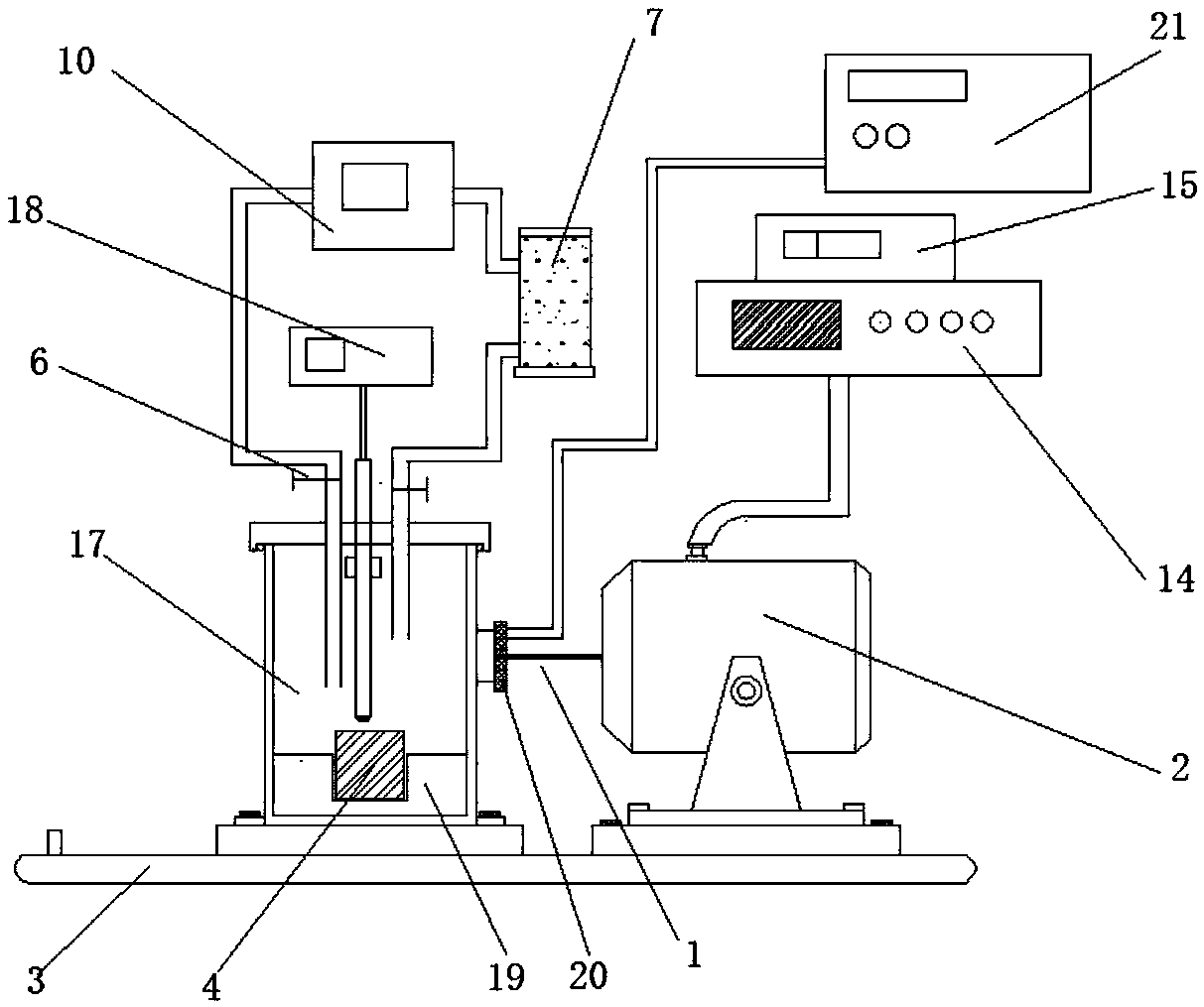
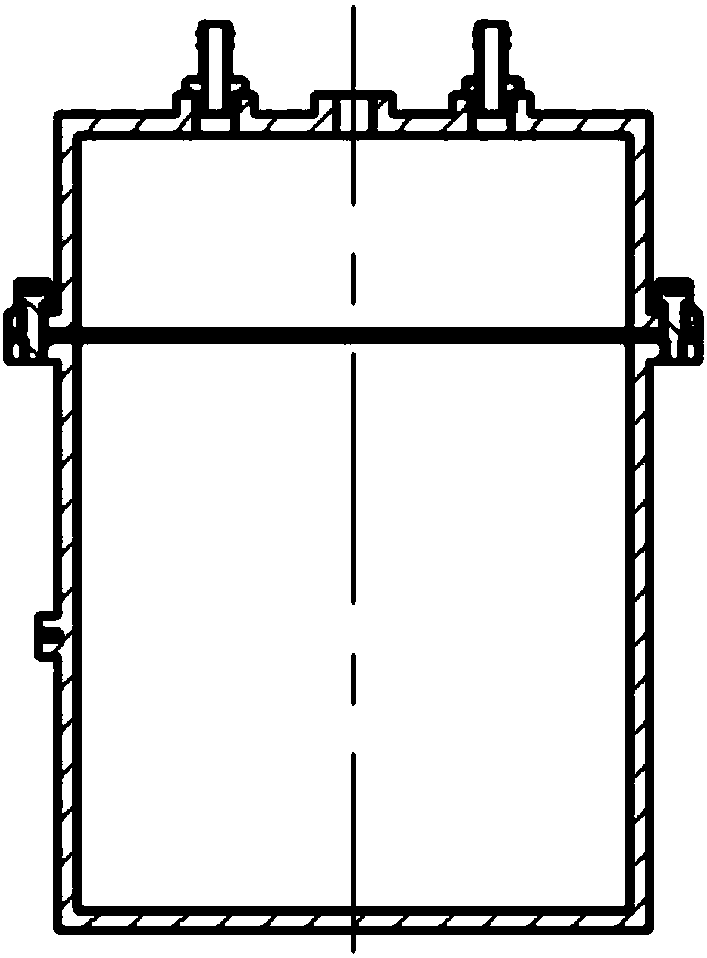
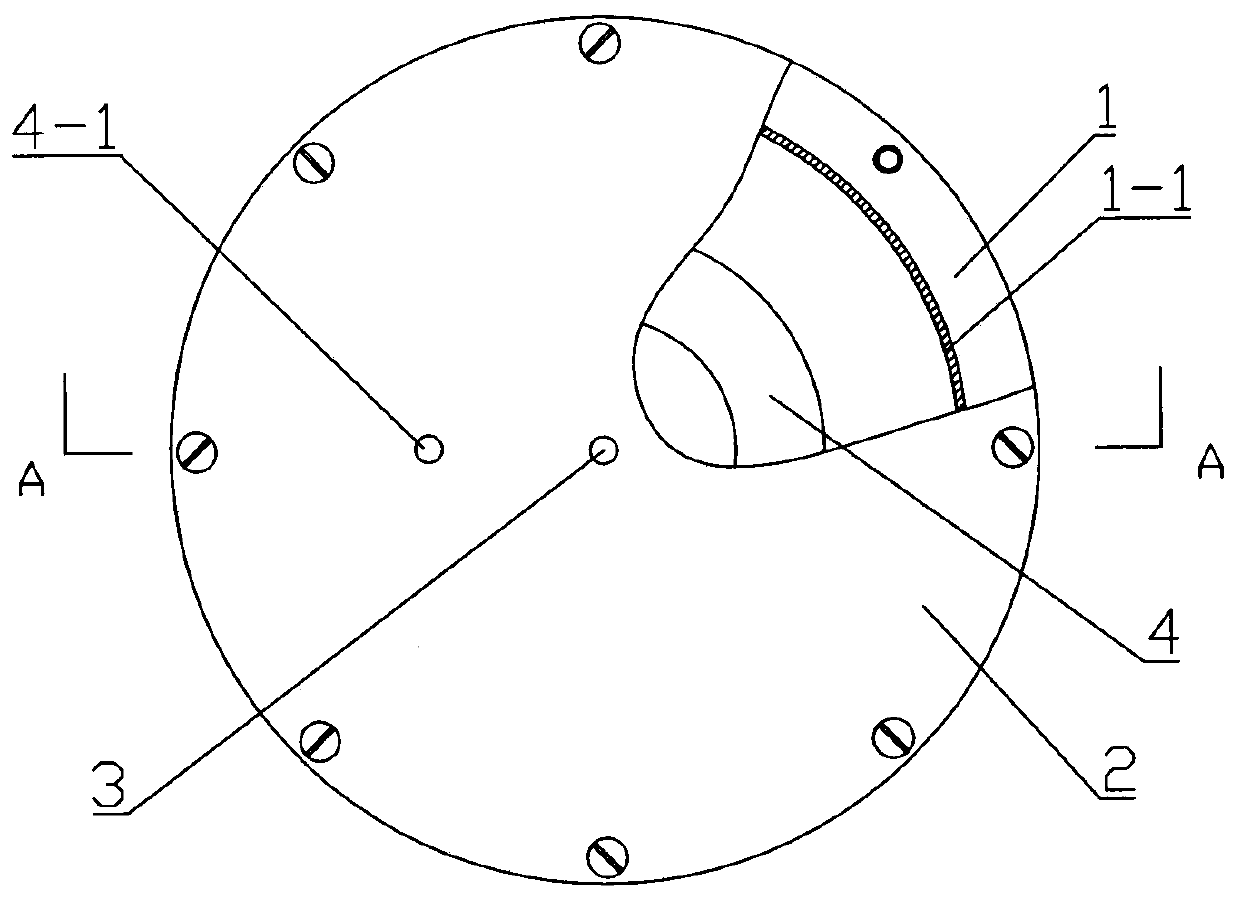
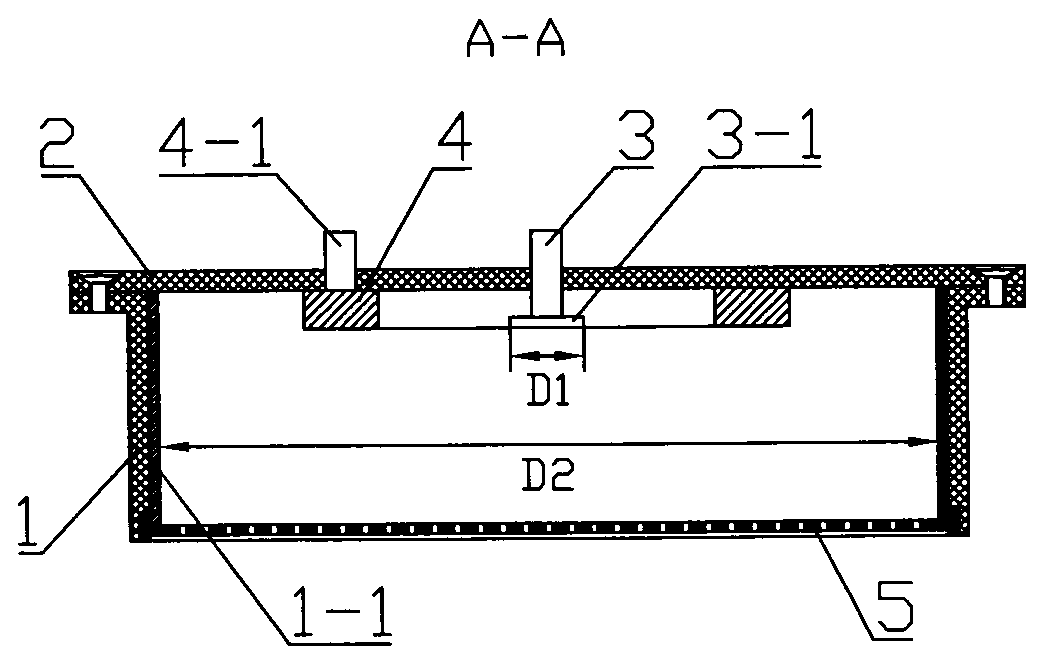
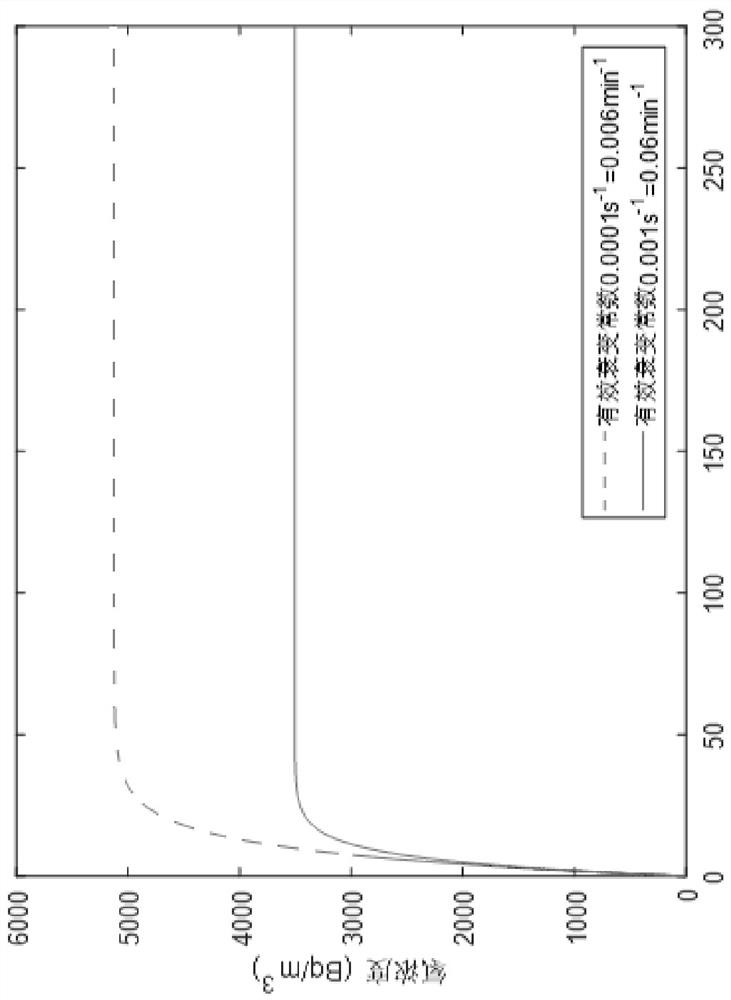
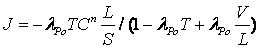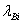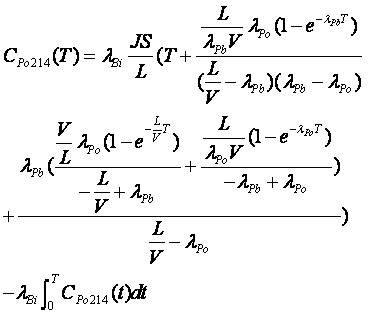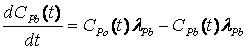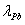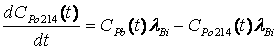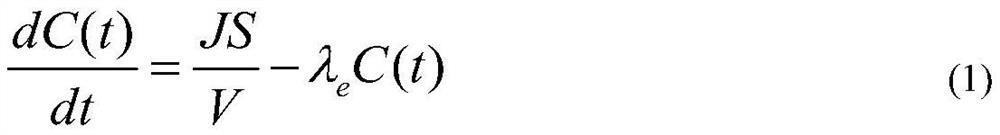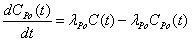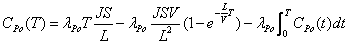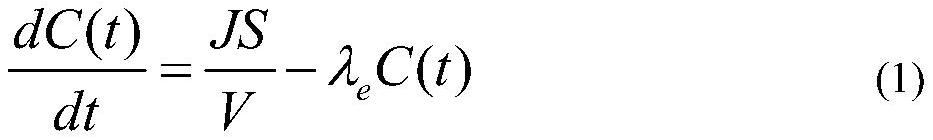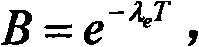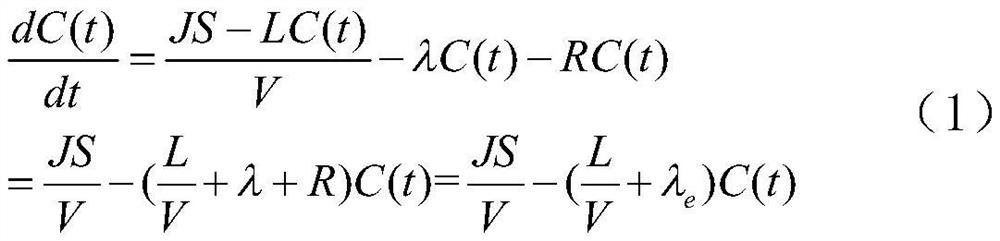Patents
Literature
40 results about "Radon flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
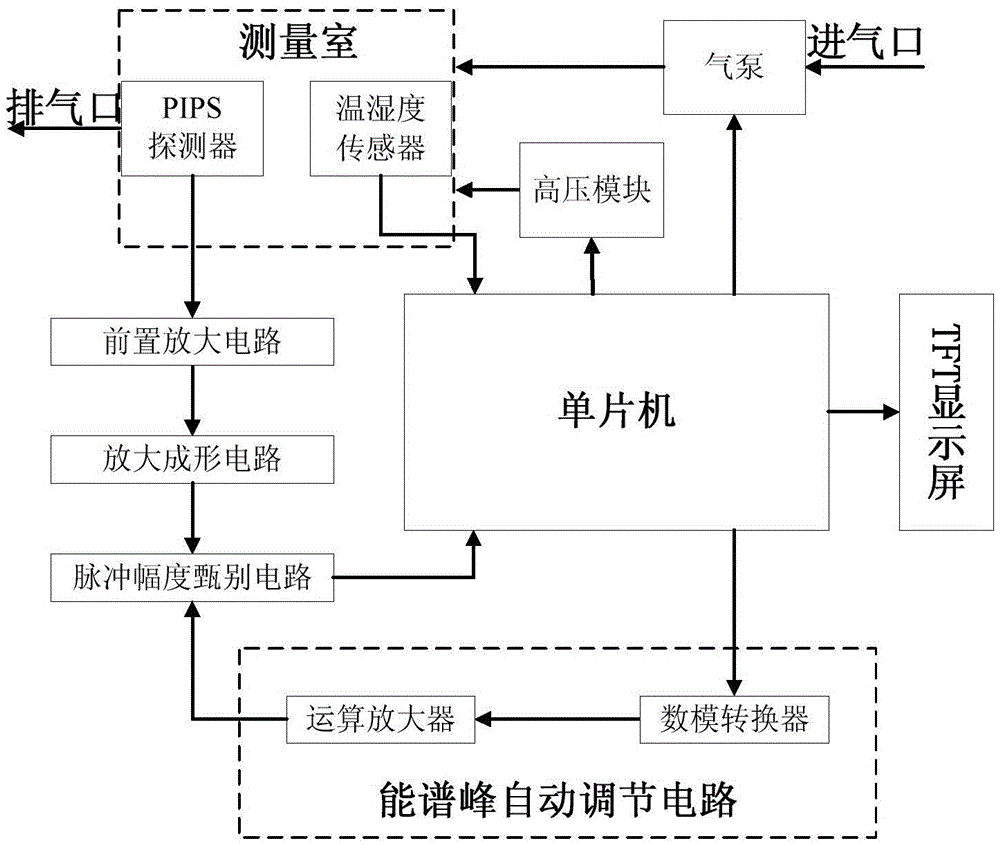
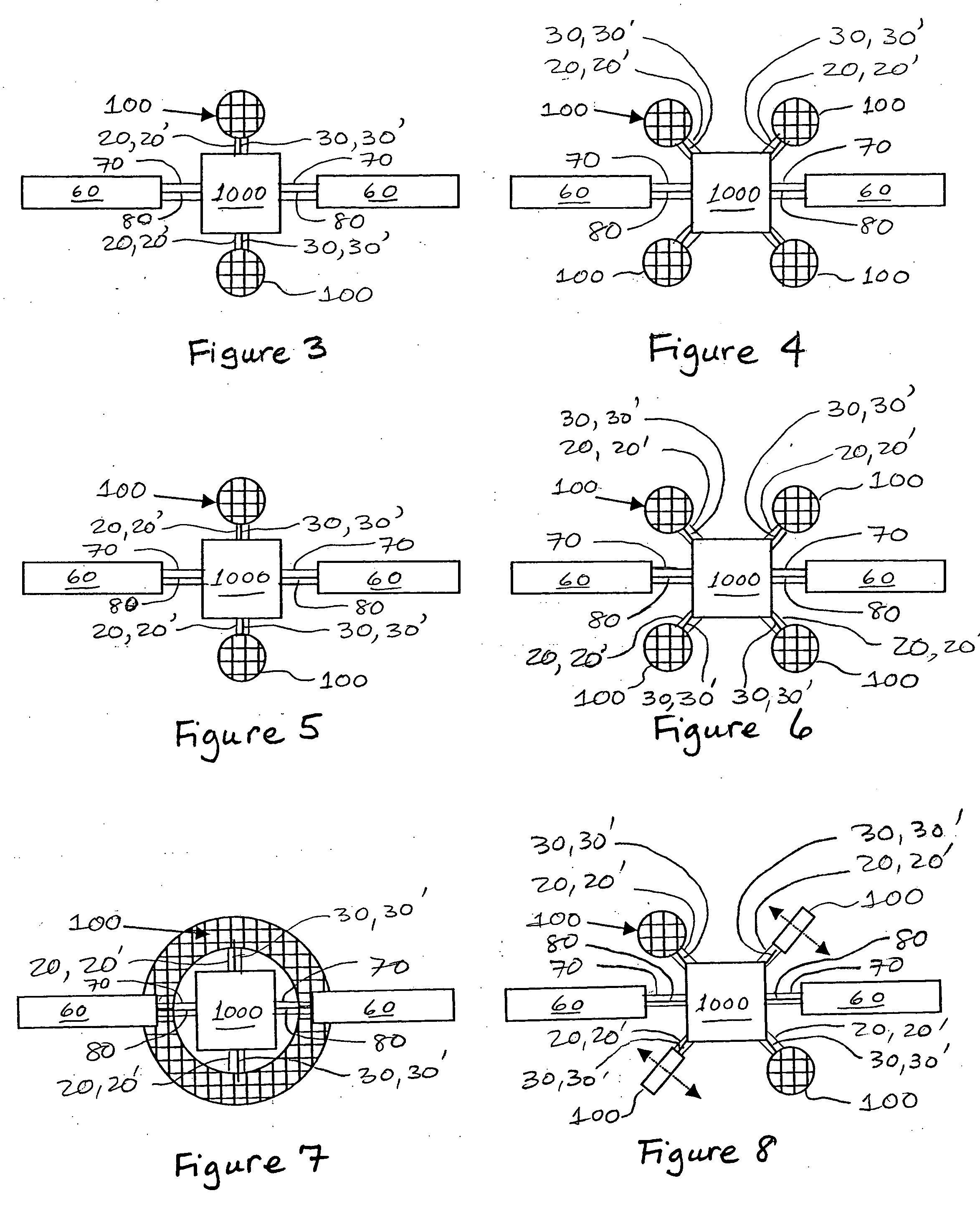
Method for open-loop measurement of radon exhalation rate by utilizing total count of 218Po and 214Po
InactiveCN102830418AAccurate radon exhalation rateHigh measurement accuracyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentTotal countRadon flux
The invention discloses a method for open-loop measurement of a radon exhalation rate by utilizing a total count of 218Po and 214Po. The method comprises the following steps: a radon collection cover is buckled on the surface of a medium to be measured during measurement, clean air with the radon concentration of near zero is continuously pumped from outside by utilizing a pump of a radon measuring apparatus, and the radon exhalation rate can be obtained by measuring a radon concentration change rule in the radon collection cover. According to the conventional static collection method radon measuring apparatus, the change of the radon concentration is obtained by only measuring a daughter 218Po with the decayed radon. As for a medium with low exhalation rate, a radon concentration value in the radon collection cover is low, the count of high-energy alpha particles emitted by 218Po decay is only measured, and the statistical fluctuation is larger due to few counts. According to the invention, the count of high-energy alpha particles emitted by 218Po decay and the count of high-energy alpha particles emitted by 214Po decay in a longer time period are simultaneously measured, and two radon exhalation rates are respectively obtained and are averaged, so that the accurate radon exhalation rate is obtained.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
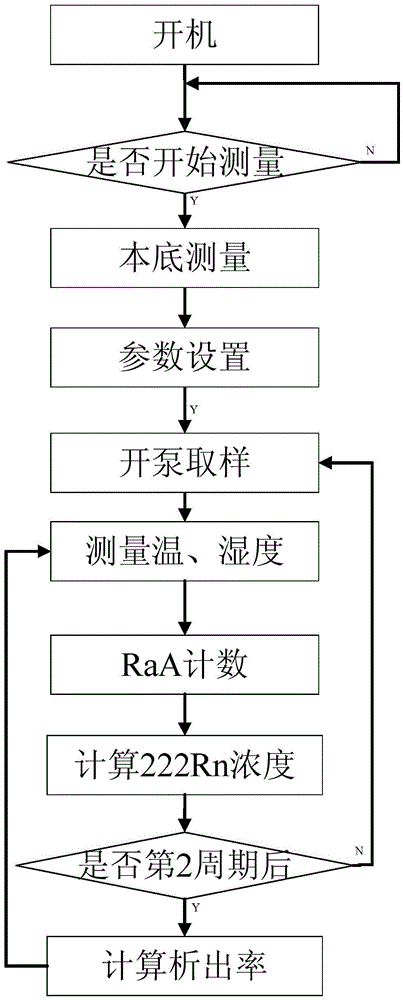
System and method for measuring evolution rate of radon
InactiveCN105425267AReliable measurementGood measurement needsRadiation intensity measurementSoil scienceDielectric surface
The invention discloses a system and method for measuring the evolution rate of radon. The system does not need a drying tube to dry sample gas, thereby reducing the impact on the evolution rate of radon of the internal dielectric surface of a radon collection cover from a drying agent. In a natural environment, a measurement instrument can accurately measure the instantaneous concentration of radon, and does not need to correct the measured concentration of radon for calculation. The measurement instrument can automatically solve the evolution rate of radon through the measured concentration of radon, and can obtain the value of the evolution rate of radon with no need of a PC for linear fitting processing. An experiment indicates that the measurement error of the radon evolution rate measurement instrument is within the range 5% on a radon evolution rate standard device. After measurement, the evolution rate of radon is directly obtained, thereby meeting the demands of on-site measurement of the evolution rate of radon. The system and method are easy to implement, and are high in measurement efficiency.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
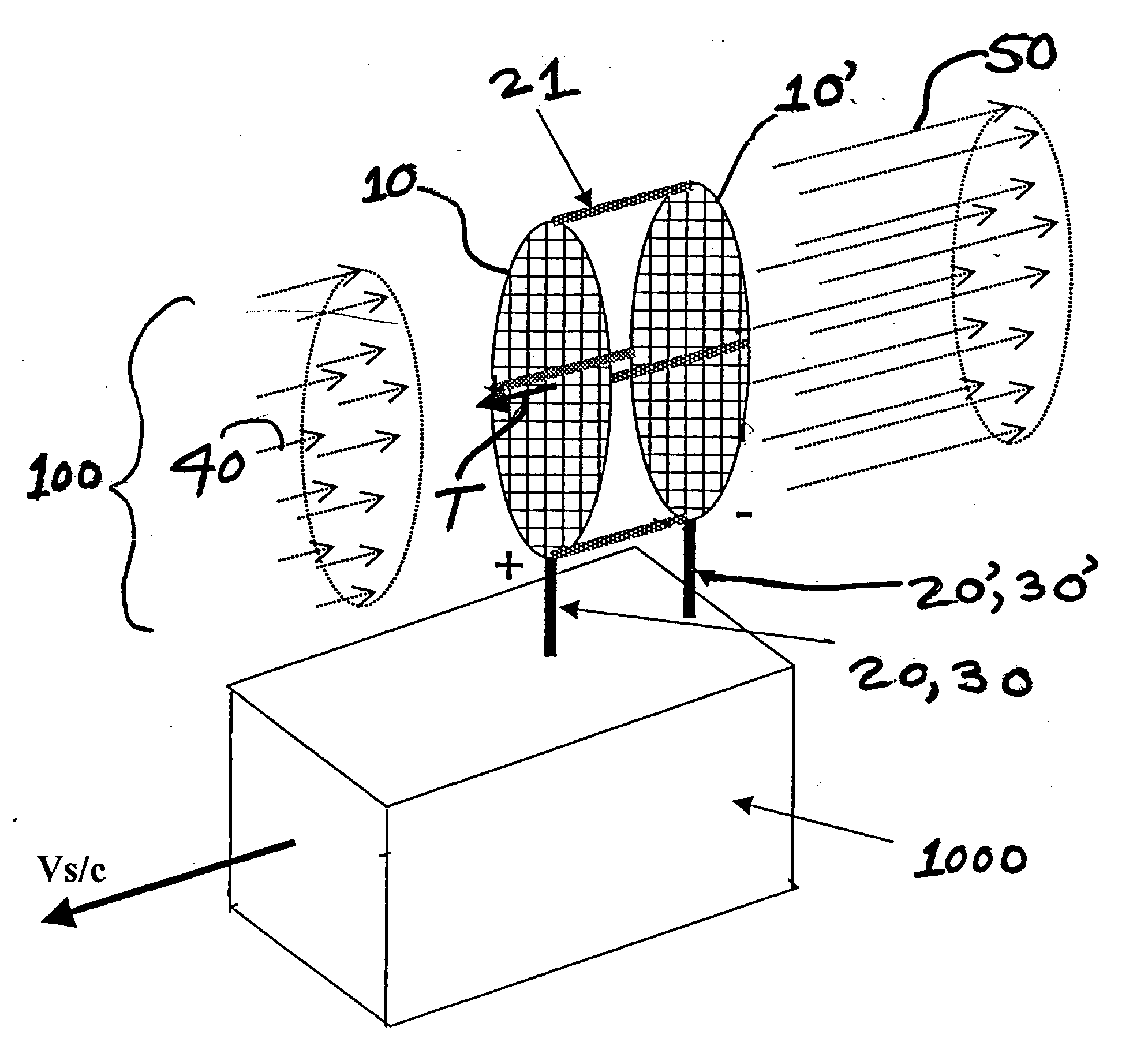
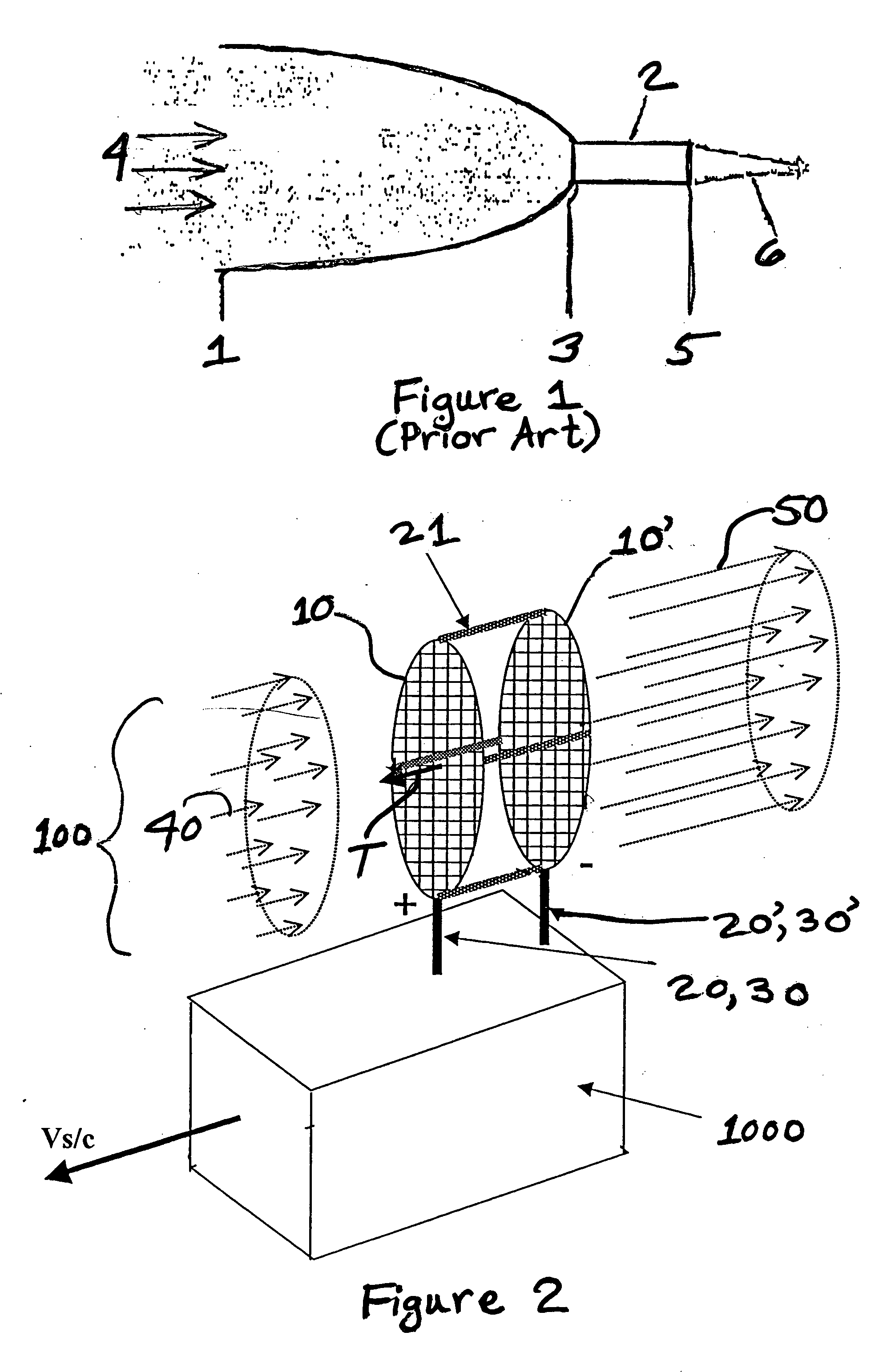
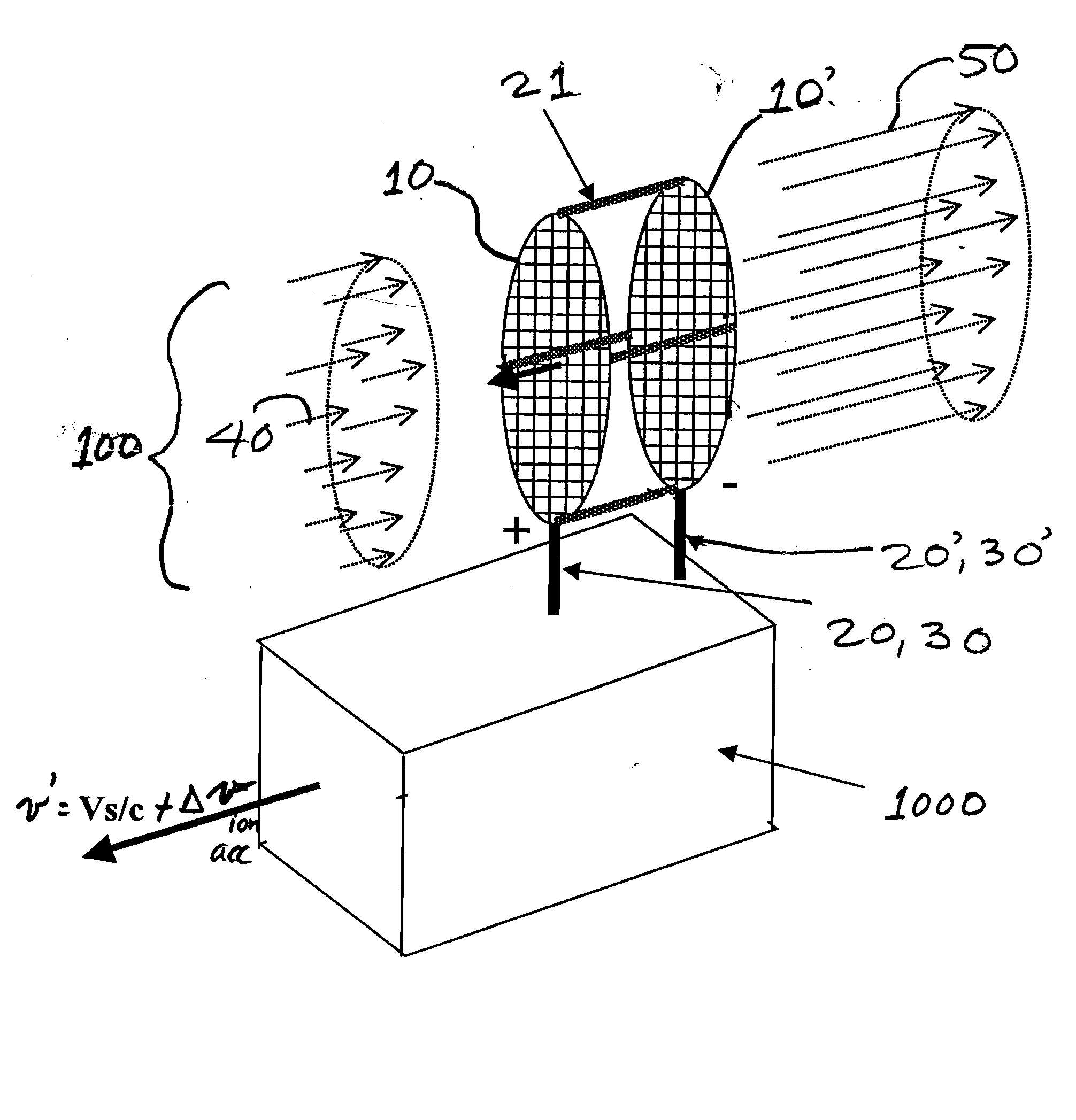
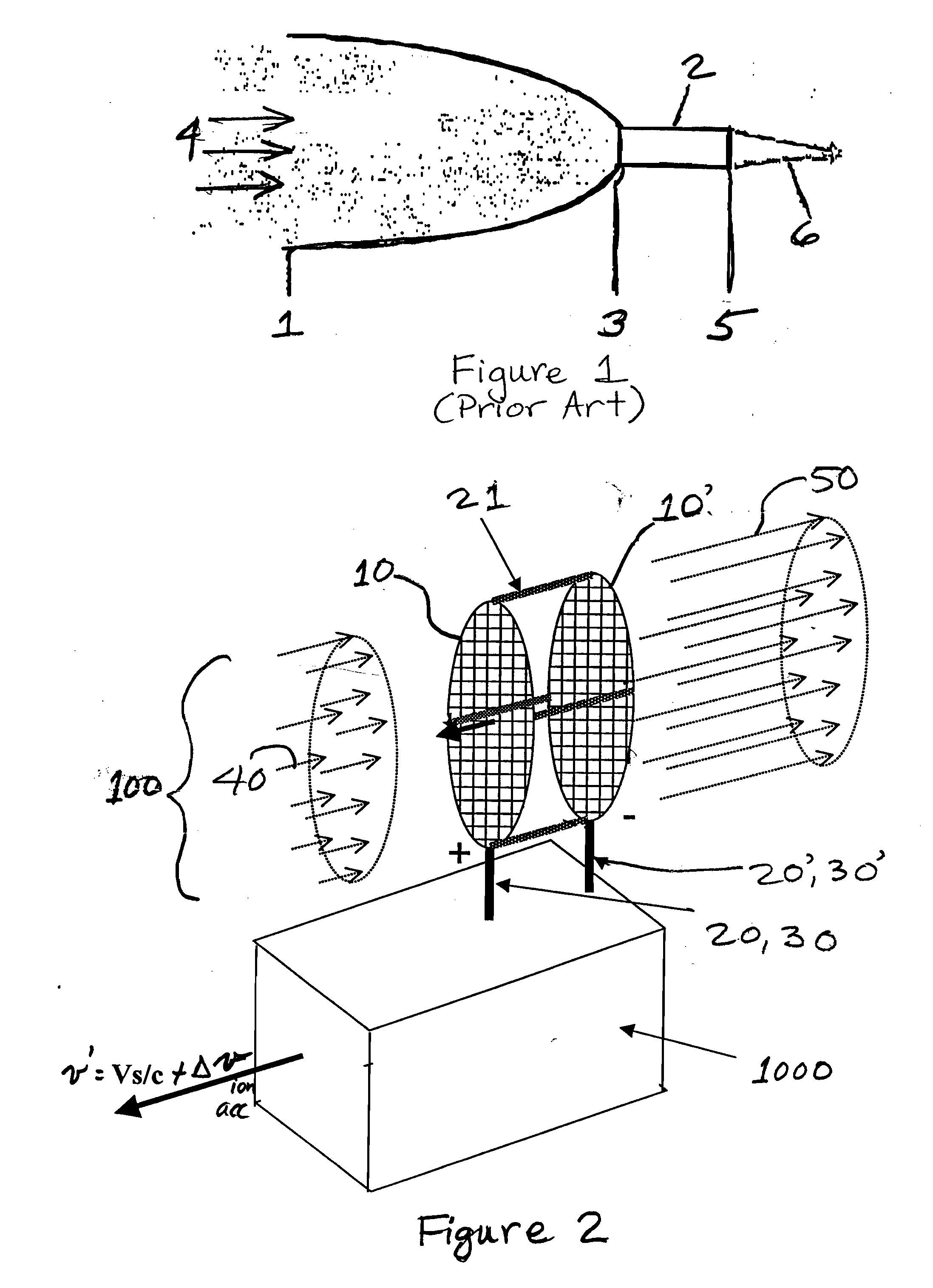
System and method for an ambient atmosphere ion thruster
ActiveUS20050178919A1Significant performanceSignificant costCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCelestial bodyRadon flux
A system and a method for an ambient atmosphere ion thruster having a pair of permeable electrical members for accelerating ambient atmosphere ions which enter the thruster due to a craft's relative velocity. Neutral ambient atmosphere molecules in the intake mass flux may also be ionized and subsequently accelerated by the pair of permeable electrical members. Acceleration of any entering mass comprises an exhaust mass flux which then produces a net thrust. Such net thrust is then vectored by configuring and orienting the thrusters for imparting axial and lateral accelerations as well as pitch, yaw, and roll controls. The present invention is operational in proximity to any celestial body having a sensible atmosphere during a portion of the free trajectory or during orbiting at altitude. Useful net thrust is thereby produced without need for carrying reaction mass onboard a spacecraft.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method for closed-loop measurement of radon exhalation rate by utilizing total count of 218Po and 214Po
InactiveCN102830417ARaise countHigh measurement accuracyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentRadon exhalationElectric field
The invention discloses a method for closed-loop measurement of a radon exhalation rate by utilizing a total count of 218Po and 214Po. The method comprises the following steps: a radon collection cover is buckled on the surface of a medium to be measured during measurement, or the medium is arranged in the radon collection cover, and the radon concentration in the radon collection cover is increased. After a daughter of the radon in the radon collection cover is filtered through a drying tube and a filter membrane, the radon is always pumped into a measurement room of a radon measuring apparatus at a constant flow speed by a pump, and then the radon returns the radon collection cover, so that the radon concentration in the measurement room of the radon measuring apparatus is balanced to the radon concentration in the radon collection cover. The 218Po and the 214Po in the measurement room of the radon measuring apparatus are absorbed on a semiconductor detector at a high speed under the action of an electric field, and the count of alpha particles discharged by decay of the 218Po and the count of alpha particles discharged by decay of the 214Po can be respectively measured. By measuring at a short measuring period or a long measuring period, the radon exhalation rate can be obtained by utilizing the total count of the 218Po and the 214Po at each measuring period.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Continuous measurement device and measurement method for radon exhalation rate
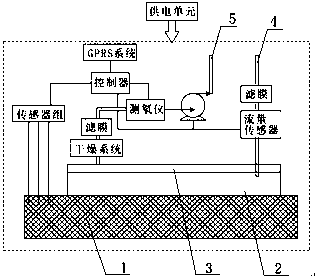
ActiveCN107831524AContinuous monitoring of radon gas exhalation rateHigh measurement accuracyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentContinuous measurementAir pump
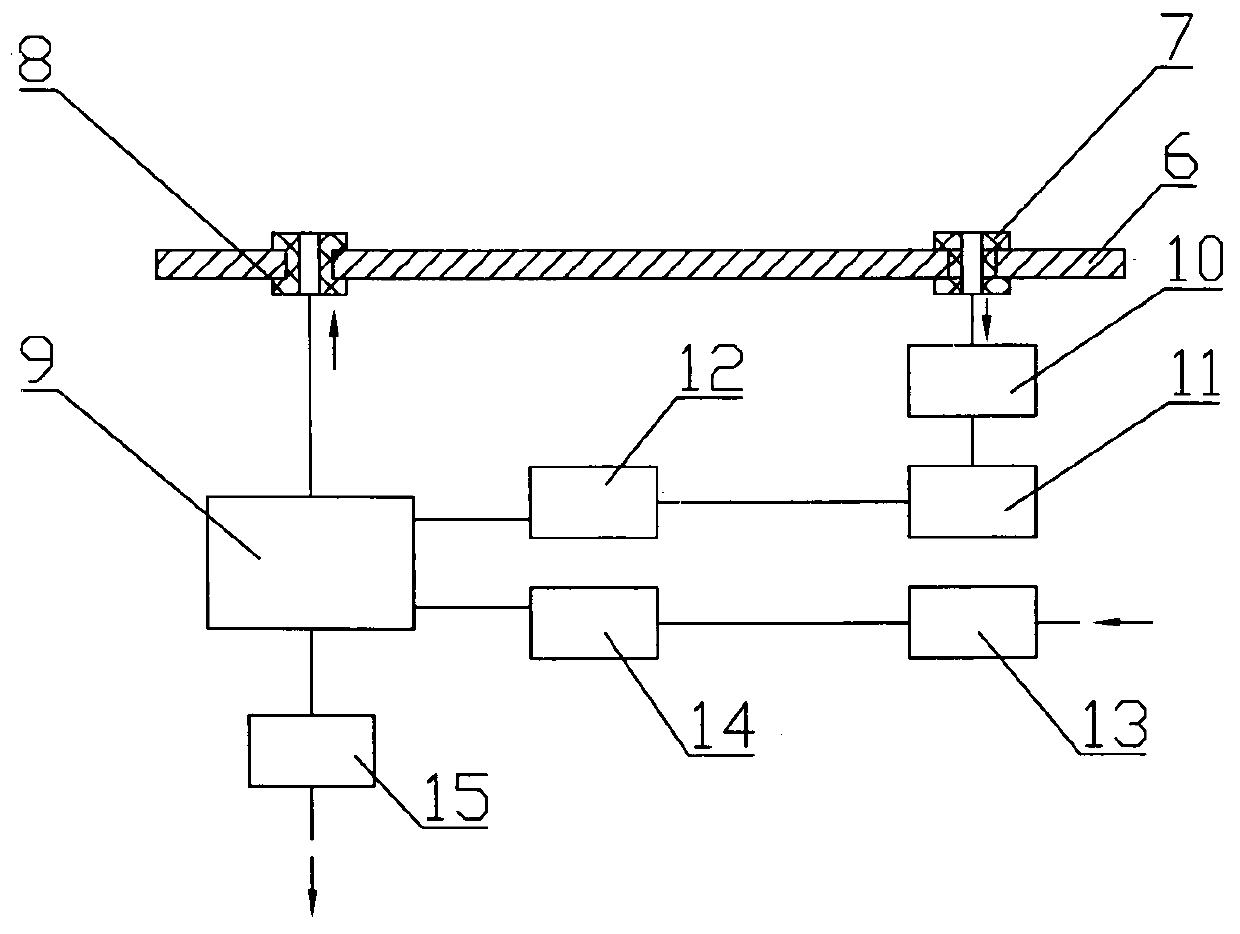
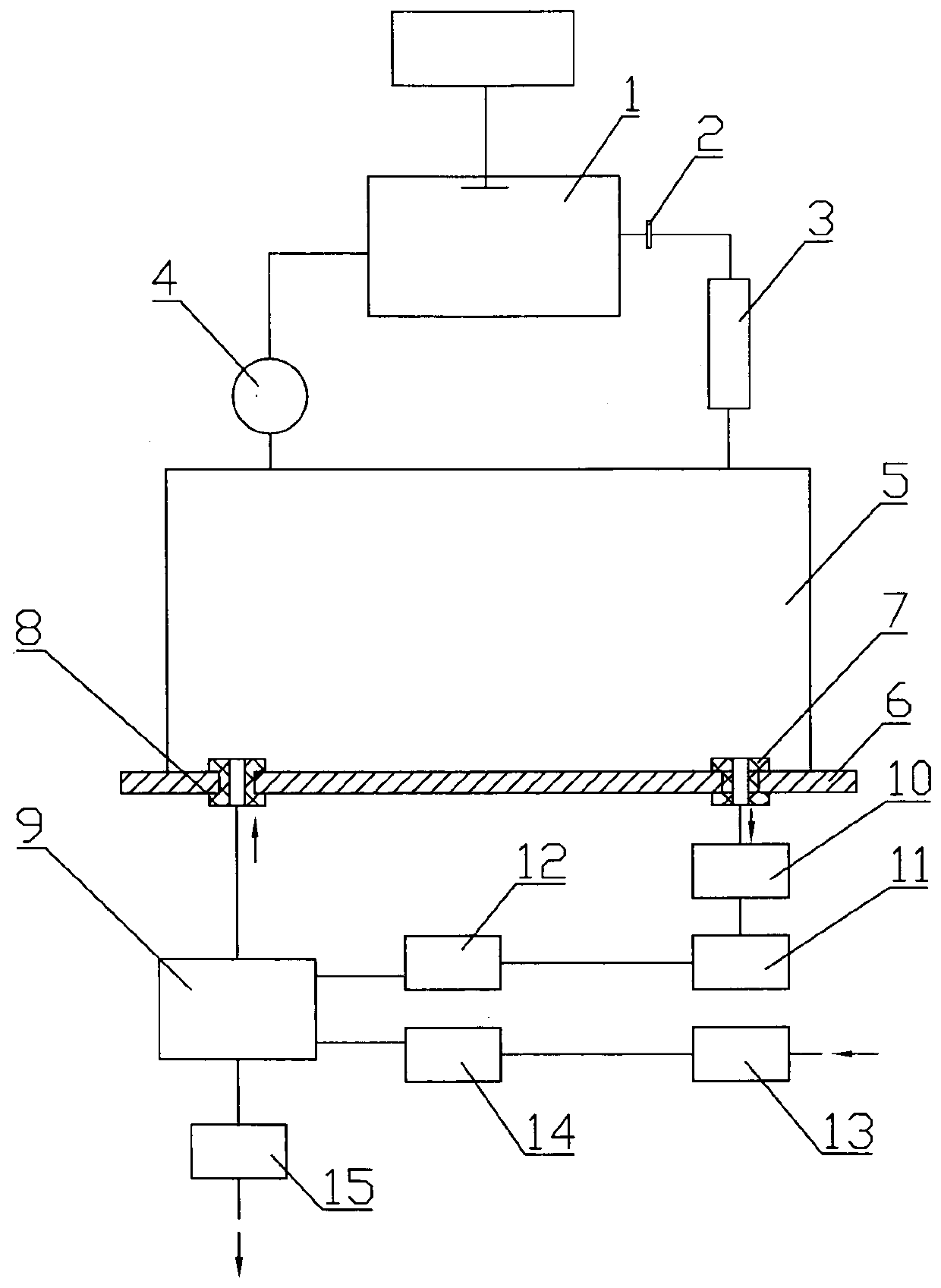
The invention discloses a continuous measurement device and a measurement method for the radon exhalation rate. The continuous measurement device comprises a radon measurer, wherein the radon measurercomprises a gas storage tank; the continuous measurement device further comprises a controller and a radon collection hood; the radon collection hood is a hood body; a flow guide plate is arranged atthe inner top of the hood body; the size of the gas storage tank is 10% less than that of the radon collection hood; a gas feeding pipe is arranged at one end of the radon collection hood, and a gasdischarging pipe is arranged at the other end of the radon collection hood; the radon measurer is arranged on the gas discharging pipe, and is connected with the controller; the continuous measurementdevice further comprises an air flow measurement and control unit, a drying system, a sensor group, a GPRS system and a power supply unit. The continuous measurement device can change the state of the environment of a measurement position; the humidity of measured gas is controlled by the drying system; the gas with high gas flow becomes uniform through the flow guide plate; the radon concentration in the radon collection hood is adjusted through a controllable gas pump, so that a measurement process is in a state free of interference caused by the humidity, the radon concentration and a radon inverse diffusion coefficient, and the measurement precision is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Position sensing by measuring intensity of magnetic flux passing through an aperture in a movable element
InactiveUS6894485B2Improve performanceEliminate needBraking action transmissionSolid-state devicesLinear relationshipRadon flux
An apparatus and method are provided for sensing the position of a point of contact through use of a sensor having a movable element, disposed between a sensing element and a source of magnetic flux, and having an aperture therein for allowing a portion of the magnetic flux from the source of magnetic flux to pass through the aperture and impinge on the sensing element. The aperture may have various shapes to provide a desired linear or non-linear relationship between the position of the movable element and the intensity of the flux that passes through the aperture and impinges on the sensing element for a given position of the movable element.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
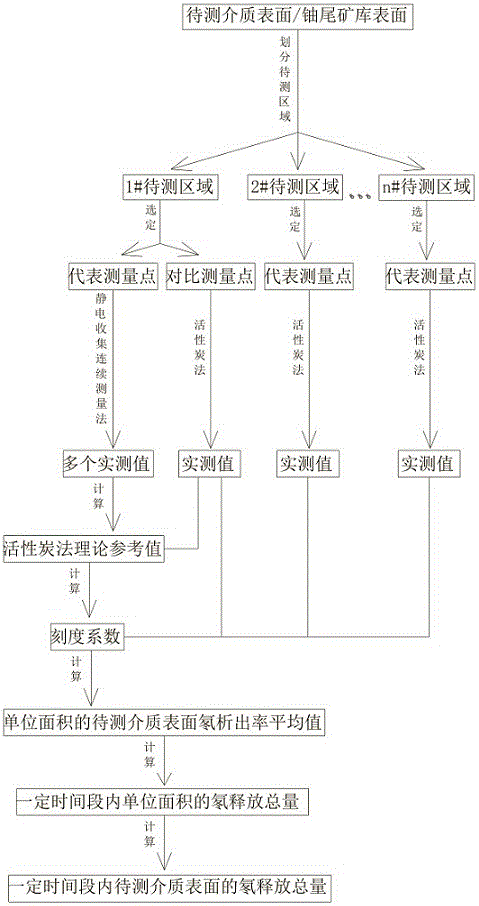
Method and system for measuring total release rate of radon on surface of medium within certain time period
ActiveCN106707325AAccurate measurementEasy to sampleX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNuclear radiationContinuous measurement
The invention discloses a method and a system for measuring a total release rate of radon on the surface of a medium within a certain time period, and relates to the technical field of nuclear radiation detection. The method comprises the following steps of distributing and sampling; computing an average value of a radon precipitation rate on the surface of a to-be-measured medium in single measurement according to a sampling measurement result; computing the total release rate of the radon in unit area of a to-be-measure region within the certain time period; computing the total release rate of the radon on the surface of the medium within the certain time period. According to the method and the system for measuring the total release rate of the radon on the surface of the medium within the certain time period, disclosed by the invention, a region distribution rule on the surface of the medium can be measured through an activated carbon-gamma energy spectrum method, continuous measurement on the radon precipitation rate representing a measurement point can be carried out by using a radon precipitation rate continuous measurement method based on electrostatic collection, the change rule can be obtained, and a radon precipitation rate measuring instrument is used as a standard for correcting an activated carbon measurement result, so that an accurate average radon precipitation rate value is obtained, and the total release rate of the radon on the surface of the medium within the certain time period is obtained.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
Neutron flux and energy spectrum measuring system of helium cooling solid multiplication agent tritium producing cladding
ActiveCN1948997ASimple designNuclear energy generationNeutron radiation measurementBiological activationHelium gas
The invention relates to fusion reactor tritium generating cladding neutron measuring. Helium cooling solid breeding agent tritium generating cladding neutron flux and spectrometry measuring system includes packaging foil pneumatic transmitting activation analysis subsystem which includes activation foil and pneumatic transmitting device. The activation foil is set in the measuring tube connected with operating station through cooling layer and biological shielding layer. The operating station is set helium cooling circuit and connected with helium gas dynamic force union station and HPGe measuring station connected with electronics and data gaining system. The solid breeding agent tritium generating cladding is also set micro-fission chamber combination detector and natural diamond neutron energy spectrum detector which are connected with operating station through current sensitive preamplifier and charge sensitive preamplifier, which is connected with electronics and data gaining system.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
Method and apparatus for X-ray irradiation having improved throughput and dose uniformity ratio
InactiveUS6940944B2Maximize throughputLess complex to maintainPackage sterilisationIrradiation devicesDose uniformityX-ray
The present invention is related to a method and apparatus of radiation processing of a product package in a device having a radiation source, a collimator having a variable aperture, and a turntable, said radiation processing resulting in a point in the product package where the dose is minimal (Dmin point) and a point in said product package where the dose is maximal (Dmax point) comprising the steps of:determining a first value of the collimator aperture, by increasing said aperture from a small value, where the Dmax point is located near the centre of the product package, up to a value where the Dmax point moves near to the centre of a small side of said package's rectangular horizontal cross-section;determining a second value of the collimator aperture, by further increasing the collimator aperture up to a point where the Dmin point moves from a point near the corner of the product package to the centre of said package;processing said package with radiation, the collimator aperture being kept at a constant value comprised between said first and said second value, the turntable being rotated at a variable speed.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Radon precipitation simulation device based on low-frequency vibration and radon precipitation rate measurement method
PendingCN107678054AAvoid partial damageImprove reliabilityX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentLow frequency vibrationRadon exhalation
The invention discloses a radon precipitation simulation device based on low-frequency vibration and a radon precipitation rate measurement method. The simulation device comprises a power amplifier, asweep signal generator, a radon precipitation module, a dryer and a radon measuring instrument; wherein the radon precipitation module comprises a vibration exciter, a radon precipitation tank, a topcover, a vibrating rod and a sliding rail. The radon precipitation tank contains a uranium ore rock test block, the vibration exciter is fixed on the sliding rail and connected with the power amplifier, and the vibration rod is arranged between the vibration exciter and the radon precipitation tank. A base platform capable of moving along the sliding rail is arranged on the sliding rail, the radon separation tank is fixed on the base platform, and an airflow loop is formed between the top cover and the radon measuring instrument. The drier is arranged on a pipeline path communicated with thegas outlet of the radon precipitation tank and the gas inlet of the radon measuring instrument. According to the device, the radon precipitation of a uranium mine rock in the low-frequency vibration can be simulated, and experimental data can be obtained. A data basis for researching the change rules of the continuous radon precipitation rate of uranium ore rocks under the action of low-frequencydisturbance loads is provided.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
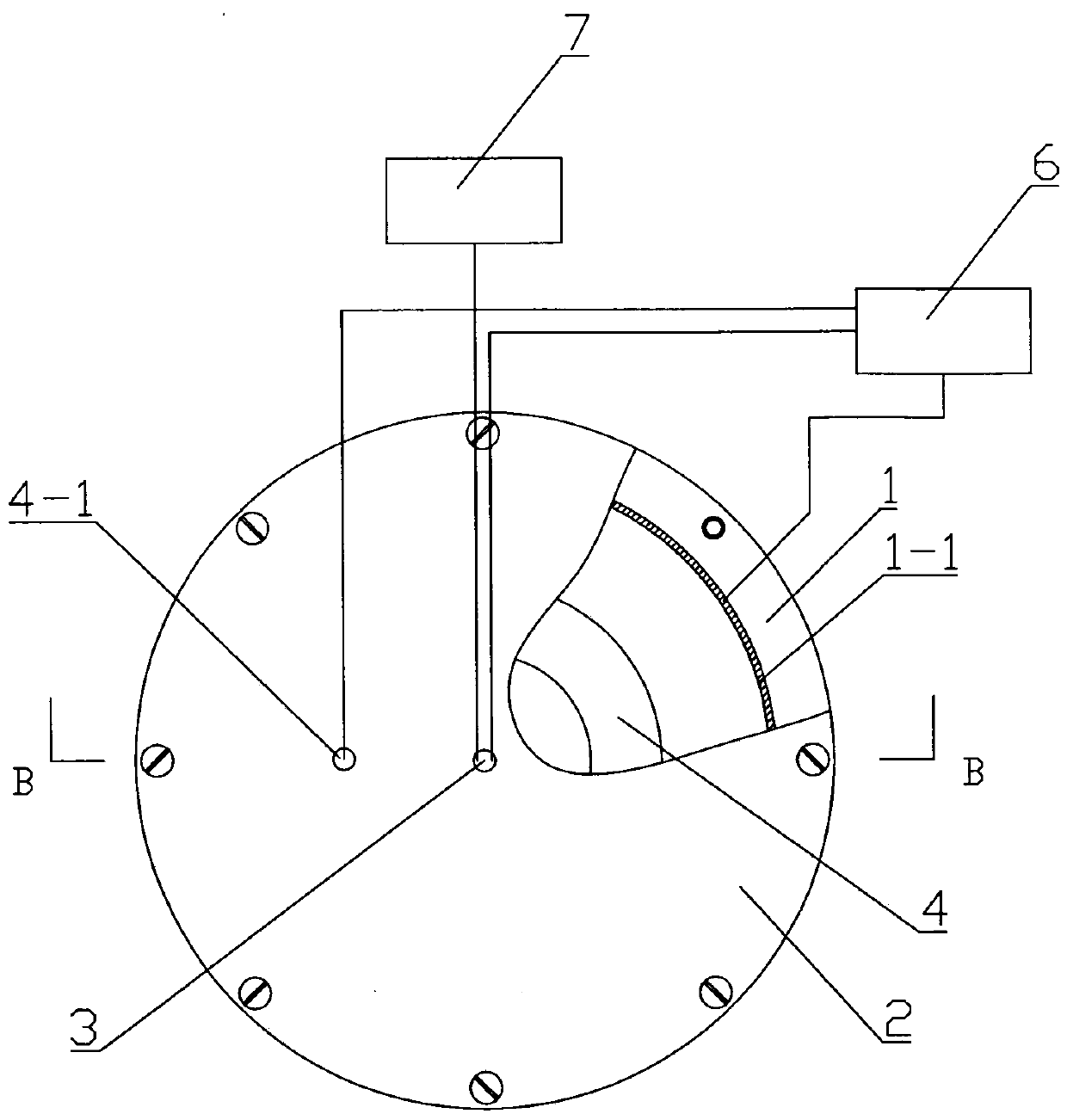
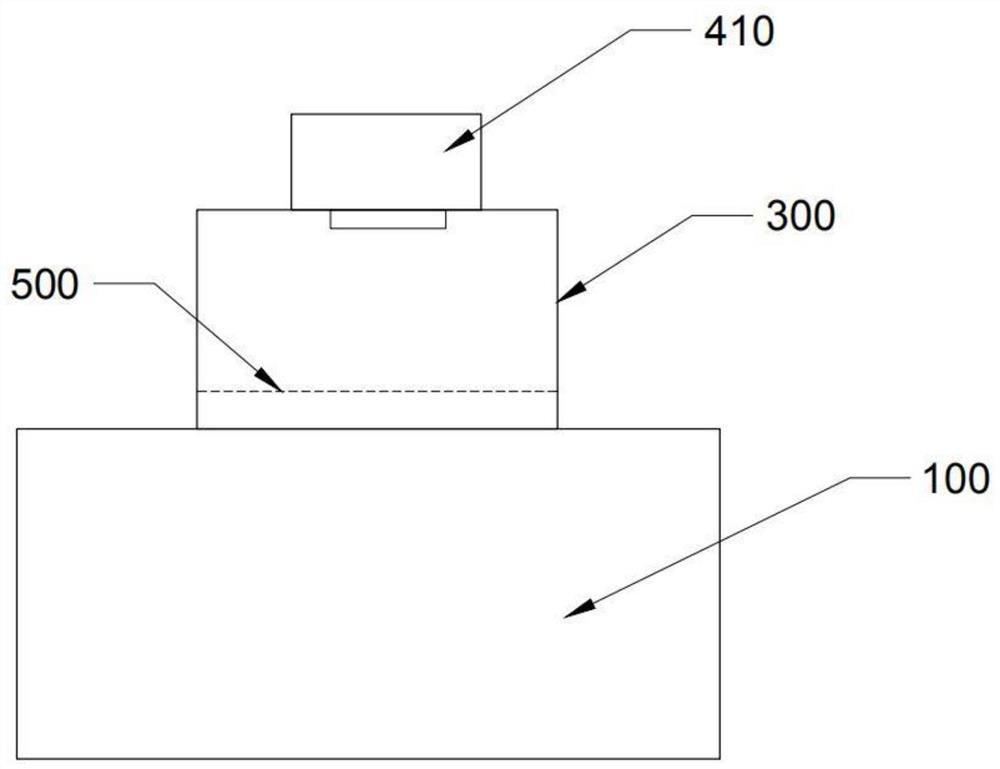
Measurement chamber for improving 218Po collection efficiency of radon precipitation rate measuring instrument through annular electrode and method thereof
ActiveCN109655857ASimple structureHigh detection sensitivityRadiation intensity measurementEngineeringPrecipitation
The invention discloses a measurement chamber for improving 218Po collection efficiency of a radon precipitation rate measuring instrument through an annular electrode and a method thereof. The innerwall of the measurement chamber is a conductive layer. The bottom of the measurement chamber is provided with a metal filter screen. A semiconductor detector is mounted at the central part on an insulating end cover. The annular electrode is mounted at the lower part of the insulating end cover. The insulating end cover is fixed to the open end of the chamber. The semiconductor detector, the conductive layer on the inner wall of the chamber and a terminal on the first annular electrode are connected with a high-voltage module through leads. The semiconductor is connected with a secondary instrument. The measurement chamber is placed in a radon chamber so that radon concentration in the chamber is same with that in the radon chamber. The high-voltage module respectively regulates voltage between the conductive layer and the semiconductor detector and the annular electrode. The secondary instrument is used for obtaining a 218Po decaying counting rate which is measured by the semiconductor detector. After the measurement chamber is adjusted, the measurement chamber directly buckles the surface of a to-be-measured chamber, and then the radon concentration change rule in the measurementchamber is measured through the secondary instrument. Then the radon precipitation rate is calculated through data fitting.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
System and Method for an Ambient Atmosphere Ion Thruster
InactiveUS20070176050A1Maximize throughputSignificant costCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCelestial bodyRadon flux
A system and a method for an ambient atmosphere ion thruster having a pair of permeable electrical members for accelerating ambient atmosphere ions which enter the thruster due to a craft's relative velocity. Neutral ambient atmosphere molecules in the intake mass flux may also be ionized and subsequently accelerated by the pair of permeable electrical members. Acceleration of any entering mass comprises an exhaust mass flux which then produces a net thrust. Such net thrust is then vectored by configuring and orienting the thrusters for imparting axial and lateral accelerations as well as pitch, yaw, and roll controls. The present invention is operational in proximity to any celestial body having a sensible atmosphere during a portion of the free trajectory or during orbiting at altitude. Useful net thrust is thereby produced without need for carrying reaction mass onboard a spacecraft.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for X-ray irradiation having improved throughput and dose uniformity ratio
InactiveUS20050053194A1Maximize throughputLess-expensive to buildPackage sterilisationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationDose uniformityX-ray
The present invention is related to a method and apparatus of radiation processing of a product package in a device having a radiation source, a collimator having a variable aperture, and a turntable, said radiation processing resulting in a point in the product package where the dose is minimal (Dmin point) and a point in said product package where the dose is maximal (Dmax point) comprising the steps of: determining a first value of the collimator aperture, by increasing said aperture from a small value, where the Dmax point is located near the centre of the product package, up to a value where the Dmax point moves near to the centre of a small side of said package's rectangular horizontal cross-section; determining a second value of the collimator aperture, by further increasing the collimator aperture up to a point where the Dmin point moves from a point near the corner of the product package to the centre of said package; processing said package with radiation, the collimator aperture being kept at a constant value comprised between said first and said second value, the turntable being rotated at a variable speed.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Device and method for randomly adjusting radon precipitation rate and effective decay constant by gas-flow type radon source
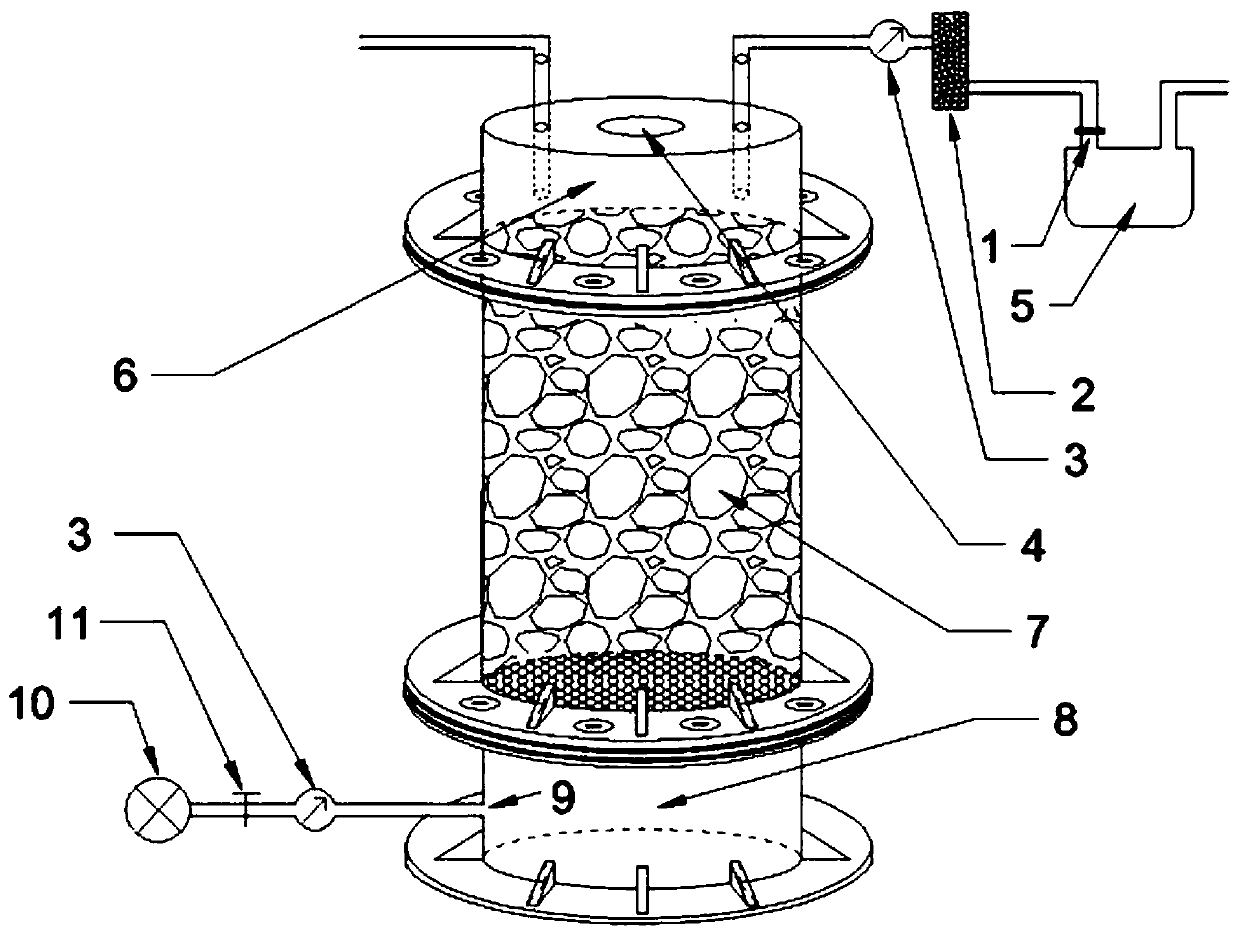
The invention relates to a device and method for randomly adjusting a radon precipitation rate and an effective decay constant by using a gas-flow type radon source. The device is characterized in that a gas outlet joint and a gas inlet joint in the device are arranged on a compact material plate, a first adjustable micro pump, a first electronic flow meter and a first adsorption pipe are sequentially connected between the gas outlet joint and first gas inlet of the gas-flow radon source, a first gas outlet of the gas-flow radon source is connected with the gas inlet joint, a gas inlet of a second adjustable micro pump is communicated with the atmospheric environment, a second adsorption pipe is connected between a gas outlet of the second adjustable micro pump and a second gas inlet of the gas-flow radon source, and the second gas outlet of the gas-flow radon source is connected with a gas inlet of the second electronic flow meter, and a gas outlet of the second electronic flow meteris communicated with the atmospheric environment. During measurement, a radon collecting cover is buckled on the compact material plate, the radon precipitation rate and effective decay constant of aradon precipitation rate standard device are arbitrarily adjusted by utilizing a gas-flow radon source, and the radon collecting cover is used for testing accuracy and reliability of the method and device for measuring the radon precipitation rate on the surface of a medium.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Multilayer radon-reducing covering material and application thereof, and method for reducing radon exhalation rate of waste rock heap of uranium mine
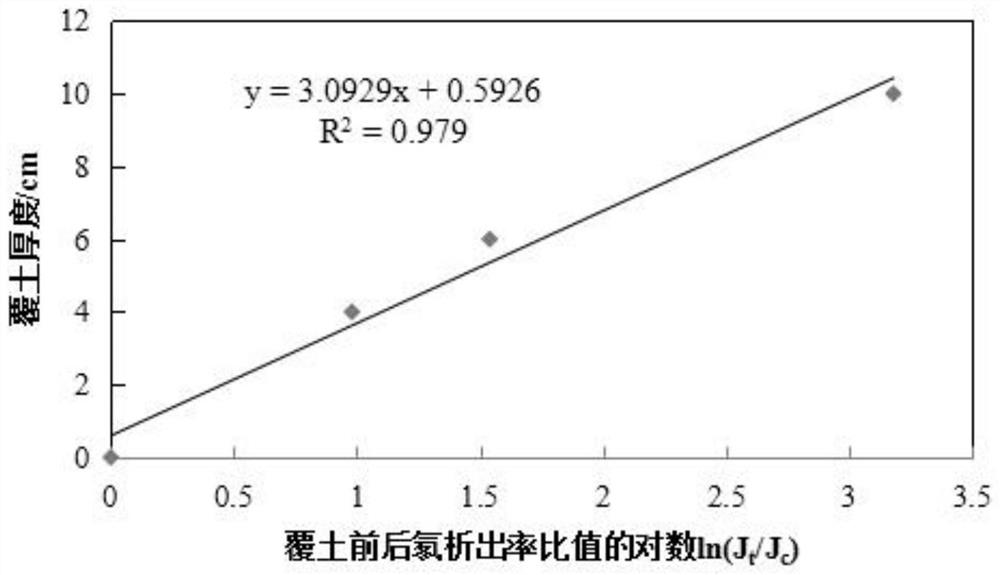
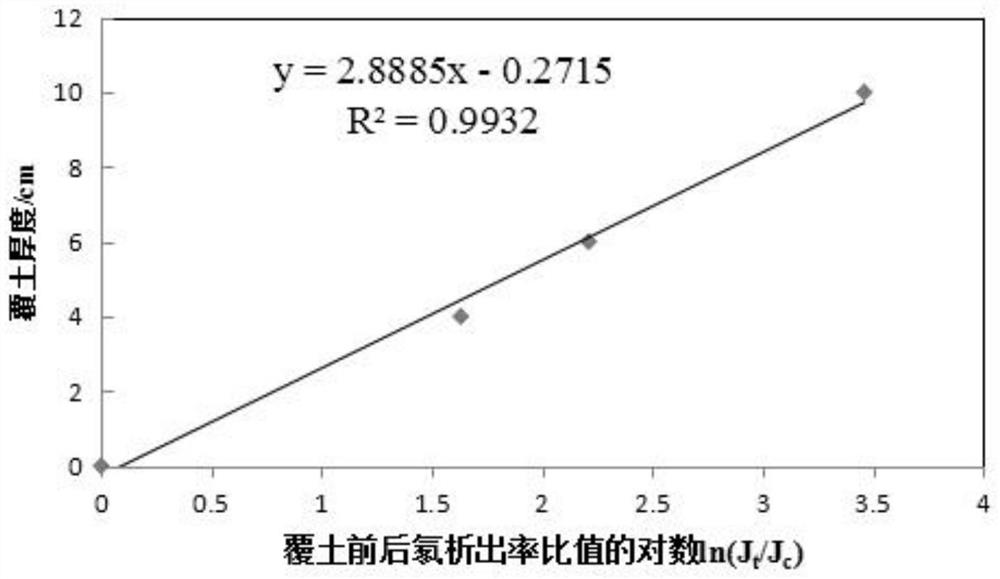
The invention relates to the technical field of decommissioning treatment of nuclear facilities, in particular to a multilayer radon-reducing covering material, application thereof and a method for reducing the radon exhalation rate of a waste rock heap of a uranium mine. The invention provides a multi-layer radon-reducing covering material. The multi-layer radon-reducing covering material comprises a bentonite layer, a first loess layer located on the surface of the bentonite layer and a second loess layer located on the surface of the first loess layer. The bentonite is used as a bottom layer soil covering material, has high adsorption capacity on radon, effectively prevents radon nuclide migration, can reduce the thickness and compactness of covering soil, can be applied to waste rock piles where mechanical equipment is difficult to reach and construction areas where the common soil compactness cannot meet design requirements, and has wide application prospects. The method has a good decommissioning treatment effect on uranium mine waste rock piles; the loess is adopted as the middle-layer covering material and the top-layer covering material, the radon exhalation rate reduction effect and the gamma radiation reduction effect can be further improved, the treatment cost is low, and later vegetation recovery is facilitated.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
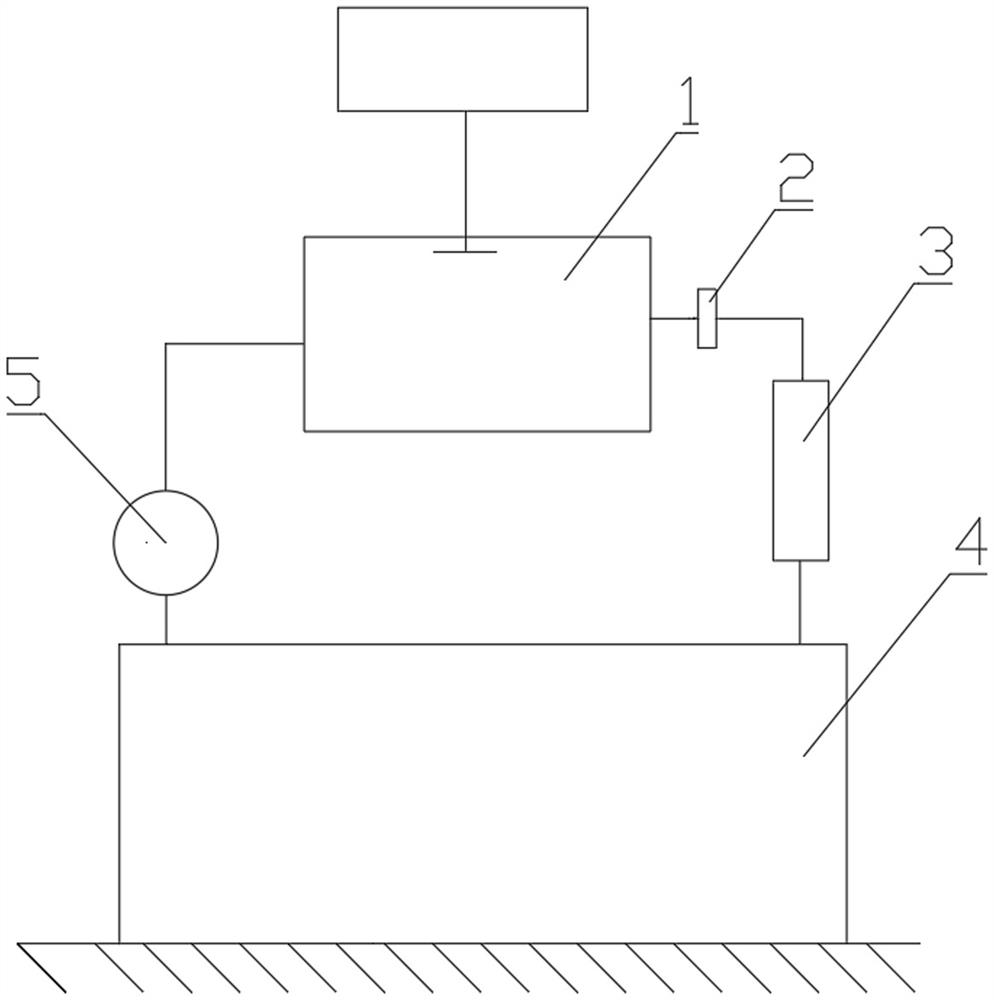
Method of adjusting radon exhalation rate and effective decay constant by using radon chamber
ActiveCN113325461BEasy to measureX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMeasuring instrumentEnvironmental engineering
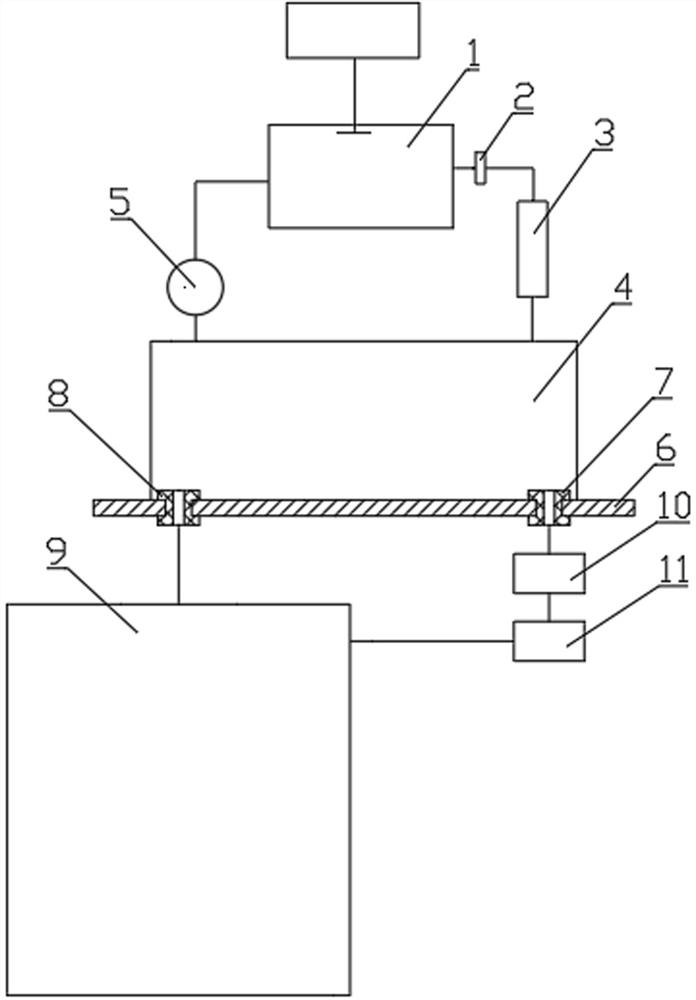
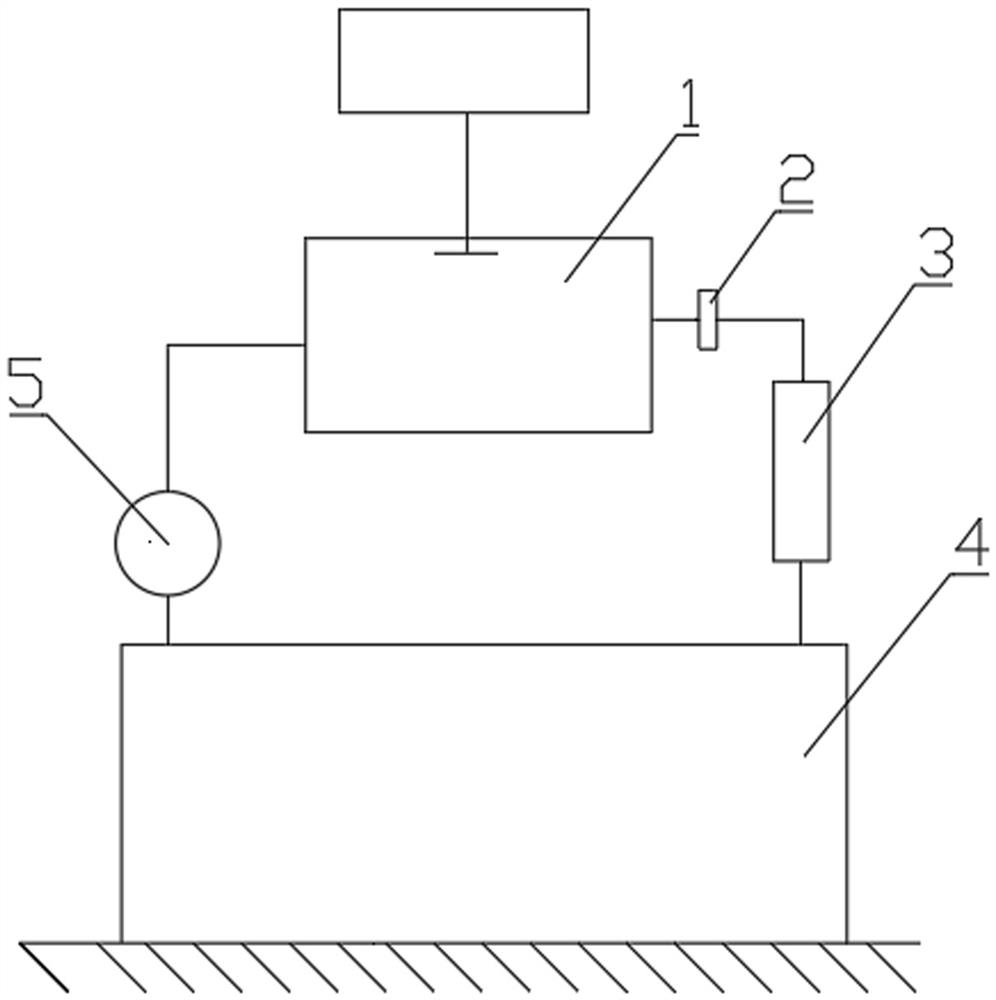
A device and method for adjusting radon exhalation rate and effective decay constant by using a radon chamber, one end of the filter membrane in the device is connected to the measuring room of the measuring instrument through a pipeline, the other end of the filter membrane is connected to a drying pipe through a pipeline, and the other end of the drying pipe is passed through The pipeline is connected to the radon collecting hood, one end of the pump is connected to the measuring chamber of the measuring instrument through the pipeline, the other end of the pump is connected to the radon collecting hood through the pipeline, the gas outlet joint and the air inlet joint are respectively installed on the dense material plate, and the gas outlet joint passes through the pipeline It is connected with an adjustable micropump, the other end of the adjustable micropump is connected with a flowmeter through a pipeline, the other end of the flowmeter is connected with a radon chamber through a pipeline, and the other end of the radon chamber is connected with an air inlet joint through a pipeline. The measurement method includes the conventional radon exhalation rate measurement process and the process of using a radon chamber to adjust the radon exhalation rate and effective decay constant of the radon exhalation rate standard device. By adjusting the flow rate of the adjustable micropump in the device, the radon exhalation rate can be adjusted and the effective decay constant.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
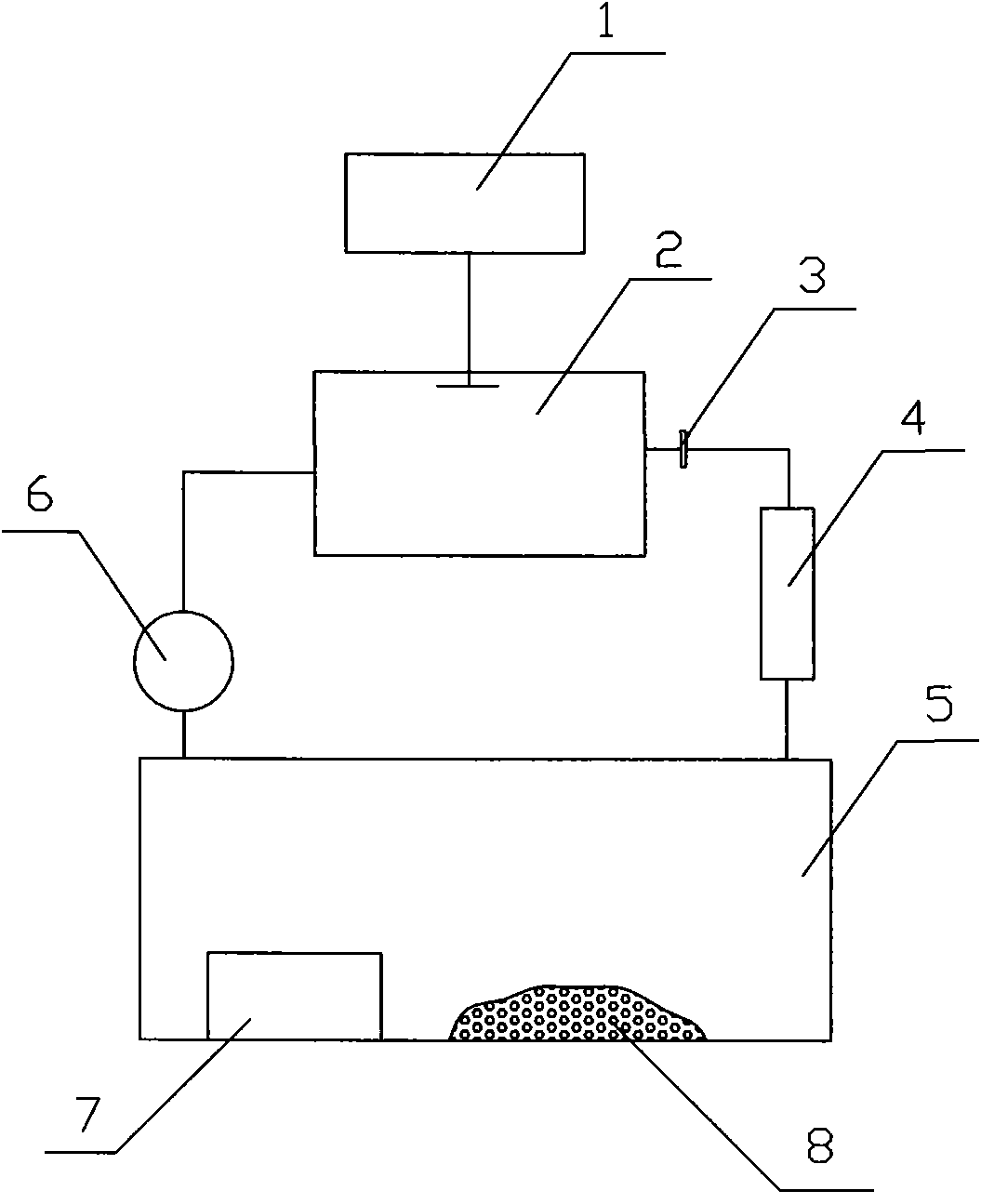
An open-loop method and device for measuring radon exhalation rate of emanation medium
The invention discloses a method and device for measuring the emanation medium radon exhalation rate in an open-loop mode. According to the method, the measurement of the radon exhalation rate is carried out by using the device. The device comprises a radon measuring instrument and a test column used for containing a to-be-tested emanation medium, a gas collecting cover is arranged above the testcolumn, the gas inlet of the radon measuring instrument is communicated with the gas collecting cover through an air pipe, the gas outlet of the radon measuring instrument is communicated with an external environment, a hole communicated with the external environment is formed in the upper surface of the gas collecting cover, a gas pressure equalizing chamber is arranged below the test column, thegas pressure equalizing chamber is connected with a gas pump through the gas pipe, and a flow regulator is arranged on the gas pipe between the gas pressure equalizing chamber and the gas pump. The method has the advantages that the free diffusion of the radon on the surface of the medium is considered, and the influence of the seepage effect is also considered. In addition, the device can accurately measure the radon exhalation rate of the surface of the medium in a short time.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Open-loop type quick measurement method of radon exhalation rate
InactiveCN102520434BQuick measurementX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentFast measurementEnvironmental engineering
An open-loop type quick measurement method of radon exhalation rate includes two measurement modes. In the first measurement mode, multiple shorter cycles which respectively last for 1-20 minutes are measured after a radon collection case is capped on the surface of a to-be-measured medium so that the radon concentration sequence is acquired, the measurement data of each cycle are approximately regarded as the concentration 218Po of the center point of each measurement cycle, and then the radon exhalation rate can be acquired by means of non-linear data fitting. In the second measurement mode, a longer cycle which lasts for 20-200 minutes is measured after the radon collection case is capped on the surface of the to-be-measured surface, and the radon exhalation rate can be solved by the aid of the measurement value of the longer measurement cycle according the formulas (14) and (15). The open-loop type quick measurement method of the radon exhalation rate is quick in measurement, and the radon exhalation rate can be obtained by calculation according to the measurement data before the radon in the radon collection case balances.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Radon exhalation rate measuring instrument
PendingCN113238272AEnsure safetyImprove accuracyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentRadon ProgenyMeasuring instrument
The invention relates to the technical field of radon measurement, and provides a radon exhalation rate measuring instrument which comprises a radon exhalation cover, a radon measurement chamber and a detector. The radon measurement chamber is arranged in the radon exhalation cover, a collection electric field is formed because of a voltage difference between the detector and the radon measurement chamber, and radon daughters generated after radon decay carry positive charges and tend to one side with low potential energy of the electric field, so that the radon exhalation rate of the surface of an object to be measured in a natural state is measured.
Owner:赛睿环仪(北京)科技有限公司
Method for adjusting radon exhalation rate and effective decay constant of radon exhalation rate standard device
The device and method for adjusting the radon exhalation rate and the effective decay constant of the radon exhalation rate standard device, one end of the filter membrane in the device is connected with the measuring chamber of the measuring instrument through a pipeline, the other end of the filter membrane is connected with a drying pipe through a pipeline, and the other end of the drying pipe is One end is connected to the radon collecting hood through a pipeline, one end of the pump is connected to the measuring chamber of the measuring instrument through a pipeline, and the other end of the pump is connected to the radon collecting hood through a pipeline. It is connected to the adjustable micropump through the pipeline, the other end of the adjustable micropump is connected to the flowmeter through the pipeline, the other end of the flowmeter is connected to the flow-type radon source through the pipeline, and the other end of the flow-type radon source is connected to the inlet joint through the pipeline . The measurement method includes the conventional radon exhalation rate measurement process and the process of adjusting the radon exhalation rate and effective decay constant of the radon exhalation rate standard device. By adjusting the flow rate of the adjustable micropump in the device, the radon exhalation rate and effective decay constant can be adjusted. .
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Method for measuring precipitation rate of radon
InactiveCN101609154BMeet the needs of fast measurementEasy to operateX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSoil scienceRadon flux
The invention relates to a method for measuring the precipitation rate of radon, which comprises a measuring step and a calculating step. A radon collection cover is covered on the surface of a medium to be tested or the medium is put in the radon collection cover, a group of radon concentration data is obtained after measuring at time intervals, and the radon concentration data obtained by measure are fitted in a nonlinear way to obtain the precipitation rate of radon according to a formula (9); or measure data after 20 min are fitted in a nonlinear way to obtain the precipitation rate of radon according to a formula (10).
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
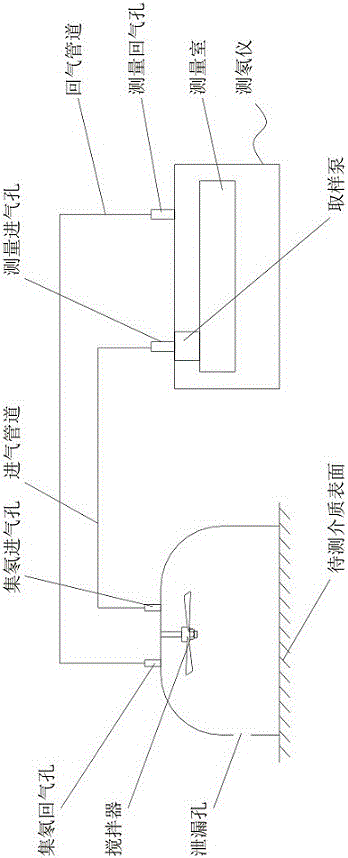
Method and device for measuring radon exhalation rate on medium surface
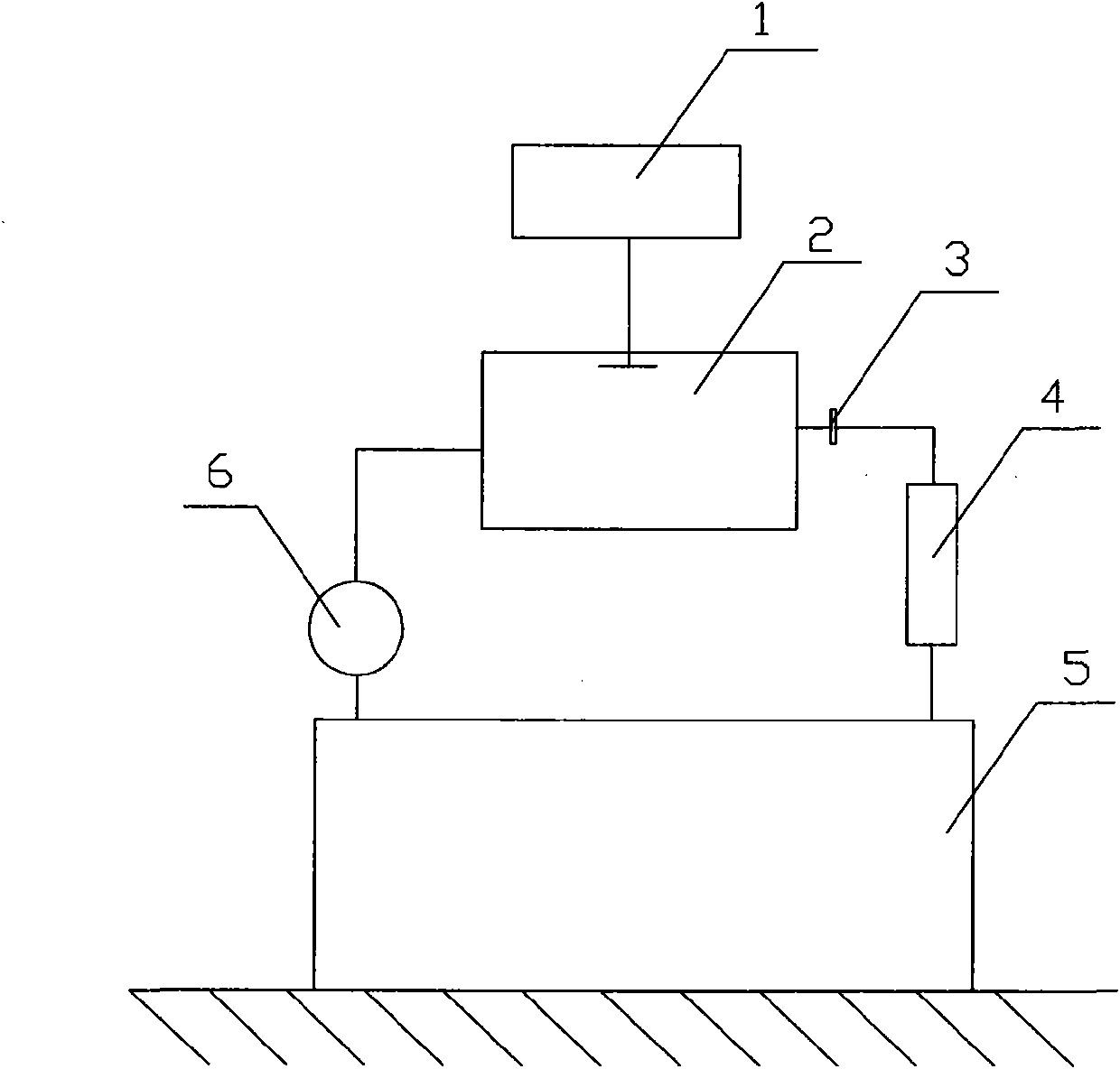
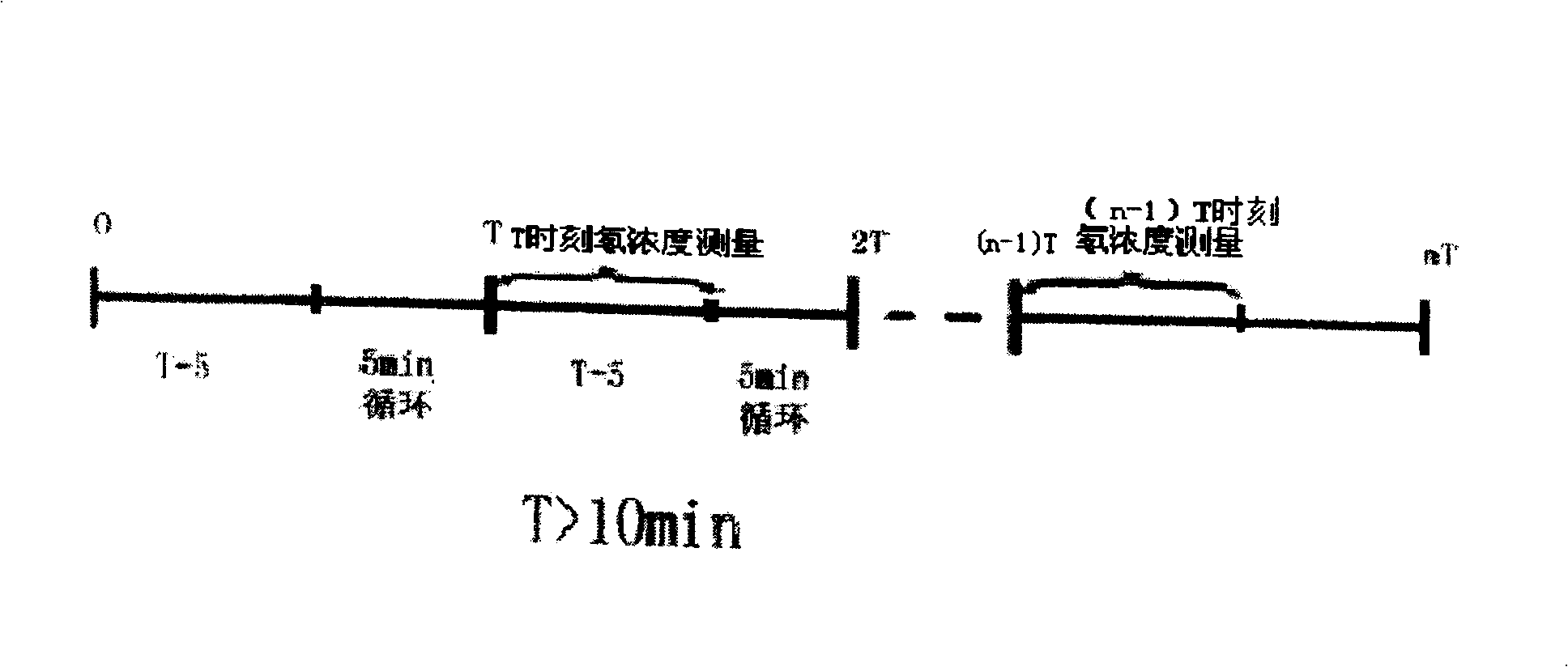
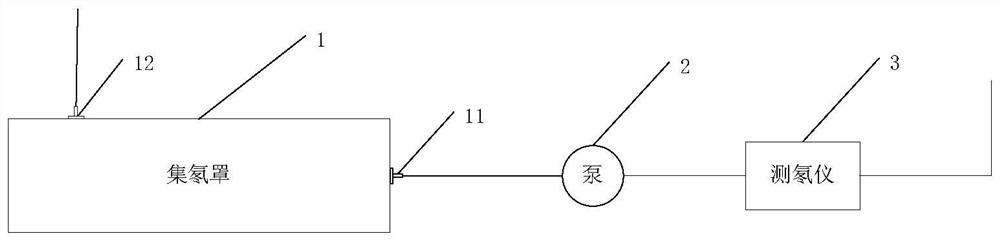
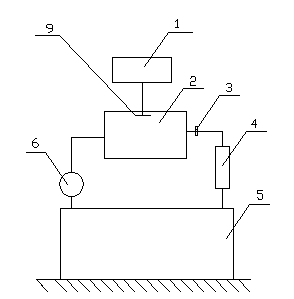
ActiveCN101644700BEliminate emanation interferenceEliminate leaksX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMaterial analysisAir pumpEngineering
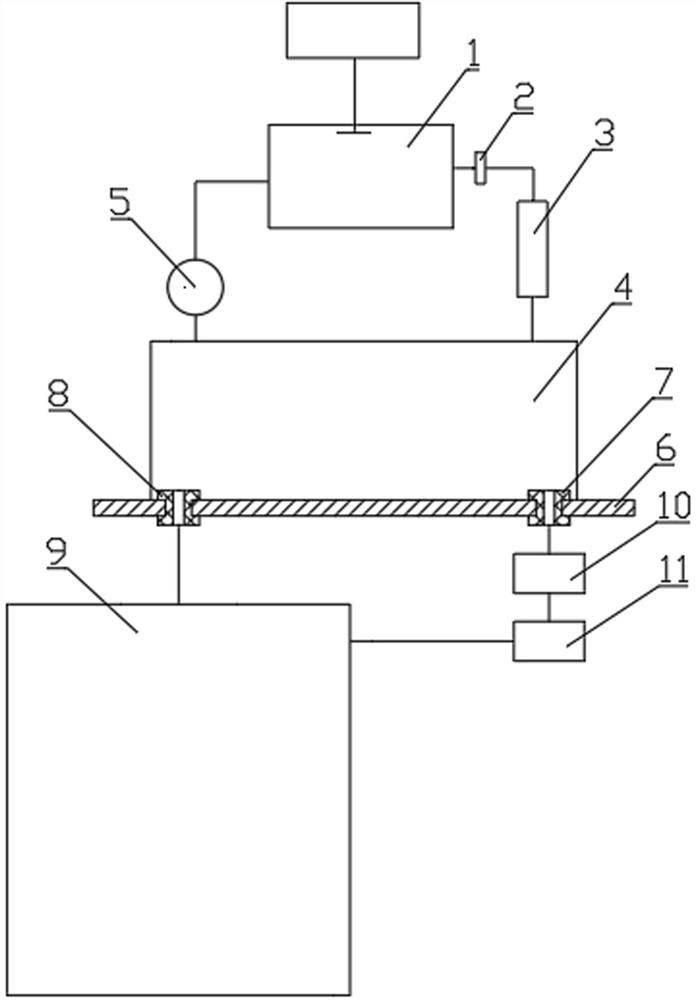
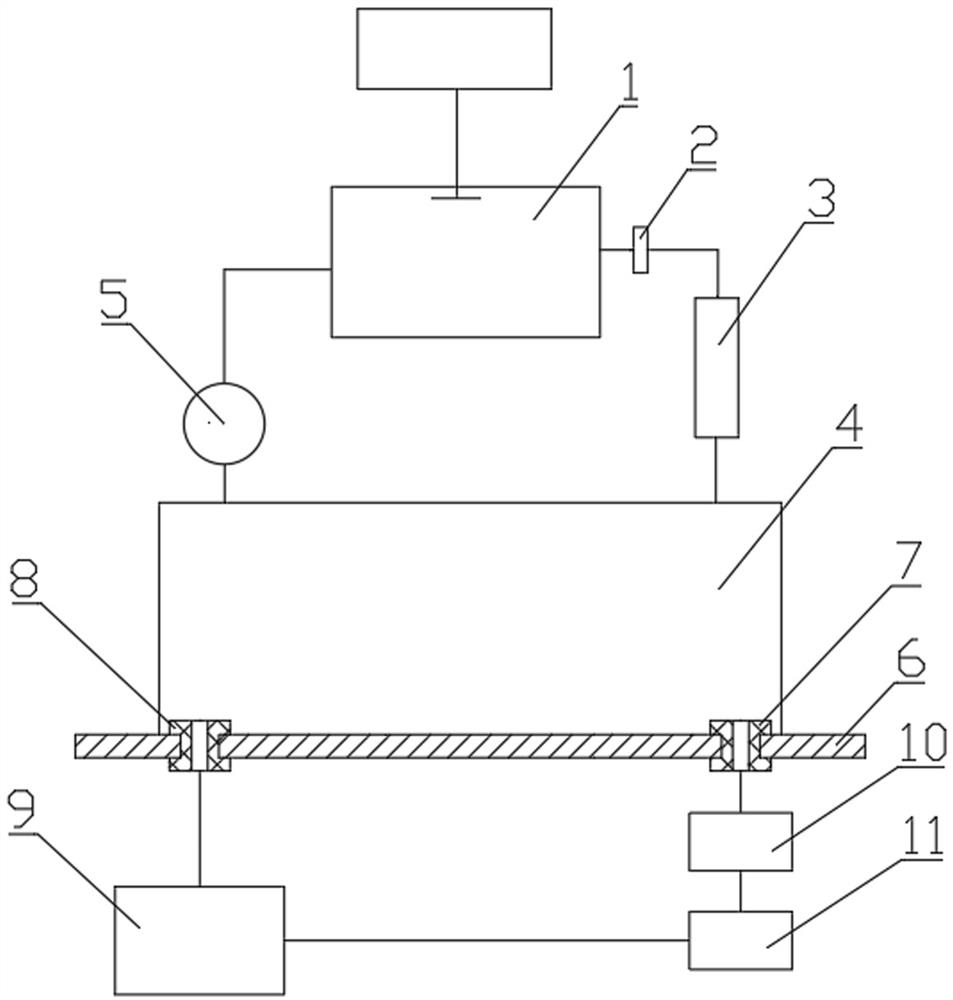
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring a radon exhalation rate on a medium surface. The measuring method comprises a measuring process and a calculating process. The measuring method comprises the following steps: during measurement, inversely covering a radon accumulation chamber on the surface of a medium to be measured; connecting a sealed measuring chamber with the radon accumulation chamber to form a loop; after collecting a certain time period of 5 minutes, turning on an air pump to mix the radon in the radon accumulation chamber and the measuring chamber at a smallflow rate less than 3L / min for 5 minutes, wherein at this time, the radon concentration in the measuring chamber is the radon concentration in the radon accumulation chamber at the time T; repeatedlymeasuring the radon concentration in the radon accumulation chamber to obtain a group of data of radon concentration in the radon accumulation chamber at equal time intervals by taking T which is greater than or equal to 10 minutes as a period; and solving the radon exhalation on the surface of the medium to be measured according to a theoretical formula. The measuring device consists of the radon accumulation chamber, the air pump, the measuring chamber, a secondary instrument and a drying pipe, wherein one end of the air pump is connected with the radon accumulation chamber, while the otherend is connected with the measuring chamber through a pipe; one end of the drying pipe is connected with the radon accumulation radon through a pipe, while the other end is connected with the measuring chamber through a pipe; and the secondary instrument is connected with the measuring chamber.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
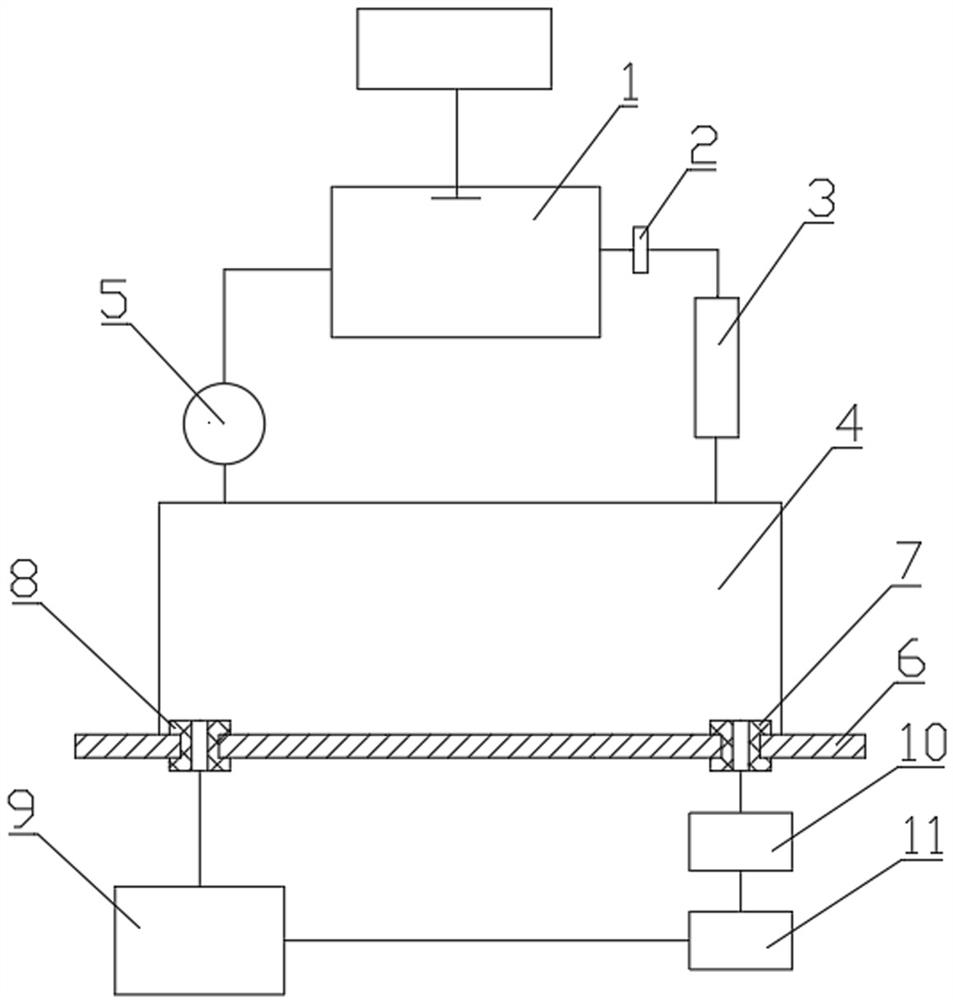
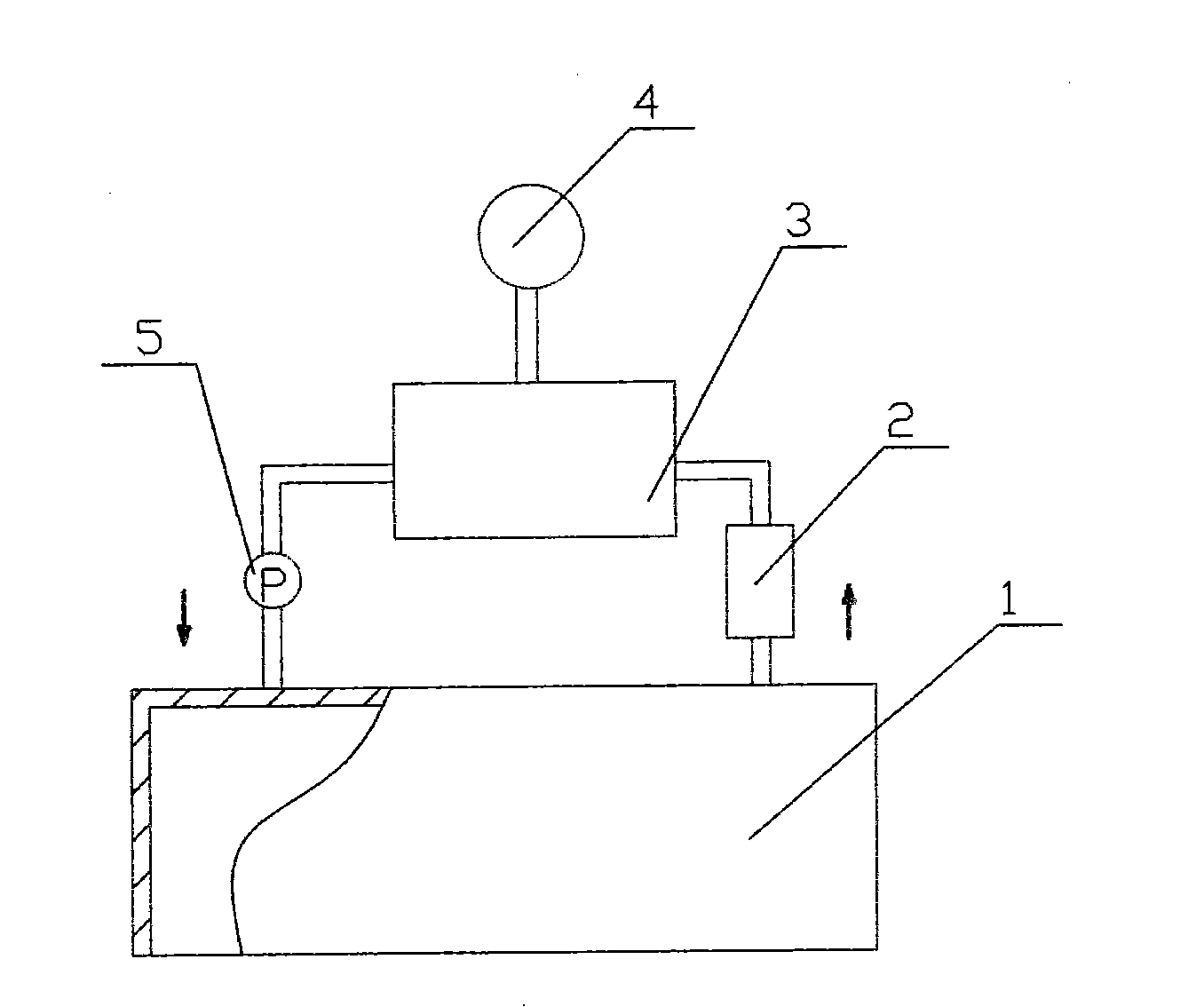
Device and method for adjusting radon exhalation rate and effective decay constant by using radon chamber
ActiveCN113325461AEasy to measureAdjust the radon exhalation rate arbitrarilyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMeasuring instrumentEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a device and a method for adjusting radon exhalation rate and effective decay constant by using a radon chamber. In the device, one end of a filter membrane is connected with a measuring chamber of a measuring instrument through a pipeline, the other end of the filter membrane is connected with a drying pipe through a pipeline, the other end of the drying pipe is connected with a radon collecting cover through a pipeline, and one end of a pump is connected with the measuring chamber of the measuring instrument through a pipeline; the other end of the pump is connected with the radon collecting cover through a pipeline, the gas outlet connector and the gas inlet connector are respectively installed on the compact material plate, the gas outlet connector is connected with the adjustable micro pump through a pipeline, the other end of the adjustable micro pump is connected with the flow meter through a pipeline, and the other end of the flow meter is connected with the radon chamber through a pipeline; the other end of the radon chamber is connected with the gas inlet connector through a pipeline. The measurement method comprises a conventional radon exhalation rate measurement process and a process of adjusting the radon exhalation rate and the effective decay constant of the radon exhalation rate standard device by using the radon chamber. Therefore, the radon exhalation rate and the effective decay constant can be adjusted by adjusting the flow rate of the adjustable micro pump in the device.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Device and method for adjusting radon exhalation rate and effective decay constant of radon exhalation rate standard device
ActiveCN113325460AEasy to measureAdjust the radon exhalation rate arbitrarilyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMeasuring instrumentEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a device and a method for adjusting radon exhalation rate and effective decay constant of a radon exhalation rate standard device. One end of the filter membrane in the device is connected with a measuring chamber of a measuring instrument through a pipeline; the other end of the filter membrane is connected with a drying pipe through a pipeline, and the other end of the drying pipe is connected with a radon collecting cover through a pipeline; one end of the pump is connected with a measuring chamber of the measuring instrument through a pipeline, the other end of the pump is connected with the radon collecting cover through a pipeline, the gas outlet connector and the gas inlet connector are respectively installed on the compact material plate, the gas outlet connector is connected with the adjustable micro pump through a pipeline, and the other end of the adjustable micro pump is connected with the flowmeter through a pipeline; the other end of the flowmeter is connected with the gas flow type radon source through a pipeline, and the other end of the gas flow type radon source is connected with the gas inlet connector through a pipeline. The measurement method comprises a conventional radon exhalation rate measurement process and a process of adjusting the radon exhalation rate and the effective decay constant of the radon exhalation rate standard device. Herein, the radon exhalation rate and the effective decay constant can be adjusted by adjusting the flow rate of the adjustable micro pump in the device.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
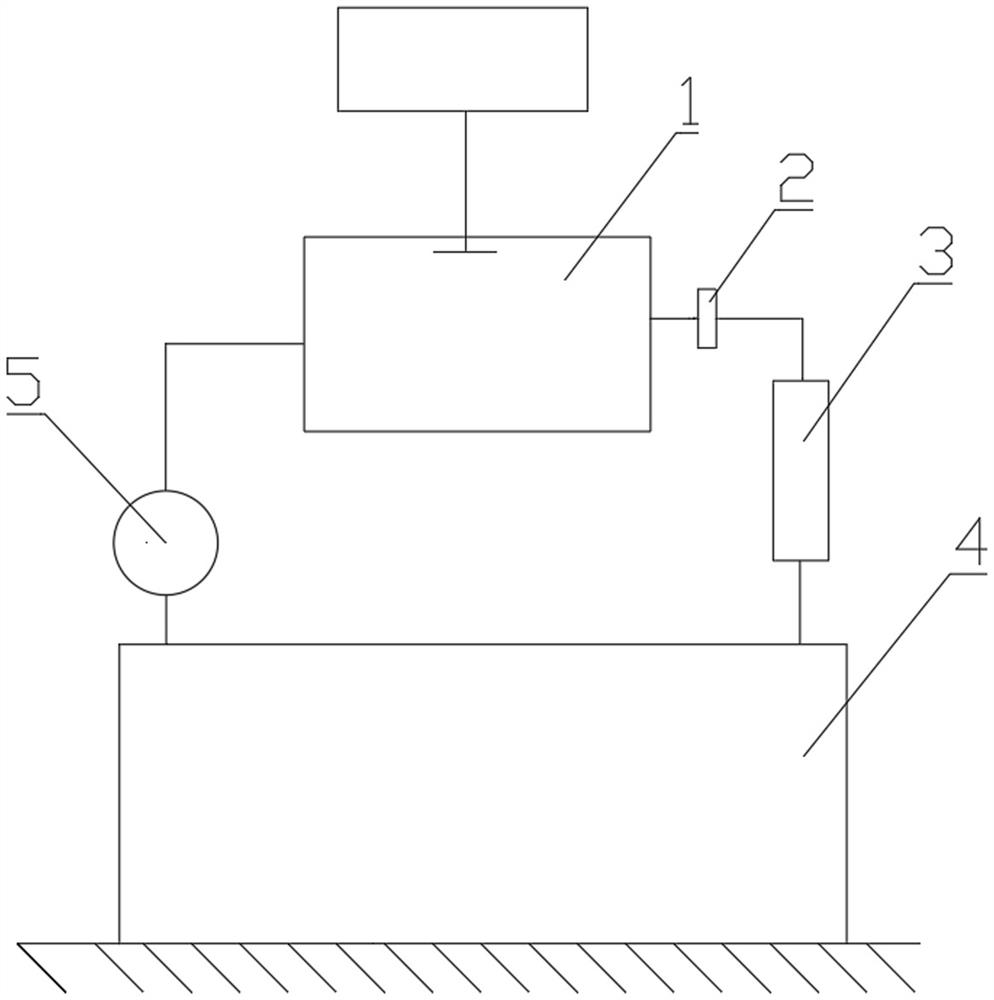
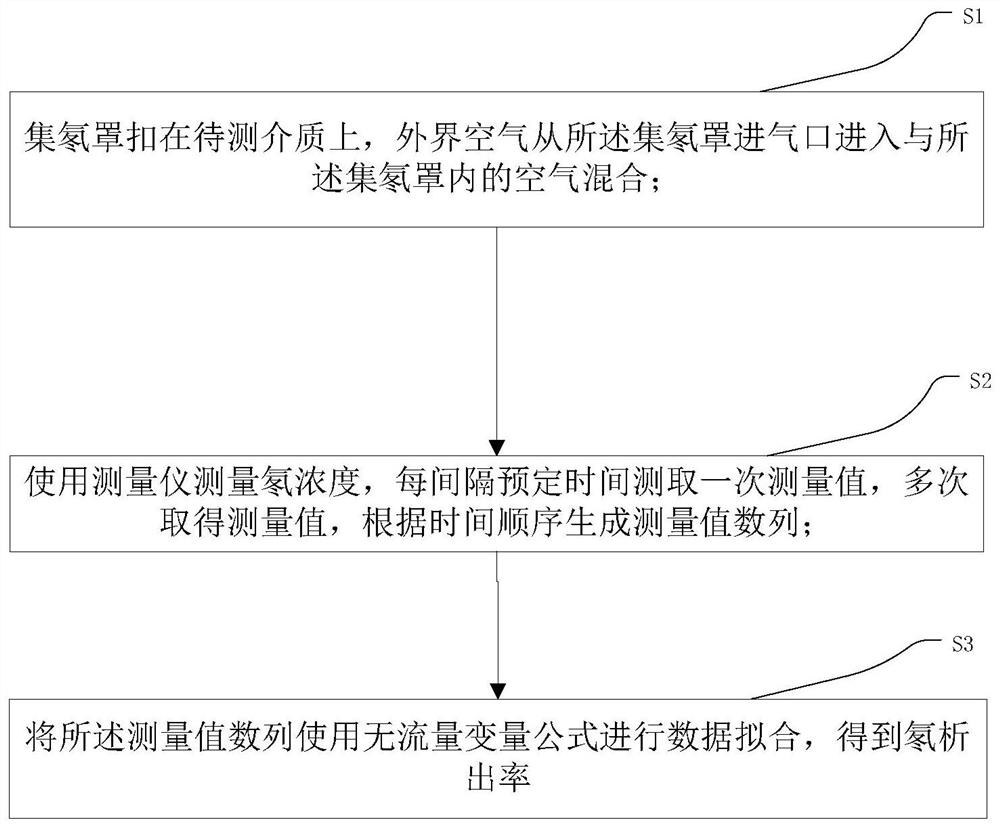
Method, device and system for rapid open-loop measurement of radon exhalation rate without flowmeter
ActiveCN110456406BSimplified calculation formulaThe result is accurateX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMeasuring instrumentEngineering
The invention relates to a method, a device and a system for rapidly open-loop measuring the exhalation rate of radon without a flow meter. The method for fast open-loop measurement of radon exhalation rate without a flow meter comprises steps: S1, pre-processing: the radon collecting hood is buckled on the medium to be measured, and the outside air enters from the radon collecting hood air inlet and is connected with the radon collecting hood Air mixing in the interior; S2, measurement: use a measuring instrument to measure the radon concentration, obtain measured values multiple times, and generate a sequence of measured values according to time sequence; S3, calculate: use the sequence of measured values to perform data fitting using the no-flow parameter formula, Get the radon exhalation rate. The method, device and system for rapid open-loop measurement of radon exhalation rate without a flow meter provided by the present invention, through analyzing the radon concentration rising curve data in the radon collecting hood collection room, the reference variables and simplified calculation formulas are reduced, and the results are accurate .
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Method for measuring radon emanation rate by adopting two-stage method
InactiveCN102426379BEasy to operateMeet the needs of fast measurementX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentThermodynamicsSoil science
The invention relates to a method for measuring radon emanation rate by adopting a two-stage method, in particular to a method for measuring radon concentration variation in a radon collecting cover by adopting an electrostatic collecting method to obtain the radon emanation rate. The method comprises a measuring process and a calculating process, radon concentration in two longer periods in the radon collecting cover are measured, and the radon emanation rate can be solved by utilizing formulas (2) and (3), or the formulas (4) and (5), or the formulas (6) and (7), or the formulas (8) and (9)or the formulas (10) and (11); radon concentration in three longer periods in the radon collecting cover are measured, a first measuring period is 20 minutes, data of a second measuring period and a third measuring period are utilized, and the radon emanation rate can be solved by utilizing the formulas (13) and (14), or the formulas (15) and (16), or the formulas (17) and (18), or the formulas (19) and (20), or the formulas (21) and (22), or the formulas (23) and (24) or the formulas (25) and (26). The measuring and calculating method and the measuring device are simple and are convenient tooperate, and rapid radon emanation rate measuring requirement is met.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
Synchronous value setting device and method for radon exhalation rate measuring instrument
ActiveCN108614289BFast setting speedShorten the time of setting valueRadiation measurementNuclear radiationMeasuring instrument
The invention, which relates to the technical field of nuclear radiation detecting, provides a synchronous setting apparatus and method of a radon precipitating rate measuring instrument. The synchronous setting apparatus comprises a filling block connected to the inner wall of a radon collection room of a radon precipitating rate measuring instrument detachably and a rapid radon precipitating rate setting unit connected in series to an air inlet pipe or an air return pipe. A radon precipitating rate value measured by the rapid radon precipitating rate setting unit is used as a standard for setting of the radon precipitating rate measuring instrument. To be specific, the rapid radon precipitating rate setting unit carries out equivalent processing on a changing radon concentration by usinga difference method; and on the basis of a corresponding scale factor value and alpha particle counting data collected by a detector during the measuring process, a radon concentration value of a next measuring cycle is calculated by combining a radon concentration value of a previous measuring cycle; The radon precipitating rate setting speed is fast; the time of radon precipitating rate measuring instrument setting is reduced substantially; the deviation caused by too long time during the setting process is reduced; and the setting value accuracy is enhanced.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV +1
Method for continuously measuring radon exhalation rate based on change of leakage coefficient and back-diffusion coefficient
PendingCN114088313AEasy to measureCalculation method is simpleMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateDiffusion analysisHydrologyRadon flux
According to a method for continuously measuring the radon exhalation rate according to the change of a leakage coefficient and a back-diffusion coefficient, before the leakage coefficient and the back-diffusion coefficient are not changed, the effective decay constant is firstly measured, and the radon exhalation rate is directly calculated through the effective decay constant. When rainfall or geological conditions are changed, and the leakage coefficient and the back-diffusion coefficient are changed, each measurement period is set to be 2 to 60 minutes, n measurement periods are set as one group, m groups are continuously measured, m is an even number, the flow rate of the pump is L1 when the first, third, fifth,... and (m-1) th groups are measured, the flow rate of the pump is L2 when the second, fourth, sixth,... and m th groups are measured, and the difference between L1 and L2 is more than 20%; and the radon exhalation rate and the effective decay constant are calculated through a formula by using the data of the first and second groups, the data of the third and fourth groups,..., and the data of the m-1 and m groups. According to the method, after the leakage coefficient and the back-diffusion coefficient are changed, the accurate radon exhalation rate and the effective decay constant can still be obtained, and the calculation precision of the radon exhalation rate is improved.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
A closed-loop method and device for measuring radon exhalation rate in emanation medium
ActiveCN108919329BRapid determination of radon exhalation rateShorten the timeX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMeasuring instrumentHydrology
The invention discloses a closed-loop method and device for measuring a radon exhalation rate of a gas emitting medium. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a gas pump is opened, and theflow rate entering a gas equalizing chamber is controlled to be Q through a flow regulator; the radon concentration C0 in the external environment measured by a radon measuring instrument is taken asthe radon concentration C0 of a gas collecting hood at zero time t0; when the radon concentration in the gas collecting hood is measured, the radon concentrations C1, C2,... and Cn ( n>=5) is recordedat this time in sequence at the same time interval delta T; and (2) the solution of differential equation (shown in the description) is fitted with the above measured values, and then radon exhalation rate J is calculated. The radon exhalation rate and equivalent decay constant can be obtained by the method before the radon concentration is balanced, the closed-loop method and device for measuring the radon exhalation rate of the gas emitting medium have the advantages of short time and accurate calculation.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Neutron flux and energy spectrum measuring system of helium cooling solid multiplication agent tritium producing cladding
ActiveCN1948997BSimple designNuclear energy generationNeutron radiation measurementBiological activationHelium gas
The invention relates to fusion reactor tritium generating cladding neutron measuring. Helium cooling solid breeding agent tritium generating cladding neutron flux and spectrometry measuring system includes packaging foil pneumatic transmitting activation analysis subsystem which includes activation foil and pneumatic transmitting device. The activation foil is set in the measuring tube connectedwith operating station through cooling layer and biological shielding layer. The operating station is set helium cooling circuit and connected with helium gas dynamic force union station and HPGe measuring station connected with electronics and data gaining system. The solid breeding agent tritium generating cladding is also set micro-fission chamber combination detector and natural diamond neutron energy spectrum detector which are connected with operating station through current sensitive preamplifier and charge sensitive preamplifier, which is connected with electronics and data gaining system.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com