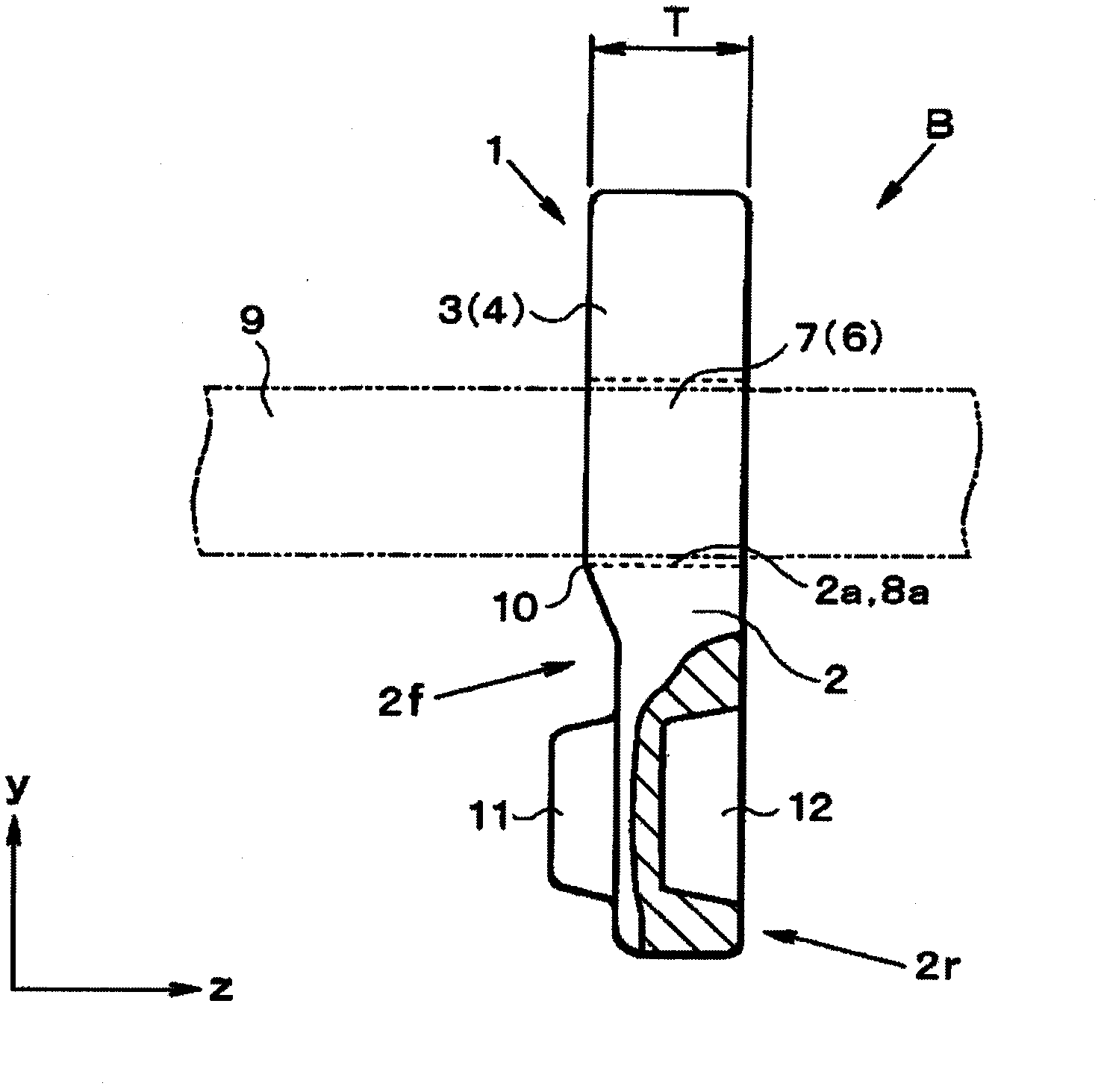
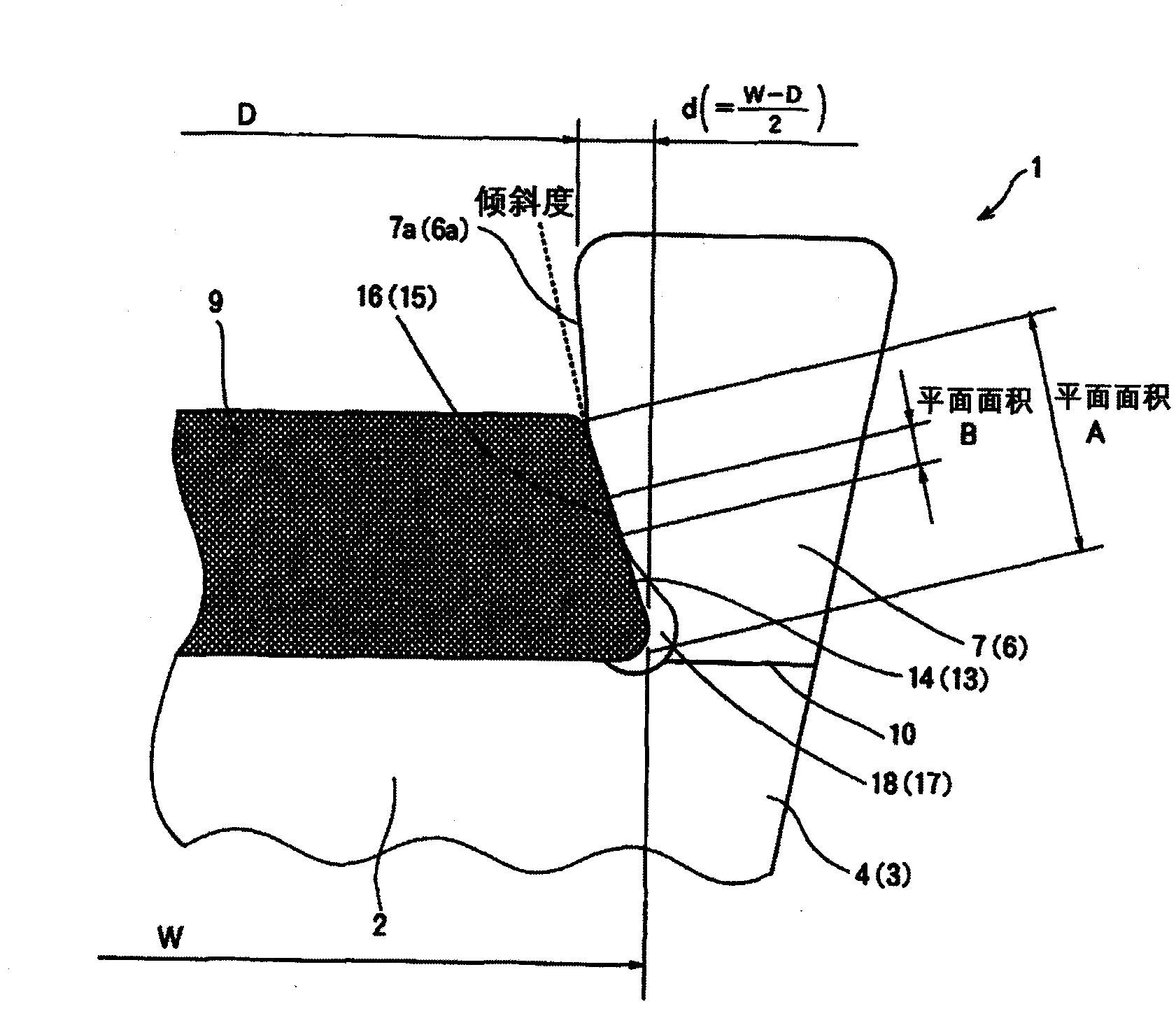
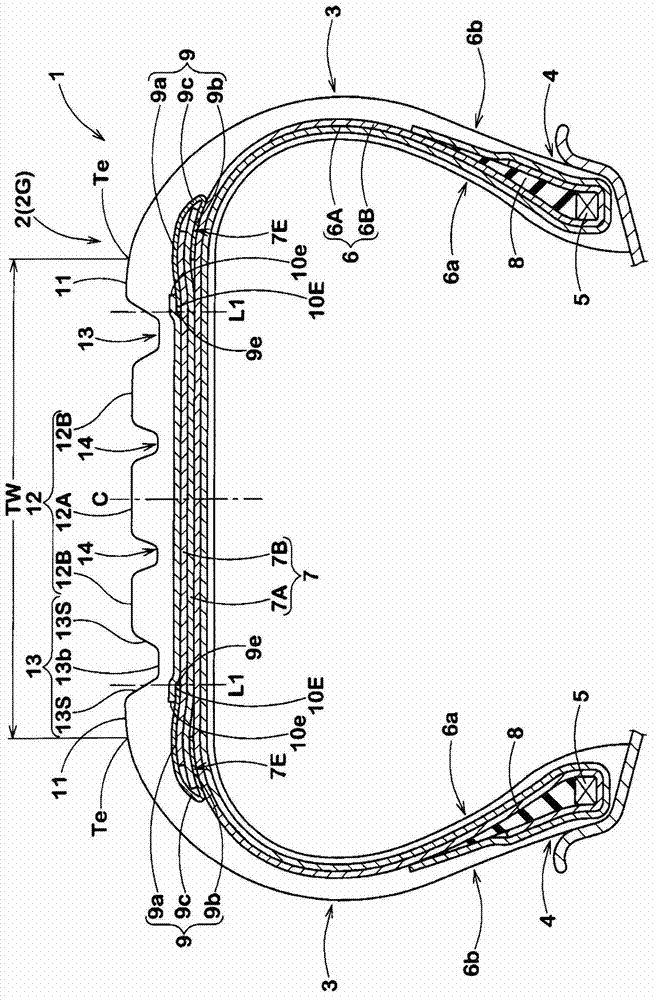
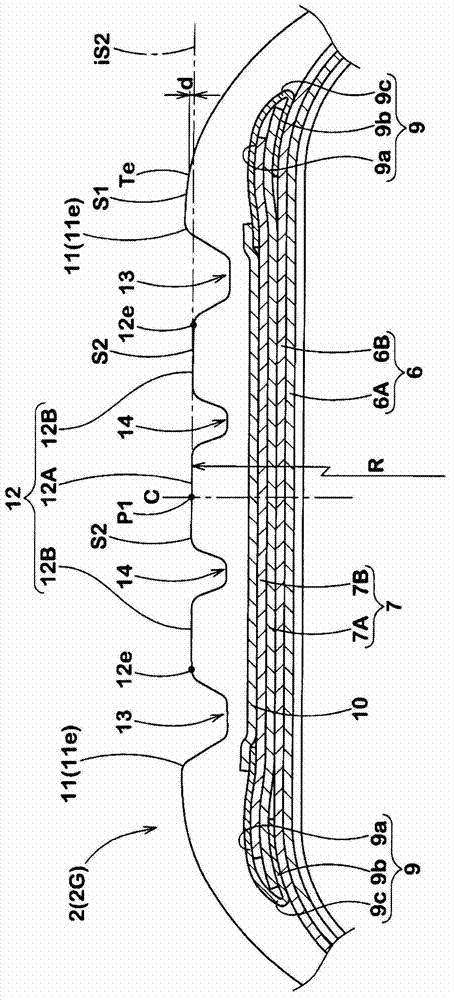
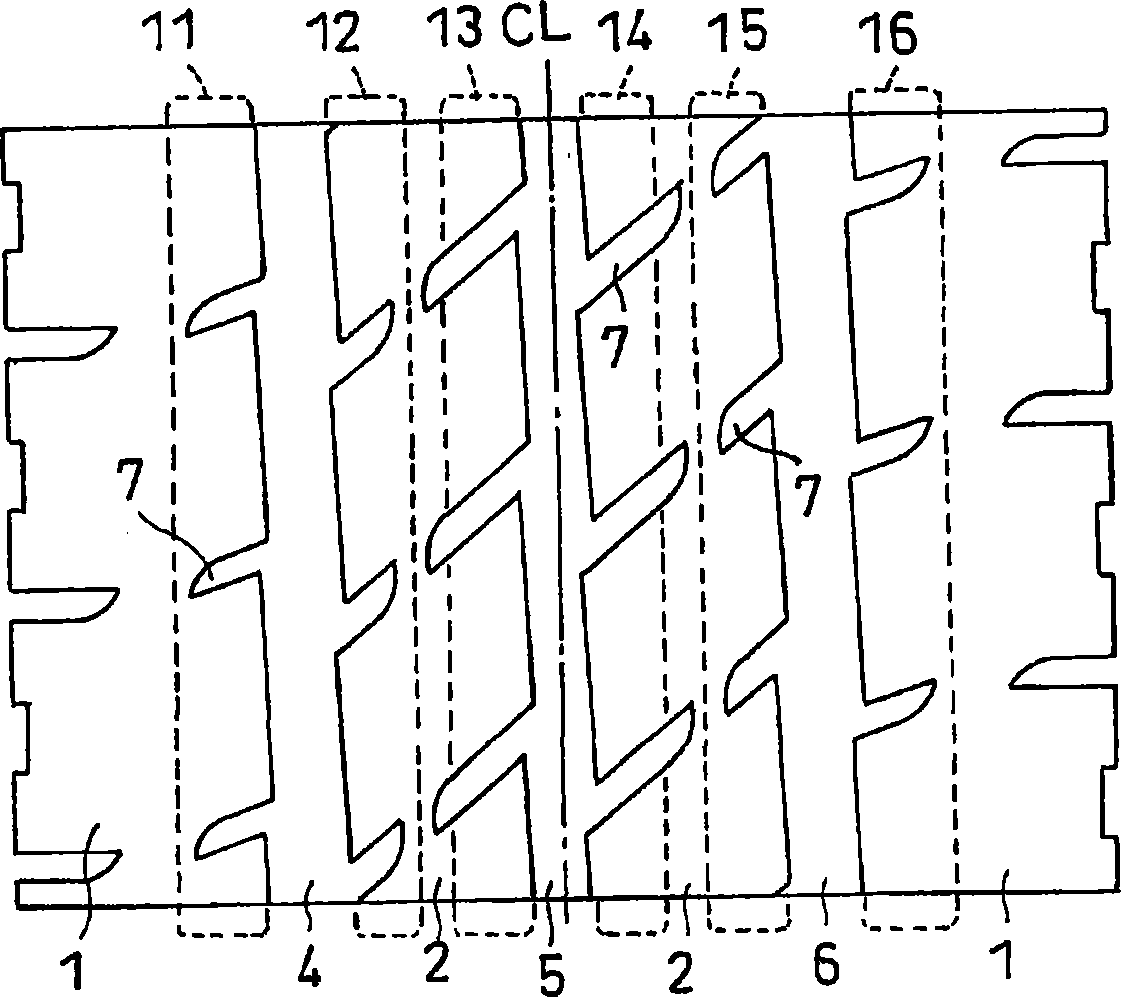
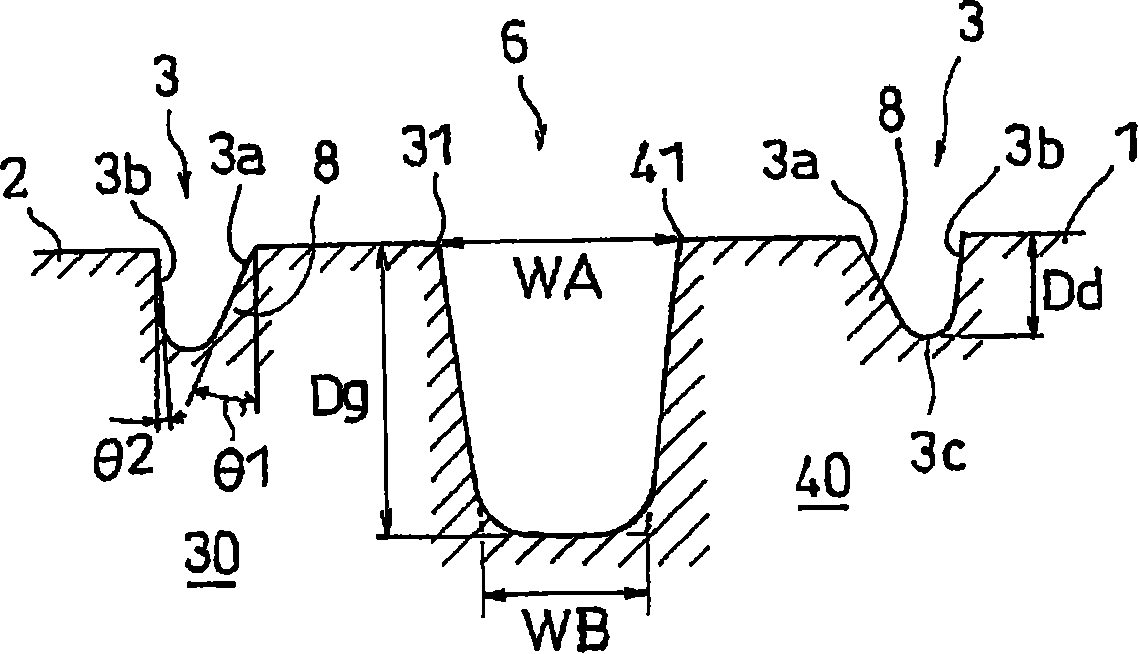
Patents
Literature
75results about How to "Inhibits uneven wear" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
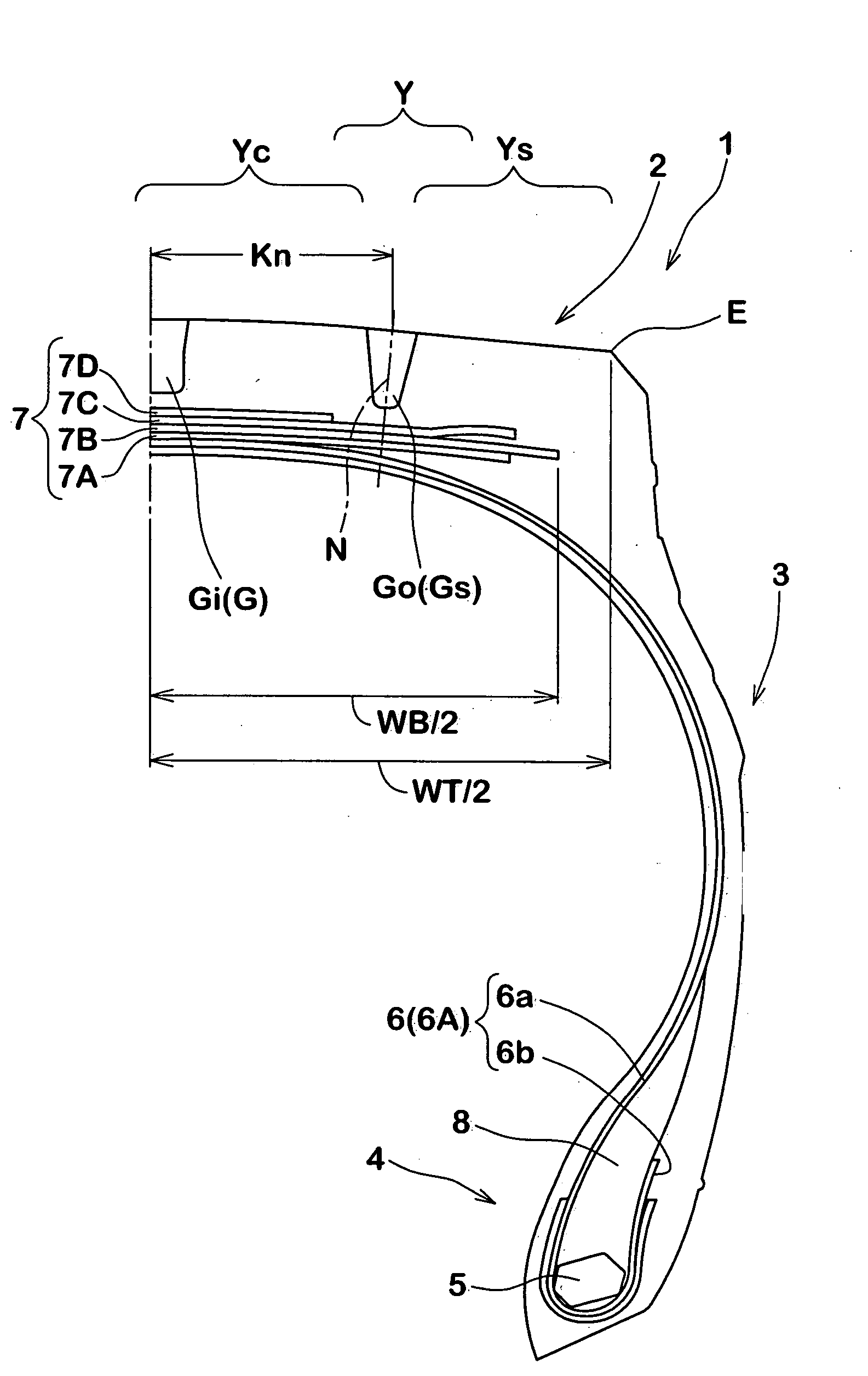
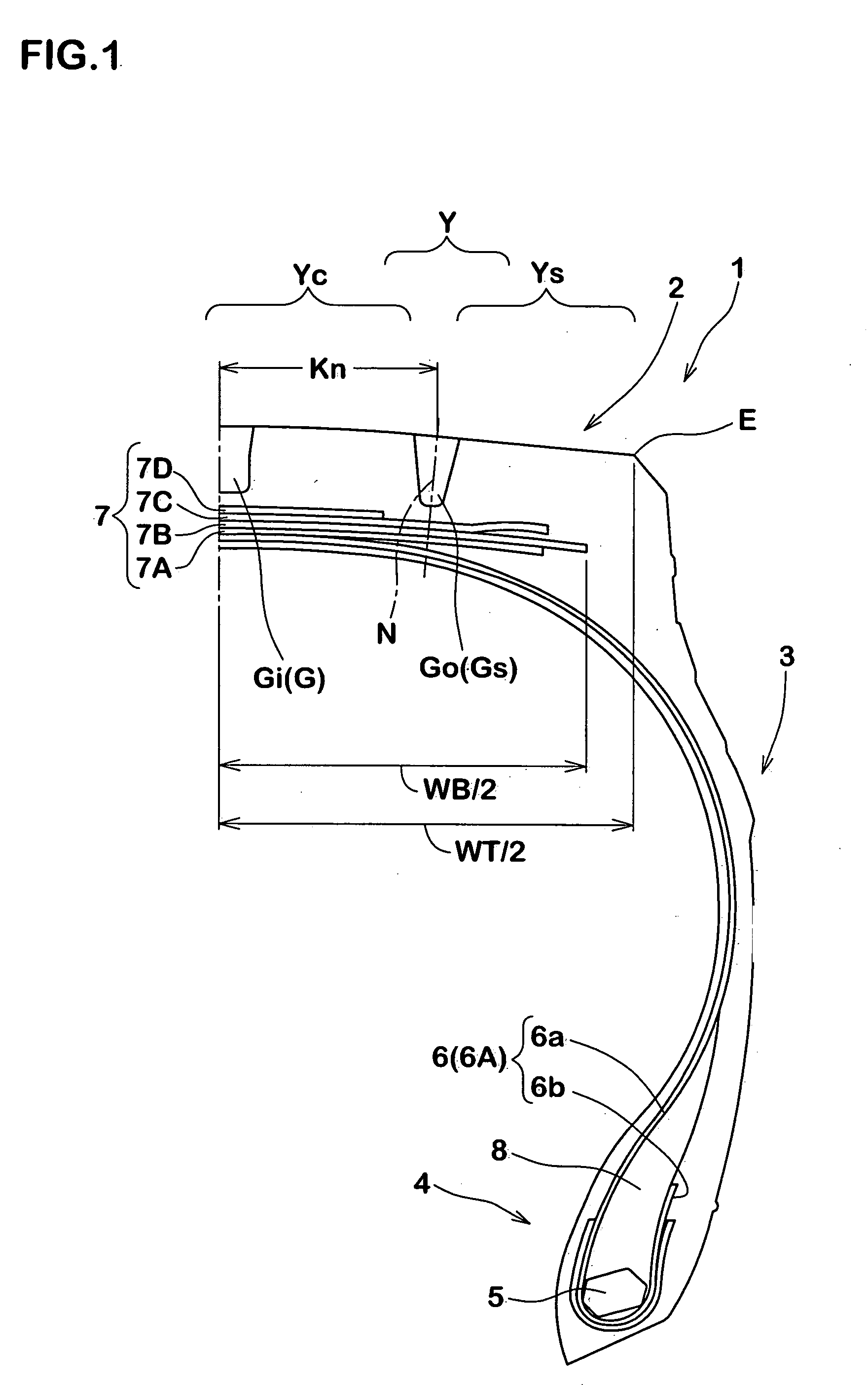
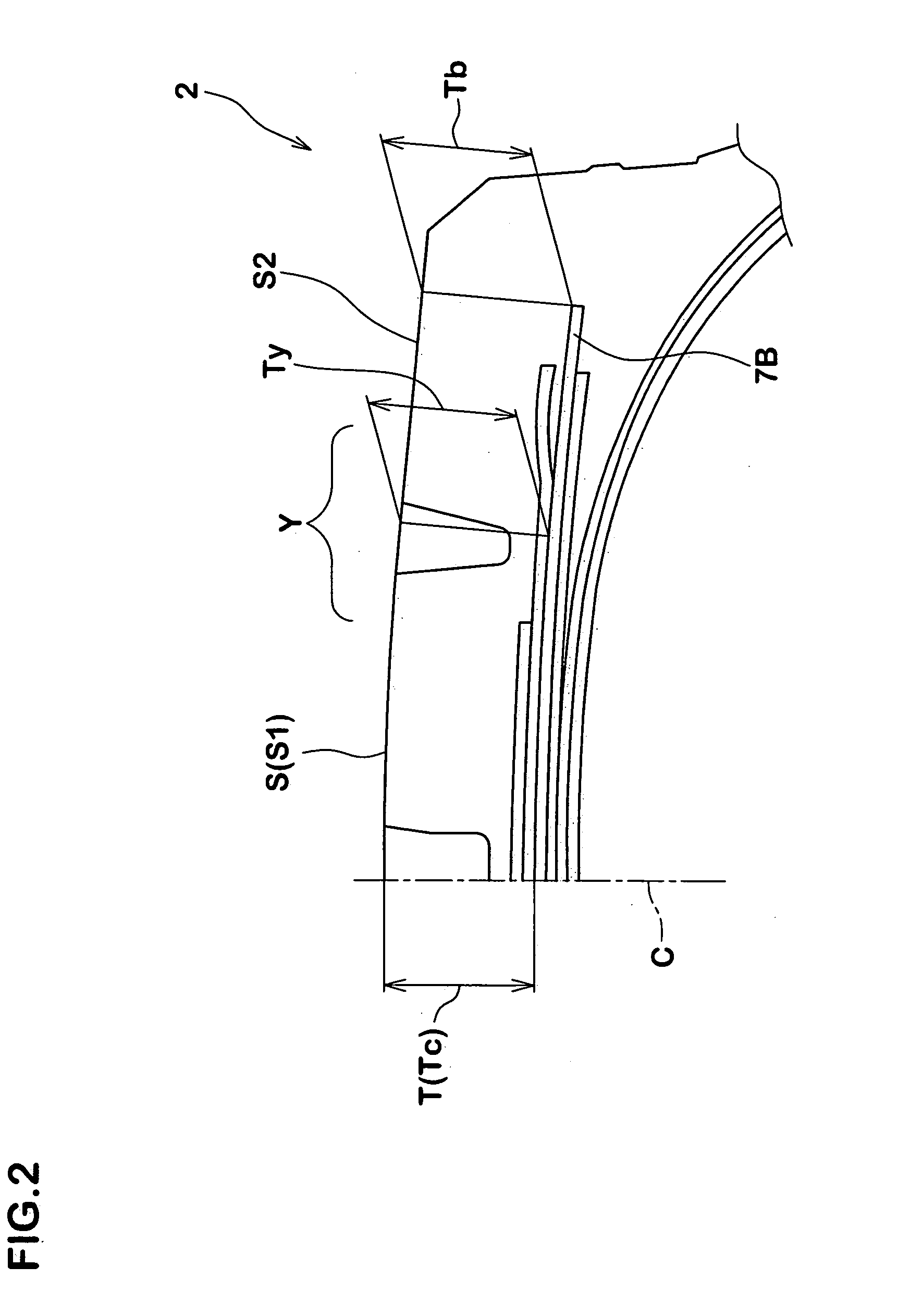
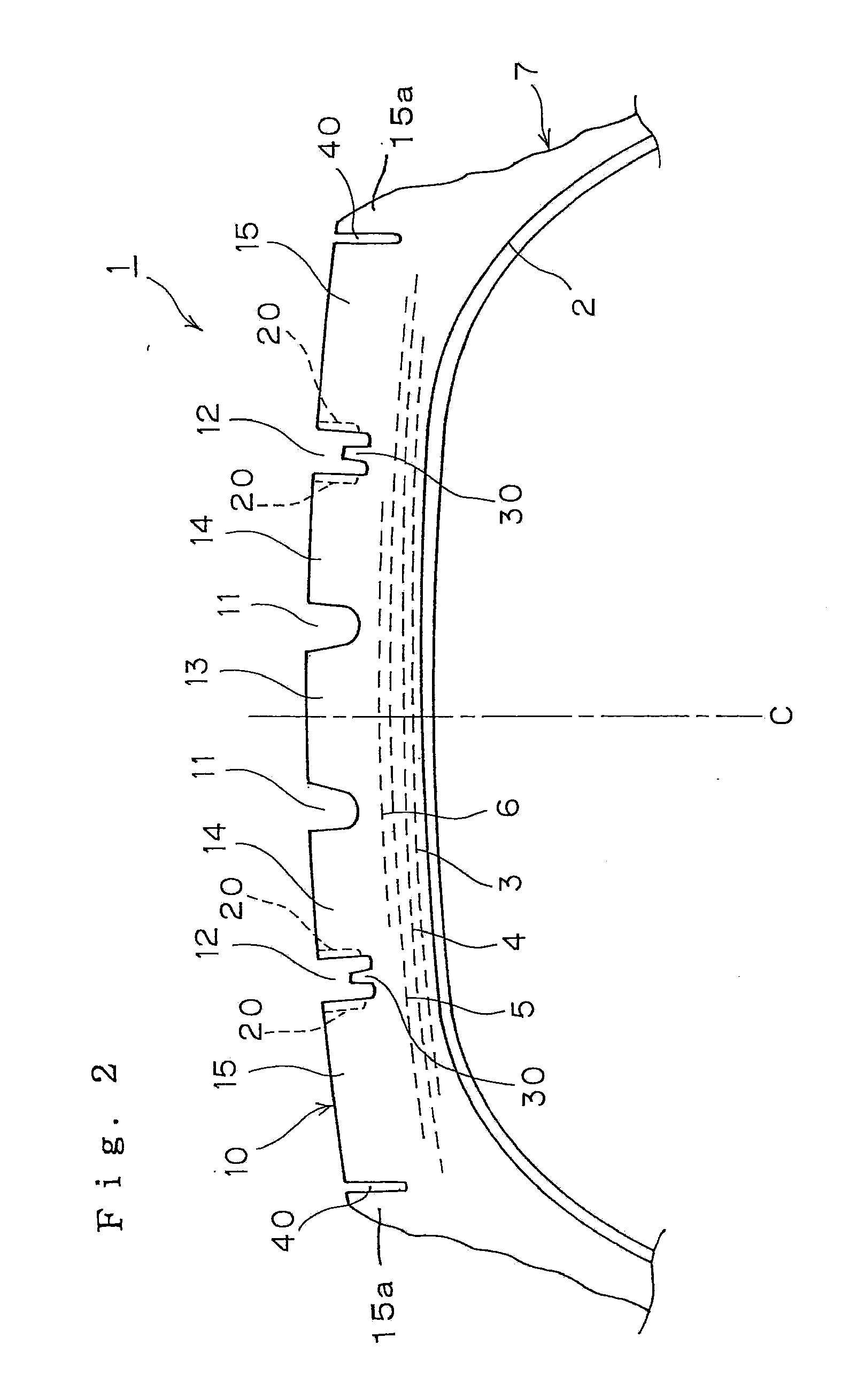
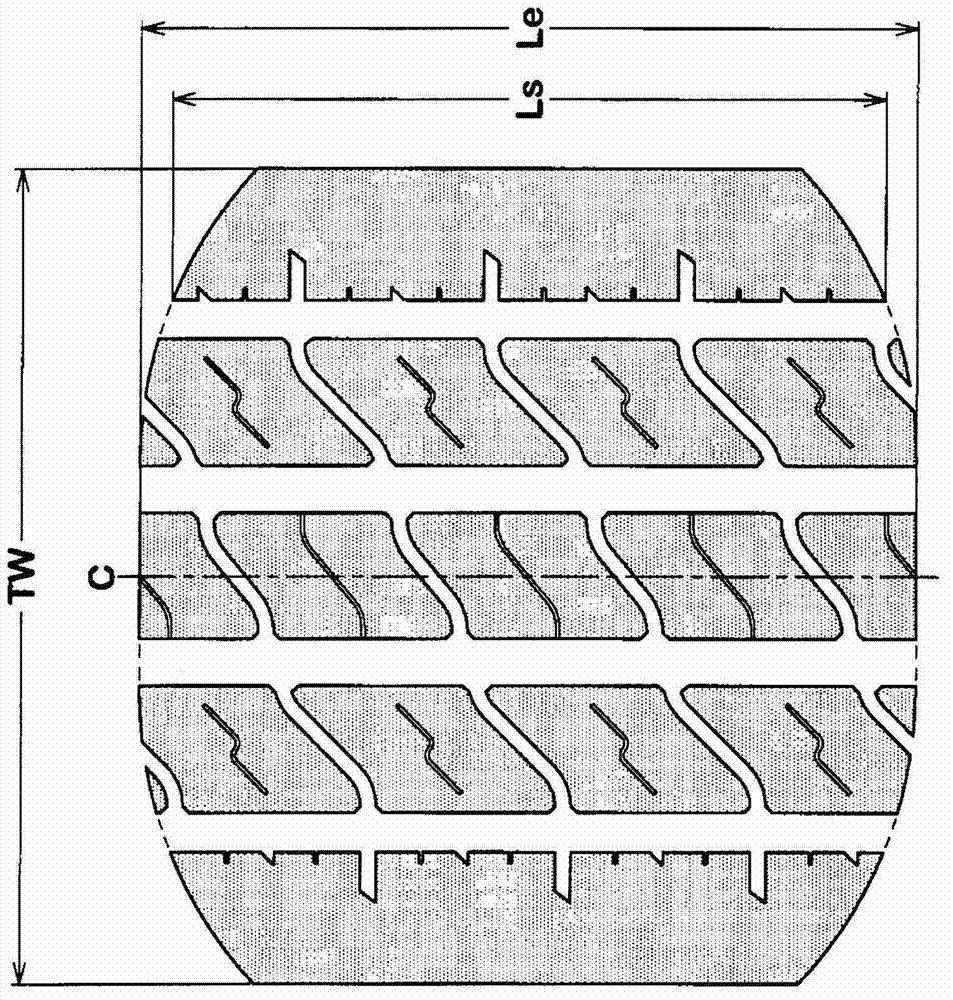
Heavy-duty tire
InactiveUS20050016656A1High level of equalizationInhibits uneven wearPneumatic tyre reinforcementsTyre beadsGround contactEngineering
In a ground-contact surface shape of a tire, when a tangent angle formed between an axial direction of the tire and a tangent X at each point P on a profile line of the tire is defined as θ, a tangent angle θ1 in a ground-contact end point Pd is 25° or smaller. When a minimum value of the tangent angle θ in a region Y which is separated away from a tire equator C by a distance in a range of not less than 0.4 times but not more than 0.7 times a half of the ground-contact width of the tread is defined as θ2, and a tangent angle at a 0.9 times point Pq which is separated away from the tire equator C by a distance of 0.9 times the half of the ground-contact width of the tread is defined as θ3, a difference (θ3−θ2) is set in a range of not less than −10° but not more than +10°.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Pneumatic tire
ActiveUS20130192731A1Improve rigidityAvoid uneven wearTyre tread bands/patternsNon-skid devicesGround contactMarine engineering
A tread portion of a pneumatic ti re includes inner land portions between outer circumferential main grooves disposed most on tread ground-contact end sides and at least one inner circumferential main groove on the inner side thereof. The inner land portions are divided into inner blocks by inner lateral grooves inclined at an angle α of 10 to 40°. The inner lateral grooves consist of first inner lateral grooves and second inner lateral grooves which are alternately arranged in a circumferential direction. The first inner lateral grooves include a wide-width part connecting to the outer circumferential main groove and a narrow-width part connecting to the inner circumferential main groove.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Pneumatic Tire
InactiveUS20080128063A1Improve wear resistanceImprove rigidityTyre tread bands/patternsNon-skid devicesGround contactEngineering
A pneumatic tire is provided which can realize an increase in stone-catching resistance while suppressing uneven wear such as river wear in a tread portion. In a pneumatic tire in which a center rib and intermediate ribs which are defined by four straight-line main grooves, which extend continuously in a circumferential direction of the tire and shoulder ribs which are defined by the main grooves which are situated closer to shoulders of the tire and straight-line thin grooves which extend continuously in the circumferential direction of the tire in the vicinity of tread ground-contacting edges are formed on the surface of a tread of the tire, inclination angles of a shoulder side groove wall of the main groove which defines the shoulder rib and a tire's equator line side groove wall of the thin groove are both such an angle that the shoulder side groove wall and the tire's equator line side groove wall are inclined at an angle of not more than five degrees in a direction in which the width of a proximal portion of the rib is expanded relative to normal lines to the tread.
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
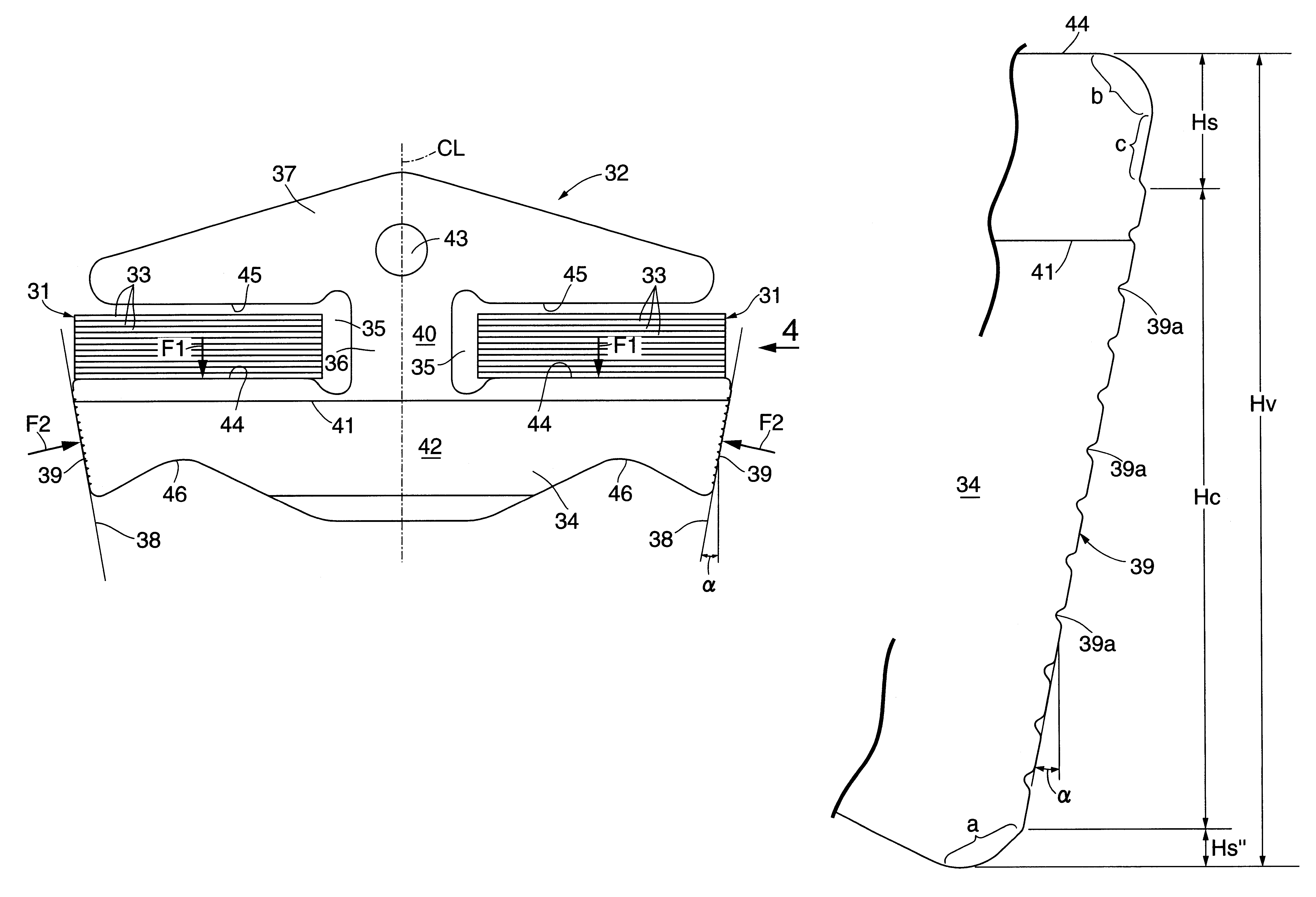
Belt for continuously variable transmission
InactiveUS6599212B2Decreasing V-face heightInhibits uneven wearV-beltsDriving beltsEngineeringPulley
A V-face of a metal element is prevented from being inclined due to a load from a pulley by increasing the height Hs of an upper non-contact portion of the V-face of the metal element. For example, when the height of the V-face is represented by Hv (mm), and the height of the upper non-contact portion of the V-face is represented by Hs (mm), the height Hv of the V-face and the height Hs of the upper non-contact portion are set so that a relationshipis established.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Electric brake
InactiveUS20070062764A1Avoid uneven wearInhibits uneven wearDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesElectrodynamic brake systemsPosition controlPiston
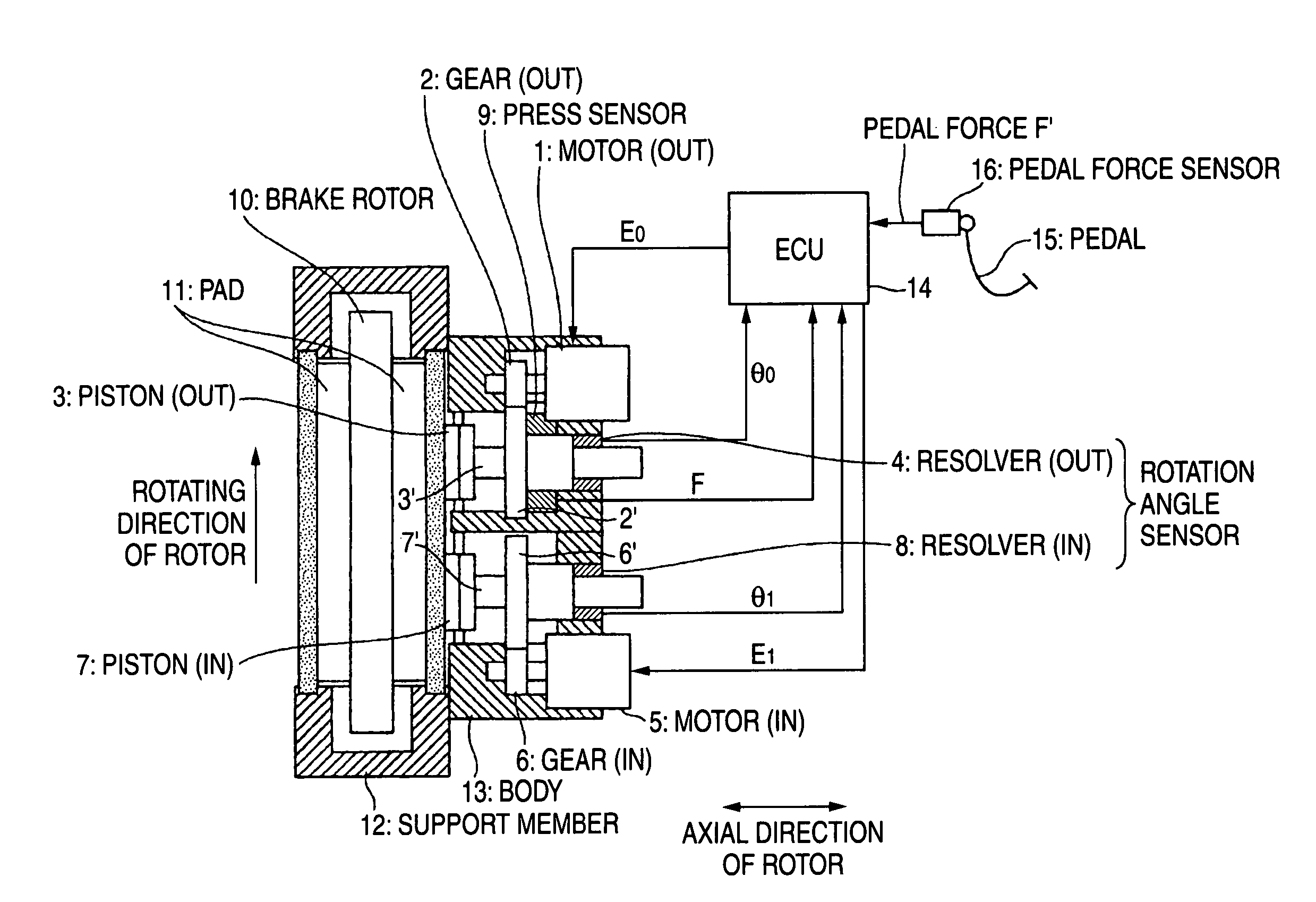
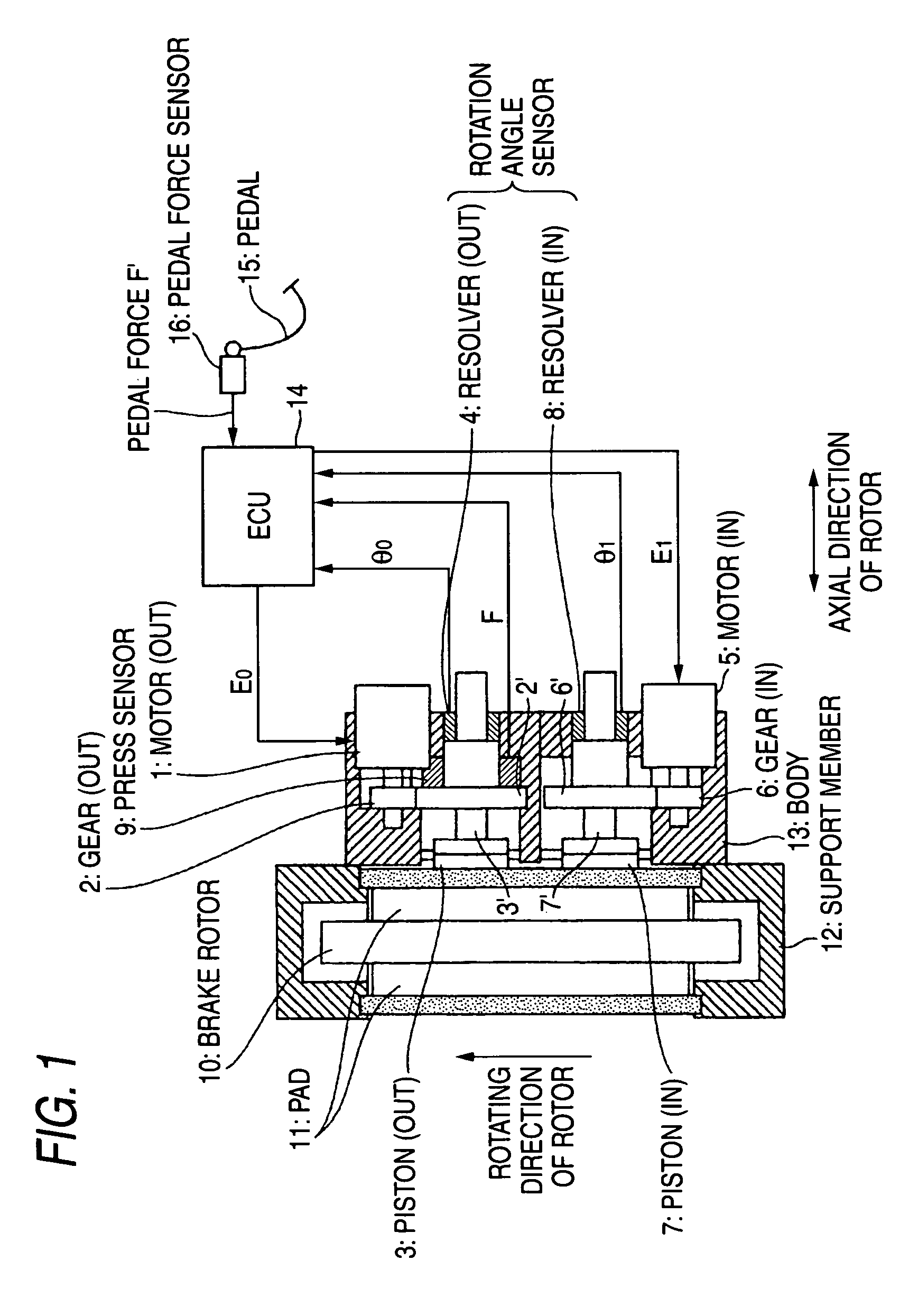
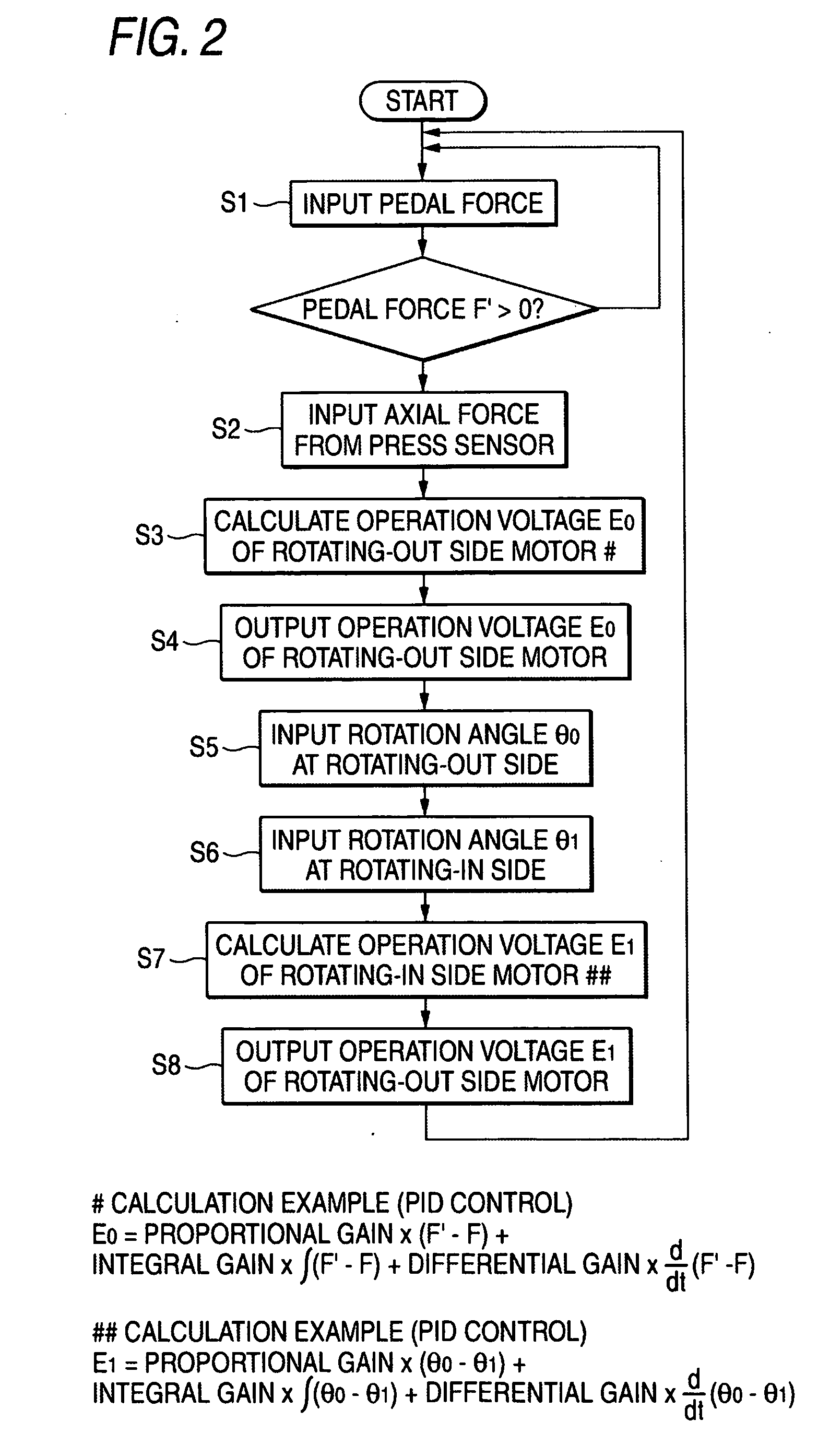
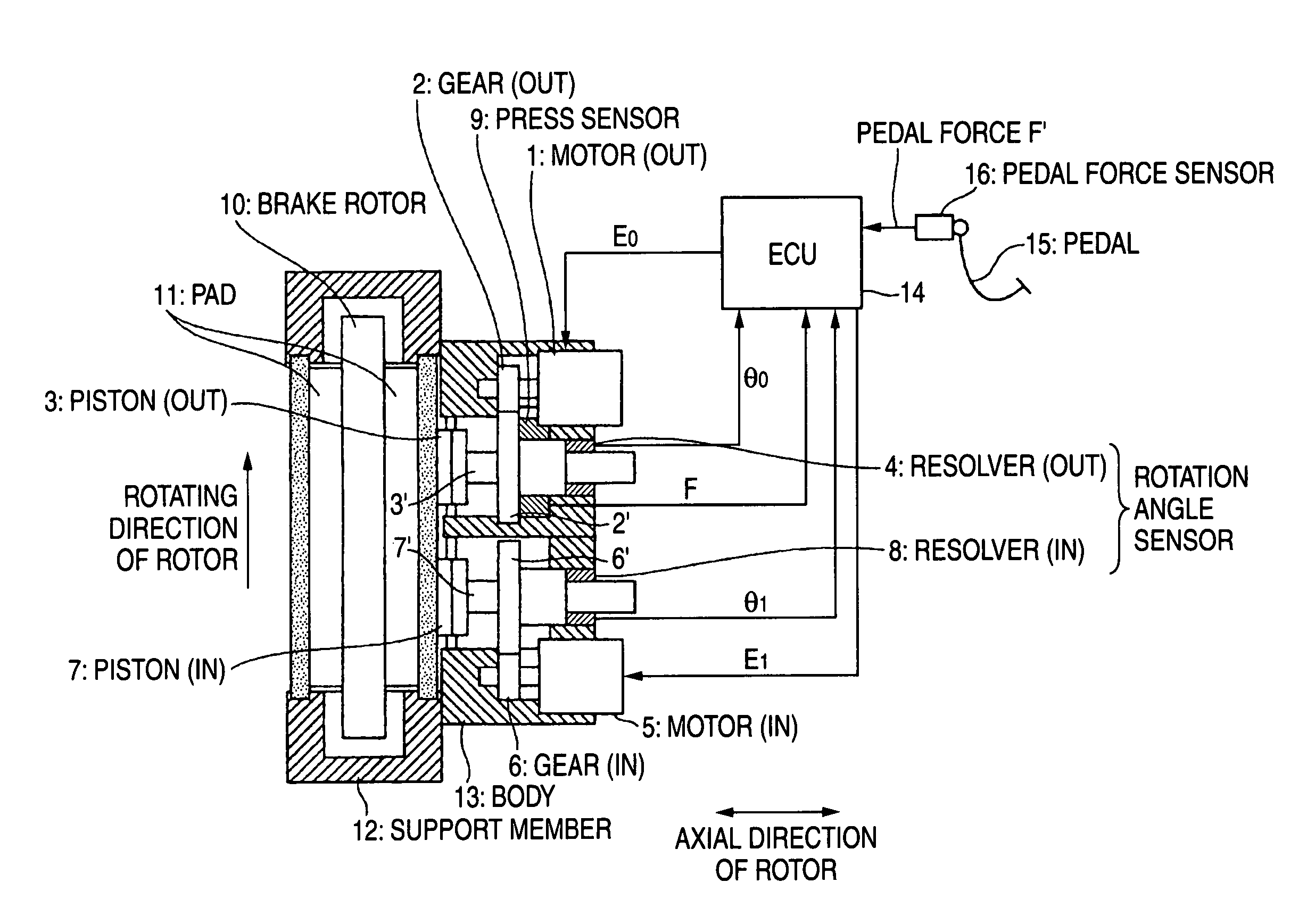
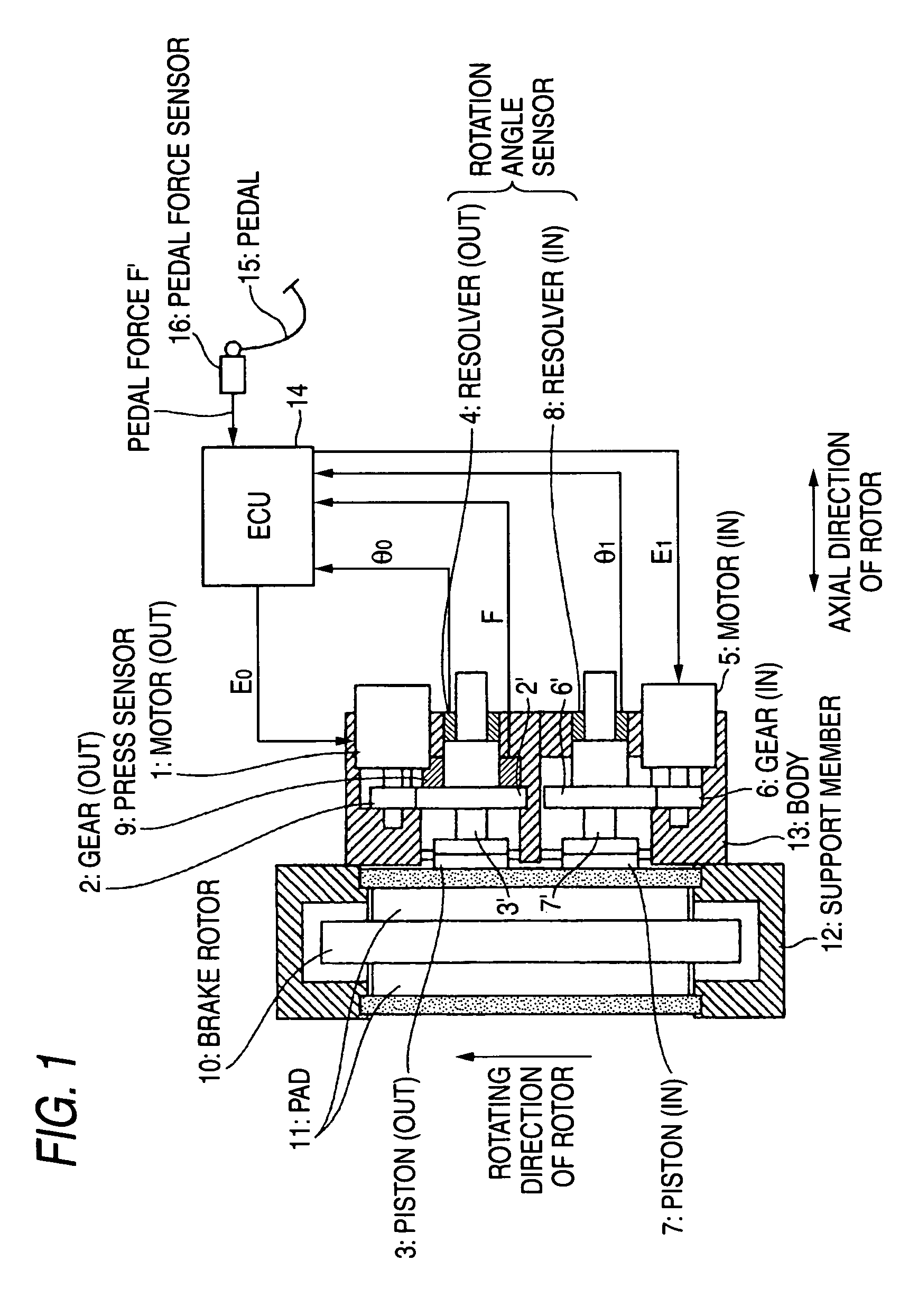
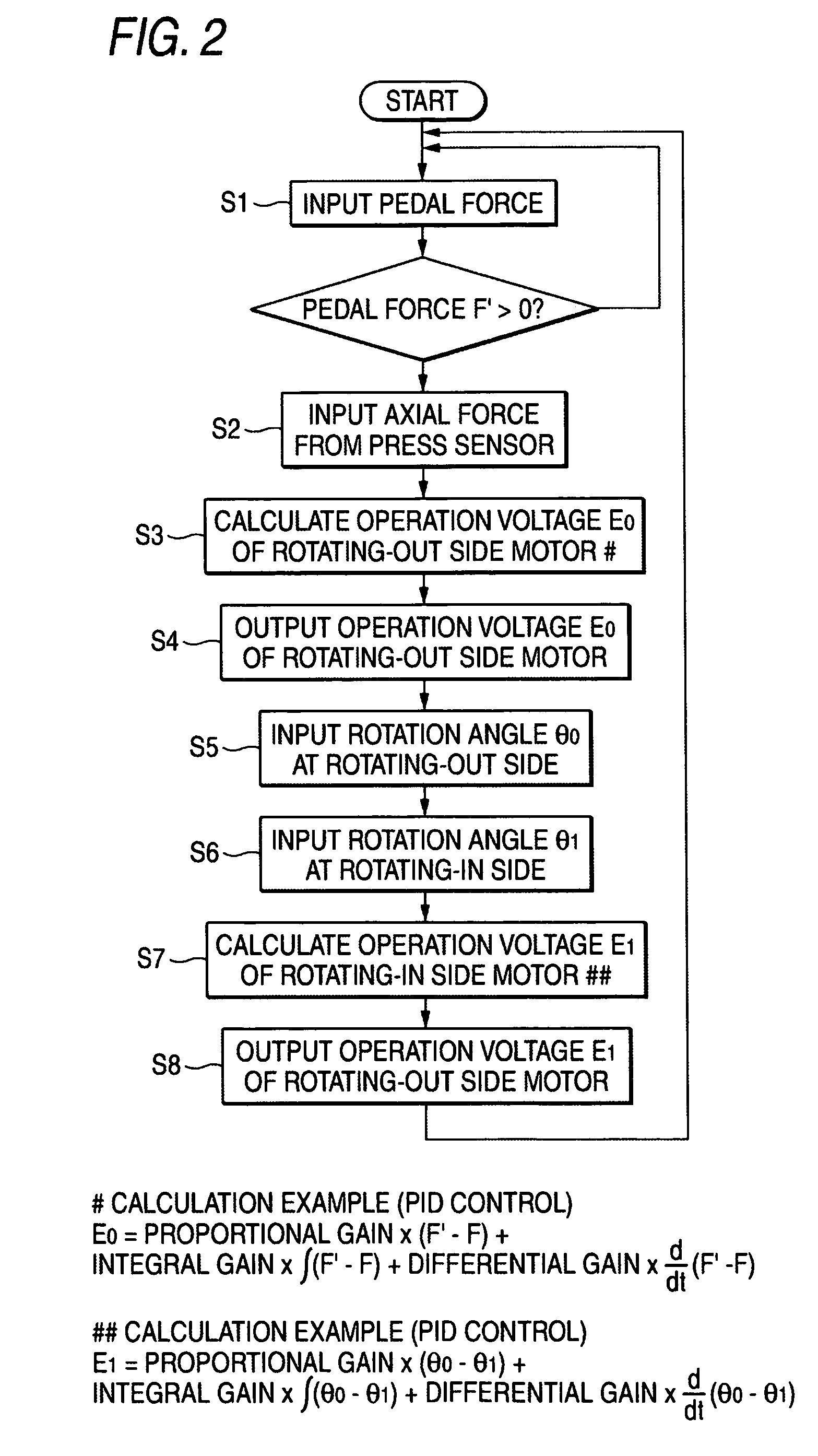
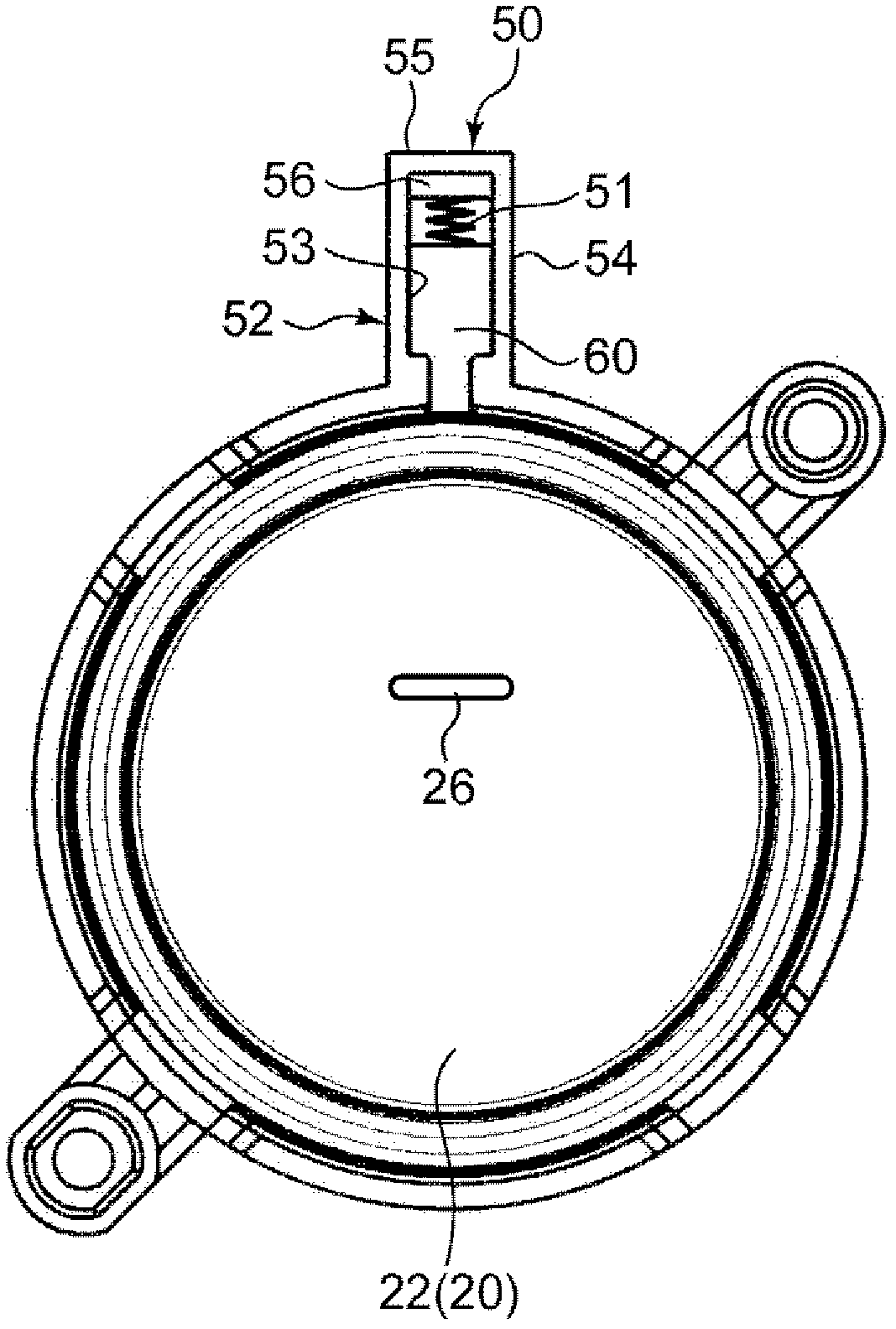
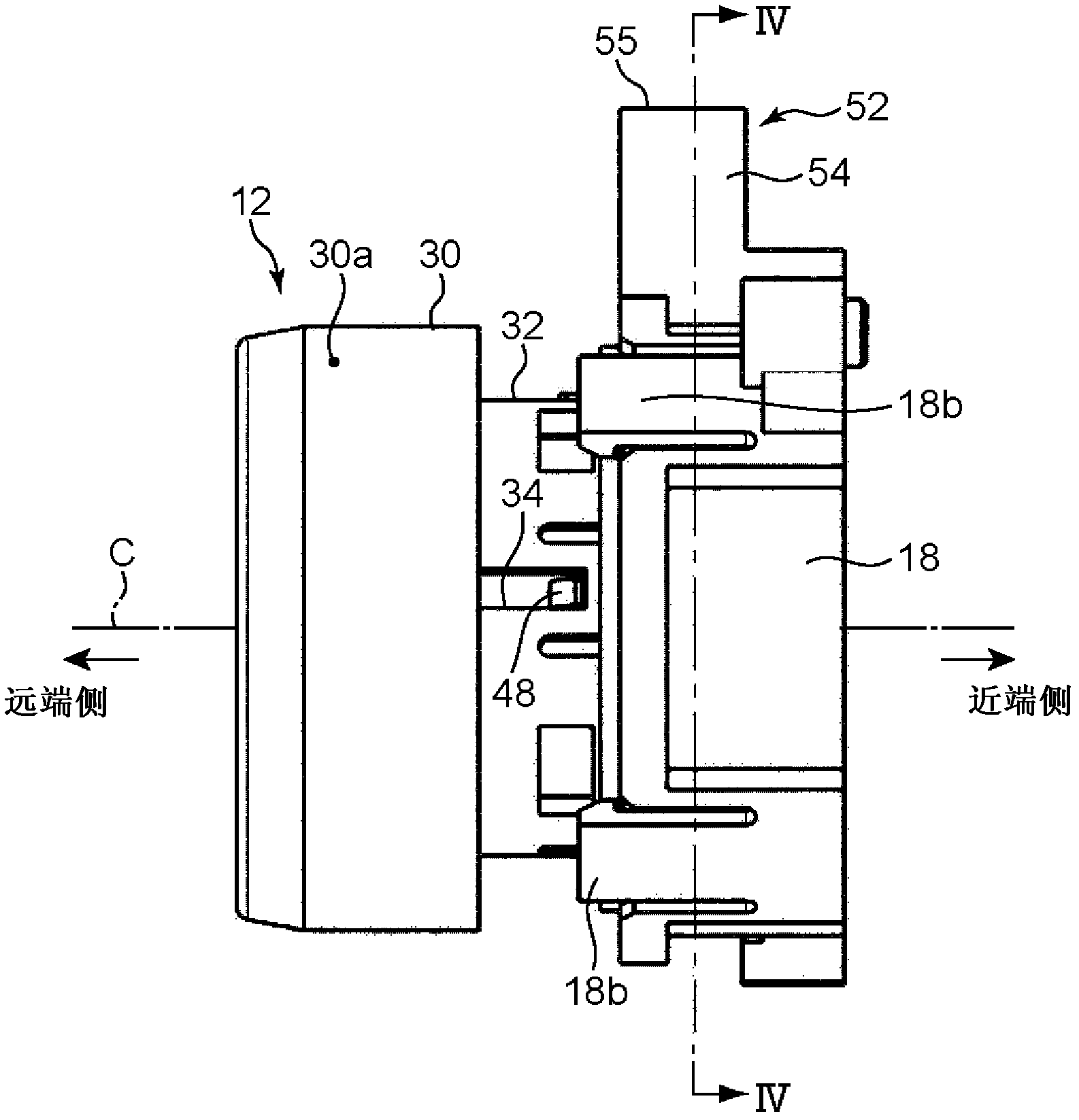
Pistons 3 and 7 are pressed to a friction member 11 at two points that are positioned at a rotating-in side and a rotating-out side in a rotating direction of a brake rotor 10. An axial force control is performed for the piston 3 on the rotating-out side, and a position control based on the position of the piston 3 on the rotating-out side is performed for the piston 7 on the rotating-in side.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE IND CO LTD
Pneumatic tire
InactiveCN101168342AImprove traction performanceImprove braking effectTyre tread bands/patternsEngineering
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
Device and method for removing burr
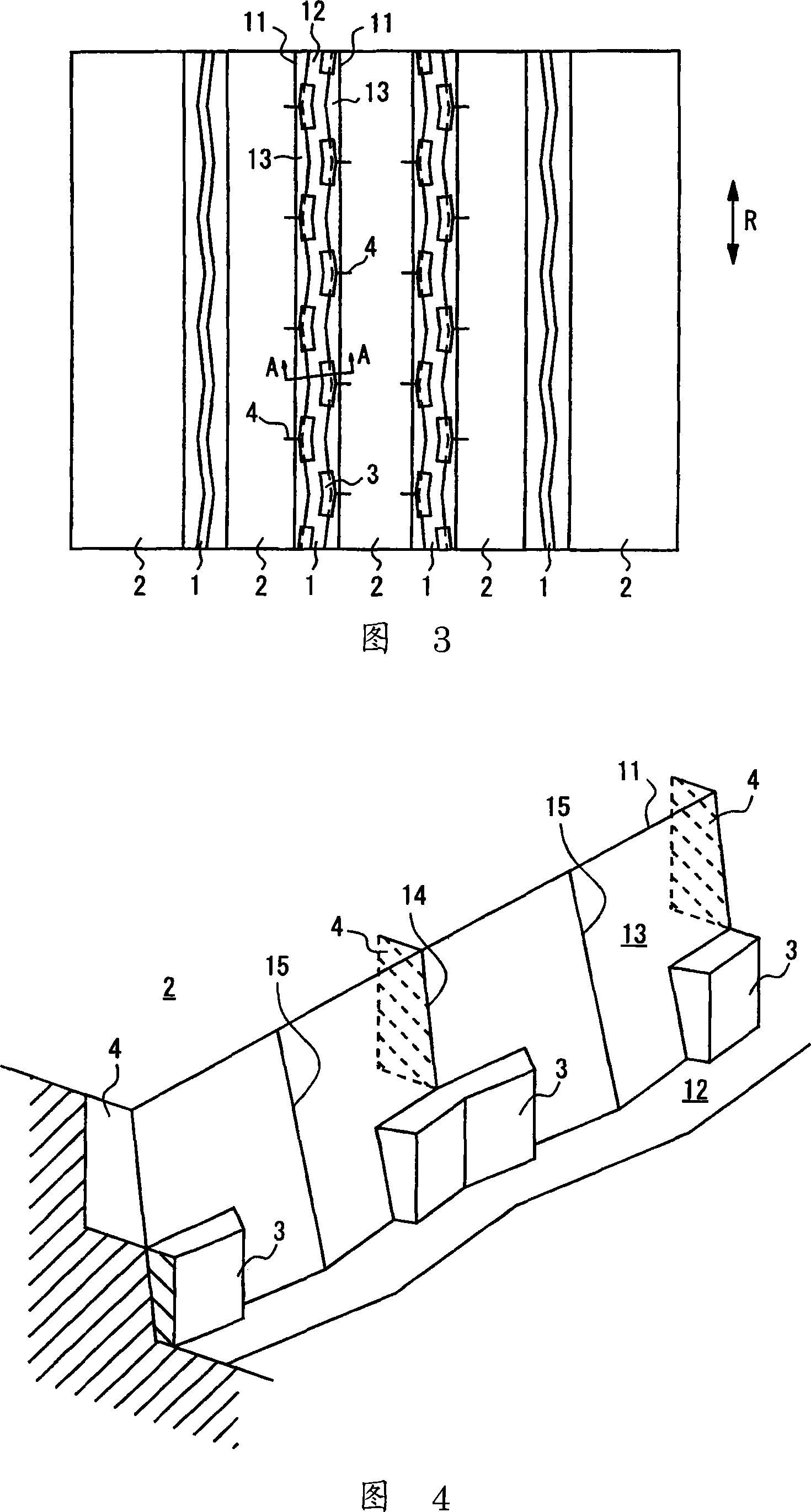
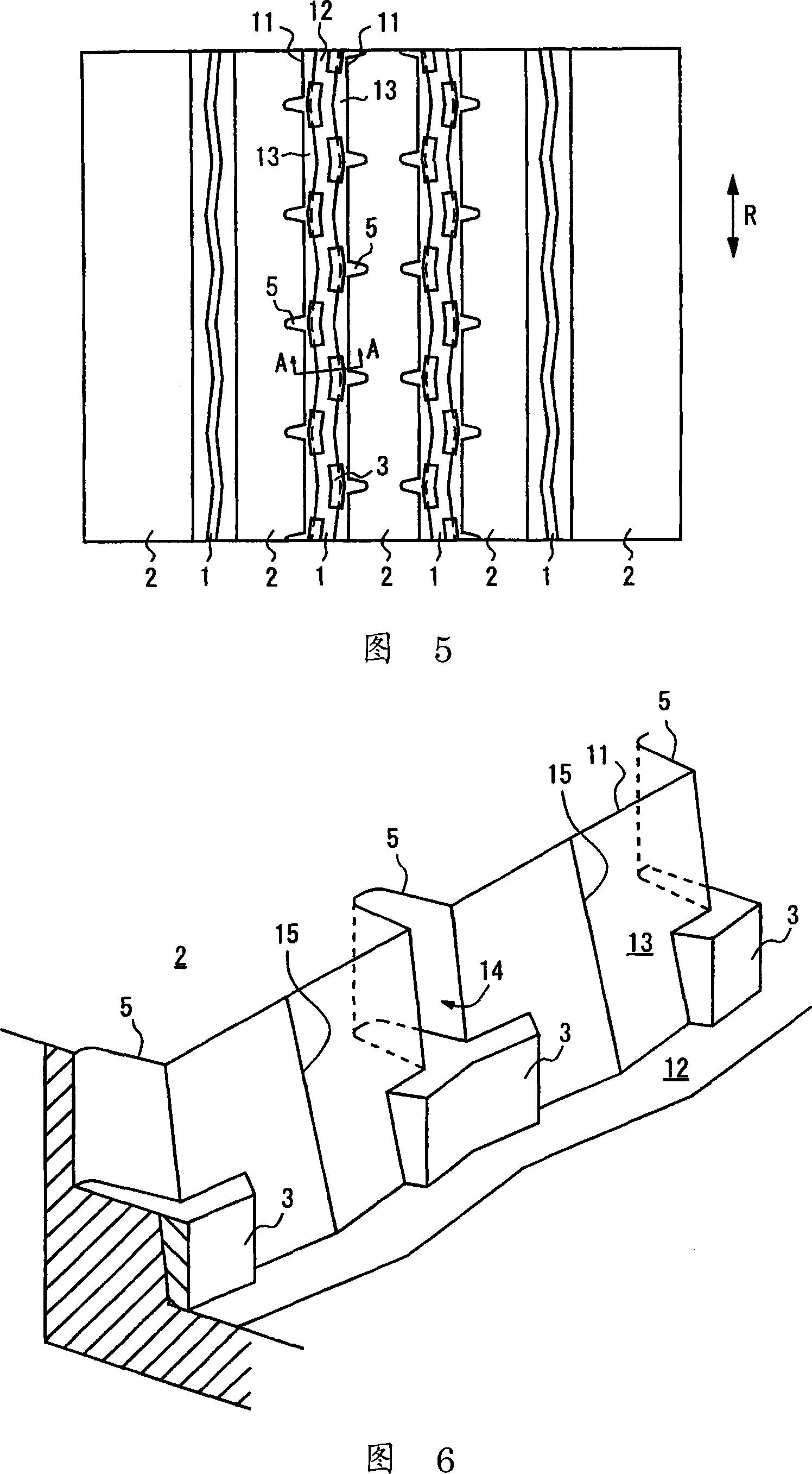
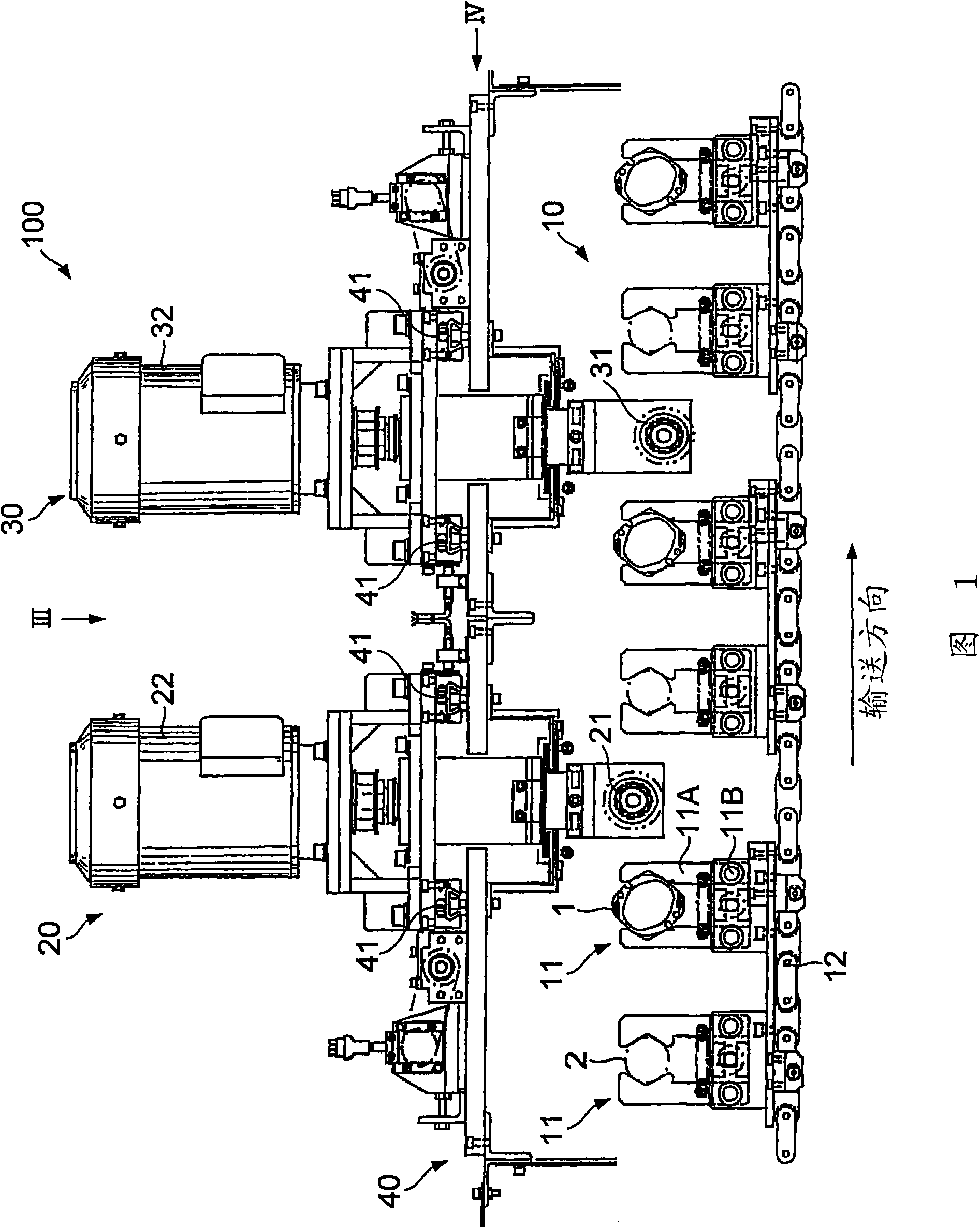
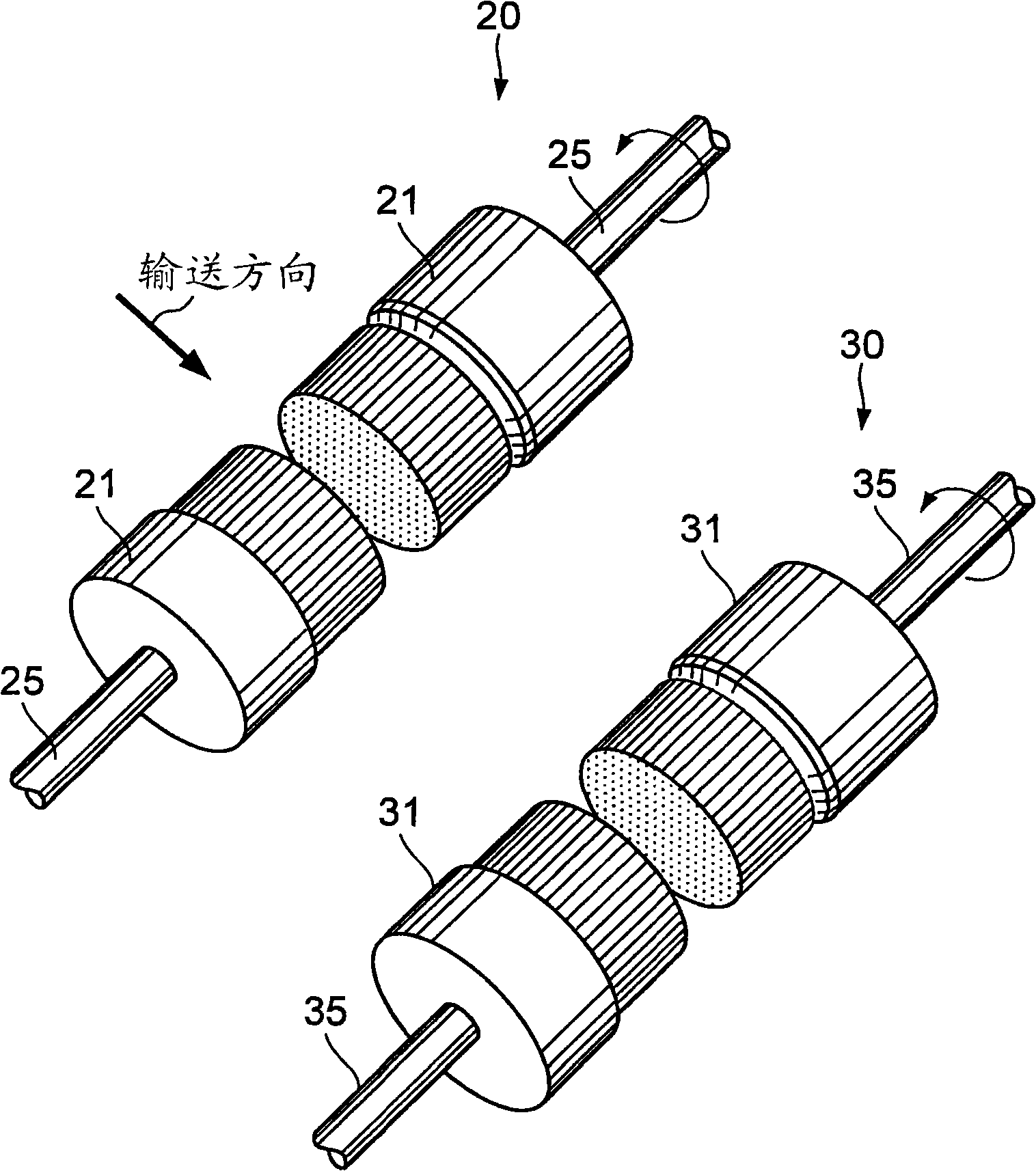
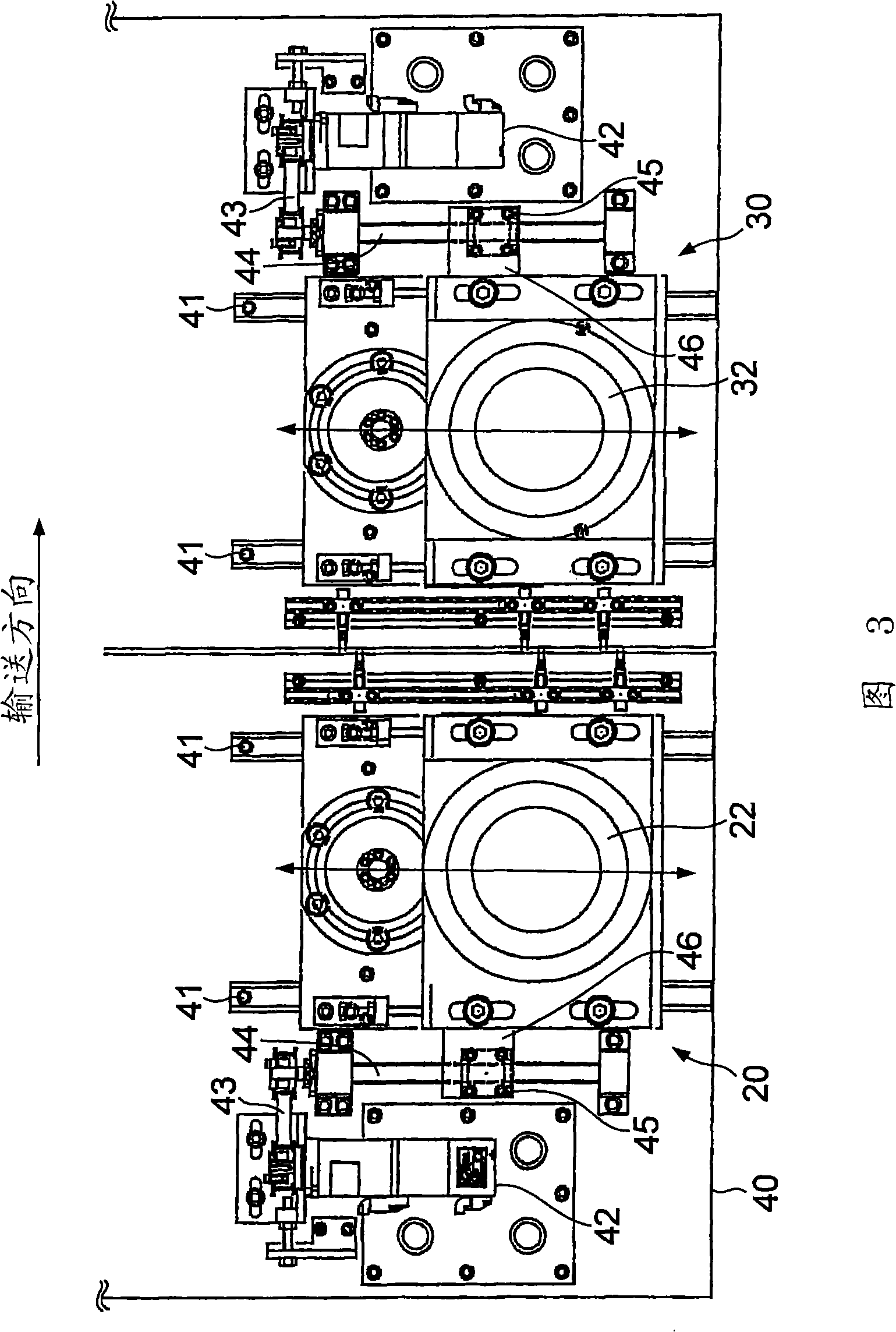
InactiveCN101274414AInhibits uneven wearHigh removal accuracyEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesEngineeringStraight path
The invention provides a burr removal device and a burr removal method. The burr removal device (100) comprises: grinding components (21, 31) which includes rotating shafts (25, 35) and grinding faces (21C, 31C) rotated along with and orthogonal to the rotating shafts (25, 35); a displacement component (10) which enables a grinded component (1) and the grinding components (21, 31) to relatively displace down a straight path; driving components (20, 30) which drive the grinding components (21, 31) to apply the grinding components (21, 31) to the grinded component (1) at a first grinding position that deviates from a central path of the grinded component (1), and to apply the grinding components (21, 31) to the grinded component (1) at a second grinding position that is isolated from the central path of the grinded component (1) and offset at one side opposite to the first grinding position.
Owner:KYB CORP
Disc brake apparatus
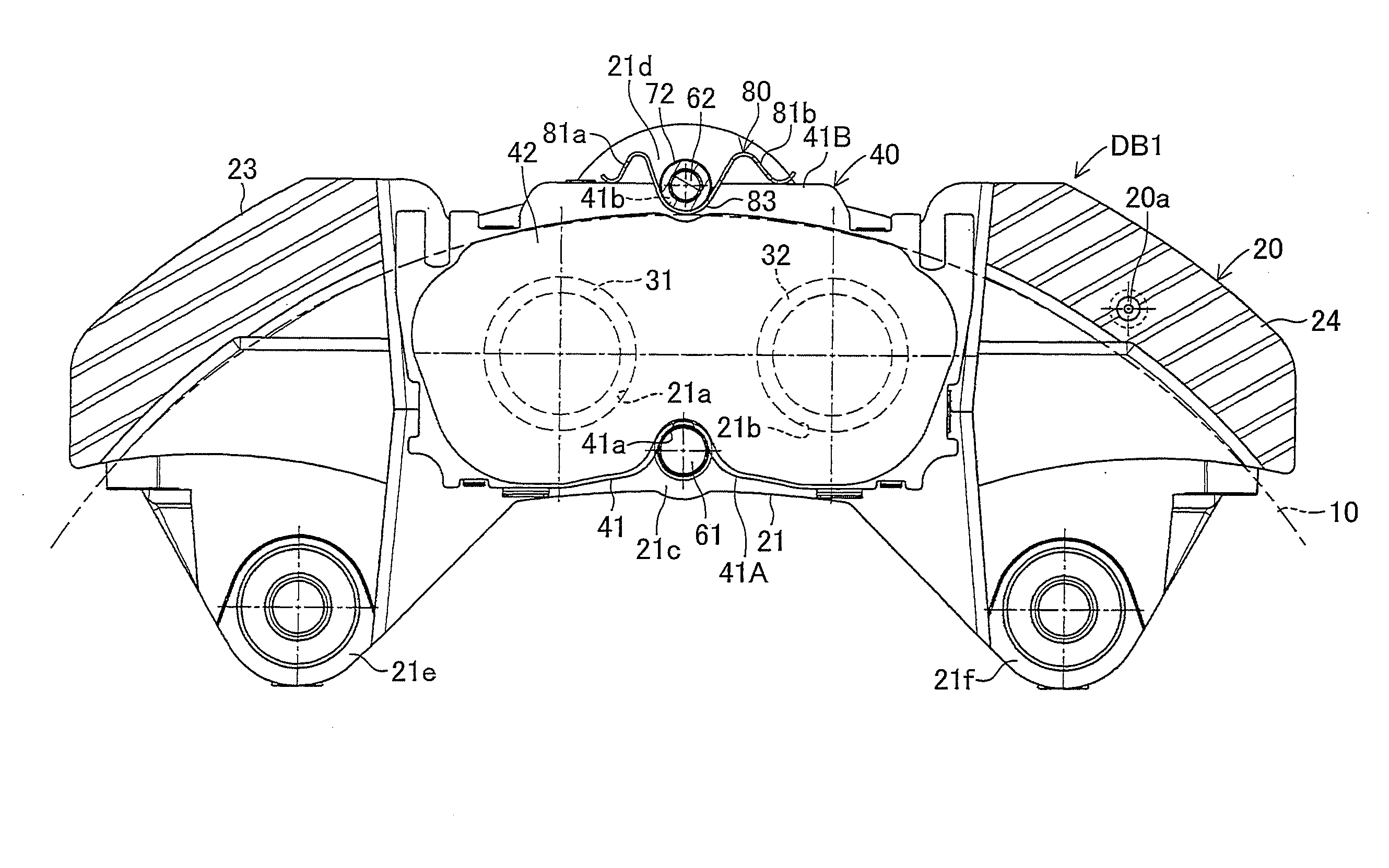
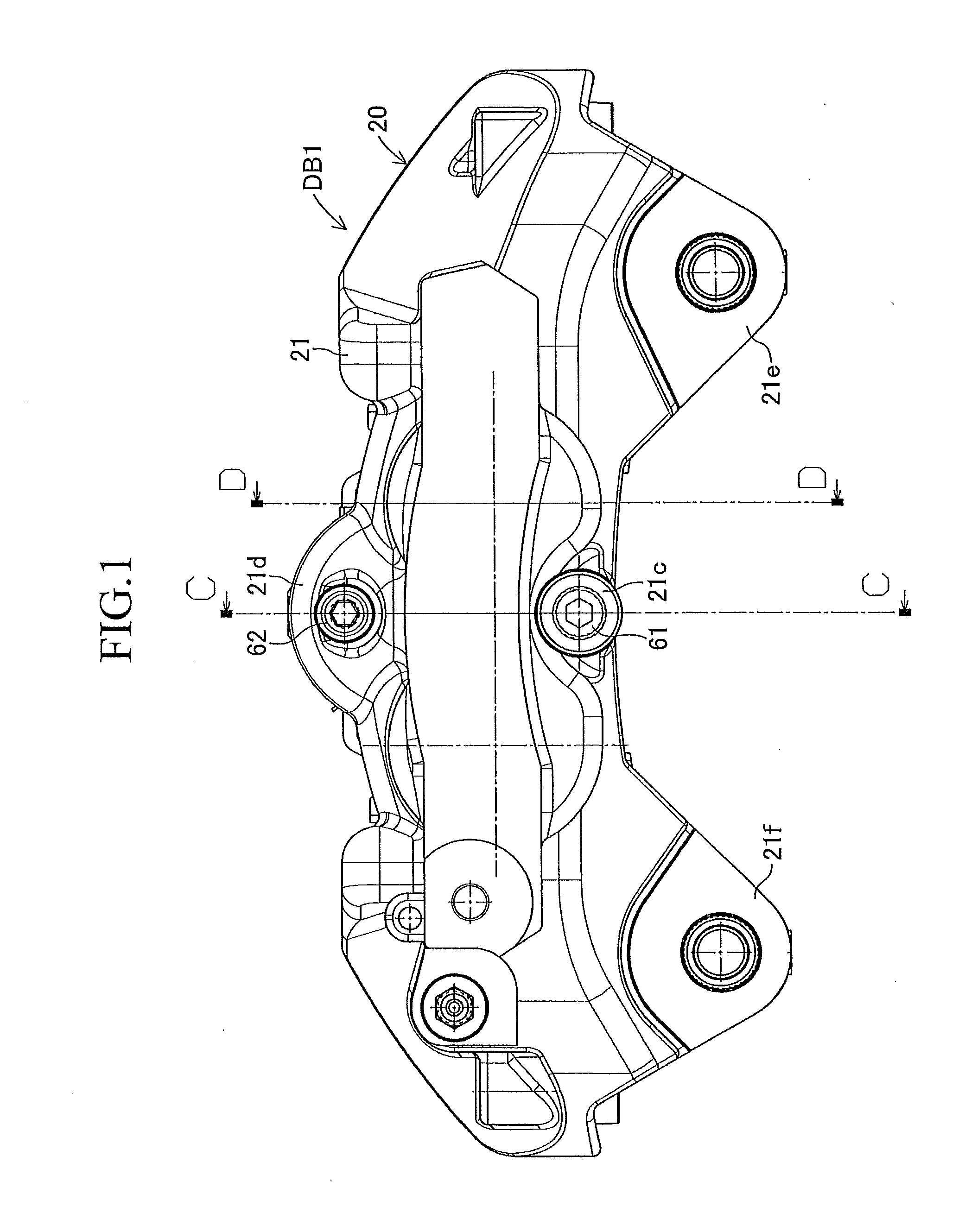
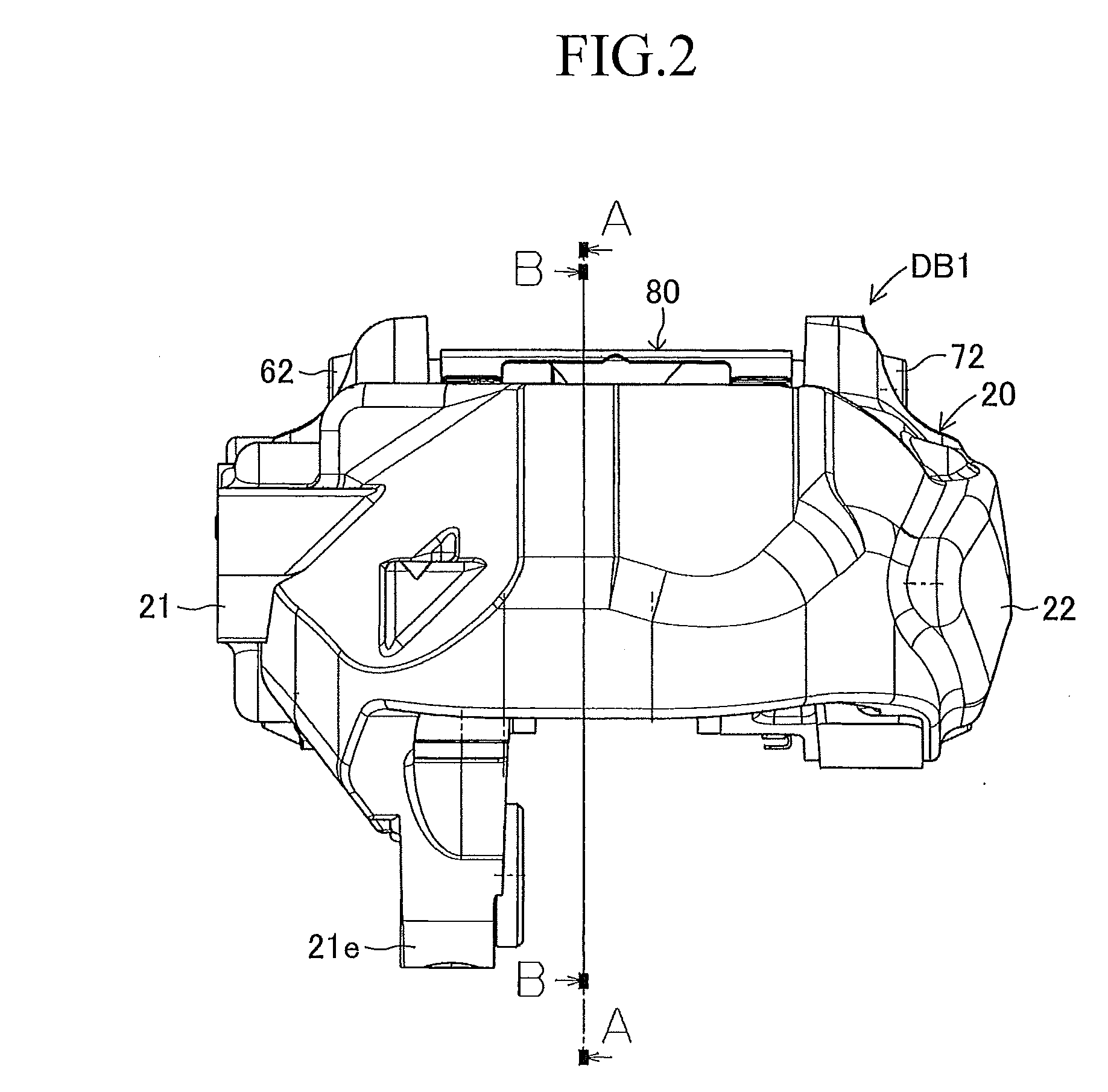
InactiveUS20100243384A1Suppress generation of brake noiseReduce processing costsAxially engaging brakesBrake actuating mechanismsRolling momentAbutment
The present invention is to stabilize behavior of brake pads at the time of braking of a disc brake so as to suppress generation of brake noise, and also to reduce the roll moment of the brake pads generated at the time of braking so as to suppress uneven abrasion of linings. A back plate (41) of a brake pad (40) is biased inward in the rotor radial direction by a plate spring (80). The back plate (41) is engaged at two points with an inner periphery support shaft (61) provided integrally with a caliper (20) on a V-shape inner peripheral abutment (41a) (provided in the back plate (41) on the inner side of a lining (42) in the rotor radial direction and on the center in the rotor circumferential direction), and engaged at one point with an outer periphery support shaft (62) provided integrally with the caliper (20) on an outer peripheral abutment (41b) (provided in the back plate (41) on the outer side of the lining (42) in the rotor radial direction and on the center in the rotor circumferential direction).
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Electric brake
InactiveUS7806241B2Avoid uneven wearInhibits uneven wearDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesAxially engaging brakesPosition controlPiston
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE IND CO LTD
Heavy duty tire
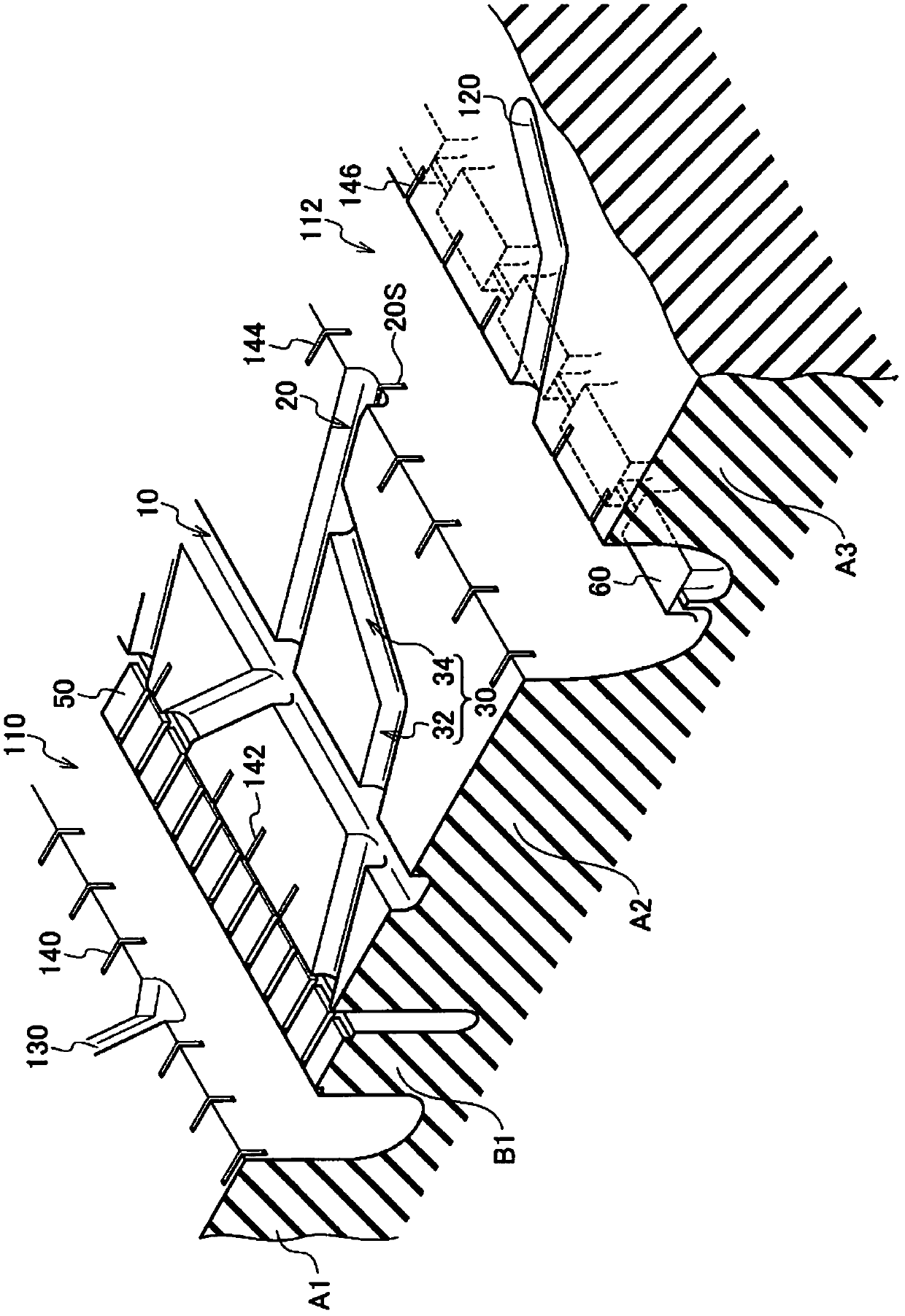
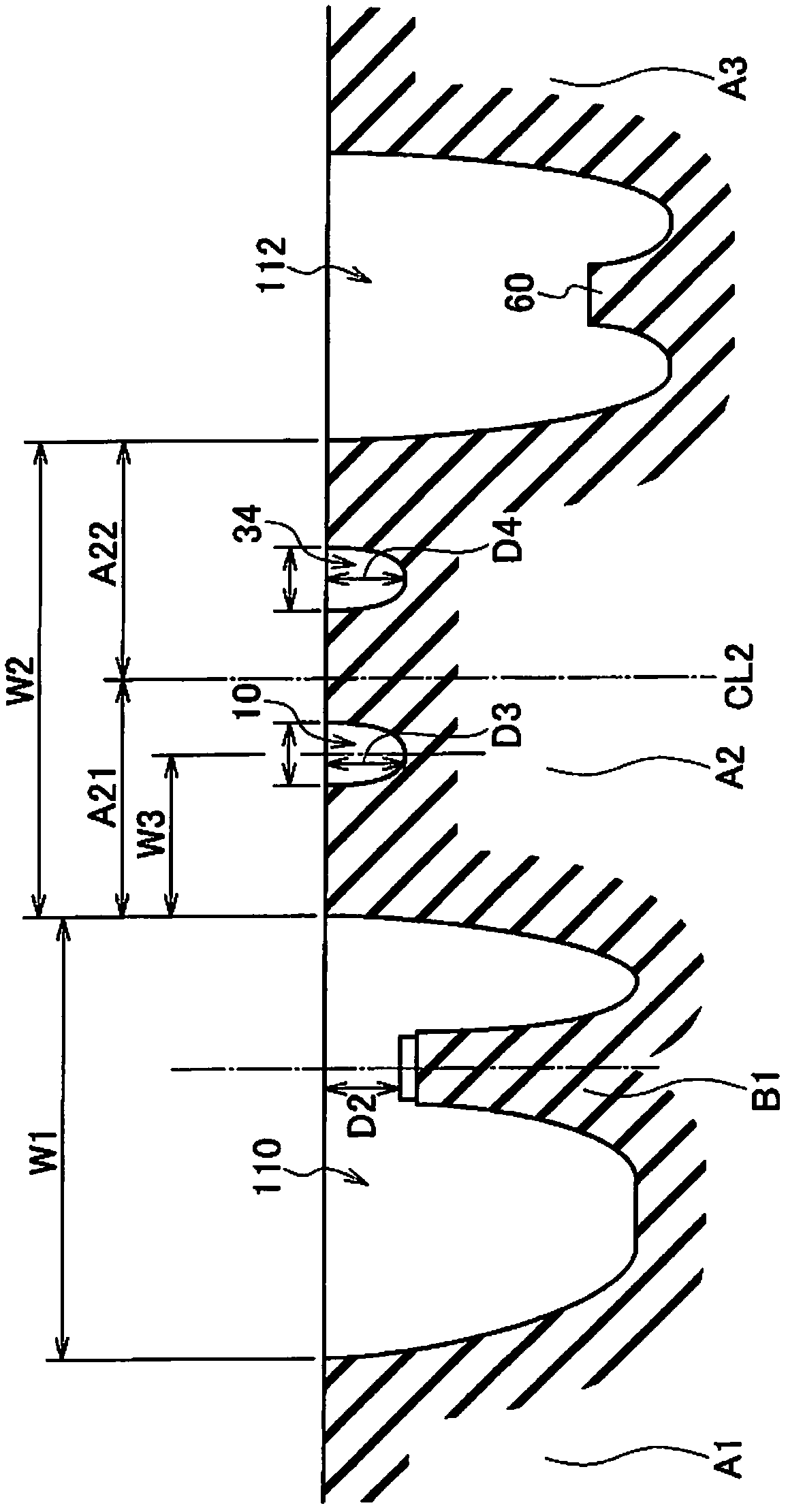
InactiveUS20120168048A1Inhibits uneven wearImprove wettabilityHeavy duty tyresHeavy duty vehicleEngineeringHeavy duty
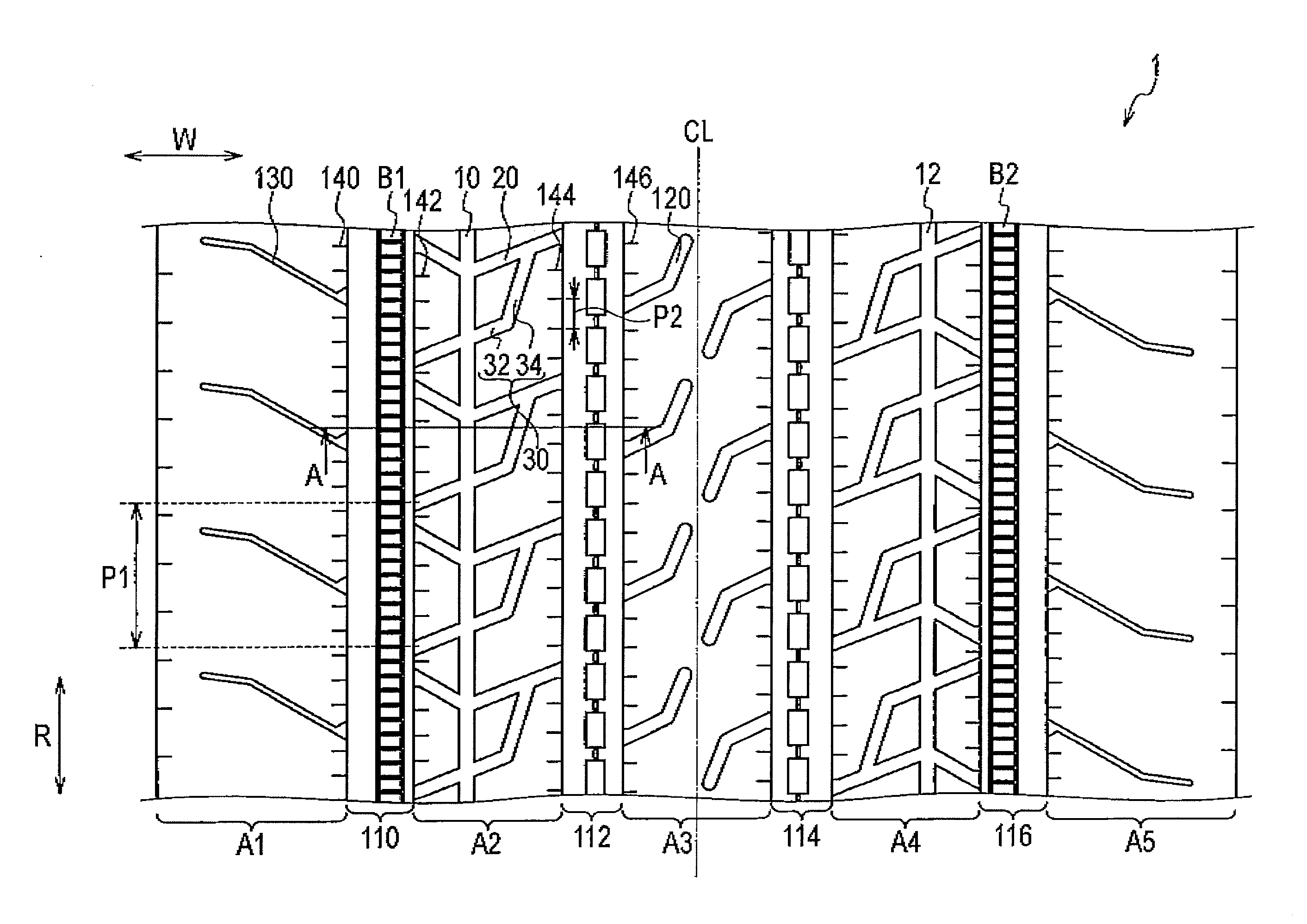
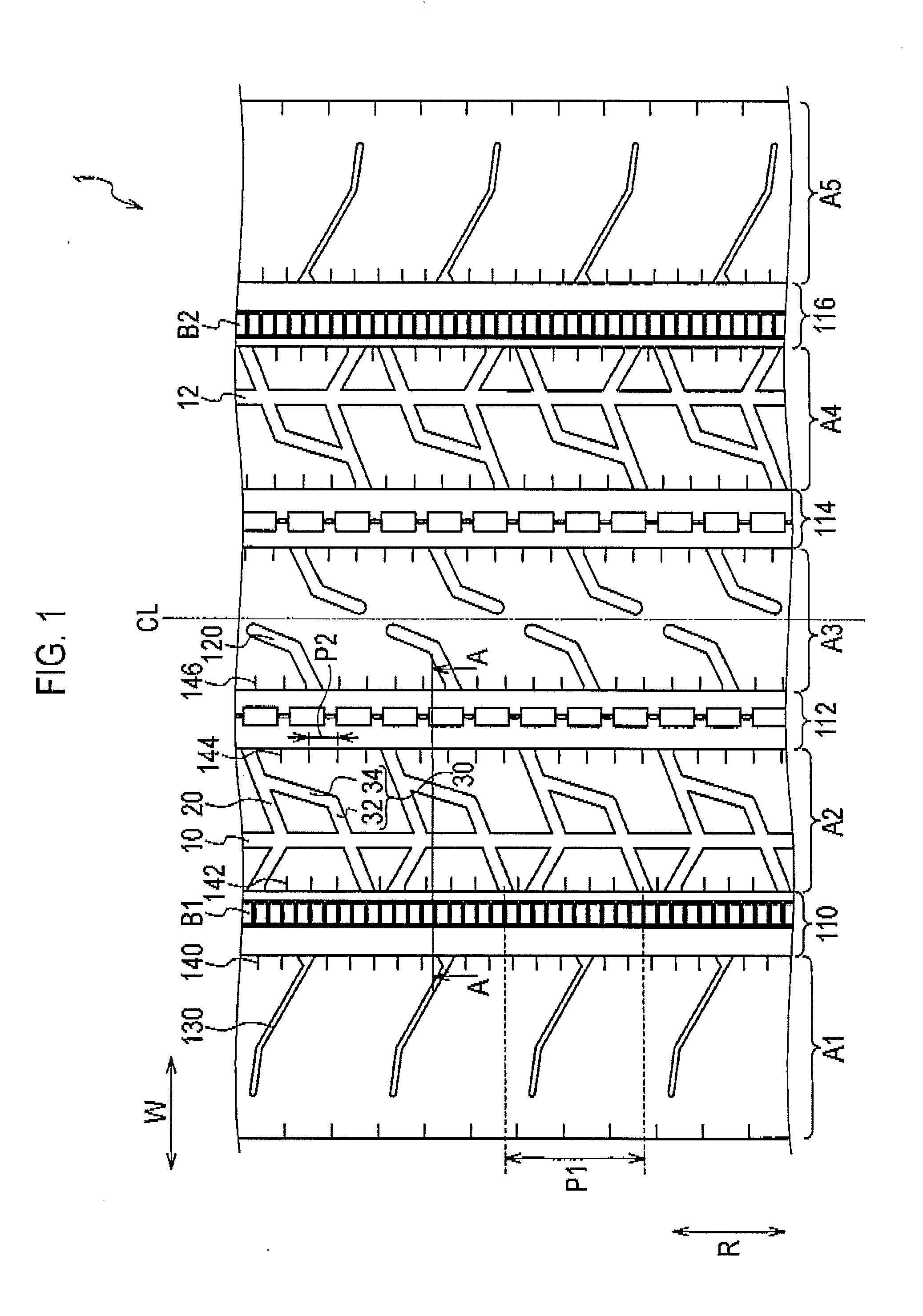
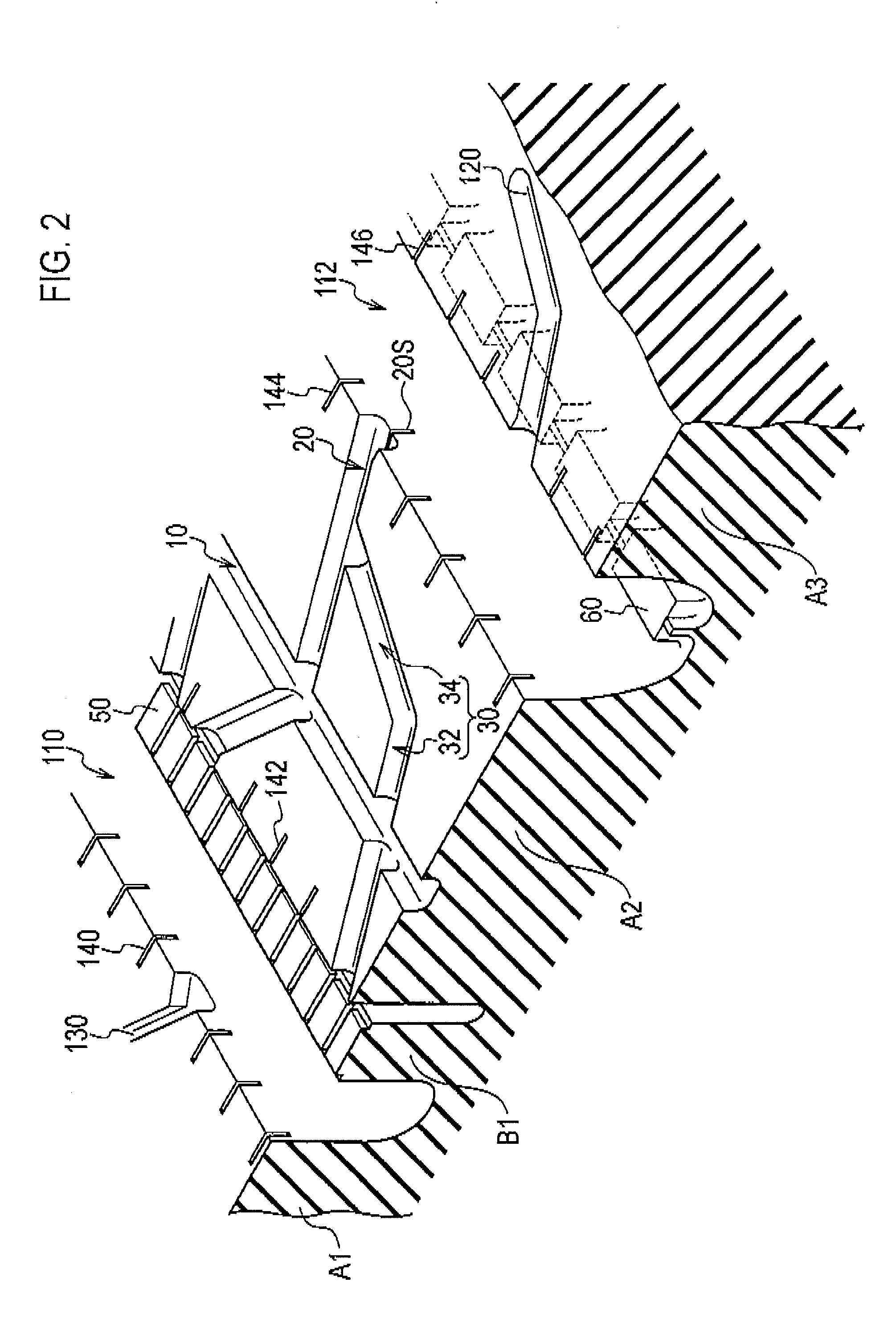
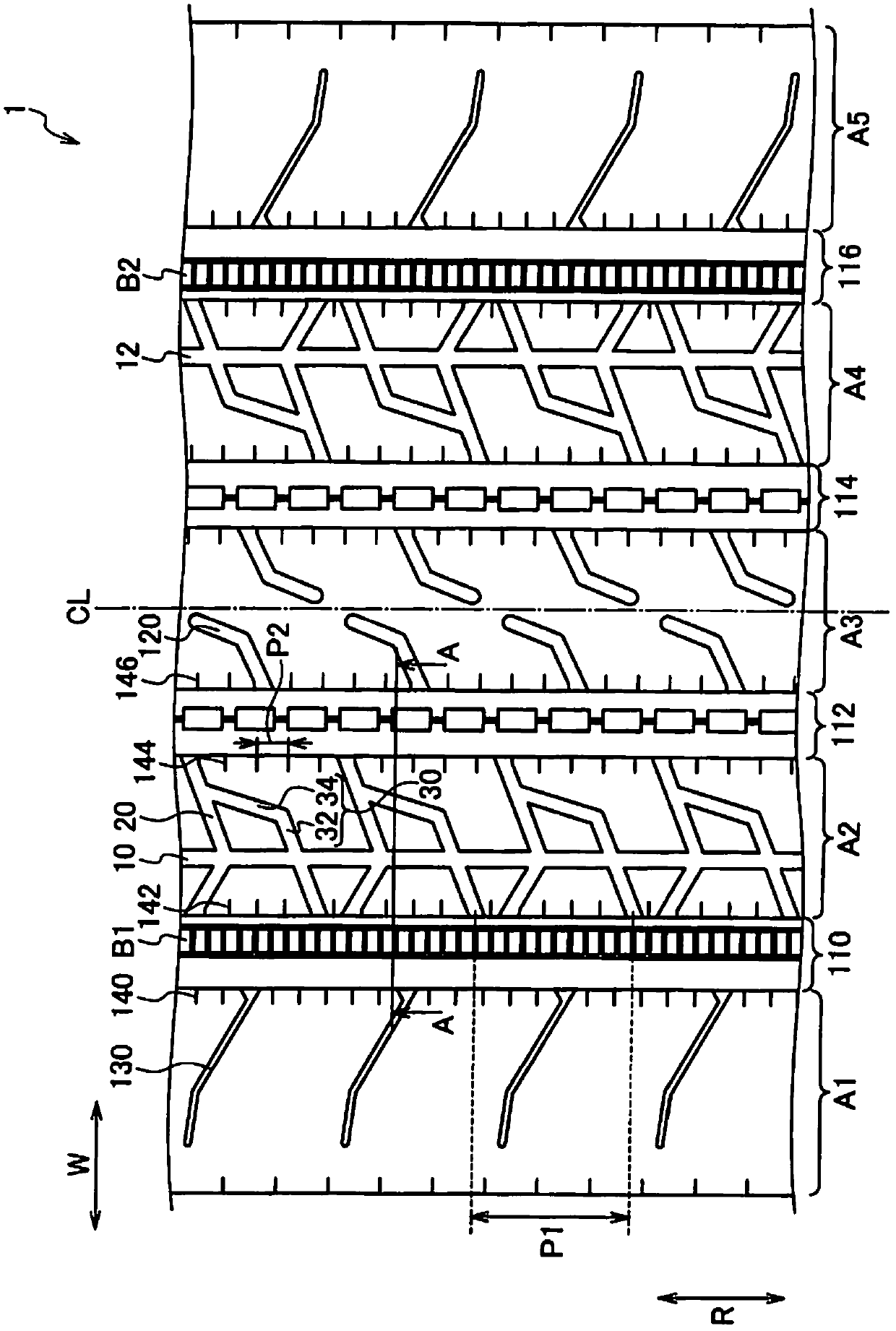
A heavy duty tire comprising: a shoulder rib (A1) (shoulder rib (A5)) which is provided to a tread shoulder unit; a second rib (A2) (second rib (A4)) which is adjacent to the shoulder rib (A1) with a circumferential groove (110) (circumferential groove (116)) interposed therebetween and is provided further toward the tire equator side than the shoulder rib (A1); and an uneven wear absorbing rib (B1) (uneven wear absorbing rib (B2)) provided within the circumferential groove (110) and located further toward the inside in the tire radial direction than the tread surfaces of the shoulder rib (A1) and of the second rib (A2). Circumferential narrow grooves (10, 12) having a smaller width than the circumferential grooves (110, 116) are formed in the second ribs (A2, A4). Each circumferential narrow groove (10, 12) is formed in such a manner that, when the tire is mounted on the vehicle, the circumferential groove (10, 12) is located on the outer side of the tire with reference to the center of the second rib (A2, A4) in the tread width direction.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Pneumatic Tire
InactiveUS20070204947A1Degraded drivabilityReduced wear resistance requirementsPneumatic tyre reinforcementsWheelsGround contactInternal pressure
The ground contact pressure on land portions 44 is uniformed so that drivability is improved and uneven wear is suppressed to improve wear resistance. The parts of the carcass layer 28 and belt layer 33 overlapping with the main grooves 42 are convexly curved toward the outside in the radial direction due to the internal pressure. The reinforcing layer 49 is arranged at the position spaced from the neutral axis of deformation in the compressed side in a certain distance, i.e. radially inside of the radially outermost carcass ply 30, and the steel cords 47 which extend in the direction including the tire width direction and its approximate direction and which act as supports for resisting against the compression force are embedded in the reinforcing layer. As a result, the above-mentioned curved deformation can be effectively suppressed.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Tire
ActiveCN104275989AInhibits uneven wearInhibit wearTyre tread bands/patternsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Provided is a tire which is configured so that driving stability and water discharge properties on a wet road surface can be maintained and so that the uneven wear of the treading surface of the tread can be minimized. A tire is configured in such a manner that the treading surface of the tread has lands defined by circumferential grooves extending in the circumferential direction of the tire, each of the lands having arranged therein lateral grooves extending across the land. The lateral grooves are arranged so that, when the lateral grooves are projected on the equatorial plane of the tire, lateral grooves adjacent to each other in the circumferential direction of the tire do not overlap each other. Each of the lateral grooves is composed of: a center region extending tilted relative to the width direction of the tread; and side regions extending from both ends of the center region toward circumferential grooves at a tilt angle relative to the width direction of the tread, the tilt angle being less than the tilt angle of the center region. Each of the side regions has a groove width expanding toward a circumferential groove. The lateral grooves have sipes extending inward in the radial direction of the tire from the bottoms of the lateral grooves, each of the sipes having a shallow bottom only in the center region, the shallow bottom being disposed near the boundary between at least the center region and a side region in such a manner that the start point of the shallow bottom is located at a distance from the boundary.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Horizontal axis wind turbine
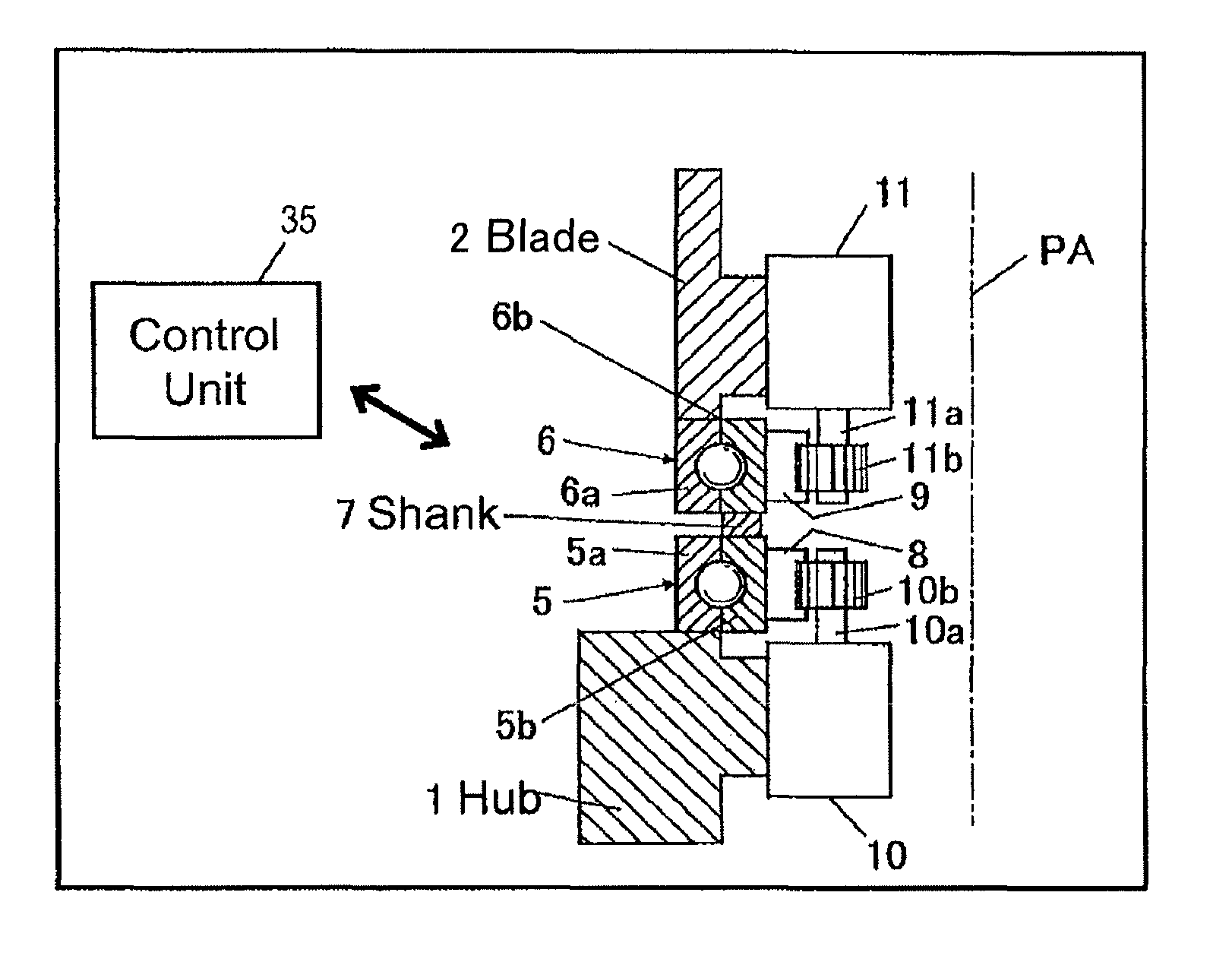
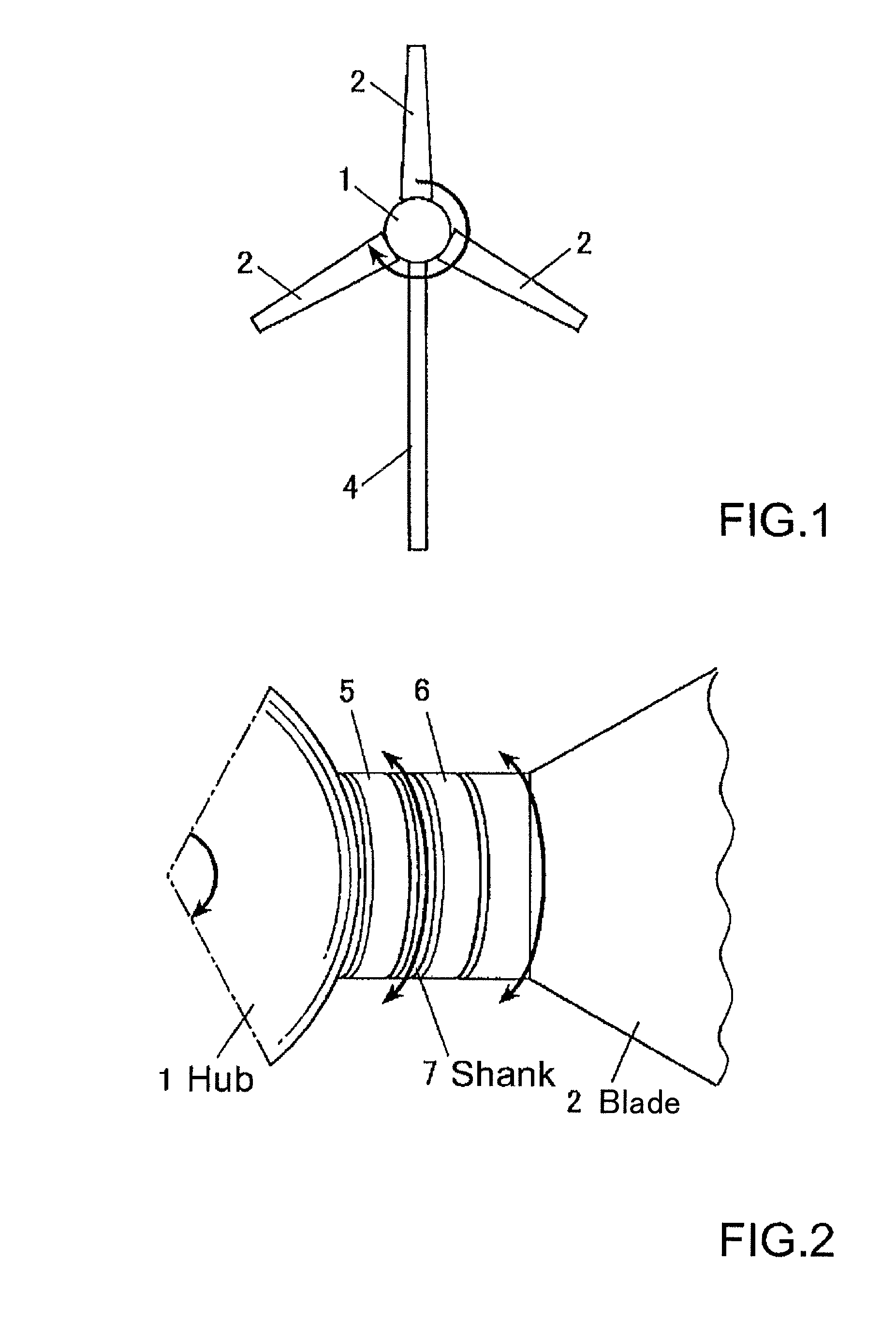
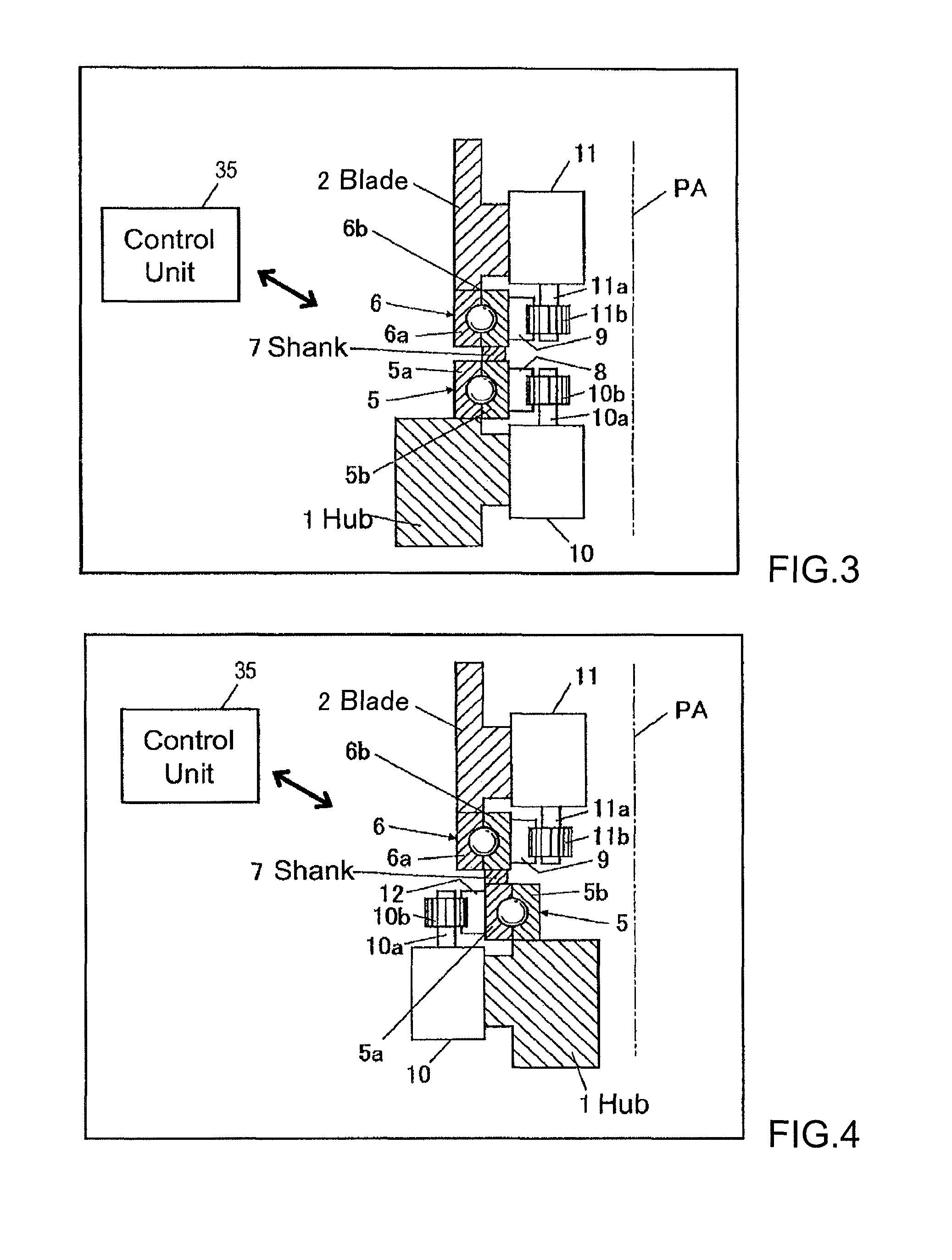
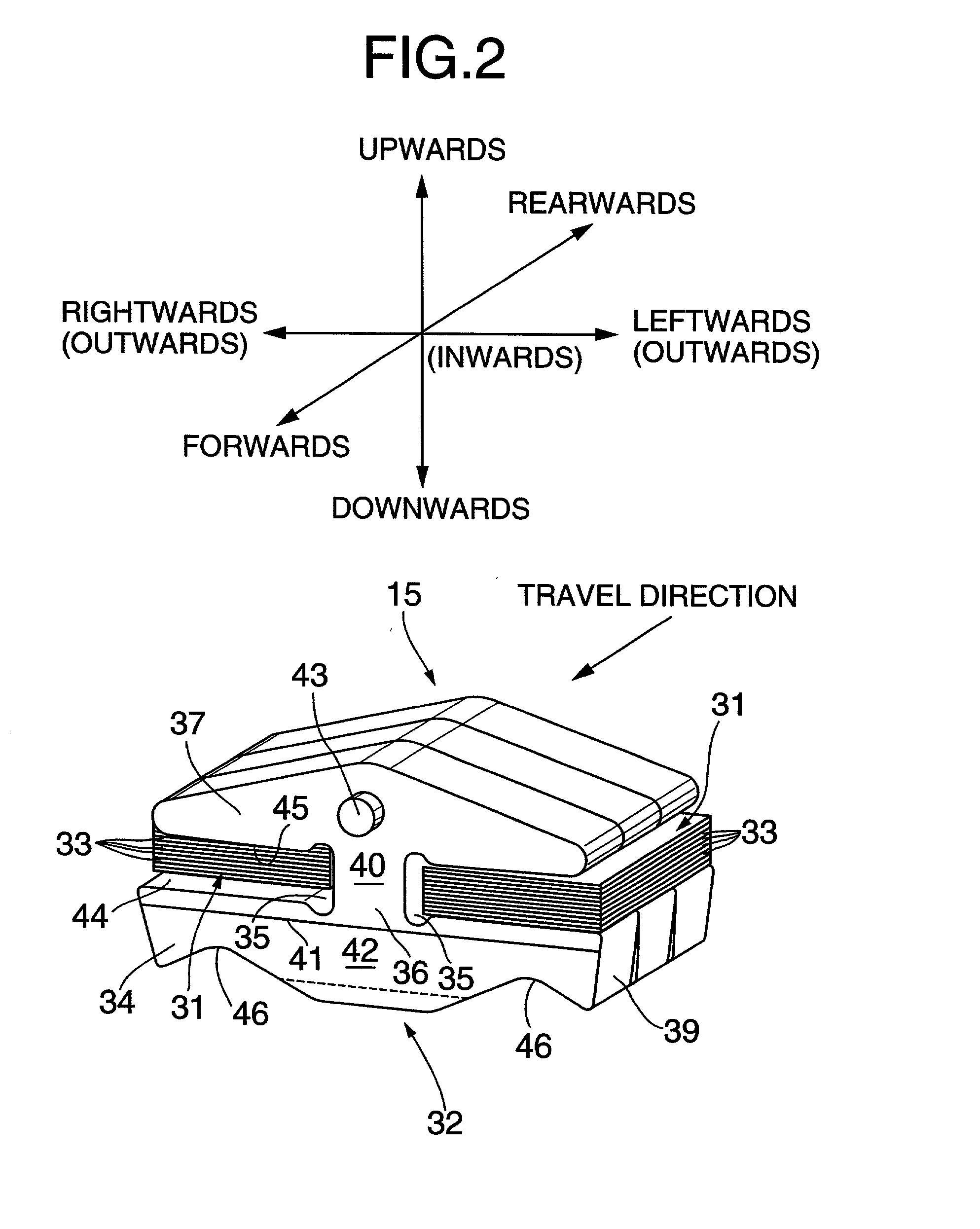
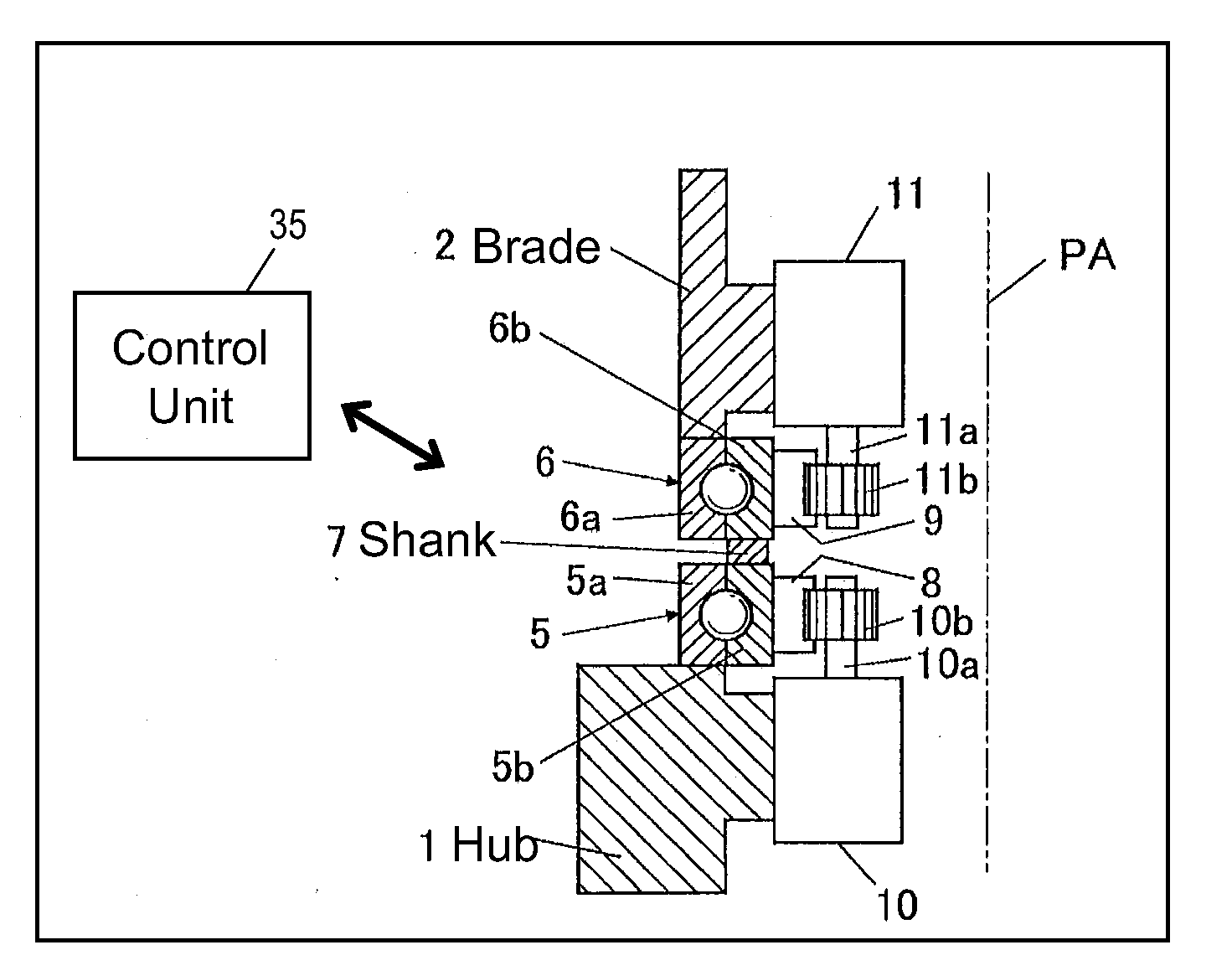
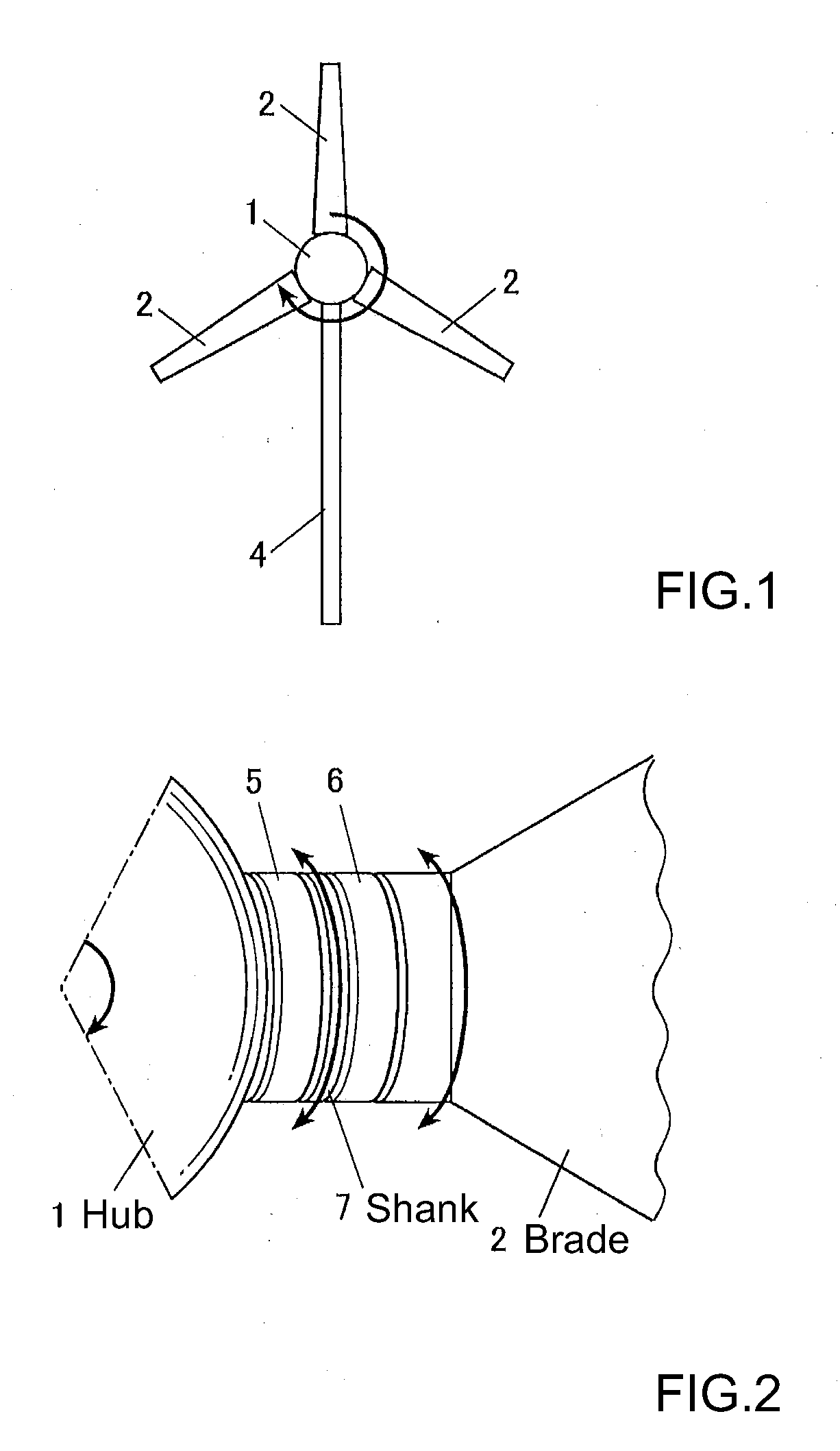
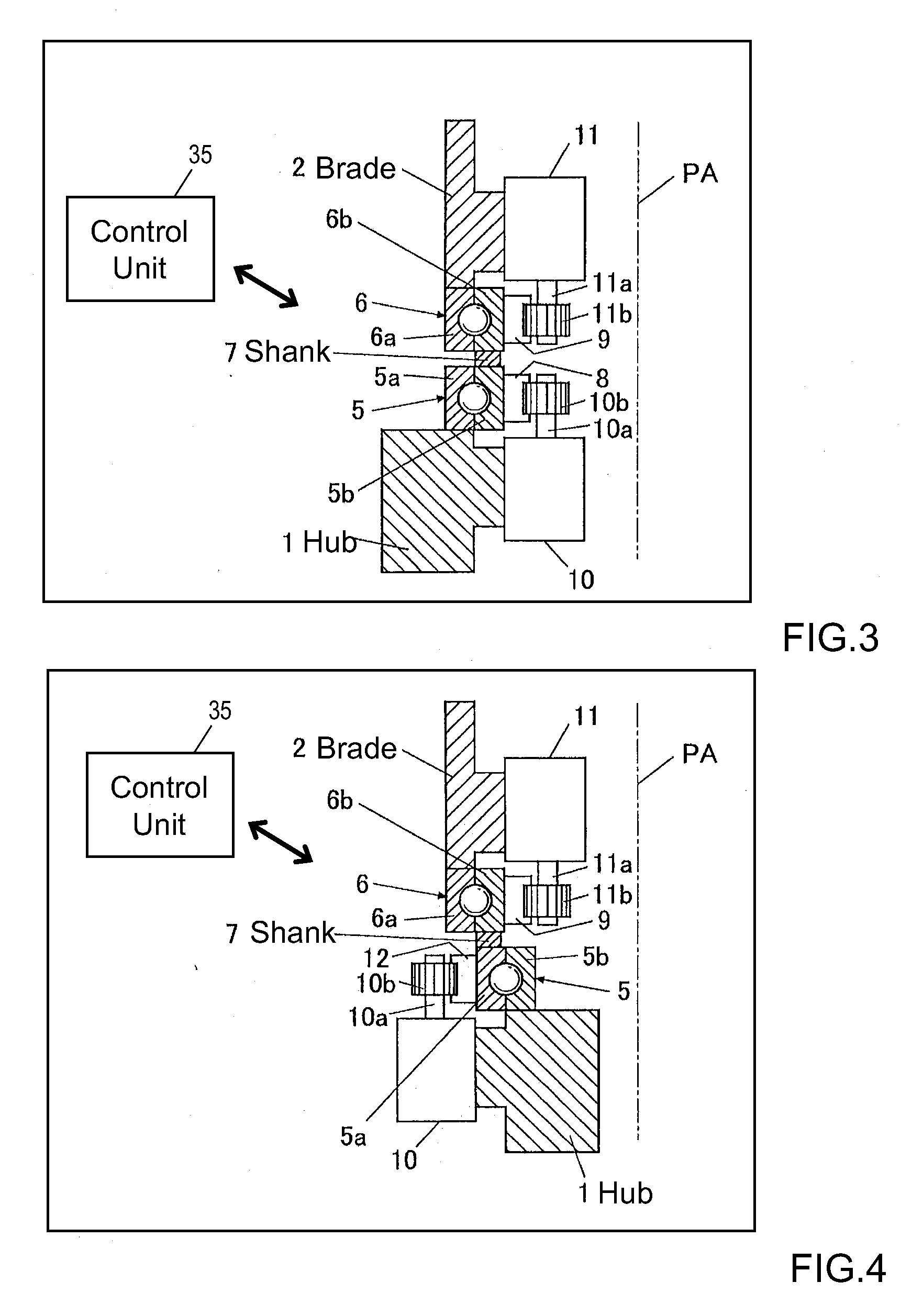
ActiveUS8459946B2Inhibits uneven wearProlong lifePropellersWind motor controlImpellerHorizontal axis
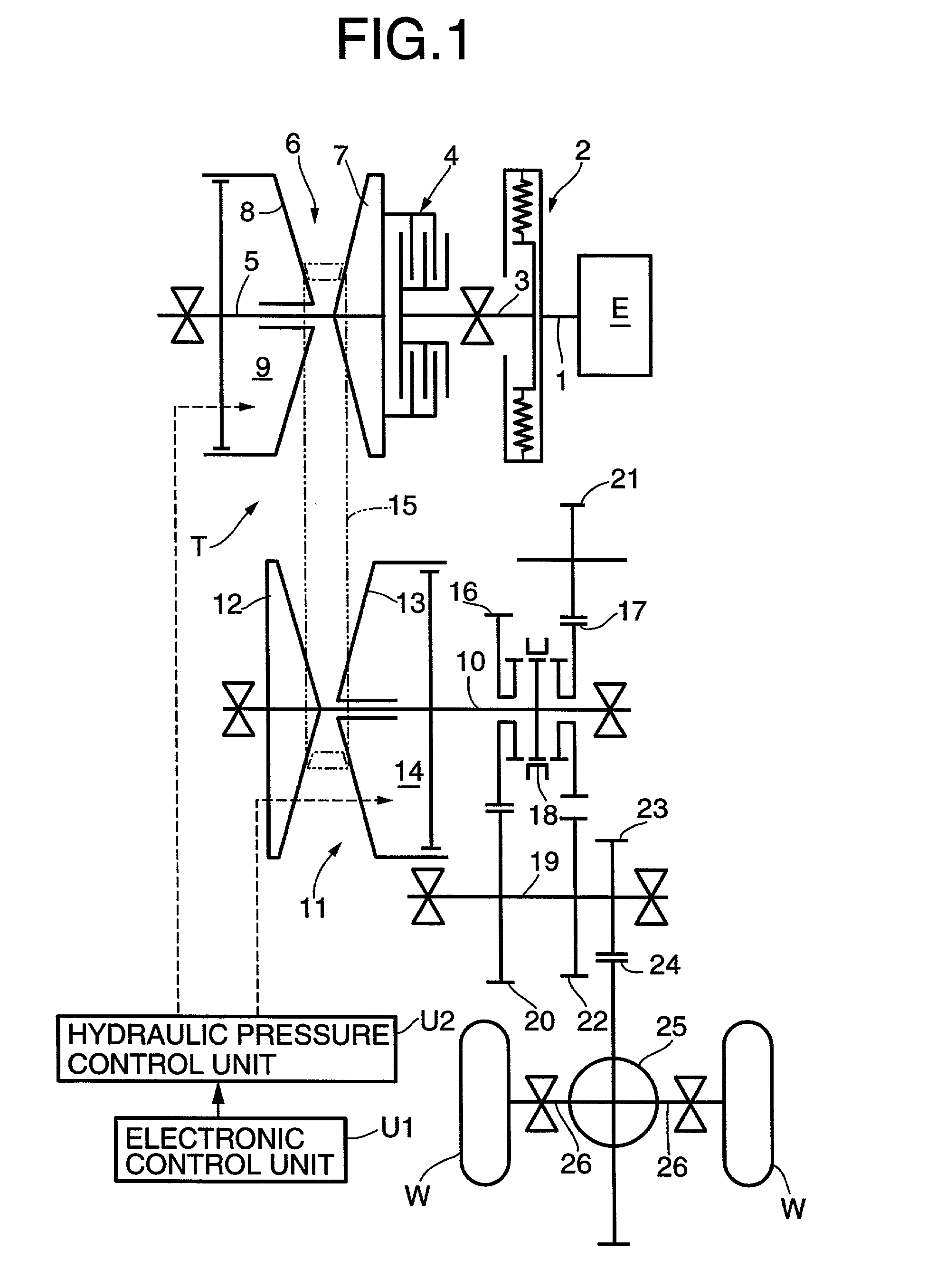
The object of the invention is to construct a horizontal-axis wind turbine comprising a dual-system pitch drive unit for one blade that is independent up to the transmission mechanism or a dual-system yaw drive unit for one wind turbine nacelle that is independent up to the transmission mechanism, and to provide the dual system with new applicability. The horizontal-axis wind turbine of the present invention has a hub 1 and a blade 2 that are connected by way of an interposed section 5b, 6b, 7 which can freely rotate around the pitch axis of the blade with respect to both the hub and the blade; and further comprises: a hub-side interposed section drive unit 10 that relatively rotates the interposed section with respect to the hub, and a blade-side interposed section drive unit 11 that relatively rotates the blade with respect to the interposed section. The horizontal-axis wind turbine further comprises a hub-side interposed section angle sensor, a blade-side interposed section angle sensor and hub-side blade angle sensor, and is configured to control the pitch angle of the blade with respect to the hub whether controlling both drive units or controlling only one drive unit. Similar connection mechanism and drive and control mechanism is applied to between a tower and a nacelle.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Oil tight type chain tensioner
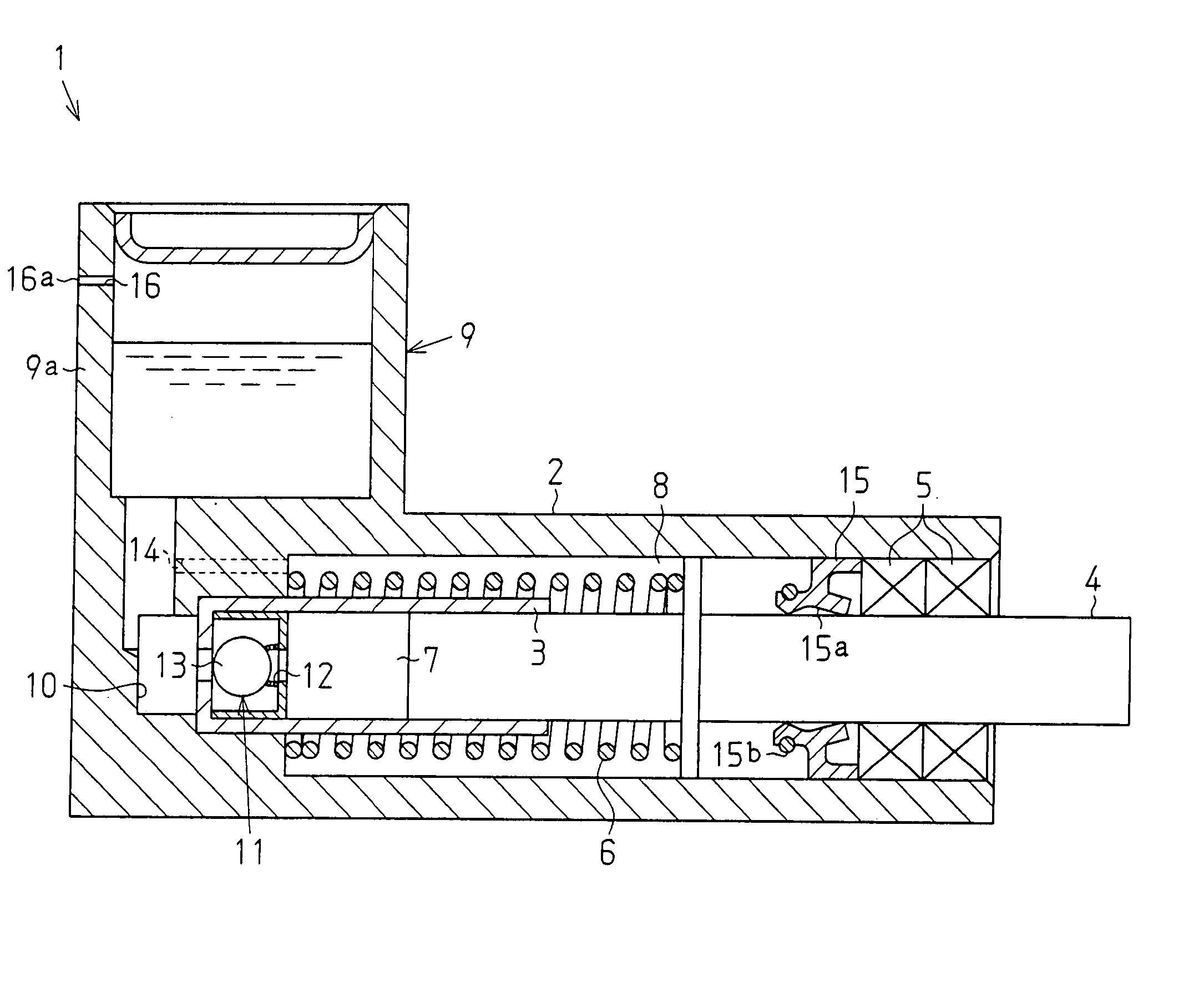
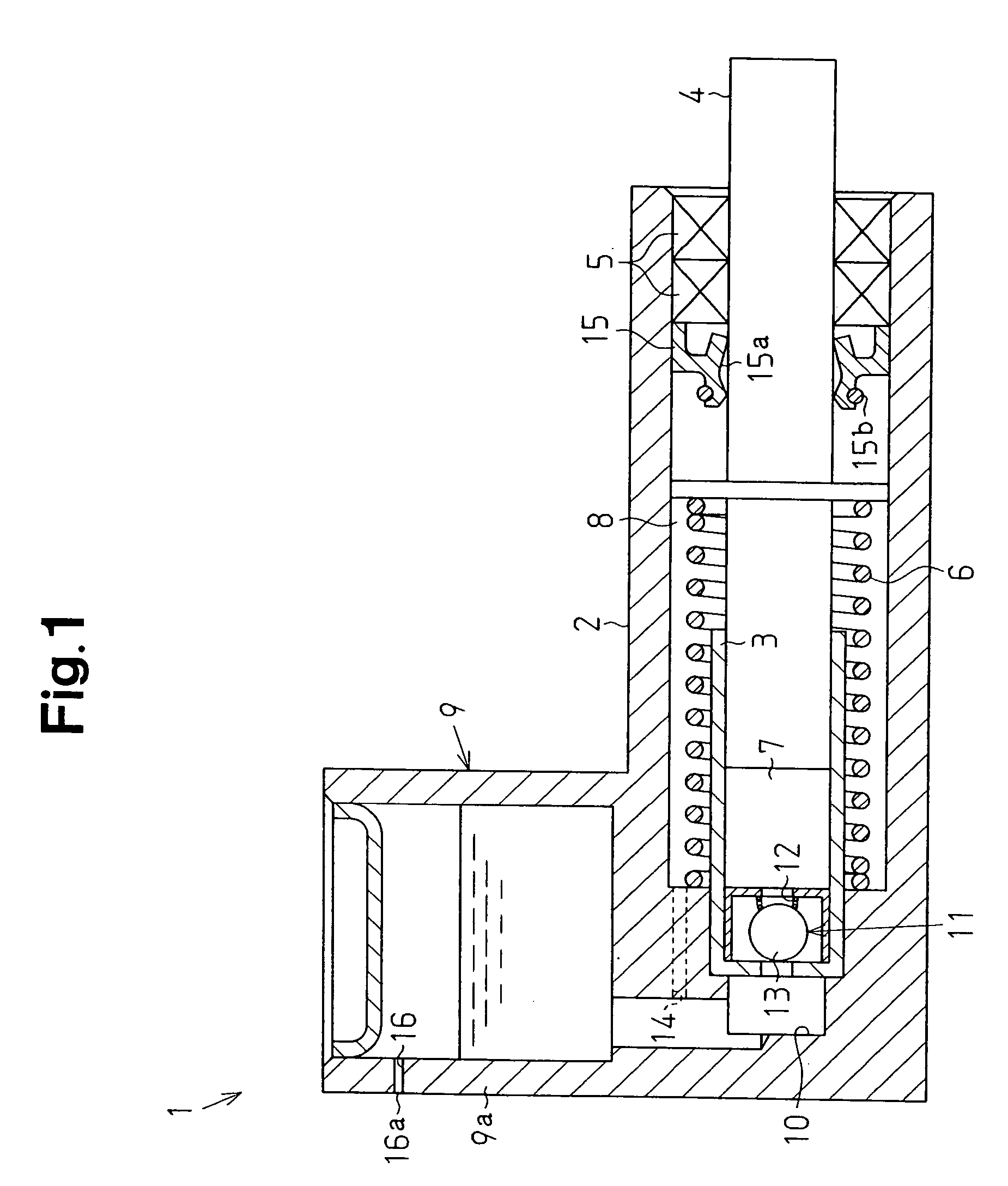
InactiveUS20050064969A1Inhibits uneven wearPrevent leakageGearingGearing detailsReciprocating motionFuel tank
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Non-pneumatic tire
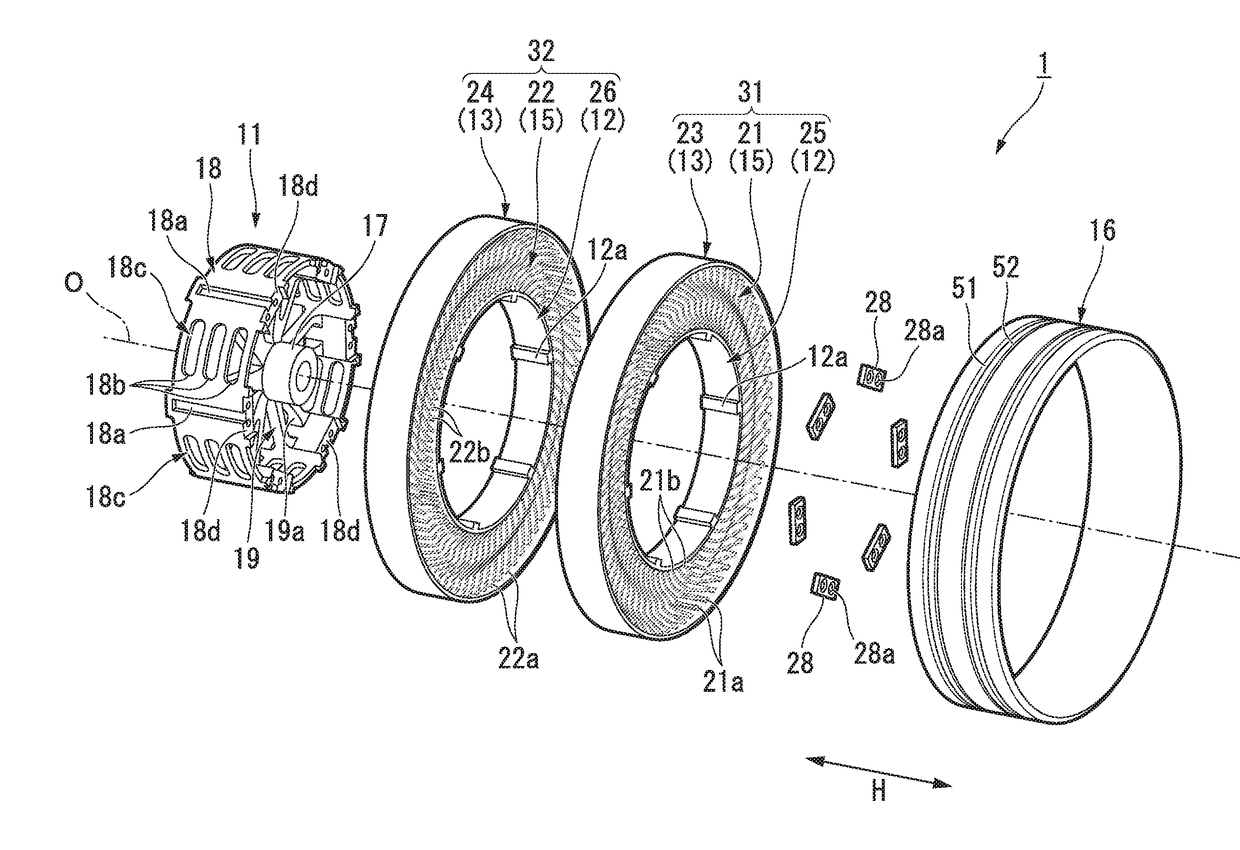
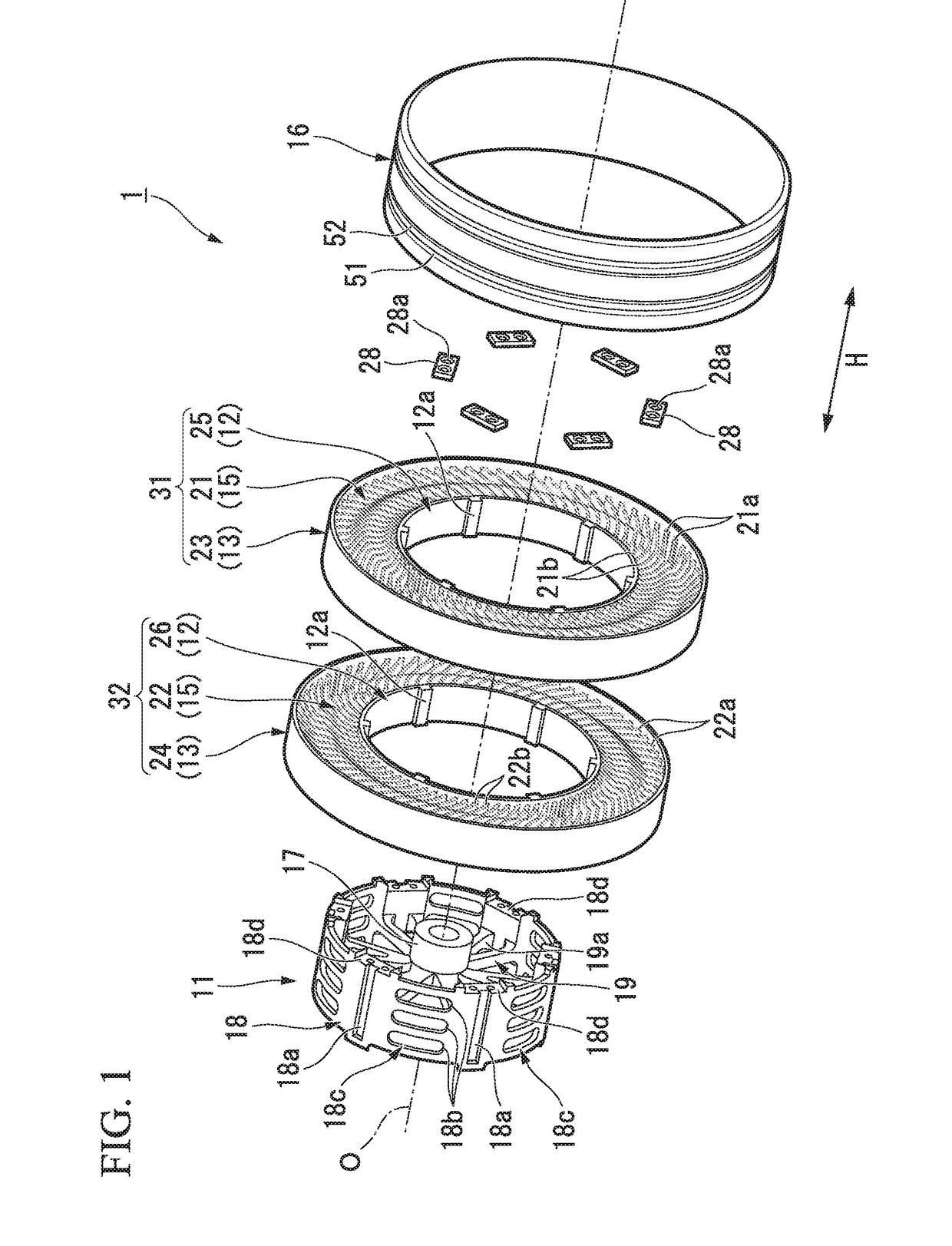
InactiveUS20170253084A1Uneven wear of tread can be limitedUneven wearNon-inflatable tyresPneumatic tyre reinforcementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention is provided with: a mounting body mounted on an axle; a ring-shaped body (13) surrounding the mounting body from an outside in a tire radial direction; a connecting member (15) configured to connect the mounting body and the ring-shaped body (13) such that the mounting body and the ring-shaped body (13) are displaceable; and a cylindrical tread member (16) mounted over the ring-shaped body (13), wherein grooves (51, 52) are formed at an outer peripheral surface of a portion located above and corresponding to a portion of the tread member (16) at which the ring-shaped body (13) and the connecting member (15) are connected.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
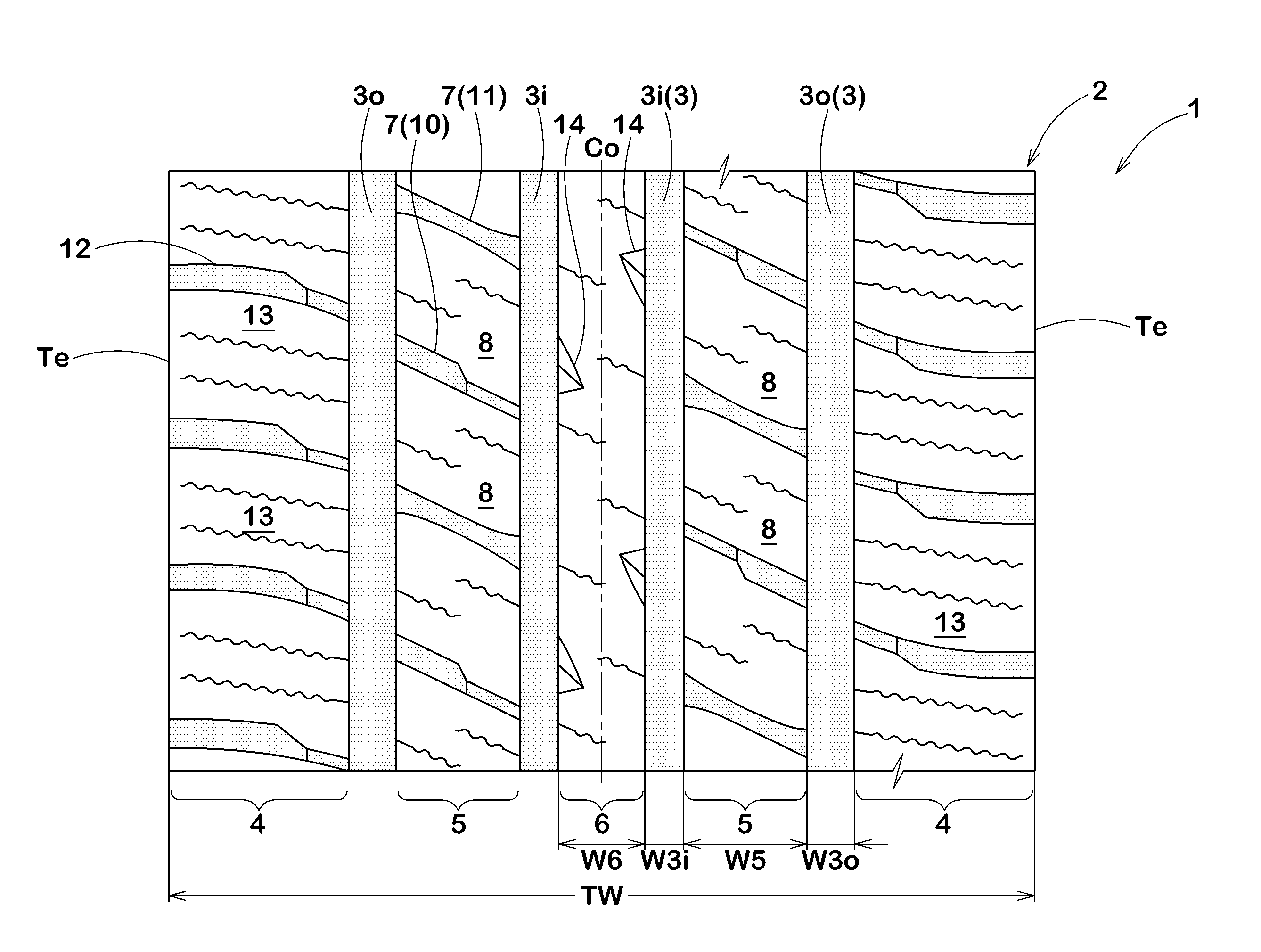
Pneumatic tyre
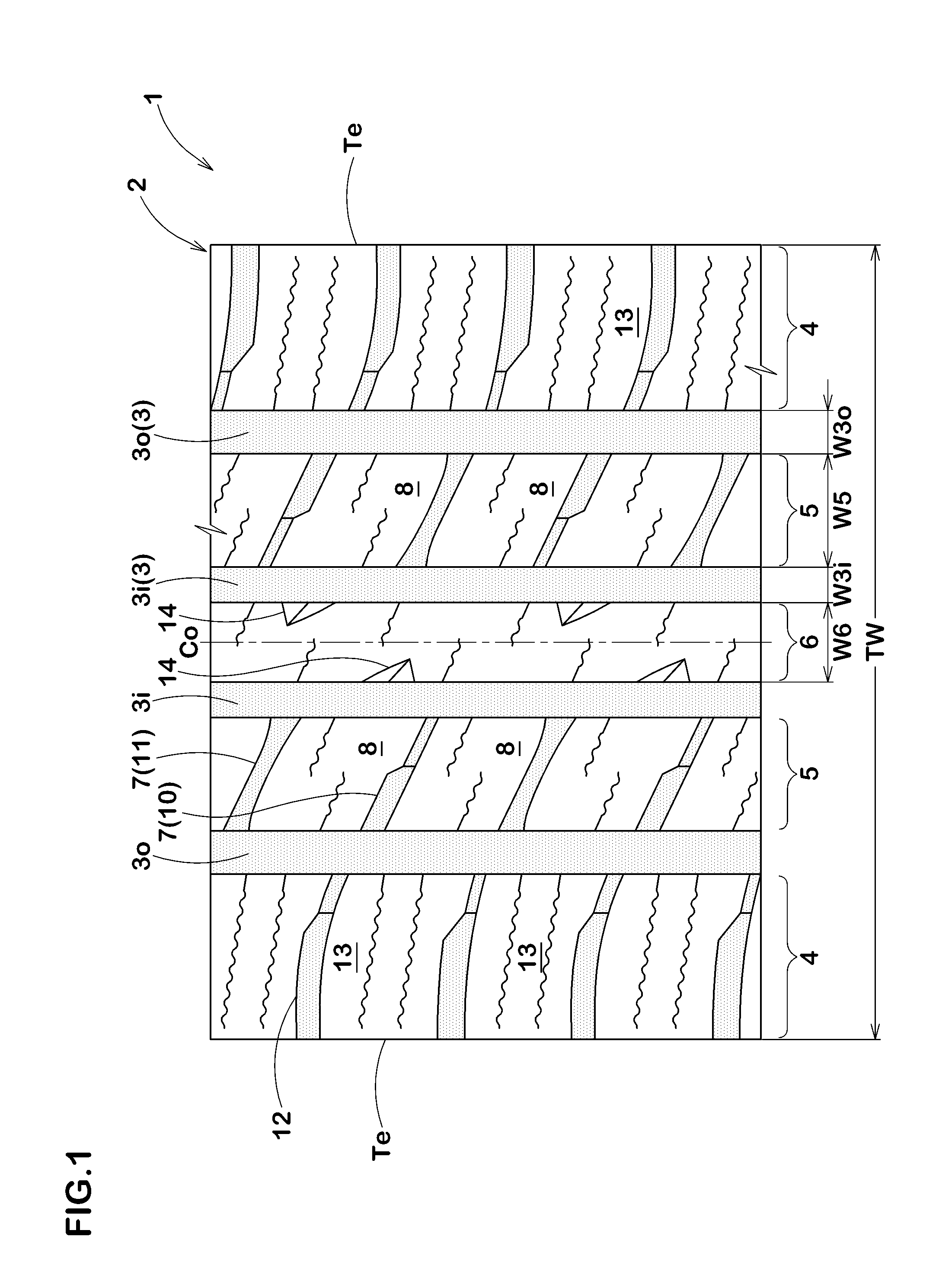
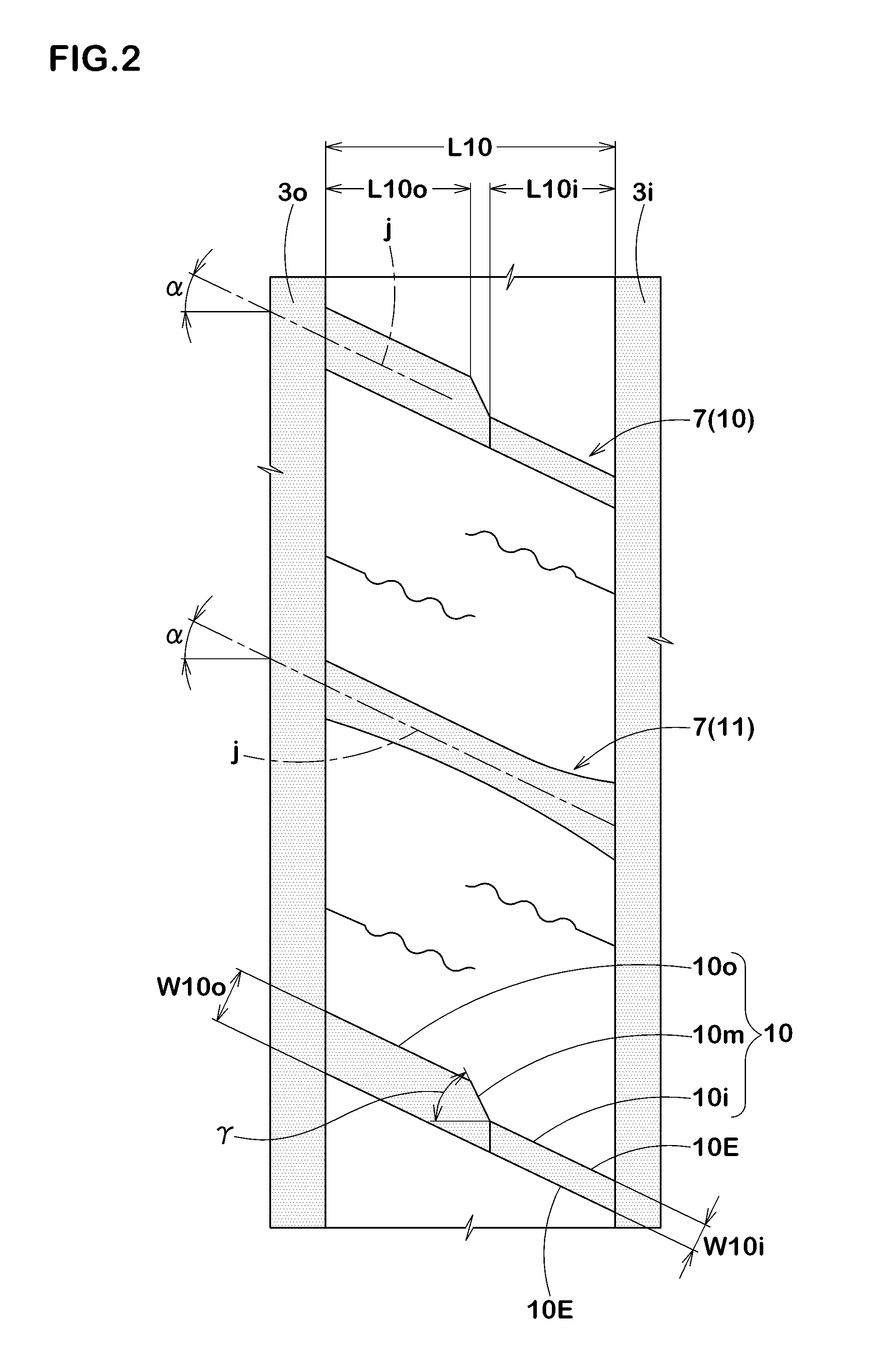
ActiveCN104275990AImprove drainage capacityRigid Distribution RationalizationTyre tread bands/patternsWear resistantTransverse groove
The present invention provides a pneumatic tyre capable of suppressing reduction of drainage performance, improving operation stability and uneven wear resistant performance. The pneumatic tyre (1), at a tyre surface portion (2), has a pair of tyre shoulder main grooves (10) configured at an inner side of a tyre surface grounding end (Te) and extending continuously along a circumferential direction of the tyre, and a pair of tyre shoulder land portions (13) arranged at a tyre axial outer side of the tyre shoulder main grooves (10). The tyre shoulder land portions (13) are provided with: a plurality of tyre shoulder transverse grooves (31) extending towards the tyre axial inner side from the tyre surface grounding end (Te) and having inner ends (31i) forming ends in the tyre shoulder land portions (13); tyre shoulder auxiliary cut slots (34) communicated between the inner ends (31i) of the tyre shoulder transverse grooves (31) and the tyre shoulder main grooves (10); and tyre shoulder thin grooves (33) which are not communicated with the tyre shoulder auxiliary cut slots (34) between the adjacent tyre shoulder auxiliary cut slots (34) in the circumferential direction of the tyre and extend along the circumferential direction of the tyre.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Pneumatic tire
InactiveUS7441576B2Large strainInhibits uneven wearPneumatic tyre reinforcementsYarnEngineeringMechanical engineering
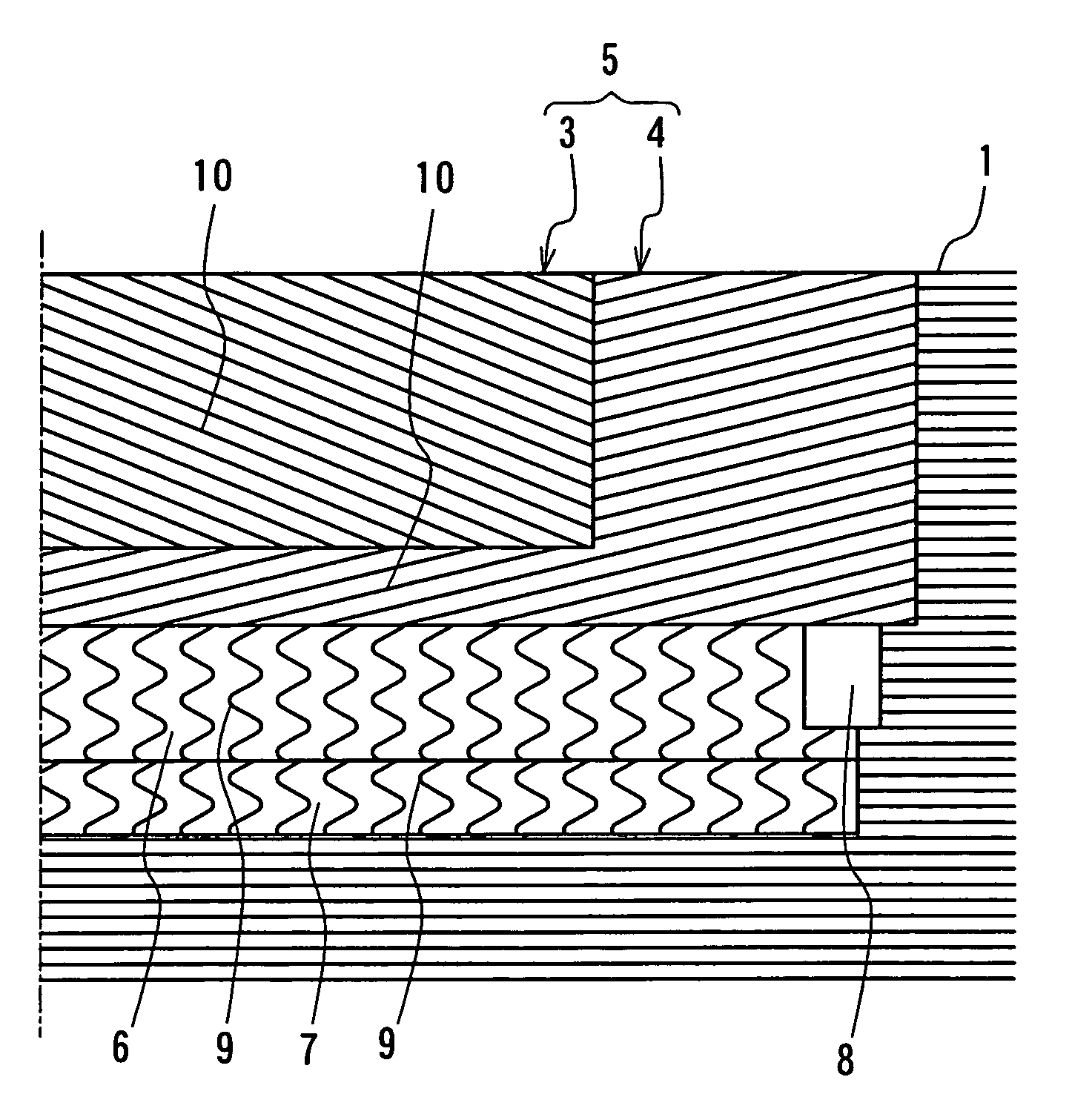
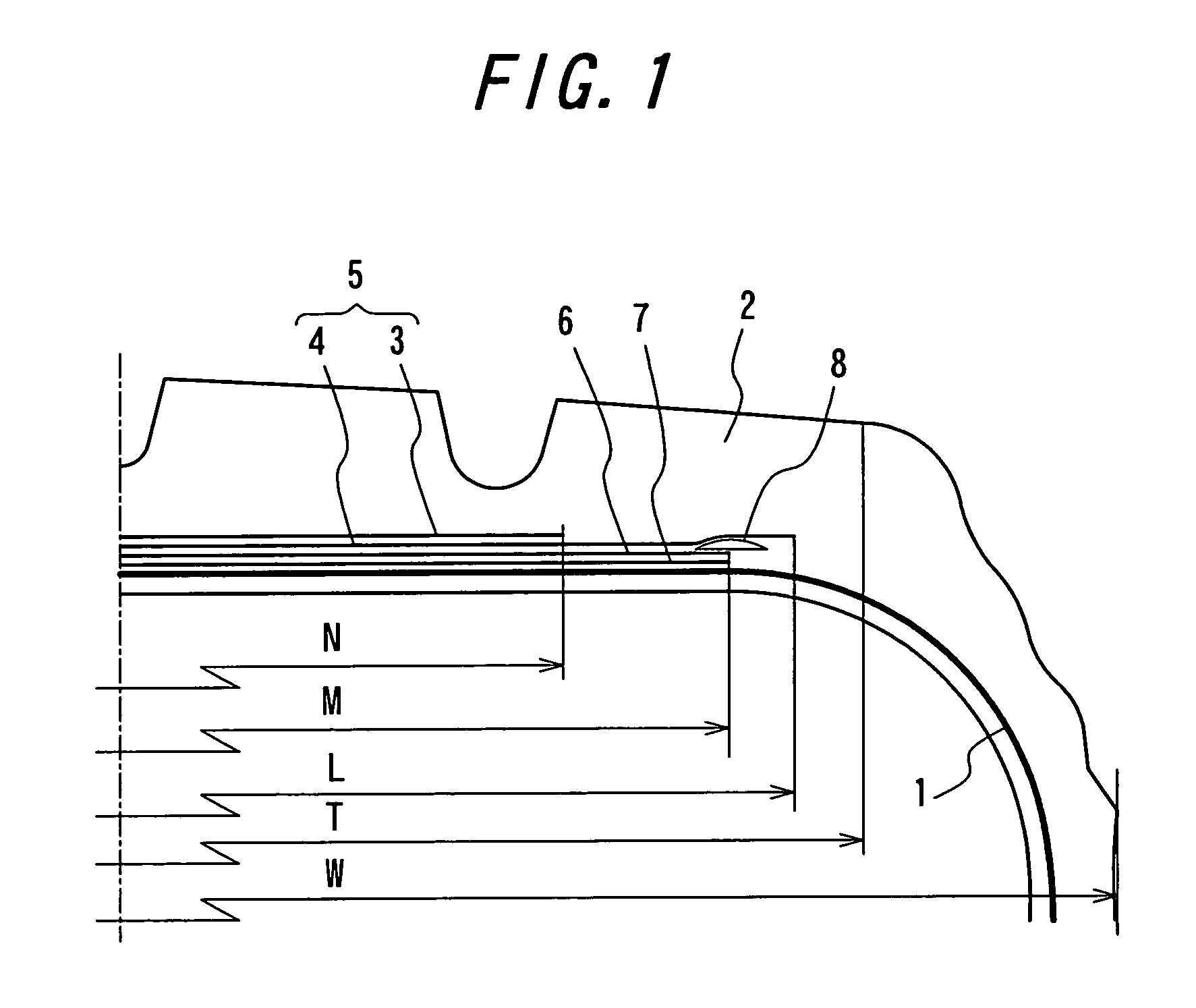
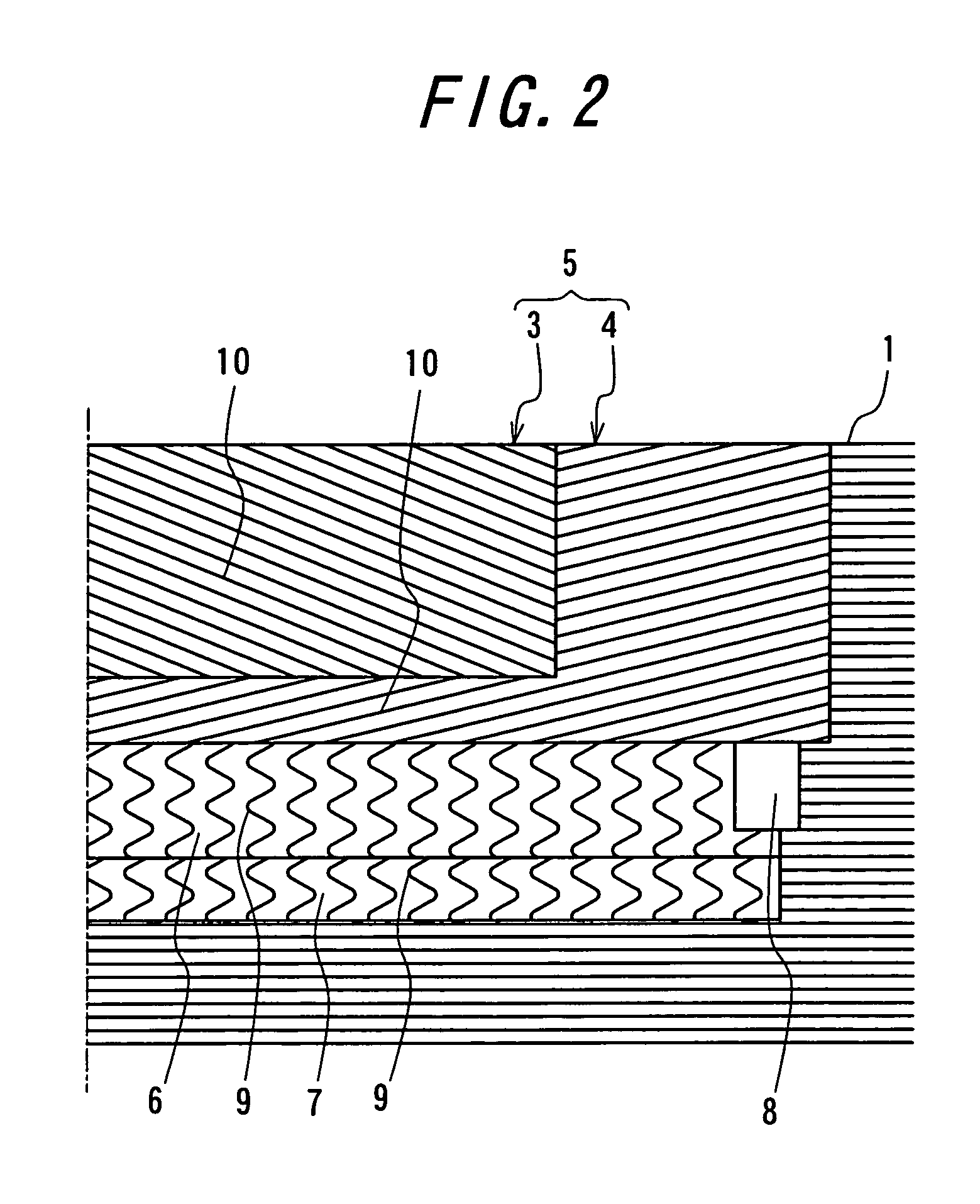
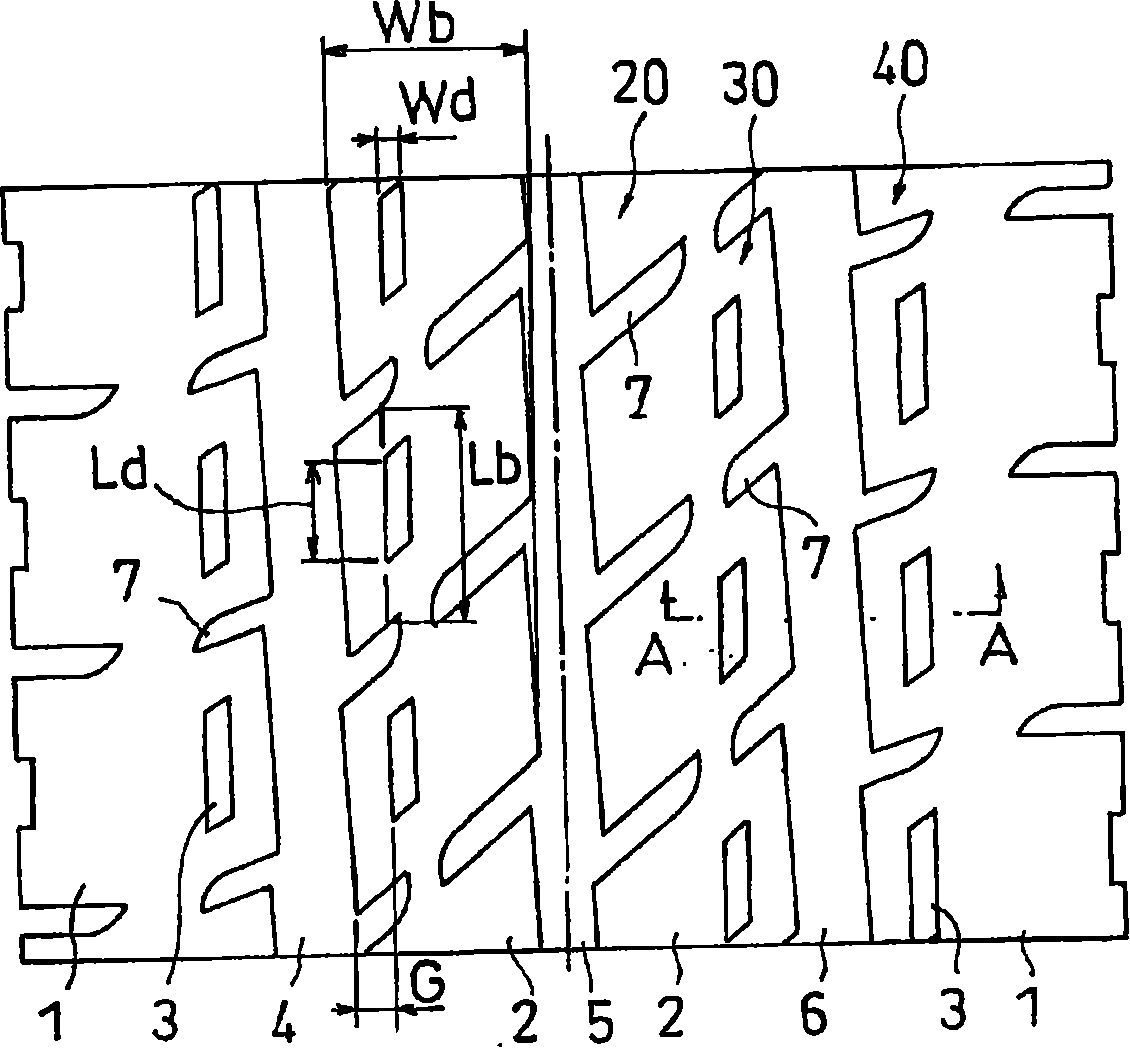
A pneumatic tire comprises a carcass 1 comprised of one or more carcass plies toroidally extending between a pair of bead portions, a tread rubber 2 arranged at an outer peripheral side of a crown portion of the carcass 1, a belt 5 arranged between the tread rubber 2 and the carcass 1 and comprised of two belt layers 3, 4, cords 10 of which layers being crossed with each other and extending in an inclination angle of 45-80° with respect to a circumferential direction of the tire, and one or more circumferential strengthening layers 6, 7 arranged at an inner peripheral side of the belt 5 and containing wavy or zigzag cords 9 extended substantially in the circumferential direction of the tire, in which a width L of a belt layer 7 located at the inner peripheral side is made larger than a width M of the circumferential strengthening layer and a width N of a belt layer located at the outer peripheral side is made smaller than the width M of the circumferential strengthening layer.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Heavy duty tire
InactiveCN102802966AInhibits uneven wearImprove wetting performanceHeavy duty tyresHeavy duty vehicleEngineeringHeavy duty
The invention provides a heavy duty tire, comprising: a shoulder rib (A1) (shoulder rib (A5)) which is provided to a tread shoulder section; a second rib (A2) (second rib (A4)) which is adjacent to the shoulder rib (A1) with a circumferential groove (110) (circumferential groove (116)) interposed therebetween and is provided further toward the tire equator side than the shoulder rib (A1); and an uneven wear absorbing rib (B1) (uneven wear absorbing rib (B2)) provided within the circumferential groove (110) and located further toward the inside in the tire radial direction than the tread surfaces of the shoulder rib (A1) and of the second rib (A2). Circumferential narrow grooves (10, 12) having a smaller width than the circumferential grooves (110, 116) are formed in the second ribs (A2, A4). Each circumferential narrow groove (10, 12) is formed in such a manner that, when the tire is mounted on the vehicle, the circumferential groove (10, 12) is located on the outer side of the tire with reference to the center of the second rib (A2, A4) in the tread width direction.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Belt for continuously variable transmission
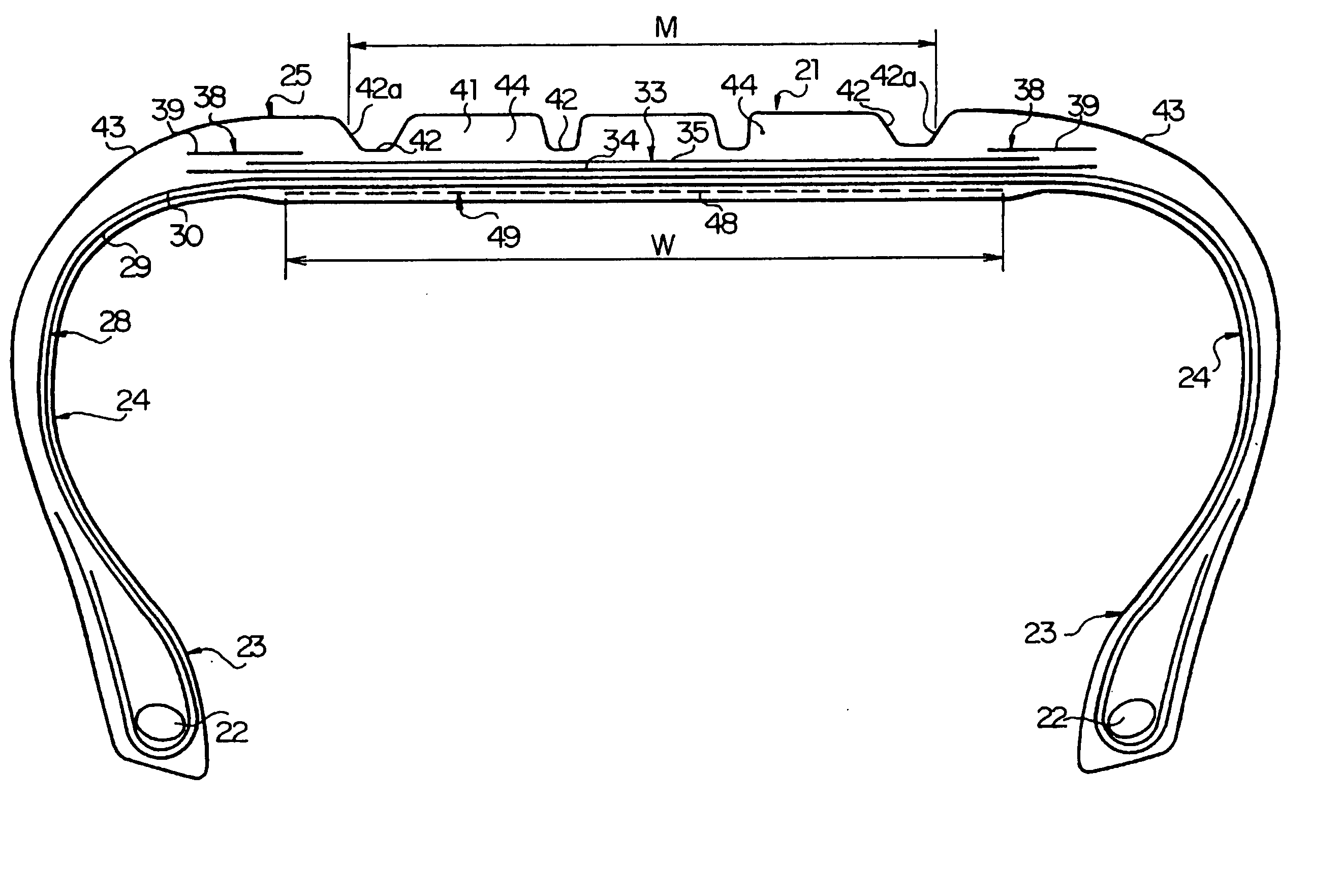
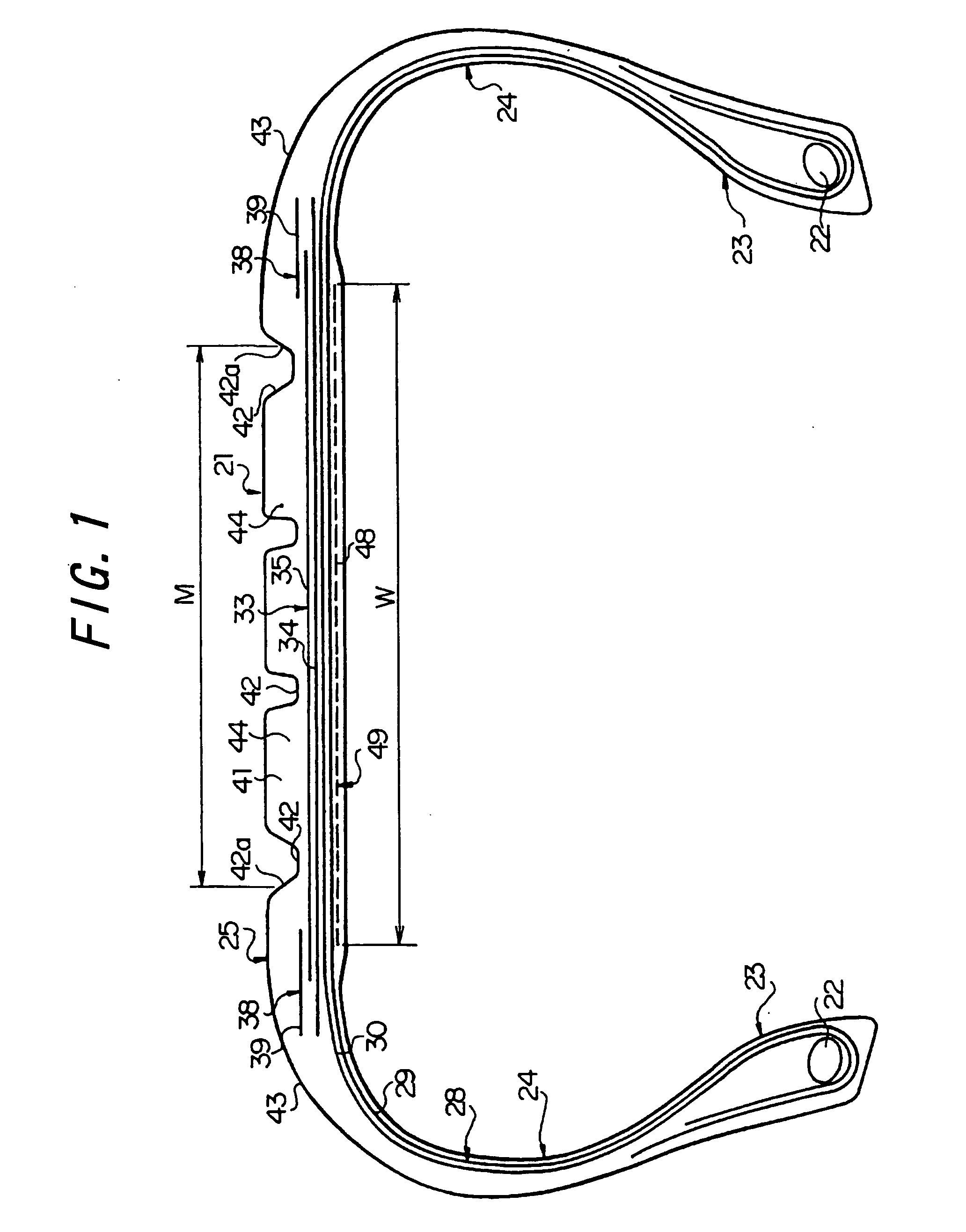
InactiveUS20020052261A1Suppress uneven wearing of metal elementDecrease heightV-beltsDriving beltsParagraphEngineering
A V-face of a metal element is prevented from being inclined due to a load from a pulley by increasing the height Hs of an upper non-contact portion of the V-face of the metal element. For example, when the height of the V-face is represented by Hv (mm), and the height of the upper non-contact portion of the V-face is represented by Hs (mm), the height Hv of the V-face and the height Hs of the upper non-contact portion are set so that a relationship <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>-0.5265Hv+2.768<=Hs<=-0.5934Hv+3.524 < / in-line-formula>is established.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Horizontal axis wind turbine
ActiveUS20100296932A1Control be possibleSuppress wearPropellersWind motor controlImpellerElectric generator
The object of the invention is to construct a horizontal-axis wind turbine comprising a dual-system pitch drive unit for one blade that is independent up to the transmission mechanism or a dual-system yaw drive unit for one wind turbine nacelle that is independent up to the transmission mechanism, and to provide the dual system with new applicability. The horizontal-axis wind turbine of the present invention has a hub 1 and a blade 2 that are connected by way of an interposed section 5b, 6b, 7 which can freely rotate around the pitch axis of the blade with respect to both the hub and the blade; and further comprises: a hub-side interposed section drive unit 10 that relatively rotates the interposed section with respect to the hub, and a blade-side interposed section drive unit 11 that relatively rotates the blade with respect to the interposed section. The horizontal-axis wind turbine further comprises a hub-side interposed section angle sensor, a blade-side interposed section angle sensor and hub-side blade angle sensor, and is configured to control the pitch angle of the blade with respect to the hub whether controlling both drive units or controlling only one drive unit. Similar connection mechanism and drive and control mechanism is applied to between a tower and a nacelle.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Pneumatic tire
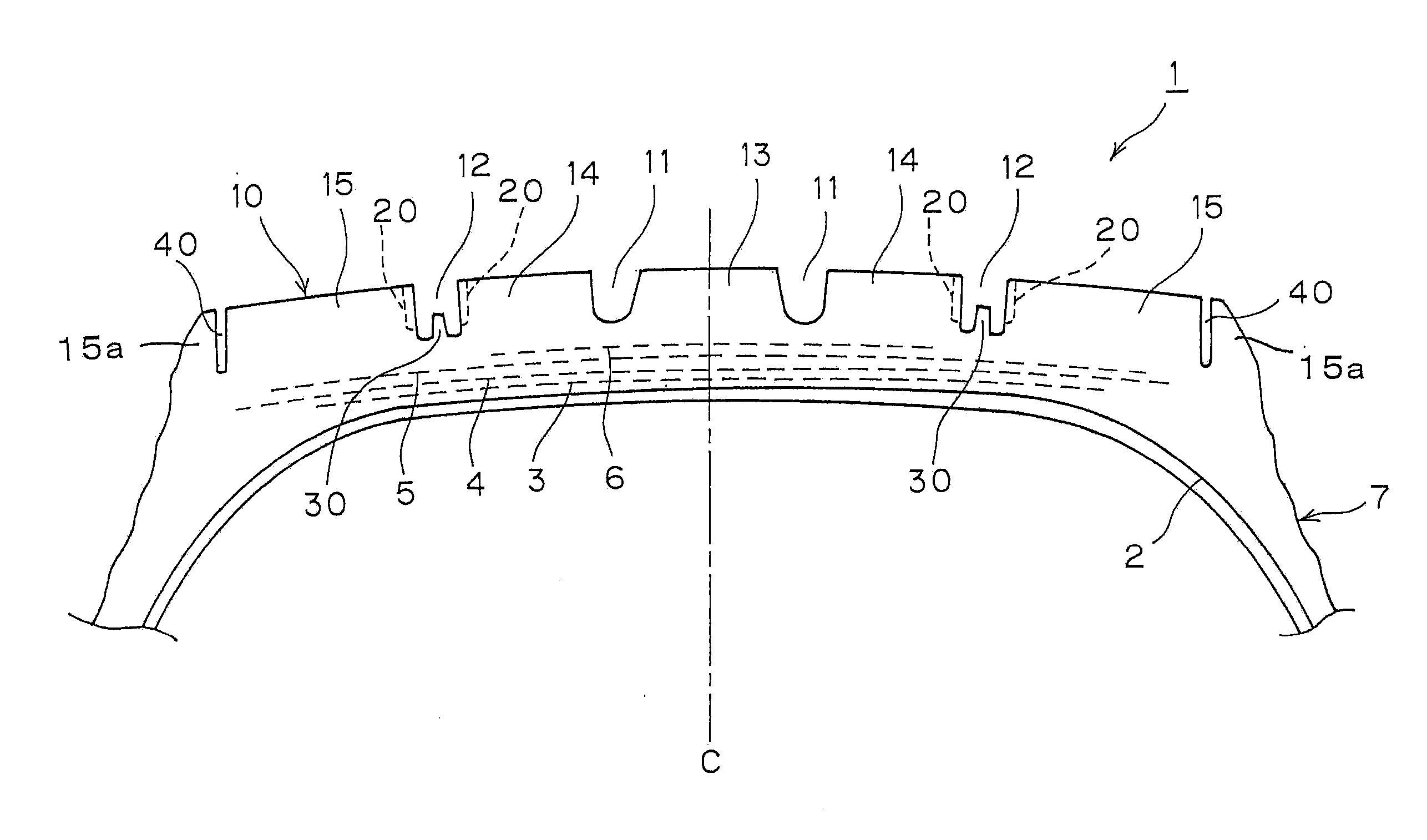
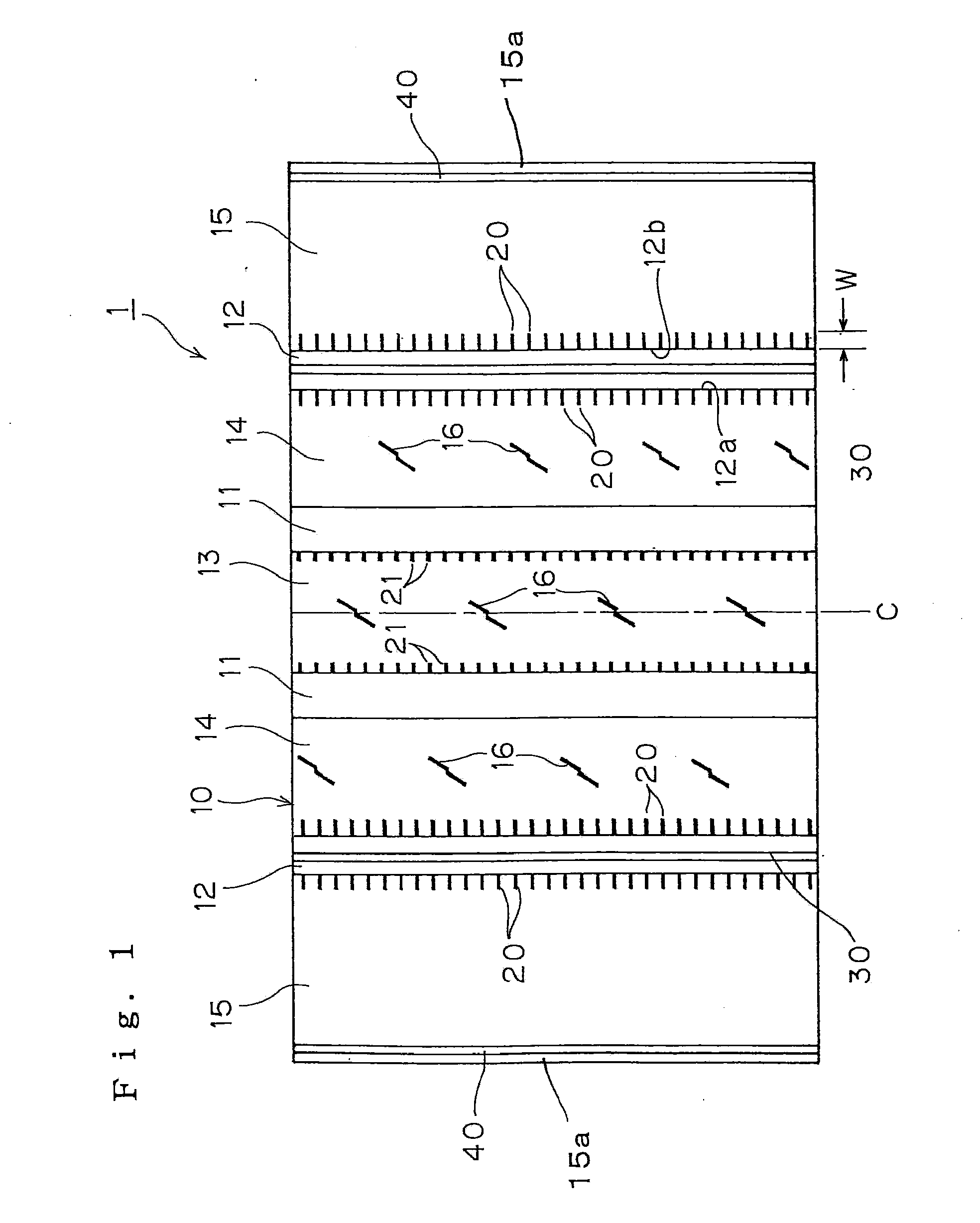
ActiveCN105365495AEfficient scrapingImprove performance on iceTyre tread bands/patternsWear resistantEngineering
The invention provides a pneumatic tire, which can be used on ice and is wear resistant. The tread (2) of the pneumatic tire (1) is provided with a pair of central main ditches (5), a central area (5), and tire shoulder areas (7). The central area (5) and each tire shoulder area (7) are provided multiple patterned blocks (12), which are defined by fine ditches (10) extending along the circumferential direction of the tire and cross ditches (11) extending along the axis of the tire. At least one of patterned blocks (12) is divided into patterned block small sheets (51) and patterned block large sheets (52) by a plurality of sipings (50); wherein the width of the patterned block large sheets (52) is larger than that of the patterned block small sheets (51). In each patterned block (12), the patterned block small sheets (51) and patterned block large sheets (52) are alternatively arranged along the circumferential direction of the tire.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Compressed trasmission belt
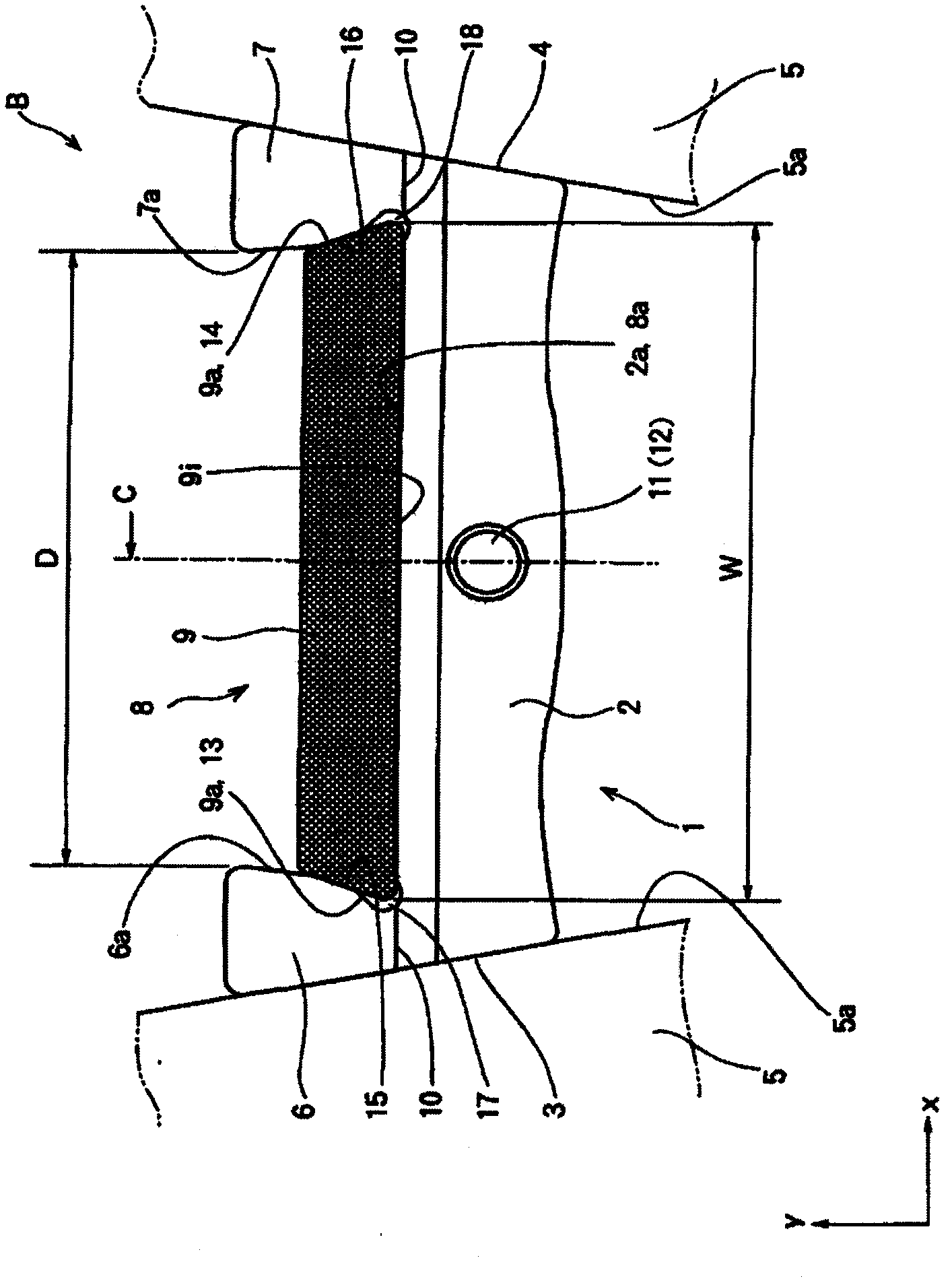
InactiveCN102144110AHigh power transmission efficiencyPrevent or suppress uneven wearV-beltsTransmission beltAbutment
Provided is a compressed transmission belt capable of eliminating loss due to internal friction within a ring, properly aligning the ring with respect to an element and preventing uneven wear or degraded durability. The compressed transmission belt (B) comprises a flat element (1) having a recess (8) at the middle of the width at the external periphery thereof and a single layer belt ring (9) made of elastic material received in the recess (8). The belt ring (9) has a left side and a right side faces (9a, 9b) each slanted symmetrically with respect to a plane (C) at the middle of the width of the ring. The recess (8) has a left side and right side faces (15, 16) slanted similarly to the faces (13, 14) but having a smaller area of abutment to the element (1) than the slant faces (13, 14).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Pneumatic tire
InactiveCN103072432AAvoid delaminationImproved high-speed durabilityPneumatic tyre reinforcementsTyre tread bands/patternsAutomotive engineering
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Pneumatic tire for motor-bicycle
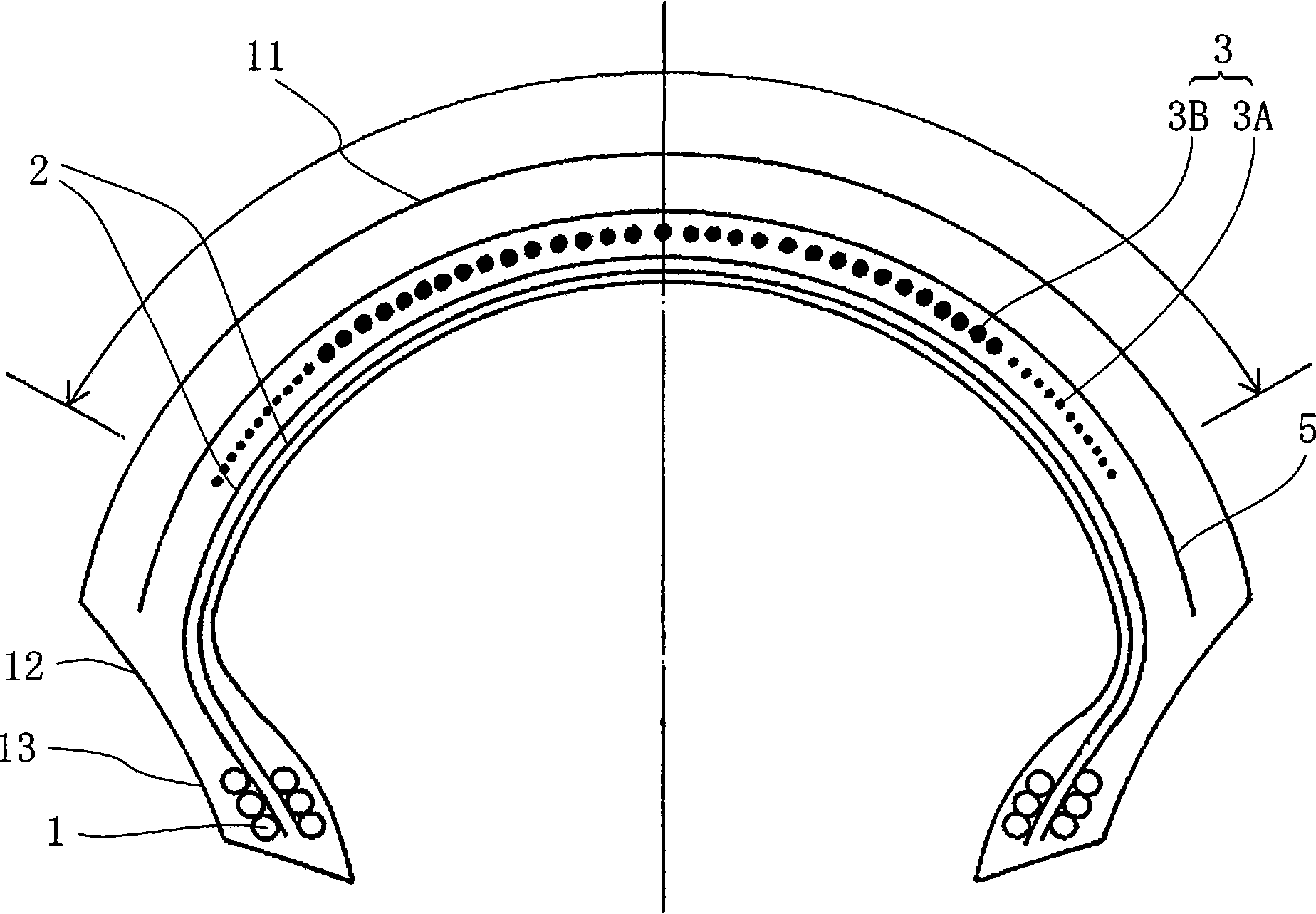
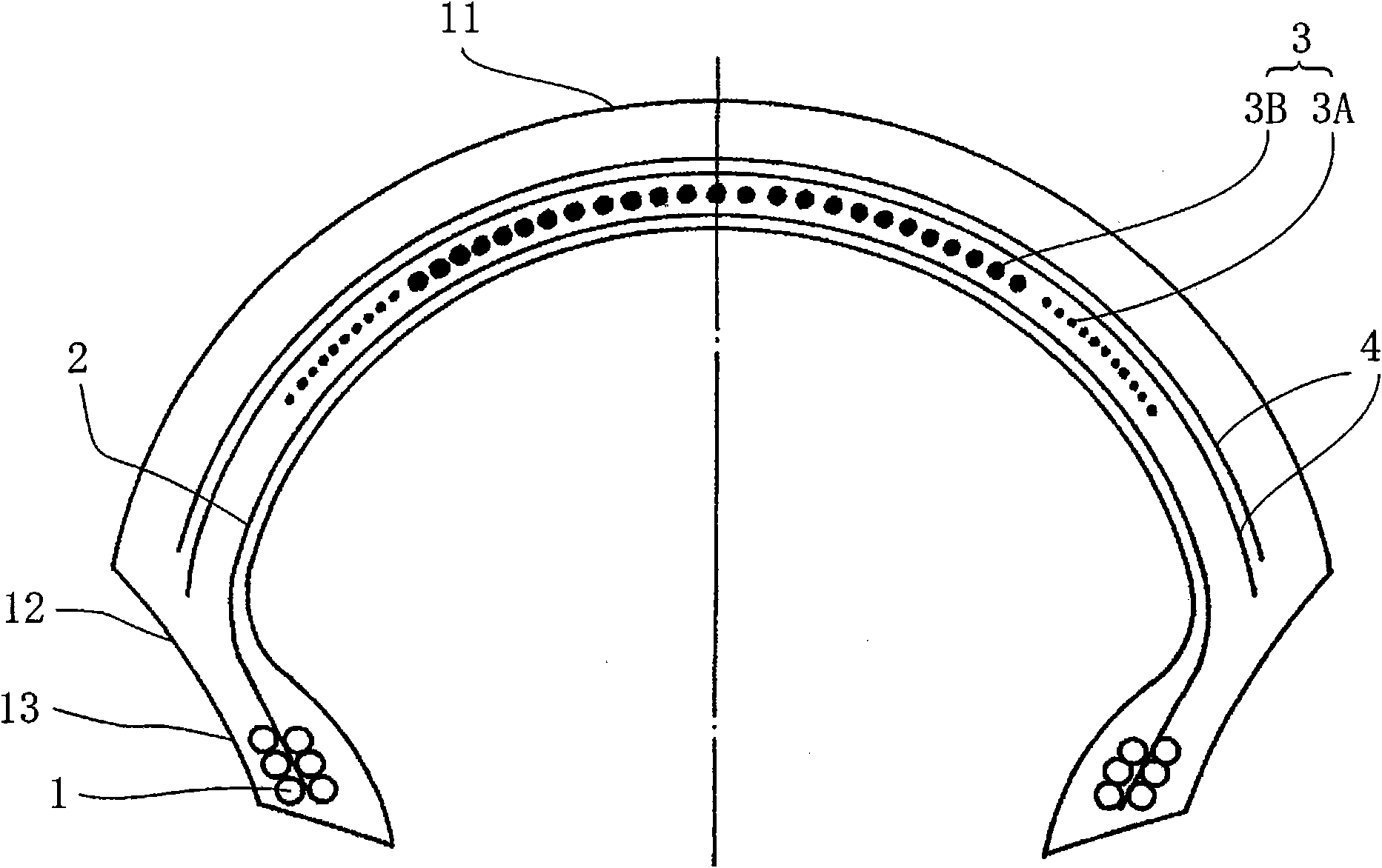
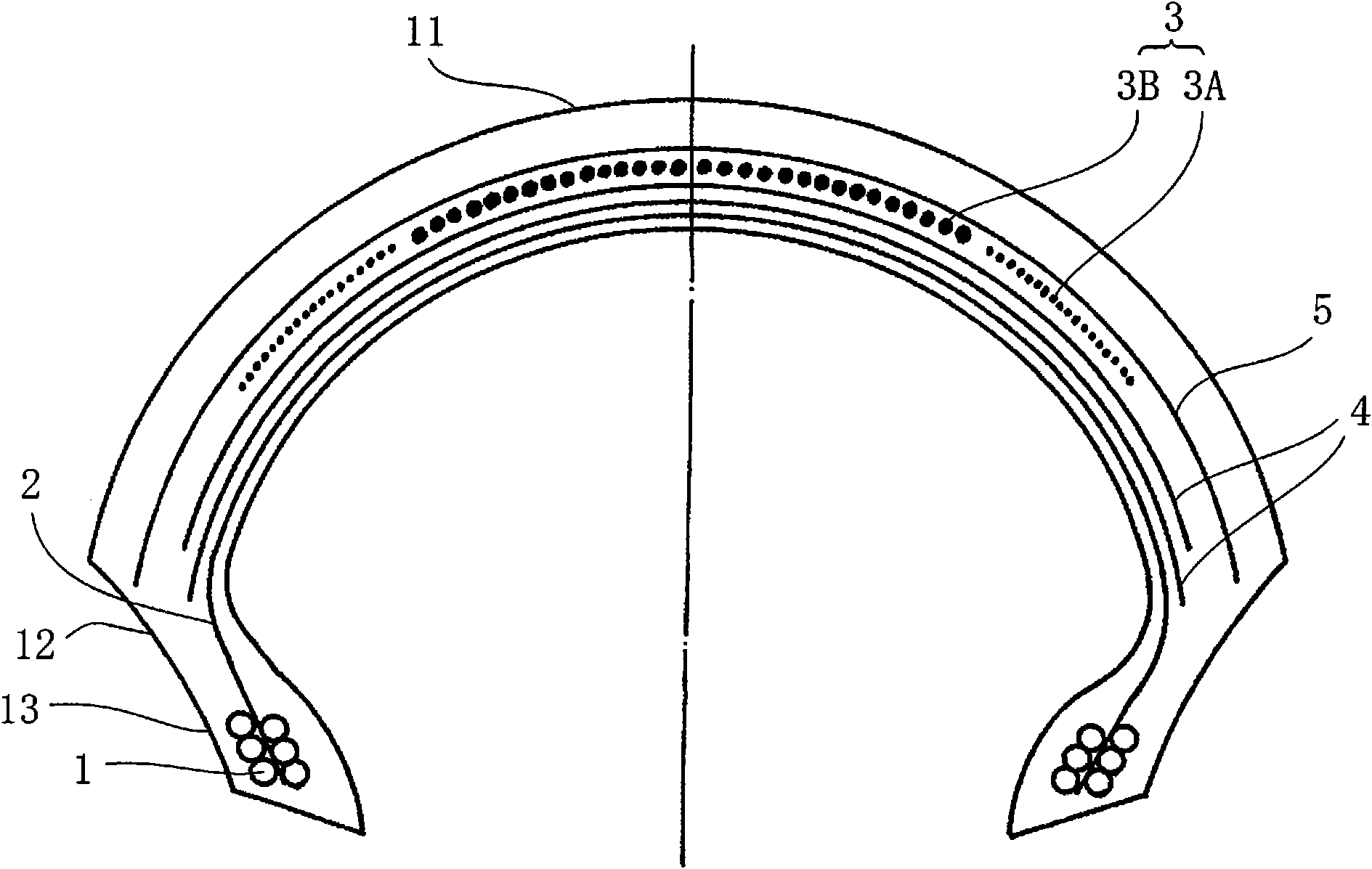
InactiveCN101855097AReduce brake deformationHigh speedMotorcycle tyresPneumatic tyre reinforcementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
This aims to provide a pneumatic tire for a motor-bicycle, which can improve a traction performance at a deep cornering time of inclining the bicycle body especially deeply and stability at the body inclining time, without deteriorating other performances. The motor-bicycle pneumatic tire comprises a tread portion (11) made annular, and a spiral belt layer (3) formed on the radially inner side of the crown portion of the tread (11) and having an angle of 0 to 5 degrees in the circumferential direction of the tire and an arrangement width of 0.5 to 0.8 times as large as the tread width. The spiral belt layer (3) is widthwise divided into three, and the tensile elastic modulus of the cords constituting the two end regions of the trisected spiral belt layer (3) is lower than that of the cord constituting the central region.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Pneumatic tire for bicycle
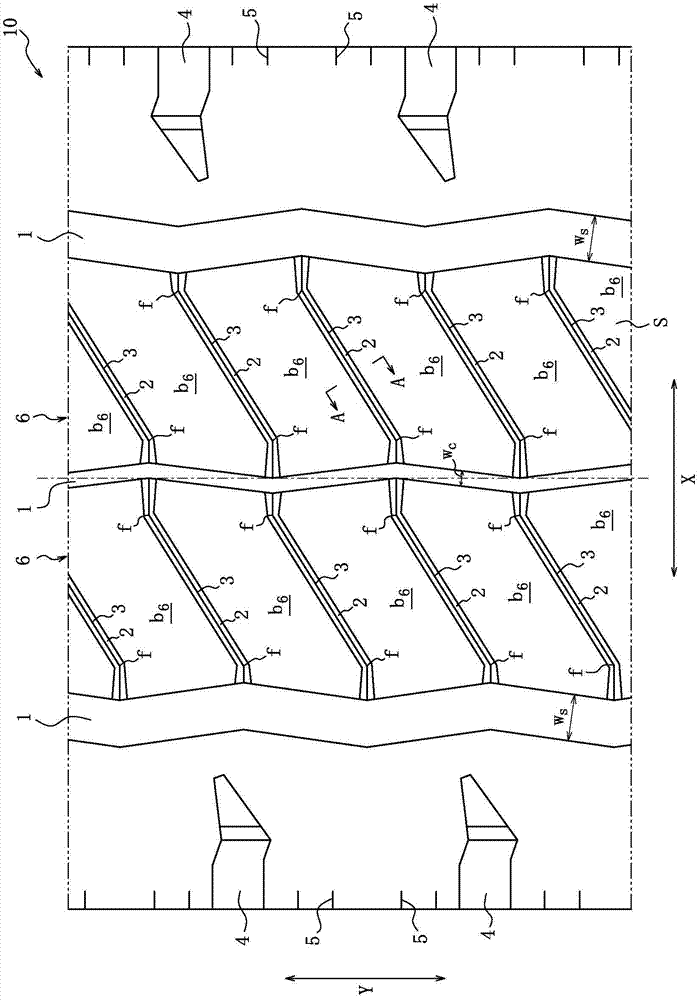
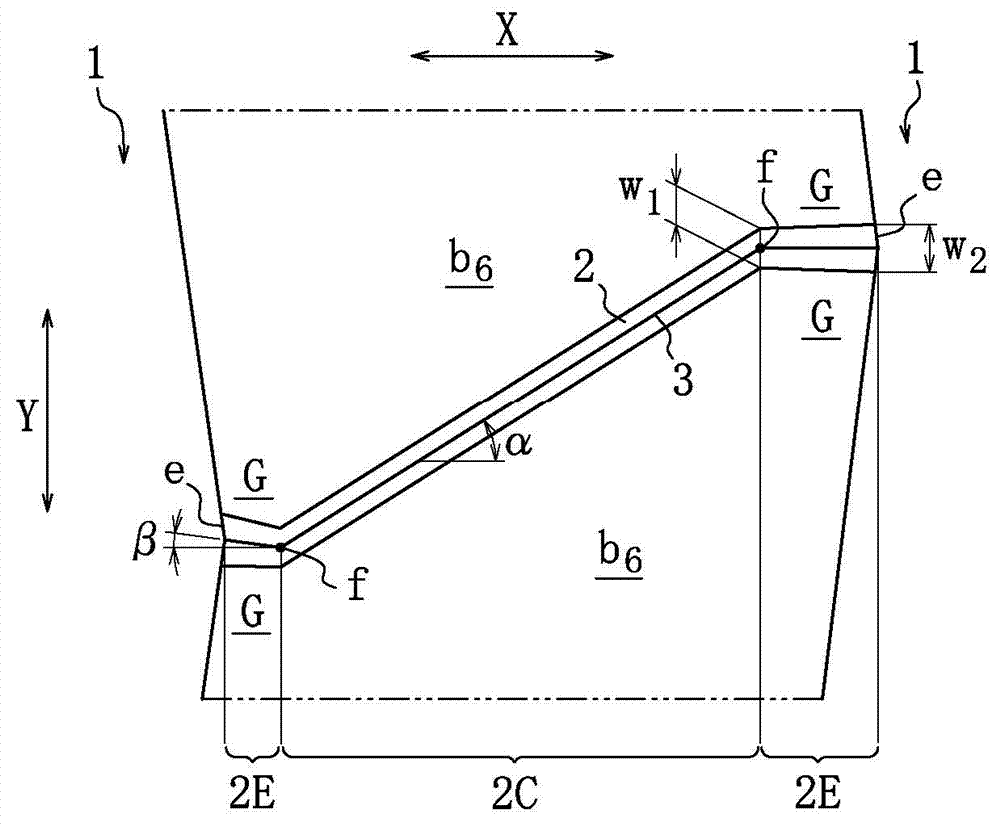
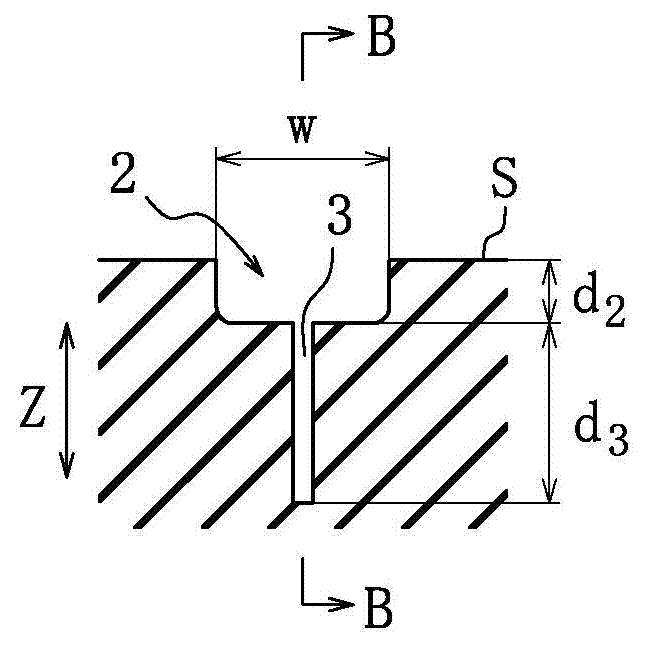
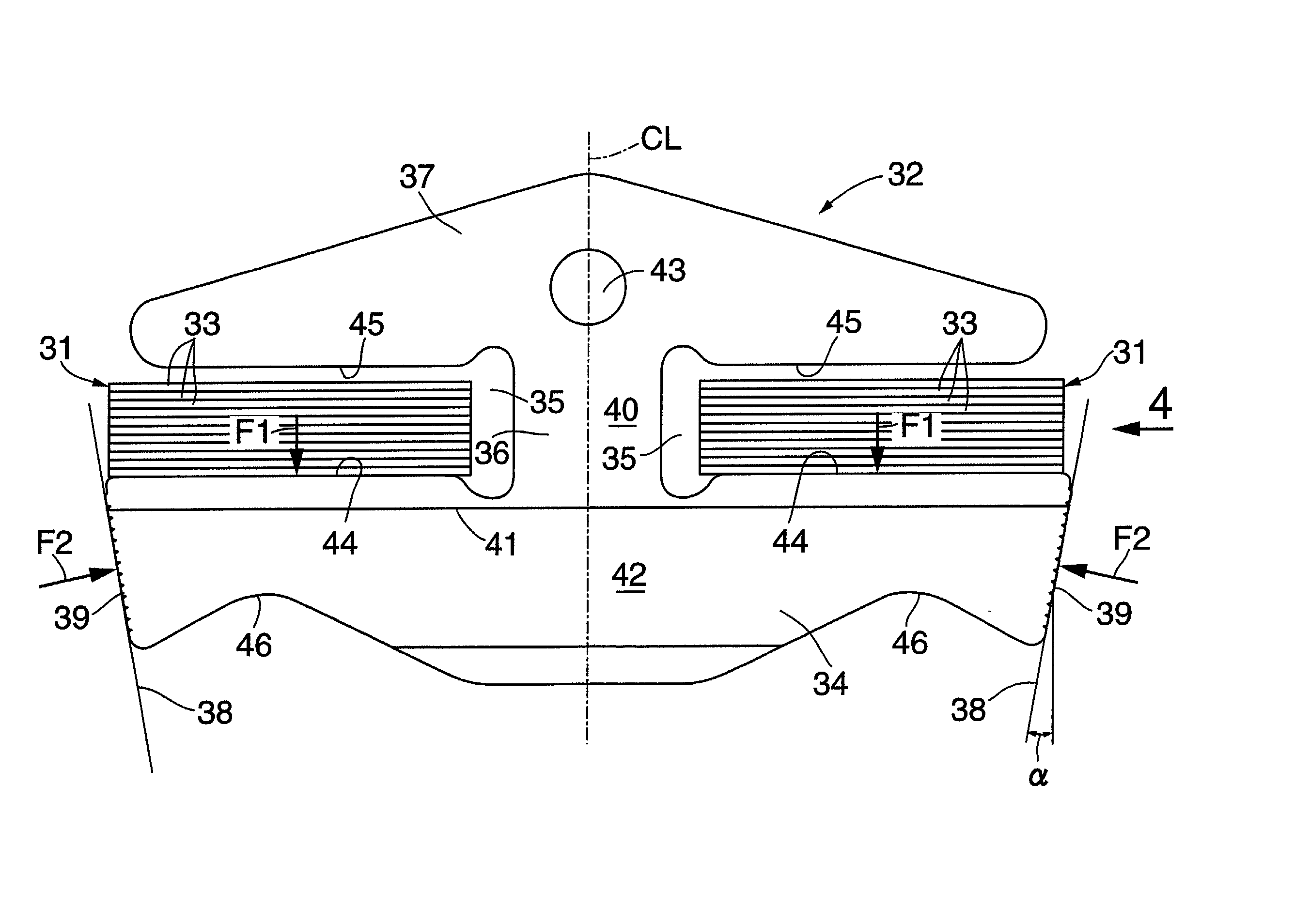
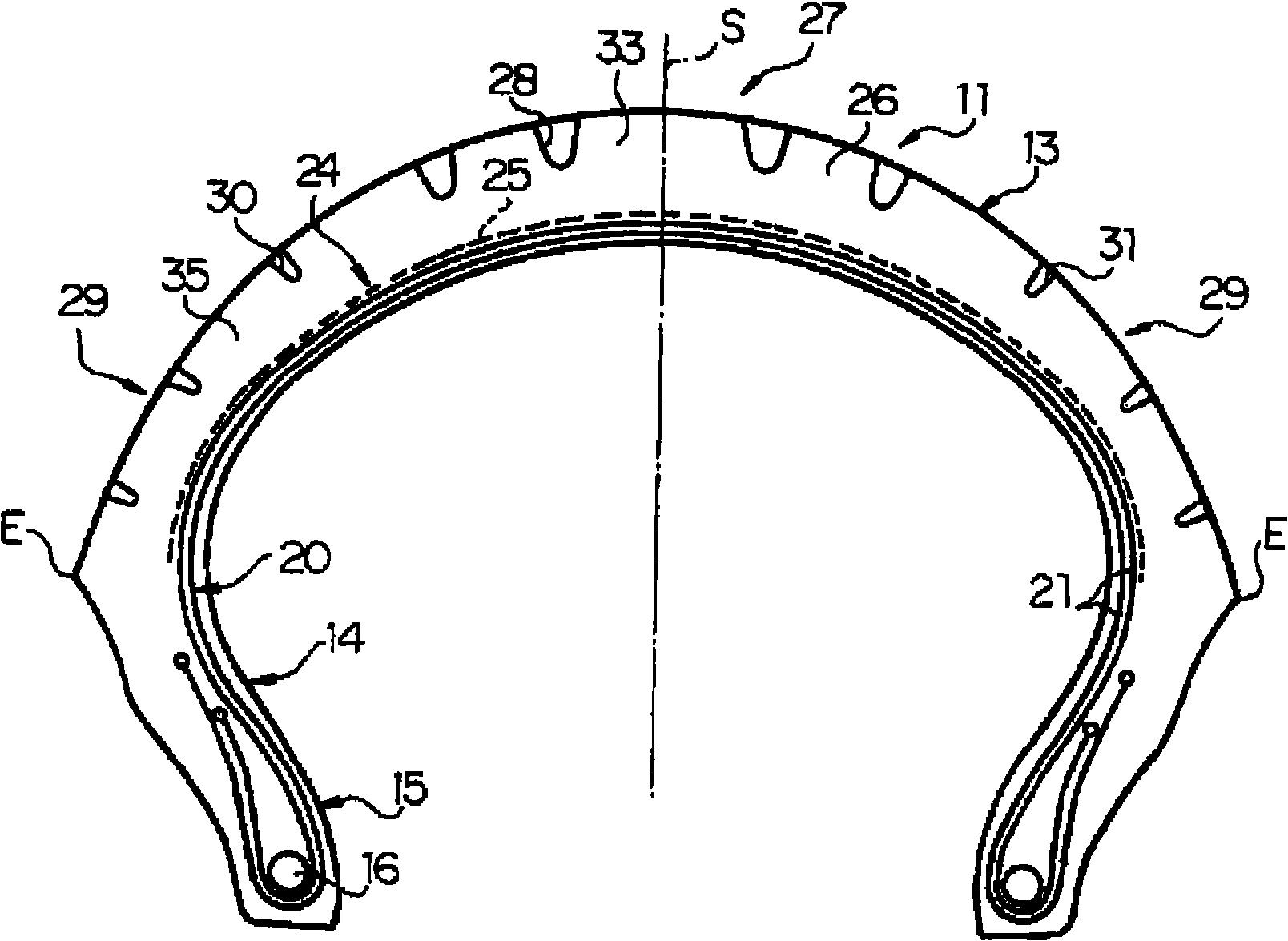
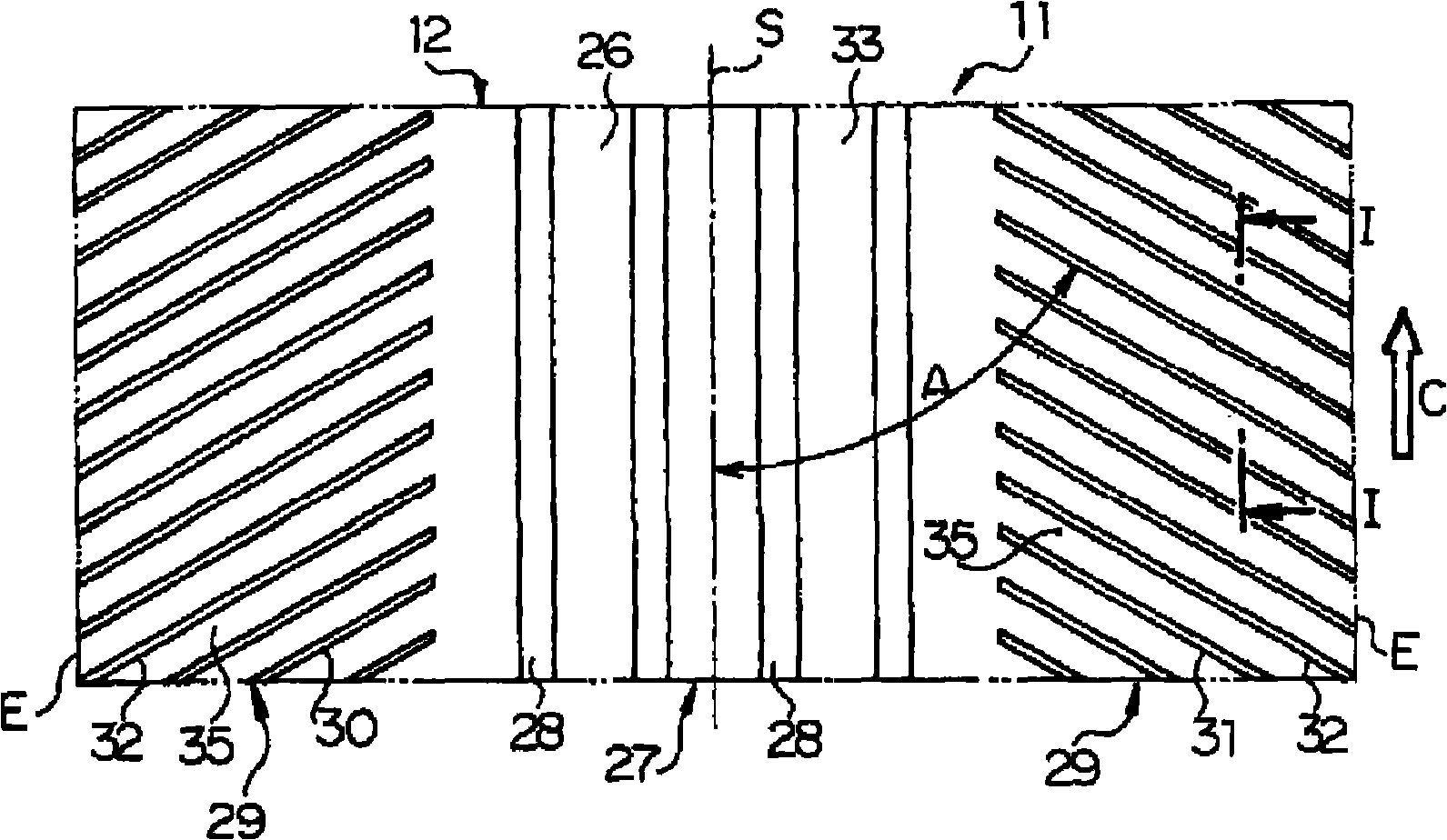
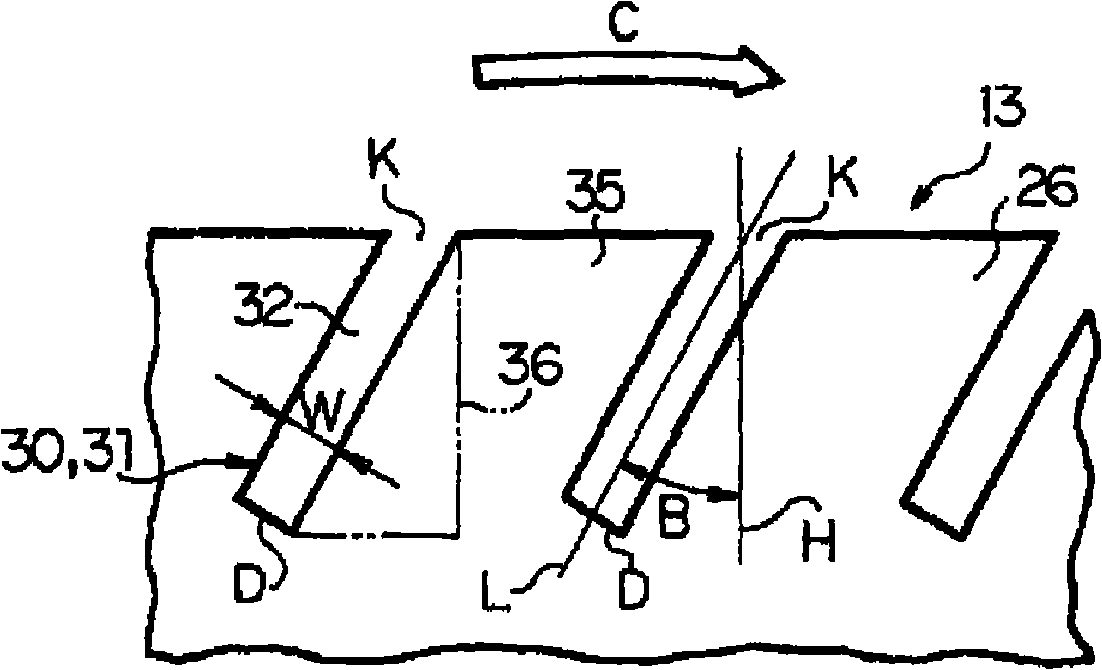
In a pneumatic tire for a bicycle having grooves (30, 31) (inclining portion (32)) formed in the outer surface of a tread (13) to extend substantially in the width direction, and having its rotational direction specified, driving performance or braking performance is enhanced. Since driving force acts on a tire for a rear wheel during acceleration traveling, the entire land (35) between the inclining portions (32) begins to tilt rearward in the rotational direction; since the inclining portions (32) are inclining forward in the rotational direction, as a whole, from a deepest portion (D) toward the end (K) of an opening, a substantially triangular brace (36) formed at the rear end of each land (35) in the rotational direction resists powerfully thus suppressing tilt at each land (35) effectively. Consequently, drive performance is enhanced by enhancement in grip force during driving, and occurrence of uneven wear is suppressed by a uniformed ground-contacting pressure.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Dial switch
InactiveCN102549696ASmooth reciprocating motionInhibits uneven wearElectric switchesEmergency protective devicesCoil springEngineering
A dial switch is provided with: a pivoting section (40) having an uneven peripheral surface (46a); a plunger (60); a holding section (52) for holding the plunger (60) so that the plunger (60) can reciprocate; and a coiled spring (51) for pressing the plunger (60). The holding section (52) has a guide surface (53) extending in the direction in which the plunger (60) moves and surrounding the plunger (60) from the outside. The plunger (60) is provided with: an outer wall section (63) which has an outer peripheral surface (63a) located close to the guide surface (53), and also has an inner peripheral surface (63b) having an inner diameter greater than the outer diameter of the coiled spring (51); and an inner shaft (64) which is located inside the outer wall section (63) and has a rear end located further toward the front side than the rear end of the outer wall section (63), the inner shaft (64) being adapted to enable the coil spring (51) to be mounted on the outer side thereof. The difference between the outer diameter of the inner shaft (64) and the inner diameter of the coiled spring (51) is less than the difference between the inner diameter of the outer wall section (63) and the outer diameter of the coiled spring (51).
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Heavy duty pneumatic tire
ActiveCN105691111AImprove performance on iceInhibits uneven wearHeavy duty tyresHeavy duty vehicleEngineeringHeavy duty
The invention provides a heavy duty pneumatic tire which can play excellent on-ice performance and the wear-resisting property. A tread portion 2 is divided into shoulder land regions 11 and middle land regions 10. The shoulder land regions 11 comprise shoulder pattern blocks 40. The middle land regions 10 comprise middle pattern blocks 16. At least one of the shoulder pattern blocks 40 and at least one of the middle pattern blocks 16 are each divided by two splitting sipes 25 into a central pattern block piece 30 and outside pattern block pieces 31 on both sides thereof. Each outside pattern block piece 31 of the middle pattern blocks 16 is provided with a closed sipe 33. Each outside pattern block piece 31 of the shoulder pattern blocks 40 is provided with an open sipe 45.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Pneumatic tire
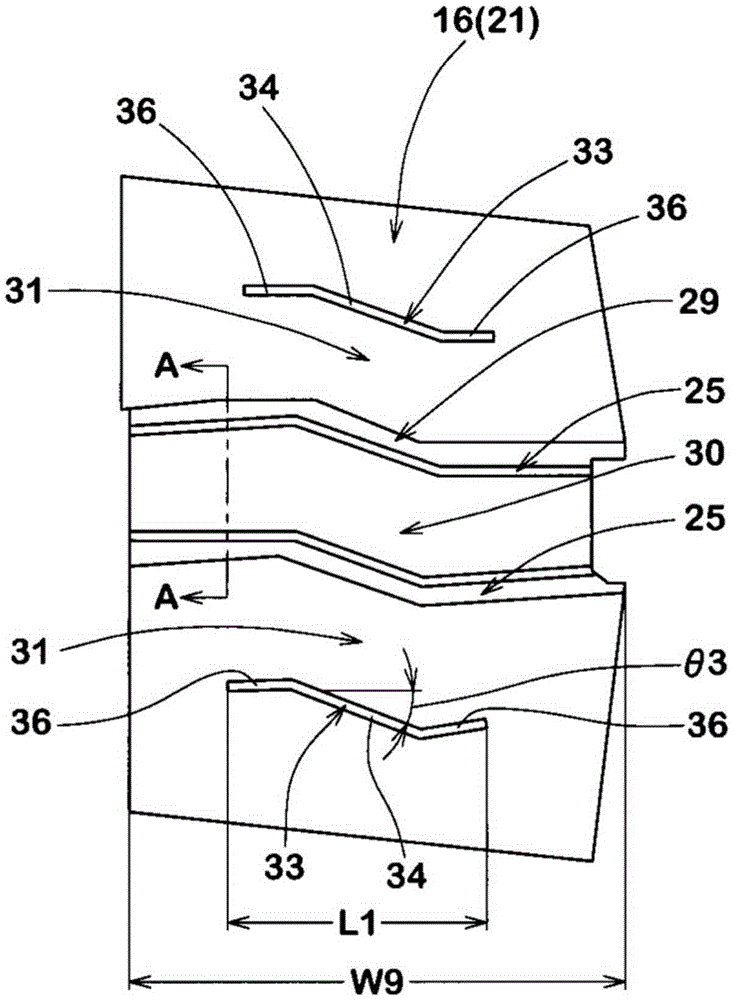
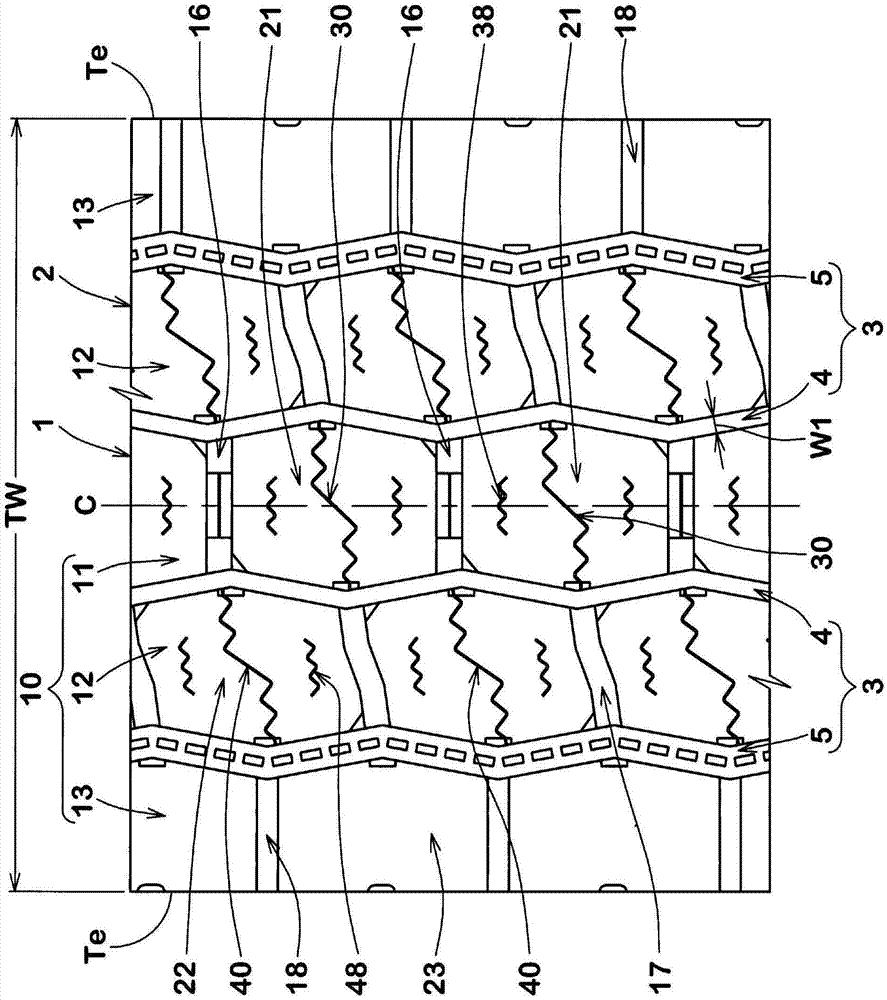
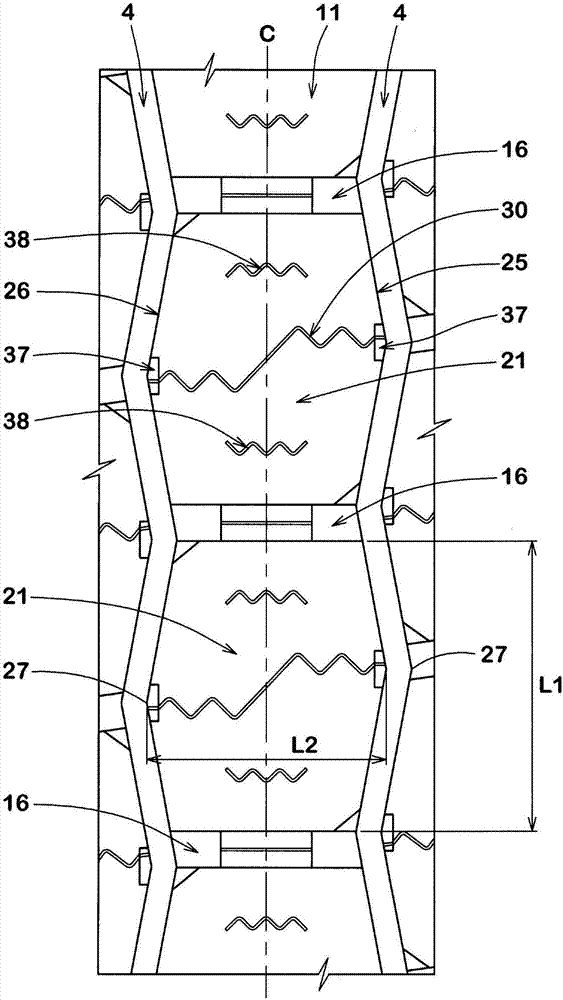
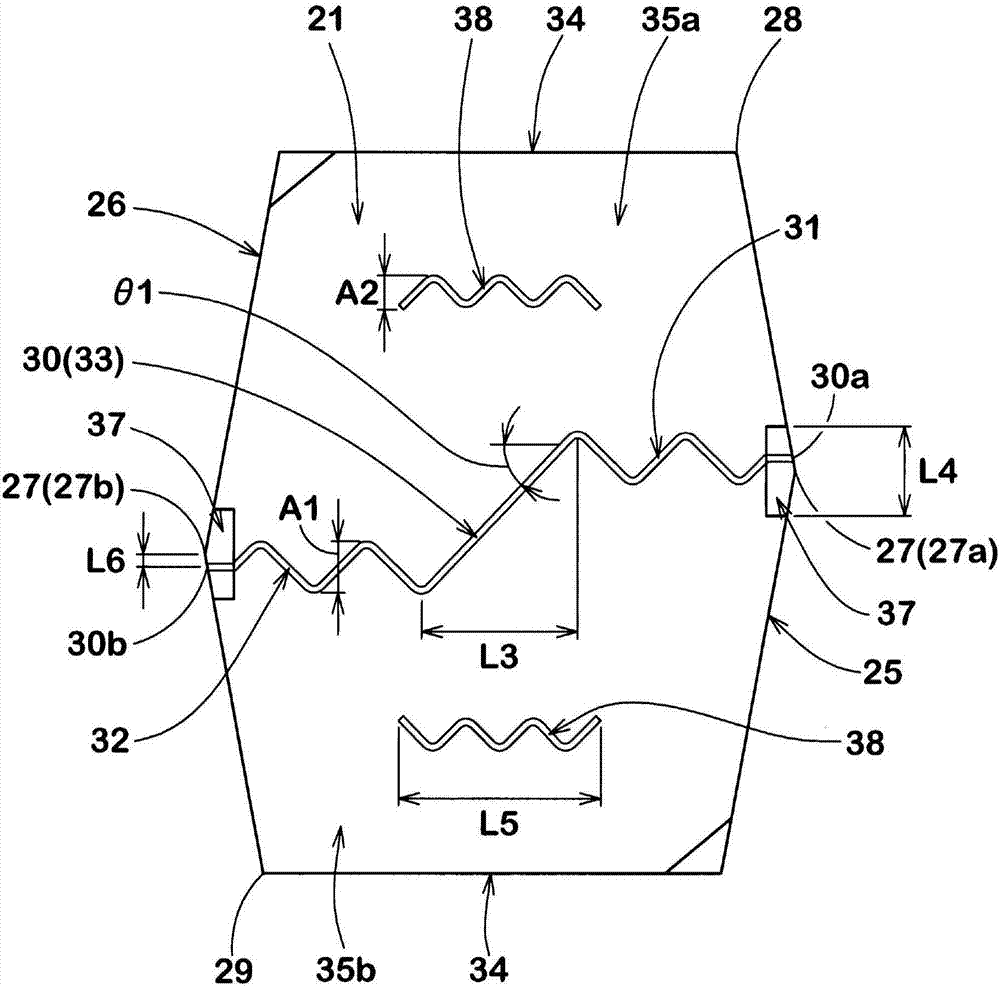
ActiveCN106985617AImprove uneven wear resistanceInhibits uneven wearHeavy duty tyresHeavy duty vehicleMechanical engineeringTread
A pneumatic tire is provided and has improved resistance to uneven abrasiveness of center blocks. The pneumatic tire (1) comprises a tread portion (2) provided with crown main grooves (4), a plurality of center axial grooves (16) and a plurality of center blocks (21). The center blocks (21) include a first block side wall (25), a second block side wall (26) and a first sipe (30). The first block side wall (25) and the second block side wall (26) are substantially V-shaped protruding from a vertex (27) respectively. At least a part of the first sipe (30) extends in a waveform manner. One end at the tire axial direction of the first sipe (30) is at one side in the tire circumferential direction of the vertex of the first block side wall (25), and the other end of the first sipe (30) at the tire axial direction is positioned on other side in the tire circumferential direction of the vertex of the second block side wall (26).
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Pneumatic tire
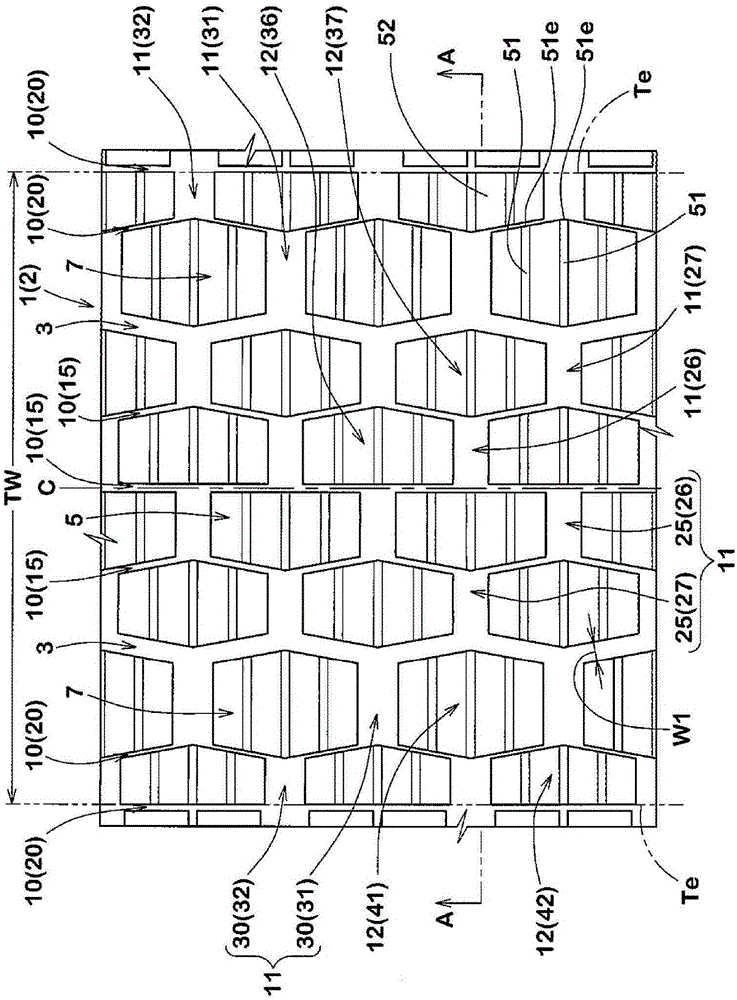
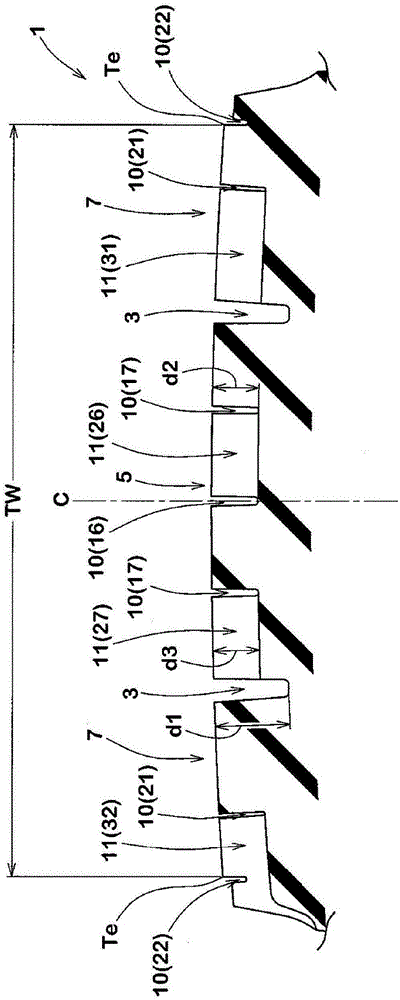
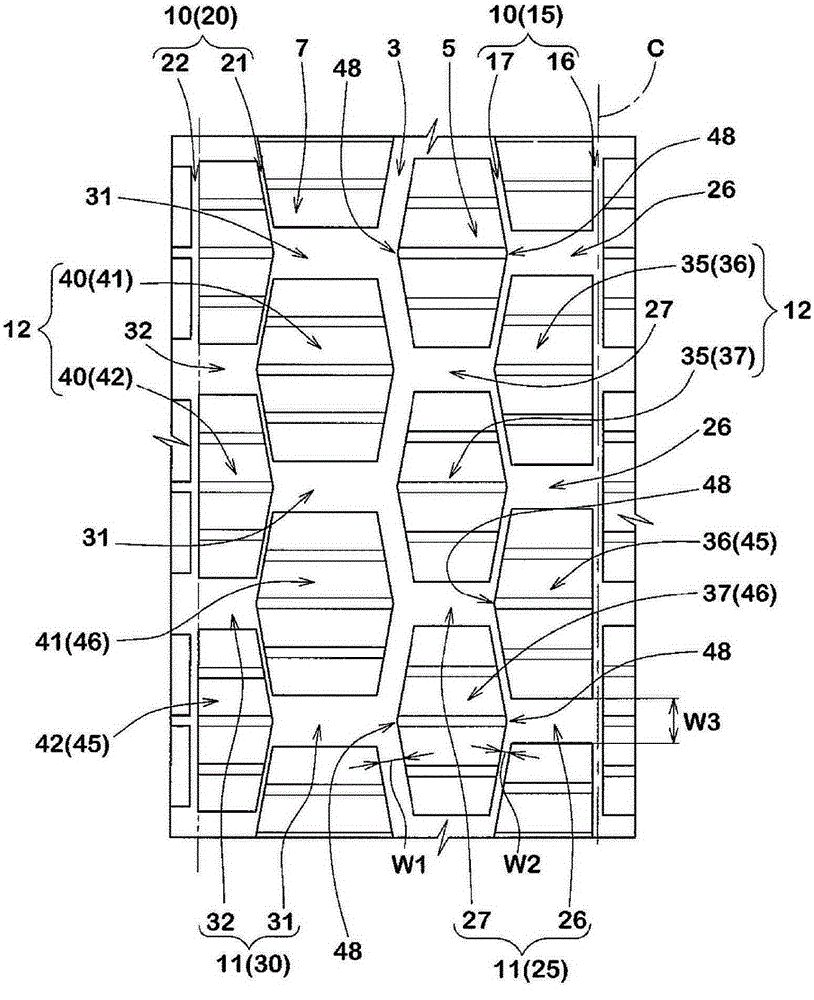
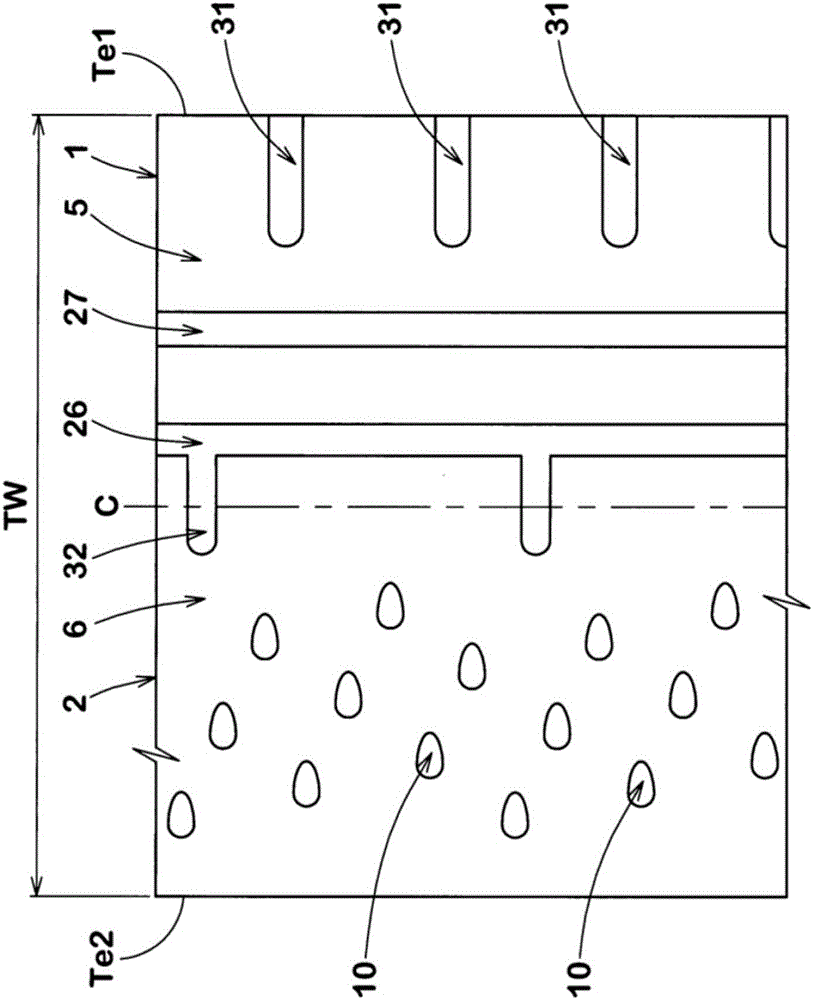
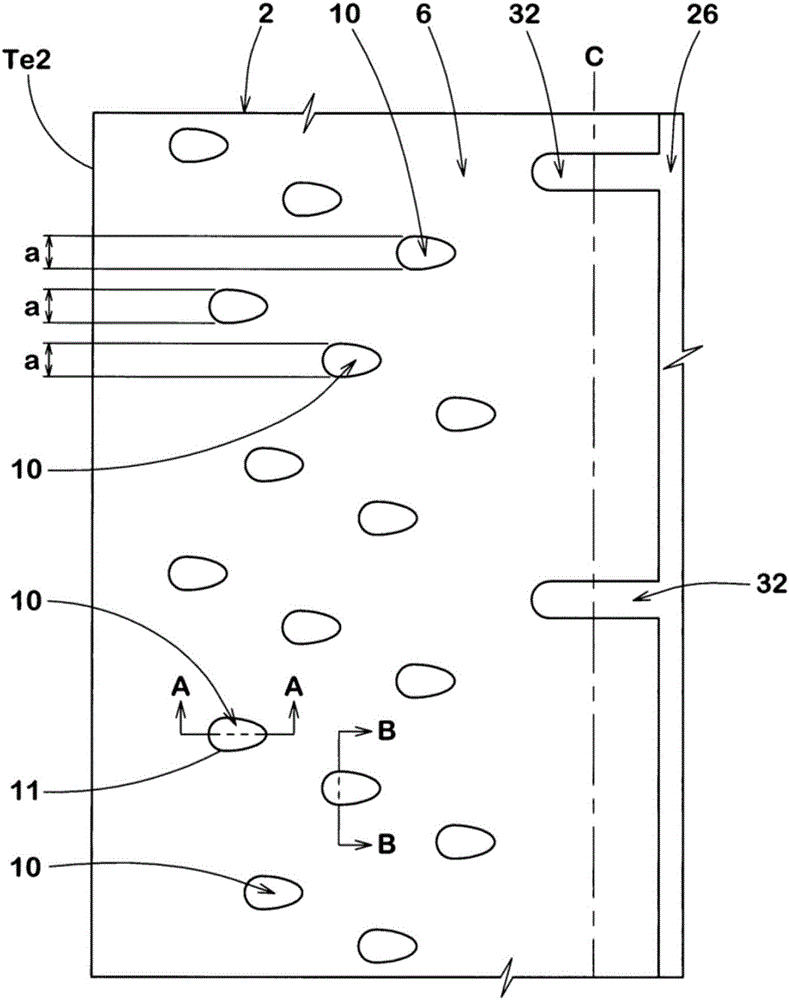
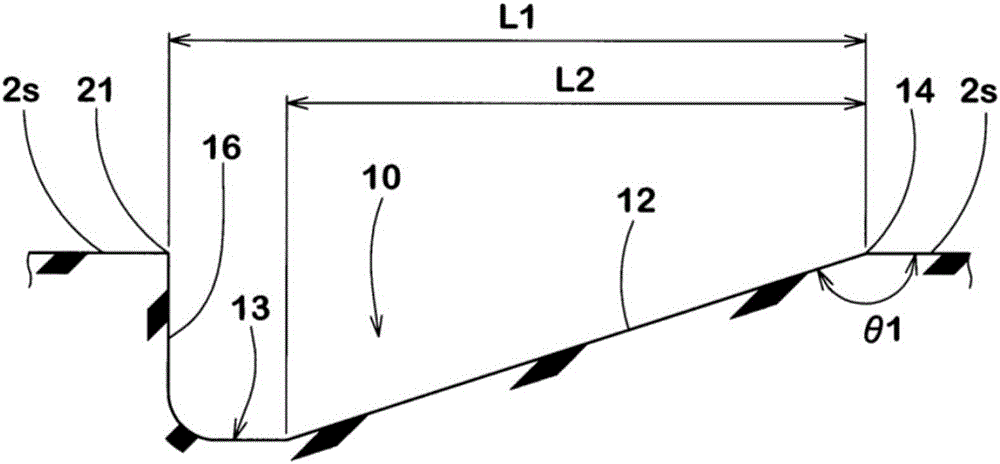
ActiveCN106427402AGuaranteed rigidityImprove cooling effectInflatable tyresTyre tread bands/patternsEngineeringWear resistance
The present invention provides a pneumatic tire which maintains both the turning performance and the nonuniform wear resistance. A plurality of recesses (10) are provided on the tread surface of the tread portion (2). Each of the recesses (10) has a closed contour shape (11) formed by a smooth curve on the surface of the tread portion (2) and has an inclined surface (12). The depth of the inclined surface (12) gradually decreases from the outer tread end (Te2) side toward the inner tread end (Te1) side in the cross section along the tire axial direction. The length of the tire in the axial direction of the inclined surface (12) is 60% or more of the length of the tire in the axial direction of the recess (10).
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Pneumatic tire
ActiveCN101168341AReduced ground areaIncrease ground pressureTyre tread bands/patternsMechanical engineeringTread
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com