Patents
Literature
42 results about "Near-field scanning optical microscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM) or scanning near-field optical microscopy (SNOM) is a microscopy technique for nanostructure investigation that breaks the far field resolution limit by exploiting the properties of evanescent waves. In SNOM, the excitation laser light is focused through an aperture with a diameter smaller than the excitation wavelength, resulting in an evanescent field (or near-field) on the far side of the aperture. When the sample is scanned at a small distance below the aperture, the optical resolution of transmitted or reflected light is limited only by the diameter of the aperture. In particular, lateral resolution of 20 nm and vertical resolution of 2–5 nm have been demonstrated.
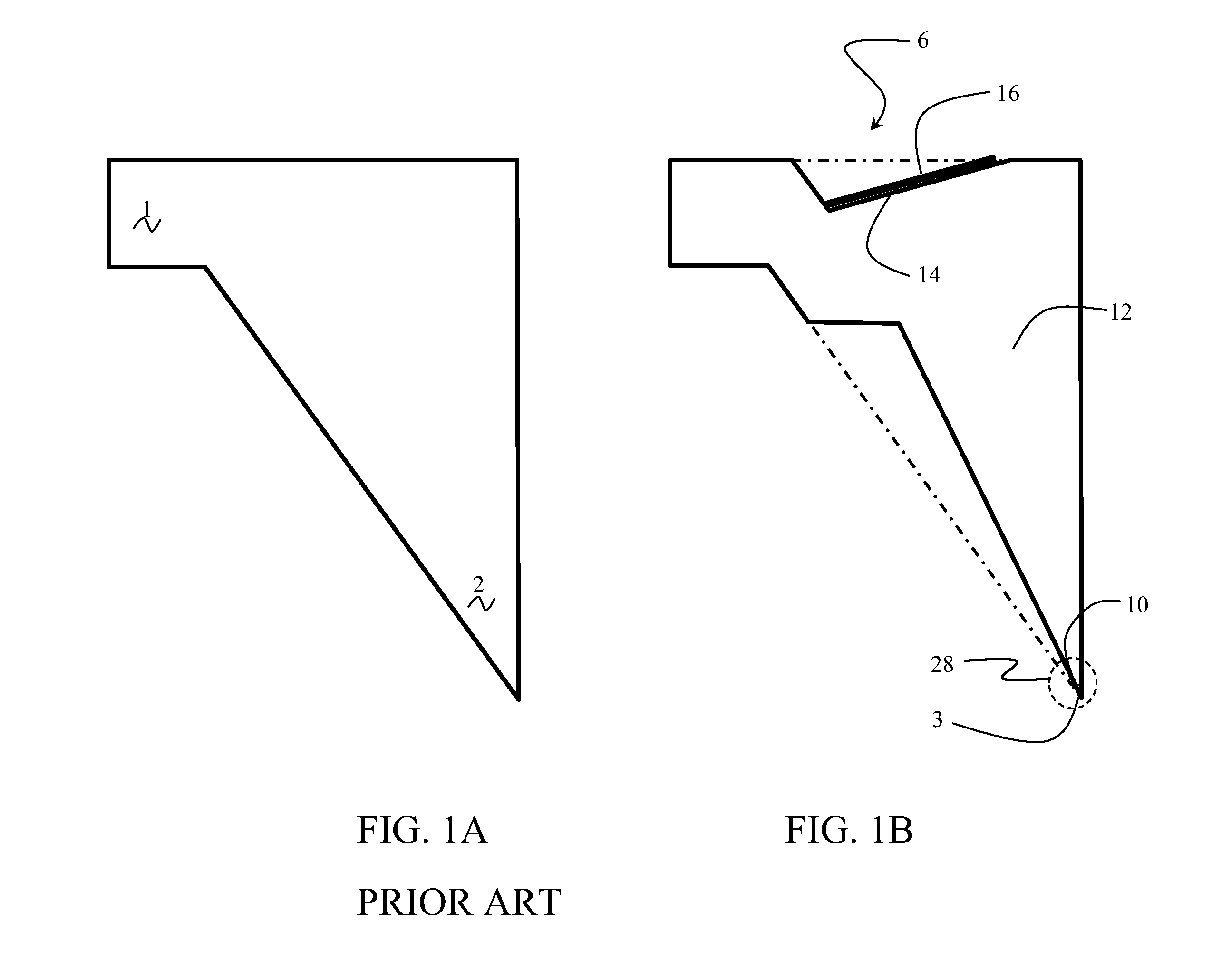
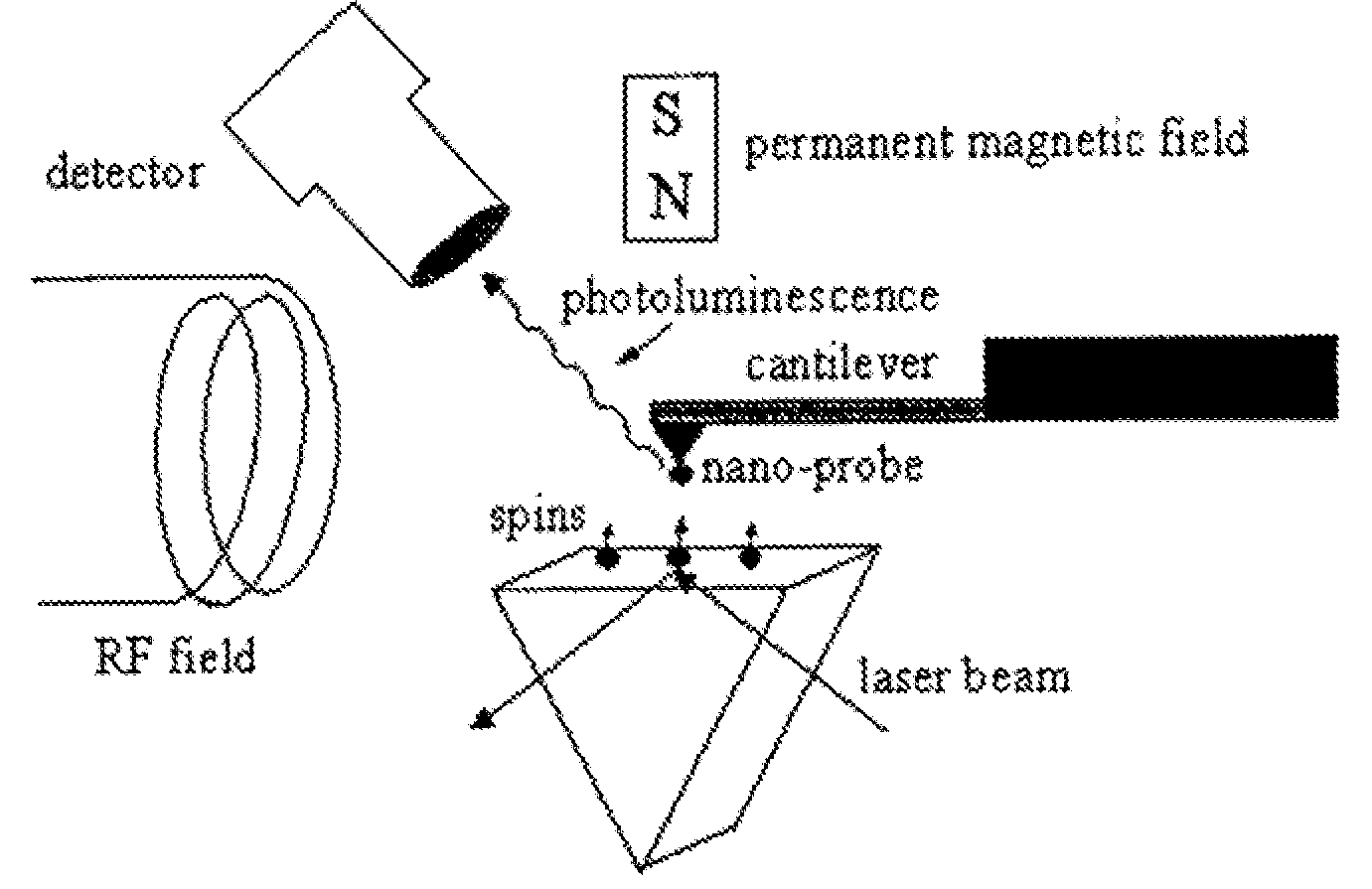
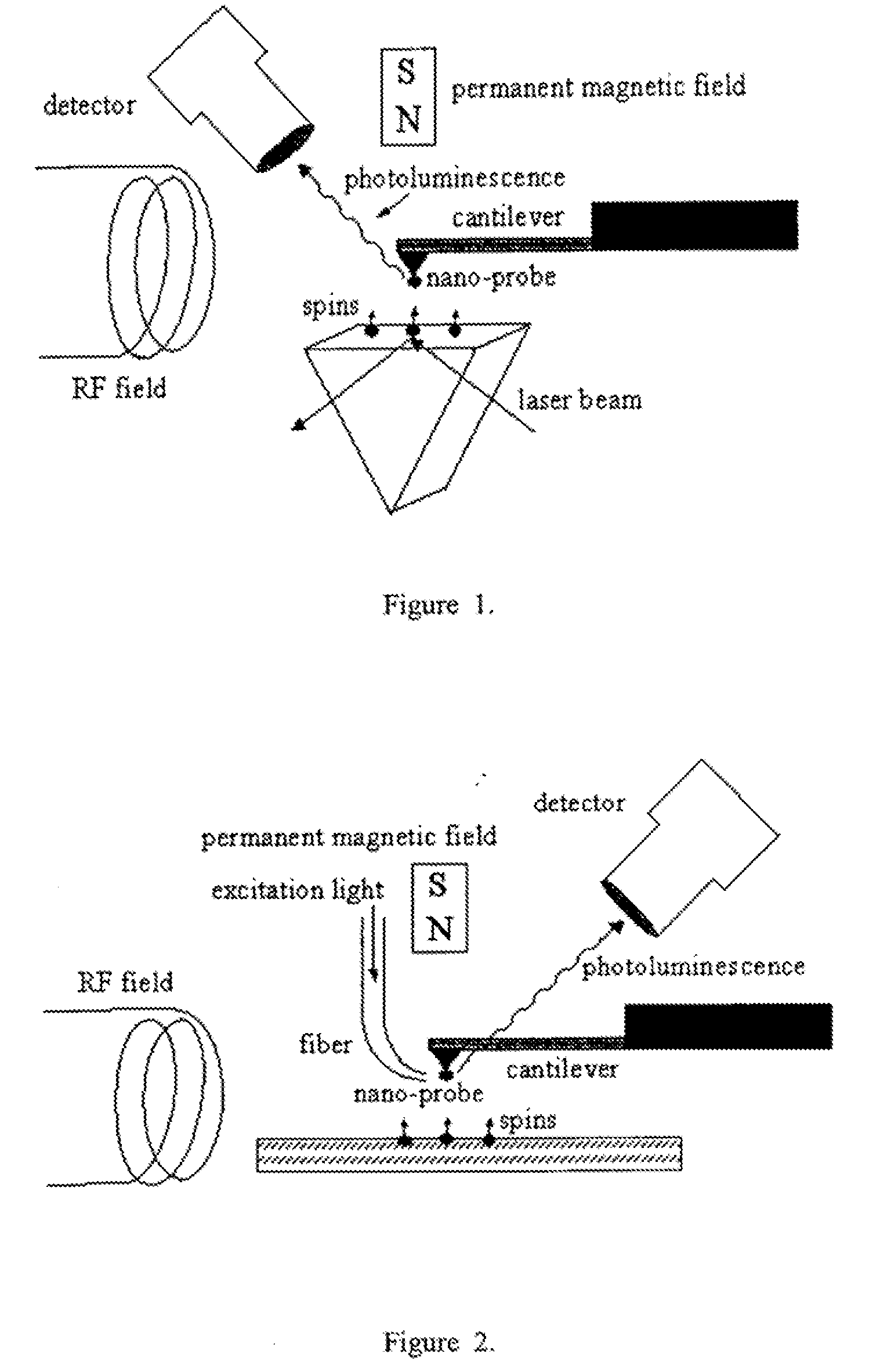
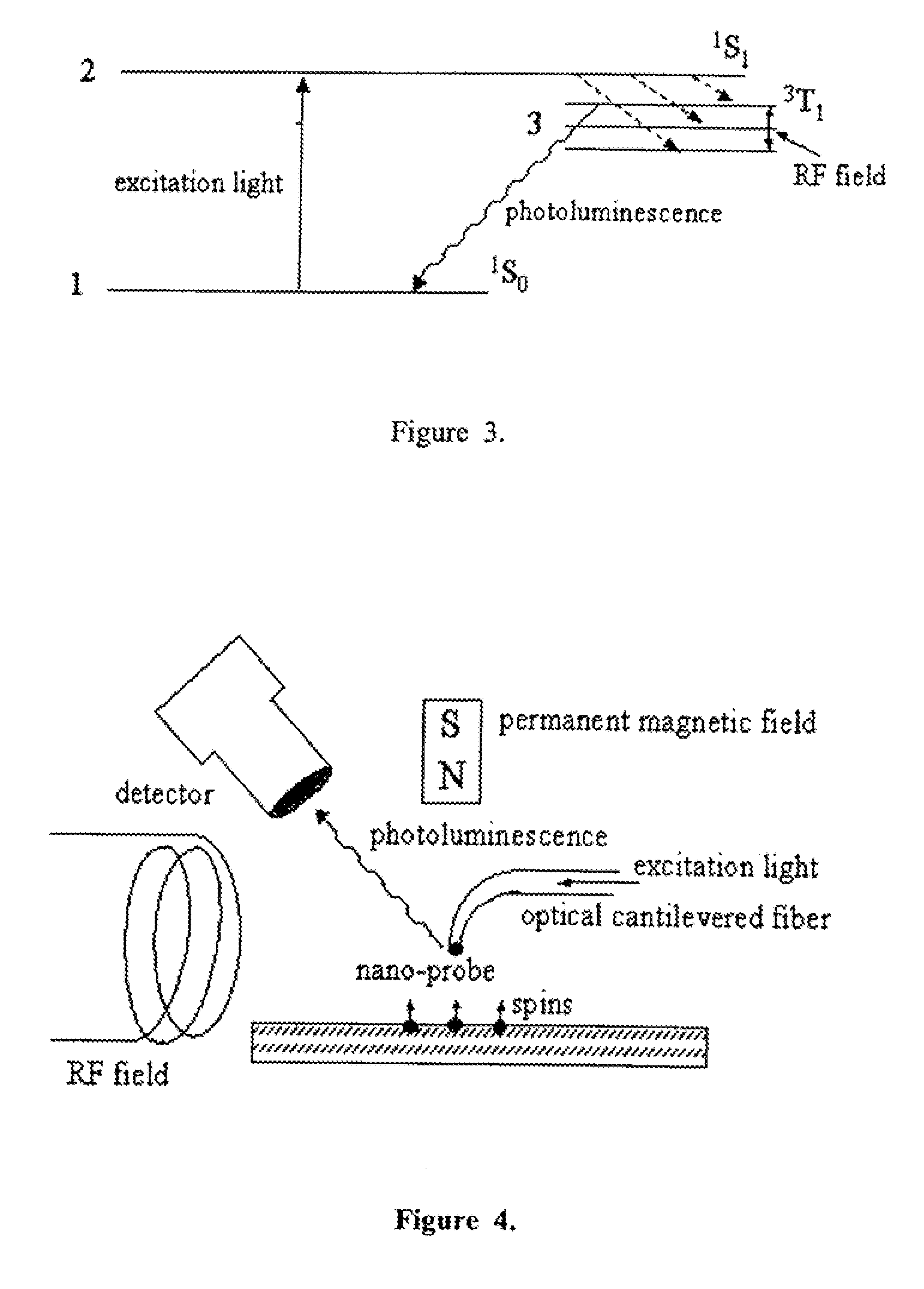
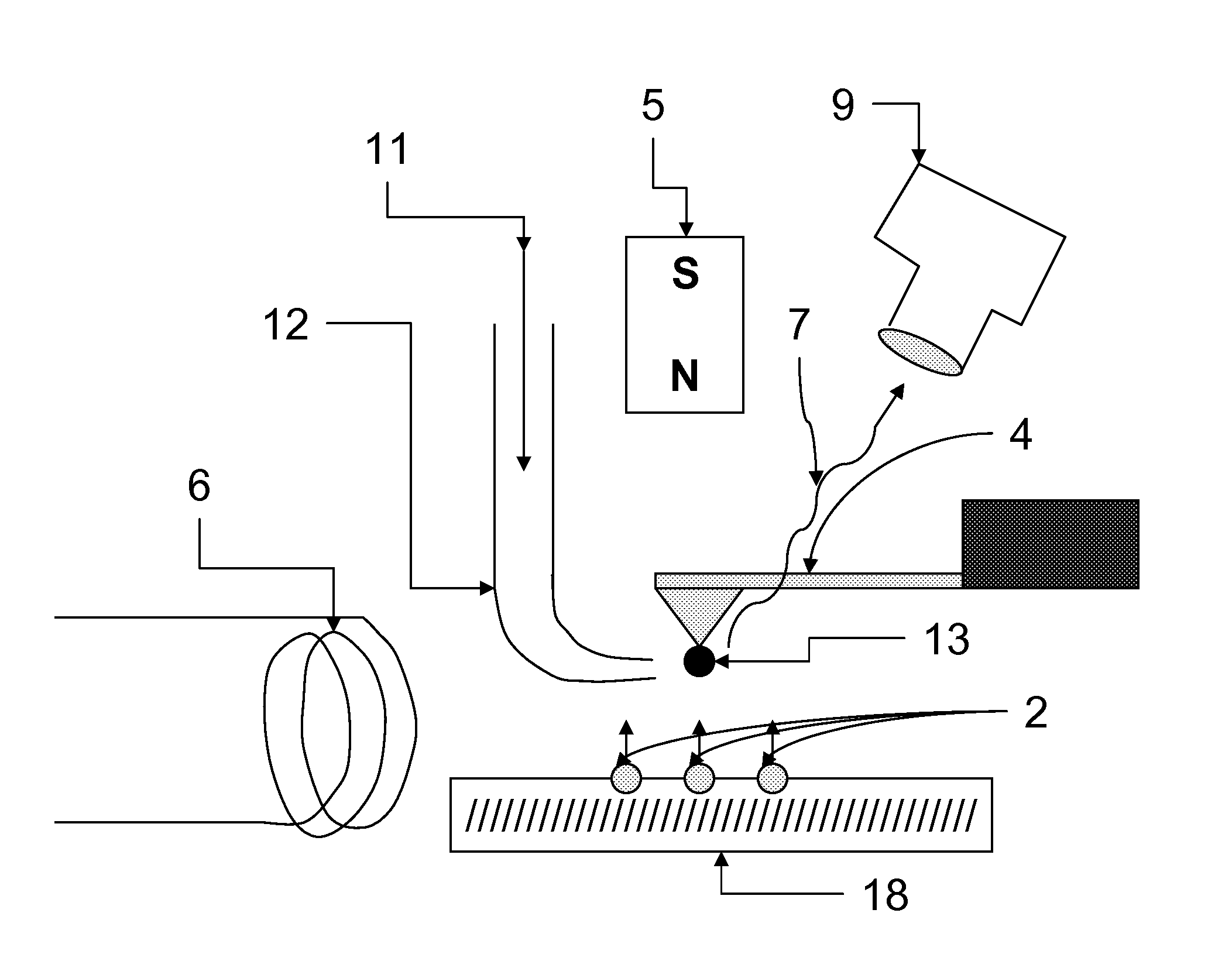
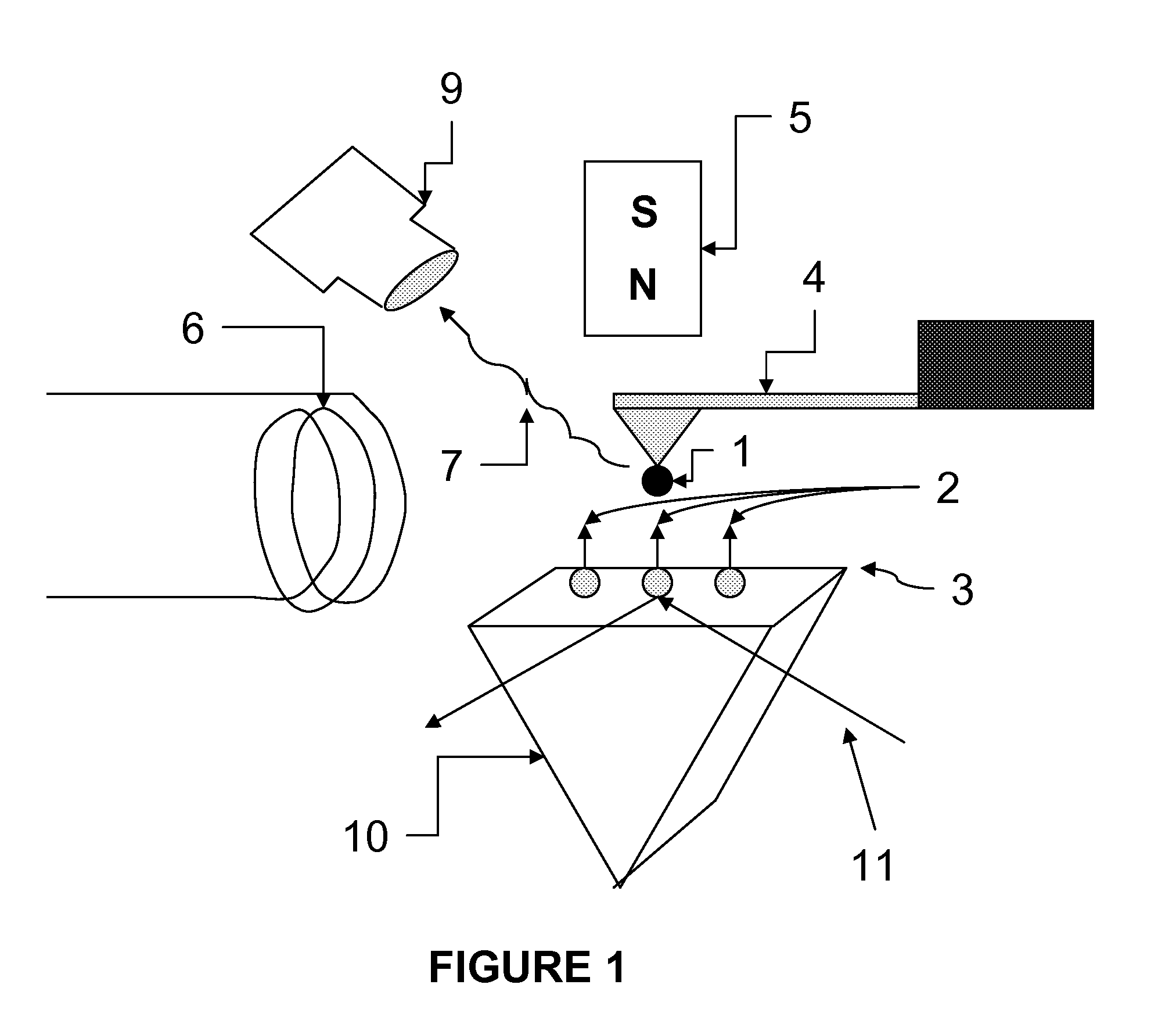
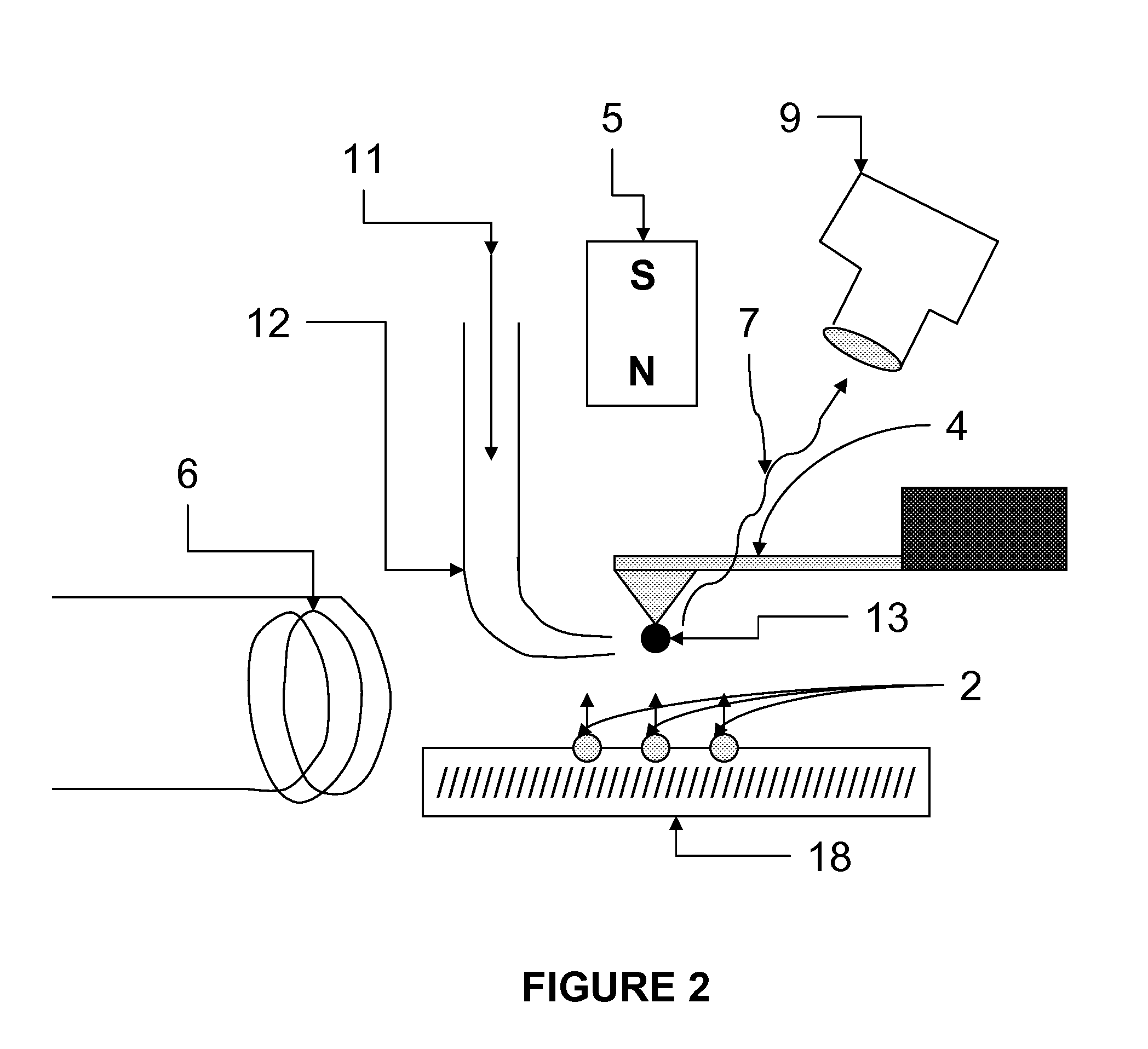
Spin microscope based on optically detected magnetic resonance
InactiveUS7608820B1NanomagnetismMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic force microscopePhotoluminescence
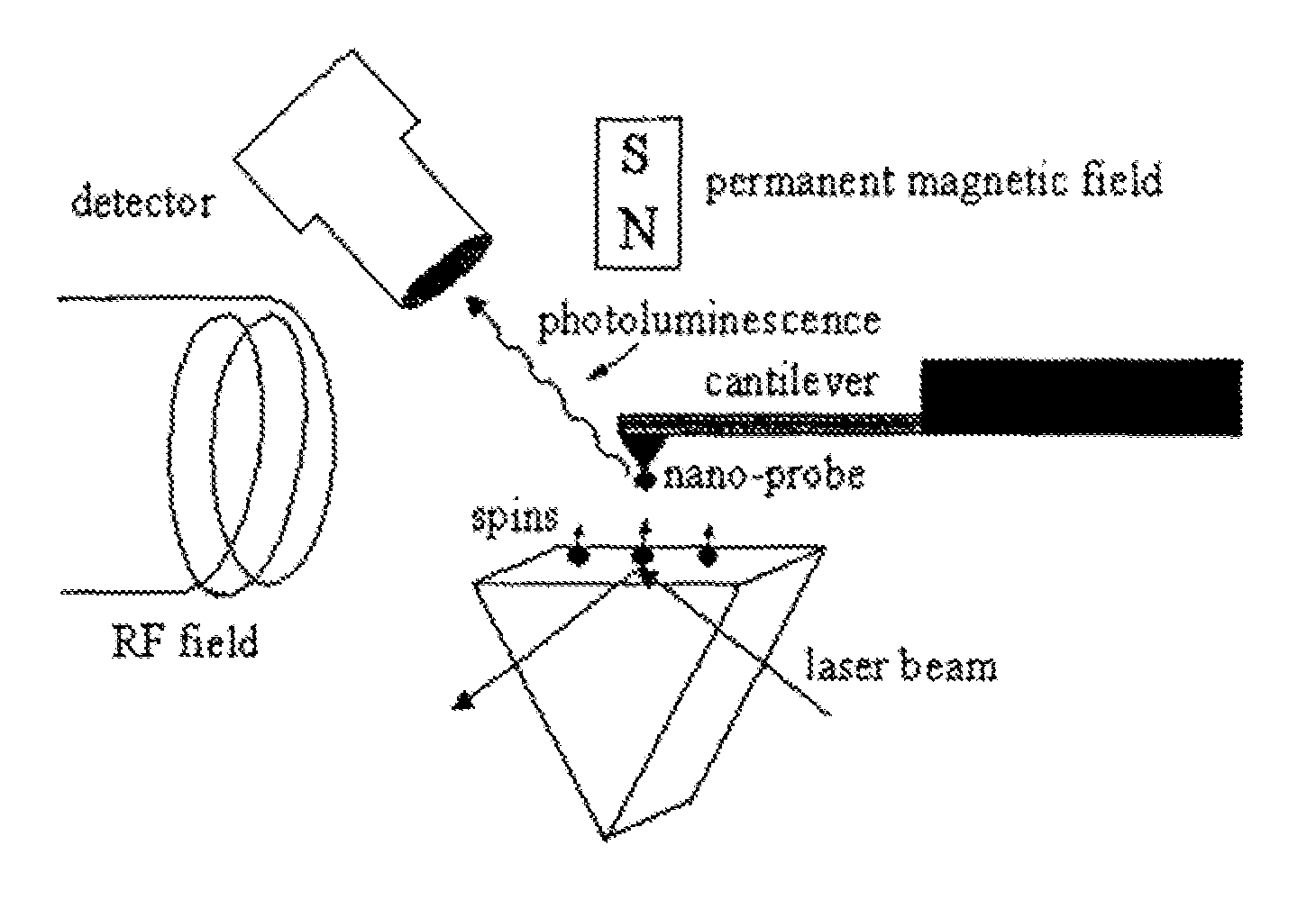
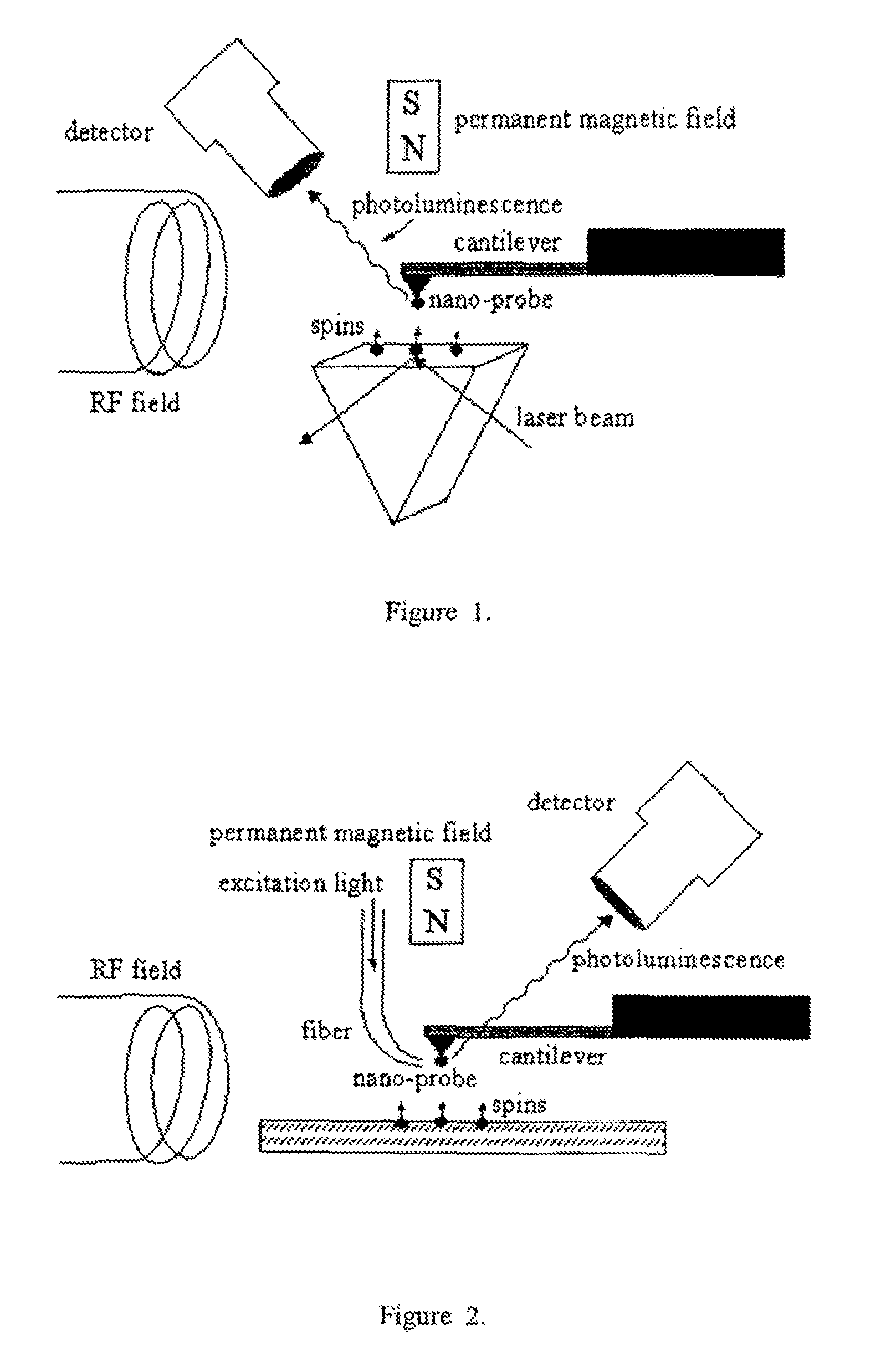
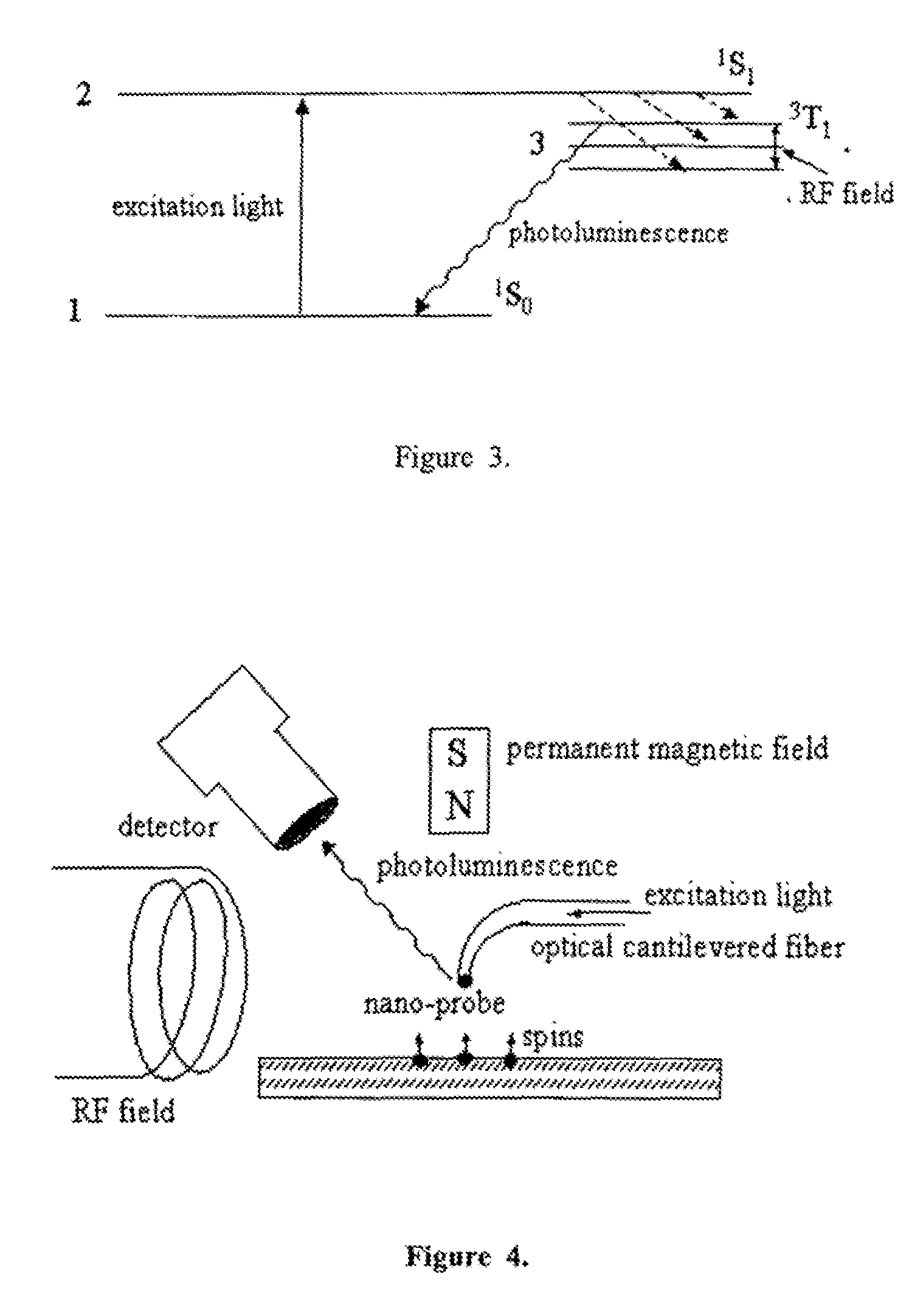
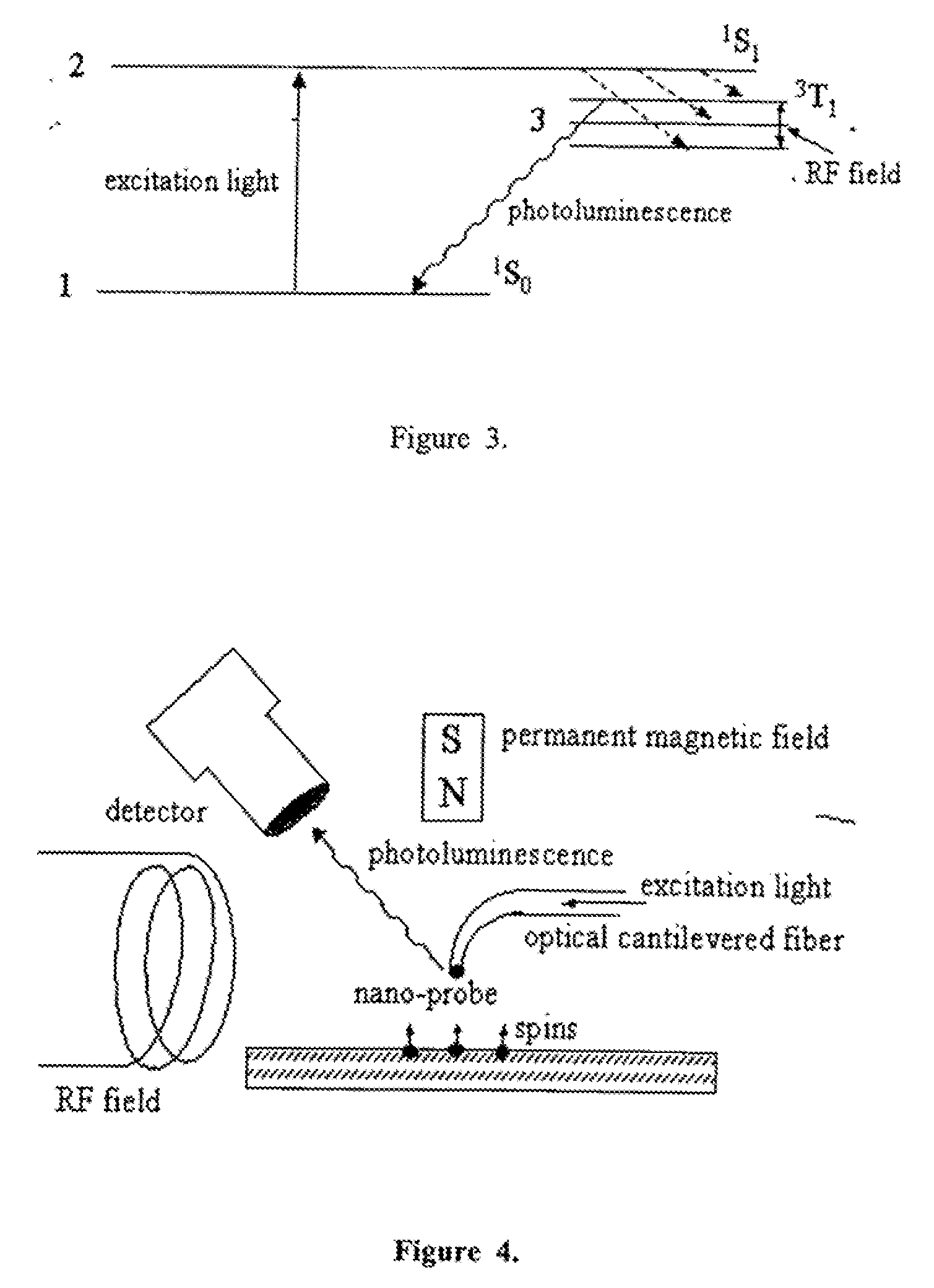
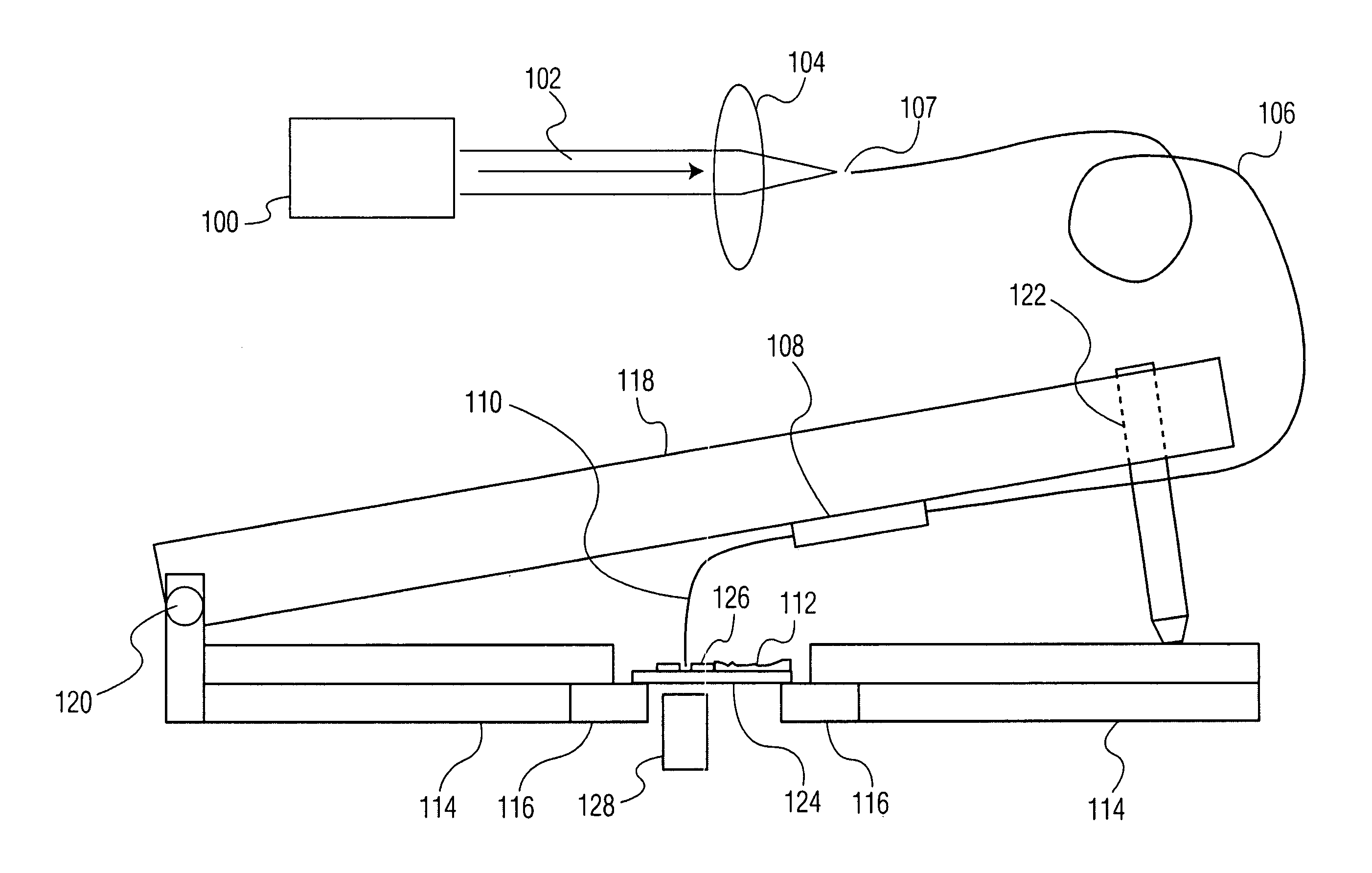
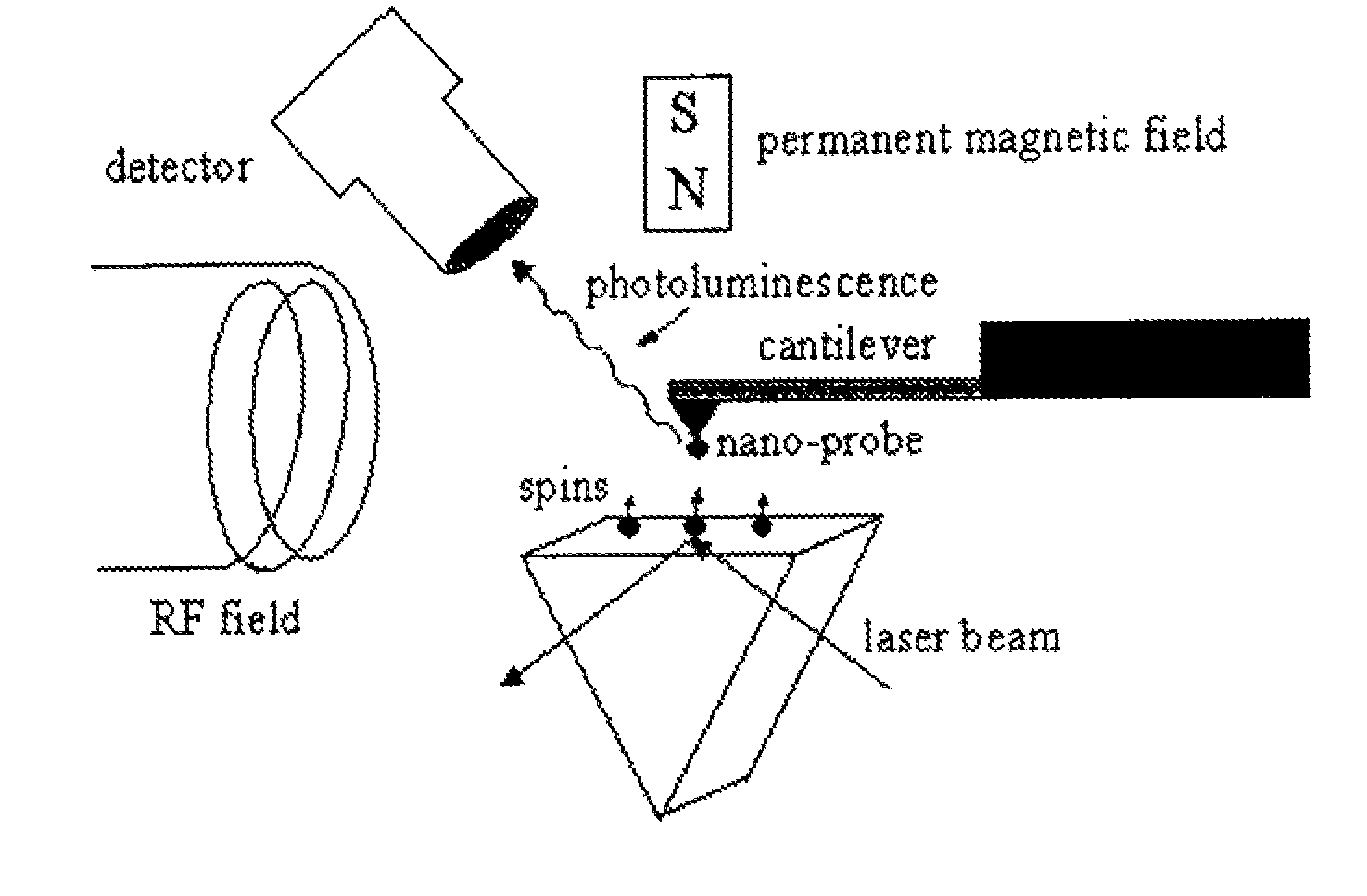
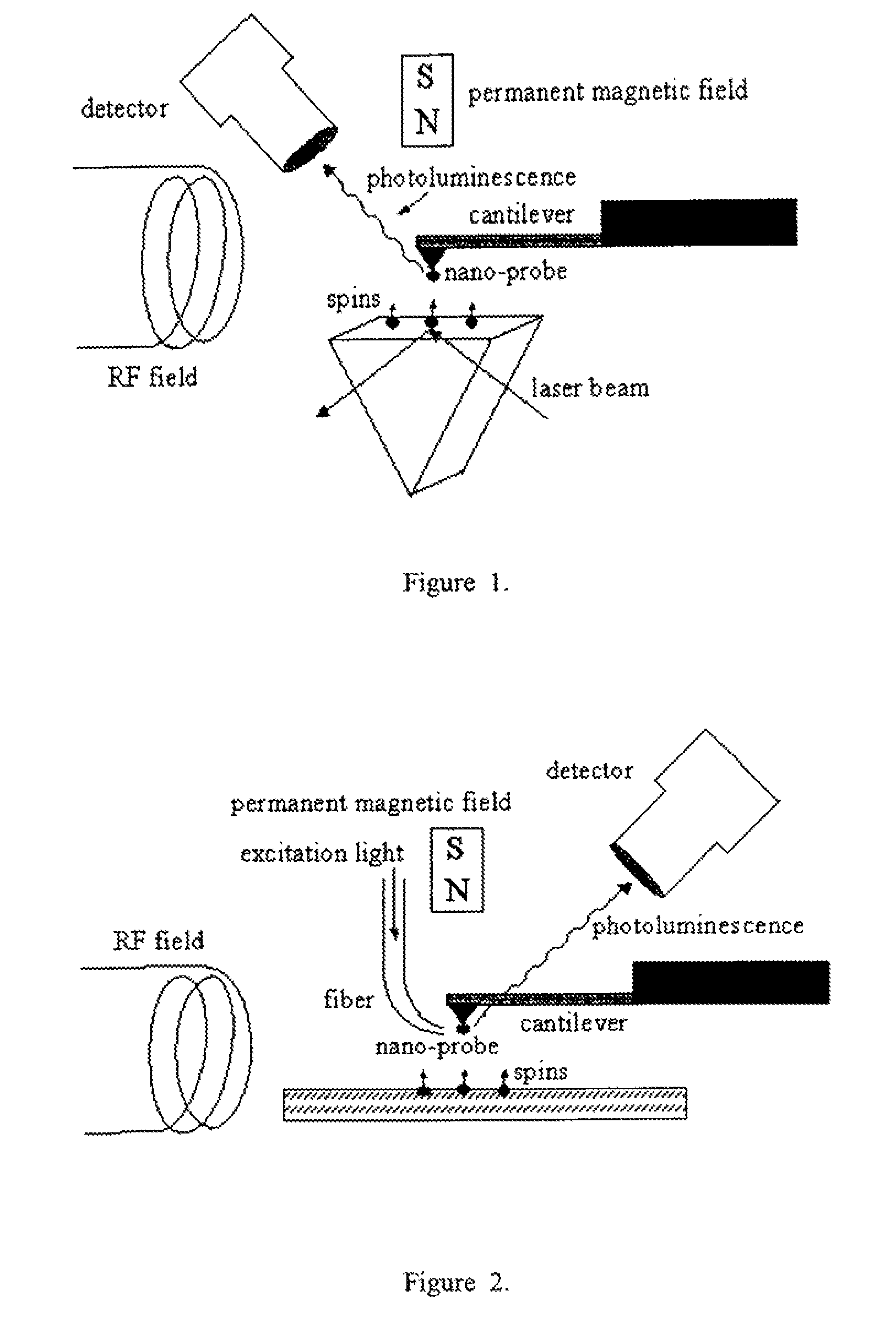
The invention relates to scanning magnetic microscope which has a photoluminescent nanoprobe implanted in the tip apex of an atomic force microscope (AFM), a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) or a near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) and exhibits optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) in the vicinity of unpaired electron spins or nuclear magnetic moments in the sample material. The described spin microscope has demonstrated nanoscale lateral resolution and single spin sensitivity for the AFM and STM embodiments.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Scanning optical microscope
InactiveUS20060007534A1Performance of was minimizedSimple methodMicroscopesLaser scanning microscopeWavefront
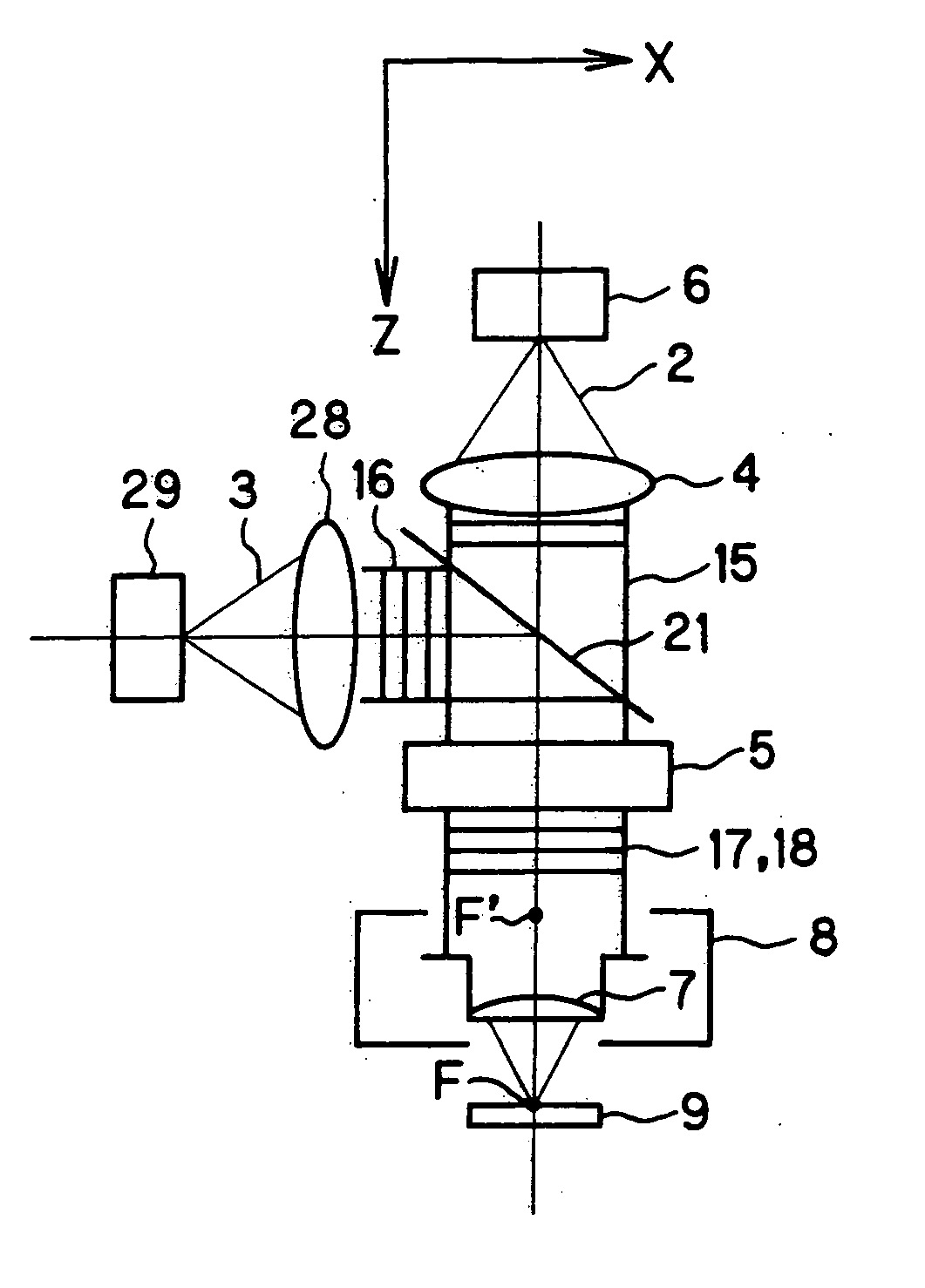
A scanning optical microscope using a wavefront converting element suffers minimum off-axis performance degradation and allows the wavefront converting element to be controlled by a simple method. Further, a pupil relay optical system is simple in arrangement or unnecessary. A laser scanning microscope includes a laser oscillator and a wavefront converting element for applying a desired wavefront conversion to a laserbeam emitted from the laser oscillator. An objective collects a wavefront-converted approximately parallel laser beam emerging from the wavefront converting element onto a sample. A detector detects signal light emitted from the sample. An actuator scans the objective along a direction perpendicular to the optical axis.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
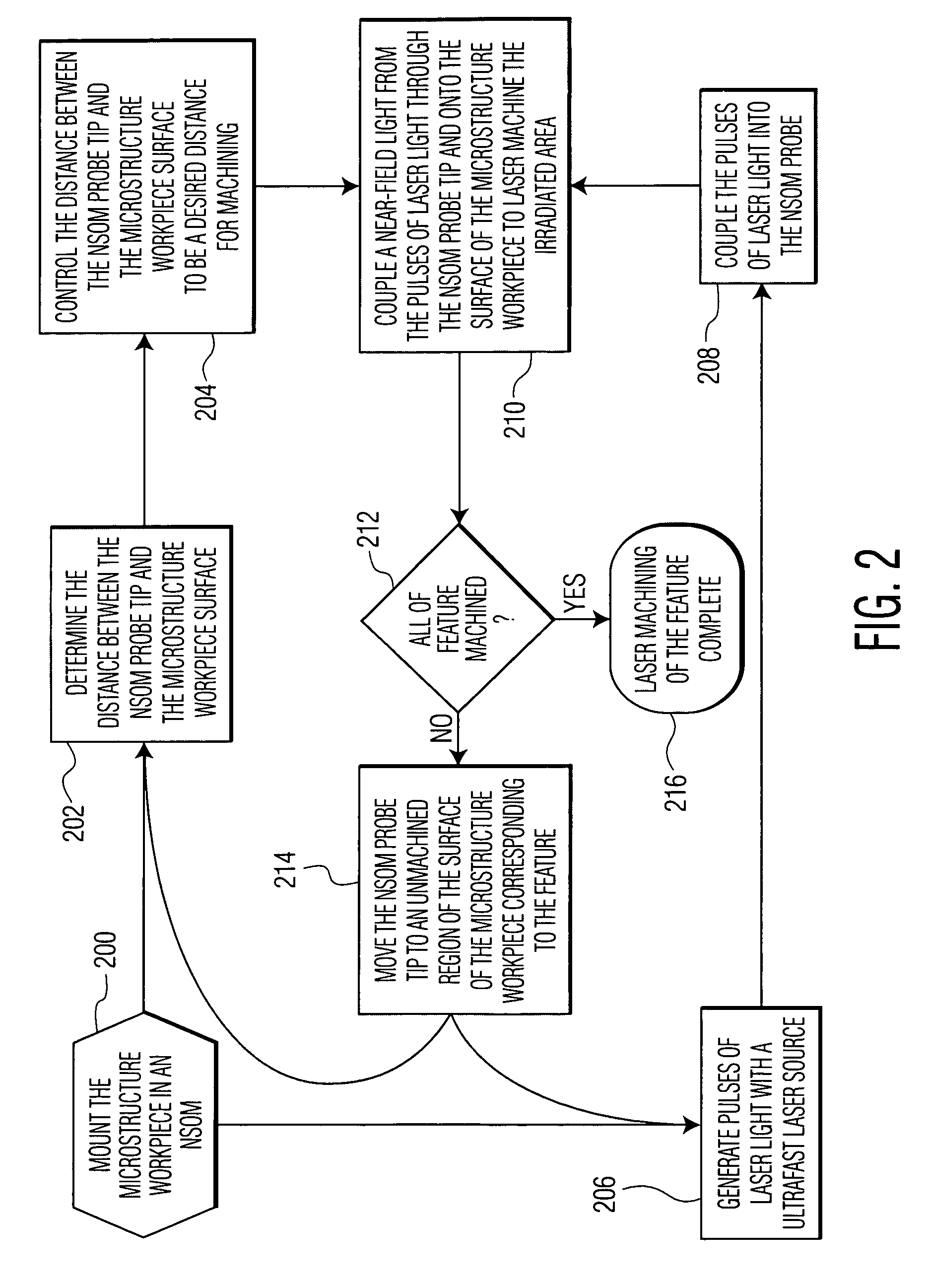
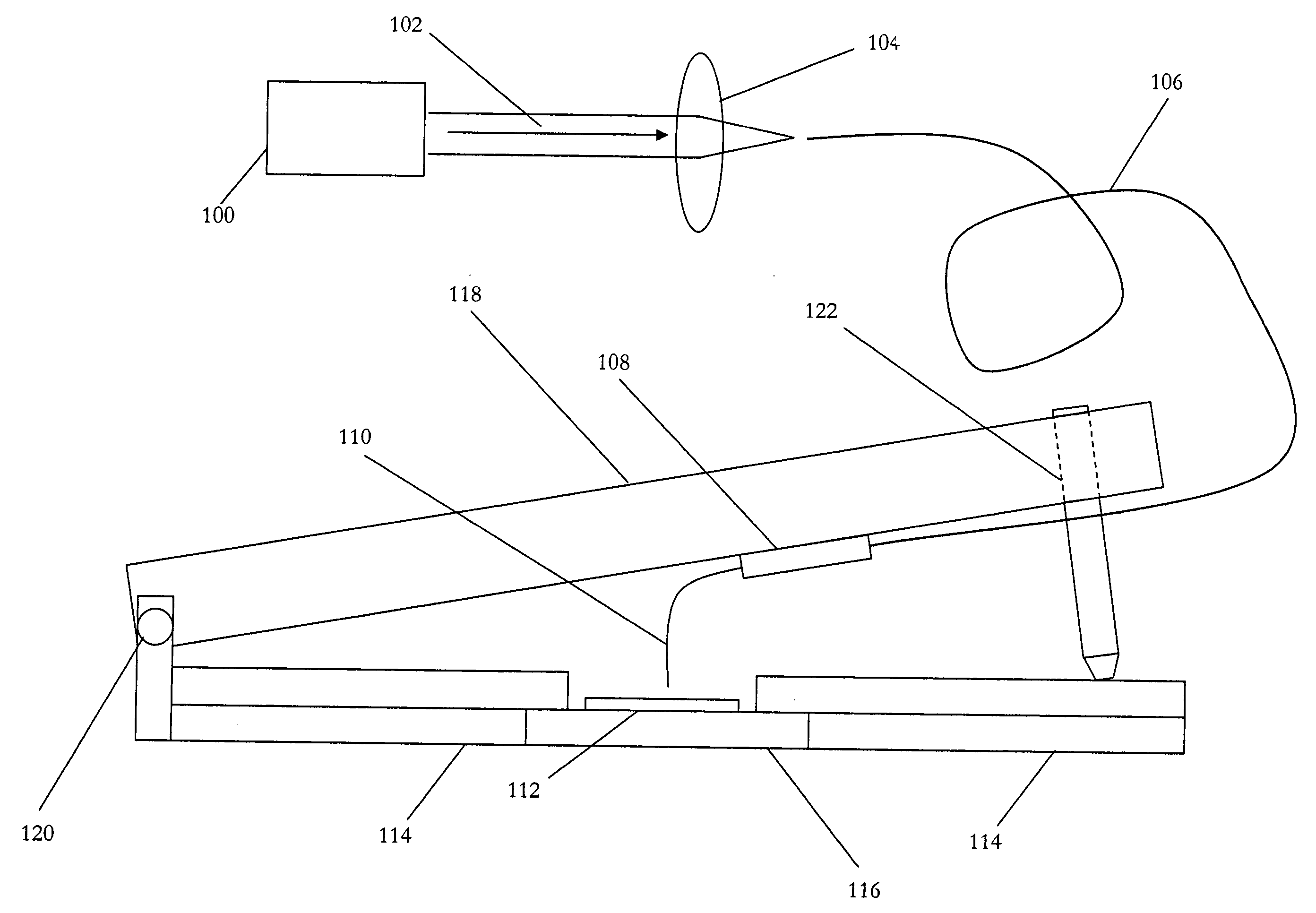
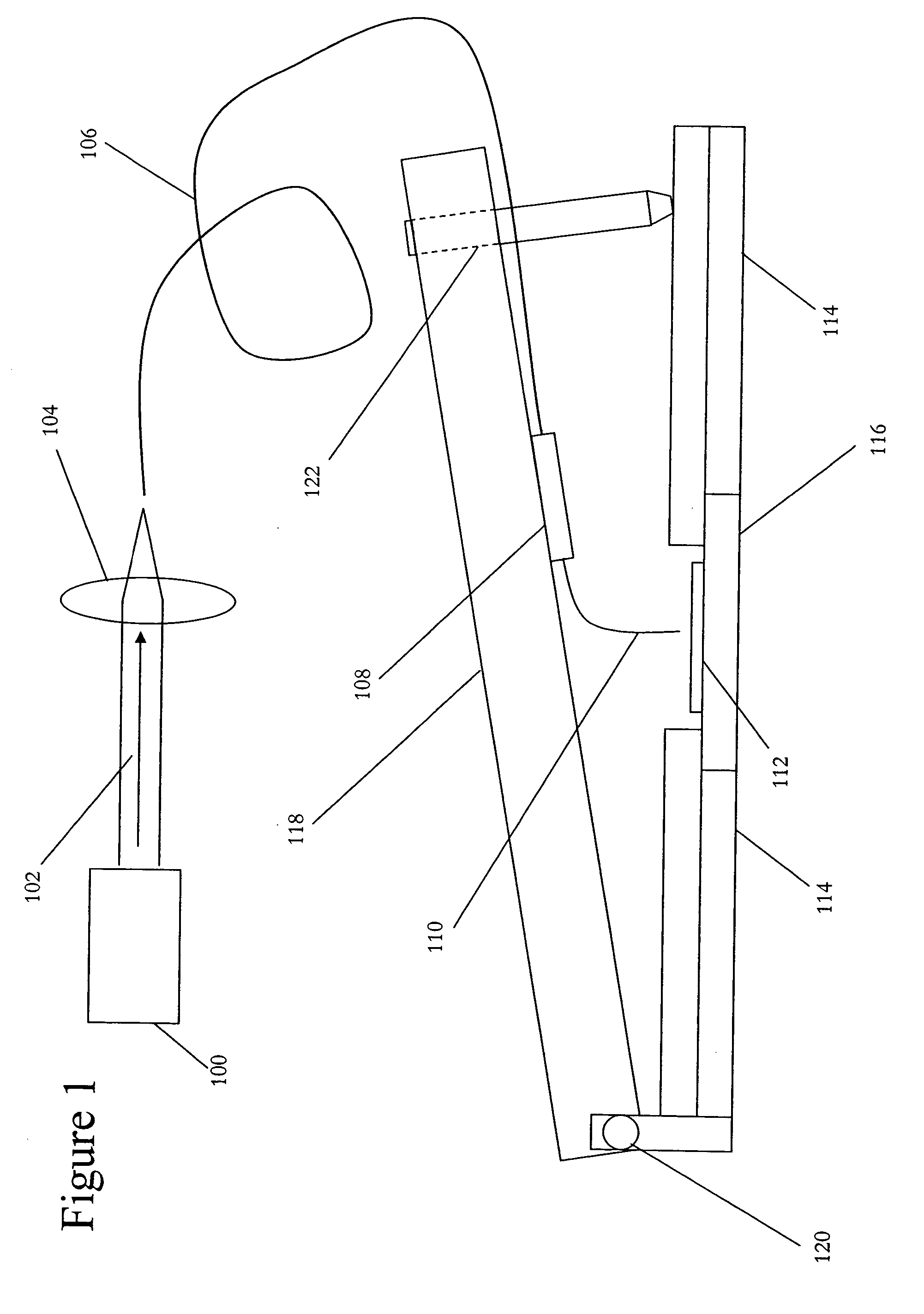
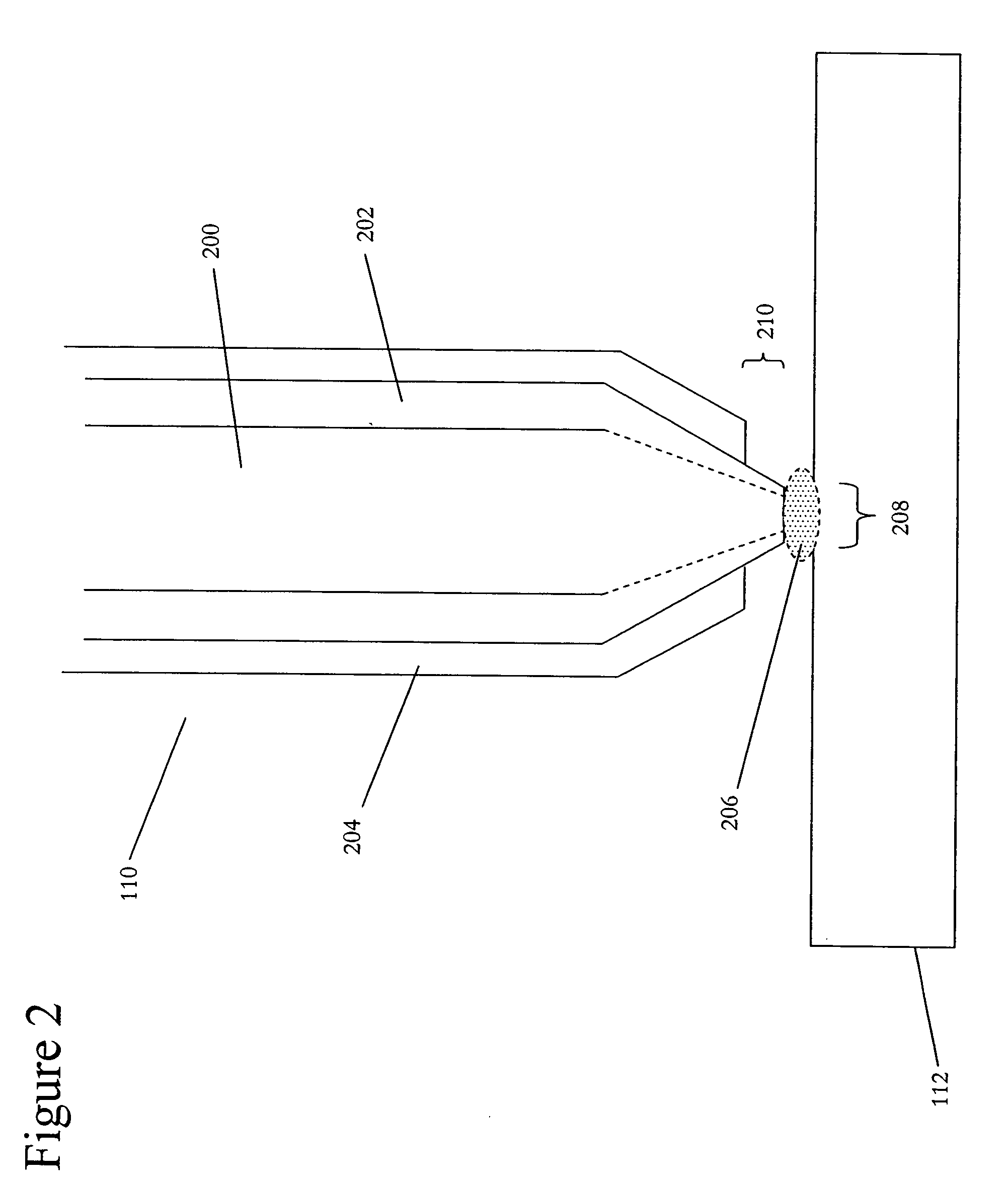
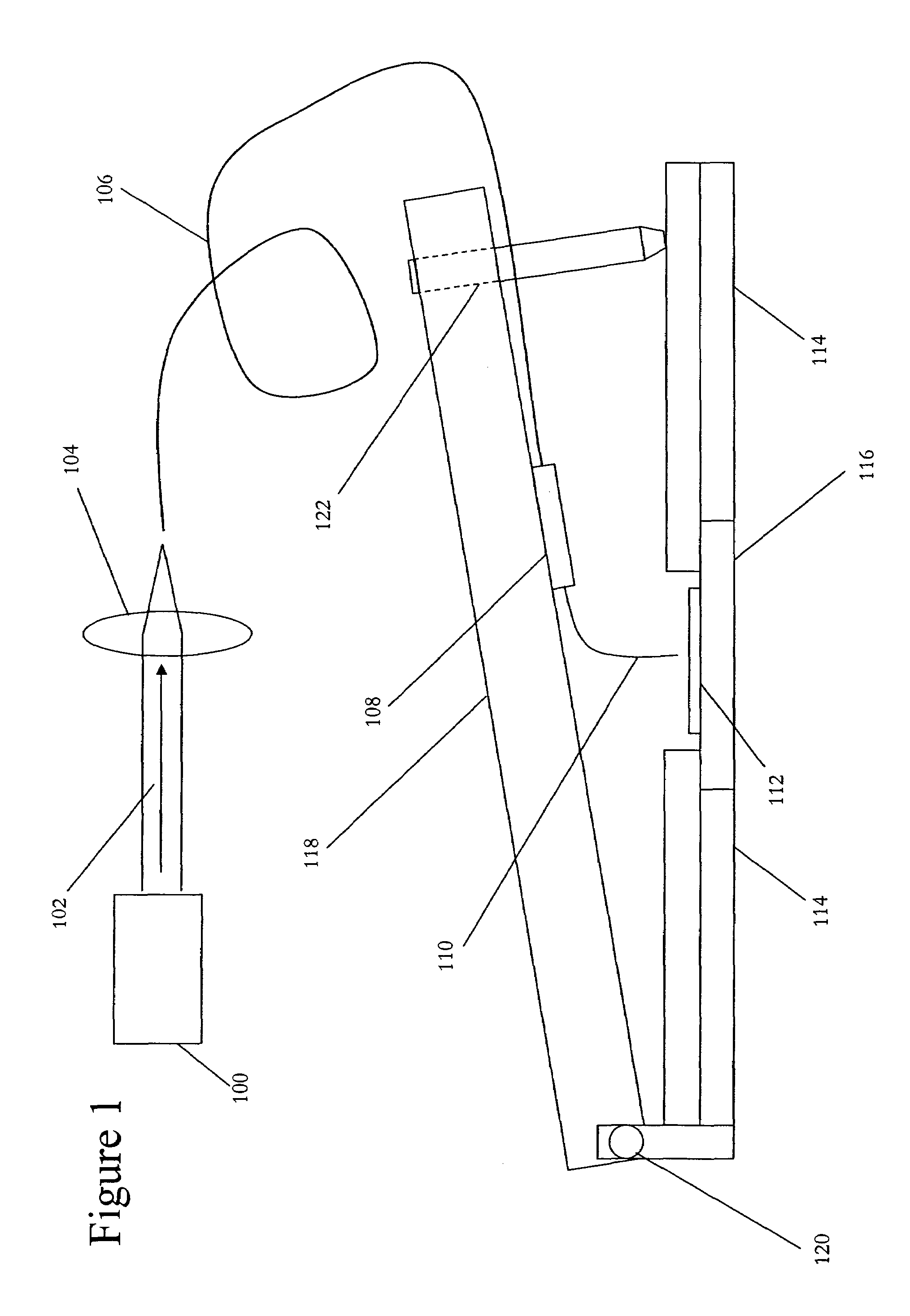
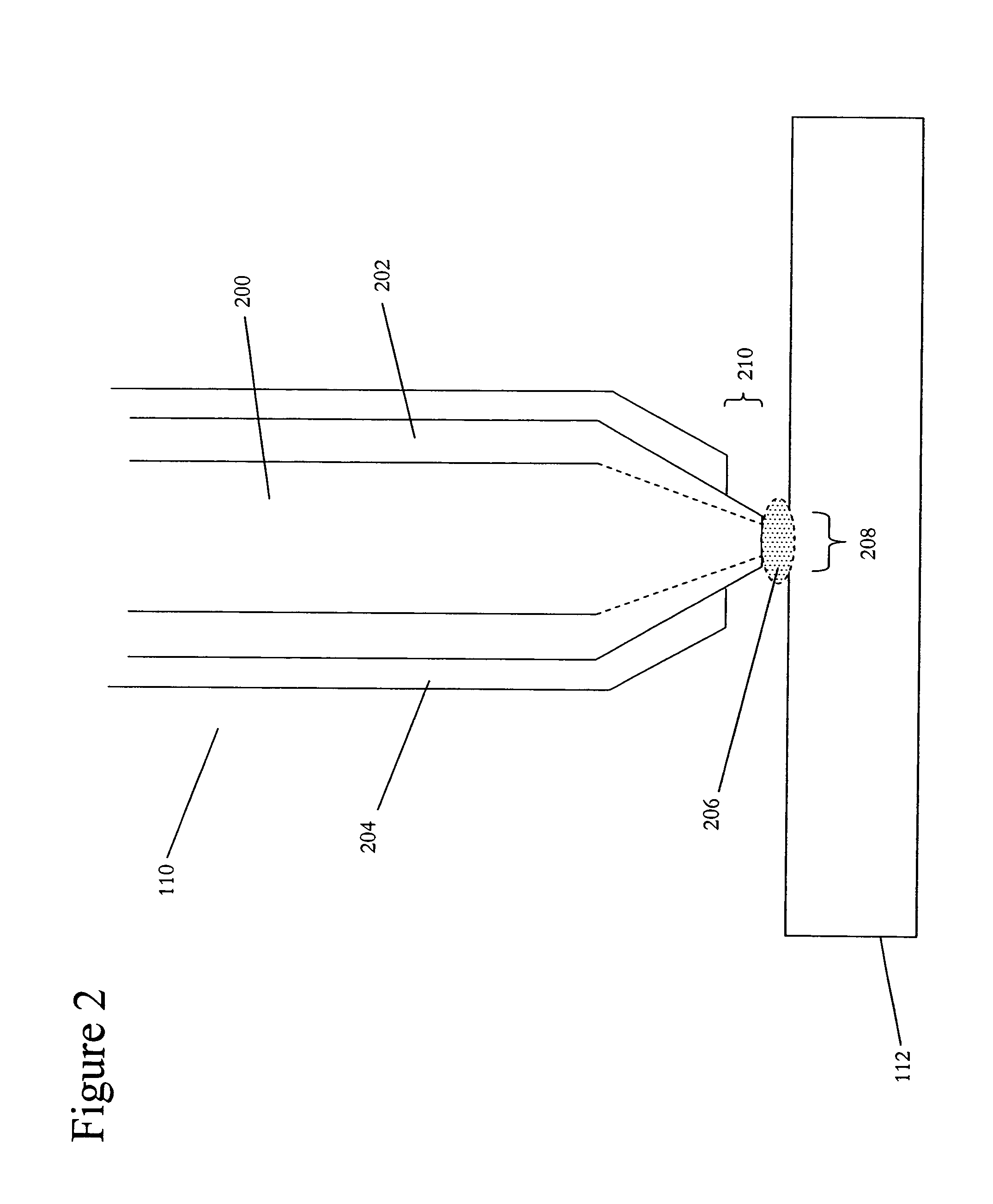
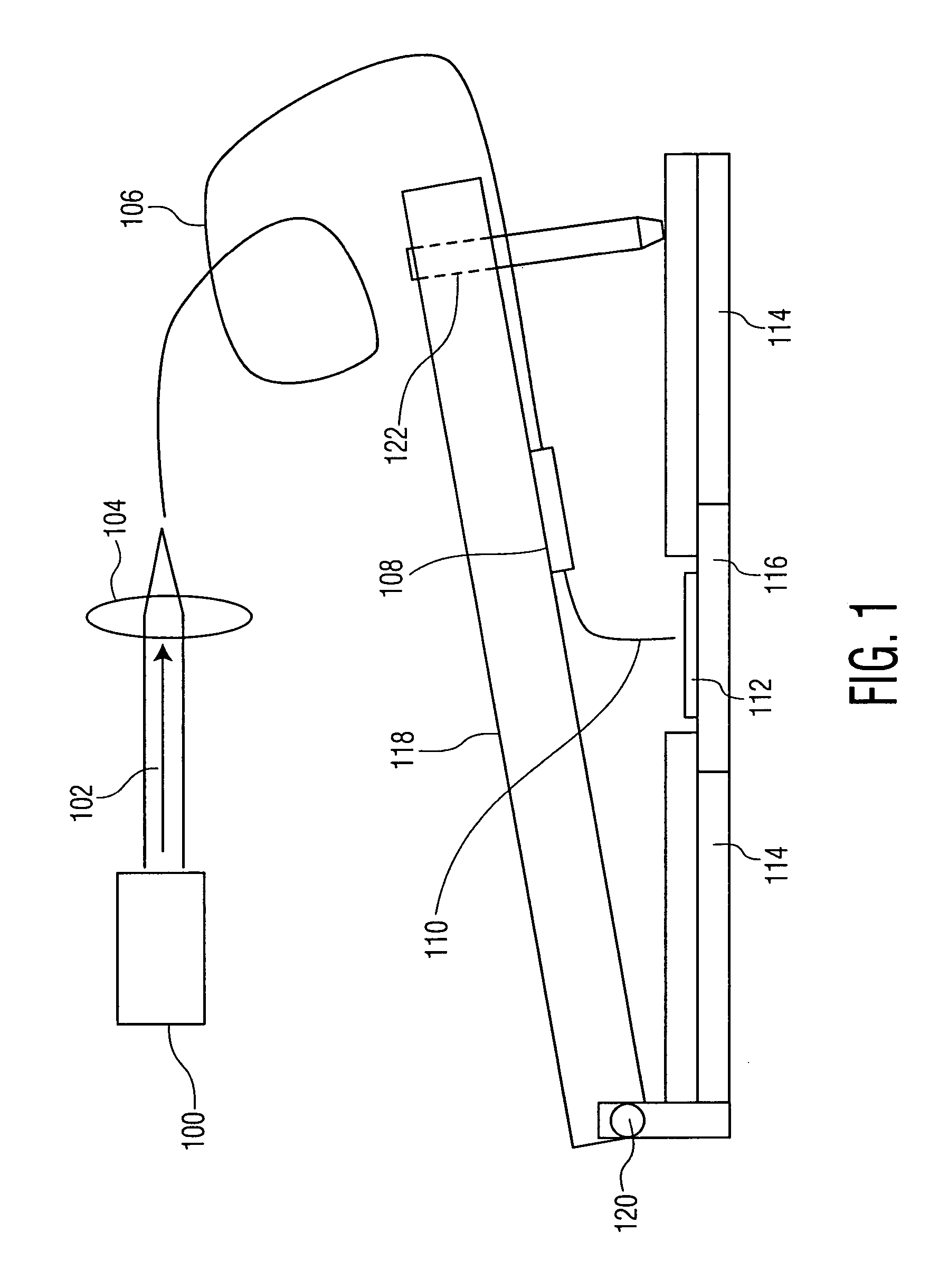
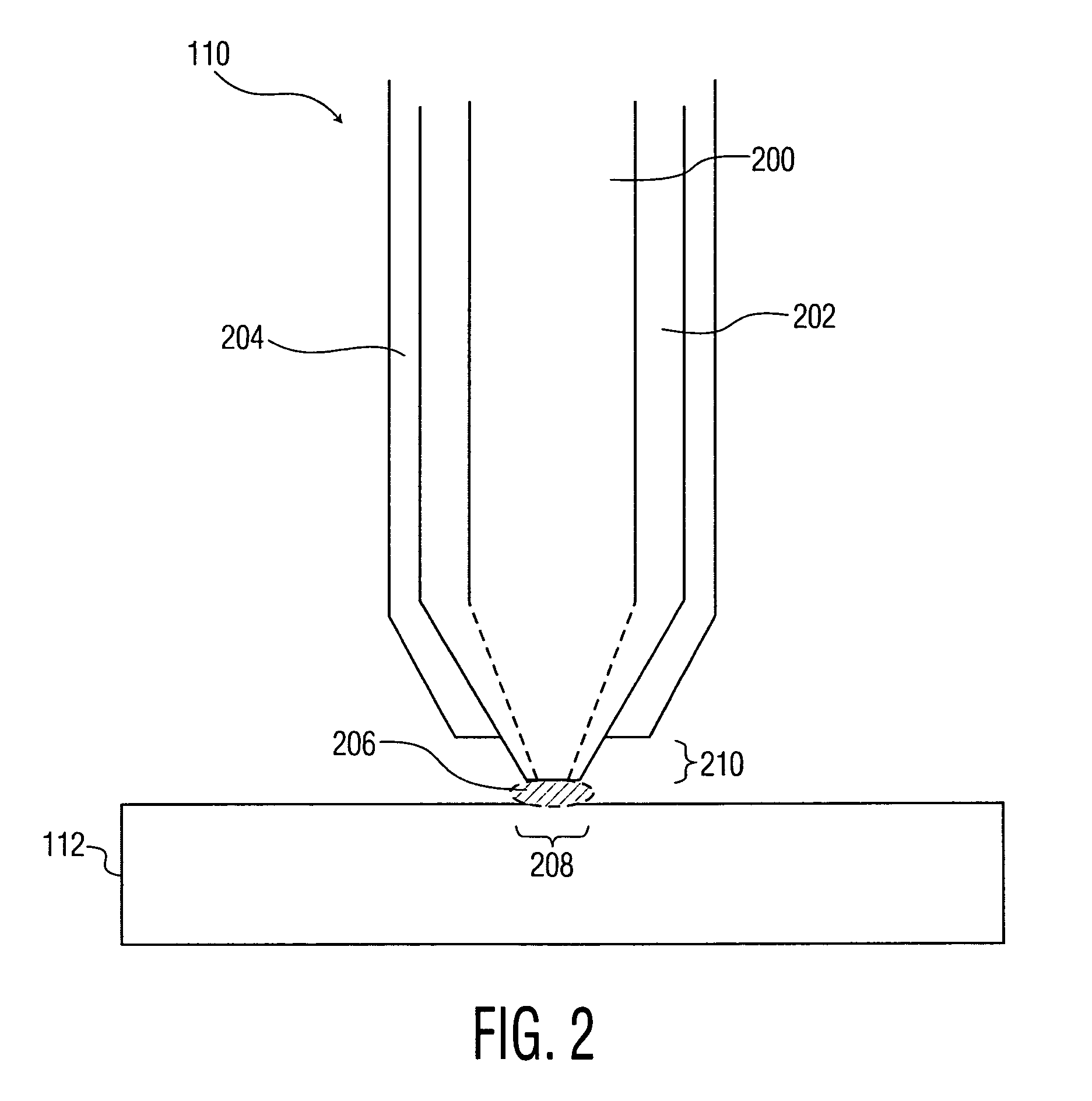
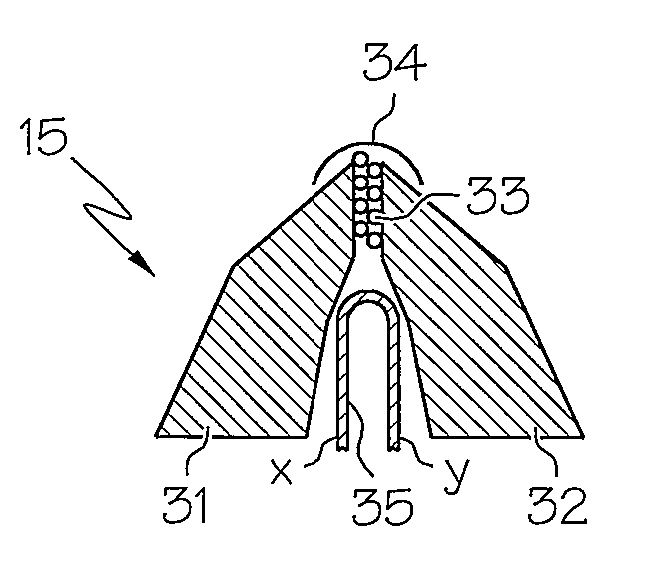
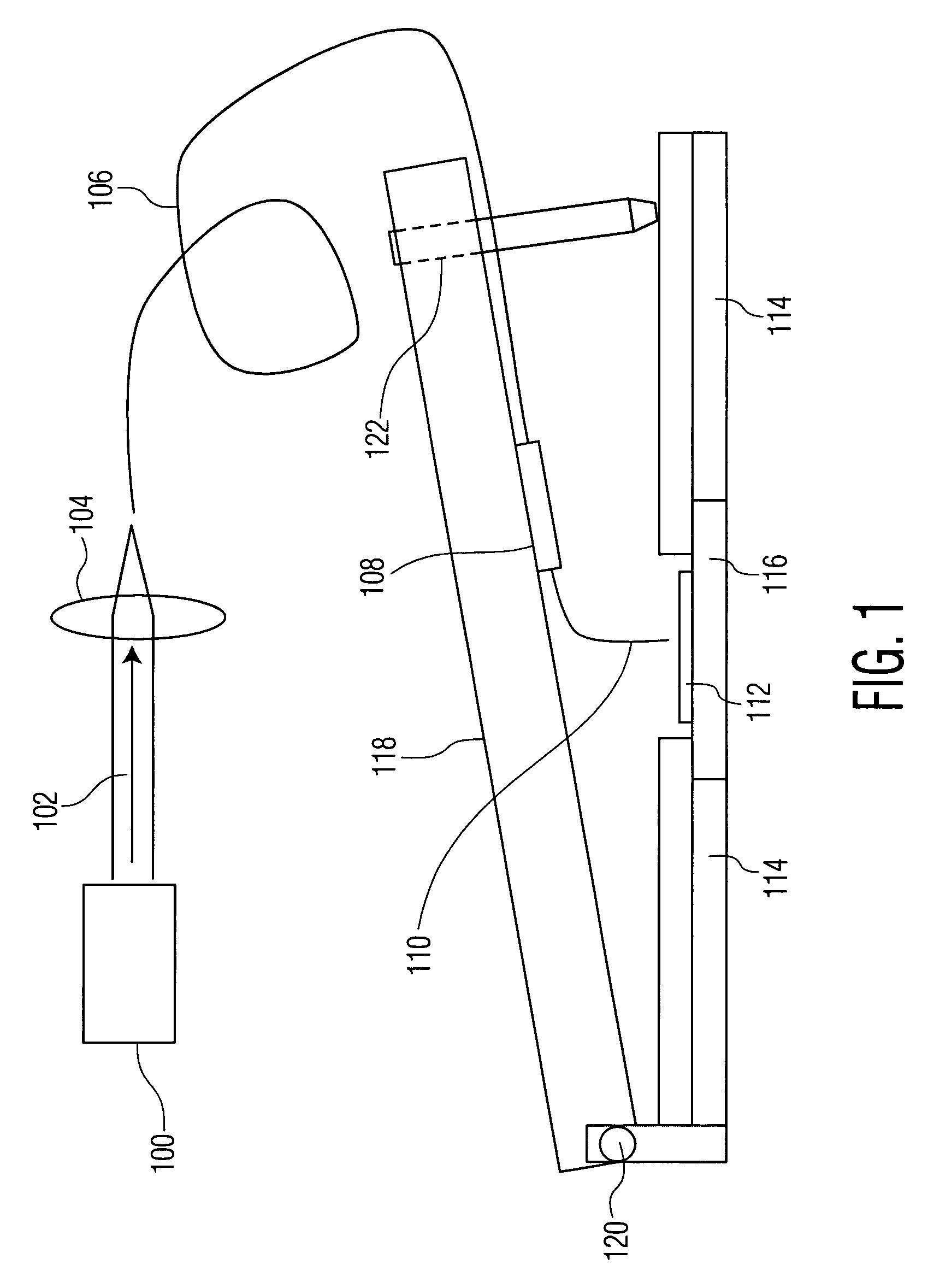
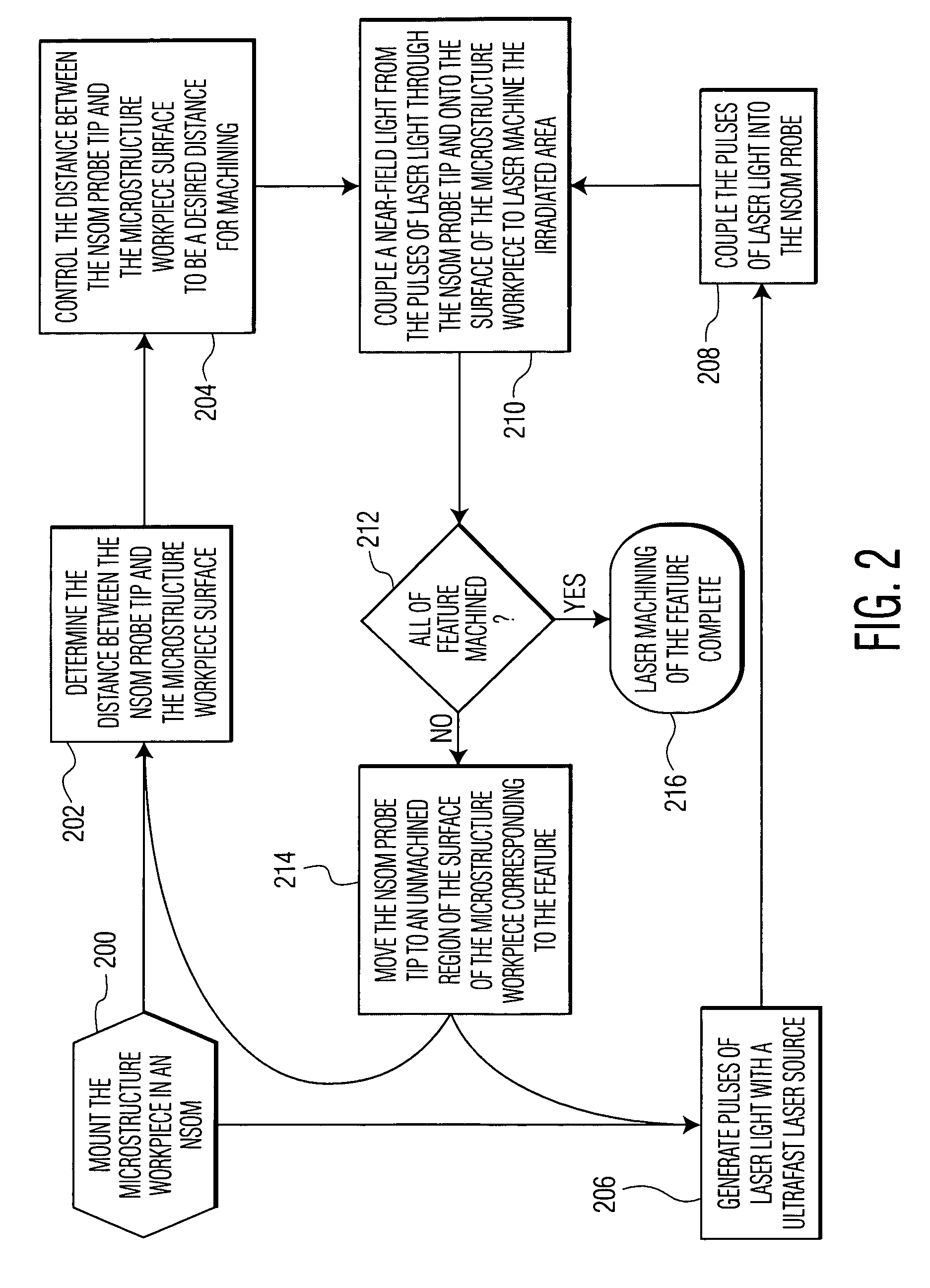
Near-field scanning optical microscope for laser machining of micro- and nano- structures
InactiveUS7053351B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLaser lightNear-field scanning optical microscope
A near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) laser micromachining system for laser machining features on surfaces using an ultrafast laser source and a method of laser machining such features. The system includes: the ultrafast laser source to generate pulses of laser light having pulse durations less than 1 ns and a peak wavelength; an NSOM probe having a substantially cylindrical shape; an NSOM mount to controllably hold the NSOM probe and the microstructure workpiece to be machined; an NSOM probe monitor coupled to the NSOM mount for determining the distance between the probe tip of the NSOM probe and the surface; and an NSOM controller coupled to the NSOM probe monitor, and motion stages in the NSOM mount. The NSOM mount includes an XY motion stage and a Z motion stage. These motion stages are couple to either the NSOM probe or the microstructure workpiece, or one motion stage to each.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
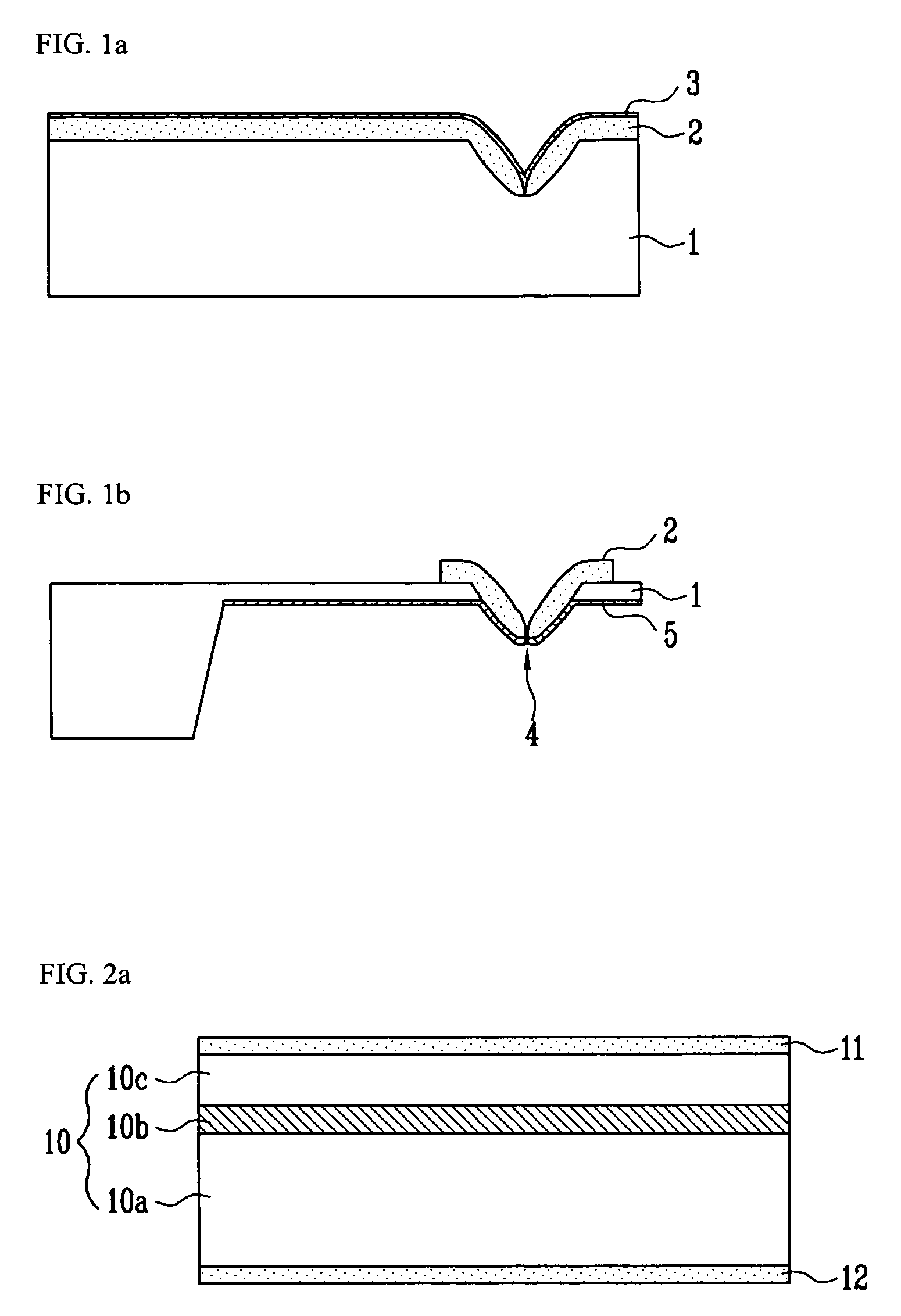
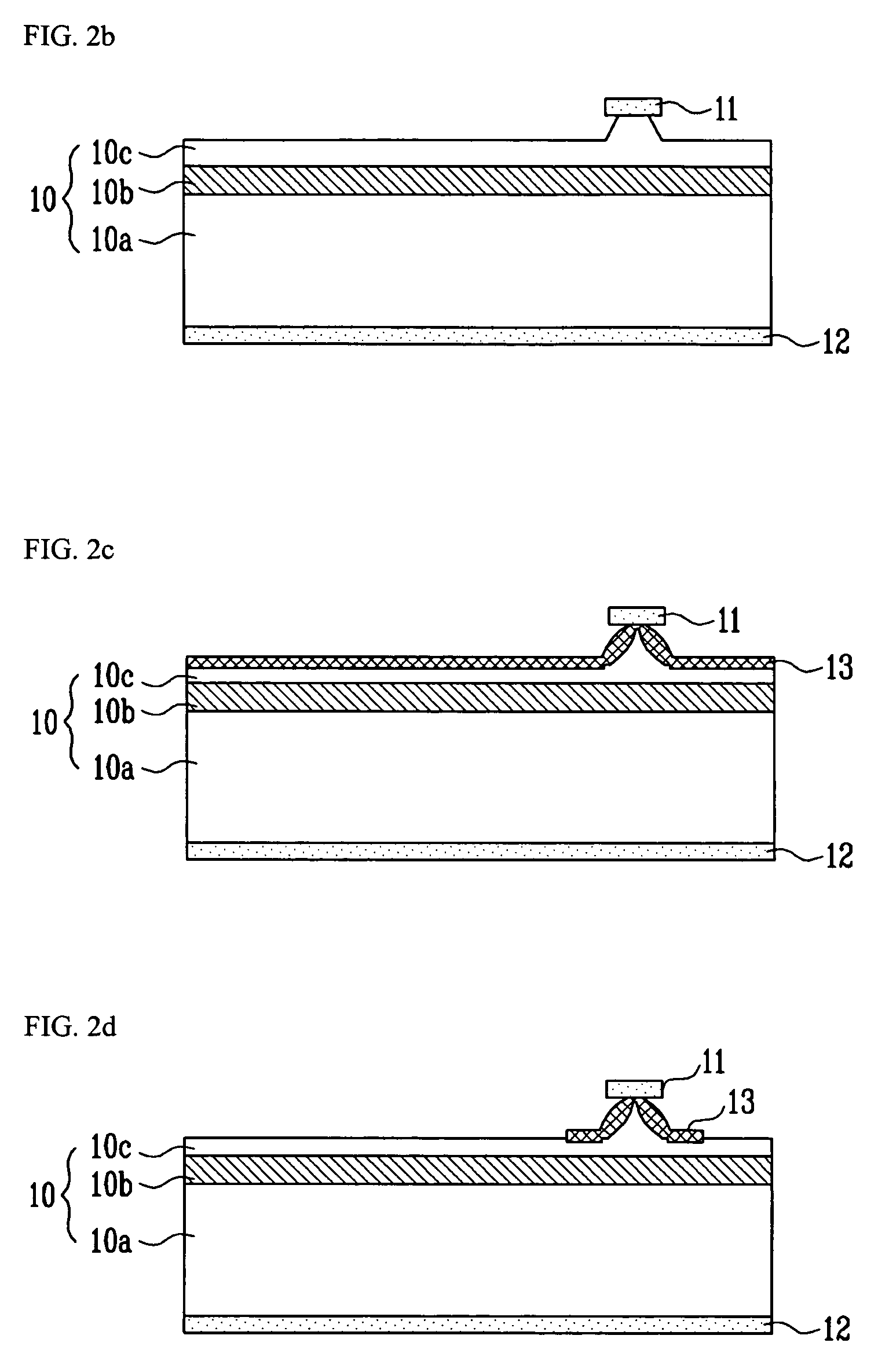
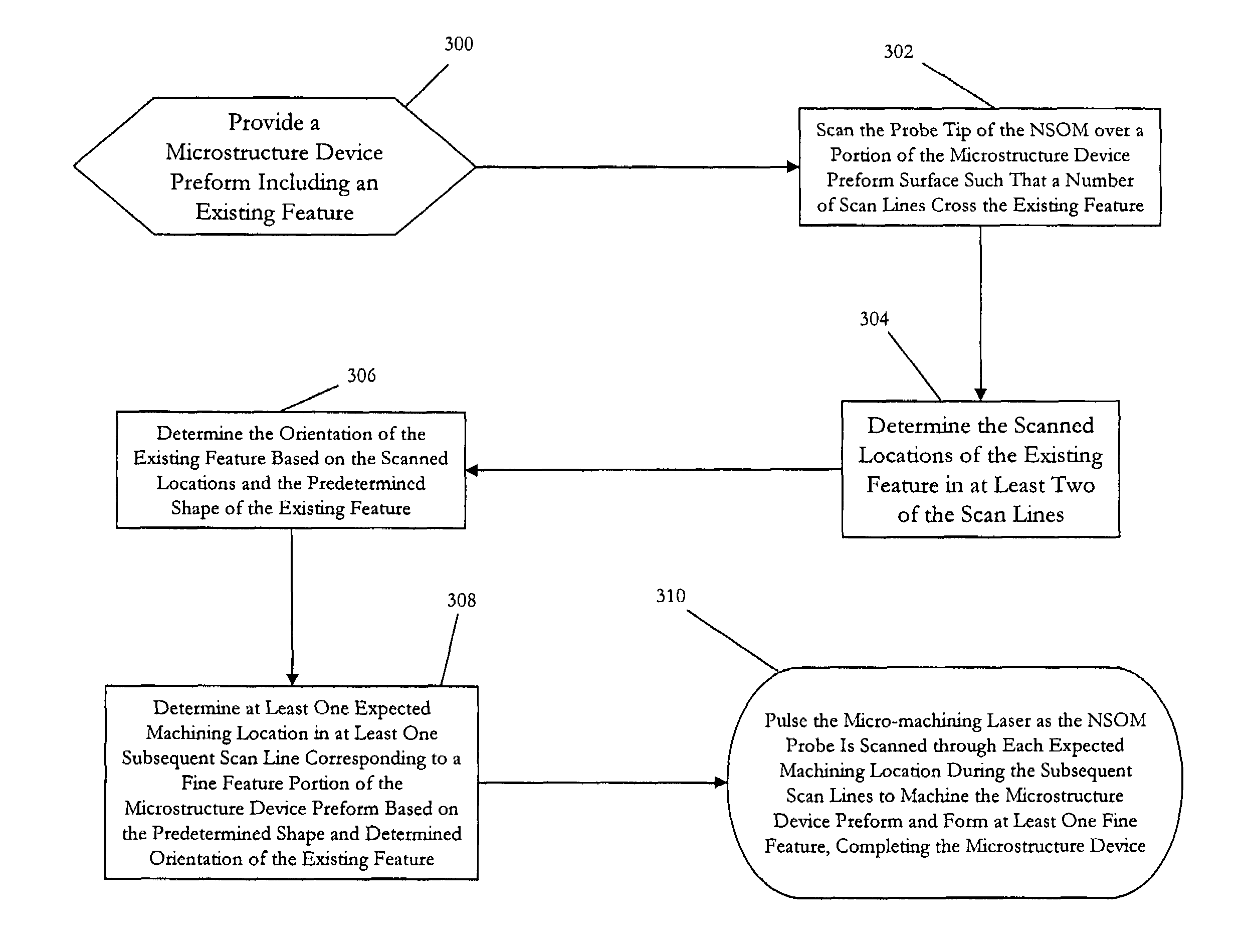
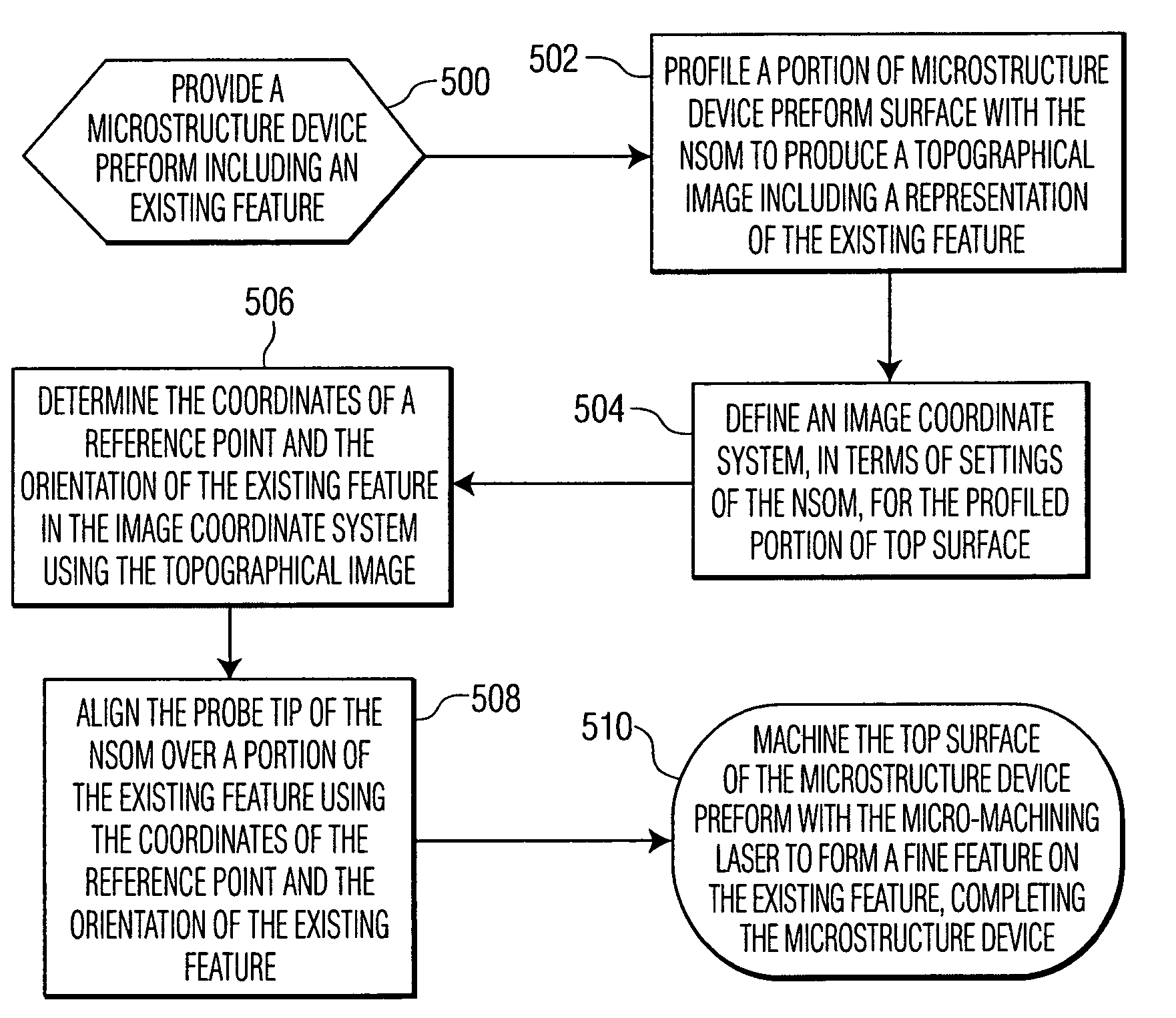
Precision machining method using a near-field scanning optical microscope
InactiveUS20060027543A1Material nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsScan lineNear-field scanning optical microscope
A method for manufacturing a microstructure device using a near field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) laser micromachining system. A microstructure device preform, including an existing feature, is provided. The NSOM probe tip is scanned over a portion of the preform selected such that a plurality of scan lines cross the existing feature. Scanned locations of the existing feature in at least two scan lines are determined. The orientation of the existing feature is determined based on the scanned locations and the shape of the existing feature. At least one expected machining location in a subsequent scan line is determined based on the shape and orientation of the existing feature. The micro-machining laser is pulsed as the NSOM probe is scanned through the expected machining location(s) during the subsequent scan lines to form at least one fine feature on the microstructure device preform, thus, completing the microstructure device.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
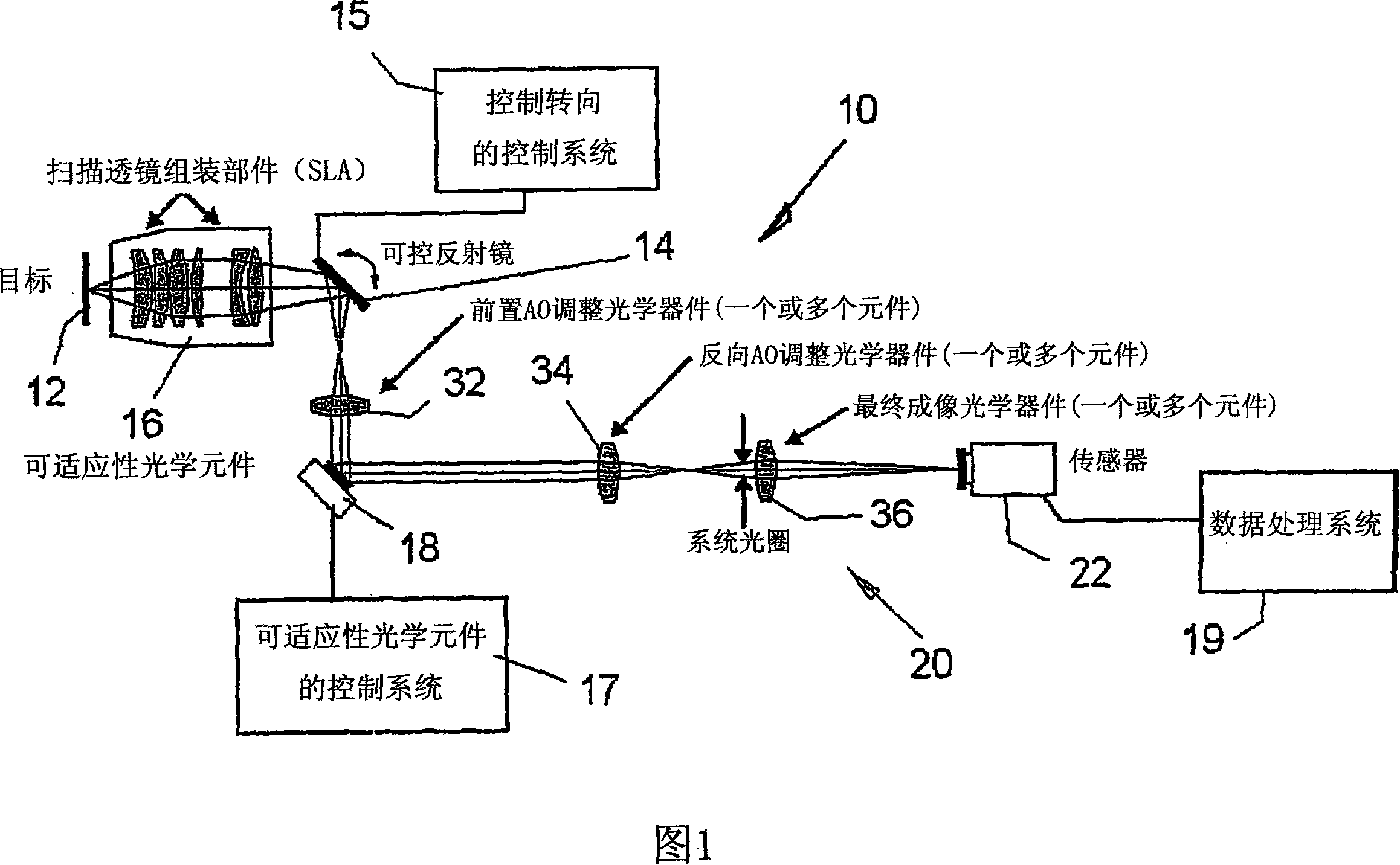
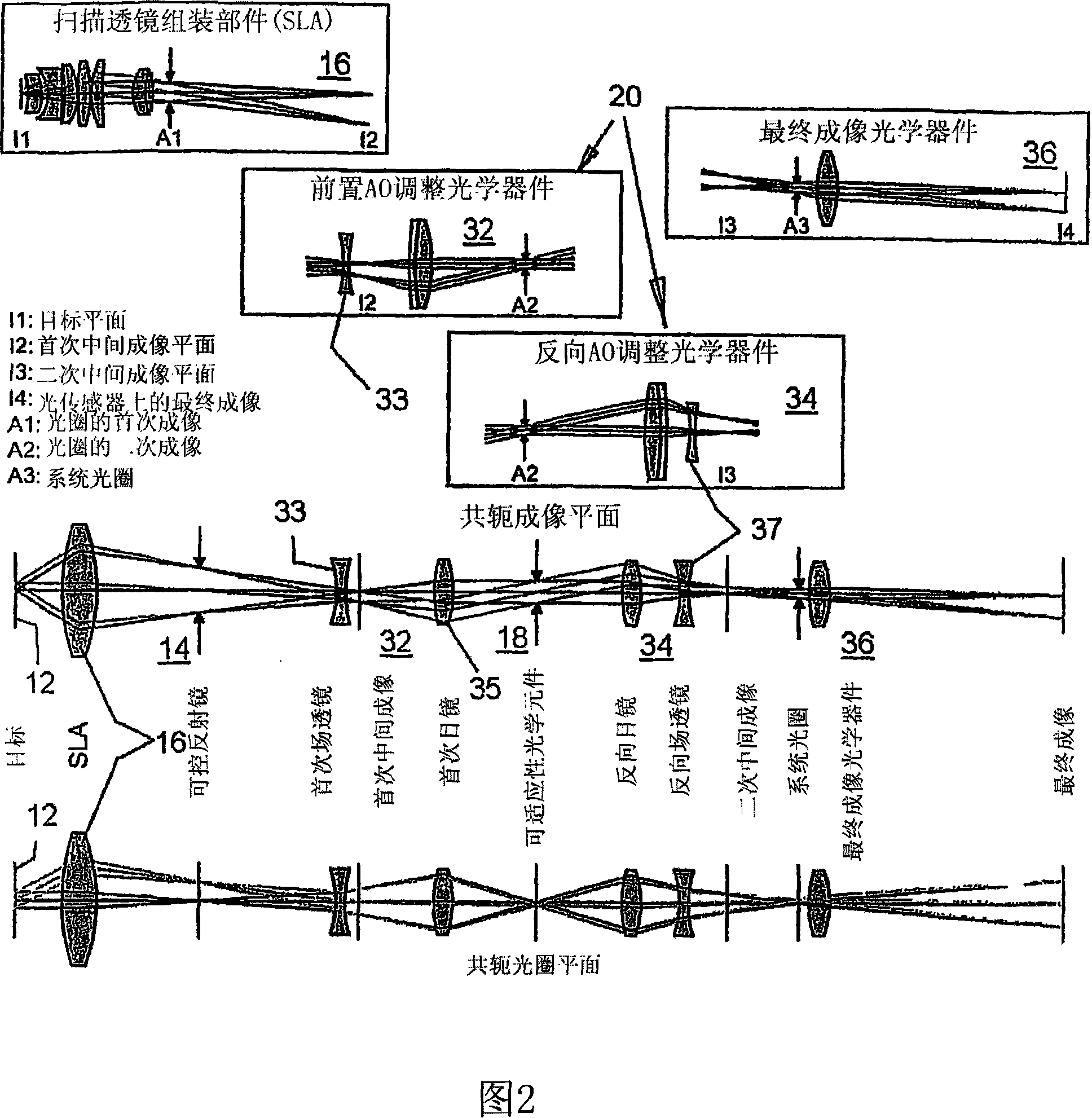
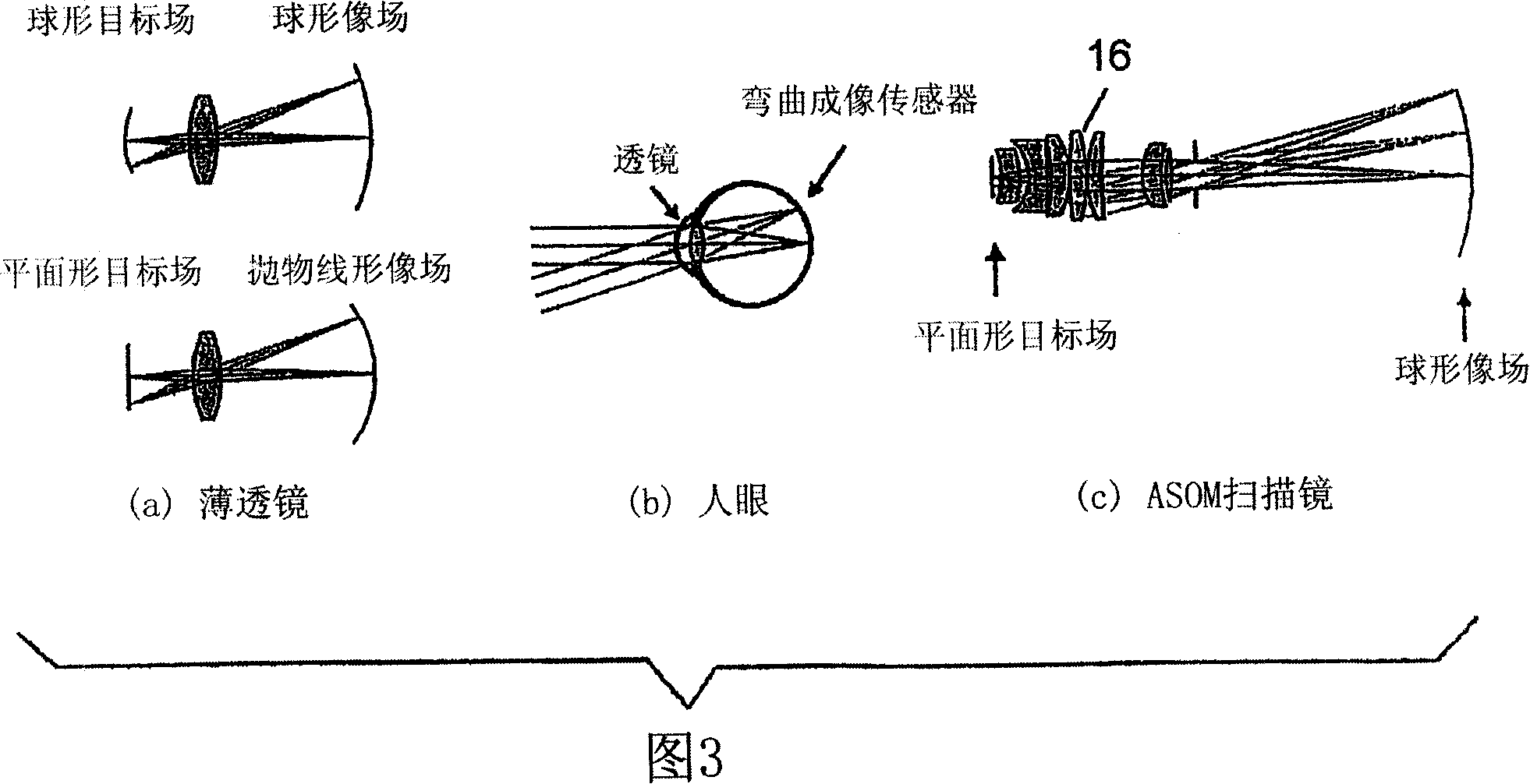
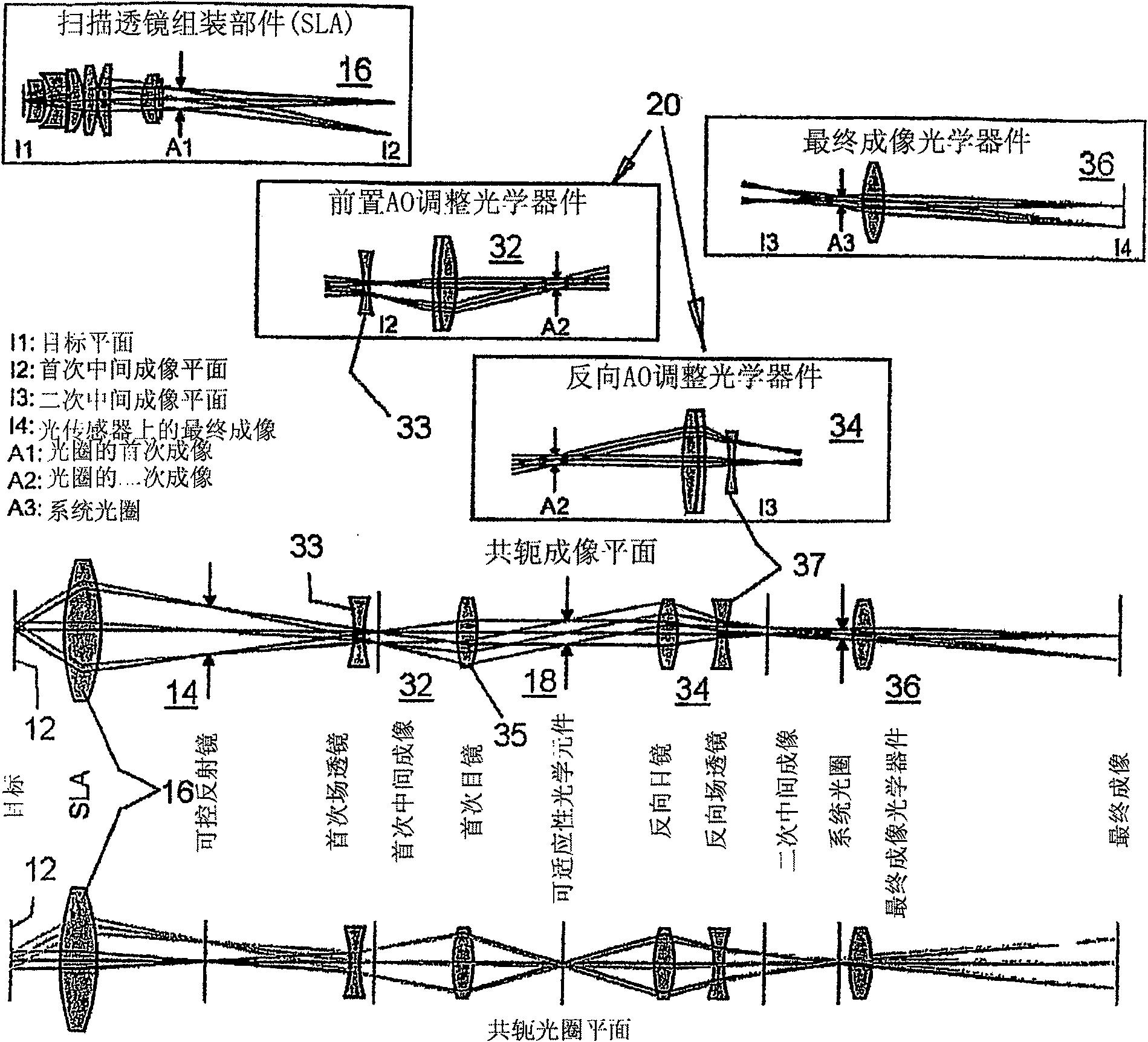
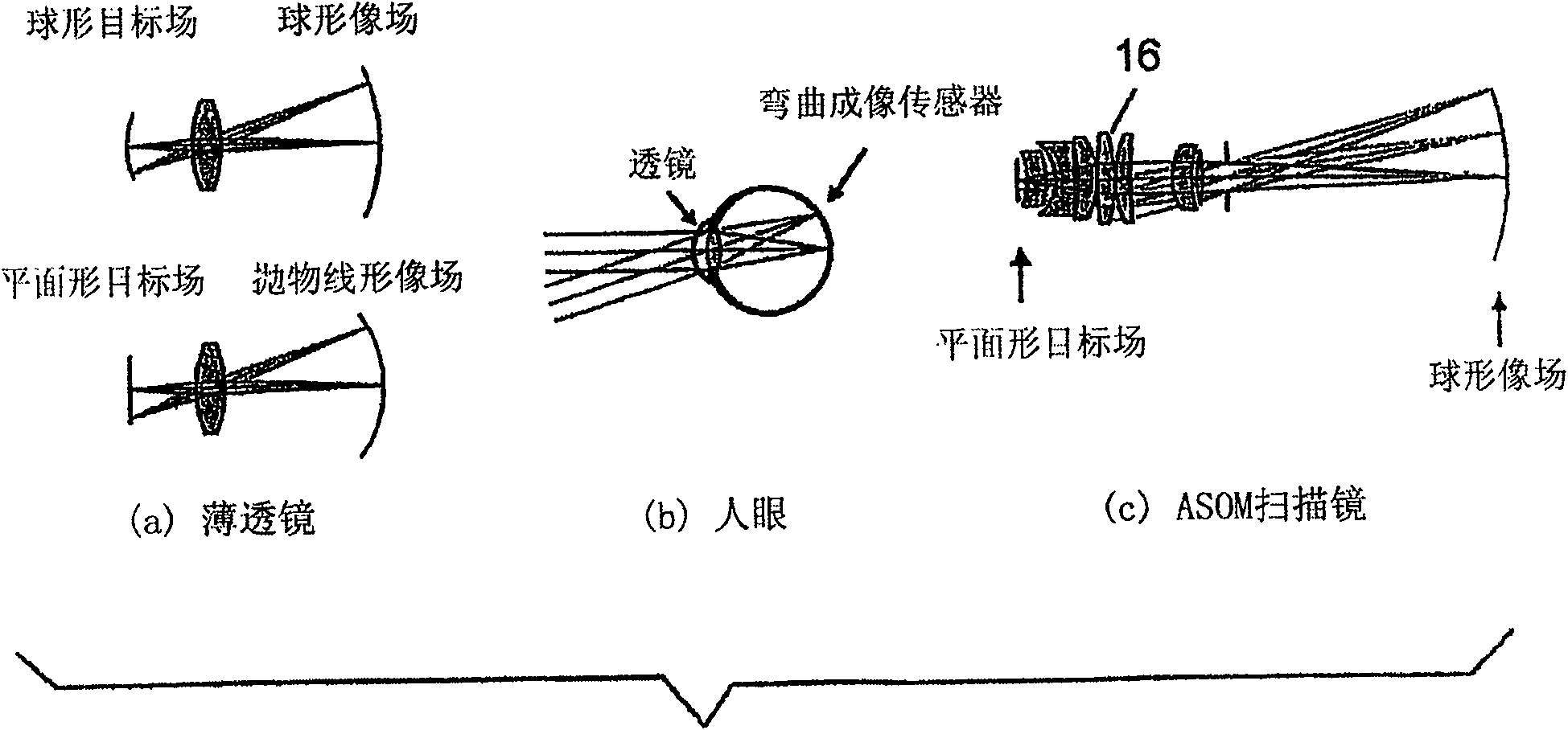
Adaptive scanning optical microscope
ActiveCN101116023AReduce complexityFast imagingMicroscopesImage formationNear-field scanning optical microscope
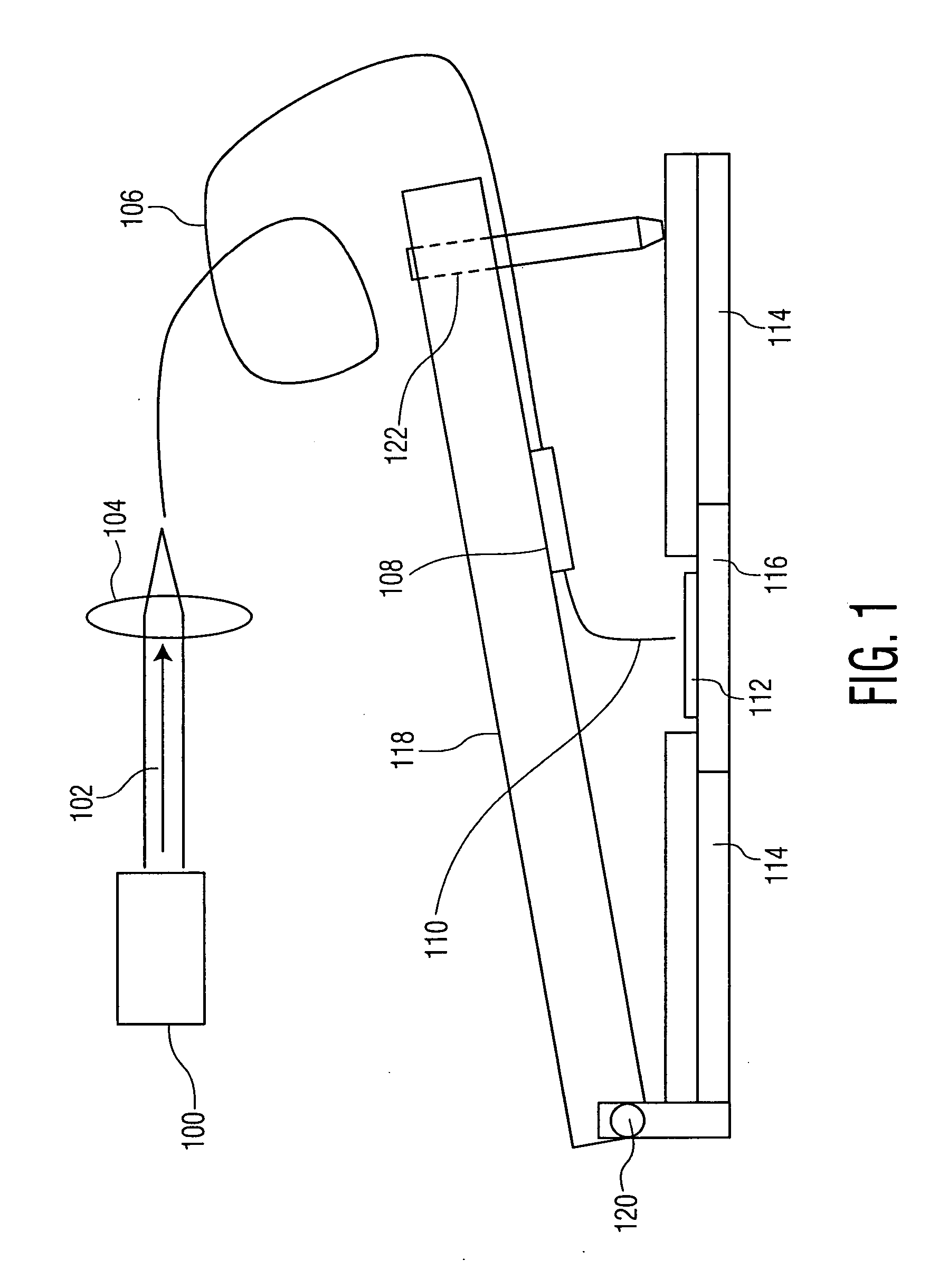
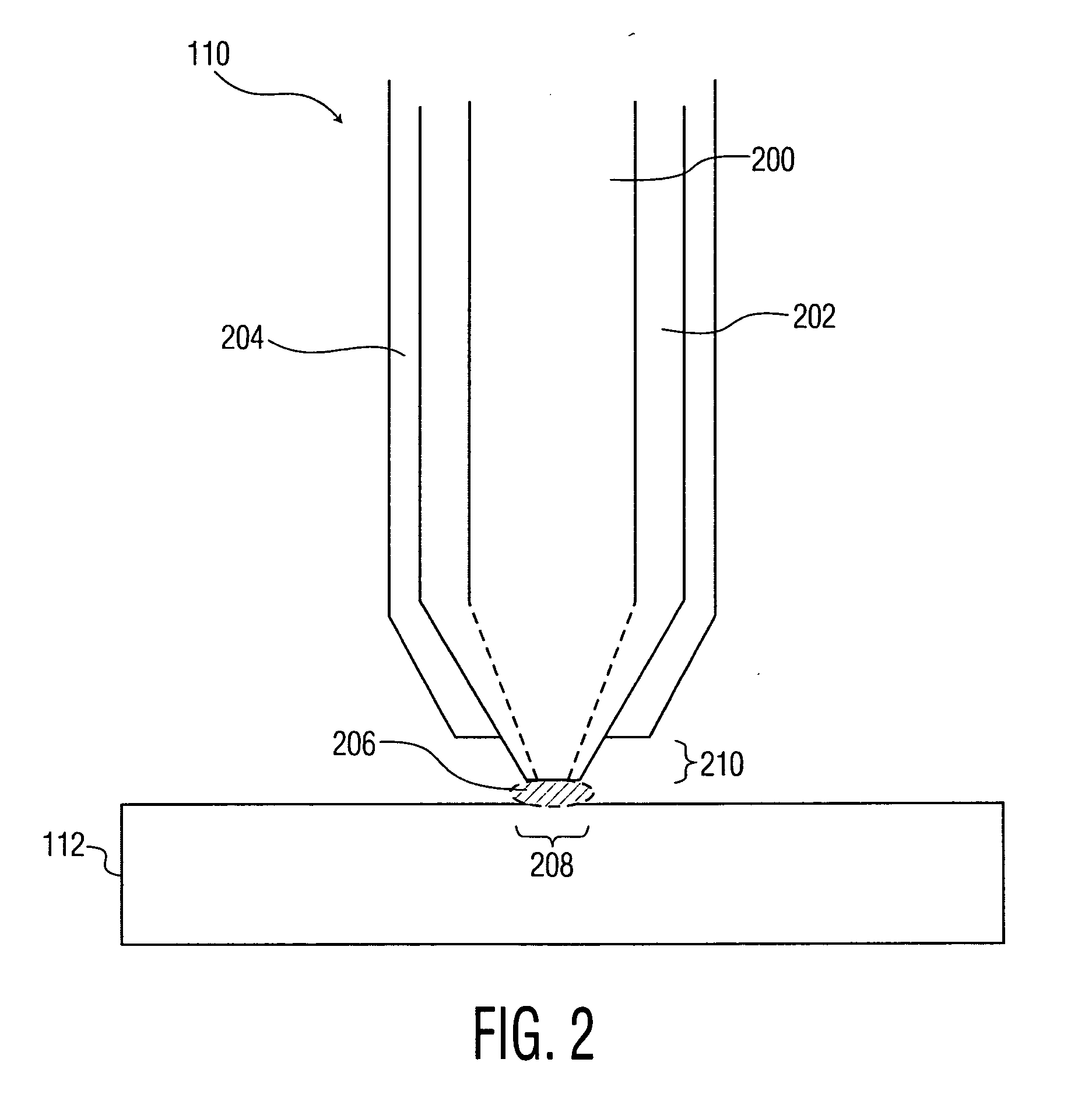
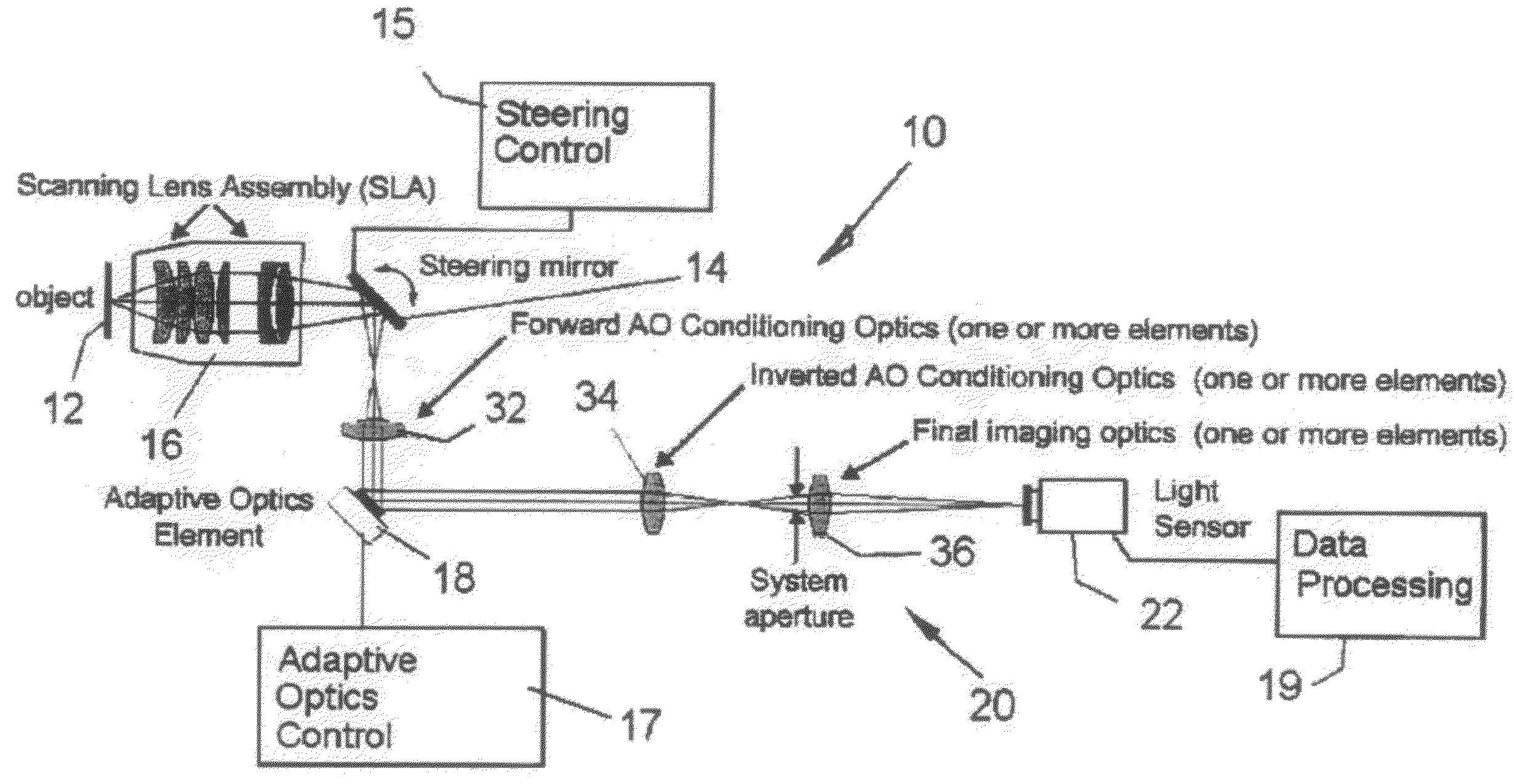
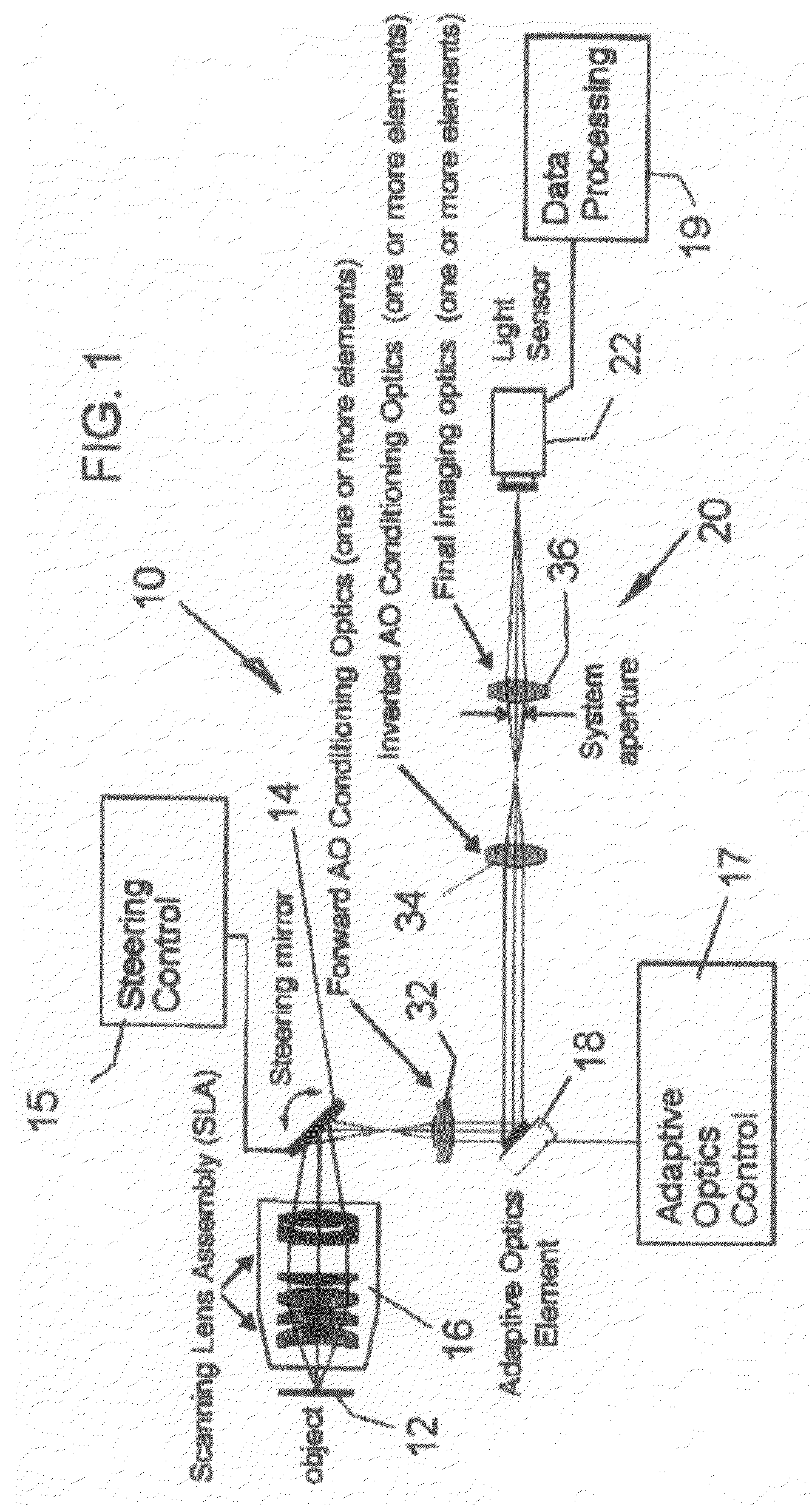
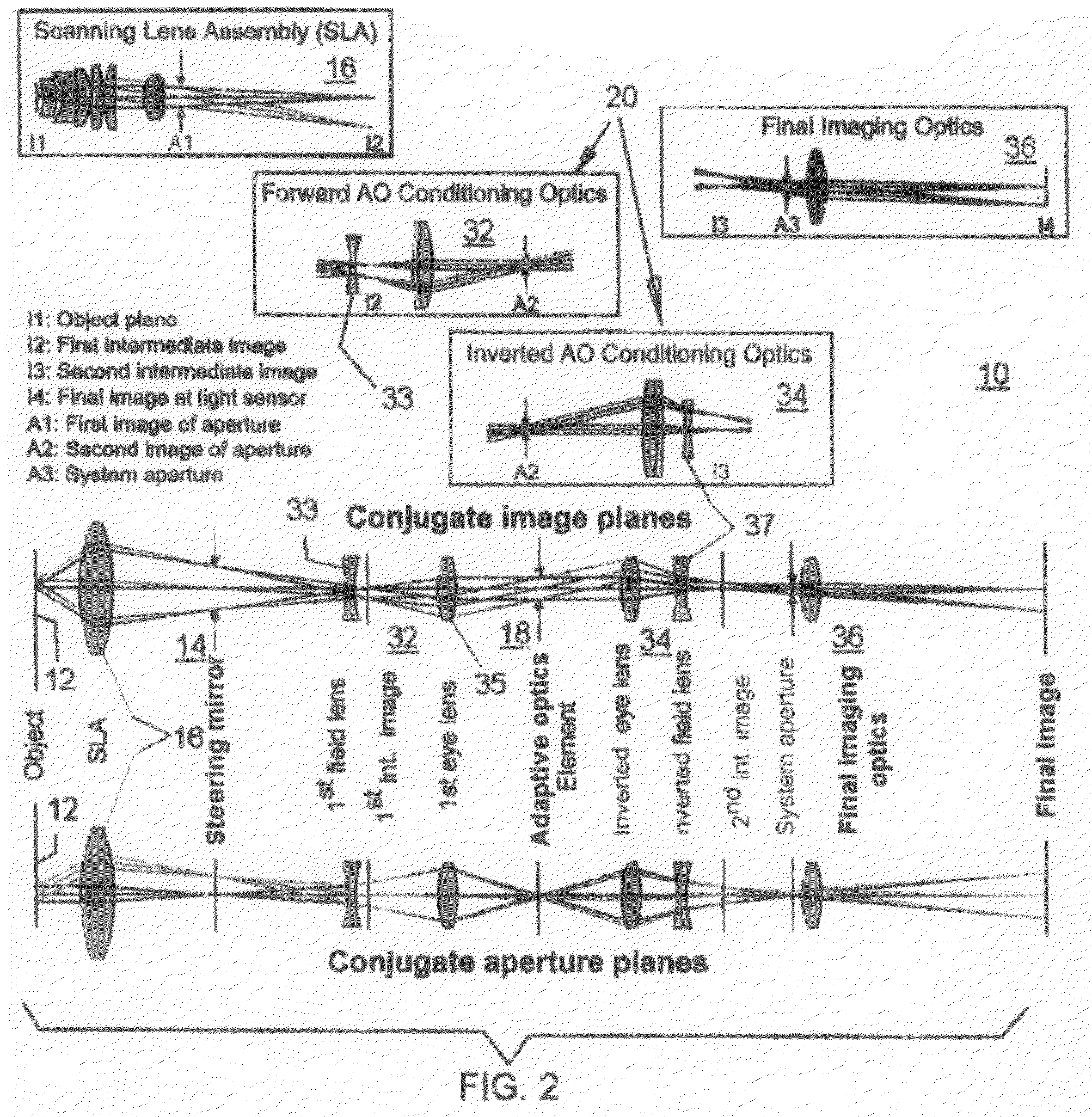
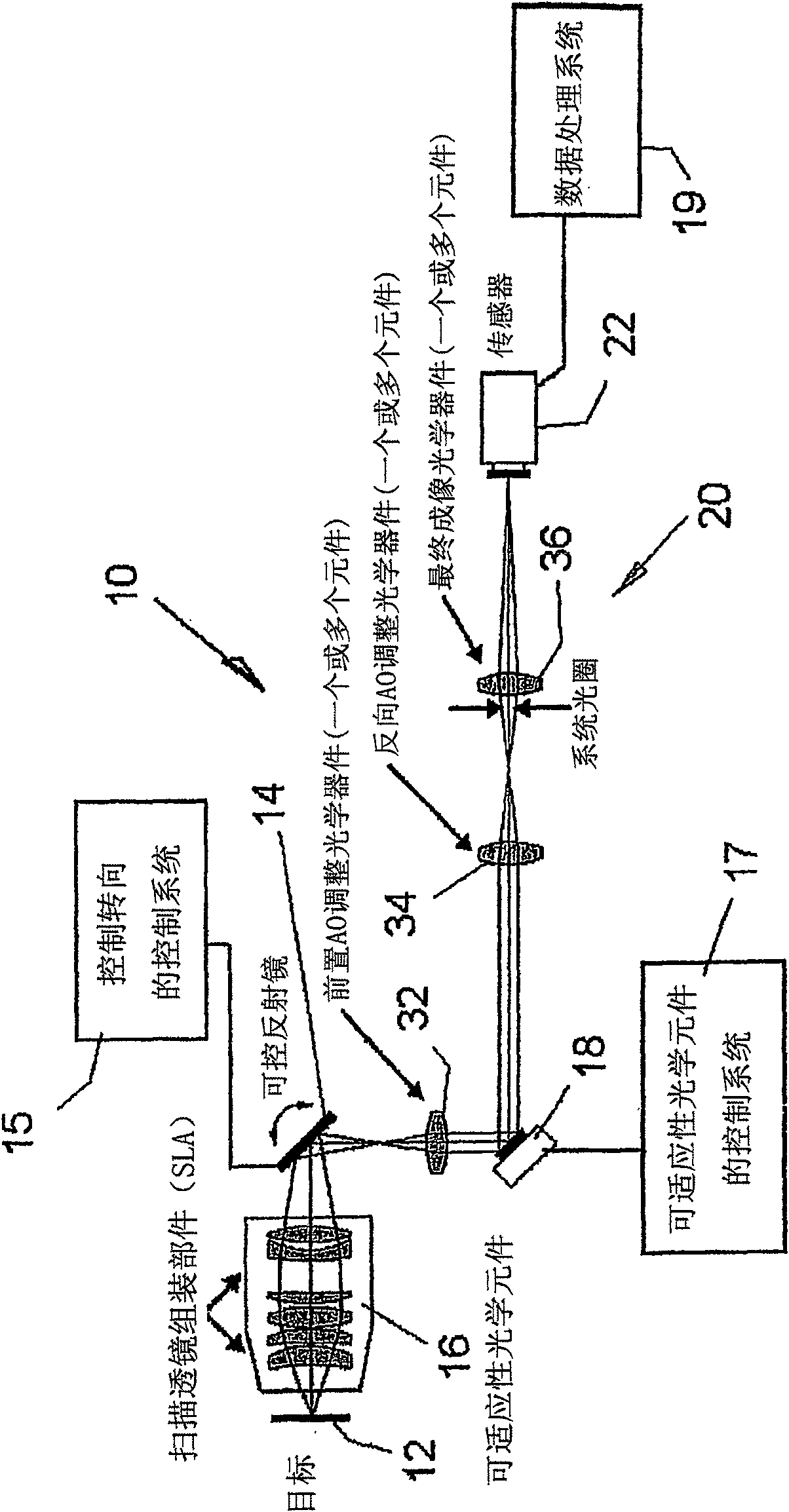
The invention relates to an adaptive scanning optical microscope. In this adaptive scanning optical microscope, a scanning lens assembly is installed, which can acquire images from different parts of the target plane, and then form a more suitable curved image field. In the resulting image field there will be at least some aberrations which vary as a function of the position of the imaging site on the object plane. A control mirror selects the imaging site and steers light from the object plane along an optical path from the object plane to the imaging plane. An adaptive optic receives light from the target, steers it, and compensates for aberrations that depend on the imaging position. There are additional optical devices on at least part of the optical path, and the optical devices will adjust and focus the light during the running process of the light from the control mirror, through the adaptive optical element, and finally to the imaging plane.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
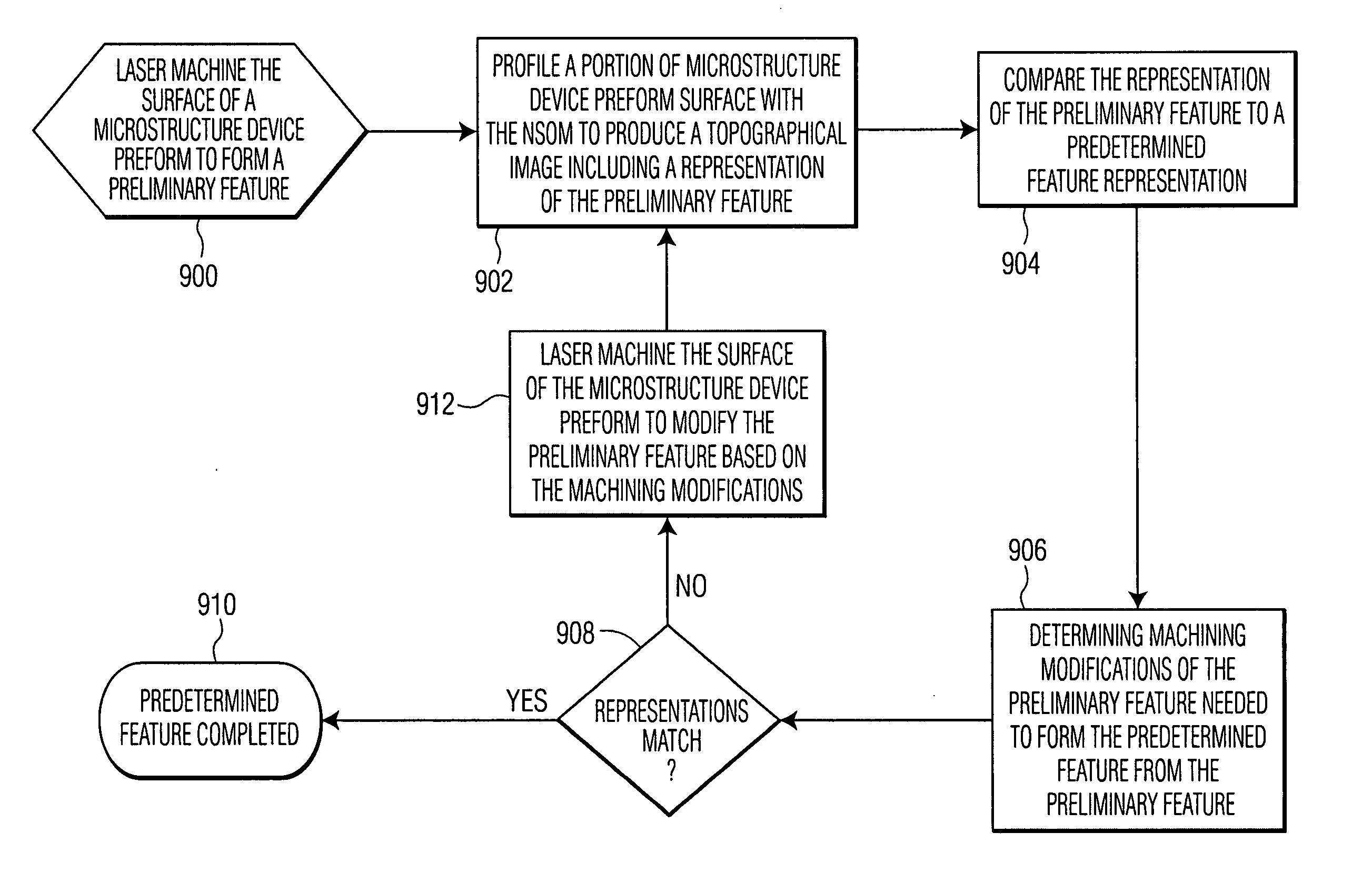
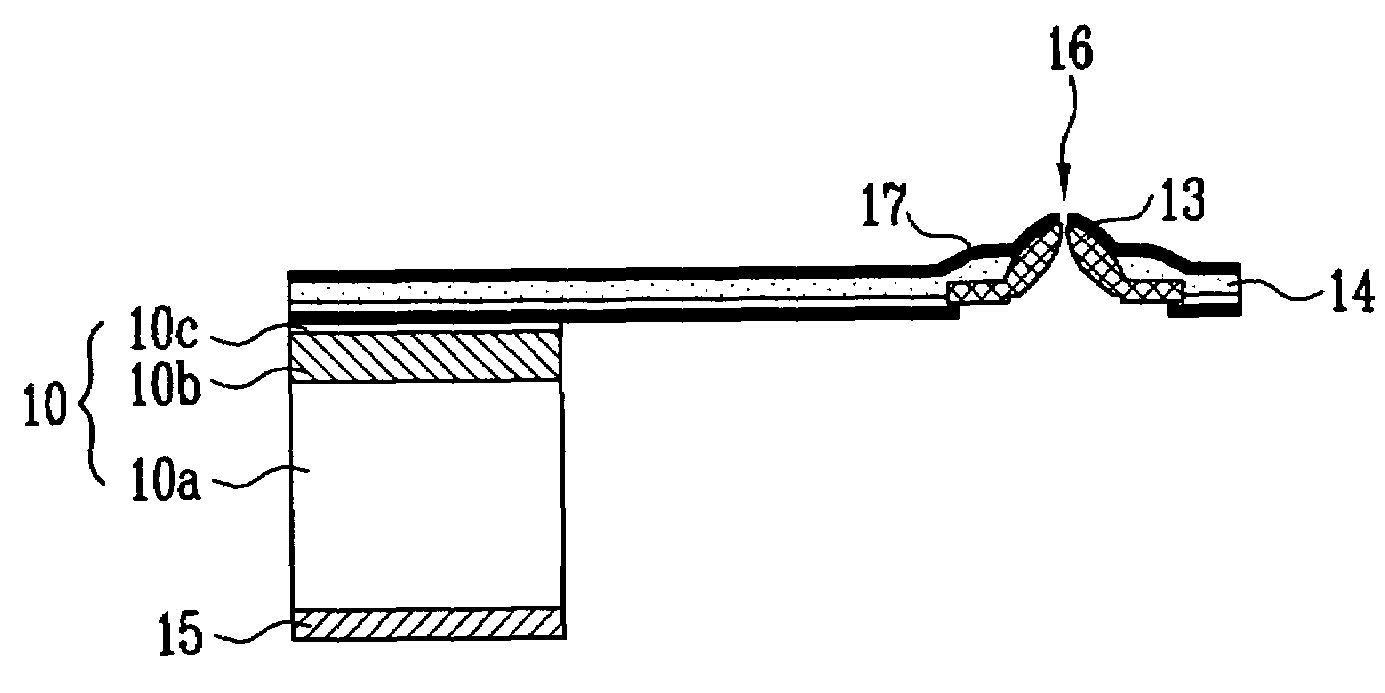
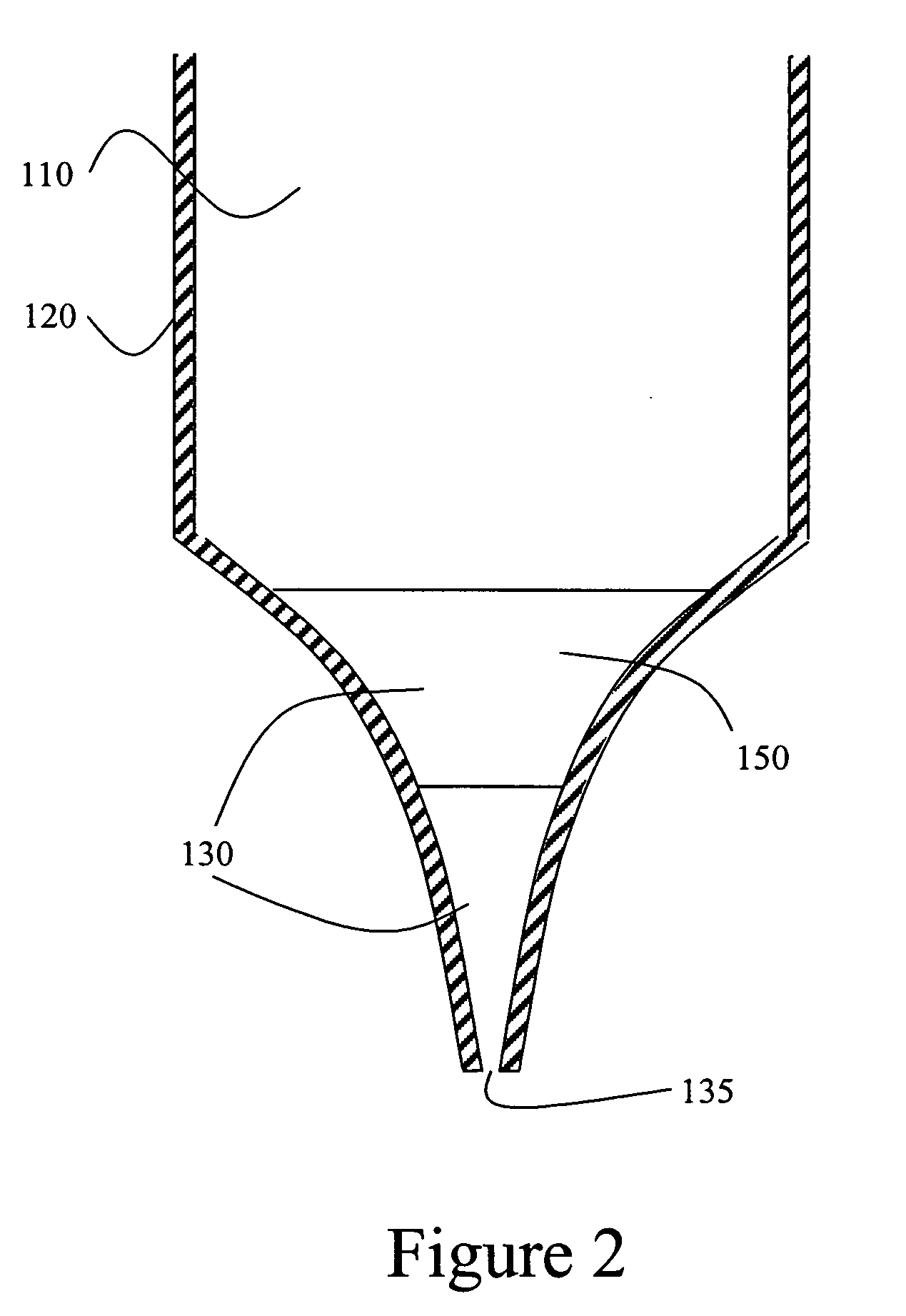
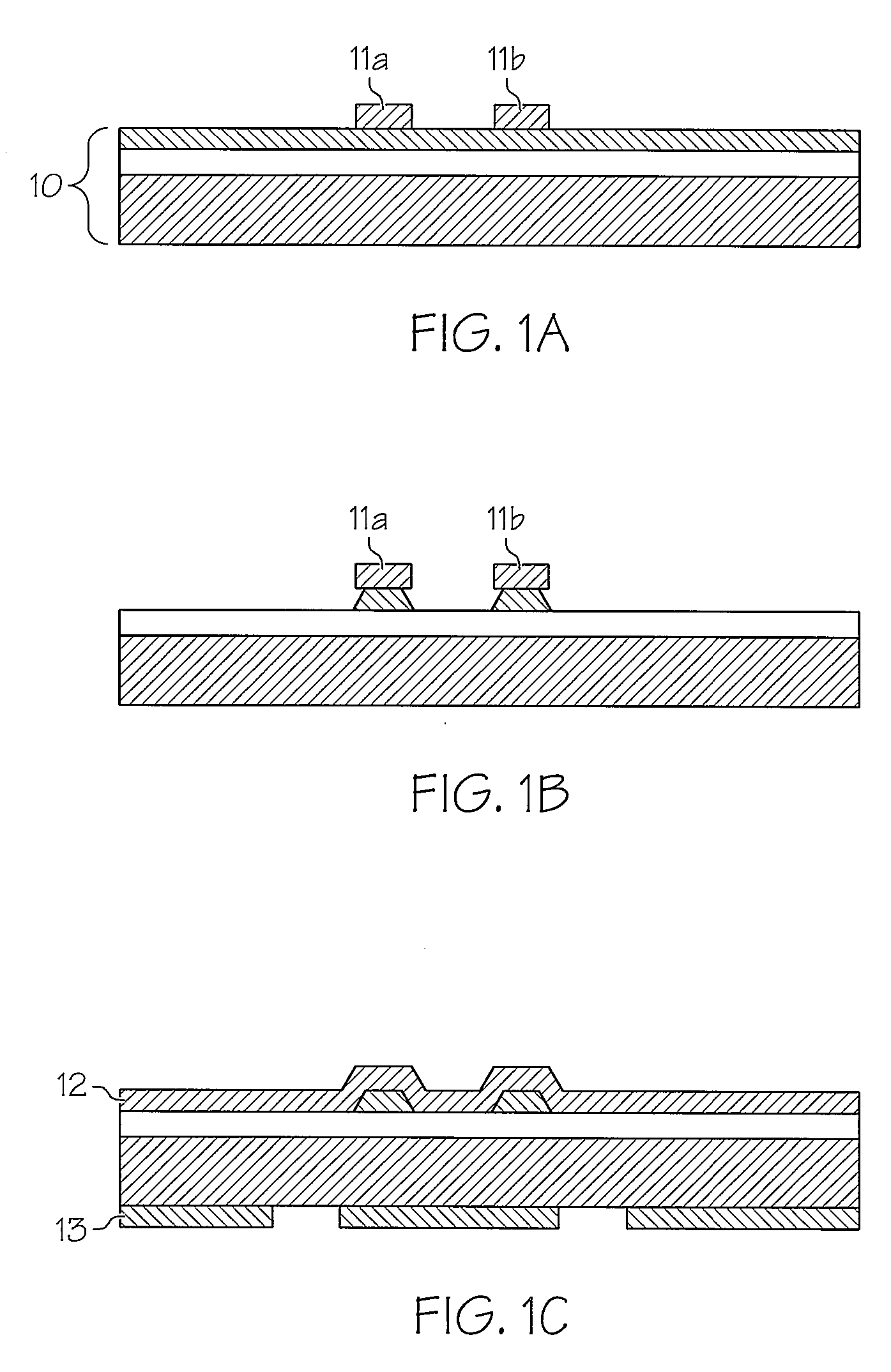
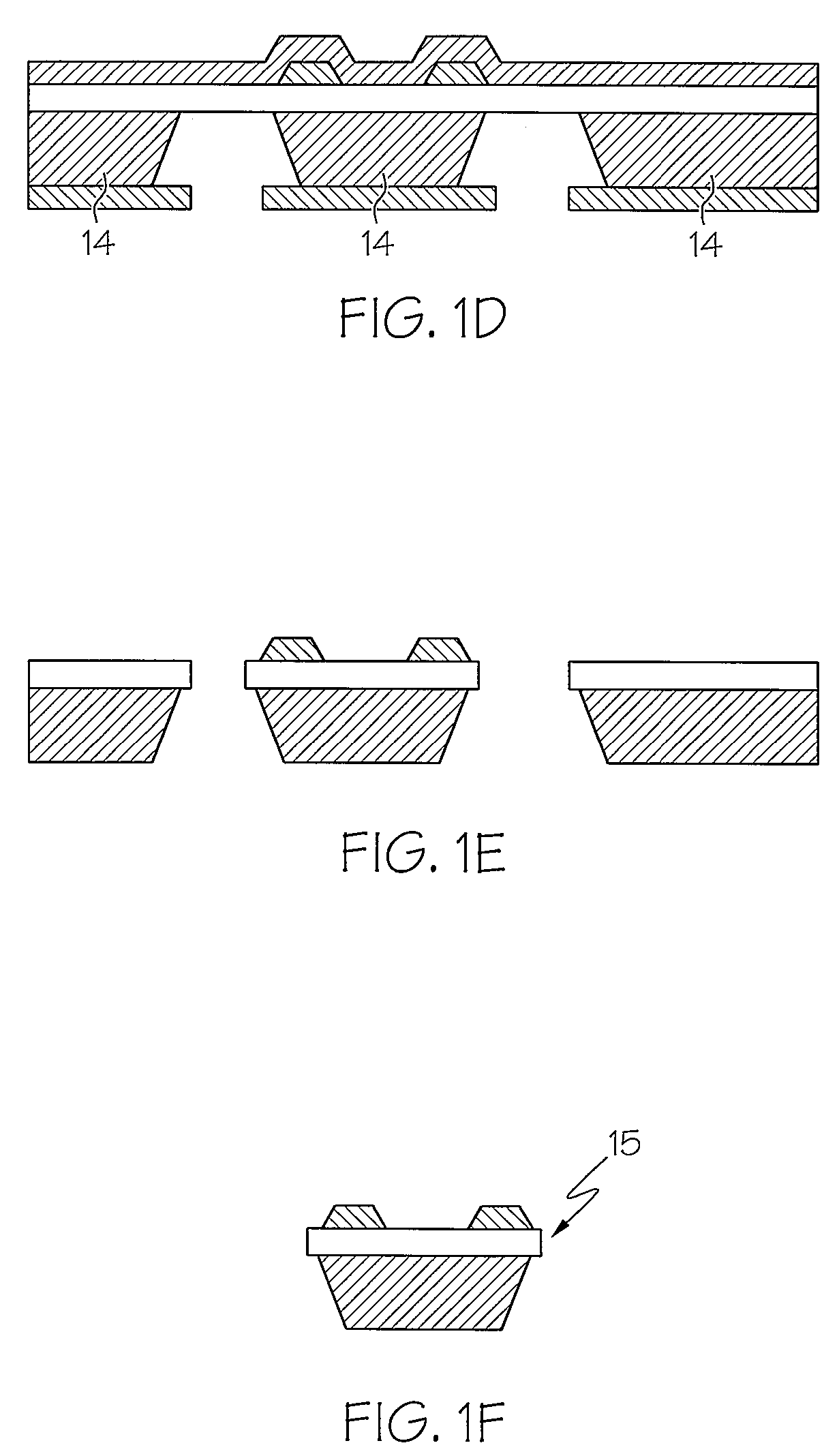
Method for modifying existing micro-and nano-structures using a near-field scanning optical microscope
InactiveUS20050221577A1Material nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsNear-field scanning optical microscopeContour analysis
A method for manufacturing a microstructure, which includes at least one fine feature on an existing feature, using an NSOM laser micromachining system. A microstructure device preform is provided. A portion of its top surface is profiled with the NSOM to produce a topographical image. This profiled portion is selected to include the existing feature. An image coordinate system is defined for the profiled portion of top surface based on the topographical image. Coordinates of a reference point and the orientation of the existing feature in the image coordinate system are determined using the topographical image. The probe tip of the NSOM is aligned over a portion of the existing feature using the determined coordinates of the reference point and the orientation of the existing feature. The top surface of the microstructure device preform is machined with the micro-machining laser to form the fine feature(s) on the existing feature.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Adaptive-scanning optical microscope
ActiveUS7742213B2Improve performanceScanner lens is simplifiedMicroscopesPosition dependentNear-field scanning optical microscope
An adaptive scanning optical microscope has a scanner lens assembly for acquiring images from different parts of an object plane and for forming a preferably curved image field having at least some aberration which varies as a function of the part of the object plane from which the image is acquired. A steering mirror selects the field of view and steers light from the object and along a light path from the object plane to a final image plane. An adaptive optics element receives the steered light from the object and compensates for the field position dependent optical aberrations and additional optics are along at least part of the light path for conditioning and focusing the light as it moves from the steering mirror, past the adaptive optics element and to the final image plane.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Method for generating rotatable optical focal field on basis of radiation field of rotating field antenna
The invention provides a method for generating a rotatable optical focal field on the basis of a radiation field of a rotating field antenna. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: S1, placing a virtual rotating field antenna composed of two dipoles which are perpendicular to each other and have a phase difference of 90 degrees at the center of a focal plane of a 4Pi focusing system, so that an electromagnetic field radiated by the virtual rotating field antenna is completely converged by two opposite high numerical aperture lenses and collimated onto a pupil plane; andS2, focusing two incident fields different for 180 degrees onto the optical focal plane of the two opposite high numerical aperture lenses by virtue of the two opposite high numerical aperture lenses. Intensity distribution of an '8'-shaped optical focal field generated by the method provided by the invention rotates at a circular frequency omega around an optical axis on the focal plane along with time. The rotatable optical focal field has important application value in the aspects of particle rotation, particle acceleration and near-field scanning optical microscopes.
Owner:QUANZHOU NORMAL UNIV
Method of fabricating near field optical probe
InactiveUS7393713B2Avoid collisionJoints with sealing surfacesDecorative surface effectsNear-field scanning optical microscopeCantilever
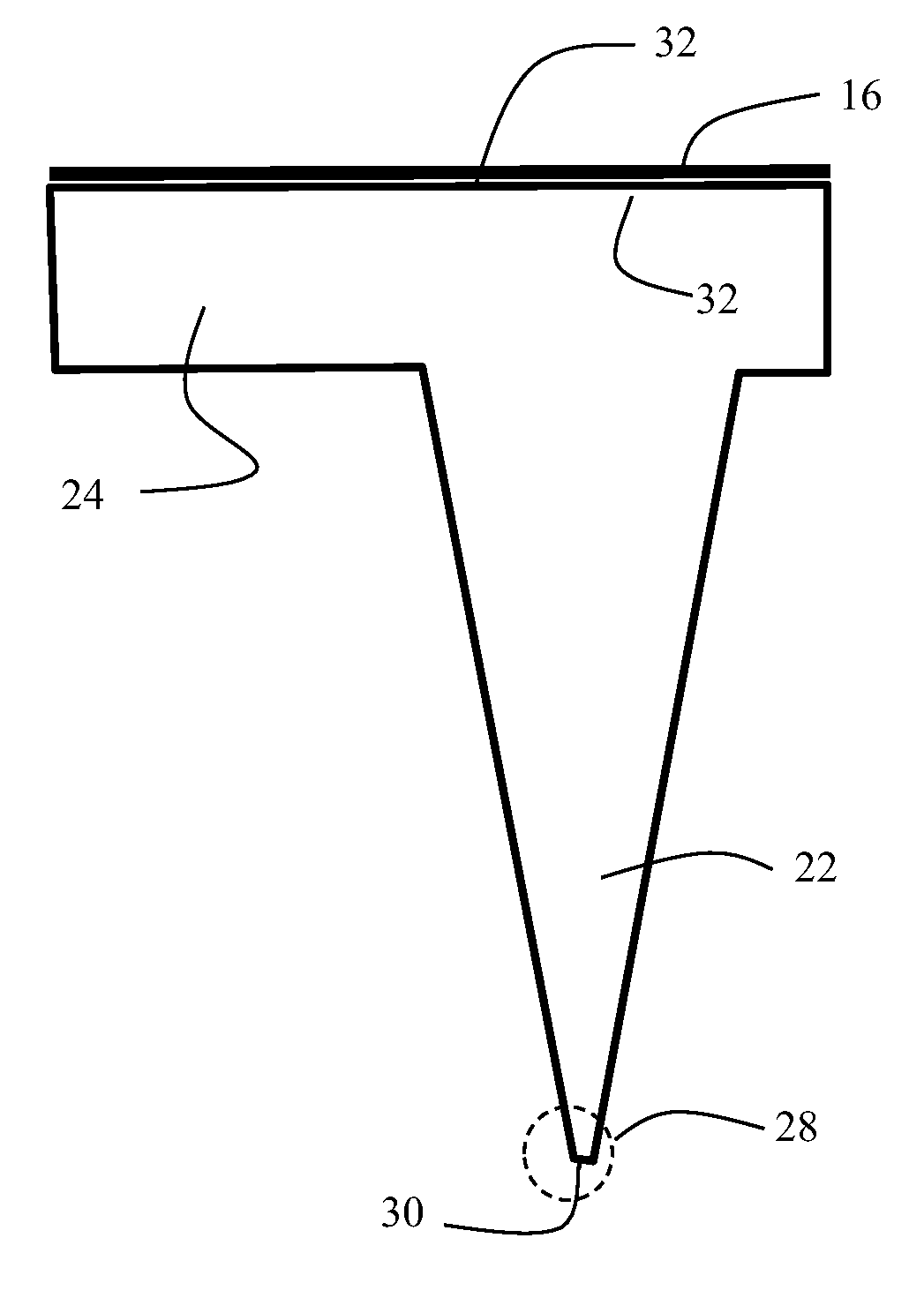
Provided is a method of fabricating a near-field optical probe adapted to a near-field scanning optical microscopy and a near-field information storage device, in which a cantilever and an optical tip are provided in one body and the optical tip is arranged to face the upper portion of the substrate. High-concentrated boron ions are implanted into an uppermost silicon layer of a silicon on insulator (SOI) substrate, and a silicon layer into which boron ions are implanted while the silicon inside the tip is etched to form the hole to act as an etch stop layer, thereby easily removing the silicon inside the tip even with the cantilever exposed, and simplifying the process due to the simultaneous fabrication of the cantilever and the tip.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Precision machining method using a near-field scanning optical microscope
InactiveUS7323657B2Material nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsScan lineNear-field scanning optical microscope
A method for manufacturing a microstructure device using a near field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) laser micromachining system. A microstructure device preform, including an existing feature, is provided. The NSOM probe tip is scanned over a portion of the preform selected such that a plurality of scan lines cross the existing feature. Scanned locations of the existing feature in at least two scan lines are determined. The orientation of the existing feature is determined based on the scanned locations and the shape of the existing feature. At least one expected machining location in a subsequent scan line is determined based on the shape and orientation of the existing feature. The micro-machining laser is pulsed as the NSOM probe is scanned through the expected machining location(s) during the subsequent scan lines to form at least one fine feature on the microstructure device preform, thus, completing the microstructure device.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for depositing material with high resolution
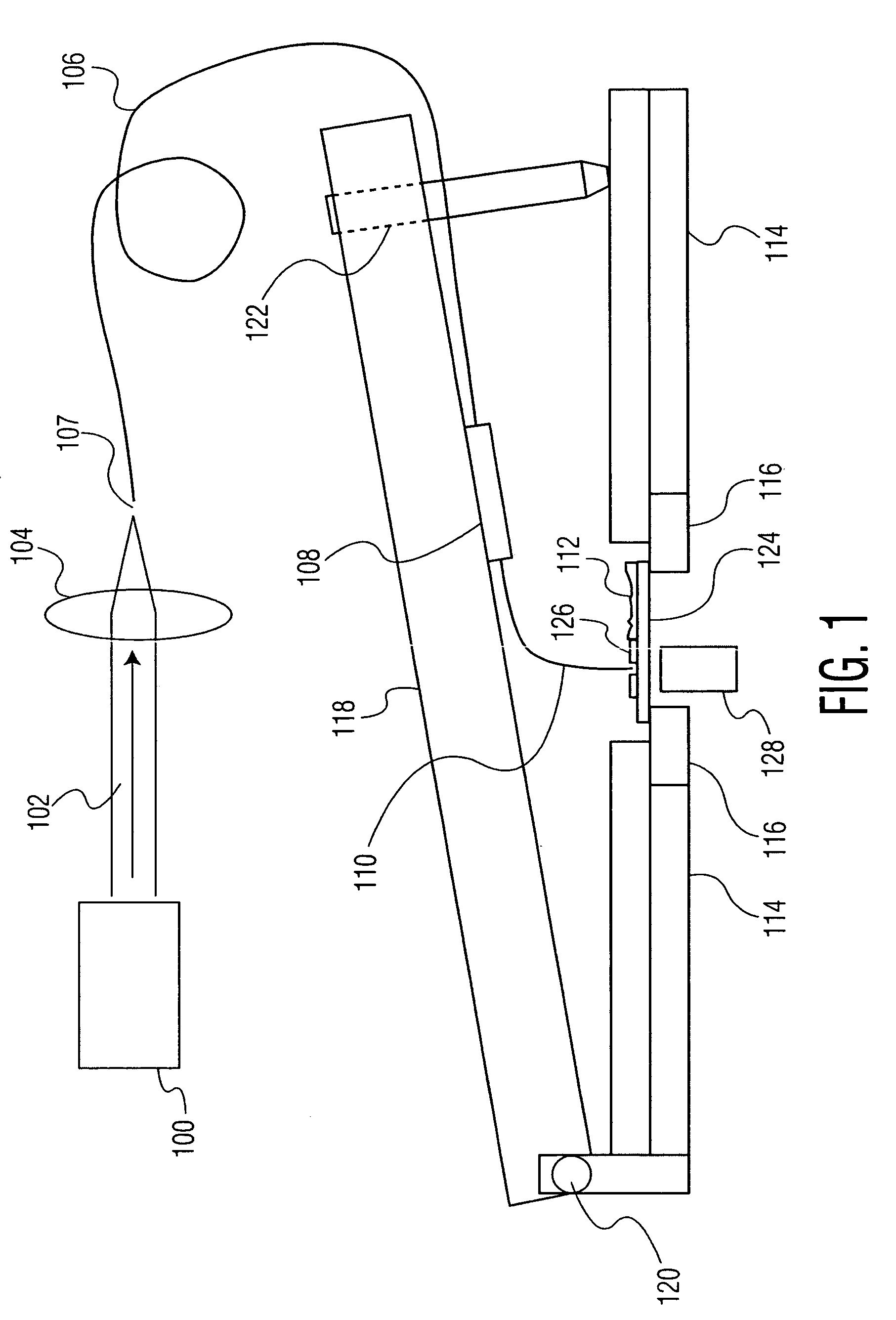
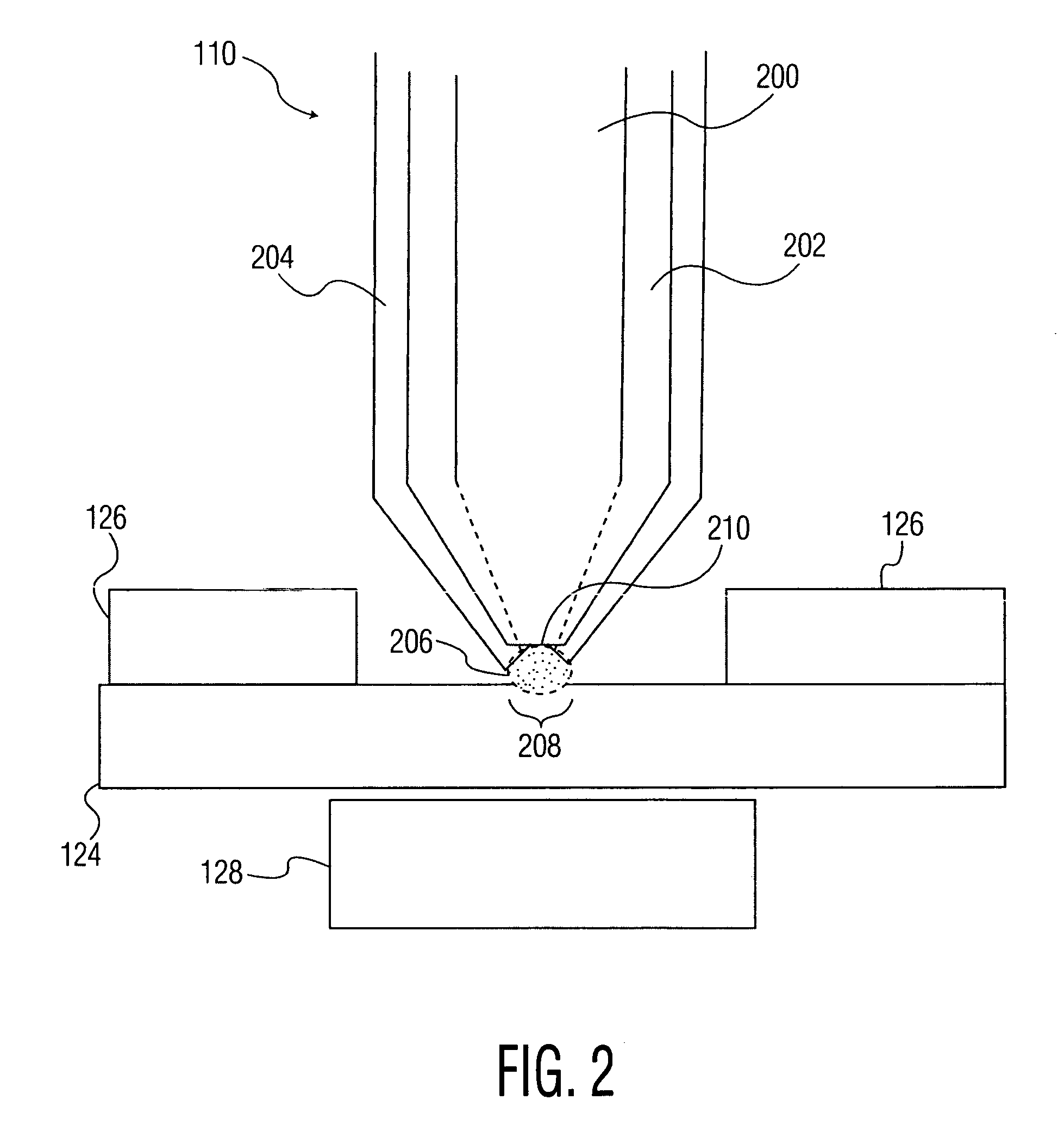
A device is provided. The device includes a base, and a reservoir disposed in the base. The reservoir is defined by a cladding and the base, and has an opening with a largest dimension of about 200 nm or less, more preferably 100 nm or less, and most preferably 60 nm or less. A material may be disposed within the reservoir. The base may be attached to a position control apparatus that may control the position of the base with an accuracy on the order of nanometers. The position control apparatus may include an atomic force microsope and / or a near field scanning optical microscope. The base may also be coupled to an energy application apparatus that may apply energy to the material. The device may be used to deposit material onto a substrate with a very high resolution, on the order of a few molecules across. The device may also be used to remove material from a substrate with a very high resolution by transmitting energy through the base. A device used for such removal may or may not include a reservoir.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Method for modifying existing micro-and nano-structures using a near-field scanning optical microscope
InactiveUS7198961B2Material nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsNear-field scanning optical microscopeComputer vision
A method for manufacturing a microstructure, which includes at least one fine feature on an existing feature, using an NSOM laser micromachining system. A microstructure device preform is provided. A portion of its top surface is profiled with the NSOM to produce a topographical image. This profiled portion is selected to include the existing feature. An image coordinate system is defined for the profiled portion of top surface based on the topographical image. Coordinates of a reference point and the orientation of the existing feature in the image coordinate system are determined using the topographical image. The probe tip of the NSOM is aligned over a portion of the existing feature using the determined coordinates of the reference point and the orientation of the existing feature. The top surface of the microstructure device preform is machined with the micro-machining laser to form the fine feature(s) on the existing feature.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Multiple plate tip or sample scanning reconfigurable scanned probe microscope with transparent interfacing of far-field optical microscopes
InactiveUS7047796B2Simple designReduce the total massMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSurface/boundary effectFiberLiquid cell
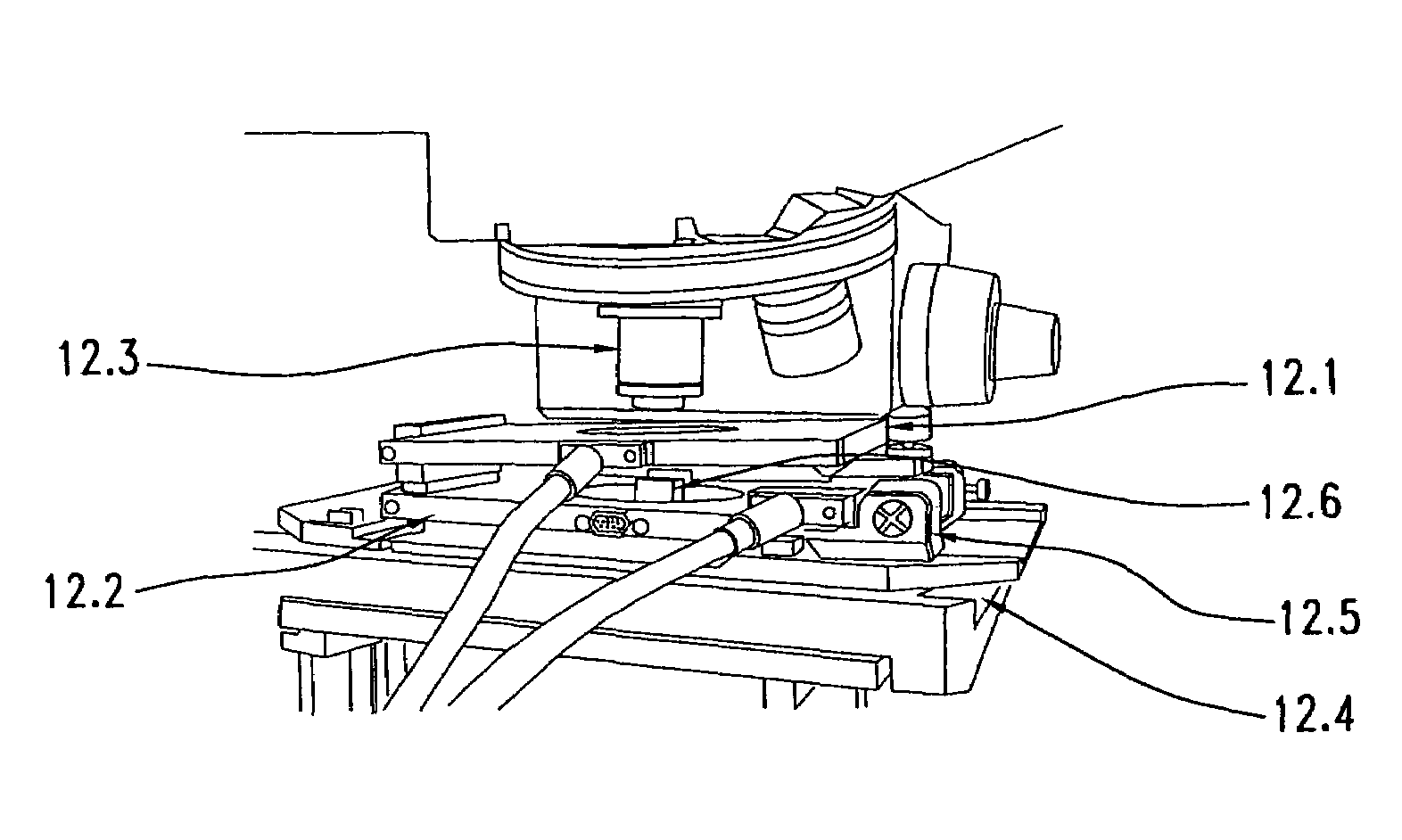
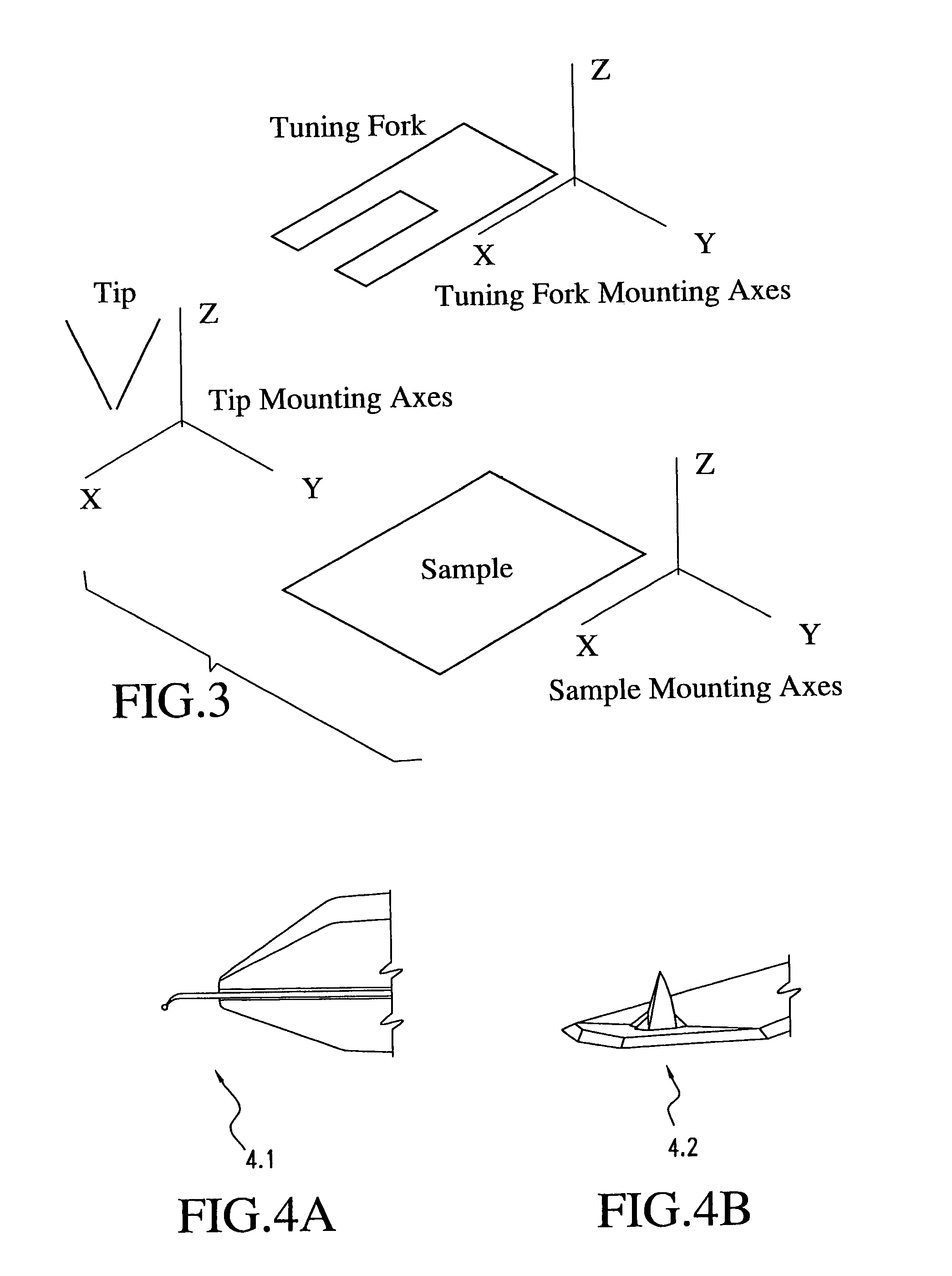
The invention is directed to a scanned probe microscope including one plate allowing for tip scanning and the other allowing for sample scanning, with the optical axis of the scanned probe microscope being free to permit incorporation into standard optical microscopes. The top plate can be hinged onto the bottom plate, or the top plate can simply be placed on the bottom plate and a rough approach is caused by a dc motor or other mechanism which will enable the two flat plate scanners to have a large z range. In another embodiment, the microscope includes three plates which allow sample scanning, tip scanning and two tips to be operational at the same time.A microscope in accordance with the invention may use a liquid cell, may use a near-field optical element made of silicon cantilever technology, or may use an apertureless probe for apertureless near-field scanning optical microscopy.The microscope may use a tuning fork for feedback in any combination of geometries of tip, sample and tuning fork and with or without gluing of the tip to the tuning fork and with control of tip attachment or near-attachment to the tuning fork. The control of tip attachment to the tuning fork may be based on near zero backlash movement technology, and the tuning fork can be used in non-contact, contact and intermittent contact modes of operation. A fiber based feedback system may use either straight or cantilevered fibers, and the detection of signals may be based on amplitude, phase, wavelength or other optical parameters that can be used to monitor the movement of an SPM sensor.
Owner:NANONICS IMAGING LTD
Apparatus and method for atomic force, near-field scanning optical microscopy
InactiveUS20150338627A1High refractive indexCladded optical fibreOptical articlesNear-field opticsRefractive index
A near-field optic has a high refractive index waveguide with a planar far field facet more than half of a wavelength across for coupling propagating light and a near field facet with the near field zone of the waveguide supporting only the fundamental optical mode in each polarization. A tapered waveguide section extends from the near field facet to transform the fundamental optical mode. A cantilever supports the tapered waveguide section.
Owner:MULTIPROBE
Spin microscope based on optically detected magnetic resonance
InactiveUS20080173812A1NanomagnetismMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic force microscopeScanning tunneling microscope
The invention relates to scanning magnetic microscope which has a photoluminescent nanoprobe implanted in the tip apex of an atomic force microscope (AFM), a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) or a near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) and exhibits optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) in the vicinity of impaired electron spins or nuclear magnetic moments in the sample material. The described spin microscope has demonstrated nanoscale lateral resolution and single spin sensitivity for the AFM and STM embodiments.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
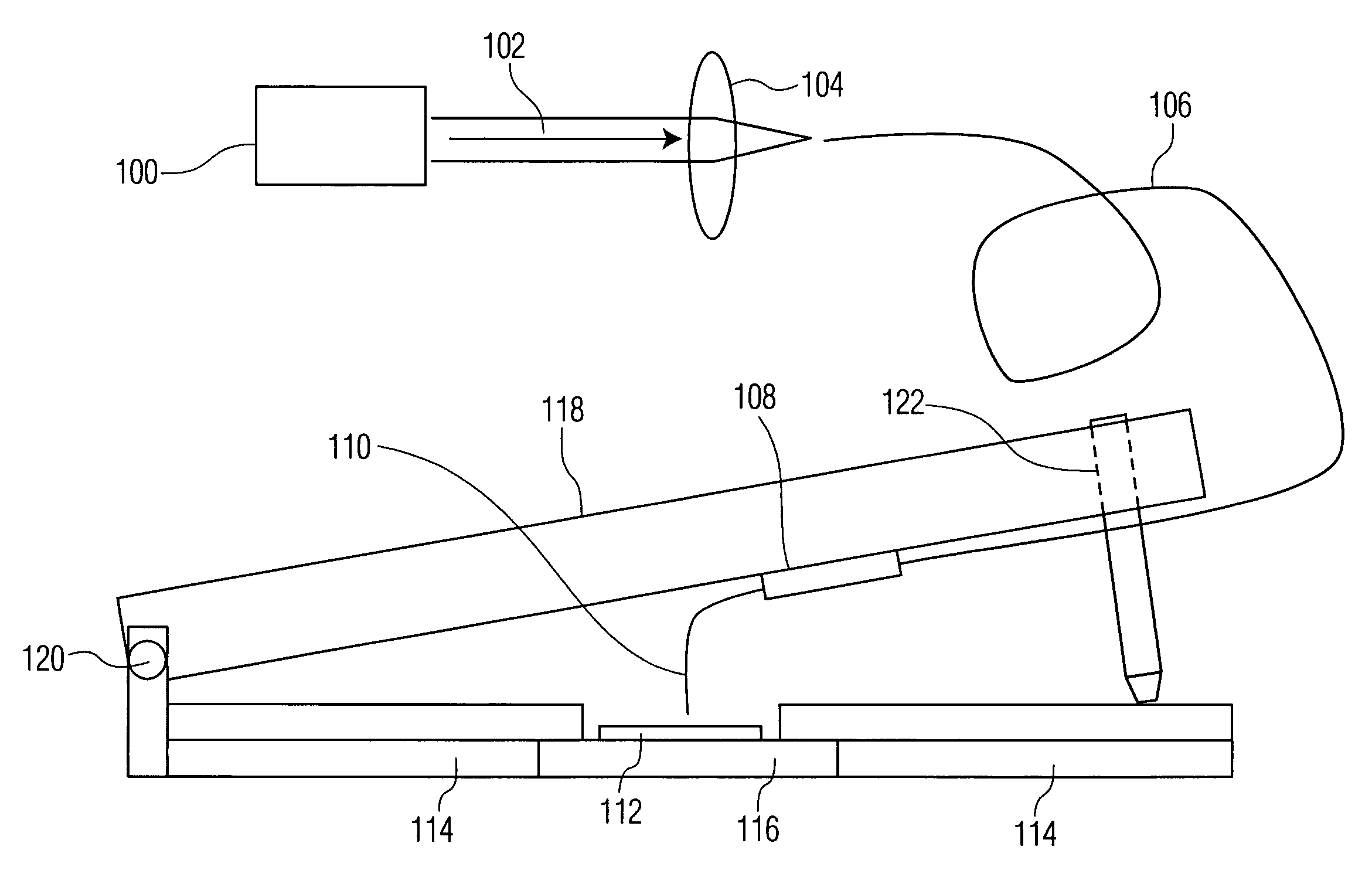
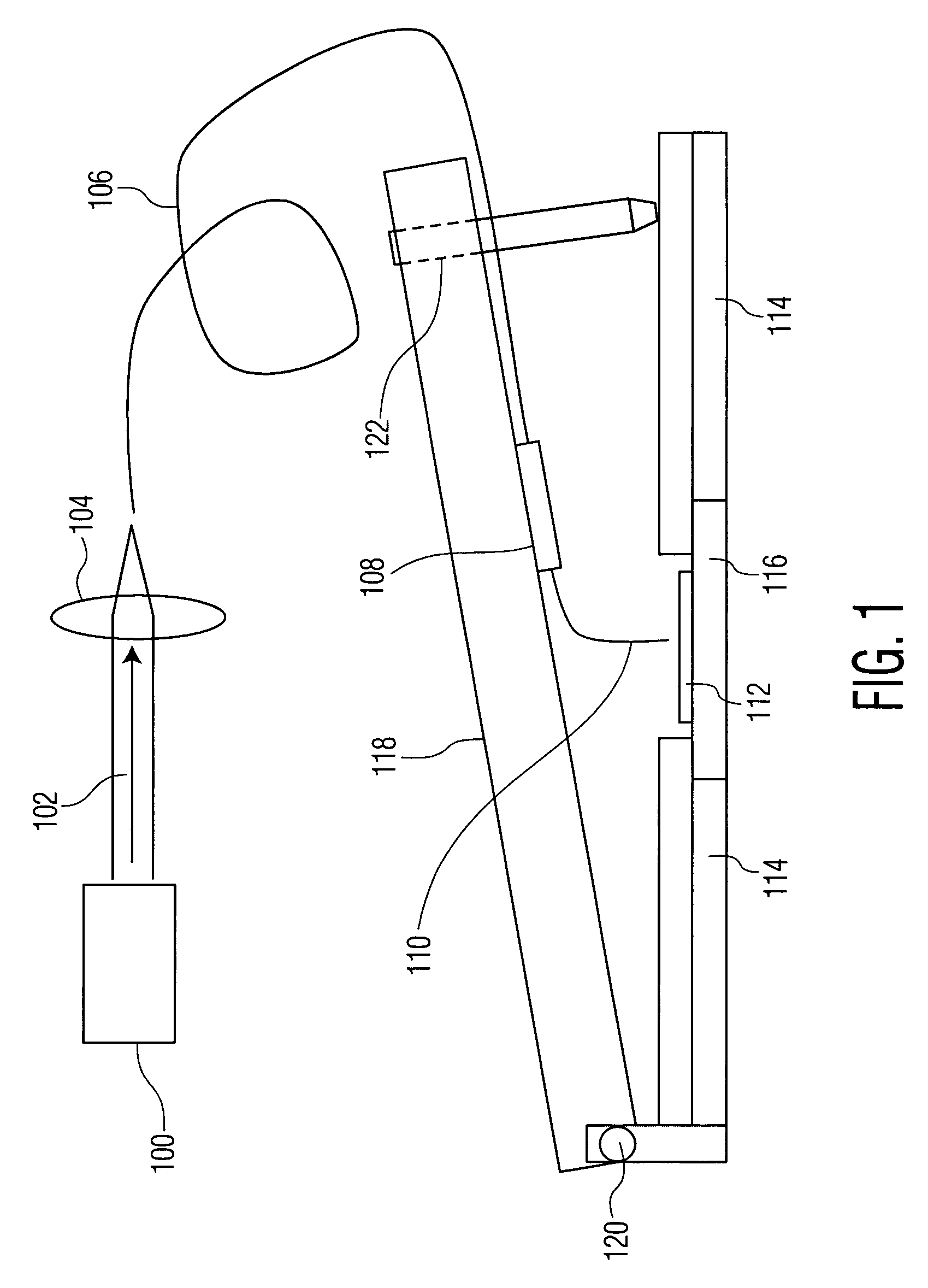
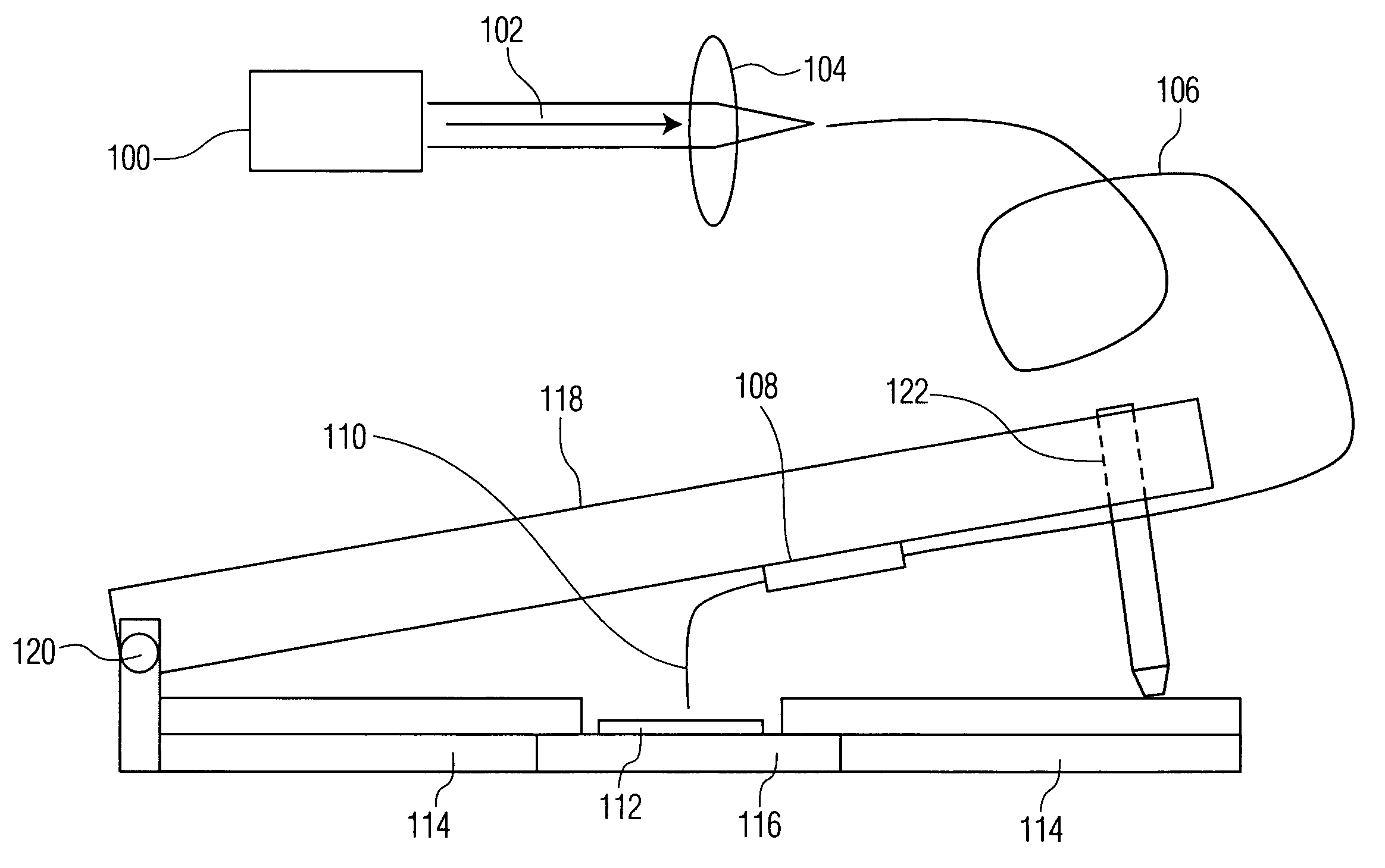
Method and apparatus for calibration of near-field scanning optical microscope tips for laser machining
A system for measuring radiation at a peak wavelength that is radiated from a probe tip of a near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) probe used for laser machining, including: a laser source; the NSOM probe; a coupling substrate that is substantially transmissive to the peak wavelength; an NSOM mount to controllably hold the probe and the coupling substrate; an NSOM probe monitor coupled to the mount; an NSOM controller; and a photodetector optically coupled to the substrate. Light is coupled into the probe. The mount includes a Z motion stage. The probe monitor determines the distance between the probe tip and the coupling substrate. The controller is coupled to the probe monitor and the motion stage. It controls the distance between the probe tip and the coupling substrate such that radiation is coupled from the probe tip into the coupling substrate. The photodetector measures the power of this radiation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Near-Field Scanning Optical Microscope Probe Having a Light Emitting Diode
InactiveUS20080054168A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsDecorative surface effectsNear-field scanning optical microscopeLight-emitting diode
An improved near-field scanning optical microscope probe is disclosed. The near-field scanning optical microscope probe includes a probe body and two electrodes extending from the probe body to form a probe tip. In addition, a light-emitting diode is disposed between the two electrodes at the probe tip to act as a light source for the near-field scanning optical microscope probe.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Near-field scanning optical microscope for laser machining of micro- and nano- structures
InactiveUS20050218315A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLaser lightNear-field scanning optical microscope
A near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) laser micromachining system for laser machining features on surfaces using an ultrafast laser source and a method of laser machining such features. The system includes: the ultrafast laser source to generate pulses of laser light having pulse durations less than 1 ns and a peak wavelength; an NSOM probe having a substantially cylindrical shape; an NSOM mount to controllably hold the NSOM probe and the microstructure workpiece to be machined; an NSOM probe monitor coupled to the NSOM mount for determining the distance between the probe tip of the NSOM probe and the surface; and an NSOM controller coupled to the NSOM probe monitor, and motion stages in the NSOM mount. The NSOM mount includes an XY motion stage and a Z motion stage. These motion stages are couple to either the NSOM probe or the microstructure workpiece, or one motion stage to each.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
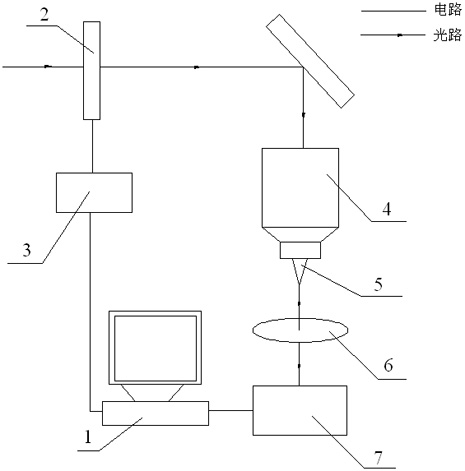
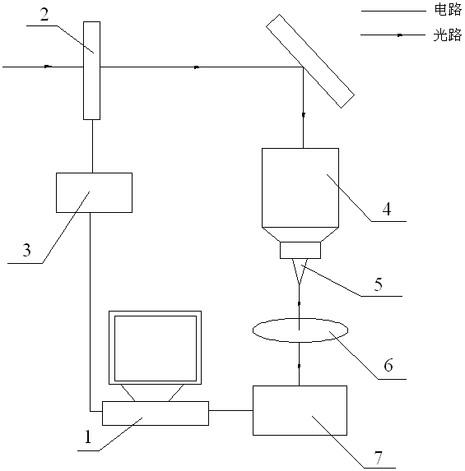
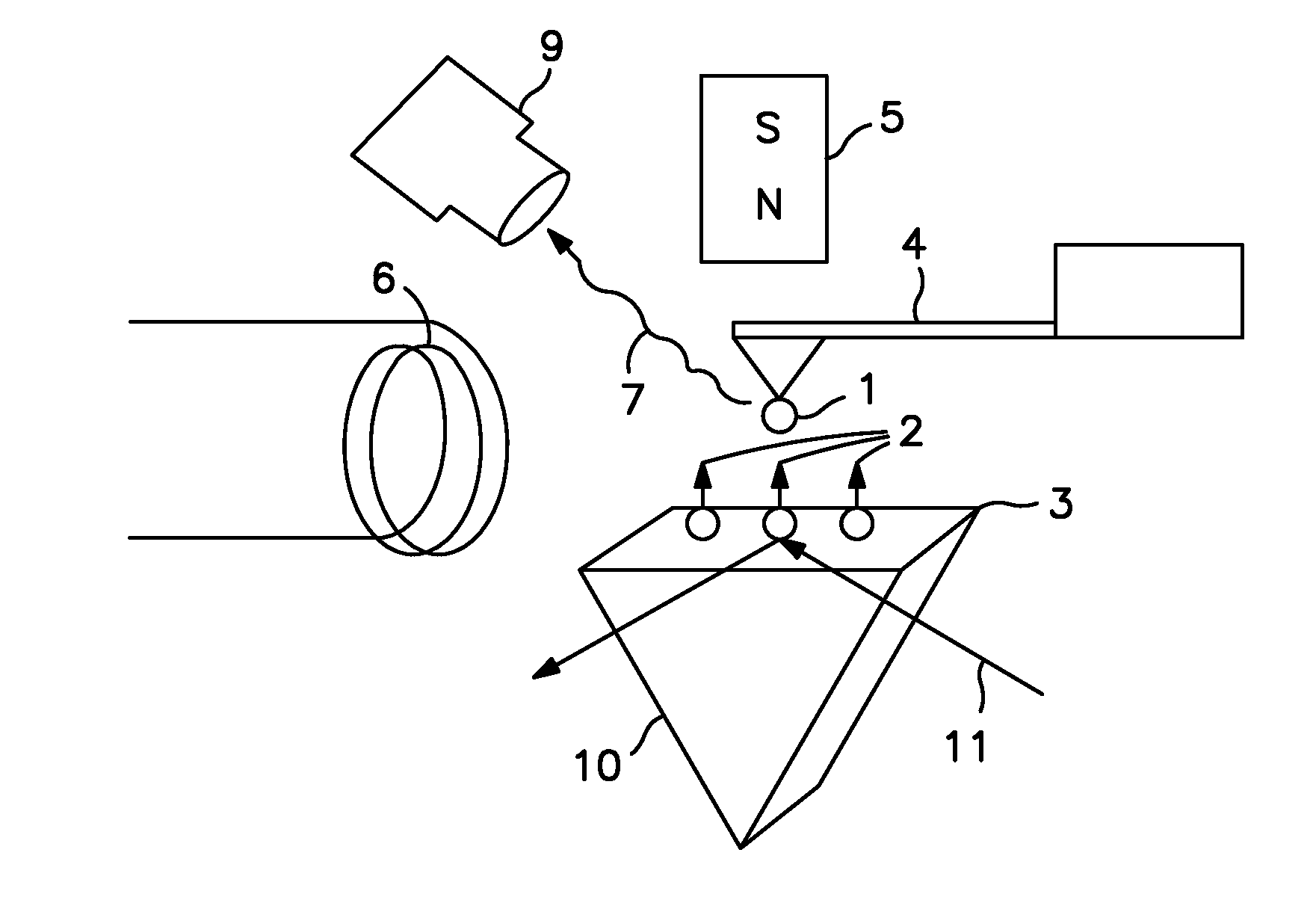
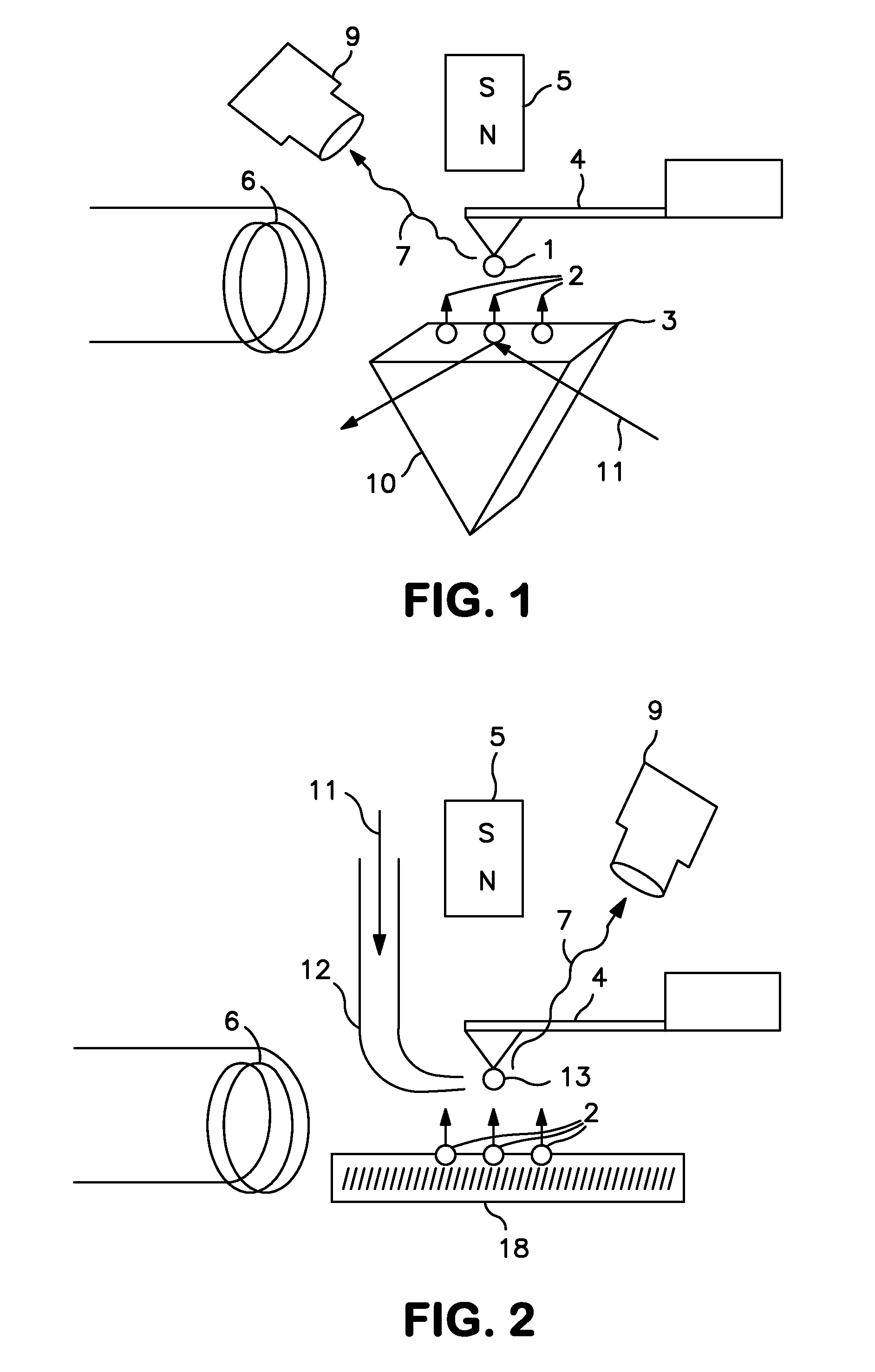
Coupling permeation efficiency optimization system of near field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) and optimization method thereof
InactiveCN102072972ANo other performance degradationSimple structureScanning probe microscopyCouplingClosed loop
The invention provides a coupling permeation efficiency optimization system of a near field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) and an optimization method thereof, relating to the field of scanning probe microtechnique. The optimization system comprises a computer, a detector, a collection mirror, a probe, a focusing mirror, a spatial light modulation instrument and a driver, wherein the computer,the detector, the spatial light modulation instrument and the driver form a closed loop circuit. In the system, the spatial light modulation instrument is introduced to modulate the light field distribution of an incident light field, so that the modulated light field is coupled with the probe, thereby having highest coupling permeation efficiency, and being incapable of reducing other performances of a microscope system.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Near-field scanning optical microscope poisitioned scanning-imaging method
InactiveCN1405548ARealize positioning scan imagingSimple structureSurface/boundary effectMicroscopesMicrometerNear-field scanning optical microscope
A method for a near field scan-optical microscope positioned scanning image is that by using micrometer dimension luminous points as the position reference points with the help of traditional optical micro scope and trimming flat table to observe by micro image device and measures in precision relative shift of the reference luminous points center and the target zone, adjusts optical probe to the center of the reference luminous optical probe, then further adjusts optical probe to the center of refrence luminous points according to the relative shift of the reference luminous points center and sample target zone, realizing NSOM positioning scanning and imaging with accuracy reaching to 1 micro meter.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Head for recording and reading optical data and method of manufacturing the same
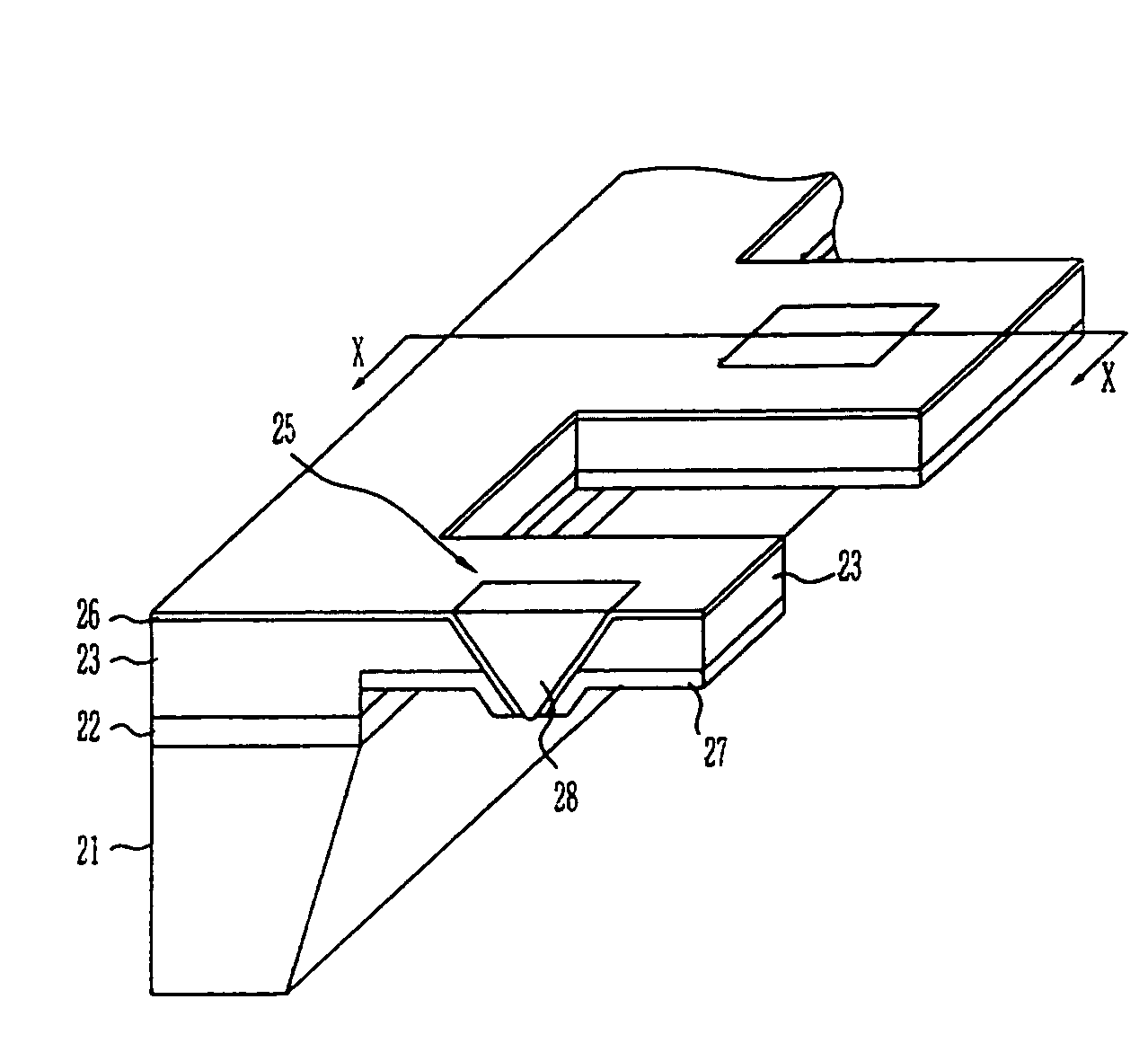
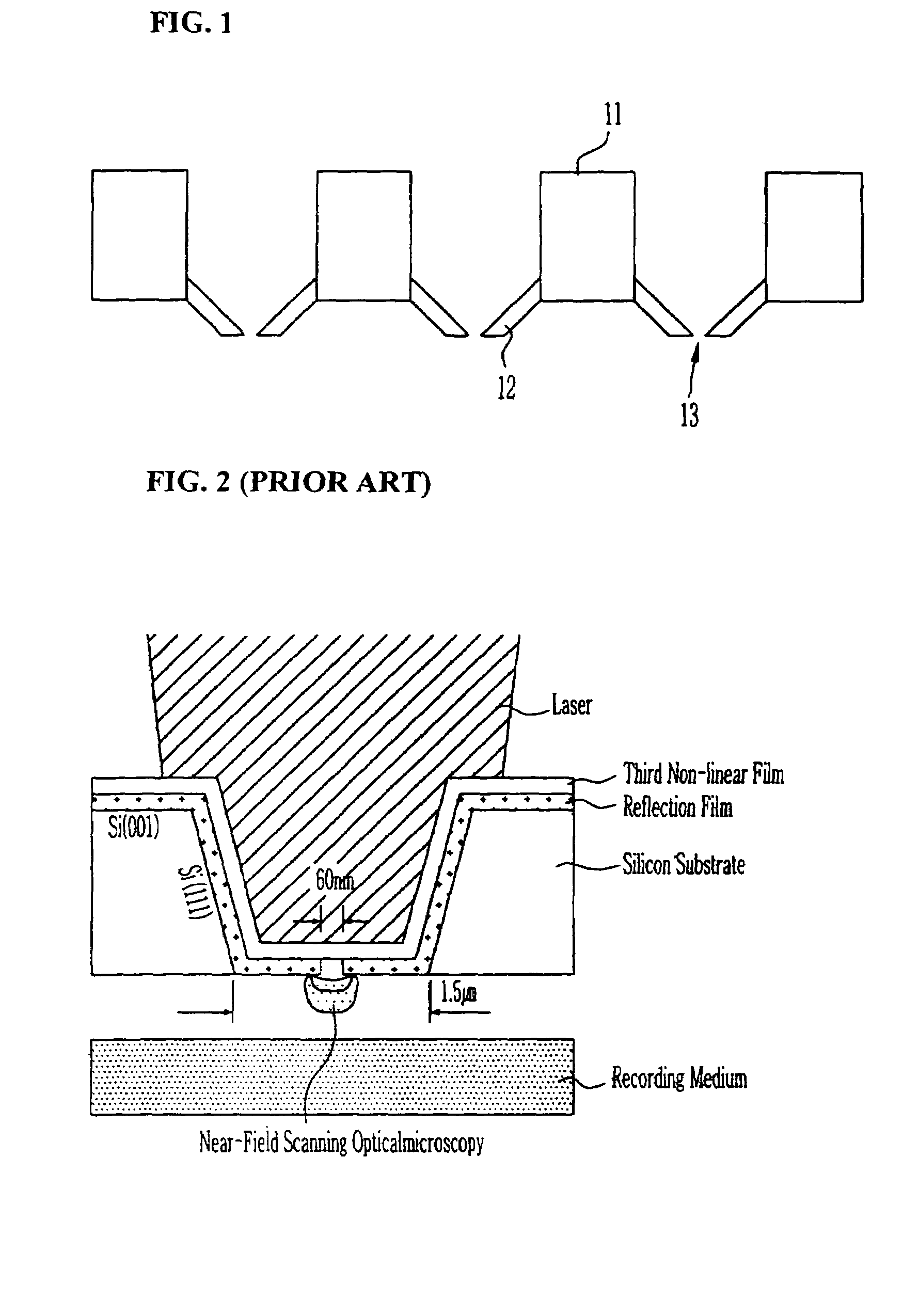
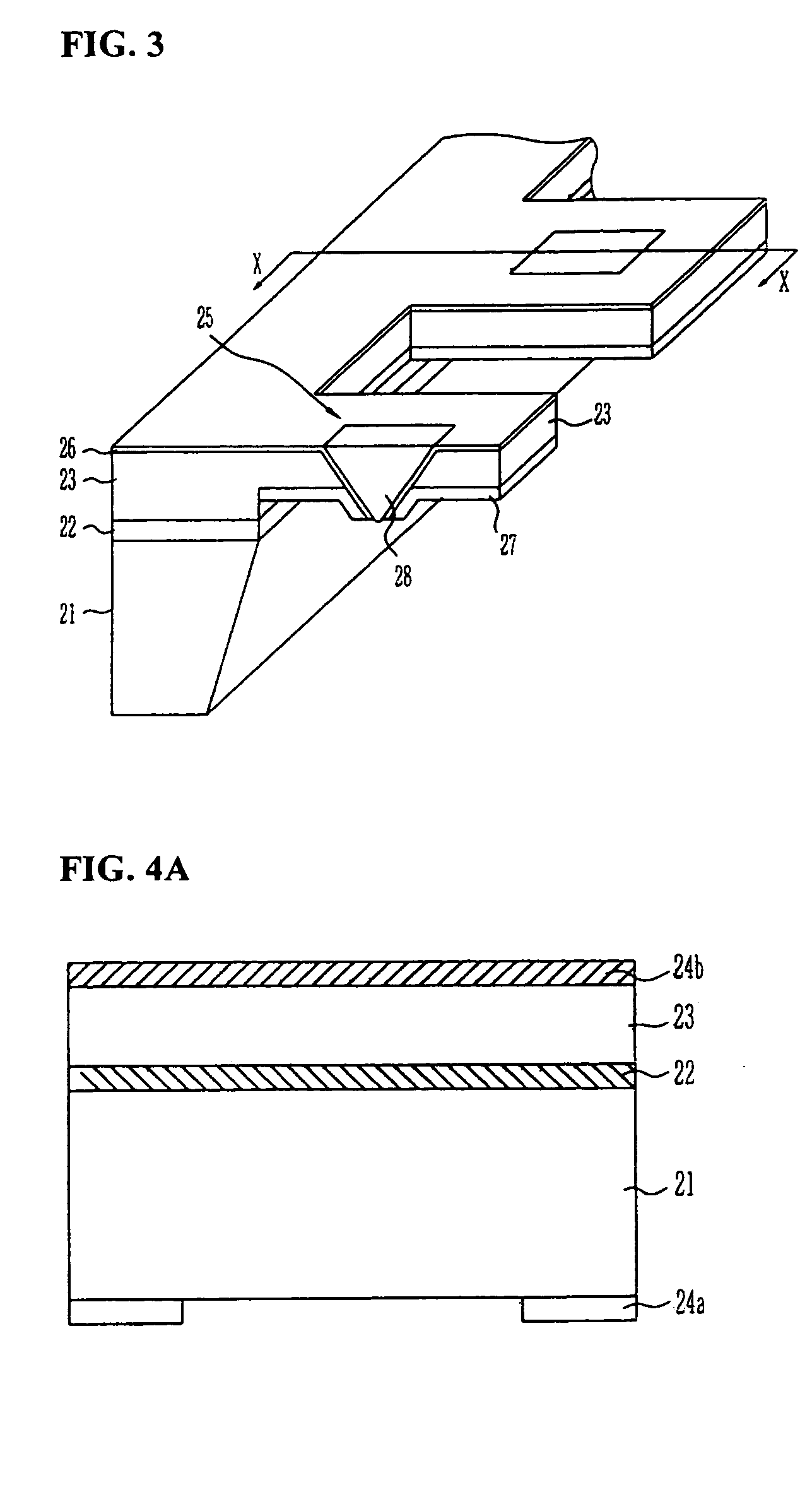
InactiveUS7379415B2Reduce the amount requiredEfficient excitationUsing microscopic probe meansNanoinformaticsTransmittanceLight beam
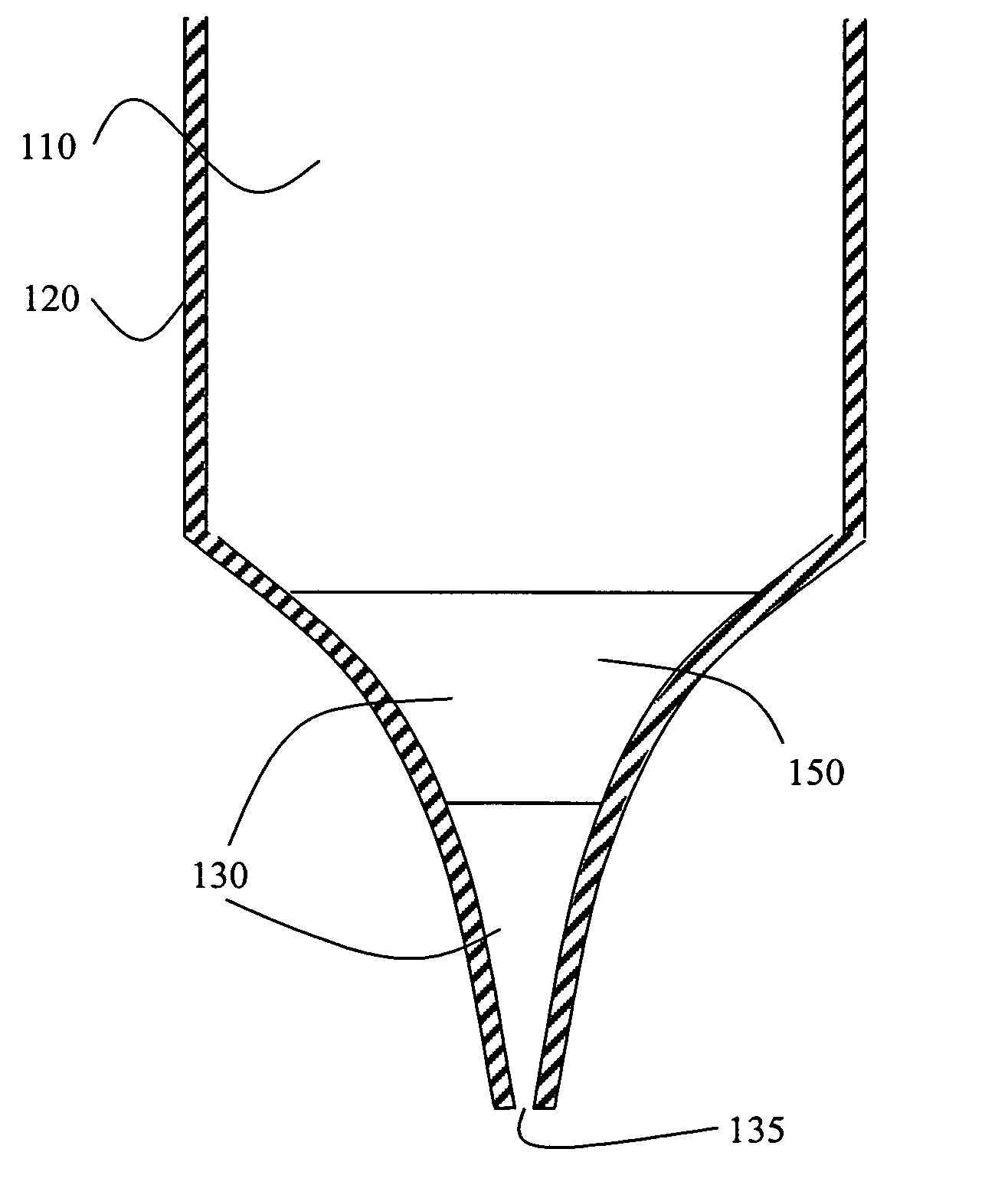
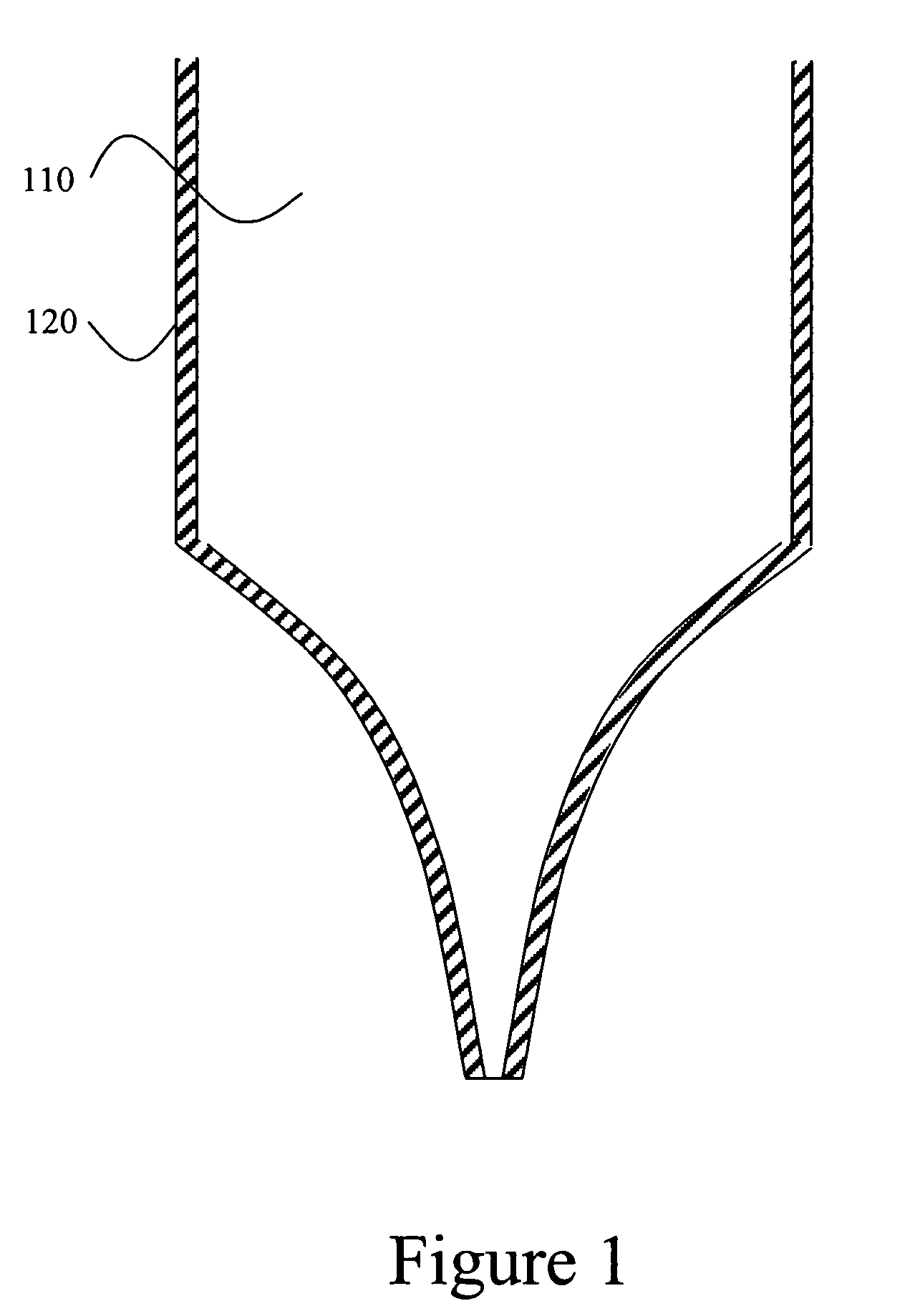
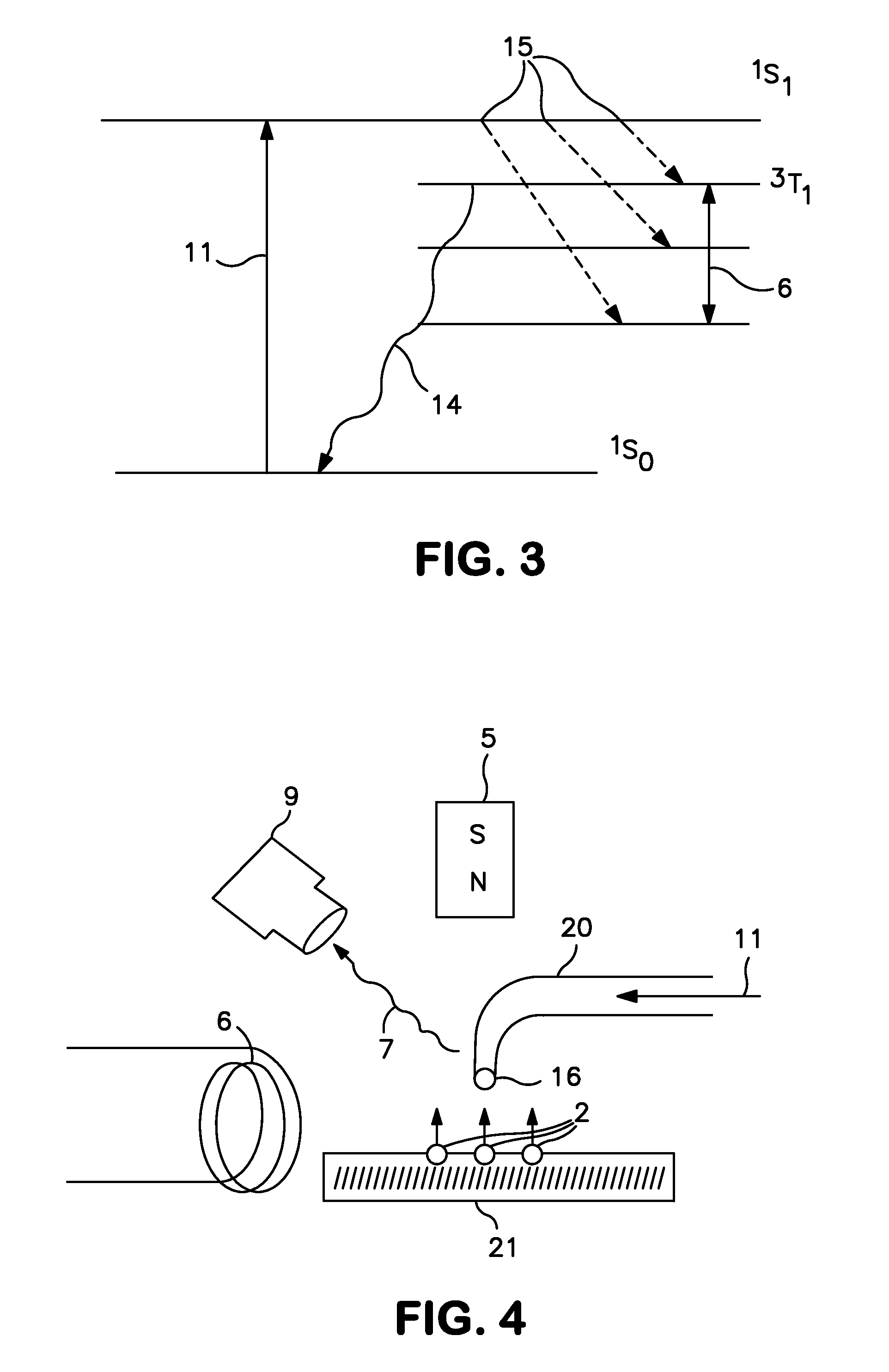
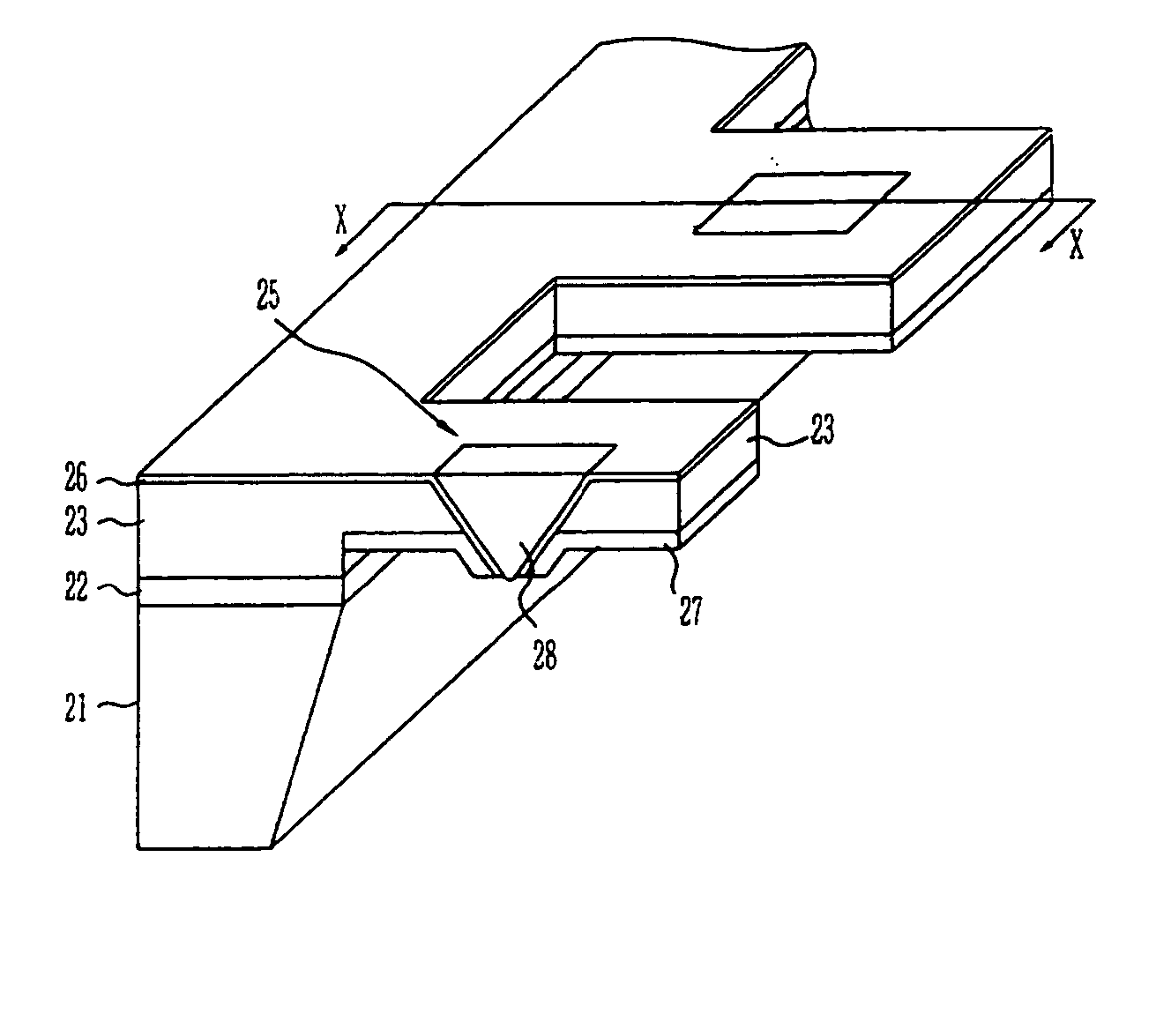
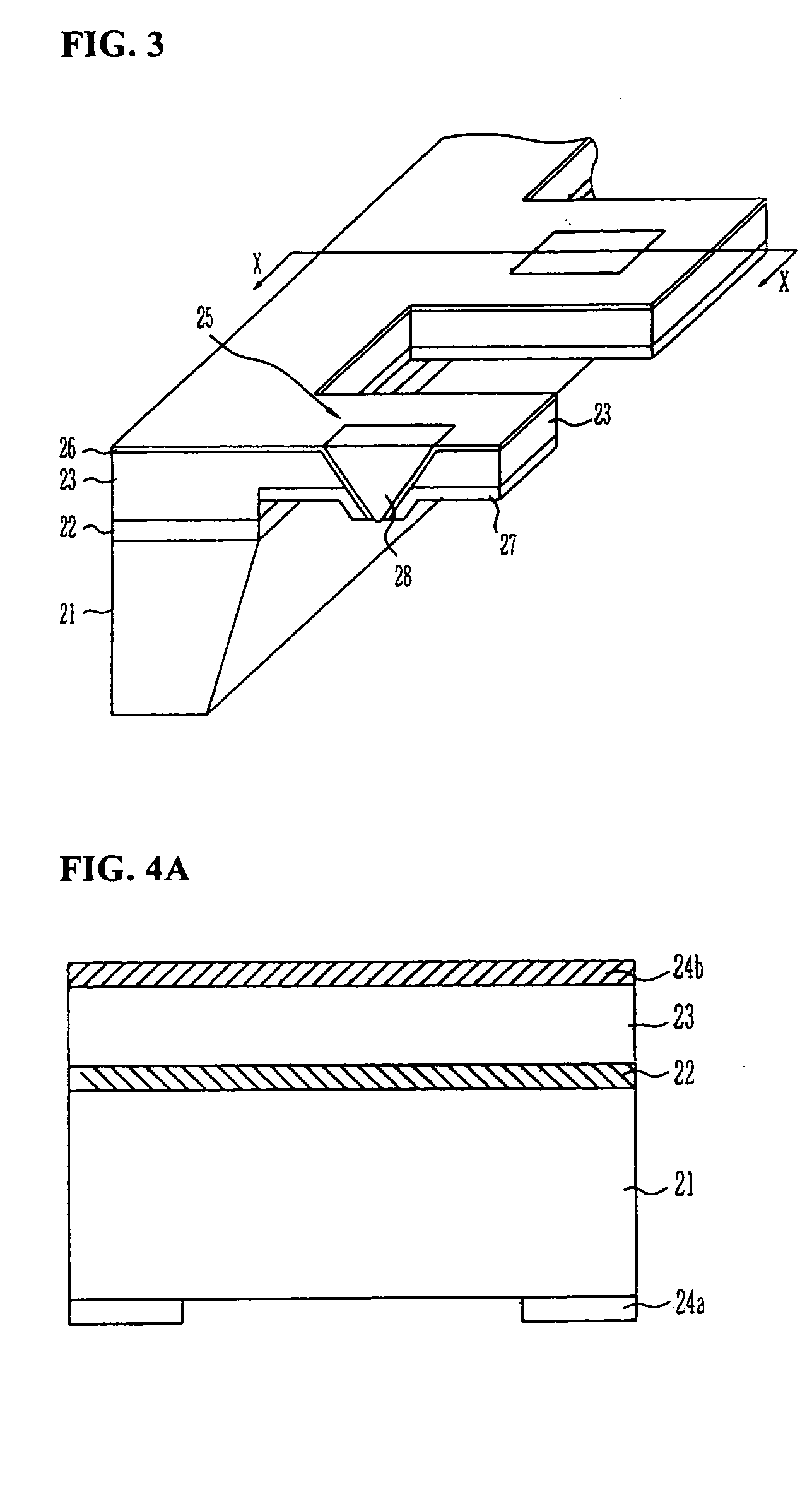
The present invention relates to a head for recording / reading optical data and method of manufacturing the same. The present invention completely buries an aperture with a material a third non-linear coefficient of which is great in order to induce self-focusing. Thus, the present invention can reduce the amount of beam by about one half wavelength and focus the beam in a parabolic shape having almost no optical loss. Therefore, the present invention can improve the transmissivity of the probe by several hundreds times compared to a conventional optical fiver probe, by effectively exciting a near-field scanning optical microscopy for the aperture at an end portion of the probe.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
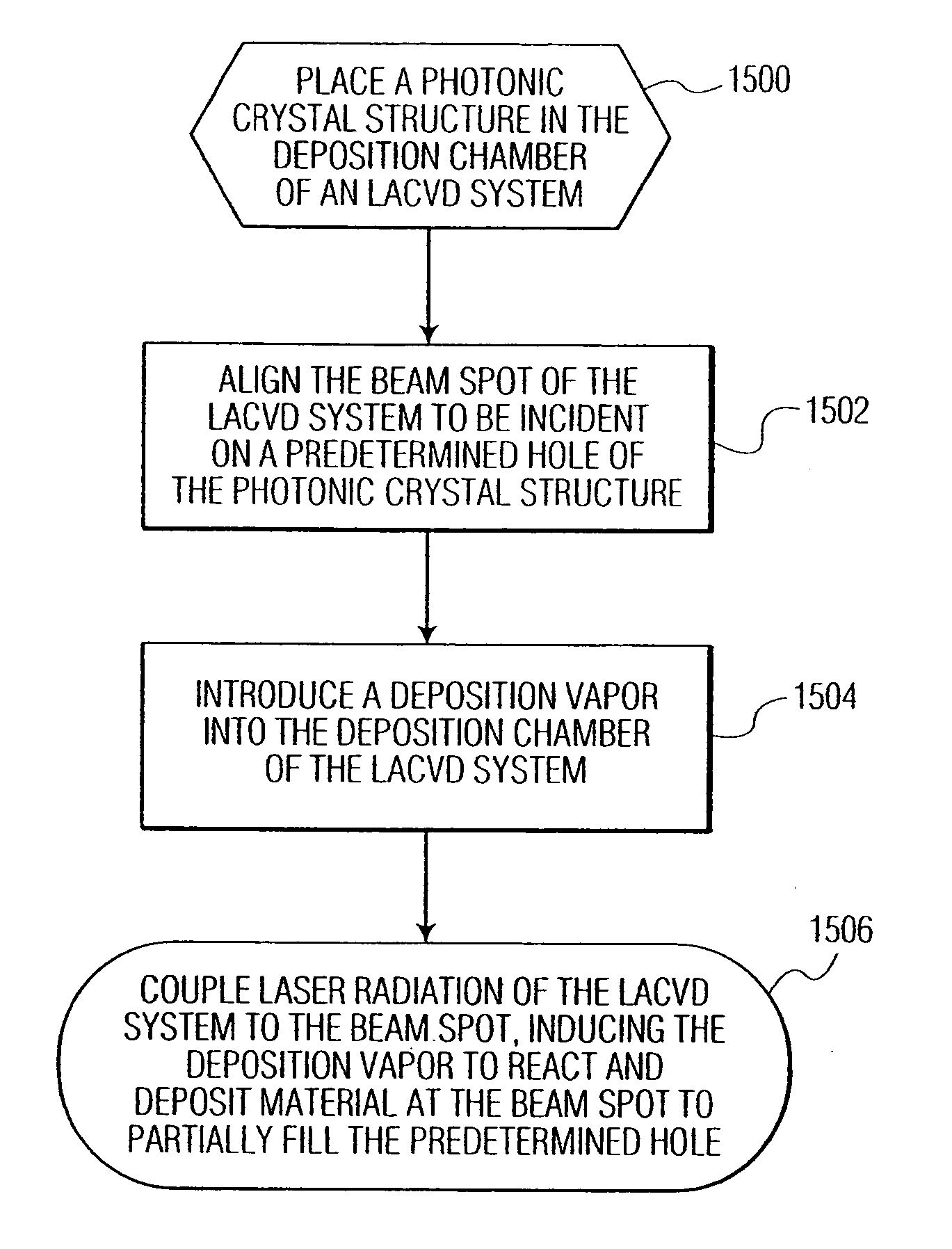
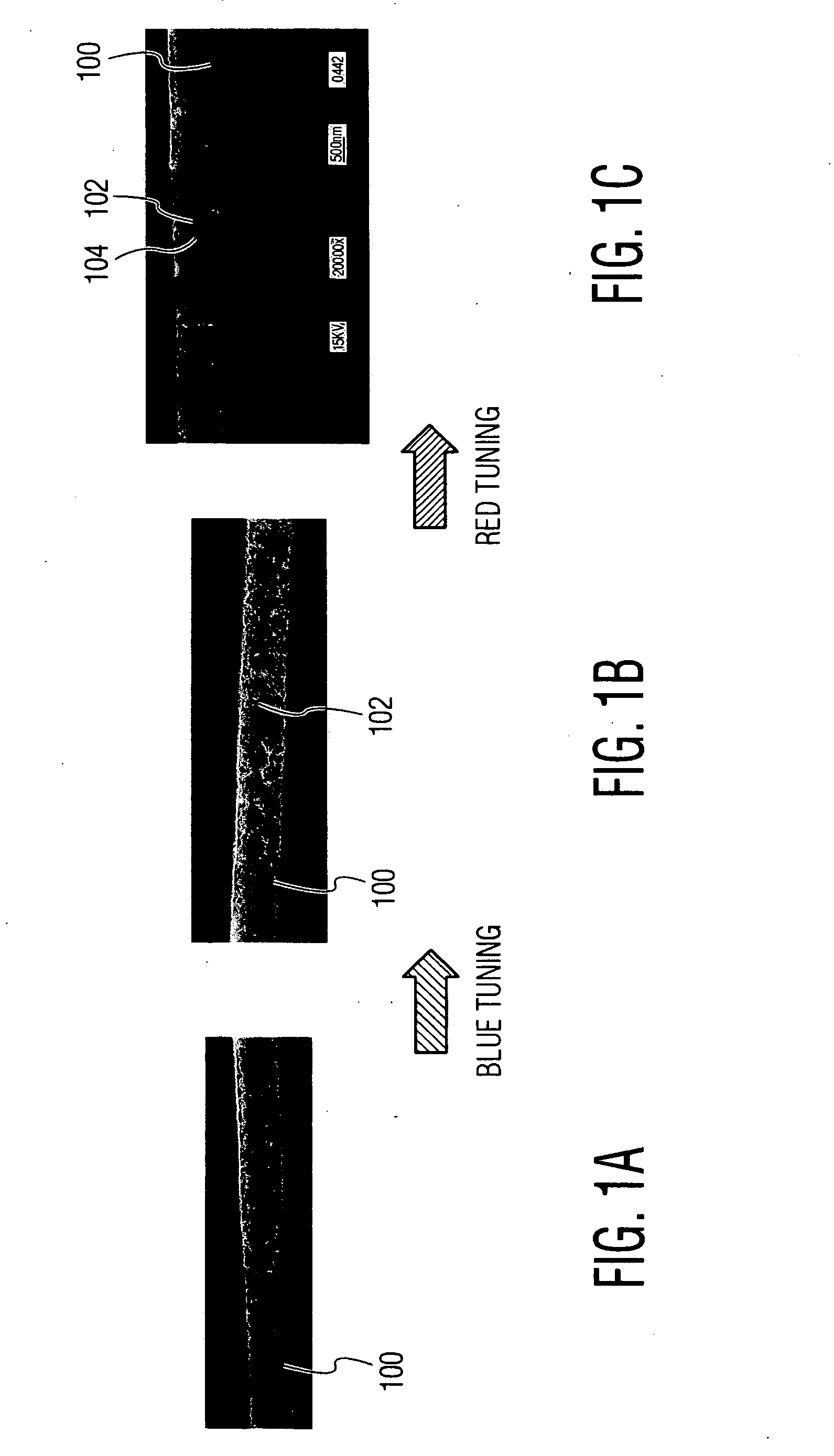
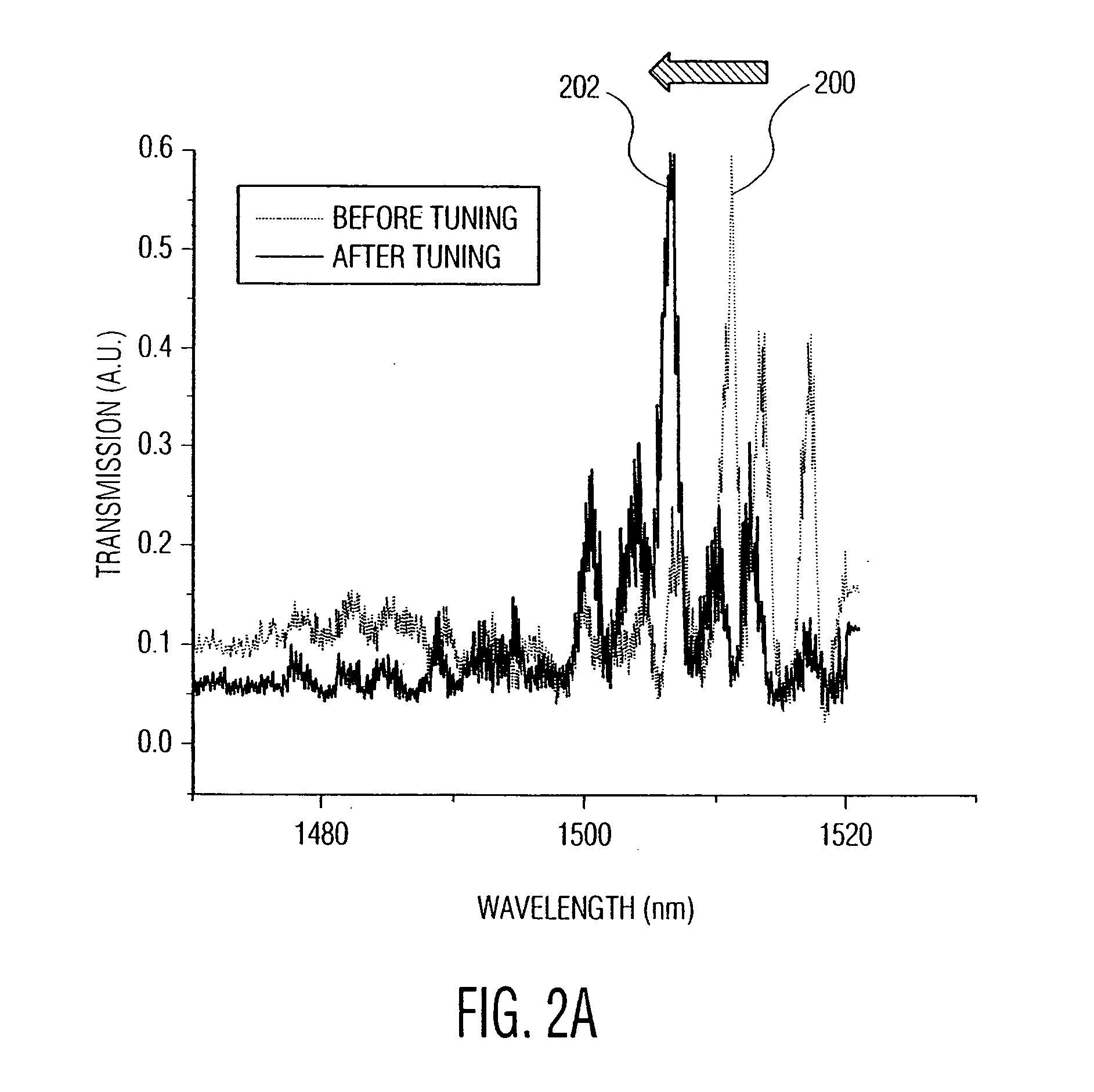
Precision resonance frequency tuning method for photonic crystal structures
A method for red-tuning the resonance frequency of a photonic crystal structure that includes a plurality of holes, using a near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) system. Part of the photonic crystal structure is ablated using the NSOM system to form submicron scale debris on a top surface of the photonic crystal structure. The tip of the NSOM system is used to move a portion of the submicron scale debris across the top surface of the photonic crystal structure to partially fill at least one predetermined hole of the plurality of holes of the photonic crystal structure. The portion of the submicron scale debris partially filling the predetermined hole(s) may be annealed.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Spin microscope based on optically detected magnetic resonance
InactiveUS7752899B1Magnetic measurementsNanotechnologyMagnetic force microscopeScanning tunneling microscope
The invention relates to scanning magnetic microscope which has a photoluminescent nanoprobe implanted in the tip apex of an atomic force microscope (AFM), a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) or a near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) and exhibits optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) in the vicinity of unpaired electron spins or nuclear magnetic moments in the sample material. The described spin microscope has demonstrated nanoscale lateral resolution and single spin sensitivity for the AFM and STM embodiments.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Method and apparatus for performing apertureless near-field scanning optical microscopy
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
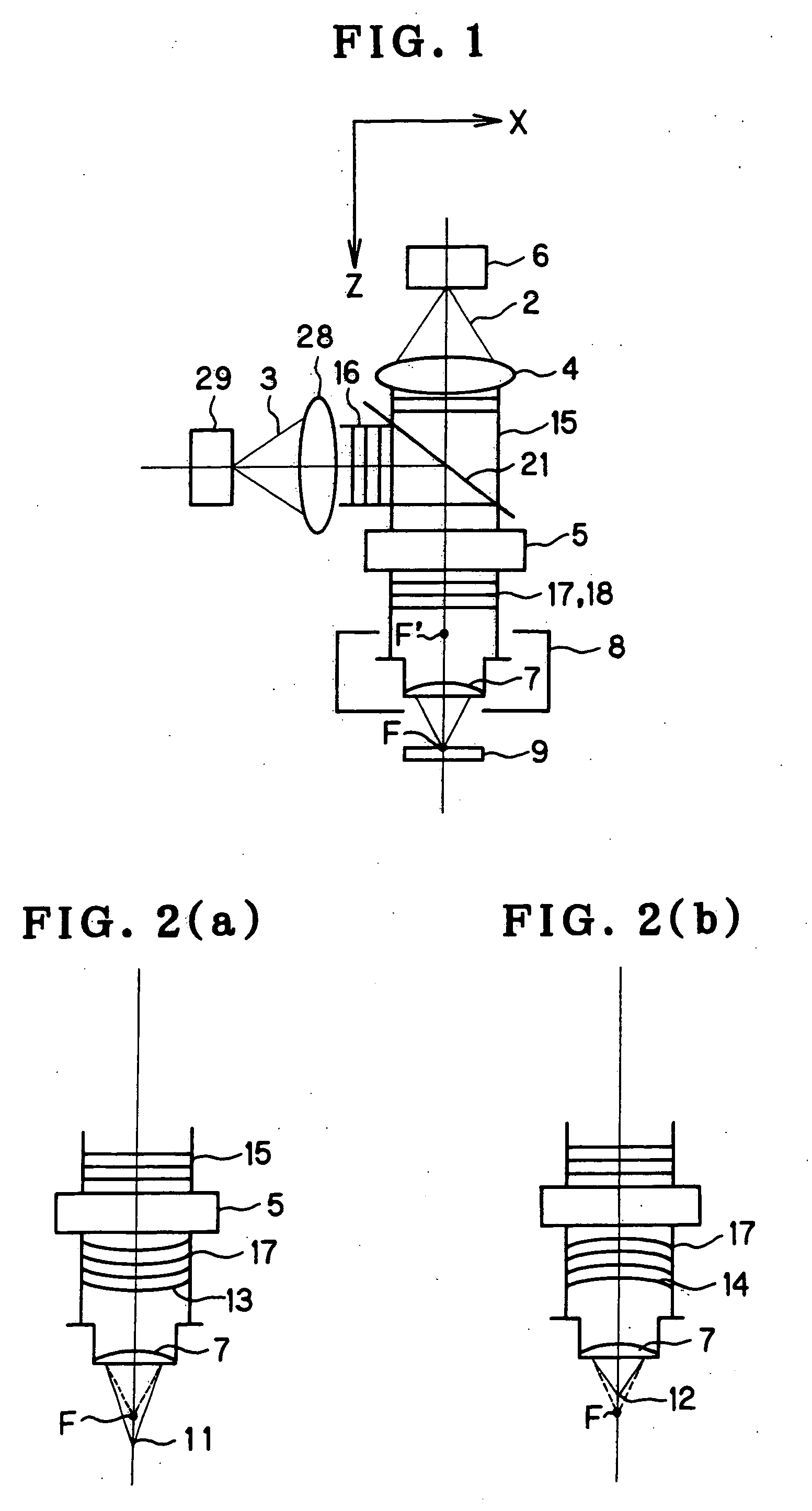
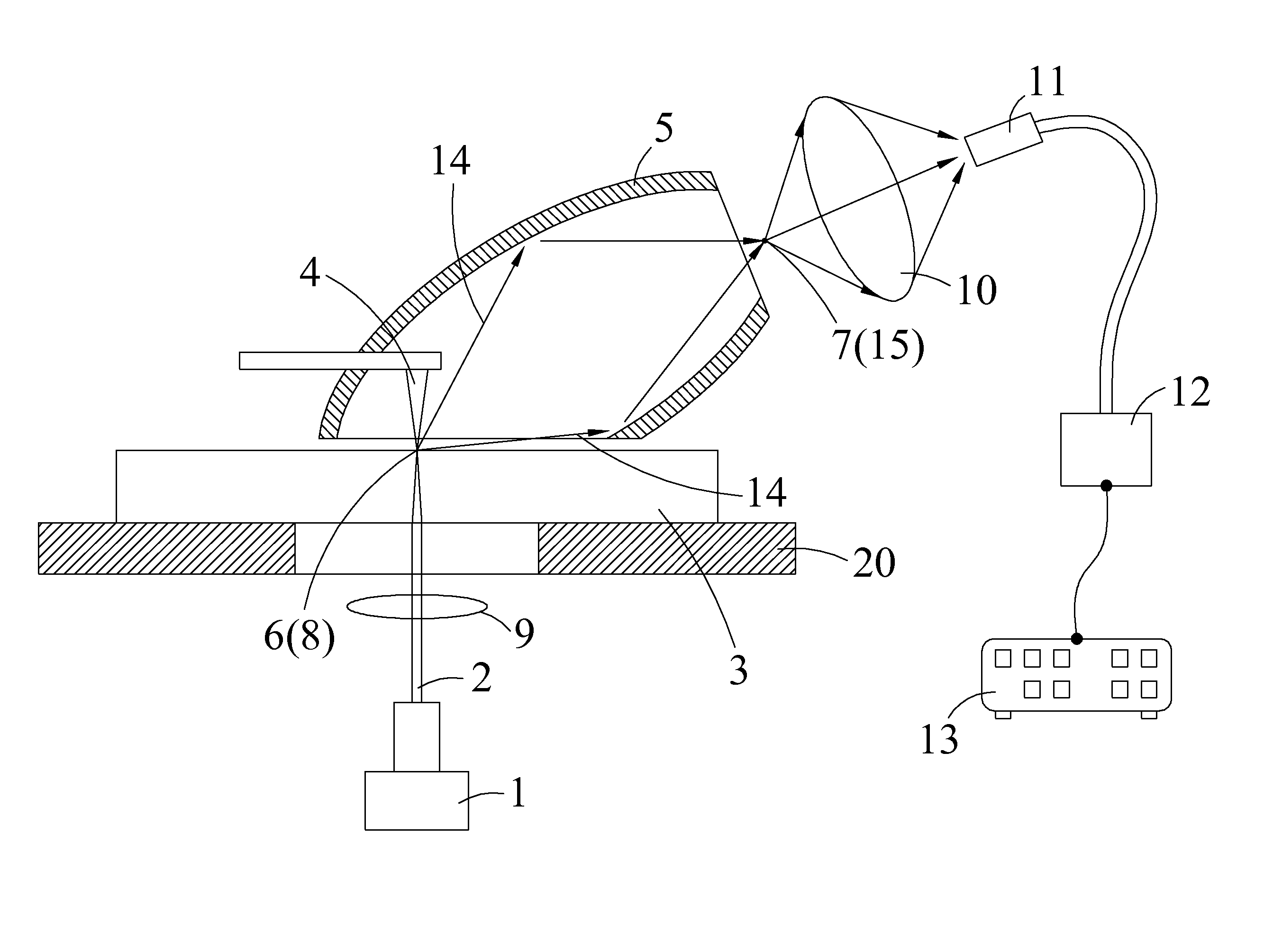
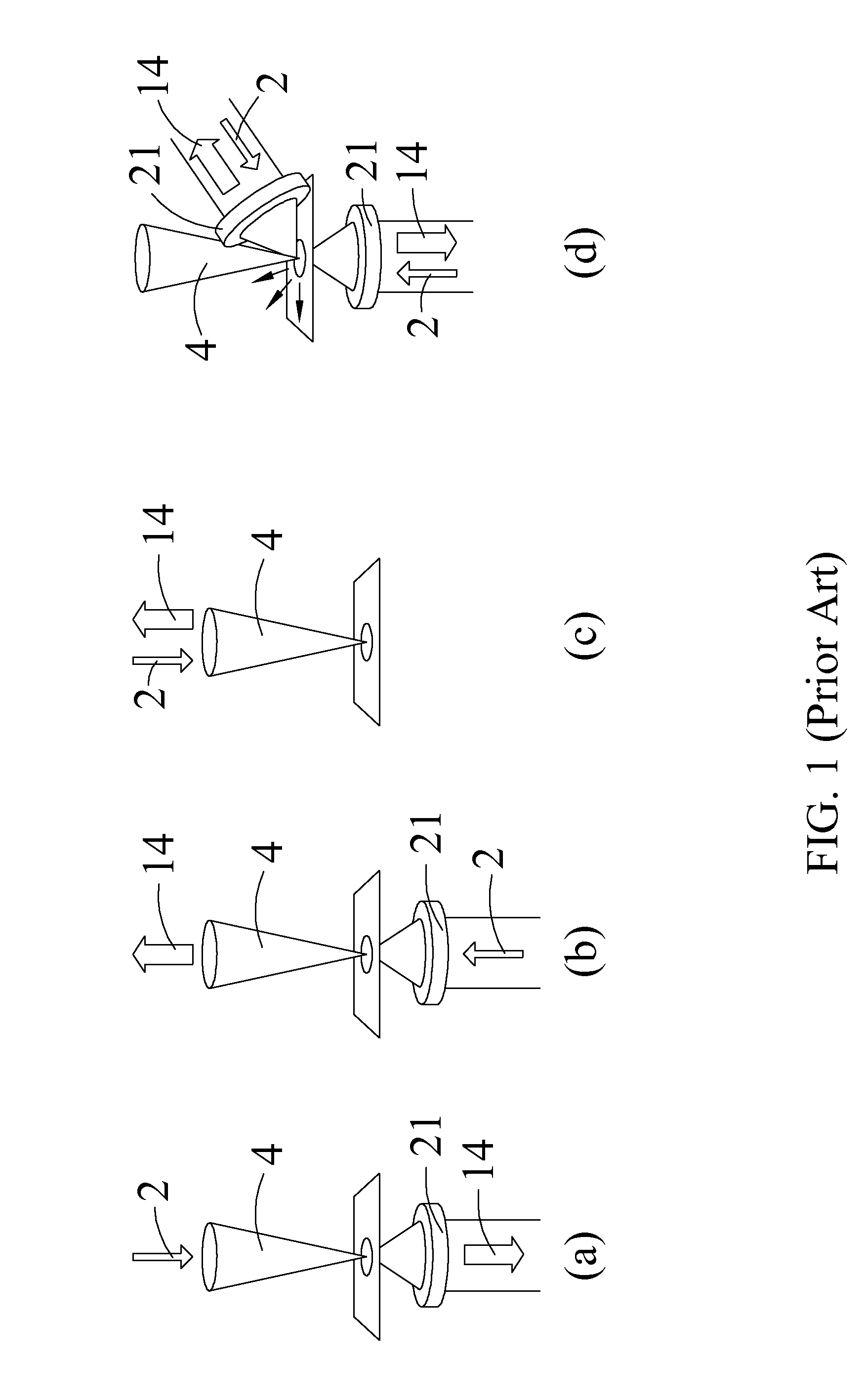
Near-field scanning optical microscope
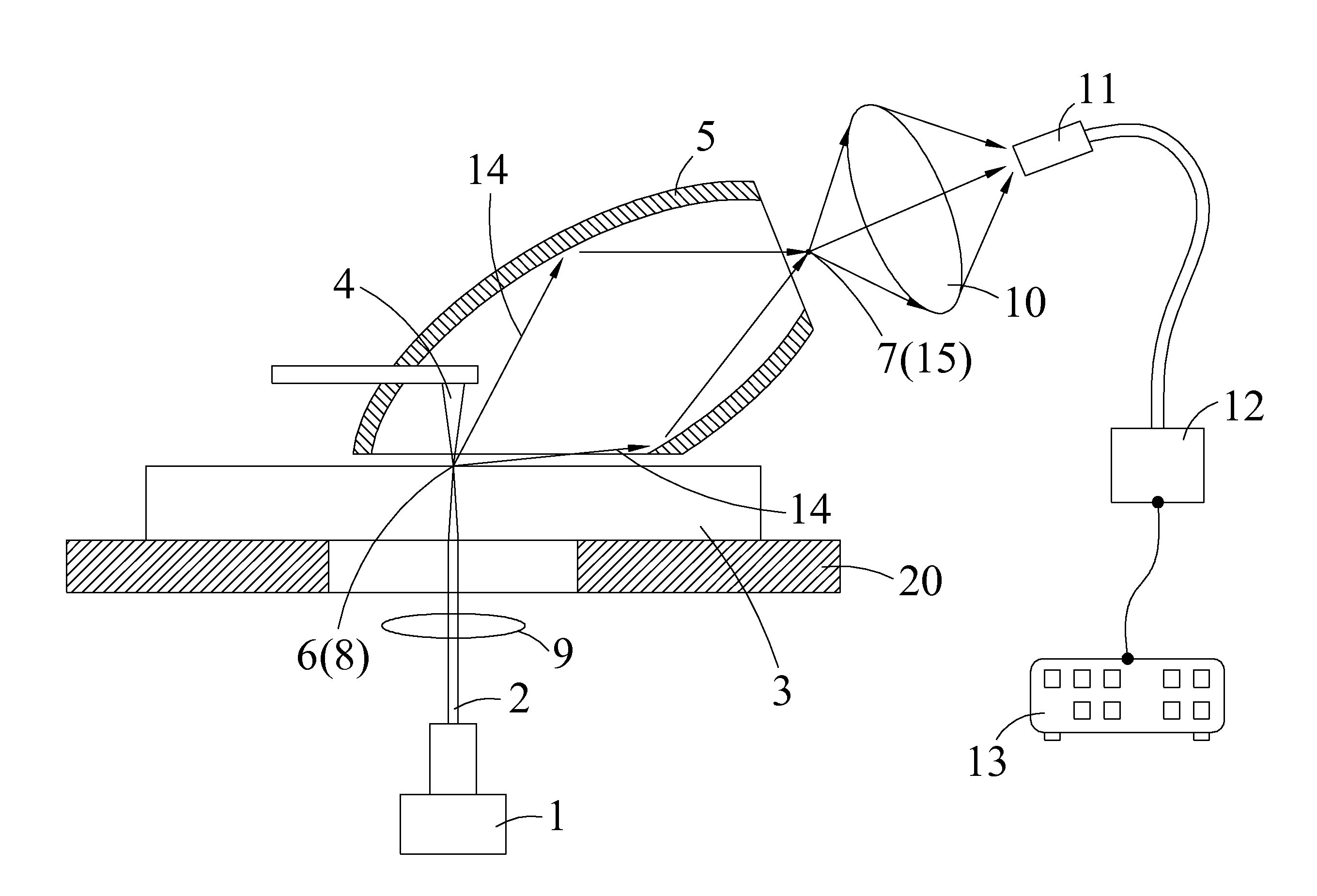
InactiveUS20120159677A1Improve concentrationGood effectNanoopticsScanning probe microscopyEllipseEffect light
A near-field scanning optical microscope is disclosed. The microscope includes a lighting component, a probe and an ellipsoidal mirror. The lighting component emits a light. The probe is disposed on one side of a testing sample, and the light is focused around a probe tip to draw the near-field light out. The ellipsoidal mirror has a first focal point and a second focal point, and the first focal point and the probe tip are disposed at the corresponding positions, and the near-field light drawn out from the probe tip is scattered from the first focal point inside the ellipsoidal mirror, and reflected and passed through the second focal point.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
Adaptive scanning optical microscope
An adaptive scanning optical microscope has a scanner lens assembly for acquiring images from different parts of an object plane and for forming a preferably curved image field having at least some aberration which varies as a function of the part of the object plane from which the image is acquired. A steering mirror selects the field of view and steer light from the object and along a light path from the object plane to a final image plane. An adaptive optics element receives the steered light from the object and compensates for the field position dependent optical aberrations and additional optics are along at least part of the light path for conditioning and focusing the light as it moves from the steering mirror, past the adaptive optics element and to the final image plane.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Spin microscope based on optically detected magnetic resonance
InactiveUS7615739B2NanomagnetismMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic force microscopeScanning tunneling microscope
The invention relates to scanning magnetic microscope which has a photoluminescent nanoprobe implanted in the tip apex of an atomic force microscope (AFM), a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) or a near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) and exhibits optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) in the vicinity of impaired electron spins or nuclear magnetic moments in the sample material. The described spin microscope has demonstrated nanoscale lateral resolution and single spin sensitivity for the AFM and STM embodiments.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Head for recording and reading optical data and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050078411A1Reduce the amount requiredEfficient excitationUsing microscopic probe meansNanoinformaticsLight beamTransmittance
The present invention relates to a head for recording / reading optical data and method of manufacturing the same. The present invention completely buries an aperture with a material a third non-linear coefficient of which is great in order to induce self-focusing. Thus, the present invention can reduce the amount of beam by about one half wavelength and focus the beam in a parabolic shape having almost no optical loss. Therefore, the present invention can improve the transmissivity of the probe by several hundreds times compared to a conventional optical fiver probe, by effectively exciting a near-field scanning optical microscopy for the aperture at an end portion of the probe.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Spin microscope based on optically detected magnetic resonance
InactiveUS7743648B1Measurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceNanotechnologyMagnetic force microscopeScanning tunneling microscope
The invention relates to scanning magnetic microscope which has a photoluminescent nanoprobe implanted in the tip apex of an atomic force microscope (AFM), a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) or a near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) and exhibits optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) in the vicinity of unpaired electron spins or nuclear magnetic moments in the sample material. The described spin microscope has demonstrated nanoscale lateral resolution and single spin sensitivity for the AFM and STM embodiments.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Near-field scanning optical microscope
InactiveUS8393010B2Improve concentrationGood effectNanoopticsScanning probe microscopyEllipseEffect light
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com