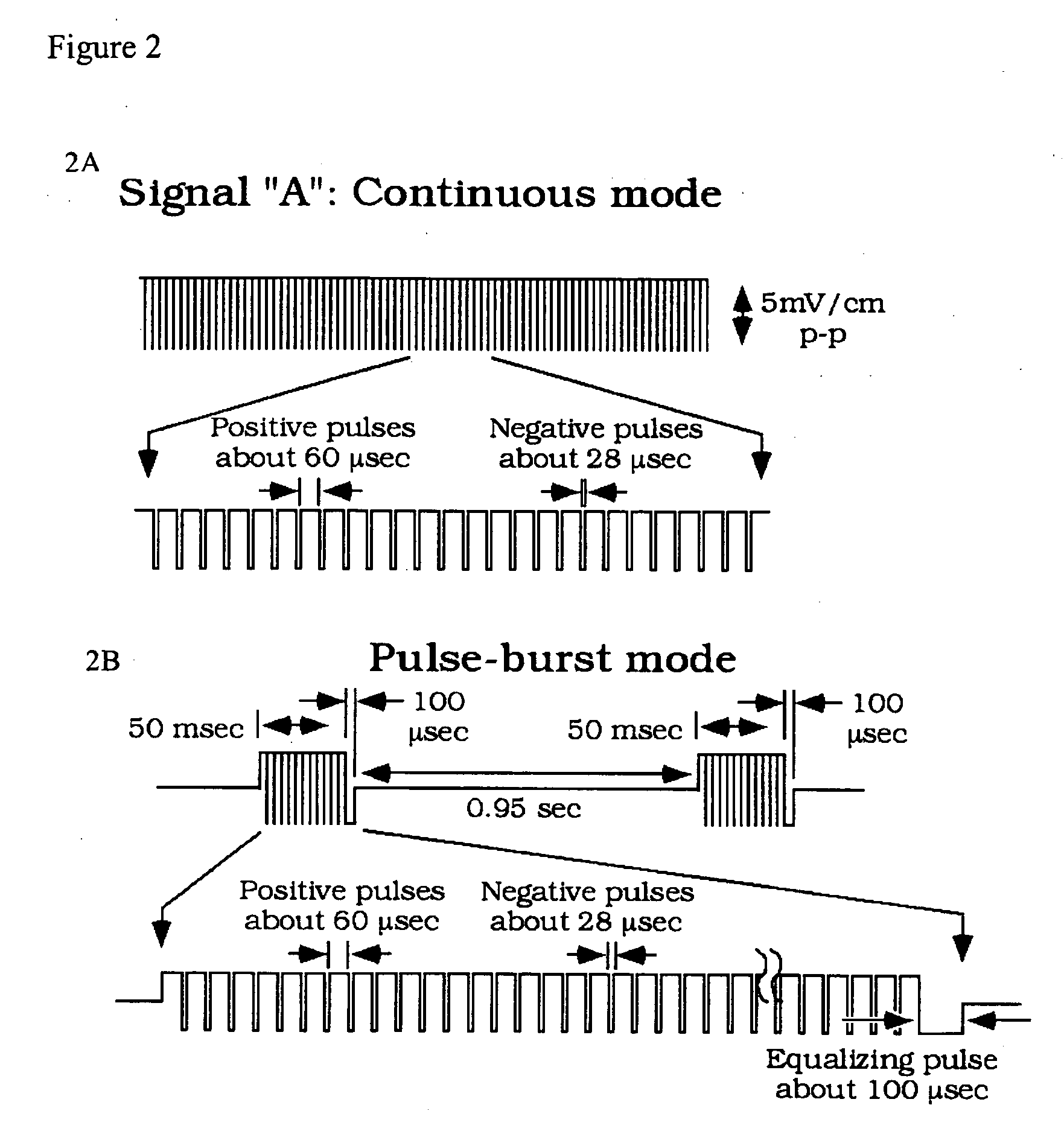
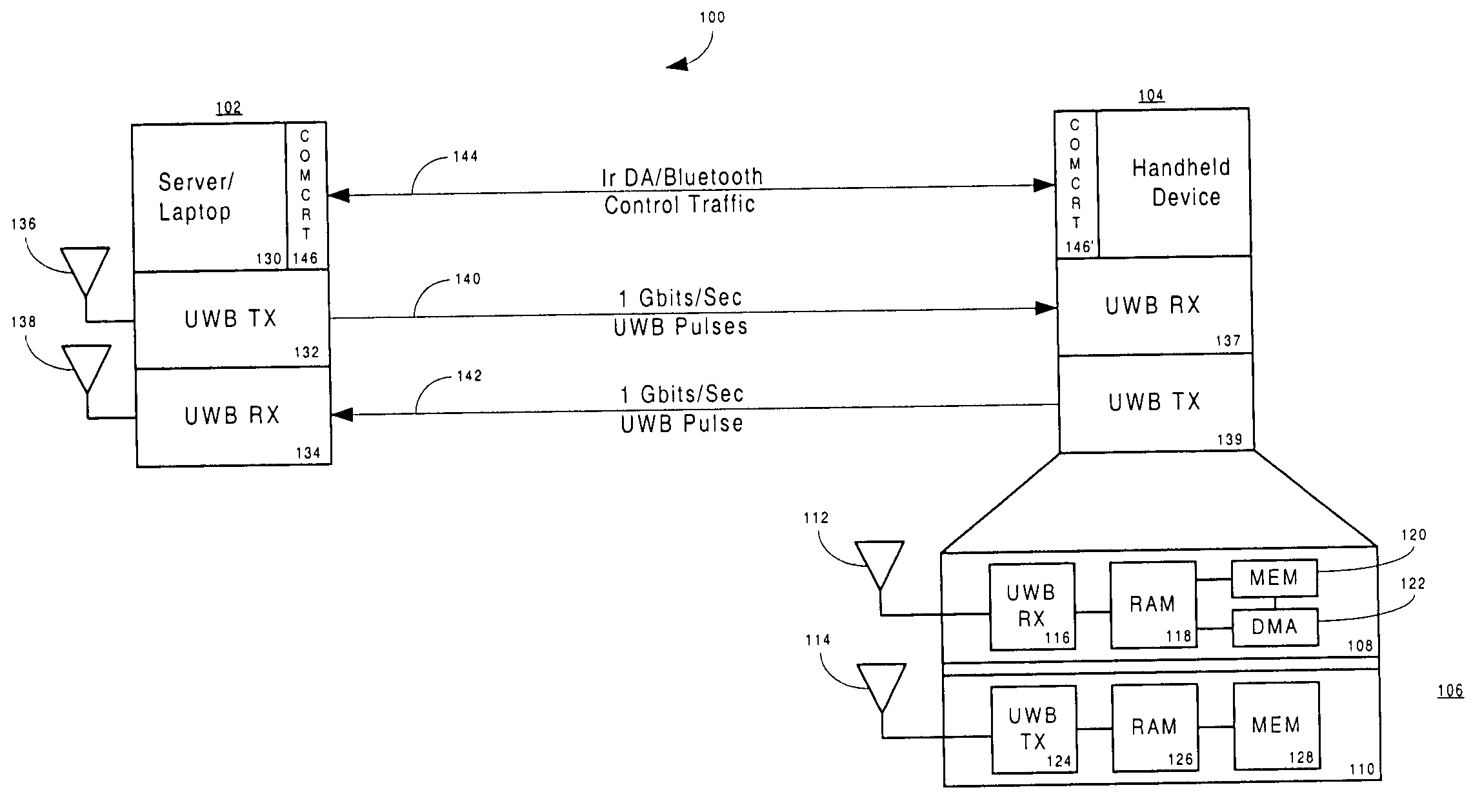
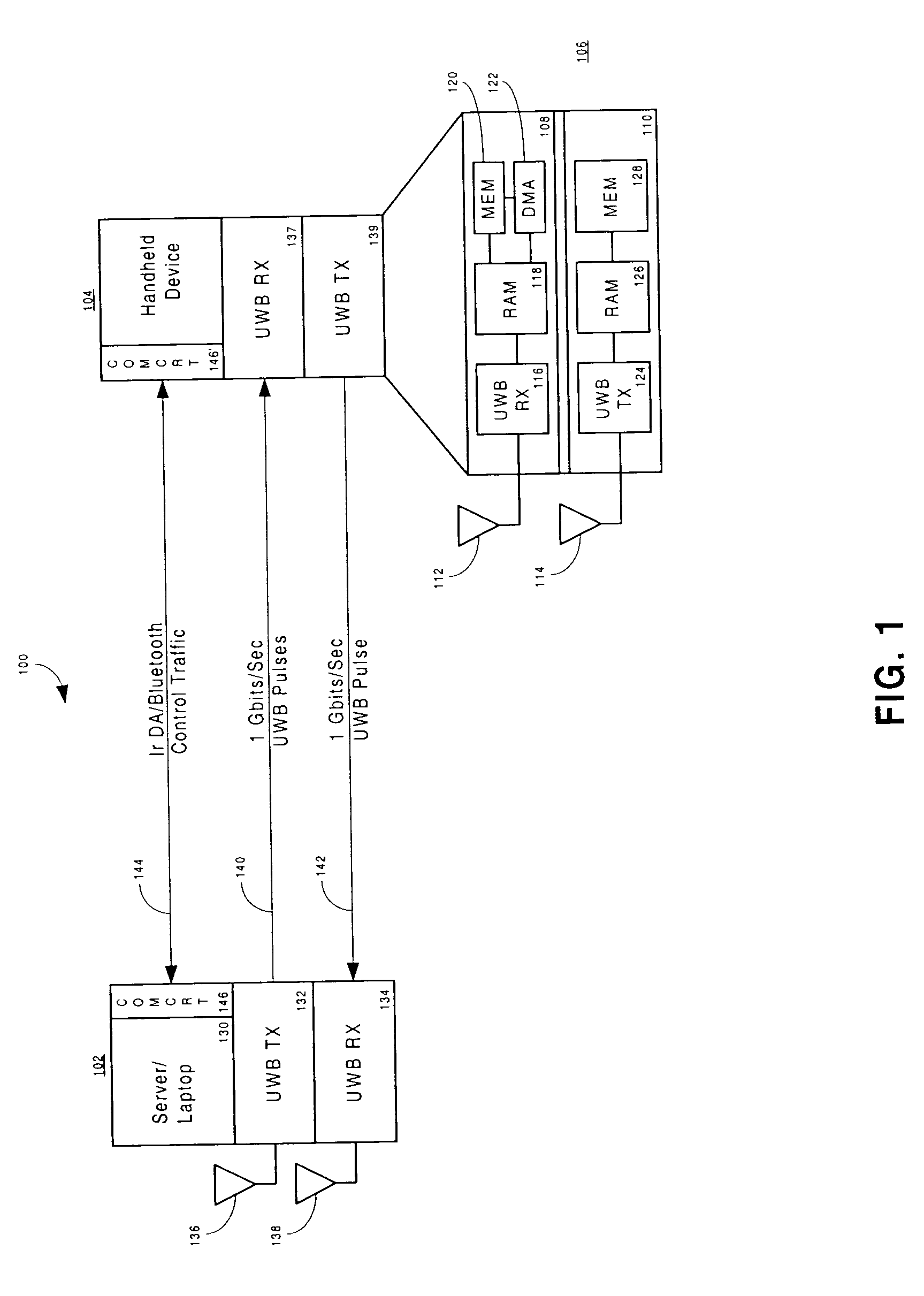
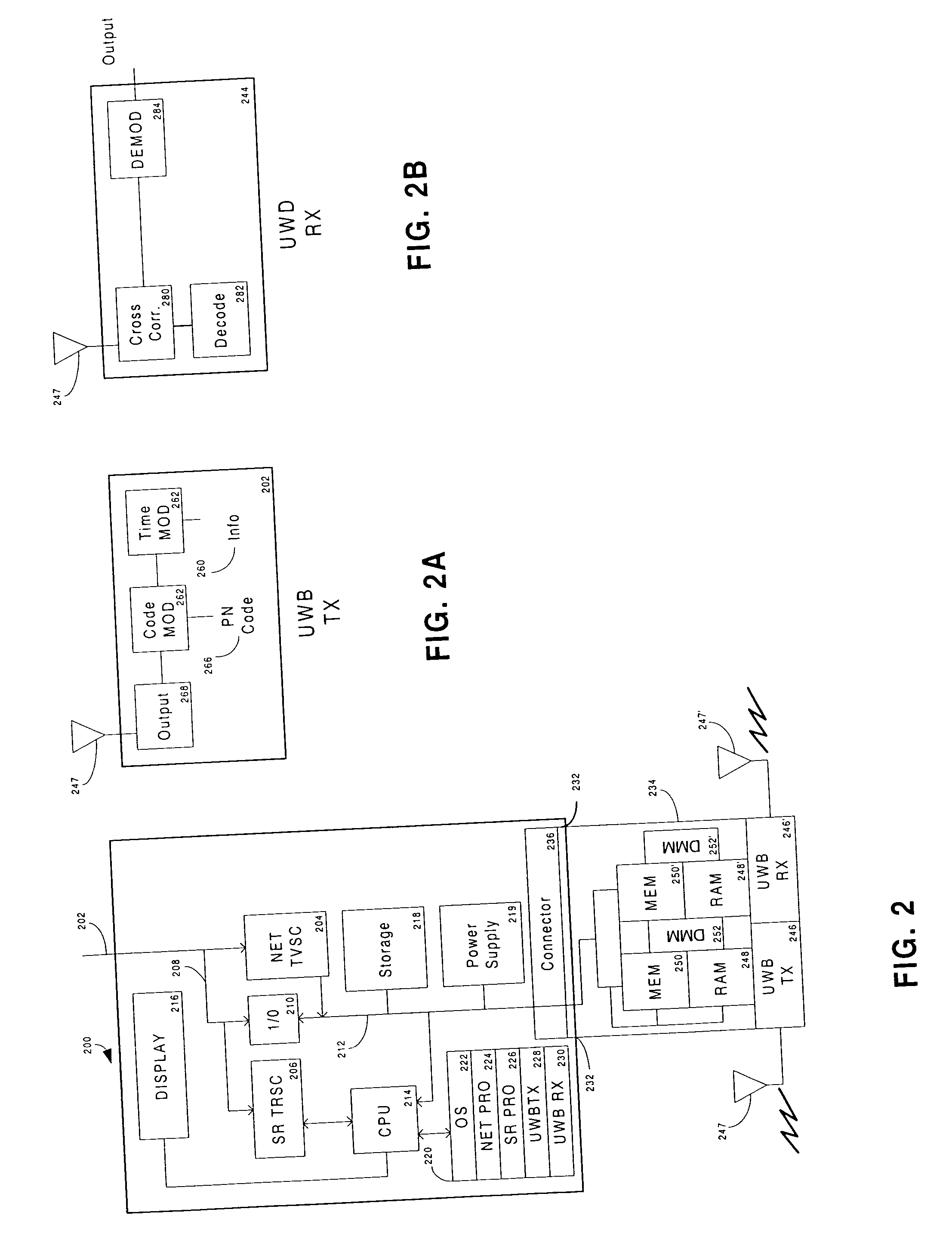
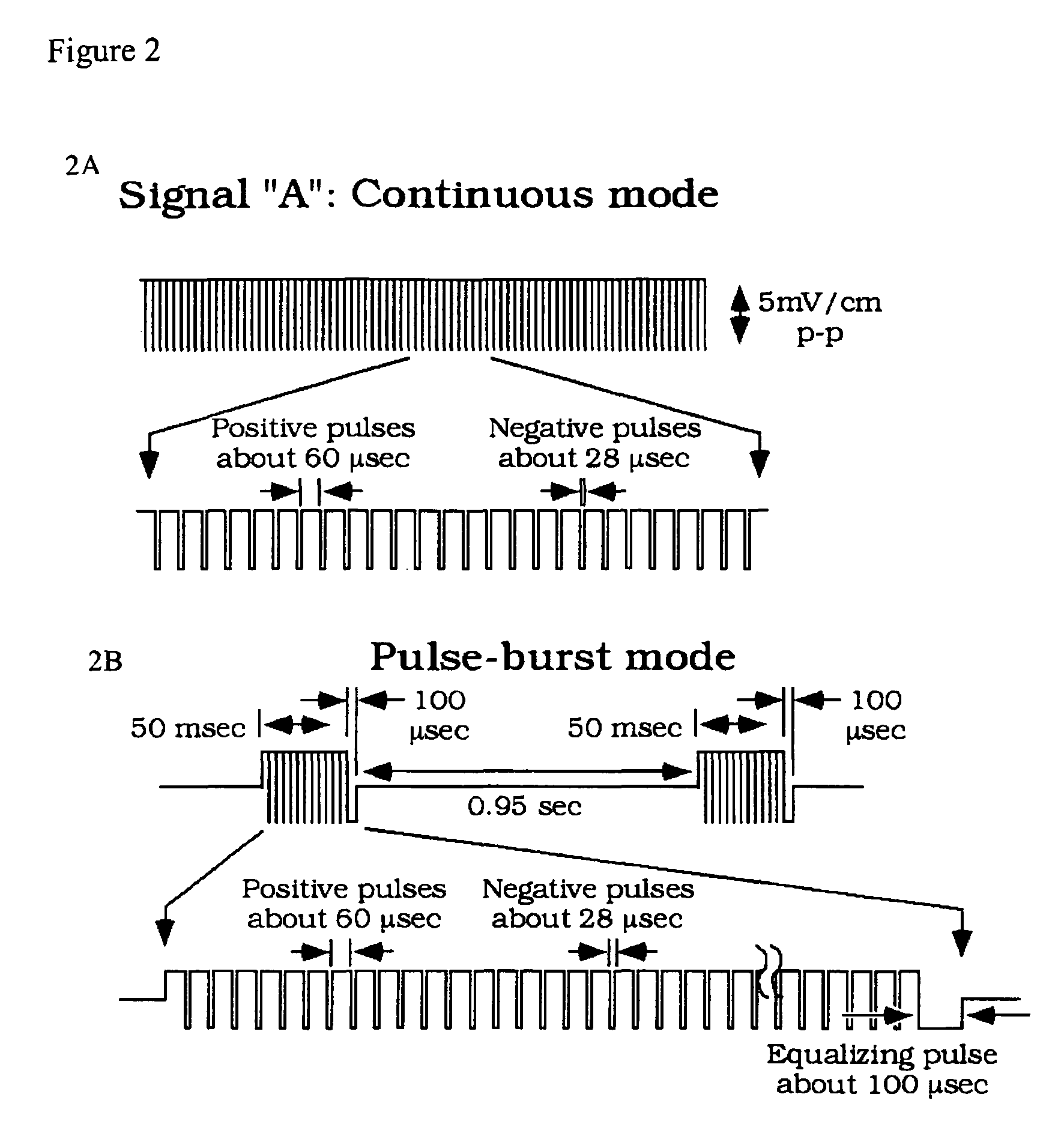
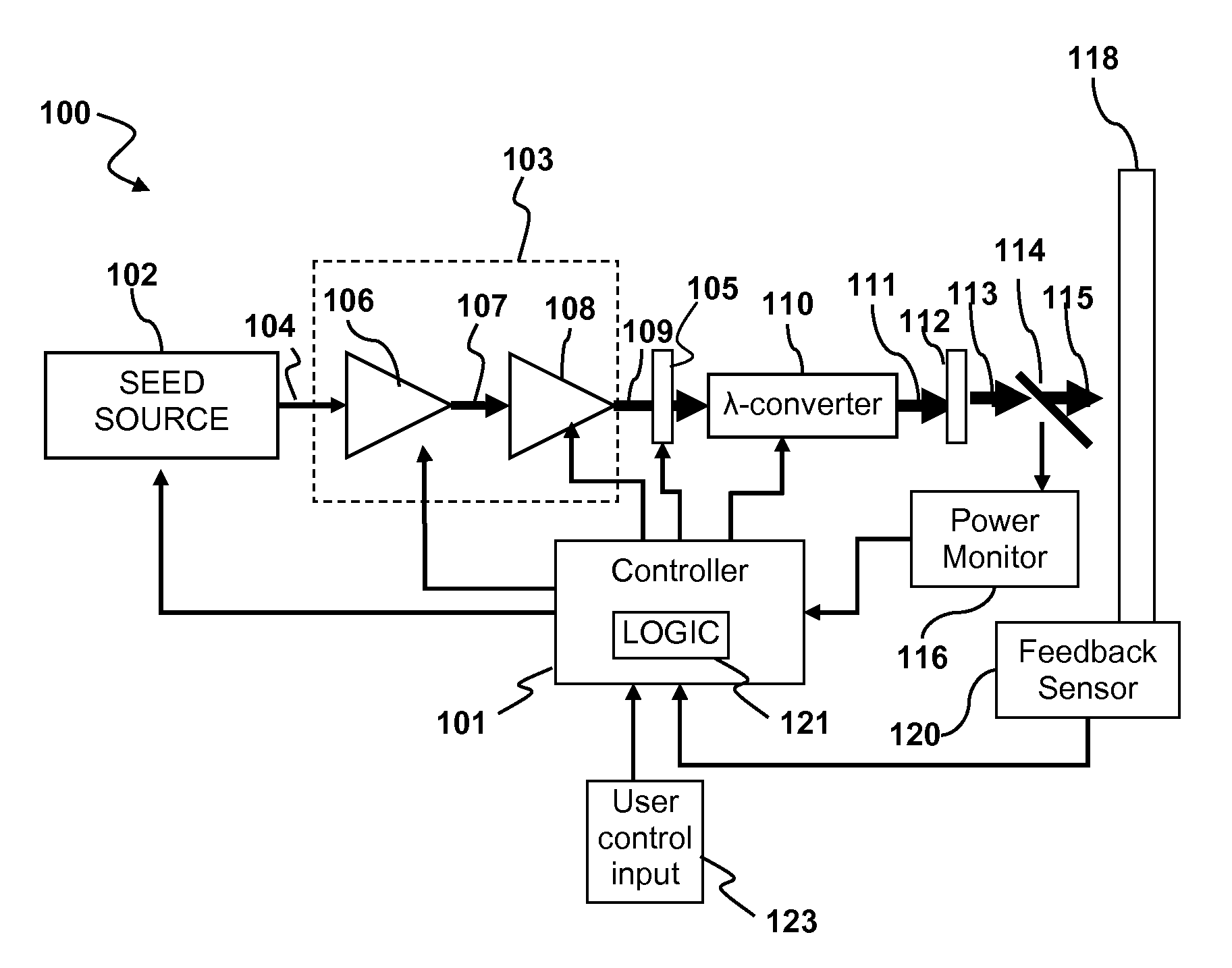
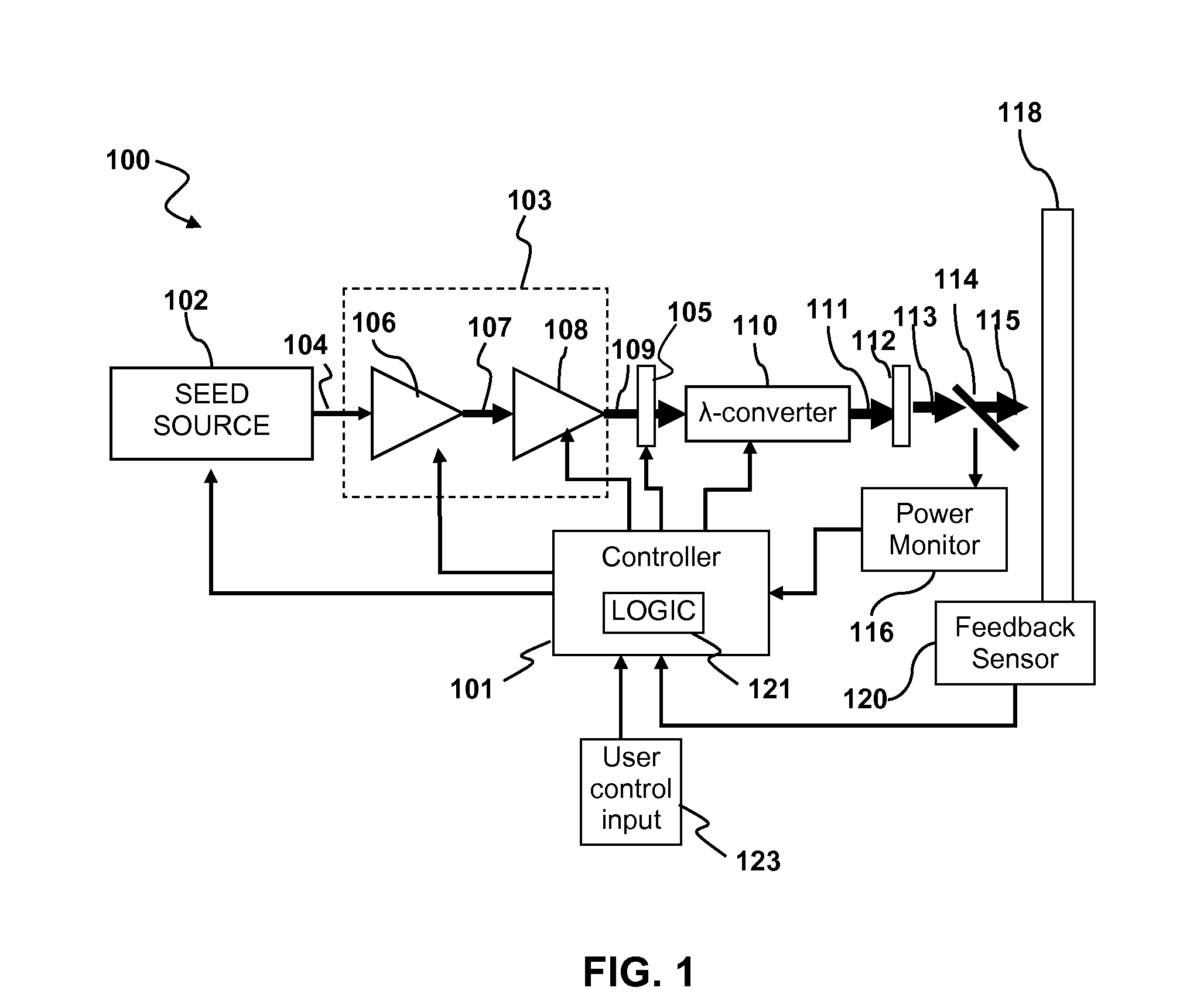
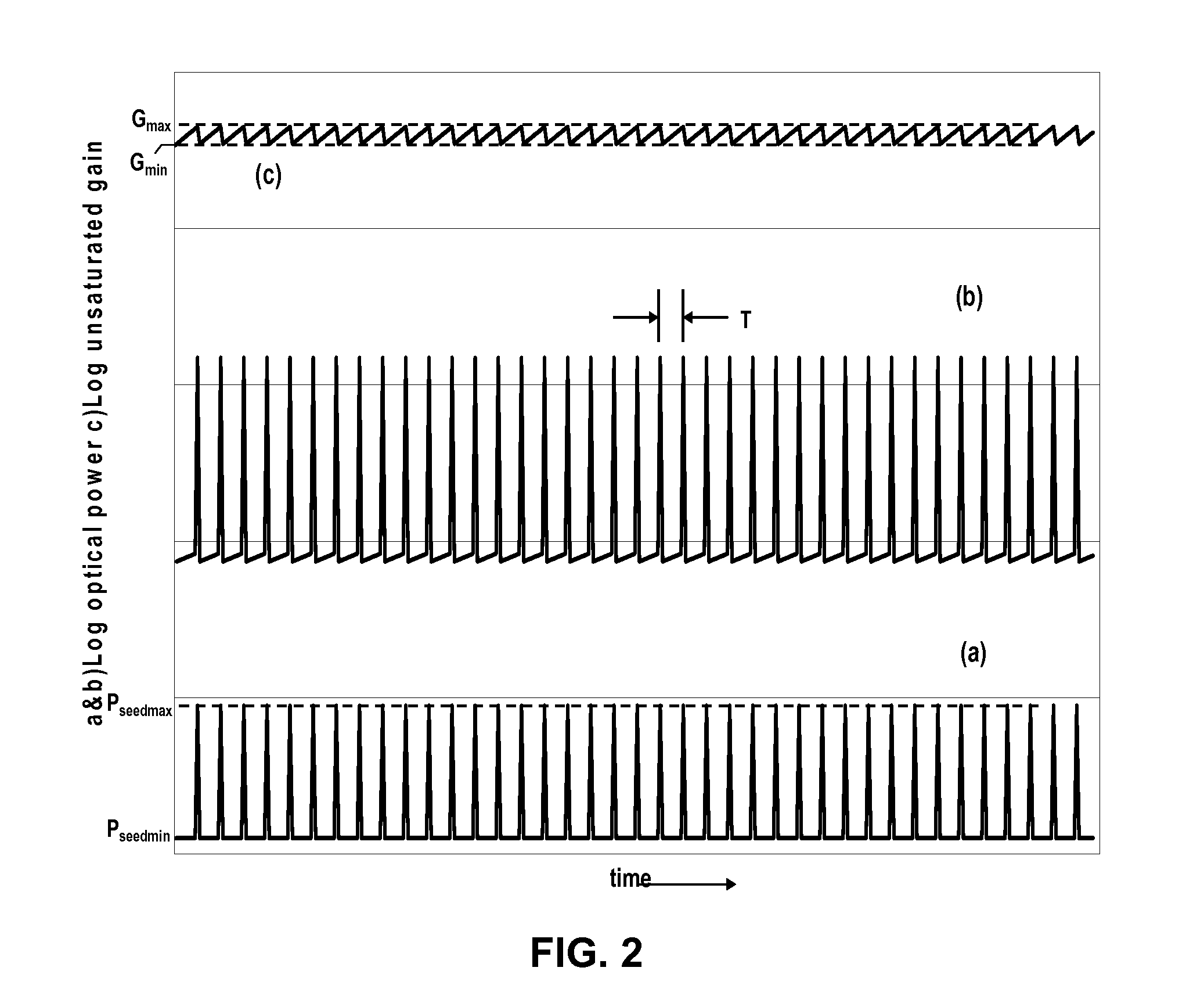
Patents
Literature
85 results about "Pulse burst" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Providing enhanced haptic feedback effects
InactiveUS7218310B2Enhanced tactile sensationStrong tactile effectInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTactile sensationEngineering
Method and apparatus for providing high strength, low frequency tactile sensations using an inertial actuator in a haptic feedback interface device, such as an actuator driving an oscillating inertial mass. A commanded low frequency is modulated or combined with a higher frequency at which the tactile sensations feel stronger, where the resulting signal is used to output a tactile sensation at the higher frequency and convey the commanded low frequency to the user. One embodiment provides higher frequency pulse bursts at the desired low frequency wherein the higher frequency pulse bursts are at or near a resonant frequency of the actuator; other embodiments modulate or otherwise vary the amplitude of the higher frequency signal according to the desired low frequency.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
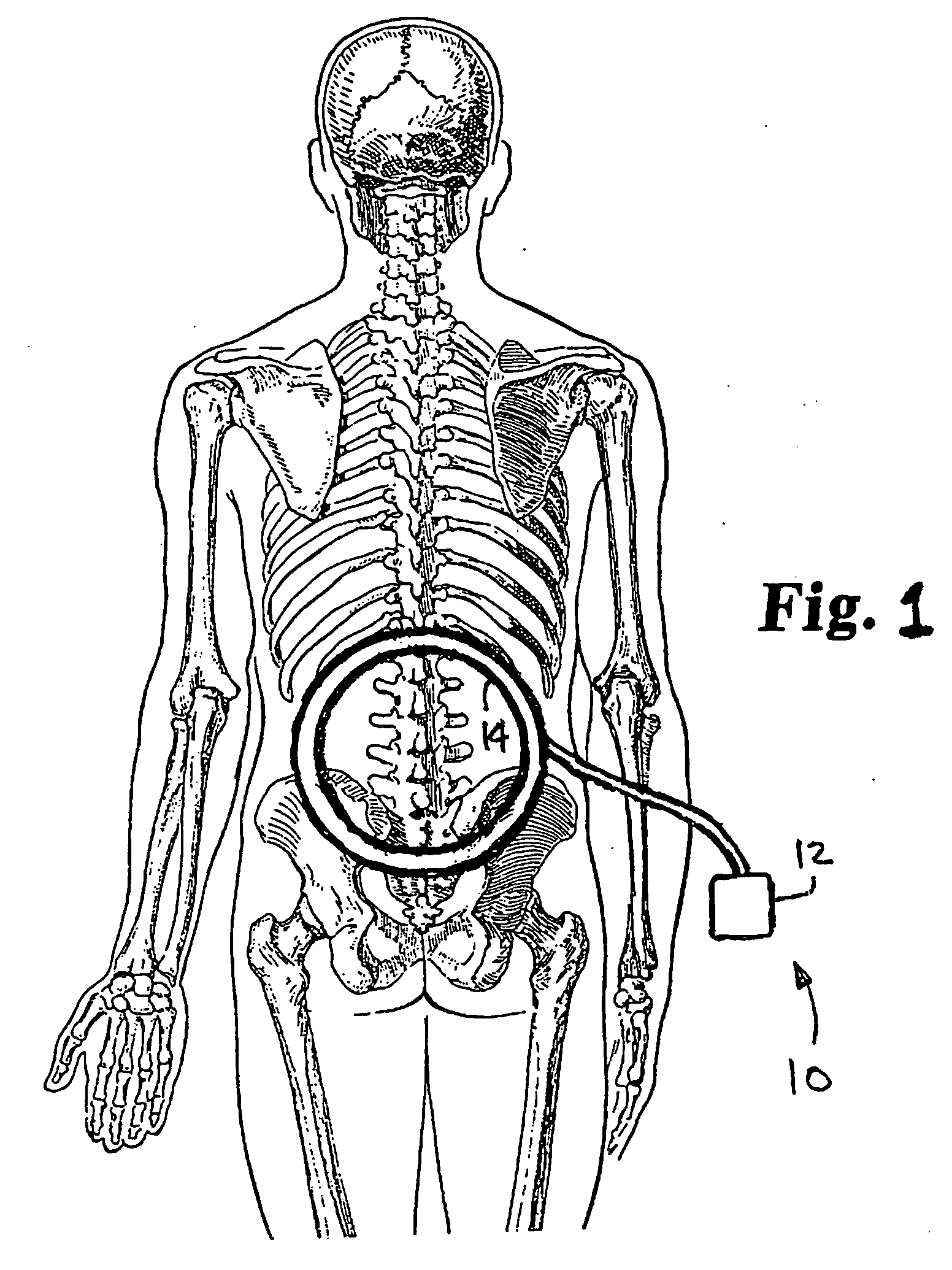
Electrical stimulation device and method for the treatment of dysphagia
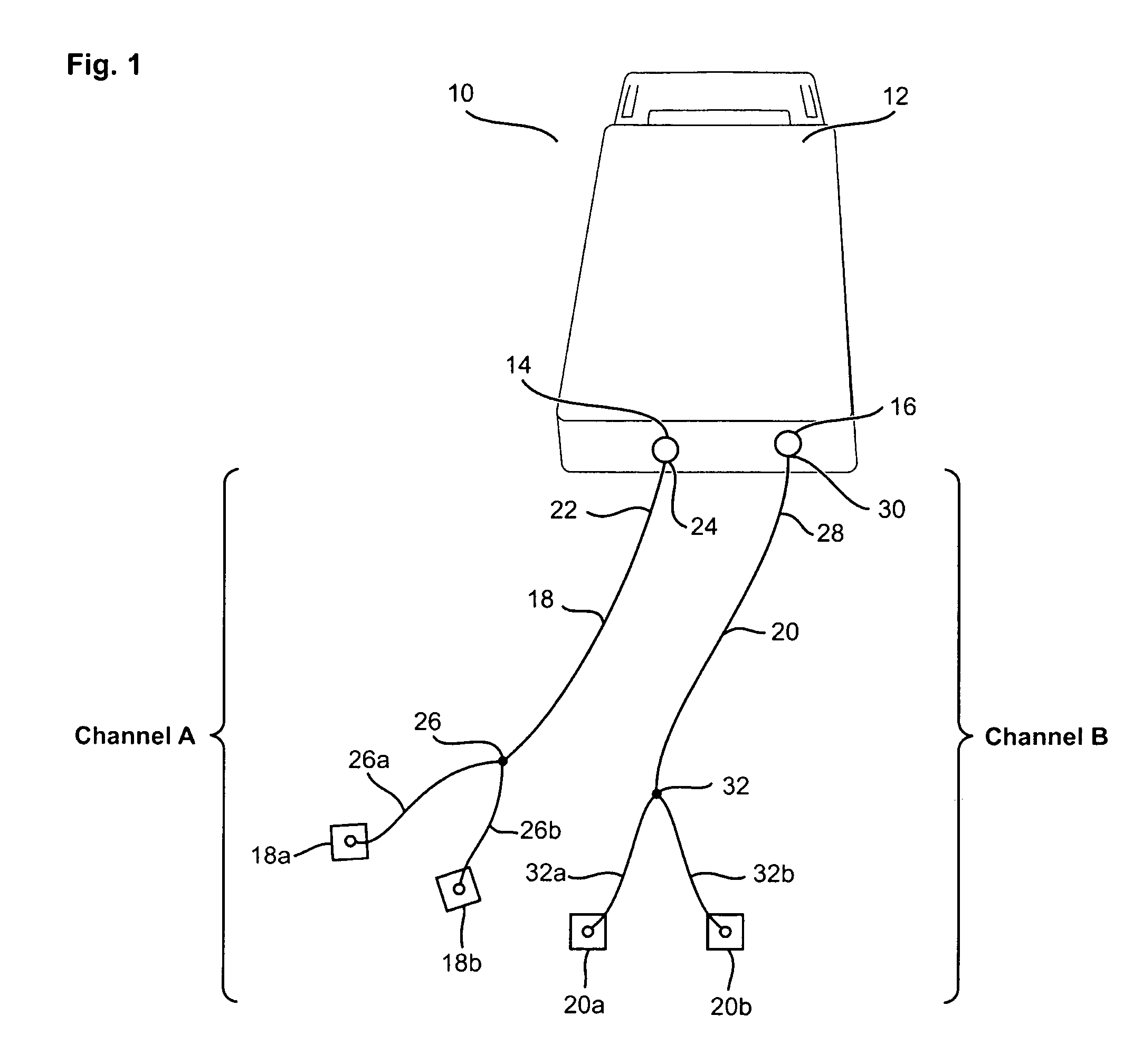
An electrical stimulation device and method for the treatment of dysphagia is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, the electrical stimulation device includes one or more channels of electrodes each of which includes a first electrode positioned in electrical contact with tissue of a target region of a patient and a second electrode positioned in electrical contact with tissue of a posterior neck region or a posterior thoracic region of the patient. A series of electrical pulses are then applied to the patient through the one or more channels of electrodes in accordance with a procedure for treating dysphagia. The series of electrical pulses may comprise: a plurality of cycles of a biphasic sequential pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a biphasic overlapping pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a triphasic sequential pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a triphasic overlapping pulse train pattern; a functional pulse train pattern; a low-frequency pulse train pattern; or a frequency-sequenced pulse burst train pattern. Various exemplary embodiments of the invention are disclosed.
Owner:ACCELERATED CARE PLUS CORP
Pulsed electromagnetic field method of treating soft tissue wounds
A pulsed electromagnetic field method of treating a soft tissue wound, wherein, in one embodiment, a patient in need of treatment for a soft tissue wound is administered a pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) having repetitive pulse bursts less than approximately 30 ms in duration, with a pulse burst repetition rate greater than approximately 5 Hz, the pulse bursts generated with a drive signal including pulses each having a first-polarity portion with a pulse width less than 1 ms and a second-polarity portion with a shorter pulse width, the electromagnetic field having a maximum amplitude less than approximately 4 mT and rising to its maximum amplitude during the first-polarity portion. According to another aspect of the invention, a soft tissue wound is treated by administering a pulsed electromagnetic field having substantially unipolar magnetic field pulses generated with a drive signal including a series of pulses each having a first-polarity portion with a pulse width less than 1 ms and a second-polarity portion with a longer pulse width, the electromagnetic field having a maximum amplitude less than 4 mT and rising to its maximum amplitude during the first-polarity portion.
Owner:EUROPEAN BIOINFORMATICS INSTITUTE
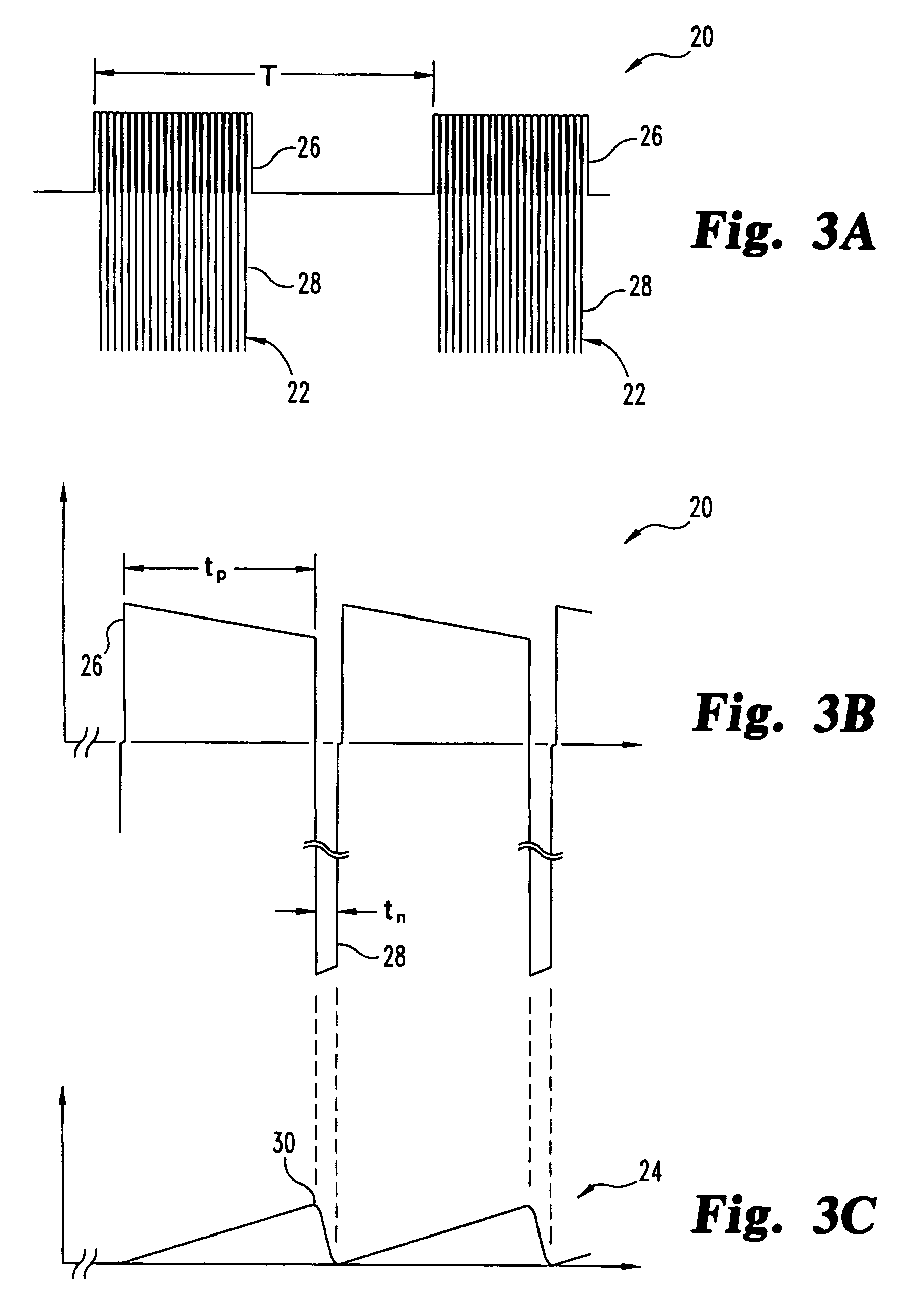
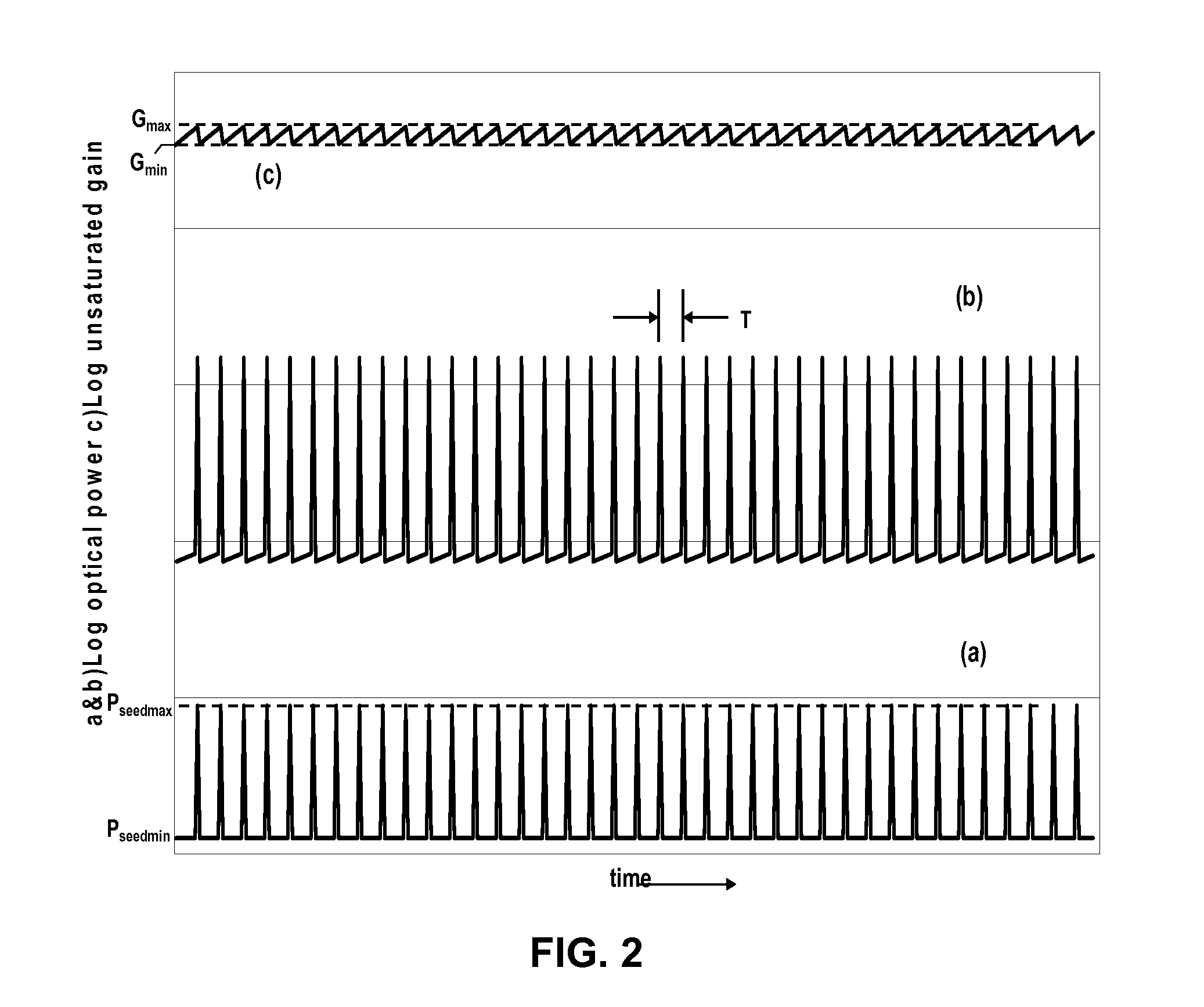
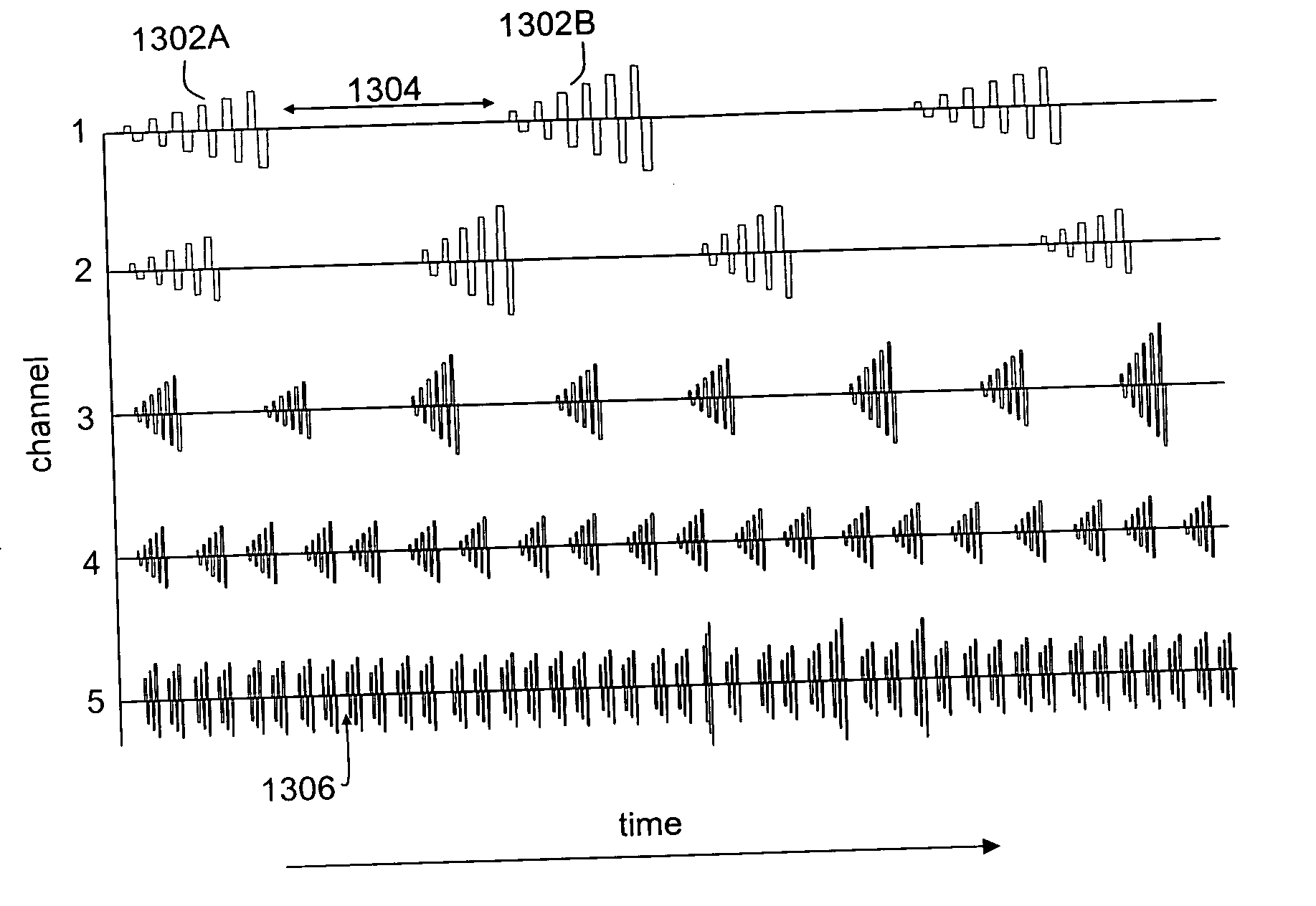
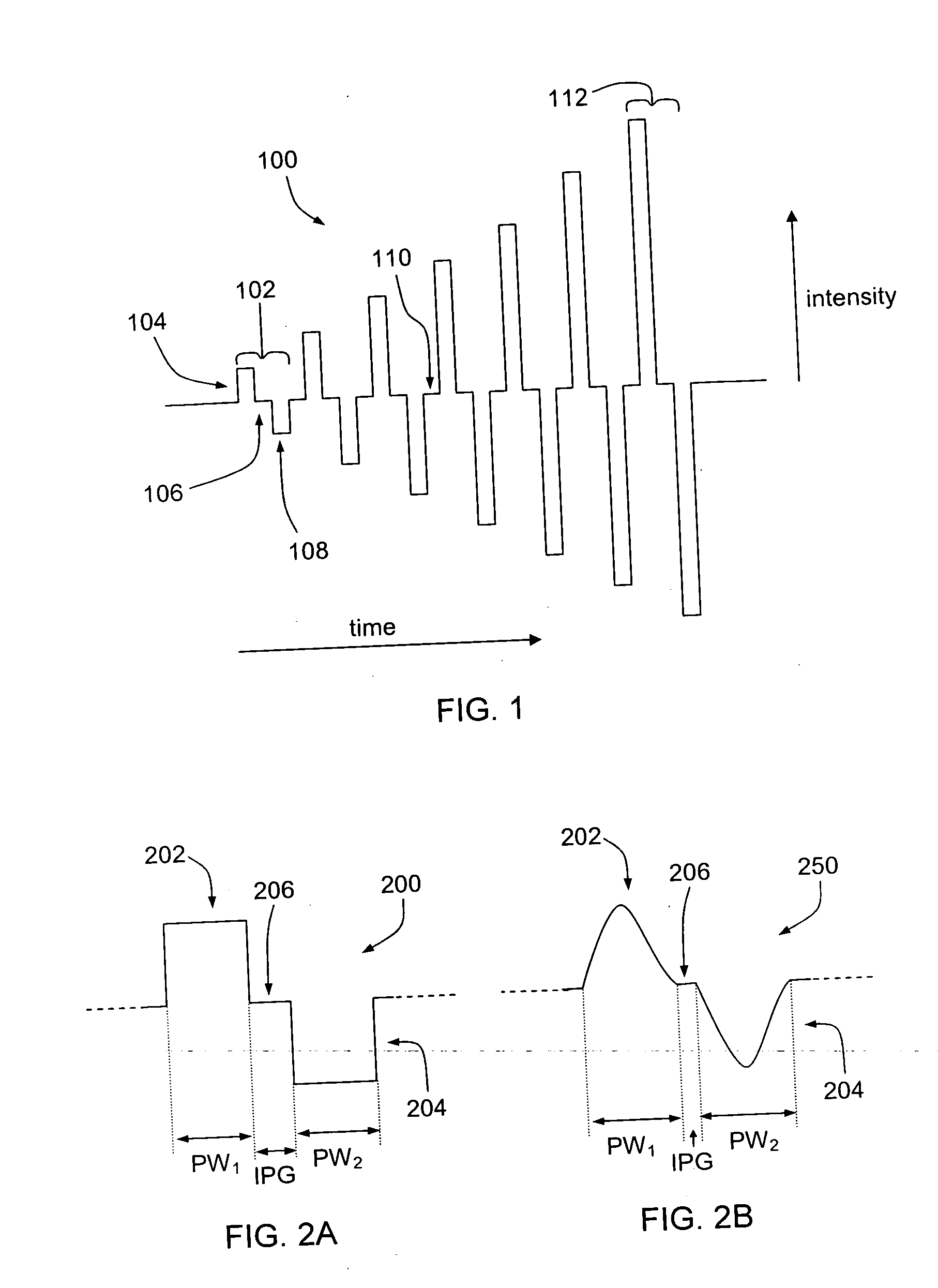
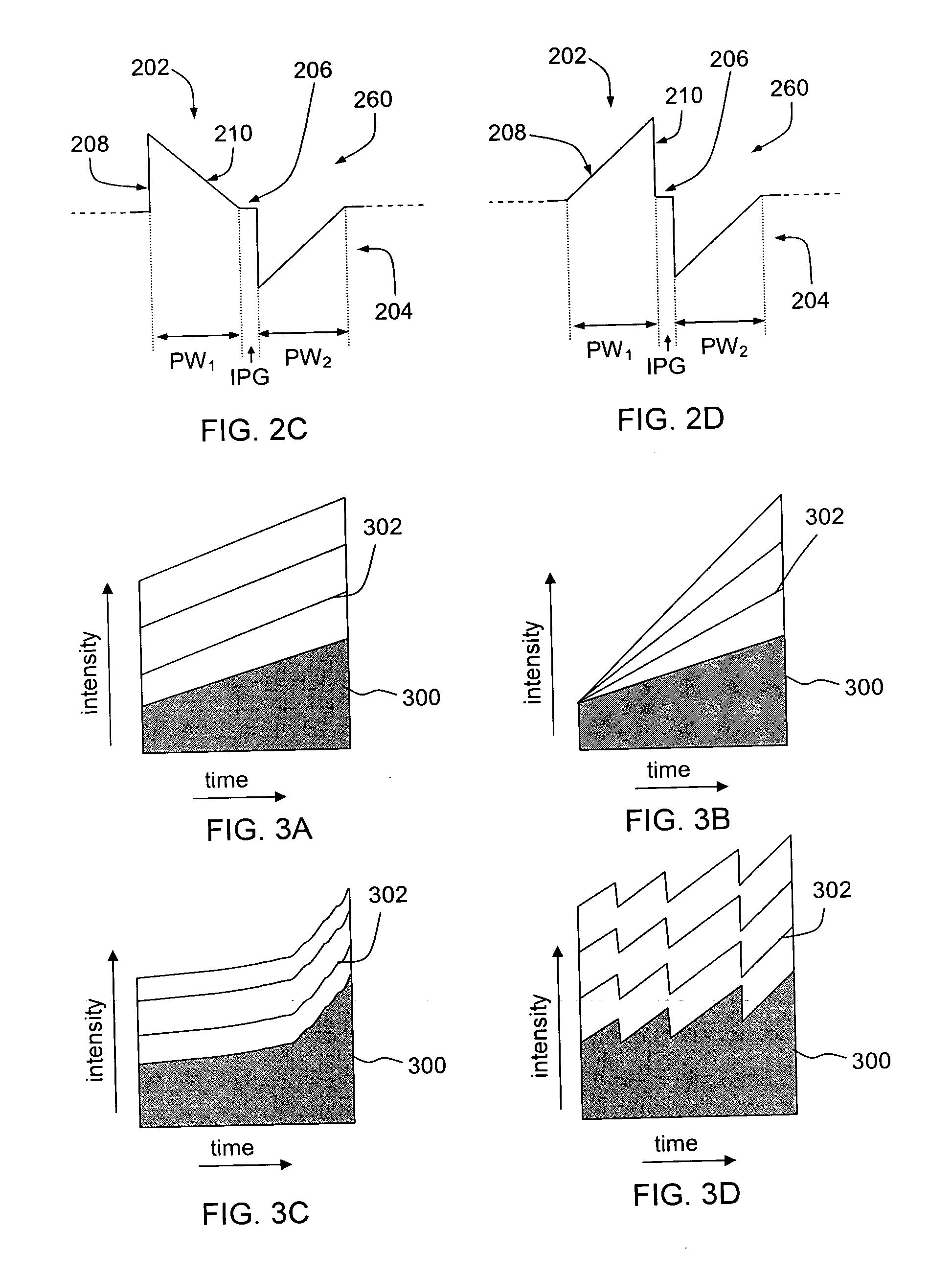
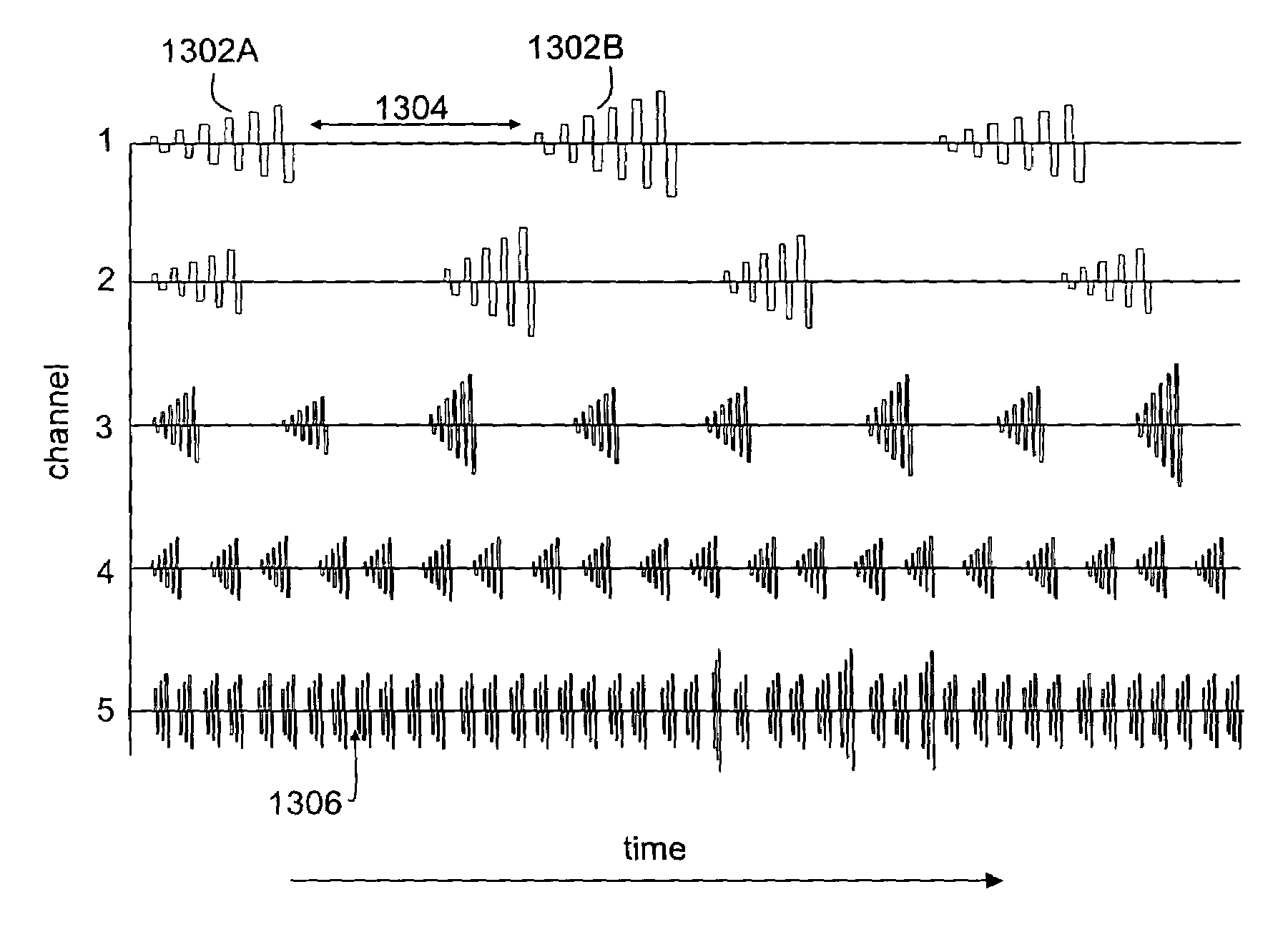
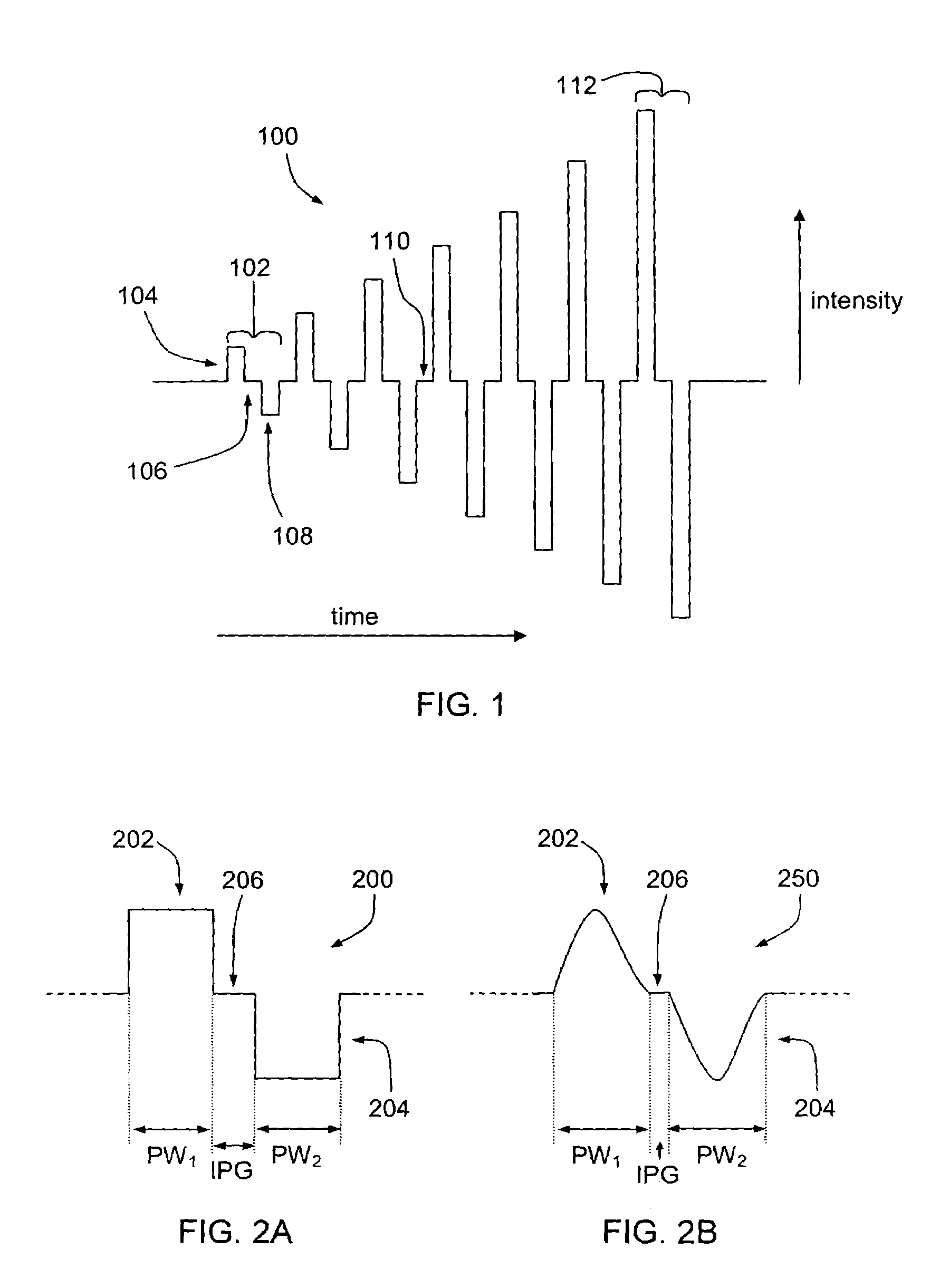
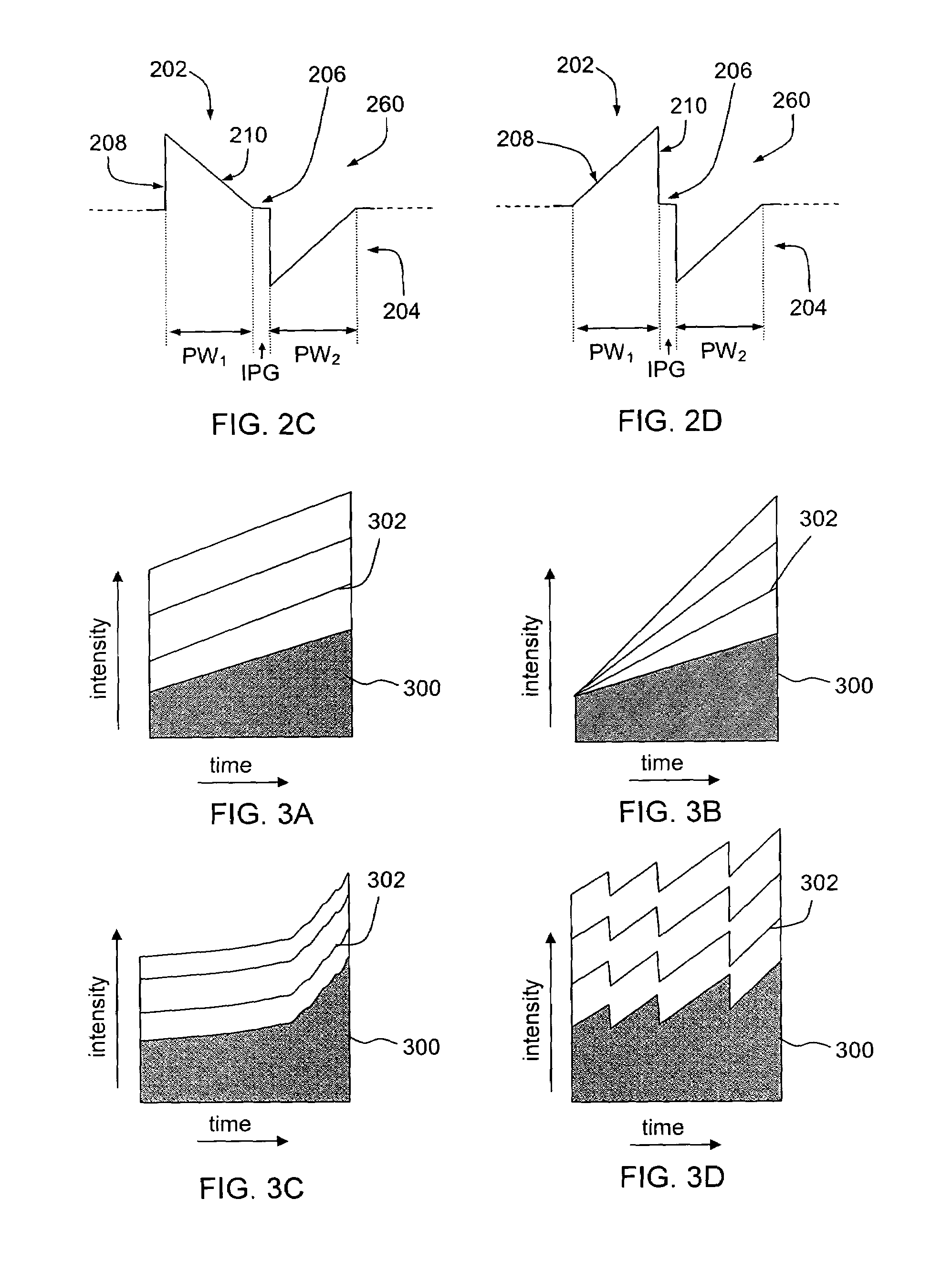
Tailored pulse burst
ActiveUS20110019705A1Raise transfer toUnprecedented level of controlLaser detailsFibre transmissionSeeds sourcePulse period
Output pulses from an optical system having a seed source and an optical amplifier coupled to the seed source may be controlled by controlling a power of a seed signal from the seed source. The seed signal may be varied between a minimum value and a maximum value in a way that the seed signal exhibits one or more pulse bursts. Each pulse burst may contain one or more pulses. During an inter-pulse period between successive pulses within a pulse burst or between successive pulse bursts, the power of the seed signal may be adjusted to an intermediate value that is greater than the minimum value and less than the maximum value. The intermediate value is chosen to control a gain in the optical amplifier such that a pulse or pulse burst that follows the period exhibits a desired behavior.
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
Pulse burst electrical stimulation of nerve or tissue fibers
A method for stimulating nerve or tissue fibers and a prosthetic hearing device implanting same. The method comprises: generating a stimulation signal comprising a plurality of pulse bursts each comprising a plurality of pulses; and distributing said plurality of pulse bursts across one or more electrodes each operatively coupled to nerve or tissue fibers such that each of said plurality of pulse bursts delivers a charge to said nerve or tissue fibers to cause dispersed firing in said nerve or tissue fibers.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Pulse burst electrical stimulation of nerve or tissue fibers
A method for stimulating nerve or tissue fibers and a prosthetic hearing device implanting same. The method comprises: generating a stimulation signal comprising a plurality of pulse bursts each comprising a plurality of pulses; and distributing said plurality of pulse bursts across one or more electrodes each operatively coupled to nerve or tissue fibers such that each of said plurality of pulse bursts delivers a charge to said nerve or tissue fibers to cause dispersed firing in said nerve or tissue fibers.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Methods for modulating osteochondral development using bioelectrical stimulation
ActiveUS20060293724A1Maximize utilizationMaximize applicationElectrotherapyStress based microorganism growth stimulationCo administrationOsteoblast
Compositions and methods are provided for modulating the growth, development and repair of bone, cartilage or other connective tissue. Devices and stimulus waveforms are provided to differentially modulate the behavior of osteoblasts, chondrocytes and other connective tissue cells to promote proliferation, differentiation, matrix formation or mineralization for in vitro or in vivo applications. Continuous-mode and pulse-burst-mode stimulation of cells with charge-balanced signals may be used. Bone, cartilage and other connective tissue growth is stimulated in part by nitric oxide release through electrical stimulation and may be modulated through co-administration of NO donors and NO synthase inhibitors. Bone, cartilage and other connective tissue growth is stimulated in part by release of BMP-2 and BMP-7 in response to electrical stimulation to promote differentiation of cells. The methods and devices described are useful in promoting repair of bone fractures, cartilage and connective tissue repair as well as for engineering tissue for transplantation.
Owner:MEDRELIEF
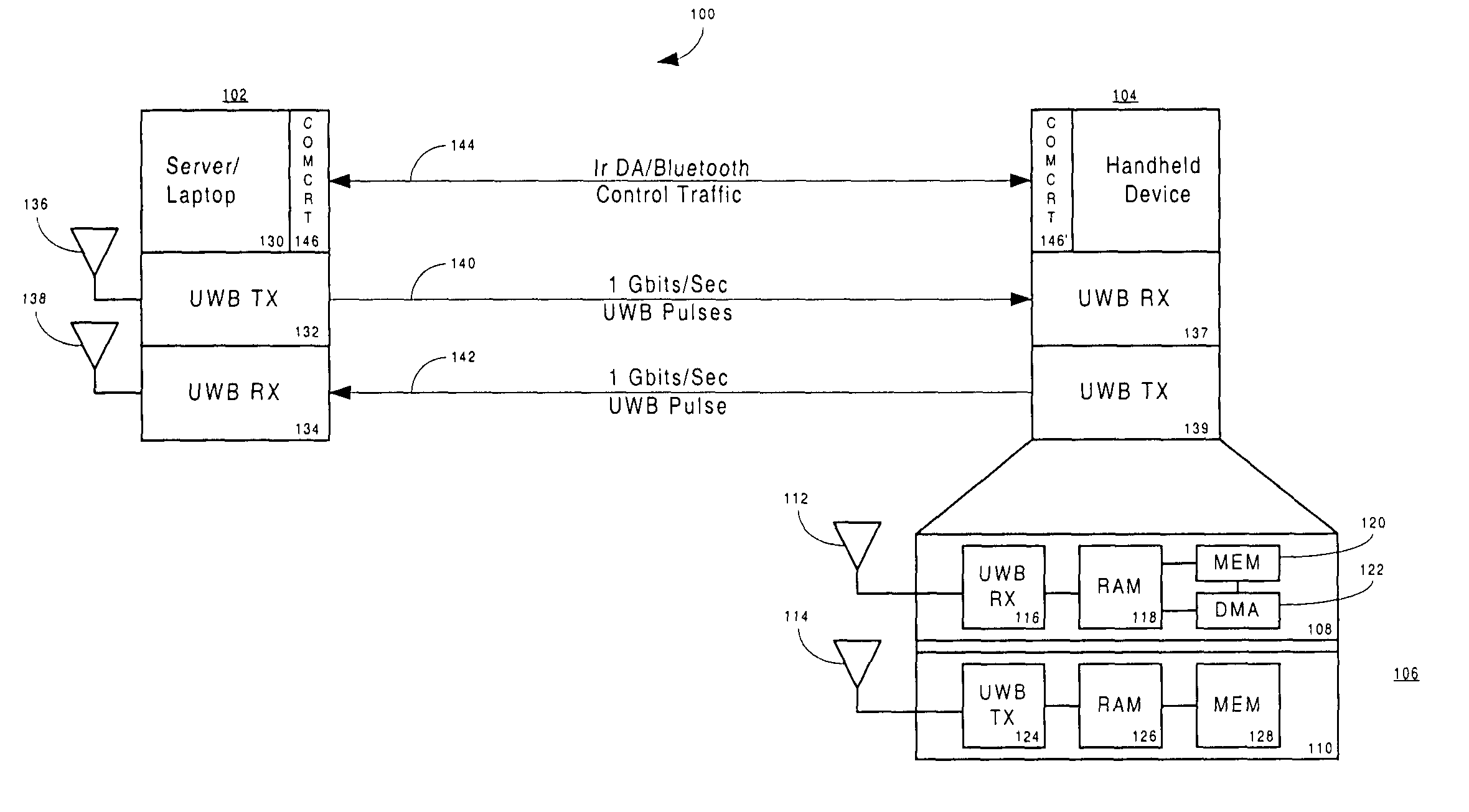
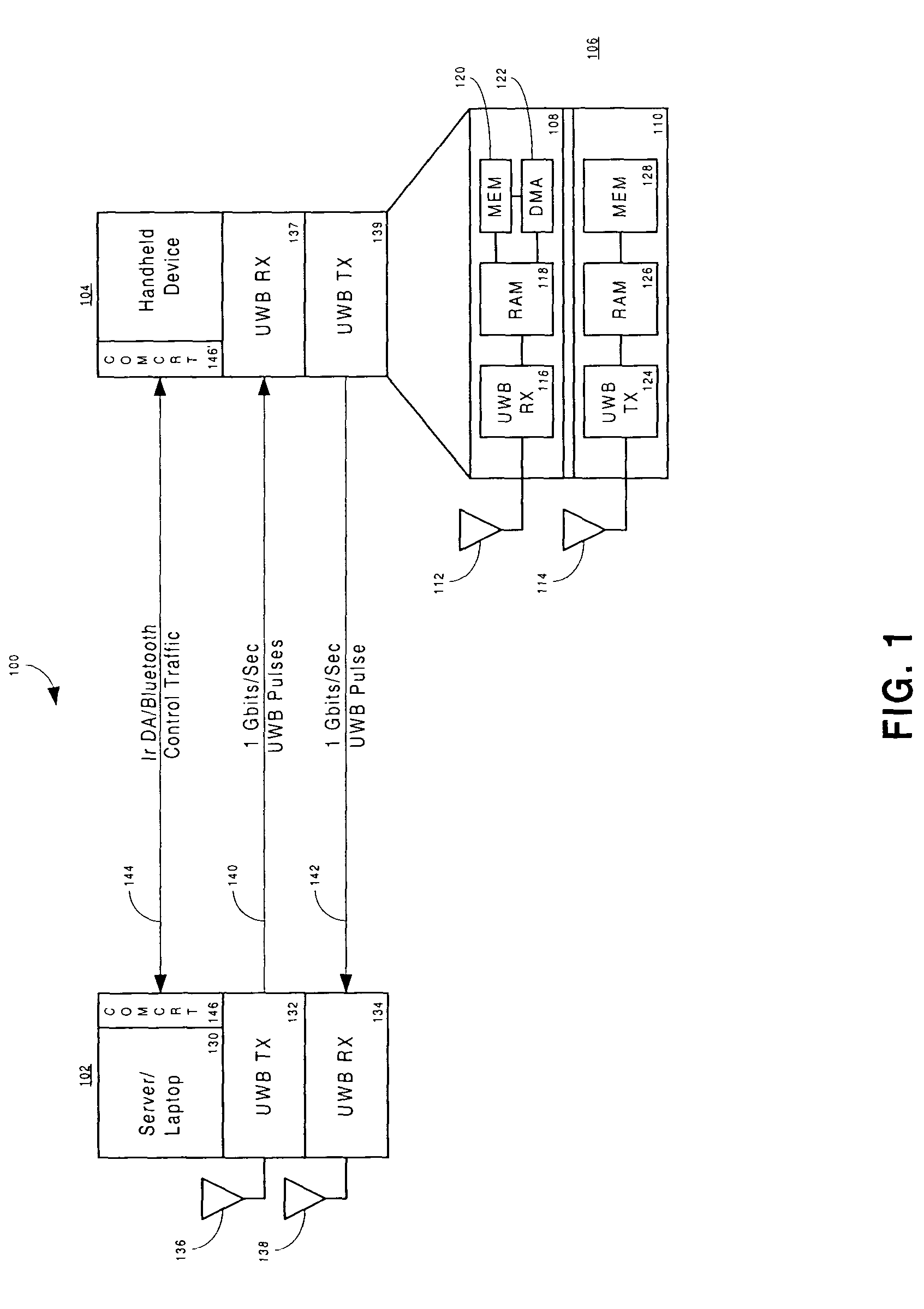
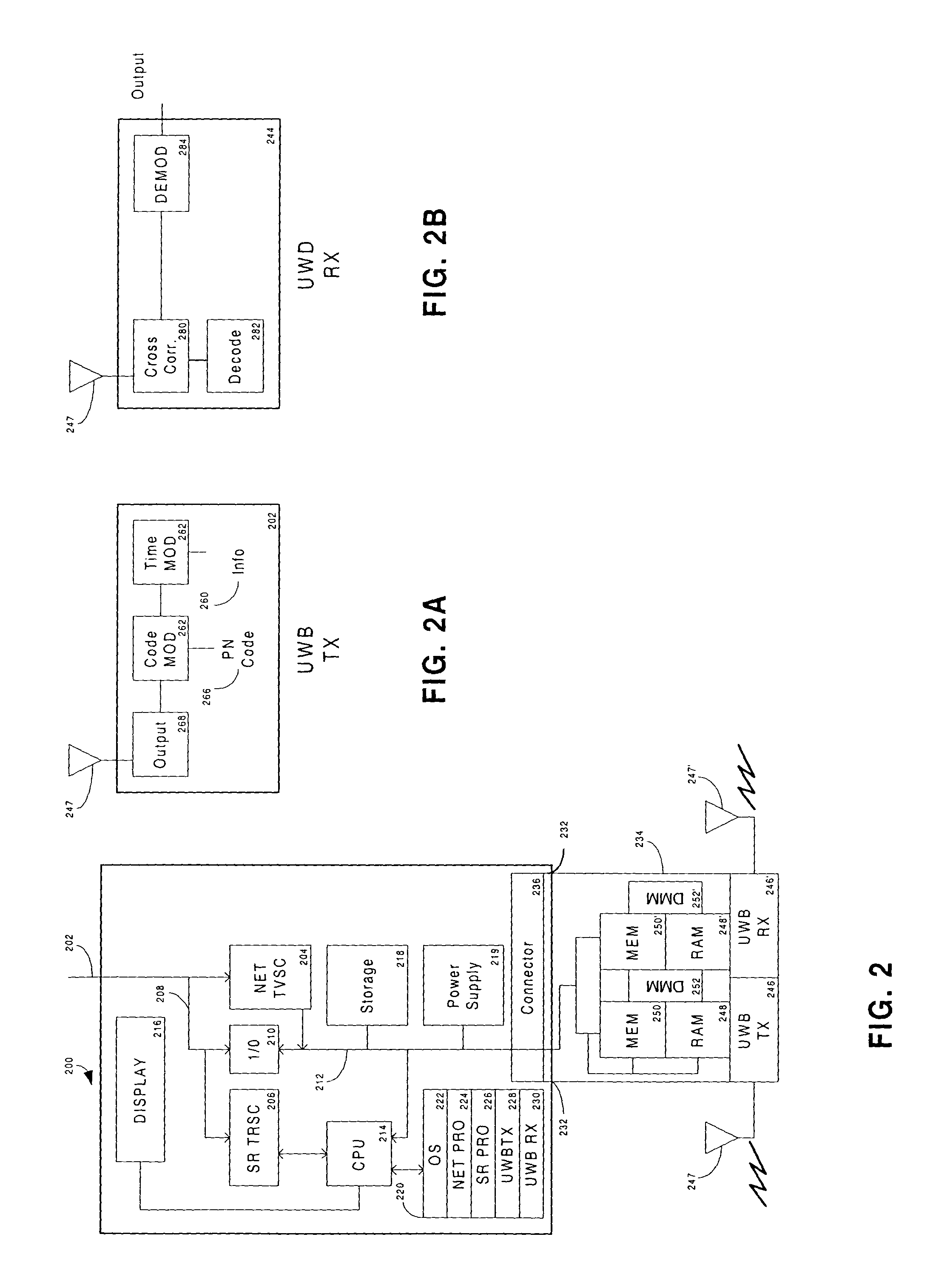
Ultra-wideband/low power communication having a dedicated memory stick for fast data downloads - apparatus, systems and methods
ActiveUS20050058152A1Enhanced BT parametersEasy to checkTime-division multiplexCo-operative working arrangementsUltra-widebandTransceiver
In a mobile environment, a mobile device includes an attached memory stick (removable memory) having a high speed—memory and storage with direct memory access embodied in an integrated circuit chip coupled to an ultra-wideband (UWB) transceiver. The mobile device communicates with other like base devices, portable or stationary, via UWB transmissions using pulse bursts up to 1 Gbit per second. Data transfers between the devices occur in the simplex or duplex mode, after a low power communication connection is established between the devices. The communication link between the devices is in the range of 10-20 meters. The communication system allows existing device bus interfaces (which are much slower than ultra-wideband transmissions) to communicate between the fast read / write cycles of the memories integrated within the memory stick. Duplex transmission can occur by pulse interleaving sending side transmitters and receiving side transmitters.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Methods for modulating chondrocyte proliferation using pulsing electric fields
Compositions and methods are provided for modulating the growth, development and repair of cartilage, bone or other connective tissue. Devices and stimulus waveforms are provided to differentially modulate the behavior of chondrocytes, osteoblasts and other connective tissue cells to promote proliferation, differentiation, matrix formation or mineralization for in vitro or in vivo applications. Continuous-mode and pulse-burst-mode stimulation of cells with charge-balanced signals may be used. Cartilage, bone and other connective tissue growth is stimulated in part by nitric oxide release through electrical stimulation and may be modulated through co-administration of NO donors and NO synthase inhibitors. The methods and devices described are useful in promoting repair of bone fractures, cartilage and connective tissue repair as well as for engineering tissue for transplantation.
Owner:HEALTHONICS INC
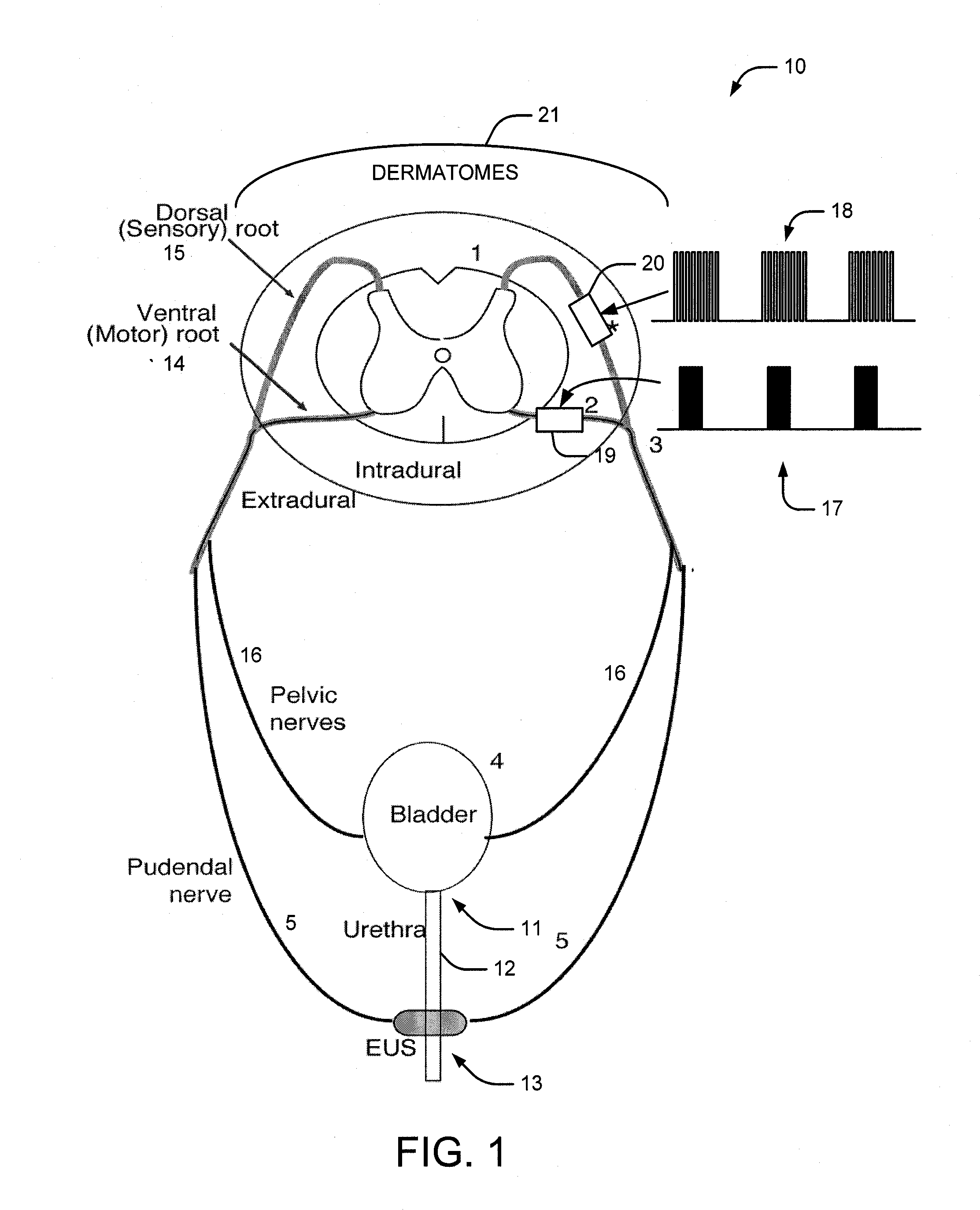
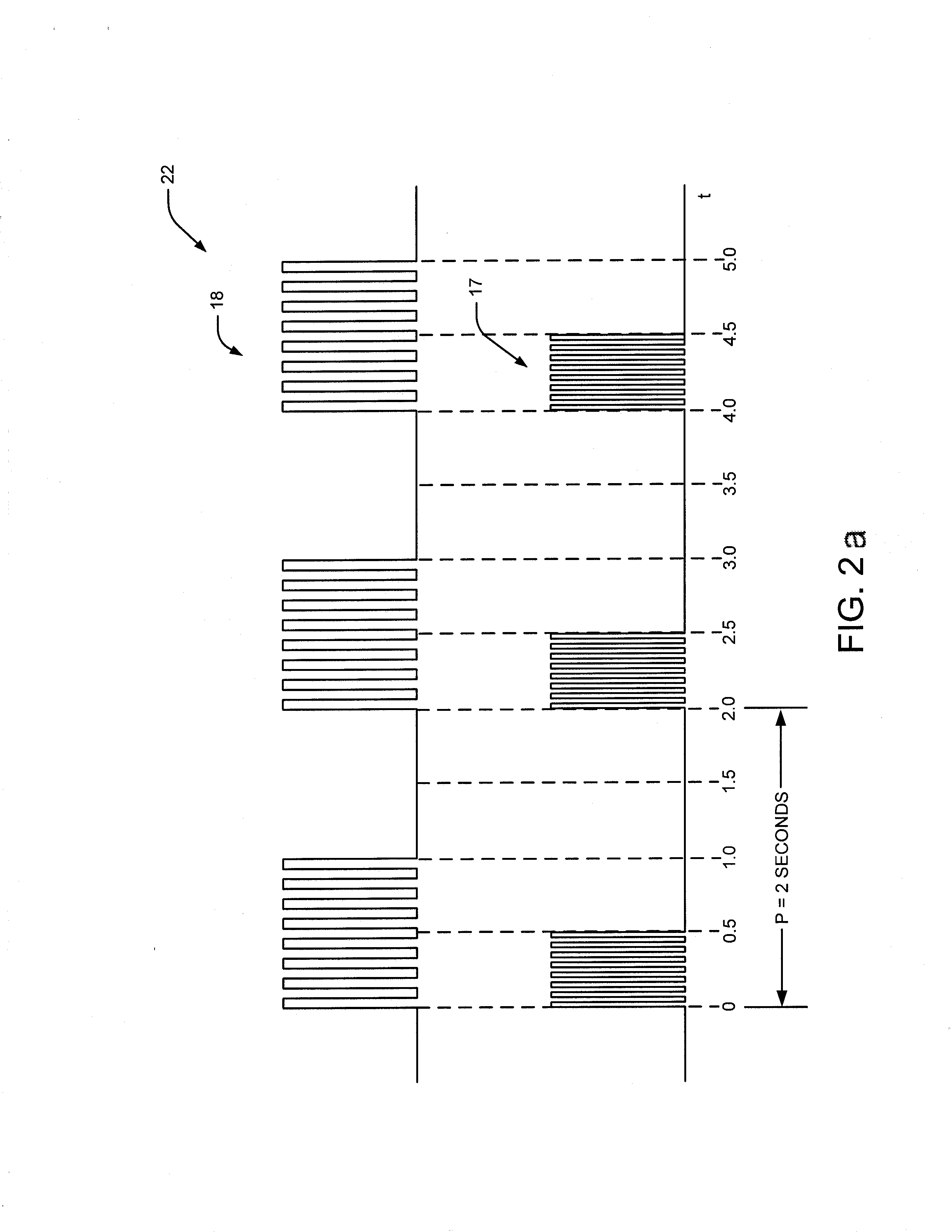
System and method of bladder and sphincter control
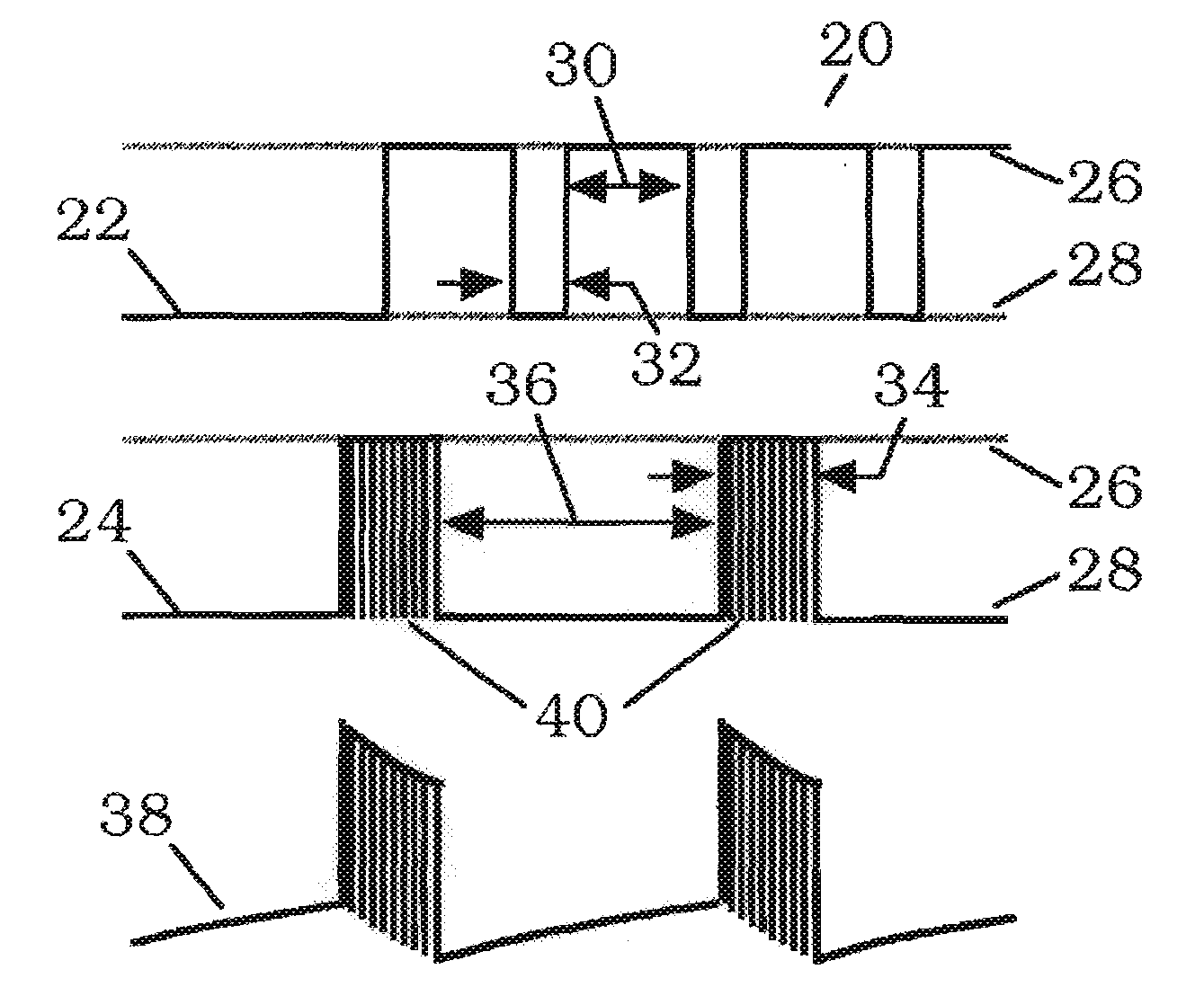
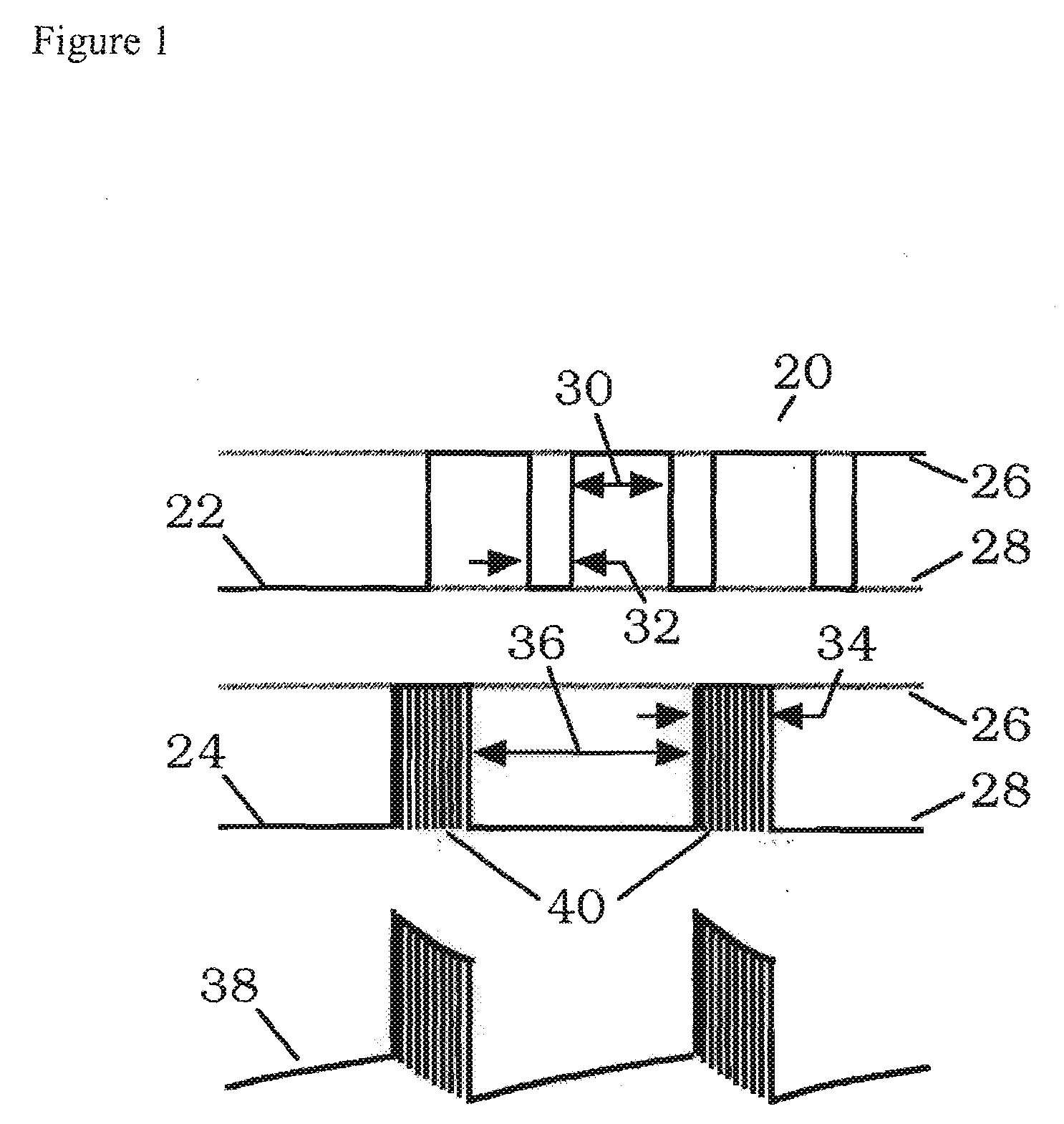
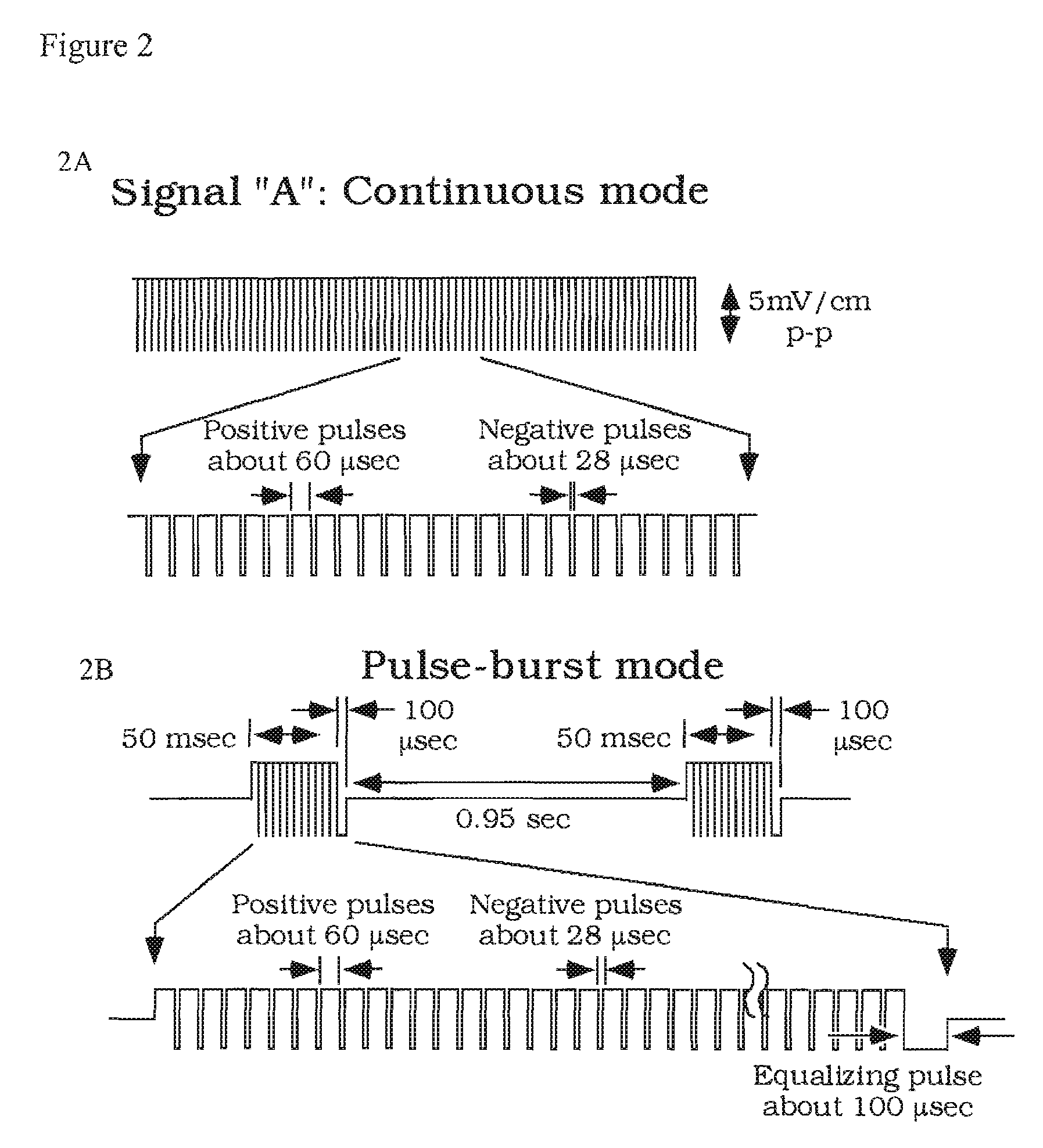
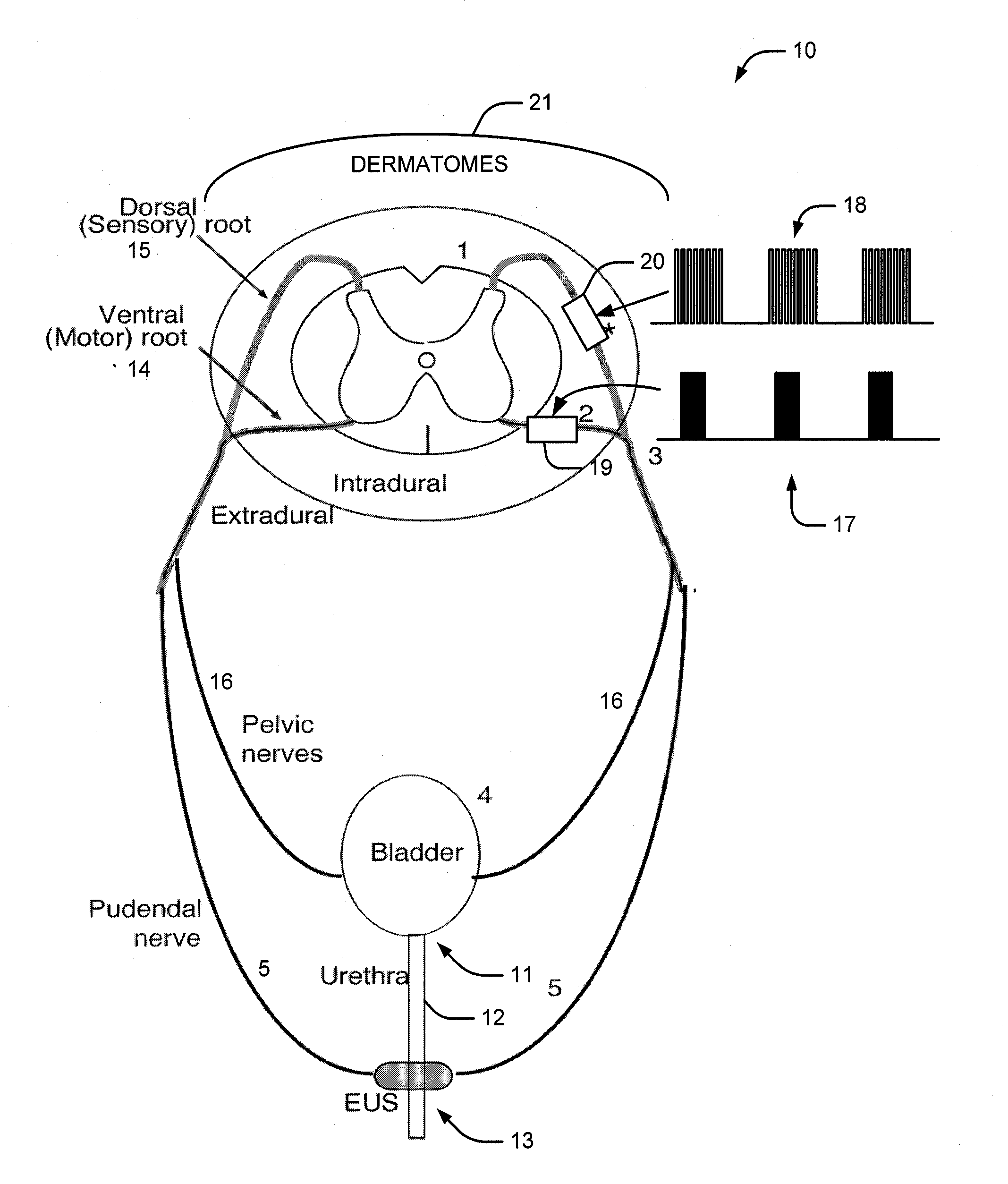
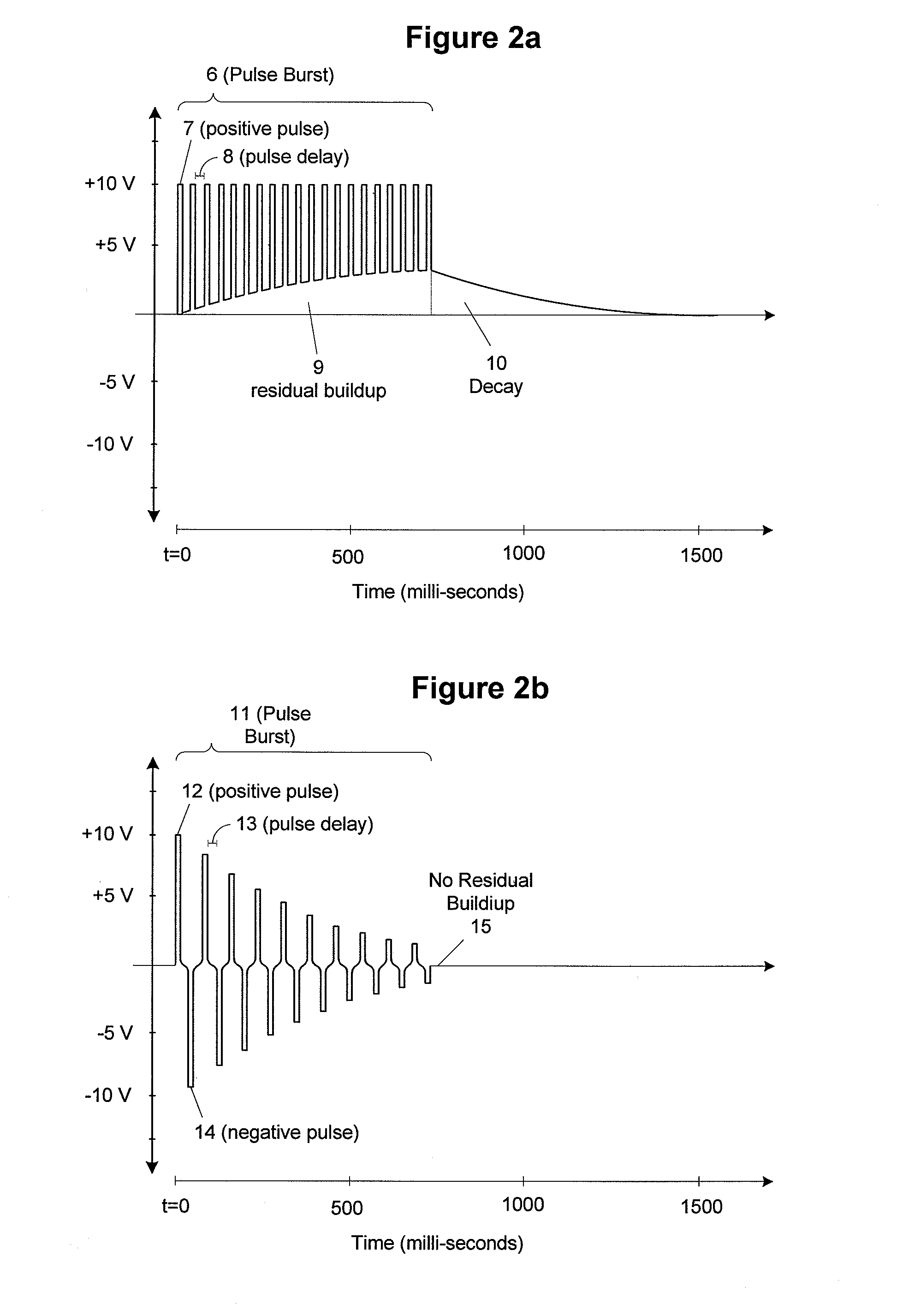
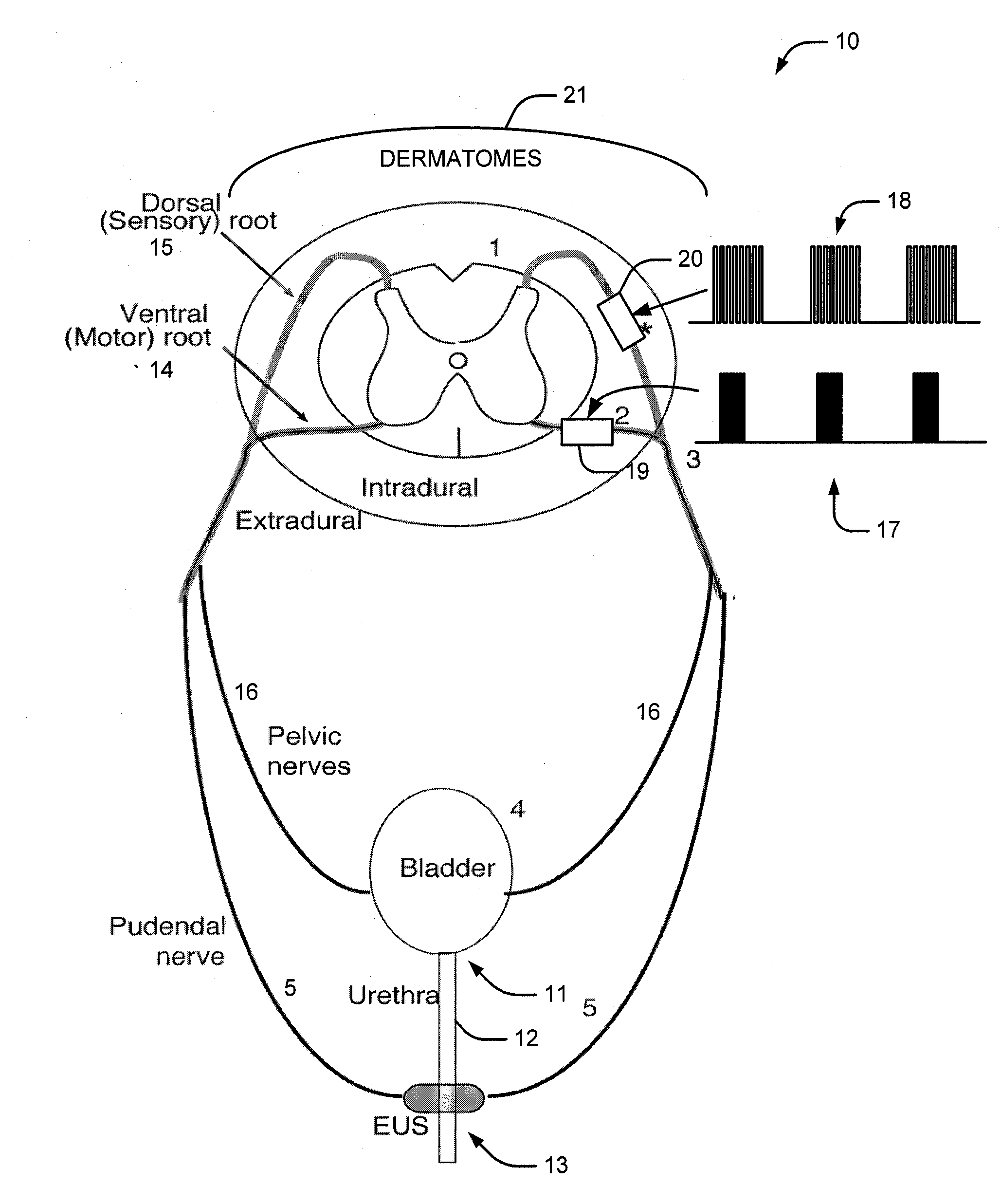
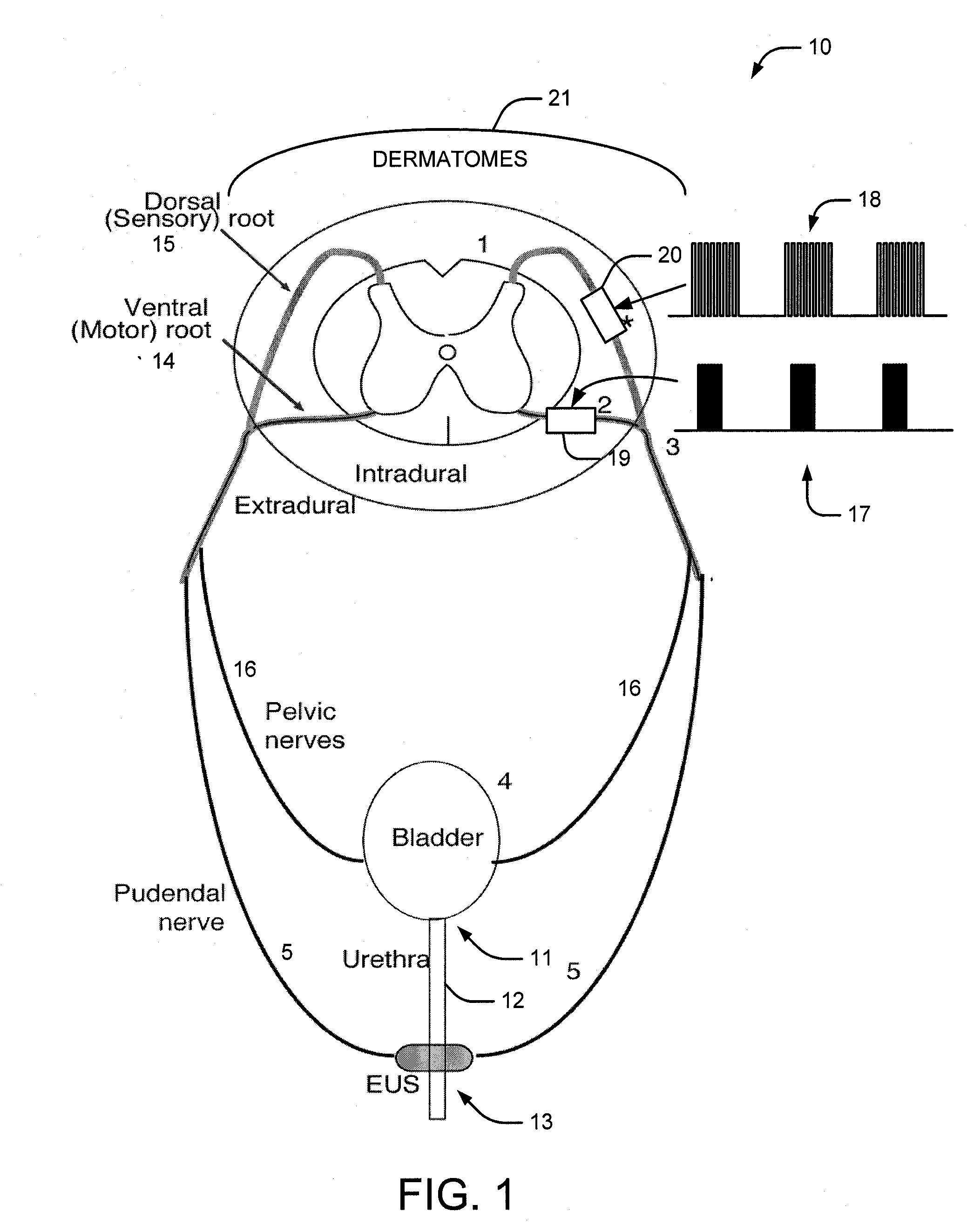
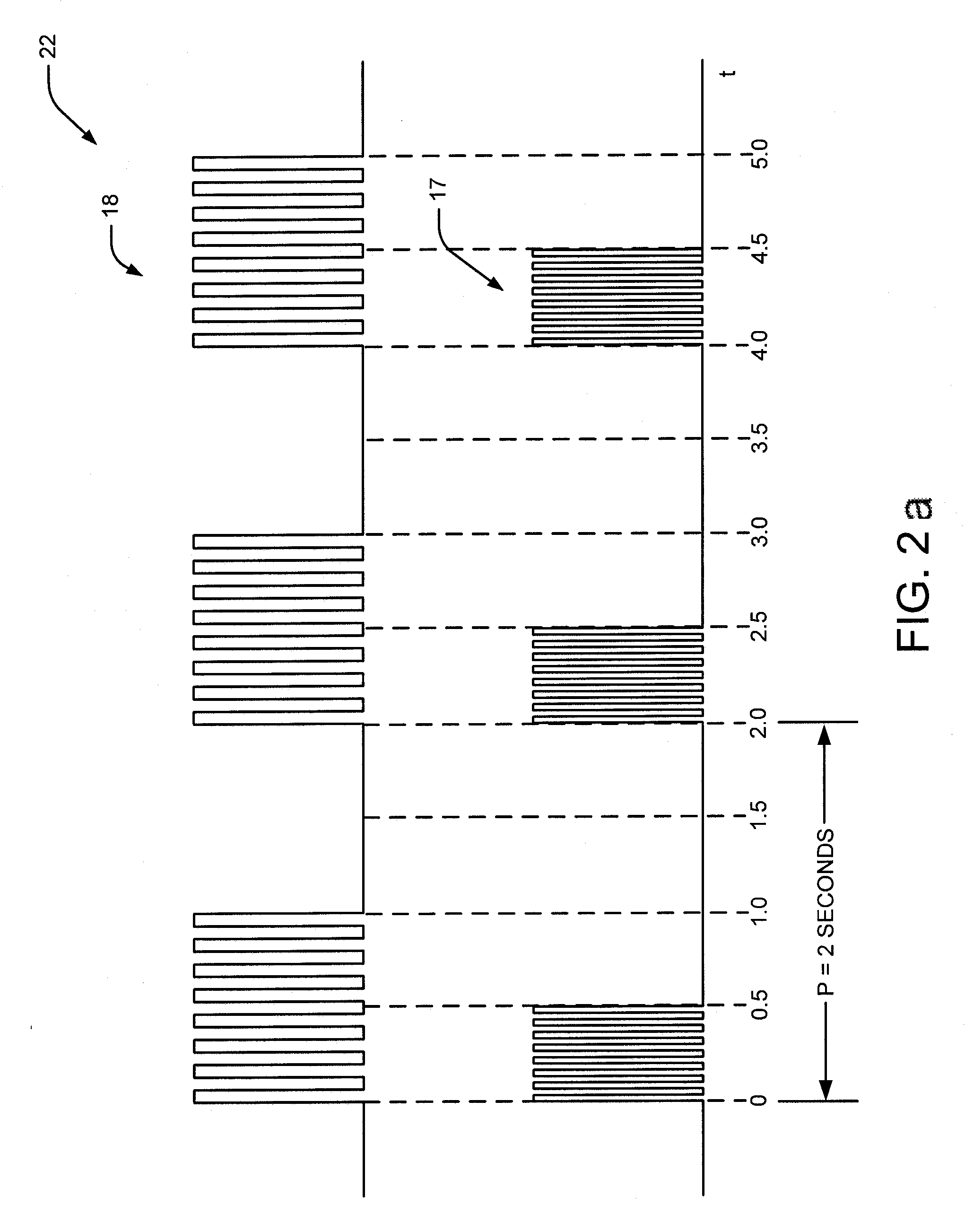
A method and system for bladder control are disclosed. In embodiments, a method for bladder control is provided that comprises coupling an electrode to an afferent nerve that is related to the bladder. Applying a plurality of pulse burst stimulations via the electrode causes voiding of urine from the bladder. In embodiments, the plurality of pulse burst stimulations to the afferent nerve reduces external urethral sphincter (EUS) contractions and evokes bladder contractions to expel urine from the subject. In embodiments, the plurality of pulse burst stimulations to the afferent nerve evokes bladder contractions alone to expel urine from the subject. In embodiments, a system for bladder control is provided that comprises an electrode for applying a pulse burst stimulus to an afferent nerve or dermatome to reduce reflex contractions and a signal generator for generating the pulse burst stimulus.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
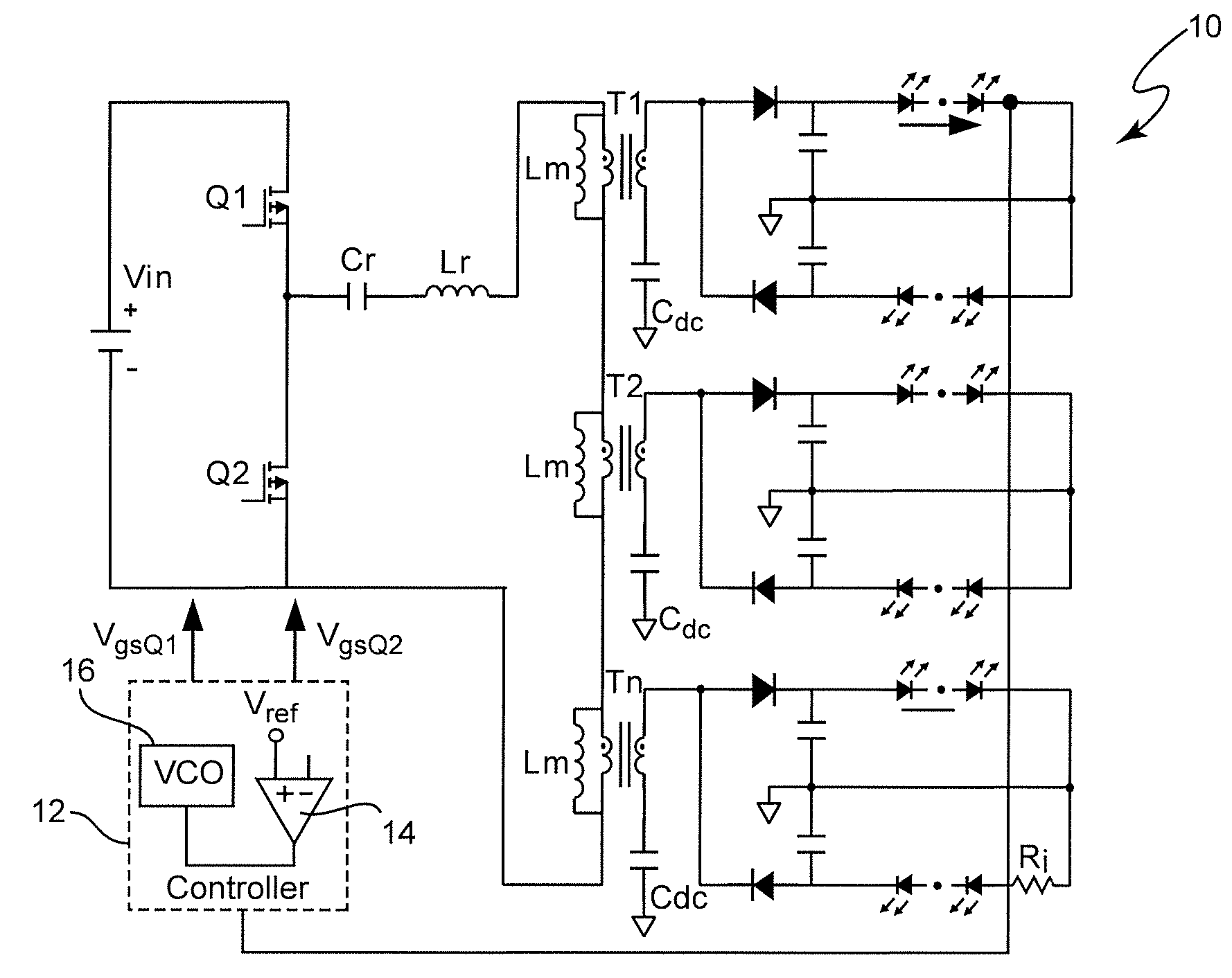
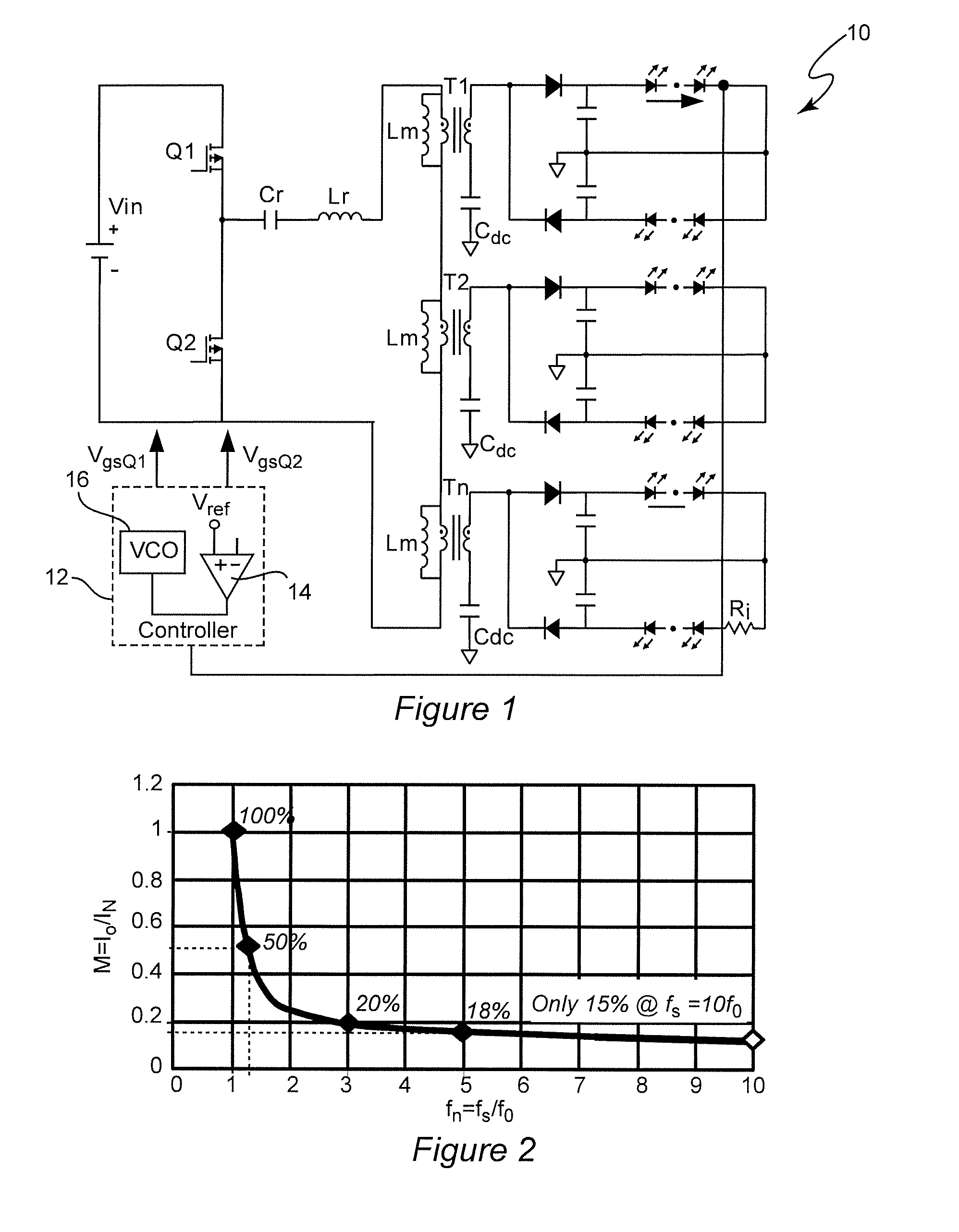
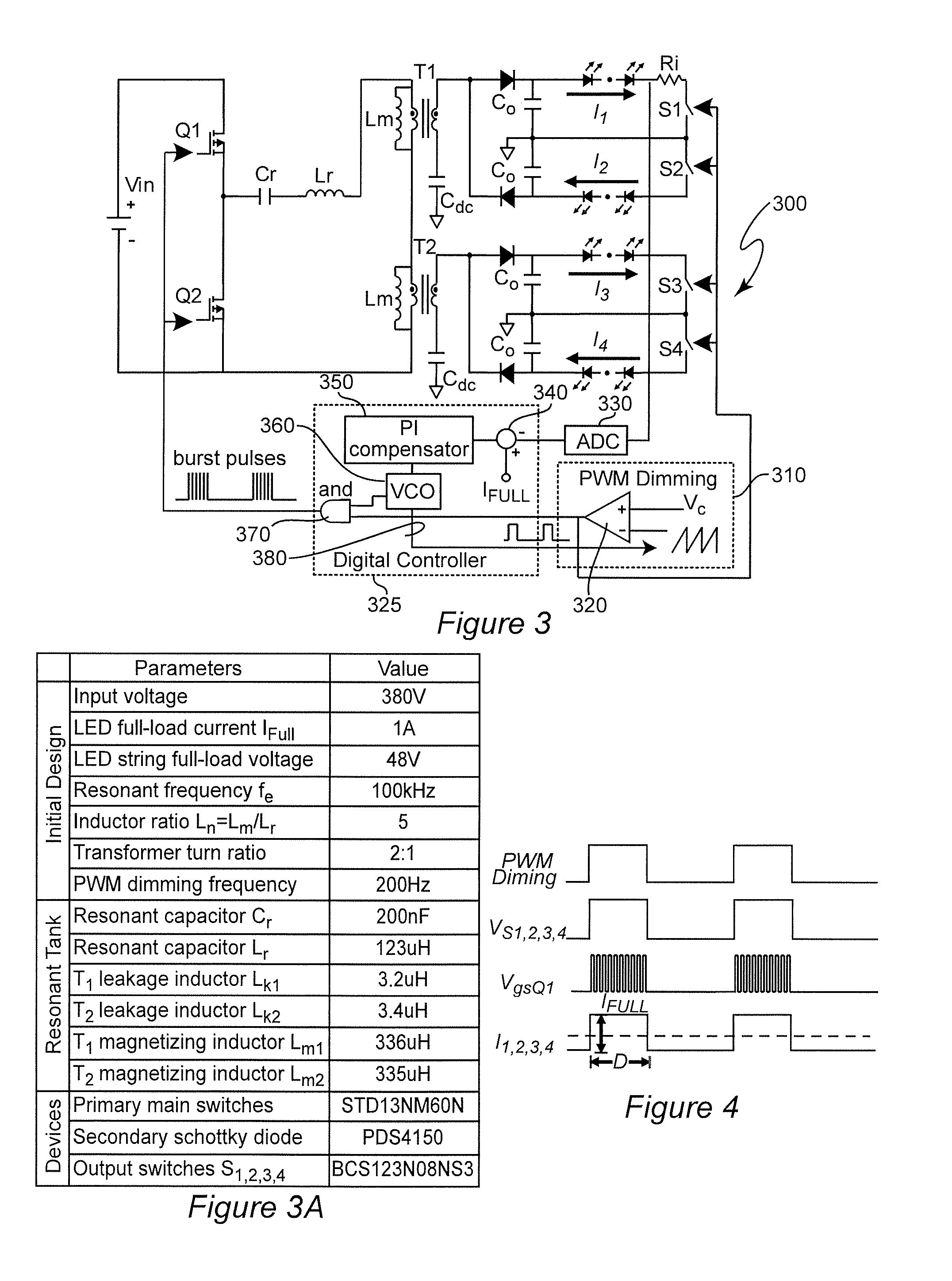
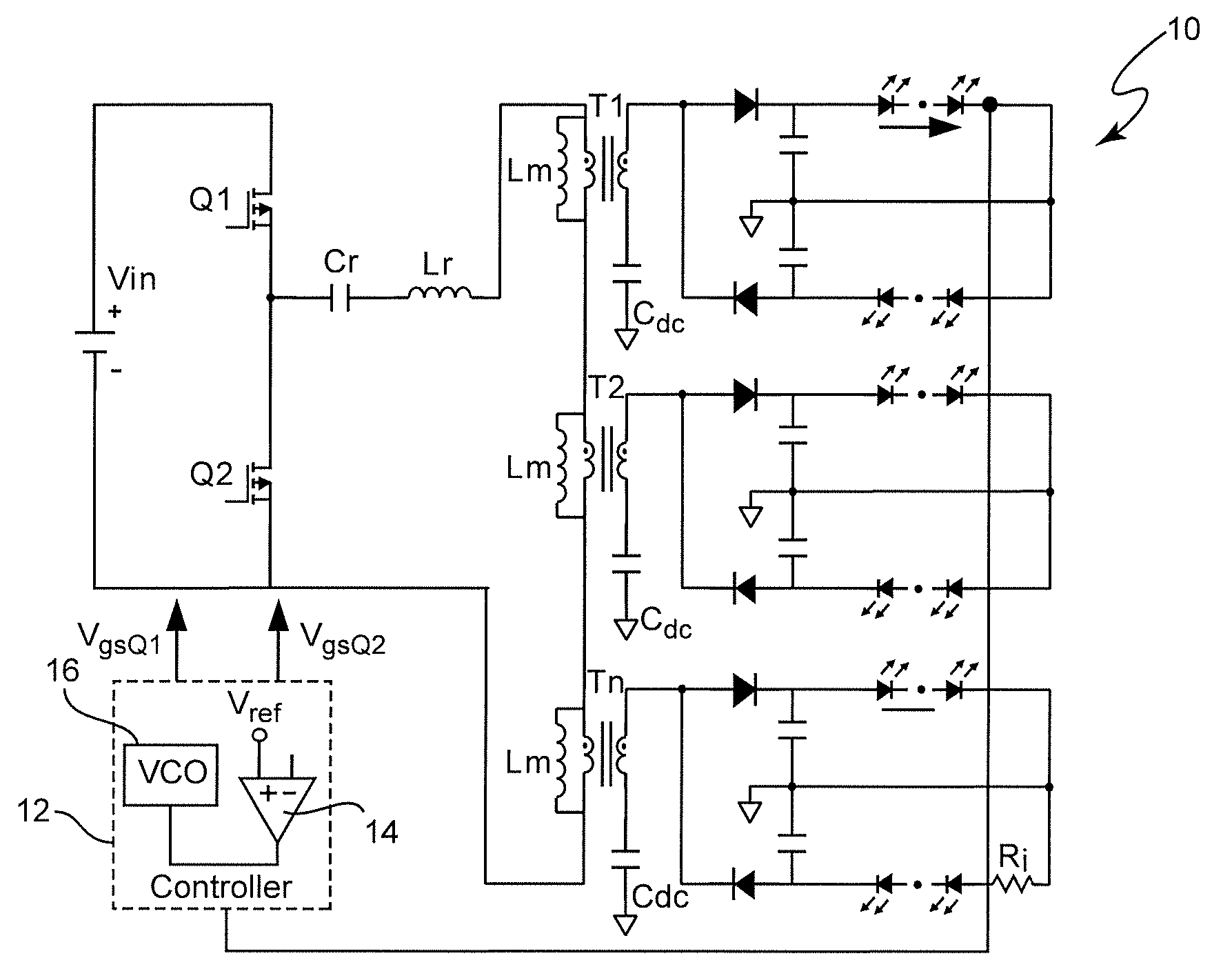
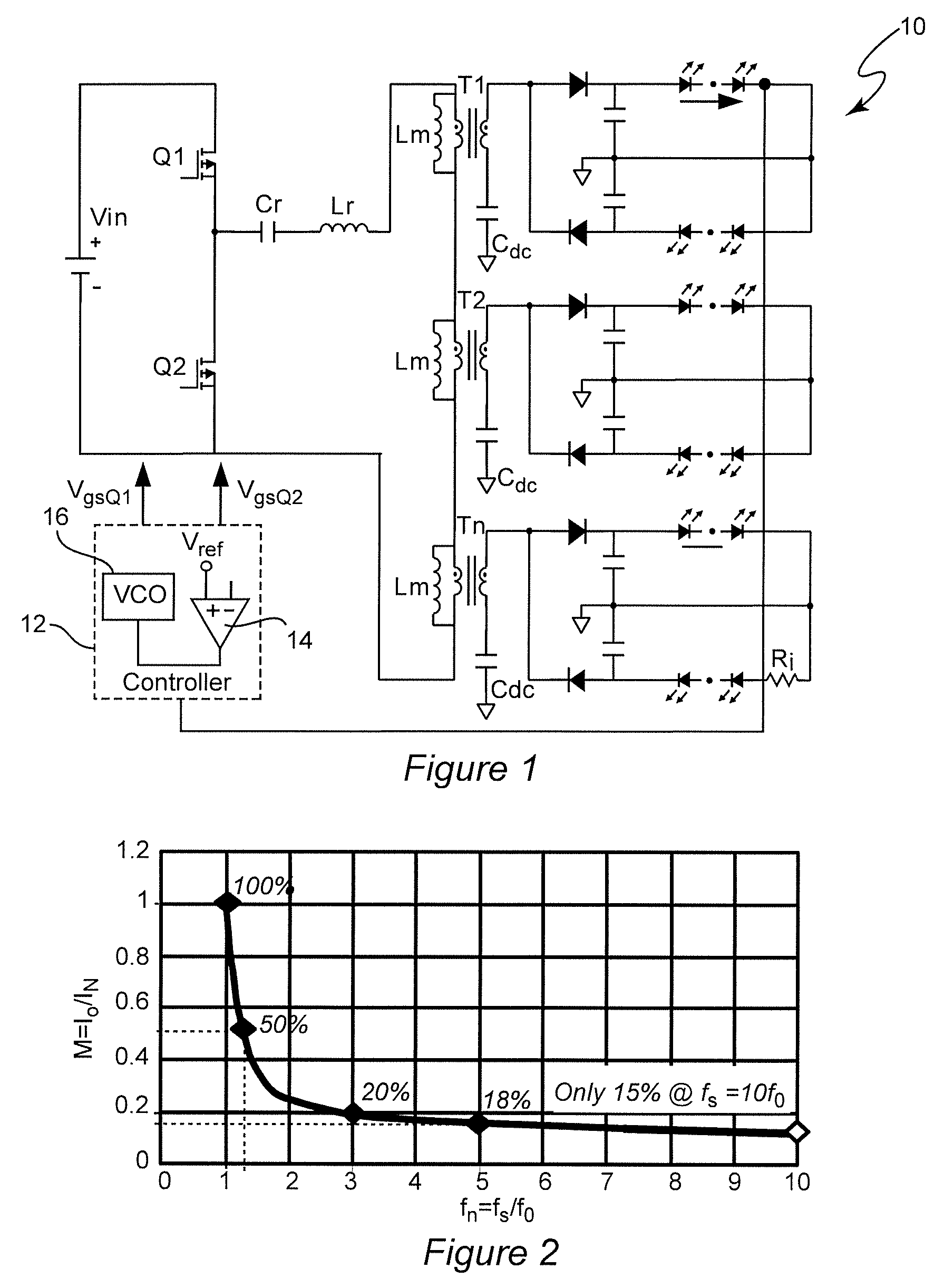
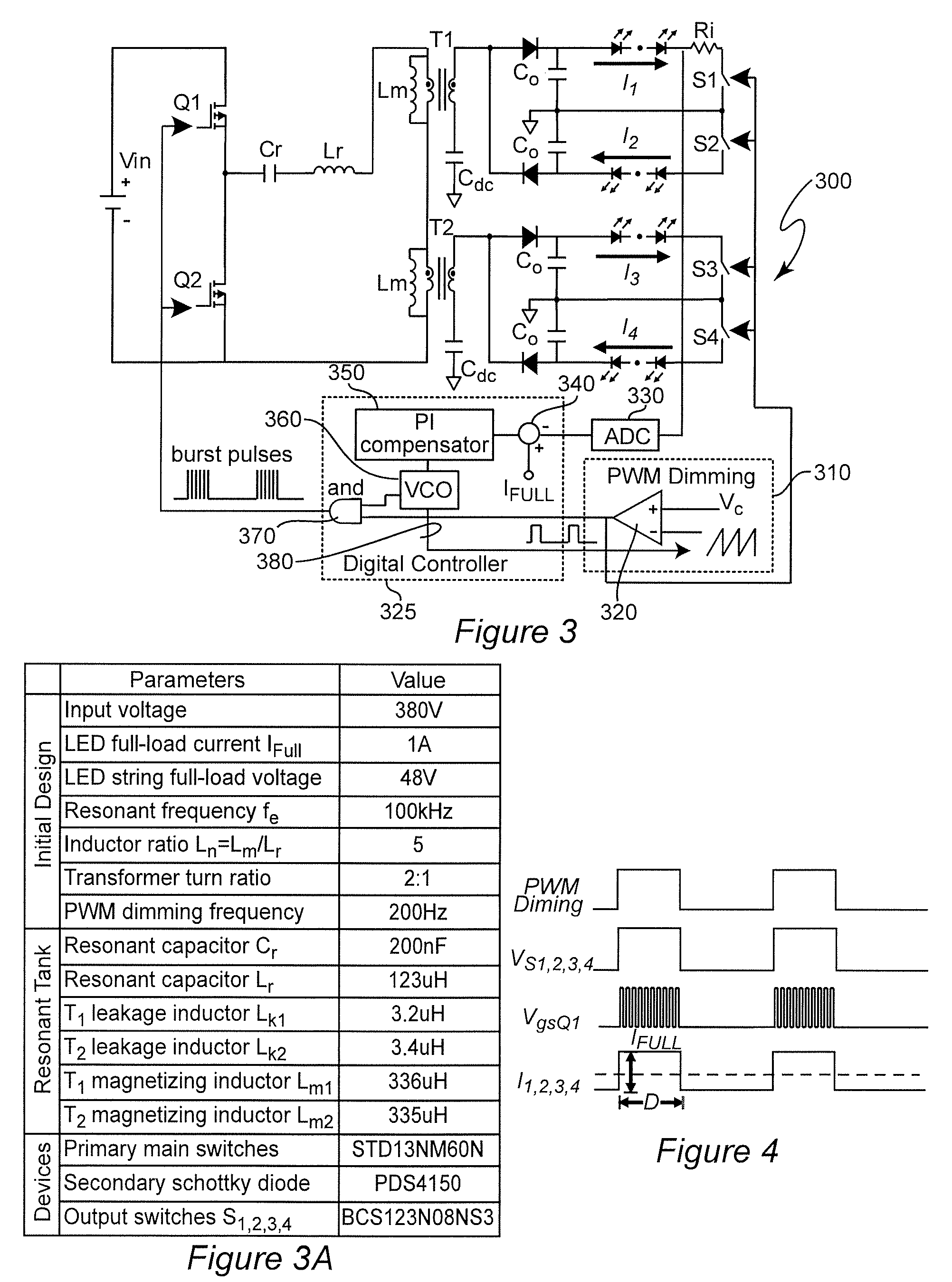
Optimal Trajectory Control for LLC Resonant Converter for LED PWM Dimming
ActiveUS20140312789A1Improve uniformityNot significantly susceptibleEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesResonant power convertersPulse-code modulation
Pulse width modulation is provided for controlling a resonant power converter, particularly for dimming of light emitting diode arrays without loss of efficiency. Dynamic oscillation due to the beginning of a pulse width modulated pulse burst is limited by shortening of the first and / or last pulse of a pulse bust such that the first pulse of a subsequent pulse burst close to or to connect with a full load steady-state voltage / current trajectory of the power converter. Pulse shortening made be made substantially exact to virtually eliminate dynamic oscillation but substantial reduction in dynamic oscillation is provided if inexact or even performed randomly.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Aluminium alloy twin-wire dipulse welding method and welding power supply thereof
InactiveCN101791733AImprove consistencyImprove dynamic response performanceArc welding apparatusSoft switchingWelding power supply
The invention discloses an aluminium alloy twin-wire dipulse welding method and a welding power supply thereof. The specific method is as follows: carrying out low frequency modulation on pulse wave shapes on the basis of high frequency to obtain periodically varied pulse bursts; and carrying out efficient and superior welding on aluminium alloy through the active phase match of two branches of the pulse bursts. The welding power supply comprises IGBT soft switching main circuits which are integrated into a whole, a DSP control circuit and a man-machine interactive system. The invention puts forward realizing dipulse aluminum alloy welding on a twin-wire welding machine for the first time, realizes all digital control, directly generates eight branches of PWM signals by utilizing a software module, controls the two main circuits, and reduces the control problems caused by communication; and simultaneously, the two main circuits are concentrated on the same welding machine so that the overall structure is much smaller than the master-slave mode welding machine, in addition methods such as instantaneous energy control and the like are adopted to realize the fine control of dipulse.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
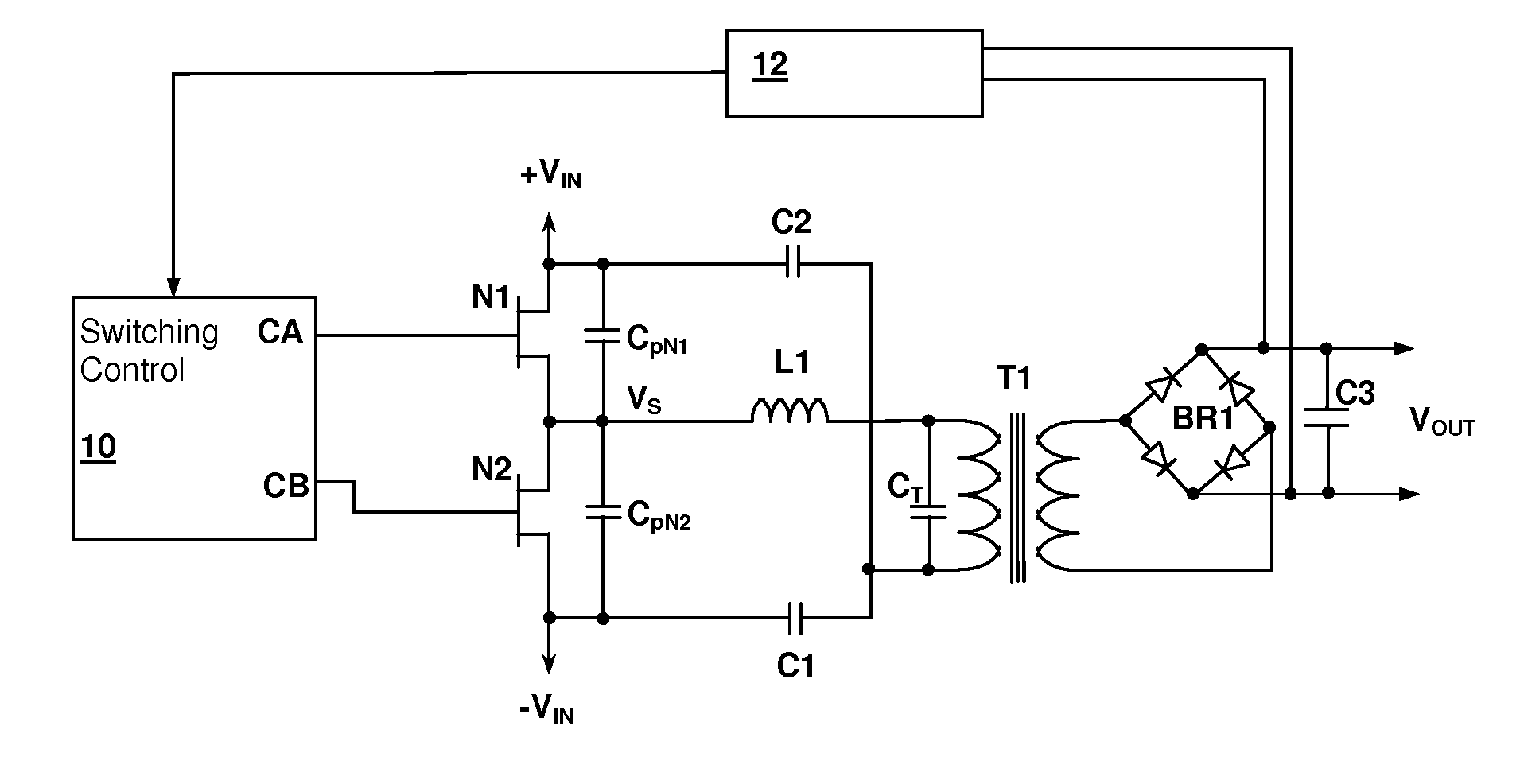
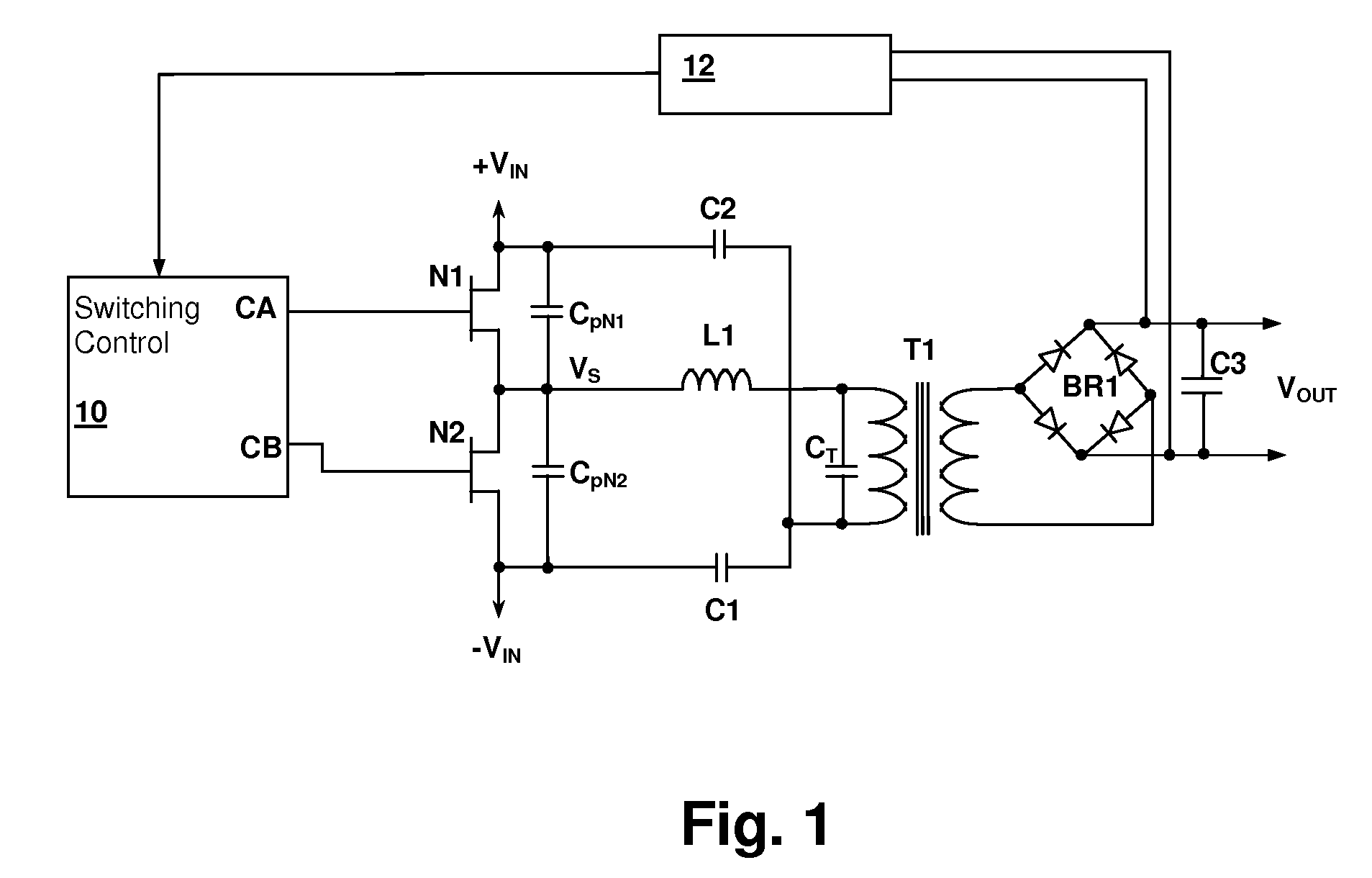
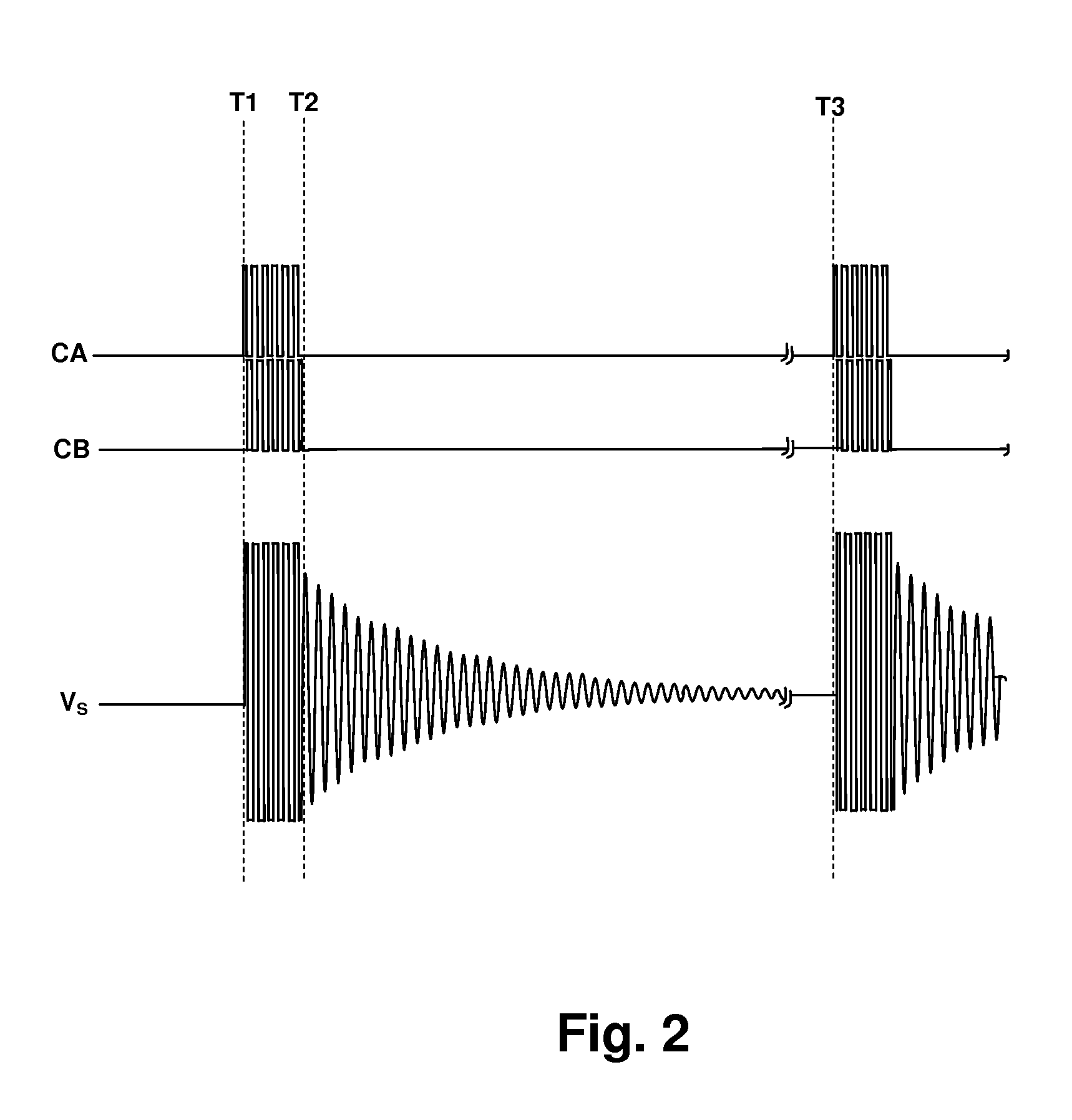
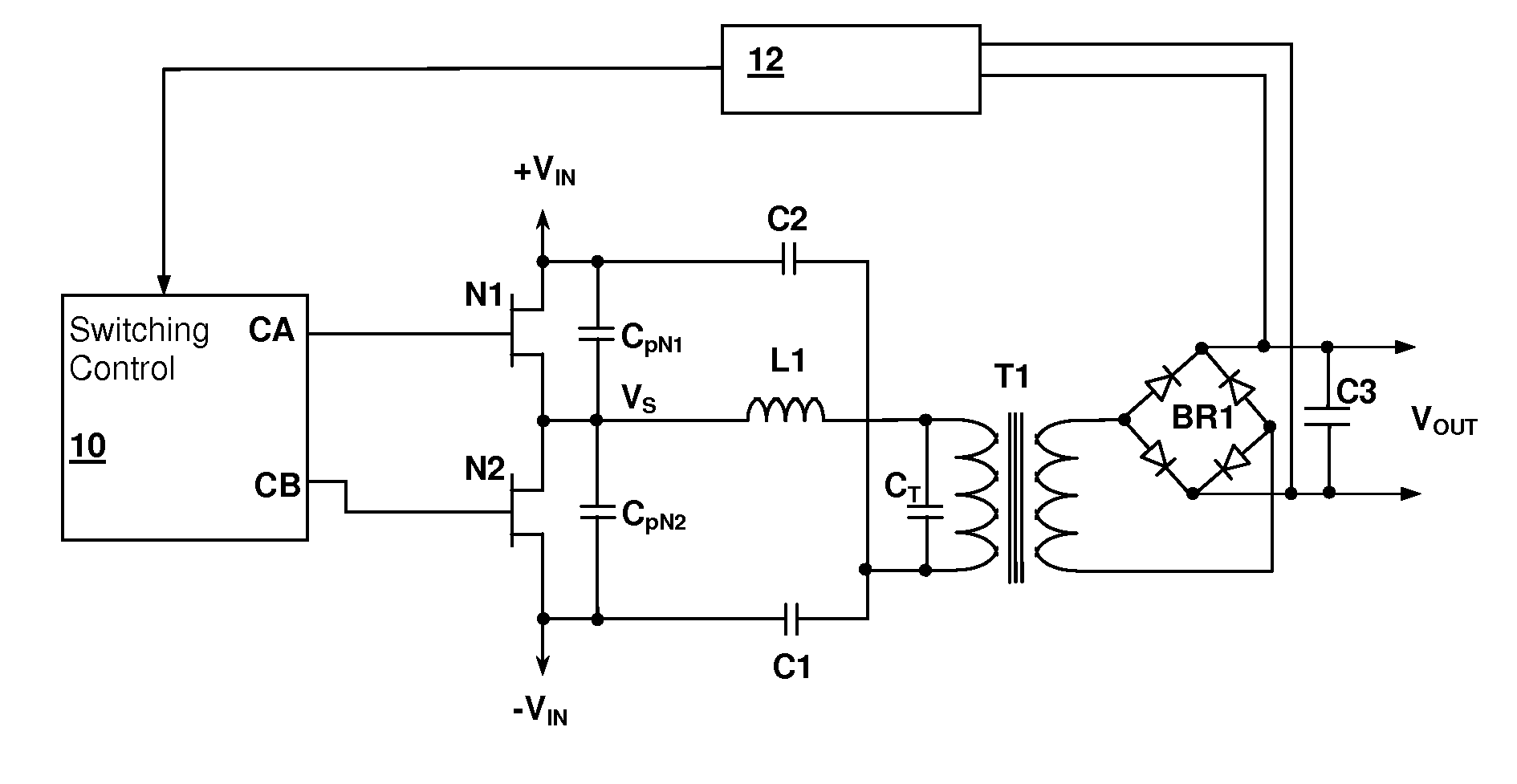
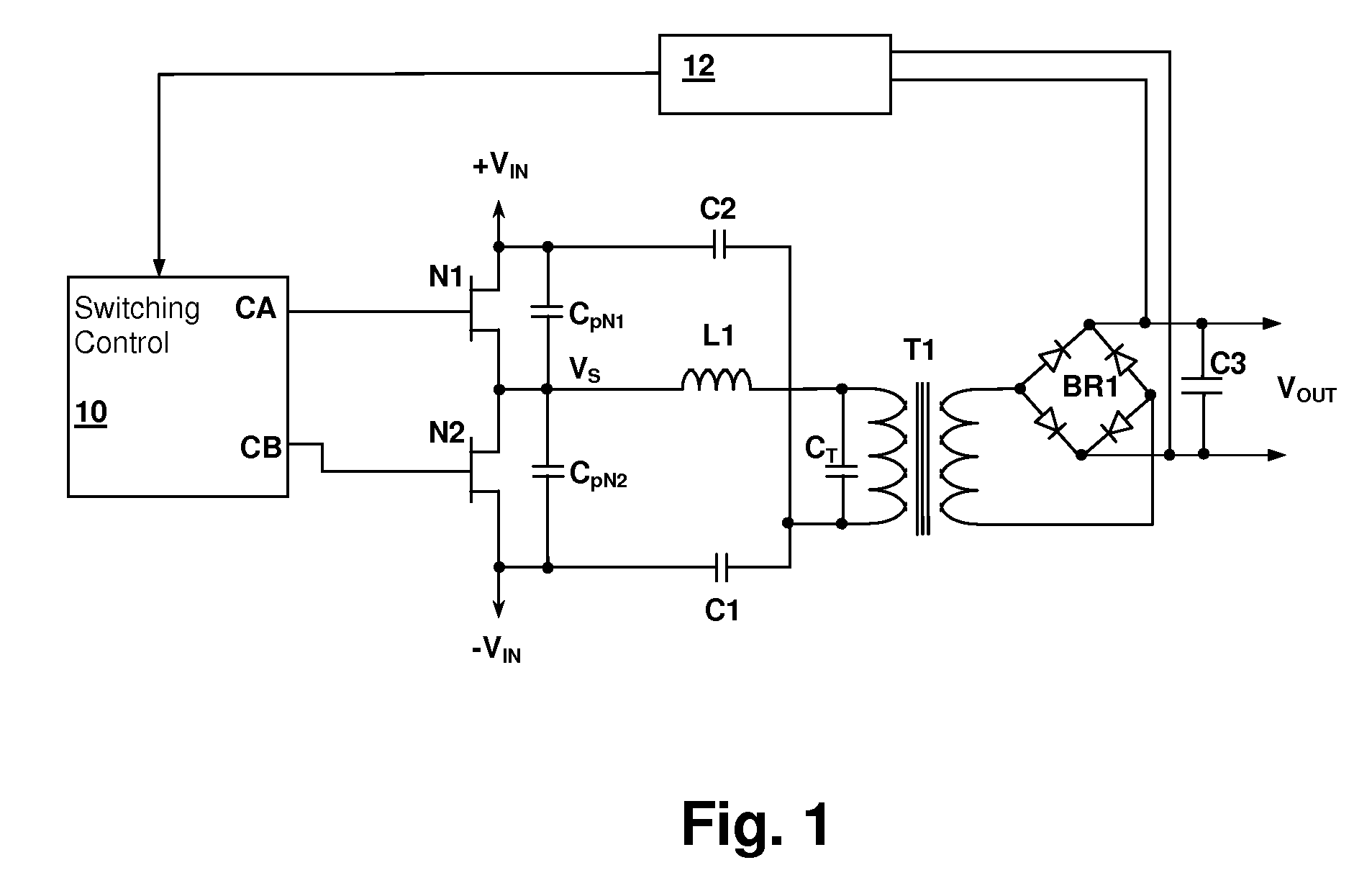
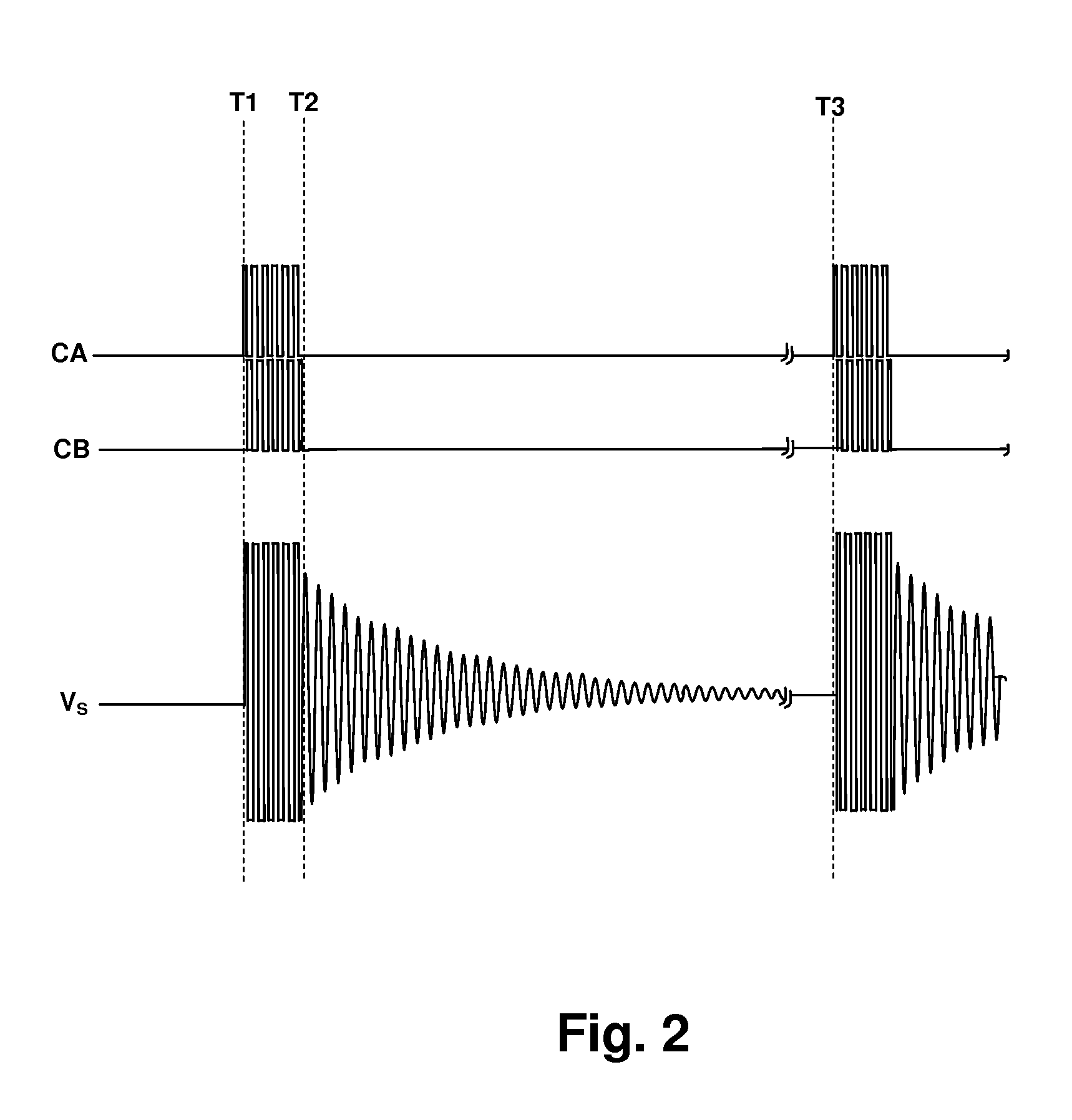
Resonant switching power converter with burst mode transition shaping
InactiveUS8014176B2Reduce vibrationReduce stressTransformersEfficient power electronics conversionTransformerTransverter
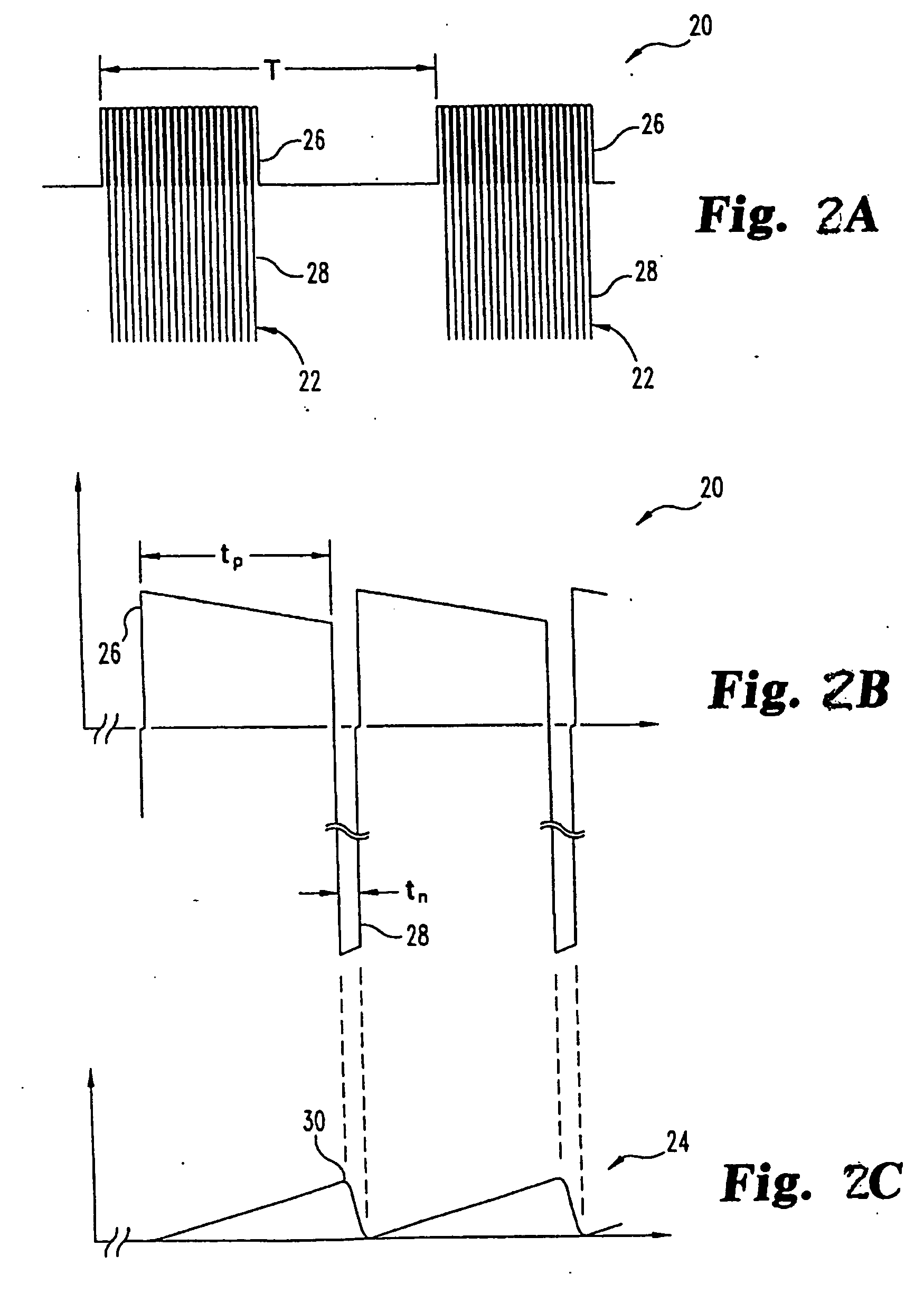
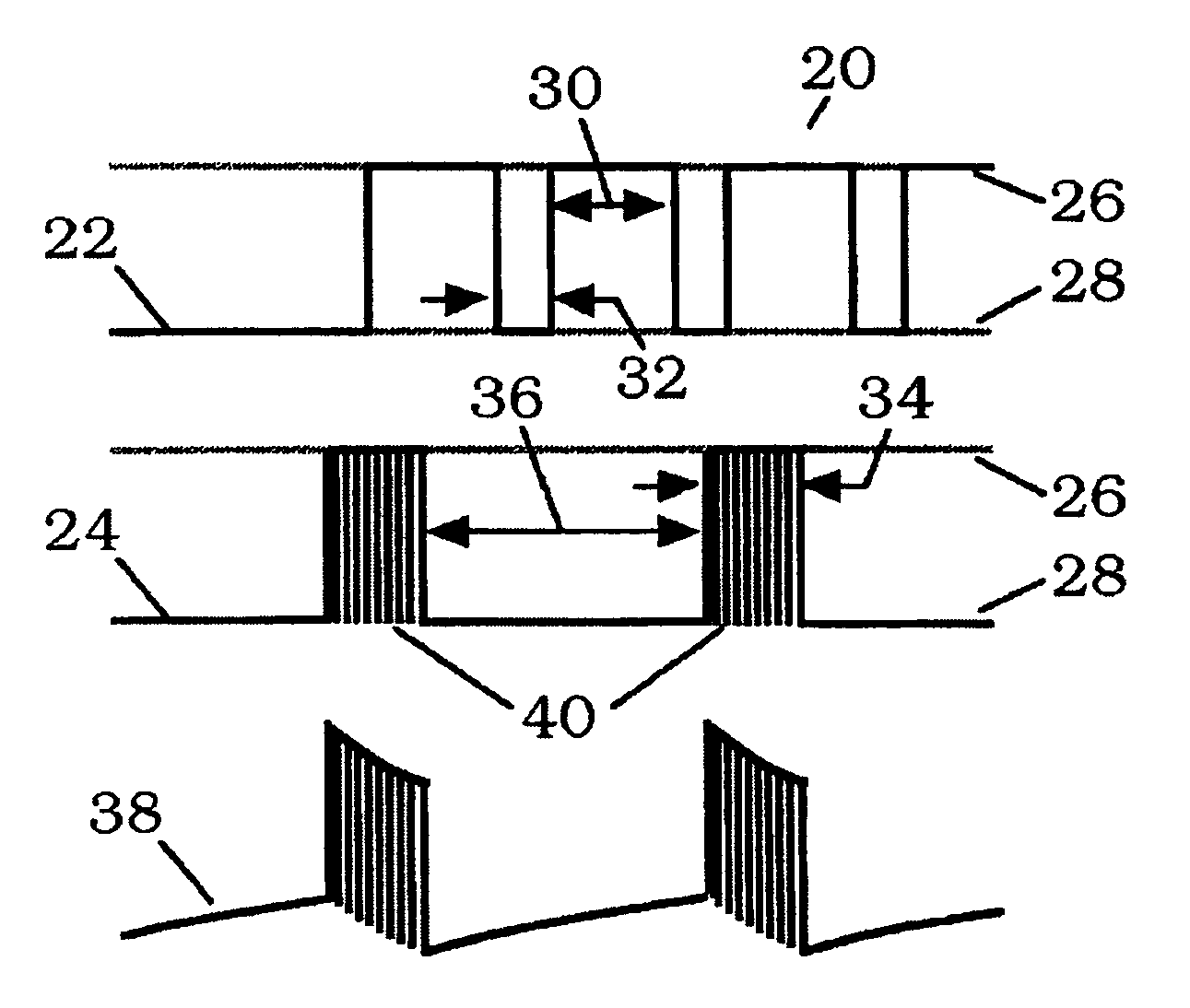
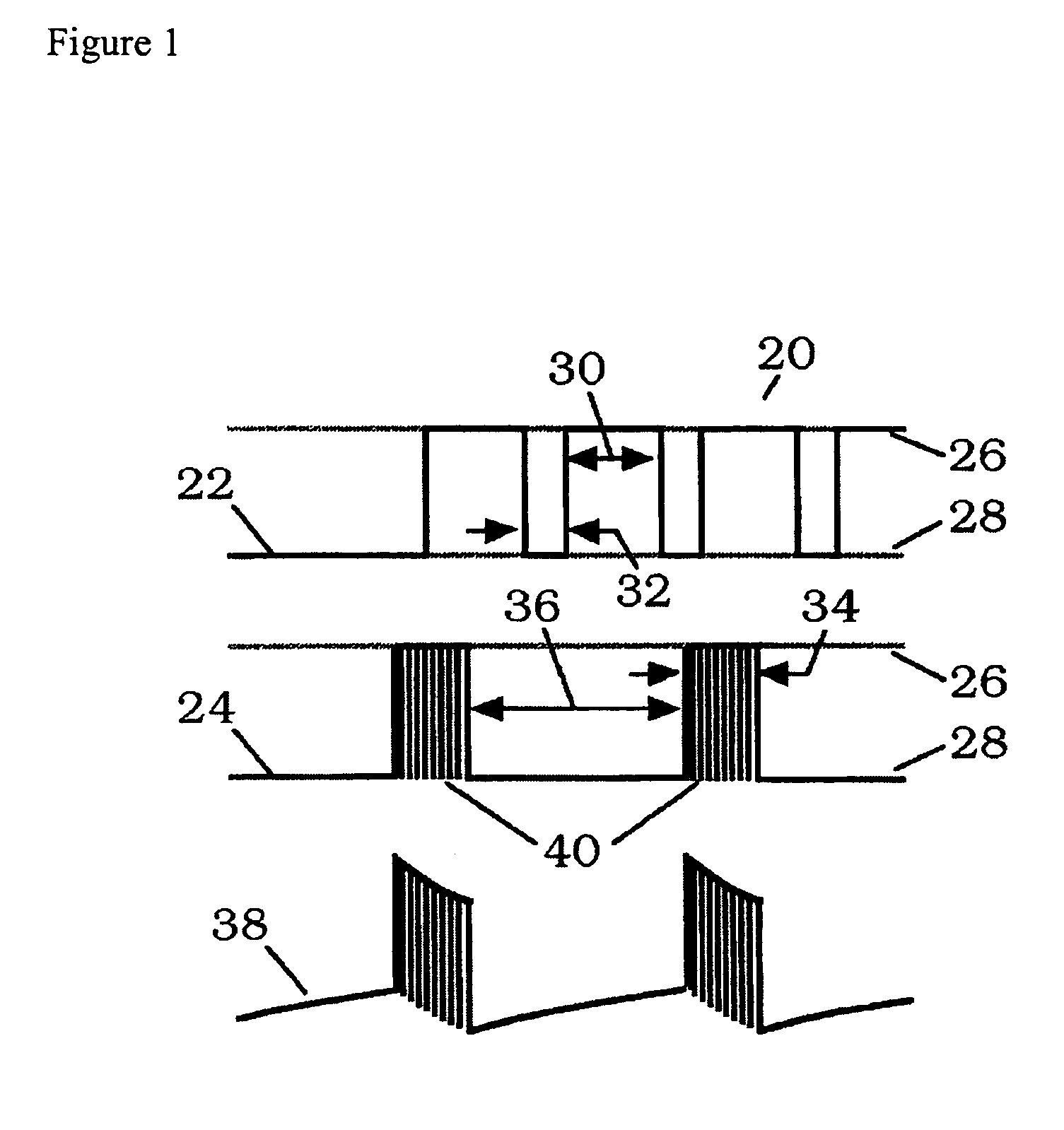
A resonant switching power converter having burst mode transitioning operates during low or zero load conditions with reduced audible noise and component stresses, while improving efficiency. Pulse bursts are generated with a beginning and / or ending pulse duration that differs from mid-burst pulse durations, in order to reduce an amplitude of transients otherwise generated at the beginning and / or end of the bursts. Alternatively, the spacing between the pulses at the beginning and / or end of the bursts may differ from the spacing between the pulses in the middle of the bursts to reduce the transient(s). A number of pulses at the beginning and / or end of the burst can also be set with gradually varying durations, to further reduce component stress and audible vibration in a transformer that couples the resonant tank to the output of the converter.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
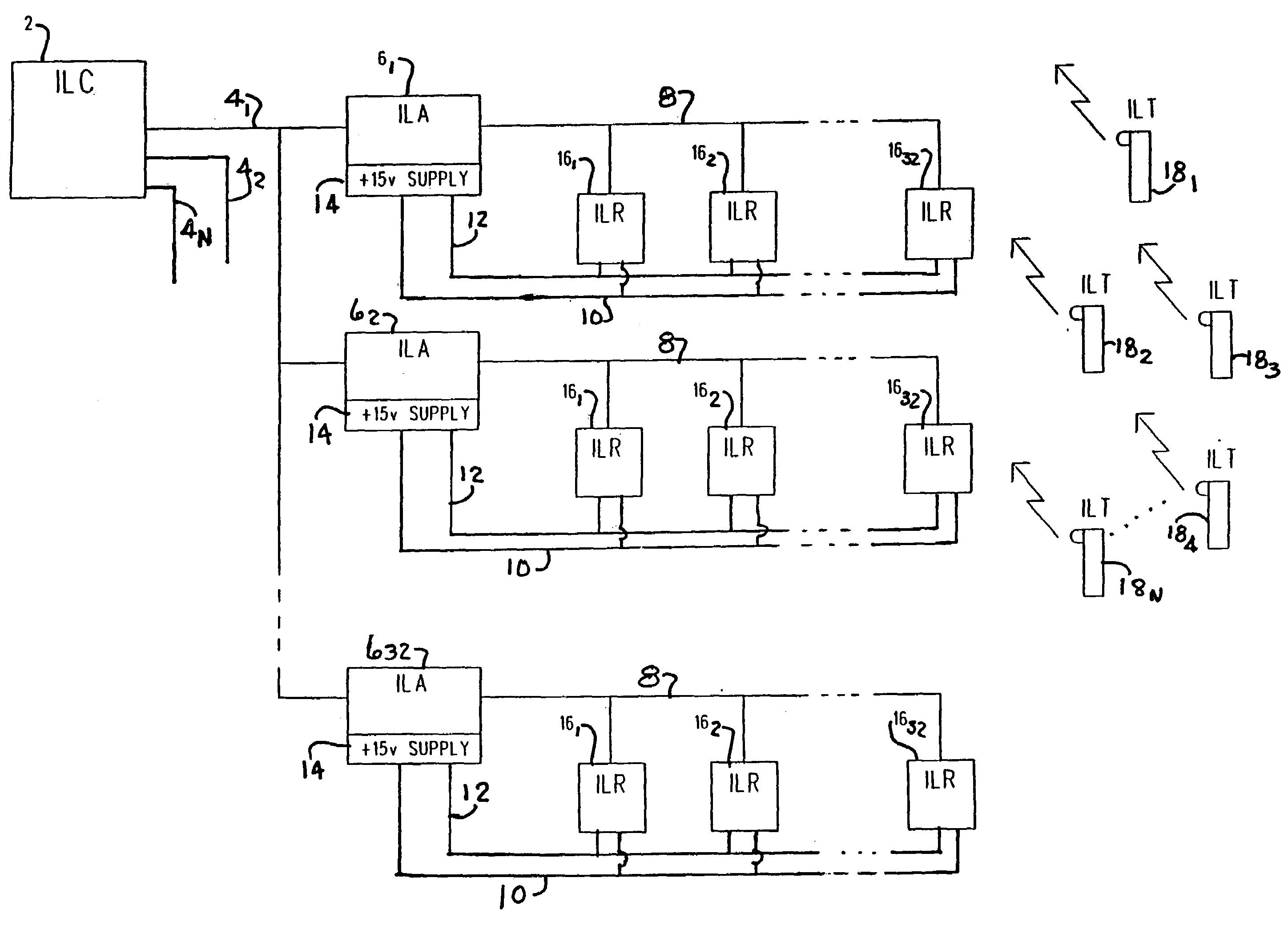
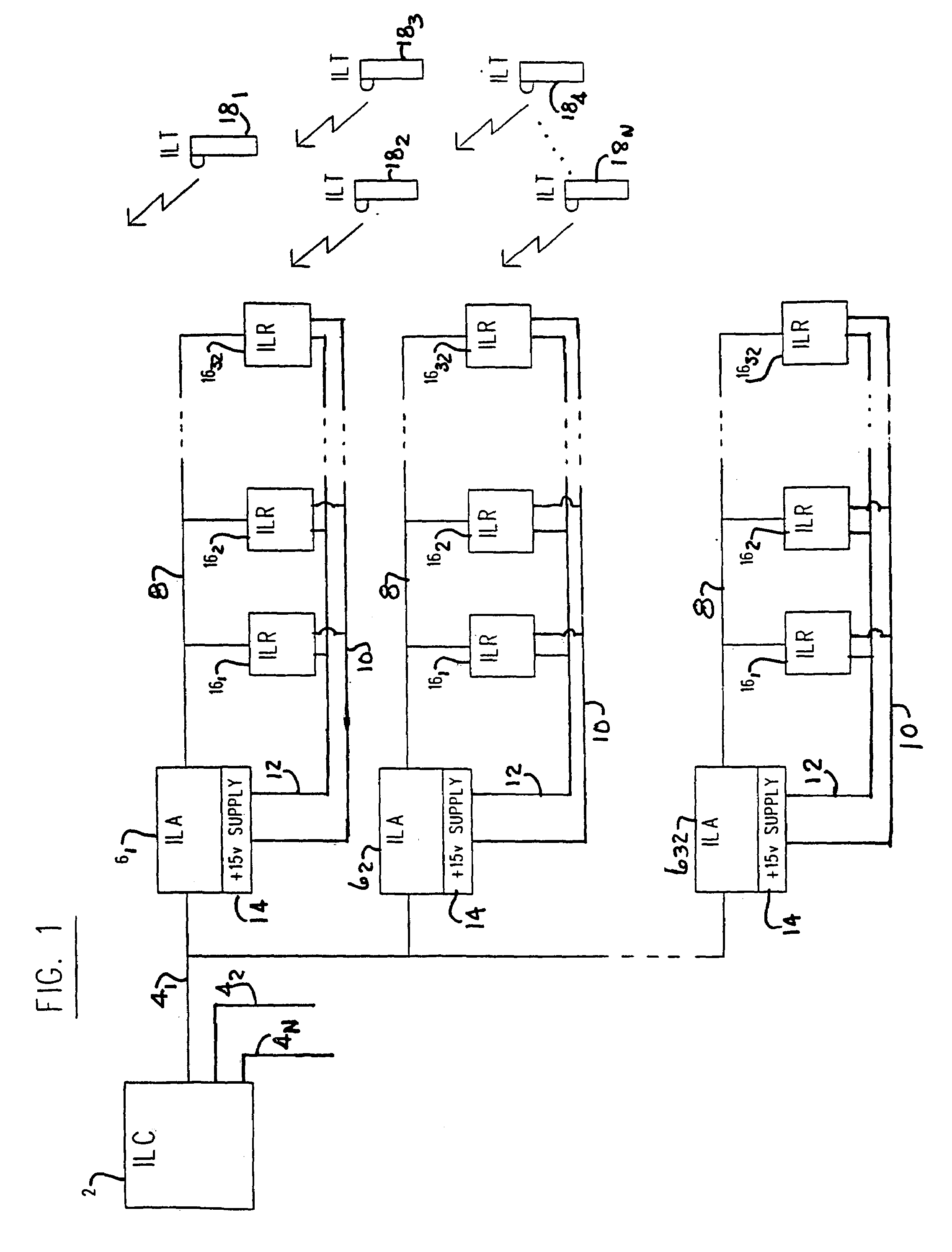
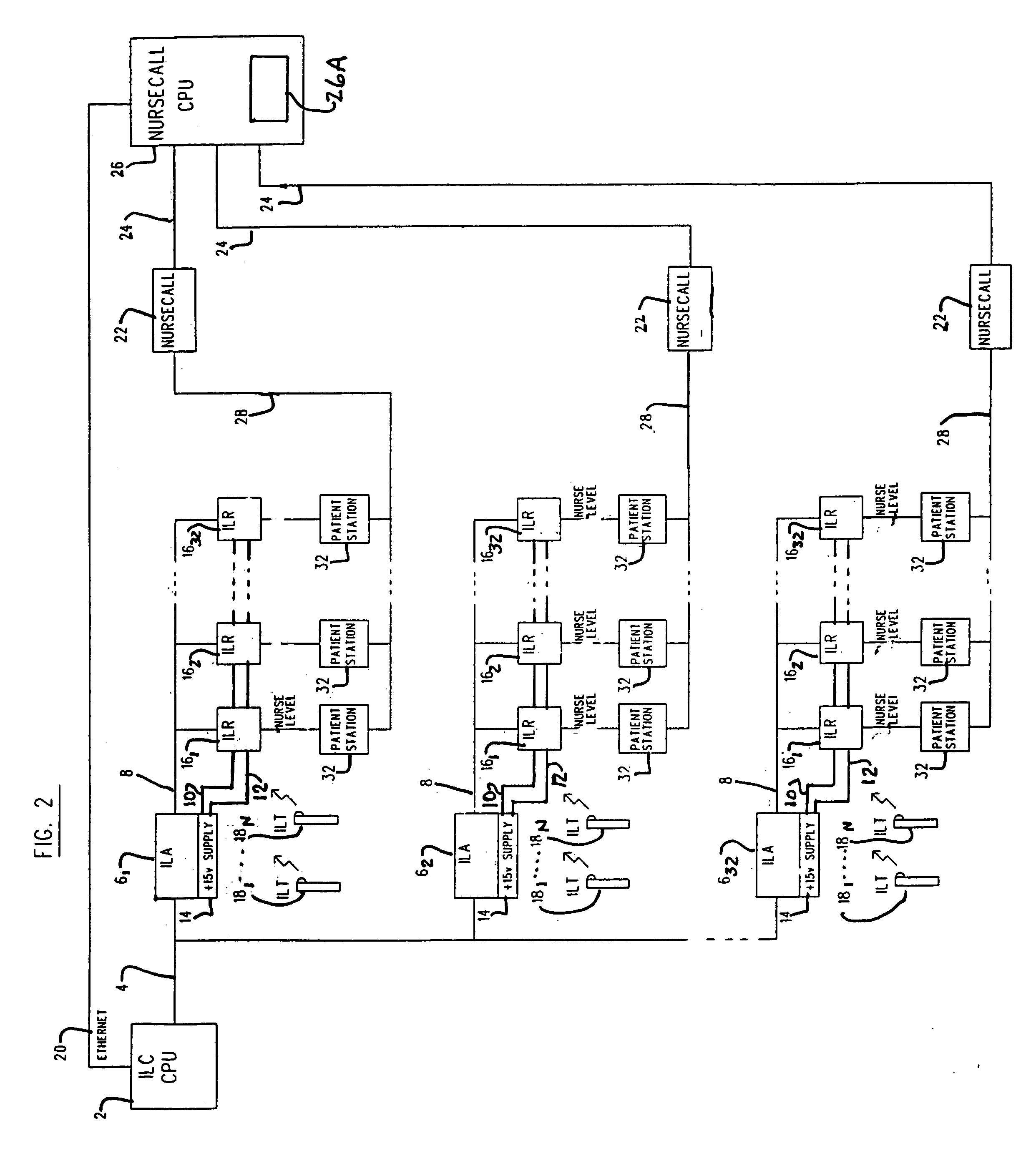
Intelligent locator system
InactiveUS7061396B1Avoid synchronizationFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelephonic communicationChecksumMonitoring system
A locating and monitoring system includes transmitters worn by a person, animal, or equipment to transmit an unique identification code while moving about a facility. The code is transmitted by pulse bursts at diverse times during predetermined time intervals to prevent synchronization with resident signals in the facility. Receivers in the walls or ceilings of the facility respond to the infrared radiation of the pulse bursts and validate the identification code by a checksum of the code through a comparison with a checksum transmitted with the code. The receivers deliver validated codes to arbitrators and receive back signals indicative of the level of an individual assigned to a class wearing the transmitters. Signals from the receivers are received by arbitrators which forward the codes to a CPU for recording start and stop events indicative of movement by transmitters into and out of the reception range of the various receivers.
Owner:DWYER PRECISION PRODS
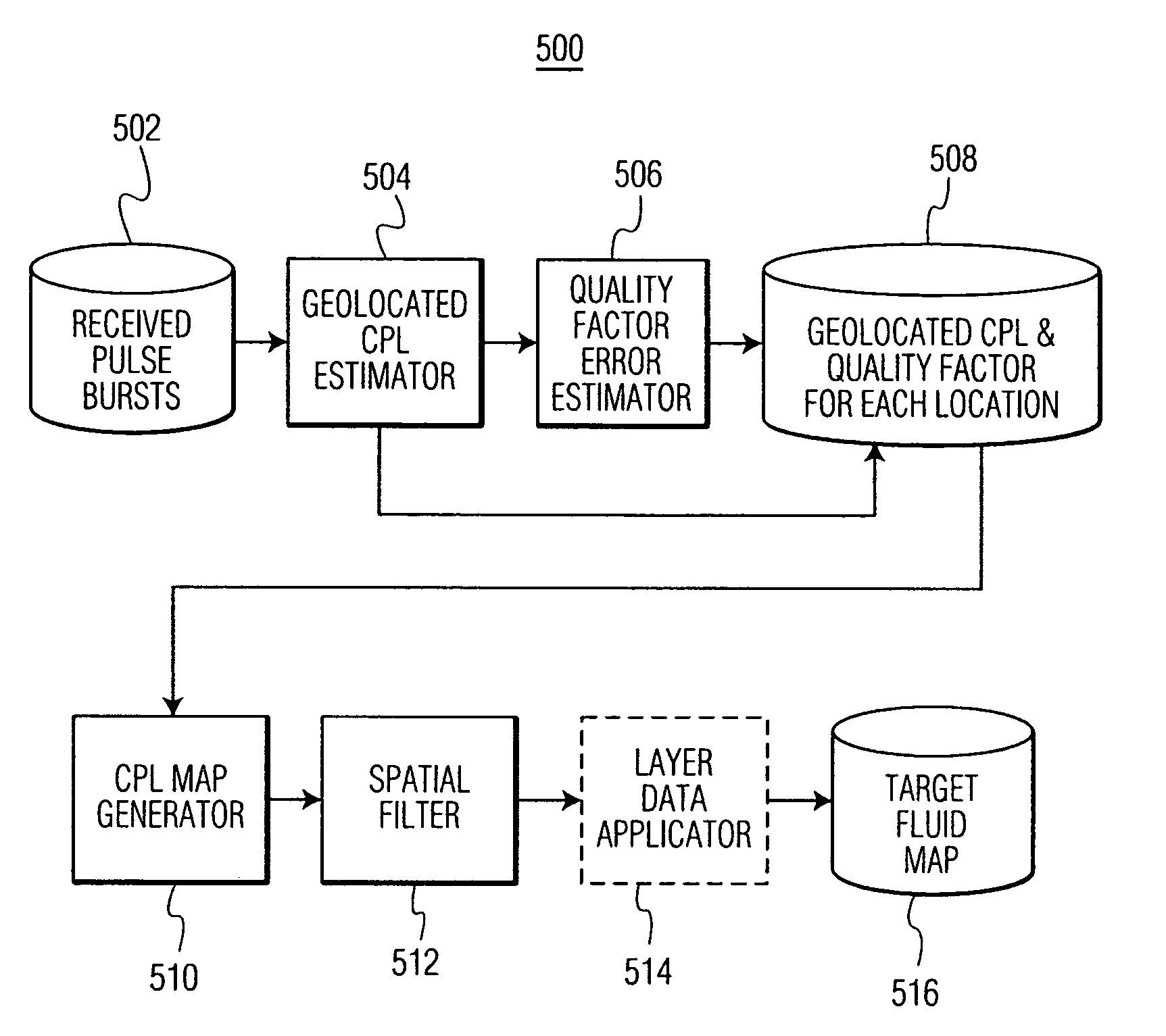
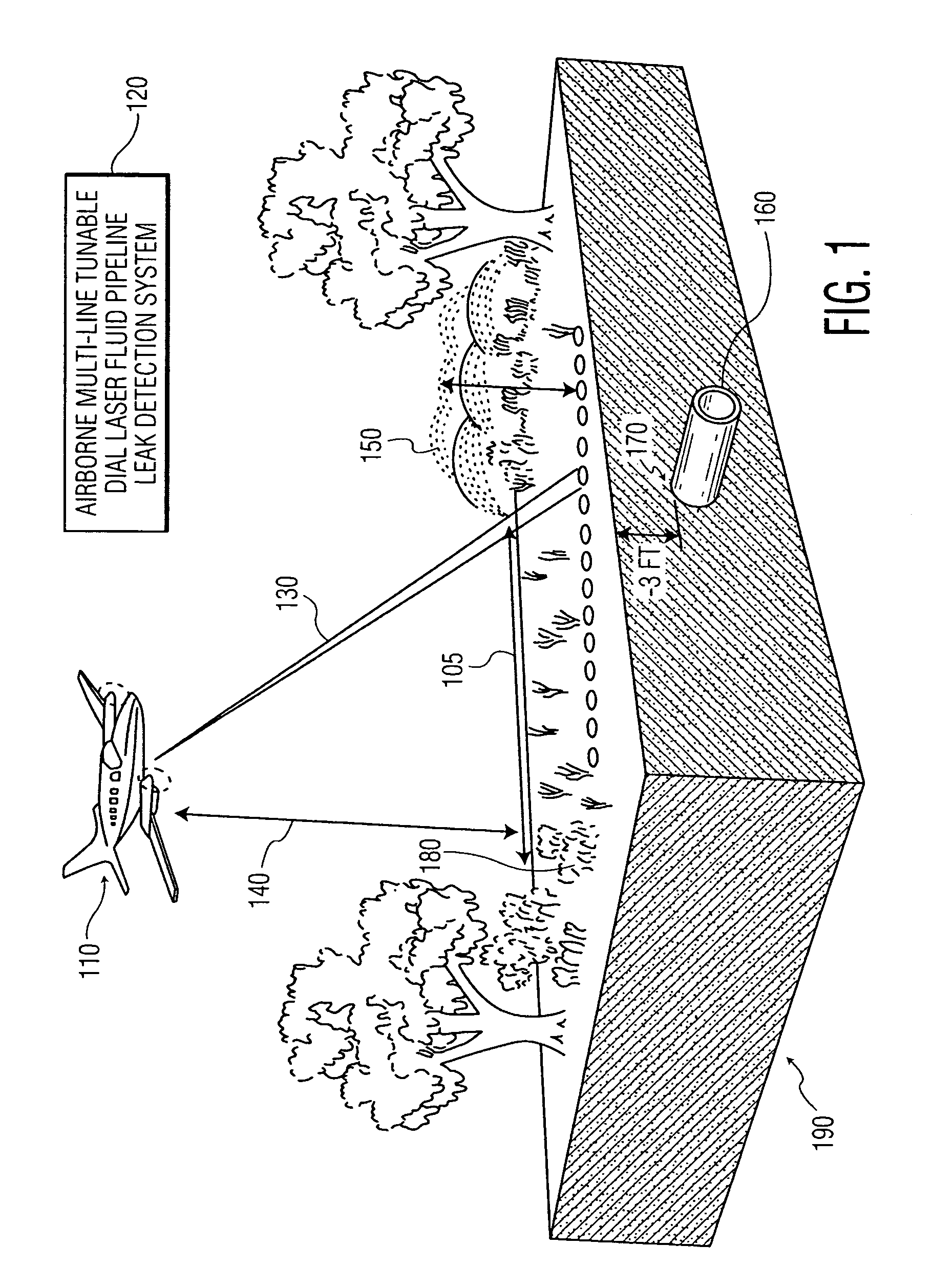
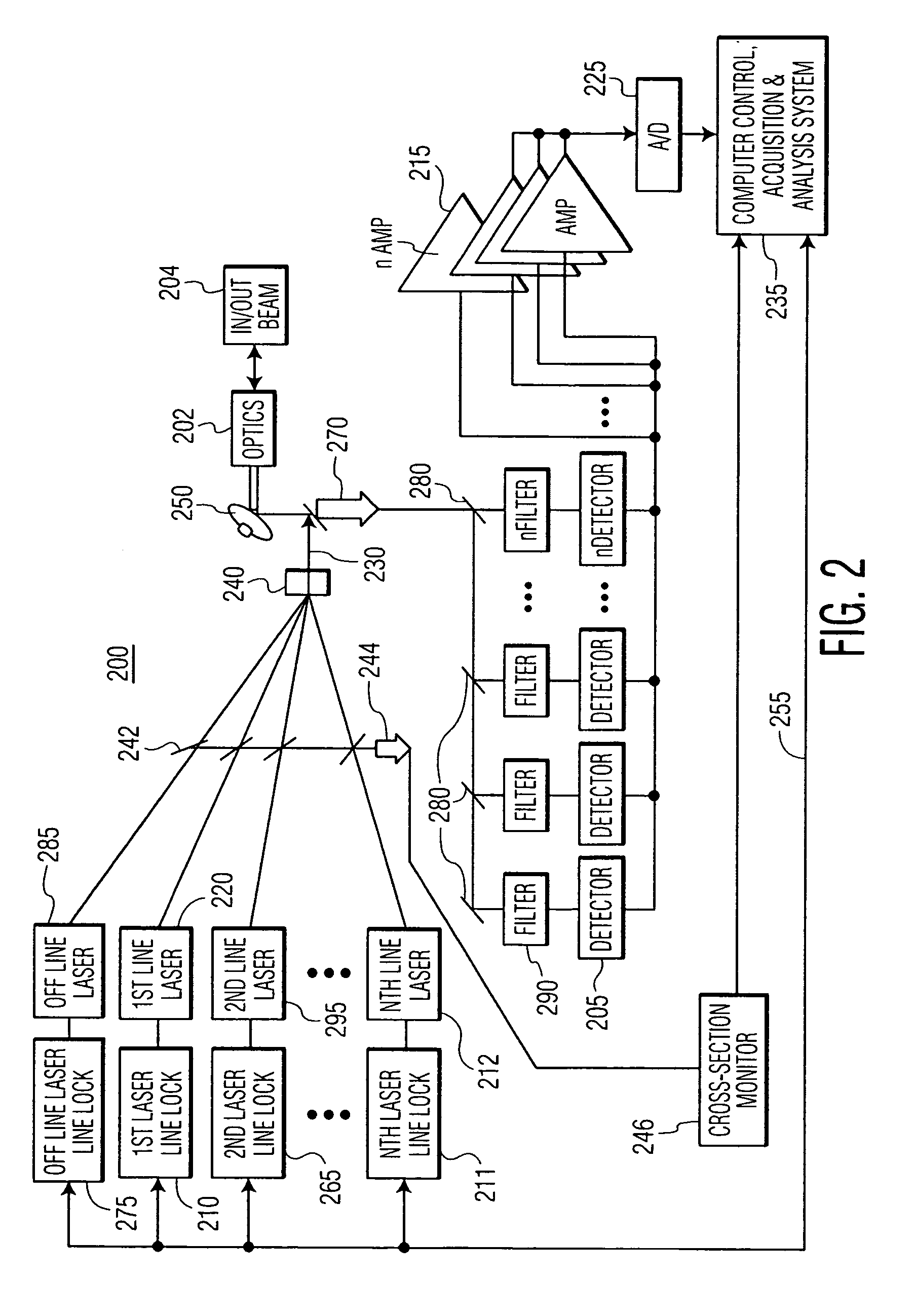
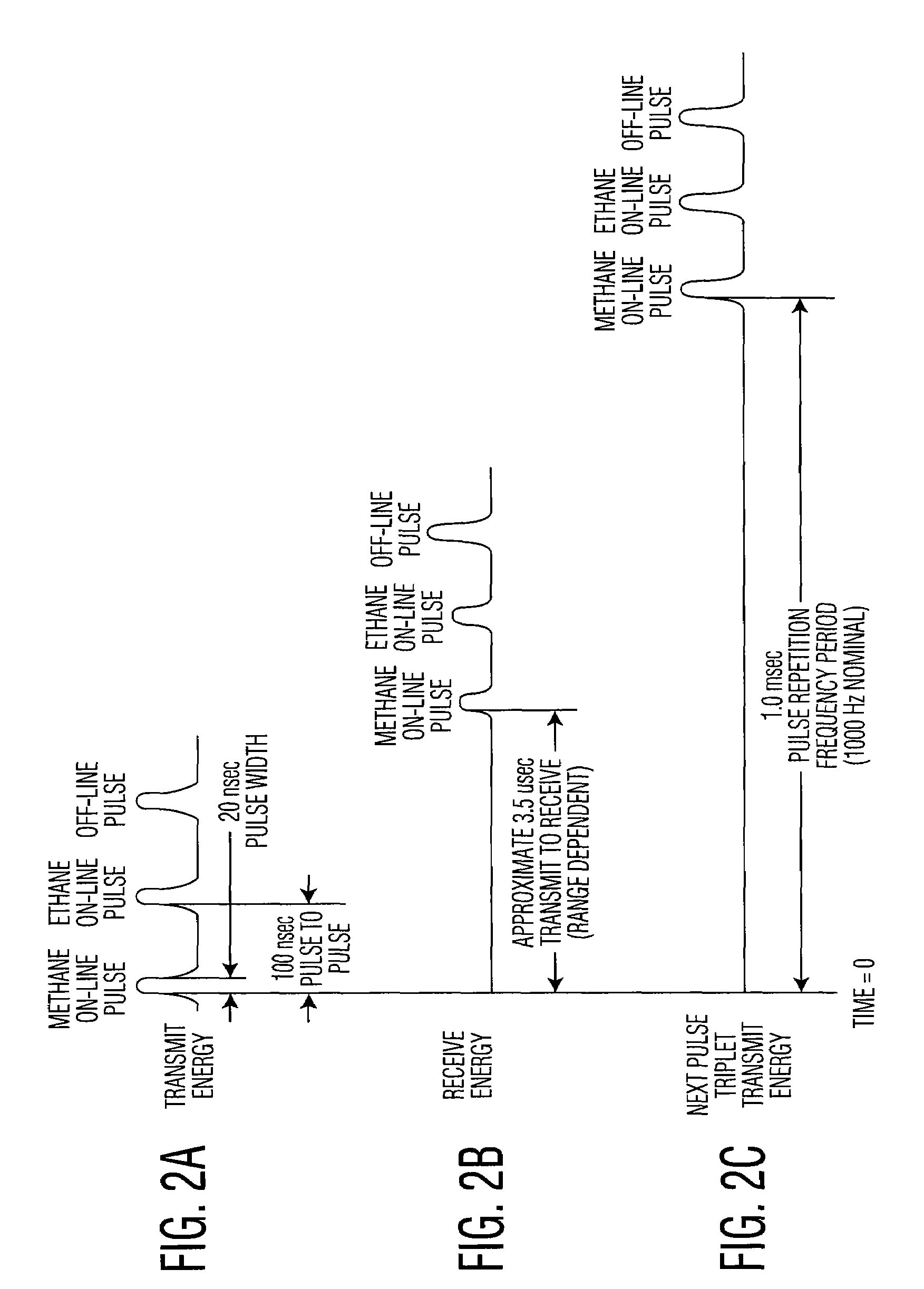
System and method for multi-target fluid concentration detection and mapping
Methods and systems for obtaining a target fluid map of a survey area using a differential absorption LIDAR (DIAL) system are provided. Pulse bursts are transmitted toward the survey area, where each pulse burst includes an off-line pulse and at least one on-line pulse. Pulse bursts, each being associated with a measurement point, are received from the survey area. A concentration path length (CPL) corresponding to a respective on-line pulse, a spatial location associated with the CPL, and an error associated with the CPL are determined for each measurement point. The CPL for each measurement point is arranged within the survey area to form the target fluid map.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
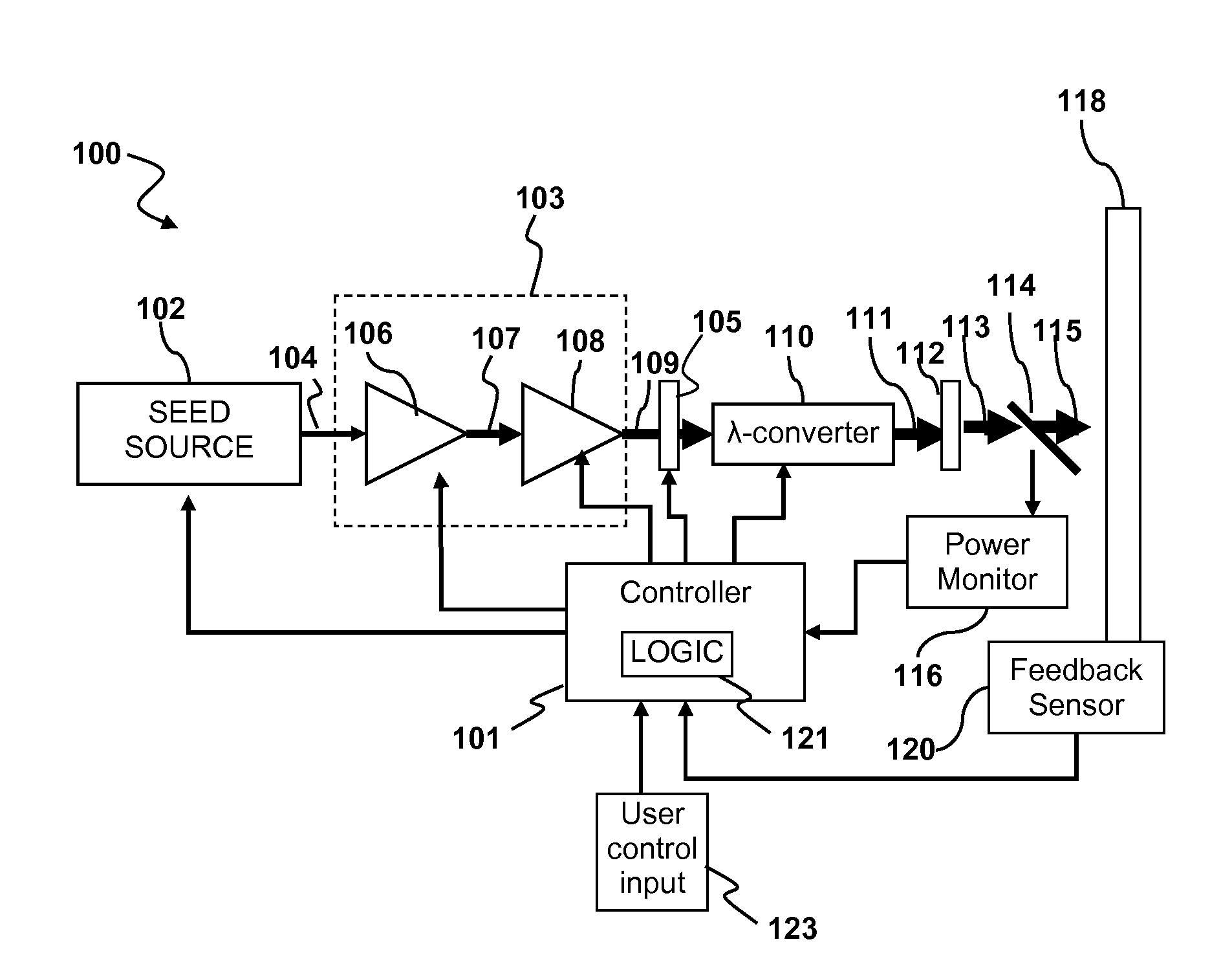
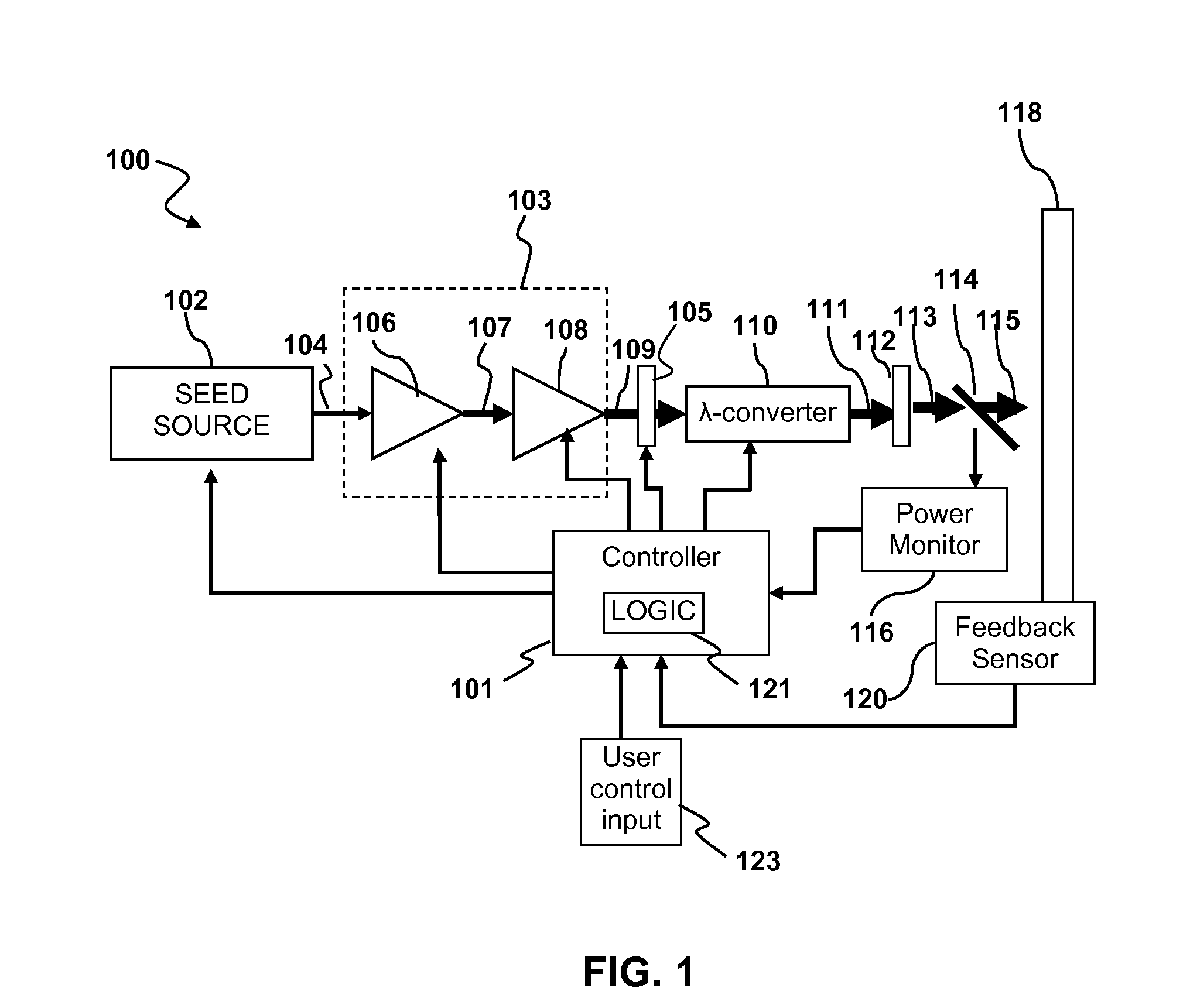
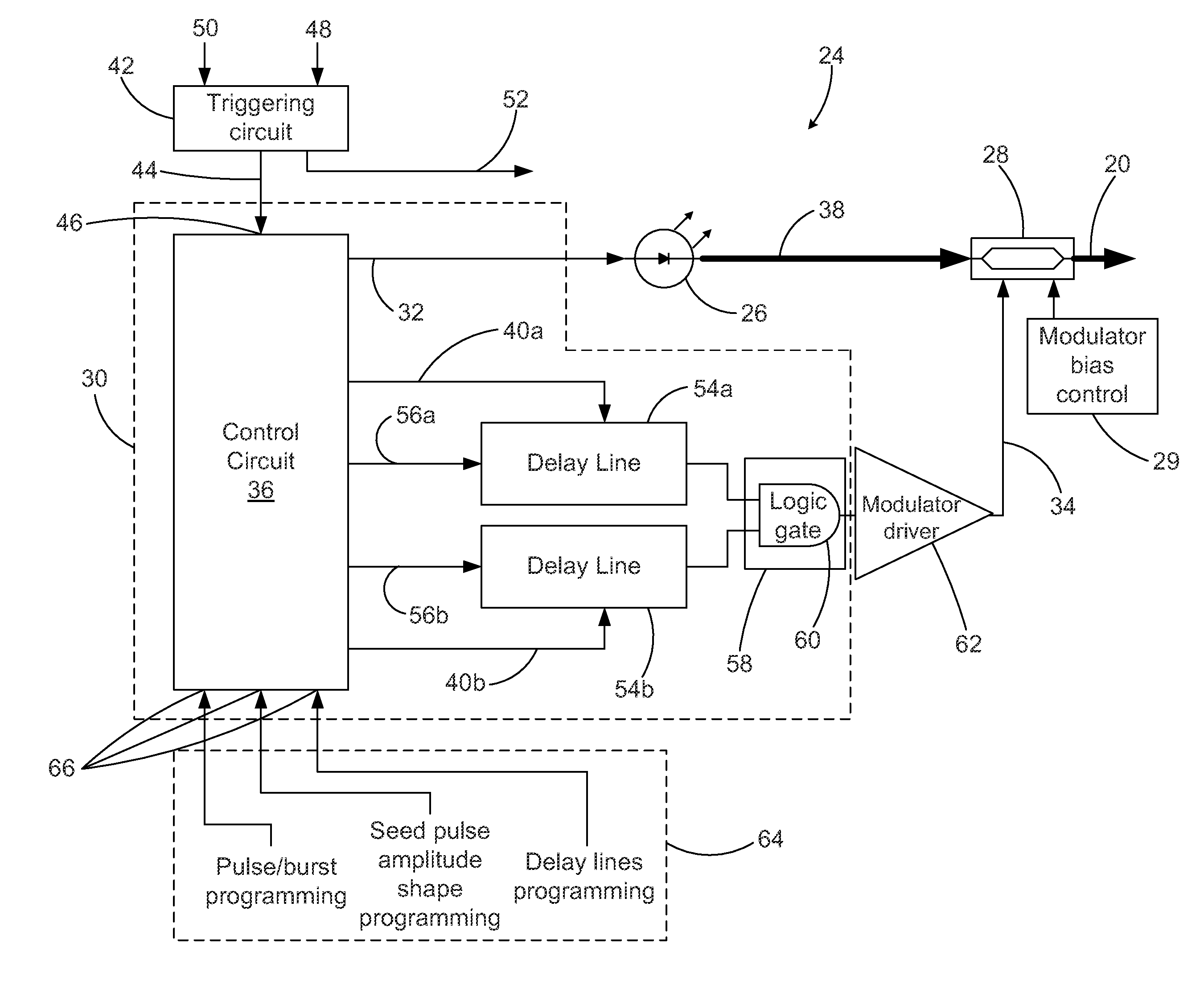
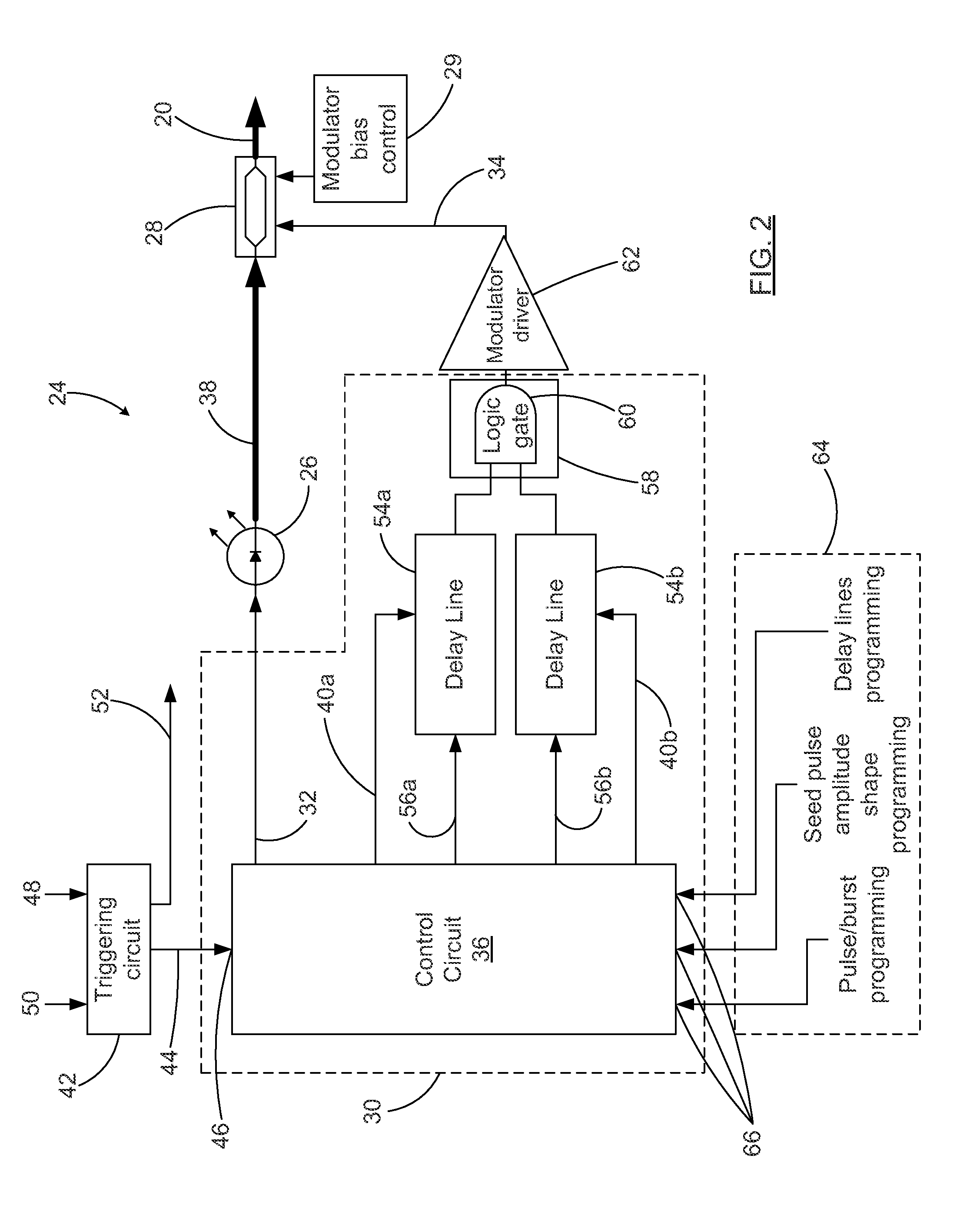
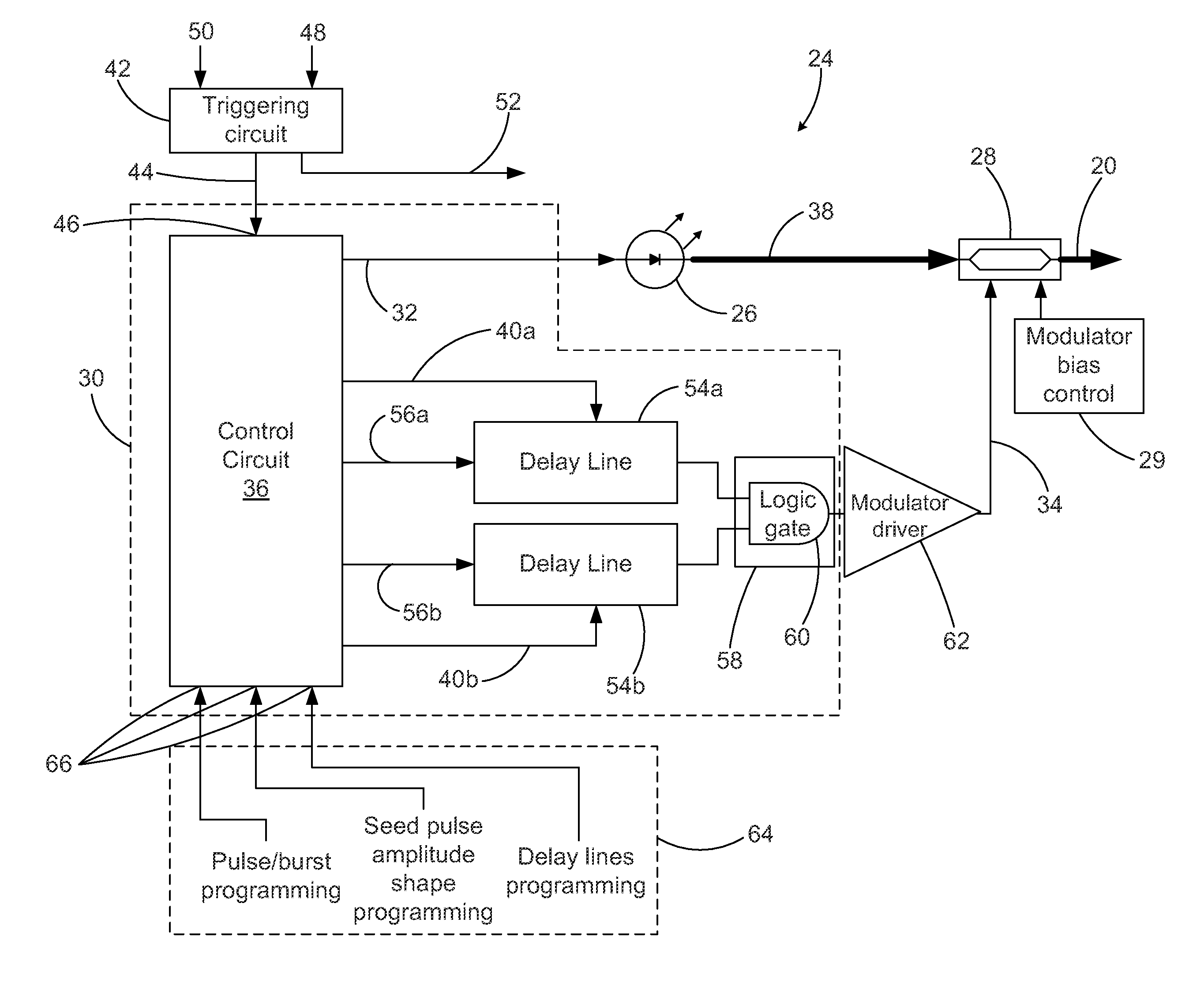
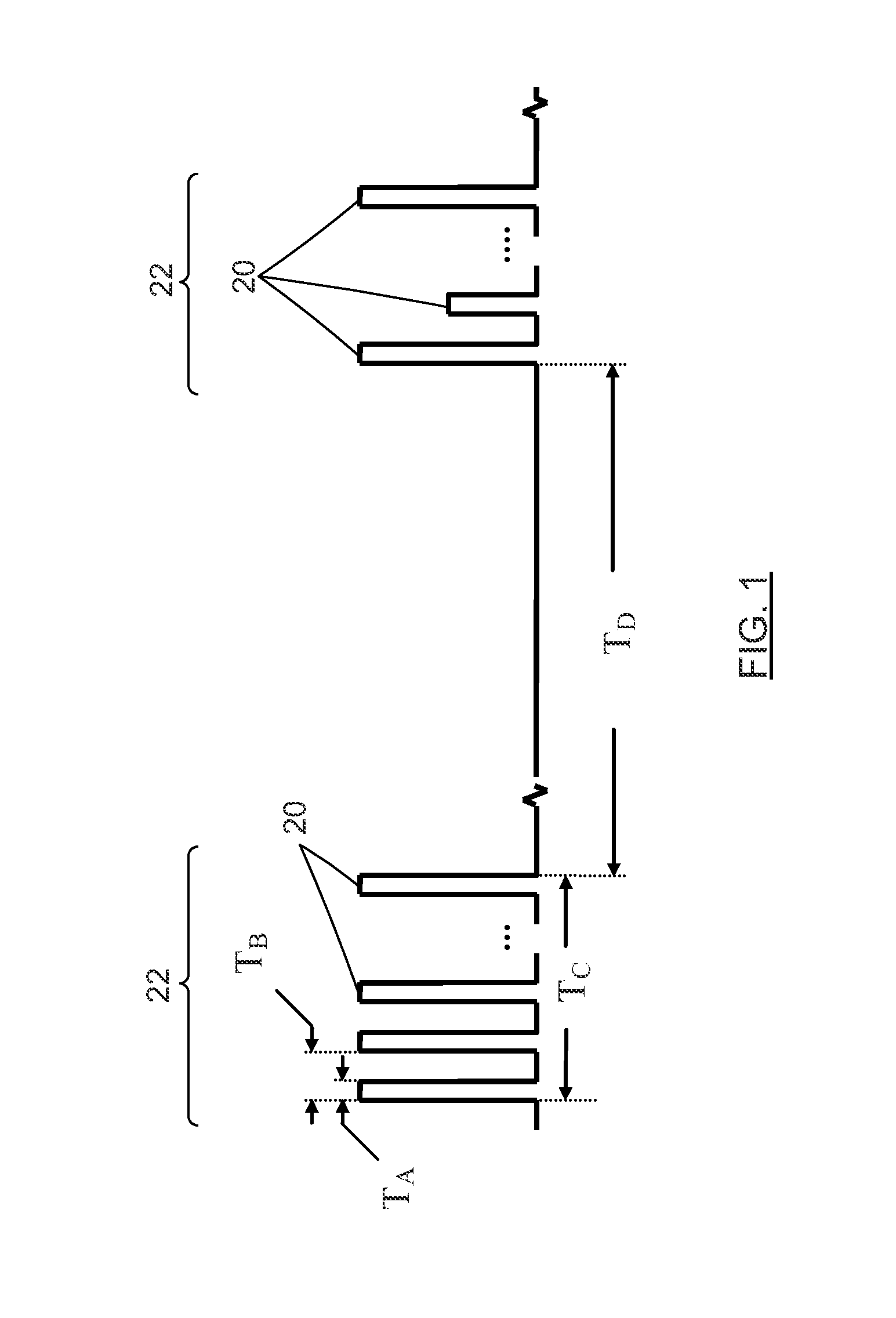
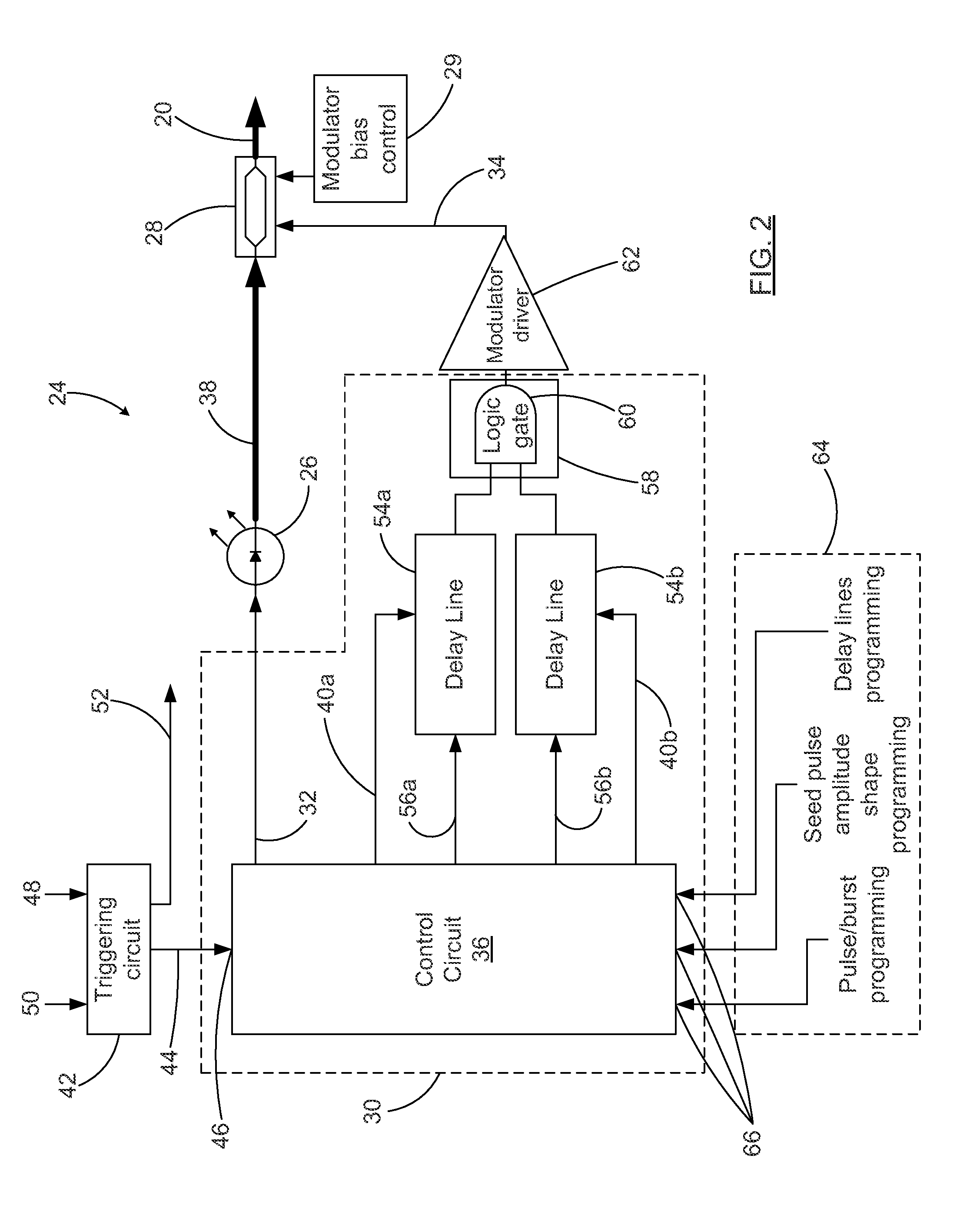
Circuit assembly for controlling an optical system to generate optical pulses and pulse bursts
A circuit assembly controlling an optical system to generate optical pulses is provided. The optical system includes a seed light source optically coupled to an amplitude modulator. The circuit assembly includes a control circuit which generates a pulsed seed drive signal for driving the seed laser source, as well as logic signals defining successions of ON and OFF states and having a predetermined relative timing relationship. One or more of the logic signals is delayed by a corresponding programmable delay line to adjust the relative timing relationship between the logic signals. A logic gating module combines the logic signals according to one or more logical rule, thereby providing a modulator drive signal. Using this circuit assembly, the optical system outputs an optical pulse at each ON state of the modulator drive signal synchronized with the passage of one of the seed optical pulses through the amplitude modulator.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Ultra-wideband/low power communication having a dedicated removable memory module for fast data downloads—apparatus, systems and methods
ActiveUS7782894B2Enhanced BT parametersEasy to checkTime-division multiplexCo-operative working arrangementsUltra-widebandTransceiver
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
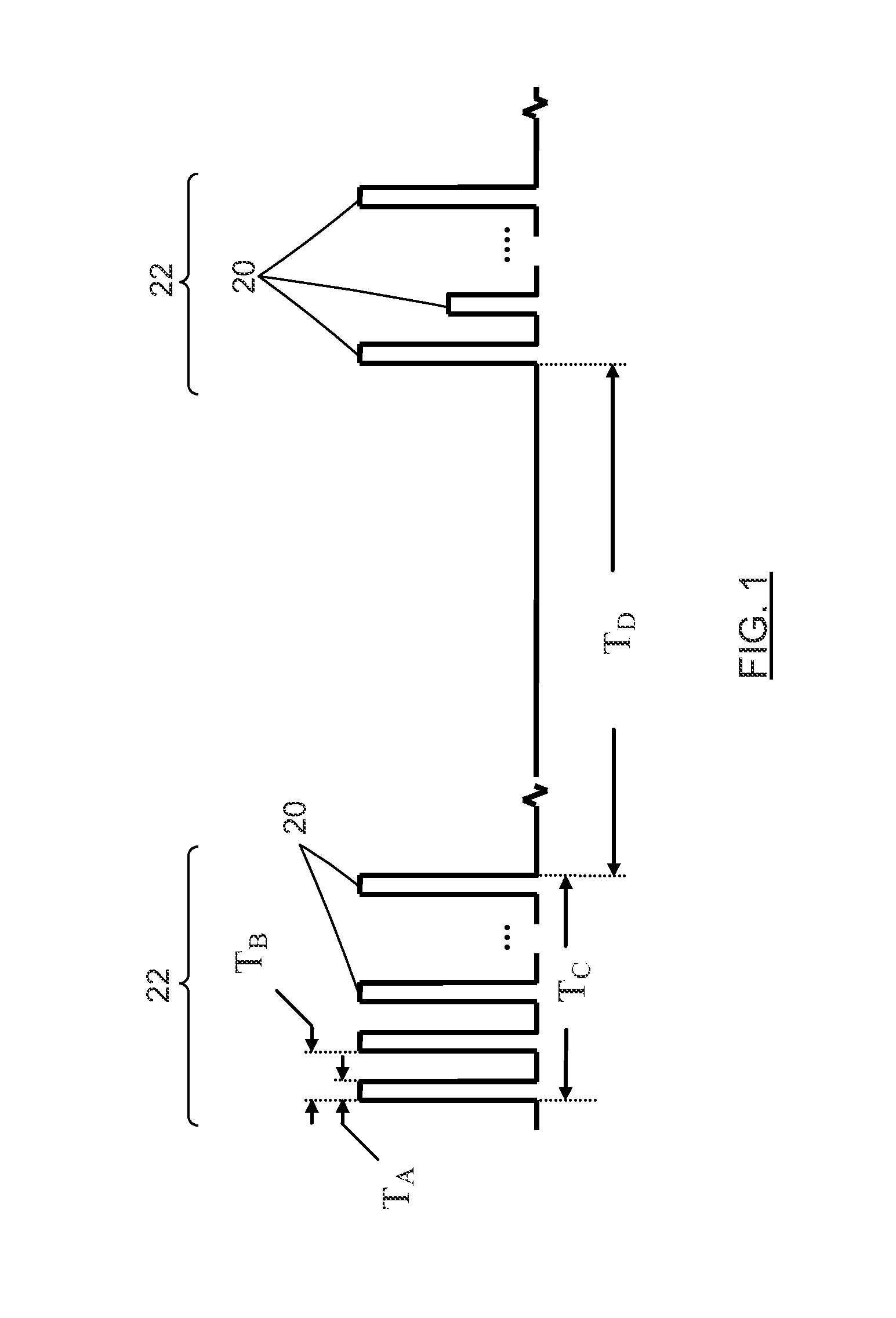
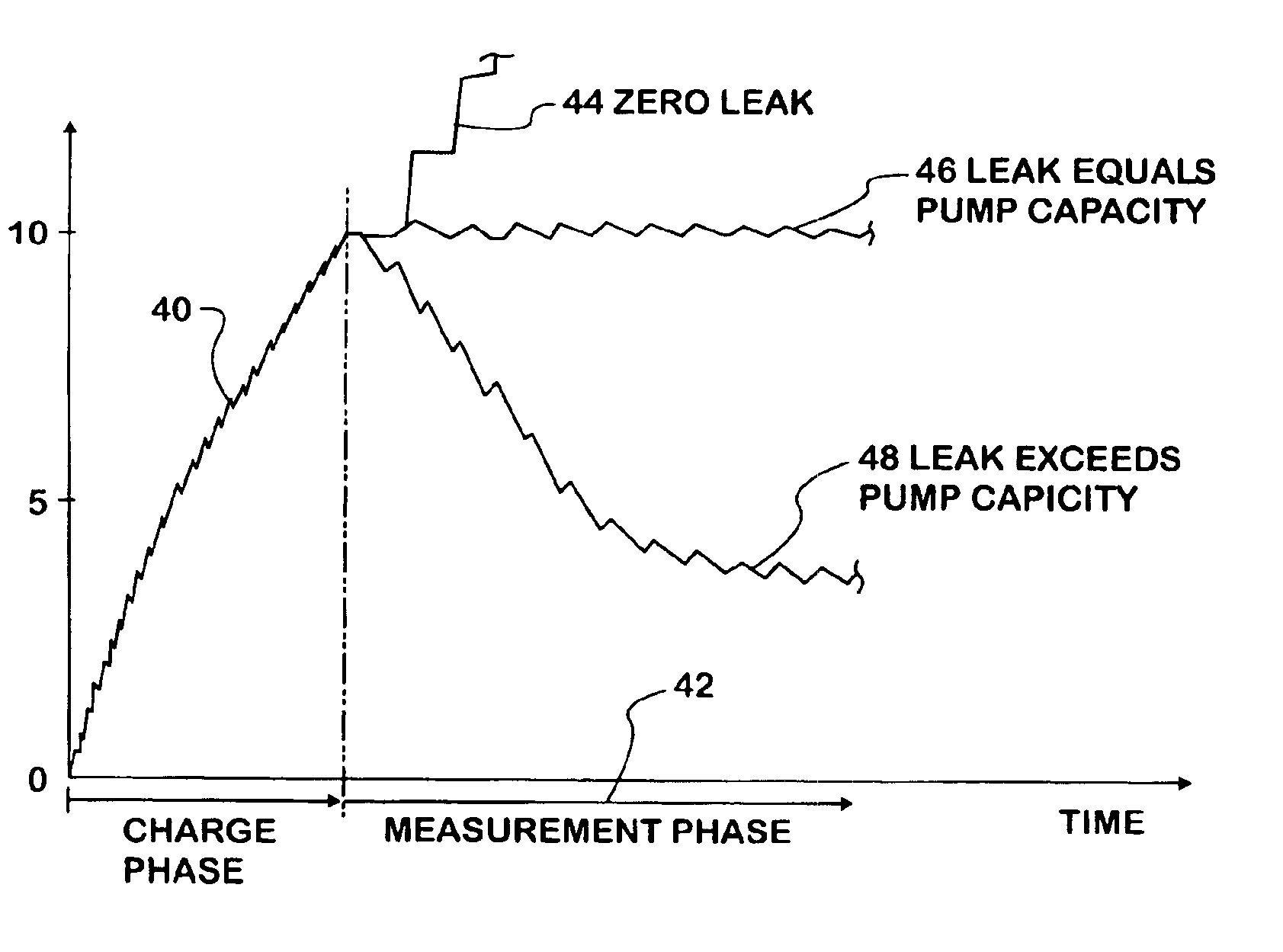
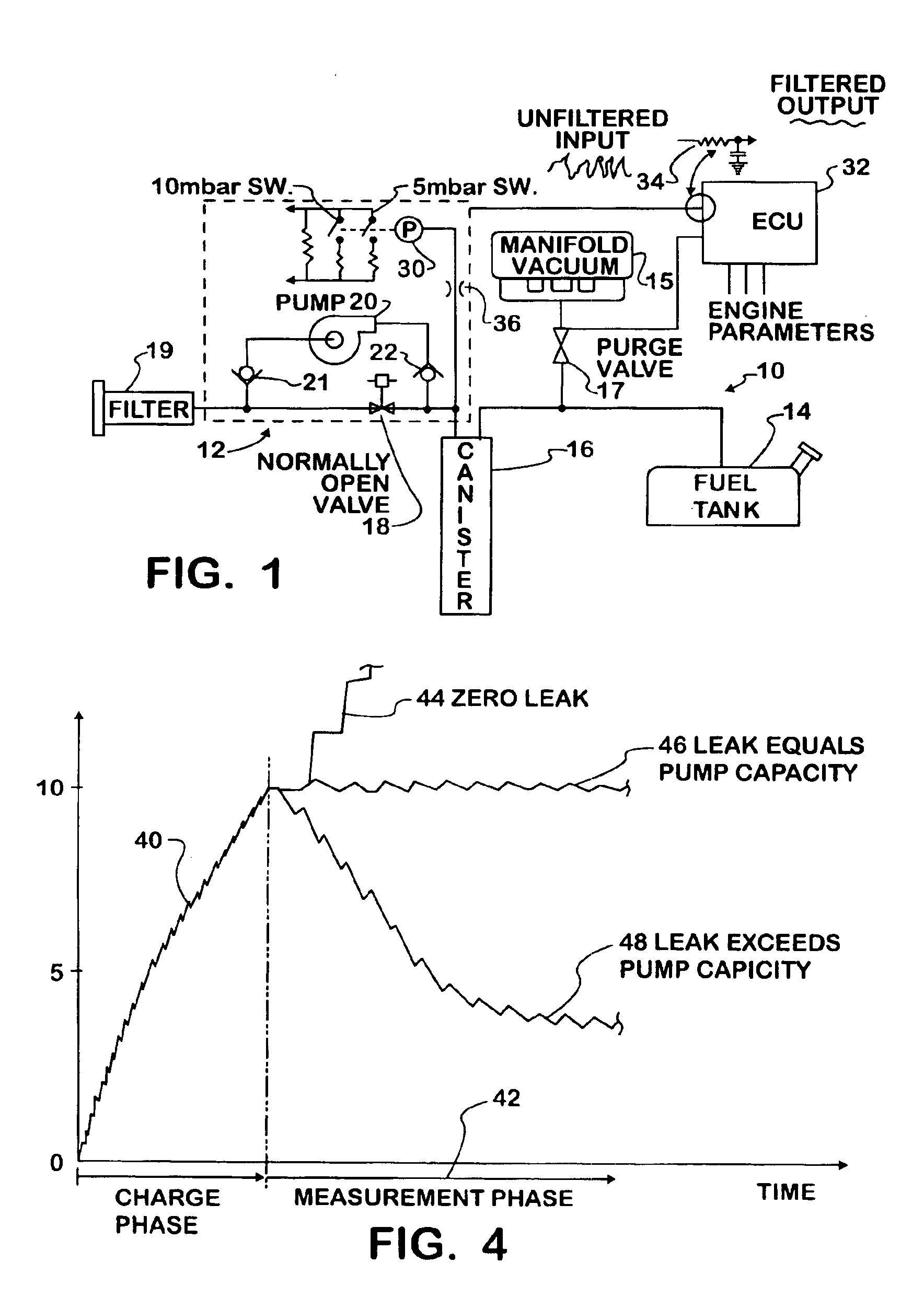
Fuel vapor leak test system and method comprising successive series of pulse bursts and pressure measurements between bursts
InactiveUS6951126B2Suitable performanceDetection of fluid at leakage pointNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringForced-air
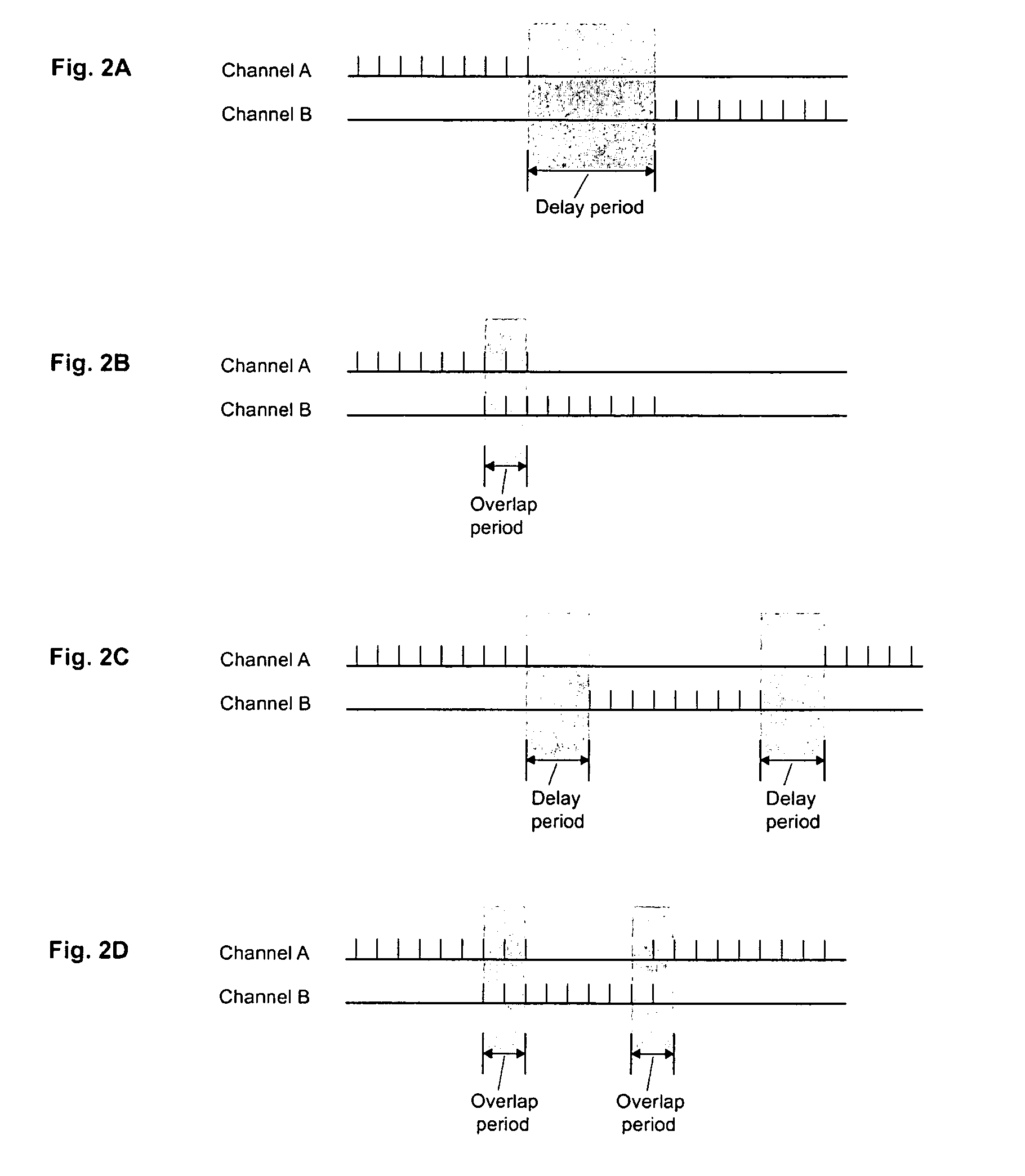
A leak test system and method for a motor vehicle fuel system. A pump forces air under pressure into vapor containment space. The pump operates in accordance with steps established by a processor. The pump creates superatmospheric pressure in the space during an initial charging phase step, and after completion of that step, the pump performs a measurement phase step that forces pulses of air into the space in a succession of pulse bursts. Each burst contains a succession of individual pulses, preferably in equal numbers, and each successive burst is delayed from an immediately prior burst by a time interval substantially longer than the time intervals between individual pulses in each burst, preferably by constant time intervals. The processor processes data corresponding to a measurement of pressure in the space after the occurrence of at least one of such bursts and as a result indicates leakage from the space.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE INC
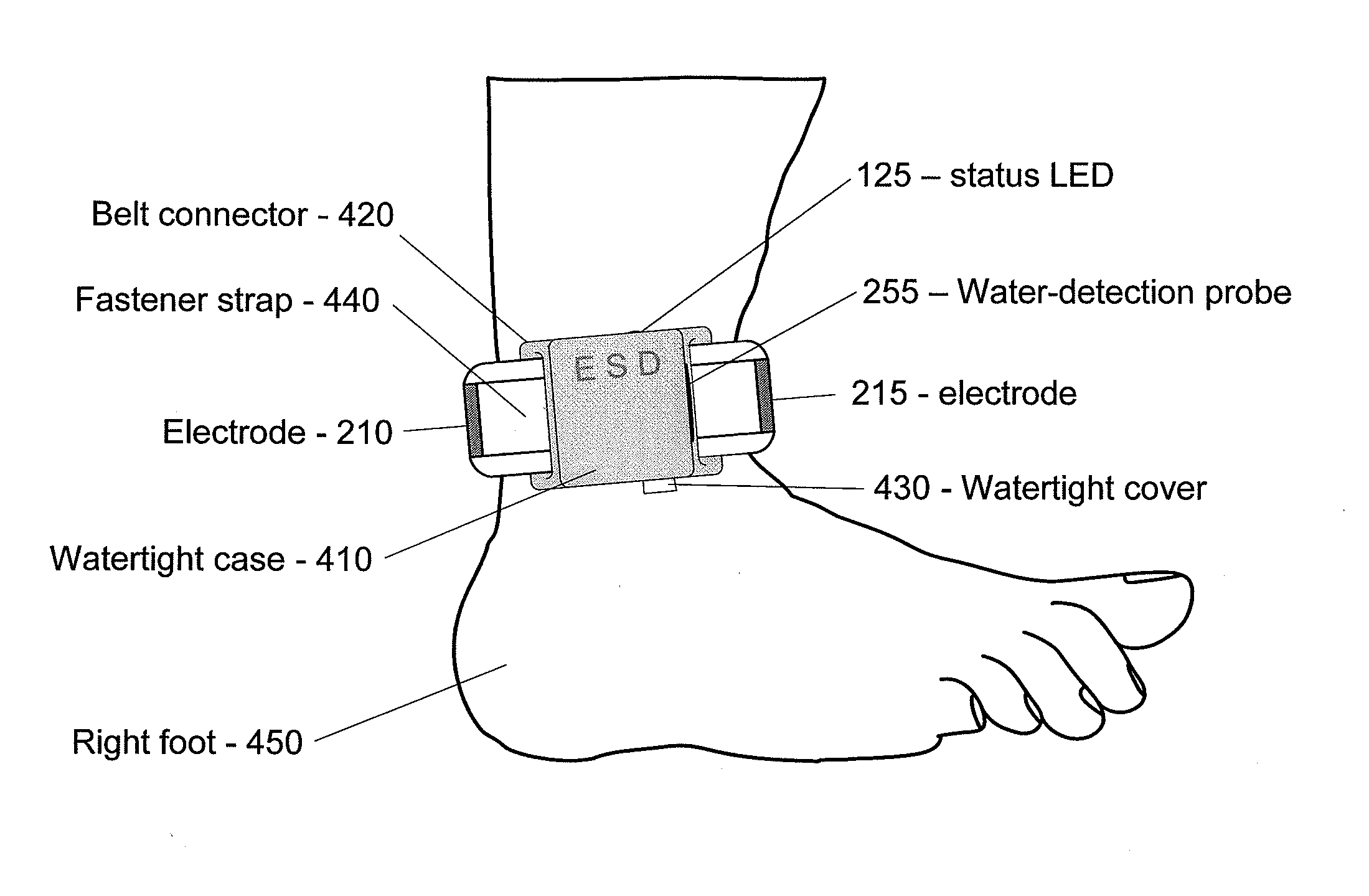
High efficacy signal format & thin-profile ankle-mounting for electronic shark deterrent
InactiveUS20110174235A1Reduces and eliminates tendencyReduce capacityBreathing protectionAlarmsElectrical polarityEfficacy
A device operable as an electronic shark deterrent has a high-voltage pulse signal waveform generator for pulses to be applied to electrodes immersed in water to deter sharks and other aquatic creatures. A preferred output waveform has a train of pulse bursts of alternating-polarity pulses in a series. Preferably, the timing intervals between pulses are of irregular duration, the amplitudes of pulses are varied to be irregular, and the interval between pulse bursts is kept to less than about 5 seconds, in order to be more effective as a shark deterrent signal. The device has the signal waveform generator enclosed in a thin, planar case mounted to a belt connector and a fastener strap for attachment to a part of a user's body. It can include a water-detection probe for automatic activation when immersed in water, a status LED indicator, and electrodes embedded in a layer at opposite ends of the fastener strap with an insulative screen layer for reducing electrostatic effects on the user.
Owner:BLUVAND INNOVATIONS
System and Method of Bladder and Sphincter Control
InactiveUS20090254144A1Reduce distractionsReduce and eliminate external urethral sphincter (EUS) contractionElectrotherapyArtificial respirationSphincterBladder control
A method and system for bladder control are disclosed. In embodiments, a method for bladder control is provided that comprises coupling an electrode to an afferent nerve that is related to the bladder. Applying a plurality of pulse burst stimulations via the electrode causes voiding of urine from the bladder. In embodiments, the plurality of pulse burst stimulations to the afferent nerve reduces external urethral sphincter (EUS) contractions and evokes bladder contractions to expel urine from the subject. In embodiments, the plurality of pulse burst stimulations to the afferent nerve evokes bladder contractions alone to expel urine from the subject. In embodiments, a system for bladder control is provided that comprises an electrode for applying a pulse burst stimulus to an afferent nerve or dermatome to reduce reflex contractions and a signal generator for generating the pulse burst stimulus.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Resonant switching power converter with burst mode transition shaping
ActiveUS20100020570A1Reduce vibrationImprove efficiencyTransformersEfficient power electronics conversionTransverterTransformer
A resonant switching power converter having burst mode transitioning operates during low or zero load conditions with reduced audible noise and component stresses, while improving efficiency. Pulse bursts are generated with a beginning and / or ending pulse duration that differs from mid-burst pulse durations, in order to reduce an amplitude of transients otherwise generated at the beginning and / or end of the bursts. Alternatively, the spacing between the pulses at the beginning and / or end of the bursts may differ from the spacing between the pulses in the middle of the bursts to reduce the transient(s). A number of pulses at the beginning and / or end of the burst can also be set with gradually varying durations, to further reduce component stress and audible vibration in a transformer that couples the resonant tank to the output of the converter.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Pulsed electromagnetic field method of treatment of degenerative disc disease
A pulsed electromagnetic field method of treating degenerative disc disease, wherein, in one embodiment, a patient in need of treatment for degenerative disc disease is administered a pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) having repetitive pulse bursts approximately 5 ms in duration, with a pulse burst repetition rate of approximately 15 Hz.
Owner:EUROPEAN BIOINFORMATICS INSTITUTE
Methods for modulating osteochondral development using bioelectrical stimulation
ActiveUS7840272B2Minimal stressAccelerated and more permanent healingElectrotherapyStress based microorganism growth stimulationCo administrationOsteoblast
Compositions and methods are provided for modulating the growth, development and repair of bone, cartilage or other connective tissue. Devices and stimulus waveforms are provided to differentially modulate the behavior of osteoblasts, chondrocytes and other connective tissue cells to promote proliferation, differentiation, matrix formation or mineralization for in vitro or in vivo applications. Continuous-mode and pulse-burst-mode stimulation of cells with charge-balanced signals may be used. Bone, cartilage and other connective tissue growth is stimulated in part by nitric oxide release through electrical stimulation and may be modulated through co-administration of NO donors and NO synthase inhibitors. Bone, cartilage and other connective tissue growth is stimulated in part by release of BMP-2 and BMP-7 in response to electrical stimulation to promote differentiation of cells. The methods and devices described are useful in promoting repair of bone fractures, cartilage and connective tissue repair as well as for engineering tissue for transplantation.
Owner:MEDRELIEF
Tailored pulse burst
ActiveUS8160113B2Raise transfer toUnprecedented level of controlLaser detailsFibre transmissionSeeds sourcePulse period
Output pulses from an optical system having a seed source and an optical amplifier coupled to the seed source may be controlled by controlling a power of a seed signal from the seed source. The seed signal may be varied between a minimum value and a maximum value in a way that the seed signal exhibits one or more pulse bursts. Each pulse burst may contain one or more pulses. During an inter-pulse period between successive pulses within a pulse burst or between successive pulse bursts, the power of the seed signal may be adjusted to an intermediate value that is greater than the minimum value and less than the maximum value. The intermediate value is chosen to control a gain in the optical amplifier such that a pulse or pulse burst that follows the period exhibits a desired behavior.
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
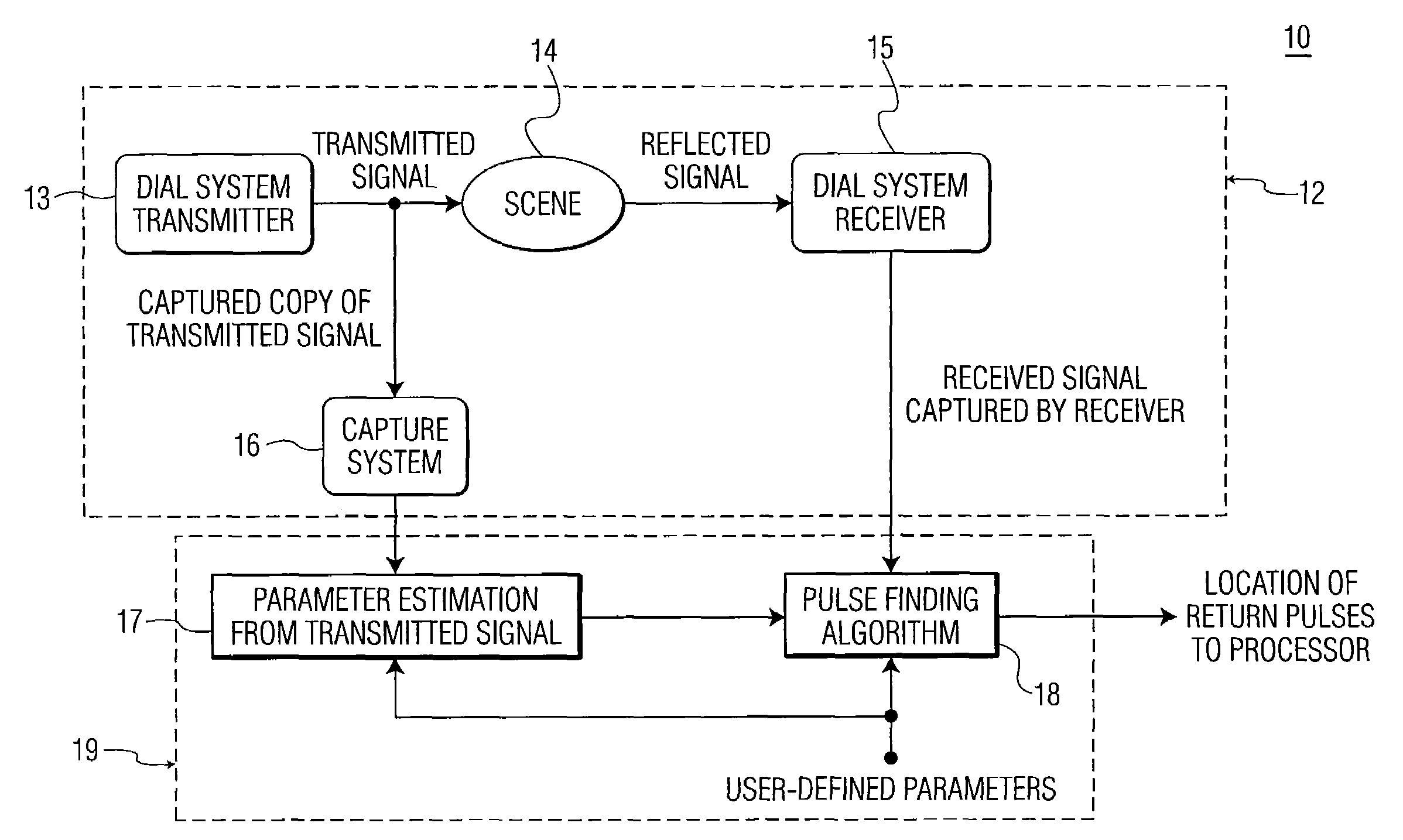
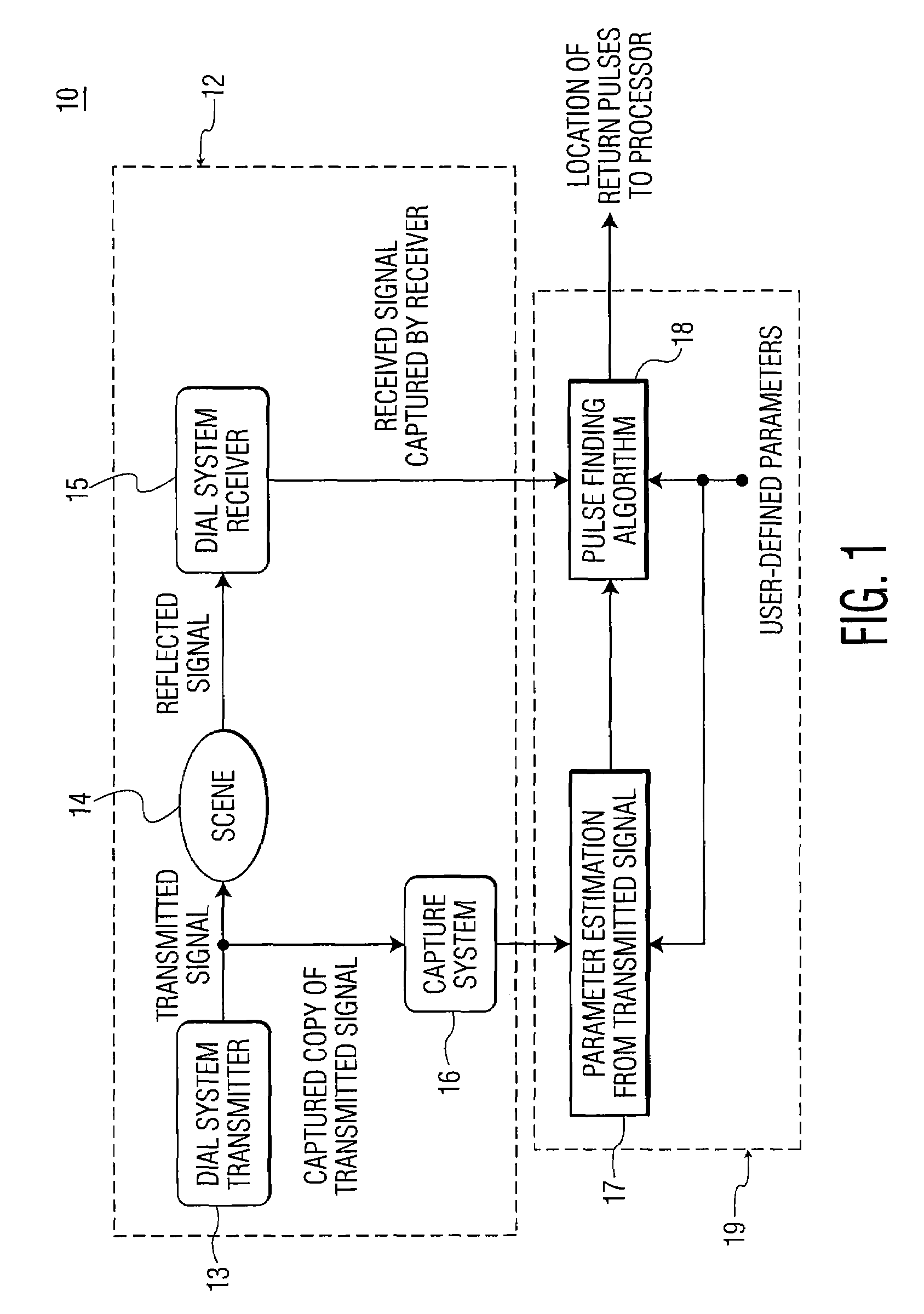
Pulse finding apparatus and method
ActiveUS7456970B1Optical rangefindersMaterial analysis by optical meansLaser transmitterPulse finding
A method of finding a temporal location of a reflected pulse in a system for remotely measuring characteristics of a target scene. The method includes steps of: (a) transmitting a pulse burst of two or more pulses toward the target scene; (b) capturing a copy of the pulse burst transmitted in step (a); (c) measuring an inter-pulse separation between at least two pulses in the pulse burst captured in step (b); (d) receiving a signal reflected from the target scene; (e) determining a temporal location of a first pulse in the signal received in step (d); and (f) determining a temporal location of a second pulse in the signal received in step (d) based on the inter-pulse separation measured in step (c). Step (a) may include transmitting an OFF-line pulse and at least one ON-line pulse in the pulse burst toward the target scene from a differential absorption LIDAR (DIAL) system, where the OFF-line pulse and the ON-line pulse are combined pulses, each individually generated from a separate pulsed laser transmitter and each having a different wavelength.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
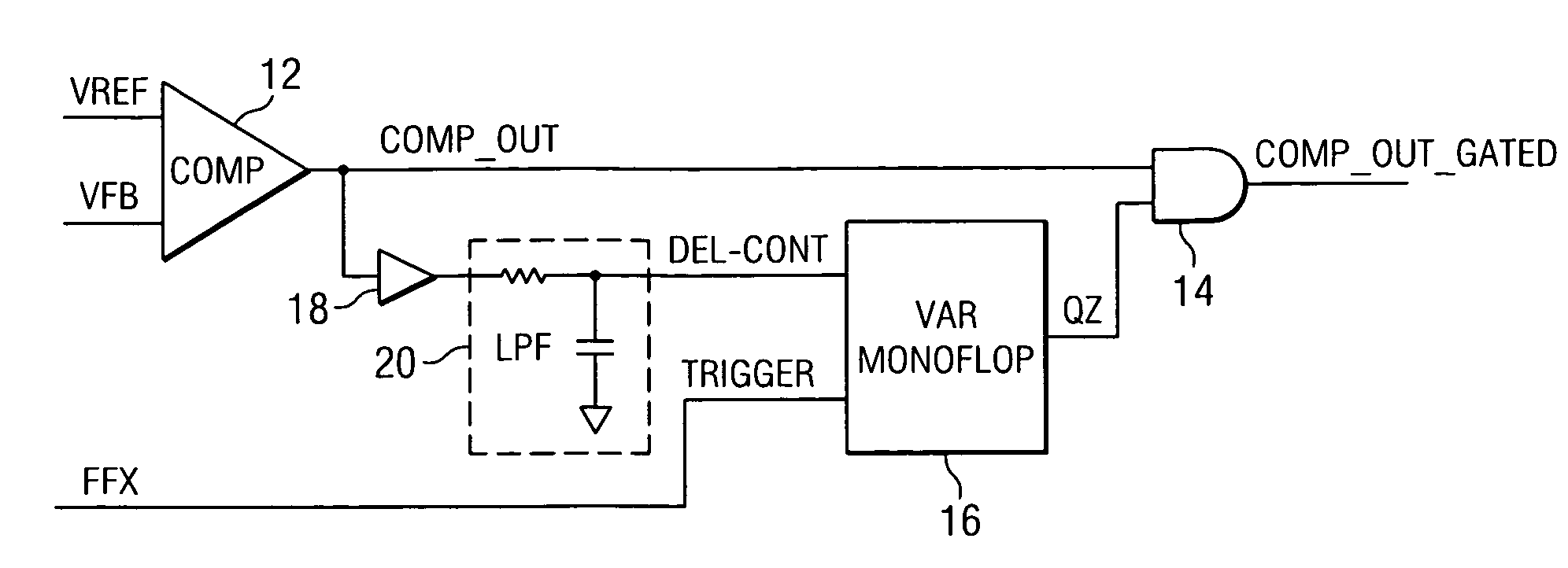
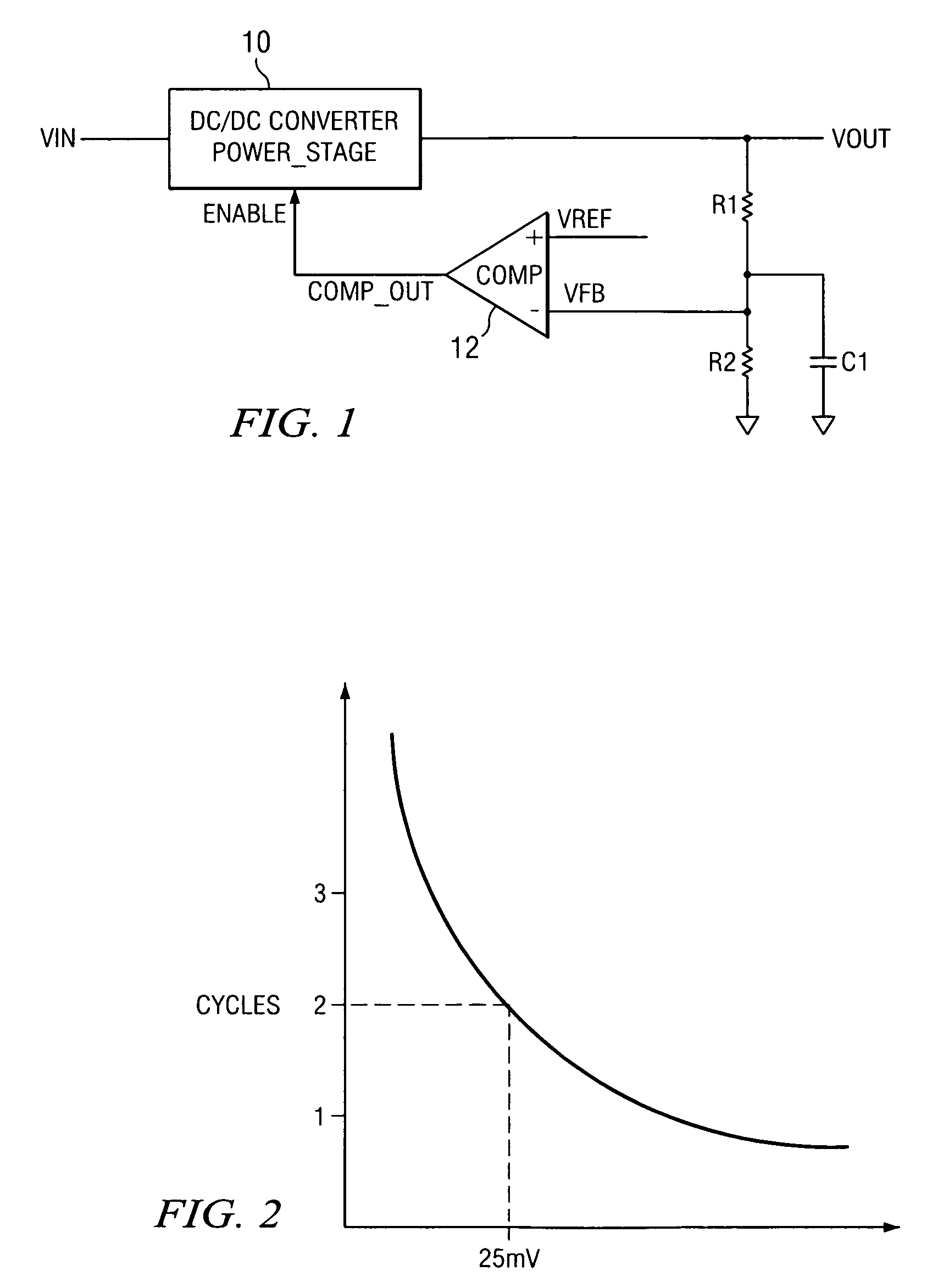
Hysteretic DC/DC converter
ActiveUS7420357B2Accurate timingImprove performanceAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsSwitching frequencyEngineering
A hysteretic DC / DC converter is proposed that operates at a high switching frequency without producing undesired pulse bursts at the output. The converter has a converter power stage with a supply voltage input, a controlled voltage output and an enable input. A comparator has a reference voltage input, a feedback input and an output, and a gating circuit connected between the output of the comparator and the enabling input of the converter power stage. The gating circuit inhibits as a function of load requirements the propagation of enabling pulses from the output of the comparator to the enabling input of the converter power stage. By gating the output of the comparator in a way to separate the output from the enabling input of the converter power stage immediately after the start of each conversion pulse, the generation of further pulses immediately after each conversion pulse is prevented, thereby keeping the output voltage ripple low.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
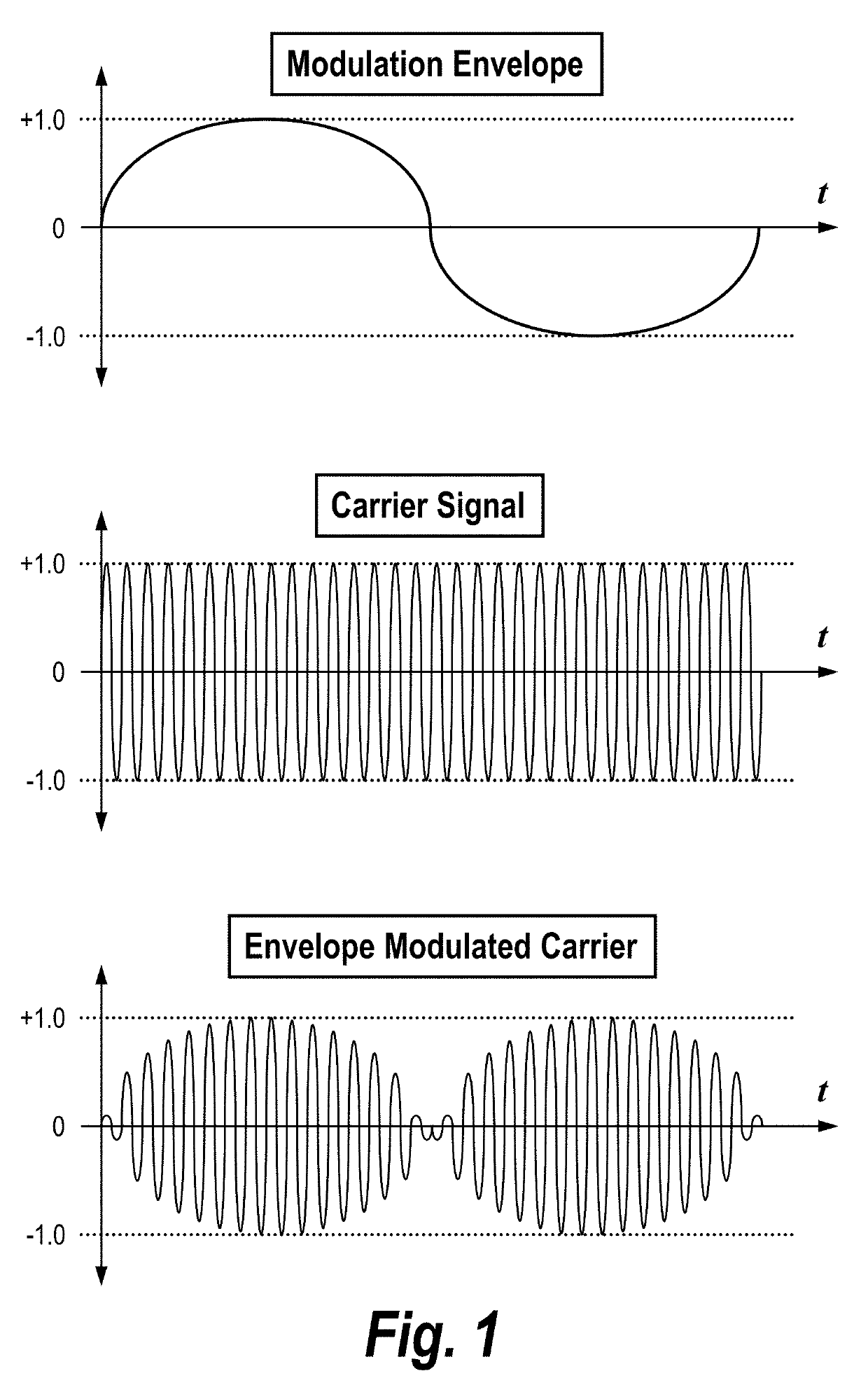
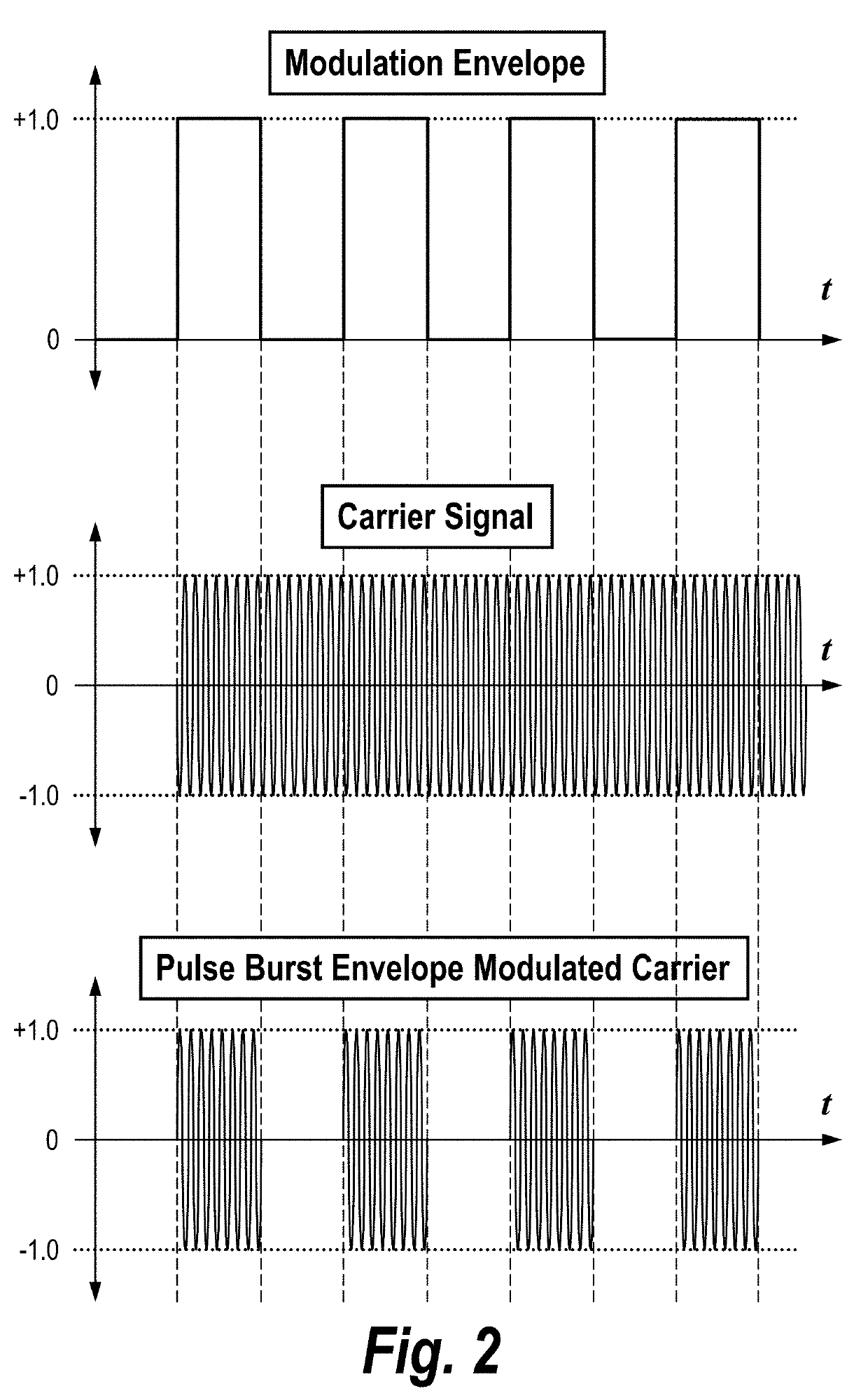
Direct detection LiDAR system and method with step frequency modulation (FM) pulse-burst envelope modulation transmission and quadrature demodulation
ActiveUS10473784B2Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPulse envelopeSignal processing circuits
A LiDAR system includes a signal generator for generating an output signal having a variable frequency. A modulation circuit receives the output signal from the signal generator and modulates the output signal to generate a pulsed modulation envelope signal configured to comprise a plurality of pulses, two or more of the plurality of pulses having two or more respective different frequencies. The modulation circuit applies the pulsed modulation envelope signal to an optical signal to generate a pulse-envelope-modulated optical signal comprising a plurality of pulses modulated by the pulsed modulation envelope signal. Optical transmission elements transmit the pulse-envelope-modulated optical signal into a region. Optical receiving elements receive reflected optical signals from the region. Receive signal processing circuitry receives the reflected optical signals and uses quadrature detection to process the reflected optical signals.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
Optimal trajectory control for LLC resonant converter for LED PWM dimming
ActiveUS9276480B2Improve uniformityNot significantly susceptibleEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesResonant inverterResonant power converters
Pulse width modulation is provided for controlling a resonant power converter, particularly for dimming of light emitting diode arrays without loss of efficiency. Dynamic oscillation due to the beginning of a pulse width modulated pulse burst is limited by shortening of the first and / or last pulse of a pulse bust such that the first pulse of a subsequent pulse burst close to or to connect with a full load steady-state voltage / current trajectory of the power converter. Pulse shortening made be made substantially exact to virtually eliminate dynamic oscillation but substantial reduction in dynamic oscillation is provided if inexact or even performed randomly.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
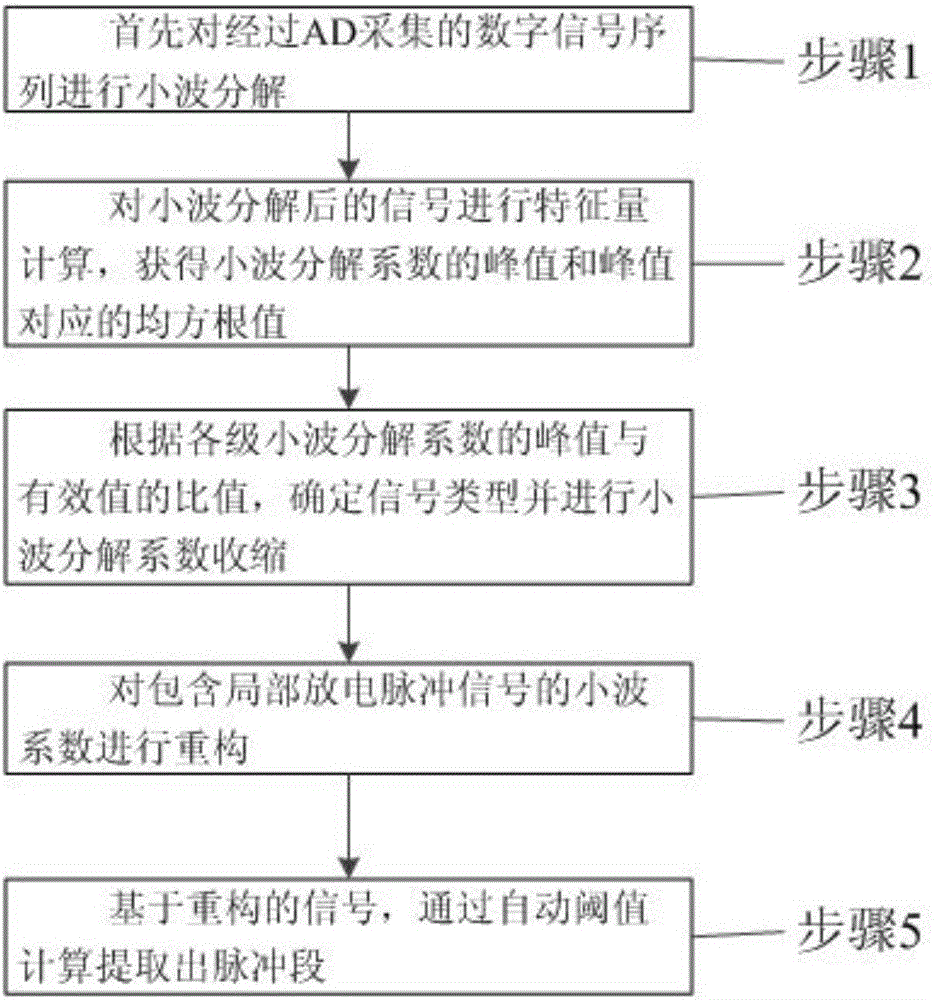
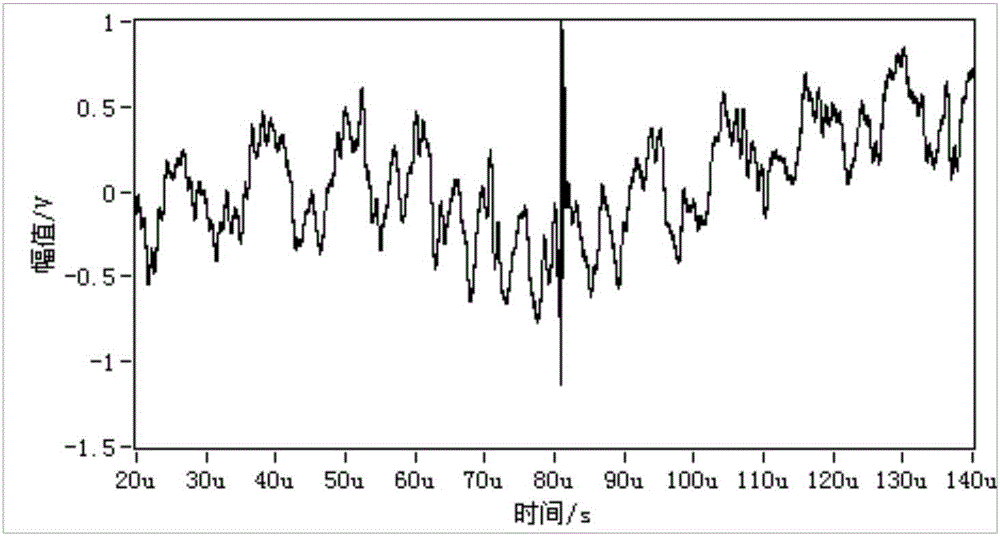
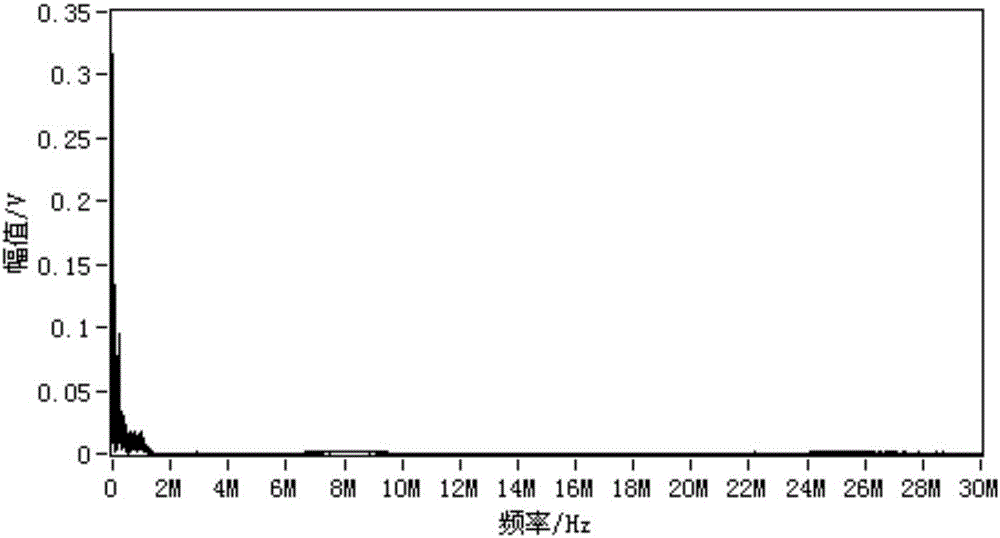
Pulse extraction method suitable for high frequency current partial discharge detection
ActiveCN106771905ASolve technical problems with poor complex effects and large calculationsReduce computational complexityTesting dielectric strengthComputation complexityPeak value
The invention discloses a pulse extraction method suitable for high frequency current partial discharge detection. The method comprises the steps of (1) carrying out wavelet decomposition on a digital signal sequence collected through an AD, (2) carrying out characteristic quantity calculation on the signal which is subjected to the wavelet decomposition, and obtaining a peak value of a wavelet decomposition coefficient and a mean square root value corresponding to the peak value, (3) determining a signal type and carrying out wavelet decomposition coefficient shrinkage according to a ratio of the peak value of each level of wavelet decomposition coefficient to an effective value, (4) reconstructing the wavelet coefficient containing a partial discharge pulse signal, and (5) extracting a pulse burst through automatic threshold calculation based on a reconstructed signal. The technical effects of computational complexity reduction, filtering efficiency improvement and real-time high performance noise suppression are realized.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Circuit assembly for controlling an optical system to generate optical pulses and pulse bursts
A circuit assembly controlling an optical system to generate optical pulses is provided. The optical system includes a seed light source optically coupled to an amplitude modulator. The circuit assembly includes a control circuit which generates a pulsed seed drive signal for driving the seed laser source, as well as logic signals defining successions of ON and OFF states and having a predetermined relative timing relationship. One or more of the logic signals is delayed by a corresponding programmable delay line to adjust the relative timing relationship between the logic signals. A logic gating module combines the logic signals according to one or more logical rule, thereby providing a modulator drive signal. Using this circuit assembly, the optical system outputs an optical pulse at each ON state of the modulator drive signal synchronized with the passage of one of the seed optical pulses through the amplitude modulator.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com