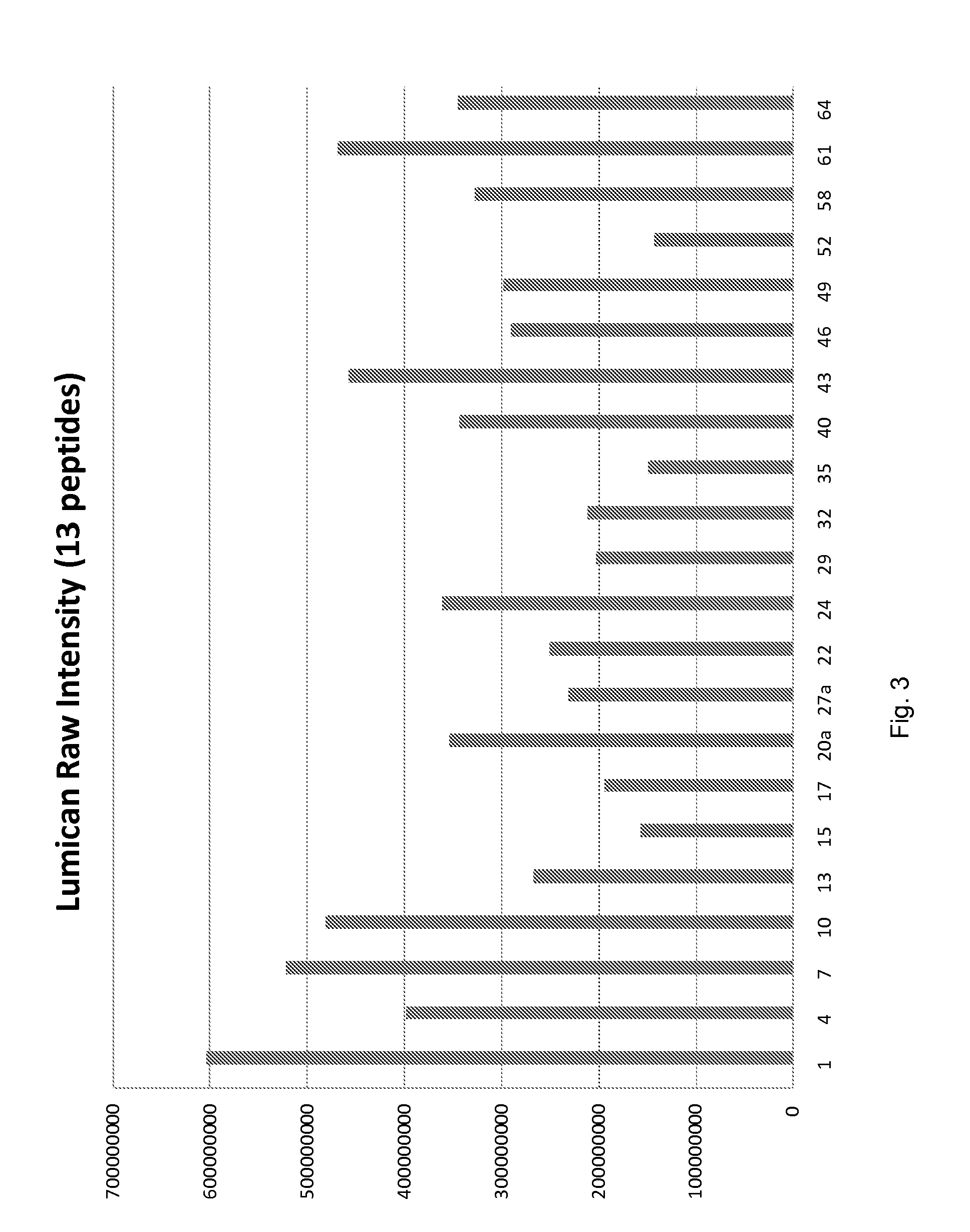
Patents
Literature
89 results about "Organ tissue transplant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An allograft is a transplant of an organ or tissue between two genetically non-identical members of the same species. Most human tissue and organ transplants are allografts.
Edg receptor agonists
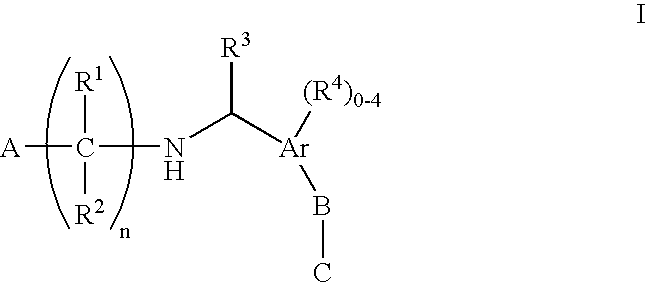
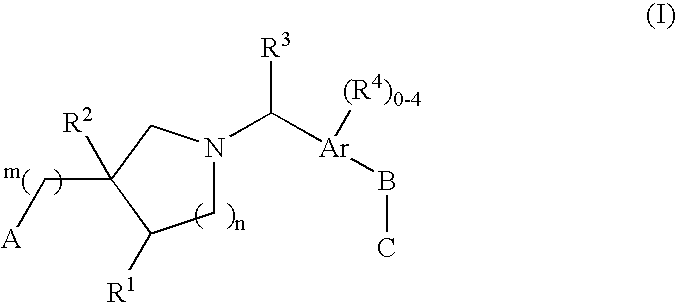
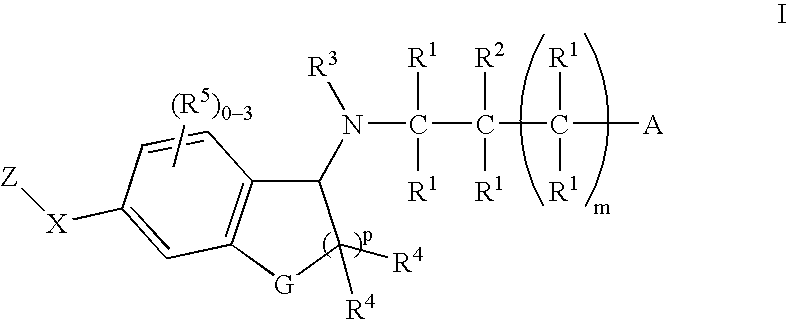
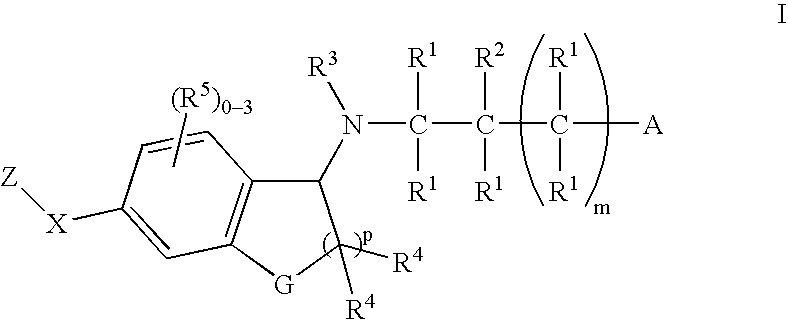
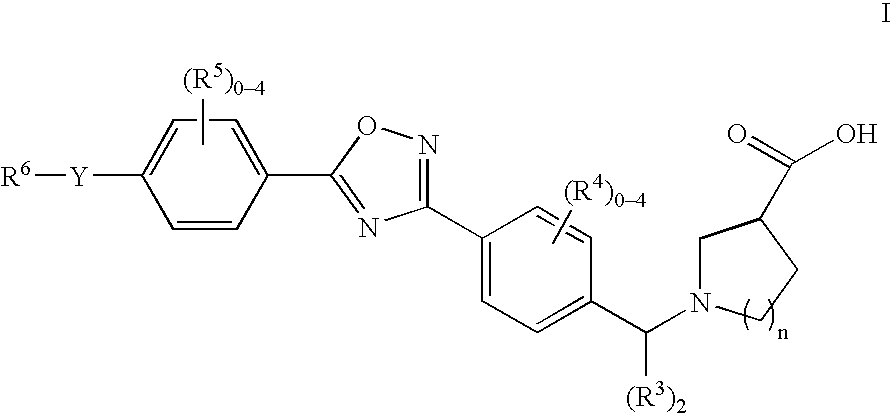
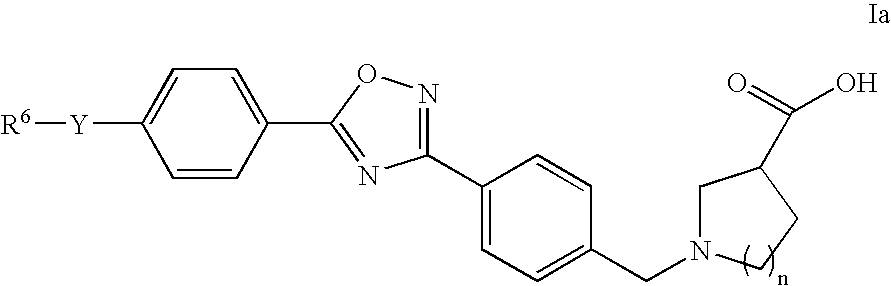
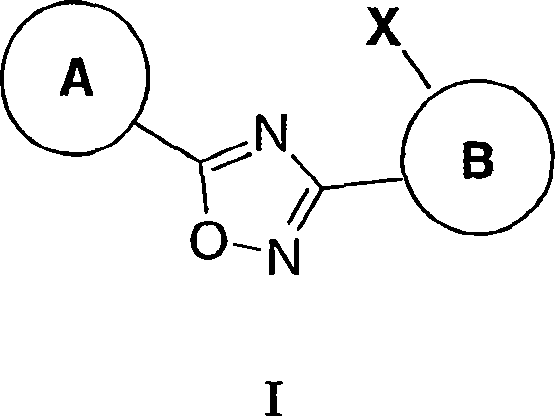
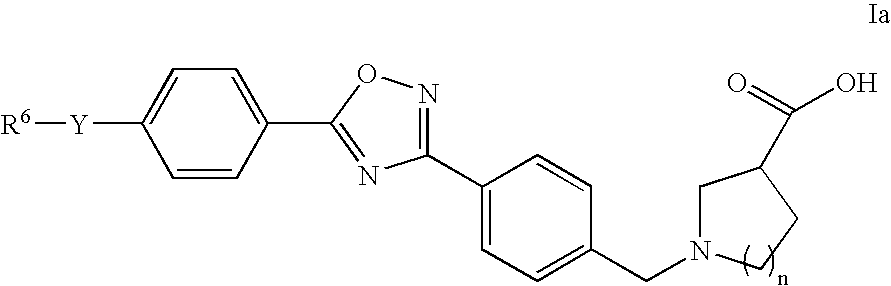
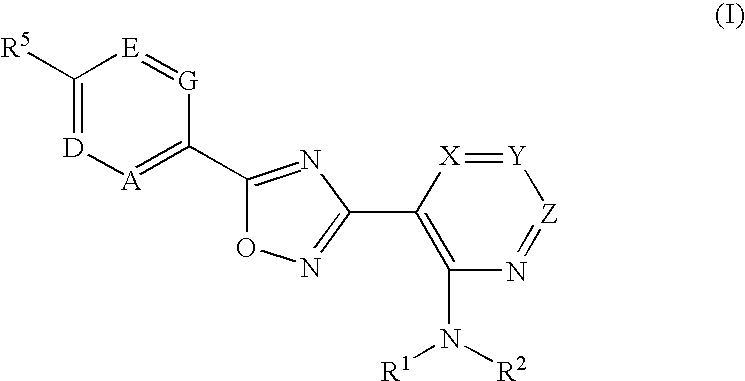
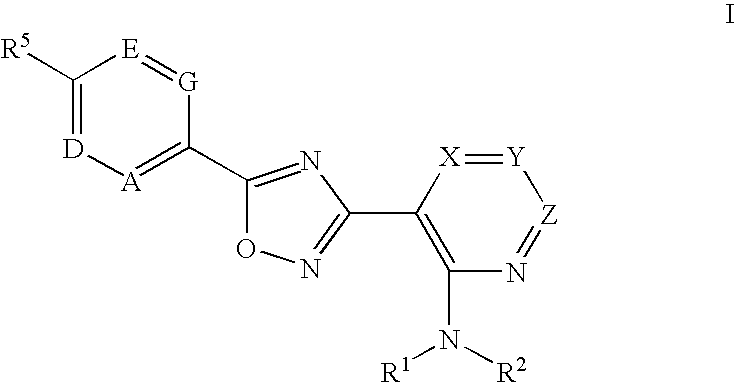
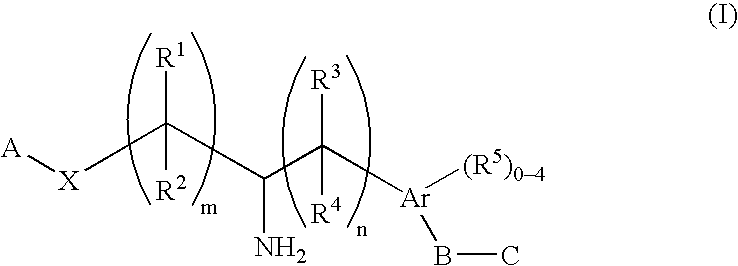
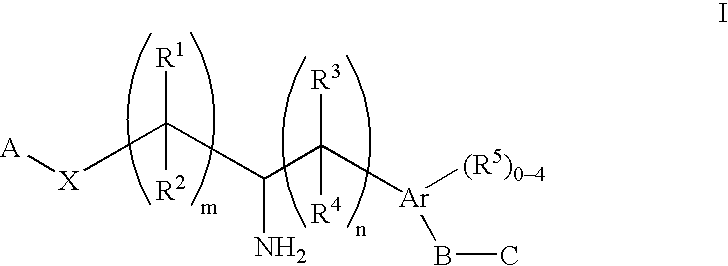
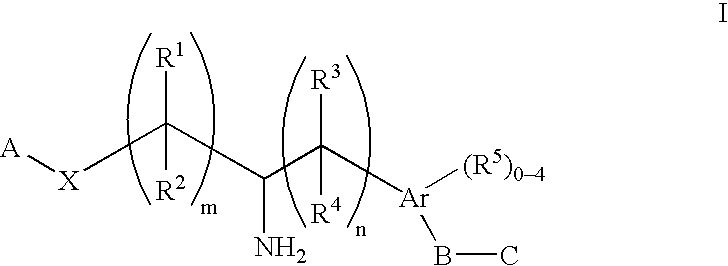
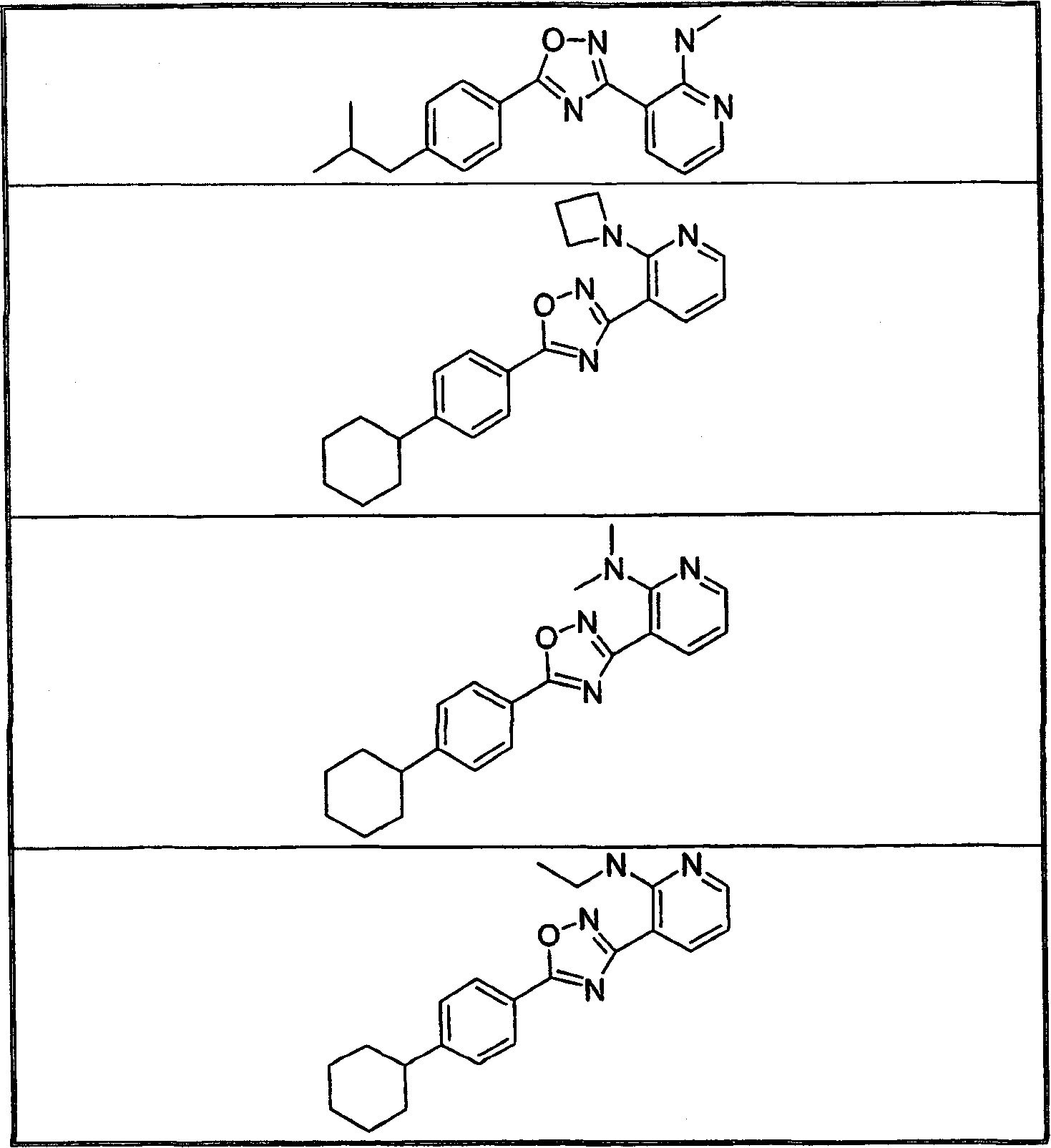
The present invention encompasses compounds of Formula 1: as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts and hydrates thereof. The compounds are useful for treating immune mediated diseases and conditions, such as bone marrow, organ and tissue transplant rejection. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use are included.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
N-(benzyl)aminoalkylcarboxylates, phosphinates, phosphonates and tetrazoles as Edg receptor agonists
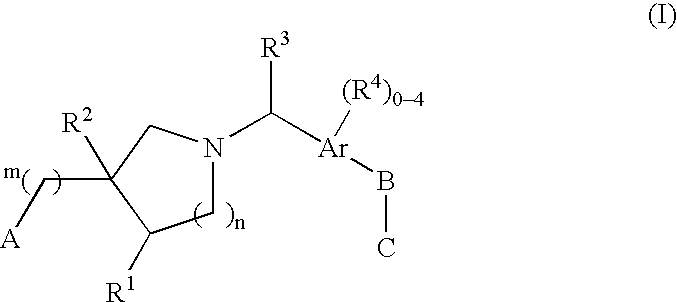
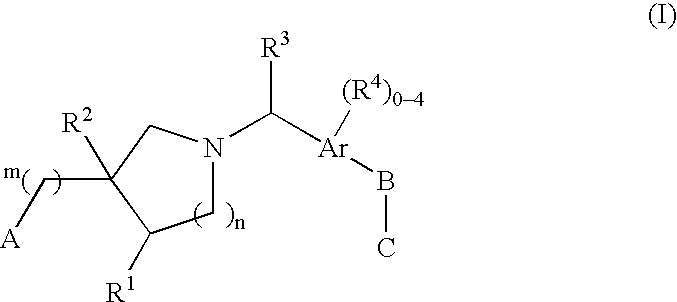
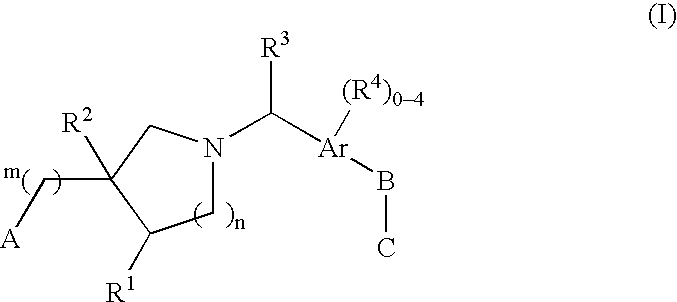
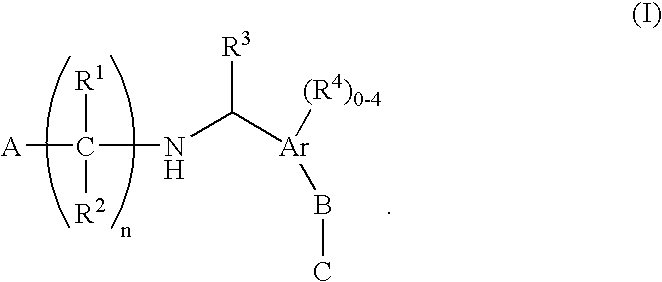
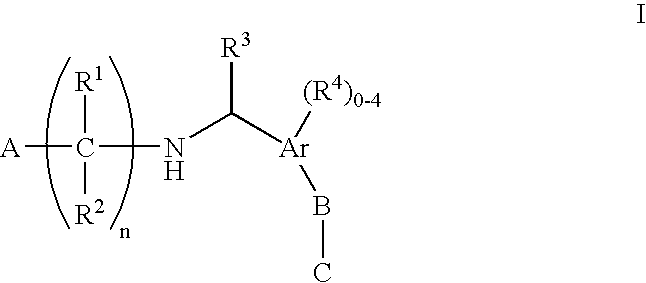
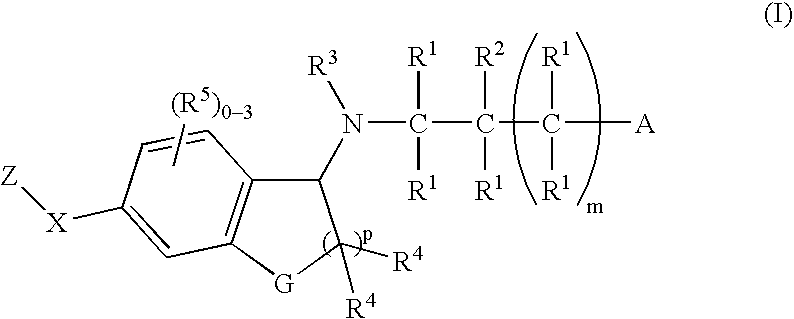
The present invention encompasses compounds of Formula (I) as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts and hydrates thereof. The compounds are useful for treating immune mediated diseases and conditions, such as bone marrow, organ and tissue transplant rejection. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use are included.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Edg receptor agonists
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
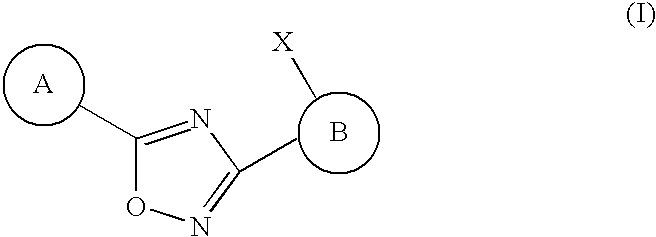
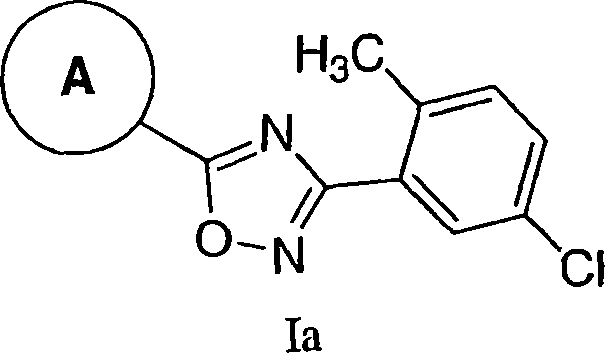
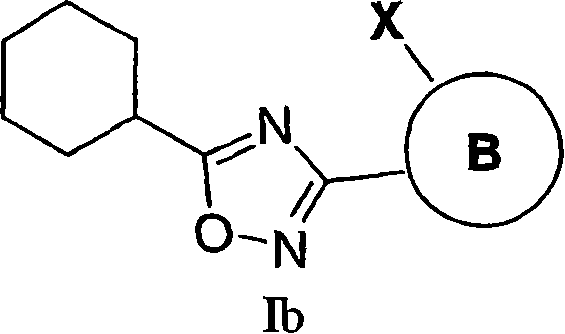
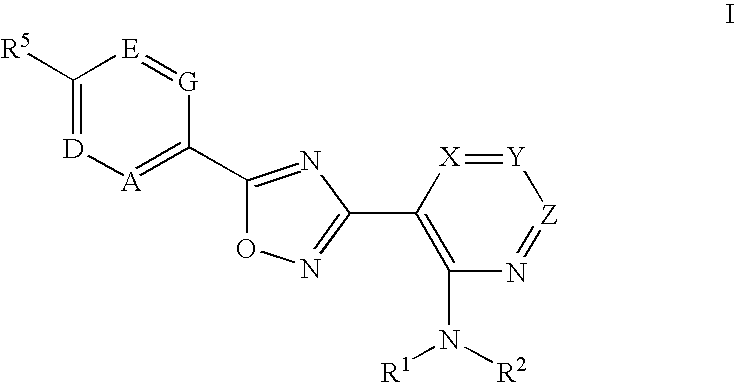
3,5-Aryl, heteroaryl or cycloalkyl substituted-1,2,4-oxadiazoles as s1p receptor agonists
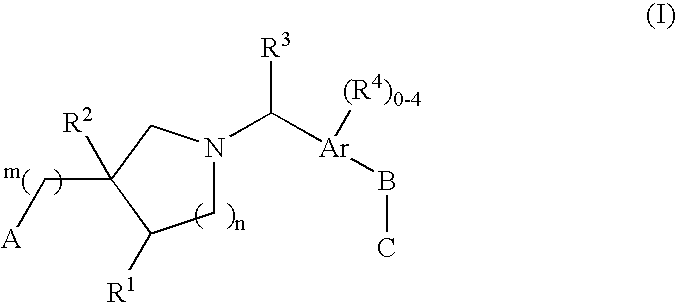
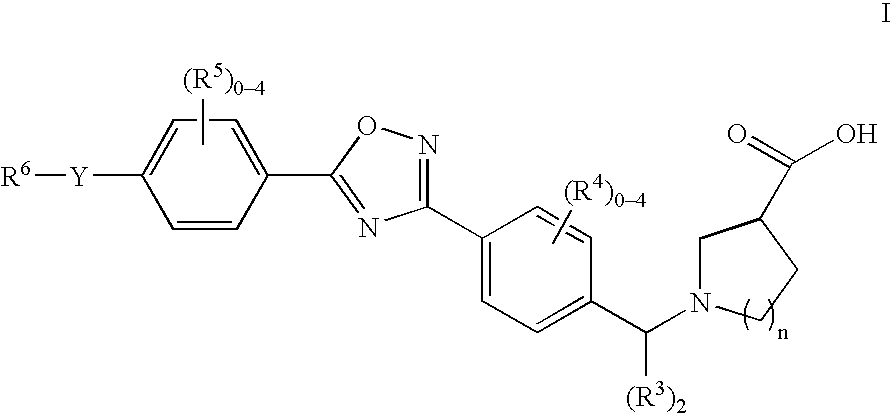
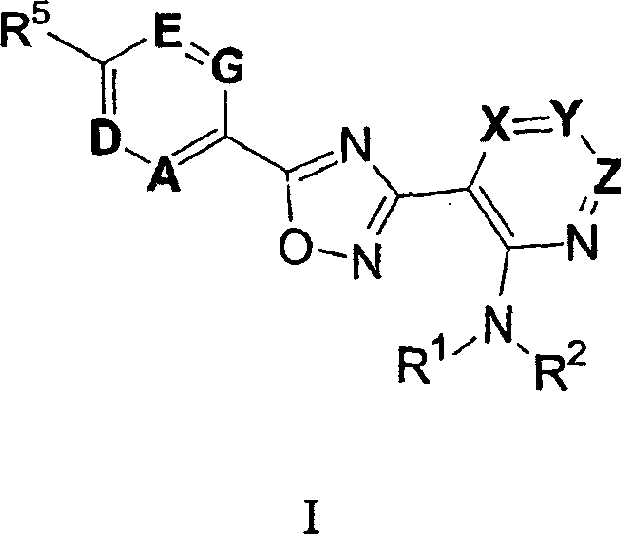
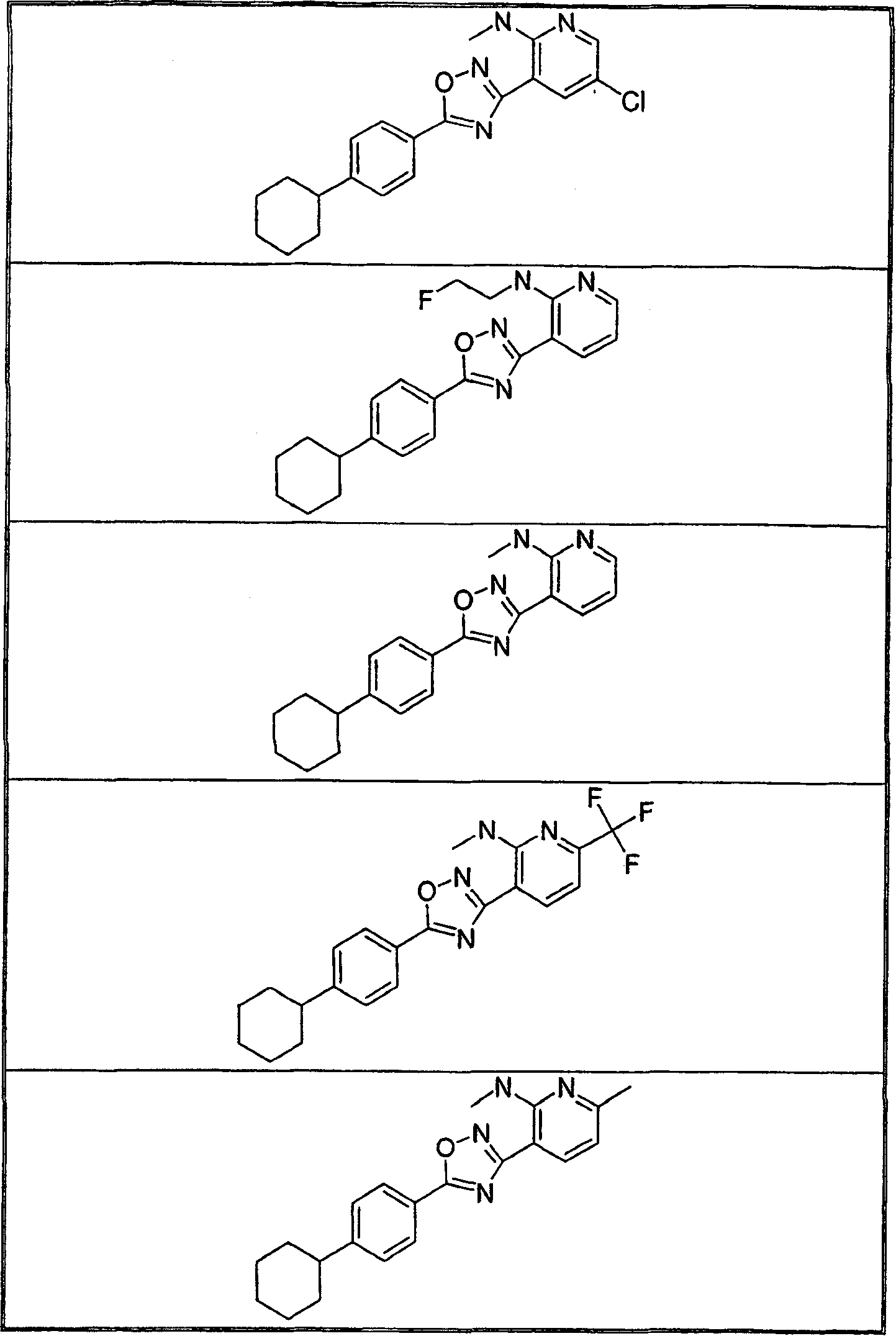
The present invention encompasses compounds of Formula I: (I) as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The compounds are useful for treating immune mediated diseases and conditions, such as bone marrow, organ and tissue transplant rejection. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use are included.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Methods and active substances for protecting organs
InactiveUS6924267B2Avoid problemsAvoid dysfunctionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsMedicineTissue transplant
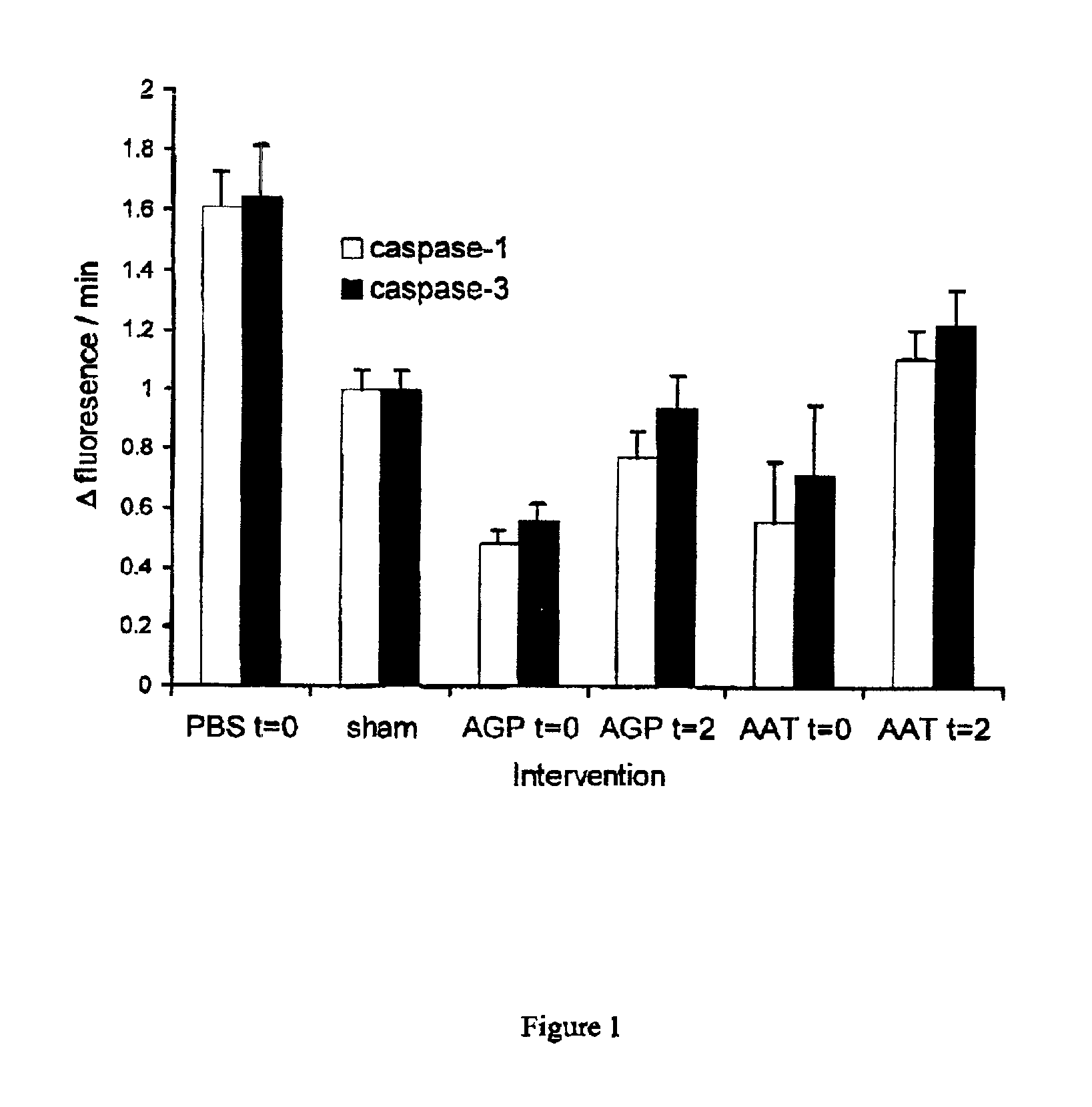
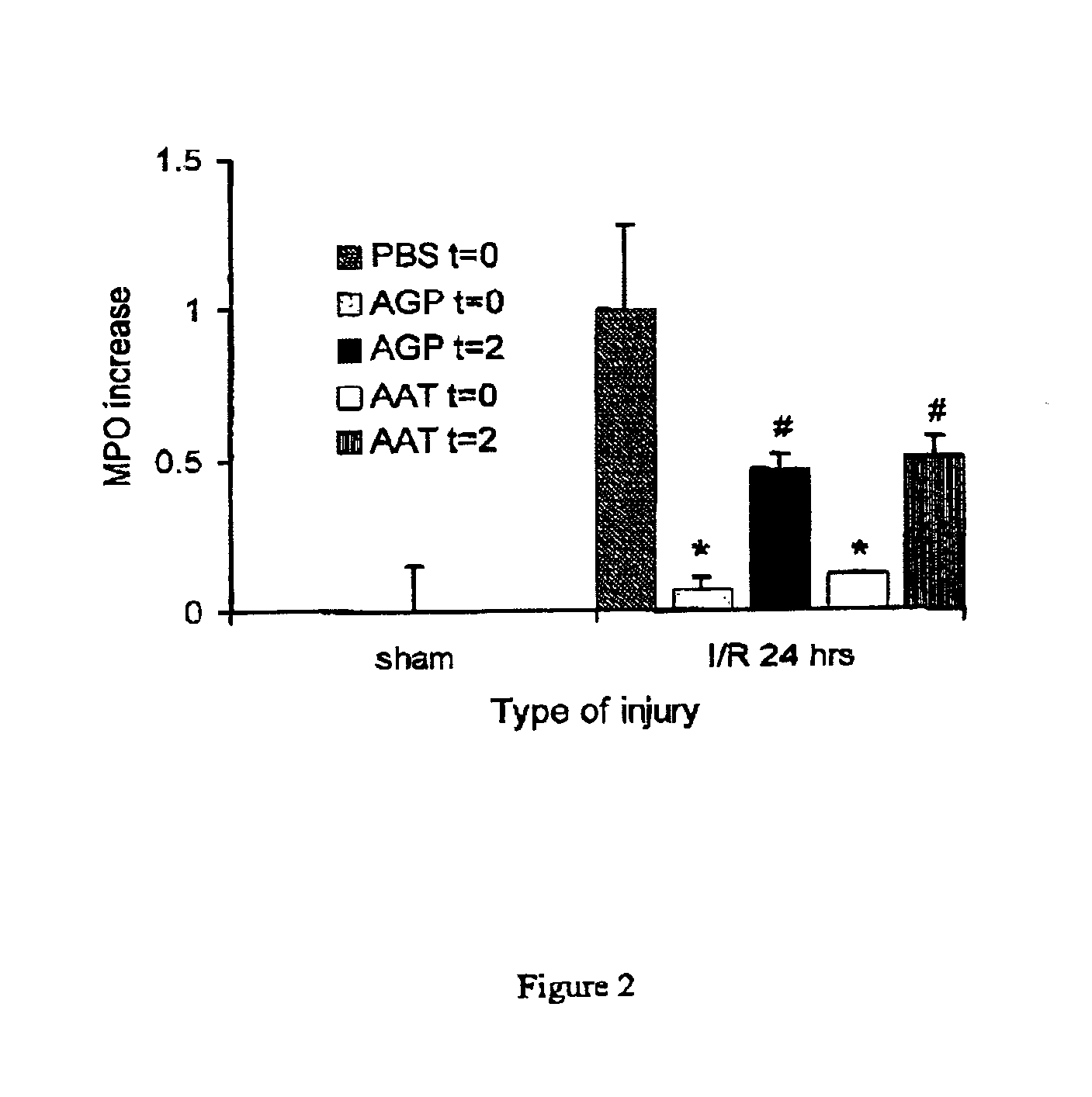
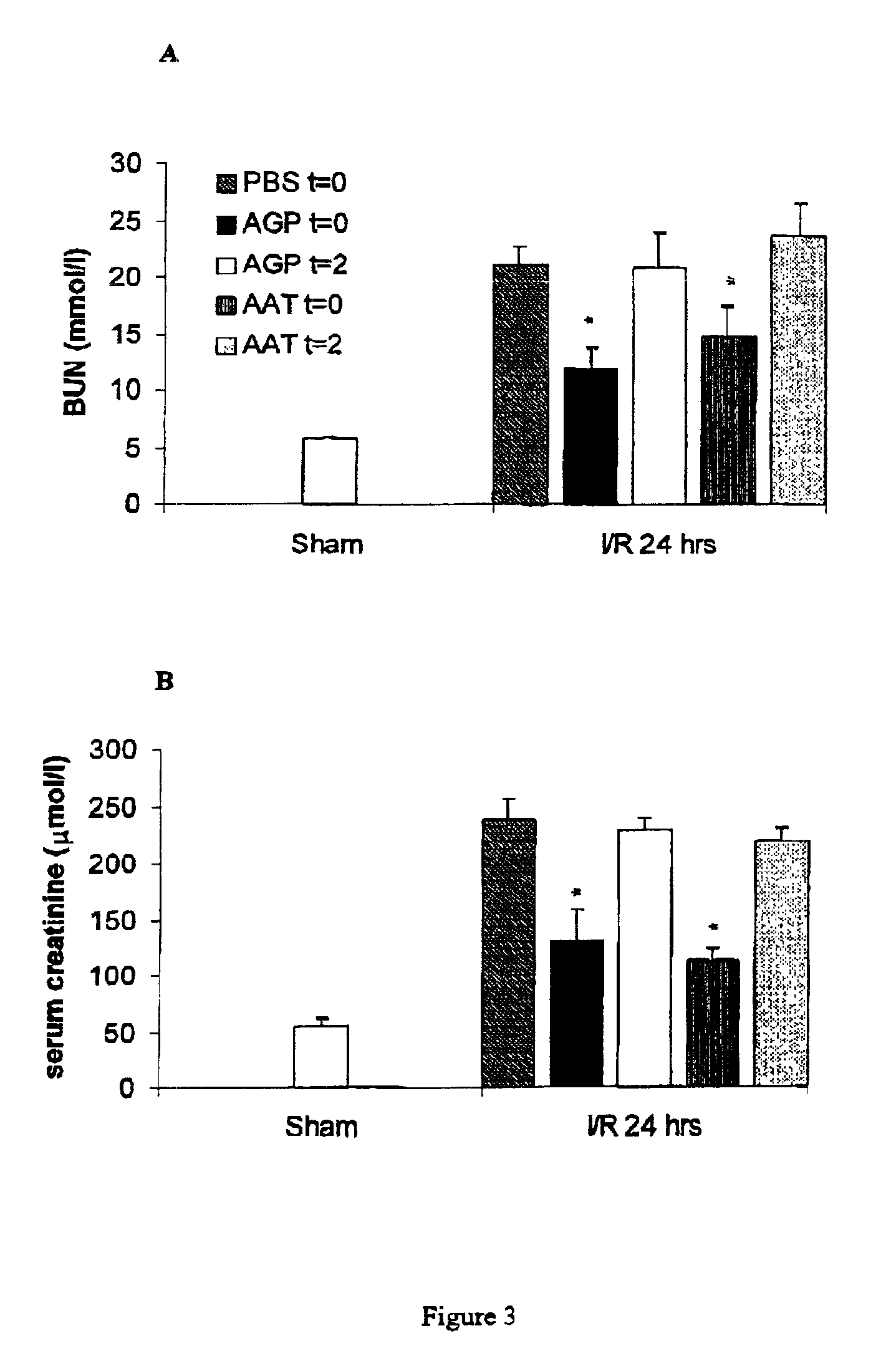
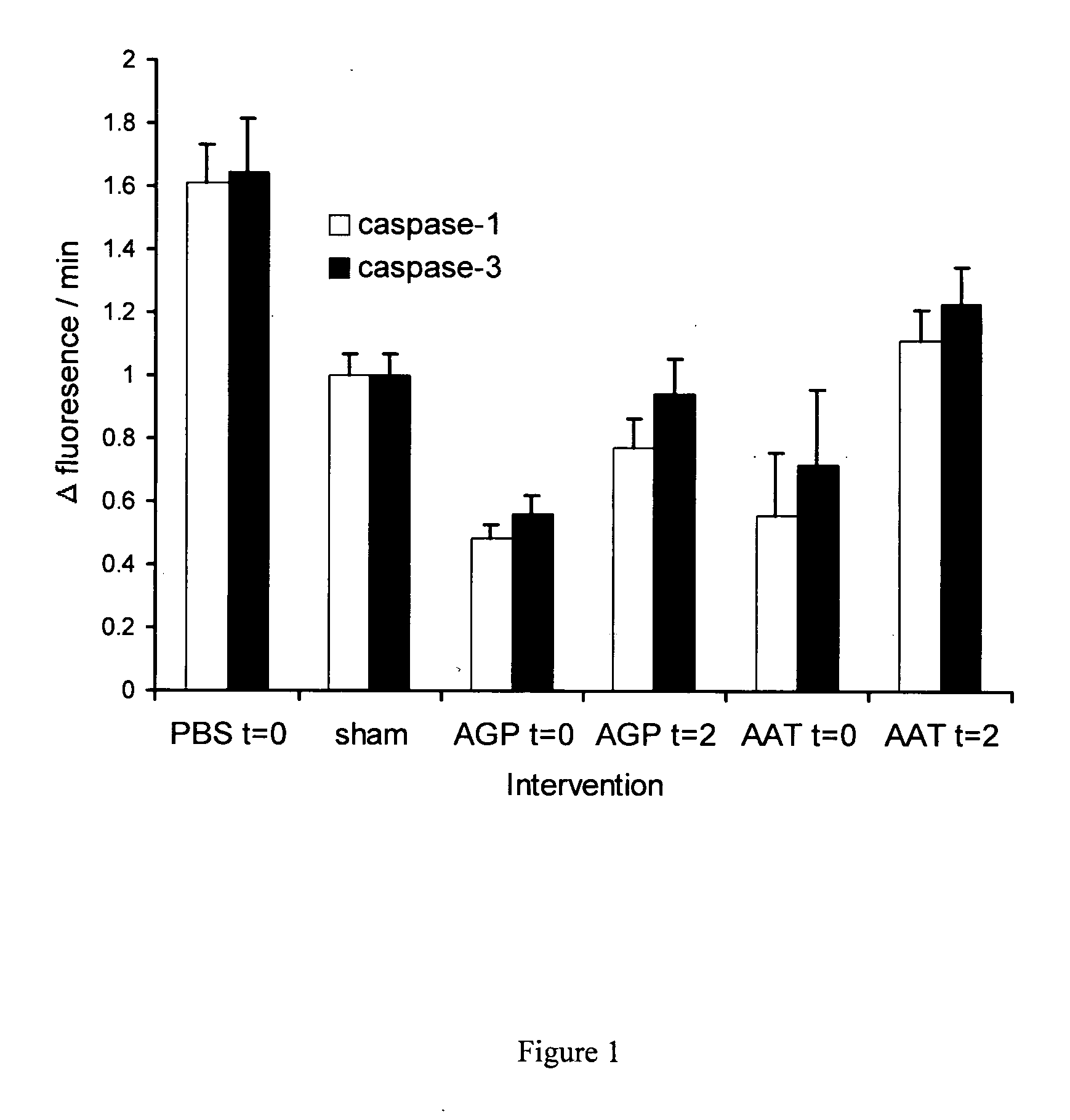
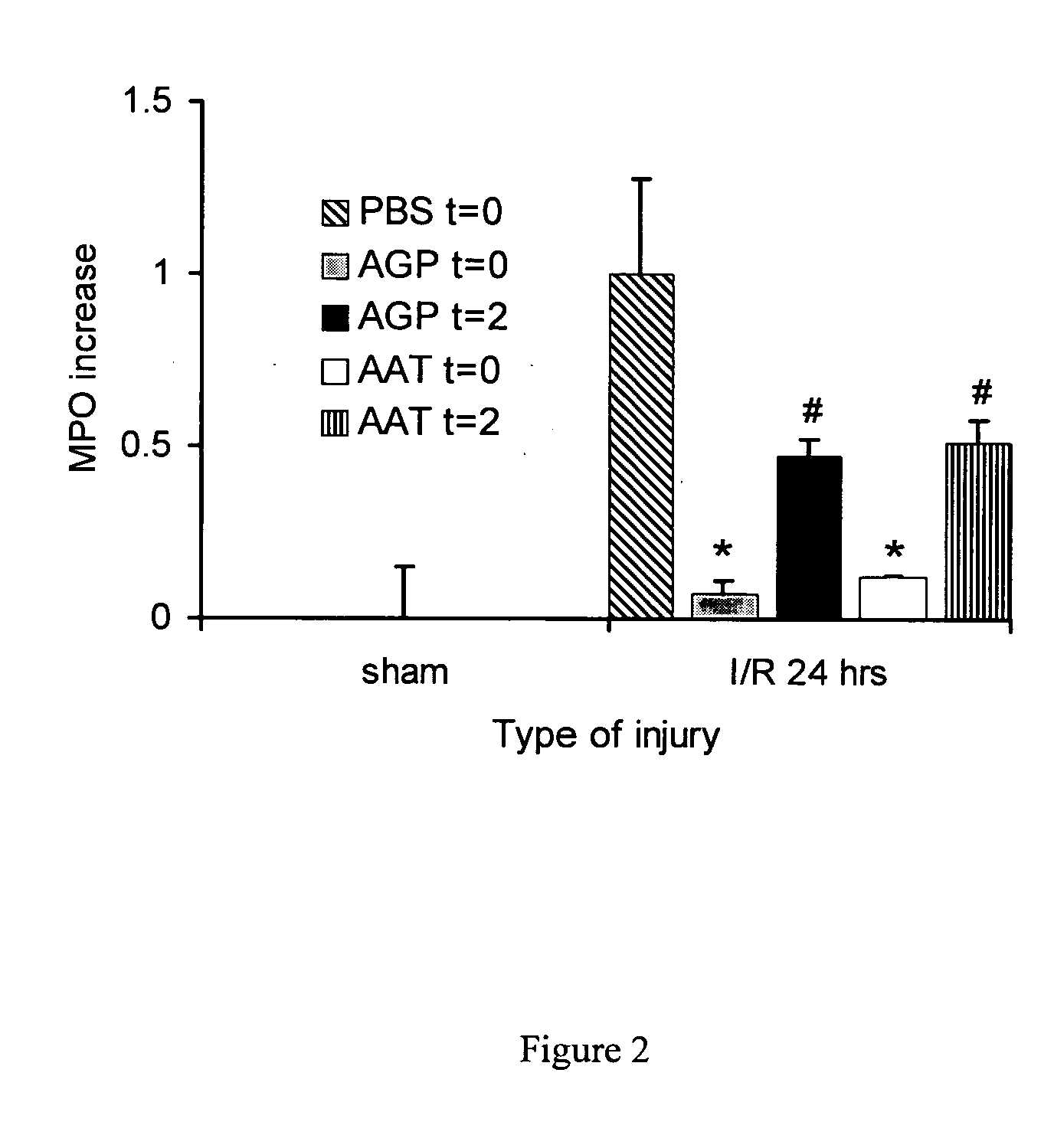
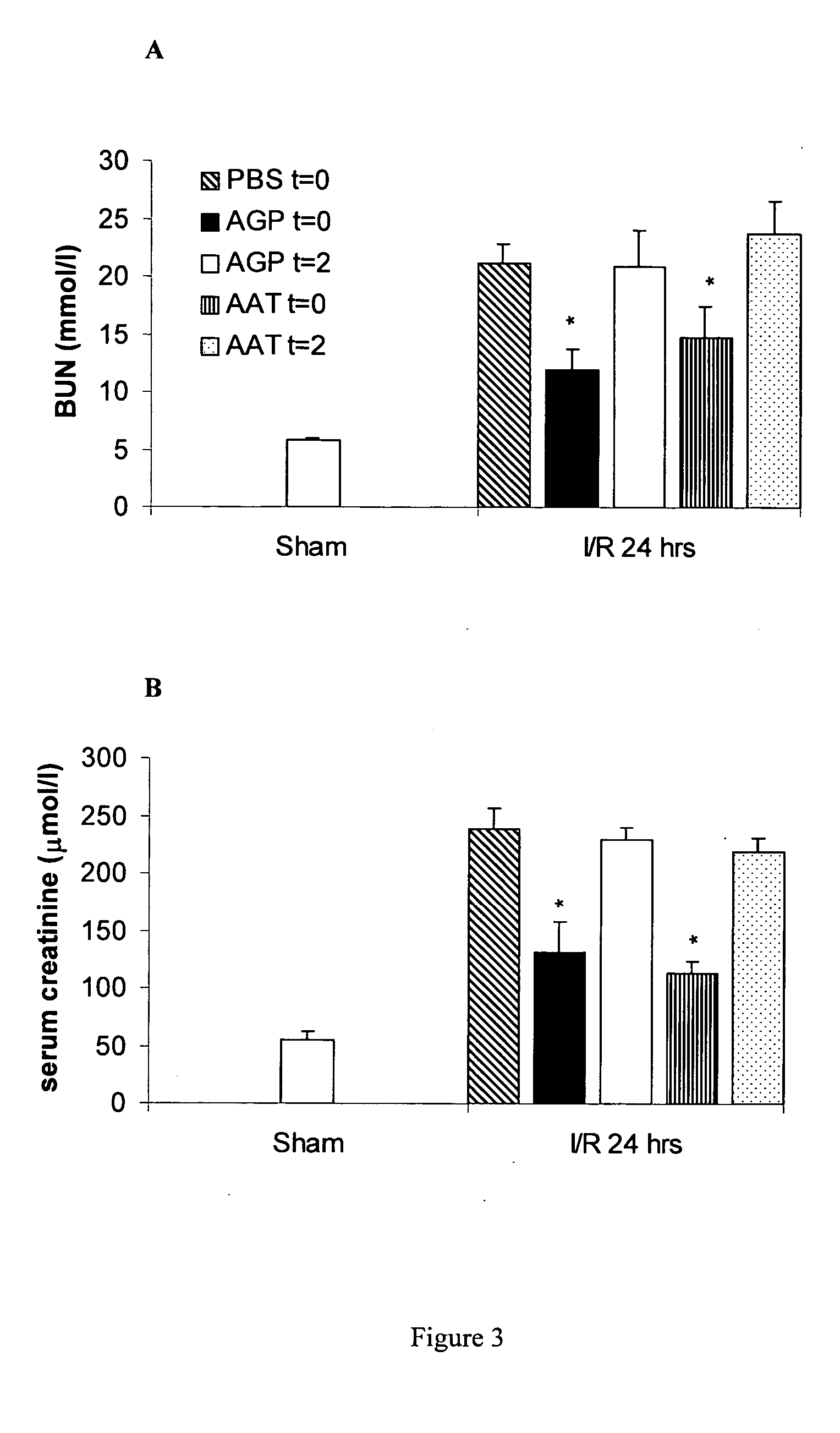
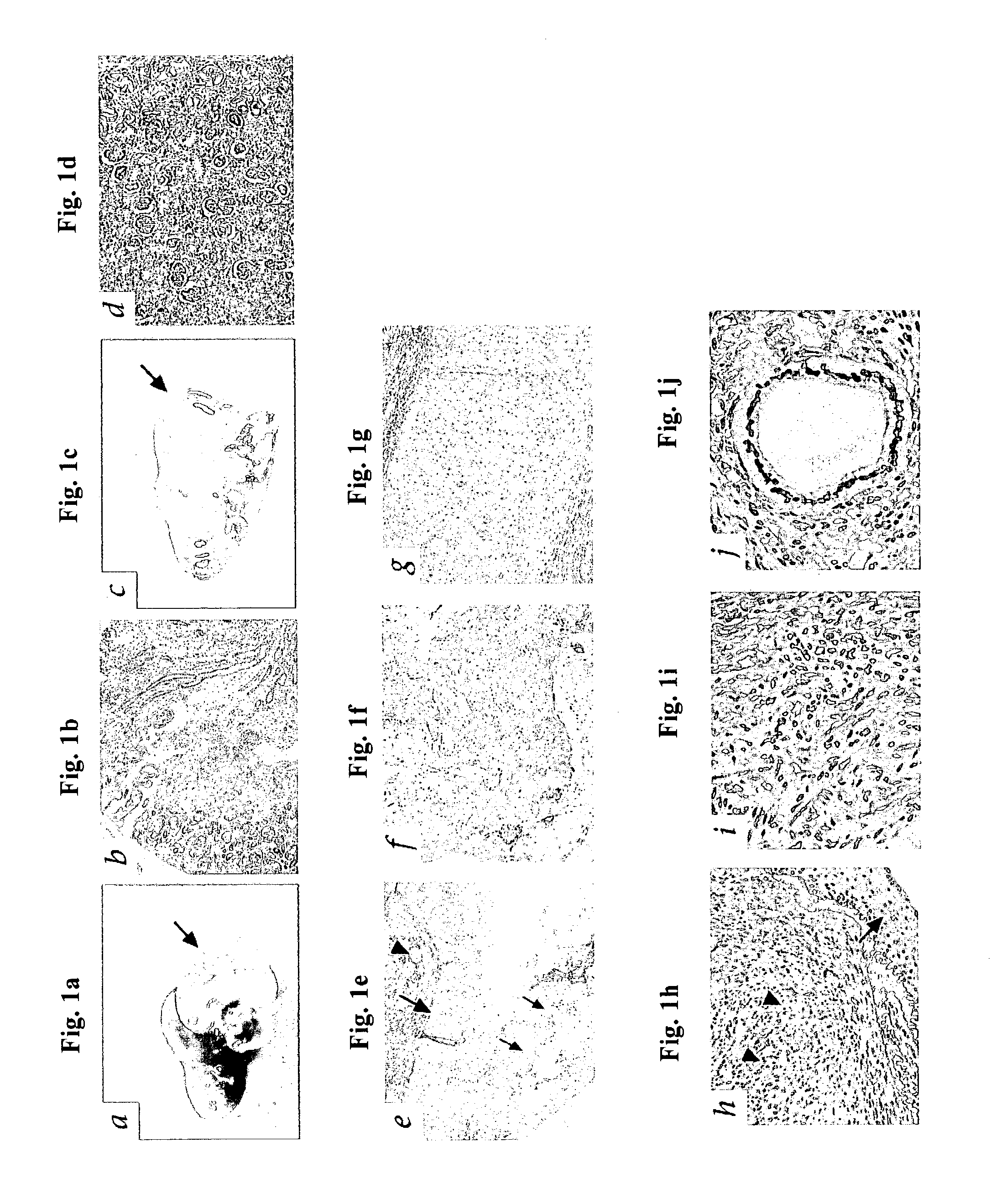
The present invention comprises a method of protecting organs or tissue susceptible to reperfusion-induced dysfunction after ischemia. The method comprises parenterally administering to a patient a therapeutical composition containing natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-1 antitrypsin or a mixture thereof. Alternatively, organ or tissue transplants can be contacted with natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-antitrypsin or mixtures by perfusing or flushing them with a solution containing natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-1 antitrypsin or mixtures thereof in a concentration of 0.1 to 5 g / l.
Owner:SUOMEN PUNAINEN RISTI VERIPALVELU
1-(Amino)indanes and (1,2-dihydro-3-amino)-benzofurans, benzothiophenes and indoles as edg receptor agonists
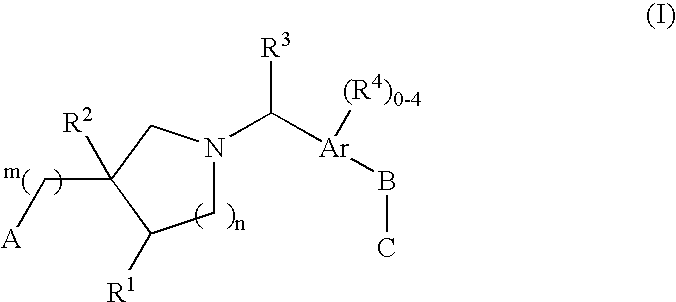
The present invention encompasses compounds of Formula (I): as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts and hydrates thereof. The compounds are useful for treating immune mediated diseases and conditions, such as bone marrow, organ and tissue transplant rejection. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use are included.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Surrogate tolerogenesis for the development of tolerance to xenografts
InactiveUS6060049AIncrease differentiationIncreased proliferationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHematopoietic cellTolerability
PCT No. PCT / US94 / 05844 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 6, 1995 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 6, 1995 PCT Filed May 24, 1994 PCT Pub. No. WO94 / 27622 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 8, 1993This invention provides a method for developing immune tolerance in xenogeneic organ graft recipients, in which lympho-hematopoietic cells from an intended organ graft recipient are differentiated within a xenogeneic surrogate, such as a fetal animal. After birth of the surrogate, the matured lympho-hematopoietic cells containing antigen specific regulatory cells, including suppressor cells, veto cells, select B cells, anti-idiotype antibodies, and other related factors responsible for antigen specific tolerance in a surrogate animal are reintroduced into the intended organ graft recipient, in conjunction with an organ transplant or a tissue transplant from the xenograft surrogate. The invention also provides an organ graft repopulated with cells from the intended organ graft recipient produced in a surrogate animal.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
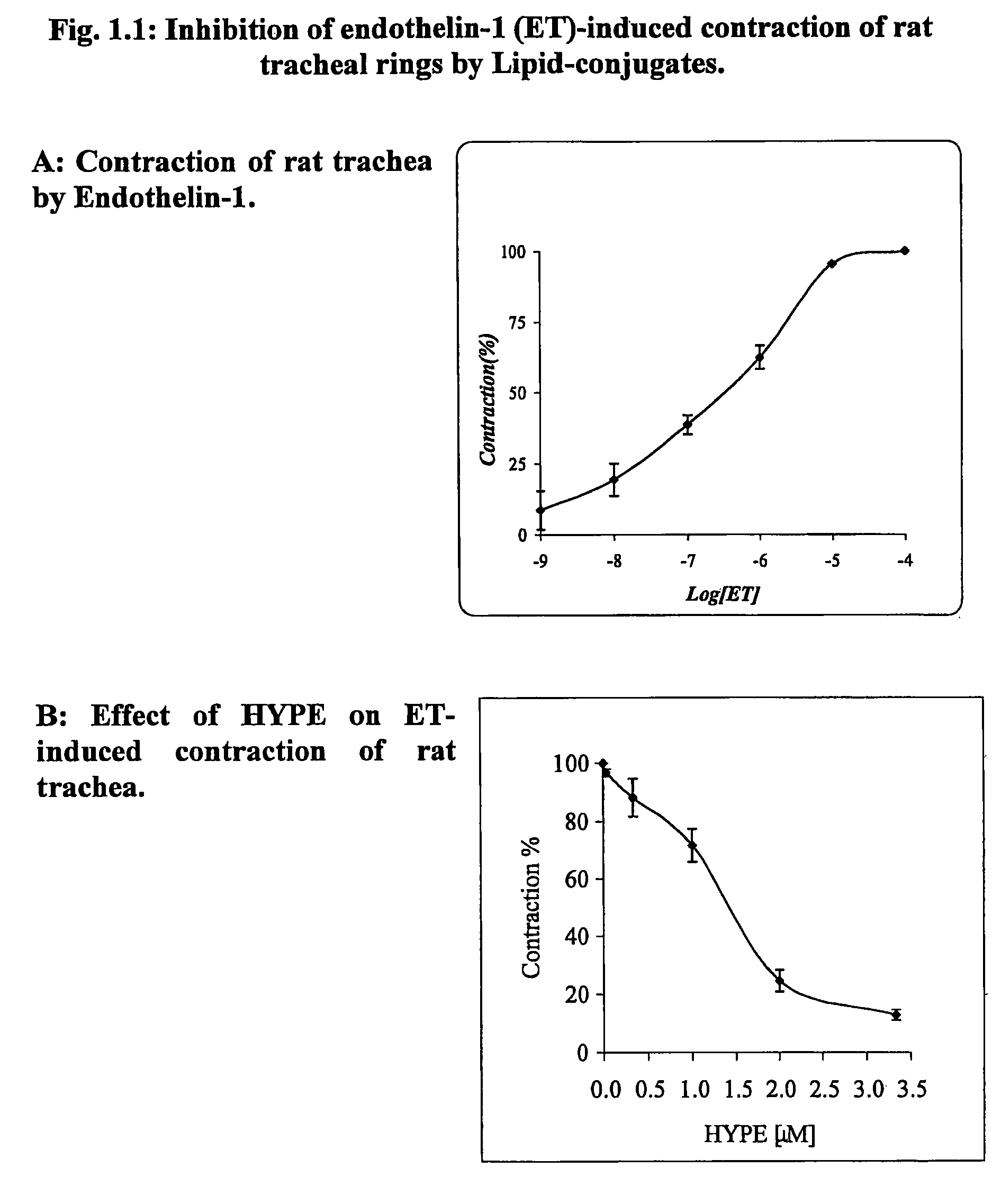
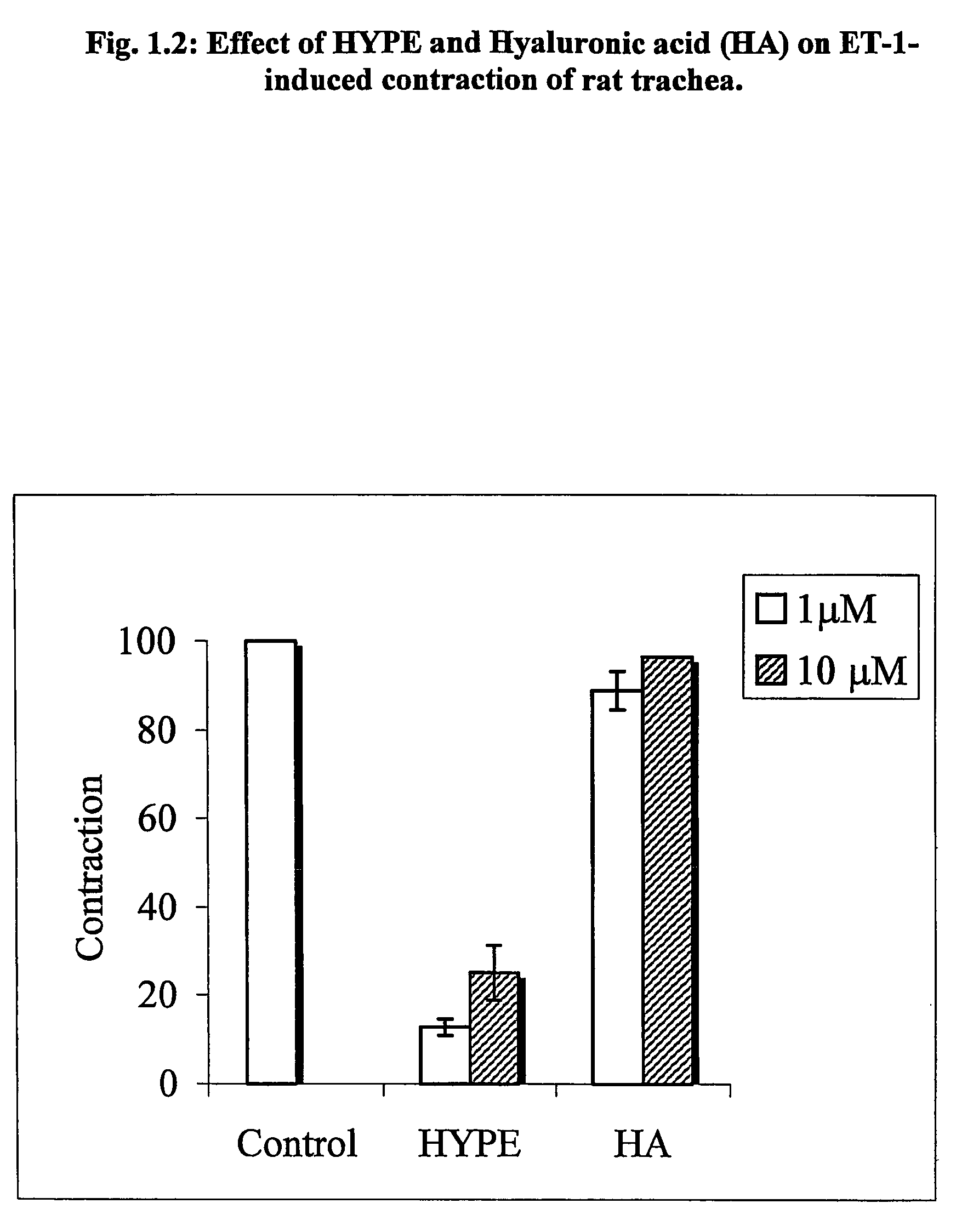
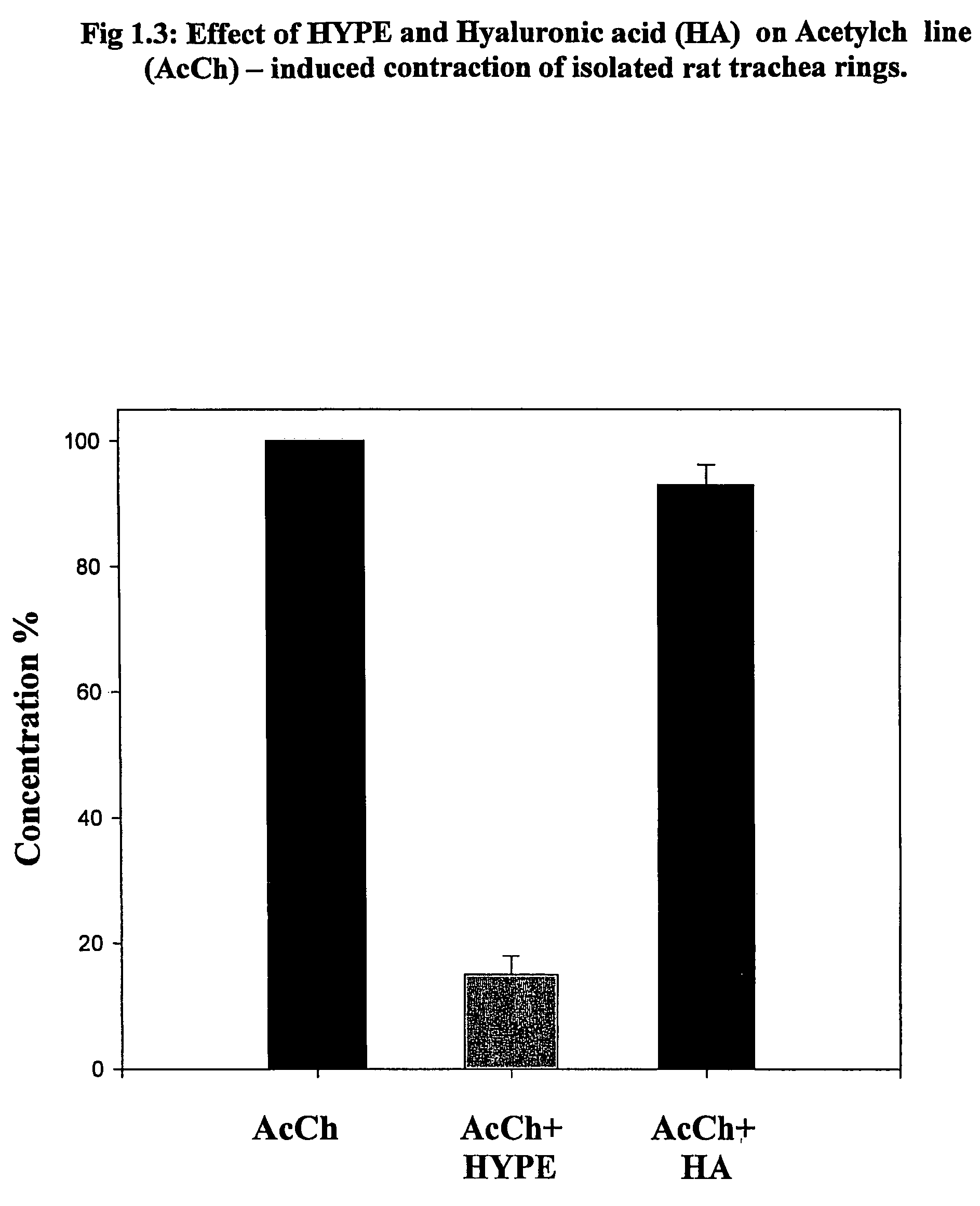
Use of lipid conjugates in the treatment of diseases
InactiveUS7101859B2Reduce molecular weightIncrease rangeAntibacterial agentsBiocideLymphatic SpreadContact dermatitis
The invention provides novel methods for treating disease based upon the medicinal use of lipids and phospholipids covalently bound to physiologically acceptable monomers or polymers. Phosphatidylethanolamine moieties conjugated to physiologically acceptable monomers and polymers (PE conjugates) manifest an unexpectedly wide range of pharmacological effects, including stabilizing cell membranes; limiting oxidative damage to cell and blood components; limiting cell proliferation, cell extravasation and (tumor) cell migratory behavior; suppressing immune responses; and attenuating physiological reactions to stress, as expressed in elevated chemokine levels. The surprisingly manifold pharmacological properties of the PL-conjugates allow for the invention, disclosed herein, of novel methods for the treatment of a diverse range of disease states, including obstructive respiratory disease, including asthma; colitis and Crohn's disease; central nervous system insult, including blood brain barrier compromise, ischemic stroke, and multiple sclerosis; contact dermatitis; psoriasis; cardiovascular disease, including ischemic conditions and prophylaxis for invasive vascular procedures; cellular proliferative disorders, including anti-tumor vasculogenesis, invasiveness, and metastases; anti-oxidant therapy; hemolytic syndromes; sepsis; acute respiratory distress syndrome; tissue transplant rejection syndromes; autoimmune disease; viral infection; and hypersensitivity conjunctivitis. The therapeutic methods of the invention include administration of phosphatidylethanolamine bound to carboxymethylcellulose, heparin, hyaluronic acid, polyethylene glycol, and Polygeline (haemaccel). Disclosed herein are also new compounds comprised of phospholipid moieties bound to low molecular weight monomers and dimers, including mono- and disaccharides, carboxylated disaccharides, mono- and dicarboxylic acids, salicylates, bile acids, and fatty acids.
Owner:YEDGAR SAUL
Devices and methods for tissue transplant and regeneration
InactiveUS20070239066A1Promote cell growthIncrease the number ofSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsIntact tissueMedicine
Devices and methods for transplanting tissue for the purpose of regeneration, for treating a patient having injured myocardial tissue, and / or for improving cardiac function through cell regrowth. More specifically, the devices and methods obviate the need for cellular alteration. The devices comprise a hollow tube with a sharp distal end, a stylet that is disposed and movable within the hollow tube, and a stopping device that constrains movement of the stylet. The methods comprise removing intact tissue from a first region of a mammalian organ and implanting the tissue in a second region of the same organ.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
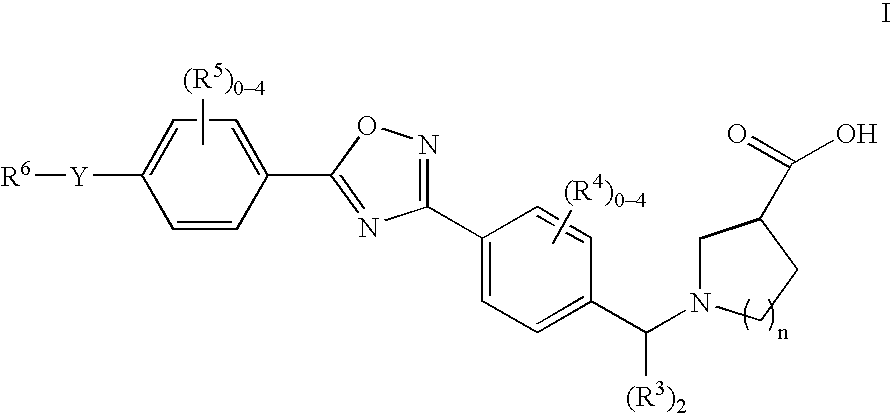
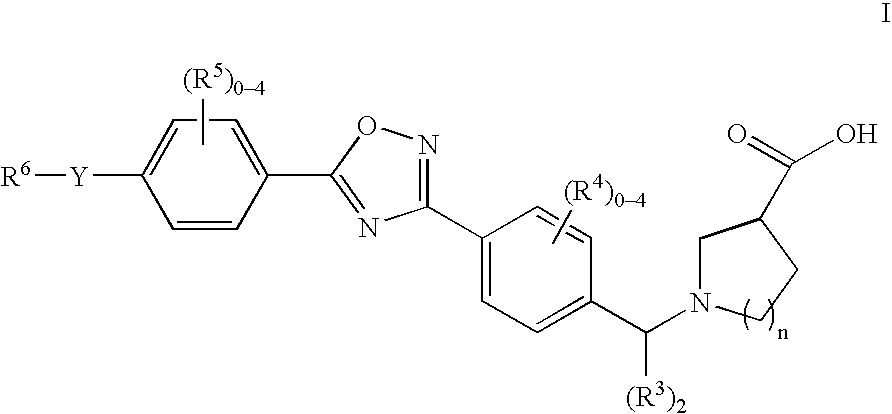
1-((5-aryl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl) benzyl)azetidine-3-carboxylates and 1-((5-aryl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)benzyl) pyrrolidine-3-carboxylates as edg receptor agonists
The present invention encompasses compounds of Formula I: as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts and hydrates thereof. The compounds are useful for treating immune mediated diseases and conditions, such as bone marrow, organ and tissue transplant rejection. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use are included.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
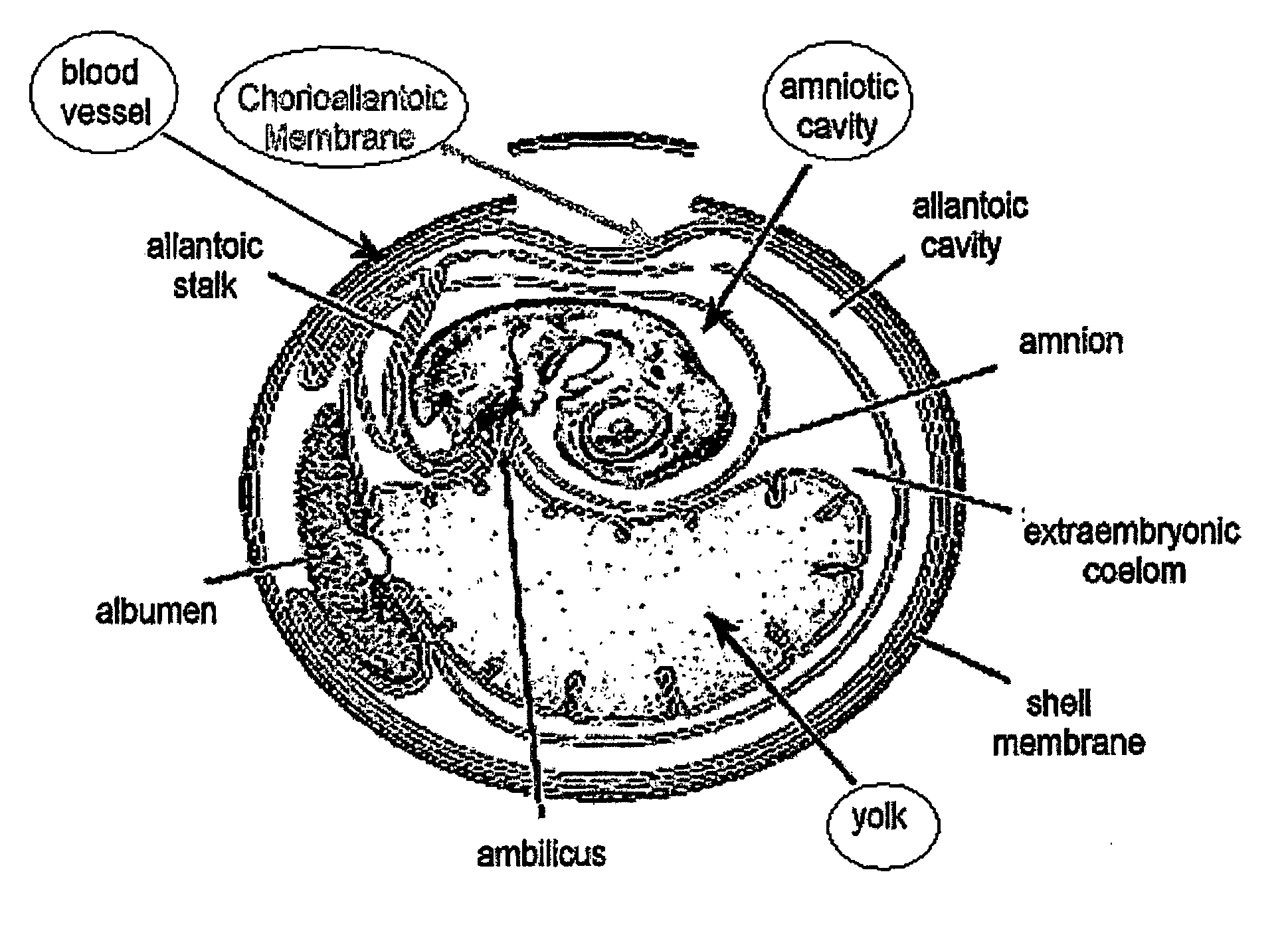
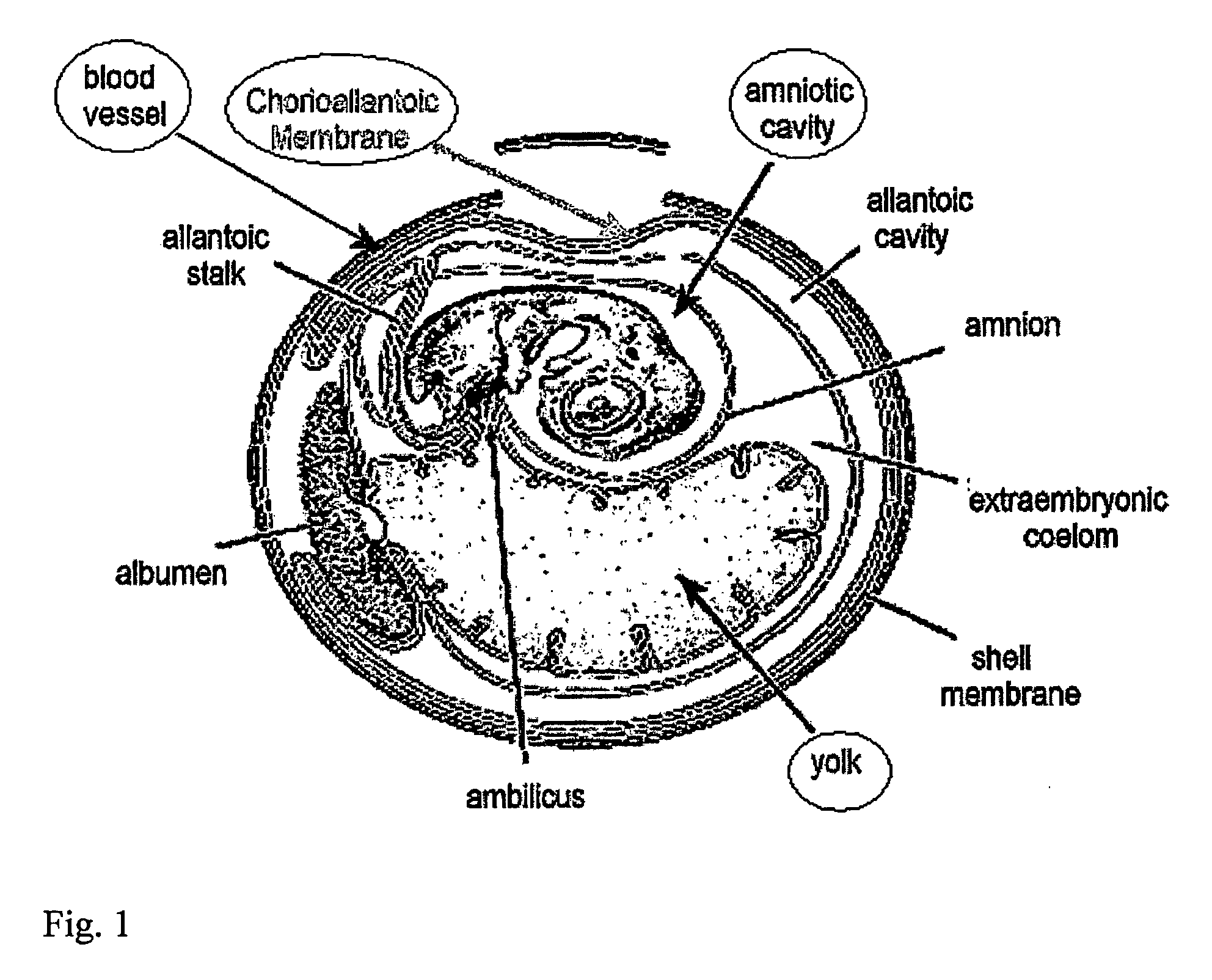
Chimeric Avian-Based Screening System Containing Mammalian Grafts
ActiveUS20090064349A1The process is convenient and fastConvenient and efficient systemCompound screeningVirusesMammalModel system
The present invention relates to animal model systems comprising a chimera between an avian embryo and a mammalian organism. Specifically, chimeric model systems comprising normal, diseased or genetically transformed mammalian cells and tissues transplanted into avian embryos, and uses thereof for in vivo testing of drugs and therapeutic modalities are disclosed.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV +1
Tissue graft
The present invention relates to a method of preparing a tissue graft material. The invention also relates to a multipurpose tissue graft material and to methods of using same as a replacement for vascular and non-vascular tissue.
Owner:CRYOLIFE
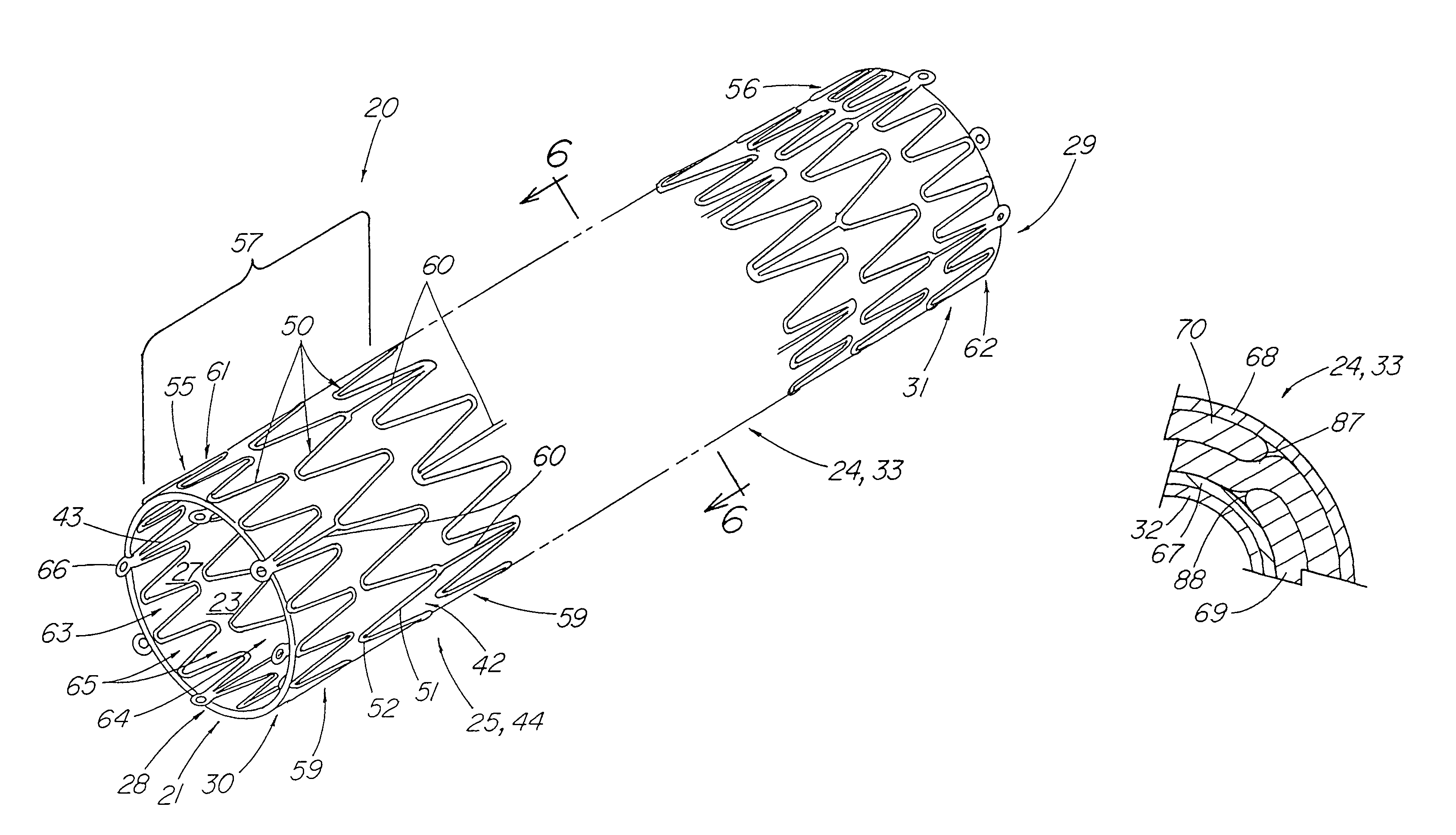
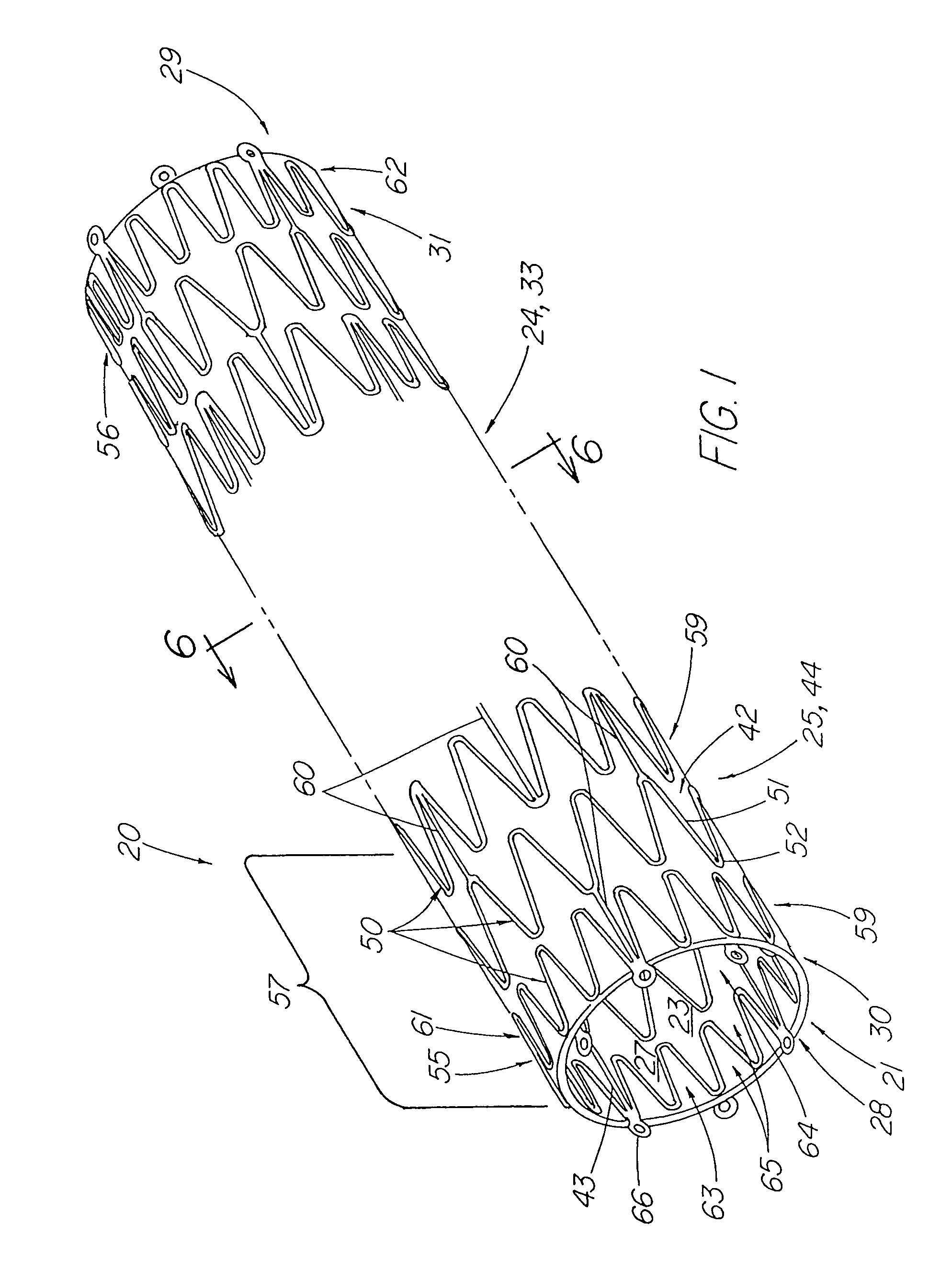
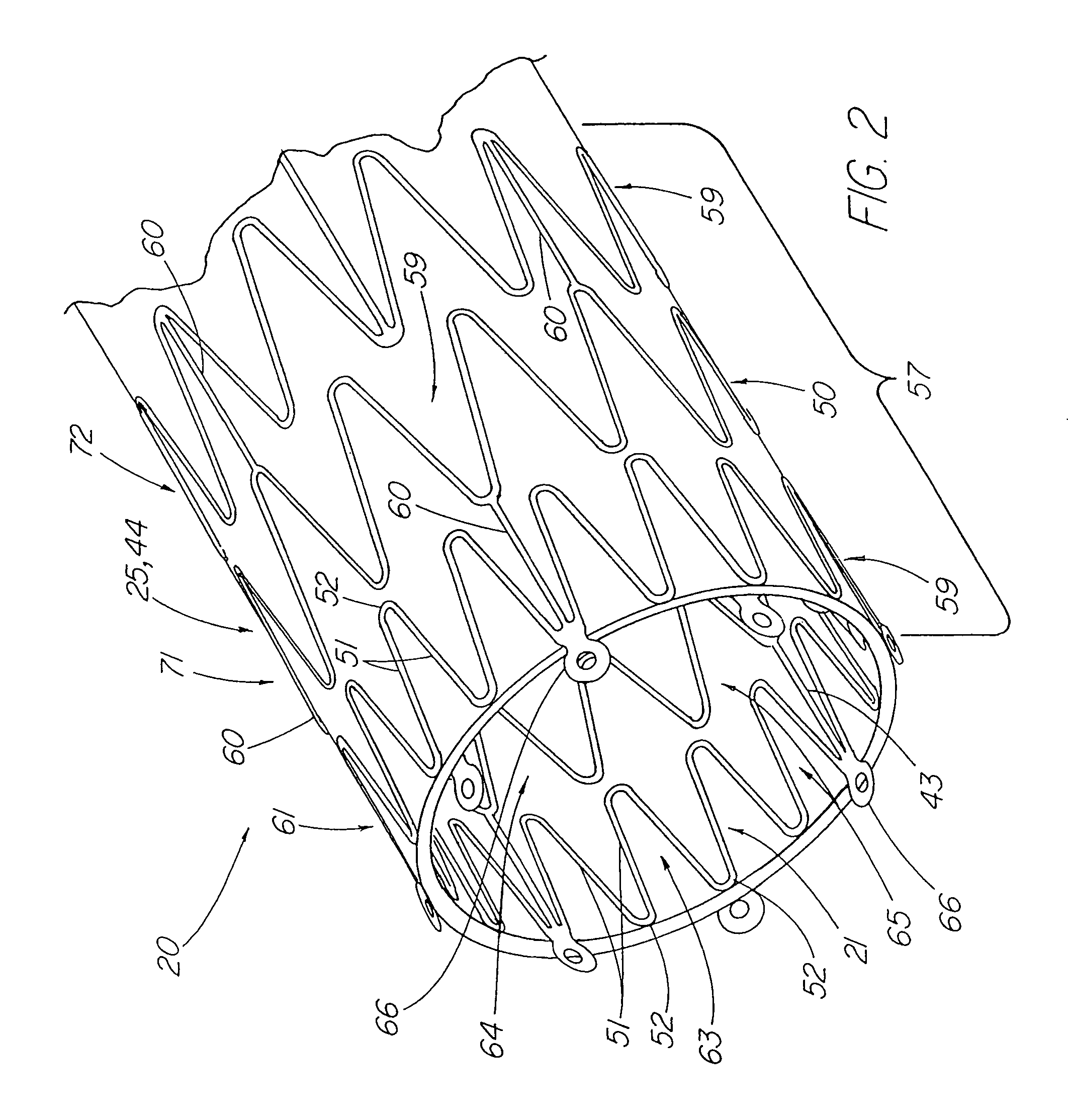
Stent tissue graft prosthesis
ActiveUS7914567B2Prevent eversionMinimize traumaStentsBlood vesselsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
A stent tissue graft prosthesis (20) for repairing, excluding and / or reinforcing a vessel, duct and the like in a patient. The prosthesis includes an inner expandable stent (21) of which a tissue graft (24) and preferably a multilayered tissue construct (33) is disposed thereon for application to the host tissue of a vessel, duct and the like. The tissue construct includes an extracellular matrix material (36) such as small intestine submucosa (37) for remodeling the host tissue into the prosthesis. The prosthesis further includes an outer tubular member (25) such as an outer expandable stent (44) for retaining the tissue graft on the inner stent. The ends of the inner and outer stents are coincident with or extend beyond the ends of the tissue graft to prevent eversion or fold back of the tissue graft during withdrawal of a delivery catheter in a placement procedure.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV +2
3,5-aryl, heteroaryl or cycloalkyl substituted-1,2,4-oxadiazoles as S1P receptor agonists
The present invention encompasses compounds of Formula I: (I) as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The compounds are useful for treating immune mediated diseases and conditions, such as bone marrow, organ and tissue transplant rejection. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use are included.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
1-((5-aryl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl) benzyl)azetidine-3-carboxylates and 1-((5-aryl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)benzyl) pyrrolidine-3-carboxylates as edg receptor agonists
The present invention encompasses compounds of Formula I: as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts and hydrates thereof. The compounds are useful for treating immune mediated diseases and conditions, such as bone marrow, organ and tissue transplant rejection. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use are included.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Methods of treating disease by transplantation of developing allogeneic or xenogeneic organs or tissues
A method of treating a disorder associated with pathological organ or tissue physiology or morphology is disclosed. The method is effected by transplanting into a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective mammalian organ or tissue graft selected not substantially expressing or presenting at least one molecule capable of stimulating or enhancing an immune response in the subject.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Methods and active substances for protecting organs
InactiveUS20050277106A1Avoid dysfunctionPreventing transplantPeptide/protein ingredientsDead animal preservationMedicineTissue transplant
The present invention comprises a method of protecting organs or tissue susceptible to reperfusion-induced dysfunction after ischemia. The method comprises parenterally administering to a patient a therapeutical composition containing natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-1 antitrypsin or a mixture thereof. Alternatively, organ or tissue transplants can be contacted with natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-1 antitrypsin or mixtures by perfusing or flushing them with a solution containing natural alpha-1 acid glycoprotein, natural alpha-1 antitrypsin or mixtures thereof in a concentration of 0.1 to 5 g / l.
Owner:SUOMEN PUNAINEN RISTI VERIPALVELU
Methods of treating disease by transplantation of developing allogeneic or xenogeneic organs or tissues
InactiveUS20040082064A1Microbiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseTissue physiology
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
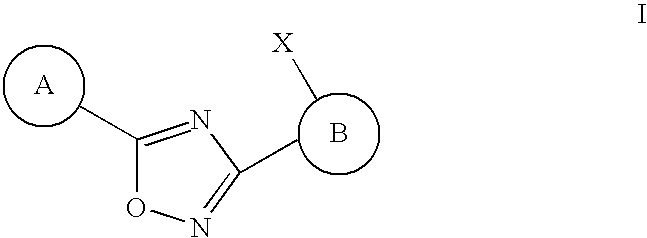
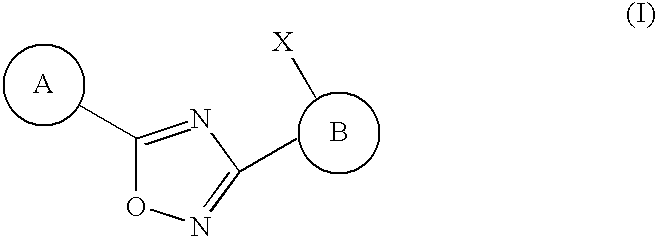
3-(2-amino-1-azacyclyl)-5-aryl-1,2,4-oxadiazoles as s1p receptor agonists
The present invention encompasses compounds of Formula (I): as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The compounds are useful for treating immune mediated diseases and conditions, such as bone marrow, organ and tissue transplant rejection. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use are included.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Aminoalkylphosphonates and related compounds as edg receptor agonists
The present invention encompasses compounds or Formula (I): as well as the pharmaceutically acceptable salts and hydrates thereof. The compounds are useful for treating immune mediated diseases and conditions, such as bone marrow, organ and tissue transplant rejection. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use are included.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Antagonist Anti-Cd40 Monoclonal Antibodies and Methods for Their Use
Compositions and methods for inhibiting CD40-directed activities that are mediated via the binding of C4BP to CD40 are provided. The compositions of the invention include anti-CD40 antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, that have the following characteristics: 1) are free of significant CD40 agonist activity when bound to CD40 antigen; and 2) are capable of specifically binding to CD40 antigen expressed on the surface of cells, wherein this binding to CD40 antigen blocks C4BP-mediated CD40 signaling, thereby inhibiting one or more CD40-directed activities. These antagonist anti-CD40 antibodies can effectively be used to treat CD40-associated diseases that are mediated by C4BP stimulation of CD40 signaling, including cancers, such as B cell-related cancers and solid tumors, and diseases or disorders that have an autoimmune and / or inflammatory component, including organ and tissue transplant rejection.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Composite for Thermo-Sensitive Cell-Tissue Transplanted Scaffold and Use thereof
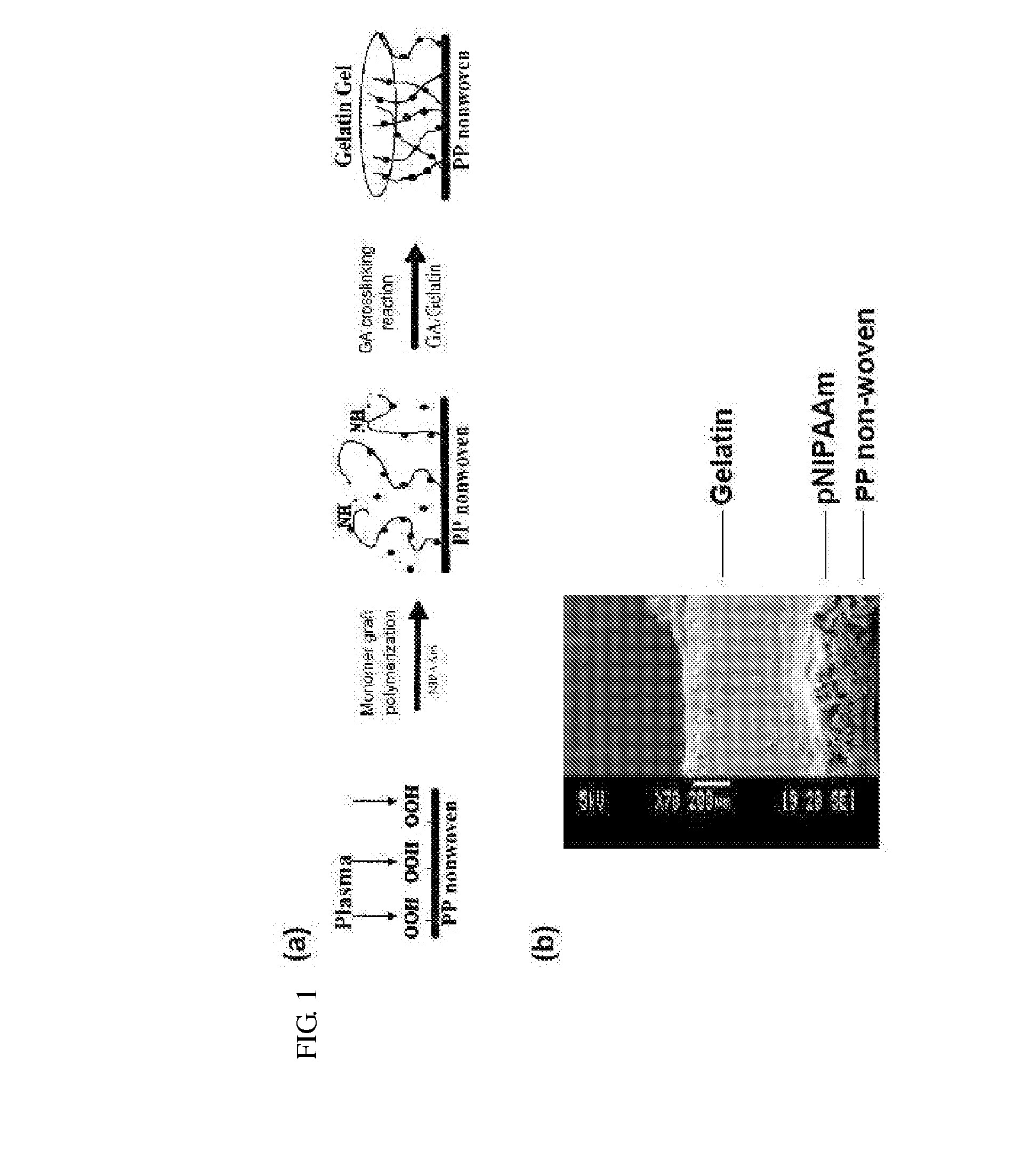
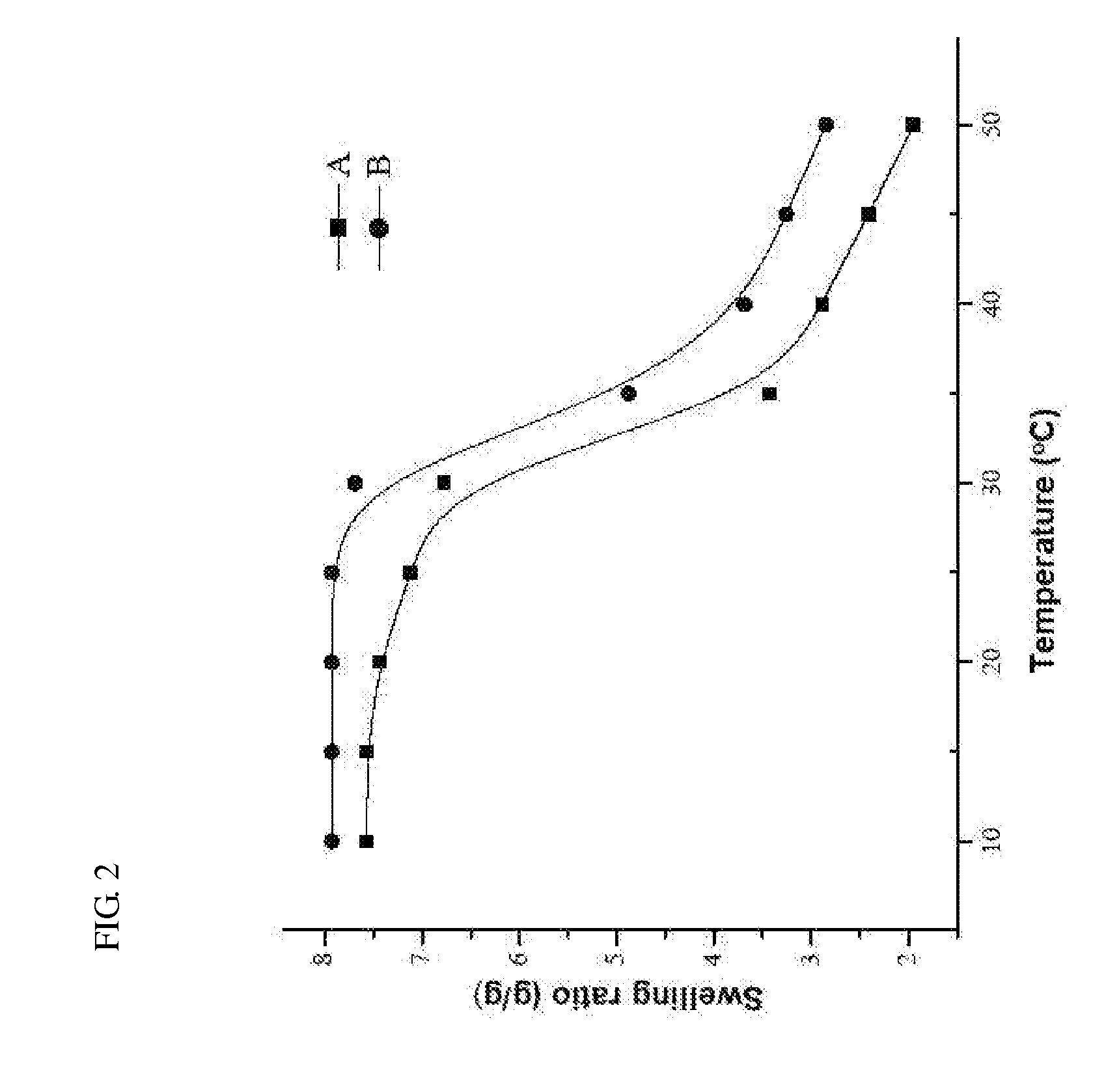
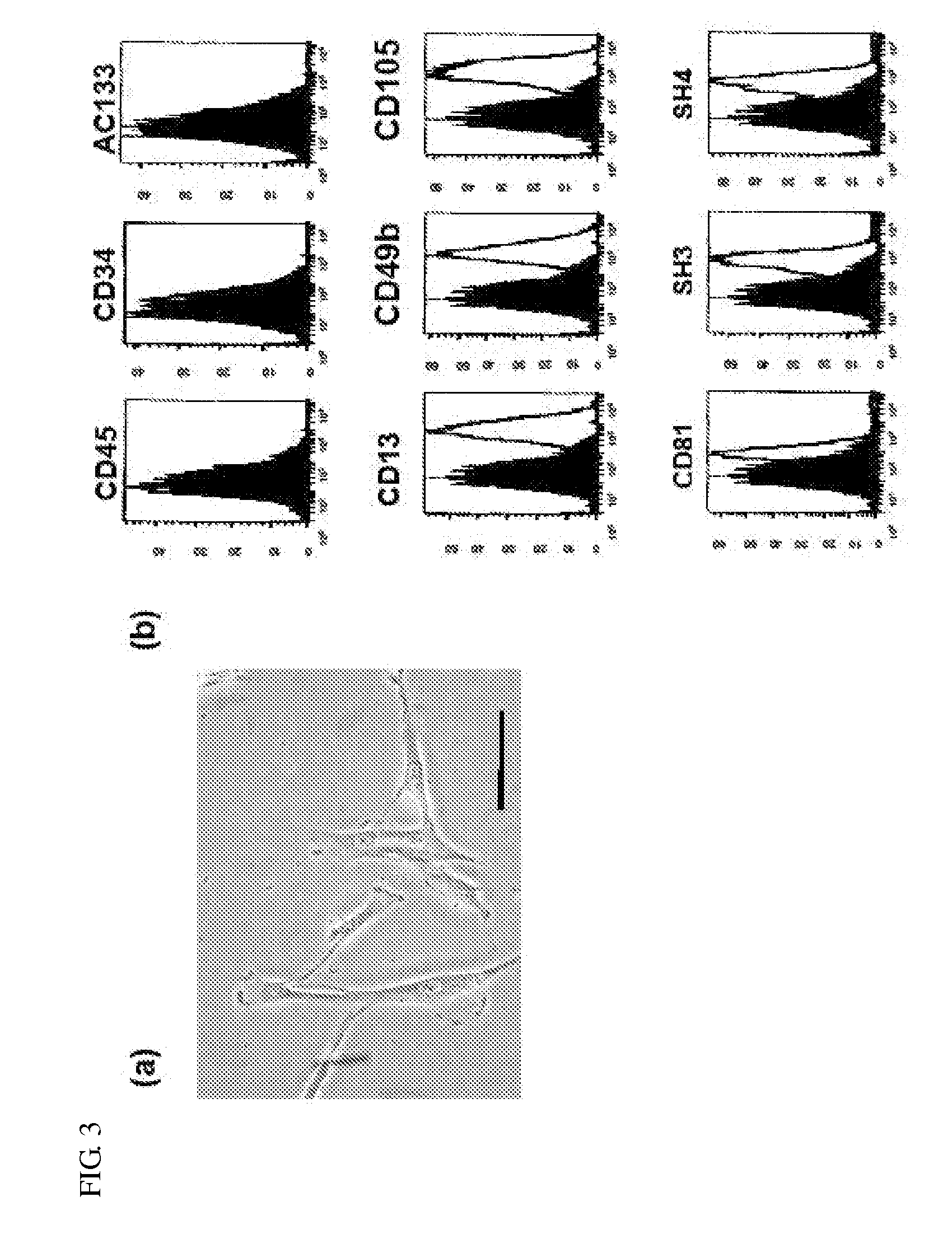
A composite comprising a stem cell; a biodegradable layer, which can provide an environment for the stem cell to grow and to differentiate, and; a N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAm), which can polymerize with the biodegradable layer and possess the temperature-responsive character for easy stripping. This invention also provides a method of treating a subject with a skin defect by covering the composite of the present invention on the skin defect of the subject in need of such treatment. Furthermore, using this composite with different growth factors, stem cells can be induced to differentiate into skin-related, neuronal cells, neuron, and insulin-positive cells in biodegradable scaffolds as well as transplanted graft. Finally, this invention also provides a quick and convenient method of monitoring cell growth or tissue engineering in an animal.
Owner:VETERANS GEN HOSPITAL TAIPEI
3-(2-amino-1-azacyclyl)-5-aryl-1,2,4-oxadiazoles as S1P receptor agonists
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
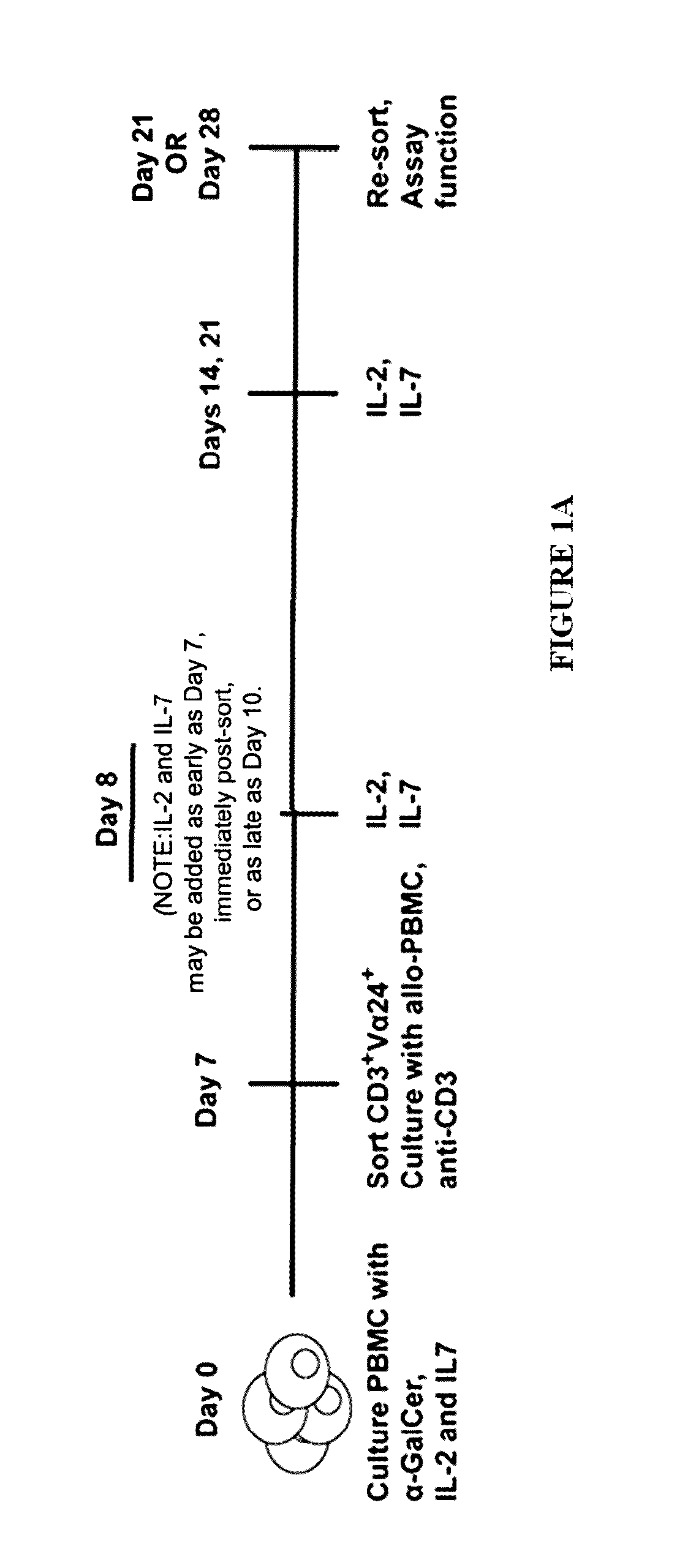
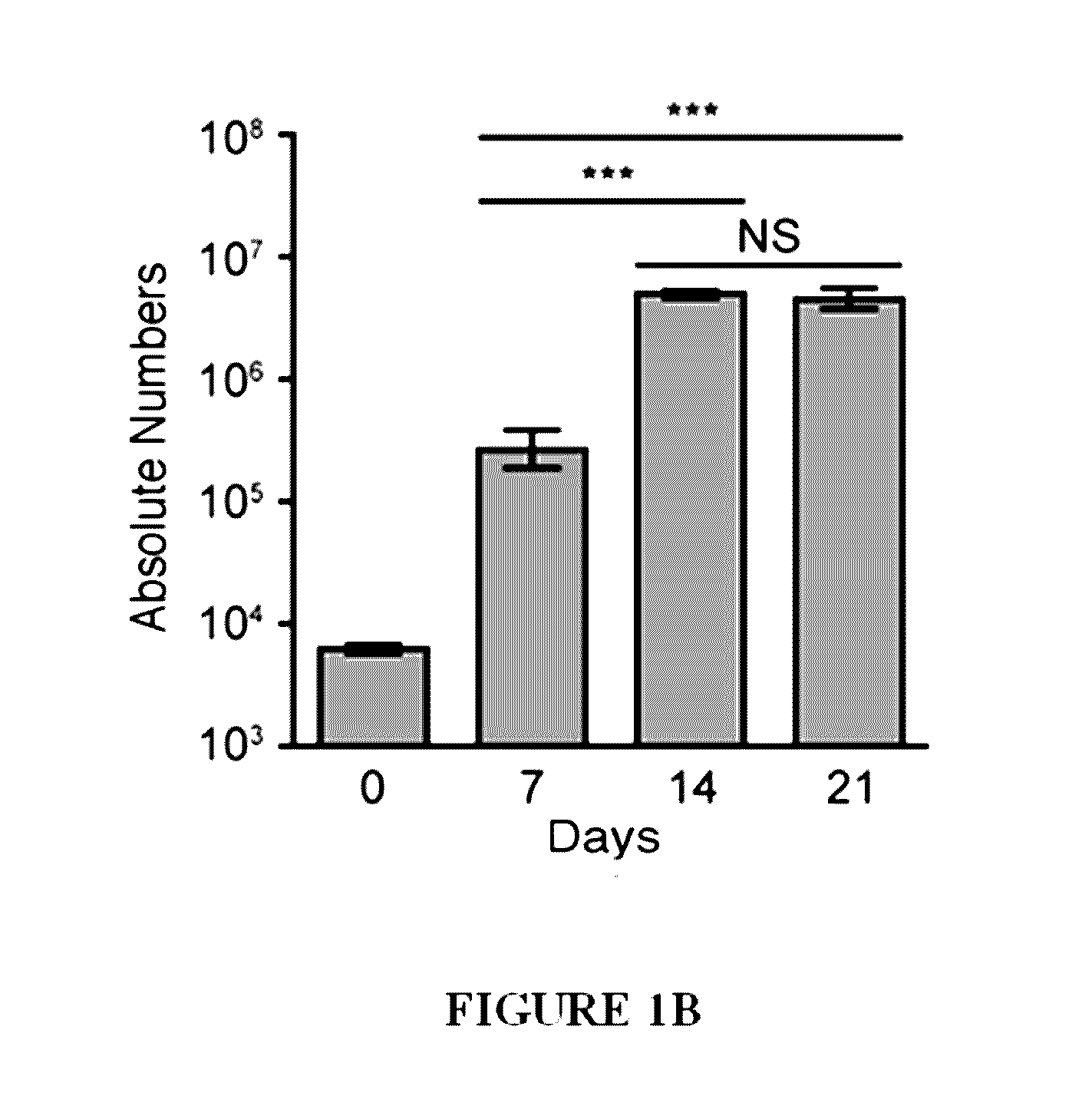
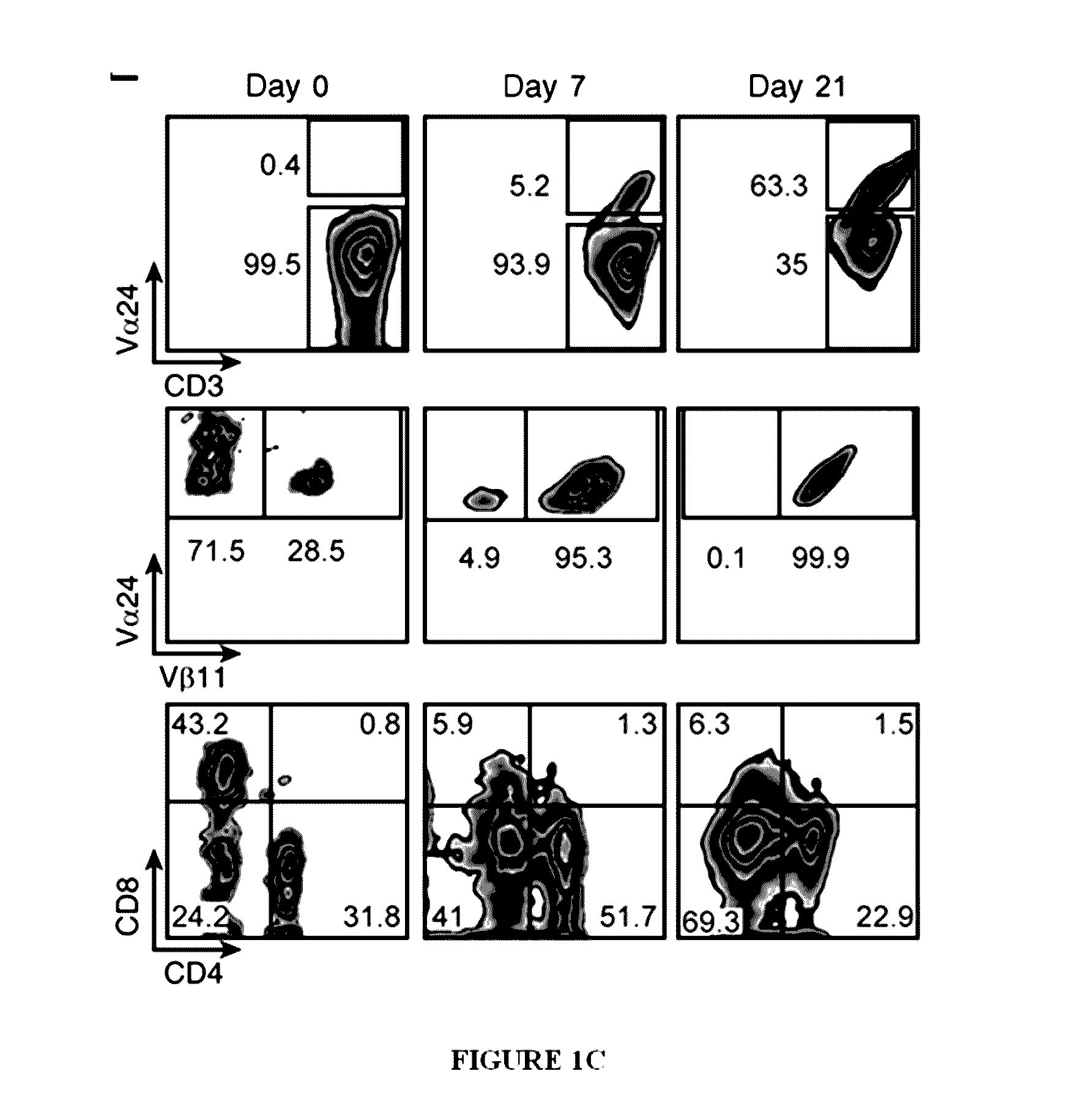
Methods of expanding ex vivo natural killer t (NKT) cells and therapeutic uses thereof
InactiveUS20170029777A1Strong cytotoxicityCulture processMammal material medical ingredientsAutoimmune responsesTissue transplant
The present invention is directed to novel methods of producing ex vivo natural killer T (NKT) cells, and therapeutic uses thereof for treatment of certain conditions including cancer, autoimmunity, inflammatory disorders, allergic disorders, tissue transplant-related disorders, and infections.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Method for Decellularization of Tissue Grafts
ActiveUS20160030636A1Encourage graft implantationReduced CD4+ T-cell mediated immune responseCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsCellular componentCell-Extracellular Matrix
The subject invention pertains to materials and methods for processing tissue to produce a natural, acellular replacement tissue that is immunocompatible with a recipient. According to the subject invention, harvested tissue is subjected to wash solutions wherein only amphoteric detergent(s) are used (e.g., anionic detergents are excluded). Following extraction by amphoteric detergent(s), the tissue is washed with a buffer system to facilitate the clearance of cellular components and detergent. In one embodiment, the subject invention pertains to a replacement tissue that is a nerve graft that supports axonal regeneration, guides axons toward the distal nerve end and / or is immunologically tolerated. Preferably, the nerve graft retains essential extracellular matrix scaffolding as well as biological components that promote nerve regeneration through the nerve graft.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
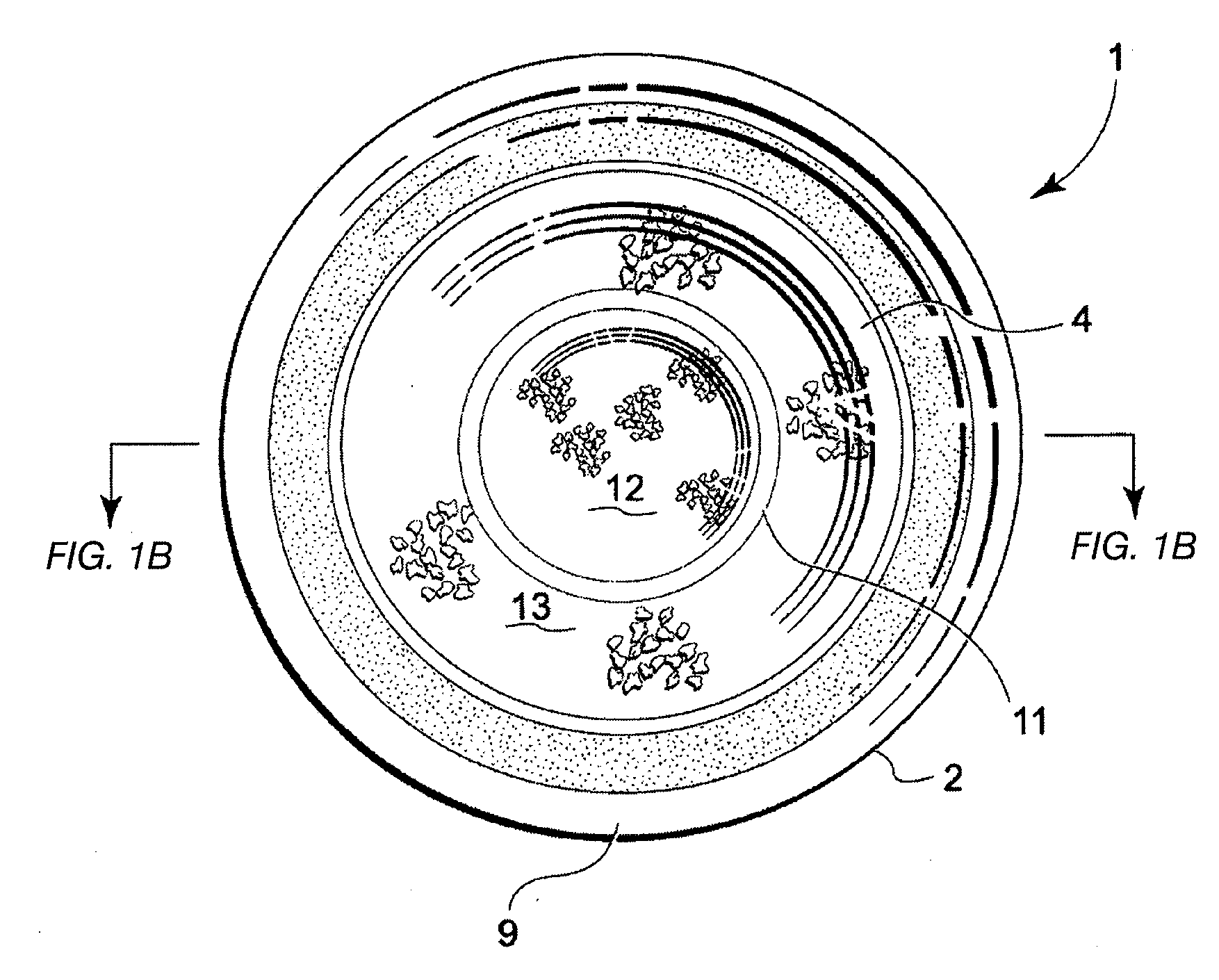
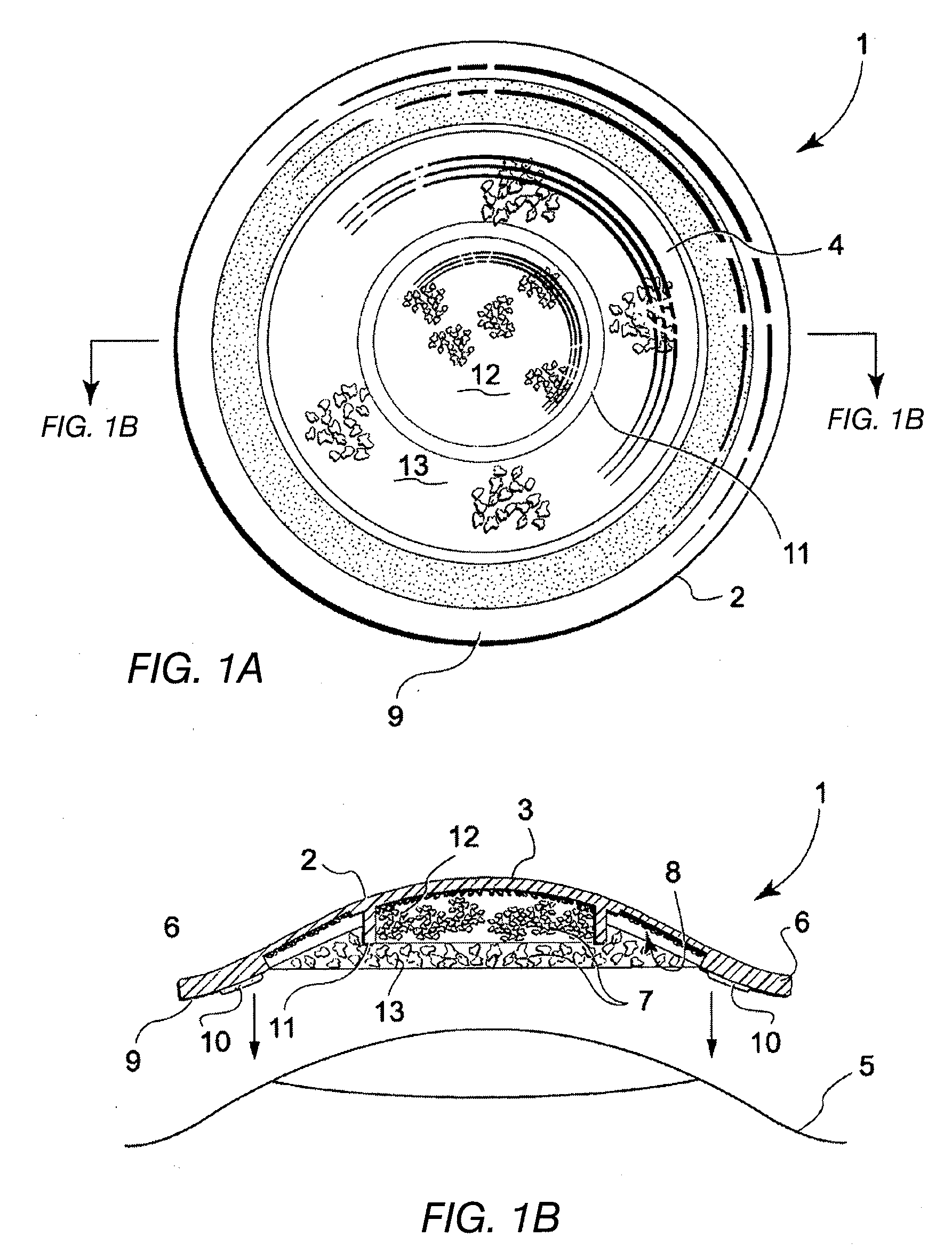
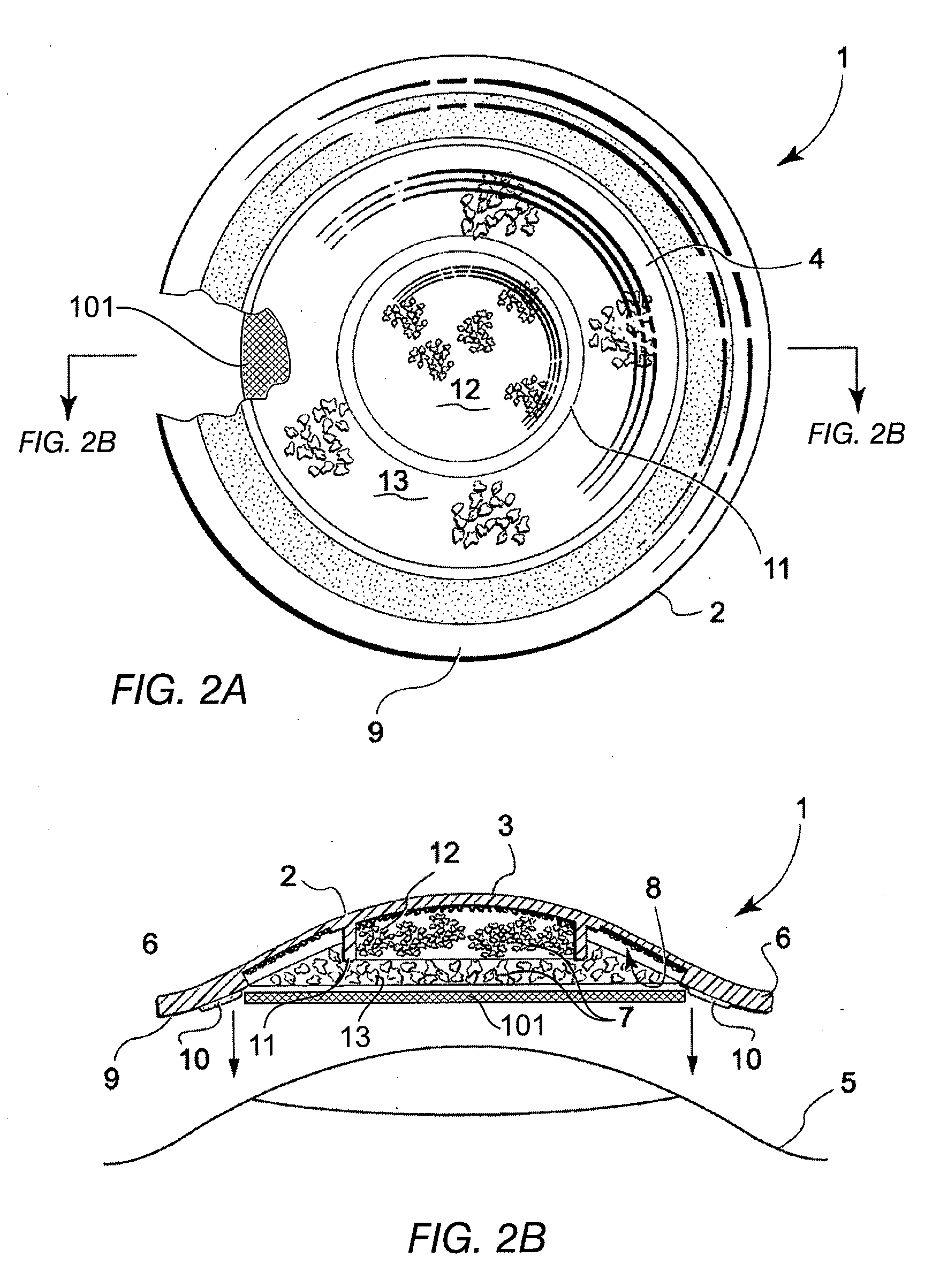
Cultured tissue transplant device
ActiveUS20120191184A1Precise positioningExact matchEye implantsSurgeryTissue transplantBiomedical engineering
A device for transplanting a graft such as a layer or layers of cultivated, autologous, allogenic or xenogenic cells to cover an accidental or surgical wound. The graft is cultivated and carried on a bed of collagen or other dissolvable or releasable material mounted on a protective substrate molded to conform to the profile of the wounded area and provided with a lateral attachment zone. The device facilitates the graft cultured in vitro to the recipient surface.
Owner:CHEN PAUL HONG DZE
Immunosuppressive drug combination for a stable and long term engraftment
InactiveUS20130183322A1Reduced graft rejectionReduce rejectionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunosuppressive drugS1P Receptor
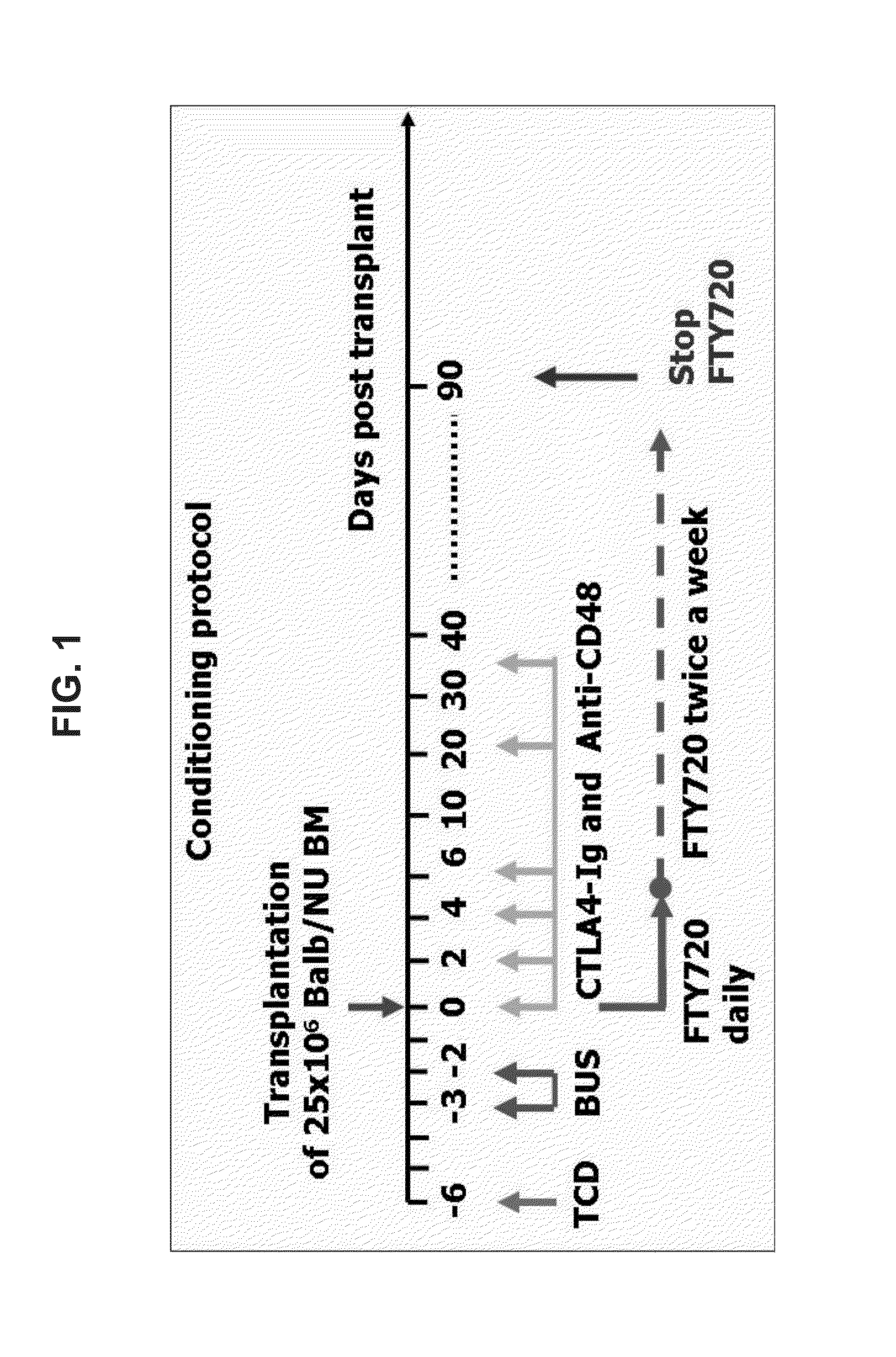
A method of treating a subject in need of a cell or tissue transplant is disclosed. The method comprising (a) transplanting a non-syngeneic cell or tissue transplant into the subject, wherein the transplant comprises bone marrow or lymphoid cells; and (b) administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of an immunosuppressive regimen comprising a Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Agonist, a B7 molecule inhibitor and a CD2 / CD58 pathway inhibitor, thereby treating the subject.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Method for inhibiting transplant rejection
A method for inhibiting rejection of tissues transplanted into a mammalian host is disclosed. Treatment of the tissues with an enzyme or combination of enzyme, particularly papain, to eliminate cell surface structures necessary for recognition by the host's immune system, particularly MHC Class I molecules, avoids or reduces the attack of the host's immune system on the transplanted tissues. Tissues that are enzymatically shaved of MHC Class I antigens and / or other critical adhesion molecules can be rendered at least temporarily resistant or immune to attack by cytolytic T lymphocytes, helper T lymphocytes, antibodies, or other effector cells of a host's immune system, thereby enhancing the survivability of the tissues in the host after transplant.
Owner:FAUSTMAN DENISE L
Protein biomarkers and therapeutic targets for autoimmune and alloimmune diseaes
ActiveUS20120077209A1Solid foundationMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAutoimmune diseaseTissue transplant
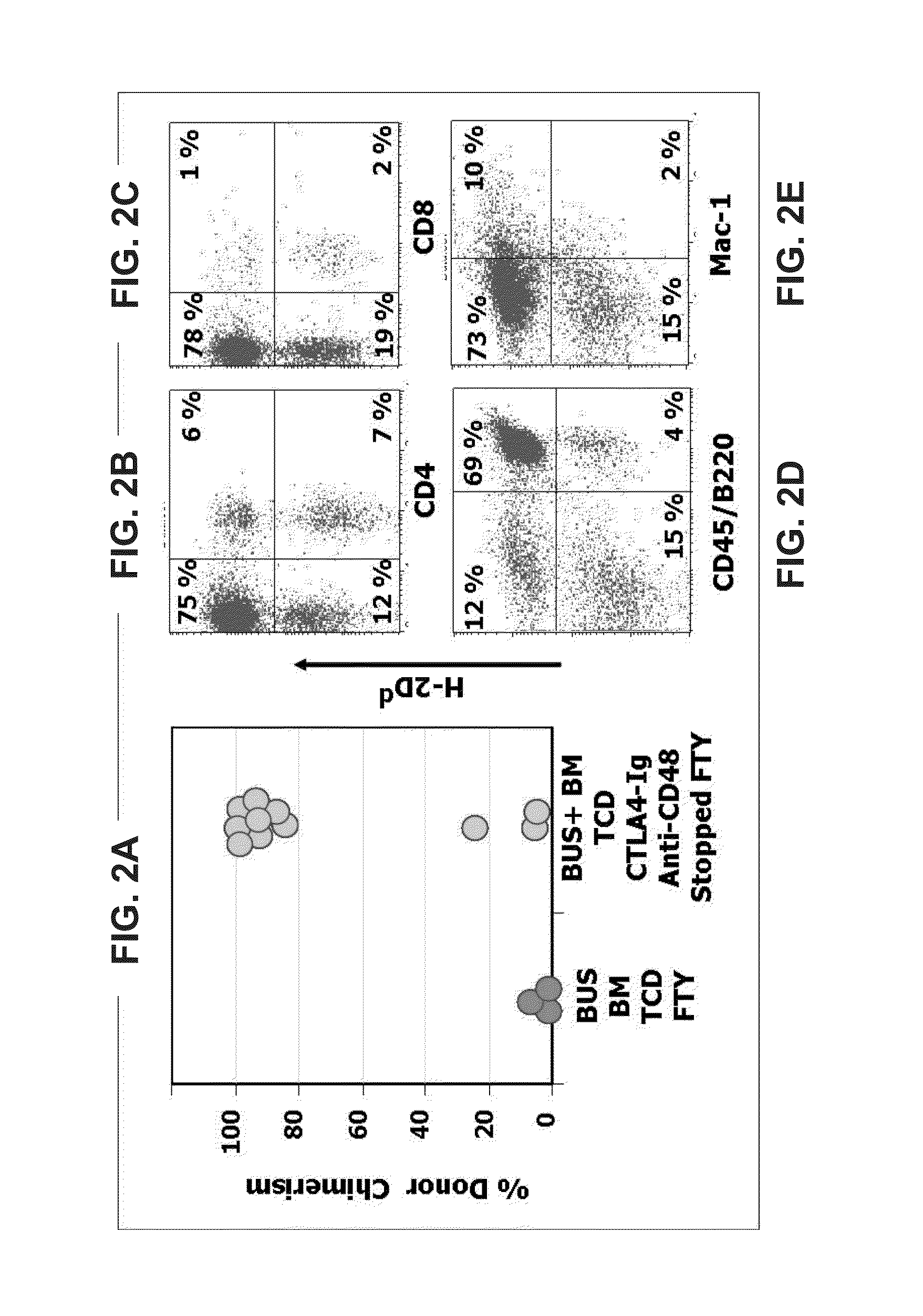
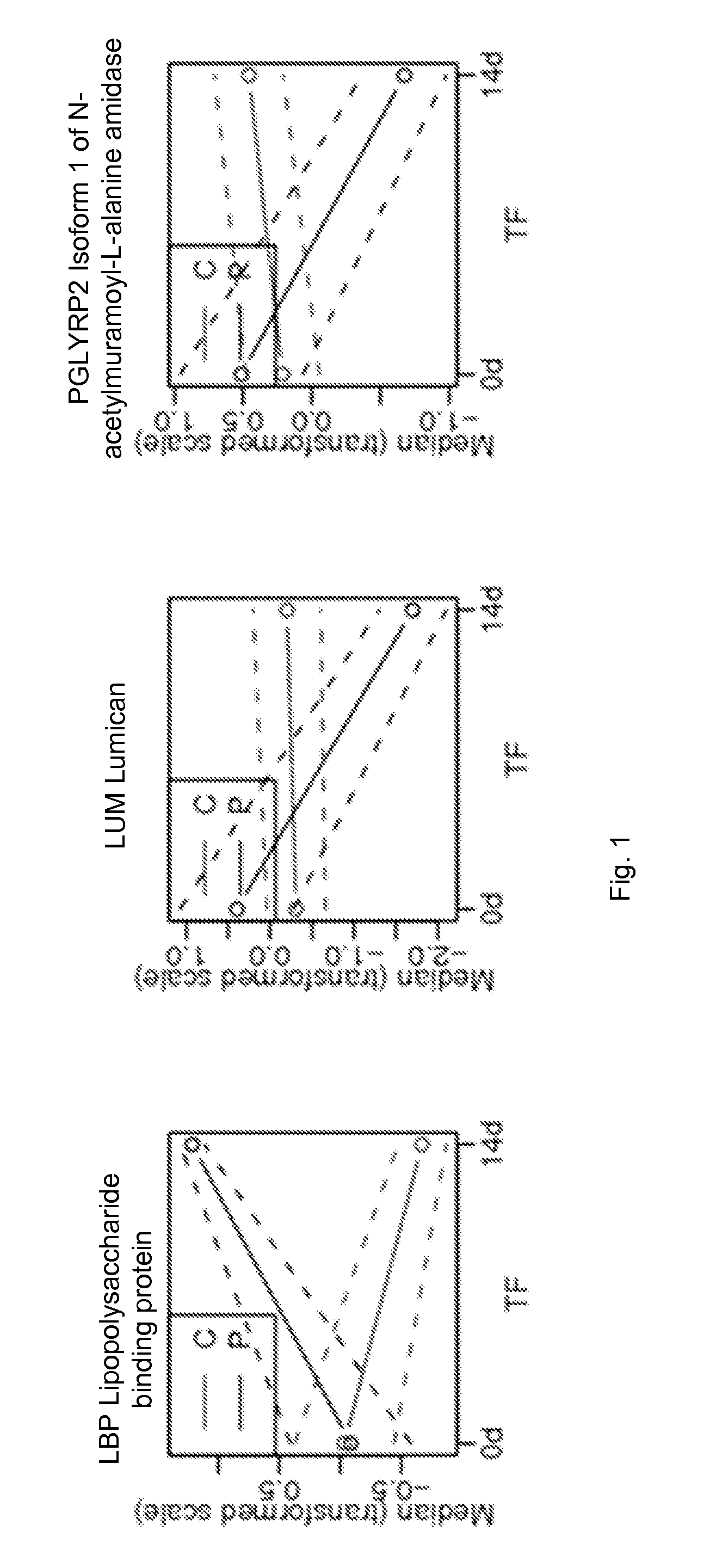
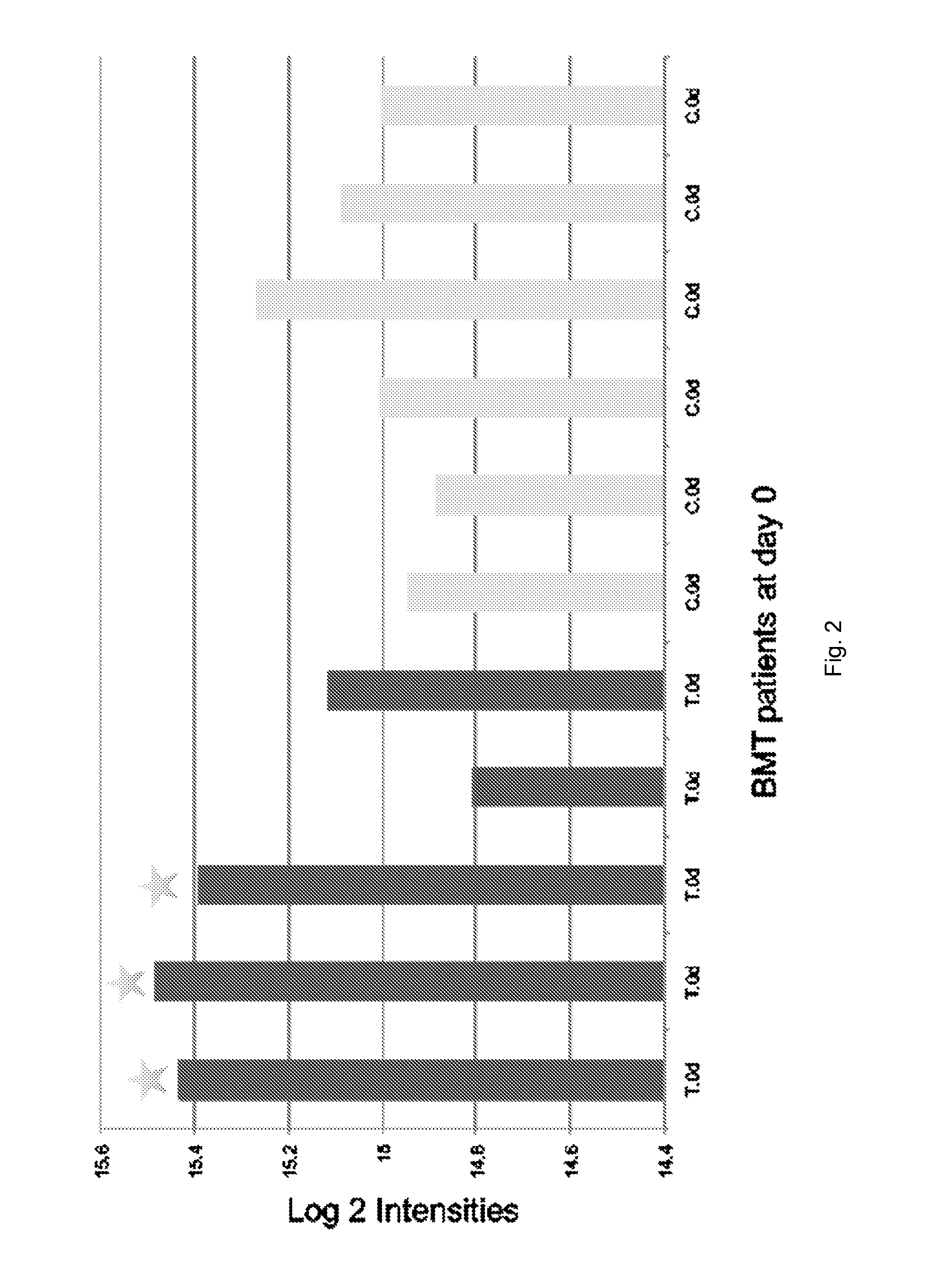
A method for characterizing the risk a subject will develop an autoimmune and / or alloimmune disease following tissue transplant includes obtaining a biological sample from the subject, wherein the subject has received the tissue transplant determining in the biological sample a level of at least one protein selected from Tables 1-4, comparing the measured level of the at least one protein to a control value, and characterizing a subject as at greater risk of developing an autoimmune disease and / or alloimmune disease if the level of at least one protein determined is increased or decreased compared to the control value.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Long-acting broad-spectrum chemotactic factor receptor inhibiting matter
A chimeric protein compound for durable and efficient suppression to different chemotactic factor receptors, its nucleic acid sequence, and the process for preparing and testing its products are disclosed. It can be used to prevent and cure HIV infection, tumor transfer, tissue transplant rejection and self immunopathy. Its advantages are high durability, broad spectrum, and high selectivity.
Owner:龚小迪
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com