Patents
Literature
43results about "Error correction/detection using non-linear codes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of Error Correction Code on Solid State Disk to Gain Data Security and Higher Performance
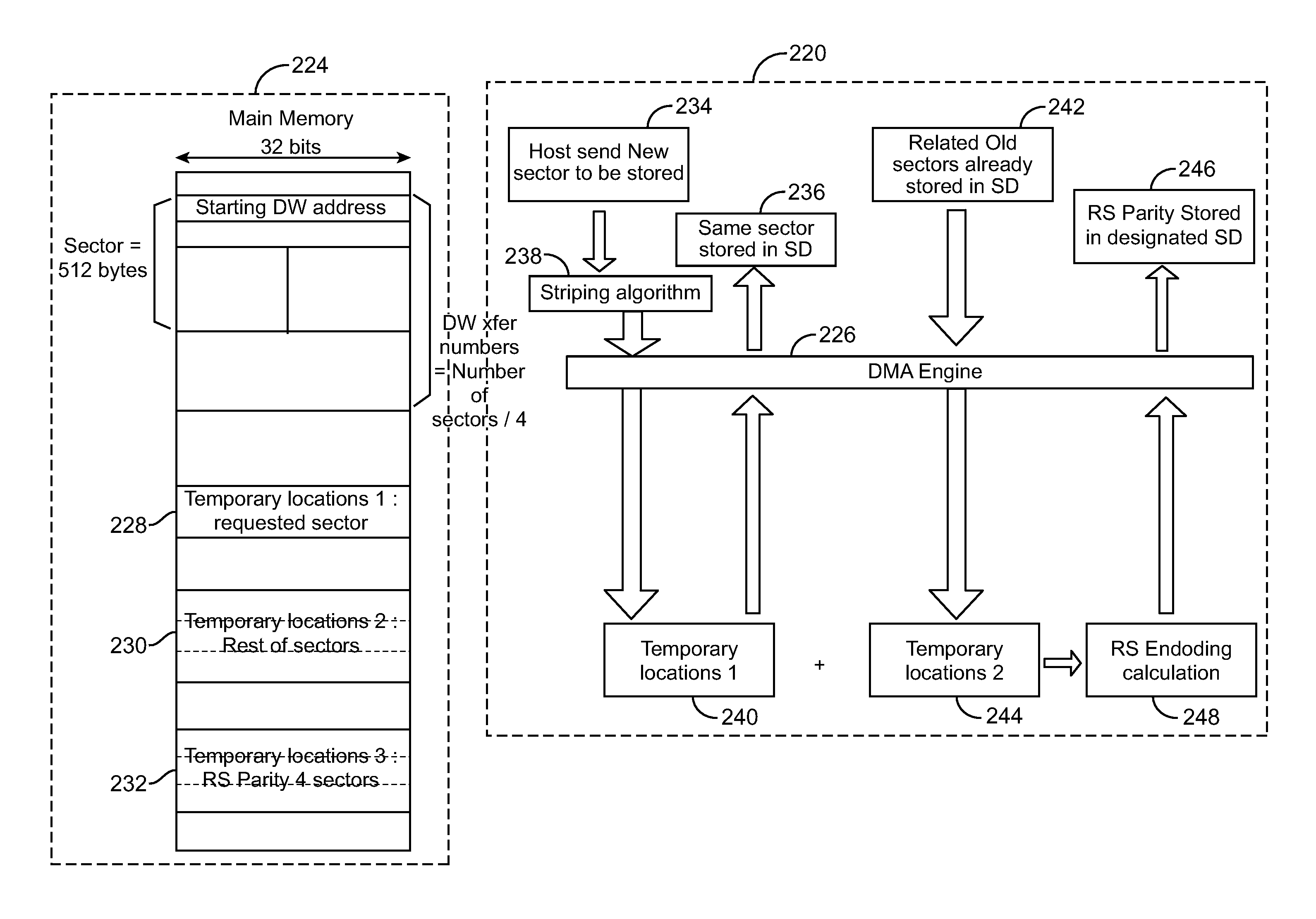
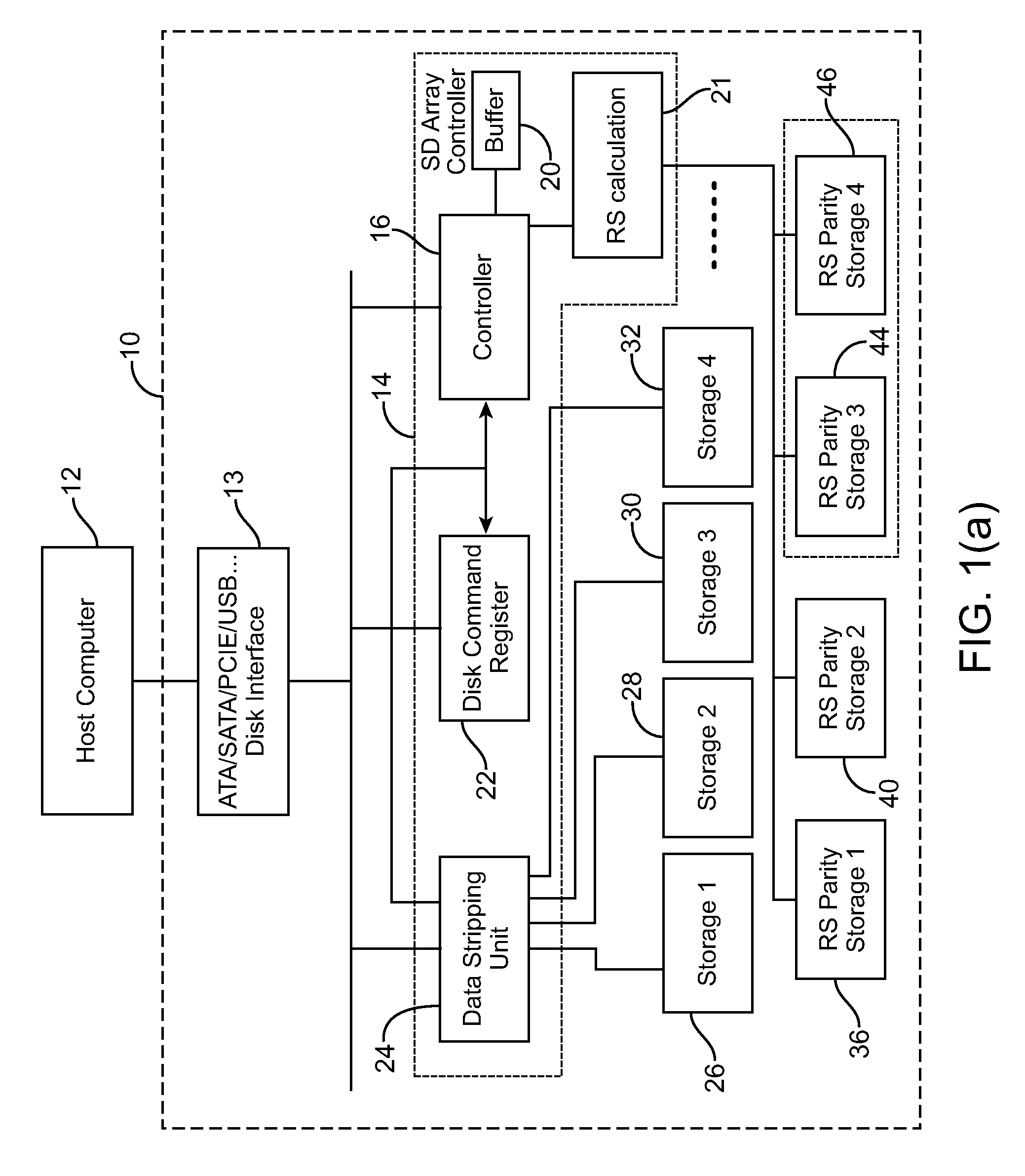
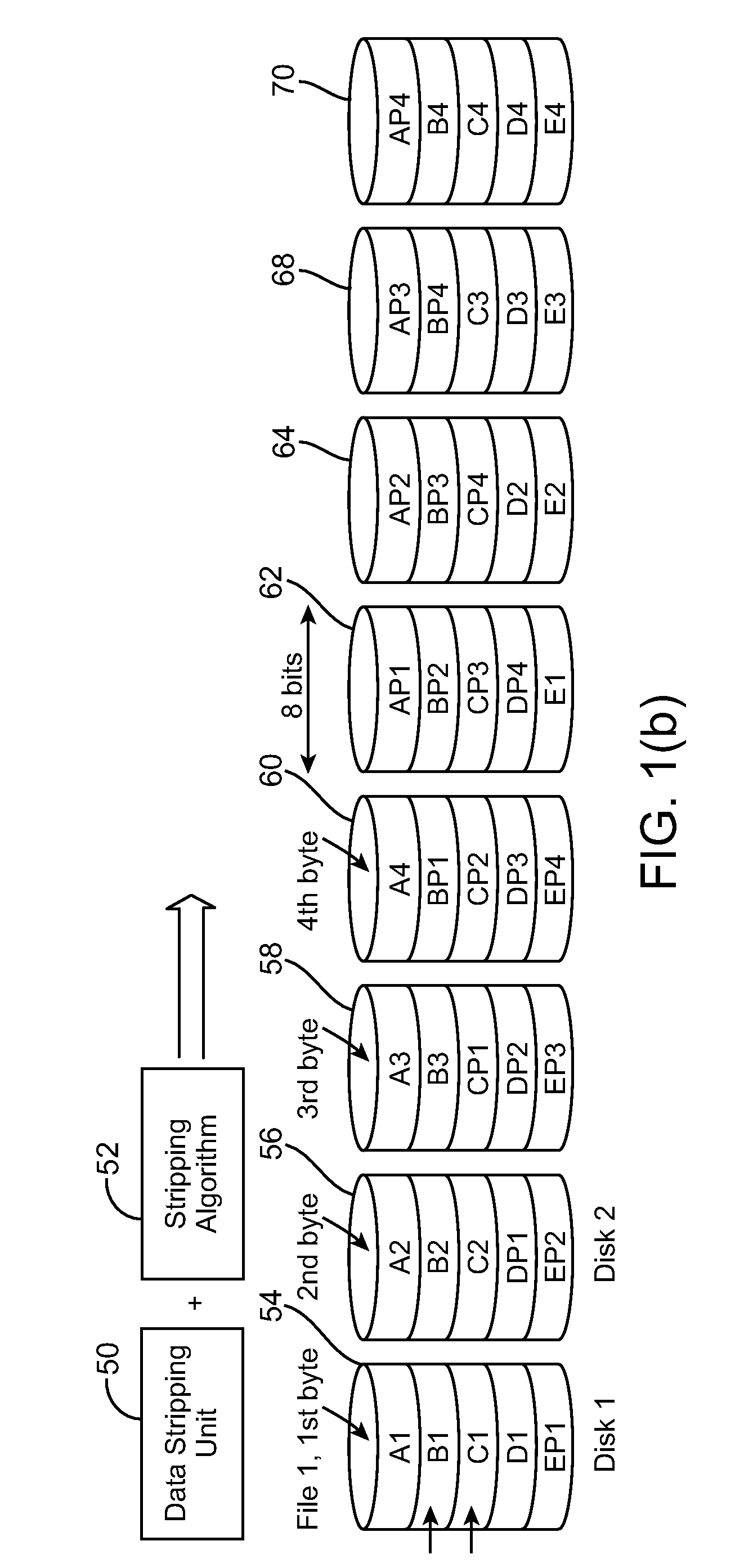
An electronic data storage device having a Reed Solomon (RS) decoder including a syndrome calculator block responsive to information including data and overhead and operative to generate a syndrome, in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. The electronic data storage device further includes a root finder block coupled to receive said syndrome and operative to generate at least two roots, said RS decoder for processing said two roots to generate at least one error address identifying a location in said data wherein said error lies; and an erasure syndrome calculator block responsive to said information and operative to generate an erasure syndrome, said RS decoder responsive to said information identifying a disk crash, said RS decoder for processing said erasure syndrome to generate an erasure error to recover the data in said disk crash.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
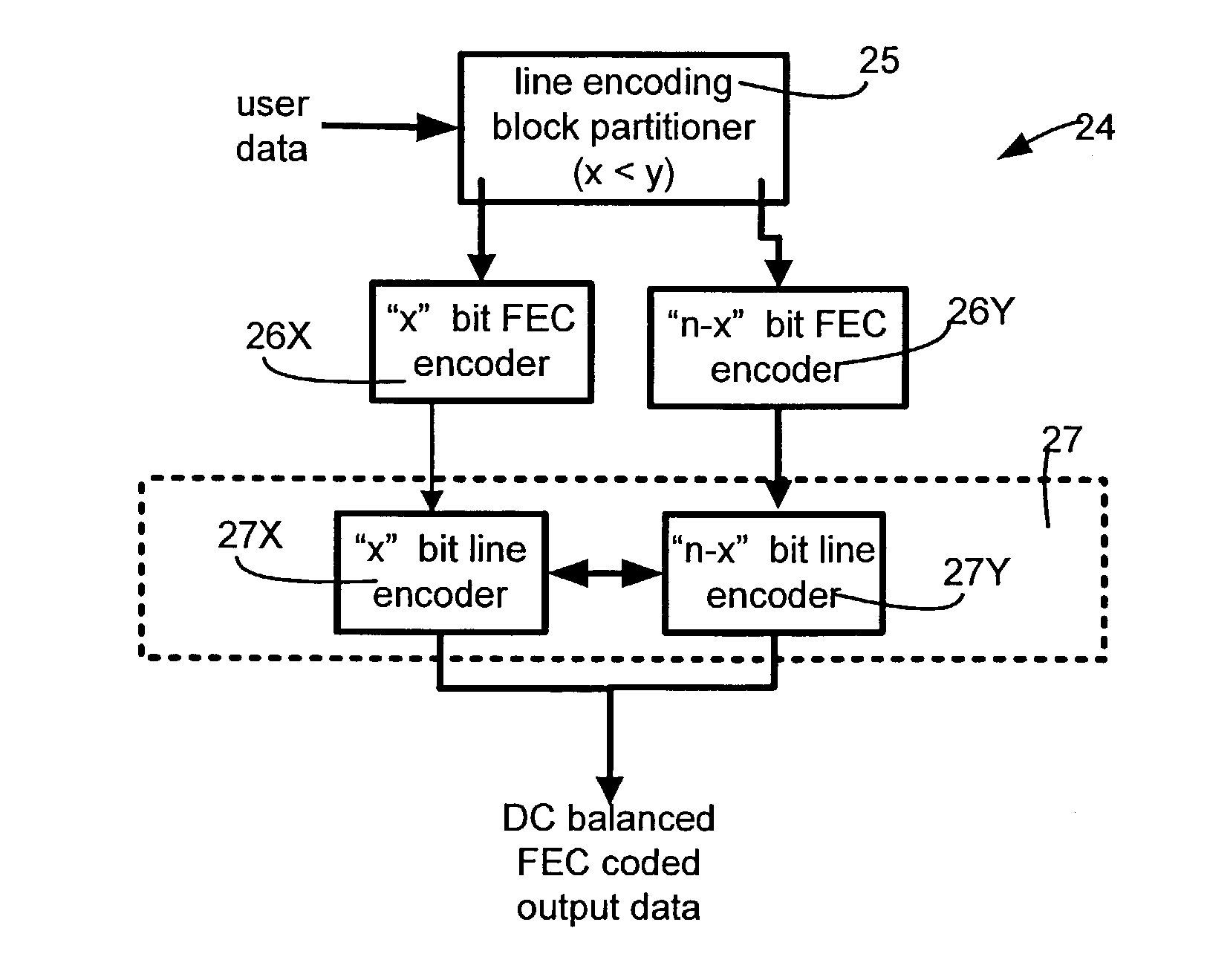
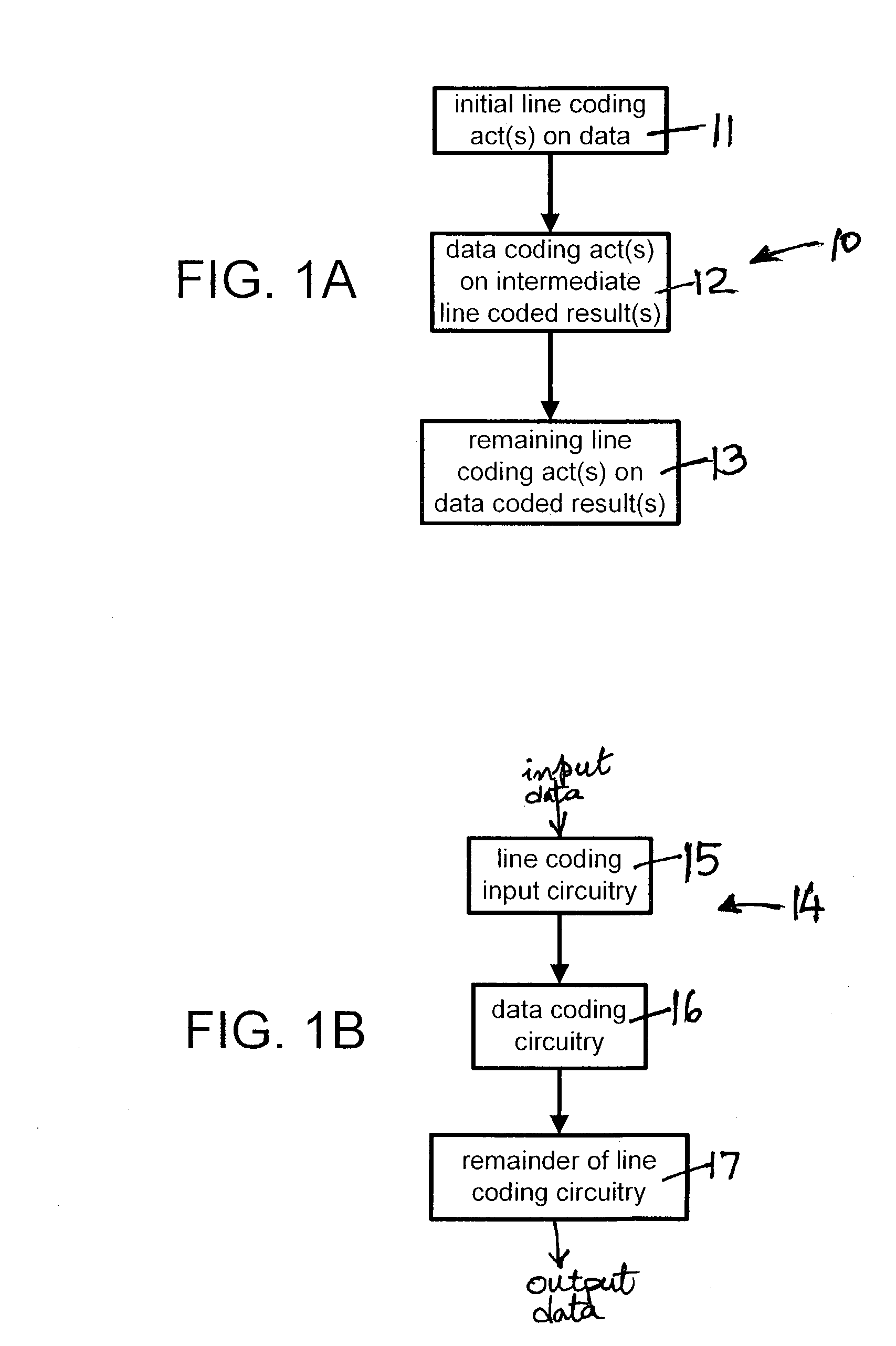
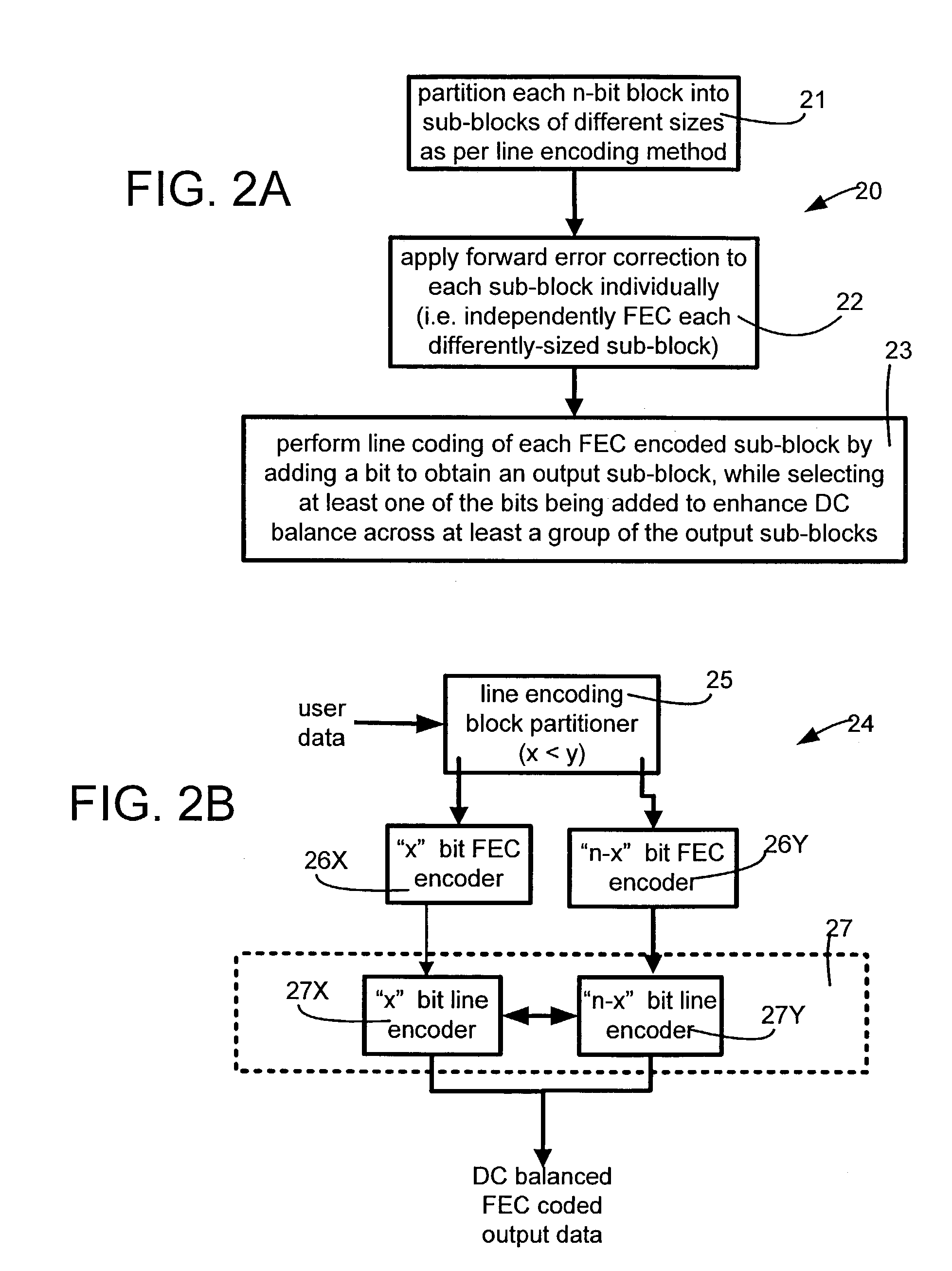
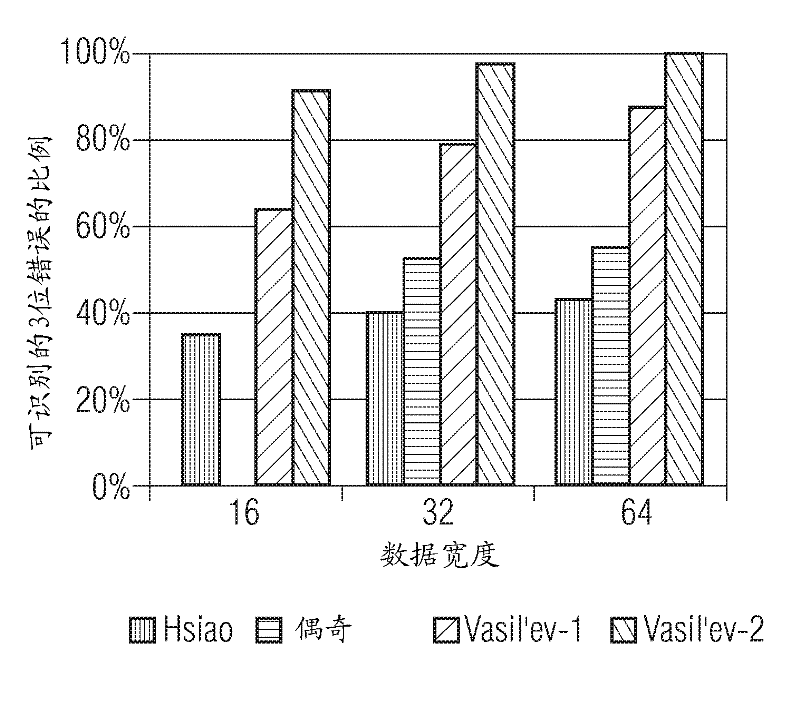
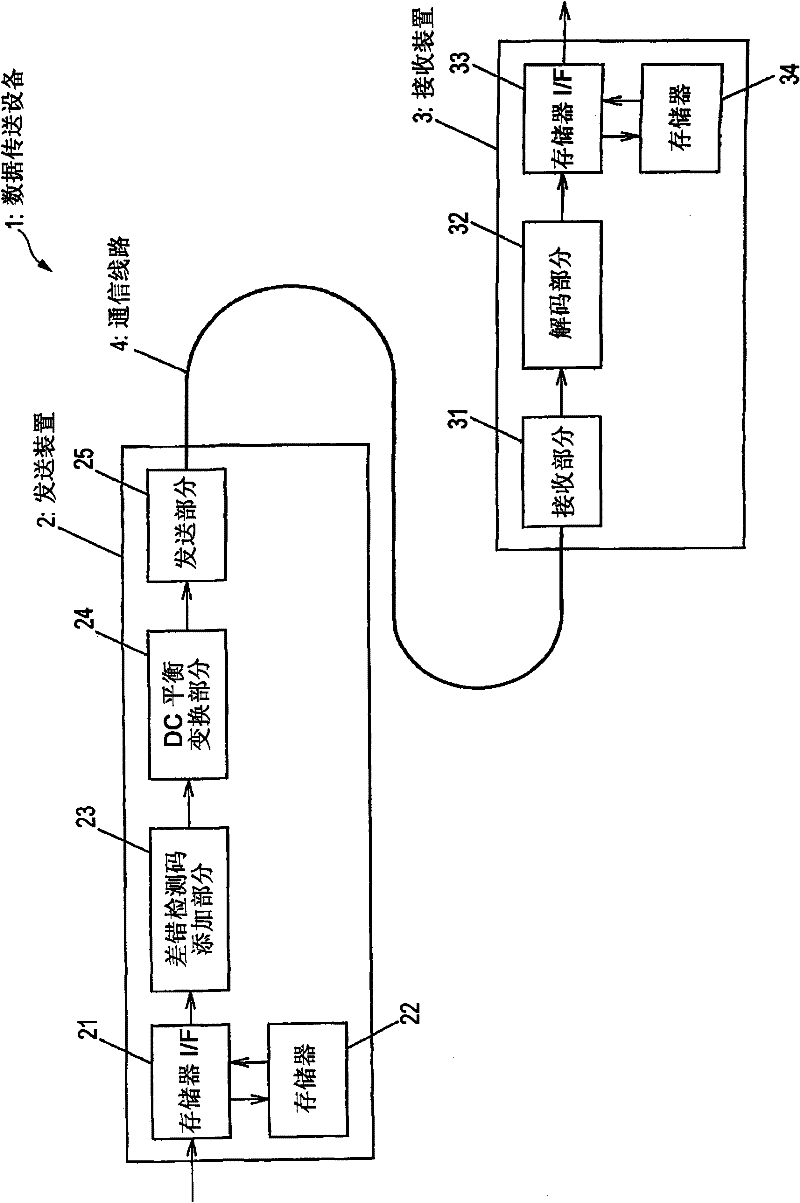
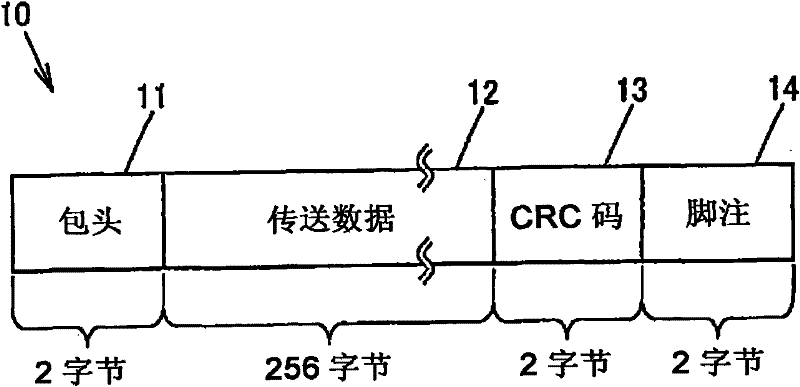
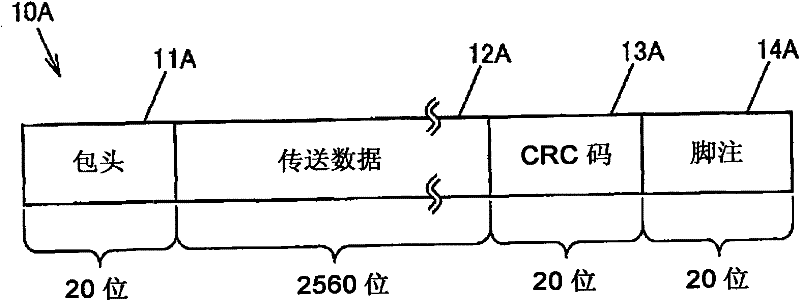
DC balanced error correction coding
ActiveUS7103830B1Simple processSmall circuitIndividual digits conversionError detection only8b/10b encodingData encoding
Two types of codings are integrated, instead of performing each coding independently. The two codings may be integrated by interleaving one or more acts of one coding method (e.g. data coding) between two or more acts of the other coding method (e.g. line coding). In some embodiments, partitioning of a block of data (e.g. a byte) for line coding (e.g. DC balance coding) is done prior to data coding (e.g. error correction coding). In such embodiments, the remaining acts of line coding may be performed after the data coding is completed. In one particular embodiment, an 8 bit byte is not directly used in error correction coding and instead, the 8 bit byte is initially partitioned into two sub-blocks (of 3 bits and 5 bits) as required by 8B / 10B encoding (which is an example of line coding). After partitioning, the 8B / 10B encoding is not continued, and instead Reed Solomon coding (which is an example of data coding) is then performed (to completion) on the individual sub-blocks (of 3 bits and 5 bits). The error correction coded sub-blocks (of 3 bits and 5 bits) are then used for the remainder of 8B / 10B encoding.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
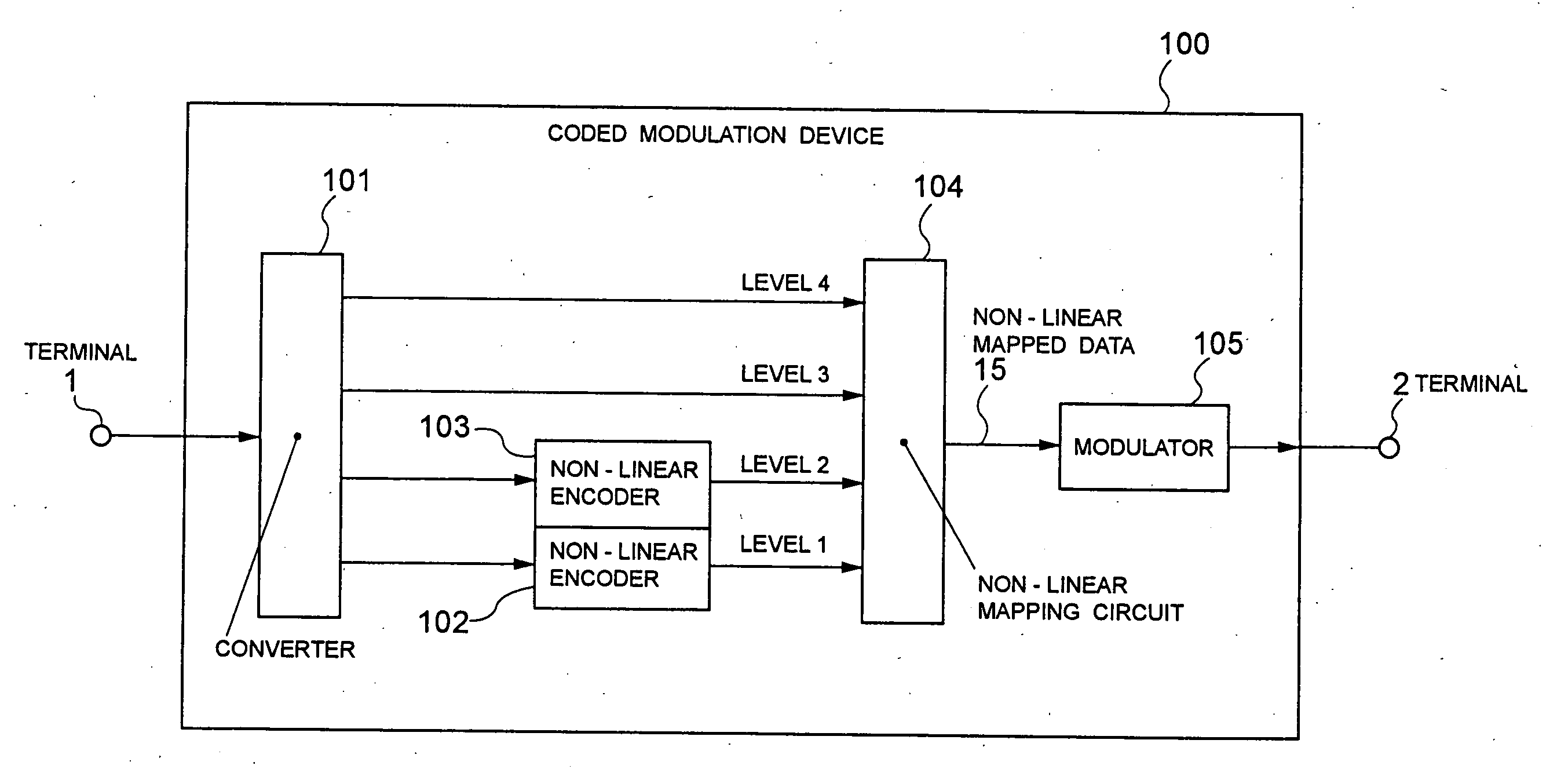
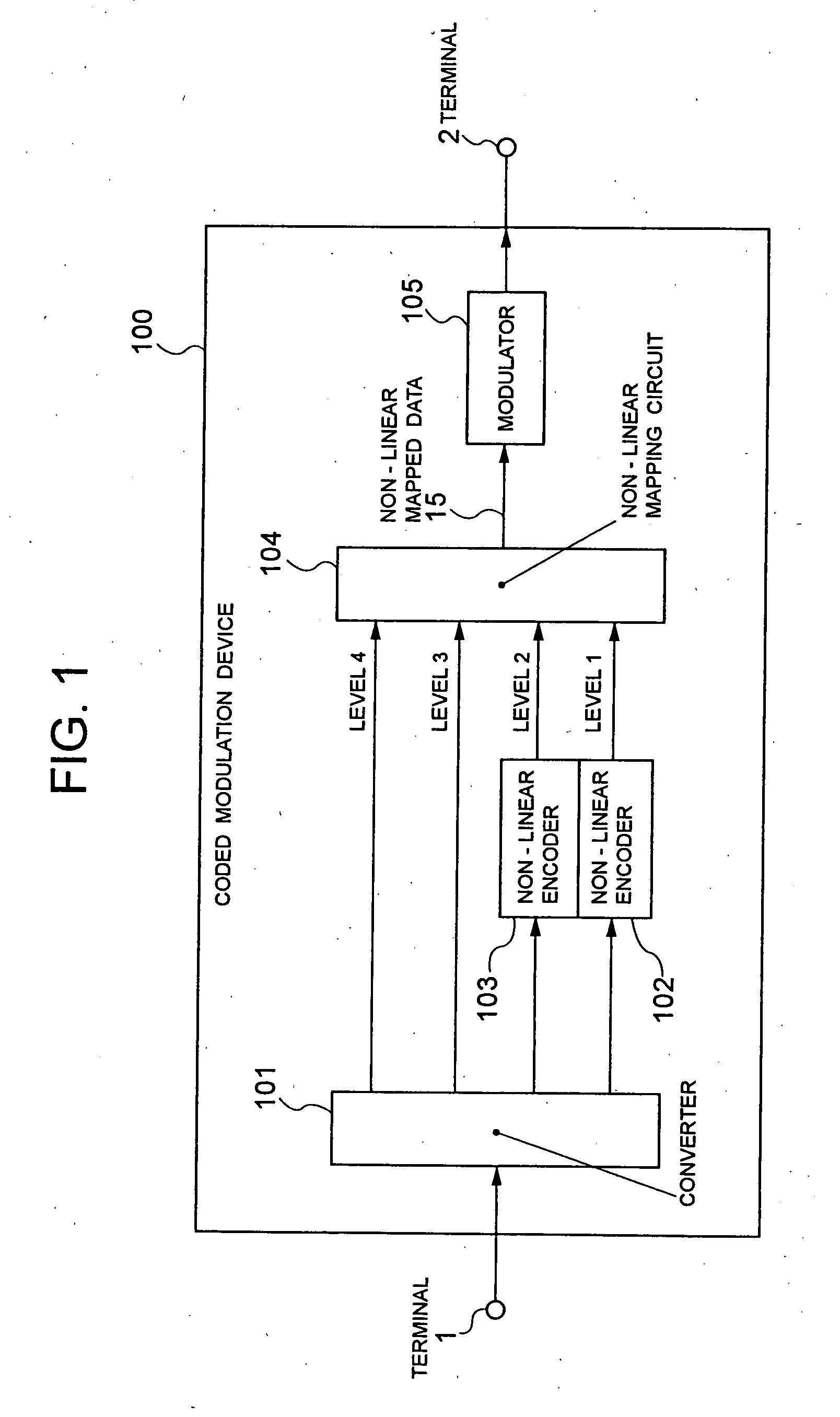
Coded modulation device and method
InactiveUS20050207507A1Higher coding gainError correction/detection using trellis codingPhase-modulated carrier systemsLinear codingCarrier signal
The present invention realizes a high coding gain employing a non-linear coding and a non-linear mapping. A converter converts one row of data that is inputted from a terminal into plural rows of data. The non-linear encoders non-linearly encode-lower level two rows of data in plural rows of converted data, and outputs them as data of level 1 and level 2 to a non-linear mapping circuit. The non-linear mapping circuit maps the data non-linearly encoded by the non-linear encoders and the uncoded data so that each codeword distance may be optimal. A modulator modulates a carrier wave with two-dimensional data that are mapped by the non-linear mapping circuit.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of compressing lookup table for reducing memory, non-linear function generating apparatus having lookup table compressed using the method, and non-linear function generating method
InactiveUS6900747B2Pulse modulation television signal transmissionSpeech analysisTerm memoryLookup table
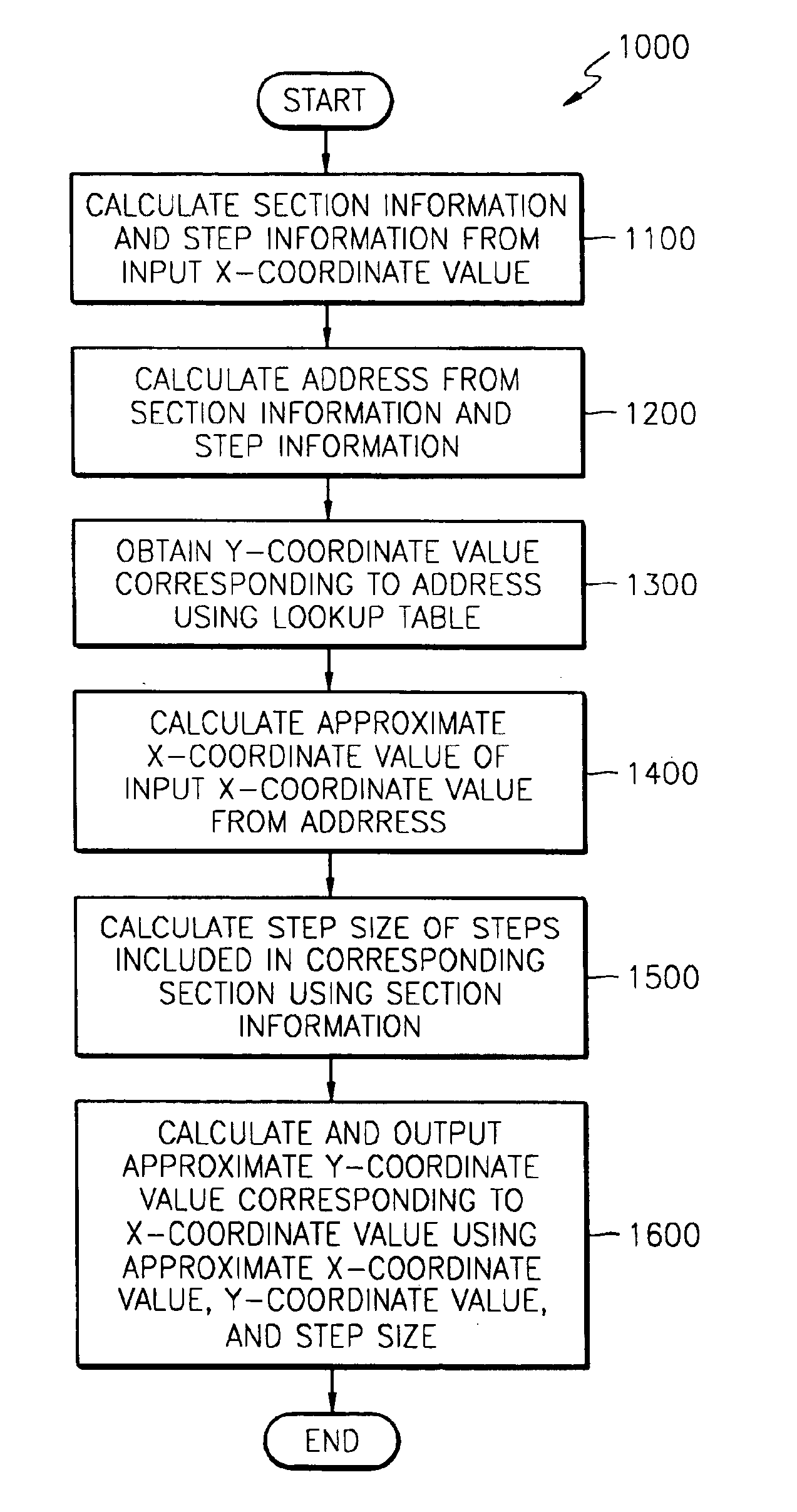
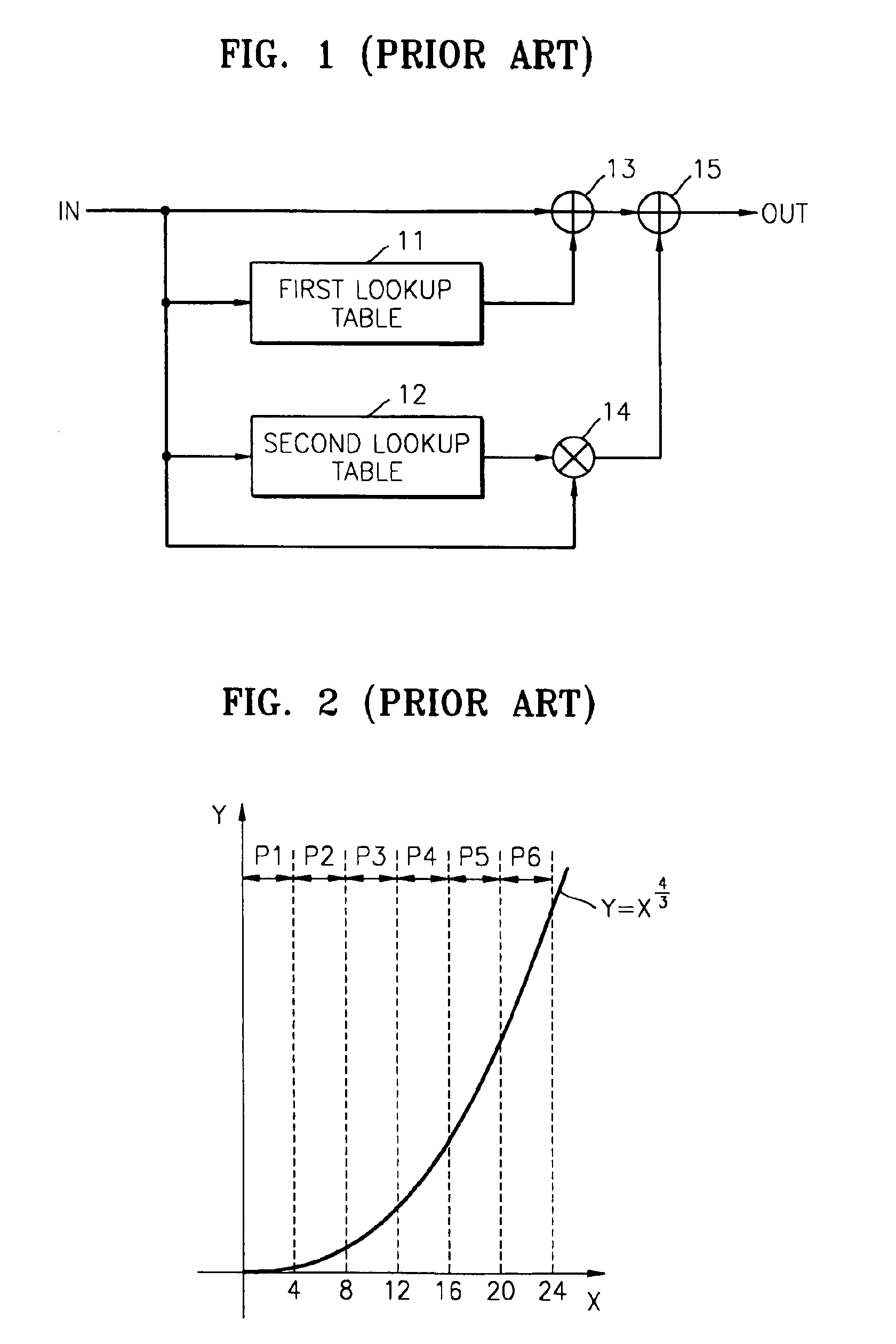
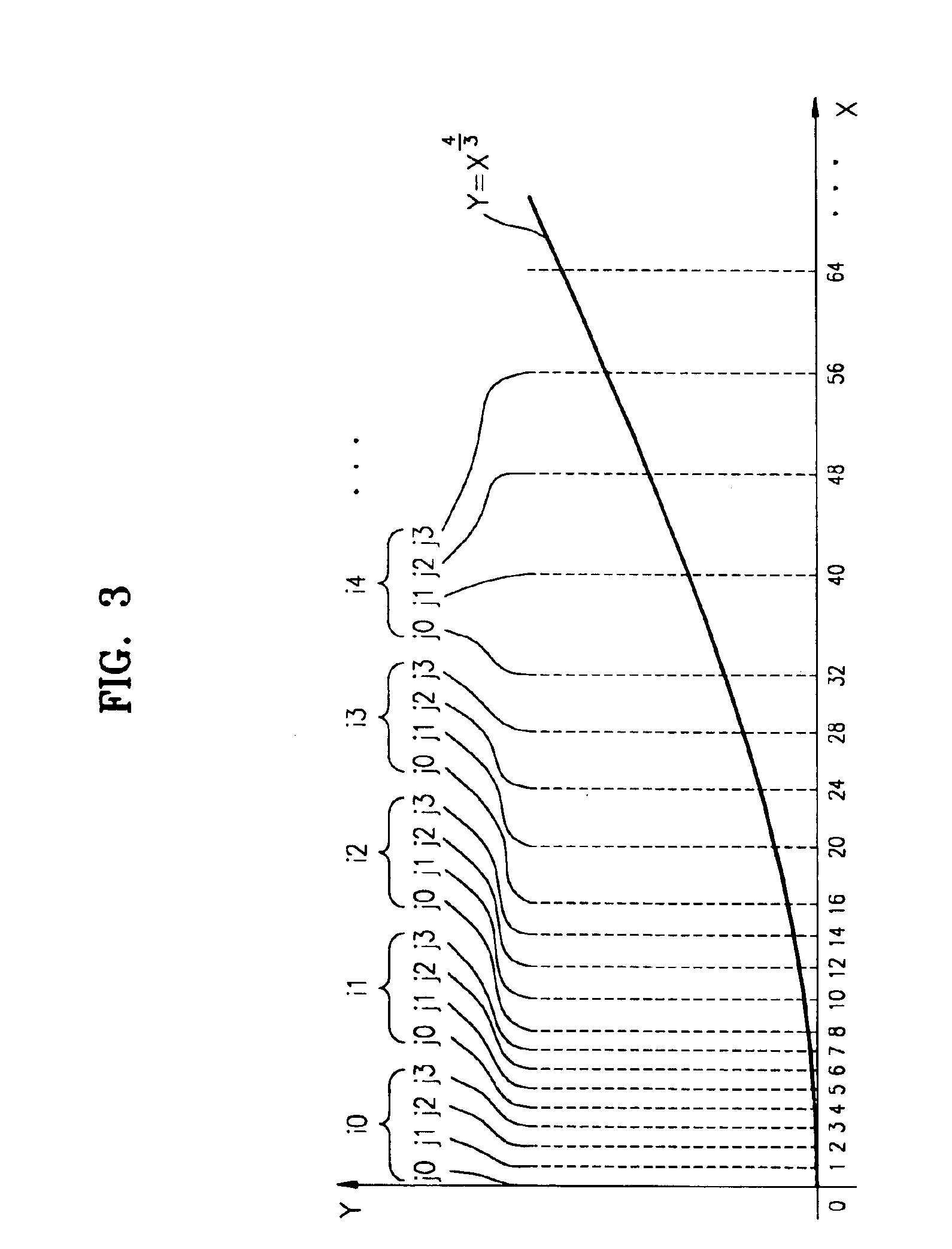
In a method of compressing a lookup table for reducing memory, a non-linear function generating apparatus having a lookup table compressed using the method, and a non-linear function generating method, X-coordinates of the non-linear function are separated into a plurality of sections including steps that have predetermined step sizes. Y-coordinate values corresponding to X-coordinate values are extracted for each step. The Y-coordinate values are stored in predetermined addresses in a memory, wherein the step sizes are different according to the sections. In this manner, memory capacity occupied by the lookup table is reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Error correction with low latency for bus structures
InactiveUS6978416B2Lower latencyElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionMultiplexerLatency (engineering)
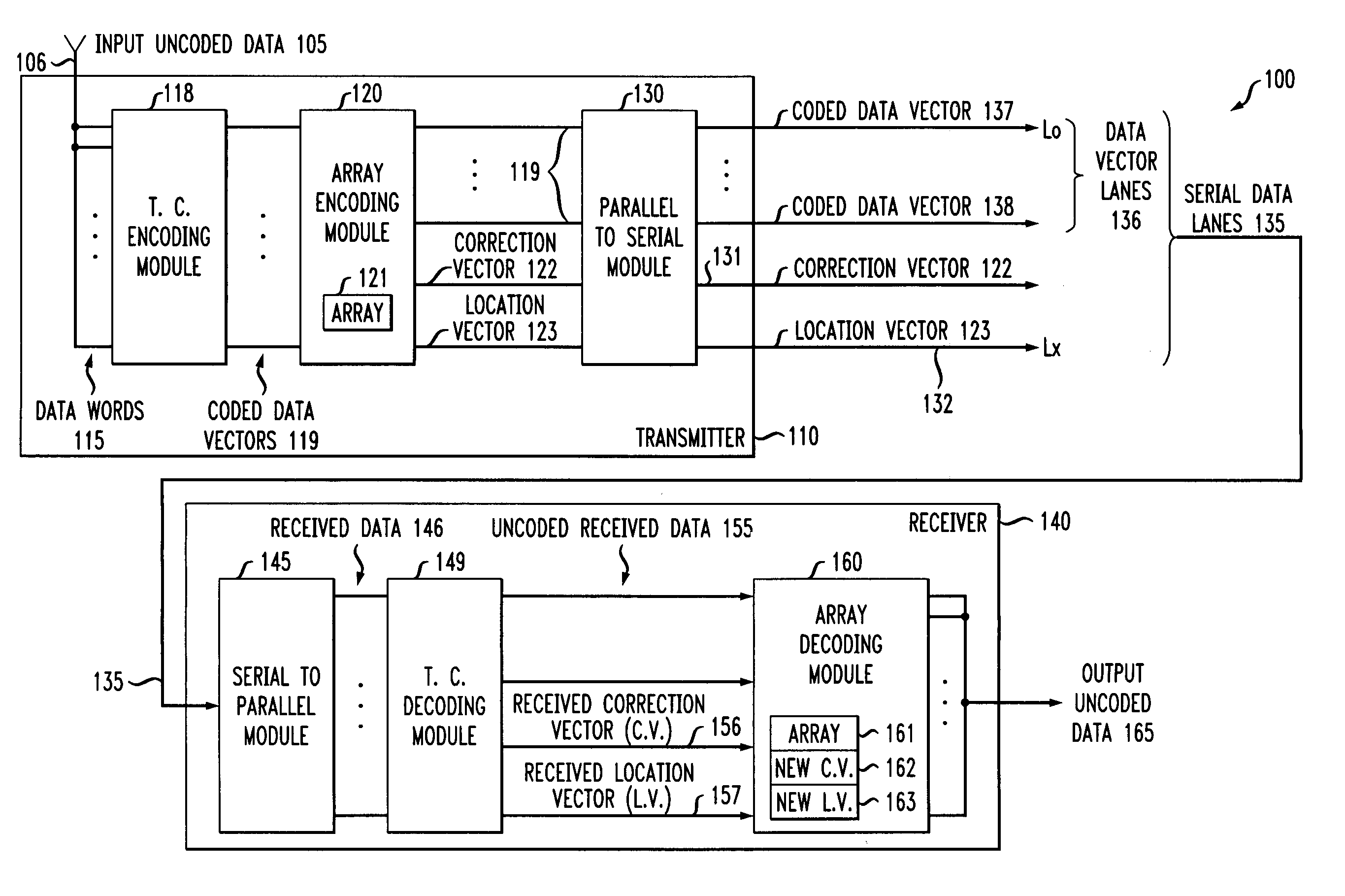
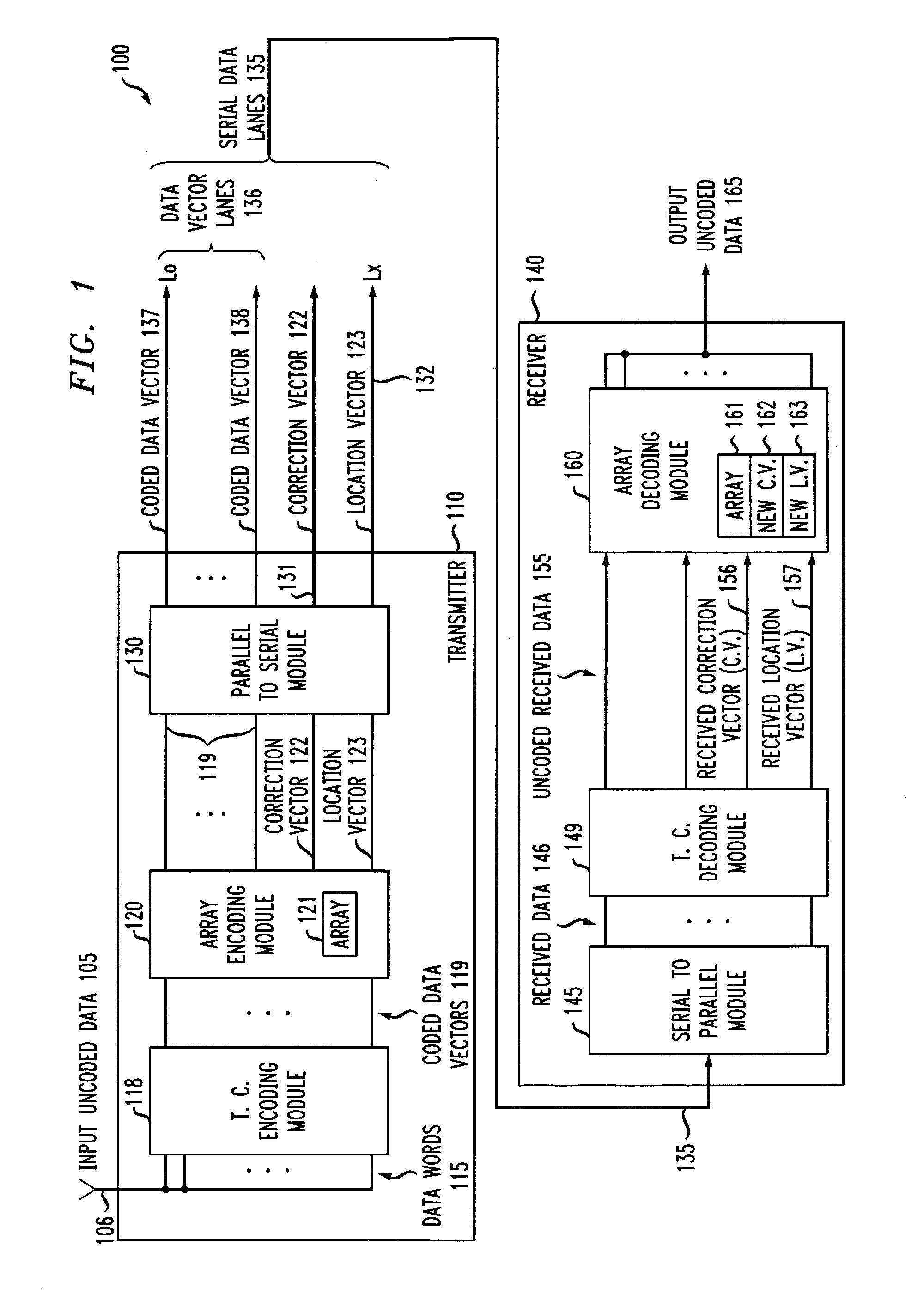
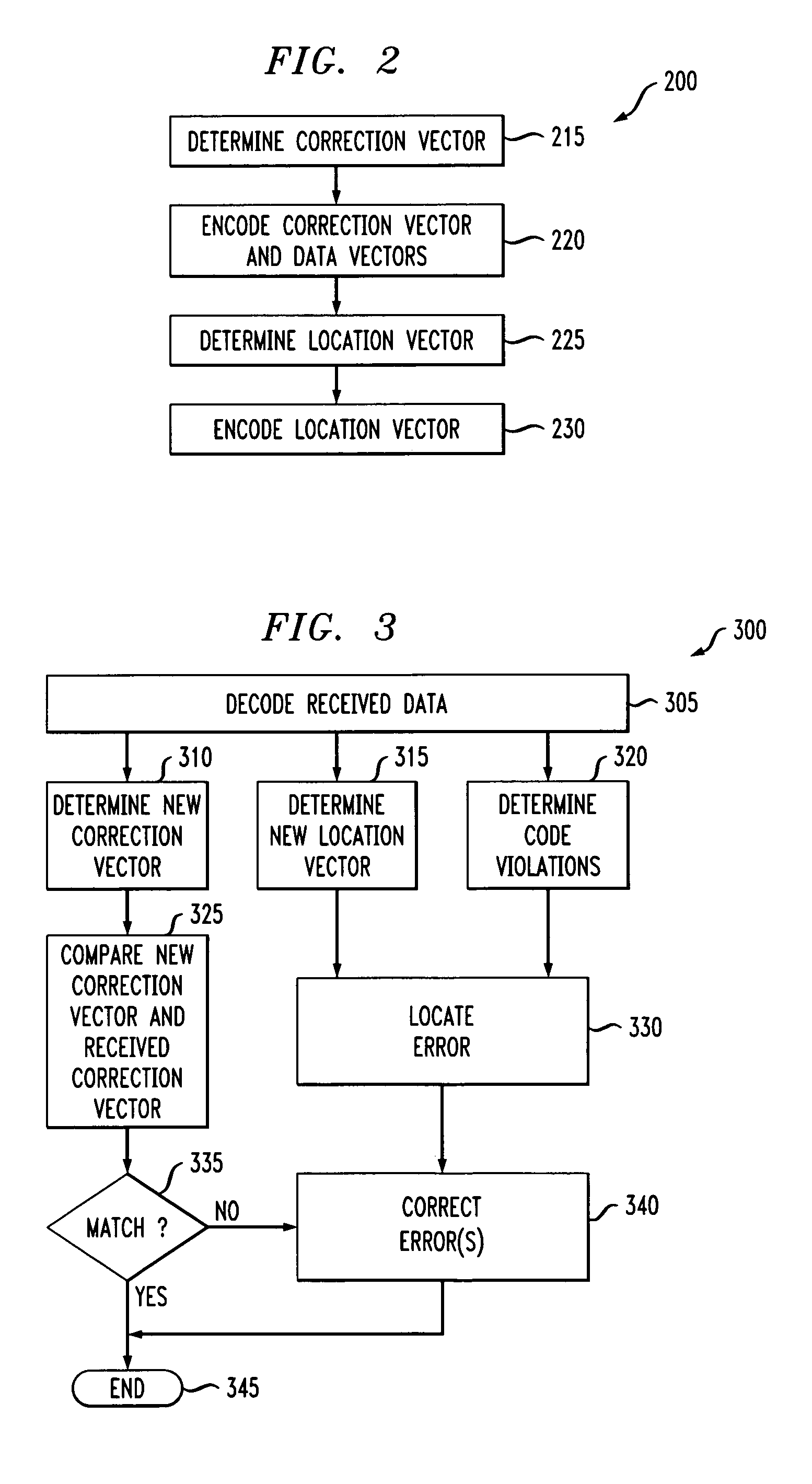
Correction and location information are determined from a number of data vectors. The location information comprises values determined from subsets of the data vectors. Two or more of the subsets have one or more data vectors in common, but also have one or more data vectors, in one or more of the subsets, that are not in other subsets. The subsets comprise groups of data vectors, and the groups of data vectors have a size that is a function of a power of two. Transmission codes are used on the data vectors and correction and location information. Received location information and determined location information are compared to determine a data vector having an error. Received correction information and determined correction information are compared to correct the data vector having the error. Failing optical lanes may be replaced efficiently by using a number of multiplexers coupled to electrical lanes and optical lanes.
Owner:IBM CORP
Channel coding/decoding apparatus and method for a CDMA mobile communication system
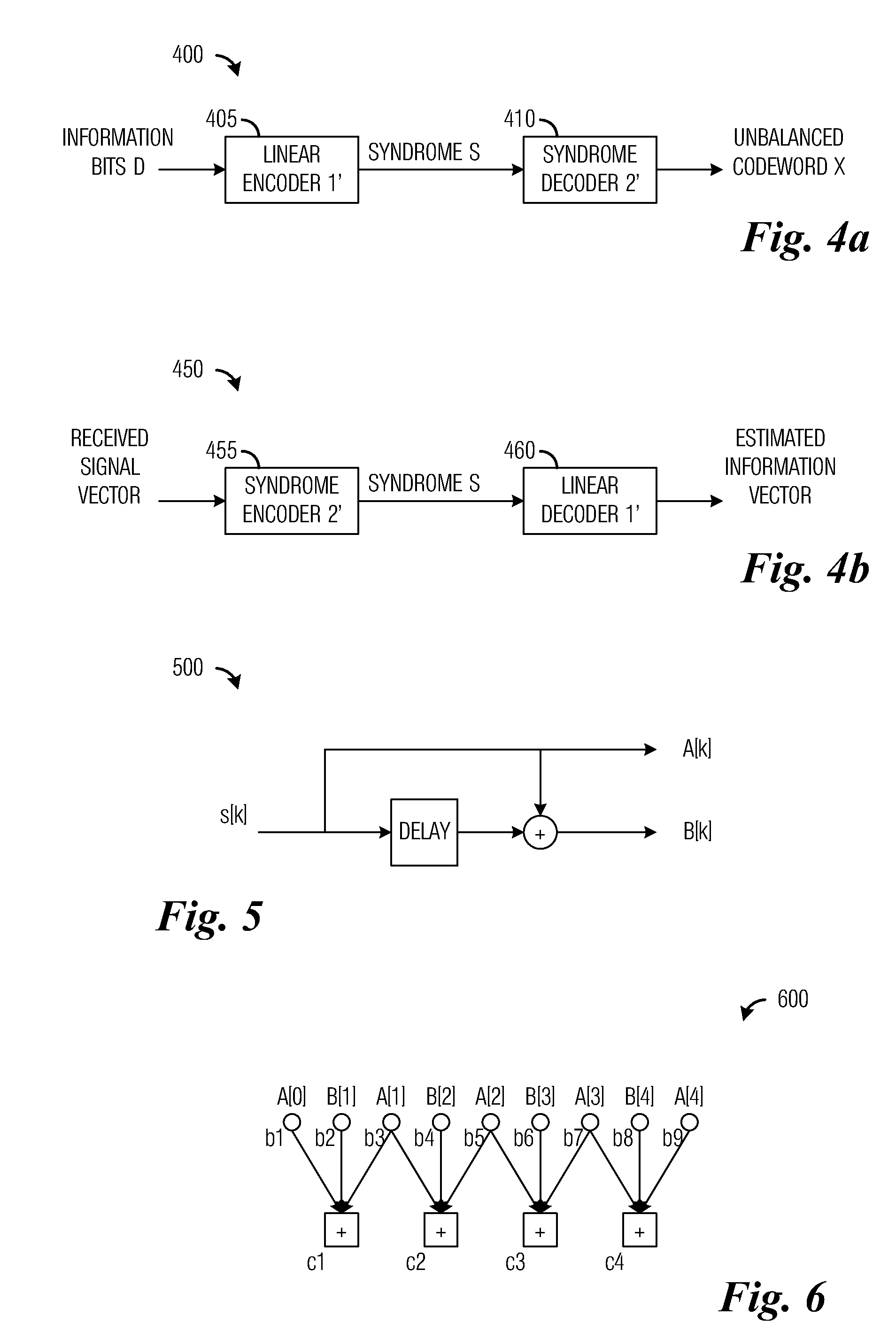
InactiveUS20050210364A1Improve error correction performanceCorrection capabilityReed-muller codesError preventionReed–Muller codeTheoretical computer science
A apparatus for generating (2k-2t) first order Reed-Muller codes from 2k first order Reed-Muller codes based on k input information bits. The apparatus includes a code generator configured to generate (2k-2t) bits first order Reed-Muller codes, and an encoder for multiplying the k input information bits with the (2k-2t) bits first order Reed-Muller codes. The encoding apparatus also includes a memory for storing a number of first order Reed-Muller codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
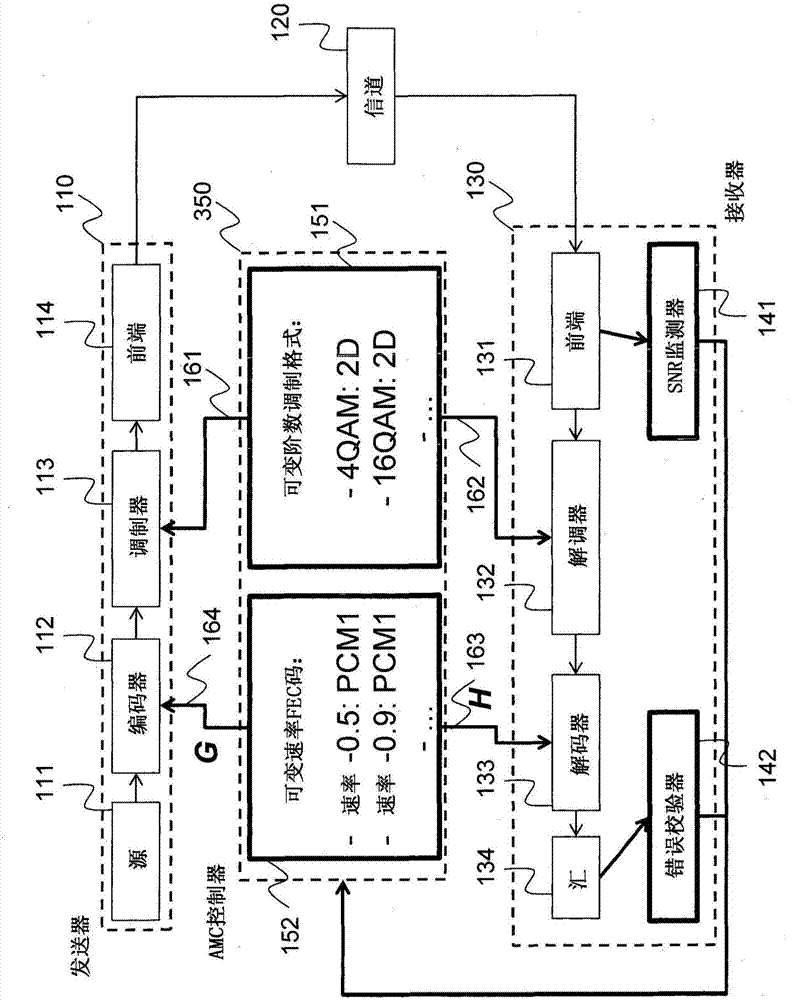
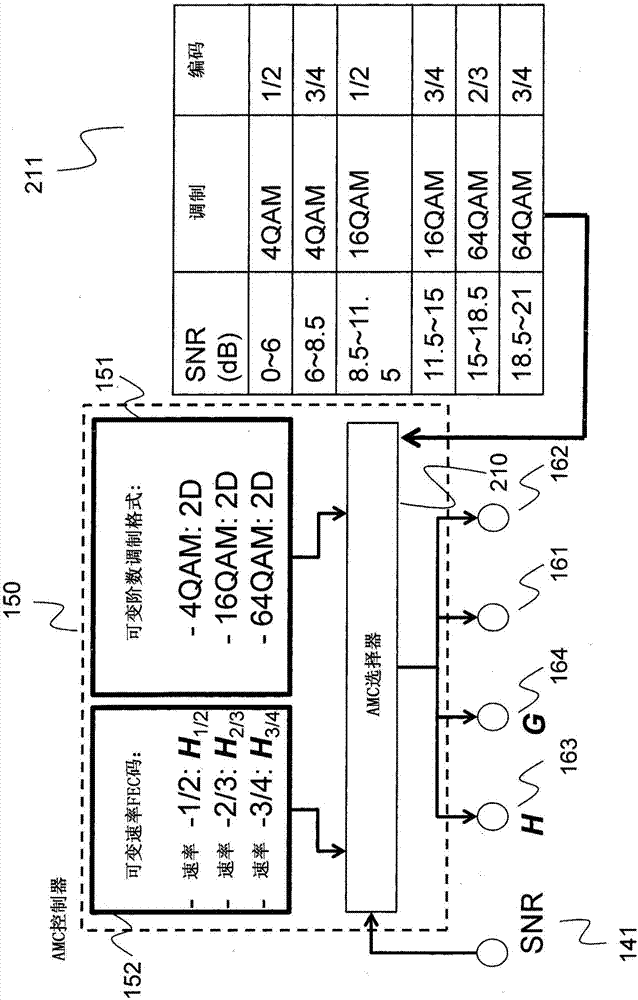
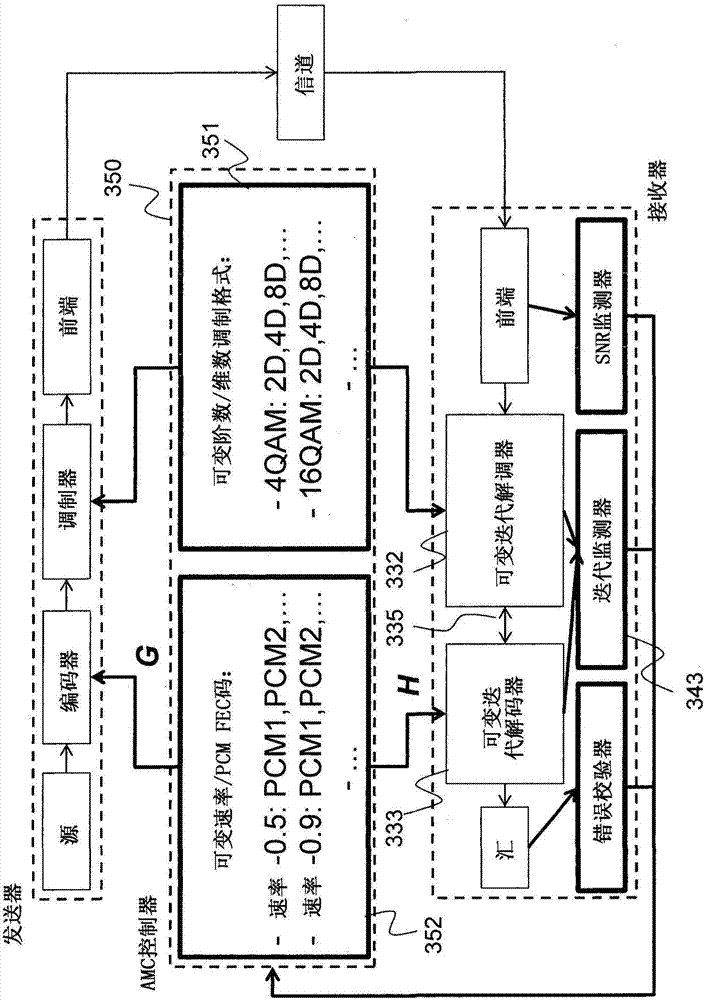
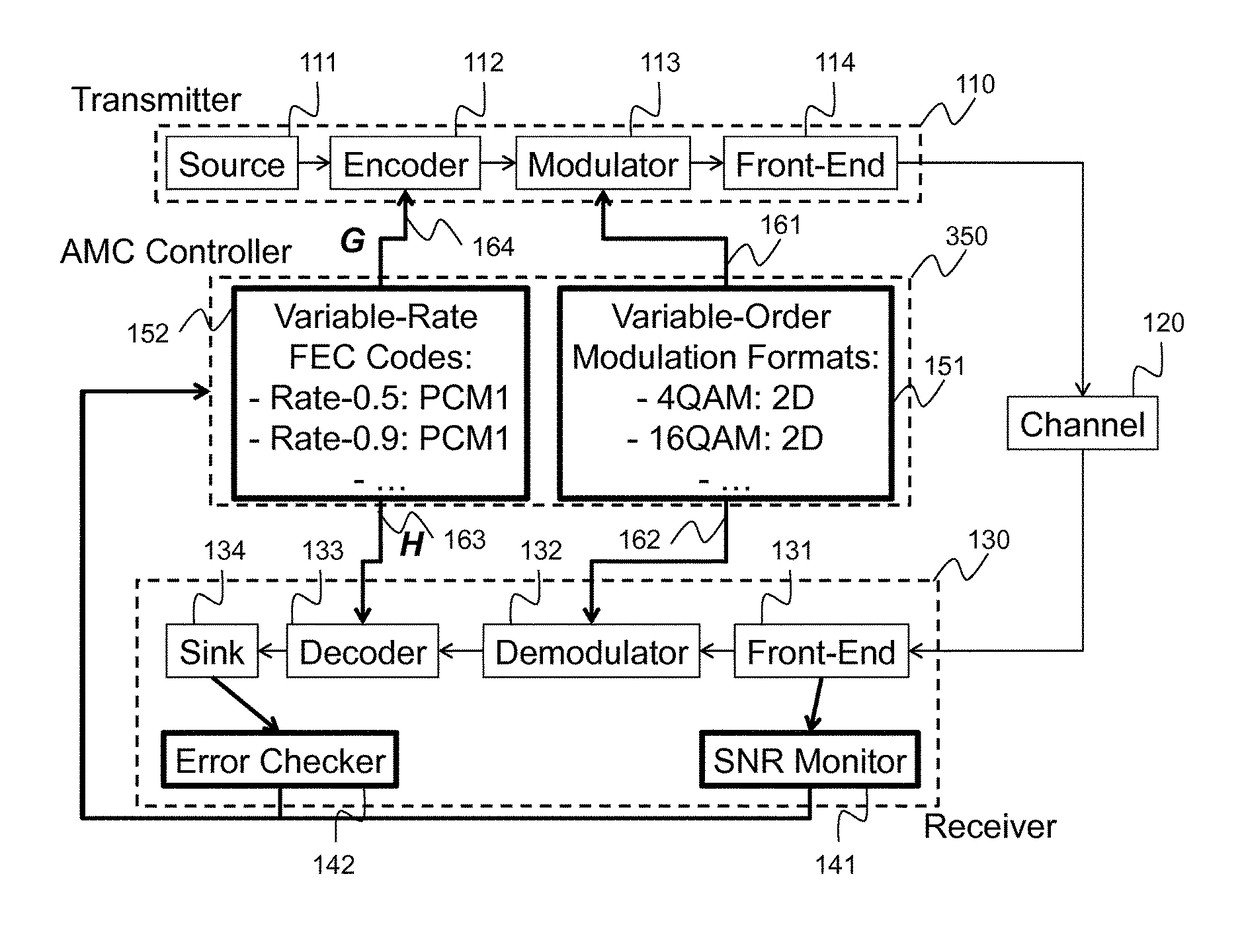
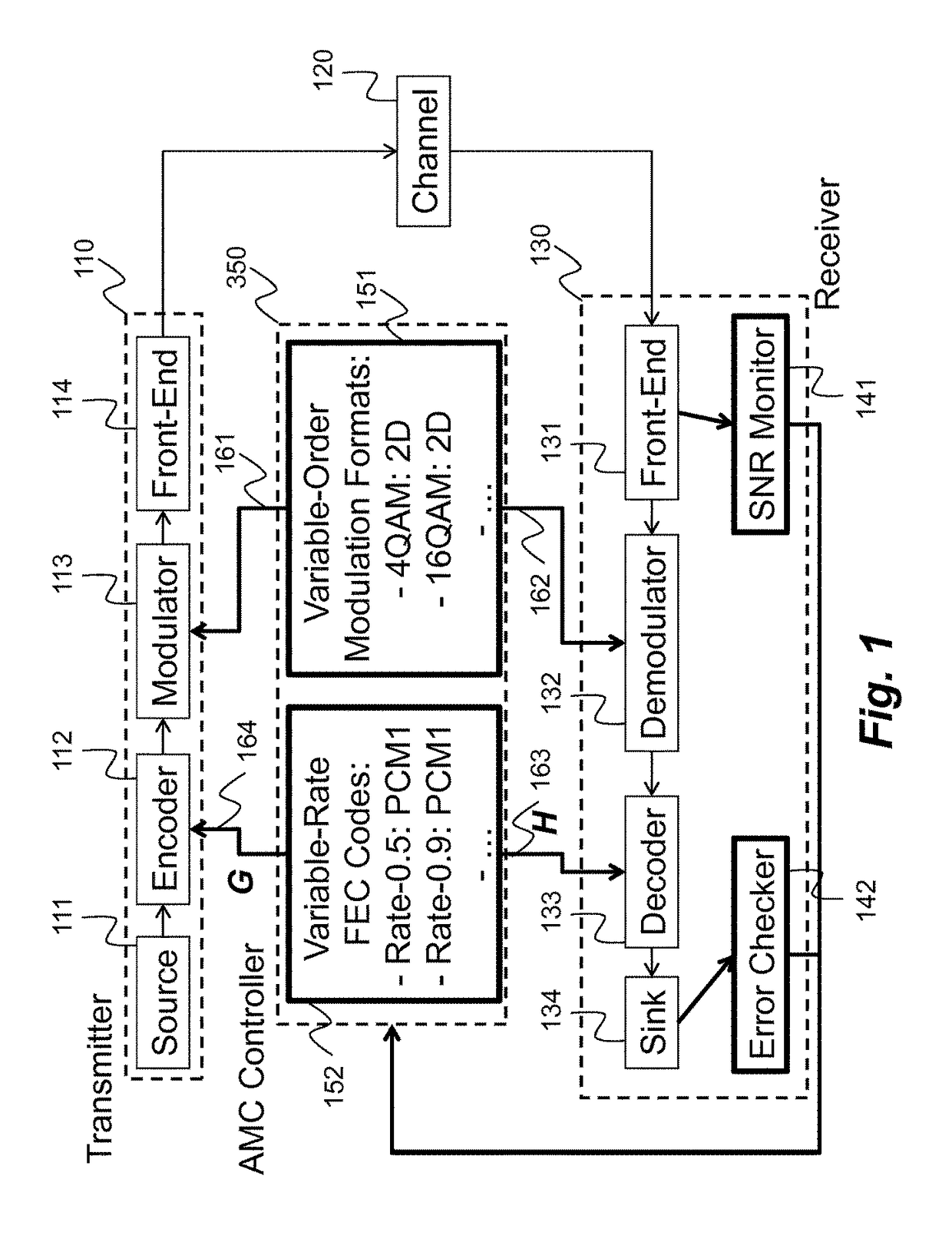
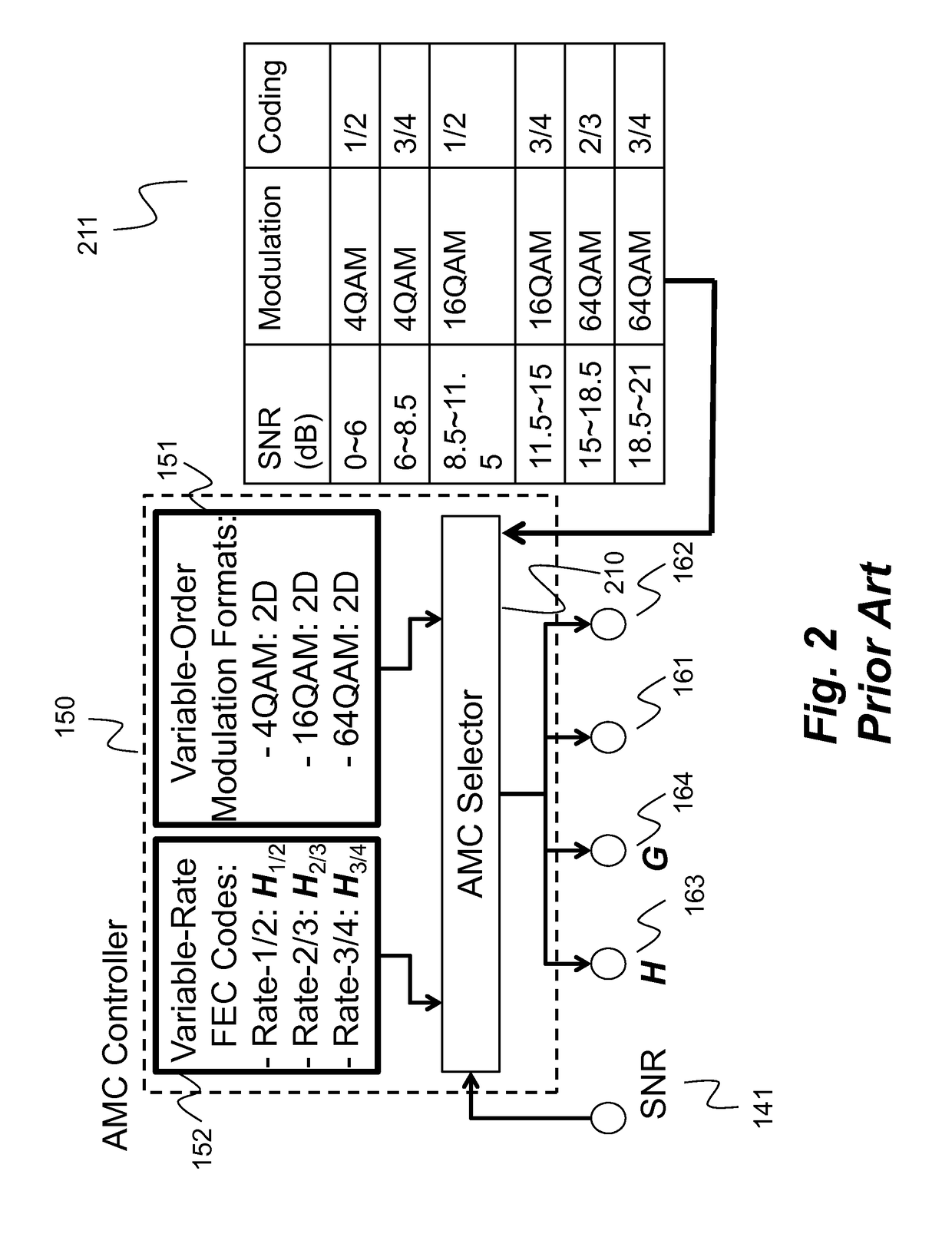
Method for adaptive modulation and coding, AMC, and AMC controller
ActiveCN107251439AMinimize power consumptionError correction/detection using block single space codingError correction/detection using LDPC codesHigh dimensionalBelief propagation
In an advanced adaptive modulation and coding (AMC) scheme, the code rate and the parity-check matrix (PCM) for low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes are adapted according to modulation formats and variable-iteration receivers. The degree distribution for the PCM adaptation is designed by heuristic optimization to minimize the required SNR via an extrinsic information transfer (EXIT) trajectory analysis for finite-iteration decoding. The method uses dynamic window decoding by generating spatially coupled PCM for quasi-cyclic LDPC convolutional coding. The method also provides a way to jointly optimize labeling and decoding complexity for high-order and high-dimensional modulations. The problem to use a large number of different LDPC codes for various modulation formats and variable-iteration decoding is also dealt with by linearly dependent PCM adaptation across iteration count to keep using a common generator matrix. This PCM adaptation can improve a convergence speed of belief propagation decoding and mitigate an error floor issue.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
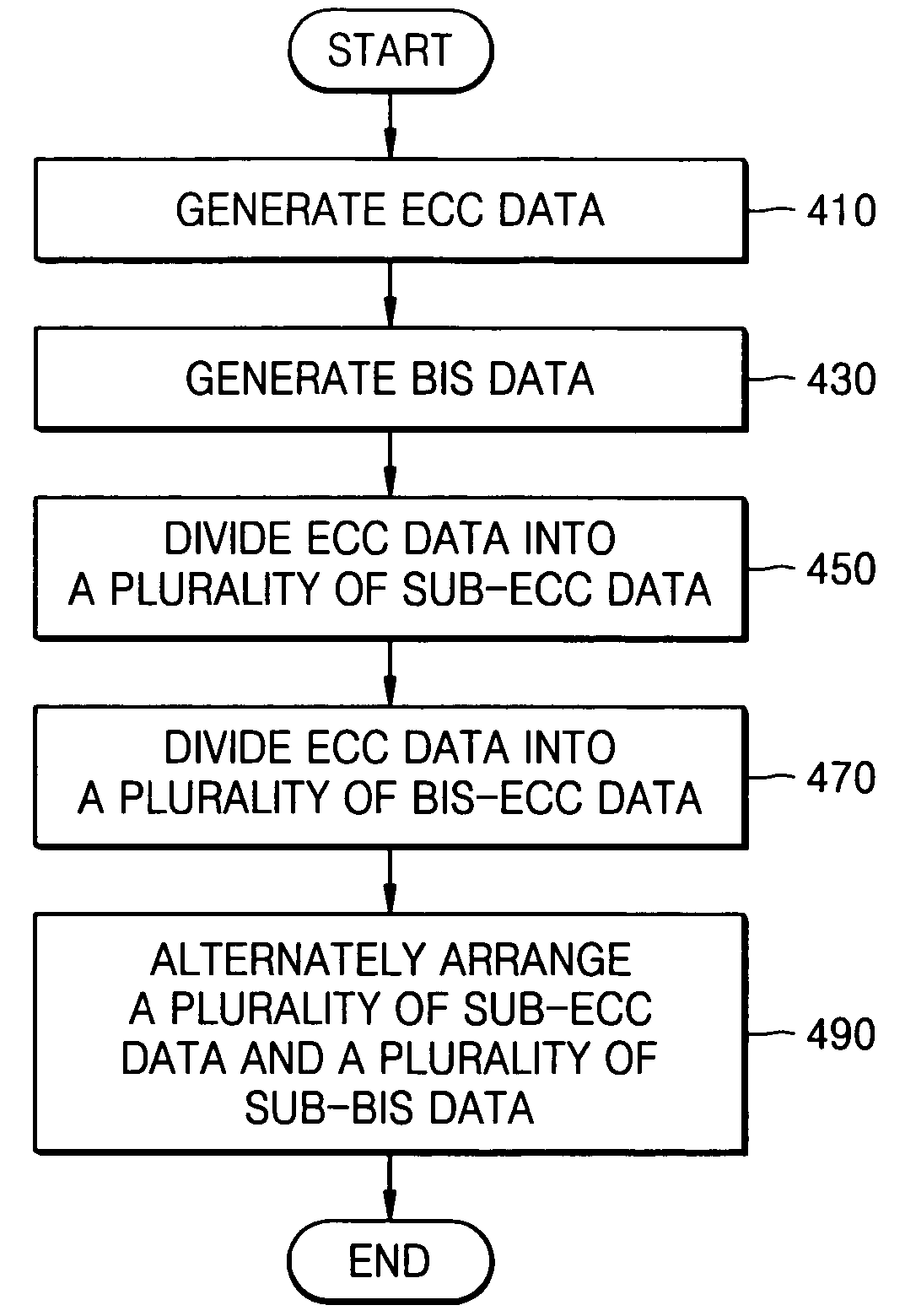
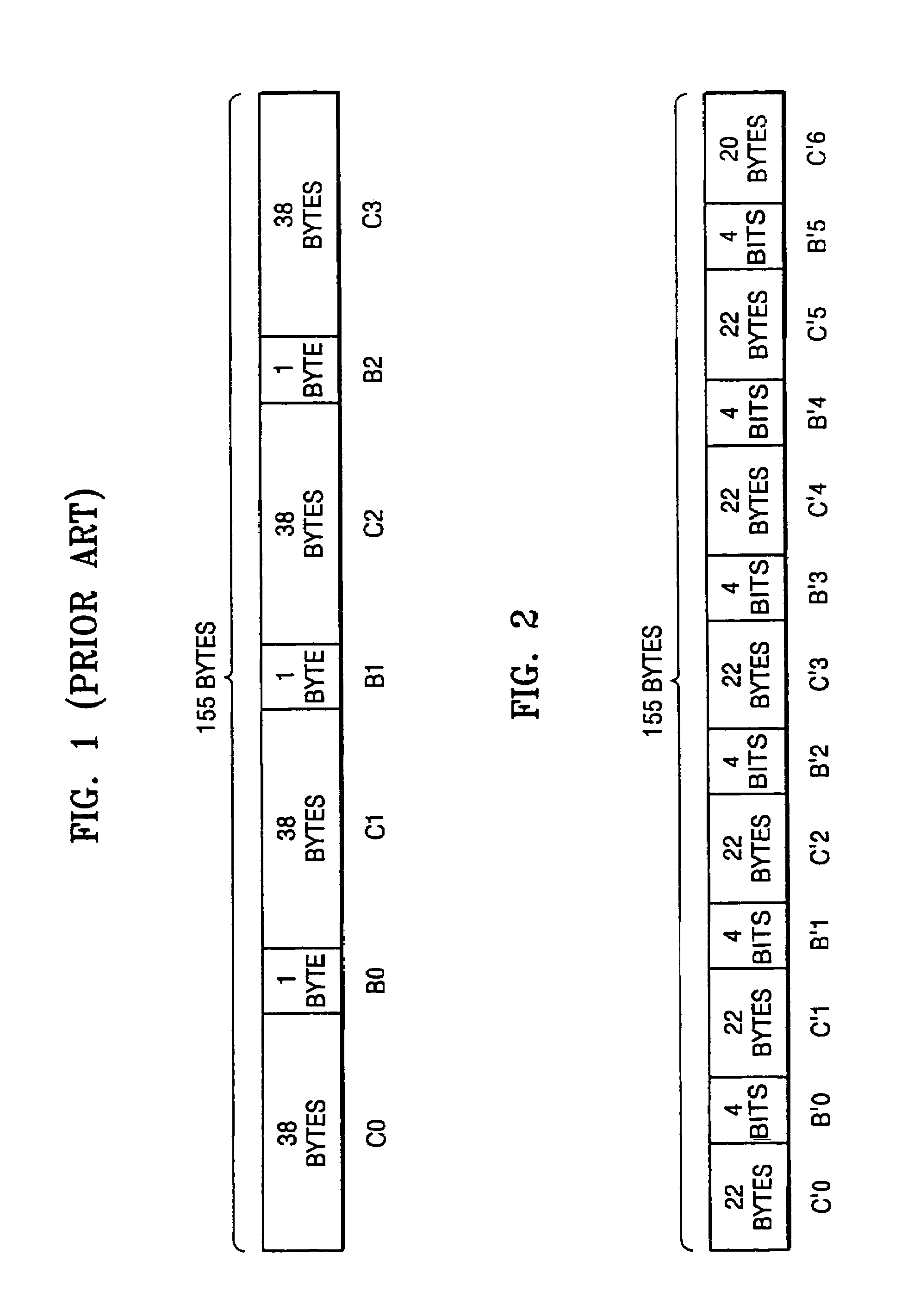
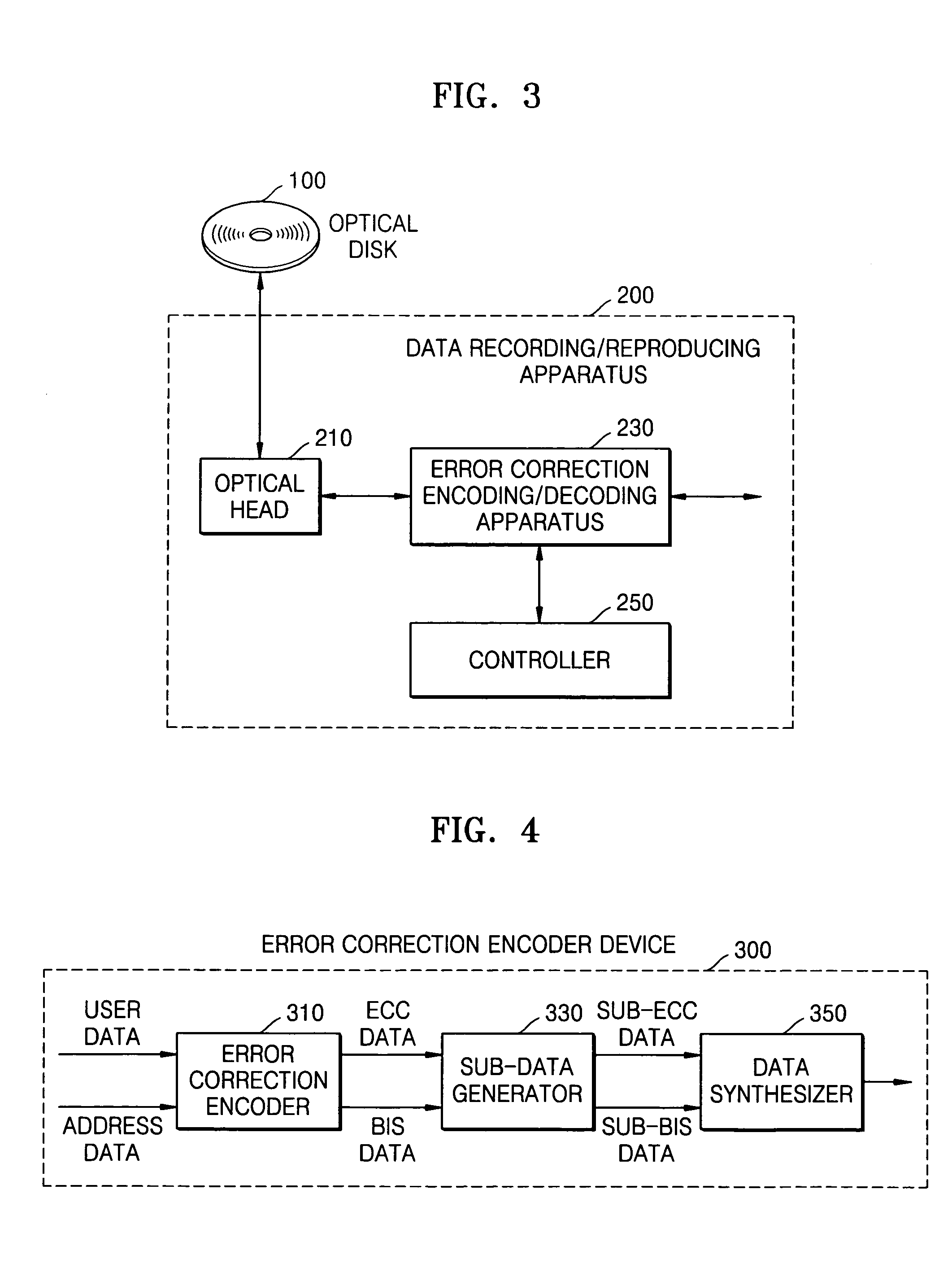
Error correction encoding apparatus and method and error correction decoding apparatus and method
InactiveUS7350133B2Erroneous dataAccurate detectionCode conversionRecord information storageByteCorrection code
An error correction encoding method including generating error correction code data, which is a predetermined number of bytes long, by error-correction-encoding user data in a predetermined manner; generating burst indicator subcode data, which is a predetermined number of bytes long and is used to detect errors that have occurred in the user data; dividing the error correction code data into a plurality of sub-error correction code data each having a length that is less than the error correction code data; dividing the burst indicator subcode data into a plurality of sub-burst indicator subcode data having a length that is less than a minimal data unit that is error-correction-encodable; and alternately arranging the plurality of sub-error correction code data and the plurality of sub-burst indicator subcode data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for digital communications with unbalanced codebooks
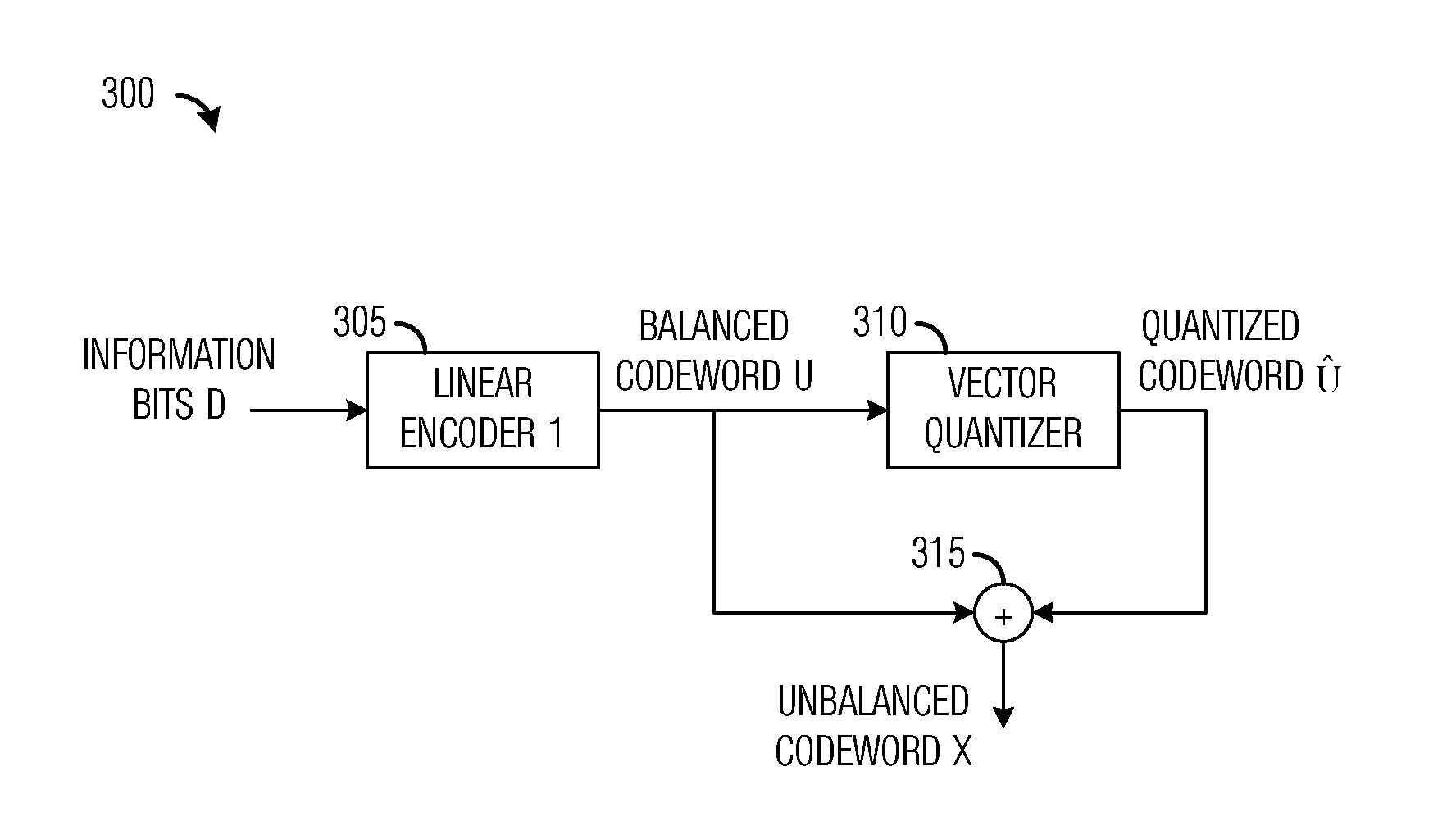
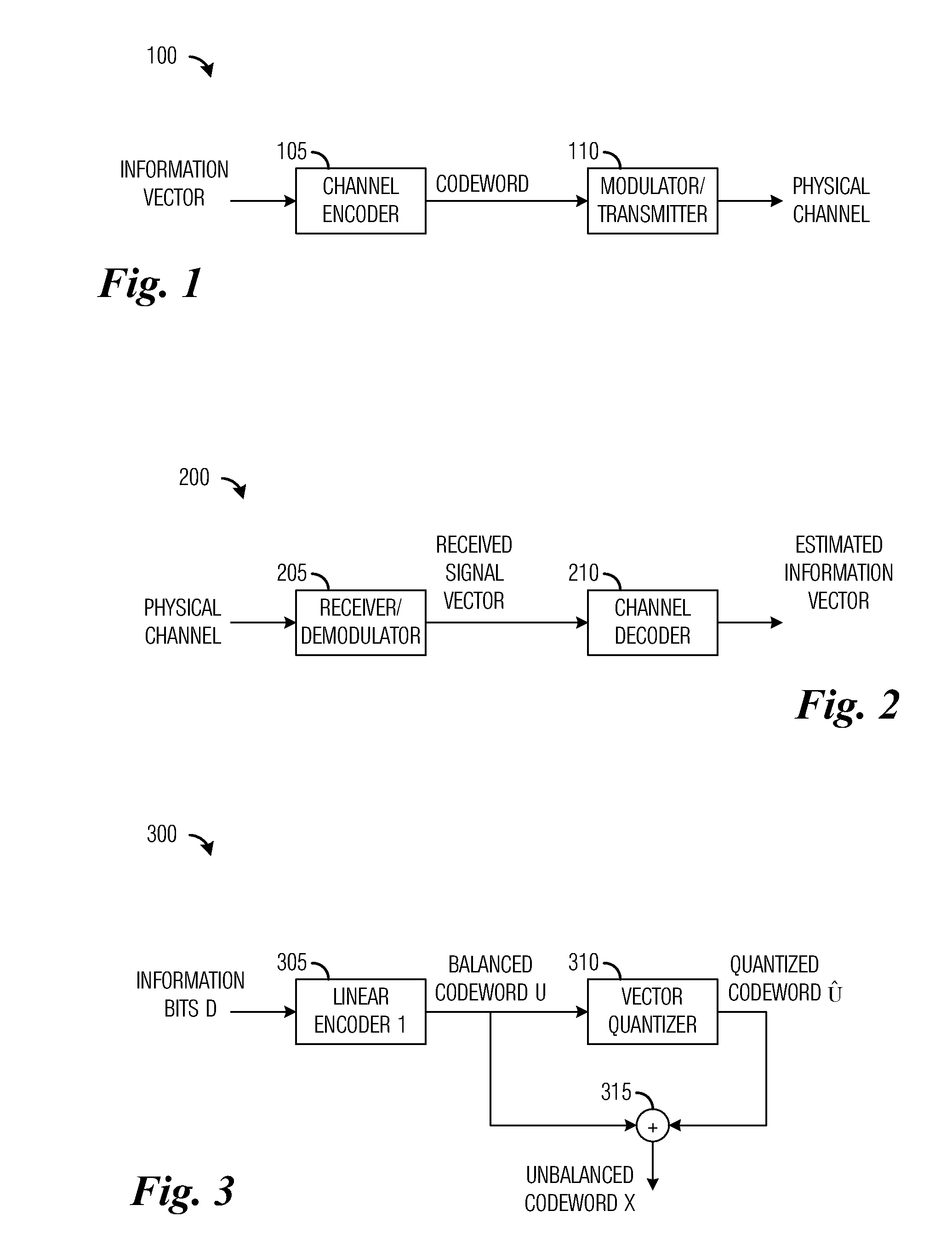
ActiveUS8325850B2Improve error correction performancePromote generationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer scienceChannel encoding
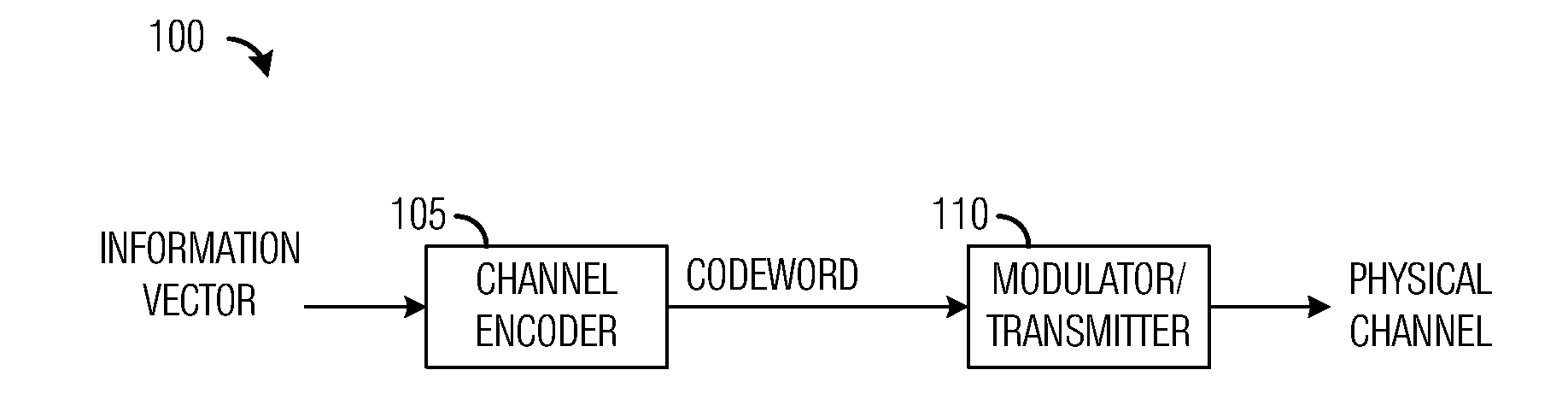
A system and method for digital communications with unbalanced codebooks is provided. A transmitter includes a channel encoder that generates an output codeword from an information vector provided by an information input, and a modulator / transmitter circuit coupled to the channel encoder. The modulator / transmitter circuit prepares the output codeword for transmission over a physical channel. The channel encoder encodes the information vector into an intermediate codeword using a first code and shapes the intermediate codeword into the output codeword having a desired distribution.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
SISO decoder for a block code
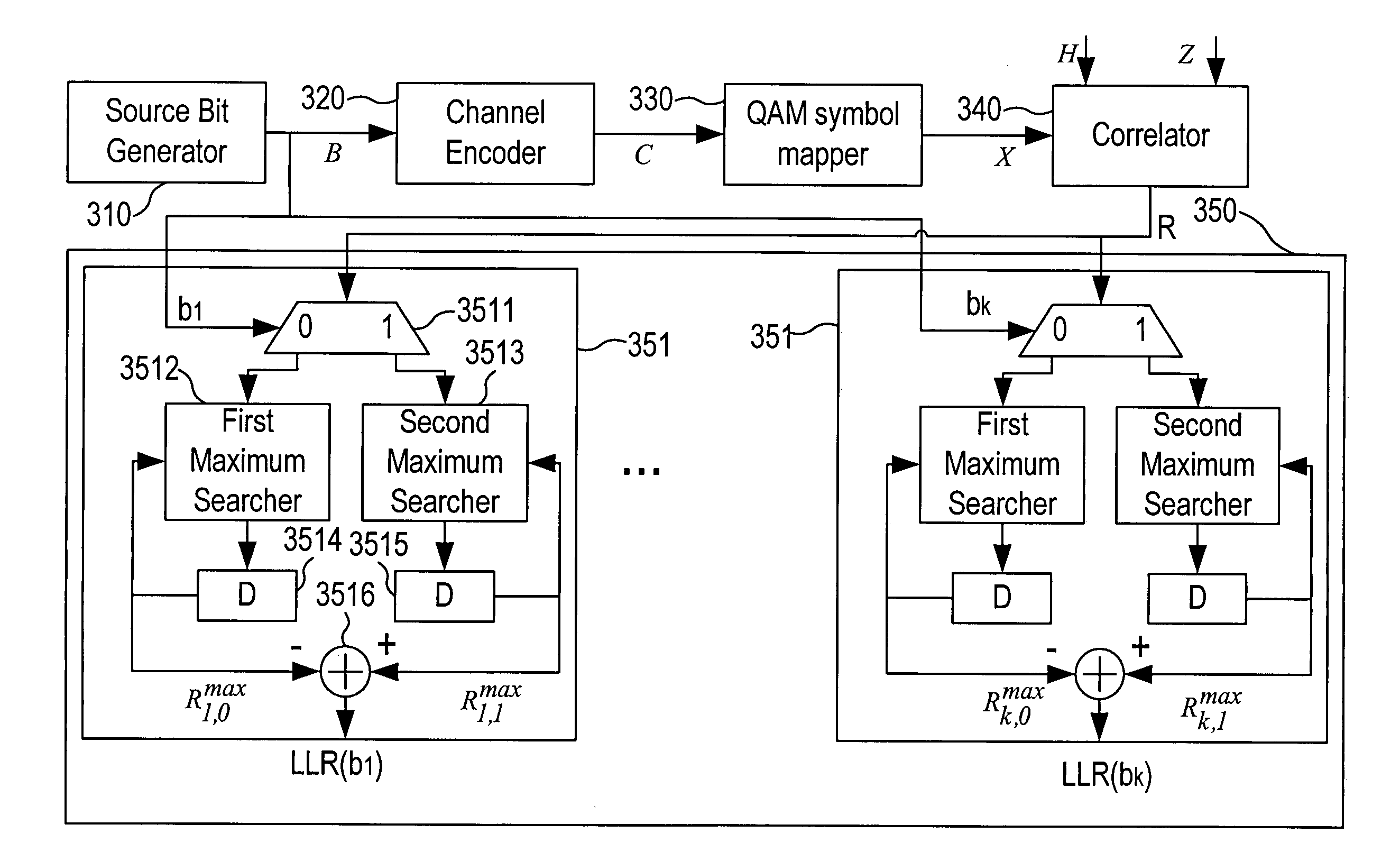
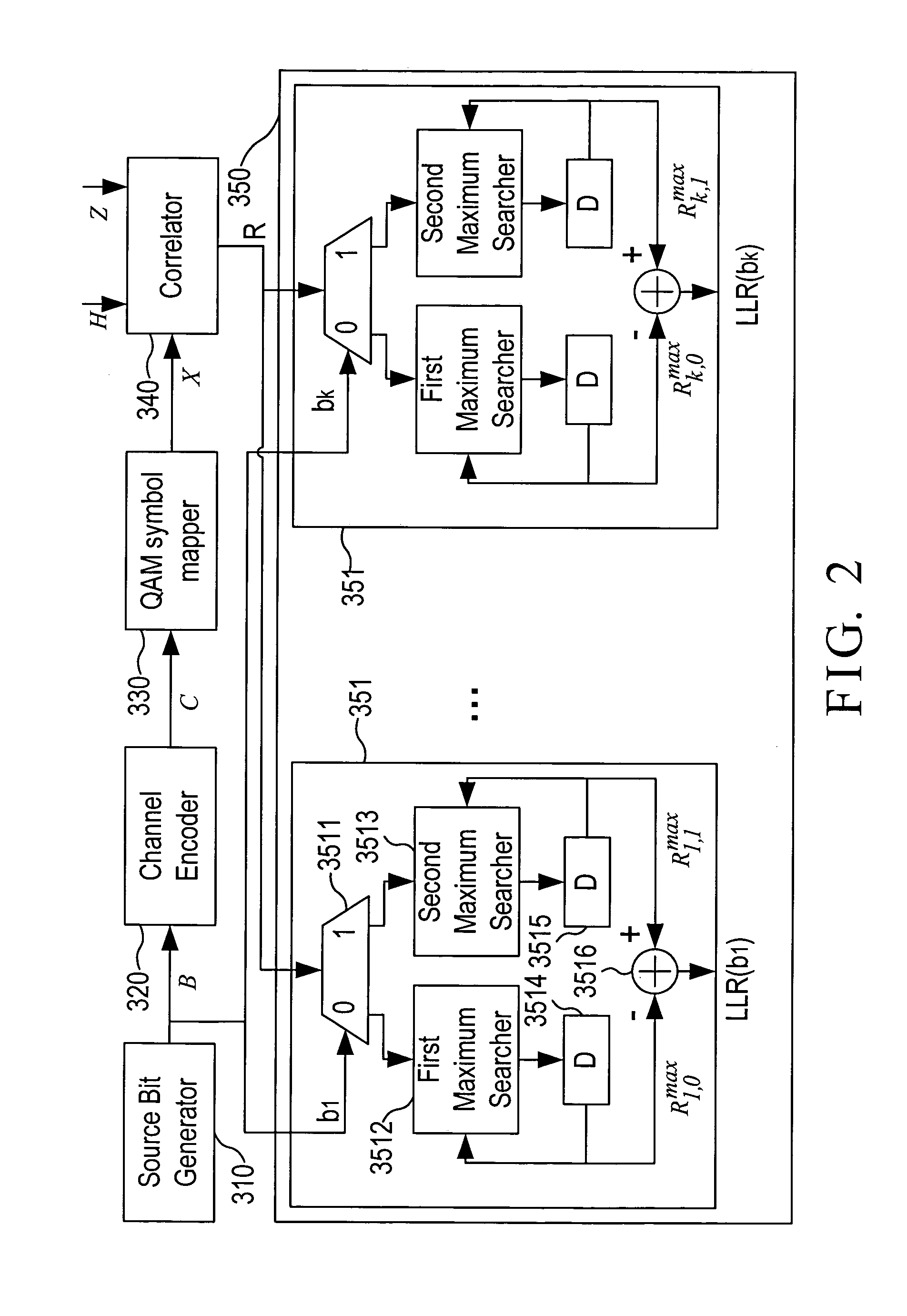
InactiveUS20120076247A1Simple and robustCode conversionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsChannel state informationBlock code
A soft-in-soft-out (SISO) decoder for a general block code includes a source bit generator which generates k guessed source bits; a channel encoder which maps the k guessed source bits to an n-bit channel codeword; a QAM symbol mapper which generates a locally generated symbol sequence comprising m consecutive QAM symbols based on the n-bit channel codeword; a correlator which receives a symbol sequence, a channel state information sequence, and the locally generated symbol sequence to calculate a correlation associated with the received symbol sequence based on the received symbol sequence, the channel state information sequence, and the locally generated symbol sequence; and a log-likelihood ratio calculator which is connected to the source bit generator and the correlator to thereby calculate the required log-likelihood ratios associated with all coded bits corresponding to the received symbol sequence.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
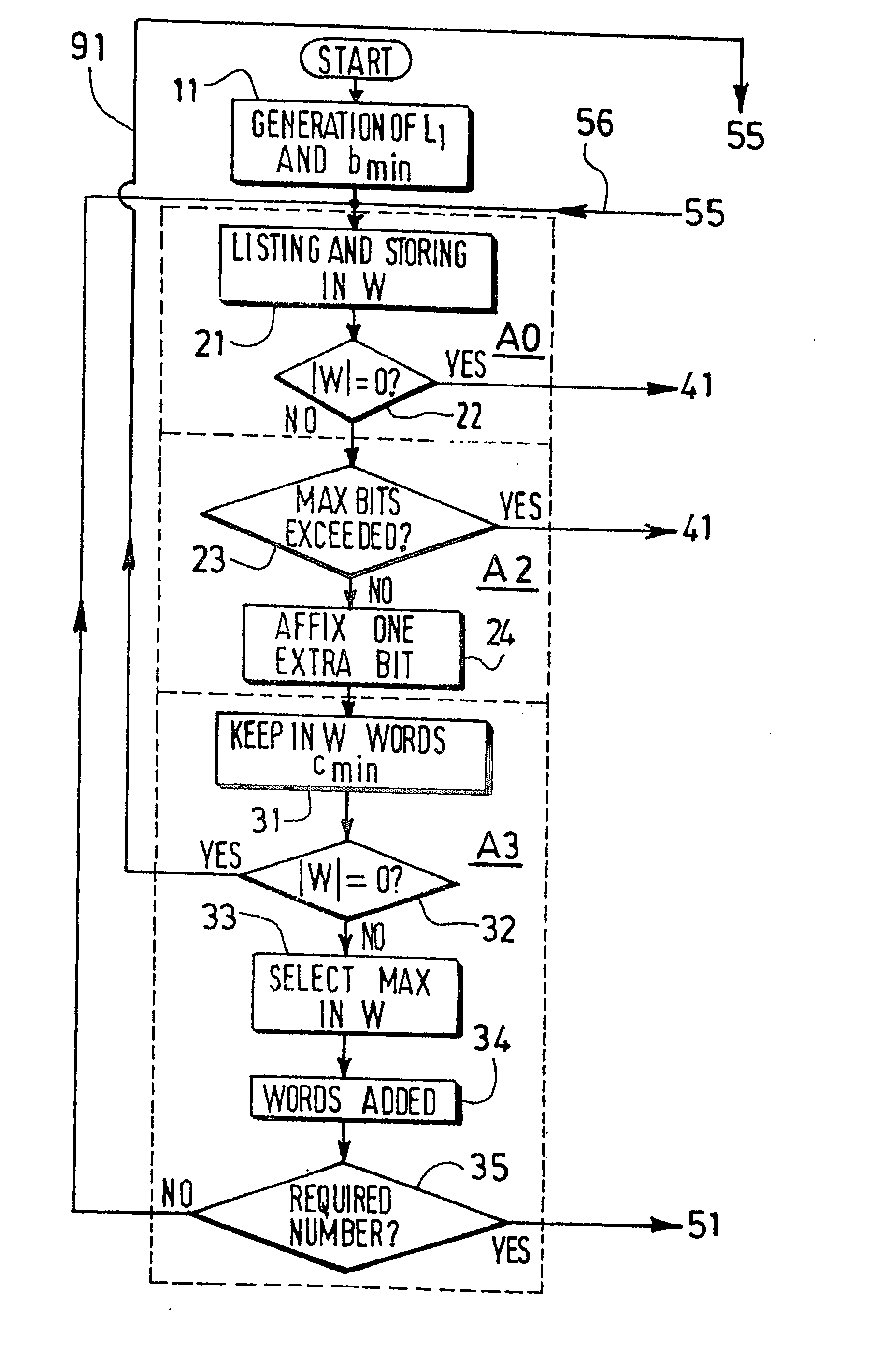
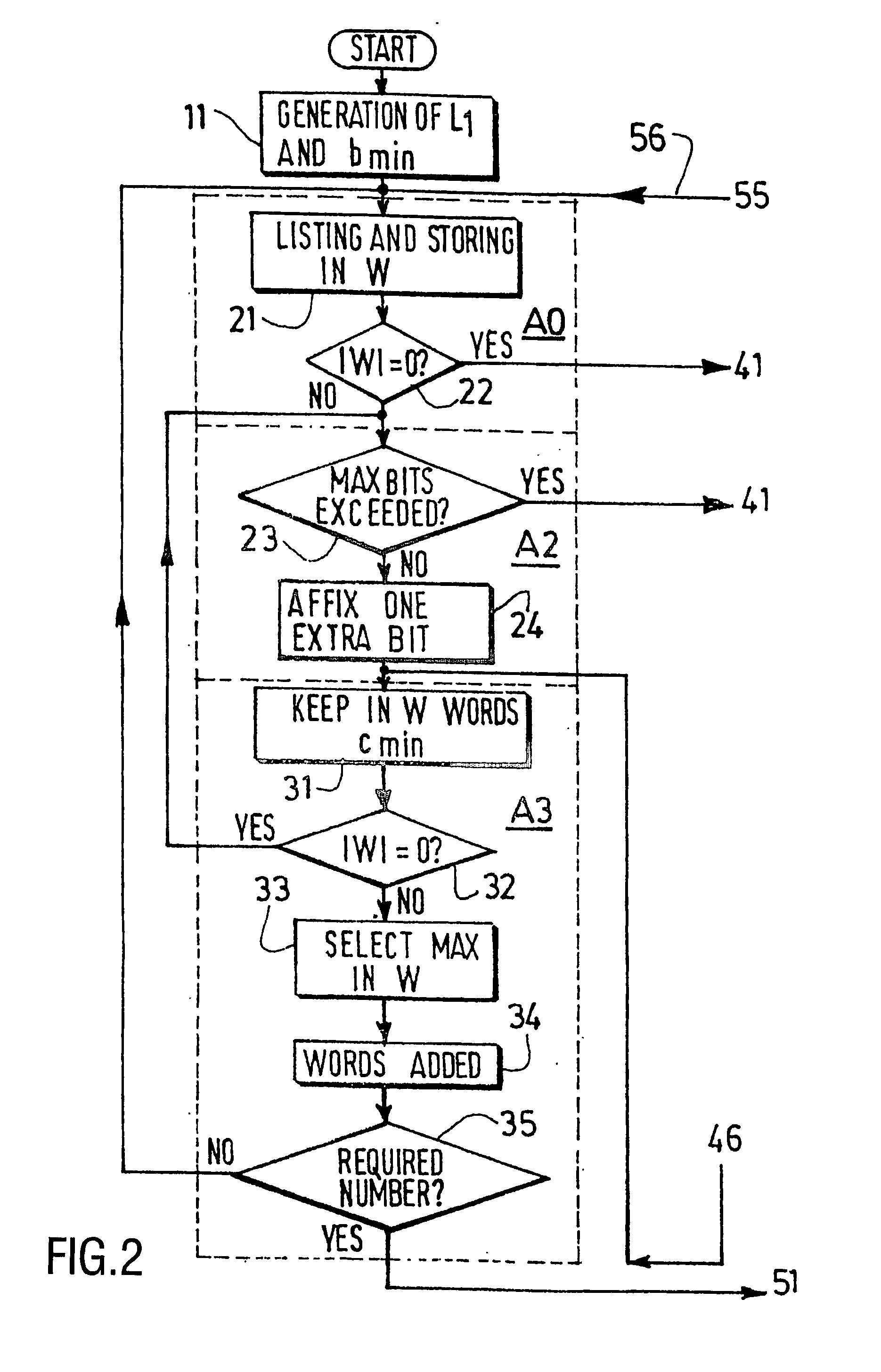
Method and device for building a variable-length error-correcting code
InactiveUS20060200706A1Easy to compressError detection/correctionCode conversionVariable lengthComputer science
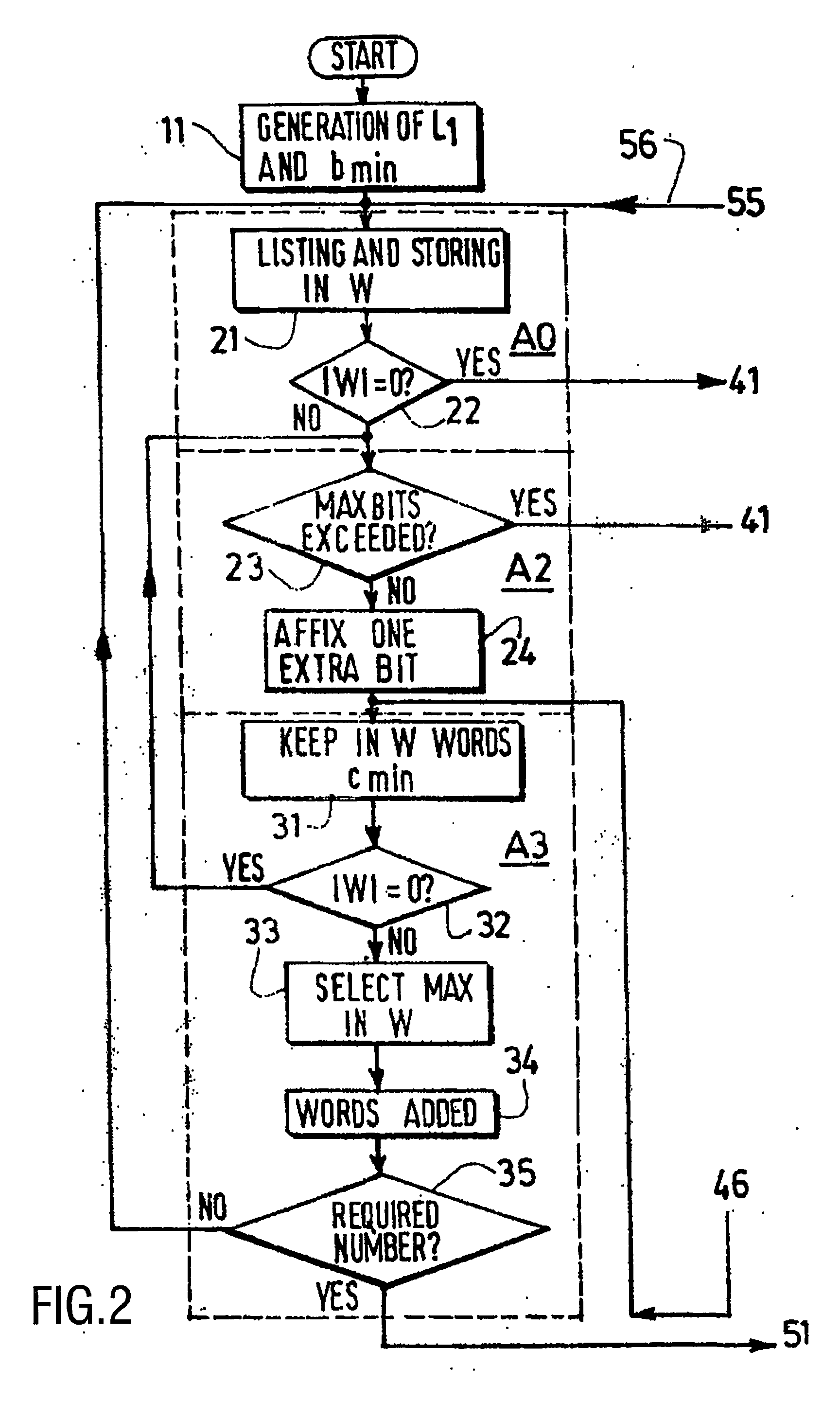
The invention relates to the construction of variable-length error-correcting (VLEC) code, using the main steps of: defining all the needed parameters, generating a code having a fixed length L1, storing in a set W thus obtained all the possible L1-tuples distant of the minimum diverging distance d′min! from the codewords (one extra-bit being affixed at the end of all words if the new set W thus obtained is not empty), deleting all words of W that do not satisfy a distance criterion with all codewords, and verifying that all words of the final set W satisfy another distance criterion. When the codeword deletion is done not anymore only in the last obtained group of the code, but in the group of a given length value Ls to which the algorithm will skip back to in the codeword deletion operation, the beginning of the best VLEC structure of each Ls is, according to the invention, kept in memory and re-used within the next search.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Digital communication method and digital communication device
InactiveUS20060093046A1Waveform distortion is minimalImprove noiseError correction/detection using convolutional codesCorrect operation testingComputer scienceCorrection method
A digital communication device includes: a modulator having encoding means for converting two-dimensional digital information signal into a three-dimensional signal and phase modulation means for modifying the carrier phase in according to the three-dimensional signal; and a demodulator having phase demodulation means for detecting information on the three-dimensional signal from the received phase-modulated wave and demodulation means for deciding the two-dimensional digital information from the information on the three-dimensional signal. The digital communication device has a bit error ratio and an occupied radio band width equivalent to a digital communication device using the conventional QPSK or π / 4 shift QPSK and the error correction method and greatly improves the amplitude fluctuation. Moreover, the digital communication device can transmit a signal with a narrower occupied frequency band width while maintaining the same constant envelope characteristic as the GMSK using the conventional error correction code.
Owner:YOKOHAMA TLO +1
Digital communication method and digital communication device
InactiveCN1703833ASmall amplitude fluctuationIncrease error resistanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesCorrect operation testingCarrier signalCorrection method
A digital communication device includes: a modulator having encoding means for converting two-dimensional digital information signal into a three-dimensional signal and phase modulation means for modifying the carrier phase in according to the three-dimensional signal; and a demodulator having phase demodulation means for detecting information on the three-dimensional signal from the received phase-modulated wave and demodulation means for deciding the two-dimensional digital information from the information on the three-dimensional signal. The digital communication device has a bit error ratio and an occupied radio band width equivalent to a digital communication device using the conventional QPSK or pi / 4 shift QPSK and the error correction method and greatly improves the amplitude fluctuation. Moreover, the digital communication device can transmit a signal with a narrower occupied frequency band width while maintaining the same constant envelope characteristic as the GMSK using the conventional error correction code.
Owner:YOKOHAMA TLO +1
System and Method for Digital Communications with Unbalanced Codebooks
ActiveUS20110182381A1Improve error correction performancePromote generationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer scienceChannel encoding
A system and method for digital communications with unbalanced codebooks is provided. A transmitter includes a channel encoder that generates an output codeword from an information vector provided by an information input, and a modulator / transmitter circuit coupled to the channel encoder. The modulator / transmitter circuit prepares the output codeword for transmission over a physical channel. The channel encoder encodes the information vector into an intermediate codeword using a first code and shapes the intermediate codeword into the output codeword having a desired distribution.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Channel coding/decoding apparatus and method for a CDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS7050417B2Correction capabilityImprove reliabilityReed-muller codesError preventionReed–Muller codeAlgorithm
Disclosed is a method for generating (2k−2t) first order Reed-Muller codes from 2k first order Reed-Muller codes based on k input information bits. The method comprises selecting t linearly independent kth order vectors; generating 2t linear combinations by linearly combining the t selected vectors; calculating 2t puncturing positions corresponding to the 2t linear combinations; selecting one k×k matrix out of a plurality of k×k matrixes having k×k inverse matrixes; calculating 2t new puncturing positions by multiplying each of the 2t puncturing positions by the selecting k×k matrix; and generating (2k−2t) first order Reed-Muller codes by puncturing the 2t new puncturing positions from the 2k first order Reed-Muller codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
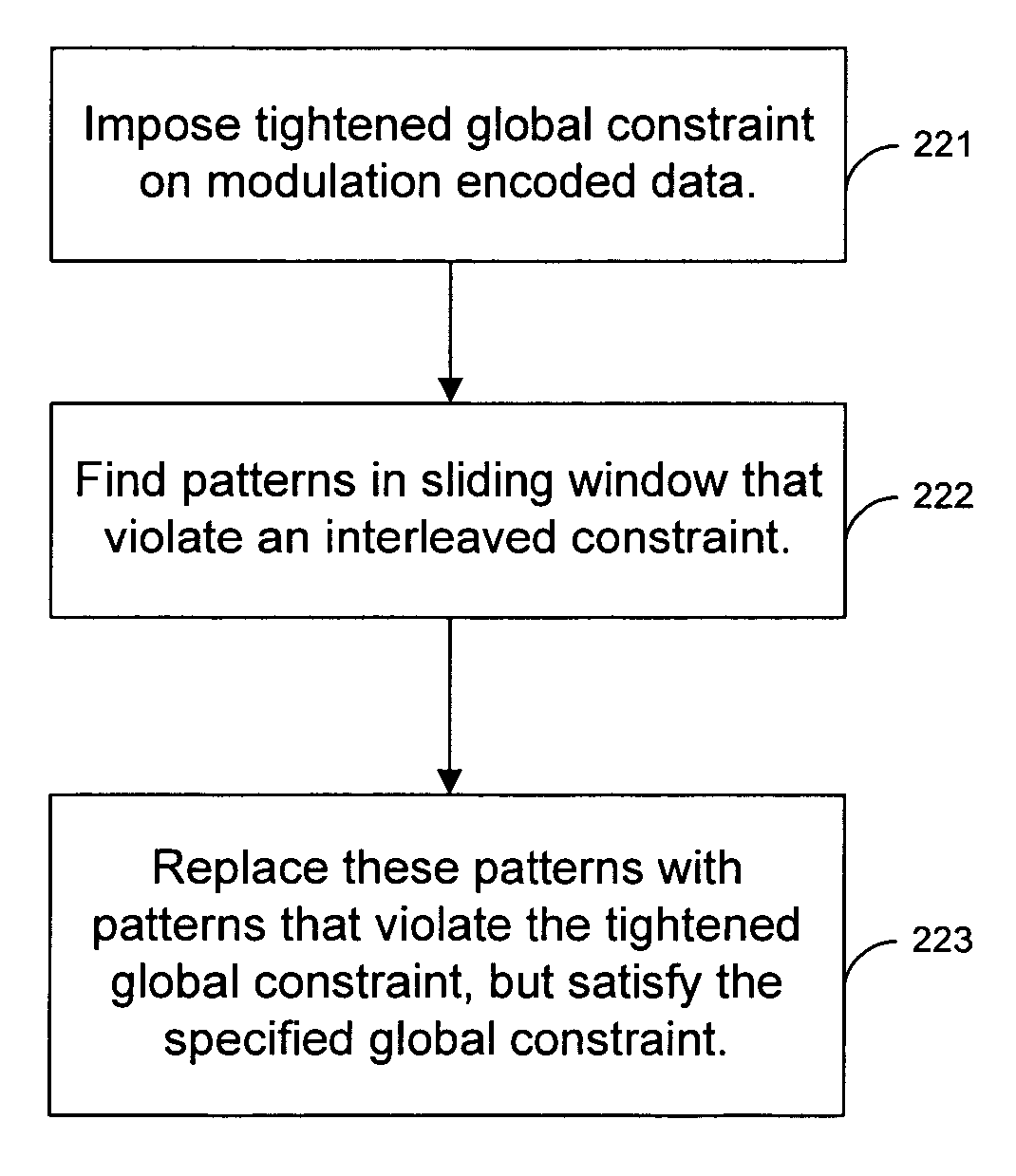
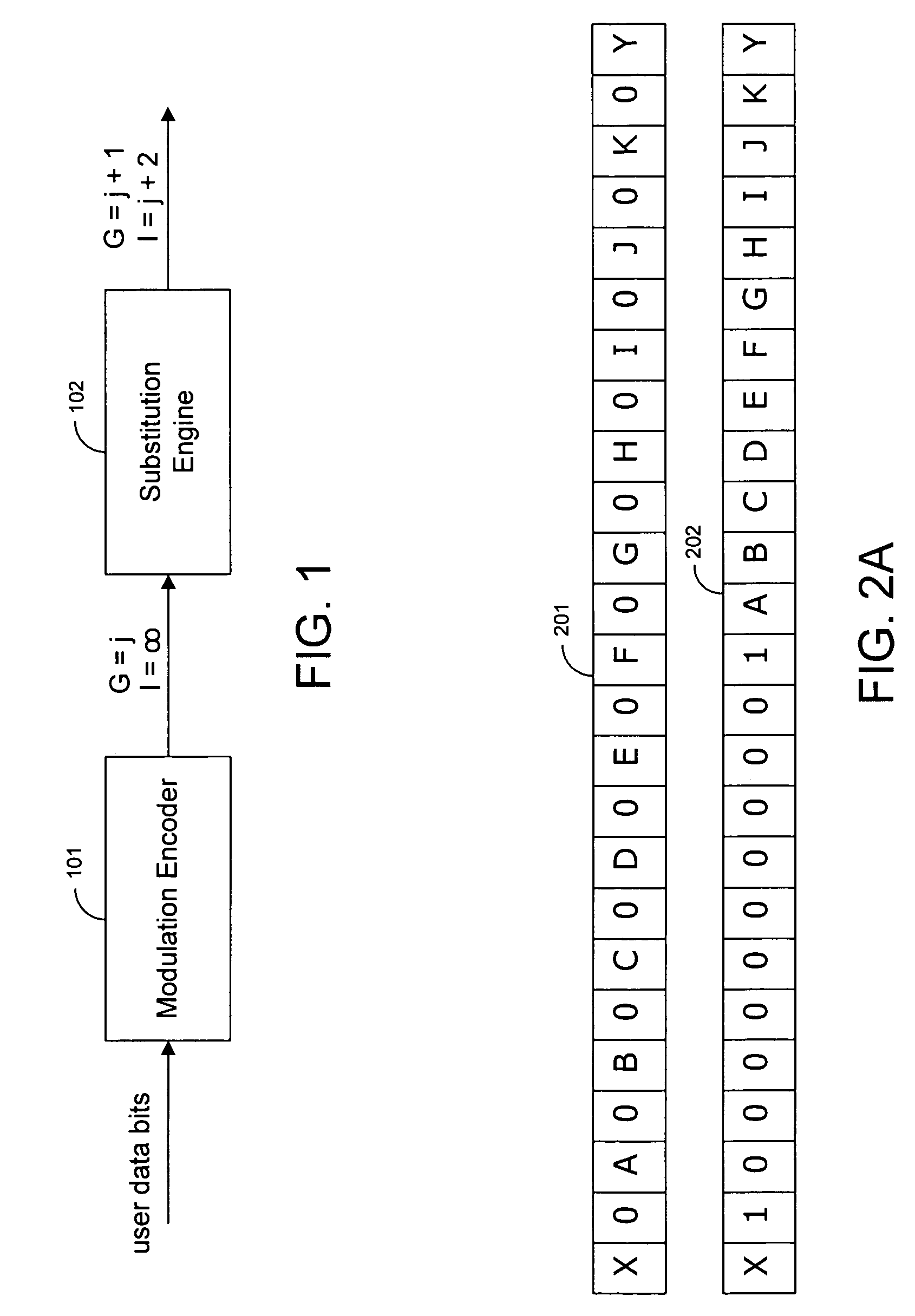
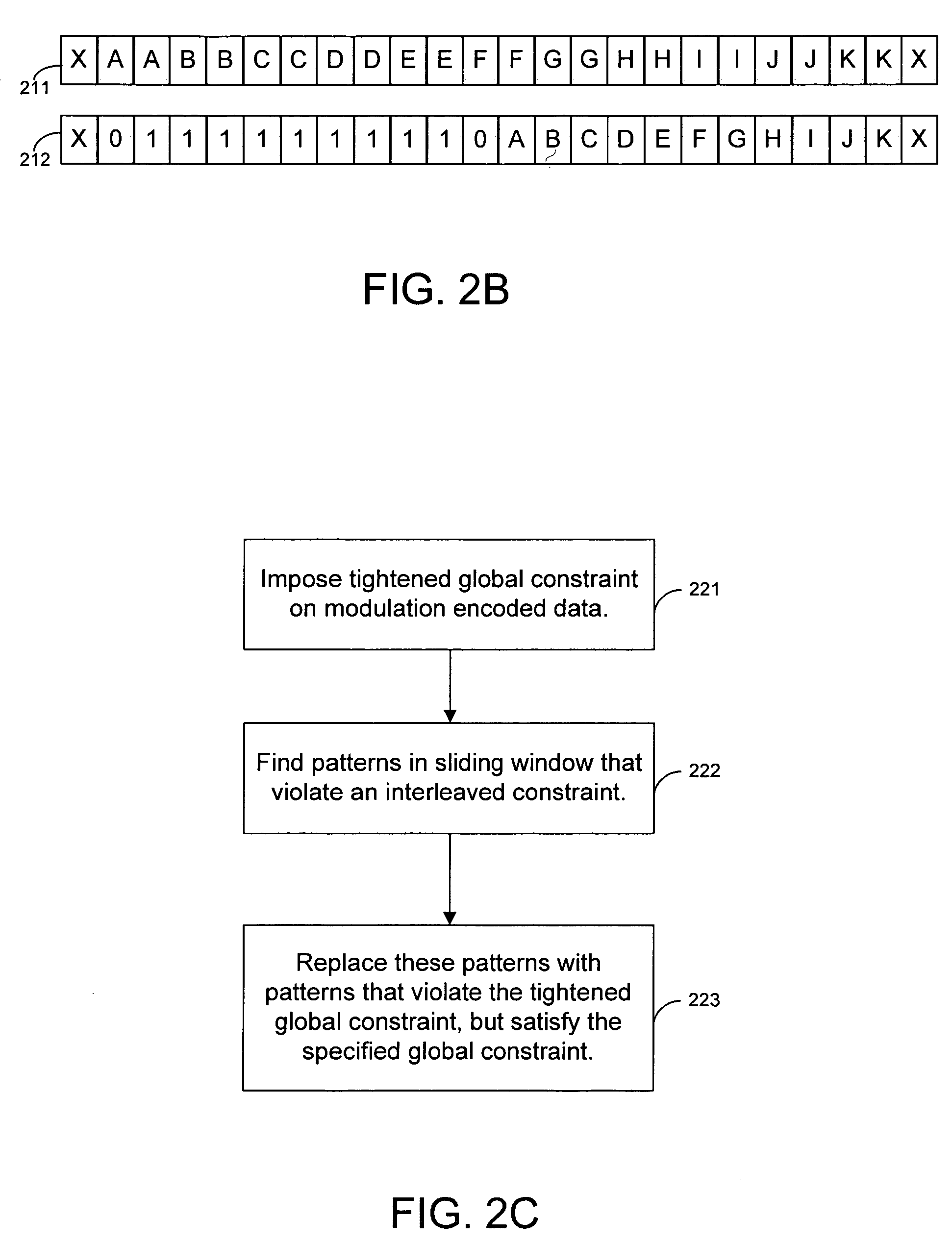
Techniques for generating modulation codes using running substitutions
Techniques are provided for performing substitutions of bit sequences that are known to cause errors. Input data is initially modulation encoded. The modulated data is then analyzed in a sliding window to determine if it contains any additional bit sequences that are known to cause errors. If an error prone bit sequence is identified in the data, a substitution engine replaces the error prone bit sequence with a predetermined pattern of bits that is less likely to cause errors. The bit stream output of the substitution engine is then recorded on a storage medium. The recorded bit stream is decoded when it read from the medium. The decoding process identifies the substituted bit pattern and replaces the substituted pattern with the original sequence of bits.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Digital encoding of parallel busses to suppress simultaneous switching output noise
ActiveUS20160164539A1Individual digits conversionChannel coding adaptationTransceiverTransmission quality
An apparatus and method for encoding data are disclosed that may allow for different encoding levels of transmitted data. The apparatus may include an encoder unit and a plurality of transceiver units. The encoder unit may be configured to receive a plurality of data words, where each data word includes N data bits, wherein N is a positive integer greater than one, and encode a first data word of the plurality of data words. The encoded first data word may include M data bits, where M is a positive integer greater than N. Each transceiver unit may transmit a respective data bit of the encoded first data word. The encoder unit may be further configured to receive information indicative of a quality of transmission of the encoded first data word, and encode a second data word of the plurality of data words dependent upon the quality.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
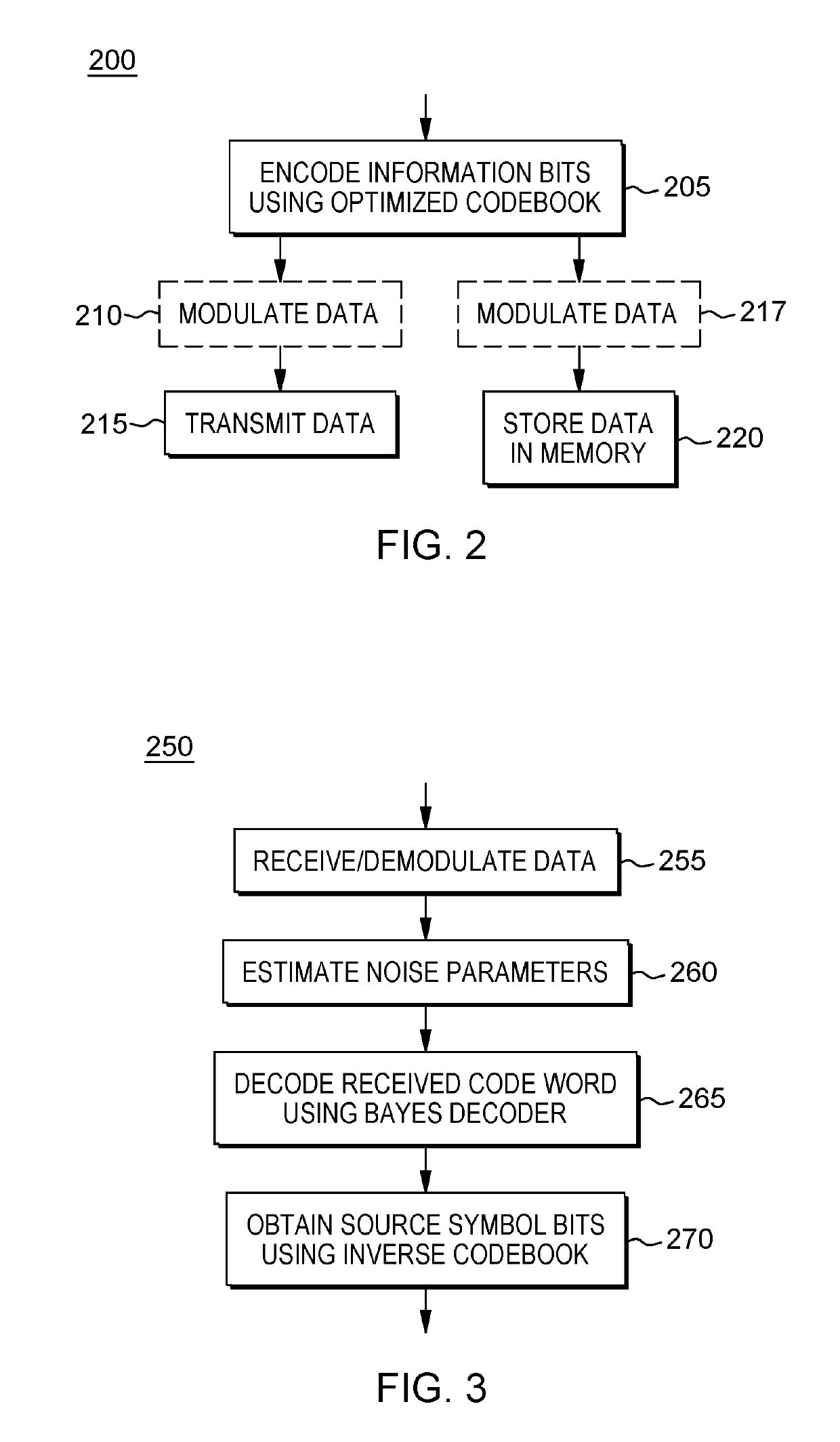
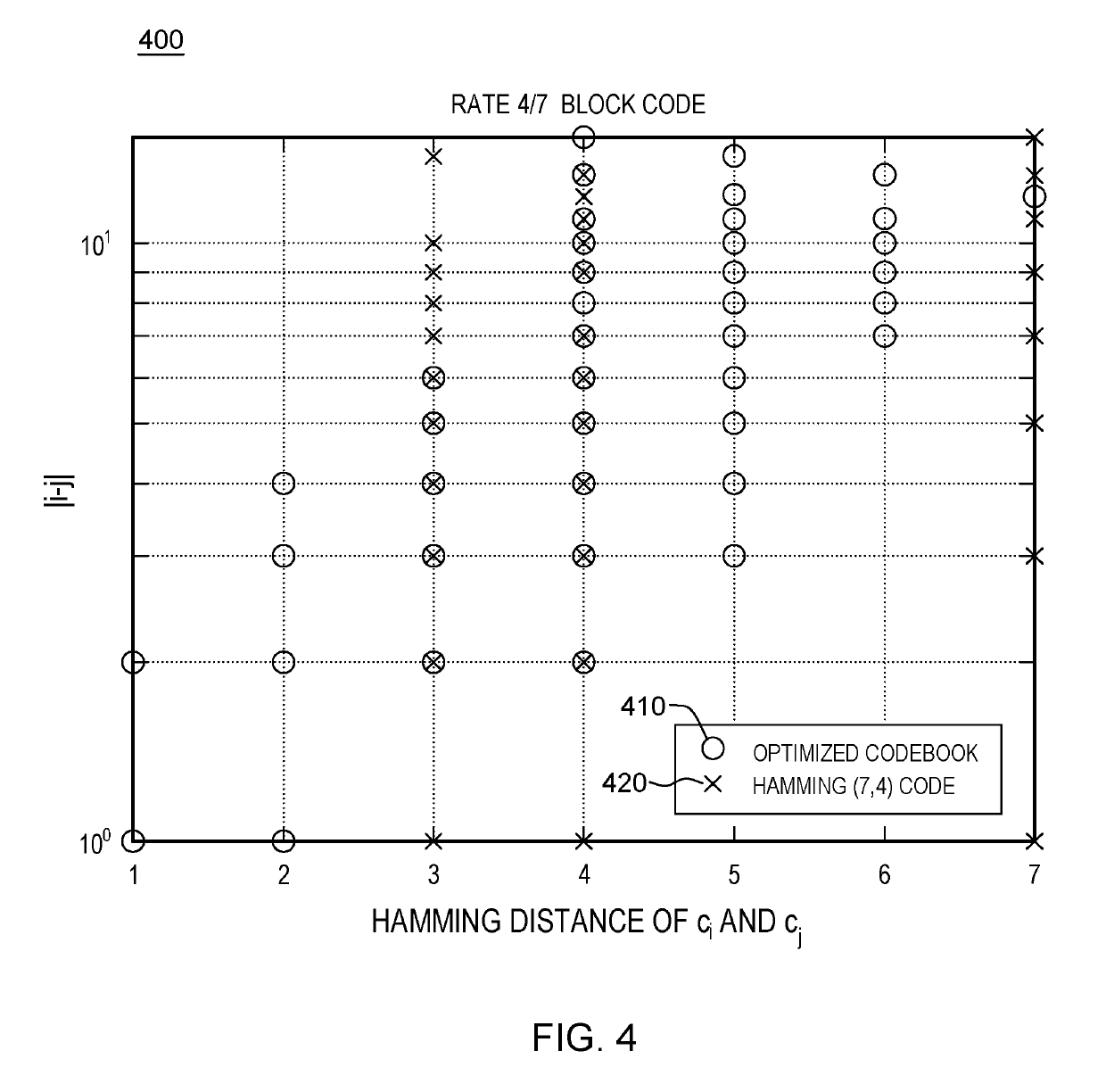
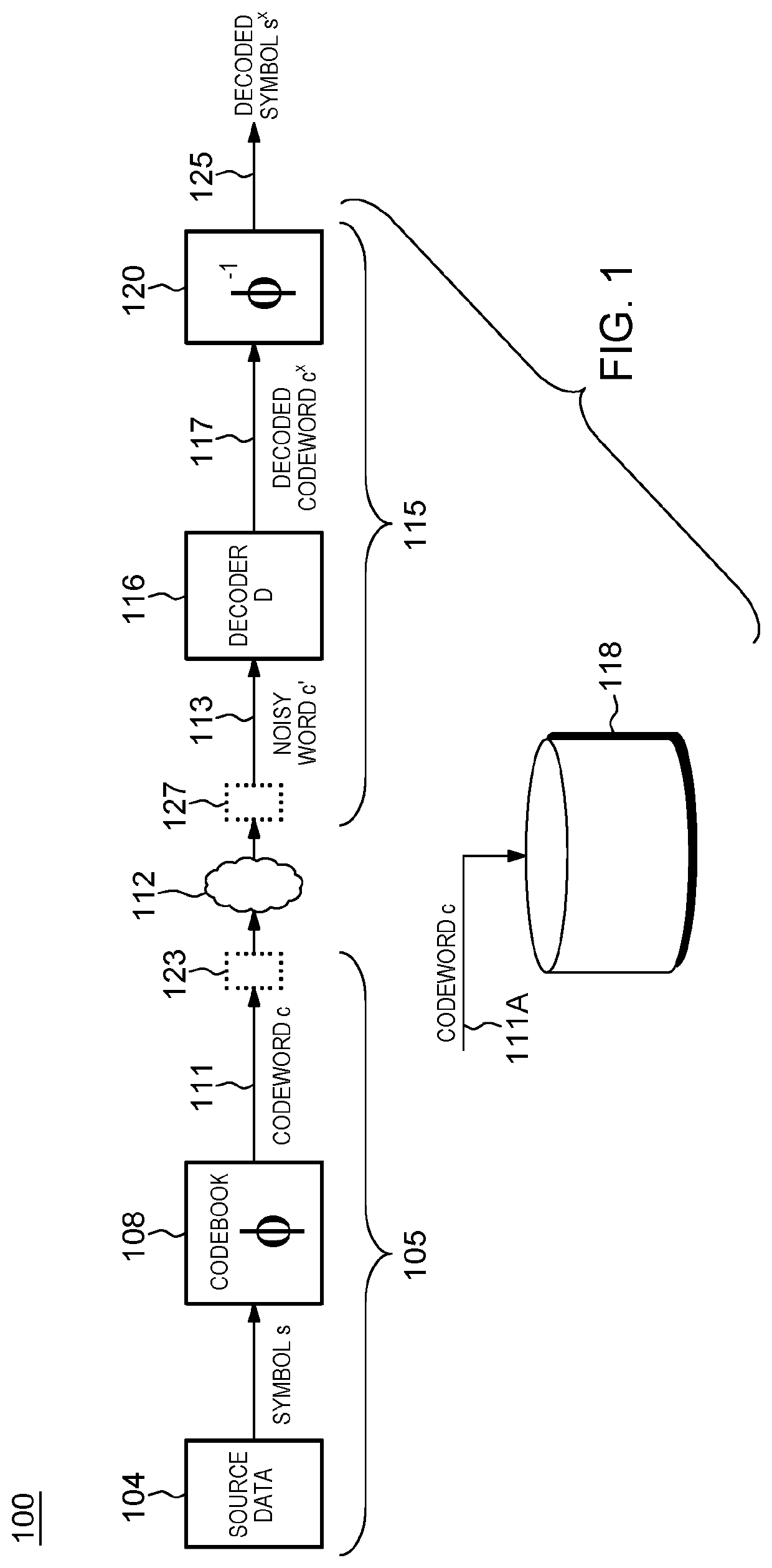
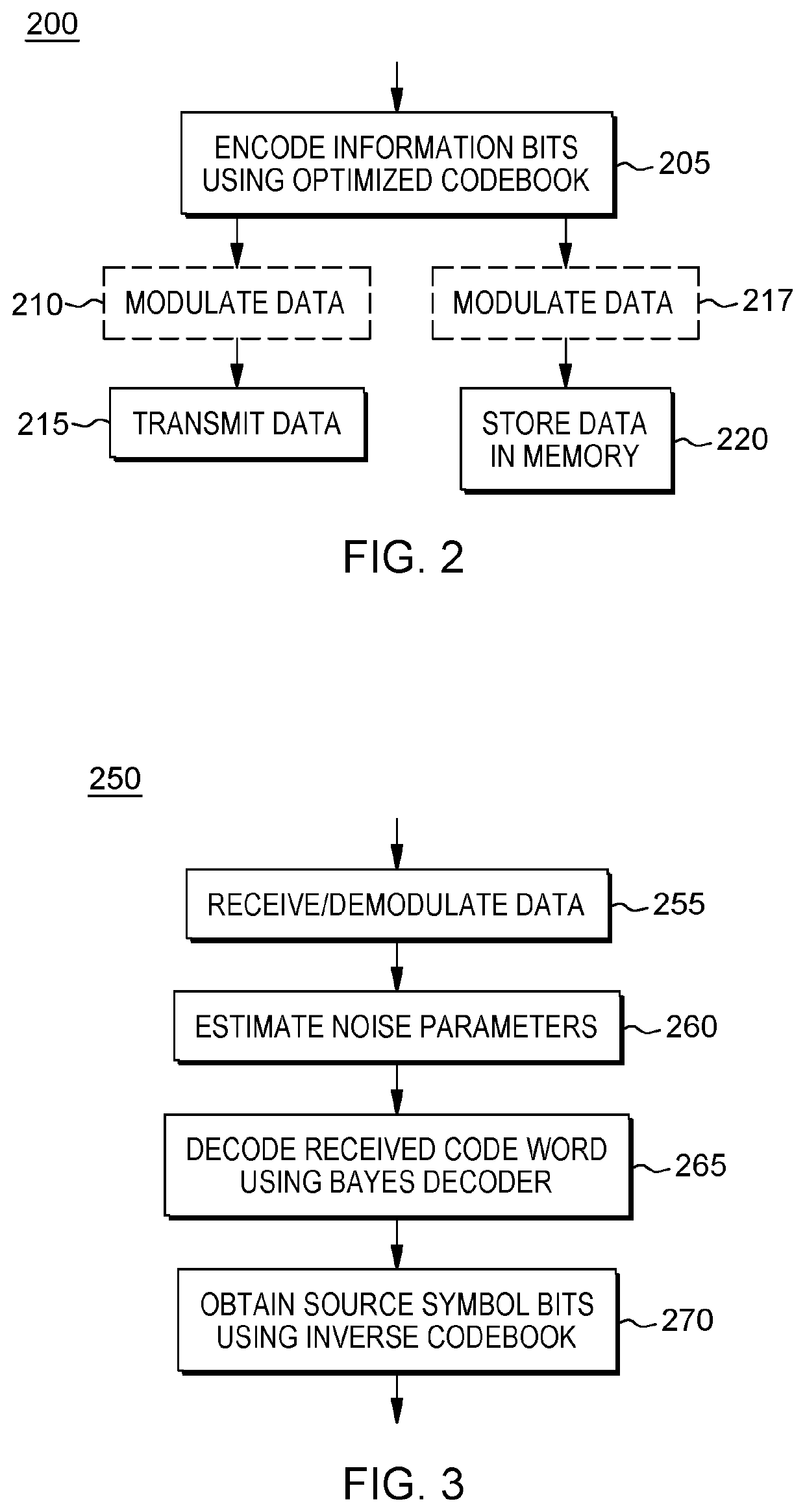
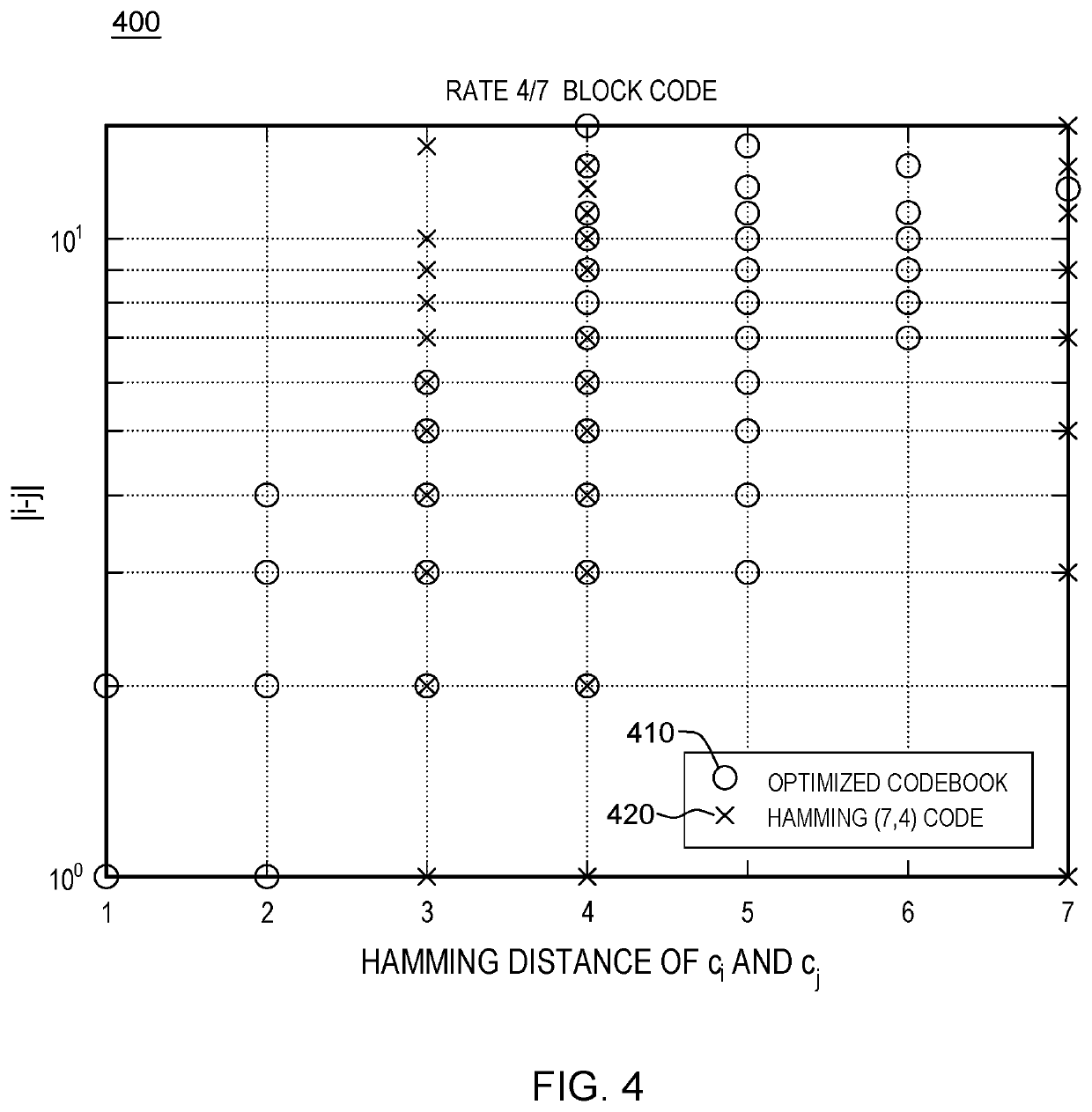
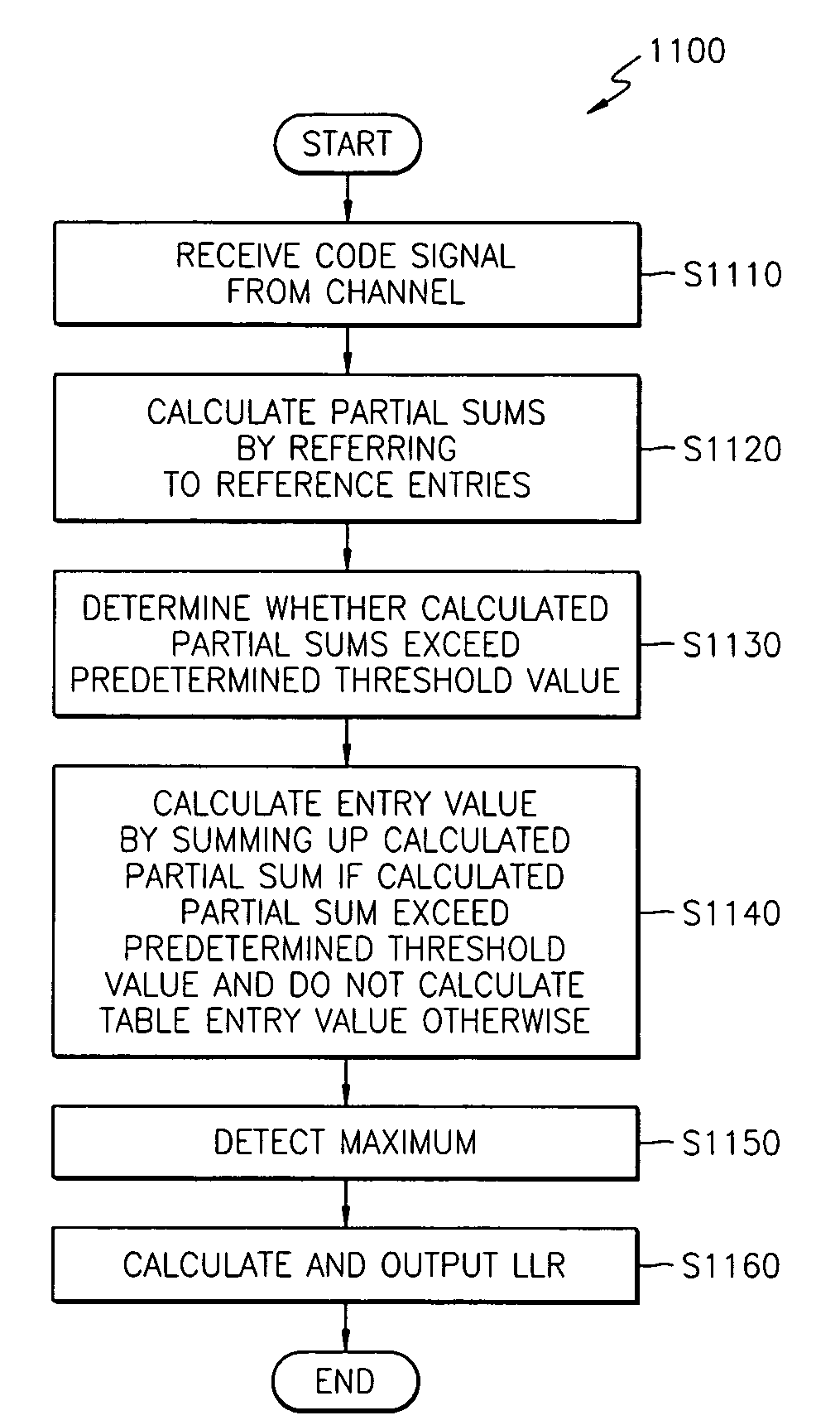
Error correcting codes with bayes decoder and optimized codebook
A framework for error correction coding that takes into account the difference in bit significance in the source symbols by using an appropriate error metric and minimizing it using a Bayes decoder and an optimized codebook. The Bayes decoder performs better than standard soft and hard minimum distance decoding and the optimized codebook performs better than classical linear block codes, e.g., Hamming codes. The error metric is a norm in information symbol space and is based on a loss function appropriately defined according to an approach for assigning significance to the various bits in the source bit stream. The Bayes decoder of this metric is defined and an optimized codebook generated that optimizes this metric under a noisy channel. The framework for error correction coding is implemented for increased reduncancy in a communications system or a data storage system and is optimized to combat noise in such systems.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for correction of a 1-bit error in a coded bit sequence
ActiveCN102436851AReduce overheadReduce processing timeCode conversionSingle error correctionComputer hardwareNon linear functions
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Data receiving apparatus, data transfer apparatus and data receiving method
InactiveCN102571267AImprove coding efficiencyError preventionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareError detection coding
The invention discloses a data receiving apparatus, a data transfer apparatus and a data receiving method. The data receiving device includes a receiving unit, an inverse conversion unit and an error correction unit. The receiving unit receives converted data, which is obtained by converting data including transfer data of a plurality of bits, and an error detection code for error detection of the transfer data, according to a predetermined first procedure. The inverse conversion unit inversely converts the received converted data according to a predetermined second procedure. If it is impossible for the inverse conversion unit to inversely convert the converted data, if it is possible for the inverse conversion unit to inversely convert inverted data obtained by inverting a portion of the bits of the converted data, and if an error is not detected in data obtained by inversely converting the inverted data based on the error detection code, the error correction unit performs error correction by inversely converting the inverted data.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Information processing method and device
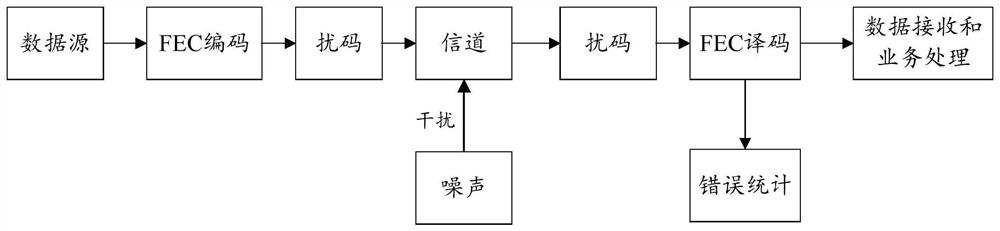
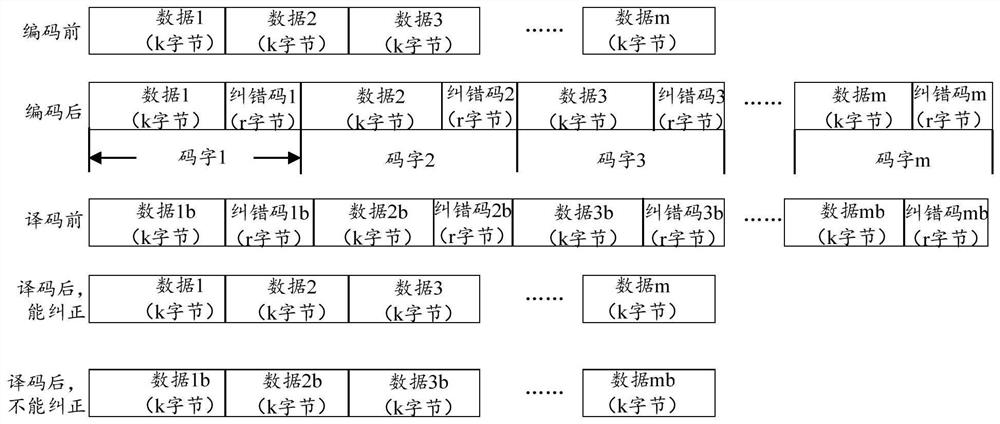
The embodiment of the invention discloses an information processing method and device, and the device comprises a decoding module which is used for receiving M first code words from at least one opposite terminal device, wherein each first code word comprises first business data of K unit lengths and error correction codes of R unit lengths; the decoding module is further used for decoding the M first code words to obtain M second code words, the length of each second code word is the sum of K unit lengths and R unit lengths, each second code word comprises second service data of the K unit lengths and error correction information, the second service data is the first service data after error correction, the error correction information is error statistical information obtained by performing error correction on the first service data with the K unit lengths according to the error correction codes with the R unit lengths; and the classification statistics module is used for determining the error rate of the first service data according to the error correction information. By adopting the embodiment of the invention, the data processing efficiency can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and system for reliable data communications with adaptive multi-dimensional modulations for variable-iteration decoding
ActiveUS9722633B2Minimize complexityMinimize power consumptionError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using block single space codingAlgorithmHigh dimensional
In an advanced adaptive modulation and coding (AMC) scheme, the code rate and the parity-check matrix (PCM) for low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes are adapted according to modulation formats and variable-iteration receivers. The degree distribution for the PCM adaptation is designed by heuristic optimization to minimize the required SNR via an extrinsic information transfer (EXIT) trajectory analysis for finite-iteration decoding. The method uses dynamic window decoding by generating spatially coupled PCM for quasi-cyclic LDPC convolutional coding. The method also provides a way to jointly optimize labeling and decoding complexity for high-order and high-dimensional modulations.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
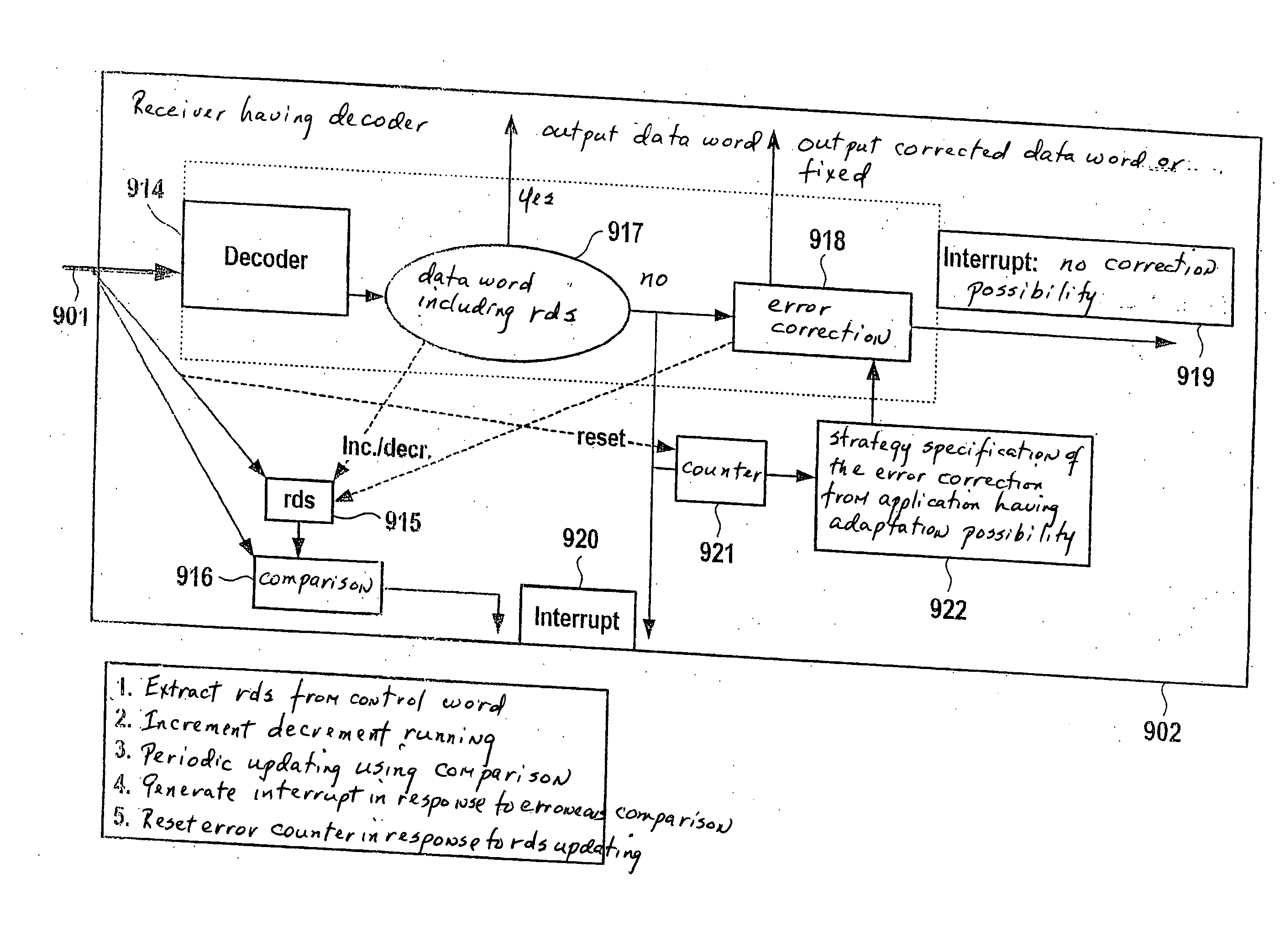
Method and Device for Error Handling in the Transmission of Data Via a Communications System
InactiveUS20070234174A1Reduce spendingAvoid disadvantagesError preventionCode conversionComputer hardwareCommunications system
A method and a device for error handling in the transmission of coded data in the form of at least one data word via a communications system, for the at least one data word a code data word being selected according to a specifiable coding rule, the data being represented as bits which are able to assume two different values, ones and zeros, at least one running digital sum being formed in such a way that a summed difference of the total number of the ones and the total number of the zeros is at least formed through the code data word and this running digital sum is transmitted, the running digital sum being determined to the following code data word and being compared to the one that is then transmitted, in the case of deviation, an error being detected.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method and device for building a variable-length error code
InactiveUS20060101318A1Small overall lengthMany stepsError preventionUnequal/adaptive error protectionVariable lengthComputer science
The invention relates to a variable-length error-correcting (VLEC) code technique, in which the main steps are: defining all the needed parameters, generating a code having a fixed length L1, storing in a set W thus obtained all the possible L1−tuples distant of the minimum diverging distance d[min] from the codewords (one extra-bit being affixed at the end of all words if the new set W thus obtained is not empty), deleting all words of W that do not satisfy a distance criterion with all codewords, and verifying that all words of the final set W satisfy another distance criterion. According to the invention, it is proposed to realize the codeword deletion not anymore only in the last obtained groupe of the code, but in the group of a given length value Ls to which the algorithm will skip back to in the codeword deletion operation, which allows to go back very quickly to smaller lengths and skip many steps of the previous methods.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Error correcting codes with bayes decoder and optimized codebook
A framework for error correction coding that takes into account the difference in bit significance in the source symbols by using an appropriate error metric and minimizing it using a Bayes decoder and an optimized codebook. The Bayes decoder performs better than standard soft and hard minimum distance decoding and the optimized codebook performs better than classical linear block codes, e.g., Hamming codes. The error metric is a norm in information symbol space and is based on a loss function appropriately defined according to an approach for assigning significance to the various bits in the source bit stream. The Bayes decoder of this metric is defined and an optimized codebook generated that optimizes this metric under a noisy channel. The framework for error correction coding is implemented for increased reduncancy in a communications system or a data storage system and is optimized to combat noise in such systems.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
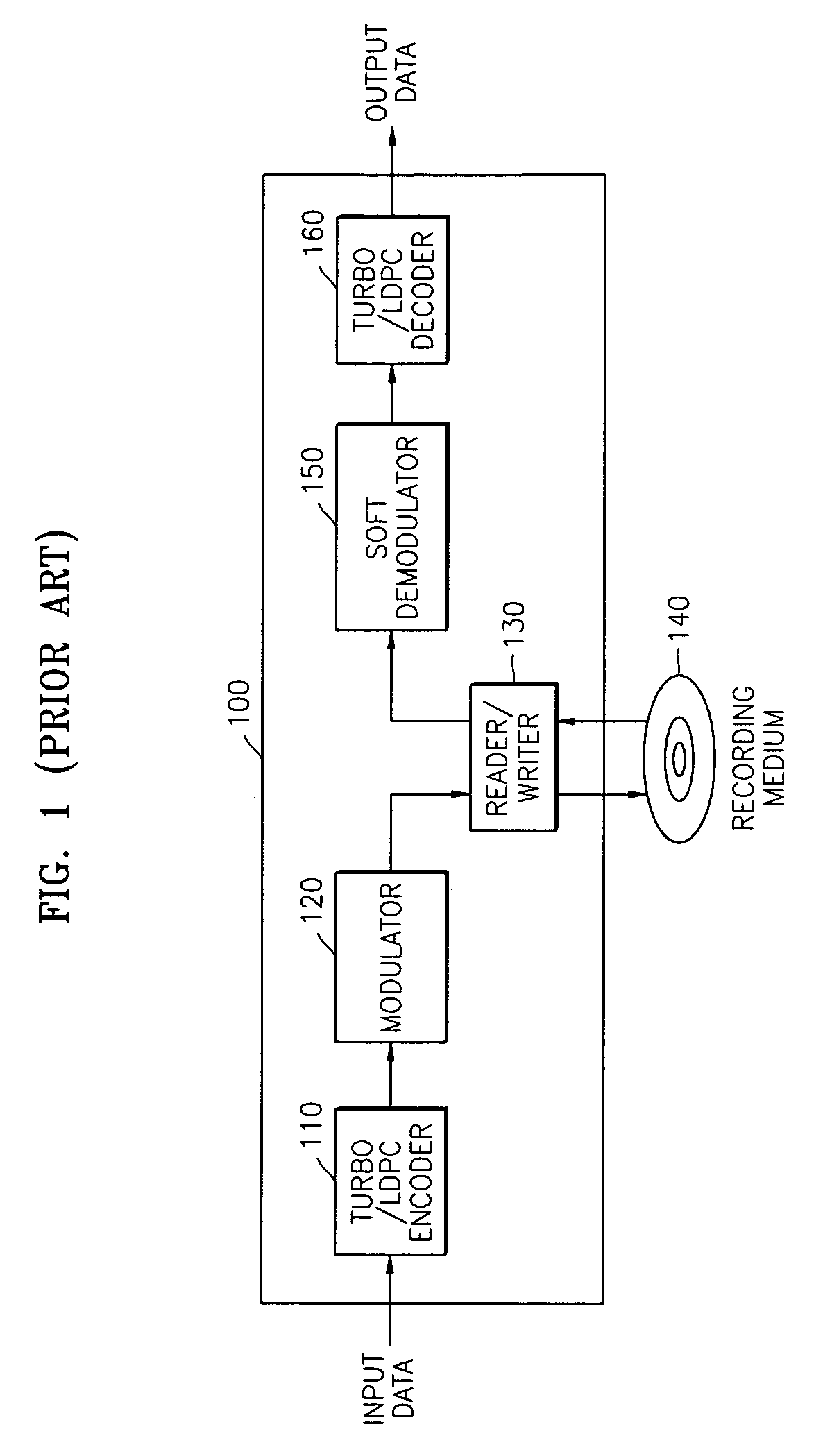
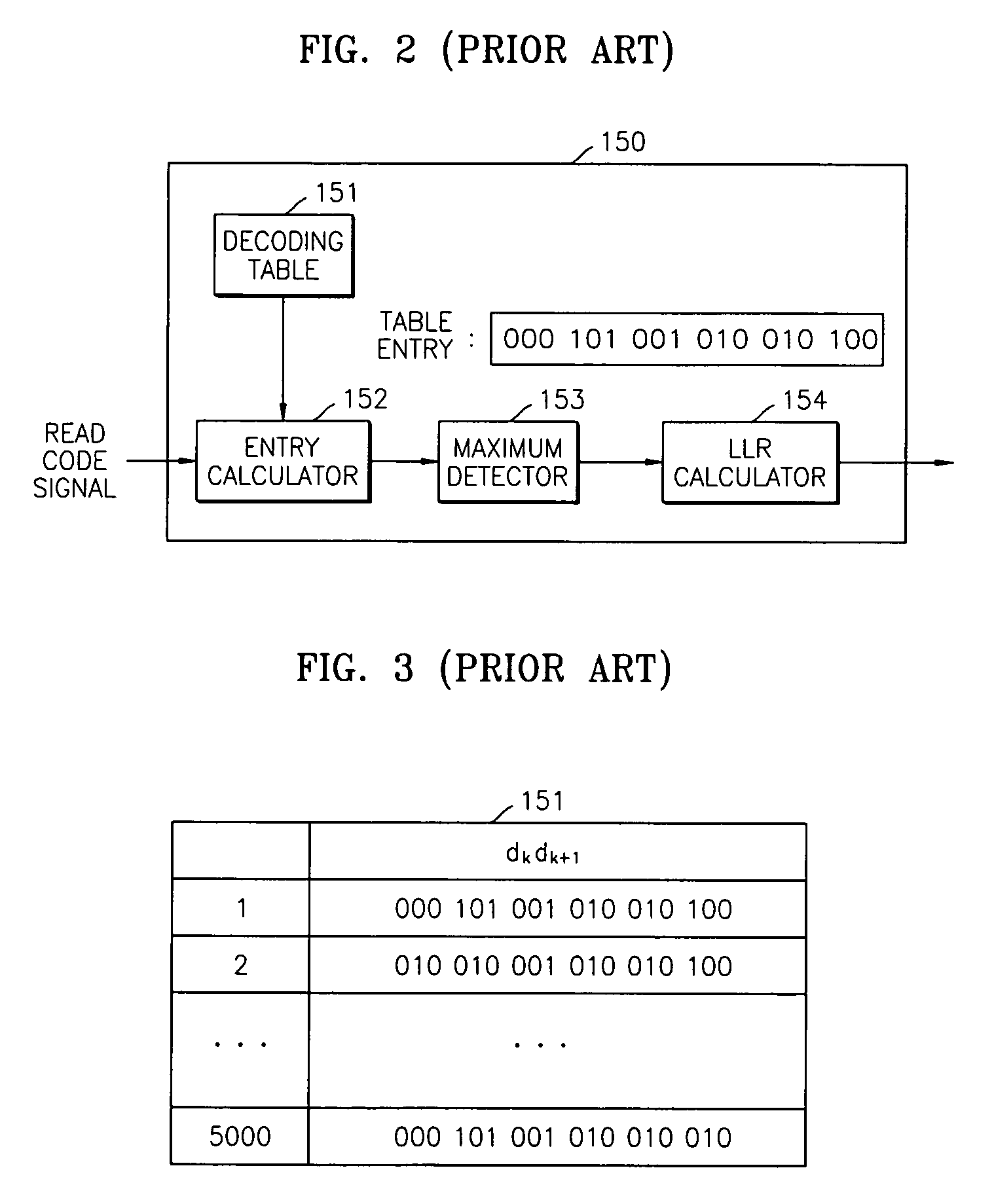
Soft demodulation method and apparatus
InactiveUS7369615B2Reduce complexityModification of read/write signalsElectric signal transmission systemsLog likelihoodComputer science
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Design and training of binary neurons and binary neural networks using error correction codes
A data processing system having a binary neural network architecture for receiving a binary network input and propagating signals via a plurality of binary processing nodes in accordance with the network input to form a network output in accordance with respective binary weights, the data processing system is configured to train each of a plurality of binary processing nodes by implementing a node function as an error correction code (e.g., an r-order Reed-Muller code, e.g., an order 1 Reed-Muller code or a coset of the order 1 Reed-Muller code) function to decode the data through a channel (e.g., a channel decoding code). A binary weight group is identified for a given input of the node that minimizes any error between an output of the node formed from a current binary weight of the node and a preferred output from the node, and the weight of the node is updated to the identified binary weight group. Such training is performed without storing and / or using any weight or other element of higher operational accuracy.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Solid state drive implementing a rate-compatible polar code
A method for extending a polar code by determining an extension number E such that E / 2<N<E whereby N is a number of codeword bits for a polar code that is to be extended and extending a codeword by adding additional redundant / extension bits. Information indicative of a bit unreliability associated with each bit in the codeword is accessed and bit positions with the highest unreliabilities are selected. Input data for an extended codeword is determined by adding a number of redundant bits in the respective selected bit positions.
Owner:MELLONI DIEGO
Parallel Encoding of Non-Binary Linear Block Codes
An encoder module includes P / L parity shift registers that are sequentially coupled, wherein an input of a first parity shift register of the parity shift registers is coupled to the input of the encoder module, an output of the last parity shift register of the parity shift registers is coupled to the output of the encoder module, each of the parity shift registers being configured to store L parity digits. The encoder module also includes a feedback circuit comprising P / L parity generation modules, wherein each of the parity generation modules is coupled to an output of a corresponding one of the parity shift registers by a switch and also coupled to the input of the first parity shift register, wherein each of the parity generation modules is configured to generate L parity digits for transmission to the input of the first parity shift register when its corresponding switch is closed.
Owner:XILINX INC
Encoder, decoder and semiconductor device including the same
ActiveUS20140317472A1Non-binary linear block codesError detection/correctionEncoder decoderDevice material
Provided is a semiconductor device configured to encode input data into a codeword including M different symbols, each of which includes Nm symbols. The semiconductor device including a first storage unit configured to store a first state value which is reset according to M and Nm; a second storage unit corresponding to any one of the M different symbols and configured to store M second state values determined through the corresponding symbol and the first state value; a third storage unit configured to store a third state value.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com