Patents
Literature
31 results about "Afferent nerves" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
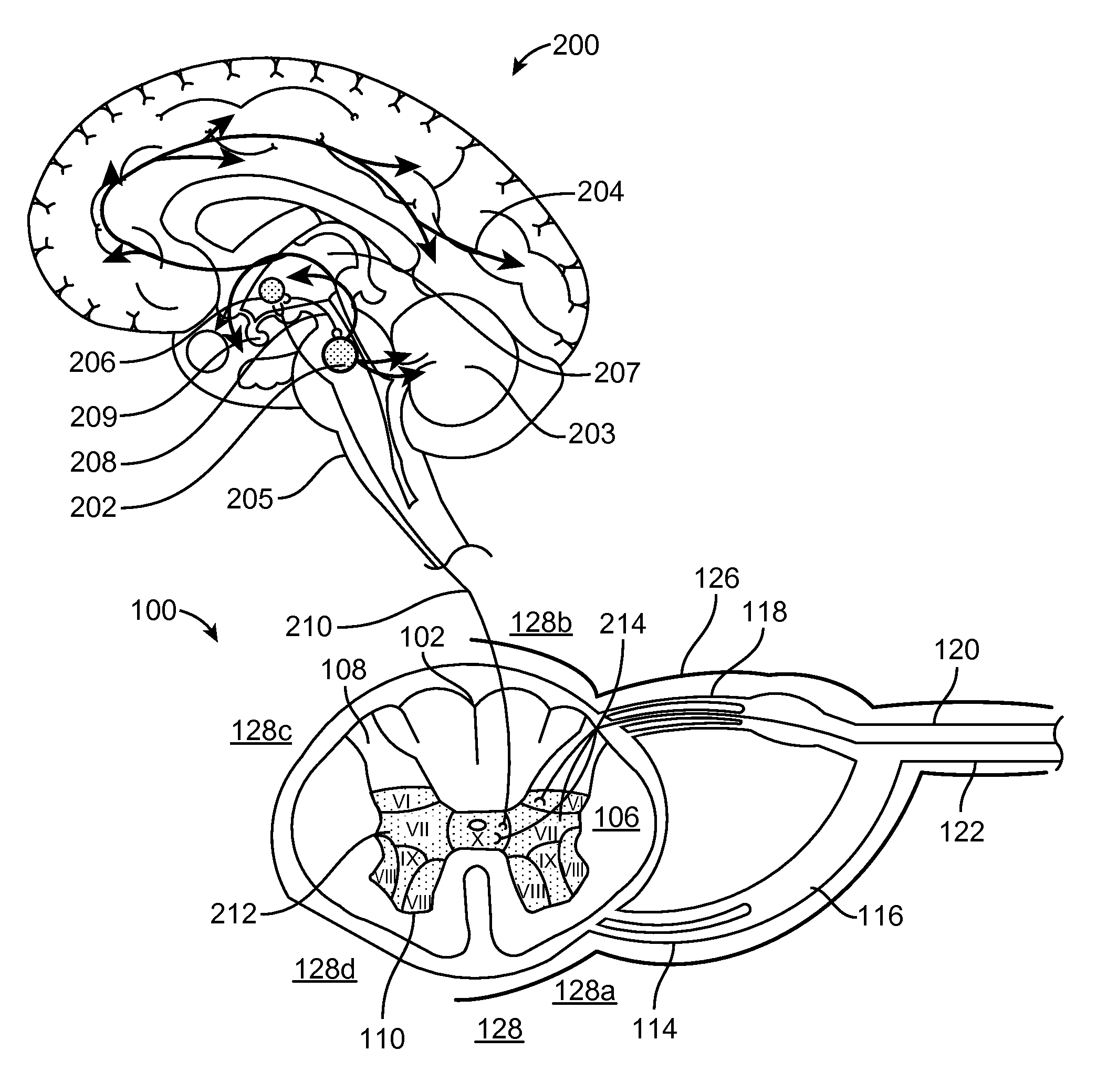
Sensory nerves, sometimes called afferent nerves, carry information from the outside world, such as sensations of heat, cold, and pain, to the brain and spinal cord. Motor nerves, or efferent nerves, transmit impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles.
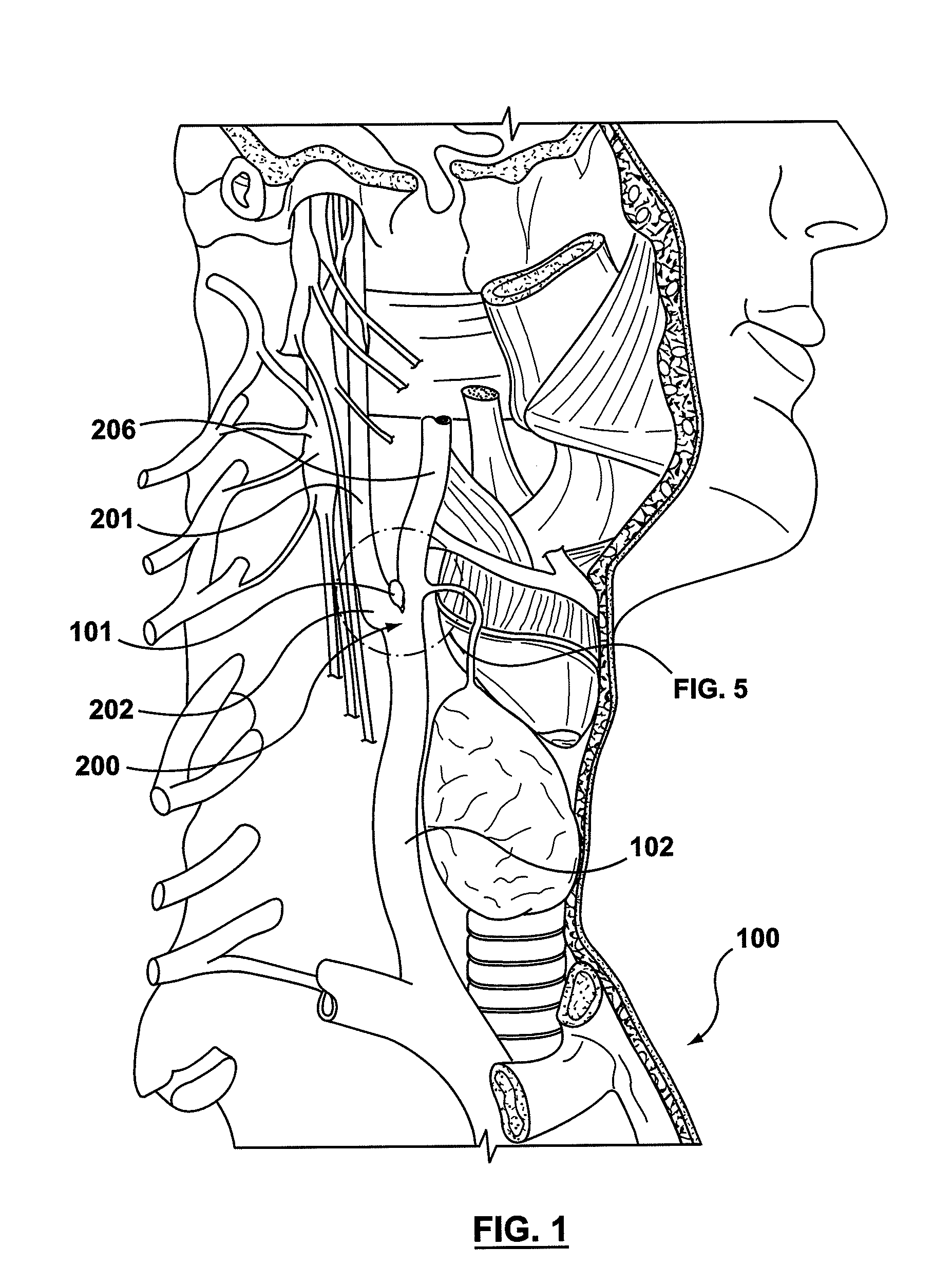
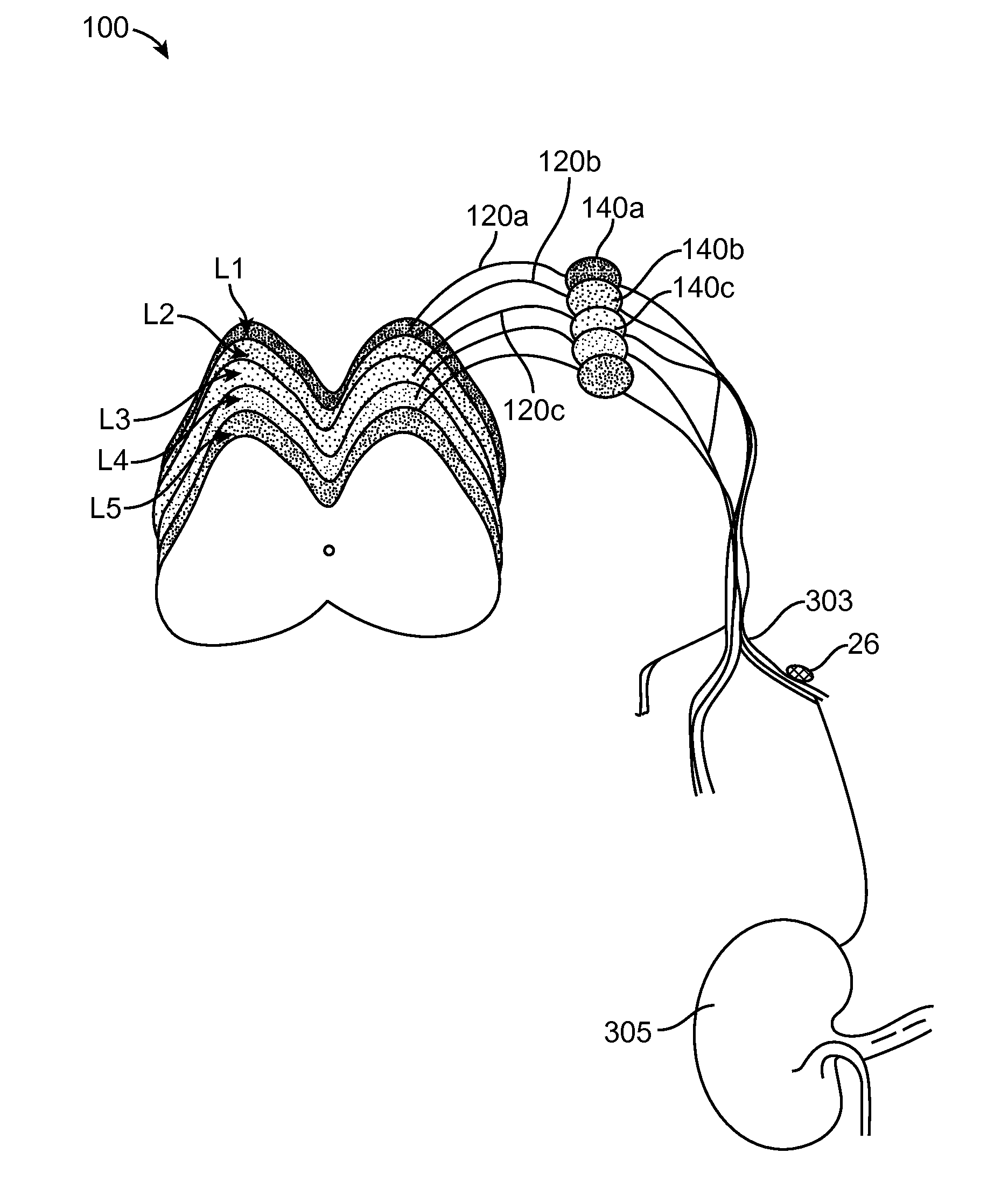
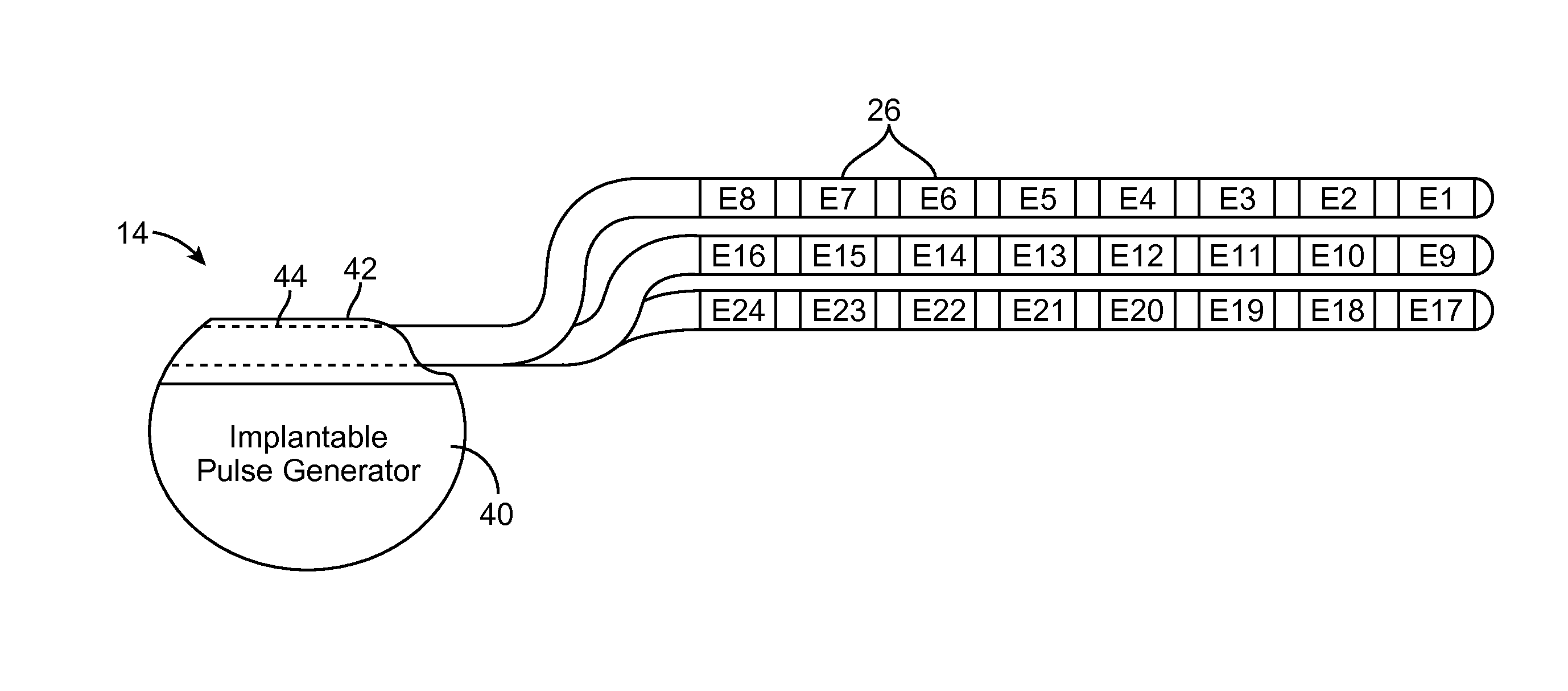
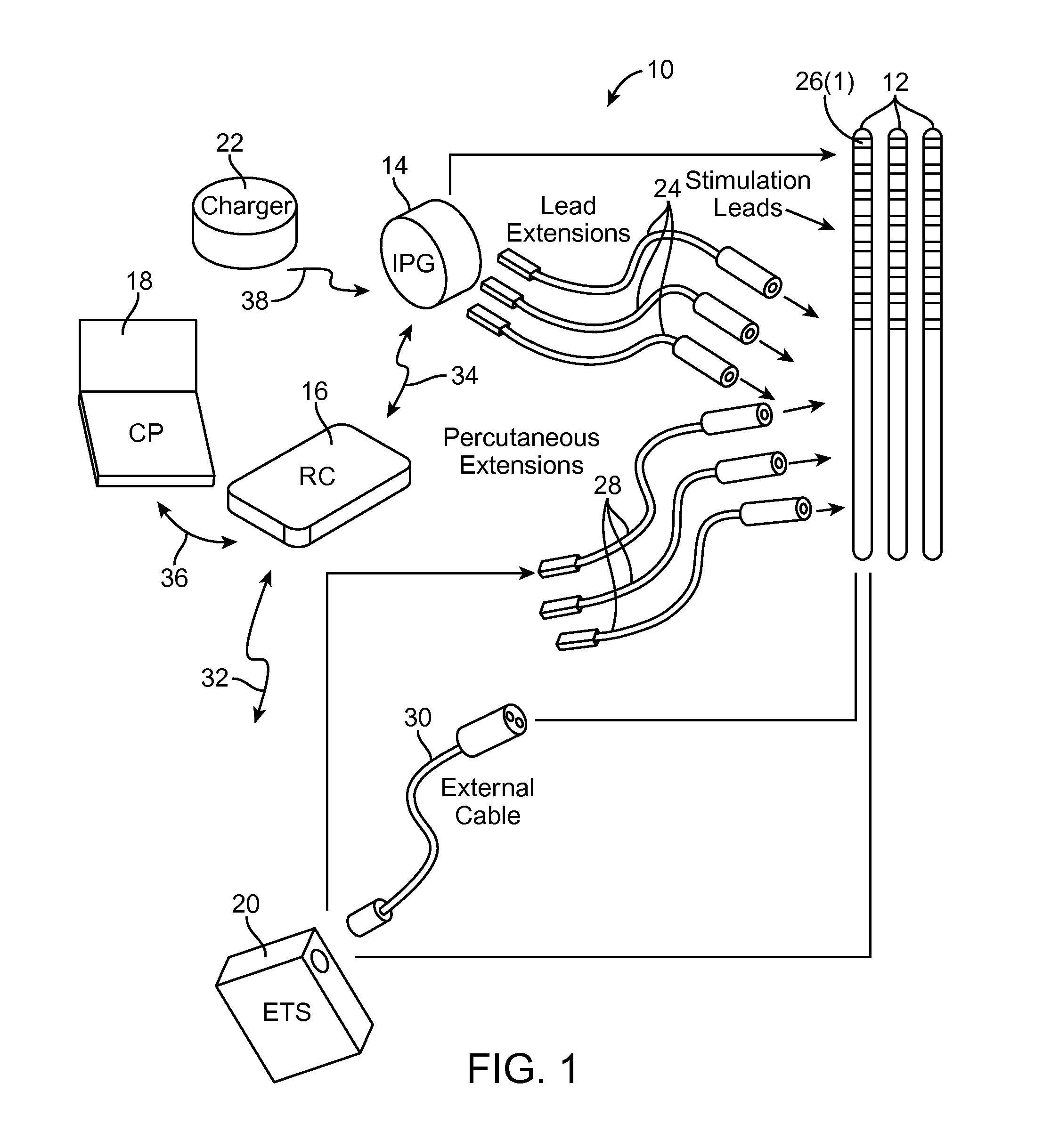
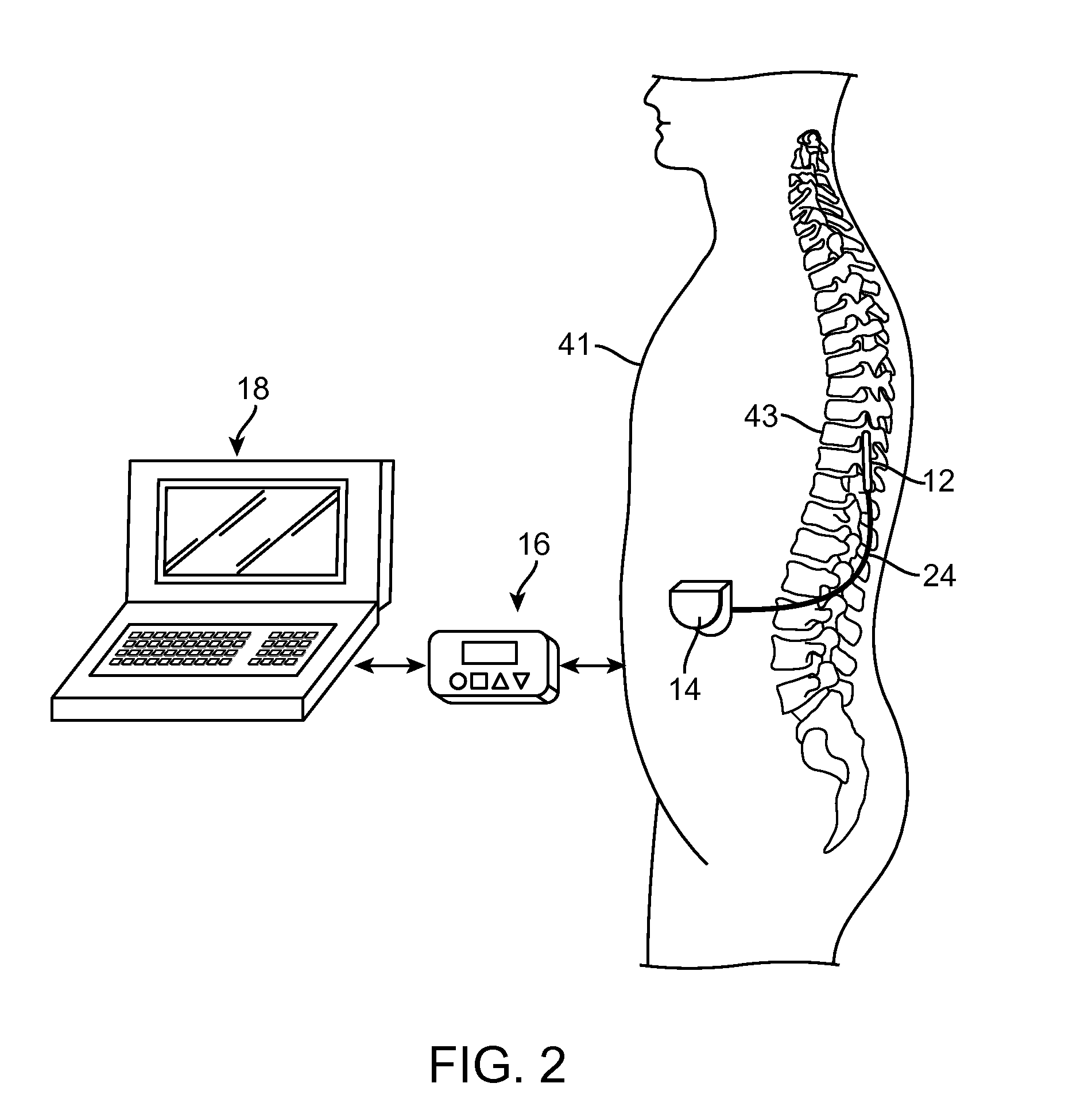
Method and Apparatus for Treating Incontinence
InactiveUS20090054950A1Alleviate and avoid symptomDigestive electrodesProsthesisSmooth muscleUrethra
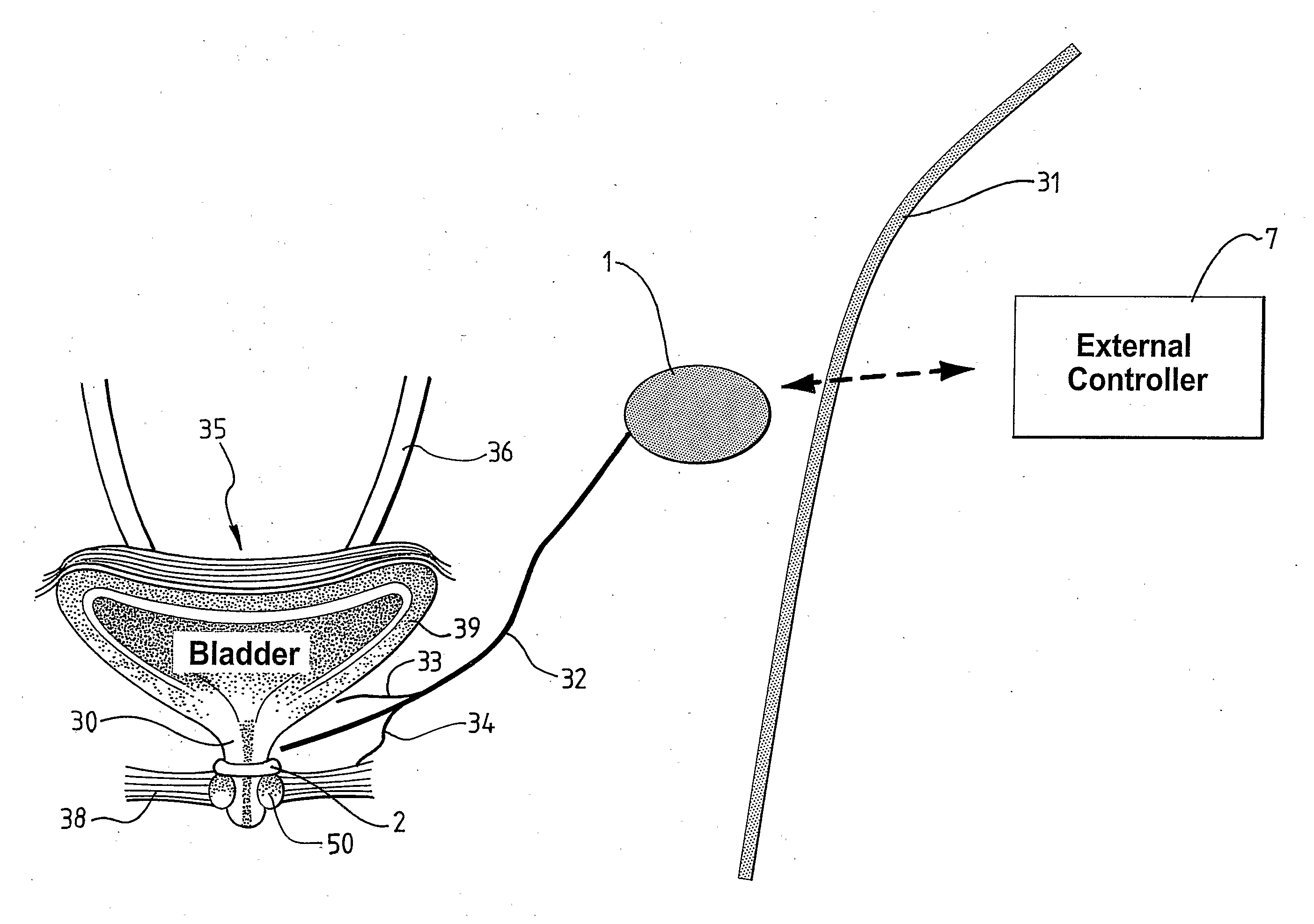
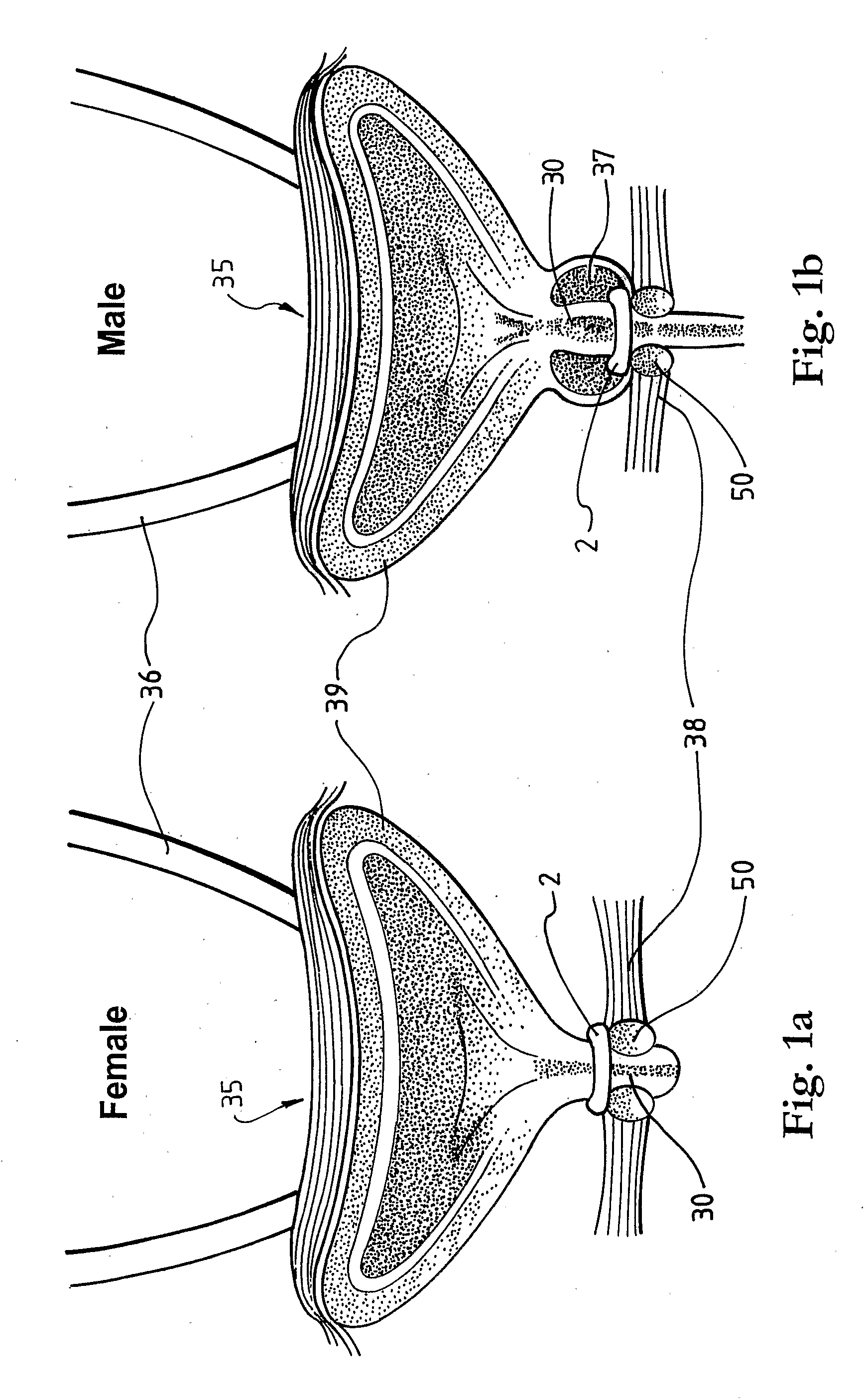
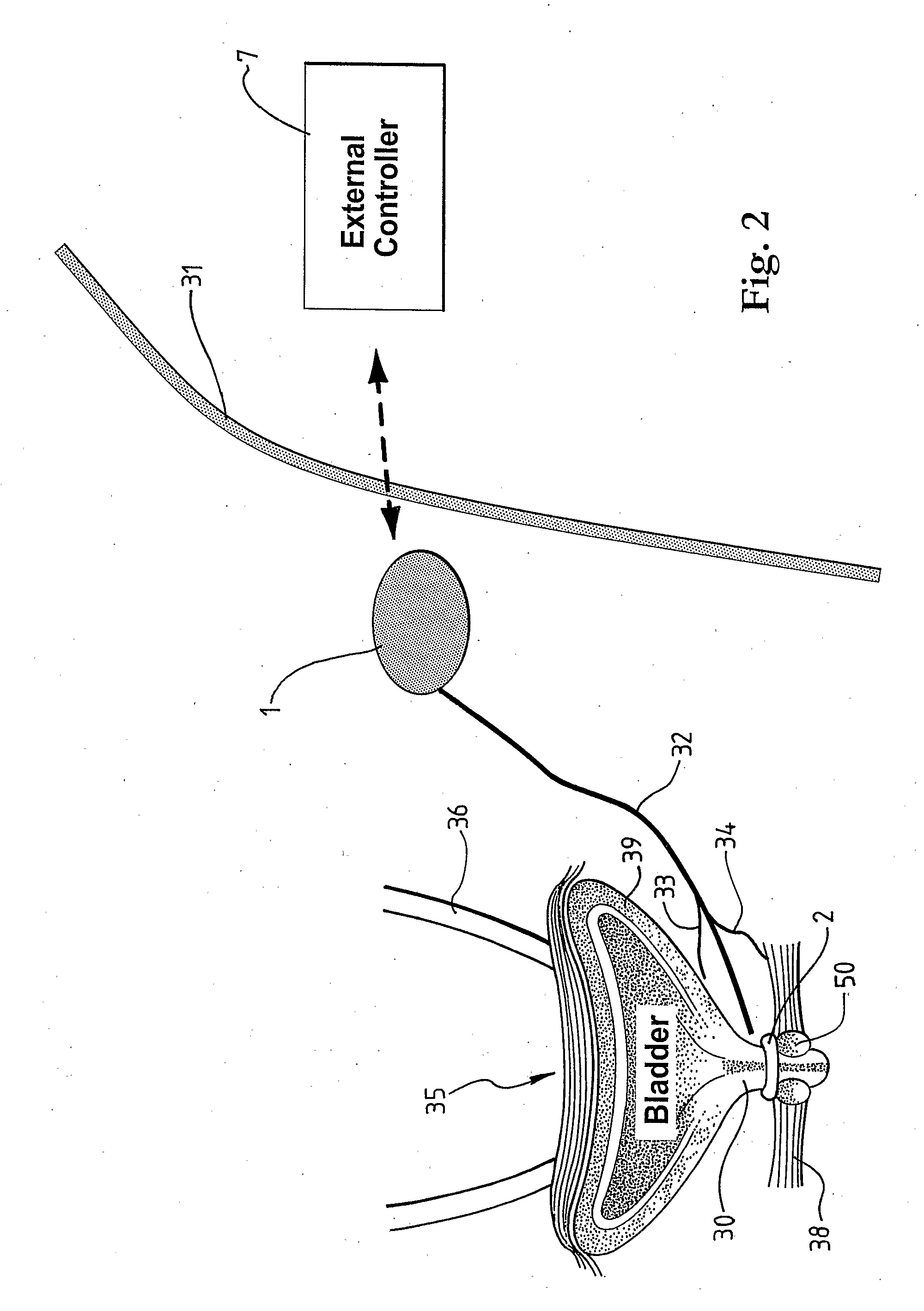
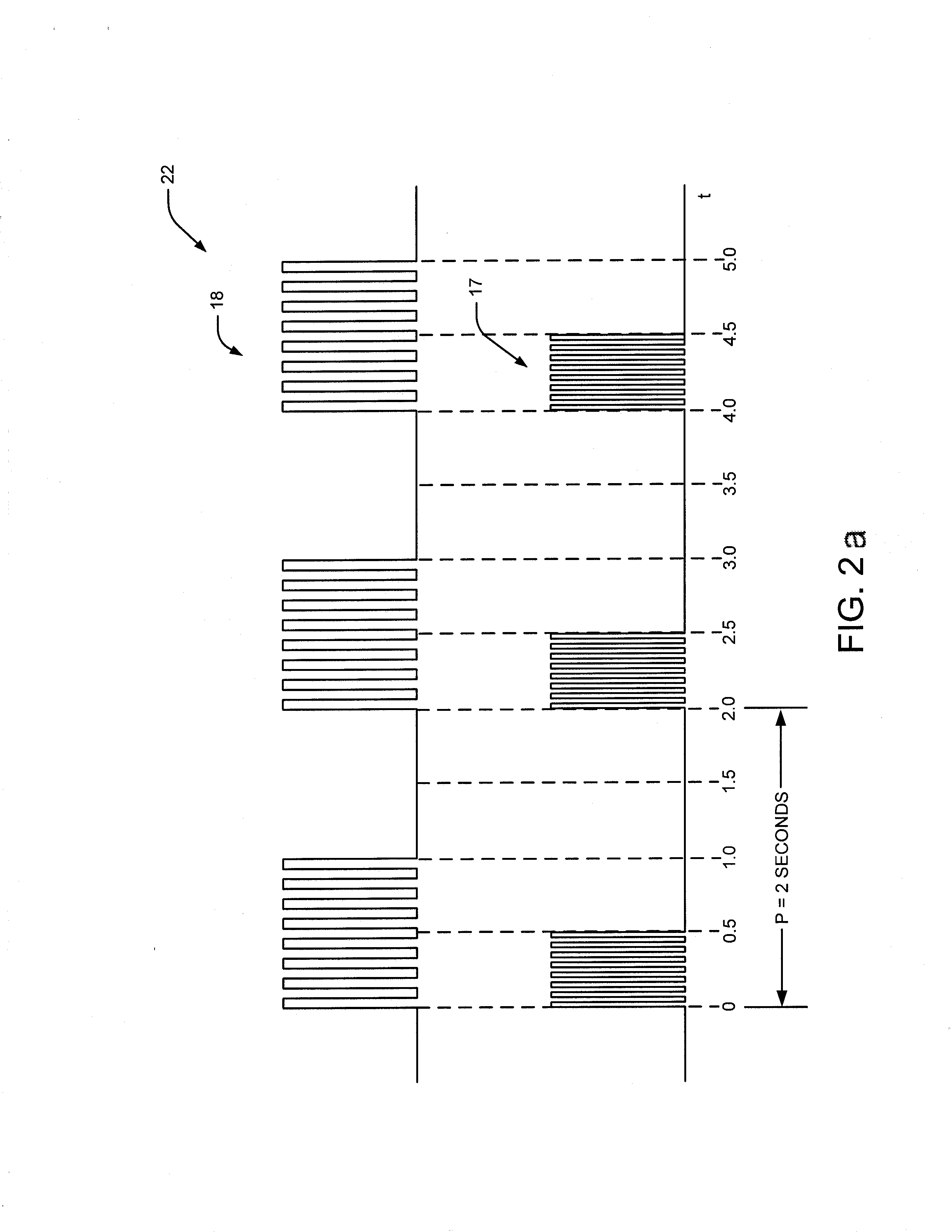
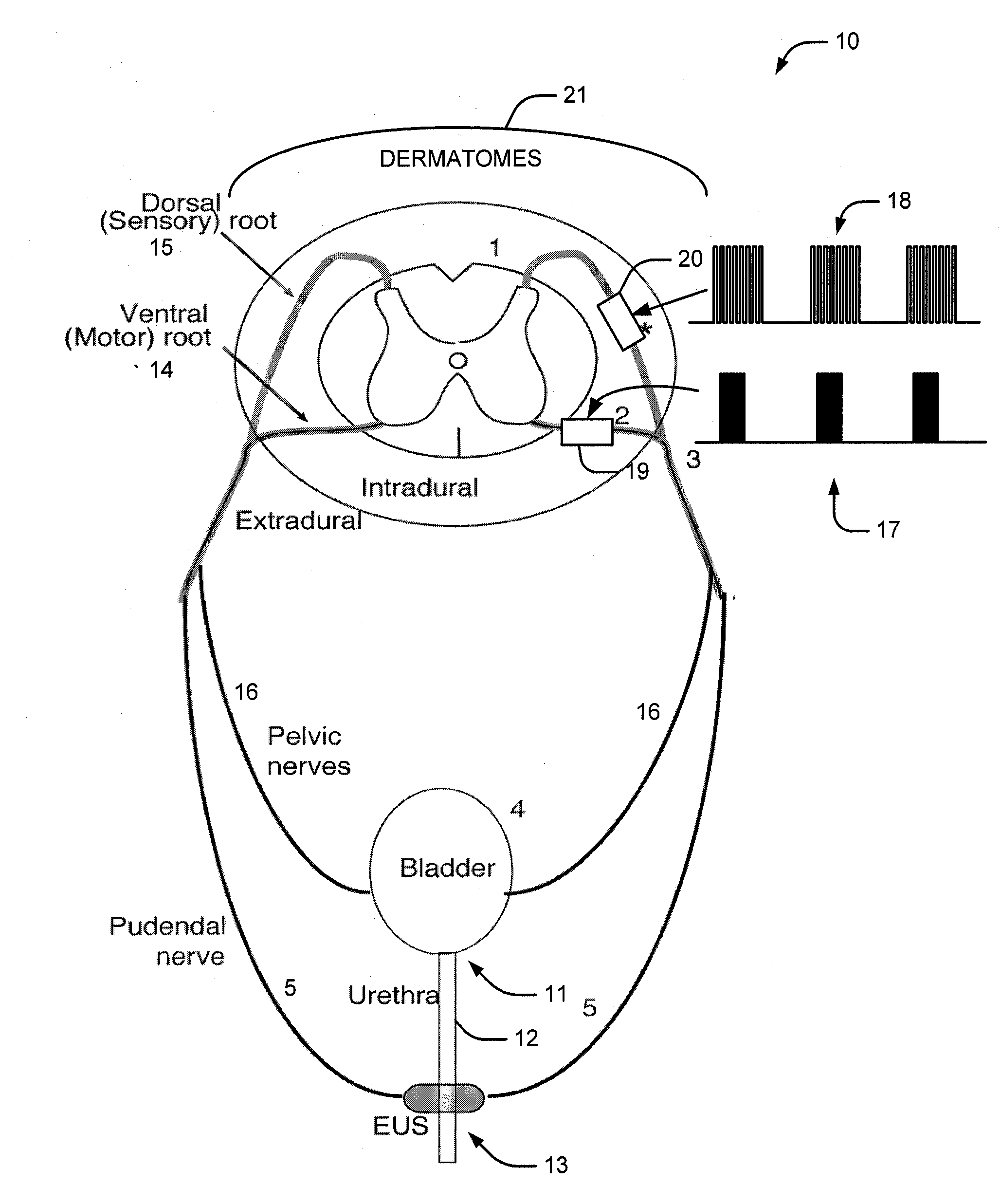
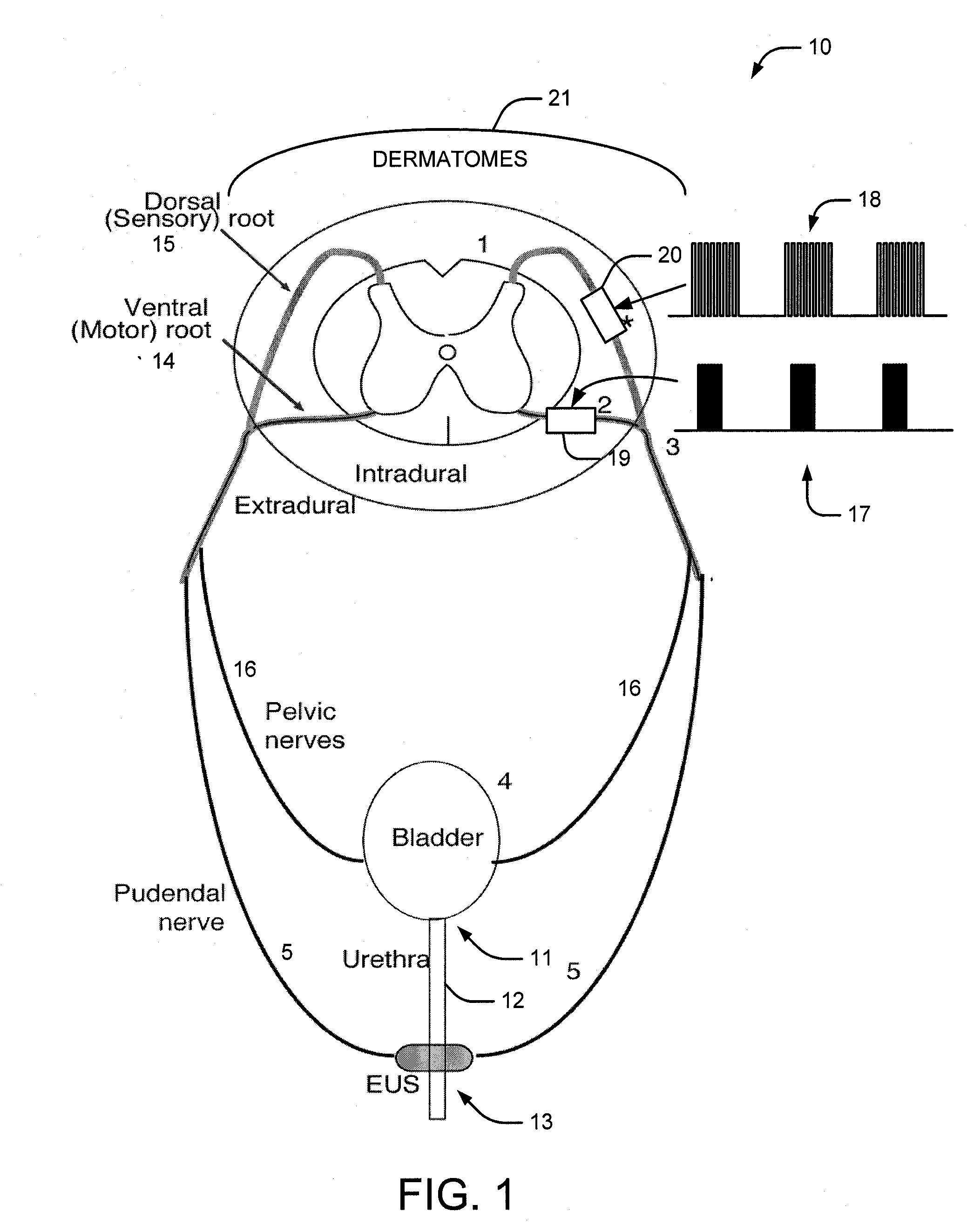
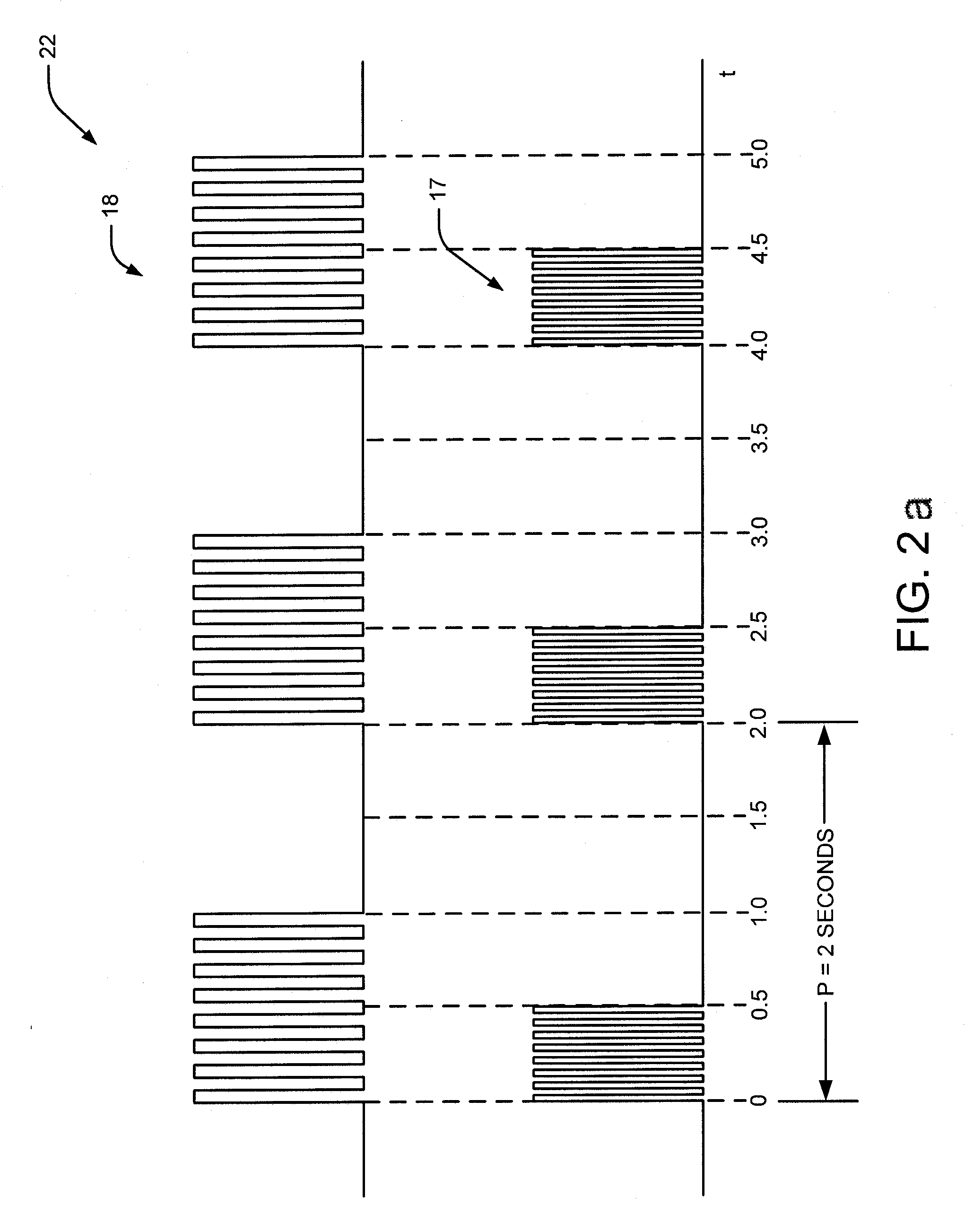
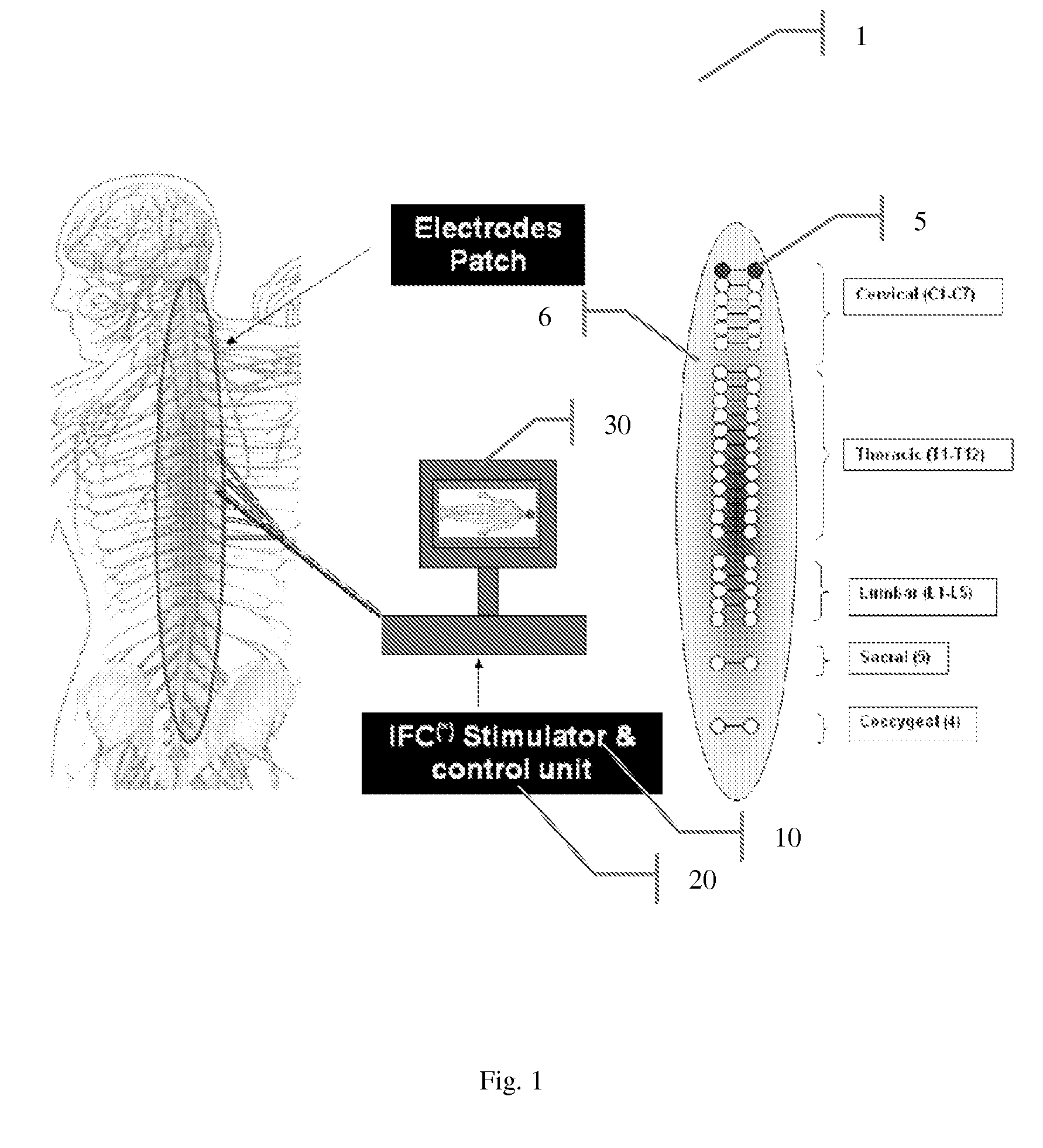
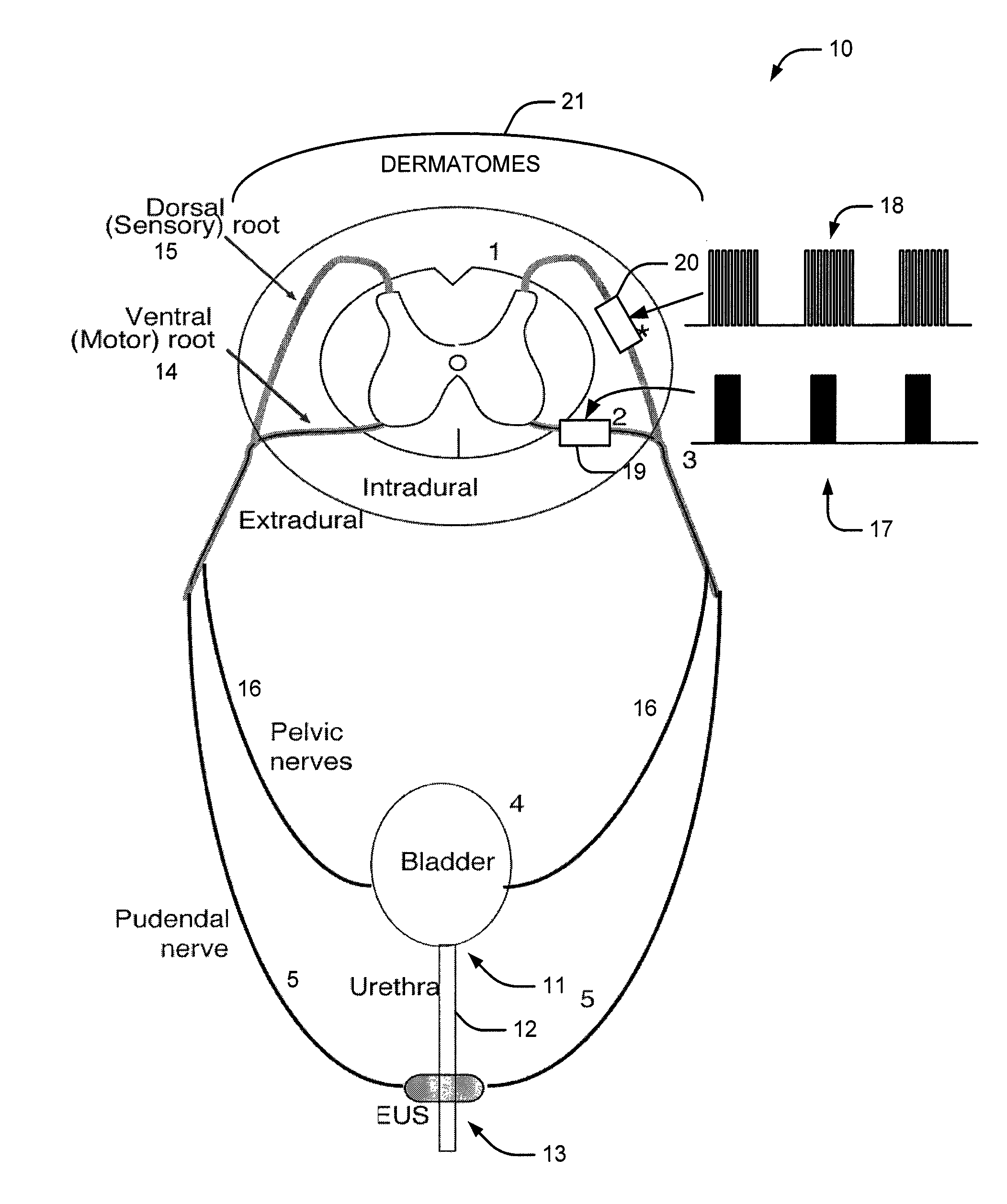
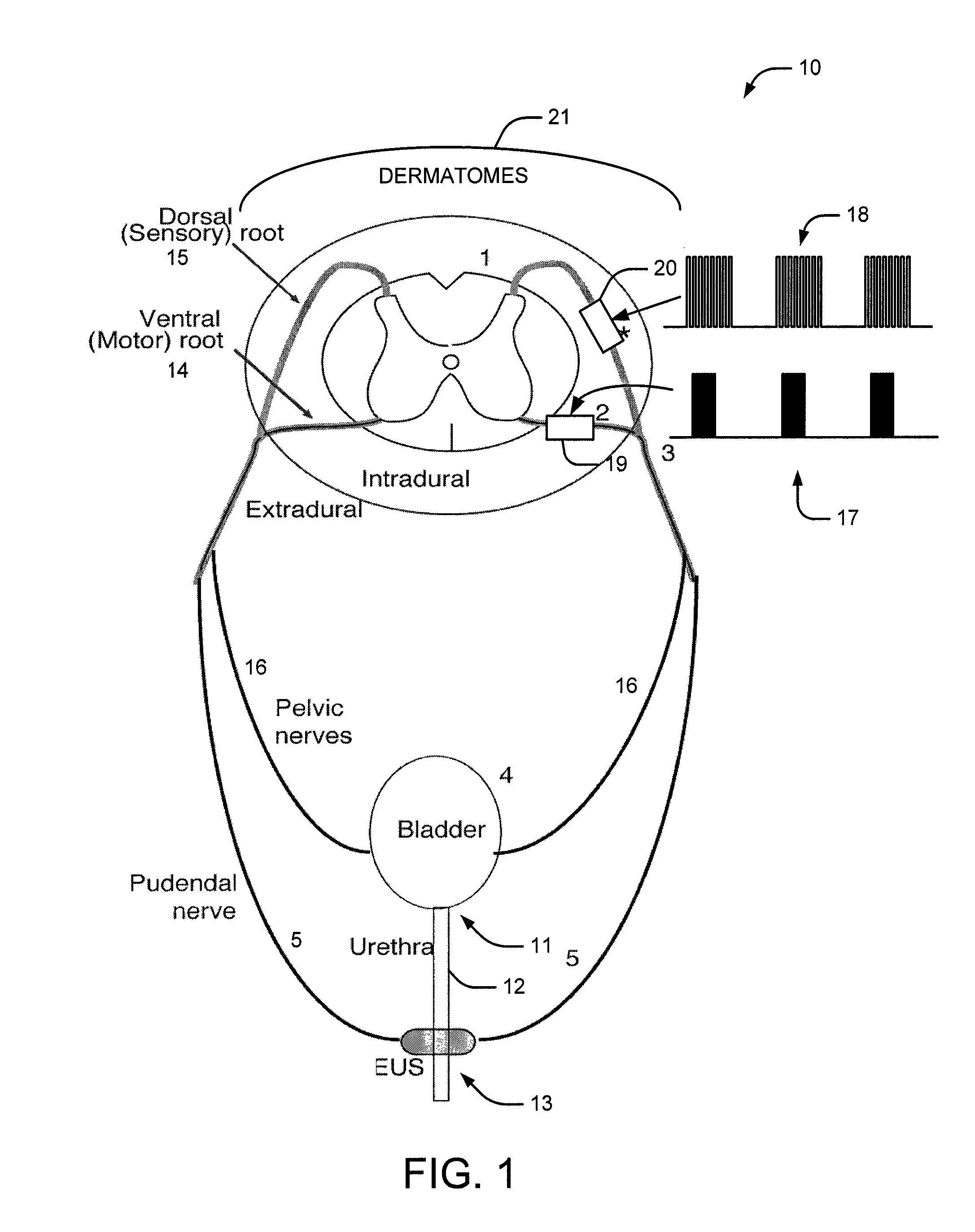
A medical condition is treated using electrical stimulation of contractile tissue, such as a sphineter, as well as electrical stimulation of afferent nerves to illicite a neuron-modulation response. The device (1) and method is particular useful for treating urge incontinence where the tissue is a smooth muscle neo-sphineter (2) about the urethra and the nerves are in the pelvic region.
Owner:CONTINENCE CONTROL SYST INT
Carotid body modulation planning and assessment
Planning for and / or assessment of an ablation procedure on one or both carotid bodies or carotid body chemoreceptors or carotid body nerves to treat patients having a sympathetically mediated cardiac, metabolic, and pulmonary disease (e.g. hypertension, CHF, diabetes, sleep disordered breathing) resulting from peripheral chemoreceptor hypersensitivity, carotid body hyperactivity, high carotid body afferent nerve signaling or heightened sympathetic activation.
Owner:CIBIEM
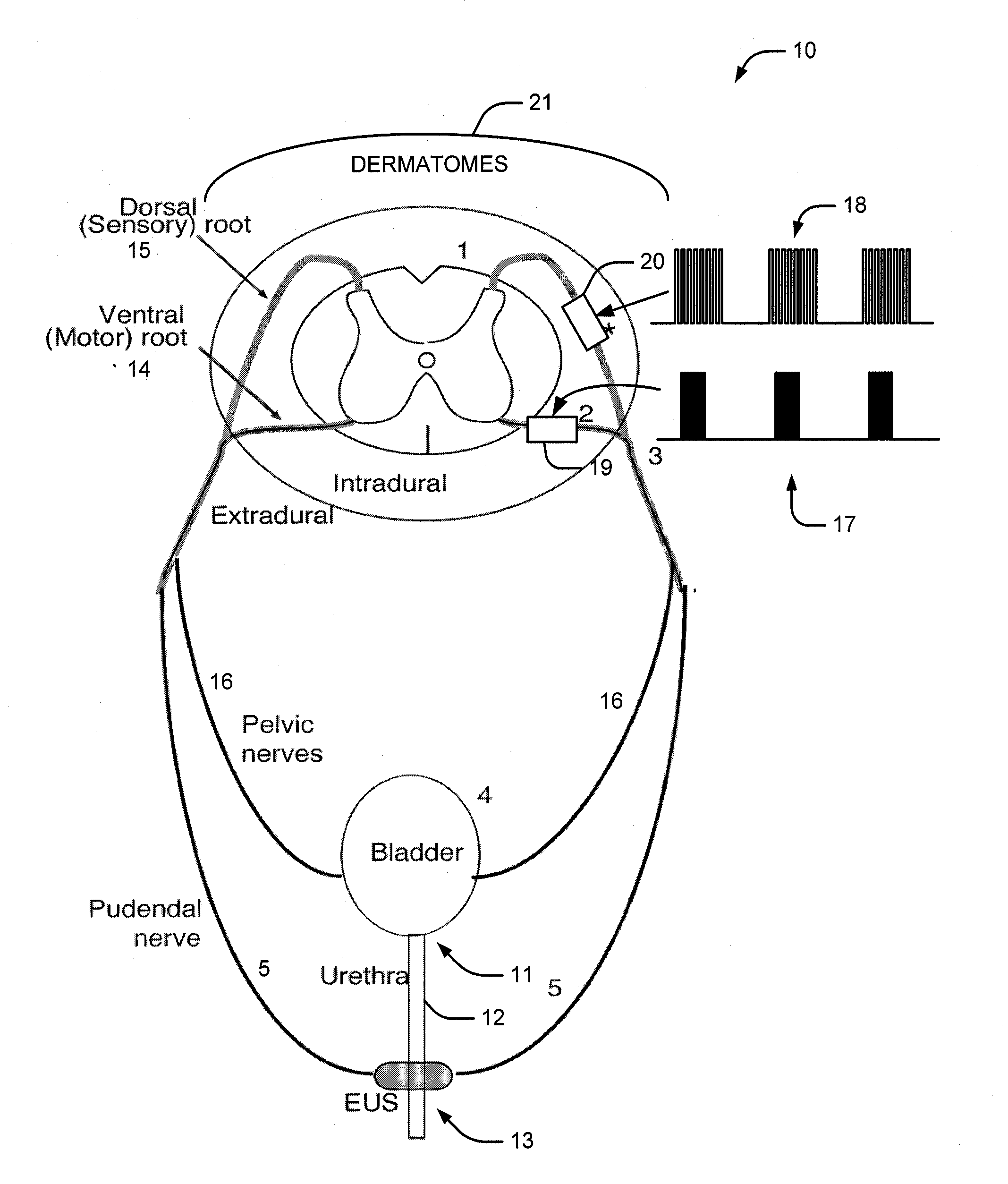
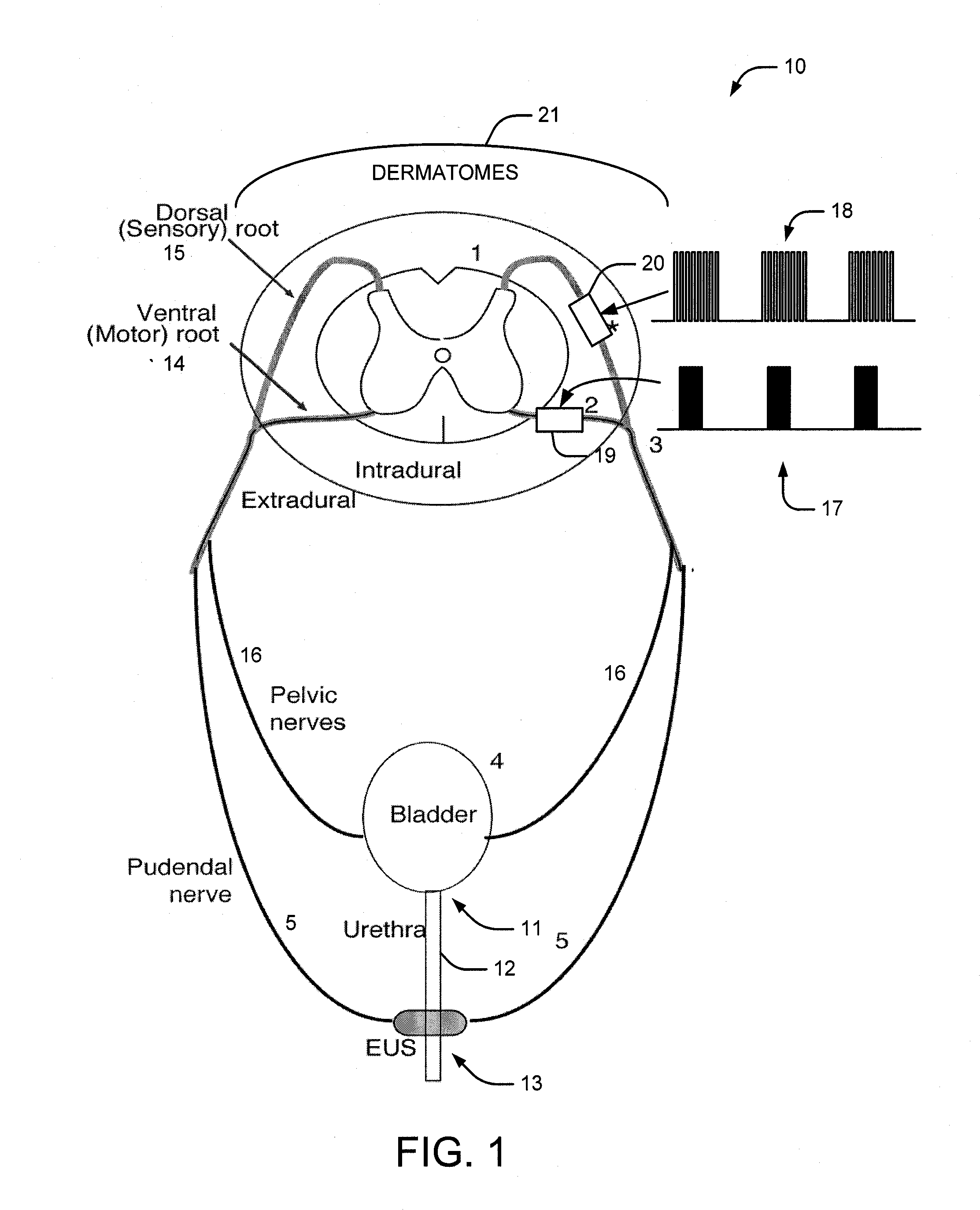
System and method of bladder and sphincter control
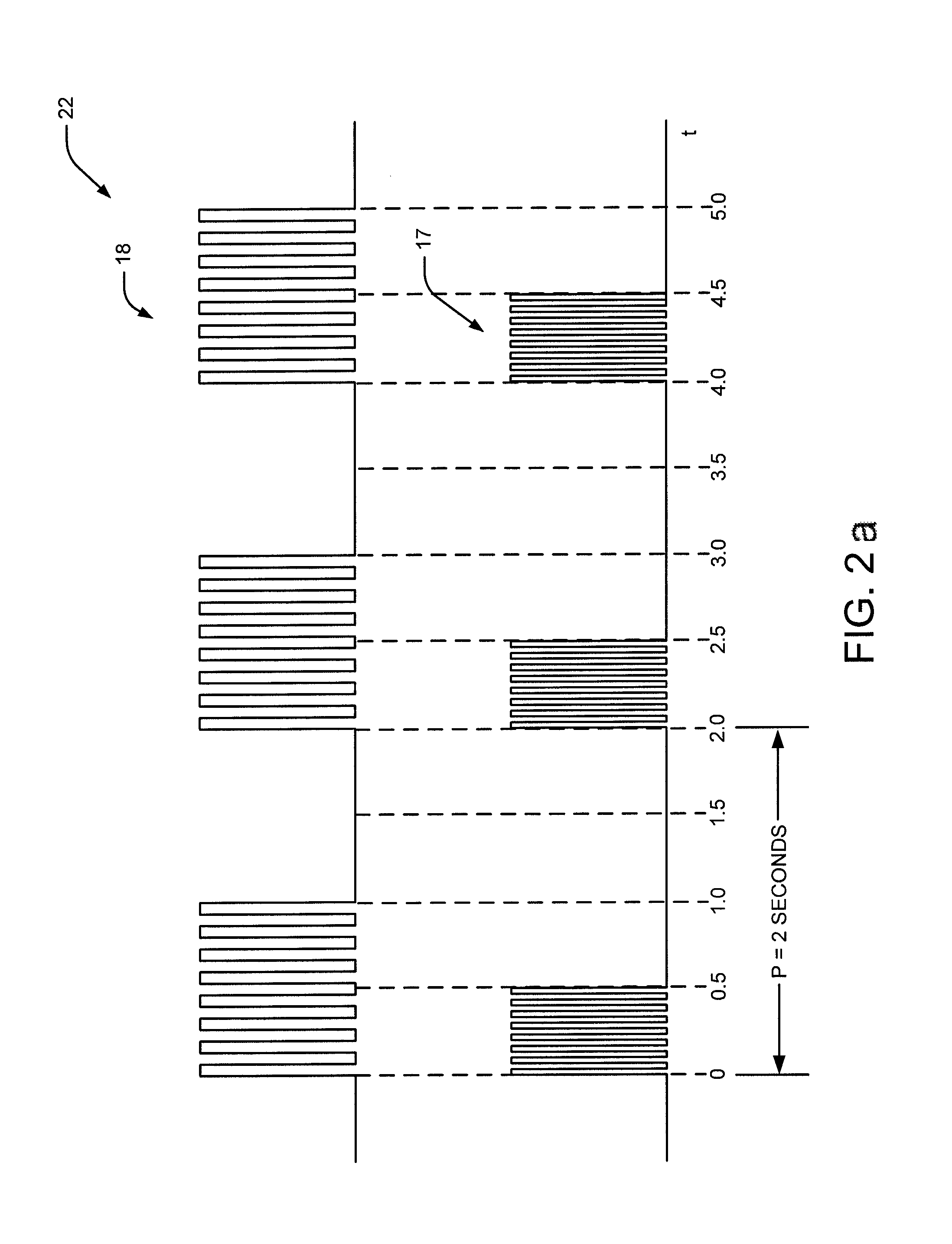
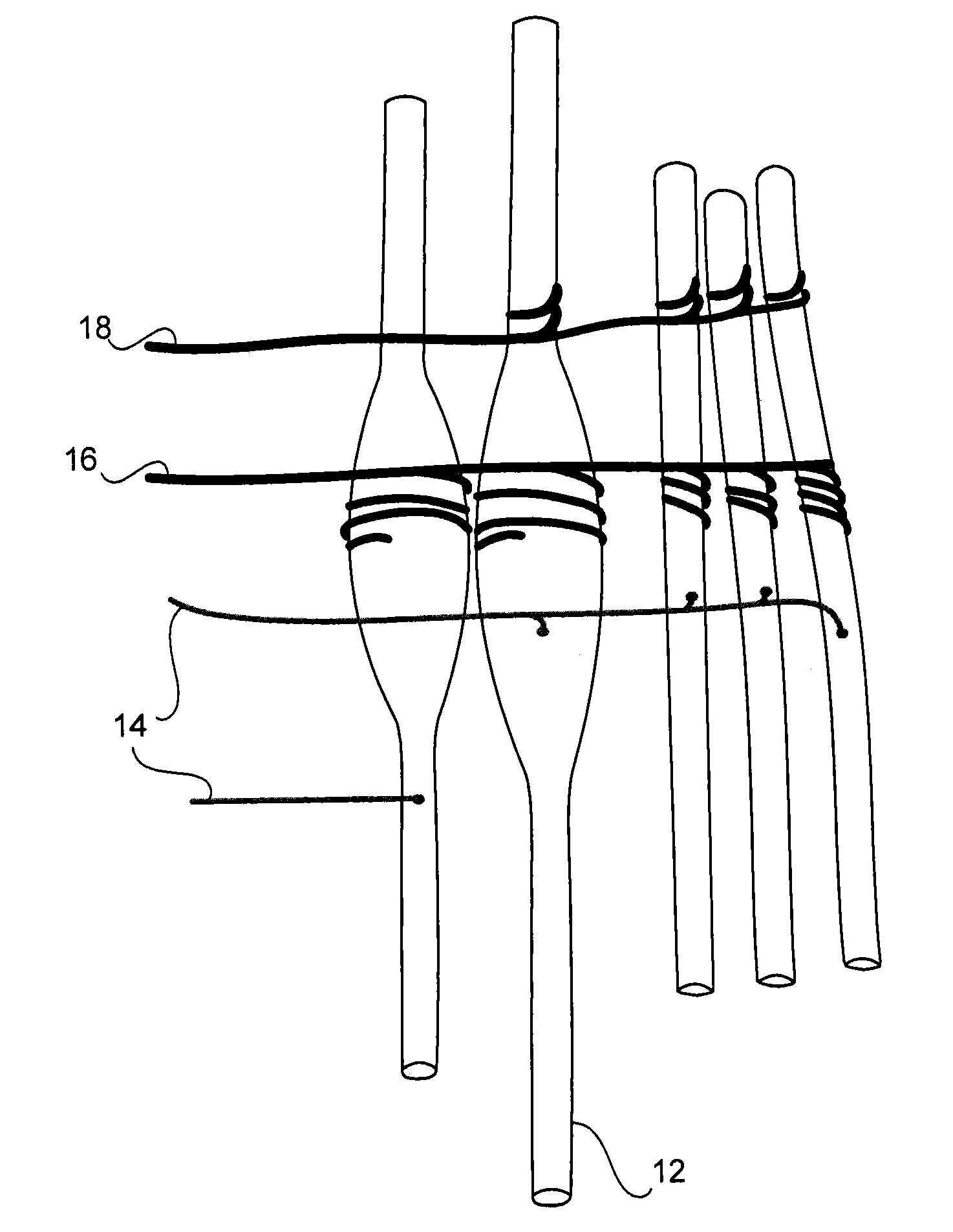
A method and system for bladder control are disclosed. In embodiments, a method for bladder control is provided that comprises coupling an electrode to an afferent nerve that is related to the bladder. Applying a plurality of pulse burst stimulations via the electrode causes voiding of urine from the bladder. In embodiments, the plurality of pulse burst stimulations to the afferent nerve reduces external urethral sphincter (EUS) contractions and evokes bladder contractions to expel urine from the subject. In embodiments, the plurality of pulse burst stimulations to the afferent nerve evokes bladder contractions alone to expel urine from the subject. In embodiments, a system for bladder control is provided that comprises an electrode for applying a pulse burst stimulus to an afferent nerve or dermatome to reduce reflex contractions and a signal generator for generating the pulse burst stimulus.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
System and Method of Bladder and Sphincter Control
InactiveUS20090254144A1Reduce distractionsReduce and eliminate external urethral sphincter (EUS) contractionElectrotherapyArtificial respirationSphincterBladder control
A method and system for bladder control are disclosed. In embodiments, a method for bladder control is provided that comprises coupling an electrode to an afferent nerve that is related to the bladder. Applying a plurality of pulse burst stimulations via the electrode causes voiding of urine from the bladder. In embodiments, the plurality of pulse burst stimulations to the afferent nerve reduces external urethral sphincter (EUS) contractions and evokes bladder contractions to expel urine from the subject. In embodiments, the plurality of pulse burst stimulations to the afferent nerve evokes bladder contractions alone to expel urine from the subject. In embodiments, a system for bladder control is provided that comprises an electrode for applying a pulse burst stimulus to an afferent nerve or dermatome to reduce reflex contractions and a signal generator for generating the pulse burst stimulus.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Method for treating hypertension via electrical stimulation of neural structures
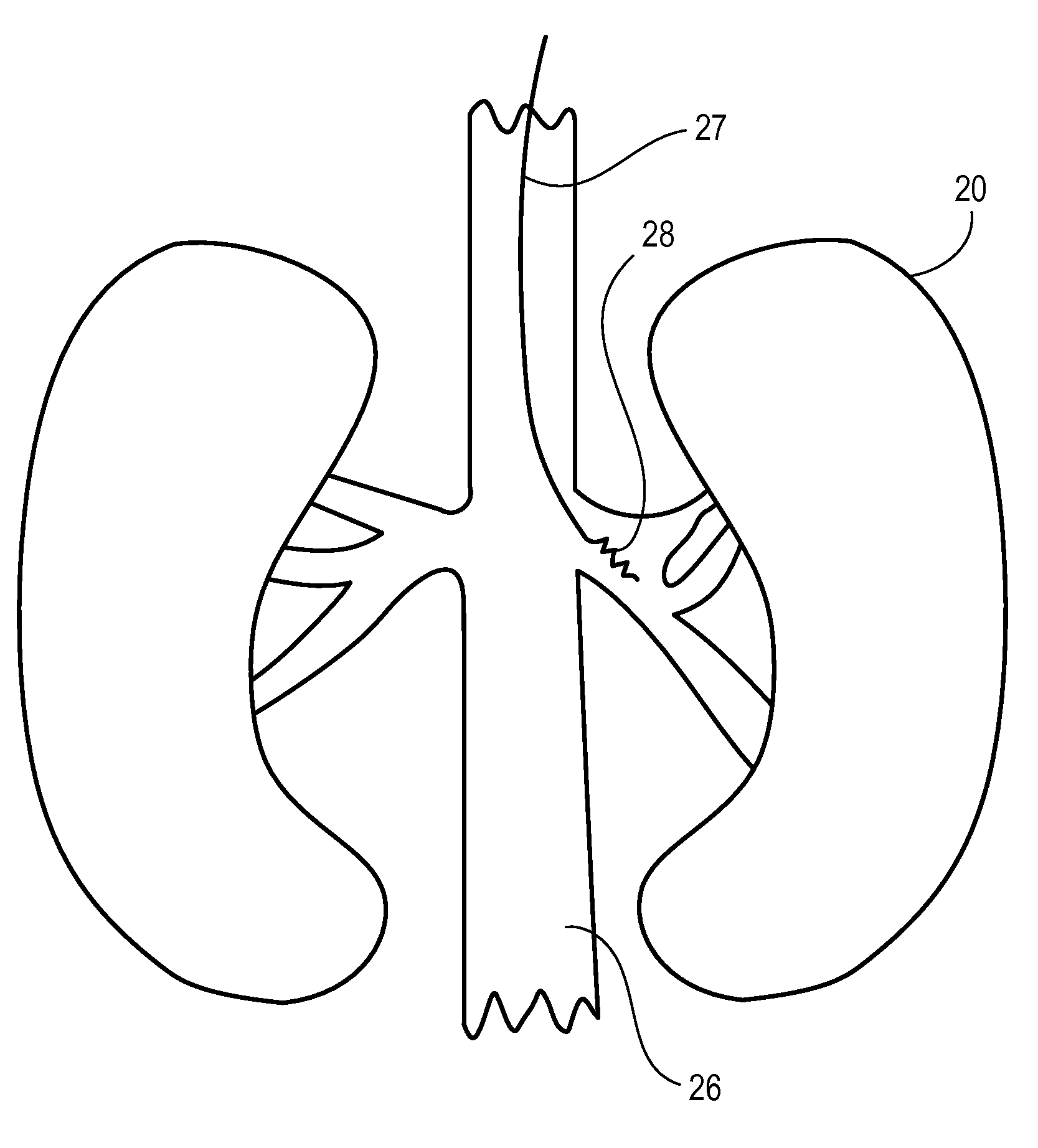
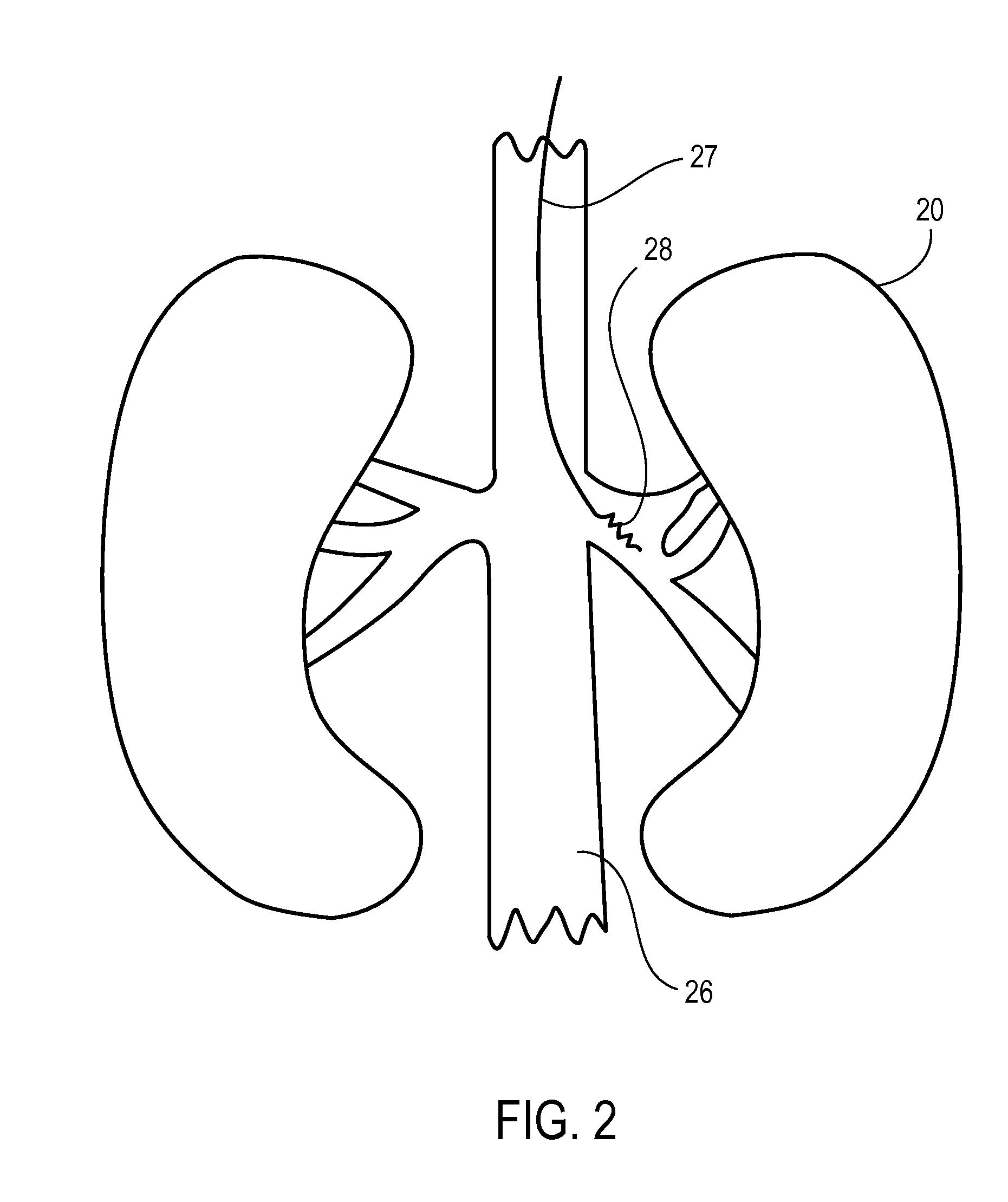
A neuromodulation system comprises a sensor configured for sensing a blood pressure of a patient, modulation output circuitry configured for conveying electrical modulation energy to at least one electrode, and a controller / processor coupled to the sensor and the modulation output circuitry. The controller / processor is configured for comparing the blood pressure sensed by the sensor to a first threshold blood pressure, and instructing the modulation output circuitry to convey the electrical modulation energy to the at least one electrode if the sensed blood pressure is greater than the first threshold blood pressure. A method for treating chronic hypertension comprises applying electrical modulation energy to a neural target site, thereby modulating an afferent nerve innervating a patient's kidney, thereby treating the chronic hypertension.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
System and method for neuromodulation of body temperature regulation system
A system for controlling and modulating a mammalian's body temperature and thermoregulation system includes: a. a display monitor; b. a pulse generator; c. at least one channel of electrical or electromagnetic stimuli connected to the pulse generator, and adapted for cutaneous application on the body's spinal cord; d. a control panel, and e. at least one Measurement Analysis and Command (MAC) unit. The control panel and the MAC units are adapted to implement the optimal stimulating procedure for blocking the afferent neural pathways, evoking the afferent neural pathways, attenuating the afferent neural pathways, blocking and evoking the efferent neural pathways, blocking and attenuating the efferent neural pathways, attenuating and evoking, or blocking, attenuating, and evoking the efferent neural pathways, involved in the thermoregulation system, thereby controlling and modulating the body's temperature and thermoregulation system.
Owner:THERMACON
Unidirectional neural stimulation systems, devices and methods
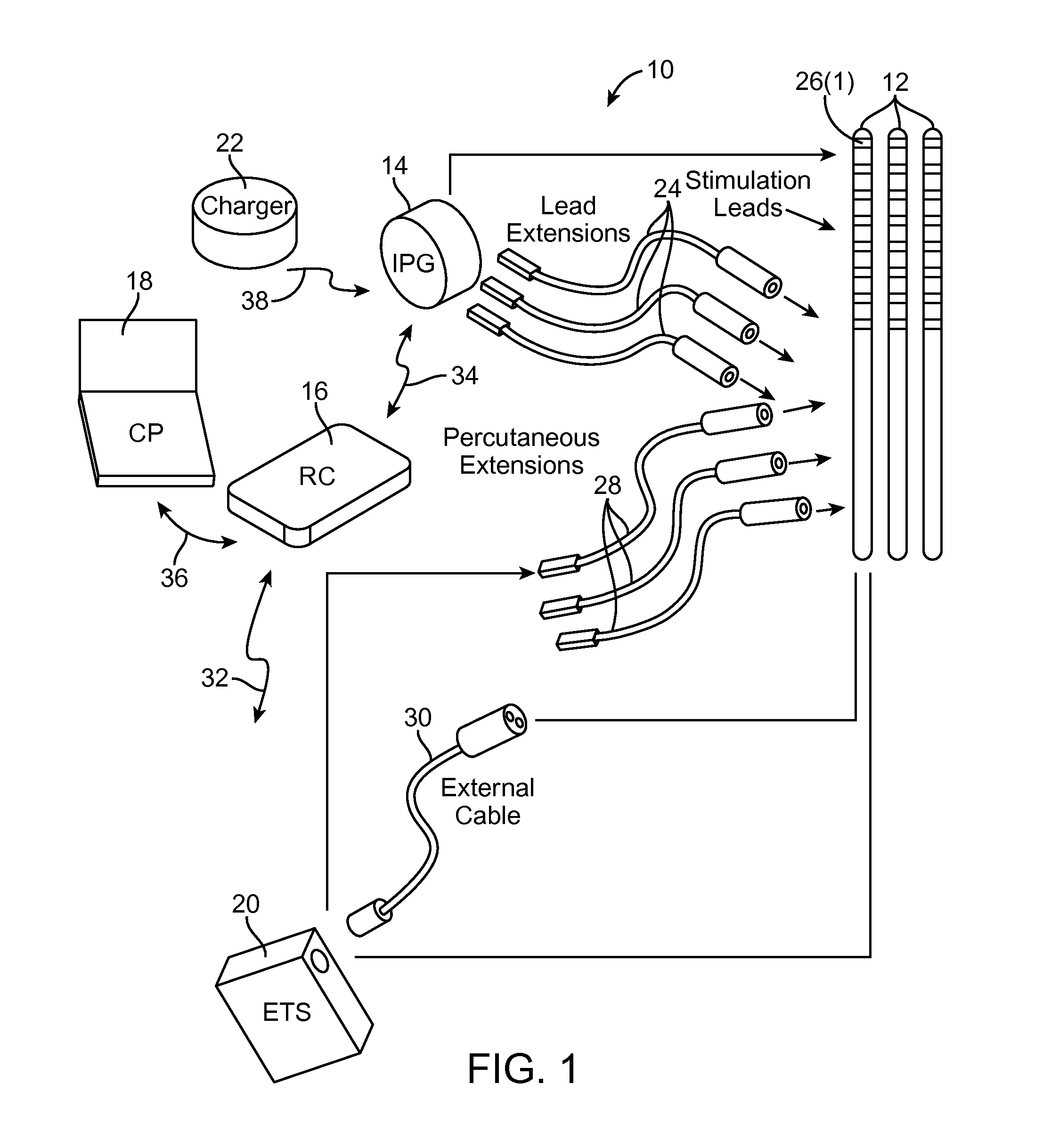
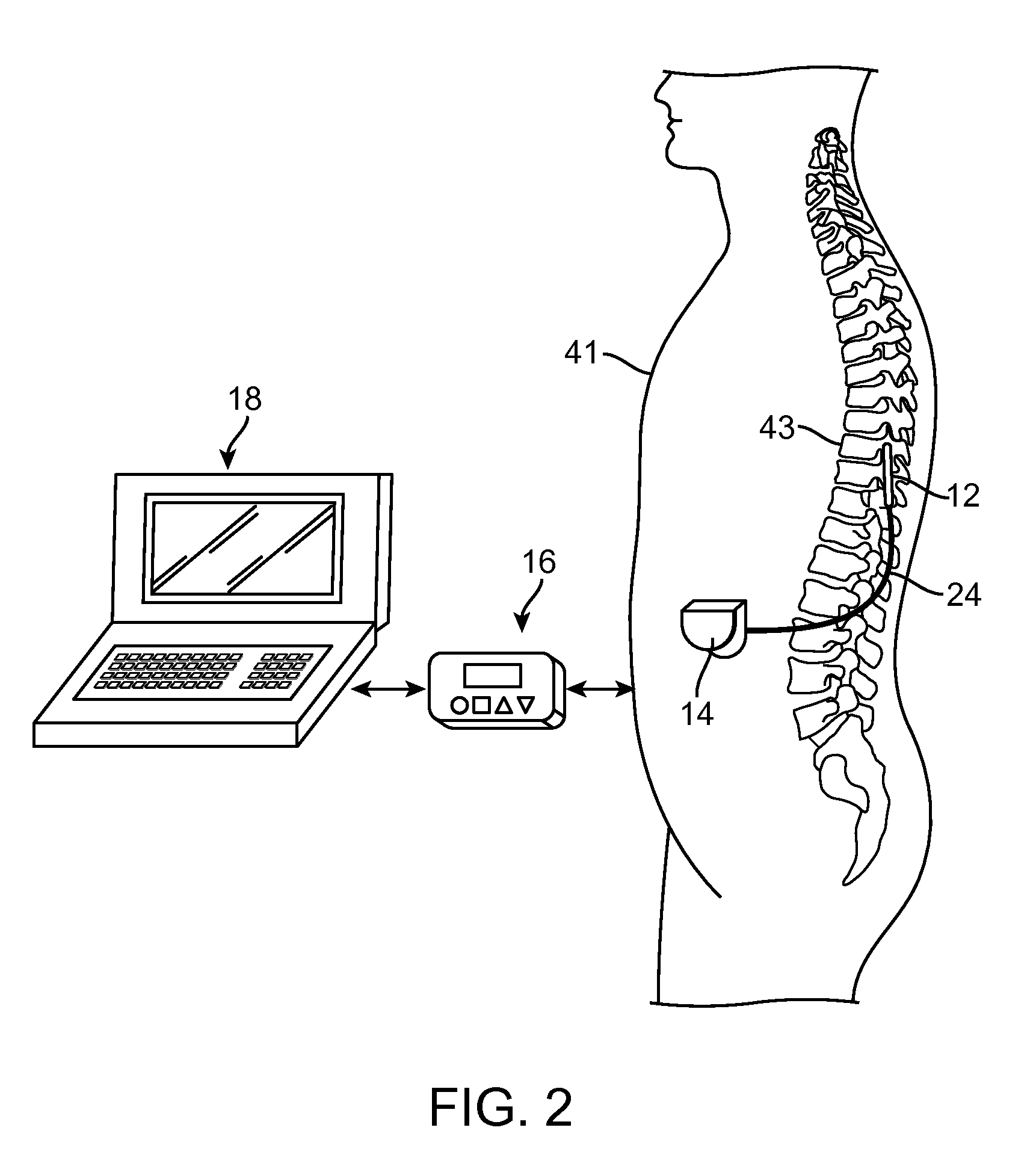
An embodiment relates to a method for delivering a unidirectional afferent nerve stimulation treatment. A test neural stimulation is delivered, and a physiologic response to the test neural stimulation is monitored. At least one neural stimulation parameter for the test neural stimulation is adjusted if the test neural stimulation does not elicit a desired physiologic response. If the test neuralstimulation does elicit the desired physiologic response, at least one treatment parameter for a unidirectional afferent nerve stimulation is determined using the at least one neural stimulation parameter for the test neural stimulation that provided the desired physiologic response. The unidirectional afferent nerve stimulation is delivered using the at least one treatment parameter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
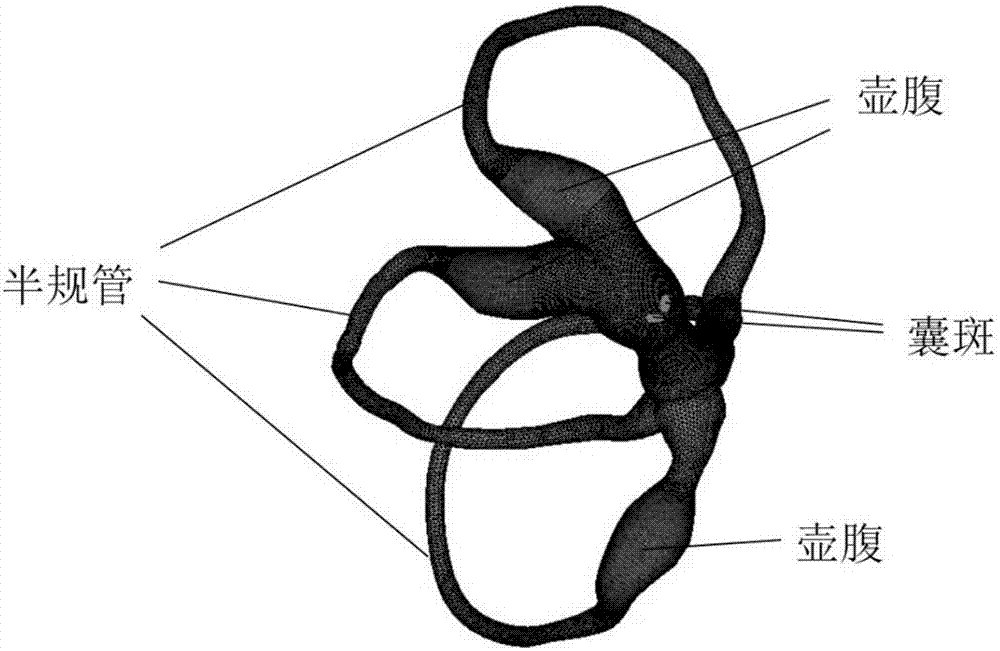
Vestibular prosthesis
InactiveUS20140081346A1Prevent fallingShort timeHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsMicrocontrollerAction potential firing
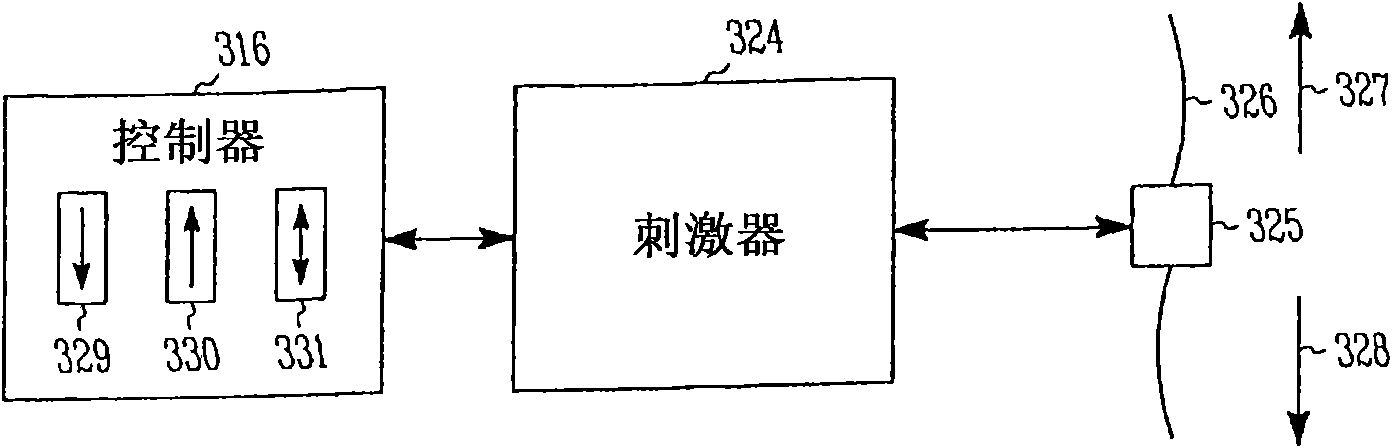
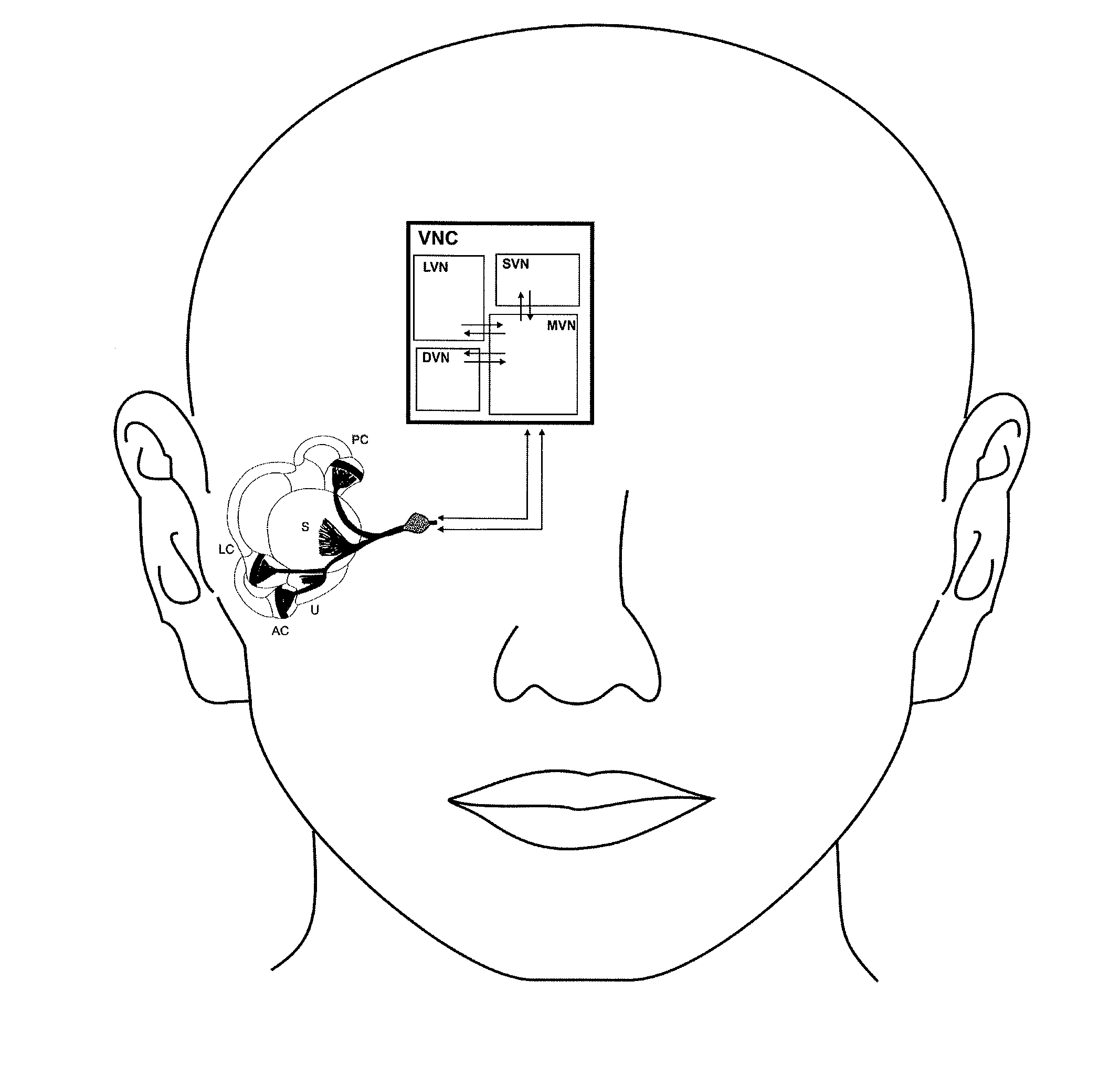
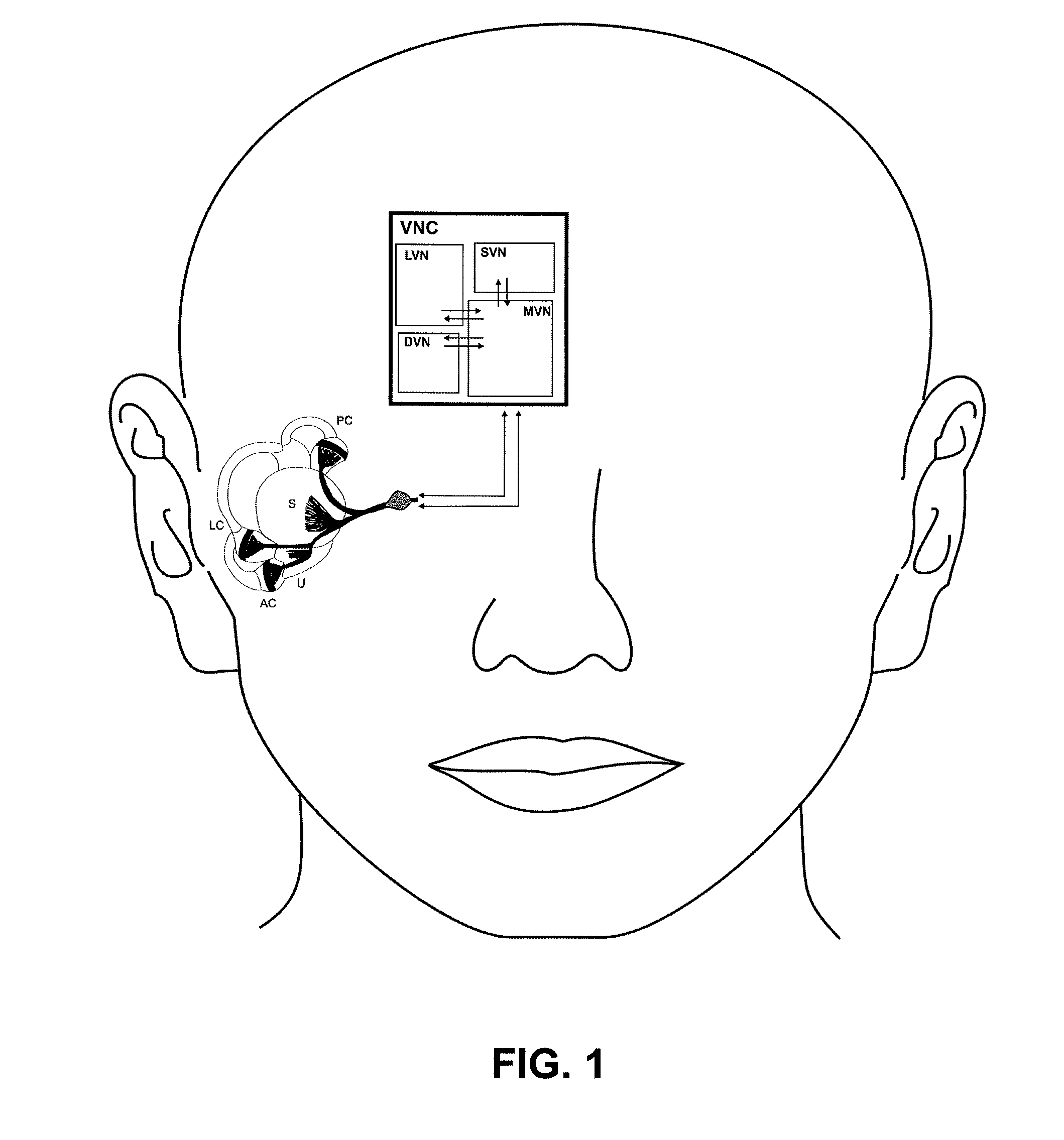
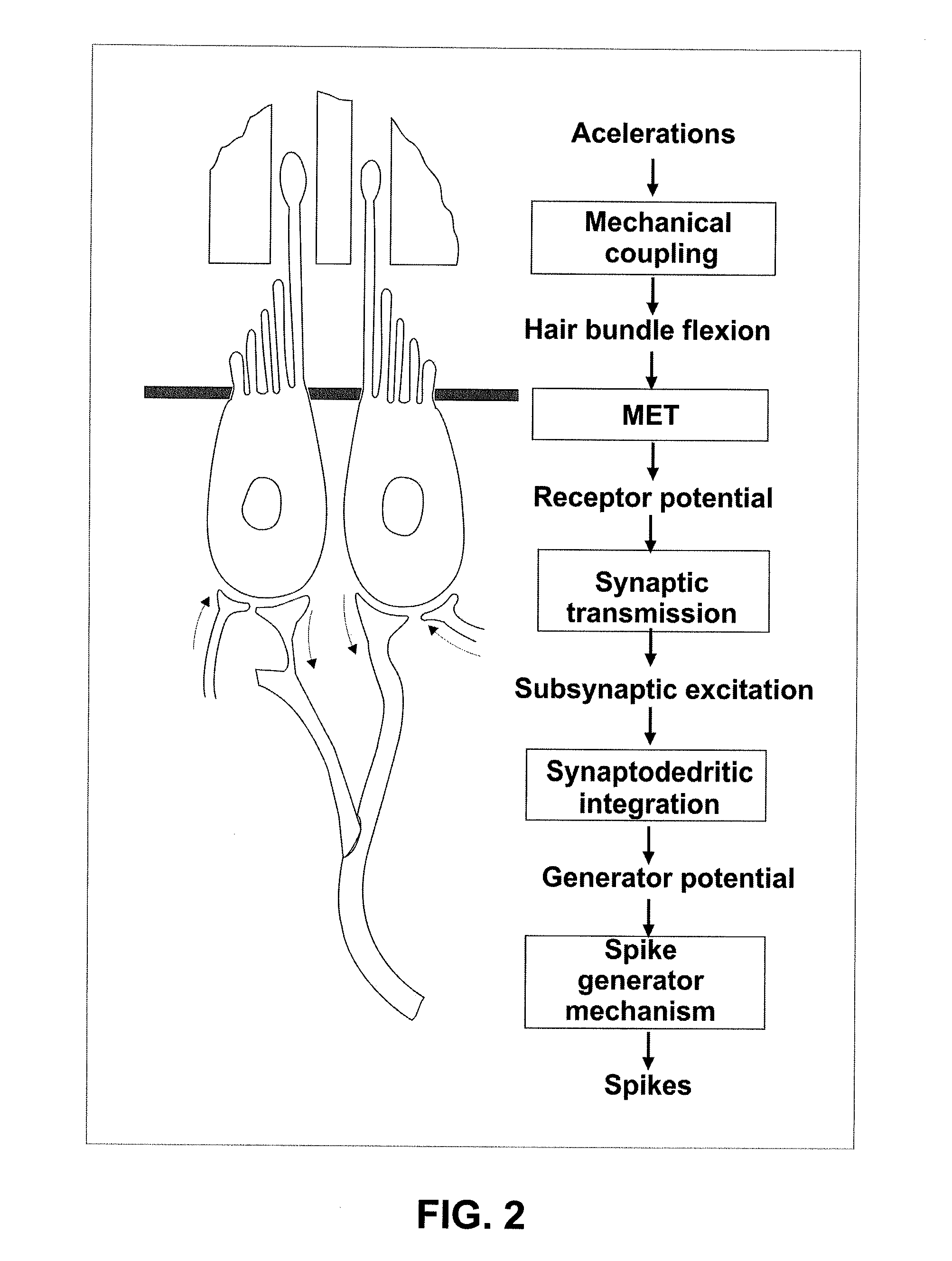
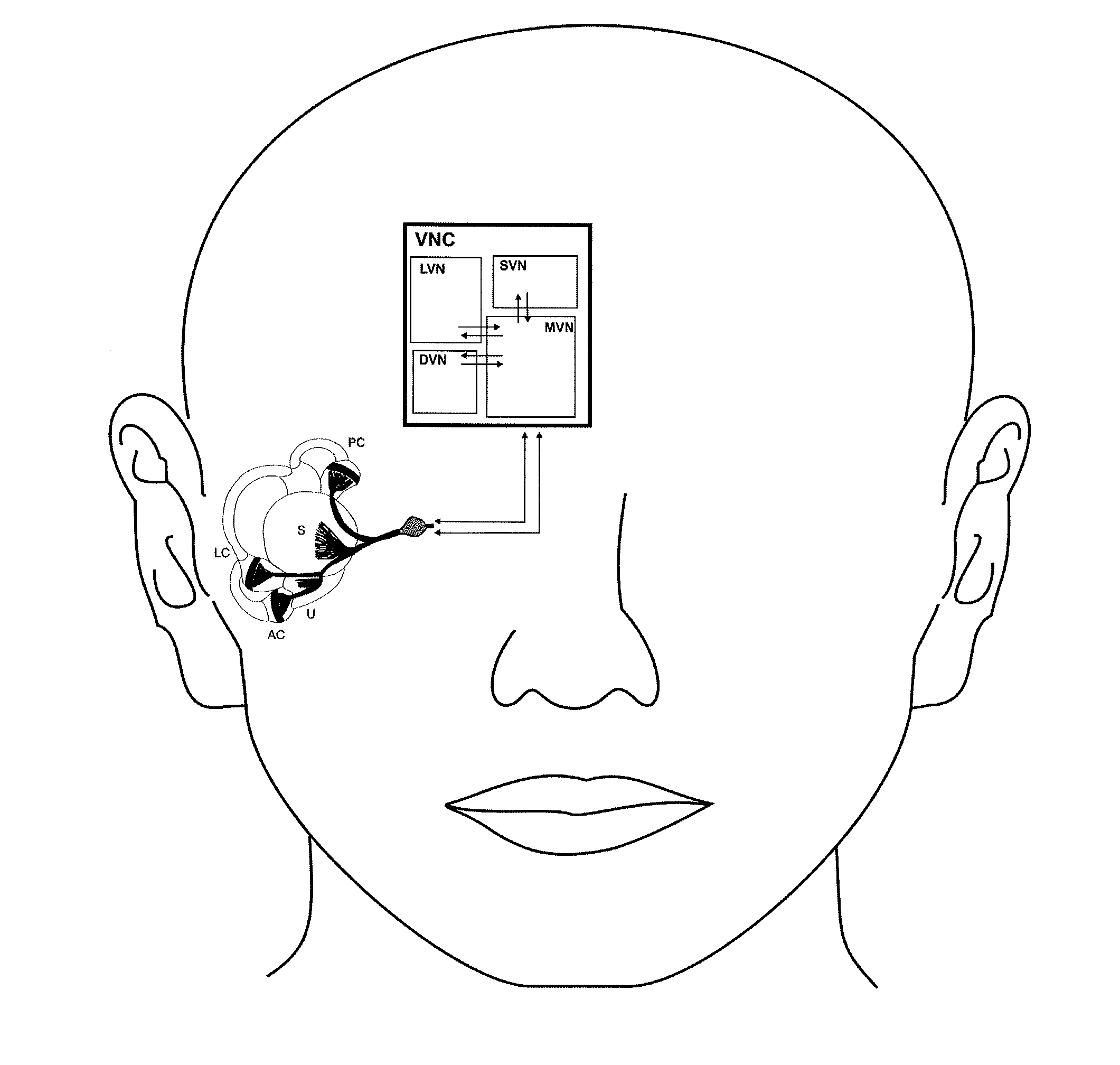
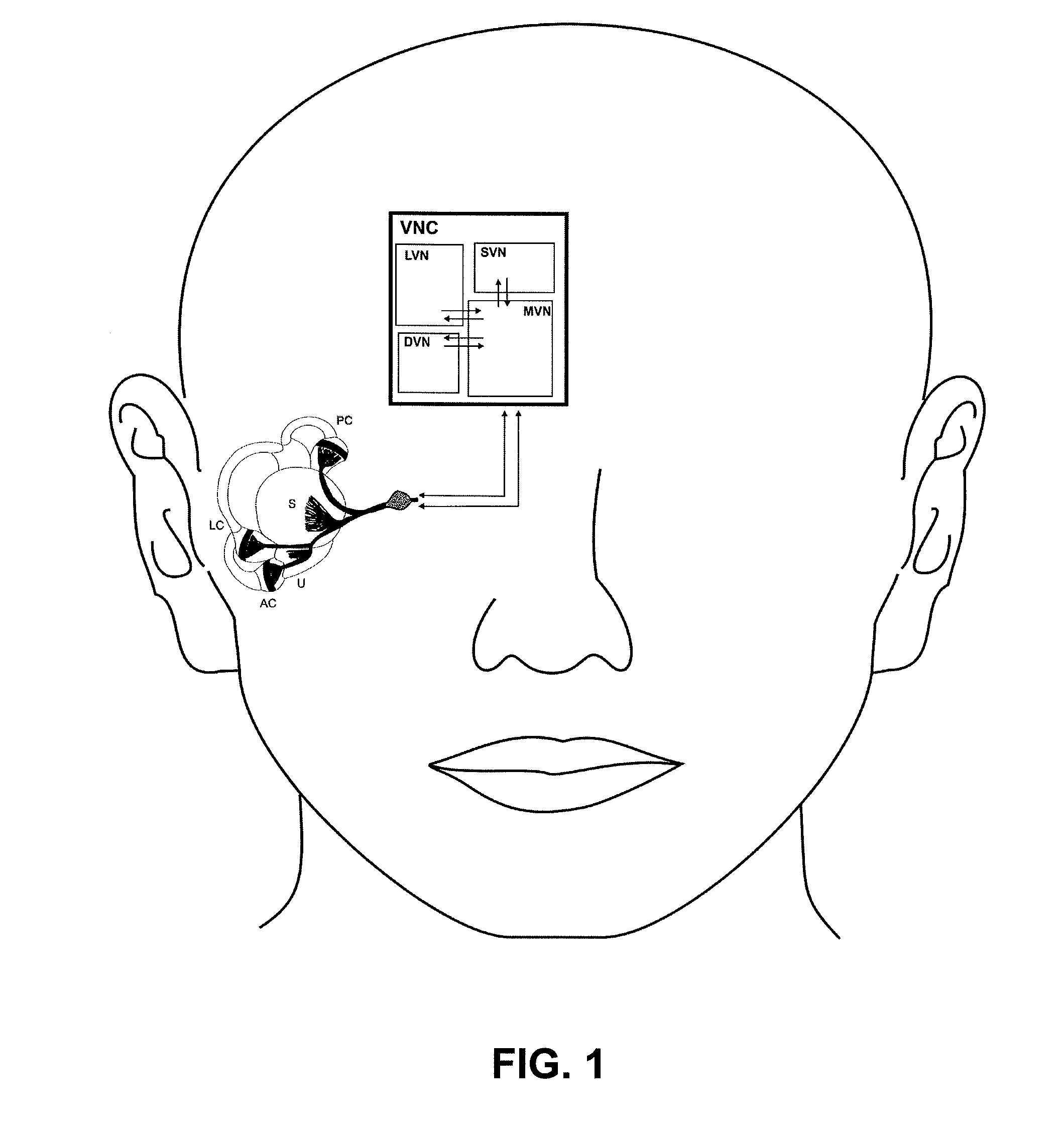
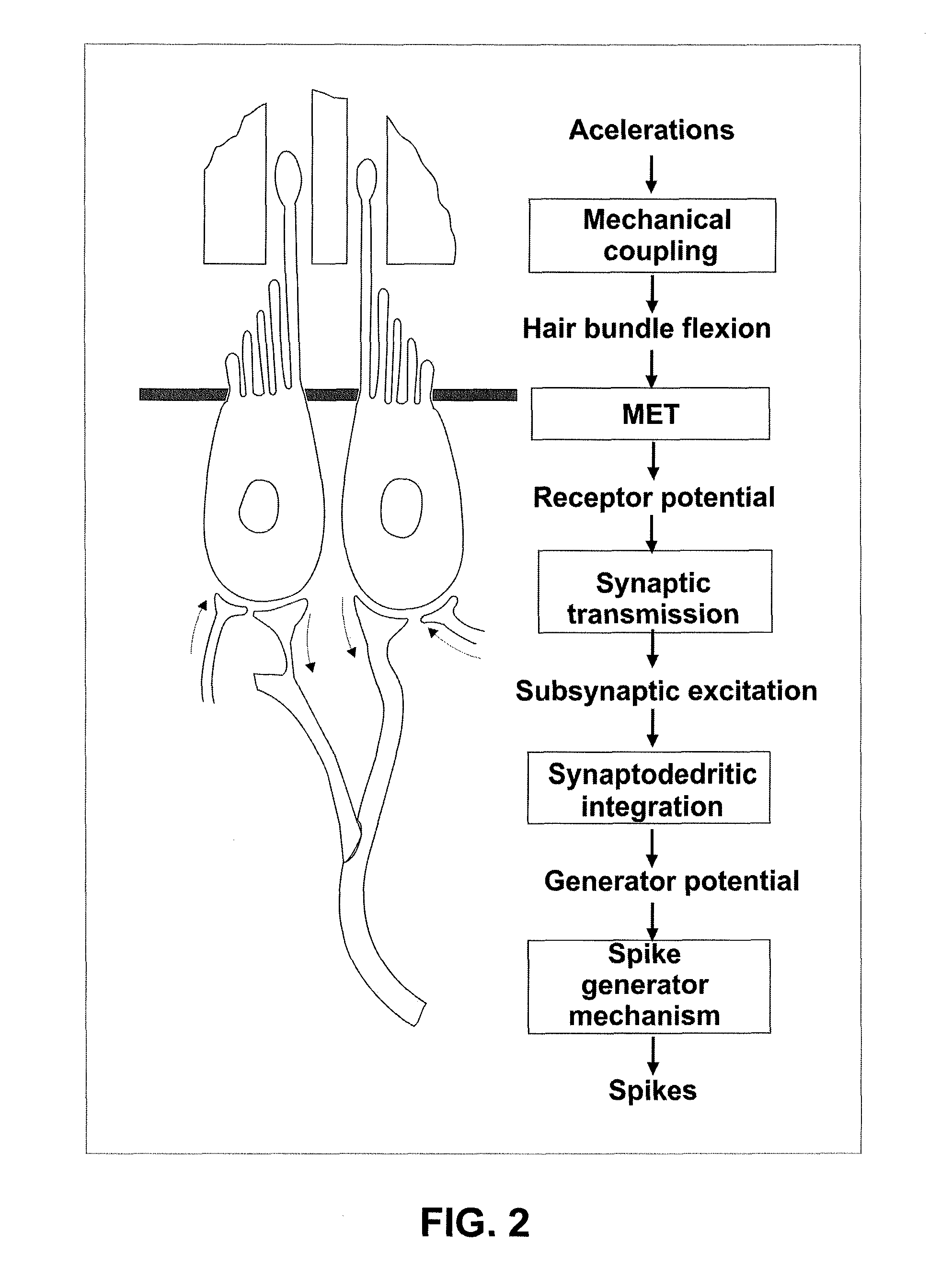
A vestibular prosthesis includes micro-electric-mechanical (MEMS) sensors, gyroscopes in each sensitivity axis (X, Y, Z), accelerometers in each sensitivity axis (X, Y, Z) to detect an angular and linear movement providing displacement measurements, gyroscopes in each one of the spatial axes (X, Y, Z), a microprocessor connected to the MEMS sensors and producing an electric pulse pattern or a continuous galvanic current pattern, a conditioning unit that amplifies and conditions the microprocessor output to apply current to the stimulation electrodes, the microcontroller being configured to determine the displacement of the cupula and the otolithic mass, determine a membrane potential as a result of a displacement detected by the MEMS sensors by means of determining a transduction current, and determine an action potential discharge pattern for the primary afferent neuron, which synapses with the hair cell by means of a mathematical model of the informative process of the vestibular mechanoreceptor.
Owner:BENEMI12RITA UNIV AUTI12NOMA DE PUEBLA
System and method of bladder and sphincter control
A method and system for bladder control are disclosed. In embodiments, a method for bladder control is provided that comprises coupling an electrode to an afferent nerve that is related to the bladder. Applying a plurality of pulse burst stimulations via the electrode causes voiding of urine from the bladder. In embodiments, the plurality of pulse burst stimulations to the afferent nerve reduces external urethral sphincter (EUS) contractions and evokes bladder contractions to expel urine from the subject. In embodiments, the plurality of pulse burst stimulations to the afferent nerve evokes bladder contractions alone to expel urine from the subject. In embodiments, a system for bladder control is provided that comprises an electrode for applying a pulse burst stimulus to an afferent nerve or dermatome to reduce reflex contractions and a signal generator for generating the pulse burst stimulus.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Method and apparatus for the treatment of focal dystonia
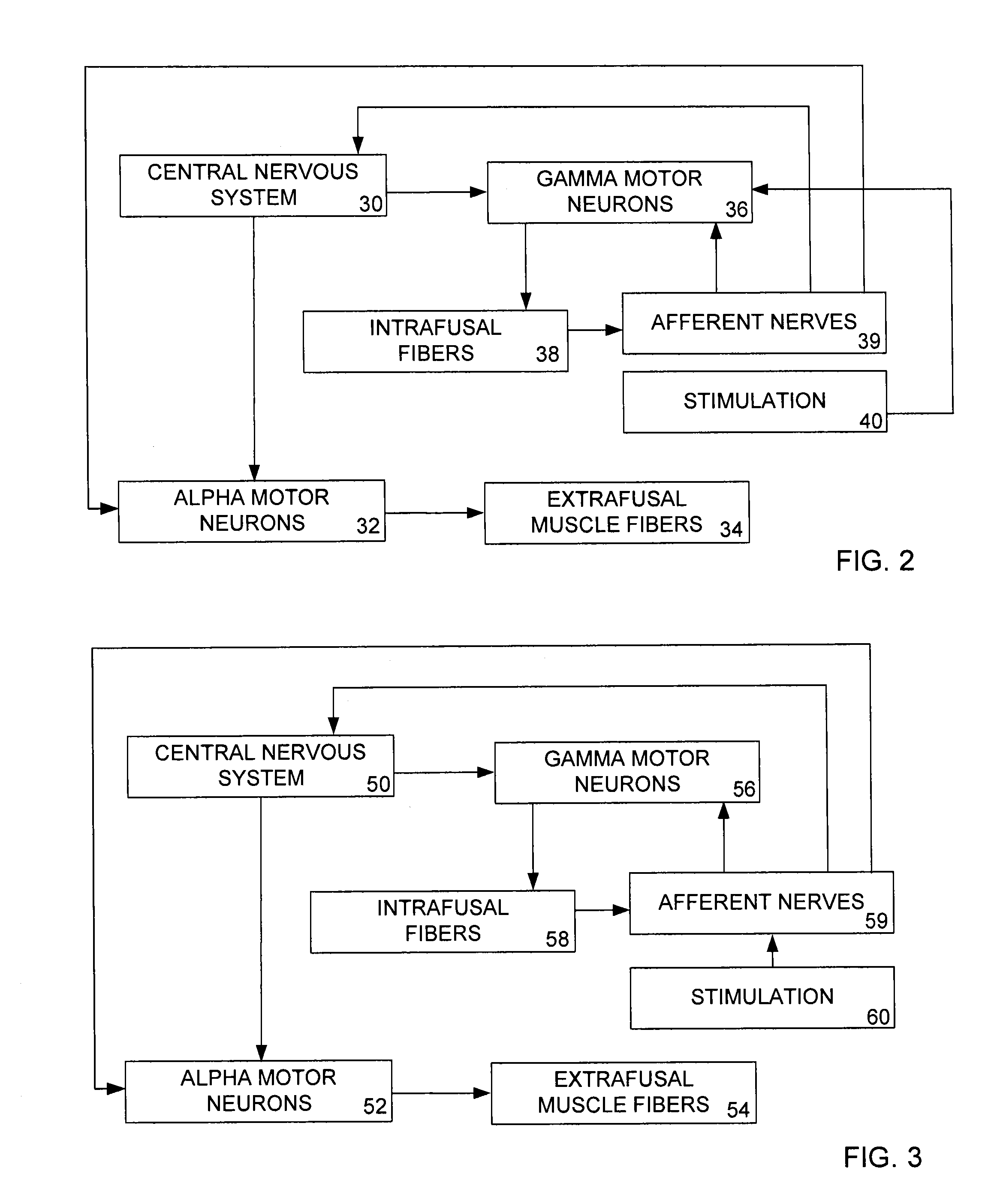
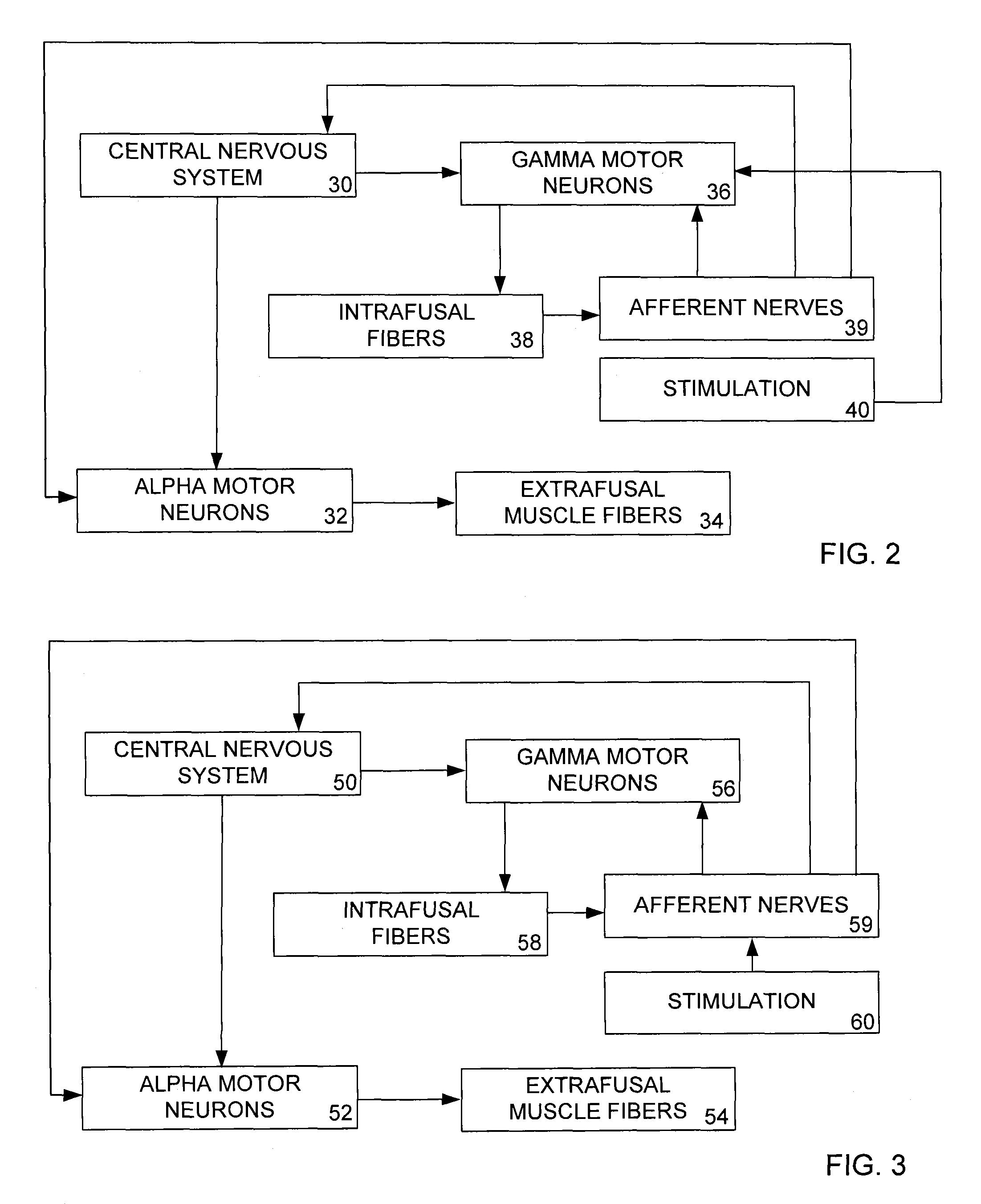
A method and apparatus for using low levels of electrical stimulation to treat focal dystonia by stimulating the afferent nervous system and / or altering the function of the gamma motor neurons innervating muscles which experience symptomatic spasms.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Vestibular prosthesis
InactiveUS8855774B2Prevent fallingShort timeHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsMicrocontrollerAction potential firing
A vestibular prosthesis includes micro-electric-mechanical (MEMS) sensors, gyroscopes in each sensitivity axis (X, Y, Z), accelerometers in each sensitivity axis (X, Y, Z) to detect an angular and linear movement providing displacement measurements, gyroscopes in each one of the spatial axes (X, Y, Z), a microprocessor connected to the MEMS sensors and producing an electric pulse pattern or a continuous galvanic current pattern, a conditioning unit that amplifies and conditions the microprocessor output to apply current to the stimulation electrodes, the microcontroller being configured to determine the displacement of the cupula and the otolithic mass, determine a membrane potential as a result of a displacement detected by the MEMS sensors by means of determining a transduction current, and determine an action potential discharge pattern for the primary afferent neuron, which synapses with the hair cell by means of a mathematical model of the informative process of the vestibular mechanoreceptor.
Owner:BENEMI12RITA UNIV AUTI12NOMA DE PUEBLA
Method and apparatus for the treatment of spasmodic dysphonia
A method and apparatus for using low levels of electrical stimulation to treat spasmodic dysphonia by stimulating the afferent nervous system and / or altering the function of gamma motor neurons innervating muscles which experience symptomatic spasms.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Modulating afferent signals to treat medical conditions
ActiveUS20150057313A1Reduce and block afferent nerve signalReduce deliveryBiocideElectrotherapyMuscle dysfunctionOrthopnea
This document provides methods and materials for modulating afferent nerve signals to treat medical conditions such as CHF, CHF respiration, dyspnea, peripheral vascular disease (e.g., peripheral arterial disease or venous insufficiency), hypertension (e.g., age-associated hypertension, resistant hypertension, or chronic refractory hypertension), COPD, sleep apnea, and chronic forms of lung disease where muscle dysfunction is a part of the disease pathophysiology. For example, methods and materials involved in using electrical and / or chemical techniques to block or reduce afferent nerve signals (e.g., nerve signals of group III and / or IV afferents coming from skeletal muscle and / or the kidneys) are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Method for treating hypertension via electrical stimulation of neural structures
A neuromodulation system comprises a sensor configured for sensing a blood pressure of a patient, modulation output circuitry configured for conveying electrical modulation energy to at least one electrode, and a controller / processor coupled to the sensor and the modulation output circuitry. The controller / processor is configured for comparing the blood pressure sensed by the sensor to a first threshold blood pressure, and instructing the modulation output circuitry to convey the electrical modulation energy to the at least one electrode if the sensed blood pressure is greater than the first threshold blood pressure. A method for treating chronic hypertension comprises applying electrical modulation energy to a neural target site, thereby modulating an afferent nerve innervating a patient's kidney, thereby treating the chronic hypertension.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
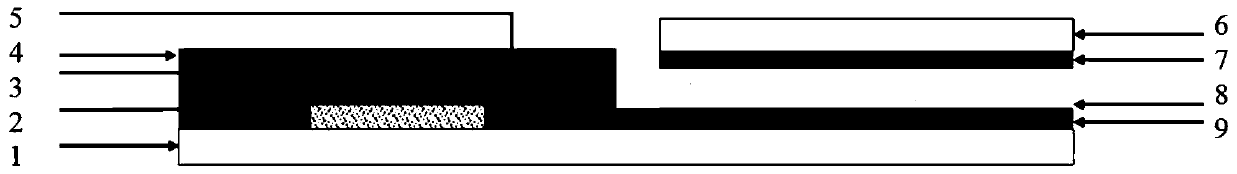
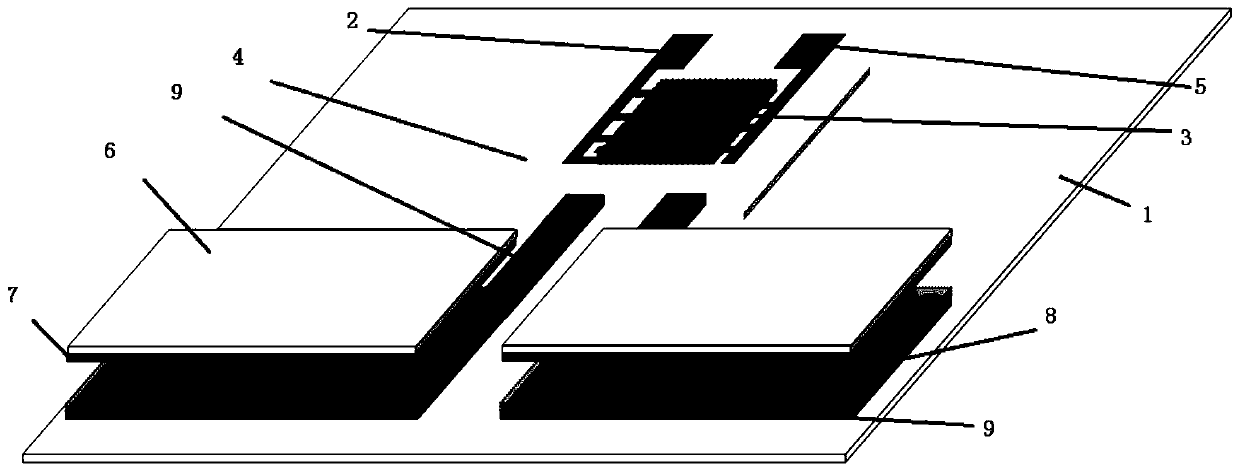
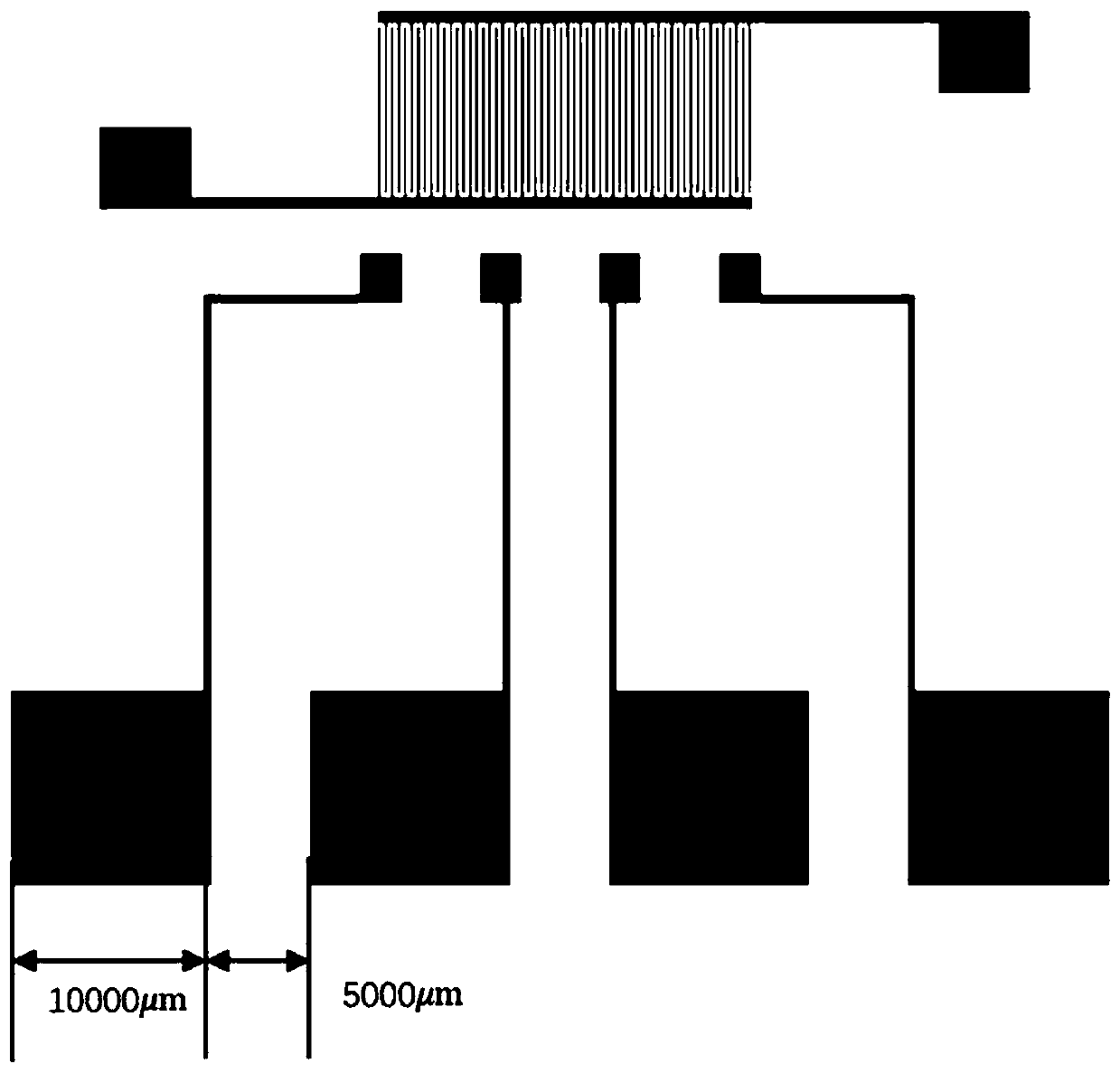
Flexible artificial afferent nervous system based on micro-nano structure force-sensitive film and preparation method of system
ActiveCN111490162AHigh sensitivityImprove performanceFluid pressure measurement using piezo-electric devicesSolid-state devicesGate dielectricNanogenerator
The invention discloses a flexible artificial afferent nervous system based on a micro-nano structure force-sensitive film, and the system comprises a substrate which is provided with a nano-generatorand an organic synaptic transistor; the organic synaptic transistor comprises a source electrode, a drain electrode, a gate electrode, a channel layer and a gate dielectric layer; the gate electrode,the source electrode and the drain electrode are located on the substrate; and the gate dielectric layer is located on the source electrode, the drain electrode and the channel layer; the nano-generator comprises a lower electrode, a dielectric layer, an upper electrode and an upper substrate from bottom to top; the lower electrode is the gate electrode; and the dielectric layer is a micro-nano structure force-sensitive film. The system has the advantages of low power consumption, small size and convenience in preparation.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methods and devices for treating pelvic conditions
ActiveUS10058381B2Modulate bladder functionEndoscopesSurgical instruments for heatingPartial denervationBladder function
A device and method that provides a minimally-invasive approach to performing treatments on soft tissue, such as that found in the bladder. The device is useful for manipulating tissue such that treatment tools can be inserted into the tissue at a controlled depth. In some implementations, the device and method described herein are suited to provide therapy to non-mucosal target tissue (or a target volume of tissue) to modulate bladder function. In an example, energy can be delivered to denervate selected portions of the bladder, such as afferent nerves.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Method for treating depression by indirectly stimulating raphe nuclei
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Unidirectional neural stimulation systems, devices and methods
An embodiment relates to a method for delivering a unidirectional afferent nerve stimulation treatment. A test neural stimulation is delivered, and a physiologic response to the test neural stimulation is monitored. At least one neural stimulation parameter for the test neural stimulation is adjusted if the test neural stimulation does not elicit a desired physiologic response. If the test neural stimulation does elicit the desired physiologic response, at least one treatment parameter for a unidirectional afferent nerve stimulation is determined using the at least one neural stimulation parameter for the test neural stimulation that provided the desired physiologic response. The unidirectional afferent nerve stimulation is delivered using the at least one treatment parameter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and method for monitoring and treating arrhythmia and cardiac function via intrinsic cardiac nervous system
The present invention includes systems and methods for measuring, monitoring and managing arrhythmia and cardiac function through an intrinsic cardiac nervous system. The system and method compare theneurological signatures of the intrinsic cardiac nervous system associated with the healthy heart muscle tissue and diseased heart muscle tissue to identify and scale incoming afferent intrinsic cardiac nerve cells whose signal transmission has been affected by diseased heart tissues. Therefore, a method of modulating afferent nerve signals from the diseased myocardium to the higher centers of the intrinsic cardiac nervous system, the intrathoracic extracardiac ganglion, and the cardiac nerve axis is used as a novel treatment method for ischemic heart diseases.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Pyrazole derivative, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof
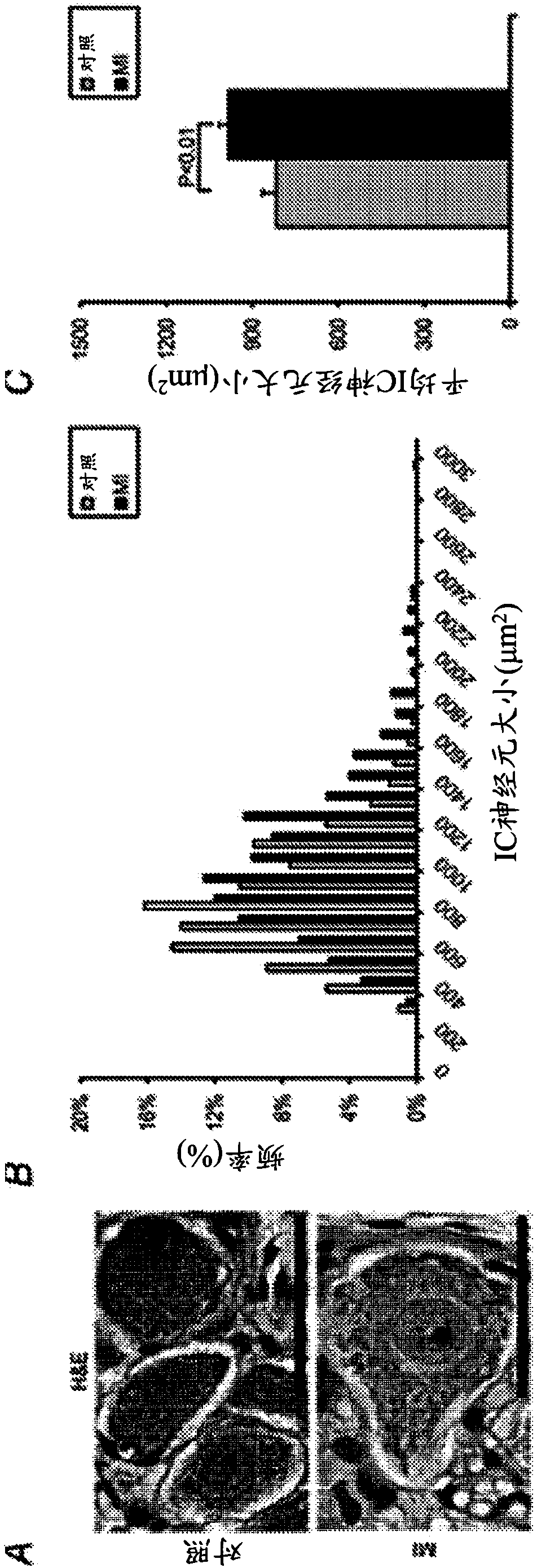
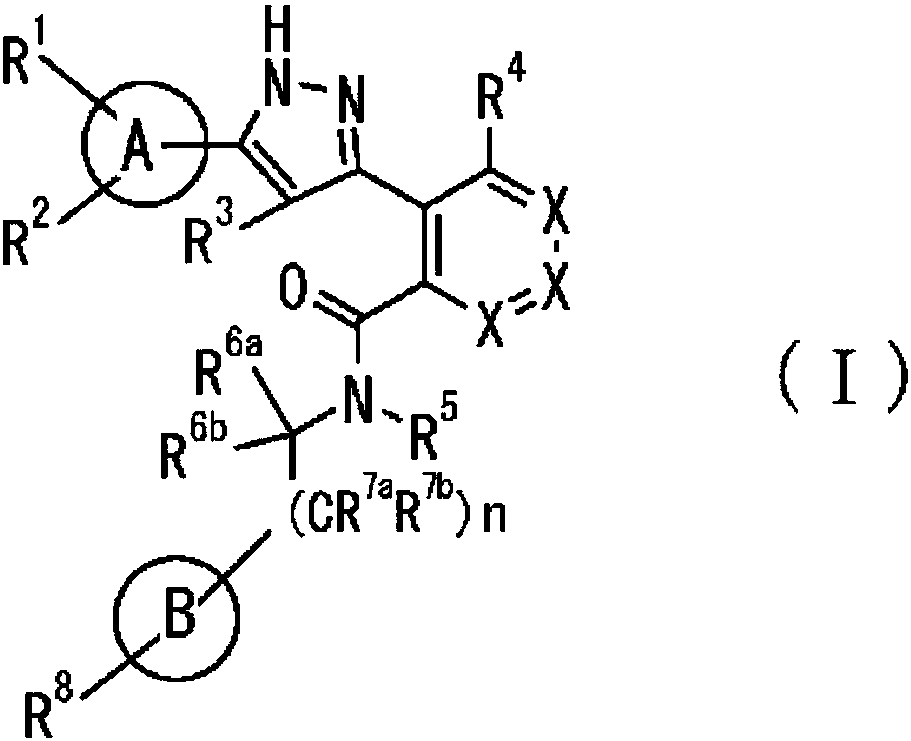
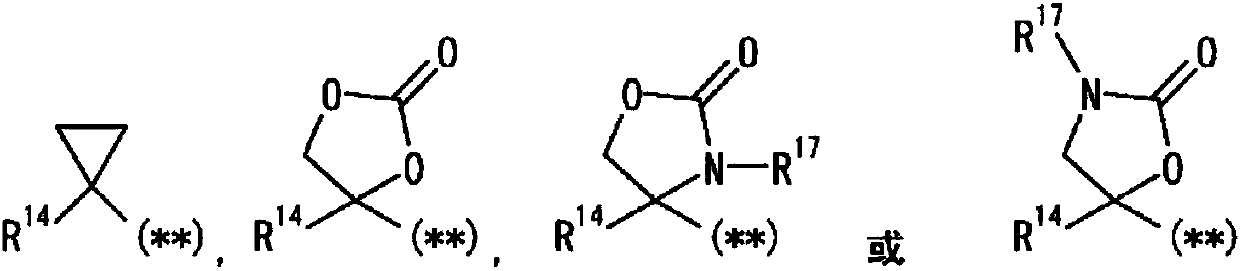
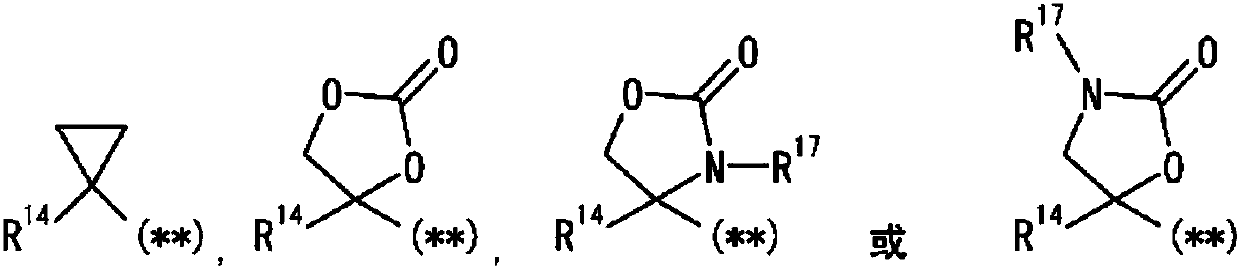
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a novel pyrazole derivative, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing same and a pharmaceutical usethereof. The present invention provides a composition having a TRPM8 inhibitory activity and represented by formula (I) (in the formula, ring A is C6-10 aryl or the like, X is CR4a or the like, R1 and R2 are a hydrogen atom or the like, R3 is a hydrogen atom or the like, R4 is a hydrogen atom or the like, ring B is C6-10 aryl or the like, R5 is a hydrogen atom or the like, R6a is a hydrogen atomor the like, R7a is a hydrogen atom or the like, R7b is a hydrogen atom or the like, R6b is a hydrogen atom or the like, R8 is a hydrogen atom or the like, and n is 0, 1, or 2), or a pharmaceuticallyacceptable salt thereof. Furthermore, the composition of the present invention represented by formula (I) or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can be used as a therapeutic agent or prophylactic agent for diseases or conditions caused by hyperexcitability or disorders of afferent nerves.
Owner:KISSEI PHARMA
Method for treating depression by indirectly stimulating raphe nuclei
A method for treating a patient suffering from depression, the method including applying electrical stimulation energy to afferent nerve fibers leading to the medial preoptic region of the hypothalamus of the patient, thereby activating serotonin in the raphe nuclei to treat depression.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
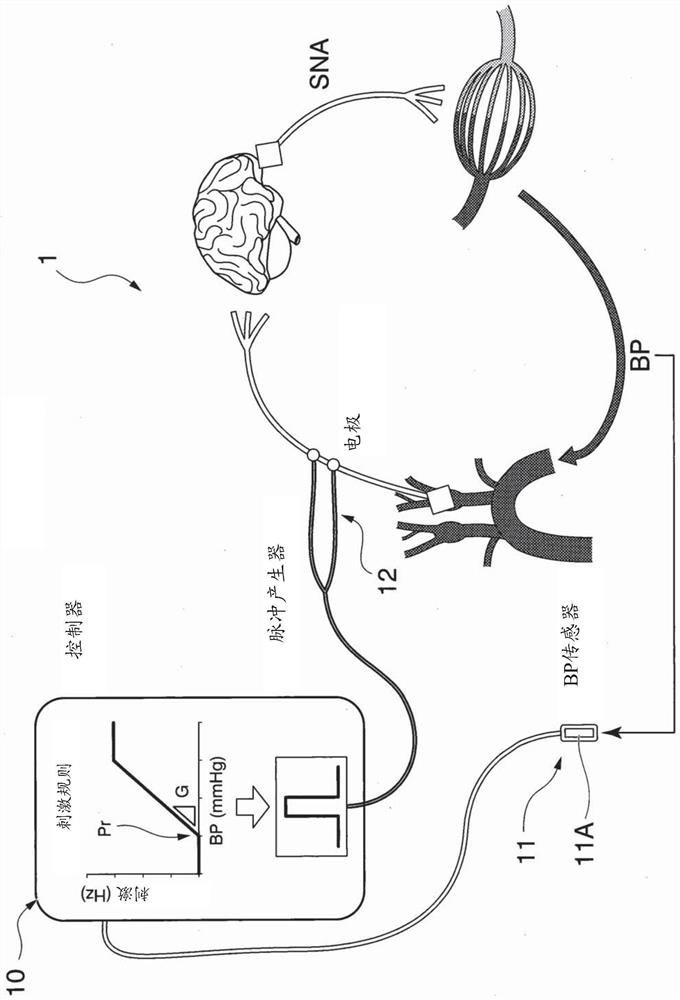
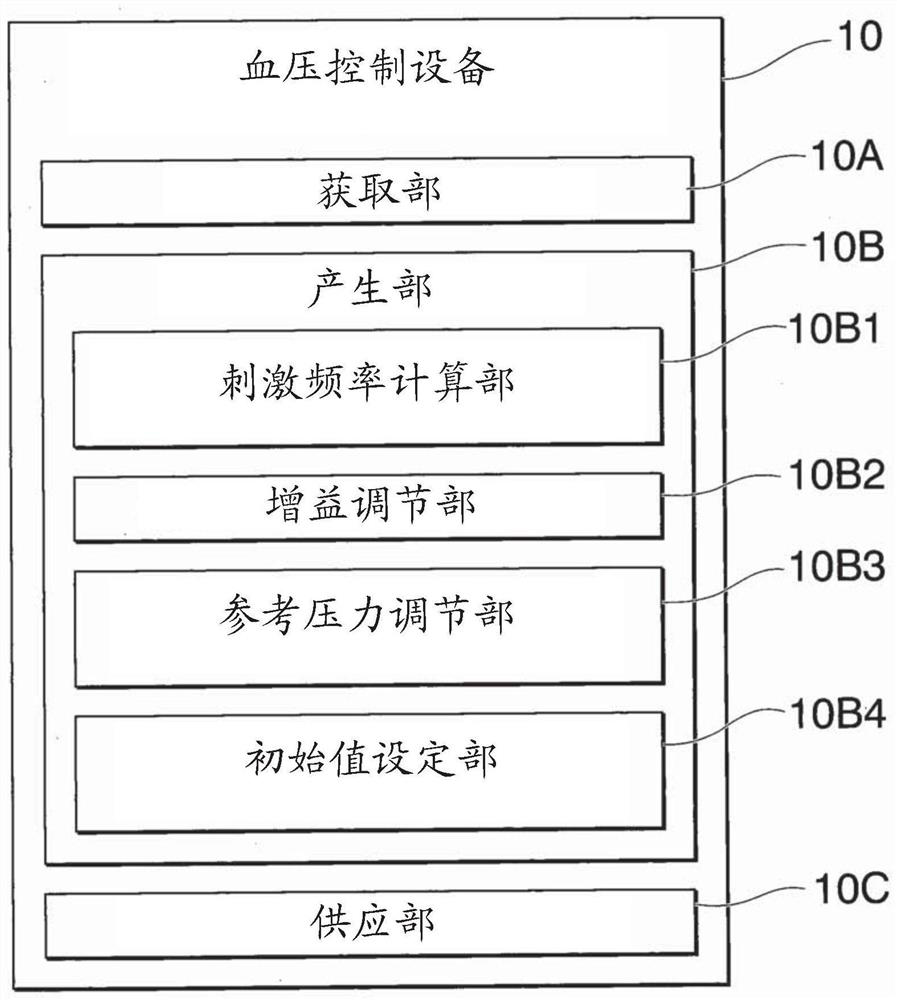
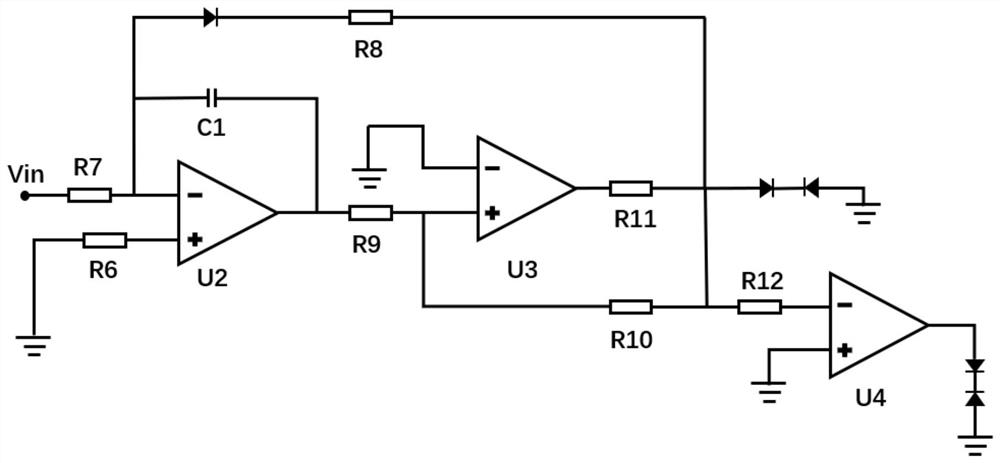
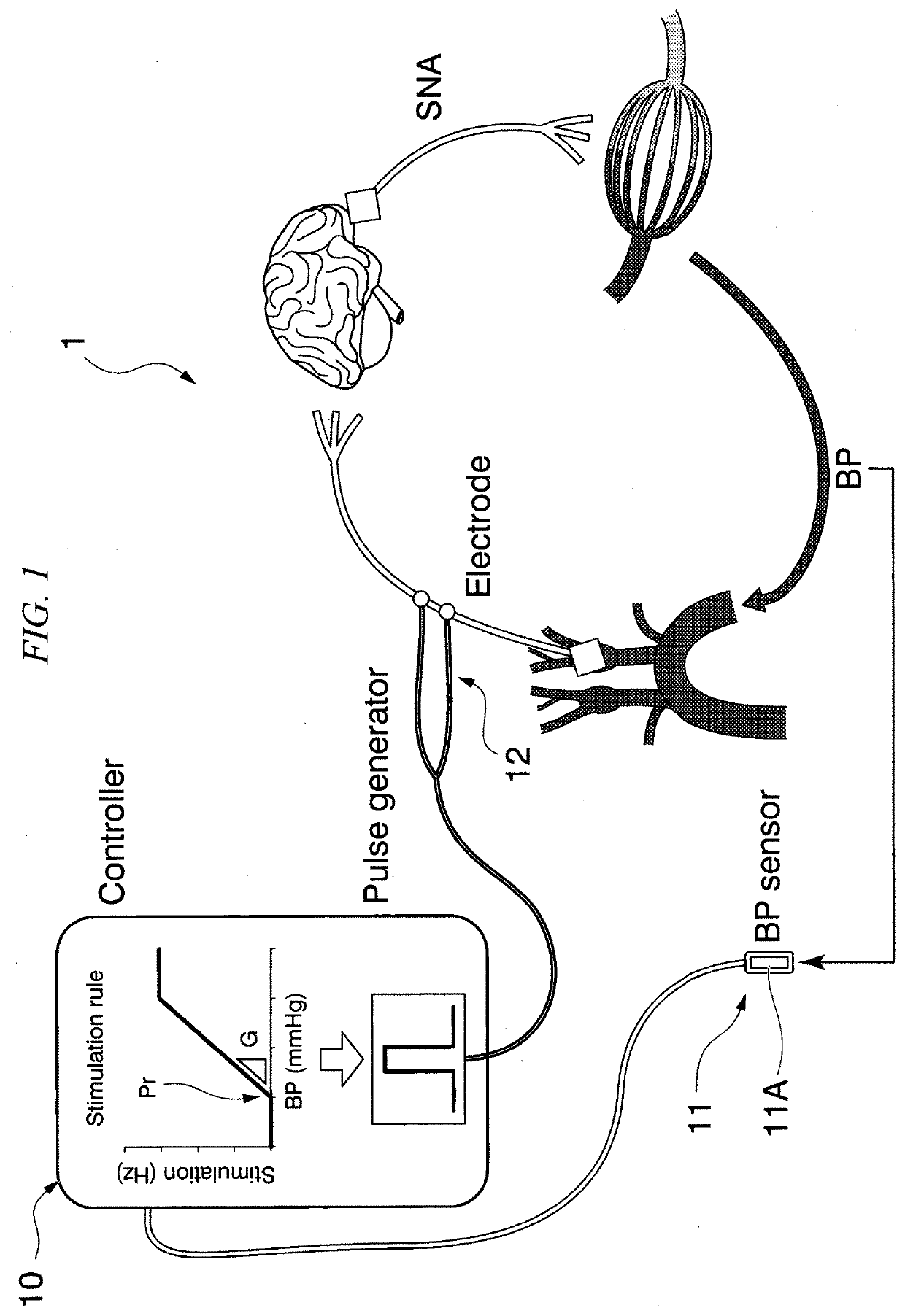
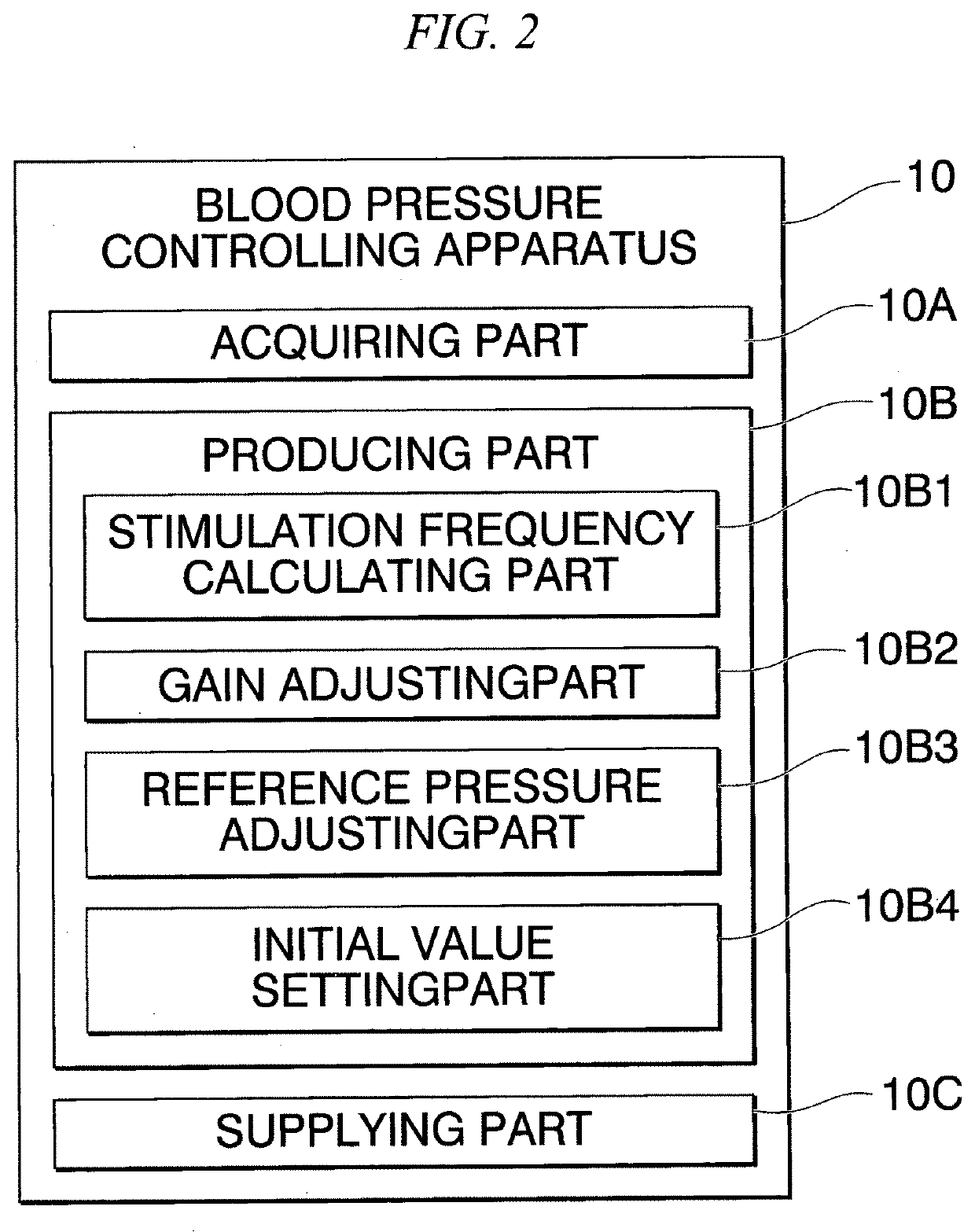
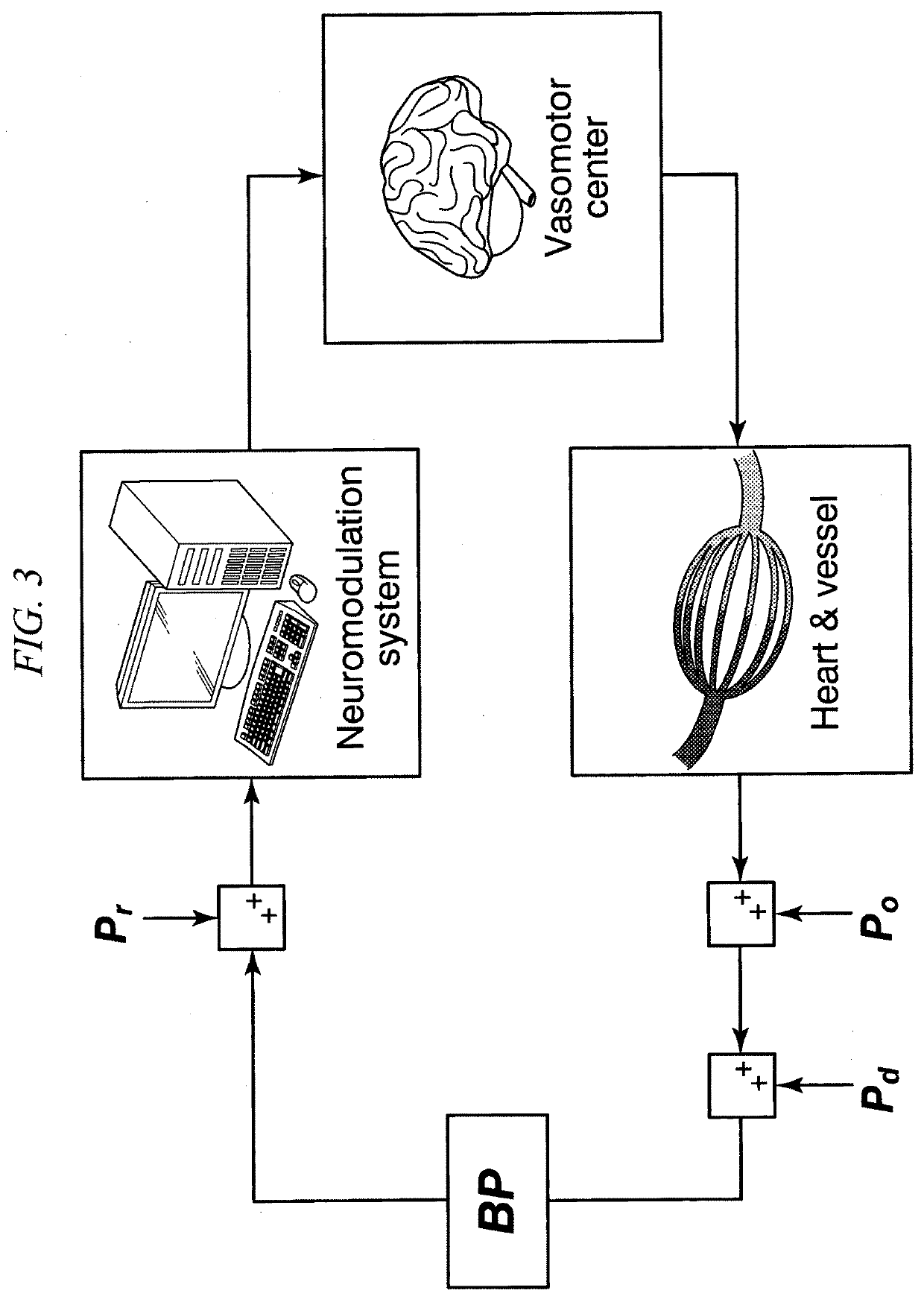
Blood pressure controlling apparatus, non-transitory computer readable recording medium storing control program of blood pressure controlling apparatus, and method for controlling blood pressure
PendingCN112955210AImprove volume toleranceResolve lung congestionElectrotherapyArtificial respirationElectric current flowAfferent nerves
A blood pressure controlling apparatus includes an acquiring part configured to acquire biological information indicating blood pressure of a subject, a producing part configured to produce a frequency modulated pulse string on the basis of the biological information, and a supplying part configured to supply an electrical current on the basis of the frequency modulated pulse string, to an electrode attached to the subject. The electrical current stimulates baroreceptor afferent nerves of the subject.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
Robot stress protection system based on synaptic transistor
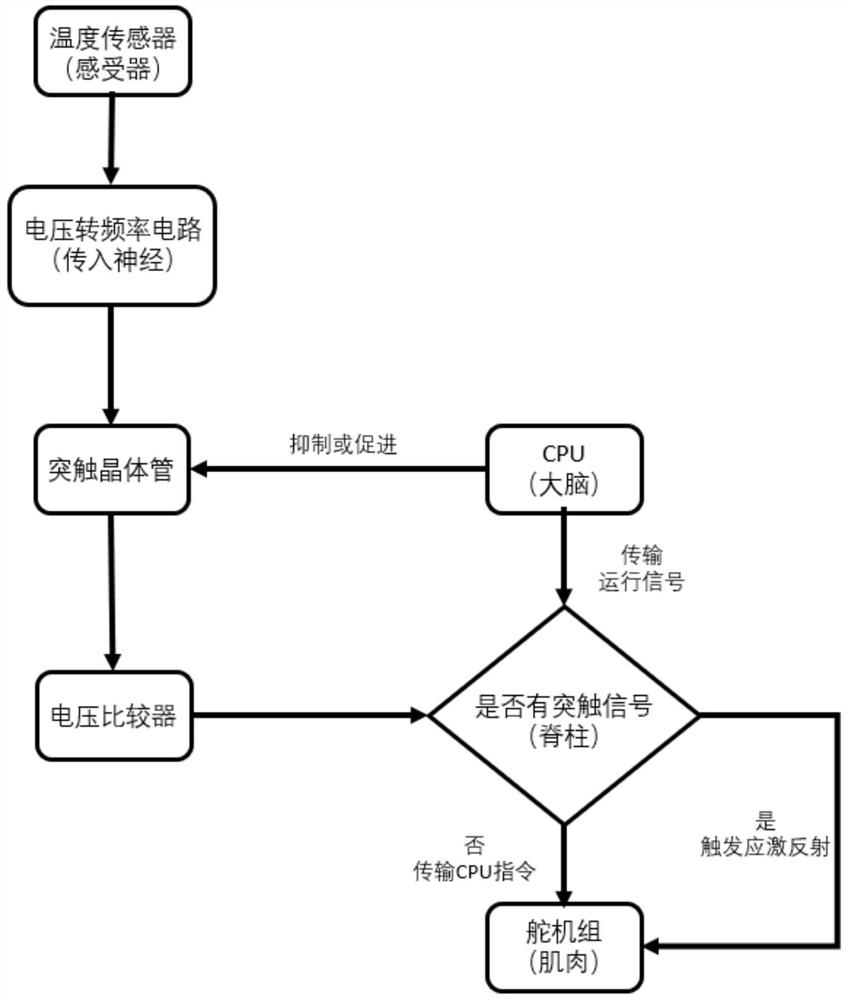
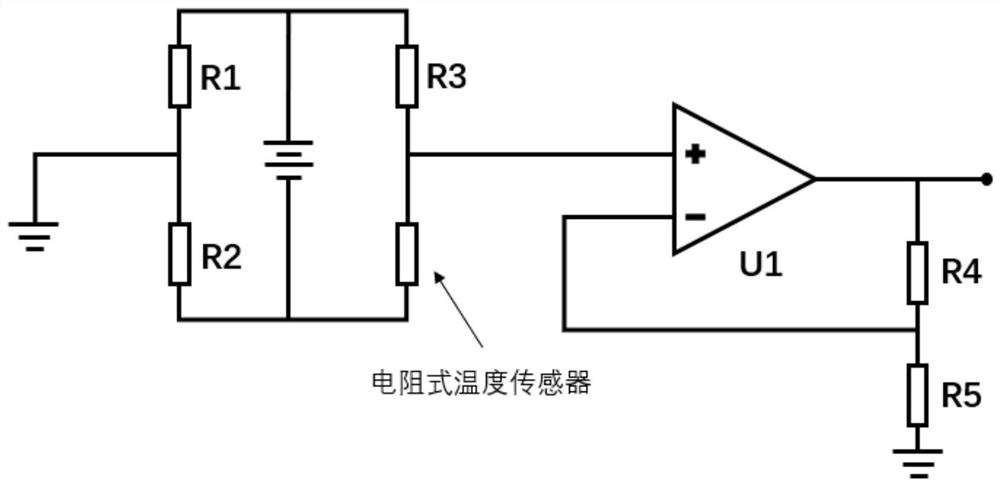
PendingCN113977639AEnsure safetySimple calculationProgramme-controlled manipulatorSolid-state devicesExcitatory synapseHemt circuits
The invention discloses a robot stress protection system based on a synaptic transistor, which comprises a resistive temperature sensor, a Wheatstone bridge, a voltage-to-frequency circuit, a synaptic transistor, a voltage comparison circuit and a robot. The robot mainly comprises a microprocessor and a steering engine set. The resistive temperature sensor and the Wheatstone bridge are used for simulating a receptor of an animal and correspondingly converting the temperature into a voltage signal. The voltage-to-frequency circuit simulates afferent nerves for converting the voltage signal into an electric pulse with a corresponding frequency. The synaptic transistor can generate an excitatory post-synaptic current according to the amplitude, frequency and duration of an input pulse of a side gate, and the post-synaptic current is promoted or suppressed under the control of a main gate. When the post-synaptic current reaches a threshold of a voltage comparator, the stress protection is triggered. By simulating behaviors and mechanisms of organisms, a humanoid robot can obtain higher sensitive perception ability and damage prevention ability. Therefore, the adaptive capacity under severe working conditions can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Blood pressure controlling apparatus, non-transitory computer readable recording medium storing control program of blood pressure controlling apparatus, and method for controlling blood pressure
PendingUS20210393963A1Increase volumeResolving pulmonary congestionElectrotherapyArtificial respirationFrequency modulationElectric current flow
A blood pressure controlling apparatus includes an acquiring part configured to acquire biological information indicating blood pressure of a subject, a producing part configured to produce a frequency modulated pulse train on the basis of the biological information, and a supplying part configured to supply an electrical current on the basis of the frequency modulated pulse train, to an electrode attached on the subject. The electrical current stimulates baroreceptor afferent nerves of the subject.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
Afferent neuron circuit and mechanoreceptive system
PendingUS20220253684A1Simple structureSolid-state devicesNeural architecturesAfferent neuronControl engineering
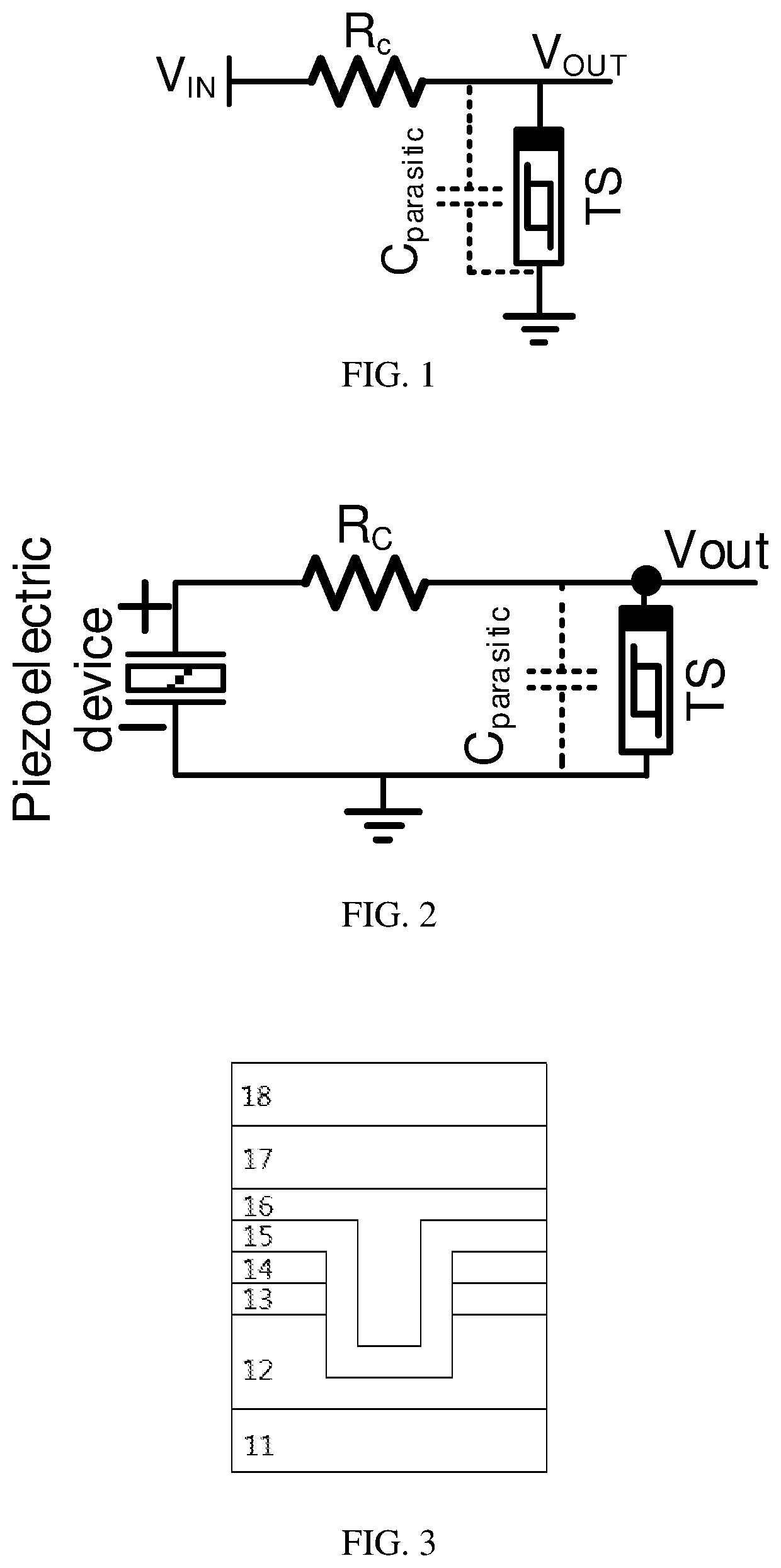
Disclosed is an afferent neuron circuit, which includes: a resistance Rc and a volatile threshold switching device TS, wherein the volatile threshold switching device TS is provided with a parasitic capacitor Cparasitic; a first end of the resistance Rc serves as a signal input terminal, and a second end of the resistance Rc serves as a signal output terminal; and a first end of the volatile threshold switching device TS is connected to the signal output terminal, and a second end of the volatile threshold switching device TS is grounded. The afferent neuron circuit provided in the content of the present disclosure has a simple structure and good scalability and is suitable for large-scale integration.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Neuronal communication system
ActiveUS11344725B2Facilitates directly eliciting certain sensory perceptImprove communication bandwidthHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsNeuronal stimulationAfferent neuron
The present invention relates to a system for providing neuronal stimulation signals configured to elicit sensory percepts in the cortex of an individual, comprising means for obtaining spatial information relating to the actual or planned position of at least one neuronal stimulation means relative to at least one afferent axon targeting at least one sensory neuron in the cortex of the individual and means for determining at least one neuronal stimulation signal to be applied to at least one afferent axon via the at least one neuronal stimulation means based at least in part on the obtained spatial information.The present invention further relates to a system for communicating conceptual information to an individual, comprising means for selecting at least one neuronal stimulation signal to be applied to at least one afferent axon targeting at least one sensory neuron in the cortex of the individual, wherein the at least one neuronal stimulation signal corresponds to the conceptual information to be communicated and means for transmitting the at least one neuronal stimulation signa to at least one neuronal stimulation means of the individual.
Owner:CEREGATE GMBH
Modulating afferent signals to treat medical conditions
ActiveUS10300281B2Reduce and block afferent nerve signalReduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyDiseaseMuscle dysfunction
This document provides methods and materials for modulating afferent nerve signals to treat medical conditions such as CHF, CHF respiration, dyspnea, peripheral vascular disease (e.g., peripheral arterial disease or venous insufficiency), hypertension (e.g., age-associated hypertension, resistant hypertension, or chronic refractory hypertension), COPD, sleep apnea, and chronic forms of lung disease where muscle dysfunction is a part of the disease pathophysiology. For example, methods and materials involved in using electrical and / or chemical techniques to block or reduce afferent nerve signals (e.g., nerve signals of group III and / or IV afferents coming from skeletal muscle and / or the kidneys) are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Devices and methods for treating conditions caused by affarent nerve signals
ActiveUS10555746B2Less invasiveEasy to implementSurgical scissorsEndoscopesAnatomyOveractive bladder
Devices and methods for treating conditions, such as overactive bladder, caused by afferent nerve signals involving the creation of dissection planes that interrupt the afferent nerve signals.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Methods and materials for treating syncope
This document provides methods and materials for treating syncope (e.g., neurocardiogenic syncope). For example, methods and materials involved in using electrical techniques to stimulate nerves (e.g., renal efferent and / or afferent nerves) in a manner that results in systemic blood vessel constriction and / or increased blood pressure are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Non-contact type motion sickness reliving method
InactiveCN107280847ANo side effectsMotion sickness reliefEar treatmentTherapeutic coolingExternal Auditory CanalsMotion sickness
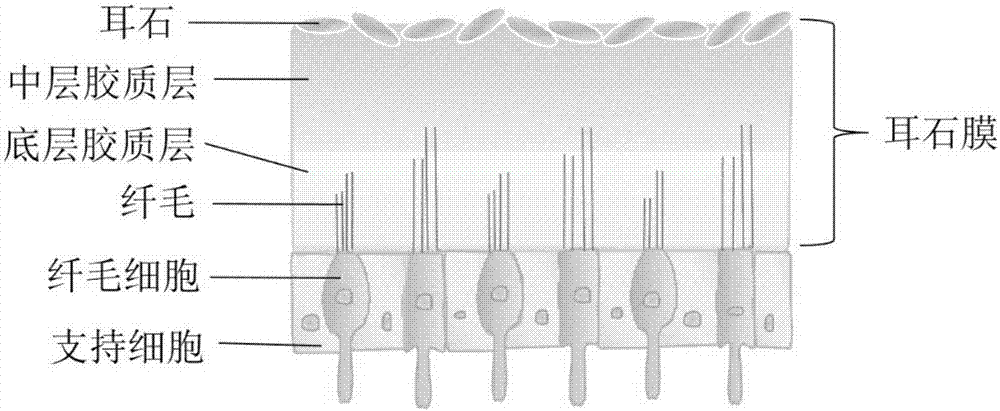
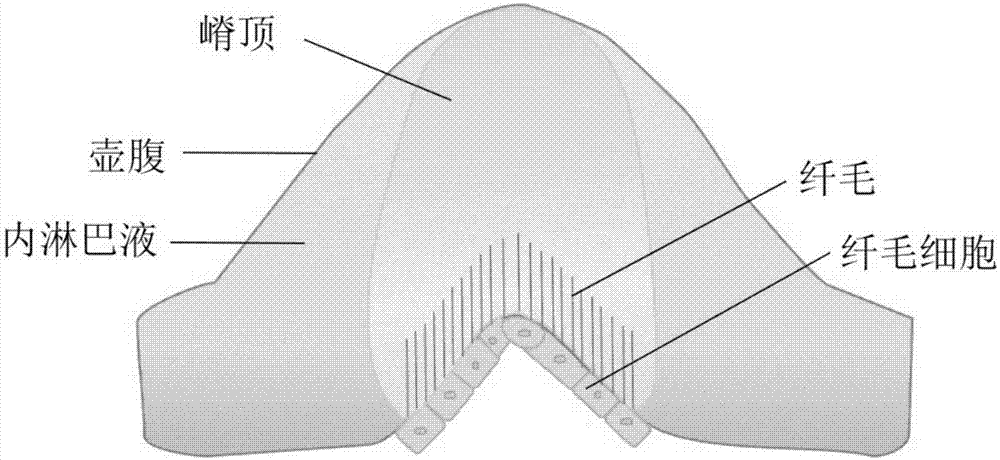
A non-contact method for relieving motion sickness. When the external auditory canal is stimulated by continuous low temperature, due to heat conduction, the temperature at the position closest to the temporal bone in the horizontal semicircular canal of the inner ear will be the first to decrease, and the temperature change will continue to spread through the endolymph. Finally, the temperature of the crest and otolithic membrane in the inner ear is lowered; after the temperature of the crest and otolithic membrane in the inner ear is lowered, the Young's modulus becomes larger, the hardness of the crest and the otolithic membrane will increase, and it will resist deformation Enhanced ability; after cooling, the crest and cilia in the otolithic membrane become less flexible, and the nerve signals generated by the stimulated ciliated cells become weaker, and the nerve signals transmitted to the nerve center are used as input information and the experience information stored in the nerve center The probability of mismatch will be greatly reduced, which will alleviate the effect of motion sickness. The invention has no side effect on the human body, and has good effect of alleviating motion sickness.
Owner:刘文龙
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com