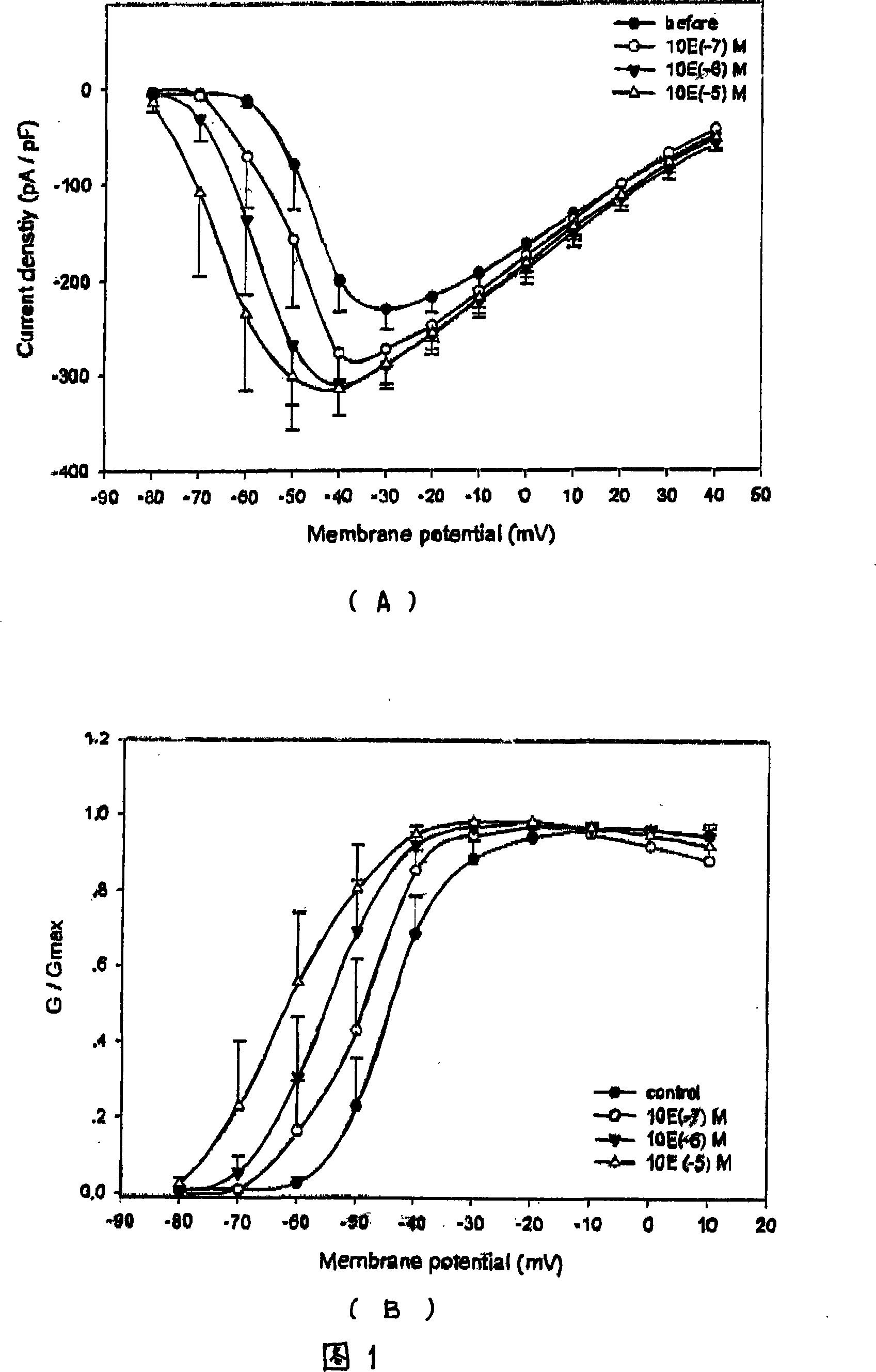
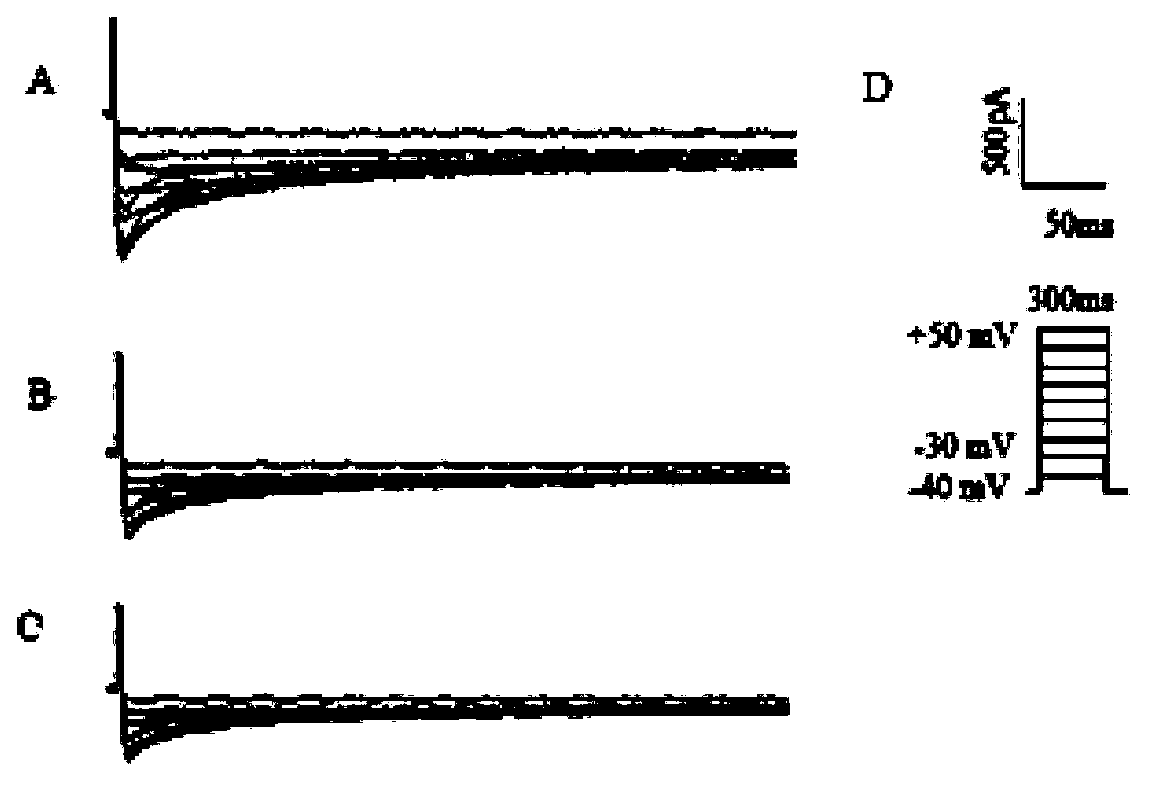
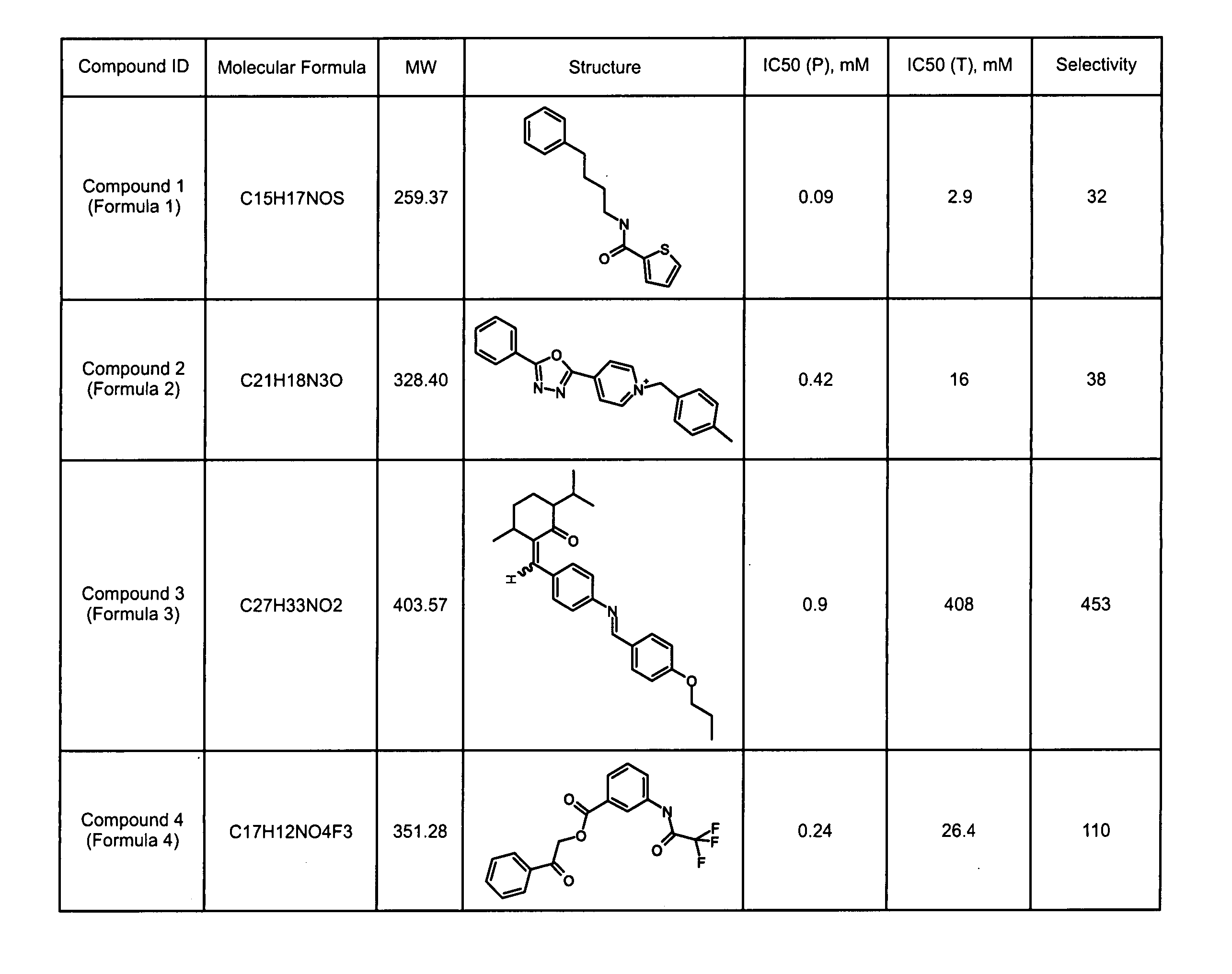
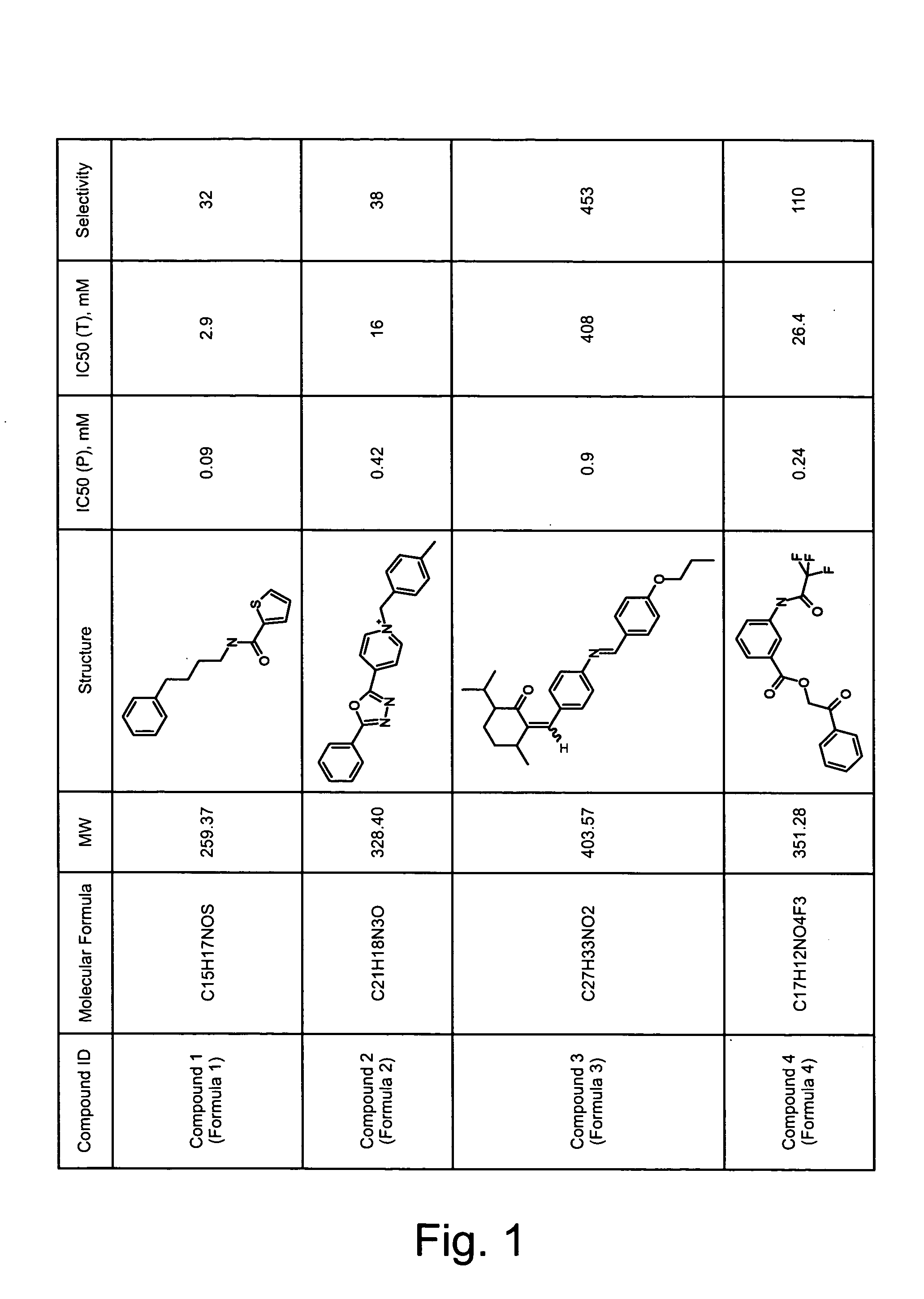
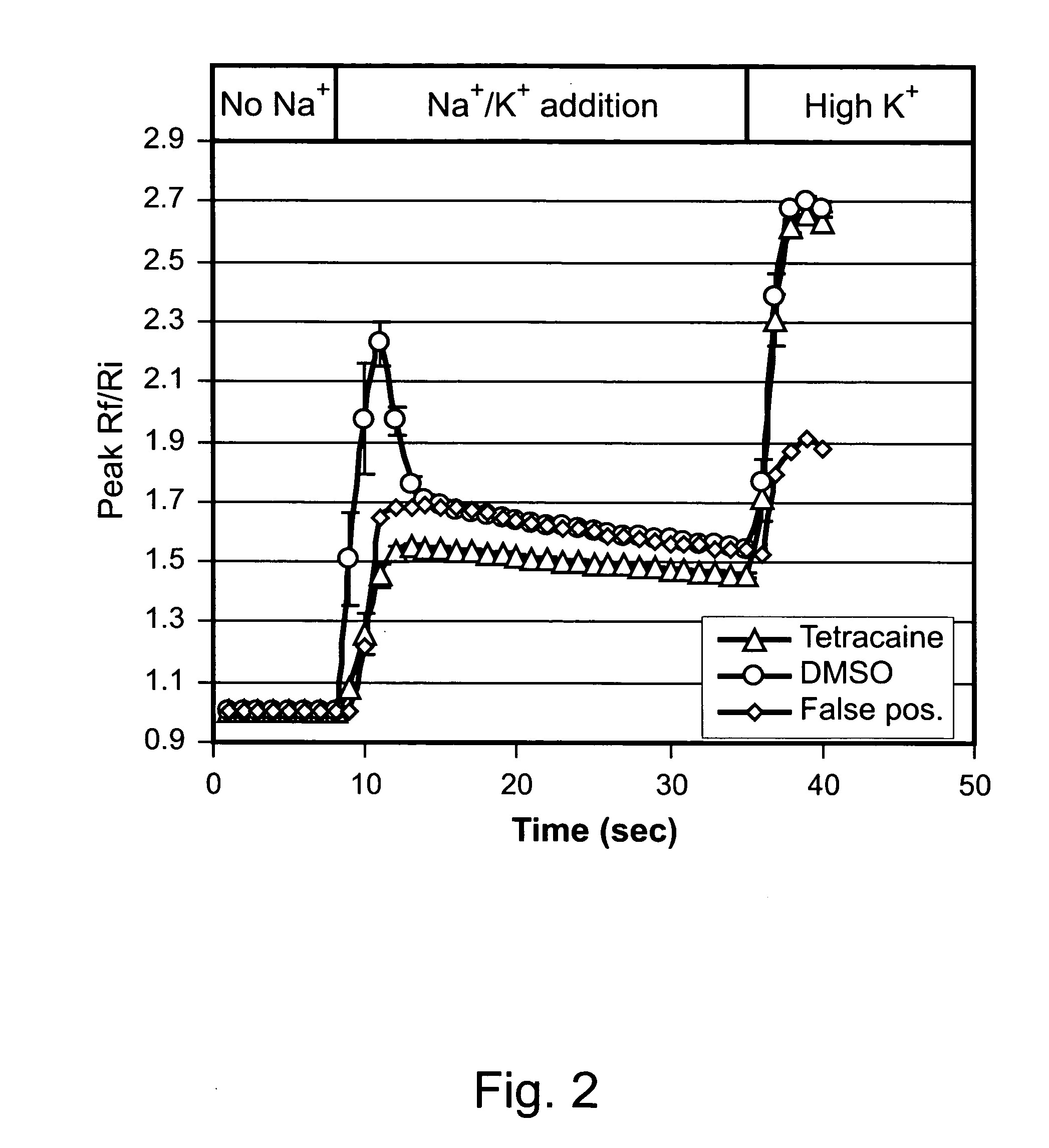
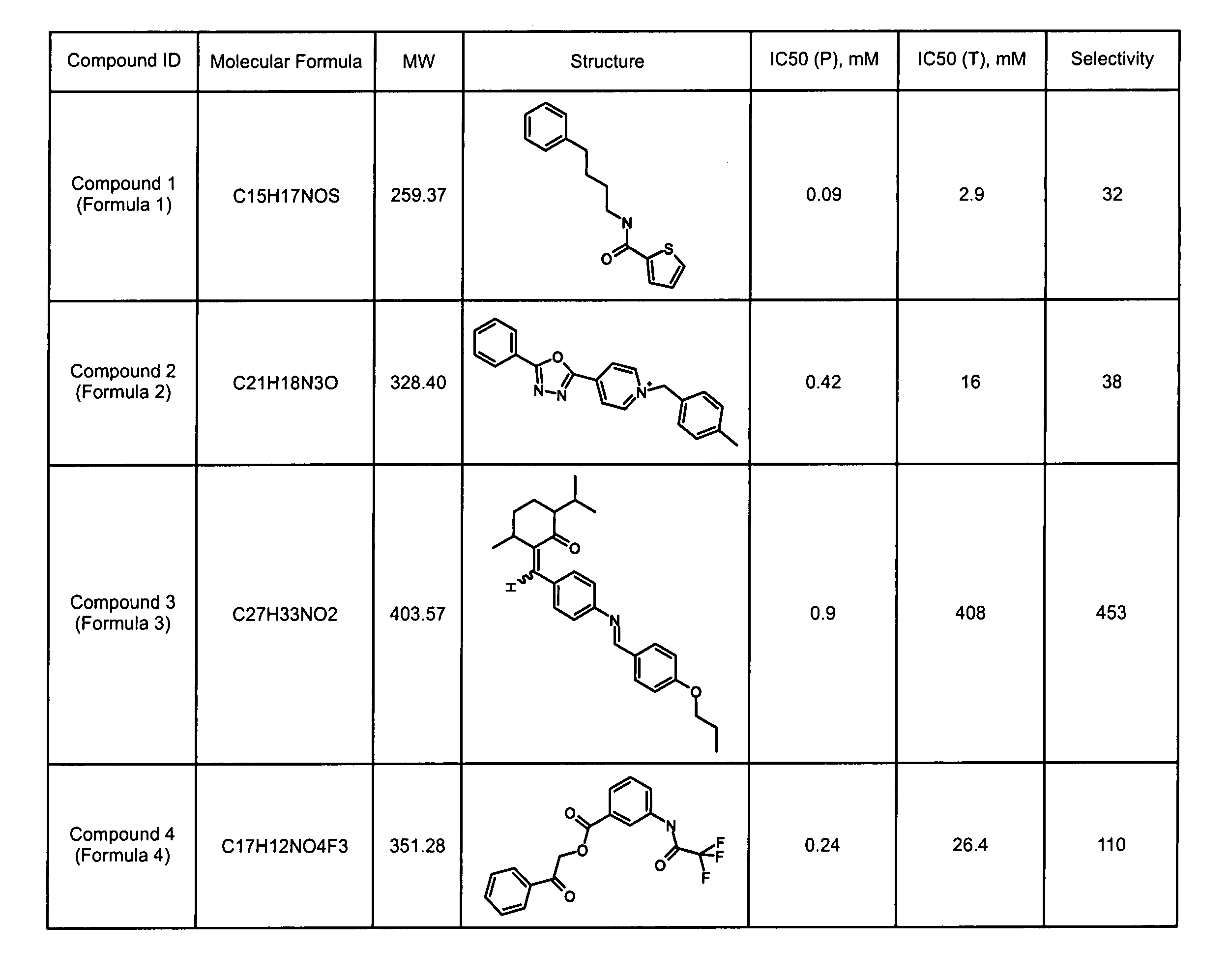
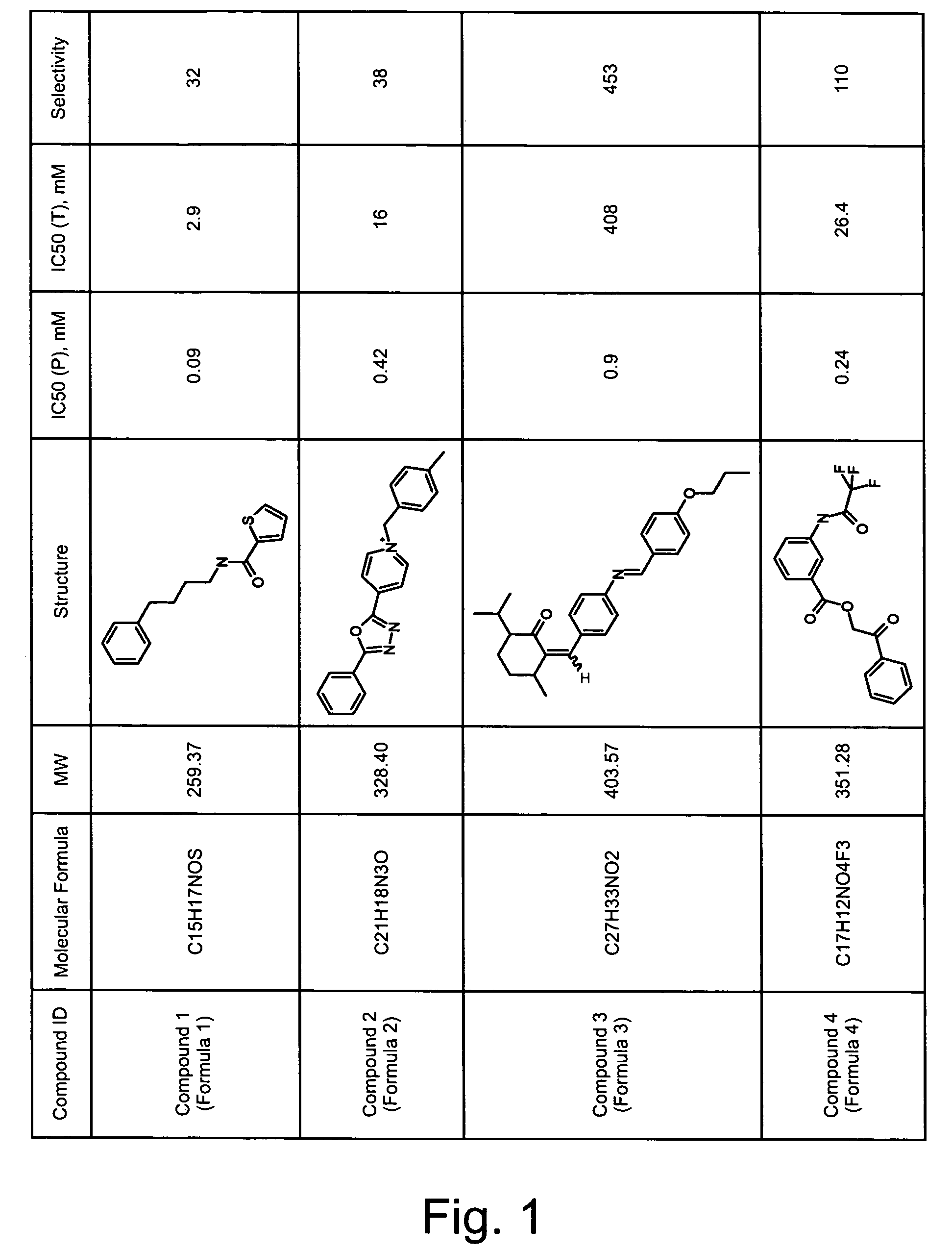
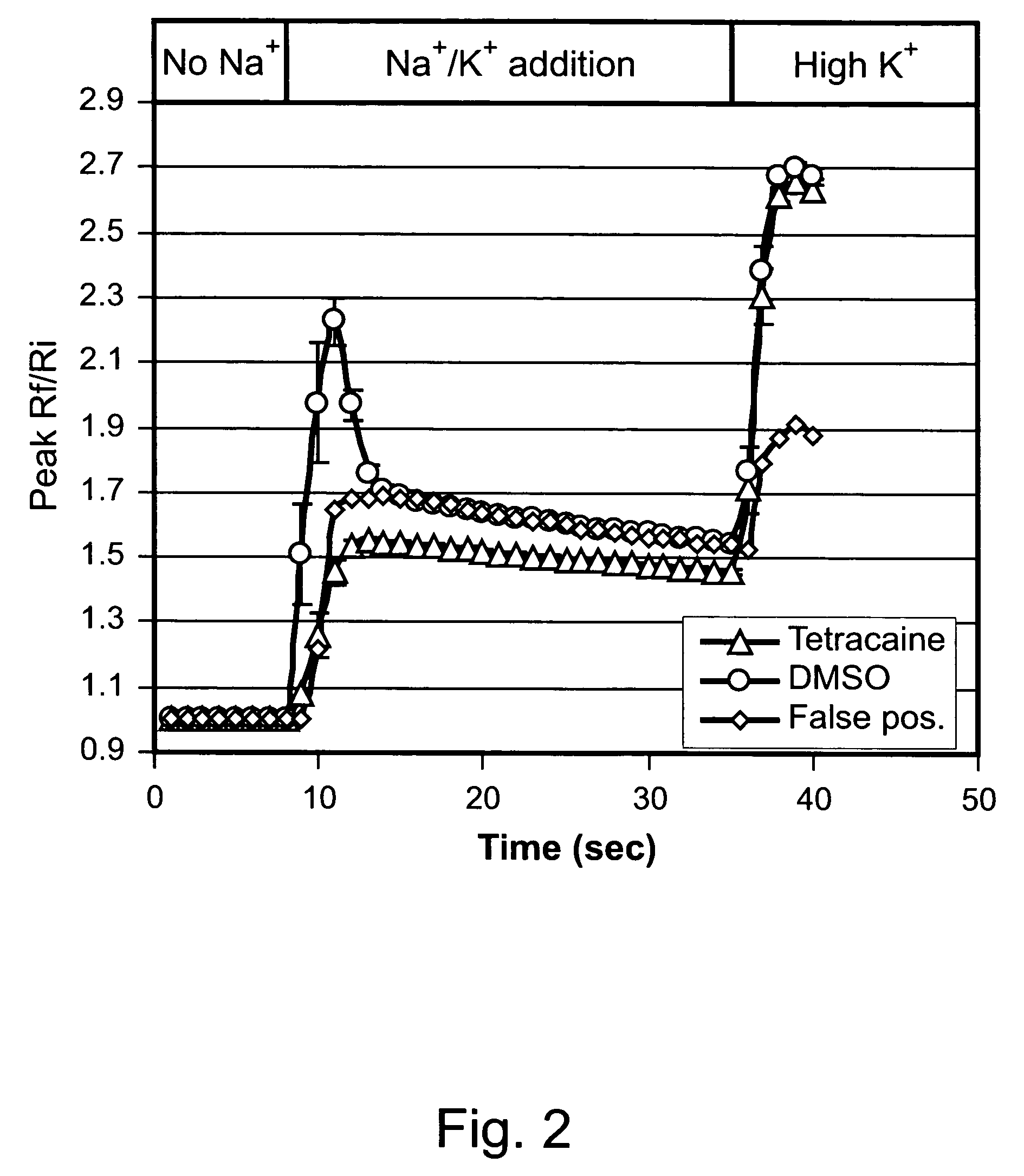
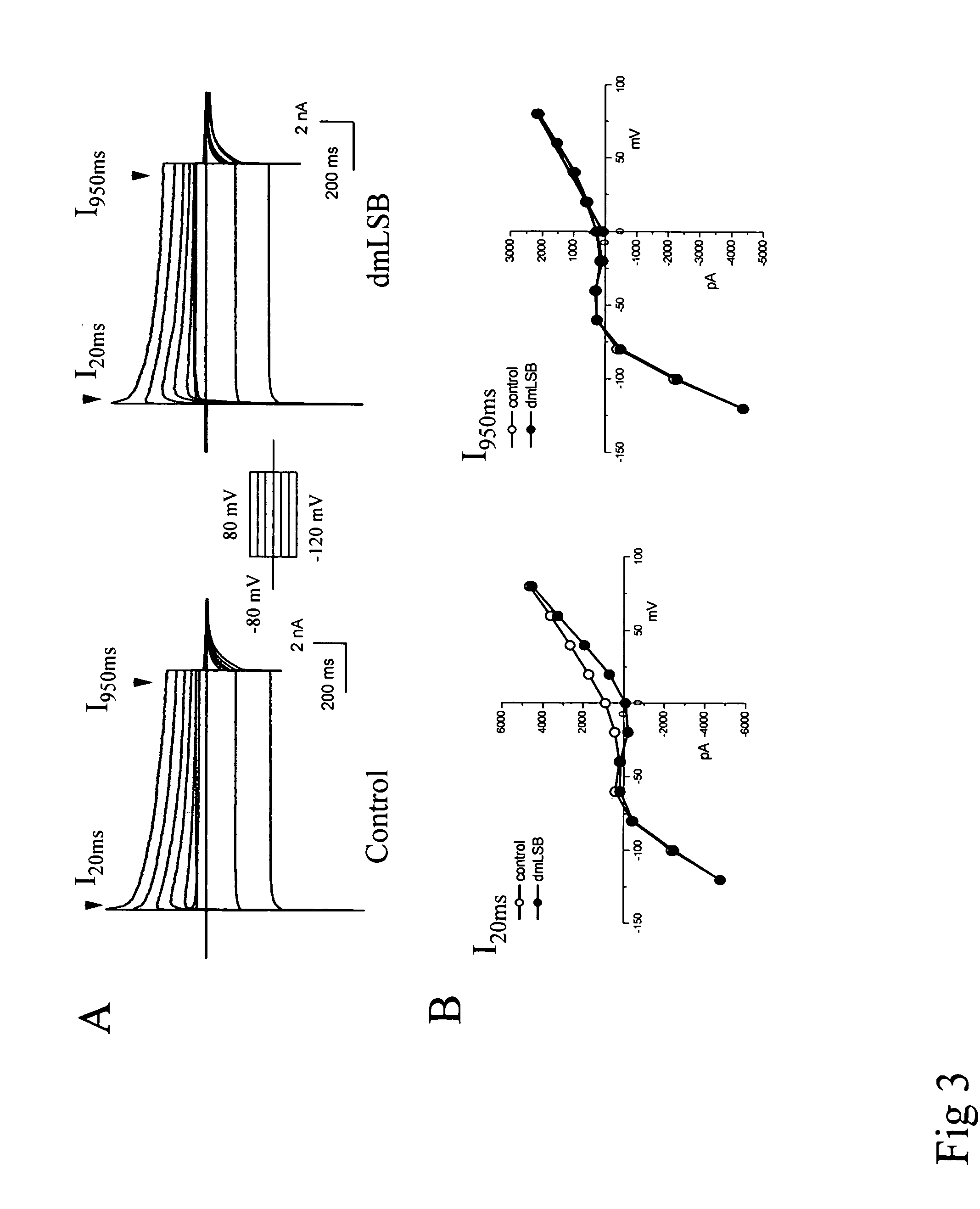
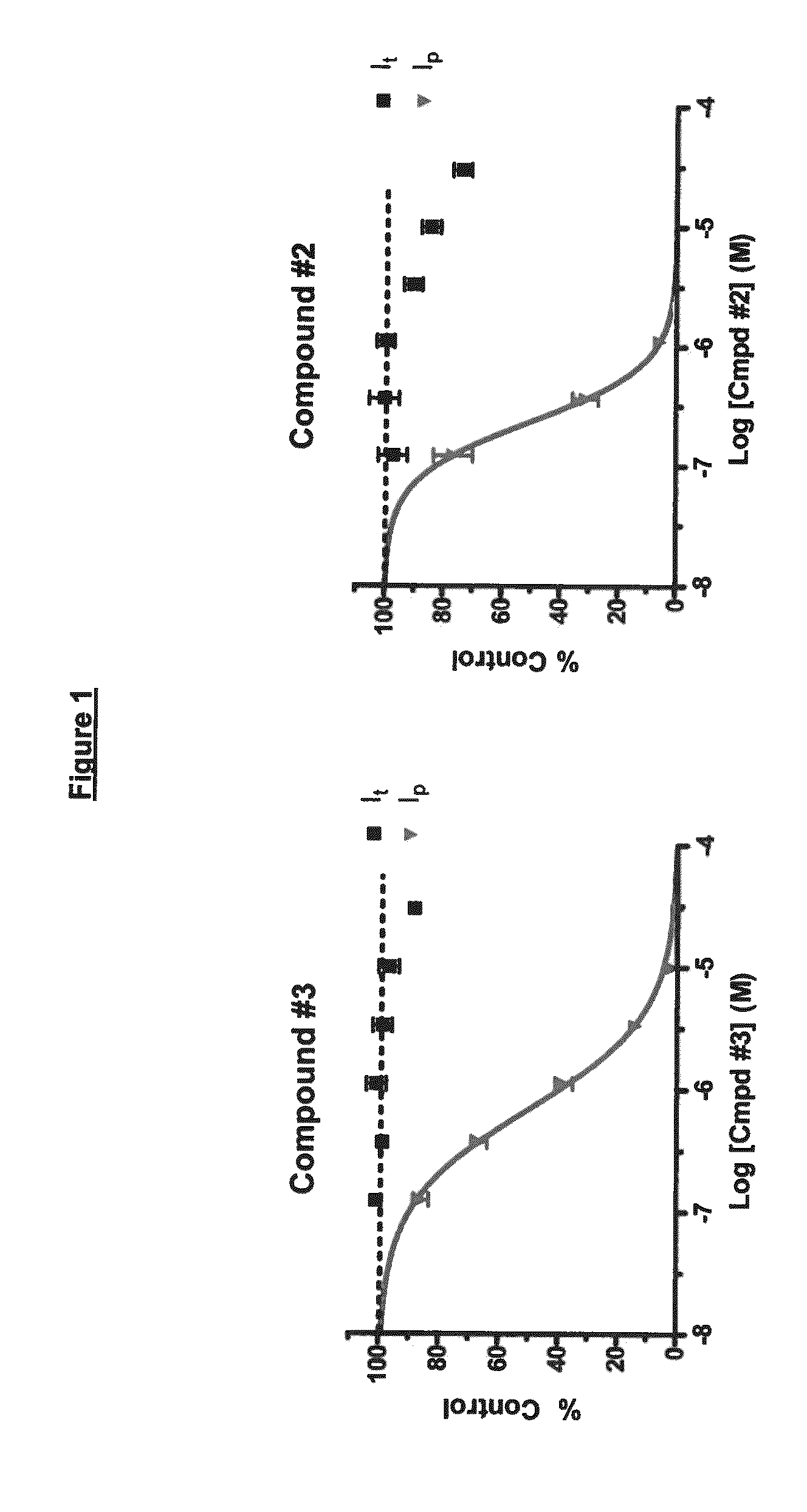
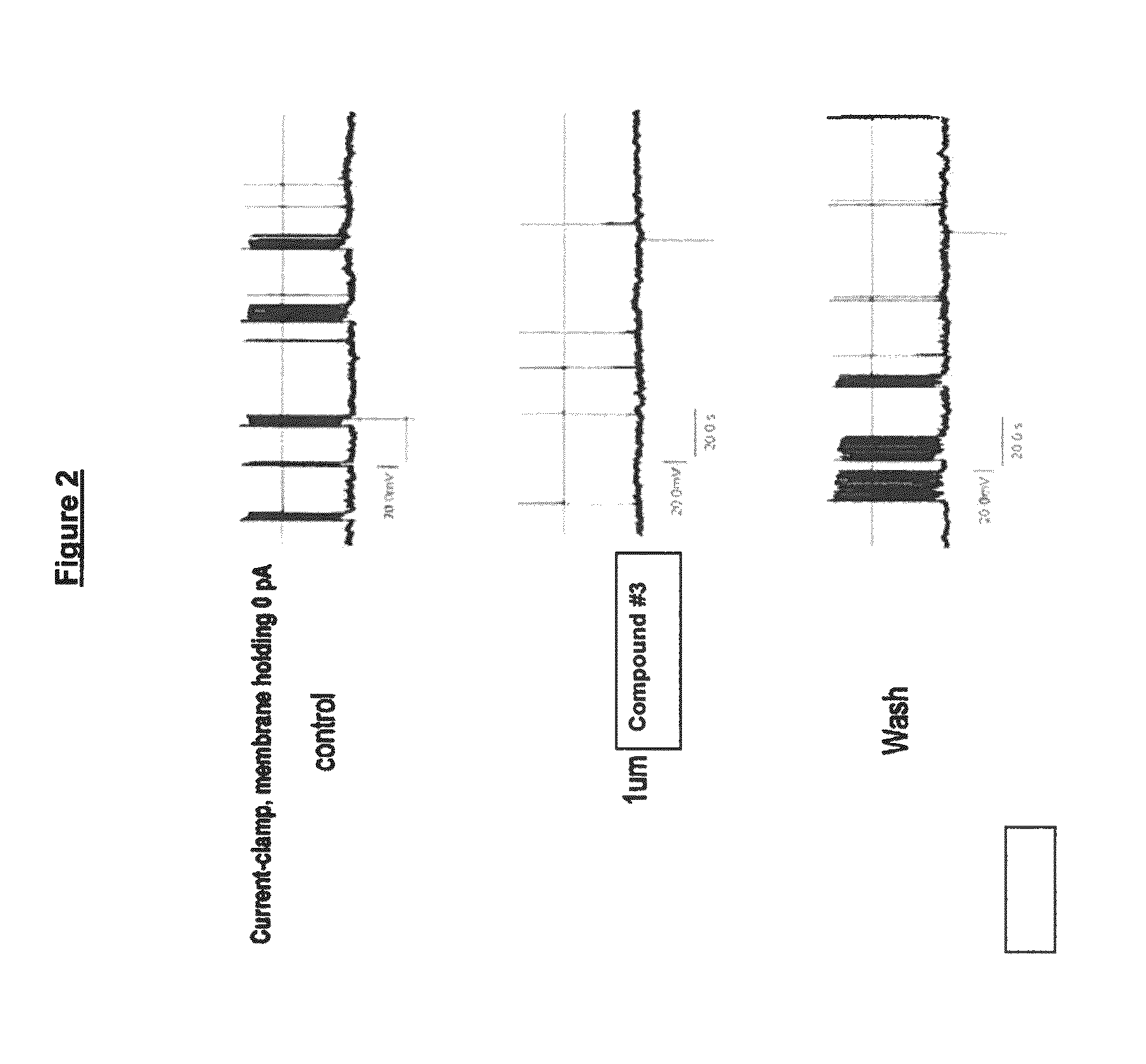
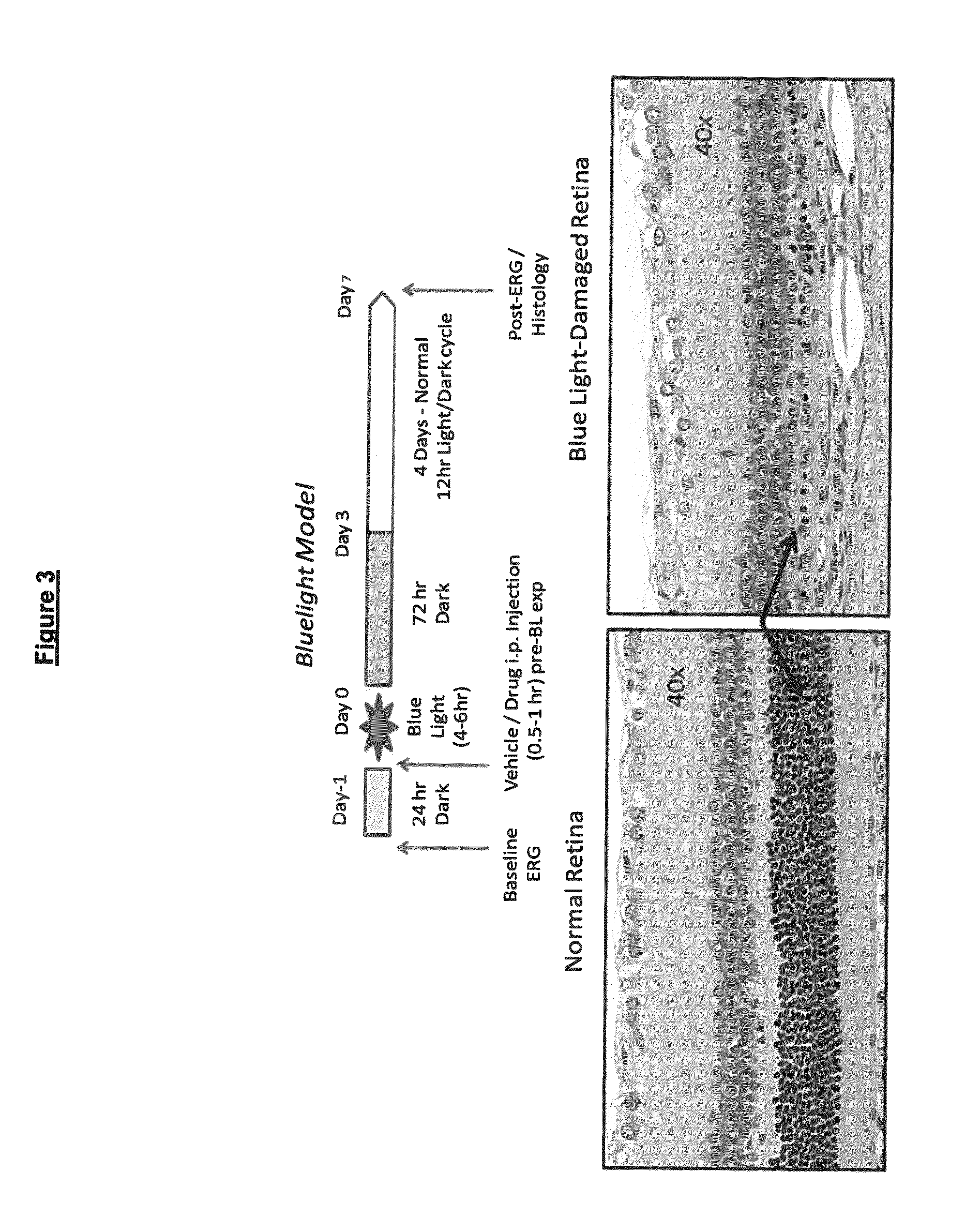
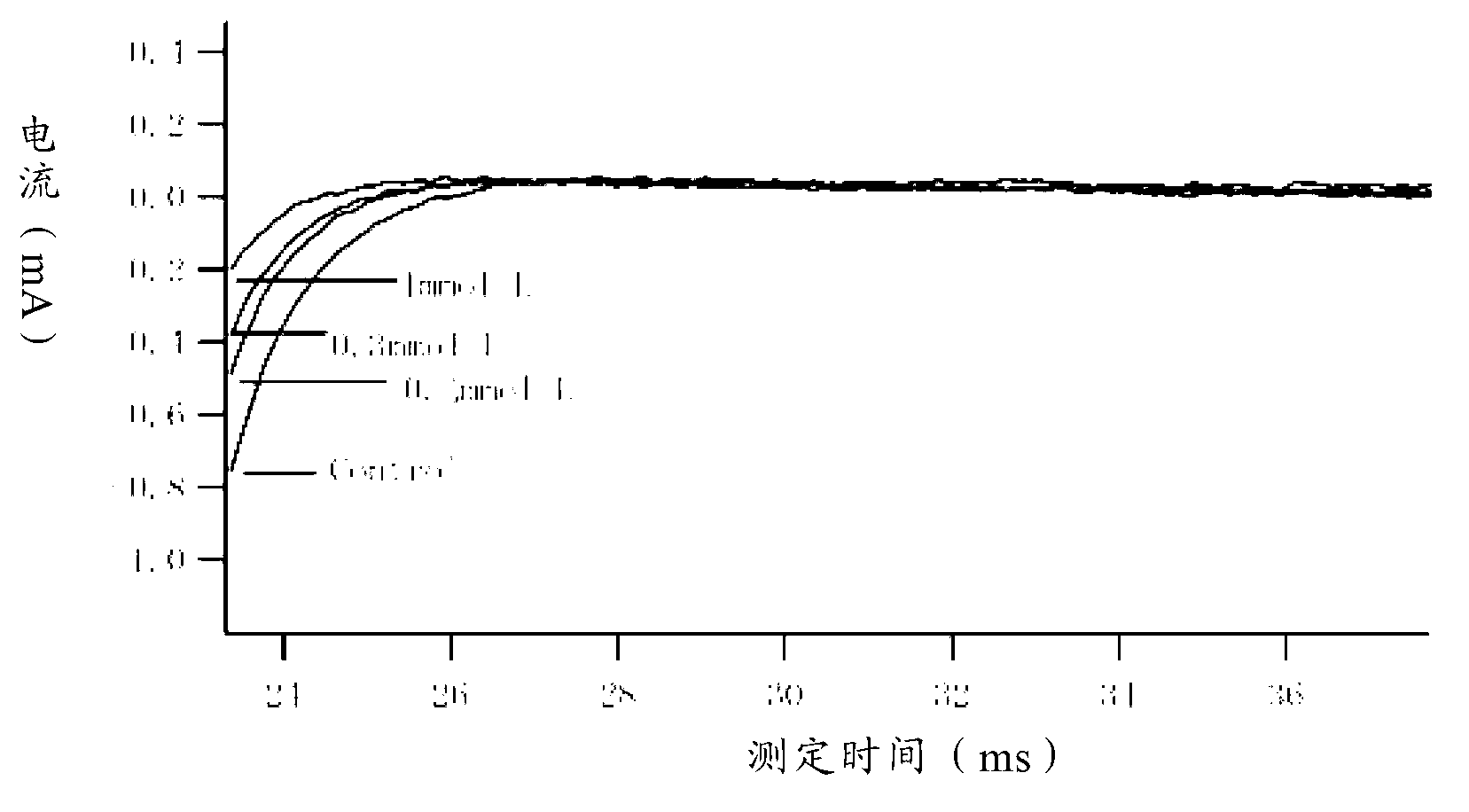
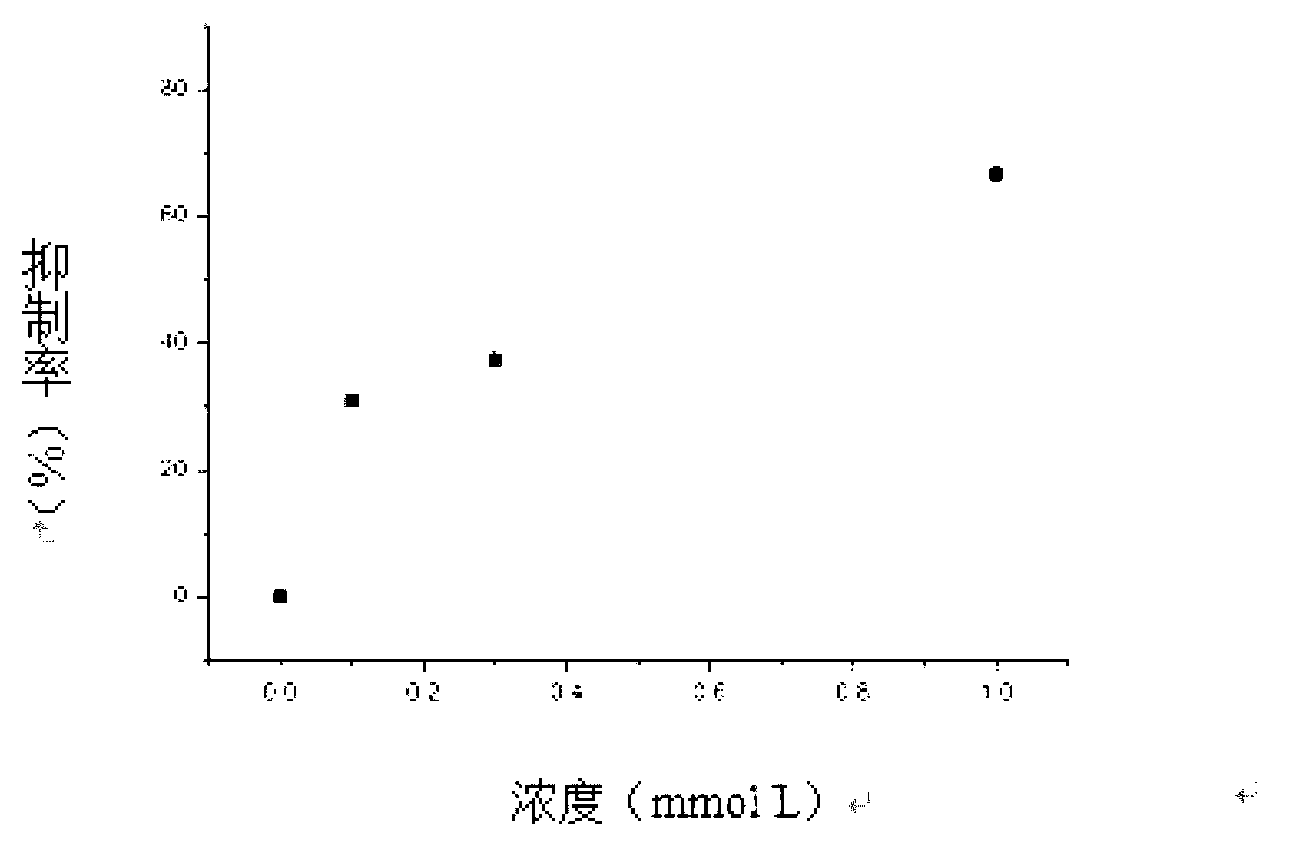
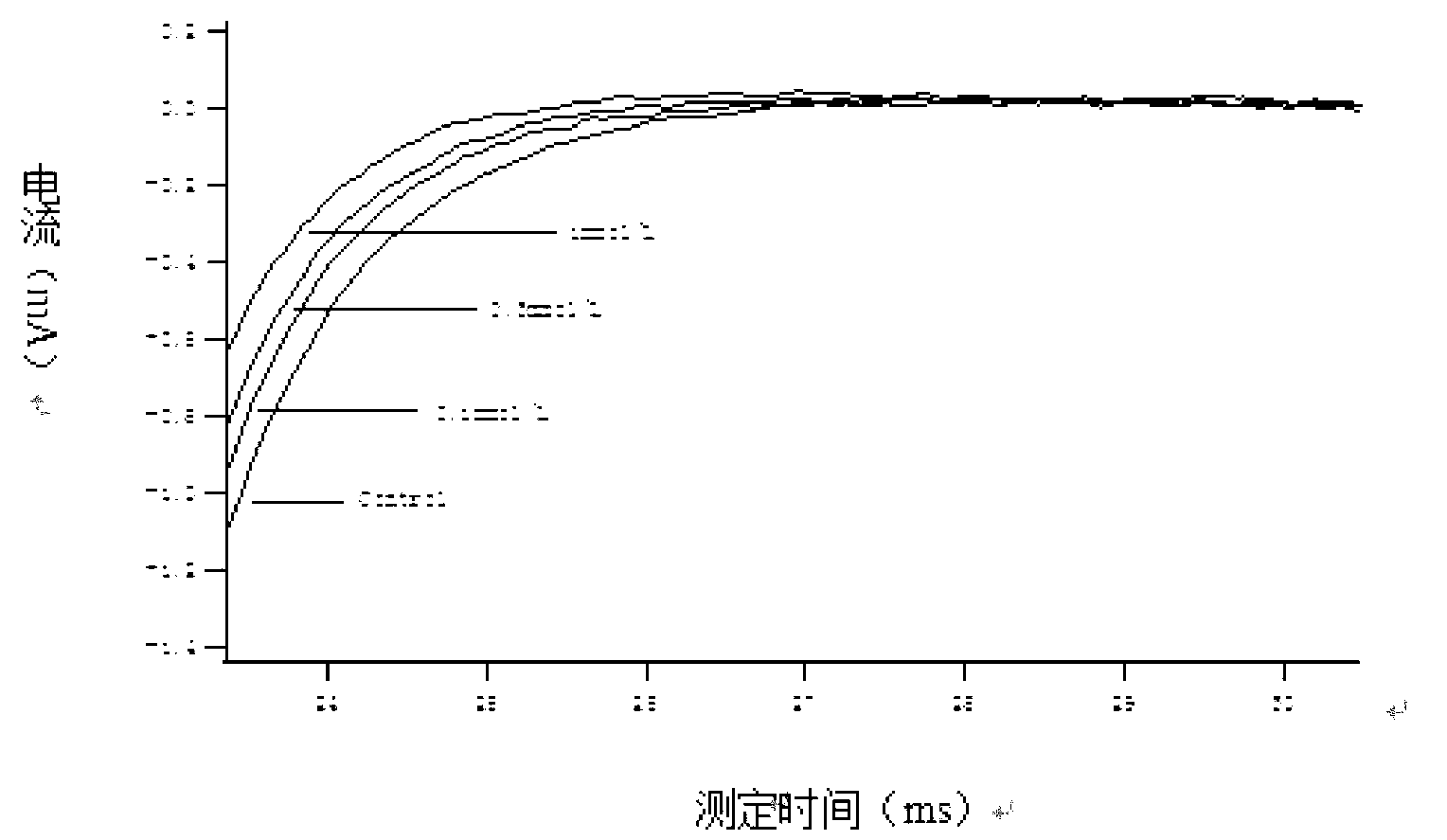
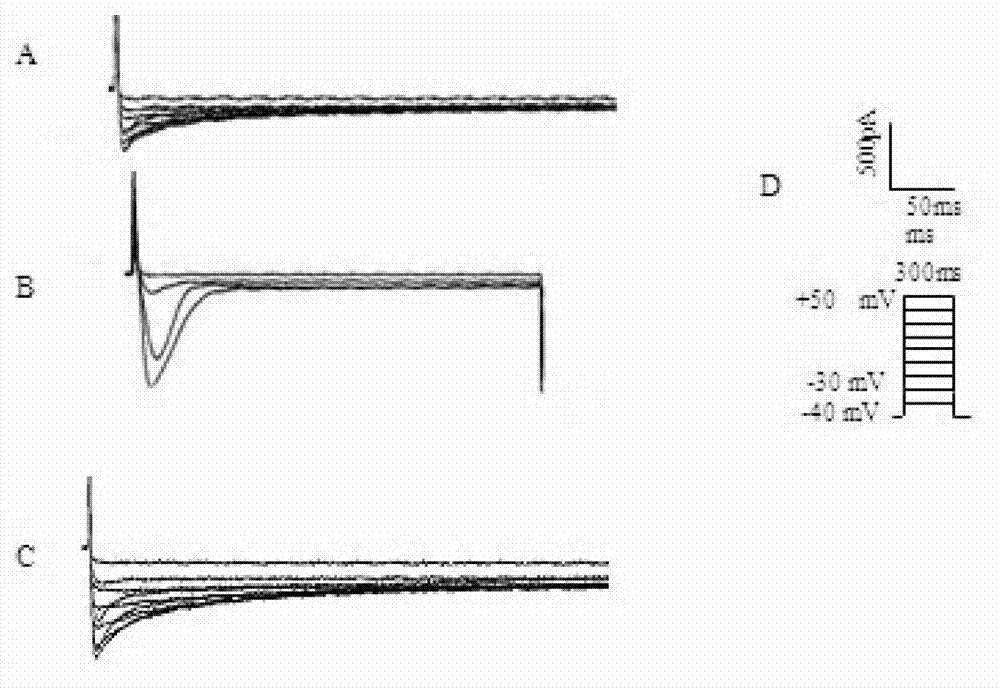
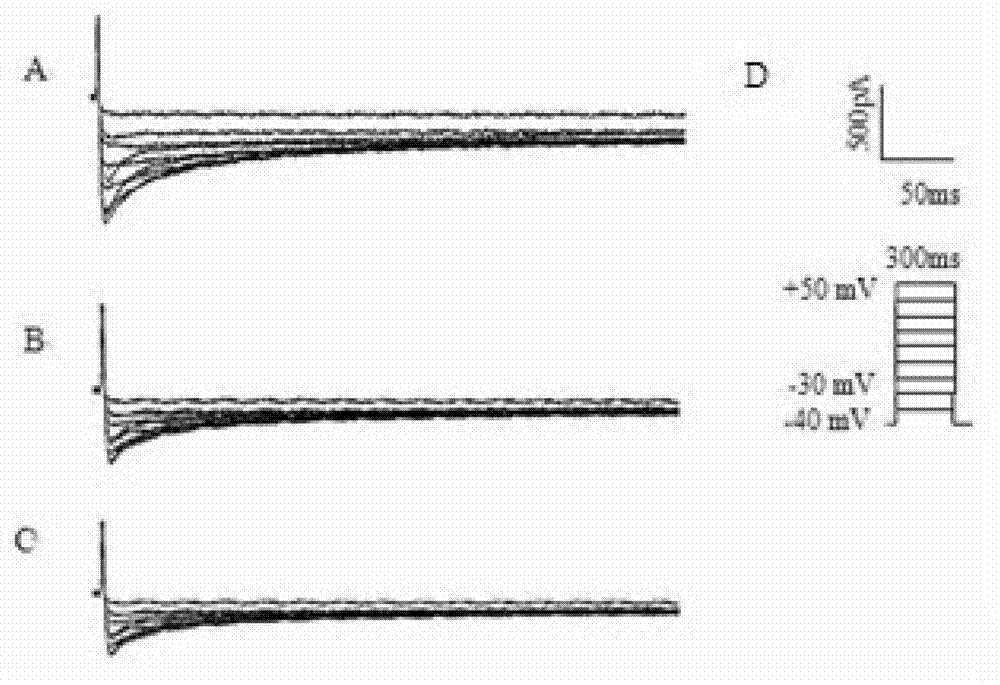
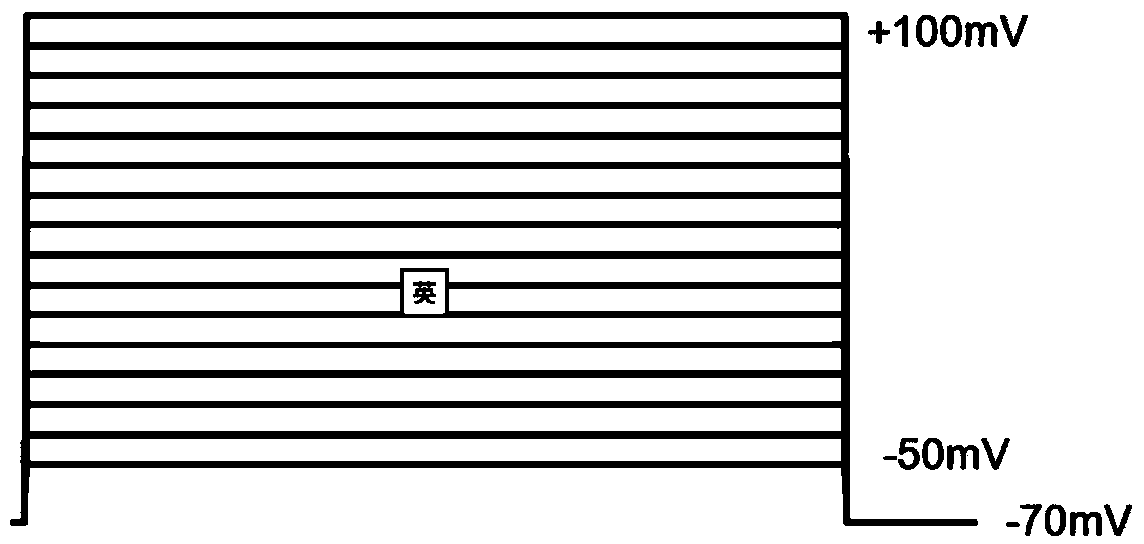
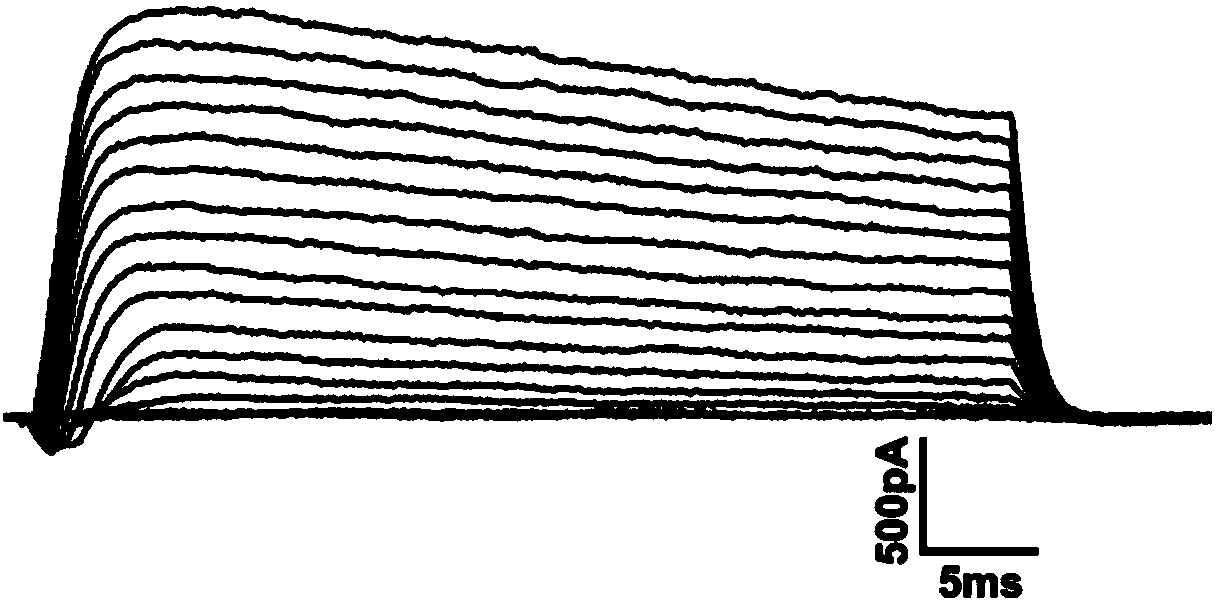
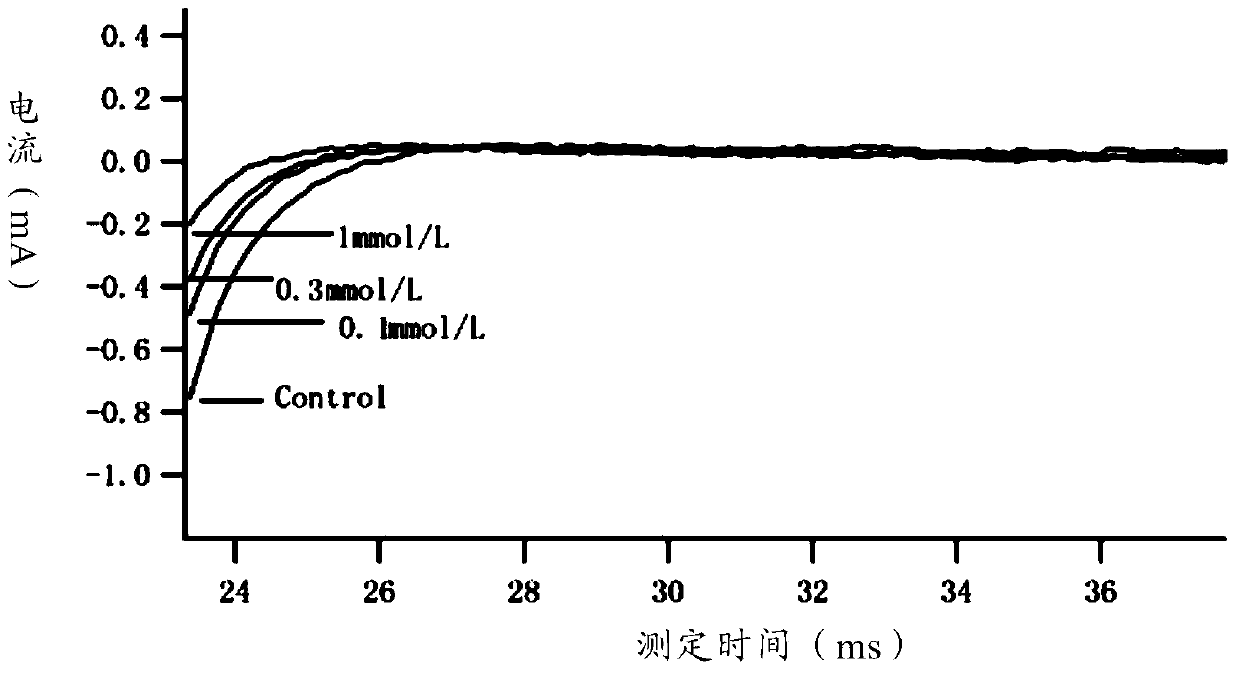
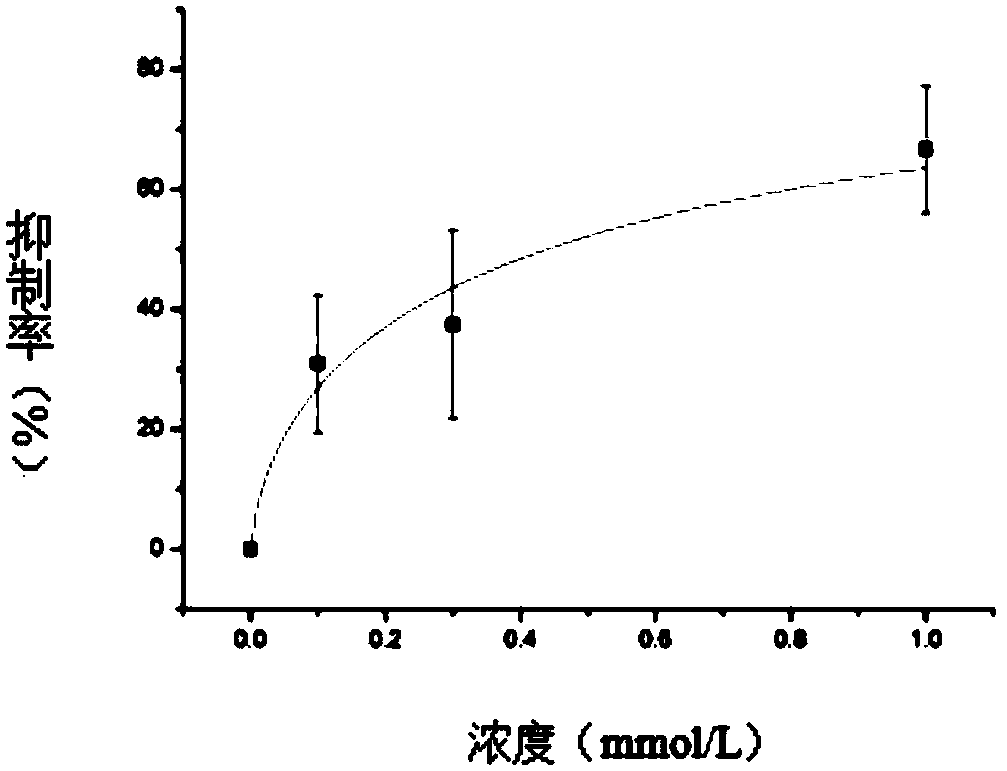
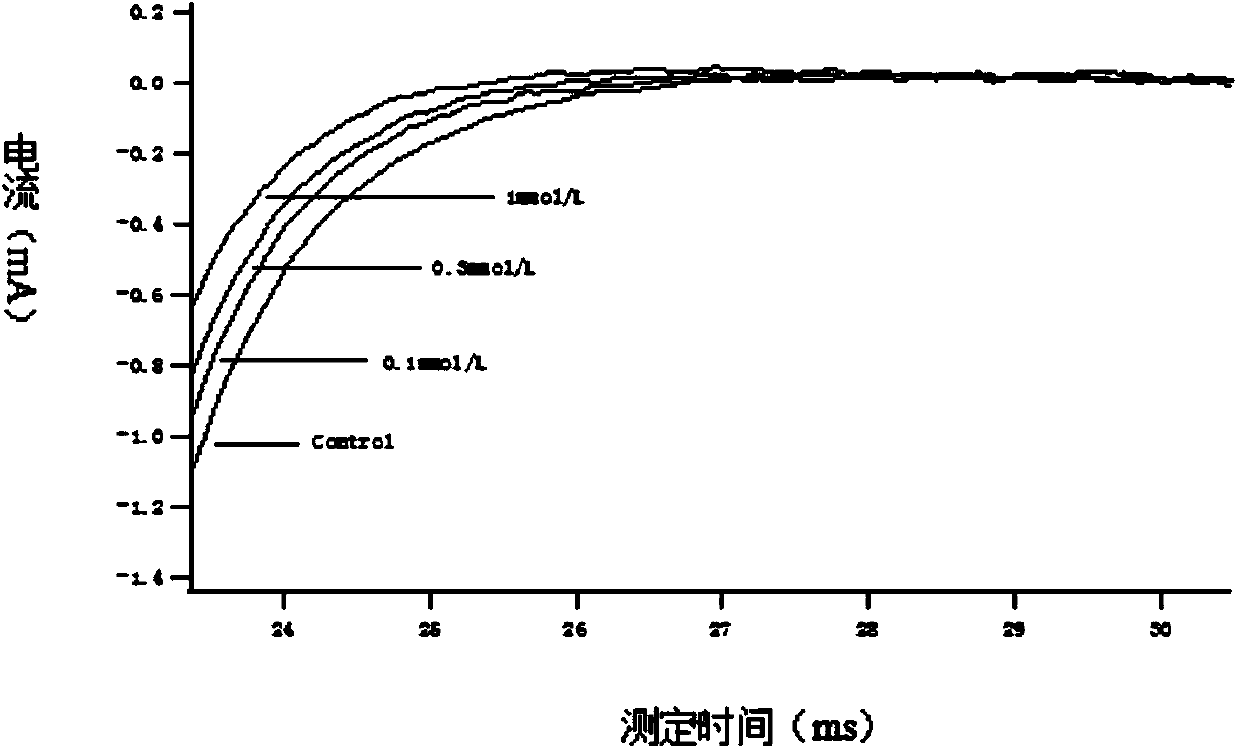
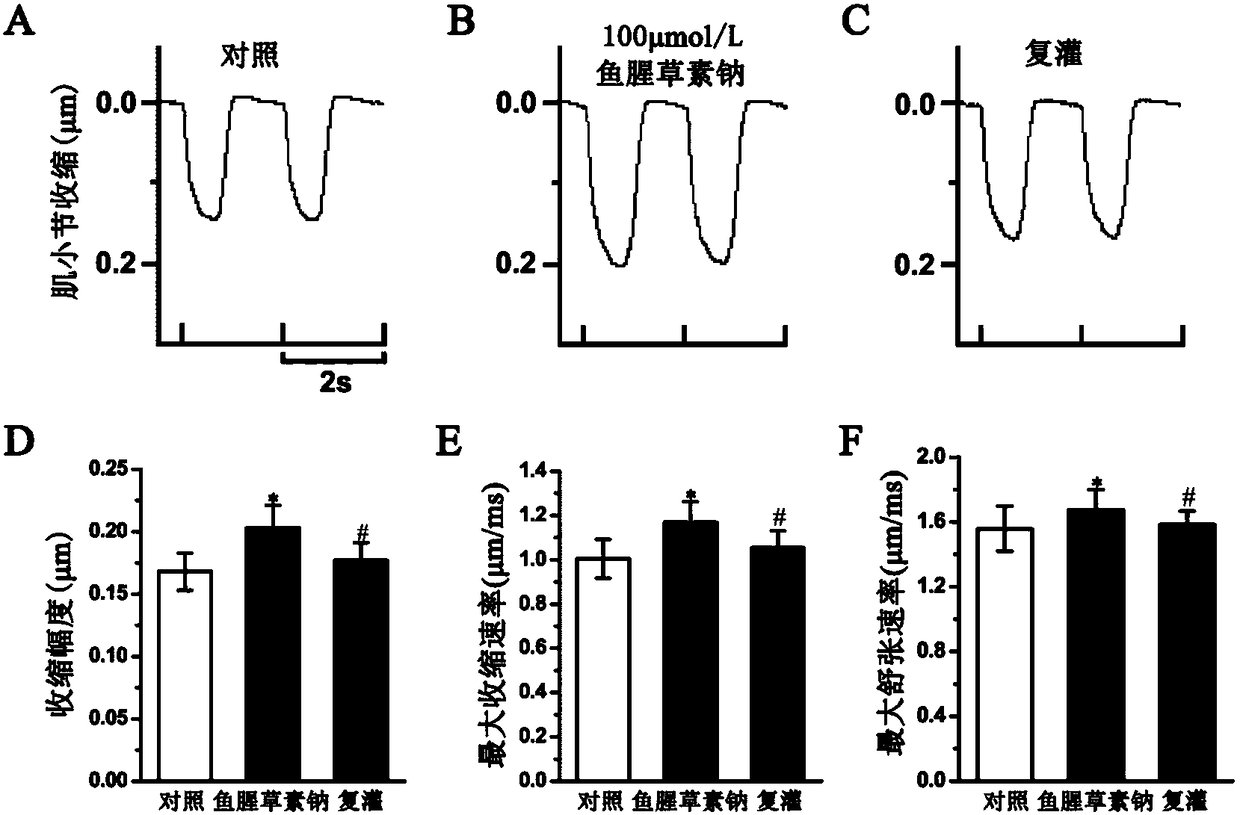
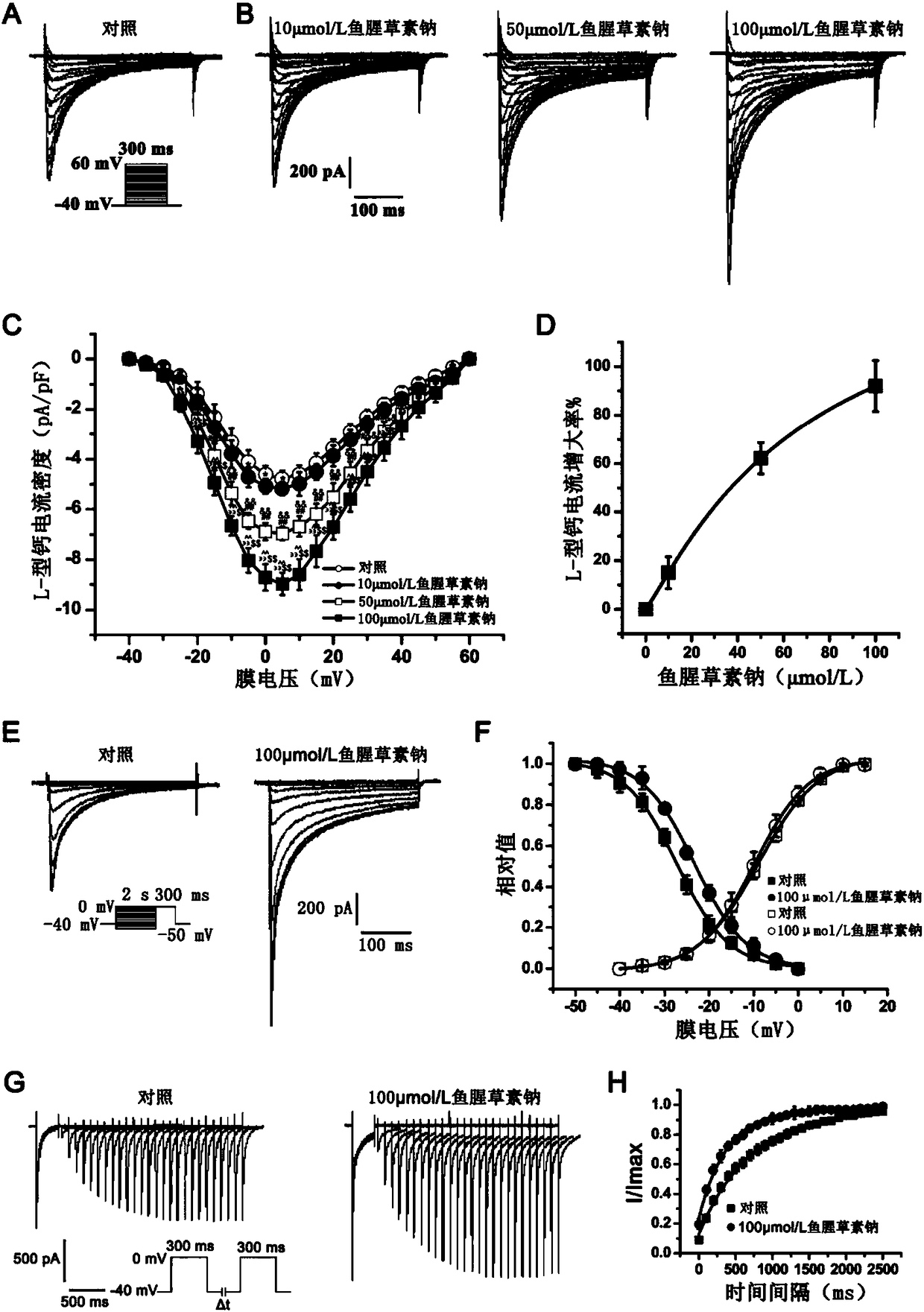
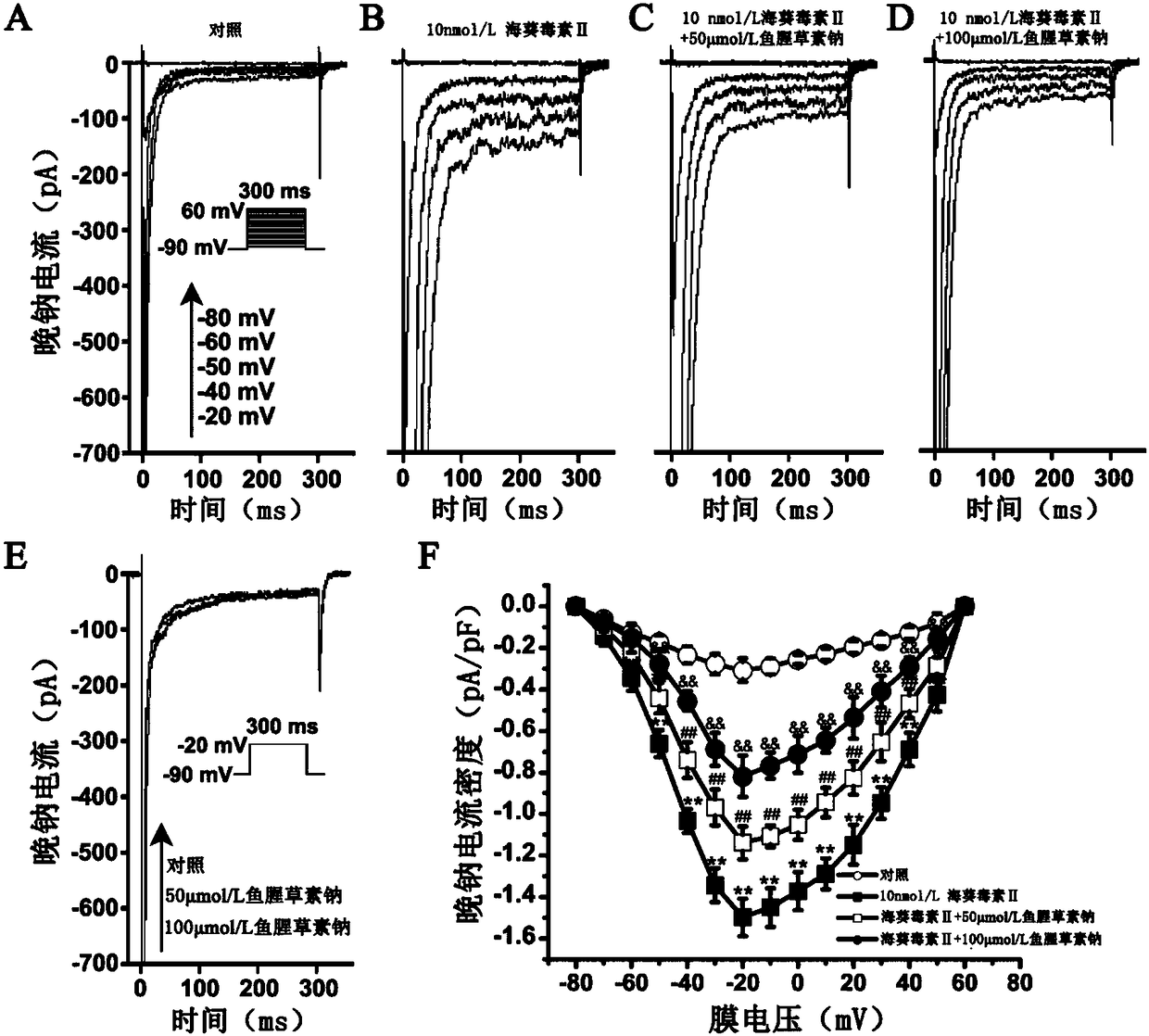
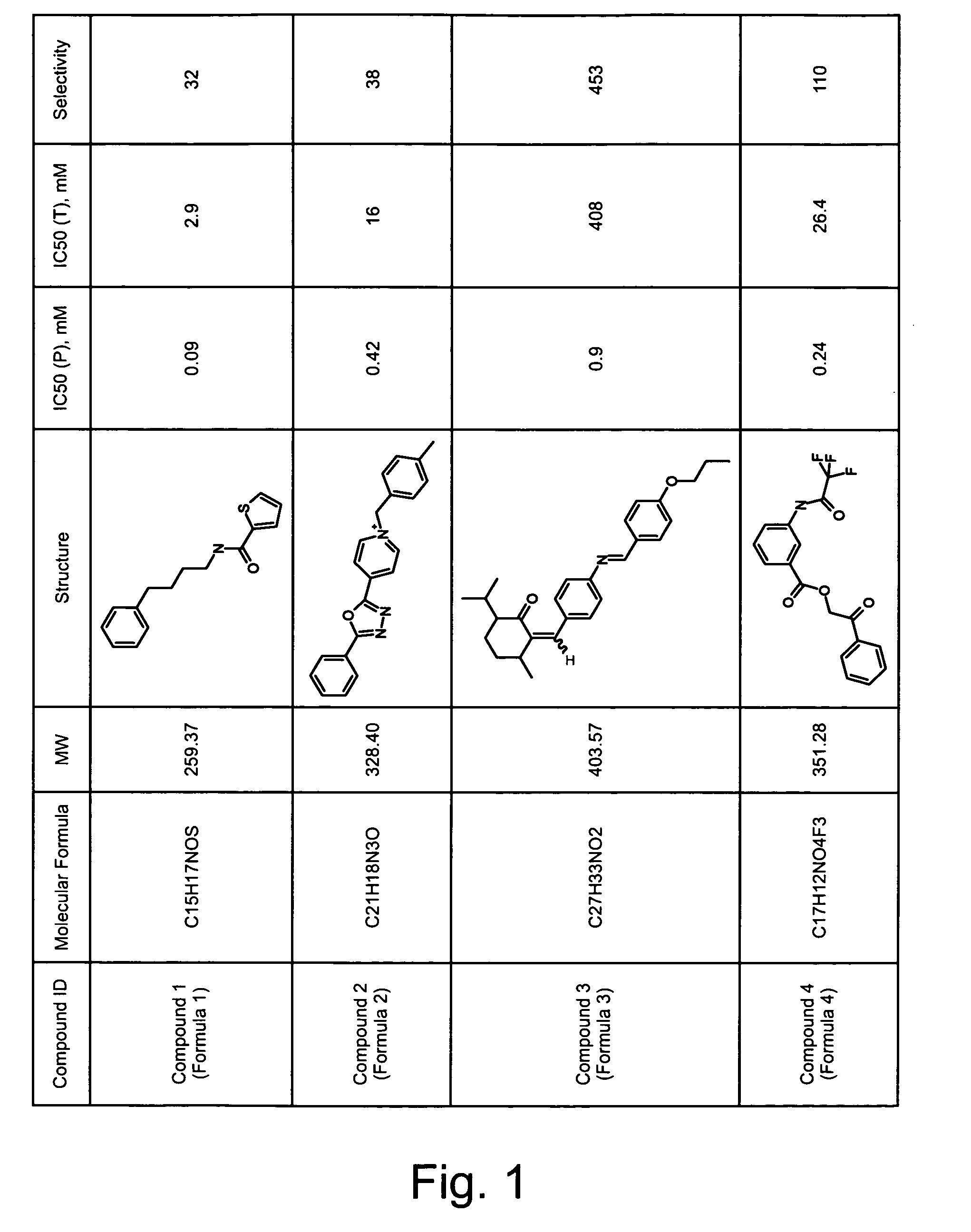
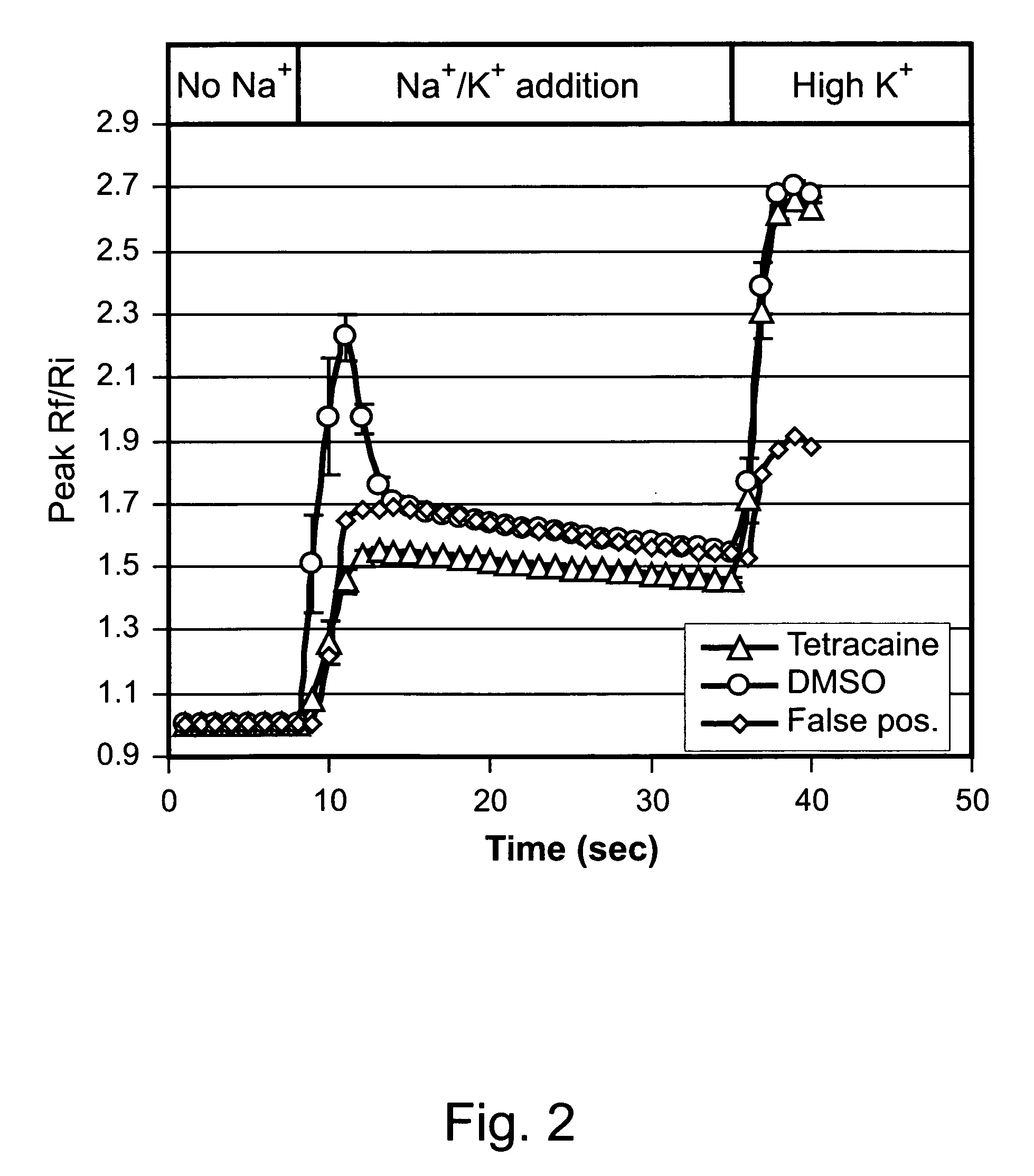
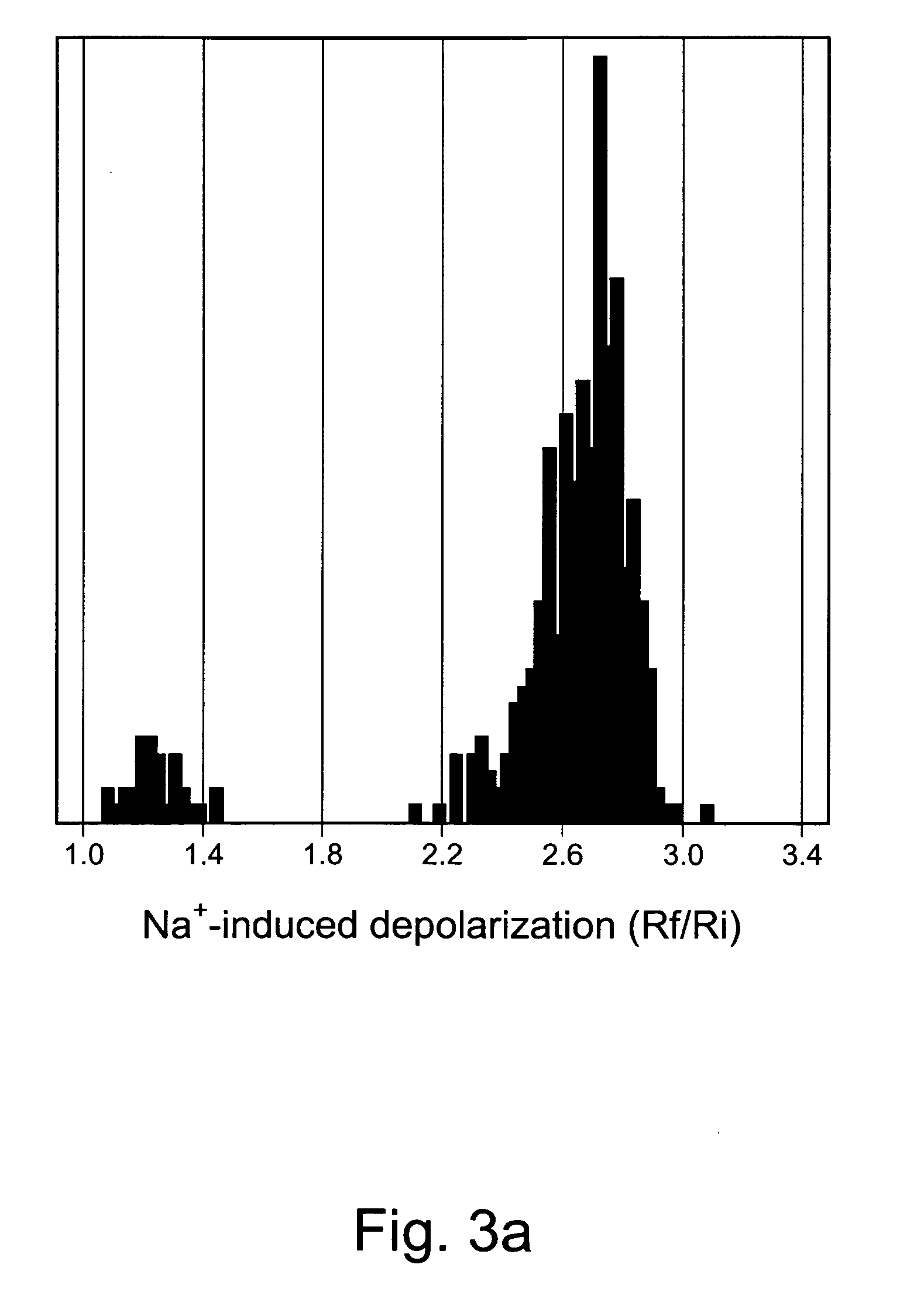
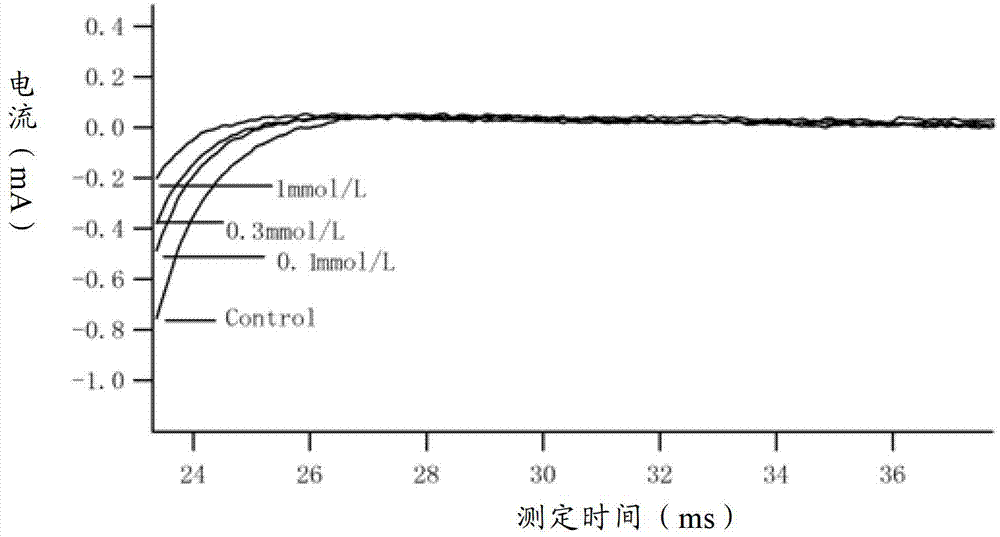
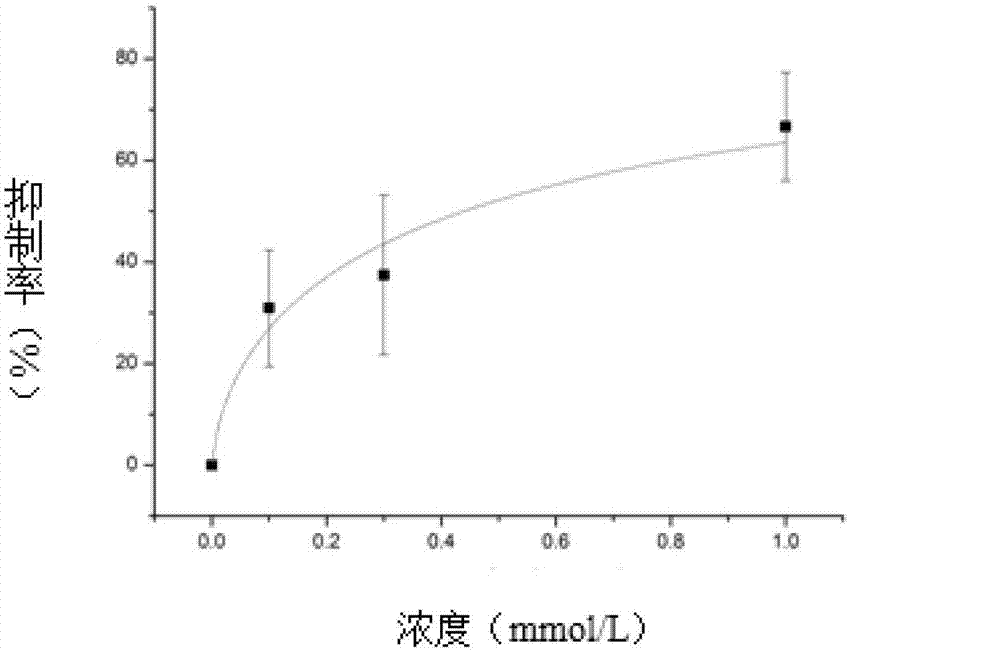
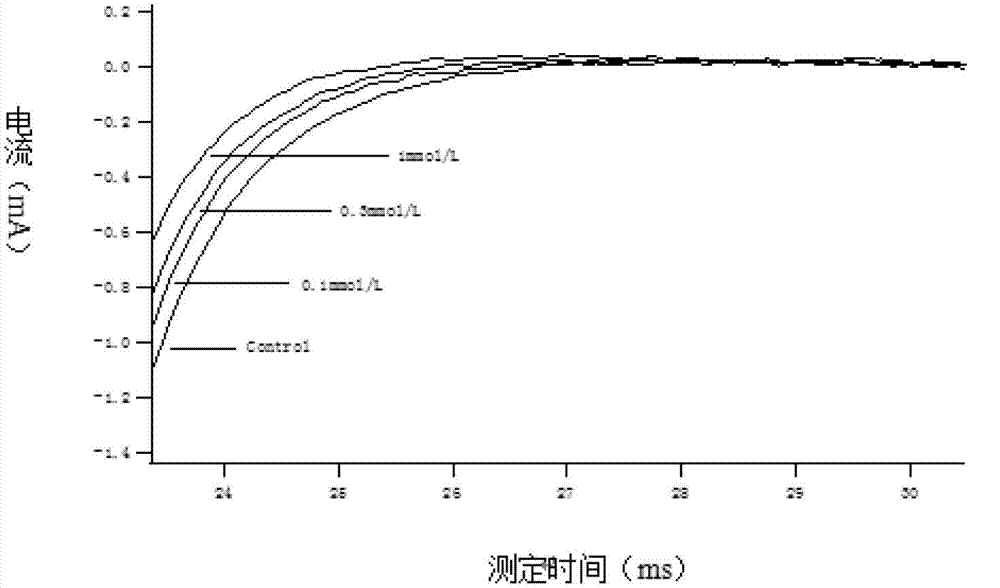
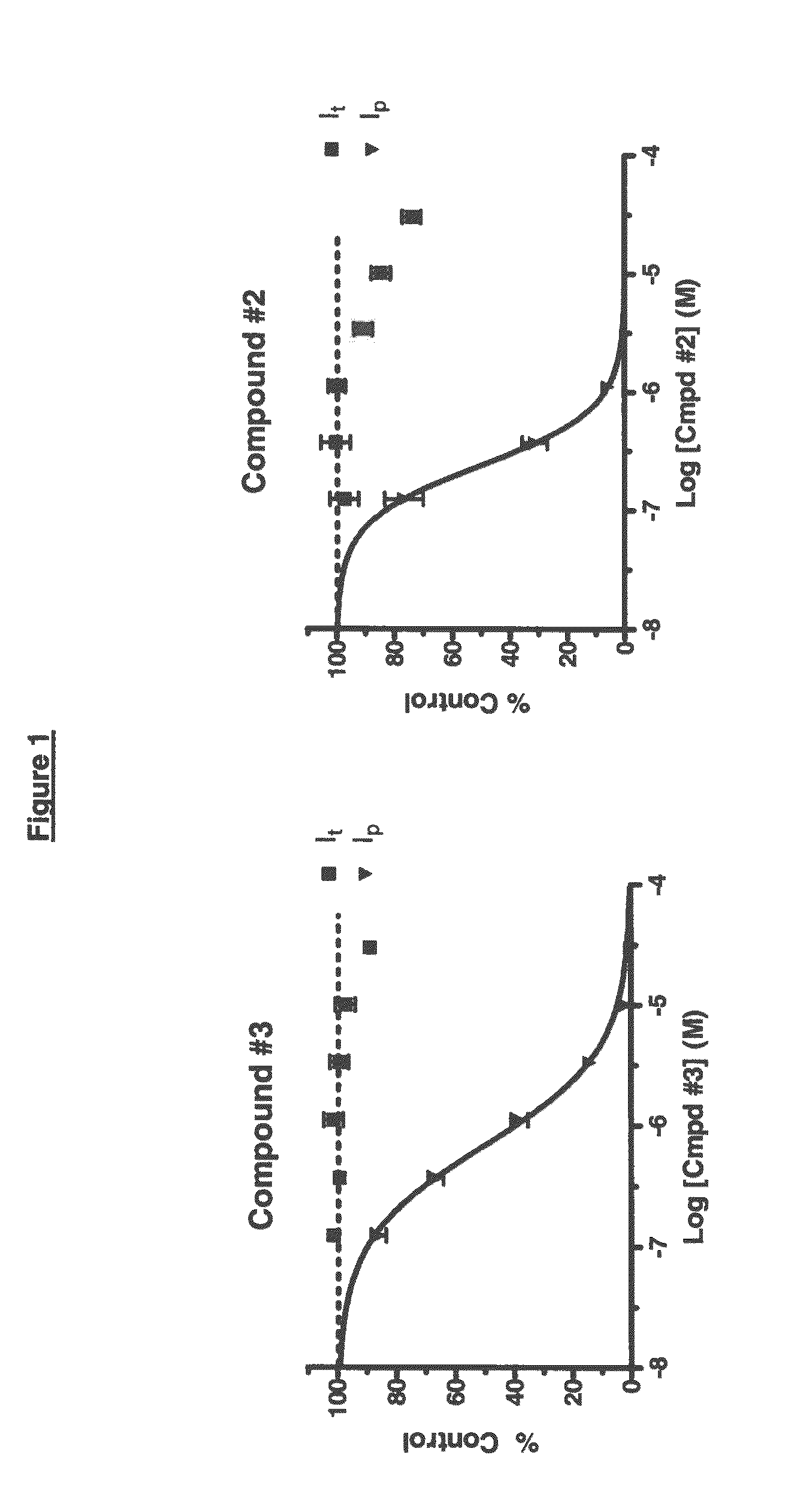
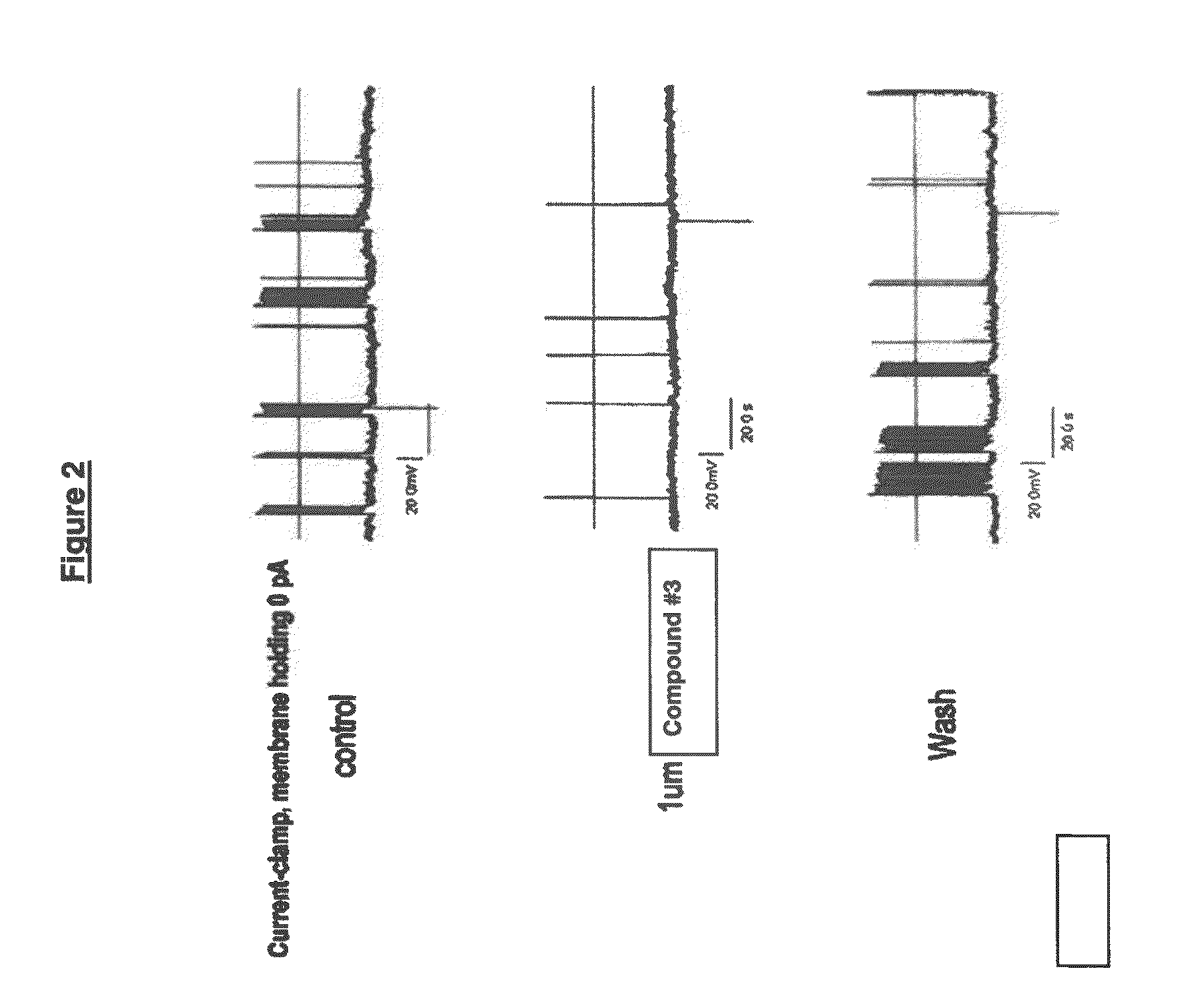
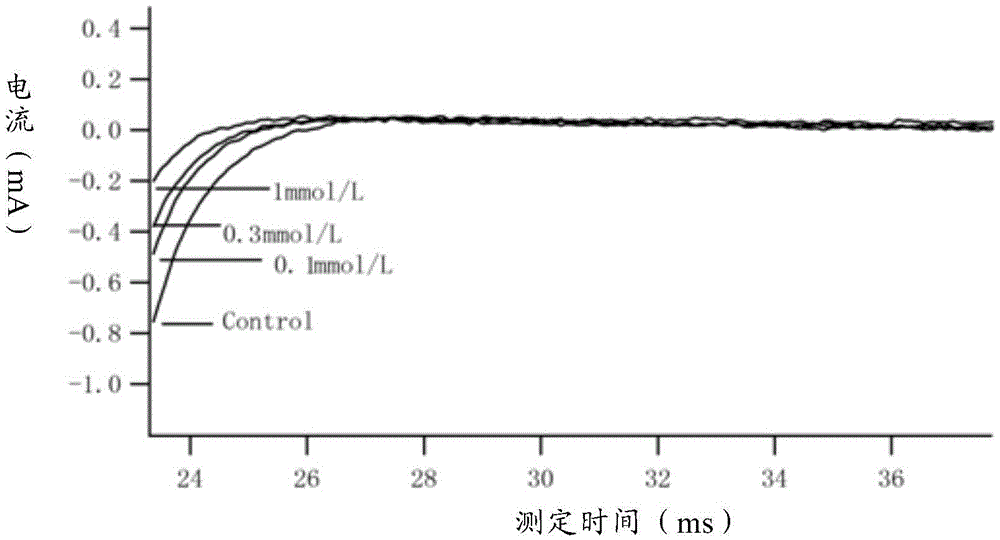
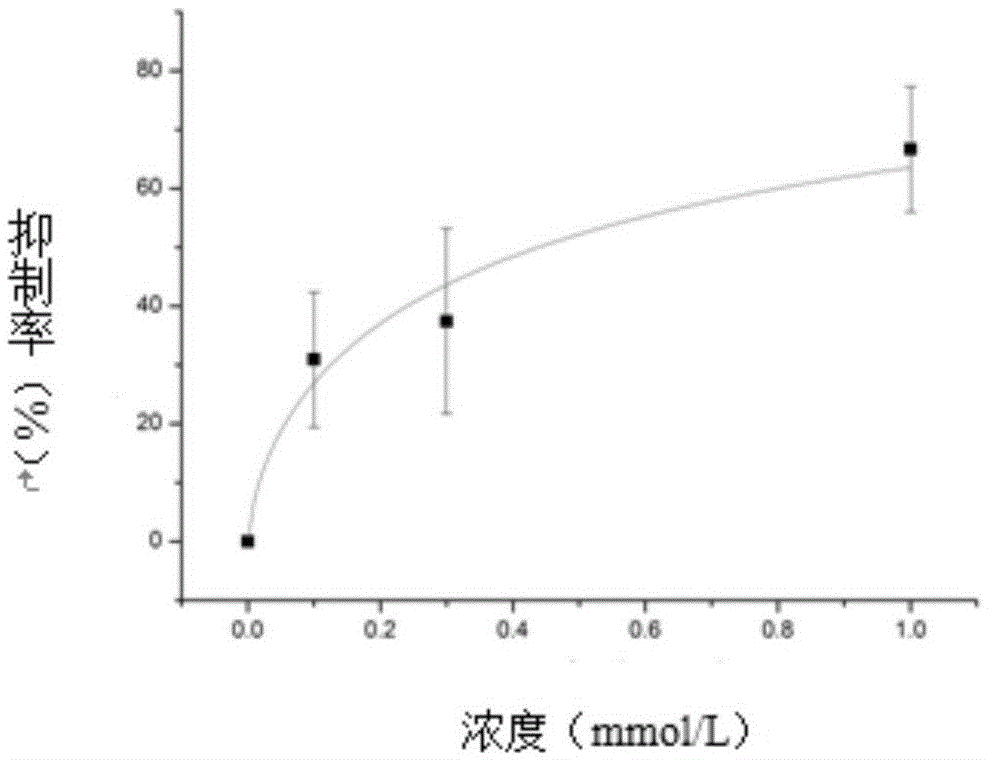
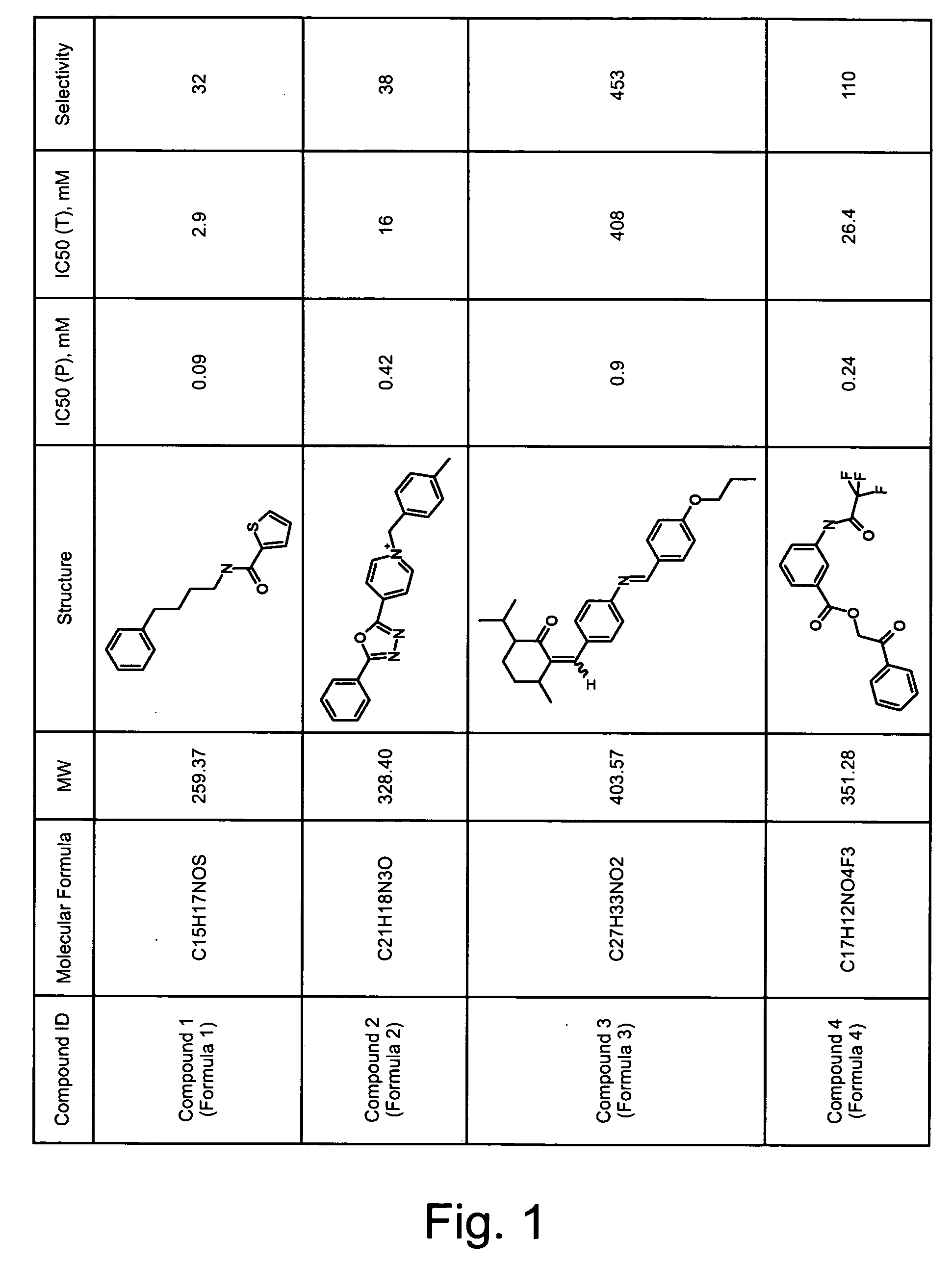
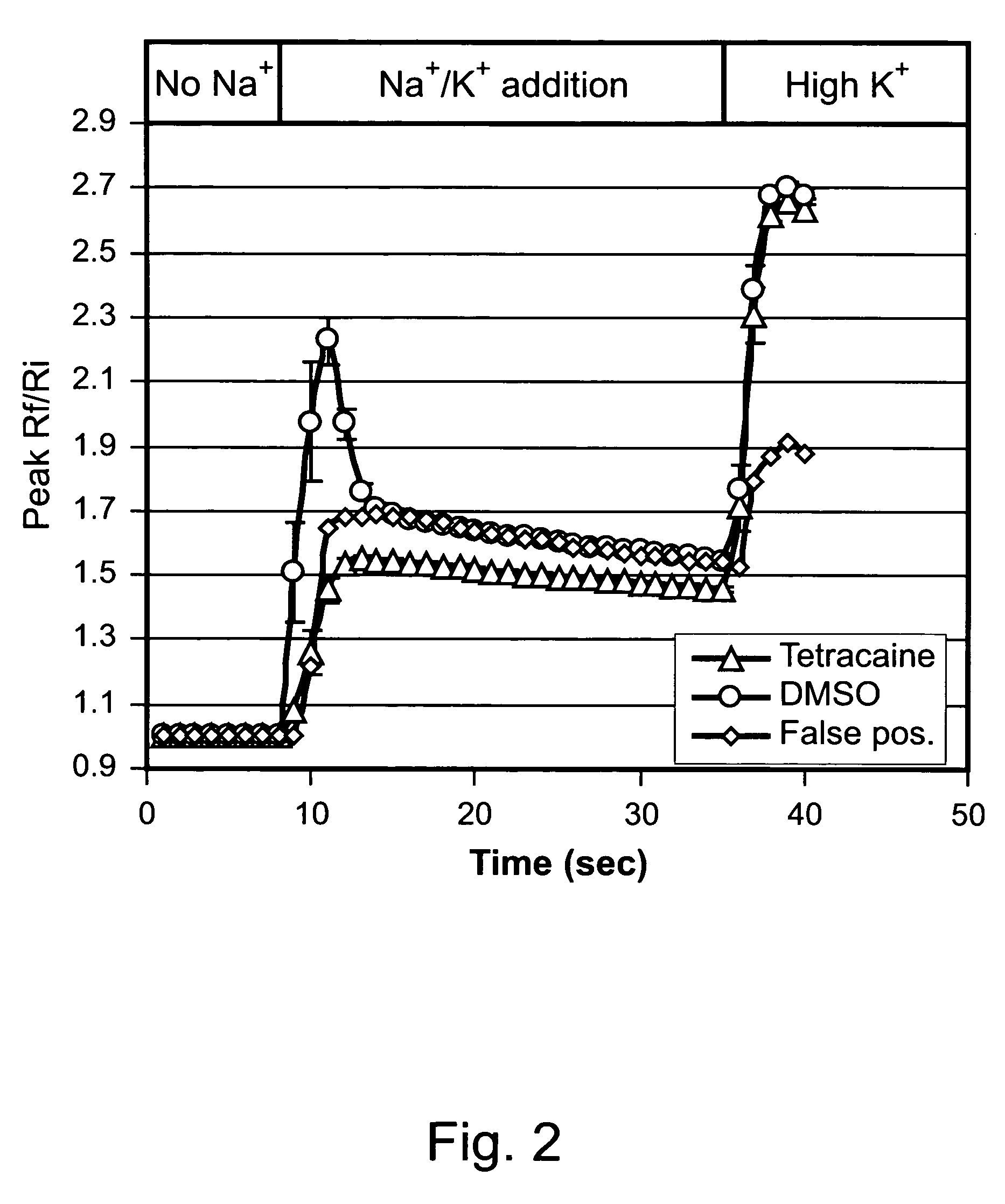
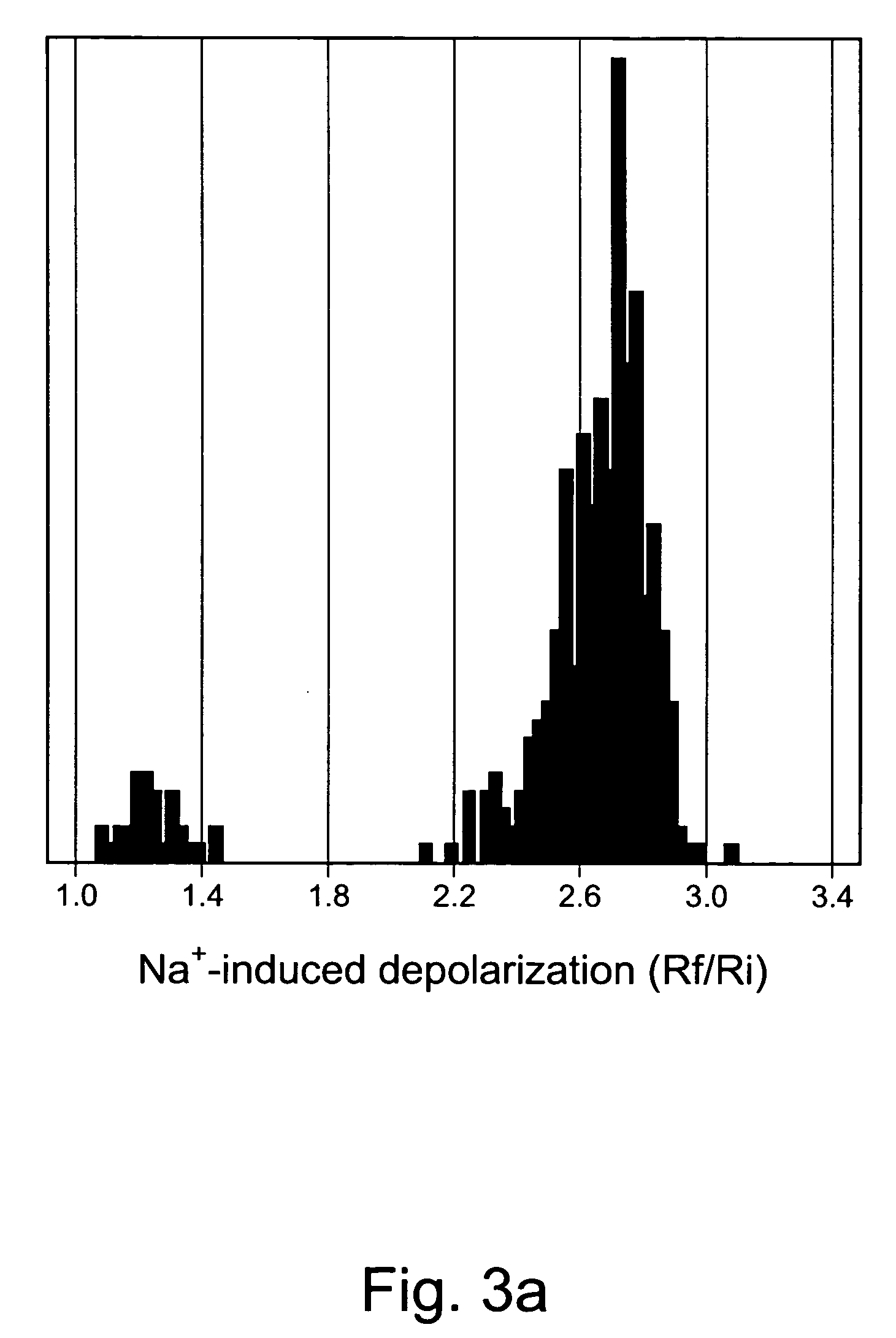
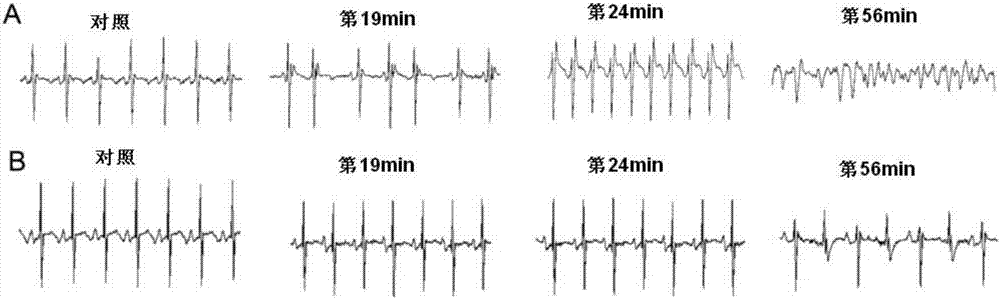
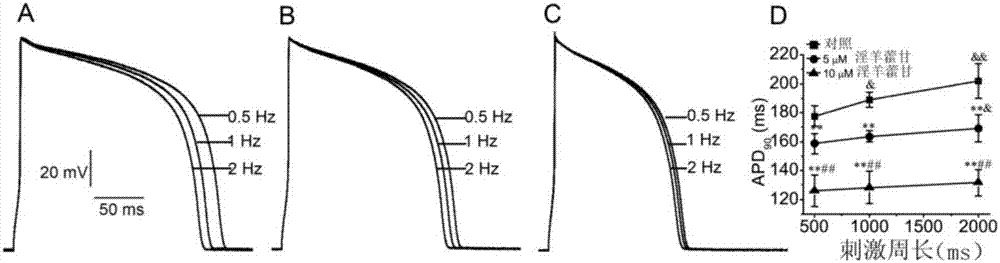
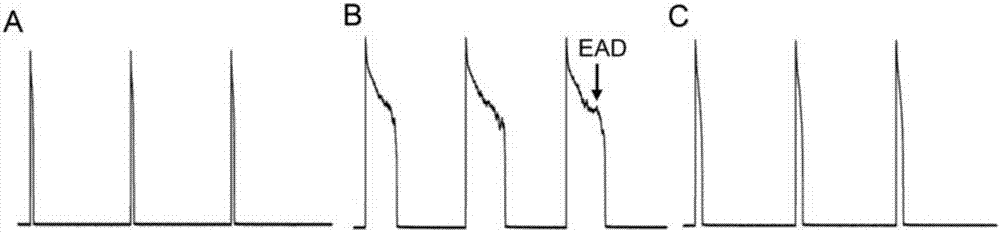
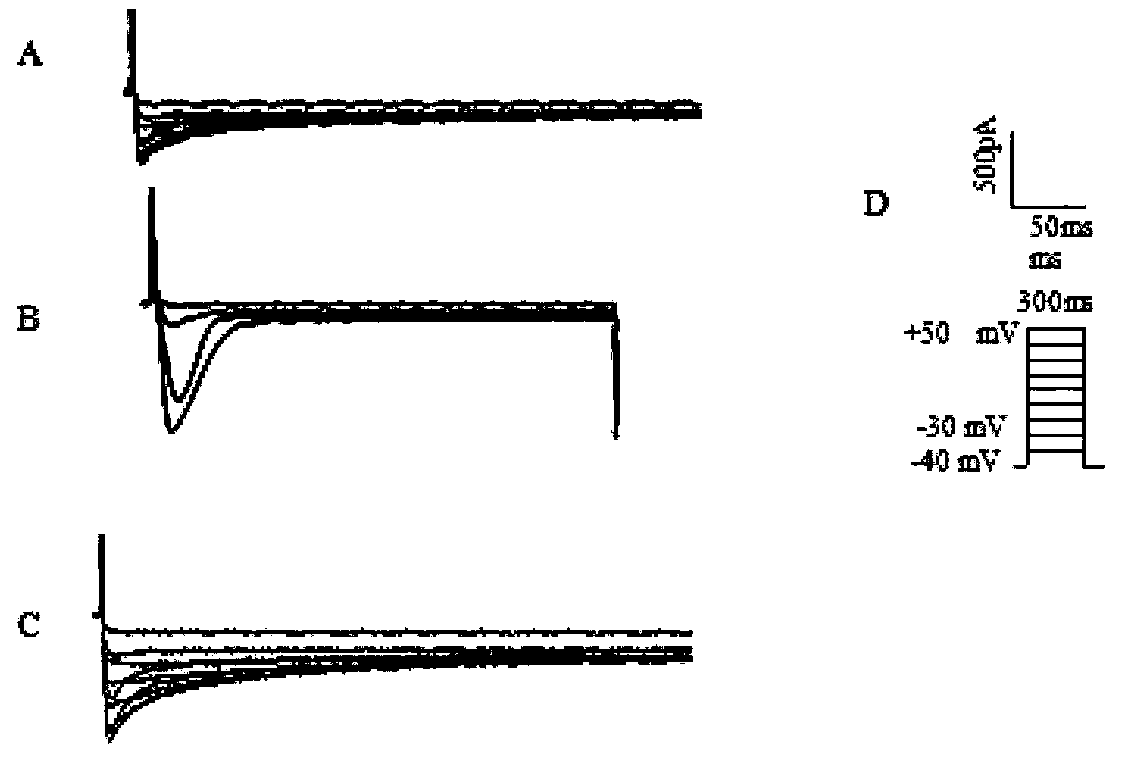
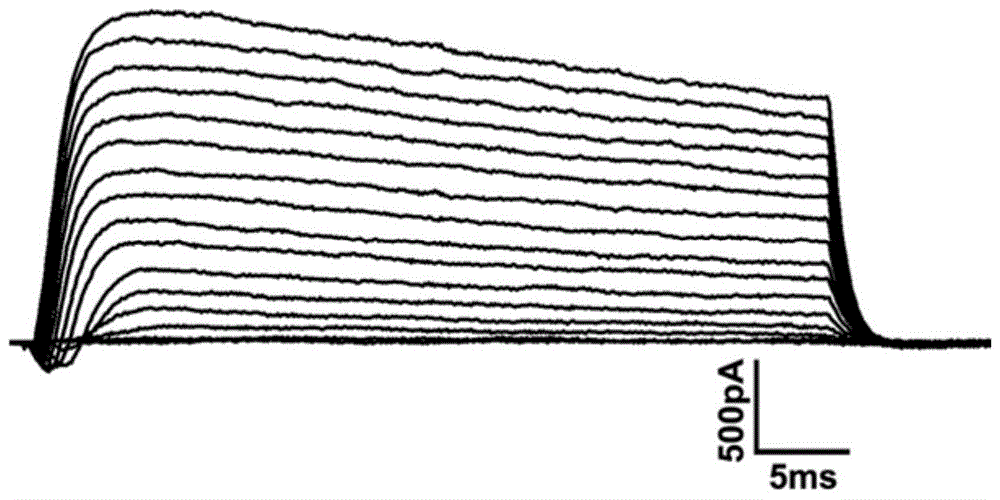
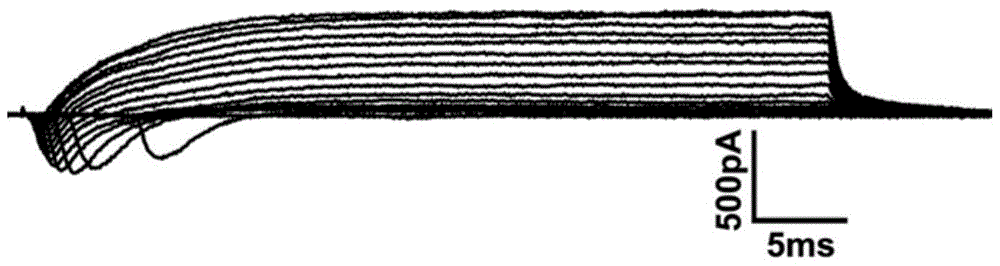
ActiveCN114044773ALower sodium currentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSpinal cord lesionIonic Channels
The invention relates to application of a 3-phenylfuran substituted 2-phenyl-4H-benzo[1,3]oxazine derivative. The invention provides a sodion channel blocker. The sodion channel blocker is a 3-phenylfuran substituted 2-phenyl-4H-benzo[1,3]oxazine derivative. The compound can effectively inhibit a sodion channel and reduce sodium current, and has the potential of treating neuropathic pain, such as post-herpes zoster neuralgia, diabetic neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, spinal cord injury and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Application of bulleyaconitine A in preparing medicament for treating primary erythermalgia
ActiveCN101468000BSuppression of pain impulsesOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseasePrimary Erythermalgia
Owner:YUNNAN HAOPY PHARM LTD
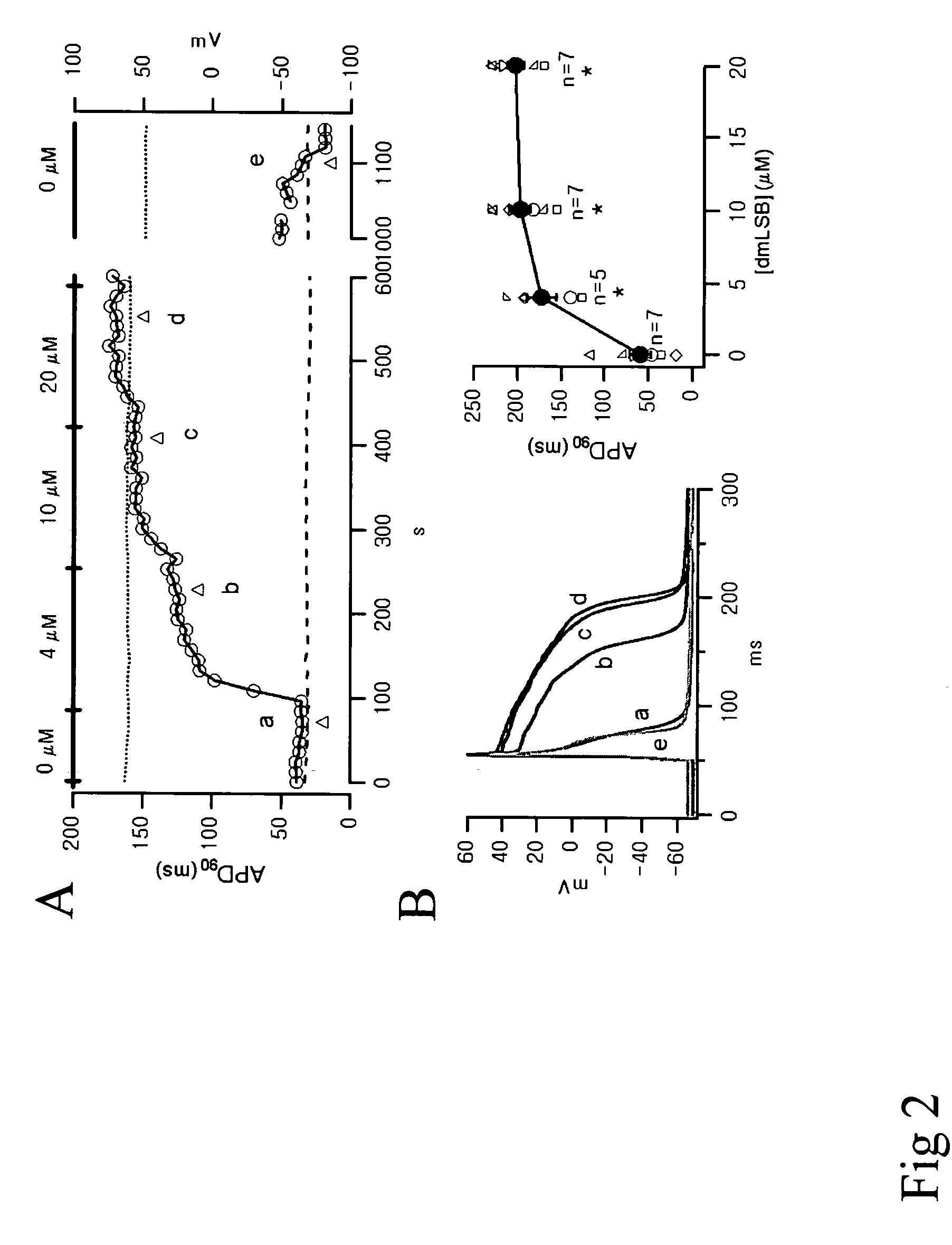
Delaid ingoticotramine -based cylinder phenolohol hybridization compound and its drug composition and application
ActiveCN111233886BIncluding myocardial ischemiaIncluding anginaOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseRanolazine
The invention provides dearomatized isopentenyl acylated phloroglucinol heteroterpene hypulatone A and hypulatone B, their preparation method, and a pharmaceutical composition using them as active ingredients, which are used in medicine, especially in the treatment of myocardial ischemia , angina pectoris, arrhythmia and heart failure and other diseases in the drug application. The novel compounds hypulatone A and hypulatone B provided by the invention are heteroterpene compounds of sesquiterpene with complex structure and dearomatization isopentenyl acylated phloroglucinol. hypulatone A and hypulatone B have selective and significant inhibitory activity on late sodium currents, with significant Na v 1.5 Sodium ion channel inhibitory activity, among which the compound hypulatone B is currently the most active natural inhibitor, and its effect is 30 times that of the positive control ranolazine, which has obvious advantages and potential medicinal value. It can be used to prepare medicines for preventing and / or treating diseases of the heart system.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel conotoxin modulating sodium channels
InactiveUS20070037743A1Prevent rotAvoid inactivationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalHamster
A 26 residue peptide (Am2766) with the sequence CKQAGESCDIFSQNCCVGTCAFICIE-NH2 has been isolated and purified from the venom of the molluscivorous snail, Conus amadis, collected of the southeastern coast of India. Chemical modification and mass spectrometric studies establish that Am2766 has three disulfide bridges. Cterminal amidation has been demonstrated by mass measurements on the C-terminal fragments obtained by proteolysis. Sequence alignments establish that Am2766 belongs to the δ-conotoxin family. Am2766 inhibits the decay of the sodium current in brain rNav1.2a voltage-gated Na+ channel, stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. Unlike δ-conotoxins have previously been isolated from molluscivorous snails, Am 2766 inhibits inactivation of mammalian sodium channel.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR BIOLOGICAL SCI TATA INST OF NAT CENT FOR BIOLOGICAL SCI TATA INST OF FUNDAMENTAL RES
Treatment of non-neuronal and non-myocardial cell, tissue and organ damage and associated pain with persistent sodium current blockers
The present invention relates to a method for slowing the development of mammalian organ, tissue and cellular damage and death by using a persistent sodium current blocker (or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or derivative thereof). The present invention further relates to a method for preventing damage and death in mammalian organs, tissues and cells or reducing the extent of damage and death in mammalian organs, tissues and cells. In particular the invention relates to a method for the treatment, amelioration or prevention of non-neuronal and non-myocardial cell or tissue damage or death and for reducing the pain associated with non-neuronal and non-myocardial cell or tissue damage.
Owner:OZTEO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com





![Application of 3-phenylfuran substituted 2-phenyl-4H-benzo[1,3]oxazine derivative Application of 3-phenylfuran substituted 2-phenyl-4H-benzo[1,3]oxazine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/8f251372-34fa-4a1a-ae7f-a45d32a605f2/HDA0003378152420000011.png)
![Application of 3-phenylfuran substituted 2-phenyl-4H-benzo[1,3]oxazine derivative Application of 3-phenylfuran substituted 2-phenyl-4H-benzo[1,3]oxazine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/8f251372-34fa-4a1a-ae7f-a45d32a605f2/HDA0003378152420000012.png)
![Application of 3-phenylfuran substituted 2-phenyl-4H-benzo[1,3]oxazine derivative Application of 3-phenylfuran substituted 2-phenyl-4H-benzo[1,3]oxazine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/8f251372-34fa-4a1a-ae7f-a45d32a605f2/FDA0003378152400000011.png)