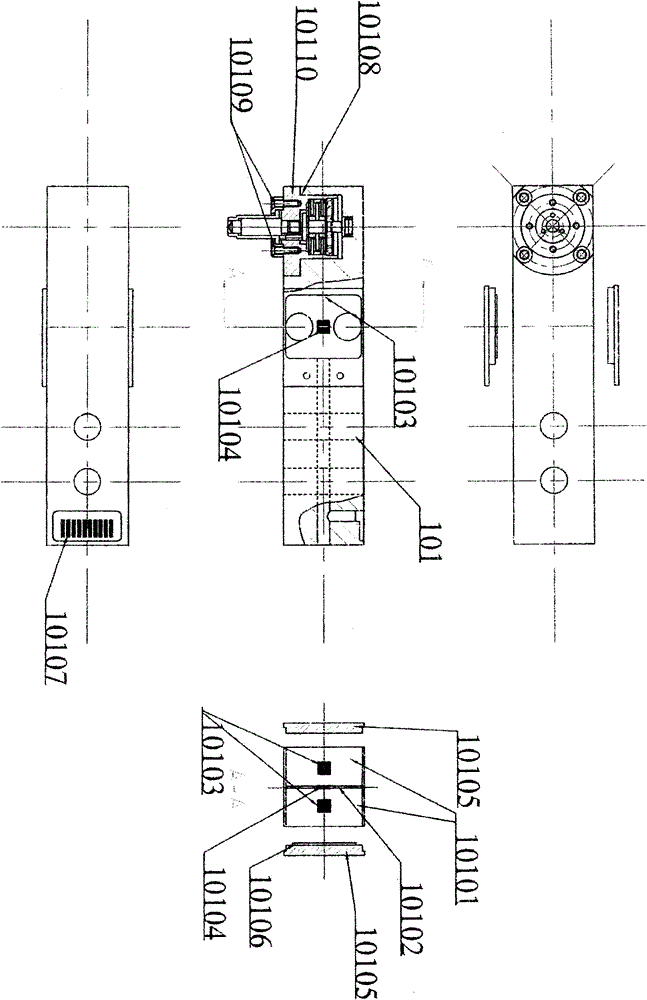
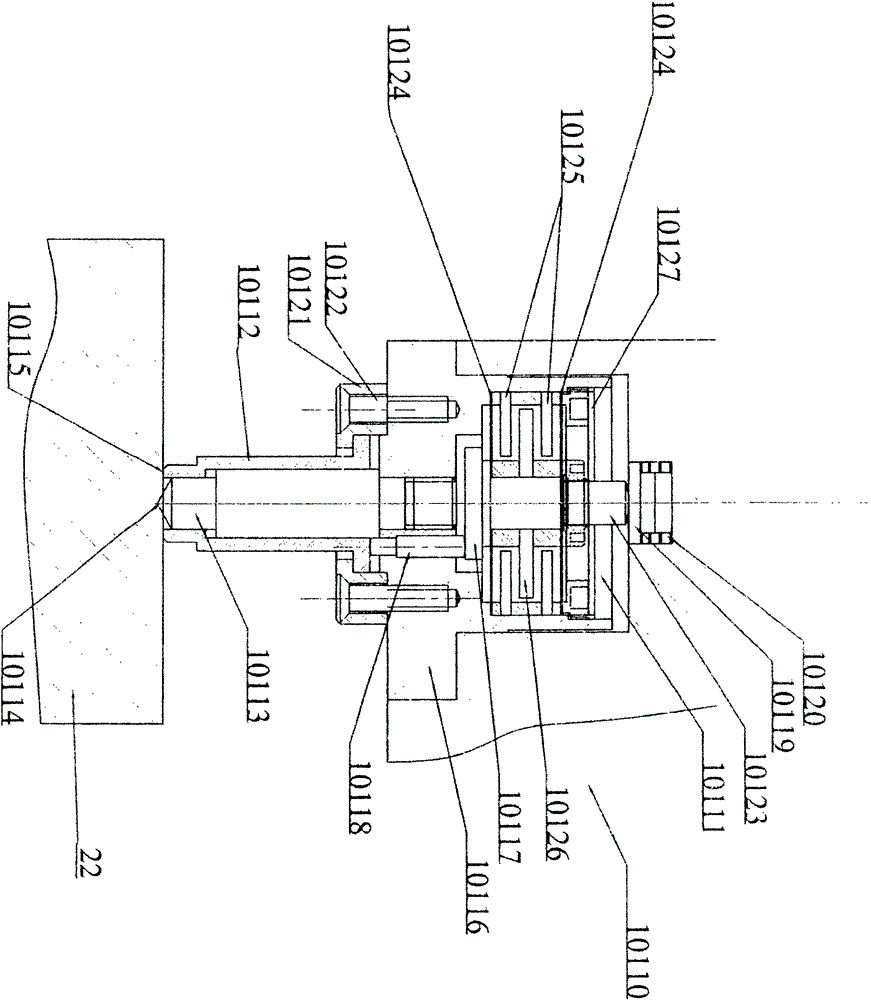
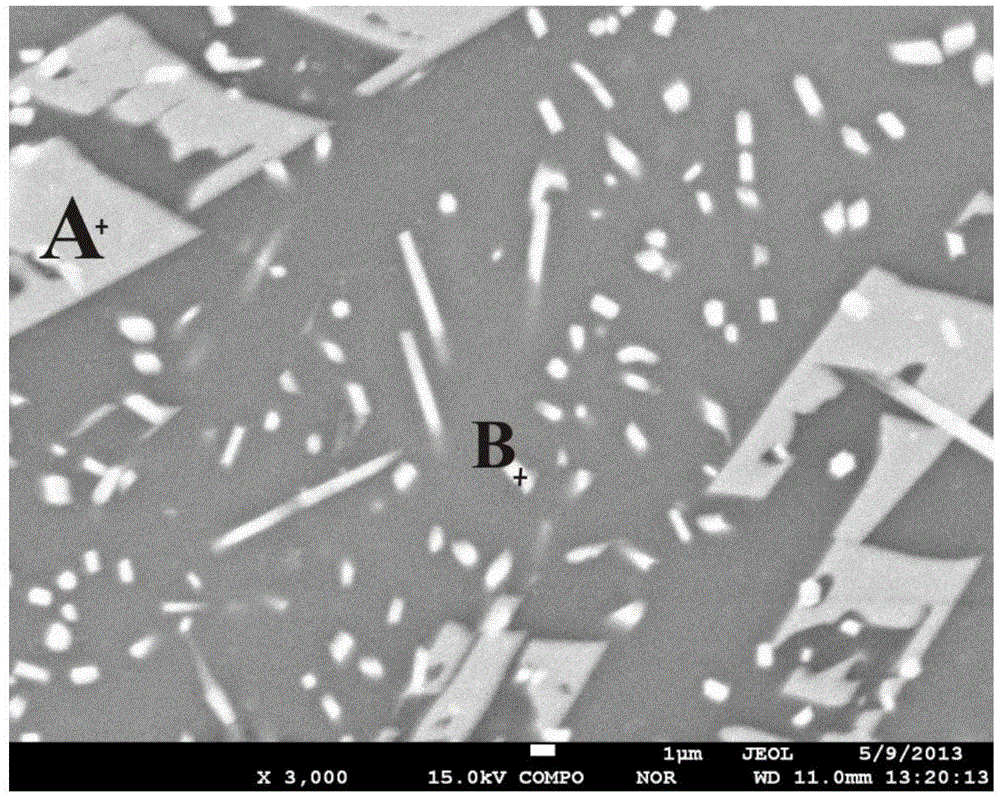
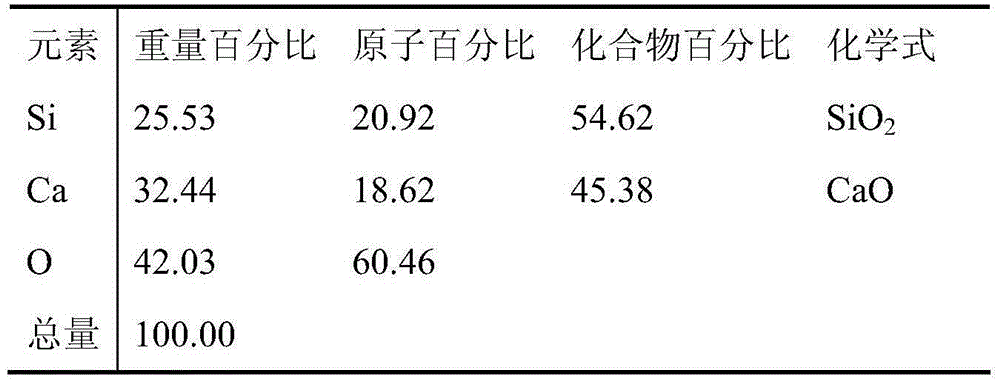
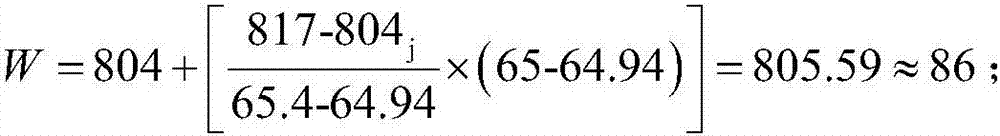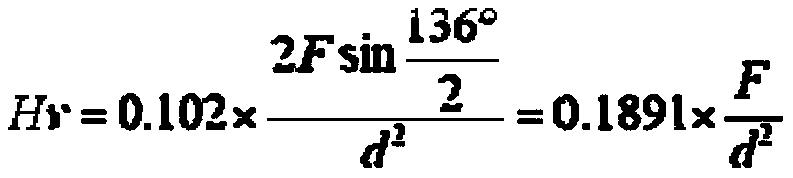Patents
Literature
35 results about "Vickers hardness test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
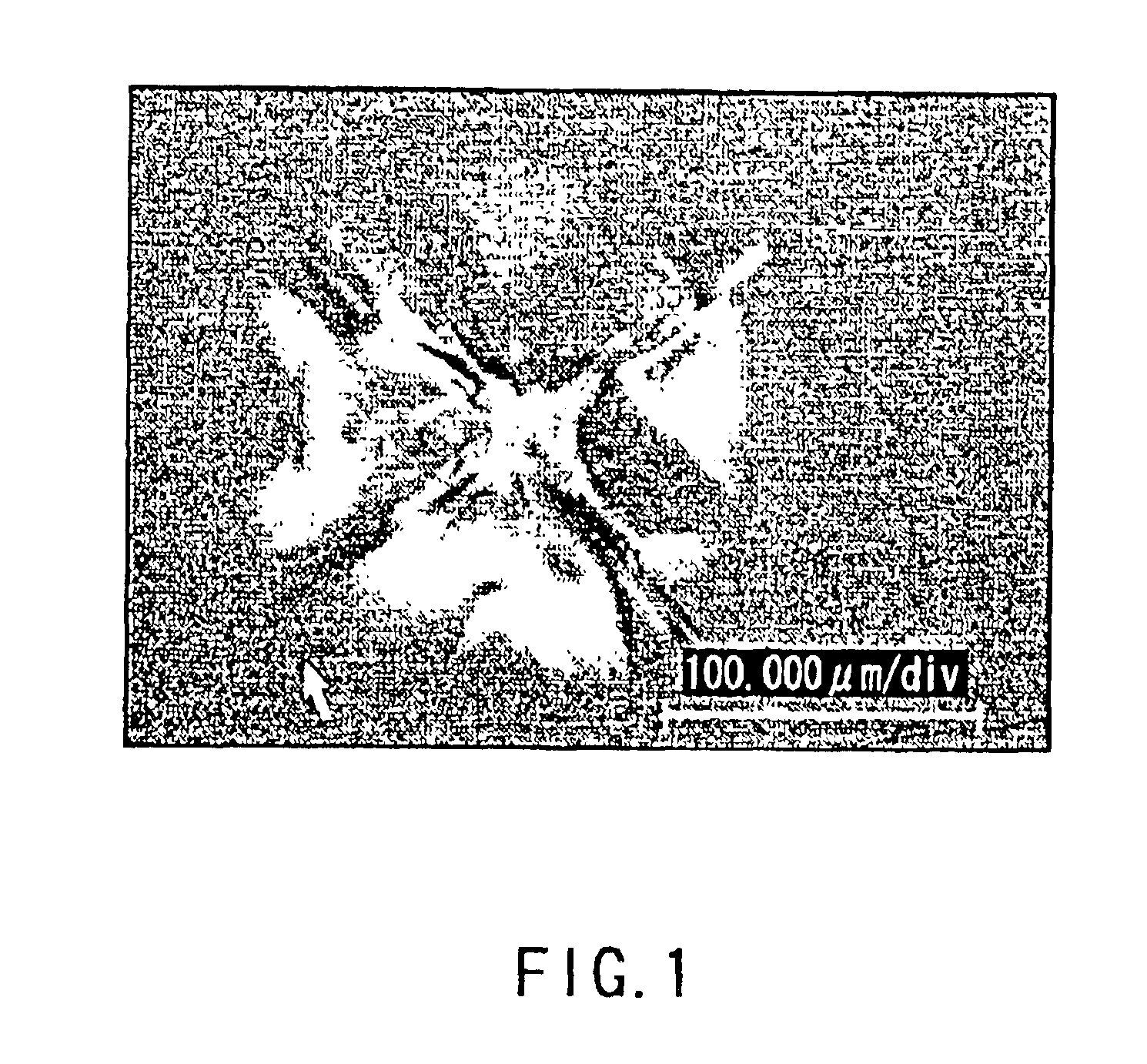
The Vickers hardness test was developed in 1921 by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers test is often easier to use than other hardness tests since the required calculations are independent of the size of the indenter, and the indenter can be used for all materials irrespective of hardness. The basic principle, as with all common measures of hardness, is to observe a material's ability to resist plastic deformation from a standard source. The Vickers test can be used for all metals and has one of the widest scales among hardness tests. The unit of hardness given by the test is known as the Vickers Pyramid Number (HV) or Diamond Pyramid Hardness (DPH). The hardness number can be converted into units of pascals, but should not be confused with pressure, which uses the same units. The hardness number is determined by the load over the surface area of the indentation and not the area normal to the force, and is therefore not pressure.
Universal testing machine
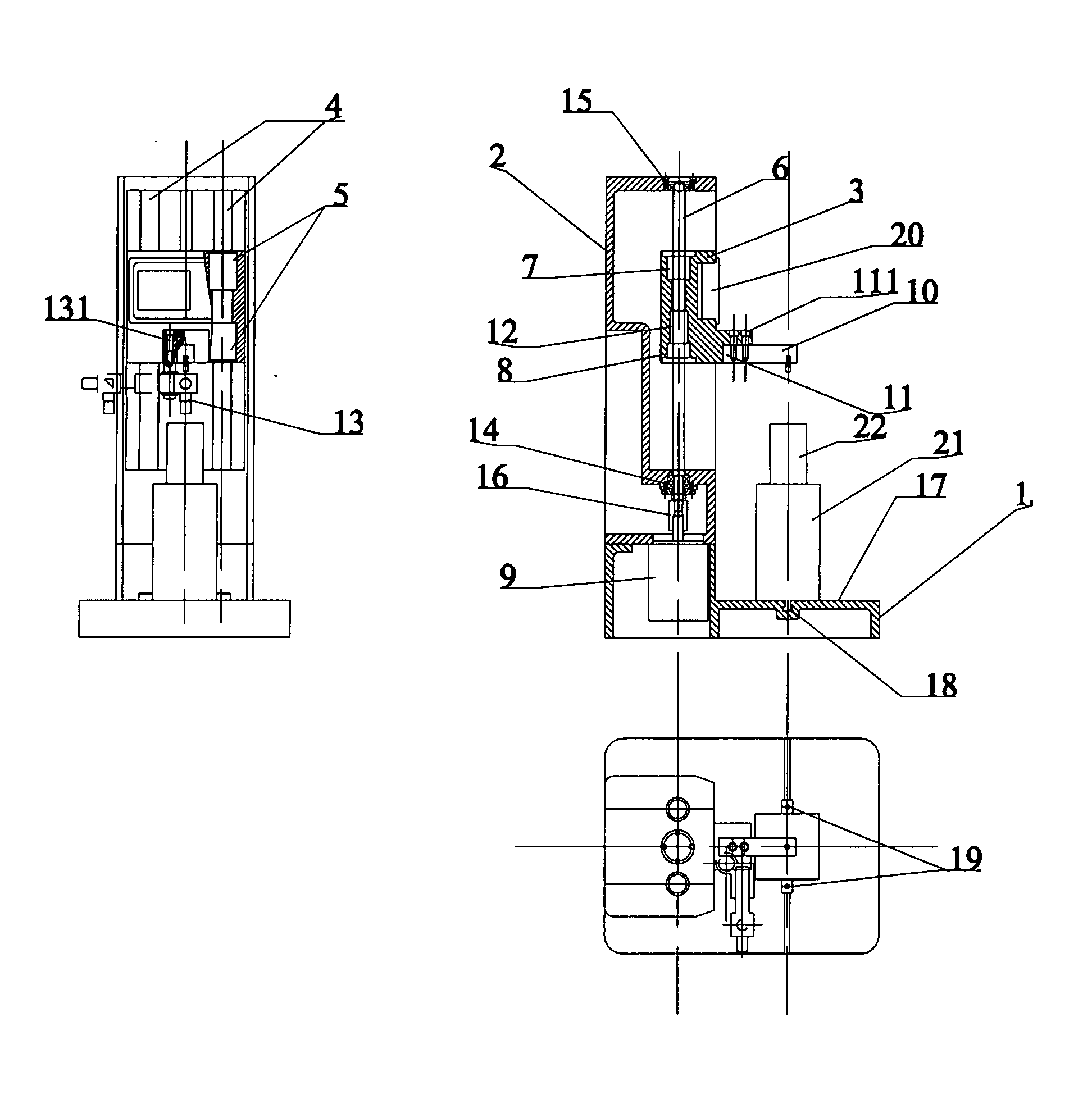
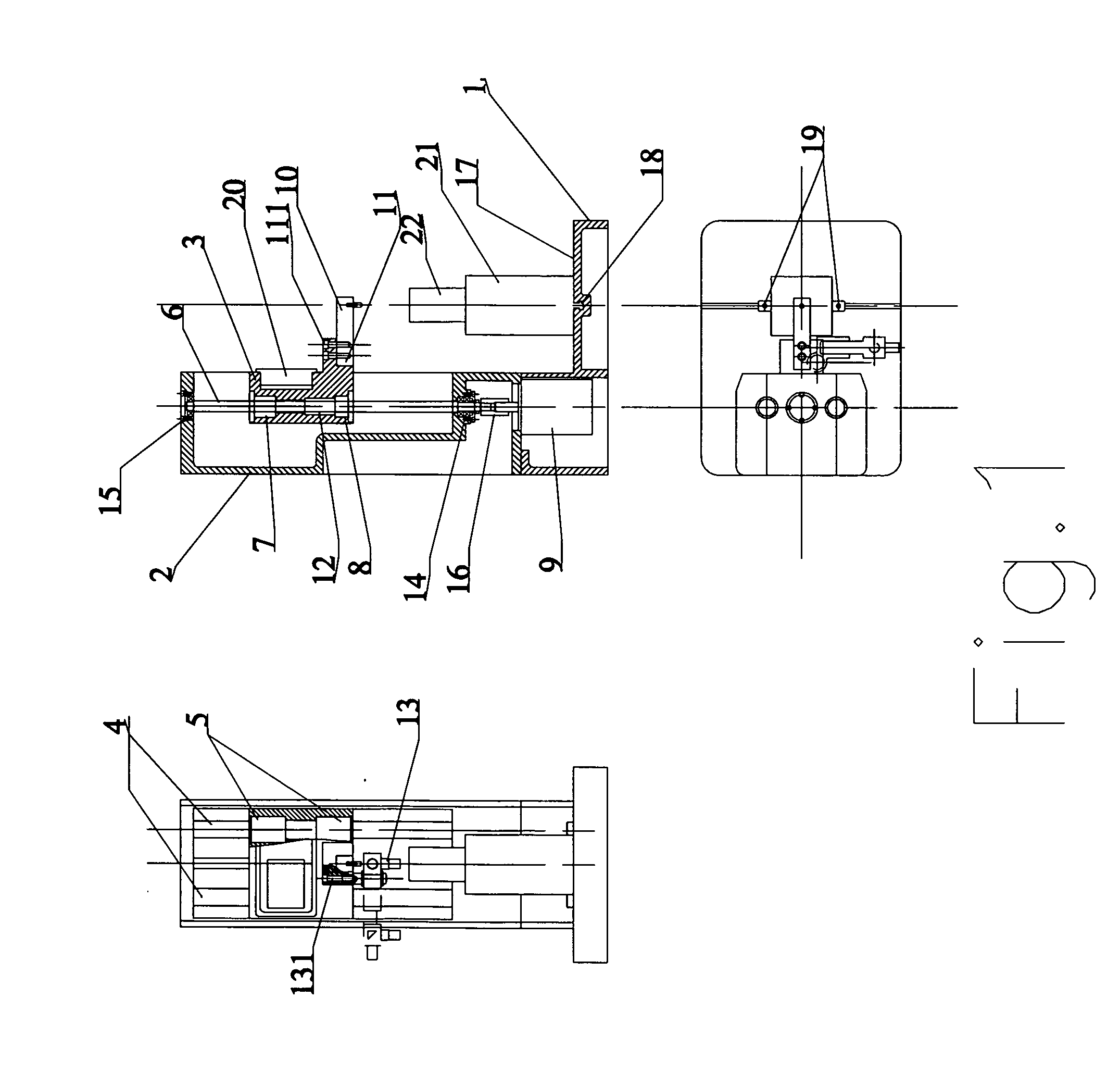
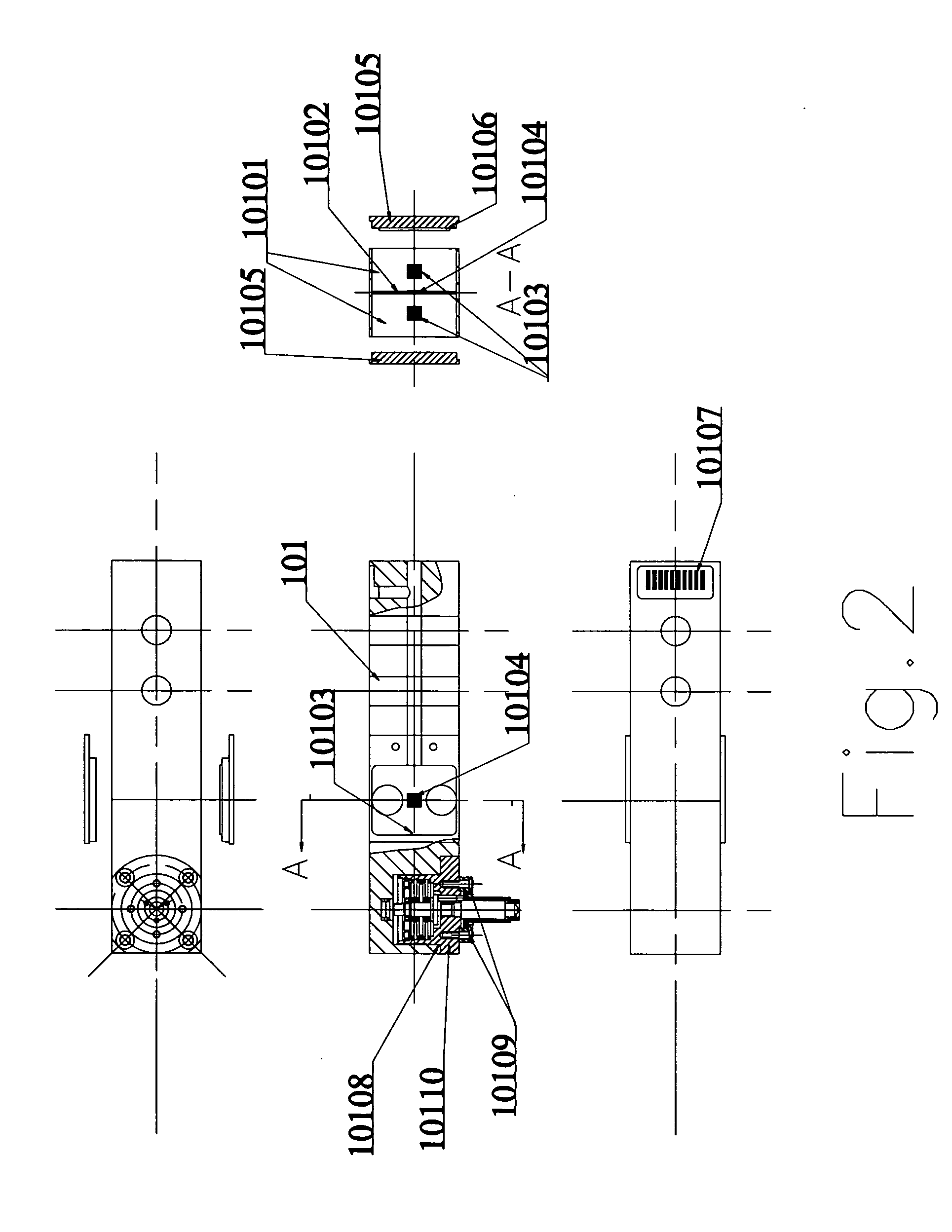
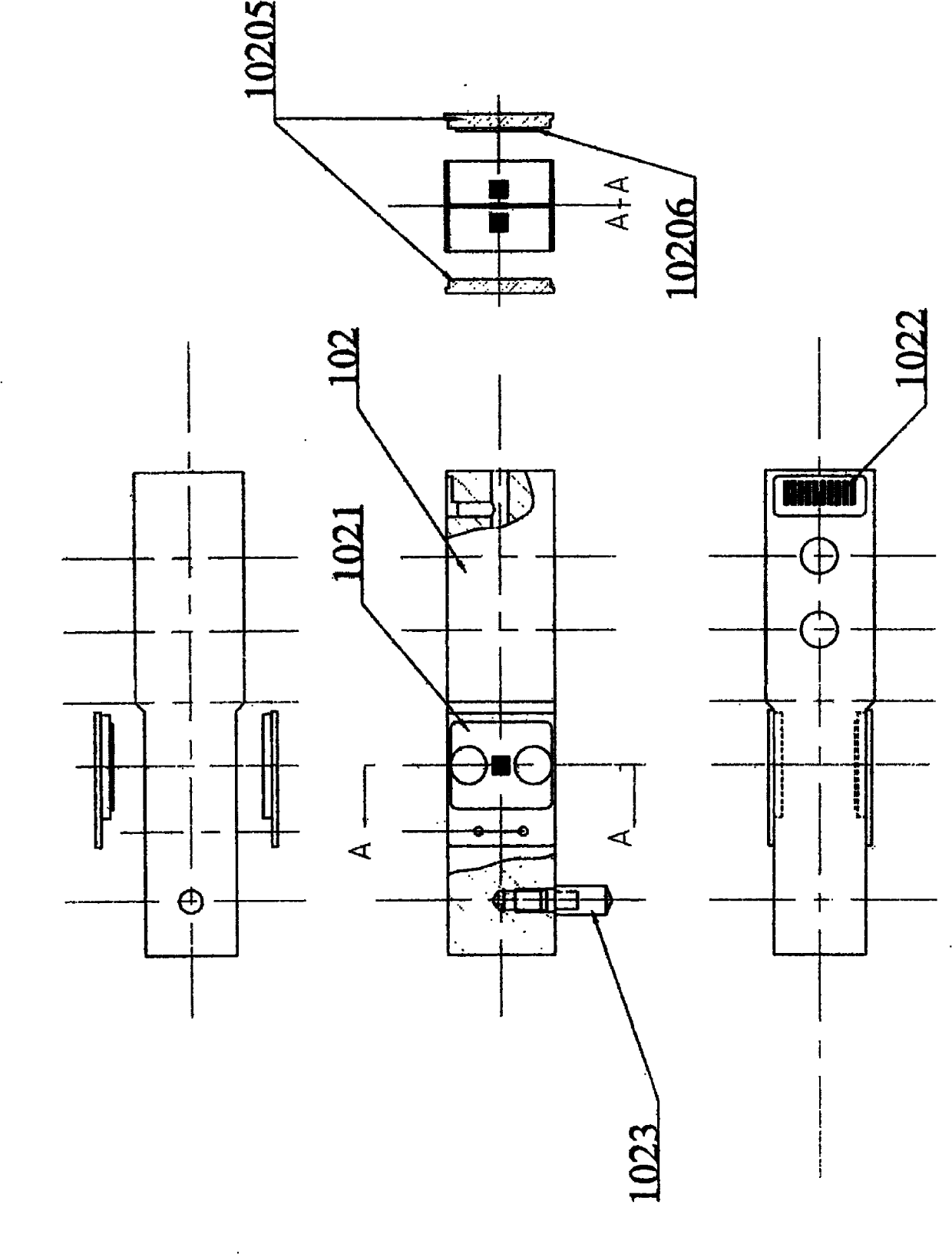
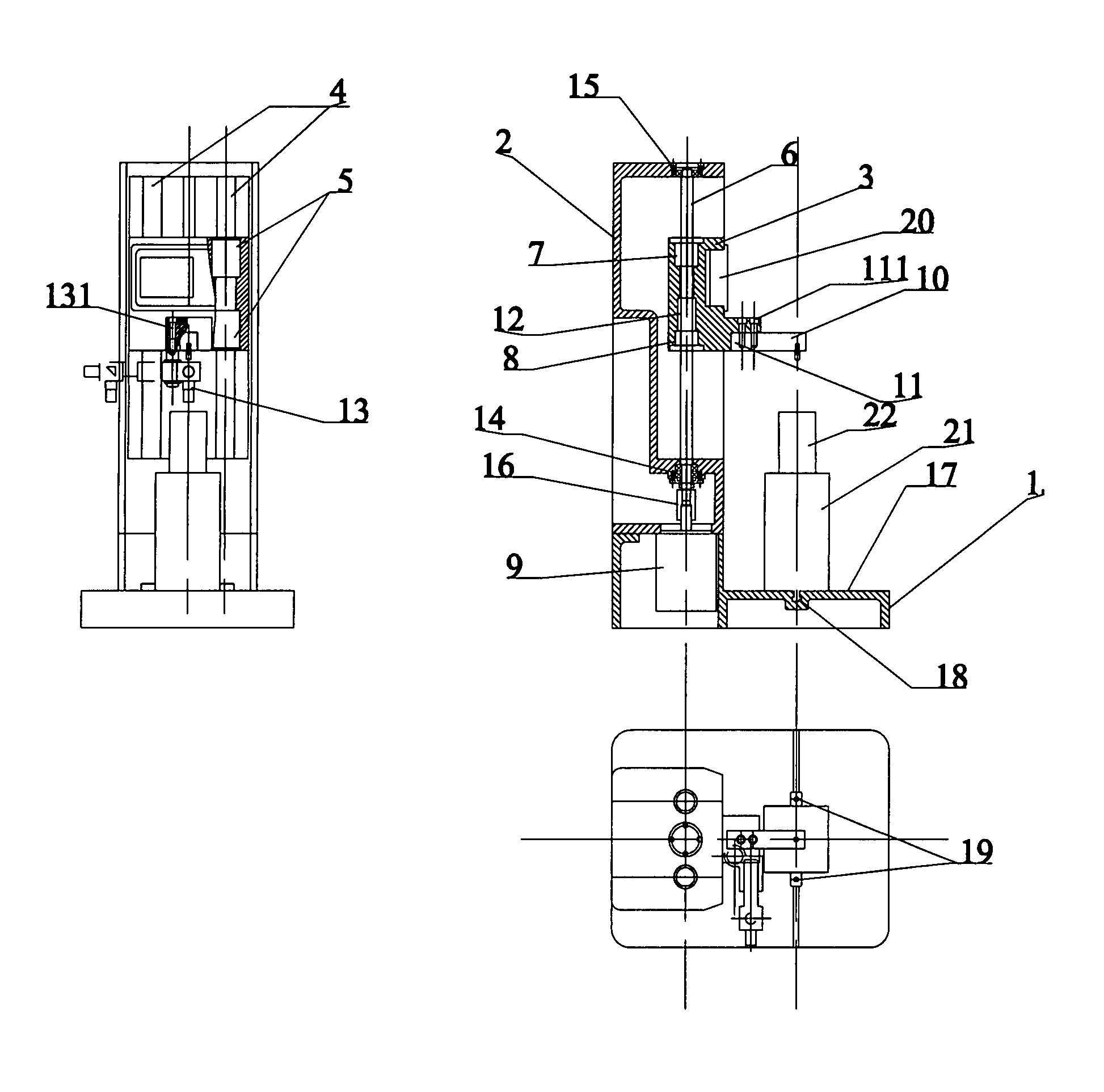
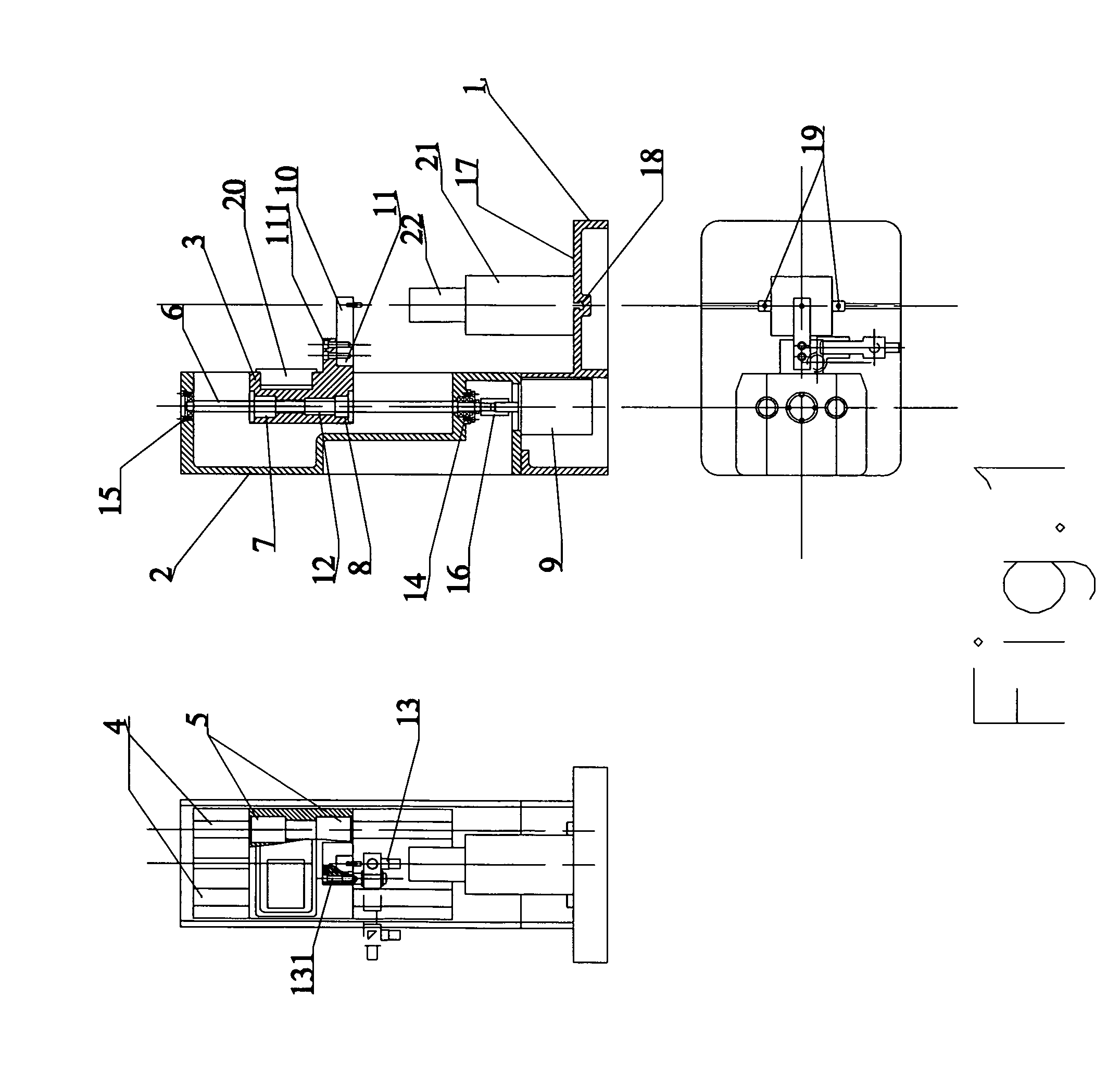
ActiveUS20110132078A1Easy to switchEasy to mountMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesInvestigating material hardnessDigital dataEngineering
A testing machine includes a stand and a test device. The stand includes a base, box frame, a slide device driven to slide by a motor, and a control system controls the force applied on the test specimen. The test device is coupled at the slide device for performing various hardness tests consisting of Rockwell hardness test, Vickers hardness test, Brinell hardness test, micro-hardness test, and tension-compression test. The test device includes a force sensor and a data processing circuit converting an analog signal of the force sensor into digital data to interface with the control system.
Owner:WUSOMING +1
Universal testing machine
ActiveCN102213661AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesInvestigating material hardnessKnoop hardness testDigital data
A testing machine includes a stand and a test device. The stand includes a base, box frame, a slide device driven to slide by a motor, and a control system controls the force applied on the test specimen. The test device is coupled at the slide device for performing various hardness tests consisting of Rockwell hardness test, Vickers hardness test, Brinell hardness test, micro-hardness test, and tension-compression test. The test device includes a force sensor and a data processing circuit converting an analog signal of the force sensor into digital data to interface with the control system.
Owner:吴绍明 +1
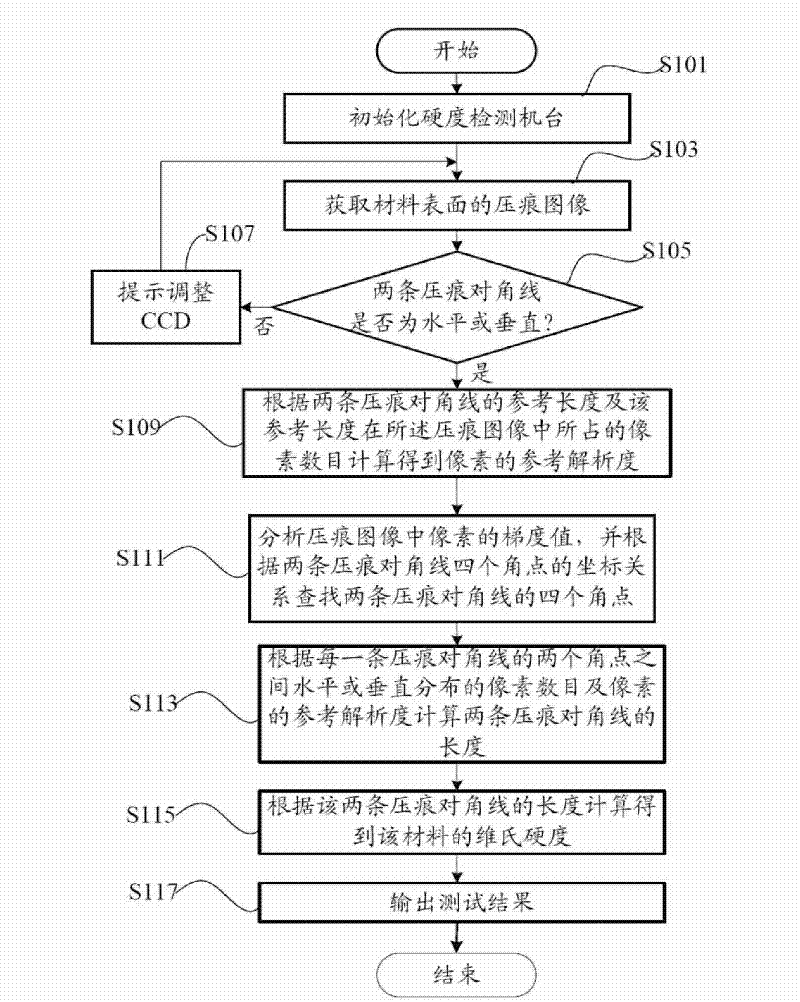
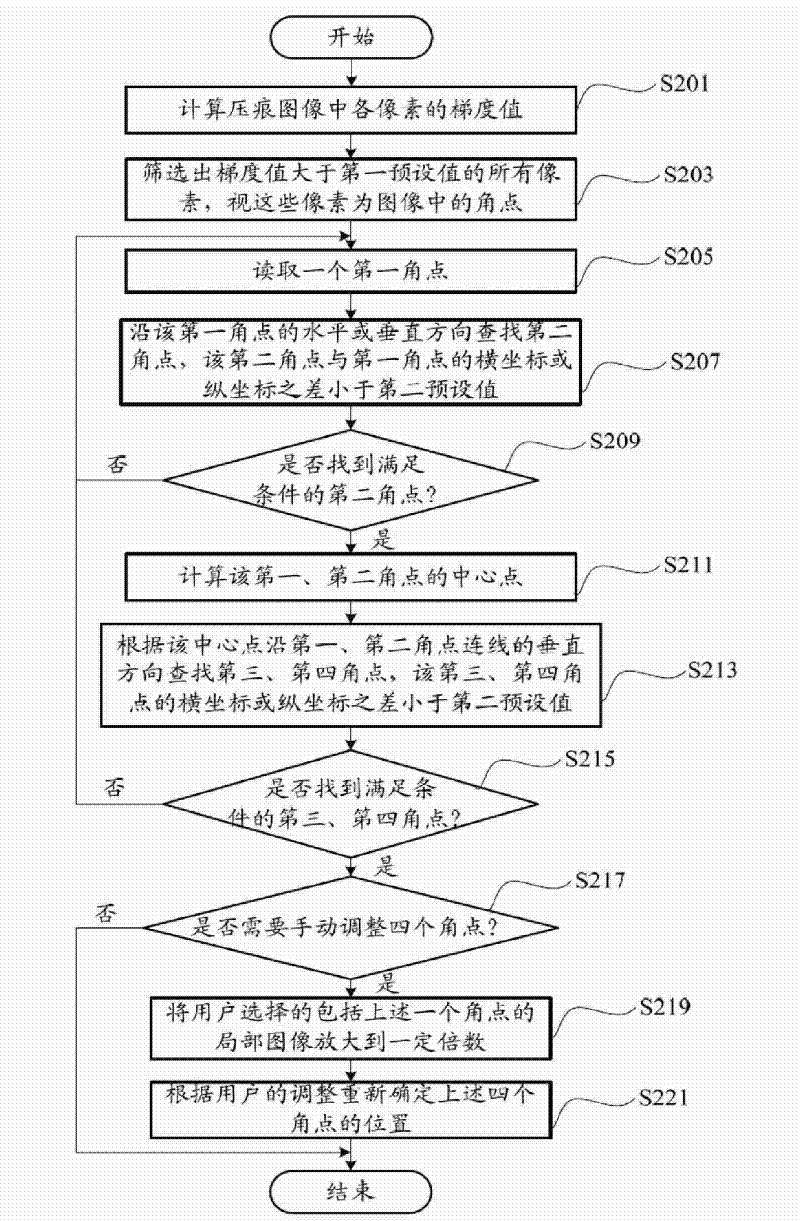
Vickers hardness test system and method
InactiveCN101839832AAccurately determineHigh precisionImage analysisInvestigating material hardnessKnoop hardness testSystems analysis
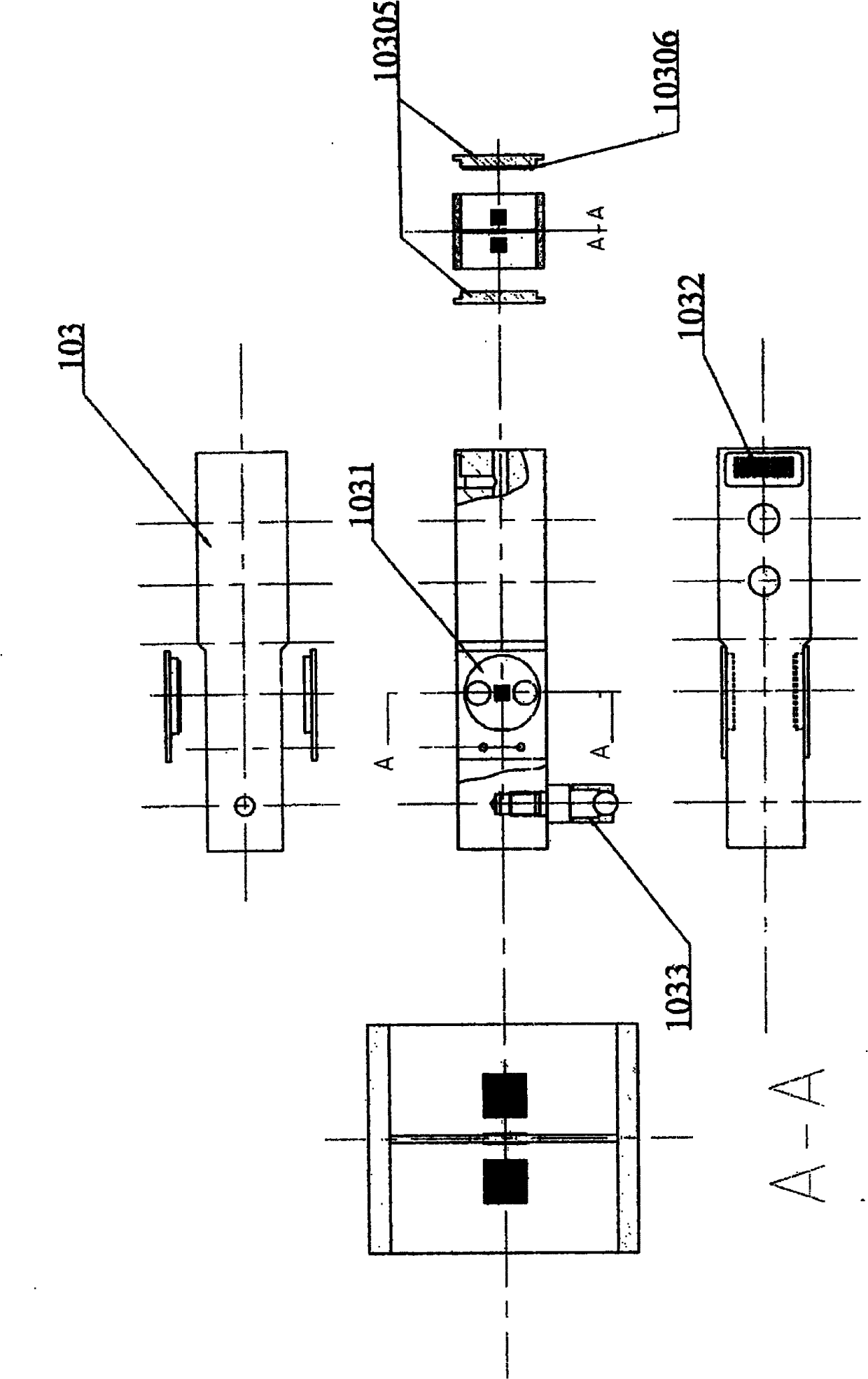
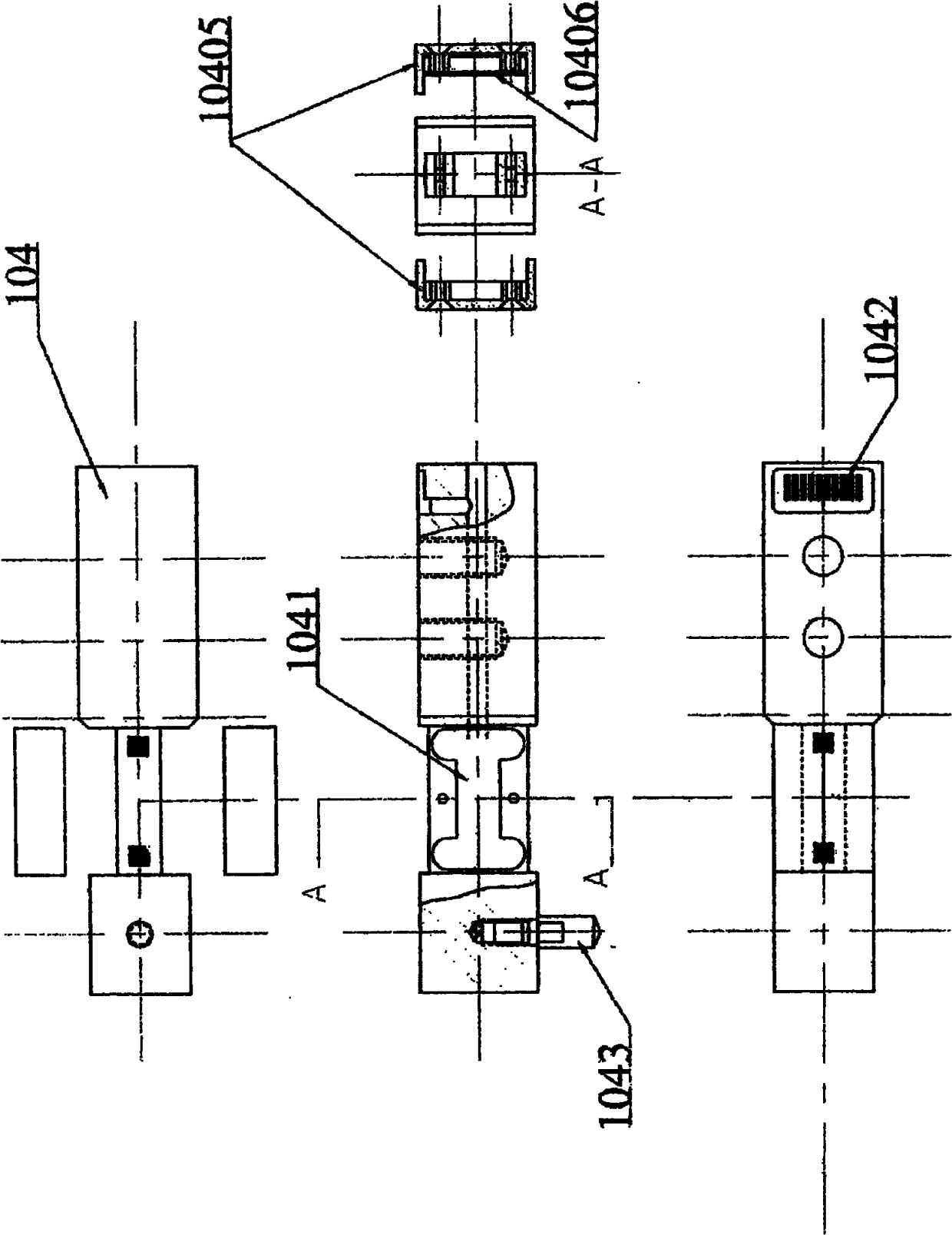
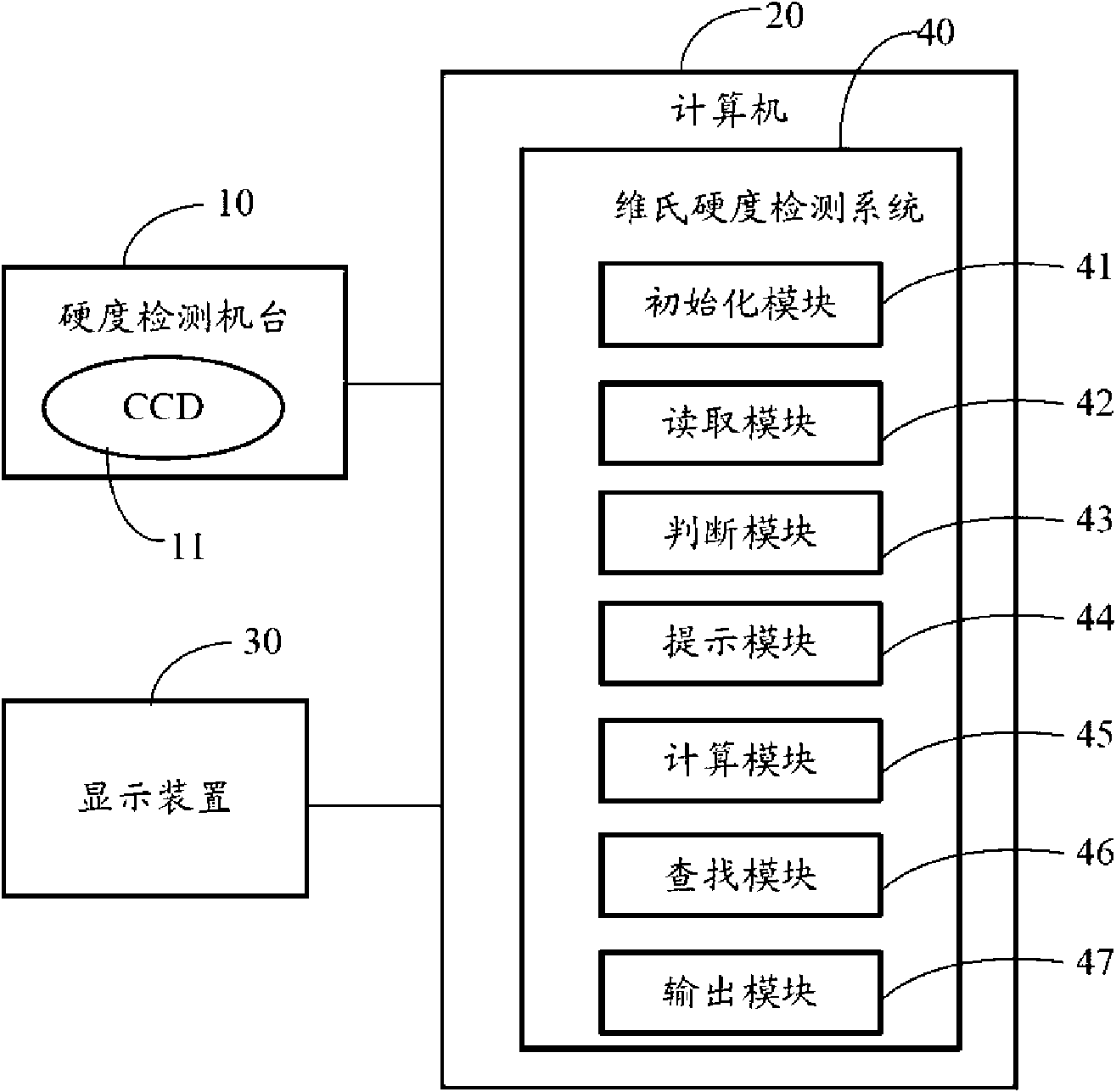
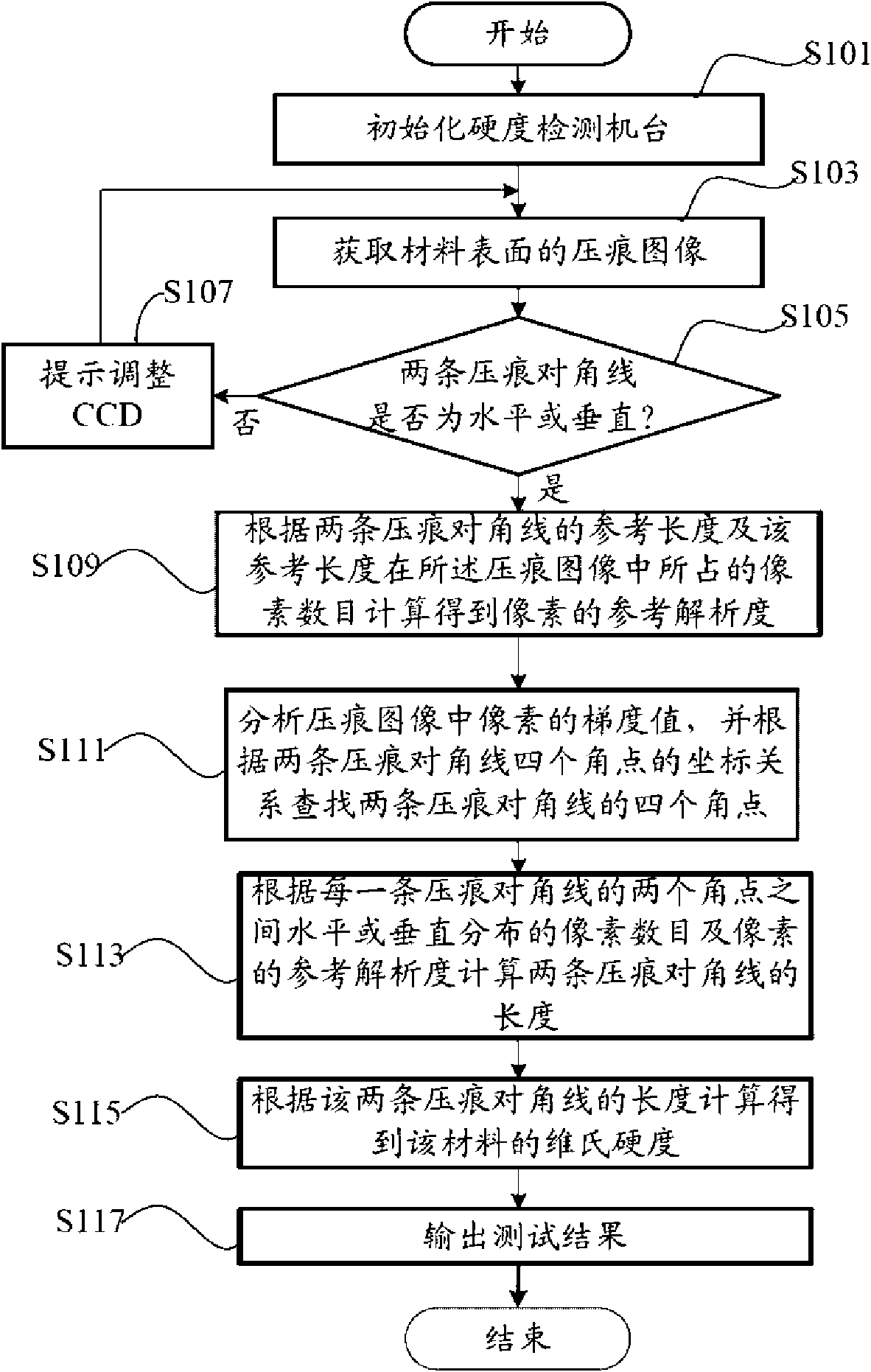
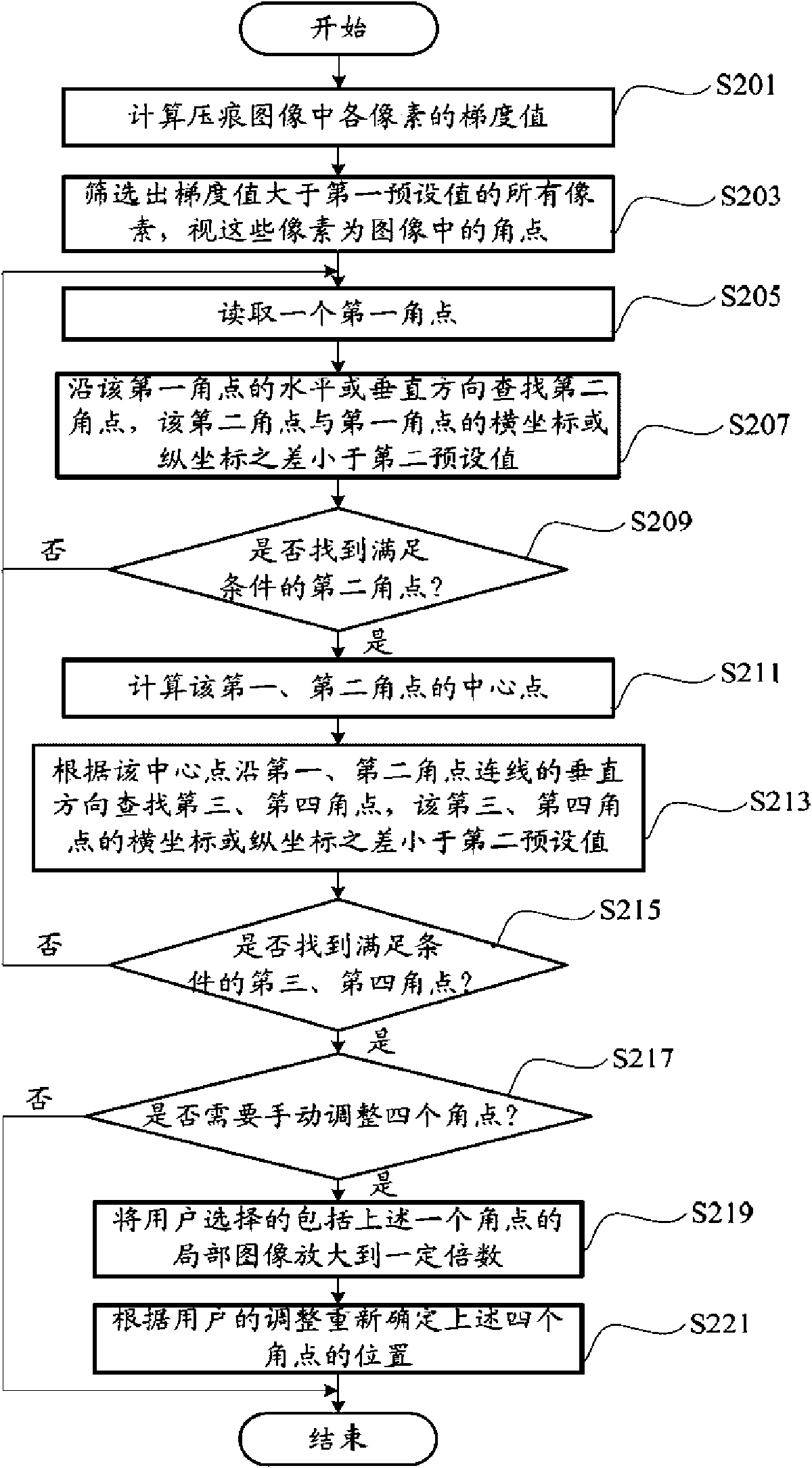
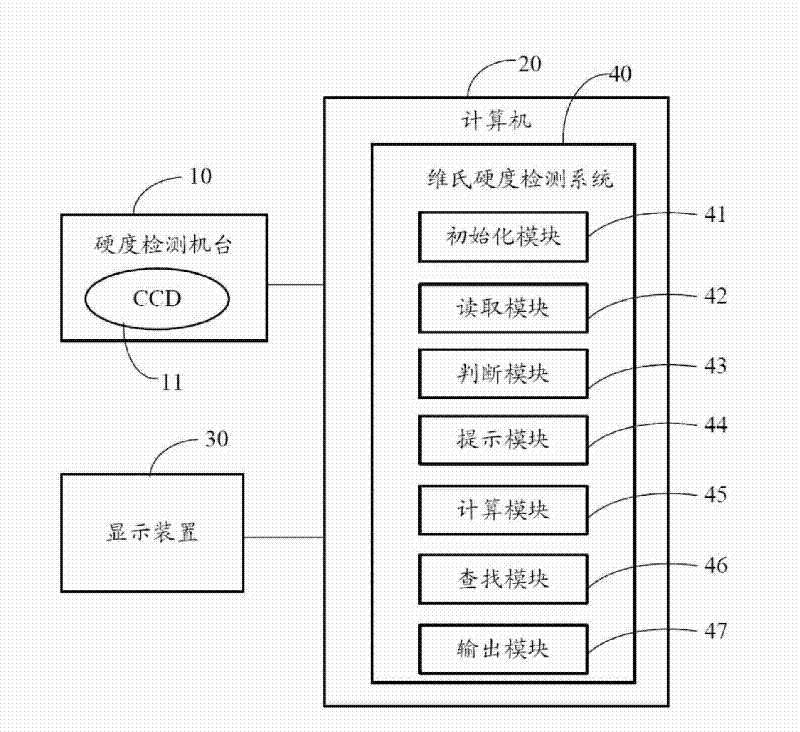
The invention provides a Vickers hardness test system, which is run on a computer, and the computer is connected with a hardness test platform. The hardness test platform utilizes an industrial optical lens and a charge-coupled device to acquire the indentation image of the surface of material to be tested, and transmits the indentation image to the computer. The computer utilizes the Vickers hardness detection system to carry out analysis in order to obtain the positions of the four corners of two indentation diagonals in the indentation image, the lengths of the two indentation diagonals are calculated according to the four corners, the Vickers hardness of the material to be tested is then calculated according to the lengths of the two indentation diagonals, and a test result is outputted to a display device connected with the computer. The invention also provides a Vickers hardness test method. The invention can accurately determine the position of the indentation of the surface of material, and therefore the precision of hardness test is increased.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Glass composition for an electric lamp, stem and bulb for an electric lamp using the same, and electric lamp using the same
InactiveUS6812175B2Reduce brittlenessGas discharge lamp detailsMaterials scienceVickers hardness test
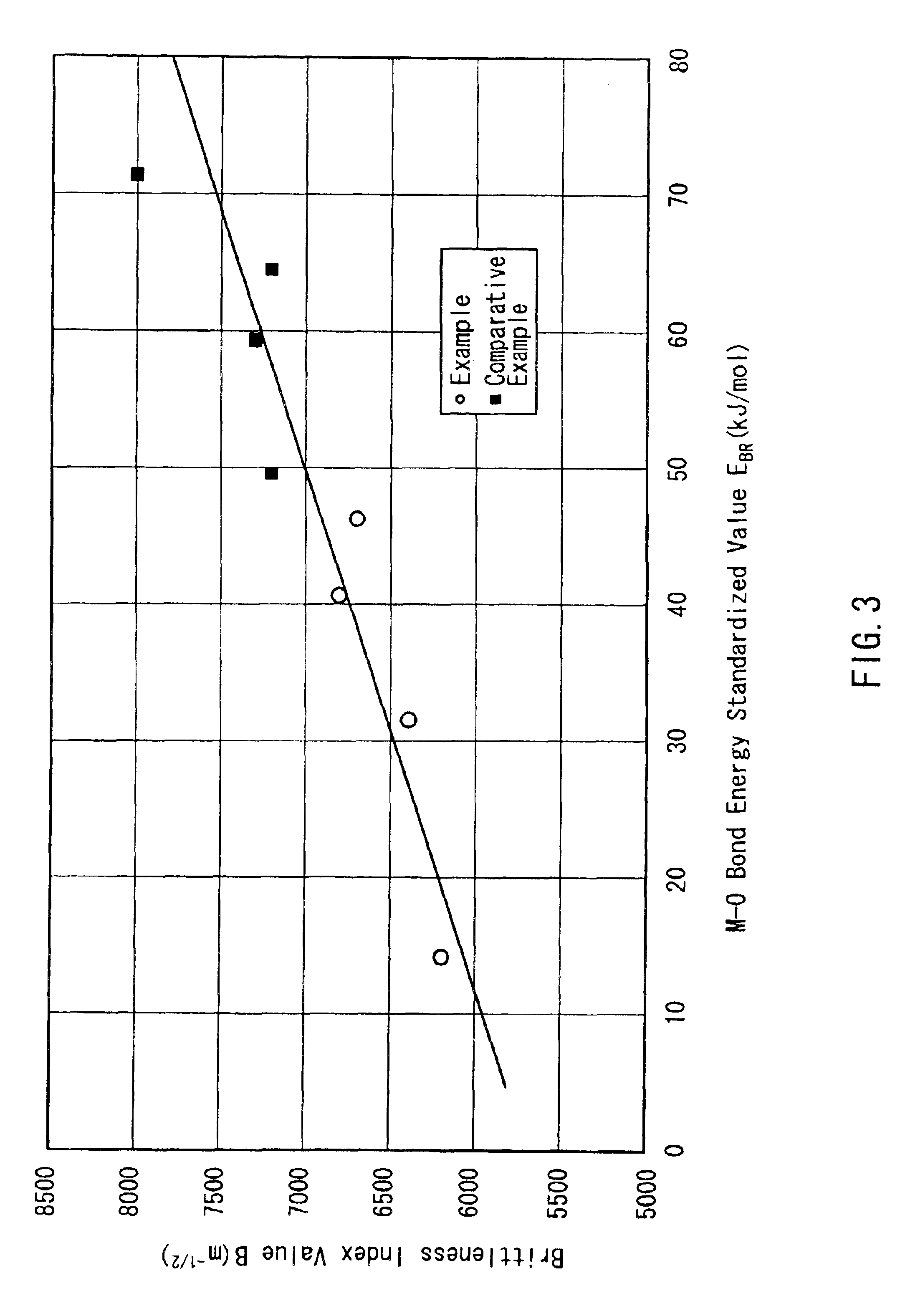
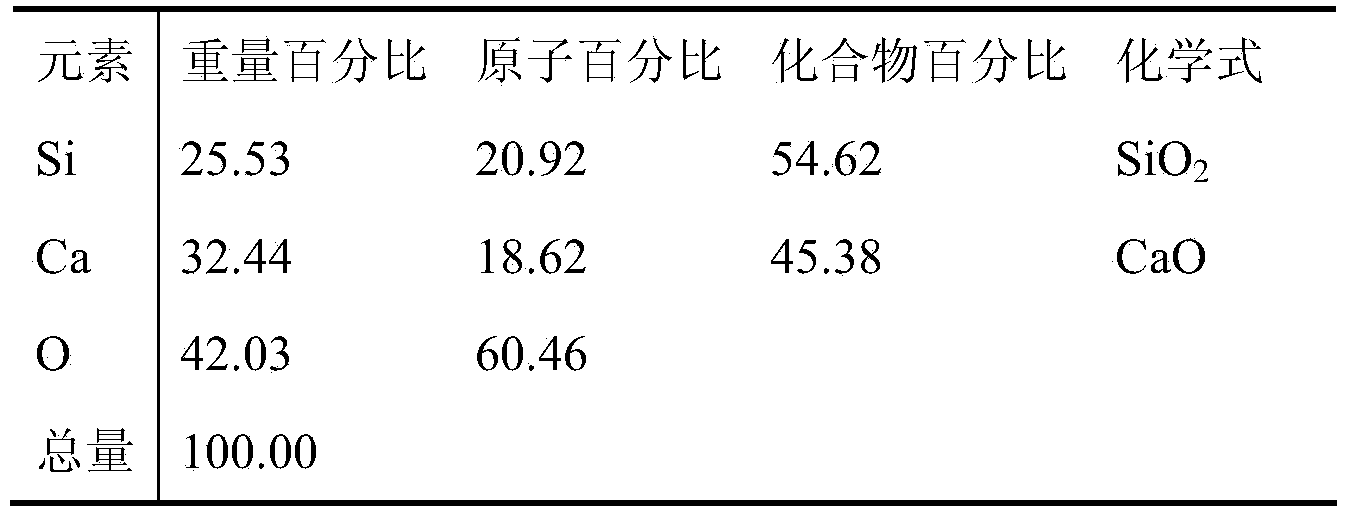
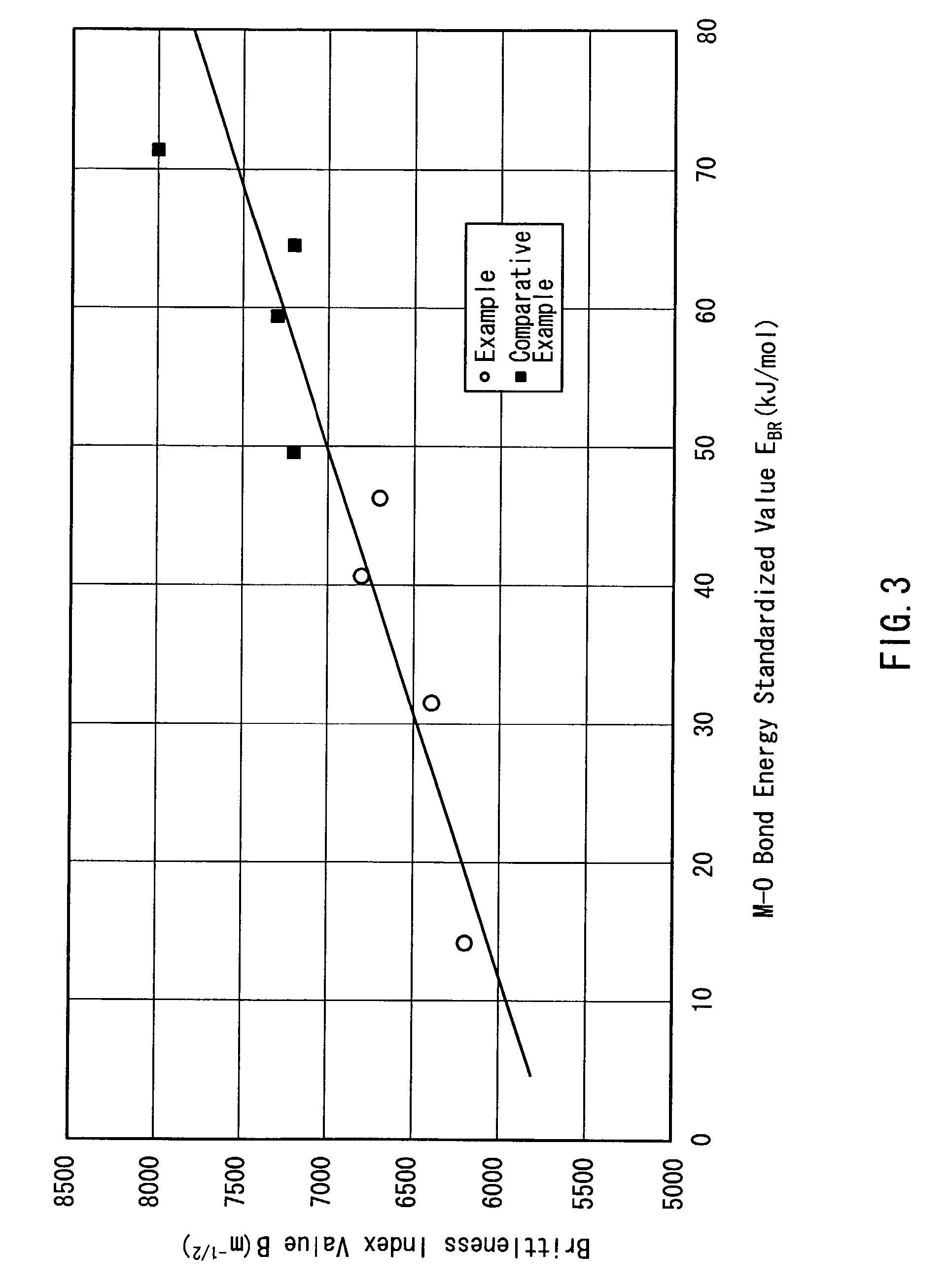
To suppress breakage of glass for an electric lamp in a process in which the glass that has already been formed is processed further, a glass composition for an electric lamp is provided. The glass composition contains, expressed in mol %, 70 to 85% of SiO2, 12 to 17% of R2O, and 2 to 8.5% of MO (where R represents at least one selected from Li, Na and K, and M represents at least one selected from Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Zn and Pb). In the glass composition, the respective contents of CaO, MgO, BaO and SrO satisfy the relationship, CaO+MgO>BaO+SrO. The glass composition has a brittleness index value B determined by the Vickers hardness test of 7,000 m<-1 / 2>. Preferably, the contents of SrO and BaO are 0 to 0.5% and 0.1 to 1%, respectively. More preferably, the respective contents of K2O and Na2O satisfy the relationship, K2O>Na2O.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Universal testing machine
ActiveUS8132447B2Easy to operateHigh precision measurementMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesInvestigating material hardnessDigital dataEngineering
A testing machine includes a stand and a test device. The stand includes a base, box frame, a slide device driven to slide by a motor, and a control system controls the force applied on the test specimen. The test device is coupled at the slide device for performing various hardness tests consisting of Rockwell hardness test, Vickers hardness test, Brinell hardness test, micro-hardness test, and tension-compression test. The test device includes a force sensor and a data processing circuit converting an analog signal of the force sensor into digital data to interface with the control system.
Owner:WUSOMING +1
Beige tooth microcrystalline glass compounded by frits of wollastonite and apatite
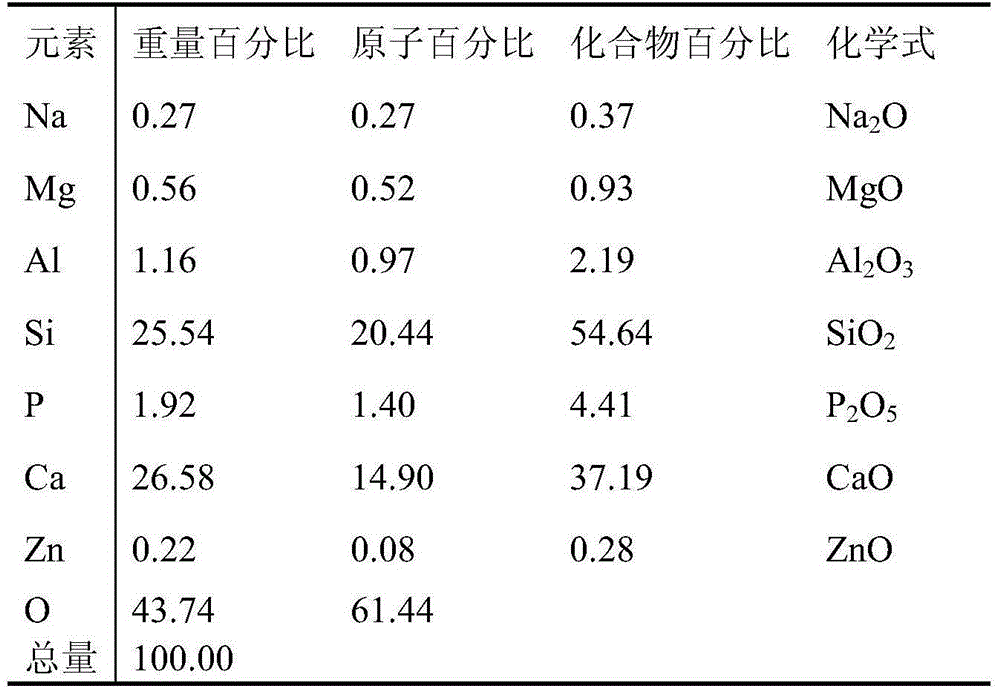
The invention discloses a beige tooth microcrystalline glass compounded by frits of wollastonite and apatite. The beige tooth microcrystalline glass is prepared through a sintering method after smashing and mixing white microcrystalline glass frits in a single wollastonite crystalline phase and beige microcrystalline glass frits in a single apatite crystalline phase, the bending strength of the prepared material is less than or equal to 80 Mpa, the Vickers hardness tested by an FM-700 type microhardness tester is less than or equal to 5.80 GPa (HV 0.5). According to the invention, through the adjustment of frit composition proportion and the mixing ratio of the two types of frits, microcrystalline glass similar to teeth of different crowds in color can be prepared; under the premise that the constituent ratio in a unitary system is not needed to be adjusted, the mechanical property and the color of the microcrystalline glass can be adjusted through changing the mixing ratio of the mixing frits,; the preparation technology requirements are low; industrialized popularization and application are facilitated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rockwell hardness judging method of thin-specification Cr-Ni system austenite stainless steel plate
The invention provides a Rockwell hardness judging method of a thin-specification Cr-Ni system austenite stainless steel plate. The Rockwell hardness judging method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) selecting two groups of products produced by one unit, wherein the thickness of each product in the first group is more than 1.50mm and the first group comprises at least 50 products; the thickness of each product in the second group is less than or equal to 1.50mm and the second group comprises at least 50 products; (2) testing the first group of products by using a method specified by Metal Material Rockwell Hardness Testing Method to obtain a hardness number HRB average value in production; (3) obtaining a metallic Vickers hardness number HV average by testing the second group of products according to Metal Material Vickers Hardness Test; and (4) judging by utilizing a formula HRB=HV / 1.98: if the HRB=HV / 1.98 meets goods ordering standard requirements, judging that the thin-specification Cr-Ni system austenite stainless steel plate is qualified; and if the HRB=HV / 1.98 does not meet the goods ordering standard requirements, judging that the thin-specification Cr-Ni system austenite stainless steel plate is unqualified. The Rockwell hardness judging method disclosed by the invention solves the difficulty of a thin sheet plate HRB test.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
Glass composition for an electric lamp, stem and bulb for an electric lamp using the same, and electric lamp using the same
InactiveUS20030050176A1Reduce brittlenessGas discharge lamp detailsMaterials scienceVickers hardness test
To suppress breakage of glass for an electric lamp in a process in which the glass that has already been formed is processed further, a glass composition for an electric lamp is provided. The glass composition contains, expressed in mol %, 70 to 85% of SiO2, 12 to 17% of R2O, and 2 to 8.5% of MO (where R represents at least one selected from Li, Na and K, and M represents at least one selected from Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Zn and Pb). In the glass composition, the respective contents of CaO, MgO, BaO and SrO satisfy the relationship, CaO+MgO>BaO+SrO. The glass composition has a brittleness index value B determined by the Vickers hardness test of 7,000 m-½. Preferably, the contents of SrO and BaO are 0 to 0.5% and 0.1 to 1%, respectively. More preferably, the respective contents of K2O and Na2O satisfy the relationship, K2O>Na2O.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electrophotographic photoreceptor, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20100330473A1Reduce solubilityReduce the amount of solutionElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeHardnessMelamine
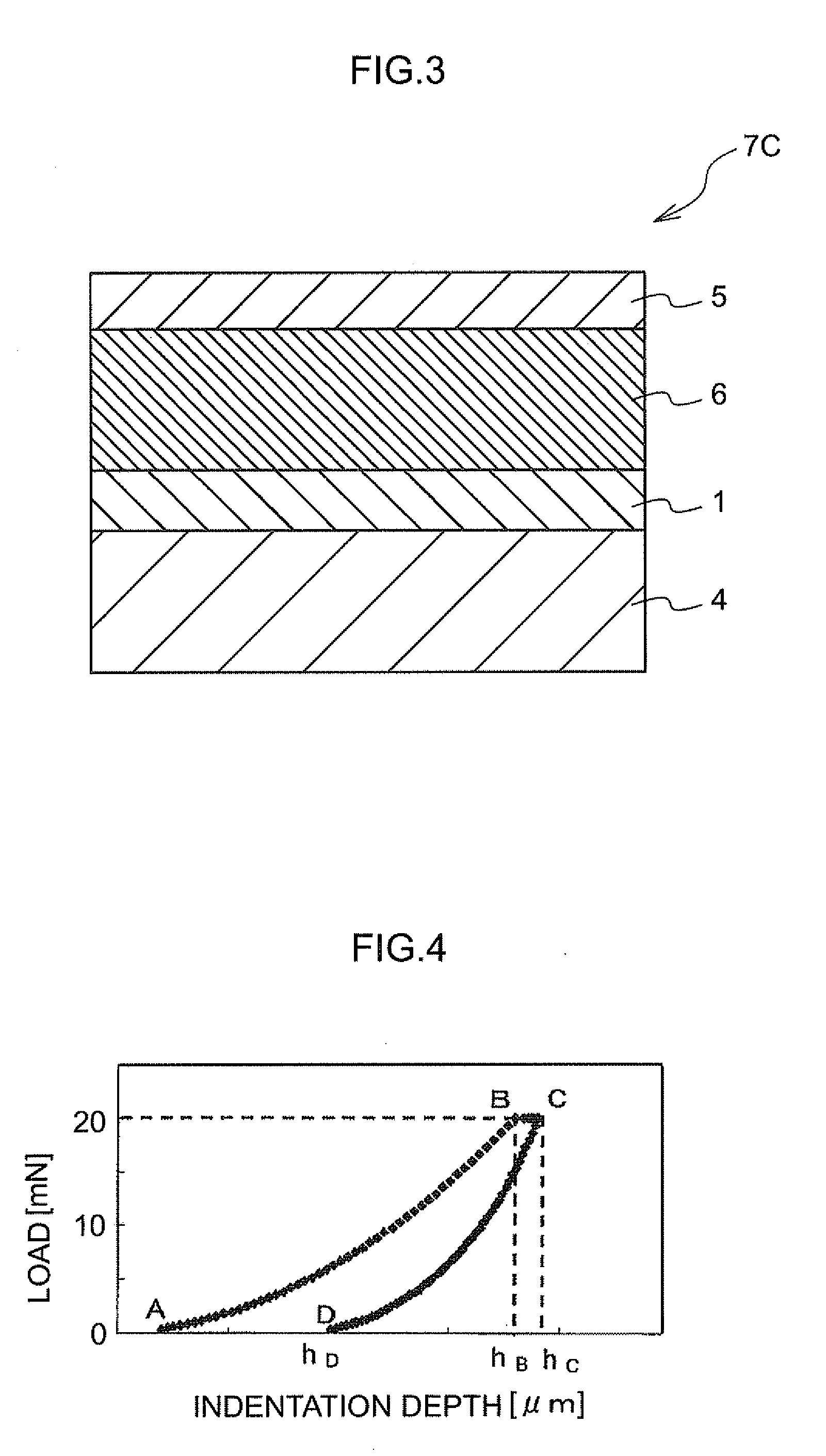
The invention provides an electrophotographic photoreceptor having a surface protection layer that satisfies the following requirements: (1) including a crosslinked substance of at least one selected from a guanamine compound or a melamine compound, and at least one charge transporting material having at least one substituent selected from —OH, —OCH3, —NH2, —SH or —COOH; (2) including the at least one of a guanamine compound or a melamine compound in an amount of from about 0.1 to about 5% by weight; and (3) having a universal hardness of from about 180 to about 220 N / mm2 and a creep ratio of from about 5% to about 8%, the universal hardness and the creep ratio being obtained by performing a hardness test by pushing a Vickers quadrangular pyramid diamond indenter against the surface protection layer at a maximum load of 20 mN, in an environment of 25° C. and a relative humidity of 50%.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Method for achieving plasticity parameter parametric inversion recognition of welding nuclear area material
InactiveCN107314938AHigh precisionImprove recognition efficiencyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesInvestigating material hardnessAlgorithmHardness
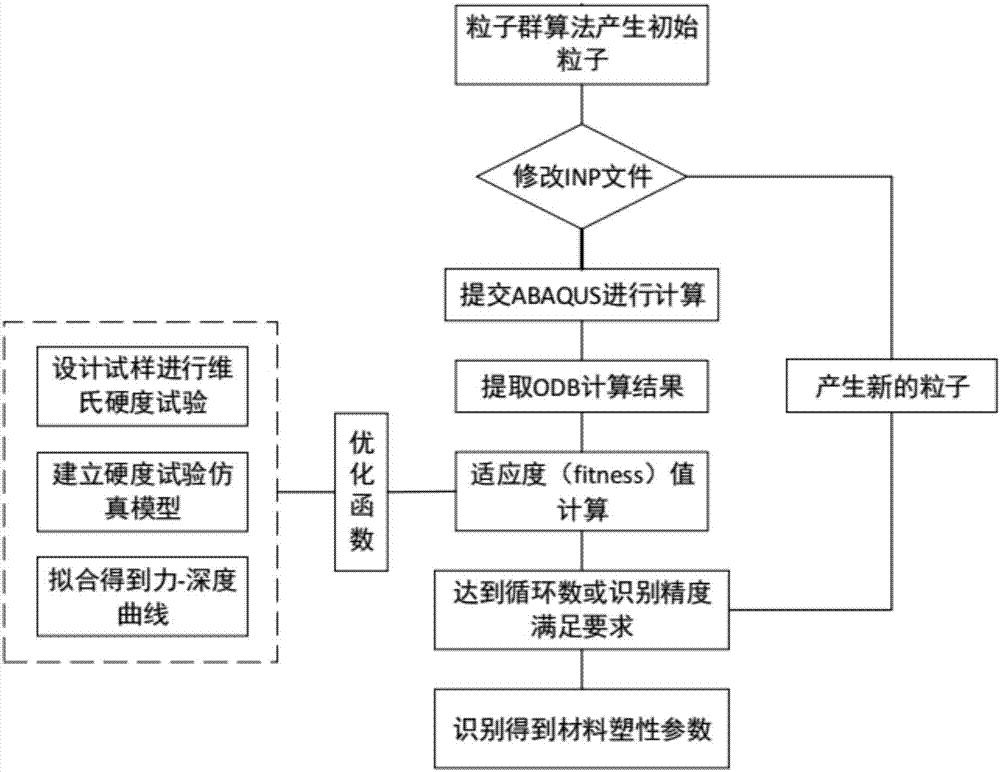
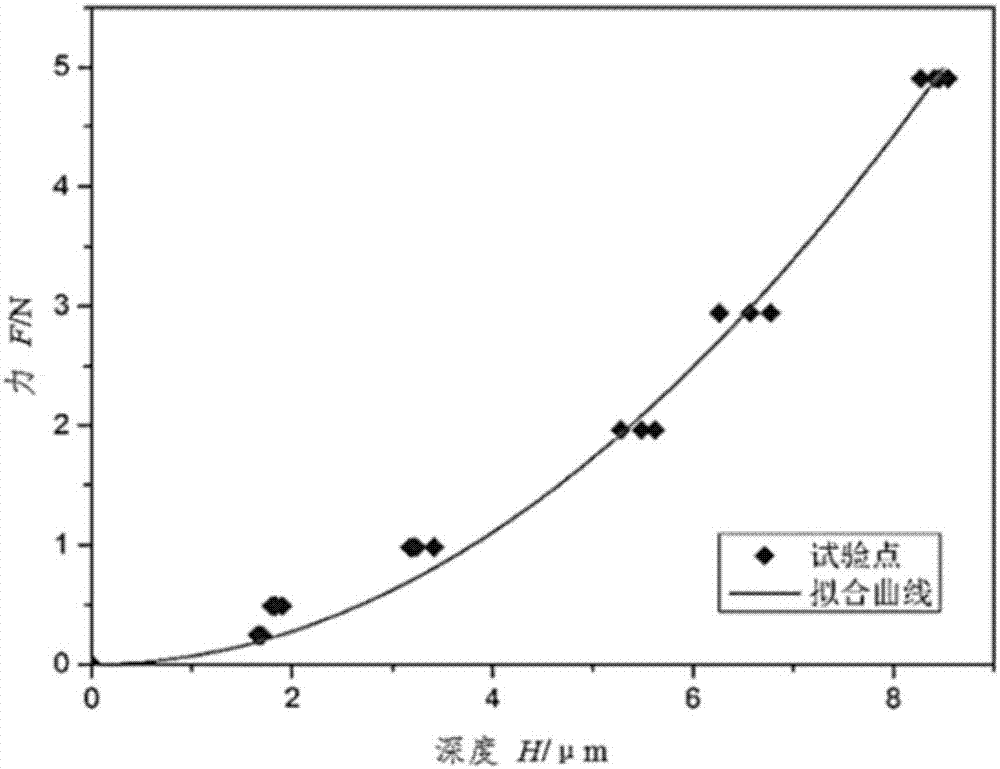
The invention discloses a method for achieving plasticity parameter parametric inversion recognition of a welding nuclear area material. The method comprises the following steps: testing the Vickers hardness of a material to be tested so as to obtain force-depth data, establishing a fitness optimization function, performing parameter optimization on a particle group algorithm according to the fitness optimization function, and performing recognition by using the optimized particle group algorithm, thereby obtaining optimal fitting plasticity parameters of the material to be tested. By adopting the method, the recognition precision and efficiency of plasticity parameters of materials can be remarkably improved, and a foundation can be made for improving the CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) simulation precision of a welding point structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Vickers hardness and Rockwell hardness conversion method for 8Cr4Mo4V steel
InactiveCN107421830AAchieve conversionSolve the problem of conversion errorsInvestigating material hardnessHardnessData reliability
The invention relates to a Vickers hardness and Rockwell hardness conversion method for 8Cr4Mo4V steel and aims to solve the problems that during the hardness tests of existing 8Cr4Mo4V steel small bearing parts, errors exist when the Vickers hardness is converted into the Rockwell hardness according to the standards GB / T1172-1999 Black Metal Hardness and Strength Conversion Value, data reliability is low, and the prior art does not have a Vickers hardness and Rockwell hardness conversion method. The method includes the steps of firstly, preparing a detection sample; secondly, calibrating hardness testers and determining indication errors; thirdly, collecting sample hardness data, and performing conversion according to a formula as shown in the specification. The Vickers hardness and Rockwell hardness conversion method has the advantages that the method aims at the 8Cr4Mo4V steel small bearing parts and uses the actually detected sample data of the Rockwell hardness tester and the Vickers hardness tester to achieve Vickers hardness and Rockwell hardness conversion; the obtained conversion data is identical with the actually detected data, errors are small, and high data reliability is achieved.
Owner:AVIC HARBIN BEARING
Steel sheet for coal/ore carrier hold
ActiveCN110536973AReduce water seepageReduced Possibility of ContaminationMetal rolling arrangementsSheet steelDislocation
A steel sheet for coal / ore carrier holds that is a ferrite-pearlite steel sheet of specified components, wherein: the microstructure is a structure configured with the ferrite area fraction in the 1 4thickness region being 80-95% and the pearlite area fraction at the 1 4 thickness region being 5-20%, the average aspect ratio of the ferrite grains in the 1 4 thickness region being 1.0-1.5, the average grain size of the ferrite grains in the 1 4 thickness region being 5-20 microns, and the average dislocation density in the ferrite in the 1 4 thickness region being 7*10<12> / m2 or less; in a 1 mm pitch Vickers hardness test, the average Vickers hardness from the steel sheet surface to the 1 4 thickness region or from the 3 4 thickness region to the back surface is 80-105% of the average Vickers hardness from the 1 4 thickness region to the 3 4 thickness region; and the maximum Sn concentration in the 1 2 thickness (sheet thickness) + / - 10% range in the sheet thickness direction is 0.01-5.0%.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
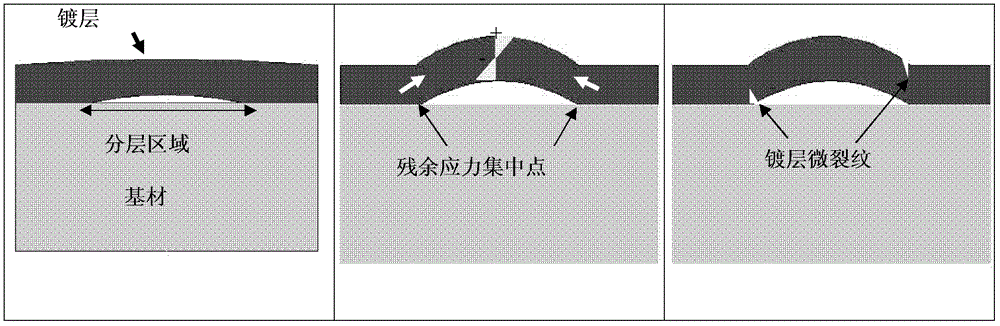
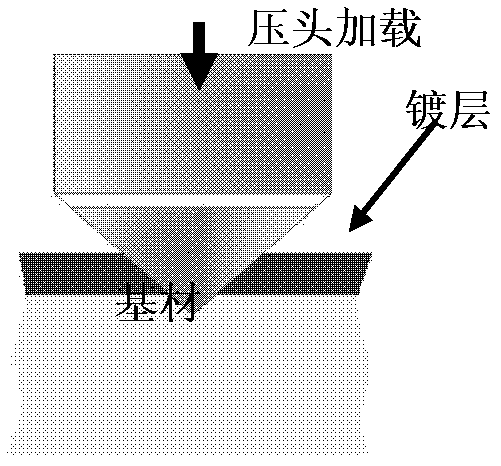
A kind of metal thin film coating bonding quality detection method
InactiveCN102507355BReduce restrictionsDoes not affect appearanceInvestigating material hardnessProgram counterLarge sample
Owner:ZTE CORP
Image forming apparatus
An elastic deformation rate of a photoconductor, an additive amount of inorganic fine particles, and a rotary member are set to satisfy a relation of 0.6≦(D / (A×B / C)) / (1+E / 20)≦0.82, where A is a thickness of fibers of a brush, B is a bristle density of the fibers of the brush, C is a length of the fibers of the brush, D is an elastic deformation rate obtained from a hardness test conducted using a Vickers diamond pyramid indenter at a temperature of 23° C. and a humidity of 50%, and E is the additive amount of the inorganic fine particles relative to 100 parts by mass of toner particles.
Owner:CANON KK
Diamond polycrystal and tool provided with same
ActiveCN110933944APolycrystalline material growthMilling cuttersCrystallographyCondensed matter physics
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
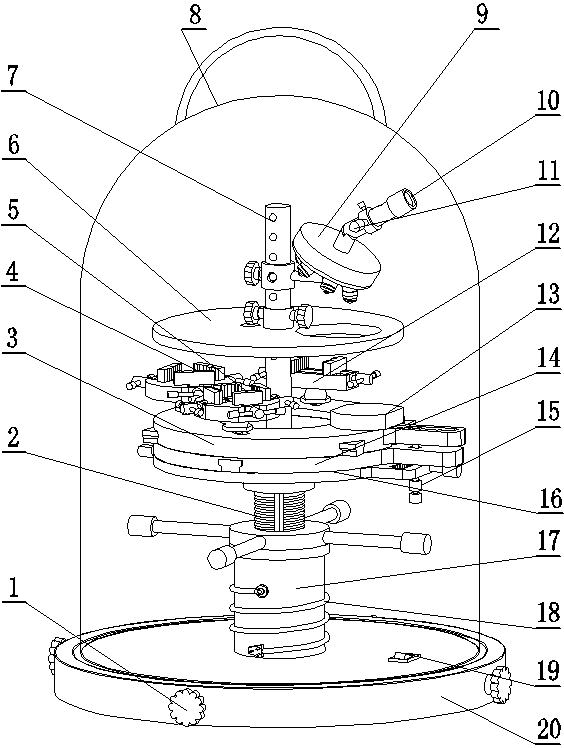
Portable microstructure observation and Vickers hardness testing machine
ActiveCN105510164BMeet the test requirementsEasy to carry outMaterial analysis by optical meansInvestigating material hardnessEyepieceTest sample
A portable microscopic structure observation and Vickers hardness test all-in-one machine is provided with a base, and the base is provided with a fixing knob, a power source wire and a switch. The center of the base is perpendicularly and upwards provided with a lifting screw column, a screw column lifter and a center column in a matched mode; the screw column lifter is provided with a lead screw handle; the upper portion of the lifting screw column is provided with a rotary disc, a transverse translation table and a longitudinal translation disc; the longitudinal translation disc is provided with a sample carrying platform, three-jaw clamp pliers, four-jaw clamp pliers and butt clamp pliers; the upper portion of the lifting screw column is perpendicularly provided with the center column, and the upper portion of the center column is sequentially provided with a flattening disc and an objective lens pressure head convertor; the top of the objective lens pressure head convertor is provided with an eyepiece and a measurer. The portable microscopic structure observation and Vickers hardness test all-in-one machine is compact in structure, novel in style, easy and convenient to operate and convenient to carry, has the wide magnification times and test force range, is provided with multiple test sample special fixtures, can meet the detection requirements of different materials and complex-shaped test samples and can easily process and storage observation images and measured data.
Owner:江苏圣奥电器有限公司
Image forming apparatus
An elastic deformation rate of a photoconductor, an additive amount of inorganic fine particles, and a rotary member are set to satisfy a relation of 0.6≤(D / (A×B / C)) / (1+E / 20)≤0.82, where A is a thickness of fibers of a brush, B is a bristle density of the fibers of the brush, C is a length of the fibers of the brush, D is an elastic deformation rate obtained from a hardness test conducted using a Vickers diamond pyramid indenter at a temperature of 23° C. and a humidity of 50%, and E is the additive amount of the inorganic fine particles relative to 100 parts by mass of toner particles.
Owner:CANON KK
Universal measuring instrument
ActiveCN102213661BMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesInvestigating material hardnessDigital dataMeasurement device
A testing machine includes a stand and a test device. The stand includes a base, box frame, a slide device driven to slide by a motor, and a control system controls the force applied on the test specimen. The test device is coupled at the slide device for performing various hardness tests consisting of Rockwell hardness test, Vickers hardness test, Brinell hardness test, micro-hardness test, and tension-compression test. The test device includes a force sensor and a data processing circuit converting an analog signal of the force sensor into digital data to interface with the control system.
Owner:吴绍明 +1
Wollastonite-apatite frit compounded medical glass ceramic and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a wollastonite-apatite frit compounded medical glass ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The wollastonite-apatite frit compounded medical glass ceramic is prepared by mixing and sintering wollastonite glass ceramic frits and apatite glass ceramic frits according to a certain proportion, the bending strength of the prepared material is more than or equal to 80MPa, the Vickers hardness tested by an FM-700 type microhardness tester is more than or equal to 5.80GPa (HV0.5), and the mechanical performance is adjustable. By respectively melting the two frits and mixing and sintering according to the proportion, the sintering and crystallization treatment temperature zones of the two frits are consistent, the sintering compatibility of the two frits can be guaranteed, and further the uniformity of structures and mechanical performance of the glass ceramic products can be guaranteed; and on the premise of having no need of regulating the composition matching of a single system, the mechanical performance of the glass ceramic can be adjusted by changing the mixing proportion of the mixed frits, the requirement of the preparation technology is low so as to facilitate the industrial popularization and use.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Beige dental glass-ceramic composite of wollastonite and apatite frit
InactiveCN103964688BColor adjustableThe temperature range of sintering and crystallization treatment is consistentApatiteFrit
The invention discloses a beige tooth microcrystalline glass compounded by frits of wollastonite and apatite. The beige tooth microcrystalline glass is prepared through a sintering method after smashing and mixing white microcrystalline glass frits in a single wollastonite crystalline phase and beige microcrystalline glass frits in a single apatite crystalline phase, the bending strength of the prepared material is less than or equal to 80 Mpa, the Vickers hardness tested by an FM-700 type microhardness tester is less than or equal to 5.80 GPa (HV 0.5). According to the invention, through the adjustment of frit composition proportion and the mixing ratio of the two types of frits, microcrystalline glass similar to teeth of different crowds in color can be prepared; under the premise that the constituent ratio in a unitary system is not needed to be adjusted, the mechanical property and the color of the microcrystalline glass can be adjusted through changing the mixing ratio of the mixing frits,; the preparation technology requirements are low; industrialized popularization and application are facilitated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Surface leveling and fixing device for Vickers hardness test of cylindrical inlaid sample
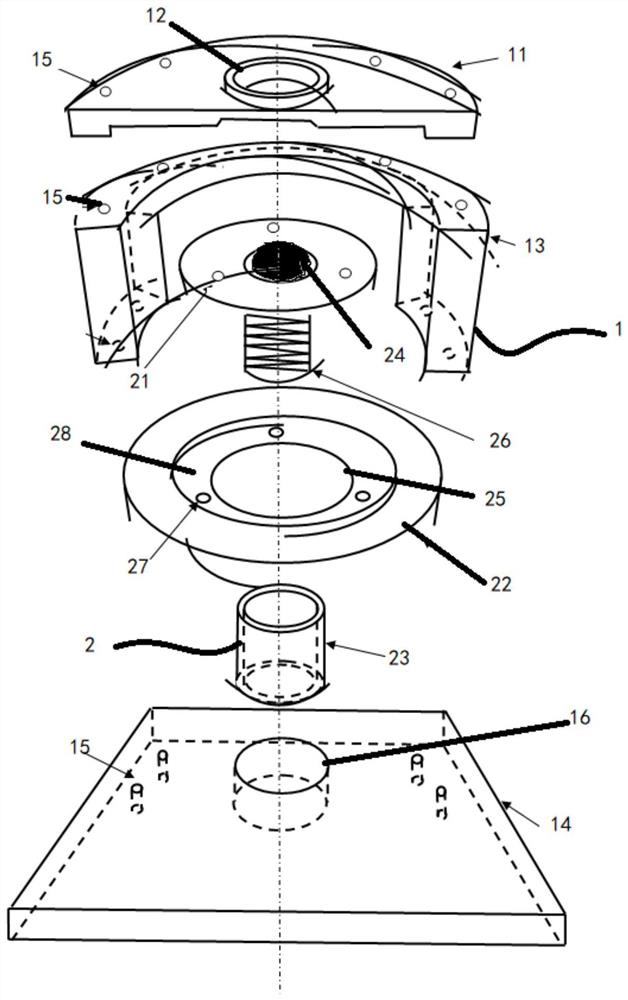
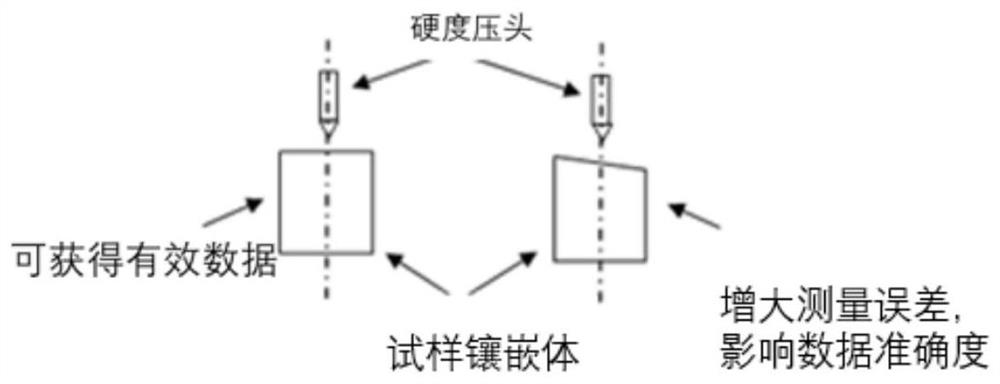
PendingCN112630071ASolve the problem of experimental errorReasonable settingInvestigating material hardnessEngineeringSurface level
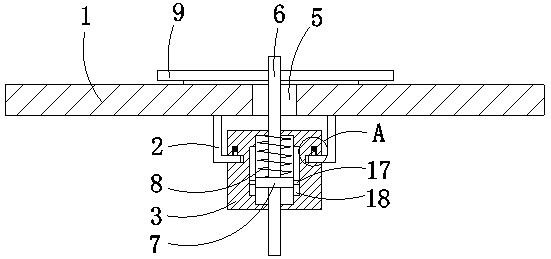
The invention discloses a surface leveling and fixing device for Vickers hardness testof a cylindrical inlaid sample. The device comprises a supporting module device and a fixing device, the supporting module device comprises a shell and a top cover, the top cover is arranged on the upper end face of the shell, and a first through hole is formed in the center of the top cover. The fixing device is arranged in the shell; the fixing device comprises a ball bull eye, a rotating disc, an internal thread connecting ring and a ball; the ball is arranged on the upper end surface of the ball bull eye; a second through hole is formed in the rotating disc; the ball bull eye is arranged on the rotating disc based on the second through hole; the ball bull eye comprises a first screw rod; and the internal thread connecting ring is arranged at the bottom of the shell. By arranging the supporting module and the fixing module, top covers with different central apertures can be replaced, the height can be adjusted through the rotating disc, the device can adapt to inlay bodies with different heights, balls on ball bull eyes can rotate, the test surfaces of the inlay bodies can be leveled in the test process, and the problem of experiment errors caused by inclination of the detection surfaces is effectively solved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGXI POWER GRID CO LTD
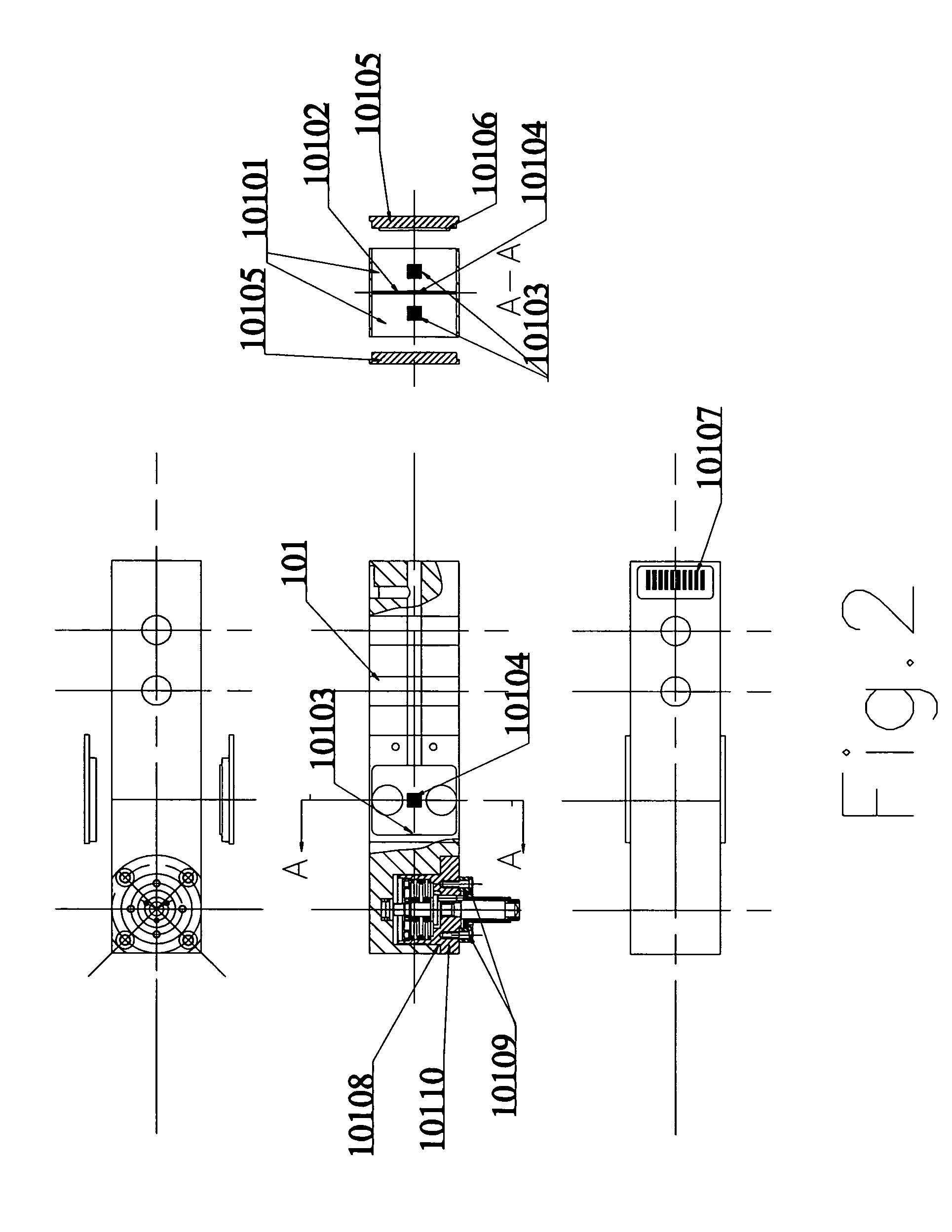
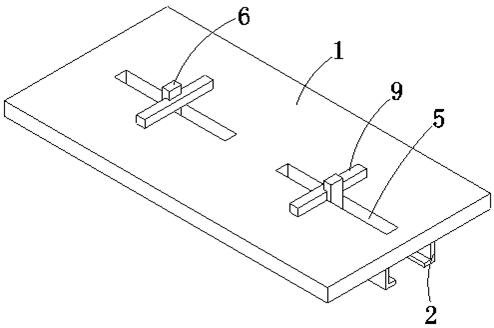
Vickers hardness test auxiliary device
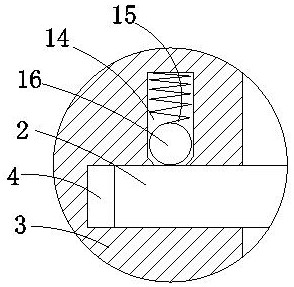
PendingCN113267414AEasy to adjustEasy to fixInvestigating material hardnessStructural engineeringCylinder block
The invention discloses a Vickers hardness test auxiliary device which comprises a test bed and cylinder bodies, strip-shaped holes are formed in the top of the test bed, sliding rails are fixedly connected to the bottom of the test bed, sliding grooves are formed in the outer side faces of the cylinder bodies, the cylinder bodies are slidably connected into the sliding rails through the sliding grooves, and the two sets of cylinder bodies are located under the corresponding strip-shaped holes respectively; a linkage rod matched with the strip-shaped hole is movably inserted into the cylinder body, a limiting plate and a first compression spring are further arranged in the cylinder body, the upper end of the linkage rod extends to the position above the strip-shaped hole, the lower end of the linkage rod extends to the outer side of the cylinder body, the linkage rod is sleeved with the first compression spring, and the lower end of the first compression spring makes contact with the limiting plate. Clamping plates are arranged on the upper portions of the linkage rods, and a containing space is formed between every two adjacent clamping plates. By means of the auxiliary device, the positions of the clamping plates can be adjusted conveniently, clamping time is saved, and the auxiliary device is simple in structure, convenient to operate, high in practicability and beneficial to application and popularization.
Owner:GUIZHOU AEROSPACE PRECISION PRODS
Diamond polycrystal and tool including same
ActiveUS20200340139A1Improve crack resistanceImprove fracture toughnessPolycrystalline material growthMilling cuttersCrystallographyEngineering
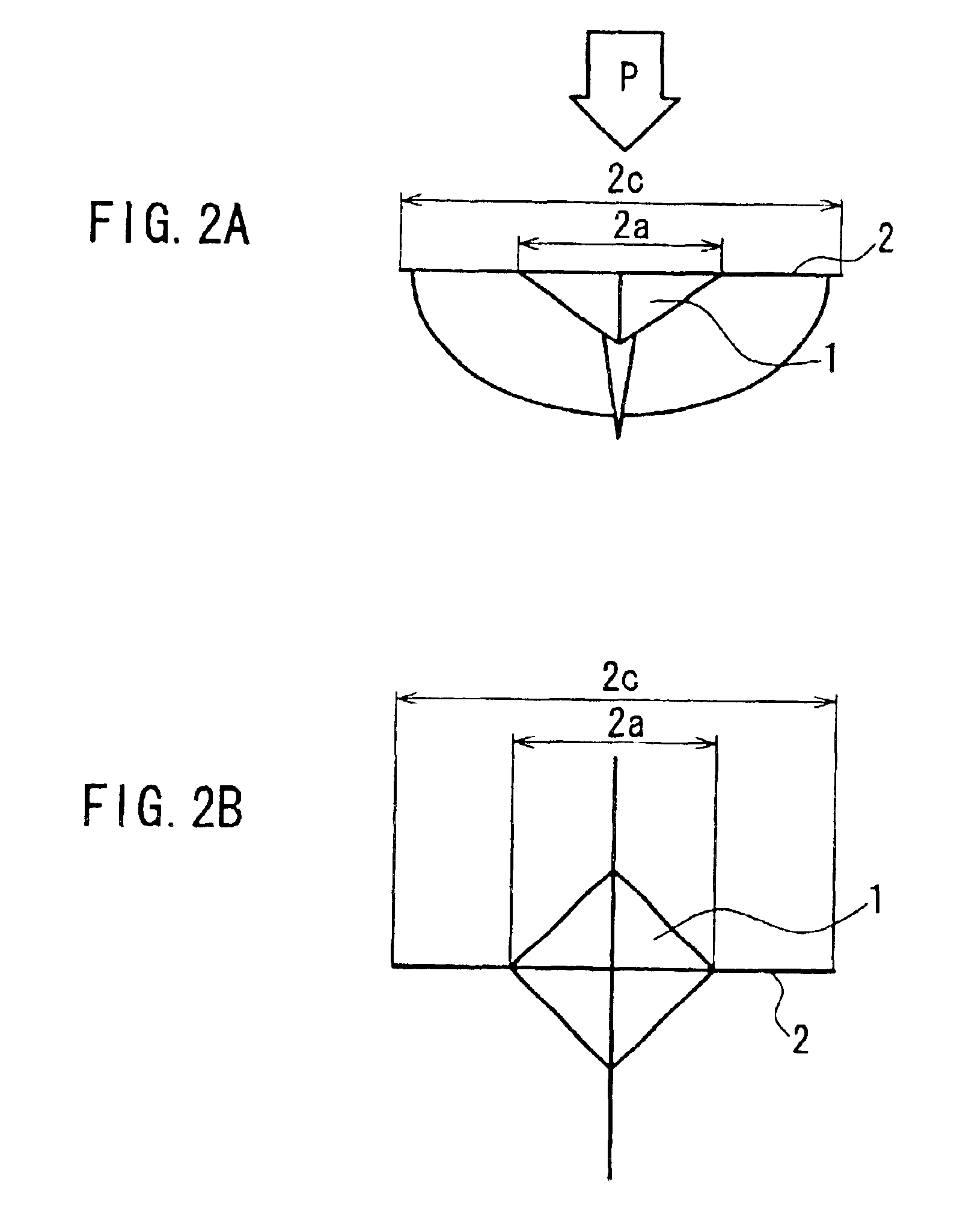
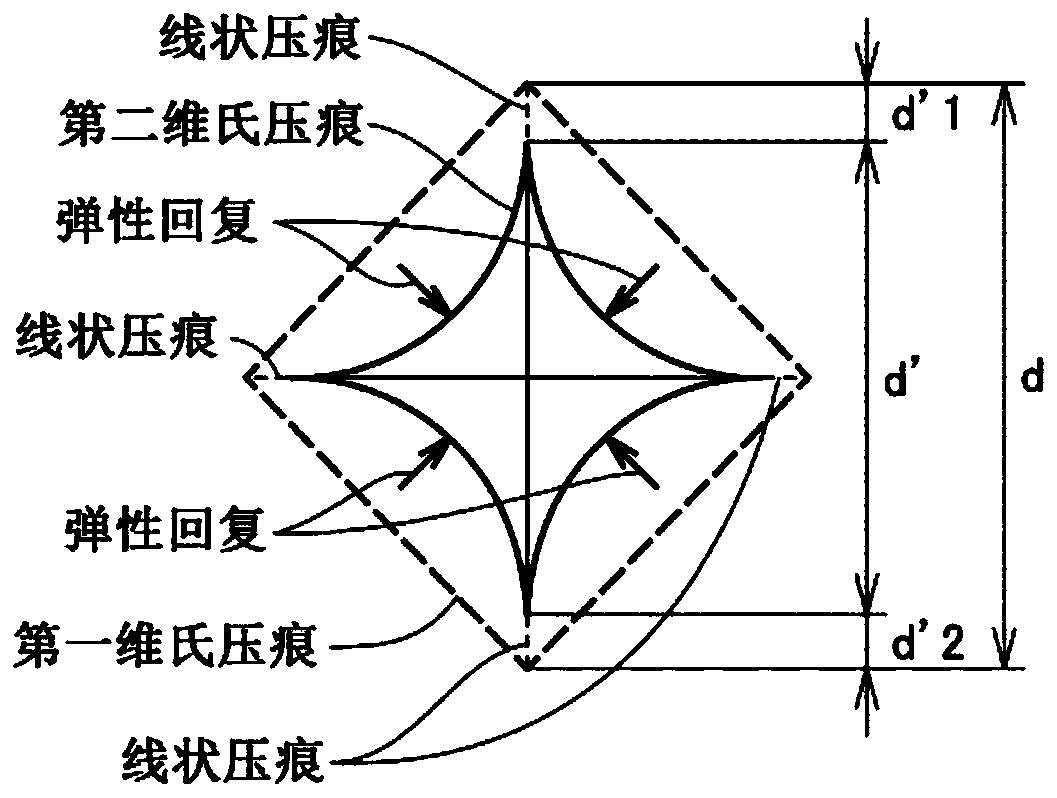
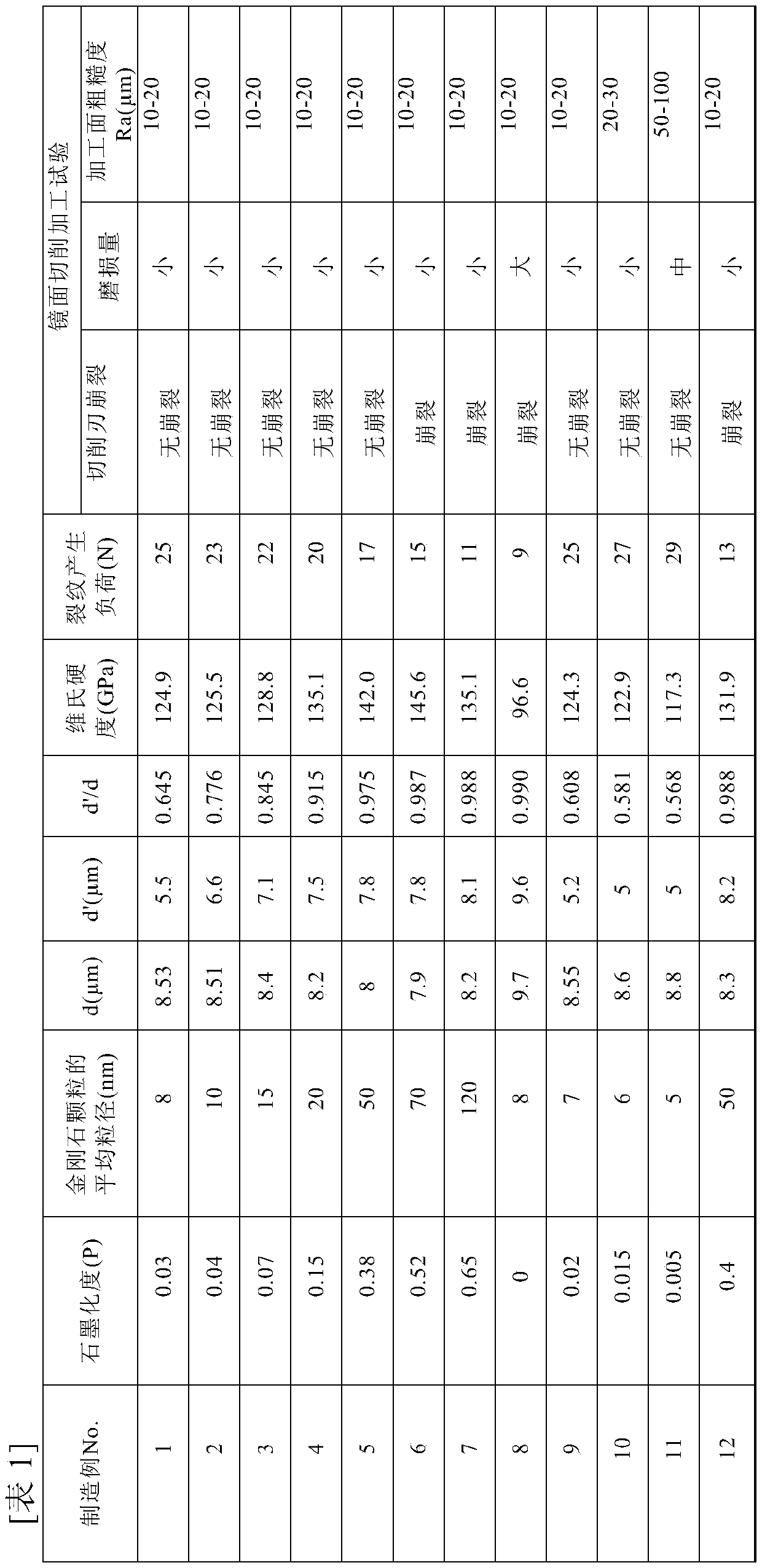
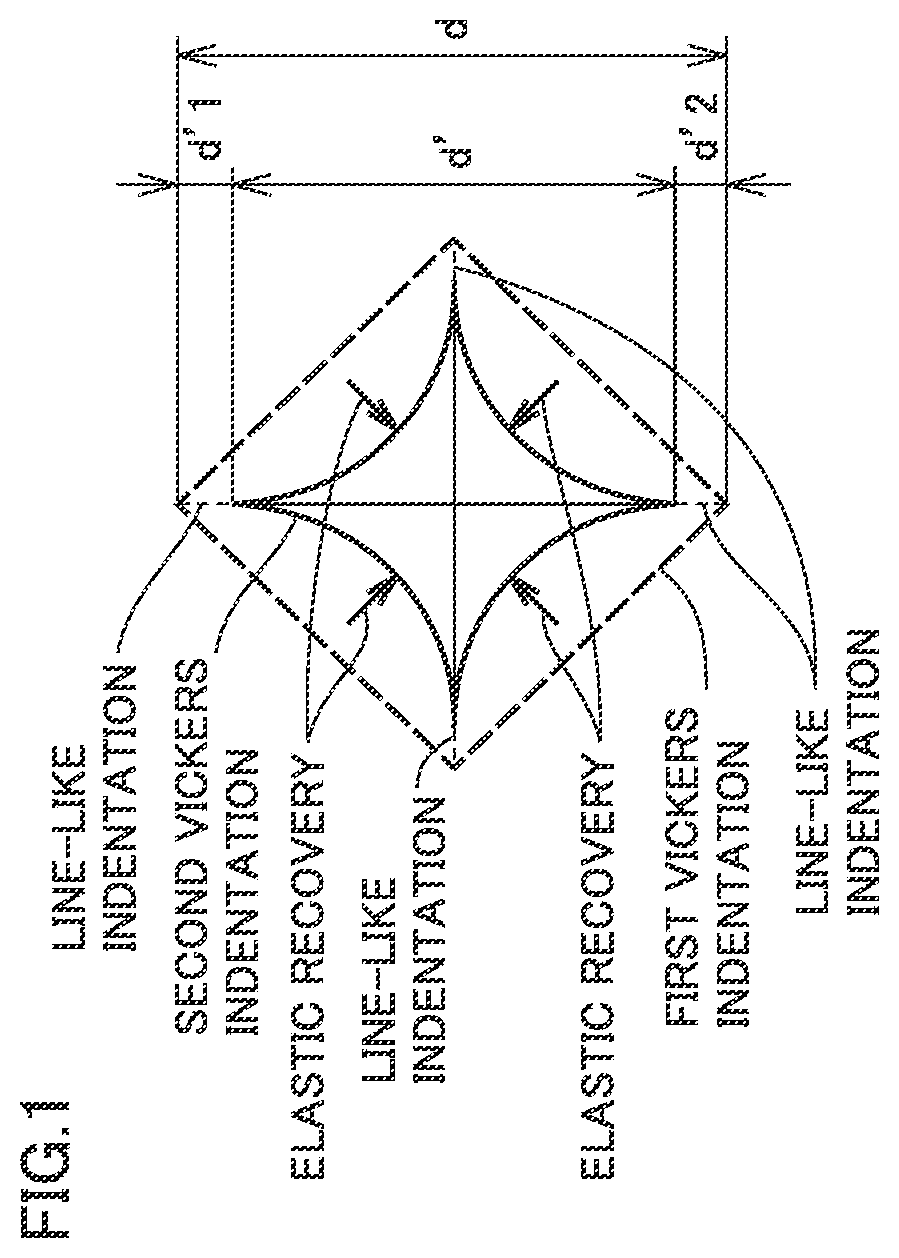
In a diamond polycrystal, a value of a ratio (d′ / d) of d′ to d is less than or equal to 0.98 in a Vickers hardness test performed under a condition defined in JIS Z 2244:2009, where the d represents a length of a diagonal line of a first Vickers indentation formed in a surface of the diamond polycrystal when a Vickers indenter with a test load of 4.9 N is pressed onto the surface of the diamond polycrystal, and the d′ represents a length of a diagonal line of a second Vickers indentation remaining in the surface of the diamond polycrystal after releasing the test load.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Vickers hardness test system and method
InactiveCN101839832BAccurately determineHigh precisionImage analysisInvestigating material hardnessSystems analysisMeyer hardness test
The invention provides a Vickers hardness test system, which is run on a computer, and the computer is connected with a hardness test platform. The hardness test platform utilizes an industrial optical lens and a charge-coupled device to acquire the indentation image of the surface of material to be tested, and transmits the indentation image to the computer. The computer utilizes the Vickers hardness detection system to carry out analysis in order to obtain the positions of the four corners of two indentation diagonals in the indentation image, the lengths of the two indentation diagonals are calculated according to the four corners, the Vickers hardness of the material to be tested is then calculated according to the lengths of the two indentation diagonals, and a test result is outputted to a display device connected with the computer. The invention also provides a Vickers hardness test method. The invention can accurately determine the position of the indentation of the surface ofmaterial, and therefore the precision of hardness test is increased.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
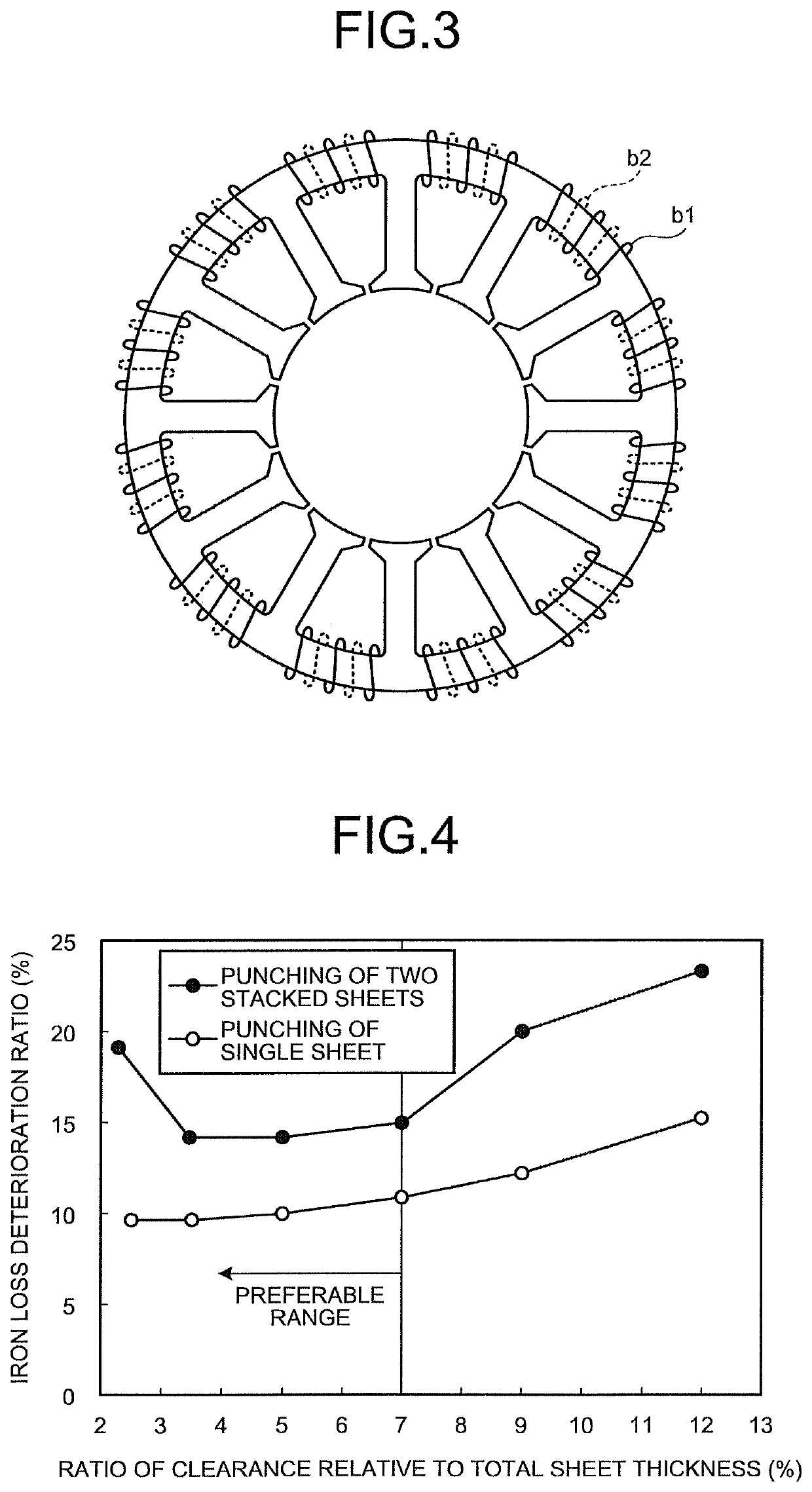
Punching method, punching device, and method for manufacturing laminated iron core
ActiveUS10919081B2Reduce wearInhibit deteriorationMetal-working feeding devicesElectric machinesPunchingElectrical steel
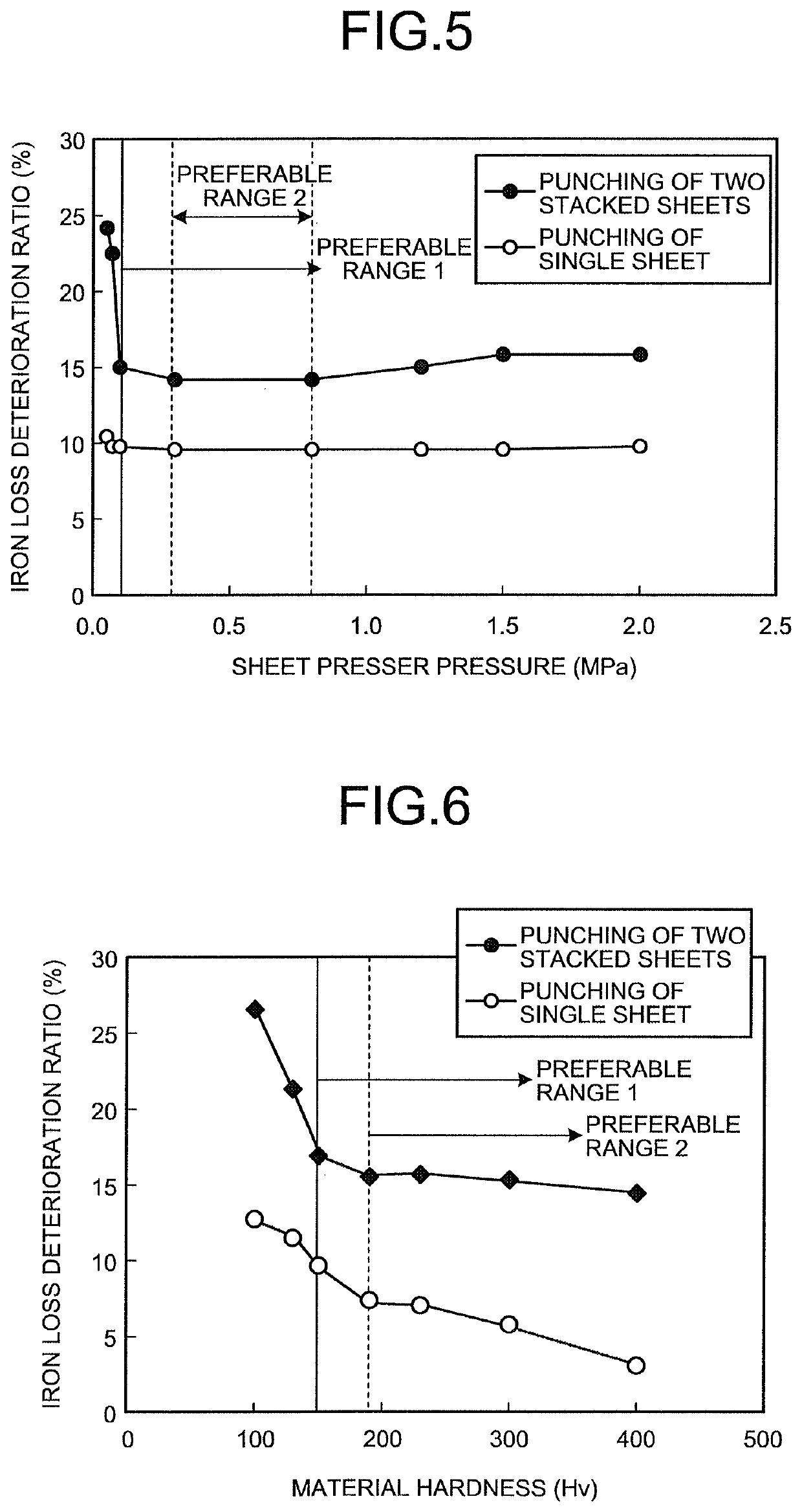
A punching method includes: punching out a plurality of electrical steel sheets in a stacked state by a mold, wherein sheet thicknesses of the electrical steel sheets are set to be 0.35 mm or less, a Vickers hardness (test force 1 kg) of the sheets is set to be 150 to 400, and an average crystal grain size of the sheets is set to be 50 to 250 μm, a clearance of the mold is set to be 7% or more of a minimum sheet thickness of the sheet thicknesses of the electrical steel sheets and equal to or lower than 7% of a total sheet thickness of the electrical steel sheets, and a pressure that a sheet presser of the mold applies to the electrical steel sheets is set to be 0.10 MPa or more.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Steel plates for cargo hold of coal/ore carrier
ActiveCN110536973BReduce water seepageReduced Possibility of ContaminationMetal rolling arrangementsThick plateHardness
A steel sheet for coal / ore carrier holds that is a ferrite-pearlite steel sheet of specified components, wherein: the microstructure is a structure configured with the ferrite area fraction in the ¼ thickness region being 80-95% and the pearlite area fraction at the ¼ thickness region being 5-20%, the average aspect ratio of the ferrite grains in the ¼ thickness region being 1.0-1.5, the average grain size of the ferrite grains in the ¼ thickness region being 5-20 µm, and the average dislocation density in the ferrite in the ¼ thickness region being 7×1012 / m2 or less; in a 1 mm pitch Vickers hardness test, the average Vickers hardness from the steel sheet surface to the ¼ thickness region or from the ¾ thickness region to the back surface is 80-105% of the average Vickers hardness from the ¼ thickness region to the ¾ thickness region; and the maximum Sn concentration in the ½ thickness (sheet thickness) ± 10% range in the sheet thickness direction is 0.01-5.0%.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
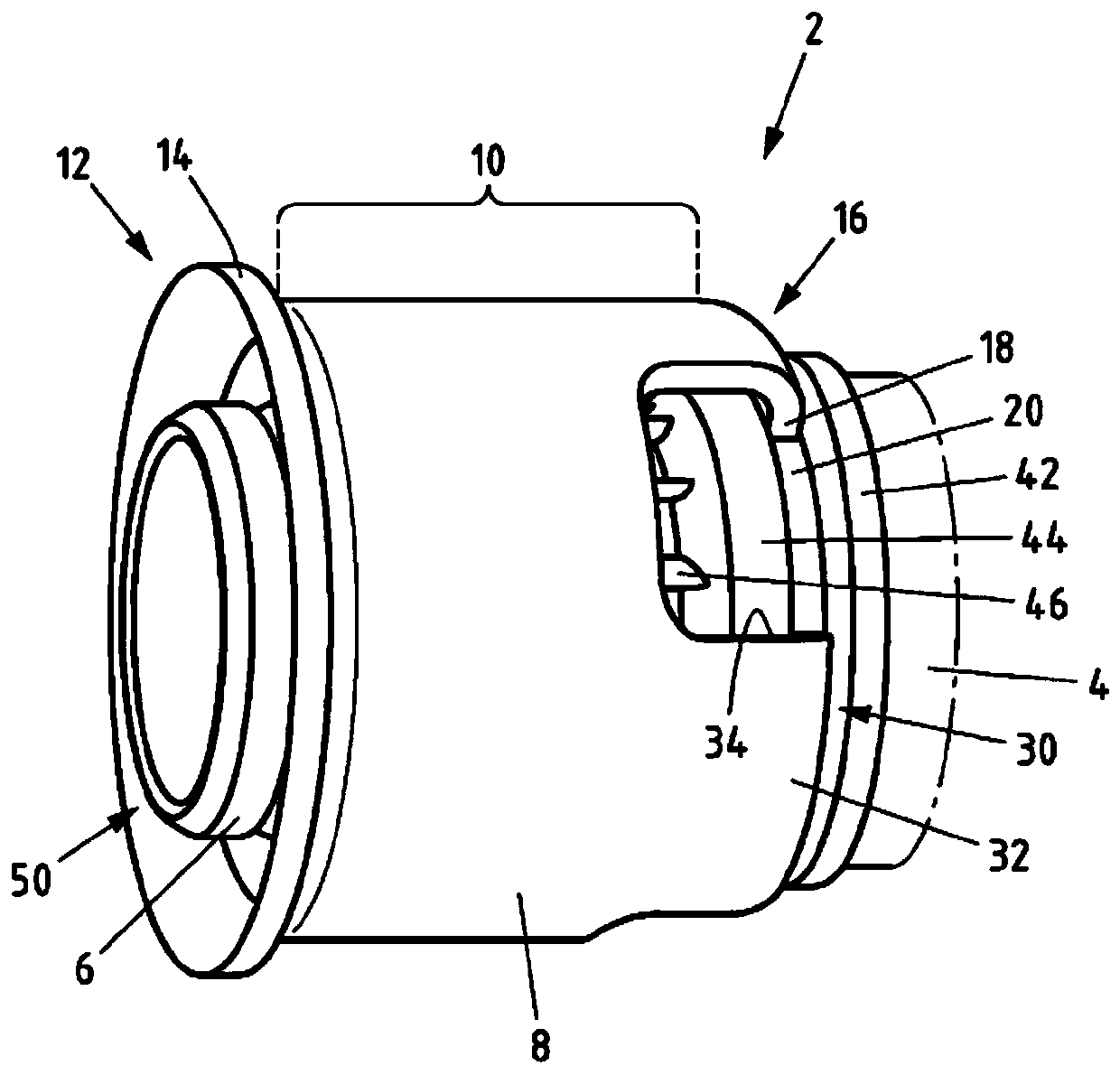
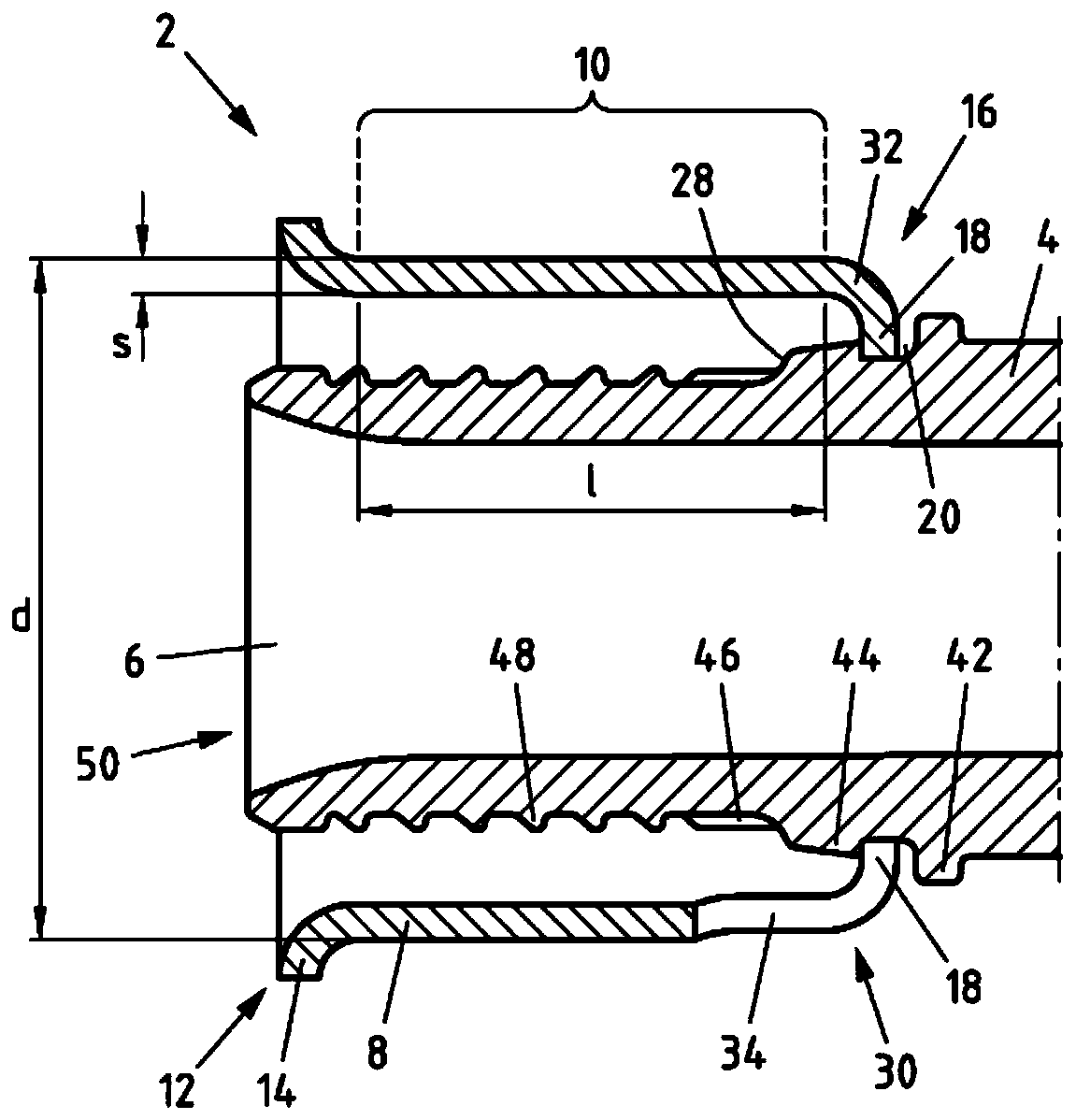
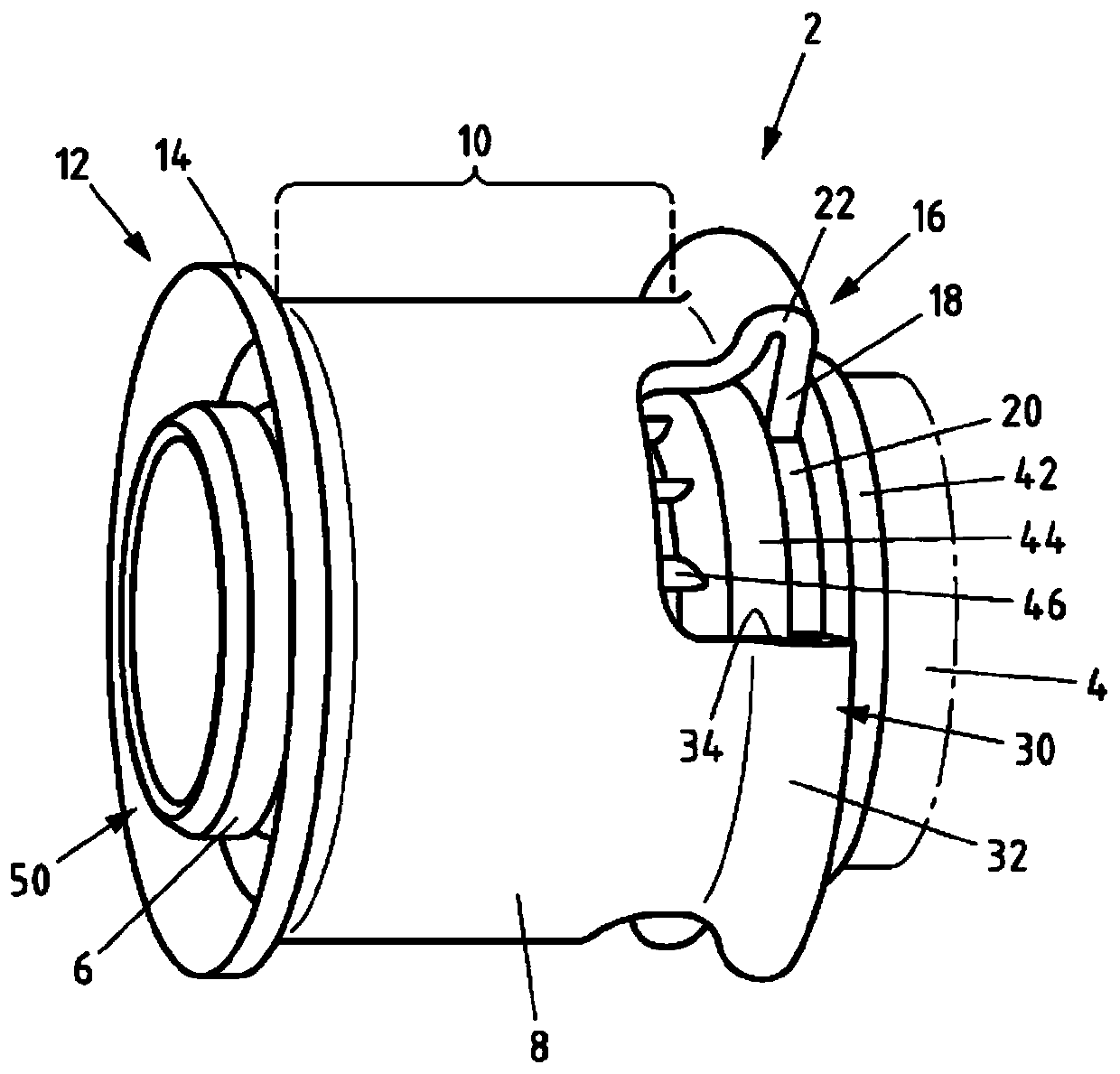
Fitting for connecting to at least one pipe and method for producing a connection
The invention relates to a fitting for connecting to at least one pipe, in particular a plastic pipe or plastic-metal composite pipe, comprising a main body (4), at least one support body (6) connected to the main body (4) and for introducing into a pipe end, and at least one press sleeve (8) connected to the main body (4) and for receiving the pipe end, wherein the press sleeve (8) has a cylindrical press section (10). The technical problem of improving the fitting for pressing, in particular with small motor-driven or hand-operated pressing tools, is achieved in that the press sleeve (8) isproduced from a metal with a micro-hardness of less than 65HV1, in particular less than 50HV1, preferably in the range between 40 and 50HV1, measured according to Vickers hardness test, and in that the ratio of the wall thickness (s) of the press section (10) to the outer diameter (d) of the press section (10) is less than 0.06, preferably in the range between 0.03 and 0.06. The invention also relates to a method for producing a connection.
Owner:VIEGA TECH GMBH & CO KG
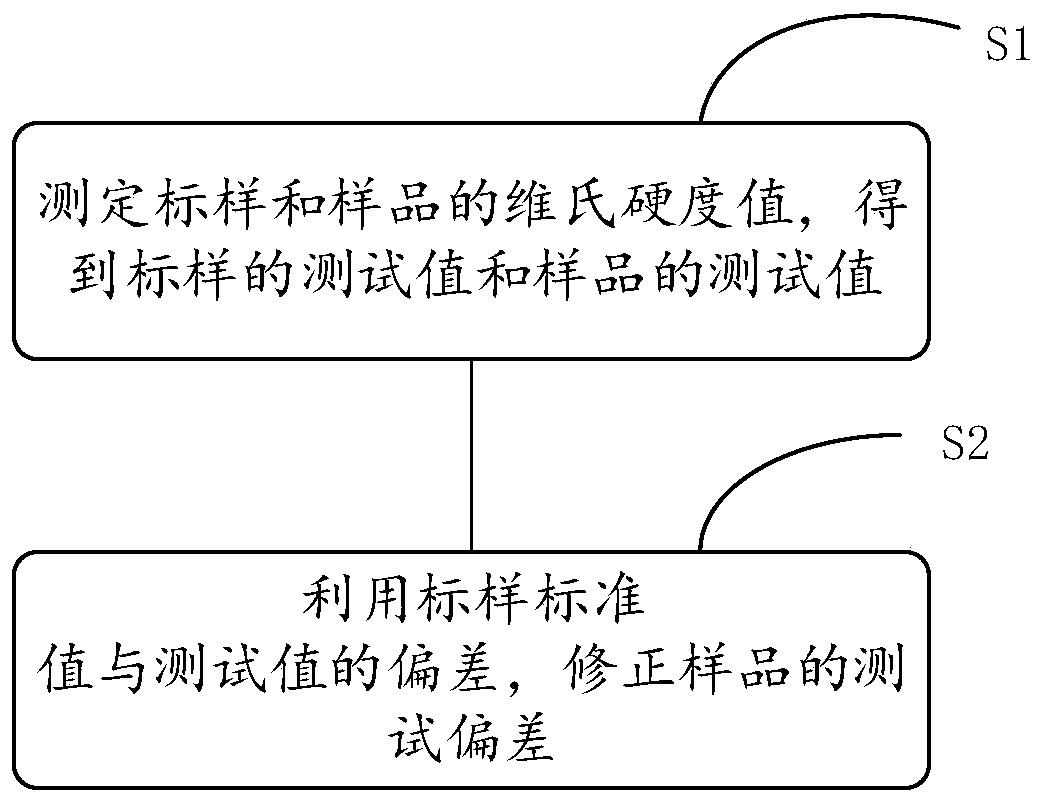
Electronic glass Vickers hardness test deviation correcting method
The invention discloses an electronic glass Vickers hardness test deviation correcting method, which relates to the field of liquid crystal glass testing. The electronic glass Vickers hardness test deviation correcting method comprises the steps of: 1) measuring Vickers hardness values of a standard microscopic Vickers hardness block and a sample to obtain a test value of the standard microscopicVickers hardness block and a test value of the sample, wherein the test conditions of the standard microscopic Vickers hardness block and the sample are the same; and 2) correcting the test deviationof the sample by utilizing the deviation between a standard value and the test value of the standard microscopic Vickers hardness block. According to the electronic glass Vickers hardness test deviation correcting method disclosed by the invention, the electronic glass Vickers hardness test deviation is effectively reduced through introducing the test of the standard microscopic Vickers hardness block and carrying out simple data processing.
Owner:IRICO DISPLAY DEVICES
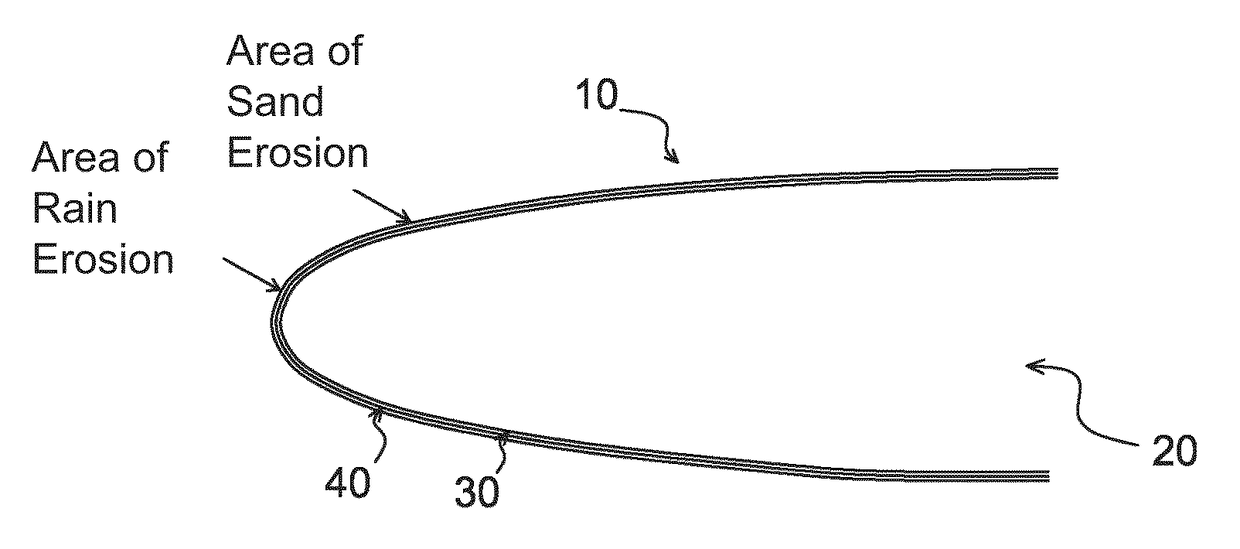
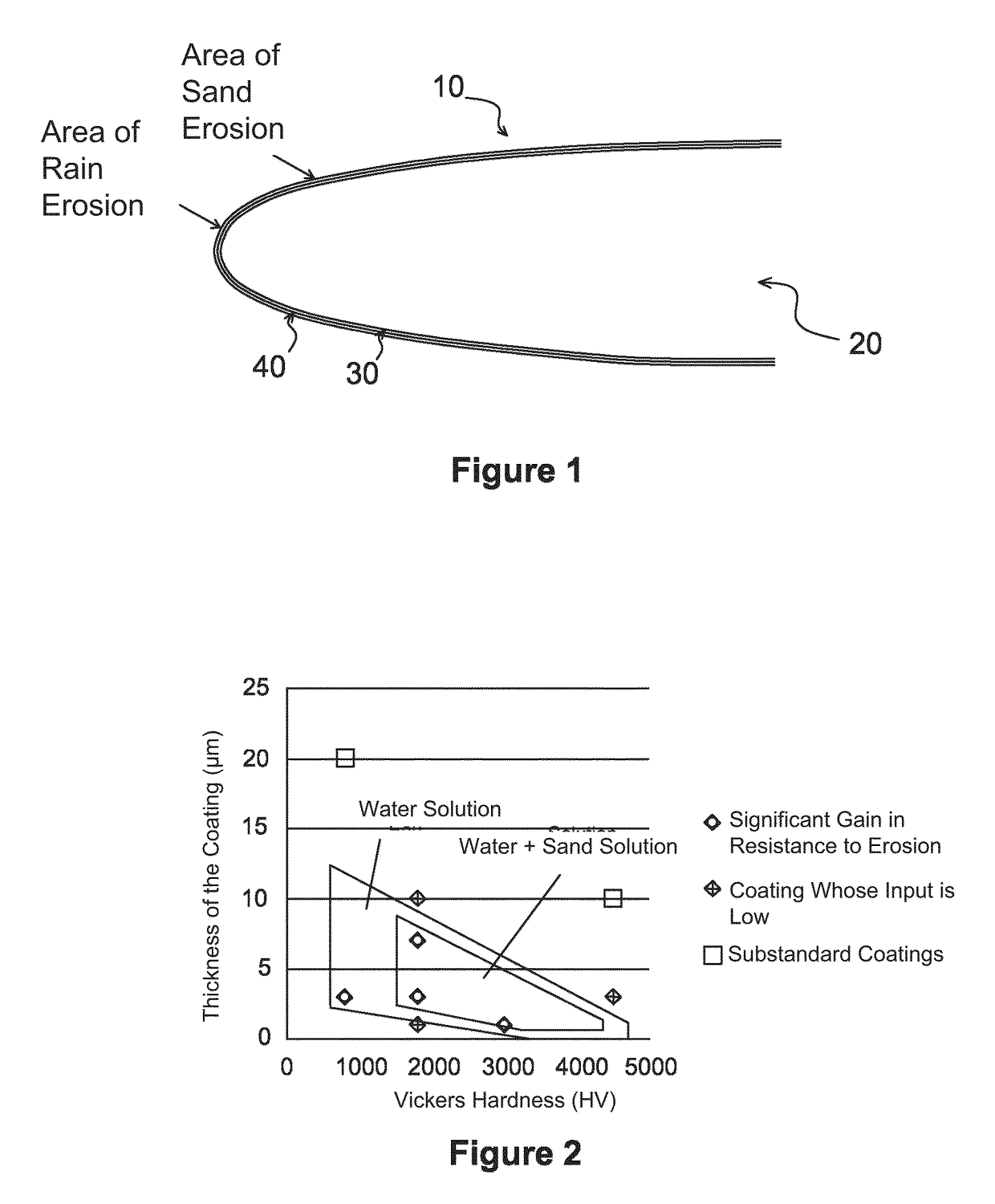
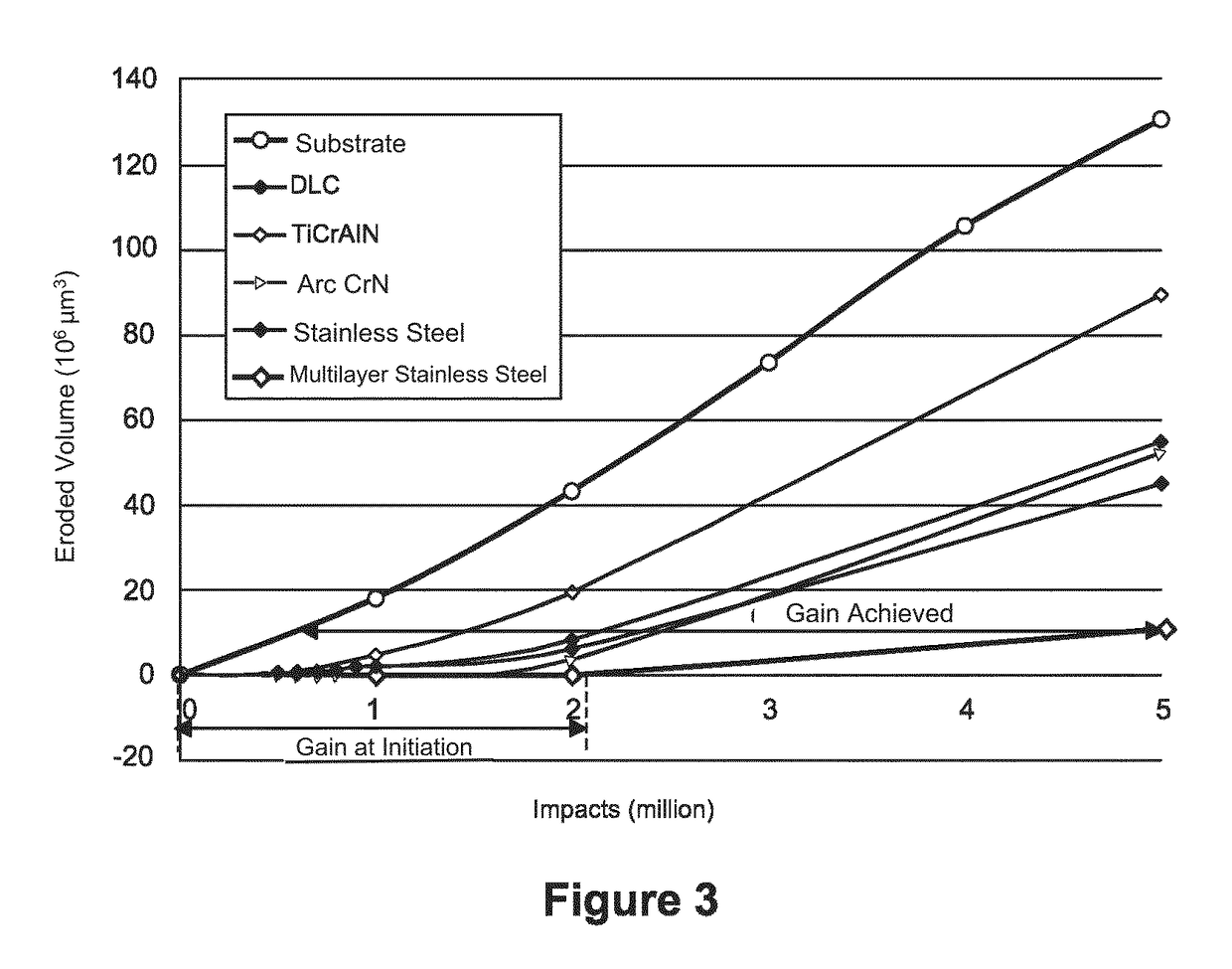
Anti-erosion structure for aircrafts
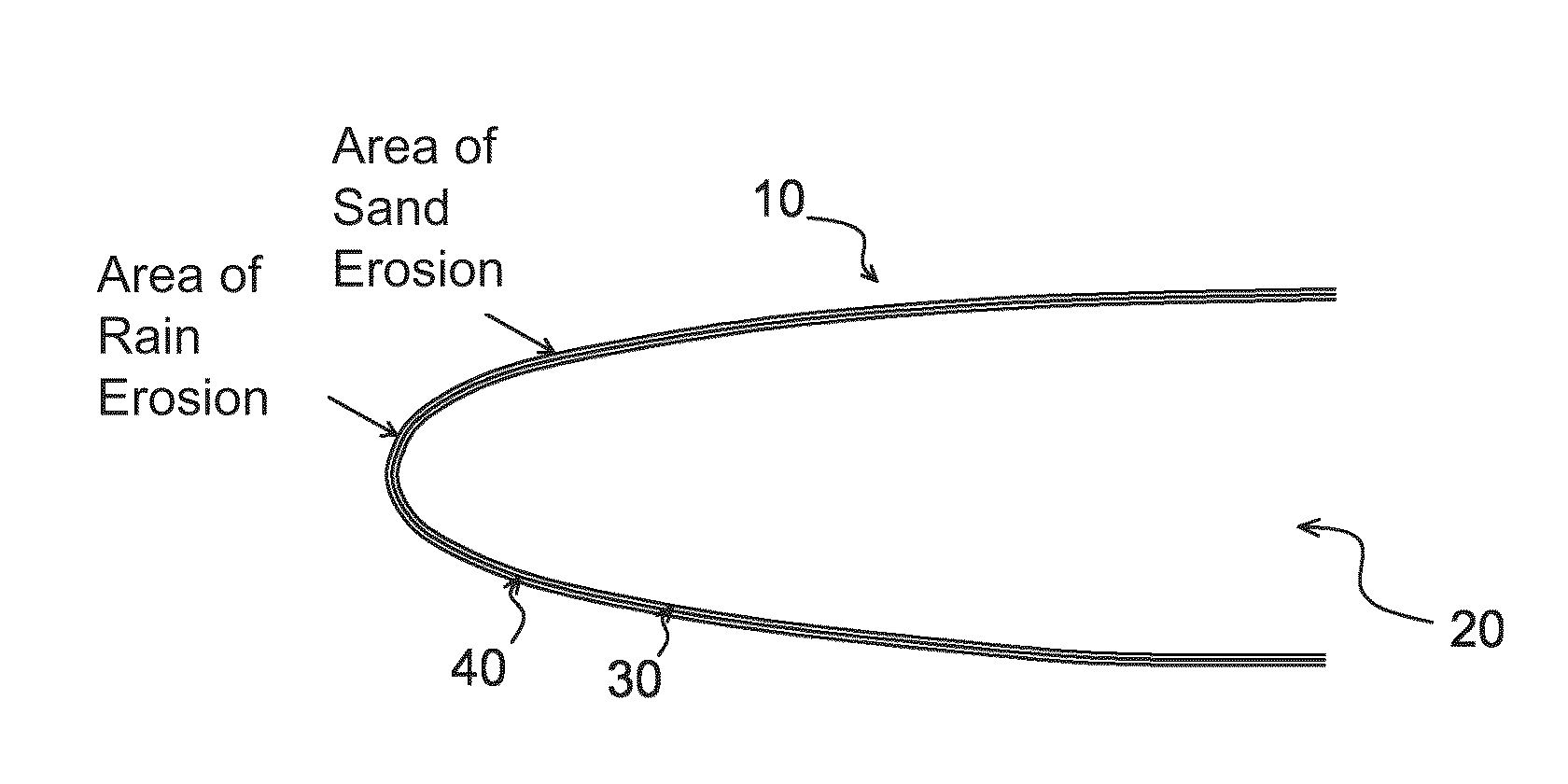
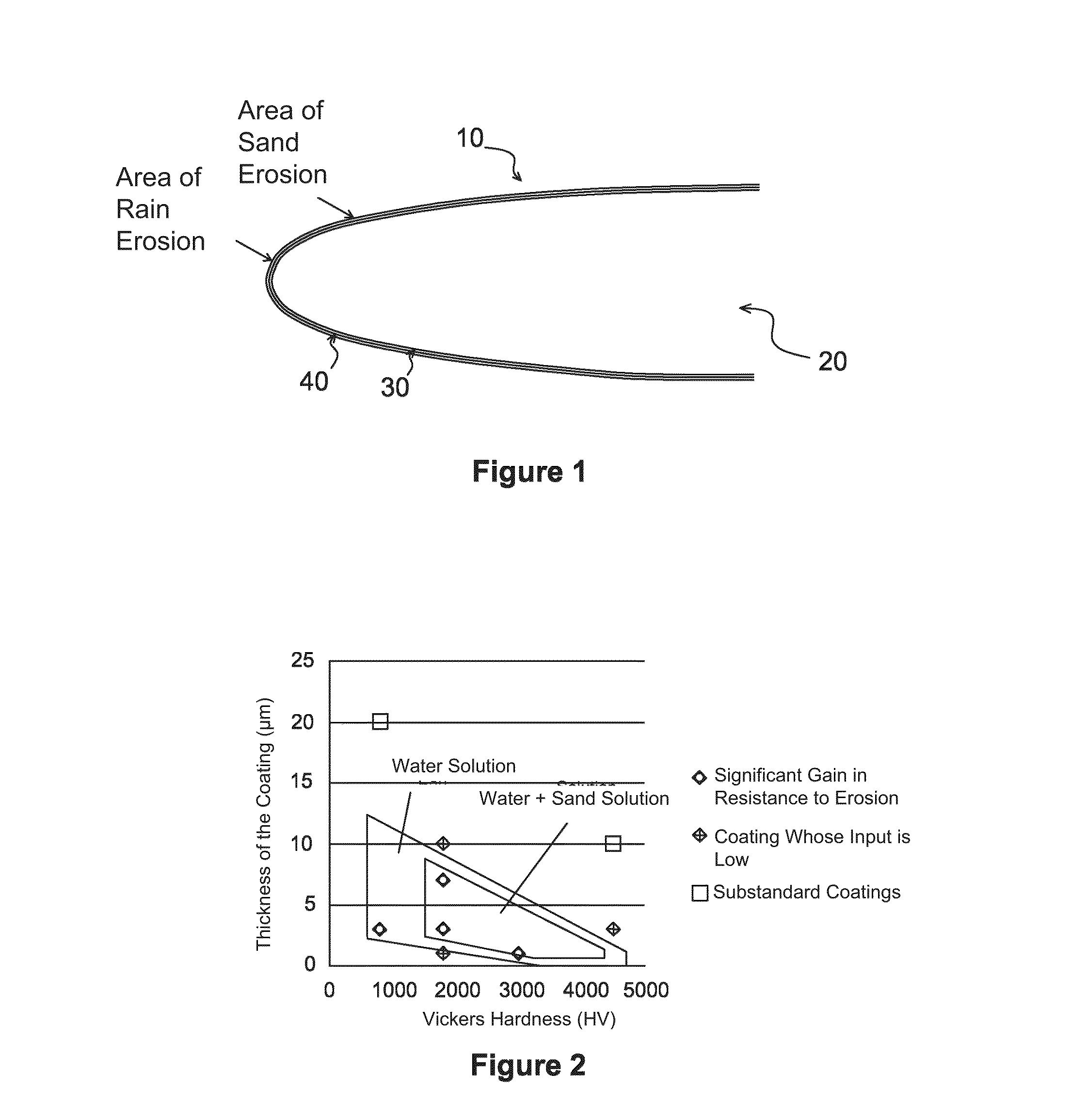
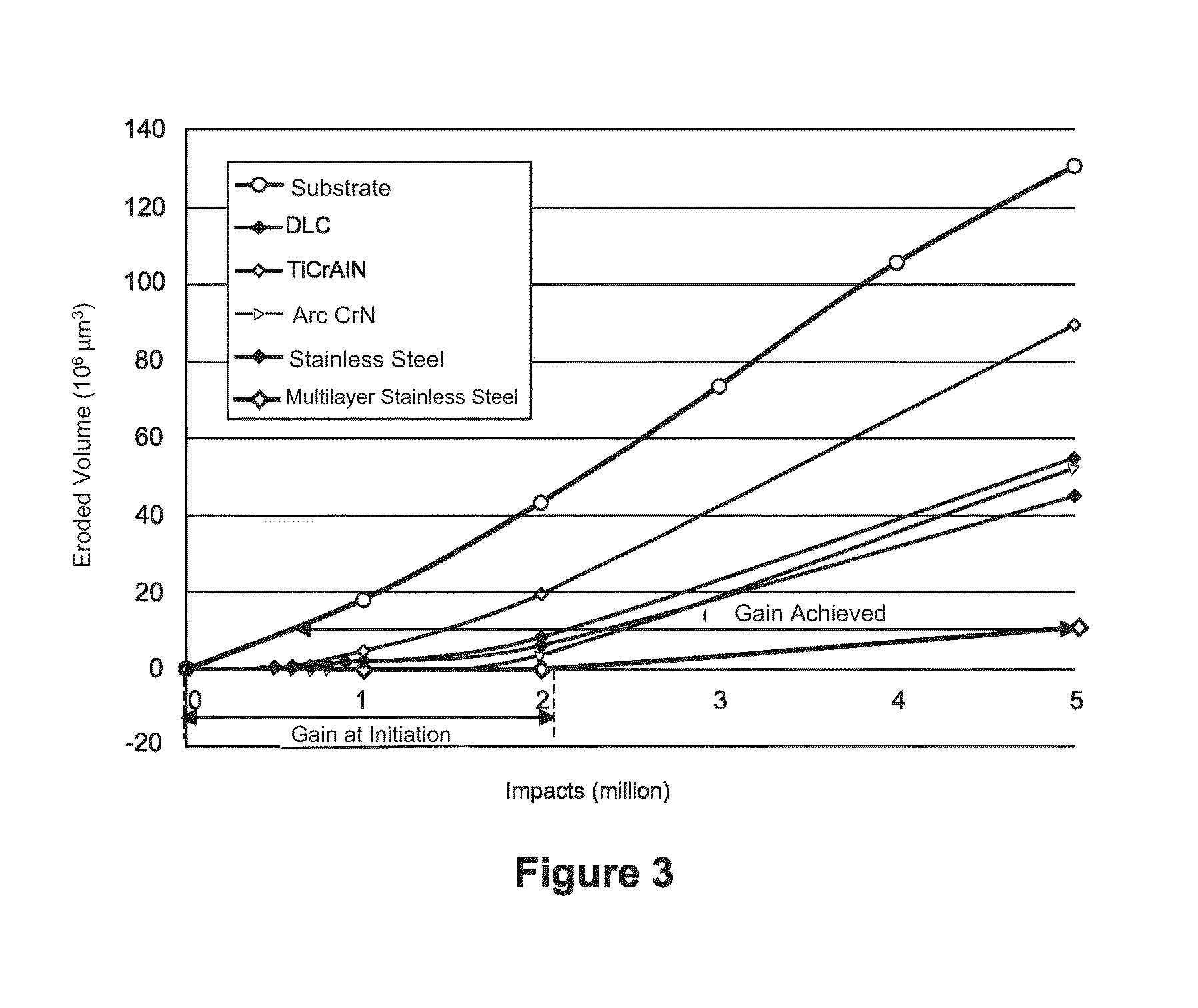
ActiveUS20160046370A1Resist erosionPromote absorptionBlade accessoriesVacuum evaporation coatingLeading edgeMicrometer
A structure (10) for aircrafts, includes a part (20) including a metal leading edge (30), the leading edge (30) being covered by a coating (40) having a thickness which is less than or equal to ten micrometers and having a hardness higher than six hundred in the Vickers hardness test (HV). According to a mode of embodiment, the coating (40) is a multilayer stainless steel coating consisting of a superposition of layers with a low nitrogen gradient and layers with a high nitrogen gradient, the layers having a thickness essentially equal to a micrometer. An aircraft including such a structure is also described.
Owner:EURON AERONAUTIC DEFENCE & SPACE +1
Anti-erosion structure for aircrafts
ActiveUS9981739B2Promote absorptionImprove the immunityBlade accessoriesVacuum evaporation coatingLeading edgeMicrometer
A structure (10) for aircrafts, includes a part (20) including a metal leading edge (30), the leading edge (30) being covered by a coating (40) having a thickness which is less than or equal to ten micrometers and having a hardness higher than six hundred in the Vickers hardness test (HV). According to a mode of embodiment, the coating (40) is a multilayer stainless steel coating consisting of a superposition of layers with a low nitrogen gradient and layers with a high nitrogen gradient, the layers having a thickness essentially equal to a micrometer. An aircraft including such a structure is also described.
Owner:EURON AERONAUTIC DEFENCE & SPACE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com