Patents
Literature
196 results about "Copying Processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
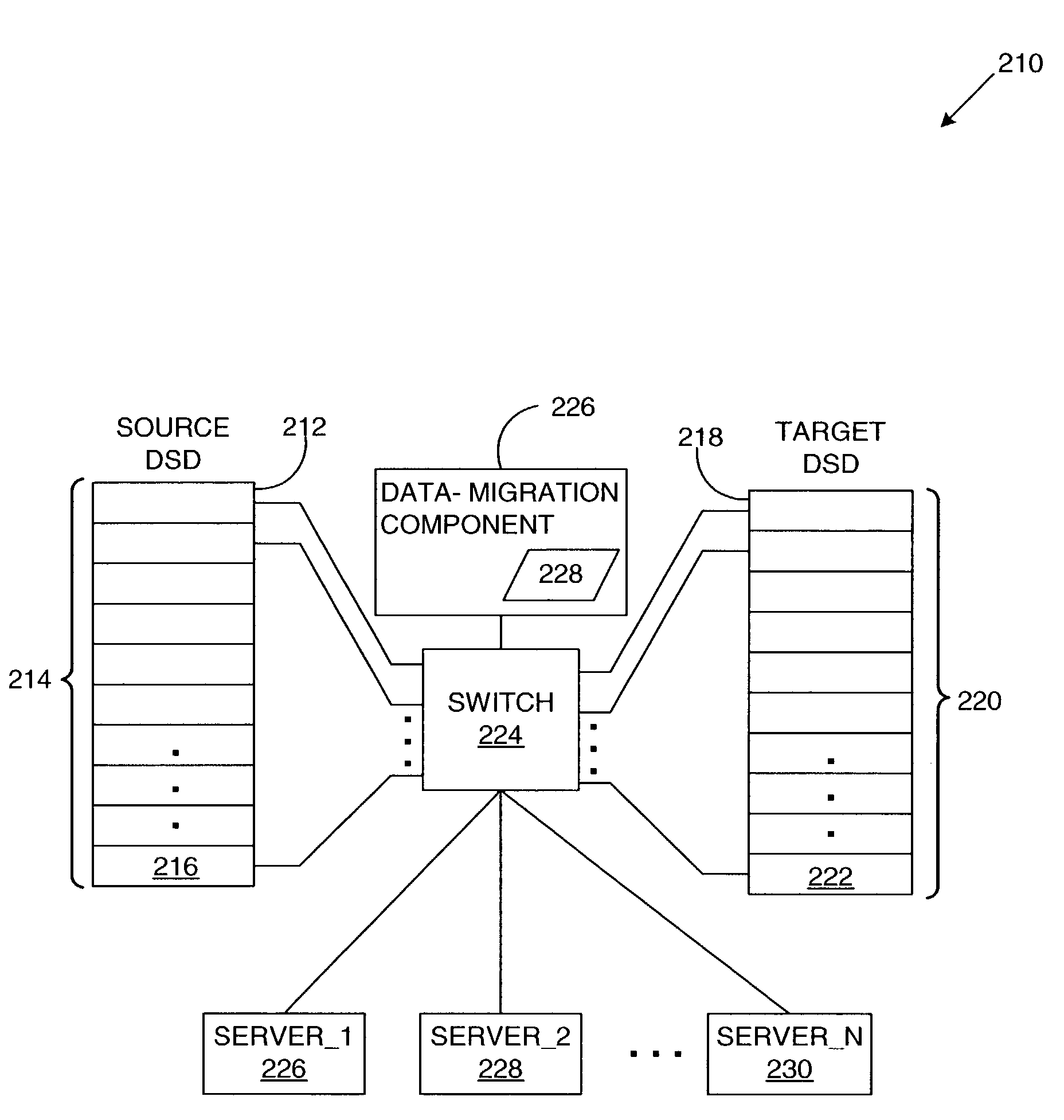
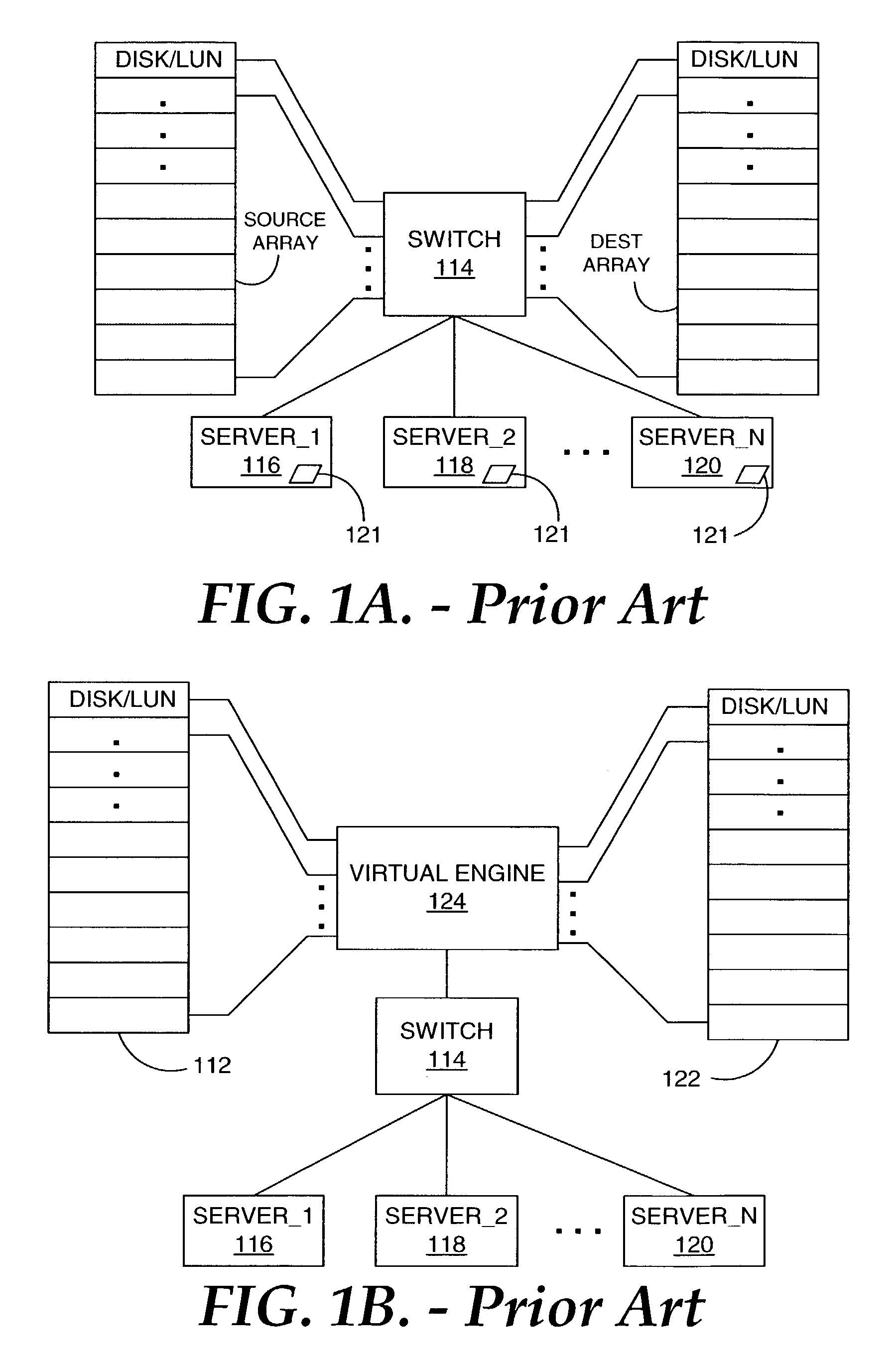
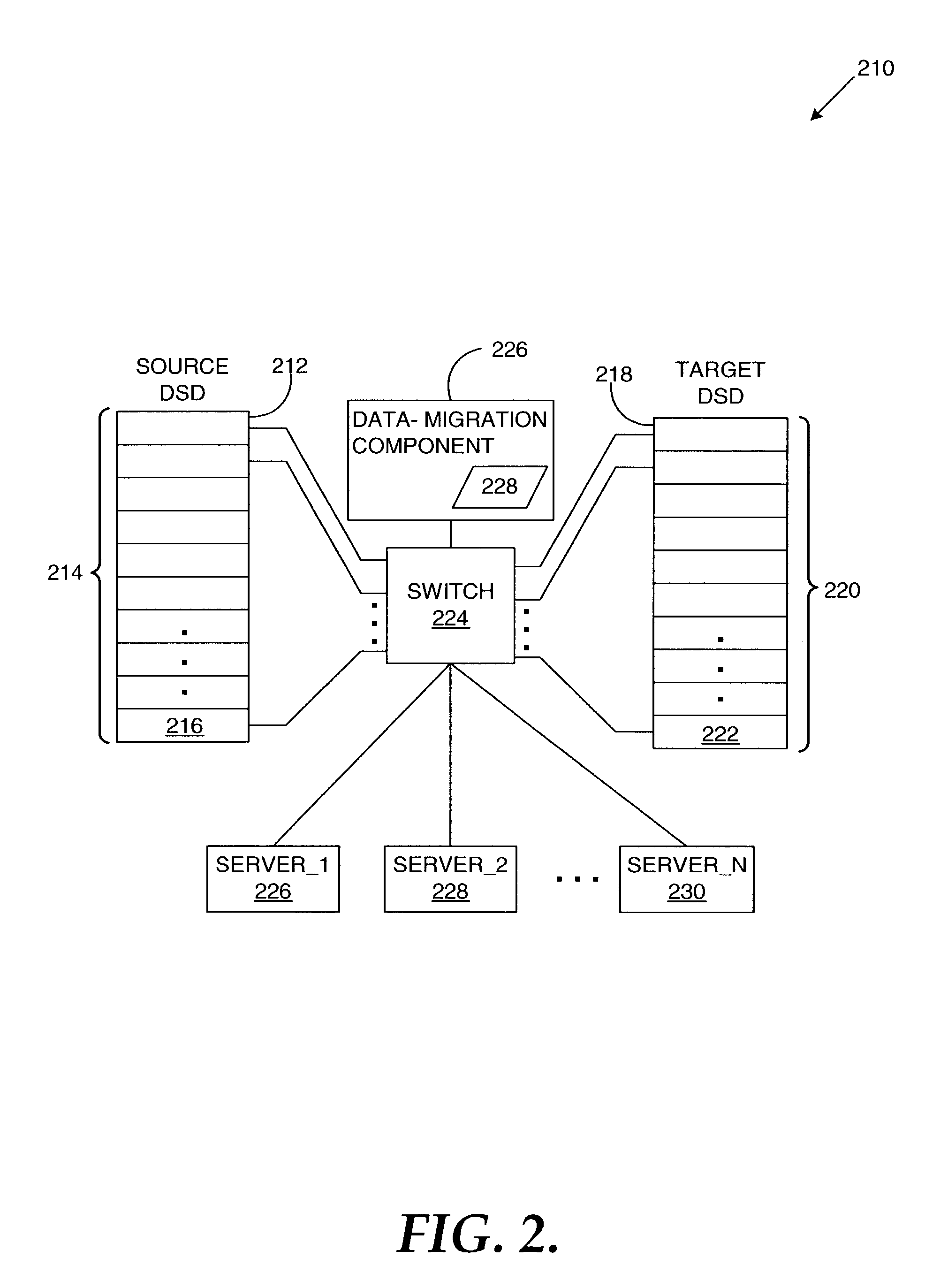
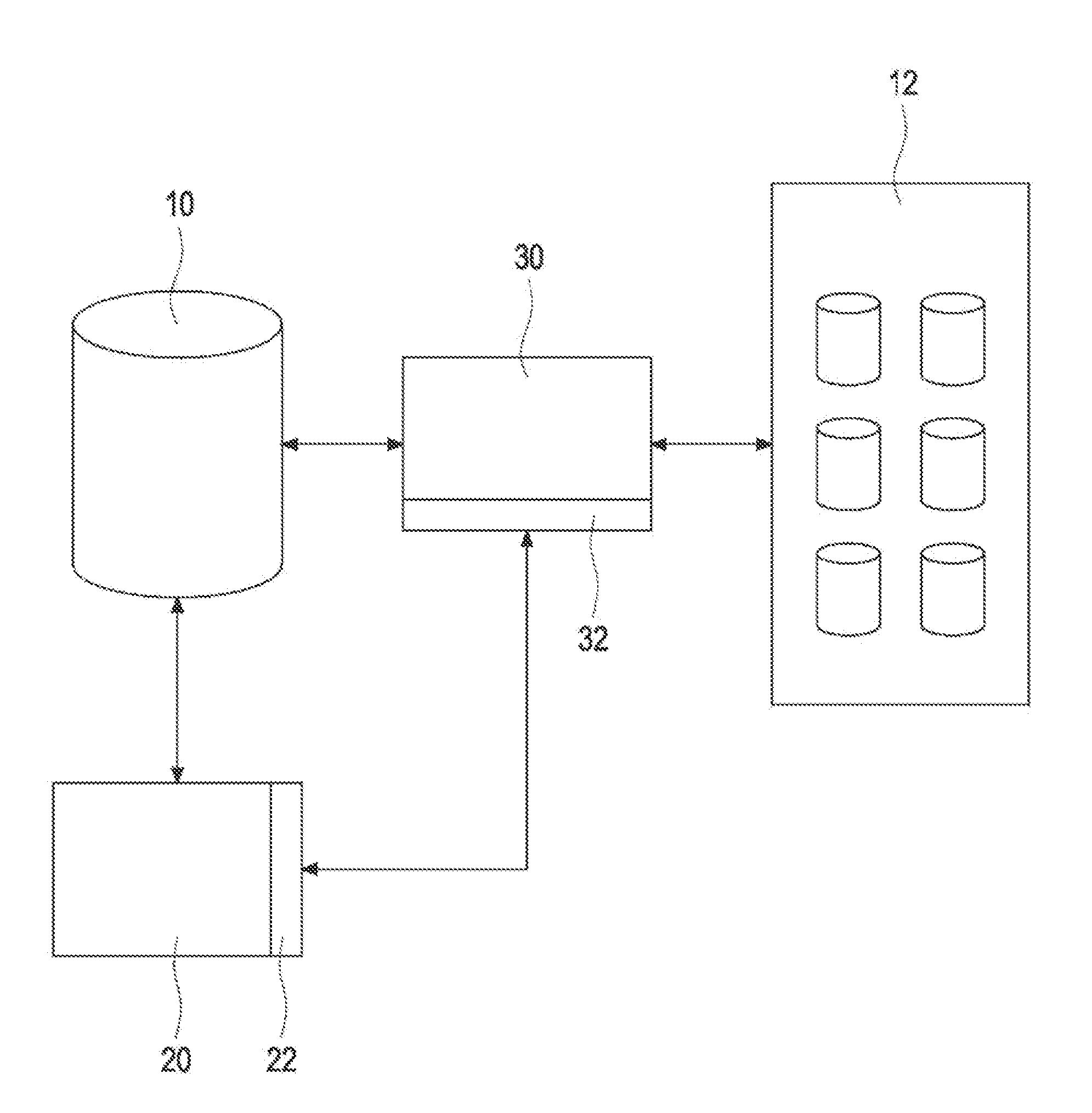
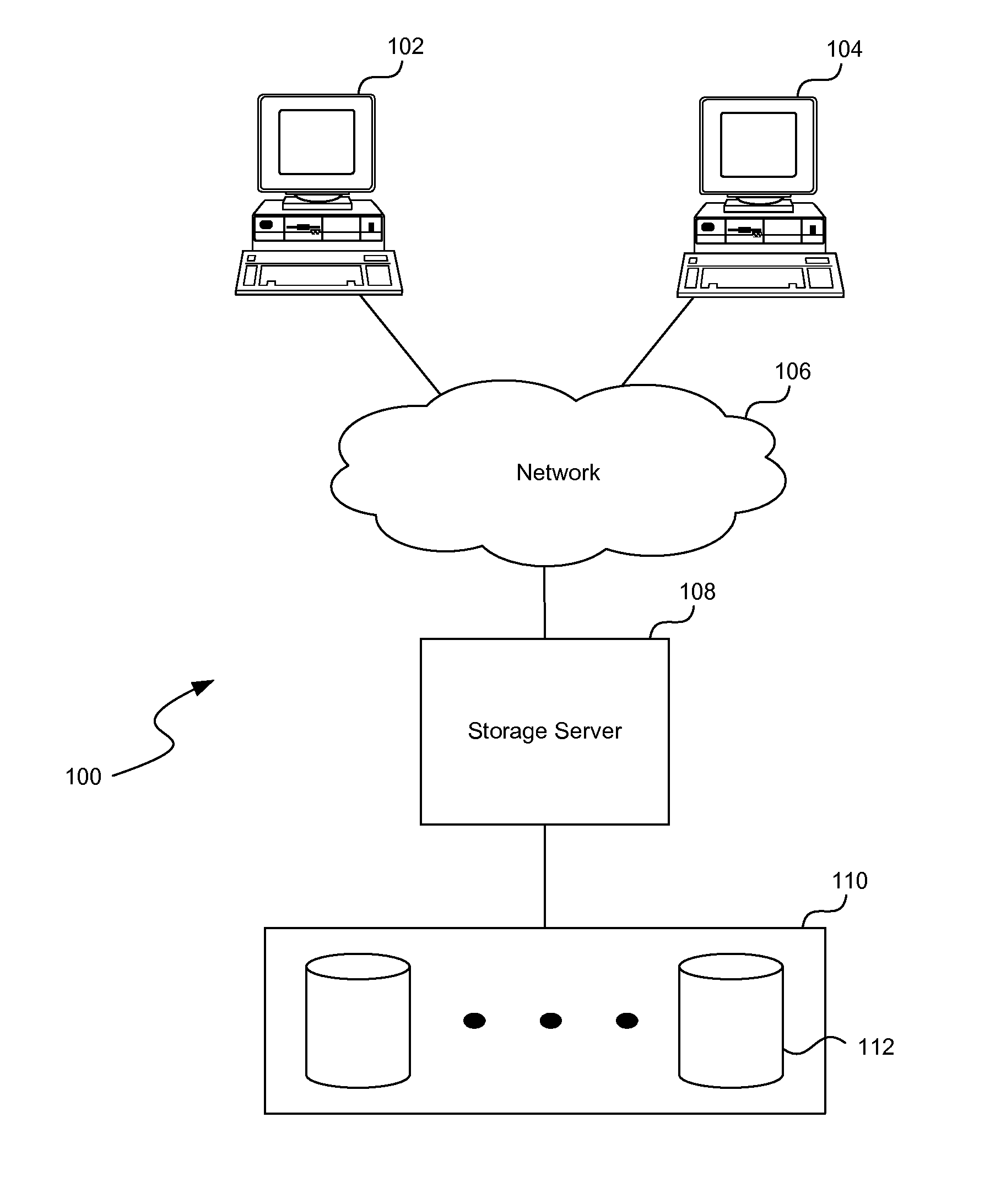
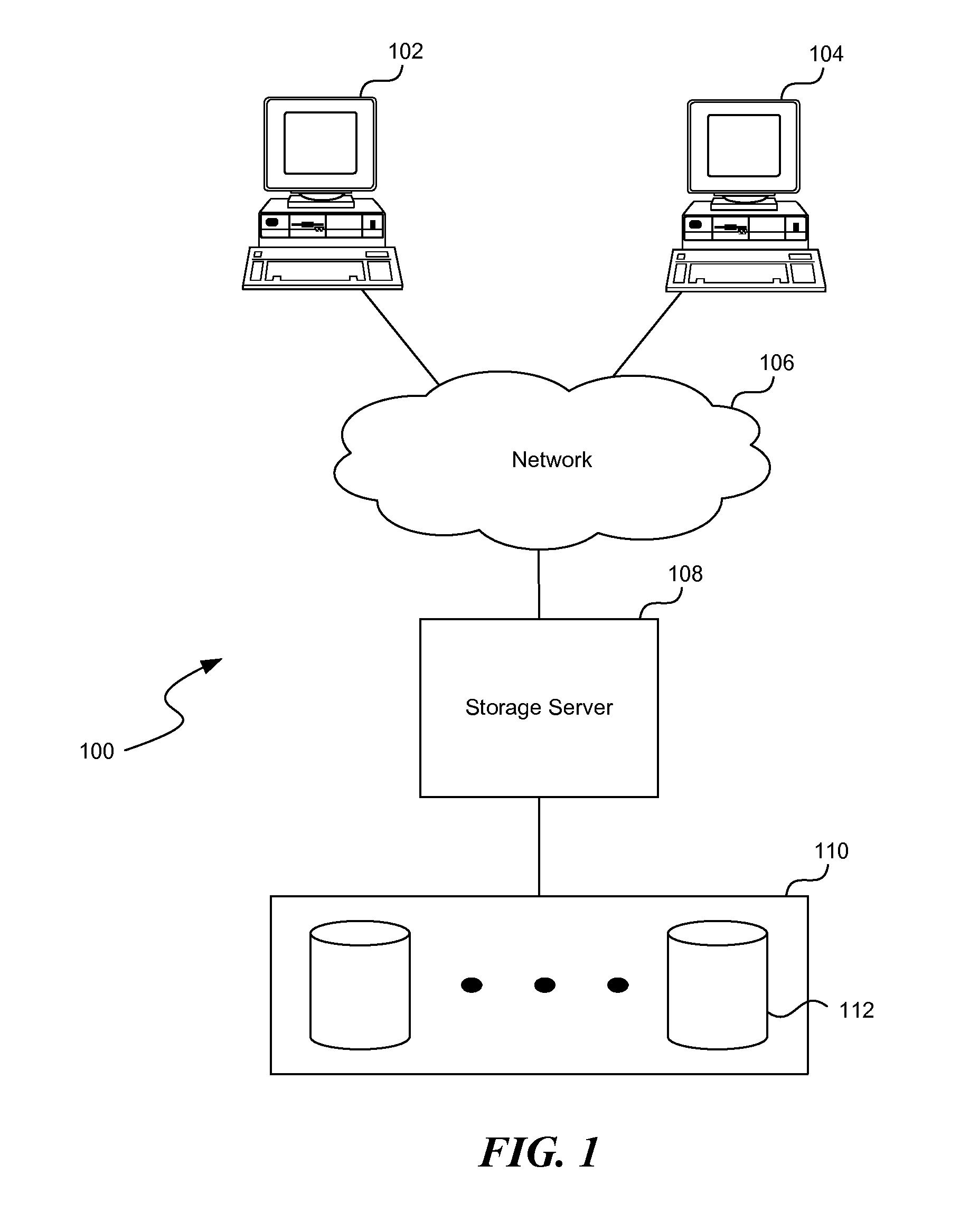
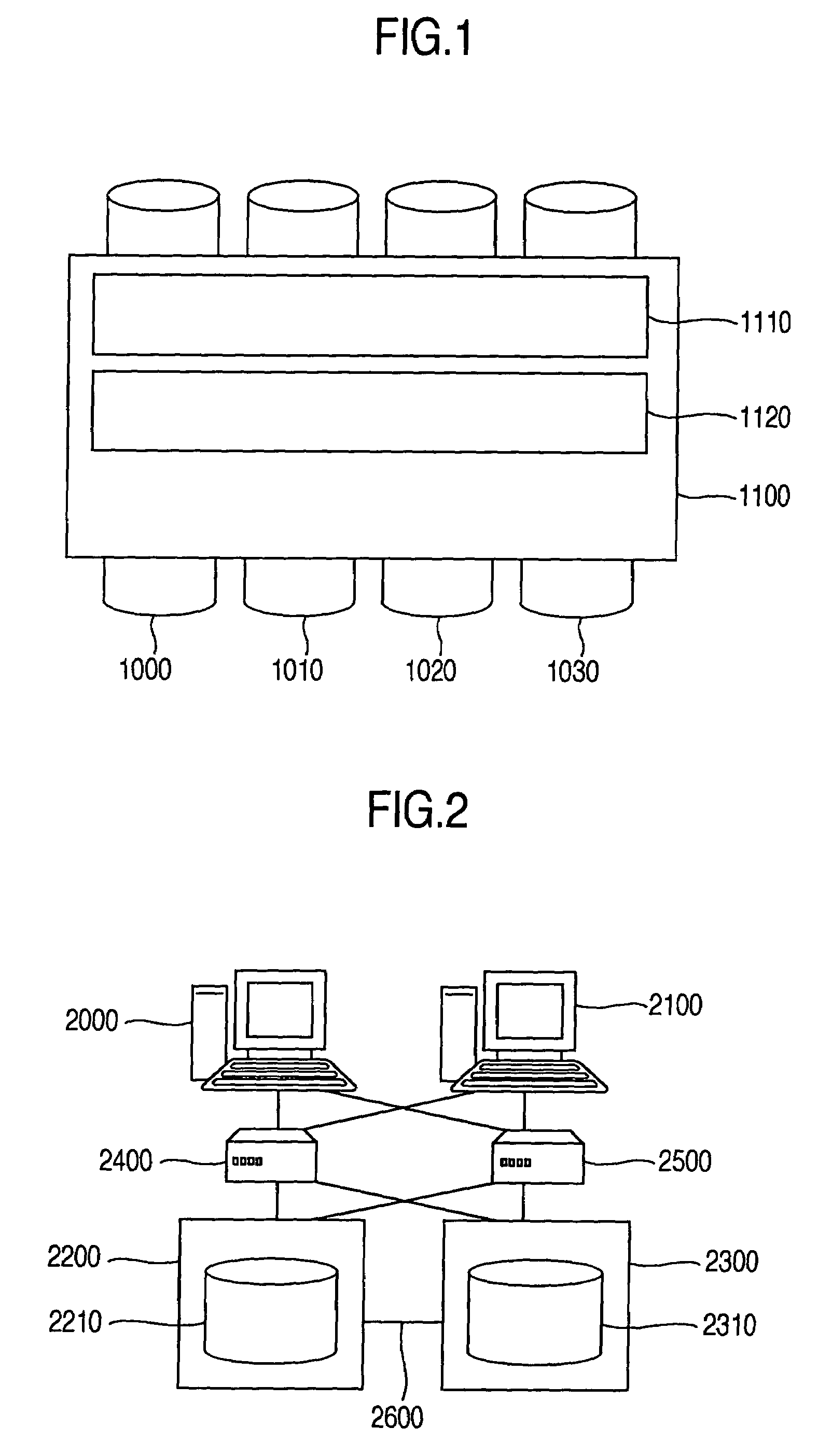
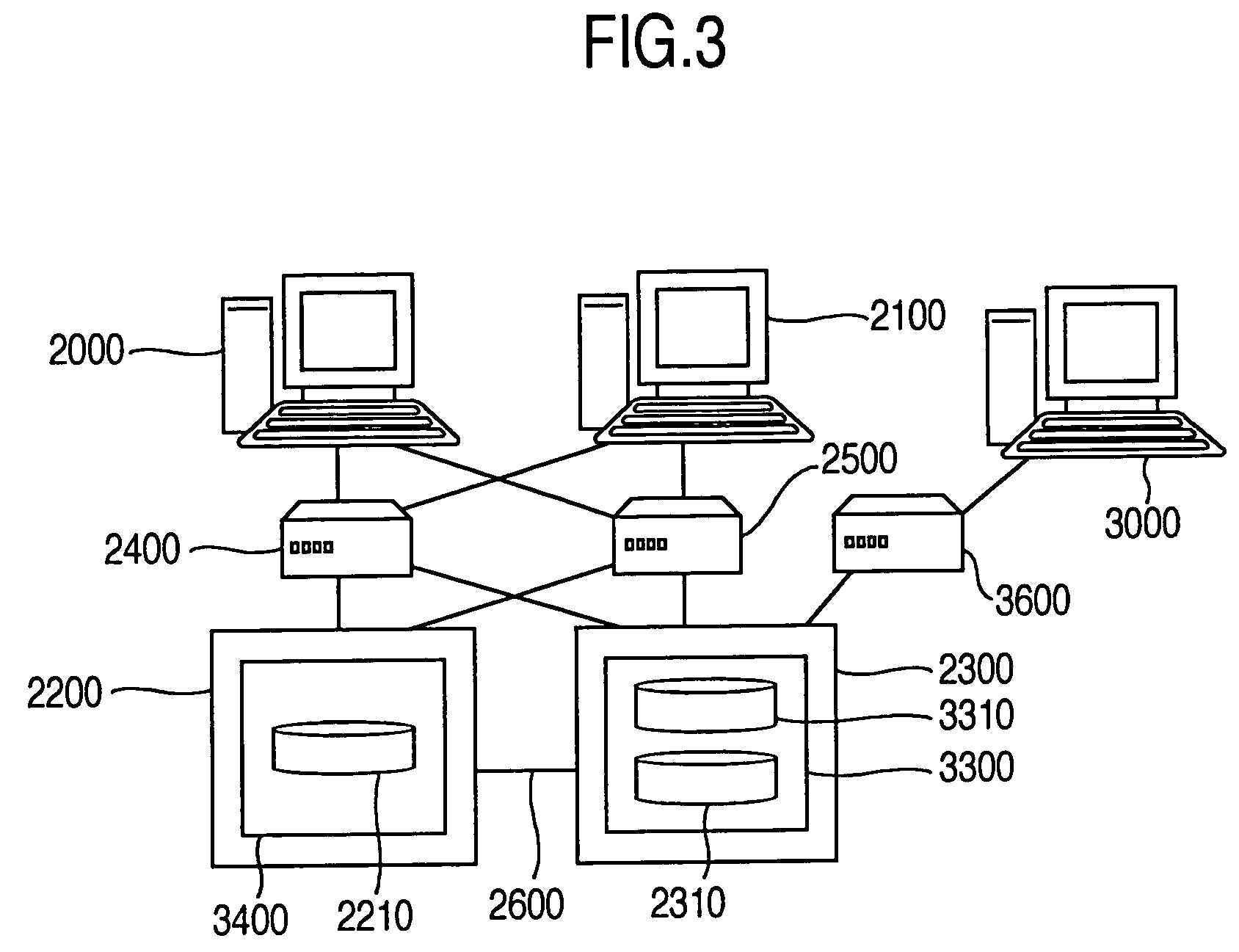
Reproduction of data in a new location or other destination, leaving the source data unchanged, although the physical form of the result may differ from that of the source.
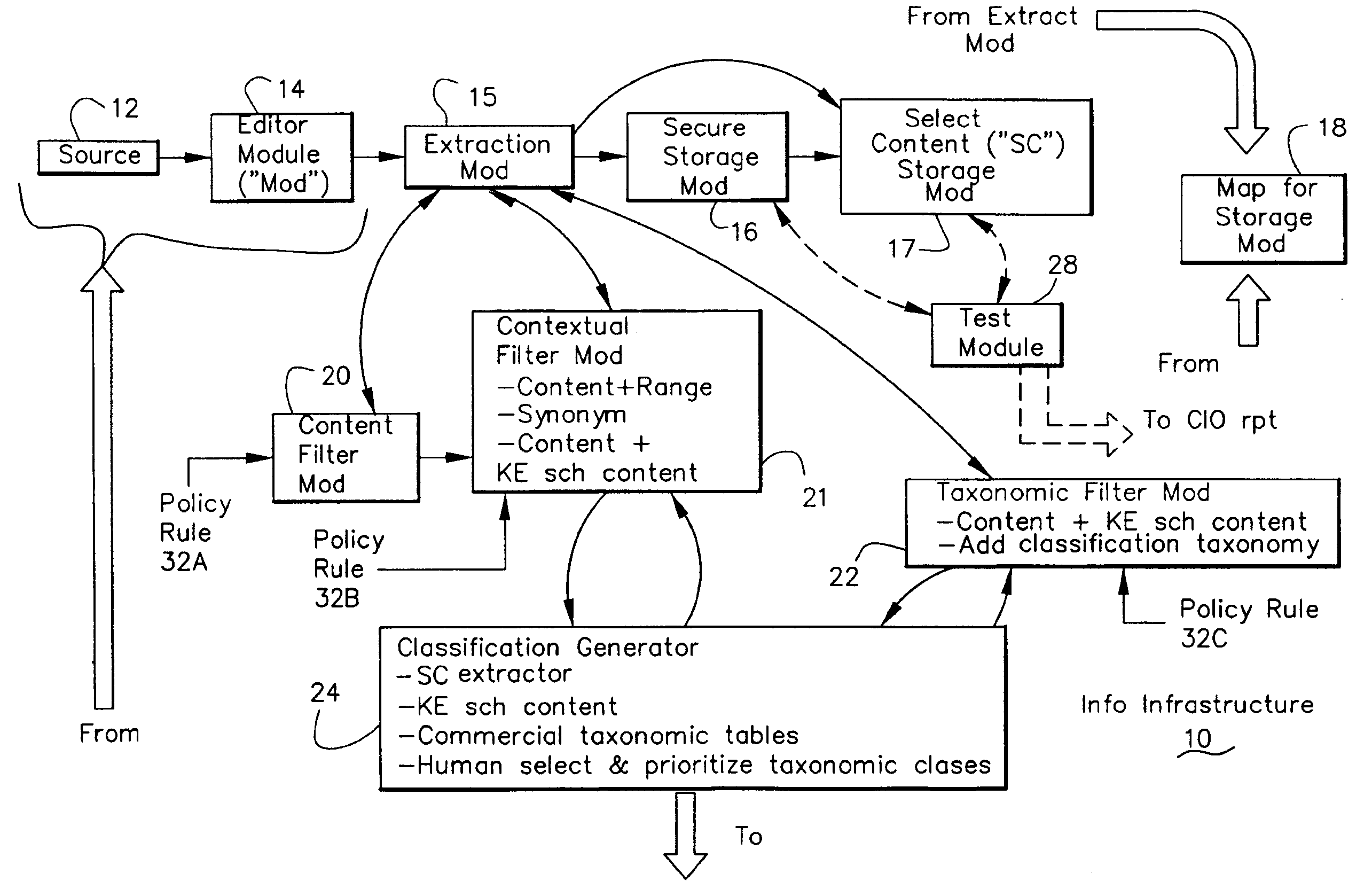
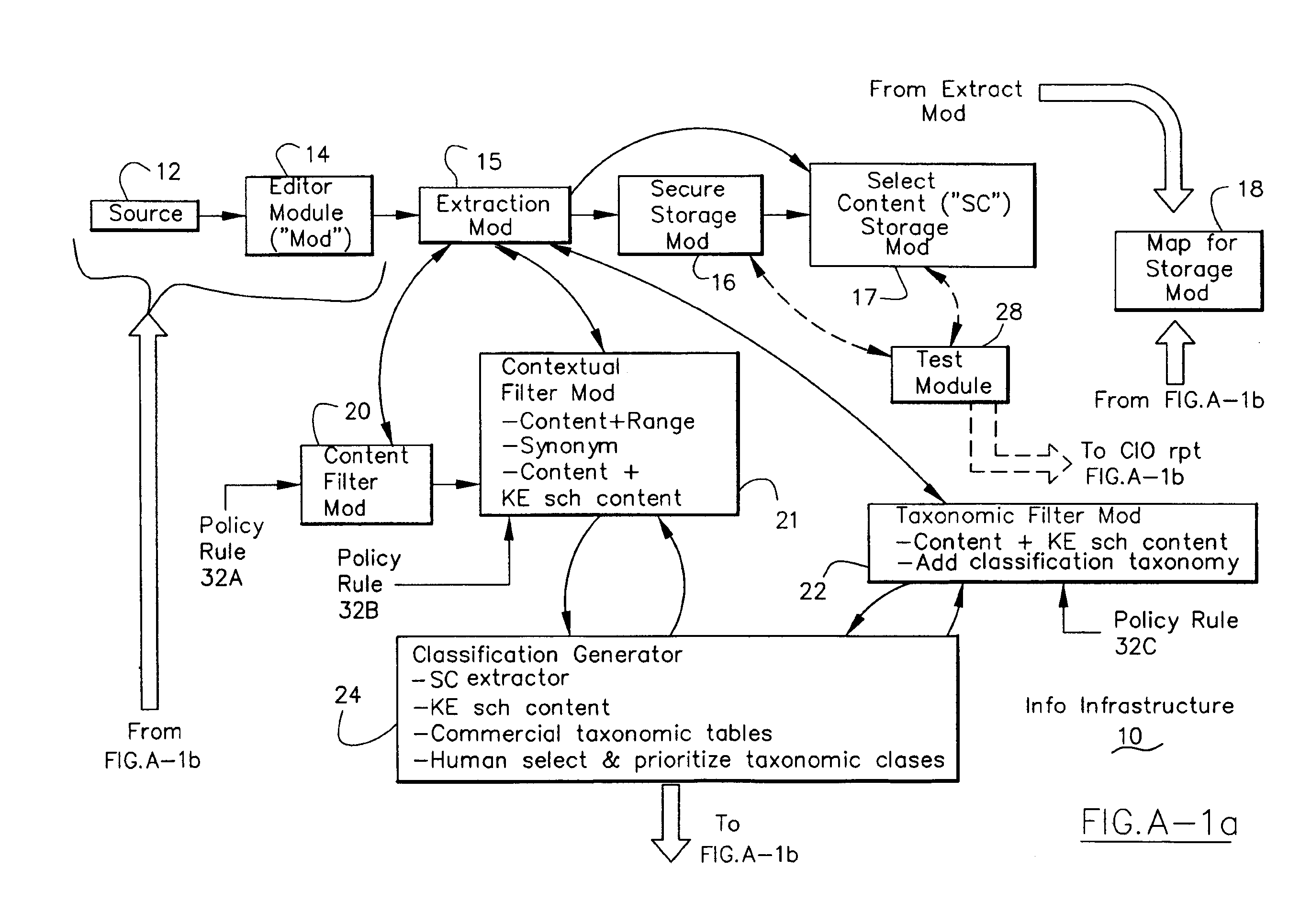
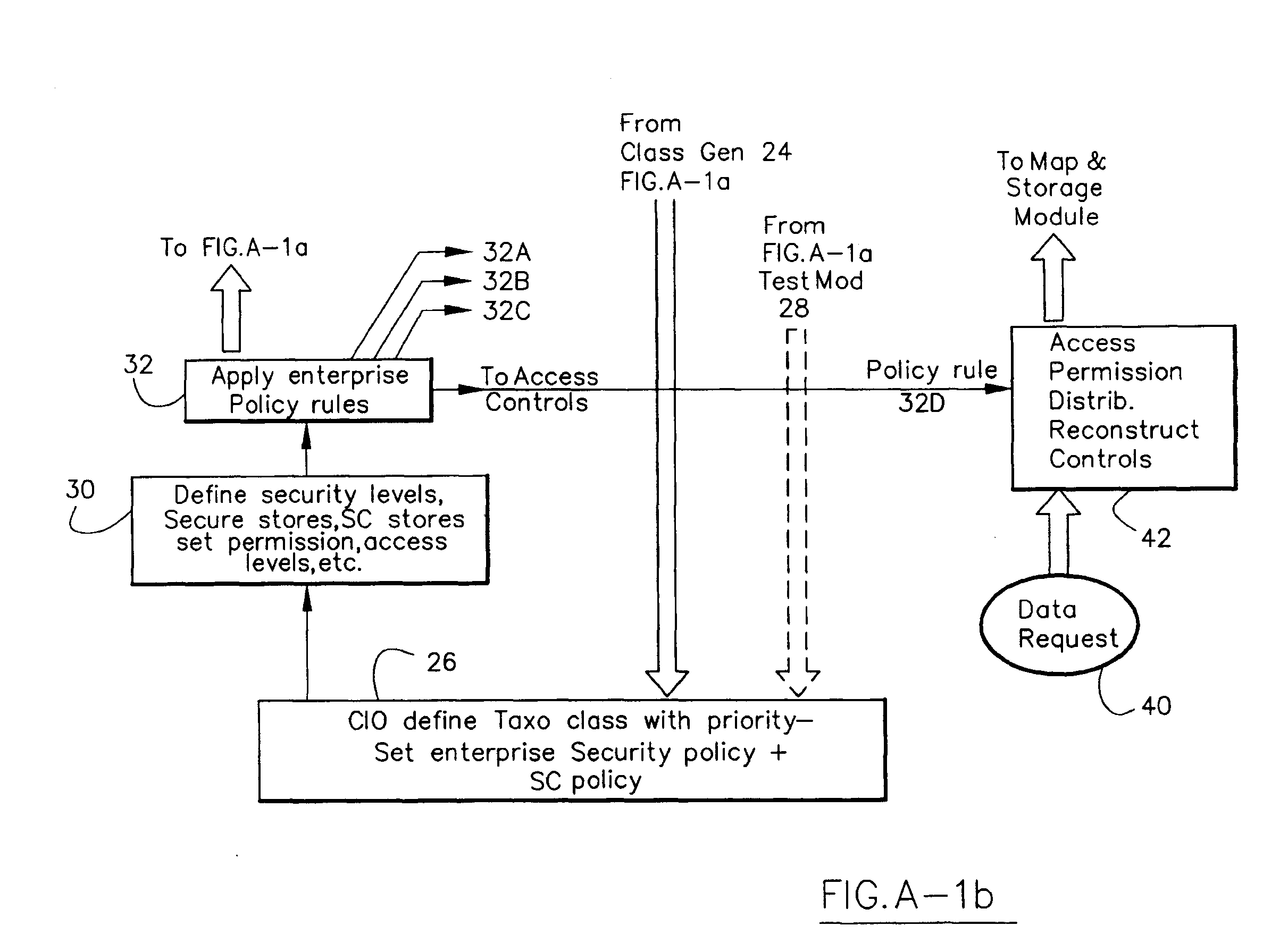
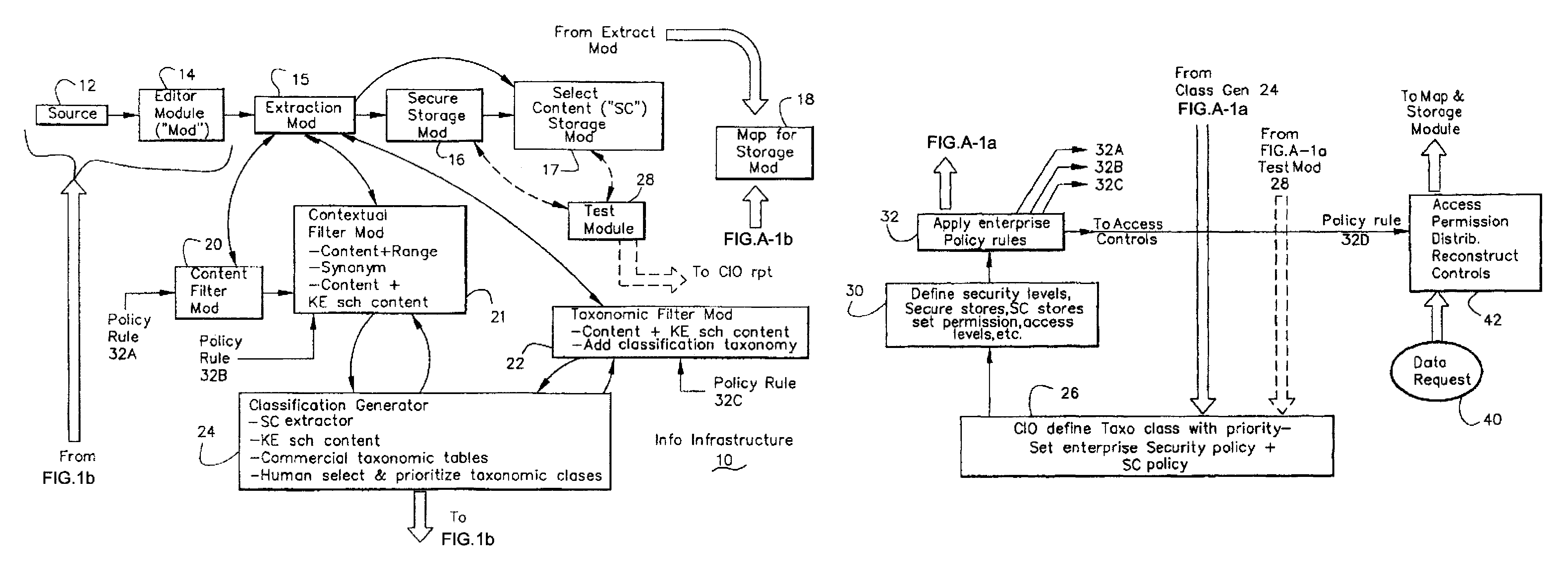
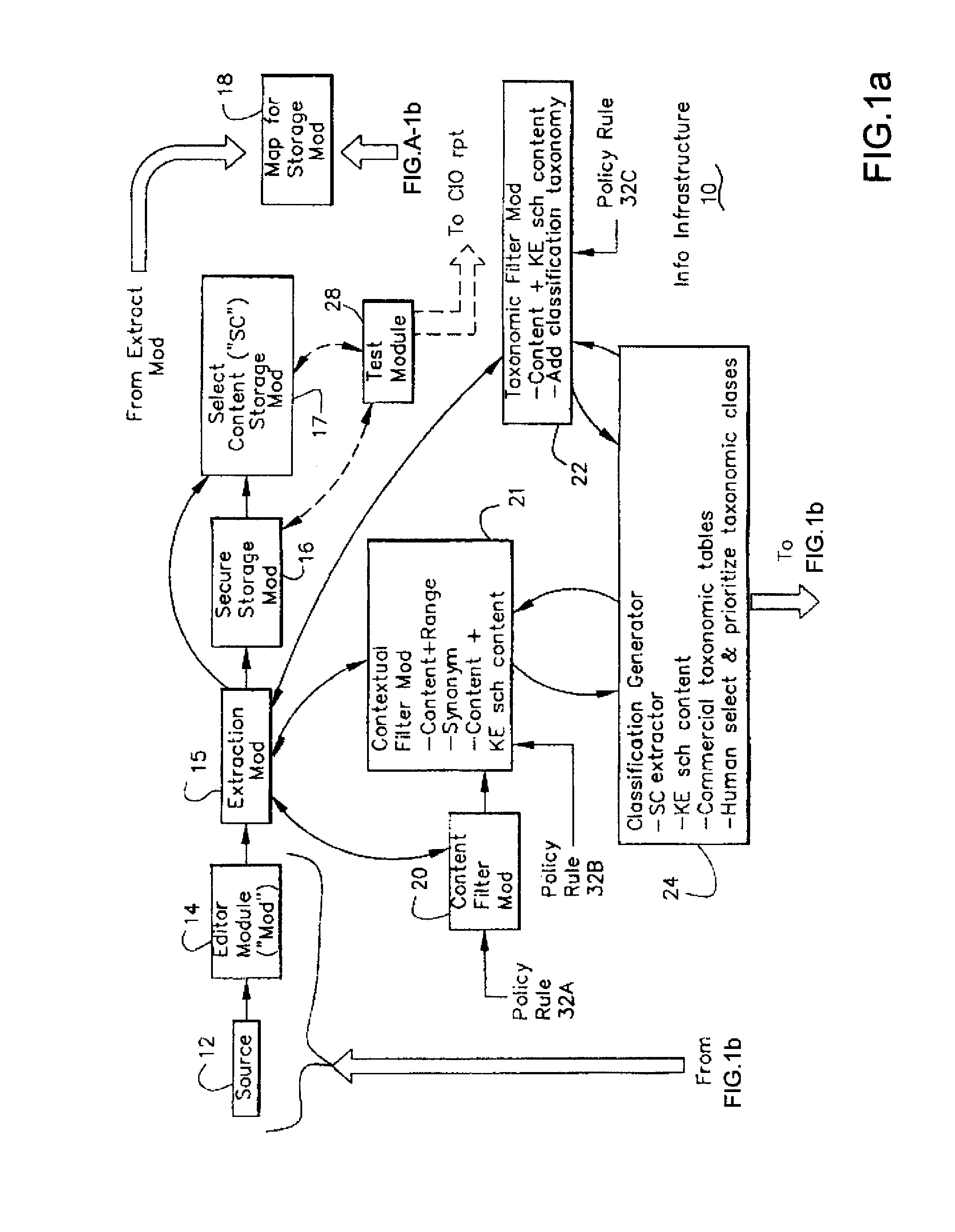
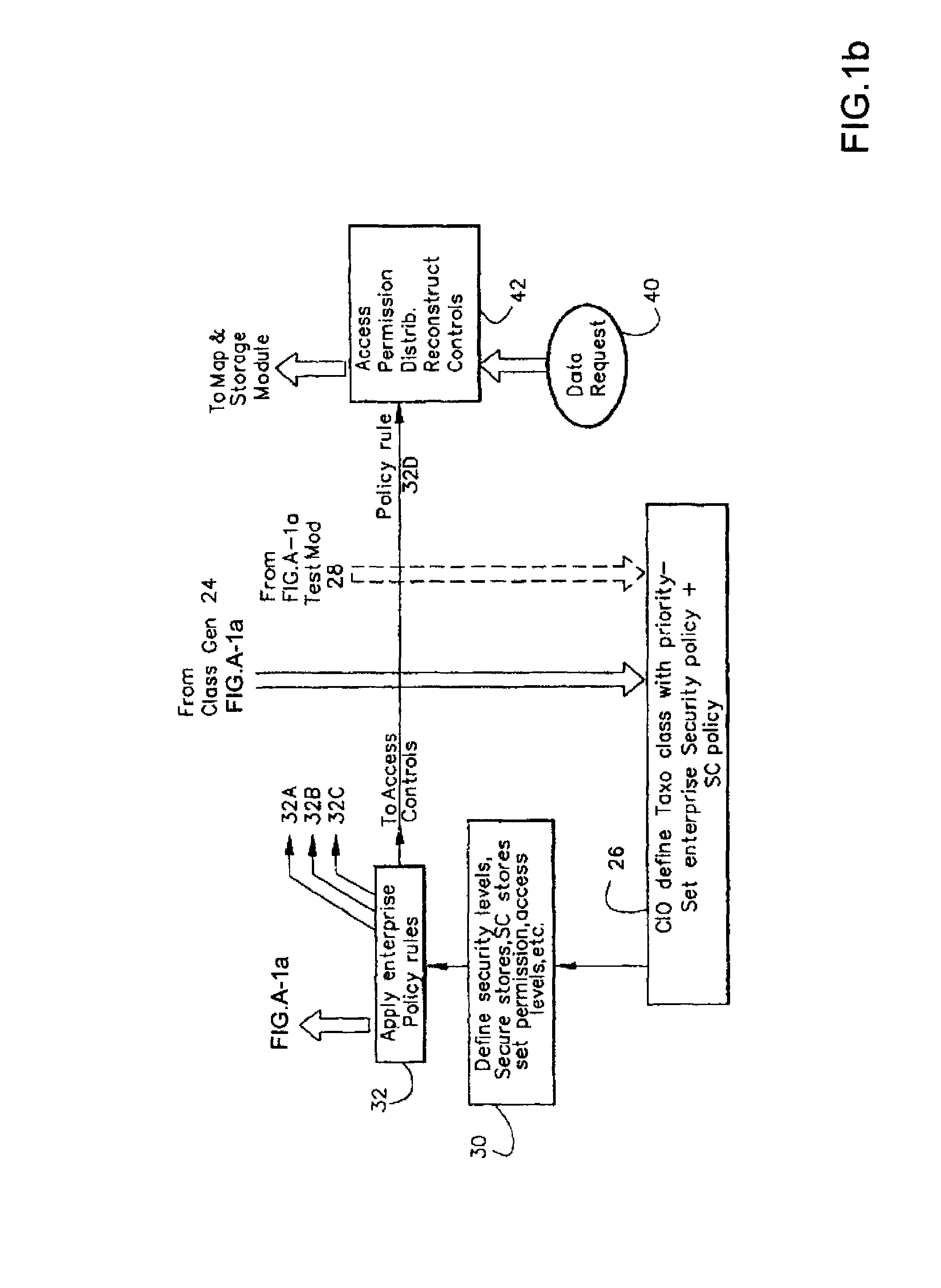
Information Infrastructure Management Tools with Extractor, Secure Storage, Content Analysis and Classification and Method Therefor
The present invention is a method of organizing and processing data in a distributed computing system. The invention is also implemented as a computer program on a computer medium and as a distributed computer system. Software modules can be configured as hardware. The method and system organizes select content which is important to an enterprise operating said distributed computing system. The select content is represented by one or more predetermined words, characters, images, data elements or data objects. The computing system has a plurality of select content data stores for respective ones of a plurality of enterprise designated categorical filters which include content-based filters, contextual filters and taxonomic classification filters, all operatively coupled over a communications network. A data input is processed through at least one activated categorical filter to obtain select content, and contextually associated select content and taxonomically associated select content as aggregated select content. The aggregated select content is stored in the corresponding select content data store. A data process from the group of data processes including a copy process, a data extract process, a data archive process, a data distribution process and a data destruction process is associated with the activated categorical filter and the method and system applies the associated data process to a further data input based upon a result of that further data being processed by the activated categorical filter utilizing the aggregated select content data.
Owner:DIGITAL DOORS
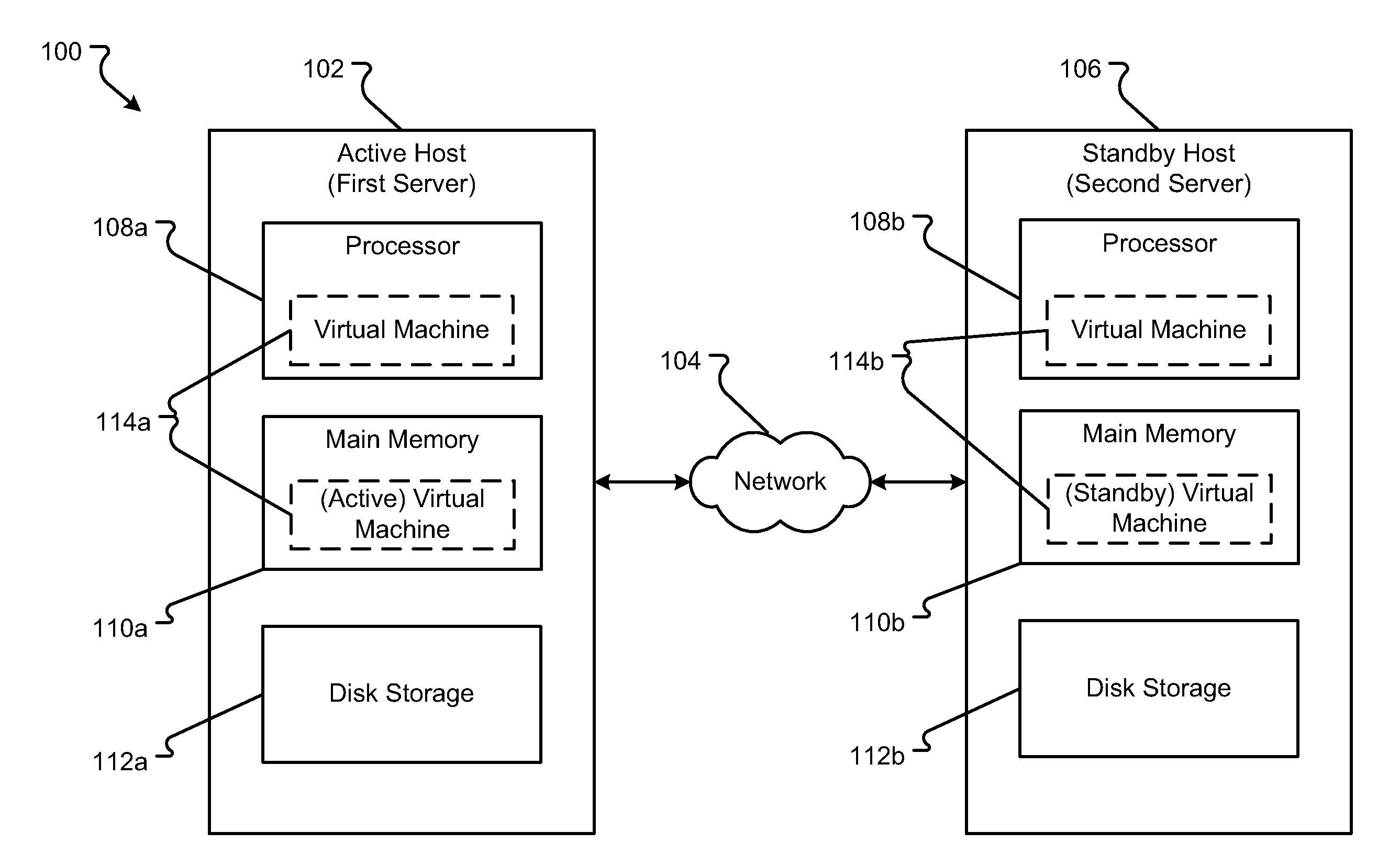
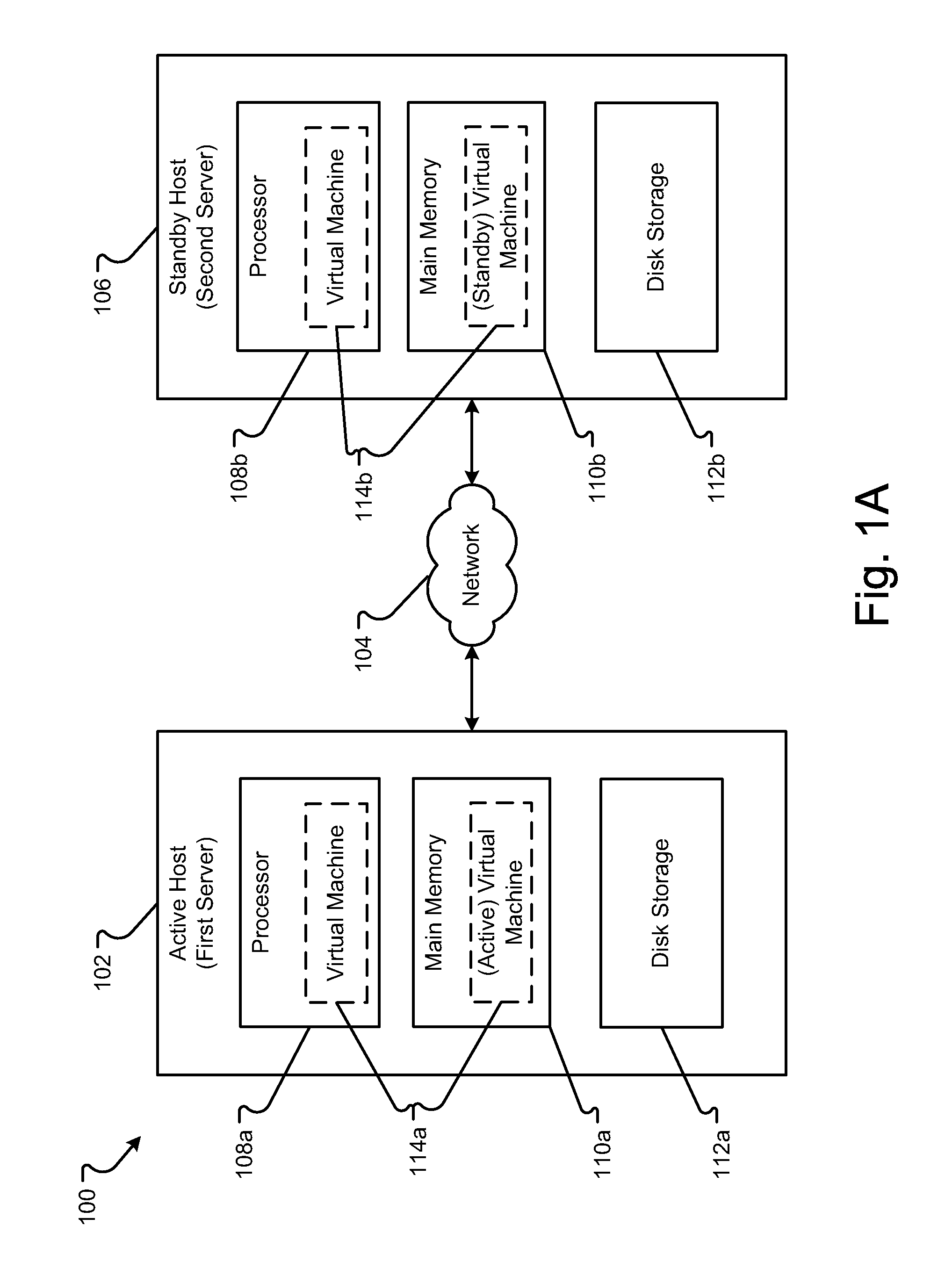
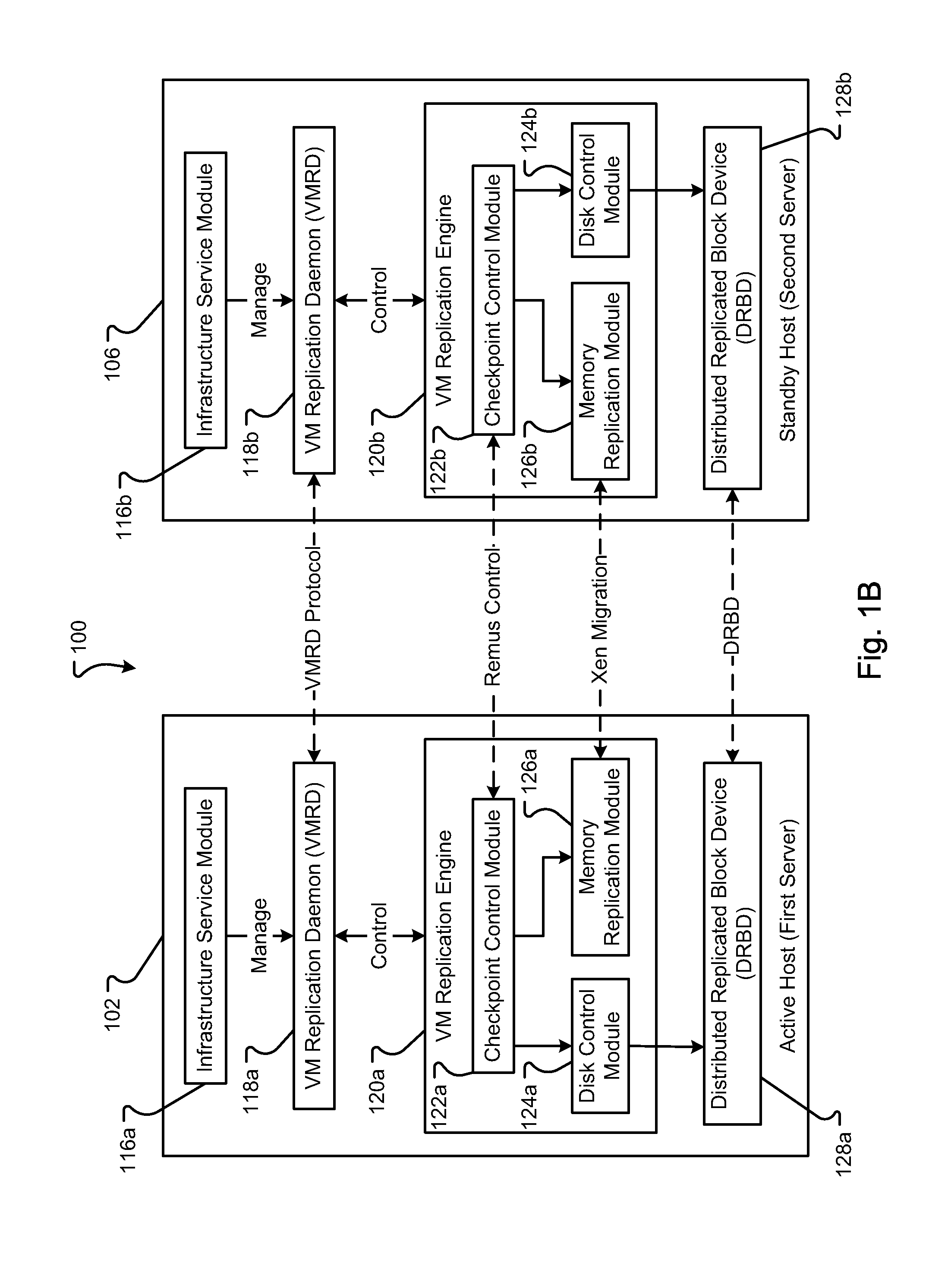
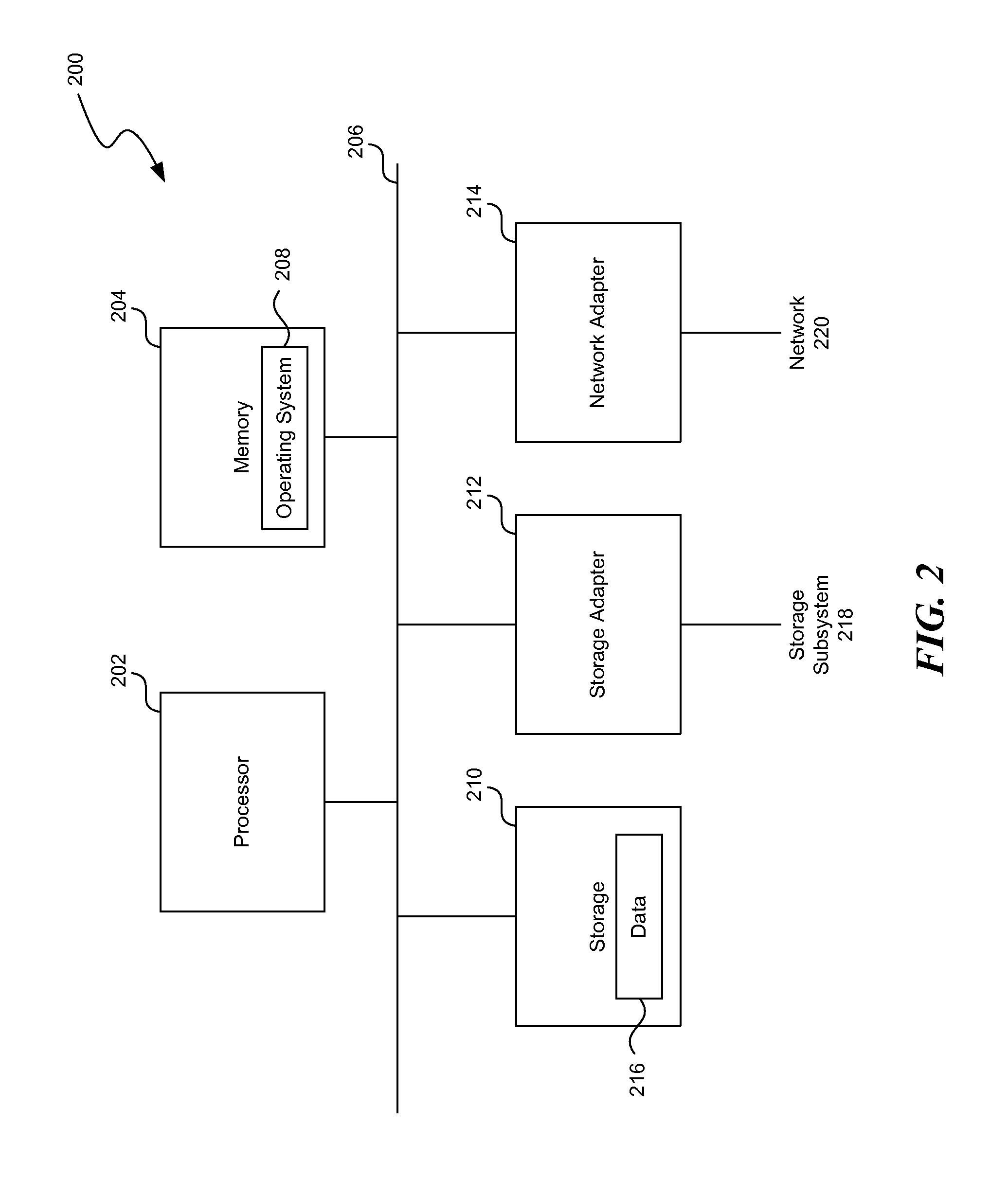
Method and Apparatus for Efficient Memory Replication for High Availability (HA) Protection of a Virtual Machine (VM)
ActiveUS20120084782A1Prevents buffer overflowSmall bufferMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionDirty pageBuffer overflow
High availability (HA) protection is provided for an executing virtual machine. At a checkpoint in the HA process, the active server suspends the virtual machine; and the active server copies dirty memory pages to a buffer. During the suspension of the virtual machine on the active host server, dirty memory pages are copied to a ring buffer. A copy process copies the dirty pages to a first location in the buffer. At a predetermined benchmark or threshold, a transmission process can begin. The transmission process can read data out of the buffer at a second location to send to the standby host. Both the copy and transmission processes can operate substantially simultaneously on the ring buffer. As such, the ring buffer cannot overflow because the transmission process continues to empty the ring buffer as the copy process continues. This arrangement allows for smaller buffers and prevents buffer overflows.
Owner:AVAYA INC
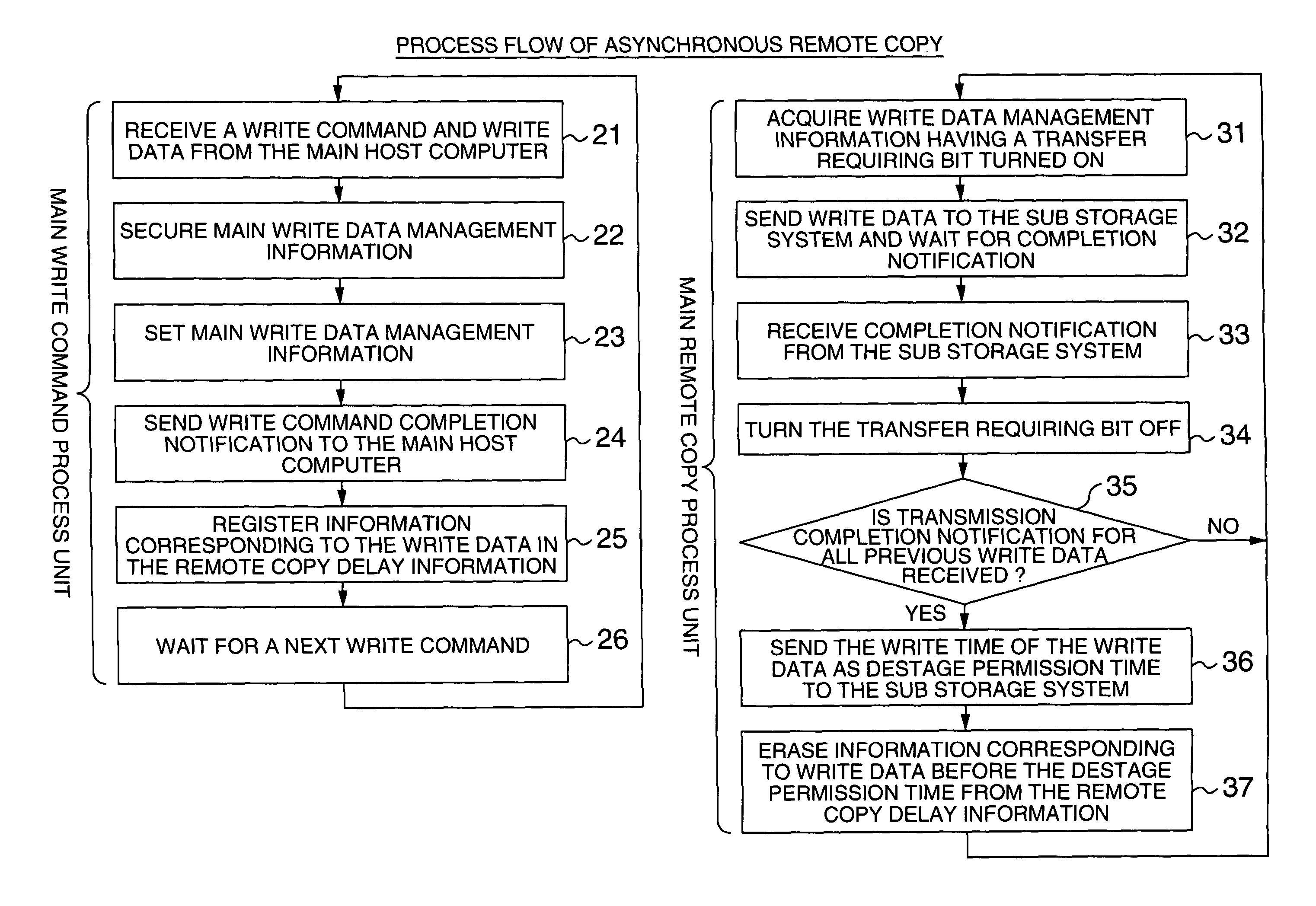
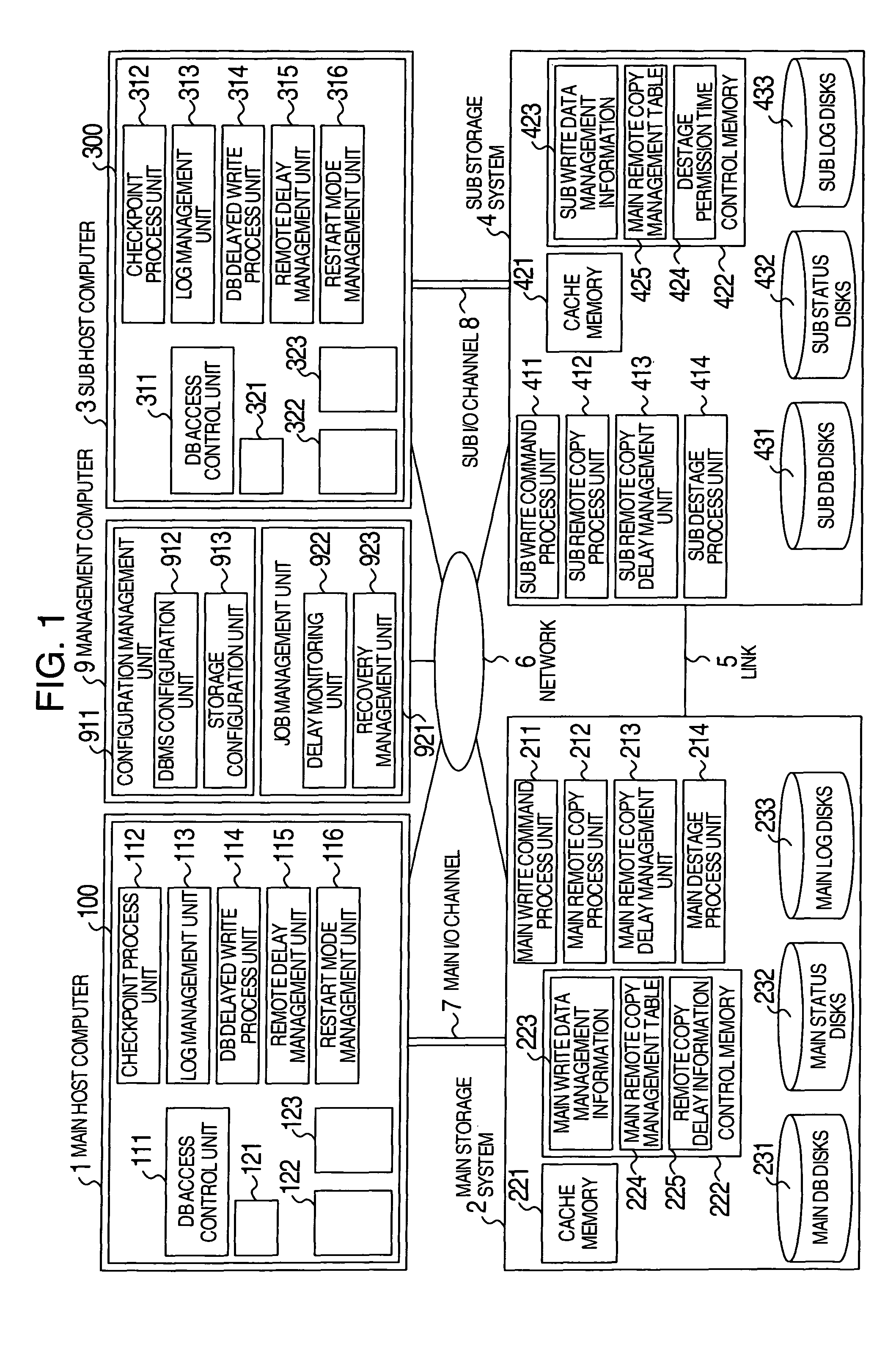
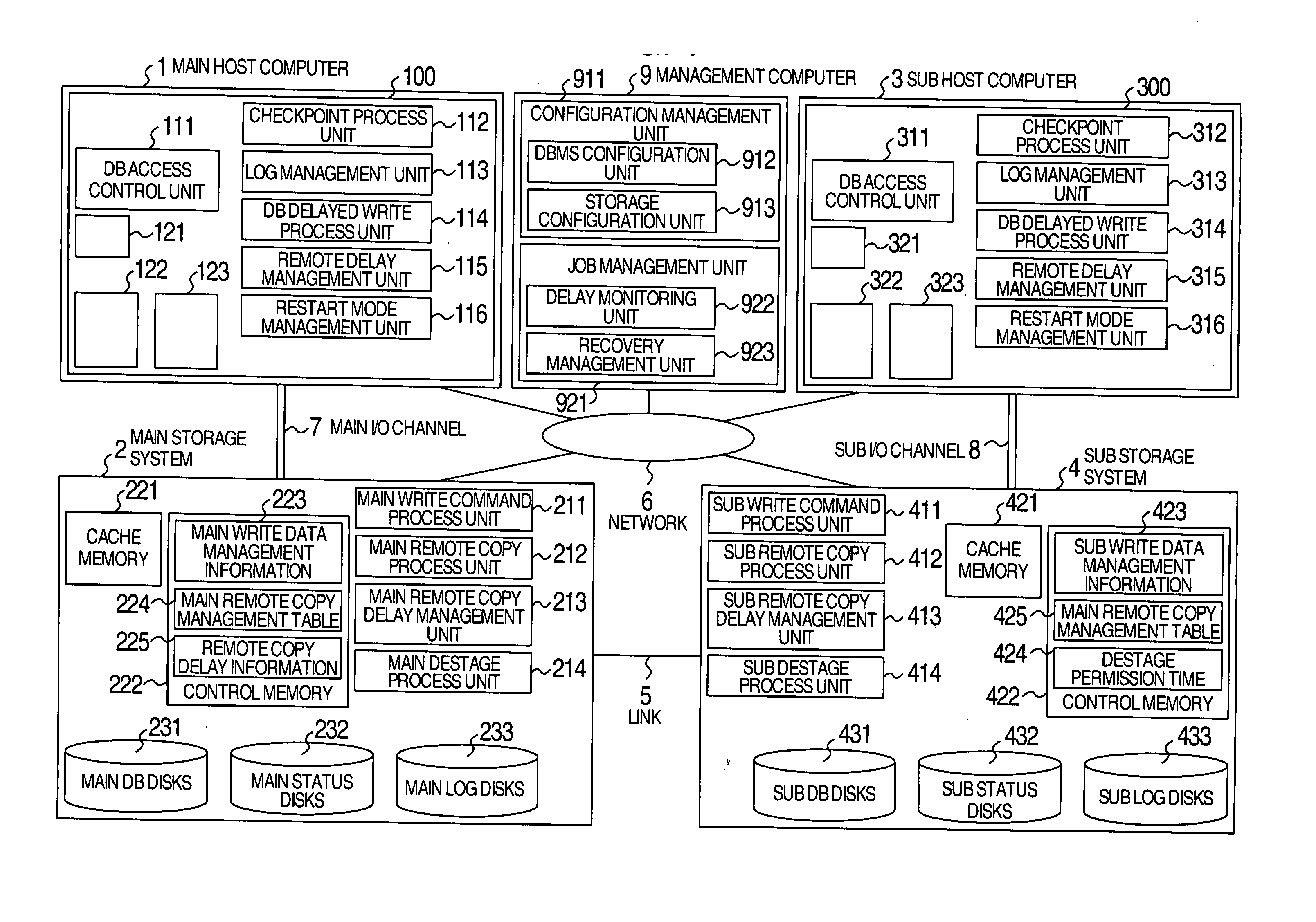
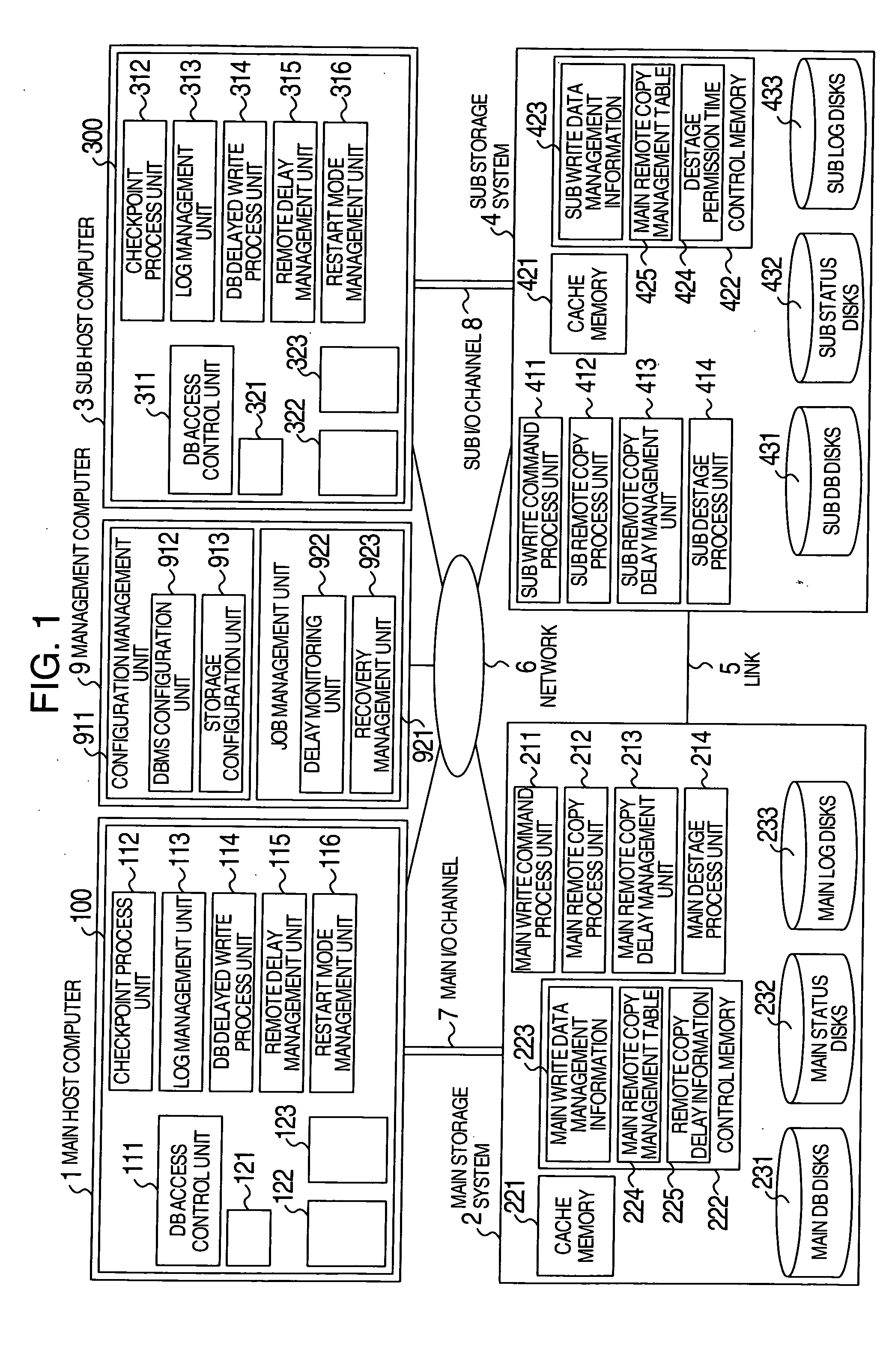
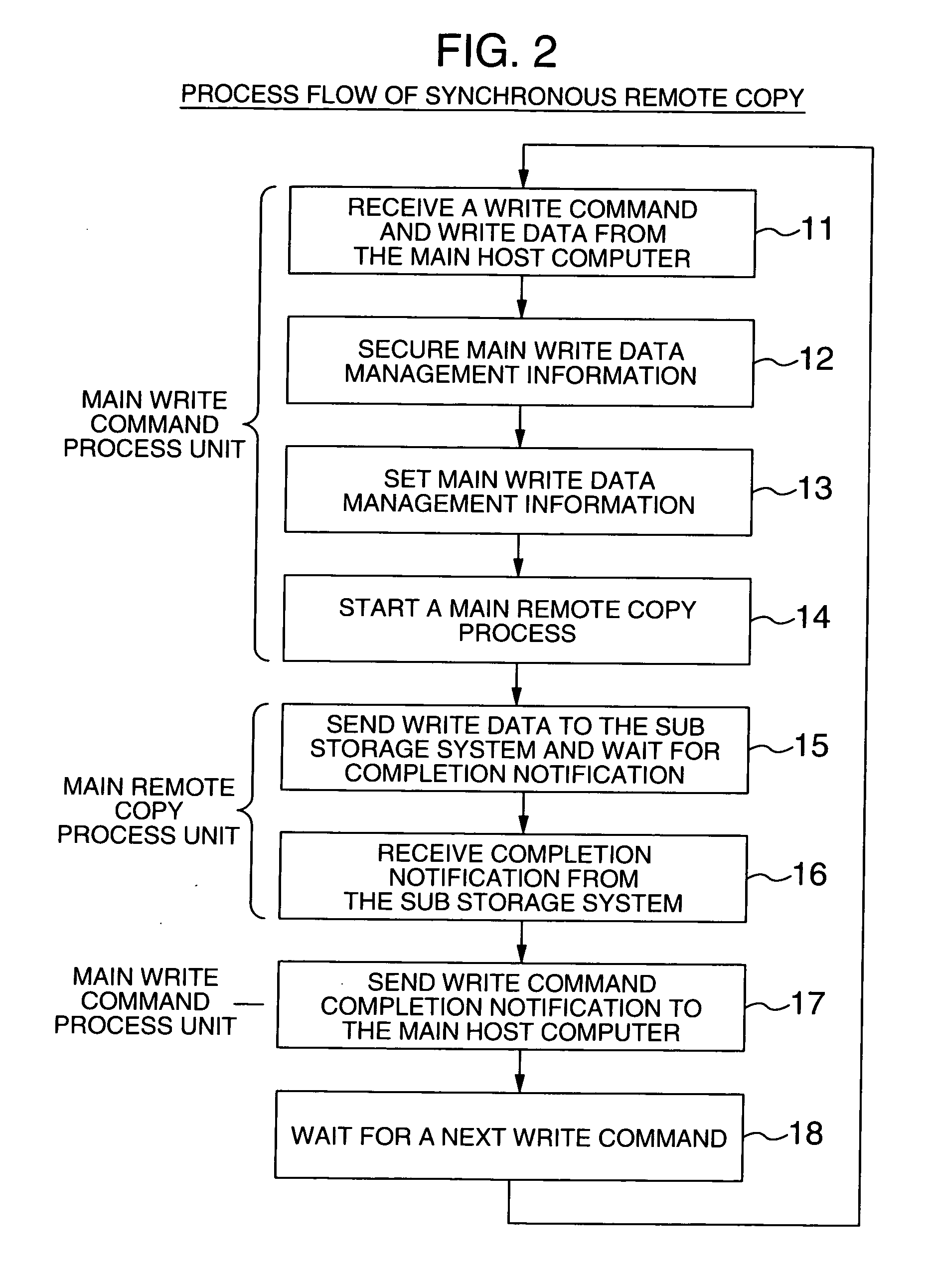
System executing log data transfer synchronously and database data transfer asynchronously
InactiveUS7890461B2Missing of transactionDeterioration in performance of an active database management system is preventedInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsData lossData library
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System and method for management of data replication
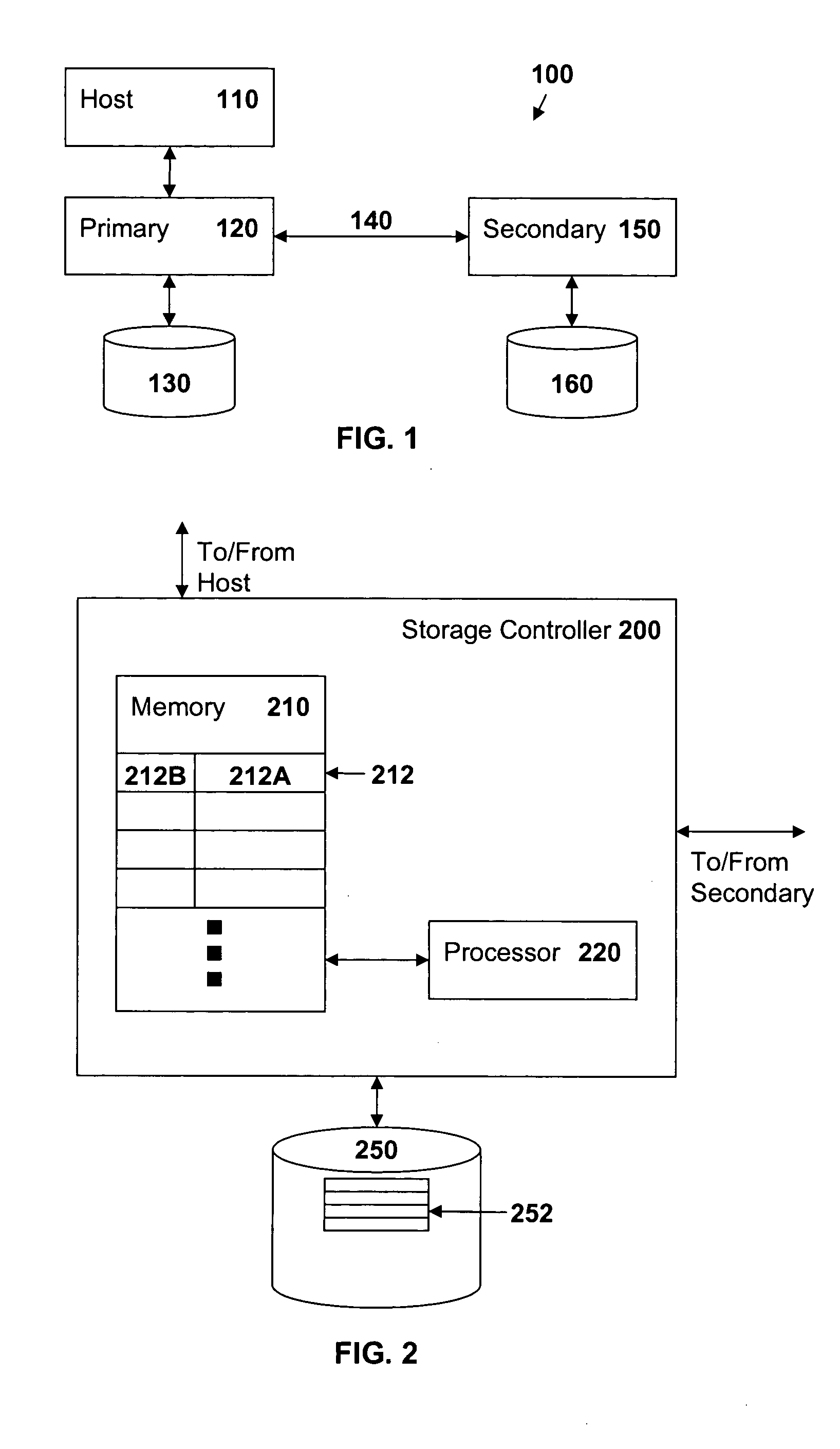
This invention is a system and method for managing replication of data in a data storage environment by grouping logical devices. The system is enabled for configuring, monitoring, and controlling replication processes in accordance with a replication policy that is particularly useful when combined with grouping of logical devices used in replication. The invention is useful for replicating essentially an entire copy of a production-level database such that the copy may be used essentially as the production-level database itself.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
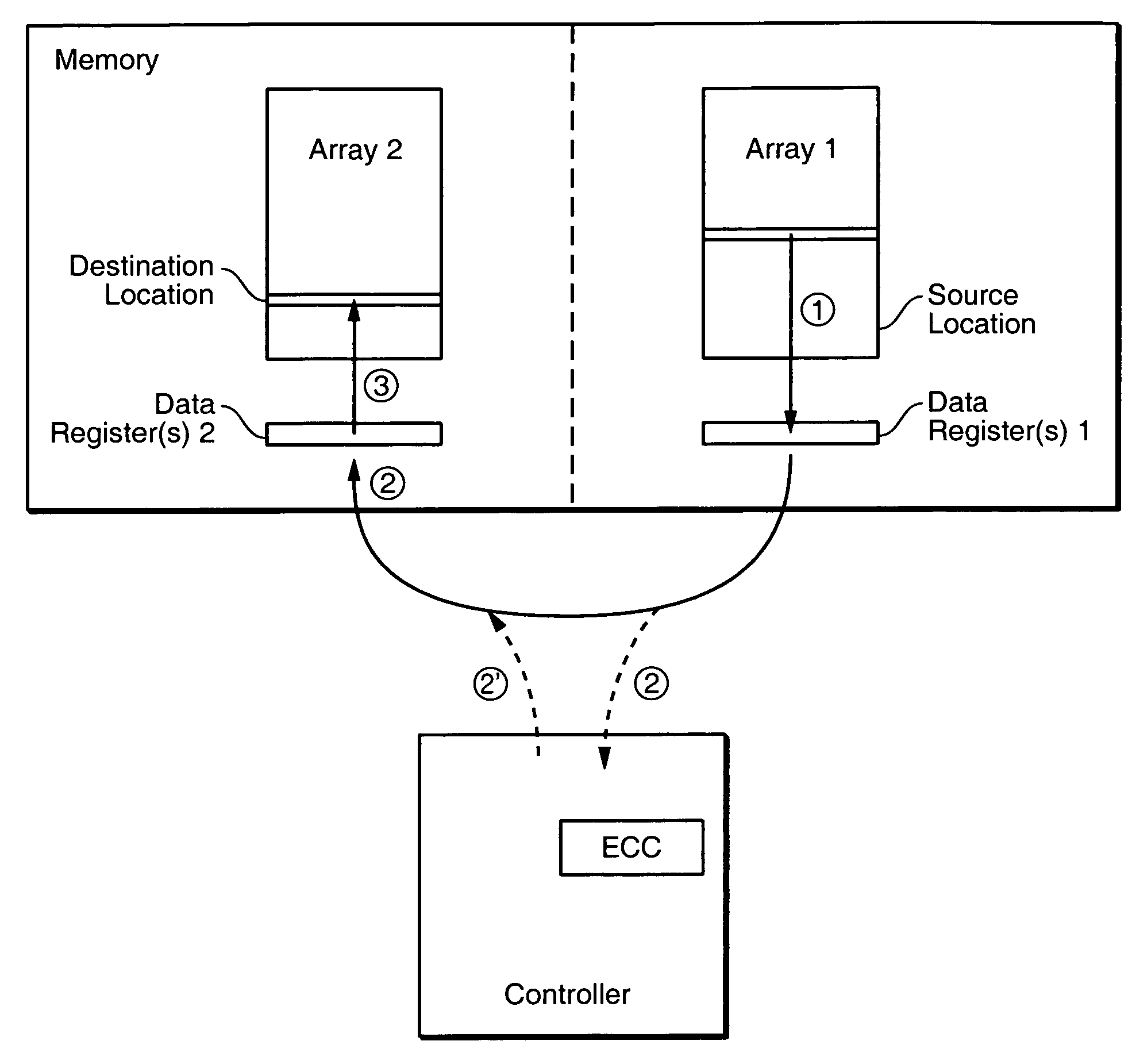
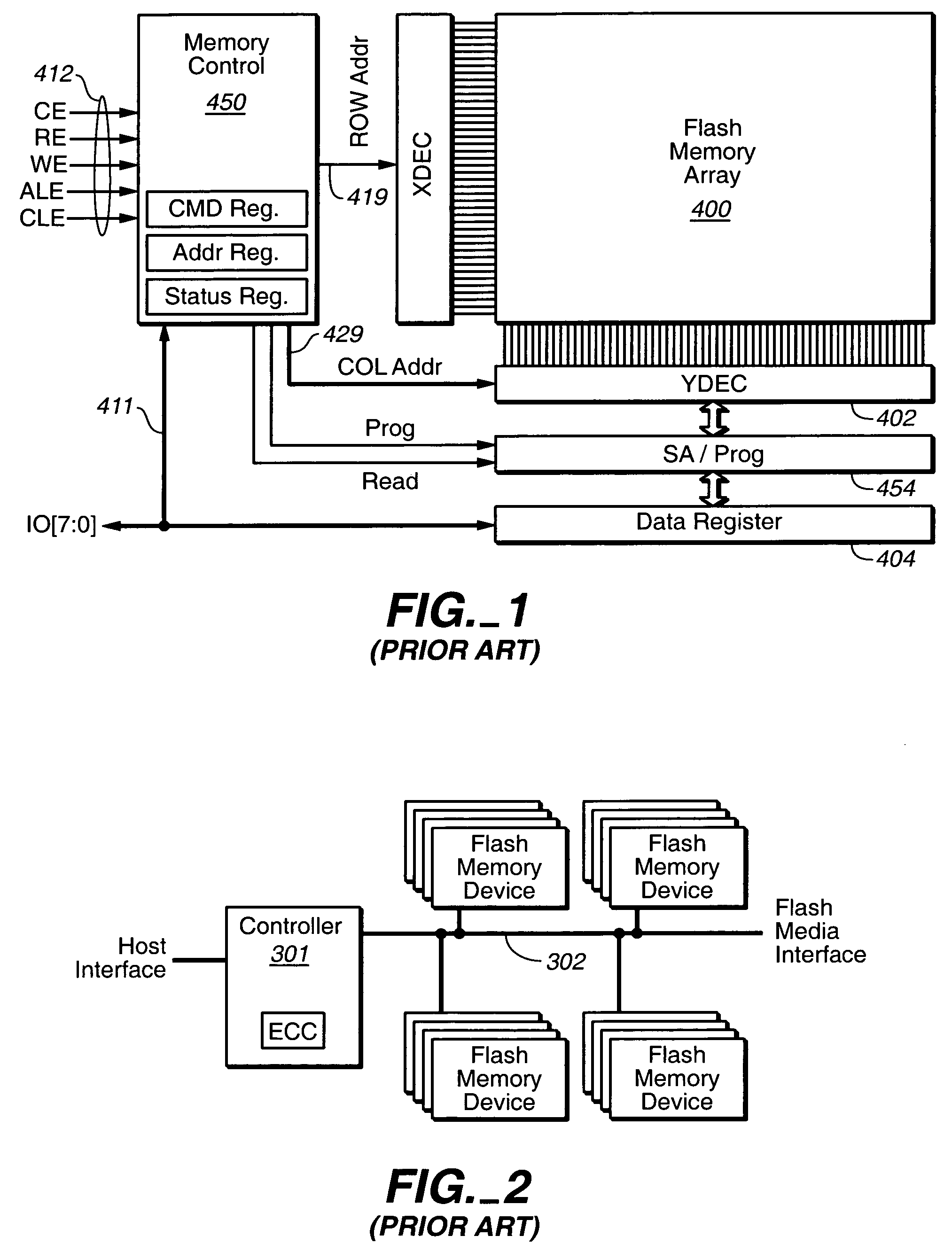
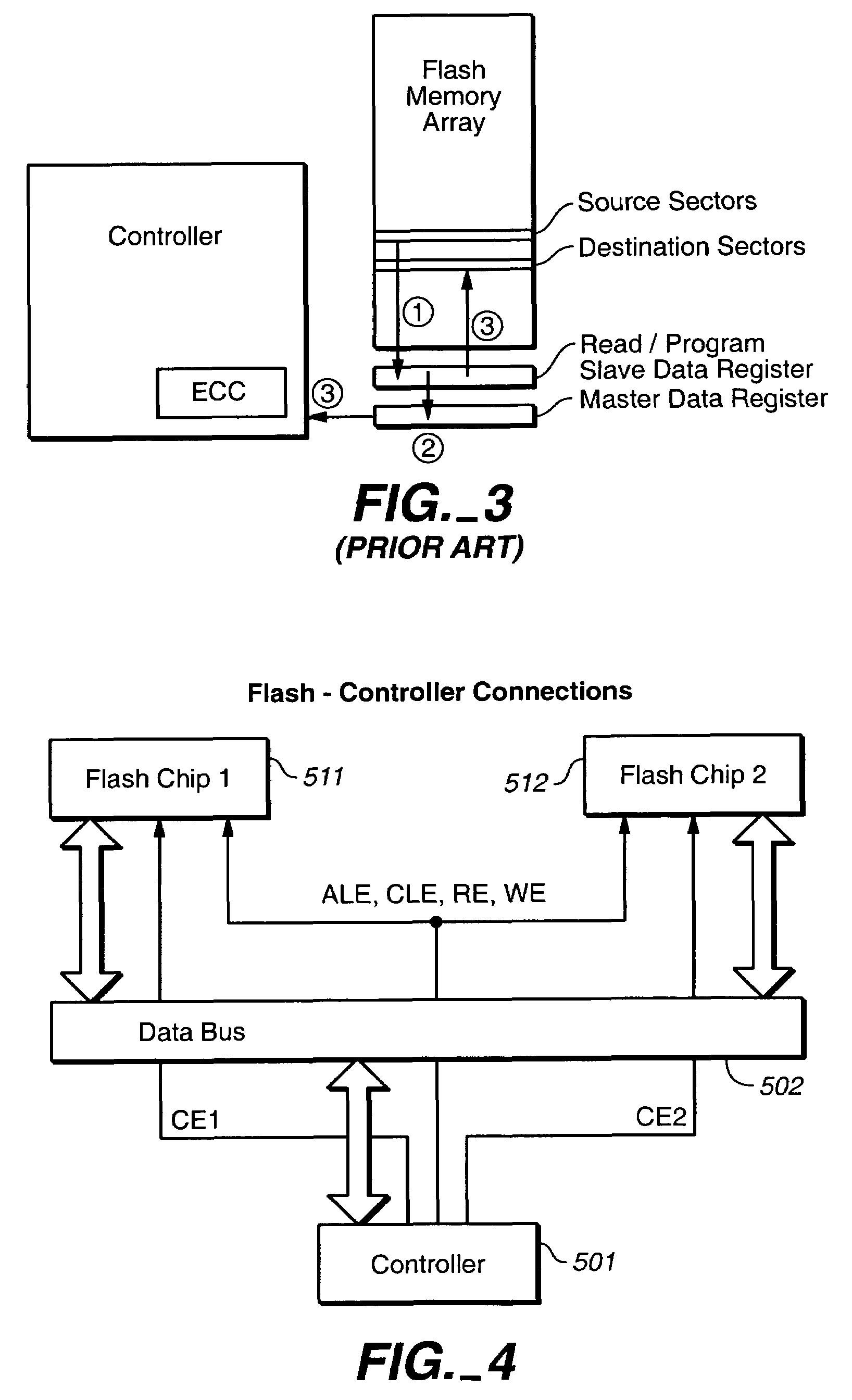
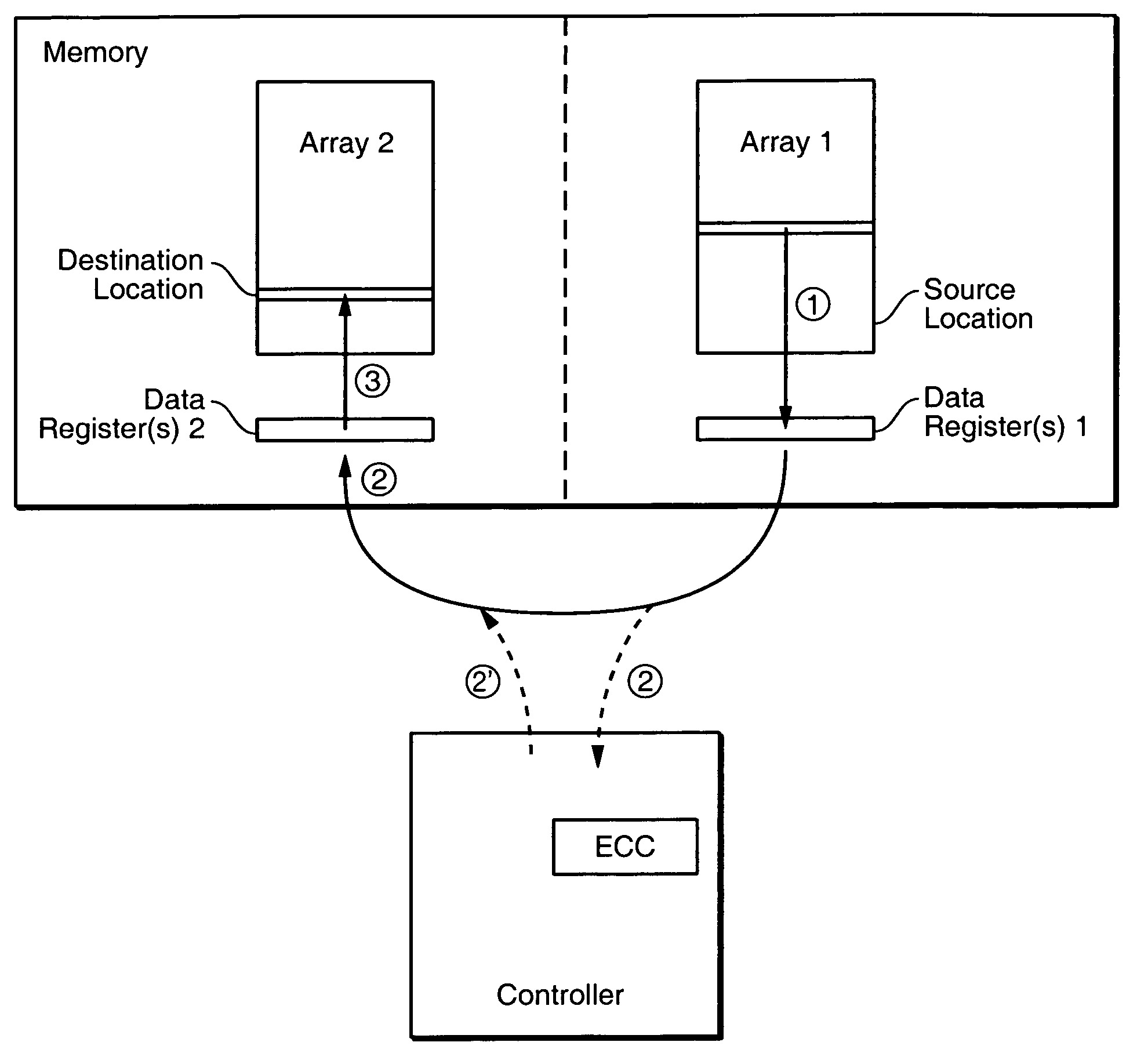
Off-chip data relocation
ActiveUS7409473B2Reduce frequencyEasy to operateRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer hardwareData set
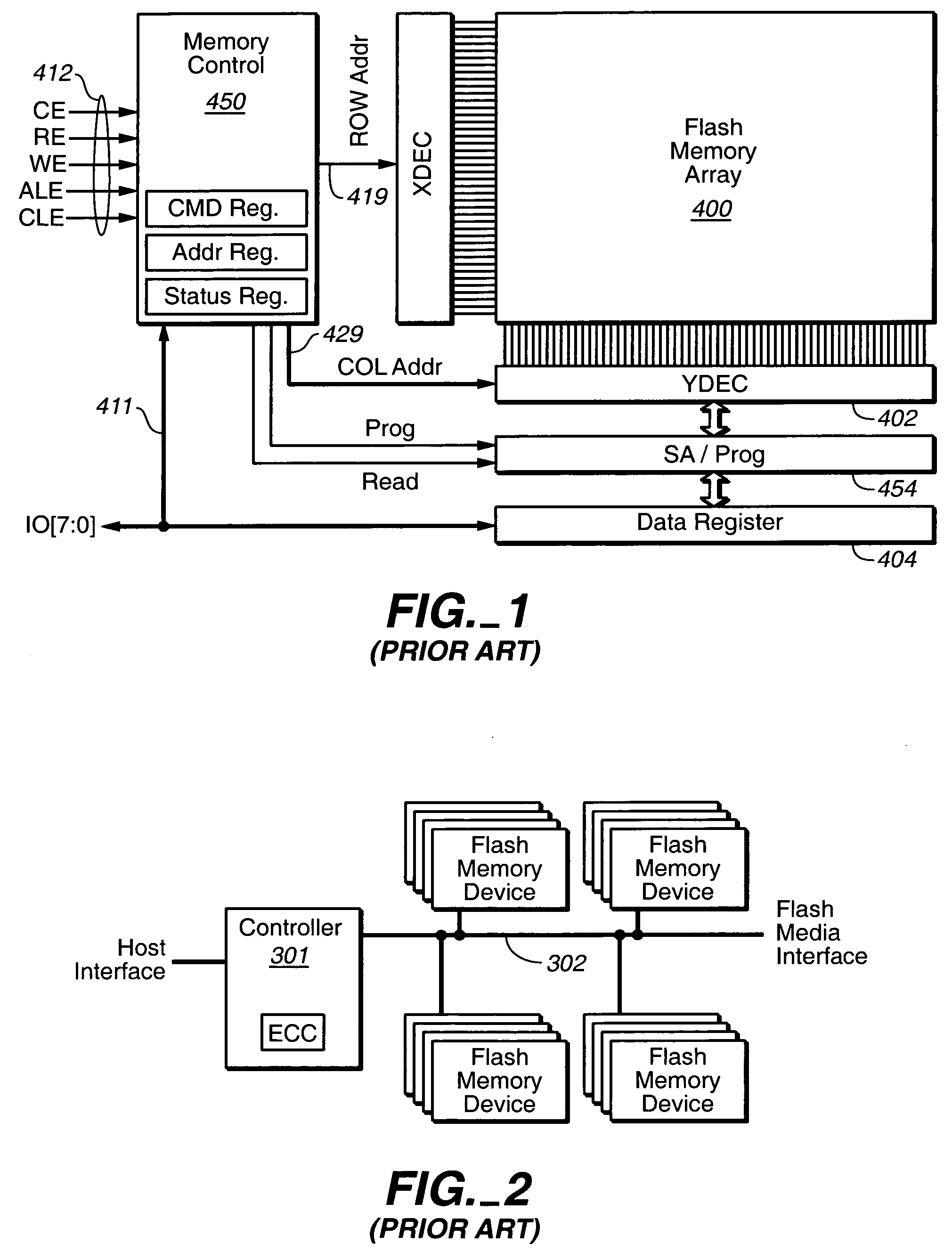
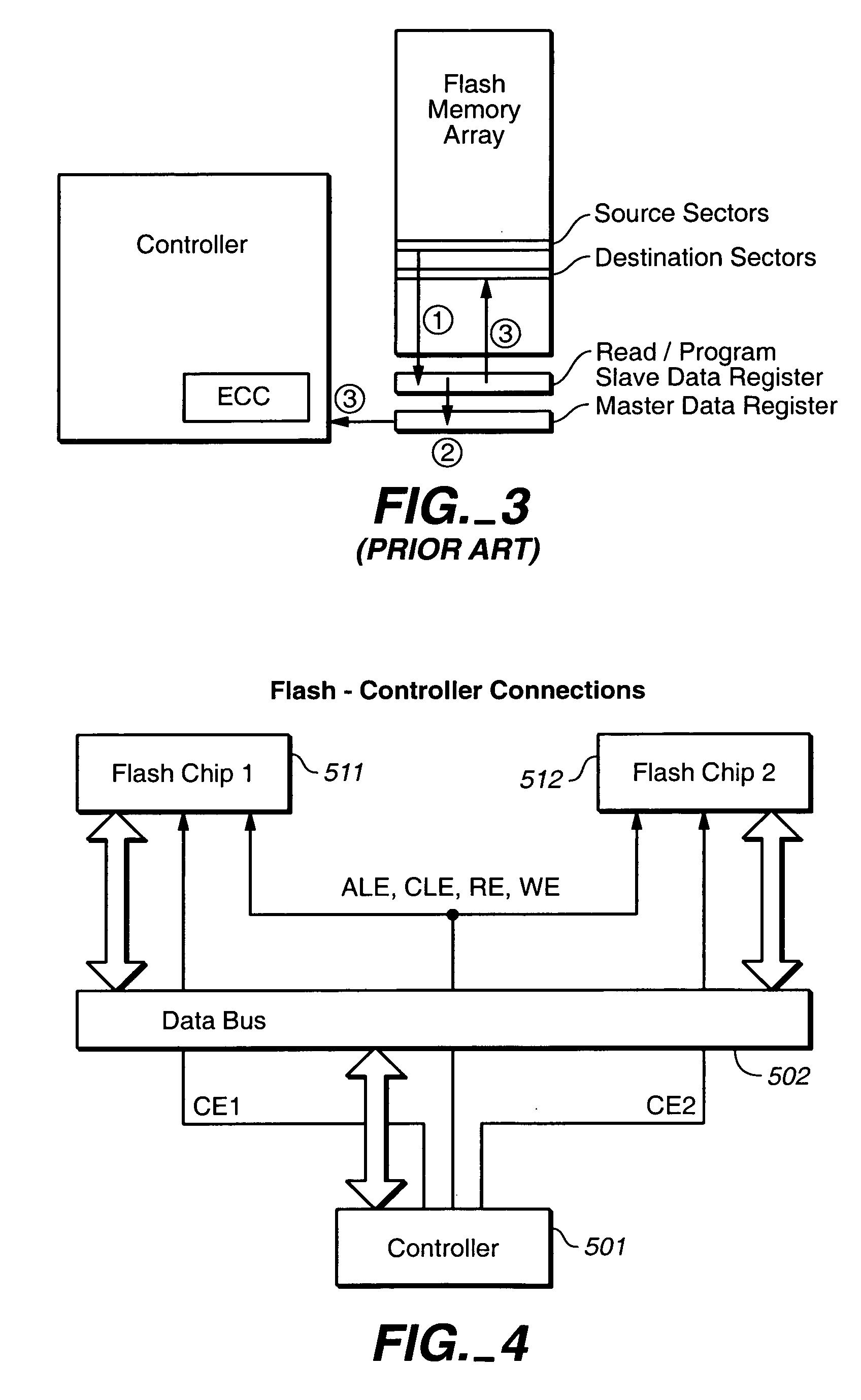
The on-chip copy process is extended so that the data may be copied between two blocks that may be on different chips, different planes on the same chip, or the same plane of the same chip. More specifically, the methods described here provide a single data copying mechanism that allows data to be copied between any two locations in a memory system. An exemplary embodiment uses an EDO-type timing. According to another aspect, selected portions of the relocated data, such as chosen words in a transferred page, can be updated in the controller on the fly. In addition to transferring a data set directly from a read buffer of a source array to a write buffer of a destination array, the data set can concurrently be copied, if desired, into the controller where an error detection and correction operation can be performed on it.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Off-chip data relocation
ActiveUS20060136687A1Reduce frequencyEasy to operateMemory loss protectionRead-only memoriesComputer hardwareData set
The on-chip copy process is extended so that the data may be copied between two blocks that may be on different chips, different planes on the same chip, or the same plane of the same chip. More specifically, the methods described here provide a single data copying mechanism that allows data to be copied between any two locations in a memory system. An exemplary embodiment uses an EDO-type timing. According to another aspect, selected portions of the relocated data, such as chosen words in a transferred page, can be updated in the controller on the fly. In addition to transferring a data set directly from a read buffer of a source array to a write buffer of a destination array, the data set can concurrently be copied, if desired, into the controller where an error detection and correction operation can be performed on it.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
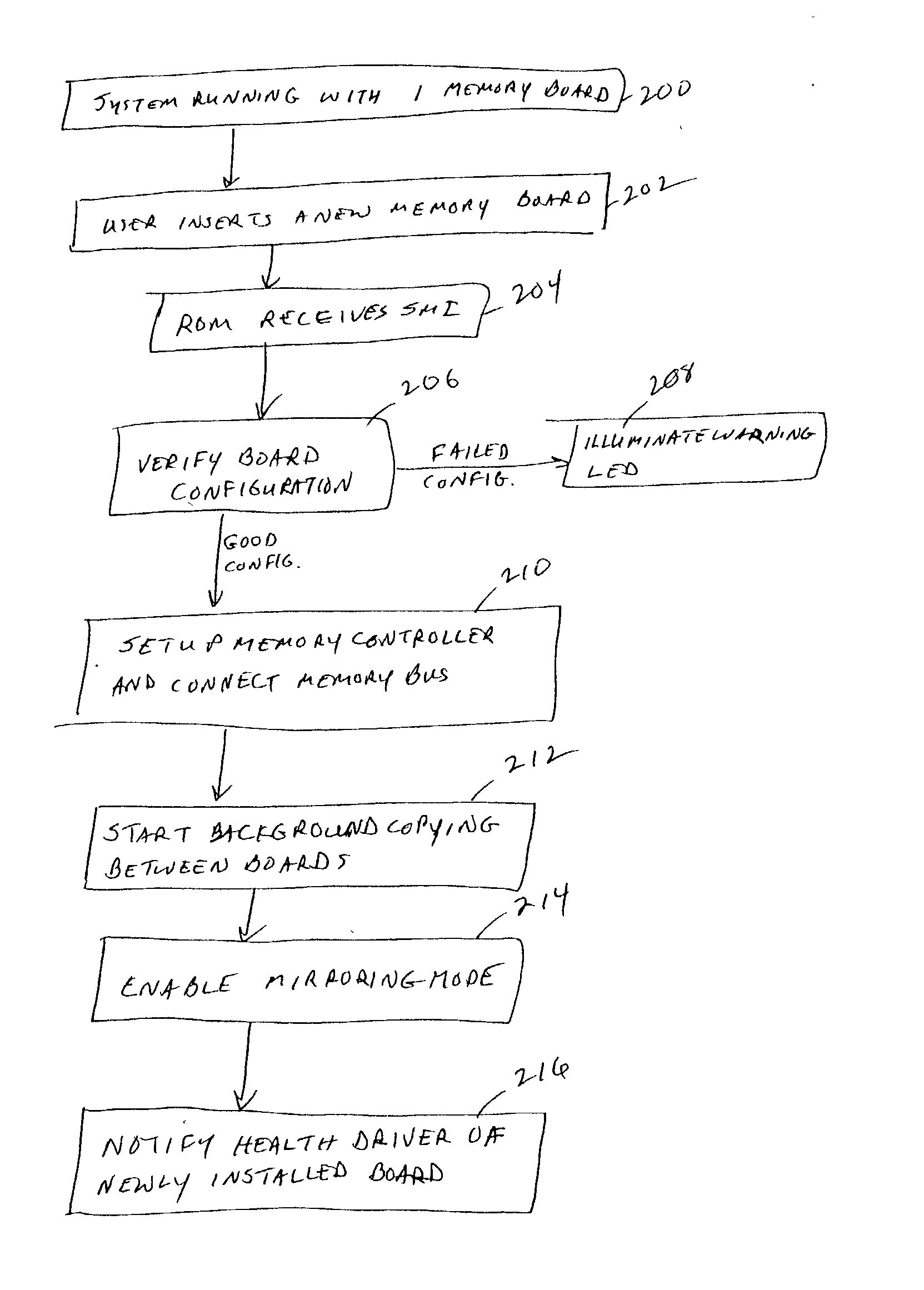
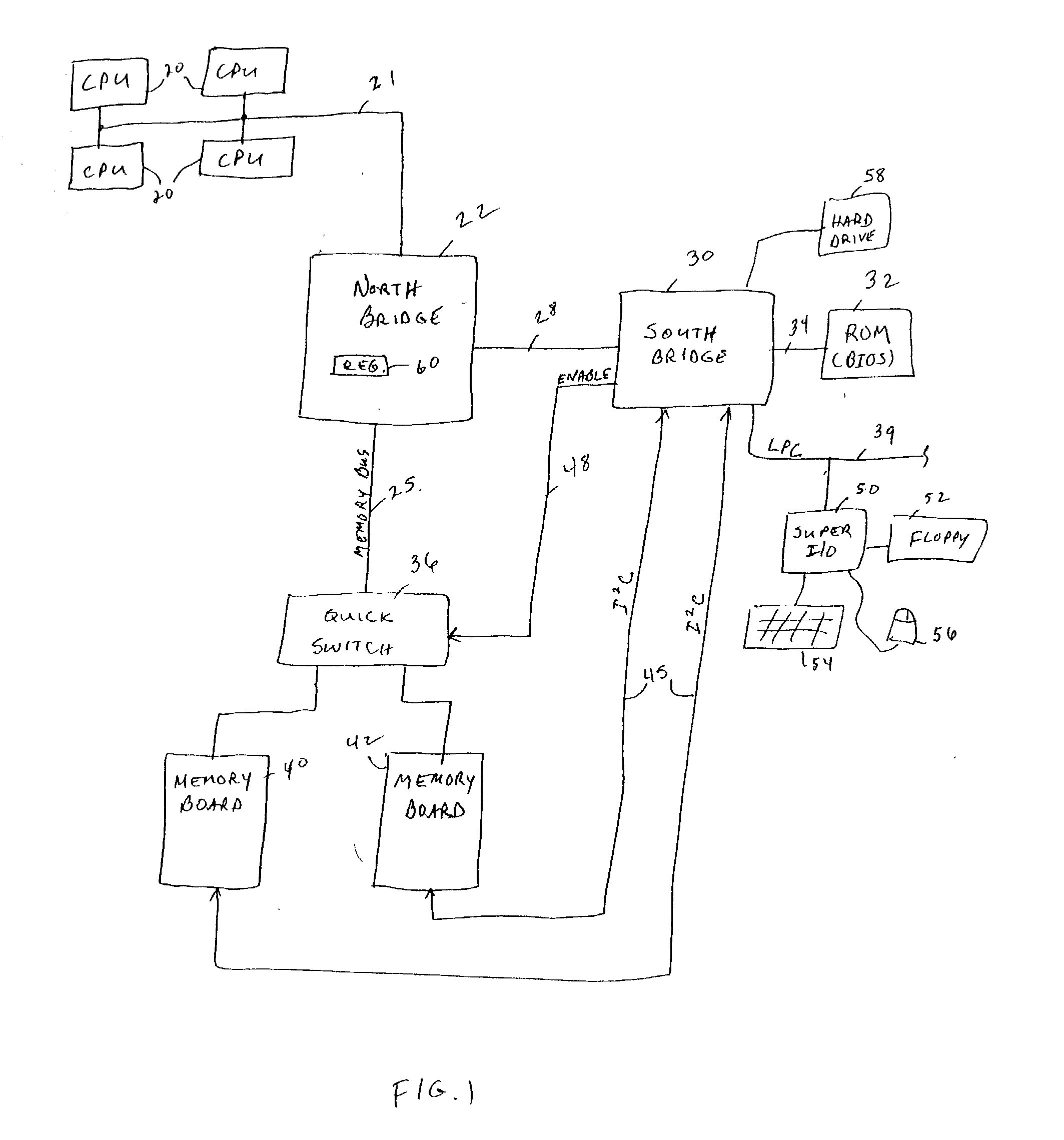
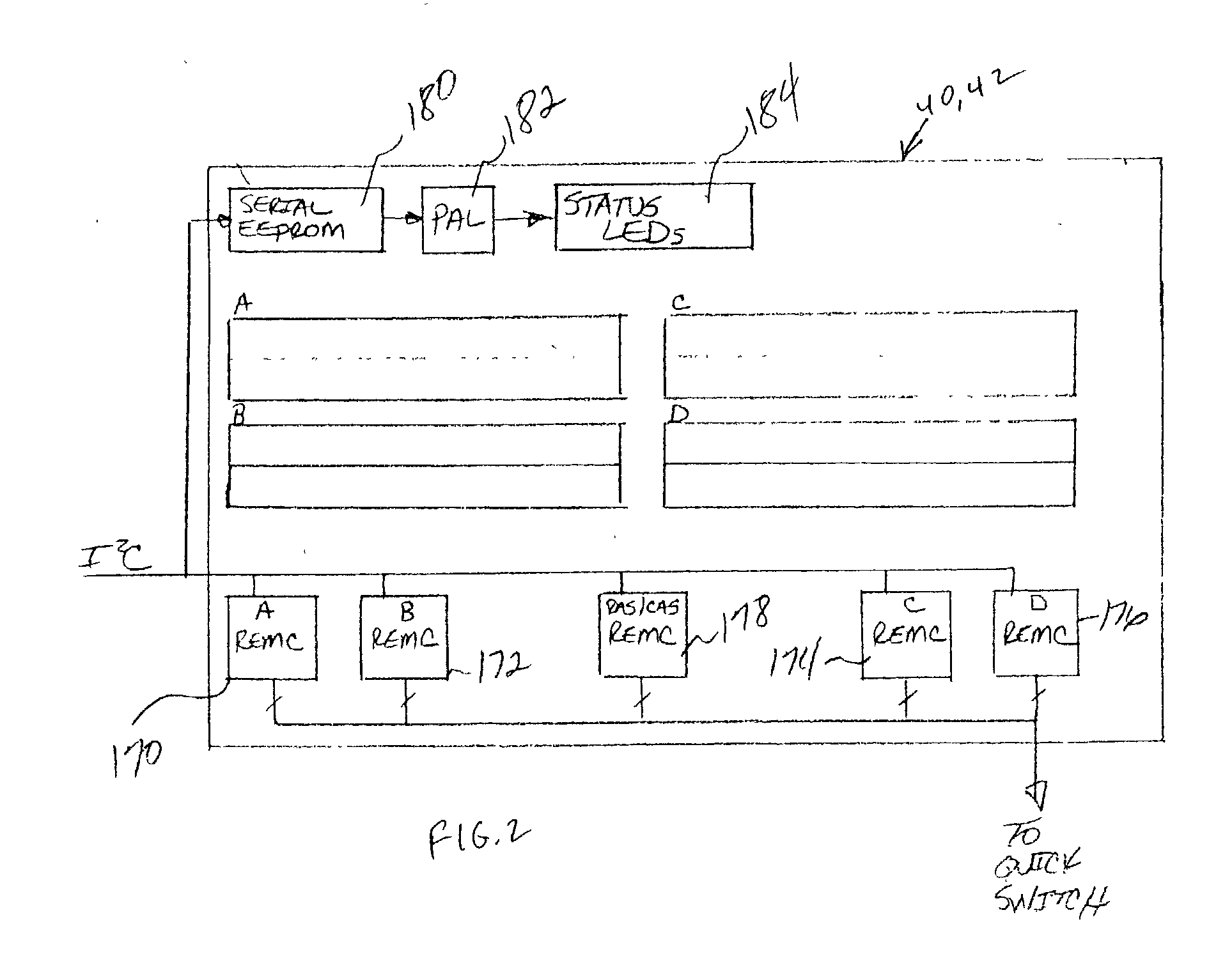
Hot mirroring in a computer system with redundant memory subsystems
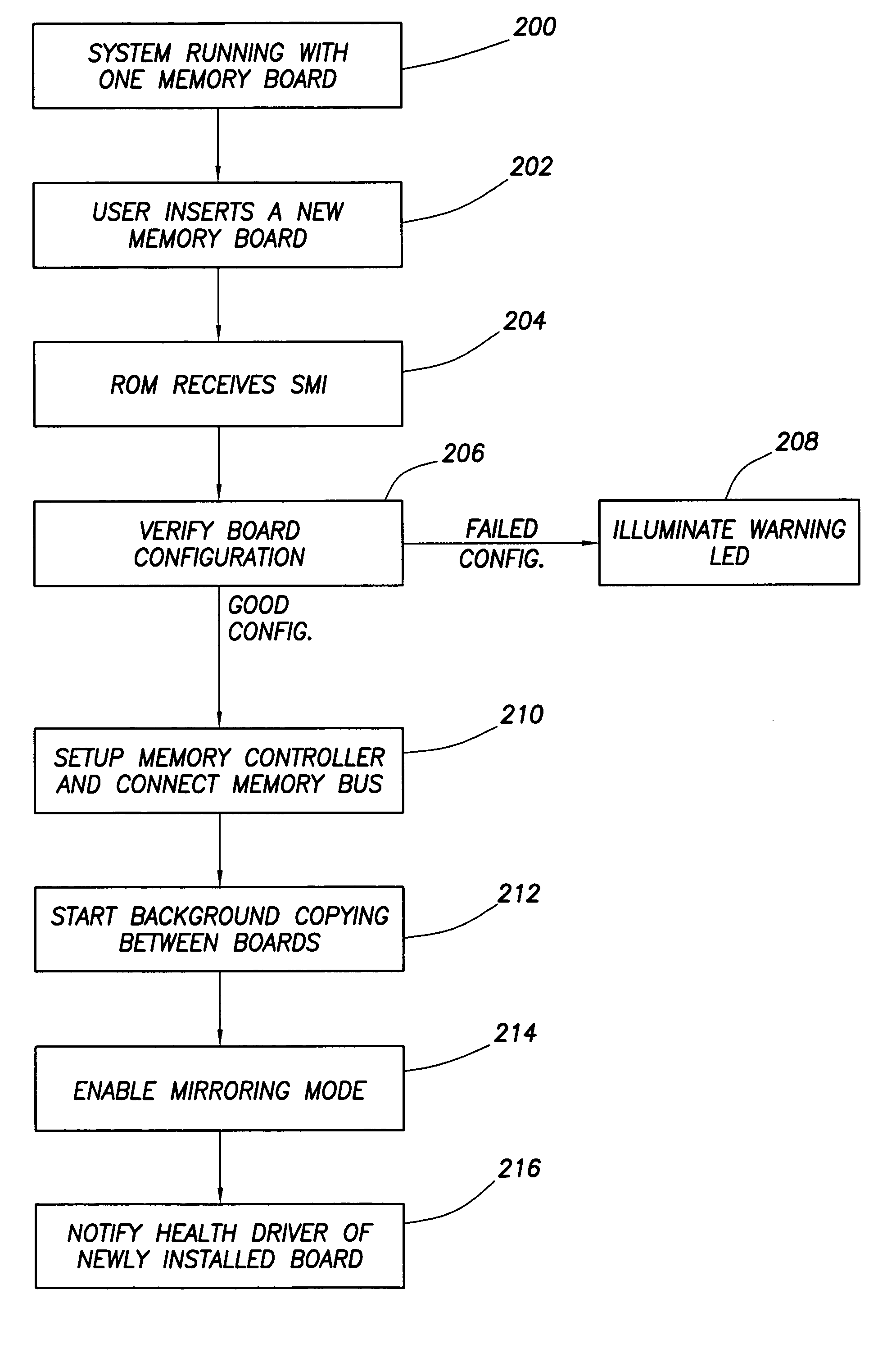
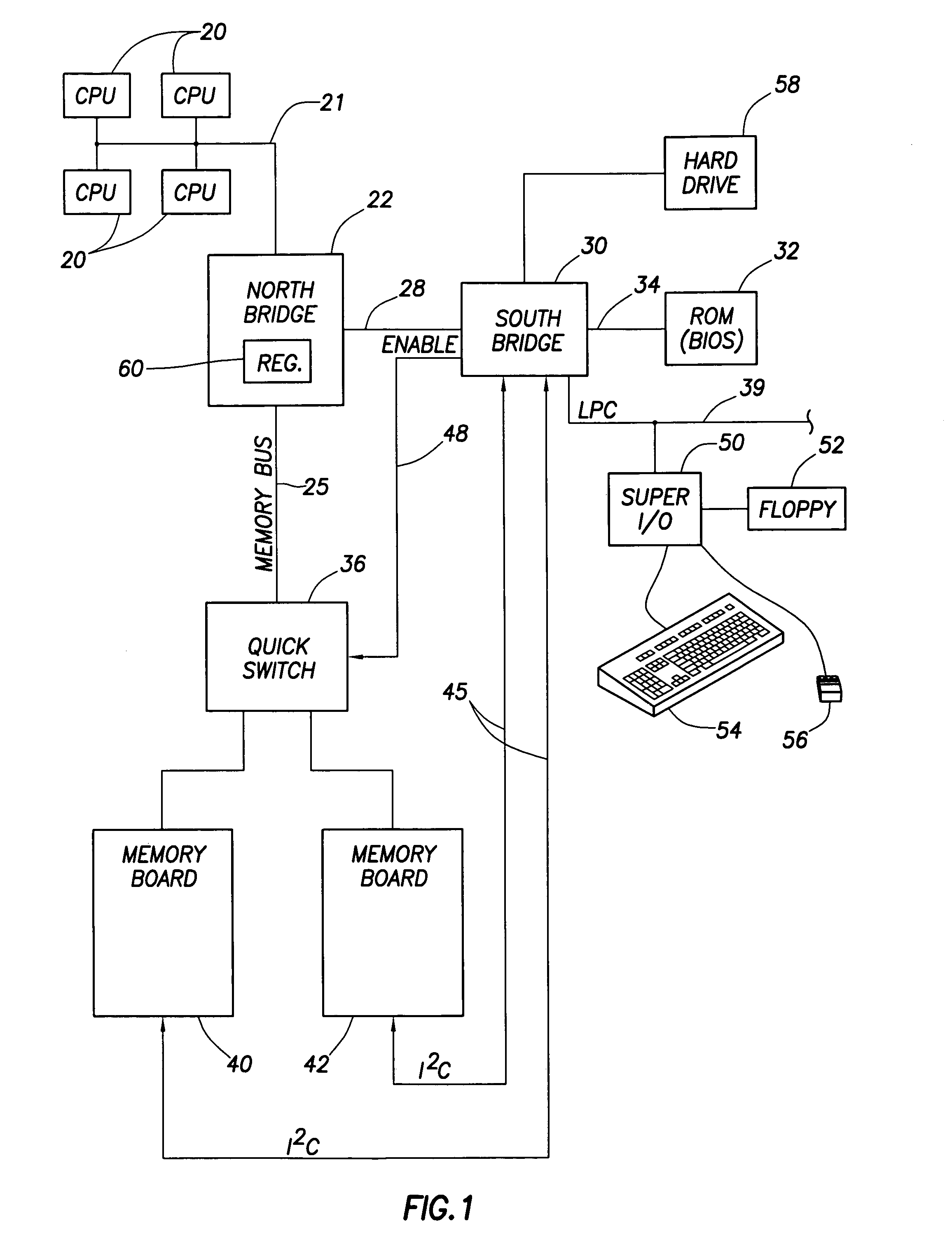
A computer system implements hot mirroring for main system memory. That is, the computer system permits a user to hot plug a new memory board into the system and the system will respond by switching to a mirrored memory mode in which write cycles are performed to both memory boards (new and old). Once a new board is hot plugged into the system, the contents of the old board are copied over, in a background mode, to the new board so that both boards will have the same data. Because this background copying process may take a non-trivial amount of time and may detrimentally interfere with other system traffic, the system a user to exert control over the relative speed of the background copying so as to trade-off the time it takes to switch over to the mirroring mode versus the impact on on-going system behavior.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
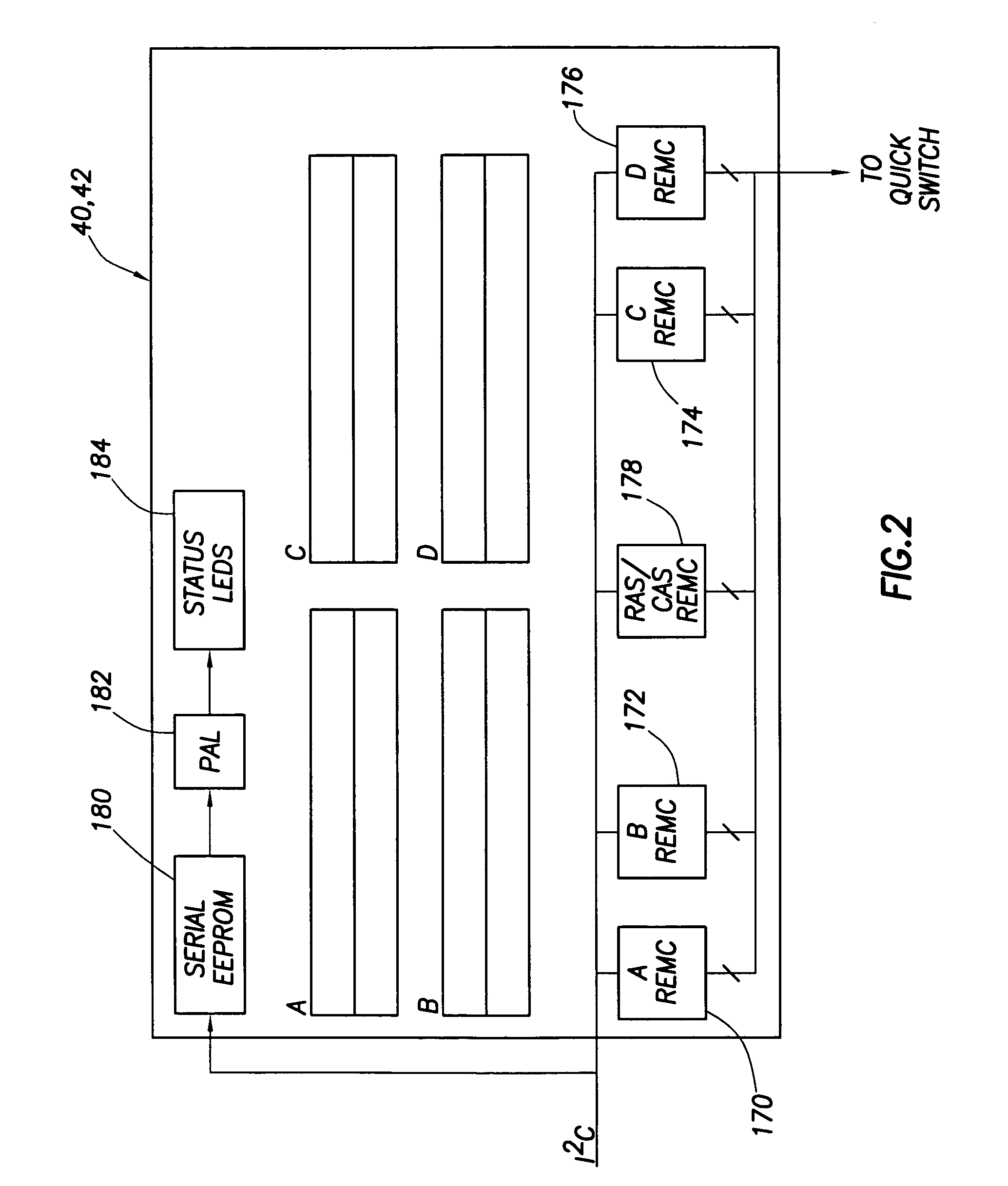
Information infrastructure management tools with extractor, secure storage, content analysis and classification and method therefor
ActiveUS9015301B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsManagement toolData memory
The present invention is a method of organizing and processing data in a distributed computing system. The invention is also implemented as a computer program on a computer medium and as a distributed computer system. Software modules can be configured as hardware. The method and system organizes select content which is important to an enterprise operating said distributed computing system. The select content is represented by one or more predetermined words, characters, images, data elements or data objects. The computing system has a plurality of select content data stores for respective ones of a plurality of enterprise designated categorical filters which include content-based filters, contextual filters and taxonomic classification filters, all operatively coupled over a communications network. A data input is processed through at least one activated categorical filter to obtain select content, and contextually associated select content and taxonomically associated select content as aggregated select content. The aggregated select content is stored in the corresponding select content data store. A data process from the group of data processes including a copy process, a data extract process, a data archive process, a data distribution process and a data destruction process is associated with the activated categorical filter and the method and system applies the associated data process to a further data input based upon a result of that further data being processed by the activated categorical filter utilizing the aggregated select content data.
Owner:DIGITAL DOORS
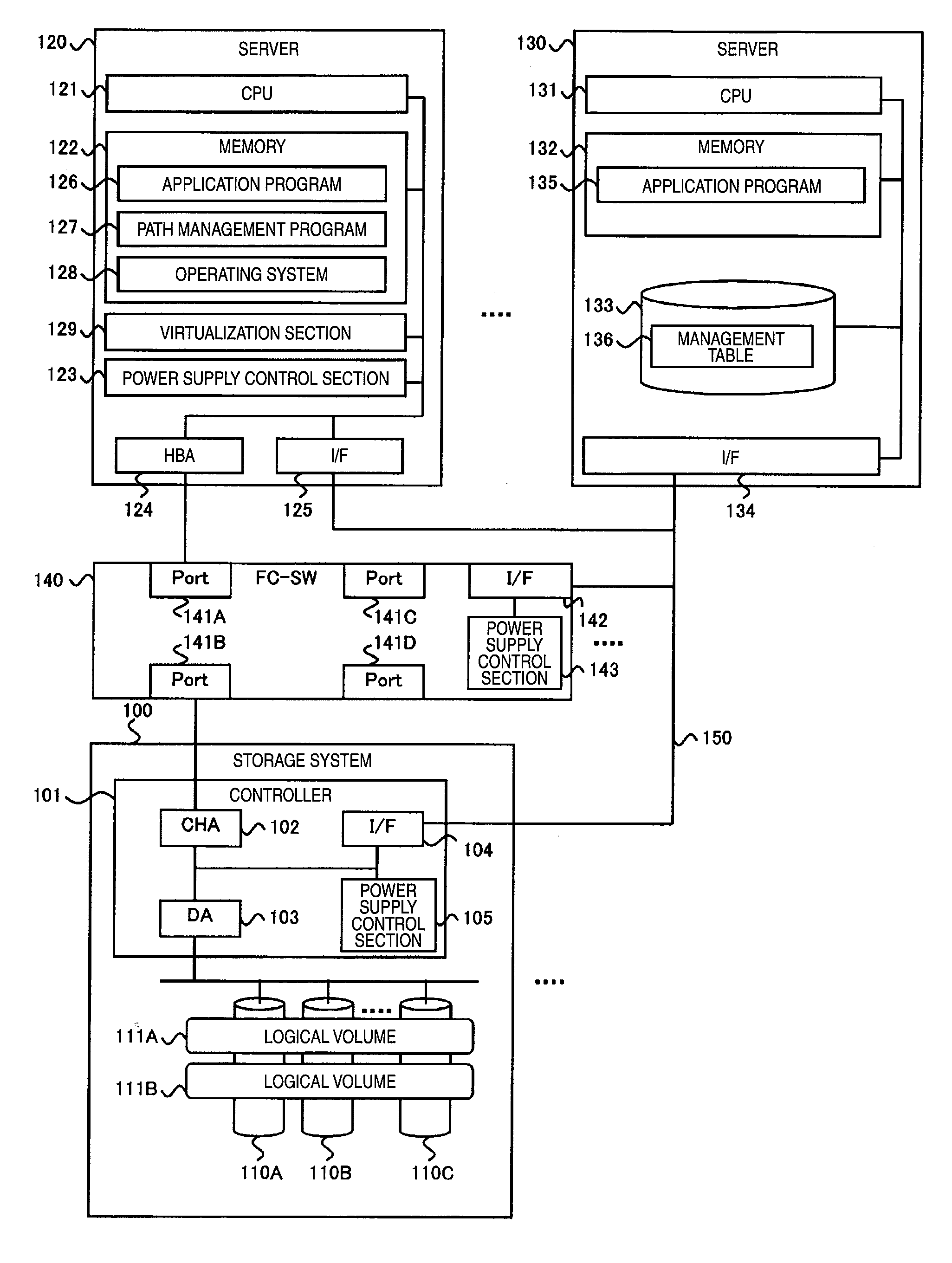
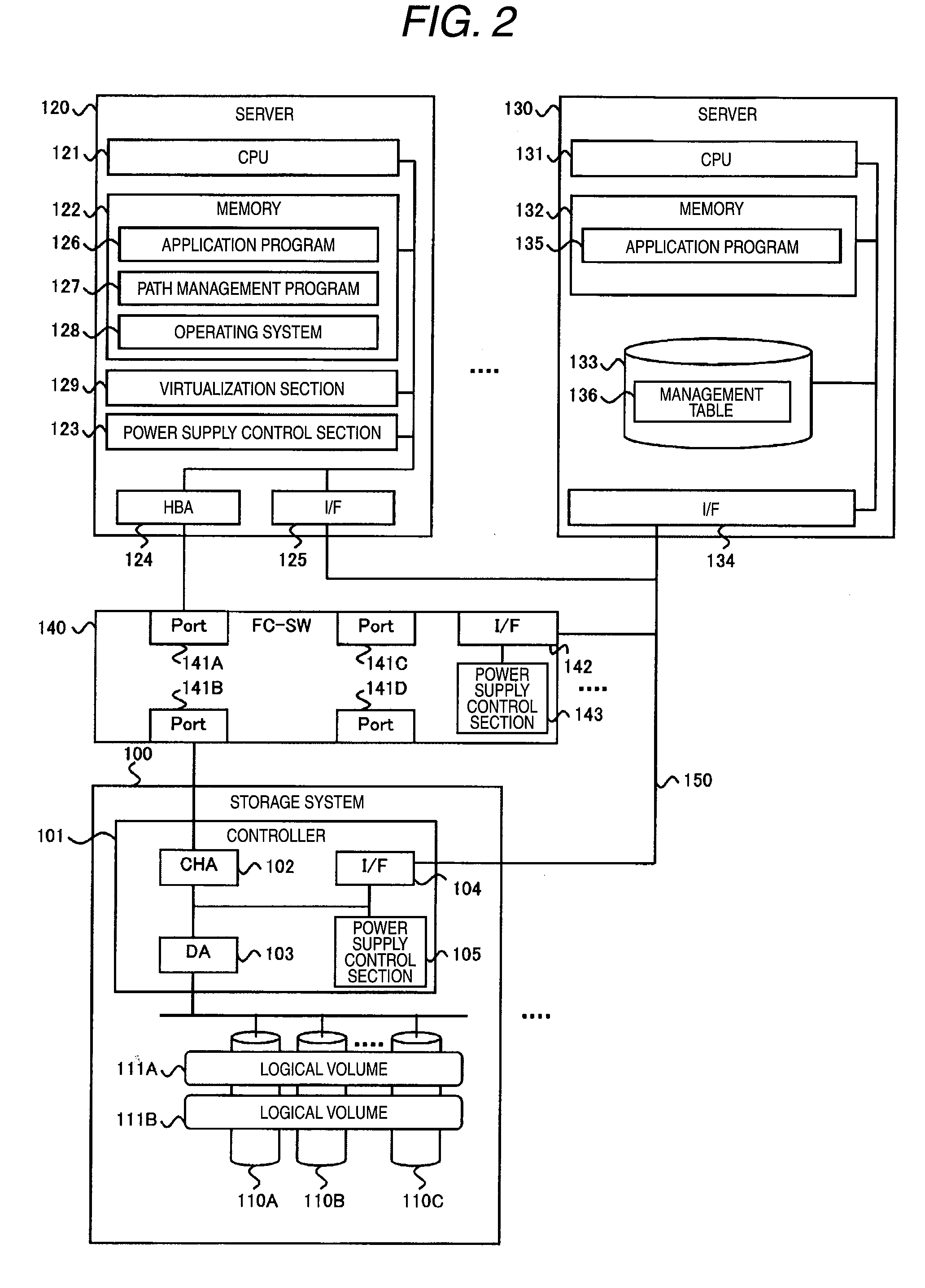
Application migration and power consumption optimization in partitioned computer system
InactiveUS20100100696A1Reduce total powerEnergy efficient ICTMemory loss protectionComputer architectureComputerized system
A storage device including a logical volume being a migration source of an application copies data stored in the logical volume being a migration source into a logical volume being a migration destination of the application. After such a copy process is started, the storage device stores the data written into the logical volume being a migration source as differential data without storing the data into the logical volume being a migration source. When the copy process is completed for the data stored in the logical volume being a migration source, a management computer starts copying of the differential data, and in a time interval after the copying of the data stored in the logical volume being a migration source is completed but before the copying of the differential data is completed, a computer being a migration destination of the application is turned ON. With such a logically-partitioned computer system, power consumption at the time of application migration can be reduced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System executing log data transfer synchronously and database data transfer asynchronously
InactiveUS20050210073A1Missing of transactionAvoid missingInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsData lossData buffer
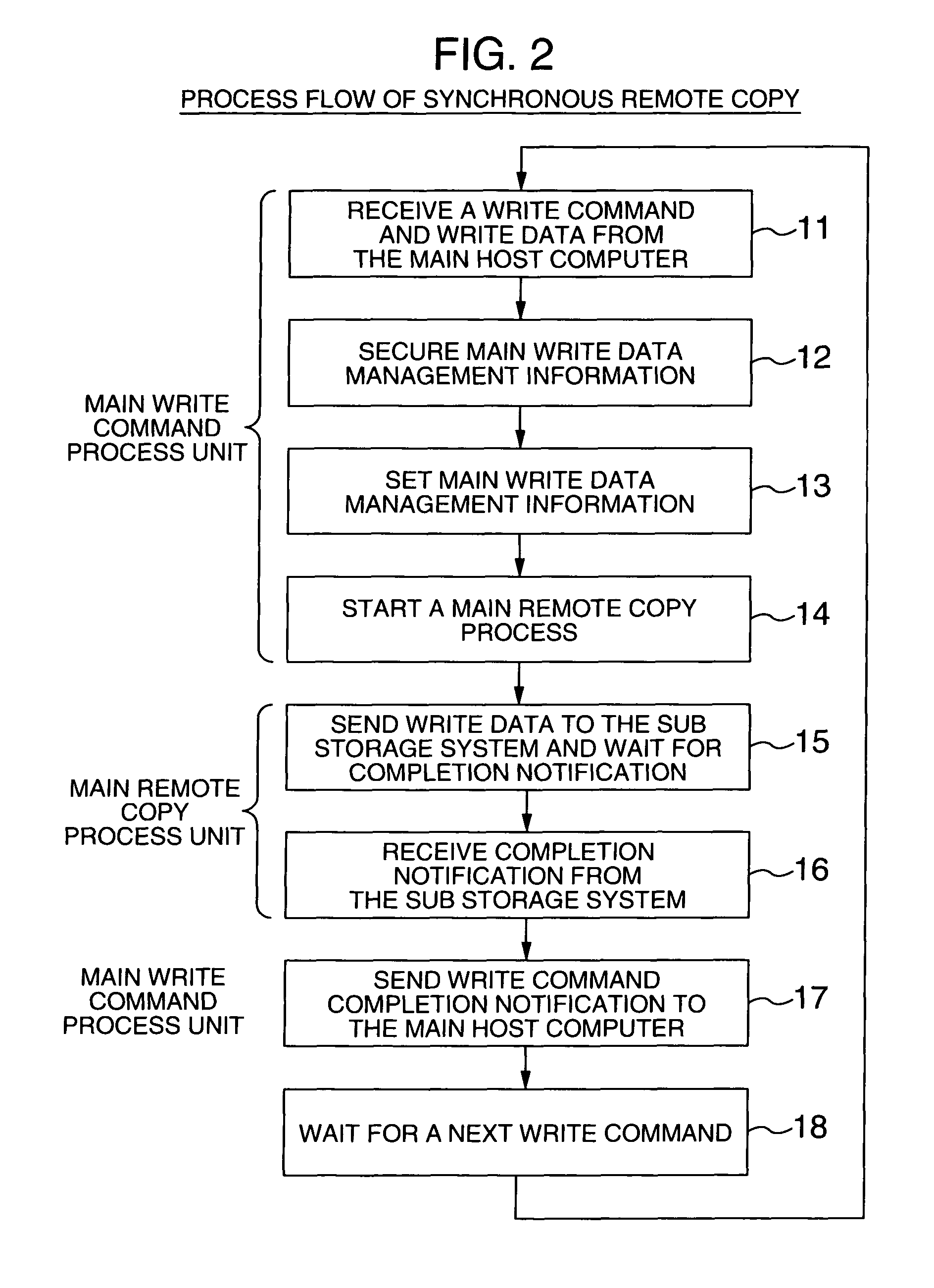
A disaster recovery system and a method therefor, having: a function for receiving write requests from a host computer to write log information indicating the contents of a database process executed for a database buffer on a main site, database data updated on the database buffer and status information indicating the position of log information used for disaster recovery; a function for transferring the received write request for log information to a recovery site by a synchronous remote copy process; and a function for transferring the received write request for database data to the recovery site by an asynchronous remote copy process. While remote copy can be executed at a long distance without data loss, the deterioration of the performance of a database process on a main site can be suppressed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
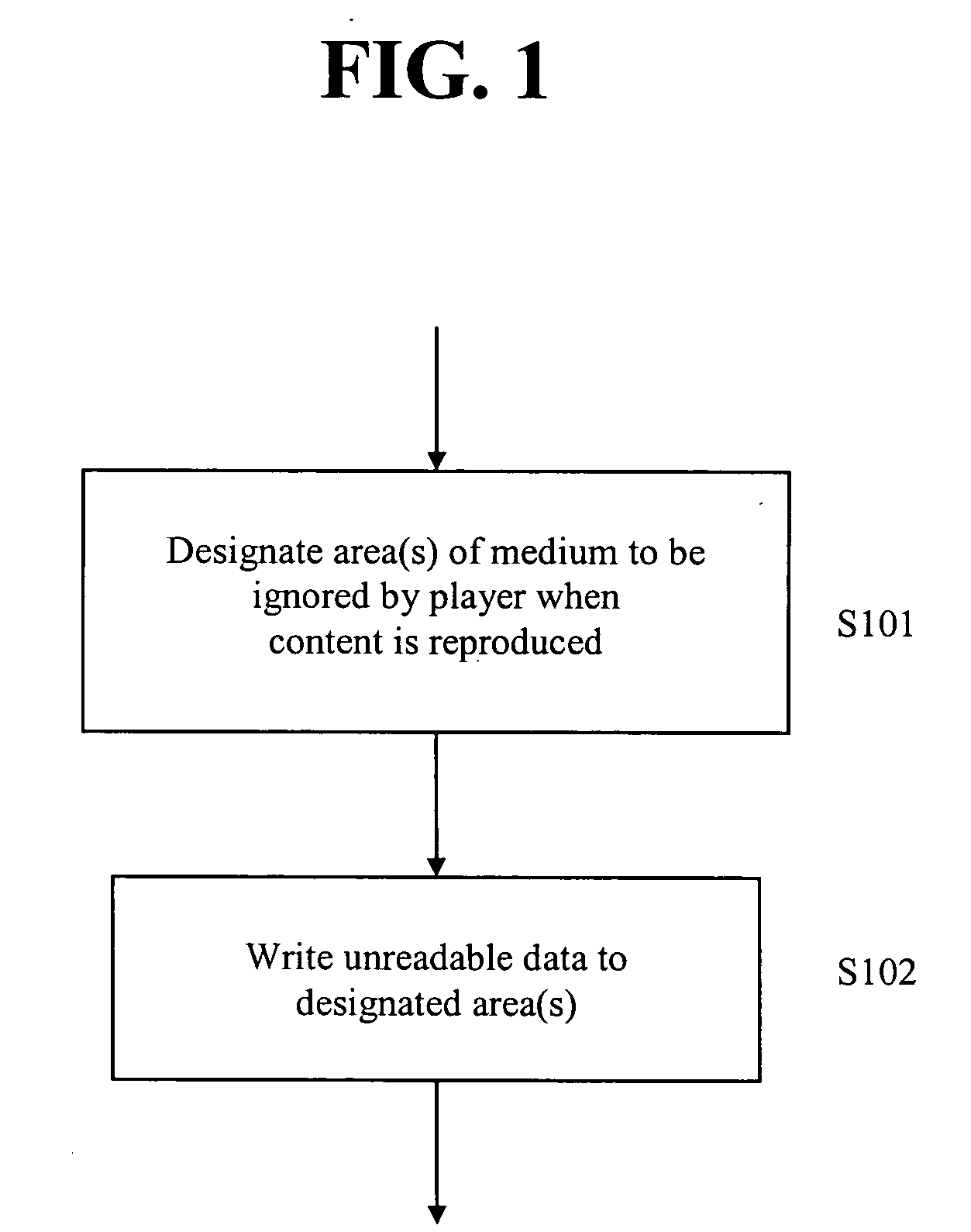
Method and apparatus for protecting against copying of content recorded on optical recording media
InactiveUS20060023598A1Combination recordingRecord information storageComputer hardwareOptical recording
Methods and apparatuses for protecting against copying of content recorded on optical recording media are provided. An area of an optical recording medium is designated to be ignored by a standards-compliant optical media player reproducing content recorded on the optical recording medium. Unreadable data is written to the designated area which is ignored by the standard-compliant optical media player. When an optical medium drive attempts to read the unreadable data in order to perform a one-to-one copy process on data recorded on the recording medium, the optical medium drive is unable to complete the one-to-one copy process.
Owner:CINRAM GRP
Managing filesystem versions
InactiveUS7139781B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile systemParallel computing
A system and method for managing logical versions of a filesystem made through a near-instantaneous copy process is provided. Each logical version of the filesystem, including the primary version, is assigned a unique epoch number or other identifying value, and each filesystem object is assigned two epoch numbers that define the space of logical versions for which the object exists. A list of all valid epoch numbers are maintained in a version table. The near-instantaneous creation of a logical version of the filesystem requires inserting a unique epoch number entry in the version table (106) and the next epoch number to the new logical version. An original state of the system is preserved through the use of a copy-on-write procedure for filesystem objects that are reference by that logical filesystem version (120). Accordingly, filesystem versions are maintained and original states of previous states of the logical filesystem versions are preserved.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for migrating data
ActiveUS7133984B1Consume considerable timeLimited bandwidthData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData storingData store
A method, system, and medium for replicating data stored on a storage array is provided. Source data, which may change during the copy process, is copied to a target device. The source data is checked to determine whether any changes were made to the data. If so, the respective data bin is copied to the target component.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
Performing a background copy process during a backup operation
ActiveUS20120101999A1Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsEvaluated dataData bank
In one embodiment, a system includes a performance monitoring facility of a database adapted for measuring performance of the database regularly, a data protection manager for controlling a backup operation of the database on a storage subsystem, logic adapted for providing an interface between the performance monitoring facility of the database and the data protection manager, logic adapted for starting the backup operation while informing the performance monitoring facility about the starting of the backup operation, logic adapted for continuously evaluating performance of the database to determine when a predefined performance criterion is violated, and logic adapted for sending information from the performance monitoring facility to the data protection manager to cause compliance with the predefined performance criterion in response to the predefined performance criterion being violated.
Owner:IBM CORP
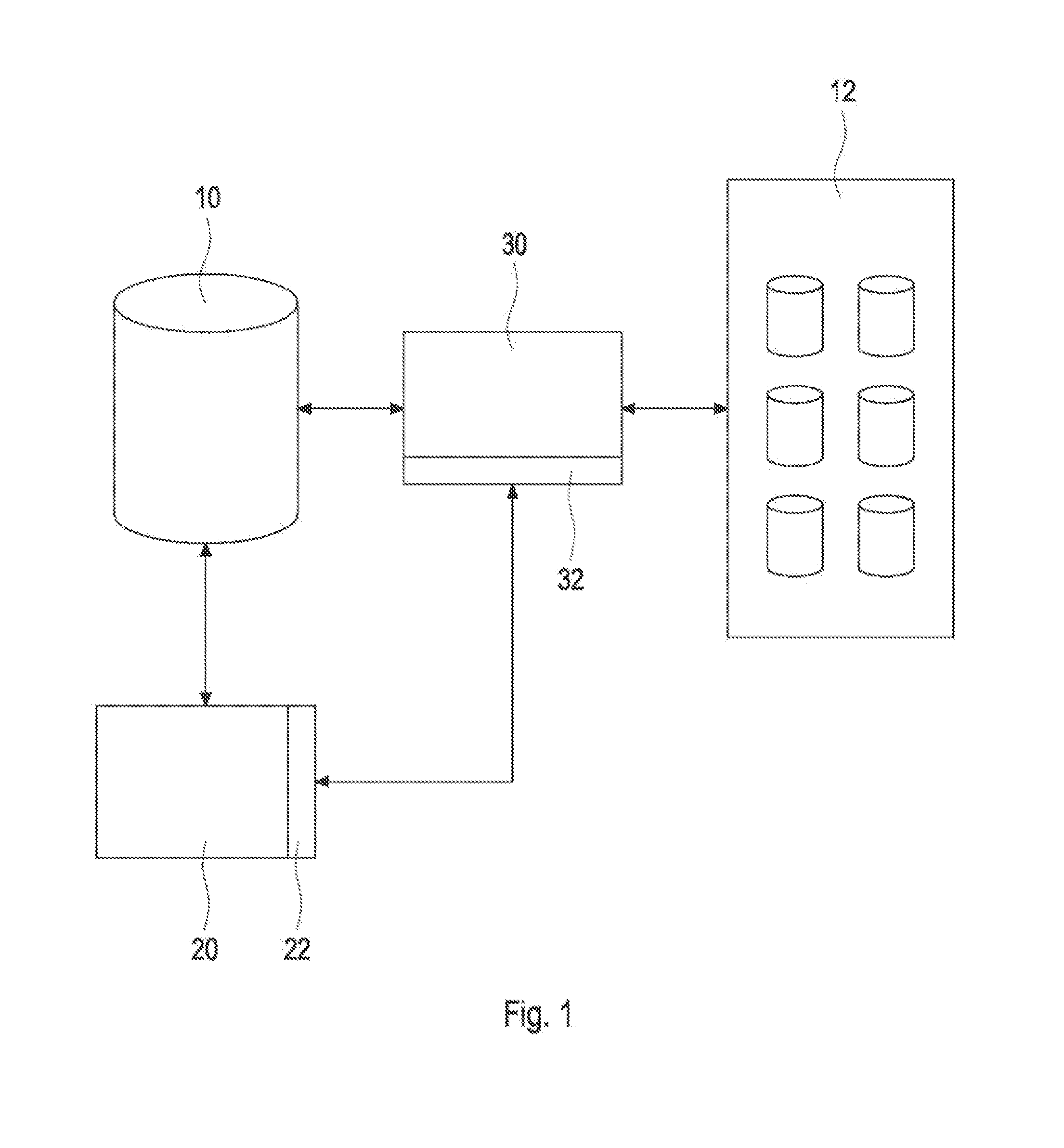
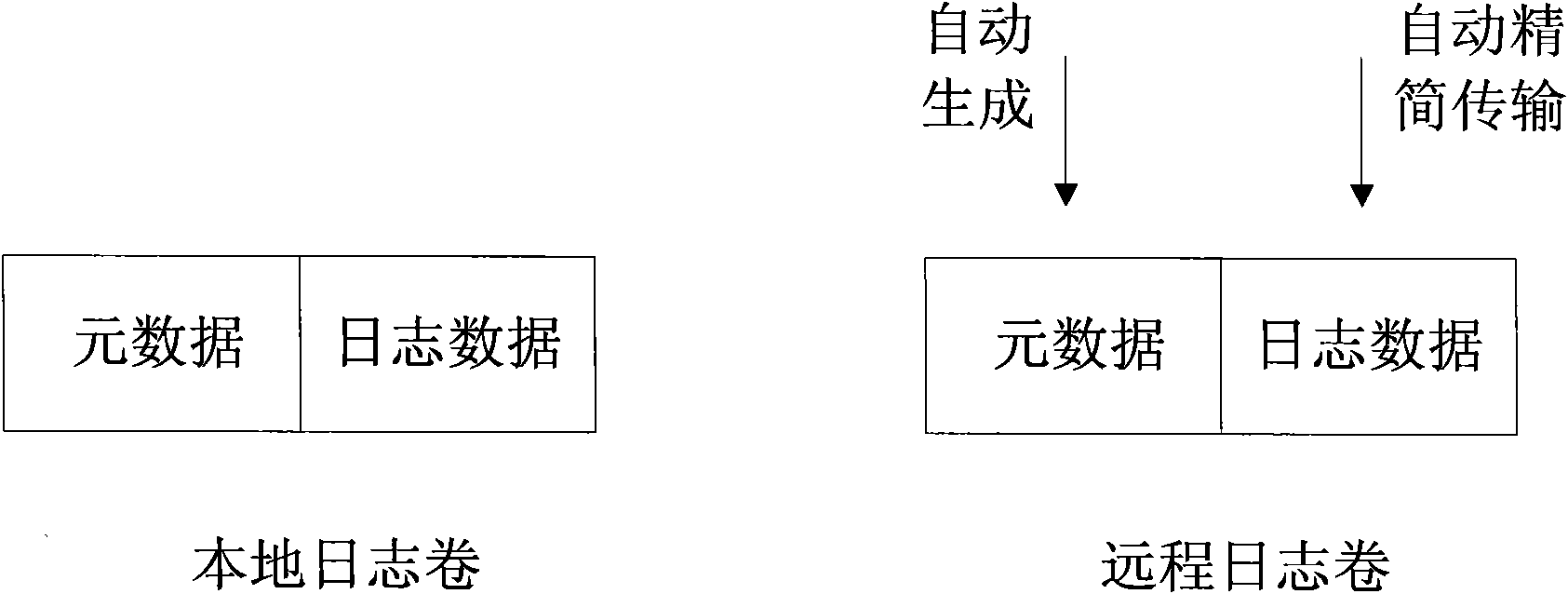
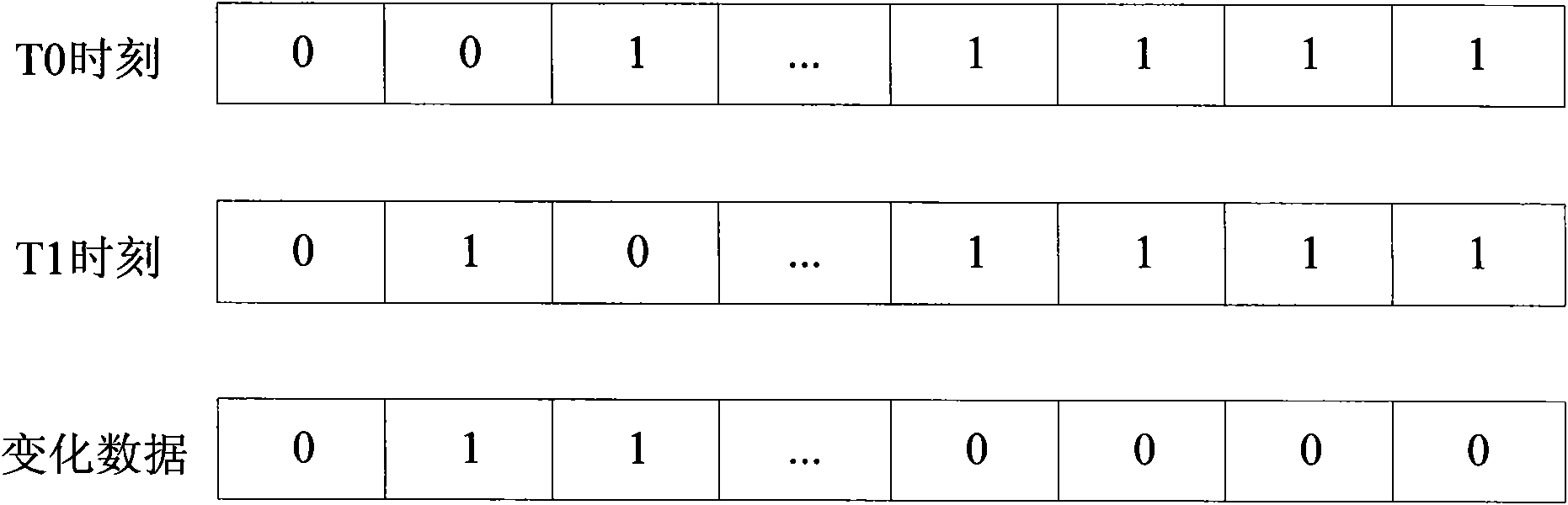
Long-distance duplicating system and method
InactiveCN102014152AReduce transfer dataStreamlined and Efficient TransmissionTransmissionWeb transportMetadata
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
Method and system for providing substantially constant-time execution of a copy operation
ActiveUS8484164B1Reduce disruption and disruptionDigital data processing detailsFile system administrationData segmentFile system
A system and method for providing a substantially constant-time copy operation for file system objects managed by a network storage server begins by generating a new file based on metadata in a source file. The system then generates a snapshot of the source file or the logical volume in which the source file resides. The system then copies each of the indirect blocks of the source file to a corresponding location in the destination file. During the copy process, a modified set of file system operations can be executed on the destination metadata container. In response to a read request directed to a target block in the destination file, the system determines if target block has been copied. If the block has not been copied, the system provides a data segment from the corresponding data block in the snapshot. Write requests are processed by generating a new data block and adding a reference to the new data block to the target location in the destination metadata container. During the copy process, the system checks each block reference before copying to determine if the block reference has been modified by a write operation. If the block was modified, the system skips copying that particular block reference. The system provides additional operations to execute truncate and append operations during the copy process.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
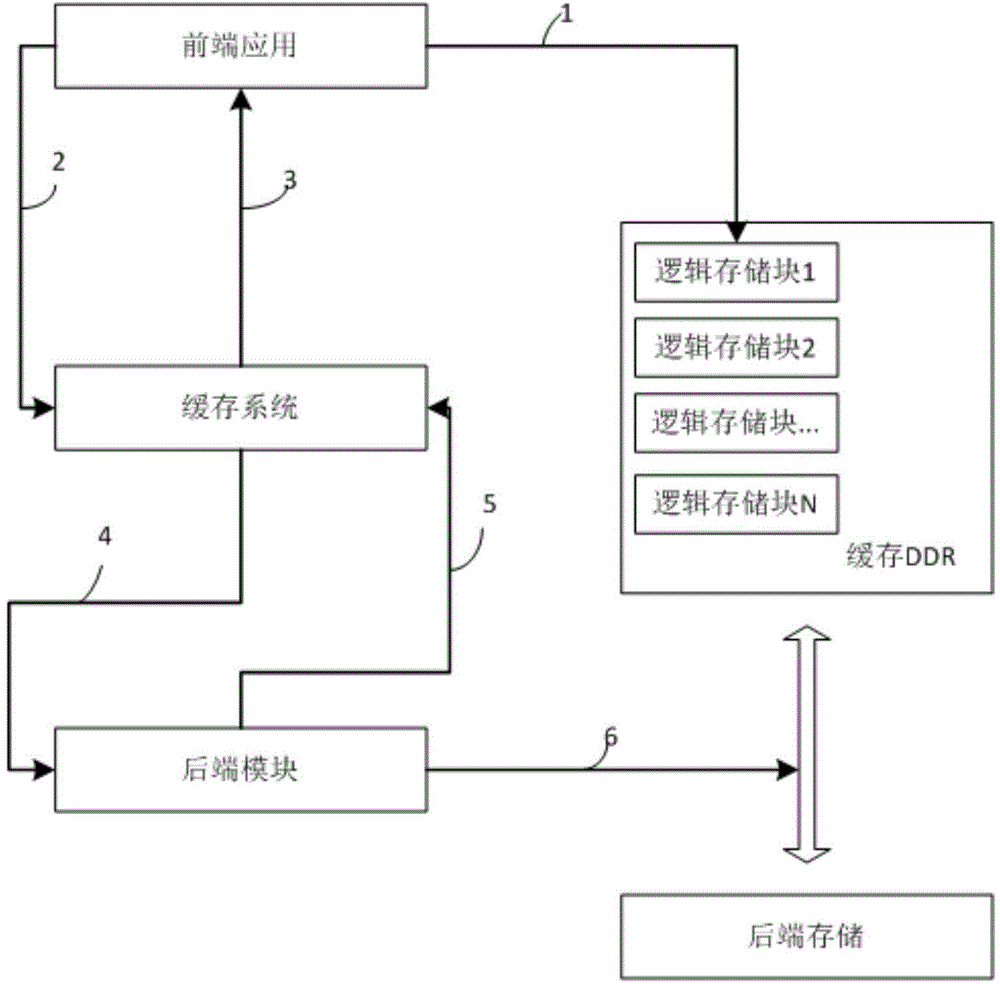
Flash memory storage system and reading, writing and deleting method thereof
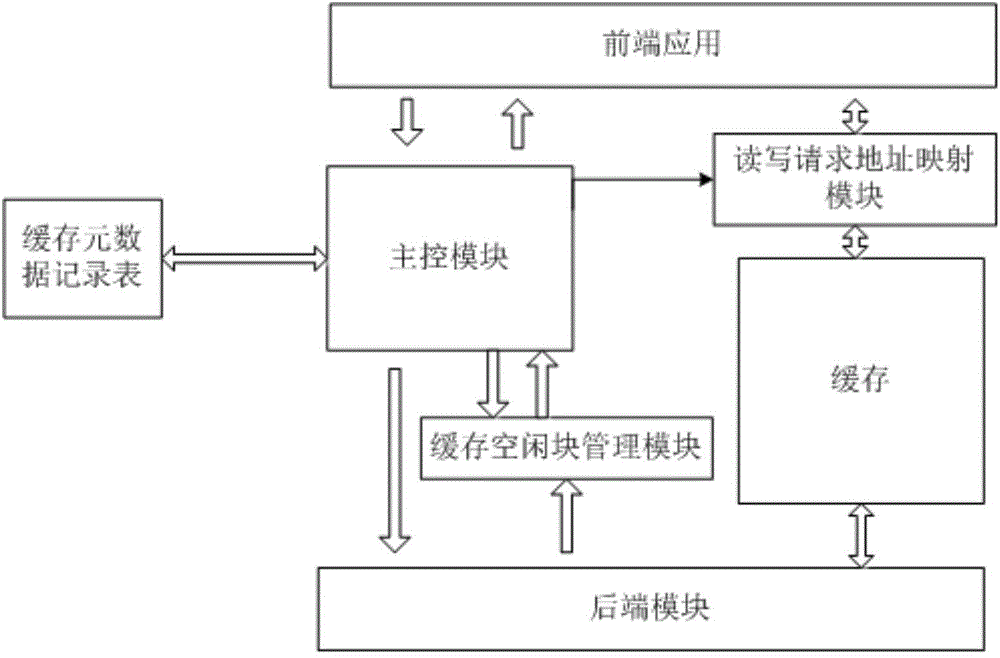
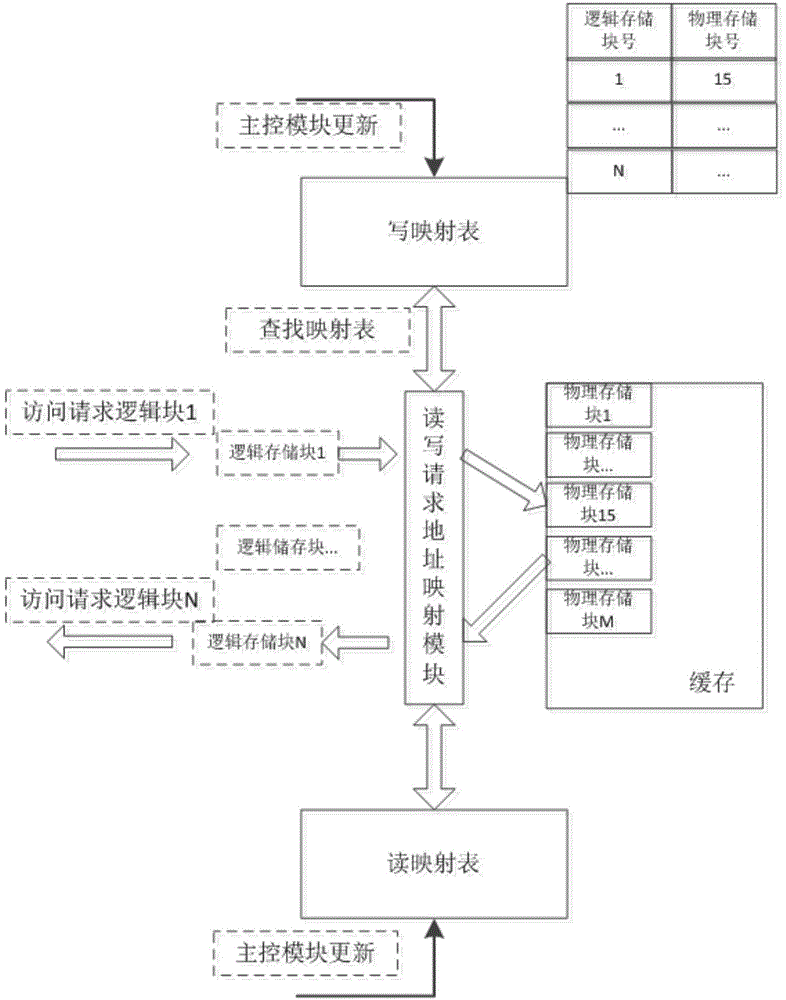
ActiveCN104636285AAchieve zero copyWrite lessMemory adressing/allocation/relocationZero-copyMetadata record
The invention discloses a flash memory storage system and a reading, writing and deleting method thereof. The flash memory storage system comprises a cache, a main control module, a cache metadata record sheet, a read mapping table and a write mapping table. The write mapping table is used for being stored in the cache and writing in the correspondence of a logical storage block and a physical storage block. The read mapping table is used for being stored in the cache and reading out the correspondence of the logical storage block and the physical storage block. The cache metadata record sheet is used for storing correspondences of metadata sheet addresses, the physical storage blocks and rear end flash memory addresses. By means of the flash memory storage system, the unnecessary write-in or read-out of a rear end flash memory can be reduced, the zero copy on a read-write data channel is achieved, the unnecessary intermediate copy process is omitted, and therefore the read-write efficiency is improved; the size of the read-write access of a front end application can be matched with the size of the rear end flash memory.
Owner:BEIJING ZETTASTONE TECH CO LTD
Online data migration method
InactiveCN102103629AImprove migration efficiencyImprove versatilitySpecial data processing applicationsBitmapUse equipment
The invention discloses an online data migration method, which is used for solving the technical problems of low efficiency and low universality of the conventional data migration method. The technical scheme comprises the following steps of: copying data in a logic unit number (LUN) of a source logic unit into the LUN of a target logic unit, and continuously running a system and a service in a data migration process; simultaneously copying the data updated into the LUN of the source logic unit into the LUN of the target logic unit in the migration process; simultaneously reflecting updating and copying processes by using a single bitmap mapping table; and after the data migration process is finished, using and updating used equipment at any time, and deleting the used equipment. The system and the service are continuously run in the data migration process, so the data migration efficiency and the data migration universality are improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Systems and methods for backing up data files
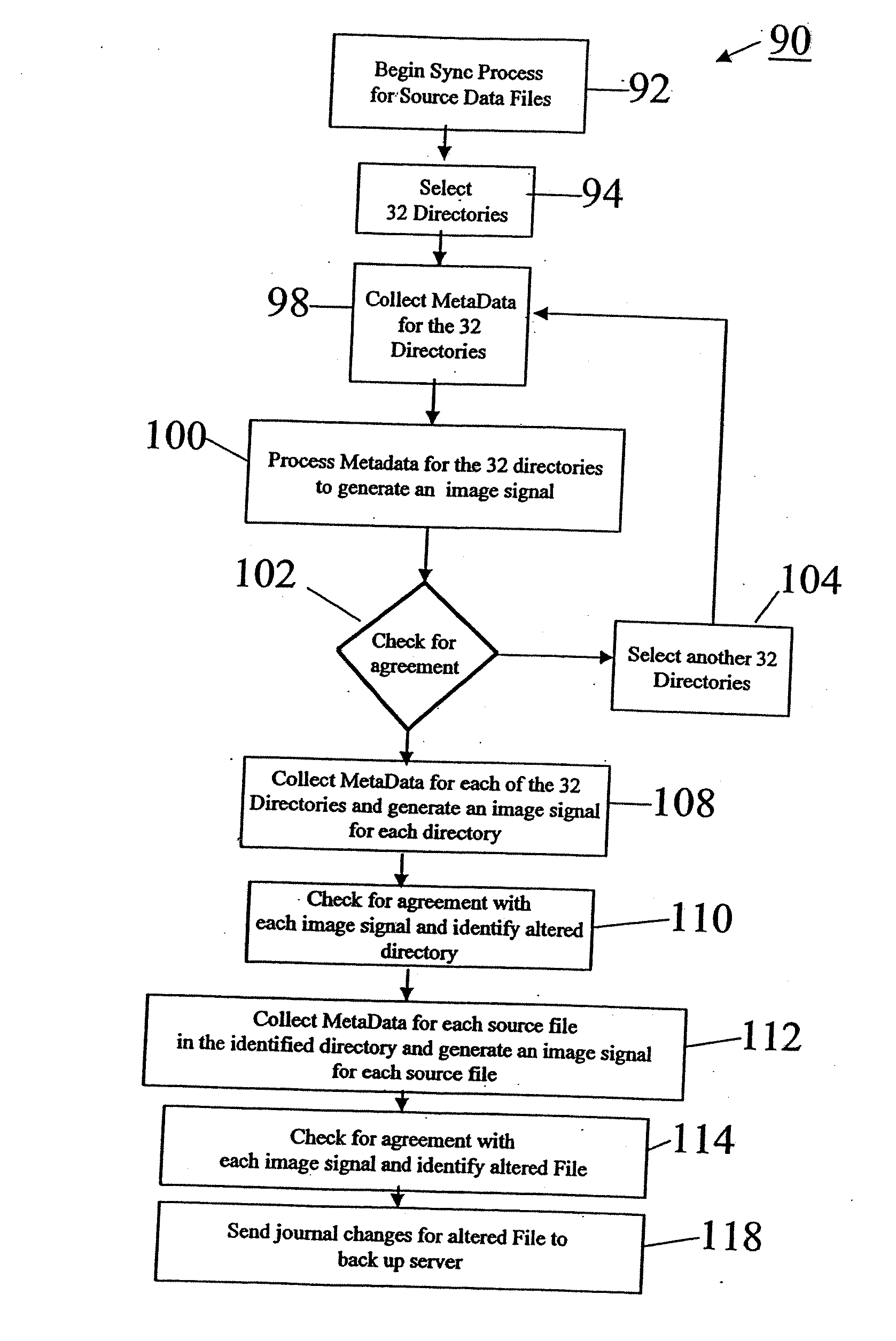
InactiveUS20070208783A1Reduce demandData processing applicationsMemory loss protectionBaseline dataData file
The invention provides systems and methods for continuous back up of data stored on a computer network. To this end the systems of the invention include a synchronization process that replicates selected source data files data stored on the network and to create a corresponding set of replicated data files, called the target data files, that are stored on a back up server. This synchronization process builds a baseline data structure of target data files. In parallel to this synchronization process, the system includes a dynamic replication process that includes a plurality of agents, each of which monitors a portion of the source data files to detect and capture, at the byte-level, changes to the source data files. Each agent may record the changes to a respective journal file, and as the dynamic replication process detects that the journal files contain data, the journal files are transferred or copied to the back up server so that the captured changes can be written to the appropriate ones of the target data files.
Owner:KEEPITSAFE INC
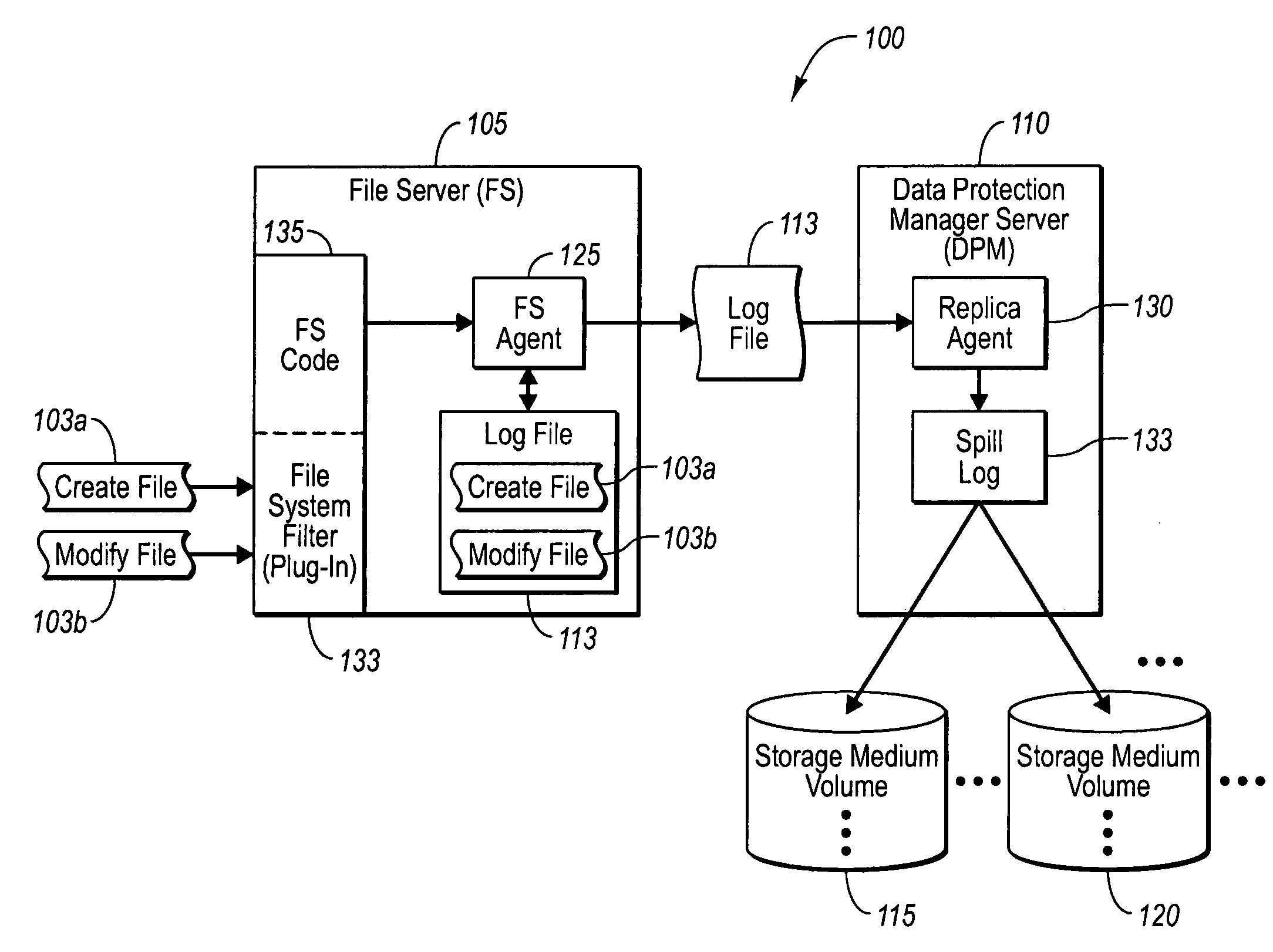
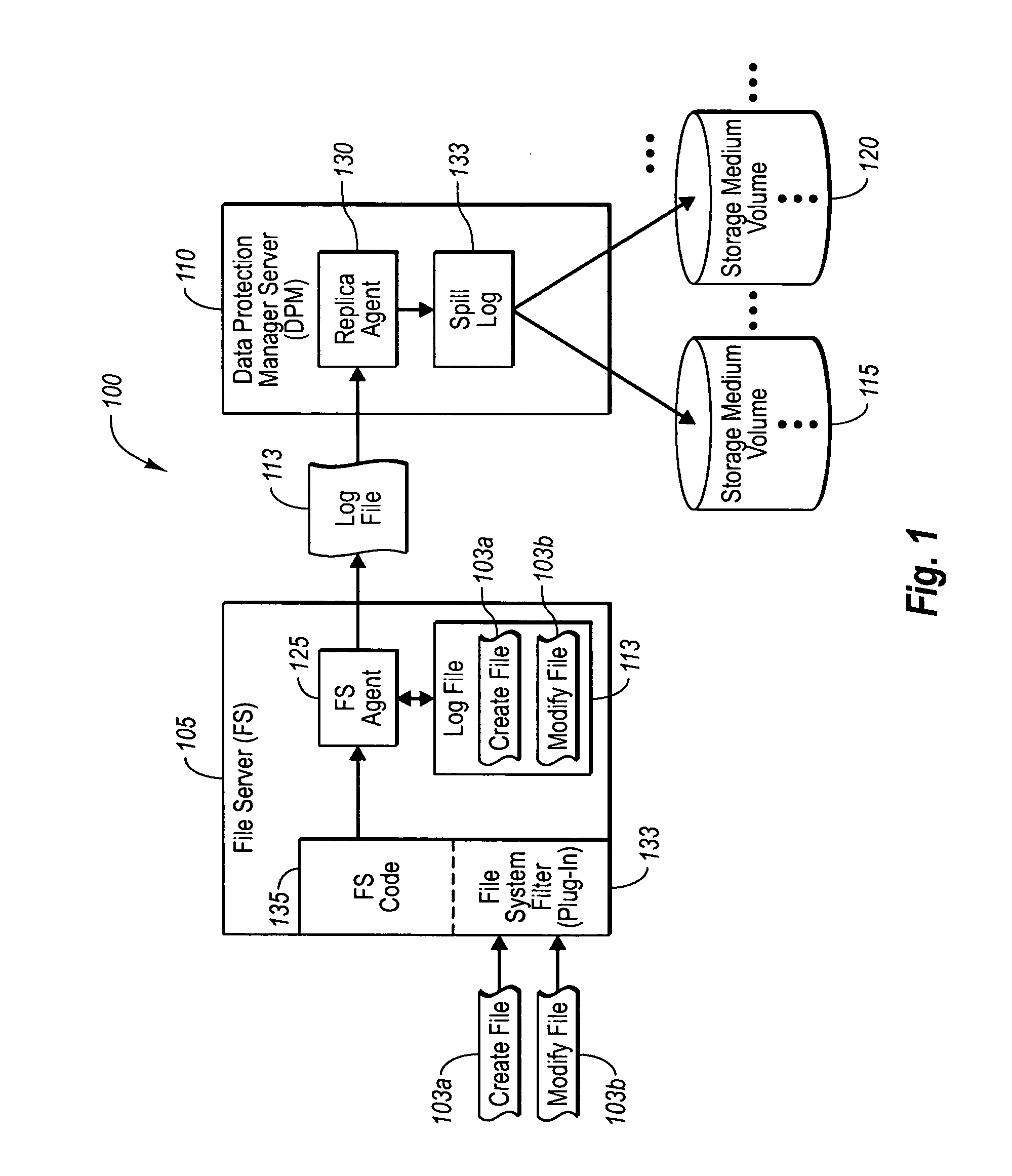
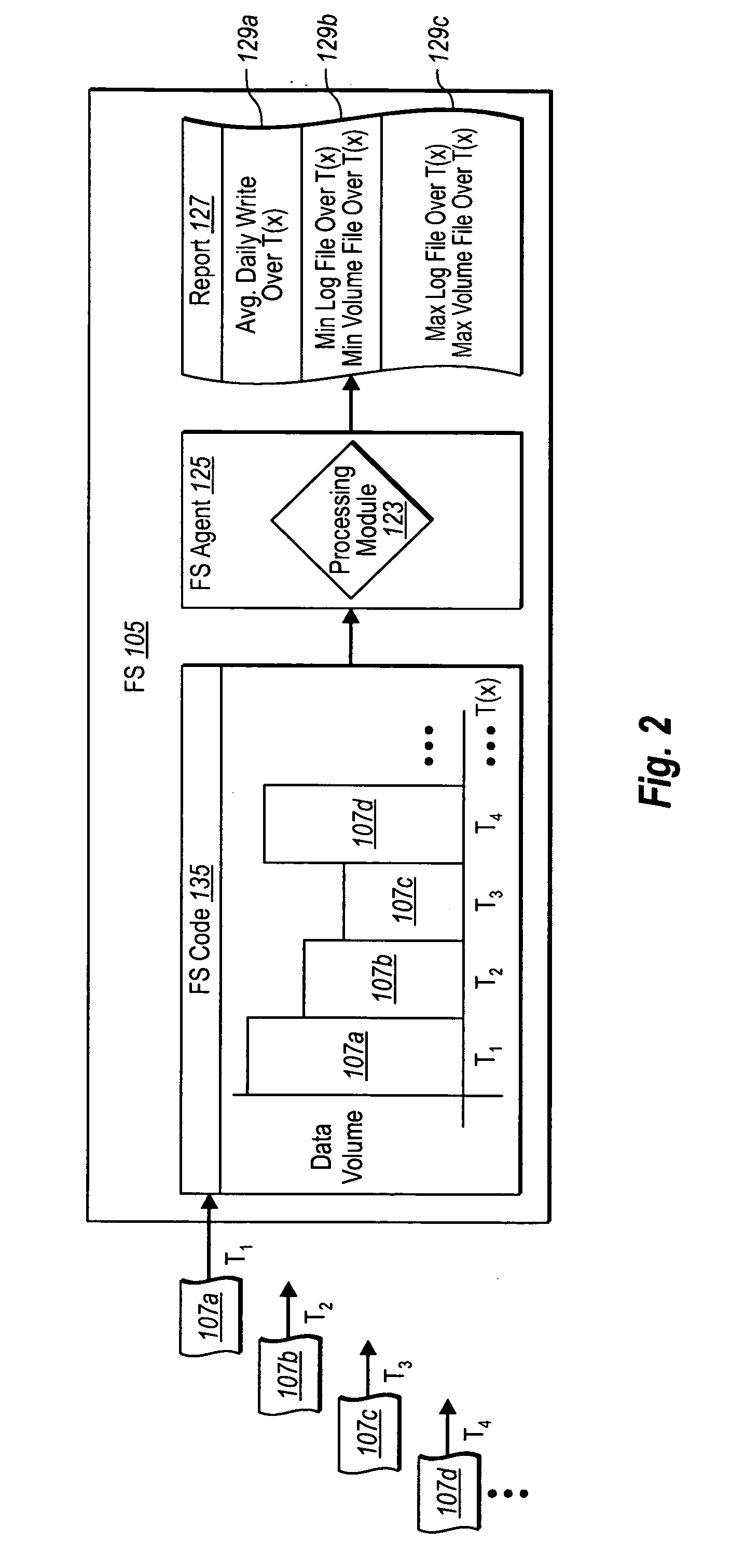
Protecting storage volumes with mock replication
ActiveUS20070136395A1Effective distributionDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionFile serverDatabase
A file server and a data protection manager server can work in tandem to efficiently backup protected volumes, and also provide efficient access to replicas of the protected volumes. In one implementation, a file server institutes a mock replication process, in which the file server observes data associated with write operations in one or more protected volumes. Appropriate volume allocation information can then be determined, which can be used to allocate log file, spill log file, replica volume, and shadow copy volume sizes, both at the file server and at the data protection manager server. In one implementation, the file server or data protection manager server automatically determines volume allocation information and automatically provides this information to the data protection manager server. The data protection manager server can then compare the volume allocation information with identified characteristics of its storage mediums, and implements an appropriate, efficient backup policy.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Hot mirroring in a computer system with redundant memory subsystems
A computer system implements hot mirroring for main system memory. That is, the computer system permits a user to hot plug a new memory board into the system and the system will respond by switching to a mirrored memory mode in which write cycles are performed to both memory boards (new and old). Once a new board is hot plugged into the system, the contents of the old board are copied over, in a background mode, to the new board so that both boards will have the same data. Because this background copying process may take a non-trivial amount of time and may detrimentally interfere with other system traffic, the system a user to exert control over the relative speed of the background copying so as to trade-off the time it takes to switch over to the mirroring mode versus the impact on on-going system behavior.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Determining regions when performing intra block copying
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
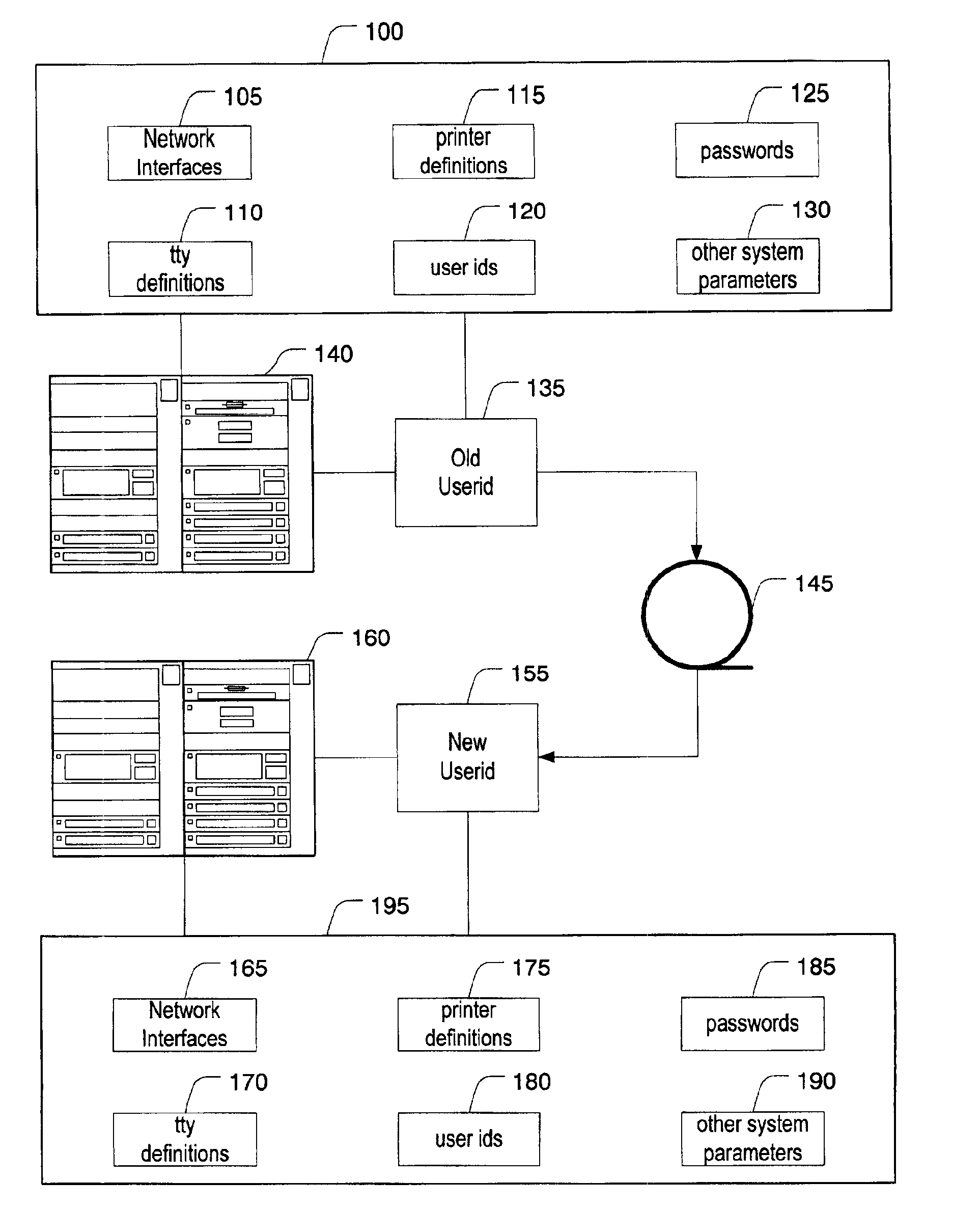
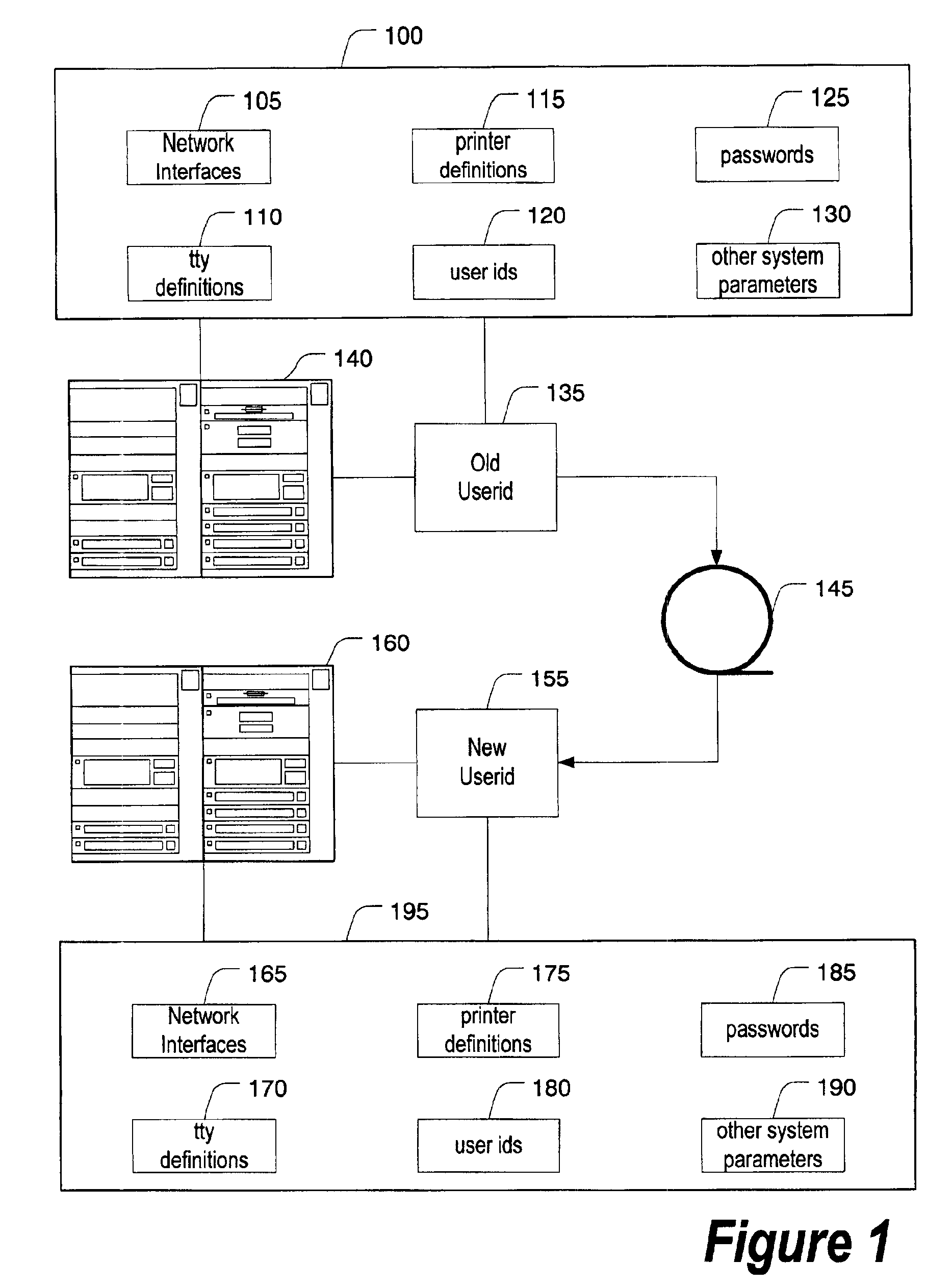
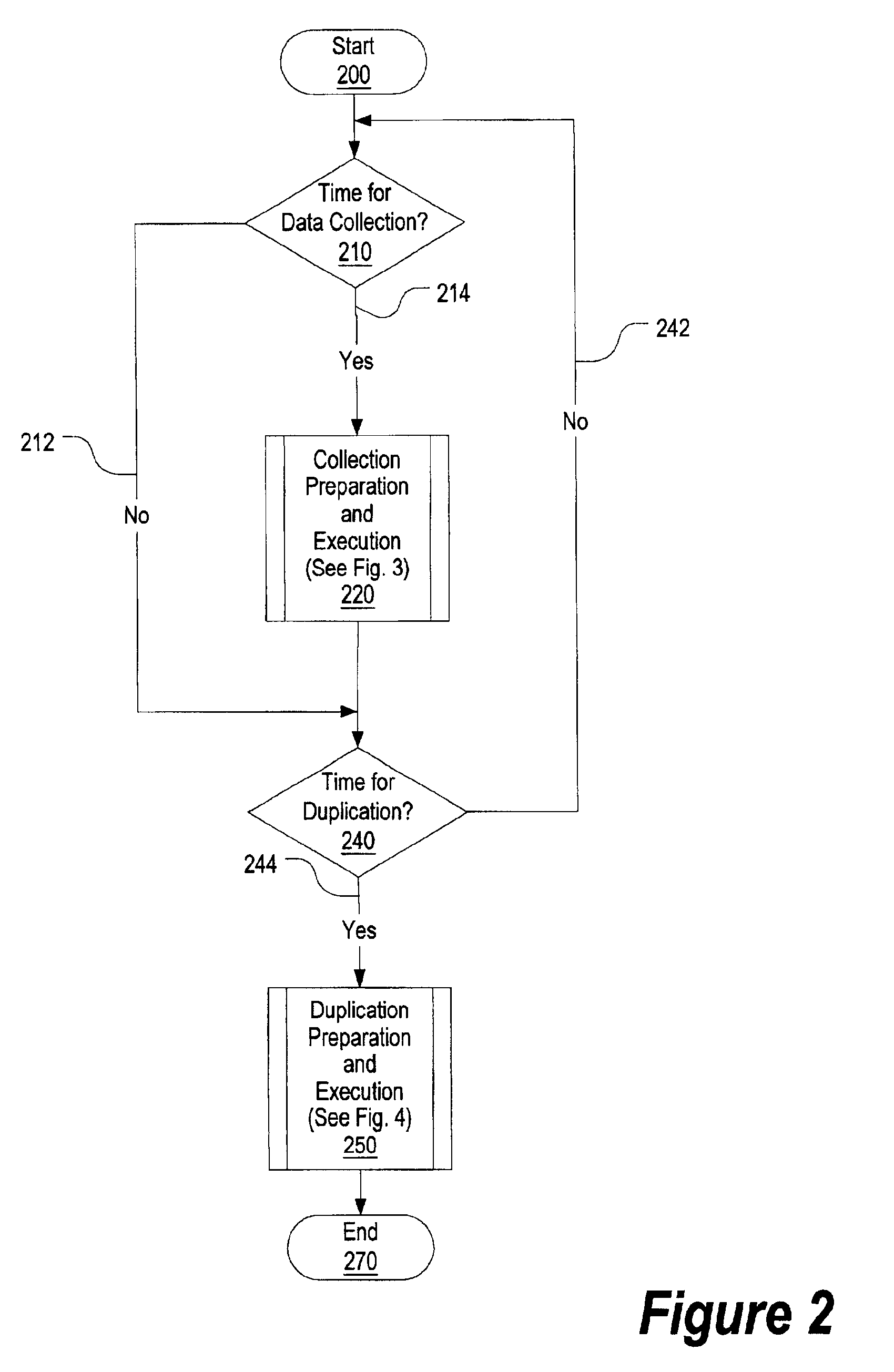
System and method for collecting and restoring user environment data using removable storage
InactiveUS6944790B2Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionRemovable mediaApplication software
A data collection program collects data from a user's workstation and captures the user environment data, including user settings and program application data. The user environment data is stored on a removable nonvolatile storage media for duplication processing. The stored user environment data is processed by a duplication process to duplicate the user environment data from the old workstation onto a new workstation or for recovery from a catastrophic system failure. A variety of user environment settings, not traditionally captured and restored by traditional backup software, are captured and restored. For example, licensing information and application personality data is identified, stored, and recovered along with other user-specific information such as hostnames, IP addresses, and the like.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
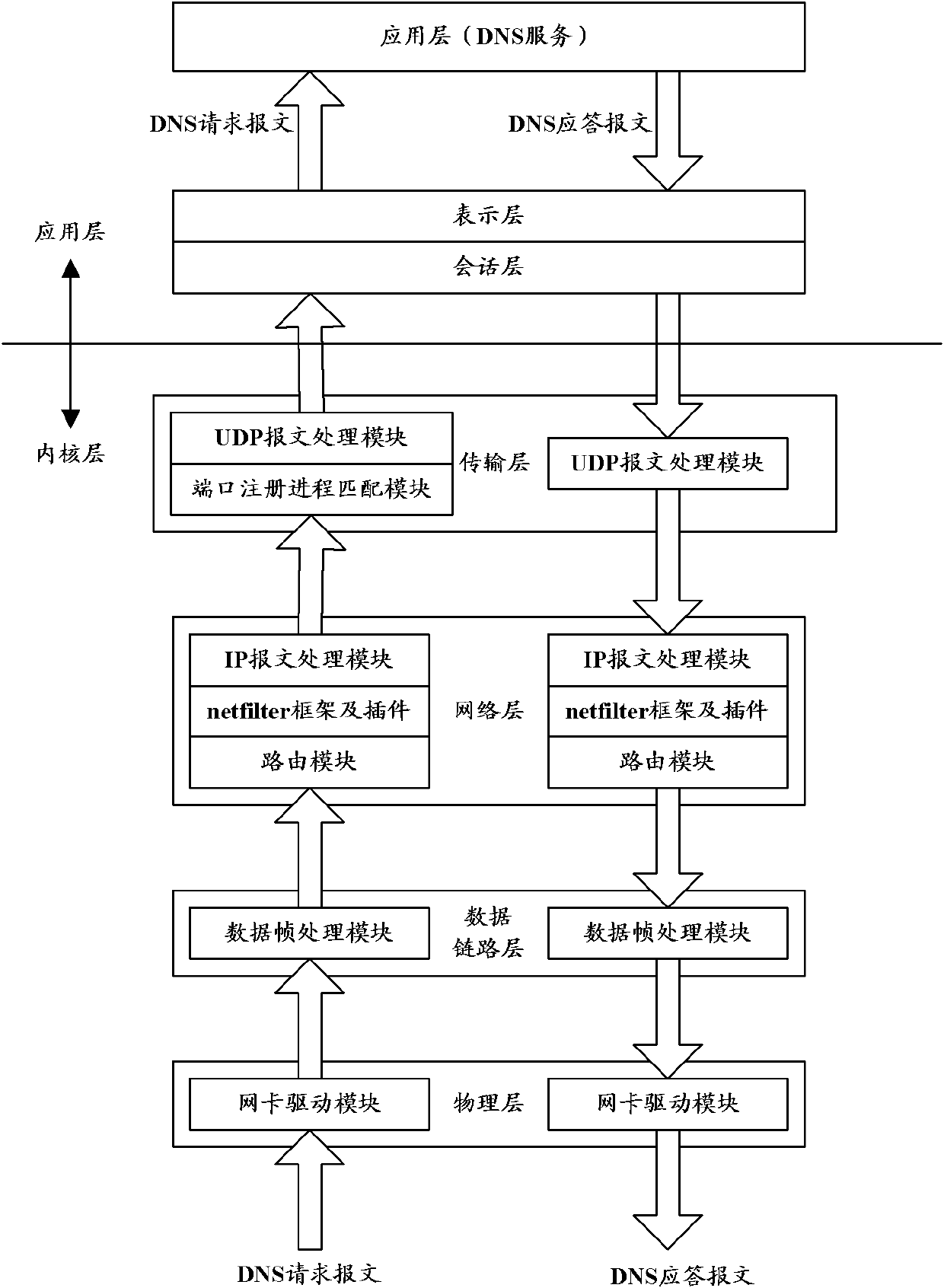
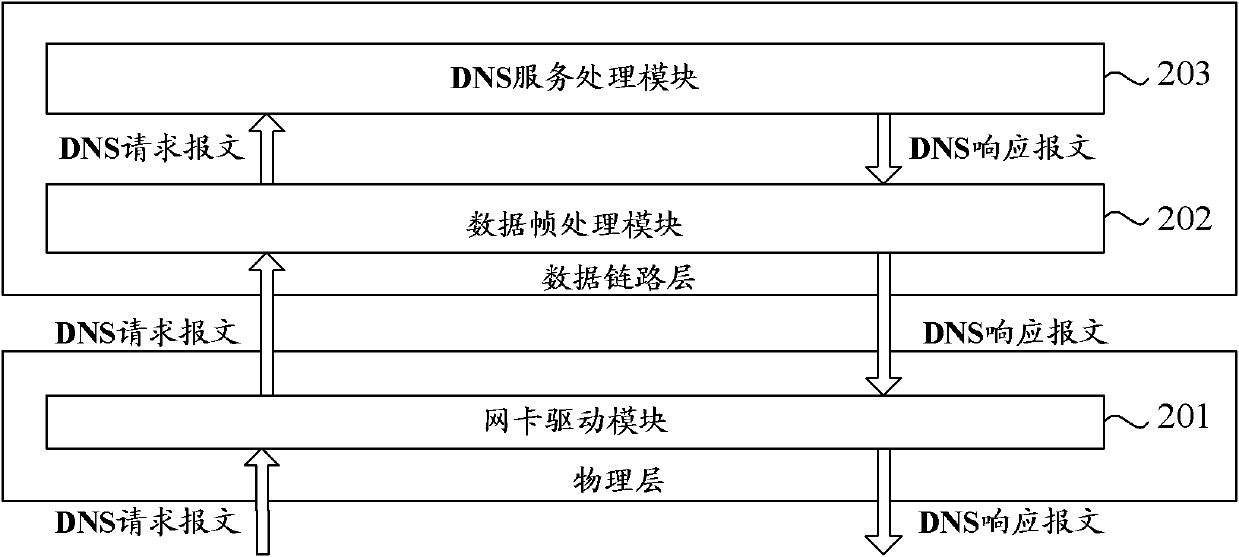
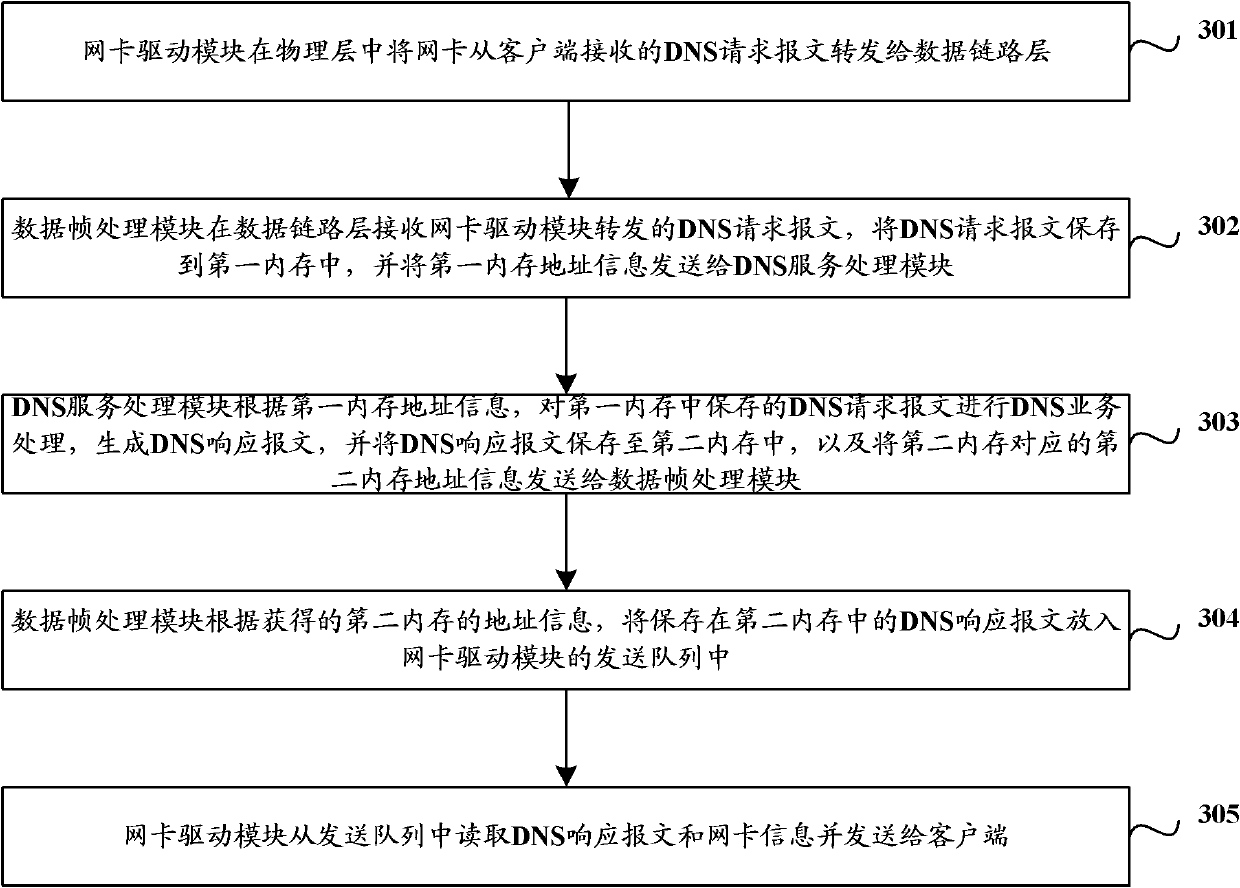
DNS (domain name system) service system and method based on Linux operation system
ActiveCN102185936AImprove processing efficiencyData switching networksOperational systemProtocol Application
The invention relates to the computer technology, in particular to a DNS (domain name system) service system and method based on a Linux operation system. In the embodiment of the invention, a DNS service processing module is placed in the data link layer of a kernel; a data frame processing module is used for receiving a DNS request message forwarded by a network card driving module, storing theDNS request message in a memory, and calling a DNS service processing module of the kernel to process the DNS request message; and the DNS service processing module is used for generating a DNS response message, storing the DNS response message into another memory, and calling the data frame processing module to read the DNS response message to the memory from the another memory, add the DNS response message to the transmission queue and transmit the DNS response message to a client. The data frame processing module and the DNS service processing module are located in the data link layer of the kernel so as to obviate the processing of other kernel modules and obviate the two copy processes from the kernel to the application layer and from the application layer to the kernel layer, thereby improving the DNS service processing efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI YAMU COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
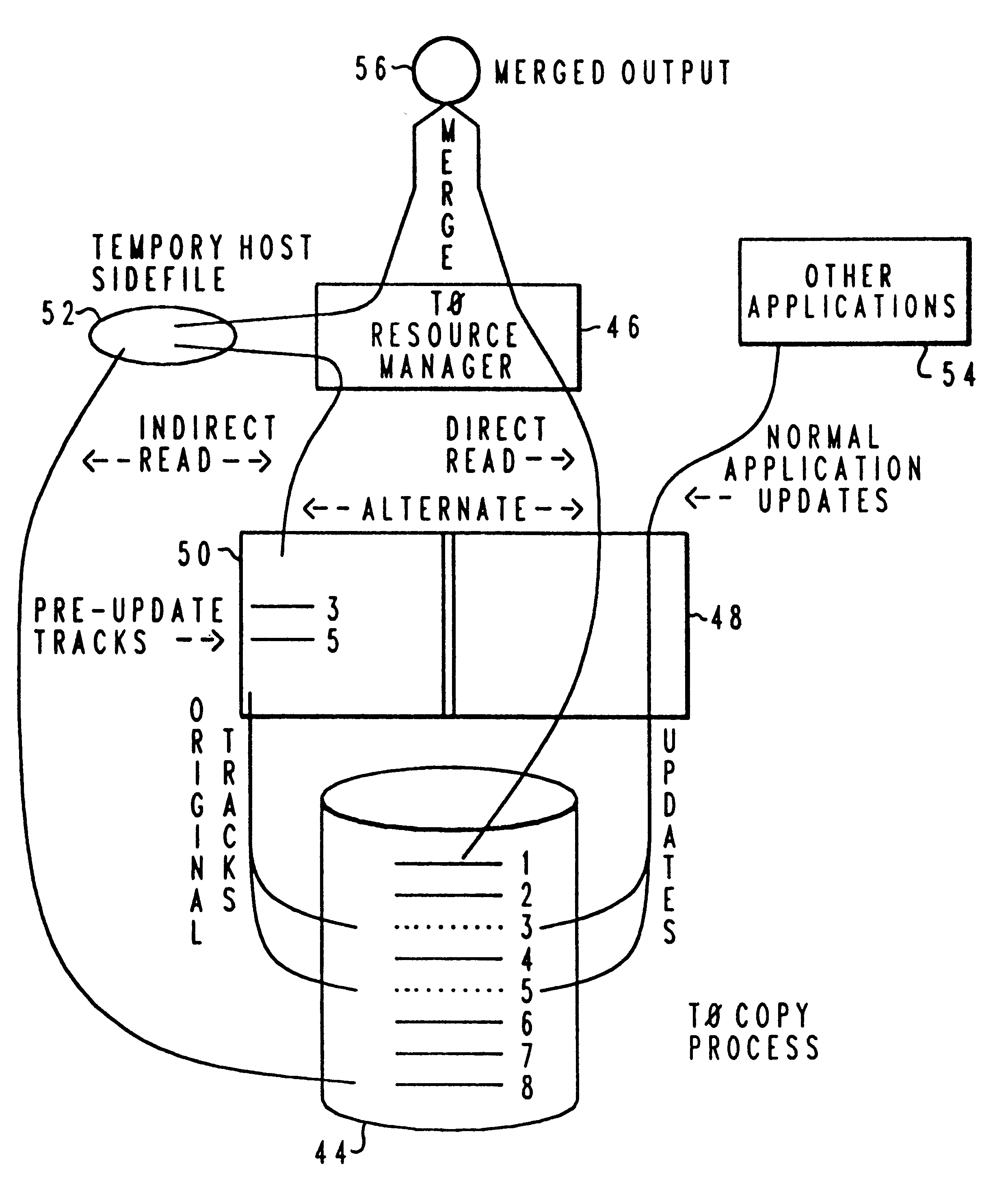
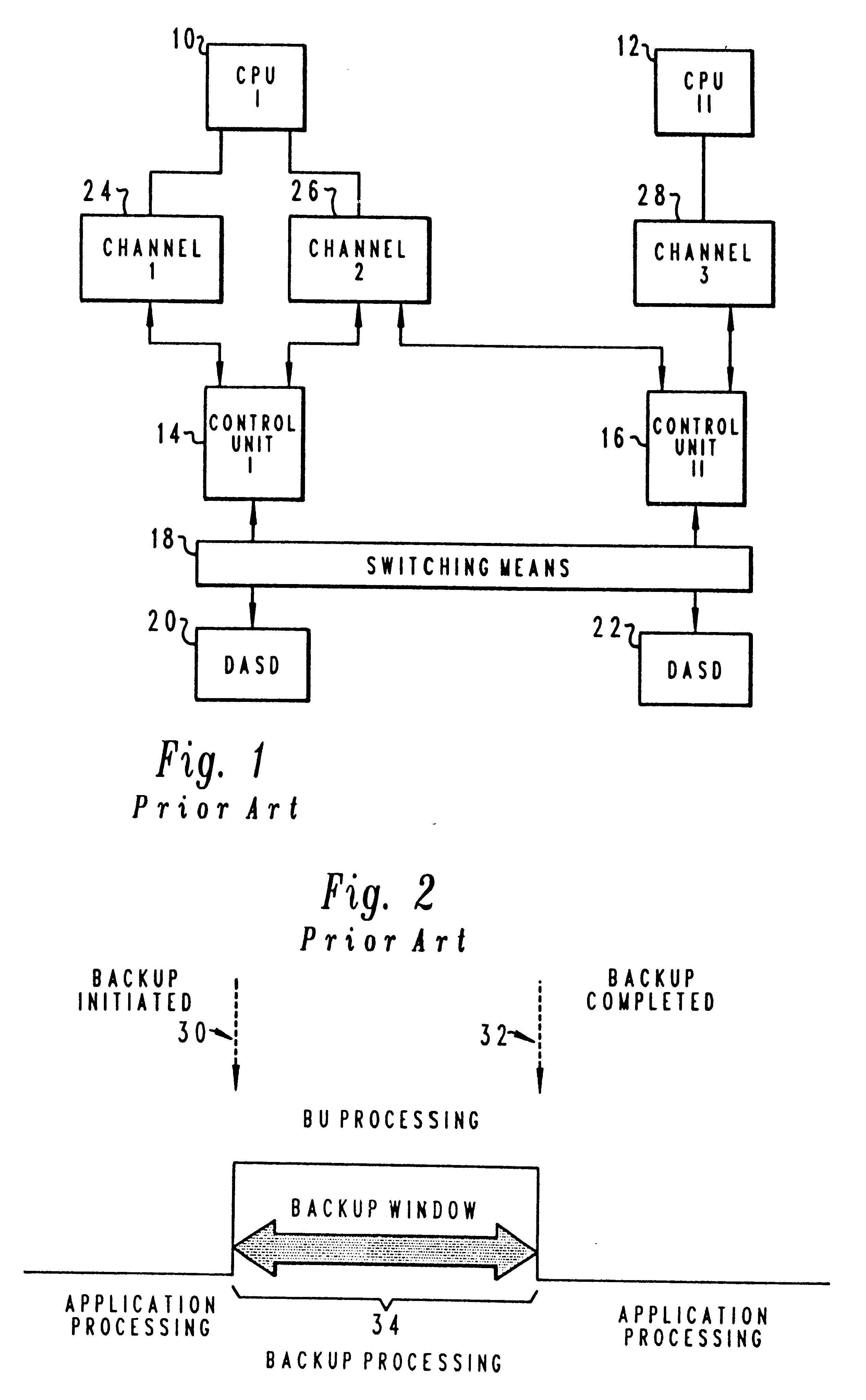
Method and system for automated termination and resumption in a time zero backup copy process
InactiveUSRE37038E1Reduce suspensionReliability increasing modificationsData processing applicationsSuccessful completionData processing system
A method in a data processing system for automatically terminating or resuming backup copy sessions after an abnormal interrupt or reset notification occurrence during a backup copy process. A status indication is entered into activity tables associated with a plurality of storage subsystems and devices within a data processing system in response to initiation of a backup copy session. Status indications are then entered upon successful completion of a backup copy session within the data processing system. The indications within the activity tables are reviewed to determine the status of a backup copy session upon restarting a resource manager, abnormal termination of a backup copy program, or an operating system initial program load. If a backup copy session has been initiated but not completed, the backup copy session is then terminated. The indications within the activity tables are also reviewed to determine the status of a backup copy session if a reset notification is raised by a storage subsystem. The tracks extents which are active for a volume associated with a particular session identification are determined. A comparison is then made between the tracks extents which are active and the volume and extent information associated with a physical session identification. If a match exists between the tracks extents which are active and the volume and extent information associated with a physical session identification, the backup copy session resumes. If a match does not exist, the backup copy session is terminated.
Owner:IBM CORP
Metadata access during error handling routines
InactiveUS20050193230A1Digital computer detailsRedundant operation error correctionData integrityControl store
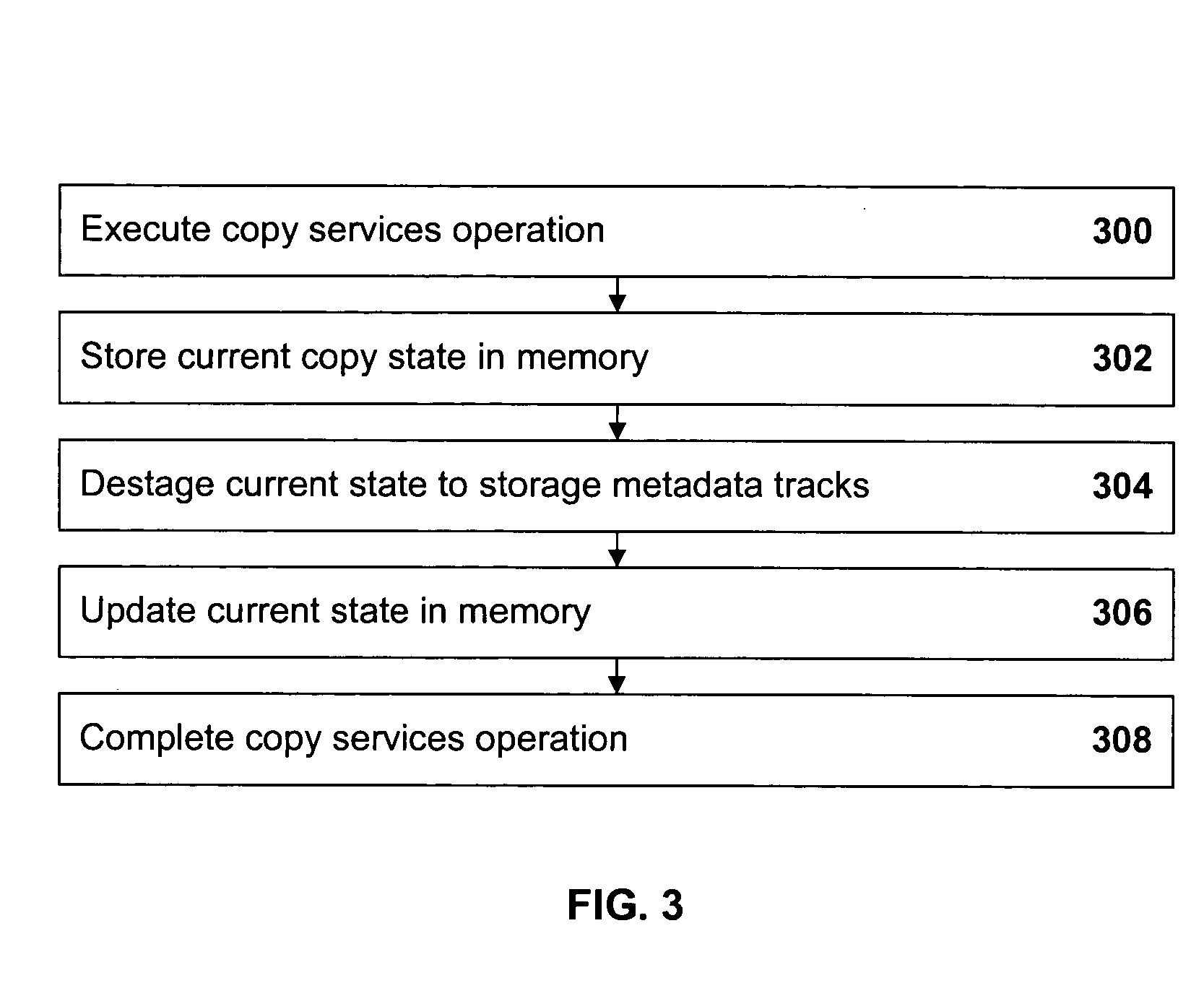
A data storage control unit is coupled to one or more host devices and to one or more physical storage units. Data is stored in one of the storage units and, for data integrity, copied to another storage unit. An updated state of the copy process (metadata) is maintained and updated in metadata tracks in a memory of the storage controller and periodically destaged to corresponding metadata tracks of a storage unit. If the copy process is interrupted, such as by a power failure, an error handling routine commences. Track state fields associated with each in-memory metadata track are initialized to an ‘invalid’ state and background staging of metadata tracks from the storage unit to the memory. After a track is staged, the associated track state field is changed to a ‘valid’ state. If a request is received to access a track of copy state data and the track has been staged (as indicated by the state of the associated track state field), the track is accessed. If the requested track has not been staged, requester waits while the requested track is staged; then the requested track is accessed. Once the error handling routine is completed, normal I / O operations with customer data may resume. Preferably, completion of the error handling routine is independent of the completion of the staging of copy state data tracks.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for the Production of a Substrate Having a Holographic Appearance
InactiveUS20080258339A1Reduce rigidityIncrease substrate temperatureThree-dimensional effectsLight effect designsPaper sheetMechanical force
A means of digitizing the topography of an art work is disclosed. A means of reproducing said art work and the related apparatus are also disclosed. The art reproduction process disclosed employs a thin sheet of thermoformable plastic onto which a permanent image of an art work has been created and which is heated prior to either a dot matrix print head, a daisy wheel print head, or both being employed to apply mechanical force to said thin sheet of thermoformable plastic sheet so as to create an accurate three-dimensional relief reproduction of an original artwork. An alternative embodiment is also disclosed wherein the art reproduction process employs a thin sheet of paper or cardboard onto which a permanent image of an art work has been created and which is heated and humidified with steam prior to either a dot matrix print head, a daisy wheel print head, or both being employed to apply mechanical force to said thin paper or cardboard sheet so as to create an accurate three-dimensional relief reproduction of an original artwork.
Owner:2089275 ONTARIO
Intelligent and efficient raid rebuild technique
A method for servicing a redundant array of independent storage drives (i.e., RAID) includes performing a service call on the RAID by performing the following steps: (1) determining whether the RAID includes one or more consumed spare storage drives; (2) in the event the RAID includes one or more consumed spare storage drives, physically replacing the one or more consumed spare storage drive with one or more non-consumed spare storage drives; and (3) initiating a copy process that copies data from a storage drive that is predicted to fail to a non-consumed spare storage drive associated with the RAID. The service call may then be terminated. After the service call is terminated, the method waits for an indication that a number of non-consumed spare storage drives in the RAID has fallen below a selected threshold. A corresponding apparatus and computer program product are also disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for adjusting performance of logical volume copy destination
InactiveUS7047360B2Smoothly and efficiently copiedInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionFailoverComputer science
When data written into a volume (source volume) in a parity group in a storage apparatus is written into a volume (destination volume) in a parity group in a storage apparatus using a remote copy function, it is determined during the copy whether or not one or both of the following two specified conditions are satisfied for this set of volumes: (1) the performance of the destination volume after a failover is equal to or higher than the performance of the source volume before the failover; and (2) the performance of the destination volume is equal to or higher than the performance of the source volume during the copy. If the condition(s) is not satisfied, the storage apparatus in which the destination volume is defined is changed in configuration to satisfy the condition.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for preventing counterfeiting or alteration of a prited or engraved surface
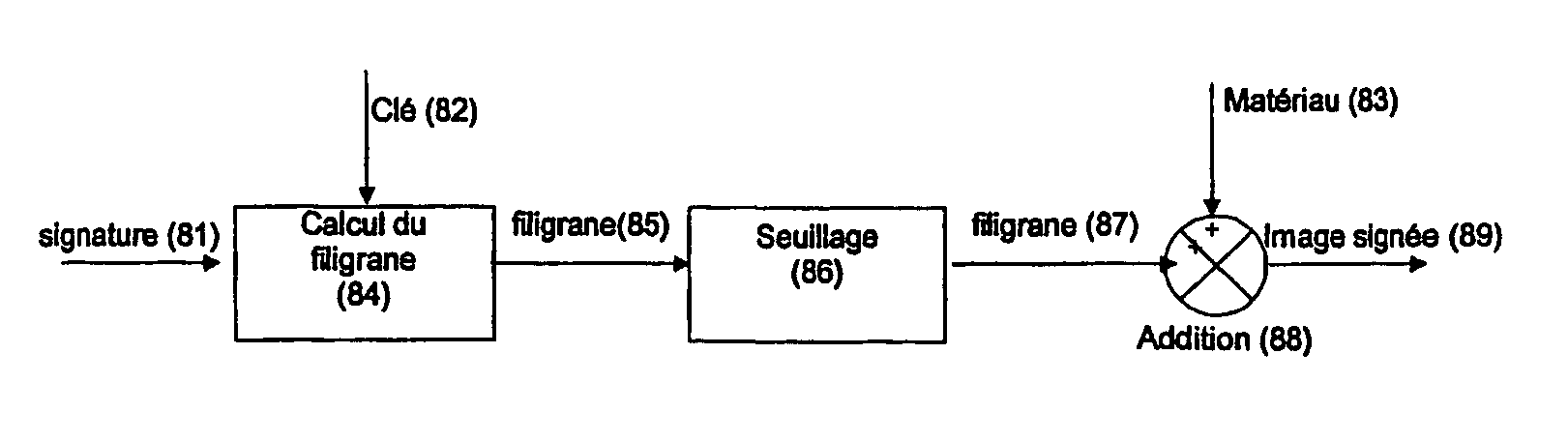
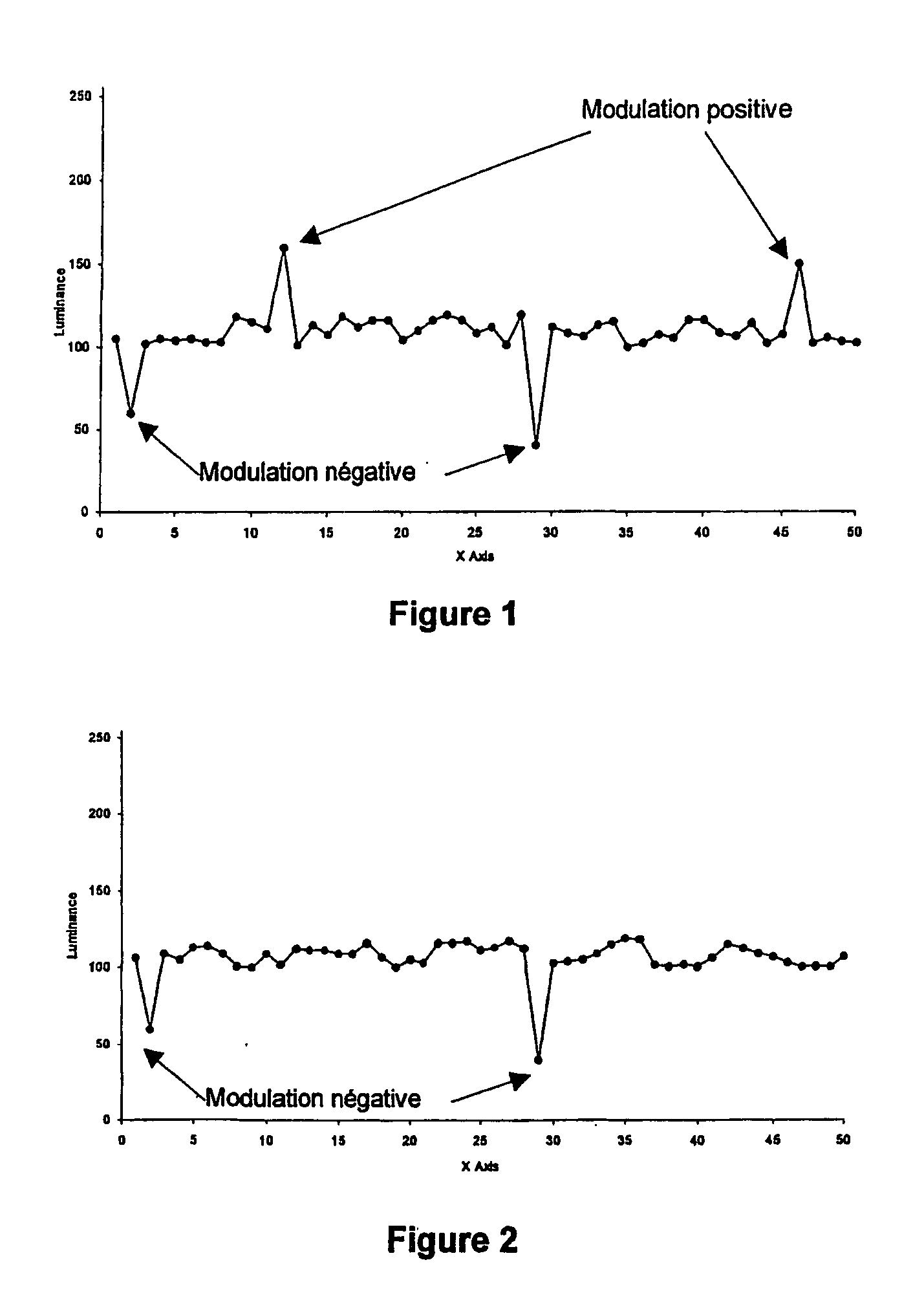
ActiveUS20040013285A1Decrease in luminanceDigitally marking record carriersOther printing matterEngineeringDocumentation
The invention describes a process to prevent counterfeiting or alteration of a printed or engraved surface, characterized by the incorporation of a signature of the form of a digital mark into parts or the entire document, and in particular a digital mark technology to hide information in an invisible way through over-printing by using a method called asymmetric amplitude modulation. This method can be applied to any type of printed material such paper, packaging, or any other surface. Visible information can also be printed over the digital mark. As an application example, applied to a paper document the digital mark can be used to guarantee the document authenticity, as it would be destroyed by a copy process.
Owner:ALPVISION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com