Patents
Literature
88 results about "Flexion extension" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
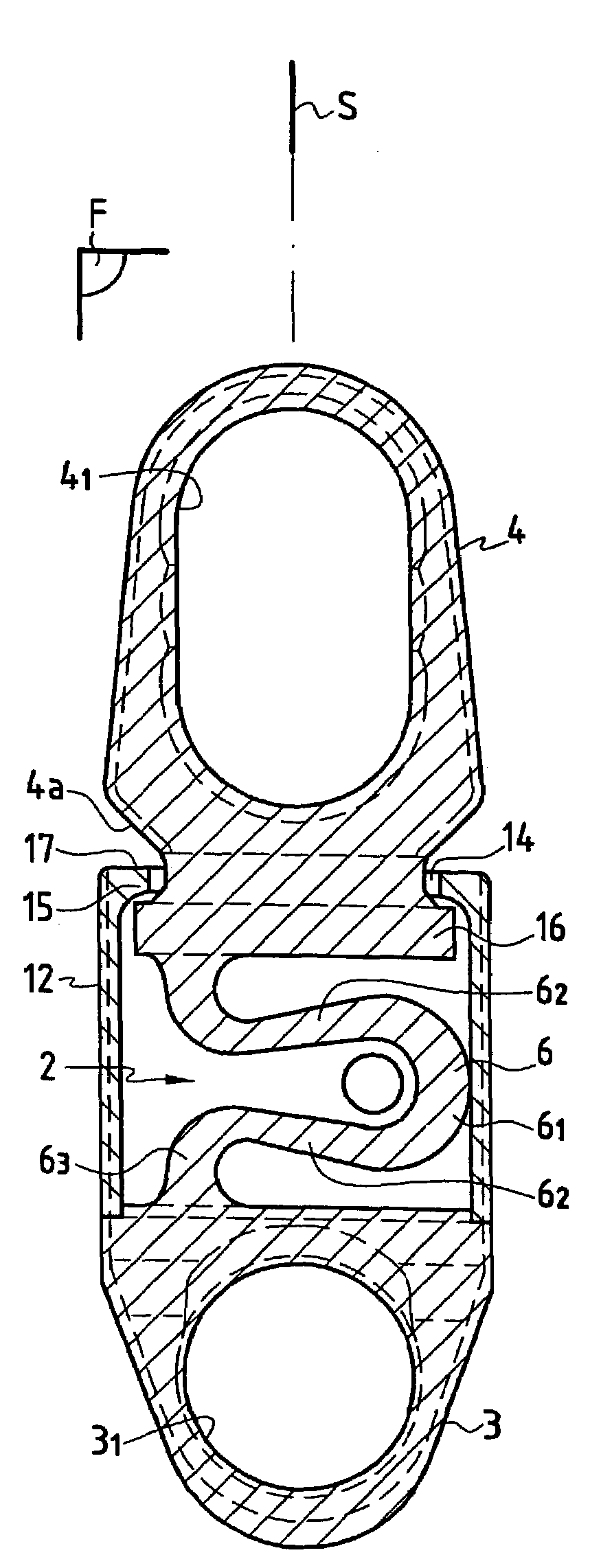
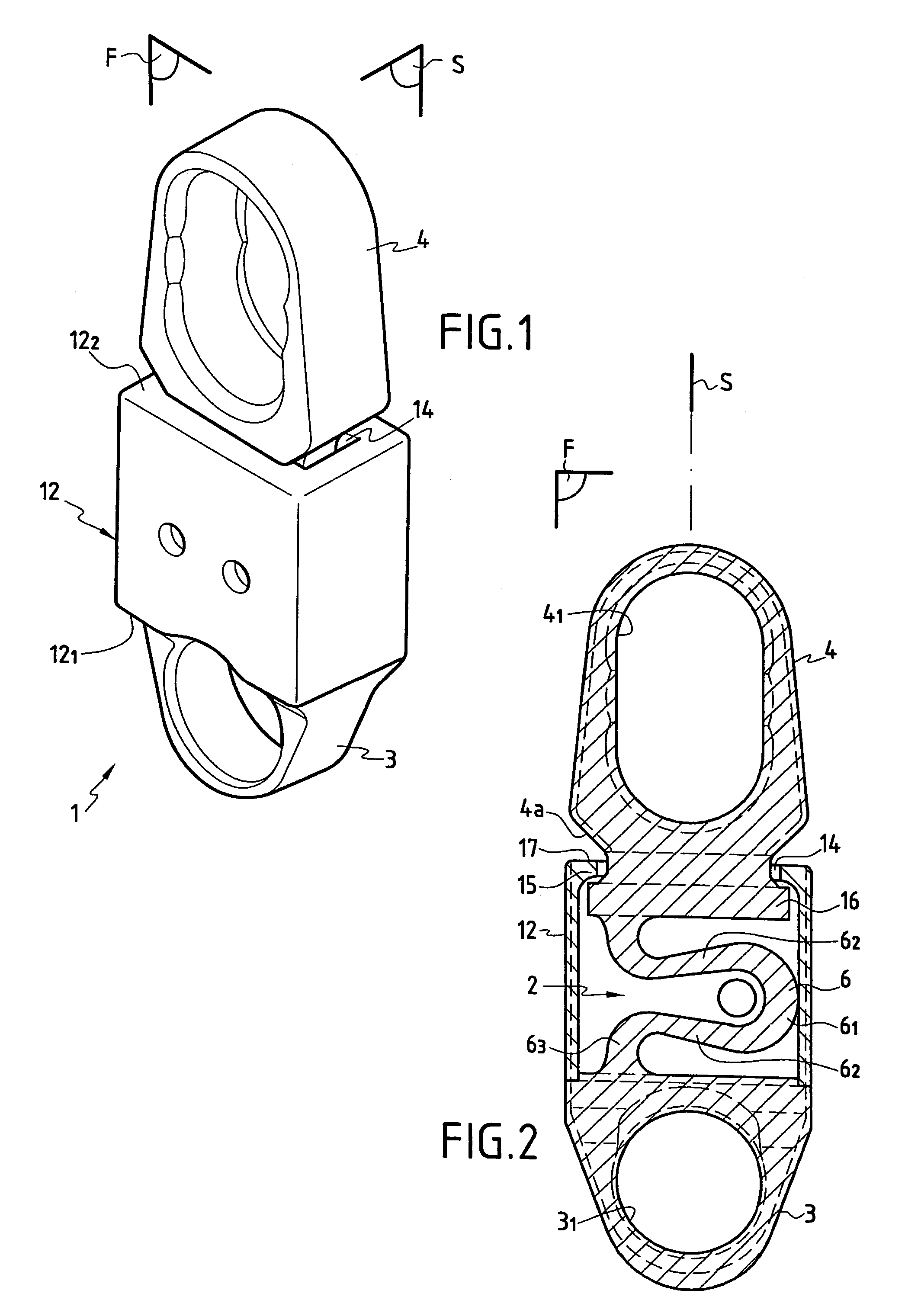
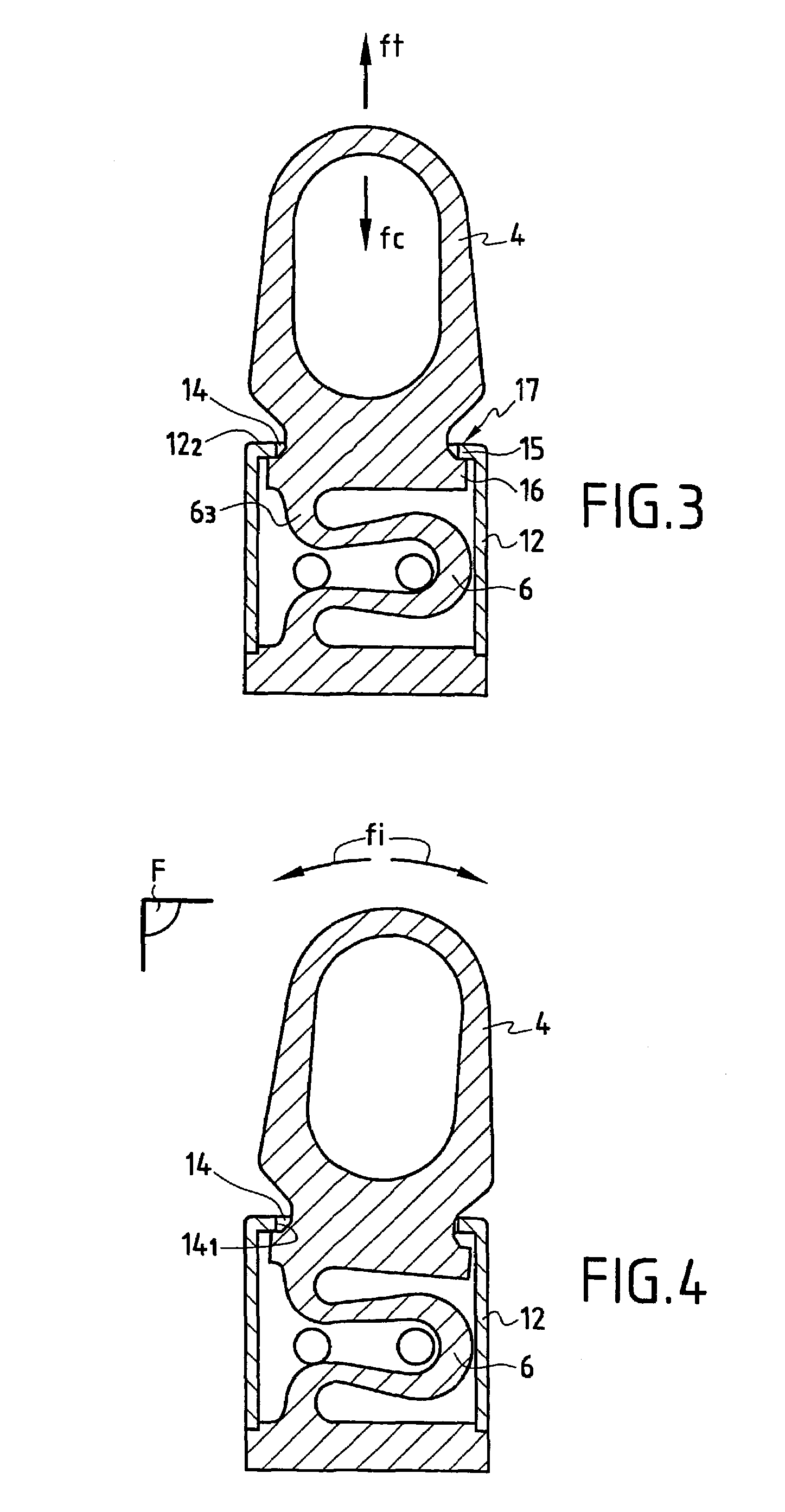
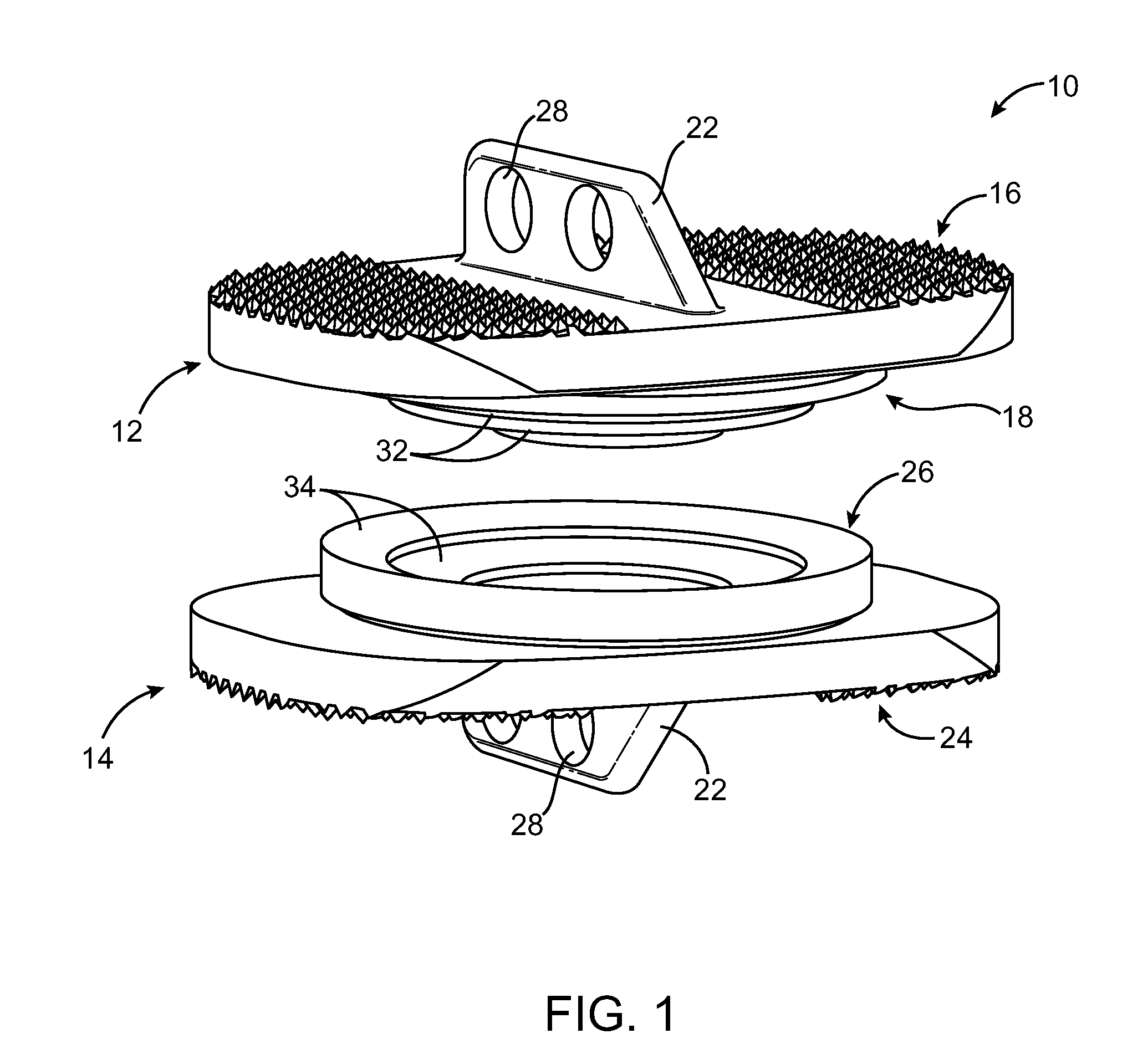
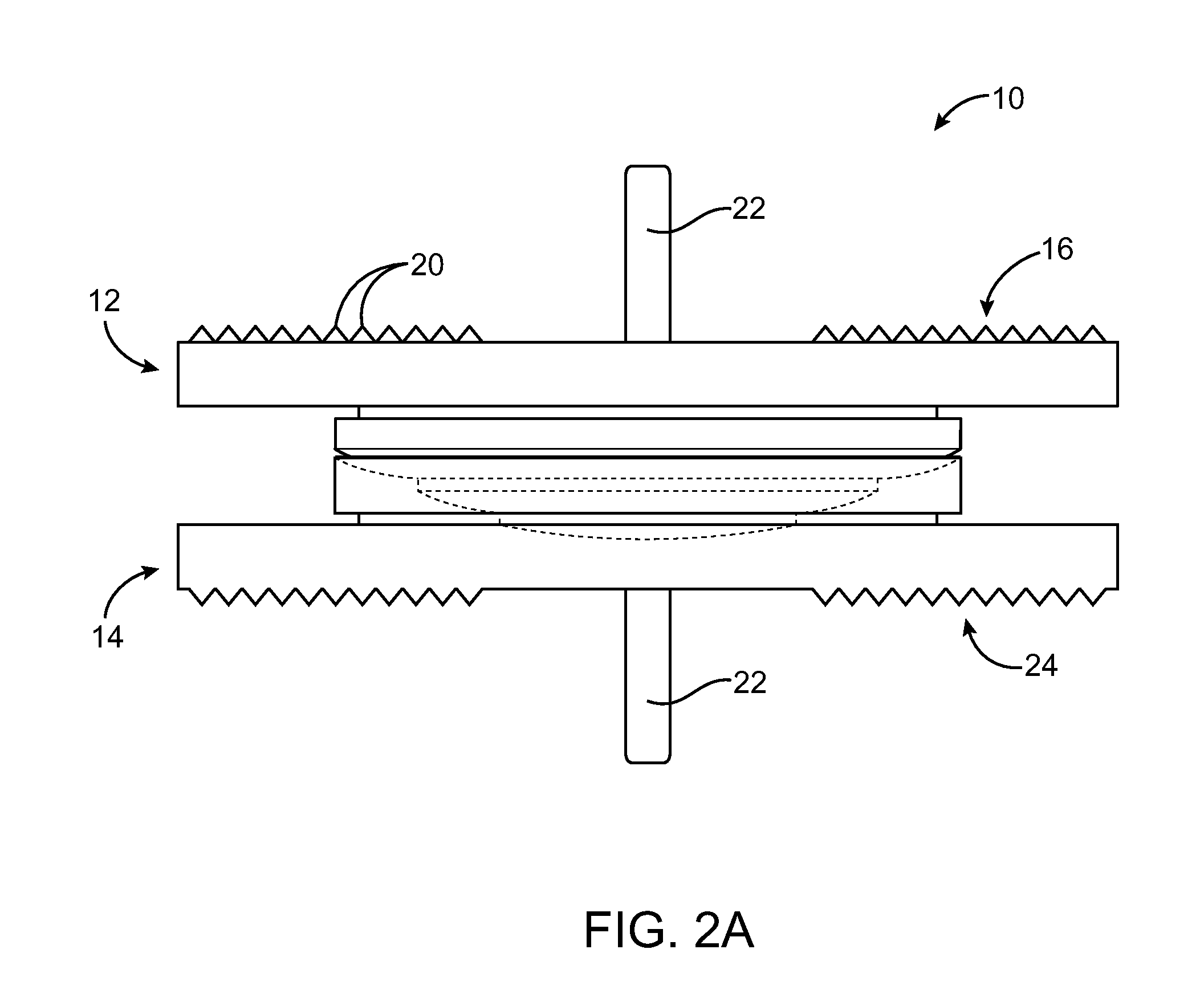
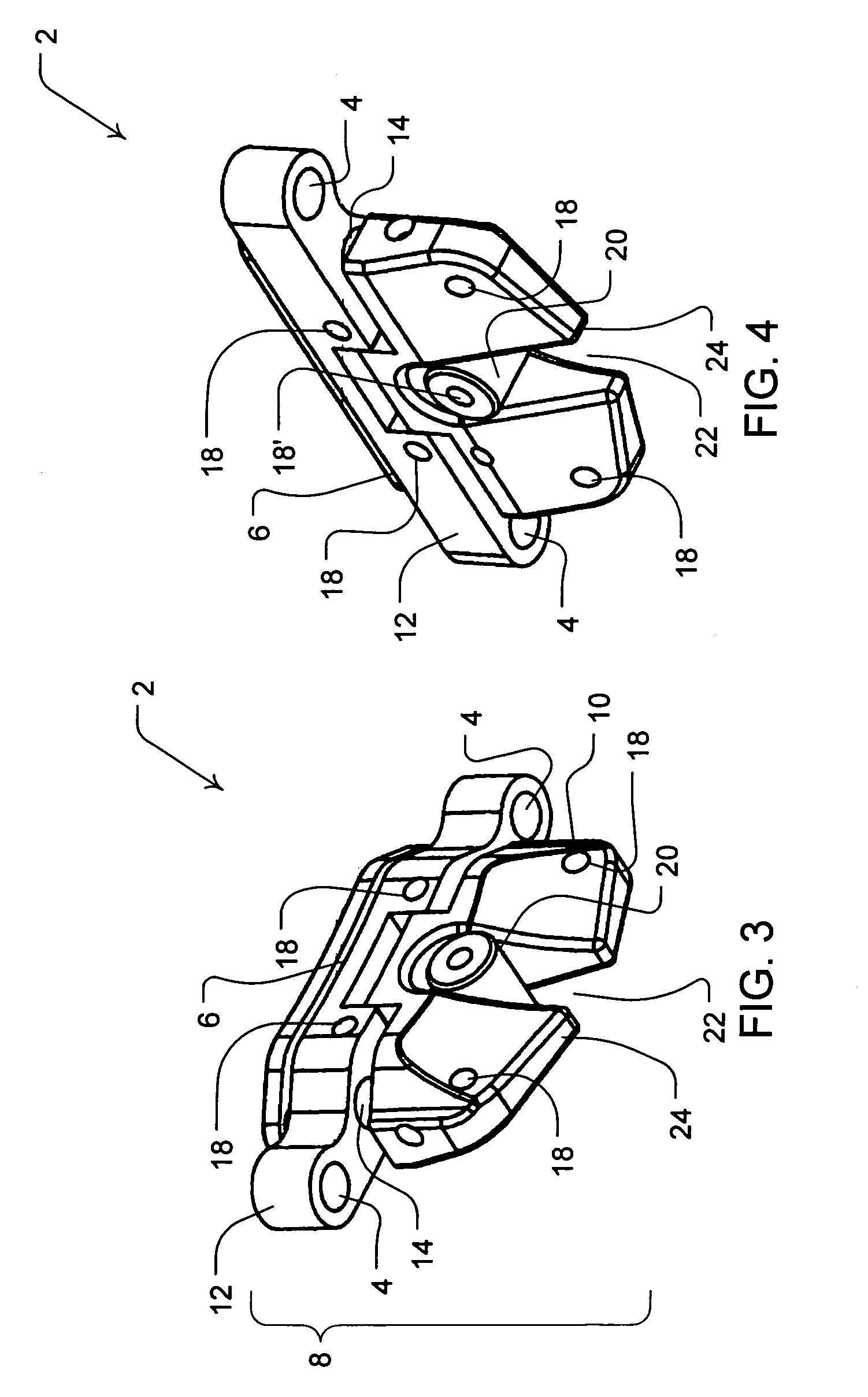
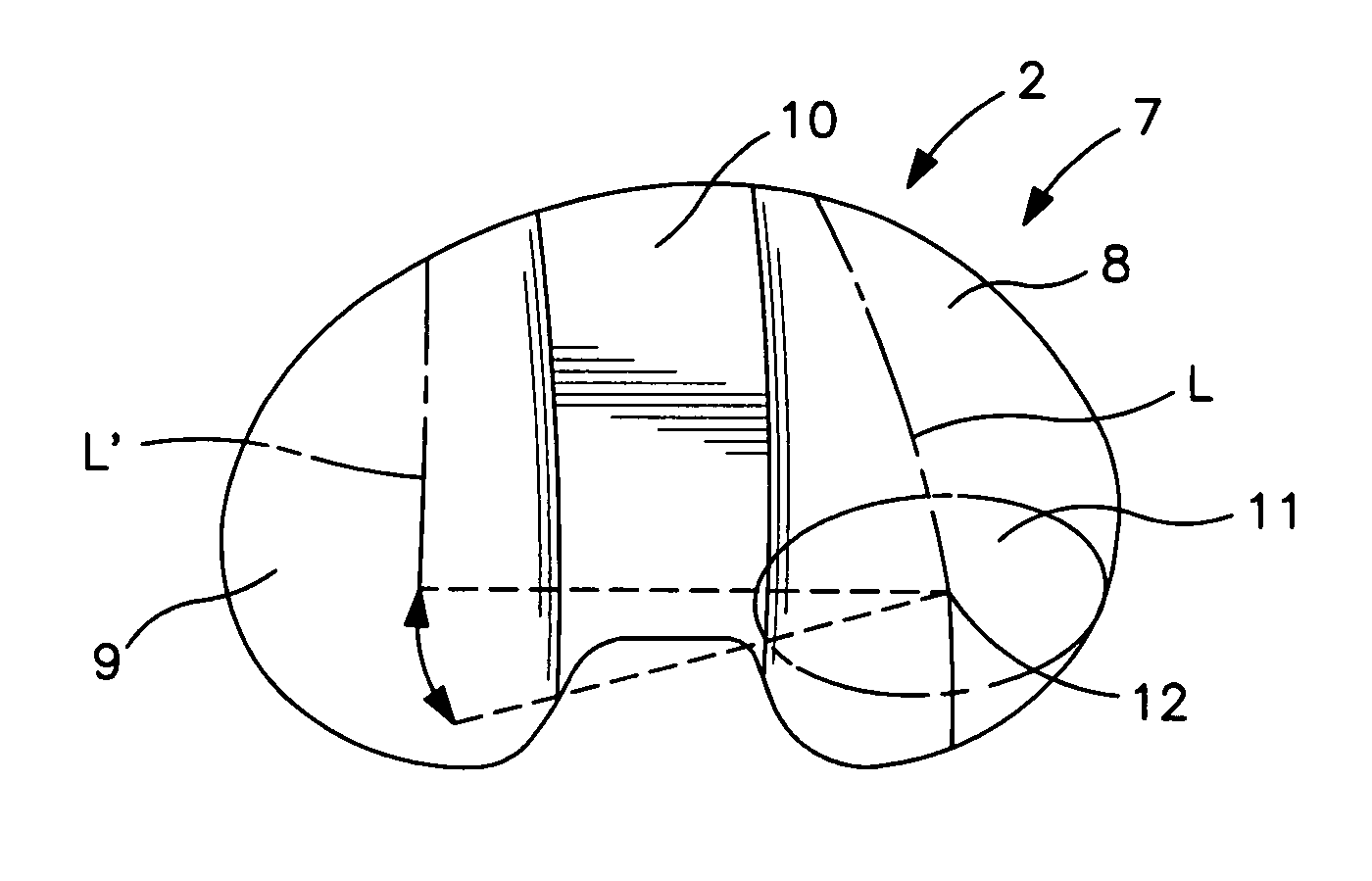
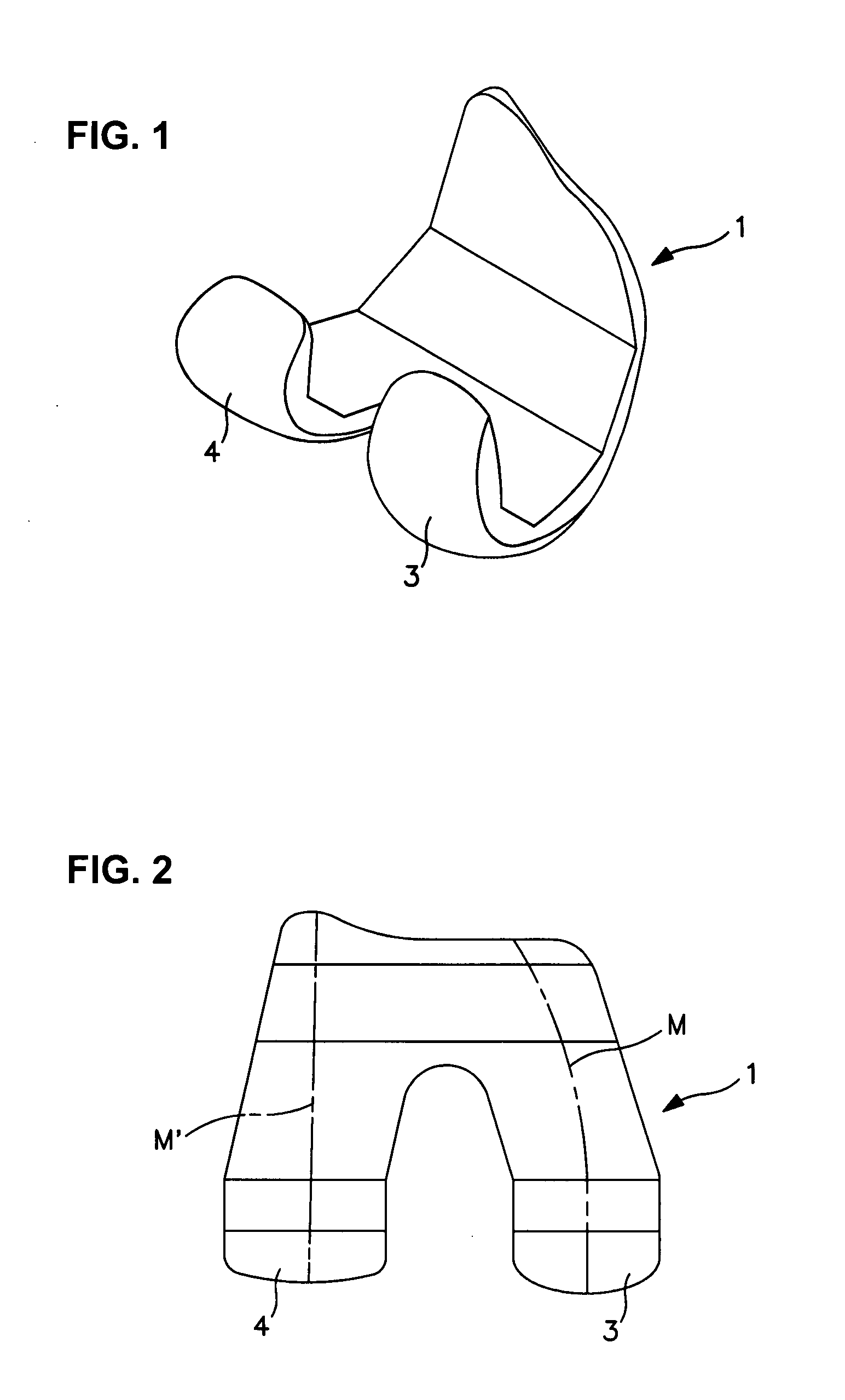
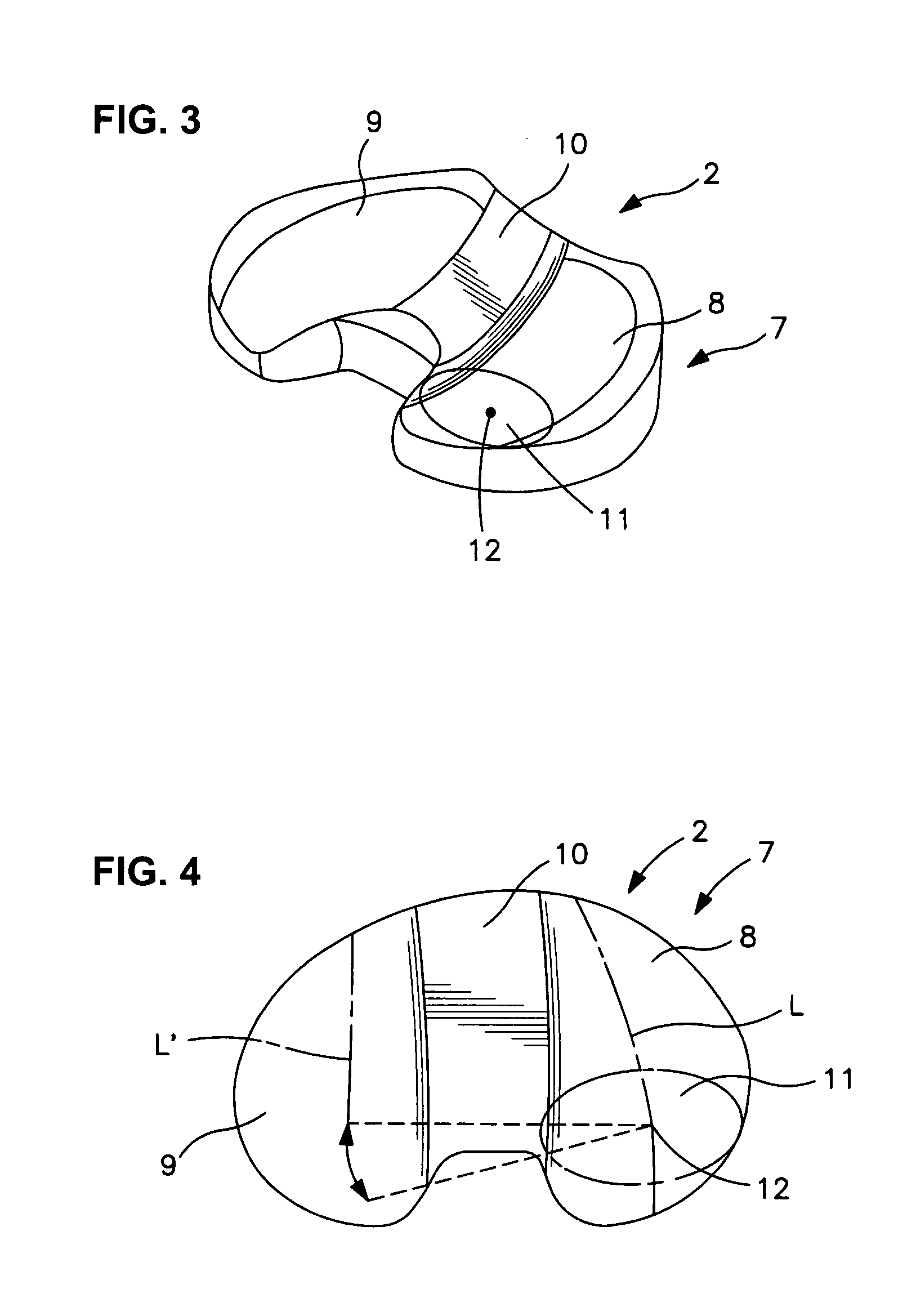
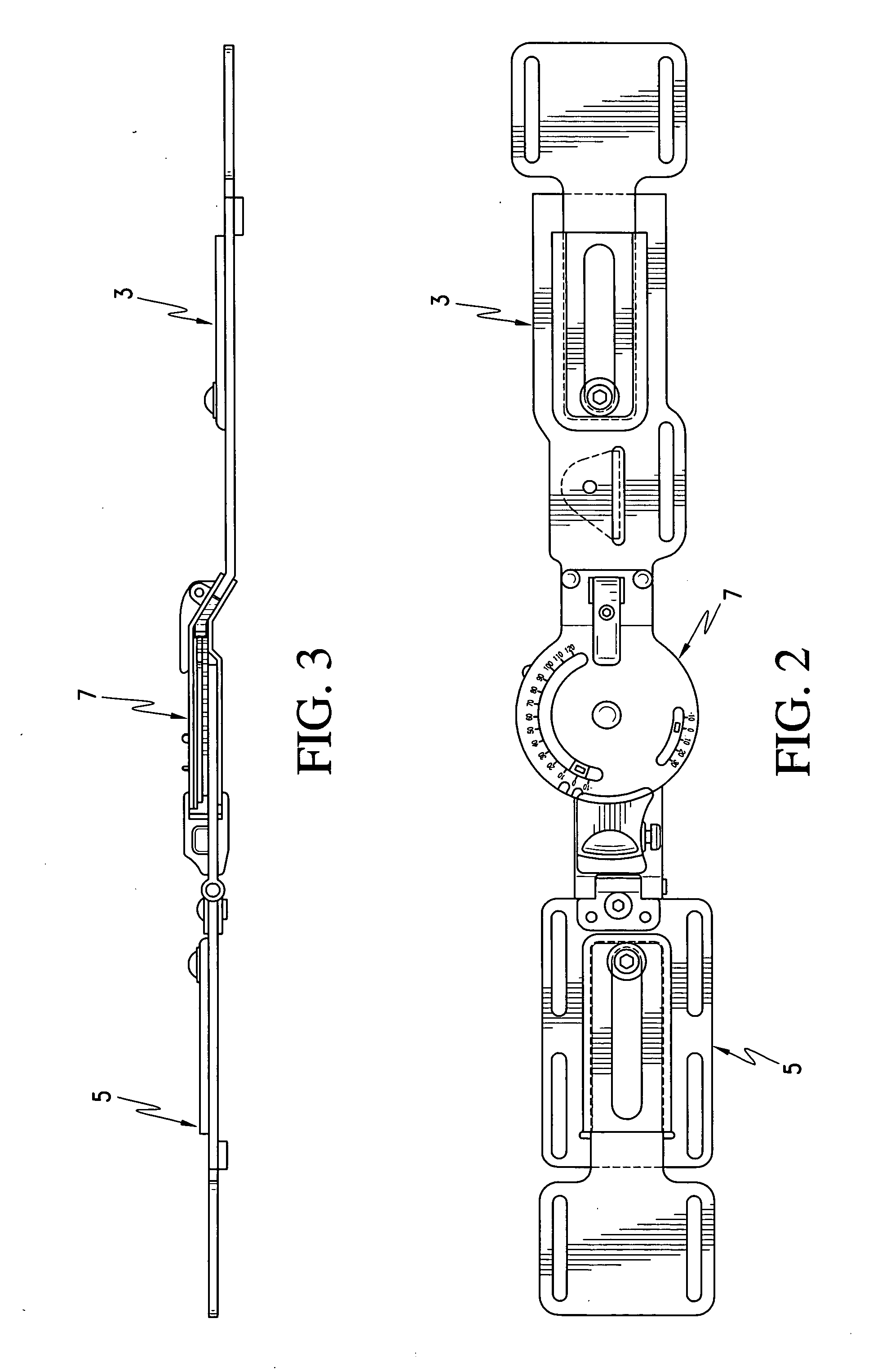
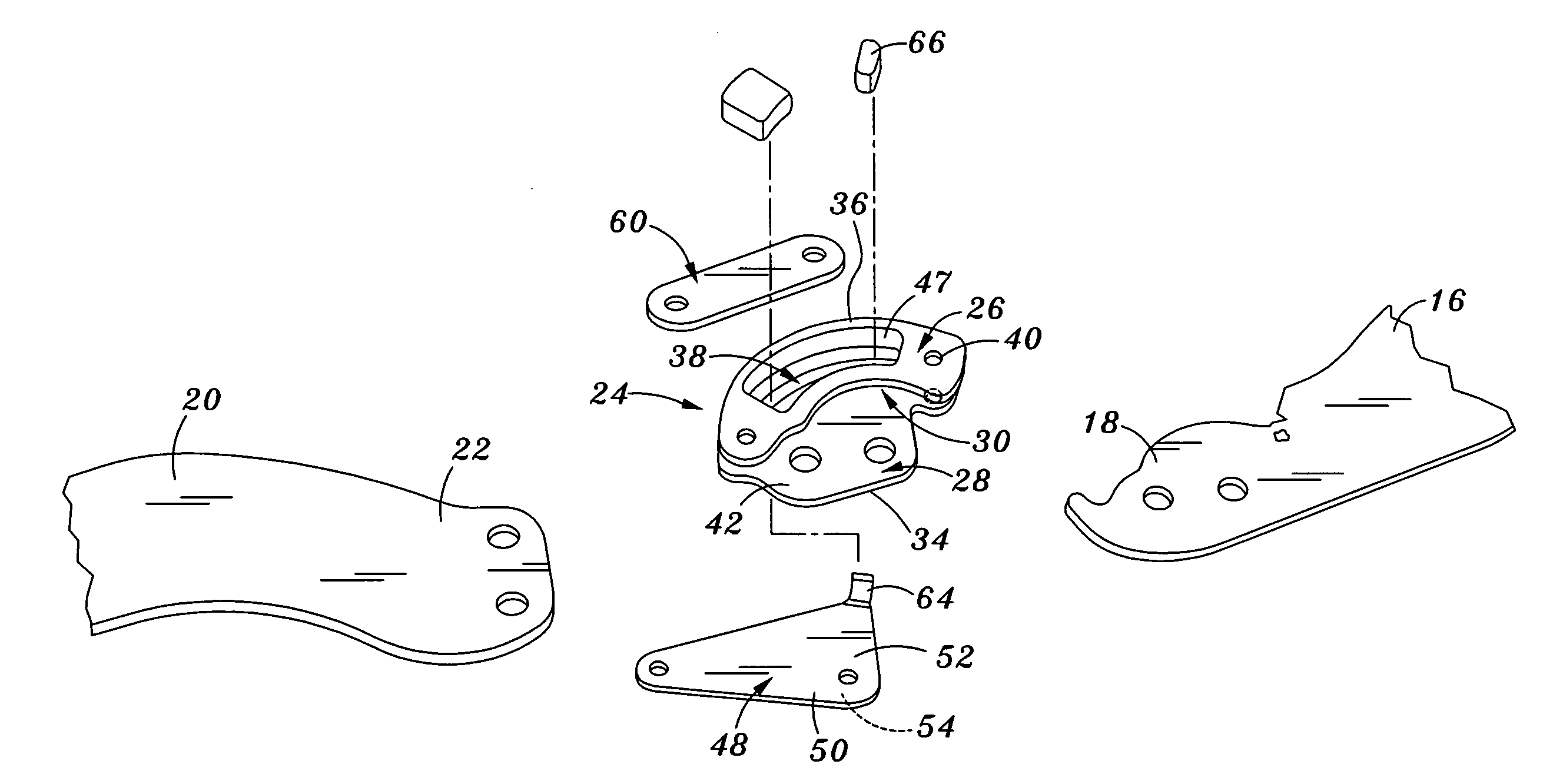
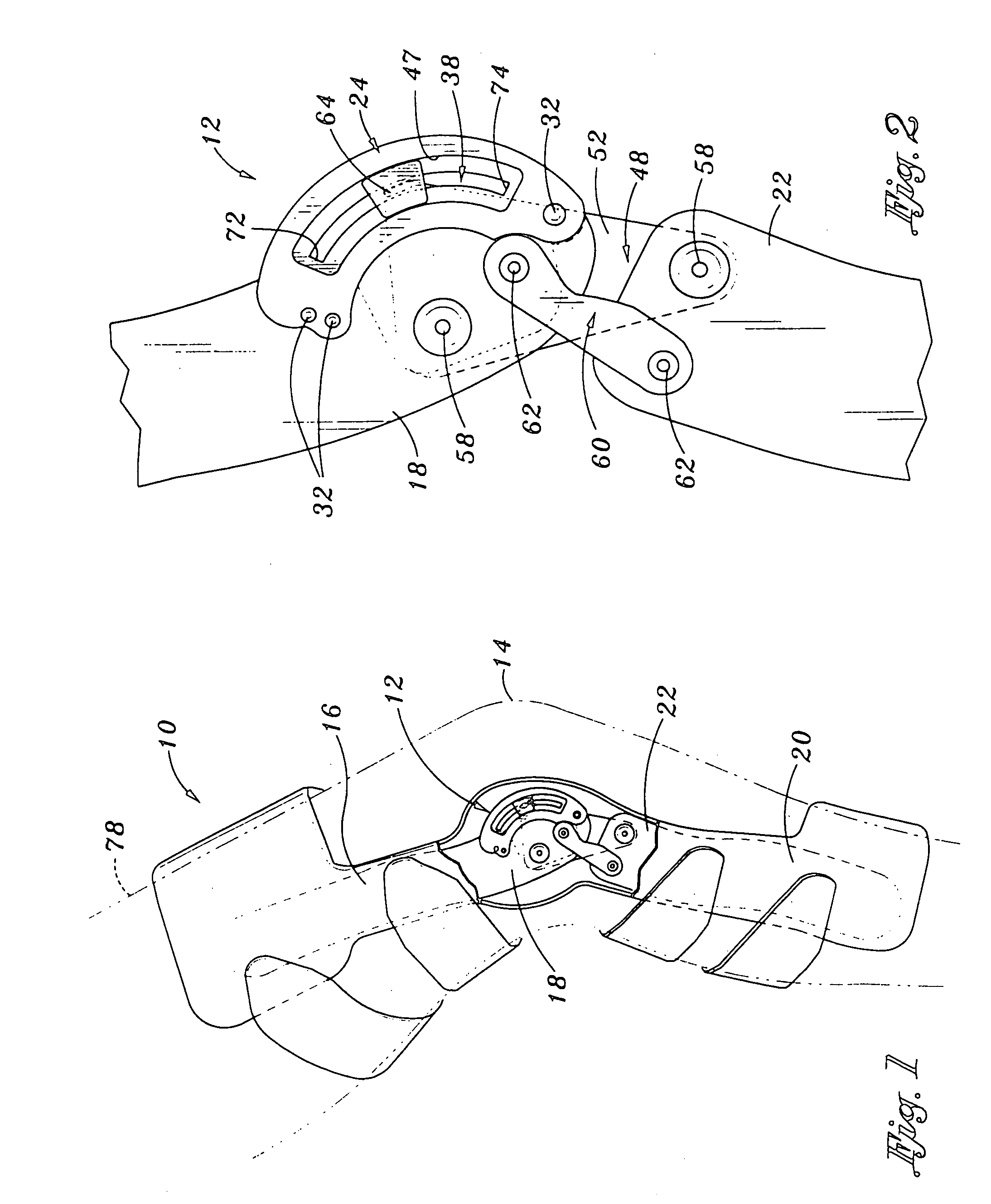
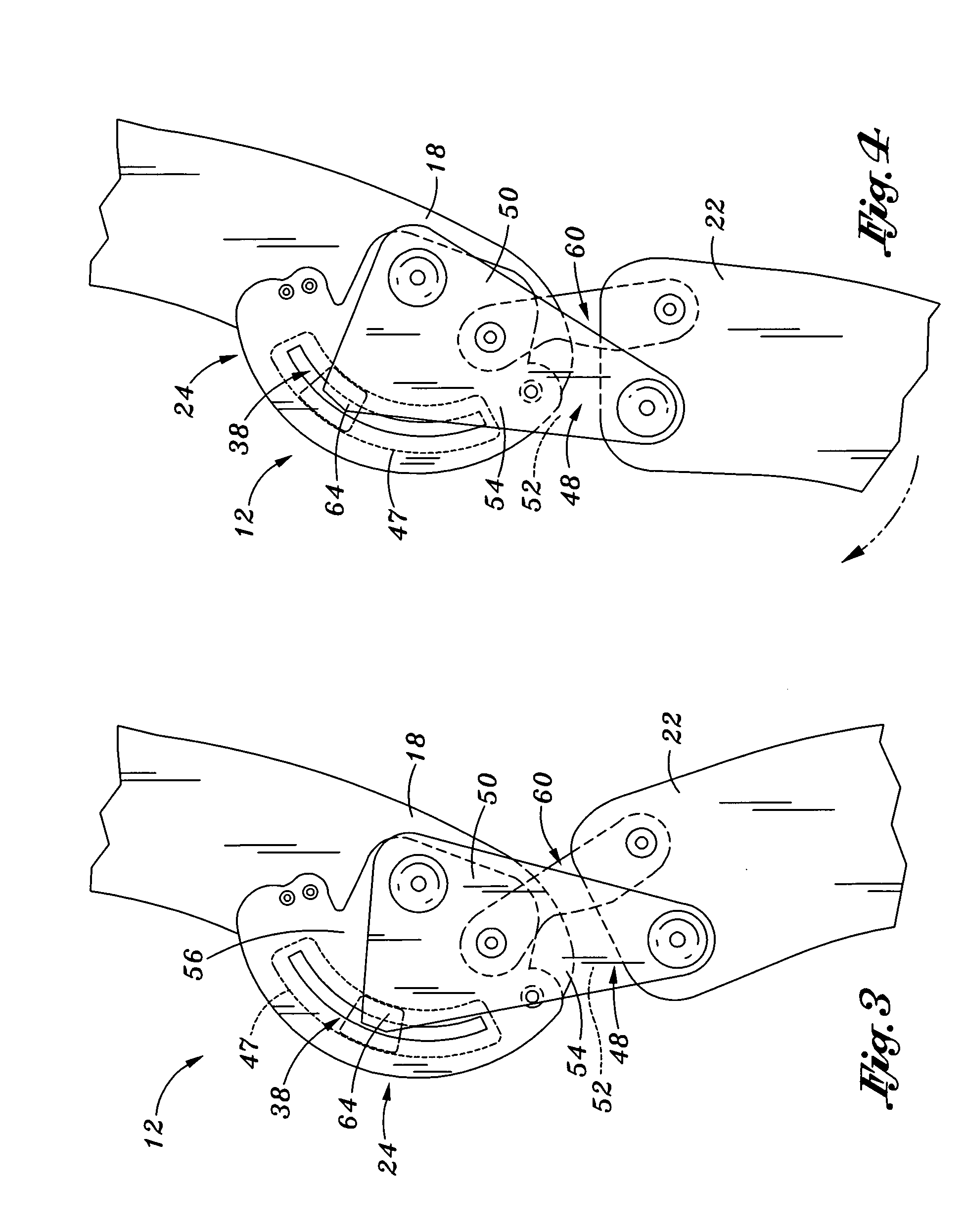
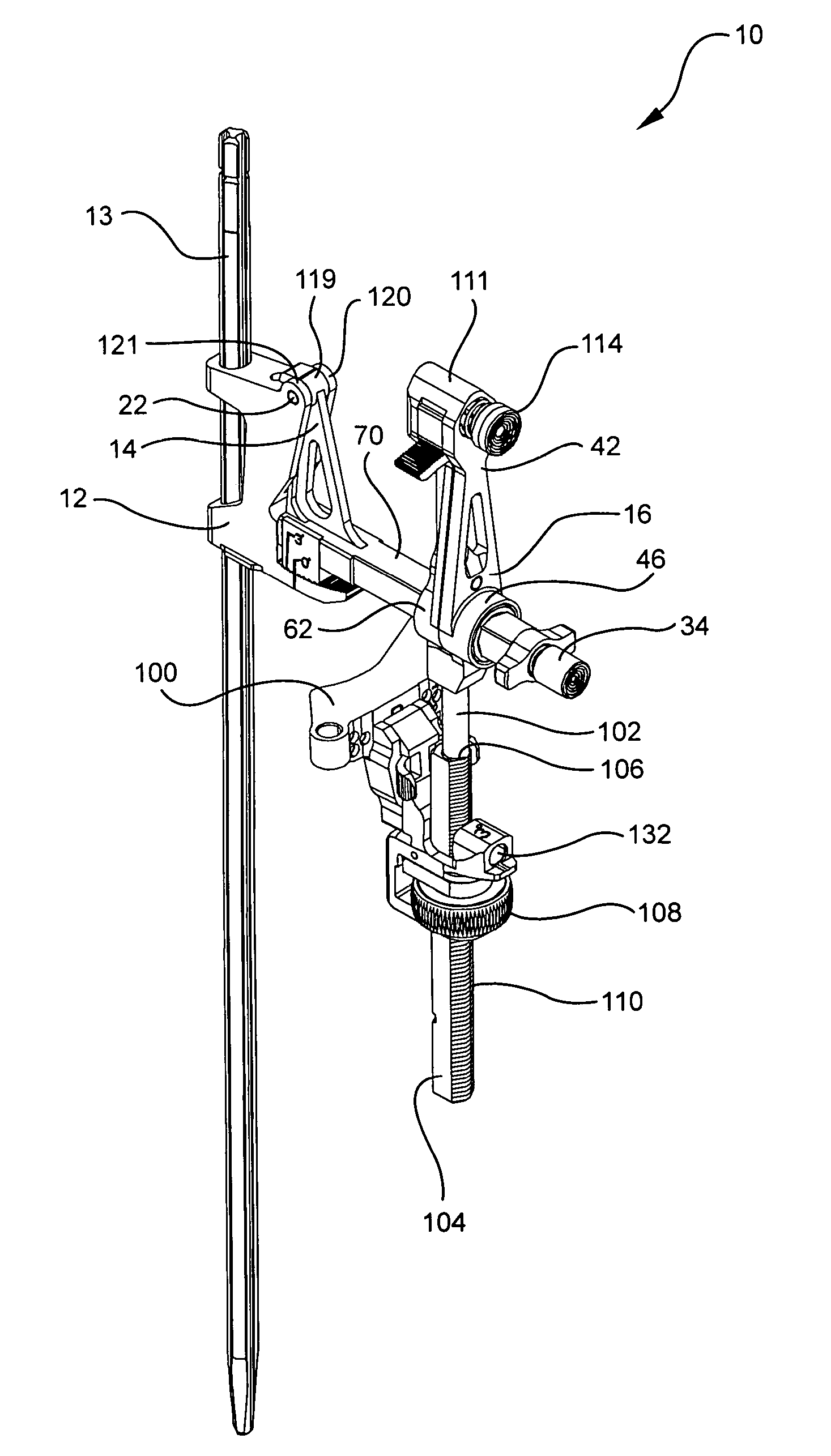
Spine stabilization system
InactiveUS6989011B2Relief the painPrevent rotationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringImage stabilization
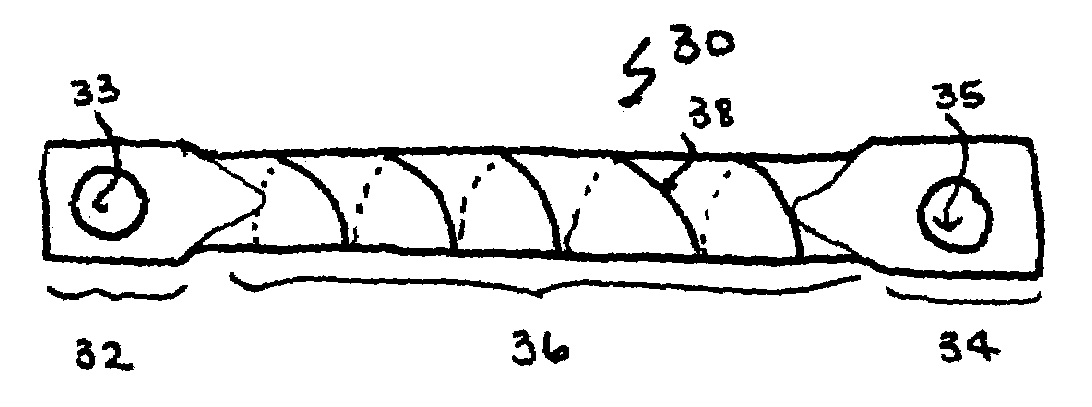
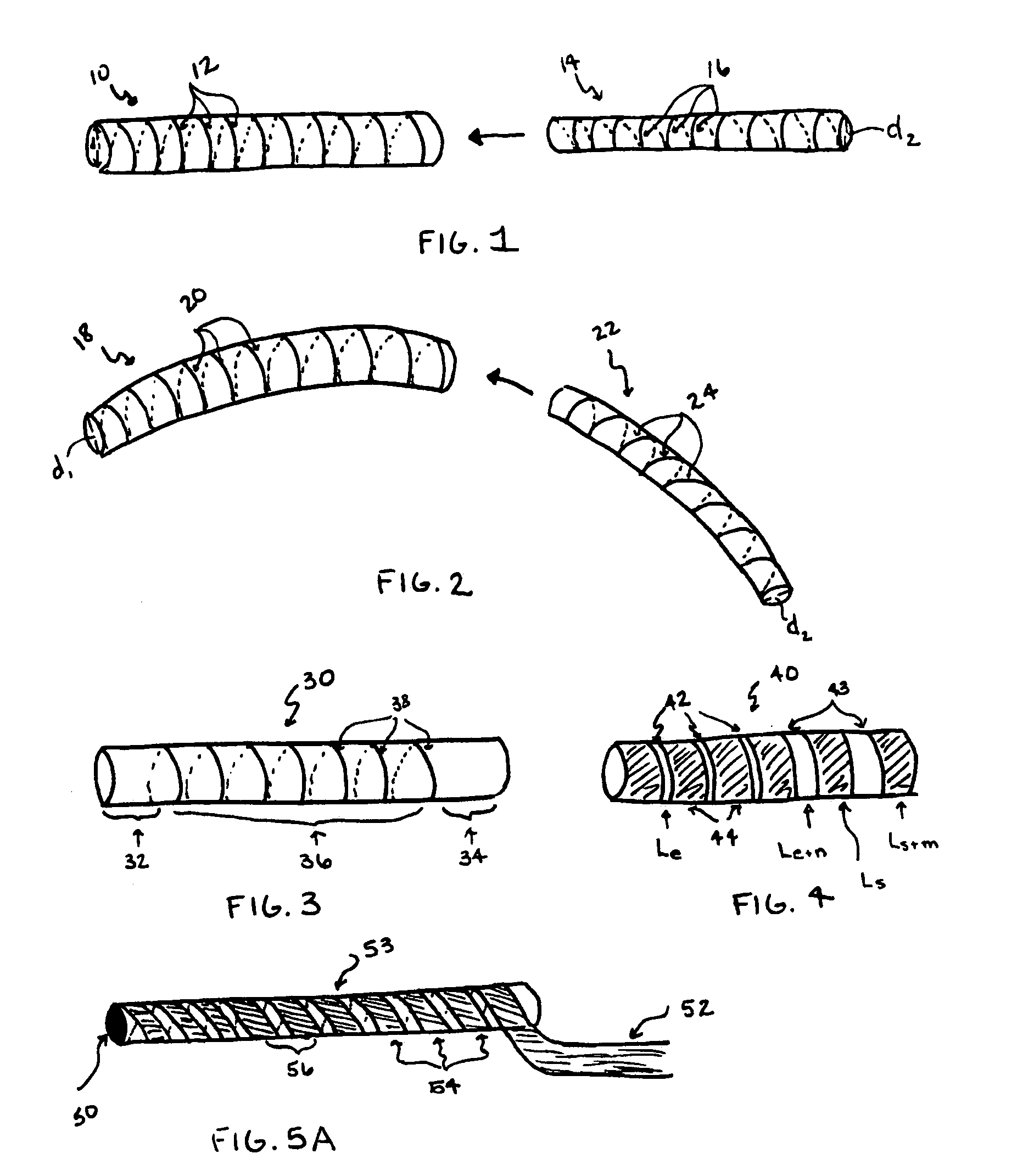
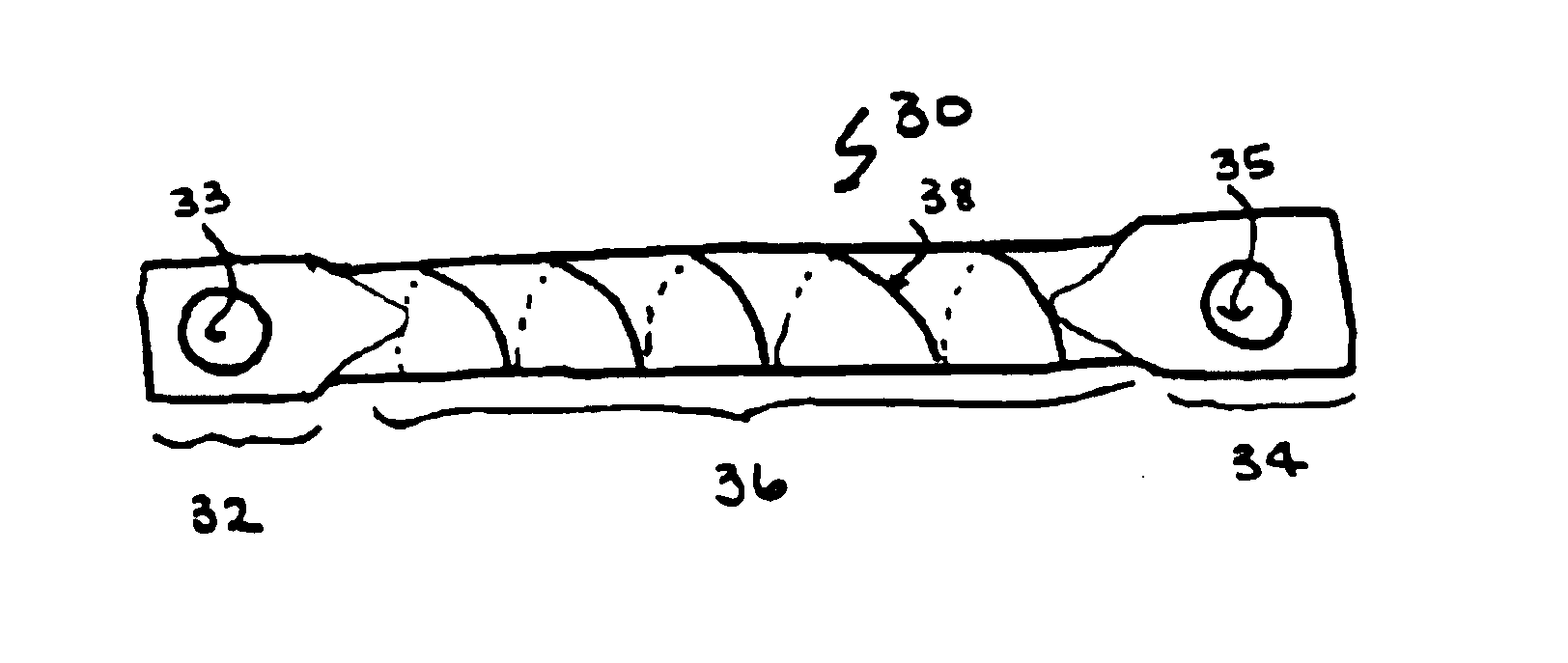
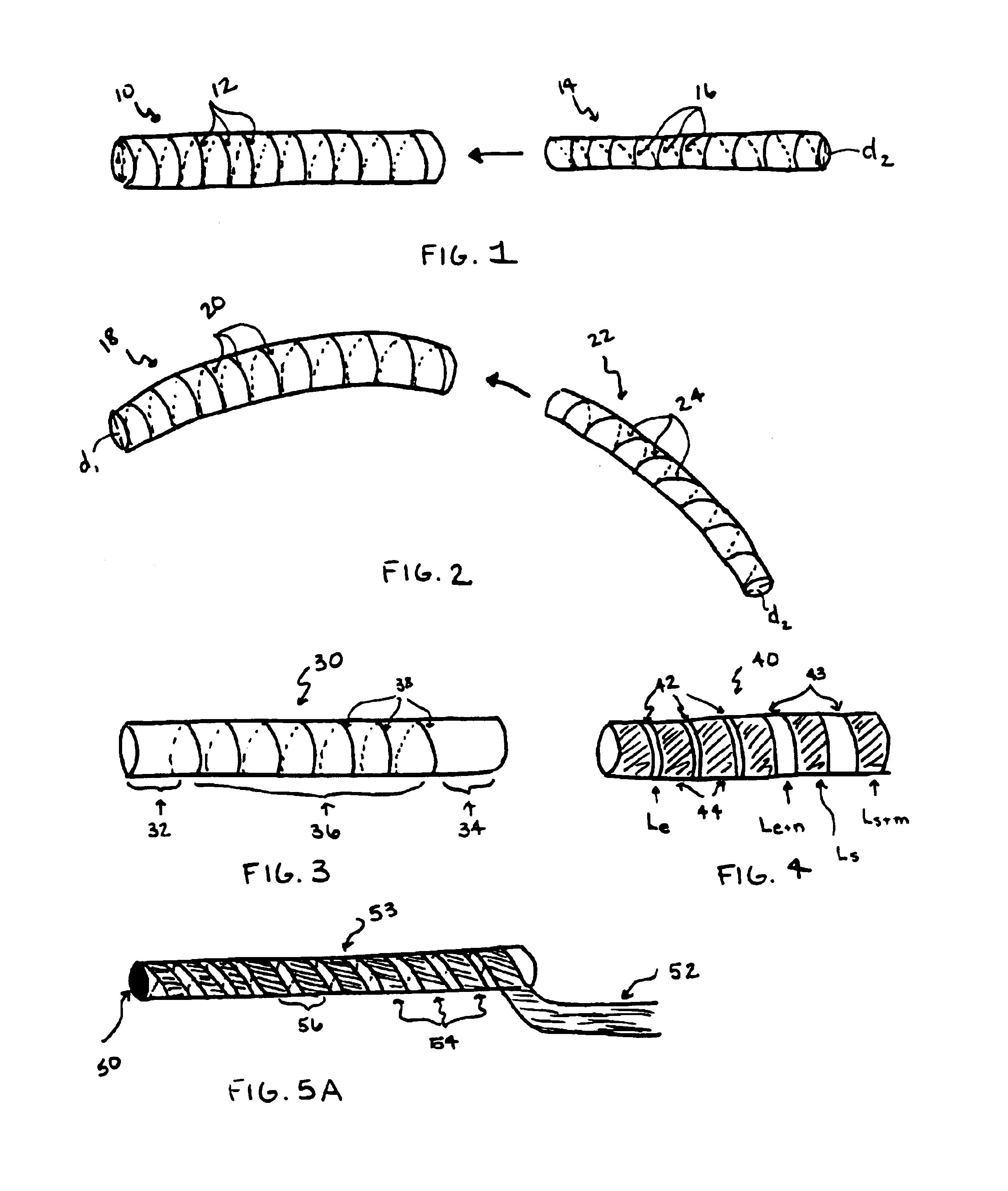
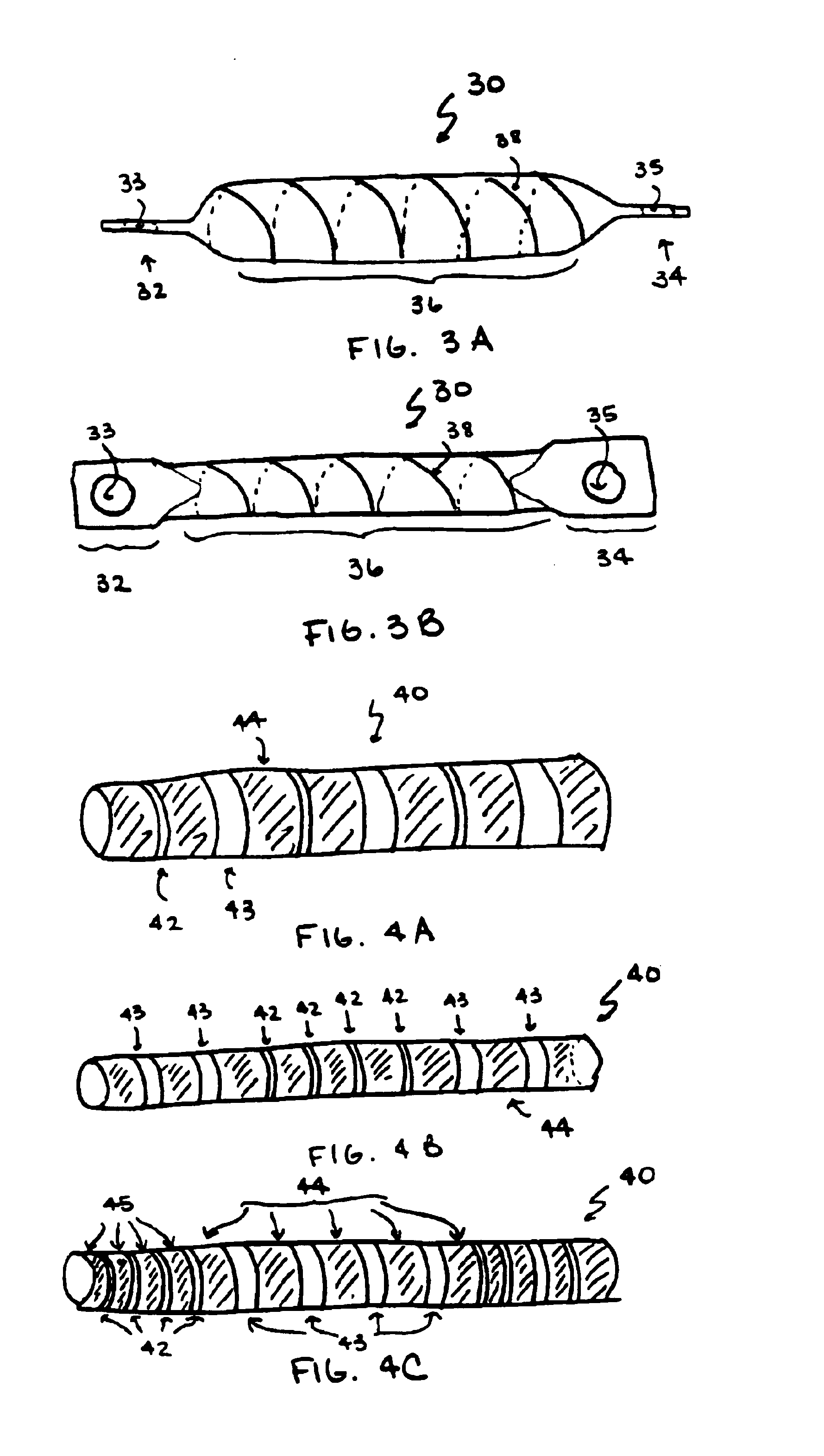
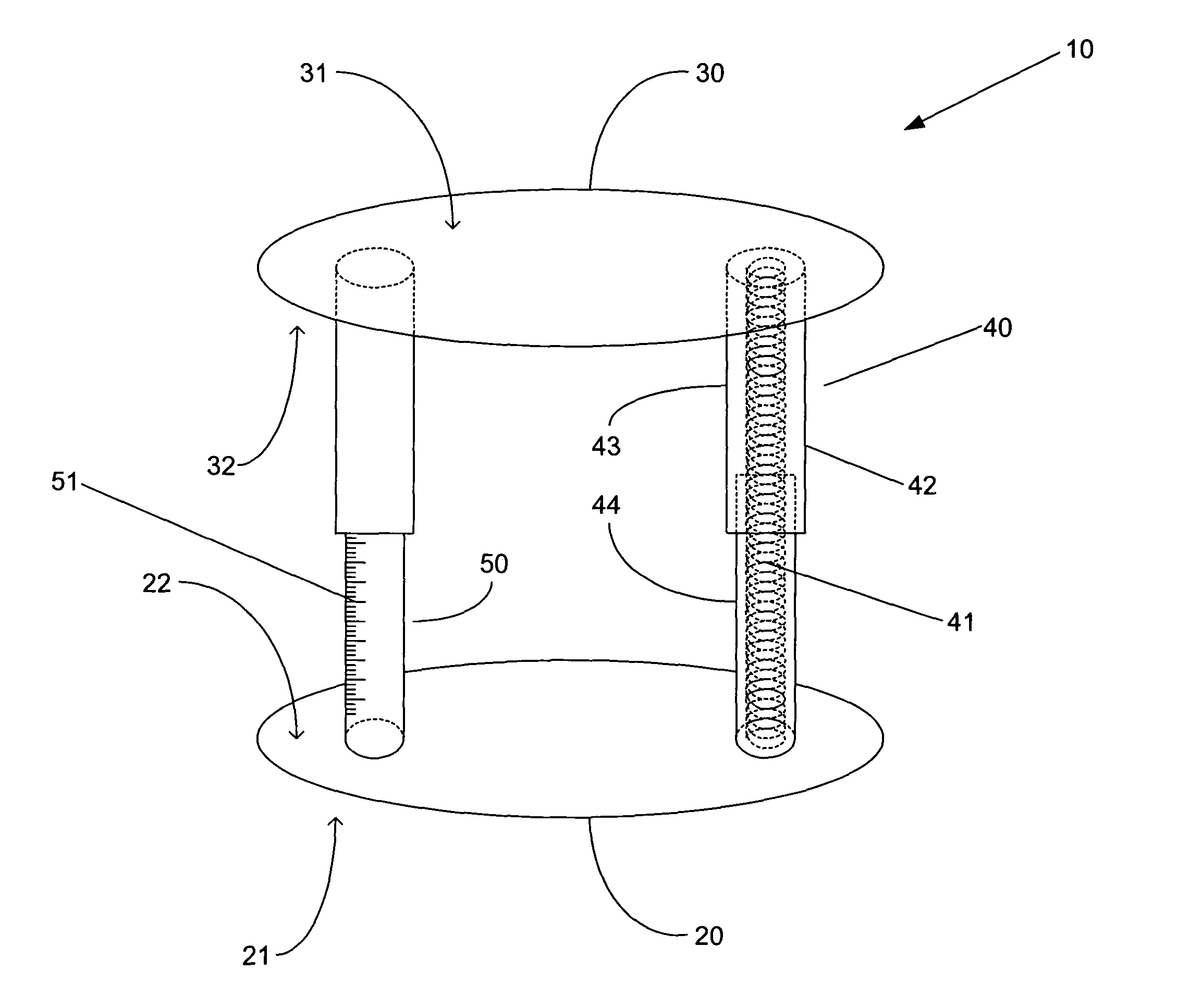
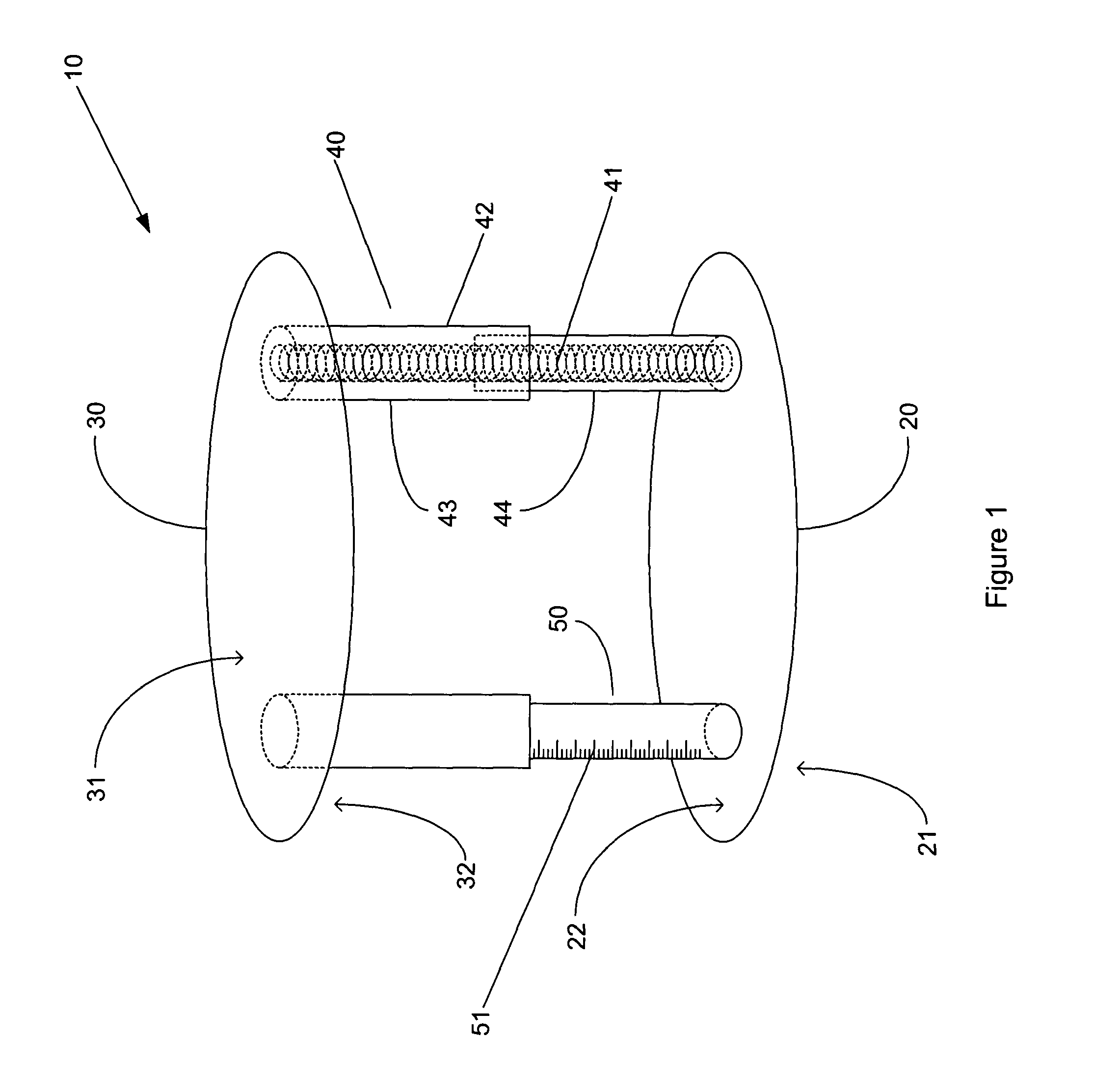
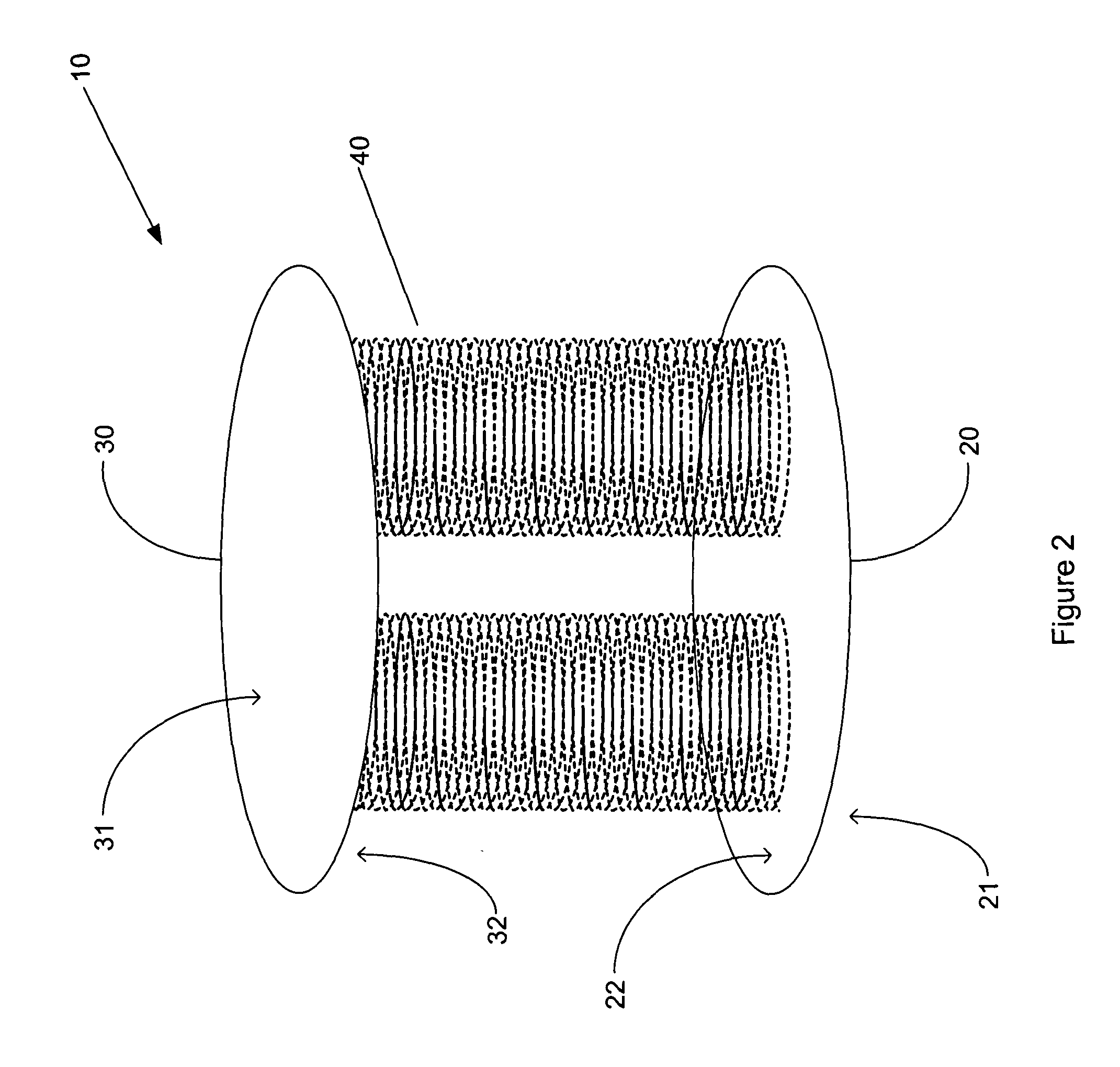
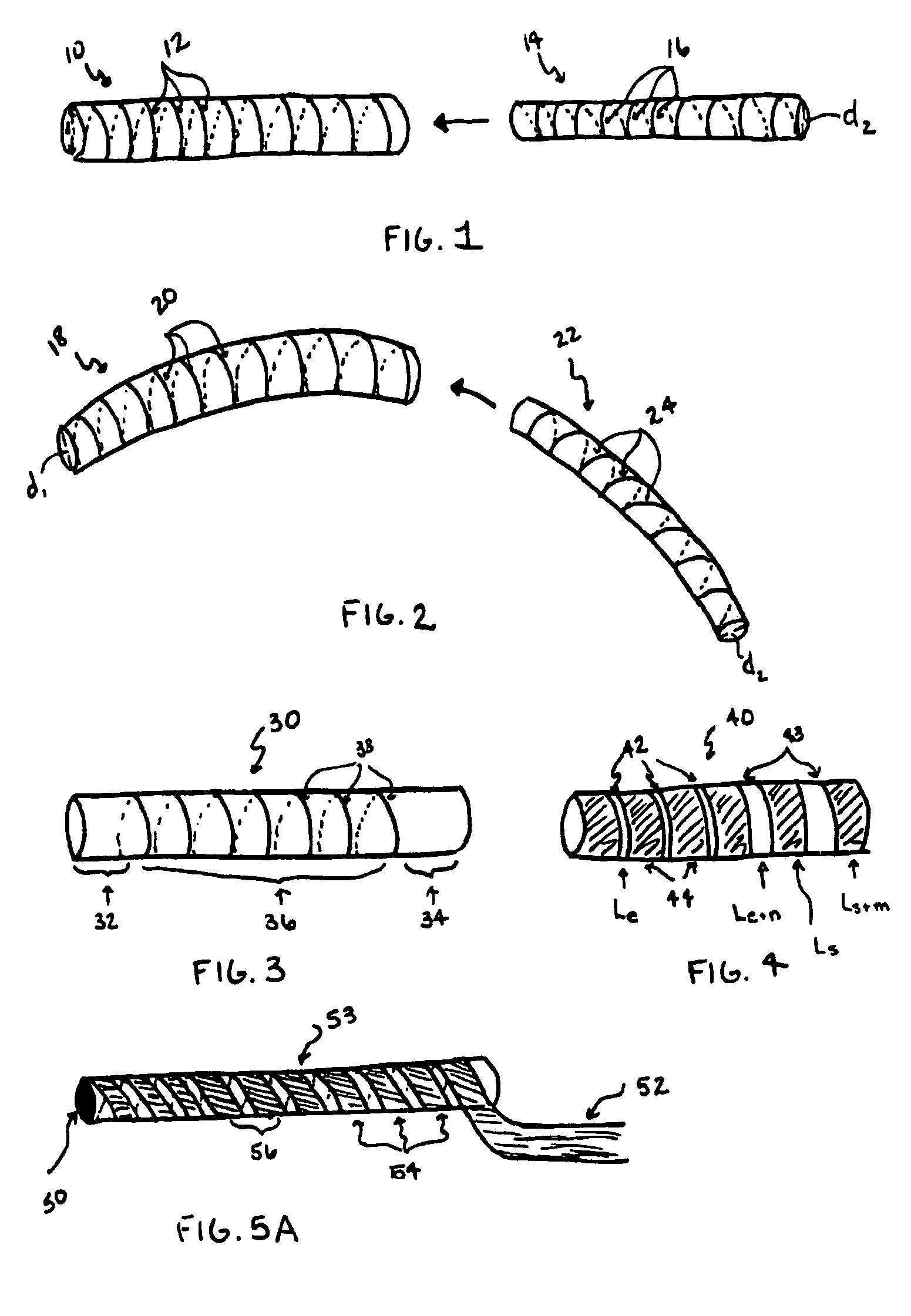
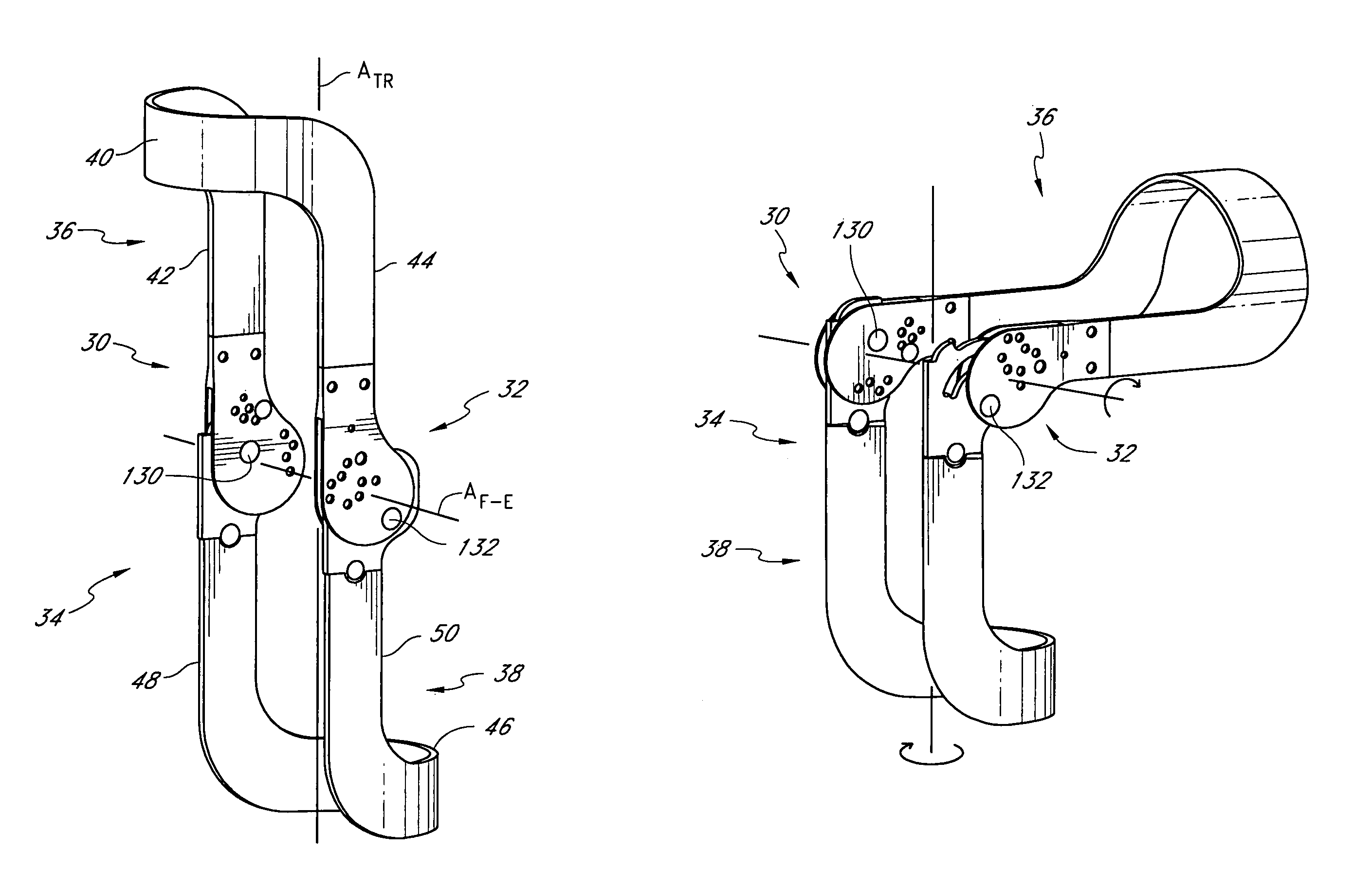
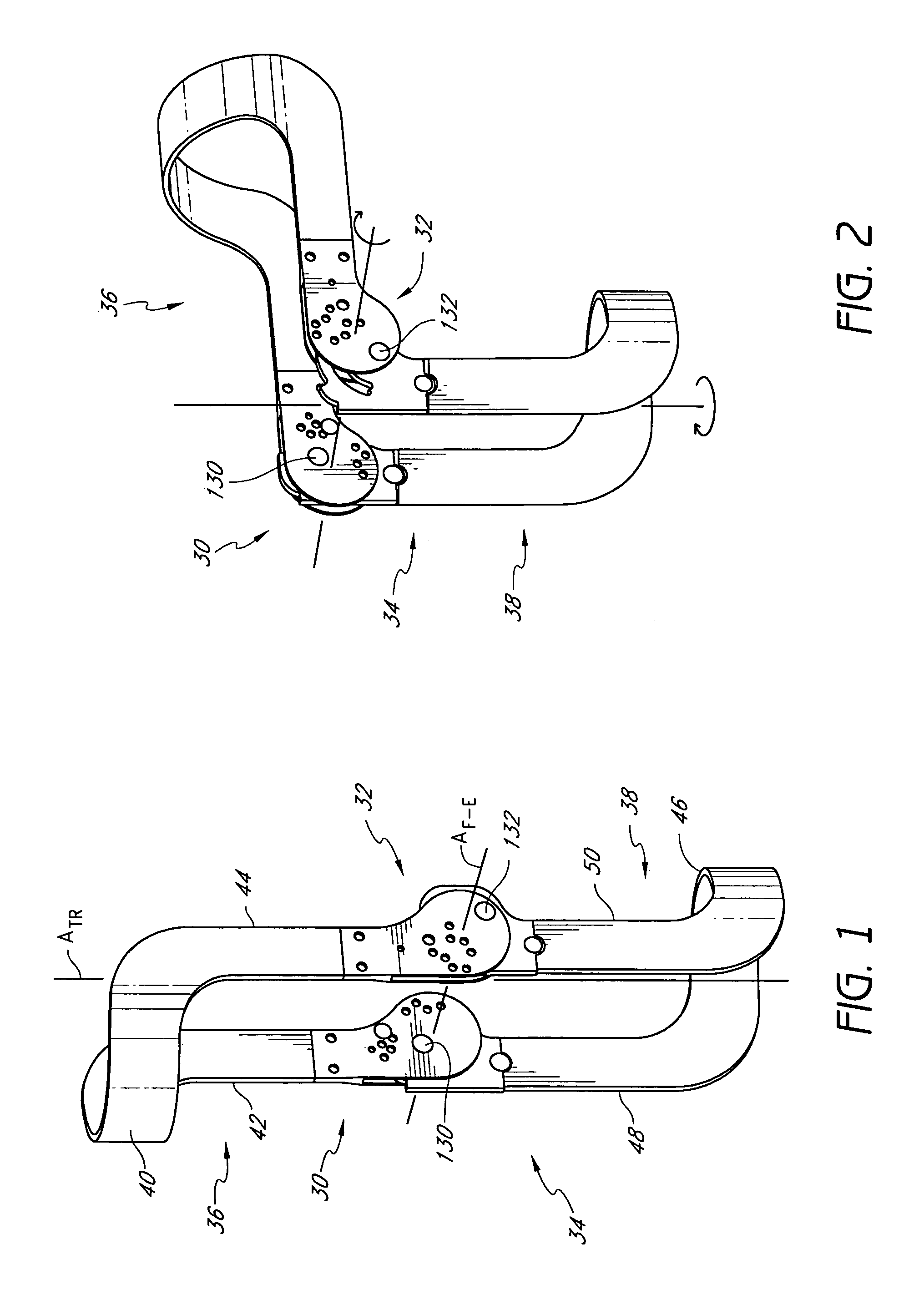
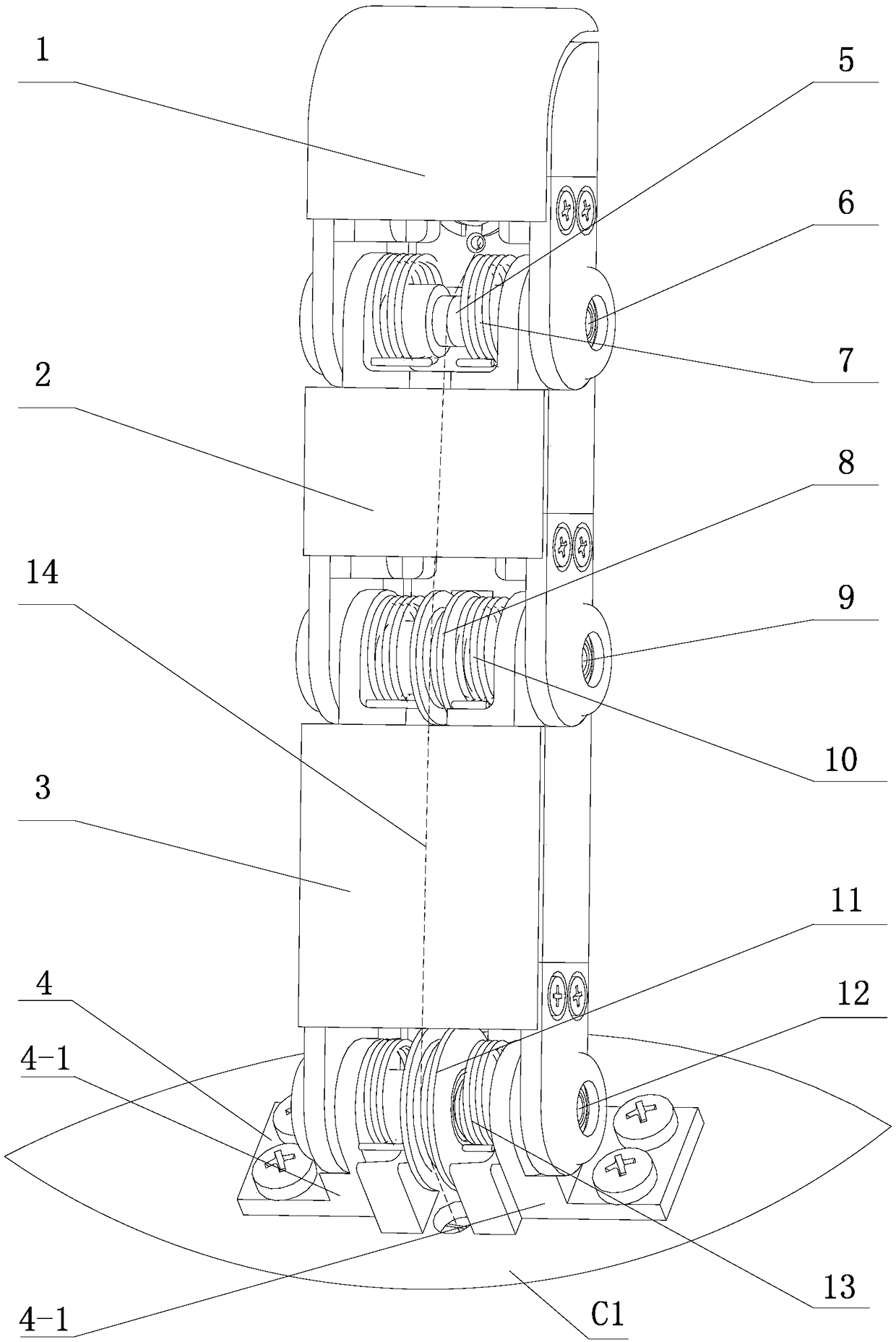
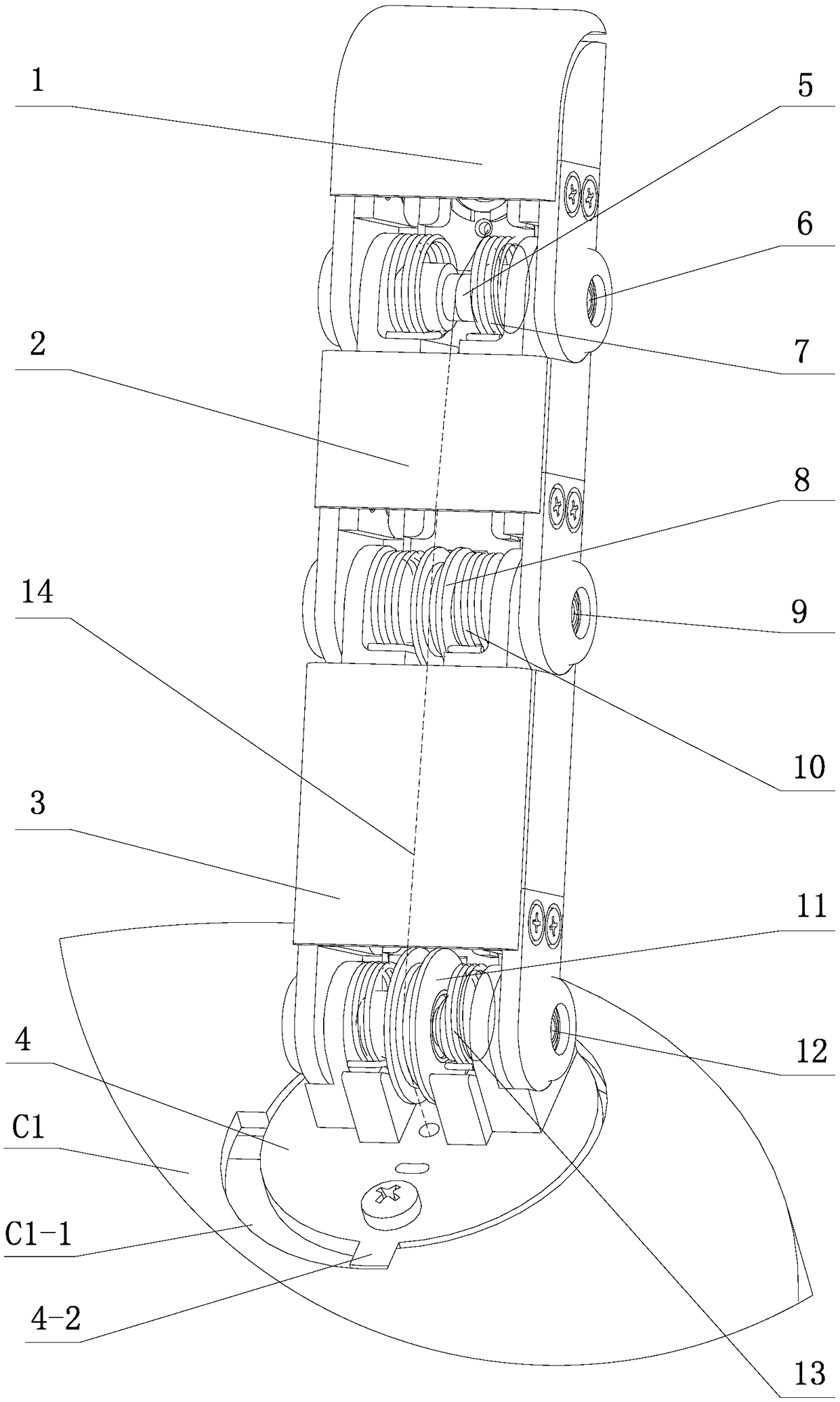
The invention generally concerns a spine stabilization system having one or more flexible elements having an opening or slit. The flexible element may be integrally formed in a rod having ends capable of receiving fasteners. The flexible element may limit rotation, flexion-extension, or lateral bending of the spine. The slit or opening may form helical pattern on the rod, and more than one slit or opening may be provided. The flexible element may be conformable to the natural spinal movement.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Spine stabilization system
InactiveUS6986771B2Relief the painPrevent rotationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsLocking mechanismImage stabilization
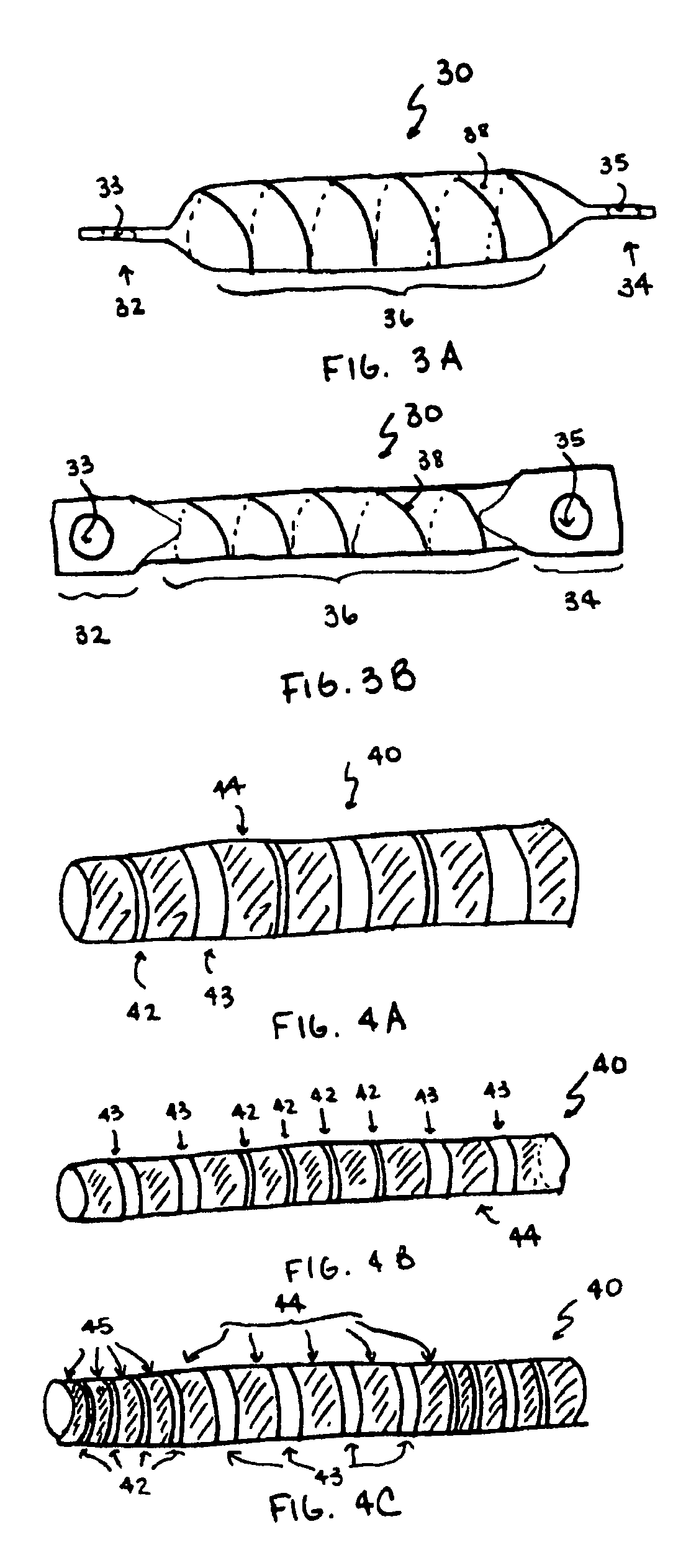
A spine stabilization system having one or more flexible elements with tubular structures with openings or slits. The flexible elements may limit rotation, flexion-extension, or lateral bending of the spine. The system also may have a locking mechanism that secures one or more flexible elements in a rigid configuration. A flexible element may be disposed within another flexible element, and the slits may form helical patterns on the tubular structures. The flexible element may be conformable to the natural spinal movement.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
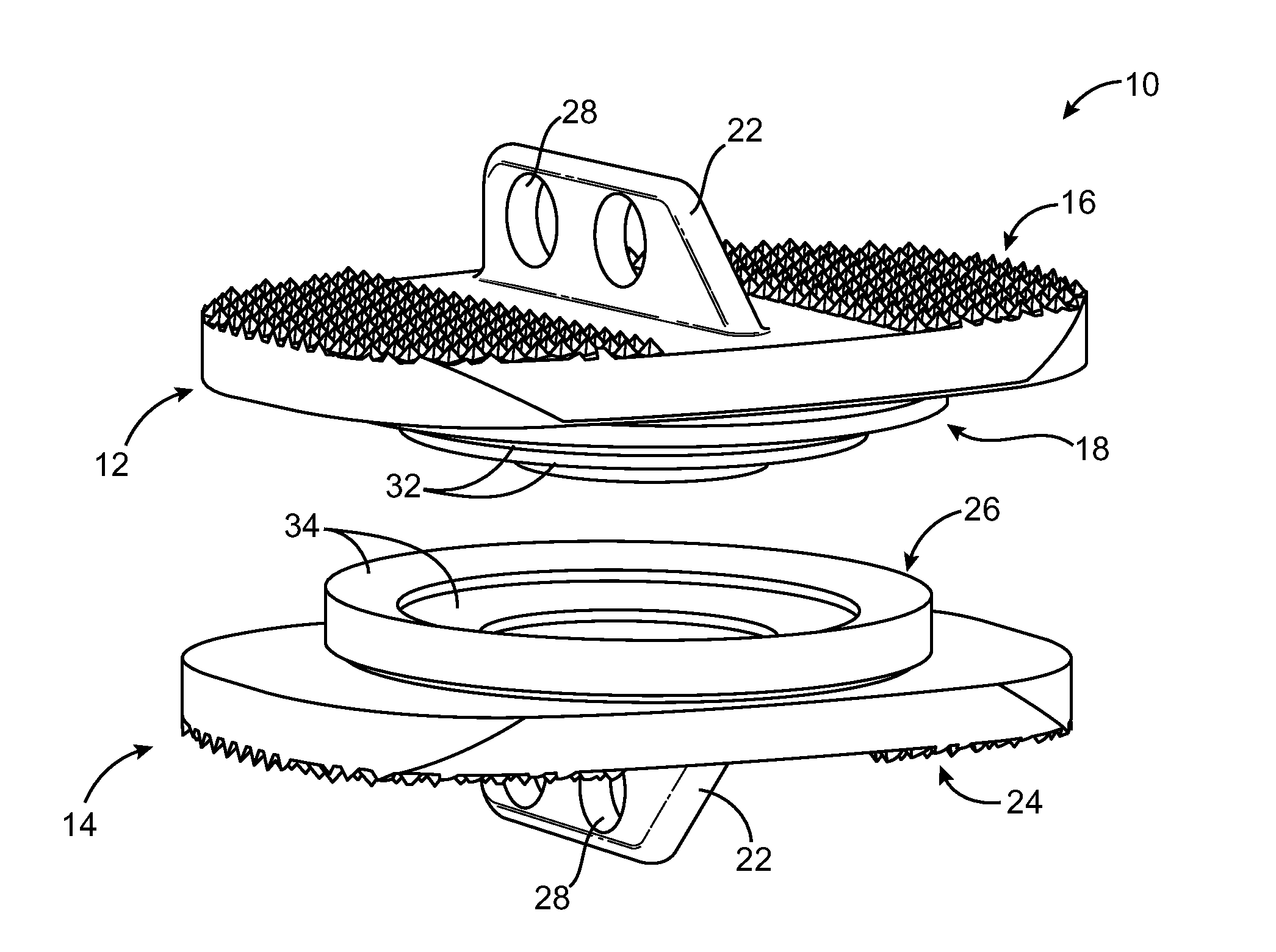
Dynamic spacer for total knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS20050020941A1Easy to useEasy constructionSurgeryPerson identificationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSurgical instrumentation
A dynamic spacer is provided for measuring flexion-extension gap during total knee arthroplasty. The dynamic spacer is an improved surgical instrumentation system that it easy to use, simple in construction, and accurately measures flexion-extension gaps under repeatable soft tissue tension. The dynamic spacer generally comprises a first planar member having a lower tissue engaging surface, a second planar member having an upper tissue engaging surface. A tensioner is disposed between the first planar member and the second planar member for applying a tensile force acting upon the first and second planar members. The tensioner is fixedly attached to the first and second planar members, such that the first planar member is held substantially parallel to the second planar member in the absence of compressive load. The dynamic spacer allows for accurately measuring flexion-extension gaps and angular deviation in flexion indicating the appropriateness of femoral rotation.
Owner:TARABICHI SAMIH
Dynamic intervertebral connection device with controlled multidirectional deflection
InactiveUS7335200B2Simple designInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSagittal planeMechanical engineering
Owner:SCIENTX
Limited Motion Prosthetic Intervertebral Disc
A prosthetic intervertebral disc includes an upper plate and a lower plate and employs congruent stepped features to provide limited articulating motion between the plates. The stepped features can be used to provide articulating motion of a rocking type rather than a rubbing or translating type of motion provided in many artificial discs. Each of two parts of the intervertebral disc includes two or more stepped bearing surfaces, having curved or flat shapes, which mate with one another to provide the articulation to the disc. The stepped features can be designed to restrict motion in flexion-extension or lateral bending to less than a predetermined angle. The stepped design can be modified to either allow or prevent rotational motion between the plates. The limited motion disc substantially prevents translation, however some limited translation can be provided by modification of the relative sizes of the stepped features.
Owner:SIMPLIFY MEDICAL PTY LTD
Navigated drill guided resection block
A bone cutting guide block has a cutting tool guide surface and a navigation mount for a navigation tracker component for computer aided positioning of the guide for a resection procedure. In various embodiments, the guide includes a rotation means. Preferably, a swivel with a pivot apparatus is provided to limit rotation to permit controlled flexion-extension angle about the pivot with respect to the cutting guide surface. A fixing member through the swivel permits for varus-valgus adjustment of the guide surface. Optionally, a positioning actuator and / or biased resistance actuator implements more regulated flexion-extension angle adjustment with the swivel. Various traversing mechanisms, such as a threaded wheel or pivoted cam tool permit controlled proximal-distal adjustment of the cutting guide surface.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
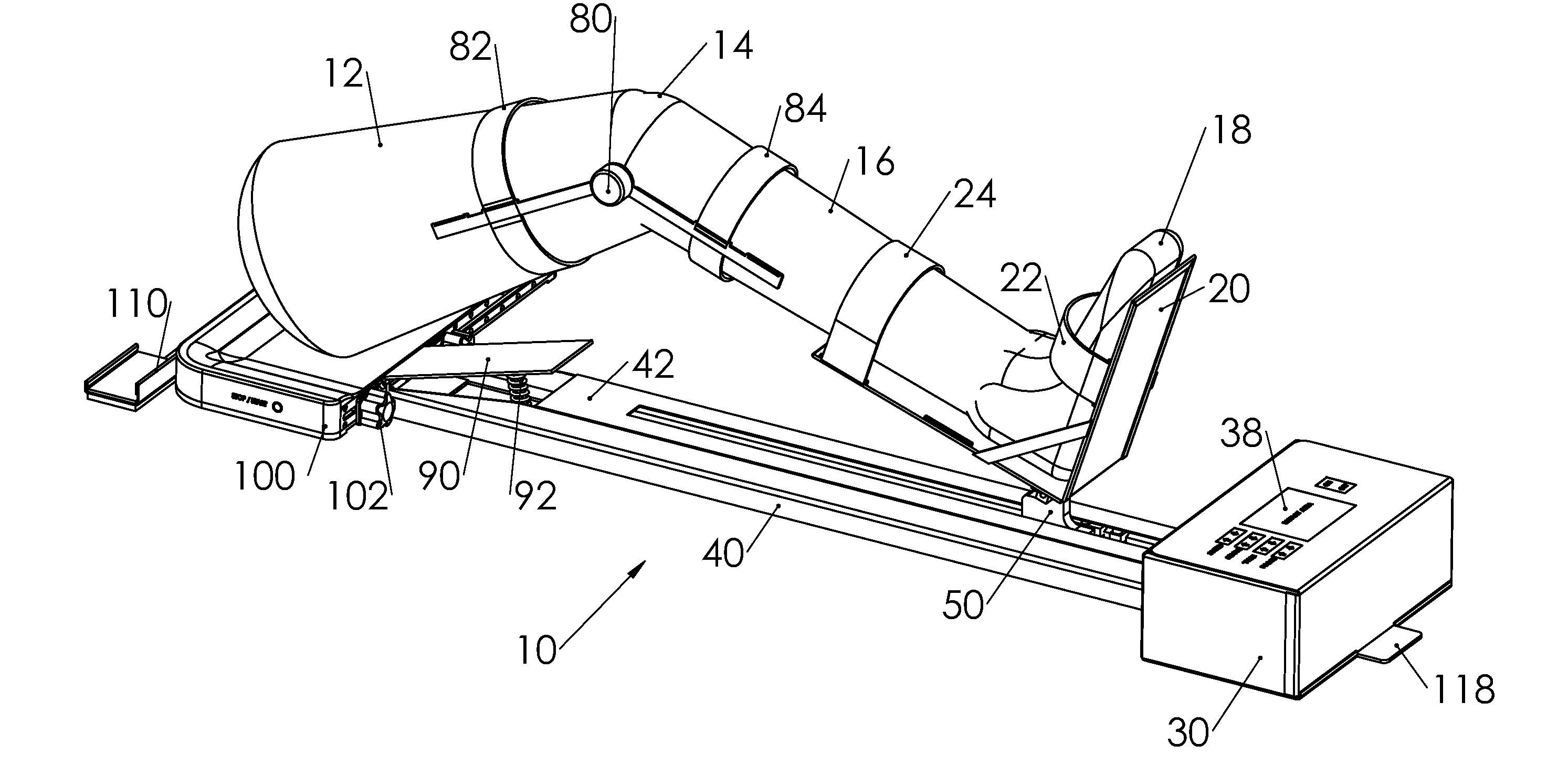
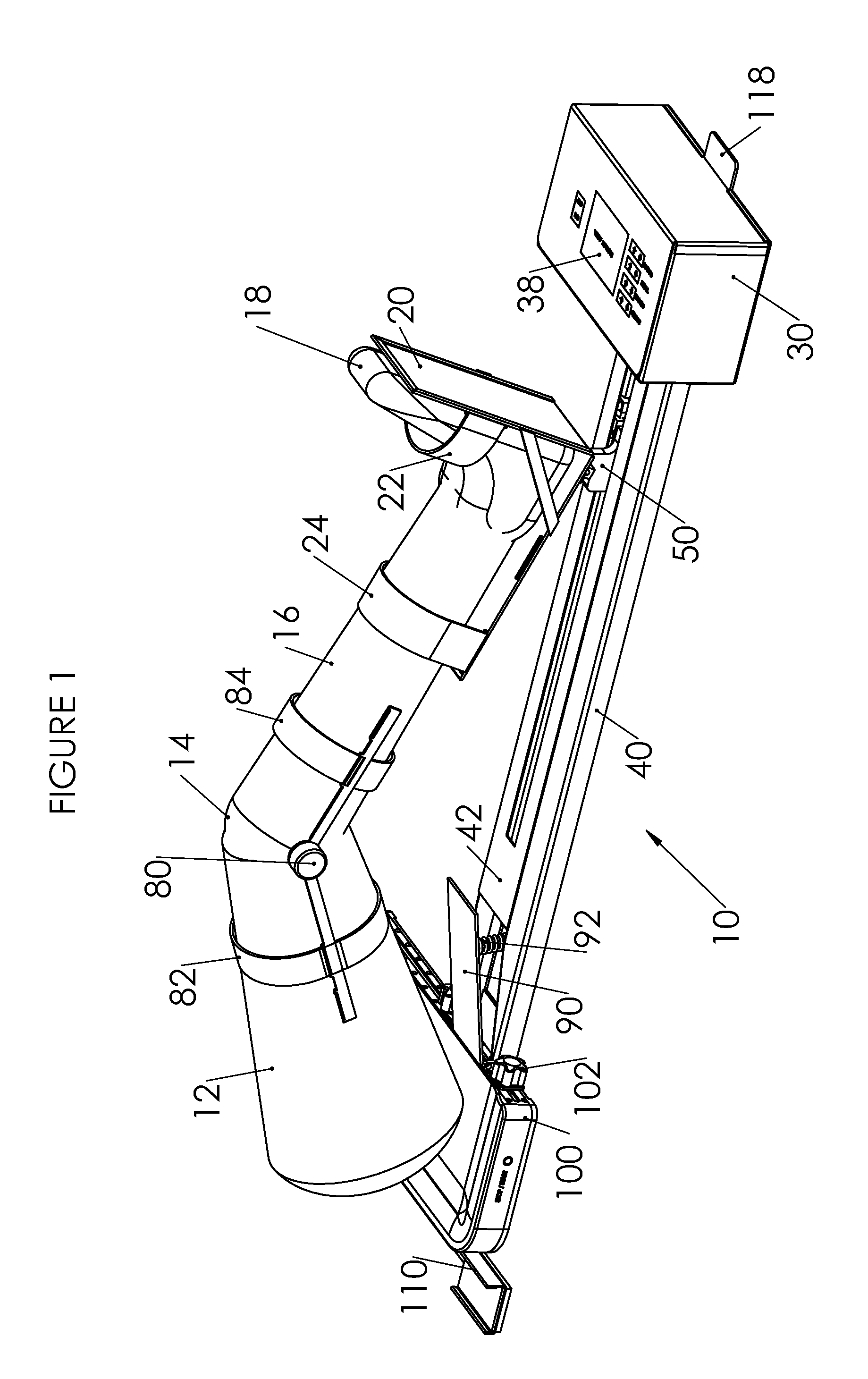
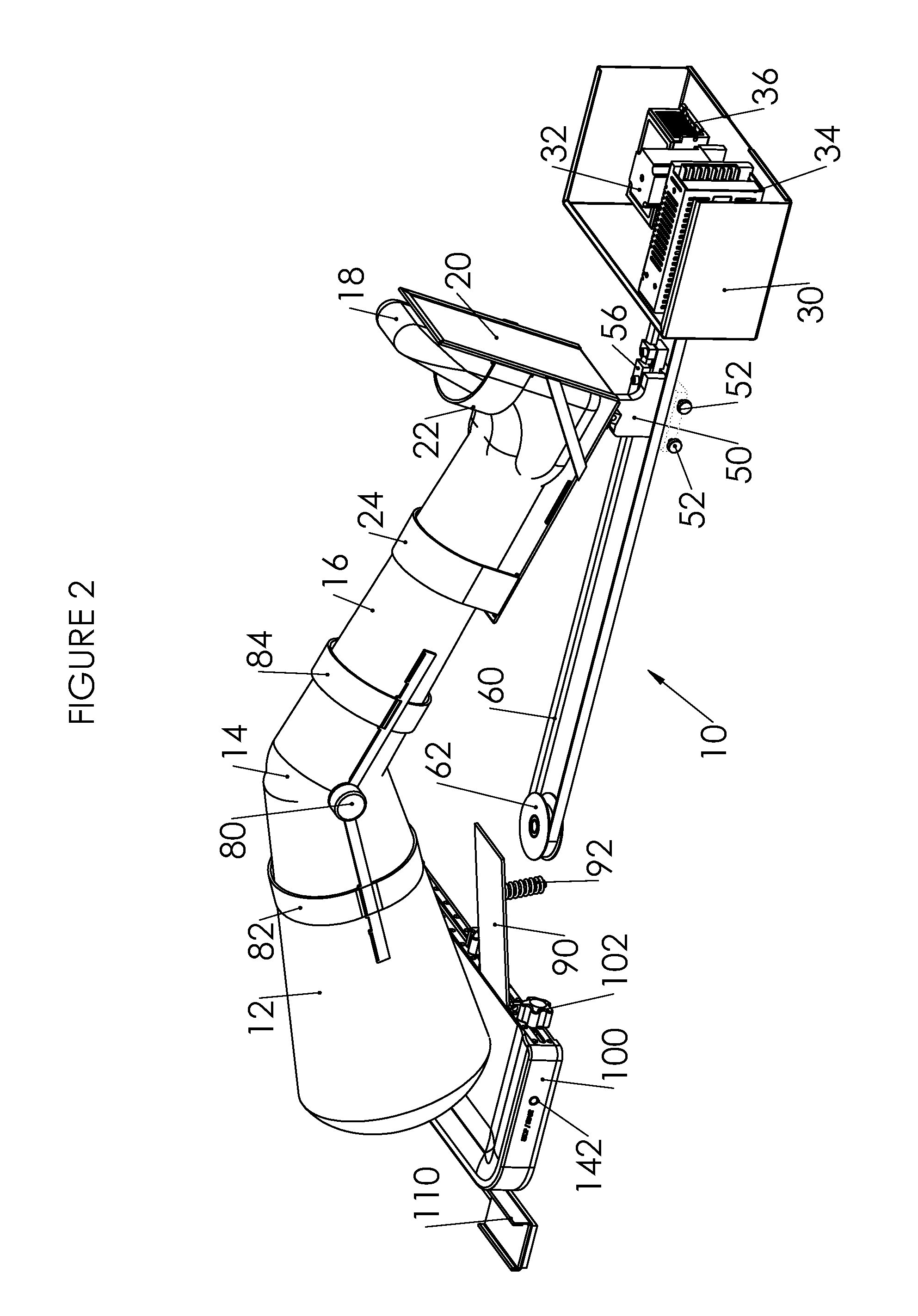
Device and Method for Knee Rehabilitation
InactiveUS20140094721A1Function increaseIncrease muscle strengthElectrotherapyChiropractic devicesStretch exerciseKnee rehabilitation
A device for increasing the range of motion of a patient's knee joint comprising of a longitudinal track frame, having a sitting platform at one end and a movable leg and foot platform at the other end, driven back and forth by a foot actuation mechanism in a flexion-extension motion, linearly along the longitudinal track by an electronically controlled motor in accordance with user defined settings and operable in a passive, active or resistive mode in either a supine or sitting position.
Owner:DIALLO IBRAHIMA
Artificial knee joint
InactiveUS7264635B2Easy to getSmooth flexion-extensionJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesTibia
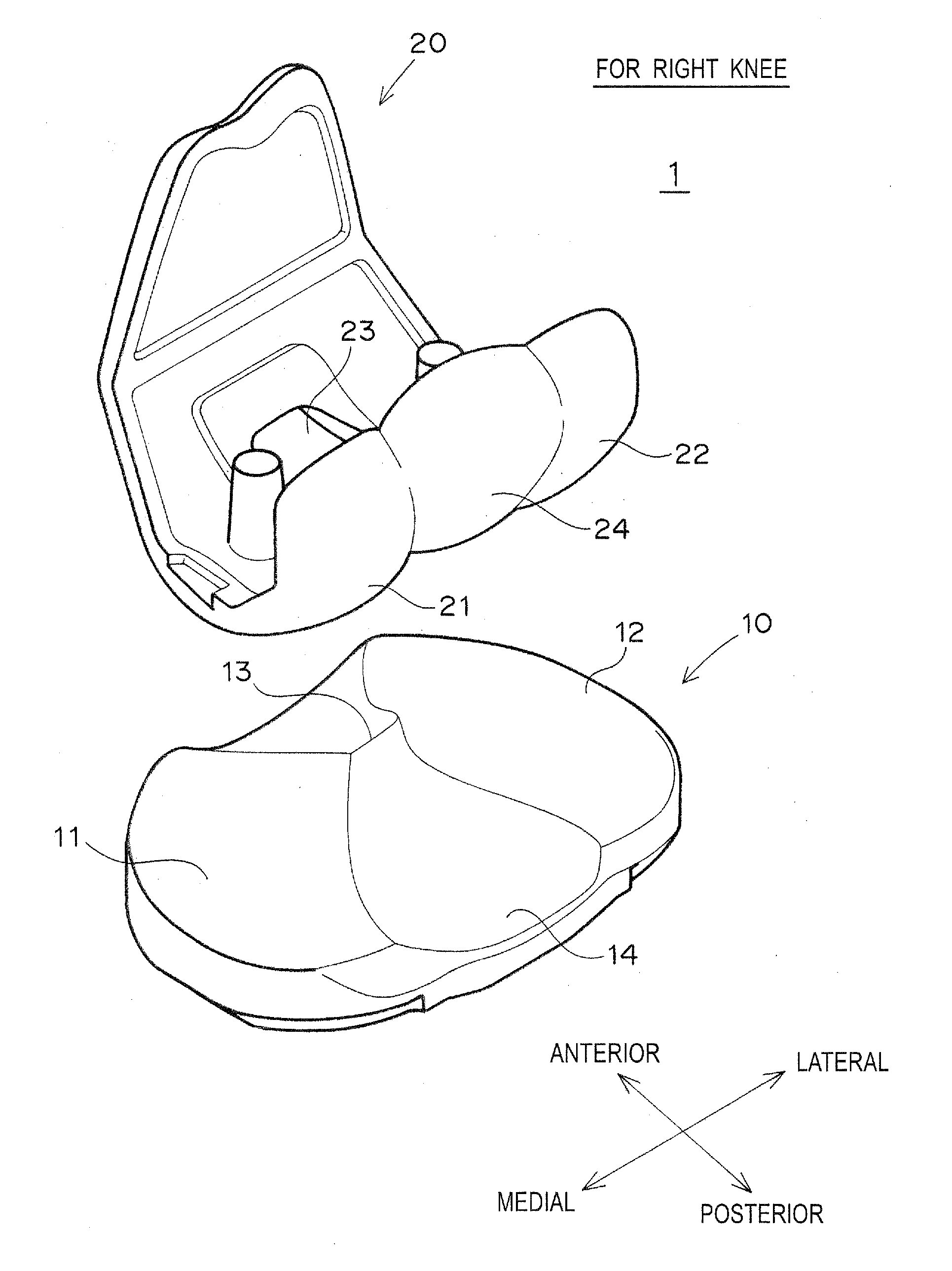
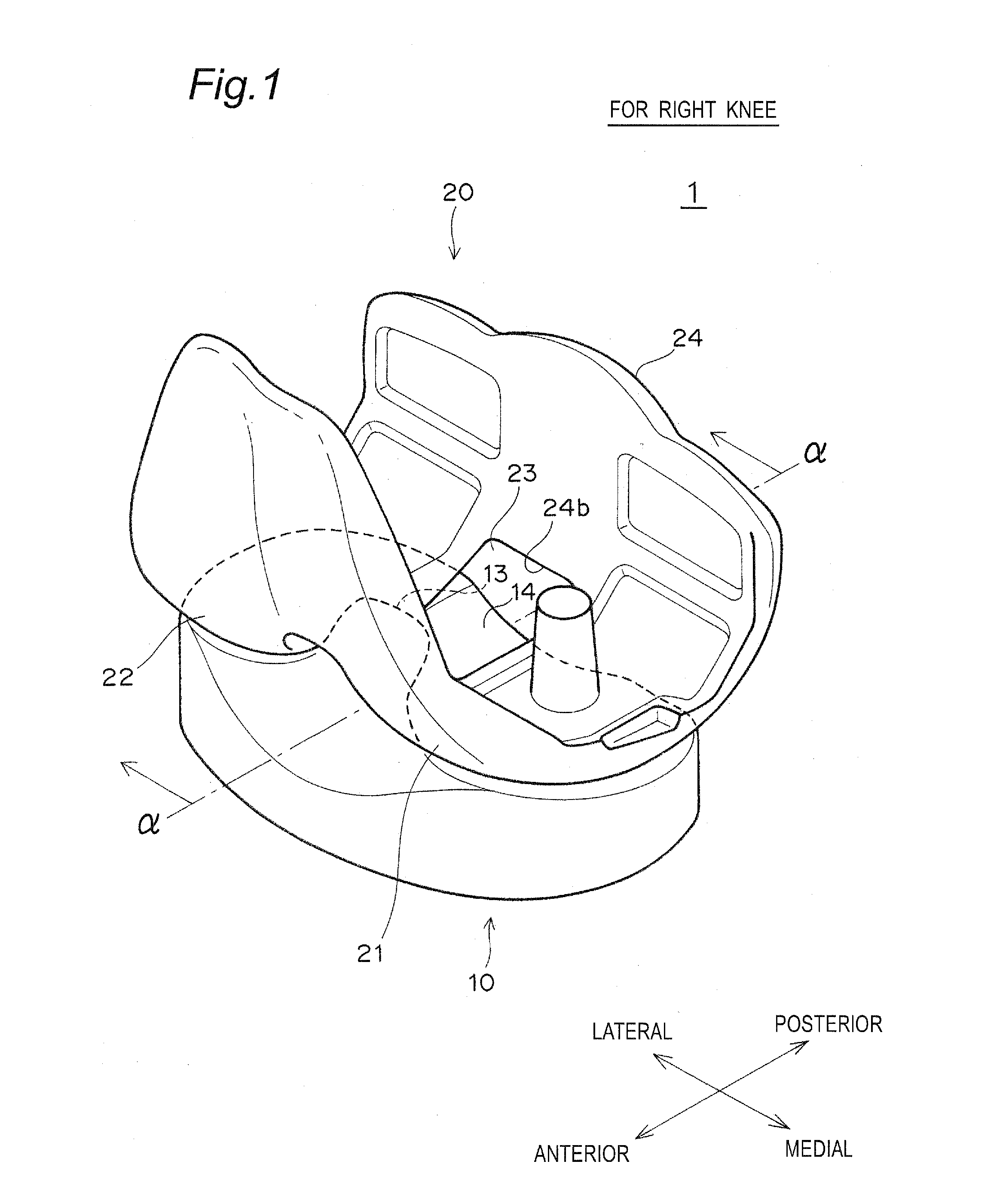
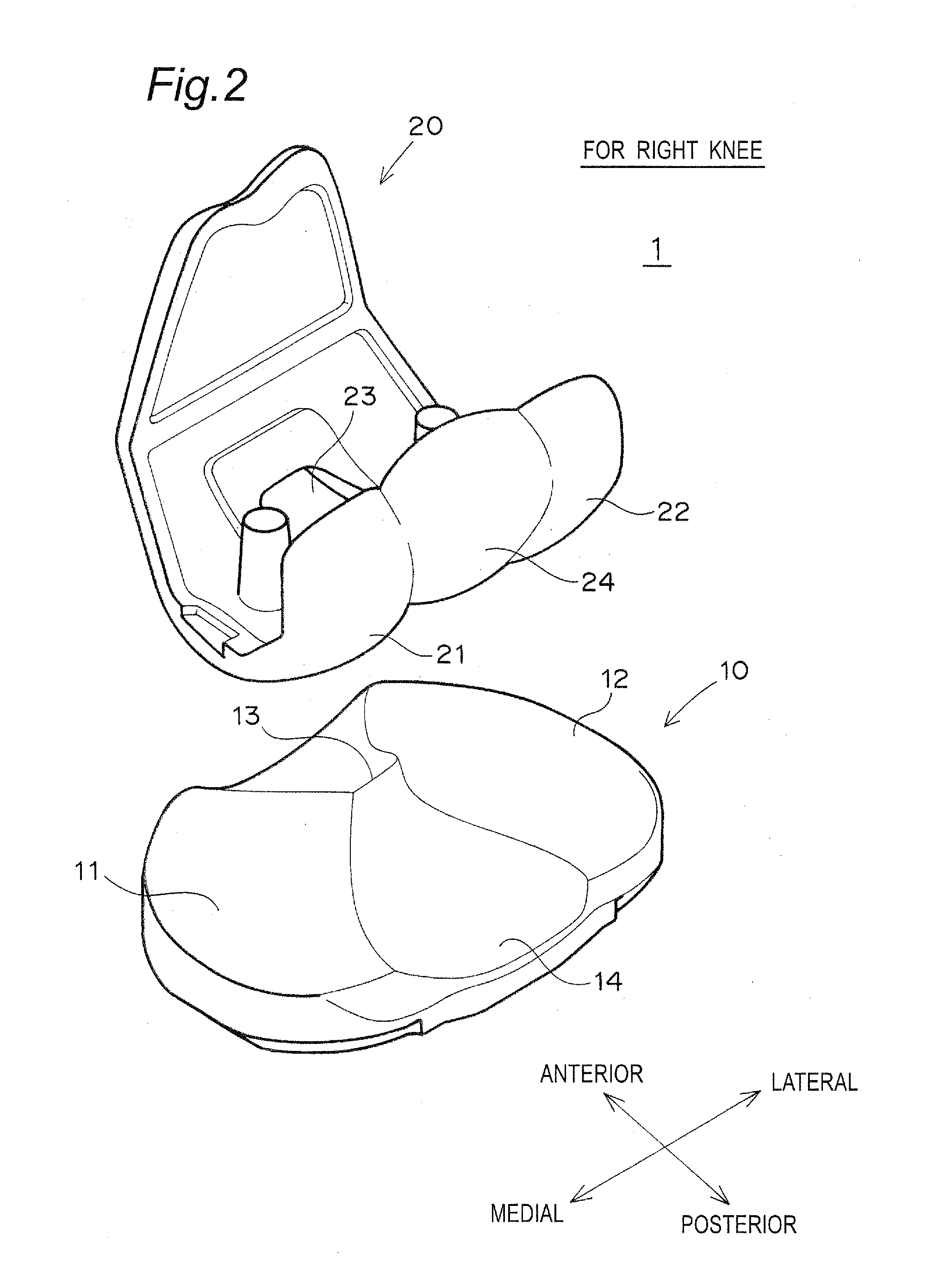
An artificial knee joint including a femoral component to be attached to a femur and a tibial component to be attached to a tibia, wherein in the femur component a medial condyle thereof is thicker than a lateral condyle thereof; in the tibial component, a medial articular surface thereof, which supports the medial condyle of the femur component, is thinner or deeper than a lateral articular surface thereof, which supports the lateral condyle of the femur component; and a joint line joining the lowest points of contact surfaces between the medial and lateral condyles of the femur component and the medial and lateral articular surfaces of the tibial component in a longitudinal cross section in a medial-lateral direction is inclined inward at virtually the same angle over the entire region of an angle of flexion-extension.
Owner:NAKASHIMA PROPELLER +1
Spine stabilization system
ActiveUS7559942B2Relief the painPrevent rotationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsImage stabilizationLateral bending
The invention generally concerns a spine stabilization system having one or more flexible elements having an opening or slit. The flexible element may be integrally formed in a rod having ends capable of receiving fasteners. The flexible element may limit rotation, flexion-extension, or lateral bending of the spine. The slit or opening may form helical pattern on the rod, and more than one slit or opening may be provided. The flexible element may be conformable to the natural spinal movement.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Post operative knee brace with multiple adjustment features
InactiveUS20060206045A1Easy and economical to produceEasy to useNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaRange of motion
A knee brace having adjustment mechanisms that are easy and economical to produce while being very user friendly, and which is more comfortable to wear. The brace has a joint mechanism formed of a plurality of plates with notches, openings and range of motion surfaces, the relative positions of which are used as part of a flexion-extension stop arrangement and also as part of an adjustable locking arrangement by which the brace can be locked, temporarily released or indefinitely released. Furthermore the lateral-medial angulation of the femoral strut is able to be adjusted relative to the joint mechanism and tibial strut.
Owner:TOWNSEND IND INC
Compliant interbody fusion device with deployable bone anchors
An interbody fusion implant with deployable bone anchors includes a support member, a monolithic body that accommodates the support member, and a longitudinal hole along a vertical length of the support member. The support member includes a first end and a second end. The second end includes two flanges. The flanges are configured to dig into an endplate of a vertebral body. The flanges of the support member provide a location fixation on an implantation of the interbody fusion implant into the vertebral body. The support member may also include at least one of a clip shaped support member and an I-shaped support member. The I-shaped support member may allow a rigidity and a support in flexion-extension through a living-hinge positioned in a middle of the I-shaped support member. The longitudinal hole sustains loads imported on the interbody fusion implant and allows the interbody fusion implant to flex freely.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
Hinge system for regulating knee joint flexion and extension
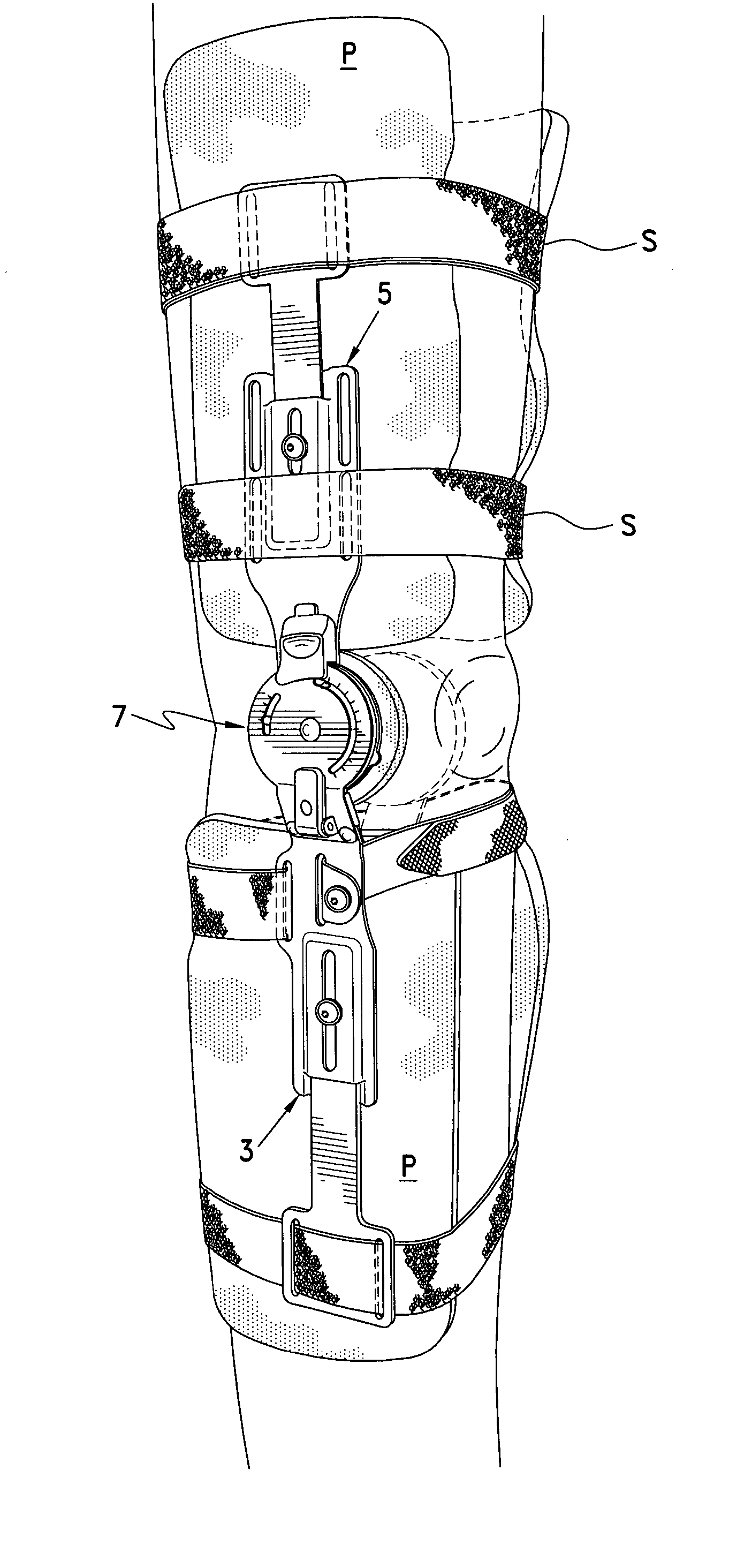
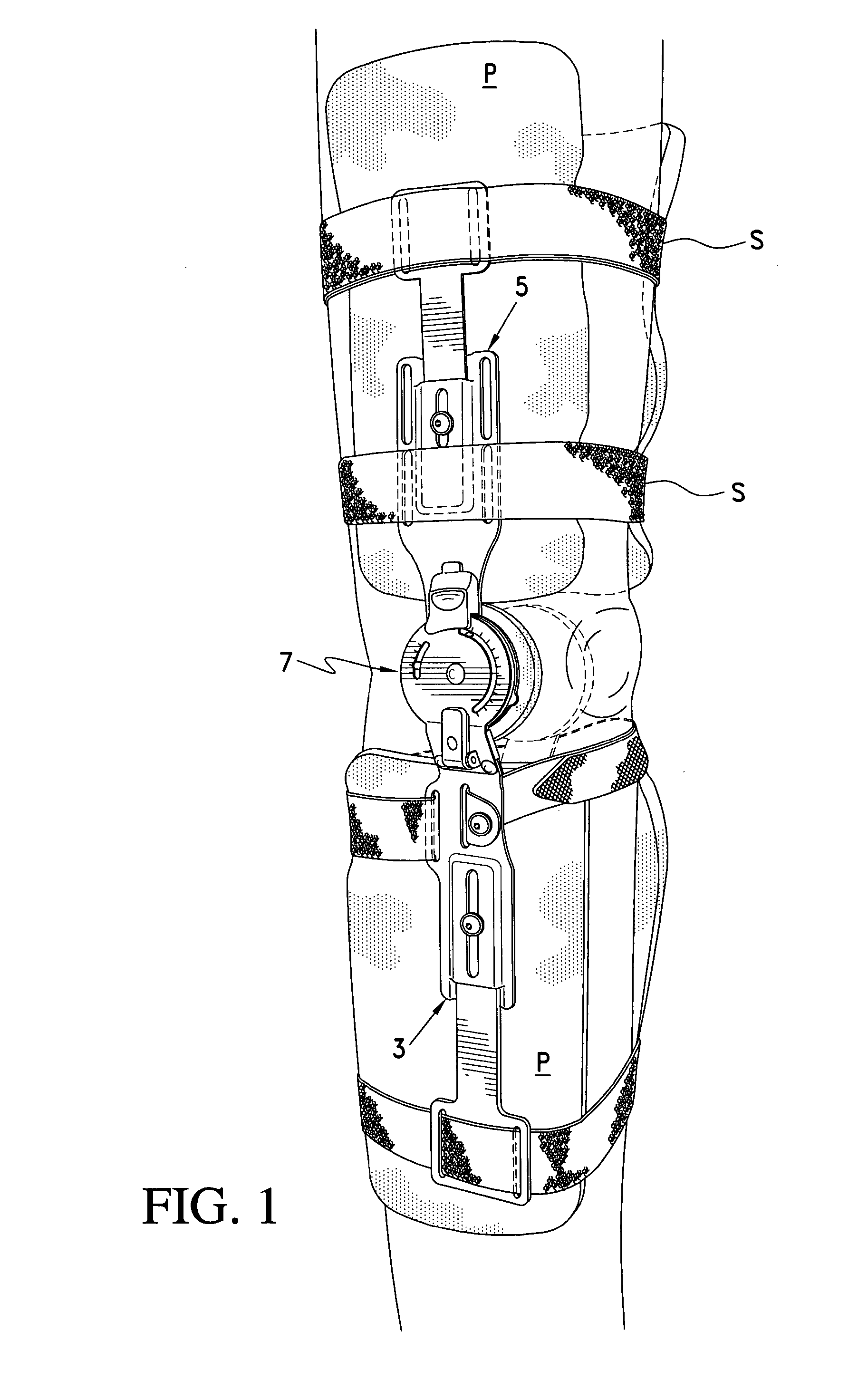
ActiveUS7044925B2Avoid re-injuryAlleviates the above-referenced deficienciesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesRange of motionKnee Joint
A hinge system for a knee brace features a flexion-extension regulating device which is adapted to engage an end portion of the knee brace's upper strut. An elongated main slot is formed through the regulating device to provide a fixed boundary for limiting range of motion. A motion limiting member is connected to the regulating device and is further adapted for connection to an end portion of the knee brace's lower strut. The motion limiting member includes a motion limiter that is disposed within the main slot. The motion limiter is caused to move therealong when the upper and lower struts pivot about a user's knee joint. By confining the motion limiter within the fixed boundary formed by the main slot, the hinge system ensures that the user's knee joint flexes and extends within the prescribed range of motion.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Locking intramedullary jig
ActiveUS20060184173A1Easy to operateEasy to adjustJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaIntramedullary rod
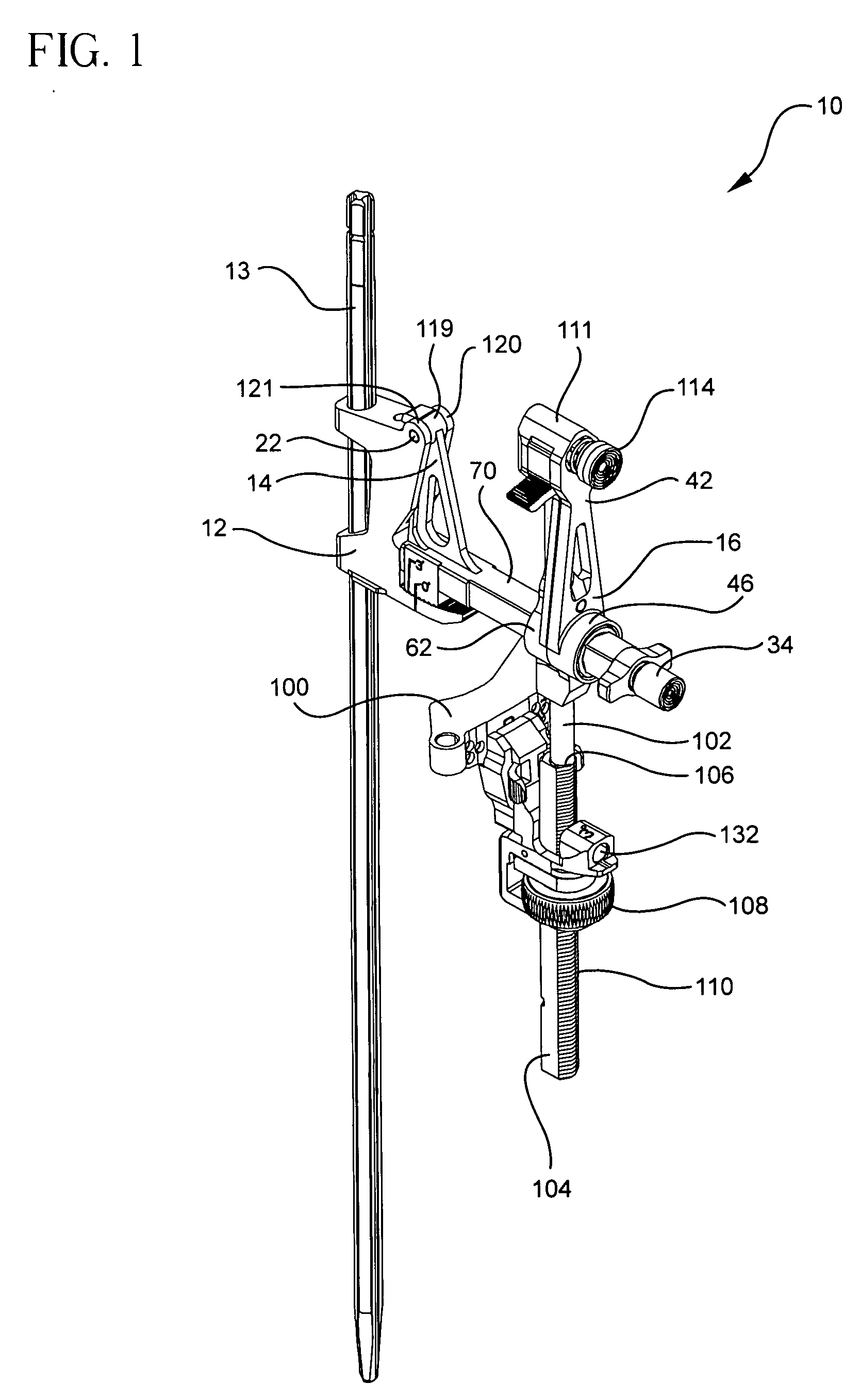
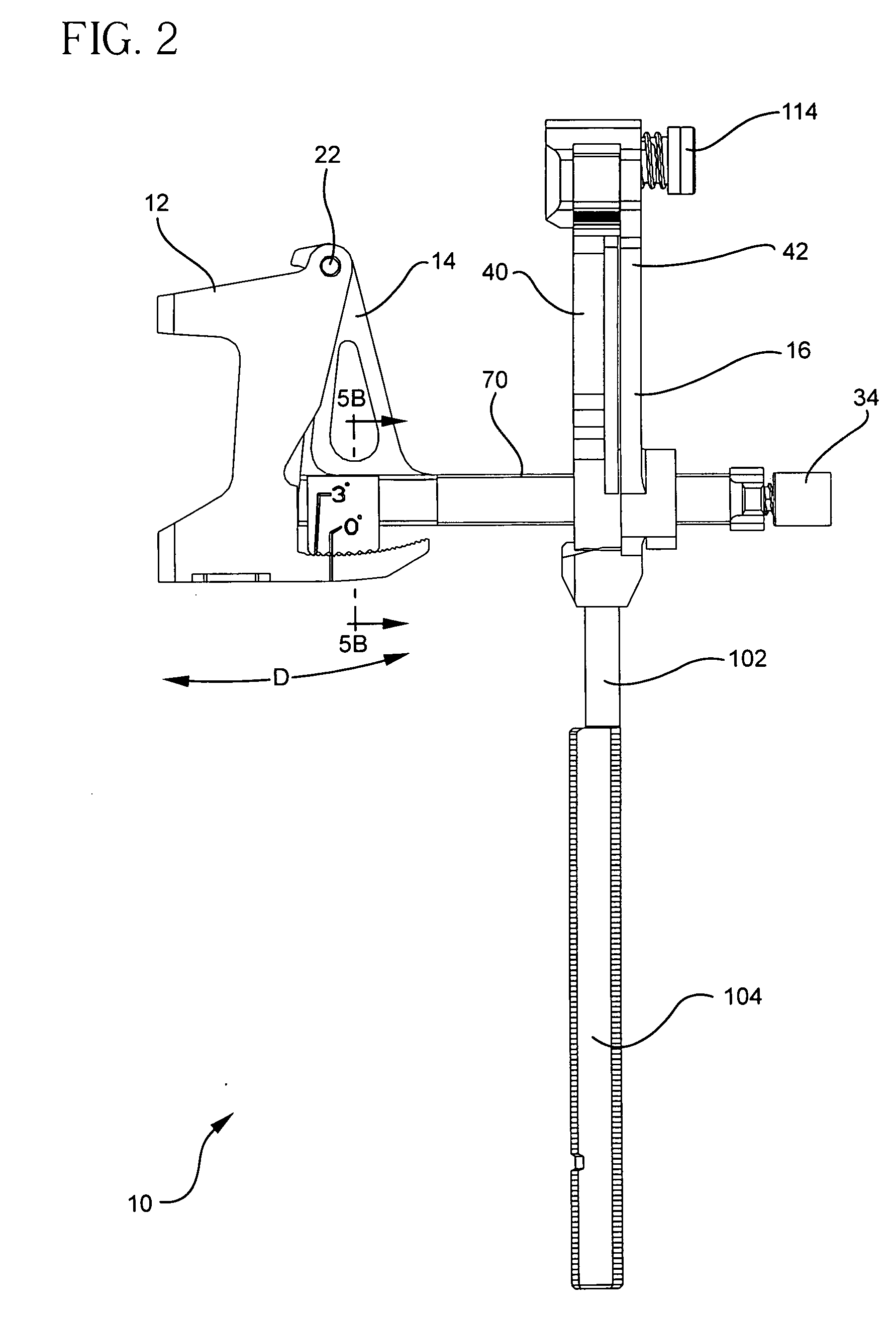
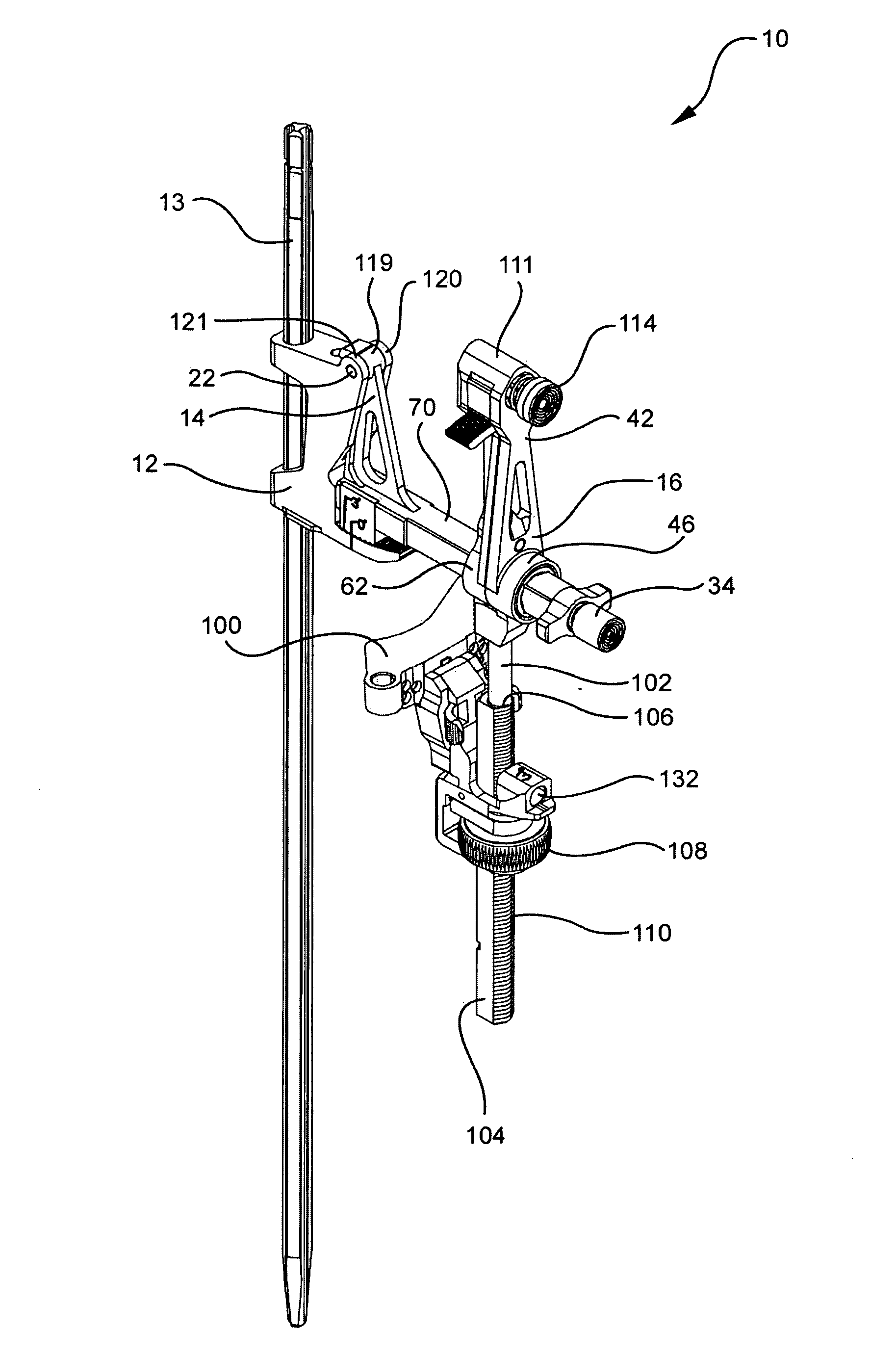
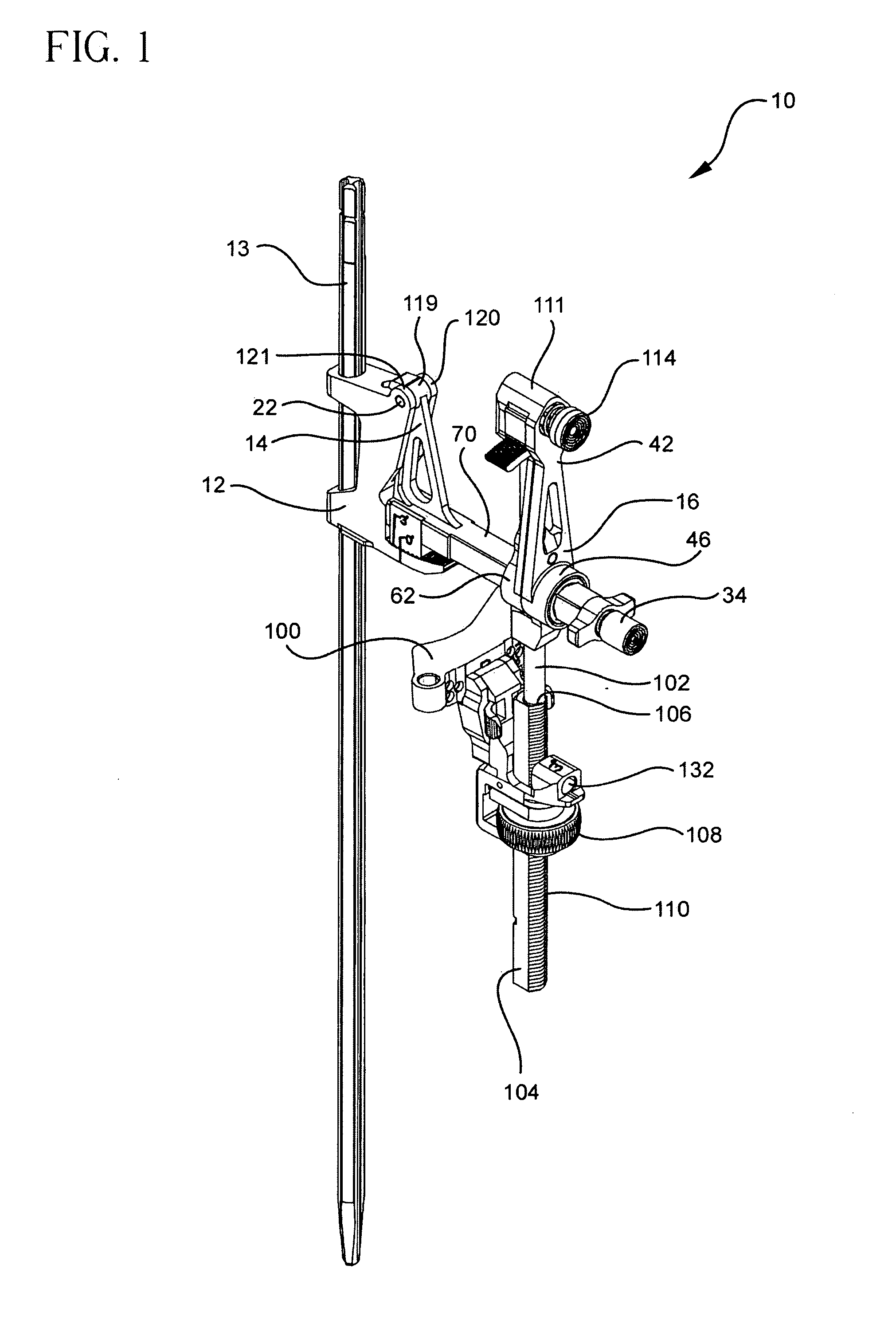
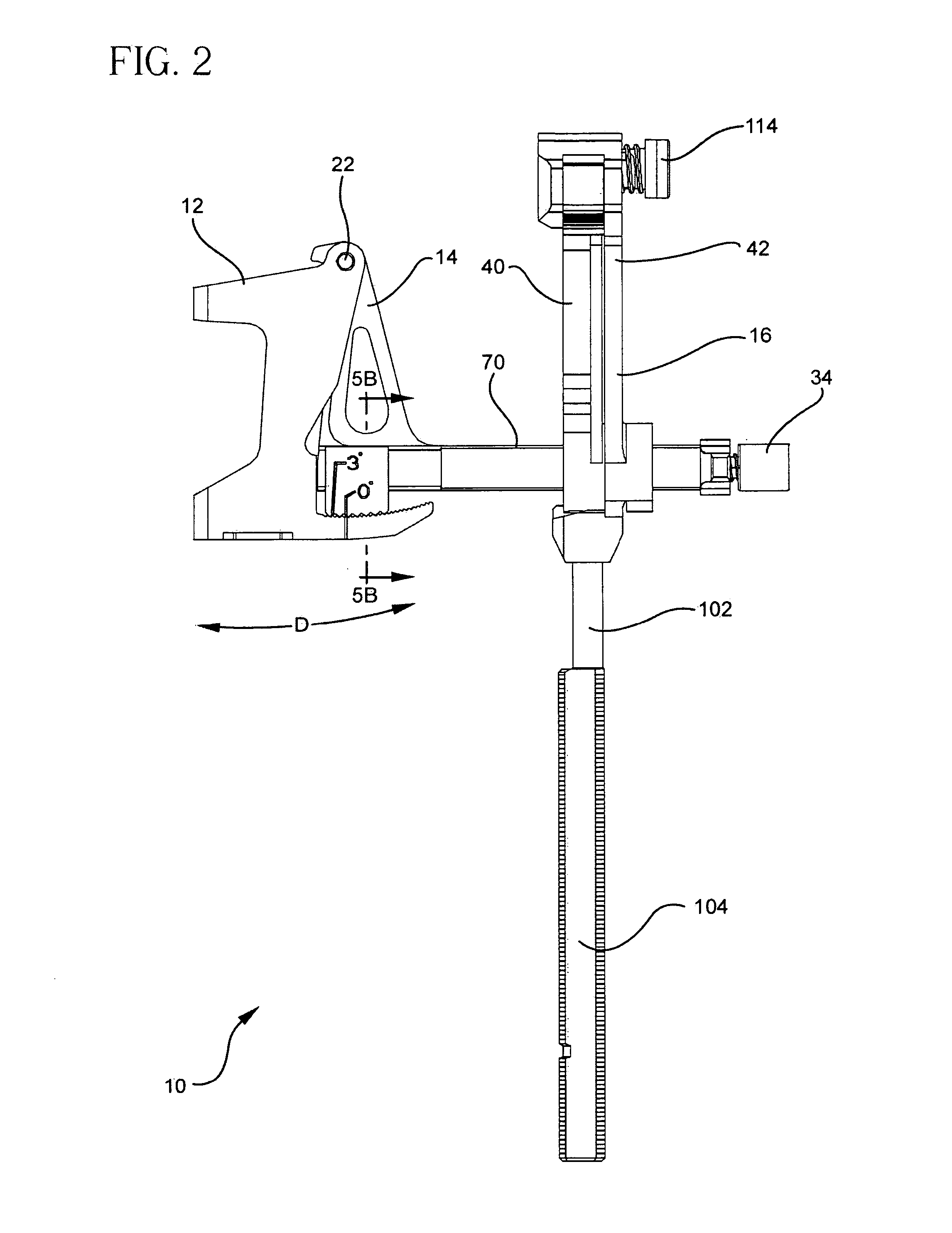
A locking intramedullary alignment jig for use in bone resection, especially for the proximal tibial has an axially extending intramedullary rod for insertion into the medullary canal of the tibia. A slidable anchoring block is mounted on the rod for movement along the rod in the axial direction, which on the tibia is the proximal-distal direction. The anchoring block has a pivot point at one end thereof and a tooth portion at a second end thereof. A first rotating body is pivotally coupled to the pivot point on the anchoring block for rotation about a first axis. The rotating body includes a toothed locking member for releasable locking engagement with the toothed portion the anchoring block. A second rotating body, including a bone resection guide is connected to the first rotating body. Movement of the first and second rotating bodies allow rotation of the resection guide in both the flexion-extension and varus-valgus directions.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Compliant Interbody Fusion Device With Deployable Bone Anchors
An interbody fusion implant with deployable bone anchors includes a support member, a monolithic body that accommodates the support member, and a longitudinal hole along a vertical length of the support member. The support member includes a first end and a second end. The second end includes two flanges. The flanges are configured to dig into an endplate of a vertebral body. The flanges of the support member provide a location fixation on an implantation of the interbody fusion implant into the vertebral body. The support member may also include at least one of a clip shaped support member and an I-shaped support member. The I-shaped support member may allow a rigidity and a support in flexion-extension through a living-hinge positioned in a middle of the I-shaped support member. The longitudinal hole sustains loads imported on the interbody fusion implant and allows the interbody fusion implant to flex freely.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
Exoskeleton assisting mechanism for lower limb
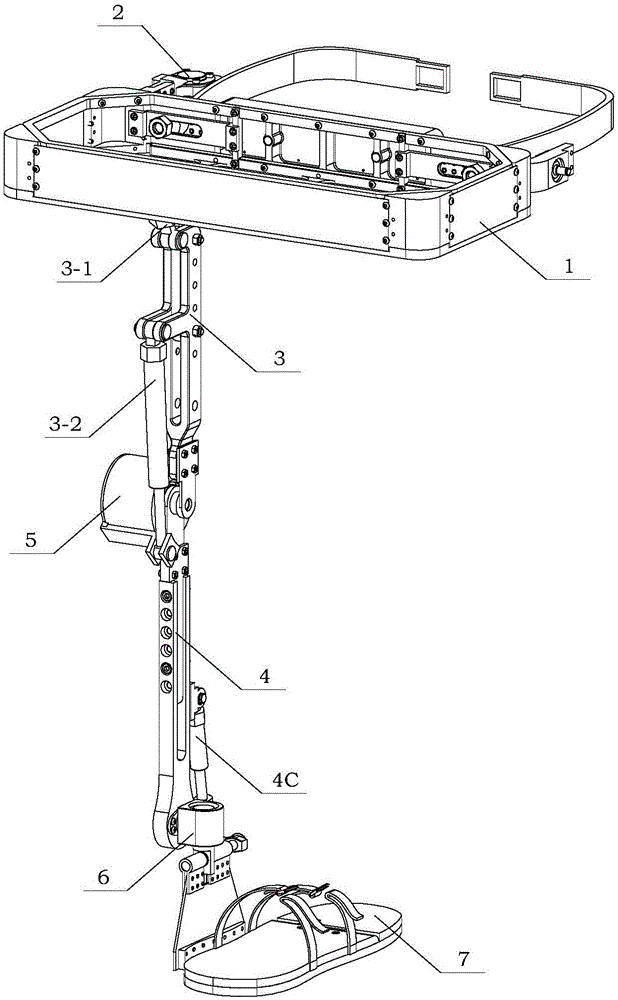
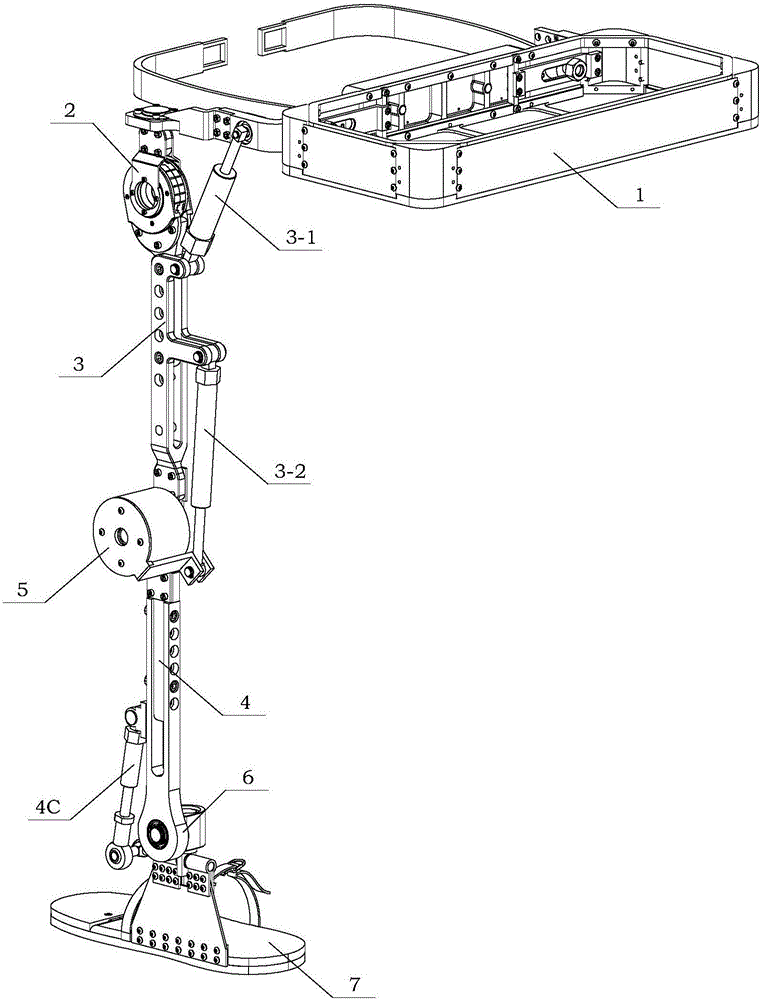
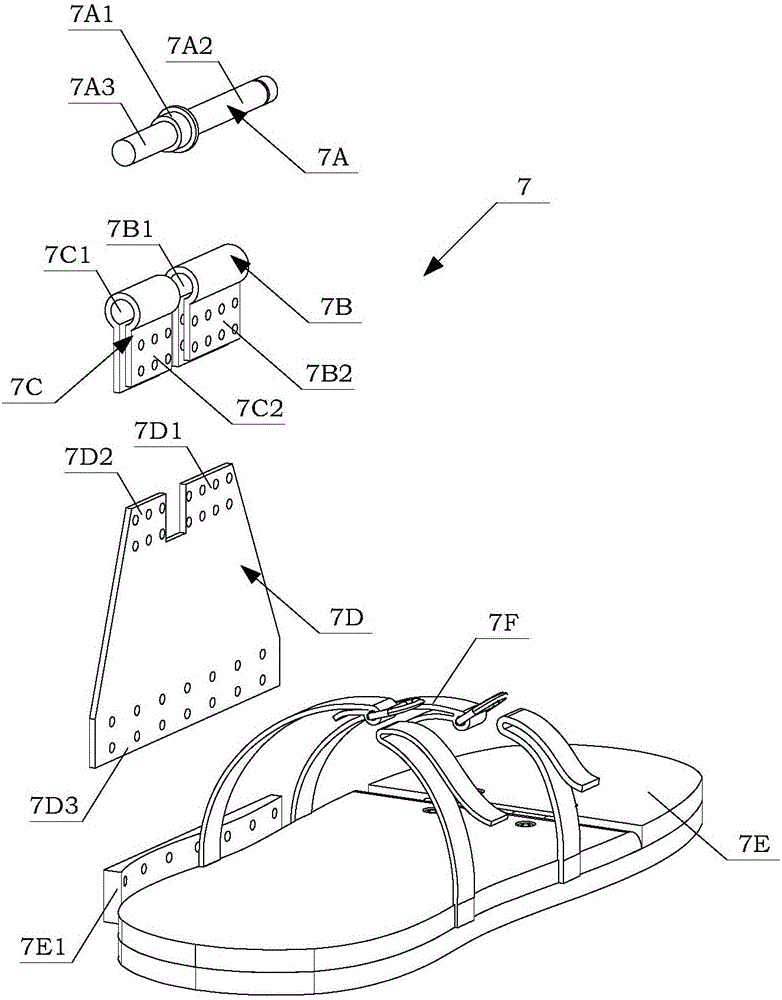
InactiveCN106426097APracticalSimple structural designProgramme-controlled manipulatorThighSagittal plane
The invention discloses an exoskeleton assisting mechanism for a lower limb. The exoskeleton assisting mechanism comprises a waist bearing unit, a thigh unit, a shank unit and a foot unit. The waist bearing unit and the thigh unit are fixed through the connection of an AA connecting piece and a CE connecting piece; the thigh unit and the shank unit are fixed through the connection of a CB connecting piece and a shank regulating rod; and the shank unit and the foot unit are fixed through the connection of a shank swing rod and an ankle joint shaft. The exoskeleton assisting mechanism for the lower limb is a single-leg seven-degree-of-freedom connecting rod bionic mechanism and is driven by three hydraulic mechanisms. In a human walking process, a thigh connecting rod is matched with a flexible coupling of a hip joint to finish flexion-extension motion in a sagittal section under the push of one of the hydraulic mechanisms, a shank connecting rod is matched with a flexible coupling of a knee joint to finish flexion-extension motion in the sagittal section under the push of the other hydraulic mechanisms, and the foot unit finishes flexion-extension motion in the sagittal section around a DC rotating shaft under the push of another hydraulic mechanism.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
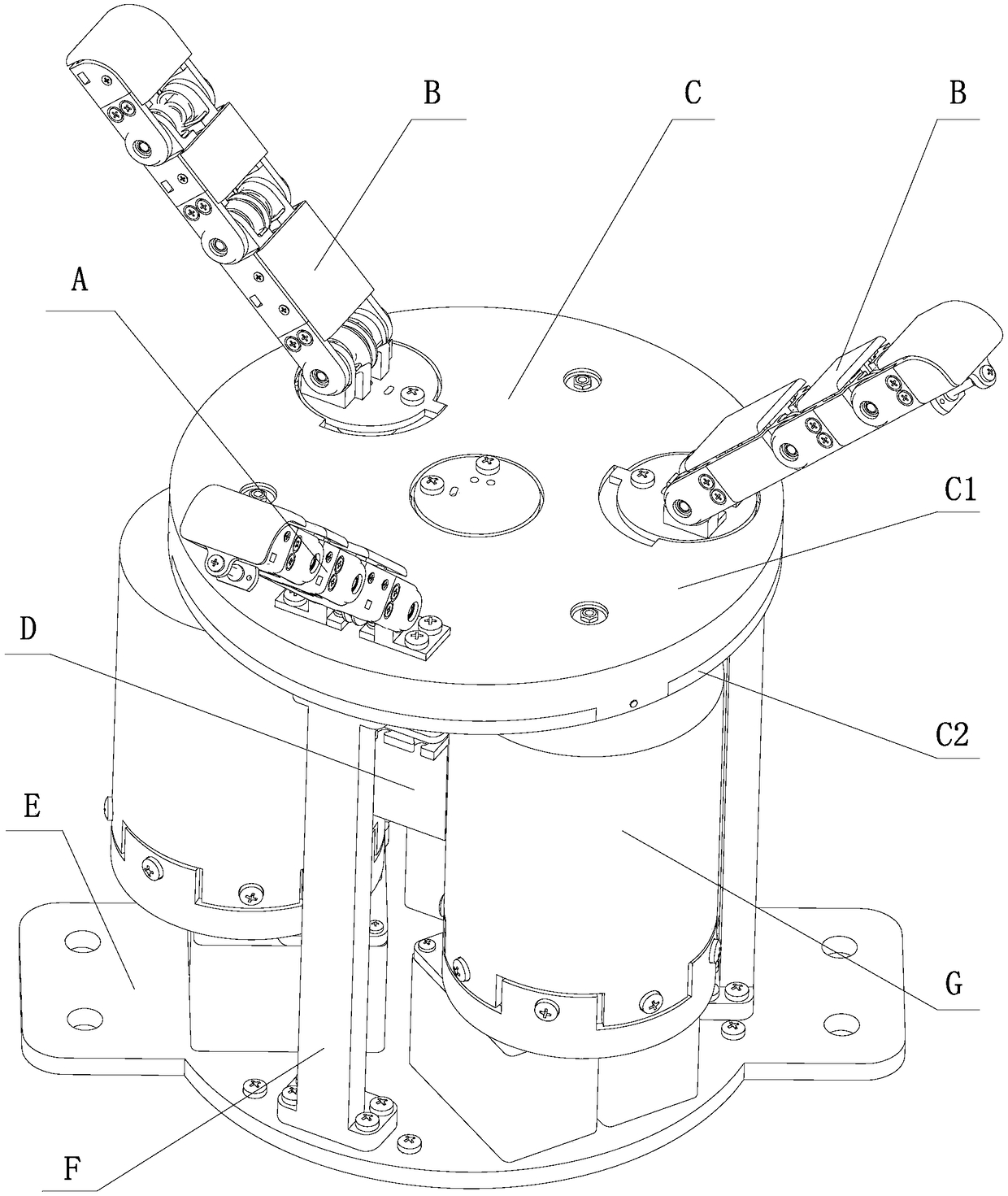
Underactuated variable-stiffness manipulator based on variable-stiffness elastic joints
PendingCN108748254AImprove gripImprove response speedJointsGripping headsVariable stiffnessSacroiliac joint
The invention provides an underactuated variable-stiffness manipulator based on variable-stiffness elastic joints, relates to a variable-stiffness manipulator, and aims to solve the problem about application limitations of a stiff manipulator and a flexible manipulator in the prior art. The underactuated variable-stiffness manipulator comprises the three variable-stiffness elastic joints, and further comprises a palm, a motor, a base, supporting columns and three fingers, wherein the three fingers comprise one flexion-extension finger and two coupling rotary flexion-extension fingers; the palmis arranged above the base; the palm and the base are connected through the supporting columns; the vertically-arranged motor and the three variable-stiffness elastic joints are mounted on the base;the flexion-extension finger and the two coupling rotary flexion-extension fingers are arranged on the palm along the circumferential direction of the palm; through a steel wire rope, the two couplingrotary flexion-extension fingers are driven by an output shaft of the motor to perform rotary motion; output shafts of the three variable-stiffness elastic joints are arranged in a one-to-one correspondence manner; and the flexion-extension motion of the flexion-extension finger and that of the two coupling rotary flexion-extension fingers are driven through the steel wire rope. The underactuatedvariable-stiffness manipulator provided by the invention belongs to the field of robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Dynamic spacer for total knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS7455647B2Easy to useEasy constructionSurgeryPerson identificationTotal hip arthroplastyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A dynamic spacer is provided for measuring flexion-extension gap during total knee arthroplasty. The dynamic spacer includes a first planar member having a lower tissue engaging surface, and a second planar member having an upper tissue engaging surface. A tensioner is disposed between the first planar member and the second planar member for applying a tensile force acting upon the first and second planar members. The tensioner is attached to the first and second planar members, such that the first planar member is held substantially parallel to the second planar member in the absence of compressive load. The dynamic spacer allows for accurately measuring flexion-extension gaps and angular deviation in flexion indicating the appropriateness of femoral rotation.
Owner:TARABICHI SAMIH
Vertical type total knee replacement patella movement test device
InactiveCN105266932AAchieve relative motionMeasure and record exercise parametersJoint implantsHydraulic cylinderTibia
The invention relates to a vertical type total knee replacement patella movement test device. The vertical type total knee replacement patella movement test device is composed of a supporting structure, a femur movement mechanism, a patella movement mechanism, a tibia movement mechanism and a driving mechanism of the tibia movement mechanism; the supporting structure can realize fixed connection of the test device and movement support of a femur; the movement support is provided by the piston rod of a hydraulic cylinder and is connected with the femur movement mechanism; the femur movement mechanism drives a proximal femur to move up and down and rotate, so that the flexion-extension movement of the femur can be realized; a linkage mechanism of patella and femur movement is adopted, so that patella movement which is coordinated and consistent with the flexion-extension process of the femur can be generated; and the tibia movement mechanism and the driving mechanism thereof are installed at the bottom plate of the supporting structure, and generate flexion-extension movement and self rotation movement of a tibia. According to the vertical type total knee replacement patella movement test device of the invention, the actual movement situation of a replacement prosthesis in the knee of a human being is simulated, so that the movement of the patella can be tested; multiple kinds of movement such as the upward / downward movement of the proximal femur, the flexion-extension movement of the femur, the displacement of patellar ligaments as well as the flexion-extension movement and self rotation movement of the tibia are measured, so that the movement performance of the patella can be obtained.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Artificial knee joint
InactiveUS20130190884A1Increase widthIncrease flexibilityJoint implantsKnee jointsEllipseFemoral component
An artificial knee joint comprises a femoral component a tibial plate slidably receive the femoral component. The femoral component includes medial and lateral condyles, an opening and an elliptical spherical sliding portion are formed therebetween. The elliptical spherical sliding portion couples posterior ends of the medial and lateral condyles, and slides with respect to the tibial plate when flexing the knee joint. The tibial plate includes a medial fossa and a lateral fossa, and a spine and a concave sliding surface are formed therebetween. The spine moves within the opening in an antero-posterior direction in response to flexion-extension action of the knee joint, and comes into contact with the sliding portion when flexing. The concave sliding surface forms a posterior surface of the spine, and slidably receives the elliptical spherical portion. A width of the elliptical spherical sliding portion is widened from the opening toward a posterior end.
Owner:KYOCERA MEDICAL CORP
Locking intramedullary jig
InactiveUS20080183178A1Easy to operateThe right amountNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical sawsTibiaIntramedullary rod
A locking intramedullary alignment jig for use in bone resection, especially for the proximal tibial has an axially extending intramedullary rod for insertion into the medullary canal of the tibia. A slidable anchoring block is mounted on the rod for movement along the rod in the axial direction, which on the tibia is the proximal-distal direction. The anchoring block has a pivot point at one end thereof and a tooth portion at a second end thereof. A first rotating body is pivotally coupled to the pivot point on the anchoring block for rotation about a first axis. The rotating body includes a toothed locking member for releasable locking engagement with the toothed portion the anchoring block. A second rotating body, including a bone resection guide is connected to the first rotating body. Movement of the first and second rotating bodies allow rotation of the resection guide in both the flexion-extension and varus-valgus directions.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
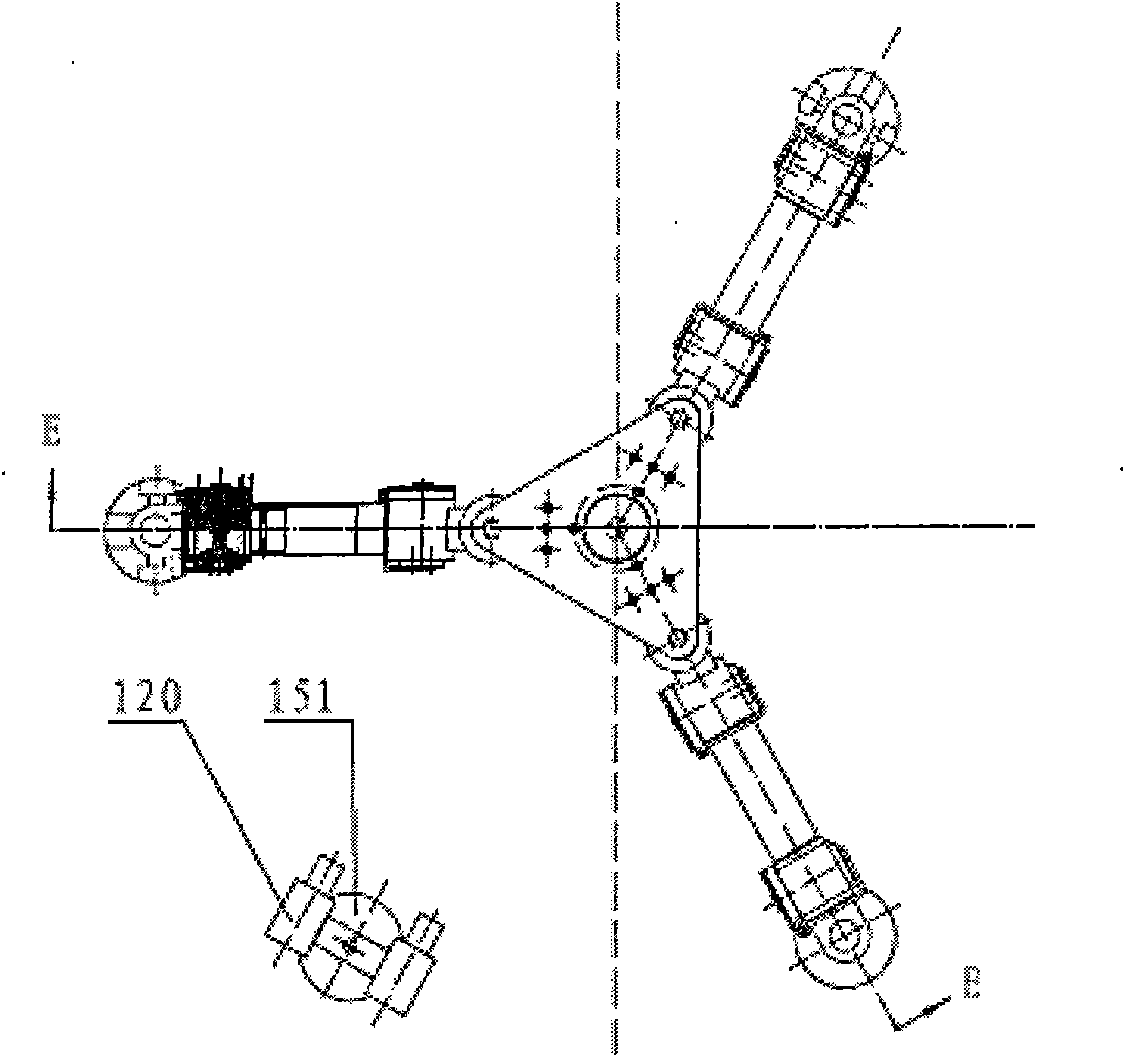
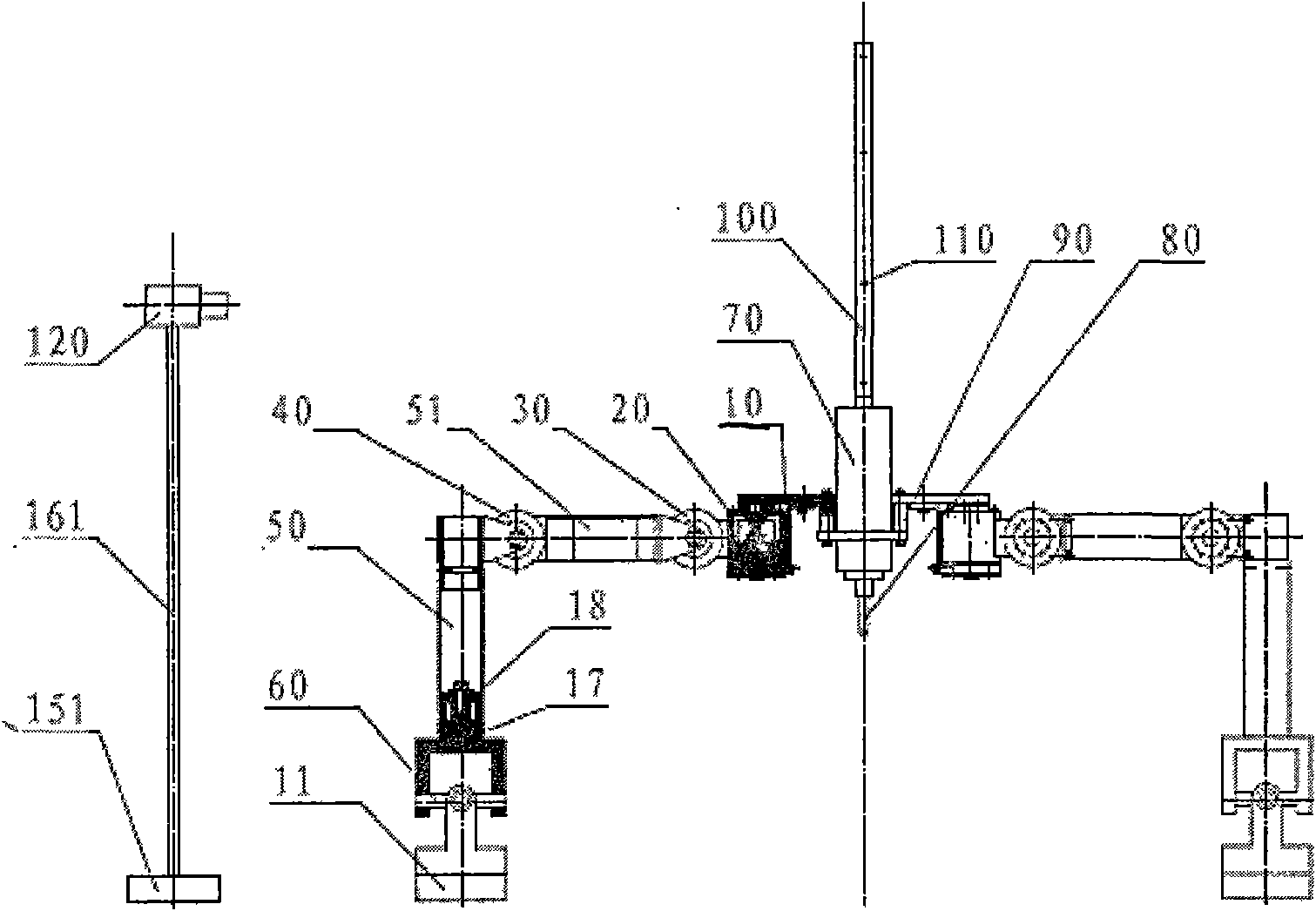
Open-type field six-degree-of-freedom series-parallel processing robot
InactiveCN101664881ARealize global positioning controlRealize multi-axis linkage NC machiningAutomatic control devicesWelding/cutting auxillary devicesEngineeringParallel processing
The invention discloses an open-type field six-degree-of-freedom series-parallel processing robot, which comprises a platform, at least three support legs, a processing spindle and a processing cutter. The support legs are symmetrically mounted on the corners of the platform around the center of the platform and each support leg consists of a swinging joint, a leg lifting joint, a flexion-extension joint, a foot ball joint and a foot. The processing spindle is mounted in the middle of the platform, and the processing cutter is installed on the processing spindle. The robot further comprises avisual benchmark, a visual camera, three force sensors and an intelligent controller. The visual benchmark is installed on the processing spindle and is located in the visual range of the visual camera, the processing spindle is connected with the platform by means of three symmetrically arranged force sensors, and the visual camera and the force sensors are all connected with the intelligent controller. The series-parallel processing robot has the advantages of compact structure, small size, low cost and high processing and measuring precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Preparing method for repetitive-gradient porous titanium alloy for promoting sacralization
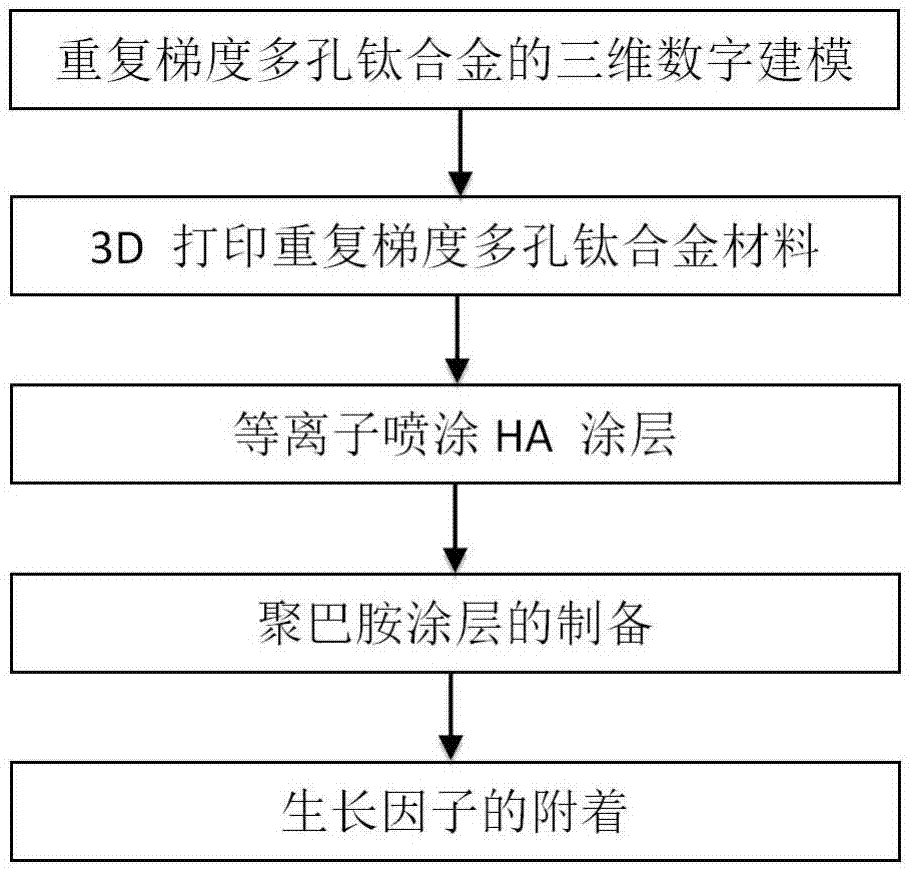
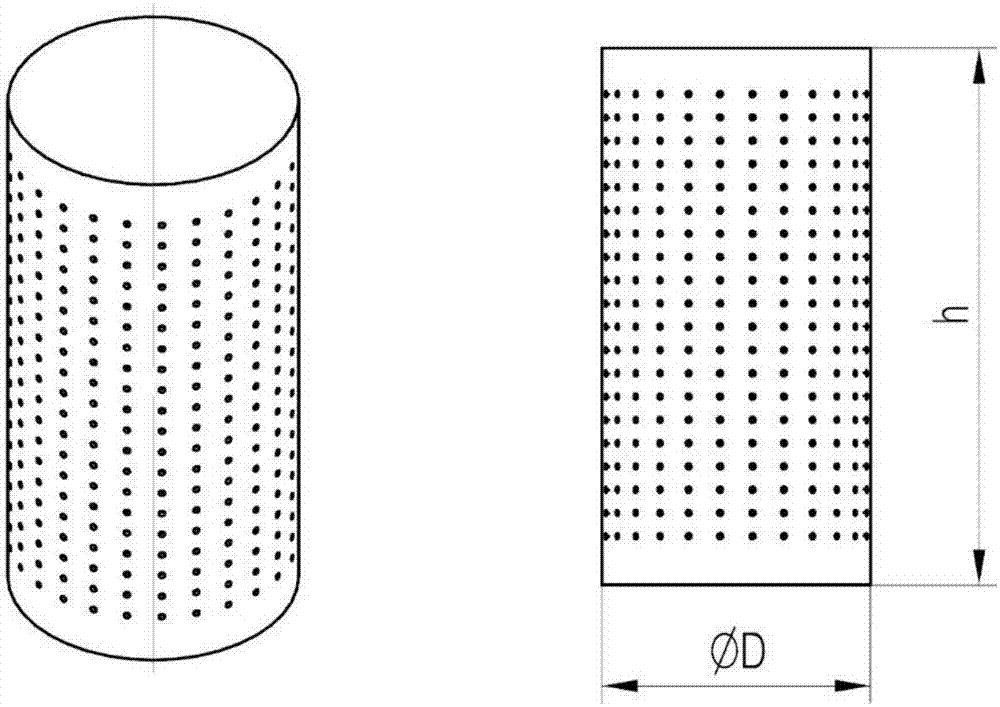
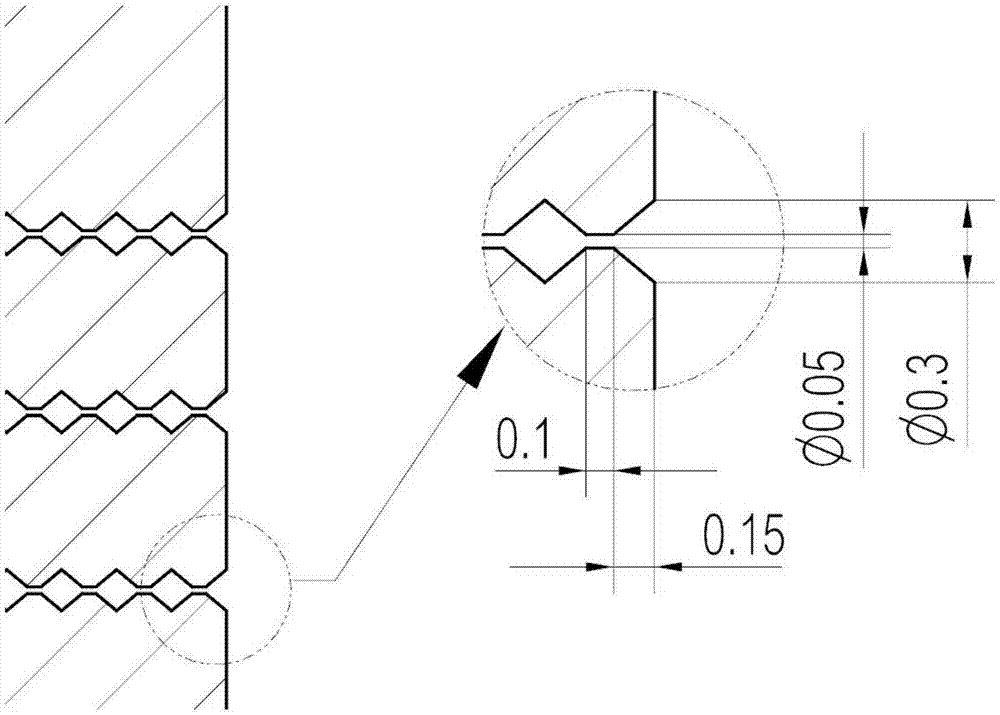
ActiveCN107349472AGuaranteed rigidityIncrease growth rateTissue regenerationCoatingsOsteocyteTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a preparing method for repetitive-gradient porous titanium alloy for promoting sacralization. The repetitive-gradient porous titanium alloy takes titanium alloy powders as raw materials, and repetitive-gradient porous titanium alloy bar materials are prepared by 3D printing; elasticity modulus of the gradient porous titanium alloy is at 0.53-13.2 GPa, and the compression and flexion-extension strength is changed at 22-356 Mpa, and the elasticity modulus of the gradient porous titanium alloy is matched with the elasticity modulus of natural bones. The preparing method for the repetitive-gradient porous titanium alloy for promoting sacralization comprises the following steps that hydroxyapatite (HA) coating with bioactivity is constructed on the surface of the repetitive-gradient porous titanium alloy through a plasma spraying technique; and the growth factor (VEGF) is fixed to surfaces of materials by utilizing dopamine as an intermediate medium. The porous titanium alloy materials prepared through the preparing method is loaded with the growth factor and the HA and has the characteristics that histocompatibility is high, and migration and growth of osteocyte can be promoted; and according to the repetitive-gradient porous structure, the fusion strength of bones is increased, and pullout force is increased.
Owner:浙江德康医疗器械有限公司
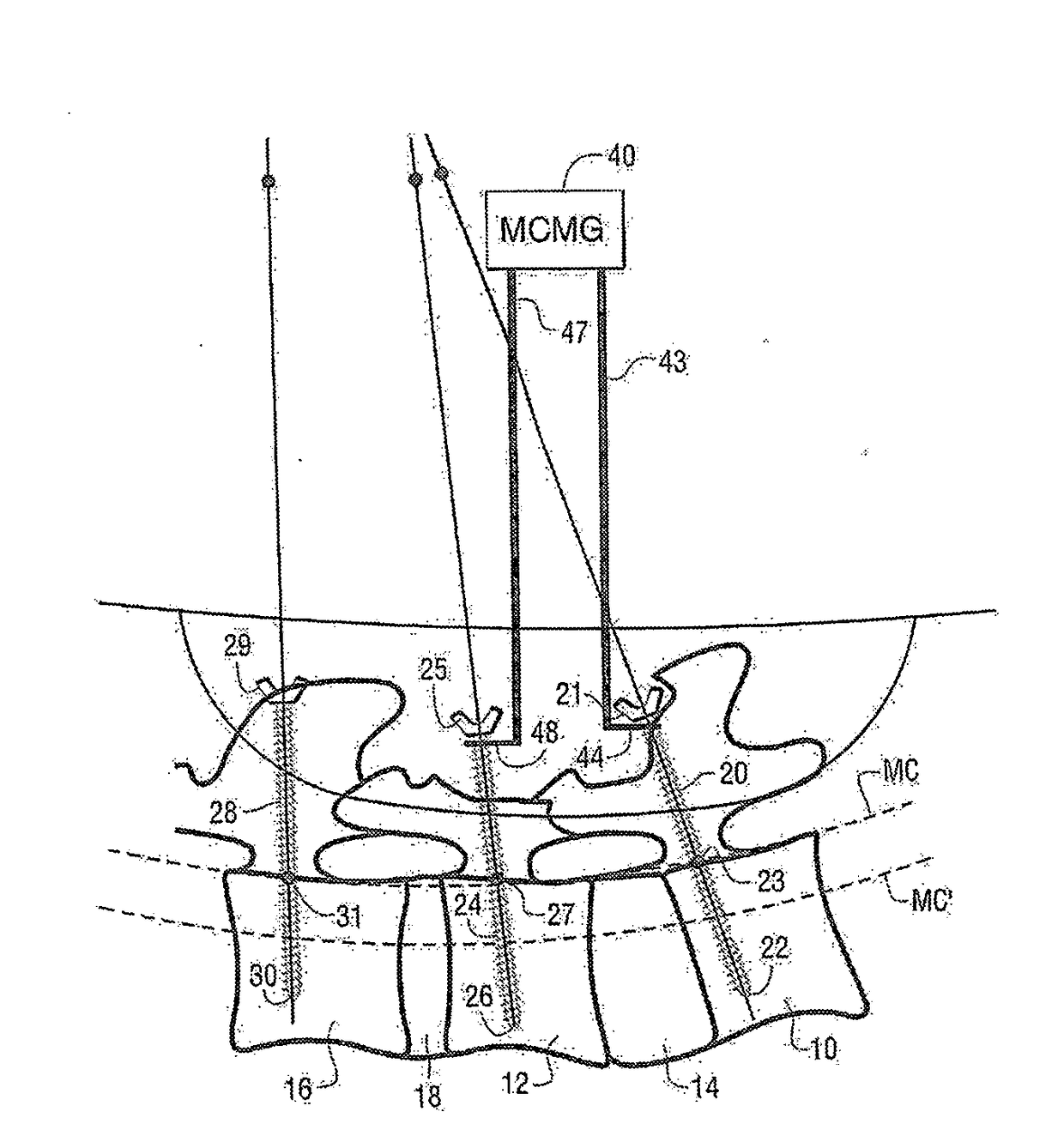
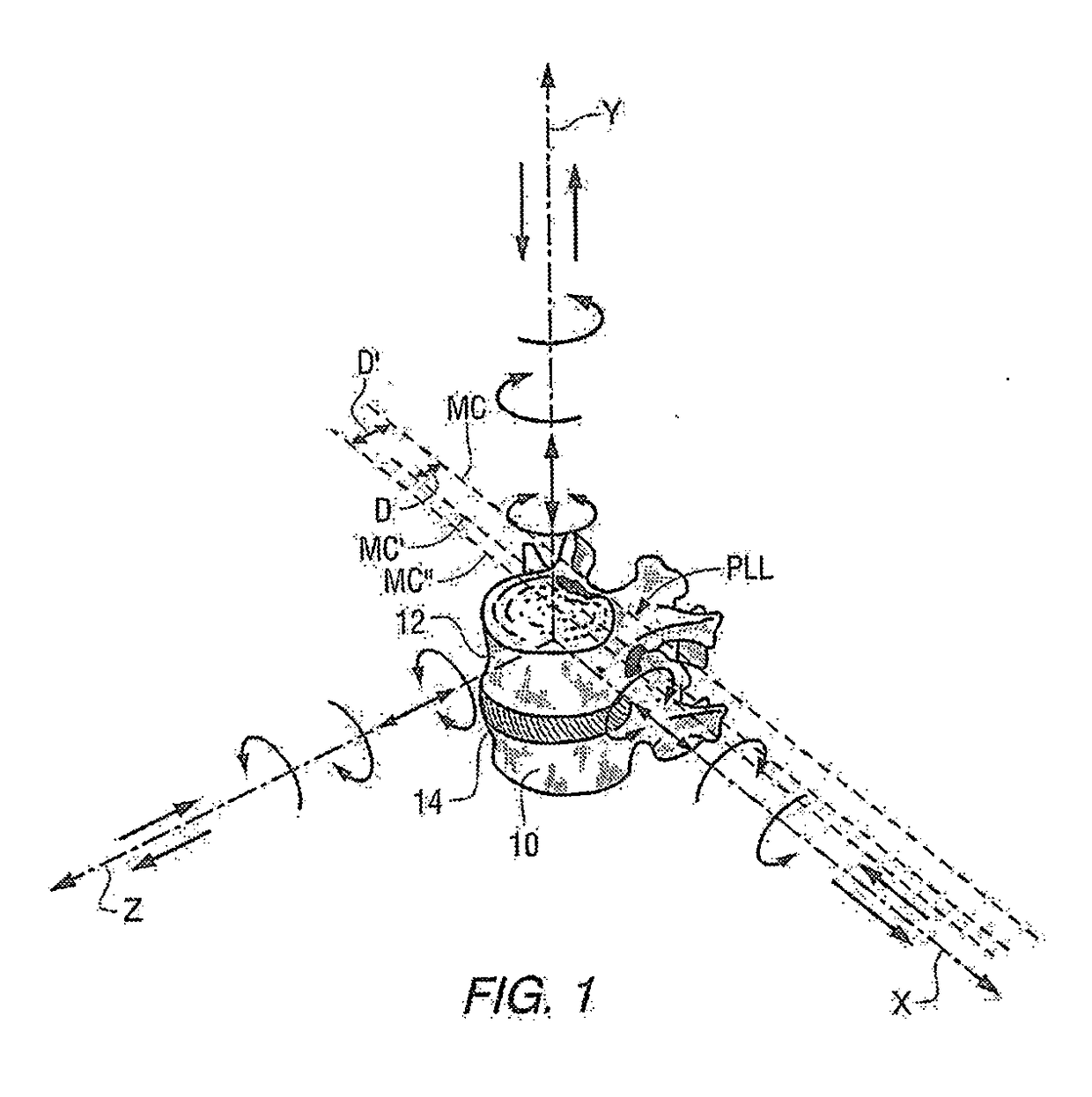
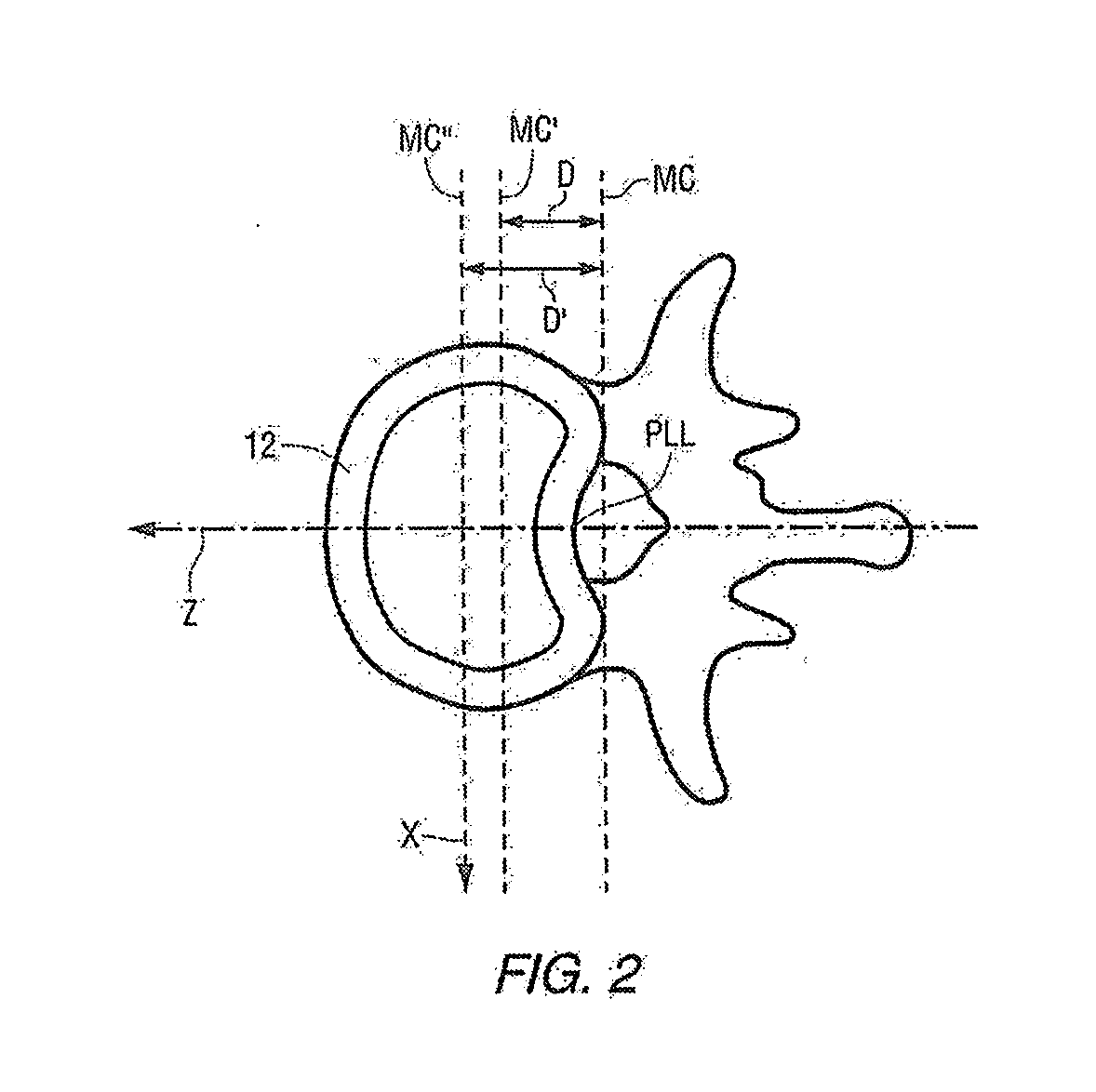
Methods and apparatus for spinal reconstructive surgery and measuring spinal length and intervertebral spacing, tension and rotation
ActiveUS20180125598A1Insufficient releaseImprove guidanceInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSpinal columnIntervertebral disc
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for performing spinal reconstructive surgery, including measuring spinal length in the Y-axis at the middle column, measuring intervertebral spacing in the Y-axis at the middle column, measuring intervertebral tension applied to the posterior longitudinal ligament, establishing the height of intervertebral spacers along the Y-axis at the middle column based on one or more of such measurements, measuring intervertebral rotation around the Y-axis, and measuring flexion-extension or anterior-posterior rotation around the X-axis.
Owner:MEDICREA INT SA
Whole lower extremity exoskeleton and operation method thereof
InactiveCN106901949AReduce the burden on the lower limbsWalking aidsDiagnostic recording/measuringThigh partExoskeleton
The invention relates to the technical field of lower extremity exoskeletons and discloses a whole lower extremity exoskeleton and an operation method of the whole lower extremity exoskeleton. The whole lower extremity exoskeleton comprises a skeleton system, wherein the skeleton system comprises a waist-hip frame (1), a left leg frame and a right left frame, wherein each of the left leg frame and the right left frame comprises a thigh part (2), a shank part (3) and a foot part (11); an auxiliary internal and external leg expansion device (4), an auxiliary internal and external leg rotating device (5) and an auxiliary leg flexion-extension device (6) are arranged between the waist-hip frame (1) and each thigh part (2); each auxiliary internal and external leg rotating device (5) comprises a first rotating shaft (51); and the direction of each first rotating shaft (51) is vertical to the horizontal plane. The whole lower extremity exoskeleton has the function of strengthening or partially replacing the lower limb movement capacity of a user, and is suitable for users with amputated lower limbs or poor lower limb movement capacity.
Owner:艾施科(杭州)科技有限公司
Reconfigurable exoskeleton upper limb rehabilitation robot for different body types
ActiveCN111281741AReconfigurableGuaranteed wearing comfortChiropractic devicesUpper limb rehabilitationExoskeleton
The invention discloses a reconfigurable exoskeleton upper limb rehabilitation robot for different body types. According to the reconfigurable exoskeleton upper limb rehabilitation robot, a shoulder joint internal and external rotation assembly, a scapulohumeral adjustment assembly, a shoulder joint flexion extension and retraction assembly, an upper arm length adjustment assembly, an upper arm rotary motion assembly, an elbow joint flexion and extension assembly, a forearm rotary motion assembly, a forearm length adjustment assembly and a wrist joint flexion and extension assembly are connected in sequence; the robot has six freedom degrees, and six-freedom-degree rehabilitation movement and compound movement of the upper limbs can be achieved corresponding to six active executing mechanisms; a liftable base is suitable for people with different heights; the scapulohumeral adjustment assembly is suitable for rising and sitting postures of different patients; the forearm length adjustment assembly and the upper arm length adjusting assembly are suitable for patients with different forearm and upper arm lengths. The reconfigurable exoskeleton upper limb rehabilitation robot has reconfigurability, multiple passive adjusting mechanisms, a left and right hand interchange using mode, and a light exoskeleton structure, requirements of patients with different disease conditions can bemet, and the treatment cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Hand exoskeleton device on basis of pre-bending elastic wire tube drive
ActiveCN108524184AMovement flexibility and comfortGood flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesEngineeringFlexion extension
The invention provides a hand exoskeleton device on the basis of pre-bending elastic wire tube drive. The hand exoskeleton device comprises a thumb movement assembly, a thumb drive assembly, four-finger movement assemblies and a four-finger drive assembly. The thumb drive assembly is rotatably connected to the thumb movement assembly, the thumb movement assembly can be driven by the thumb drive assembly to bend, extend and swing, the four-finger drive assembly is connected to the four-finger movement assemblies, the four-finger movement assemblies can be driven by the four-finger drive assembly to bend and extend, the thumb drive assembly is rotatably connected to the four-finger drive assembly, and the thumb movement assembly and the four-finger movement assemblies are based on the pre-bending elastic wire tube drive. The hand exoskeleton device has the advantage that the hand exoskeleton device can rotate in consistency with flexion-extension and swinging of human fingers and is highin flexibility.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
Pressure orthotics device
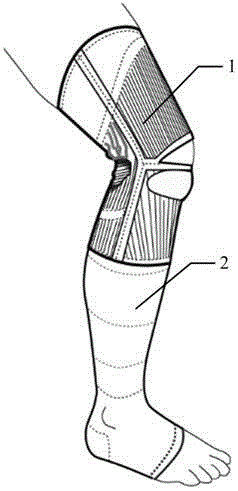
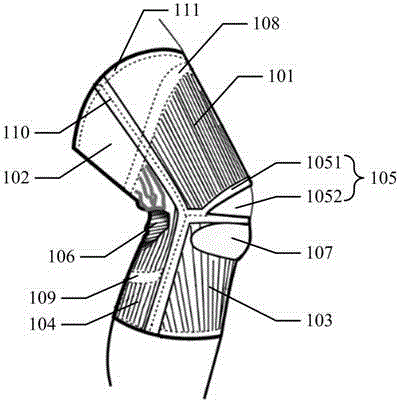
ActiveCN105996224AReduce tensionRelieve knee painProtective garmentPressure decreaseLower limb circumference
The embodiment of the invention discloses a pressure orthotics device. The pressure orthotics device comprises a knee guard part and a leg guard part, wherein the knee guard part and the leg guard part are of an integral type or a sleeving-wearing type; the knee guard part is woven by three-dimensional knitting, and forms a plurality of functional blocks which are differently stretched in a limb biaxial direction, apply support force or pressure on a knee joint and the periphery thereof, and are seamlessly connected; the leg guard part is woven by three-dimensional knitting, and forms a plurality of pressure blocks which produce pressures decreasing step by step from bottom to top in a lower limb circumference direction, and are seamlessly connected. The pressure orthotics device can be used for preventing and treating lower limb knee pain and chronic venous insufficiency; by means of systemic pressure management, the tensioned state of thigh muscles can be relieved, the knee joint and a flexion-extension angle thereof are controlled and stabilized, and lower limb blood circulation is promoted; besides, the woven blocks of the knee guard part and the leg guard part are respectively seamlessly connected, so the wearing comfort of the pressure orthotics device can be improved.
Owner:CHEMTAX IND
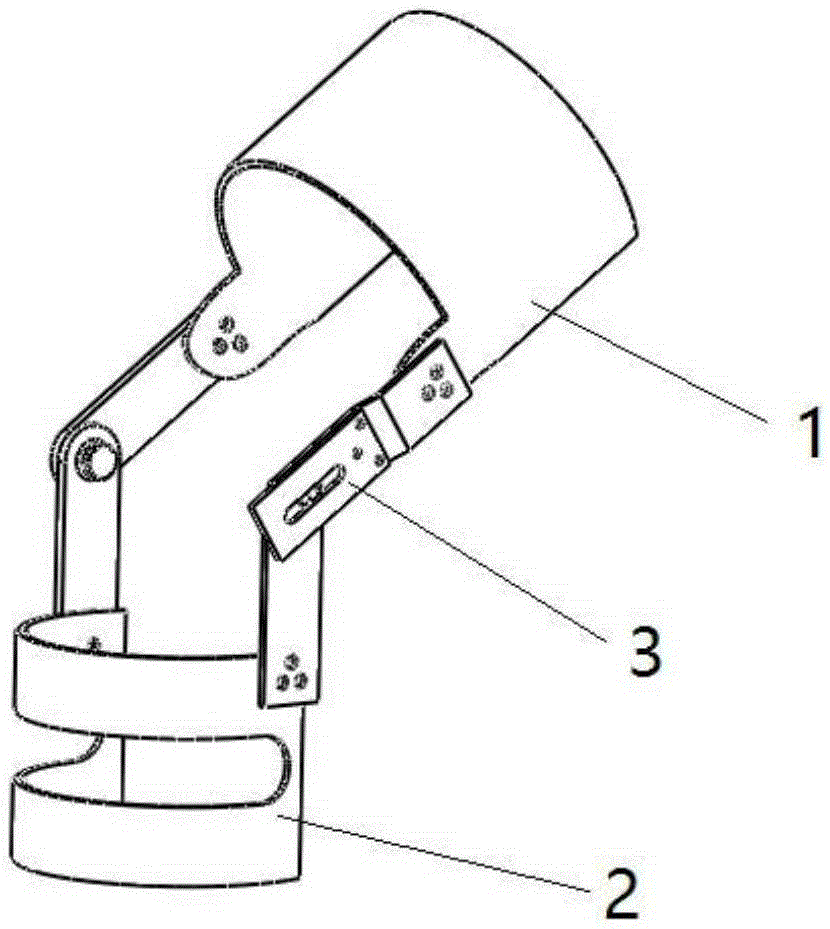
Load-balanced knee joint orthopedic brace and implementation method thereof
The invention discloses a load-balanced knee joint orthopedic brace and a 3D printing method thereof. The printing method includes designing and printing of a thigh supporting part, a shank supporting part and a connecting part; both the thigh supporting part and the shank supporting part are represented as an annular curved surface; the connecting part comprises a leg inner side connecting unit and a leg outer side connecting unit; and the designing includes 3D scanning and modeling, manifold, relaxation, offsetting and shelling. The brace disclosed by the invention is simple in structure and reasonable in design, and is capable of preventing further abrasion of a knee joint under a flexion-extension state; and the printing method, which conducts 3D printing by virtue of polylactic acid fiber, has a good physical effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
System and method for capturing hand movement function based on data glove and position tracker
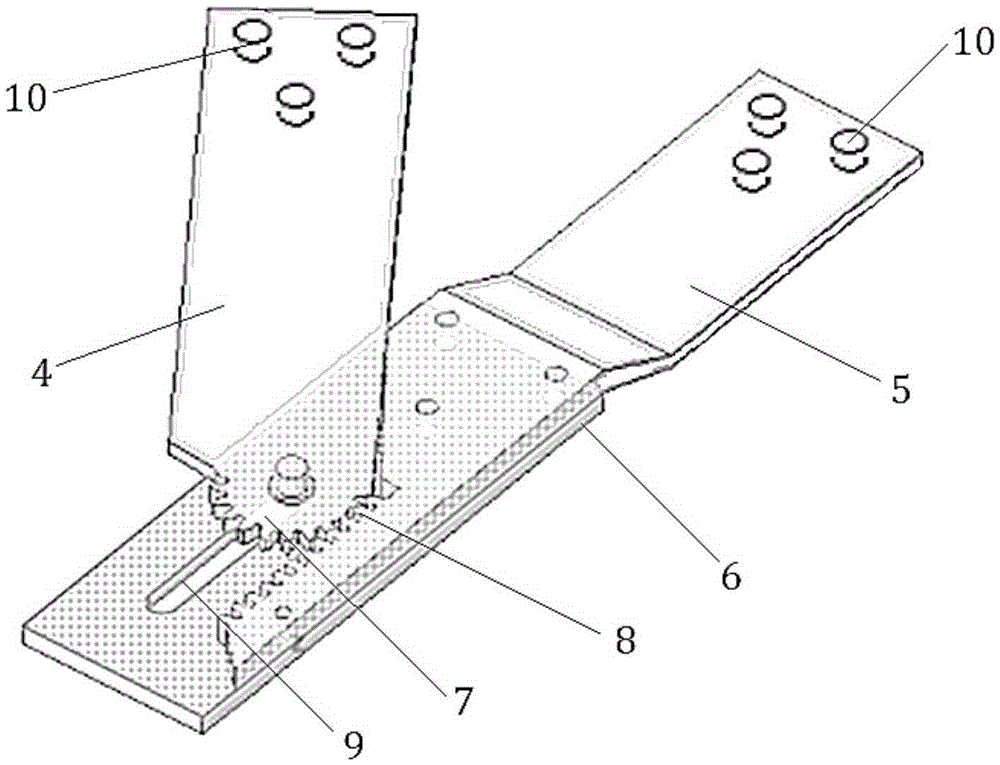
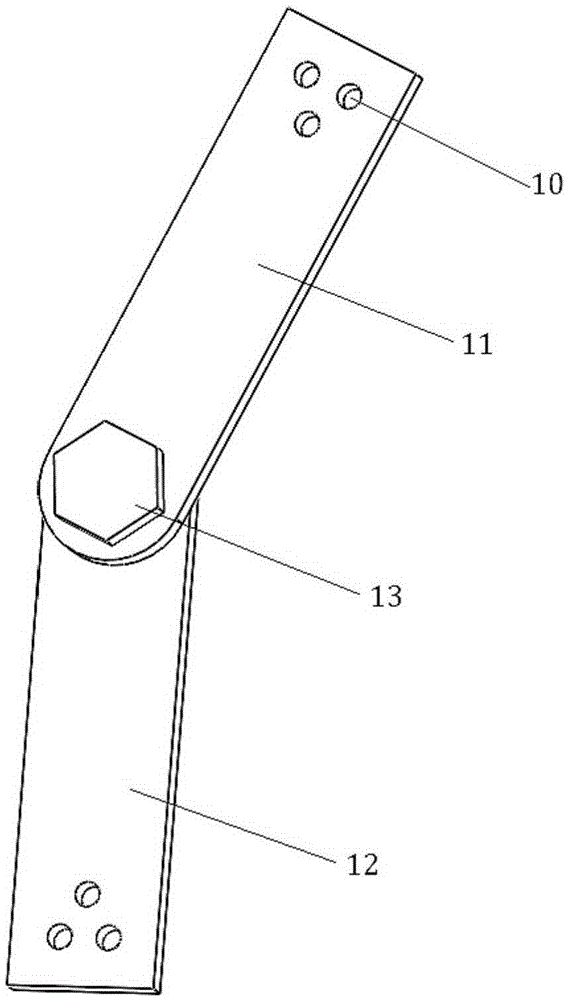
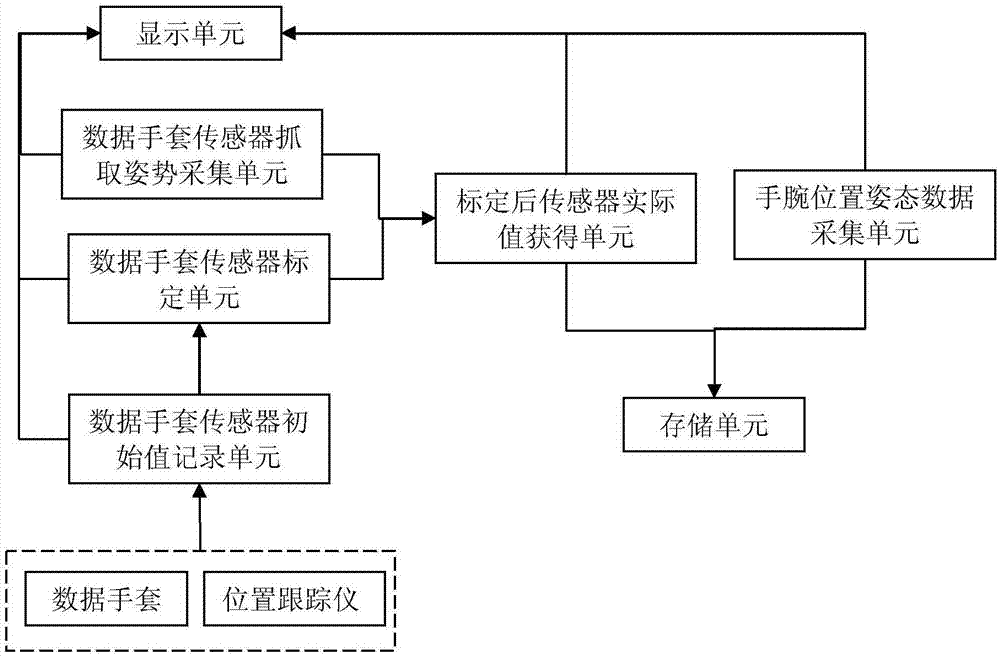
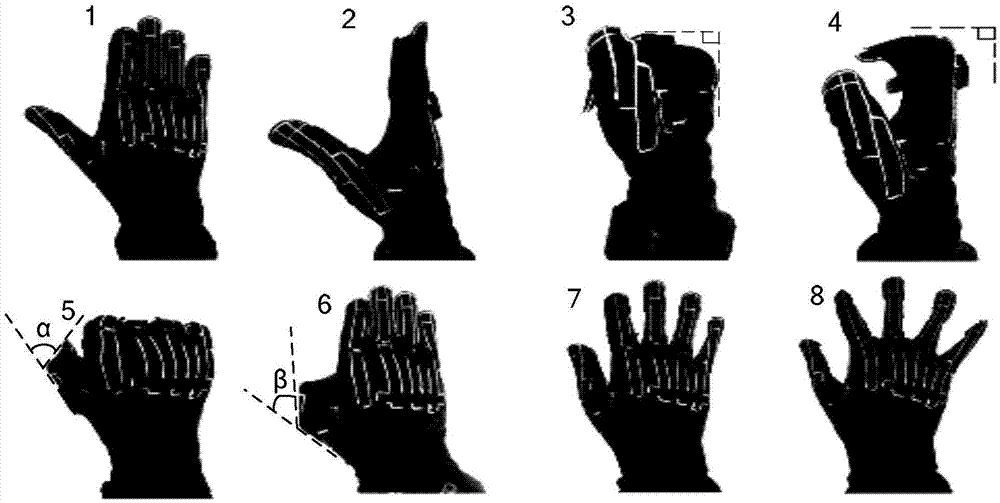
ActiveCN105446485AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingHand graspGross motor functions
The invention relates to a system and method for capturing a hand movement function based on a data glove and a position tracker, relates to the field of hand movement function capturing systems, and aims to solve the problems that the hand movement function is difficult to capture and the existing data glove is difficult to record hand grasping posture data scaling. According to the system and method for capturing the hand movement function based on the data glove and the position tracker disclosed by the invention, hand joint flexion-extension angle information is acquired through the data glove; scaling of the data glove is completed rapidly and accurately through 8-posture data glove scaling experimental paradigms; according to hand movement function experimental requirements, multiple grasping postures of many people for many times can be effectively recorded in combination with wrist position posture data of the position tracker; therefore, the hand movement function capturing accuracy and efficiency are greatly increased; and the system and the method are applied to capturing hand postures.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com