Patents
Literature
31 results about "Propagation pattern" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
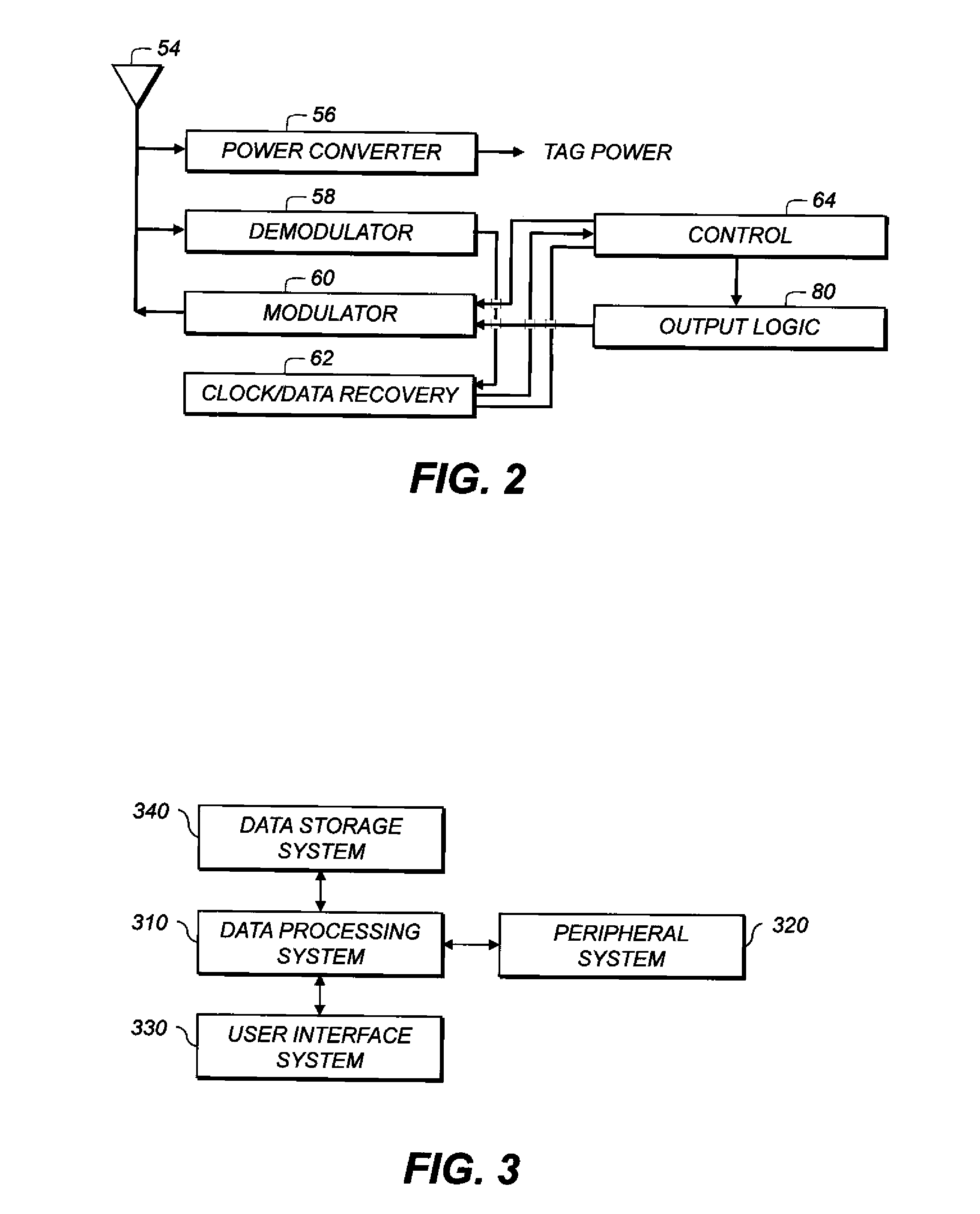
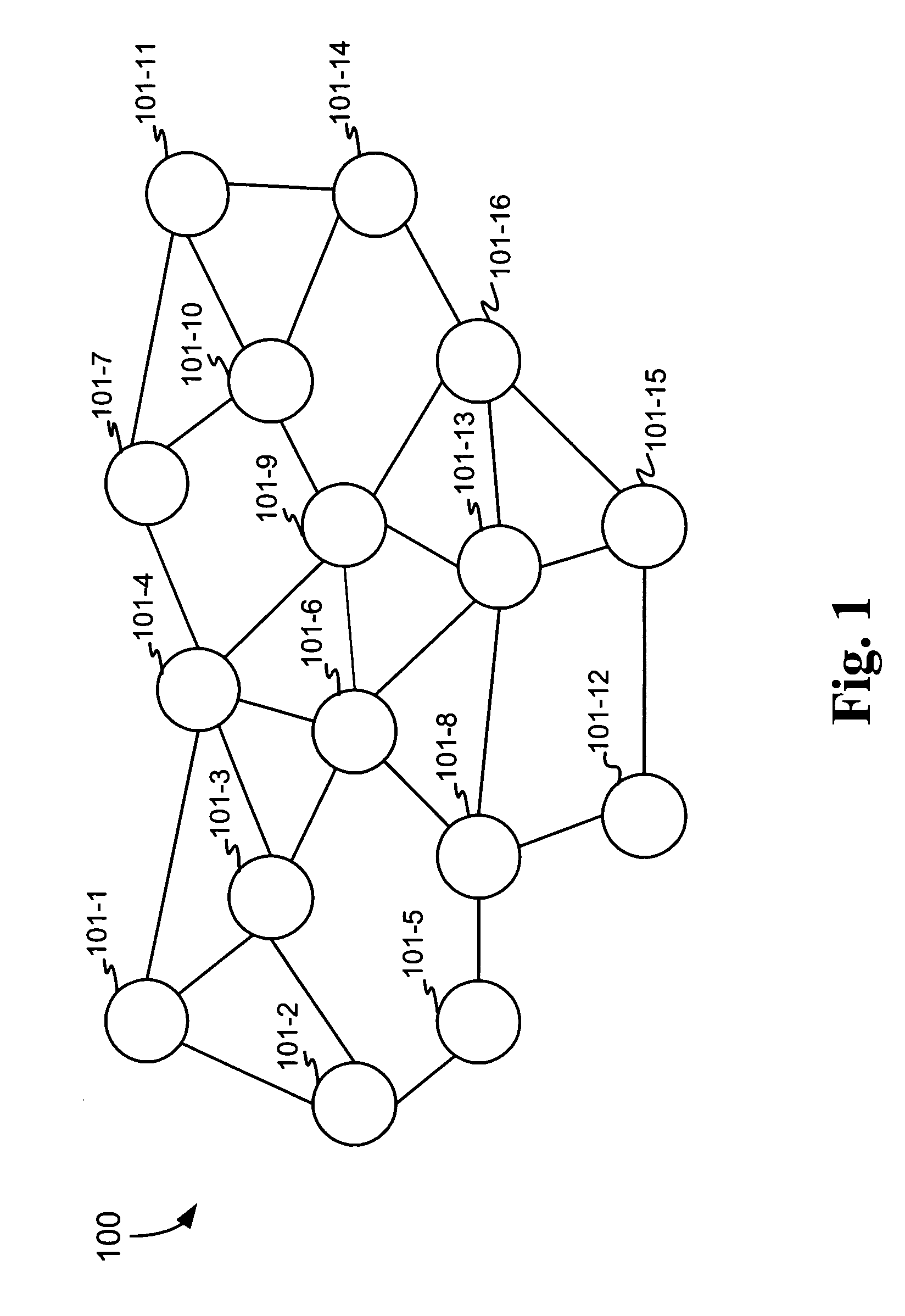
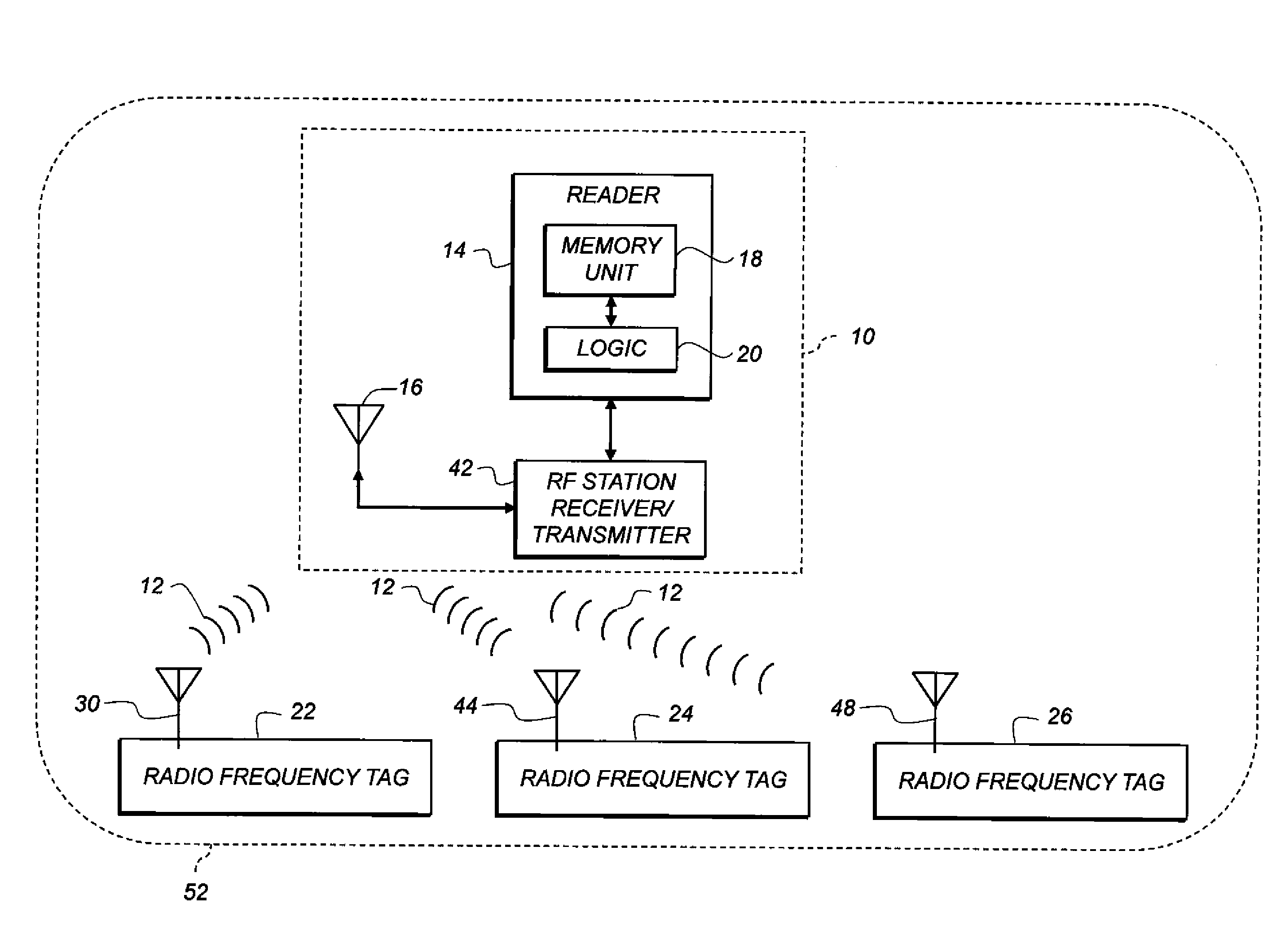
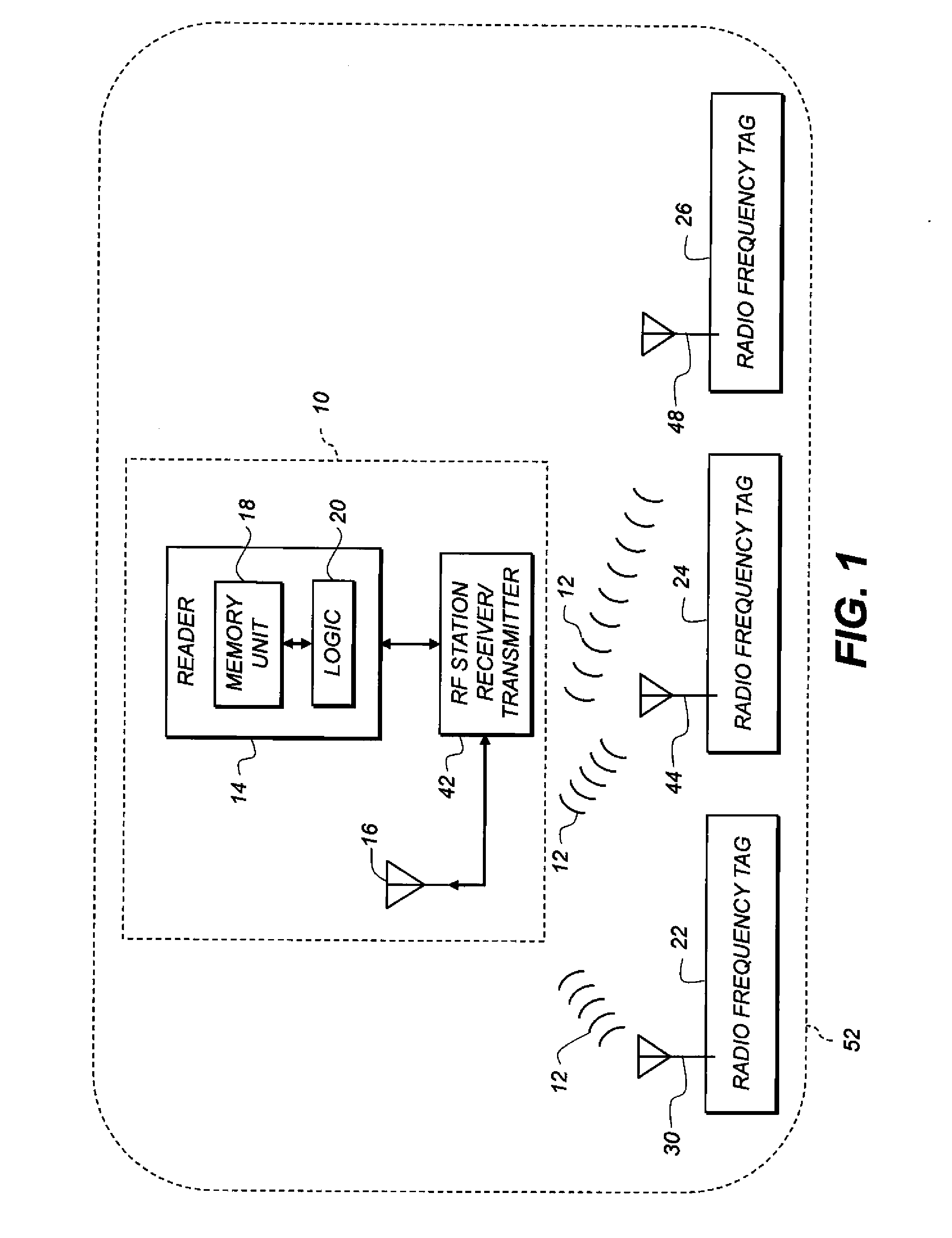
Virtual dynamic cellular infrastructure based on coordinate information
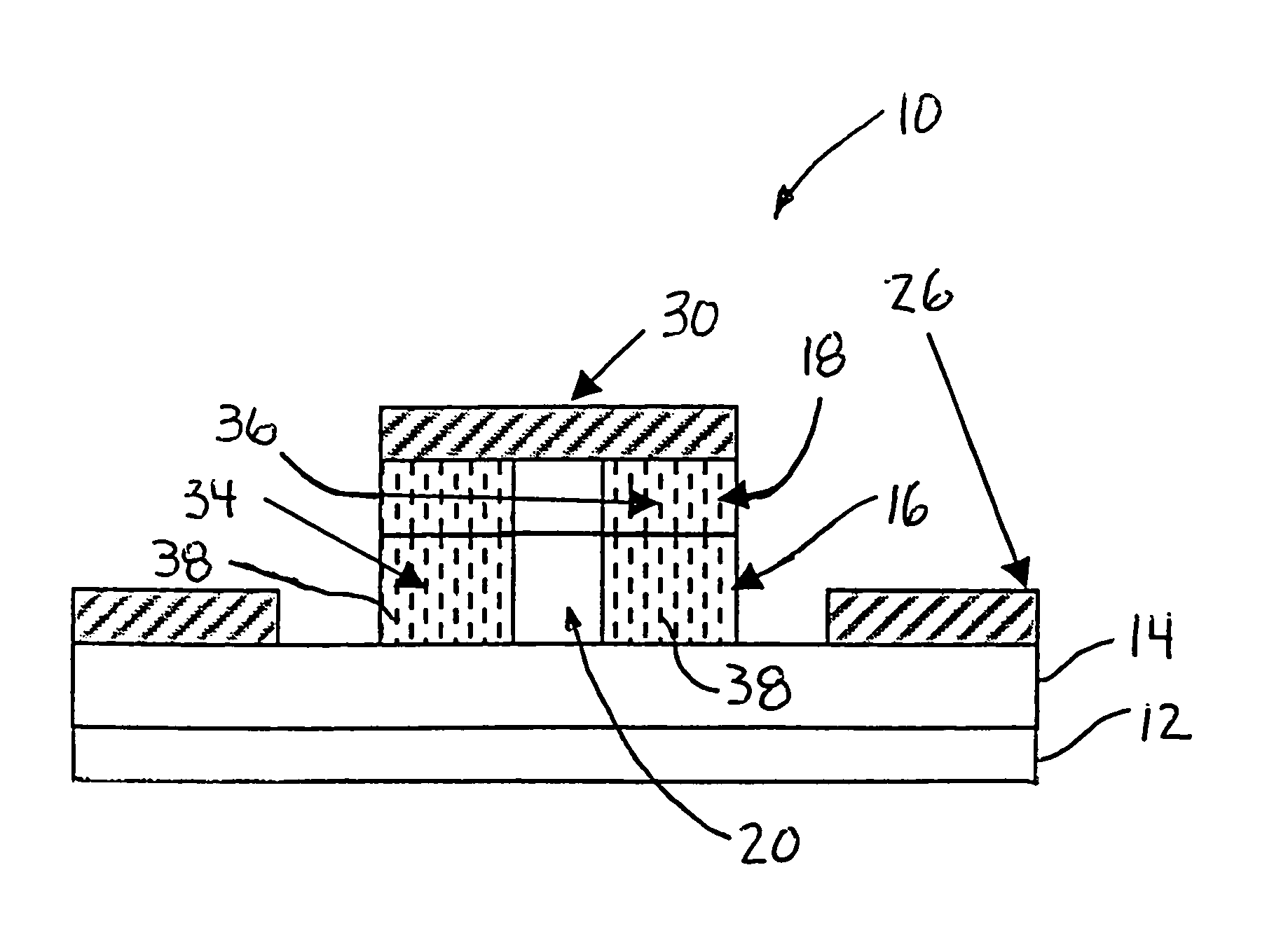
InactiveUS6839542B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork topologiesCommunications systemPropagation pattern
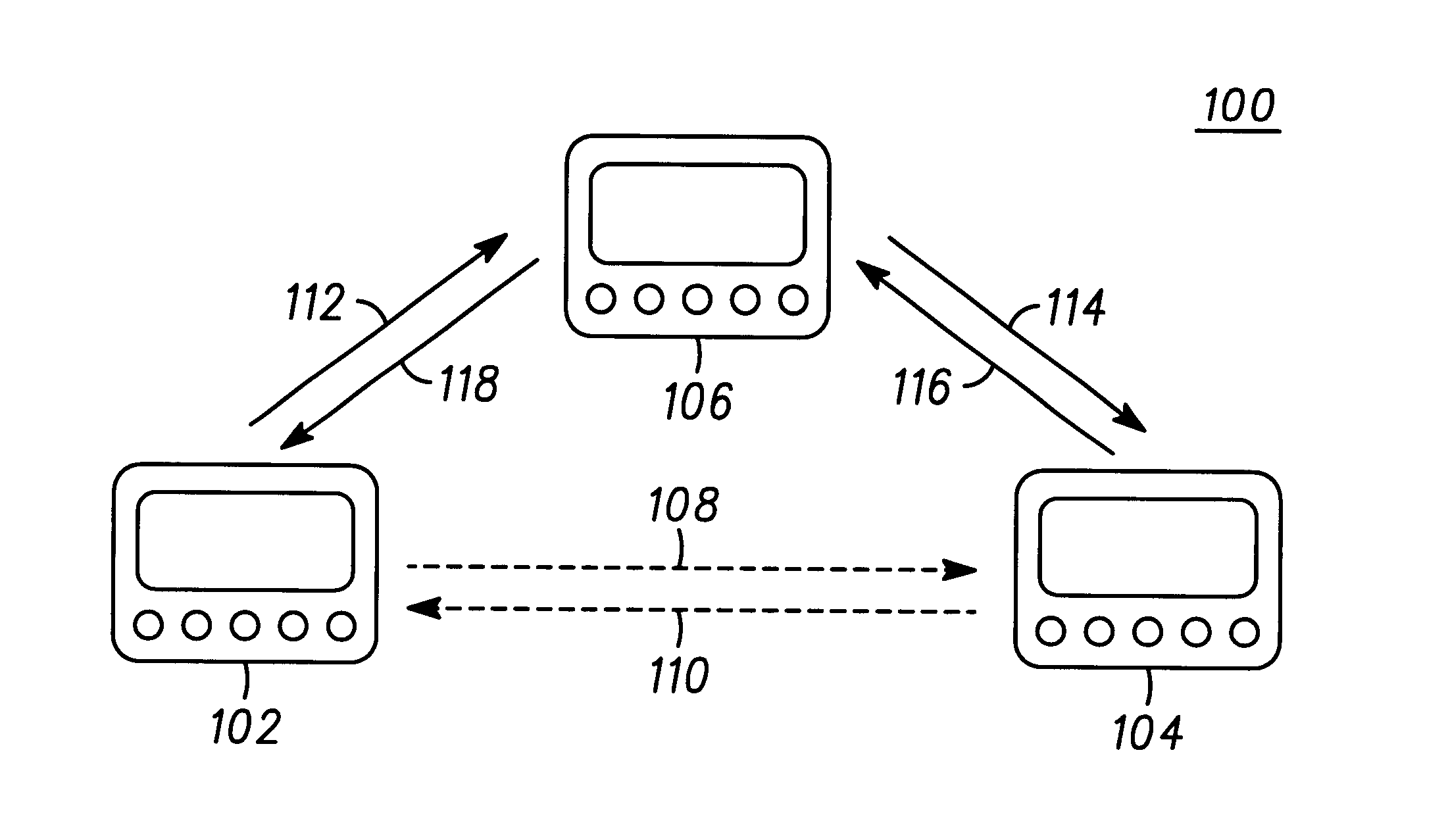
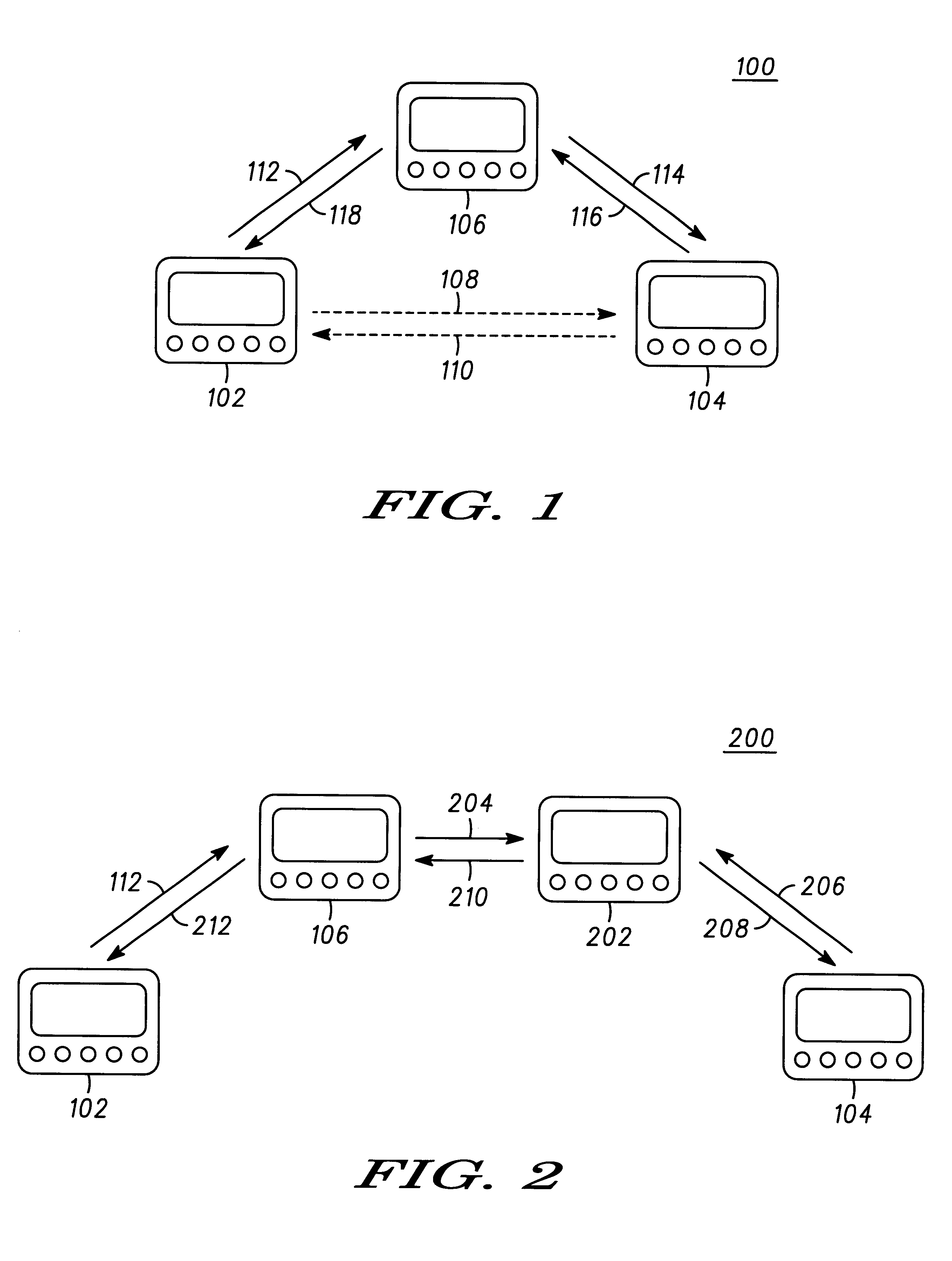
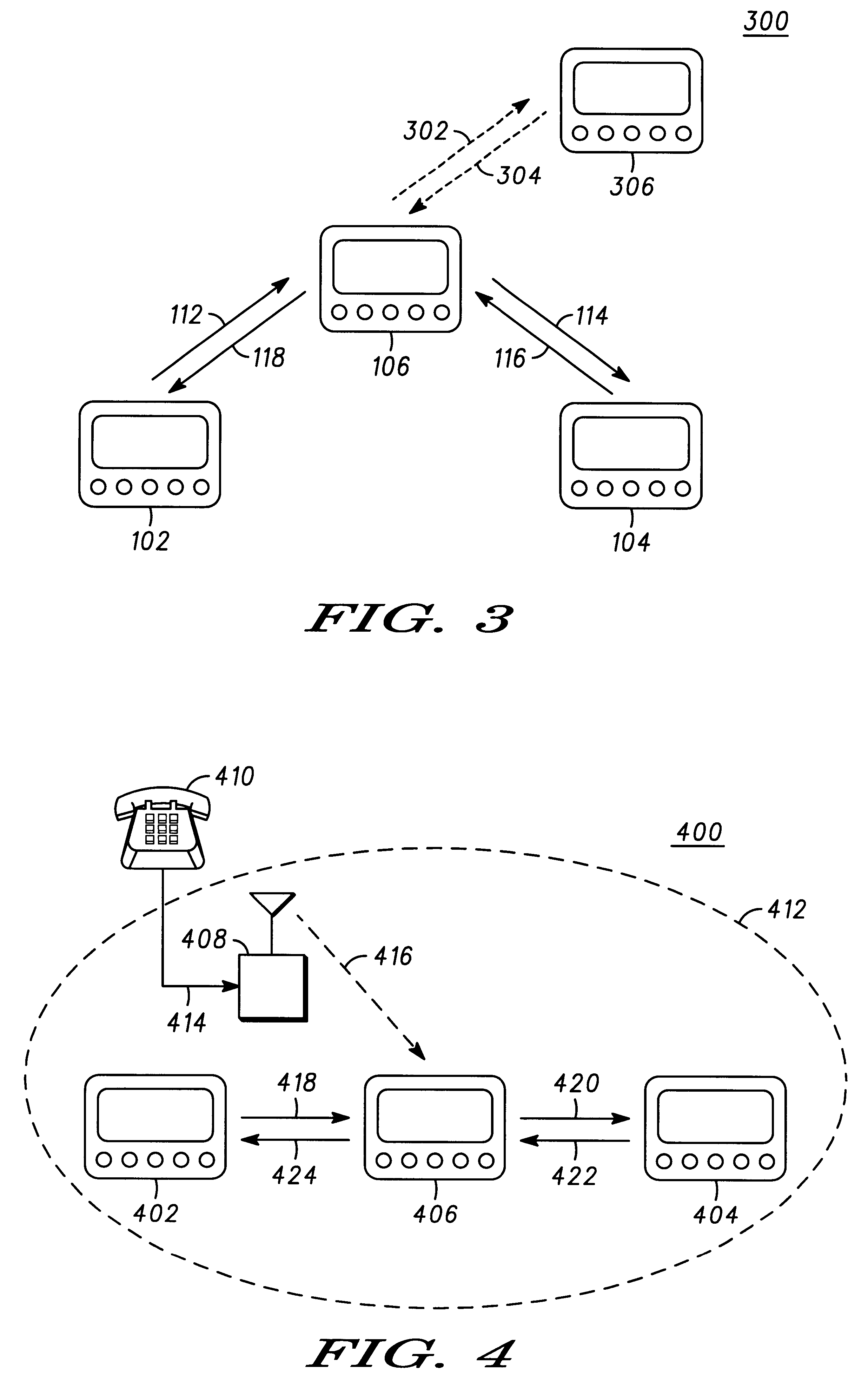
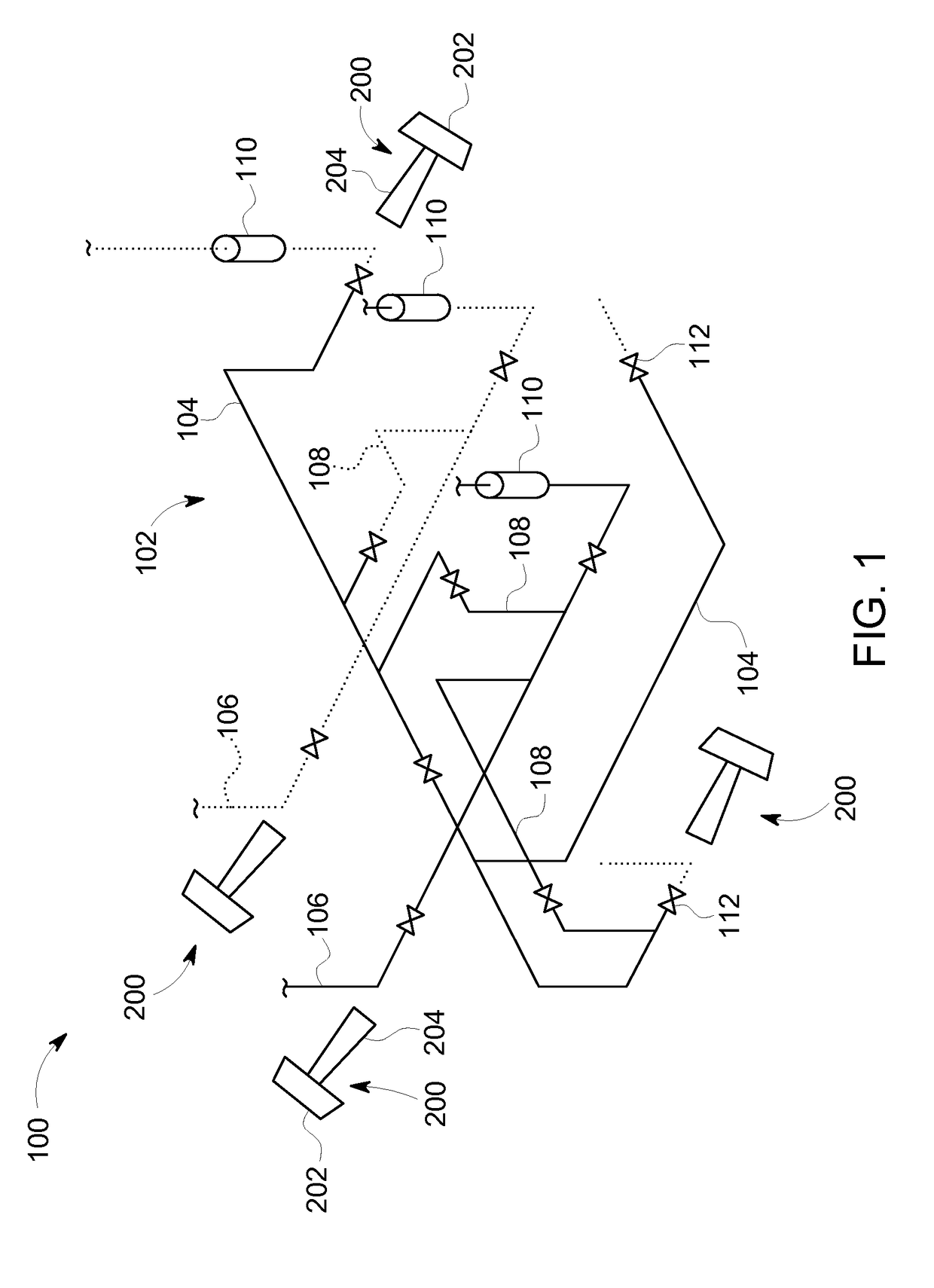
A wireless communication system (100) having portable communication devices (102, 104, and 106) capable of establishing direct terminal (102)-to-terminal (104) communication (108 and 110) and indirect terminal (102)-to-terminal (104) communication (112, 118 and 114, 116) through another terminal (106) without having a fixed base station. A portable communication device (106) used as a terminal is capable functioning as a router for communication (112, 118 and 114, 116) between other portable devices (102 and 104) in the system. While functioning as a router, the portable device (106) is capable establishing and maintaining a separate direct communication (302 and 304) with another portable communication device (306). A wireless communication system(600) utilizing predetermined cell- and location-specific communication parameters (808) and non-repeating propagation patterns (1200) for portables communication devices in the system for establishing communications.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
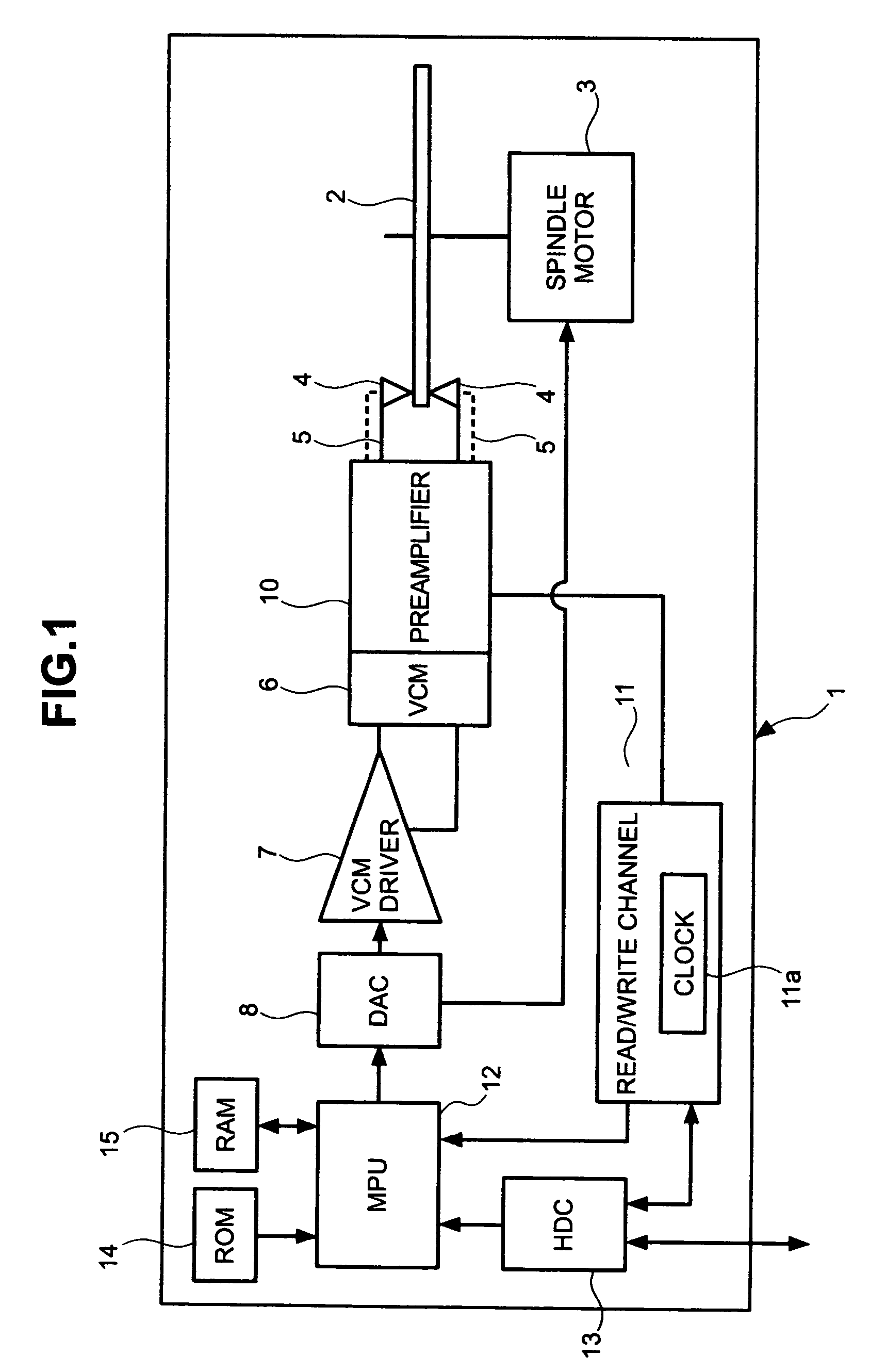
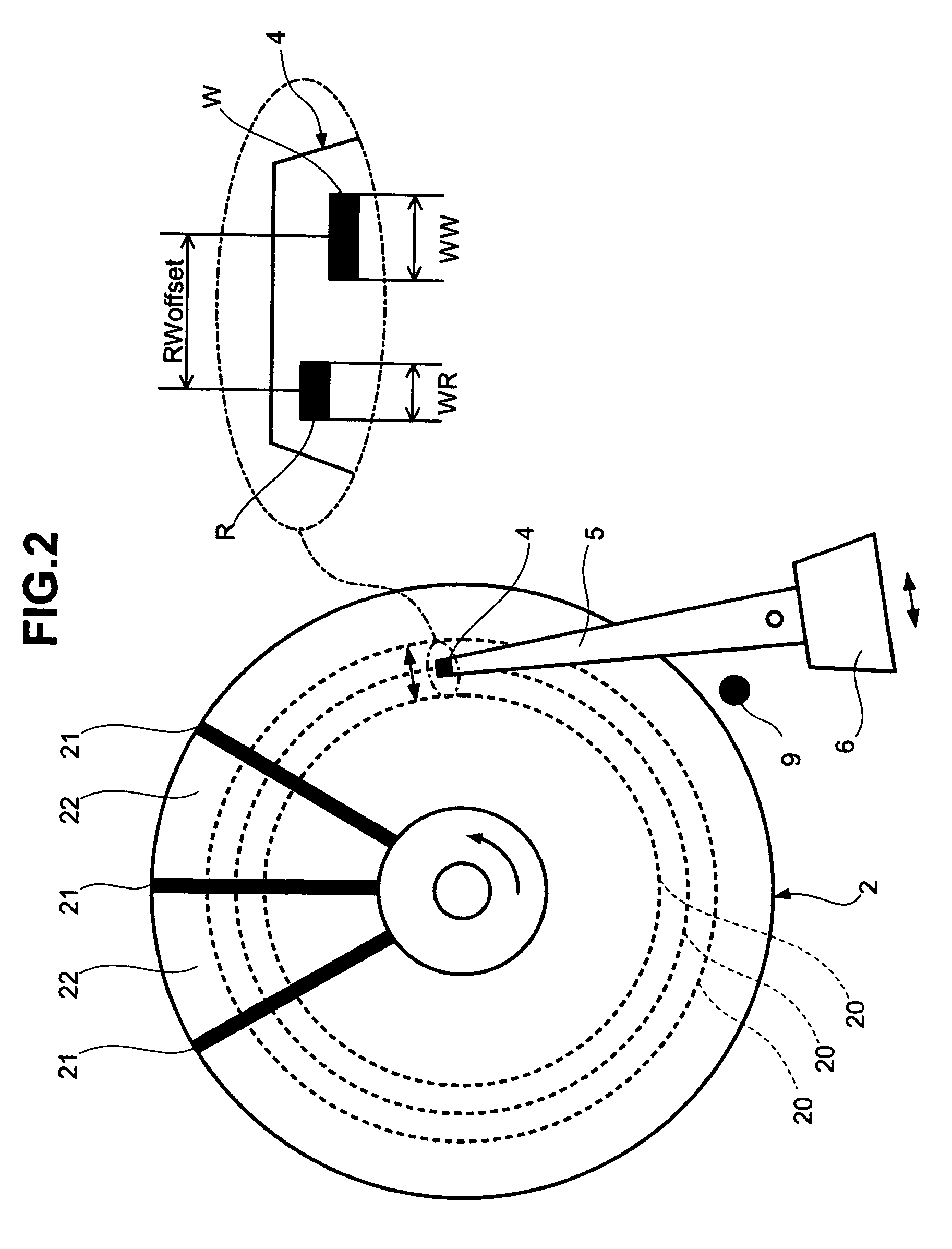
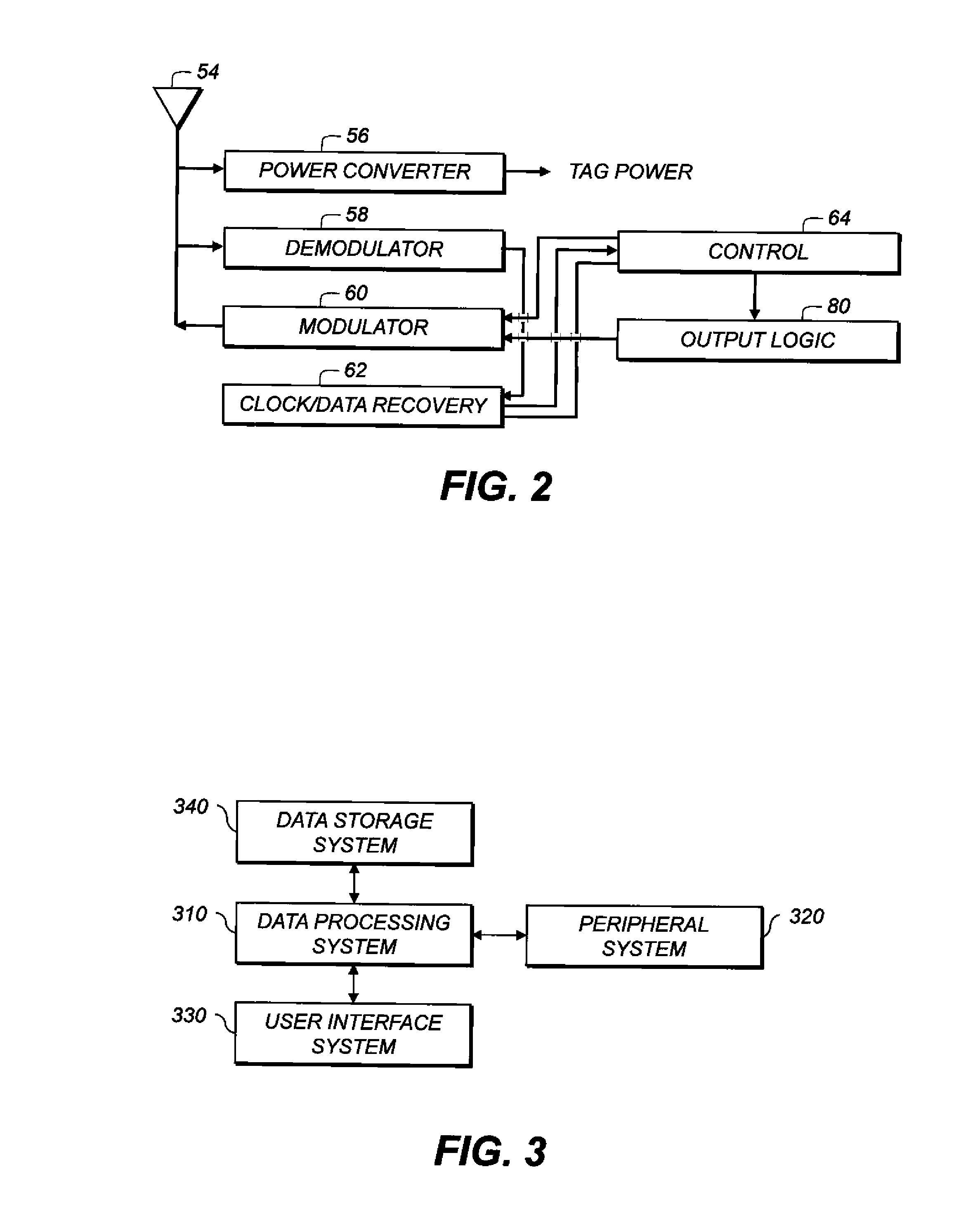
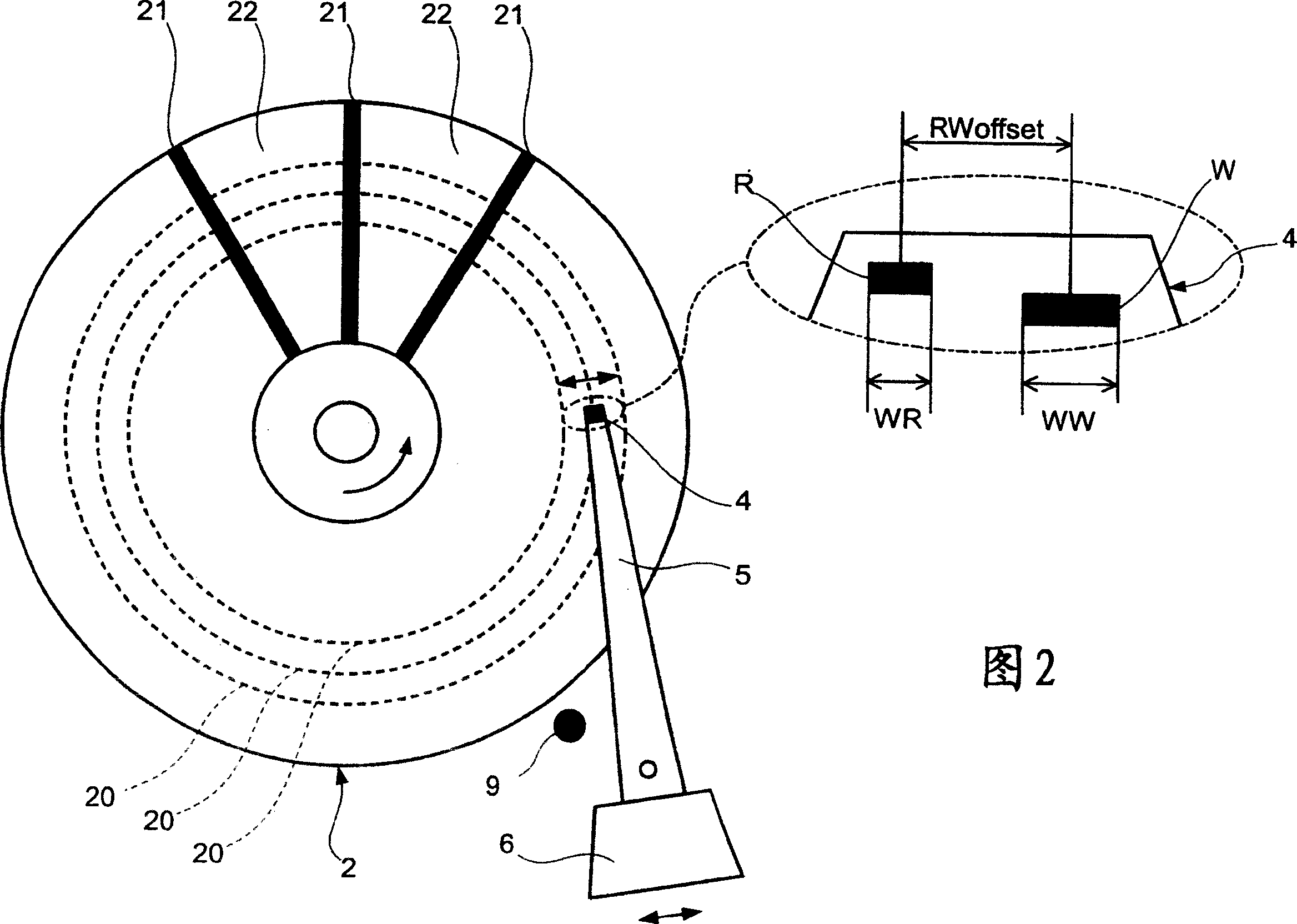
Servo information write method, servo control method, data storage device, and program
InactiveUS7019933B2Improve positioning control accuracyHigh positioning accuracyTrack finding/aligningRecord information storagePropagation patternPosition control
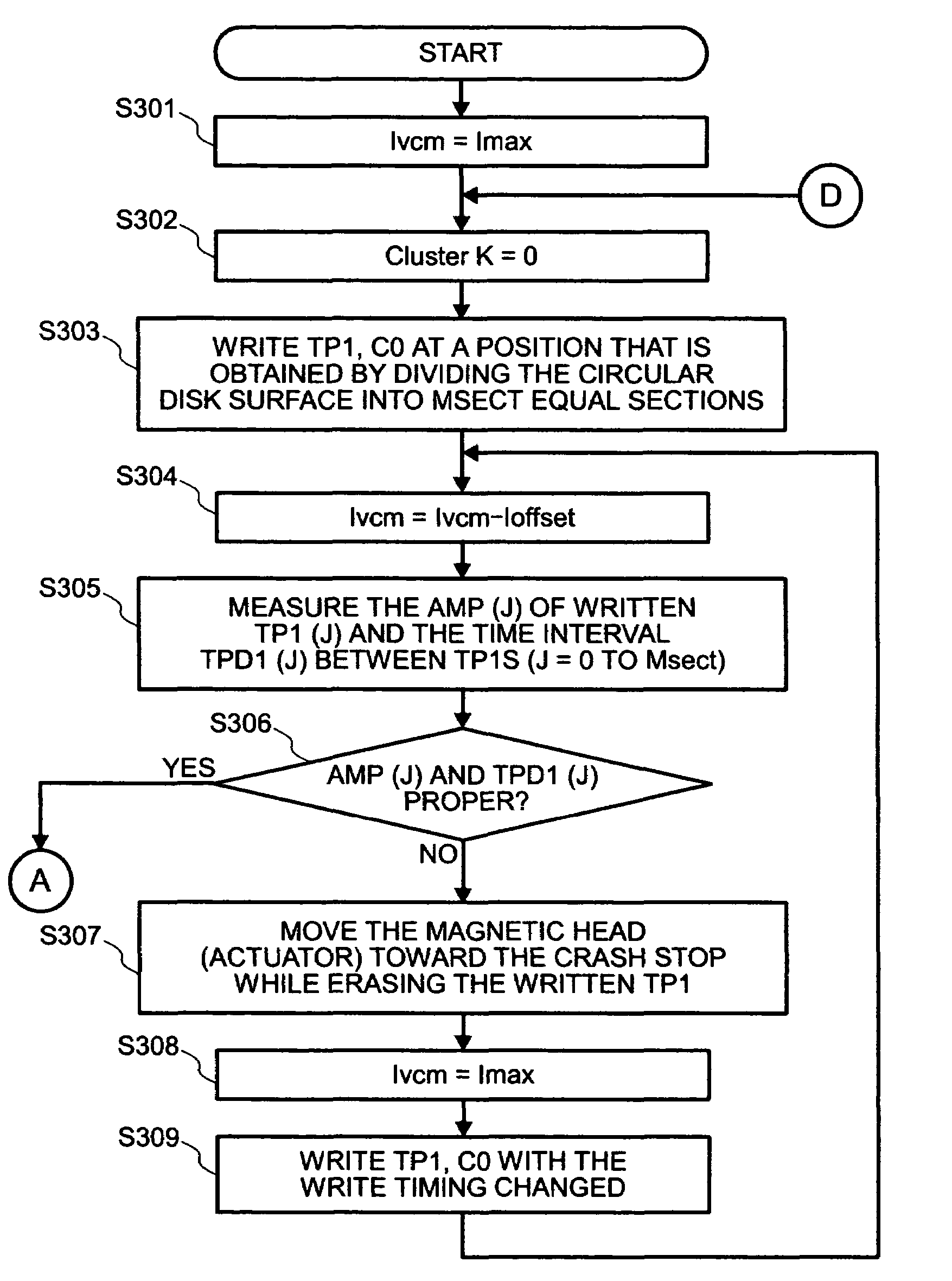
A servo system wherein a read head R detects a servo pattern that is written on a magnetic disk by a write head W. Position control of the write head W is exercised in accordance with the detected servo pattern, and the read head R detects a propagation pattern that is written on the magnetic disk by the write head W. Position of the write head W is corrected in accordance with the detected propagation pattern.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
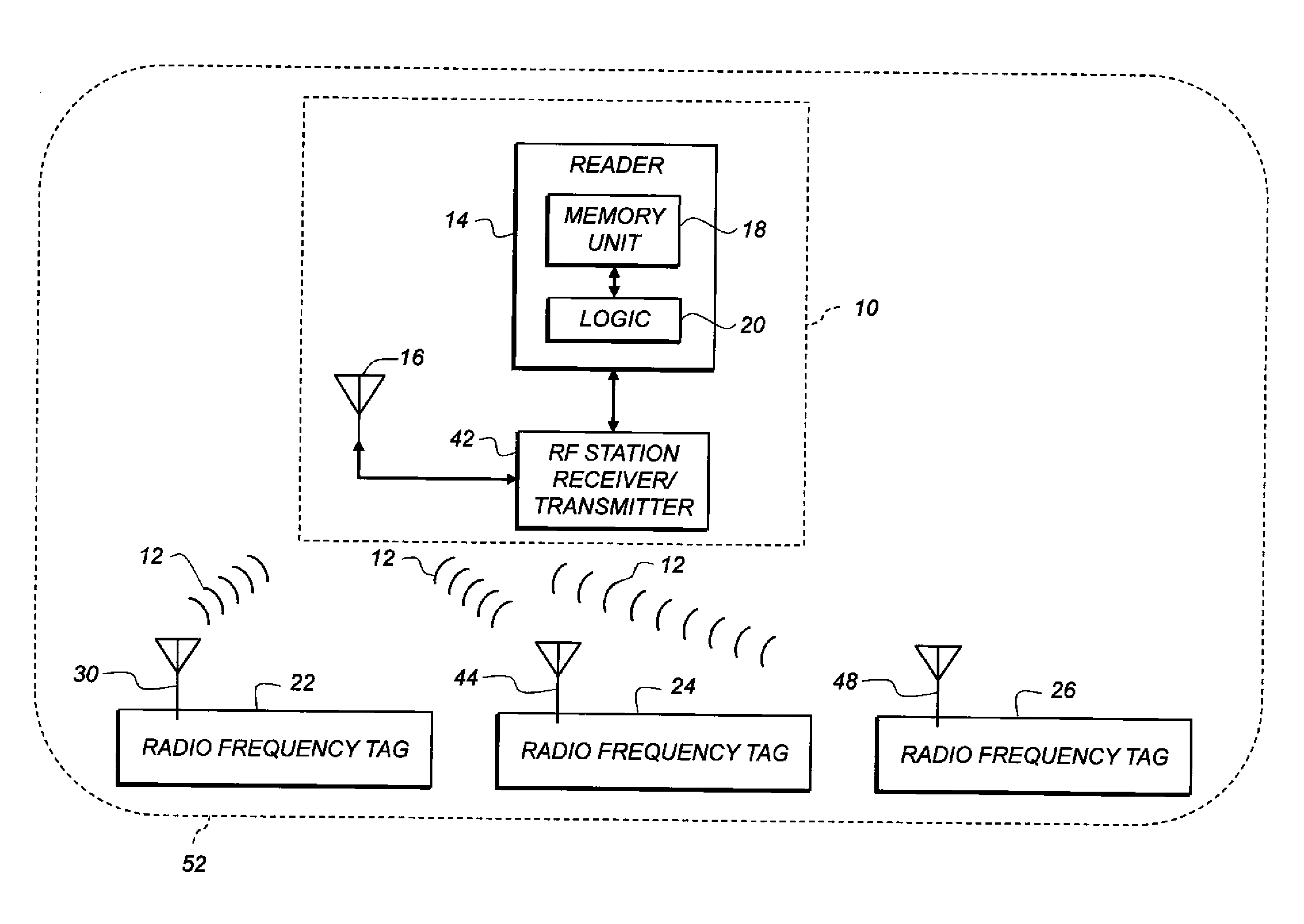
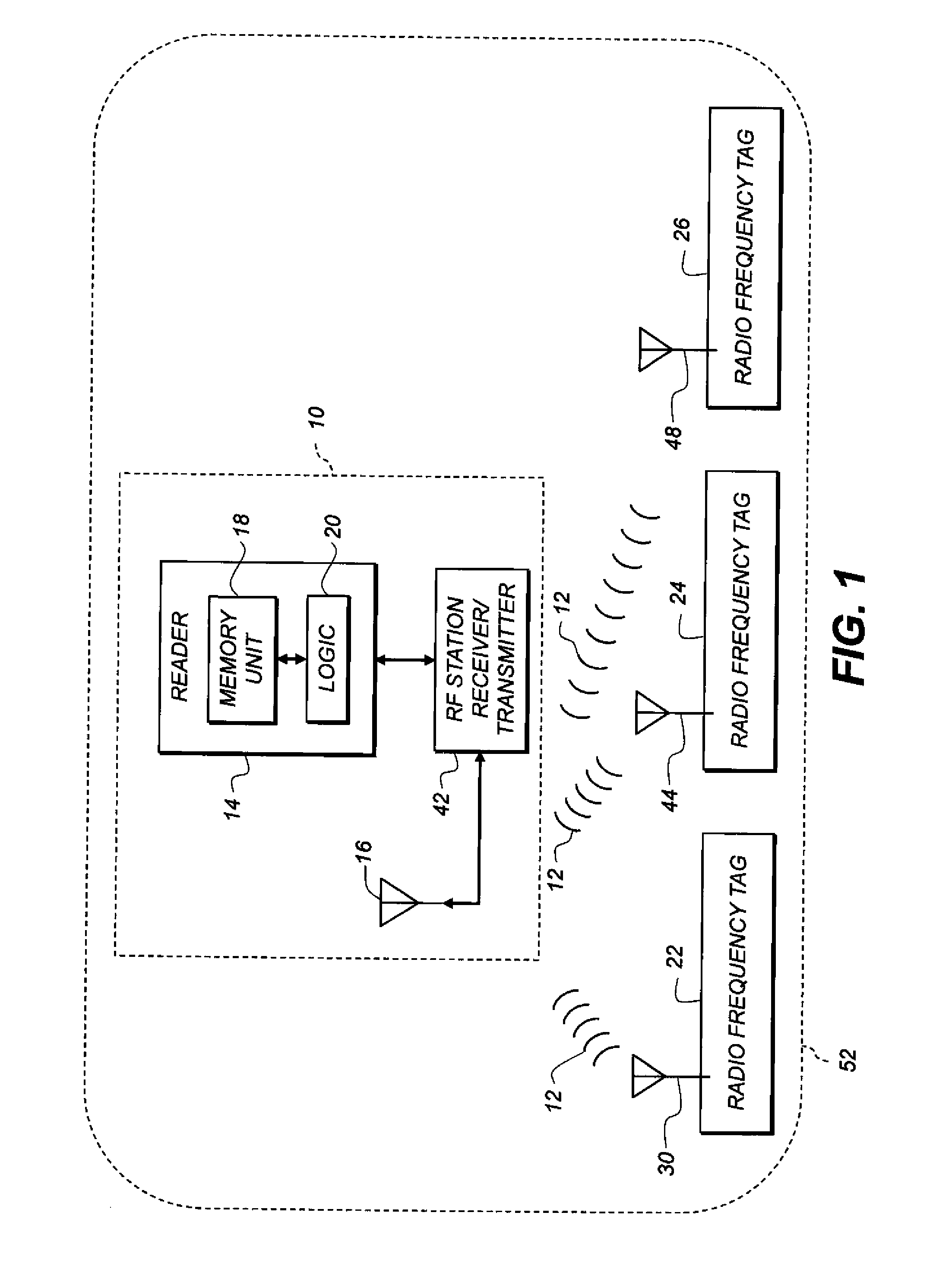
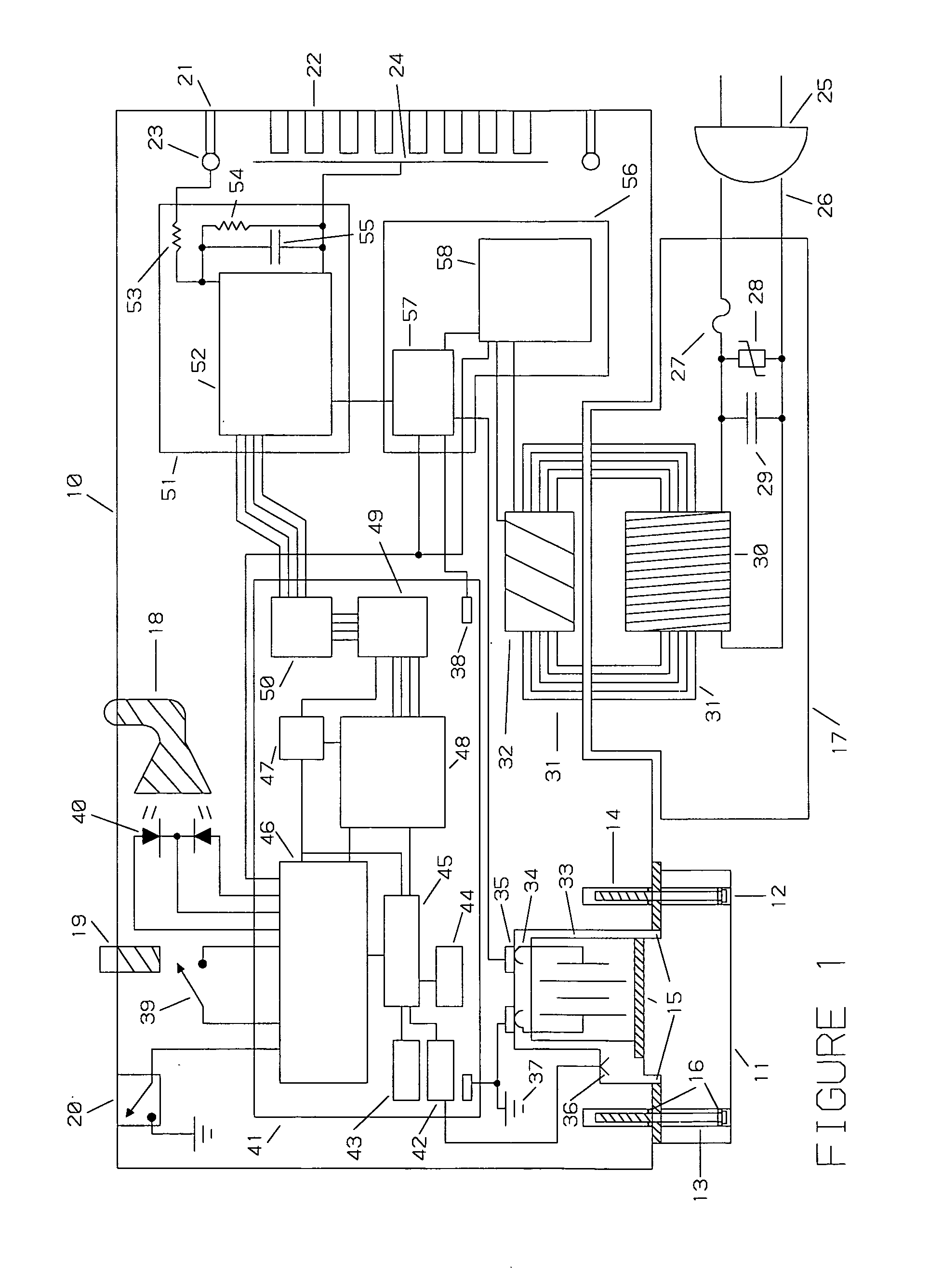
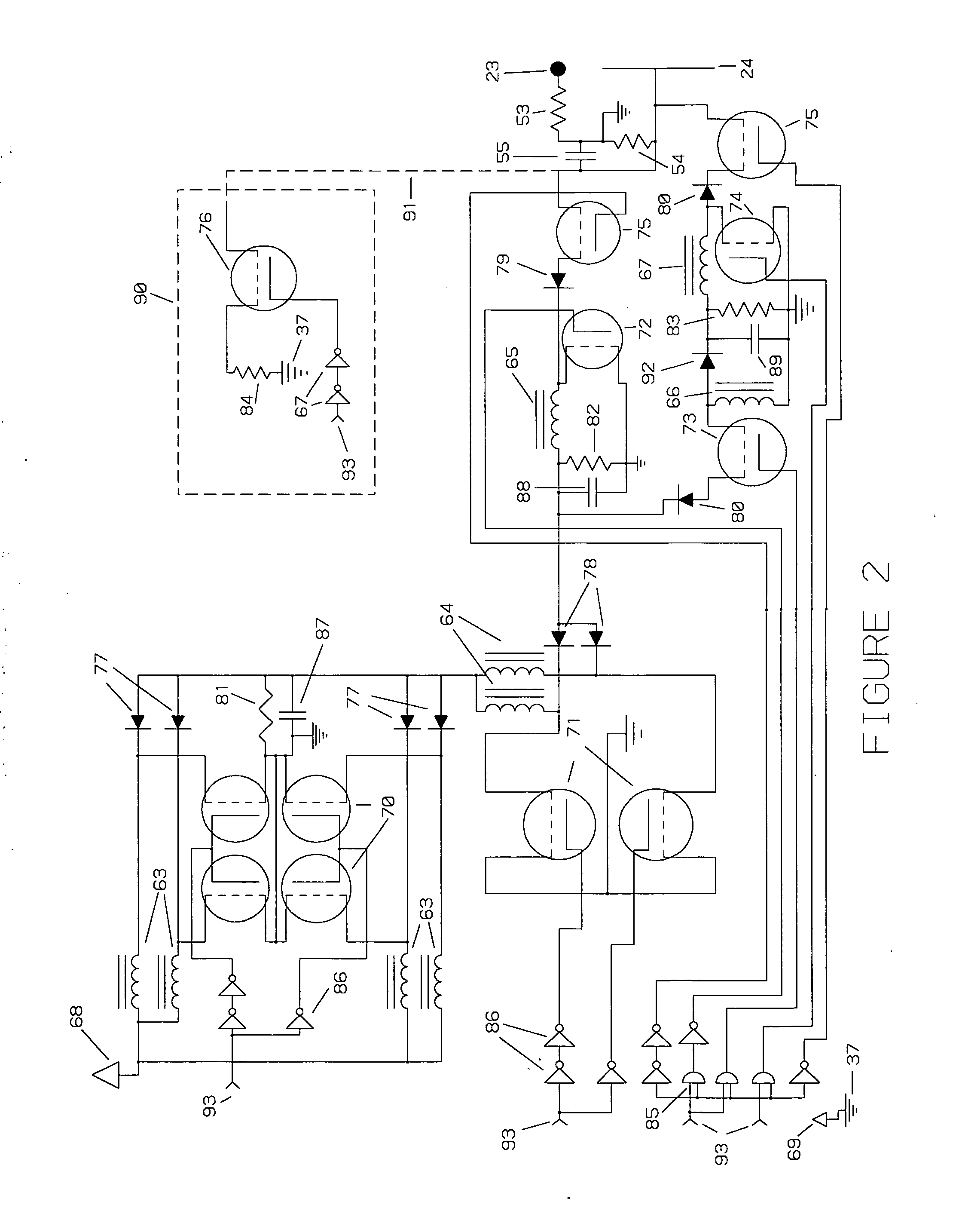
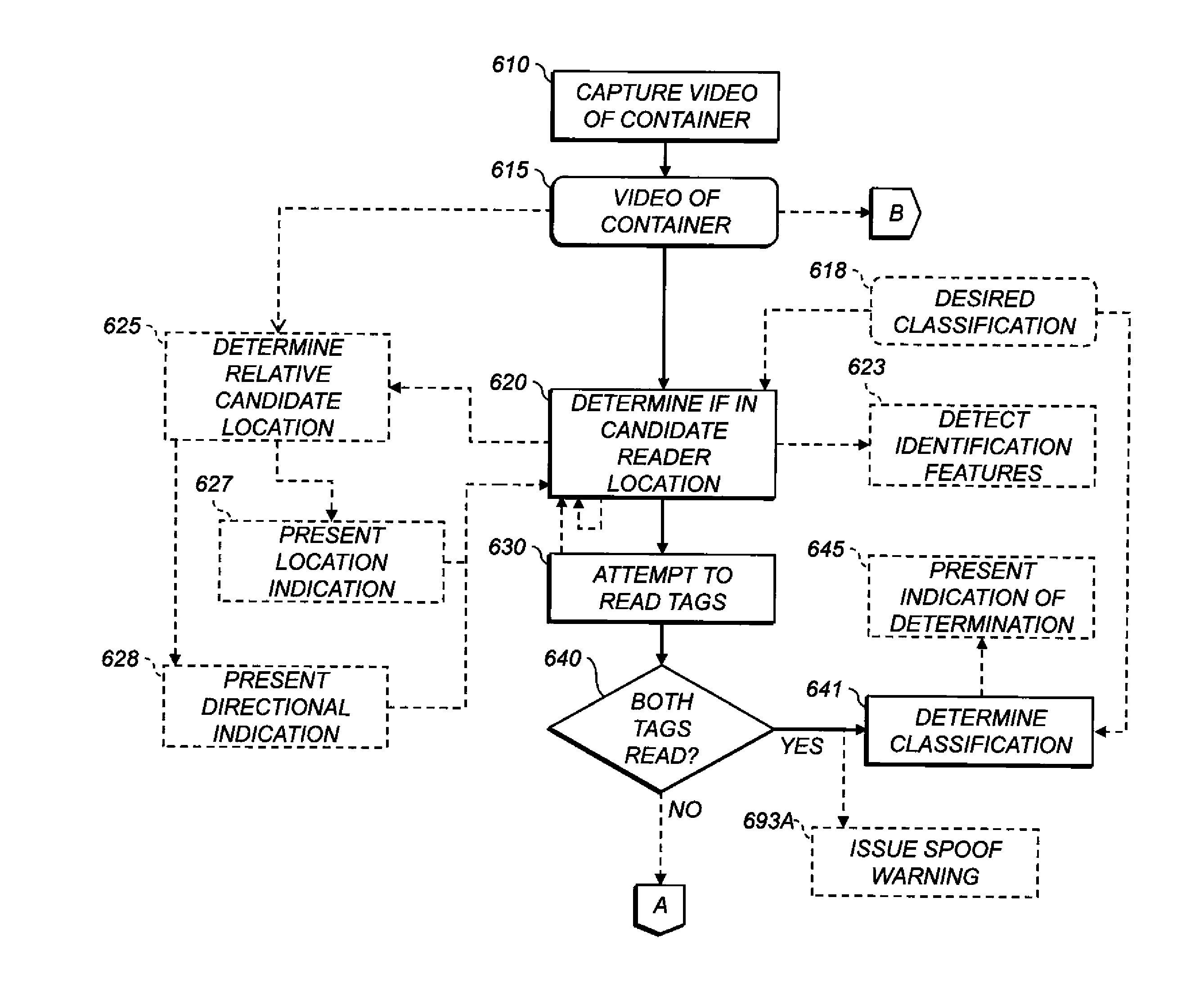
Container-classification identification using directional-antenna RFID
InactiveUS20130314534A1Clear feedbackProvide goodColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsPropagation patternDirectional antenna
A classification of a container is identified using a mobile station including an image capture device and an RFID reader having a reader antenna. The container has two RFID tags affixed thereto at respective, different locations. Each tag has a directional antenna steered in a different direction, so that a reader location is defined in the intersection of the antenna propagation patterns. Using the image capture device, one or more images of the container are captured. A controller determines, using the captured image data, whether the mobile station is in a candidate reader location. When the mobile station is in the candidate reader location, the RFID reader attempts to read both tags. If both tags are read while the mobile station is in the candidate reader location, the controller determines the classification of the container is a classification corresponding to the candidate reader location.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
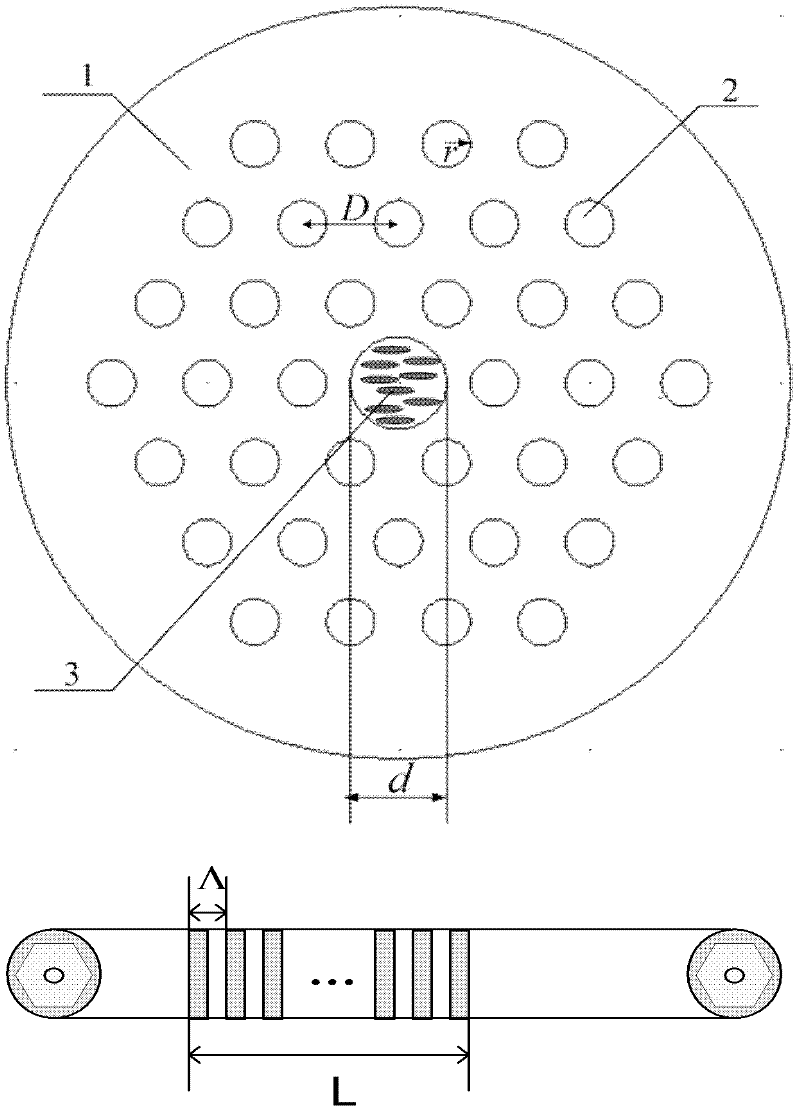
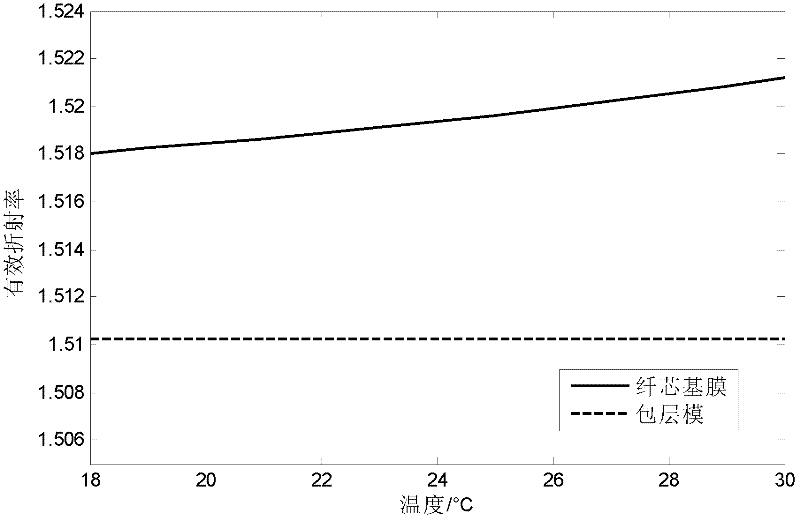
Photonic crystal fiber grating temperature sensor with tunable wavelength
InactiveCN102243113AChanging the Mode Refractive IndexNo need to change geometryCladded optical fibreThermometers using physical/chemical changesGratingPropagation pattern
The invention relates to a temperature sensor. In order to solve the problem that the detecting waveband of the conventional photonic crystal fiber sensor cannot be changed once the photonic crystal fiber sensor is manufactured, the invention provides a photonic crystal fiber grating temperature sensor with tunable wavelength. According to the technical scheme of the invention, a photonic crystal fiber for sensing is provided with a cladding and a long-period grating written in a fiber core, wherein the cladding consists of air vent holes which are in triangular periodical arrangement, the air vent holes in the center of the cladding serve as the fiber core, and the radius of the fiber core is larger than that of the air vent holes in the cladding; temperature sensitive nematic liquid crystals are filled in the fiber core; the central wavelength of the long-period grating is determined by the period of a controlled long-period grating; the refractive index of the nematic liquid crystal changes with the temperature of the surrounding working environment, and the propagation pattern through grating coupling is controlled by controlling the temperature of the working environment of the liquid crystal, so that temperature change represents drifting of spectrum, and thus the wavelength tunable temperature sensing characteristic is realized. The invention is mainly applied to design and manufacture of temperature sensors.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
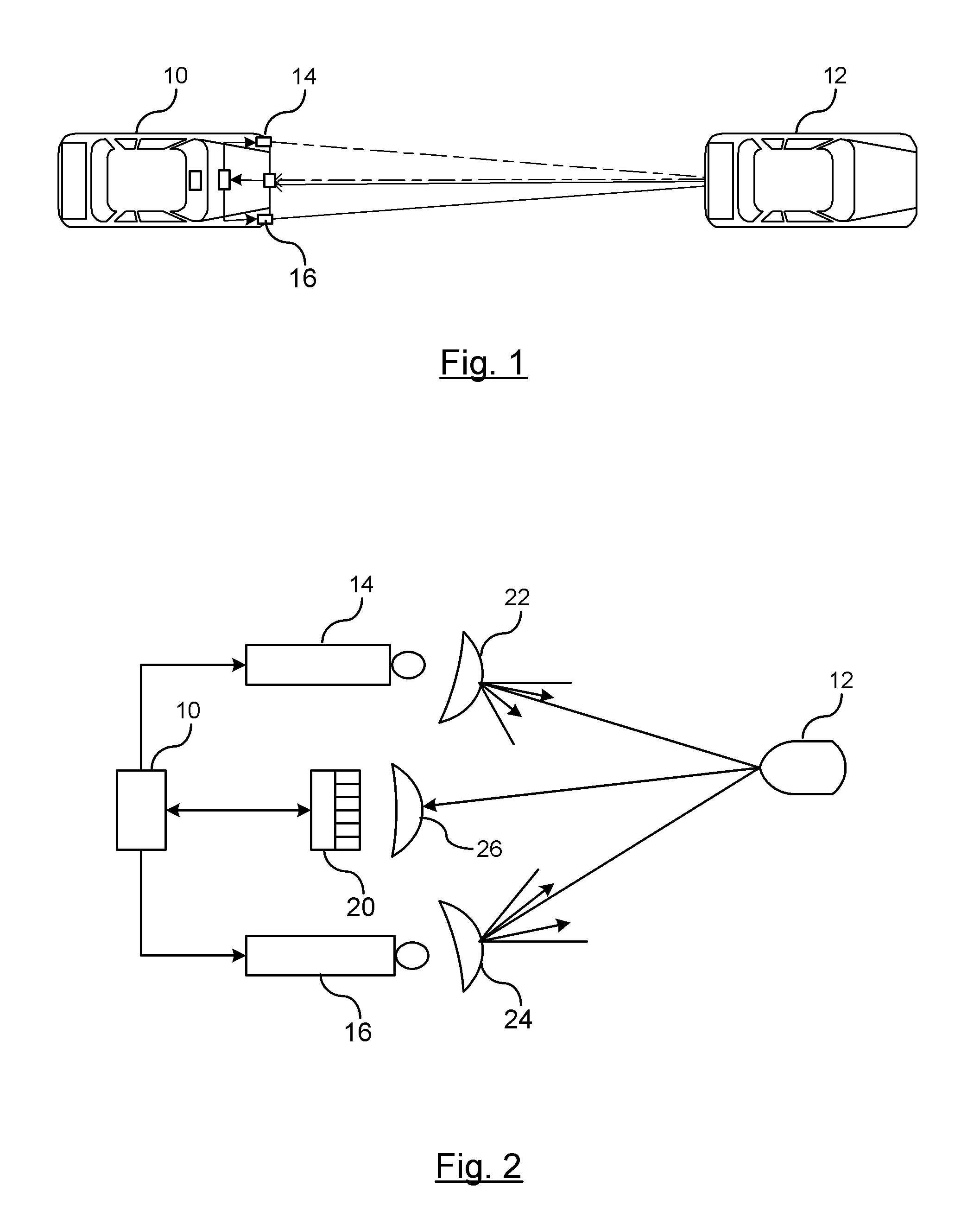
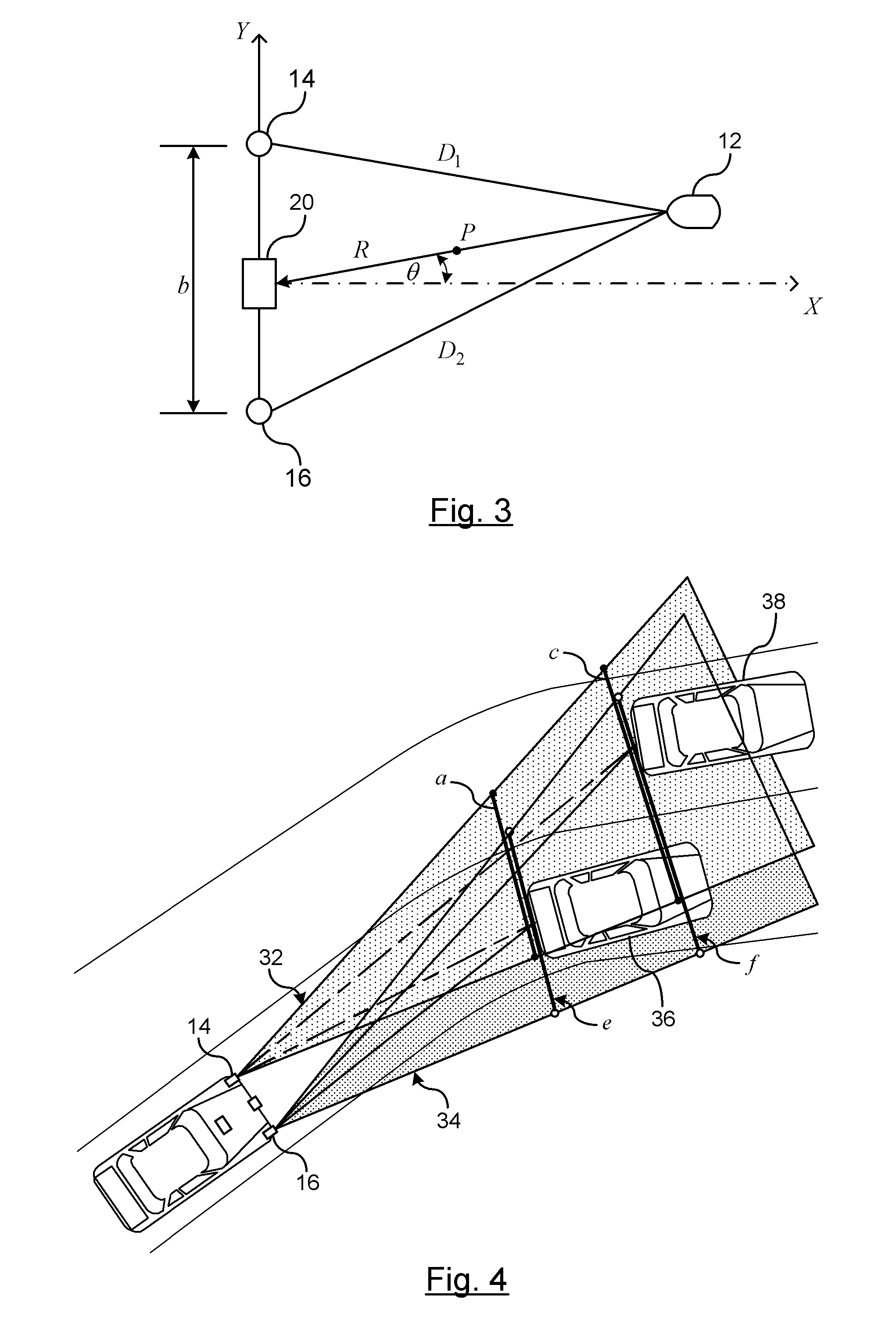
Method and apparatus for an object detection system using two modulated light sources
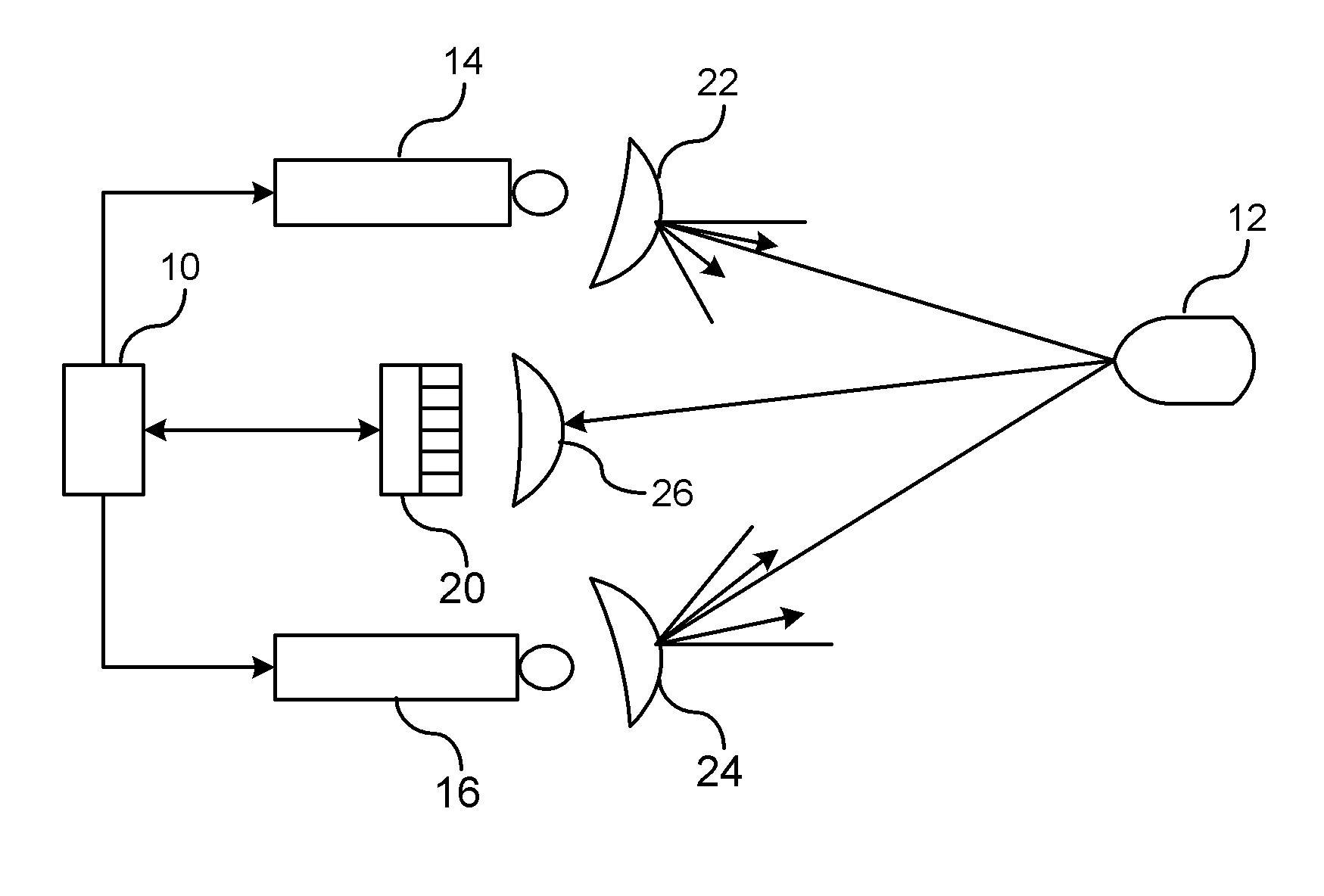
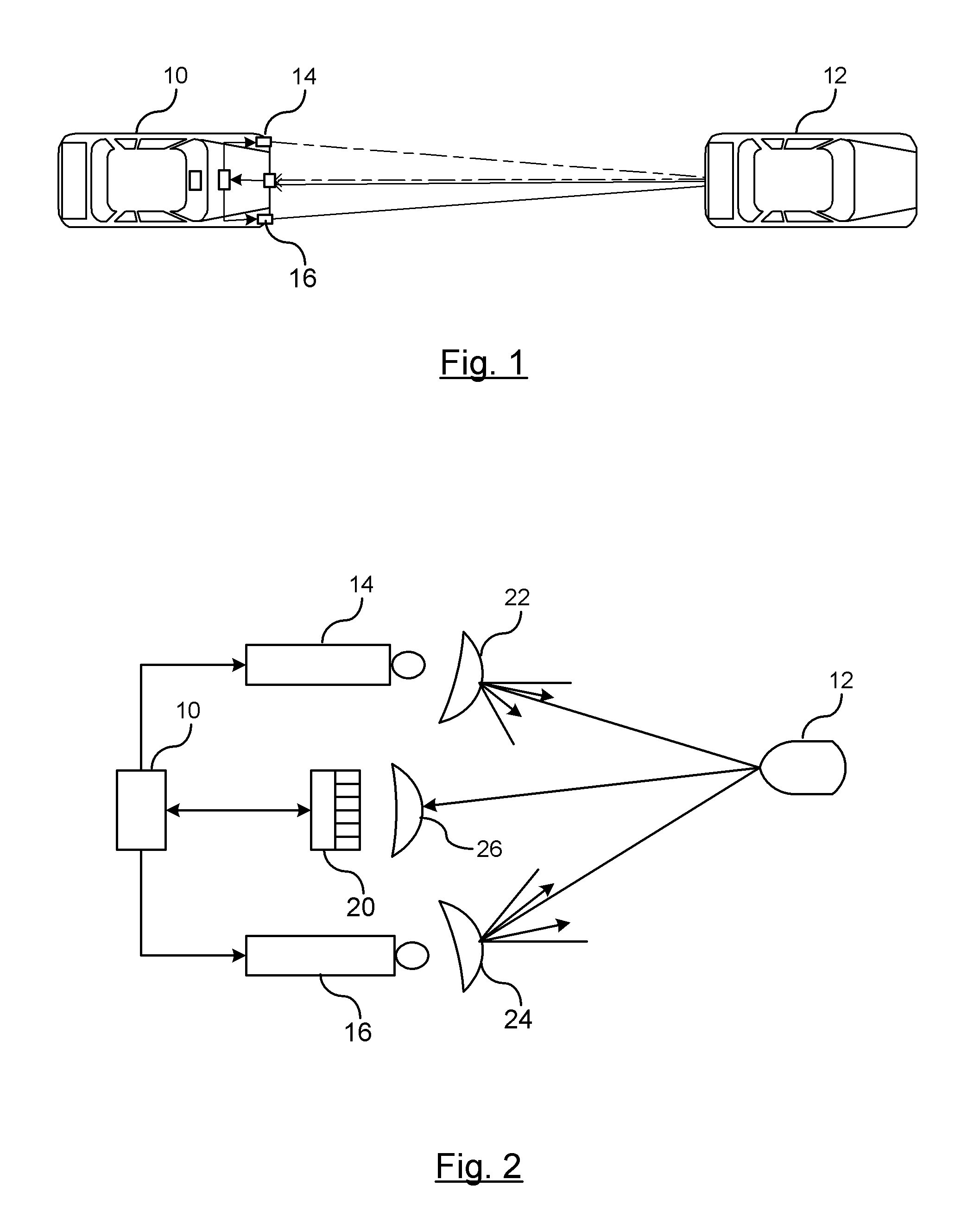
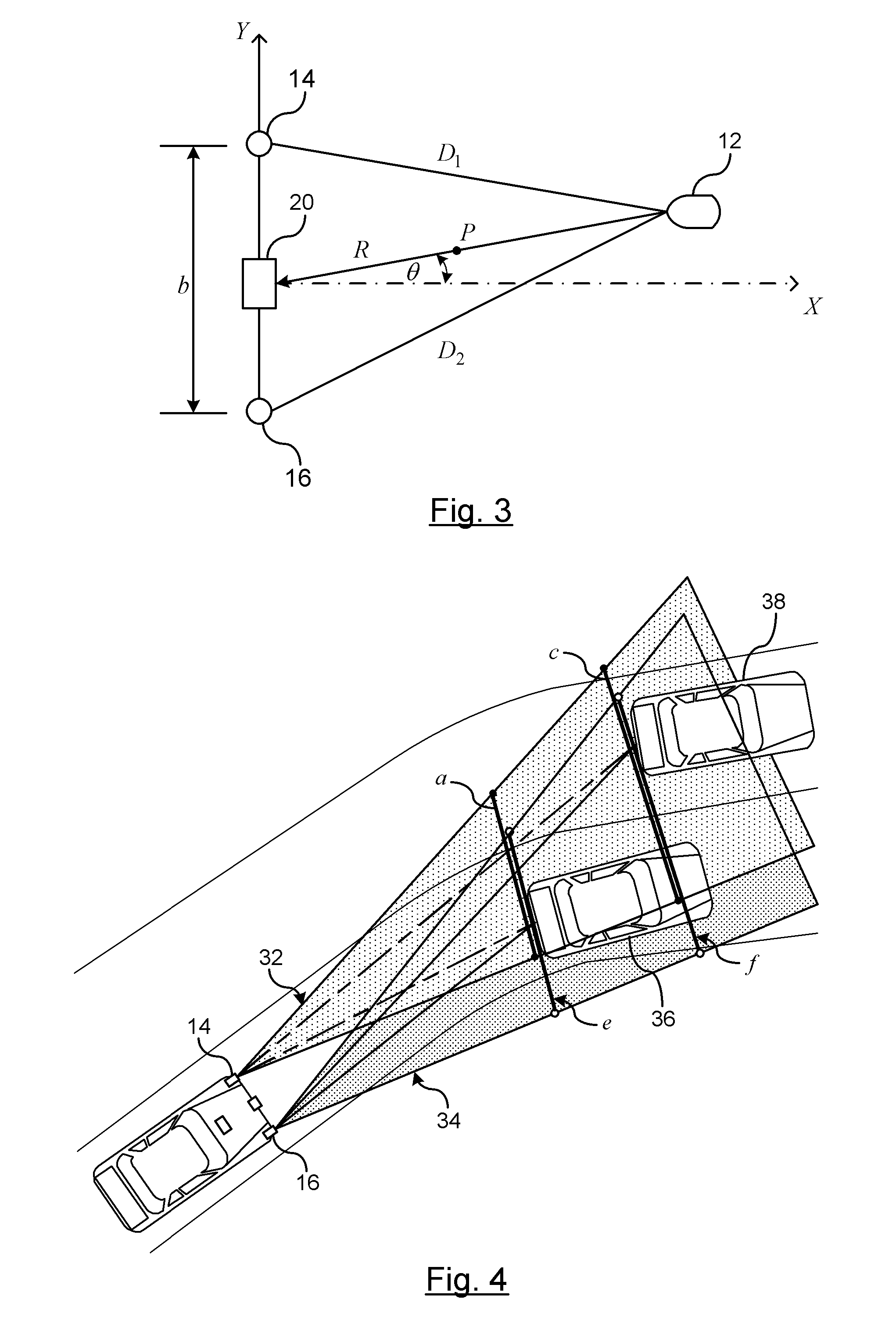
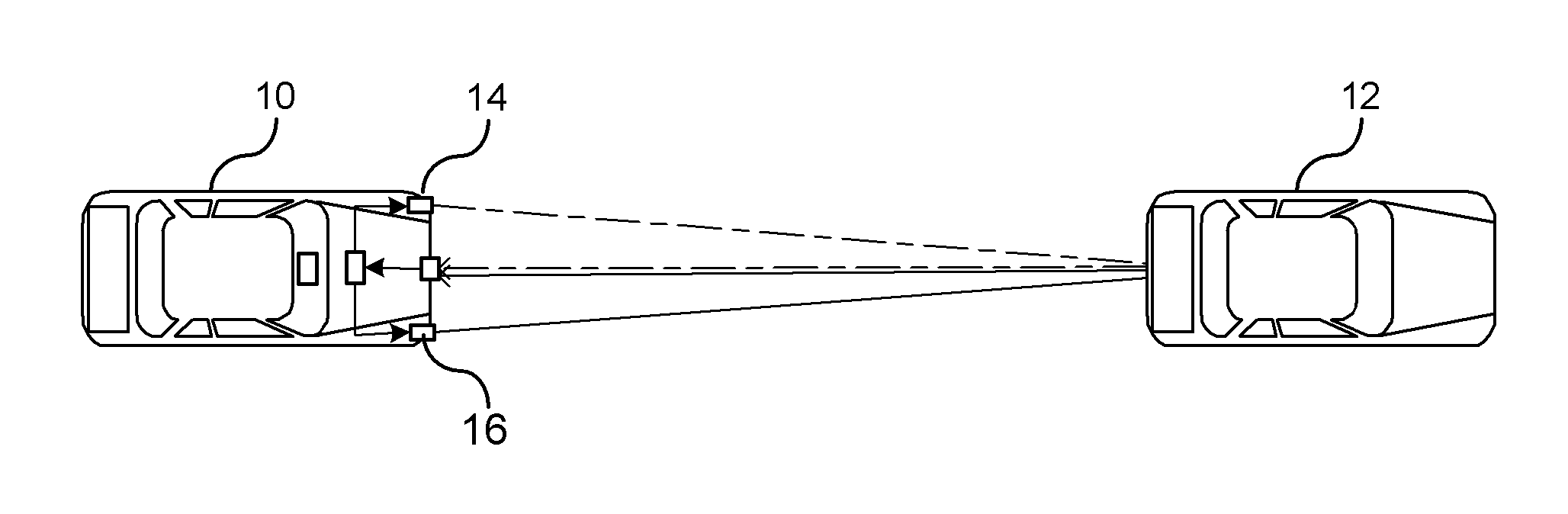
An object detection tracking system for a vehicle includes a first modulated light source for transmitting a first light signal with a first propagation pattern into a target region and a second modulated light source for transmitting a second light signal with a second propagation pattern into the target region. A sensor measures light reflected off objects in the target region. A controller demodulates the measured light to detect when the first or second light signals are received. The controller determines respective ranges for generating a first set of range data for the first light signal and a second set of range data for the second light signal. The controller maintains an object tracking list that includes a position of detected objects relative to the vehicle. The position of each object is determined using trilateration of the first and second sets of range data.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and Apparatus for an Object Detection System Using Two Modulated Light Sources
ActiveUS20120256764A1Arrangements for variable traffic instructionsUsing optical meansPropagation patternLight signal
An object detection tracking system for a vehicle includes a first modulated light source for transmitting a first light signal with a first propagation pattern into a target region and a second modulated light source for transmitting a second light signal with a second propagation pattern into the target region. A sensor measures light reflected off objects in the target region. A controller demodulates the measured light to detect when the first or second light signals are received. The controller determines respective ranges for generating a first set of range data for the first light signal and a second set of range data for the second light signal. The controller maintains an object tracking list that includes a position of detected objects relative to the vehicle. The position of each object is determined using trilateration of the first and second sets of range data.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
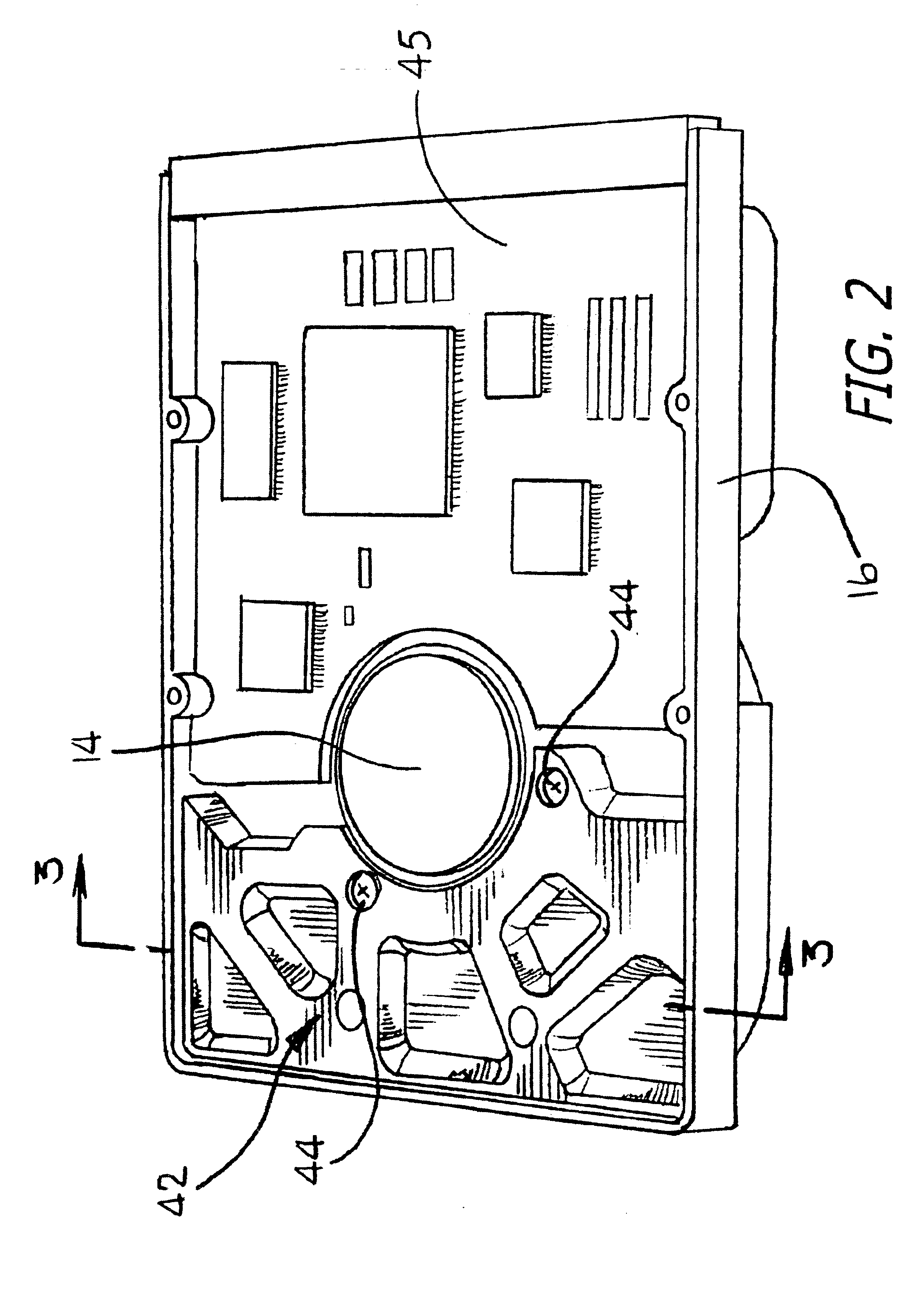
Wave stringer for controlling acoustic noise and shock vibration in a storage device
InactiveUS6947252B2Weaken energyUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionFluid-dynamic spacing of headsHard disc driveLongitudinal wave
A hard disk drive that includes a wave stringer. The wave stringer can attenuate energy which propagates through a base plate of the disk drive. The wave stringer may be designed by initially analyzing propagation patterns of both acoustic and shock waves applied to the drive. The wave stringer is then designed, constructed and assembled to the disk drive to attenuate critical frequencies at weak points of the disk drive. The wave stringer may have a plurality of ribs designed to vary the mechanical impedance of the drive to attenuate the propagated energy.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
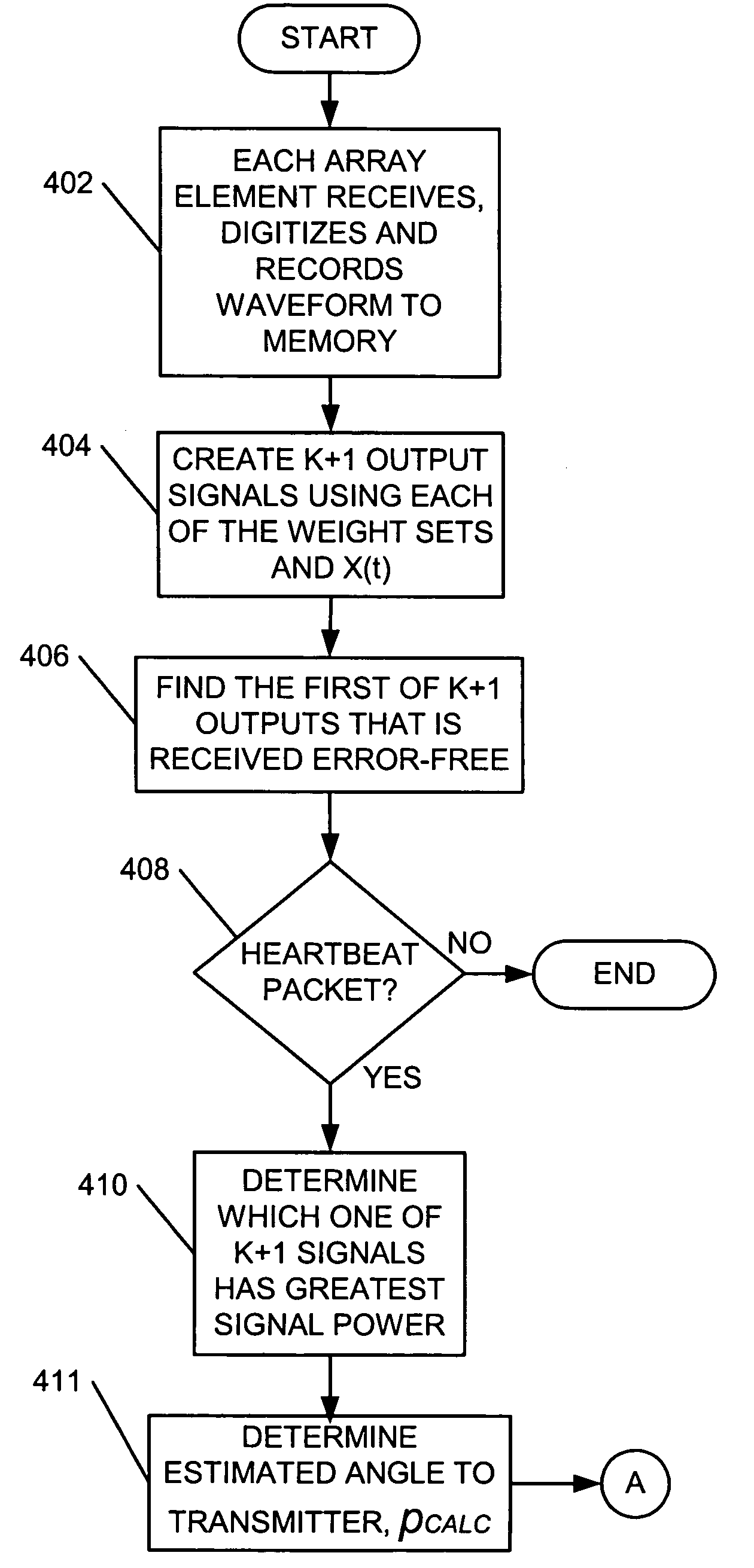
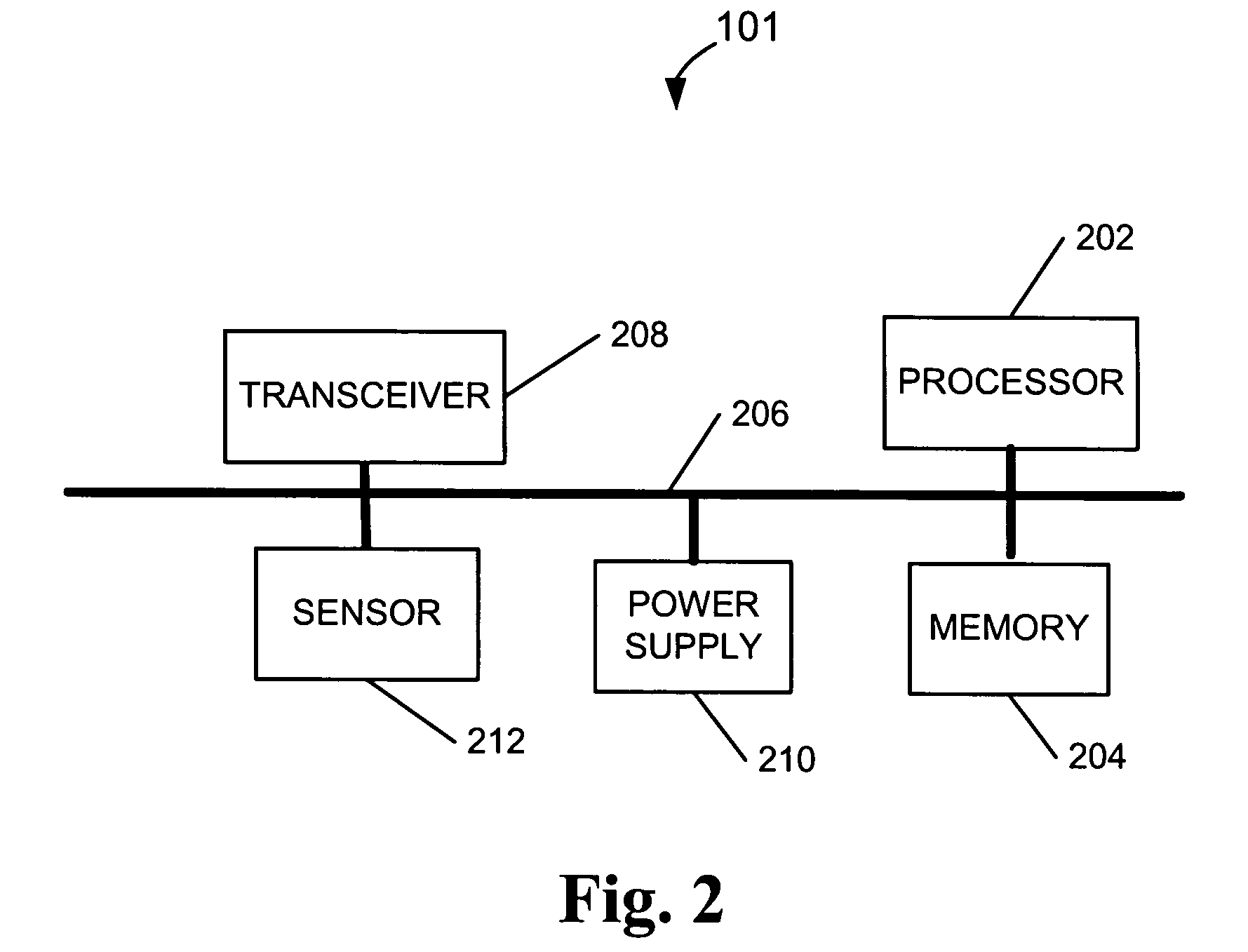
Dynamic beamforming for ad hoc networks
A method, a node and a machine-readable medium are provided for dynamically adjusting a beam of an adaptive antenna array (302). A receiving node (101) receives, via a group of antenna array elements (302), a signal from a transmitting node (101). Each received signal from the antenna array elements (101) is digitized and recorded. K+1 output signals are generated from the recorded digitized signal. The k+1 output signals are generated by applying each of a group of weight sets to the recorded digitized signal. Each of the weight sets corresponds to a different one of k known neighboring nodes (101) and a weight set for generating an omnidirectional propagation pattern. Which one of the k+1 output signals to process is determined. The determined one of the k+1 output signals is processed and the packet encoded in the determined one of the k+1 output signals is decoded.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC +1
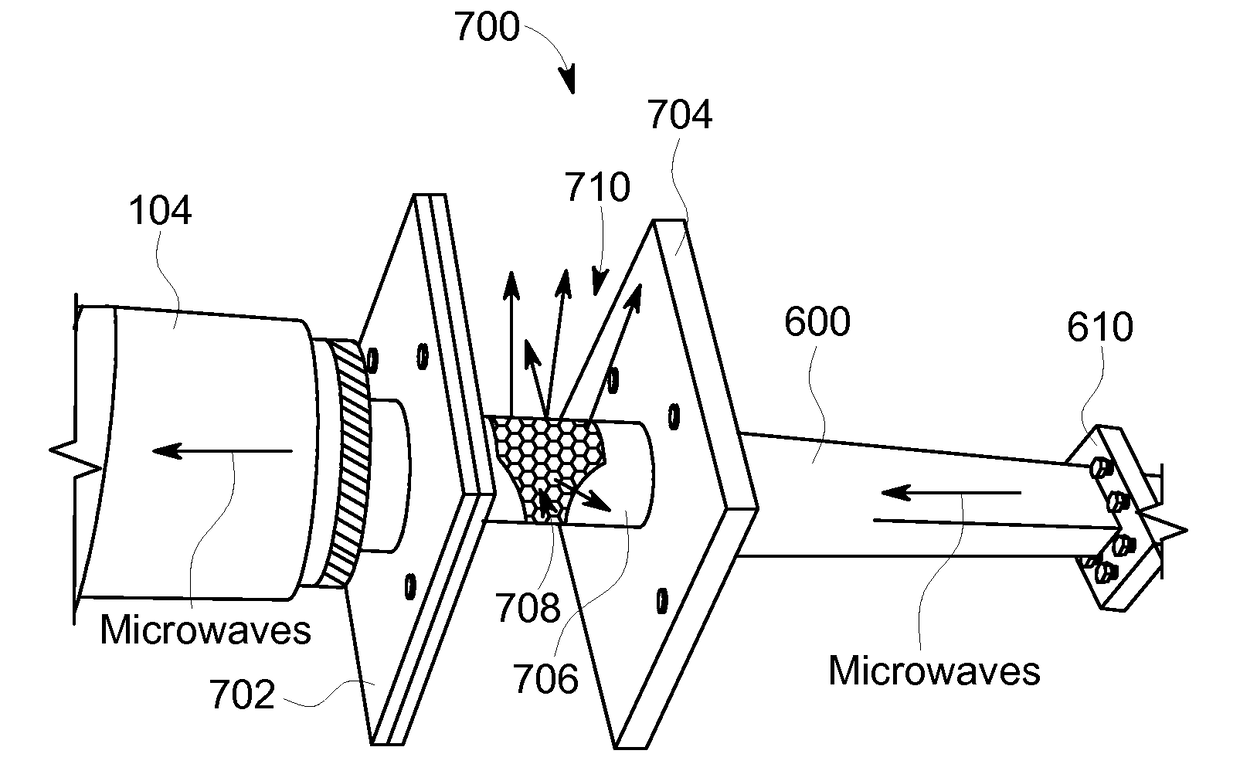
Microwave-based fluid conduit heating system and method of operating the same
A fluid conduit heating system includes a fluid transport conduit including a wall including a radially inner surface and a radially outer surface. The radially inner surface has a predetermined topography and the fluid transport conduit is configured to transport a hydrocarbon fluid therethrough. The system also includes a microwave heating device in radio frequency (RF) communication with the fluid transport conduit. The microwave heating device includes a microwave generator configured to generate microwave radiation and a waveguide coupled to the microwave generator. The waveguide is configured to conform a propagation pattern of the microwave radiation generated by the microwave generator to the predetermined topography of the radially inner surface.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-factorial electronic shark repellant
InactiveUS20120031343A1Lower average currentInefficiency can be toleratedShark screensPisciculture and aquariaPropagation patternElectrical battery
In abstract this invention is a pressure and water sealed unit small enough to be worn by a swimmer. It contains a rechargeable battery, control interface logic, digital signal generation, and amplification circuitry. It uses a ground balanced electrode system to produce electric fields in the very low impedance environment of water. These fields are organized into patterns called words. These words are presented in a hierarchal pseudo random manner to prevent target organisms from learning and adapting to them. The presentation of these words is controlled by upgradable programing stored within memory. The words evoke central nervous system (CNS) responses which result in sharks leaving the area of operation. These words represent stimuli of predators, navigation signals, noxious events, CNS interference patterns, and other sequences found to repel sharks from the protected area. Reprogrammability allows upgrades to newer sequences. The amplifier uses switching stages to multiply the battery voltage up to about one thousand times. An inversion unit provides for positive and negative signals. The switching circuit is logic level and pulse width modulation controlled. The switching typology permits micro miniaturization and efficient power consumption prolonging battery life. The unit has no user adjustable parameters except for go no-go control and shark alarm. Unit and battery status is indicated by flashing light signals. Electrode typology generates a spherical electric wave propagation pattern in water. A recharging cradle projects magnetic energy into the unit providing for automatic battery recharging and conditioning without electrical connections exposed to an aqueous environment.
Owner:DELUZE JAMES ROBERT
Container-classification identification using directional-antenna RFID
InactiveUS8947528B2Clear feedbackProvide goodPosition fixationColor television detailsTelecommunicationsPropagation pattern
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
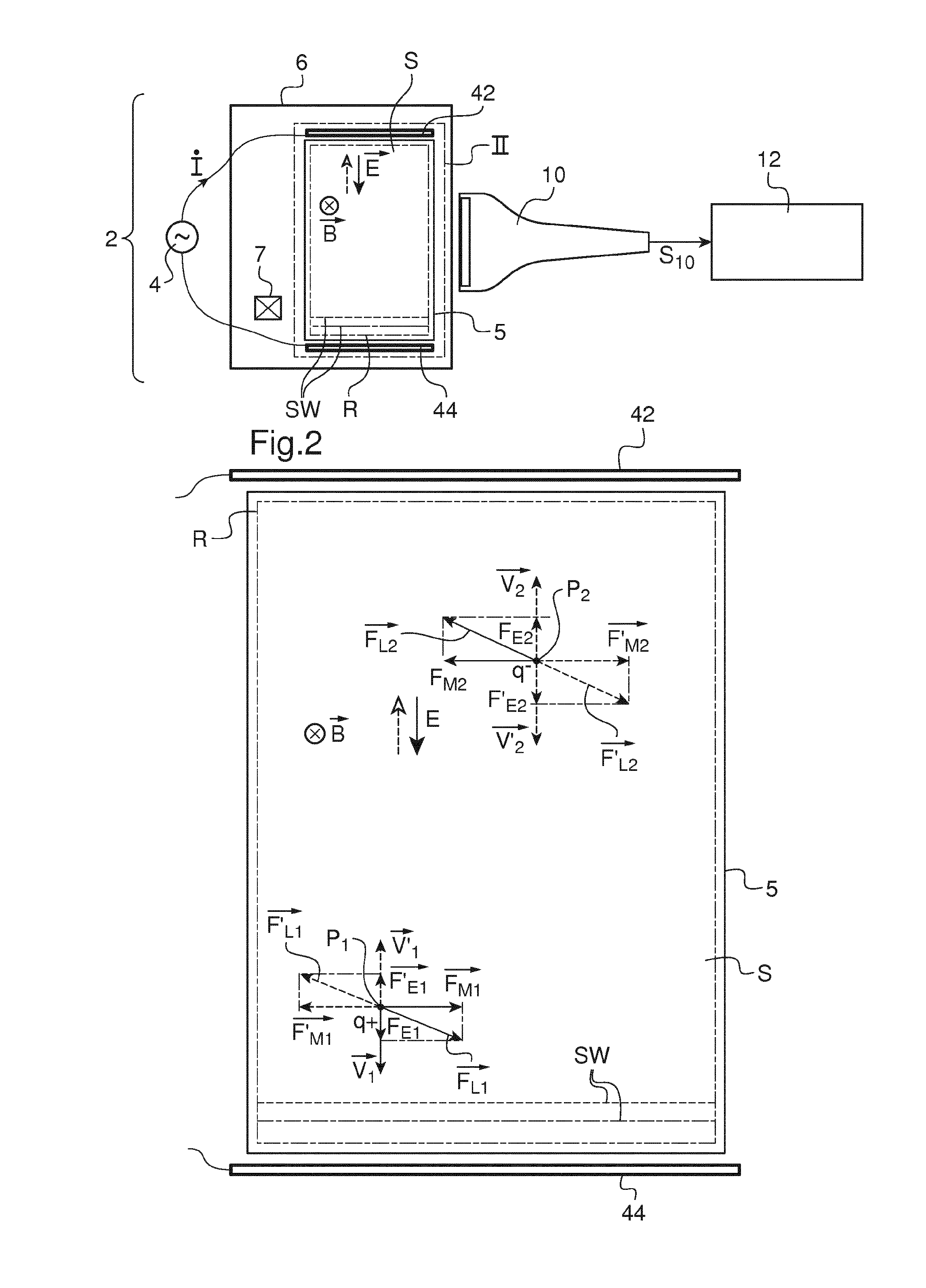
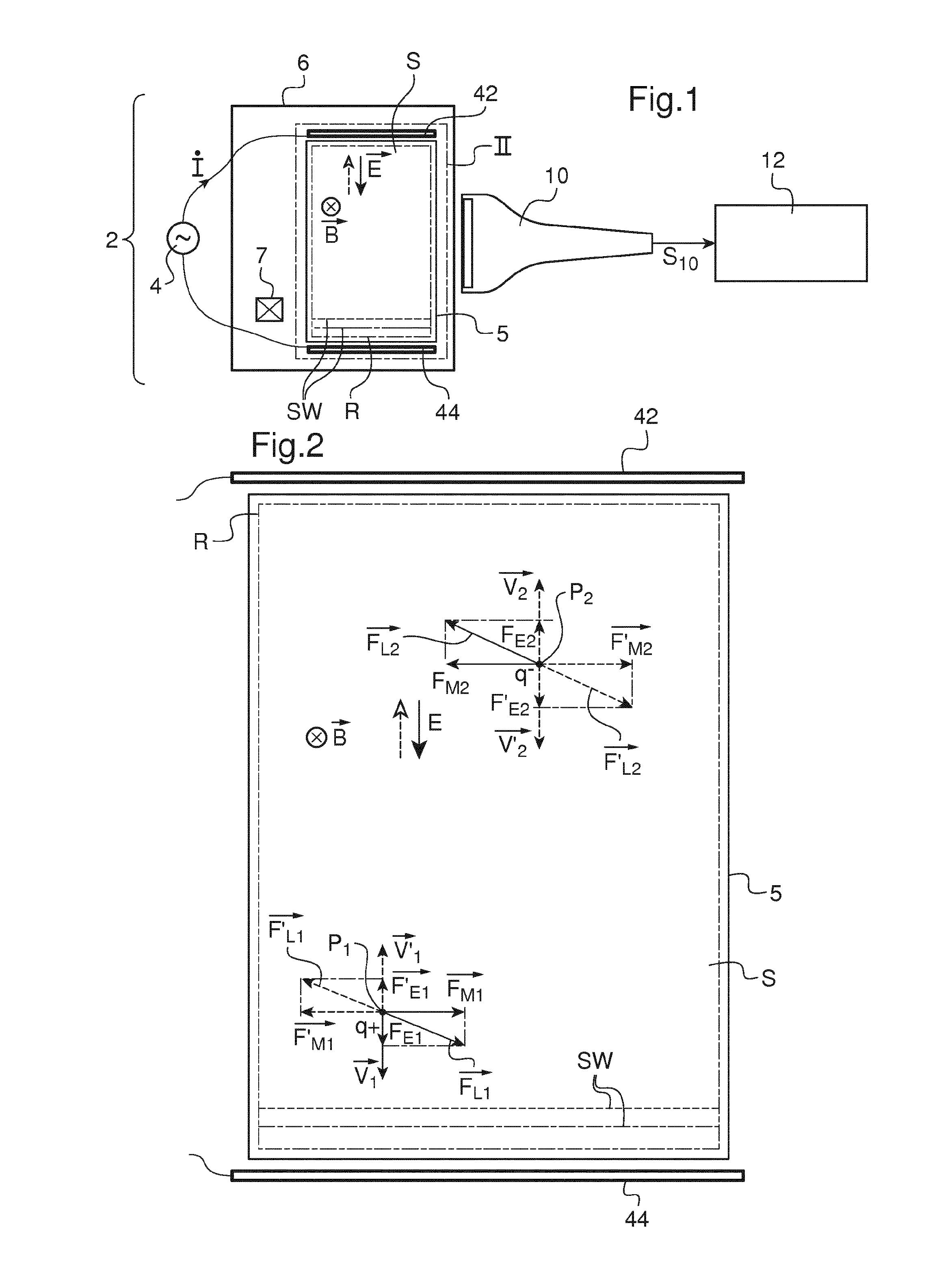
Shear Wave Imaging Method and Installation for Collecting Information on a Soft Solid
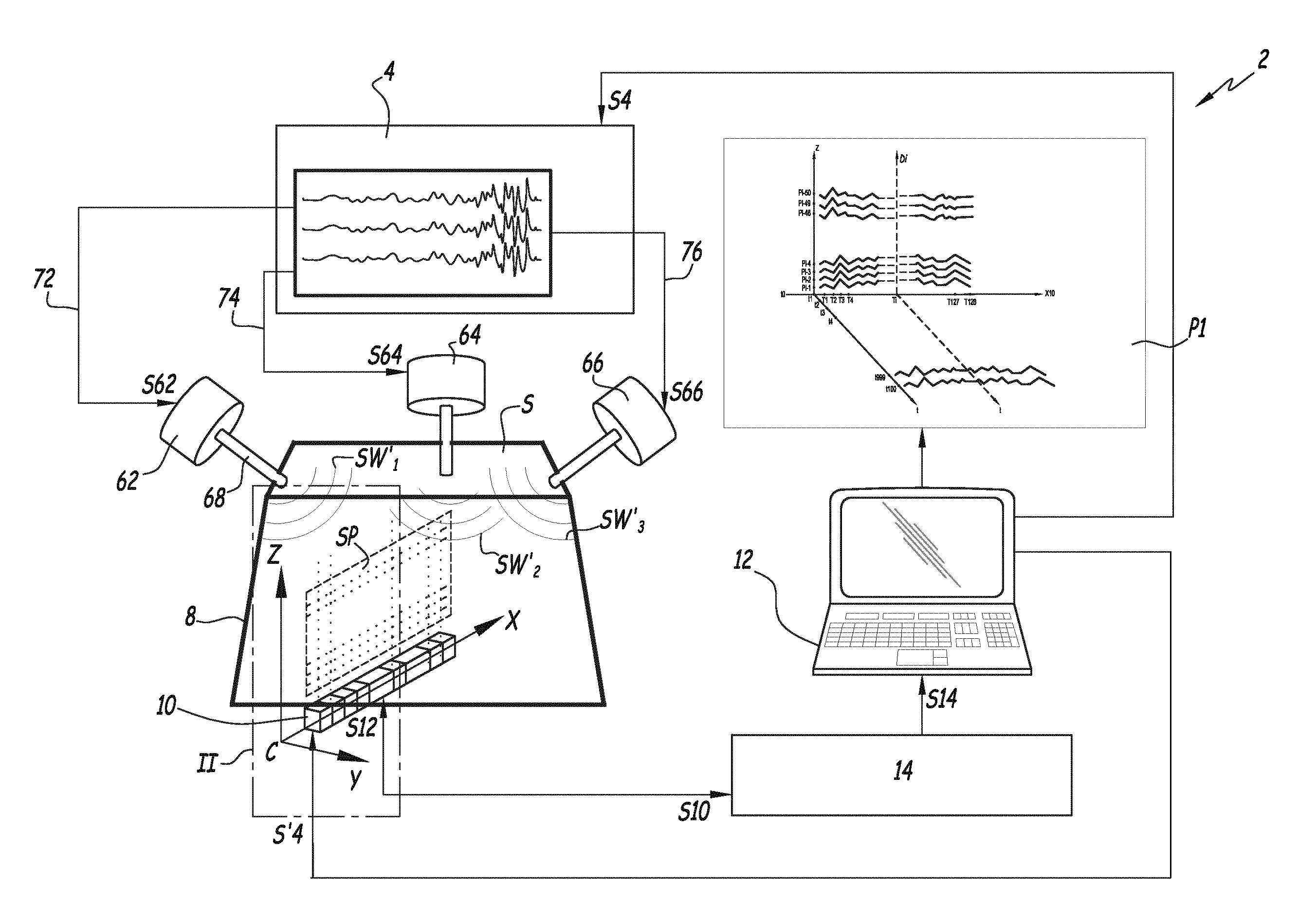
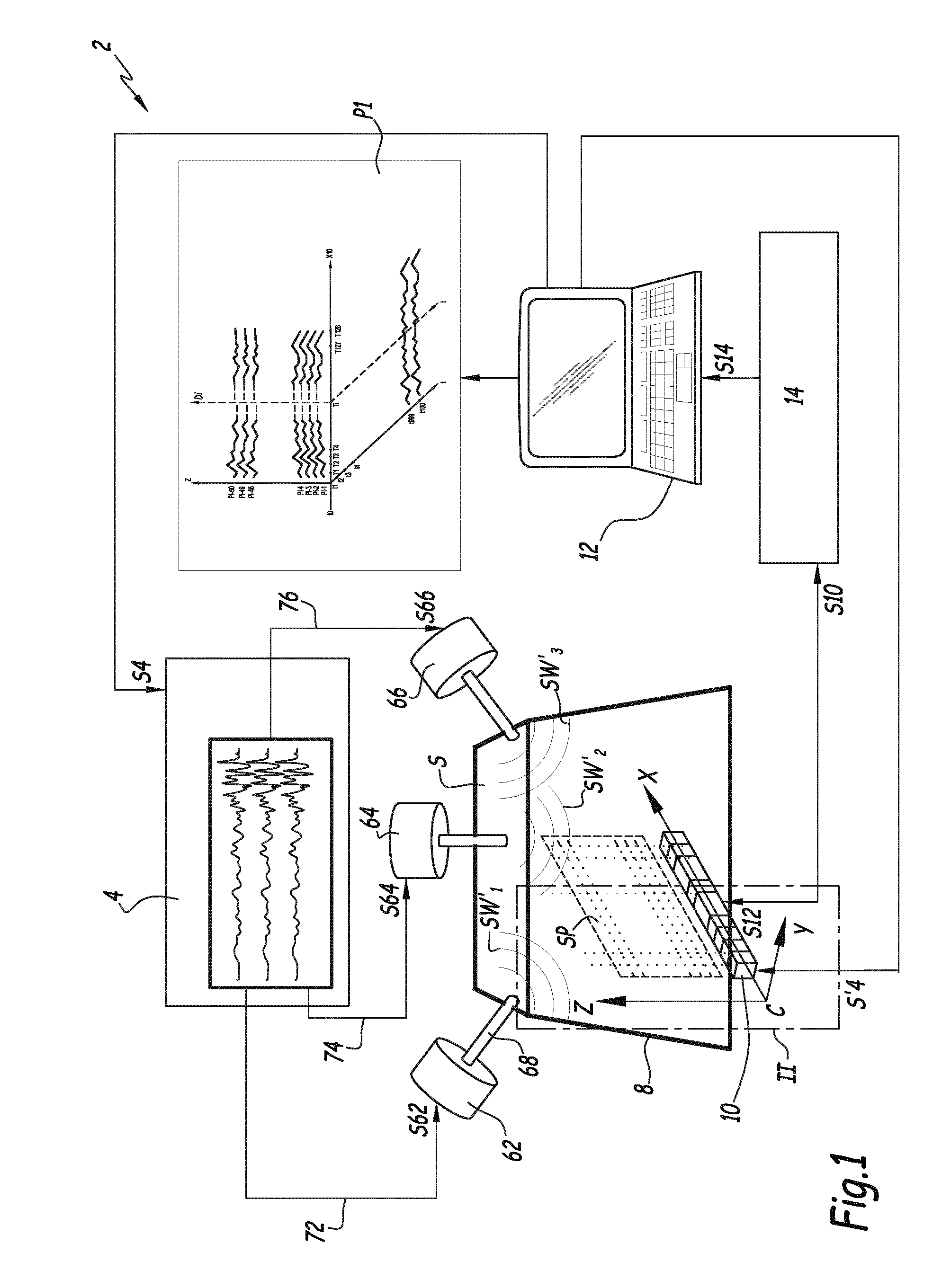
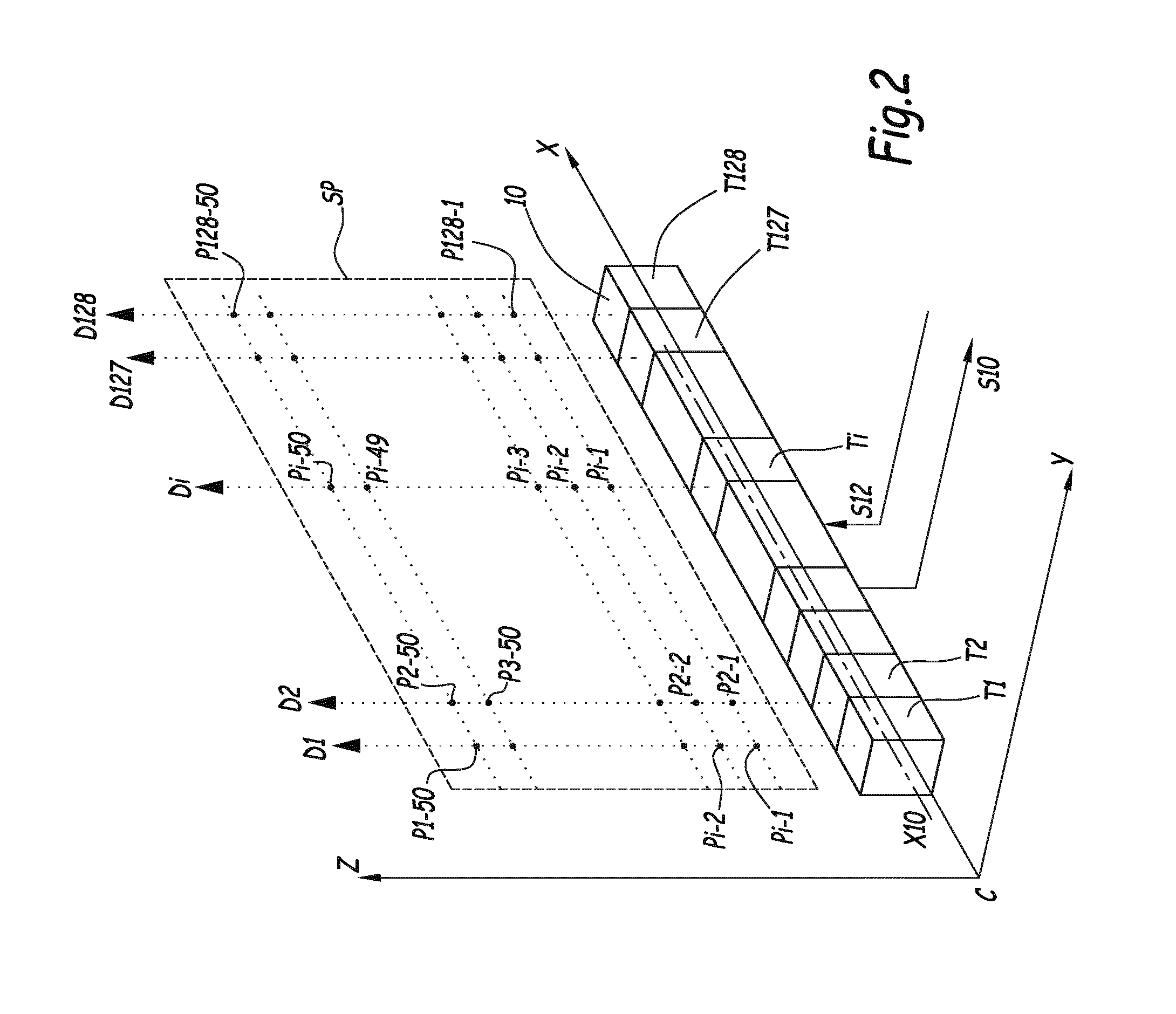
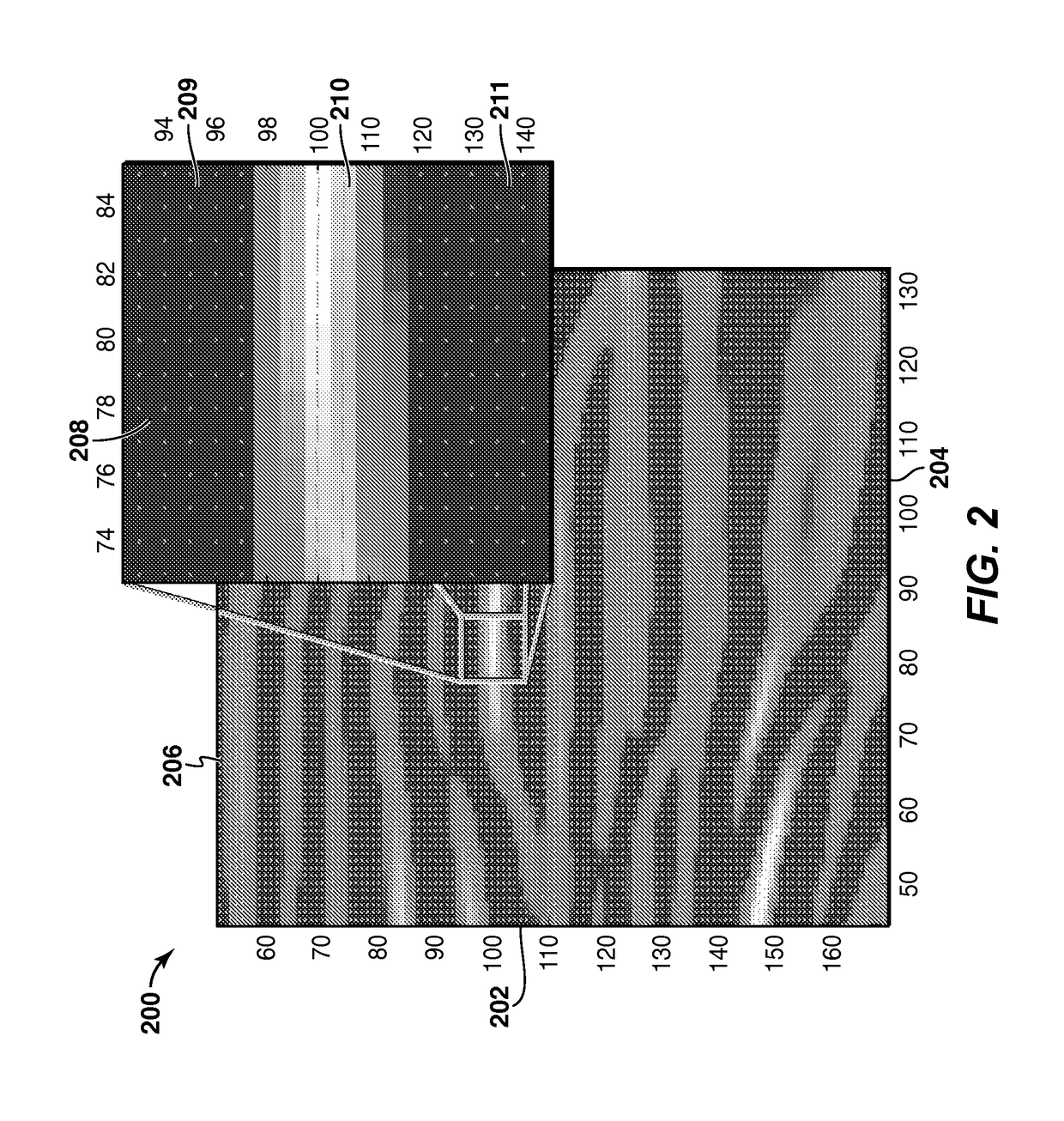
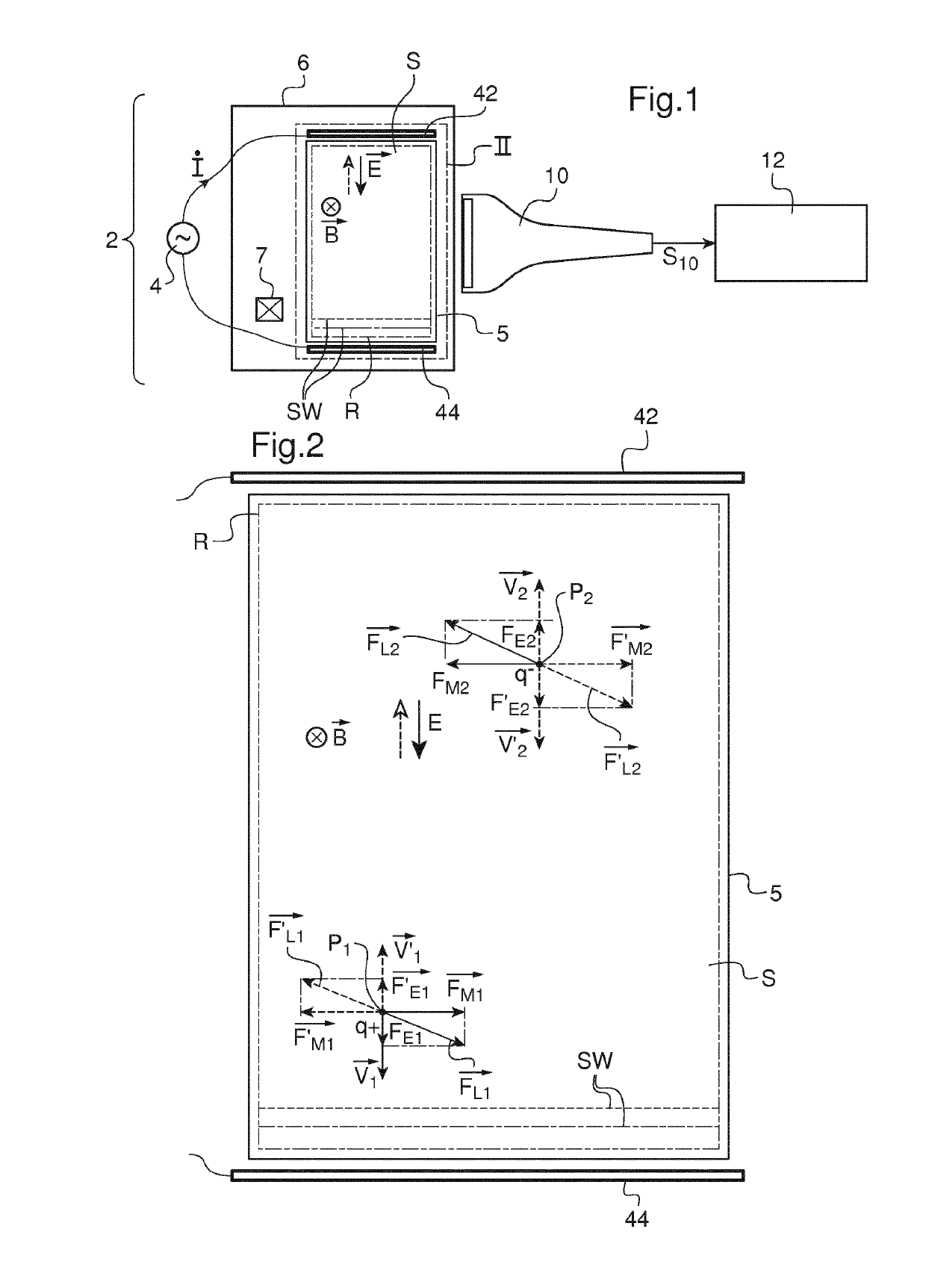
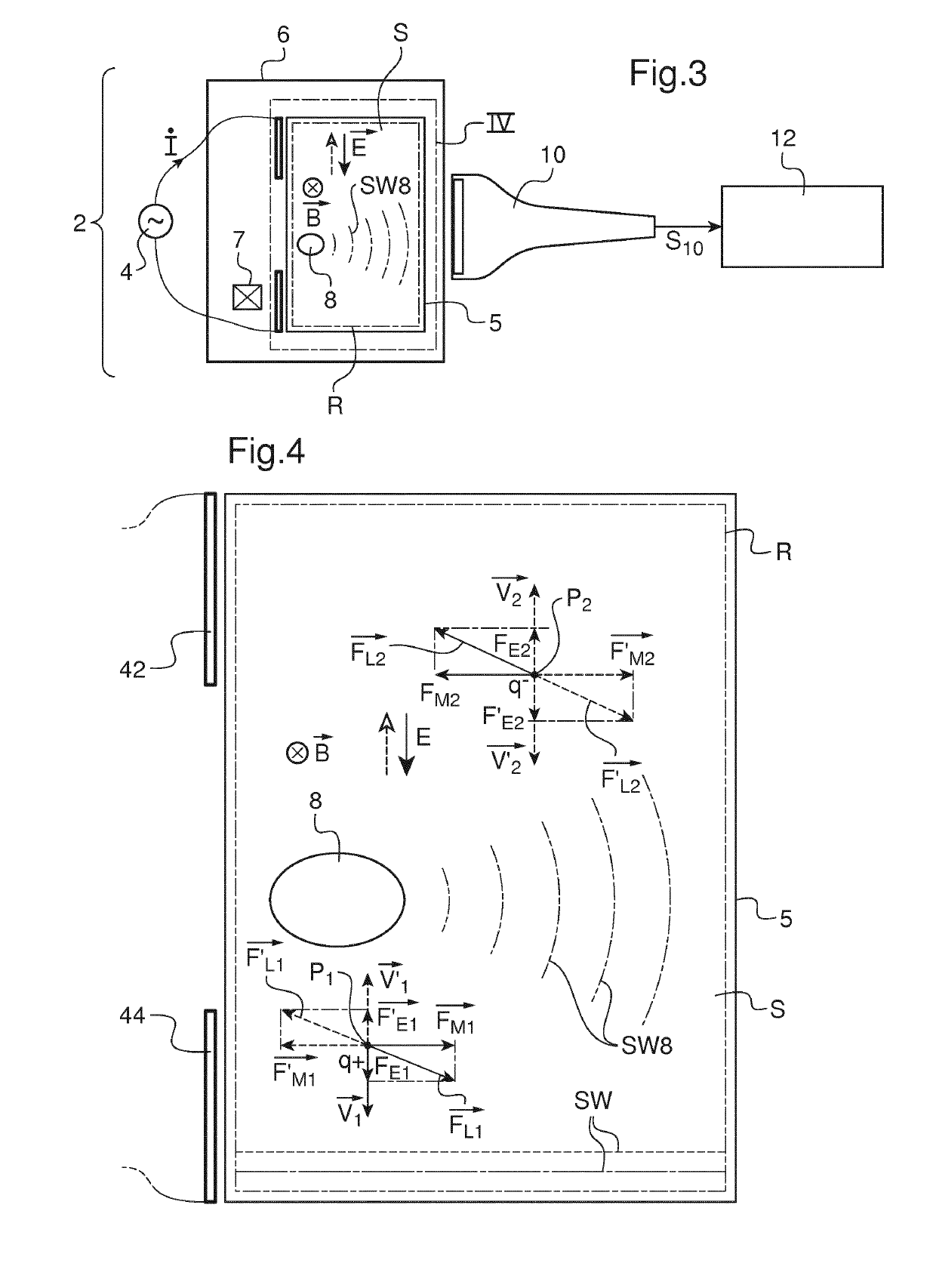
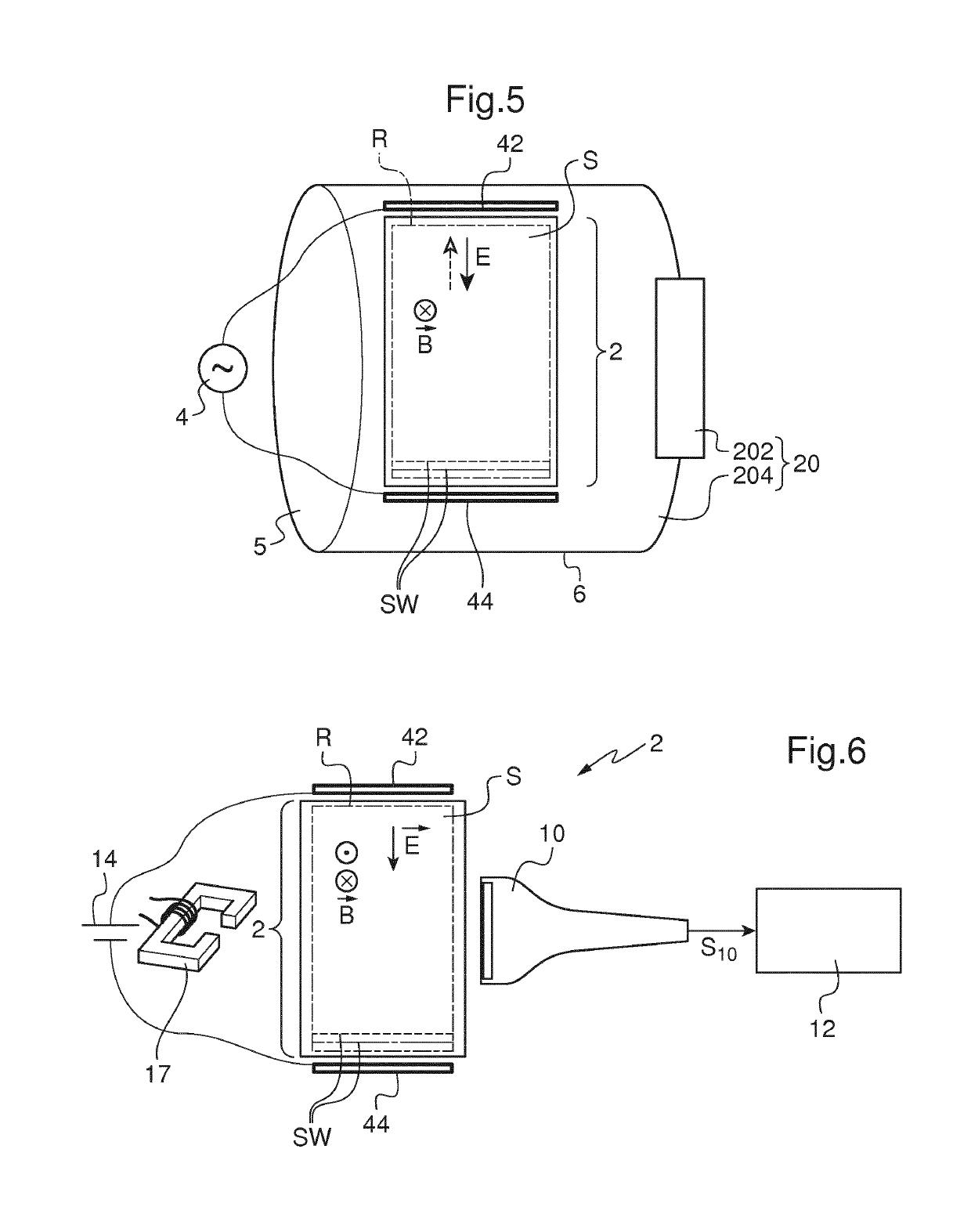
InactiveUS20160367143A1Easy to implementGenerate efficientlyMagnetic measurementsDiagnostics using vibrationsPropagation patternClassical mechanics
This shear wave imaging method, for collecting information on a target region (R) of a soft solid (S), comprises at fi least the steps a) of generating at least one shear wave (SW) in the target region, and b) of detecting a propagation pattern of the shear wave in the target region. Step a) is realized by applying to particles of the target region (R) some Lorentz forces resulting from an electric field (E) and from a magnetic field (B). At least one of the electric field (E) and the magnetic field (B) is variable in time, with a central frequency (fo) between 1 Hz and 10 kHz. Alternatively, both the electric and magnetic fields (E, B) are variable in time, with a central difference frequency (Δfo) between 1 Hz and 10 kHz. The shear wave imaging installation comprises a first system (4, 7) for generating at least one shear wave (SW) in the target region (R) and a second system (10) for detecting a propagation pattern of the shear wave. The first system includes first means (4) to apply an electric field (E) through the target region (R) and second means (7) to apply a magnetic field (B) through the target region. The first and second means are configured to apply to particles of the target region some Lorentz forces resulting from the electric field (E) and the magnetic field (B), where at least one of these fields is a quantity variable in time, with a central frequency (fo) between 1 Hz and 10 kHz, or both fields are quantities variable in time, with a central difference frequency (Δfo) between 1 Hz and 10 kHz.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
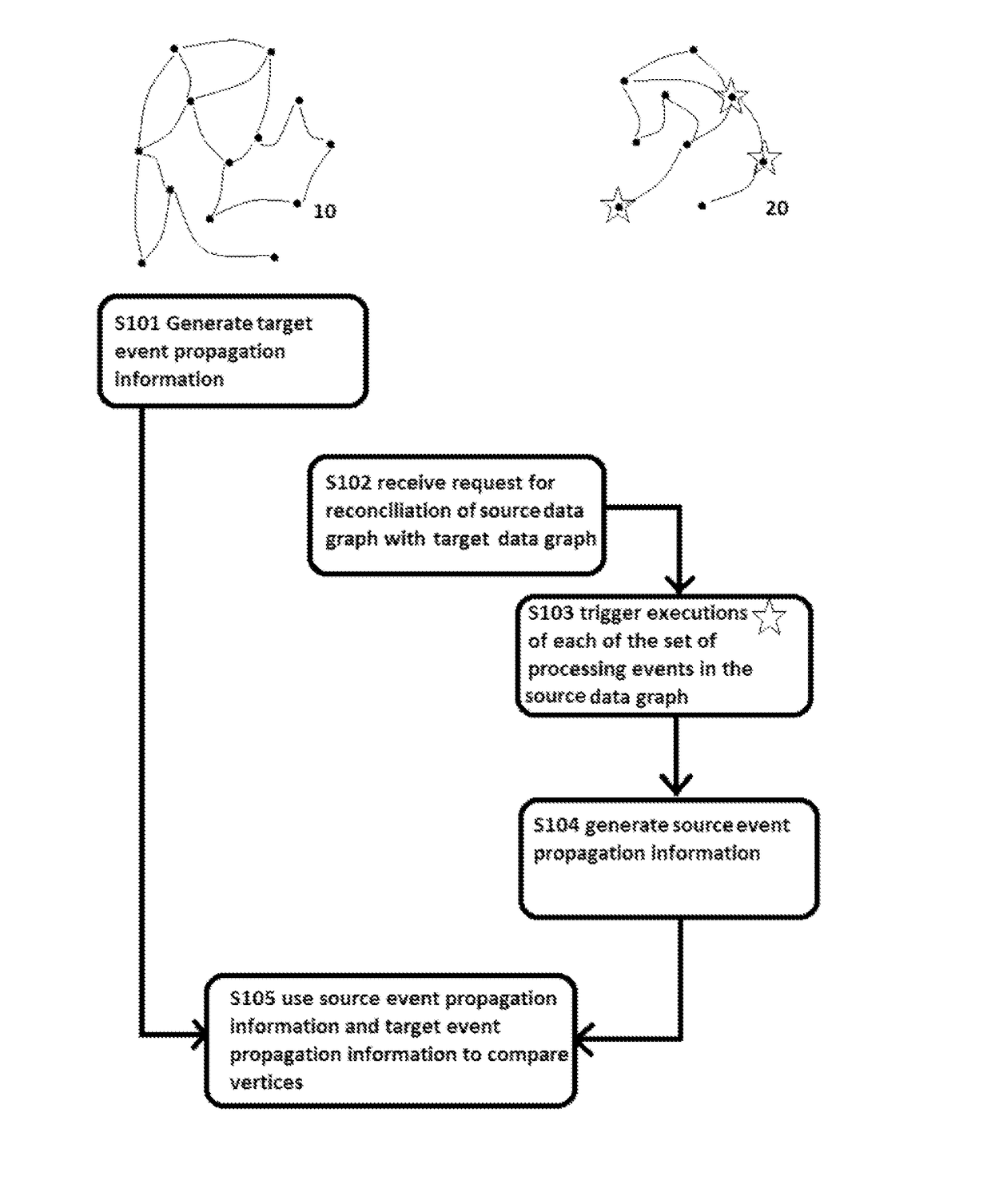
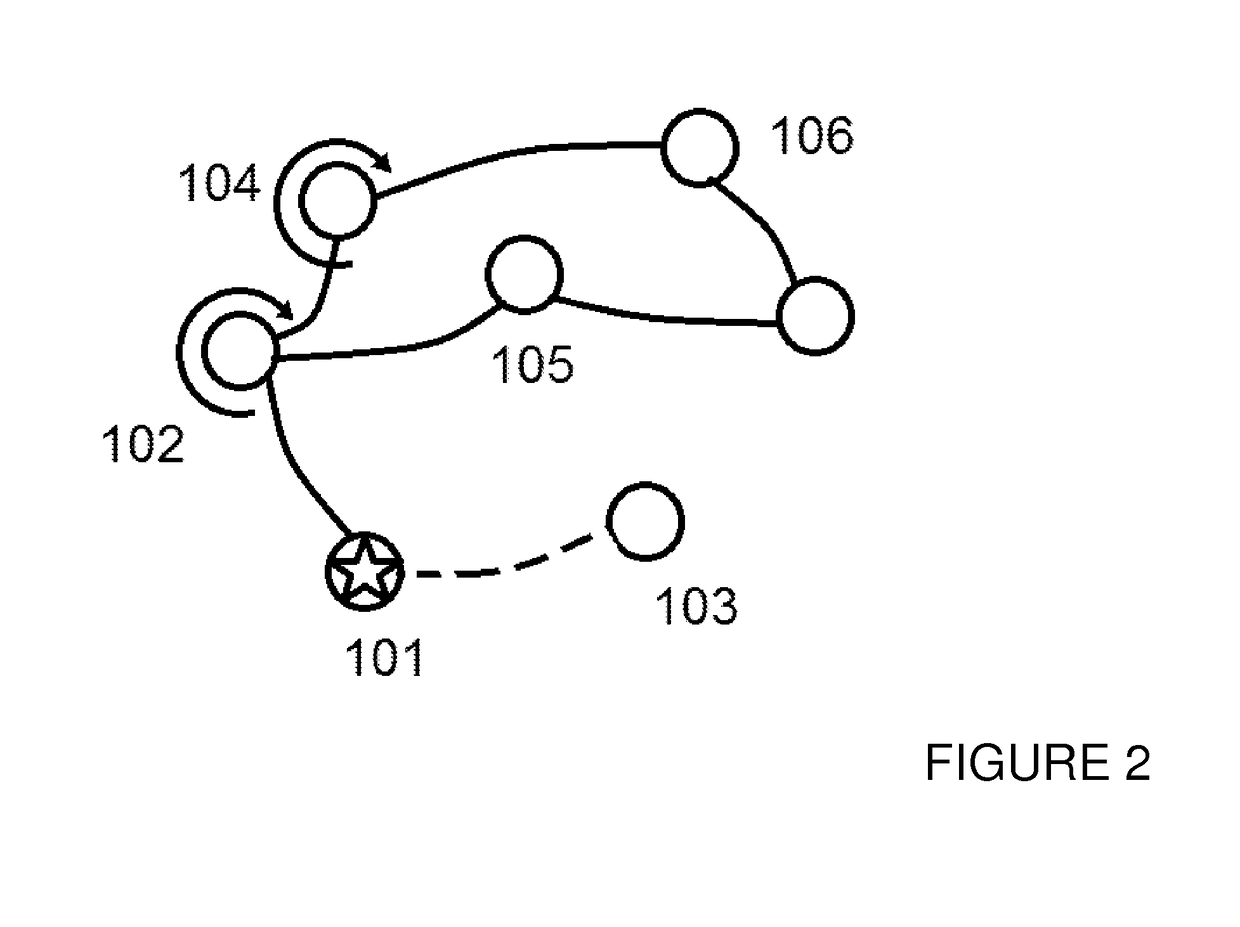
Method, Controller, Program, and Data Storage System for Performing Reconciliation Processing
InactiveUS20170177737A9Reduce processing burdenReconciling the data graphsKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsPropagation patternAlgorithm
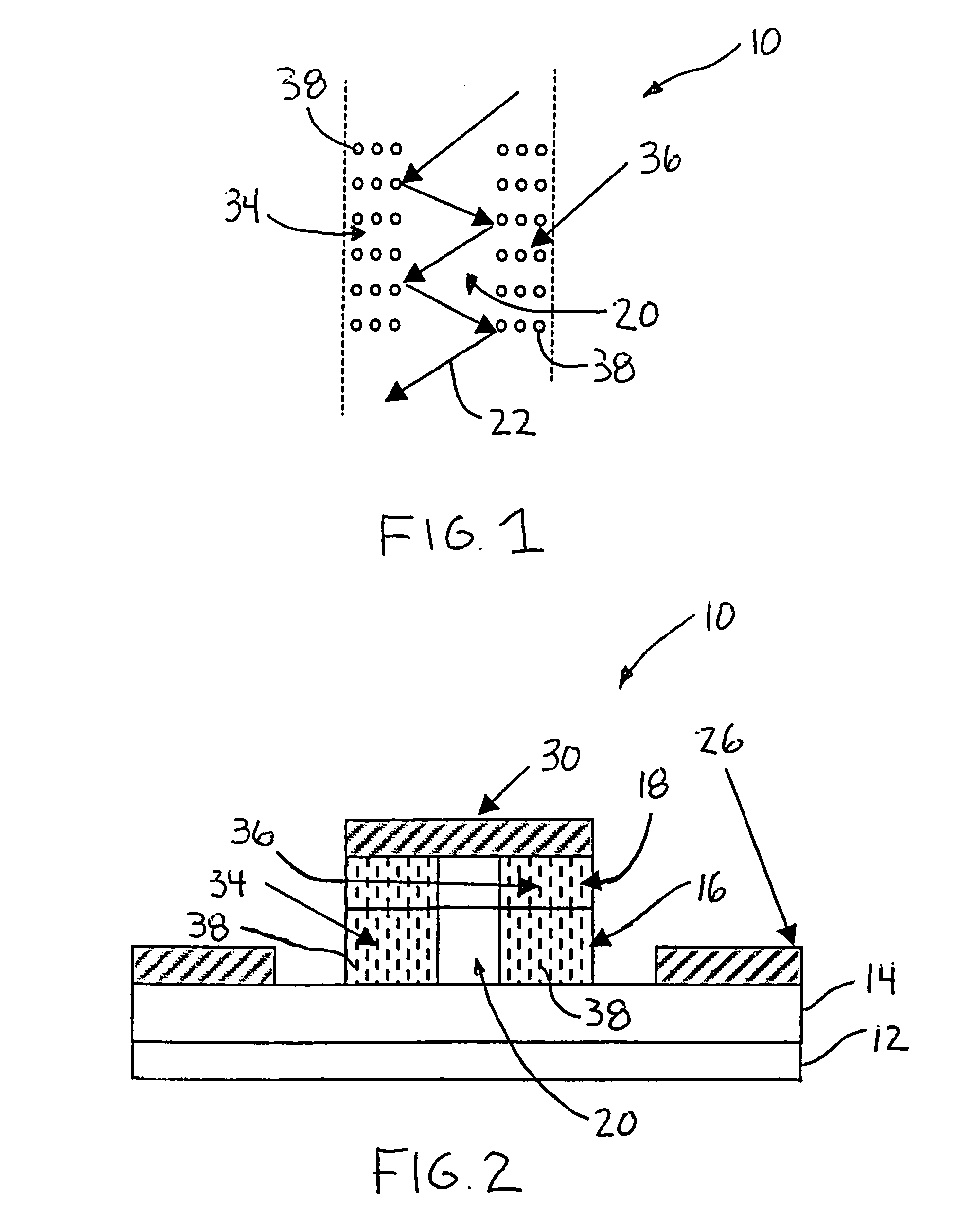
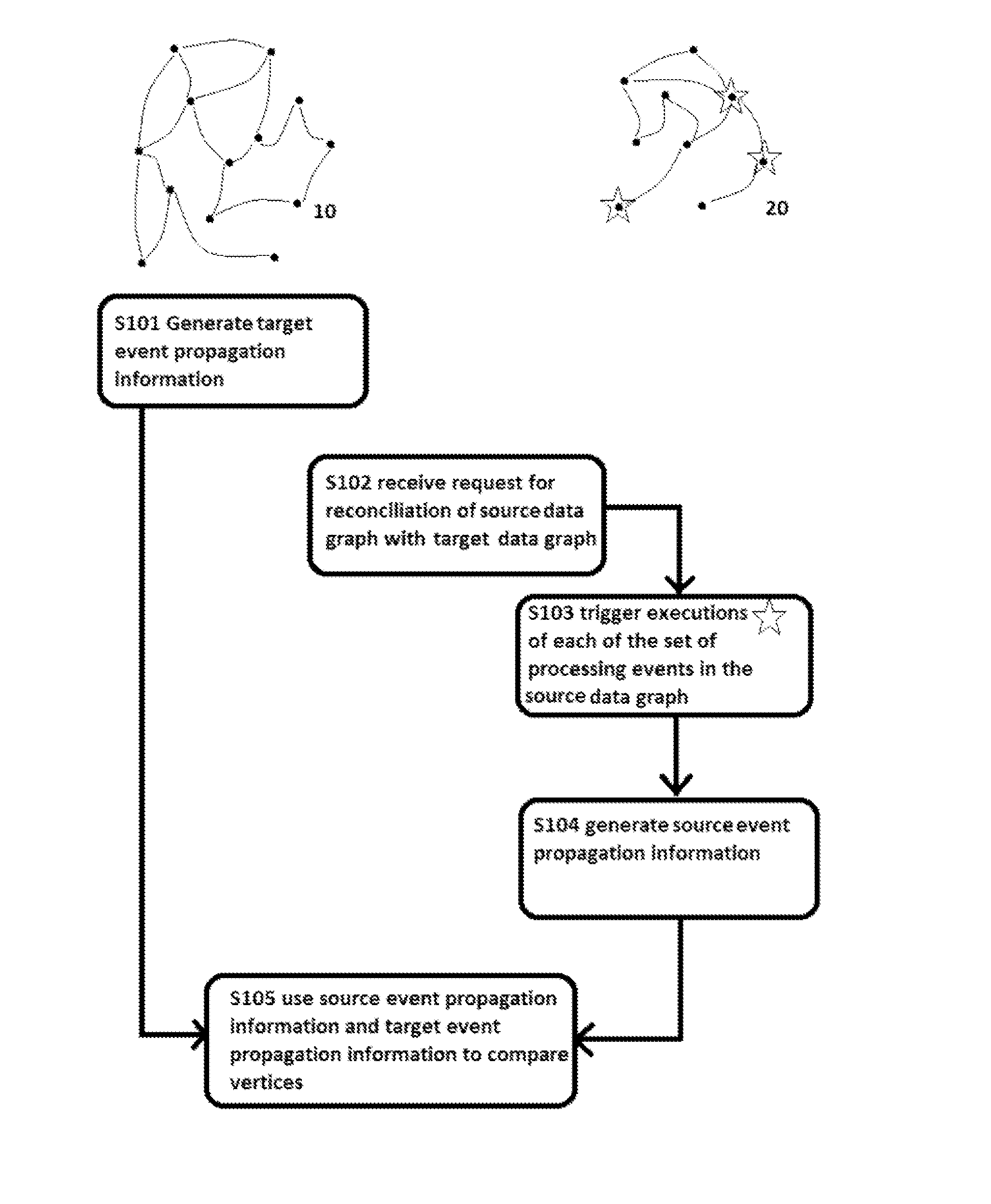
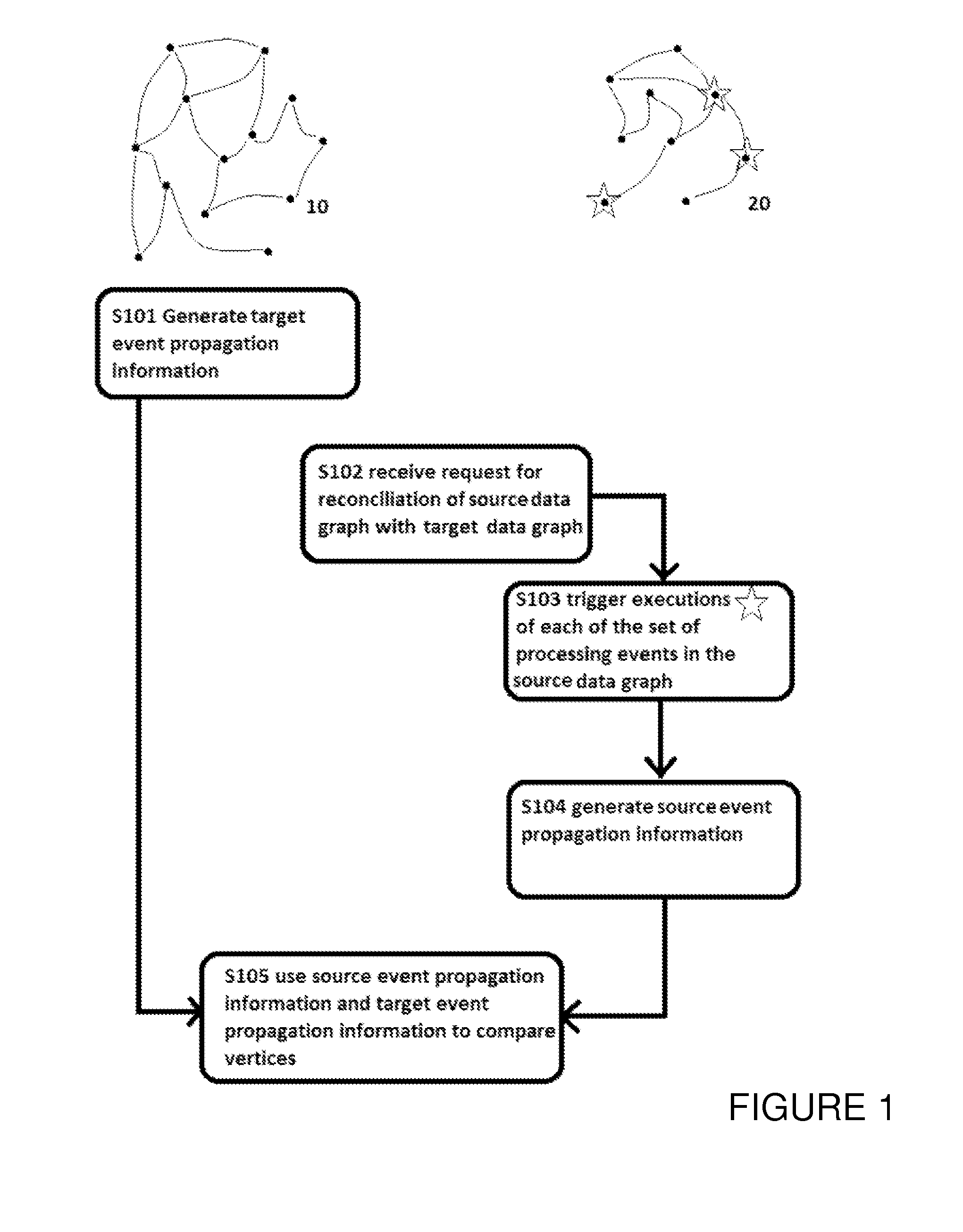
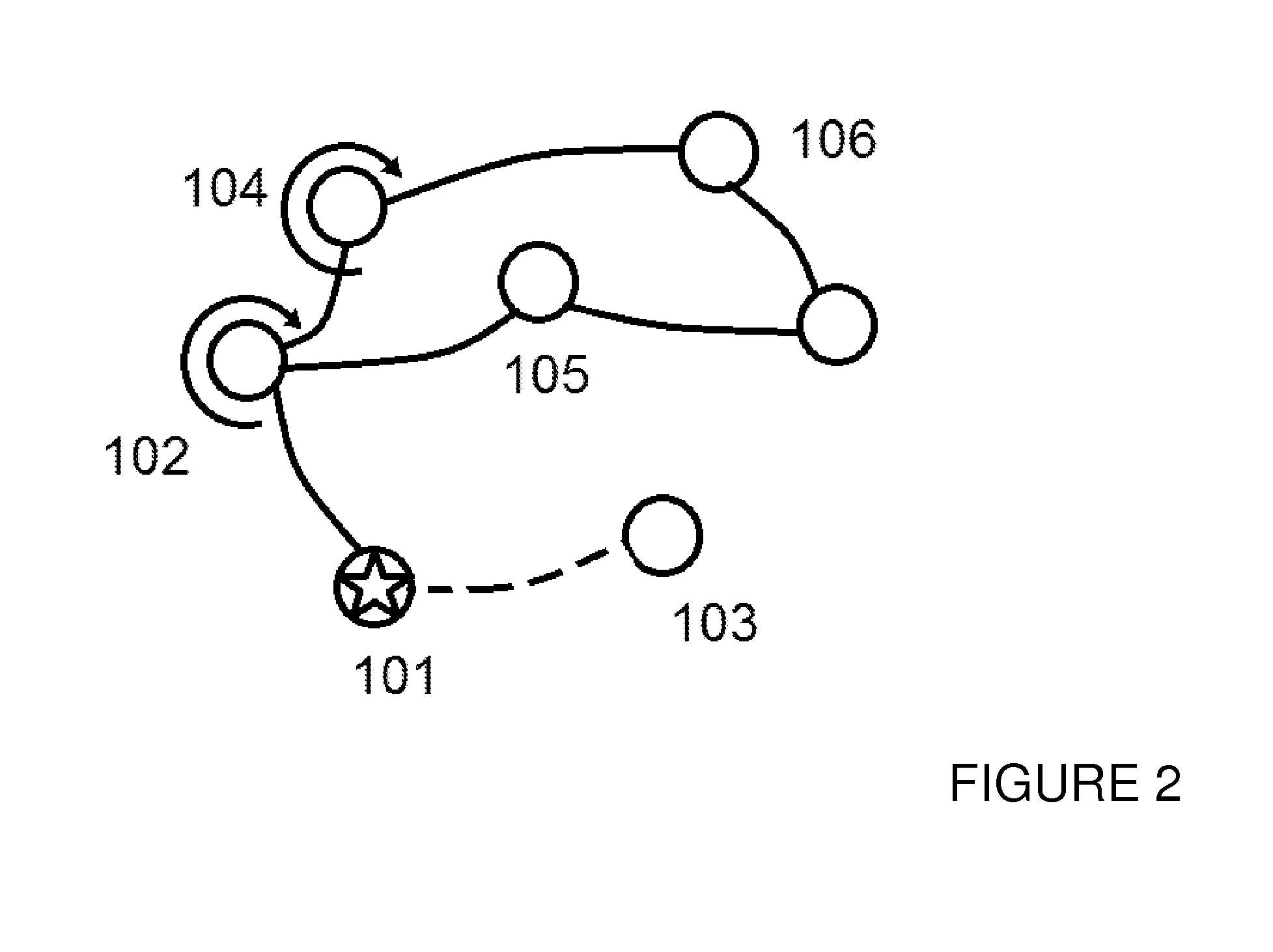
A method for reconciling a source data graph with a target data graph, the source graph and the target graph each comprising: and a interconnections, the interconnections each connecting two vertices from and representing a relationship between the connected vertices. The method comprises: generating target event propagation information representing the propagation pattern of executions of each of a set of processing events in the target graph; receiving a request to reconcile the source and graph, and in response to the request, triggering the executions of each of the set in the source graph; generating source event propagation information representing the pattern of each of the executions triggered in the source graph; and using the target event propagation information and the source event propagation information to assess the similarity of pairs of vertices comprising one vertex from each of the source graph and the target graph.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
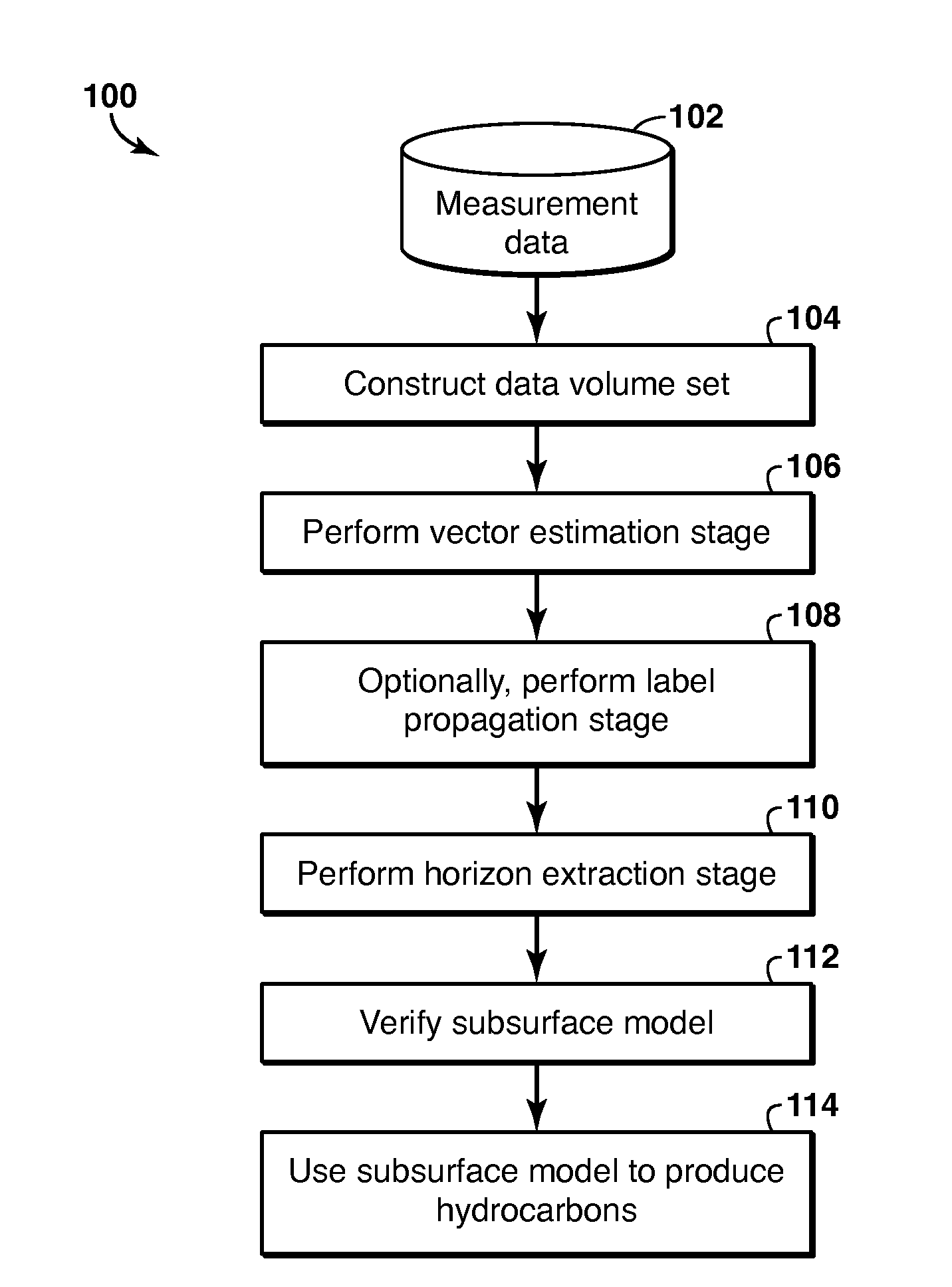
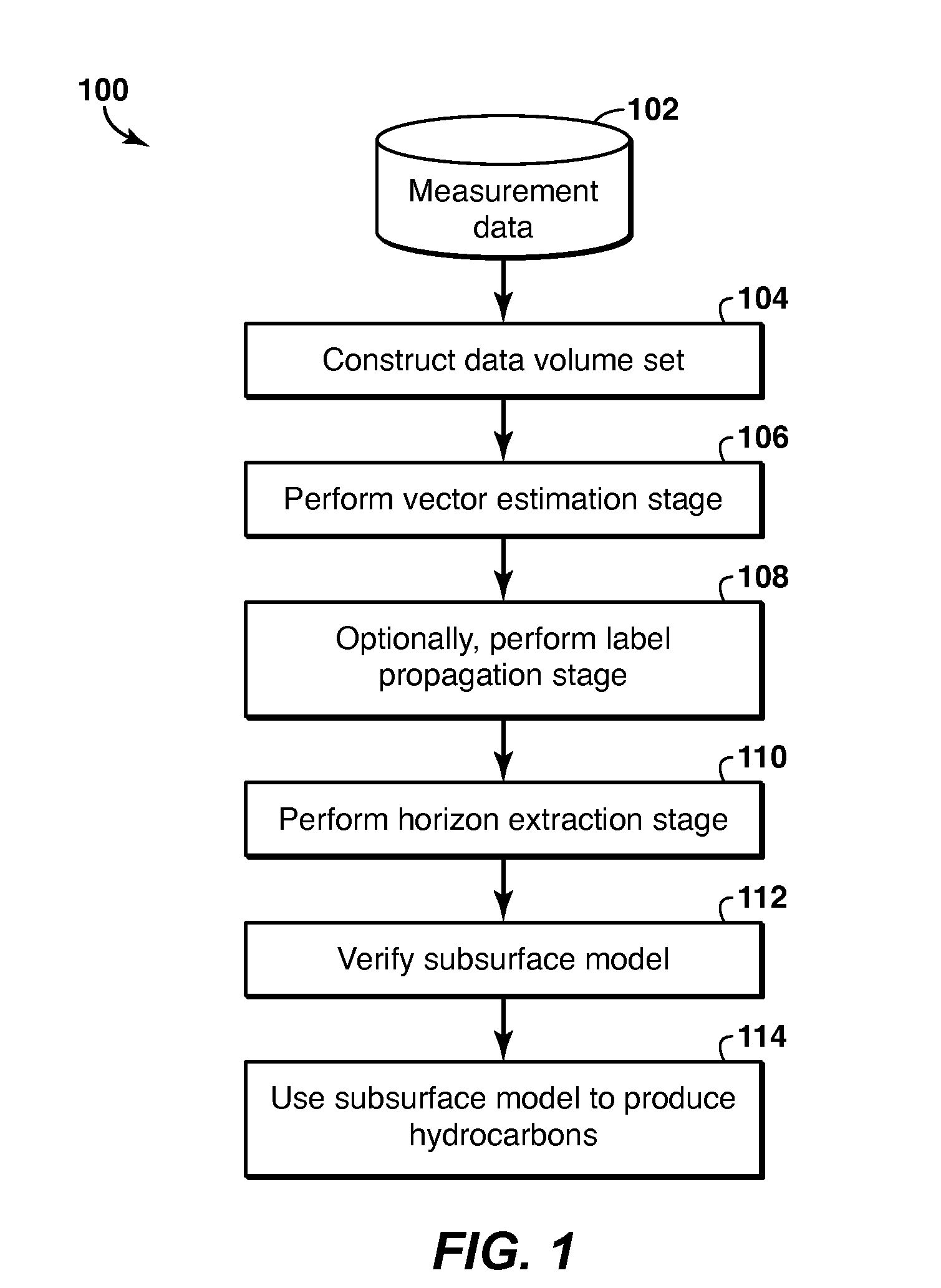
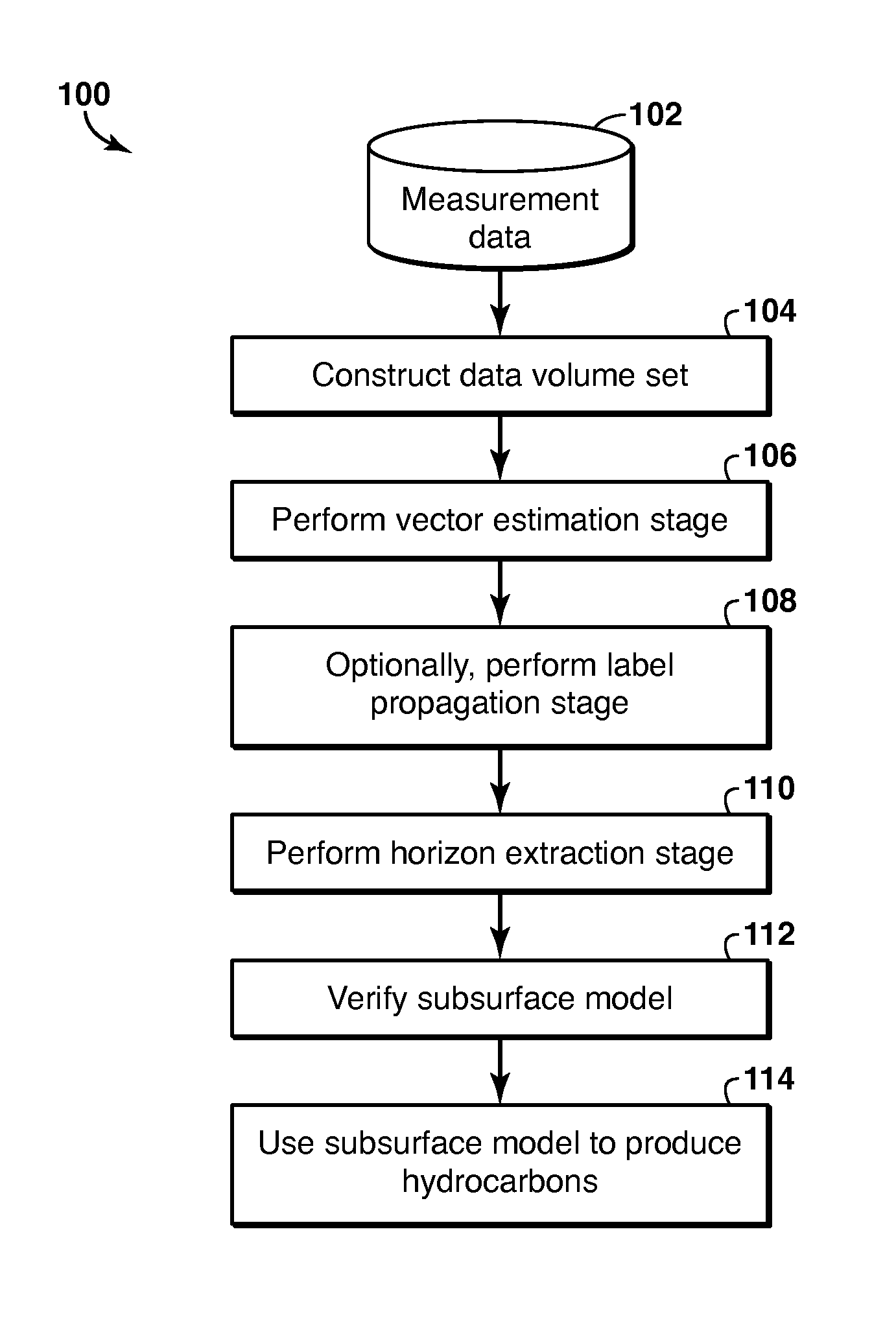
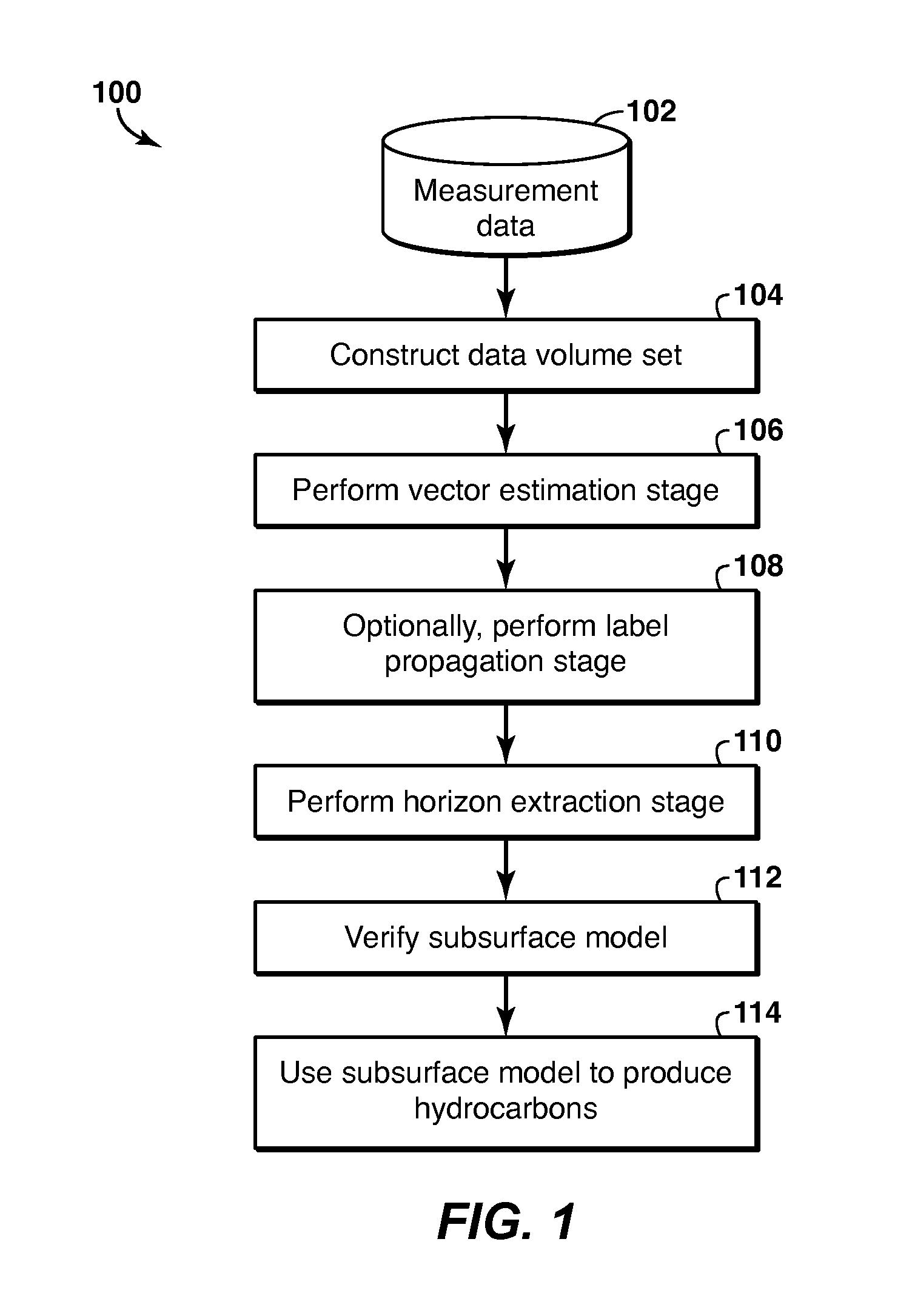
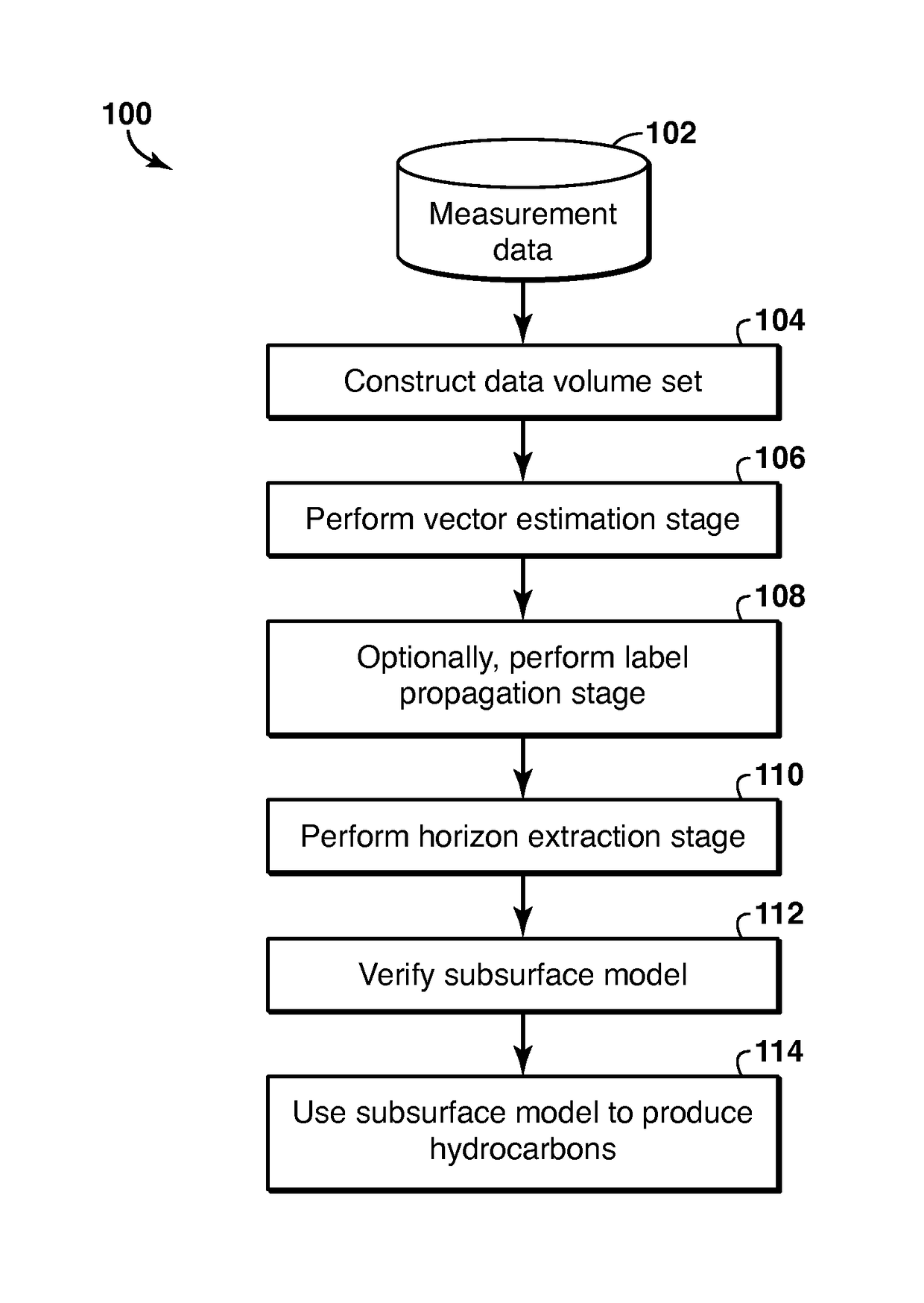
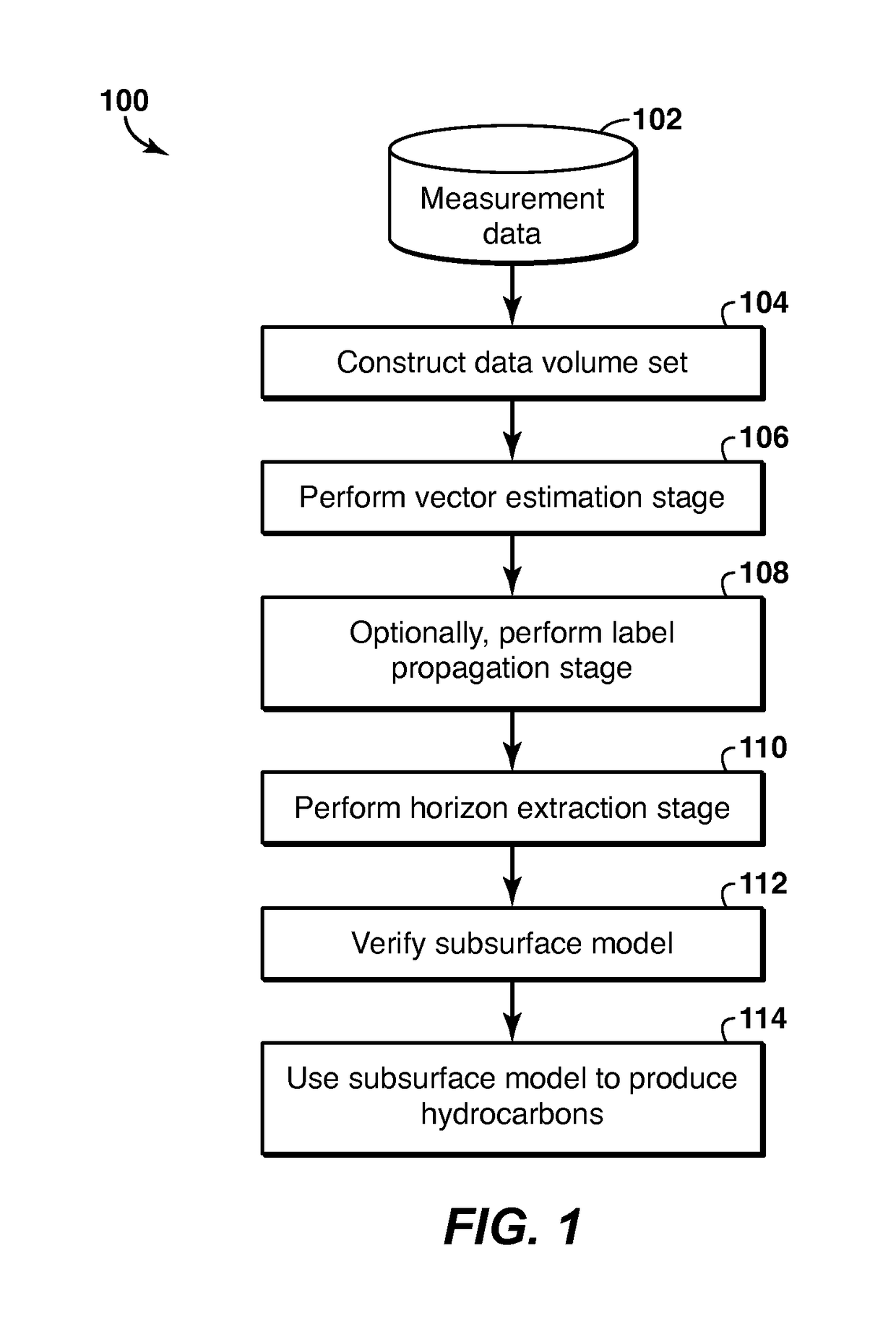
Geophysical Modeling of Subsurface Volumes Based on Horizon Extraction
Method and system is described for modeling one or more geophysical properties of a subsurface volume. The method includes extracting locations from the data volume and combining them into an object, for example a horizon. The extraction may begin with selecting one or more initial traces, assigning labels to each sample of each trace, selecting a propagation pattern, and propagating the labels from the initial traces along a vector volume. Then, locations with the same label are extracted (1106). As an alternative to label propagation, a specific type of labeled volume (1102) may be obtained, such as a stack of surfaces (1132). The object may then be further modified or utilized to enhance the process of producing hydrocarbons.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
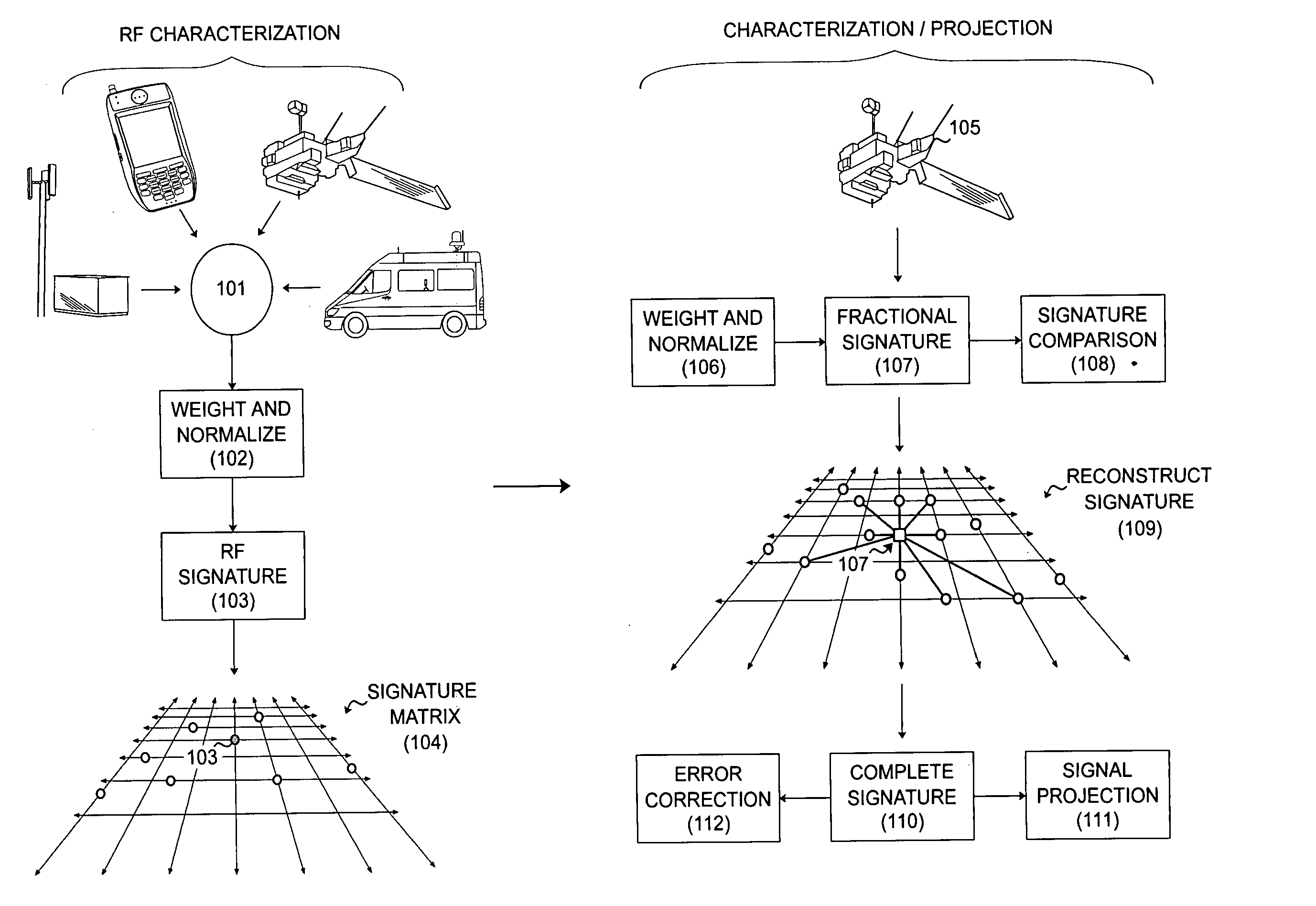
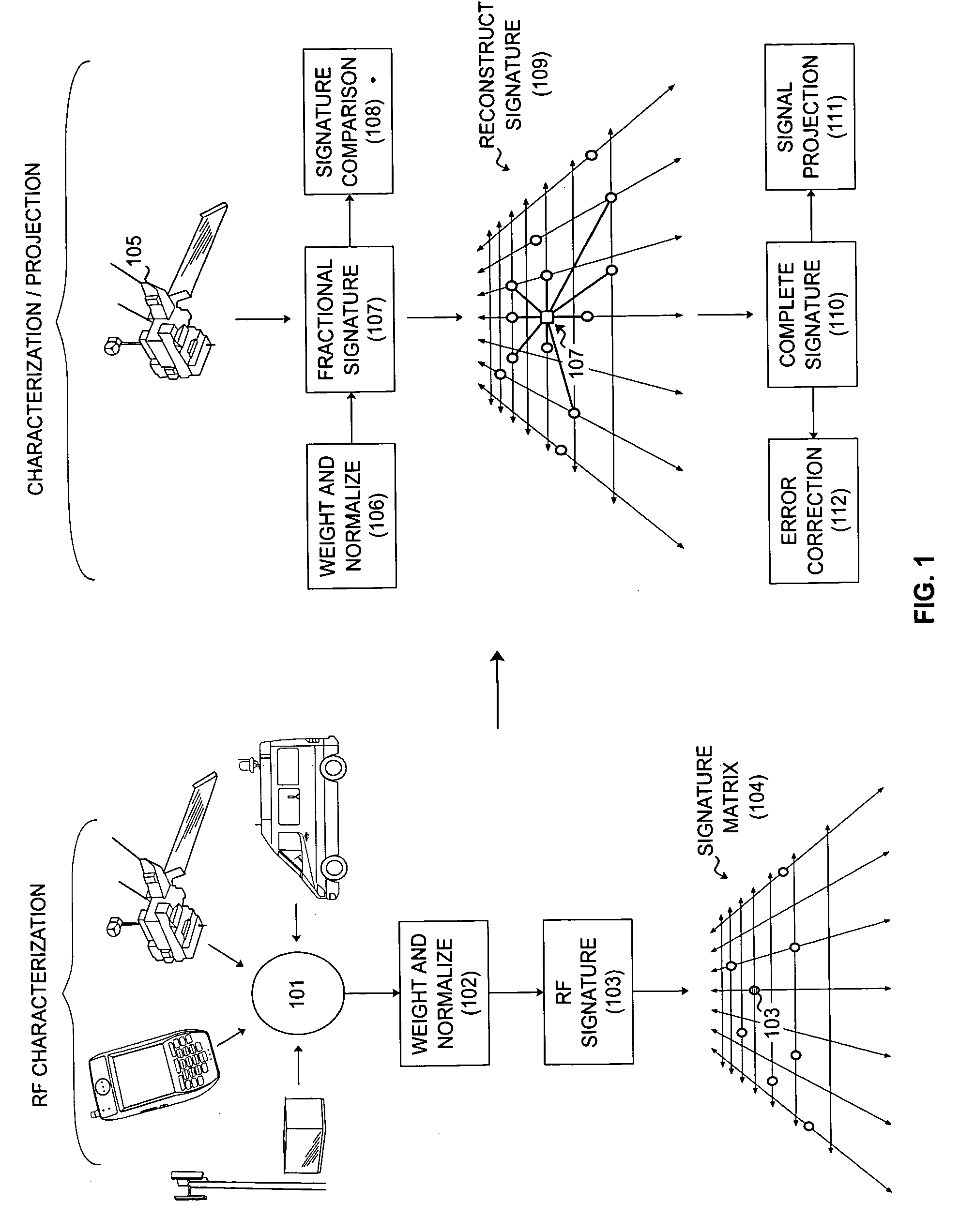
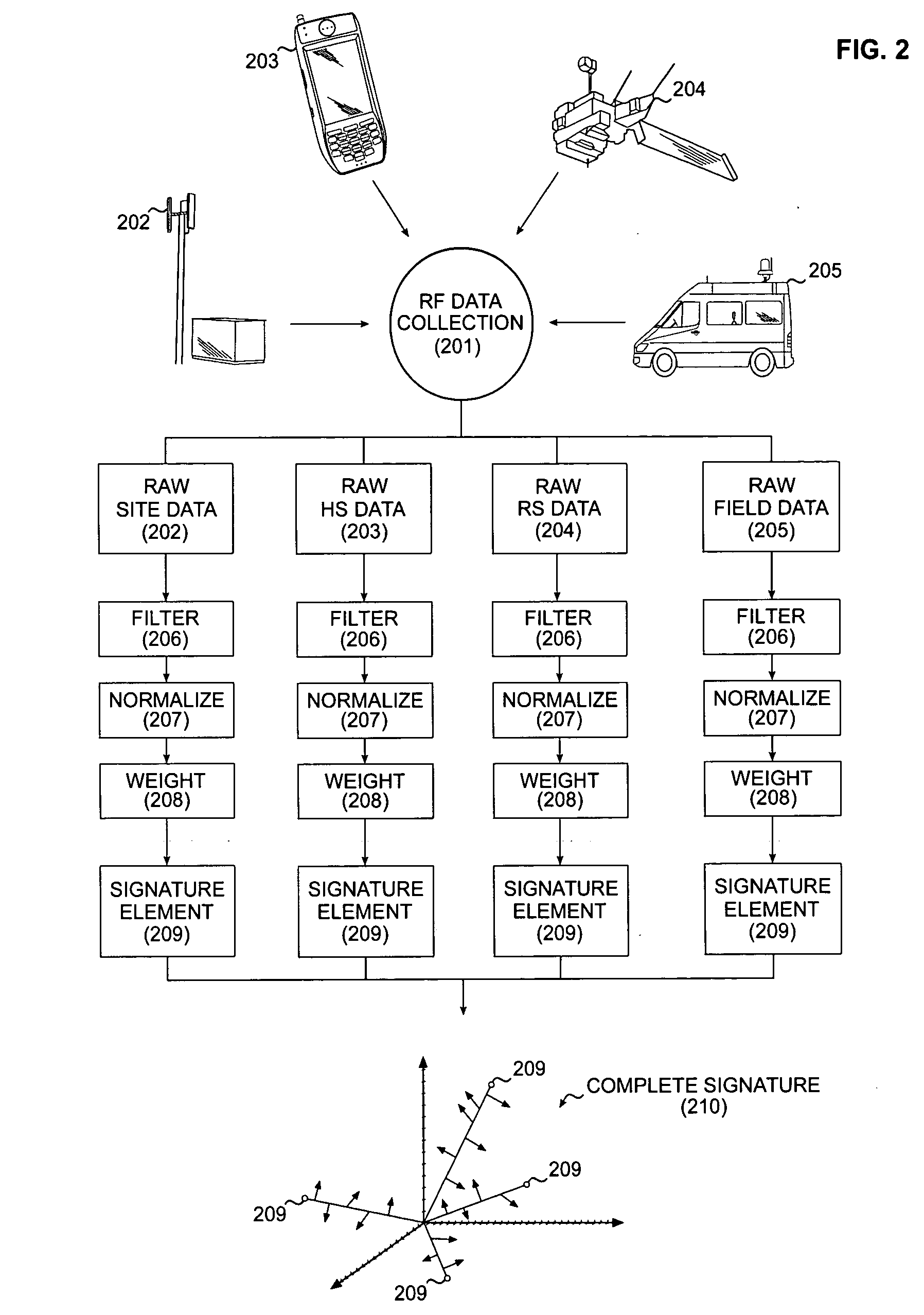
System and method for the ultra-precise analysis and characterization of RF propagation dynamics in wireless communication networks
InactiveUS20070010207A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyReceivers monitoringRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPropagation patternRadio frequency
The present invention relates to a system and method for the ultra-precise analysis and characterization of RF propagation dynamics in complex wireless communication networks. The invented system includes sub-systems for the collection of network specific performance and environmental data, the consolidation of said data into representative signature elements, and the organization of said signature elements into a relational matrix. Through the invented methodology, RF performance and environmental composition data are closely correlated in uniformly weighted signature elements. These signatures, arranged in a relational matrix, represent a multiplicity of propagation pattern extrema. Limited RF data is compiled and formed into fractional signature elements. Fuzzy logic based reconstructive techniques are used to integrate these fractional elements into the normal signature matrix, allowing rapidly gathered and severely abbreviated data to produce extremely detailed and accurate characterization of RF propagation in localized coverage zones.
Owner:DOOLEY JOHN ALDRICH
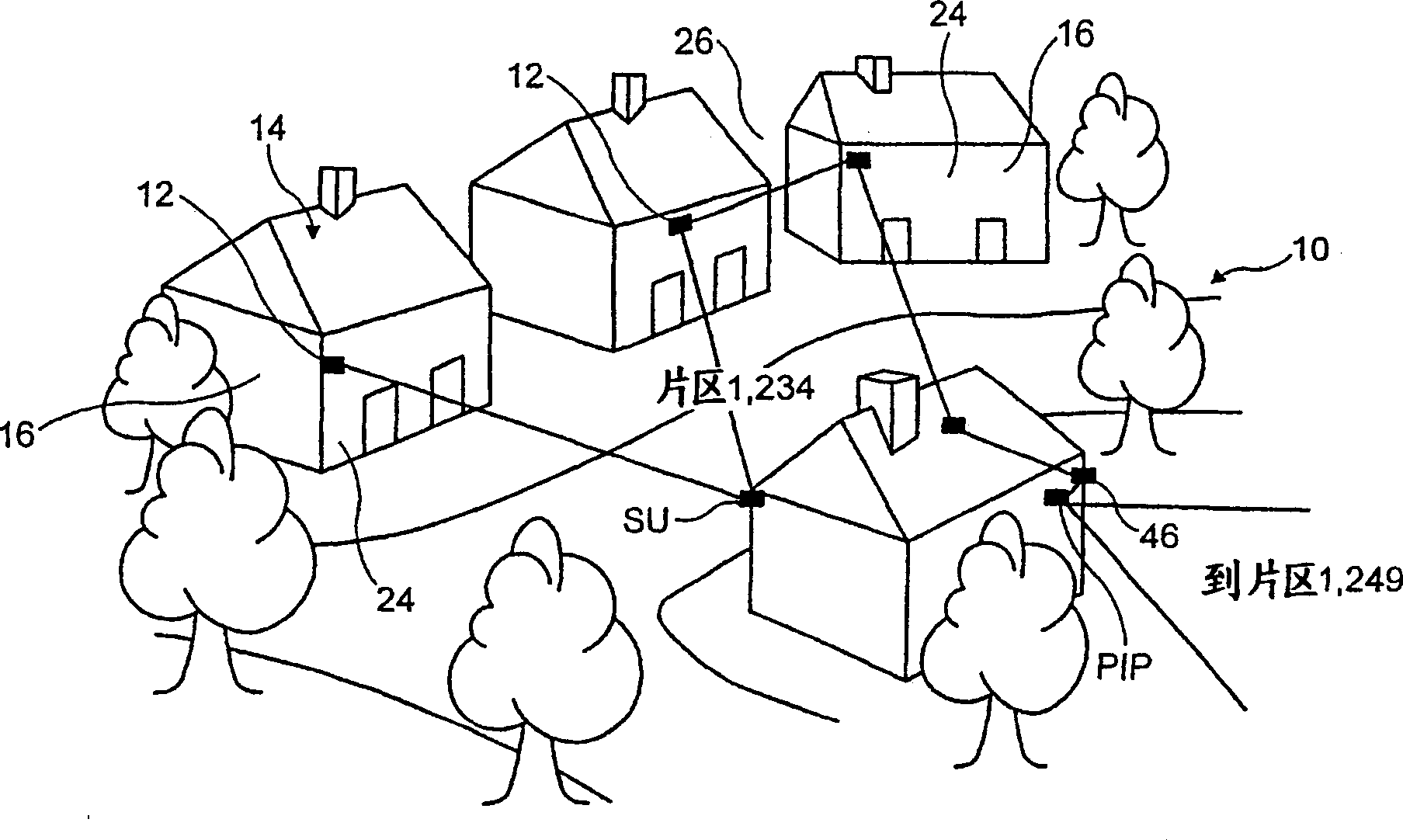
System and method for mass broadband communications
InactiveCN1554161ANo interferenceSame spectral bandwidthLine-of-sight transmissionInfraredCommunication unit
After the claims, please insert the following Abstract:-The invention provides a broadband mass communications network system and method comprising a plurality of patches (10), each patch including a plurality of subscribers, and each subscriber having a respective subscriber unit (12) for transmitting signals to and receiving signals from other subscribers. Each subscriber unit comprises an indoor interface unit (20) for user access to the system and an outdoor mounted communication unit (18) for the transmission and reception of signals. The signals are impressed on a carrier signal operating at frequencies in the range from infra-red to ultra-violet, the subscriber units of a respective patch being arranged to transmit the carrier signals substantially omni-directionally and to communicate by way of direct line of sight connections within the patch. Objects (16) within and / or around the respective patch are employed to determine and / or modify the propagation pattern of the carrier signal and to define boundaries for the patch. Respective patches are inter-connected by way of patch interface points (46), each patch interface point being connected to respective subscriber units from at least two adjacent patches by communication means other than that between respective subscriber units within the patches.
Owner:REDWAVE TECH LTD
Slow wave optical waveguide for velocity matched semiconductor modulators
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method, Controller, Program, and Data Storage System for Performing Reconciliation Processing
InactiveUS20160171121A1Reduce processing overheadReduce processing burdenDigital data processing detailsKnowledge representationData graphAlgorithm
A method for reconciling a source data graph with a target data graph, the source graph and the target graph each comprising: and a interconnections, the interconnections each connecting two vertices from and representing a relationship between the connected vertices. The method comprises: generating target event propagation information representing the propagation pattern of executions of each of a set of processing events in the target graph; receiving a request to reconcile the source and graph, and in response to the request, triggering the executions of each of the set in the source graph; generating source event propagation information representing the pattern of each of the executions triggered in the source graph; and using the target event propagation information and the source event propagation information to assess the similarity of pairs of vertices comprising one vertex from each of the source graph and the target graph.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Slow wave optical waveguide for velocity matched semiconductor modulators
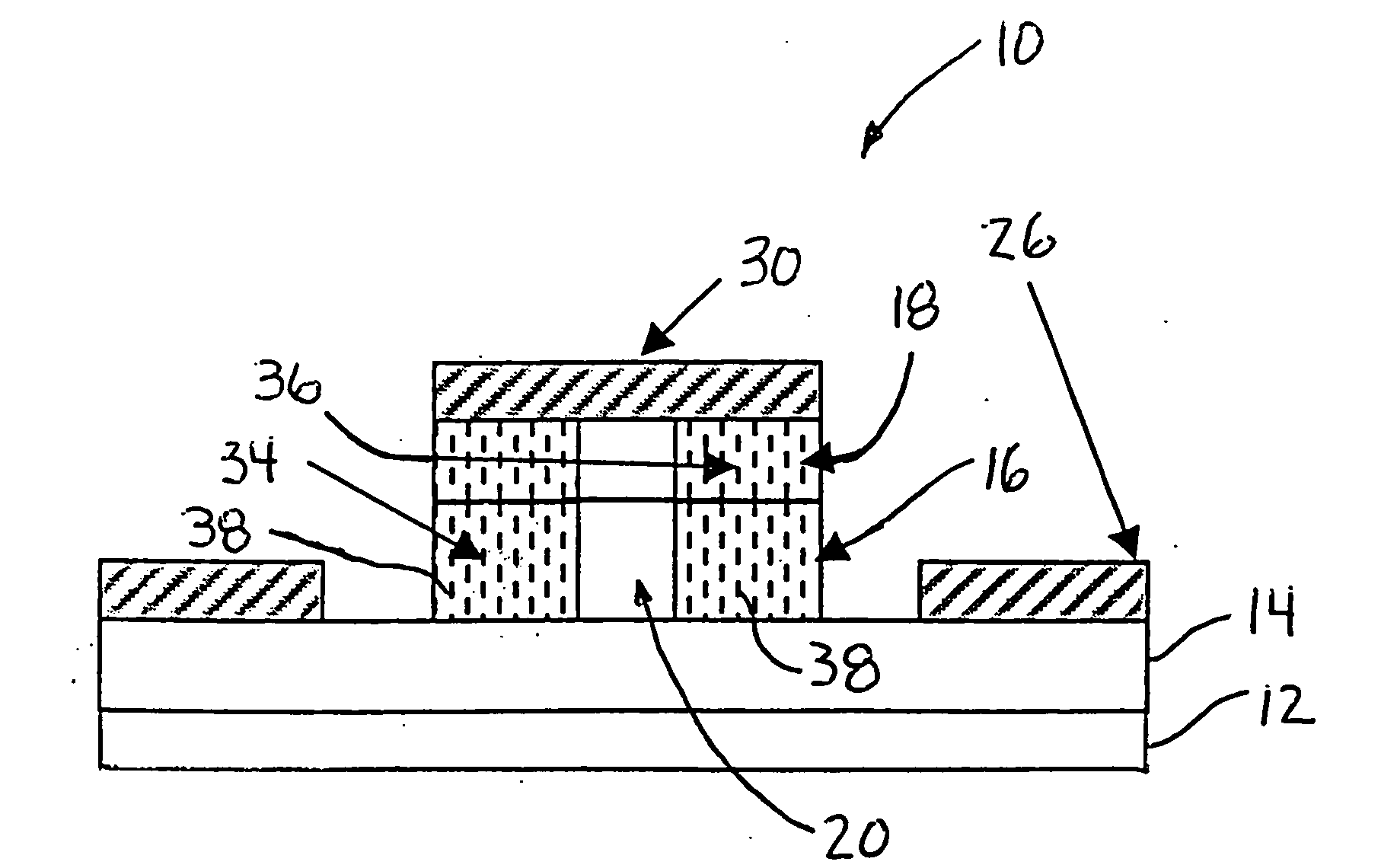
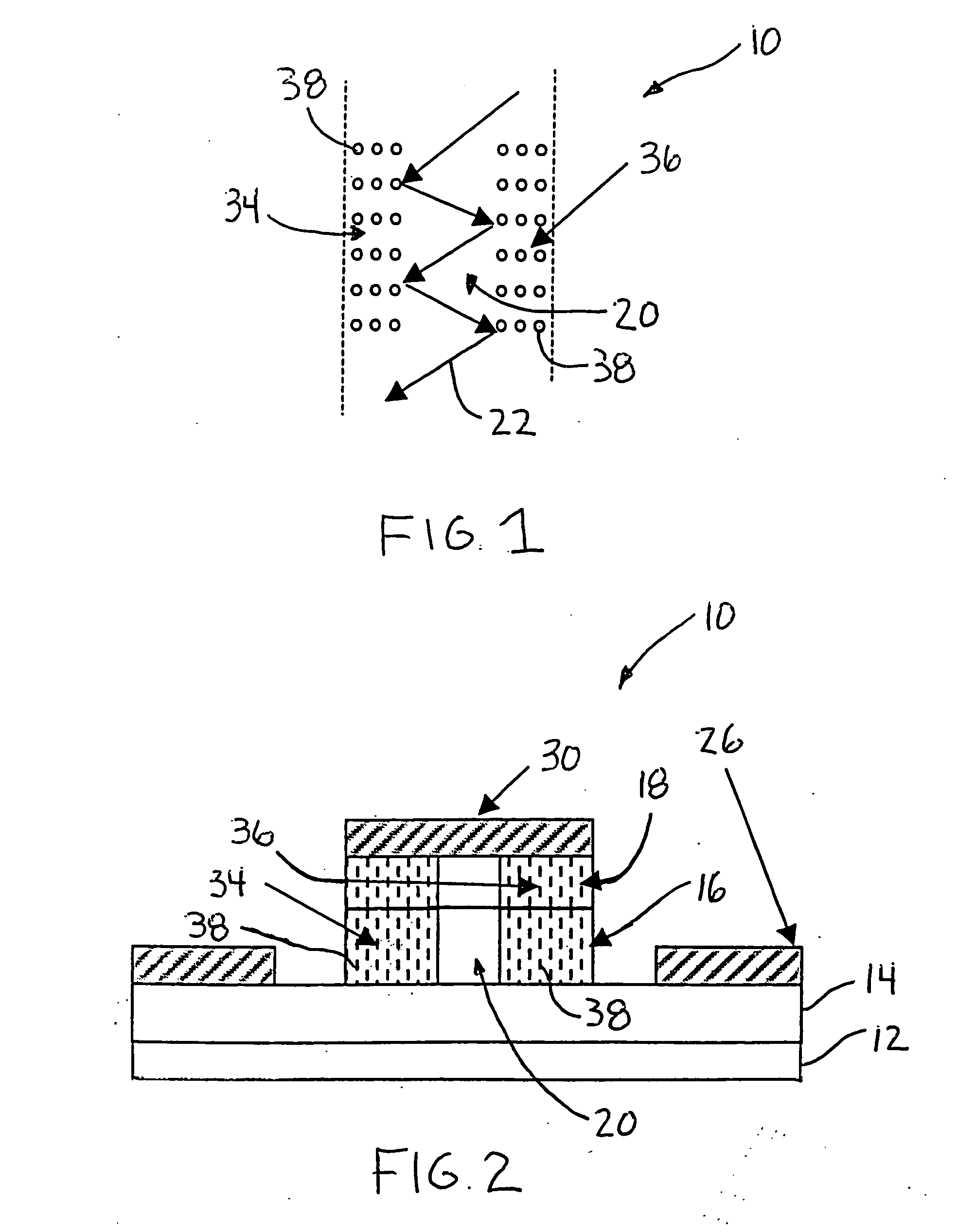
A PIN electro-optical traveling wave modulator (10) including diffraction gratings (34, 36) positioned at opposing sides of an optical waveguide (20) that act to change the propagation pattern of the waveguide (20). The modulator (10) includes an N-type layer (14), a P-type layer (18) and an intrinsic layer (16) acting as the waveguide (20). A metal electrode (26) is in electrical contact with the N-type layer (14), and a metal electrode (30) is in electrical contact with the P-type layer (18). The electrodes (26, 30) define an RF transmission line. An optical wave (22) propagates along the waveguide (20) and interacts with the gratings (34, 36) which slow the optical wave (22) to match its speed to the speed of the RF wave in the transmission line. In one embodiment, the gratings (34, 36) are 2-D gratings formed by vertical holes (38) in the waveguide (20).
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Geophysical modeling of subsurface volumes based on horizon extraction
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
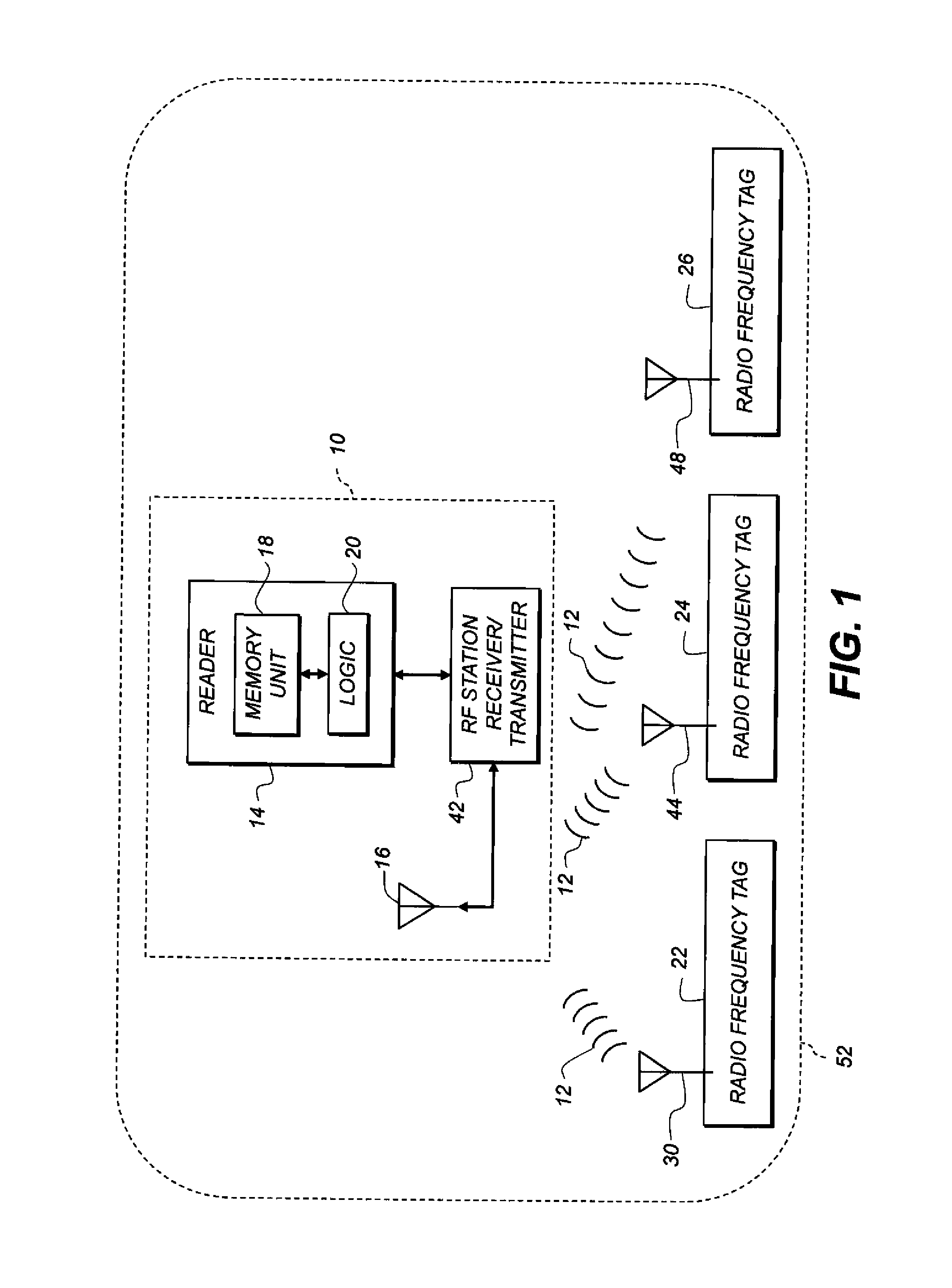
Container-type identification using directional-antenna RFID
InactiveUS20130314211A1Sensing detailsSubscribers indirect connectionPropagation patternDirectional antenna
RFID tags are read using an RFID reader. A non-RFID-active object has two RFID tags affixed thereto at respective, different tag locations. Each tag has a respective directional antenna steered in a respective, different direction. Respective directional propagation patterns are thus defined and a reader location is defined in the intersection of the propagation patterns. An RFID reader with a reader antenna located at the reader location is provided. The RFID reader is activated to read both tags.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Servo information writing method, servo control method, data memory equipment and program
A servo system wherein a read head R detects a servo pattern that is written on a magnetic disk by a write head W. Position control of the write head W is exercised in accordance with the detected servo pattern, and the read head R detects a propagation pattern that is written on the magnetic disk by the write head W. Position of the write head W is corrected in accordance with the detected propagation pattern.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
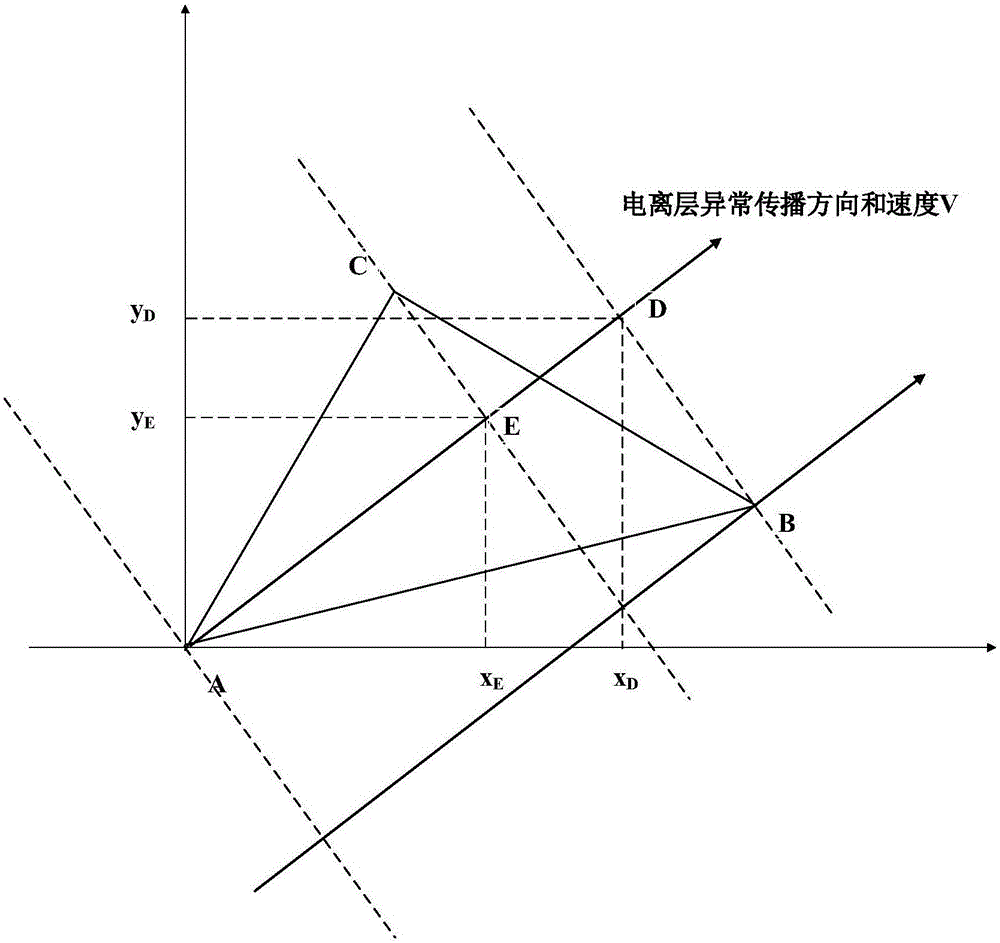
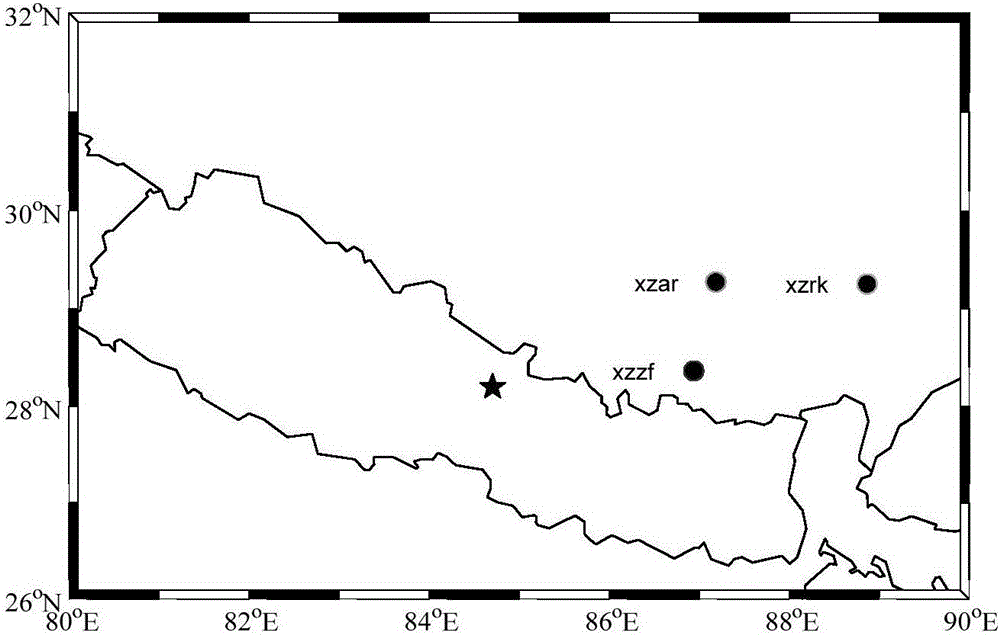
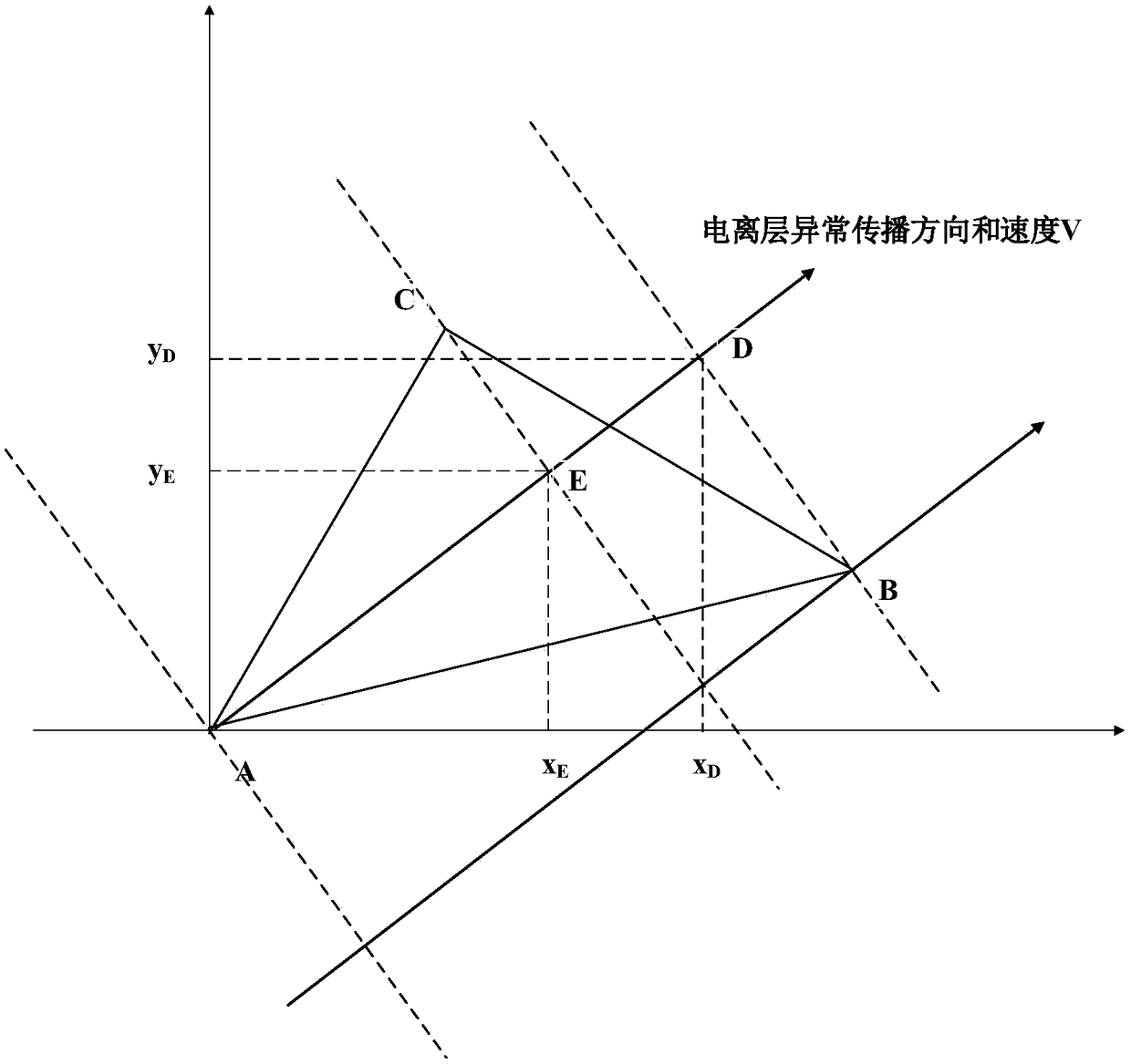
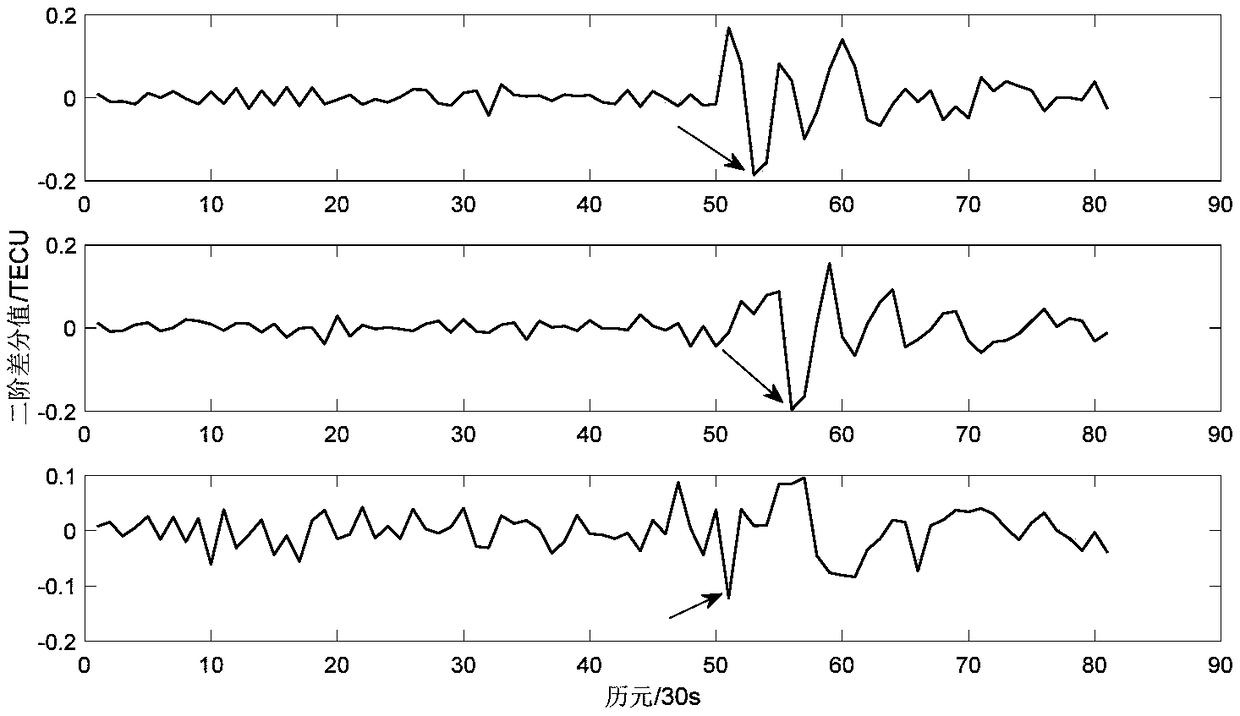
Three observation station data feature point-based ionospheric disturbance propagation measurement method and system
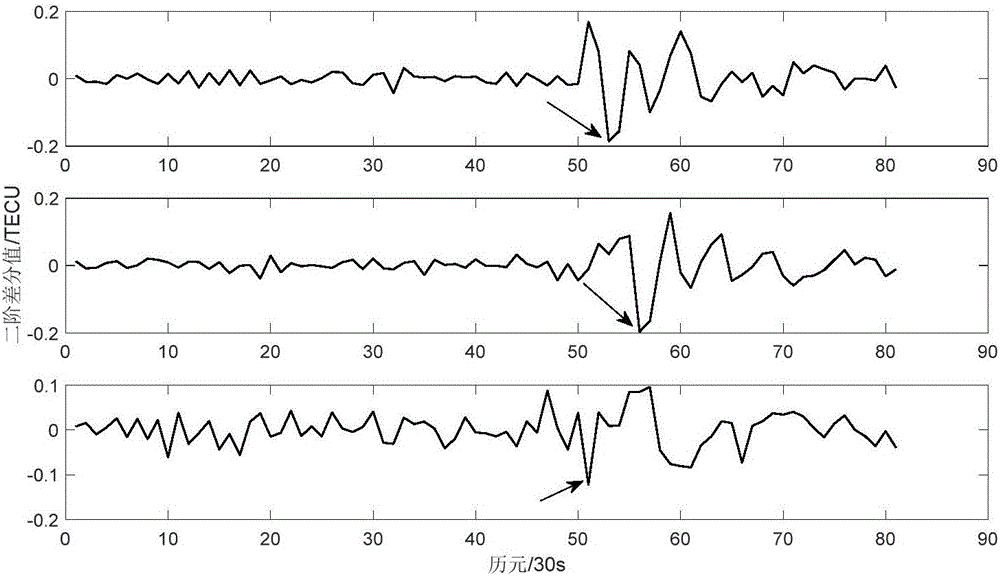
The invention discloses a three observation station data feature point-based ionospheric disturbance propagation measurement method and system. The method includes the following steps that: a local coordinate system is built, monitoring data feature points are selected, and time when an anomaly arrives at three points is obtained, and the propagation time difference of anomaly disturbance is obtained; and the slope of an anomaly propagation path and the coordinates of projection points in a disturbance propagation direction are calculated, and the propagation velocity and azimuth angle of the anomaly are calculated, and measurement results are obtained. According to the three observation station data feature point-based ionospheric disturbance propagation measurement method and system of the invention, the velocity and direction of ionospheric disturbance propagation can be accurately and automatically calculated with only a small number of feature points based on the precise geometrical relationships of observation station puncture points under a condition that ionospheric disturbance time is short. The three observation station data feature point-based ionospheric disturbance propagation measurement method and system have great scientific significance and application value for the study of the solar-terrestrial space environment, ionosphere, magnetosphere coupling and traveling ionospheric disturbance propagation patterns.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
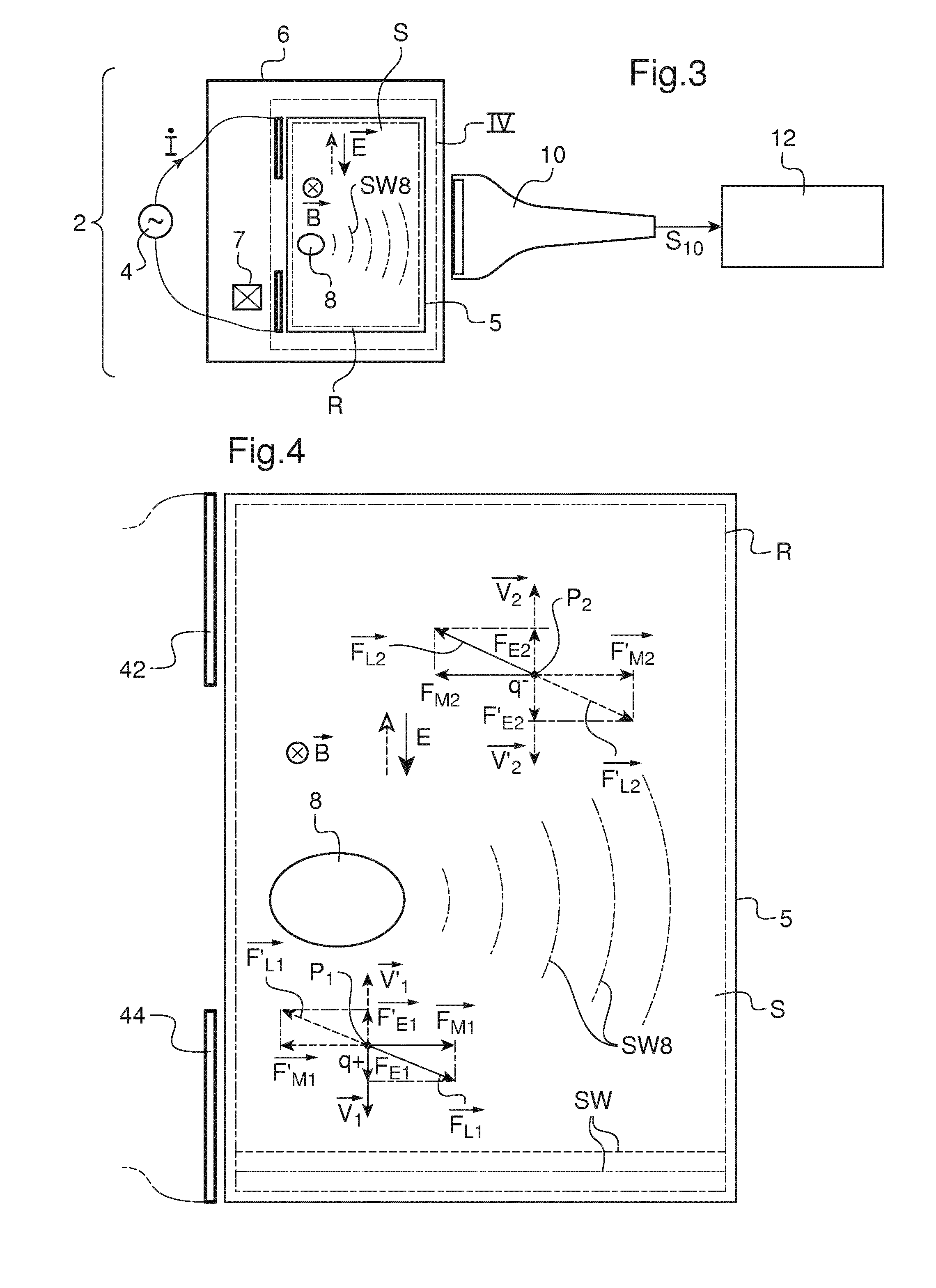
Shear wave generation method, shear wave imaging method and thermal mapping or treating method utilizing such a generation method and installation for generating at least one shear wave
ActiveUS20170007206A1Easy to detectHigh pressureOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationUltrasonic sensor
Method for generating a shear wave in a target region of a soft solid, includes the following steps: a) generating at least two shear waves with a first and a second source of shear waves in the target region; b) detecting a propagation pattern of the shear wave in the target region with a detector unit including a row of ultrasonic transducers aligned on a first direction perpendicular to a detection direction of each or a single ultrasonic transducer movable along a first direction perpendicular to its detection direction; c) proceeding to a time reversal of the detected propagation pattern; and d) submitting the target region to an inverted excitation set of forces based on the temporally inverted propagation pattern. During step b), a first propagation pattern is detected when only the first source is active and a second propagation pattern is detected when only the second source is active.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
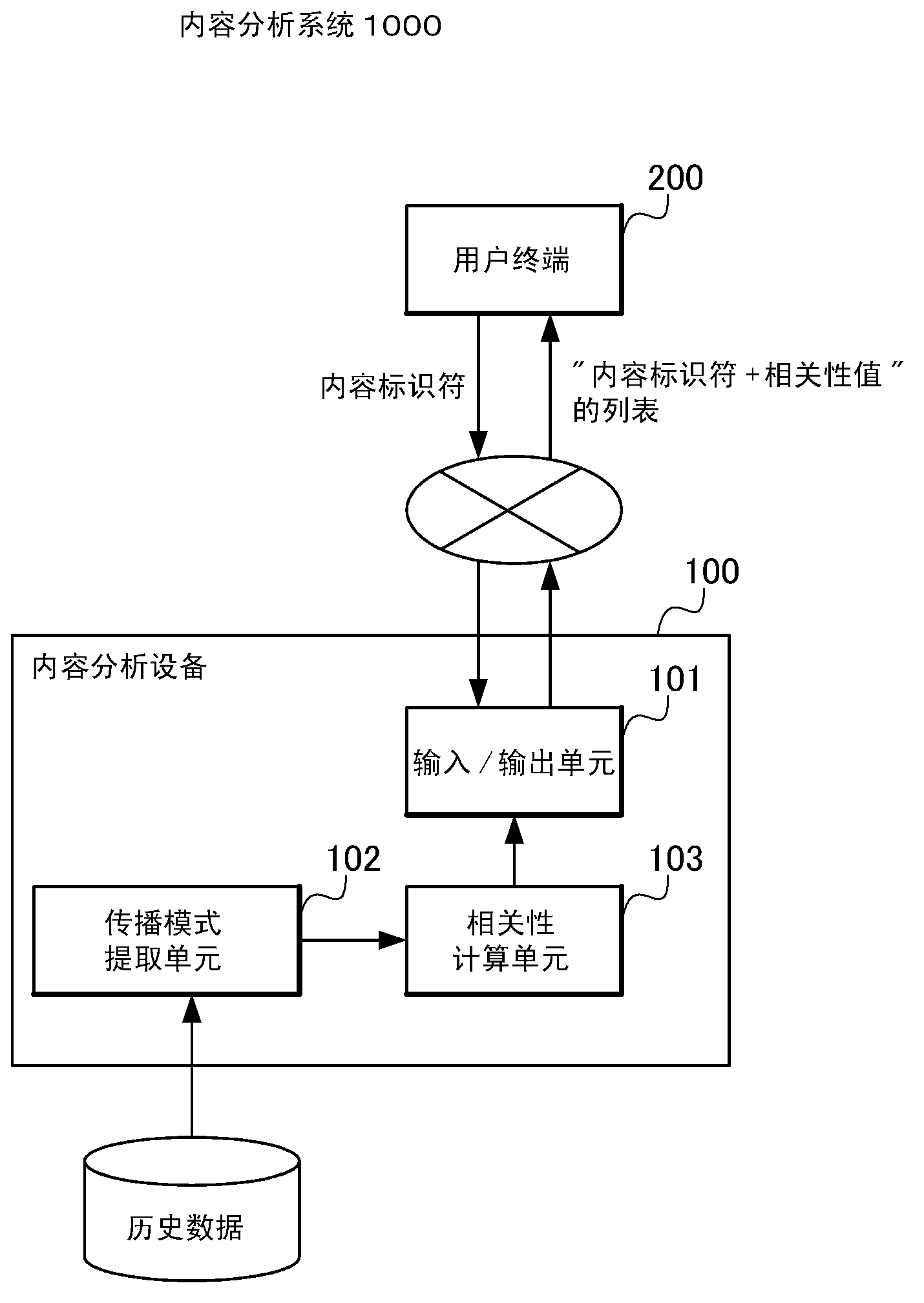
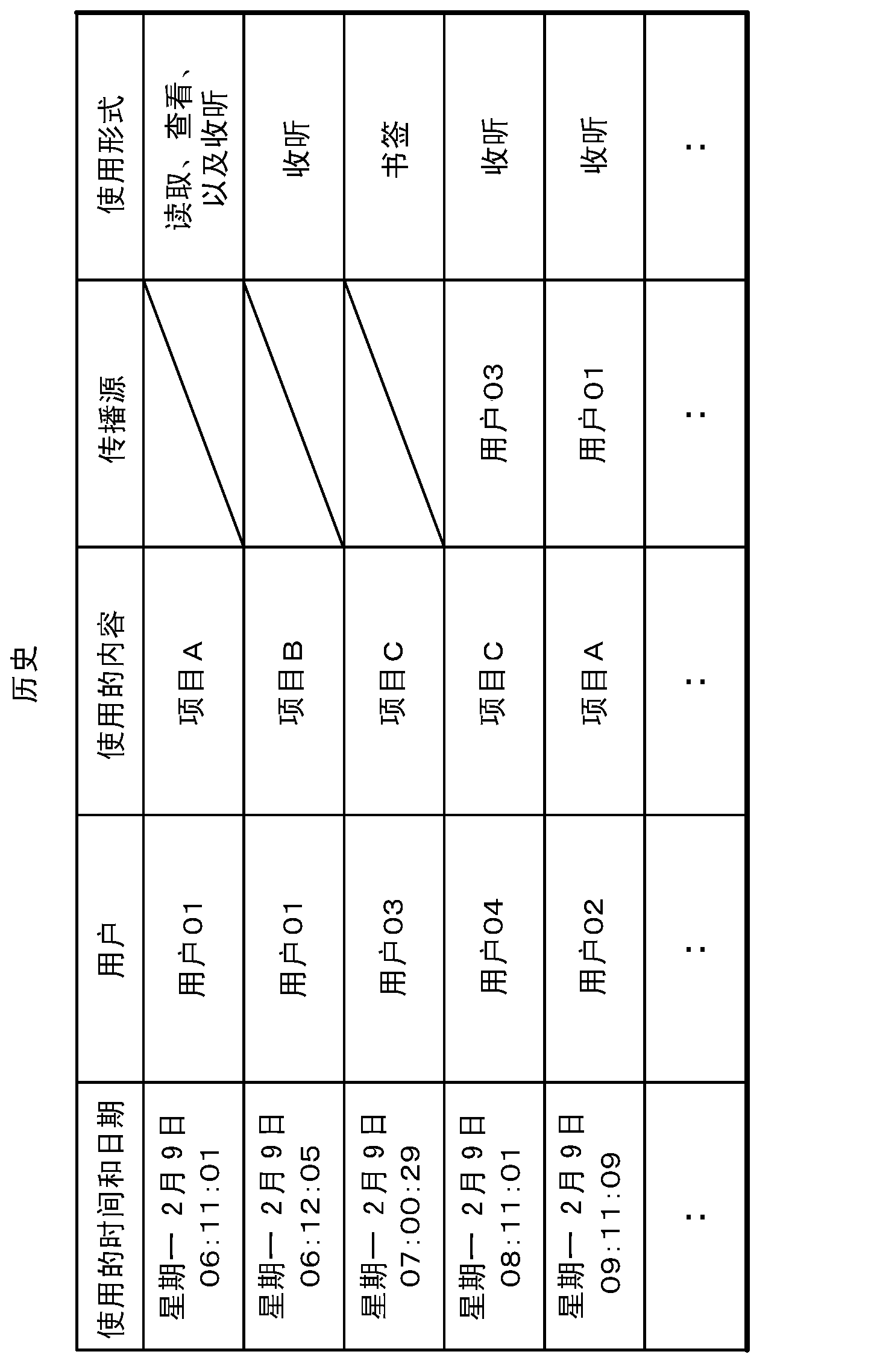
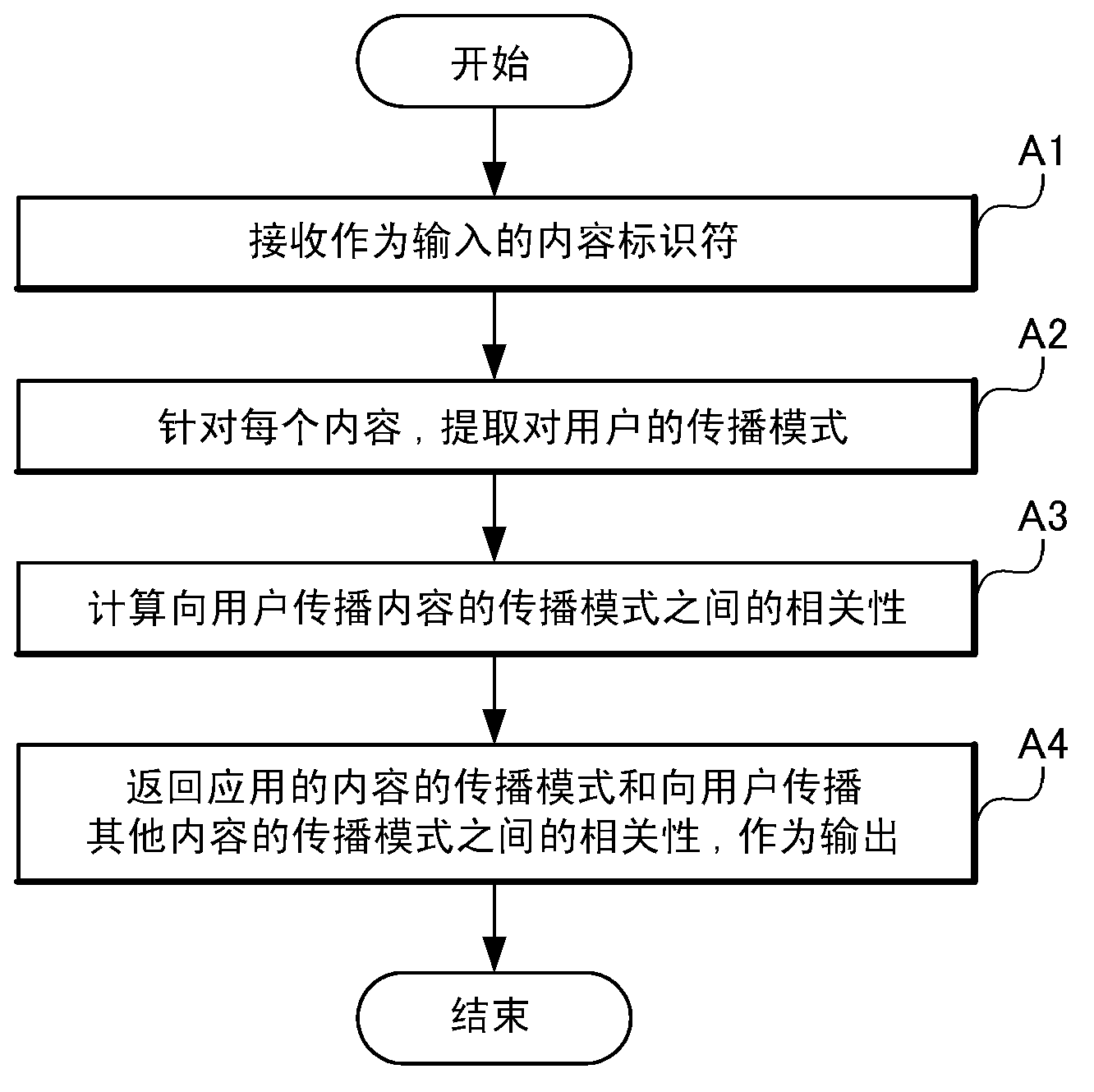
Content analyzing system, content analyzing apparatus, content analyzing method, and content analyzing program
InactiveCN103154945ABuying/selling/leasing transactionsSpecial data processing applicationsPropagation patternContent analytics
Owner:NEC CORP
Ionospheric Disturbance Propagation Measurement Method and System Based on Three Station Data Feature Points
The invention discloses a three observation station data feature point-based ionospheric disturbance propagation measurement method and system. The method includes the following steps that: a local coordinate system is built, monitoring data feature points are selected, and time when an anomaly arrives at three points is obtained, and the propagation time difference of anomaly disturbance is obtained; and the slope of an anomaly propagation path and the coordinates of projection points in a disturbance propagation direction are calculated, and the propagation velocity and azimuth angle of the anomaly are calculated, and measurement results are obtained. According to the three observation station data feature point-based ionospheric disturbance propagation measurement method and system of the invention, the velocity and direction of ionospheric disturbance propagation can be accurately and automatically calculated with only a small number of feature points based on the precise geometrical relationships of observation station puncture points under a condition that ionospheric disturbance time is short. The three observation station data feature point-based ionospheric disturbance propagation measurement method and system have great scientific significance and application value for the study of the solar-terrestrial space environment, ionosphere, magnetosphere coupling and traveling ionospheric disturbance propagation patterns.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method and system for geophysical modeling of subsurface volumes based on label propagation
Method and system are described for generating a stratigraphic model of a subsurface volume. Measured geophysical data are converted into a vector volume (106) by assigning to each sample in each trace in the data volume a vector representing dip, azimuth or confidence. Then a labeled volume is generated from the vector volume by assigning a label to each sample in an initial trace (1006), then selecting a propagation pattern (1008) and propagating the labels to other traces (1010). Horizons can be extracted (110) from the labeled volume, and utilized to enhance the process of producing hydrocarbons (114).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Shear wave generation method, shear wave imaging method and thermal mapping or treating method utilizing such a generation method and installation for generating at least one shear wave
ActiveUS10485516B2Increase temperatureGenerate efficientlyOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasonic sensorSonification
Method for generating a shear wave in a target region of a soft solid, includes the following steps: a) generating at least two shear waves with a first and a second source of shear waves in the target region; b) detecting a propagation pattern of the shear wave in the target region with a detector unit including a row of ultrasonic transducers aligned on a first direction perpendicular to a detection direction of each or a single ultrasonic transducer movable along a first direction perpendicular to its detection direction; c) proceeding to a time reversal of the detected propagation pattern; and d) submitting the target region to an inverted excitation set of forces based on the temporally inverted propagation pattern. During step b), a first propagation pattern is detected when only the first source is active and a second propagation pattern is detected when only the second source is active.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Shear wave imaging method and installation for collecting information on a soft solid
InactiveUS10368750B2Generate efficientlyEasy to implementMagnetic measurementsDiagnostics using vibrationsPropagation patternClassical mechanics
This shear wave imaging method, for collecting information on a target region (R) of a soft solid (S), comprises at least the steps a) of generating at least one shear wave (SW) in the target region, and b) of detecting a propagation pattern of the shear wave in the target region. Step a) is realized by applying to particles of the target region (R) some Lorentz forces resulting from an electric field (E) and from a magnetic field (B). At least one of the electric field (E) and the magnetic field (B) is variable in time, with a central frequency (fo) between 1 Hz and 10 kHz. Alternatively, both the electric and magnetic fields (E, B) are variable in time, with a central difference frequency (Δfo) between 1 Hz and 10 kHz. The shear wave imaging installation comprises a first system (4, 7) for generating at least one shear wave (SW) in the target region (R) and a second system (10) for detecting a propagation pattern of the shear wave. The first system includes first means (4) to apply an electric field (E) through the target region (R) and second means (7) to apply a magnetic field (B) through the target region. The first and second means are configured to apply to particles of the target region some Lorentz forces resulting from the electric field (E) and the magnetic field (B), where at least one of these fields is a quantity variable in time, with a central frequency (fo) between 1 Hz and 10 kHz, or both fields are quantities variable in time, with a central difference frequency (Δfo) between 1 Hz and 10 kHz.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
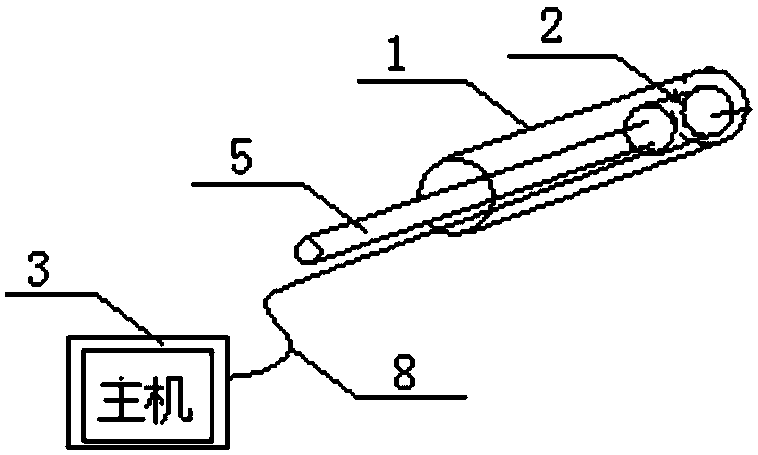
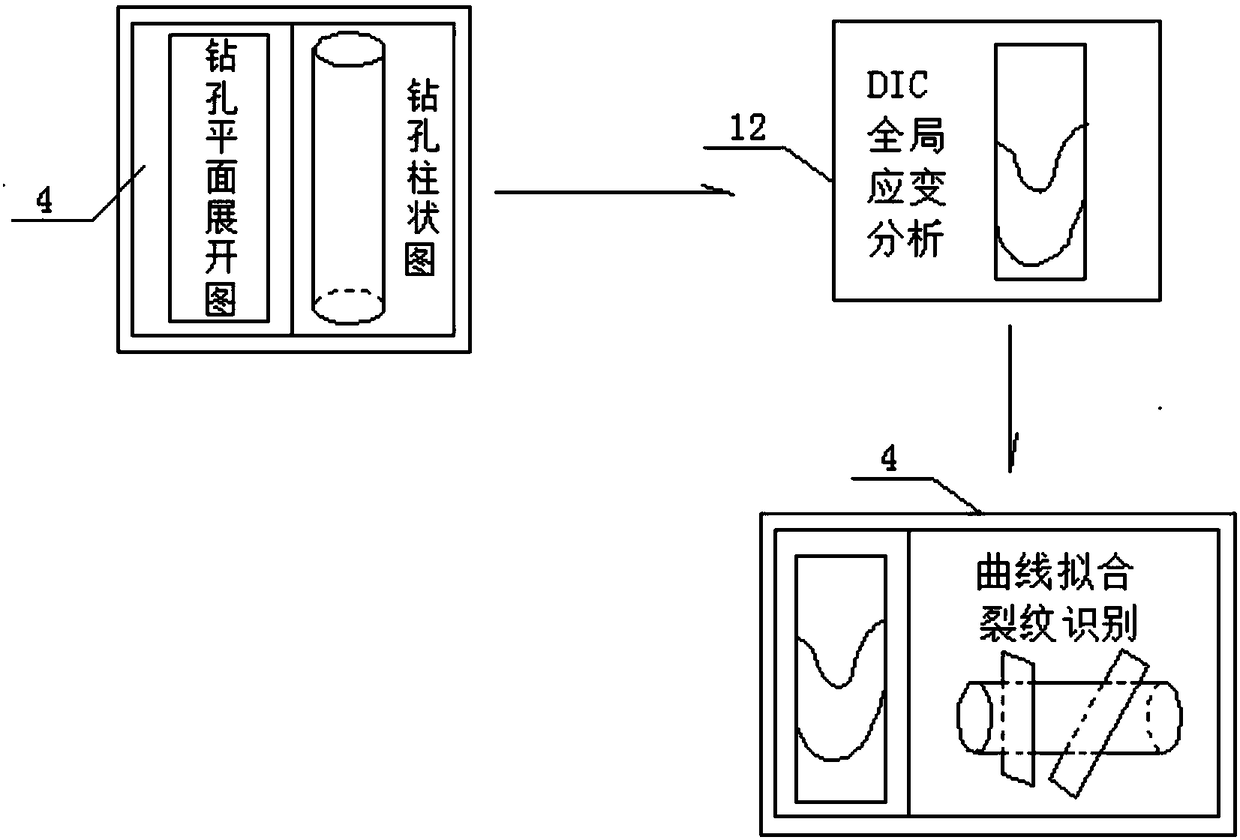
A DIC technology-based method and system for on-site rock mass crack propagation pattern recognition in holes
ActiveCN106248672BEasy to operate on siteEasy to disassembleMaterial analysis by optical meansRock corePropagation pattern
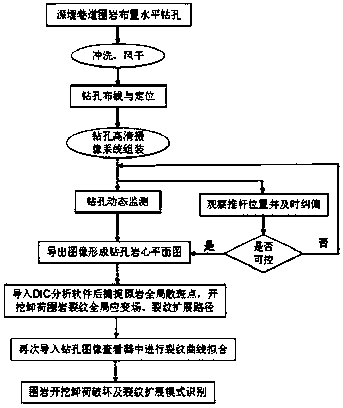
A method and a system for identifying on-site in-hole rock body crack propagation patterns based on DIC technology are disclosed. The method is as follows: horizontal boreholes are bored in an underground engineering rock body excavation site, and by synergistic effect of borehole camera technology and DIC software, a borehole three-dimensional histogram showing fitting plane space distribution of excavation-unloading-induced cracks; and according to an included angle alpha between a crack fitting plane in the borehole three-dimensional histogram and the rock core axis in the borehole three-dimensional histogram, whether the crack is a plate-fracture crack or a shear crack can be determined. The system comprises a high definition probe, a host, a push rod, guide rods and a cable, the high definition probe is connected electrically with the host by the cable, the lower parts of the two sides of the high definition probe is connected fixedly with the two guide rods, and the end surface of the tail of the high definition probe is connected fixedly with the push rod. Through organic bond of the borehole camera technology and the DIC technology, the excavation-unloading-induced cracks and original cracks can be effectively differentiated, the authenticity and reliability of the dynamic monitoring and recognition of on-site rock body excavation-induced cracks can be ensured, and the system has the advantages of convenient operation, reliable monitoring and high precision, and is especially suitable for deep-buried high-stress hard rock containing a certain natural gray level difference.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com