Patents
Literature
149results about How to "Detected as abnormality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
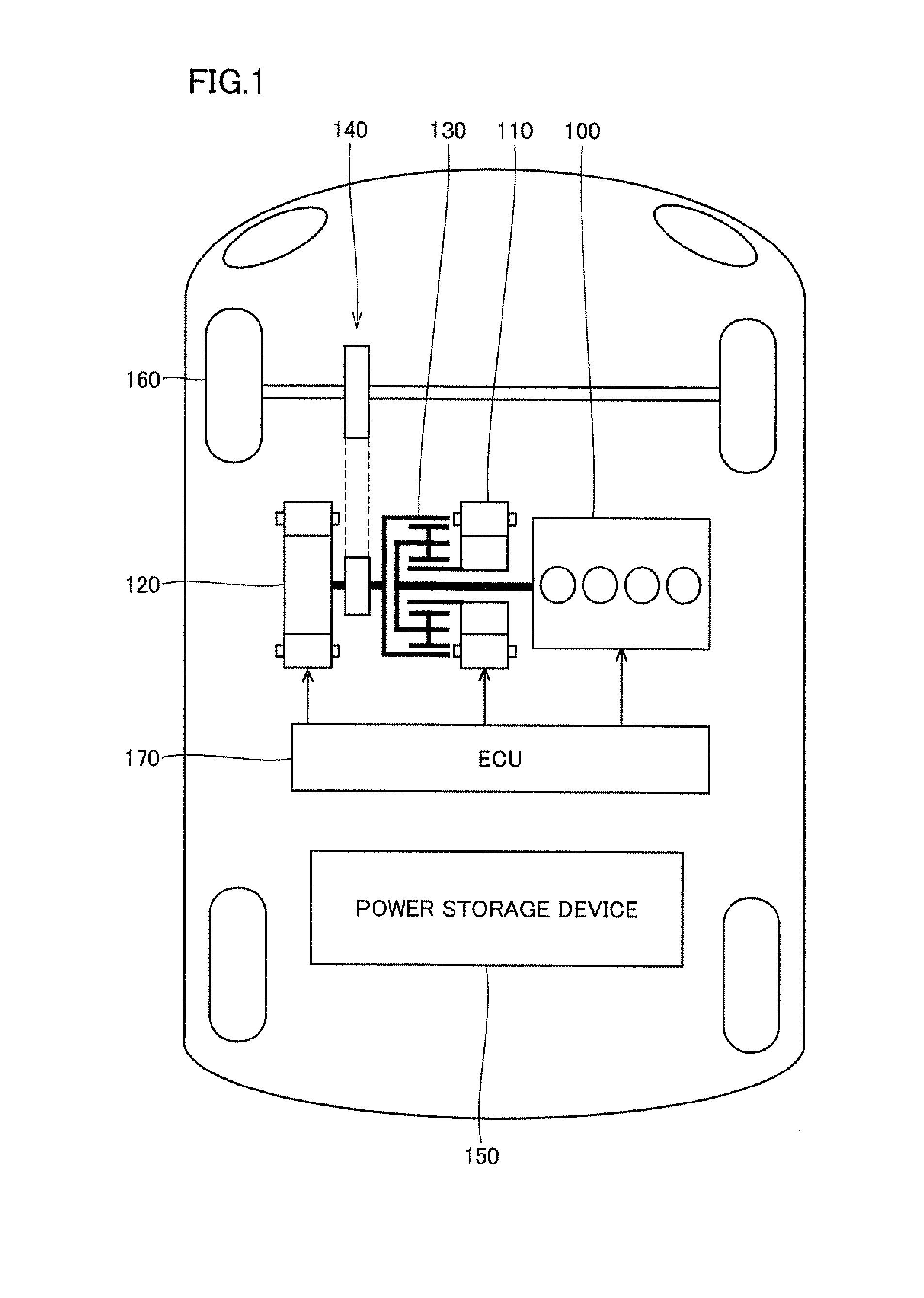
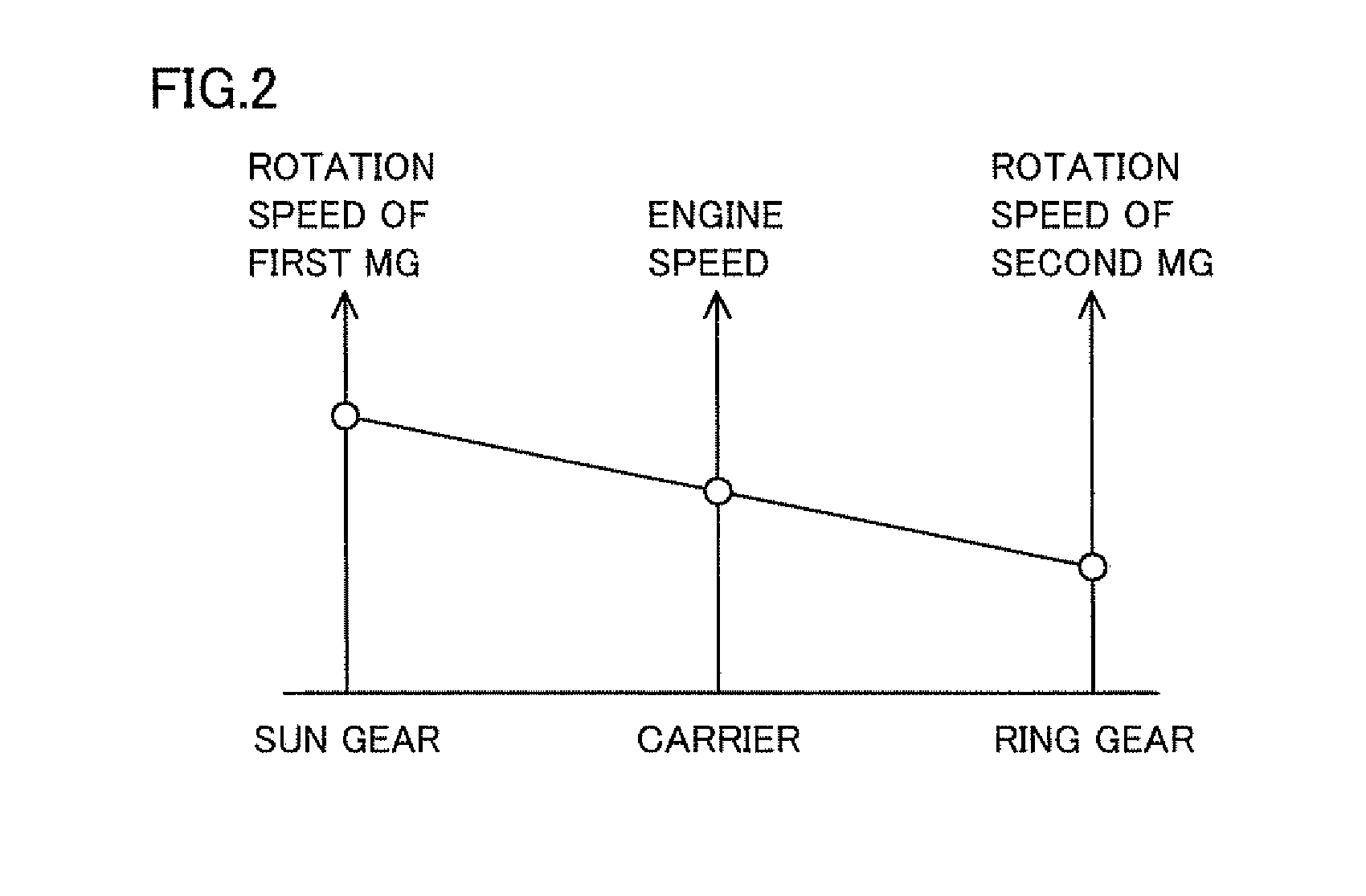
Abnormality diagnosis method and device therefor
ActiveUS10073447B2Detected as abnormalityProgramme controlRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMechanical AbnormalityDiagnosis methods
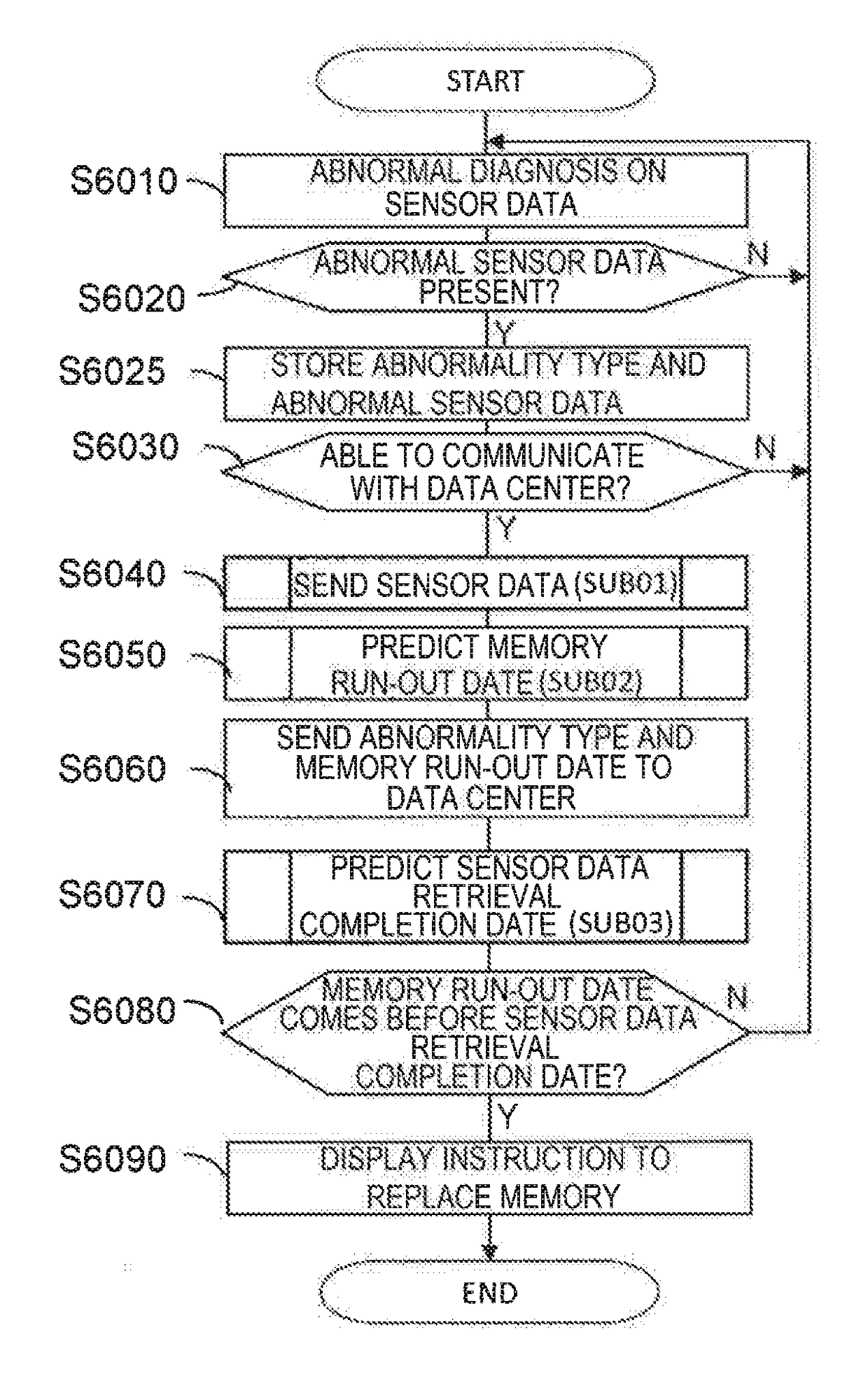
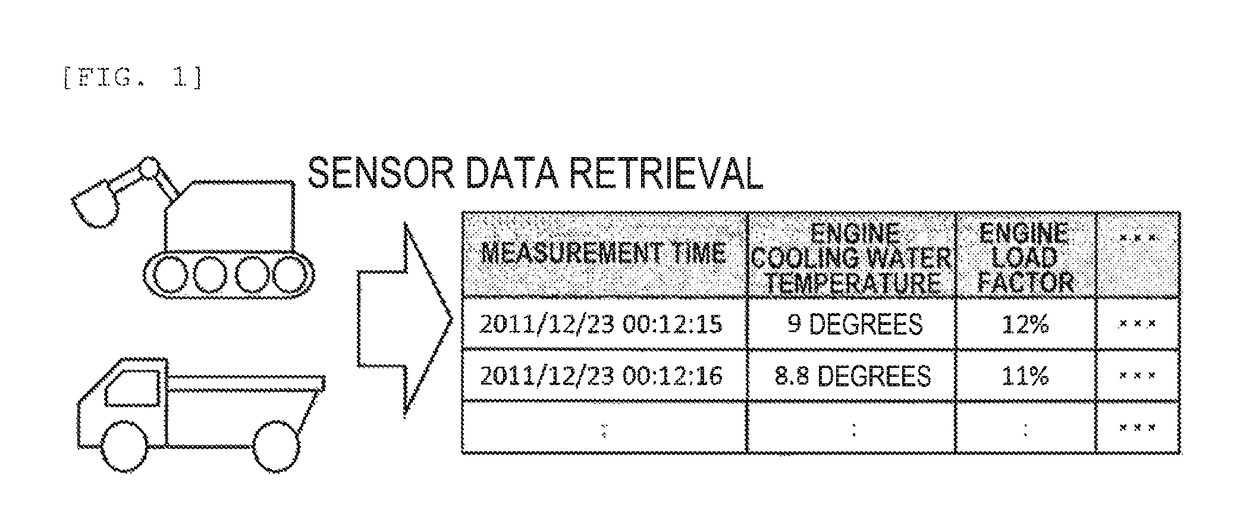
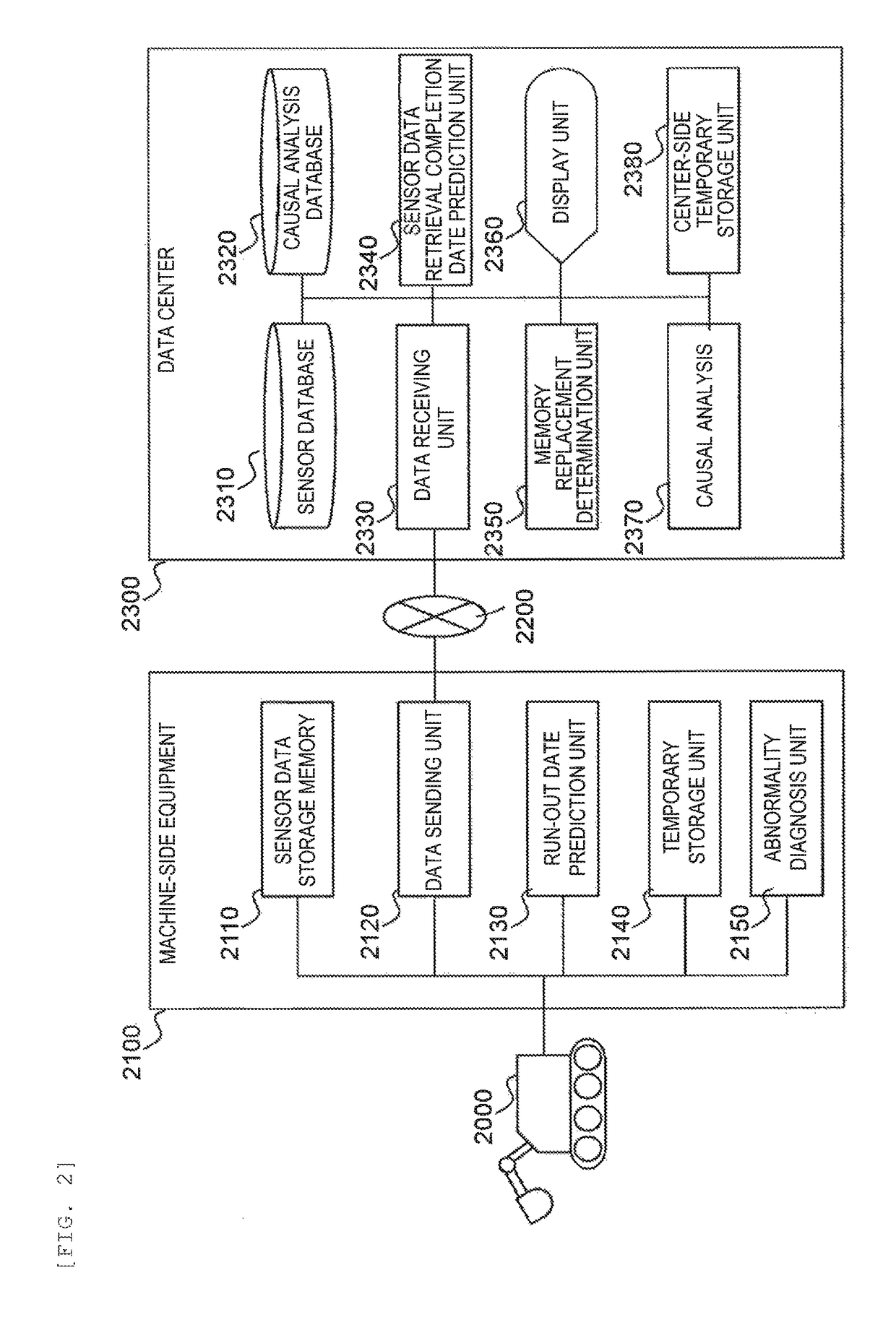
In industrial machine abnormality diagnosis, if the machine is diagnosed to have abnormality, then sensor data from the machine needs to be sent to a management center for causal analysis. However, since machines operated at a remote site cannot always communicate with a management center, it has been found that, in some cases, sensor data that has failed to be sent from a machine remains in the memory of the machine, resulting in lack of available memory capacity. In view of this, the present invention determines beforehand whether the diagnosed machine will run out of available memory capacity before the completion of sending the amount of sensor data required for causal analysis for the machine, and instructs a maintenance person to recover memory. This determination as to whether the machine will run out of available memory capacity before the completion of sending the amount of sensor data required for the causal analysis for the machine, is made as follows: (1) first, the machine predicts the run-out date on which the machine will run out of memory capacity for storing sensor data generated in the machine, and sends a notification of the predicted run-out date to the management center for the machine; and (2) next, from the amount of sensor data required for the causal analysis and the reception rate of sensor data, the management center calculates the number of days required to retrieve the necessary data for the causal analysis and determines whether the management center can retrieve the data by the predicted run-out date.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Electric household appliance remote monitoring system
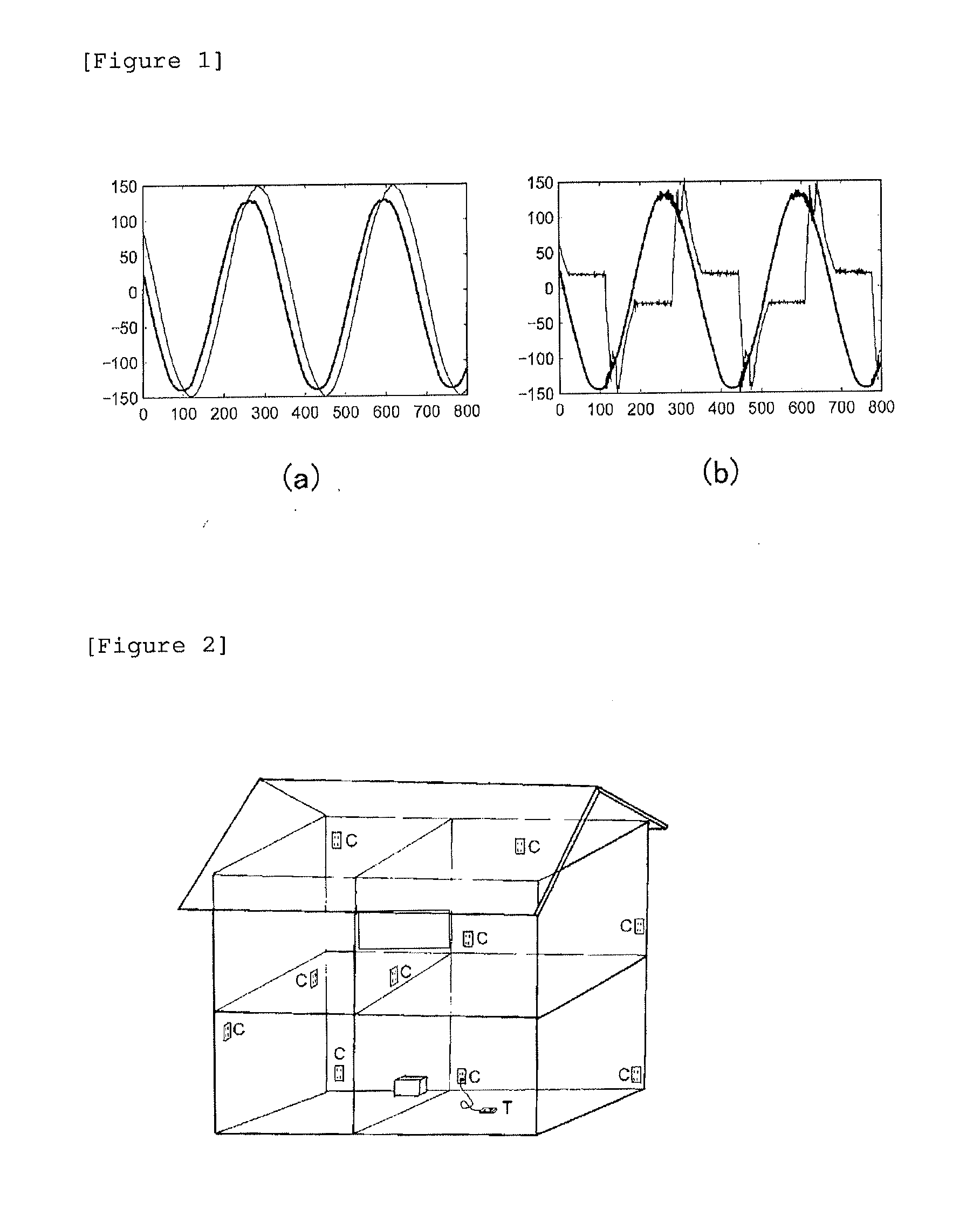
InactiveUS20150253364A1Eliminate possibility of fireDetected as abnormalityProgramme controlTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsPower flowMonitoring system
An electric household appliance remote monitoring system including a smart tap to which one or two or more power plugs of electric equipment can be inserted, an electric household appliance incorporating a smart tap function, and a server is provided. The smart tap includes voltage waveform measuring means and / or current waveform measuring means and communication means. The server has a function of judging an operation state of each piece of connected electric equipment based on the voltage waveform and / or the current waveform received from the smart tap and, when detecting abnormality of the electric equipment, transmitting the detection to an external network.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
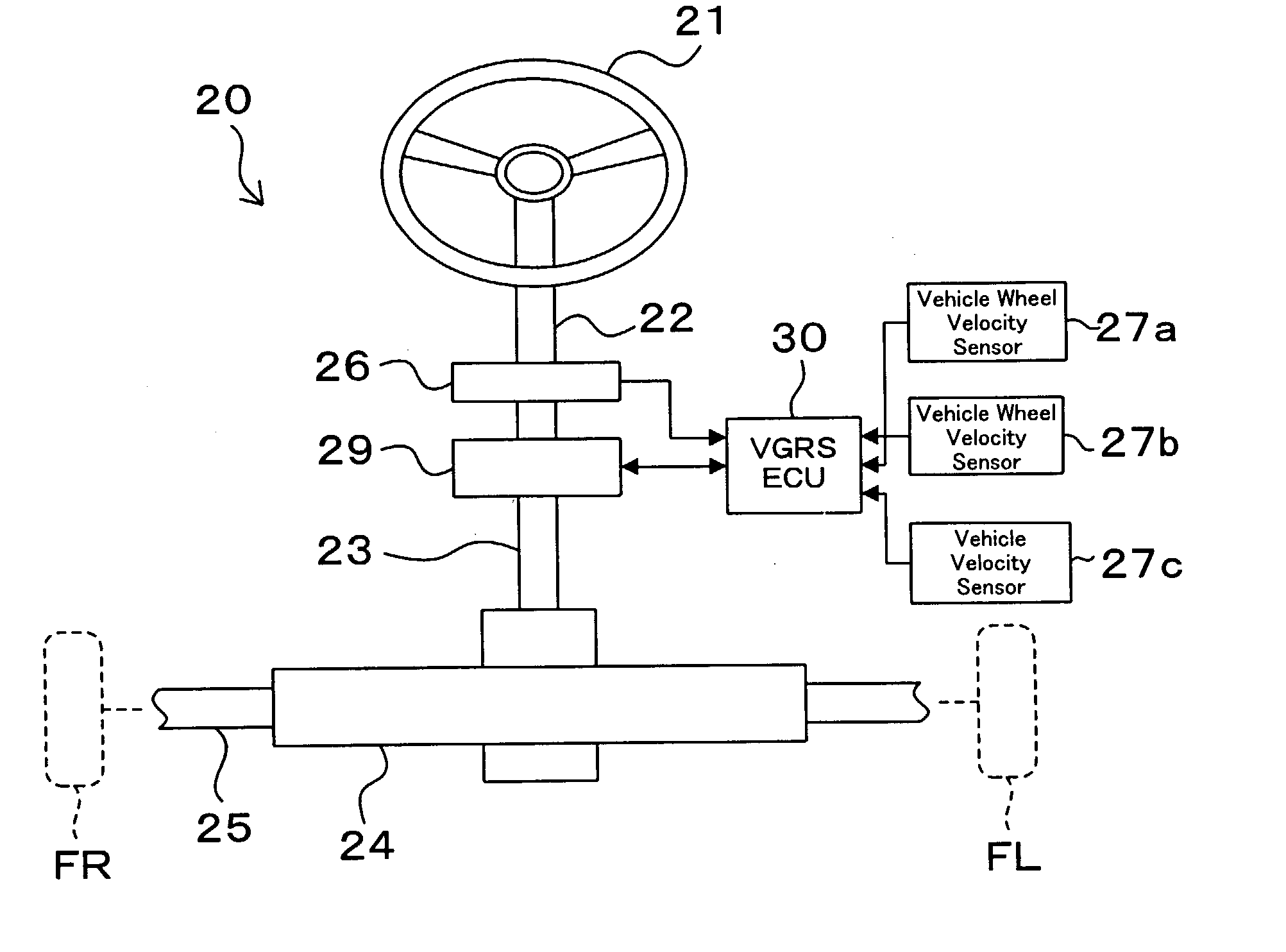
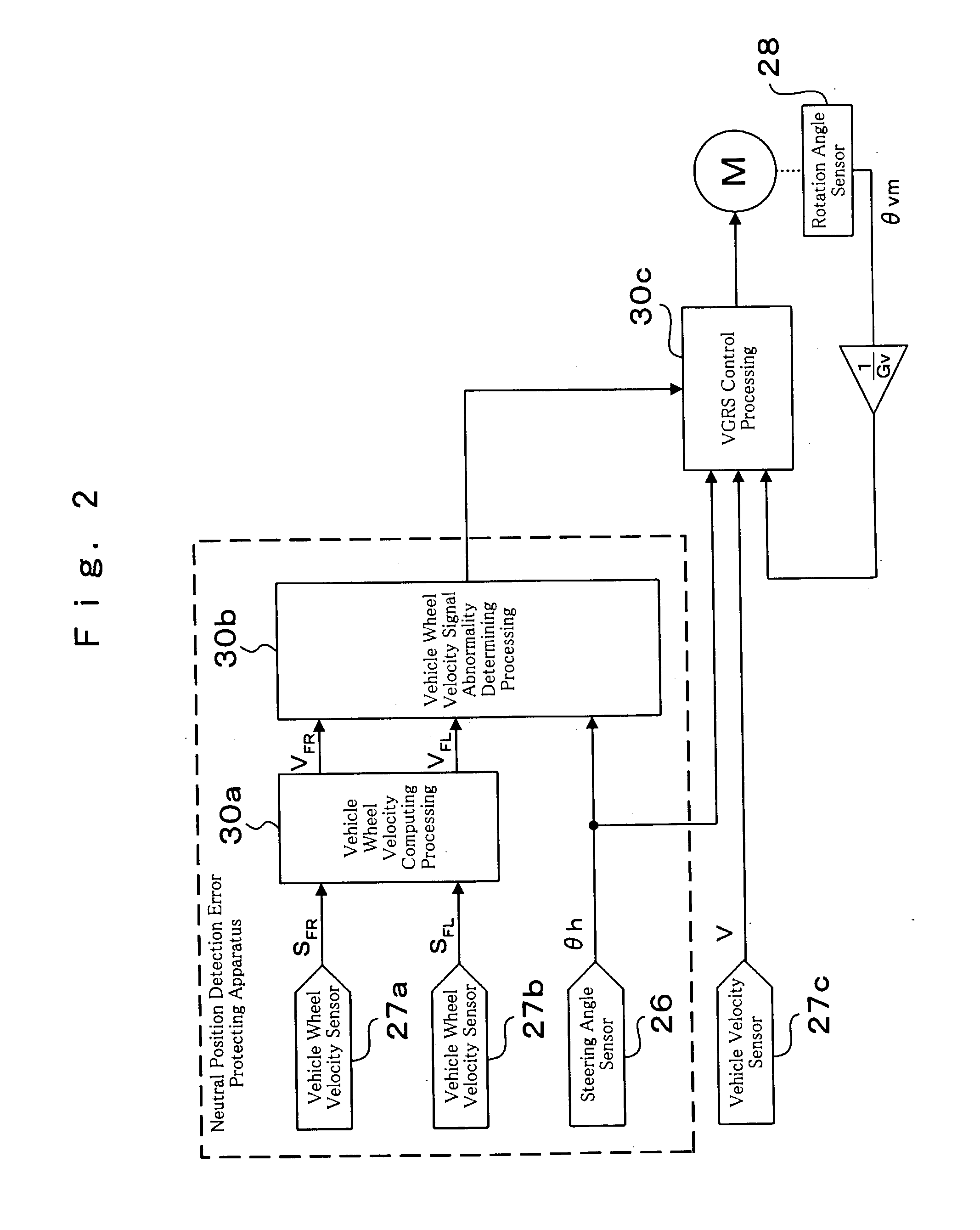
Steering angle neutral position detection error protecting method and detection error protecting apparatus
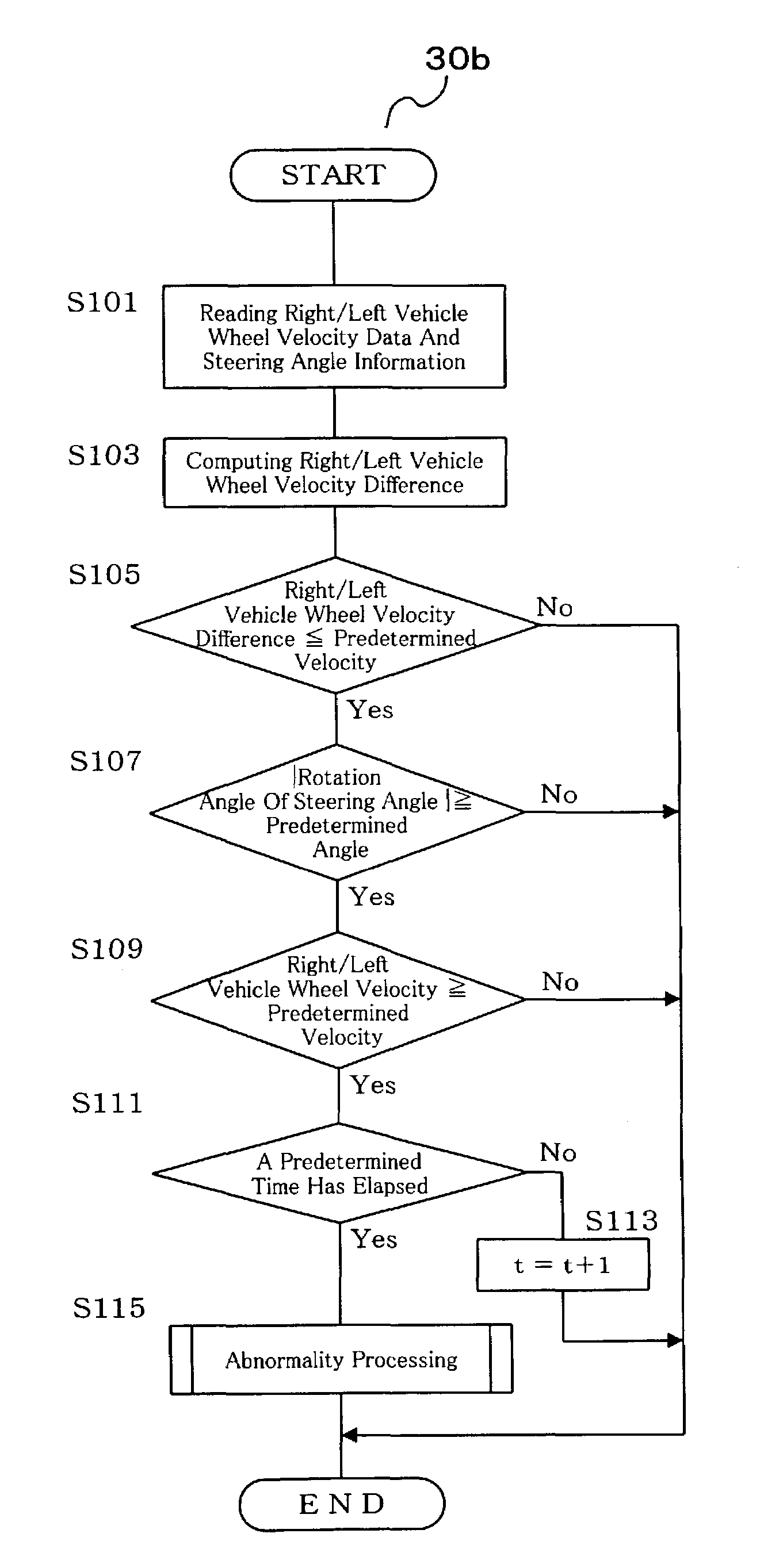
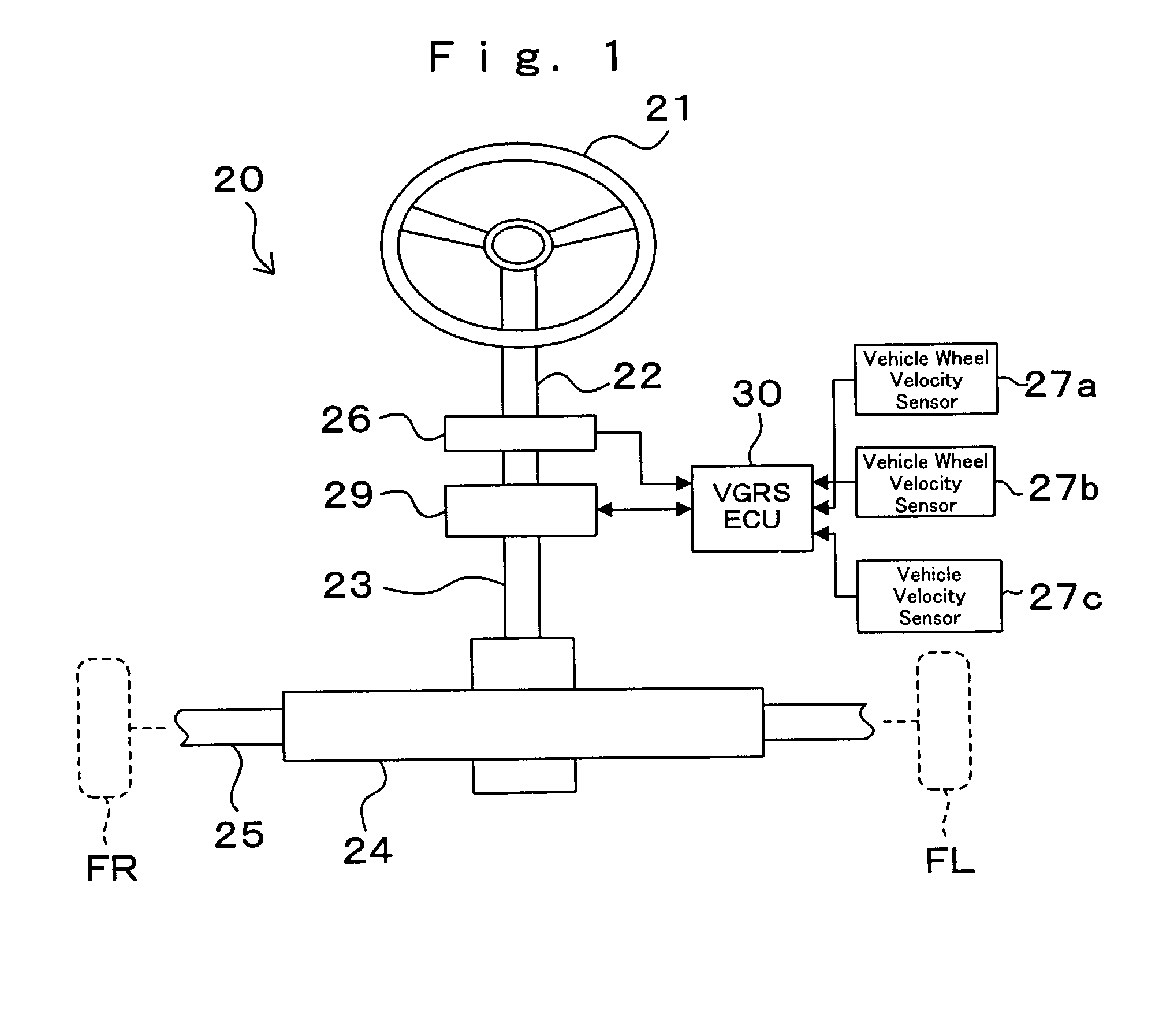
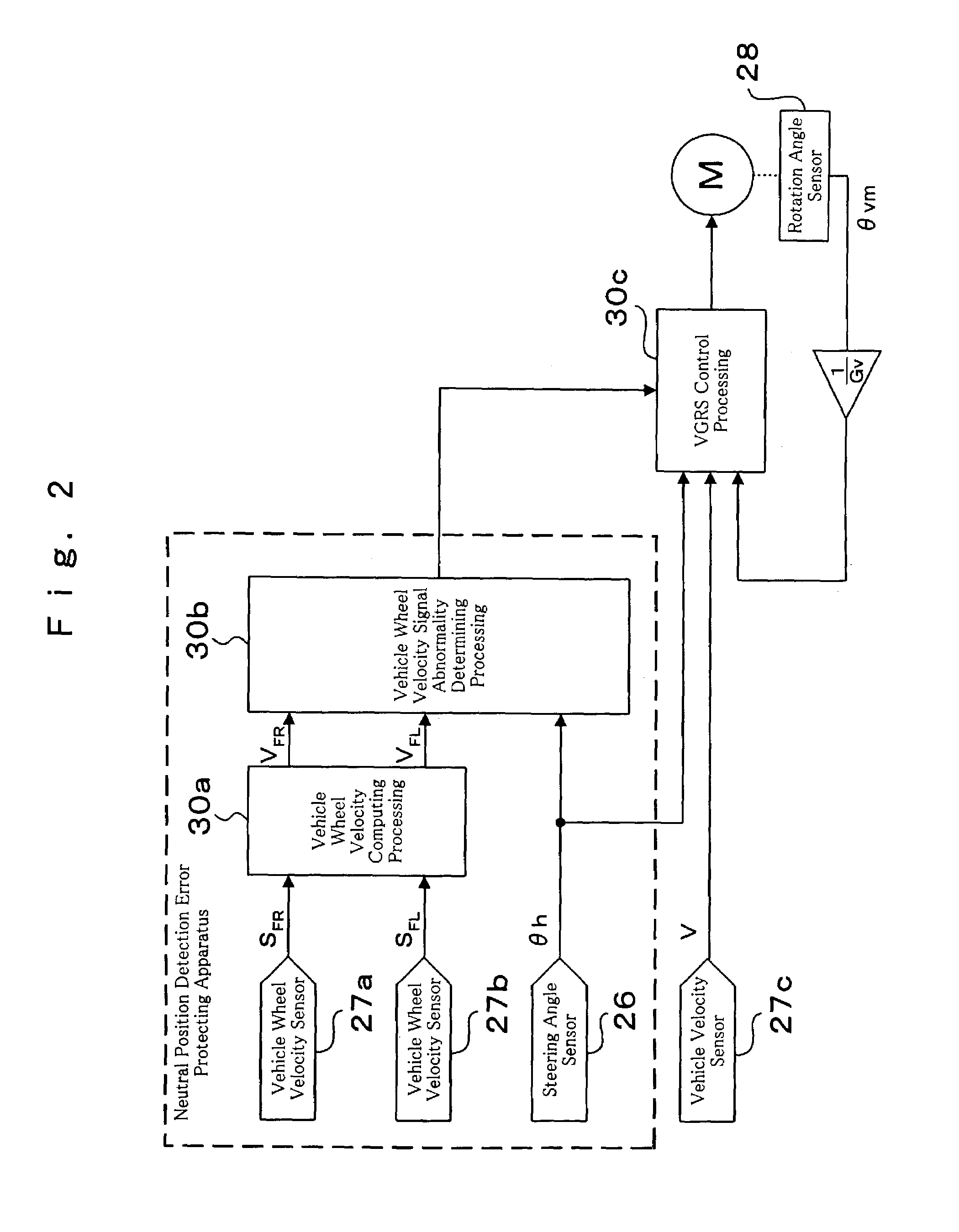
InactiveUS20040046346A1Detection errorAvoid detectionVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesLocation detectionDrive wheel
In a neutral position detection error protecting apparatus, vehicle wheel velocities SFR, SFL of right / left driven wheels FR, FL are detected by vehicle wheel sensors 27a, 27b and a right / left wheel velocity difference VFD is obtained from vehicle wheel velocities VFR, VFL of the driven wheels FR, FL through vehicle wheel velocity signal abnormality determining processing 30b so as to detect steering angle information thetah from the steering wheel 21. Then, when a condition that a right / left wheel velocity difference VFD is less than a predetermined velocity V1, a condition that a rotation angle of steering angle information thetah is more than a predetermined value thetak and a condition that a vehicle wheel velocity is more than a predetermined velocity V2 according to vehicle wheel velocities VFR, VFL of the driven wheels FR, FL are all satisfied in a predetermined period T, it is determined that there is any abnormality in the vehicle wheel velocities SFR, SFL (VFR, VFL) of the driven wheels FR, FL through vehicle wheel velocity signal abnormality determining processing 30b.
Owner:TOYODA MASCH WORKS LTD
Failure diagnosis method
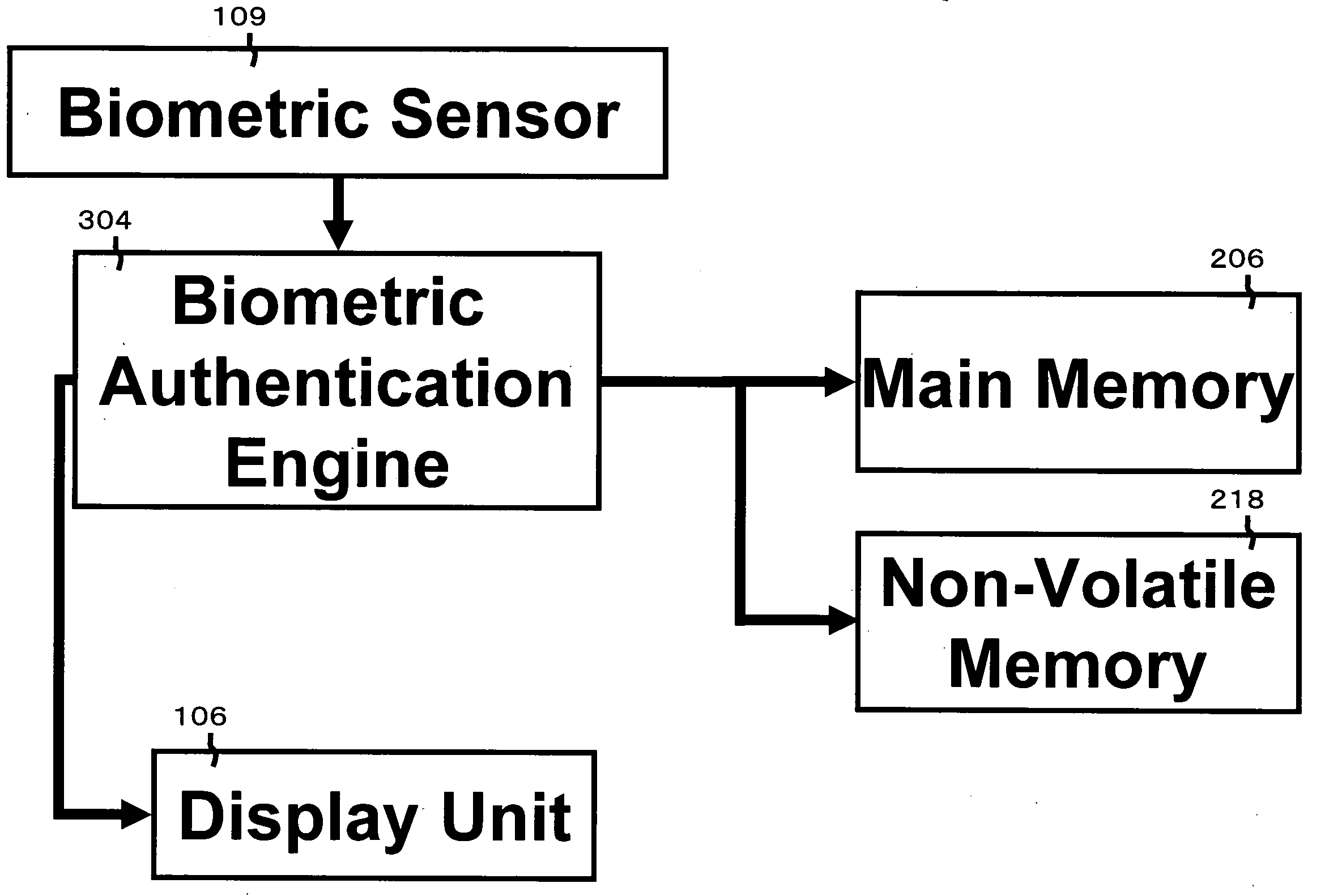
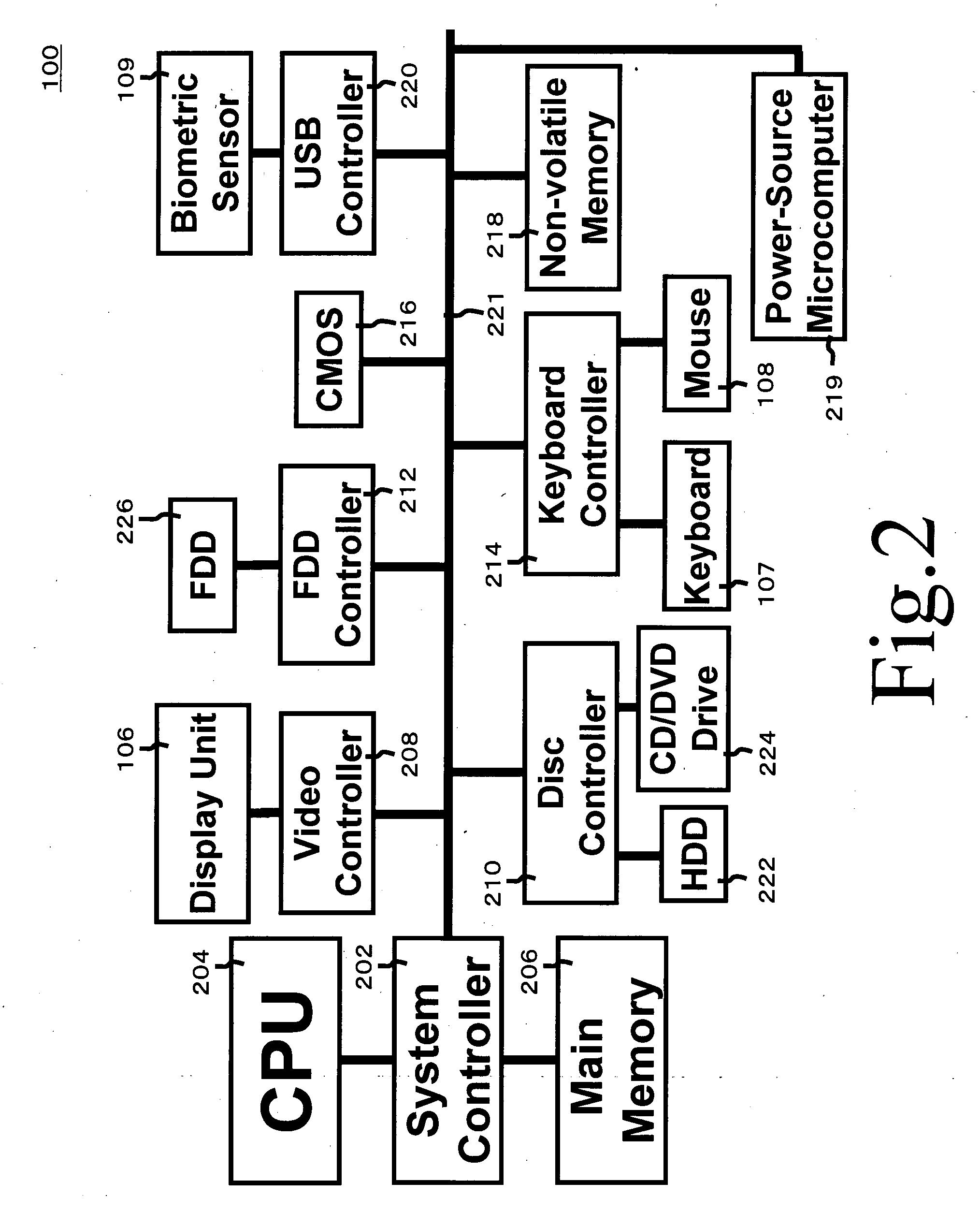
ActiveUS20080133931A1Detected as abnormalityRandom number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationInformation processingBiometric data
A method of detecting abnormality of an information processing apparatus to be started by biometric authentication without being started when the apparatus is inoperable. The information processing apparatus performs the biometric authentication using obtained biometric data of a user and pre-registered reference biometric data of the user in order to allow the apparatus to be used. When the apparatus cannot be started, the information processing apparatus outputs the reference biometric data, a detecting apparatus capable of obtaining the reference biometric data obtains the reference biometric data, the detecting apparatus obtains biometric data of the user and detects abnormality of the information processing apparatus by comparing the biometric data of the user obtained by the information processing apparatus and the obtained reference biometric data for authentication determination.
Owner:FUJITSU CLIENT COMPUTING LTD
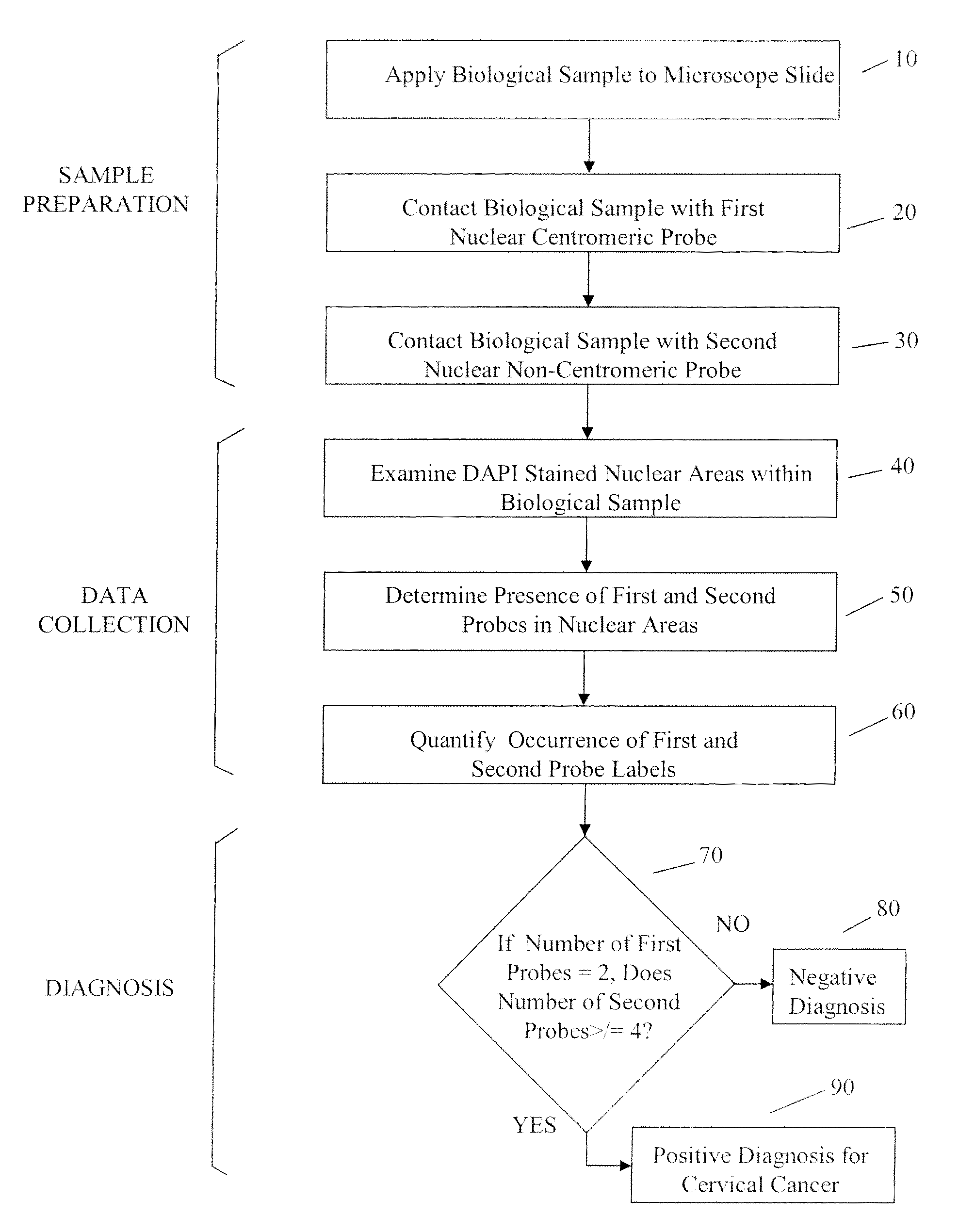
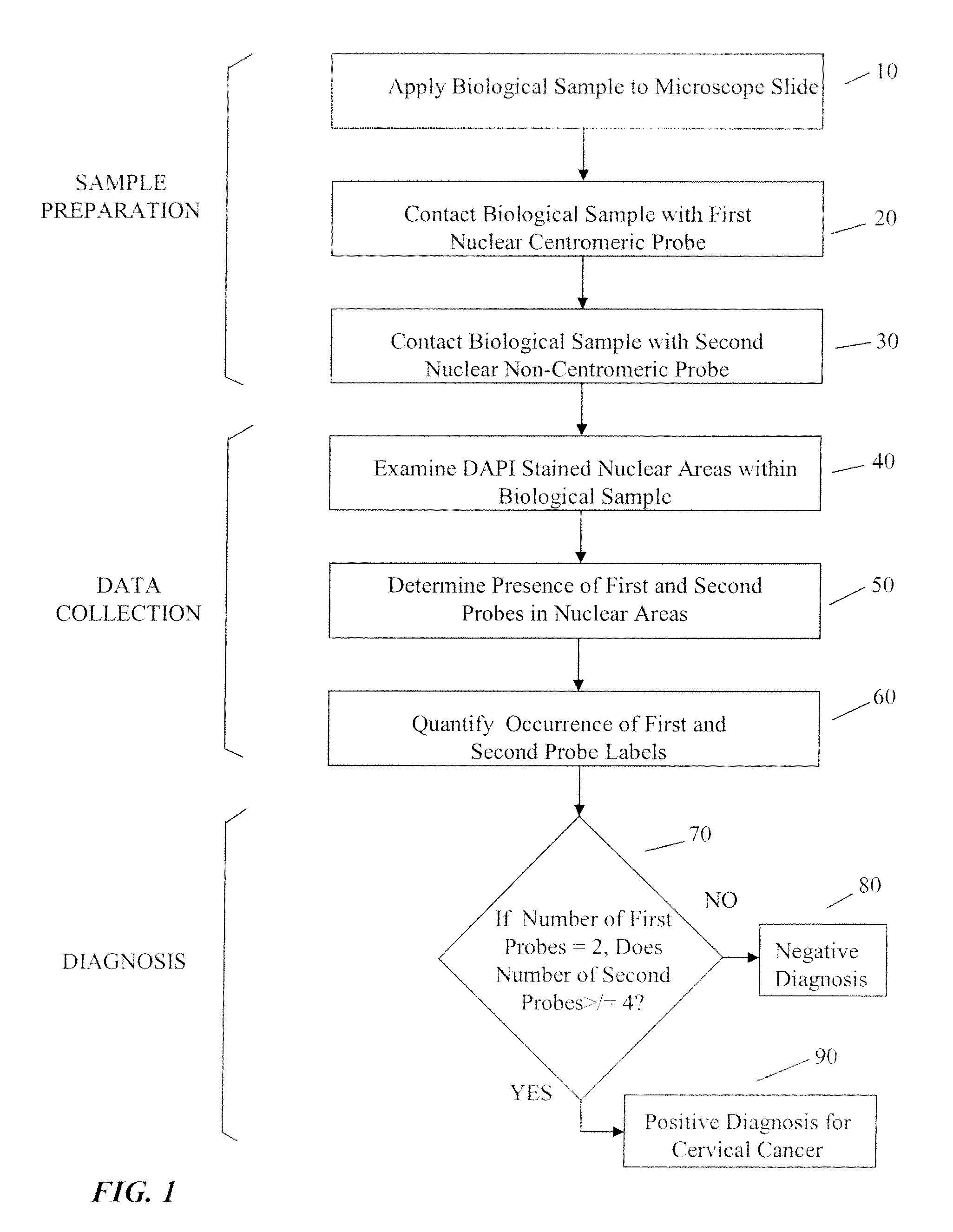
Automated method for detecting cancers and high grade hyperplasias
InactiveUS20090208965A1Quick checkDetected as abnormalityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiochemistryAutomated method
Owner:IKONISYS INC
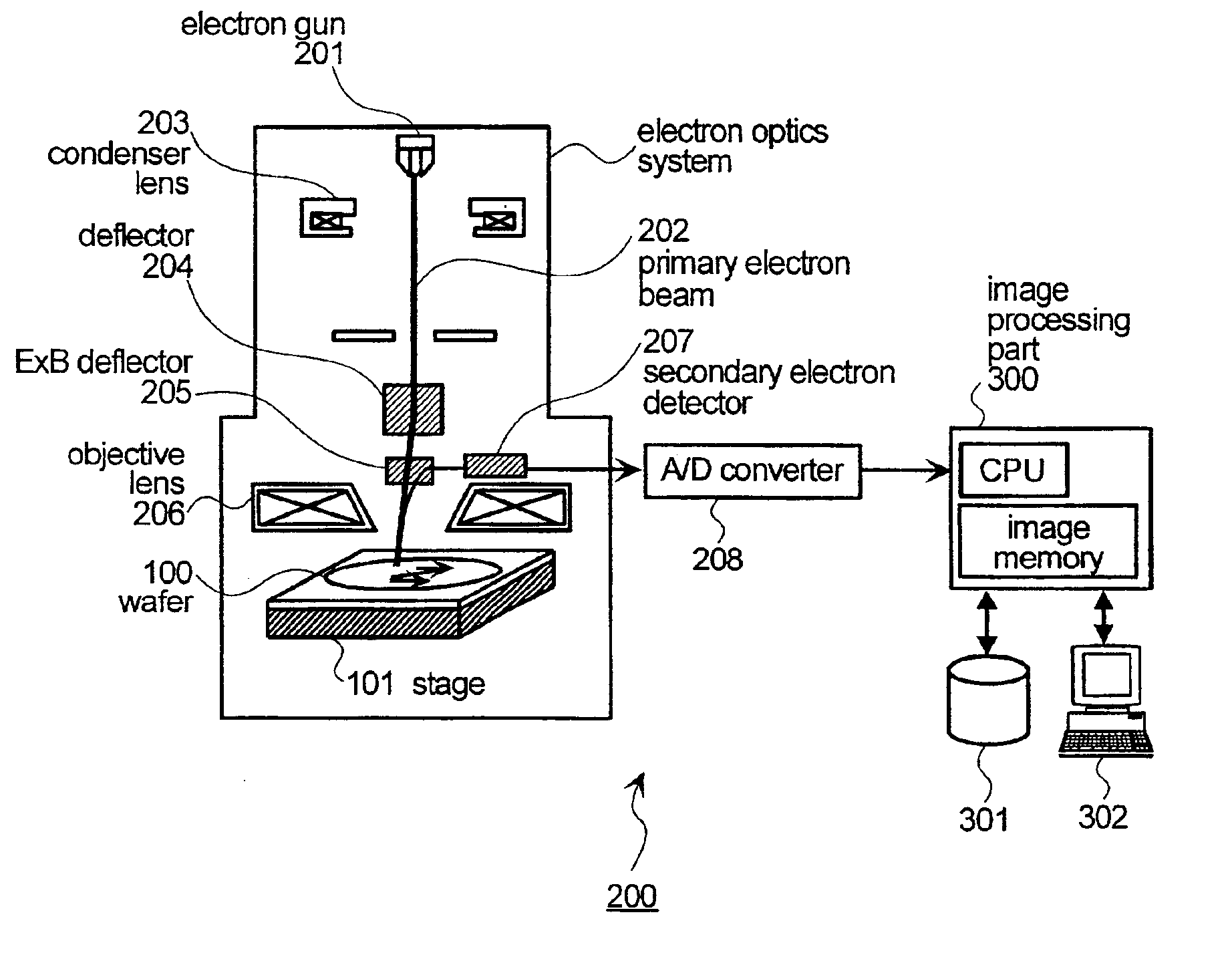
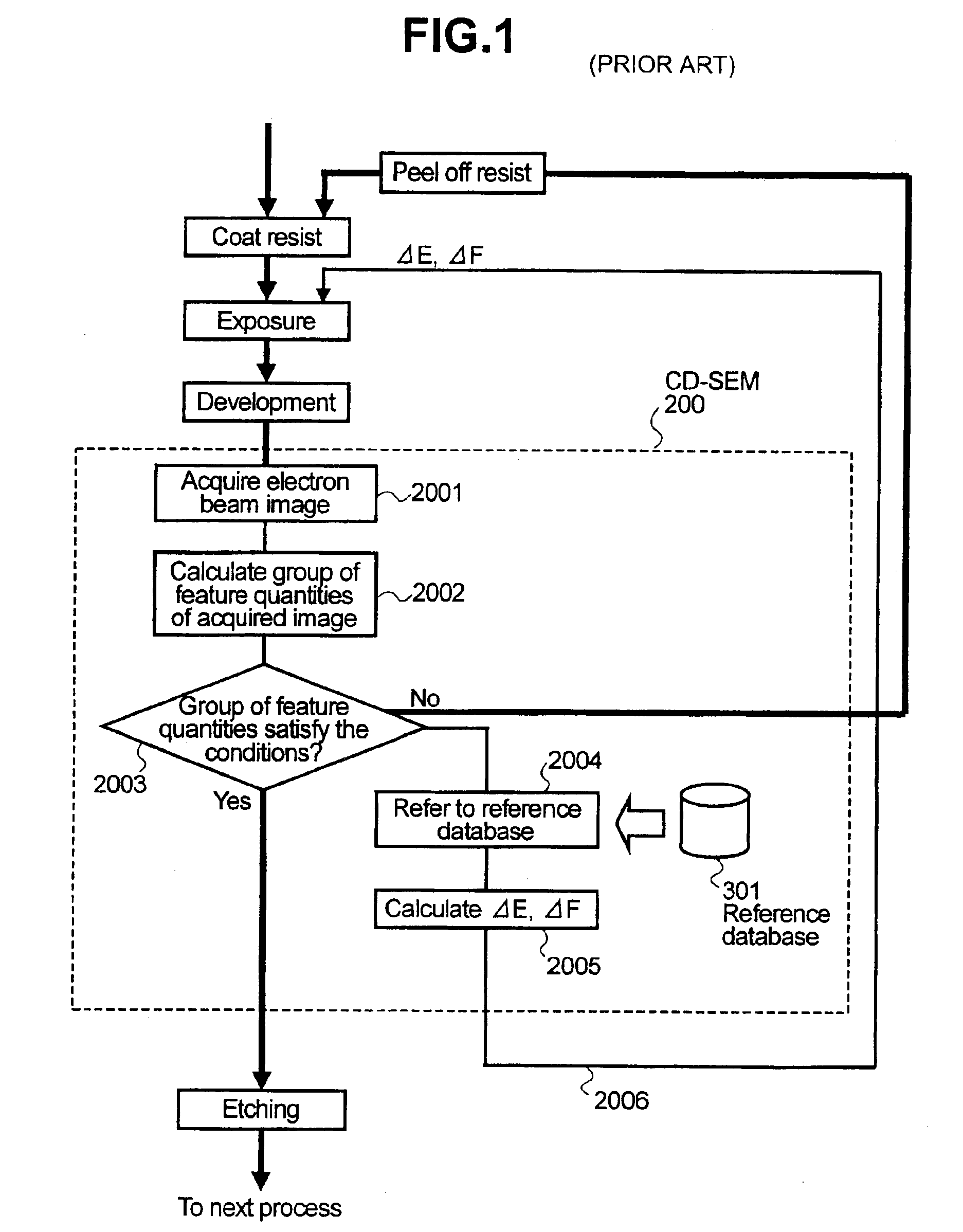
Method and system for monitoring a semiconductor device manufacturing process
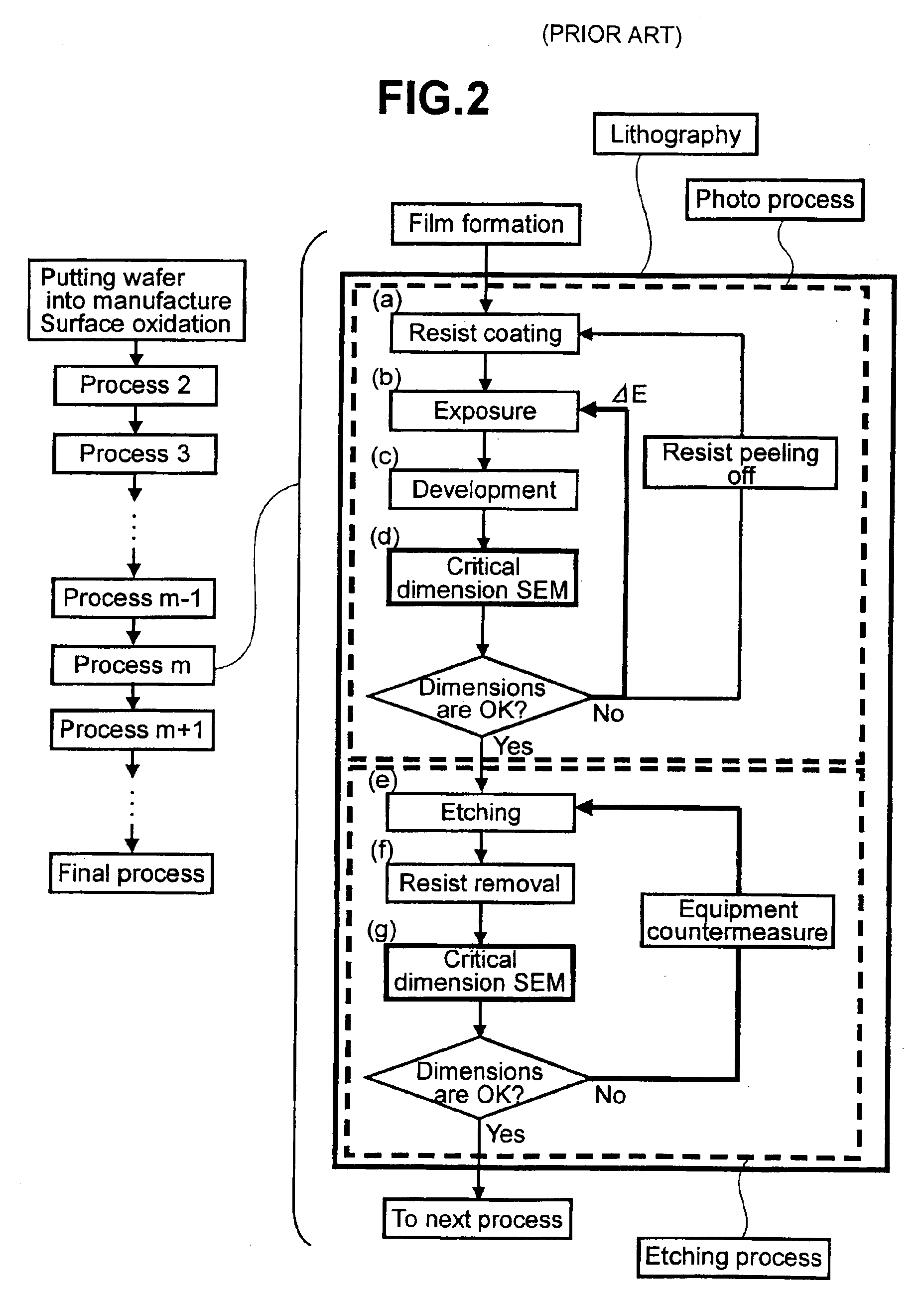
InactiveUS6909930B2Direct precise alterationAccurate monitoringMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithography processElectron
To realize a method for detecting variations in conditions (drift of the exposure and drift of the focus) in exposure equipment at a product wafer level in lithography process, the process is specified in such a way that calculation results of feature quantities such as electron beam images, line profiles, dimensions, etc. under various sets of the exposure and the focus are stored as a library, and an electron beam image of the product wafer is compared with these pieces of data in the library so that detection of drifts of the exposure and the focus a check of the results on the screen can easily be performed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
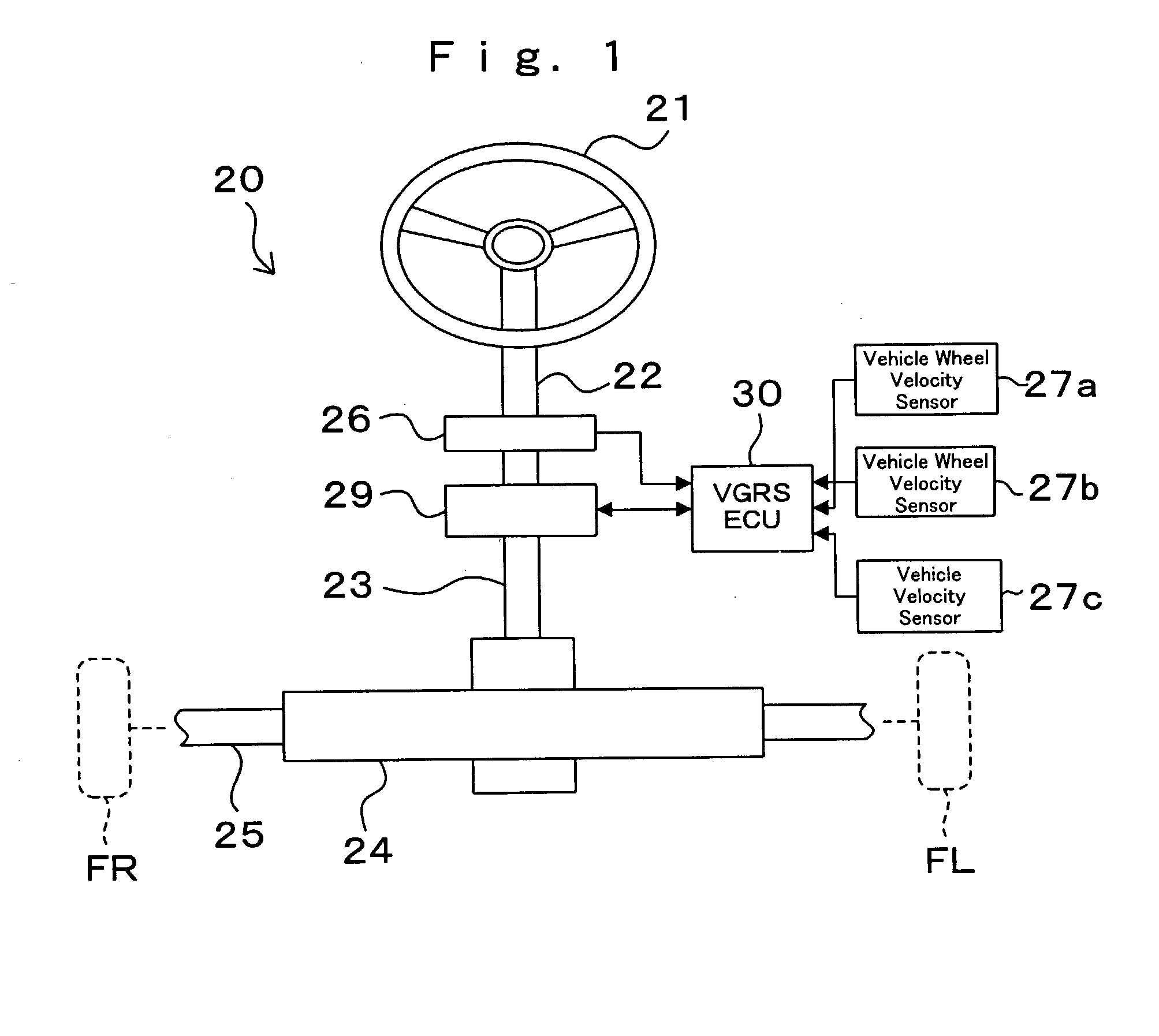
Steering angle neutral position detection error protecting method and detection error protecting apparatus
InactiveUS7028804B2Detection errorAvoid detectionVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesLocation detectionDrive wheel
In a neutral position detection error protecting apparatus, vehicle wheel velocities of right / left driven wheels are detected and a right / left wheel velocity difference is obtained. Then, when a right / left wheel velocity difference is less than a predetermined velocity a steering rotation angle is more than a predetermined value and a vehicle wheel velocity is more than a predetermined velocity in a predetermined period, it is determined that there is an abnormality in the vehicle wheel velocities.
Owner:TOYODA MASCH WORKS LTD
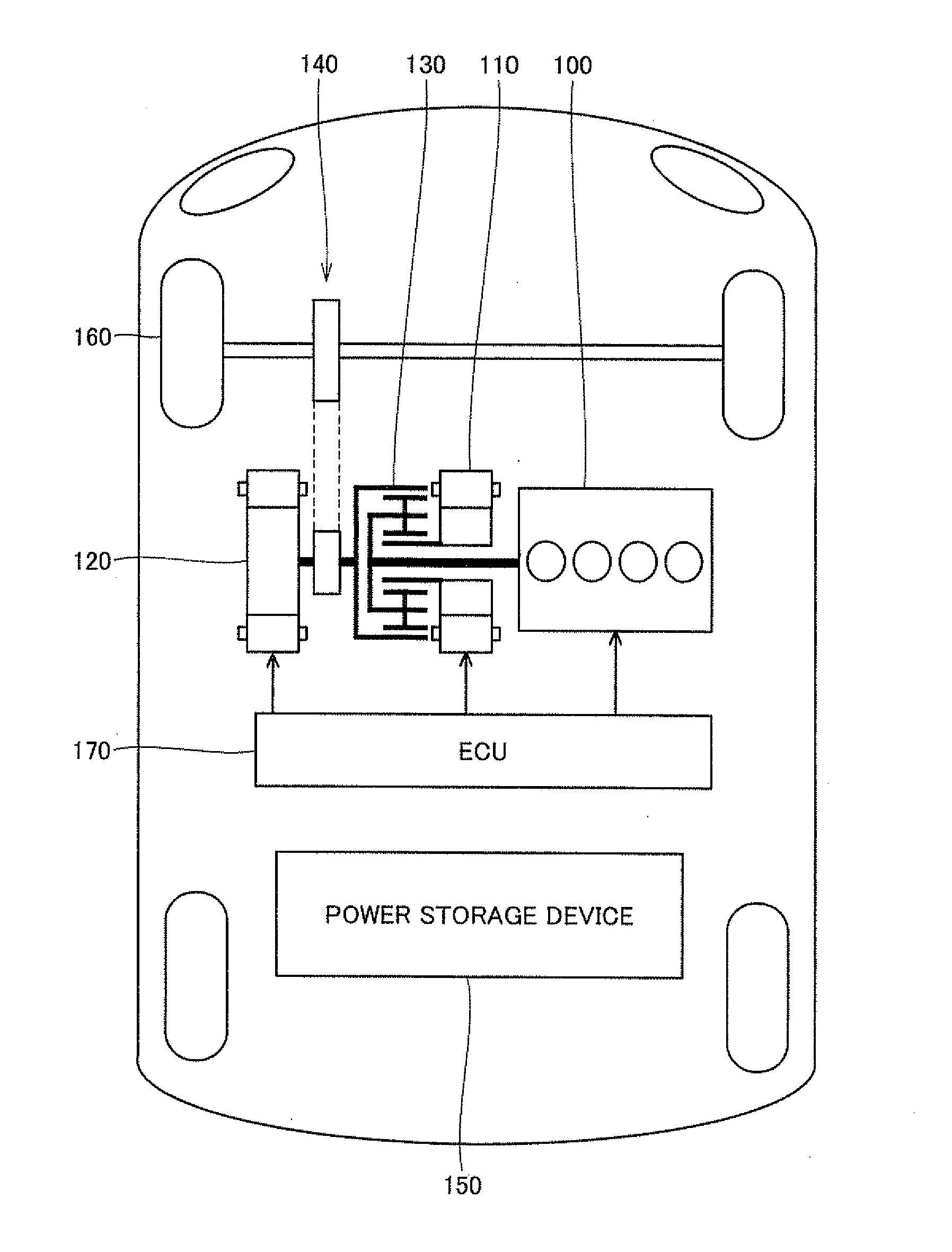
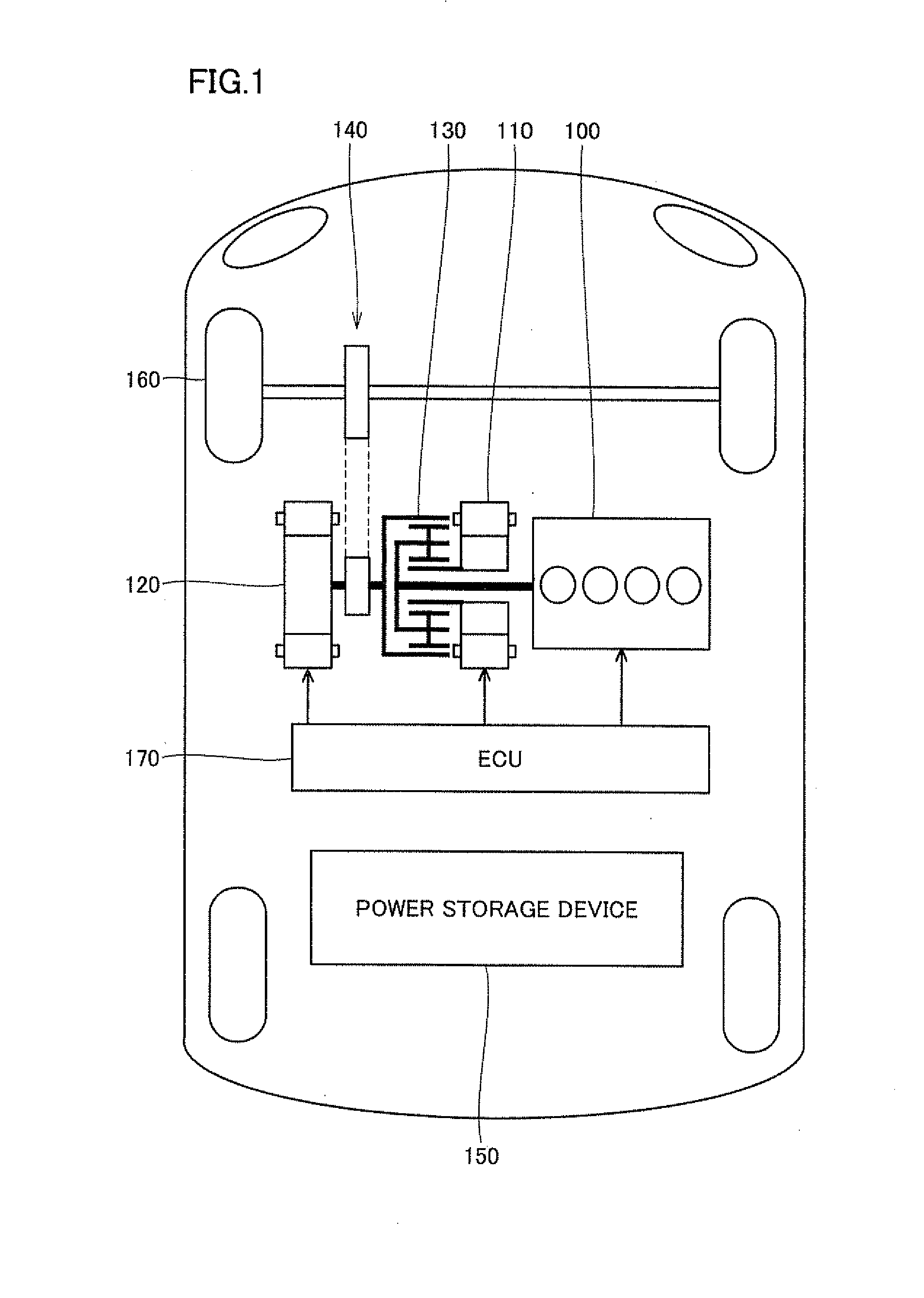
Charging control apparatus for vehicle
ActiveUS20100295507A1Easy to changeDetected as abnormalityBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectrical resistance and conductanceCharge control
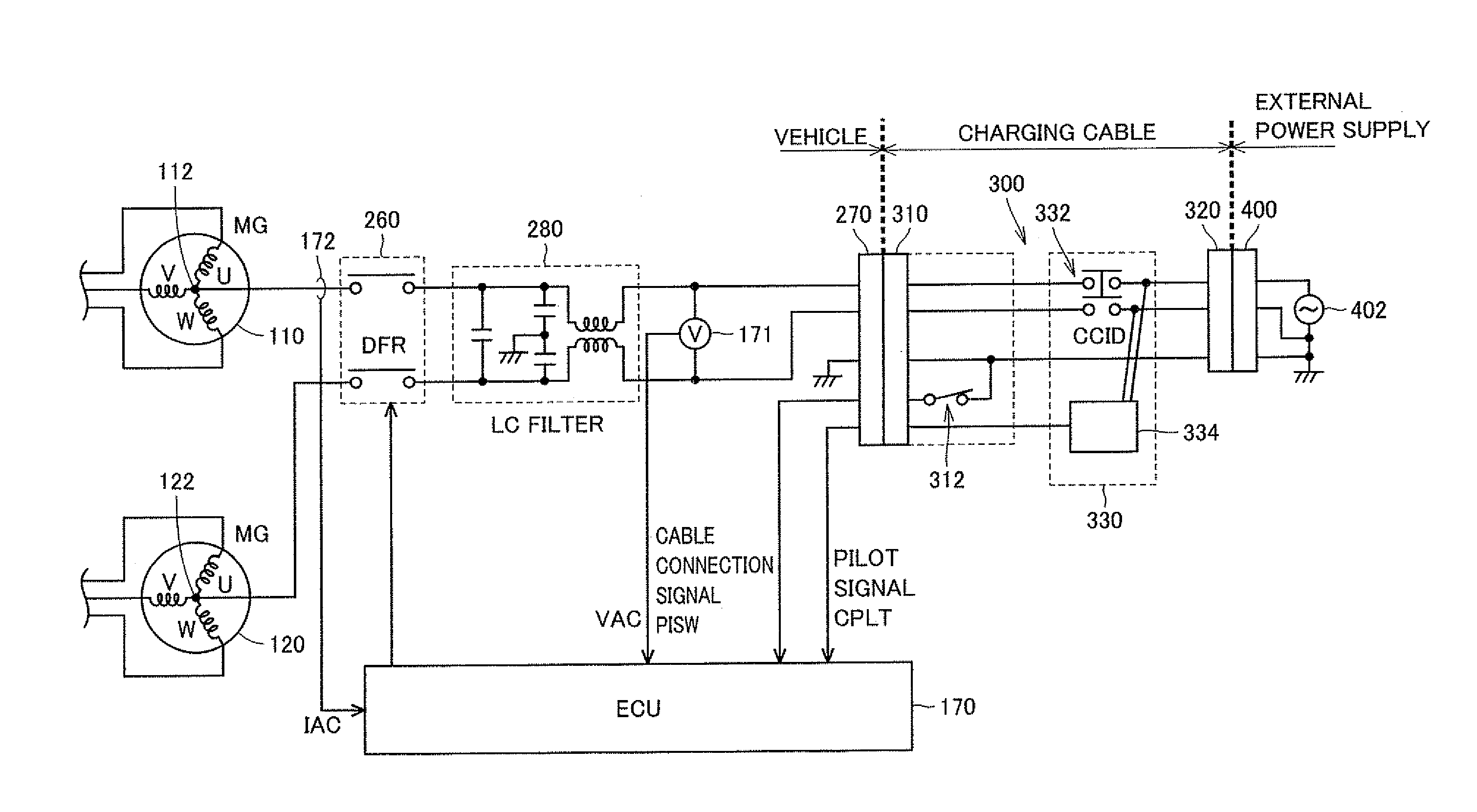
An oscillator provided in a charging cable outputs a non-oscillating signal when the potential of a pilot signal is around V(1), and outputs an oscillating signal when the potential of the pilot signal is lowered to V(2). A pull-down resistance element provided in the plug-in hybrid vehicle is connected between a control pilot line and a vehicle earth, and changes the potential of the pilot signal from V(1) to V(2). A switch is connected in series between the pull-down resistance element and the vehicle earth. When the charging cable is connected to the vehicle, the switch is turned off and the pull-down resistance element is separated from the vehicle earth.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +2
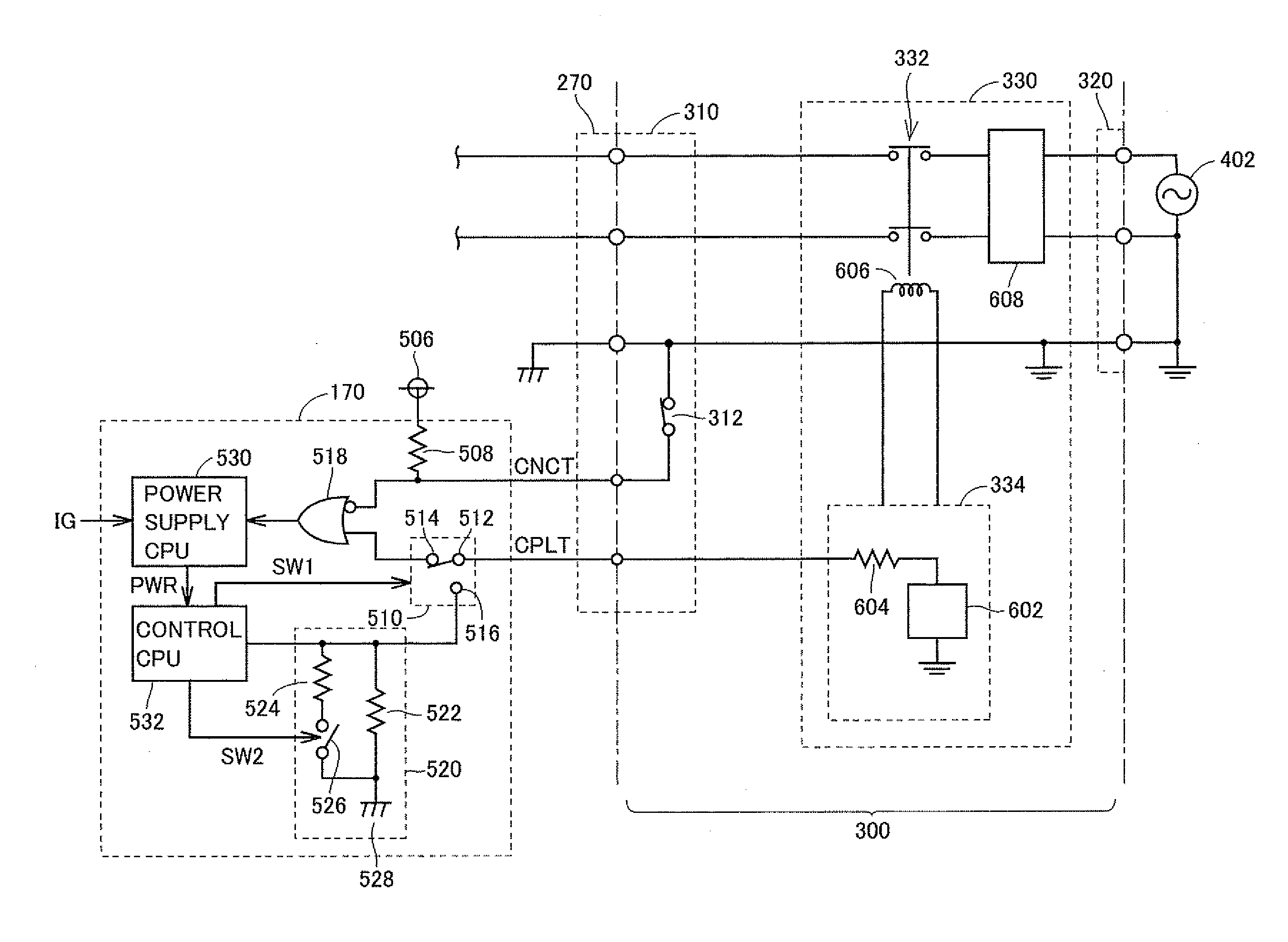
Apparatus and method for activating system of vehicle
InactiveUS20100299008A1Reliably activatedDetected as abnormalityBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceVIT signals
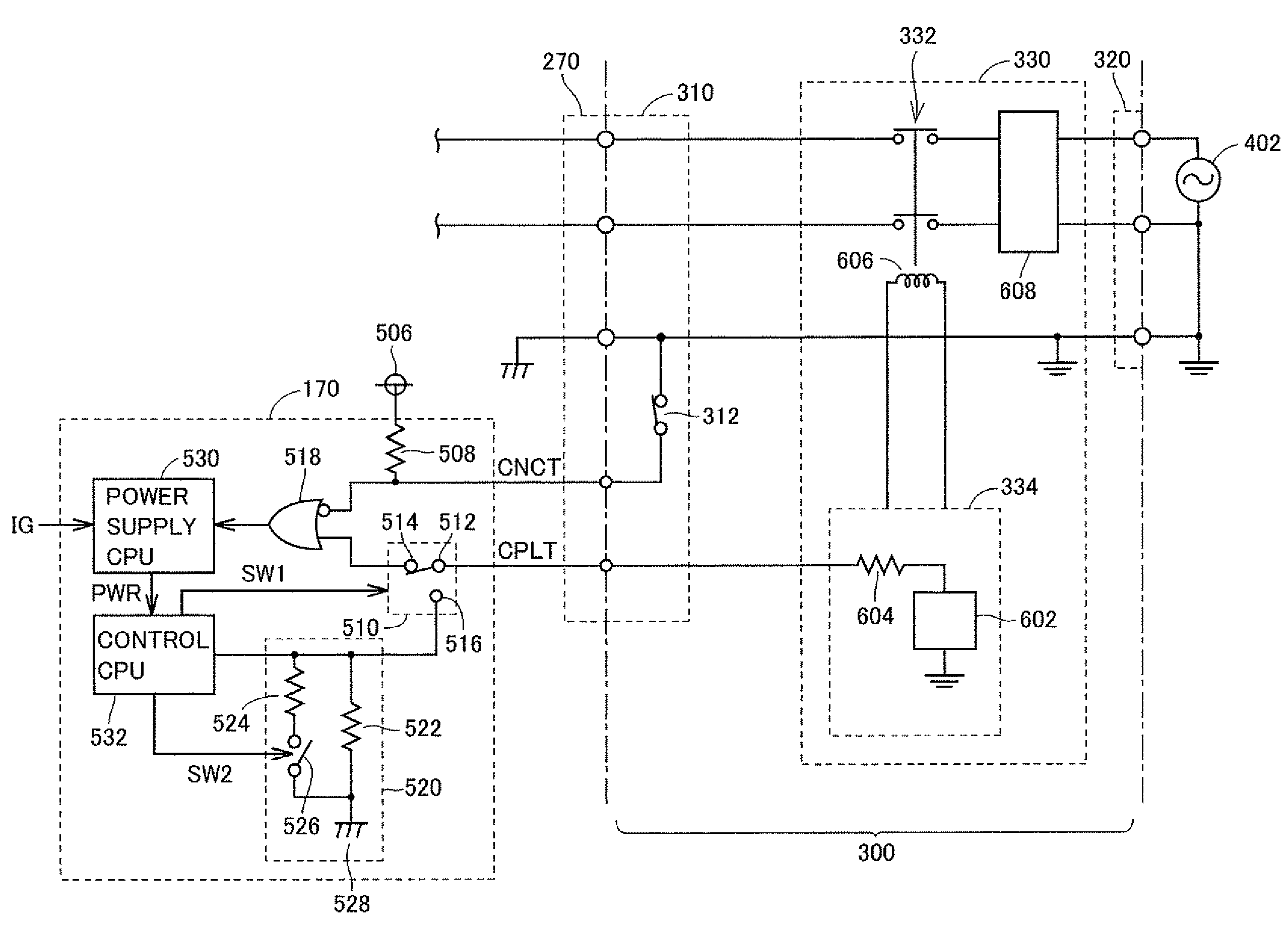
Until a vehicle system is activated, a switching circuit outputs a pilot signal to an OR circuit. As a result, lowering of the potential of the pilot signal caused by a resistance circuit is avoided, and the pilot signal is provided in a non-pulsed manner. A power supply CPU is activated in accordance with any one of a connector signal and the non-pulsed pilot signal. When the vehicle system is activated, the switching circuit switches an output destination of the pilot signal to the resistance circuit.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
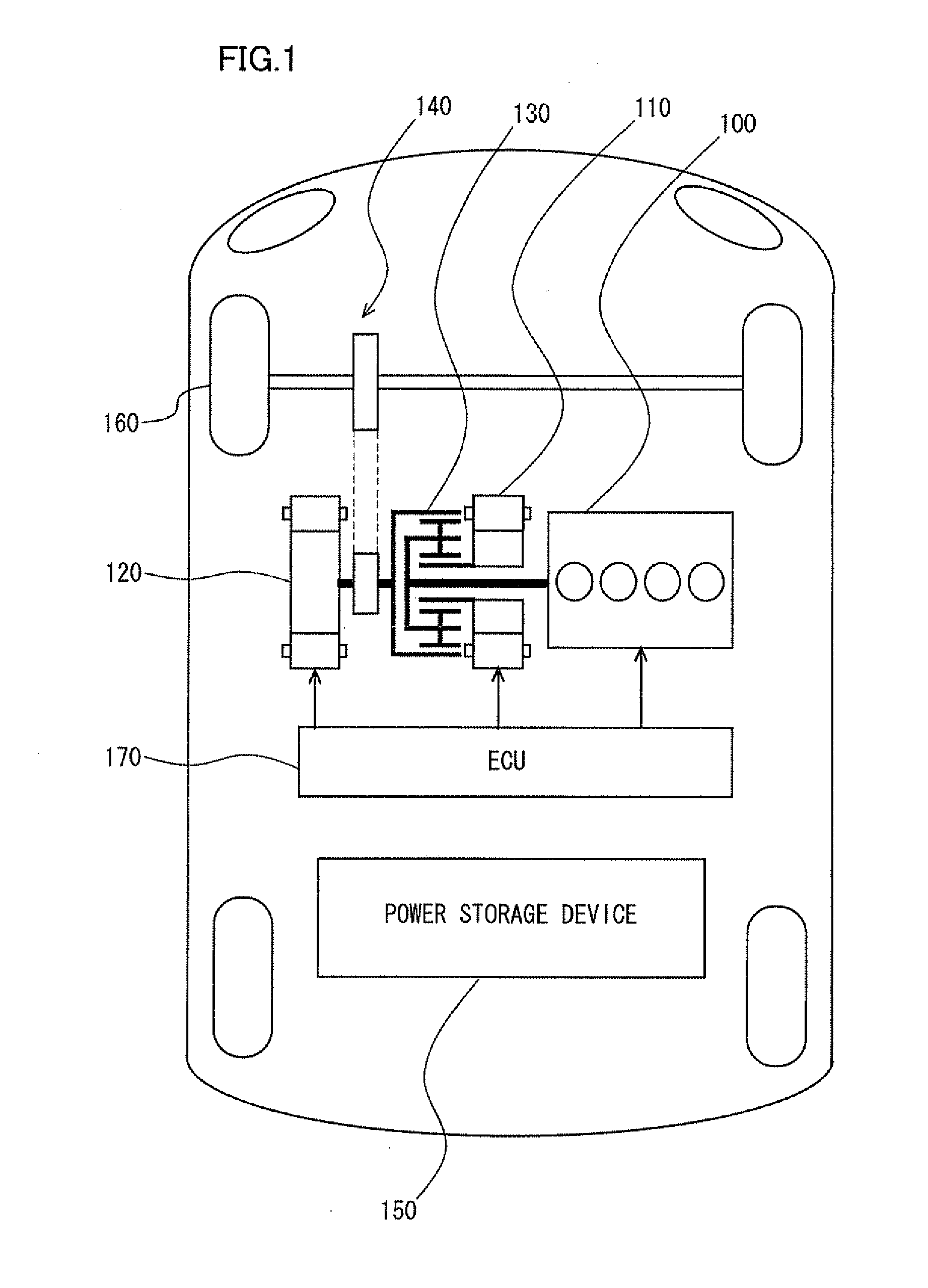
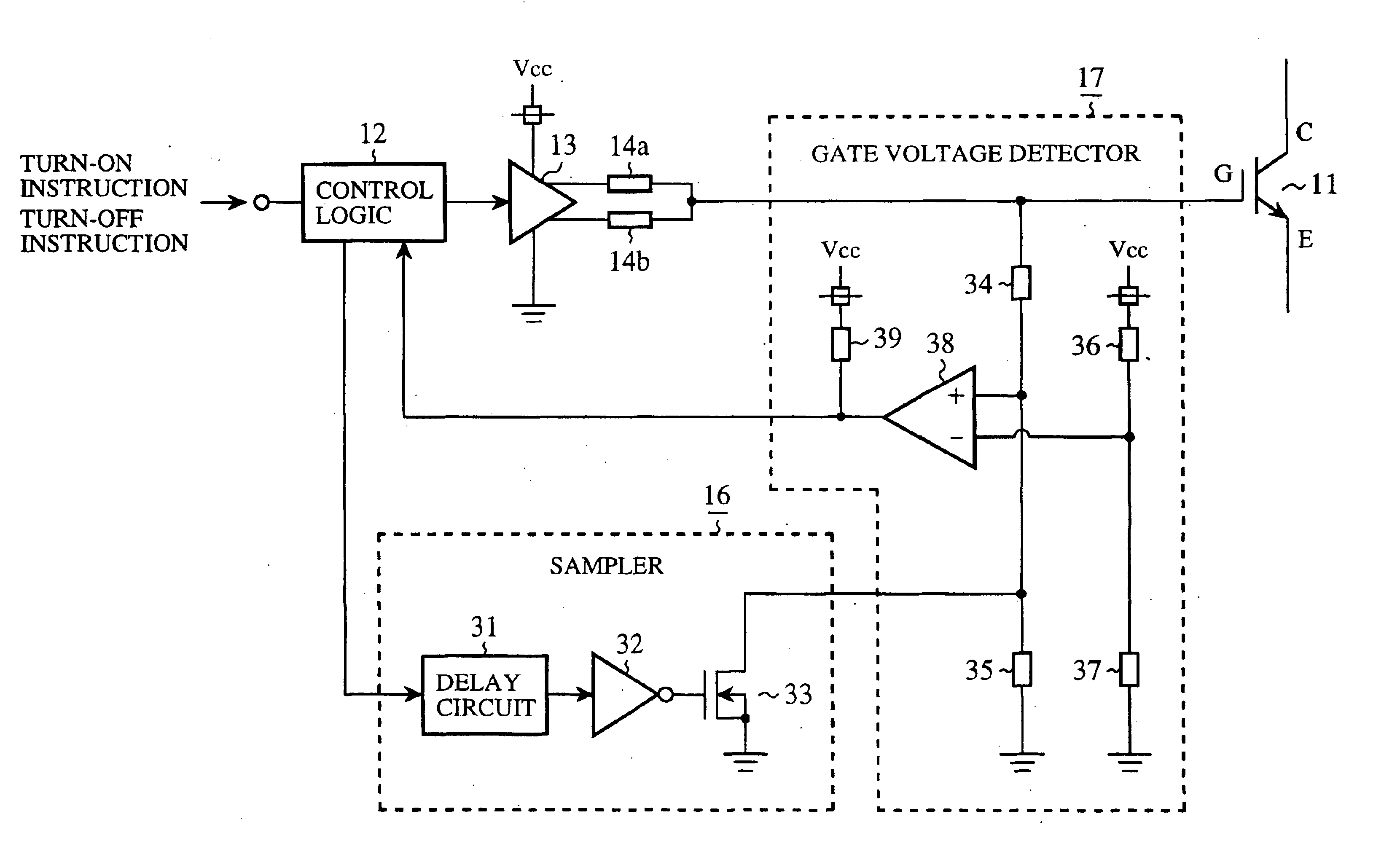
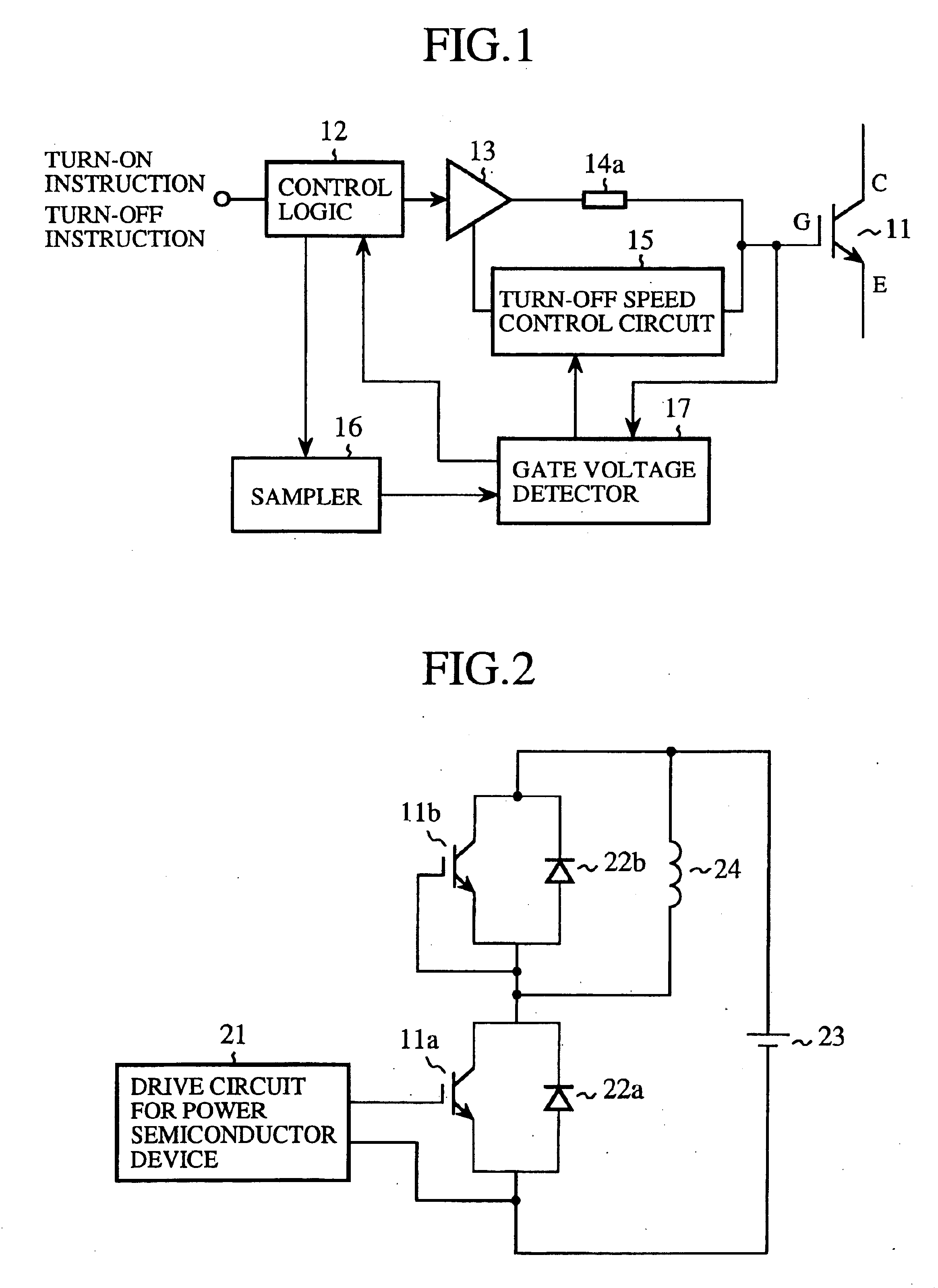
Drive circuit for driving power semiconductor device
InactiveUS6906574B2Easy to detectImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceDriver circuit
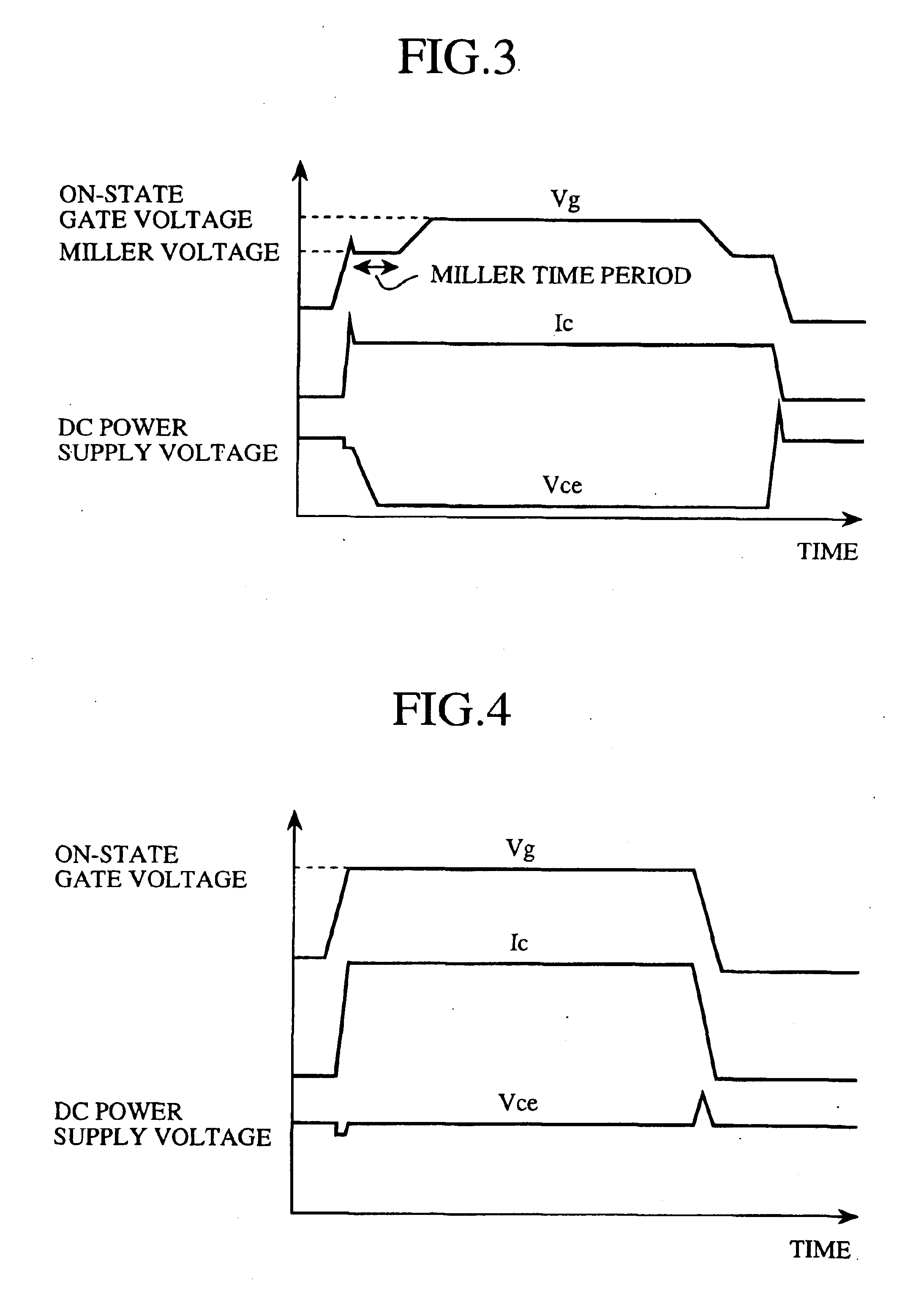
A drive circuit includes a gate voltage detector that detects a gate-emitter voltage Vge that appears between the gate and emitter of a power semiconductor device throughout a detection time period during which a sampler allows the process of detecting the gate-emitter voltage Vge, and that recognizes the occurrence of an abnormality in the power semiconductor device when the gate-emitter voltage Vge exceeds a reference value. Therefore, the drive circuit can protect the power semiconductor device with higher reliability by promptly detecting the occurrence of a short circuit even when the power semiconductor device is resistant to high voltages.
Owner:NEXGEN CONTROL SYST LLC
Photovoltaic Device Characterization Apparatus
InactiveUS20090000659A1Improve accuracyDetected as abnormalityPhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringVoltage
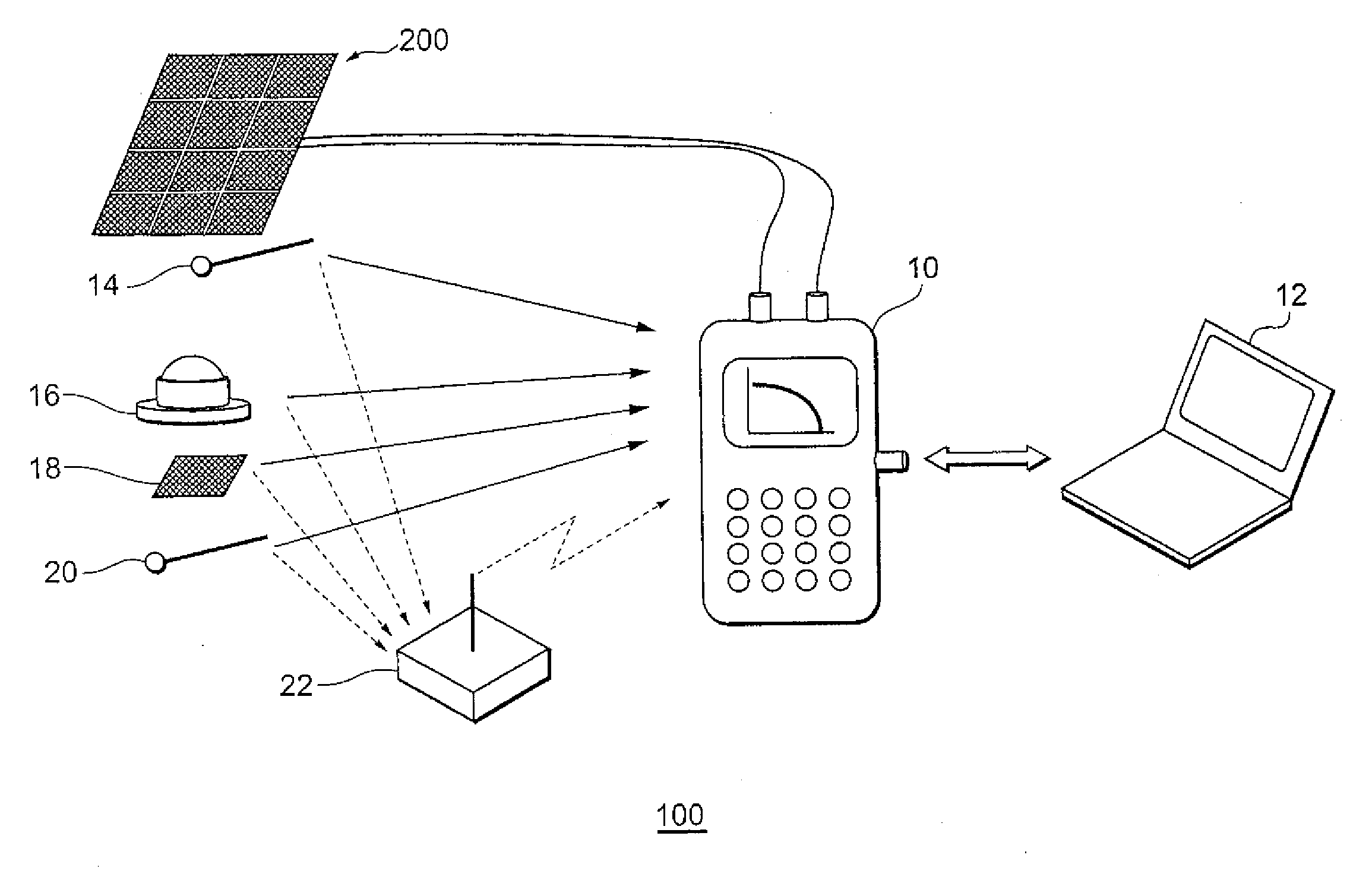
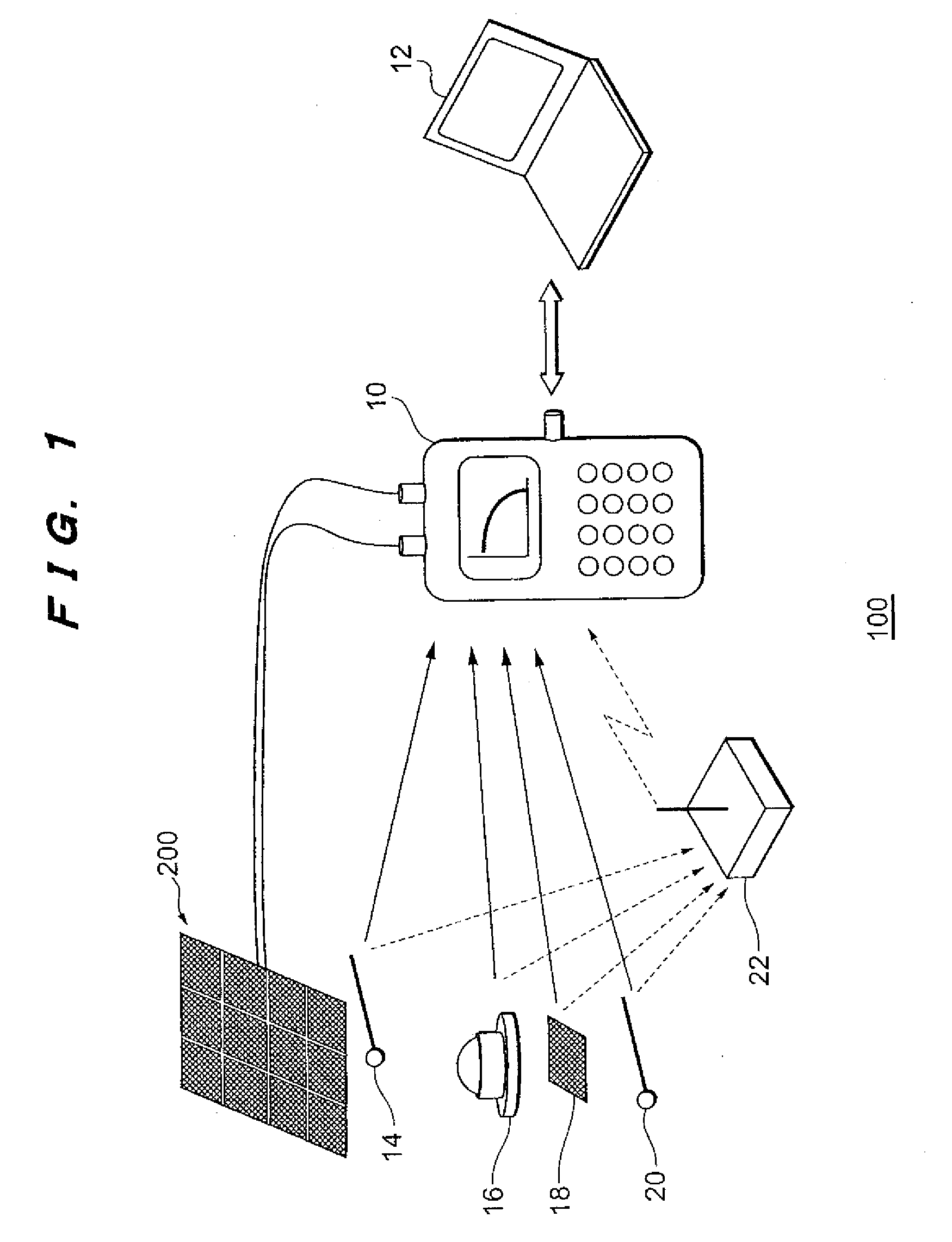
The objective is to perform a more detailed failure diagnosis of a photovoltaic device. Provided is a photovoltaic device characterization apparatus including a measurement unit (30, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46, 48, 50) for measuring current-voltage characteristic of a photovoltaic device, a conversion unit (30) for converting the current-voltage characteristic measured with the measurement unit into a prescribed reference condition, a memory (52) for storing a plurality of reference characteristics, and a determination unit (30) for comparing the current-voltage characteristic converted into the reference condition and the reference characteristics read from the memory, and determining to which one of the reference characteristics the current-voltage characteristic is closest.
Owner:EKO INSTR
Apparatus and method for activating system of vehicle
InactiveUS8301322B2Reliably activatedDetected as abnormalityBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringVIT signals
Until a vehicle system is activated, a switching circuit outputs a pilot signal to an OR circuit. As a result, lowering of the potential of the pilot signal caused by a resistance circuit is avoided, and the pilot signal is provided in a non-pulsed manner. A power supply CPU is activated in accordance with any one of a connector signal and the non-pulsed pilot signal. When the vehicle system is activated, the switching circuit switches an output destination of the pilot signal to the resistance circuit.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and device for detecting particulate matter contained in a gas to be measured
ActiveUS8860439B2Improve reliabilityImprove detection accuracyInternal combustion piston enginesResistance/reactance/impedenceParticulatesCapacitance
A particulate matter detection element includes a capacitance component disposed in parallel with a detected resistance RSEN. A direct current-power source that supplies a direct current (IDC) for particulate matter detection, and an alternating-current power source that supplies an alternating current (IAC) for disconnection detection are provided.
Owner:DENSO CORP
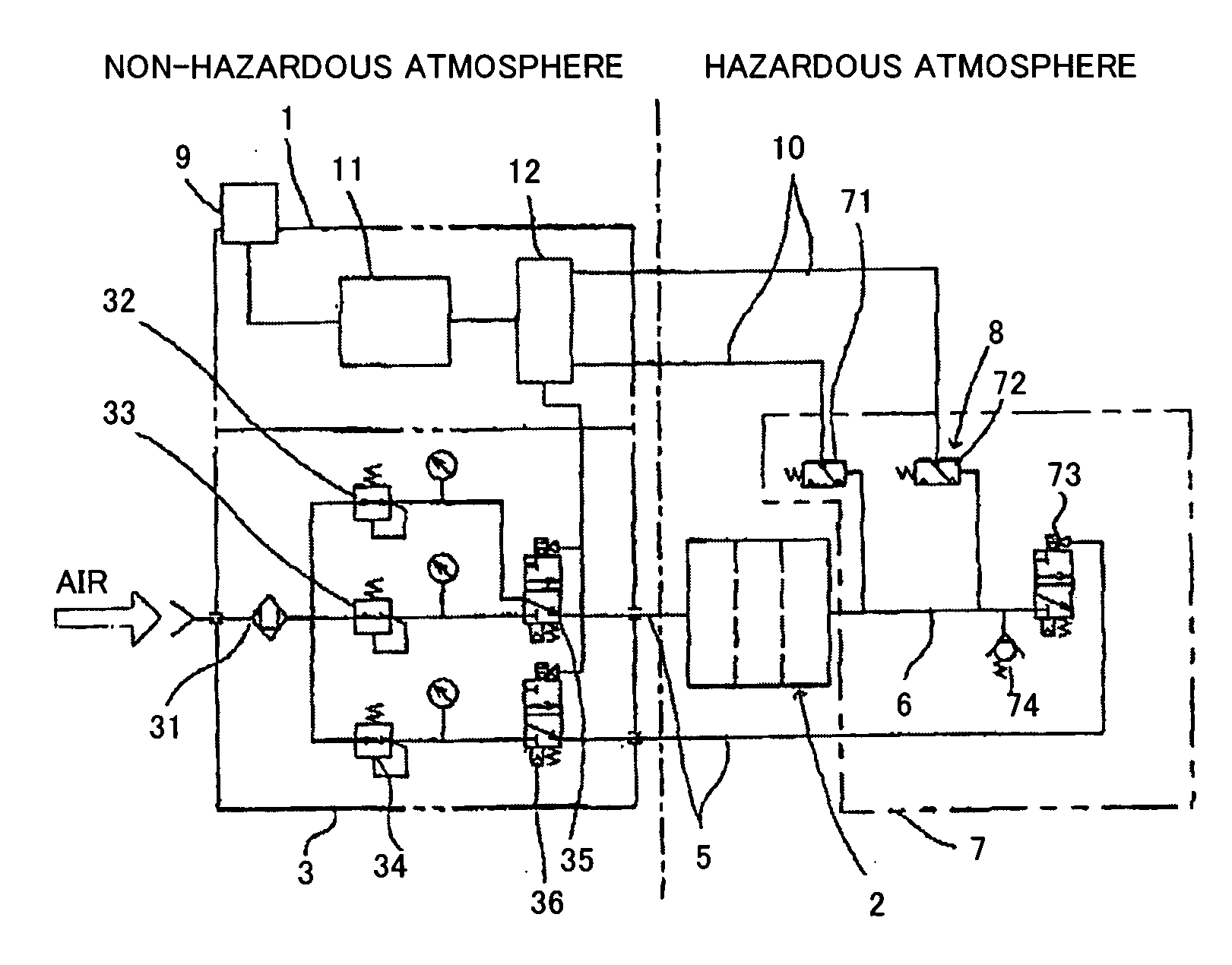
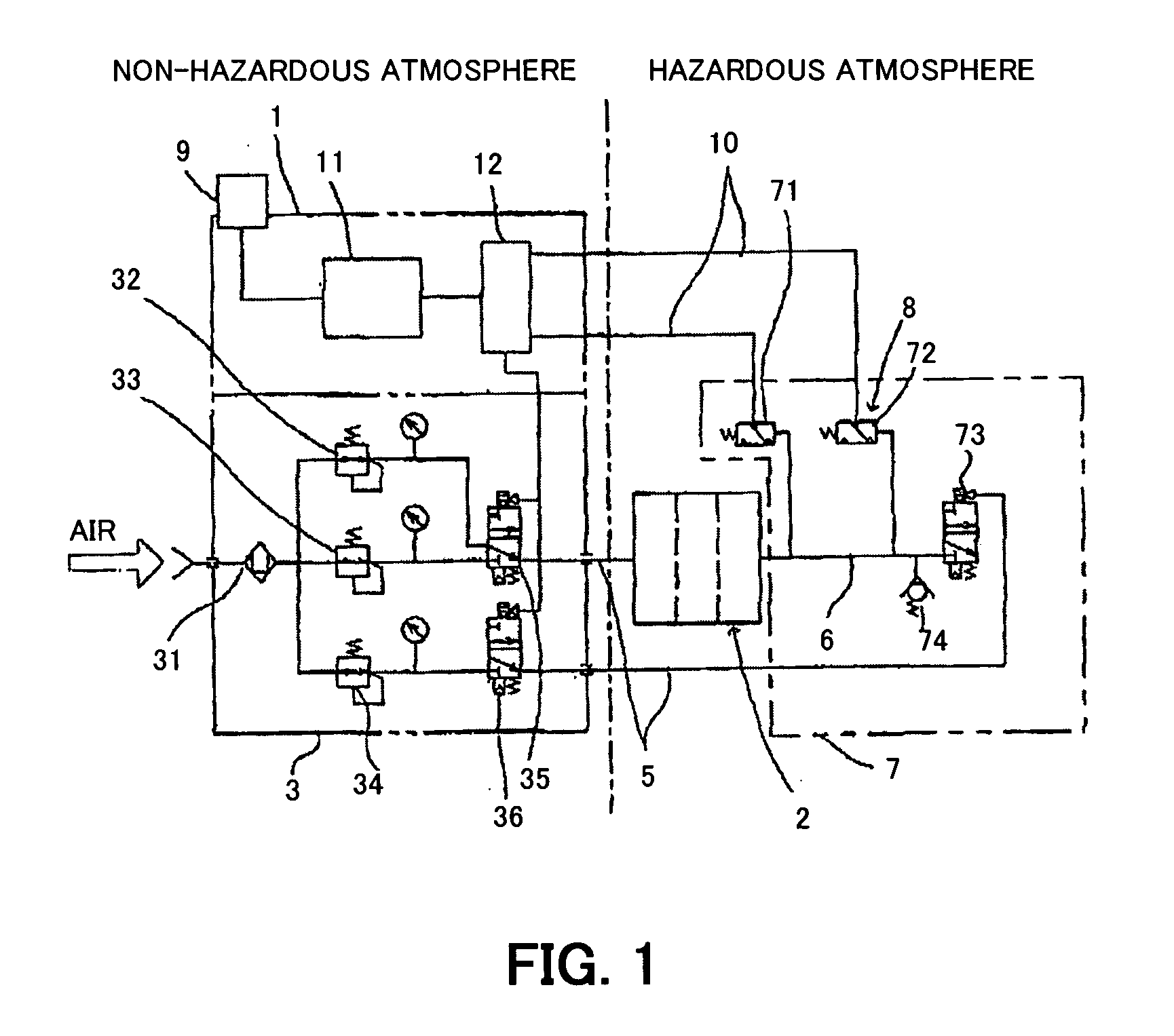
Internal pressure explosion-proof system
InactiveUS20060250025A1Guaranteed uptimeExcessive internal pressureBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsInternal pressureWorking pressure
An internal pressure explosion-proof system is provided that is capable of detecting high-pressure abnormality of an internal pressure explosion-proof mechanism, urging a check of gas / air apparatus by providing a means for notifying a user of abnormality, and decreasing excessive pressure of an internal pressure chamber. A high-pressure abnormality detector and a pressure regulating valve are provided in an air discharging portion for releasing the gas / air discharged from the internal pressure explosion-proof mechanism. The working pressure of the high-pressure abnormality detector is set to be lower than the working pressure of the pressure regulating valve. The high-pressure abnormality detector sends a signal when the pressure becomes higher than the set pressure to make the alarm give a warning and makes the open valves open to decrease the pressure of the internal pressure chamber of the internal pressure explosion-proof mechanism which became excessive.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
Method and device for detecting particulate matter contained in a gas to be measured
ActiveUS20120103059A1Improve reliabilityImprove detection accuracyInternal-combustion engine testingInternal combustion piston enginesCapacitanceParticulates
A particulate matter detection element includes a capacitance component disposed in parallel with a detected resistance RSEN. A direct current-power source that supplies a direct current (IDC) for particulate matter detection, and an alternating-current power source that supplies an alternating current (IAC) for disconnection detection are provided.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Diagnostic apparatus for vehicle cooling system
InactiveUS20100067560A1Detected as abnormalityEasy to installThermometer detailsInternal-combustion engine testingEngineeringTemperature difference
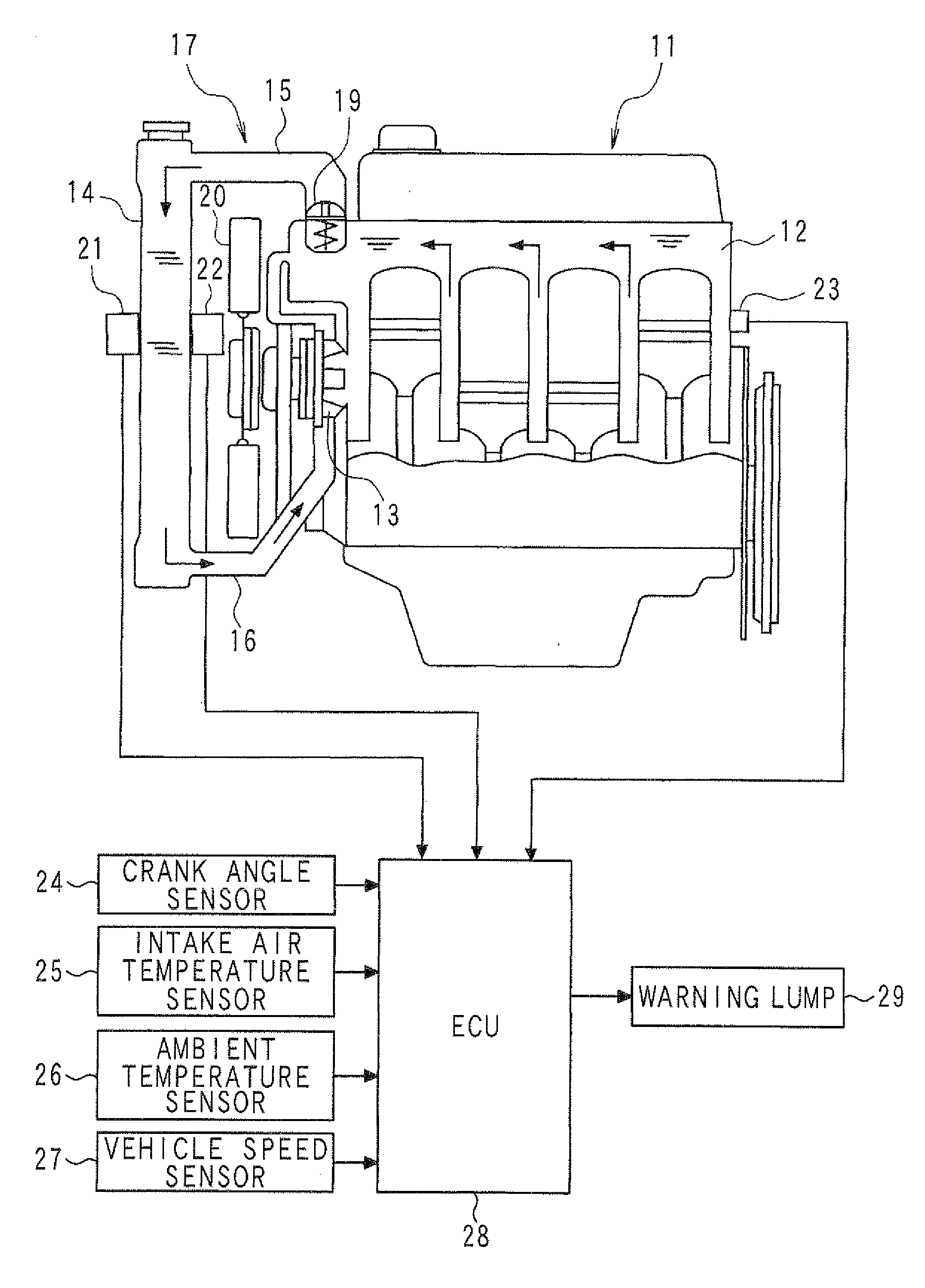
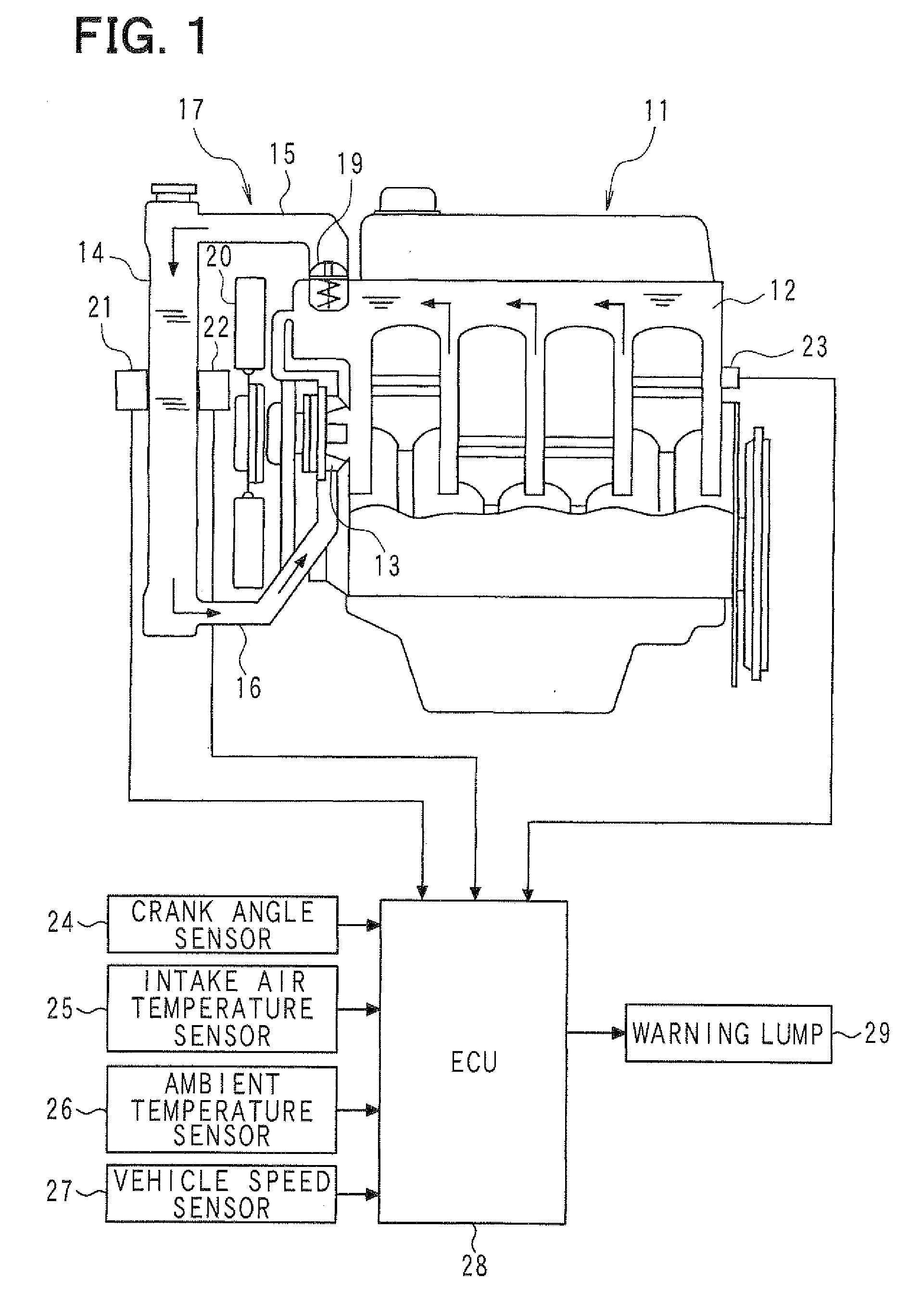
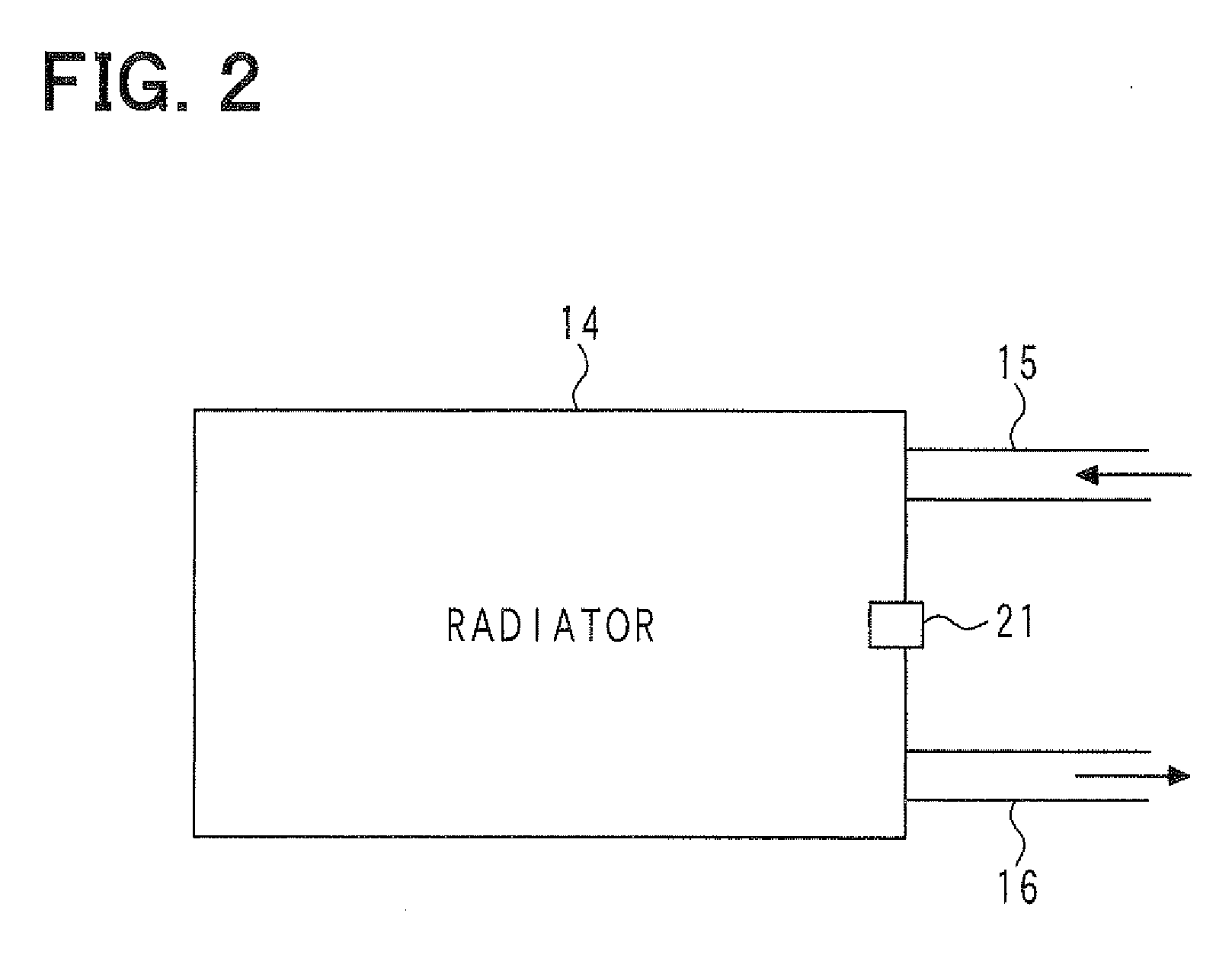
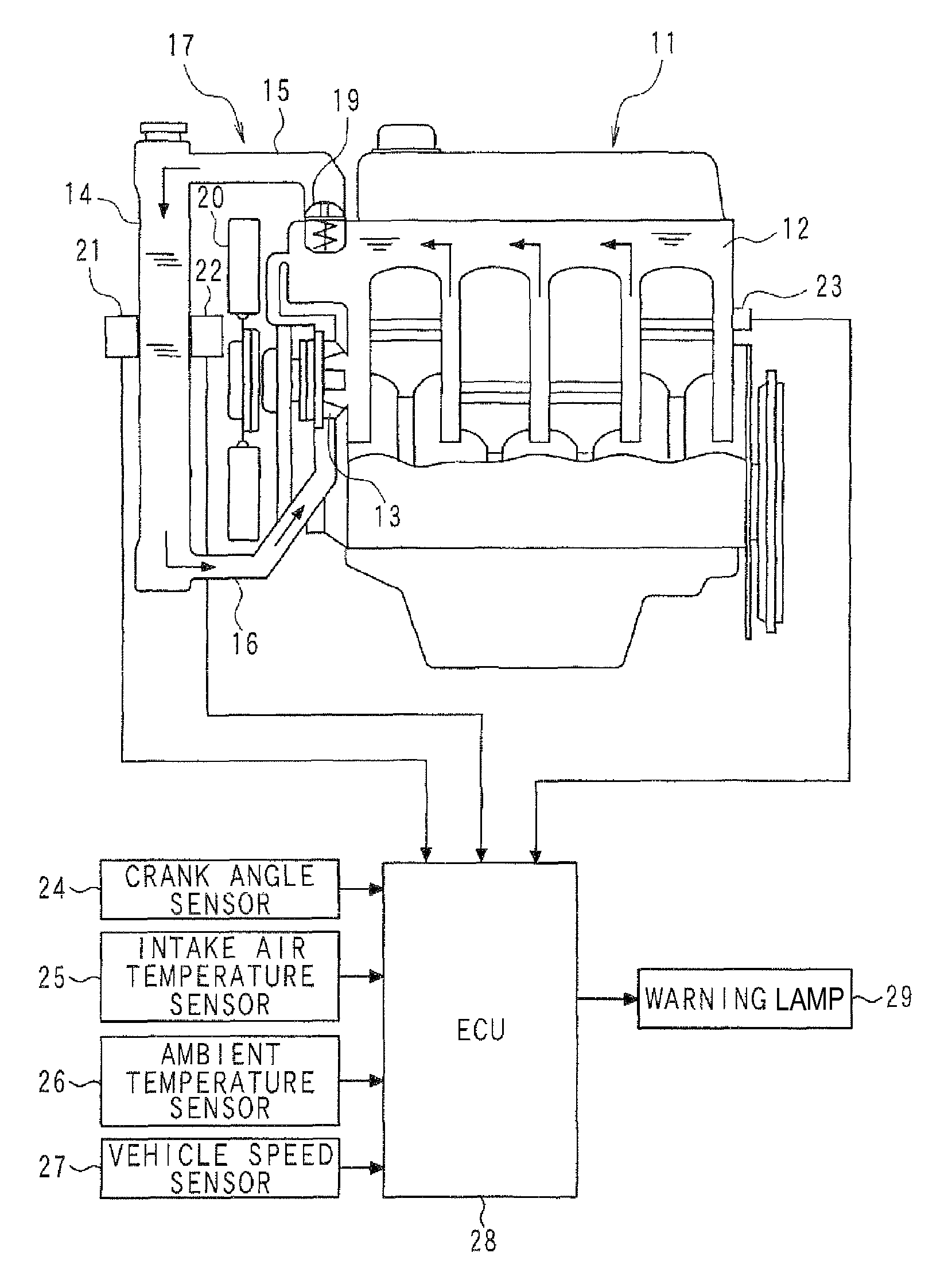
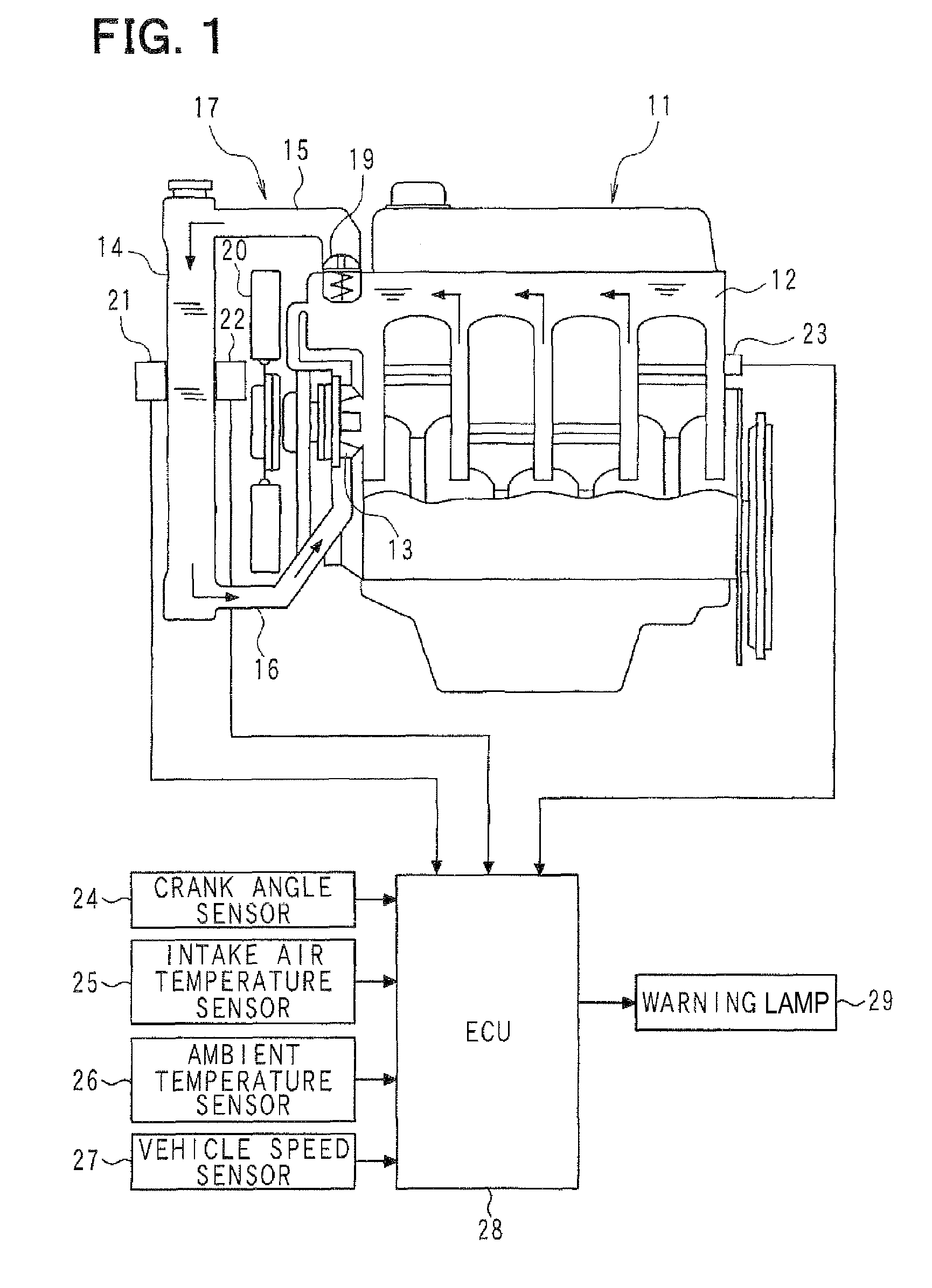
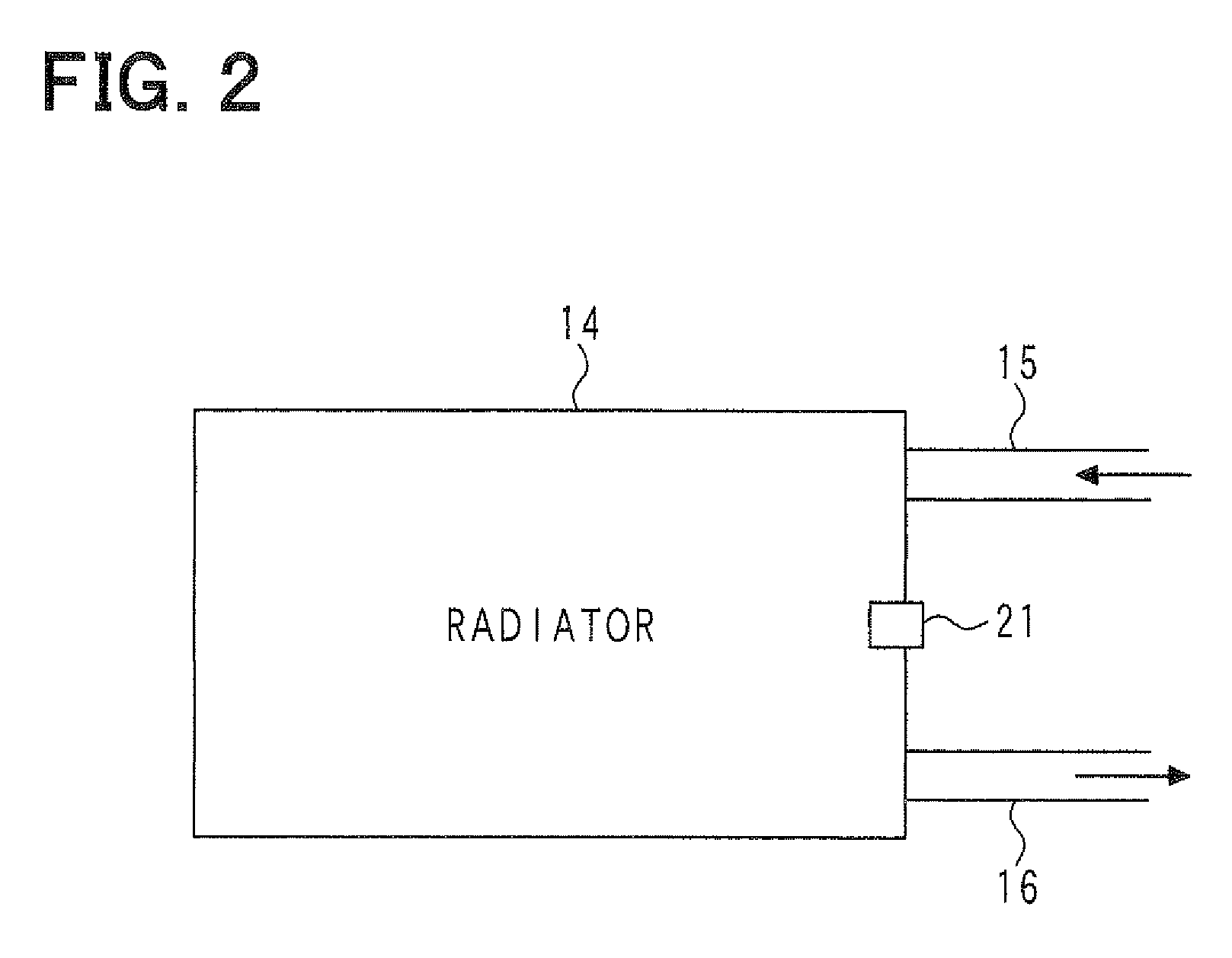
When the driving wind and the cooling wind are generated, based on the phenomenon in which the temperature difference is generated between the front surface and the rear surface of the radiator (14), the temperature difference between the detection value of the rear temperature sensor (22) and the detection value of the front temperature sensor (21) is compared with the abnormality determination value so that it is determined whether the front temperature sensor (21) and the rear temperature sensor (22) are properly fixed on the radiator (14), whereby it is determined whether the abnormality (unauthorized alteration) exists. By setting the abnormality determination value according to the ambient temperature and the vehicle speed, corresponding to a variation in temperature difference between the front surface and the rear surface of the radiator (14), the abnormality determination value is varied to be set at a proper value.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Control apparatus and method for a vehicle having idle stop function
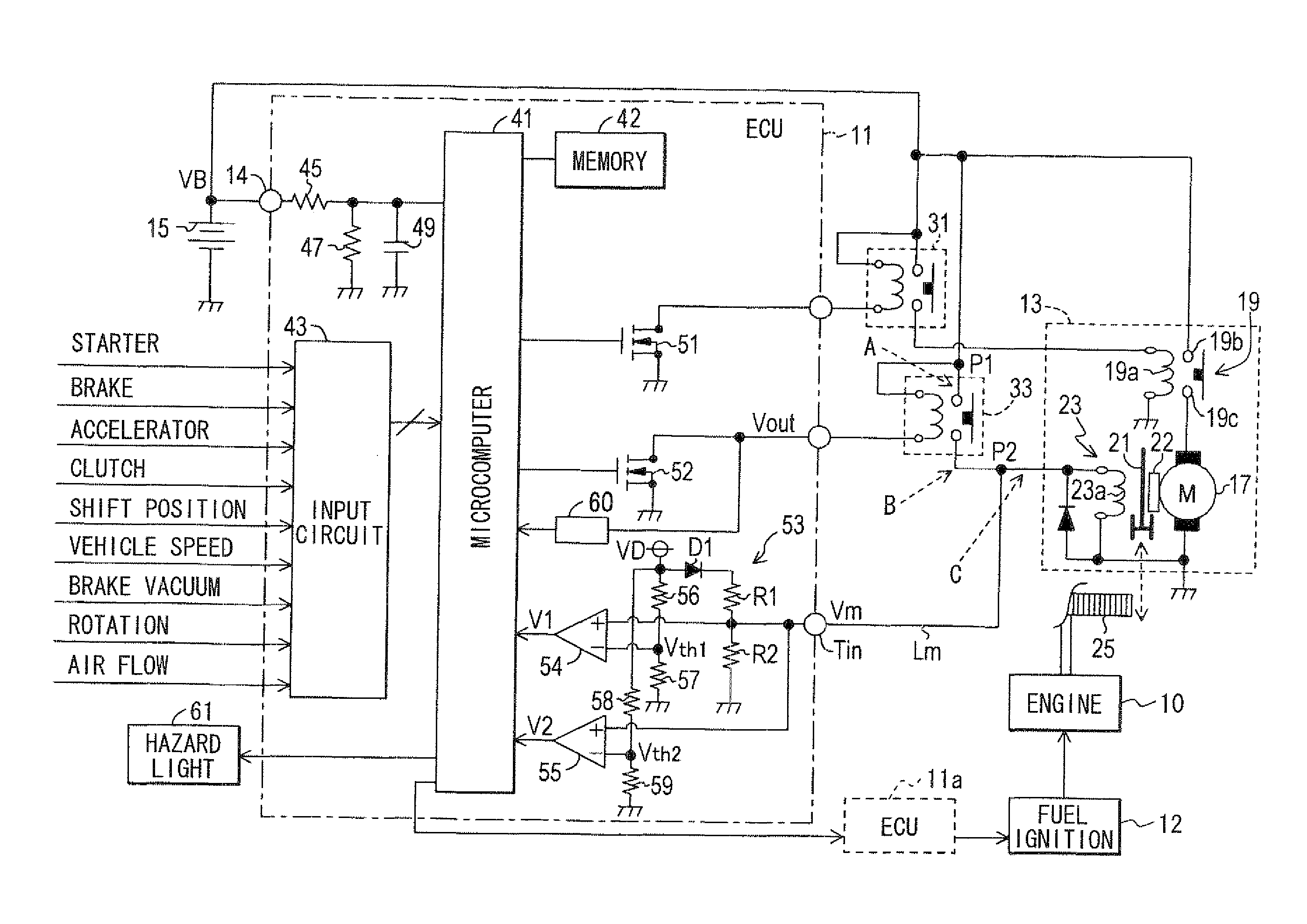
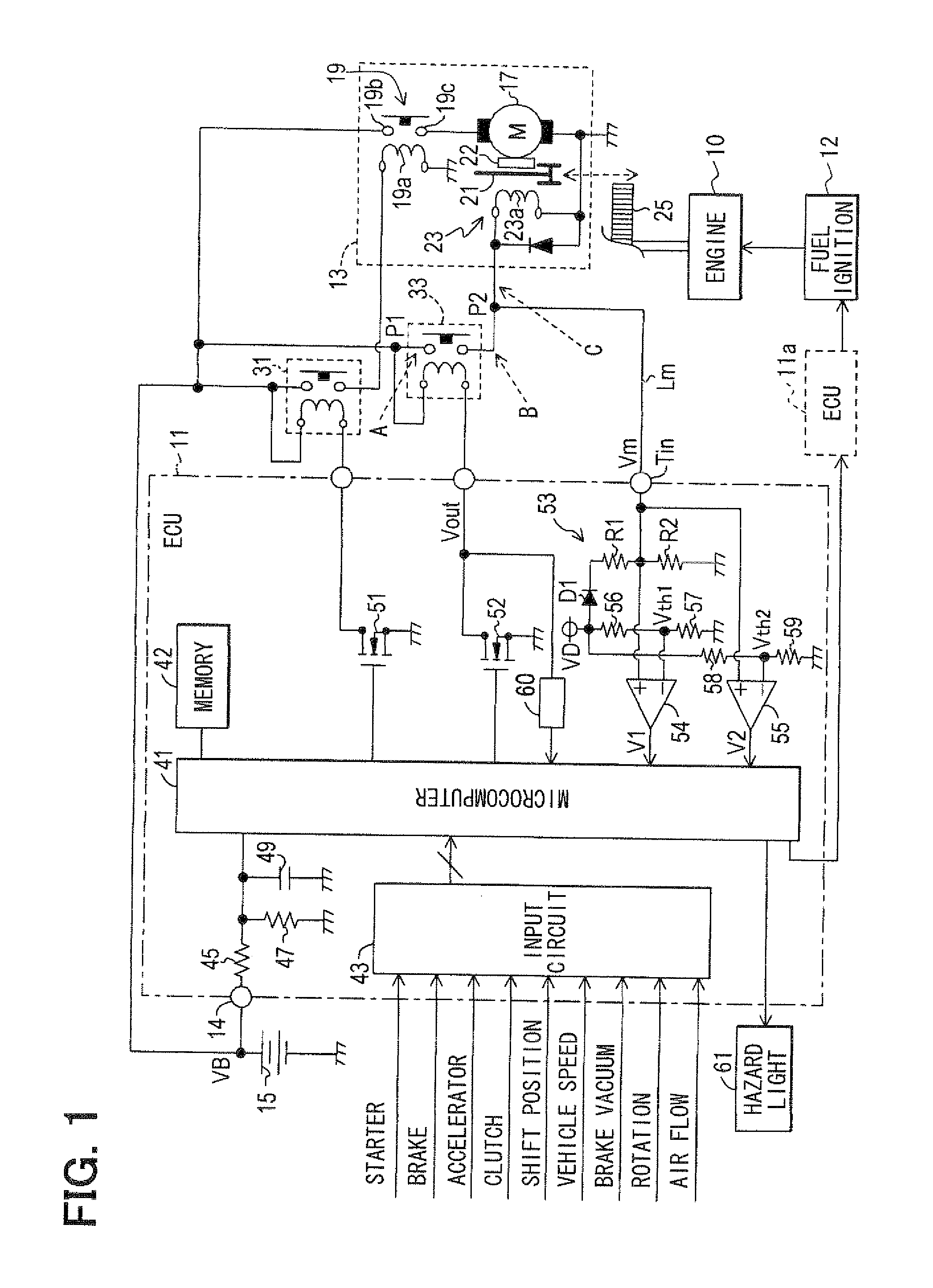
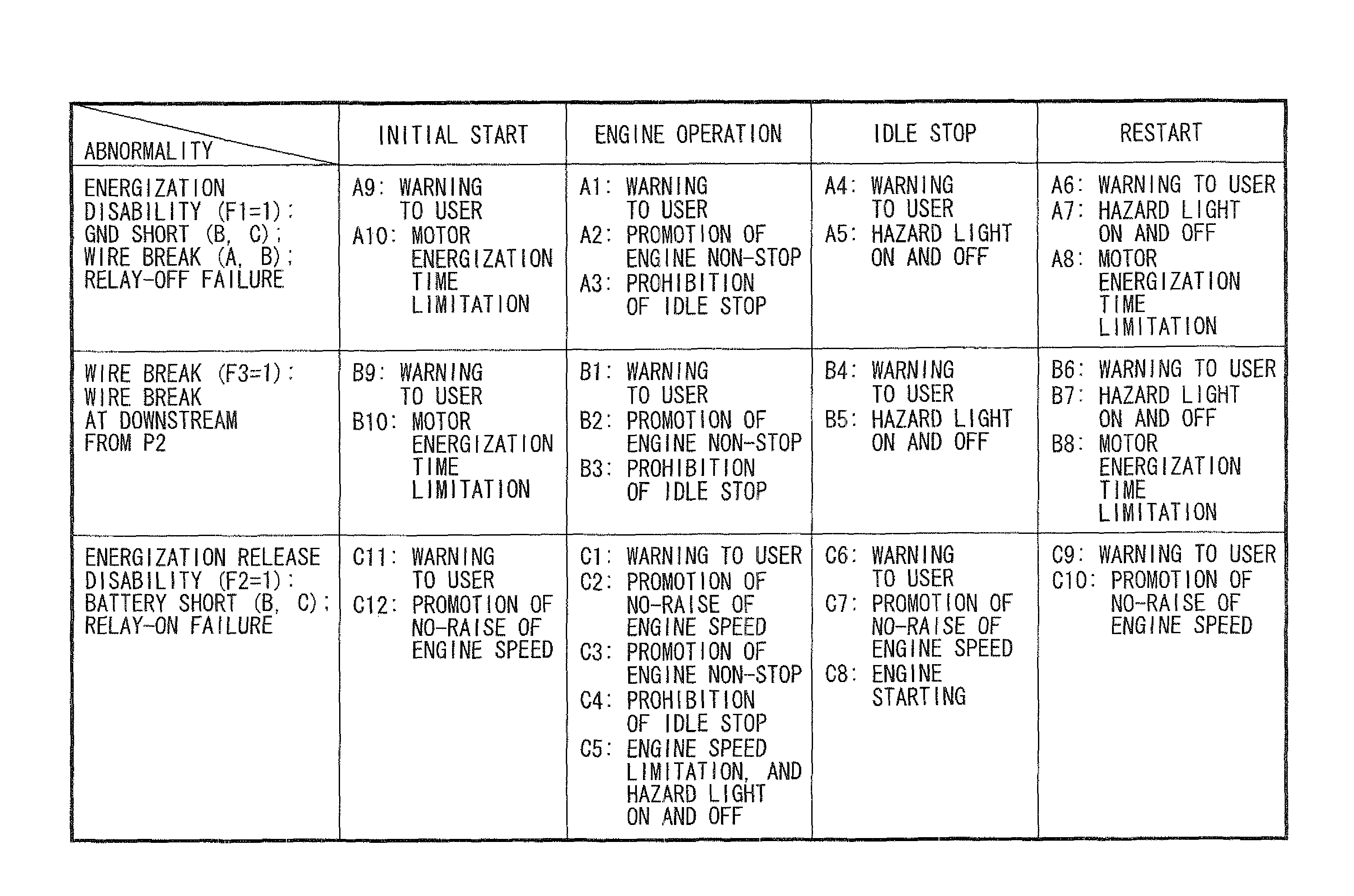
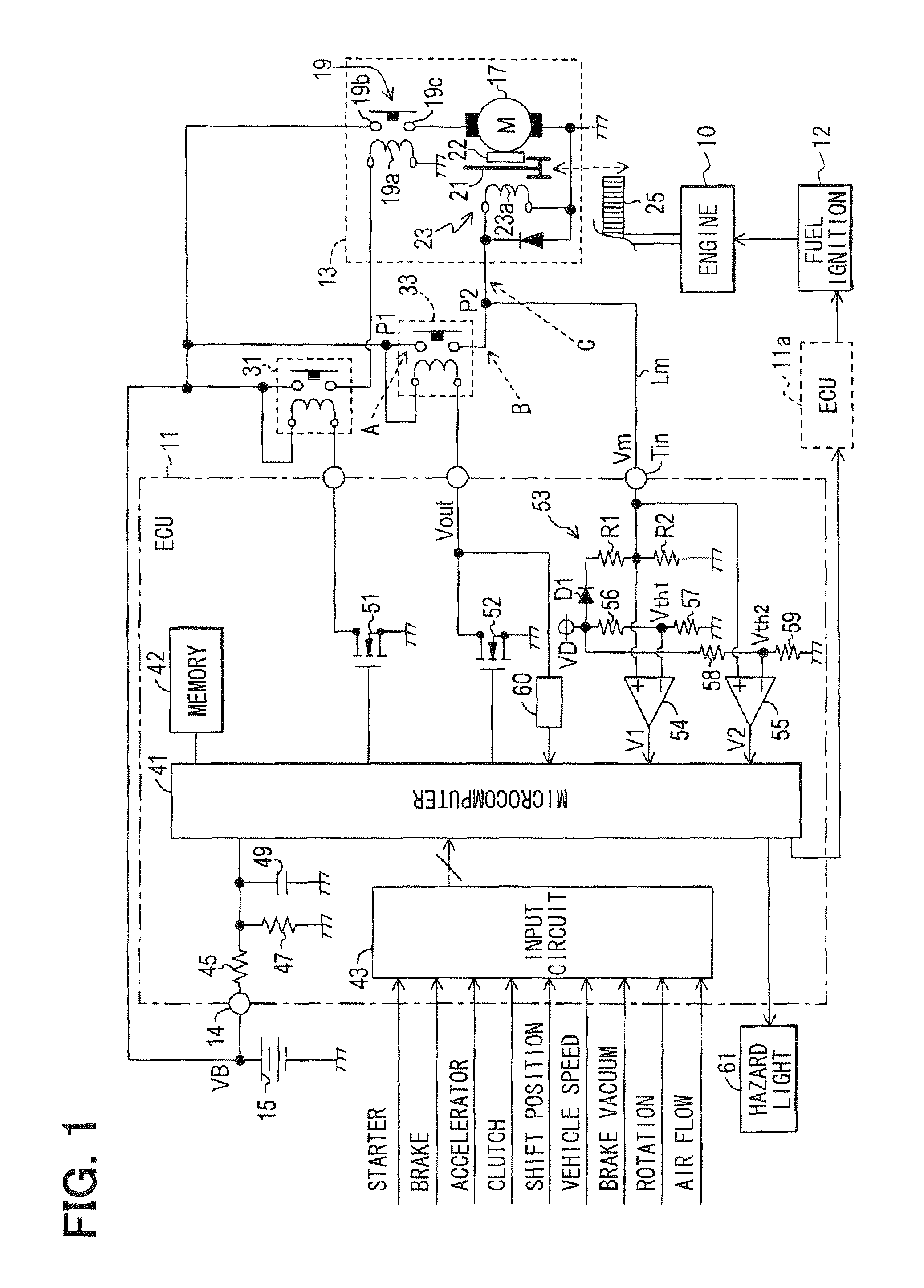
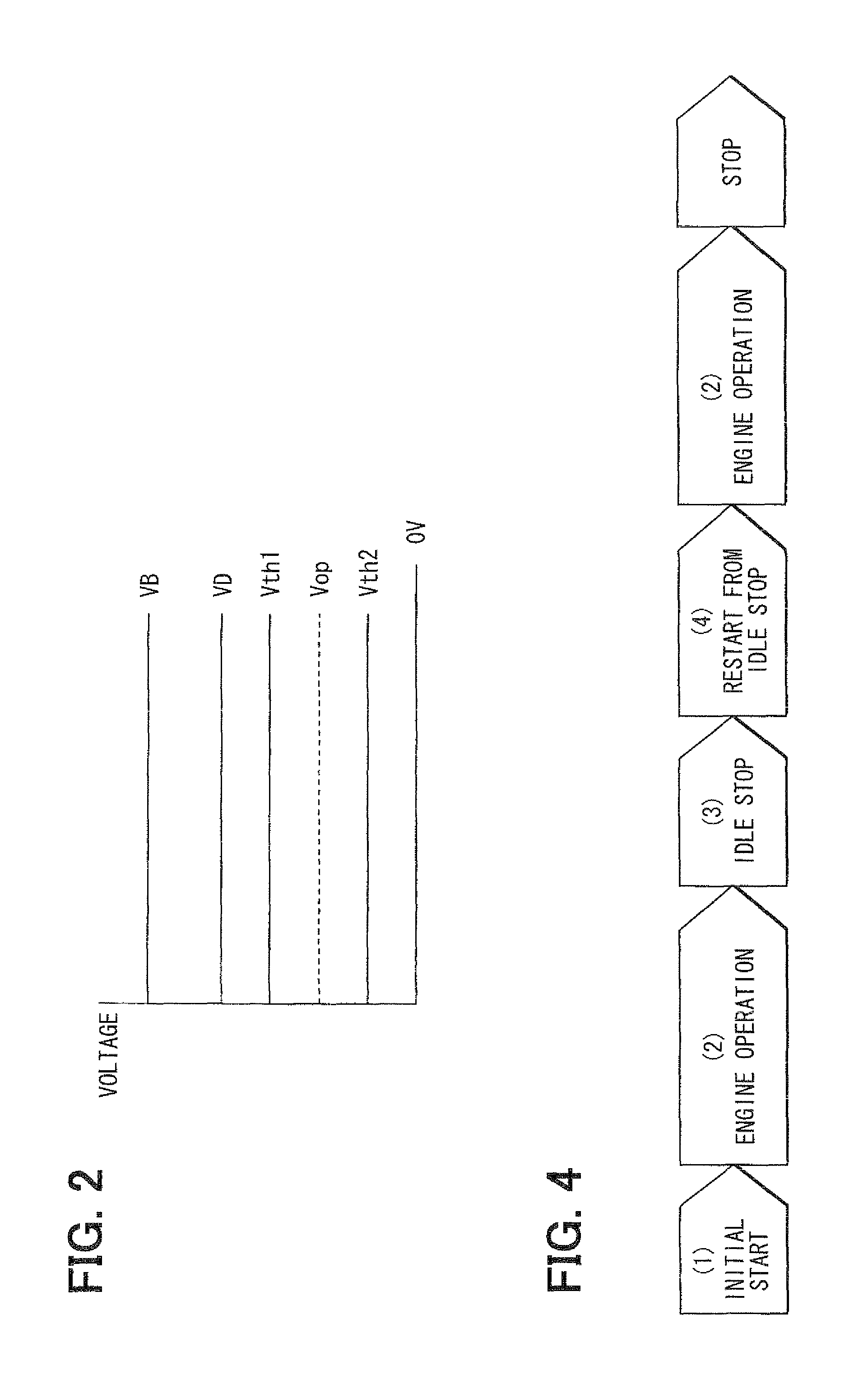
ActiveUS20110213525A1Simple configurationDetected as abnormalityVehicle testingPower operated startersVoltageEngineering
In an idle stop vehicle, a starter has separately an electromagnetic switch for energizing a motor and a pinion control solenoid for engaging a pinion gear with a ring gear. A coil of the solenoid is energized by a battery through a relay. For starting an engine, an ECU turns on the relay and the electromagnetic switch so that the starter cranks an engine. During engine operation, the ECU turns on only the relay while maintaining turn-off of the electromagnetic switch. If a voltage of a current supply path between the relay and the coil is lower than a predetermined threshold value, the ECU prohibits automatic idle stop by determining that the current supply path to the coil has abnormality.
Owner:DENSO CORP
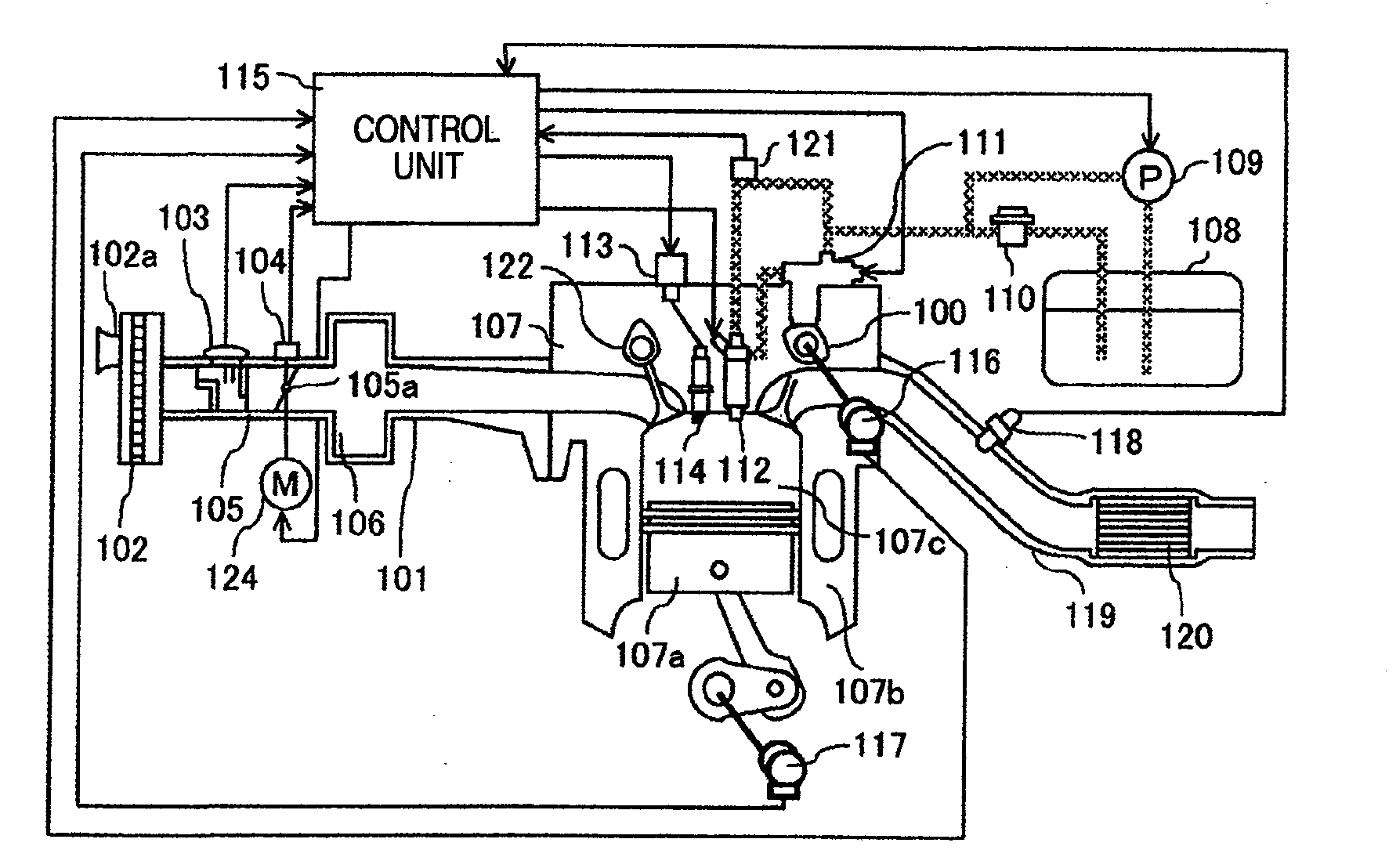
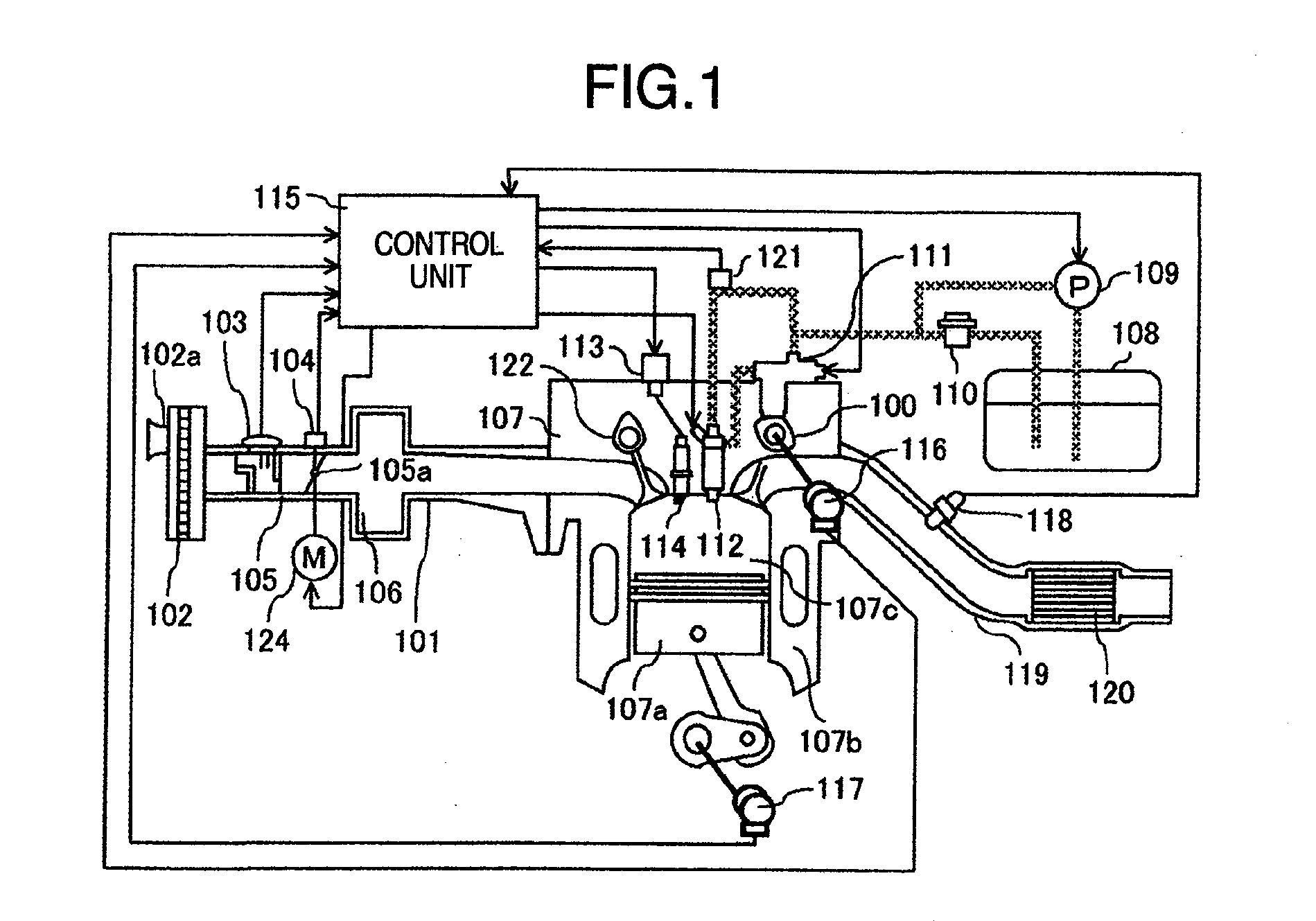
Diagnosis Apparatus for Internal Combustion Engine
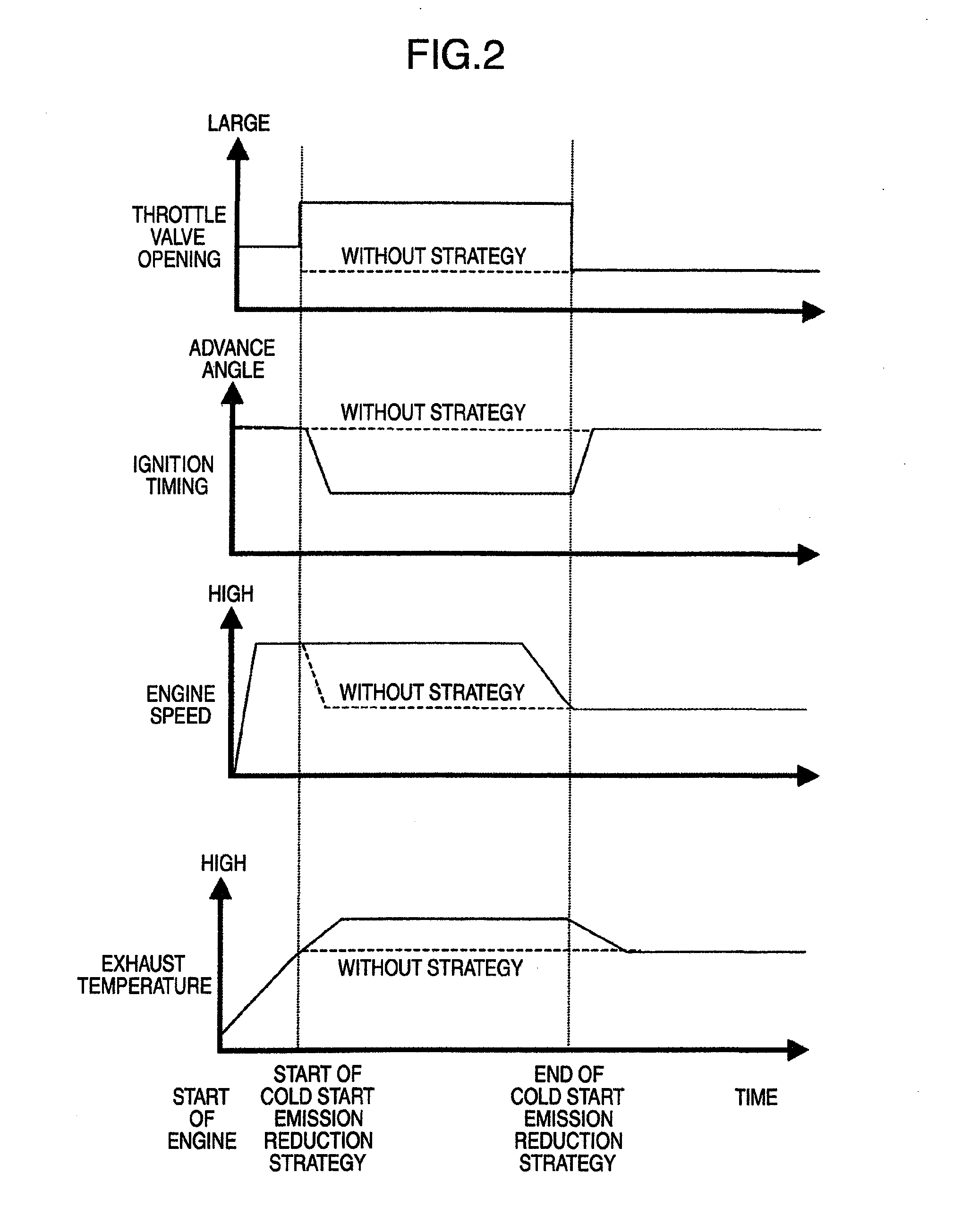
InactiveUS20090265086A1Detect abnormalityDetected as abnormalityAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A diagnosis apparatus for an internal combustion engine equipped with a cold start emission reduction strategy unit, includes: a temperature measuring unit for detecting a temperature of coolant of the internal combustion engine; a temperature estimating unit for calculating an estimated temperature of the coolant in accordance with a running state of the internal combustion engine; and a cold start emission reduction strategy abnormality judging unit for judging abnormality of the cold start emission reduction strategy unit in accordance with the temperature detected with the coolant temperature measuring means and the estimated temperature.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Abnormality detector for a motor drive system
InactiveUS6781341B2Reduce in quantitySimple and inexpensive constitutionDC motor speed/torque controlElectrical controlMotor driveAnomaly detection
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Power monitoring system and electric vehicle
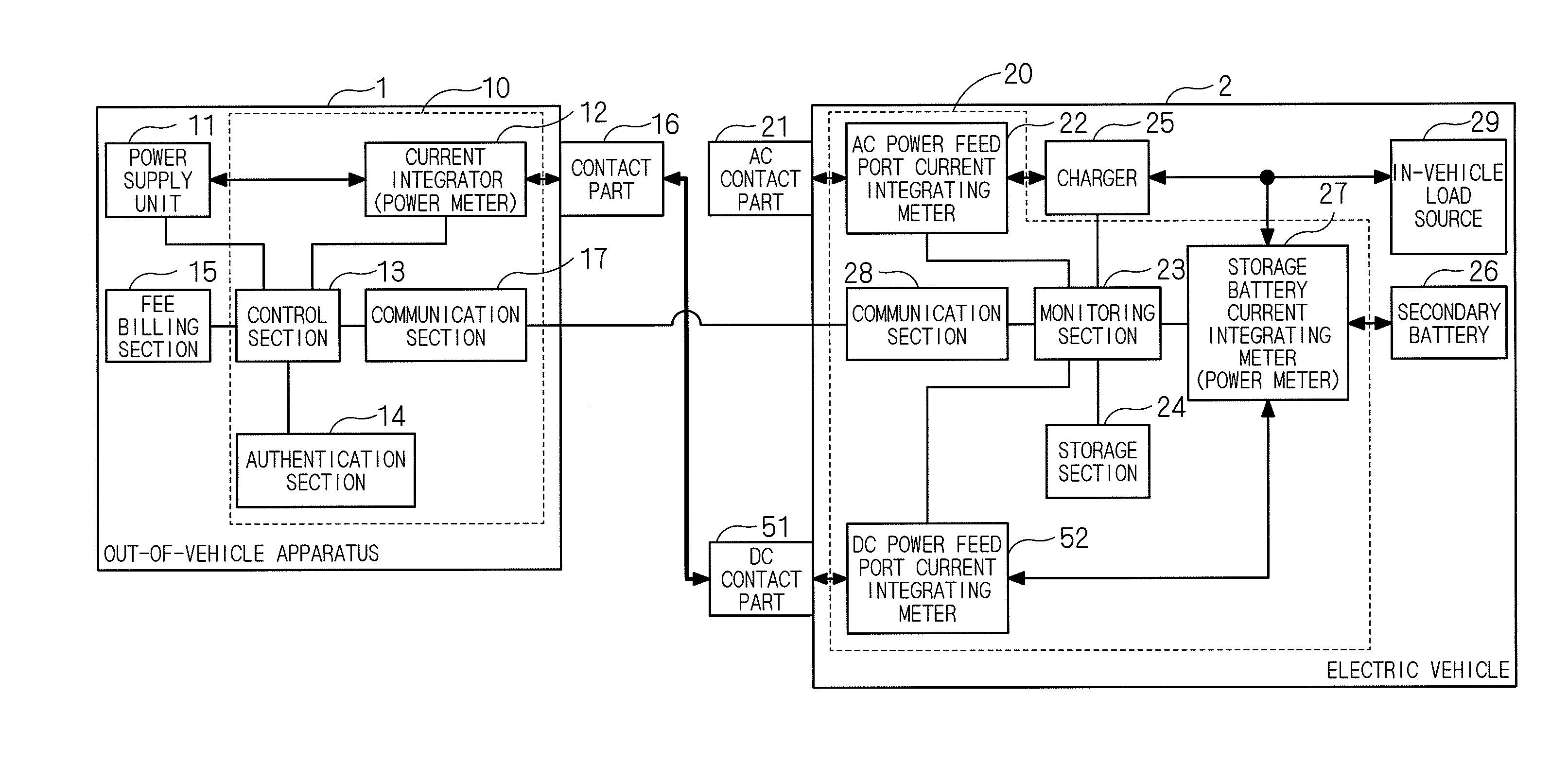
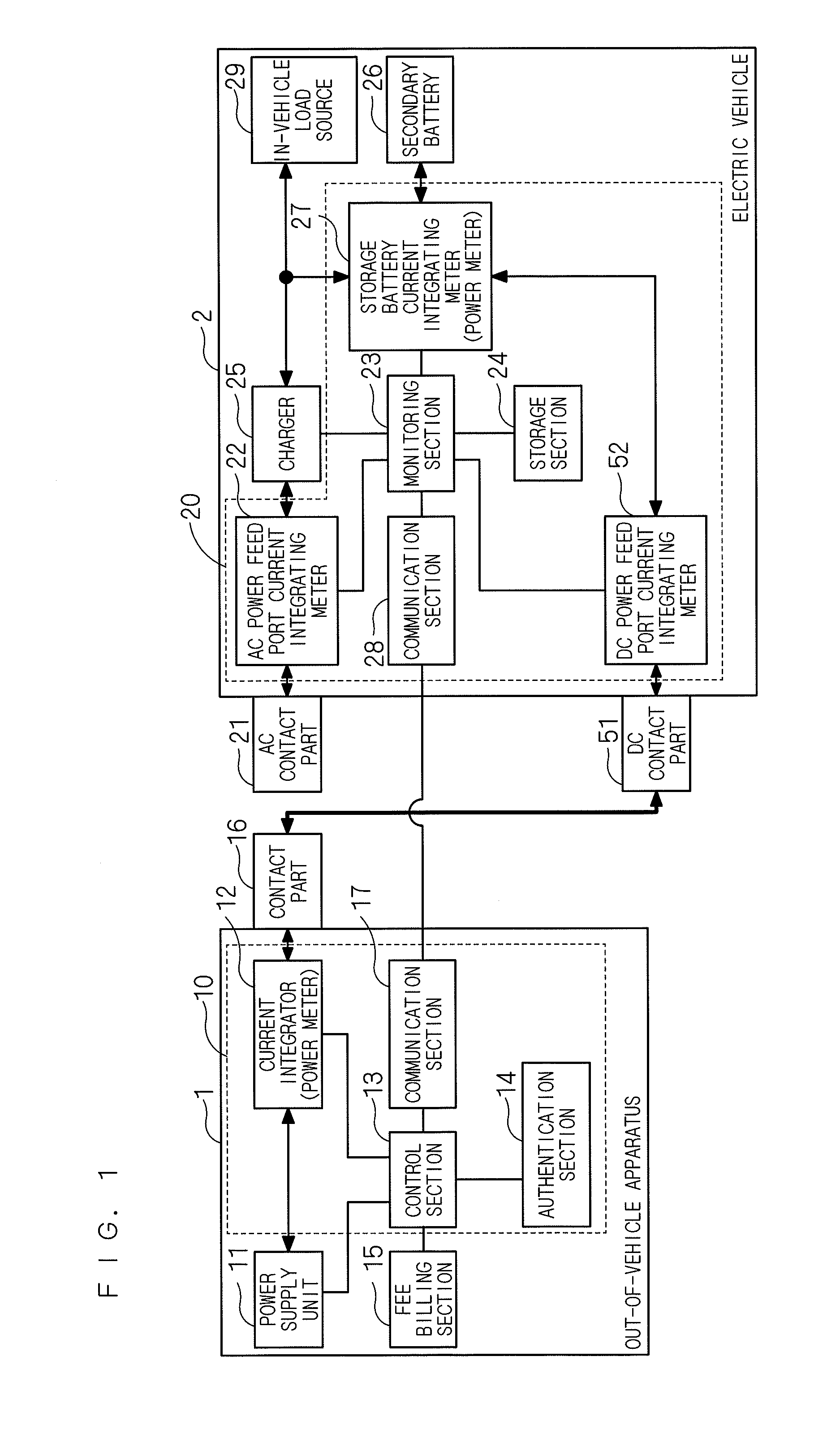
ActiveUS20130311017A1Accurate calculationDetected as abnormalityBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsMeasurement deviceIn vehicle
A power monitoring system includes an in-vehicle system that monitors a power state of a storage battery of an electric vehicle, and an out-of-vehicle system that is mounted on an out-of-vehicle apparatus and monitors power supply to the electric vehicle. The electric vehicle includes a first power feed port for supplying and receiving AC power to and from the out-of-vehicle apparatus, and a second power feed port for supplying and receiving DC power to and from the out-of-vehicle apparatus. The in-vehicle system includes first power feed port power measurement means for measuring a first amount of fed power supplied from the out-of-vehicle apparatus via the first power feed port, second power feed port power measurement means for measuring a second amount of fed power supplied from the out-of-vehicle apparatus via the second power feed port, vehicle side communication means, storage battery power measurement means, and a monitoring section.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Charging control apparatus for vehicle
ActiveUS8258744B2Easy to changeDetected as abnormalityBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectrical resistance and conductanceCharge control
An oscillator provided in a charging cable outputs a non-oscillating signal when the potential of a pilot signal is around V(1), and outputs an oscillating signal when the potential of the pilot signal is lowered to V(2). A pull-down resistance element provided in the plug-in hybrid vehicle is connected between a control pilot line and a vehicle earth, and changes the potential of the pilot signal from V(1) to V(2). A switch is connected in series between the pull-down resistance element and the vehicle earth. When the charging cable is connected to the vehicle, the switch is turned off and the pull-down resistance element is separated from the vehicle earth.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +2
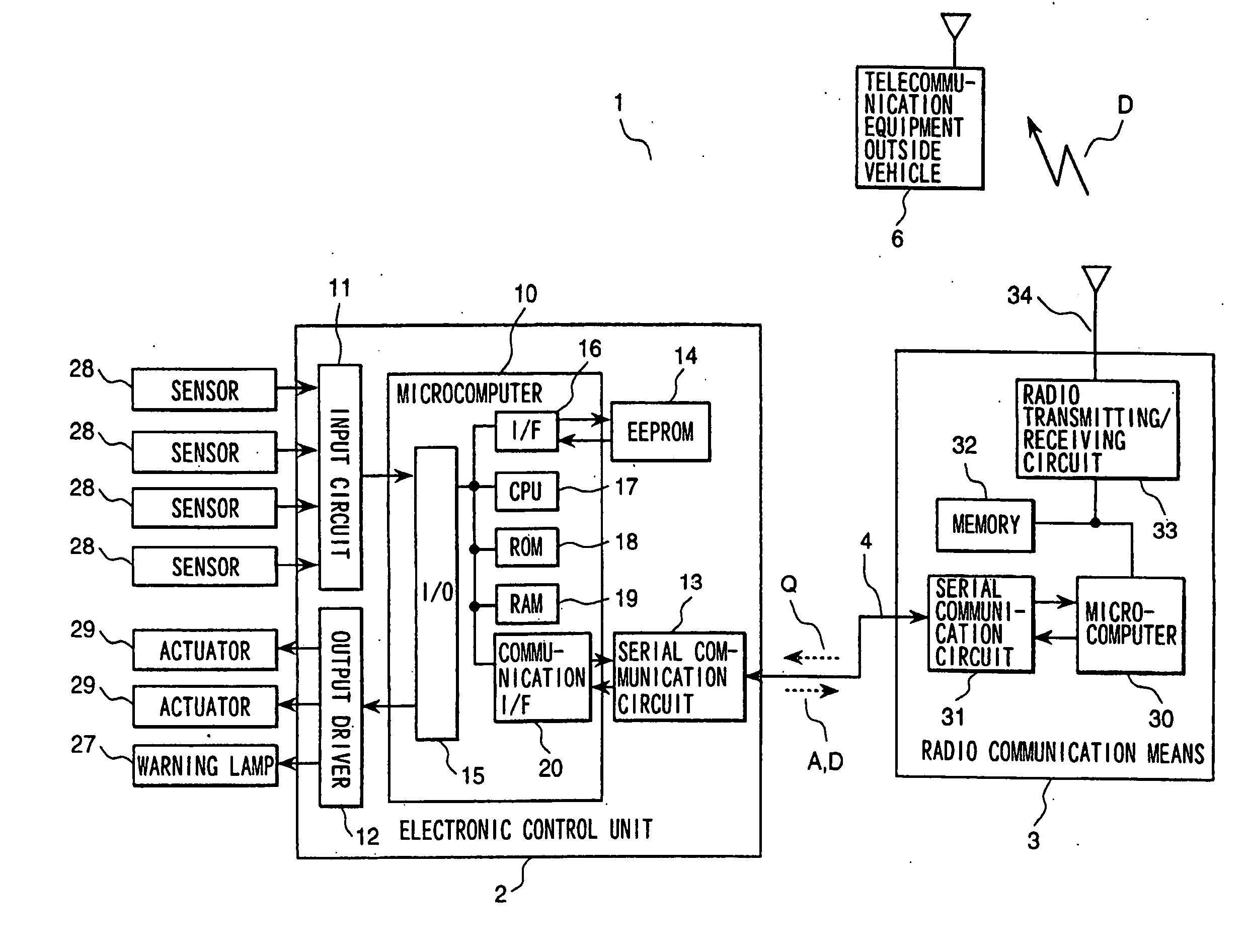
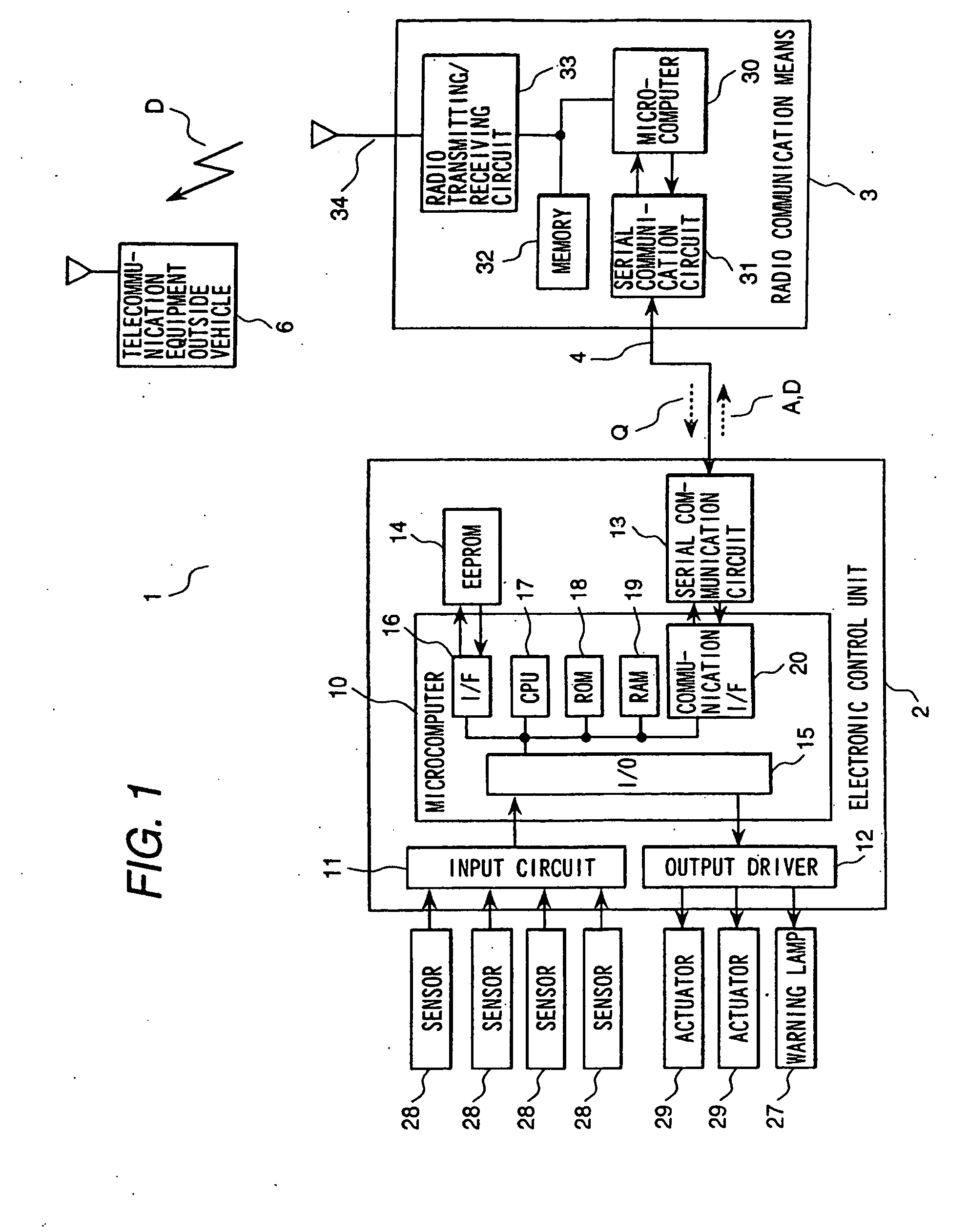
Vehicle diagnostic system
InactiveUS20070124039A1Low costDetected as abnormalityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringDiagnostic information
Owner:HITACHI LTD
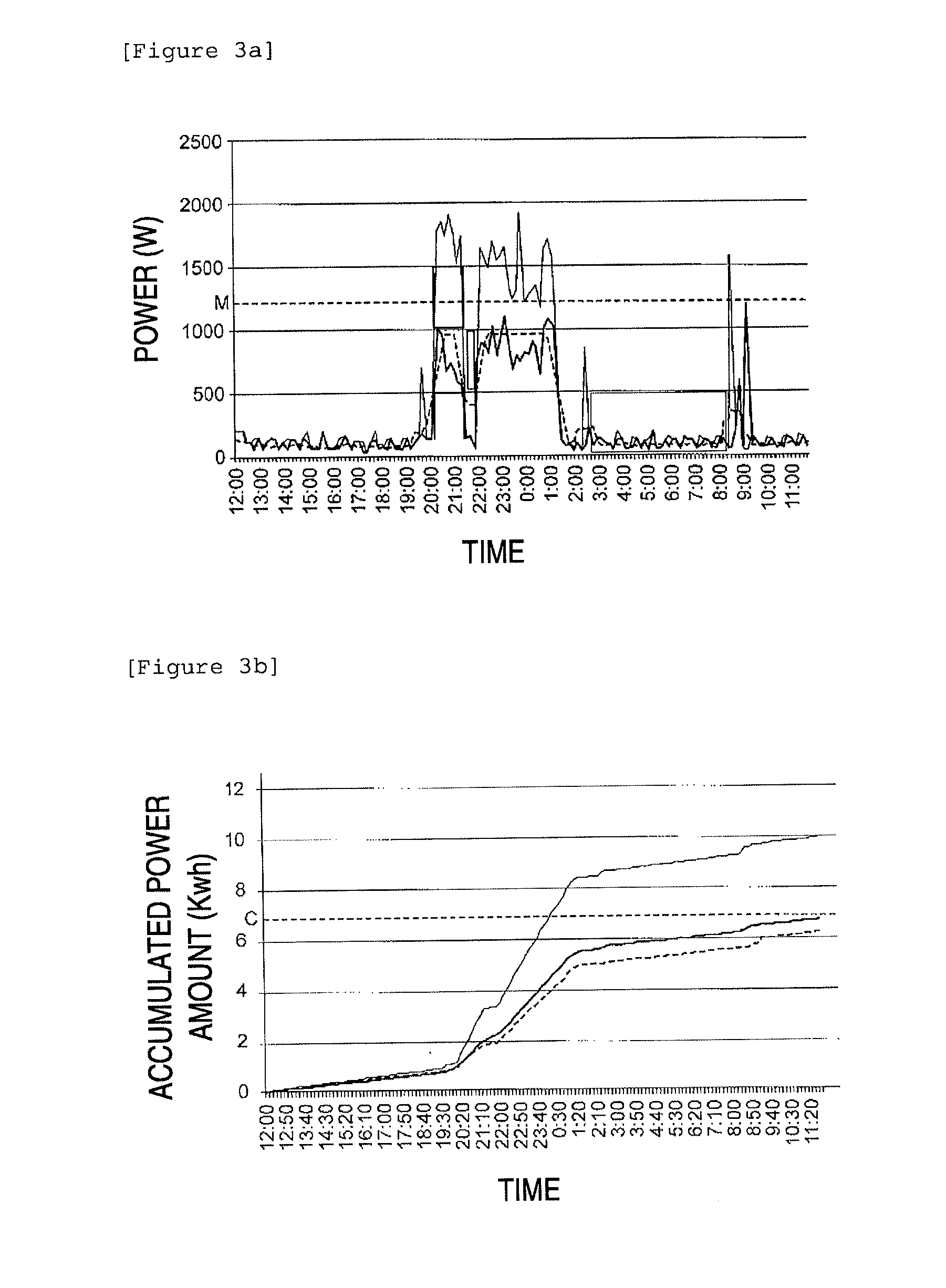
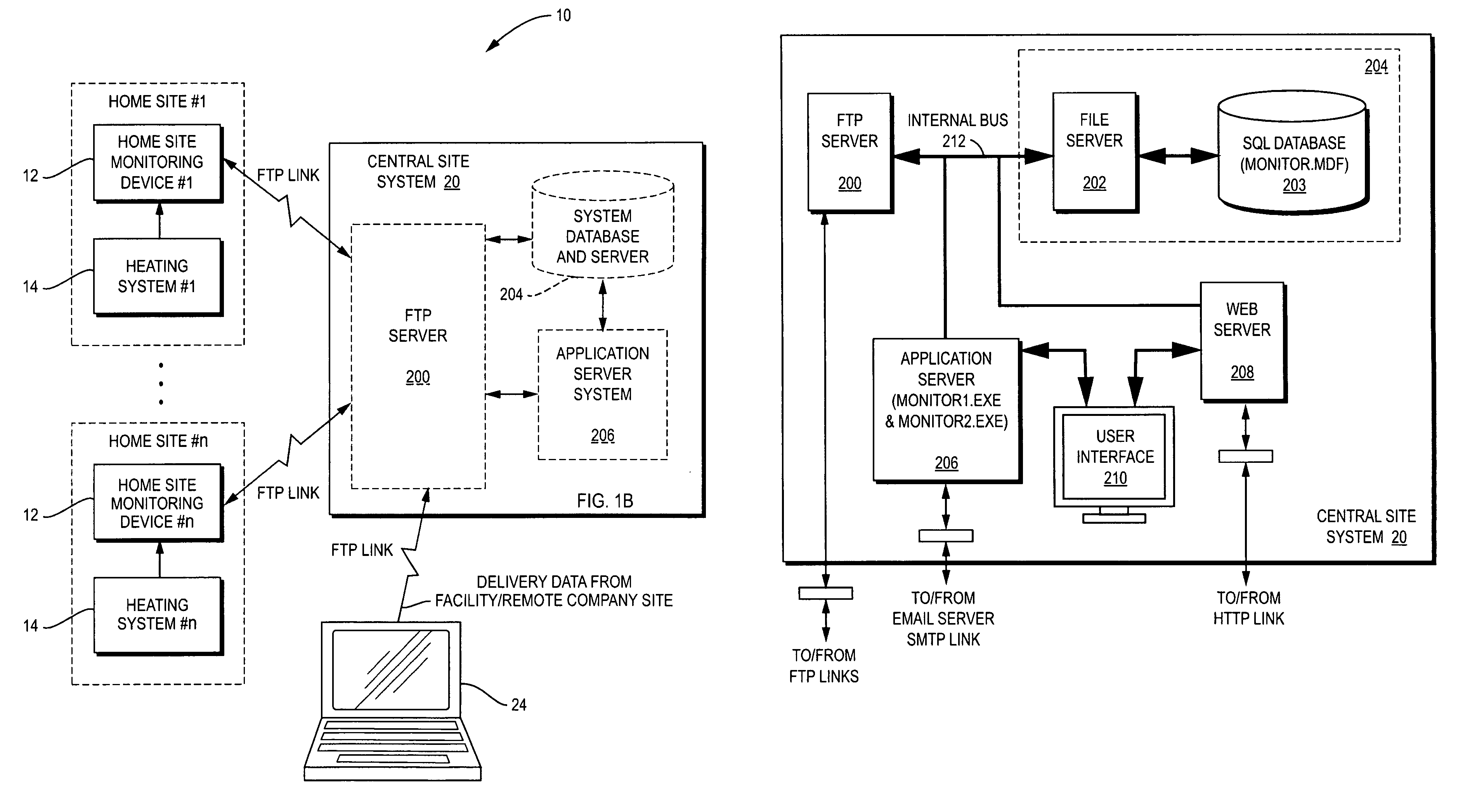
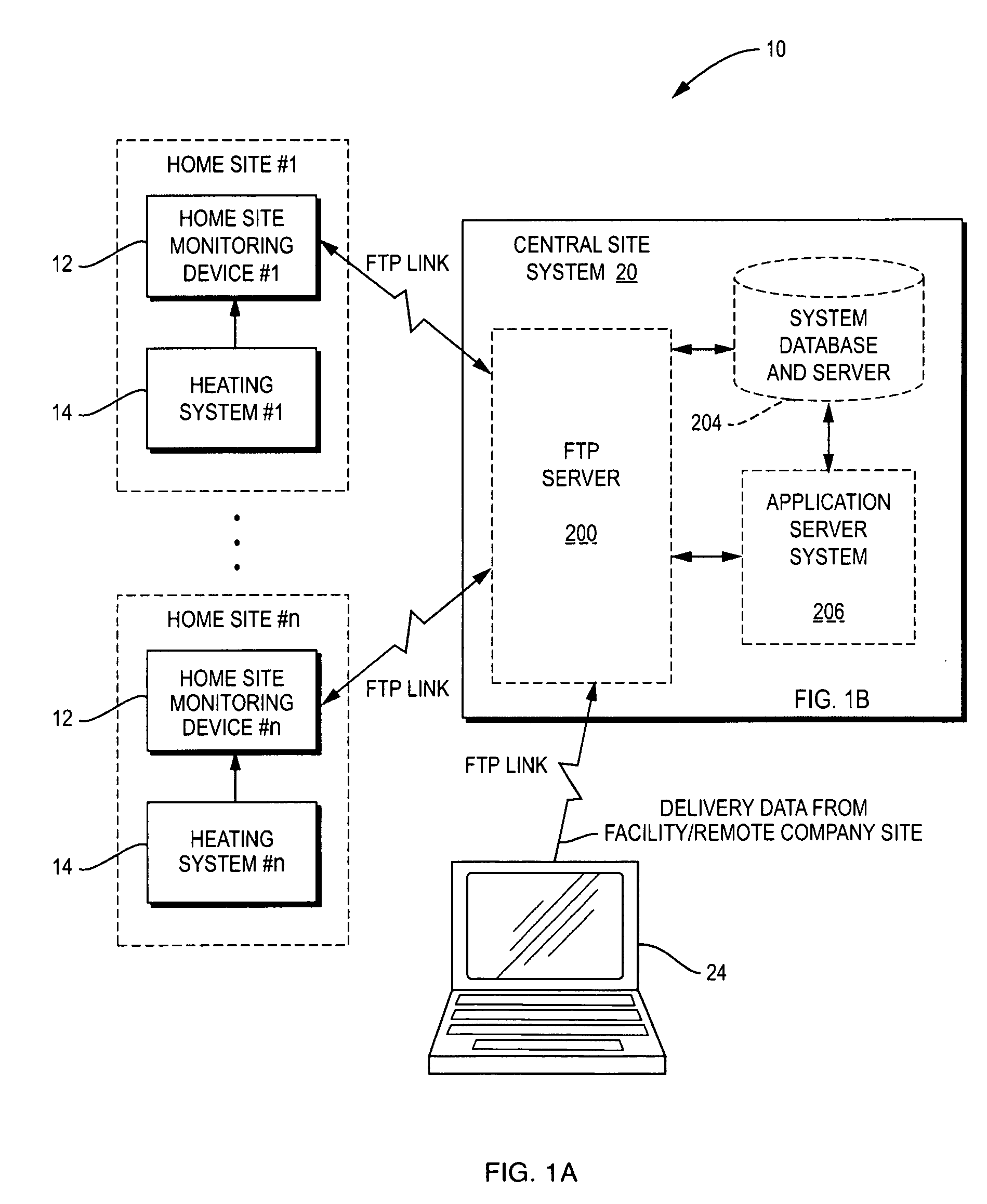
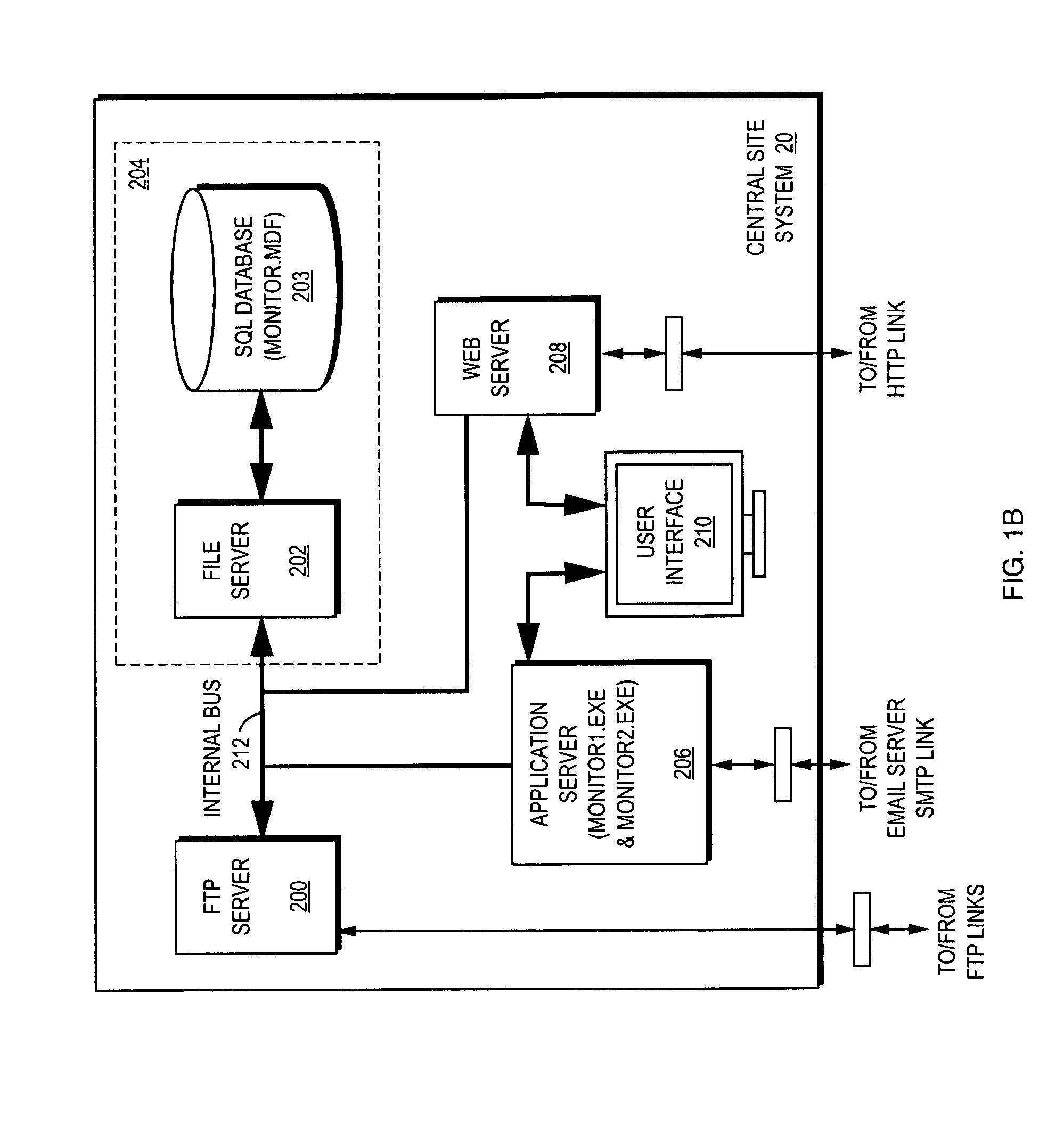
Self calibrating home site fuel usage monitoring device and system
InactiveUS20120185197A1Precise and less-costlyDetected as abnormalityFluid pressure measurementVolume meteringHeating systemEngineering
A home site fuel monitor device in conjunction with a remote central site system to provide accurate fuel usage data used in planning fuel deliveries. The fuel monitor device is U an internet based, compact, and low cost home heating site monitor device that is easily installed in the home heating site without modification to the home site's heating system. The monitor device includes a microprocessor which measures heating system run times using real time clock values. The microprocessor computes heating system fuel usage and the rate of fuel usage using heating system run times and heating burner parameters down loaded from the remote central site system. The monitor device continuously adjusts or recalibrates the rate of fuel usage defined as a burn coefficient value to coincide with the latest delivery information received from the central site system which results in increased accuracy over time.
Owner:LORDEN THEODORE J +1
Abnormality detector for a motor drive system
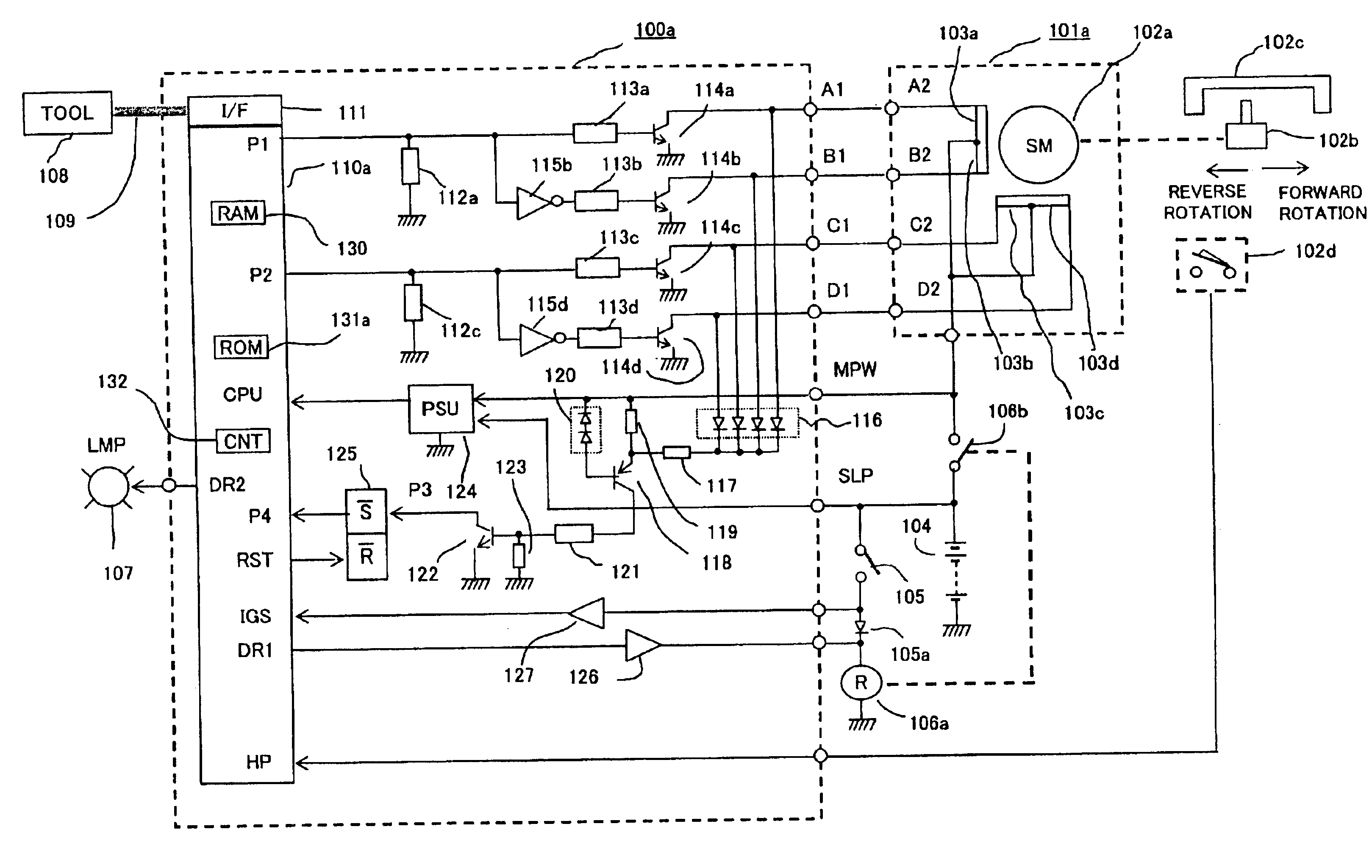
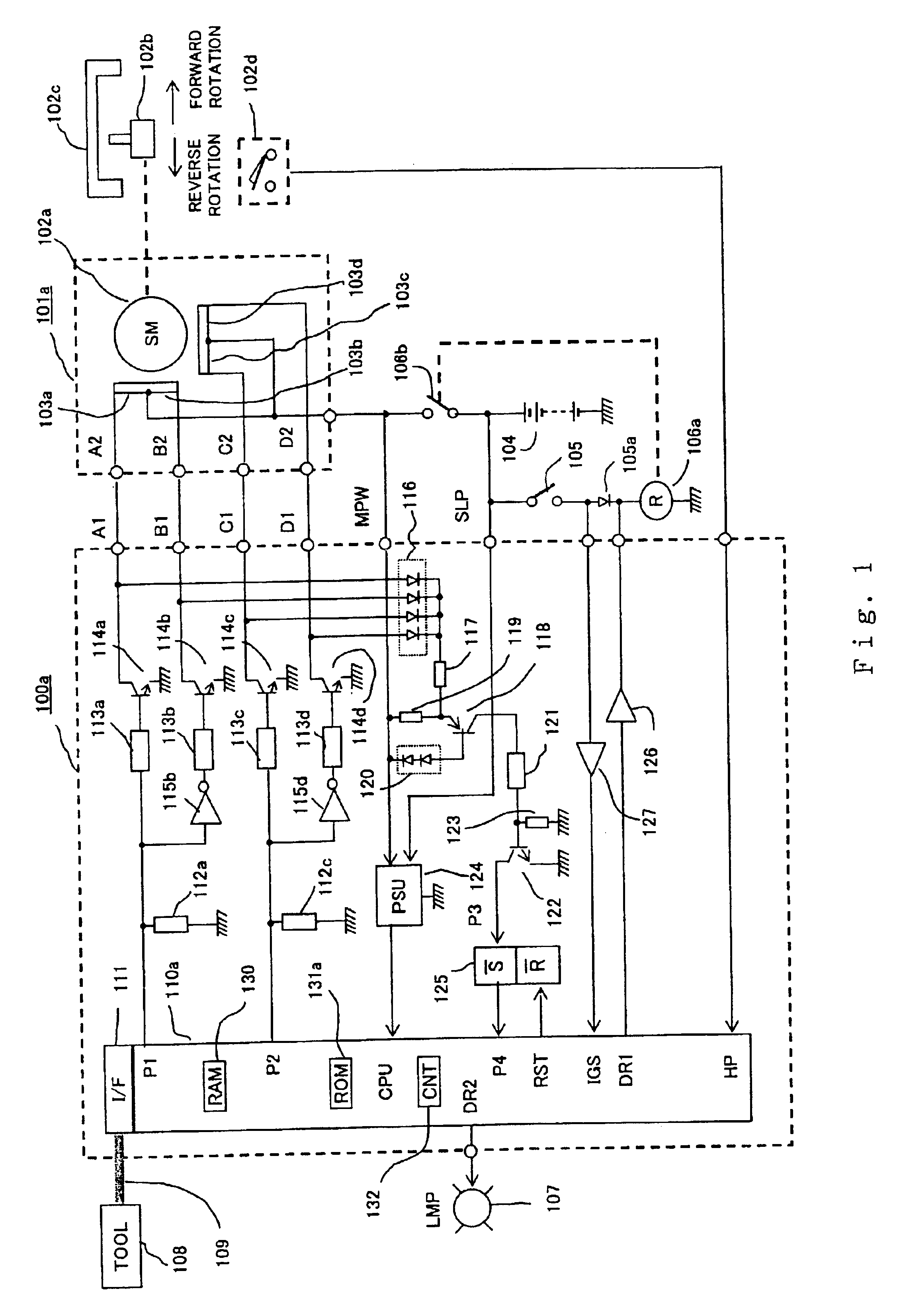
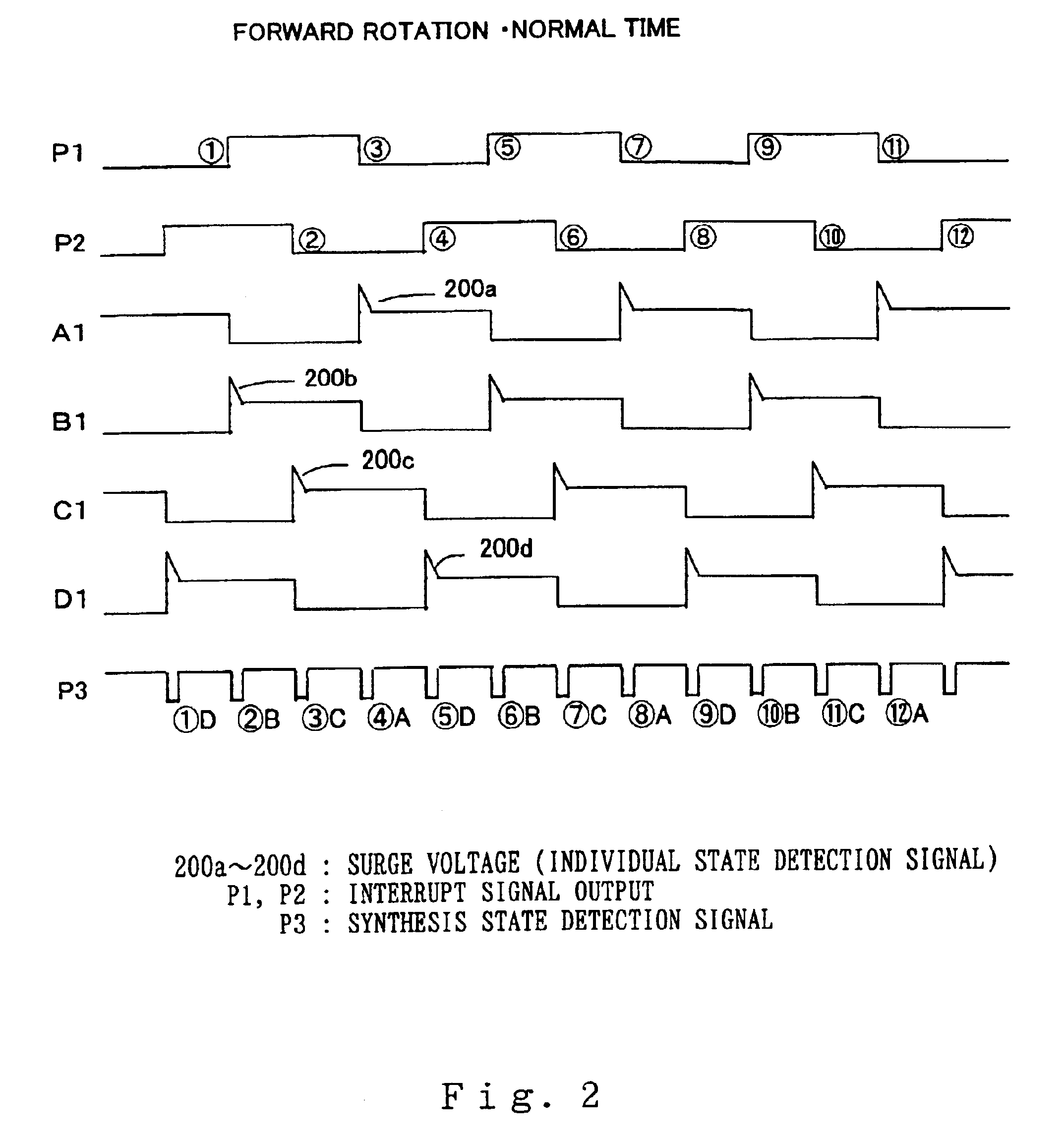
InactiveUS20030218443A1Reduce in quantitySimple and inexpensive constitutionDC motor speed/torque controlElectrical controlMotor driveAnomaly detection
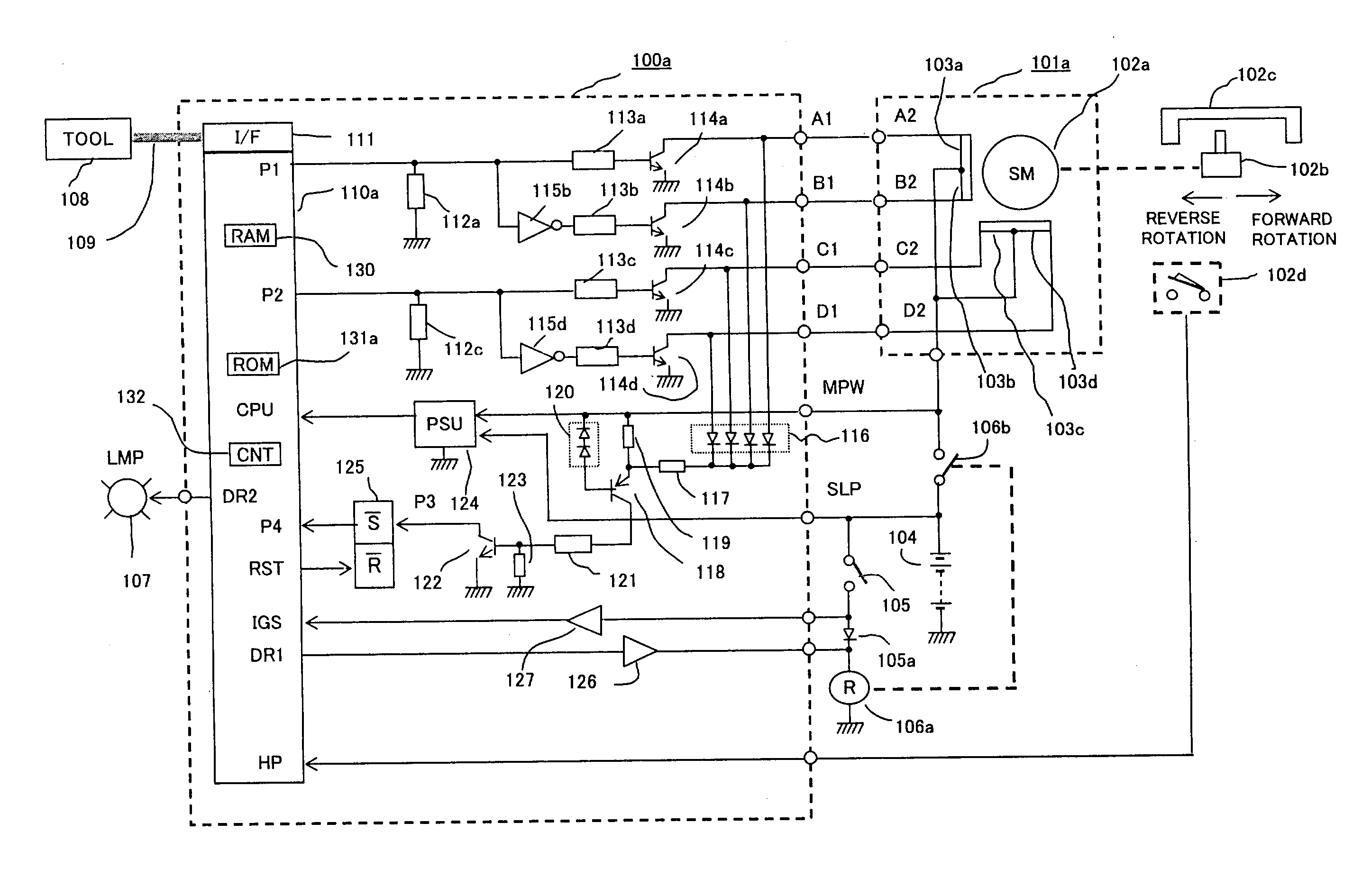
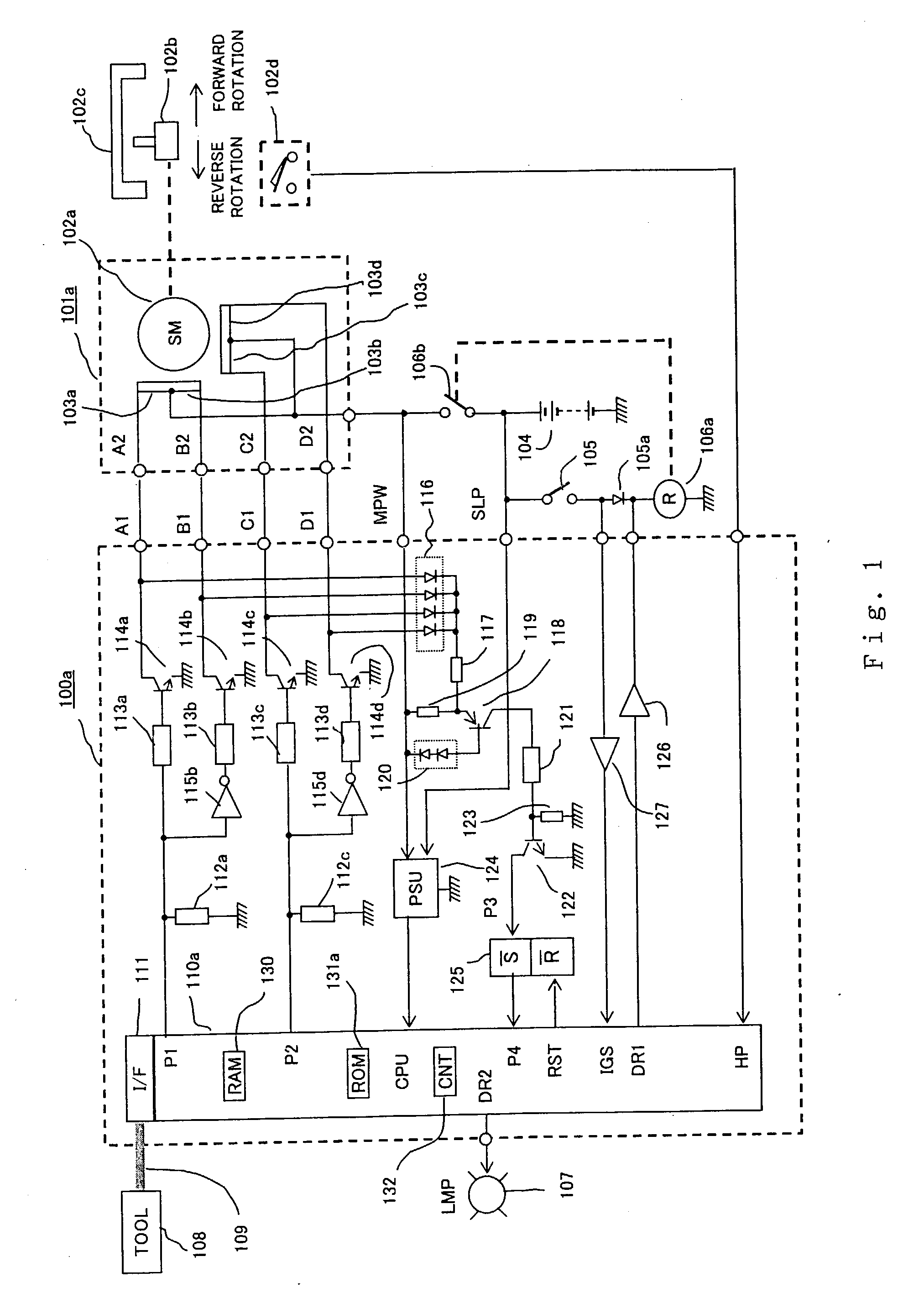
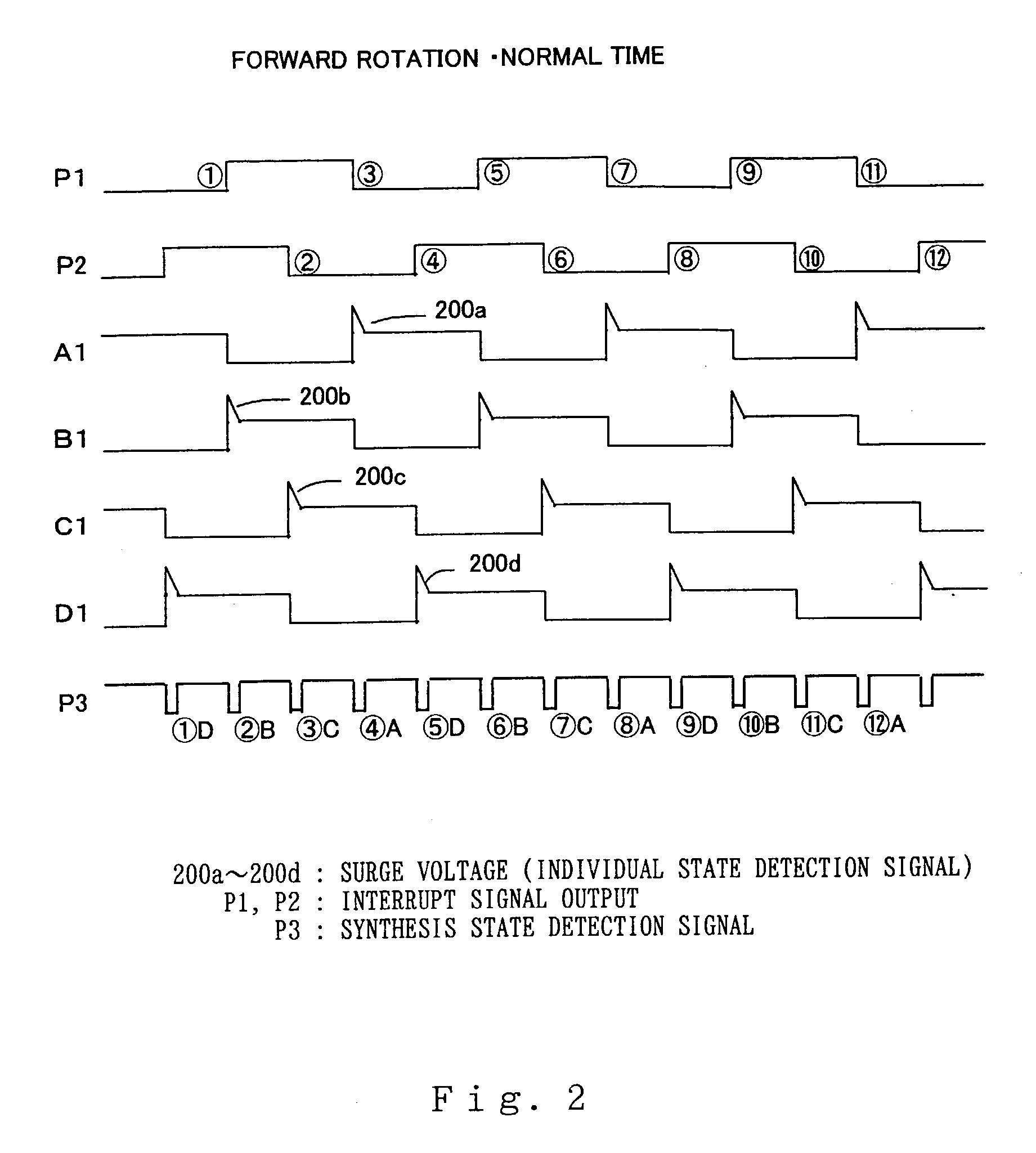
An abnormality detector for motor drive system easily detects, using a CPU, abnormality such as short circuit or disconnection in magnetic field coils of a motor, wiring, an open / close element, etc., which are controlled by a microprocessor (CPU). The open / close elements conducting an open / close operation sequentially in response to pulse outputs P1, P2 generated by the CPU, drive the magnetic field coils. Surge voltages generated upon interrupting the mentioned open / close elements are OR connected through a diode, and input to a temporary storage circuit. Then the CPU reads out, stores and resets the surge voltages using pulse edges of the pulse output P1 or P2. When any generation of the surge voltage is not stored in the temporary storage circuit, the CPU operates an abnormality alarm display.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Diagnostic method for motor
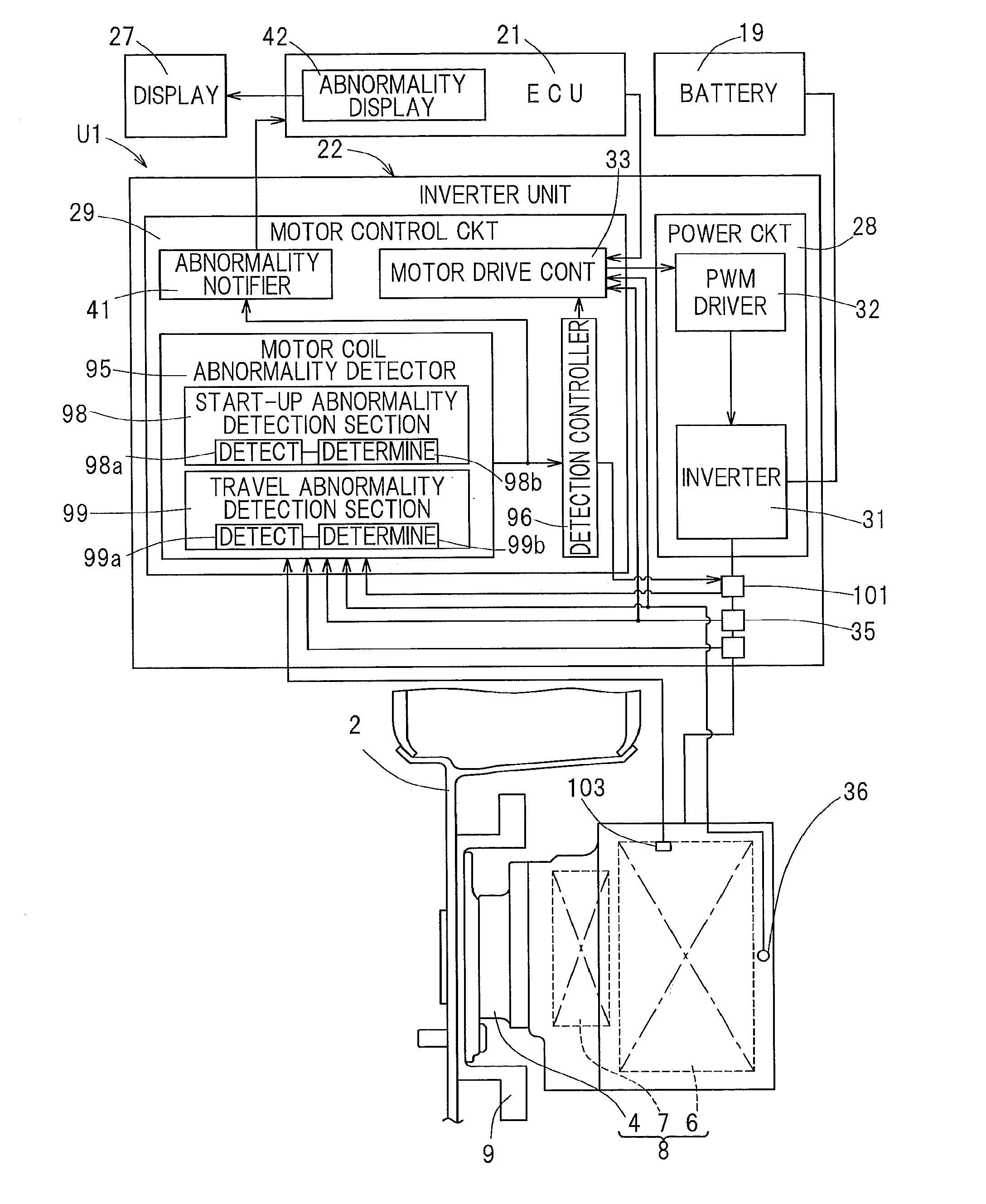
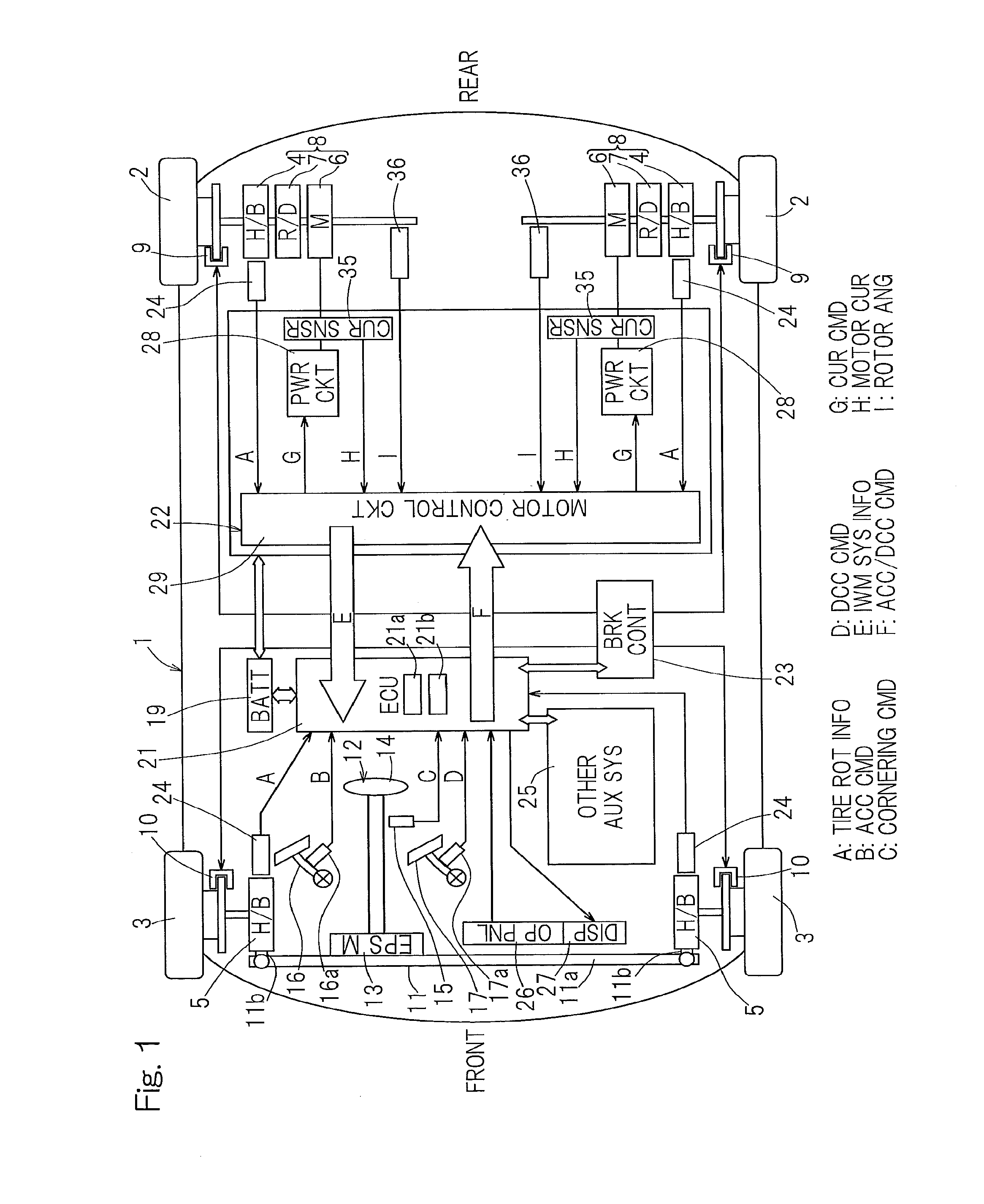
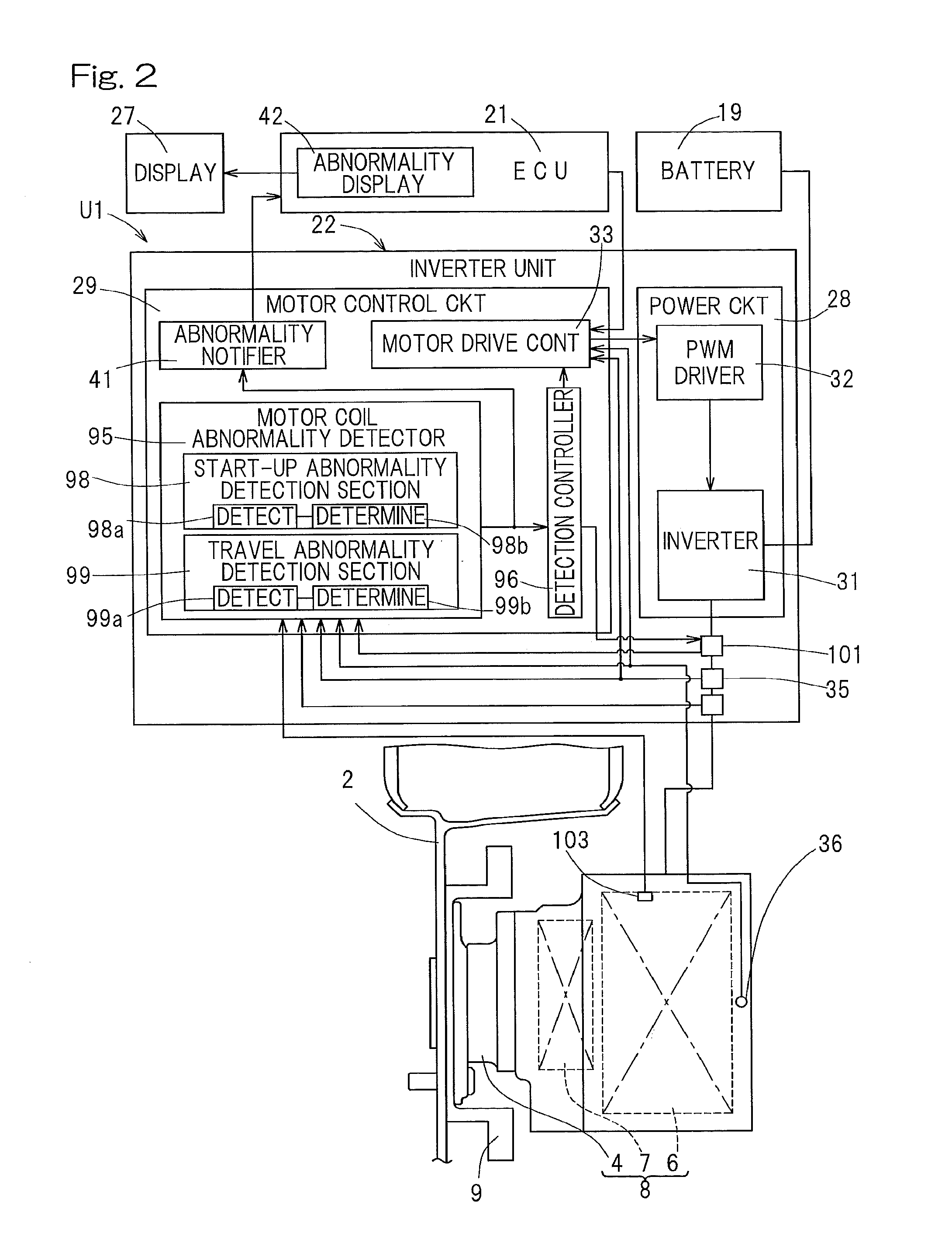
ActiveUS20130341109A1Accurate measurementSimple device structureAC motor controlVector control systemsPower flowDrive motor
A diagnostic apparatus for diagnosing a drive motor of a vehicle includes a start-up abnormality detection section to detect coil temperature, coil resistance or insulation resistance of a motor coil during a non-traveling time in which electric power supply is applied and to determine occurrence of abnormality in the motor coil when the coil temperature is greater than a threshold value or the coil resistance or insulation resistance is greater than a threshold value, and a travel abnormality detection section to detect coil temperature, rotation number of the motor, a motor applied voltage and a motor current during traveling of the vehicle and to determine occurrence of abnormality in the motor coil when the coil temperature is greater than a threshold value or the relation between the motor applied voltage and the motor current relative to the rotation number fails to fall within a predetermined range.
Owner:NTN CORP
Wireless communication system
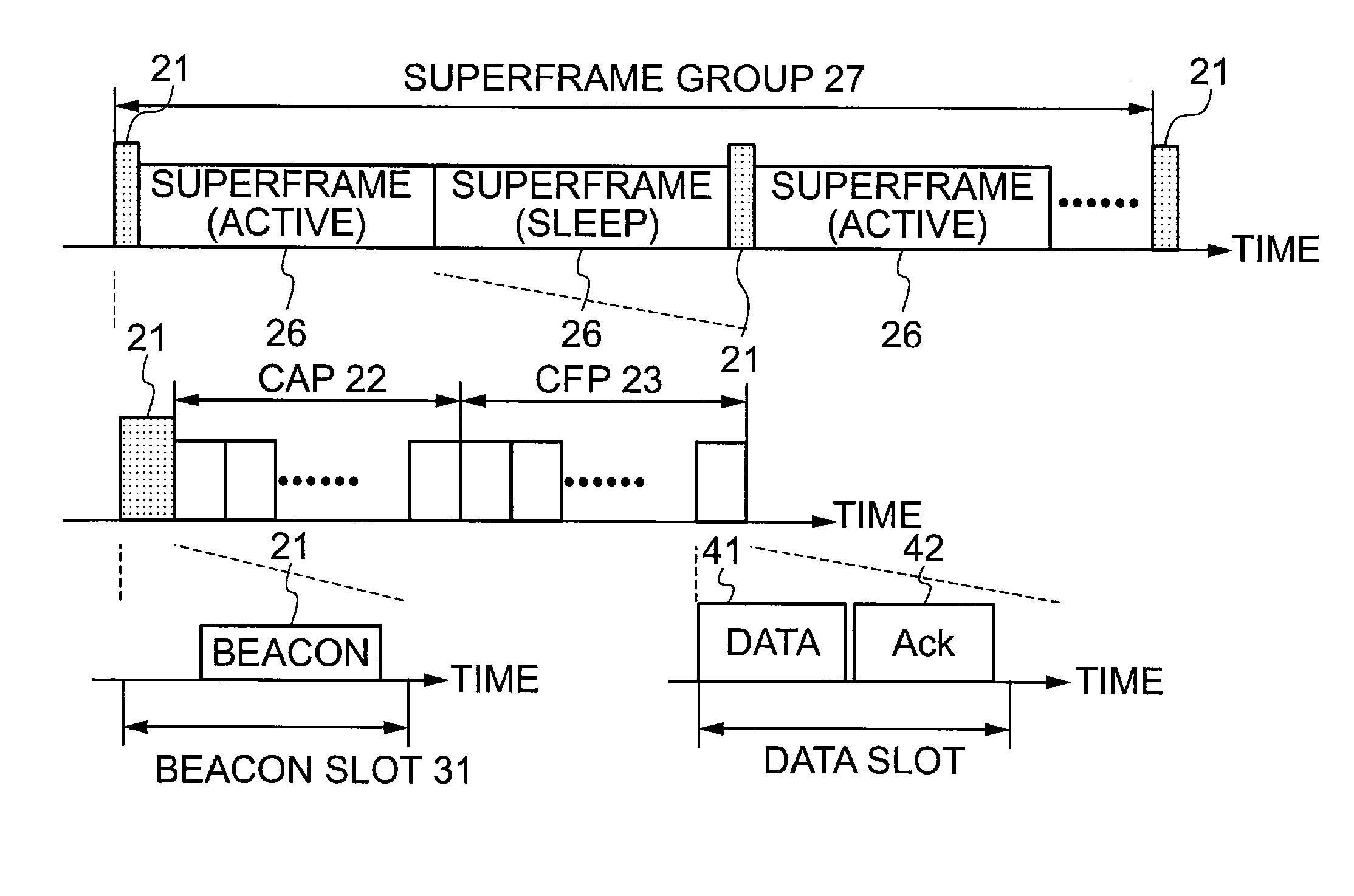
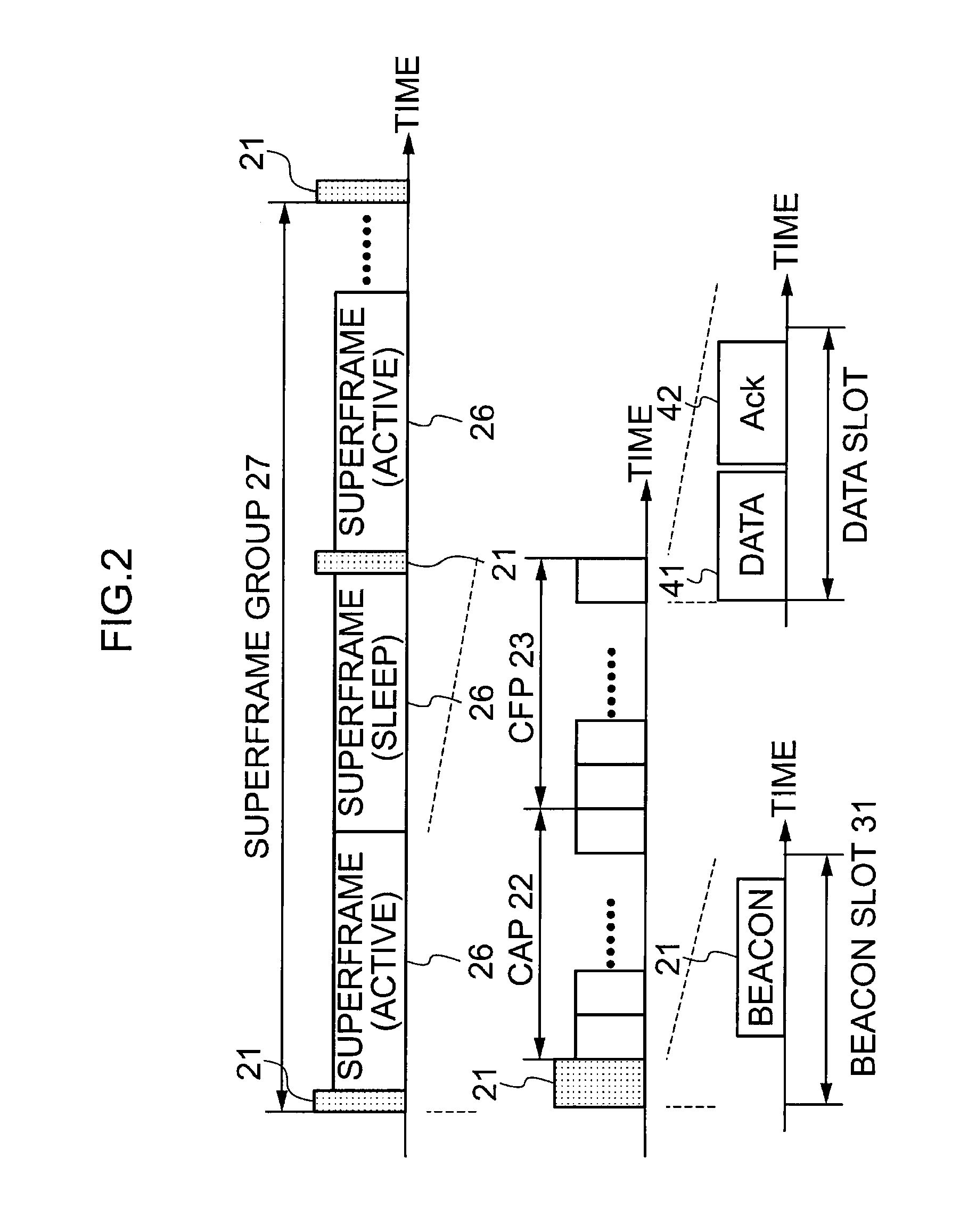
InactiveUS20110164605A1Reliably establish synchronizationSuppress power consumptionPower managementSynchronisation arrangementCommunications systemBeacon frame
A wireless communication system includes a coordinator (3) that broadcasts a beacon (21) having at least a preamble part (32) and a payload part (33), and a plurality of devices (2) each of which is synchronizable with at least the coordinator (3) by listening to the beacon (21) through a listen period set based on an own reference clock. The coordinator (3) fixes a position of the end of the beacon (21) with respect to a beacon slot constituting a superframe, and generates the beacon (21) where a start of a preamble part (32) is extended toward a start of the beacon slot over a time To. The devices (2) are synchronized with the coordinator (3) via an end time of the beacon slot detected from an end time of the preamble part (32) in the beacon frame.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Diagnostic apparatus for vehicle cooling system
InactiveUS8215833B2Detected as abnormalityEasy to installThermometer detailsEngine testingEngineeringTemperature difference
When the driving wind and the cooling wind are generated, based on the phenomenon in which the temperature difference is generated between the front surface and the rear surface of the radiator (14), the temperature difference between the detection value of the rear temperature sensor (22) and the detection value of the front temperature sensor (21) is compared with the abnormality determination value so that it is determined whether the front temperature sensor (21) and the rear temperature sensor (22) are properly fixed on the radiator (14), whereby it is determined whether the abnormality (unauthorized alteration) exists. By setting the abnormality determination value according to the ambient temperature and the vehicle speed, corresponding to a variation in temperature difference between the front surface and the rear surface of the radiator (14), the abnormality determination value is varied to be set at a proper value.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Battery unit
InactiveUS20130149572A1Simple circuitDetected as abnormalitySecondary cellsCell component detailsEngineeringBattery cell
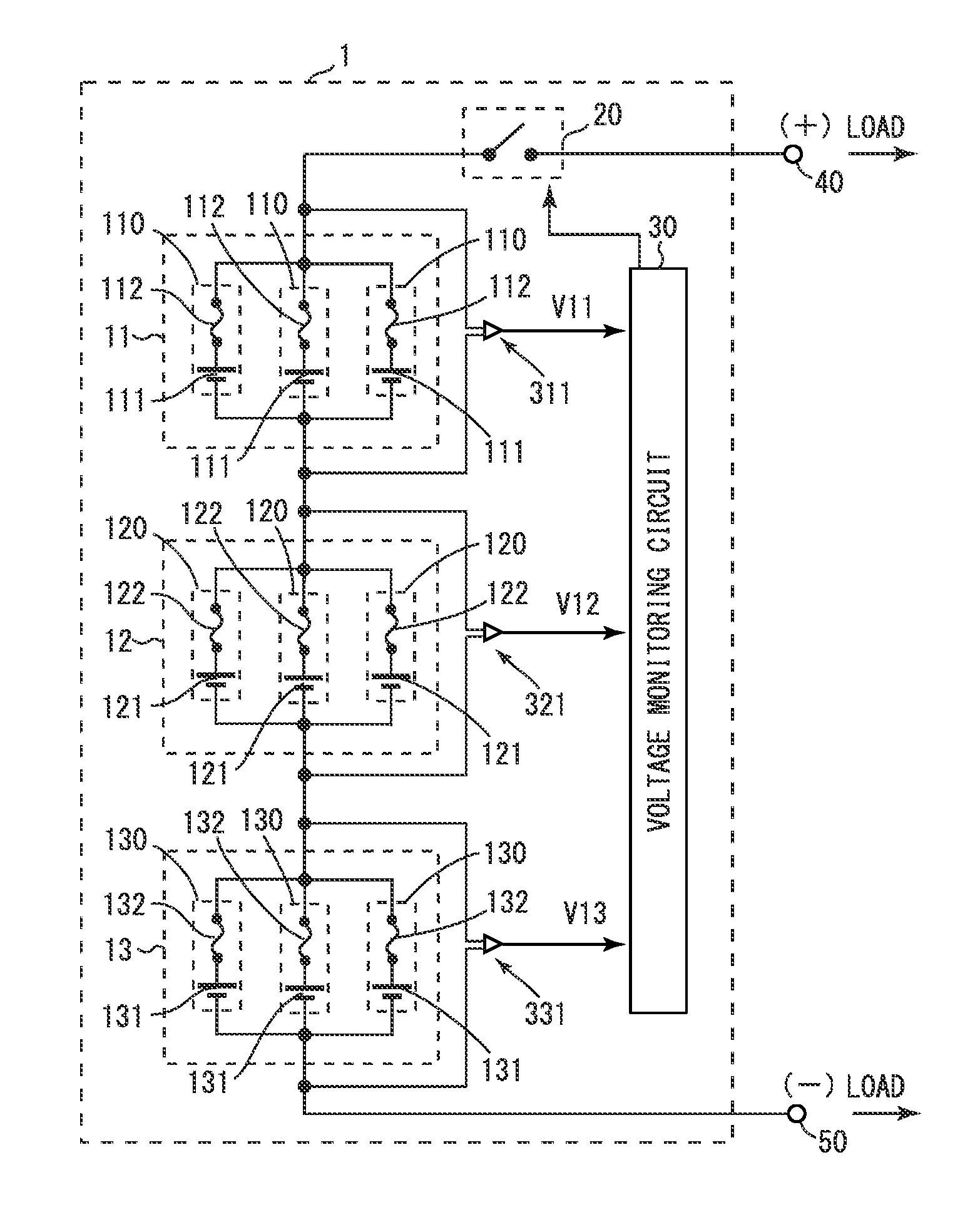
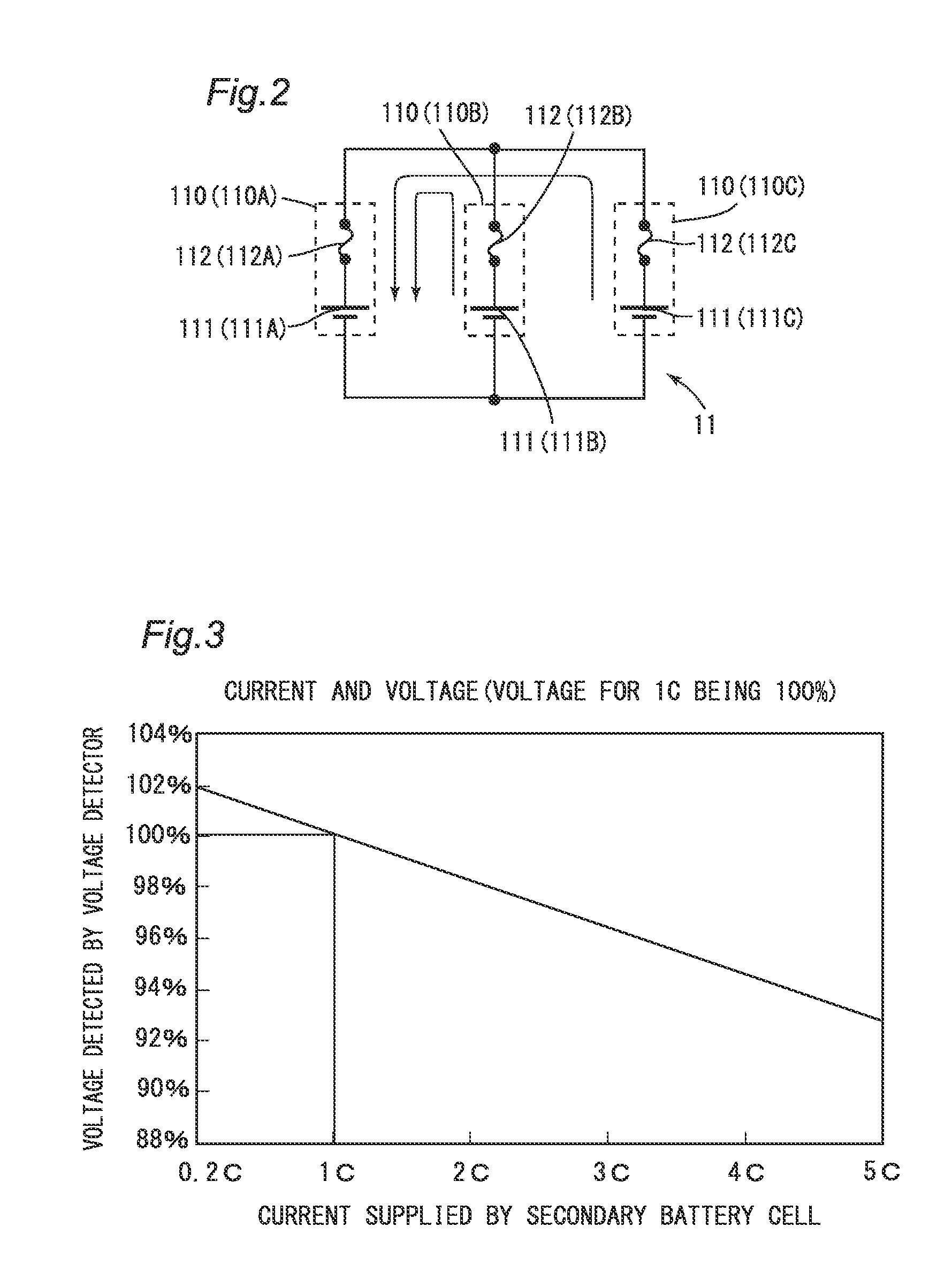
A battery unit (1) includes battery subunits (11, 12, 13) and a voltage monitoring circuit (30). The battery subunits (11, 12, 13) includes battery modules (110, 120, 130), each having a secondary battery cell (111, 121, 131) and a fuse (112, 122, 132) connected in series. The voltage monitoring circuit (30) monitors the voltage across the terminals of each of the battery subunits (11, 12, 13). Each of the battery subunits (11, 12, 13) includes one battery module or a plurality of battery modules (110, 120, 130) connected in parallel.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
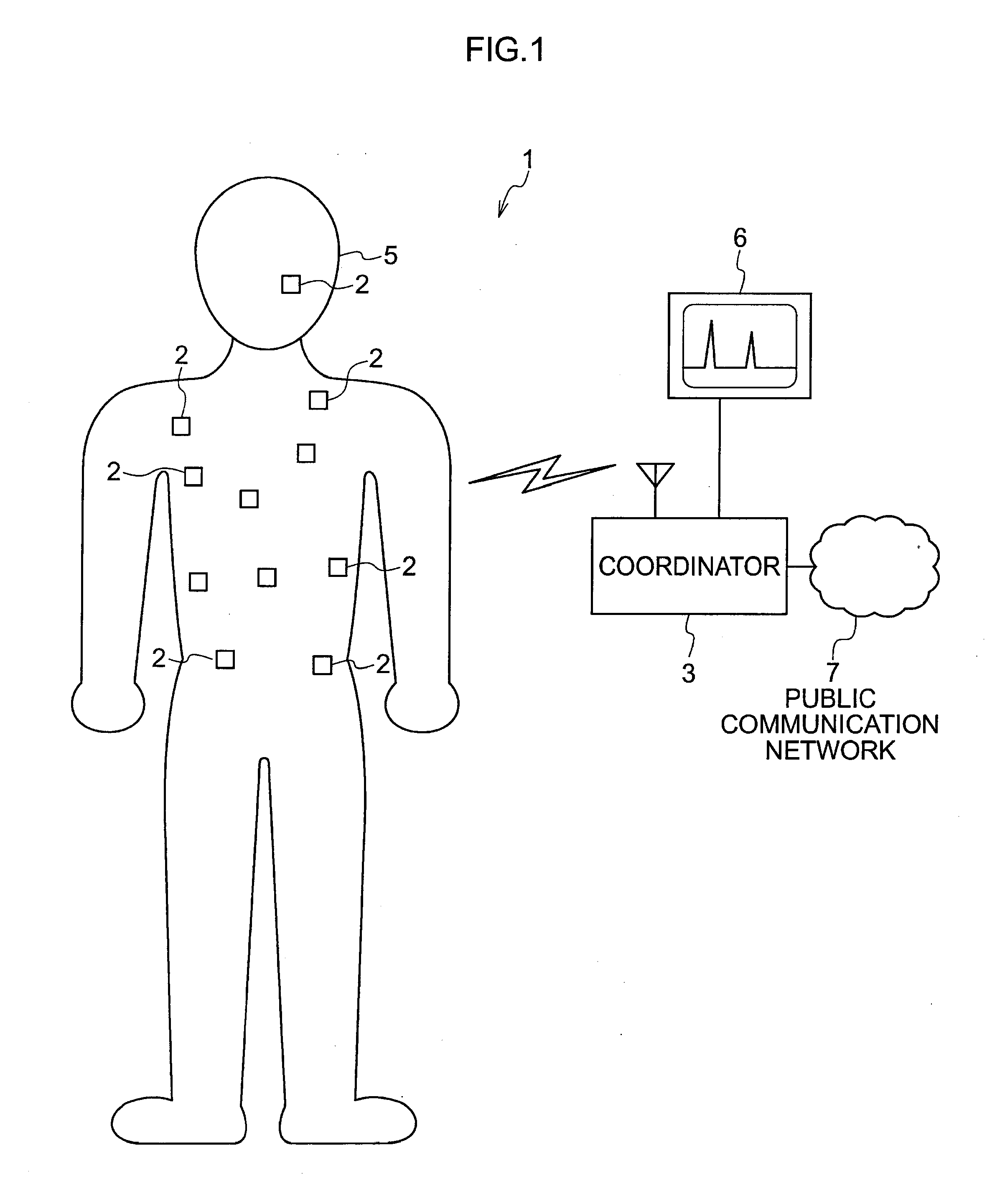
Inspection apparatus using magnetic resonance
InactiveUS20070055136A1Detected as abnormalityReduces bone densityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBone densityNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
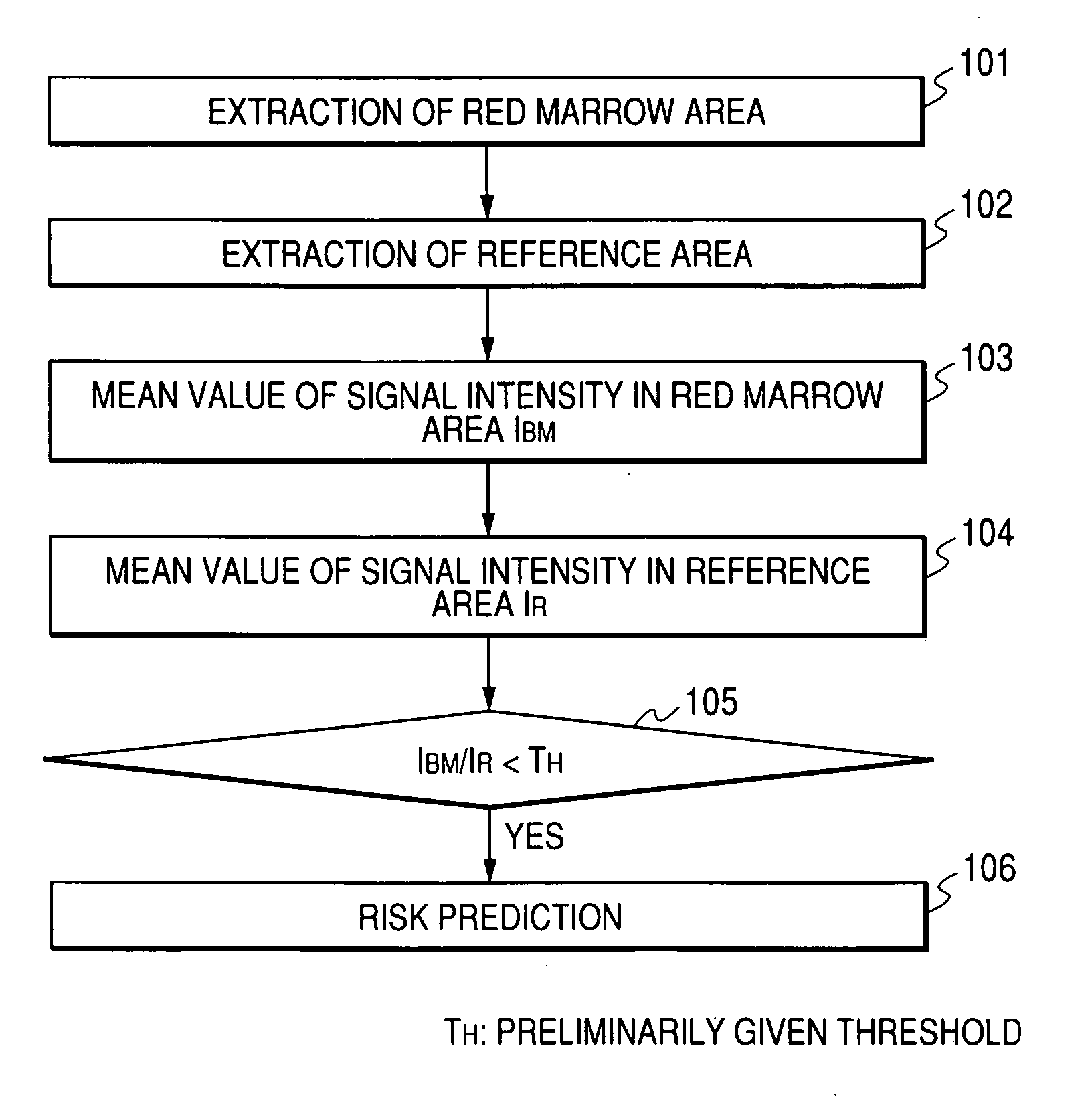
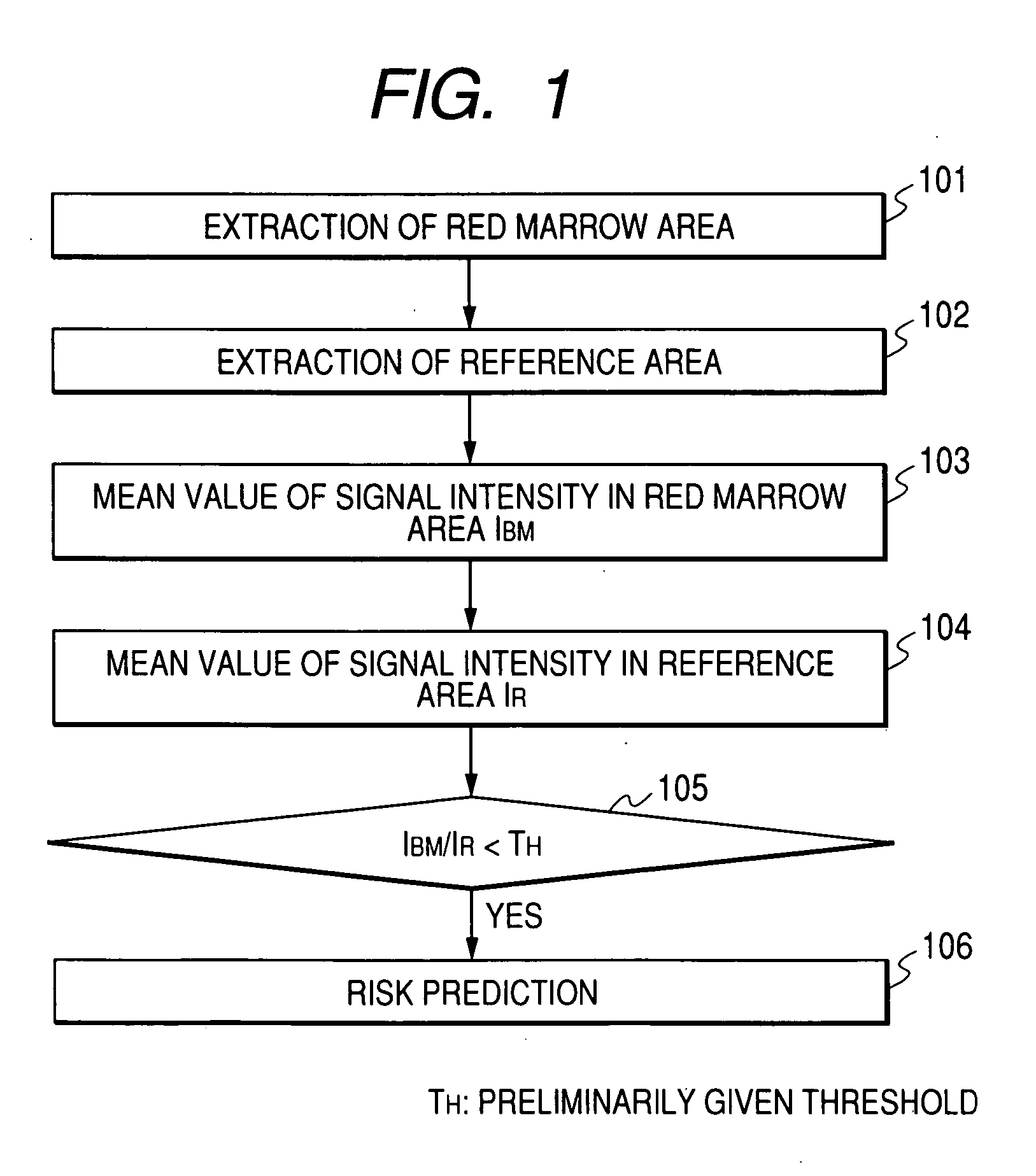
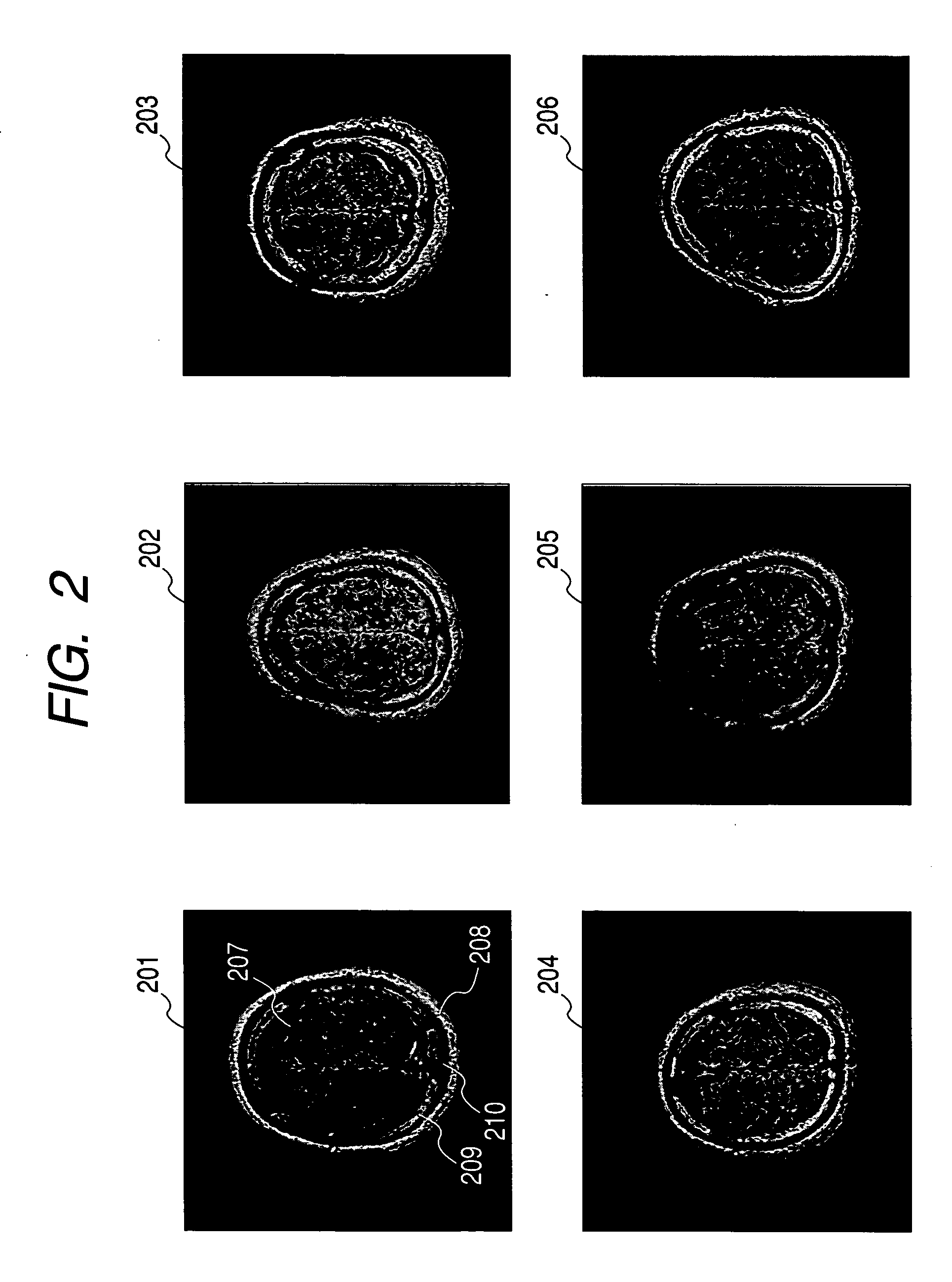
A means to predict bone density reduction before it actually begins will be provided. This invention provides a method to detect abnormalities in the bone marrow hemopoietic cells which precede the bone density reduction, by obtaining a nuclear magnetic resonance image containing a flat bone or an a long bone epiphysis, and evaluating the signal intensity in the red marrow area.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Control apparatus and method for a vehicle having idle stop function
ActiveUS8498772B2Simple configurationDetected as abnormalityVehicle testingPower operated startersIdle speedPinion
In an idle stop vehicle, a starter has separately an electromagnetic switch for energizing a motor and a pinion control solenoid for engaging a pinion gear with a ring gear. A coil of the solenoid is energized by a battery through a relay. For starting an engine, an ECU turns on the relay and the electromagnetic switch so that the starter cranks an engine. During engine operation, the ECU turns on only the relay while maintaining turn-off of the electromagnetic switch. If a voltage of a current supply path between the relay and the coil is lower than a predetermined threshold value, the ECU prohibits automatic idle stop by determining that the current supply path to the coil has abnormality.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com