Patents
Literature
337 results about "Turboprop" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
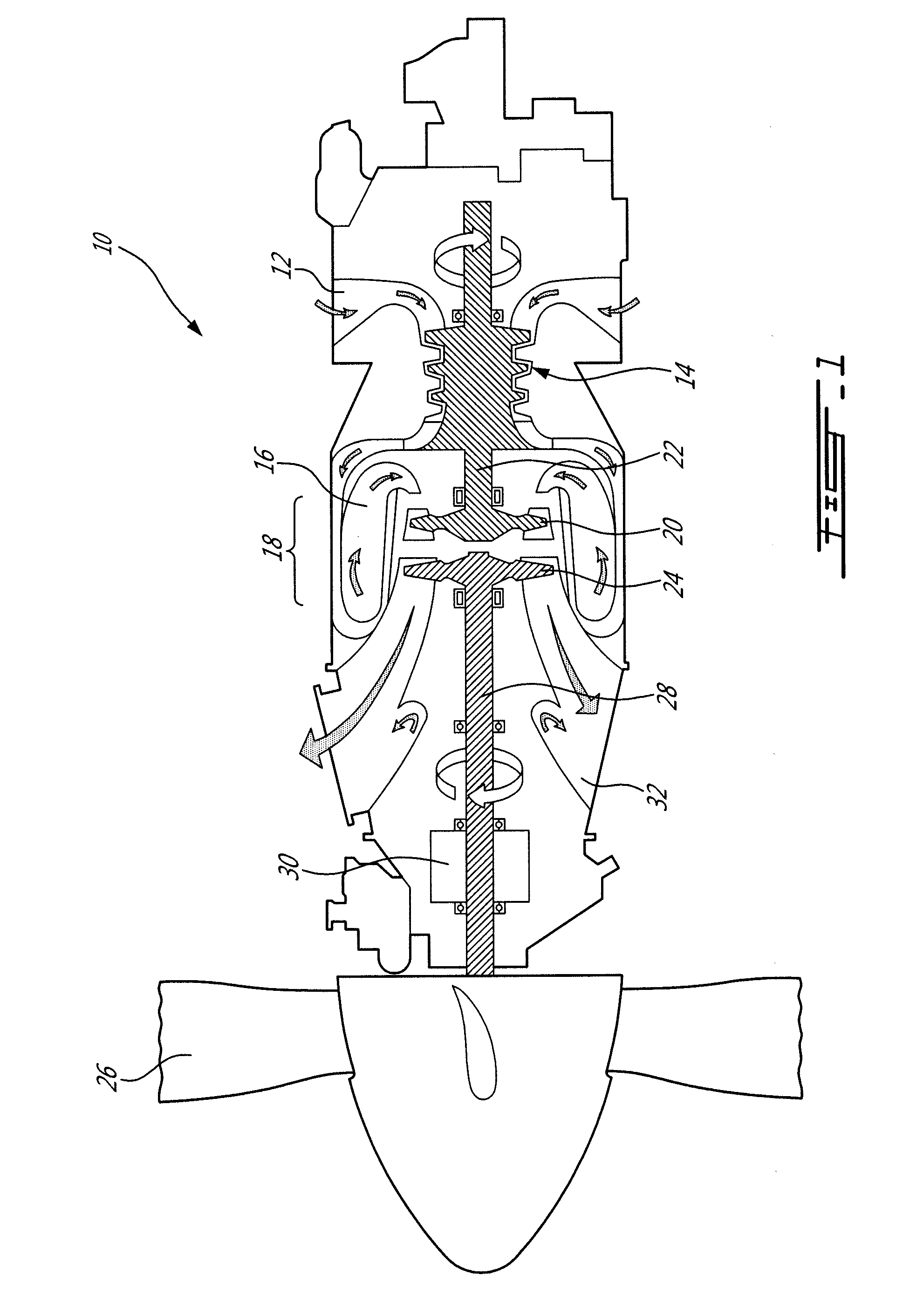
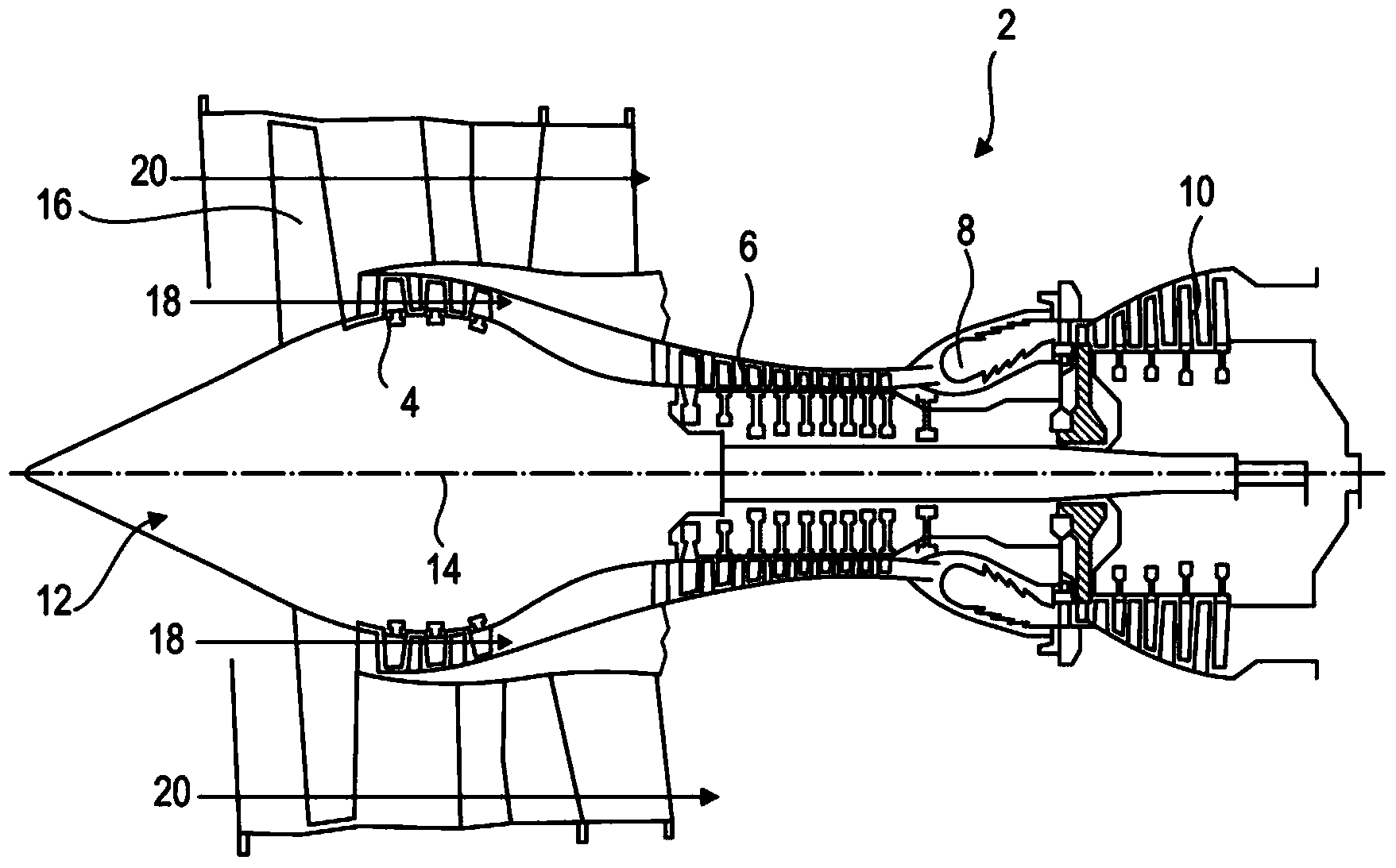
A turboprop engine is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller. In its simplest form a turboprop consists of an intake, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air is drawn into the intake and compressed by the compressor. Fuel is then added to the compressed air in the combustor, where the fuel-air mixture then combusts. The hot combustion gases expand through the turbine. Some of the power generated by the turbine is used to drive the compressor. The rest is transmitted through the reduction gearing to the propeller. Further expansion of the gases occurs in the propelling nozzle, where the gases exhaust to atmospheric pressure. The propelling nozzle provides a relatively small proportion of the thrust generated by a turboprop.
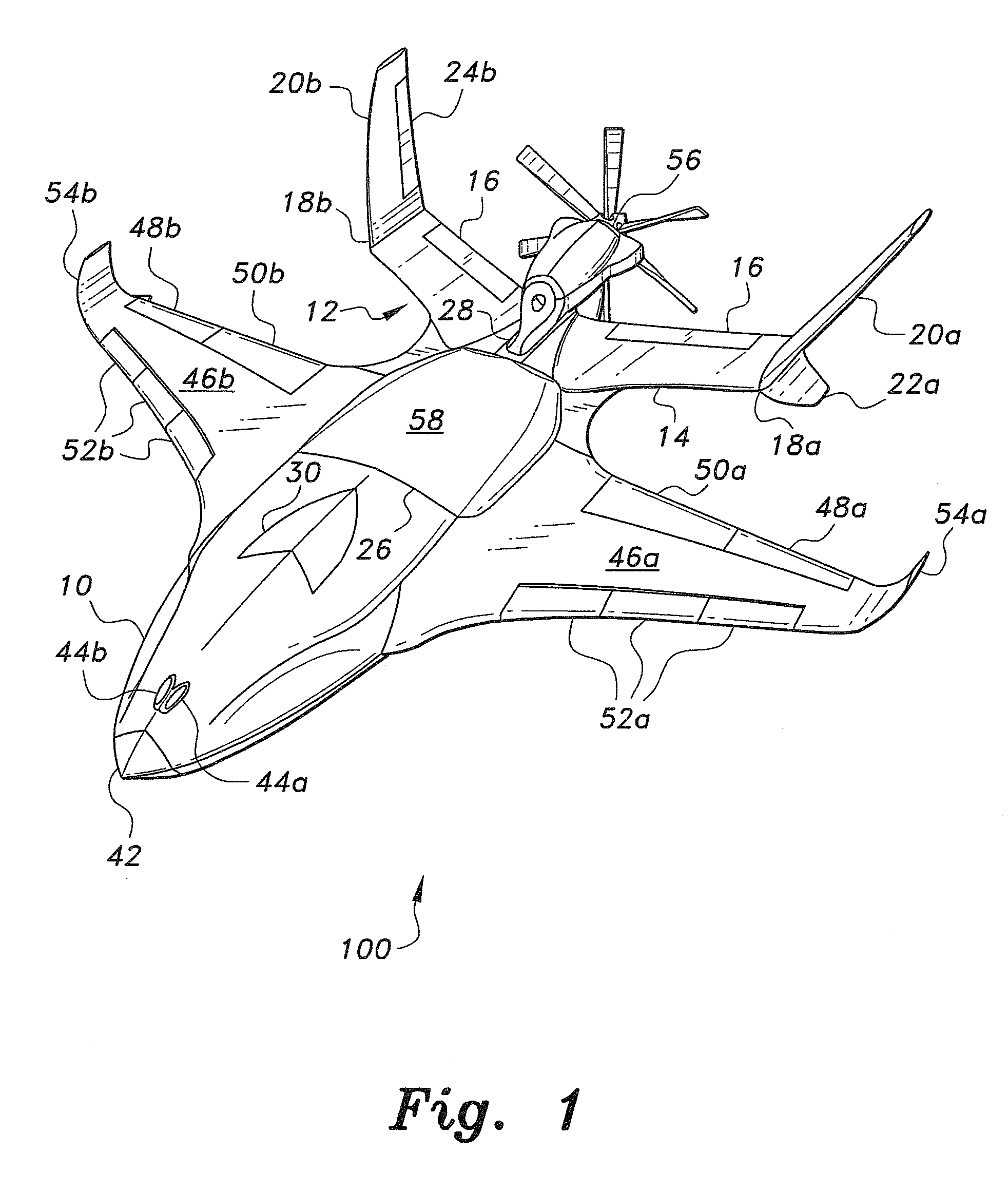
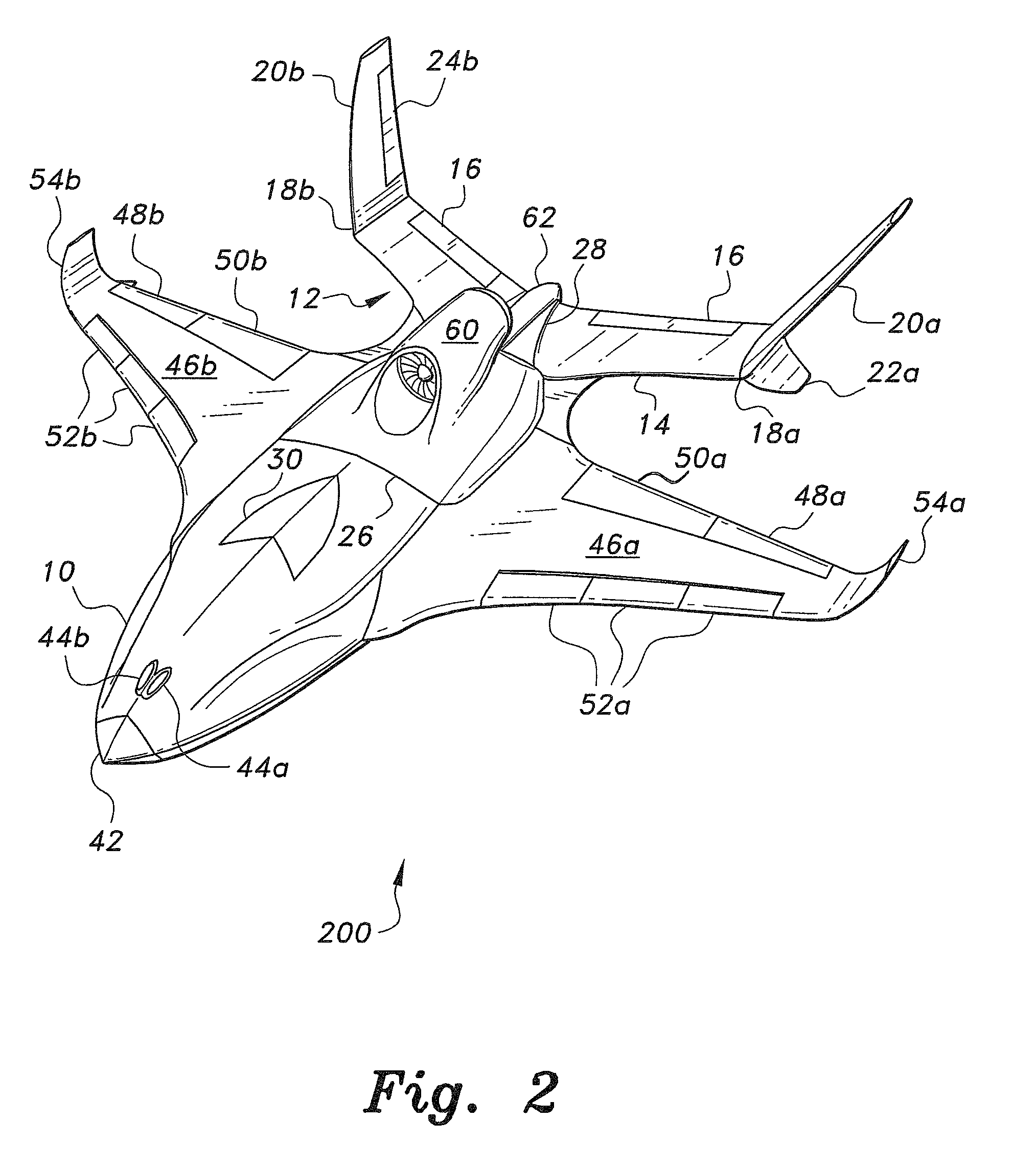
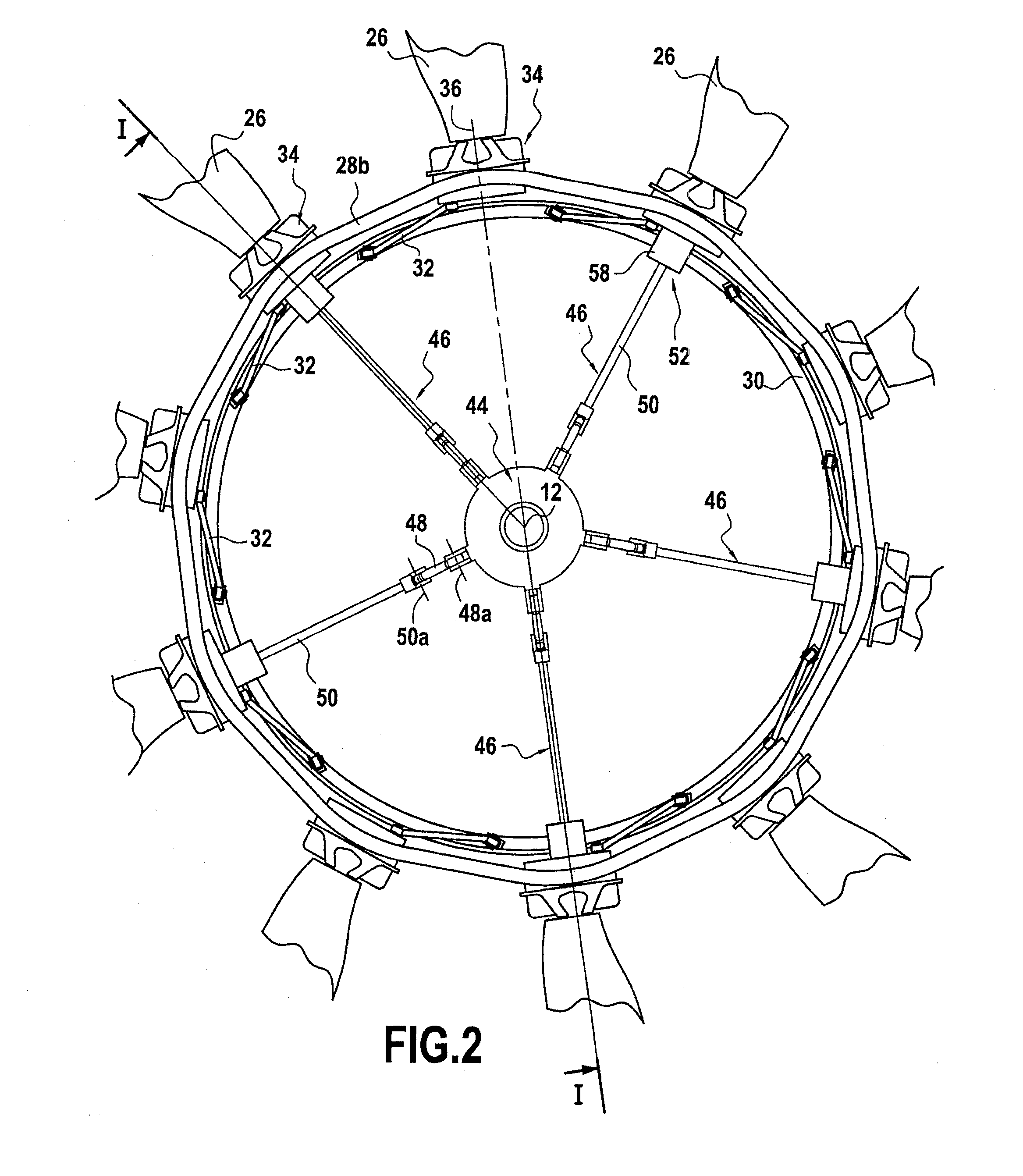
Lift, propulsion and stabilising system for vertical take-off and landing aircraft
InactiveUS20120280091A1Streamlined shapeImprove stabilityAircraft navigation controlVertical landing/take-off aircraftsTransverse axisFixed wing
The lift, propulsion and stabilising system for vertical takeoff and landing aircraft of the invention consists of applying during vertical flight on, below or in the interior of the fixed-wing aircraft one or more rotors or large fans each one with two or more horizontal blades, said rotors are activated by means of turboshafts, turbofans or turboprops with a mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic or electrical transmission, and the respective motors. Using lifting and / or stabilising and / or controlling fans and / or oscillating fins and / or air blasts. Placing the horizontal lifters near at least one end of the longitudinal axis and of the transverse axis of the aircraft. Generally said stabilising elements form 90° with one another and with the central application point of the rotor or application of that which results from the lift forces.
Owner:SALZ MANUEL
Modular aircraft system
ActiveUS9505484B1Easy constructionImprove aerodynamic performanceActuated automaticallyDe-icing equipmentsCarrying capacityFlight vehicle
The modular aircraft system includes a single fuselage having a permanently installed empennage and plural sets of wing modules and engine modules, with each wing and engine module optimized for different flight conditions and missions. The fuselage and each of the modules are configured for rapid removal and installation of the modules to minimize downtime for the aircraft. Short wings having relatively low aspect ratio are provided for relatively high speed flight when great endurance and / or weight carrying capacity are not of great concern. Long wings having high aspect ratio are provided for longer range and endurance flights where speed is not absolutely vital. A medium span wing module is also provided. Turboprop, single turbojet, and dual turbojet engine modules are provided for installation depending upon mission requirements for any given flight. The aircraft is primarily adapted for use as an autonomously operated or remotely operated unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:AL SABAH NASSER M
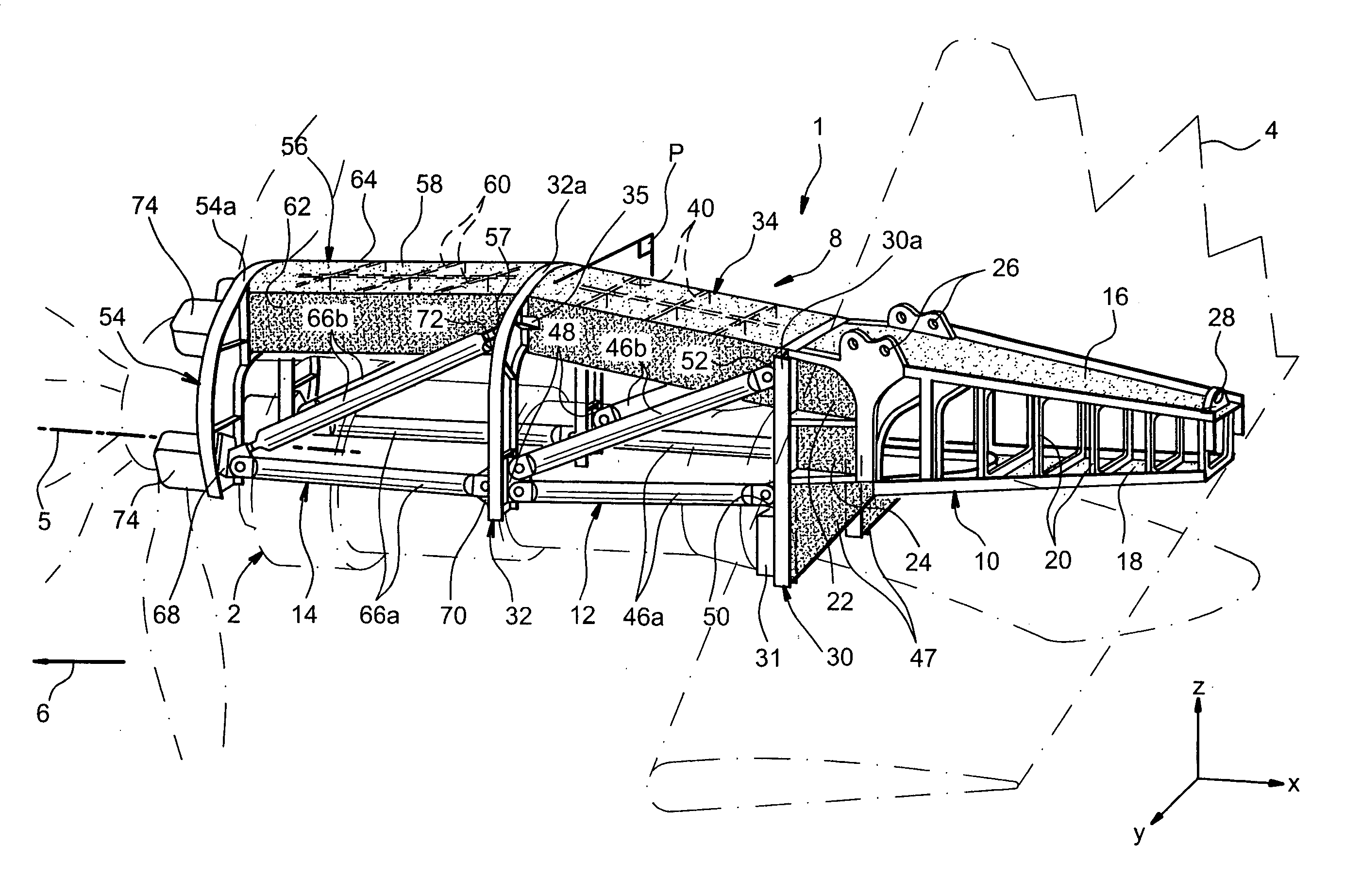
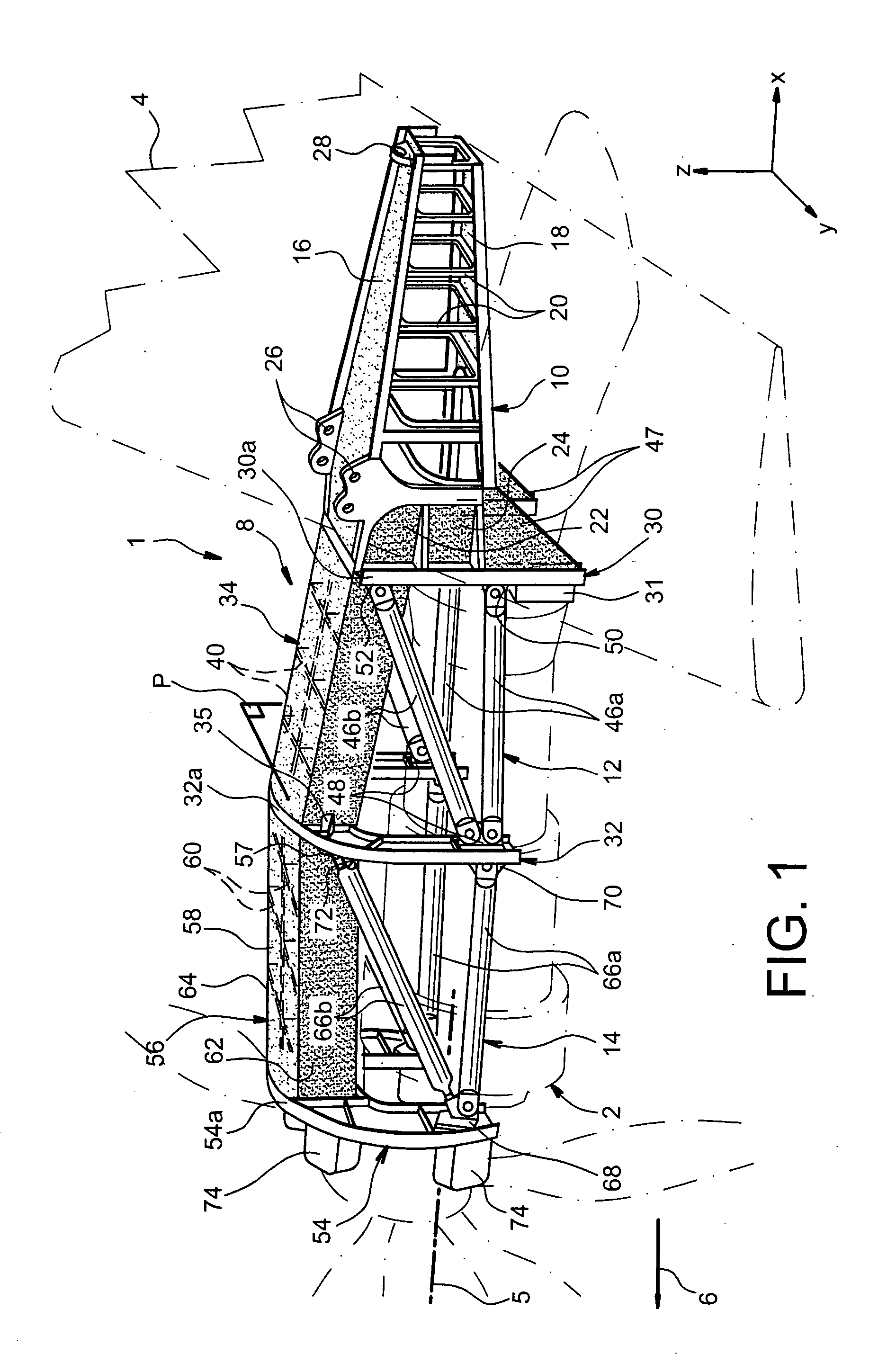
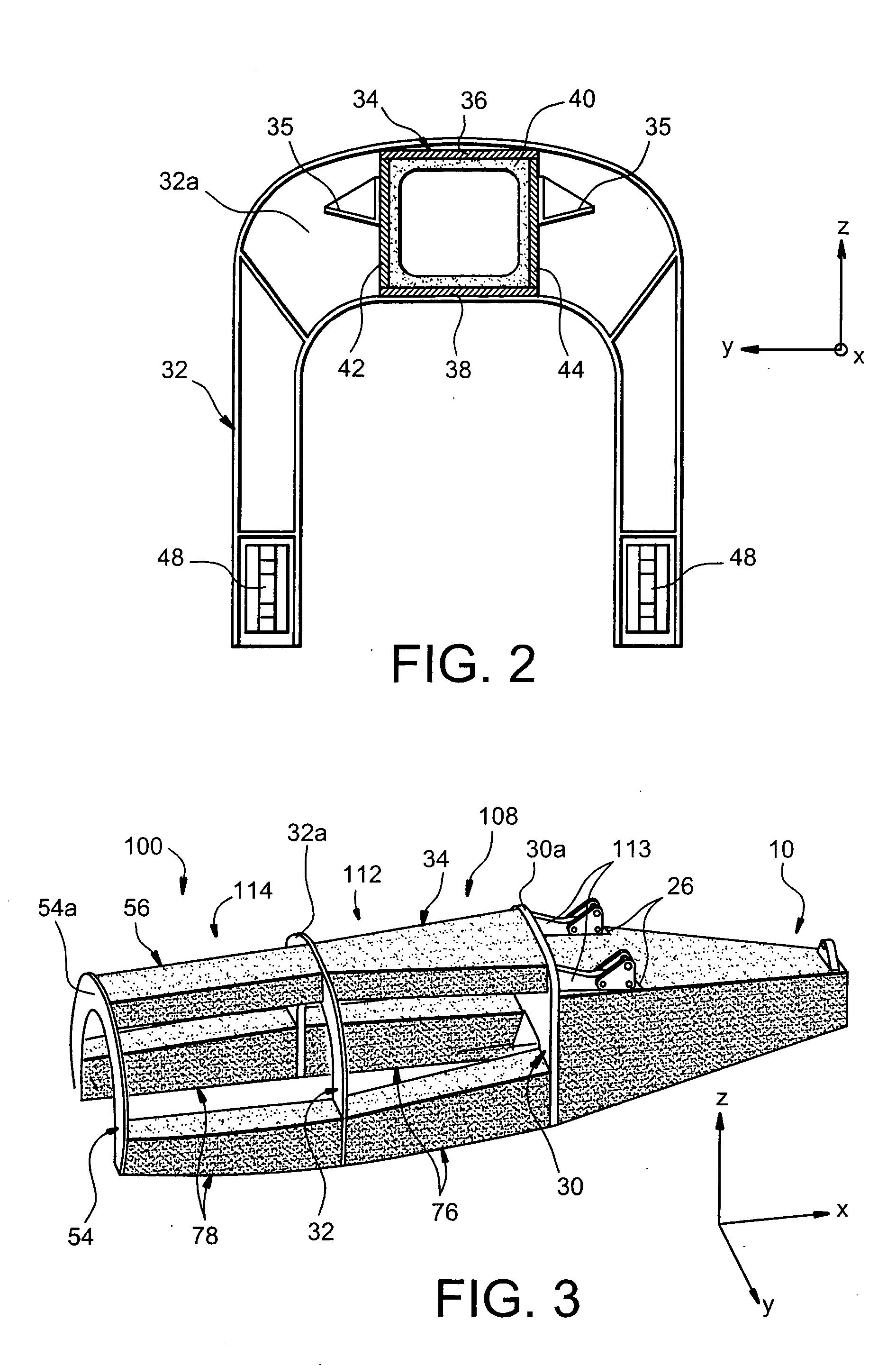
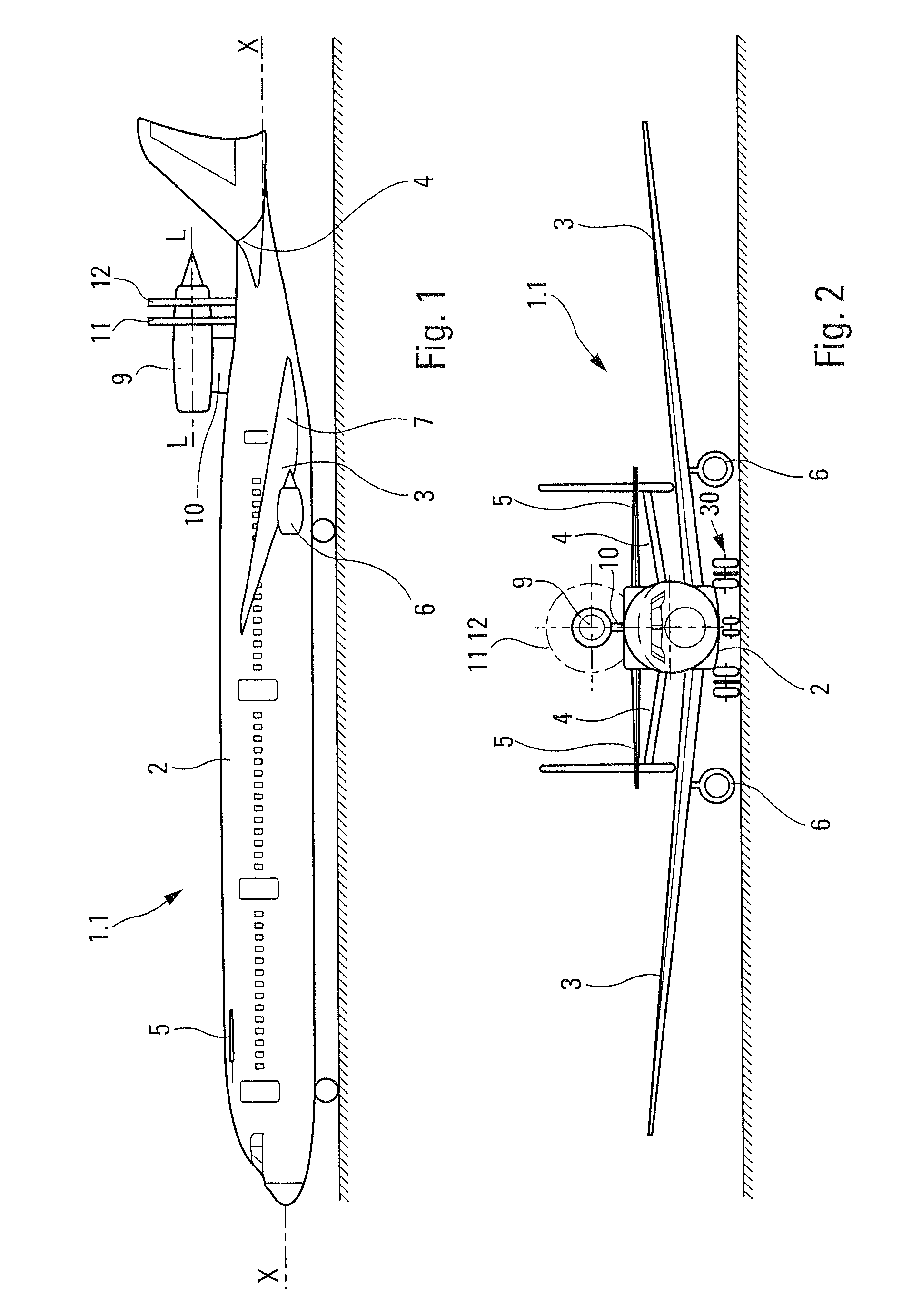
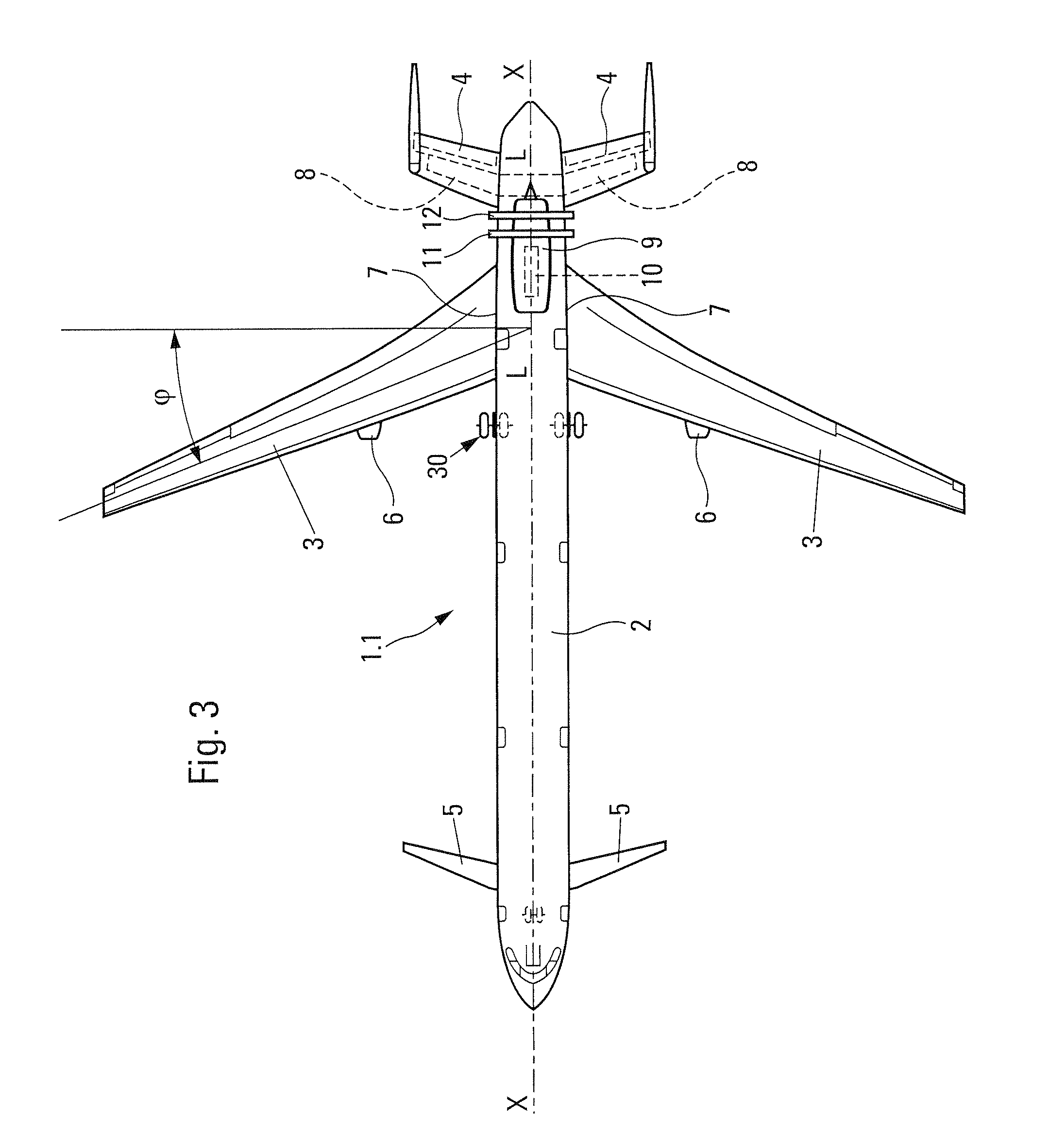
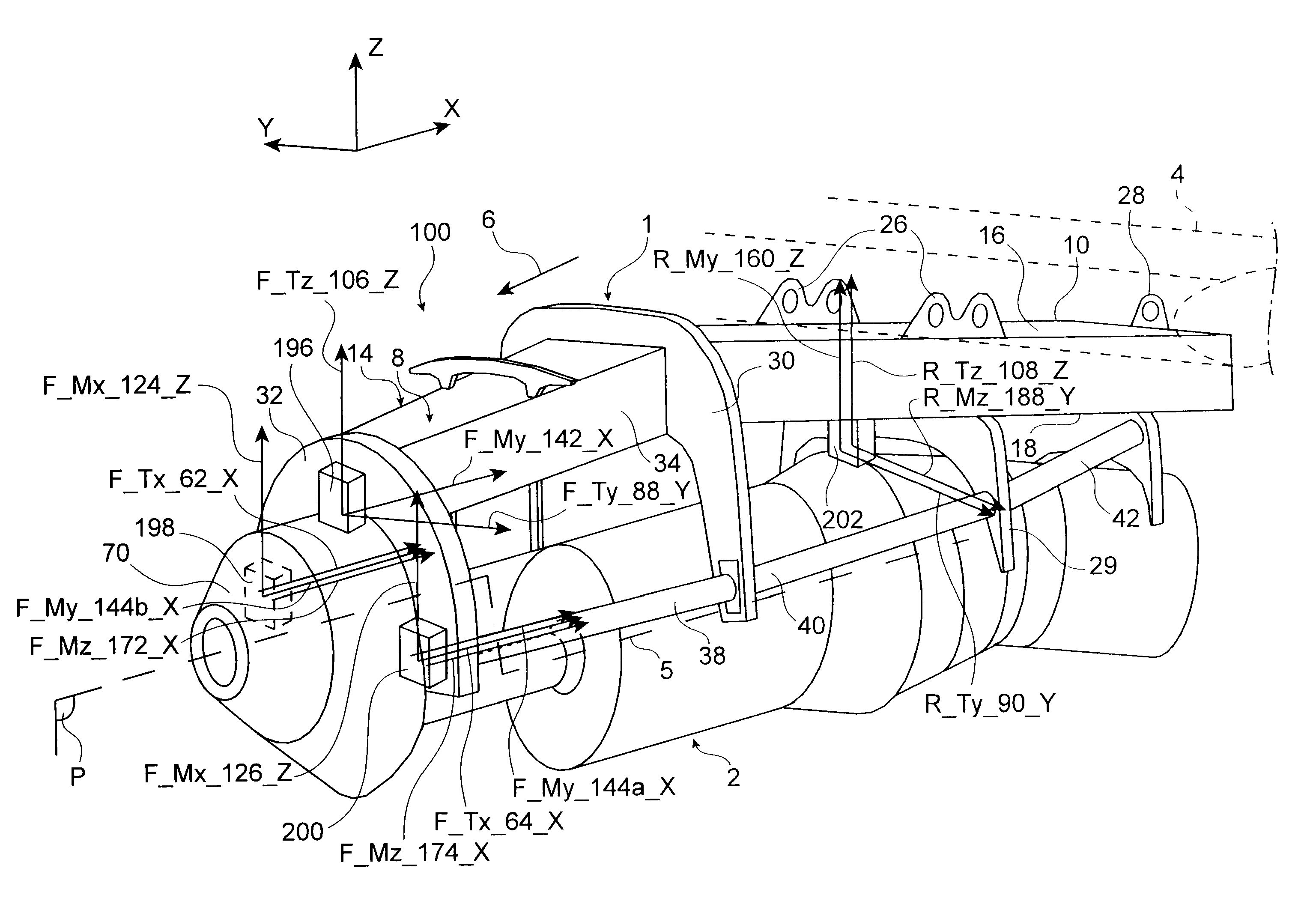
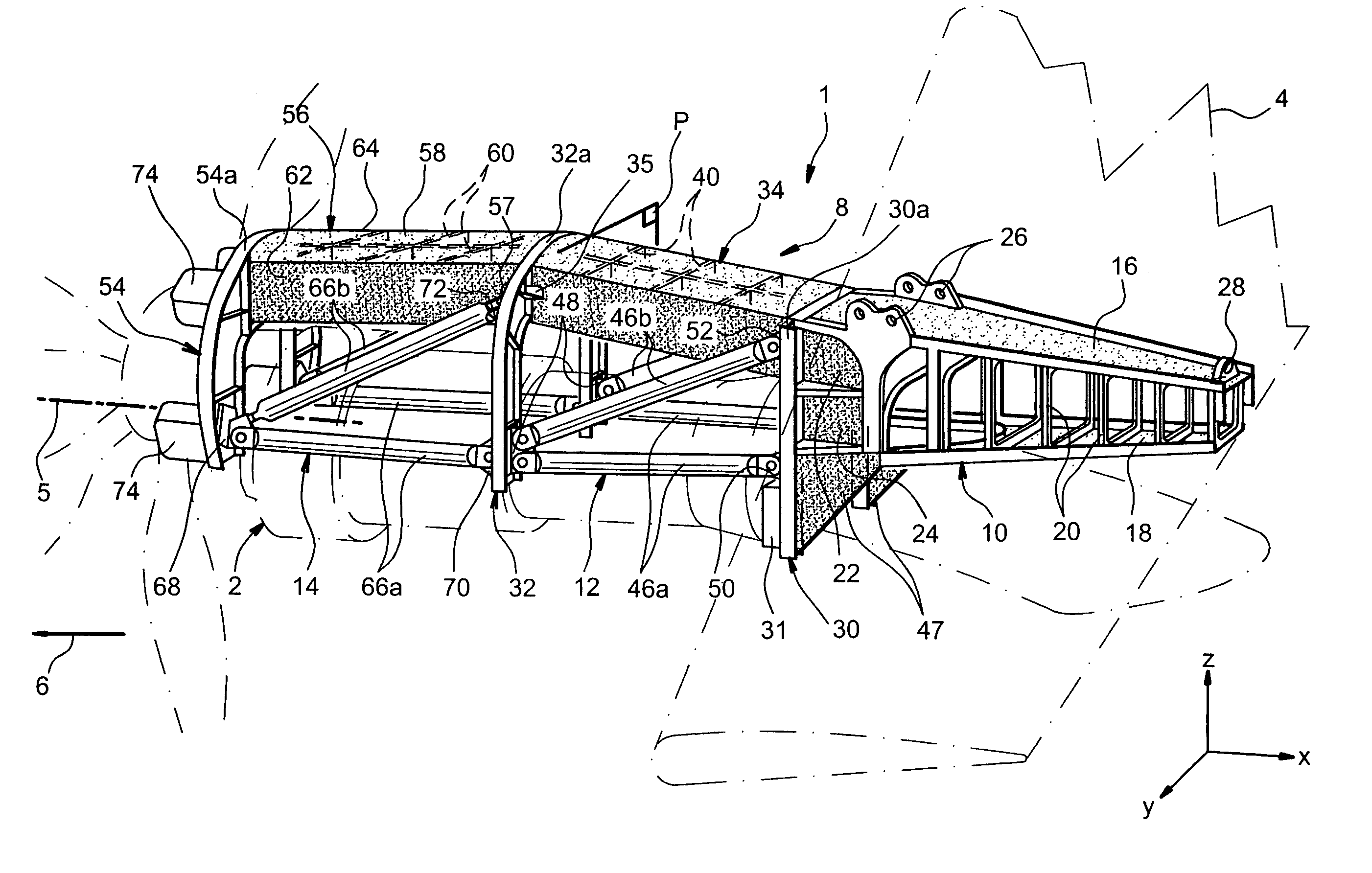
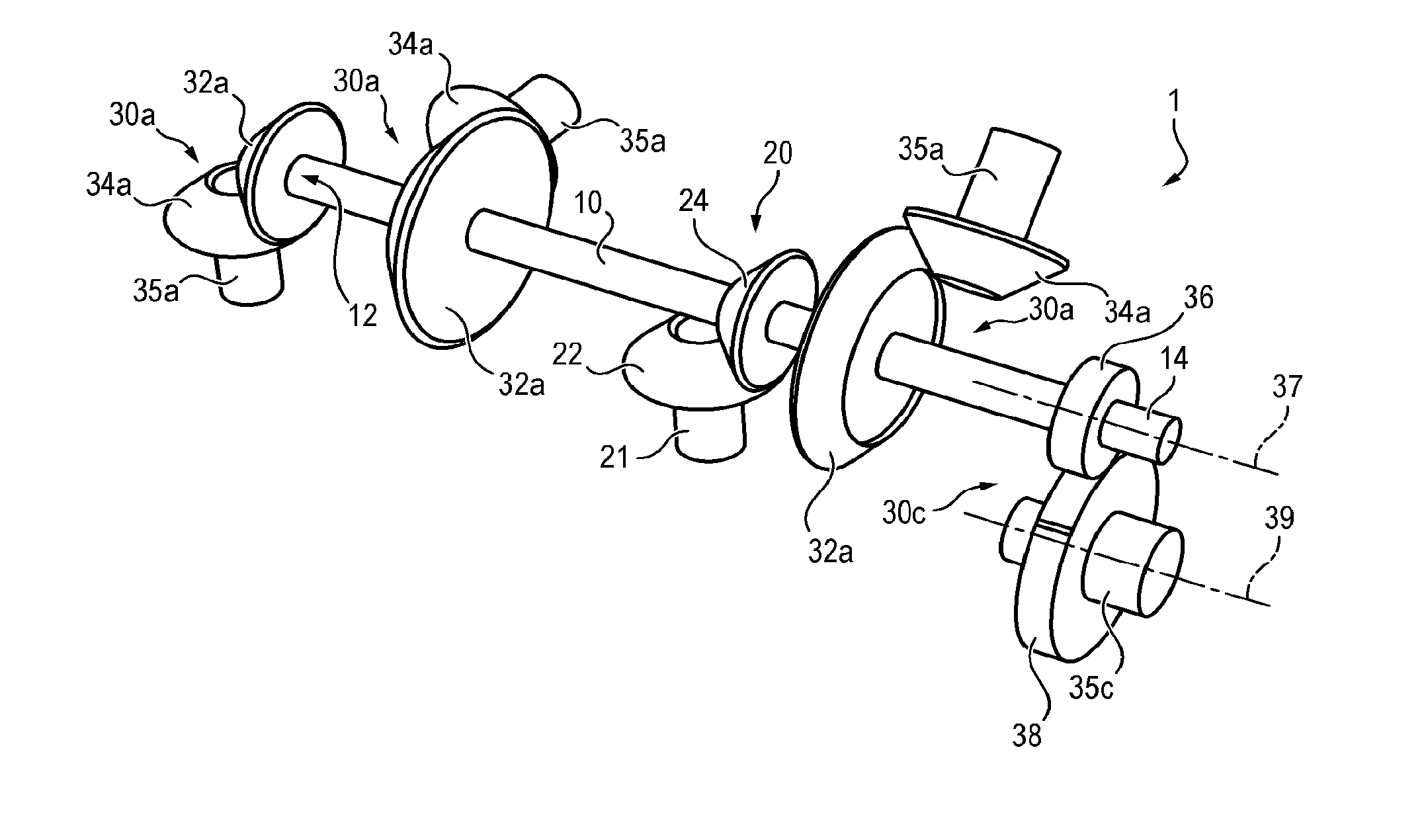
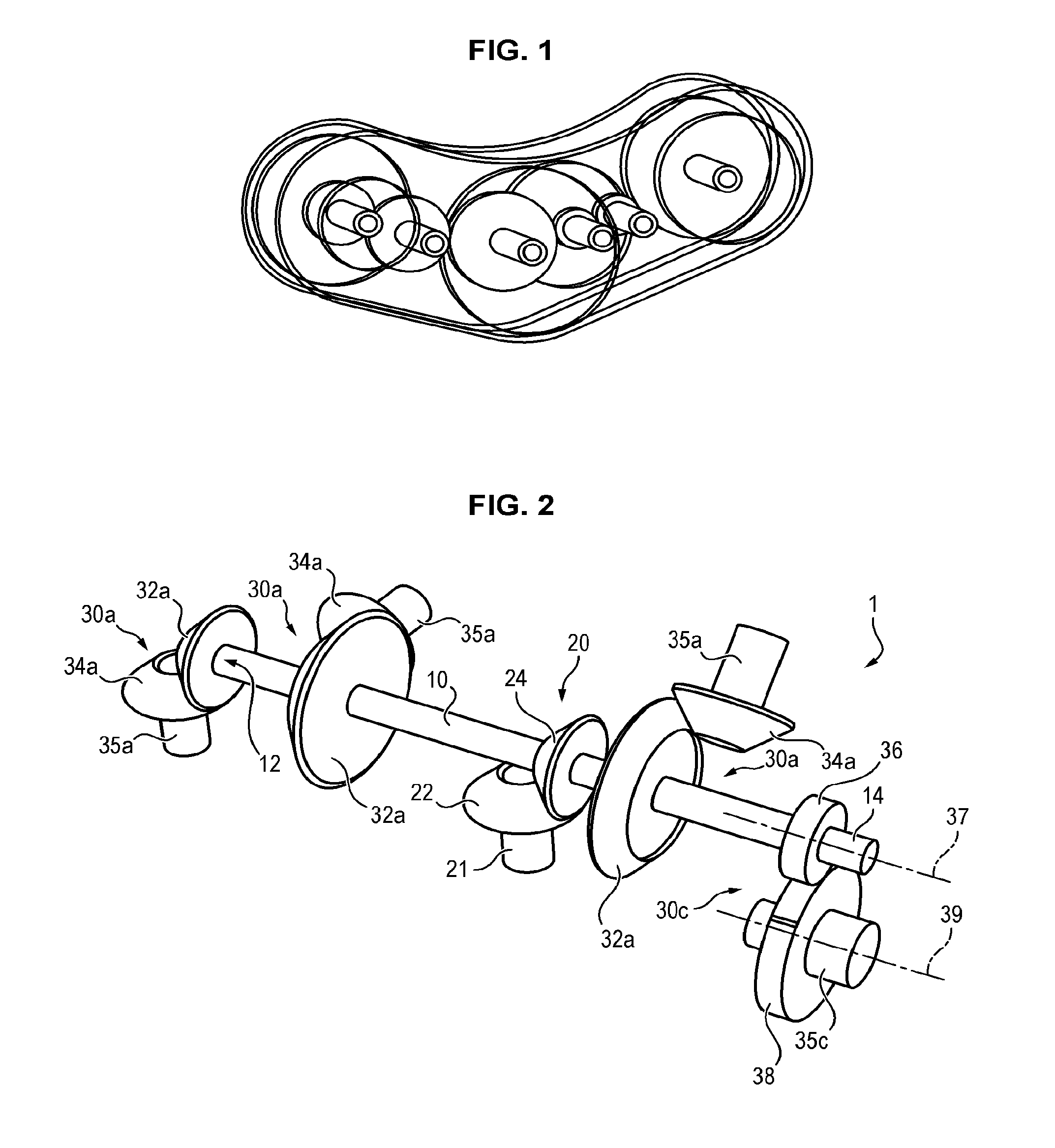
Mounting structure for mounting a turboprop under an aircraft wing
ActiveUS20050116093A1Easy resistanceGood geometric continuityGas turbine type power plantsPower plant constructionRigid structureAirplane
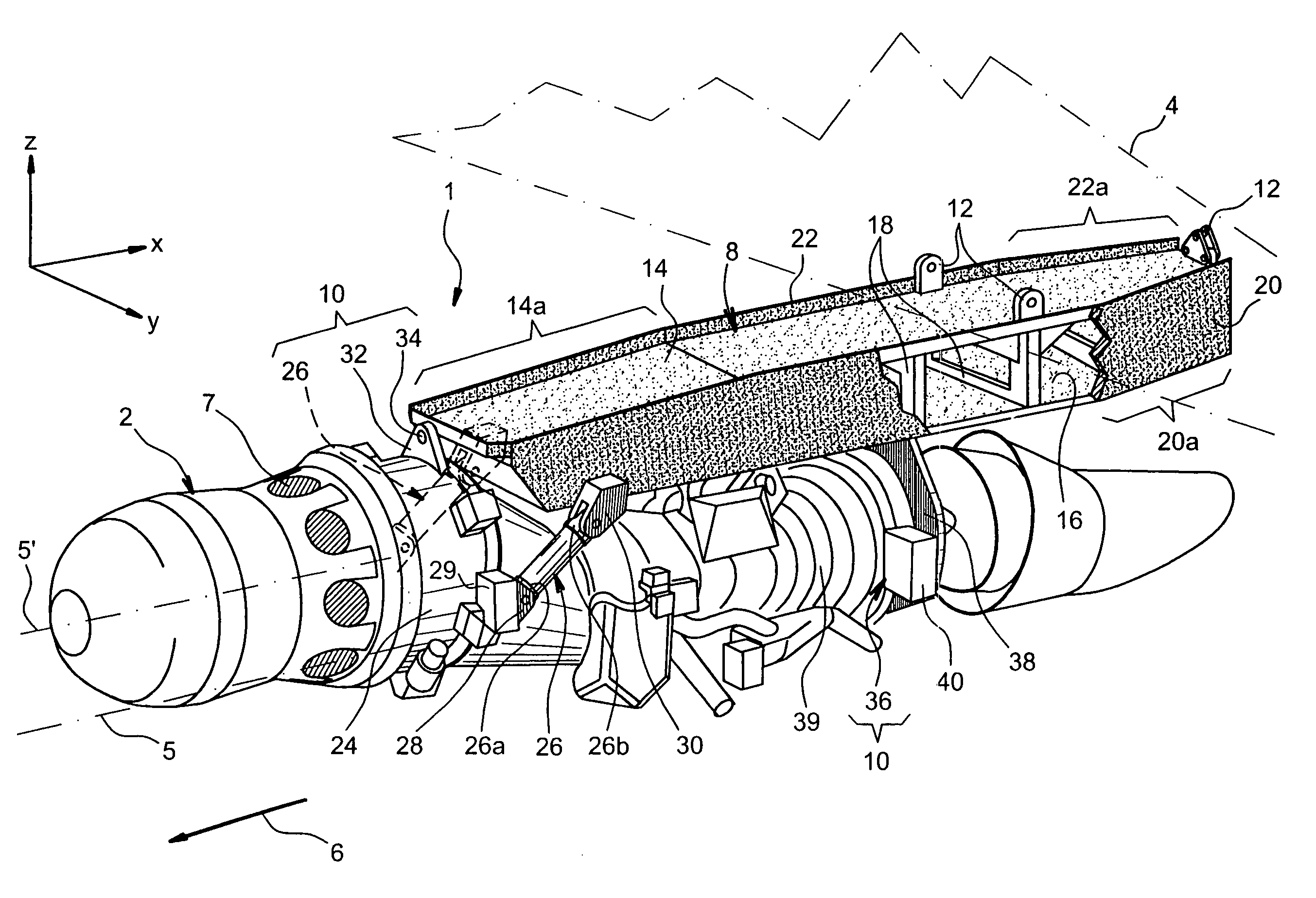
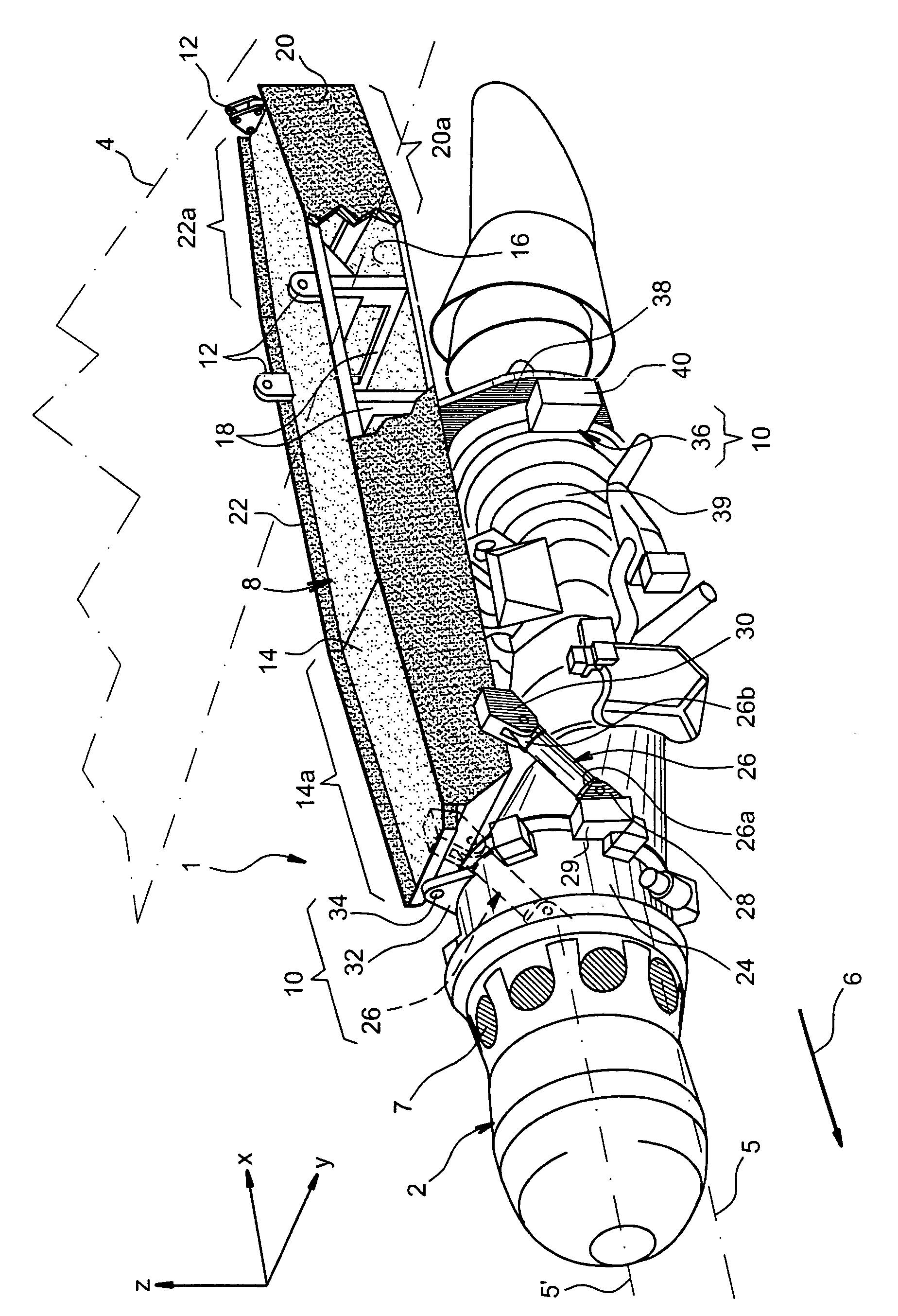
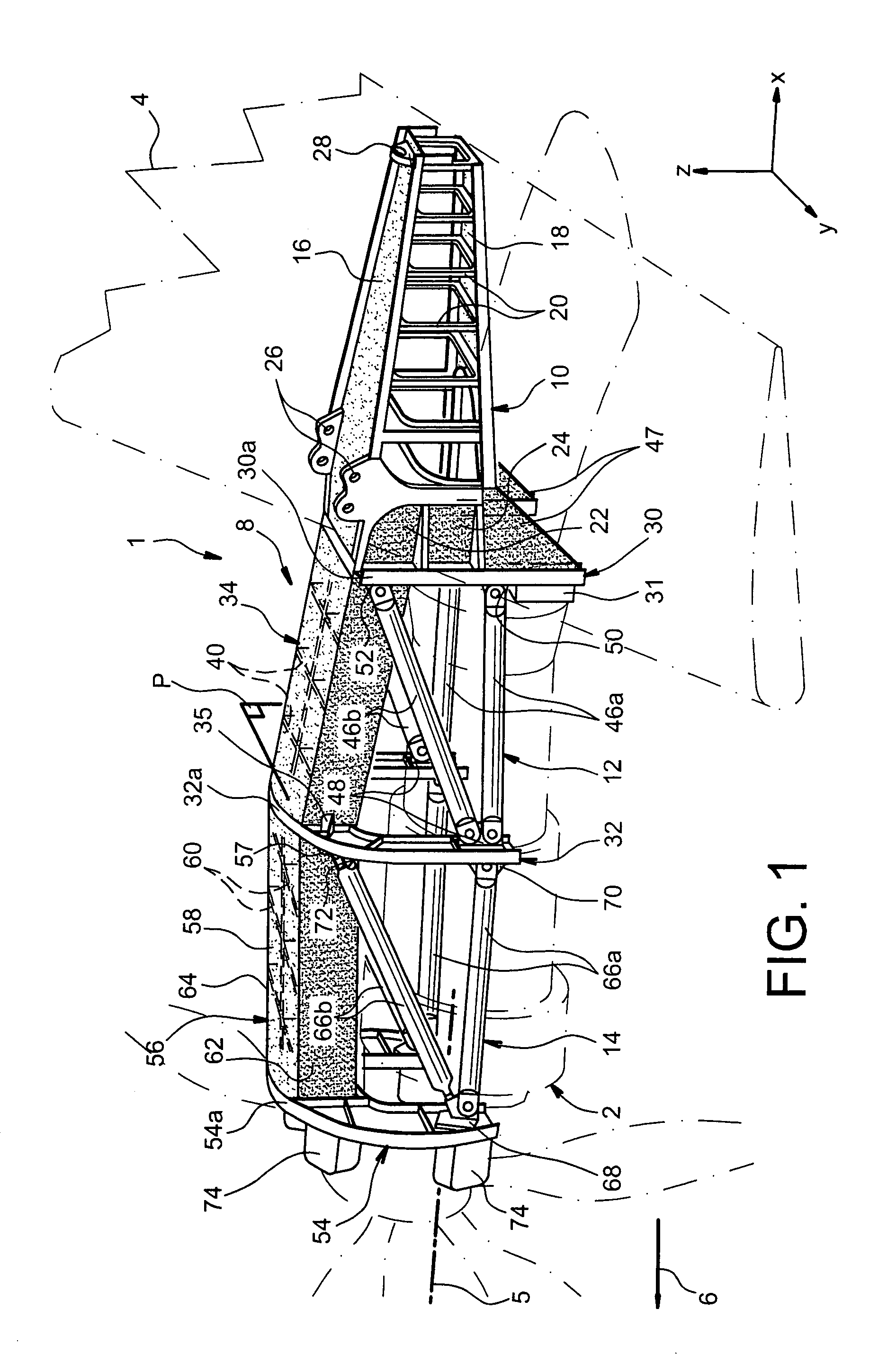
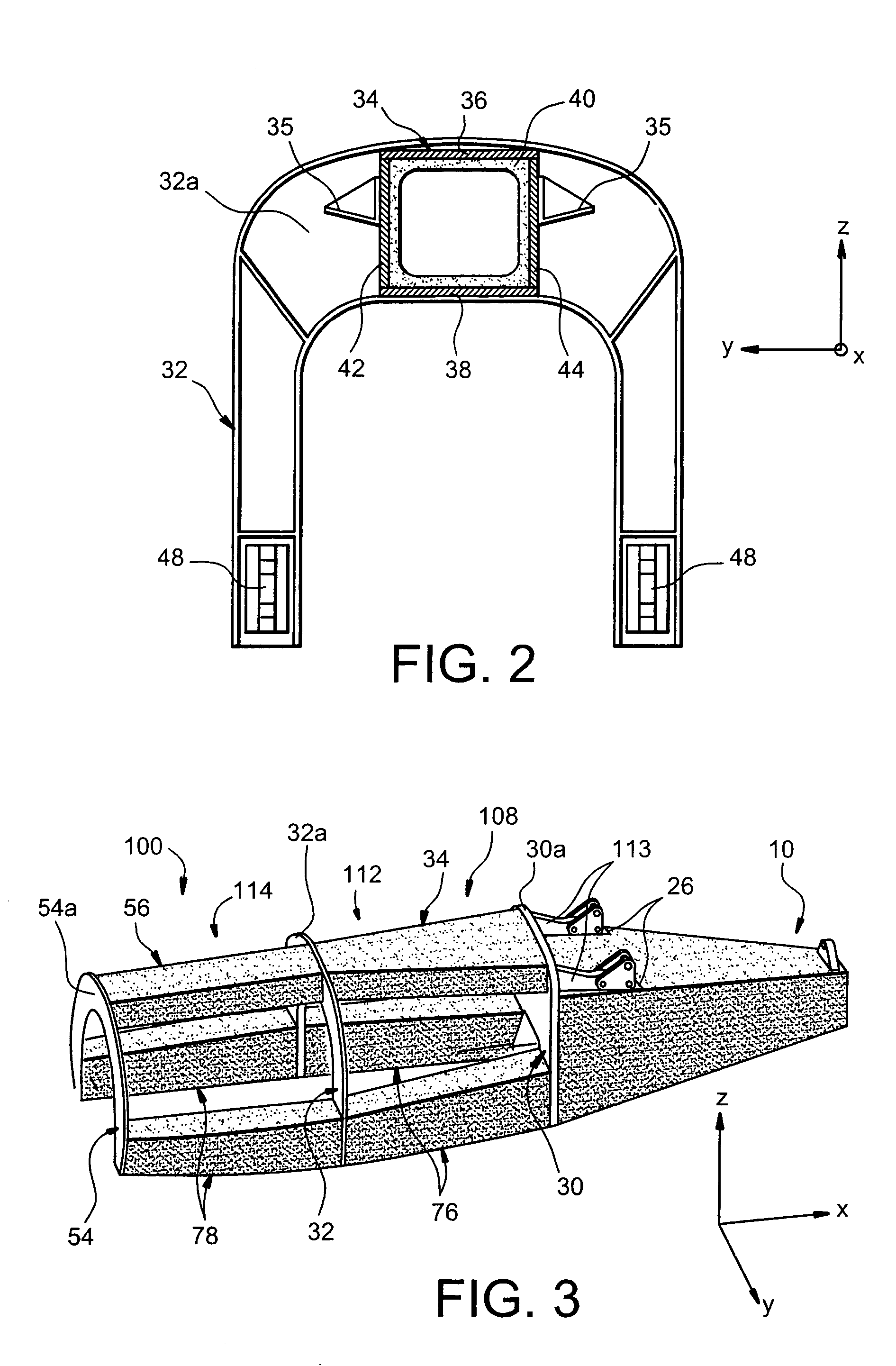
This invention relates to a mounting structure (1) for mounting a turboprop (2) under an aircraft wing (4), the structure comprising a rigid structure (8) provided with an aft underwing box (10), and at least one forward rigid segment (12, 14), each forward rigid segment having two transverse frames (30, 32, 54) at a spacing from each other. According to the invention, at least one forward rigid segment (12, 14) of the rigid structure also comprises at least one forward upper box (34, 56) connecting a top part (30a, 32a, 54a) of the two transverse frames (30, 32, 54) of the forward rigid segment.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Turboprop carrier structure and an assembly including such a carrier structure
ActiveUS20040227033A1Simple and reliable and relatively quickHigh strengthGas turbine type power plantsPower plant constructionMechanical engineeringAirplane
The carrier structure of the invention is used for carrying a turboprop and it is designed to be mounted beneath and / or in front of an airplane wing. In characteristic manner, said carrier structure comprises: a top portion comprising a front arch, a rear arch, and longitudinal beams; an upwardly-open removable bottom portion comprising at least two bottom arches and longerons; said bottom portion being demountably fixed to the top portion by centering and fixing means, said bottom and top portions together defining a housing suitable for receiving said turboprop, and a suspension for carrying said turboprop.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Turboprop-powered aircraft
InactiveUS20130283816A1Simplified system solutionEfficient workPower plant cooling arrangmentsGas turbine type power plantsLeading edgeEngineering
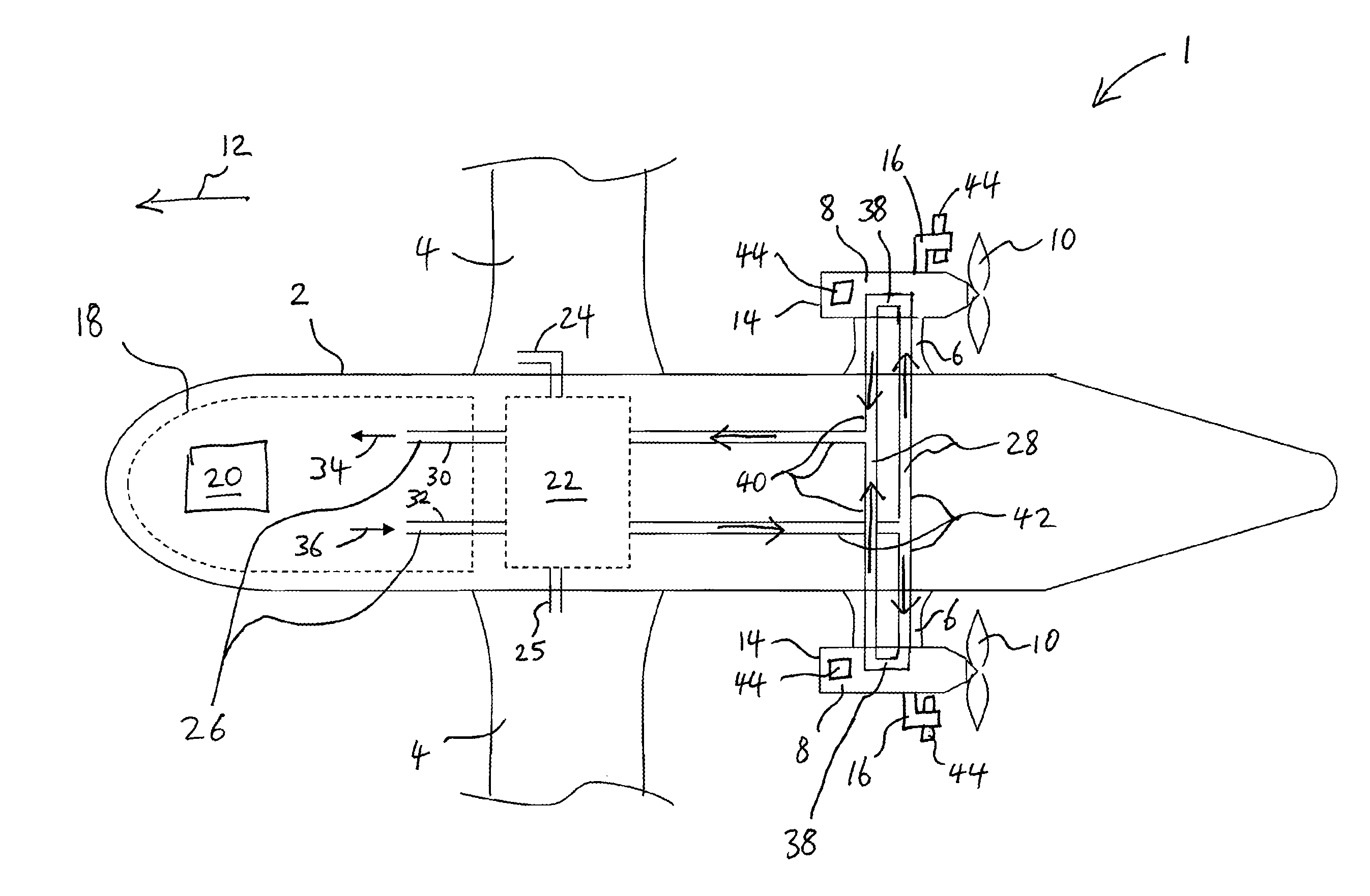
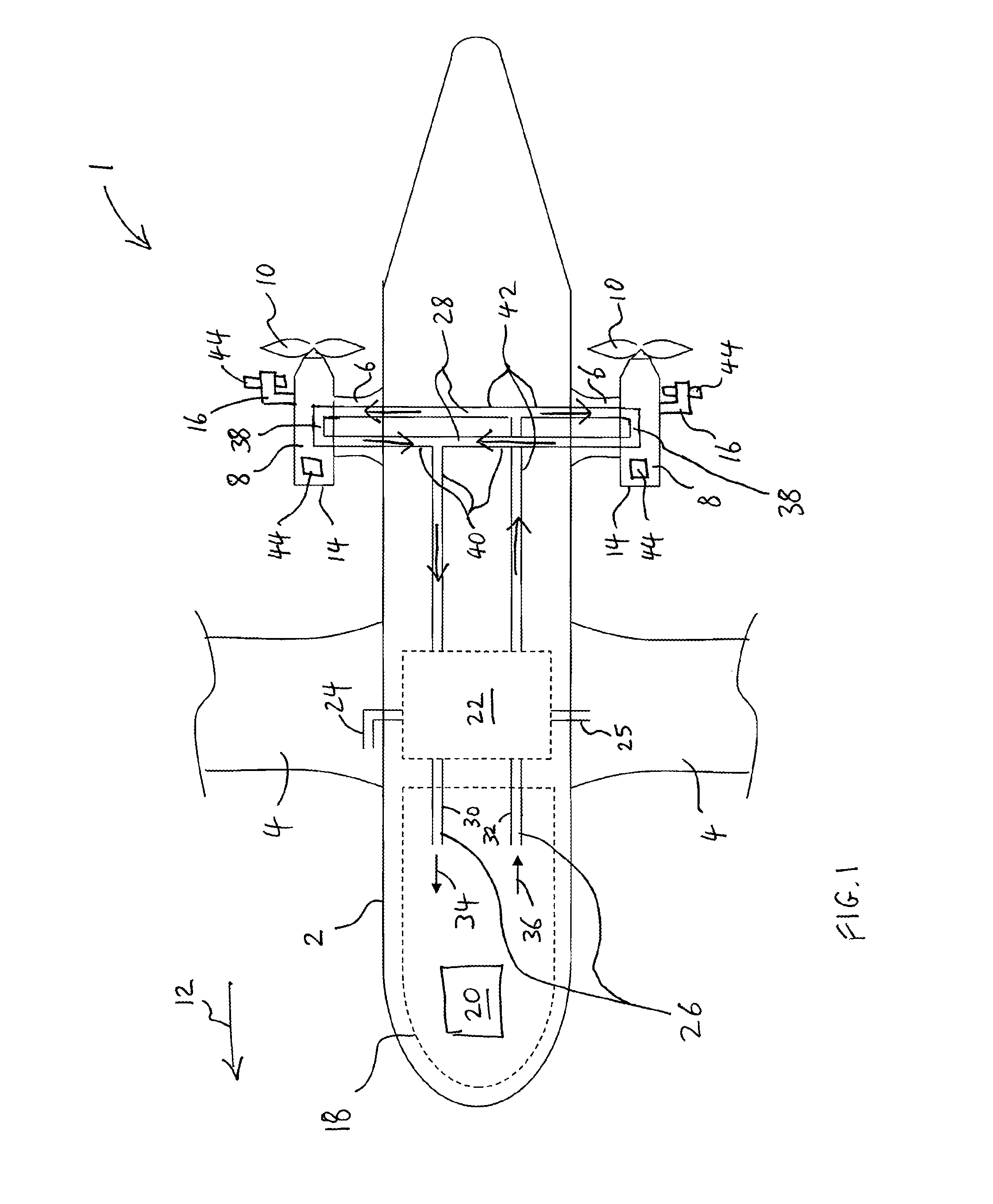
A turboprop-powered medium altitude long endurance aircraft, having a gas turbine engine; a heat scavenging device to scavenge heat from the gas turbine engine; and a heating device to use the scavenged heat to provide heating to the aircraft. The heat scavenging device may be placed on an engine casing and / or on or in an engine exhaust duct. The heating device may include a circulation path routed directly to a location in the aircraft where heating is to be performed, for example a leading edge of an engine support pylon or a leading edge of an engine-carrying wing. The heating device can include a heat exchanger.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Convertible airplane with exposable rotors
ActiveUS20180141652A1Reduce noiseSolve excessive vibrationWing adjustmentsCanard-type aircraftJet aeroplaneJet engine
Convertible-type aircraft, able to fly with the speed and the reduced operating costs of a fixed-wing aircraft and also to take-off / land vertically and hover / manoeuvre like an helicopter.The aircraft object of the invention comes in the form of a classical plane, with a fuselage (1), a fixed wing (2), an horizontal stabilizer (3) and a vertical fin (4), as well as one or several jet engines or turboprops (5) for propulsion and it comprises exposable rotors (6 and 7) installed inside the wing and possibly inside the horizontal stabilizer or the fuselage for lifting the aircraft for vertical take-off / landing and stationary flight.For the flight and the horizontal take-off / landing, the rotors are completely enclosed inside the wing and possibly inside the horizontal stabilizer or the fuselage.
Owner:DESLYPPER CHRISTIAN ROGER RENE
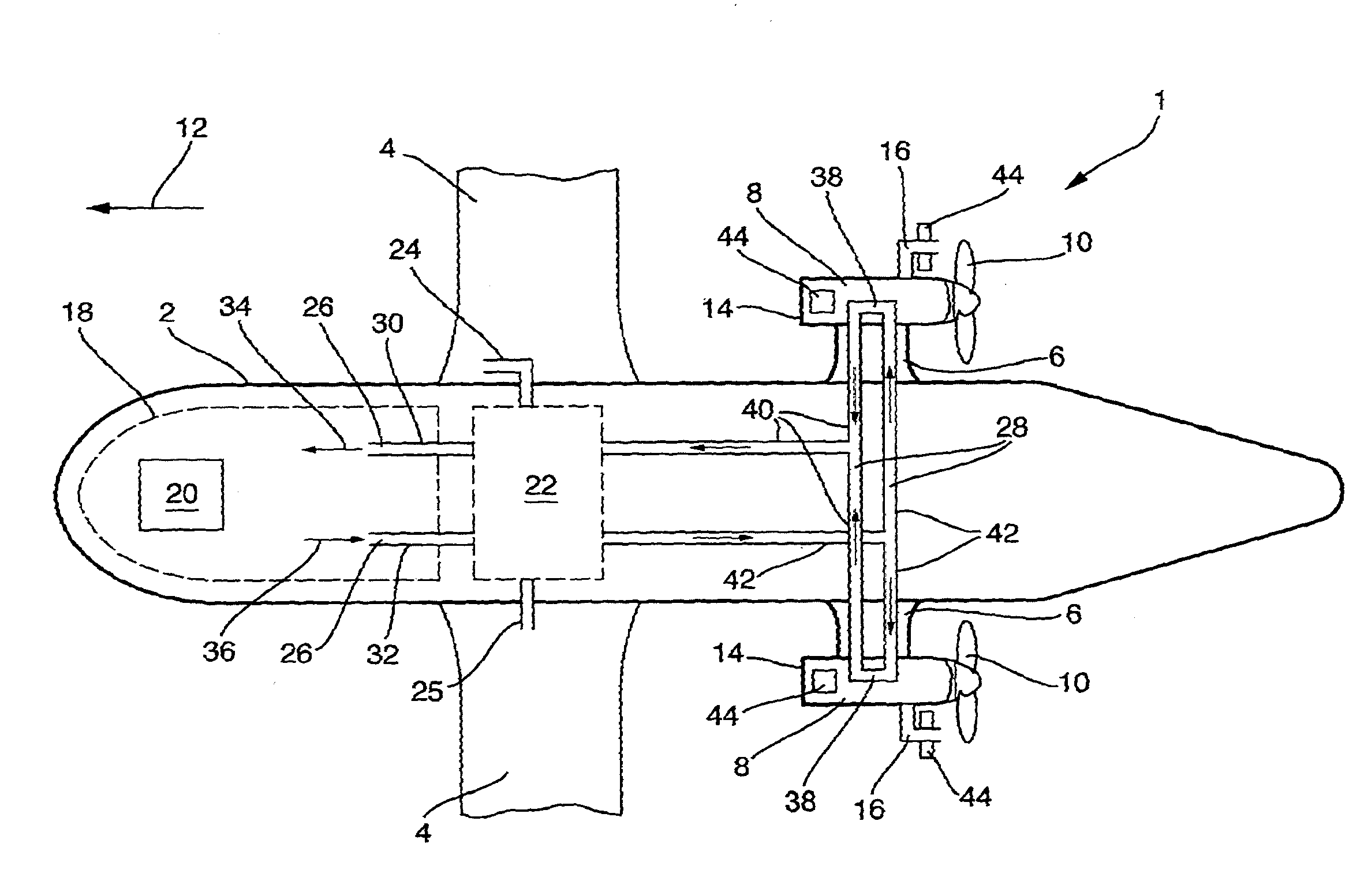
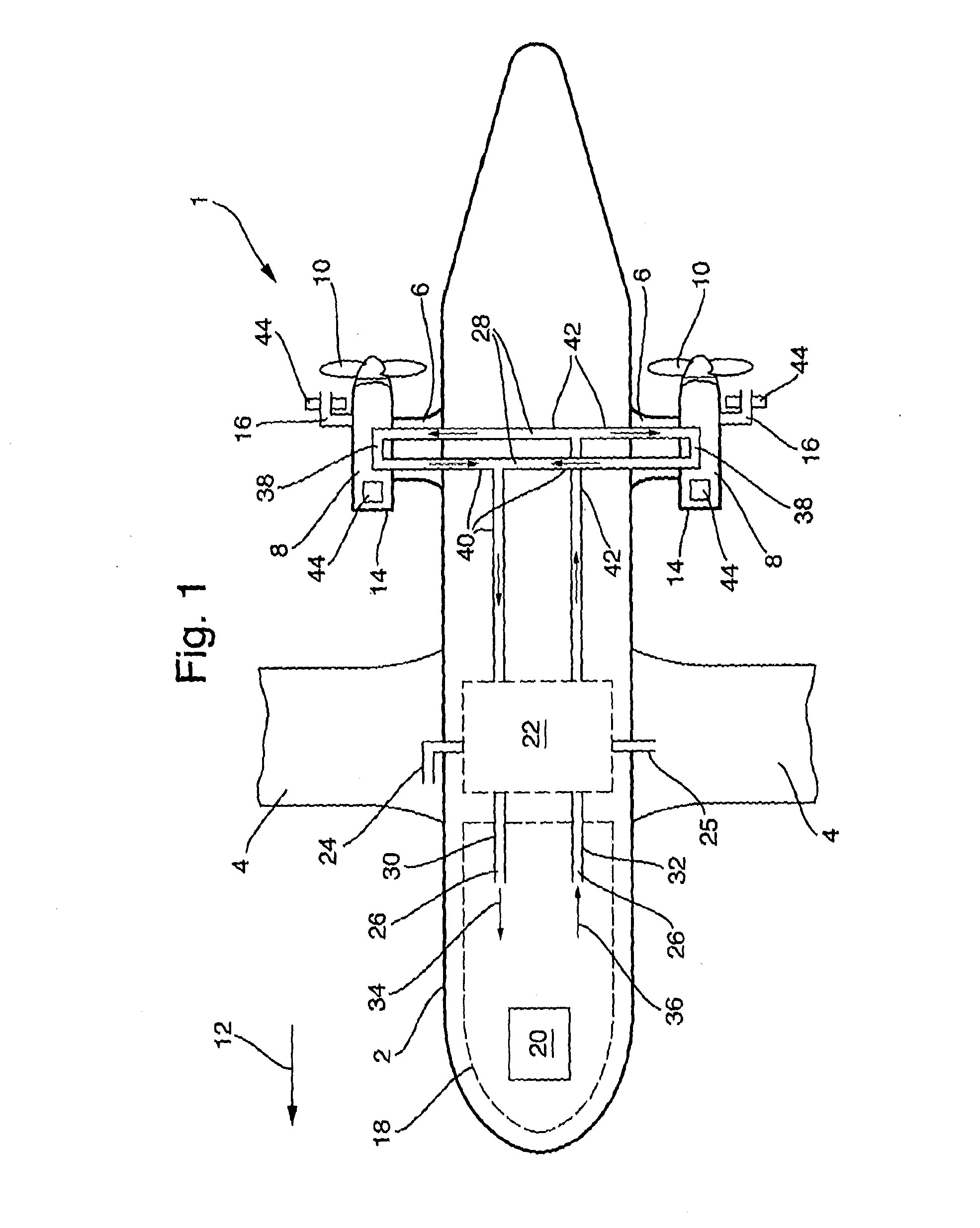
Hybrid inlet
ActiveUS20050229605A1Increase the lengthWeight increaseEngine manufactureCombustion enginesRadial planeMechanical engineering
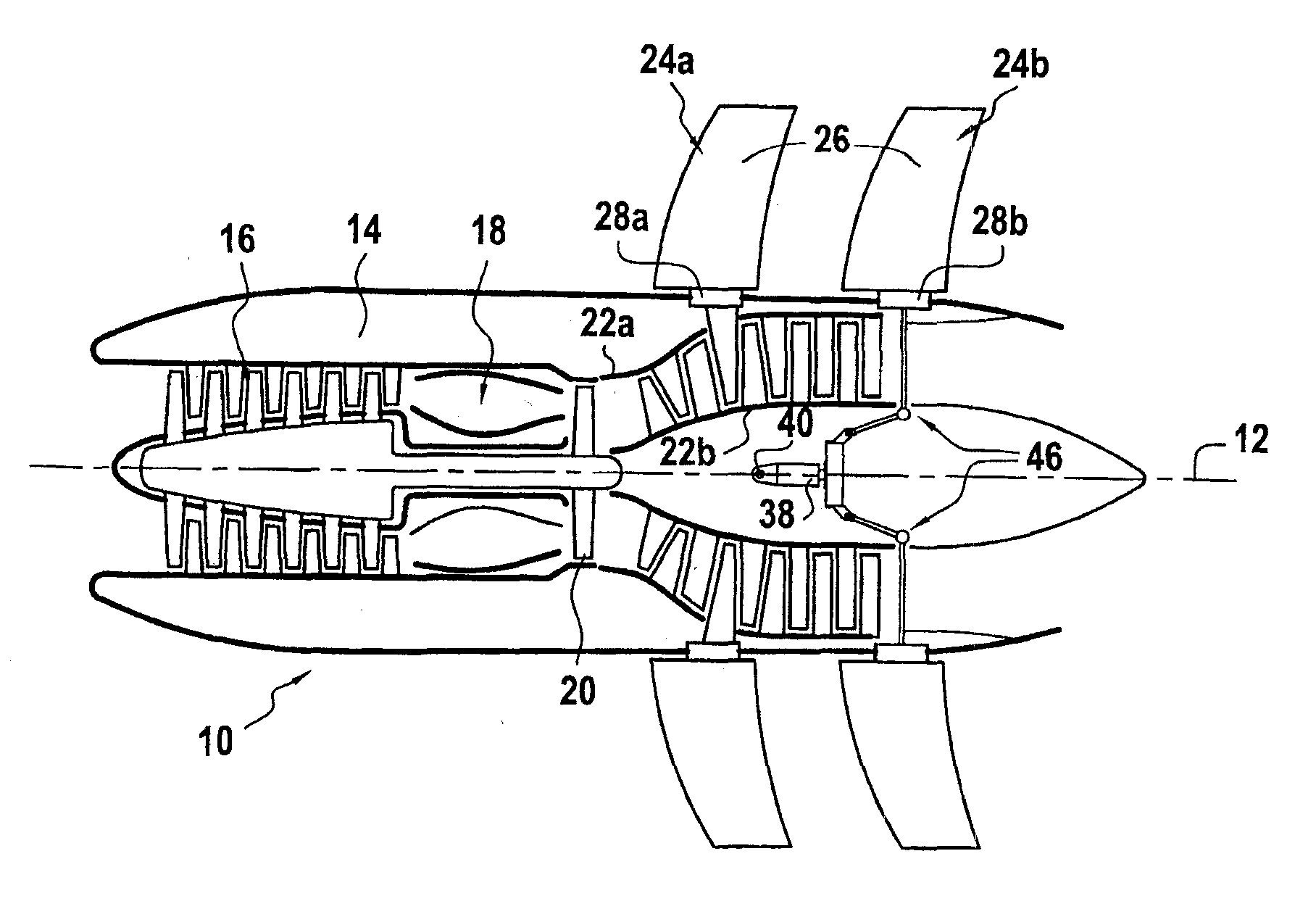
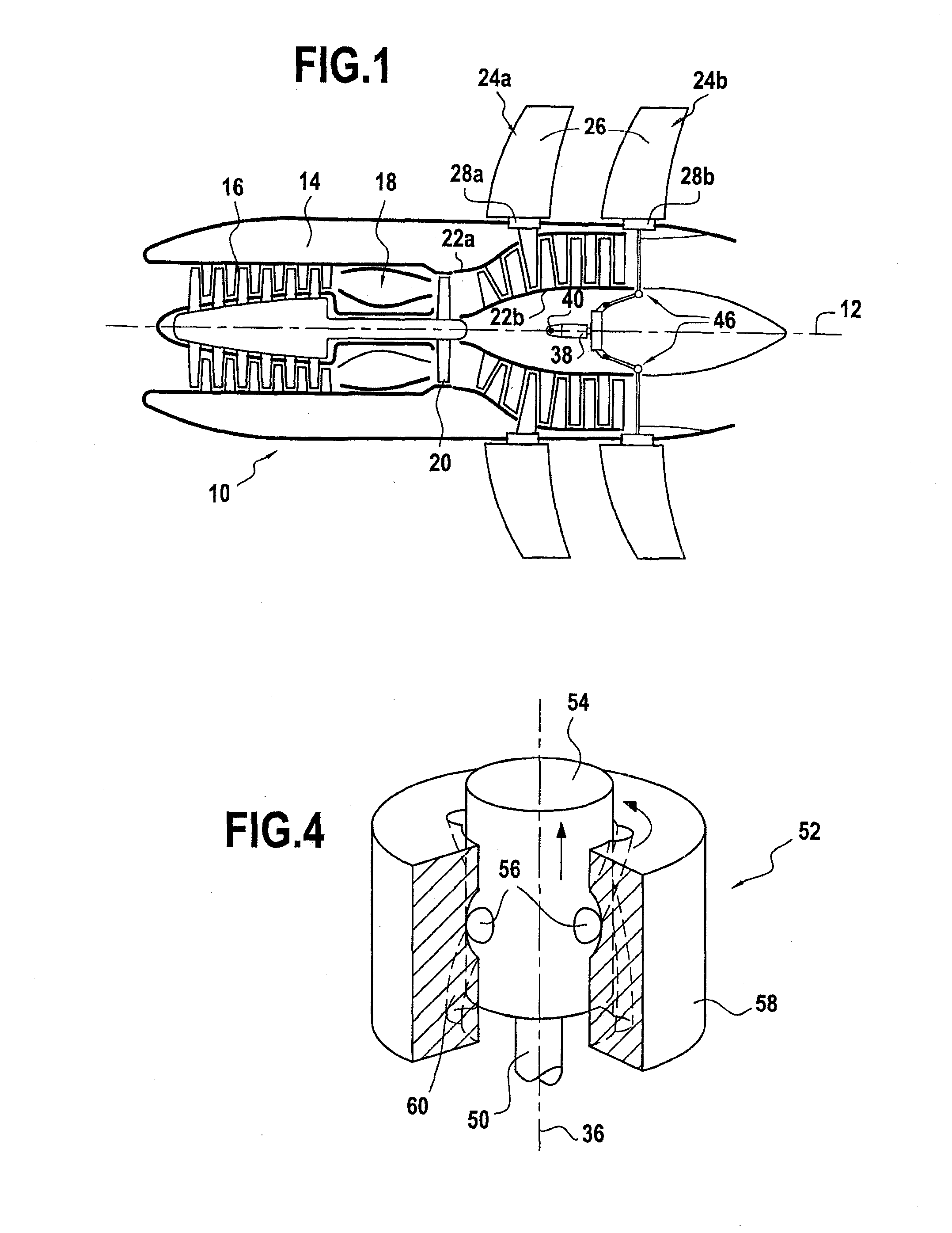
A turboprop powerplant with at least a compressor having a forward compressor inlet and a shaft extending axially through the compressor and having a shaft axis, an inlet duct encircling the shaft passing therethrough, the inlet duct having an aft end in gas communication with the compressor inlet and a forward end having at least two branches each with an inlet orifice, each inlet orifice having a centroid in a radial plane through and transverse to the shaft axis, the centroids and shaft axis defining an angle less than 180°.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Hybrid inlet
ActiveUS6990798B2Increase the lengthWeight increaseEngine manufactureCombustion enginesRadial planeMechanical engineering
A turboprop powerplant with at least a compressor having a forward compressor inlet and a shaft extending axially through the compressor and having a shaft axis, an inlet duct encircling the shaft passing therethrough, the inlet duct having an aft end in gas communication with the compressor inlet and a forward end having at least two branches each with an inlet orifice, each inlet orifice having a centroid in a radial plane through and transverse to the shaft axis, the centroids and shaft axis defining an angle less than 180°.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Tall V/STOL aircraft
InactiveUS20060032970A1Improve the stability of actionMinimizes ground effectAircraft stabilisationAll-wing aircraftLeading edgeHorizontal axis
A vertical or short takeoff and landing (V / STOL) airplane is described having a vertical form factor. Making the airplane tall has many advantages when operating in hover mode close to the ground. Several variations of the design are described. The preferred embodiment consists of two tall fuselage2 structures having an airfoil shape in plan view. As high above the ground as practical a “lift wing” spans the space between these fuselages. This wing may be equipped with lift augmentation systems to facilitate V / STOL flight. In the center of the span on the leading edge of the lift wing is placed a turboprop engine. Alternatively, the wing and attached engine can be made to tilt about a horizontal axis. For takeoff the wing will be tilted skyward. A second wing slightly below and behind the lift wing has a pusher engine located on the trailing edge. This lower wing and engine is also able to tilt about a horizontal axis parallel to the lift wing. During takeoff this lower engine is pointed downward toward the ground. This lower wing contains aerodynamic control surfaces to provide attitude and position control. Subsequent to liftoff the wings and engines tilt into a horizontal position to provide cruise lift and thrust. At the end of the flight the wings and attached engines are tilted back to provide vertical lift for hover, maneuvering, and soft landing. 2 “Fuselage” is used here even though it substantially differs from the conventional fuselage (and its French origins meaning, “spindle shaped”) since in plan view it is an airfoil shape of large thickness. It will be used here for lack of a better word. Think of fuselage as meaning “where the pilot, passengers and cargo are located”.
Owner:ALLEN NORMAN CARTER
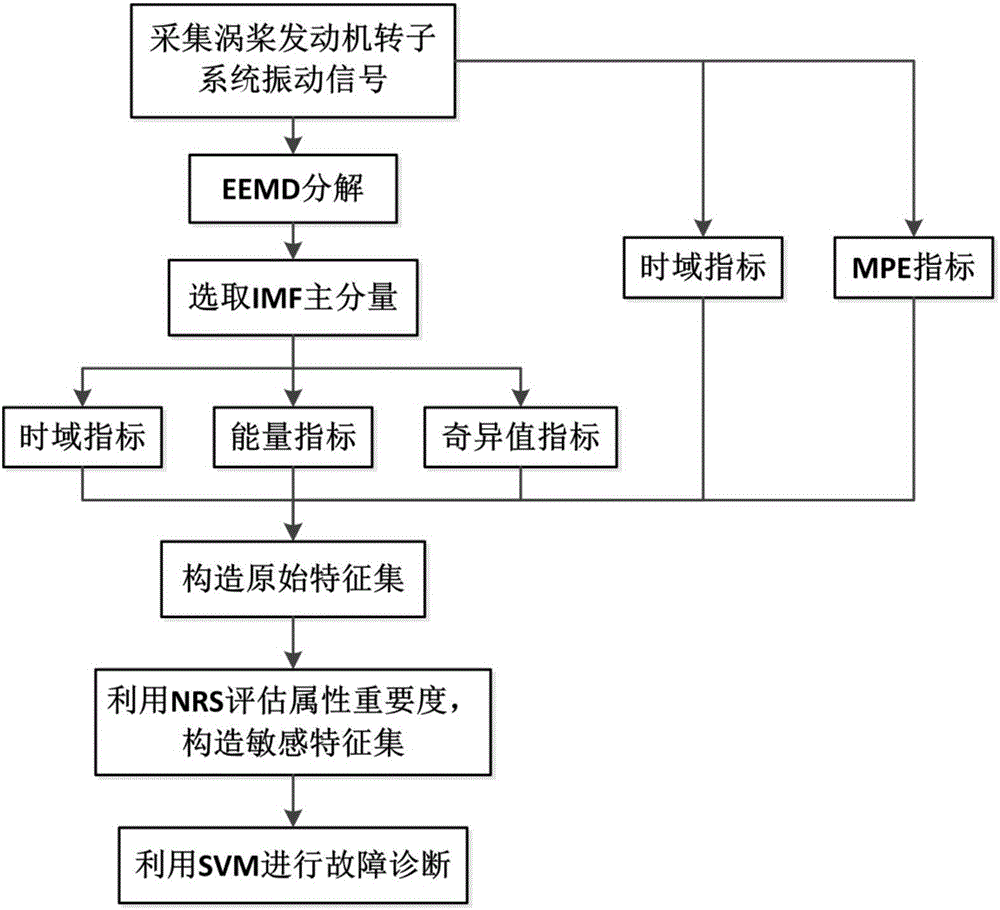
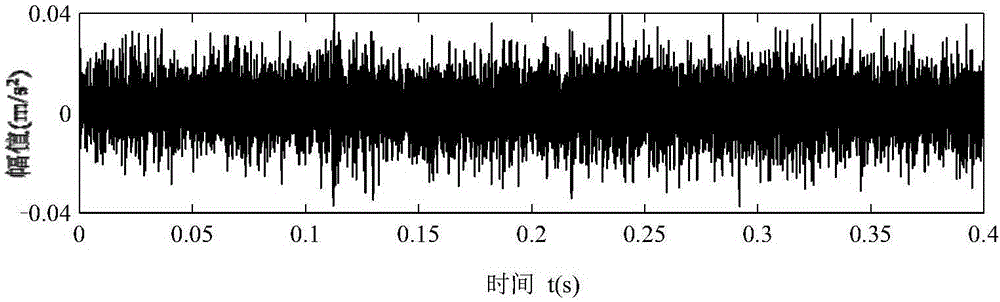
Turboprop Engine rotor system fault diagnosis method through combination of EEMD and neighborhood rough set
InactiveCN106644484AReduce complexityReduce redundancyMachine part testingEngine testingDiagnosis methodsTurboprop
The invention discloses a turboprop engine rotor system fault diagnosis method through combination of EEMD and a neighborhood rough set. The method comprises the steps of performing EEMD decomposition of an original signal of a turboprop engine rotor system in different fault states for obtaining a plurality of IMF components; extracting the original vibration signal and a plurality of different characteristic indexes contained in an IMF main component in the plurality of IMF components, and constructing an original combined characteristic set; evaluating the attribute importance of each characteristic in the original characteristic set according to a neighborhood rough set attribute reduction method, and selecting a characteristic set which is relatively sensitive to rotor system fault classification in the original characteristic set; inputting the sensitive characteristic set of a training sample into a support vector machine multi-classifier, determining an optimal combination of classifier parameters c and g in an index range, and performing classification and identification on the testing sample according to a trained SVM model. According to the turboprop engine rotor system fault diagnosis method, information which is hidden in the vibration signal and reflects a rotor system operation state can be mined in multiple aspects, thereby reducing fault characteristic redundancy and calculation complexity of the classifier.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Turboprop engine assembly with combined engine and cooling exhaust
ActiveUS20170037756A1Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusInternal combustion engineTurboprop
A turboprop engine assembly for an aircraft, including an internal combustion engine having a liquid coolant system, an air duct in fluid communication with an environment of the aircraft, a heat exchanger received within the air duct having coolant passages in fluid communication with the liquid coolant system and air passages air passages in fluid communication with the air duct, and an exhaust duct in fluid communication with an exhaust of the internal combustion engine. The exhaust duct has an outlet positioned within the air duct downstream of the heat exchanger and upstream of an outlet of the air duct, the outlet of the exhaust duct spaced inwardly from a peripheral wall of the air duct. In use, a flow of cooling air surrounds a flow of exhaust gases. A method of discharging air and exhaust gases in an turboprop engine assembly having an internal combustion engine is also discussed.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Turboprop engine with compressor turbine shroud
A turboprop engine including an annular outer case including a mount ring for attachment to an aircraft along a plane to transfer loads from a propeller and having an annular flange extending radially inwardly therefrom within the plane, an annular turbine support case received within the outer case and connected to the outer case only through a direct connection with the annular flange allowing a limited relative pivoting motion between the turbine support case and the mount ring, and a turbine section including a rotor closely surrounded by a shroud with an annular tip clearance being defined therebetween, the shroud being directly connected to and located by the turbine support case. A method of isolating a turbine shroud from propeller loads in a propeller engine is also disclosed.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
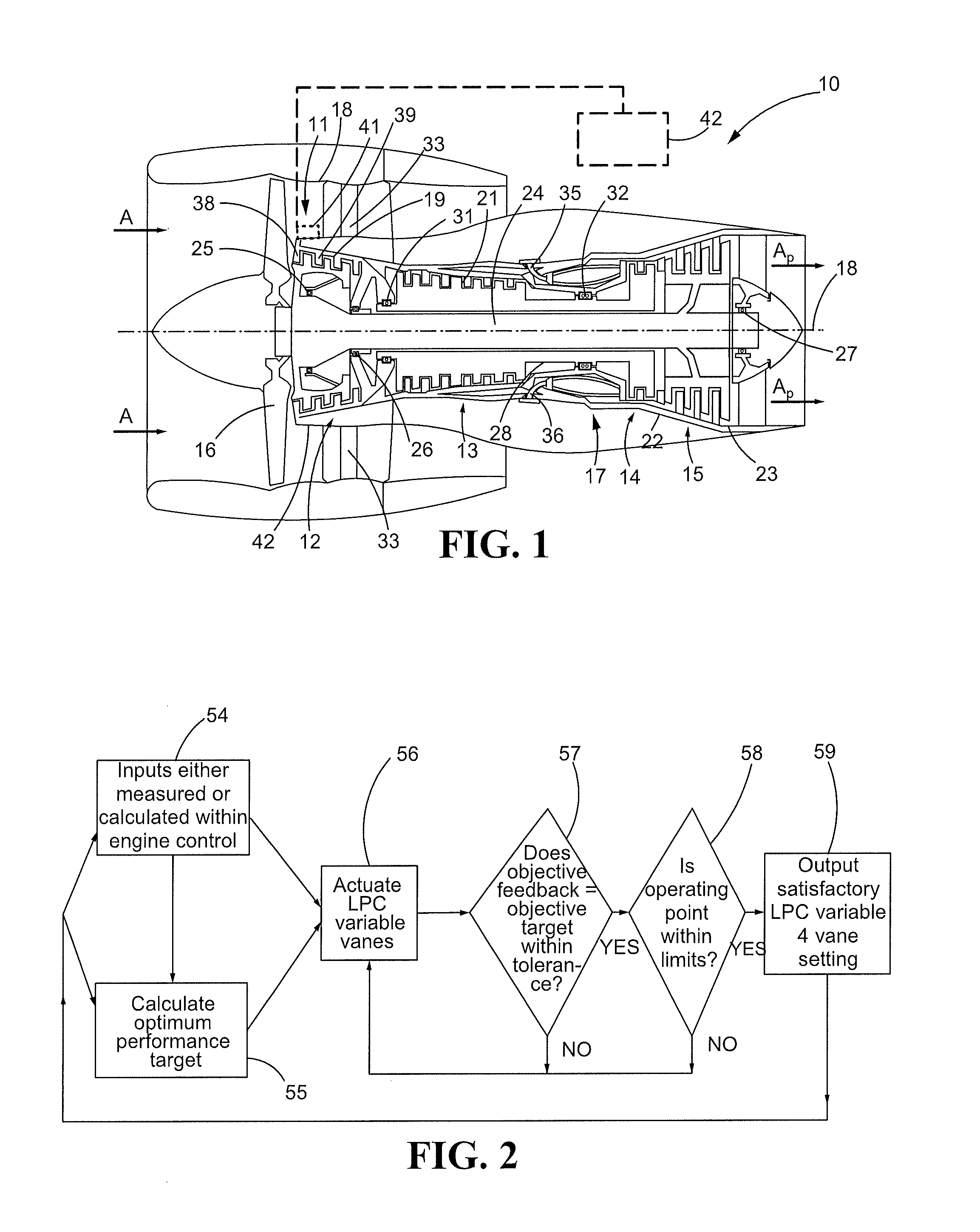
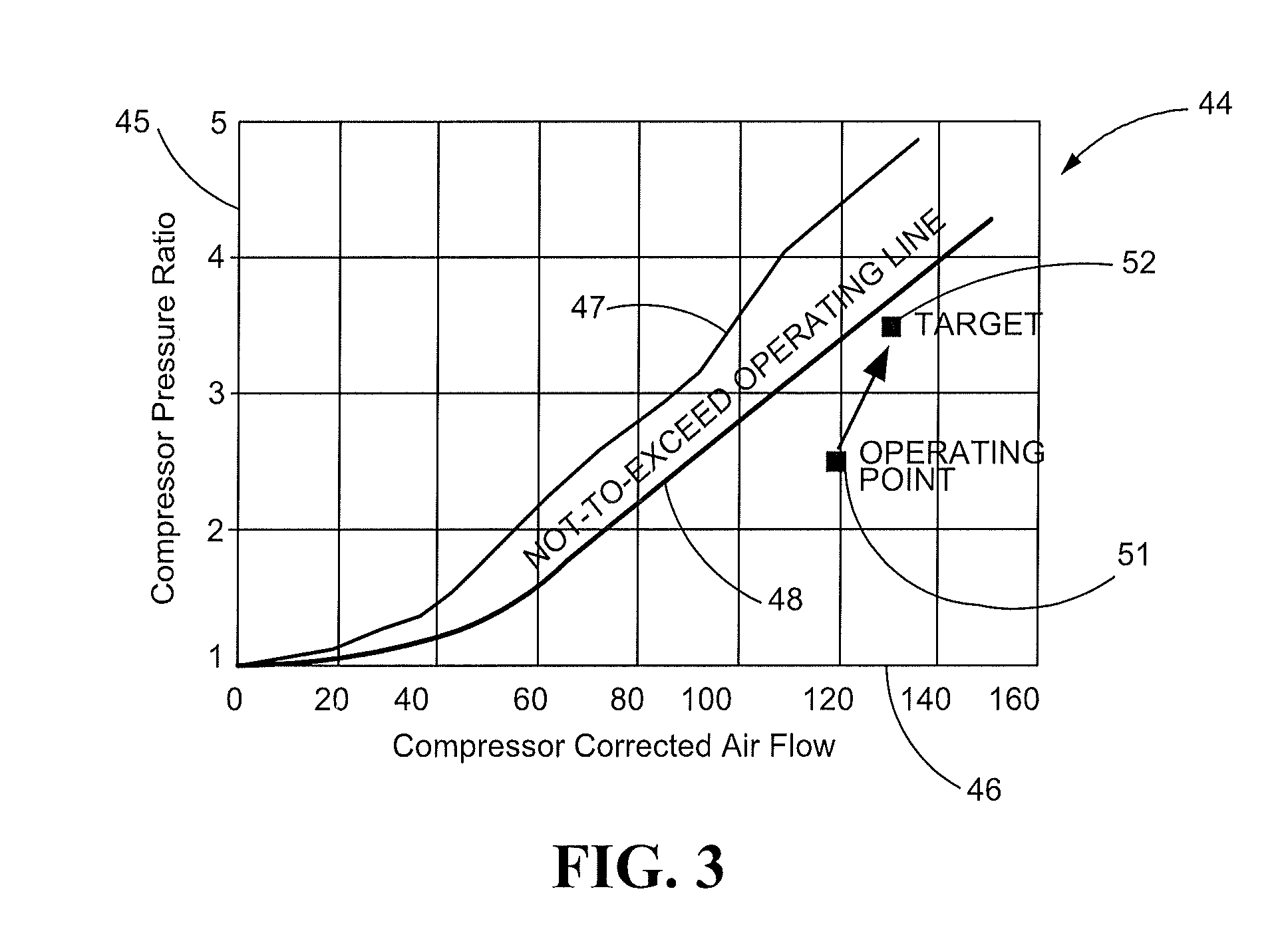
Low Pressure Compressor Variable Vane Control for Two-Spool Turbofan or Turboprop Engine
A system and a method for adjusting an angle of at least one stator vane of a low pressure compressor (LPC) of a two spool gas turbine engine is disclosed. Variable stator vanes are rotatably coupled to a stationary case in one of the stages of the LPC. An actuator is coupled to at least one of the variable stator vanes for imparting rotation of the stator vane about a radius of the case. Various coupling or linkage arrangements may be made so that rotation of one vane results in rotation of the other vanes disposed along the case. The controller includes the stored constraints, the ability to estimate operating condition, and the ability to estimate optimum targets.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP +1
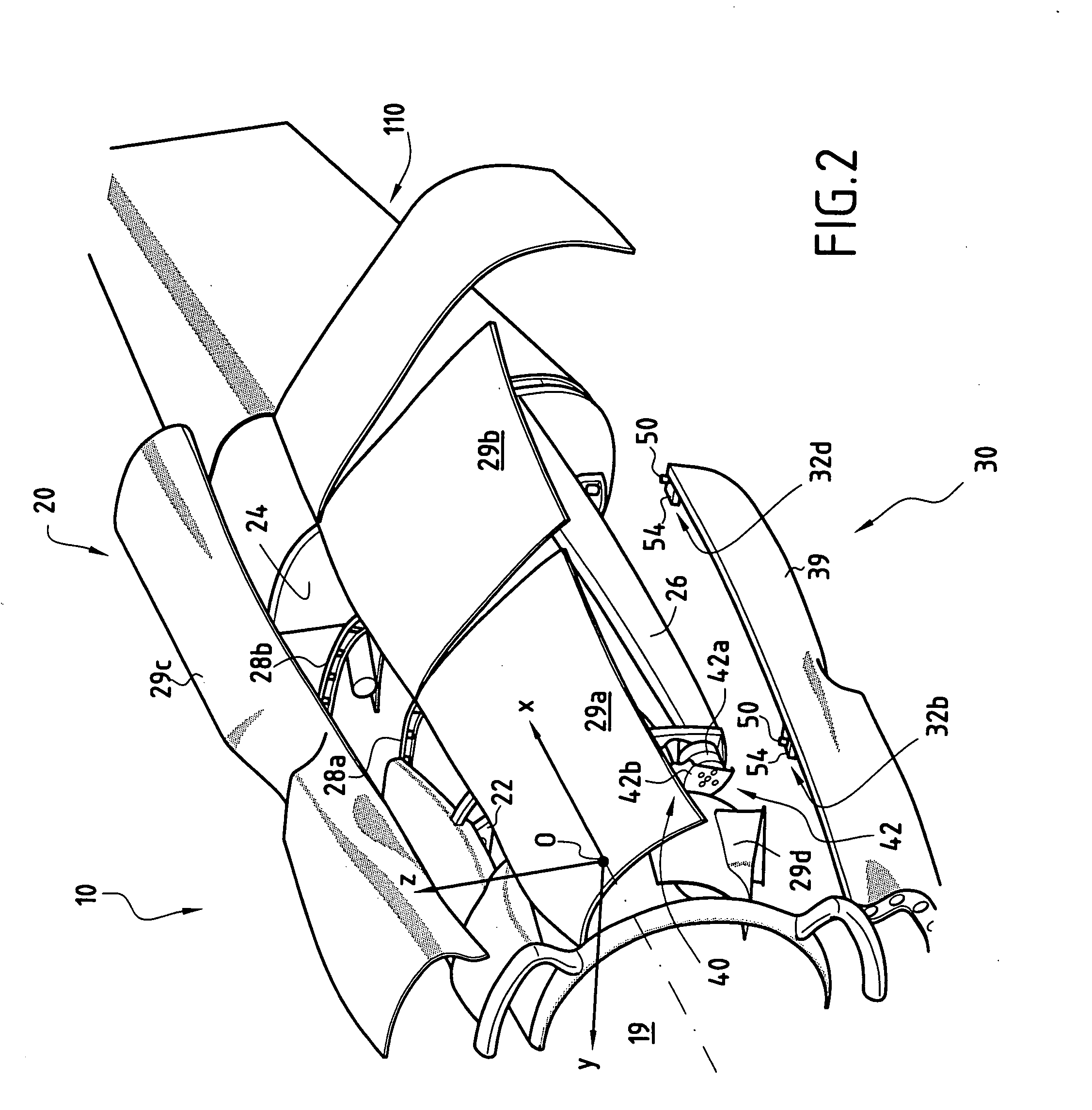
Structure for mounting a turboprop under an aircraft wing
ActiveUS20050178889A1Easy resistancePower plant constructionGas turbine type power plantsRigid structureAirplane
This invention relates to a structure (1) for mounting a turboprop (2) under an aircraft wing (4), comprising a rigid structure and means (10) of fastening the turboprop on the rigid structure. According to the invention, the rigid structure is composed of a box (8), and the mounting means comprise at least two lateral connecting rods (26) resisting the engine torque generated by the turboprop, the connecting rods (26) being arranged on each side of the box and each having a forward end (26a) connected to a gear box (24) of the turboprop (2), and an aft end (26b) connected to said box.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Structure for mounting a turboprop under an aircraft wing
ActiveUS7296768B2Easy resistanceGas turbine type power plantsPower plant constructionAircraft landingRigid structure
A structure for mounting a turboprop under an aircraft wing includes a rigid structure and a device for fastening the turboprop on the rigid structure. The rigid structure is composed of a box, and the device for fastening includes at least two lateral connecting rods resisting the engine torque generated by the turboprop, the connecting rods being arranged on each side of the box and each having a forward end connected to a gear box of the turboprop, and an aft end connected to the box.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
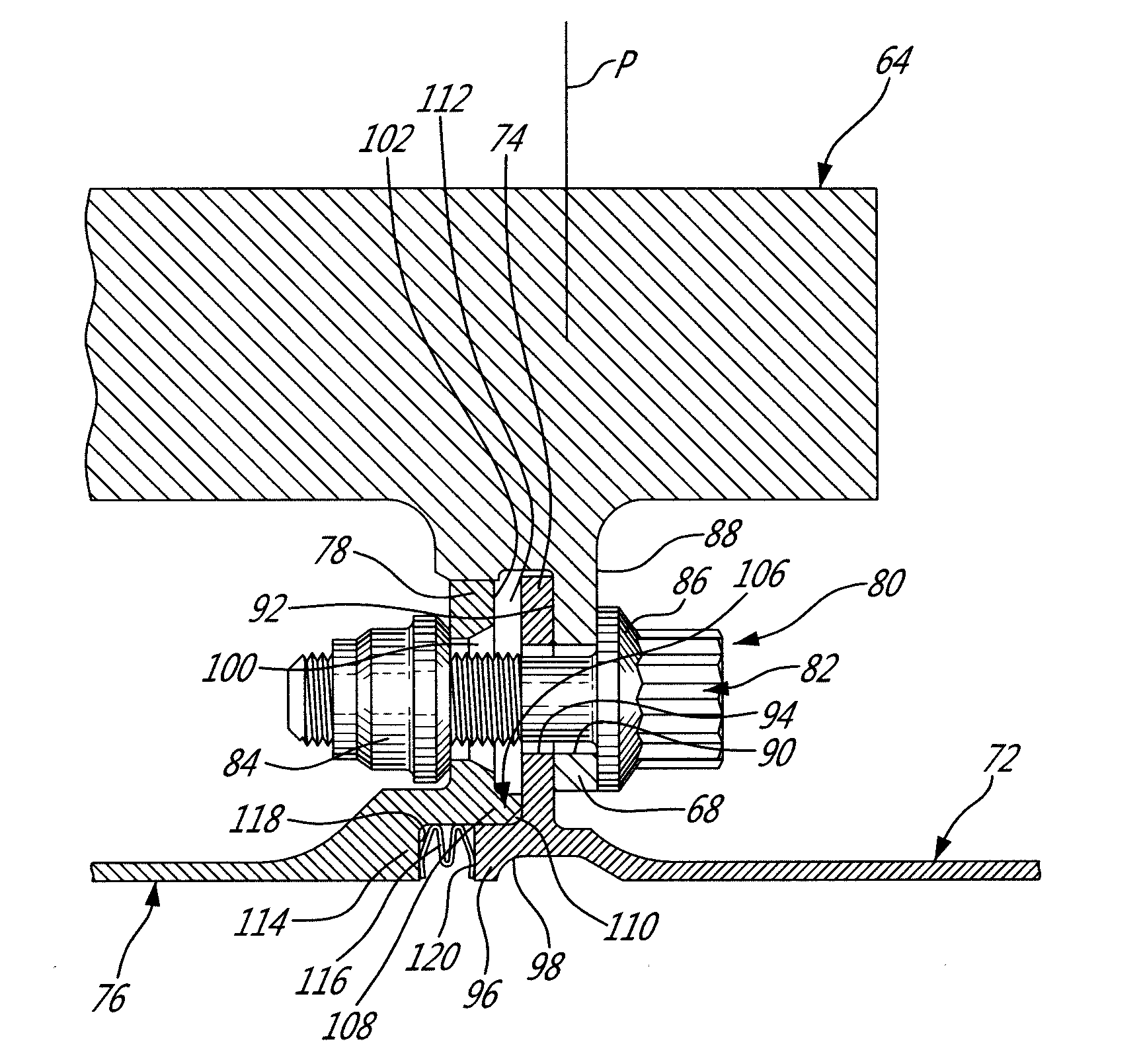
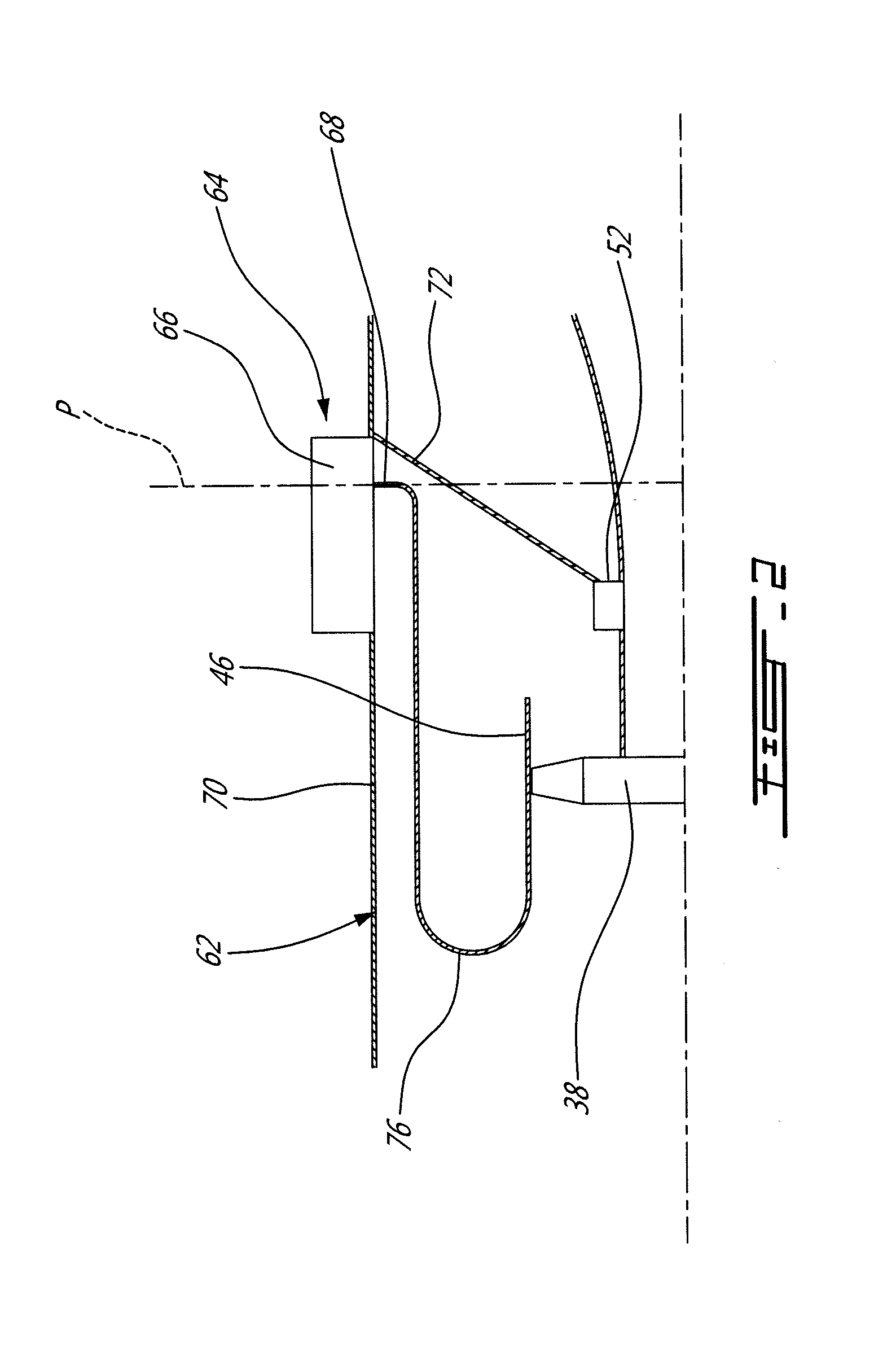
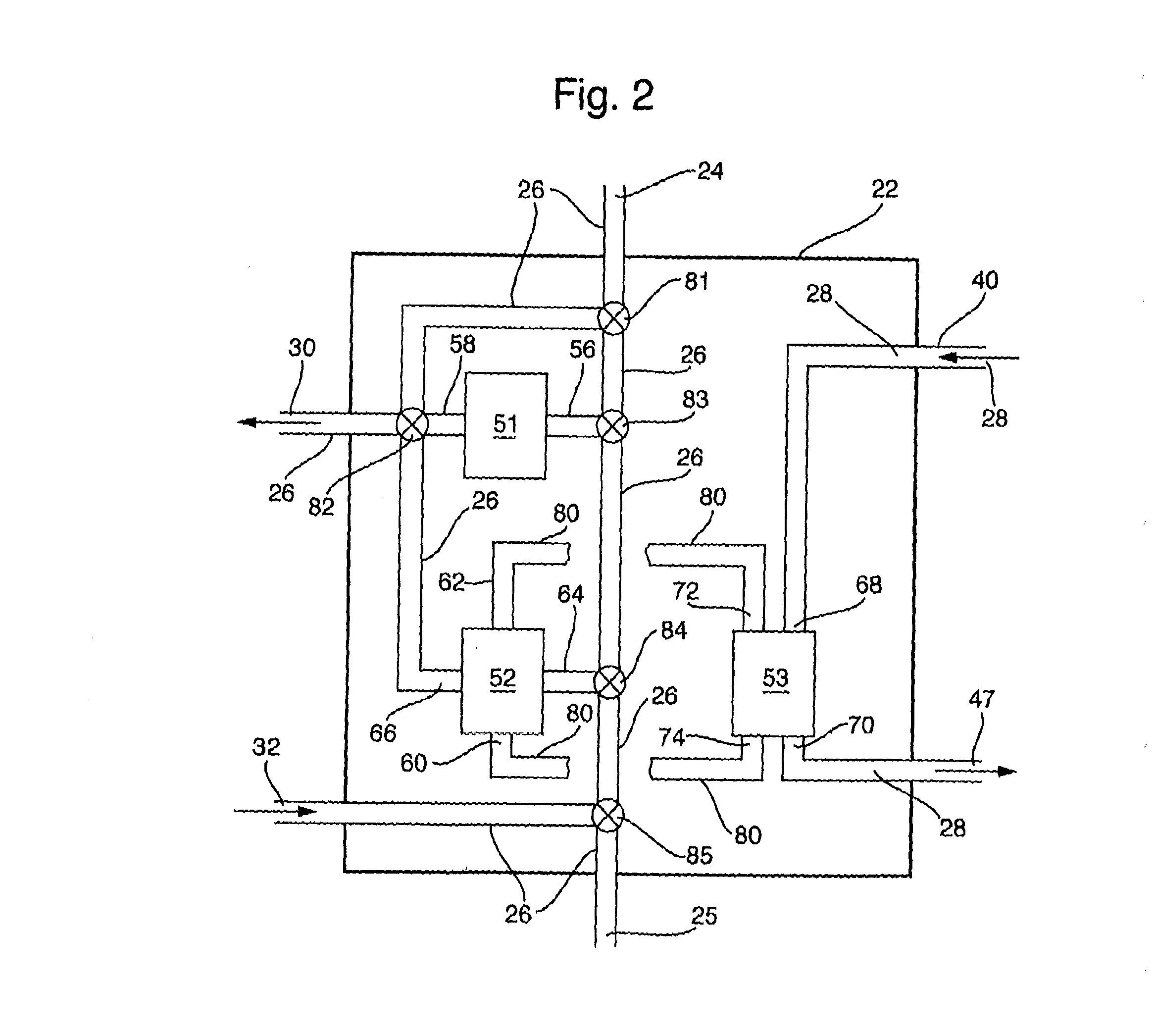
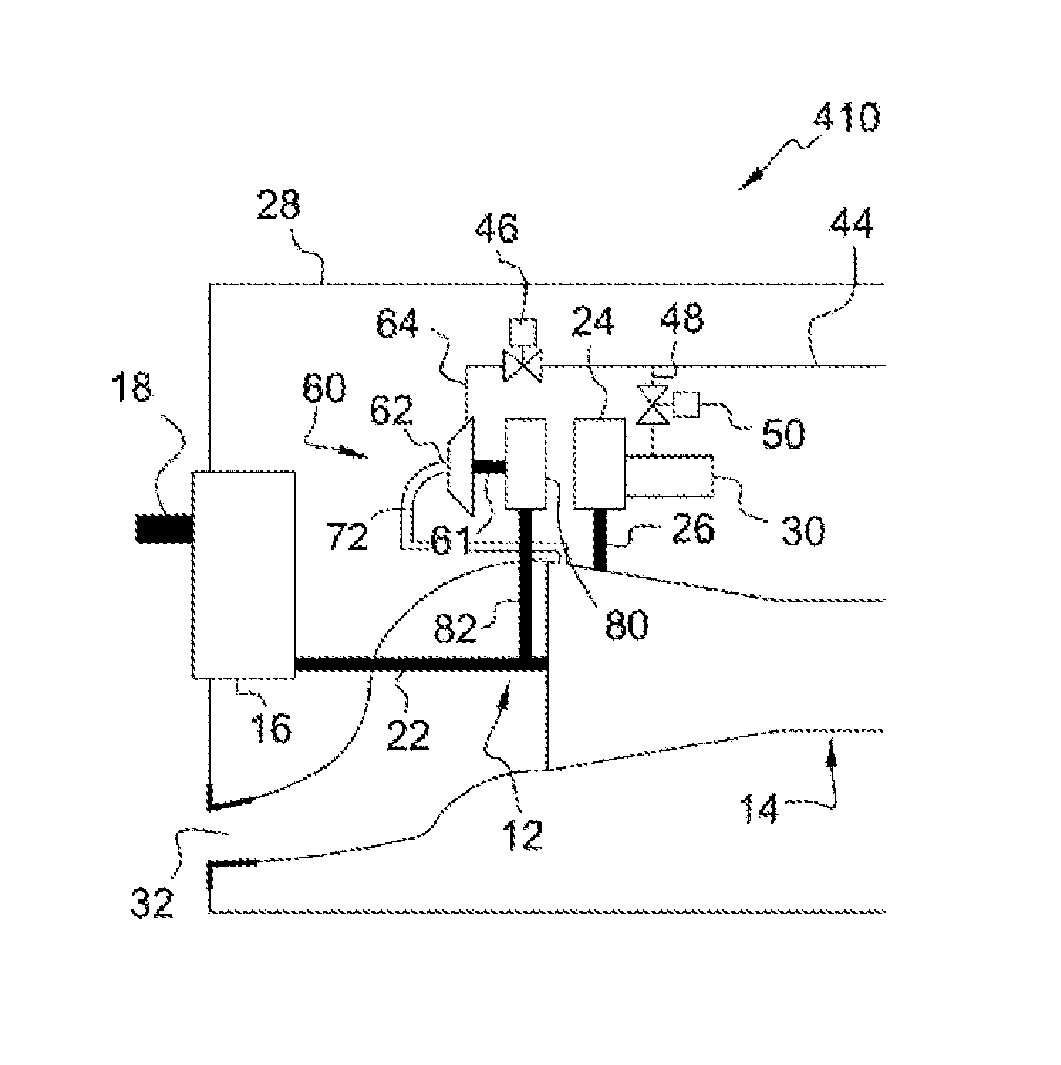
Supply of air to an air-conditioning circuit of an aircraft cabin
ActiveUS20170284408A1Significant and uncontrolled fuel consumptionRestrict air flowGas turbine type power plantsEngine fuctionsAir conditioningHigh pressure
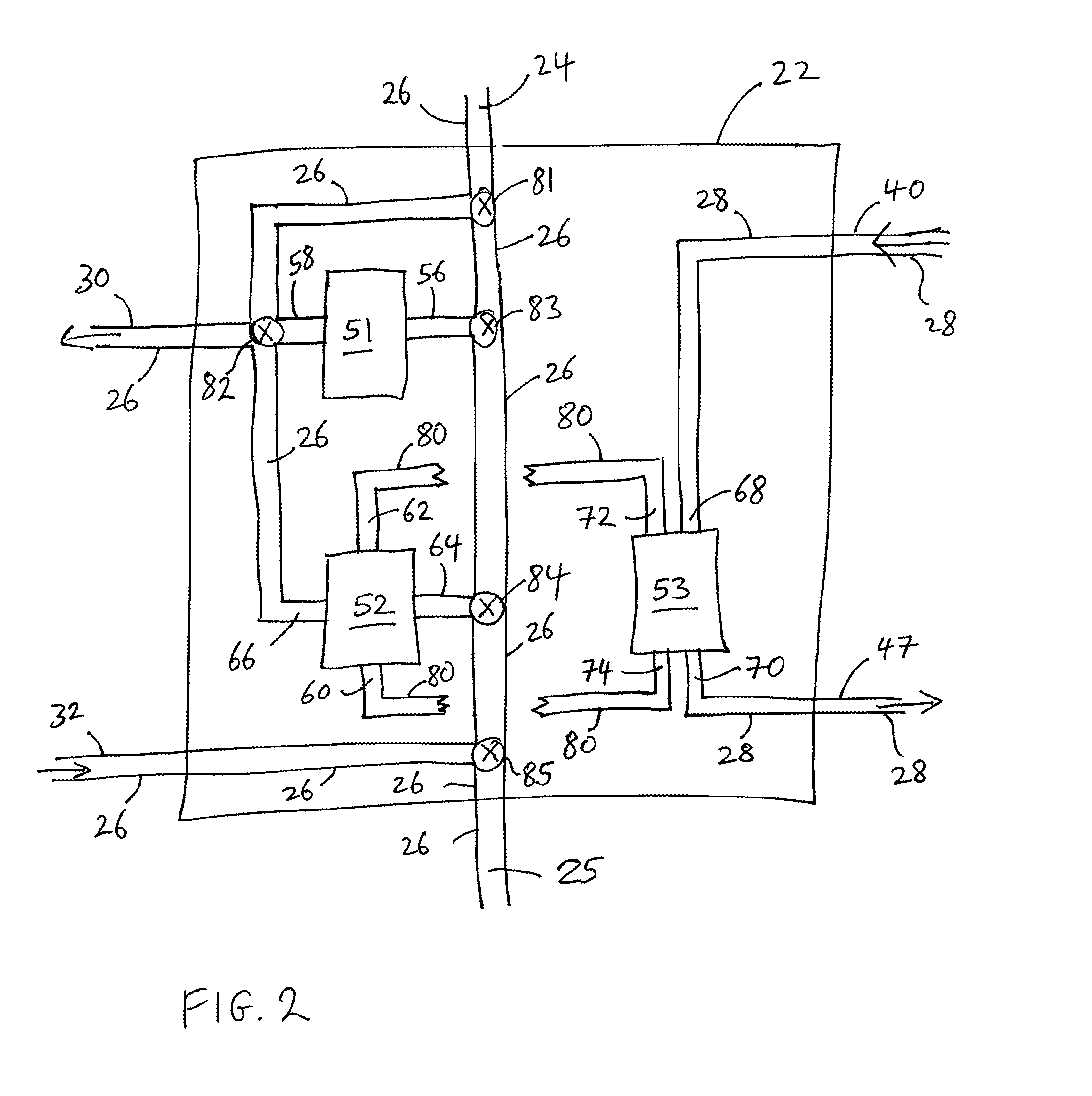
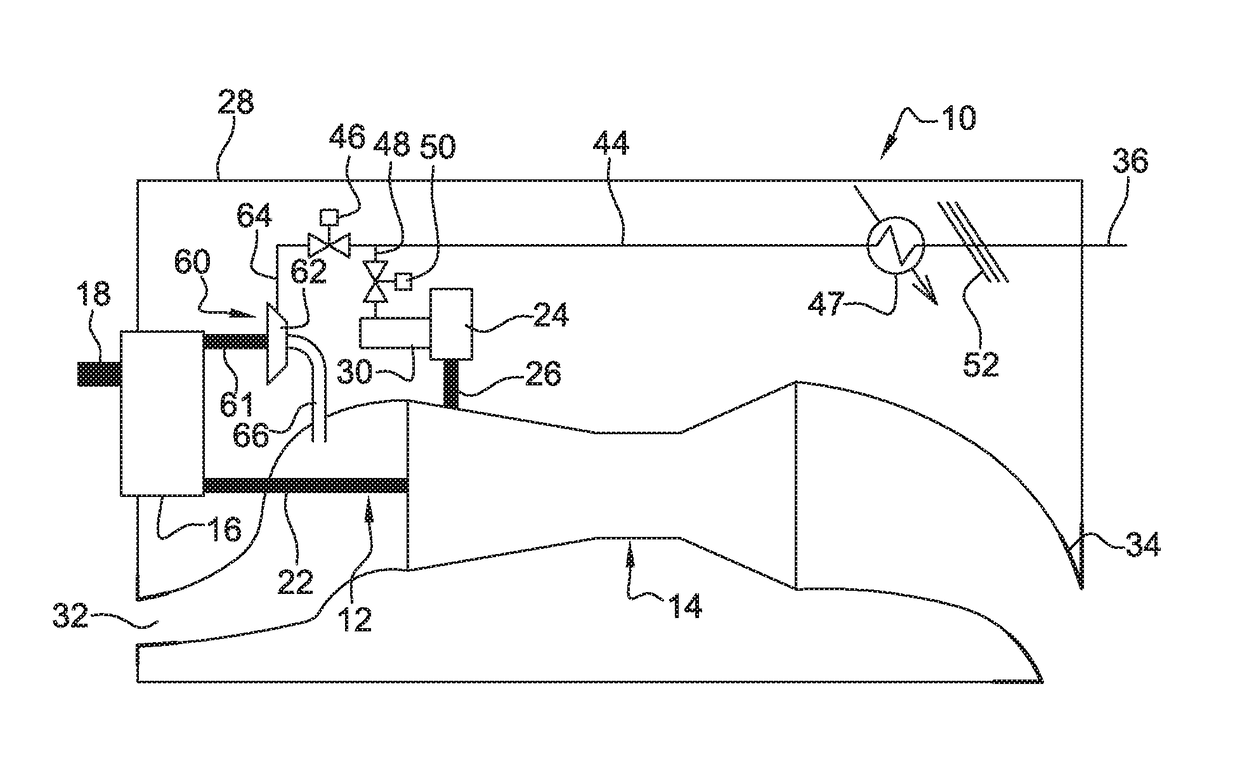
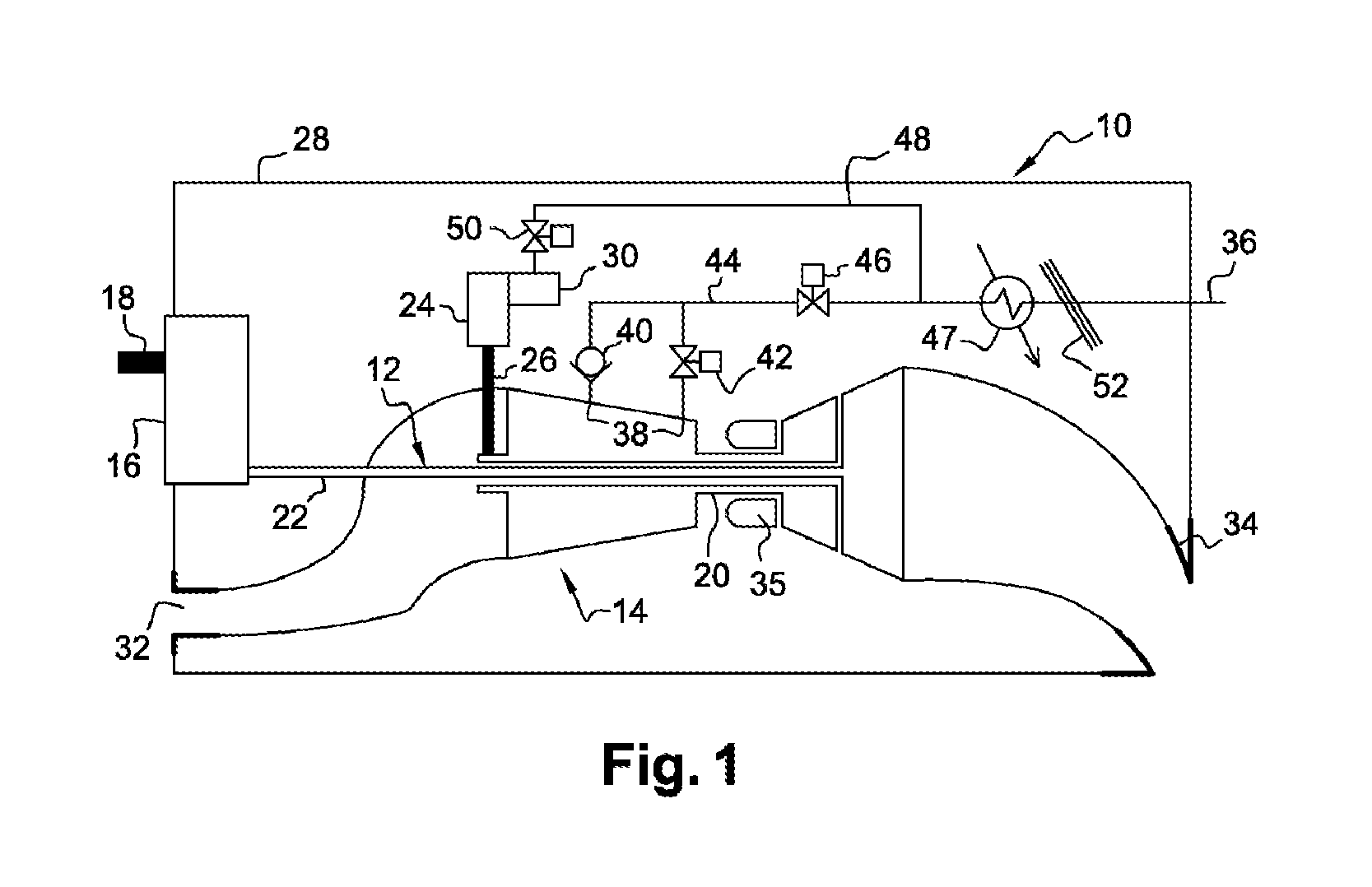
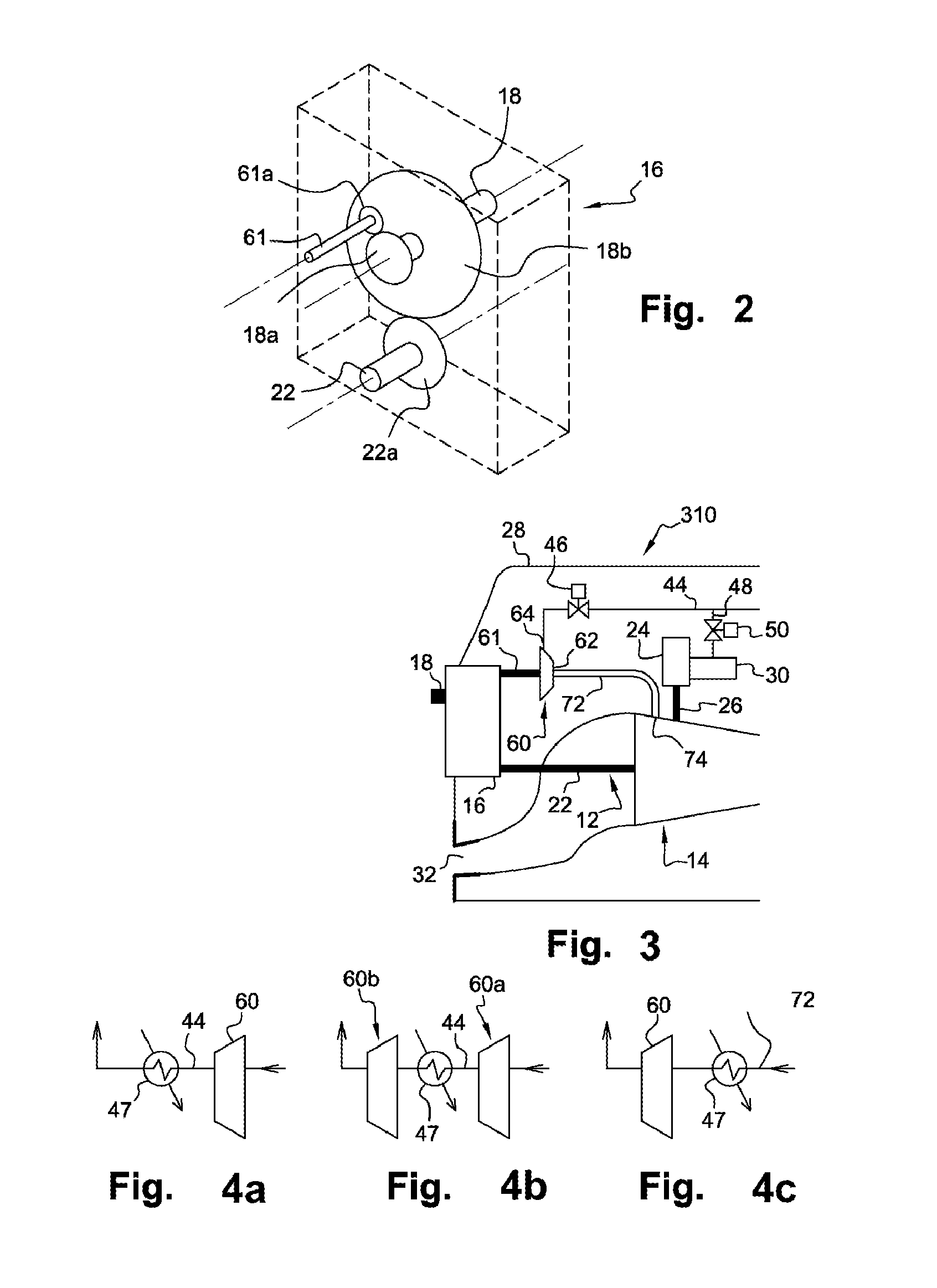
Aircraft turboprop engine (110), comprising at least one low-pressure body (12) and one high-pressure body (14), the low-pressure body driving a thrust propeller by means of a gearbox (16), the turboprop engine further comprising means for supplying air to an air-conditioning circuit (36) of an aircraft cabin, said supply means comprising a load compressor (60), a rotor (61) of which is coupled to said low-pressure body by means of said gearbox, characterised in that said supply means further comprise means for controlling the rotation speed of the rotor (61) of said compressor (60), which means comprise an electric motor (70), and a mechanical differential (72) for coupling a first output shaft (74) of said electric motor to a second output shaft (76) of said gearbox and to said compressor rotor (61), such that the rotation speed (V3) of said rotor depends on the respective rotation speeds (V1, V2) of said first and second output shafts.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
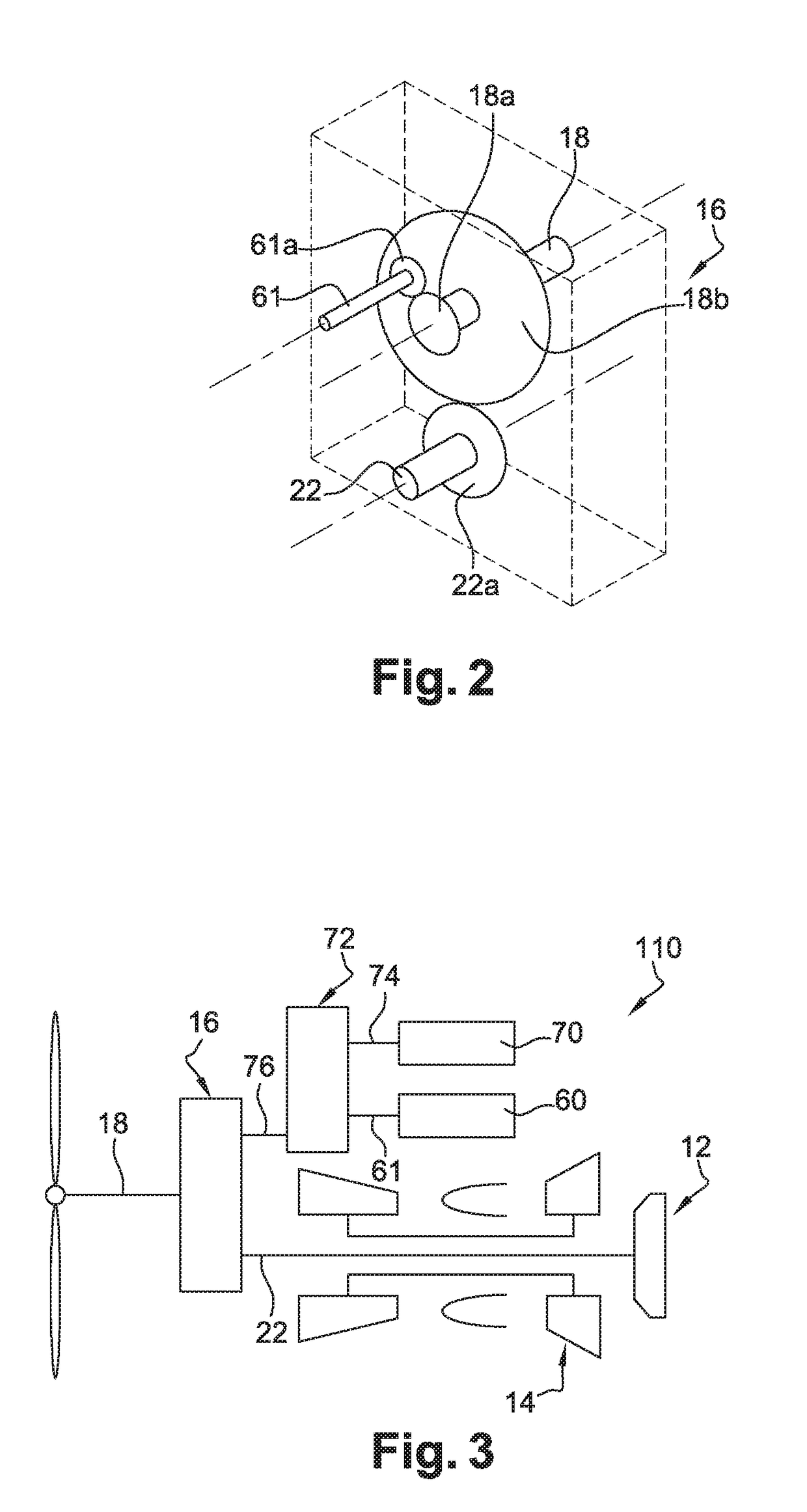
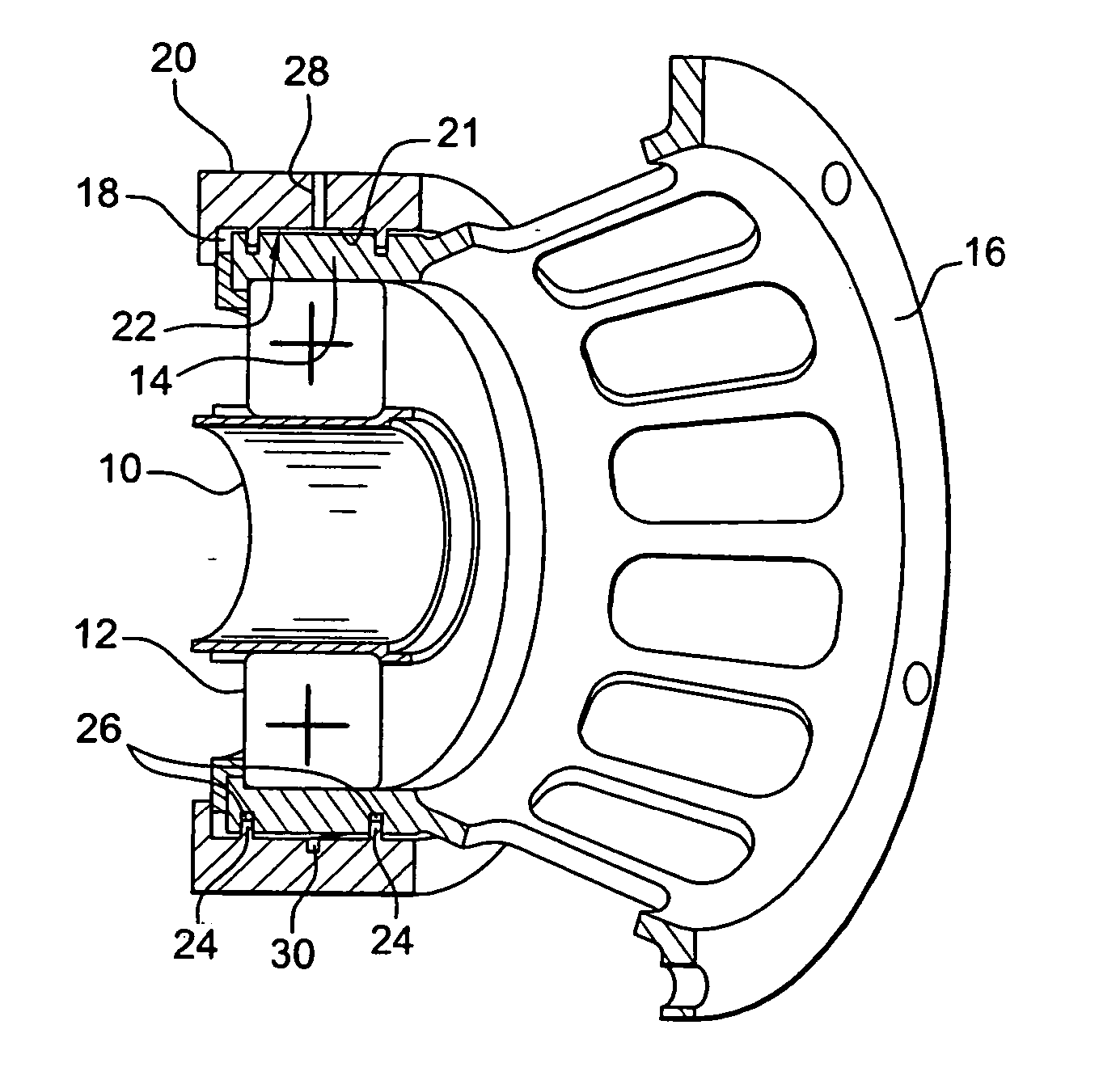
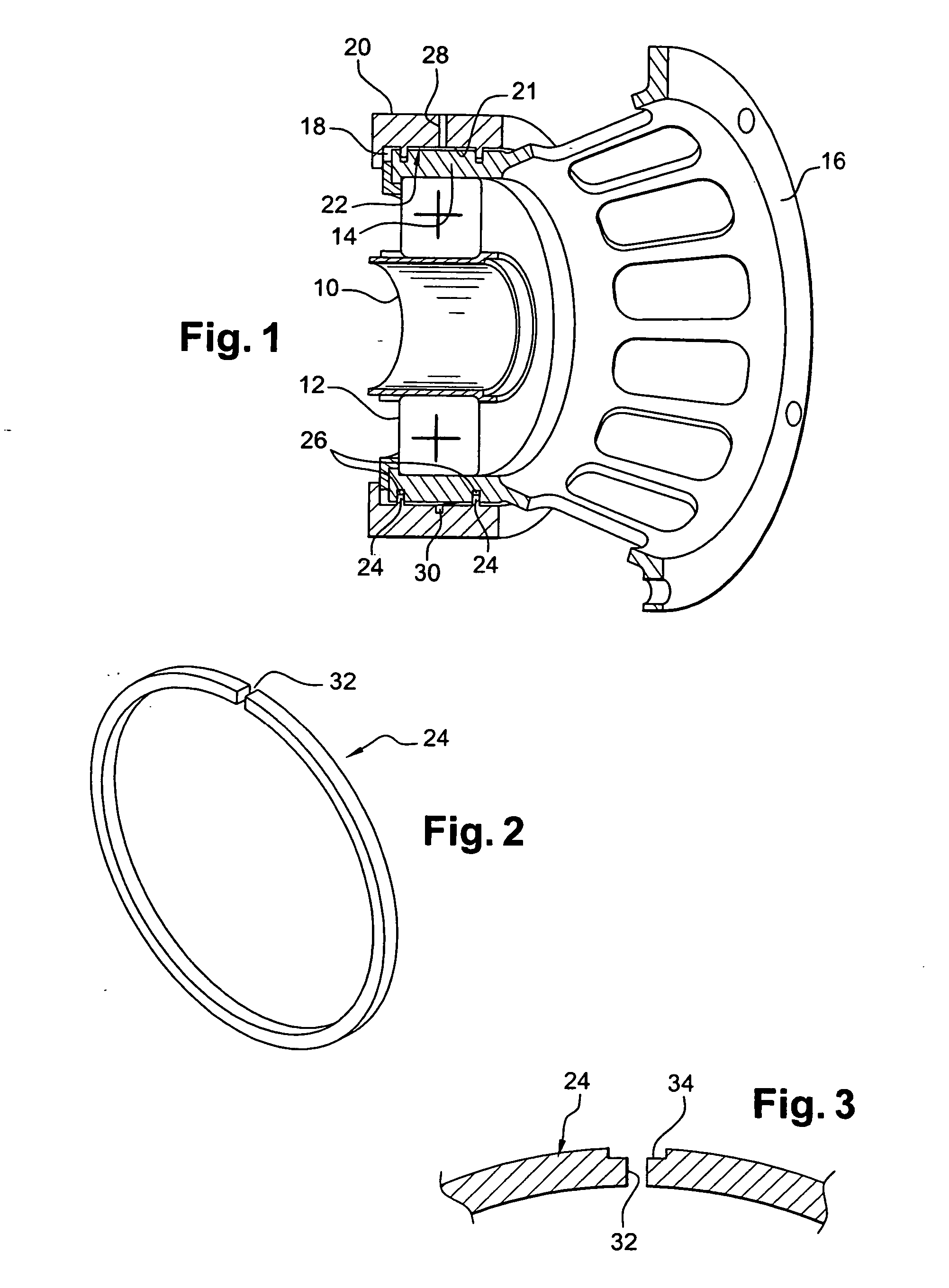
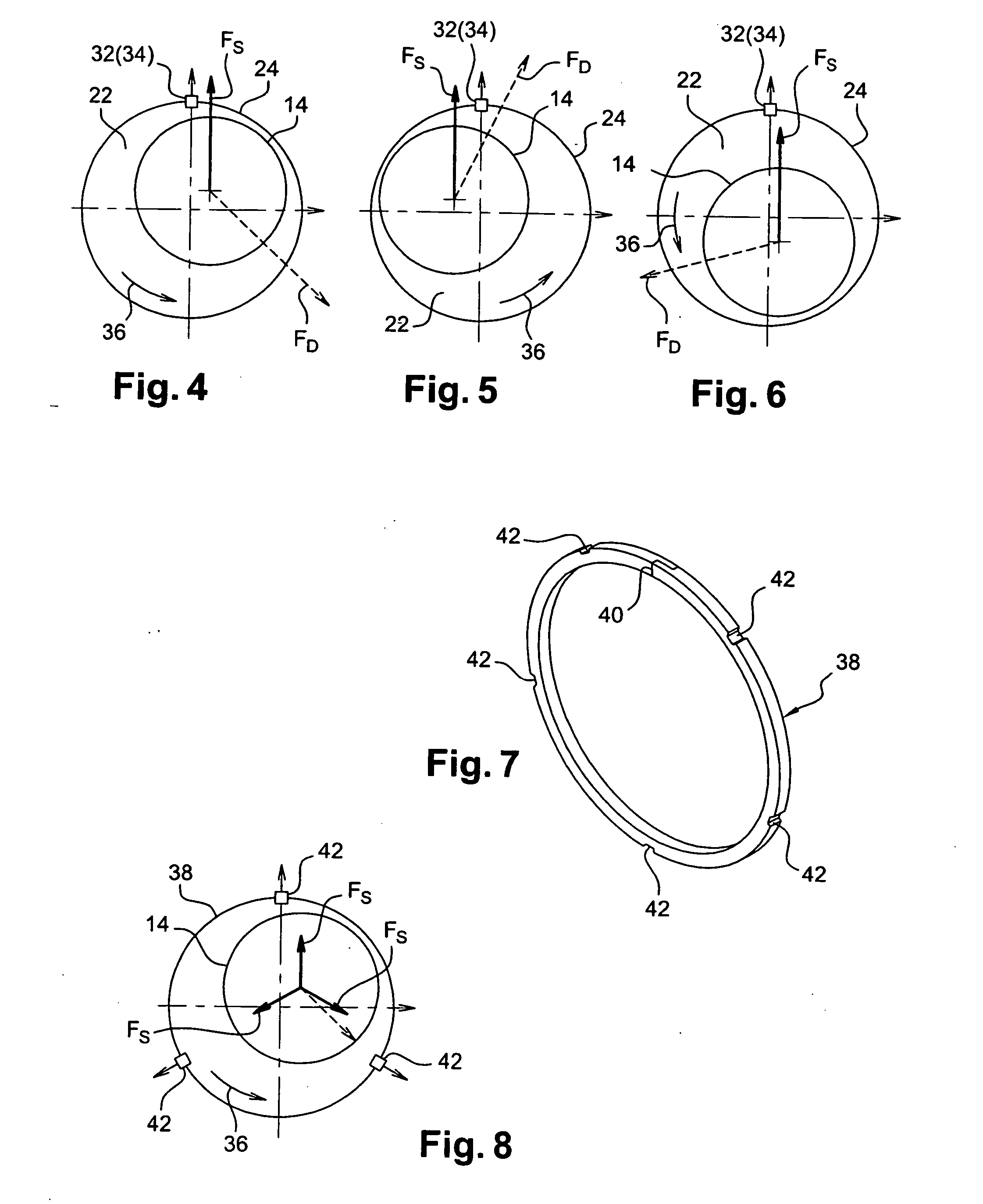
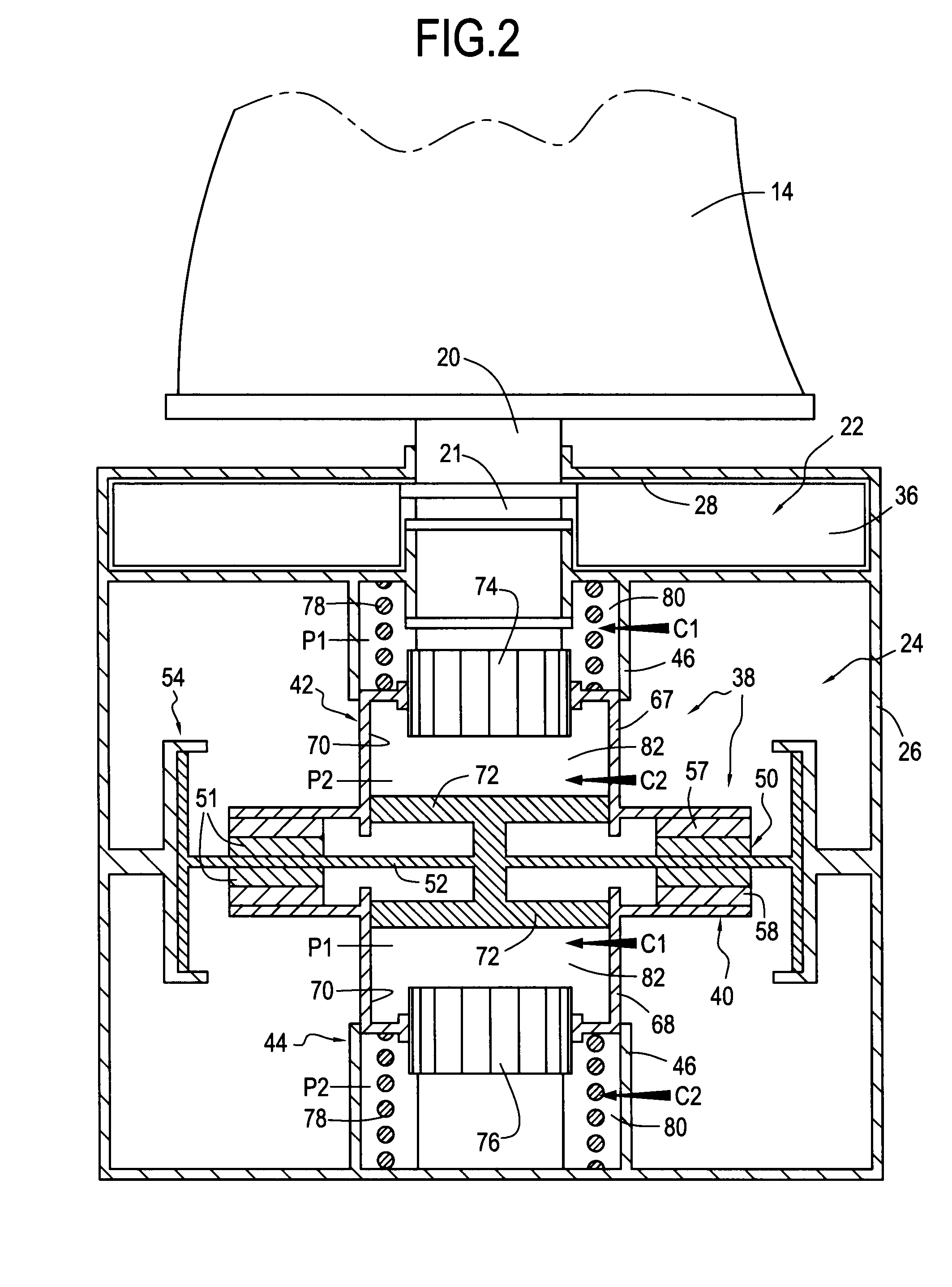
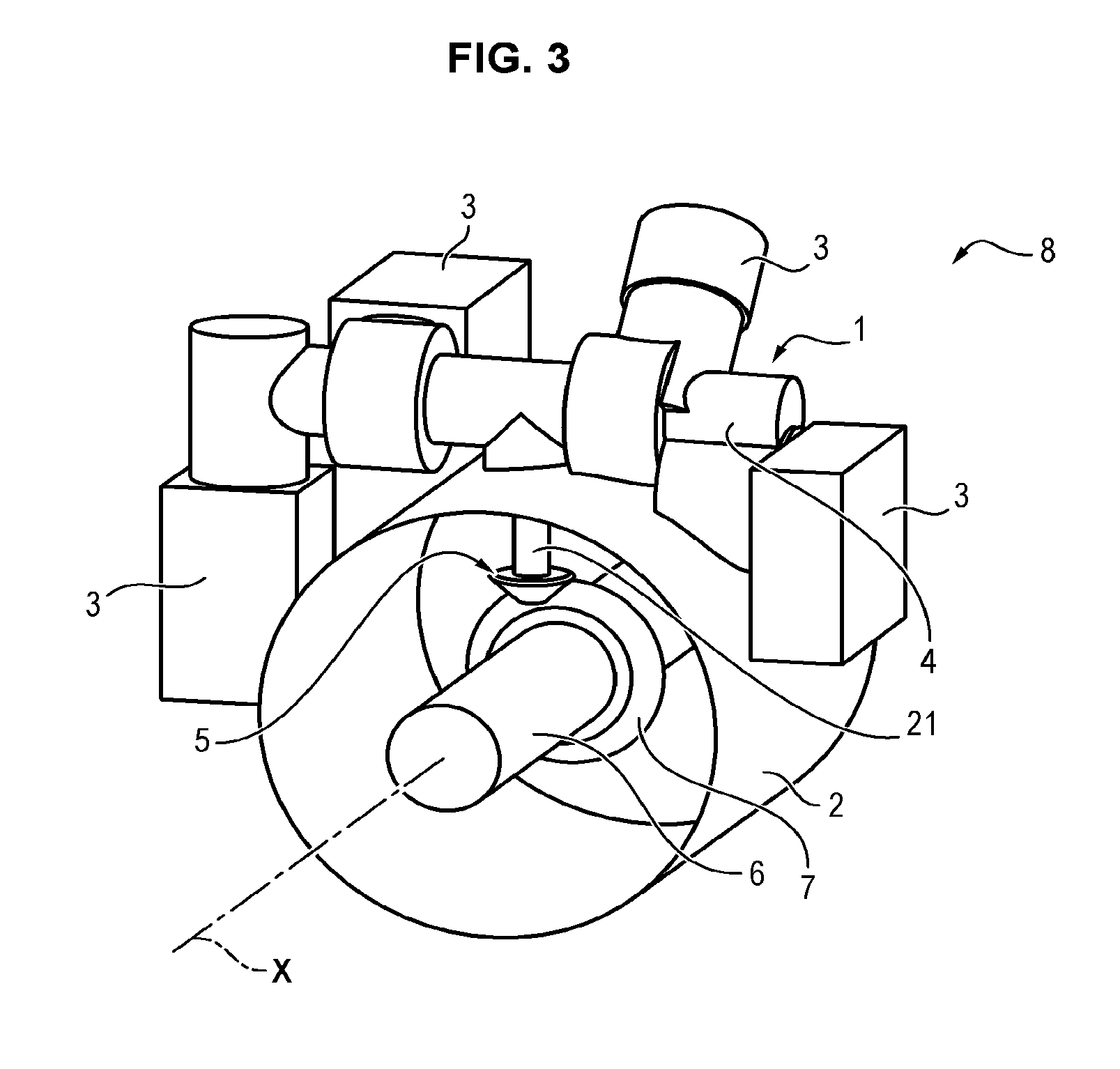
Device for supporting and guiding a rotating shaft
ActiveUS20060083449A1Simple and effective and inexpensiveReduce forceRoller bearingsShaftsRotational axisEngineering
A device for supporting and guiding a rotating shaft, in particular a rotor shaft of an airplane turboprop or turbojet, the device comprising an oil squeeze damper around each bearing of the shaft, said damper comprising an annular space surrounding the outer ring of the bearing and defined by annular sealing elements, each having a small number of calibrated oil outlet orifices formed in its outer periphery.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
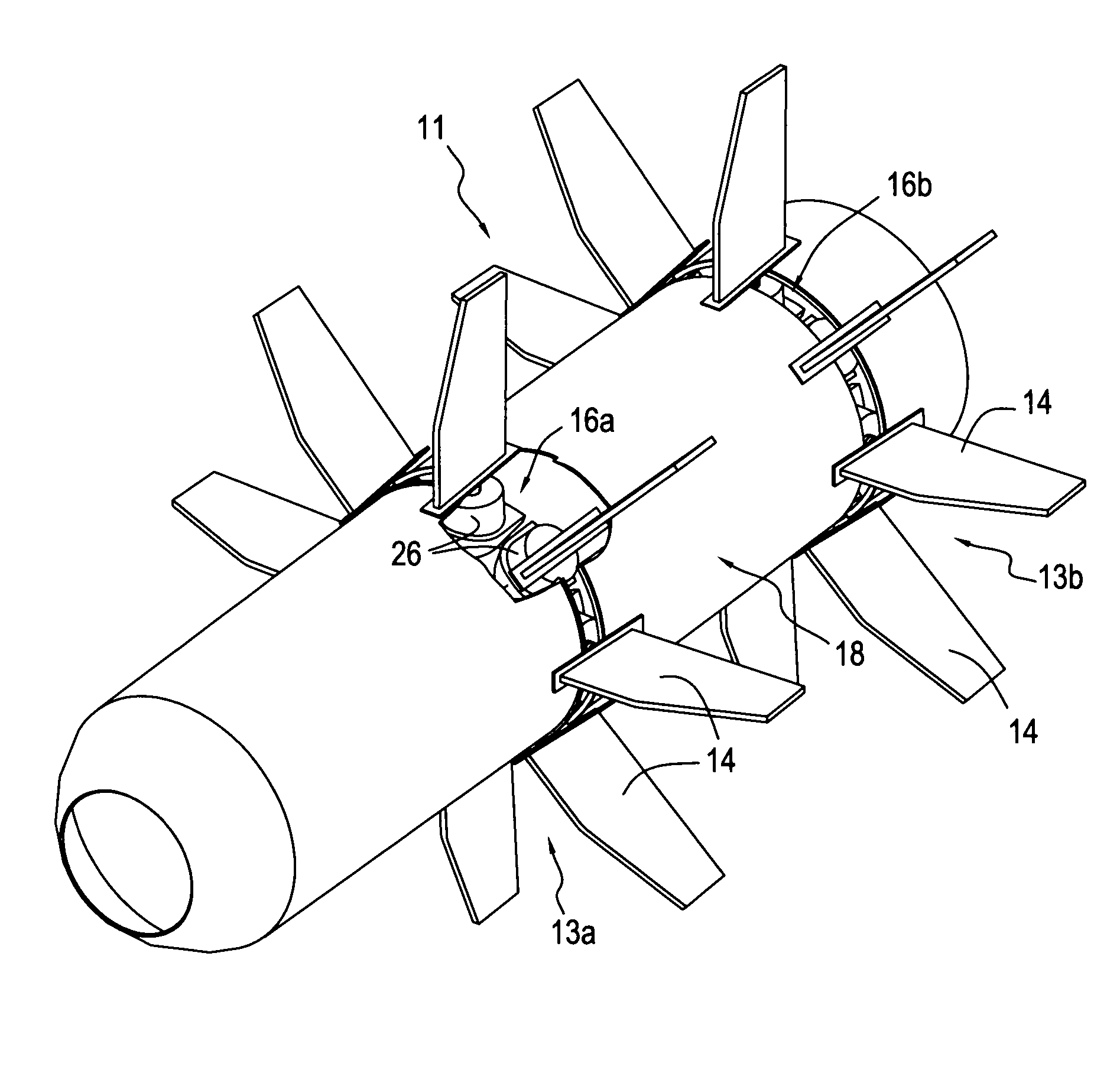
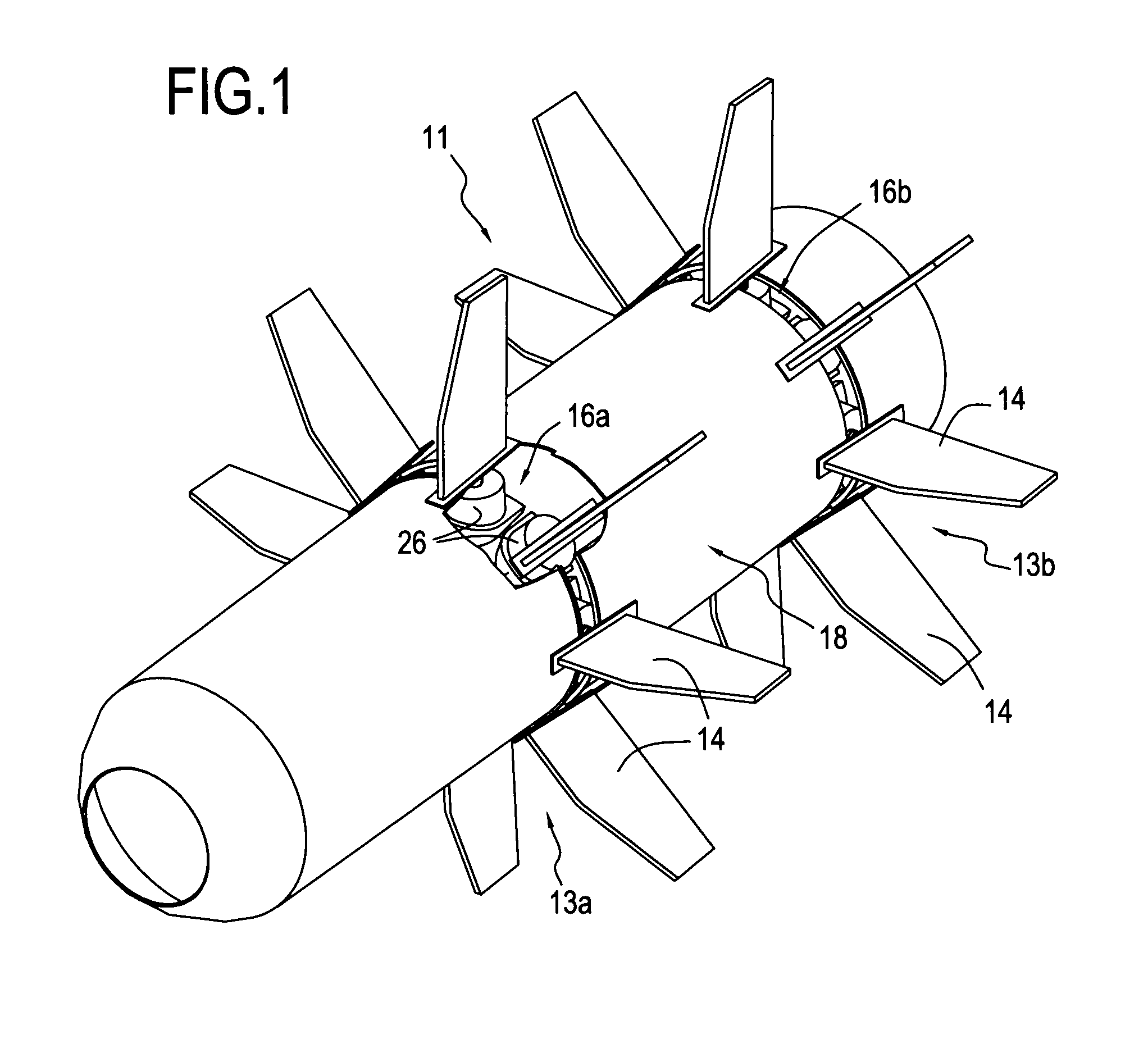
Device for controlling the pitch of fan blades of a turboprop
A device for controlling pitch of fan blades of a turboprop including at least one set of adjustable-pitch fan blades secured to rotate with a rotary ring mechanically connected to a turbine rotor, each blade of the set being coupled for pitch adjustment to a synchronization ring. The device includes a rolling bearing including an inner cage slidably mounted on a turbine casing and connected to the rod of an actuator, and an outer cage that is mechanically connected to the synchronization ring by a plurality of connection arms connected to the actuator rod and hinge-mounted on the synchronization ring such that actuating the actuator causes the synchronization ring to move in turning about the longitudinal axis.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Method for producing an aircraft with reduced environmental impact and the aircraft thus obtained
ActiveUS7926760B2Reduce environmental impactSatisfactory masking of the propeller interaction noisePropellersAircraft stabilisationAirplaneTurboprop
An aircraft with reduced environmental impact includes a turboprop, having two contra-rotating propellers, disposed on the rear portion on the back of the aircraft's fuselage so that the interaction noise of the propellers is masked, in the forward direction, by the wings and, in the rearward direction, by the aircraft's horizontal stabilizer.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
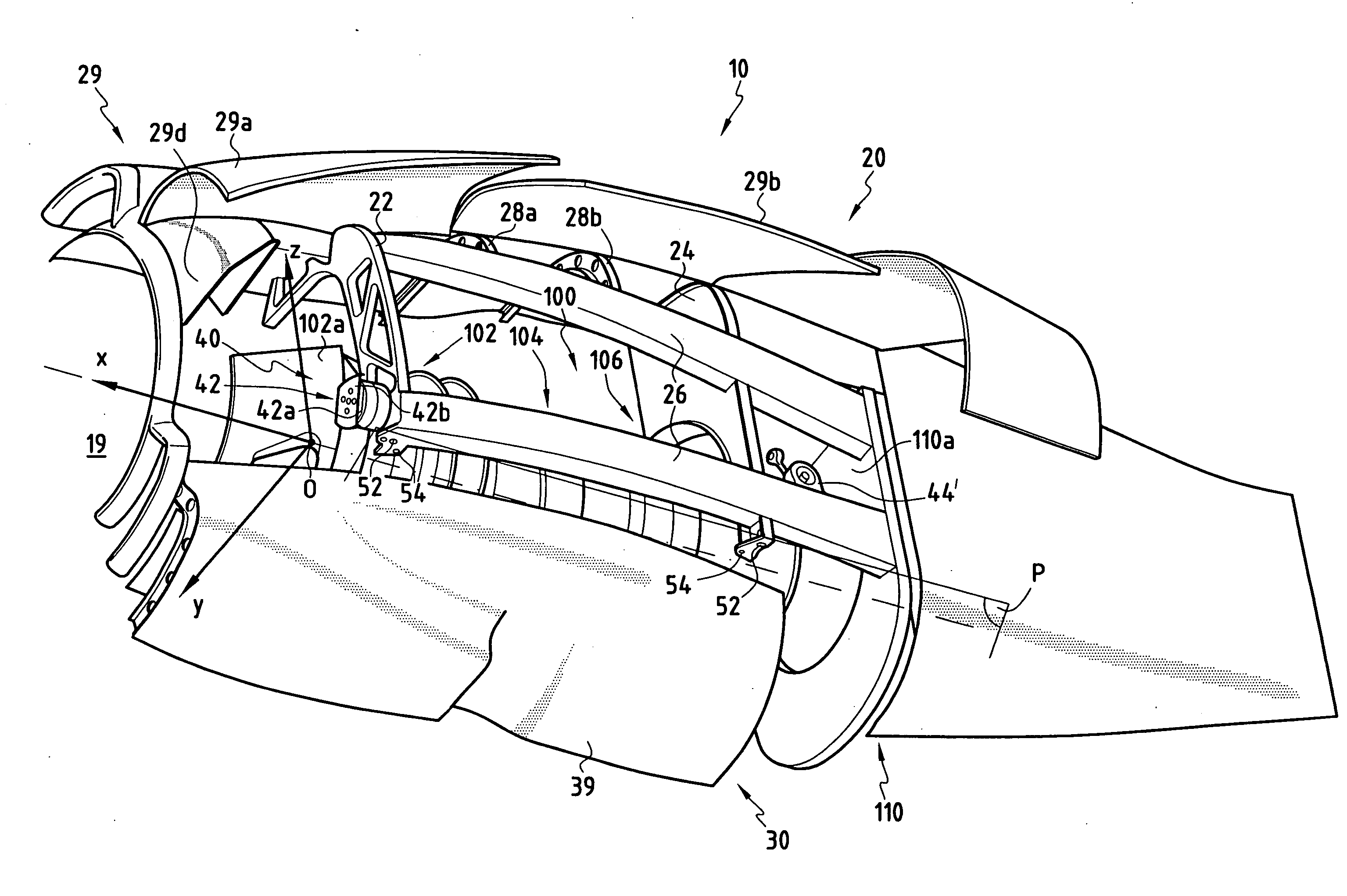
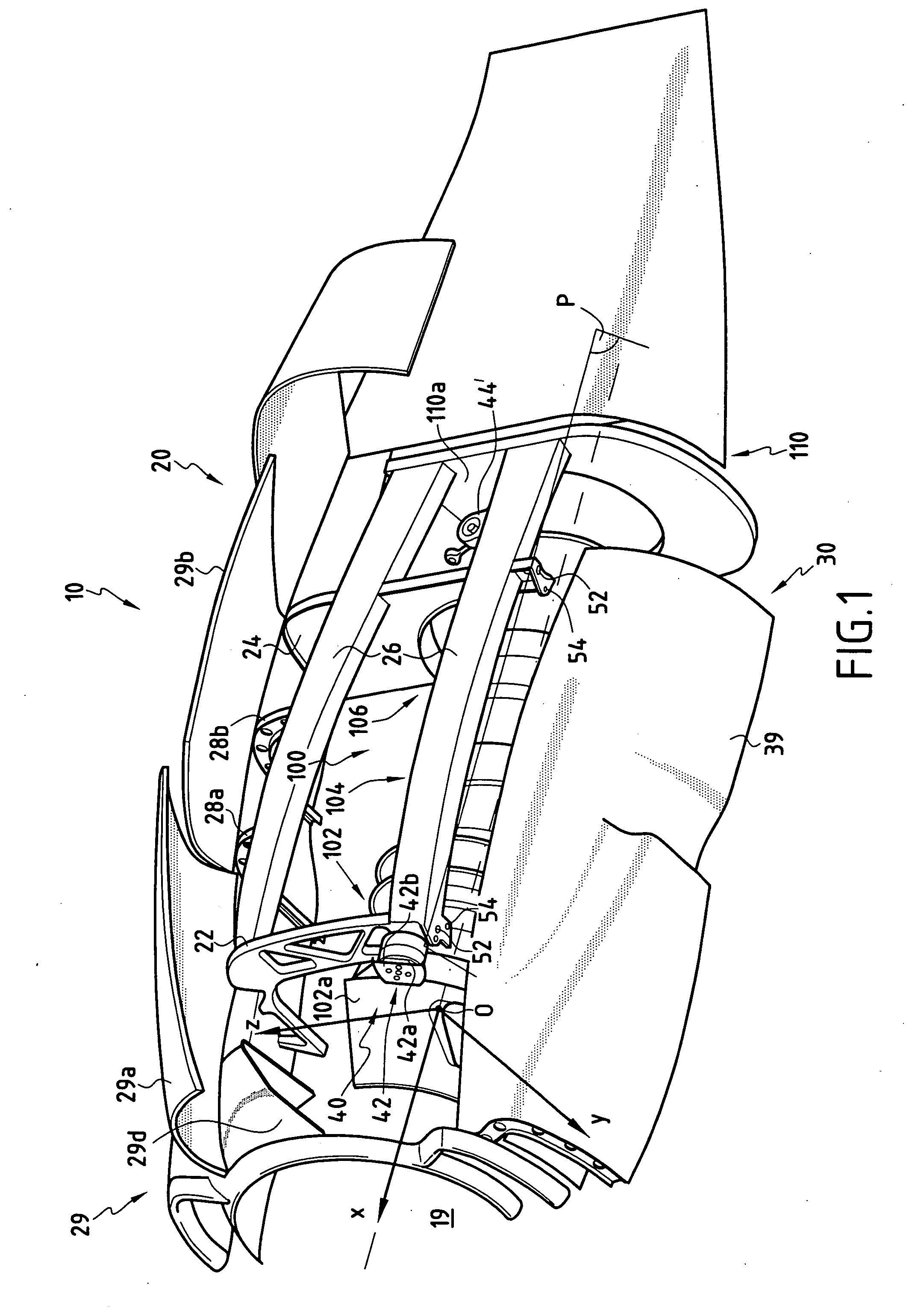
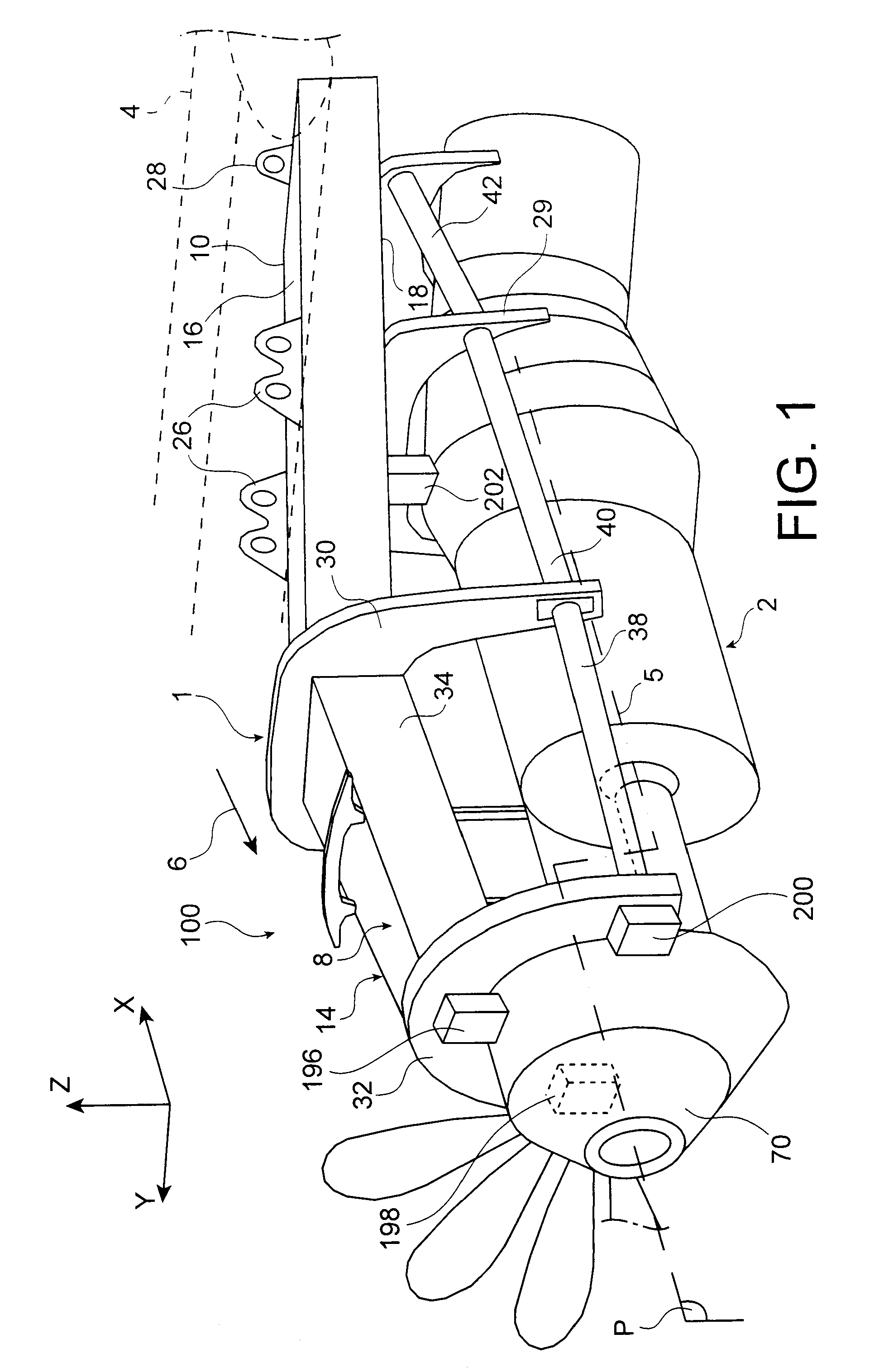
Device for mounting an aircraft turboprop engine comprising hydraulic attachments
ActiveUS8226028B2Determination of the efforts at the interfaces is facilitatedEasy to assembleGas turbine type power plantsGas turbine plantsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An engine unit for an aircraft including a turboprop engine and its device for mounting on to a wing surface. The device includes a rigid structure and a mechanism for fastening the turboprop engine on to this structure. The fastening mechanism includes six mutually independent hydraulic systems, each one exclusively dedicated to the transfer, to the rigid structure, of forces exerted respectively according to one of the six degrees of freedom of movement. Each hydraulic system includes at least one hydraulic jack with a piston attached to one of the two elements, i.e. either the turboprop engine or the rigid structure, together with a cylinder housing the piston and attached to the other of the two elements.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
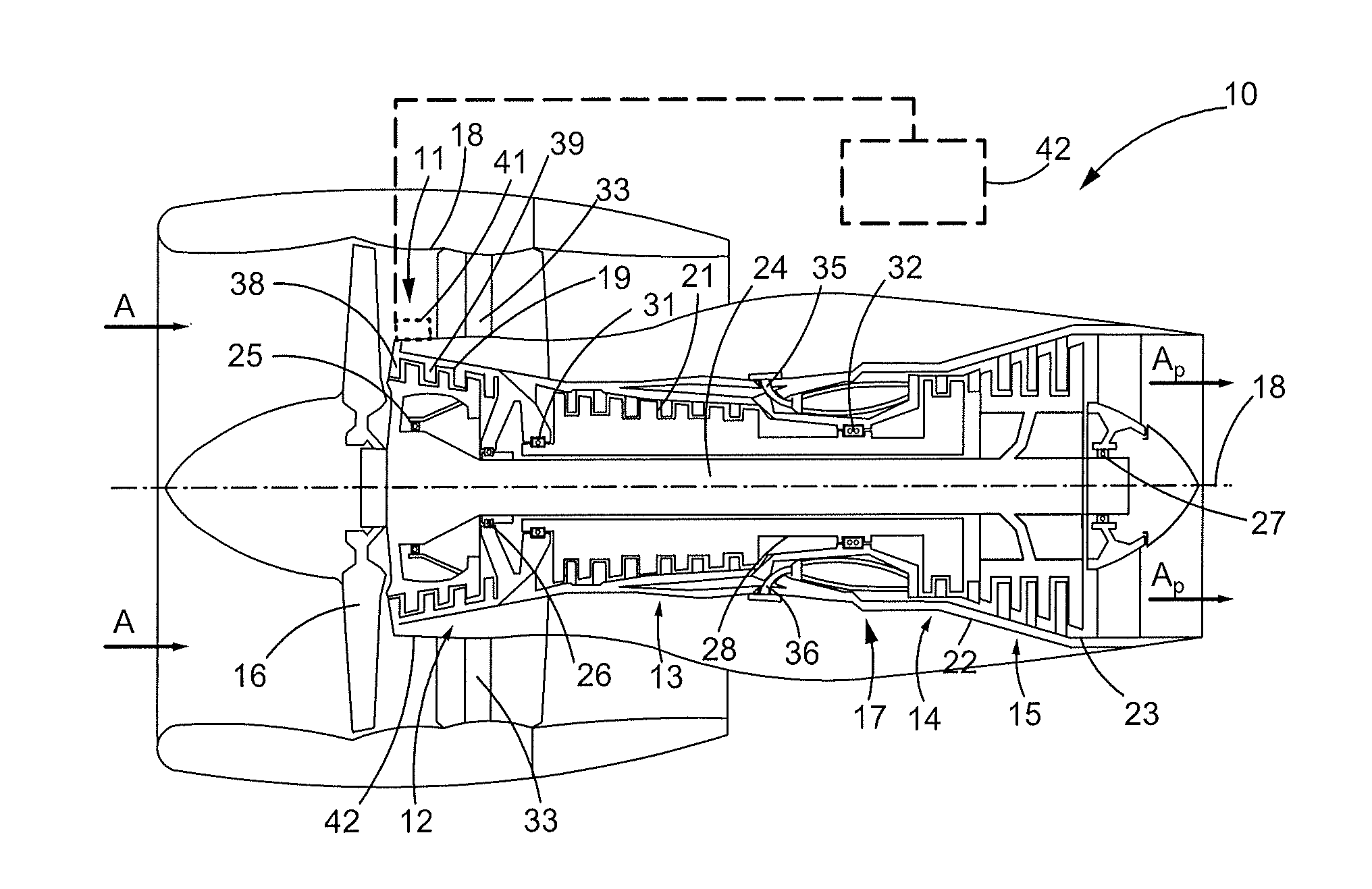
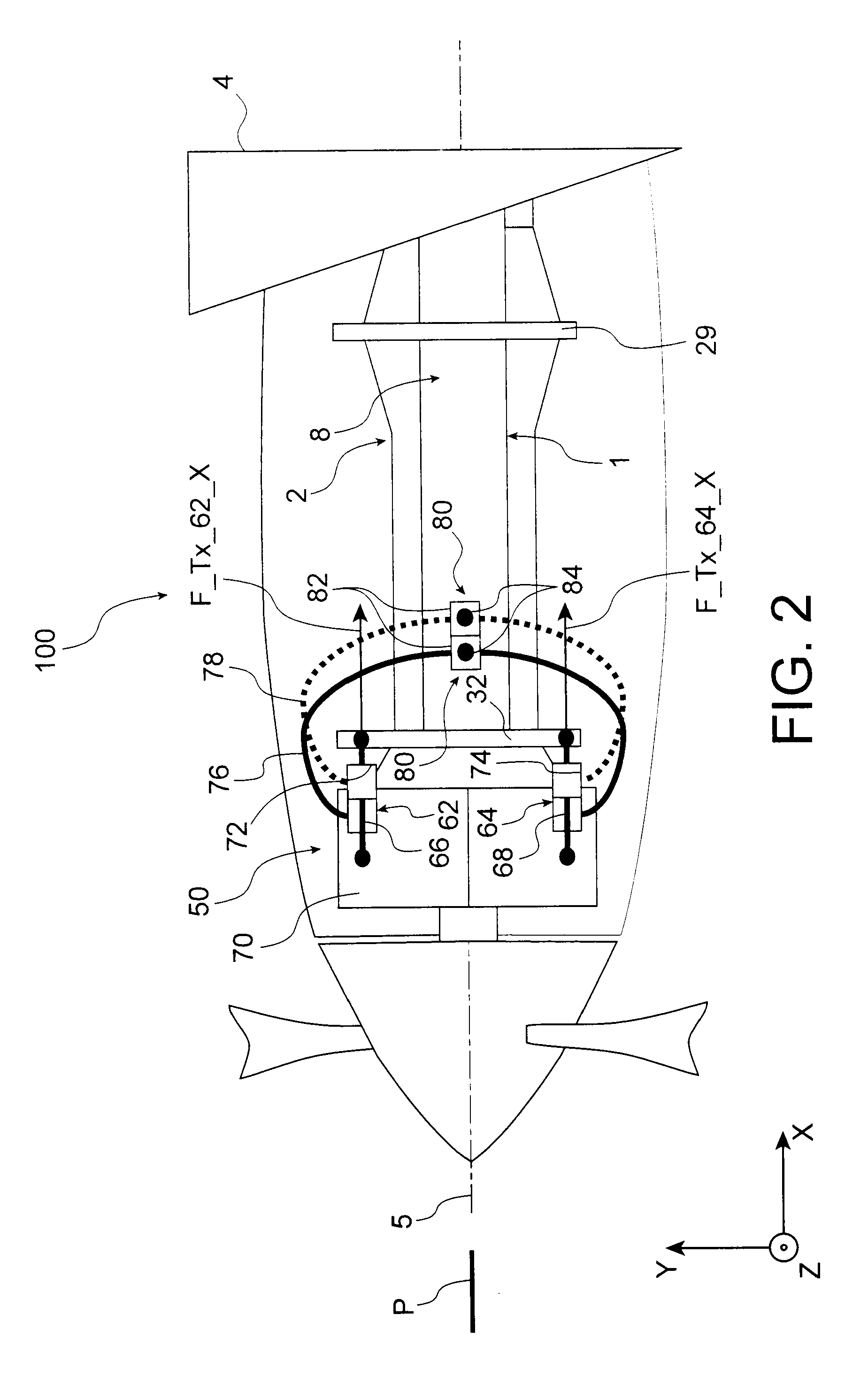
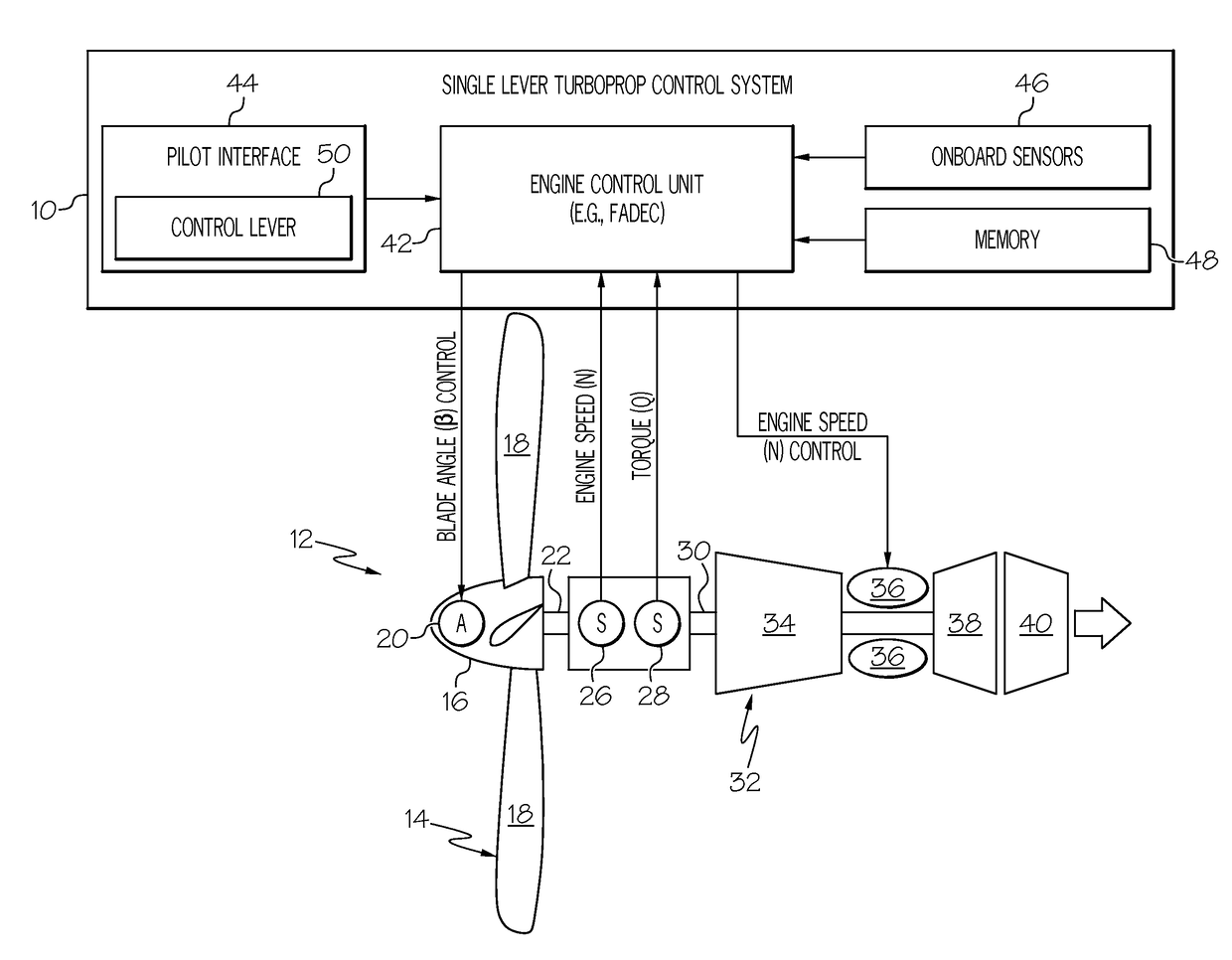
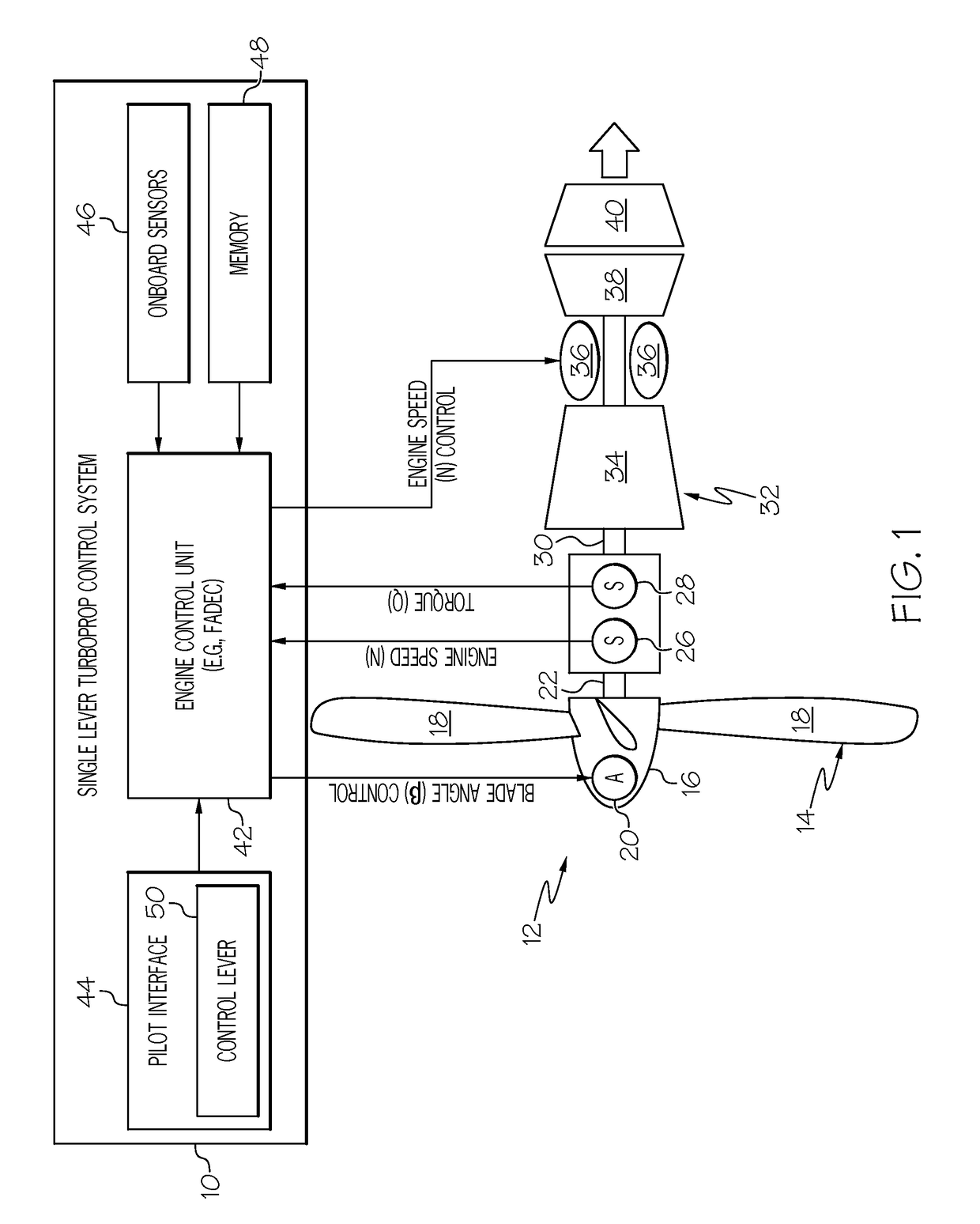
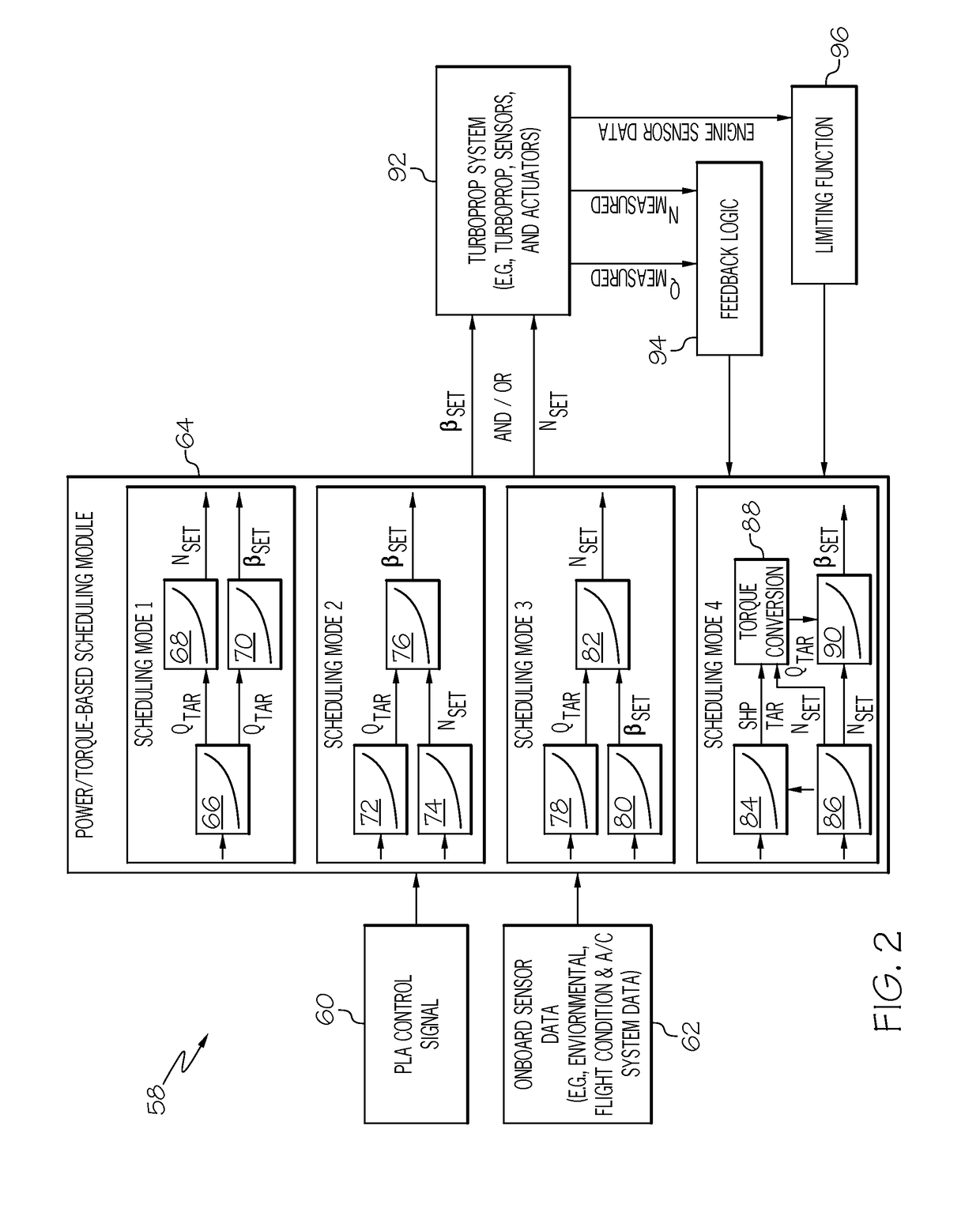
Single lever turboprop control systems and methods utilizing torque-based and power-based scheduling
Embodiments of a single lever turboprop control method and system are provided, which utilize torque-based and / or power-based scheduling to achieve a desired (e.g., substantially proportional) relationship between control lever position and the power output of a turboprop engine. In one embodiment, the method includes the step or process of monitoring, at an Engine Control Unit (ECU), for receipt of a Power Lever Angle (PLA) signal from a single lever control device. When a PLA control signal received at the ECU, a target torque or power output is established as a function of at least the PLA control signal. A first engine setpoint, such as a blade angle setpoint or an engine rotational speed setpoint, is determined utilizing the target torque output. An operational parameter of the turboprop engine is then adjusted in accordance with the first engine setpoint.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Turboprop having a propeller made up of variable-pitch blades
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Mounting structure for mounting a turboprop under an aircraft wing
ActiveUS7159819B2Easy resistanceEasily resist the entire engine torqueGas turbine type power plantsPower plant constructionAircraft landingRigid structure
A mounting structure for mounting a turboprop under an aircraft wing includes a rigid structure provided with an aft underwing box, and at least one forward rigid section. Each forward rigid section has two transverse frames at a spacing from each other. At least one forward rigid section of the rigid structure also includes at least one forward upper box connecting a top part of the two transverse frames of the forward rigid section.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Stationary actuator device for controlling the pitch of fan blades of a turboprop
A device for controlling pitch of fan blades of a turboprop including at least one set of variable-pitch fan blades constrained to rotate with a rotary ring centered on a longitudinal axis and mechanically connected to a turbine rotor, each blade coupled for pitch adjustment to a synchronization ring. A turntable is mounted via a rotary connection to a rod of an actuator that is secured to a stationary structural element of the turboprop, the turntable being mechanically connected to the synchronization ring by a plurality of connection arms hinge-mounted on the turntable and connected to the synchronization ring such that a longitudinal movement of the turntable under drive from the actuator causes the synchronization ring to turn about the longitudinal axis.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Turboprop-powered aircraft
InactiveUS20130292085A1Extended flight enduranceDuration of missionAir-treatment apparatus arrangementsEnergy efficient board measuresWaxHeat storage material
A method and apparatus are disclosed for a turboprop-powered medium altitude long endurance (MALE) aircraft, having: a heat exchanger with a heat-storage material, for example a heat-storage wax; and an air recirculation path. The heat exchanger can be arranged to cool air recirculating around the air recirculation path which is arranged to provide cooling to the MALE aircraft, for example to an equipment bay. The heat-storage material may be cooled by ground-based cooling apparatus when the aircraft is on the ground and / or by ram air when the aircraft is in flight. The heat-storage material may have a melting point selected so as to be rendered solid during ground-based cooling and / or ram air cooling, and / or selected so as to undergo melting whilst cooling the air recirculating around the air recirculation path.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
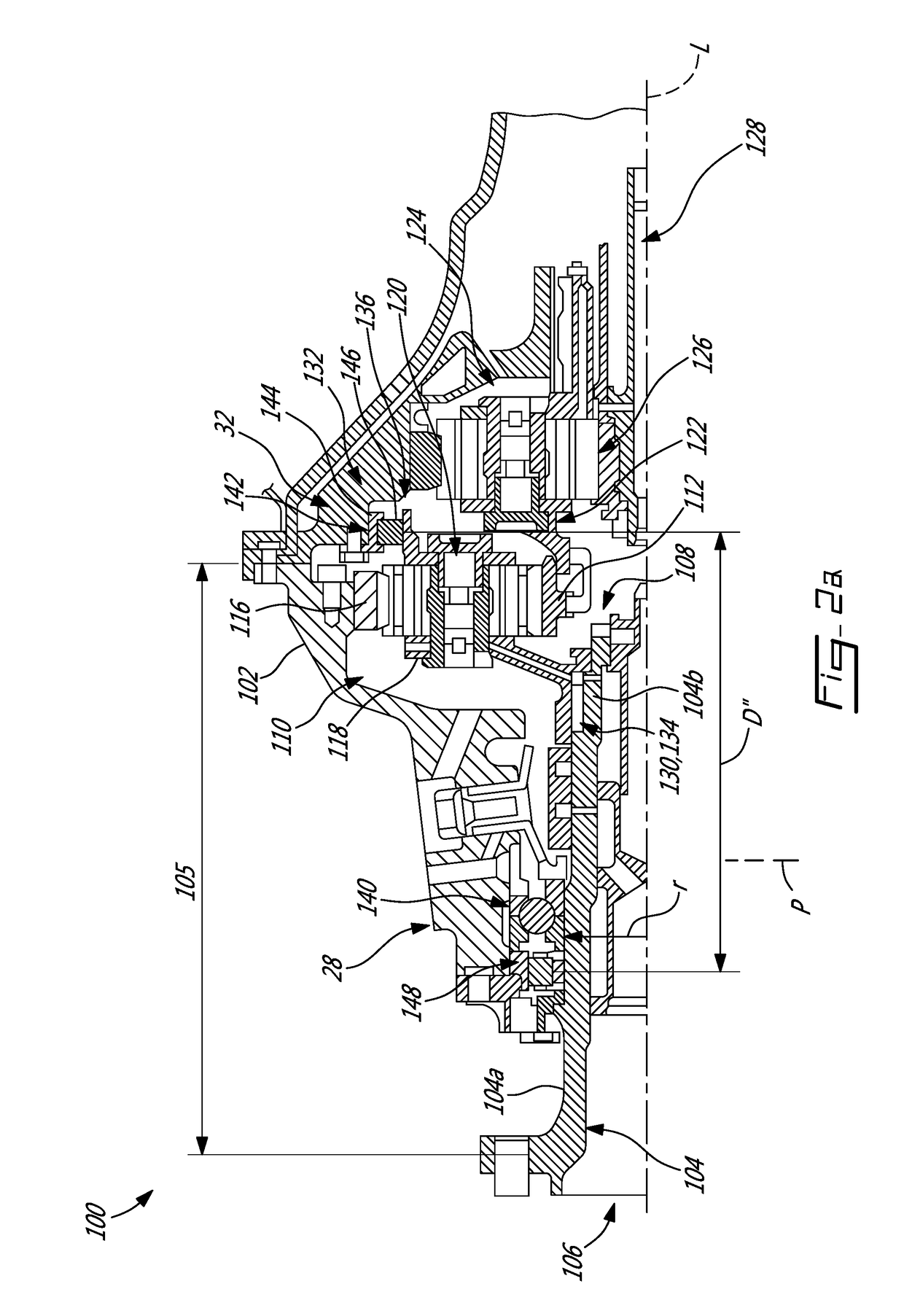
Support assembly for a propeller shaft
A turbo propeller engine comprises a housing circumferentially extending around a longitudinal axis and disposed around a gearbox. The turbo propeller engine includes a propeller outside of the housing and a shaft surrounded in part by the housing and extending along the longitudinal axis. The shaft has a front end and a rear end. The propeller is mounted to the front end. The rear end is in a driven engagement with an output of the gearbox. The shaft is rotatably supported by a first bearing and by a second bearing separated from the first bearing by an axial distance along the longitudinal axis. The first and second bearings are disposed on opposite sides of the gearbox. The first bearing is disposed between the shaft and the housing, the second bearing is disposed between the housing and a component of the gearbox to rotatingly support the component of the gearbox.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
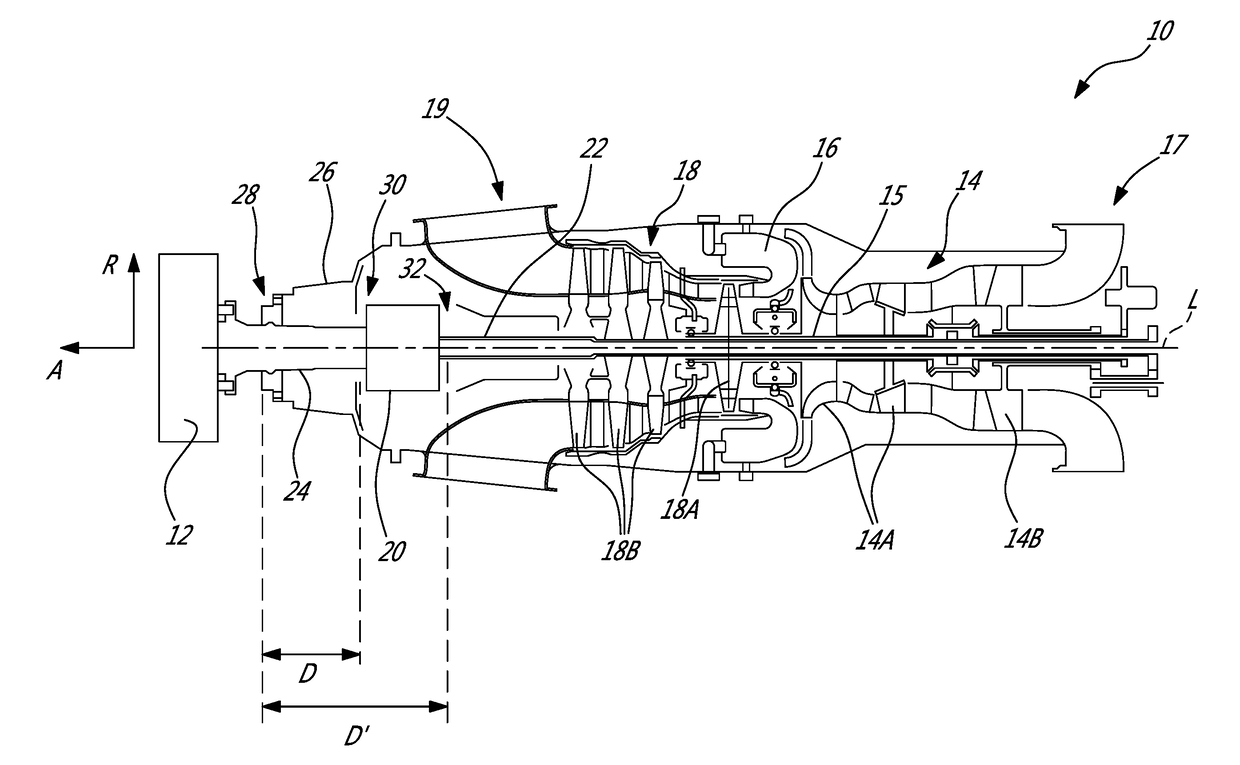
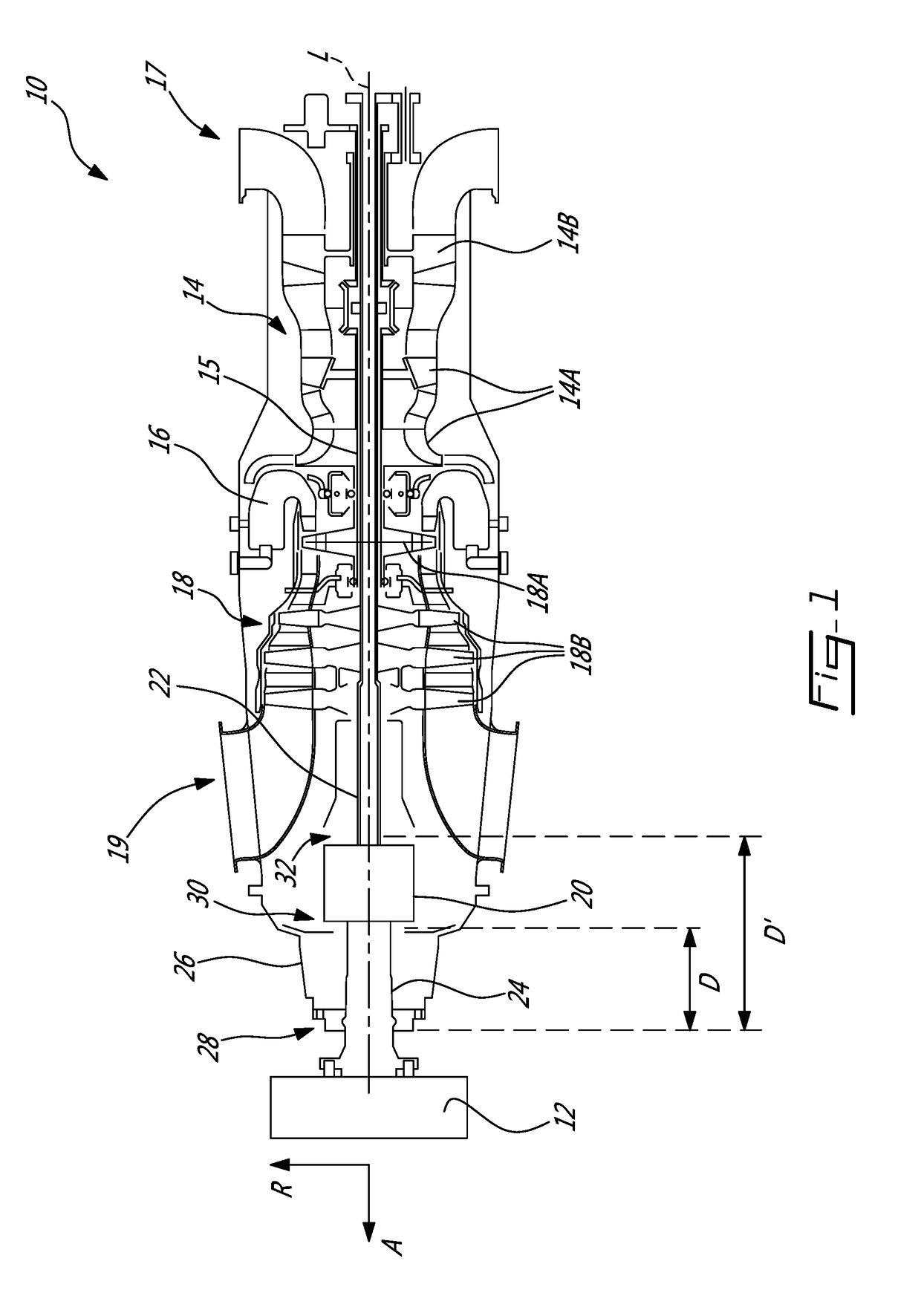
Supply of air to an air-conditioning circuit of an aircraft cabin from its turboprop engine
ActiveUS20160332736A1Simple processSaving in massGas turbine type power plantsPump componentsNacelleBleed air
The invention relates to an aircraft turboprop engine (310) comprising at least a low-pressure body (12) and a high-pressure body (14), possibly also an intermediate-pressure body, at least one of said bodies comprising a compressor, the low-pressure body driving a propeller by means of a first gearbox (16), the turboprop engine also comprising means for supplying air to an air-conditioning circuit of an aircraft cabin, characterised in that said supply means comprise at least one compressor (60) of which the rotor (61) is coupled to the low-pressure body, said load compressor (60) including an air inlet (62) connected to means (72) for bleeding air from the compressor of the turboprop engine when all of the aforementioned bodies comprise only a single compressor, or from the compressor of the low-pressure body or the compressor of the intermediate-pressure body of the turboprop engine when all of the bodies comprise at least two compressors.
Owner:SAFRAN POWER UNITS +2
Turbomachine stator internal shell with abradable material
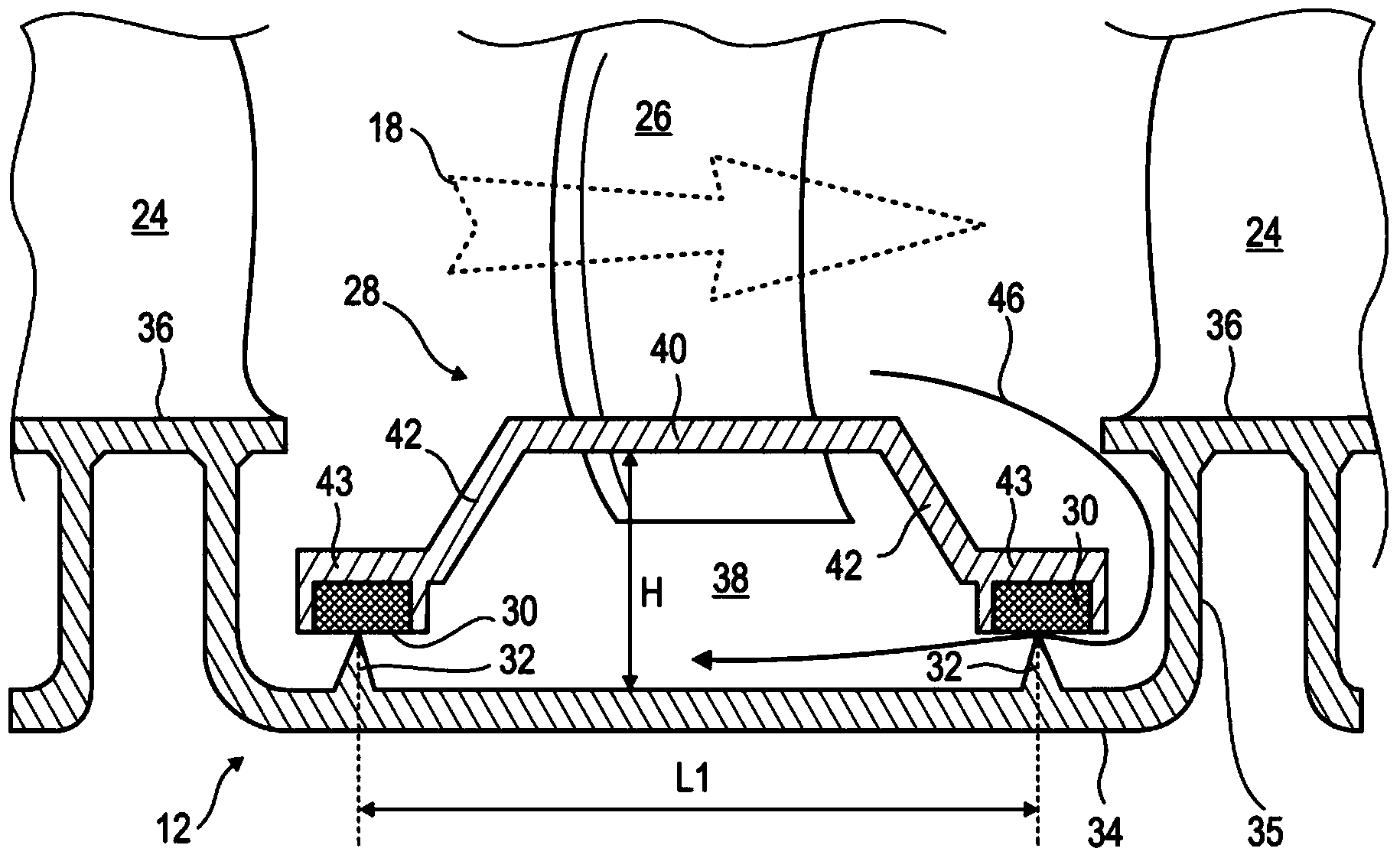
ActiveCN104141631AReduce leakageIncrease distancePump componentsEfficient propulsion technologiesLip sealTurboprop
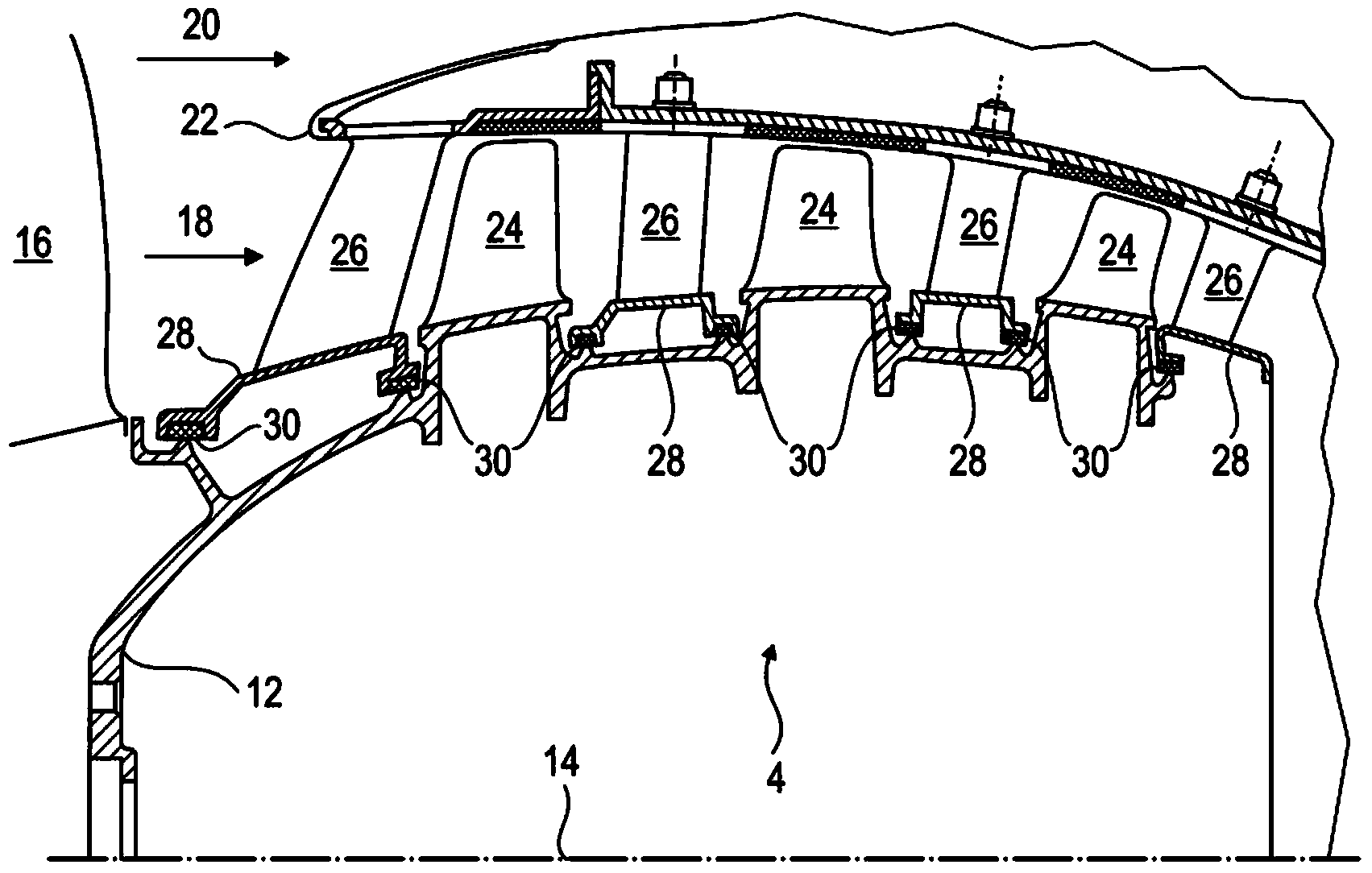
The present application relates to a compression stage of a low-pressure compressor of an axial turbomachine, such as a turboprop. The stage includes a rotor with, on its outer surface, two lip seals, each forming a radial annular rib; and a stator which includes an annular row of stator blades extending substantially radially; and an inner shell whose radial cross section includes a central part connected to the inner tips of the blades, a lateral part extending from each side of the central part to one of the two lip seals, respectively, thus forming a rotor with the annular cavity. The shell and the rotor are configured so that the radial section of the annular cavity has a length L1 and a height H, the length L1 being greater than the height H, which initiates rotational movement of the air contained therein. The speed of the air reduces its pressure, which limits downstream to upstream leaks.
Owner:SAFRAN AERO BOOSTERS SA
Fuel Efficient Fixed Wing Aircraft
InactiveUS20080099599A1Minimizing introductionEnhanced passengerAircraft navigation controlGas turbine type power plantsTurbopropAirplane
A fixed wing aircraft having a fuselage having a forward end and a rearward end, the fuselage's forward end forming a nose section; the aircraft further having a primary thrust turbo-prop engine fixedly mounted upon the fuselage's rearward end; the aircraft further having an auxiliary thrust turbo-fan jet engine; the aircraft further having a pivot axle and support strut combination interconnecting the auxiliary thrust turbo-fan engine and the fuselage, the pivot axle and support strut combination positioning the auxiliary thrust turbo-fan jet engine within the fuselage's nose section; the aircraft further having an auxiliary thrust port extending through an outer wall of the nose section, the pivot axle and support strut combination being adapted for alternately moving the turbo-fan engine between first and second positions, the turbo-fan engine residing within the nose section upon movement to the first position, the turbo-fan engine outwardly overlying the auxiliary thrust port upon alternate movement to the second position.
Owner:HUTTERER GLADYS IRENE +4
Accessory drive case for a turboprop
ActiveUS20160138414A1Moderate weightImprove distributionPump componentsEngine fuctionsEngineeringAccessory drive
A turbomachine including an accessory drive case, connected to the engine shaft via a radial shaft, wherein the accessory drive case also includes: a primary shaft which is driven by the radial shaft via a bevel gearbox, and assemblies for mechanically driving accessories, driven by the primary shaft and configured such that the related accessories lie at the upper portion and on at least one of the side edges of the engine case.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com