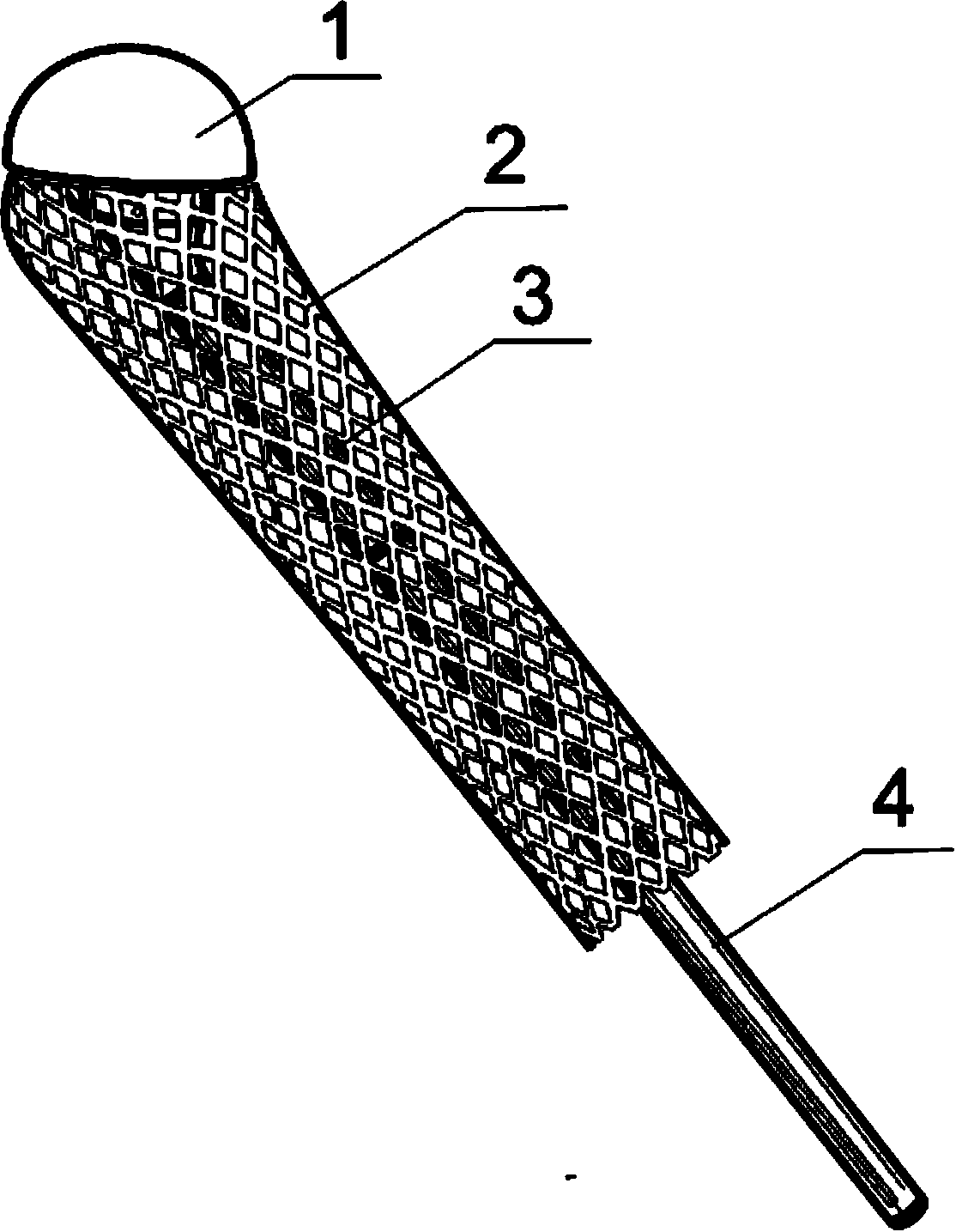
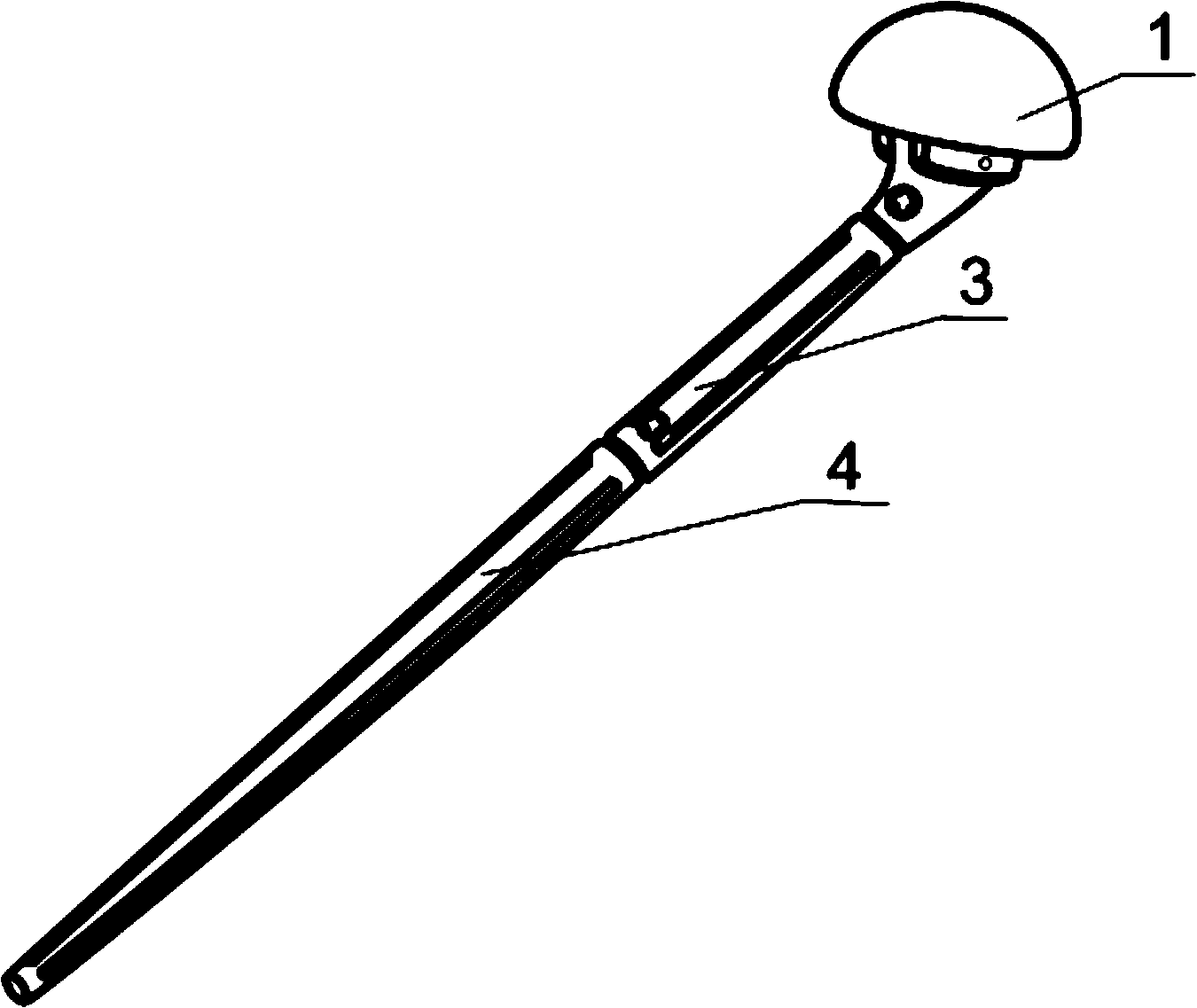
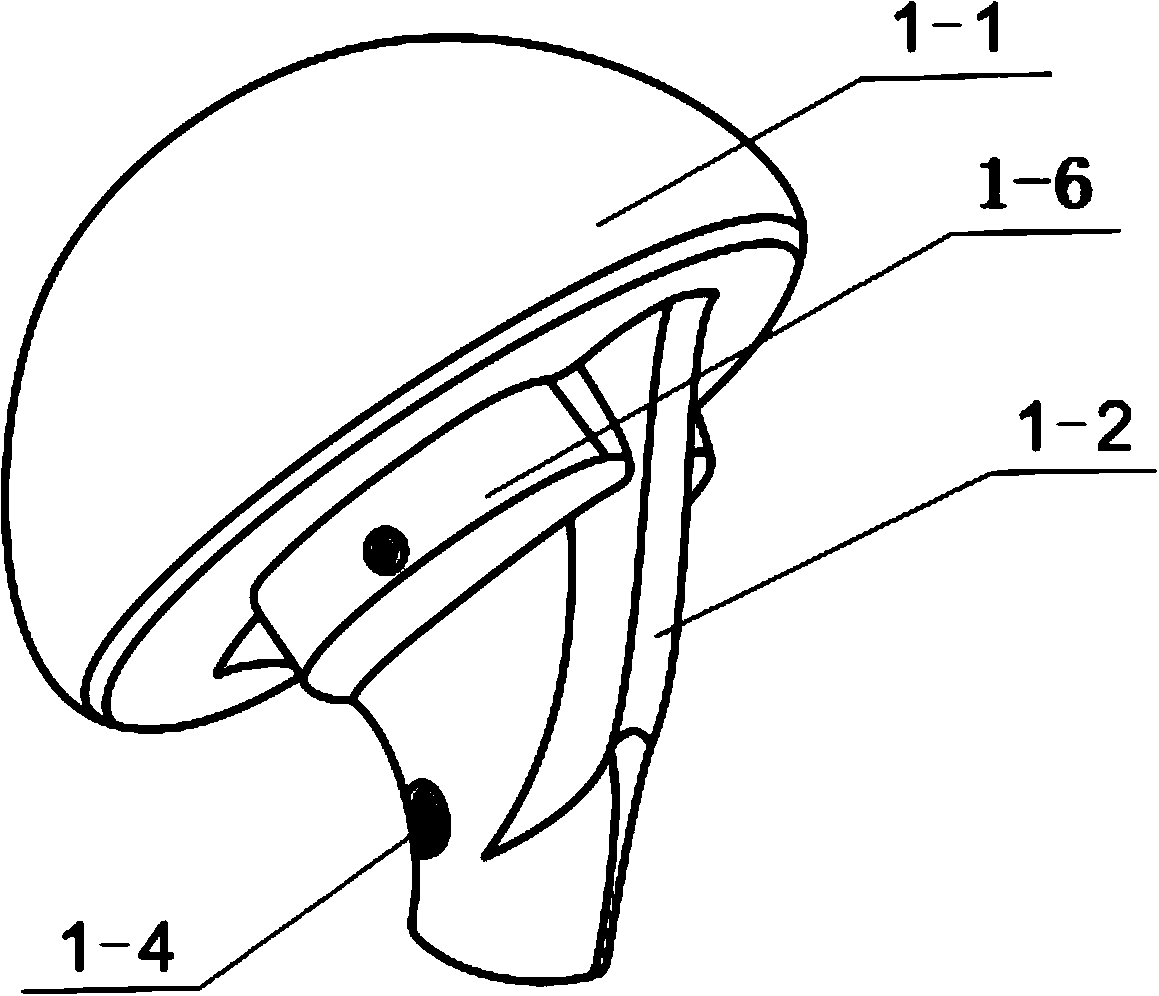
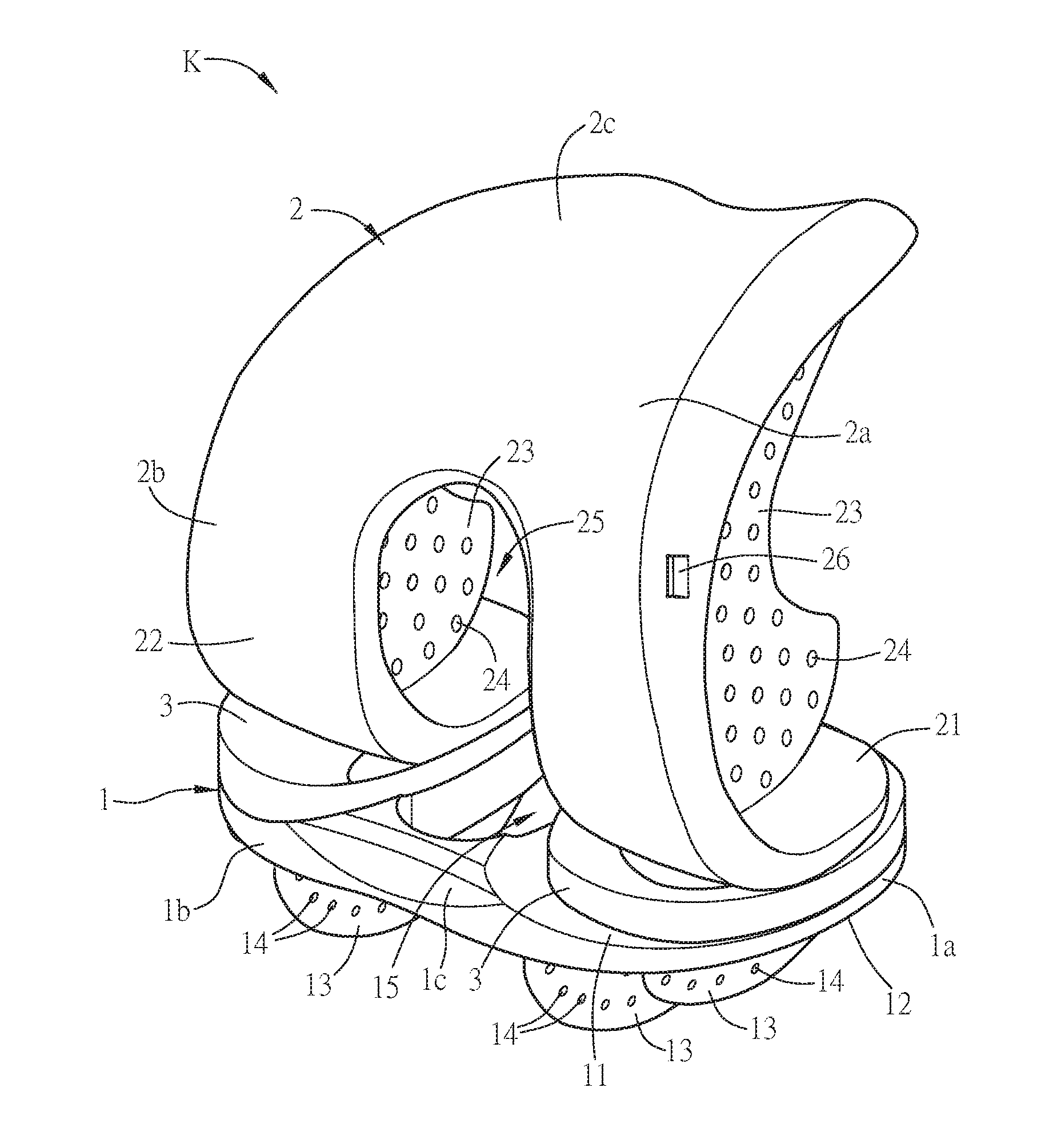
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Collum femoris" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
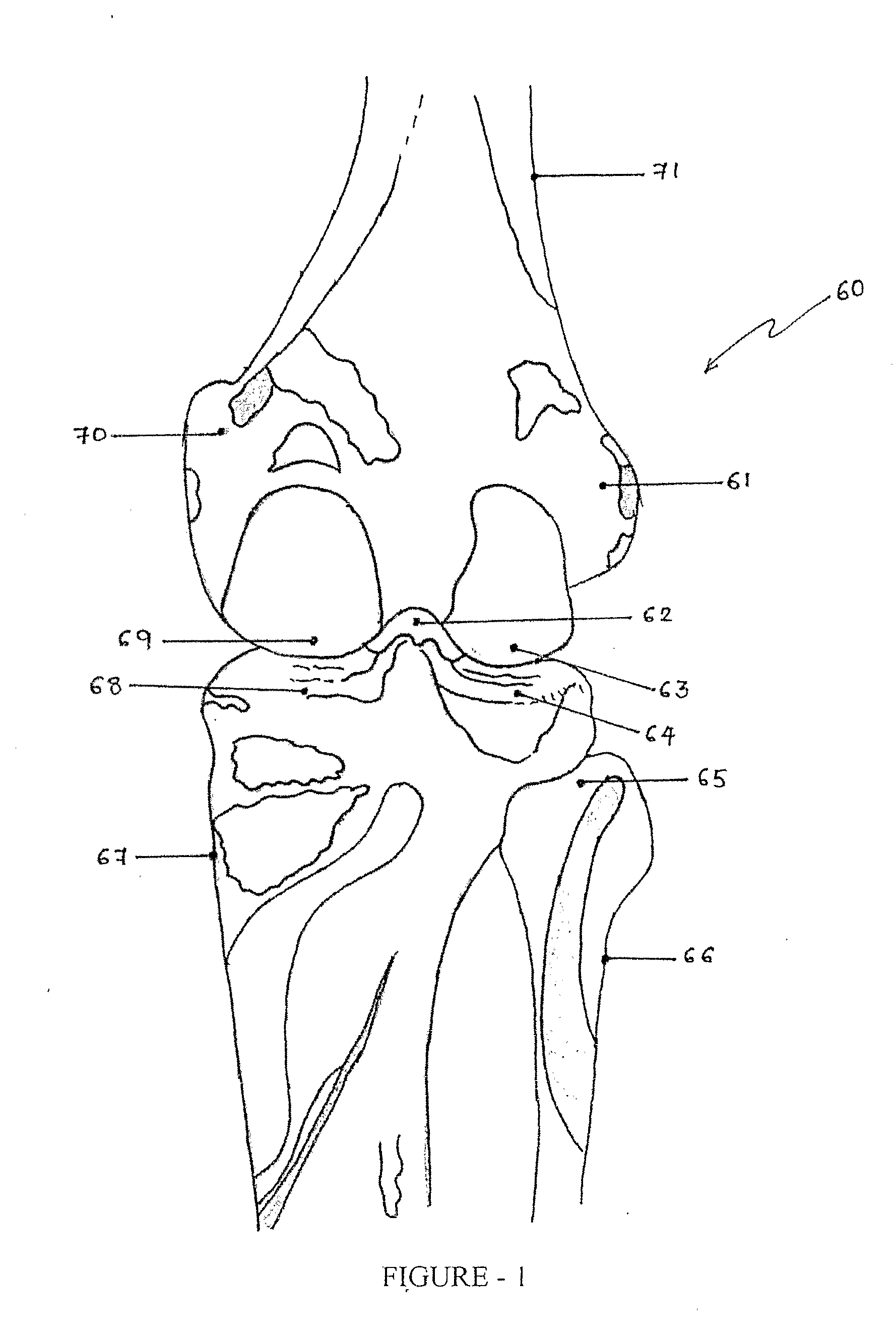
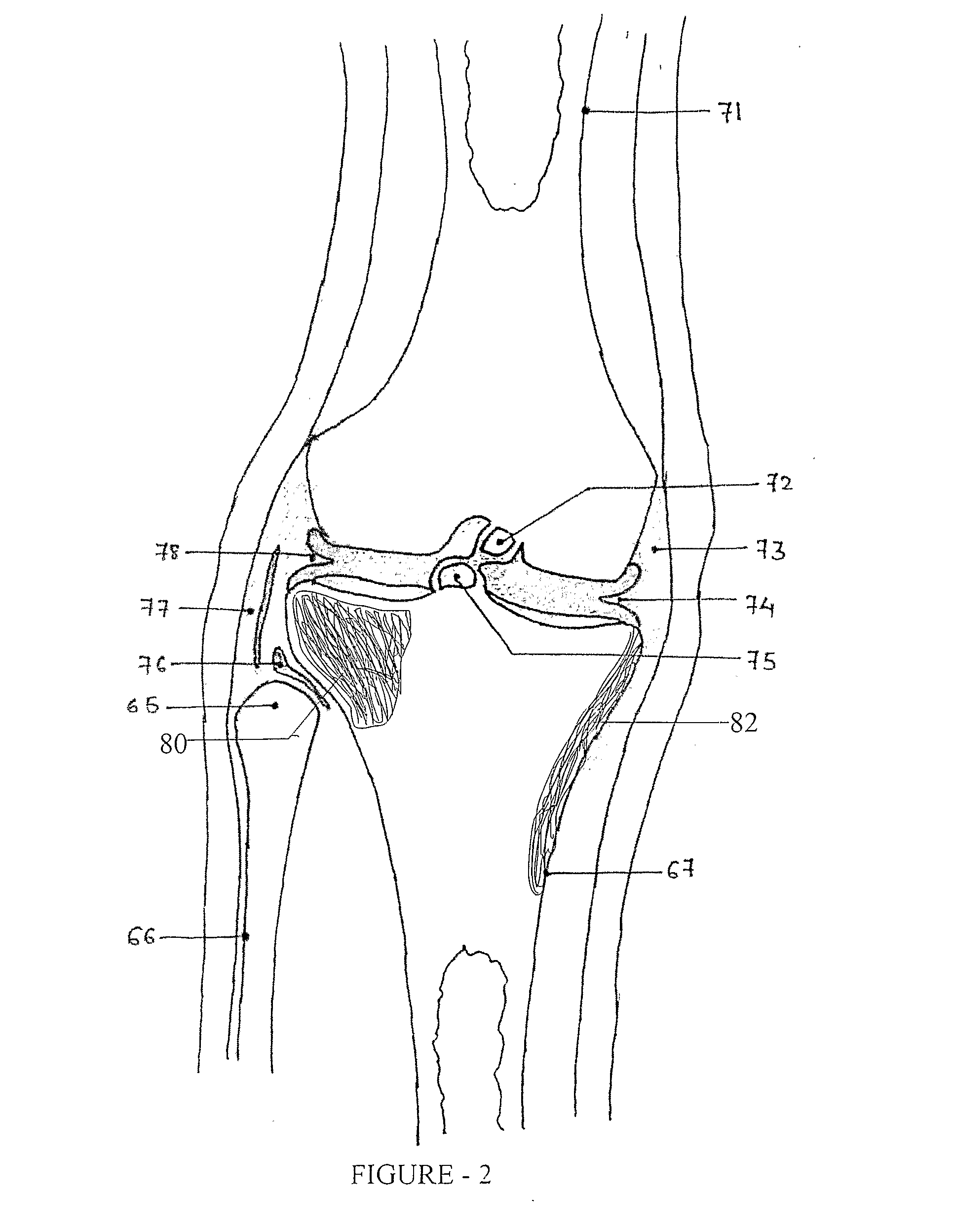
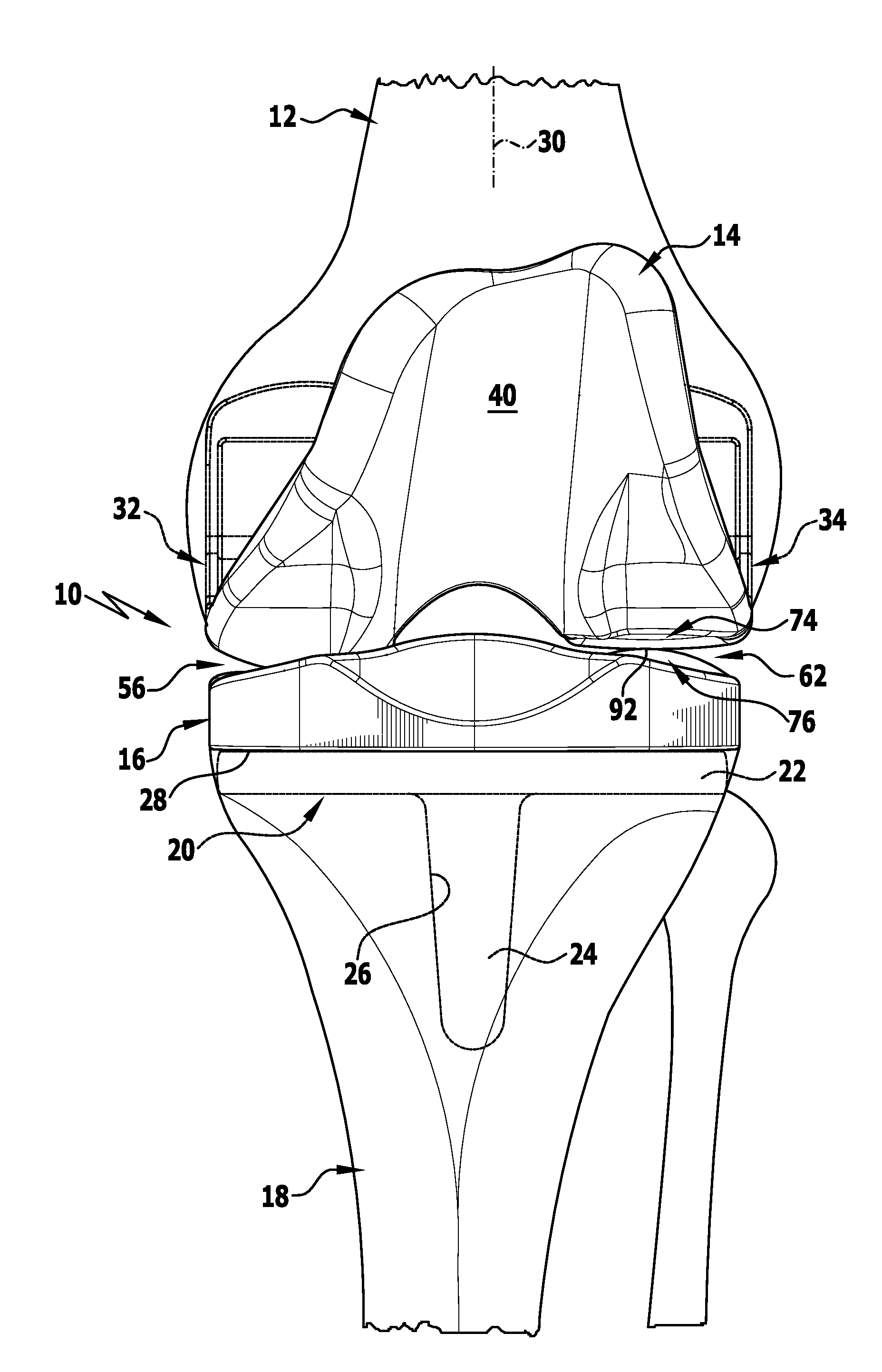
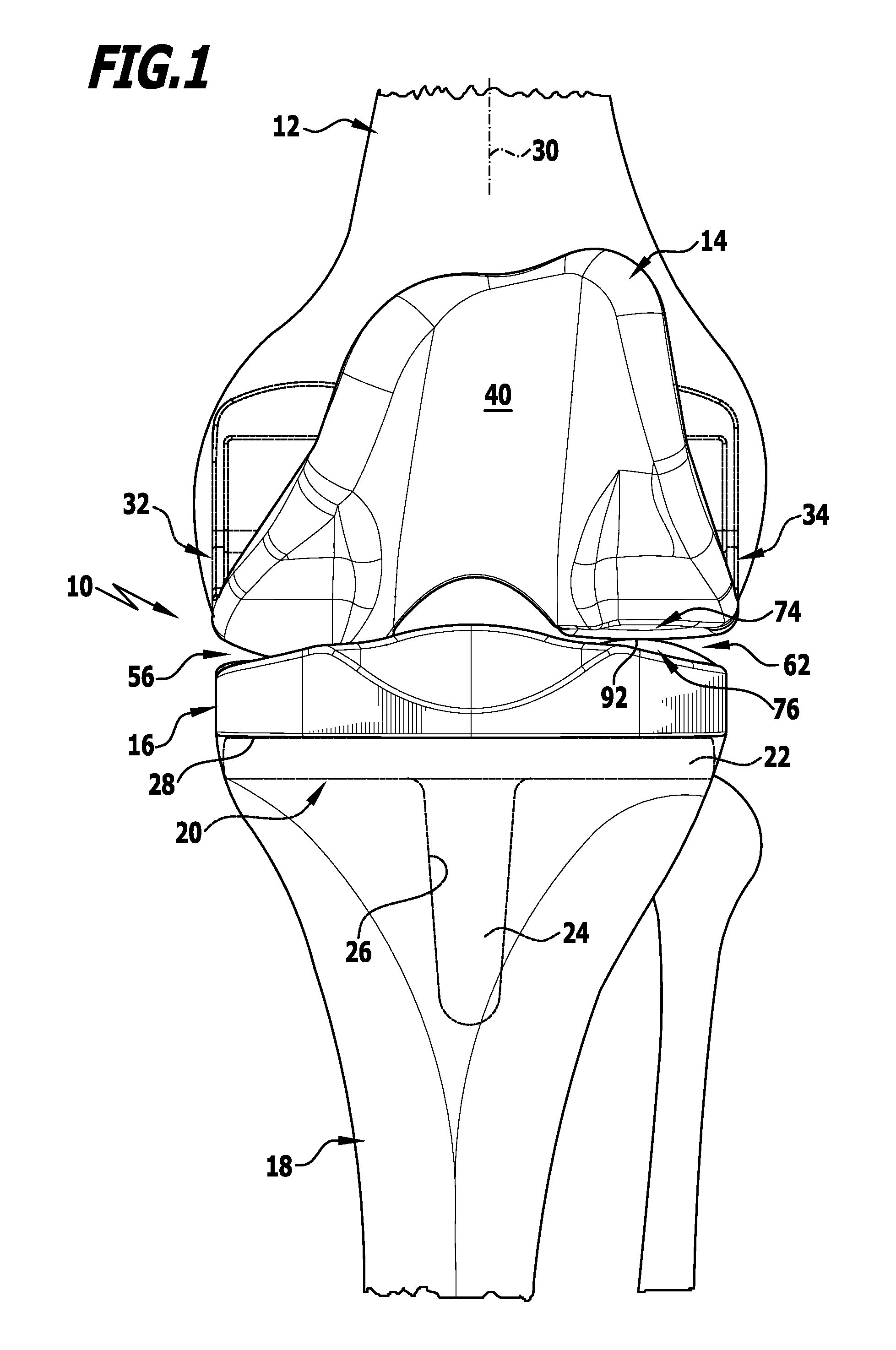
Collum femoris: MeSH: D005272: TA: A02.5.04.004: FMA: 42385: Anatomical terms of bone [edit on Wikidata] The femur neck (femoral neck or neck of the femur) is a flattened pyramidal process of bone, connecting the femoral head with the femoral shaft, and forming with the latter a wide angle opening medialward.
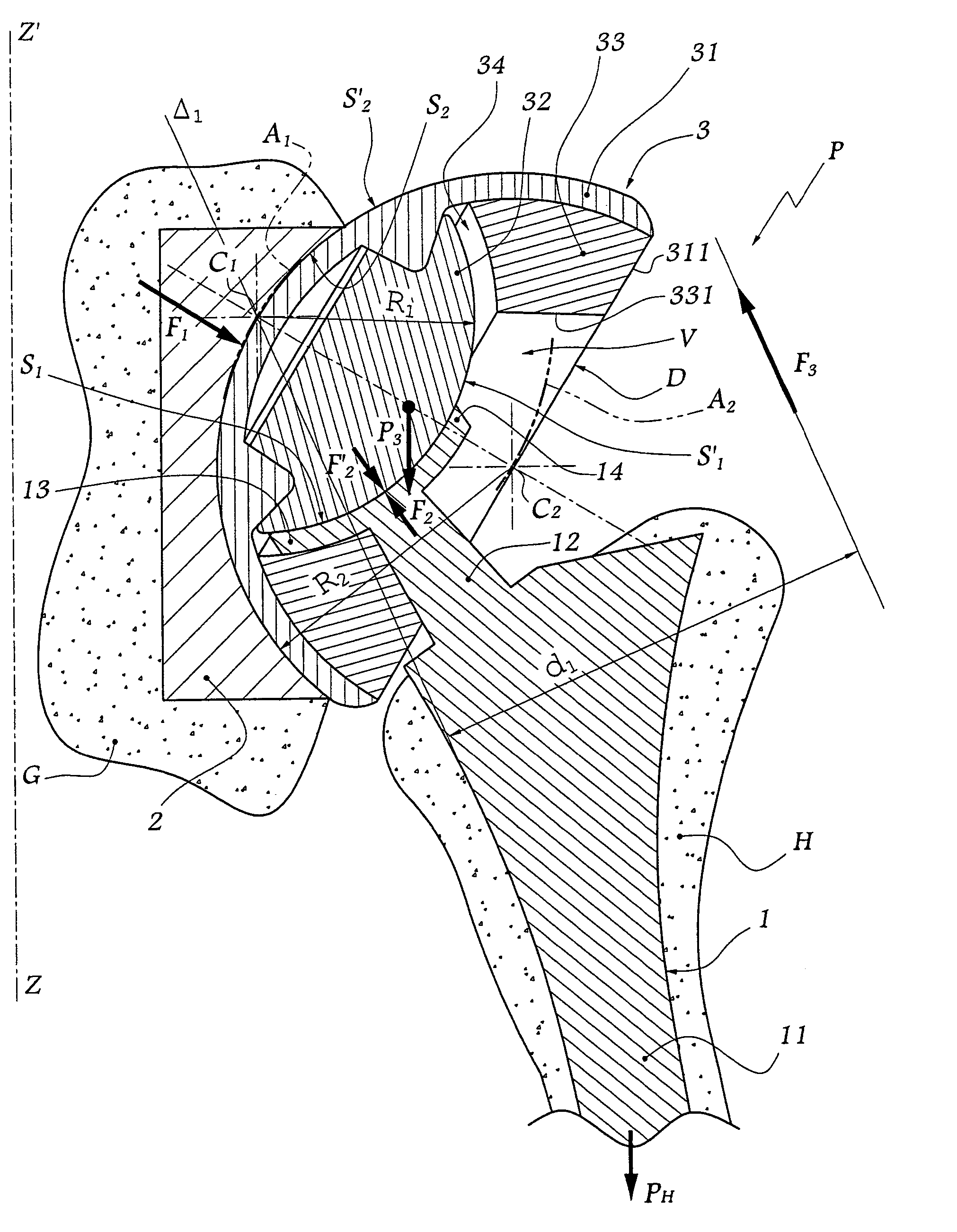
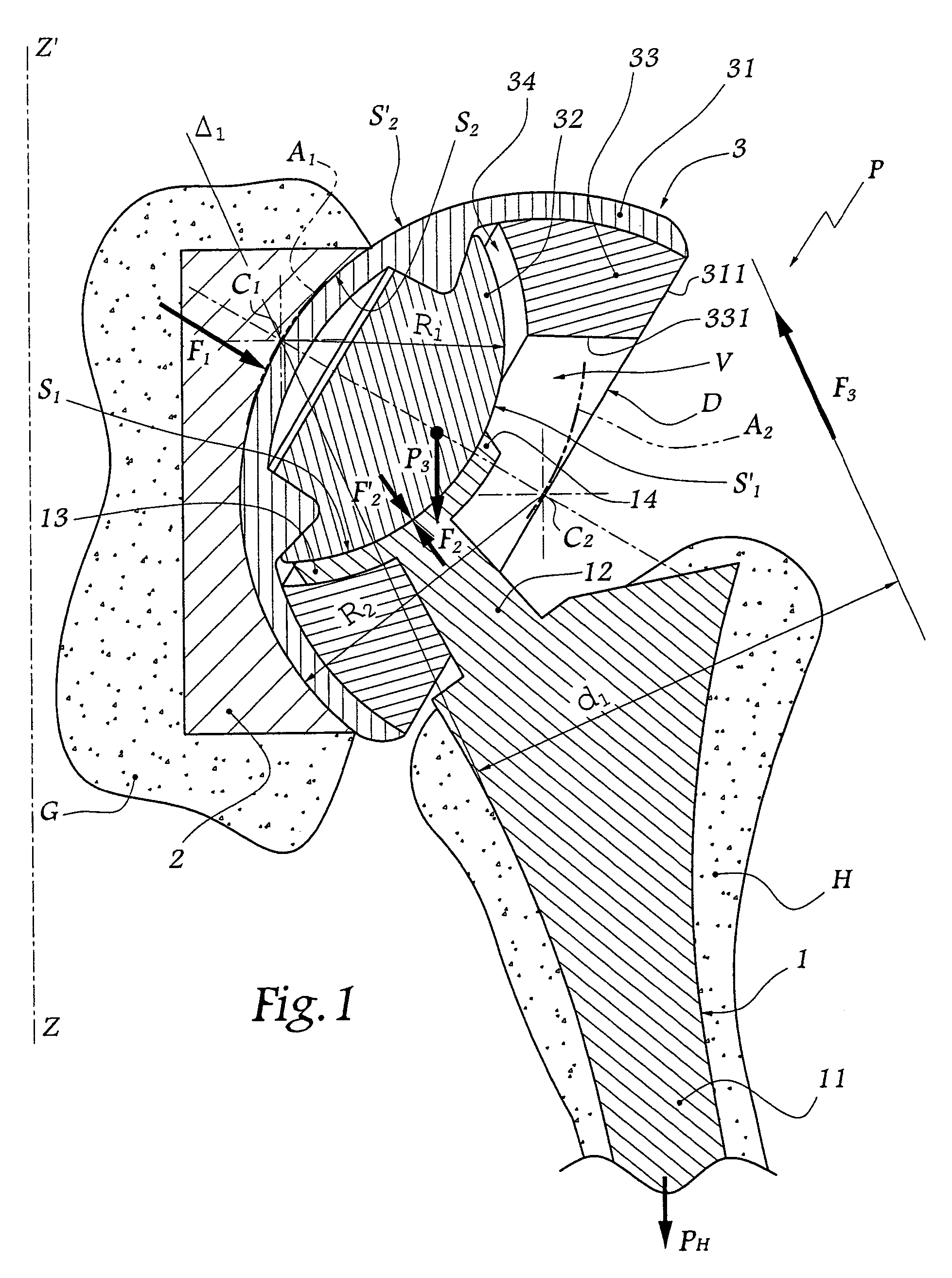
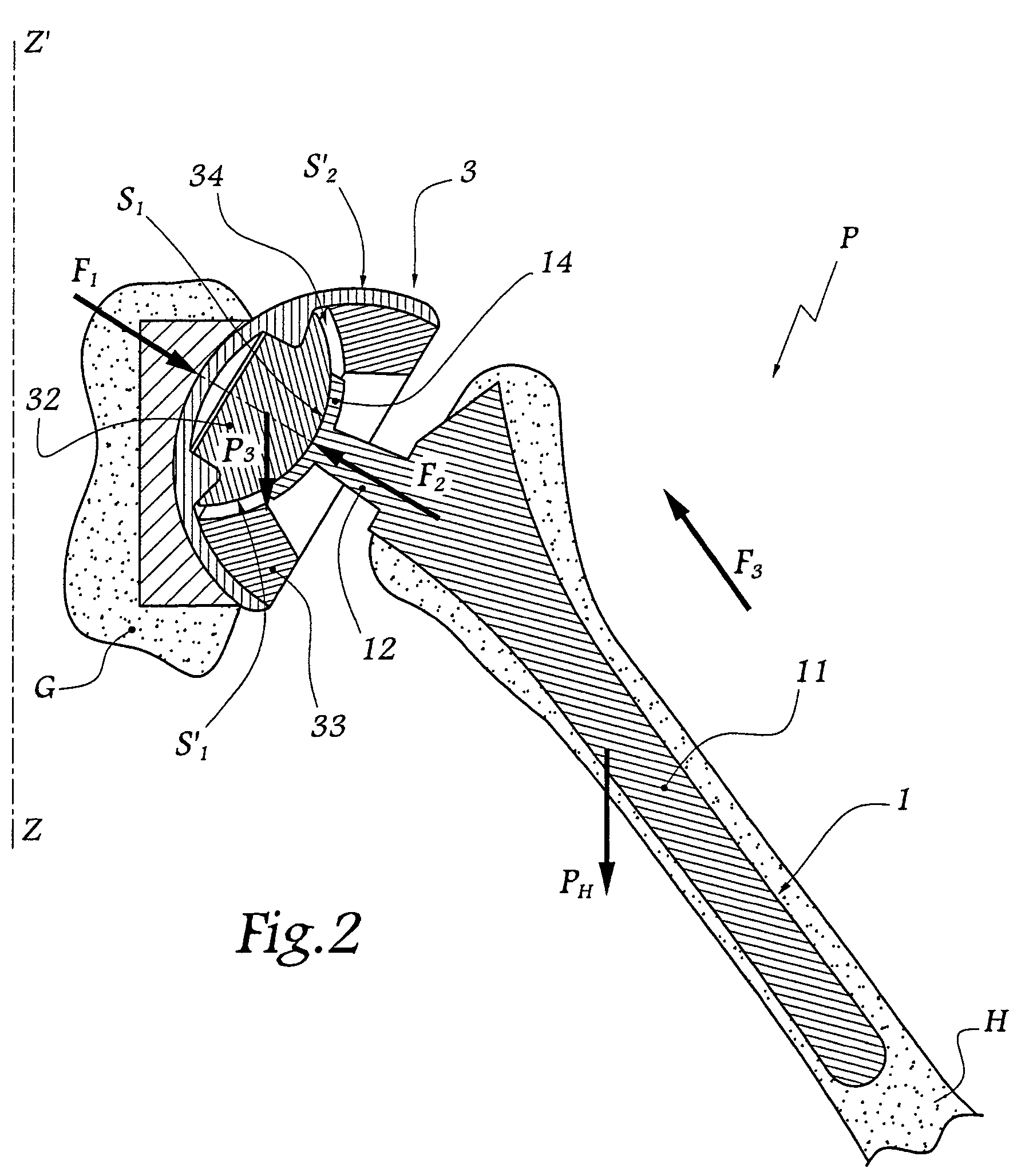
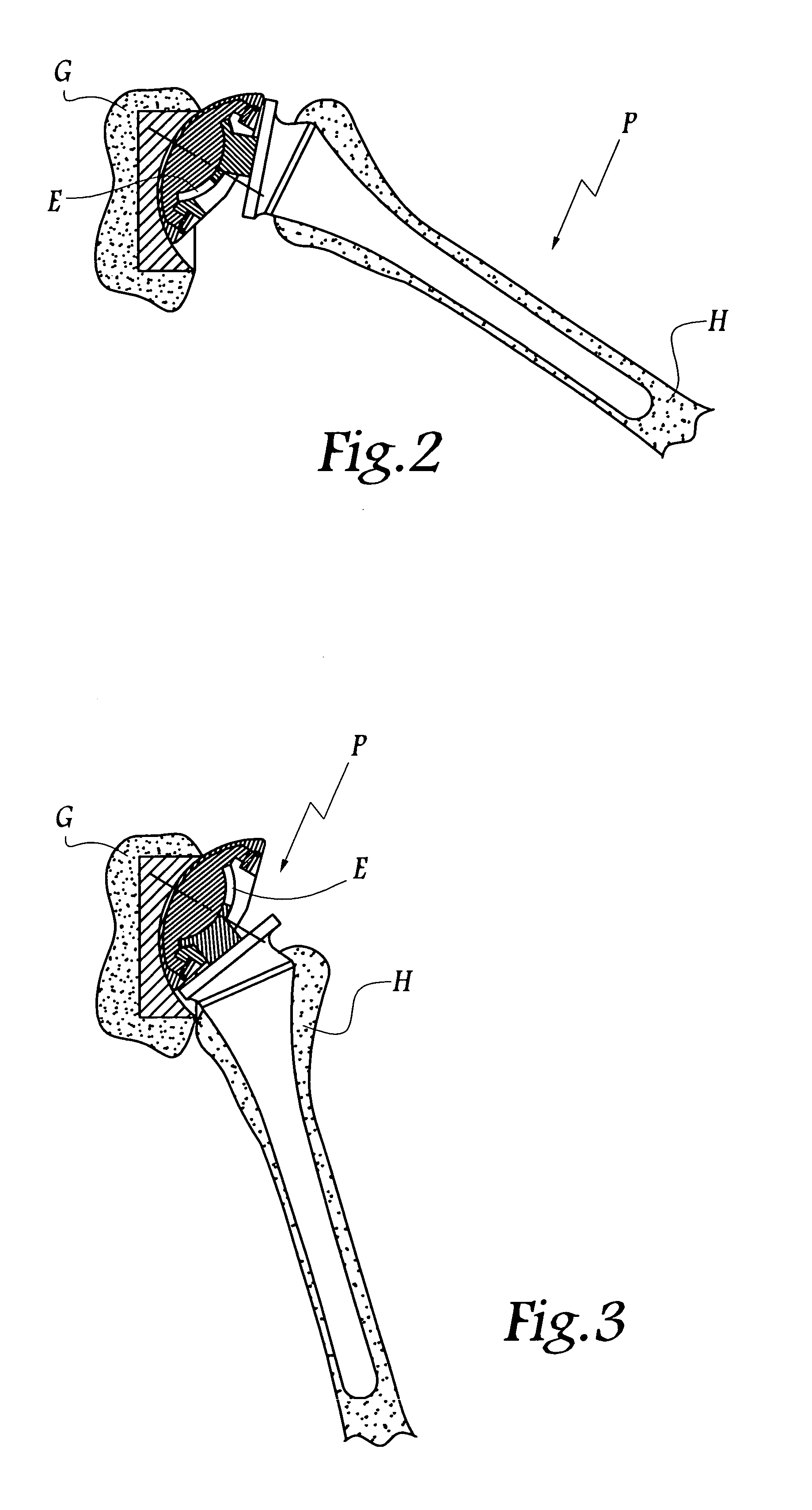
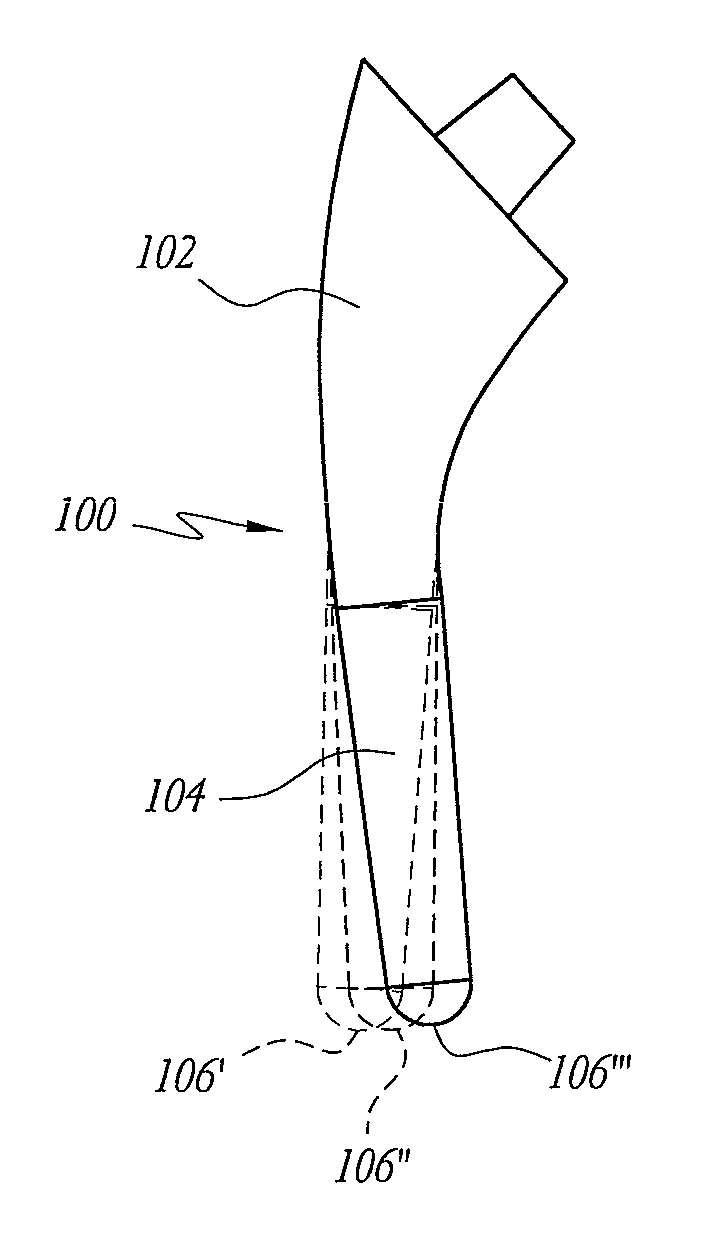
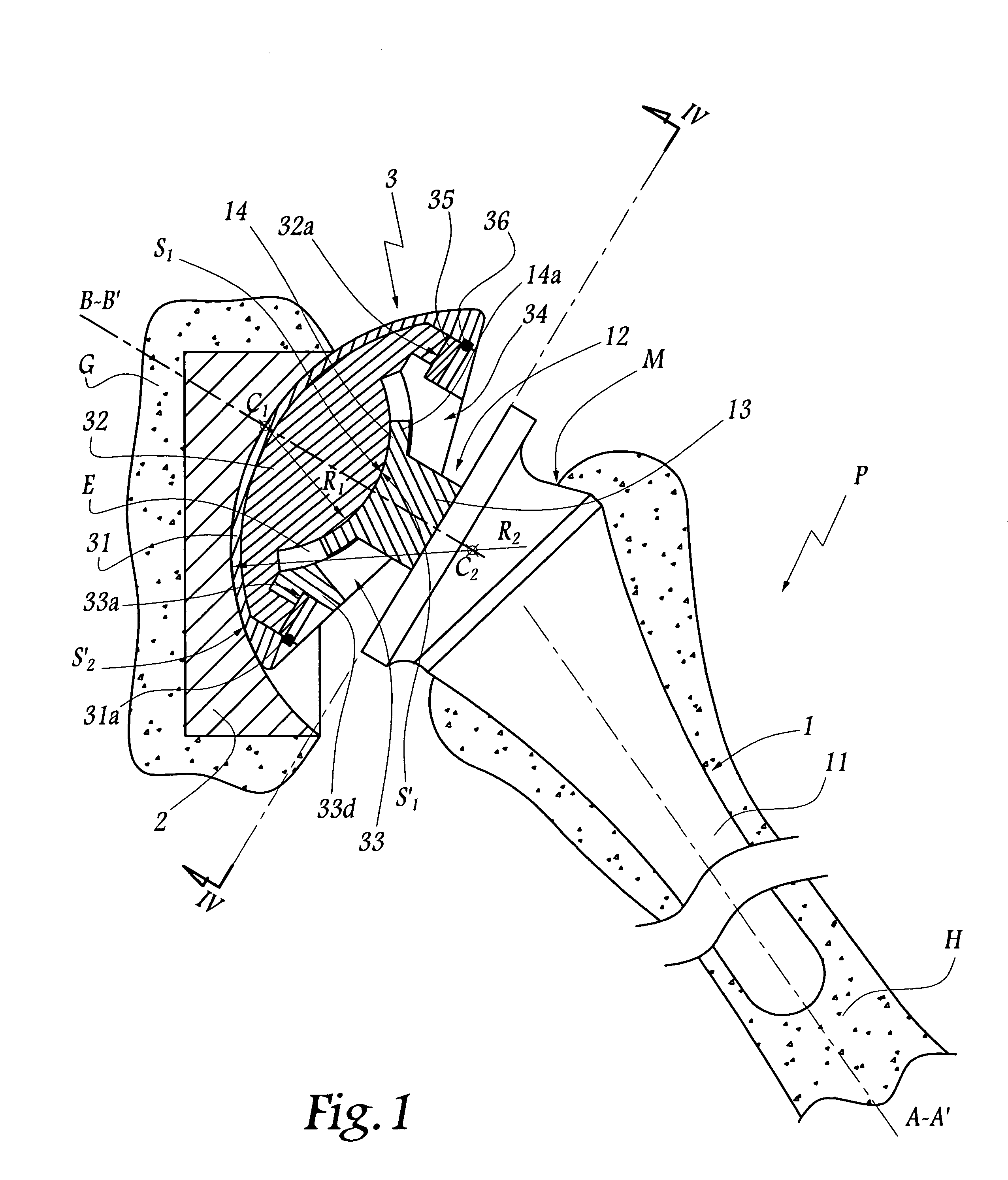
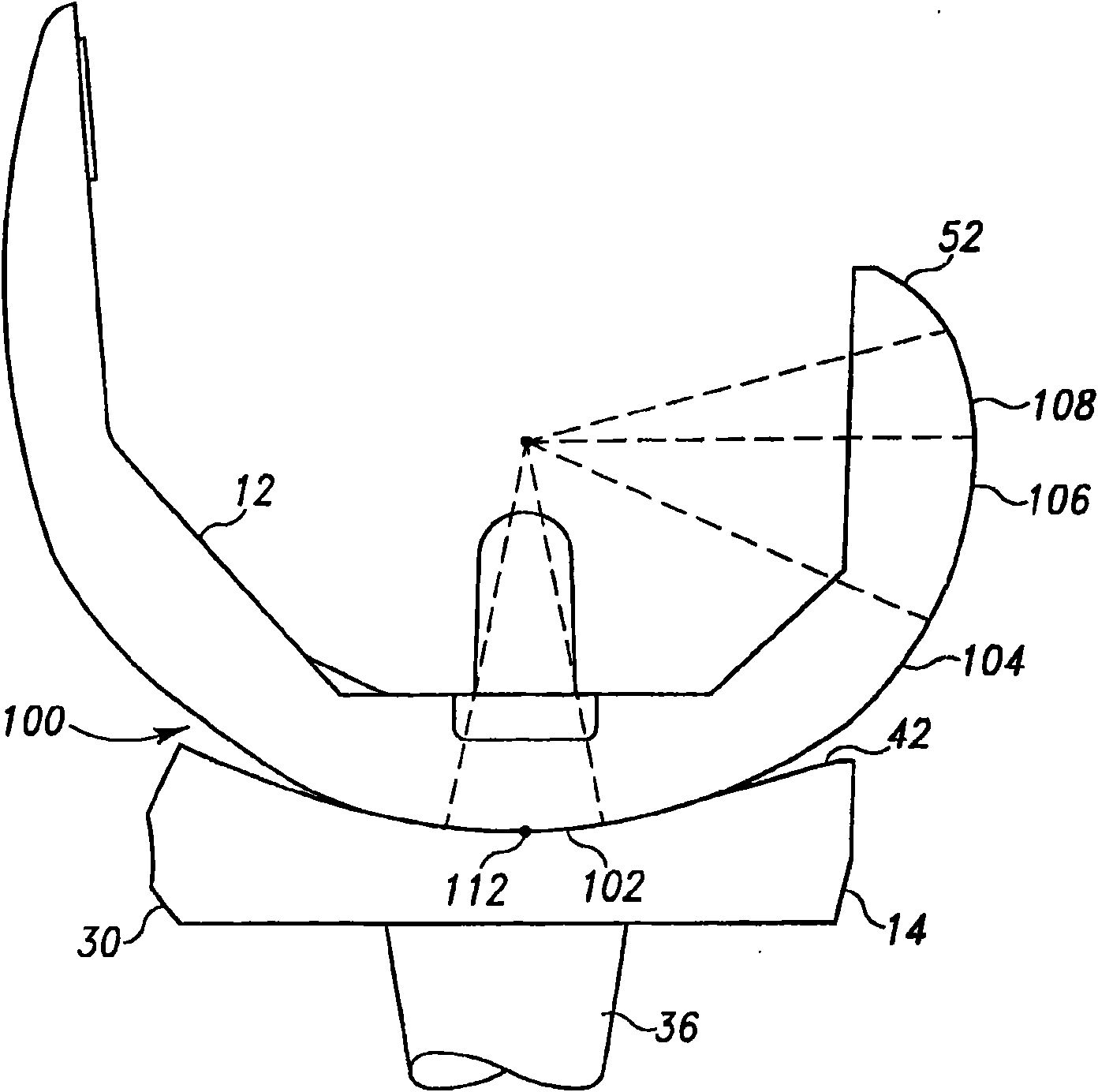
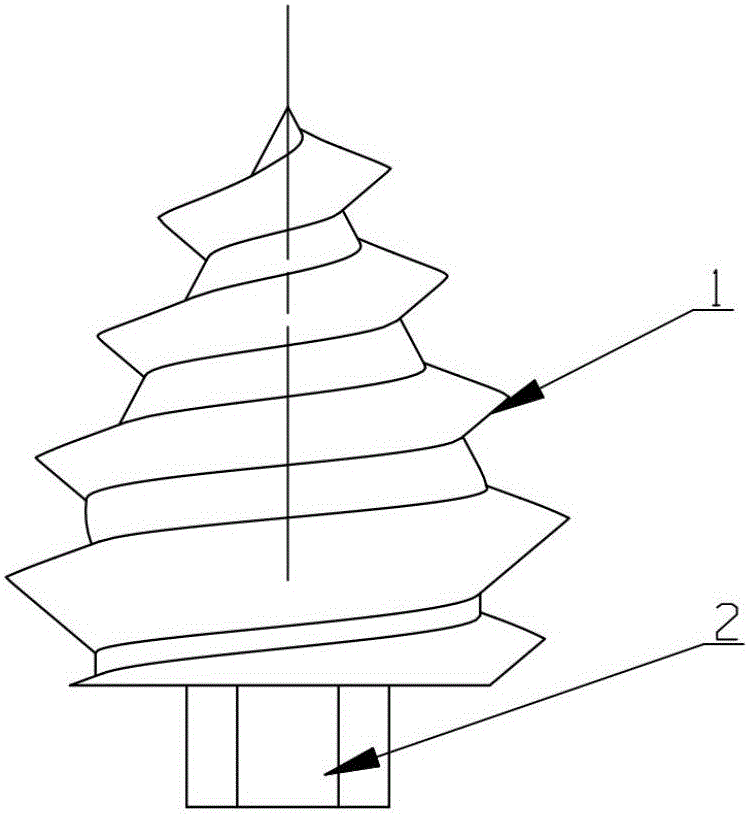
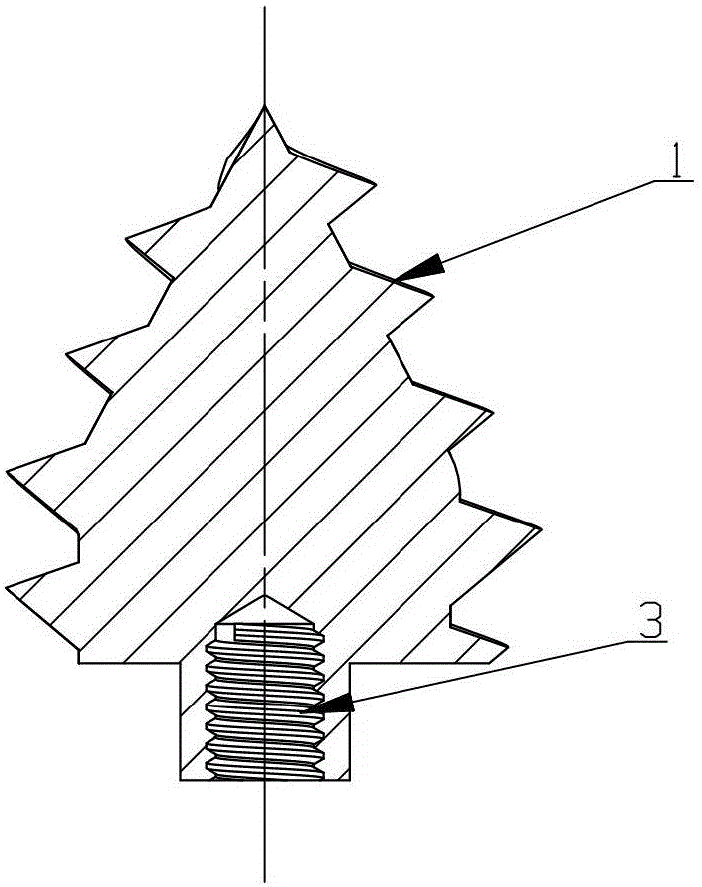
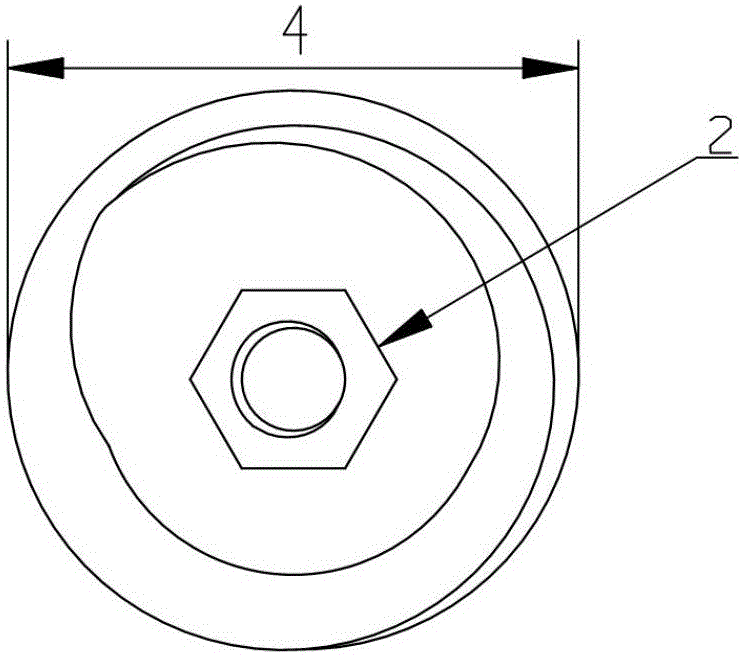
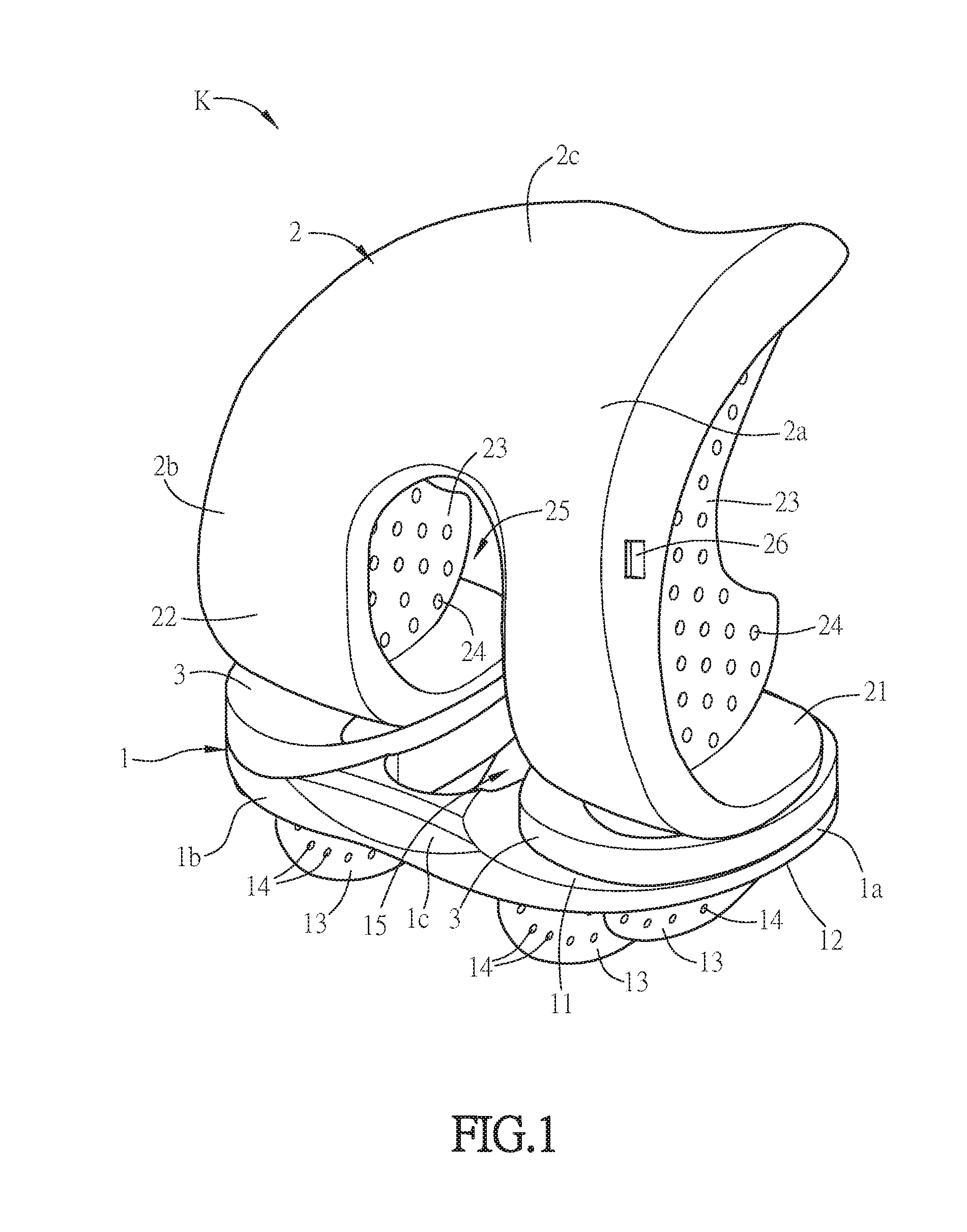
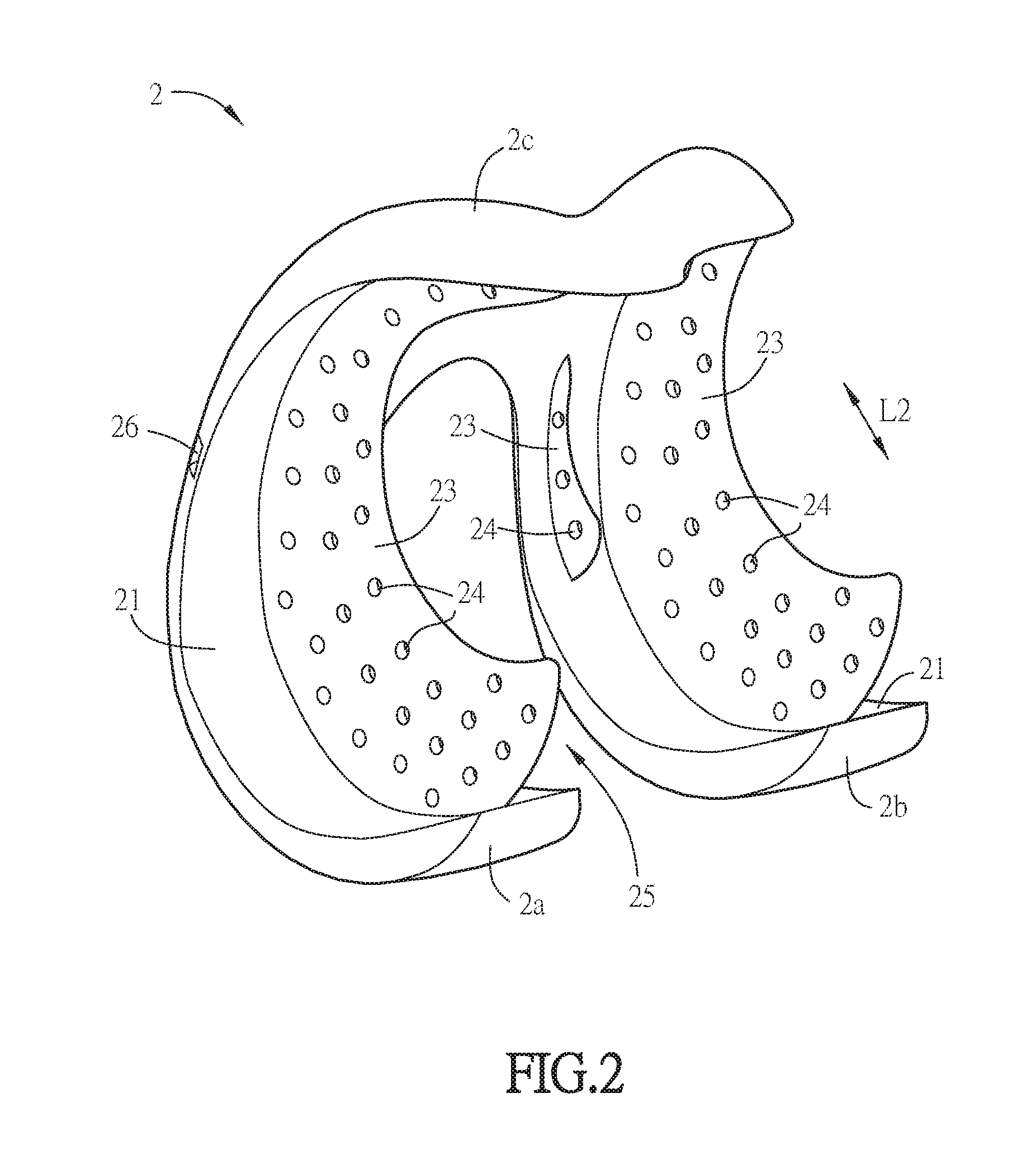
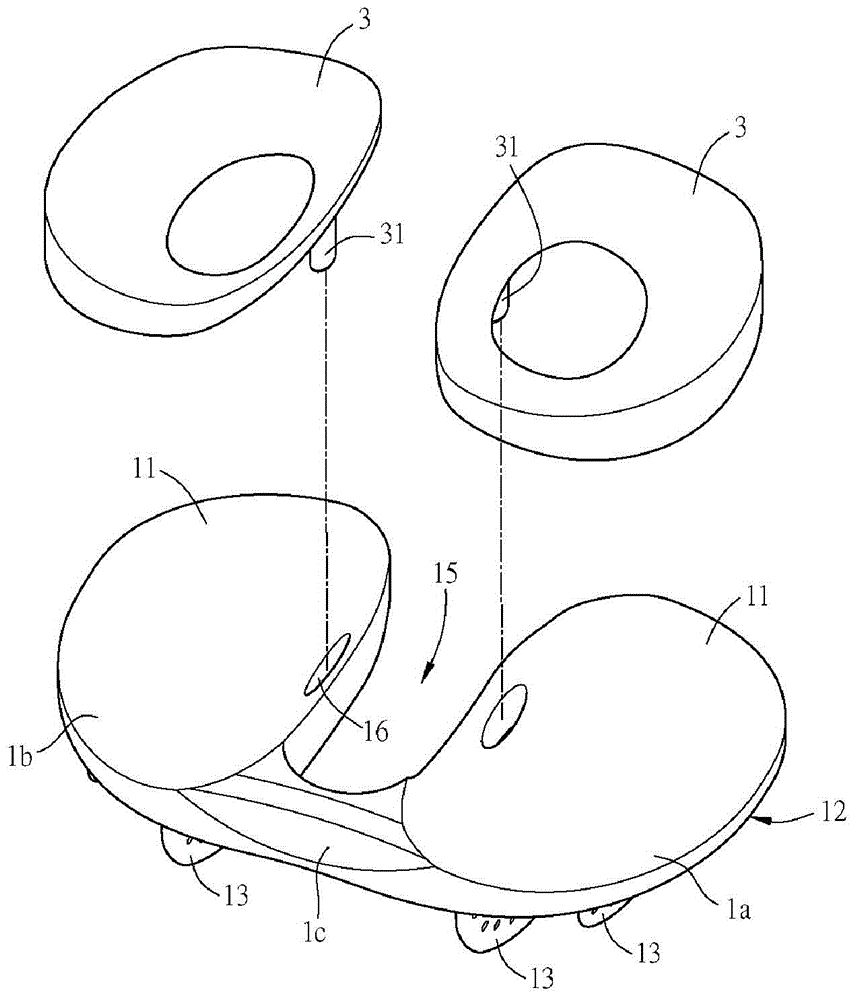
Shoulder or hip prosthesis facilitating abduction
InactiveUS7033396B2Facilitates abductionGreat effortJoint implantsFemoral headsArticular surfacesFemoral component
The prosthesis of this invention comprises a humeral or femoral component presenting a concave articulation surface, and an intermediate component presenting first and second convex articulation surfaces intended to cooperate respectively with said concave articulation surface of the humeral or femoral component and with a concave glenoid or cotyloid articulation surface. The locus of the instantaneous centers of rotation of the first convex articulation surface, with respect to the concave humeral or femoral articulation surface, and the locus of the instantaneous centers of rotation of the second convex articulation surface on the glenoid or cotyloid surface, are located on either side of the first surface.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
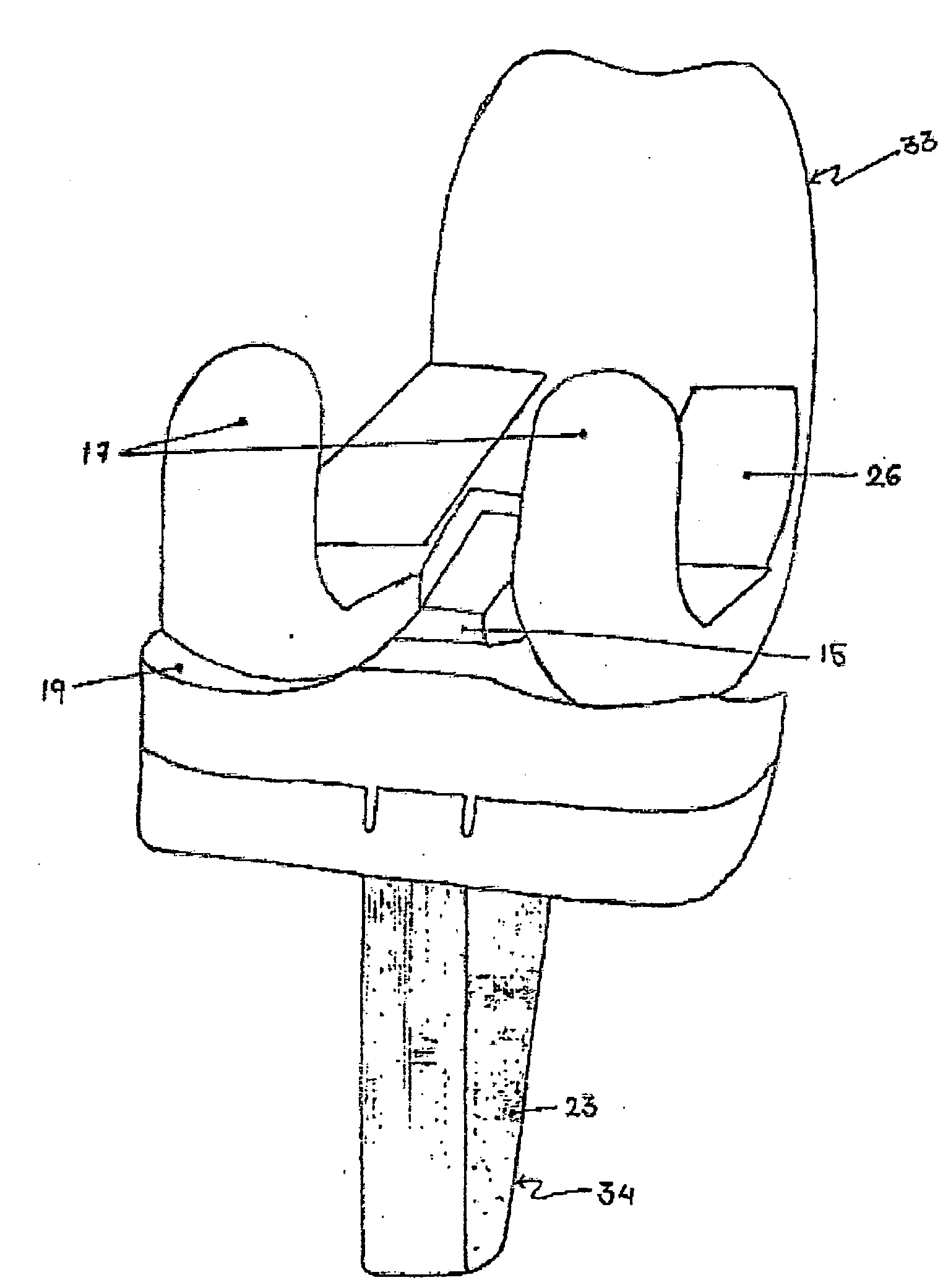
Knee Joint Prosthesis
A knee joint prosthesis is disclosed. The prosthesis has a femoral component and a tibial component. The tibial component has a tibial plateau element fitted in a tibial tray element. A hemi capstan shaped bridge member is provided between replicated condyles on the femoral component. A specially shaped post is provided between kidney shaped meniscal depression on the tibial plateau element. The bridge member and the post act together to form an additional joint for load transfer during deep flexion of the prosthesis in its operative configuration.
Owner:SANCHETI KANTILAL HASTIMAL
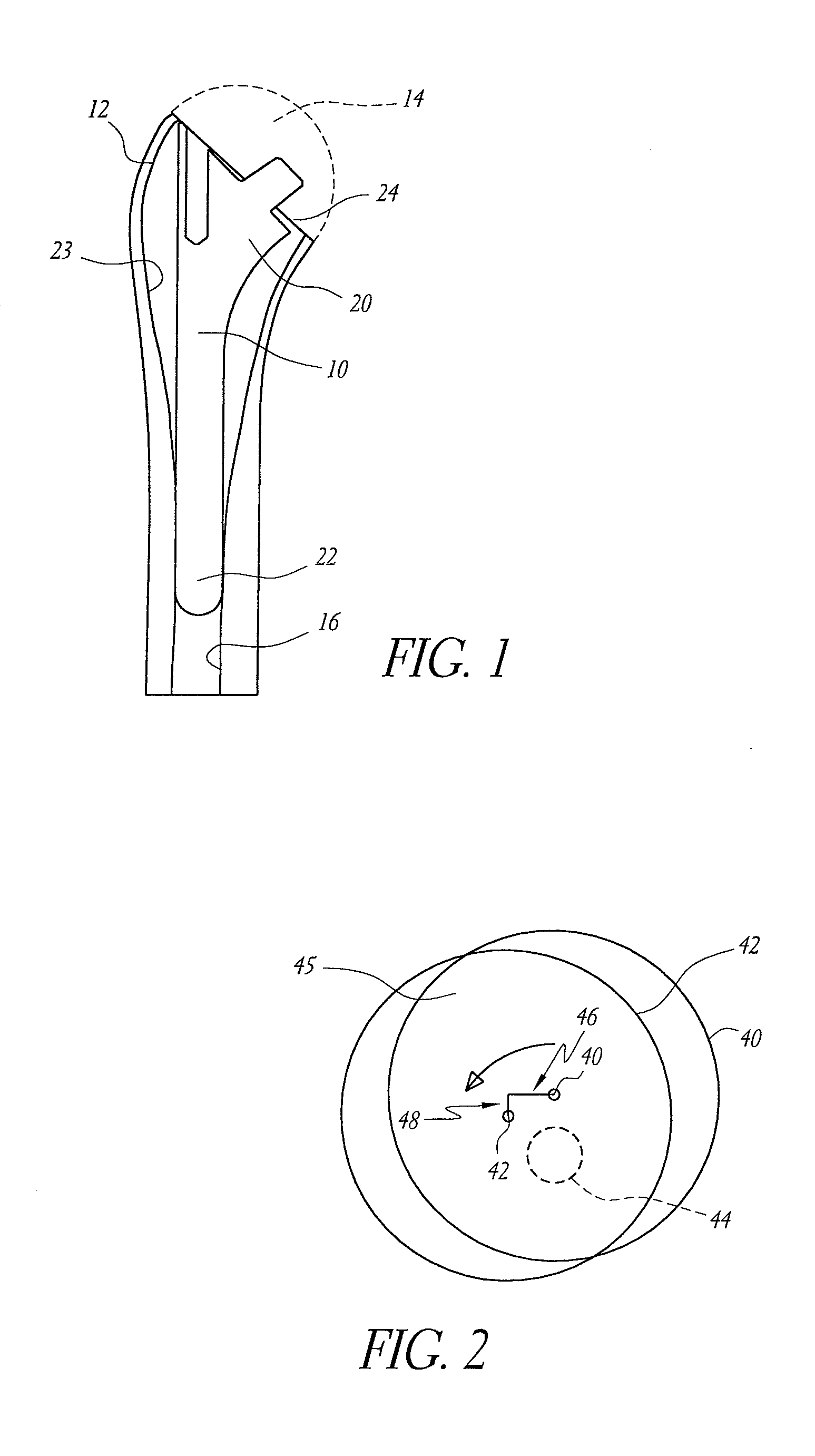
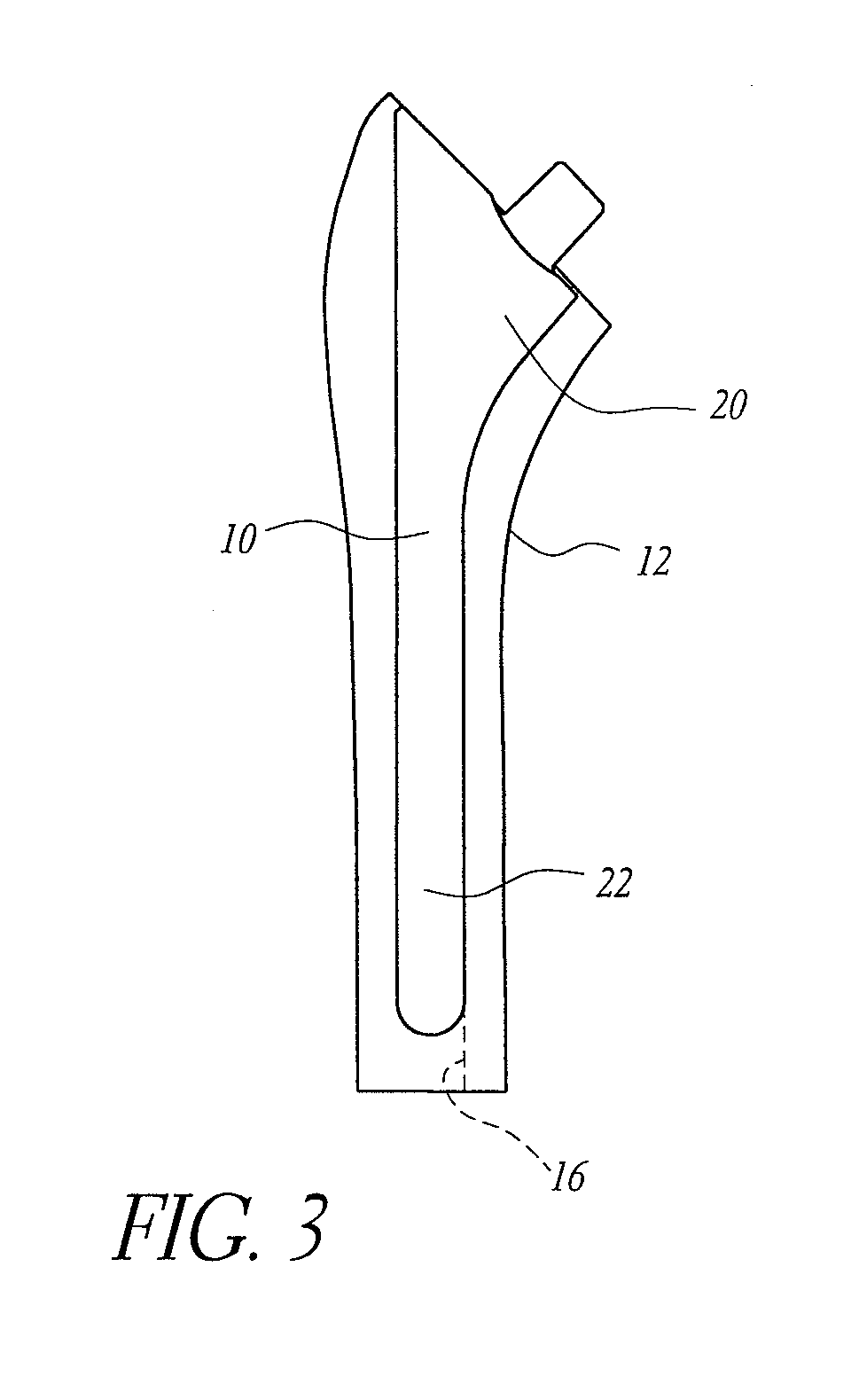
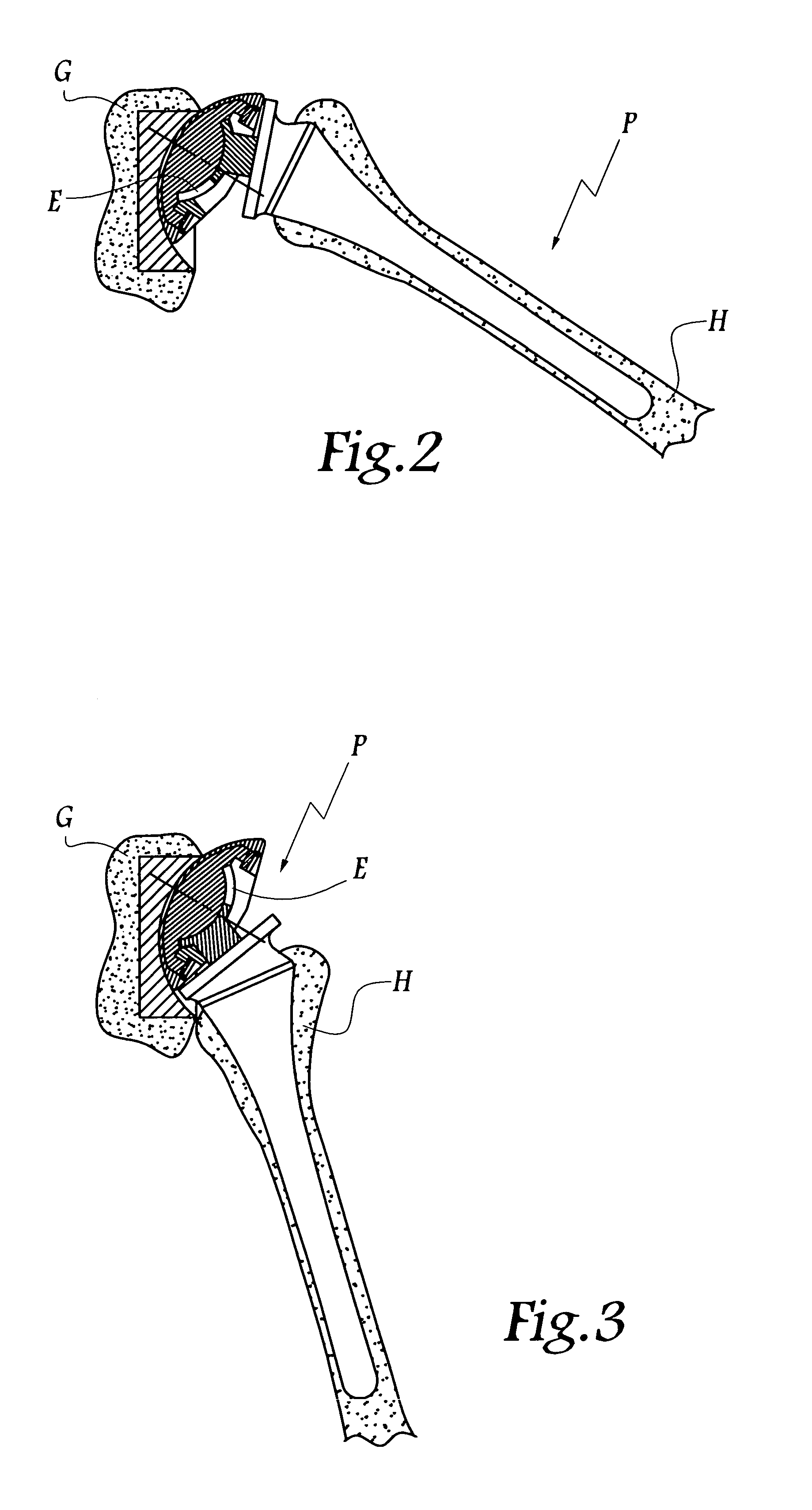
Shoulder or hip prosthesis and process for fitting same
InactiveUS20050165490A1Improve stabilityIncrease amplitudeJoint implantsFemoral headsMedicineAbutment
This prosthesis comprises a humeral or femoral component and an intermediate component. The concave surface of articulation of the humeral or femoral component is formed by a plate connected by a neck to a part of this component adapted to be anchored in the humeral or femoral medullary cavity. The intermediate component is provided with a member for retaining the humeral or femoral component in a position where the plate is in abutment against the first convex surface of the intermediate component. The retaining member defines a non-circular passage in which the neck is adapted to be displaced as a function of the movements of the humeral or femoral component with respect to the other components of the prosthesis. The retaining member defines with the first convex surface of articulation of the intermediate component a volume for receiving a part of the plate projecting radially with respect to the neck.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
Knee joint prosthesis
A knee joint prosthesis is disclosed. The prosthesis has a femoral component and a tibial component. The tibial component has a tibial plateau element fitted in a tibial tray element. A hemi capstan shaped bridge member is provided between replicated condyles on the femoral component. A specially shaped post is provided between kidney shaped meniscal depression on the tibial plateau element. The bridge member and the post act together to form an additional joint for load transfer during deep flexion of the prosthesis in its operative configuration.
Owner:SANCHETI KANTILAL HASTIMAL
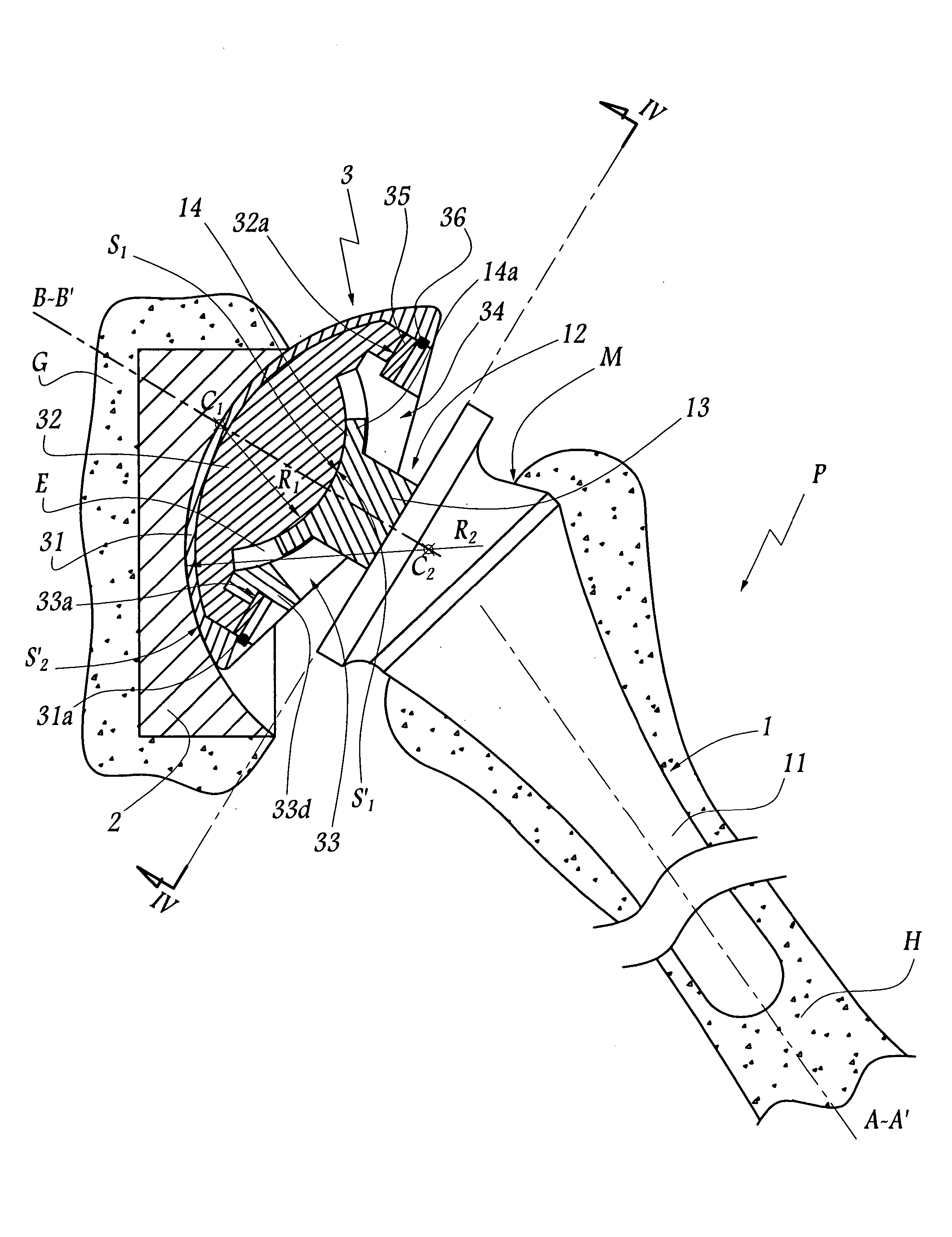
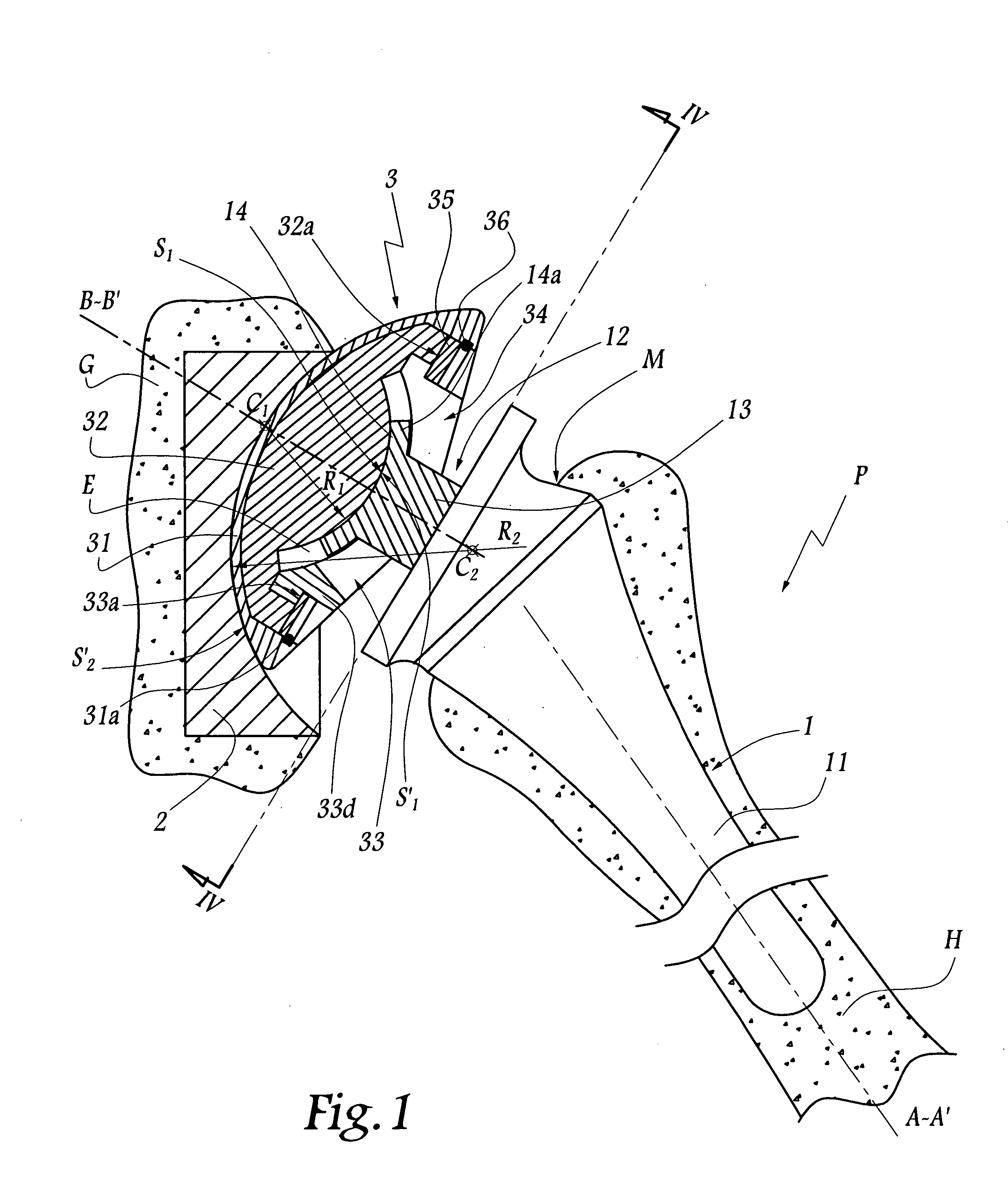
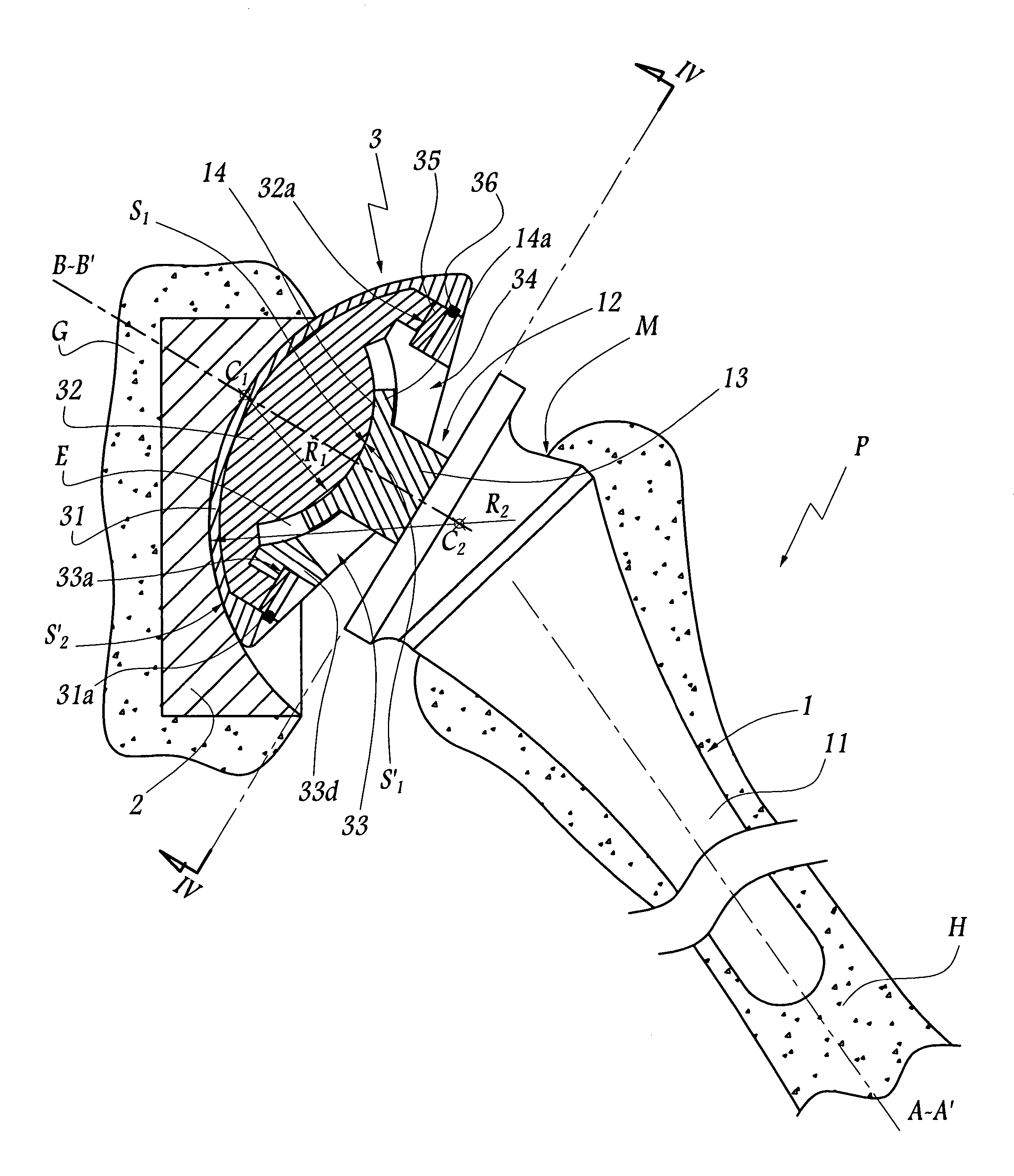
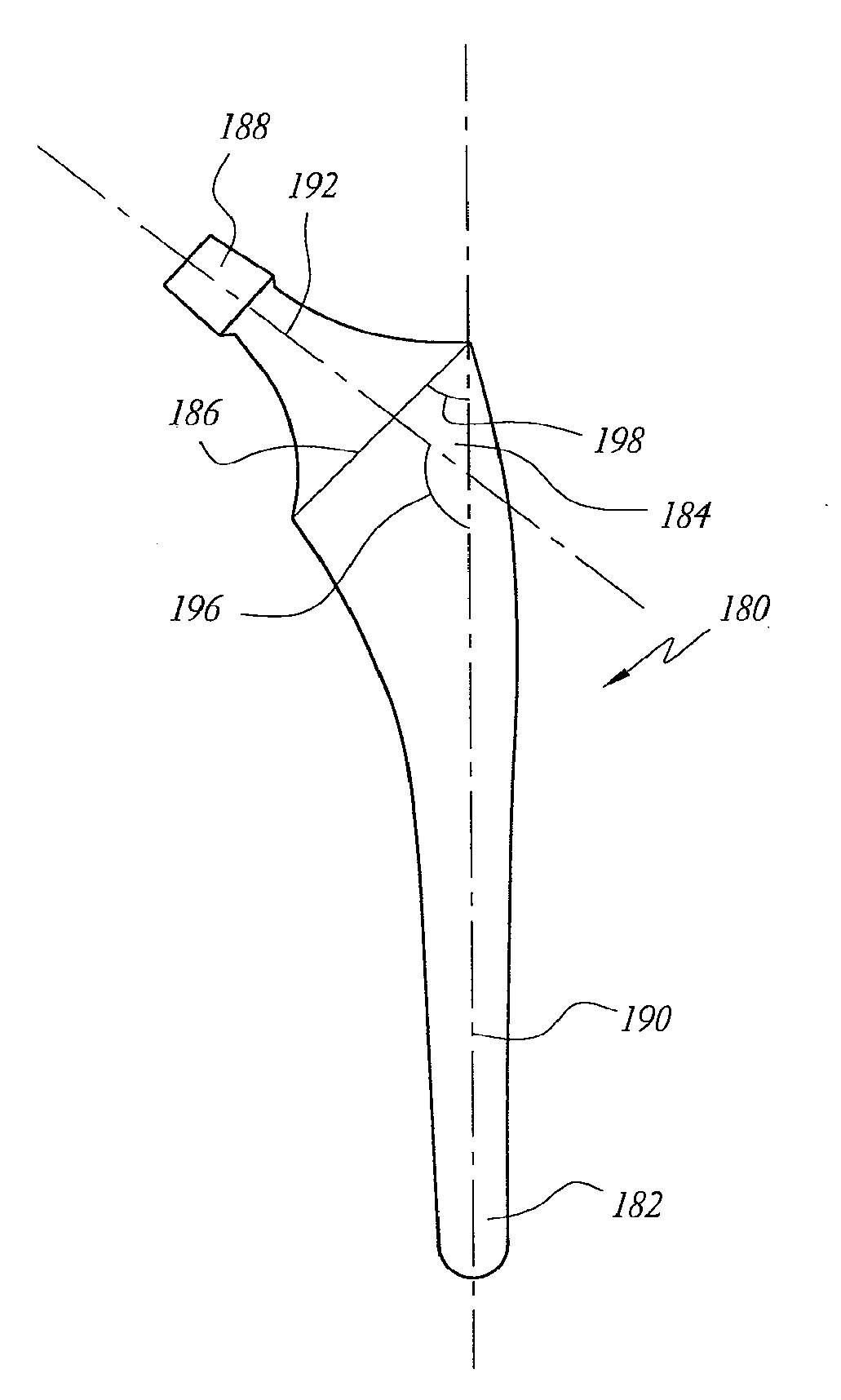
Femoral and humeral stem geometry and implantation method for orthopedic joint reconstruction
InactiveUS20070225821A1Improving conformance and fixationEasy to insertDiagnosticsSurgeryPlastic surgeryJoint reconstruction
The present inventions relate to devices and methods that improve the positioning and fit of orthopedic reconstructive joint replacement stem implants relative to existing methods. For example, an embodiment of the device provides a stem component comprising proximal and distal body portions that can be configured to mimic a geometric shape of a central cavity region created in a bone of a joint for improving conformance and fixation of the stem component thereto. Further, another embodiment provides a system of stem implants that each have a unique medial offset for facilitating the matching of an implant to the geometry of a central cavity region of a bone. Additionally, an inclination angle of a resection surface of each of the implants in the system can remain constant or vary as a function of the medial offset.
Owner:TORNIER INC
Shoulder or hip prosthesis and process for fitting same
This prosthesis comprises a humeral or femoral component and an intermediate component. The concave surface of articulation of the humeral or femoral component is formed by a plate connected by a neck to a part of this component adapted to be anchored in the humeral or femoral medullary cavity. The intermediate component is provided with a member for retaining the humeral or femoral component in a position where the plate is in abutment against the first convex surface of the intermediate component. The retaining member defines a non-circular passage in which the neck is adapted to be displaced as a function of the movements of the humeral or femoral component with respect to the other components of the prosthesis. The retaining member defines with the first convex surface of articulation of the intermediate component a volume for receiving a part of the plate projecting radially with respect to the neck.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
Anterior stabilized knee implant
A posterior cruciate ligament retaining knee implant prosthesis comprising a femoral component including a medial condyle and a lateral condyle separated from one another by an intercondylar channel adapted to accommodate throughput of a native cruciate ligament, both the medial condyle and the lateral condyle posteriorly terminate individually, the medial condyle including a medial condyle bearing surface and the lateral condyle including a lateral condyle bearing surface, the femoral component including an anterior cam, and a tibial component including a medial condyle receiver having a medial condyle receiver bearing surface, the tibial component also including a lateral condyle receiver having a lateral condyle receiver bearing surface, the tibial component also including an anterior post.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
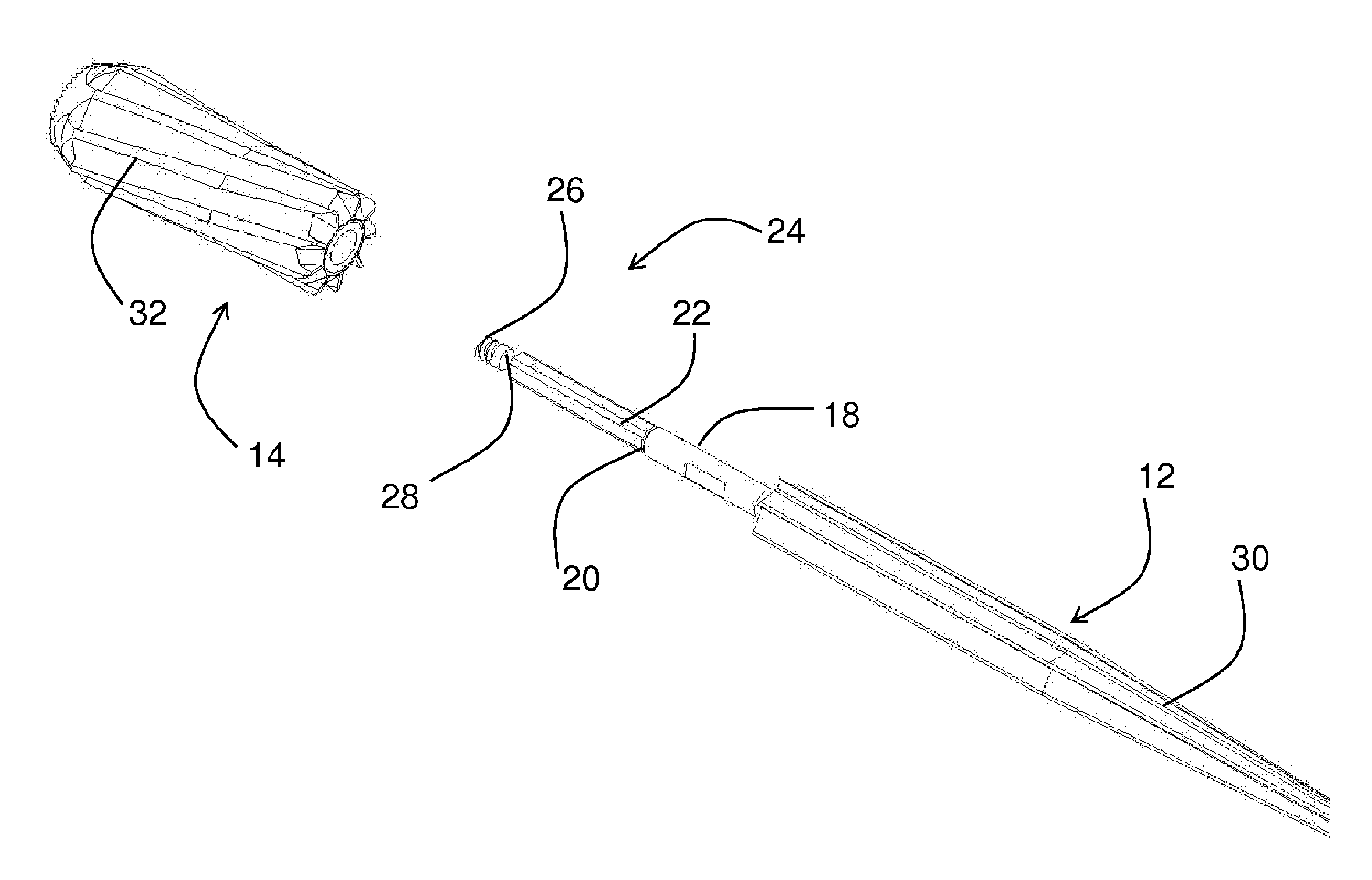
Femoral reaming system and method of performing trial reduction
InactiveUS20110112540A1Improve accuracyReduce in quantityFemoral headsOsteosynthesis devicesEngineeringReamer
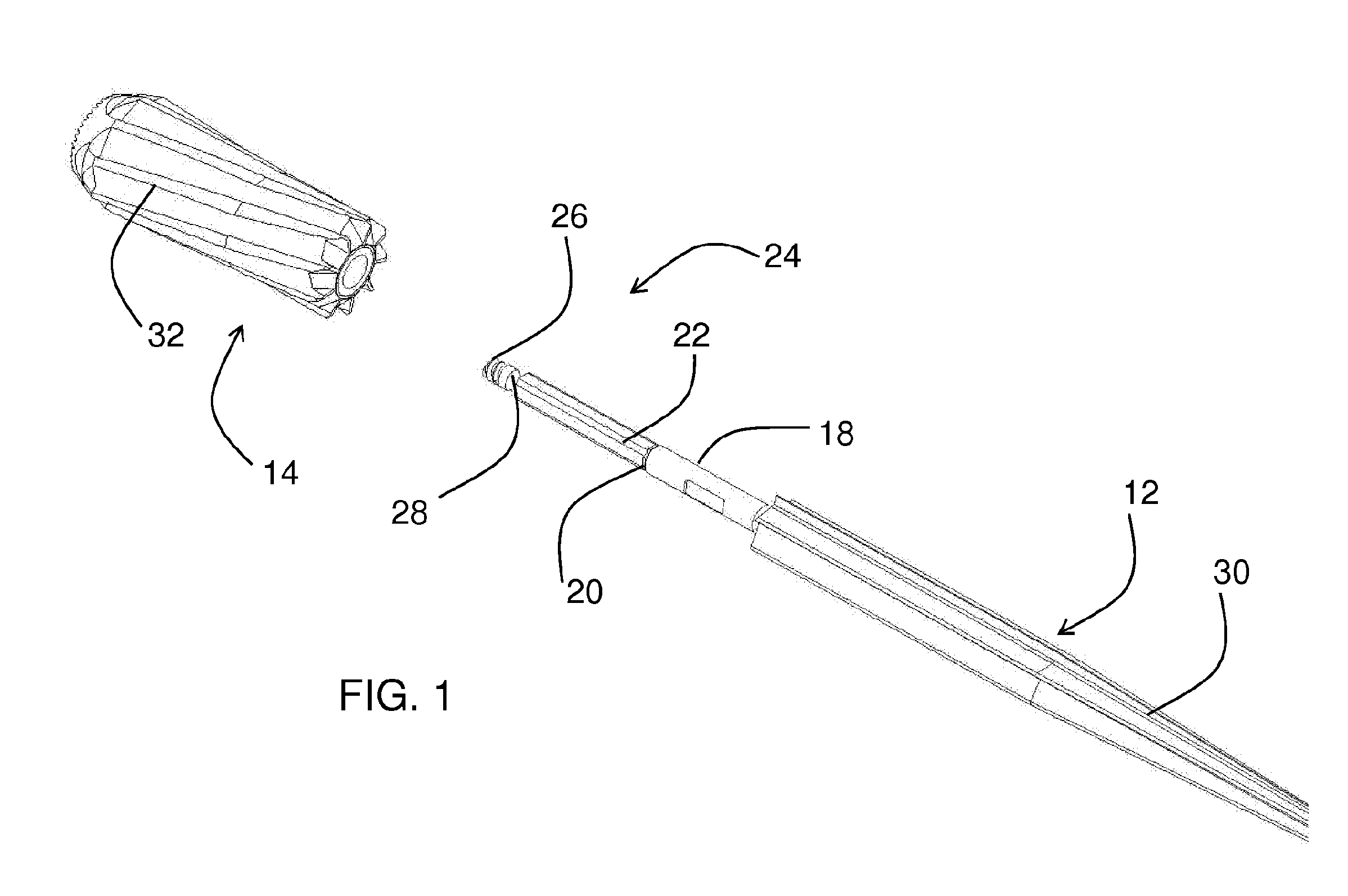
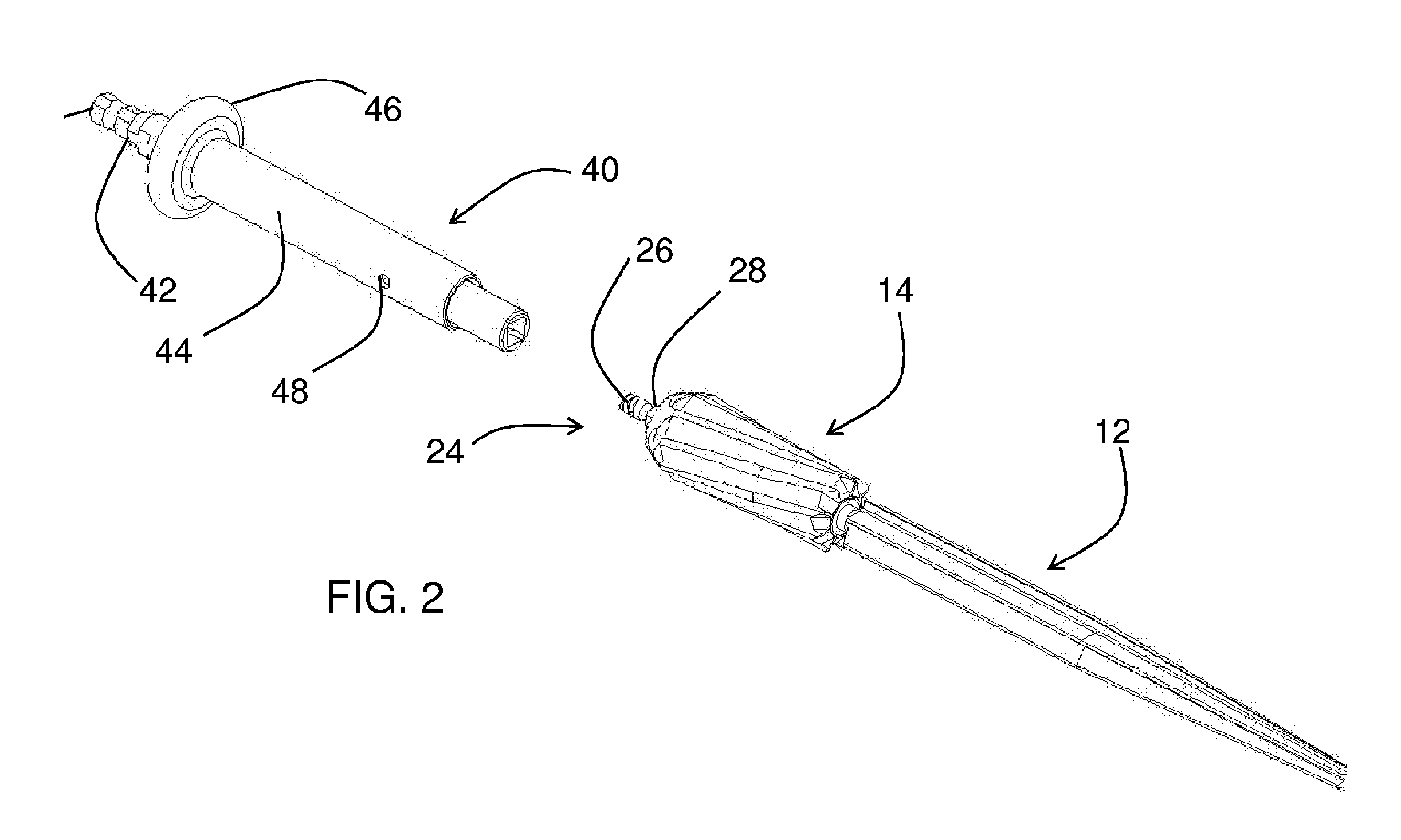
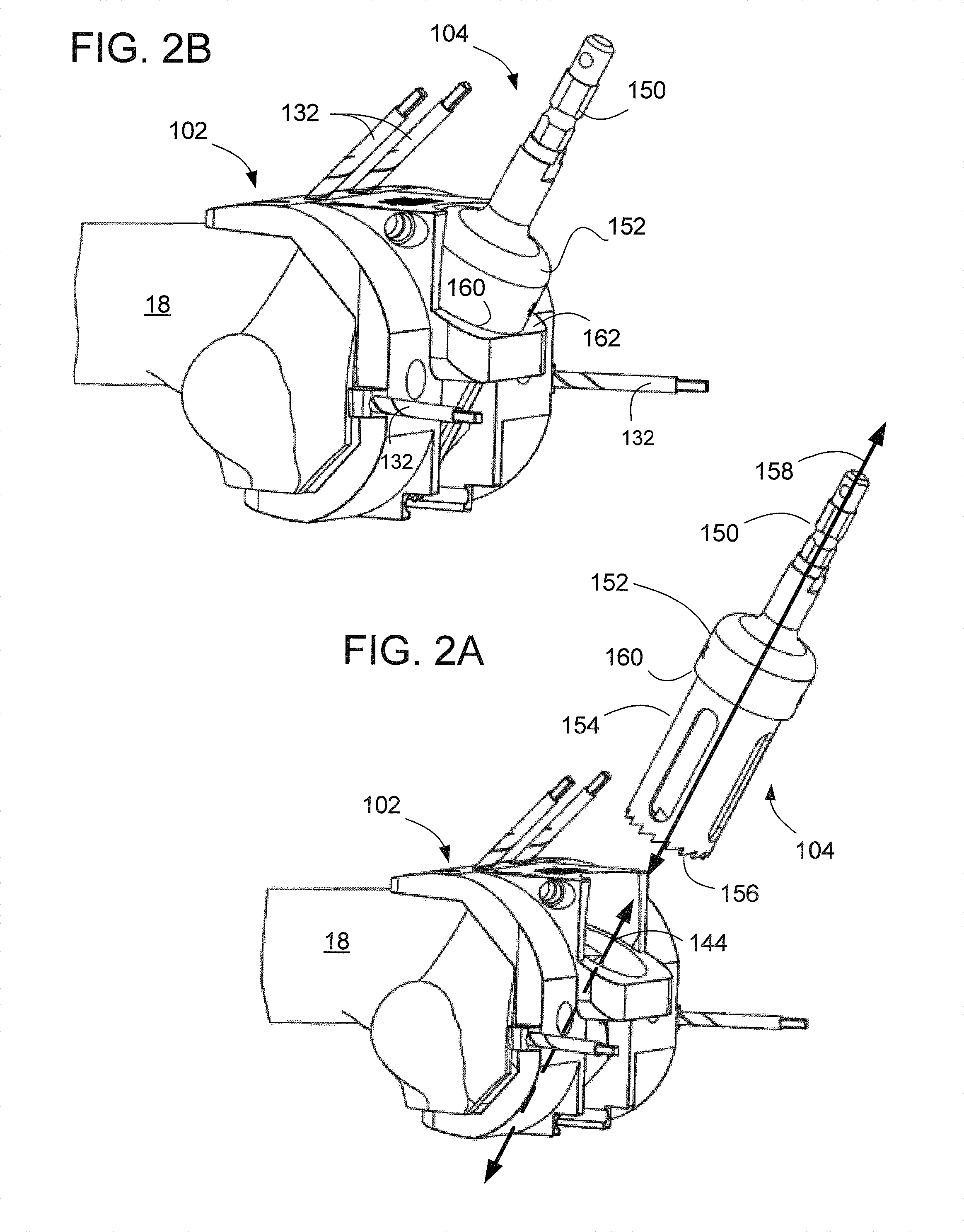
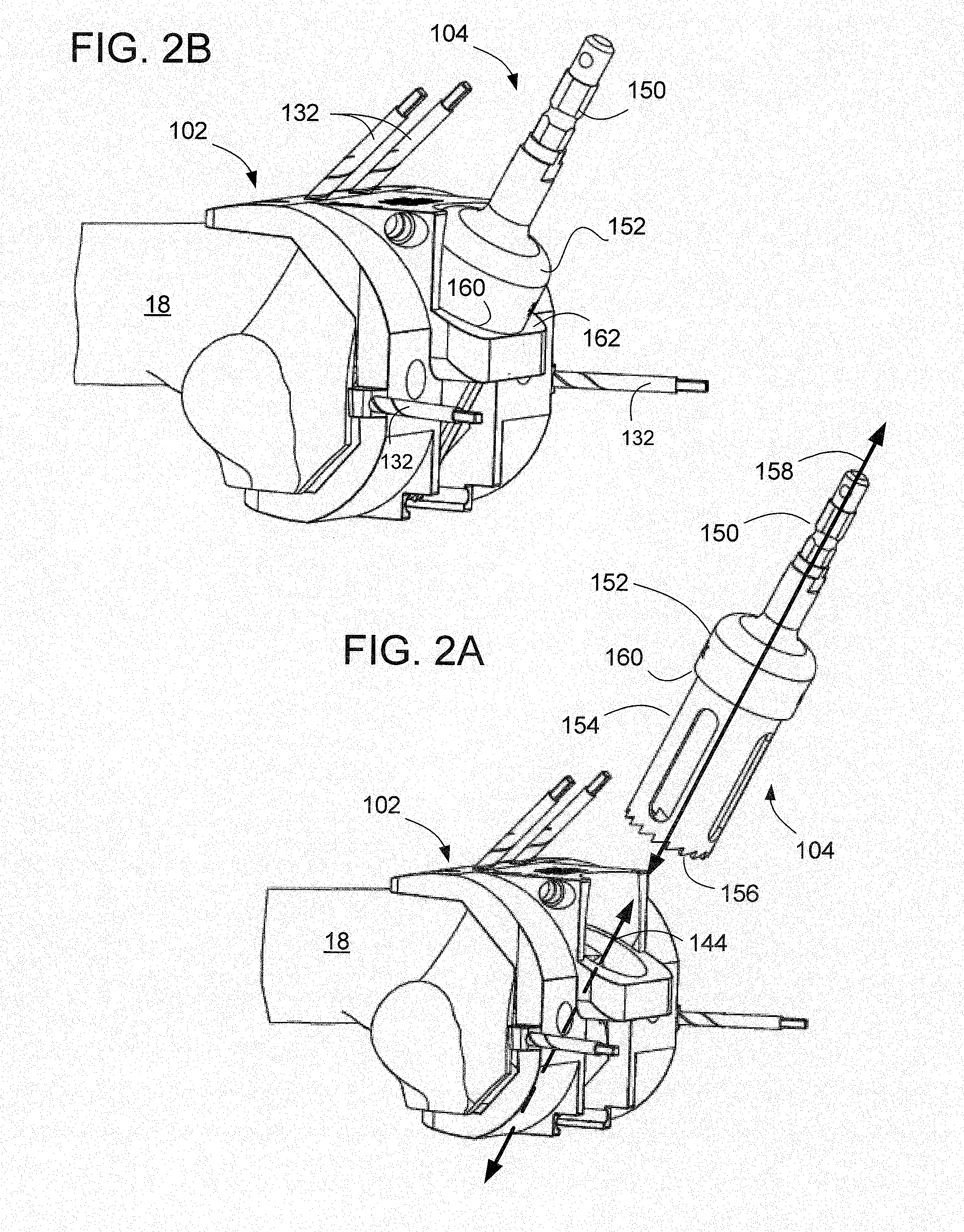
An apparatus (10) for removing bone material comprises a distal cutting instrument (12) and a proximal cutting instrument (14). The distal cutting instrument has at least one first cutting edge (30), a shoulder (20), and a shaft portion (22). The shaft portion (22) has an anti-rotation feature. The at least one first cutting edge (30) removes bone material when moved in a first direction. The proximal cutting instrument (14) is removably attached to the shaft portion (22). The proximal cutting instrument (14) has a first end portion (68) and a second end portion (66). The second end portion (66) contacts the shoulder (20) of the distal reamer (12) when the proximal reamer is mounted to the shaft portion (22). The proximal reamer (14) has at least one second cutting edge (32) and an aperture. The aperture is adapted to receive the anti-rotation feature of the shaft portion (22) of the distal reamer (12). The at least one second cutting edge (32) removes bone material when moved in a second direction.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Methods and apparatus for preparing an intercondylar area of a distal femur
Methods and apparatus provide for modifying an intercondylar notch of a patient's femur, including cutting bone from the intercondylar notch using a hole saw having a hollow cylinder and a circular cutting edge, where the hollow cylinder of the hole saw defines a central longitudinal axis which is oriented with reference to the patient's femur such that the circular cutting edge of the hole saw removes a portion of material from the intercondylar notch of the patient's femur.
Owner:ARTHREX
Knee joint endoprosthesis
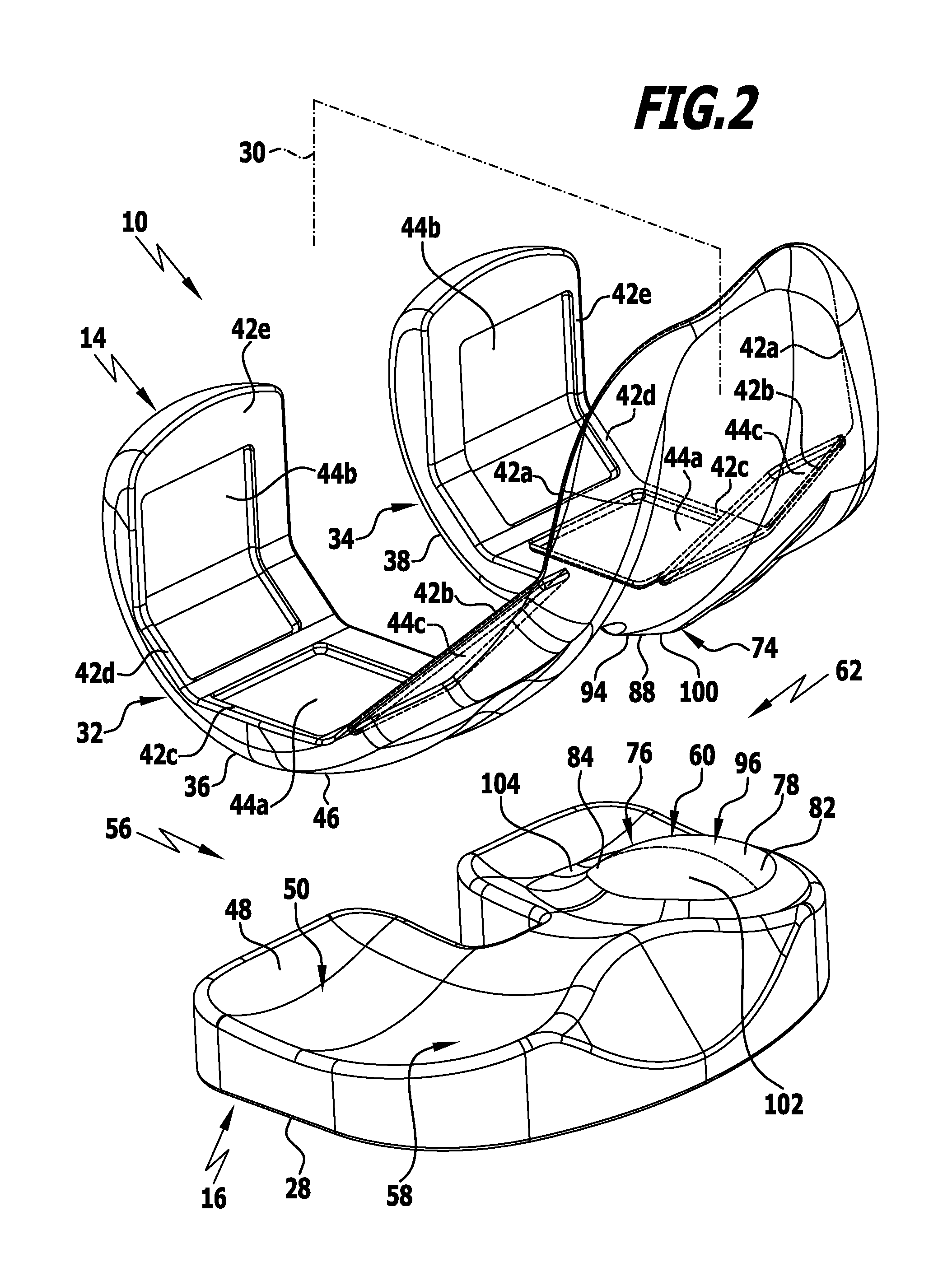
In accordance with the invention a knee joint endoprosthesis comprises a femoral component and a meniscal component mounted for movement relative to and on said femoral component. Said femoral component comprises a medial and a lateral condyle having a medial and a lateral condylar surface. Said meniscal component comprises a medial and a lateral joint surface on which the medial and lateral condylar surfaces bear at least partially. Said medial condyle and said medial joint surface are shaped so as to form a rotary joint with a rotary joint center. Moreover, a rolling motion guiding device is provided for defined rolling of the lateral condylar surface and the lateral joint surface on each other along a curved path which is defined in dependence upon an angle of flexion between femoral component and meniscal component and extends around the rotary joint center.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Lower limb traction device for intramedullary nail surgery
PendingCN110537964AImprove performanceDoes not affect the operationExternal osteosynthesisThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses a lower limb traction device for an intramedullary nail surgery. The lower limb traction device includes a bottom beam, a shank support plate, a thigh backup plate, a sliding block, a traction needle, a traction bow and a pulling mechanism, the sliding block is installed on an axial sliding channel on the bottom beam and provided with sliding block locking screws, the shanksupport plate and the thigh backup plate are hinged in a Chinese character 'ren' shape, the lower end of the thigh backup plate is rotatably connected with the head end of the bottom beam, the lowerend of the shank support plate is rotatably connected with the sliding block, thighs and shanks of a patient respectively abut against the upper part of the thigh backup plate and the upper part of the shank support plate, the traction needle penetrates through the far-end of an anklebone or a shin bone of the patient and is connected between the two ends of the traction bow, and the bow back of the traction bow is connected with the tail end of the bottom beam through the pulling mechanism. According to the lower limb traction device, the patient can be kept in the state of curved leg, reliable traction of the shin bone of the patient can be achieved, all parts are not higher than lower limbs of the patient, and surgery operation is not affected; and according to the lower limb traction device, smooth operation of the intramedullary nail implantation surgery of a thigh bone and the shin bone can be ensured, and the surgical quality and the surgical efficiency are improved.
Owner:THE THIRD HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
Posterior cructiate-retaining orthopaedic knee prosthesis having controlled condylar curvature
The invention relates to a posterior cructiate-retaining orthopaedic knee prosthesis having controlled condylar curvature. The orthopaedic knee prosthesis includes a tibial bearing and a femoral component configured to articulate with the tibial bearing. The femoral component includes a condyle surface curved in the sagittal plane. The radius of curvature of the condyle surface decreases gradually between early-flexion and mid-flexion. Additionally, in some embodiments, the radius of curvature may be increased during mid-flexion.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Femoral and humeral stem geometry and implantation method for orthopedic joint reconstruction
ActiveUS20160361173A1Improving conformance and fixationEasy to insertDiagnosticsSurgeryJoint reconstructionHumerus
The present inventions relate to devices and methods that improve the positioning and fit of orthopedic reconstructive joint replacement stem implants relative to existing methods. For example, an embodiment of the device provides a stem component comprising proximal and distal body portions that can be configured to mimic a geometric shape of a central cavity region created in a bone of a joint for improving conformance and fixation of the stem component thereto. Further, another embodiment provides a system of stem implants that each have a unique medial offset for facilitating the matching of an implant to the geometry of a central cavity region of a bone. Additionally, an inclination angle of a resection surface of each of the implants in the system can remain constant or vary as a function of the medial offset.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Knee joint prosthesis pad, shinbone base element and knee joint prosthesis
ActiveCN102614036AExtended service lifeAvoid wear and tearJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses a knee joint prosthesis, a knee joint prosthesis pad and a shinbone base element. The knee joint shinbone base element is combined with a shinbone, and comprises a base, wherein a boss is arranged on the base; and a guide channel through which an anterior cruciate ligament passes is formed on the boss and the base. The knee joint prosthesis pad is provided with a pad opening or a pad through hole for accommodating the boss of the shinbone base element. The knee joint prosthesis comprises the shinbone base element, the knee joint prosthesis pad and a shinbone element combined with the shinbone. The attaching position of the anterior cruciate ligament relative to the shinbone base element can be kept consistent with the attaching position of a human body anterior cruciate ligament in anatomy on the shinbone, so that the knee joint prosthesis can be used for rebuilding an anterior cruciate ligament, and a patient recovers body feel and moves well after replacement of the knee joint prosthesis.
Owner:北京威联德骨科技术有限公司 +1
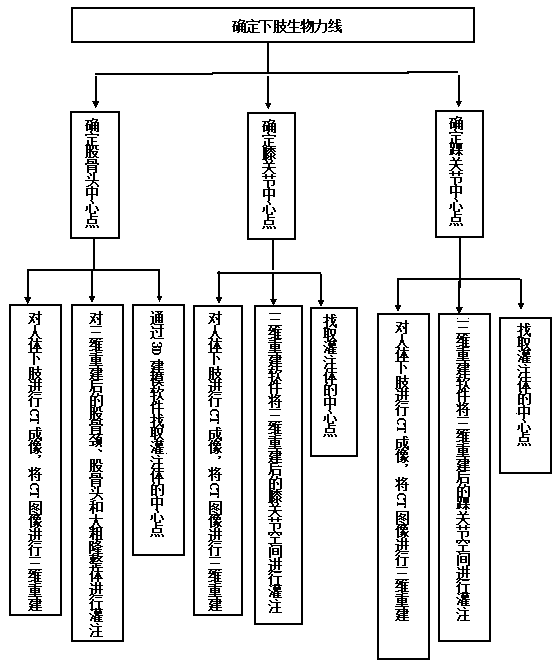
Method for determining biological force line of lower limbs in three dimensional space
InactiveCN108042217AHigh precisionMeasured in accordance withDiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingKnee JointAnkle
The invention discloses a method for determining the biological force line of lower limbs in a three dimensional space. A caput femoris central point, a knee joint central point and an ankle joint central point are determined respectively in the three dimensional space, the caput femoris central point is used for three-dimensional reconstruction of the lower limbs of the human body, perfusion is conducted on collum femoris, caput femoris and greater trochanter after three-dimensional reconstruction, and then the geometric center of a perfusion body is found through Mimics or 3D Slicer; the knee joint central point adopts the center of a knee joint non-bony space perfusion body; the ankle joint central point adopts the center of an ankle joint non-bony space perfusion body. The method avoids the defects that in the prior art, the measurement result, obtained by visual inspection, protractor measurement and body X-ray measurement on a two-dimensional platform, of the force line of the lower limbs is greatly affected by interference, data has no standard and the subjectivity is high; the accuracy of the method is higher, and the method is more in line with the measurement of the forceline of the lower limbs.
Owner:成都真实维度科技有限公司 +1
Endoprosthesis for reestablishment of knee joint cruciate ligaments under full arthroscope
ActiveCN105055049AAvoid the disadvantage of low healing rateGood curative effectLigamentsMusclesCruciate ligamentTibia
The invention discloses an endoprosthesis for reestablishment of knee joint cruciate ligaments under a full arthroscope. The endoprosthesis comprises a first bolt prosthesis and a second bolt prosthesis which are connected to a thighbone and a shinbone respectively, wherein an artificial tendon prosthesis is connected between the first bolt prosthesis and the second bolt prosthesis; each of the first bolt prosthesis and the second bolt prosthesis comprises a bolt prosthesis front section and a bolt prosthesis back section, and the bolt prosthesis front section and the bolt prosthesis back section are in detachable connection with each other; the bolt prosthesis front section is provided with a self-tapping external thread capable of tapping into the thighbone and the shinbone; the outer surface of the bolt prosthesis back section is provided with an external thread continuously butted with the self-tapping external thread of the bolt prosthesis front section, and adopts a material capable of growing together with bones; and muscle tendon fixation forcing screws are arranged between the first bolt prosthesis and the artificial tendon prosthesis and between the second bolt prosthesis and the artificial tendon prosthesis. Physical fixation and biological fixation are combined to realize the reestablishment of the knee joint cruciate ligaments without establishing a bone channel penetrating through the thighbone, a knee joint cavity and the shinbone, so that operation difficulty is obviously reduced, various complications are avoided, the tensile force of the reestablished artificial ligaments can be adjusted, the operation accuracy is improved and the operation curative effect is promoted.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for positioning human body knee joint flexible motion axis in lateral femoral condyle long-axis section
The invention relates to a method for positioning a human body knee joint flexible motion axis in lateral femoral condyle long-axis section, which comprises the steps of: acquiring image data of a human body knee joint full bone structure by using a CT machine, and constructing a lateral femoral condyle three-dimensional geometrical model by using the image data; then determining a lateral femoral condyle long-axis section and a lateral femoral condyle surface curve; dividing the lateral femoral condyle surface curve into arc sections with equal lengths; calculating positions of centers of circles of the arc sections in the lateral femoral condyle long-axis section; using the positions of the centers of circles as a human knee joint flexible motion axis; and finally, calculating a knee joint instant center curve according to the positions of the centers of circles of all arc sections. The invention realizes the positioning of important kinematics parameters of the knee joint according to the kinematics characteristics of determining the knee joint flexible motion axis by the lateral femoral condyle dissection shape, and has practical values on researching the human body individualized knee joint kinematics, the knee joint prosthesis design and the knee joint motion stimulation, and important significance for the diagnosis and the prognosis evaluation of knee joint diseases.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Customized compound bone cutter for femoral condyle
The invention relates to a customized compound bone cutter for femoral condyle which is used for cutting the bone of the femoral condyle in knee surgery. The customized compound bone cutter for femoral condyle comprises a paracondyloid positioning surface, a remote-end positioning surface, a paracondyloid fixing hole, a paracondyloid fixing inclined hole, a remote-end fixing inclined hole, a force line inspection line, a femoral condyle prosthesis positioning hole, a femoral condyle remote-end bone cutting groove, a paracondyloid bone cutting groove, a front inclined-surface bone cutting groove, a hypocondyle bone cutting groove, a rear inclined-surface bone cutting groove and an intercondylar bone cutting groove; the femoral condyle model number is determined by virtue of preoperative planning based on the CT data of a patient, and then the contact surface, the fixed point and each cutting surface can be determined; the customized compound bone cutter for femoral condyle has the advantages that various parameters are more accurate, the used operating tools are greatly reduced, the operating time is greatly shortened, the infection risk is reduced, pulp exposing is avoided, wound is reduced, and the dependency on the experience of a doctor is reduced; as a result, the customized compound bone cutter for femoral condyle is especially suitable for operations not suitable for conventional operating tools.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
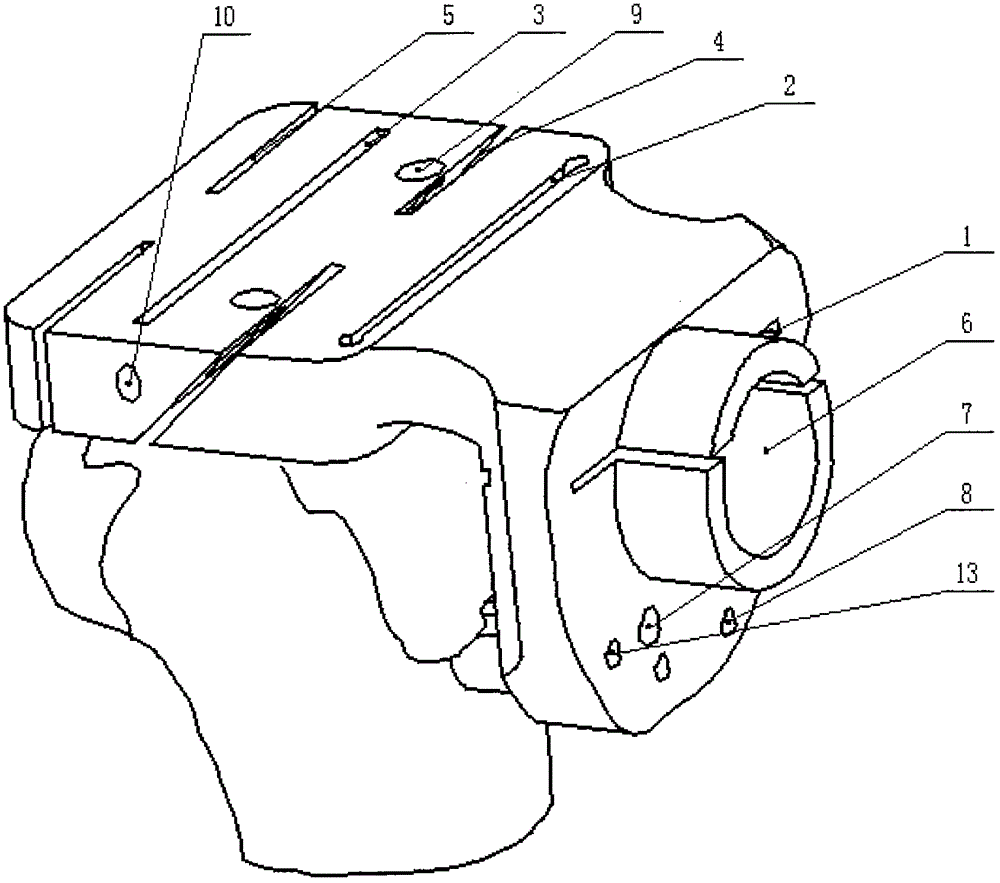
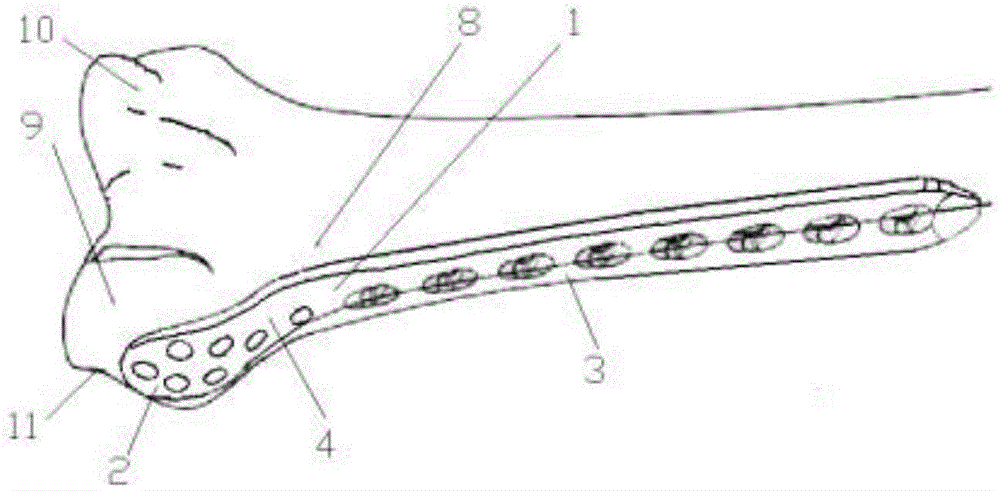
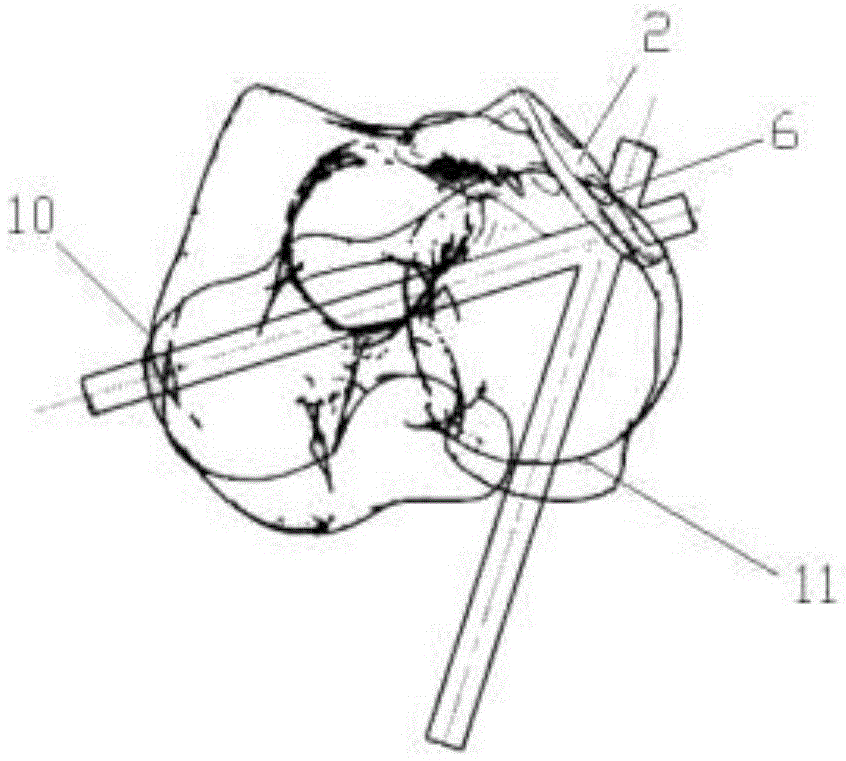
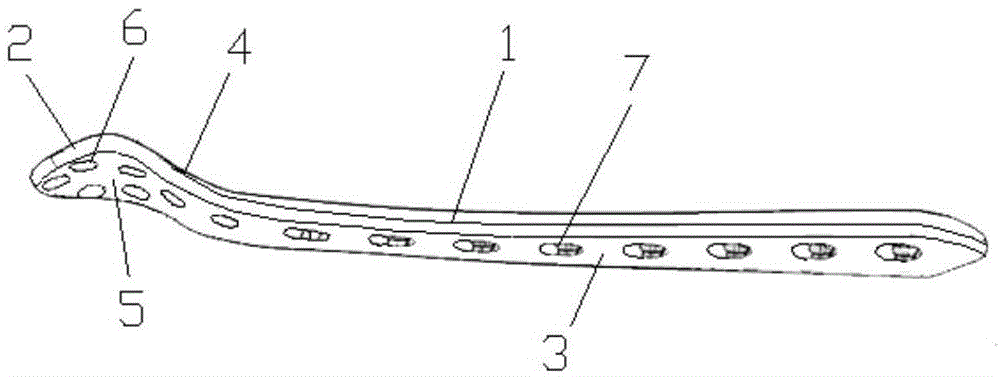
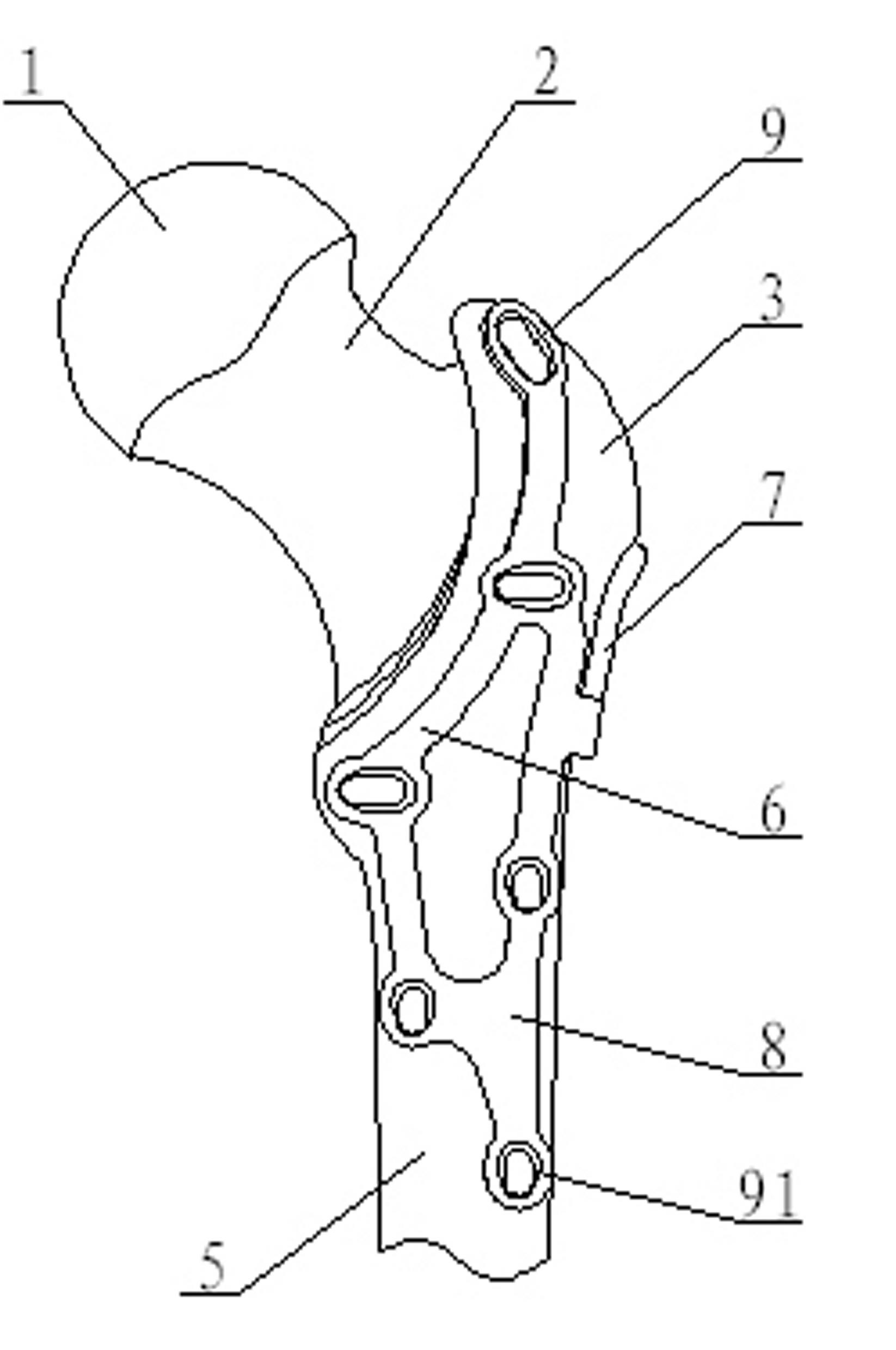
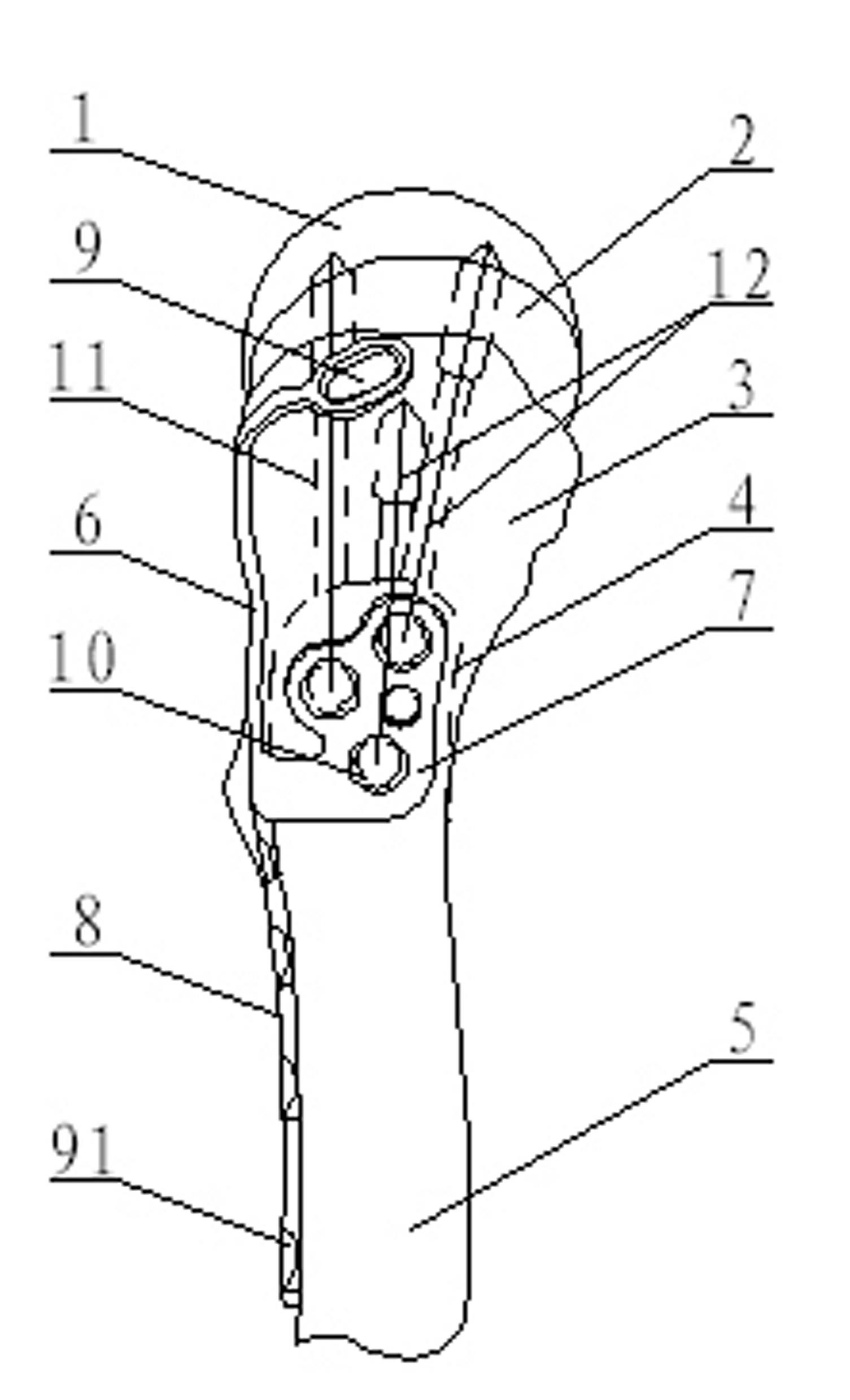
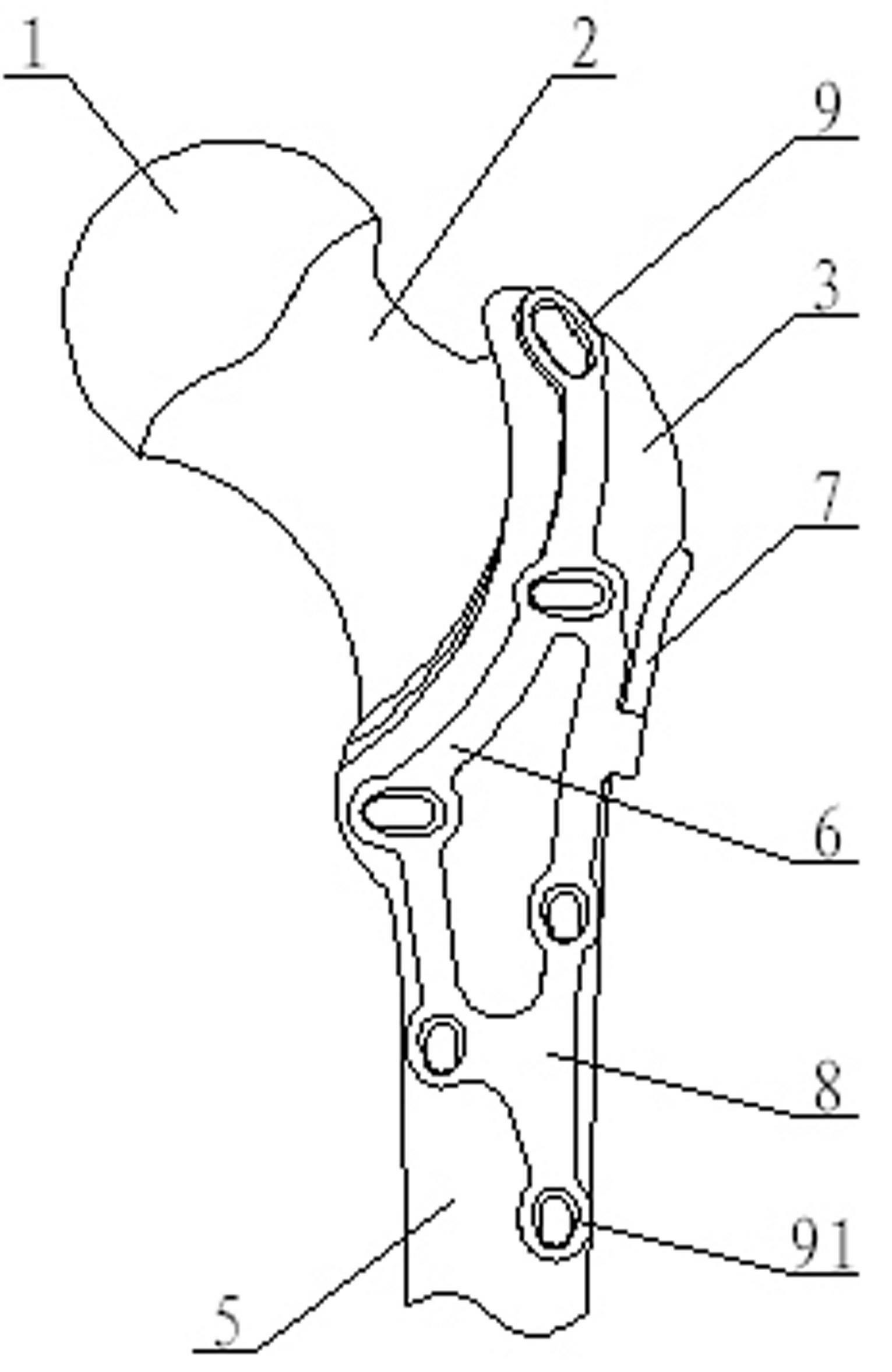
Bone plate implanted from front inner side of distal femur
ActiveCN105520777AGuaranteed to embedImprove gripInternal osteosythesisBone platesBody of femurDiaphyseal fracture
The invention provides a bone plate implanted from the front inner side of the distal femur, belonging to the technical field of medical apparatus and instruments for the department of orthopaedics, and used for treating the condylar fracture and bone shaft fracture of the distal femur. The technical scheme is as follows: the bone plate is composed of a bone plate condylar part, a transitional face and a bone plate shaft part which are connected together, wherein the bone plate condylar part is opposite to the front inner side surface of the condyle of the distal femur, the lower surface of the bone plate condylar part is adaptive to the front inner side surface of the condyle of the distal femur in shape, the bone plate shaft part is opposite to the inner side surface of the distal femur, the lower surface of the bone plate shaft part is adaptive to the inner side surface of the distal femur in shape, and a plurality of fixing holes are uniformly distributed on the bone plate condylar part and the bone plate shaft part. The bone plate provided by the invention belongs to an innovation for the bone plate for the distal femur, therefore, the problem that when the existing bone plate is implanted from the outer side of the distal femur, the fixation for the condyle fracture on the inner side of part of the distal femur is not firm is solved, and the fracture blocks on the inner side of the distal femur can be effectively and firmly fixed, so that the heal of the fracture blocks on the inner side is promoted, and therefore, the bone plate has extremely good promotion and utilization values in the industry.
Owner:侯志勇
Reconstruction device of humerus or thighbone near end
ActiveCN103519921AAchieve reconstructionReduce manufacturing costJoint implantsHip jointsRight femoral headBenign bone tumours
The invention discloses a reconstruction device of a humerus or a thighbone near end. The reconstruction device comprises a prosthesis and a titanium cage, wherein the prosthesis comprises a combined prosthesis head and a prosthesis handle; the titanium cage is arranged outside the prosthesis handle, and the upper end of the titanium cage is connected with the prosthesis head. When the prosthesis is a humerus prosthesis, the prosthesis head comprises a humerus head and neck, and the humerus head and neck is formed by a humerus head and a humerus neck connected with the humerus head; the prosthesis handle comprises a humerus handle connected with the humerus neck; when the prosthesis is a prosthesis on the upper middle section of a thighbone, the prosthesis head comprises a thighbone head and neck, and the prosthesis handle comprises a thighbone handle. According to the reconstruction device, not only can the humerus or the thighbone near end be replaced and shoulder joints or hip joints be constructed, but also reconstruction for the defect after bone tumours of the humerus or the thighbone near end are removed can be achieved, and the reconstruction device is suitable for reconstruction of severely smashed C-shaped fracture conditions of humerus (thighbone) backbone near ends.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Knee joint prosthesis and tibial component and femoral component thereof
A knee joint prosthesis and a tibial component thereof and a femoral component thereof are disclosed. The knee joint prosthesis includes a tibial component and a femoral component. The tibial component has a top surface, a bottom surface opposite the top surface and a first slot passing through the top surface and the bottom surface for accommodating a cruciate ligament. The tibial component has at least one first protrusion disposed on the bottom surface, and the first protrusion has a plurality of first through holes. The femoral component is carried by the tibial component and has a second slot for accommodating the cruciate ligament. The femoral component has at least one second protrusion disposed on a surface thereof against the tibial component, and the second protrusion has a plurality of second through holes.
Owner:HWA +1
Minimal invasive combined pressurizing and locking bone fracture plate for trochanter comminuted fracture and femoral neck fracture
ActiveCN102247205AEasy to operateSmall incisionInternal osteosythesisBone platesTreatment effectFemoral diaphysis
The invention relates to a minimal invasive combined pressurizing and locking bone fracture plate for trochanter comminuted fracture and femoral neck fracture. The bone fracture plate comprises a trochanter rear-side fixing plate and a femoral proximal-end fixing plate, which are connected into an integrated structure for respectively covering the trochanter rear side and femoral proximal end in an annular shape, wherein first locking holes are respectively formed on two ends of the trochanter rear-side fixing plate, and first locking nails which penetrate the rear side of the trochanter crown head end and the rear side of the trochanter crown bottom end are locked in the two first locking holes respectively; three second locking holes, arranged in a regular triangle way, are formed on the femoral proximal-end fixing plate, a second locking nail for locking femoral trochanter, femoral neck and bulb penetrates at least one second locking hole; and the trochanter rear-side fixing plate and the femoral proximal-end fixing plate are connected into an integrated structure for covering the trochanter rear side and femoral proximal end in an annular way. By utilizing a ball lag screw or a locking lag screw, tensioning of the trochanter, the femoral neck and the bulb and positioning lock on the femoral diaphysis are realized, so the minimal invasive combined pressurizing and locking bone fracture plate for the pulverous trochanter fracture and femoral neck fracture has the advantages of simpleness in operation, small cut, good fixing effect, firm tensioning, no potential safety hazards in long term use, no deformation and good treatment effect and is beneficial to accurate diaplasis.
Owner:泰州市中兴医械科技有限公司
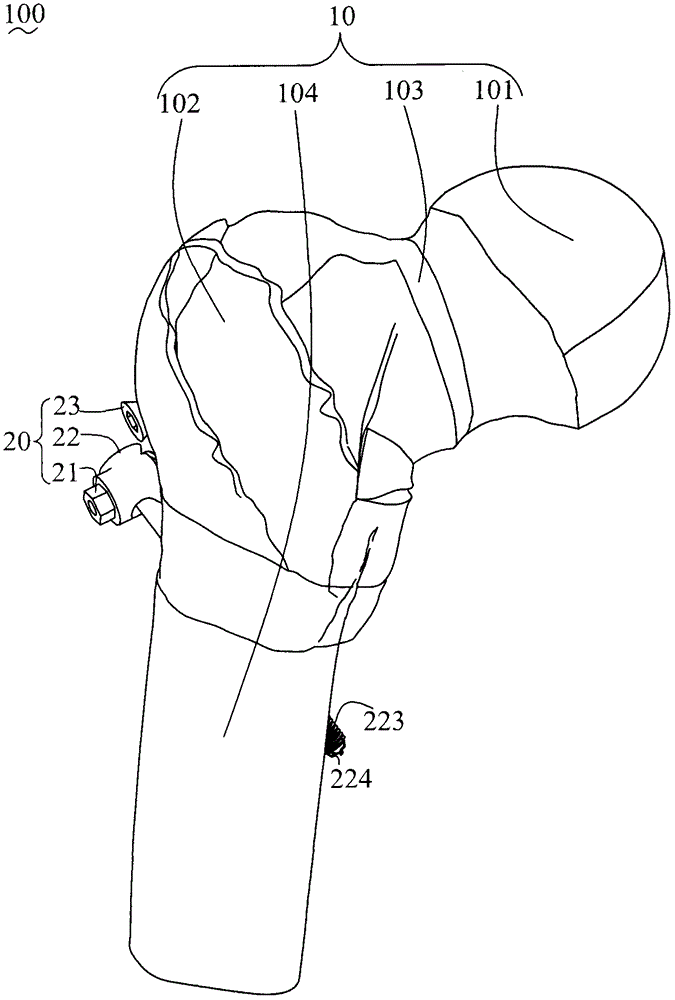
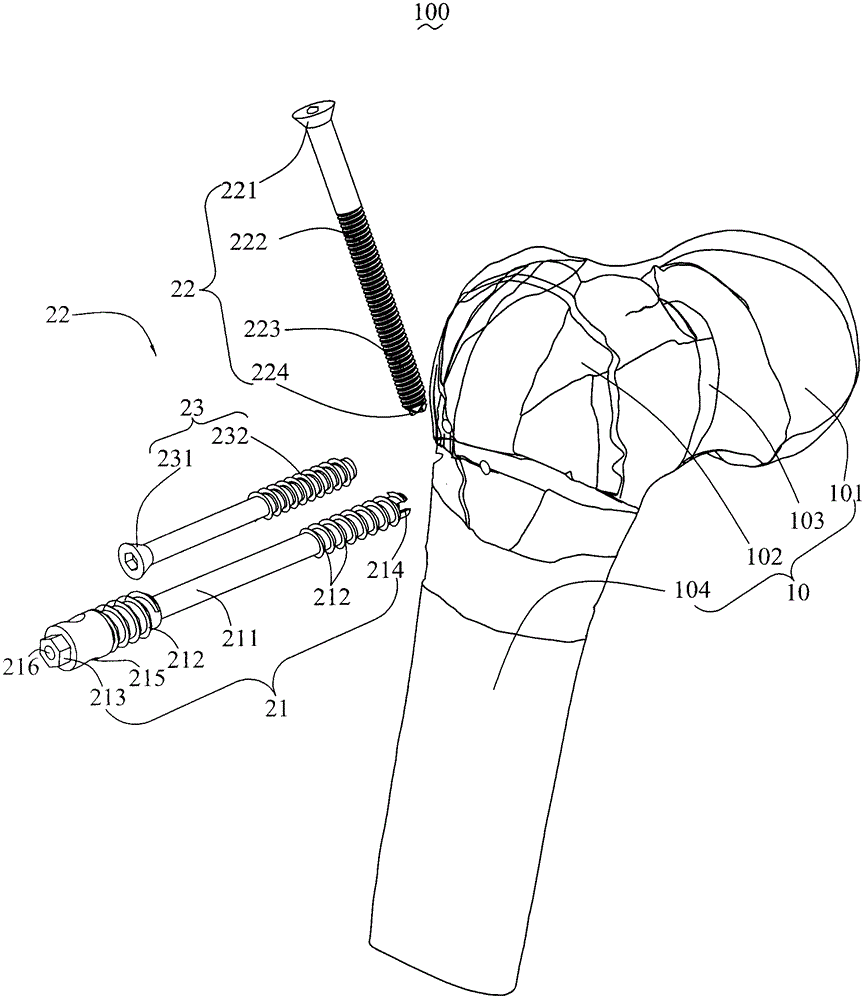
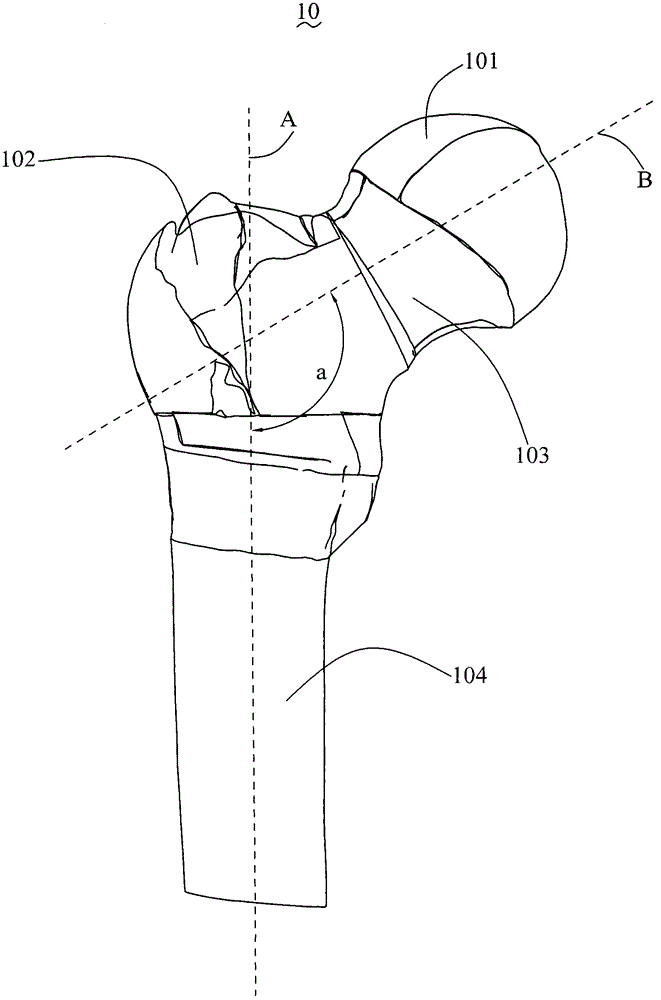
Femoral neck fixing mechanism and femoral neck fracture fixing structure thereof
InactiveCN105877832AInsufficient improvementFractures are easy to causeFastenersRight triangleBody of femur
The invention relates to a femoral neck fracture fixing structure. The femoral neck fracture fixing structure comprises a femoral neck with a fracture line and a femoral neck fixing mechanism connected with the fracture line, wherein the femoral neck fixing mechanism comprises a femoral neck screw and a rotation resistant screw; the femoral neck screw comprises a screw body, two receding resistant screw threads and a penetrating hole, wherein the receding resistant screw threads form a right triangle in the axial section of the screw body, and the hypotenuse of the right triangle faces towards the screwing-in direction of the femoral neck screw; the rotation resistant screw is arranged in the penetrating hole of the femoral neck screw in a penetrating manner and is used for preventing the femoral neck screw from automatically rotating. According to the femoral neck fixing mechanism provided by the invention, the disadvantages that in DHS, a side screw is deviated, the operation time is long, and the bleeding amount is large are overcome; defects that in PFN, anchor resultant force is insufficient and the locking is cut out are improved by utilizing the reasonable combination of the femoral neck screws.
Owner:王建平
Artificial joint femoral stem
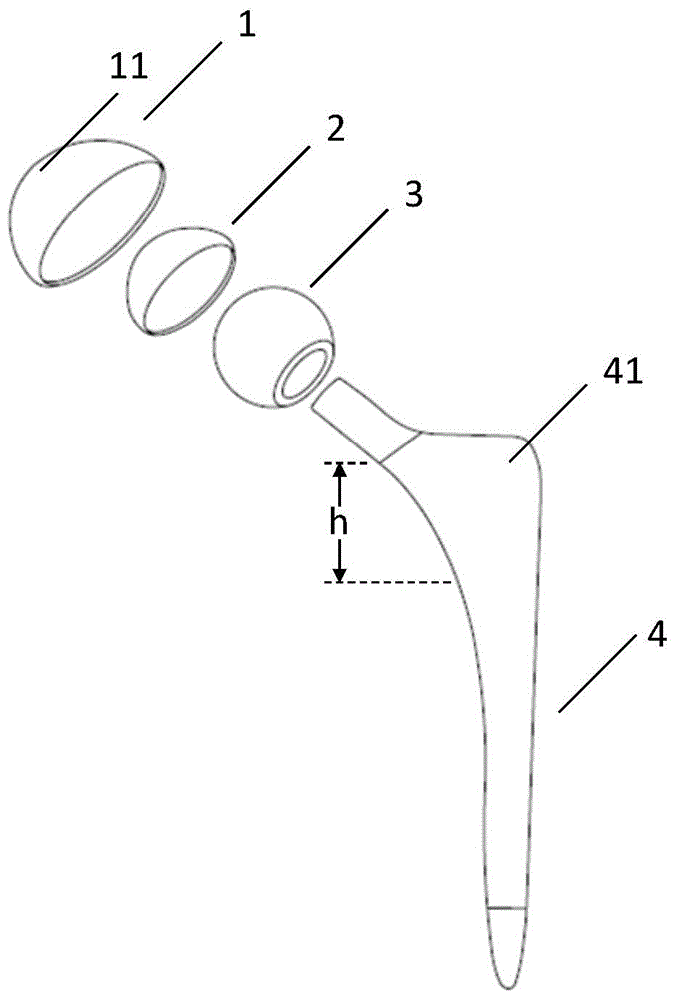
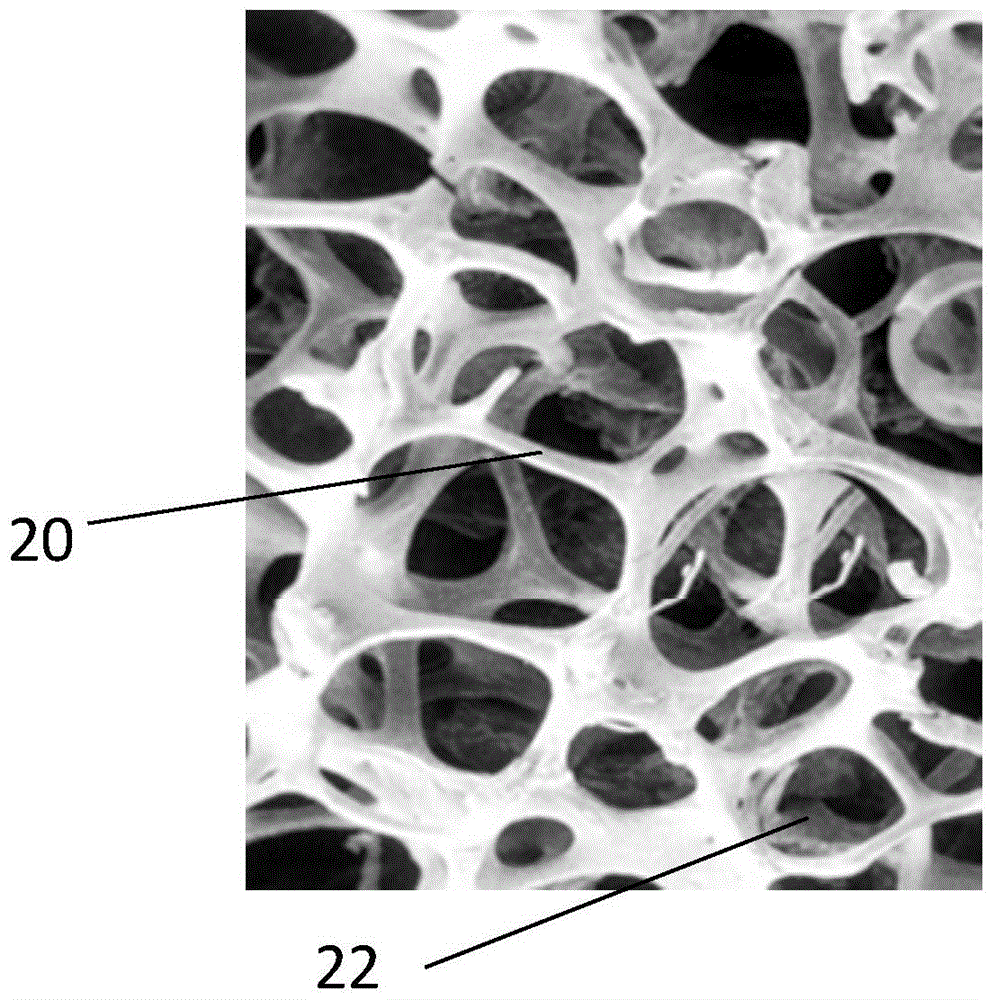
InactiveCN104874019APrevent looseningImprove fusion effectCoatingsProsthesisHuman bodyArtificial joints
The invention discloses an artificial joint femoral stem which comprises a joint femoral stem body and at least one titanium alloy layer on the partial outer surface of the end part, close to a femoral ball head, of the joint femoral stem body, wherein the titanium alloy layer adopts a sponge hole structure; walls of holes in the sponge hole structure are made of titanium alloy materials; the holes are distributed in an irregular three-dimensional net-shaped manner in the thickness direction so as to form communicated hole channels. Integration of the artificial joint femoral stem and human body bone tissue is increased, so that looseness between the artificial joint femoral stem and the bone is effectively prevented.
Owner:ZHONGAO HUICHENG TECH CO LTD
Methods And Apparatus For Preparing An Intercondylar Area Of A Distal Femur
Methods and apparatus provide for modifying an intercondylar notch of a patient's femur, including cutting bone from the intercondylar notch using a hole saw having a hollow cylinder and a circular cutting edge, where the hollow cylinder of the hole saw defines a central longitudinal axis which is oriented with reference to the patient's femur such that the circular cutting edge of the hole saw removes a portion of material from the intercondylar notch of the patient's femur.
Owner:ARTHREX
Total knee replacement substituting function of anterior cruciate ligament
ActiveUS9023111B2Prevention of excessive anterior displacementReduce saggingJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaMedicine
A total knee replacement prosthesis comprising condylar and intercondylar bearing surfaces configured to manage anterior / posterior displacement between the articulating femoral and tibial components.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
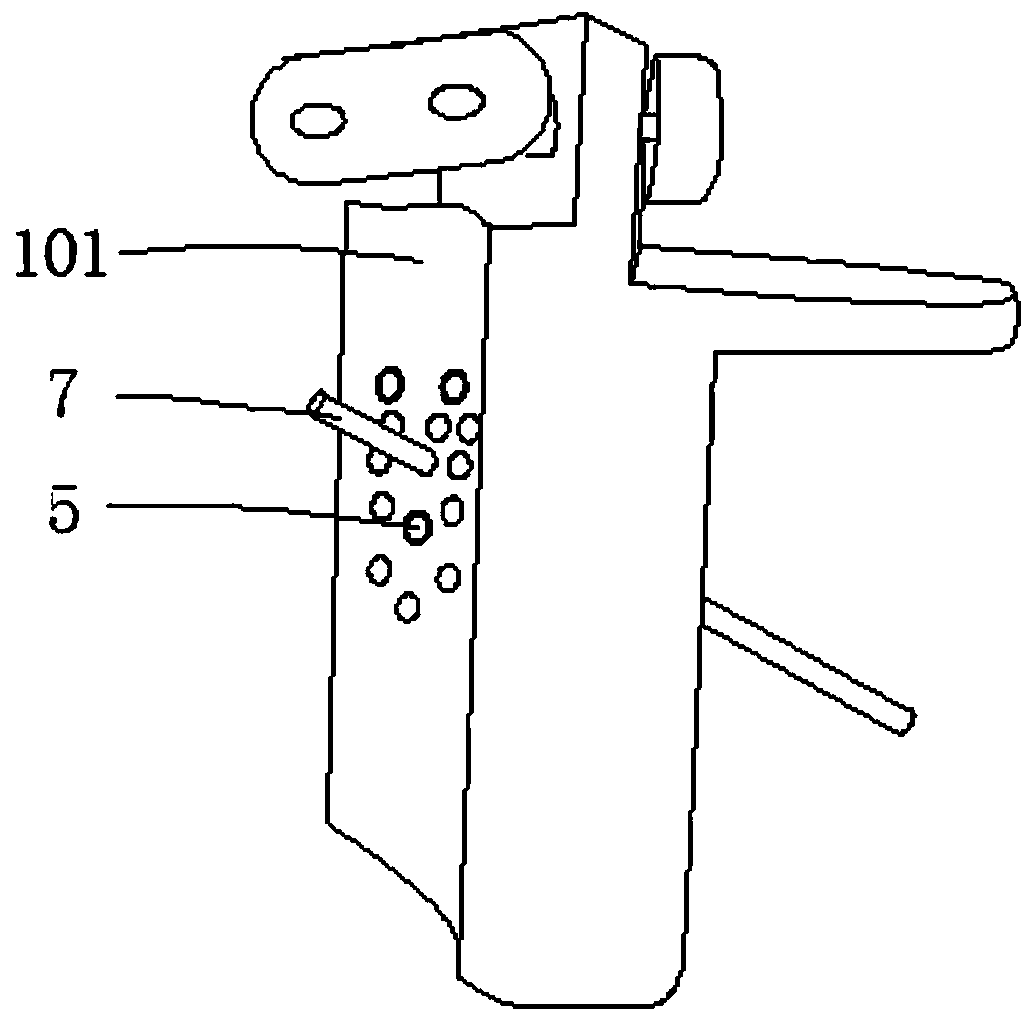
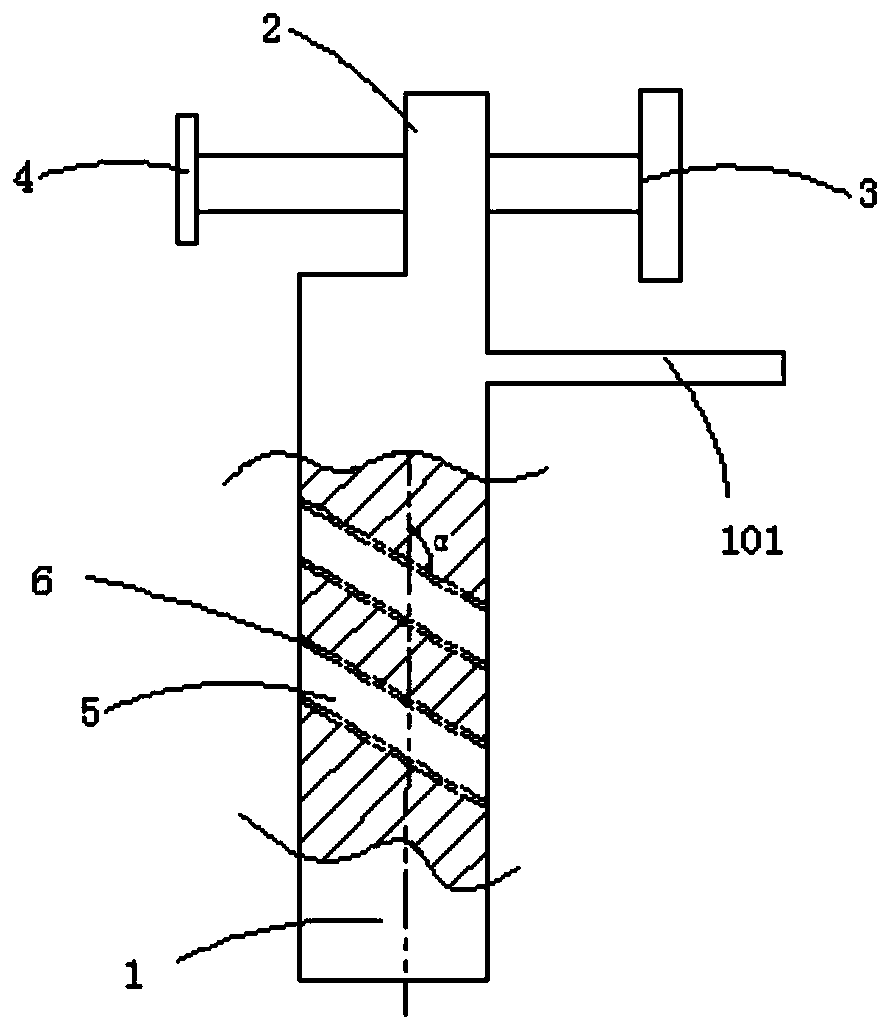
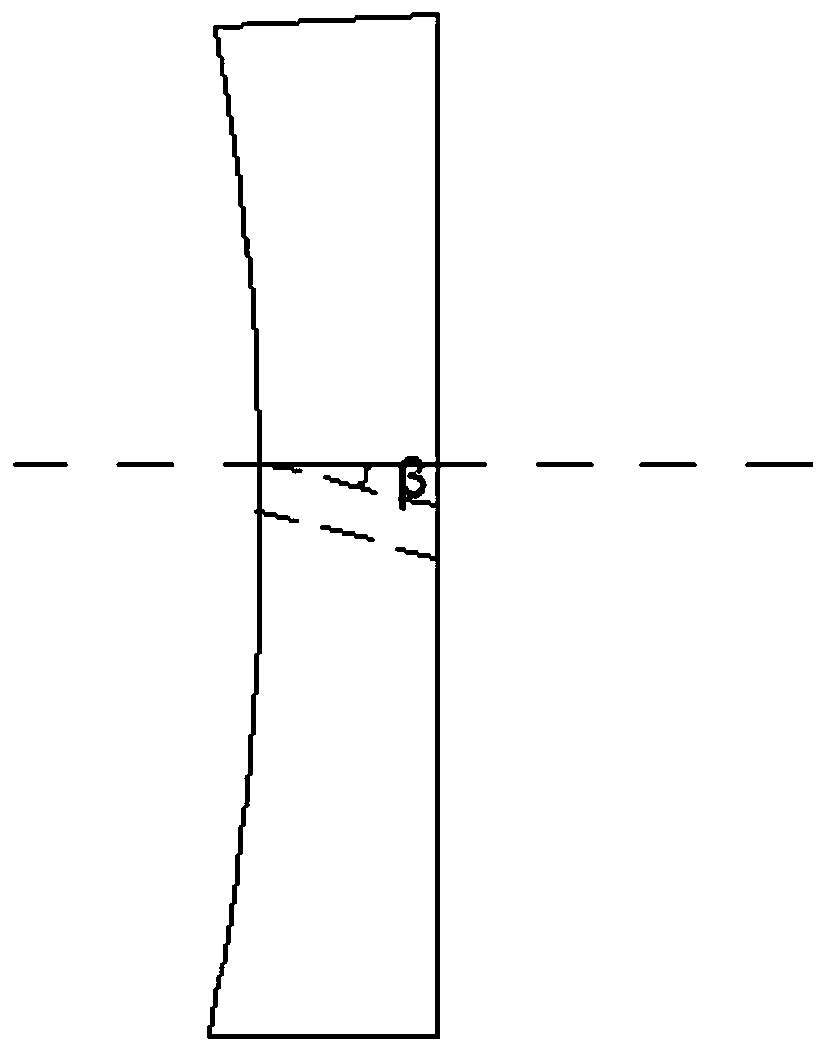
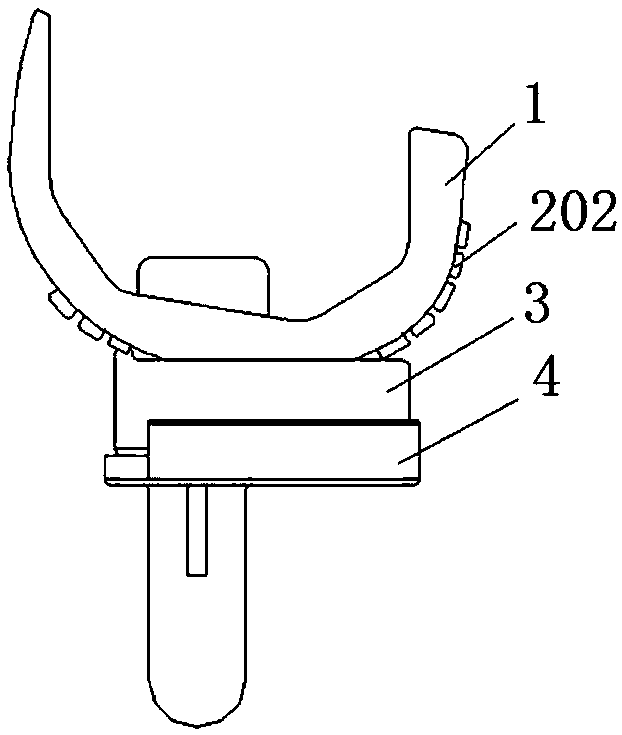
Guide plate for percutaneous implantation of hollow rivets into collum femoris
PendingCN110074855AEvenly distributedEffective implantationOsteosynthesis devicesEngineeringFemoral neck
The invention relates to a guide plate for percutaneous implantation of hollow rivets into collum femoris. The guide plate comprises a guide plate body of which the inner side is of a curved surface,the upper part of the guide plate body is provided with a flange portion which is integrally formed with the guide plate body, the outer side face of the flange portion is flush with the outer side face of the guide plate body, and the thickness of the flange portion is smaller than that of the guide plate body; two groups of bolts are installed on the flange portion, the ends of the two groups ofbolts are connected with a metal baffle plate, and the metal baffle plate is located above the inner side of the guide plate body; the guide plate body is provided with a plurality of inclined guideholes, obtuse angles formed between the central axes of the inclined guide holes and a vertical line are 115 degrees, the inclined guide holes on the guide plate body is provided with a top rake, theangle of the top rake is the same as that of the collum femoris of humans, metal conduits are installed in four inclined guide holes, and the plurality of inclined guide holes can be assembled into different inverted isosceles triangles to be used as rivet-placing positions. By adopting the guide plate, the three hollow rivets can be implanted into the collum femoris quickly, accurately and effectively, fluoroscopy times are reduced, and operation time is shortened.
Owner:JIAXING CITY NO 2 HOSPITAL
Knee joint prosthesis
PendingCN109662812AWith impact resistanceWith noise reductionJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaProsthesis
The invention discloses a knee joint prosthesis. The knee joint prosthesis comprises a femoral condyle prosthesis, a pad and a tibial plateau bracket, wherein the pad is arranged on the tibial plateaubracket; a group of ceramic sheets for reducing the abrasion of the femoral condyle prosthesis and the pad are arranged on the femoral condyle prosthesis, distributed dispersedly, and connected withthe femoral condyle prosthesis through welding, and the convex curved surfaces of the ceramic sheets are in contact with the upper surface of the pad to form a friction pair. The ceramic sheets are distributed on the femoral condyle prosthesis in the knee joint prosthesis to separate the femoral condyle prosthesis from the tibial pad in order to reduce the abrasion loss of the femoral condyle prosthesis and the tibial pad; the friction between metal and a high-molecular polymer material is converted into the friction between the metal and the ceramics, the precipitation of metal ions, caused by the friction between the metal and the high-molecular polymer, is reduced, and the knee joint prosthesis has certain impact resistance and a noise reduction effects.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Knee joint prosthesis and tibial component and femoral component thereof
A knee joint prosthesis and a tibial component thereof and a femoral component thereof are disclosed. The tibial component has a top surface, a bottom surface opposite to the top surface and a first slot passing through the top surface and the bottom surface for accommodating a cruciate ligament. The tibial component has a plurality of first protrusions disposed on the bottom surface, and each of the first protrusion has at least a first through hole. The femoral component is carried by the tibial component and has a second slot for accommodating the cruciate ligament. The femoral component has a plurality of second protrusions disposed on a surface thereof against the tibial component, and each of the second protrusion has at least a second through hole. The knee joint prosthesis is stably arranged after implantation without bone nails, and the orthopedic surgeons can adopt cruciate ligament-retaining to keep the stability of the postoperative joint and reduce the wear of the new join.
Owner:花世源 +1
Posterior thighbone internal fixation bone plate
InactiveCN105213011AEasy to fixReduce stimulationInternal osteosythesisBone platesPull forceOrthopedic department
The invention provides a posterior thighbone internal fixation bone plate, and belongs to the technical field of medical apparatuses and instruments in the orthopedics department. The posterior thighbone internal fixation bone plate is used for fixing the thighbone fracture from the posterior of a thighbone. According to the technical scheme, the bone plate is bent in the length direction, and the radian of the bending shape is matched with the forward-bending radian of the thighbone; meanwhile, the bone plate is bent in the width direction, the morphology of the bent plate face is matched with the morphology of the rear side surface of the thighbone, and locking screw holes and ordinary screw holes are distributed in the bone plate in the length direction. The traditional method that fixation is conducted from the front tension side of the thighbone is broken through, fixation is conducted from the pressure side for the fracture, innovation for the thighbone internal fracture fixation is achieved, and disadvantages of traditional thighbone operations are effectively avoided. Due to the arc-shaped design, the bone plate is tightly attached to the surface of the thighbone, the posterior thighbone internal fixation bone plate is suitable for residual displacement of different positions, further reset and fixation of fracture segments, ordinary tension screws and locking nails are combined, pressurized fixation and traction are combined, an extremely-good fixing effect is achieved, the operation time and the recovery time are greatly shortened, and pains of patients are effectively relieved.
Owner:陈卫
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com