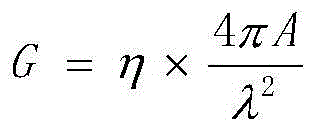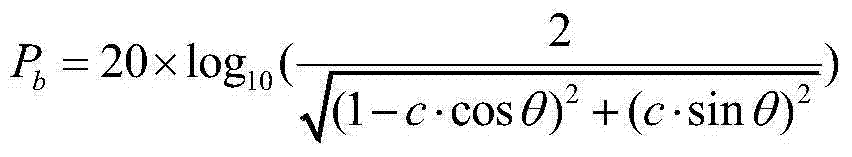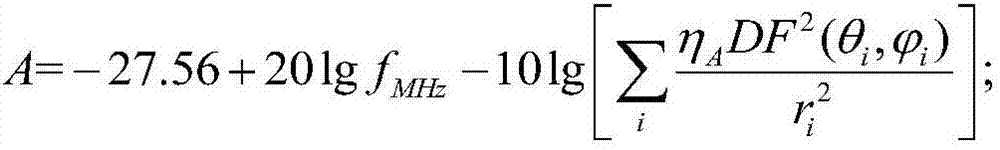Patents
Literature
82 results about "Equivalent isotropically radiated power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
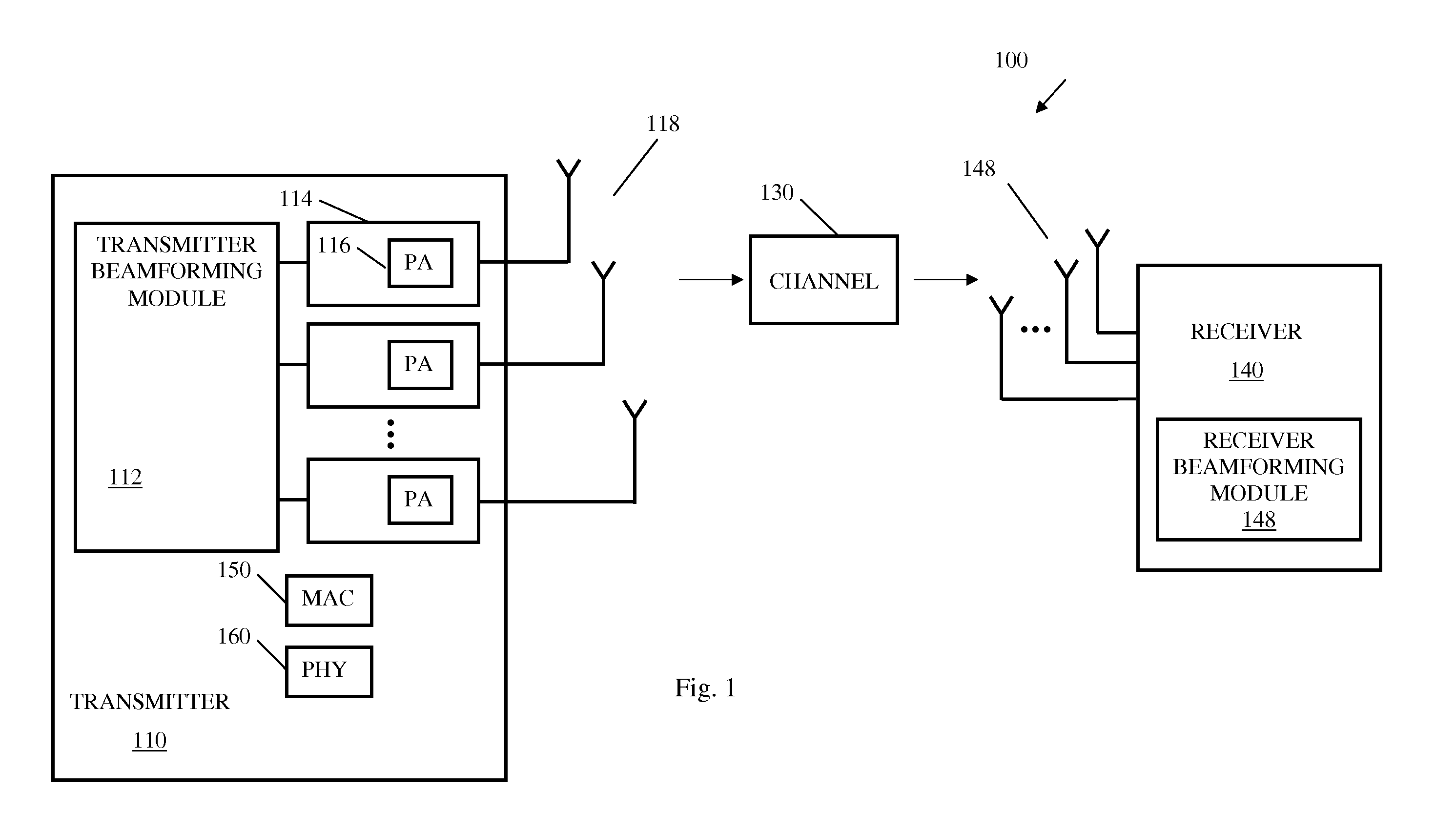
In radio communication systems, equivalent isotropically radiated power or, alternatively, effective isotropically radiated power is the amount of power that a theoretical isotropic antenna would emit to produce the peak power density observed in the direction of maximum antenna gain. EIRP can take into account the losses in transmission line and connectors and includes the gain of the antenna. The EIRP is often stated in terms of decibels over a reference power emitted by an isotropic radiator with an equivalent signal strength. The EIRP allows comparisons between different emitters regardless of type, size or form. From the EIRP, and with knowledge of a real antenna's gain, it is possible to calculate real power and field strength values. where and are in dBm, cable losses is in dB, and antenna gain is expressed in dBi, relative to a isotropic reference antenna. This example uses dBm, although it is also common to see dBW. Decibels are a convenient way to express the ratio between two quantities. dBm uses a reference of 1 mW and dBW uses a reference of 1 W. and A transmission output of 50 W is the same as 17 dBW or 47 dBm.
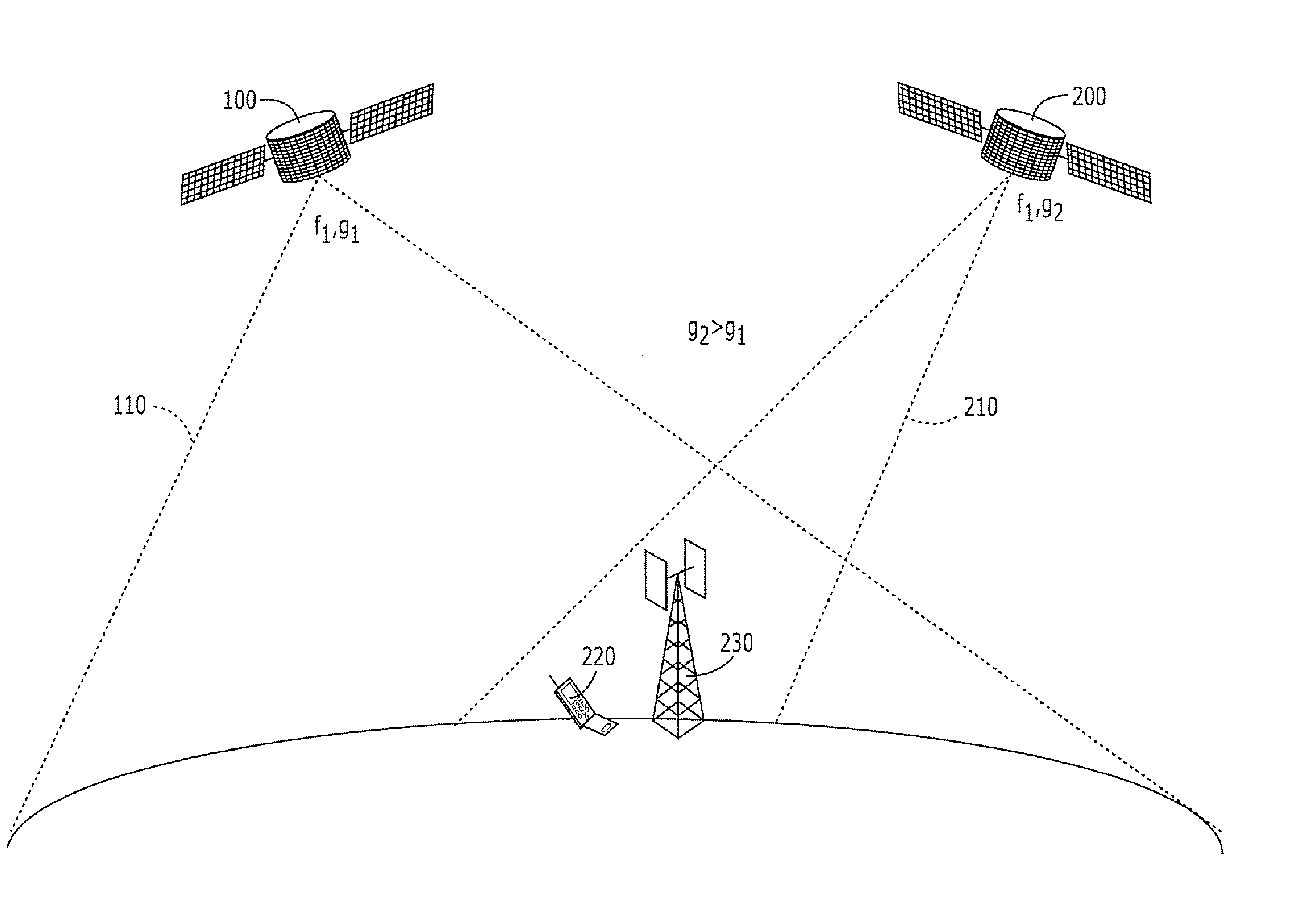
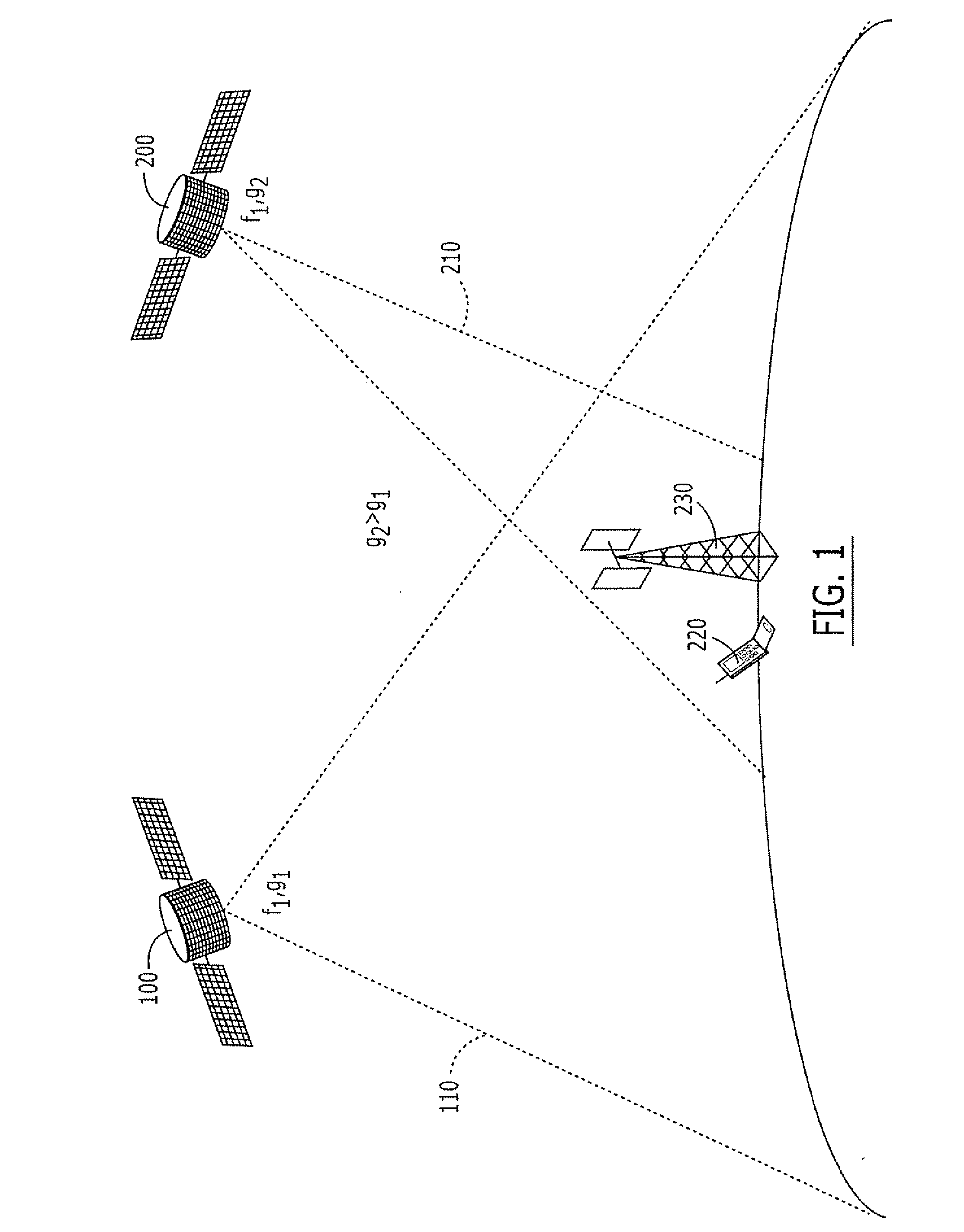
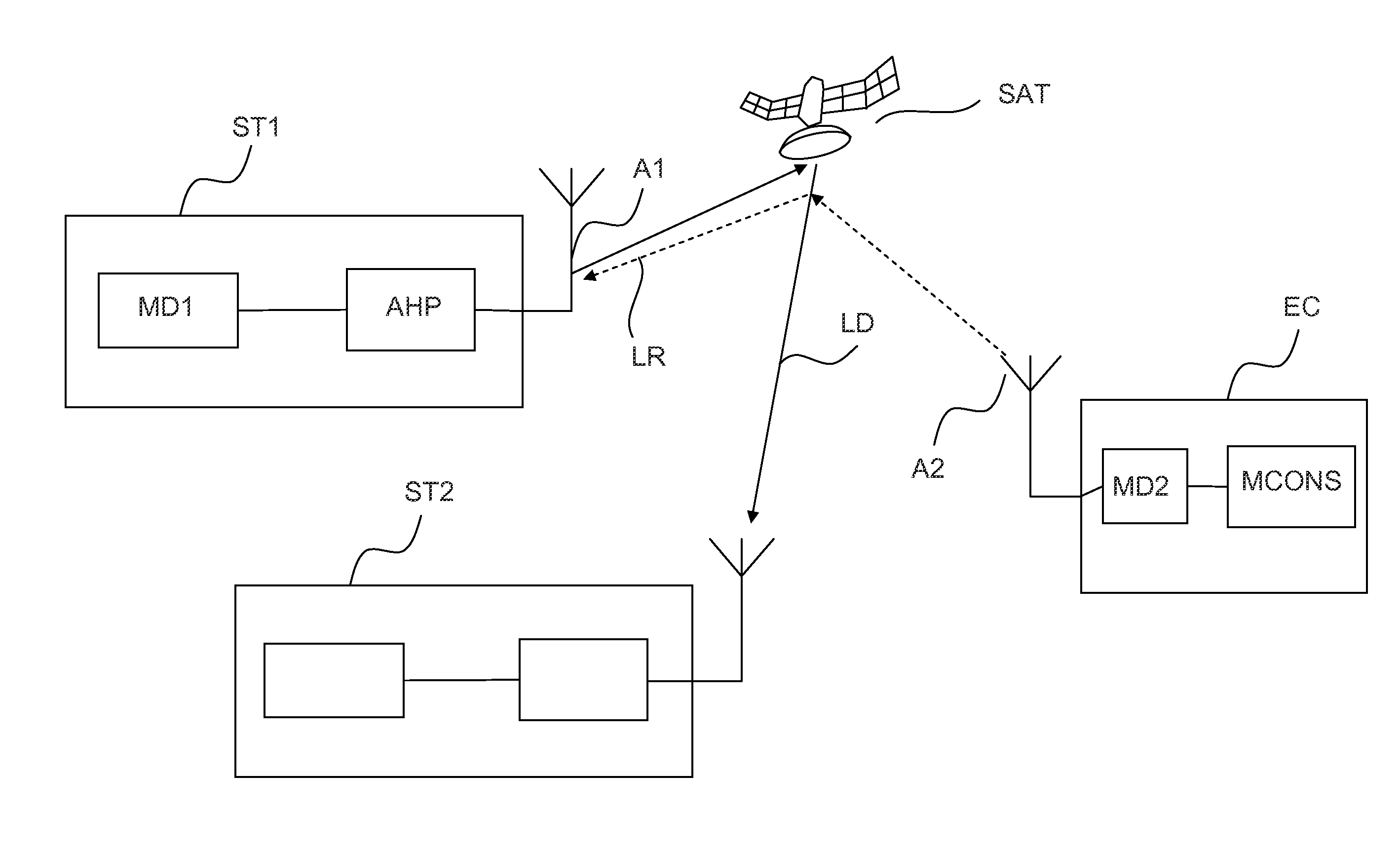
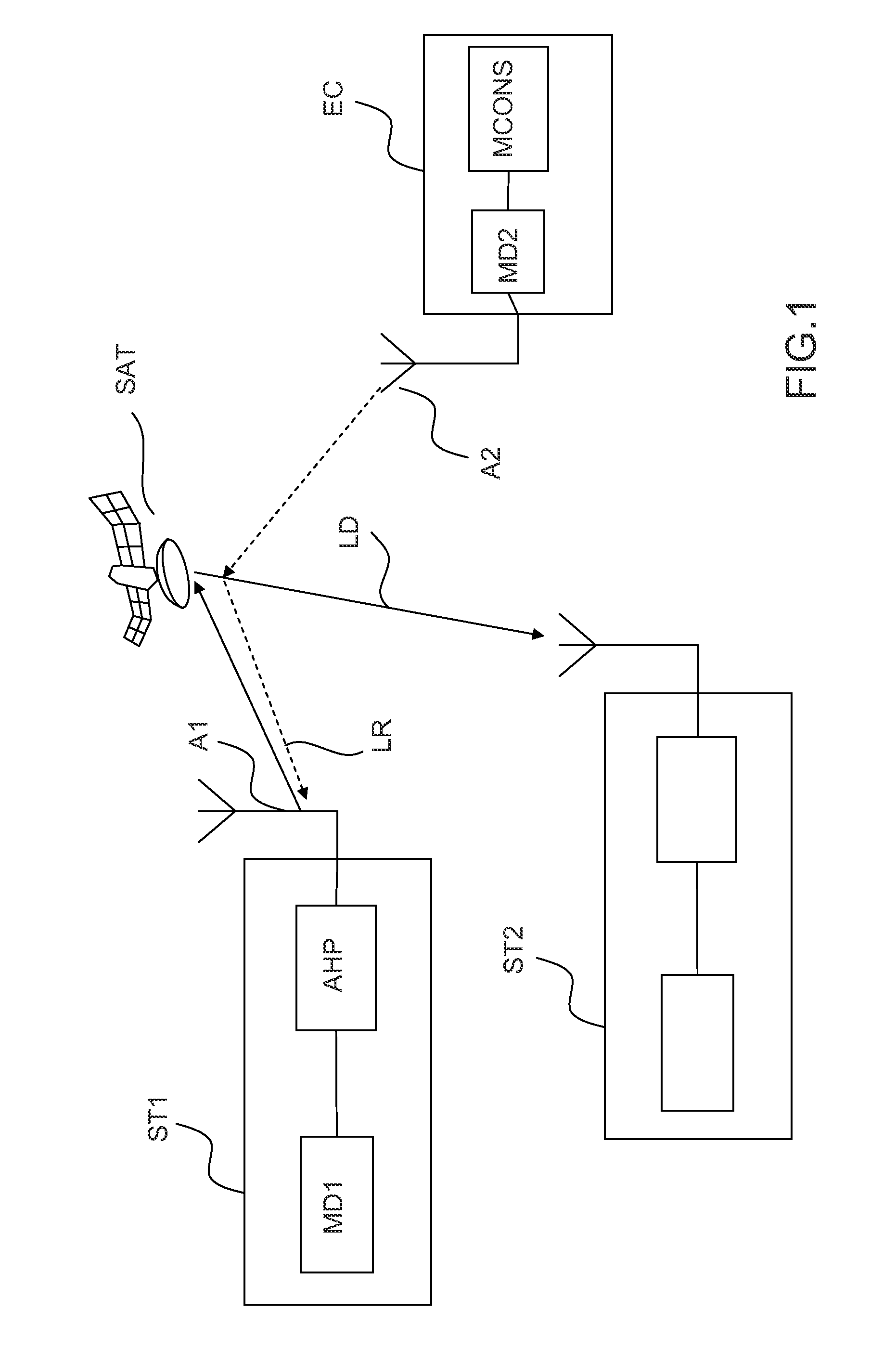
Systems and methods for inter-system sharing of satellite communications frequencies within a common footprint
ActiveUS20050064813A1Improve noiseIncrease aggregate noiseActive radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceCommunications system
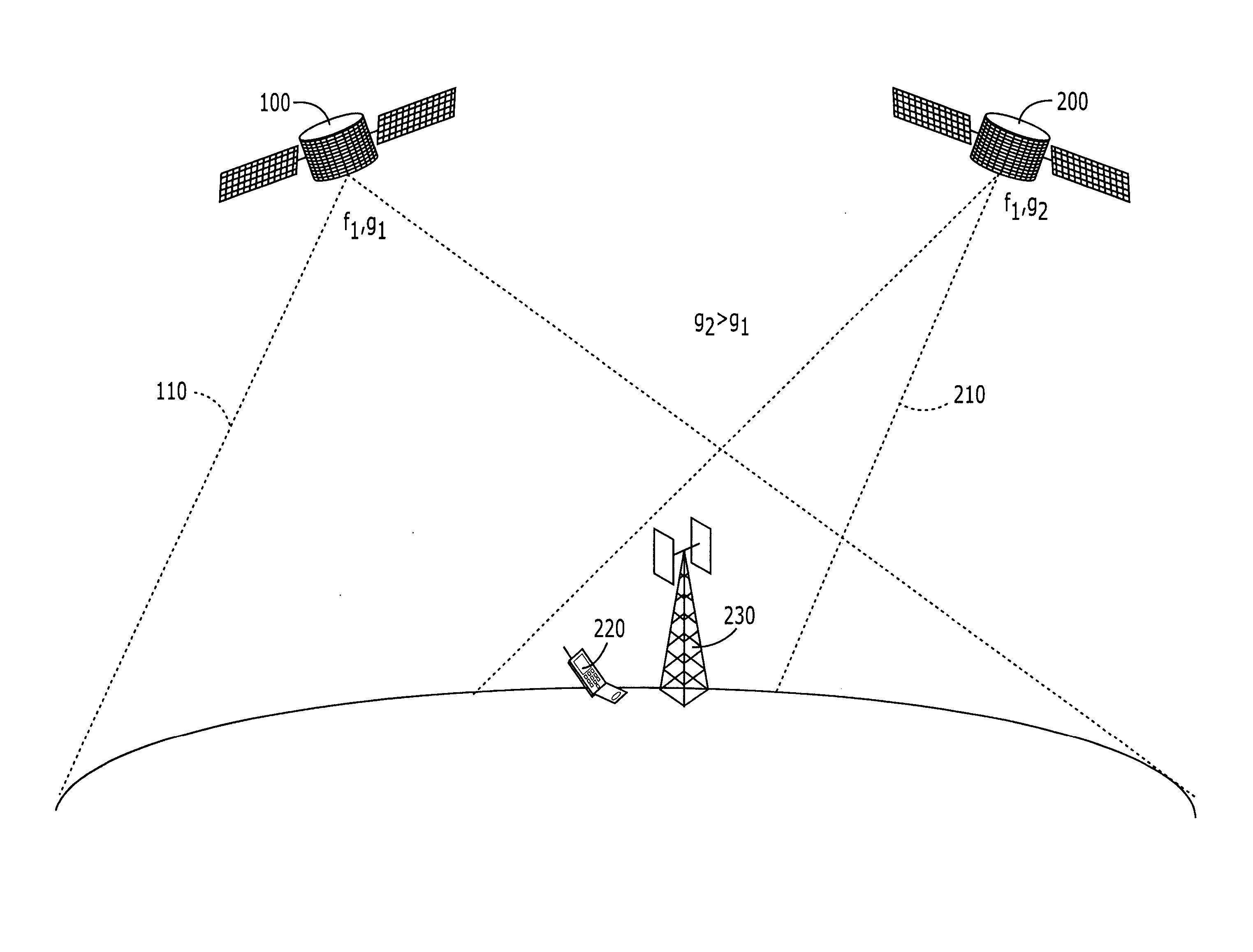
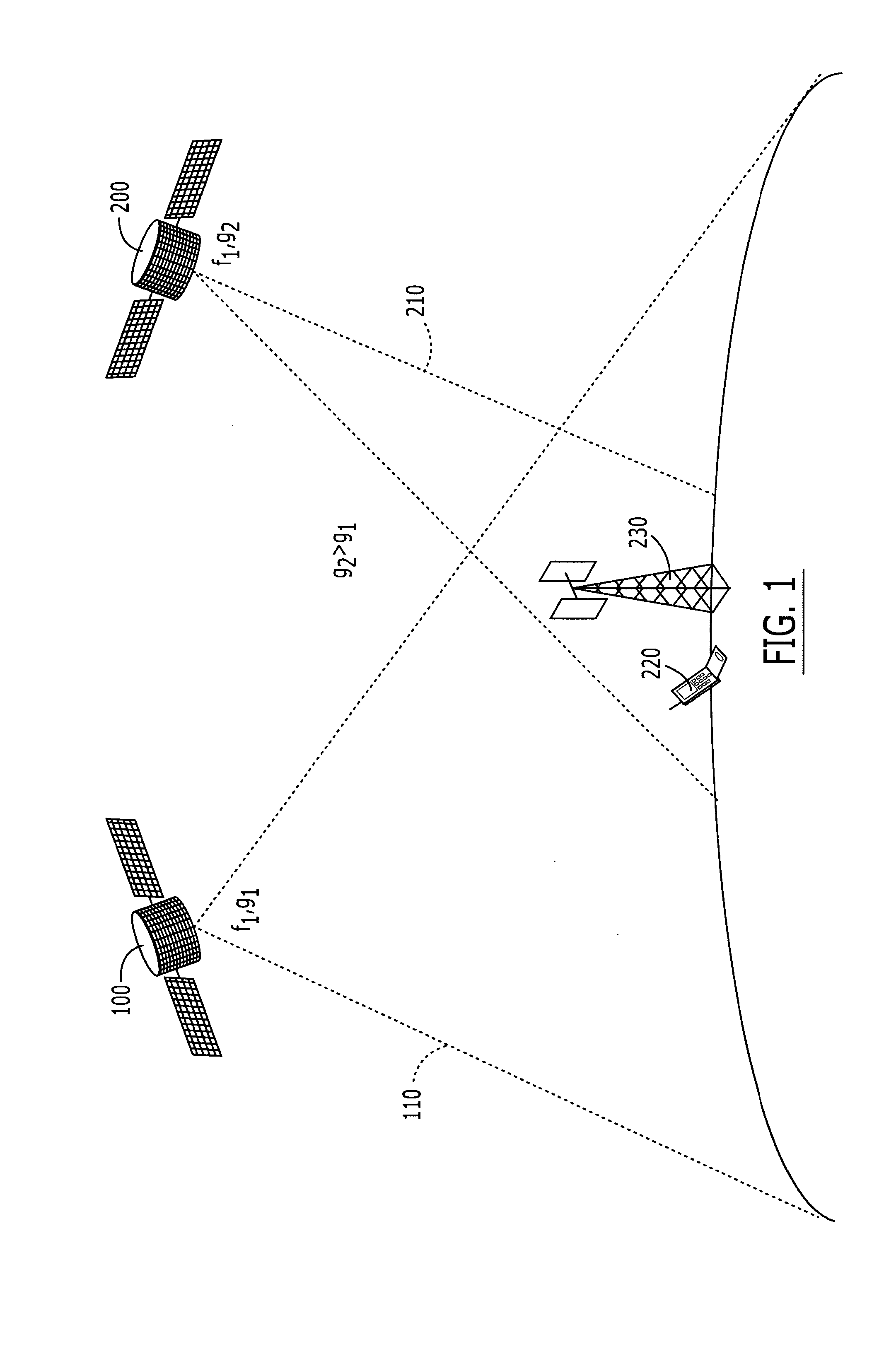
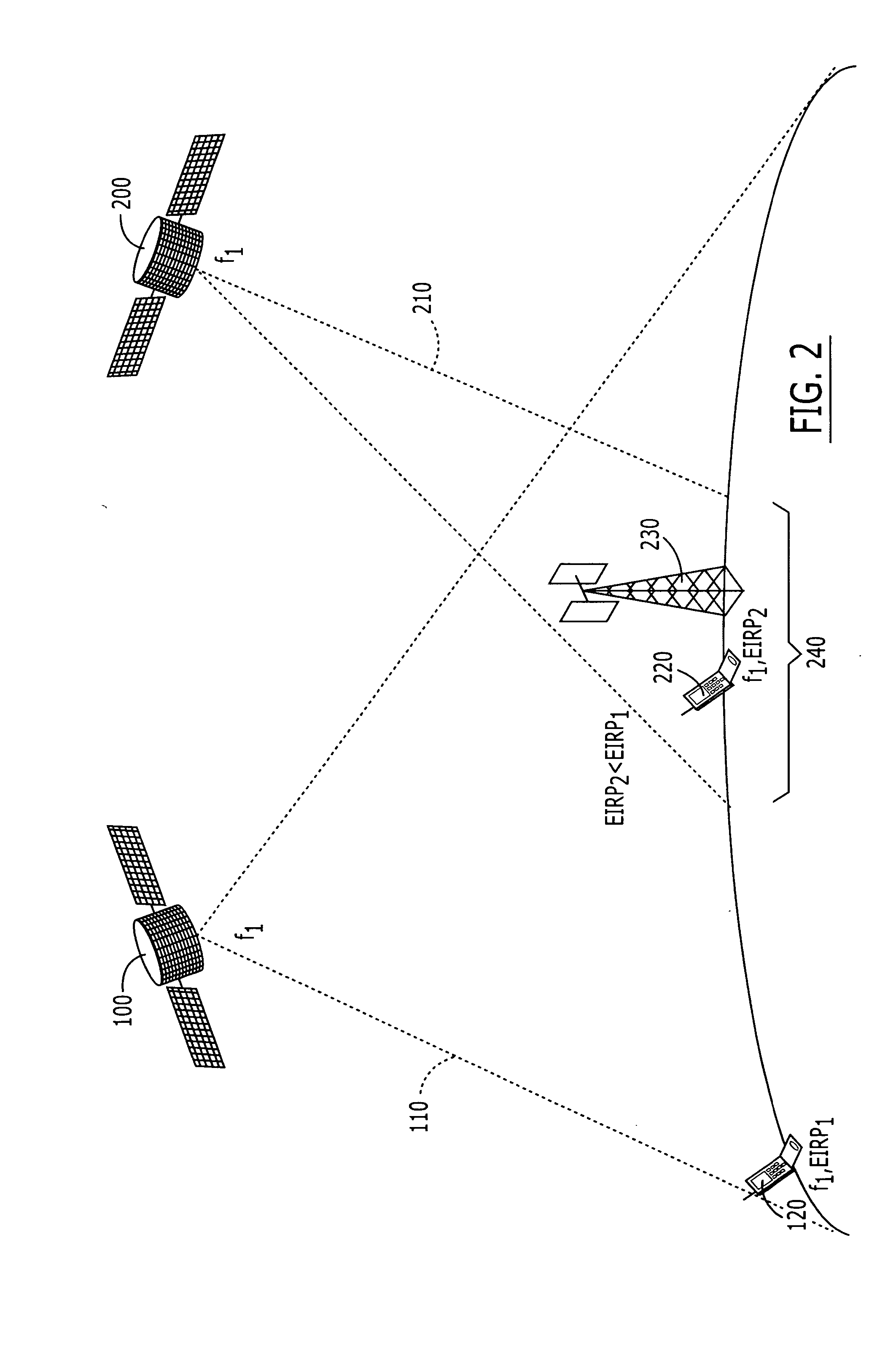
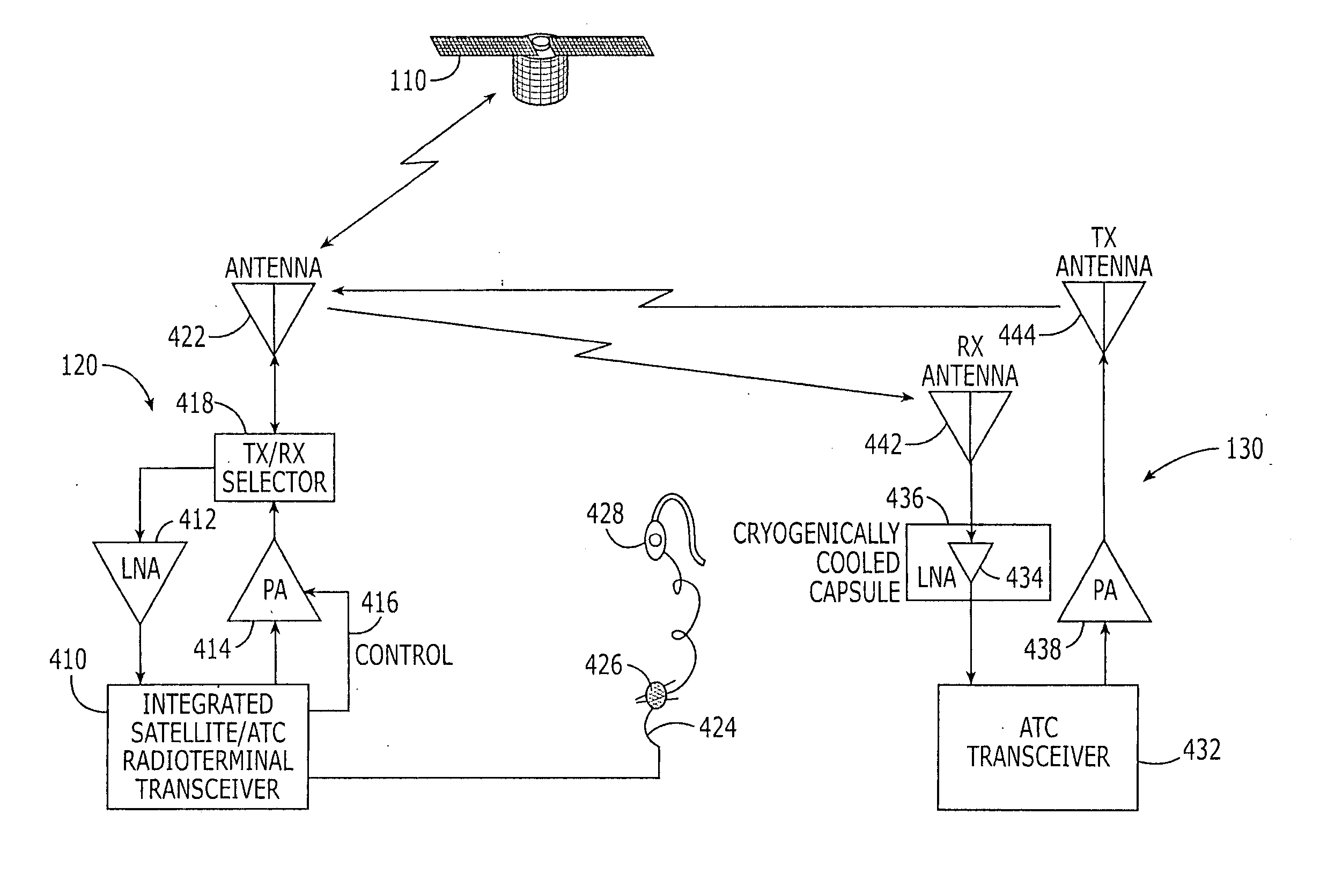
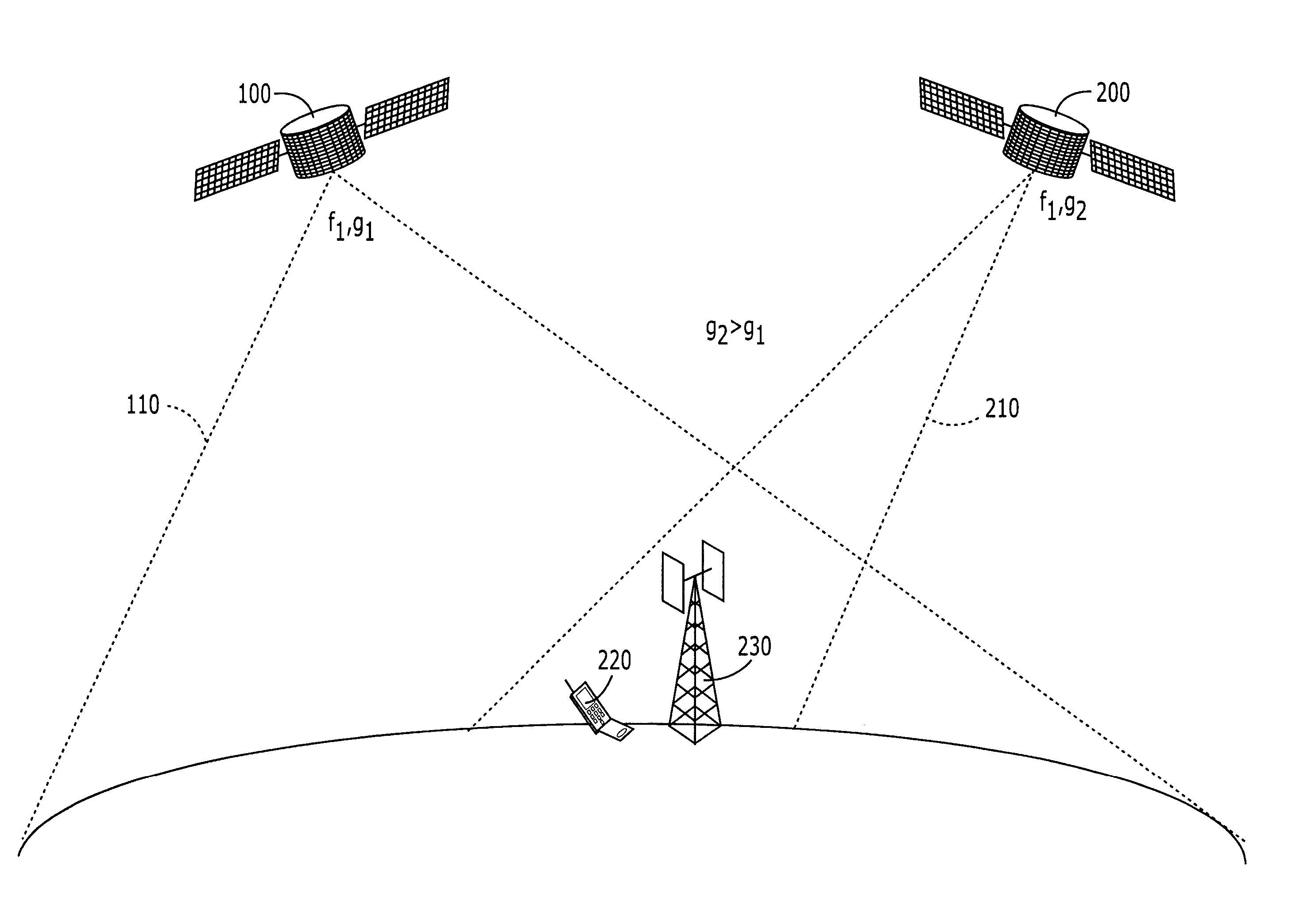
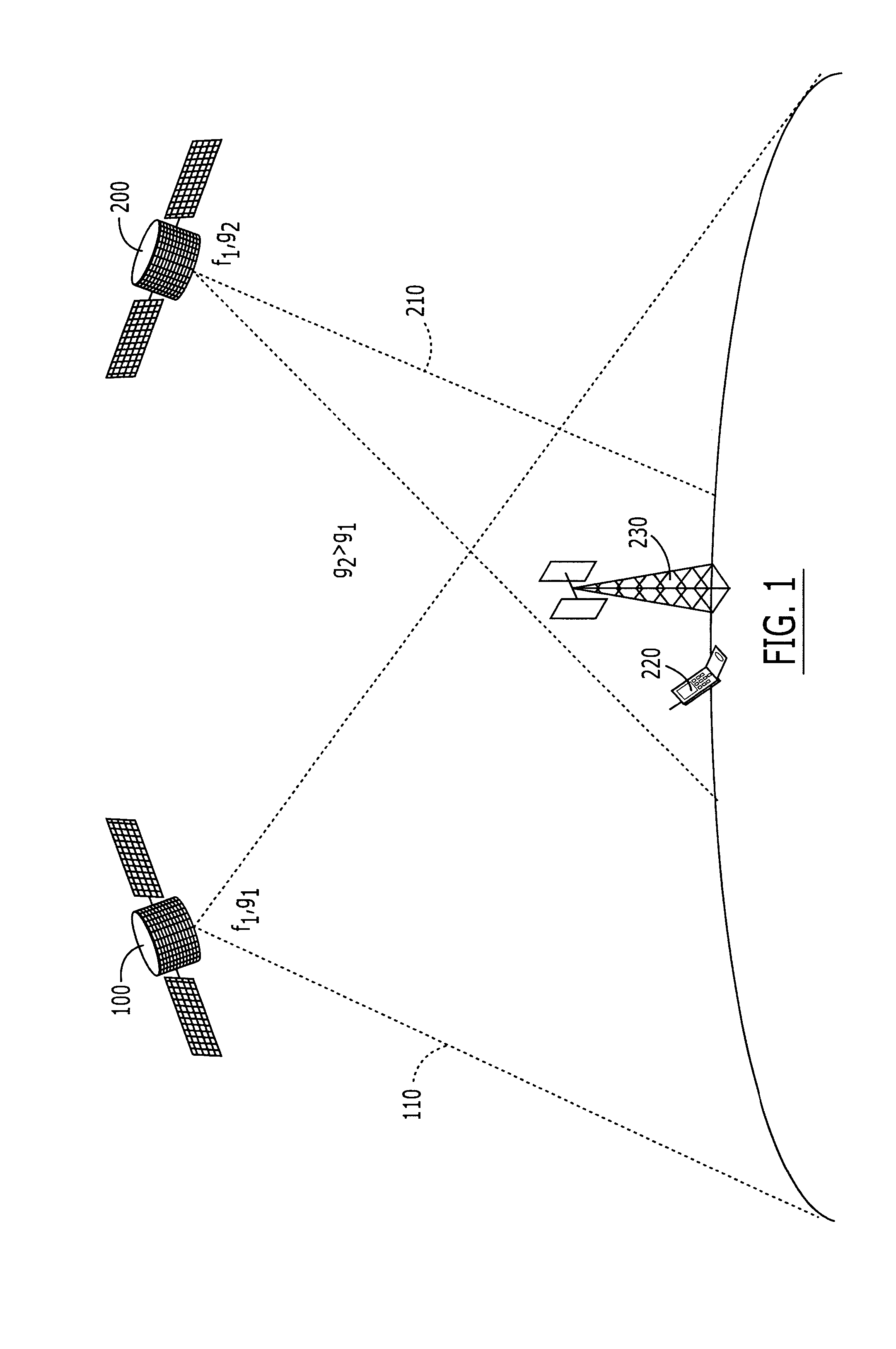
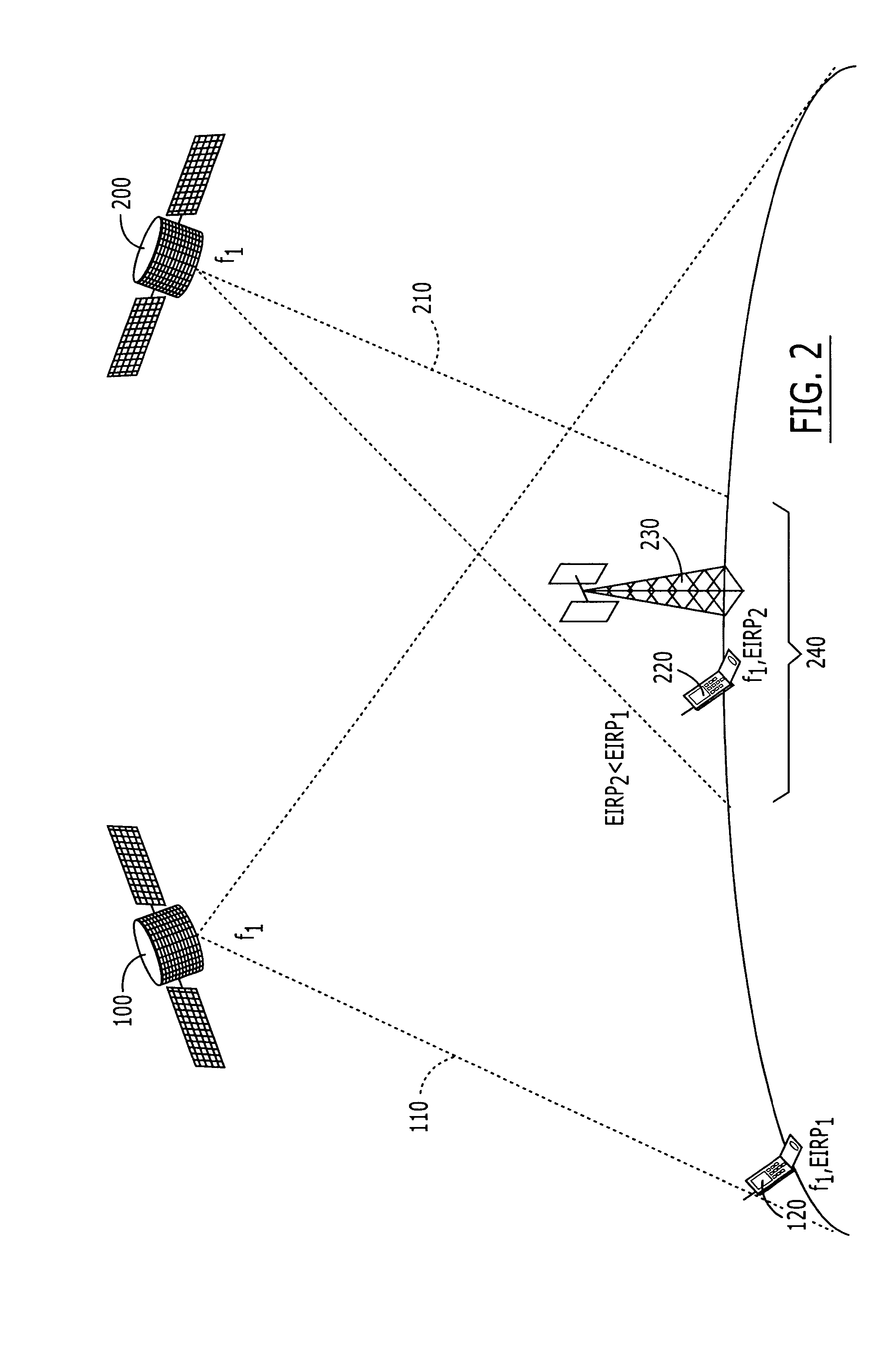
Two satellite communications systems can use the same frequency or frequencies in geographically overlapping footprints, without creating undue interference in a given system that is caused by the same frequency signal(s) that is / are used by the other system. In particular, an aggregate Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) of the radioterminals and / or ancillary terrestrial components of a second satellite communications system in the common footprint is sufficiently low, and / or the receive antenna gain of a first satellite communications system is sufficiently low compared to the receive antenna gain of the second satellite communications system, so as to increase an aggregate receiver noise that is seen by the first satellite system receivers by an amount that does not substantially change a Quality of Service (QoS) of the first satellite communications system.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
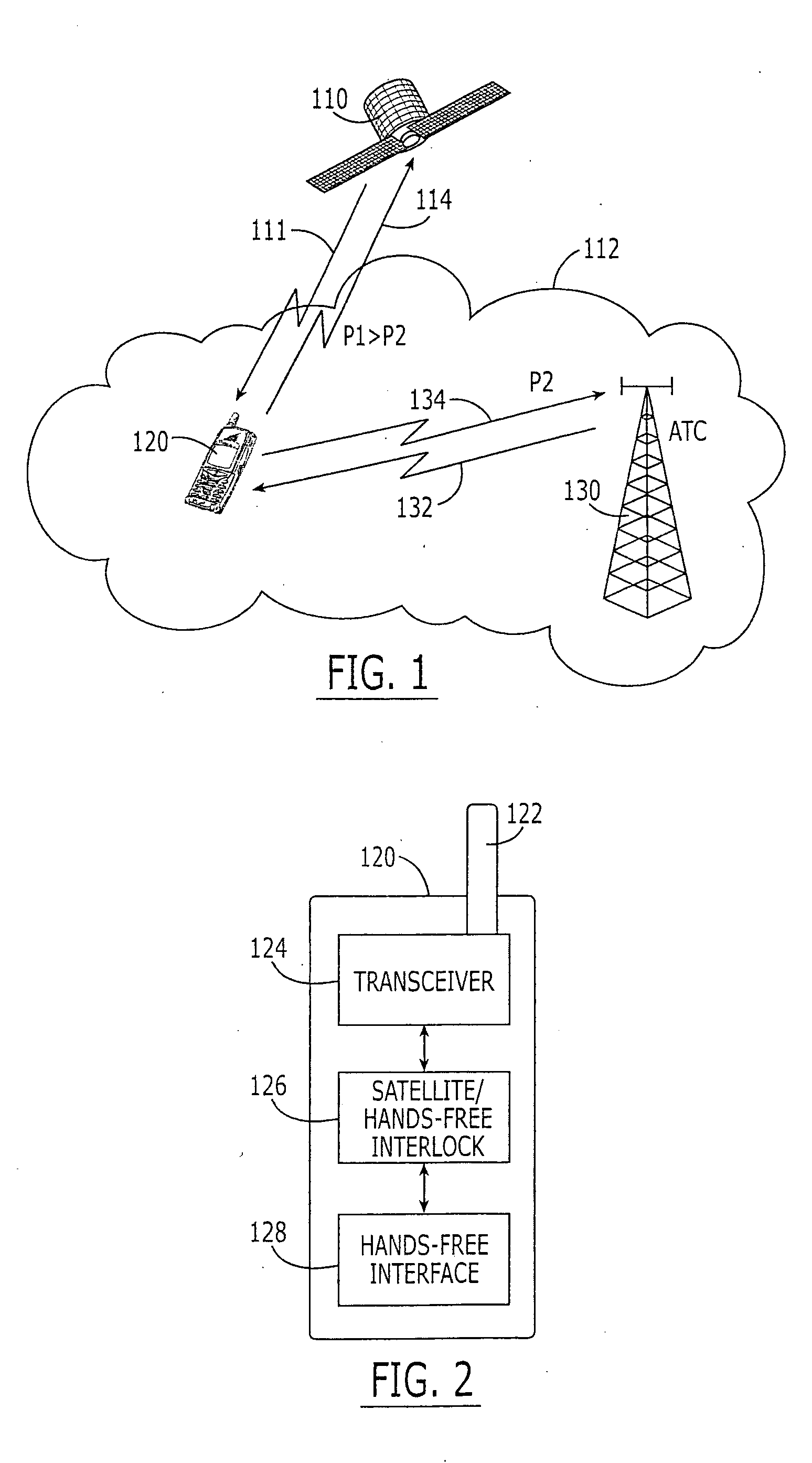
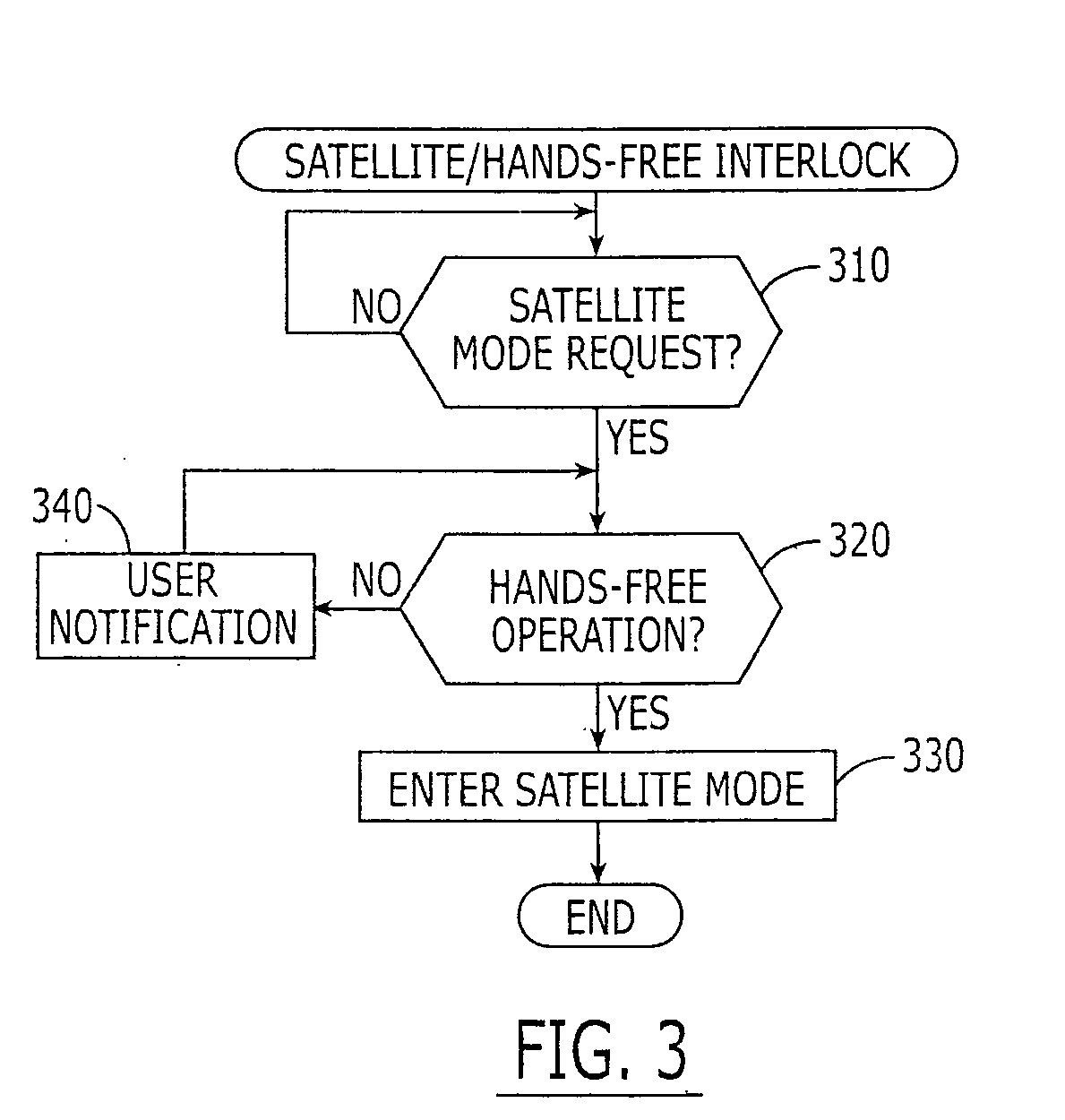
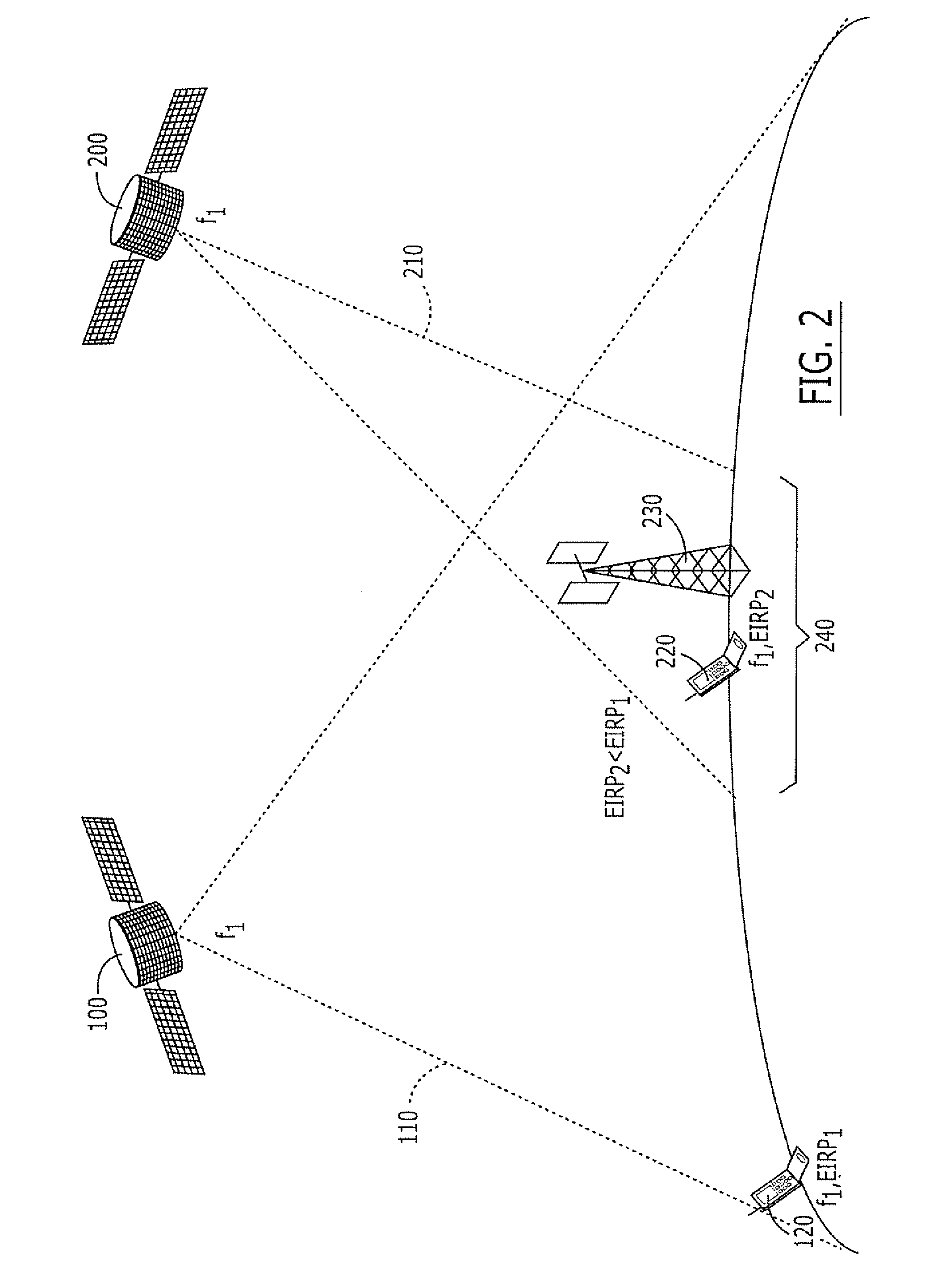
Satellite/hands-free interlock systems and/or companion devices for radioterminals and related methods
ActiveUS20050239404A1Avoid spreadingAvoid communicationPower managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverHand held
A radioterminal may include a transceiver, a hand-held interface coupled to the transceiver, and an interlock coupled to the transceiver. The transceiver may be configured to transmit and receive wireless communications, and the transceiver may be further configured to transmit high power communications at a high maximum power and / or EIRP and to transmit low power communications at a low maximum power and / or EIRP. The interlock may be configured to prevent the transceiver from transmitting high power communications at a power and / or EIRP that exceeds a threshold when the hand-held interface is activated. Related methods are also discussed.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
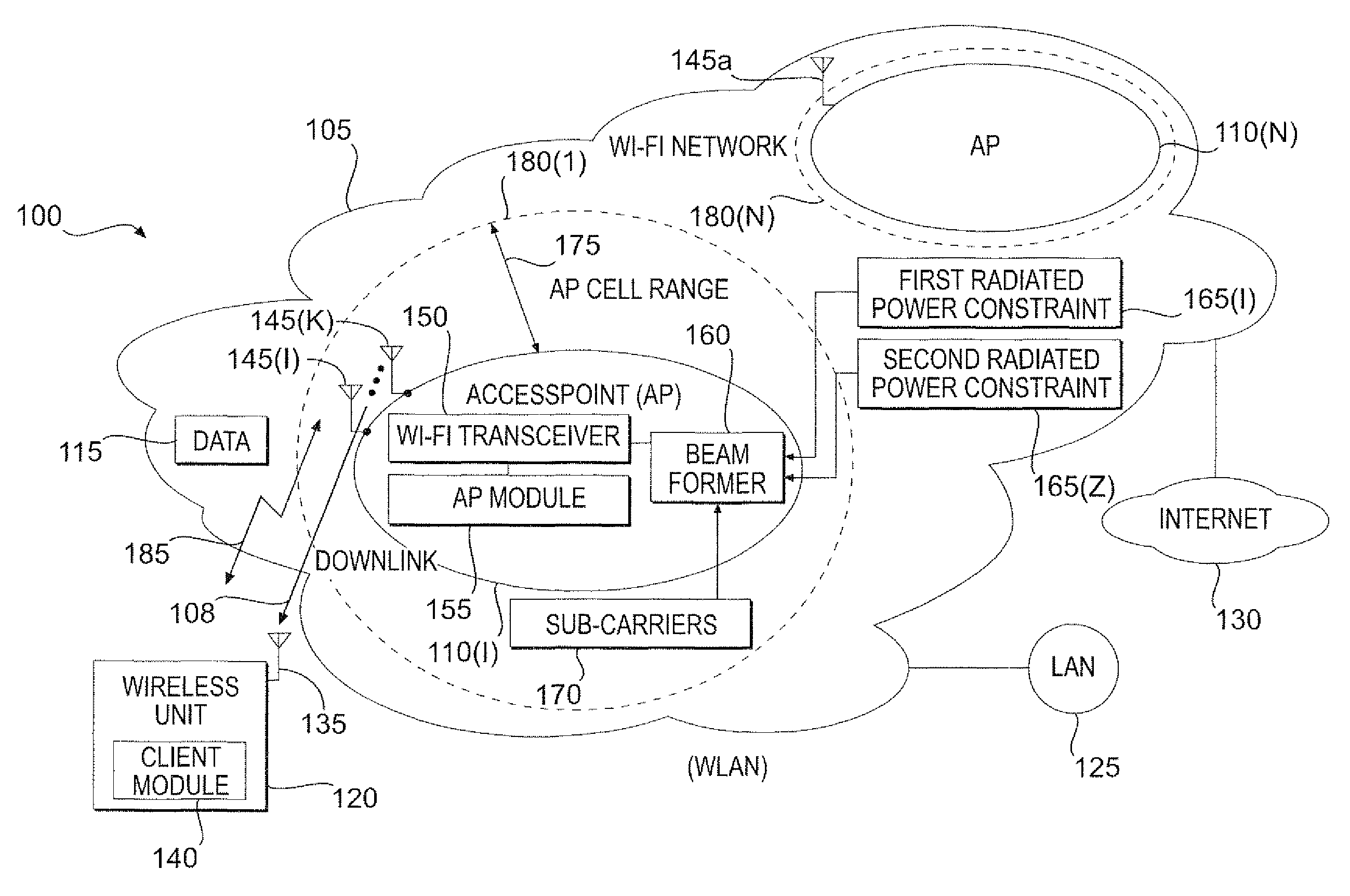
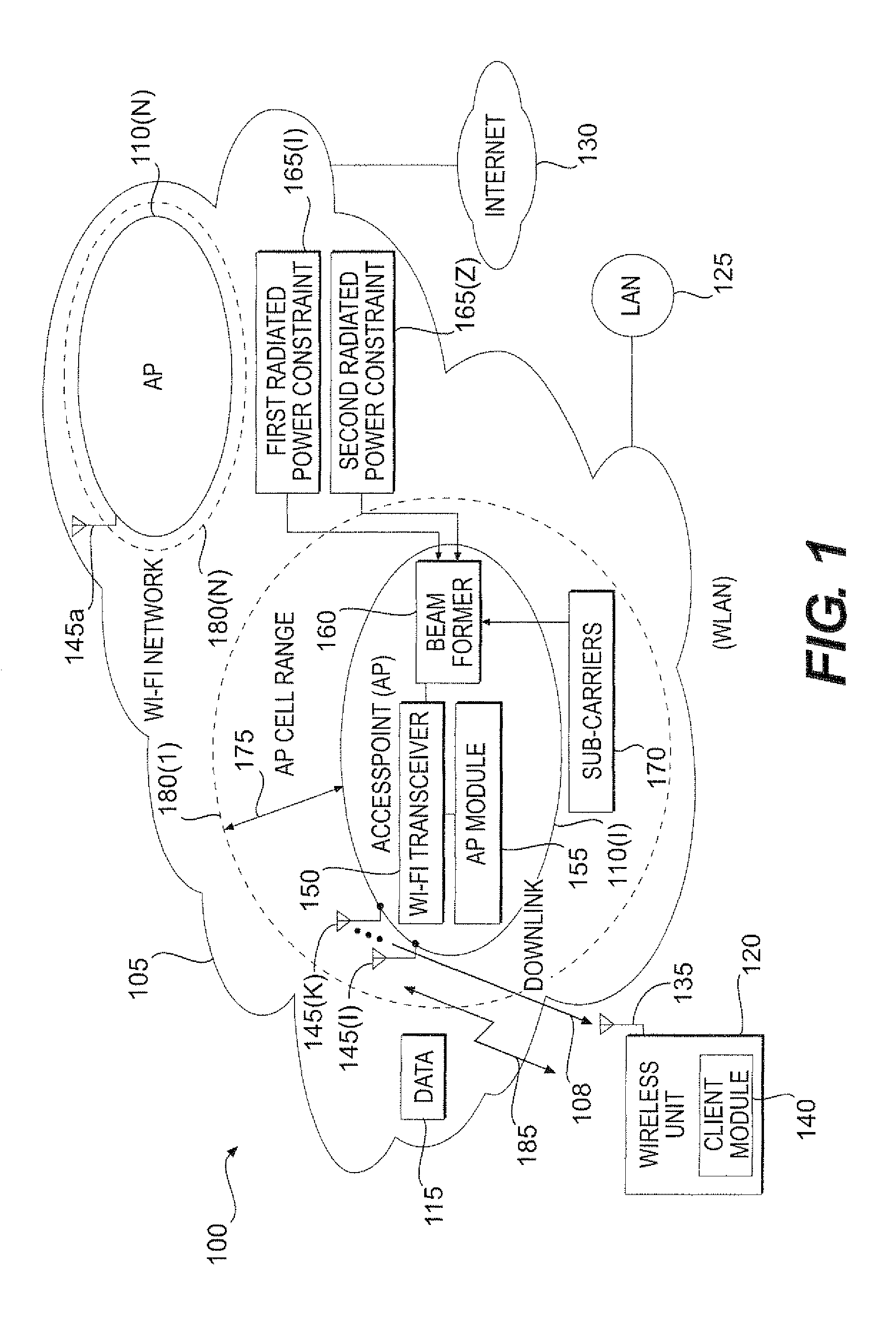
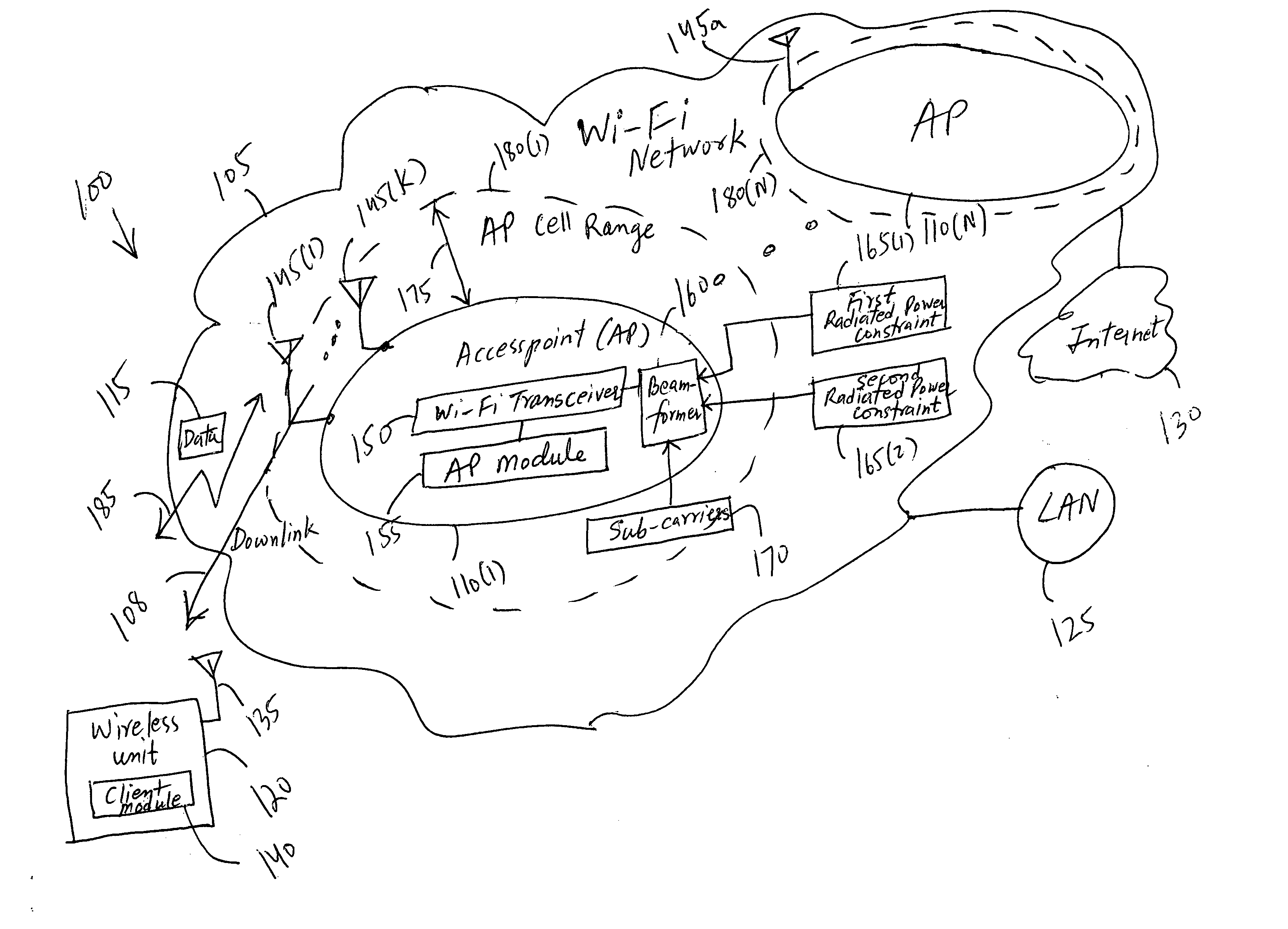
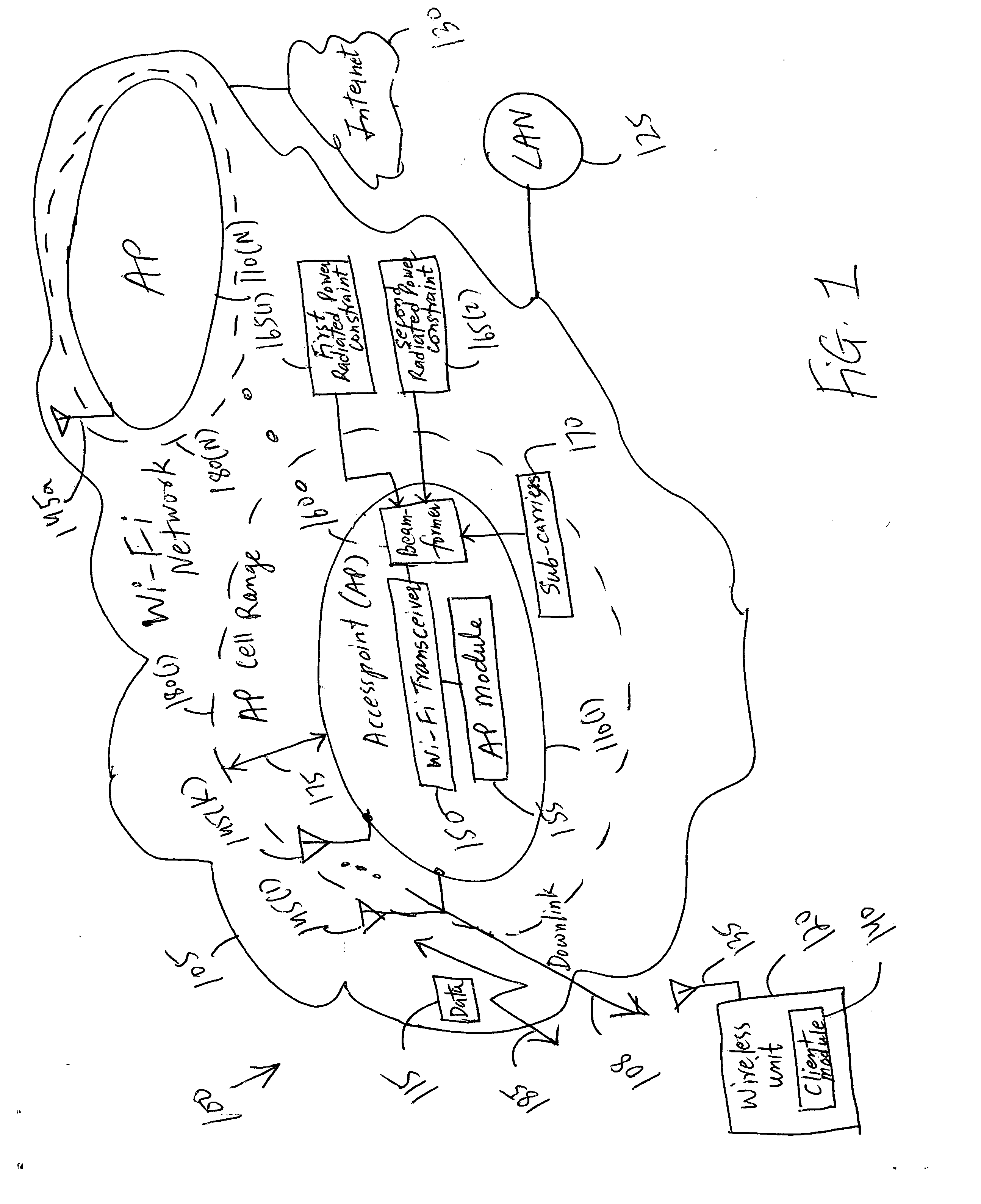
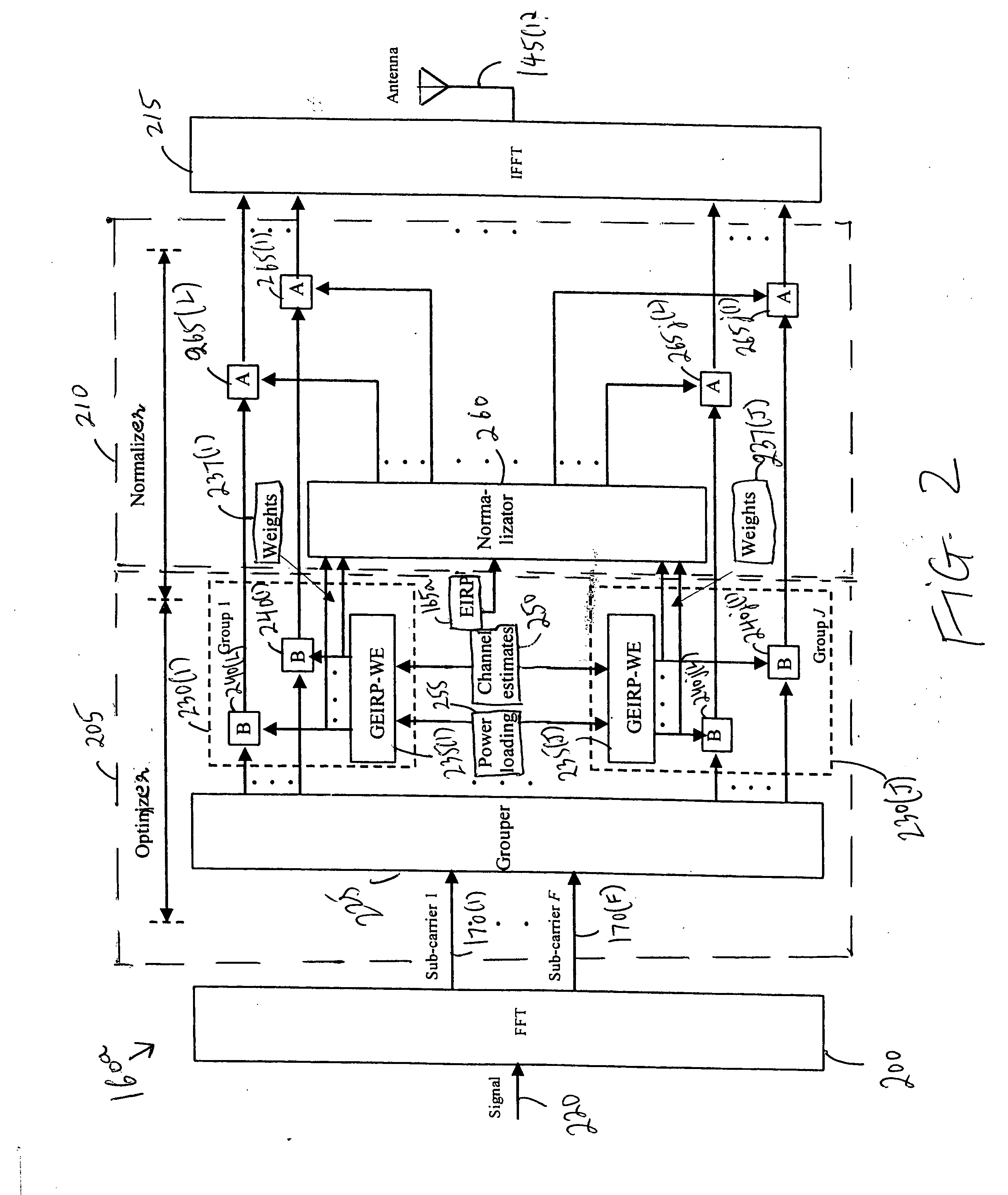
Increasing the range of access point cells for a given throughput in a downlink of a wireless local area network
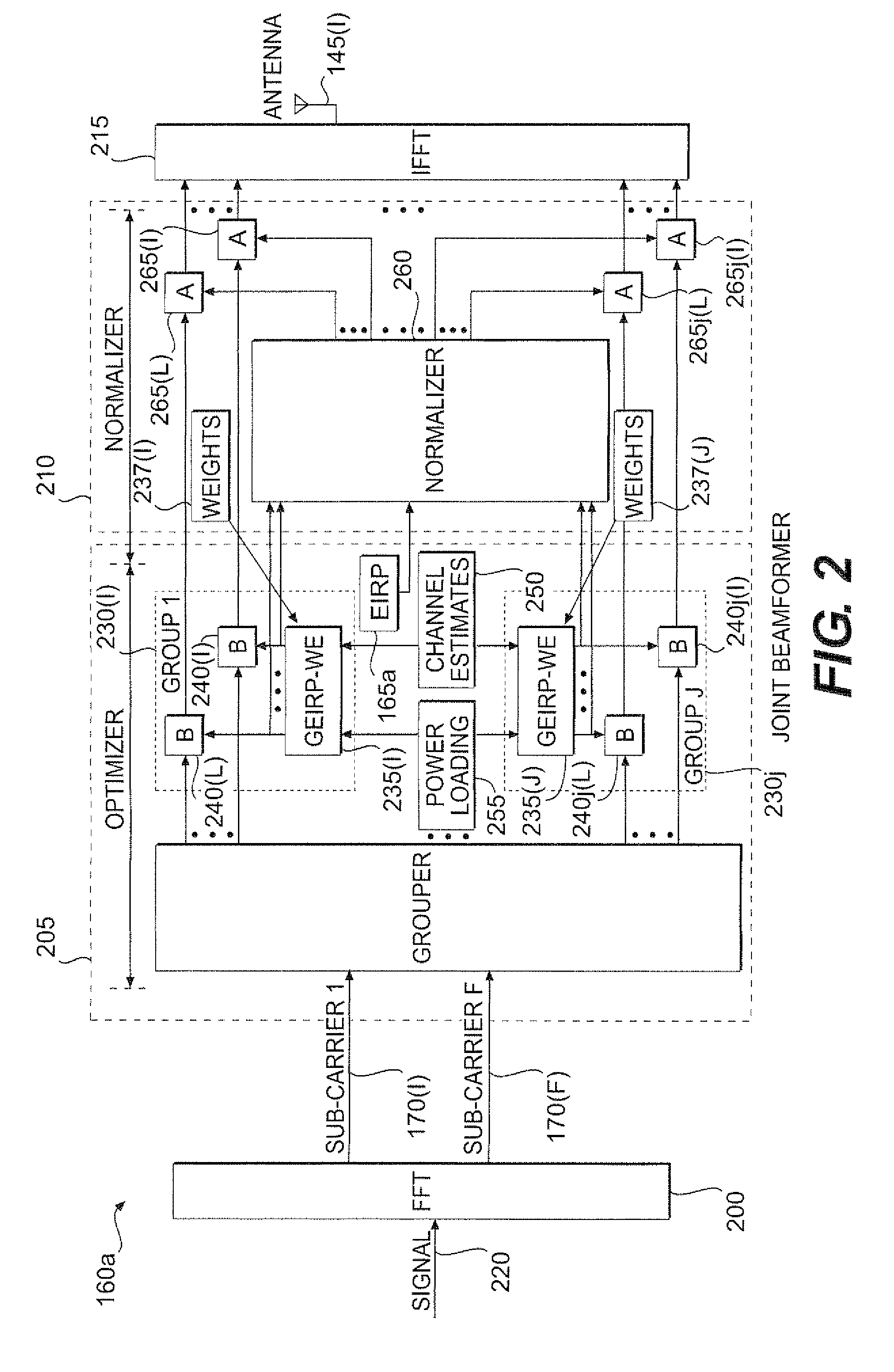
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus may increase or extend the range of wireless communication cells for a given throughput in a downlink of a wireless communication system. When transmitting data in a downlink of a plurality of access point cells in a wireless local area network (WLAN), the range of the downlink may be increased for a given throughput under one or more radiated power constraints. The method includes providing a plurality of antennas at an access point to transmit the data to a wireless unit under at least one of a first and a second radiated power constraints. The method further includes using the plurality of antennas for beamforming over a group of sub-carriers subject to the first and / or second radiated power constraints. Under one or more radiated power constraints, a multiple antenna based beamforming may extend the range of a wireless communication for a user of a wireless unit that may be located within a coverage area across the plurality of access point cells of a Wi-Fi network associated with the WLAN. A joint beamforming optimized over all of sub-carriers may account for a European regulation restriction into at least one of an averaged and a spectral density Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) constraint. In this way, an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) based joint beamformer may provide a significant performance improvement and range extension.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Systems and methods for inter-system sharing of satellite communications frequencies within a common footprint
ActiveUS7113743B2Improve noiseReduce aggregationActive radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceCommunications system
Two satellite communications systems can use the same frequency or frequencies in geographically overlapping footprints, without creating undue interference in a given system that is caused by the same frequency signal(s) that is / are used by the other system. In particular, an aggregate Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) of the radioterminals and / or ancillary terrestrial components of a second satellite communications system in the common footprint is sufficiently low, and / or the receive antenna gain of a first satellite communications system is sufficiently low compared to the receive antenna gain of the second satellite communications system, so as to increase an aggregate receiver noise that is seen by the first satellite system receivers by an amount that does not substantially change a Quality of Service (QoS) of the first satellite communications system.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Systems and Methods for Inter-System Sharing of Satellite Communications Frequencies Within a Common Footprint
ActiveUS20060246838A1Improve noiseReduce aggregationRadiating elements structural formsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceCommunications system
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Increasing the range of access point cells for a given throughput in a downlink of a wireless local area network
InactiveUS20070077968A1Well formedSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus may increase or extend the range of wireless communication cells for a given throughput in a downlink of a wireless communication system. When transmitting data in a downlink of a plurality of access point cells in a wireless local area network (WLAN), the range of the downlink may be increased for a given throughput under one or more radiated power constraints. The method includes providing a plurality of antennas at an access point to transmit the data to a wireless unit under at least one of a first and a second radiated power constraints. The method further includes using the plurality of antennas for bearnforming over a group of sub-carriers subject to the first and / or second radiated power constraints. Under one or more radiated power constraints, a multiple antenna based beamforming may extend the range of a wireless communication for a user of a wireless unit that may be located within a coverage area across the plurality of access point cells of a Wi-Fi network associated with the WLAN. A joint beamforming optimized over all of sub-carriers may account for a European regulation restriction into at least one of an averaged and a spectral density Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) constraint. In this way, an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) based joint beamformer may provide a significant performance improvement and range extension.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
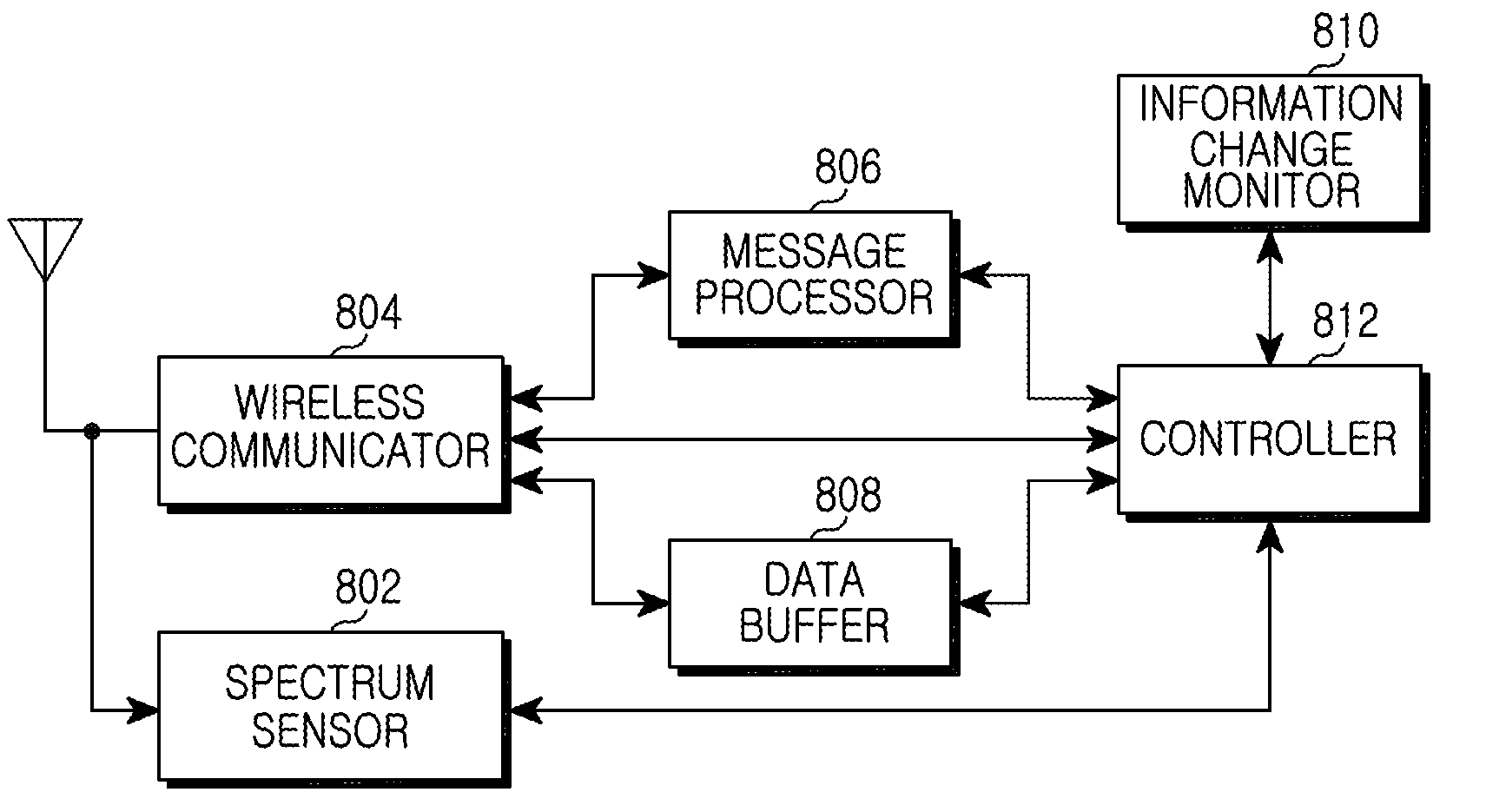
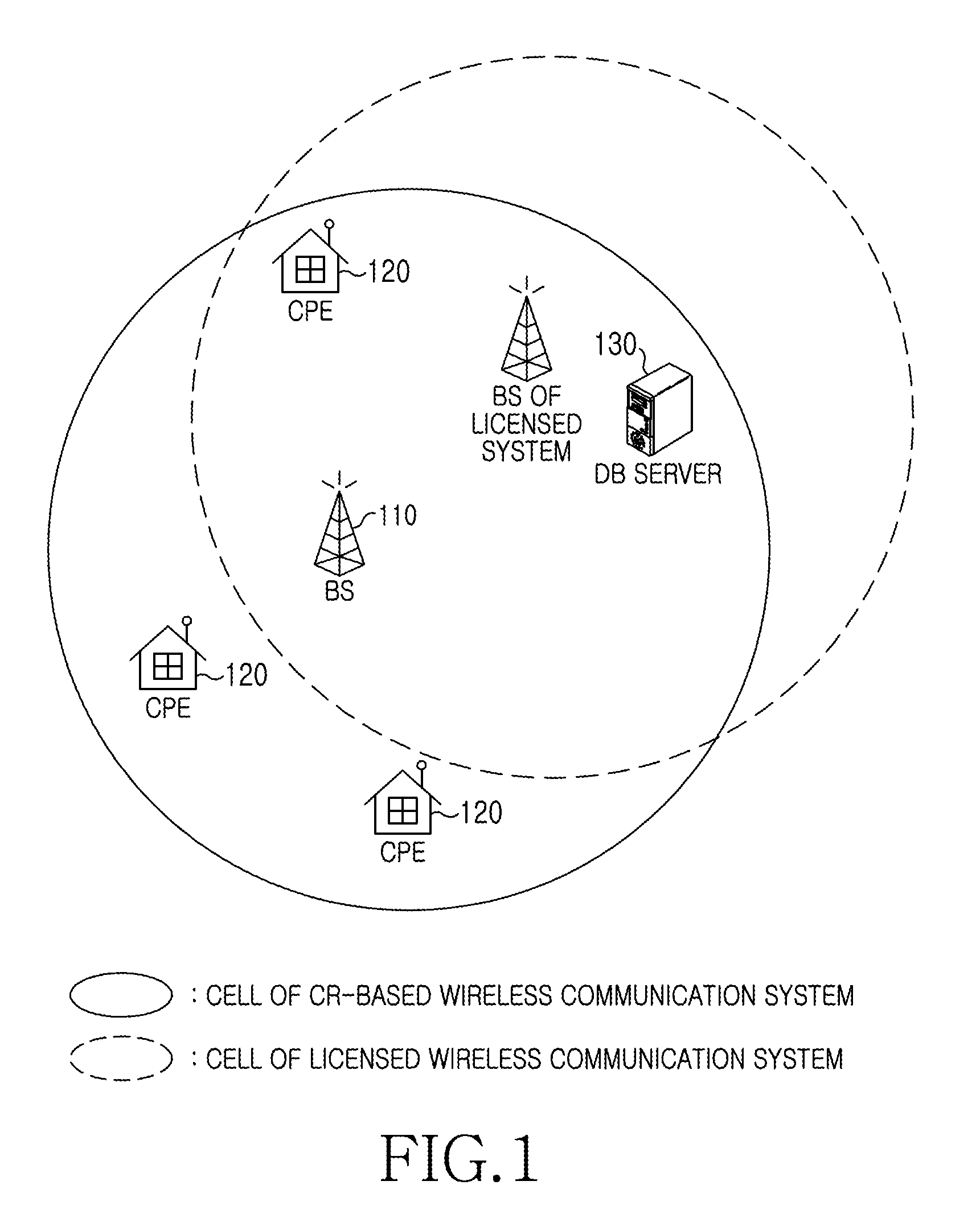
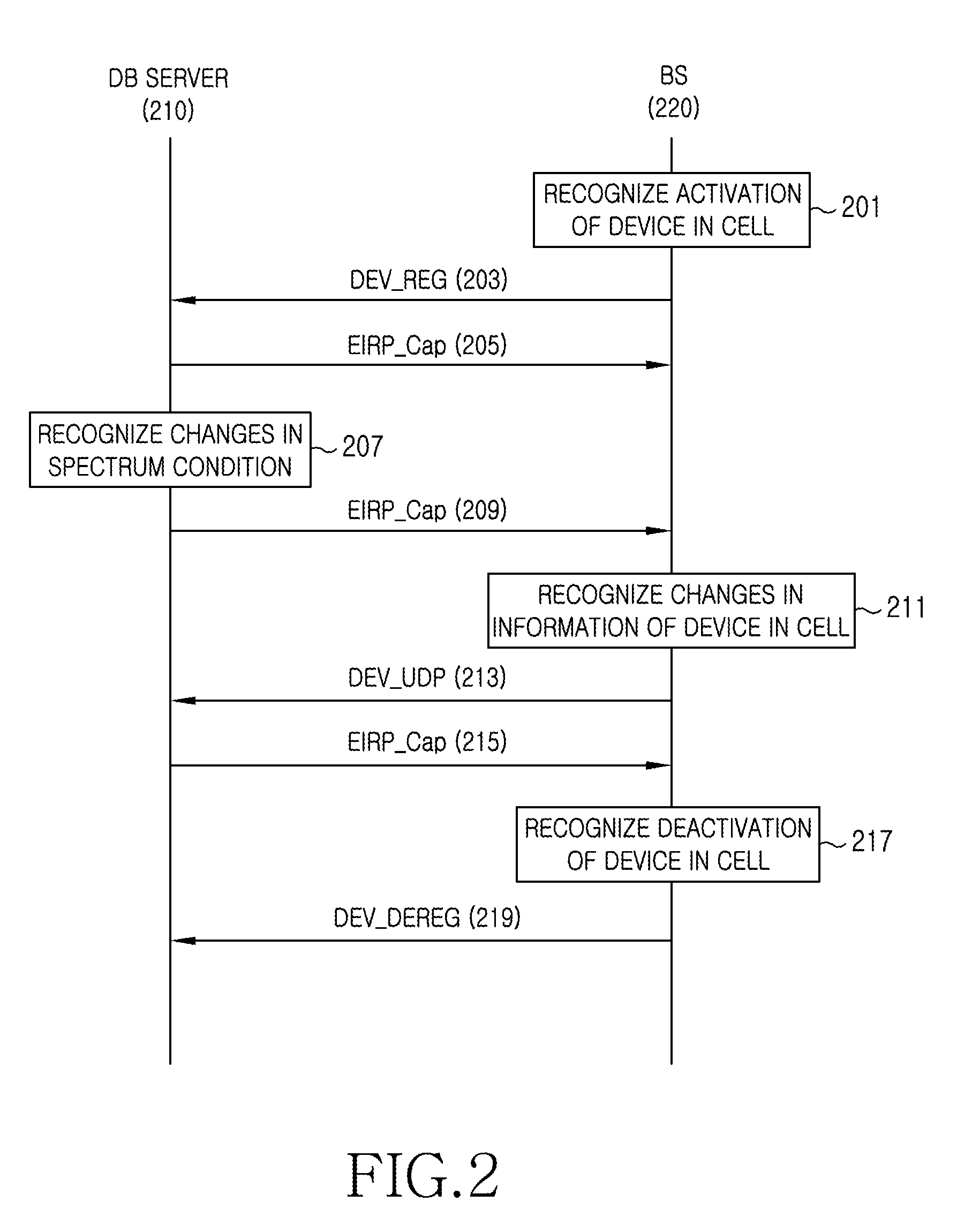
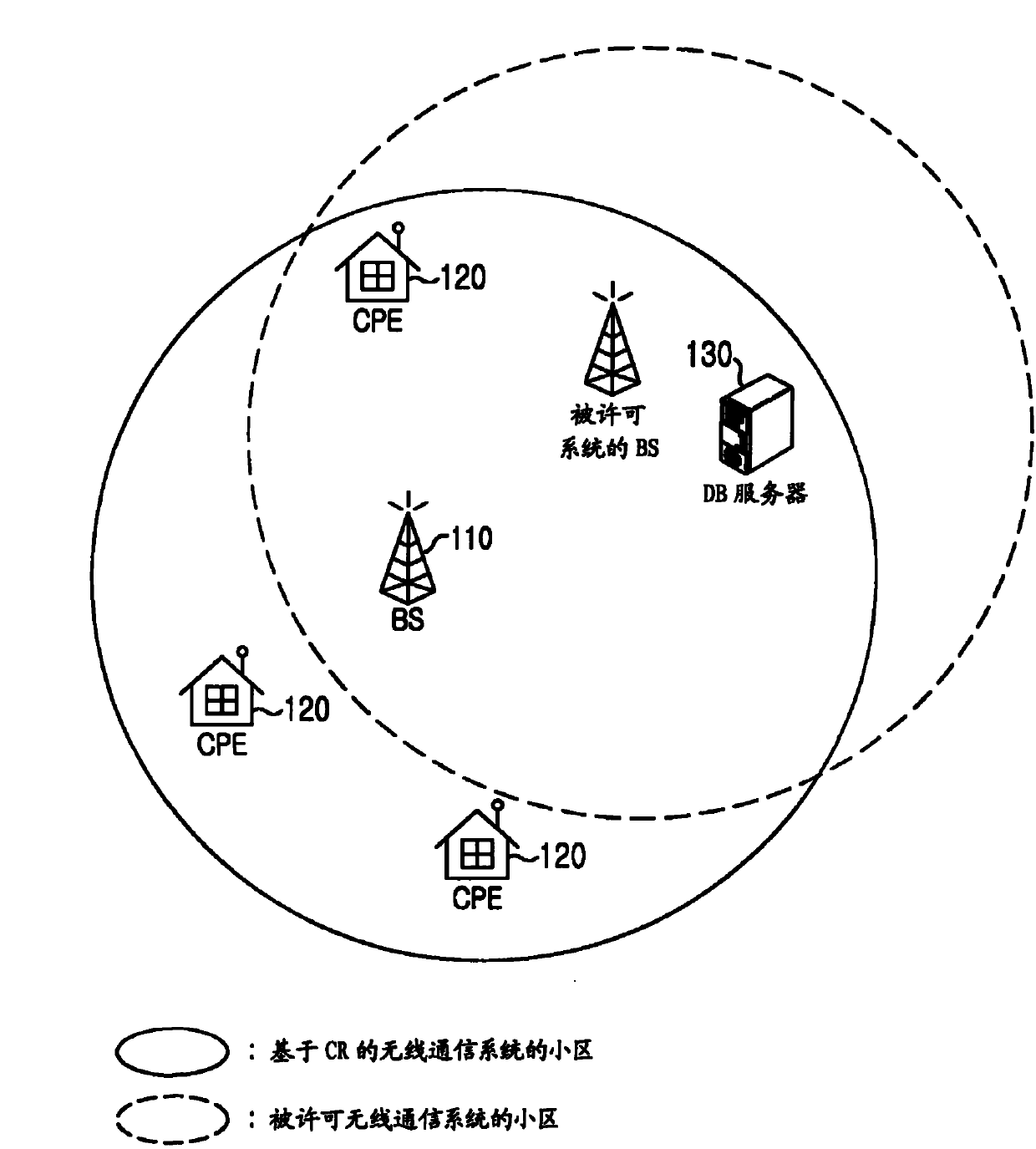
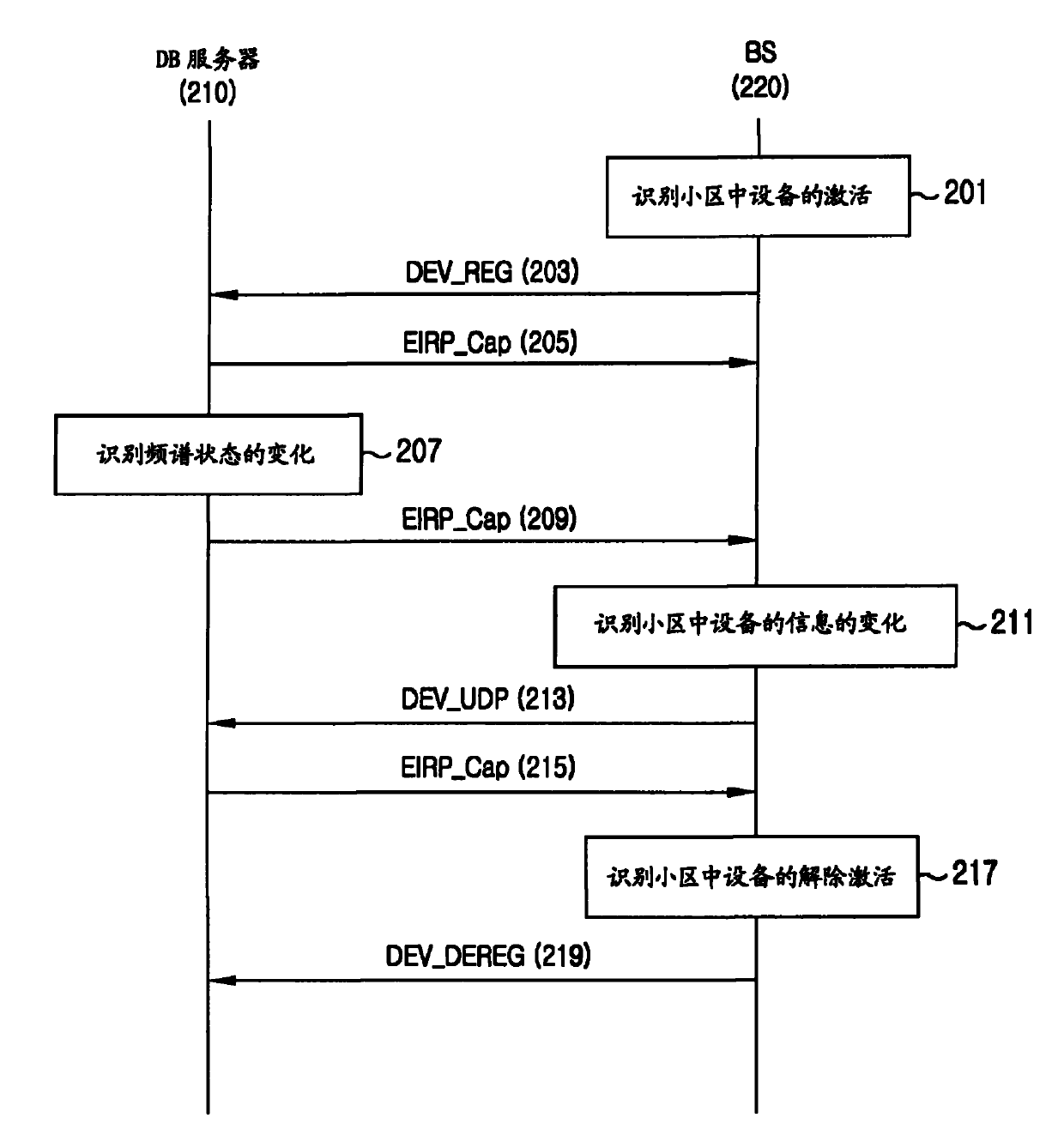
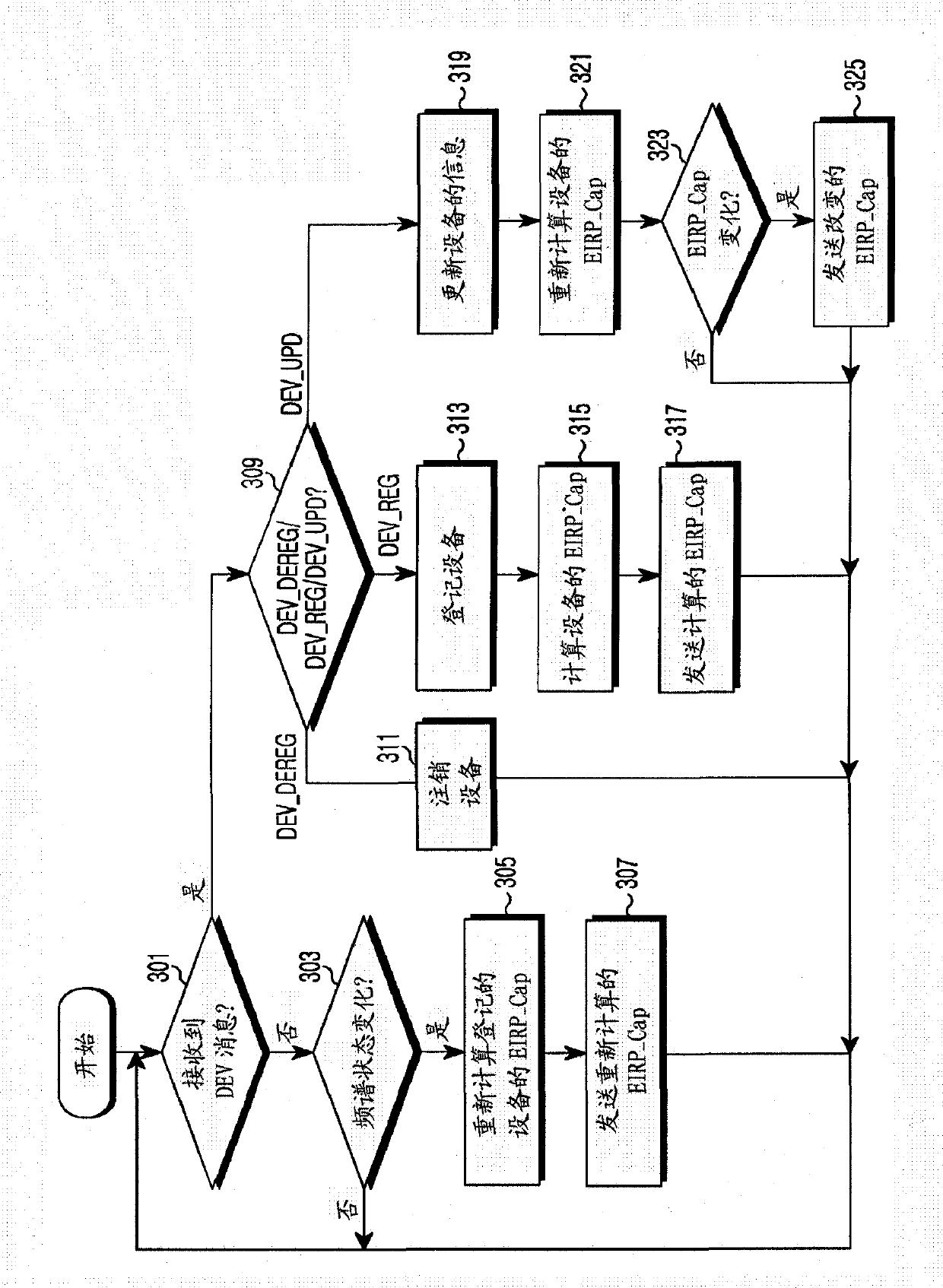
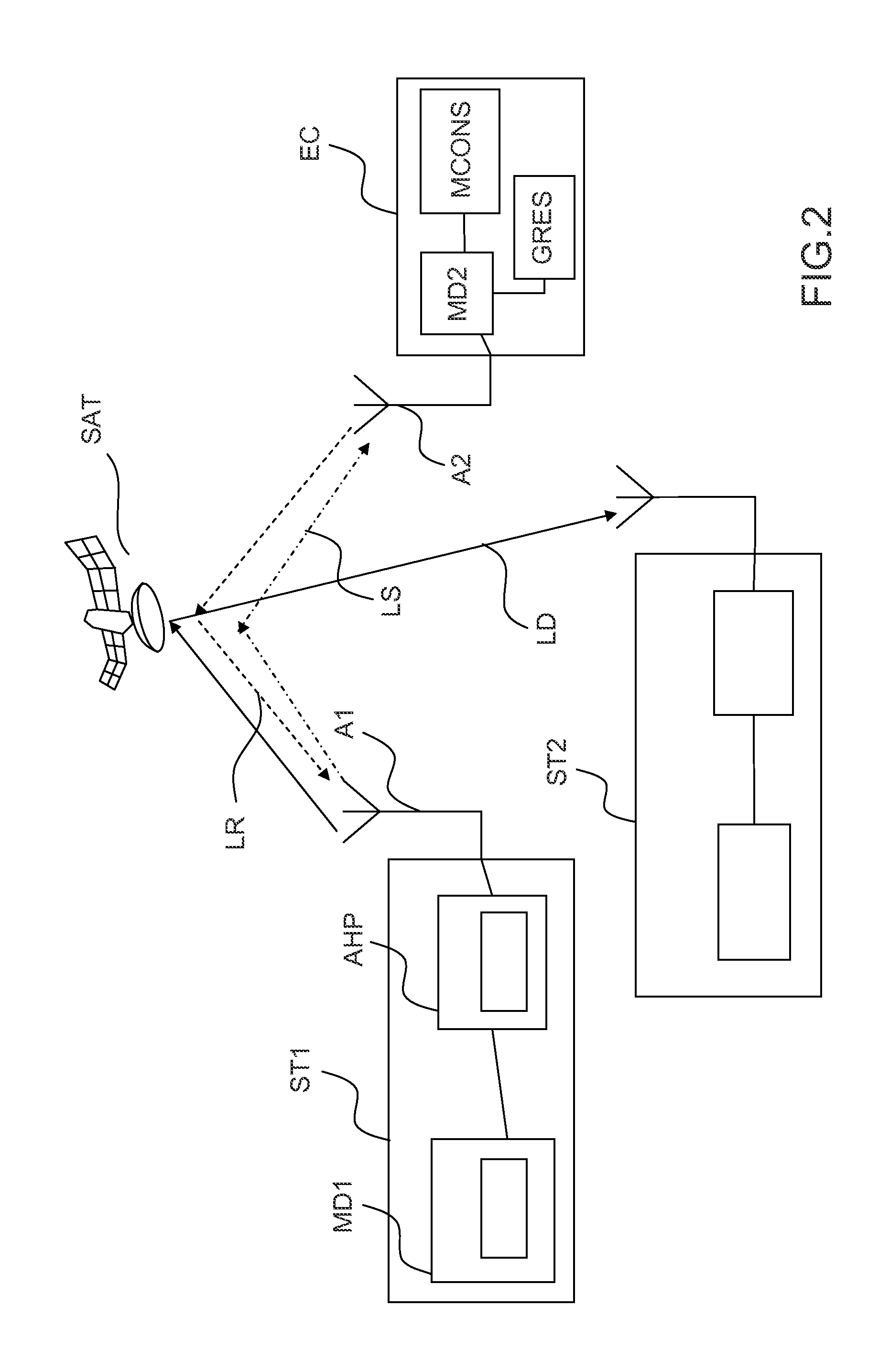
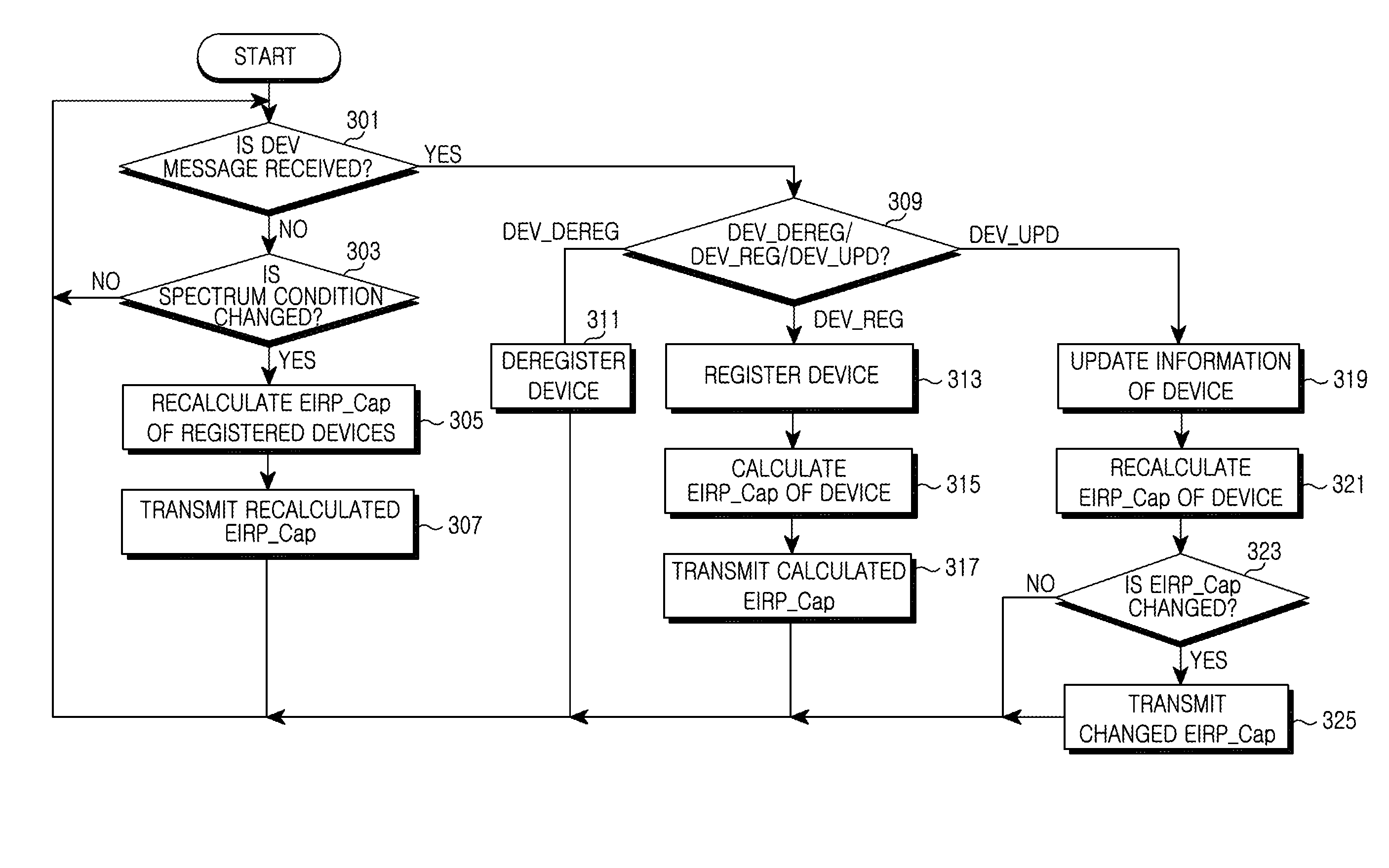
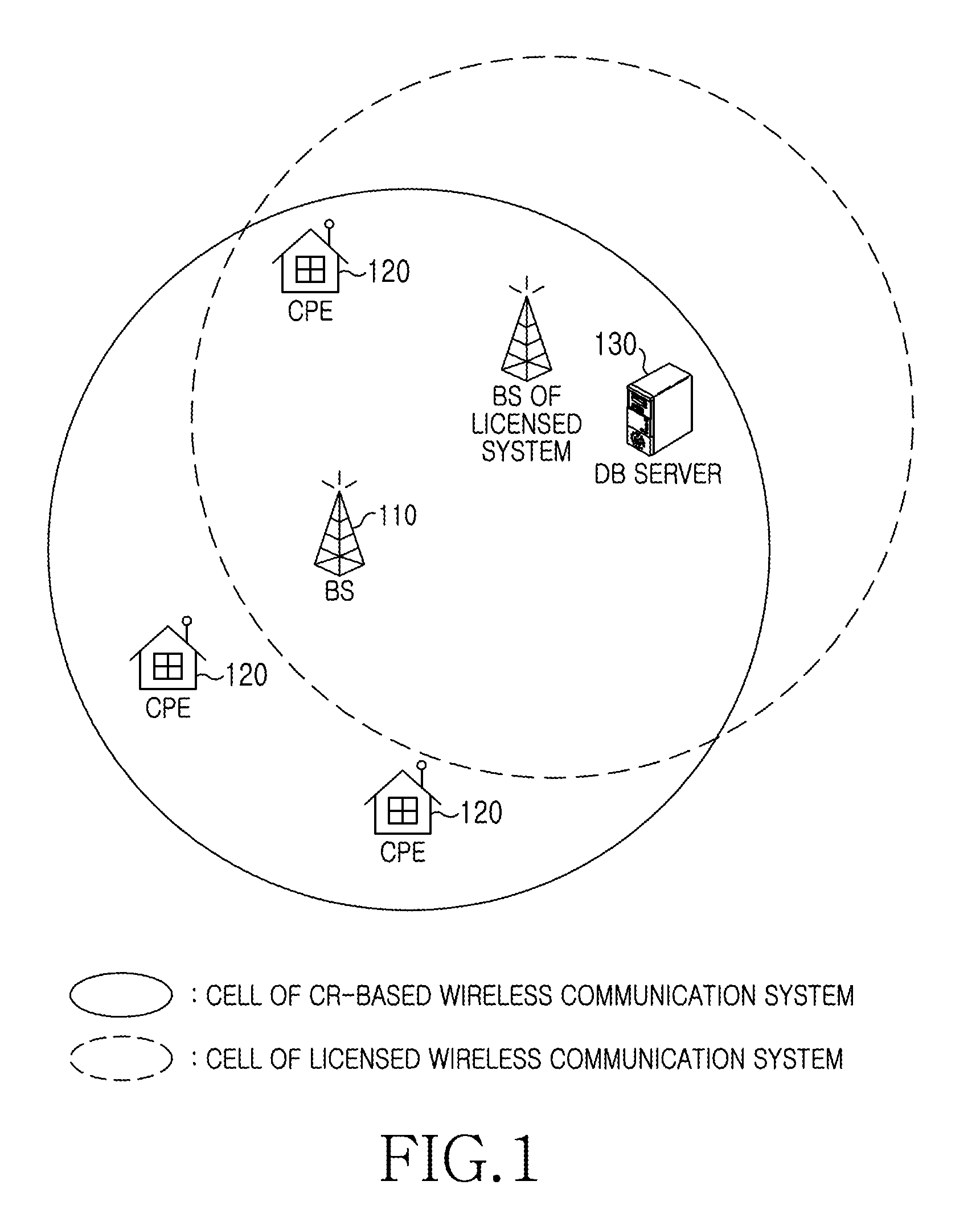
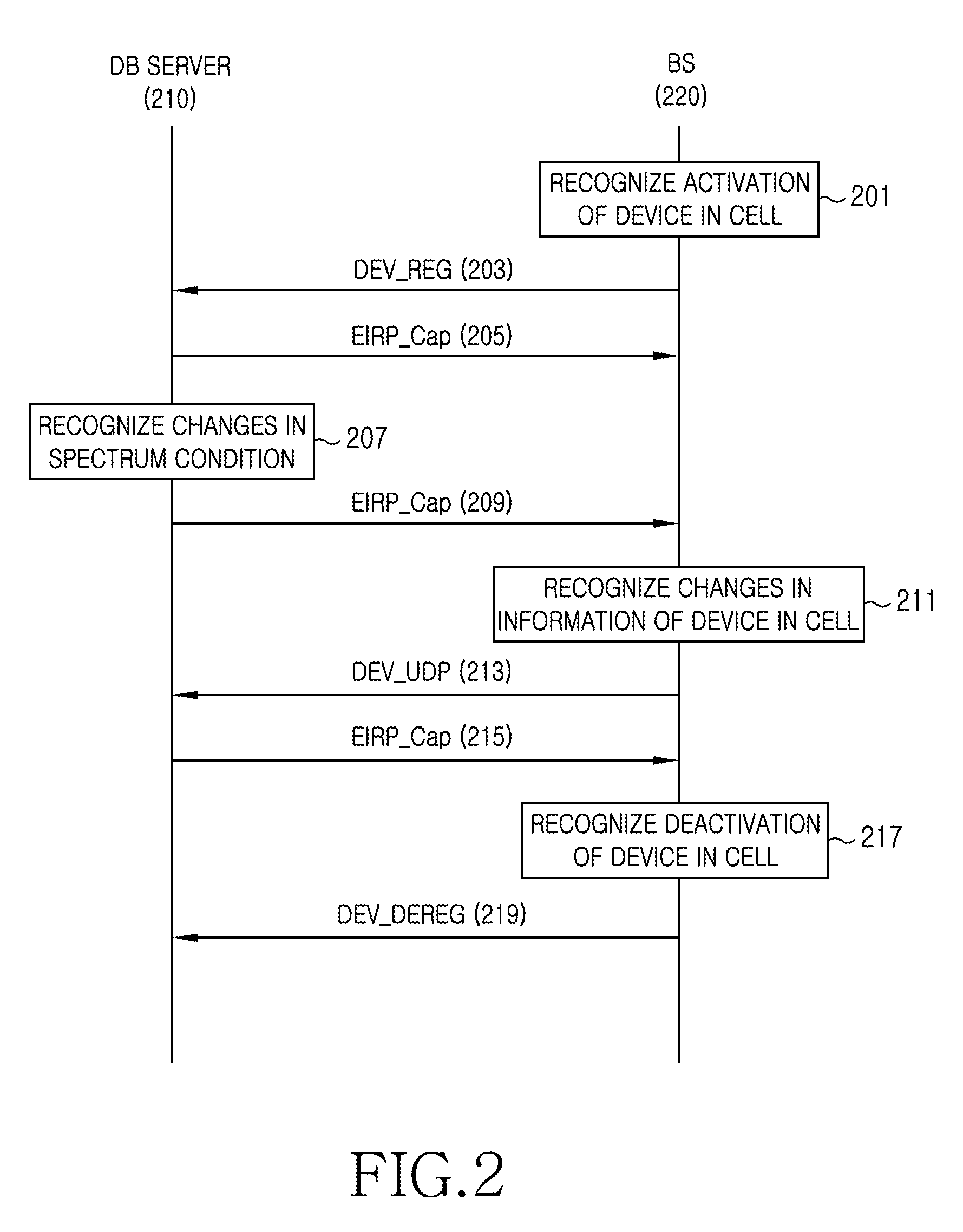
Apparatus and method for enquiring channel condition information in cognitive radio wireless communication system
A method of operating a Data Base (DB) server for storing spectrum condition information on a licensed system in a Cognitive Radio (CR)-based wireless communication system and a CR-based wireless communication system are provided. The method includes determining changes in the spectrum condition information on the licensed system, recalculating maximum Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power (EIRP) allowed for each channel of CR-based devices registered in a list, and transmitting information regarding the recalculated maximum allowed EIRP.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for power autoscaling in a resource-constrained network
ActiveUS20120225687A1Power managementSynchronisation arrangementTransmitted powerReceived signal strength indication
An electronic device may adaptively manage power consumption associated with transmission and / or reception of signals by the electronic device, wherein the adaptive power management may comprise adjusting transmit power and / or one or more power-related thresholds used during transmission or reception operations in the electronic device. Adjustments to the transmit power and / or the one or more power-related thresholds may be determined based on comparison between power measurement associated with signals received by said electronic device with original transmit power for the signals. The reception power measurement may be determined based on detected received signal strength indication (RSSI). The original transmit power may be determined based on signal transmission information embedded in at least one frame carried via said signals. The original transmission power may be embedded as an equivalent isotropic radiated power (EIRP) value.
Owner:BLACKBIRD TECH HLDG
Locating Devices in a Wireless Network
ActiveUS20120119880A1Position fixationElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingEquivalent isotropically radiated powerNoise floor
Determining the location of a wireless device to be located (DTL) by three or more locating devices (LDs). LDs operating at known locations estimate the distance to the DTL by sending wireless frames to the DTL and varying frame parameters such as transmit power and data rate, searching for the boundary at which the frame is or is not received and ACKd by the DTL. For a given set of frame parameters, the SNR required to be successfully received at the DTL is known. Given that the configuration of the LD is known, the EIRP of the DL is also known. Estimating the noise floor at the DTL, and using the SNR required to successfully receive the frame at the DTL and the EIRP at the LD transmitting the frame, the path loss can be calculated. From the path loss and operating frequency, a distance estimate is calculated. EIRP of the DTL is not and need not be known. Distance estimates from at least three LDs at known locations allow a location for the DTL to be calculated by a location engine (LE). Distance estimates from more than three LDs allow for an overdetermined solution. Distance estimates derived in this manner may be combined with distance estimates calculated using other approaches, such as measuring signal strengths, or TOA / TDOA measurements. The LE process may reside on a central controller supporting the LDs, on one of the LDs, or on any suitable device with network access.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
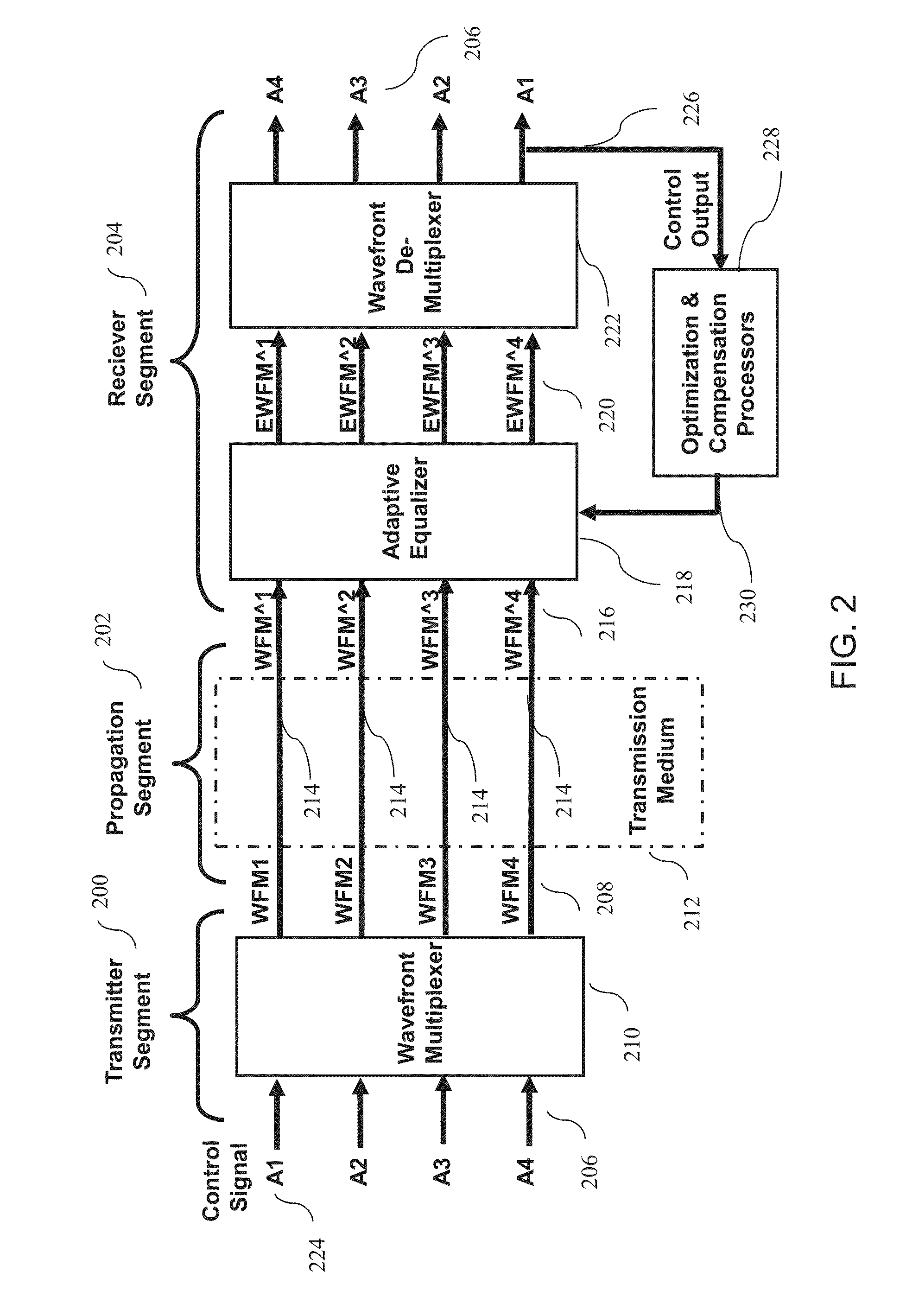
Dynamic power allocations for direct broadcasting satellite (DBS) channels via wavefront multiplexing
ActiveUS20160014786A1Increase power levelPower managementTime-division optical multiplex systemsMultiplexingWavefront
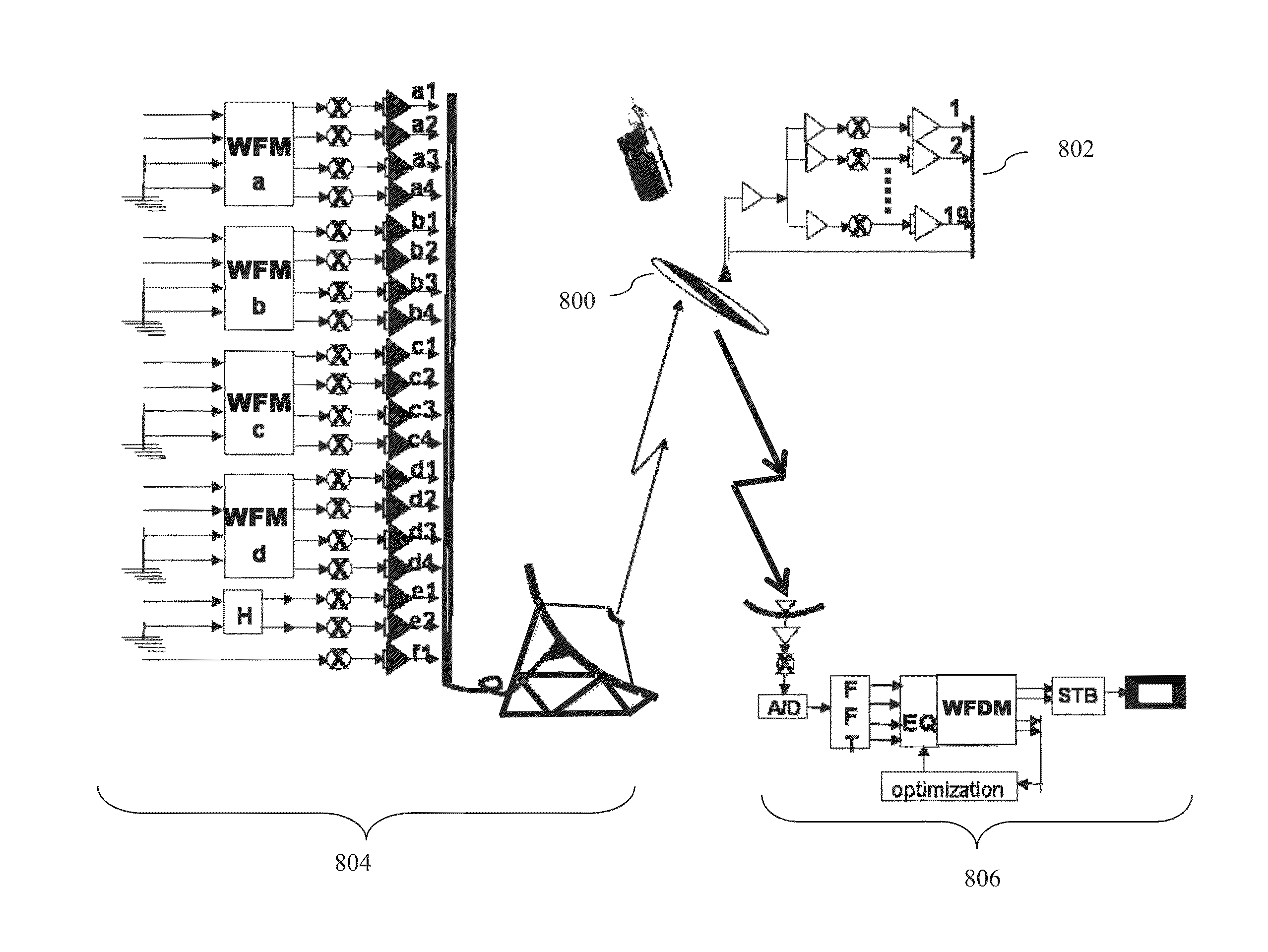
A direct broadcasting satellite (DBS) system features a capability of coherently combining amplified signals powers from various broadcasting transponders without modifying the satellite segment. Organized DBS transponders would function as an equivalent DBS transponder with a higher EIRP. Power allocations are via a mechanism in an uplink transmitter in a ground segment and power combining mechanisms are in user receivers in a user segment. Specifically, the transmitter generates mixtures of input signals by using Wavefront-Multiplexing and transmits wavefront-multiplexed (WFM) signals which are sent concurrently through multiple parallel channels of transponders in the satellite segment. A receiver in the user segment separates the mixtures of received amplified WFM signals and coherently combines amplified components by various transponders by adaptive equalizing and Wavefront De-Multiplexing processors. The WFM signal mixtures allow an operator, or automated system, at the transmitter to dynamically allocate the equivalent transponder powers according to continuously changing demands.
Owner:SPATIAL DIGITAL SYST
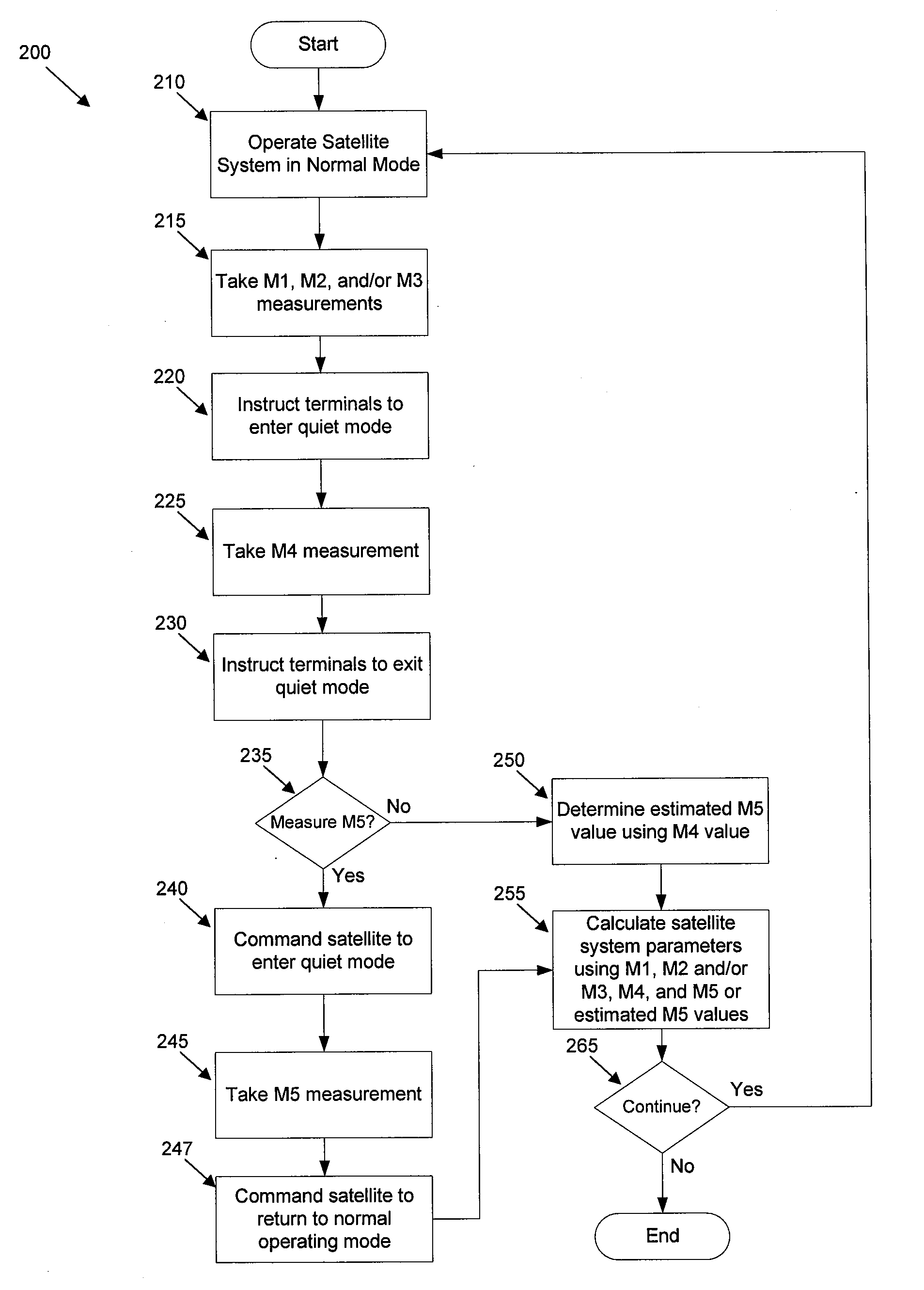
Satellite performance monitoring
ActiveUS20090195444A1Easy to operateRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesEquivalent isotropically radiated powerOptical performance monitoring
Techniques for monitoring transmission performance of a satellite communications systems are provided, including techniques for measuring the primary contributors to the end-to-end SNR, including the uplink SNR, the downlink SNR, and the C / I for each link in the network. These individual measurements are used to estimate satellite effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP), satellite antenna gain-to-noise-temperature (G / T), and loss due to an Earth Terminal pointing error. The EIRP, satellite antenna G / T and loss due to Earth terminal pointing error may then be used to determine operating parameters for the satellite communications network that enable the network to operate more efficiently.
Owner:VIASAT INC
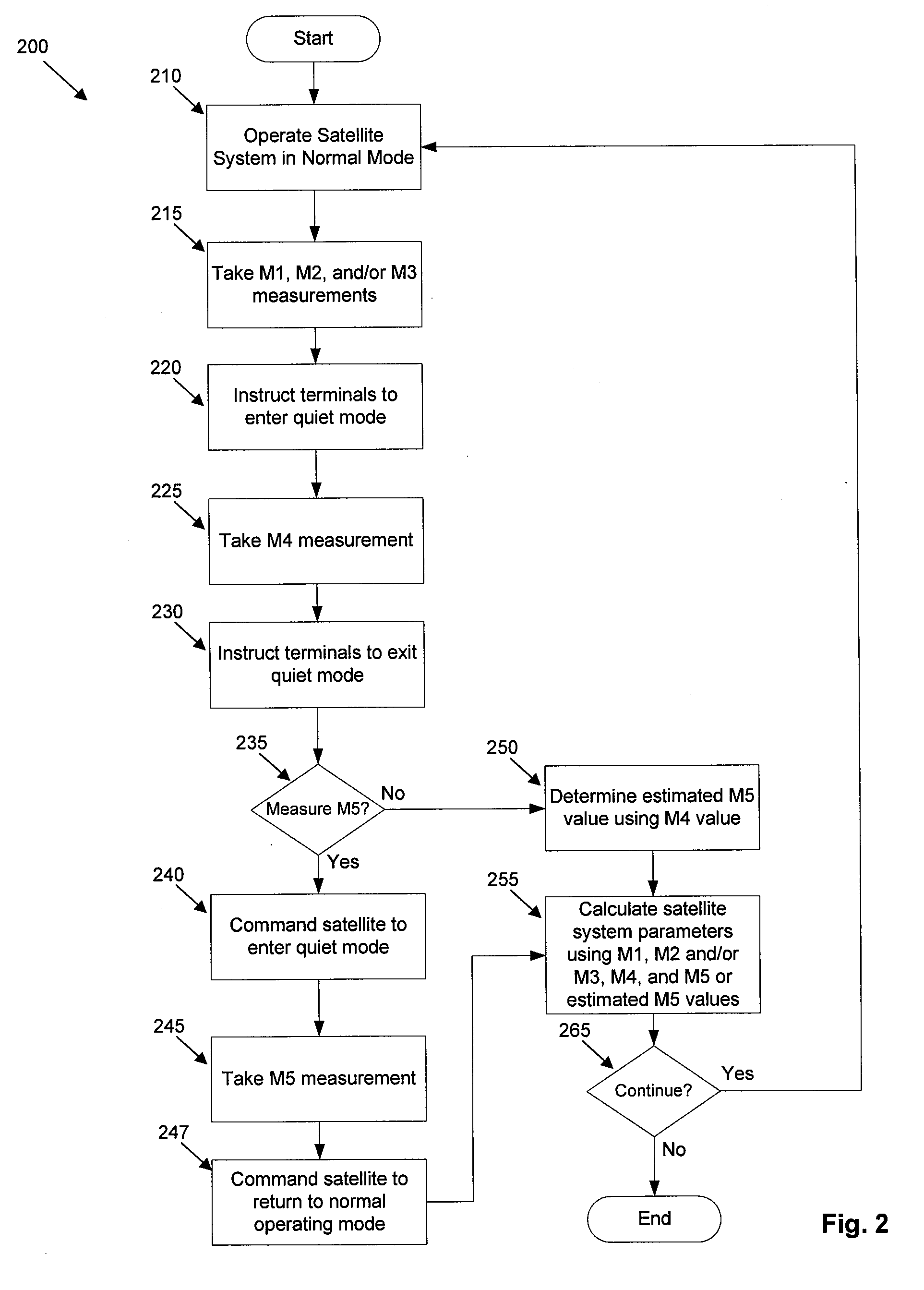
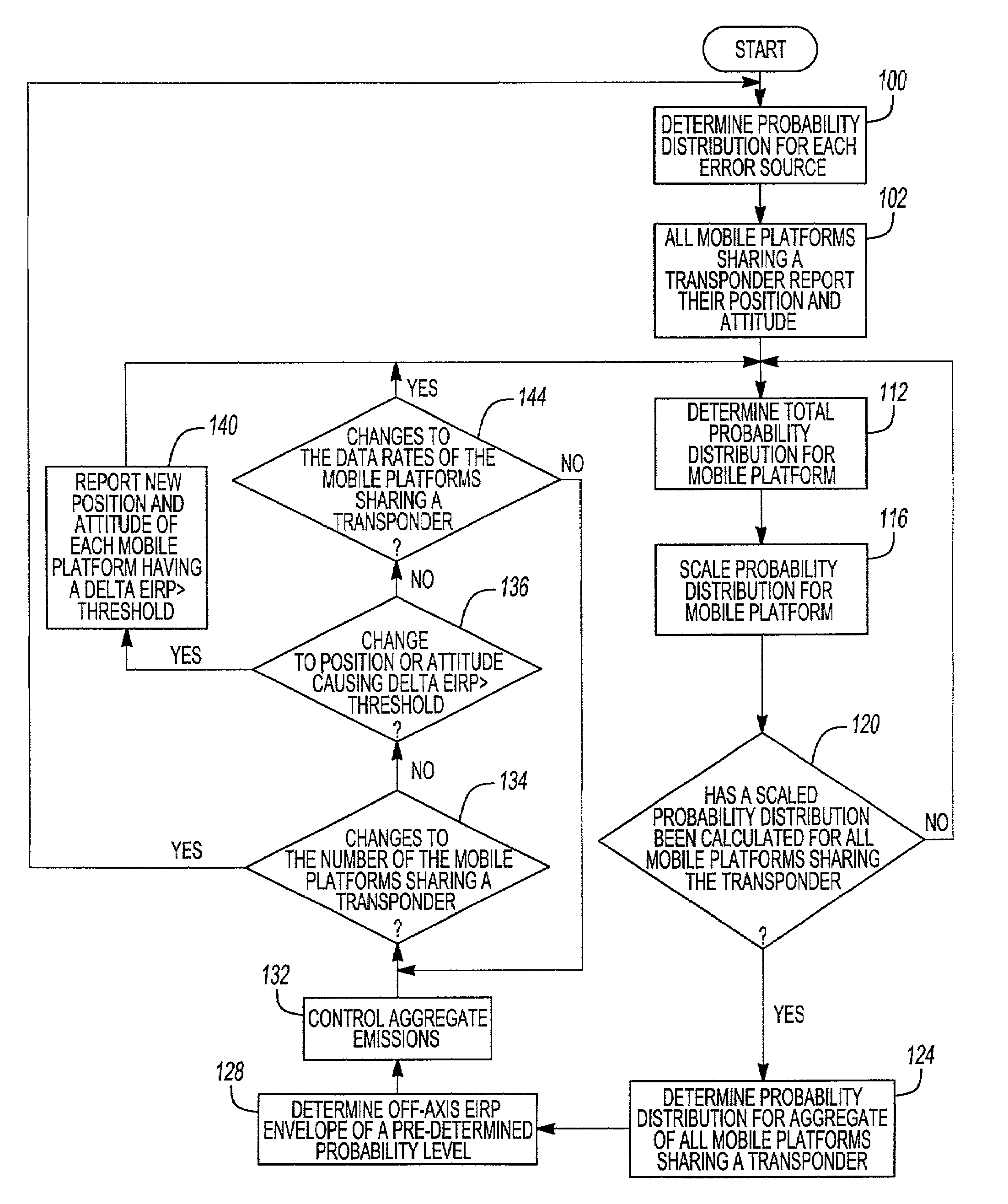
EIRP statistical calculation method
ActiveUS7437125B2GHz frequency transmissionAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesData contentEquivalent isotropically radiated power
In a system for providing data content to and from a plurality of mobile platforms where each of the mobile platforms transmits a return link having an EIRP to a predetermined location via a satellite-mounted transponder, a method for controlling an EIRP of the aggregate return link emissions of the mobile platforms. The method includes the steps of determining a probability distribution of the EIRP of the return link for each of the mobile platforms; and determining a probability distribution of the EIRP for the aggregate return link emissions using the probability distributions of the EIRP of the return link for each of the mobile platforms; determining an aggregate off-axis EIRP density envelope for a predetermined probability level and the probability distribution of the EIRP for the aggregate return link emissions.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Mobile satellite communication system
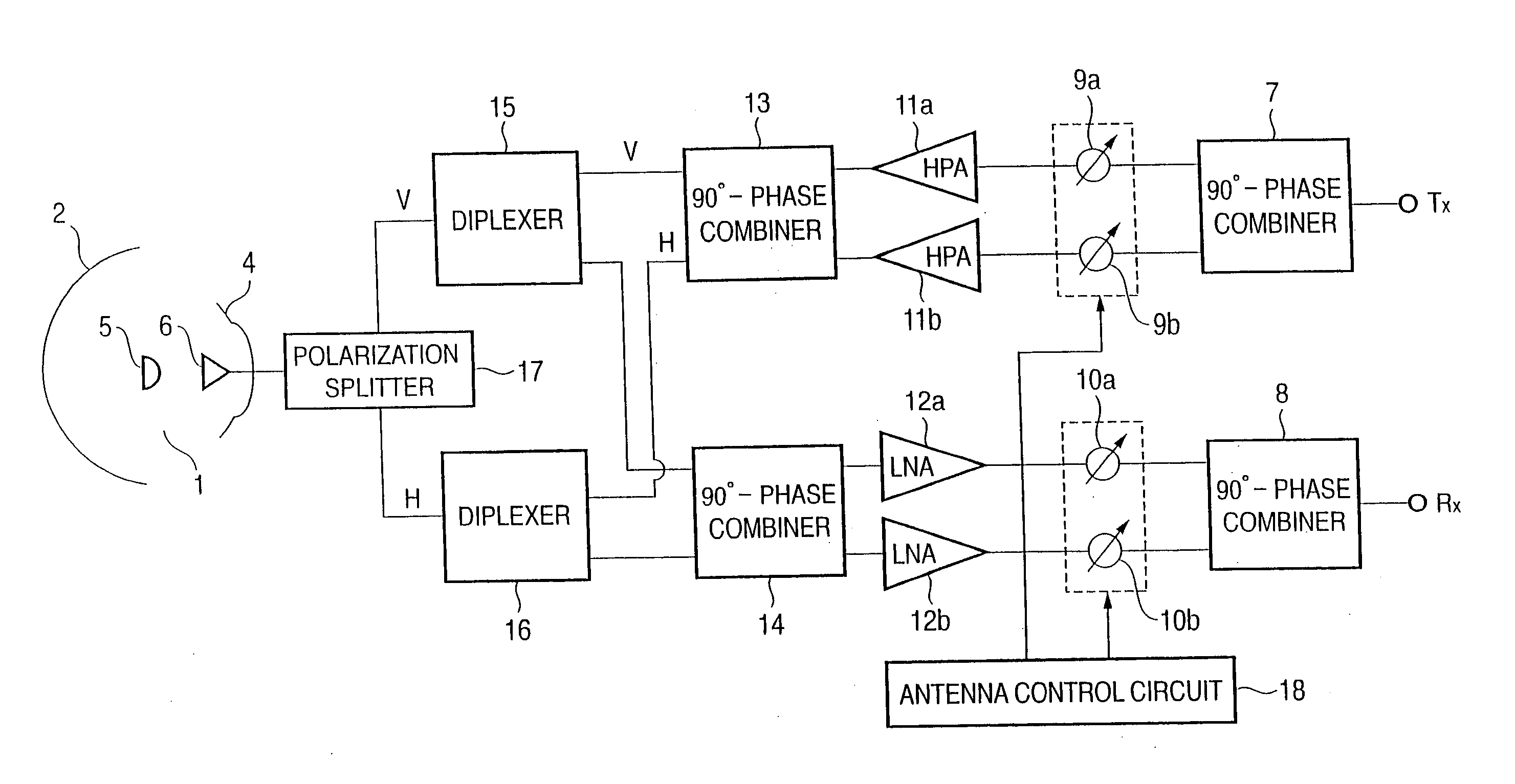
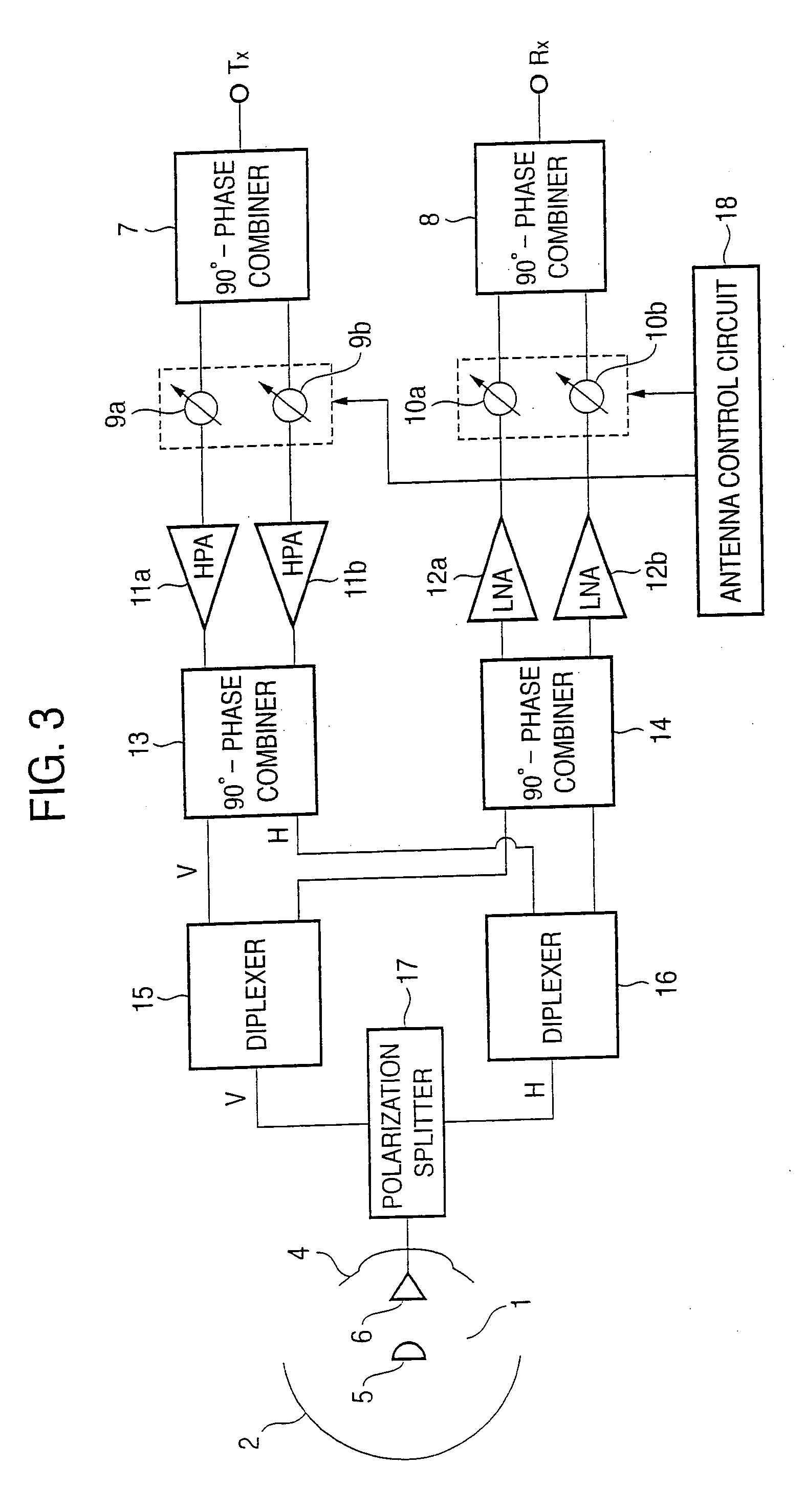
InactiveUS20060046638A1Antenna adaptation in movable bodiesActive radio relay systemsControl theoryEquivalent isotropically radiated power
In a moving body satellite communication apparatus for performing communication with a satellite by an antenna with a radome mounted on a moving body such as an aircraft, loss due to transmission through the radome, and distortion of polarization characteristics are compensated in the inside of the antenna. Variable phase shifters 9a and 9b and variable attenuators 19a and 19b, and variable phase shifters 10a and 10b and variable attenuators 20a and 20b are respectively controlled as one body in each channel, and the whole power EIRP radiated from the antenna is also optimally controlled by a common variable attenuator 21 inserted independently from the variable attenuators 19a and 19b, and therefore, radome correction and EIRP control can be simultaneously realized by a relatively simple circuit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
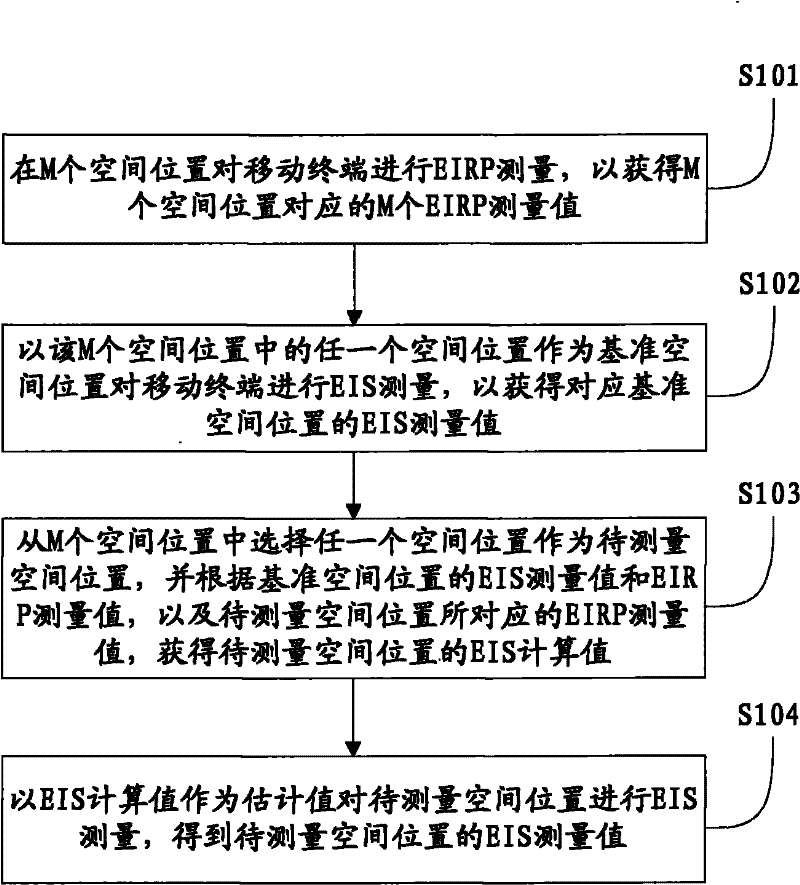
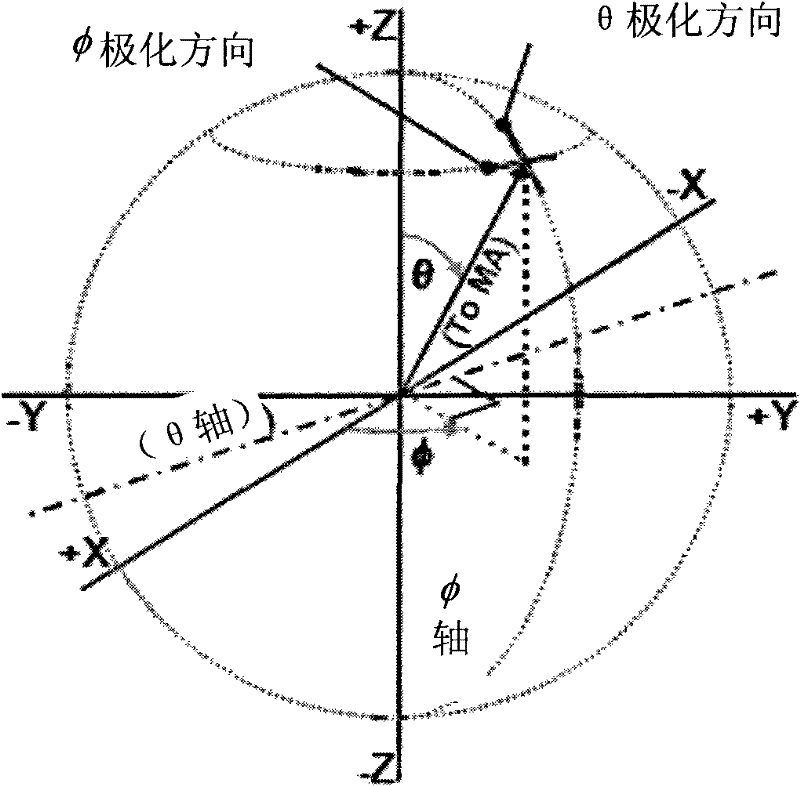
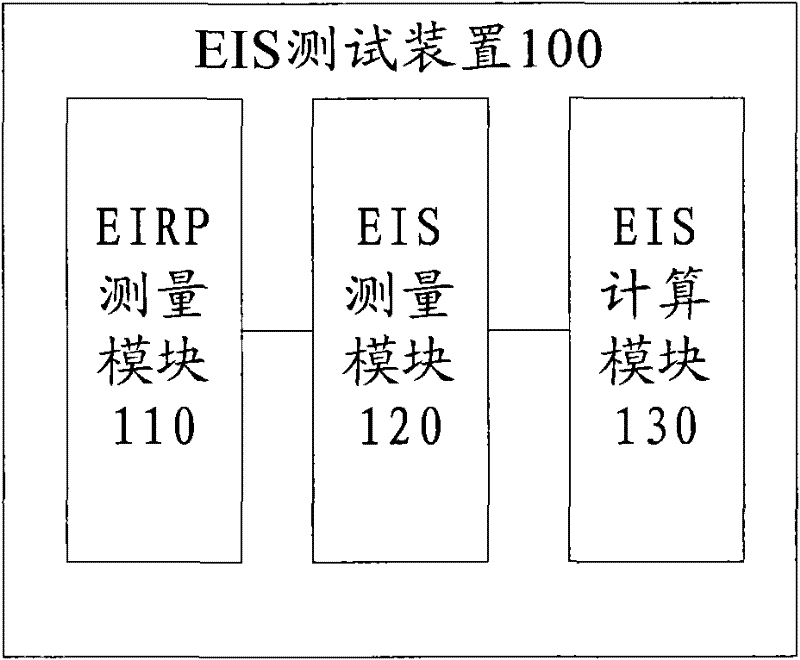
Method and device for testing effective isotropic sensitivity (EIS)
ActiveCN102237933AReduce the number of test searchesFast testReceivers monitoringAntenna radiation diagramsReference spaceEquivalent isotropically radiated power
The invention provides a method for testing EIS (Effective Isotropic Sensitivity). The method comprises the following steps of: performing EIRP (Effective Isotropic Radiated Power) measurement on a mobile terminal at a plurality of space positions to obtain a plurality of EIRP measured values corresponding to the plurality of space positions; performing EIS measurement on the mobile terminal by taking any space position in the plurality of space positions as a reference space position to obtain an EIS measured value of a corresponding reference space position; obtaining an EIS calculation value of a space position to be measured according to an EIS measured value and an EIRP measured value of the reference space position and an EIRP measured value corresponding to the space position to be measured; and performing EIS measurement on the space position to be measured by taking the EIS calculation value as an estimation value to obtain an EIS measured value of the space position to be measured. In the embodiment of the invention, the EIS calculation value obtained by calculation is accurate to take as an estimation value, so that the test searching times can be greatly reduced, and the test speed is greatly increased.
Owner:GENERAL TEST SYST
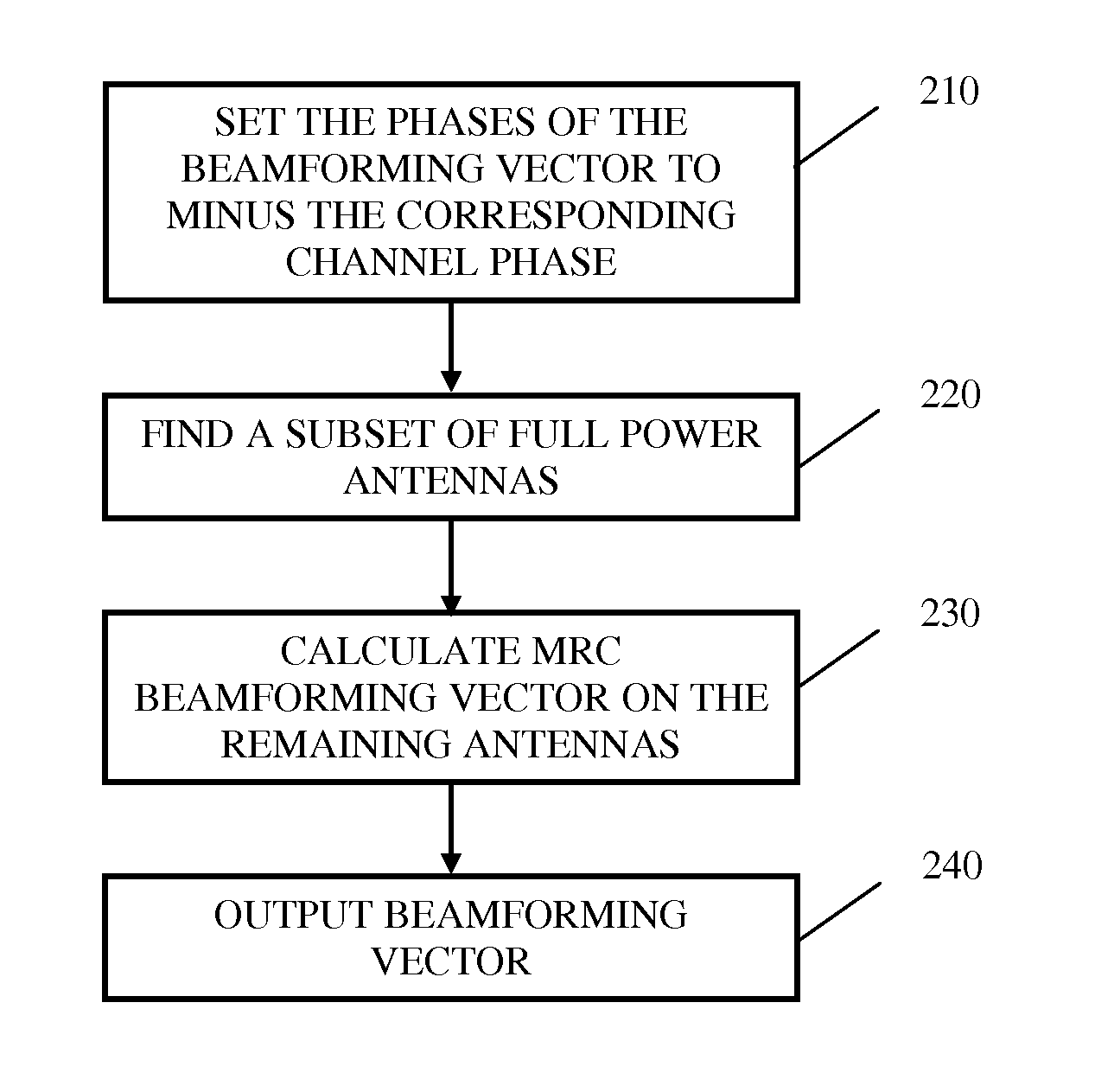
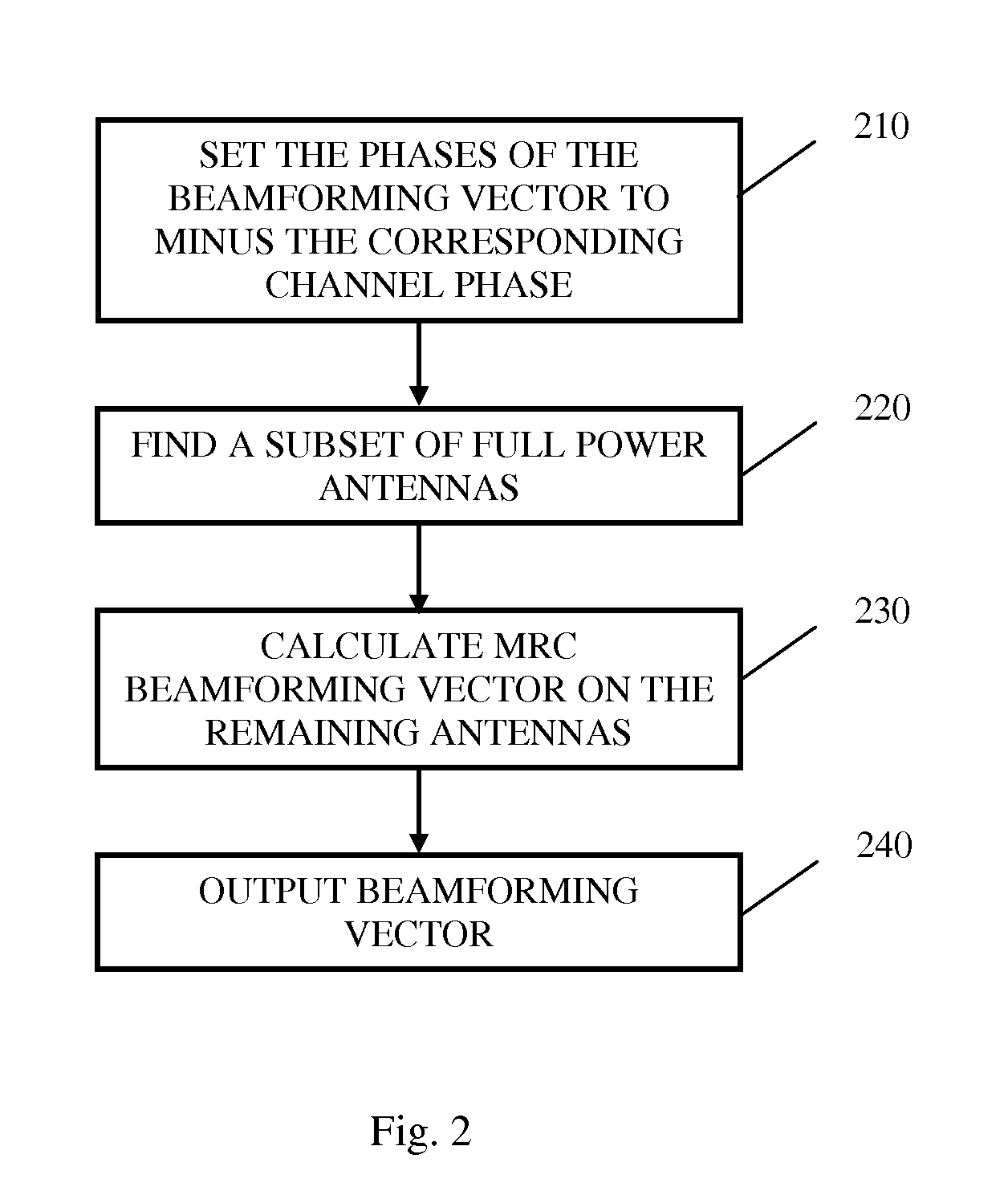
Method for single stream beamforming with mixed power constraints
ActiveUS20110210892A1Power managementEnergy efficient ICTEngineeringEquivalent isotropically radiated power
System and method for calculating a transmitter beamforming vector related to a channel vector h under per-antenna power constraints combined with total power constraint, under per-antenna power constraints combined with overall line of site (LOS) effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) and under all three constraints. Calculating a transmitter beamforming vector may be done in the transmitter, in the receiver and feedback to the transmitter or in both. The method may be adapted to perform with a multi-antenna receiver and with multi-carrier systems.
Owner:CELENO COMMUNICATIONS (ISRAEL) LTD
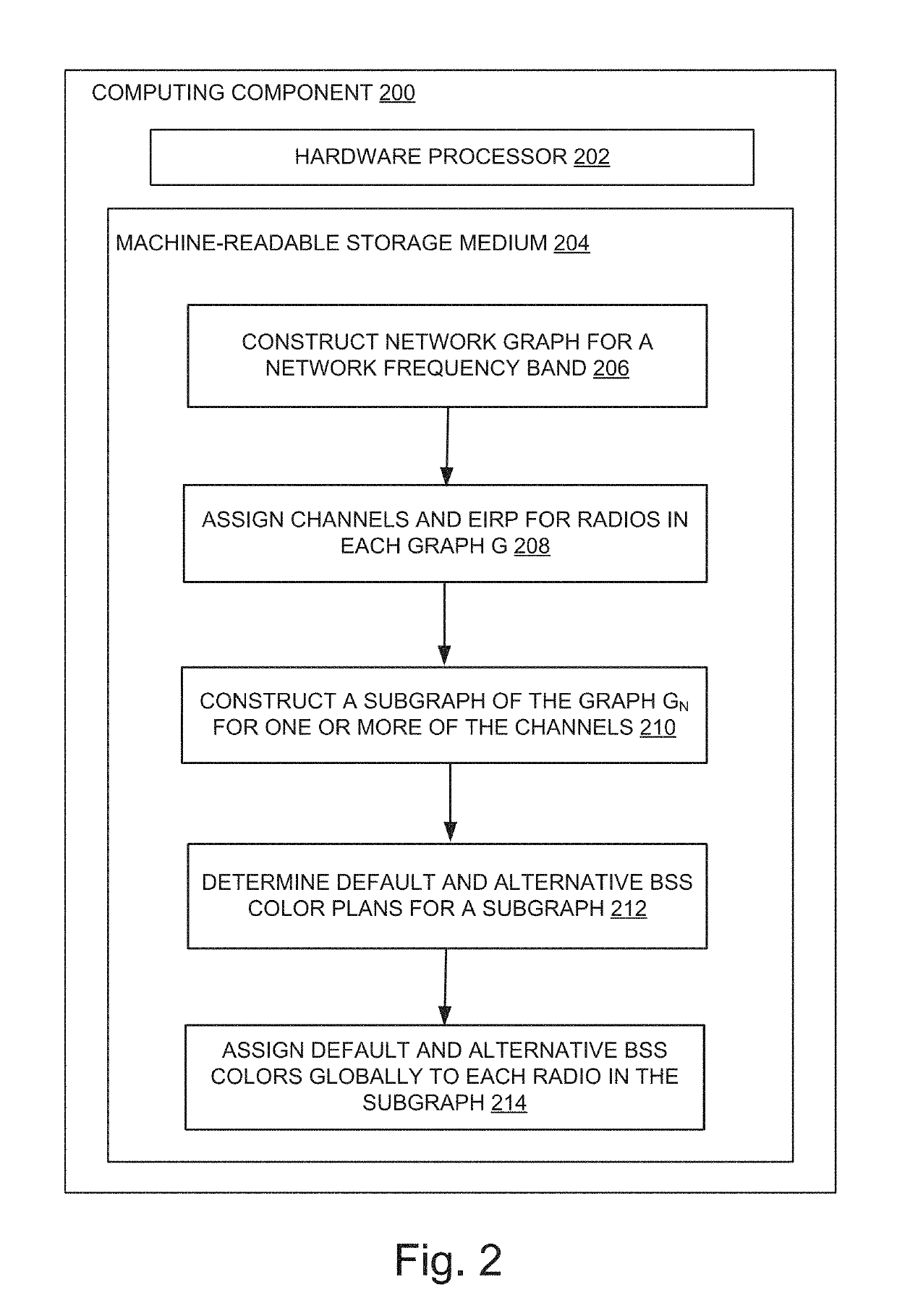
BSS color assignment in a wireless local area network
ActiveUS10397928B1Network topologiesTransmission monitoringBasic serviceEquivalent isotropically radiated power
Systems and methods for assigning default an alternative BSS colors in a wireless local area network (WLAN) including a network graph representing radio neighbors include assigning a frequency range and EIRP for each radio represented in the network graph; generating a subgraph of radios operating at the same frequency range; for the subgraph, determining a minimum number of basic service set (BSS) colors required to BSS color the subgraph without BSS color conflict; based on the minimum number of BSS colors, assigning a default BSS color to each radio in the subgraph to avoid BSS color conflict among radios in the subgraph; based on remaining BSS colors, assigning one or more alternative BSS colors to each radio in the subgraph.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Dynamic effective radiated power (ERP) adjustment
ActiveUS20180006371A1Reduce outputNavigational calculation instrumentsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesOn boardSkew angle
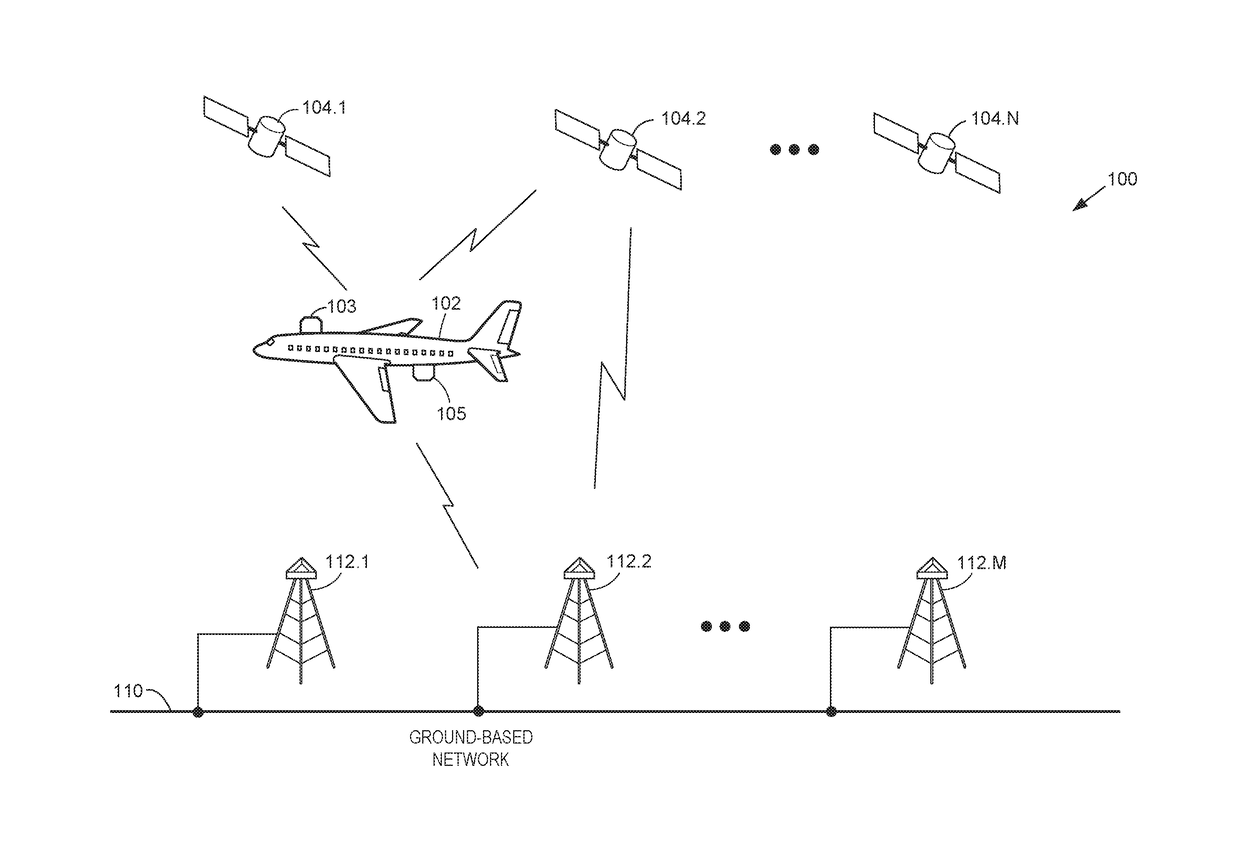
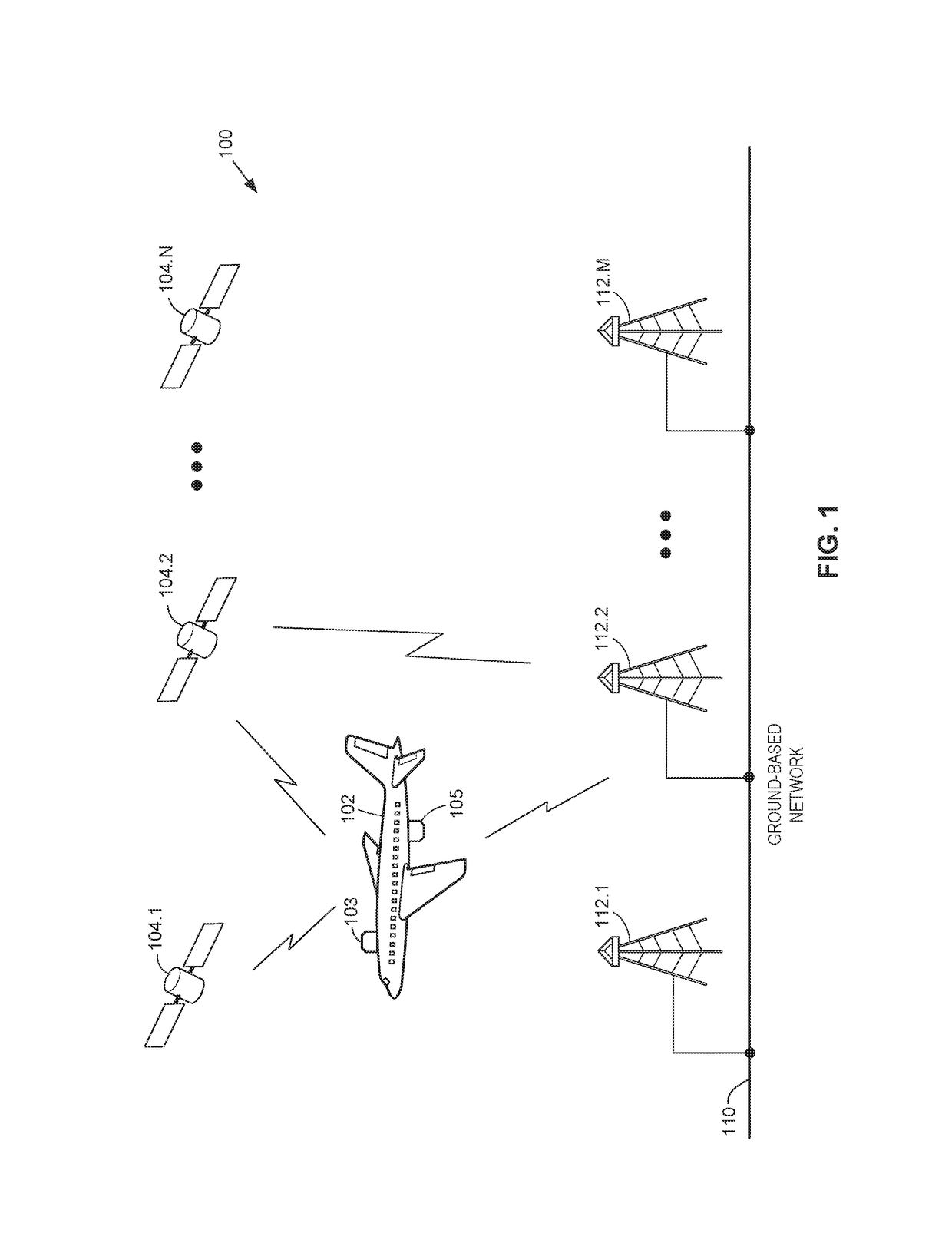
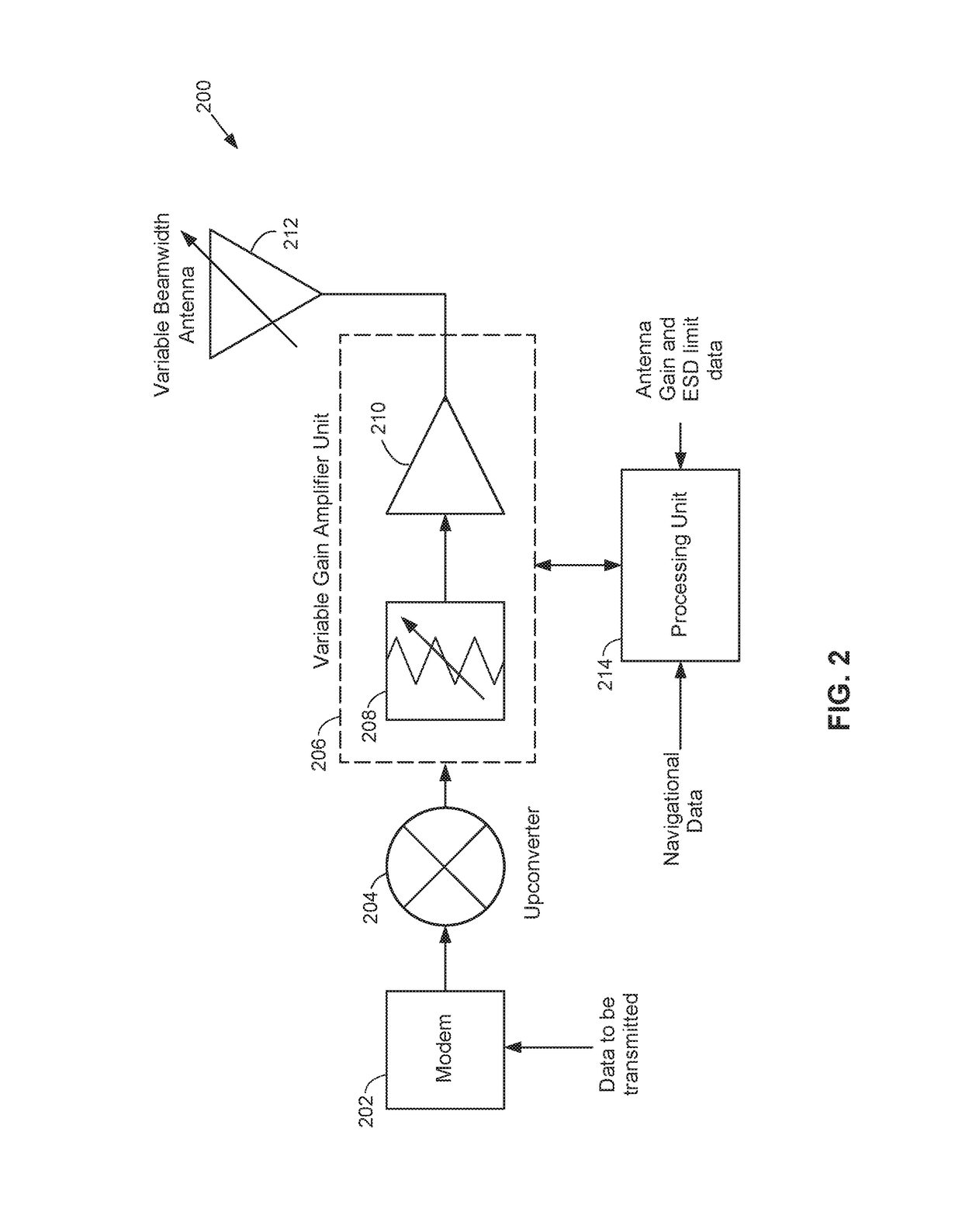
Antennas used aboard aircraft to communicate with satellites or ground stations may have complex antenna patterns, which may vary as the aircraft moves throughout a given coverage area. Techniques are disclosed for dynamically adjusting the instantaneous power fed to an antenna system to ensure that the antenna transmits at the regulatory or coordinated effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) spectral limit. The antenna may transmit, in accordance with aircraft location and attitude, steerable beam patterns at different scan and skew angle combinations, causing variations in antenna gain and fluctuations in the transmitted EIRP. Using on-board navigational data, an antenna gain and ESD limit may be calculated for a particular scan and skew angle, which may be used to adjust power fed to the antenna such that the antenna transmits substantially at maximum allowable EIRP as the steerable beam pattern is adjusted.
Owner:GOGO BUSINESS AVIATION LLC
Variable column surface/spherical surface luneburg lens antenna based on phased array feeding
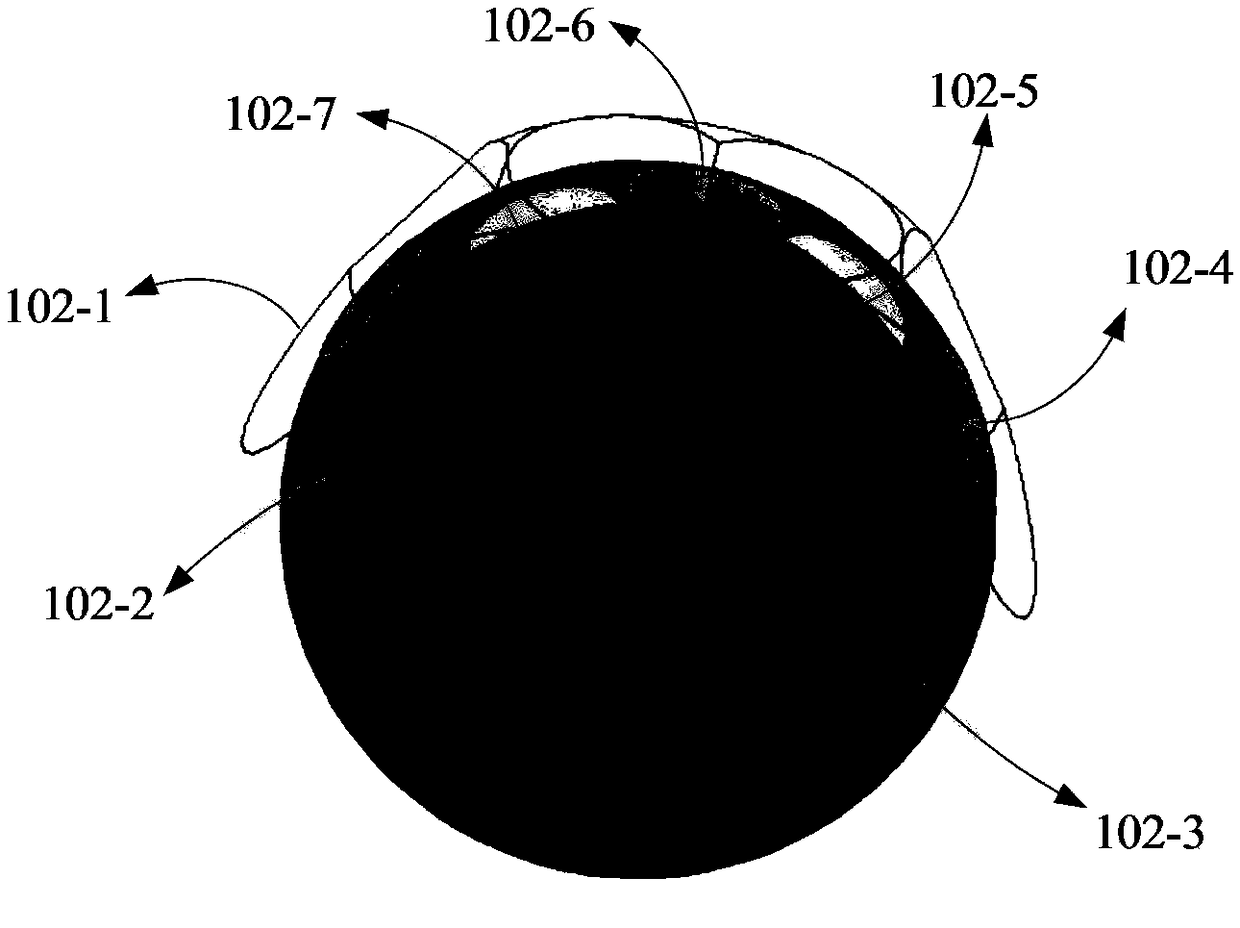
ActiveCN108808260AReduce volumeReduce weightParticular array feeding systemsDifferential interacting antenna combinationsSystem integrationElectricity
The invention discloses a variable column surface / spherical surface luneburg lens antenna based on phased array feeding, and belongs to the technical fields of wireless communication and radars. The antenna comprises a variable column surface / spherical surface luneburg lens, and a plurality groups of active plane phased array antennas serving as a feed source. By virtue of reasonable design of theposition relationship between the variable luneburg lens and the phased array antennas, and optimization of excitation coefficients of the phased array antennas serving as the feed source, wave beamsare formed in the needed direction, and wave beam electric scanning or simultaneous multi-beam wave scanning is realized. Compared with a traditional luneburg lens, the antenna disclosed in the invention has the characteristics and advantages of high gain, high effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP), high scanning precision, low mass and small volume, and convenience in processing and system integration by adopting the plane array feed source, so that the antenna can be applied to a radar and communication system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Self-adaptive distance data transmission method for aircraft-mounted terminal
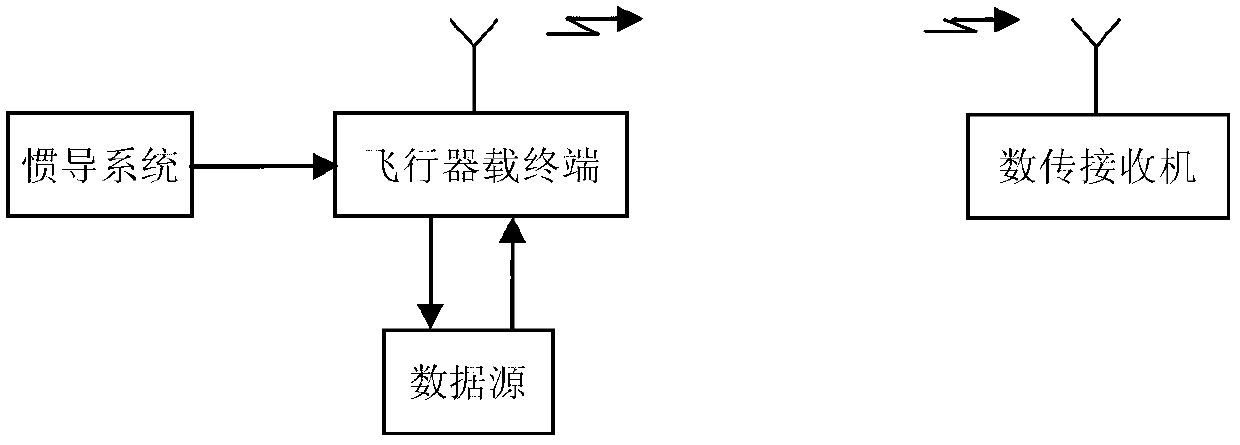
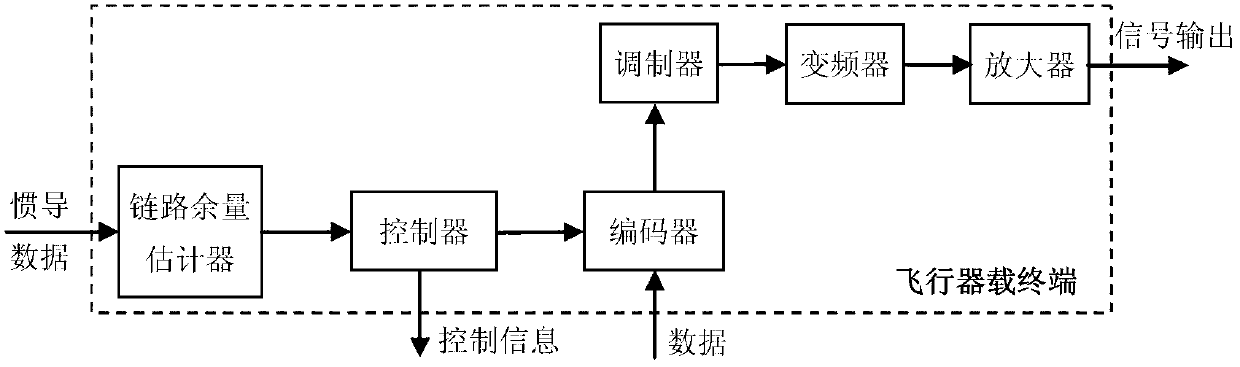
ActiveCN103312453AIncrease profitIncrease data transfer rateError preventionLink marginUp conversion
The invention provides a self-adaptive distance data transmission method for an aircraft-mounted terminal and aims to provide a data transmission method capable of improving transmission link utilization rate and data transmission efficiency and also provides a self-adaptive implementation method for the data transmission between the aircraft-mounted terminal and a data transmission receiver. The self-adaptive distance data transmission method is realized through the following technical scheme: an aircraft inertial navigation system provides inertial navigation data for the aircraft-mounted terminal in real time through a serial port, a link margin estimator of the aircraft-mounted terminal calculates the distance between an aircraft and the data transmission receiver in real time according to the inertial navigation data and works out the system margin of the data transmission link according to the stored data transmission receiver relevant parameters, the data transmission link parameters and the parameters such as the EIRP (effective isotropic radiated power) value of the antenna of the aircraft-mounted terminal, the aircraft-mounted terminal automatically selects data transmission speed, carries out coded modulation on data in different data transmission speeds through an encoder and a modulator, and transmits the data to the data transmission receiver after up-conversion and amplification processing.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
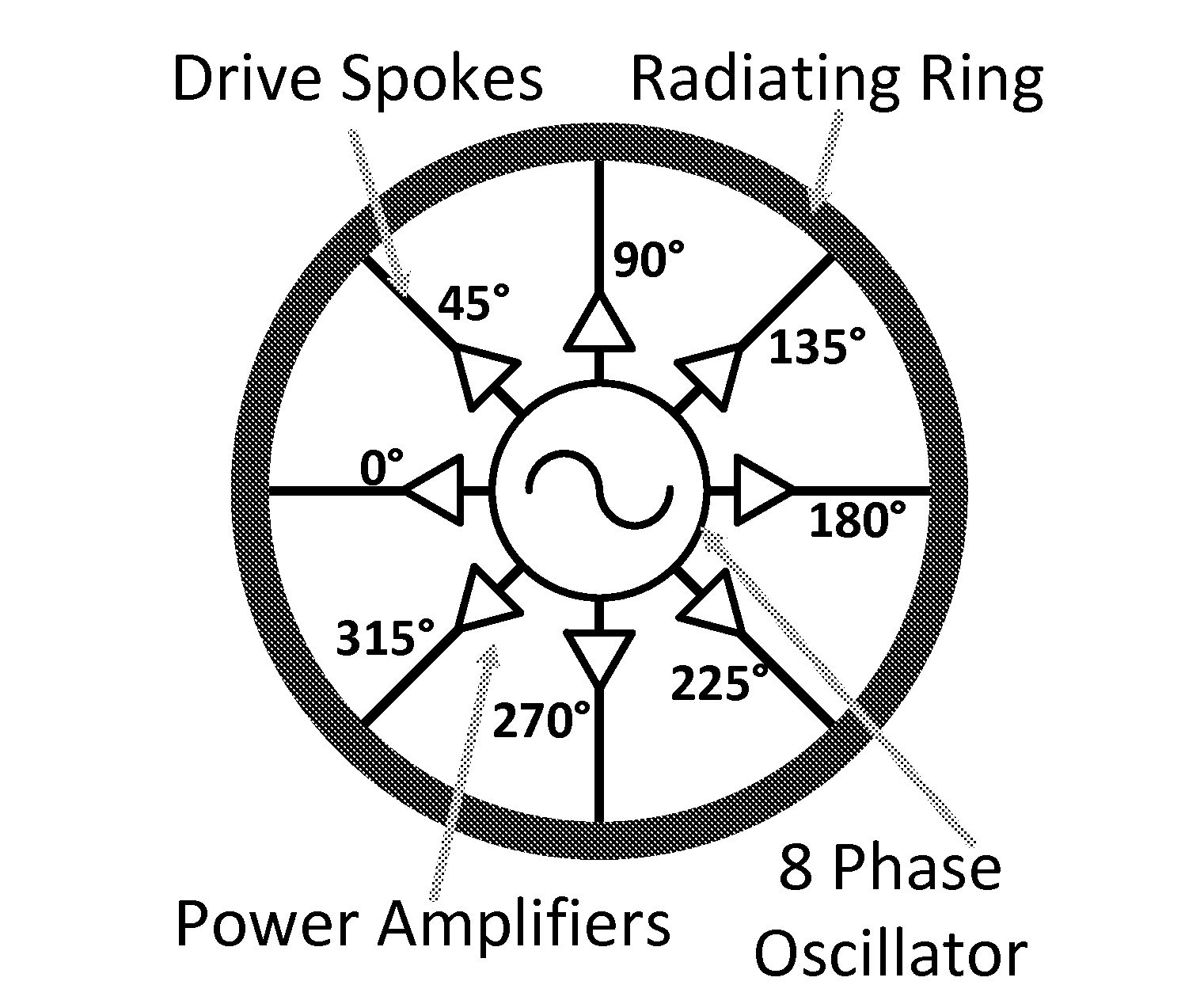
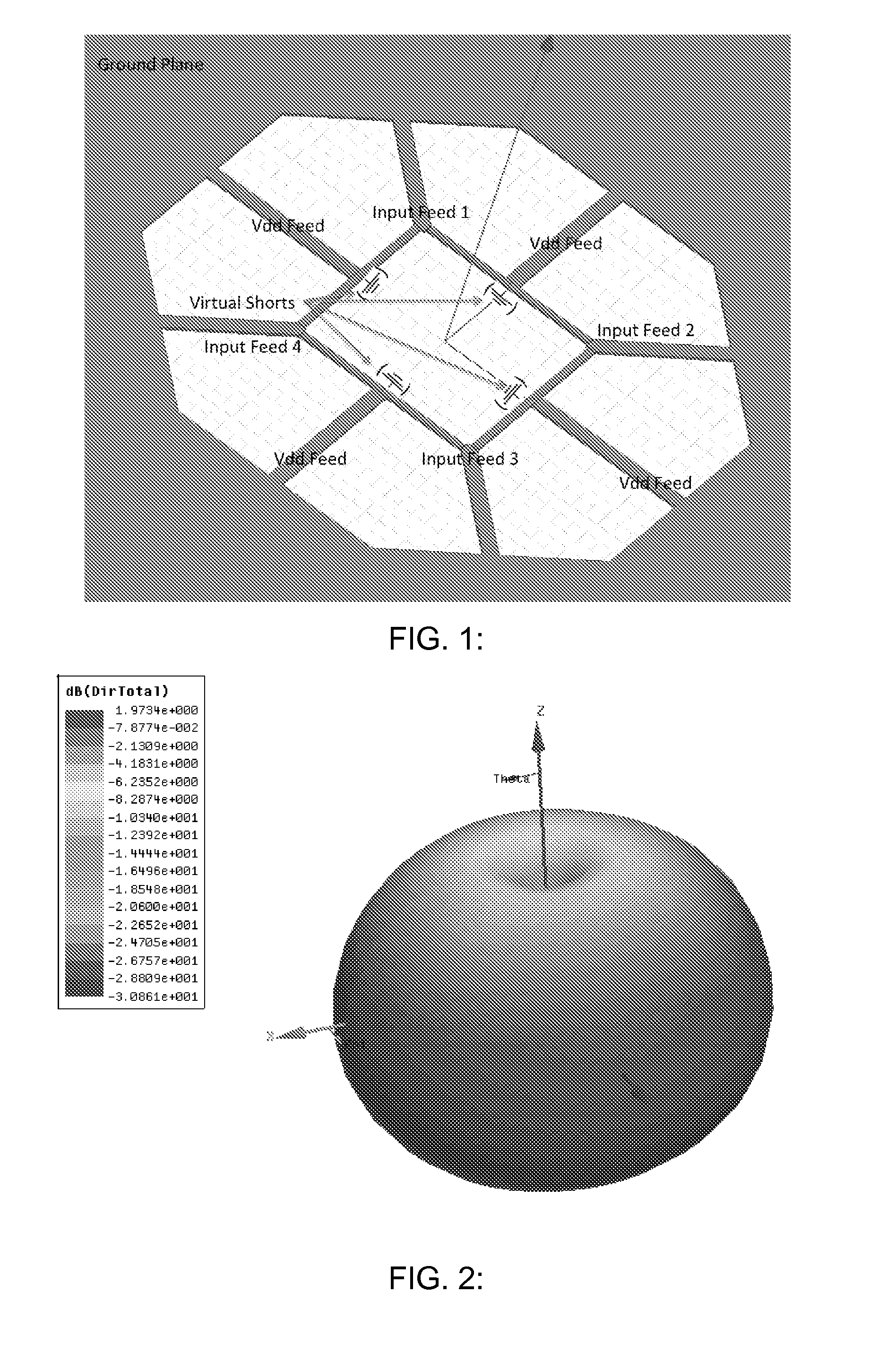
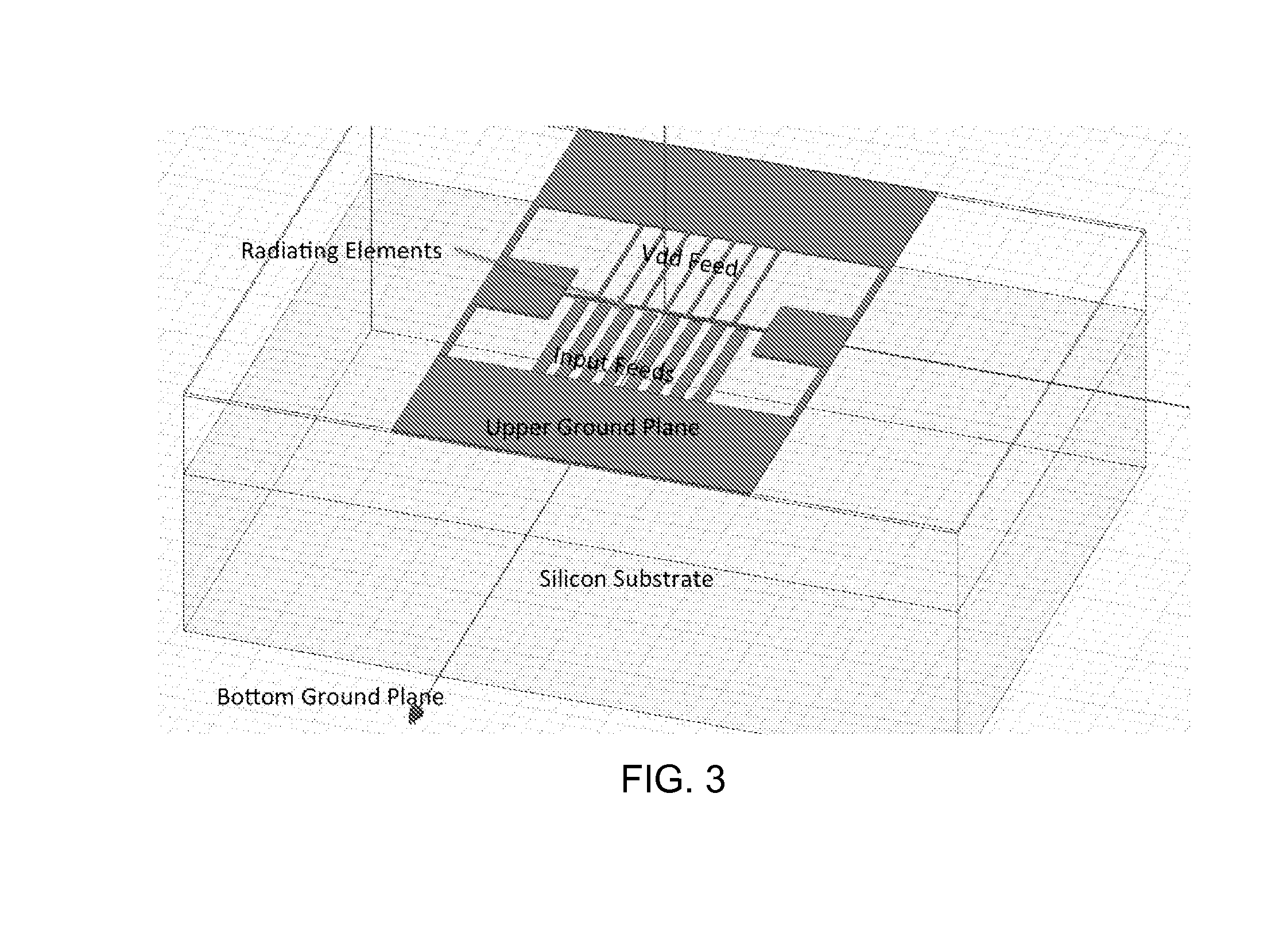
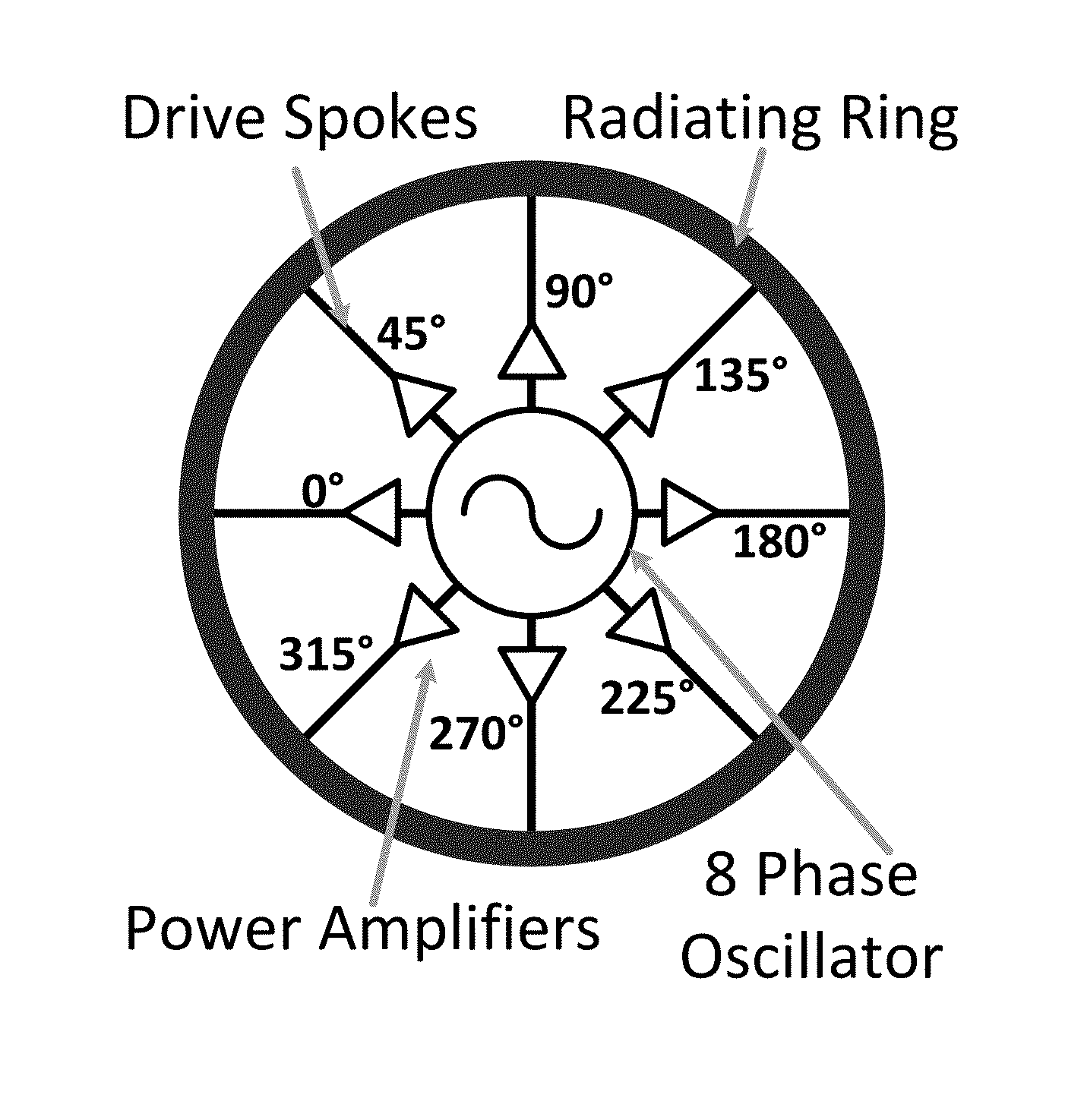
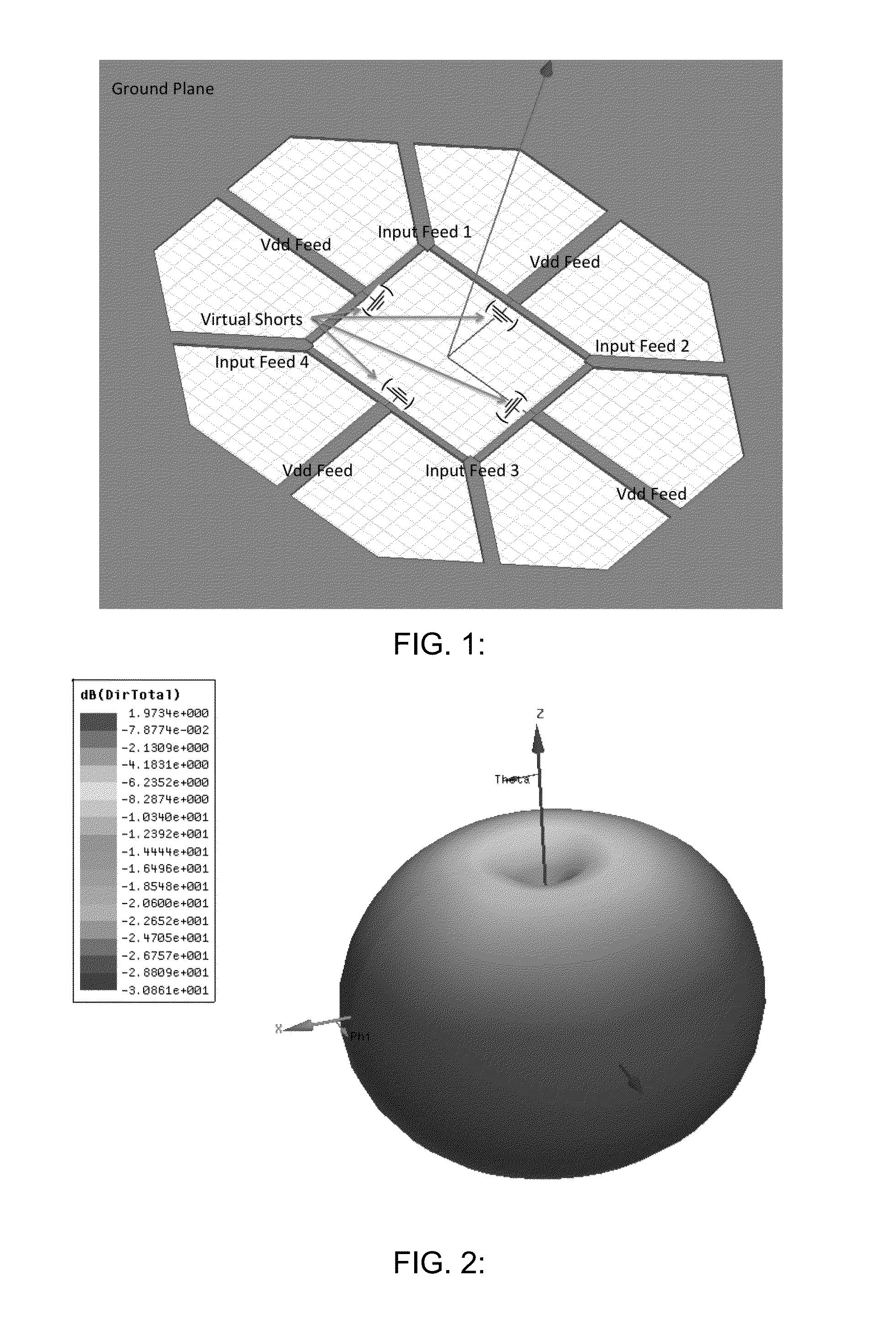
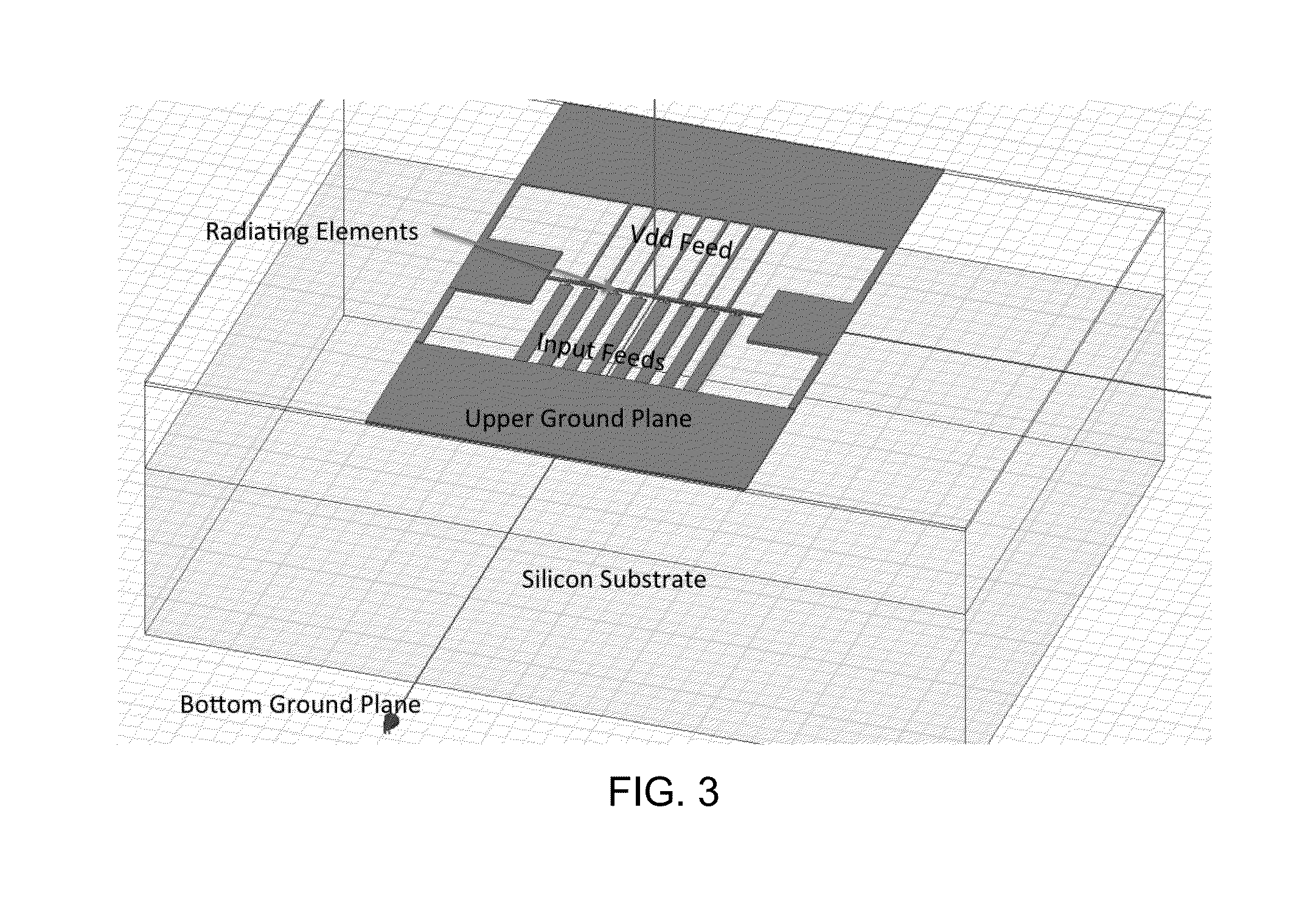
Efficient active multi-drive radiator
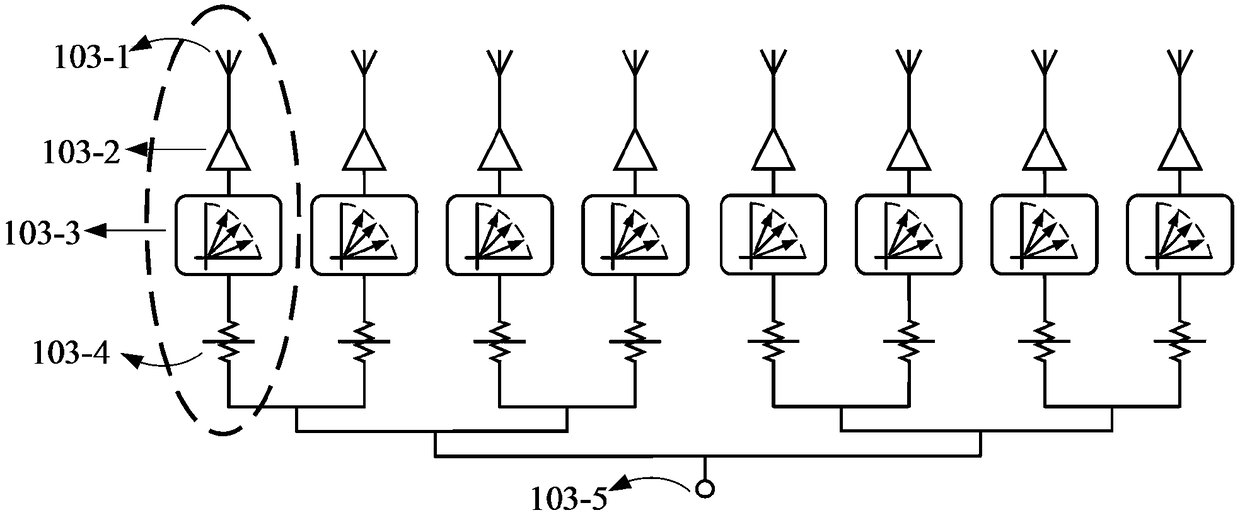
An integrated Multi-Port Driven (MPD) antenna that can be driven at many points with different signals. An integrated MPD radiating source utilizing an 8-phase ring oscillator and eight power amplifiers to drive the MPD antenna at 161 GHz with a total radiated power of −2 dBm and a single element EIRP of 4.6 dBm has been demonstrated in silicon with single lobe well behaved radiation patterns closely matching simulation.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for determining nonuniform link gain of flexible forwarding satellite system
ActiveCN104219766APrevent inversionReduce solution parametersNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesSystem capacityResource utilization
The invention discloses a method for determining nonuniform link gain of a flexible forwarding satellite system. The method includes performing resource distribution and link parameter setting; calculating link gain under different working point conditions; judging whether a link can be on or not; selecting an optimal working point for a forwarder; calculating an EIRP (effective isotropic radiated power) value of a ground uplink terminal and link gain. By the method, link gain of a nonuniform channel of the flexible forwarding satellite communication system can be determined simply and quickly, and system capacity and power resource utilization rate can be improved effectively.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for determining transmission power and a mobile communication device performing the method
ActiveUS20190349863A1Solve problemsPower managementEngineeringEquivalent isotropically radiated power
There is provided a method for determining transmission power. The method is performed by a wireless communication device and comprises: determining transmission power; and transmitting uplink signal based on the transmission power, wherein the transmission power meets a requirement for a minimum EIRP value for the spherical coverage, and wherein the requirement for the minimum EIRP value for the spherical coverage is predetermined based on a 50th percentile of a distribution of measured power.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for analyzing working performance of damaged satellite-earth data transmission antenna
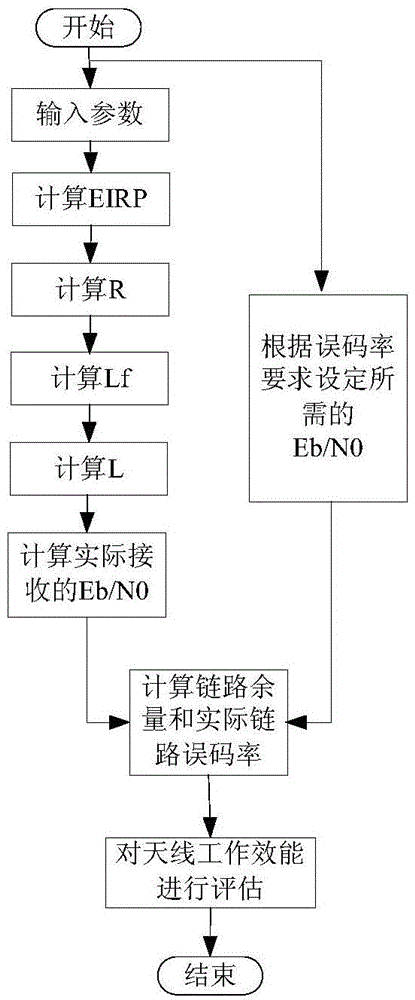
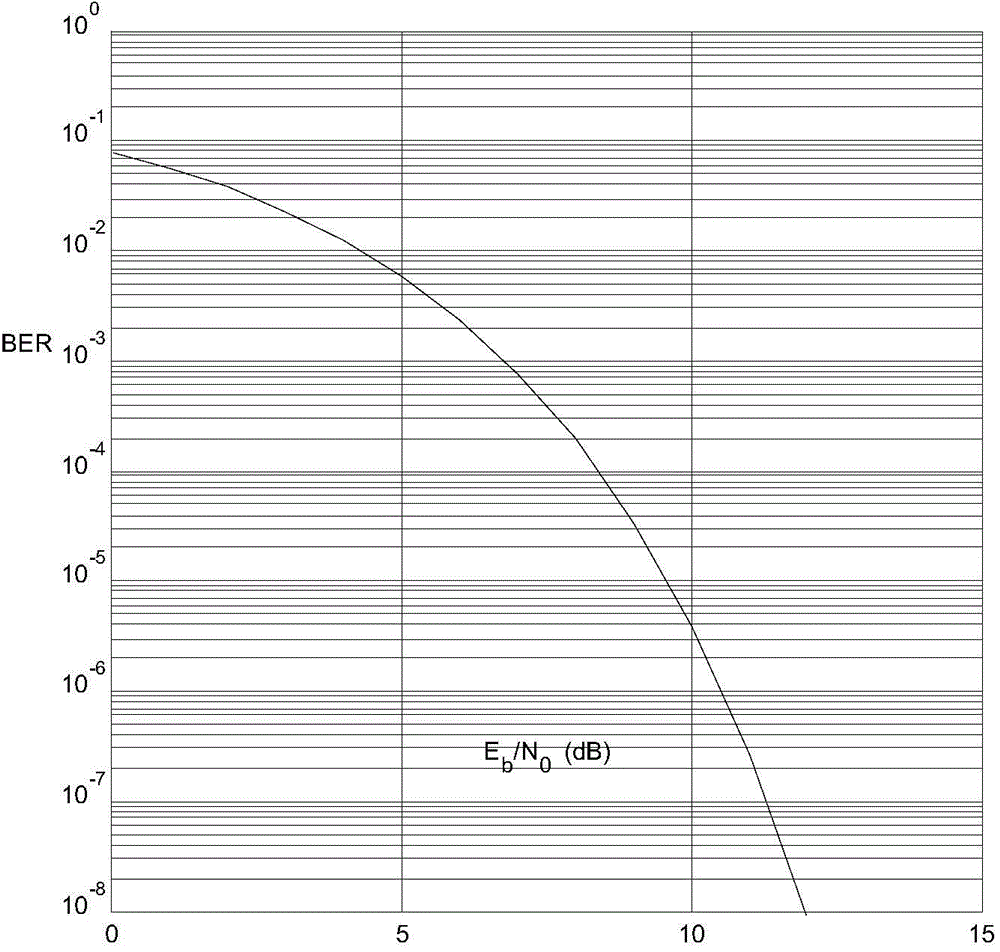
ActiveCN104467987AComprehensive assessment of work performance impactEase of evaluationTransmitters monitoringTerrainAntenna polarization
A method for analyzing the working performance of a damaged satellite-earth data transmission antenna comprises the steps of (1) calculating the equivalent isotropic radiated power (EIRP) of a satellite according to the output power of a satellite transmitter, satellite antenna gain and the transmission channel loss value; (2) calculating the maximum slant range R of signal transmission according to the mean terrain level of a satellite and the minimum elevation of a ground receiving antenna; (3) calculating the free space loss Lf of a signal according to the downlink carrier frequency of the satellite data transmission signal and R; (4) calculating all transmission losses L of the data transmission signal according to the atmosphere loss, the directivity loss of the receiving antenna, the polarization loss and atmosphere value of the receiving antenna and Lf; (5) calculating the bit signal to noise ratio of a received signal by means of the coding gain, the transmission code rate, the coding rate and the link margin; (6) calculating the bit signal to noise ratio actually needed by the received signal according to bit error rate requirements so as to obtain the channel margin, wherein if the margin is positive, the overall performance of the damaged data transmission antenna can still meet the requirements of a system, and the working performance of the data transmission antenna is affected otherwise.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Apparatus and method for enquiring channel condition information in cognitive radio wireless communication system
A method of operating a Data Base (DB) server for storing spectrum condition information on a licensed system in a Cognitive Radio (CR)-based wireless communication system and a CR-based wireless communication system are provided. The method includes determining changes in the spectrum condition information on the licensed system, recalculating maximum Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power (EIRP) allowed for each channel of CR-based devices registered in a list, and transmitting information regarding the recalculated maximum allowed EIRP.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
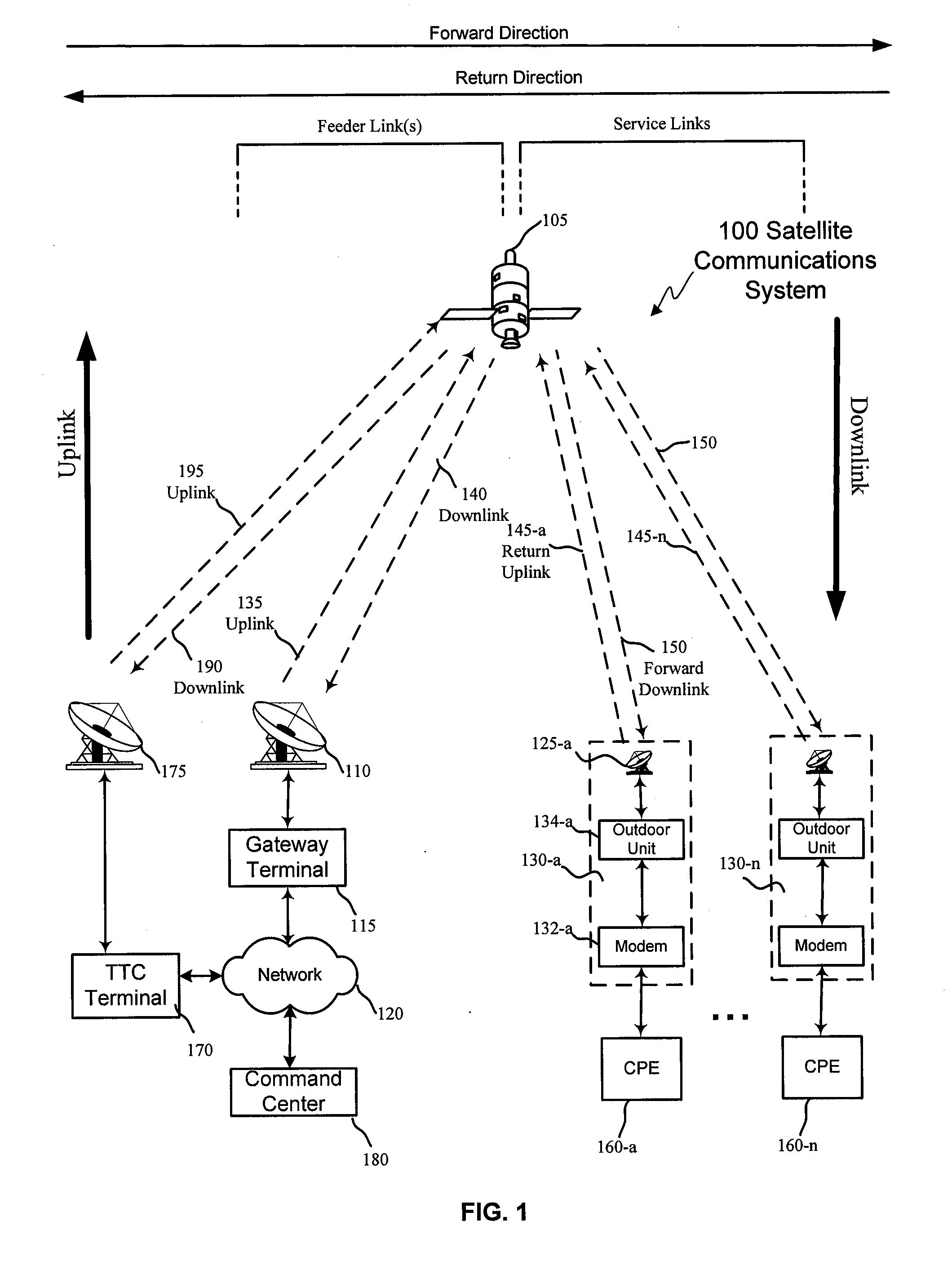
Satellite communication device, satellite communication system comprising such a device and method for managing the resources allocated within such a system
InactiveUS20150156734A1Palliate problemPower managementTransmission systemsComputer terminalEngineering
In the field of satellite communication systems, a method is provided for managing communication resources allocated by central control equipment to the various terminal communication devices within a global satellite communication system. In particular, the management of communication resources by way of the monitoring of the equivalent isotropically radiated power transmitted by a terminal of the satellite communication system is provided.
Owner:THALES SA
Apparatus and method for enquiring channel condition information in cognitive radio wireless communication system
A method of operating a Data Base (DB) server for storing spectrum condition information on a licensed system in a Cognitive Radio (CR)-based wireless communication system and a CR-based wireless communication system are provided. The method includes determining changes in the spectrum condition information on the licensed system, recalculating maximum Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power (EIRP) allowed for each channel of CR-based devices registered in a list, and transmitting information regarding the recalculated maximum allowed EIRP.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
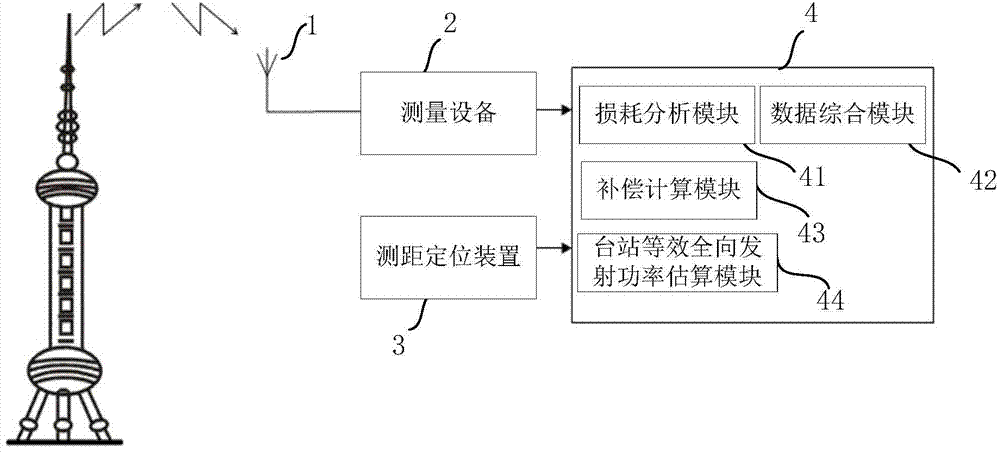
Radiation testing system for simulation television station transmitting power under open ground environment
InactiveCN104735446AComprehensive monitoringAccurate monitoringTelevision systemsTransmitted powerTelevision station
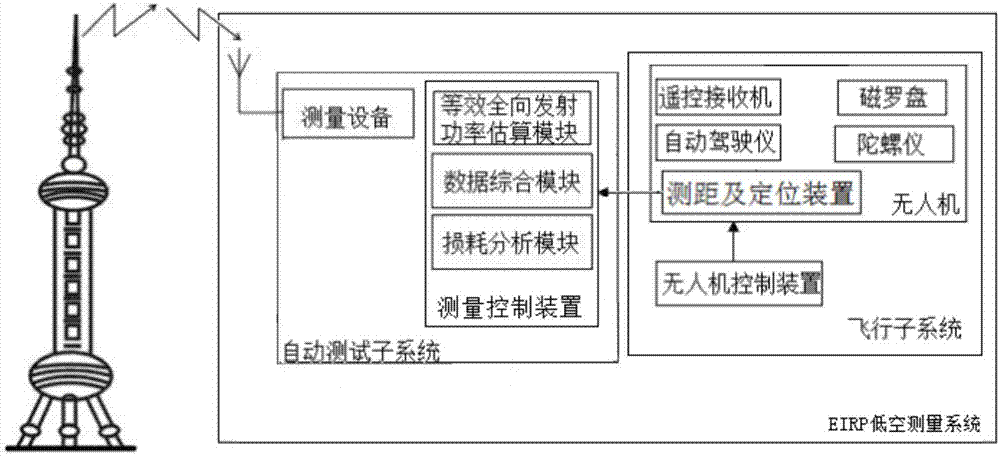
The invention provides a radiation testing system for simulation television station transmitting power under an open ground environment, and belongs to the field of radio transmission system performance index testing. The testing system comprises a directional receiving antenna, power measuring equipment, a ranging and locating device and a control device; the directional receiving antenna is used for receiving electromagnetic waves transmitted by a simulation television station, converting the electromagnetic waves into electric signals and transmitting the electric signals to the power measuring equipment; the power measuring equipment calculates the peak power Pr incident on the receiving antenna according to the electric signals; the ranging and locating device is used for measuring the height h1 of a transmitting antenna, the height h2 of the receiving antenna and the distance L between the receiving antenna and the transmitting antenna; the control module comprises a equivalent isotropic radiated power estimating module, and the equivalent isotropic radiated power estimating module is used for calculating the equivalent isotropic radiated power (EIRP) of a tested station. The radiation testing system for the simulation television station transmitting power under the open ground environment can achieve more comprehensive and accurate monitoring on a station radio transmission system including transmitters and antenna feed systems, and therefore the working flexibility and autonomy are greatly improved.
Owner:国家无线电监测中心 +2
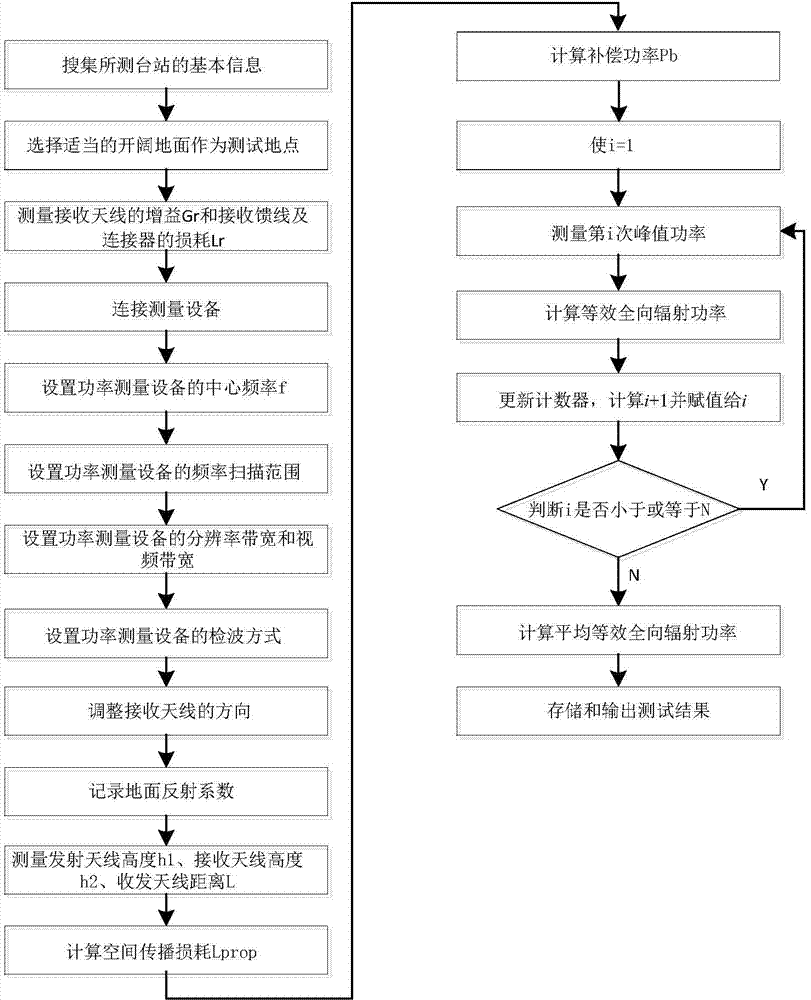
300MHz-800MHz simulation television station transmitting power radiation testing method
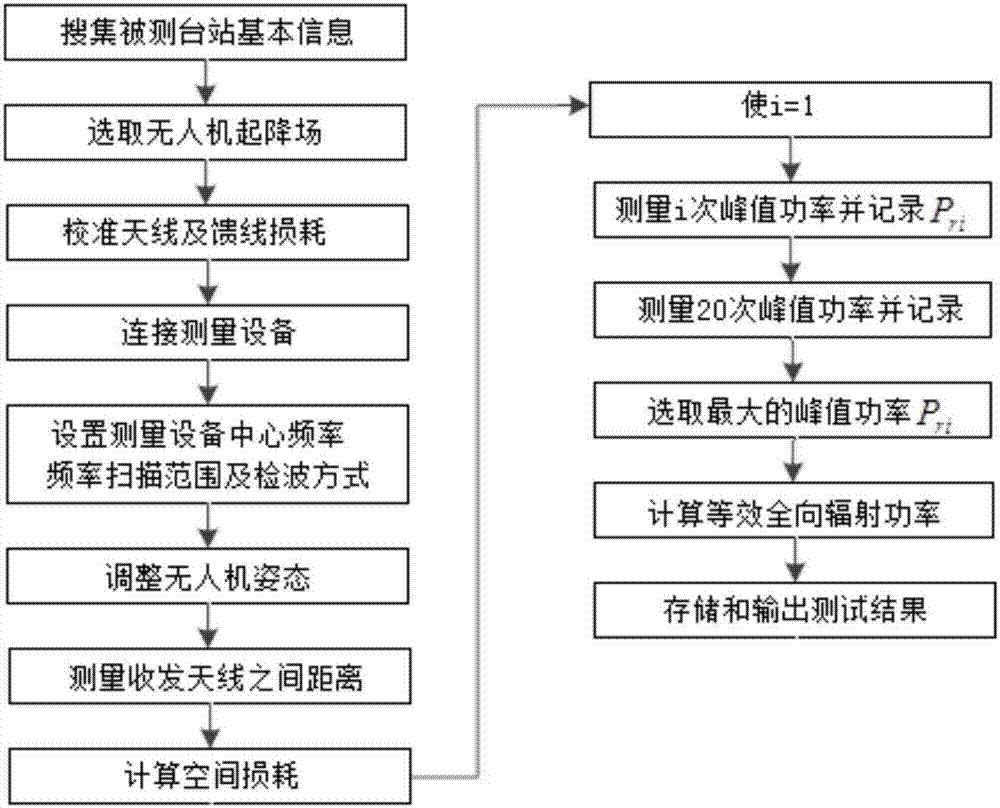
ActiveCN107968686AComprehensive monitoringAccurate monitoringTelevision system detailsTransmitters monitoringTerrainTransmitted power
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle low-altitude radiation testing method for the transmitting power of a 300MHz-800MHz simulation television station and belongs to the field of testingof performance indexes of the radio station equipment. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, information of a tested simulation television station is collected, and the unmanned aerial vehicle and the measuring equipment are preprocessed; then, the receiving antenna of the unmanned aerial vehicle is aligned to the transmitting antenna of the tested station, the unmanned aerial vehicle receives the control of an unmanned aerial vehicle control device in the air, and the attitude is adjusted in real time; the distance between the transmitting antenna and the receiving antenna is measured through a distance measuring and positioning device; finally, the measuring equipment calculates the transmission path loss A and converts an electromagnetic wave into an electric signal, the peak power Pr transmitted to the receiving antenna is calculated according to the electric signal, and the equivalent isotropic radiated power EIRP of the tested station is calculated. According to themethod in the invention, the terrain limitation is greatly reduced, the performance indexes of the broadcast television station equipment are more comprehensively and accurately detected so as to obtain a relatively high precision test result; and the timeliness, the flexibility and the autonomy of the detection work of the broadcast television station equipment are improved.
Owner:国家无线电监测中心
Efficient active multi-drive radiator
An integrated Multi-Port Driven (MPD) antenna that can be driven at many points with different signals. An integrated MPD radiating source utilizing an 8-phase ring oscillator and eight power amplifiers to drive the MPD antenna at 161 GHz with a total radiated power of −2 dBm and a single element EIRP of 4.6 dBm has been demonstrated in silicon with single lobe well behaved radiation patterns closely matching simulation.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
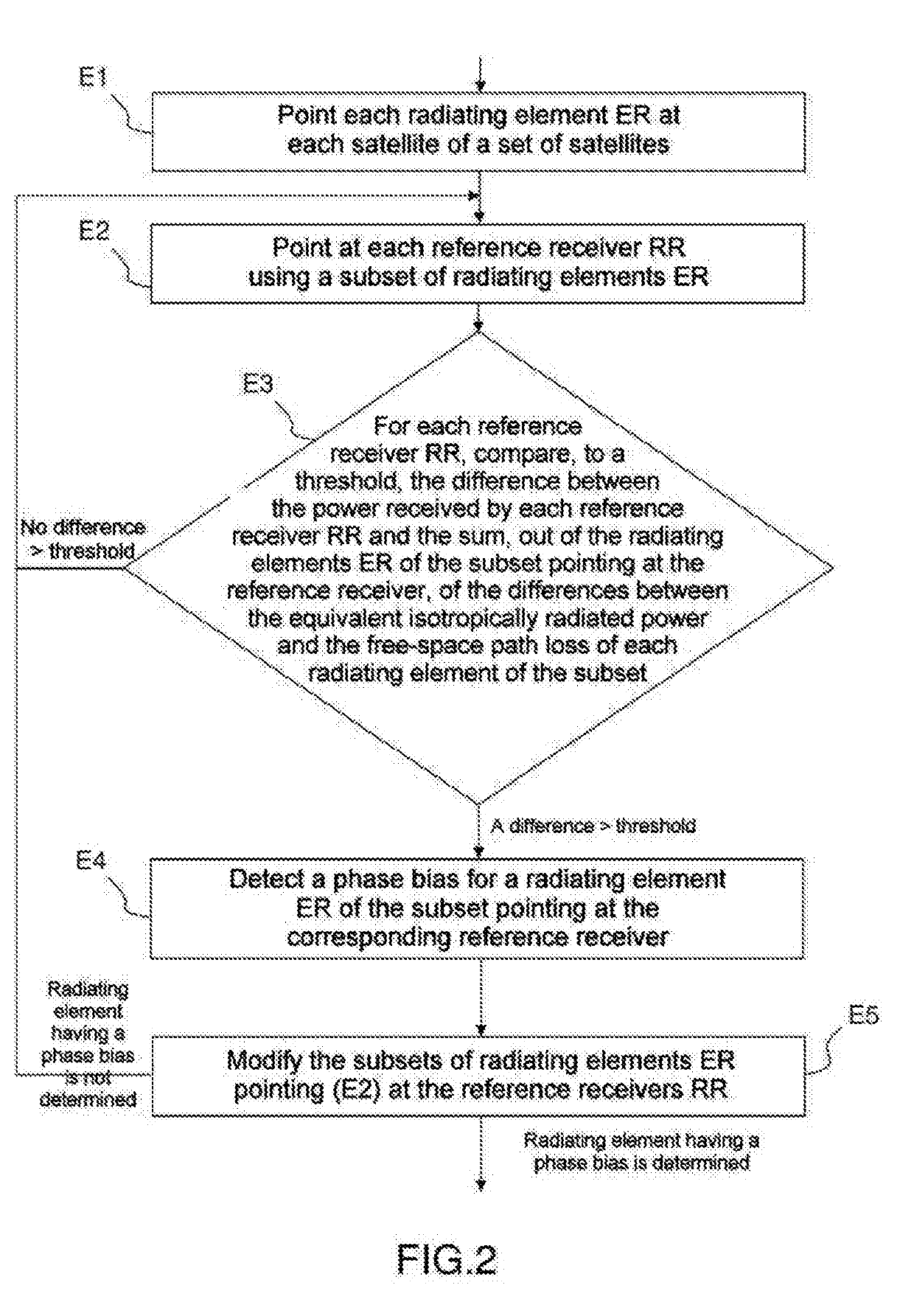
Method for determining a phase bias in the signal transmitted by at least one of the radiating elements of an active antenna, and associated device
ActiveUS20190113594A1Improve beamformingIncrease constraintsTransmitters monitoringBeacon systems using radio wavesSpace-division multiple accessEquivalent isotropically radiated power
A method for determining a phase bias in the signal transmitted by at least one of the radiating elements of an active antenna on the ground emitting signals into space using a space-division multiple access SDMA method, implementing a step, for each reference receiver, of comparing, to a threshold, the difference between the value of a measurement of the power received by each reference receiver and the sum, out of the radiating elements of the subset beamforming in the direction of the reference receiver, of the differences between the equivalent isotropically radiated power in the direction of the reference receiver and the free-space path loss of each radiating element of the subset.
Owner:THALES SA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com