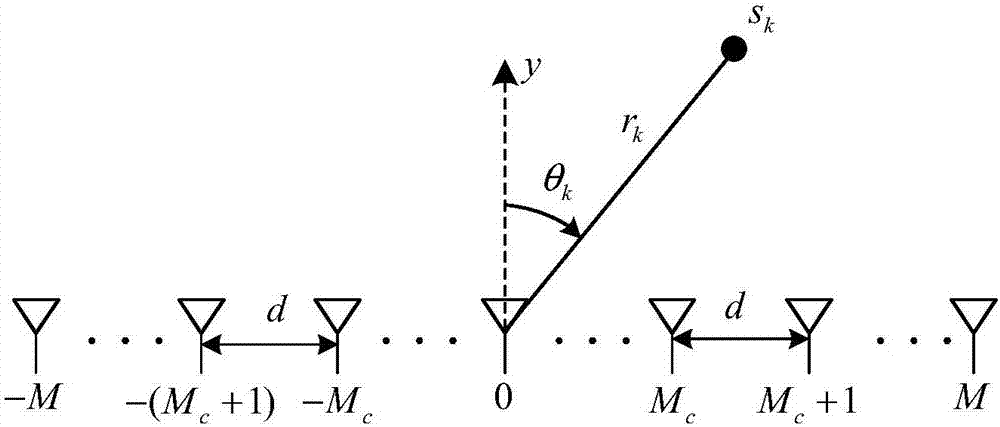
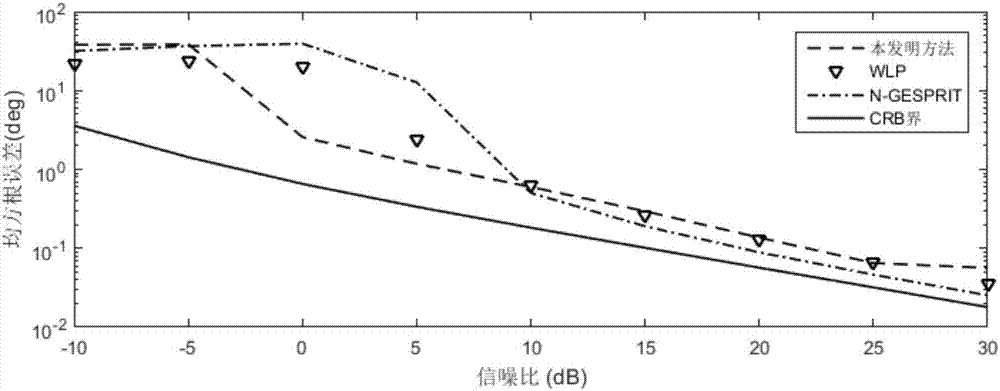
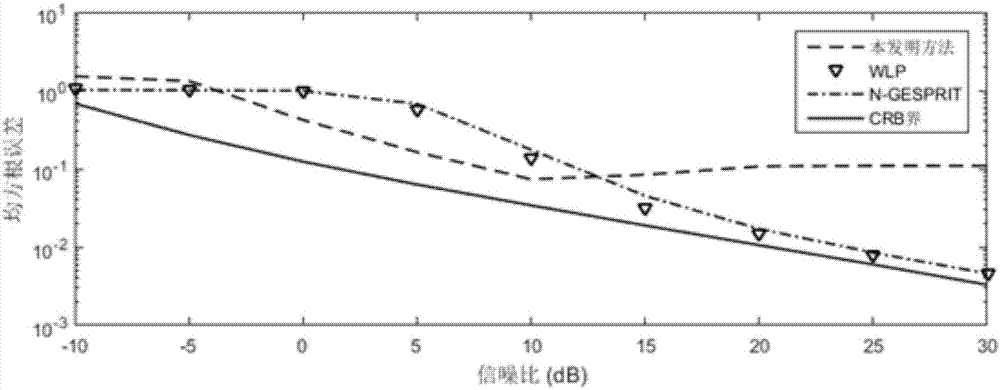
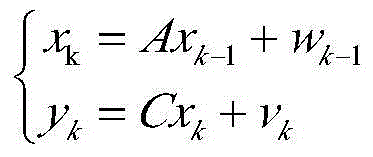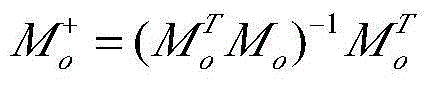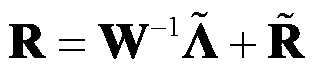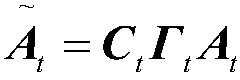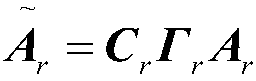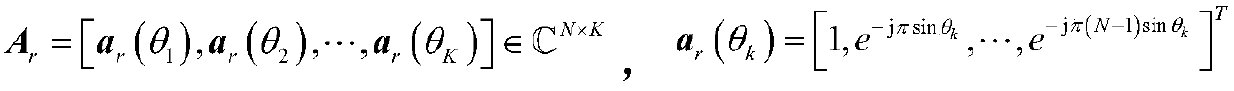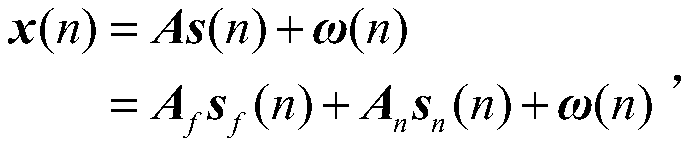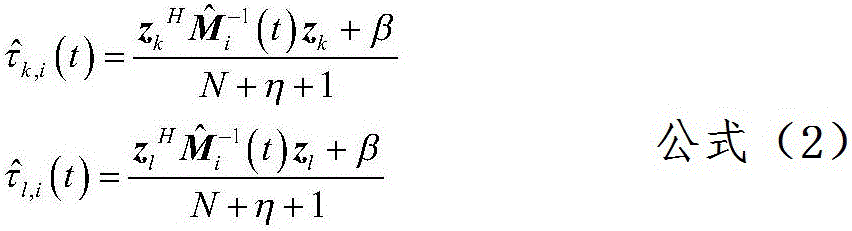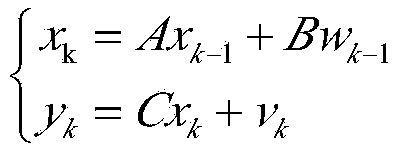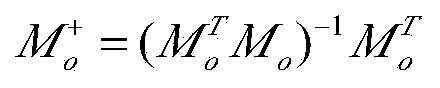Patents
Literature
67 results about "Estimation of covariance matrices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistics, sometimes the covariance matrix of a multivariate random variable is not known but has to be estimated. Estimation of covariance matrices then deals with the question of how to approximate the actual covariance matrix on the basis of a sample from the multivariate distribution. Simple cases, where observations are complete, can be dealt with by using the sample covariance matrix. The sample covariance matrix (SCM) is an unbiased and efficient estimator of the covariance matrix if the space of covariance matrices is viewed as an extrinsic convex cone in R; however, measured using the intrinsic geometry of positive-definite matrices, the SCM is a biased and inefficient estimator. In addition, if the random variable has normal distribution, the sample covariance matrix has Wishart distribution and a slightly differently scaled version of it is the maximum likelihood estimate. Cases involving missing data require deeper considerations. Another issue is the robustness to outliers, to which sample covariance matrices are highly sensitive.
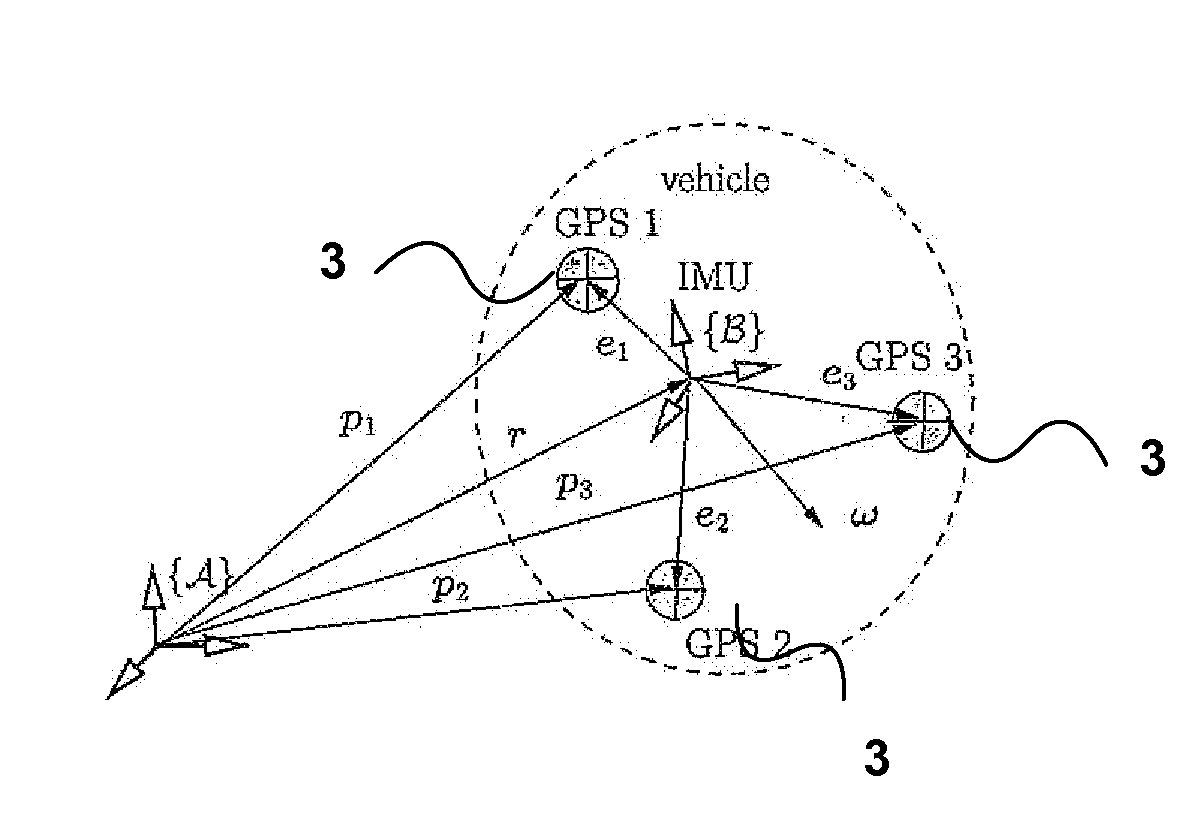
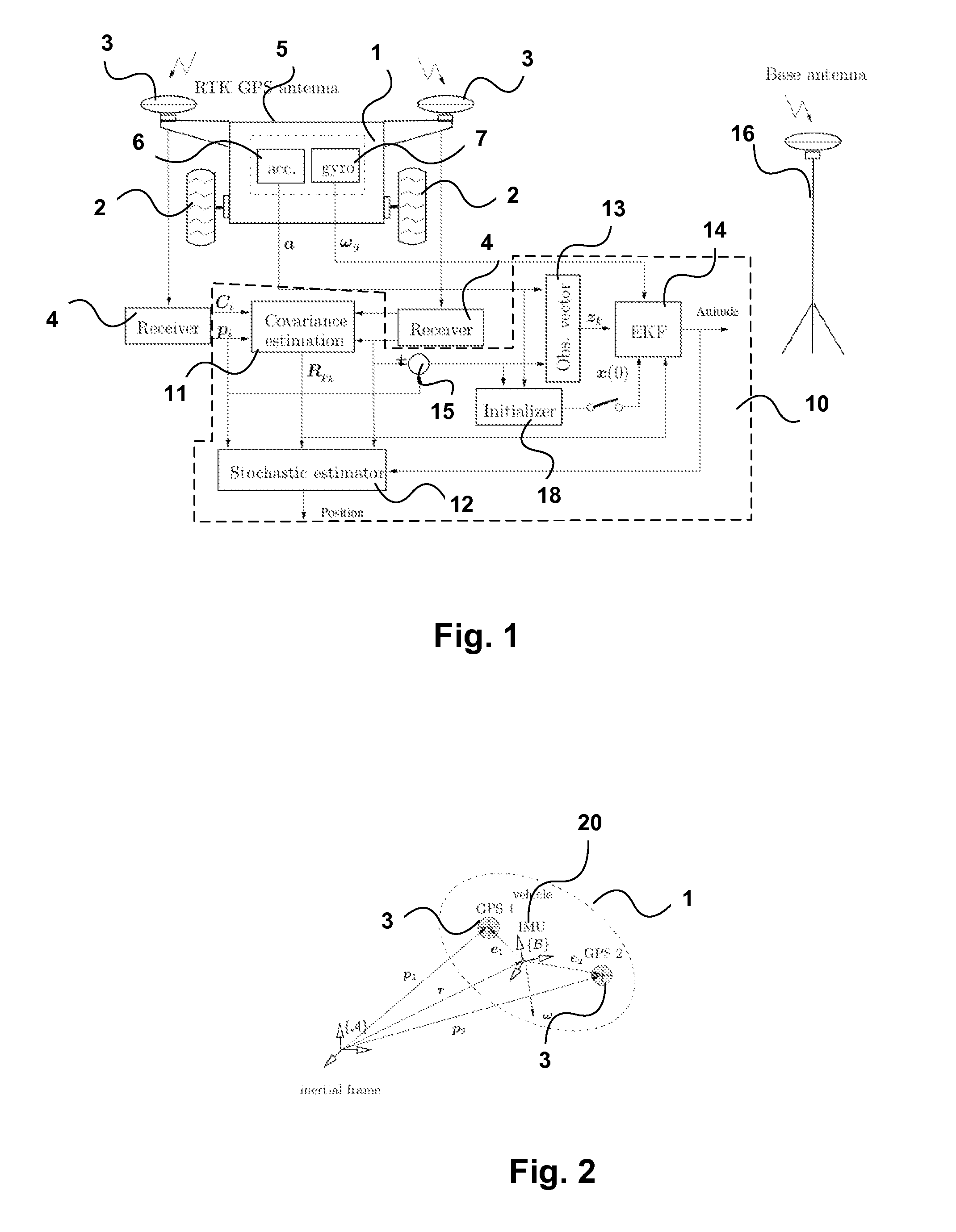
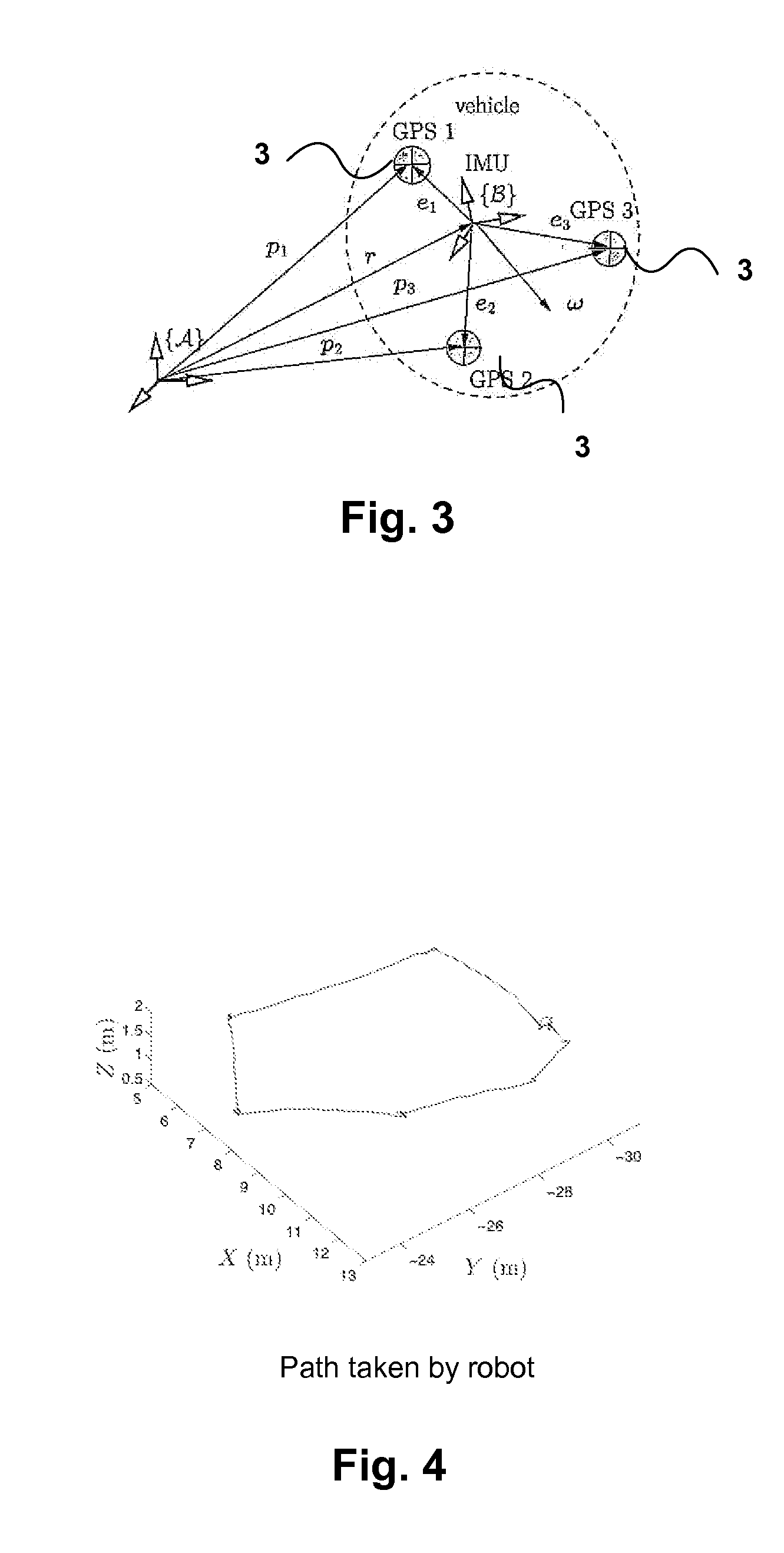
Apparatus and methods for driftless attitude determination and reliable localization of vehicles
InactiveUS20120086598A1Enhanced positional informationImprove accuracySatellite radio beaconingReal Time KinematicAttitude determination
In order to determine positional information, about a mobile robot, Real Time Kinematic (RTK) Global Satellite Navigation System (GNSS) measurement data are obtained by at least two GNSS receivers mounted on the mobile robot. Estimates of the covariance matrices of the measurement data are computed. The RTK GNSS measurement data are combined according to the covariance matrices to obtain enhanced positional information. The results may be fused with data from an IMU to obtain driftless attitude and / or localization information.
Owner:CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY
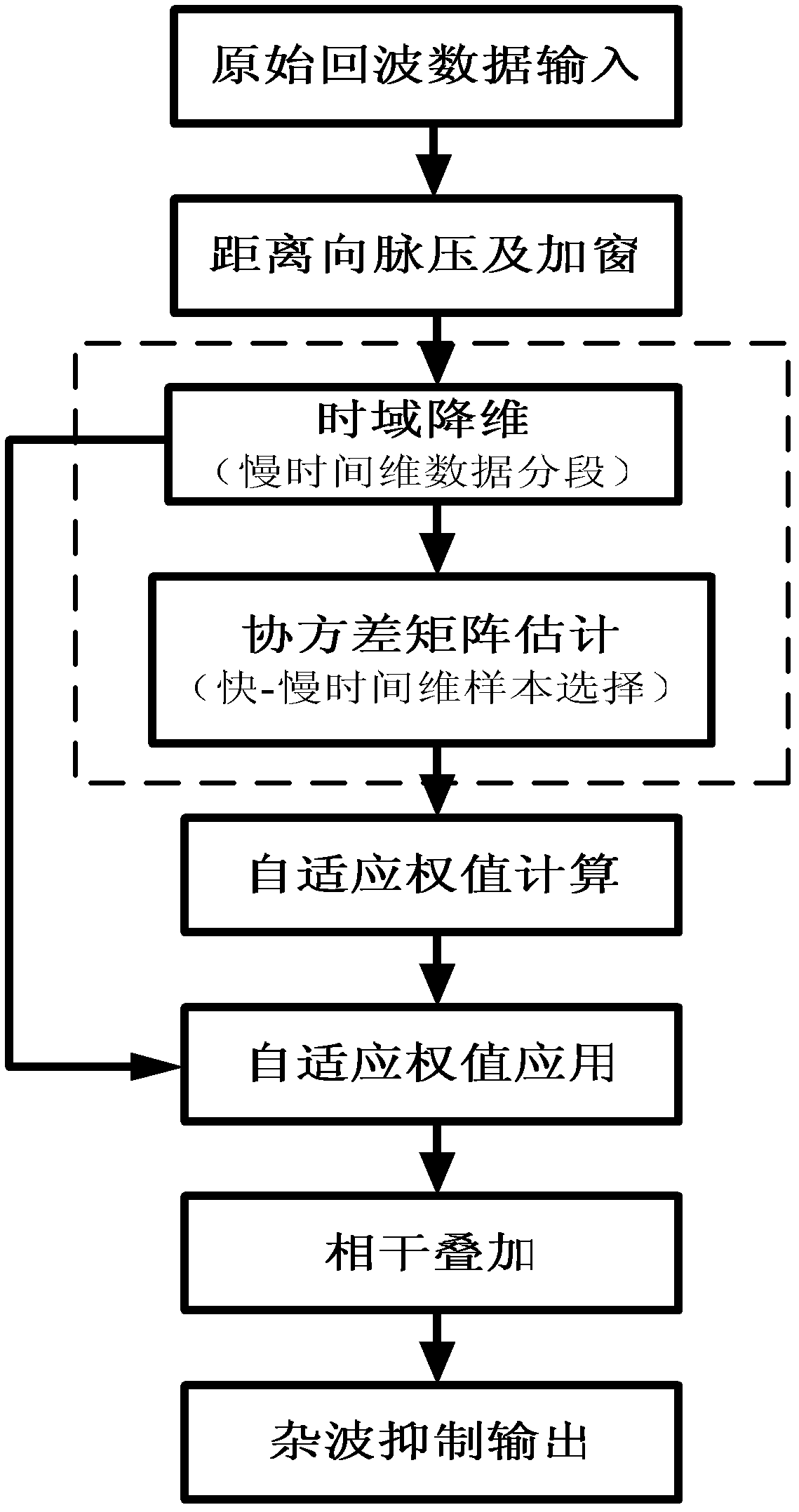
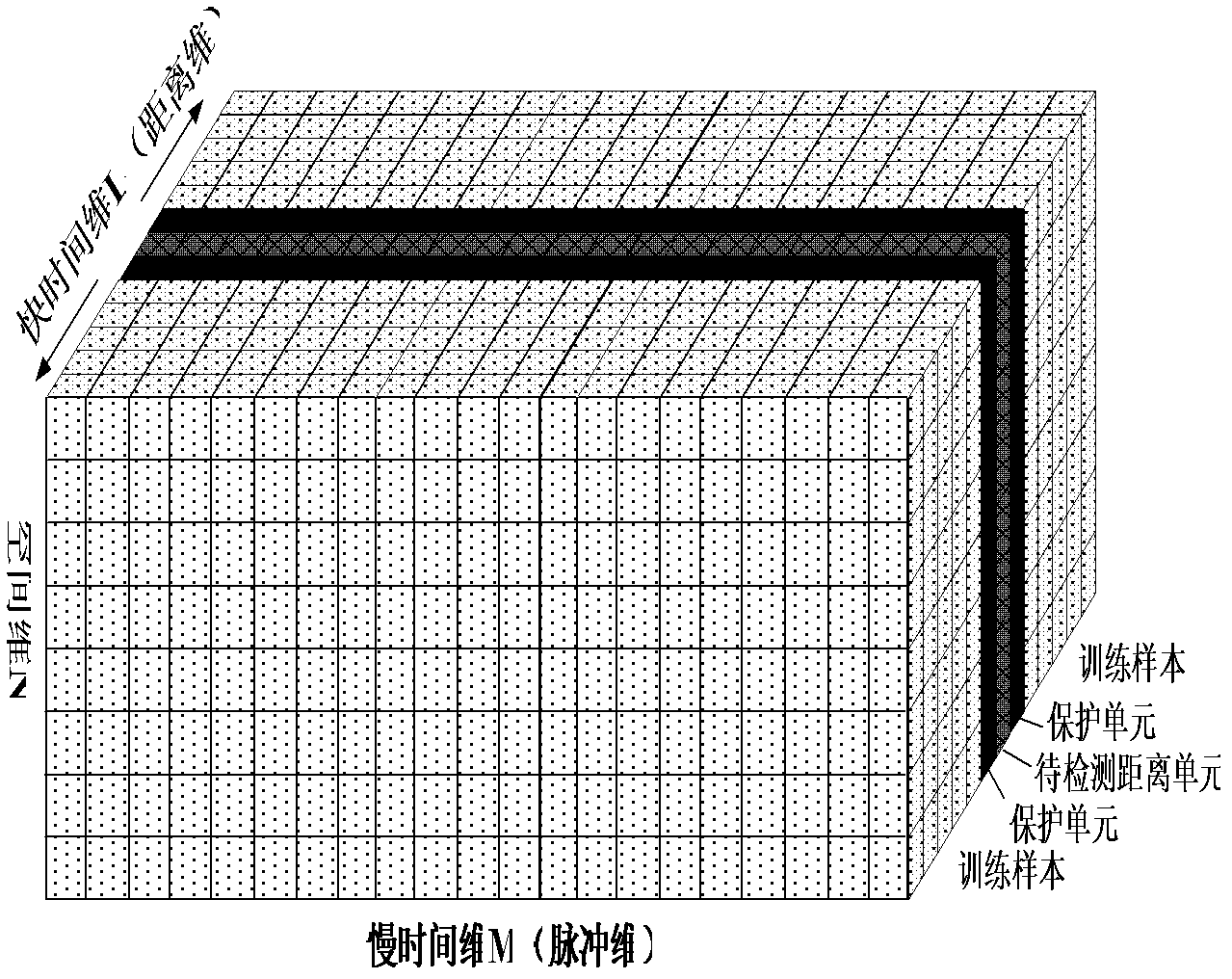
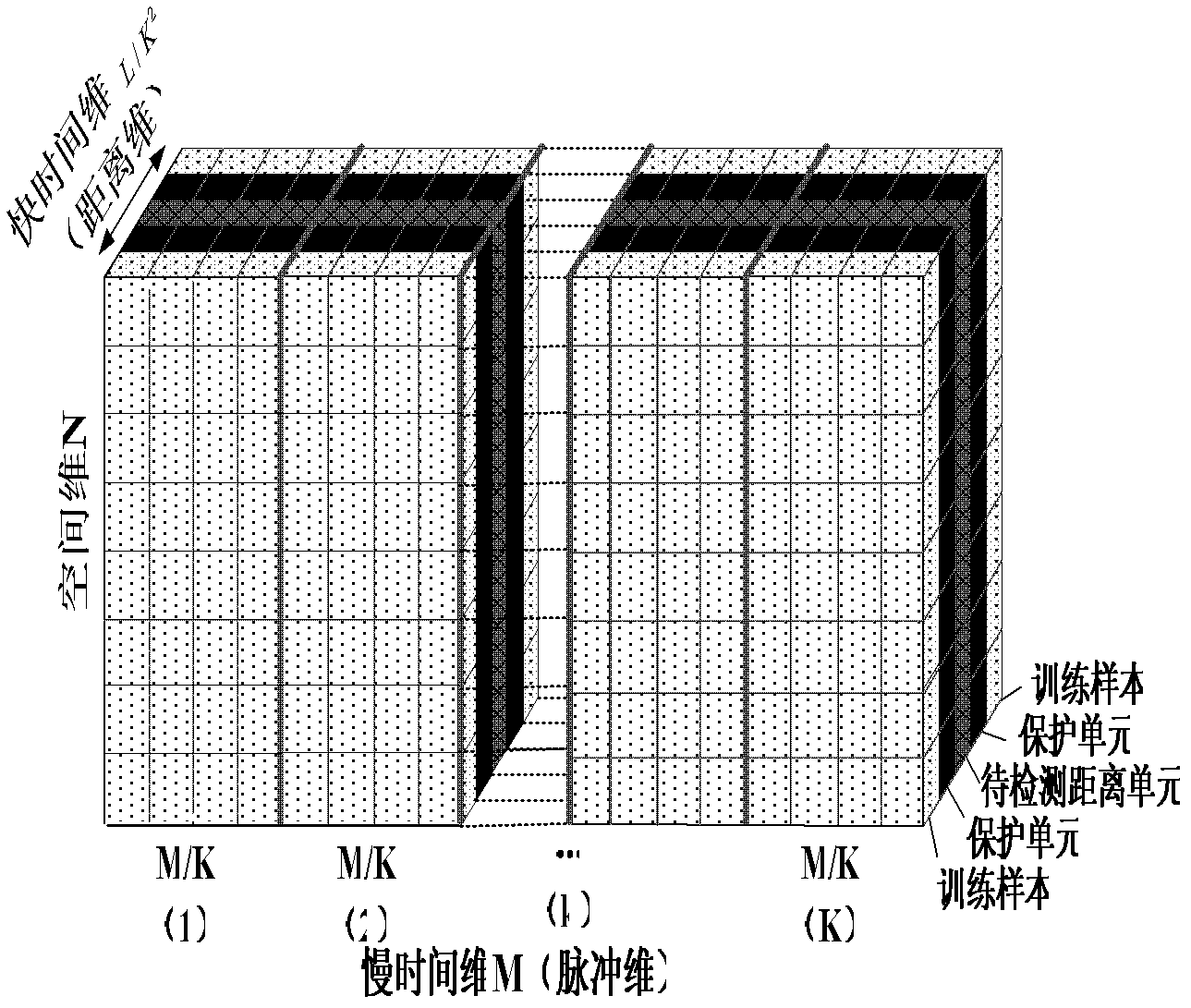
Sample-training-based non-stationary clutter suppression method of vehicle-mounted radar
InactiveCN103018727ASolve the problem of clutter distance dependenceImproved clutter suppression performanceWave based measurement systemsTime domainRadar
The invention discloses a sample-training-based non-stationary clutter suppression method of a vehicle-mounted radar, which relates to vehicle-mounted radar technology. The method comprises the steps of estimation of a clutter covariance matrix based on combined time-dimension sample training strategies, application of a self-adaptive weight, and coherence stack to output signals. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: inputting raw echo data; compressing and windowing pulses in a distance dimension; segmenting slow-time-dimension data; selecting quick-slow time dimension training samples; estimating the clutter covariance matrix; calculating and applying the self-adaptive weight; and carrying out coherence stack on the output signals. According to the method, the sample training strategies are changed under an STAP (space-time adaptive processing) time domain dimension reducing structure in light of the clutter range dependence of the vehicle-mounted radar, thus the estimation precision of the clutter covariance matrix can be effectively improved, and the clutter suppression performance of a main lobe is improved as well. The sample-training-based non-stationary clutter suppression method shows high robustness in engineering application, and is particularly applicable to detection on a slow moving object.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
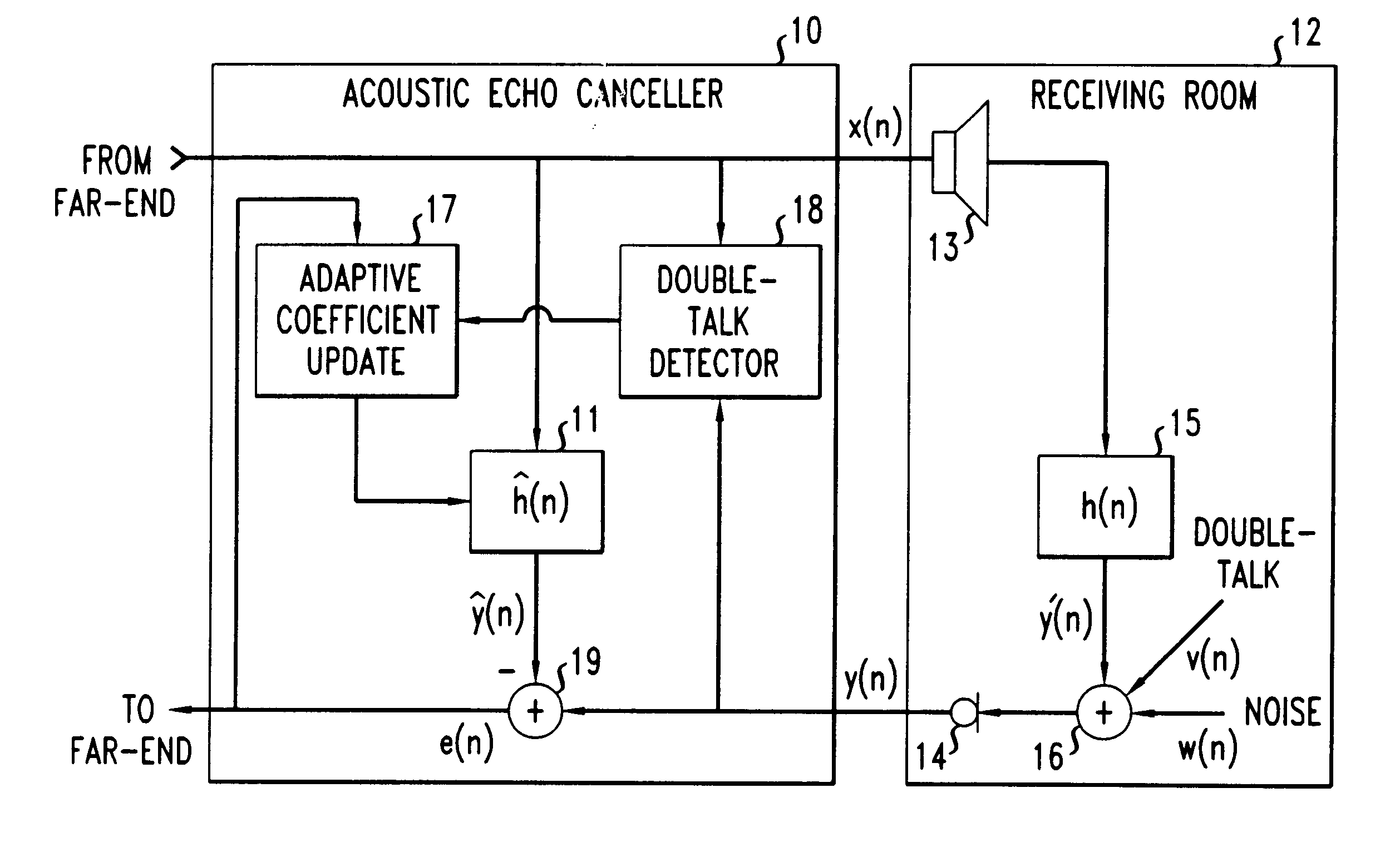
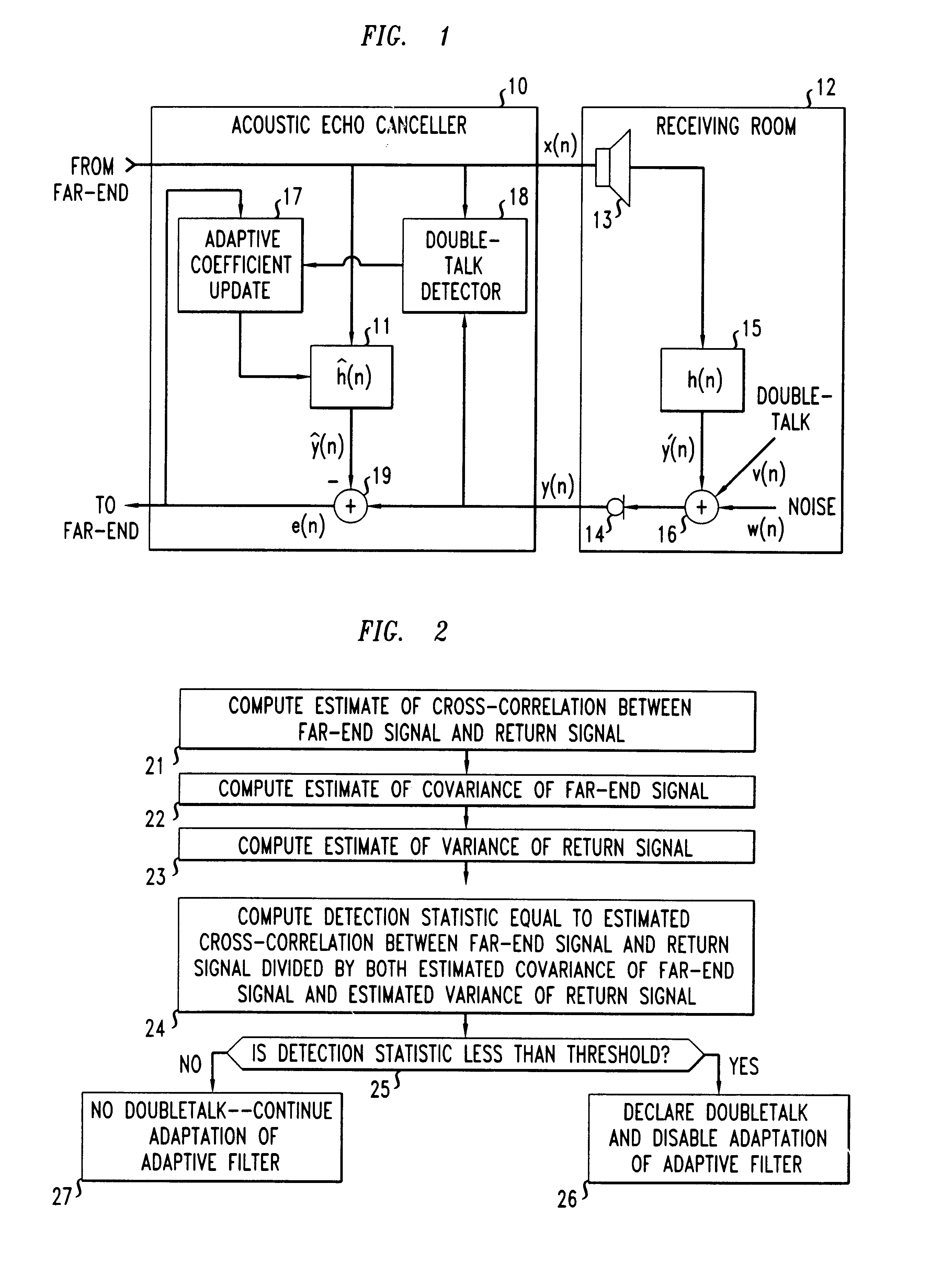
Method and apparatus for performing double-talk detection in acoustic echo cancellation
InactiveUS6766019B1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstations coupling interface circuitsTime domainEngineering
A method and apparatus for performing double-talk detection in an acoustic echo canceller in which a detection statistic is advantageously computed based on an estimate of a cross-correlation between the far-end signal and the return signal which has been normalized with use of an estimate of a covariance matrix of the far-end signal. The estimate of the cross-correlation between the far-end signal and the return signal may be further normalized with use of either an estimate of a variance of the return signal or an estimate of a covariance matrix of the return signal. In certain illustrative embodiments of the invention, one or more of these quantities may be estimated based on signal samples sampled over a predetermined time window. And in another illustrative embodiment of the present invention, the coefficients of the adaptive filter employed in the acoustic echo canceller itself are advantageously used to compute the detection statistic. These computations may be performed in either the time domain or the frequency domain. The detection statistic so computed is compared with a predetermined threshold, which threshold may be advantageously fixed at a value close to one, in order to determine whether or not double-talk has occurred.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Dimensionality reduction subspace angle measuring method suitable for millimeter wave vehicle-mounted radar
ActiveCN109975807AHigh processing robustnessReduce computational complexityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComputation complexityPrior information
The invention discloses a dimensionality reduction subspace angle measuring method suitable for a millimeter wave vehicle-mounted radar. The dimensionality reduction subspace angle measuring method comprises the steps of: firstly, proposing the adoption of a beam domain MUSIC algorithm to reduce computational complexity and memory occupation, and utilizing prior information to optimize a beamforming matrix design; secondly, proposing a new MUSIC estimator, which reflects finer scale information about a signal subspace; in addition, modifying a mathematical expression of a received signal estimation sample covariance matrix for the coherent situation of two adjacent signals under single snapshot, so as to enhance the orthogonality of a noise subspace and the signal subspace and maintain Toeplitz structure. The dimensionality reduction subspace angle measuring method adopts a sub-beam space averaging method, and improves the estimation precision of the sample covariance matrix under thecondition that each sub-beam space is full rank.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Narrowband near field signal source positioning method under non-uniform noise
ActiveCN107255796ASolve the problem of non-uniform noiseEliminate direction unknownsPosition fixationEstimation methodsDirection information
The present invention relates to a narrowband near field signal source positioning method under non-uniform noise. The method comprises the steps of firstly utilizing a principal back-diagonal element for receiving an estimated value of a data array covariance matrix to eliminate the distance unknown quantity, constructing a toeplitz structure matrix, and transforming the non-uniform noise into the uniform noise; then using a direction of arrival estimation method to estimate the information source direction information on the constructed toeplitz matrix; finally, utilizing a second back-diagonal element for receiving the data array covariance matrix and the estimated value in a direction of arrival to construct the toeplitz structure matrix only containing the distance unknown quantity, and using the toeplitz structure matrix to obtain the estimated value of a narrowband near field signal source distance. The narrowband near field signal source positioning method under the non-uniform noise of the present invention effectively solves the problem that the noise is non-uniform when a near field signal source is positioned, is simple to calculate, and has good estimation performances both on the direction of arrival and the distance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
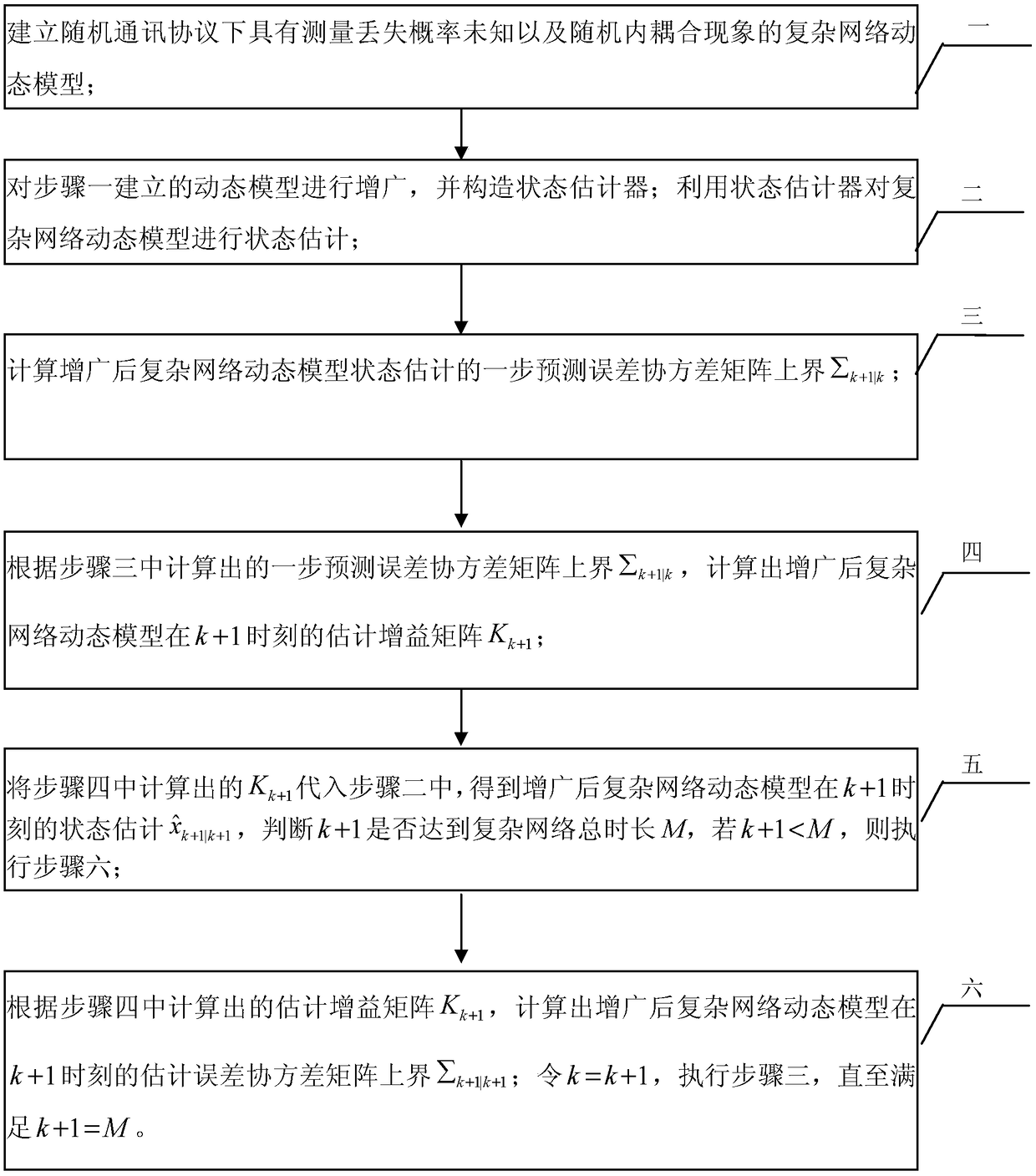
A state estimation method for complex network based on stochastic communication protocol
ActiveCN109088749ATo achieve the purpose of anti-disturbanceEasy to solveData switching networksCouplingEstimation methods
The invention relates to a state estimation method of complex network under random communication protocol, which is used in the network state estimation technical field of control system. The invention solves the problem that the existing state estimation method cannot simultaneously process the state estimation of a complex network with random internal coupling and measurement loss phenomenon. The invention simultaneously considers the measurement loss phenomenon with unknown probability and the influence of random internal coupling on the state estimation performance, comprehensively considers the effective information of the estimation error covariance matrix by using the extended Kalman filter method, and achieves the purpose of anti-disturbance. Compared with the existing complex network state estimation method under the communication protocol, the method of the invention can control the estimation error in a very small range, and can improve the estimation accuracy by more than 10% while being easy to solve. The invention can be applied to the technical field of network state estimation.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
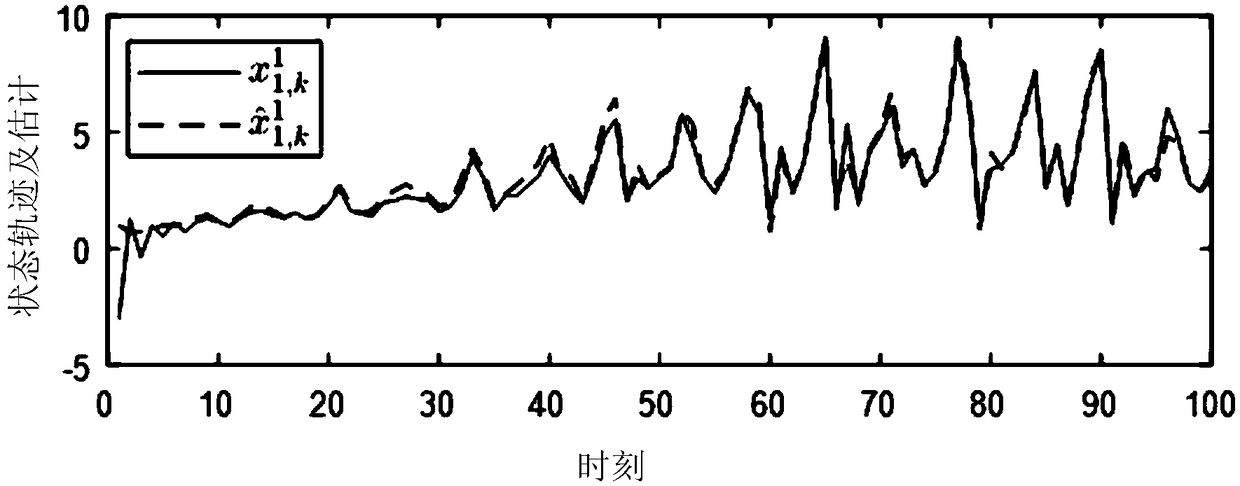
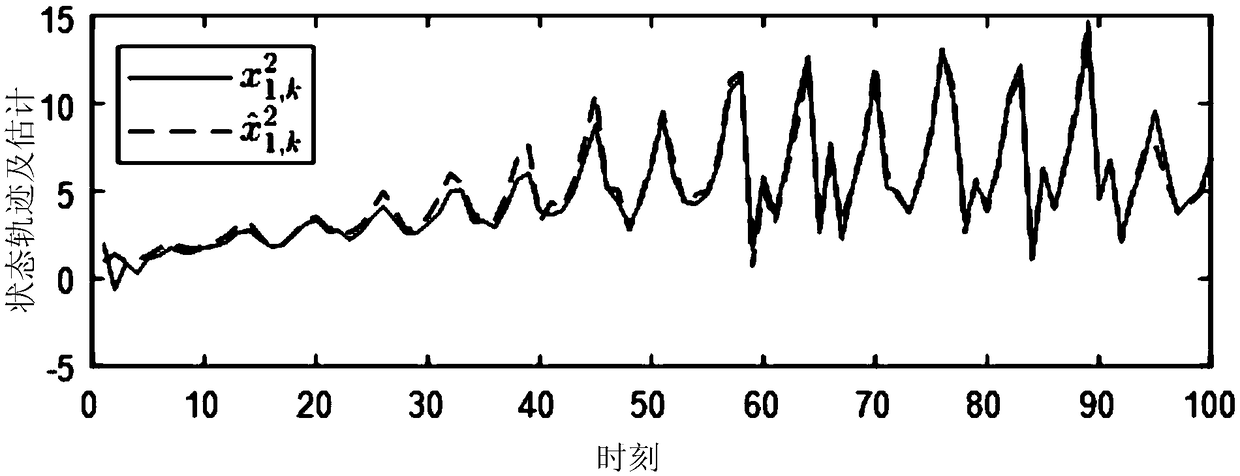
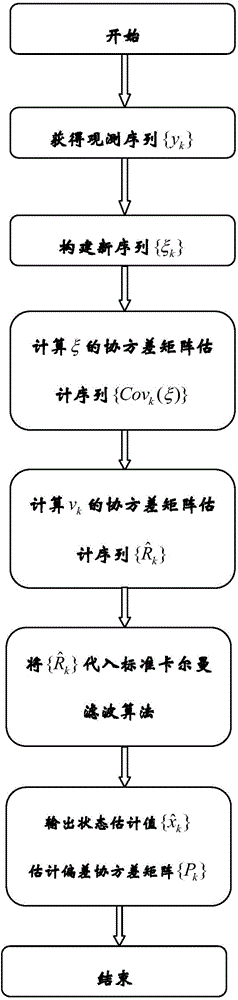
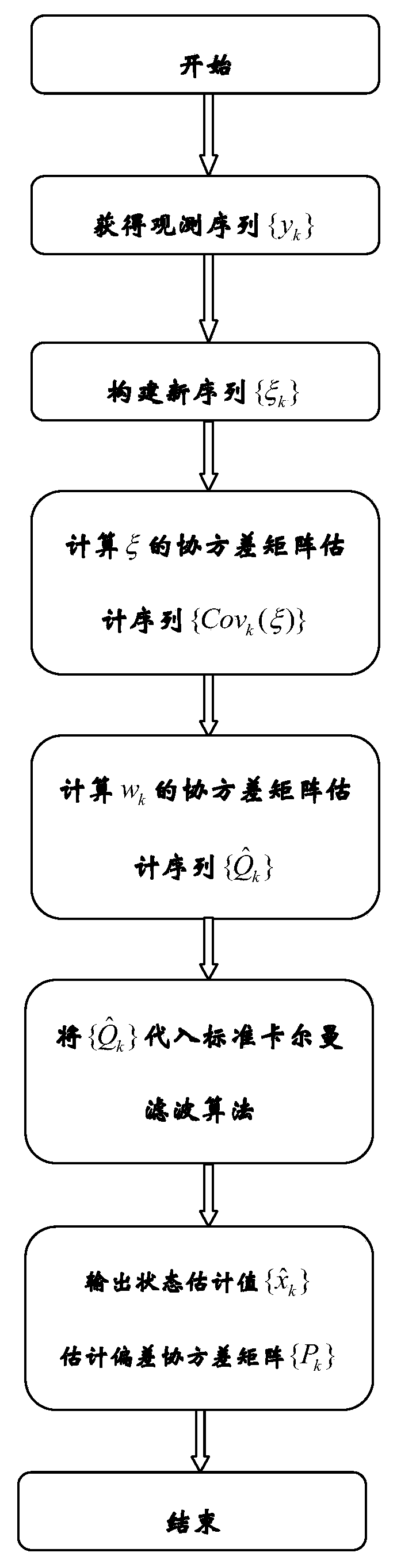
Kalman filtering method for recursive estimation under condition that observation noise covariance matrix is unknown
The invention provides a Kalman filtering method for recursive estimation under the condition that an observation noise covariance matrix of a discrete time time-invariant system is unknown, wherein the method solves the problem of system state filtering estimation under the condition that the observation noise covariance matrix of the discrete time time-invariant system is completely unknown. The method includes the steps that (1) a new statistic sequence is built by means of an observation sequence; (2) a recursion formula of the covariance matrix of the new statistic sequence is calculated; (3) an estimation sequence (f(R)k)of the observation noise covariance matrix is calculated; (4) an estimation sequence of the covariance matrix is calculated, and then real-time estimation of the observation noise covariance matrix is calculated through an algebraic relation; (5) an estimation sequence substitution true value of the observation noise covariance matrix is put into a standard Kalman filtering method, and real-time state estimation of the system and a covariance matrix of state estimation deviation are calculated.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
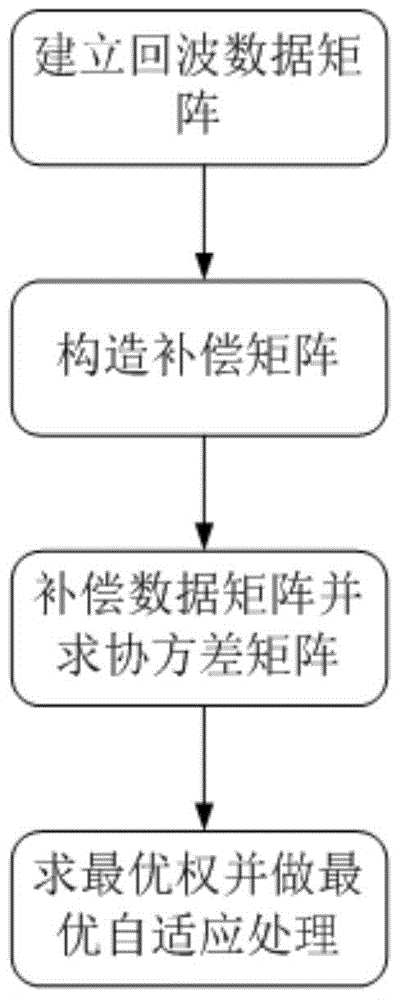
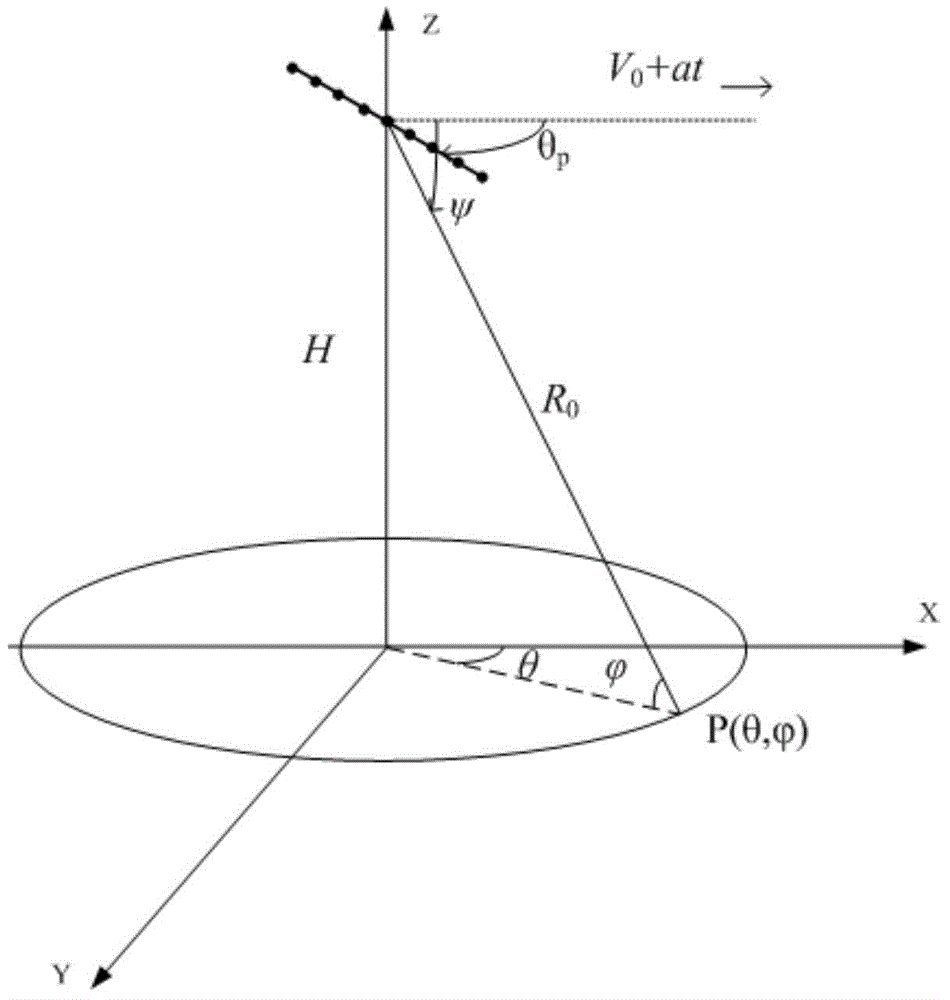
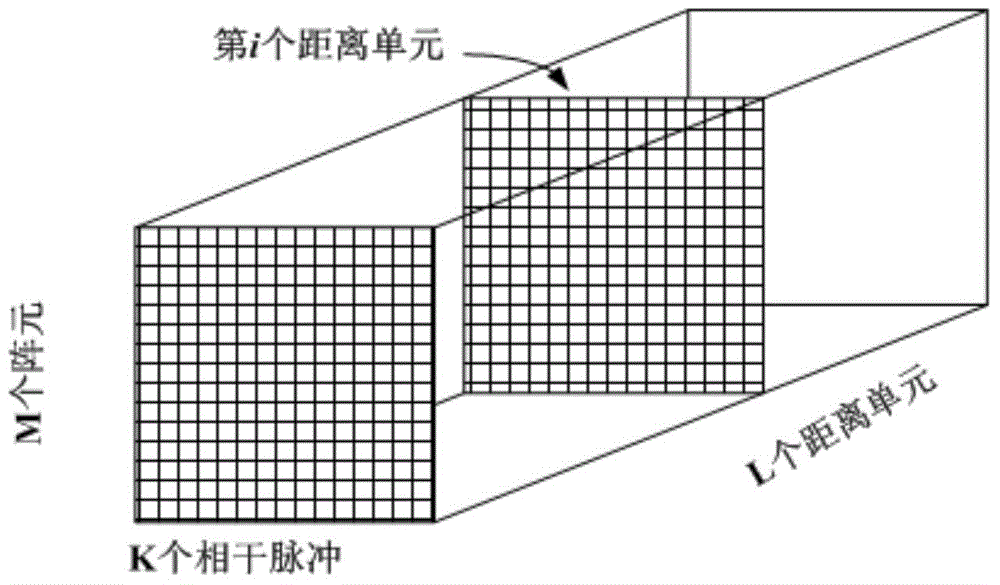
Space time adaptive processing method of constant-acceleration platform based on array element-pulse domain compensation
ActiveCN104635219AEasy to detectSimple and fast operationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmOptimal weight
The invention belongs to the technical field of motion compensation related to STAP (Space Time Adaptive Processing), and particularly relates to a space time adaptive processing method of a constant-acceleration platform based on array element-pulse domain compensation. The space time adaptive processing method comprises the specific steps: obtaining an echo data matrix rc; obtaining a compensating factor Bw; constructing a compensation matrix T by utilizing the compensating factor Bw and a pitching angle corresponding to each distance unit, and obtaining the echo data matrix after compensation, wherein = T; determining an estimate of a covariance matrix by utilizing the echo data matrix after compensation; determining a space time adaptive processing optimal weight vector Wopt by utilizing the estimate of the covariance matrix; performing space time adaptive processing on the echo data matrix rc by utilizing the optimal weight vector Wopt.
Owner:湖南鼎方电子科技有限公司
Compressed sensing based onboard phased array radar low-altitude wind shear wind speed estimation method
ActiveCN104793210AAccurate wind speed estimation resultsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationWind shearMain lobe
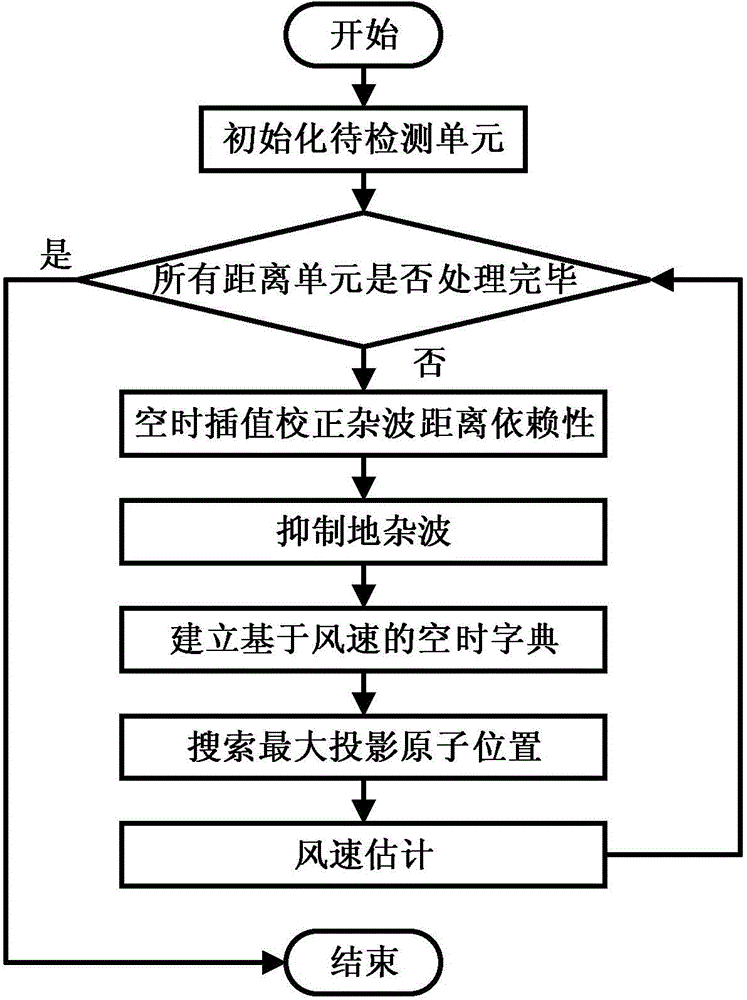
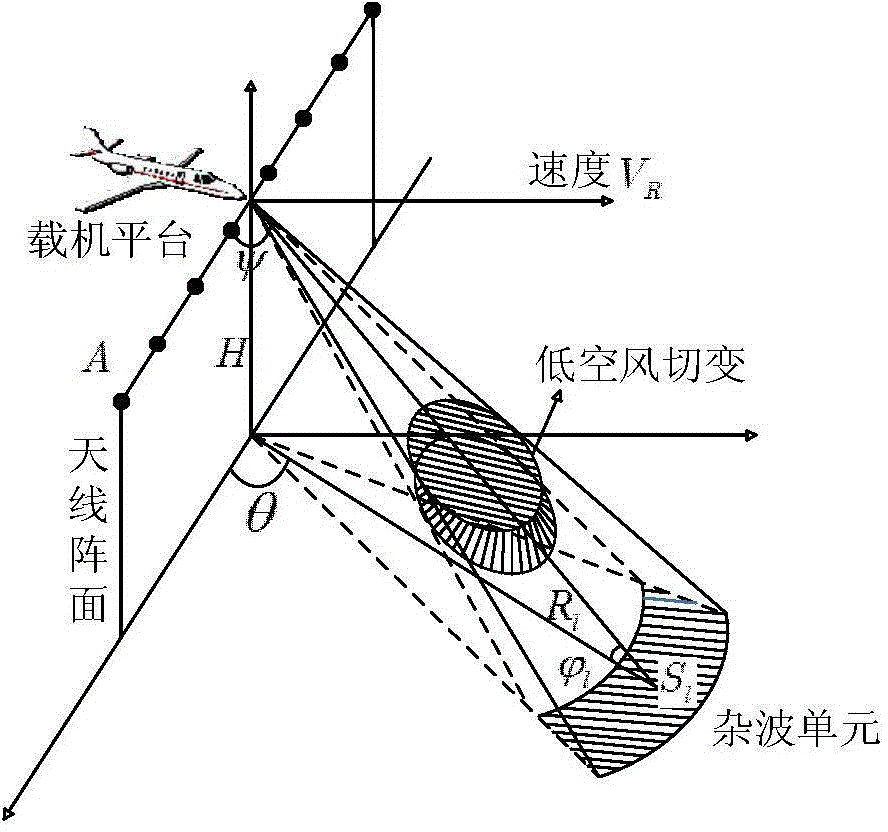
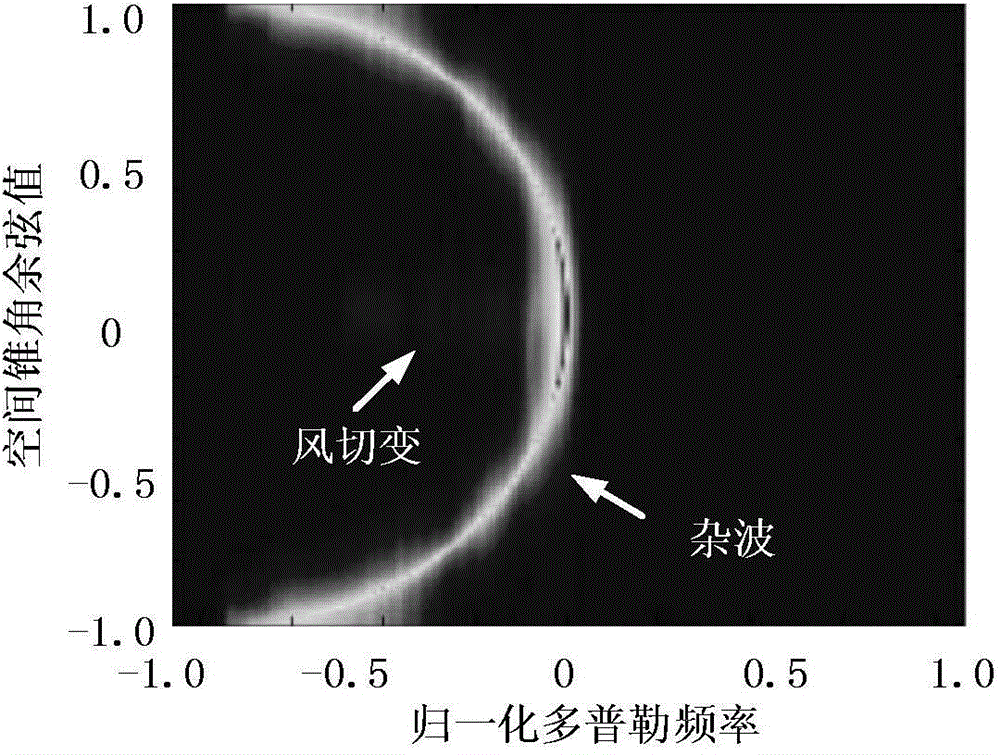
A compressed sensing based onboard phased array radar low-altitude wind shear wind speed estimation method includes creating a transformation matrix of a reference distance unit and a to-be-detected distance unit according to a space-time interpolation method, acquiring an independently and identically distributed sample of a clutter covariance matrix forming the to-be-detected distance unit, and acquiring an estimated value of the clutter covariance matrix to achieve clutter rejection; taking radar main lobe length as prior information, and creating a generalized space guide vector of a wind shear field; taking signal spectral width as prior information, and creating a generalized time guide vector of the wind shear field; according to the generalized space guide vector and the generalized time guide vector, creating a wind speed based wind shear field space-time base dictionary and creating a sparse basis matrix; observing echo signals subjected to clutter rejection in the first step, and recovering the echo signals by the aid of the sparse basis matrix to achieve wind speed estimation. The method has the advantage that accurate wind field speed estimation results can be still acquired when the number of pulses is small and the signal-to-noise ratio is low.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
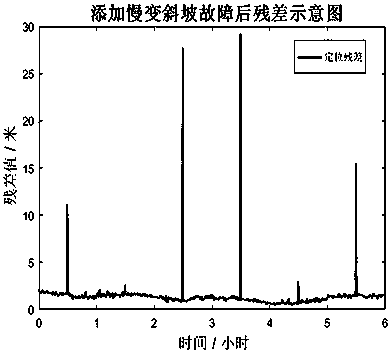
Slowly changing slope fault integrity monitoring method
InactiveCN107479069AAvoid the "transfer" phenomenon of fault errorsSatellite radio beaconingAccelerometerGyroscope
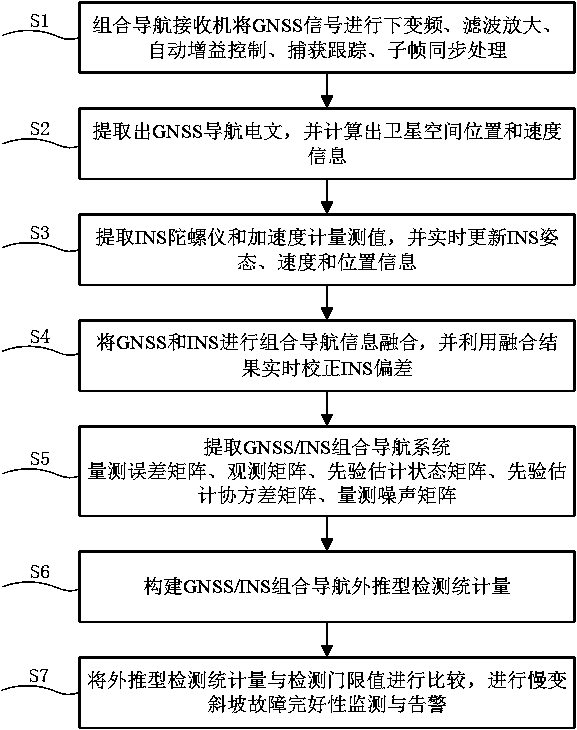
The invention discloses a slowly changing slope fault integrity monitoring method. The method performs down-conversion, filter amplification, automatic gain control, acquisition tracking and sub-frame synchronization processing of a GNSS signal, and simultaneously realizes the real-time updating of the INS attitude, speed and position information based on the INS gyroscope and the accelerometer measurement value. Through the GNSS / INS integrated navigation system to measure the error matrix, the observation matrix, the priori estimation state matrix, the priori estimation covariance matrix and the noise matrix and by means of combined navigation Kalman filter for multi-step extrapolation measurement, the construction of extrapolation test statistic and the comparison with the theoretical detection threshold, it is possible to effectively monitor and identify the fault integrity of the slowly changing slope and avoid the "transmission" error of the fault. The test statistic constructed by this method can identify slowly changing faults efficiently and effectively monitor the slow error source such as thermal noise of integrated navigation receivers.
Owner:天津博创领航知识产权有限公司
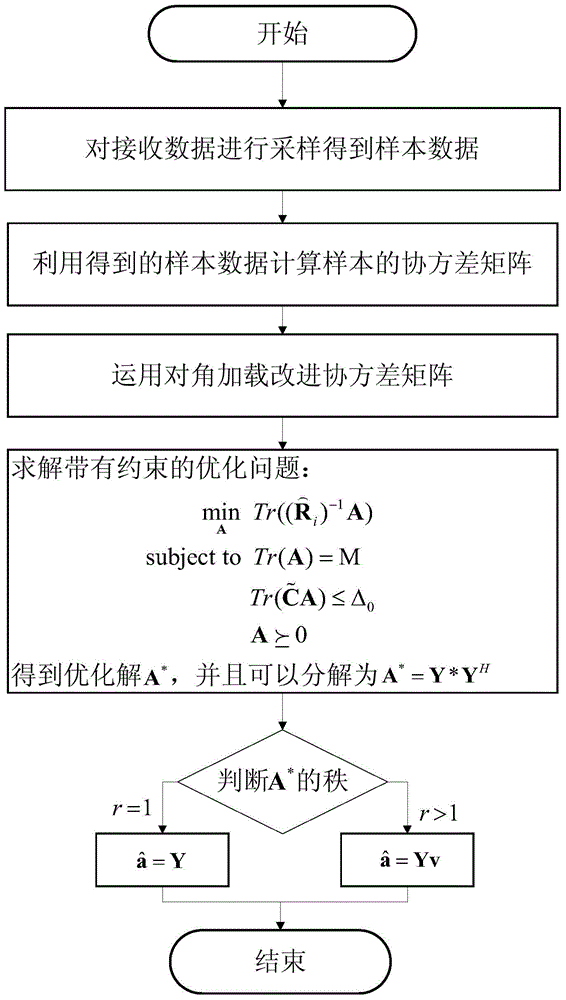
Diagonal loading based adaptive beamforming method for array antenna
ActiveCN104360338AEffective estimateReduced precision requirementsWave based measurement systemsSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringSelf adaptive
The invention belongs to the technical field of adaptive beamforming, and particularly relates to a diagonal loading based adaptive beamforming method for an array antenna. The diagonal loading based adaptive beamforming method specifically includes acquiring sample data through the array antenna, calculating a covariance matrix of the sample data, taking the value of the covariance matrix as an estimated value of an interference and noise covariance matrix, improving the covariance matrix by an diagonal loading method, and solving a guide vector of a constrained optimization problem estimation desired signal. A final simulation result verifies effectiveness of two improvement methods.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
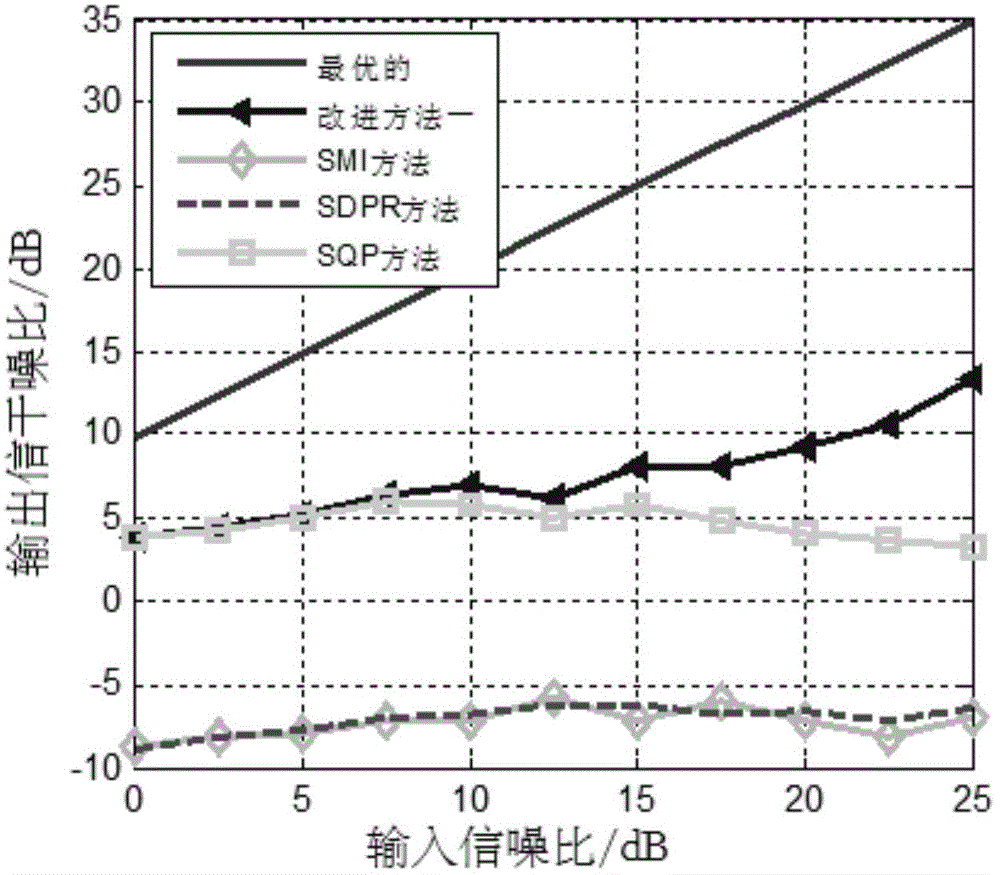
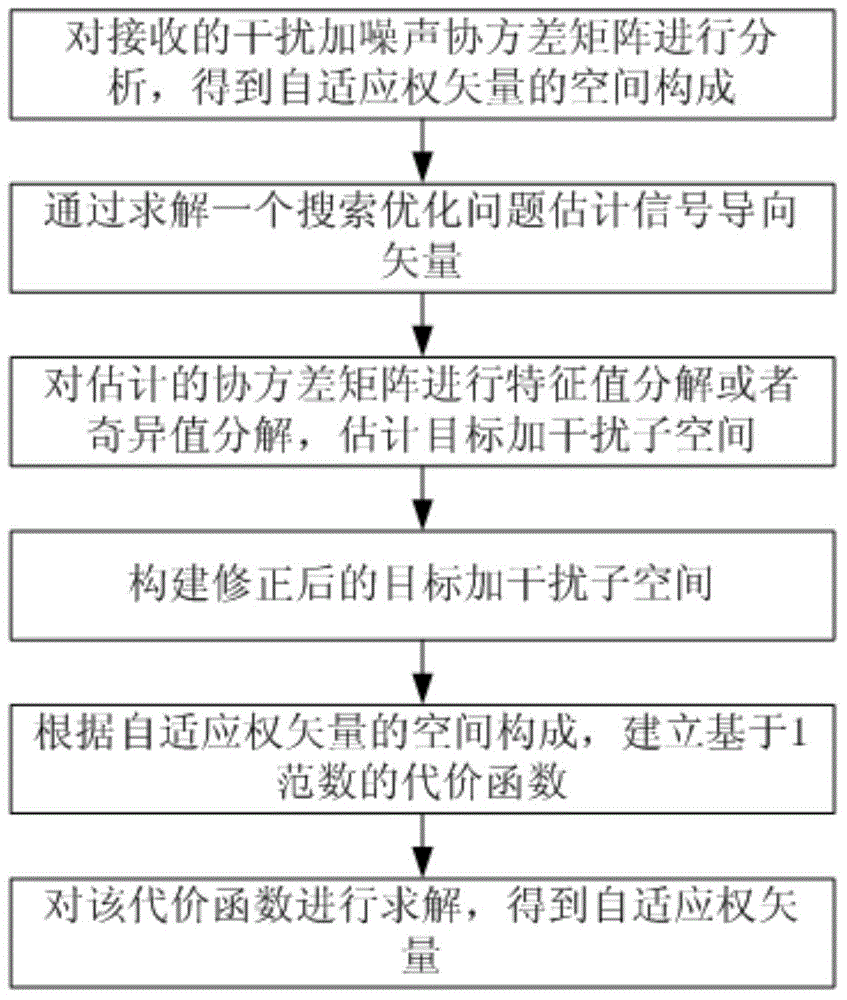
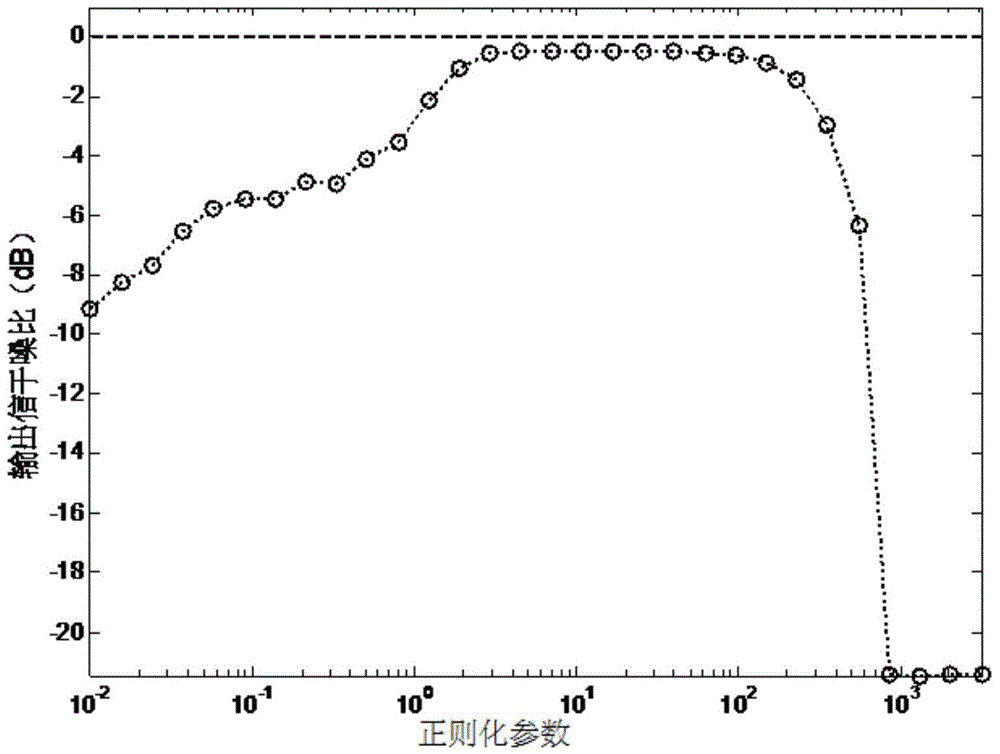
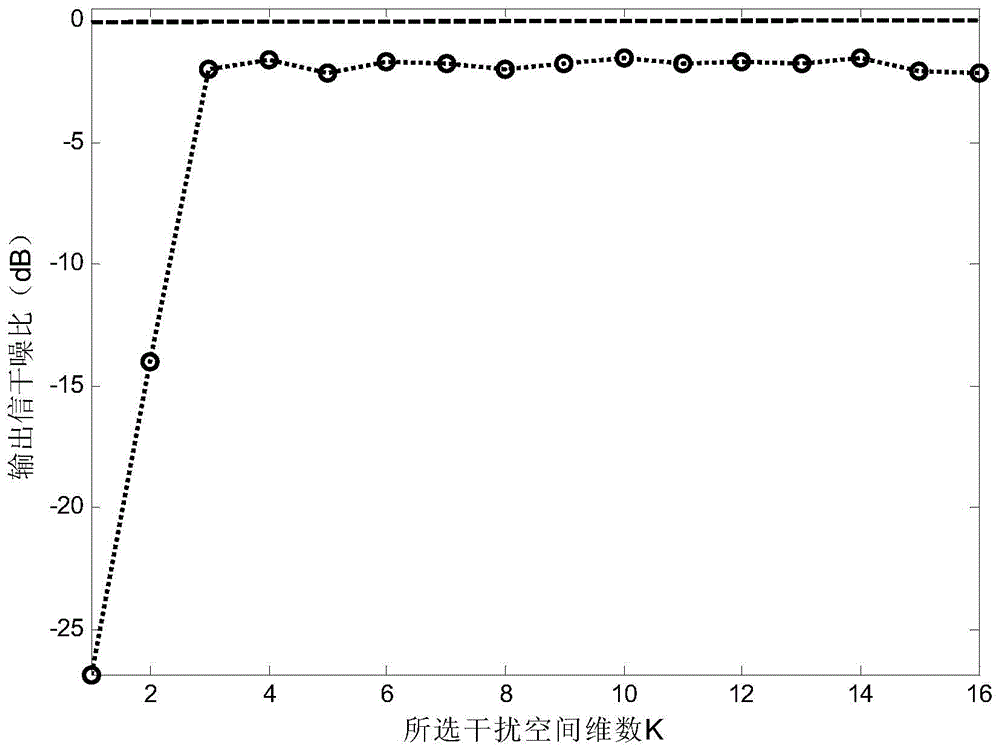
Adaptive beam forming method based on 1 norm constraint
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar adaptive beam forming, and particularly relates to an adaptive beam forming method based on 1 norm constraint. The method includes the specific steps of receiving signals through a receiving array of radar, wherein the signals received through the receiving array of the radar include the interference signal and the target echo signal, and the receiving array of the radar is a uniform linear array; making e represent the error vector between a set target guide vector s and the estimation (please see the specifications) of the target guide vector; establishing an optimization model about the vector e, and solving the optimization model about the vector e so as to obtain the estimation (please see the specifications) of the target guide vector, wherein the estimation (please see the specifications) is equal to the sum of s and e; obtaining the estimation (please see the specifications) of the covariance matrix of the received signals received by the receiving array of the radar; making U represent the matrix composed of the feature vectors corresponding to all feature values of the estimation (please see the specifications) of the covariance matrix of the received signals; making the front k lines of the matrix U serve as target and interference sub-spaces (please see the specifications), wherein the formula of the target and interference sub-spaces is equal to the formula (please see the specifications); establishing the cost function based on the 1 norm constraint; solving the cost function based on the 1 norm constraint so as to obtain a vector beta; obtaining the adaptive weight vector W[opt], wherein W[opt] is equal to the product of the target and interference sub-spaces (please see the specifications) and beta.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
STAP clutter covariance matrix estimation method
The invention belongs to the technical field of radars, and particularly relates to a STAP clutter covariance matrix estimation method based on CUT self priori knowledge. The invention discloses the clutter covariance matrix estimation method based on CUT self priori knowledge. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, reconstructing clutter of a to-be-detected frequency channel of CUT,further extracting clutter of other frequency components except the to-be-detected frequency from the CUT, and finally calculating the clutter covariance matrix of the CUT by the reconstructed clutter. By adoption of the method, the problem of estimation of the clutter covariance matrix in the STAP is solved, the estimated clutter covariance matrix is more accurate, and the rejection performanceof the clutter is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
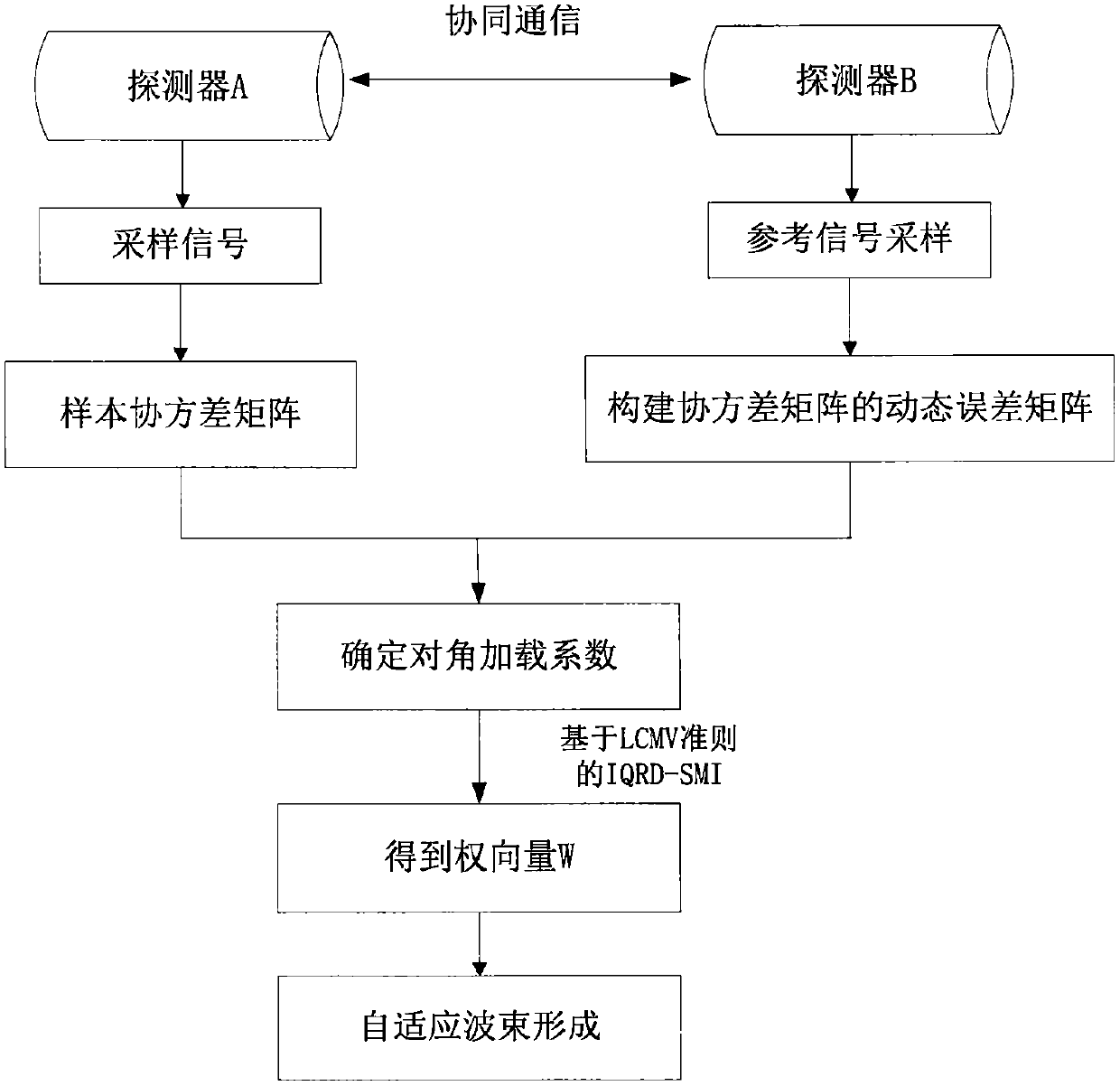
Adaptive wave beam formation method based on dynamic re-correction and system
InactiveCN105372644AImprove formation qualityReduce distractionsAcoustic wave reradiationArray elementSelf adaptive
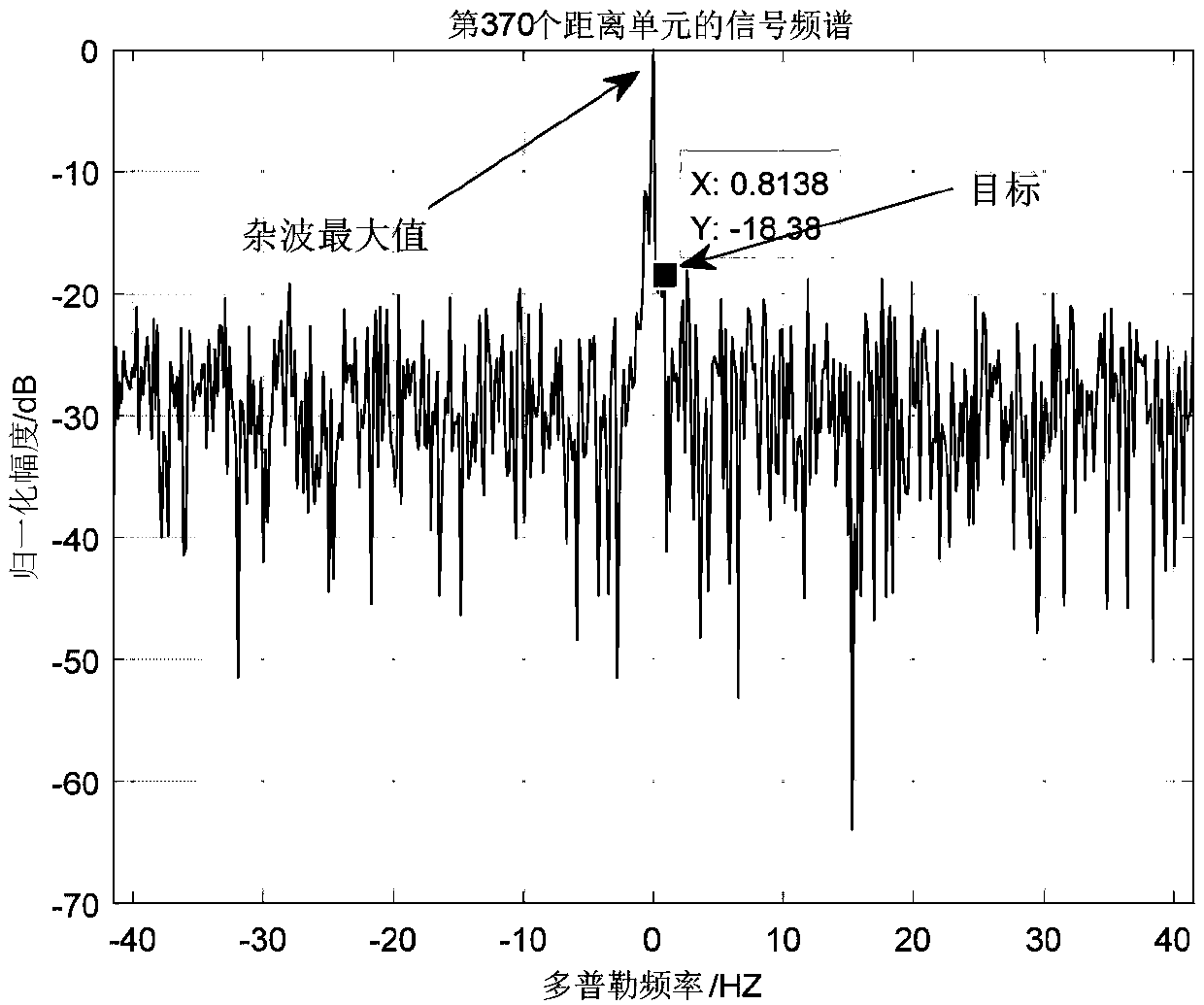
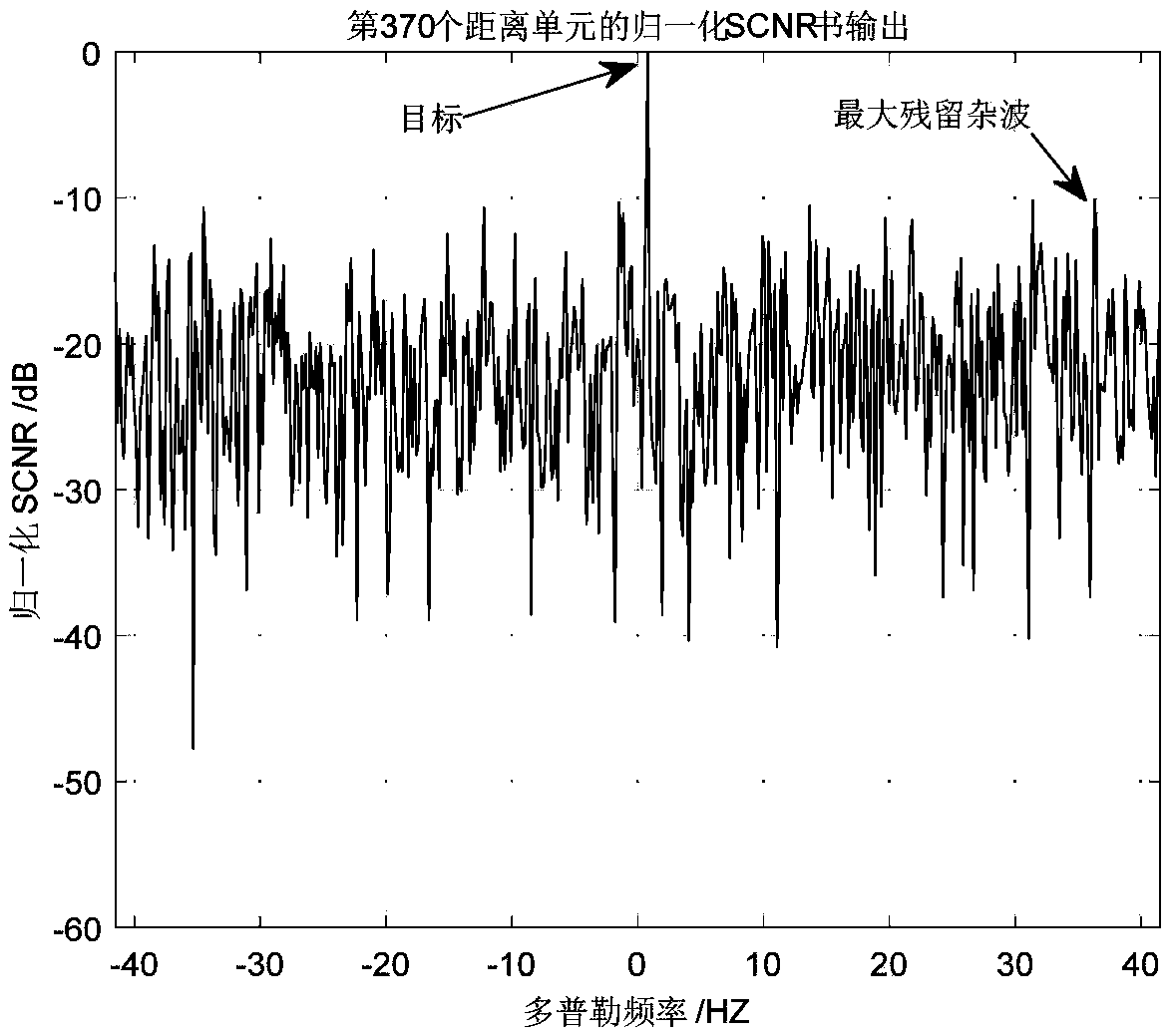
The invention discloses an adaptive wave beam formation method and an adaptive wave beam formation system. An actual input vector covariance matrix is dynamically evaluated according to cooperation communication between reception equipment and a sampling covariance matrix, a dispersion situation of characteristic values is minimized; performance of an adaptive wave beam is improved, influence of environment interference change on signal reception is reduced, and wave beam formation accuracy and wave beam formation robustness are improved. The method comprises steps that, 1), a sample is acquired through receiving end array elements, a covariance matrix of the sample data is calculated and is taken as an estimate of an interference noise addition covariance matrix; 2), an error matrix of the covariance matrix is constructed according to a reference signal sent by cooperation equipment and a pre-stored reference signal of the equipment; 3), the covariance matrix of the sample data acquired in the step 1) is dynamically adjusted by the error matrix acquired in the step 2), and the improved sample covariance matrix is acquired; 4), a diagonal loading coefficient is determined; and 5), weight vector solution is carried out by employing an IQRD-SMI algorithm based on LCMV, and adaptive wave beams are generated.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
MIMO signal covariance matrix estimation method
ActiveCN103259574AReduce estimation errorGuaranteed positive semidefiniteSpatial transmit diversityComputation complexityRound complexity
Provided is an MIMO signal covariance matrix estimation method. Through utilization of observational samples of MIMO signals, a covariance matrix of the MIMO signals on all frequency components is estimated. The method includes the steps: (1) figuring out a sample self-correlation function based on the observational samples of the MIMO signals received by a receiving terminal; (2) constructing a low-complexity SDP problem utilizing the sample self-correlation function, and obtaining an optimal solution of the problem through utilization of an SDP solving tool; (3) obtaining an estimated value of the self-correlation function of the MIMO signals through the optimal solution of the SDP problem; (4) obtaining an estimated value of the covariance matrix of the MIMO signals on all frequency components through utilization of the estimated value of the self-correlation function of the MIMO signals. The MIMO signal covariance matrix estimation method has the advantages that computation complexity is obviously reduced compared with a traditional method through utilization of the SDP problem, the estimation error can reach the minimum in the meaning of least square, and the estimated covariance matrix can be positive semi-definite on all frequencies.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
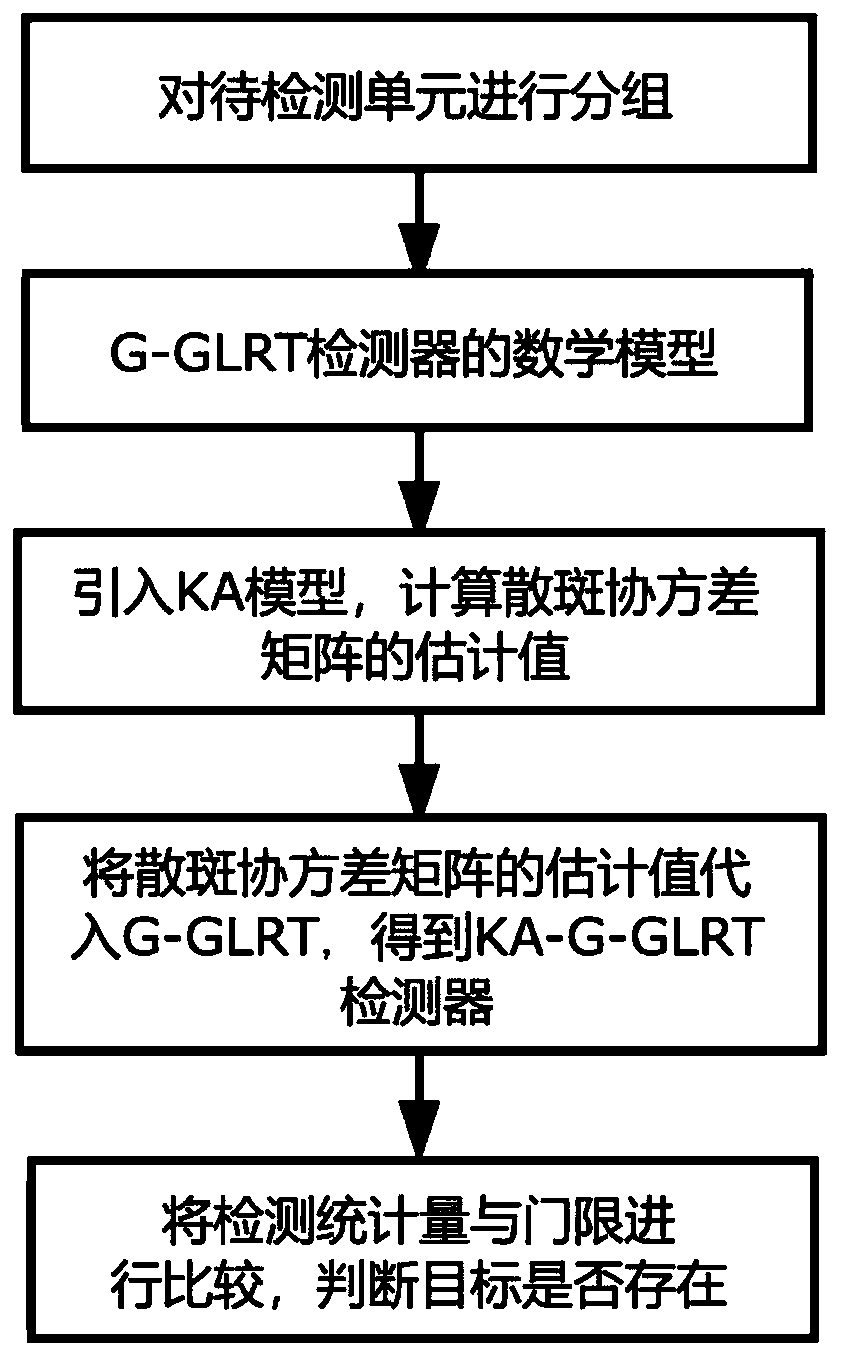
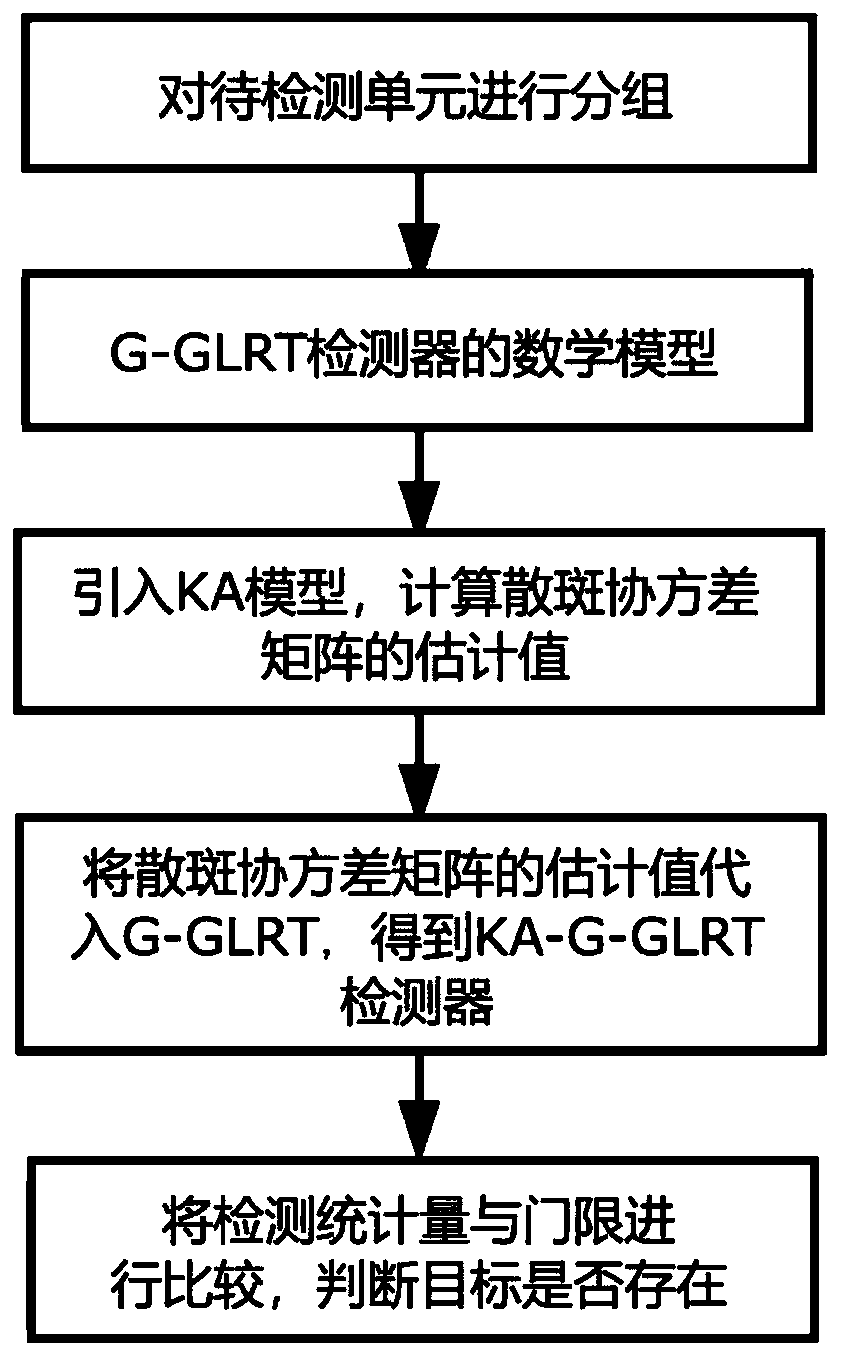
Knowledge aided (KA) grouped generalized likelihood ratio detection method
ActiveCN109709526AAchieve homogenizationConstant false alarm characteristicWave based measurement systemsPattern recognitionMathematical model
The invention provides a KA grouped generalized likelihood ratio detection method. According to the method, units to be detected are grouped; a mathematical model of a G-GLRT detector is constructed;a KA model is used to calculate an estimated value M<^> of a speckle covariance matrix; the speckle covariance matrix M in a mathematical expression of a G-GLRT detector is replaced with M<^>, and a mathematical expression of a KA-G-GLRT detector is obtained; a detection statistic quantity S is calculated on the basis of the KA-G-GLRT detector, S is compared with a threshold, and whether there isa target is thus determined. The grouped algorithm is used, uniform samples in the space part are uniformized in the groups, the texture component of sea clutters in each group satisfies inverse gammadistribution, and scale and shape parameters of the texture of each group are different. The KA-G-GLRT detector has a constant false alarm characteristic for the estimated value M<^> of the speckle covariance matrix. Compared with other detectors, the KA-G-GLRT detector can obtain a better detection performance in sea clutter data actually measuring experiments.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
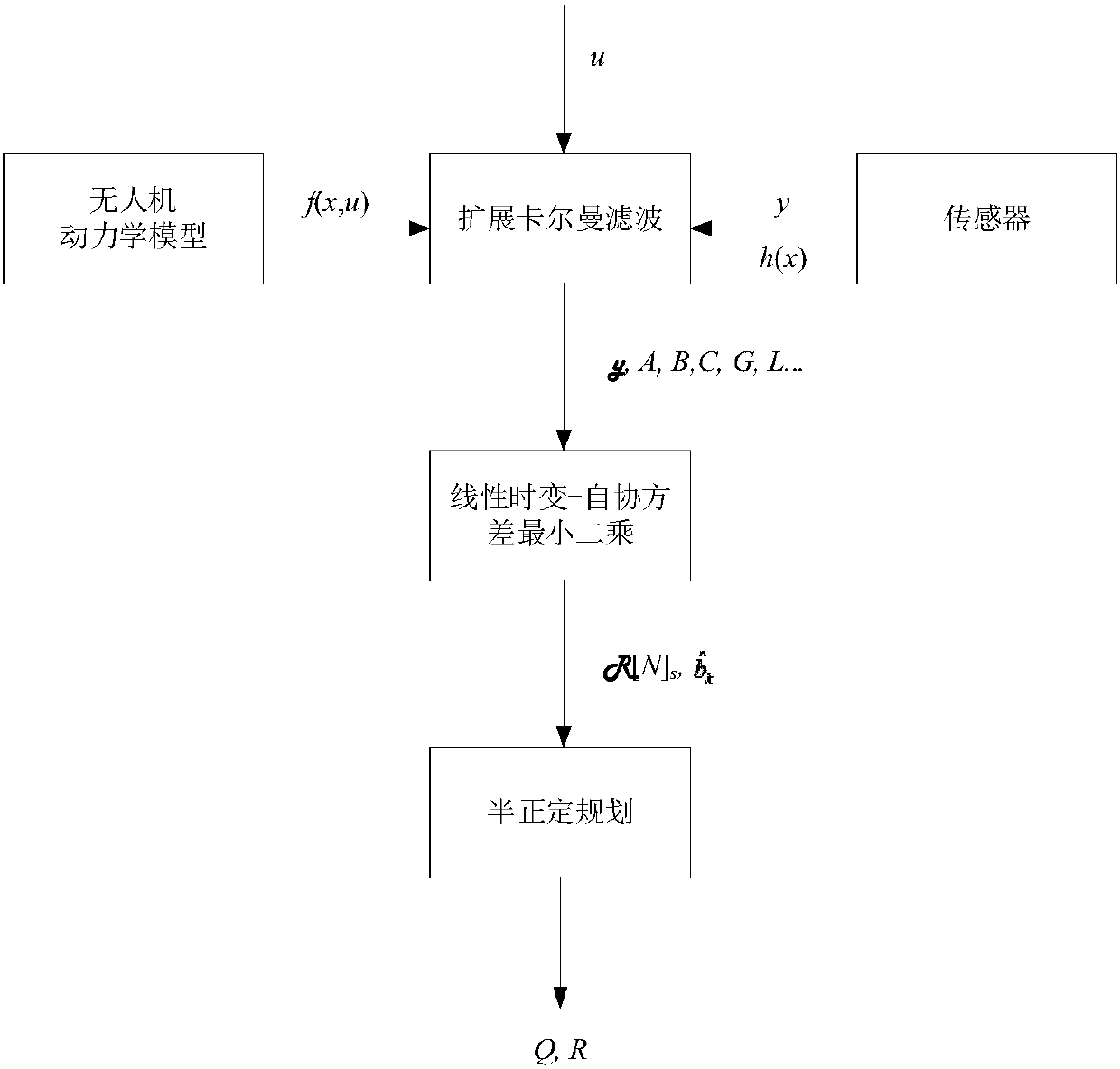
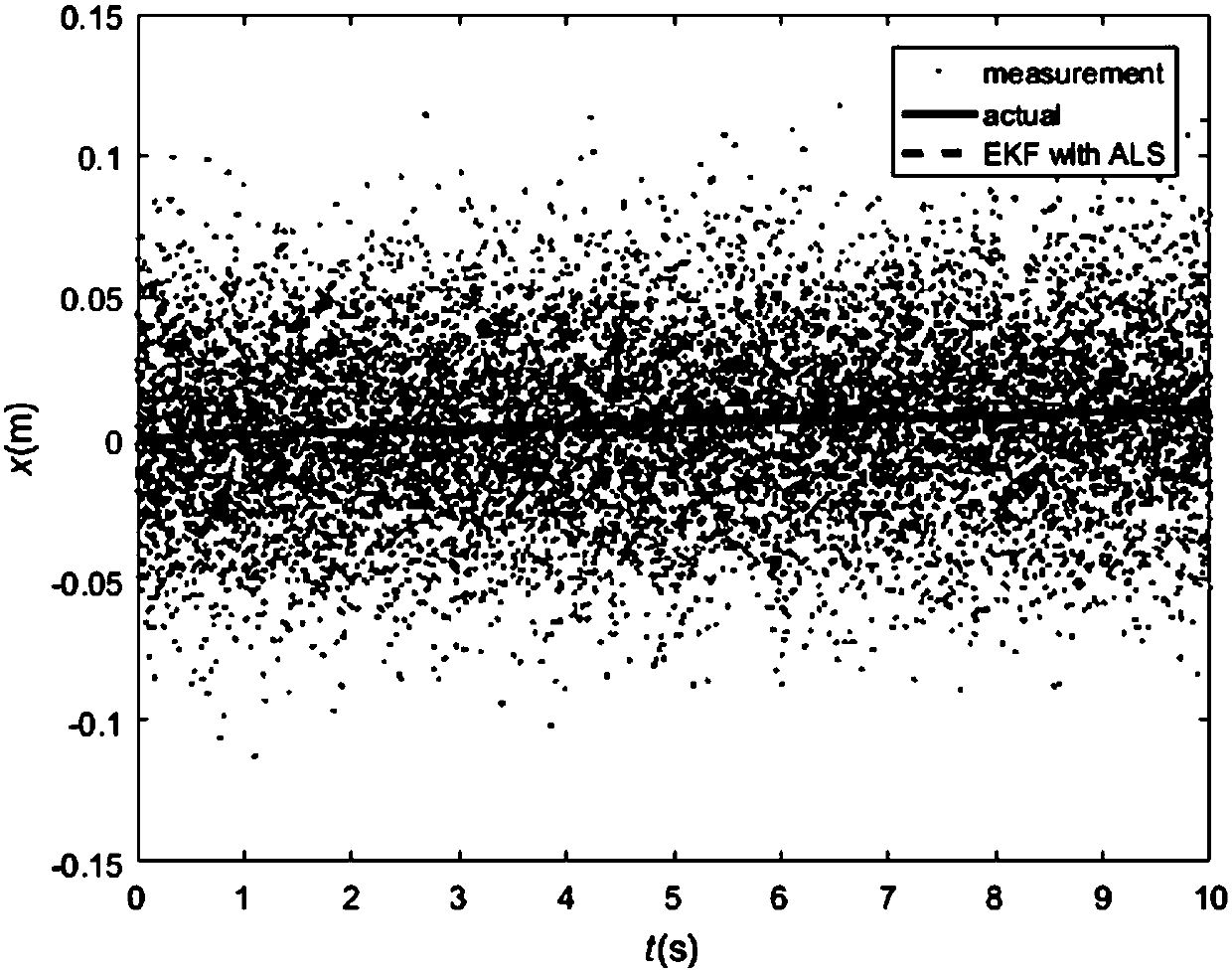
Method for estimating noise covariance of unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN107729585ALower requirementAccurate Valuation RangeGeometric CADSustainable transportationKaiman filterProcess noise
The invention provides a method for estimating a noise covariance of an unmanned aerial vehicle. A dynamics model of the unmanned aerial vehicle is linearized in combination with a control quantity and an observation value by utilizing an extended Kalman filter to obtain a linearized state estimation equation; and a coefficient matrix, a Kalman gain and an innovation obtained by the linearized state estimation equation are substituted into an auto-covariance least squares algorithm to obtain estimated values of a covariance matrix composed of an expected value of the innovation and an auto-covariance matrix composed of the expected value of the innovation, and through a semi-definite programming algorithm, a process noise covariance and a measurement noise covariance are obtained. Throughthe method for estimating the noise covariance of the unmanned aerial vehicle, the estimation accuracy of the process noise covariance Q and the measurement noise covariance R is high. Meanwhile, theestimation method provides a numerical value reference for operators, so that in general, the operators can debug the process noise covariance Q and the measurement noise covariance R more conveniently and quickly.
Owner:SHENZHEN SPROCOMM TECH CO LTD
Bistatic MIMO radar angle estimation method under joint error condition
InactiveCN108919231AGood precisionReduce computational complexityWave based measurement systemsAlternating least squaresAlgorithm
The invention discloses a bistatic MIMO radar angle estimation method under a joint error condition, comprising the following steps: performing matched filtering processing on data of a receiving array, and constructing one three-dimensional tensor model; then decomposing the three-dimensional tensor model by adopting a COMFAC algorithm and performing iterative computation on a receiving directionmatrix, a transmitting direction matrix and a target covariance matrix by utilizing an alternating least square method until convergence conditions are met, thus estimated values of the receiving direction matrix, the transmitting direction matrix and the target covariance matrix are obtained; and finally estimating DOD and DOA of a target by utilizing a least square method by virtue of a guidance vector of an auxiliary array element. The estimation method disclosed by the invention utilizes an array measurement multidimensional structure, so that precision of the estimation method is obviously better than that of a Reduced-MUSIC method; meanwhile, computational complexity of the estimation method is far below that of the Reduced-MUSIC method, and efficiency of the estimation method is higher than that of the Reduced-MUSIC method.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
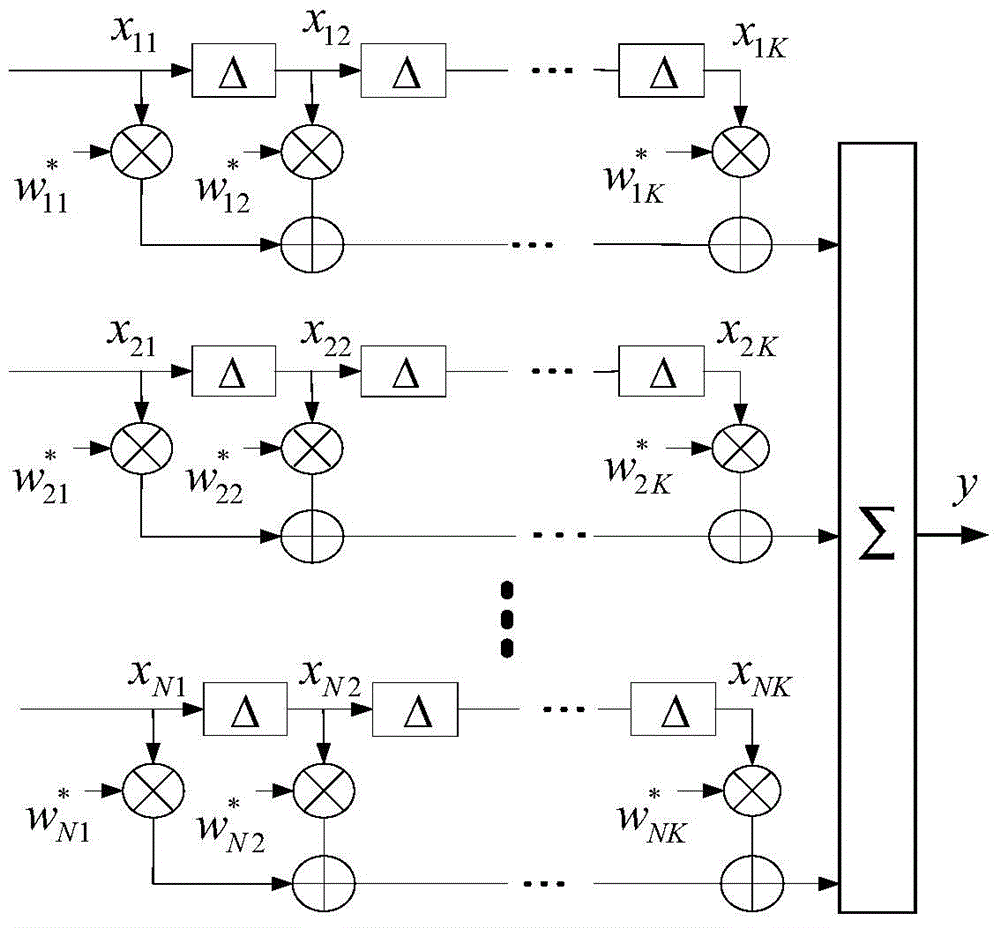
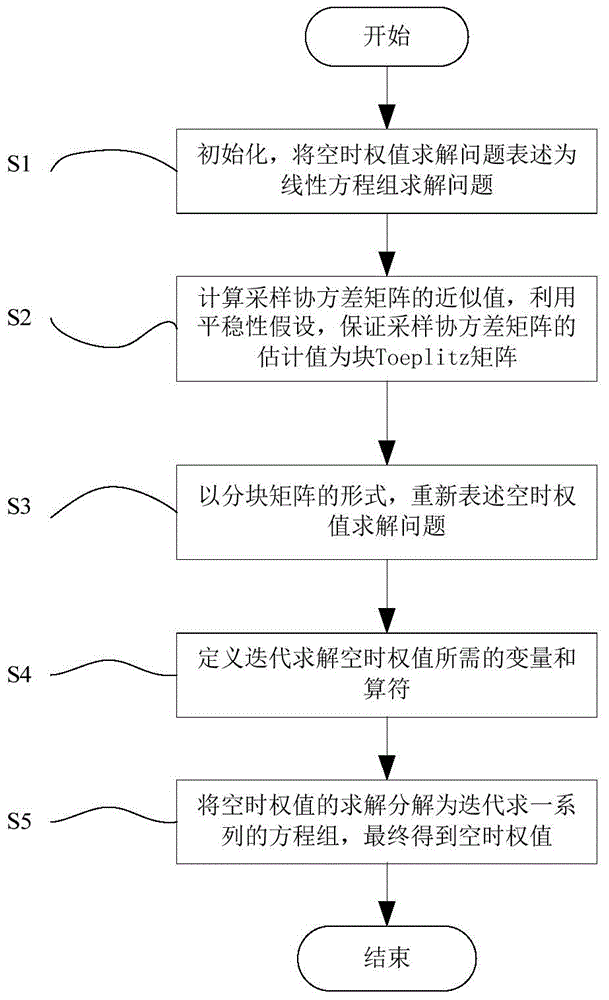
Space-time anti-interference method for block Toeplitz matrix low-complexity inversion
ActiveCN104914451AIncrease update frequencyCutting costsSatellite radio beaconingComputation complexitySignal processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of array signal processing, and relates to a space-time anti-interference method for block Toeplitz matrix low-complexity inversion. The method specifically comprises the following steps: (S1) performing initialization, and expressing a space-time weight solving problem as a linear equation set solving problem; (S2) calculating the approximate value of a sampling covariance matrix, and using stationarity assumption to ensure that the estimated value of the sampling covariance matrix is a block Toeplitz matrix; (S3) re-expressing the space-time weight solving problem in the form of a partitioned matrix; (S4) defining variables and operators required for iterative solving of the space-time weight; and (S5) decomposing the solving of the space-time weight into iterative solving of a series of equation sets to obtain the space-time weight finally. The invention puts forward a low-complexity method for iteratively solving the space-time weight. The method has the same performance as a traditional SMI method on the premise of adopting the same anti-interference principles. By adopting the method of the invention, the computational complexity is reduced greatly.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
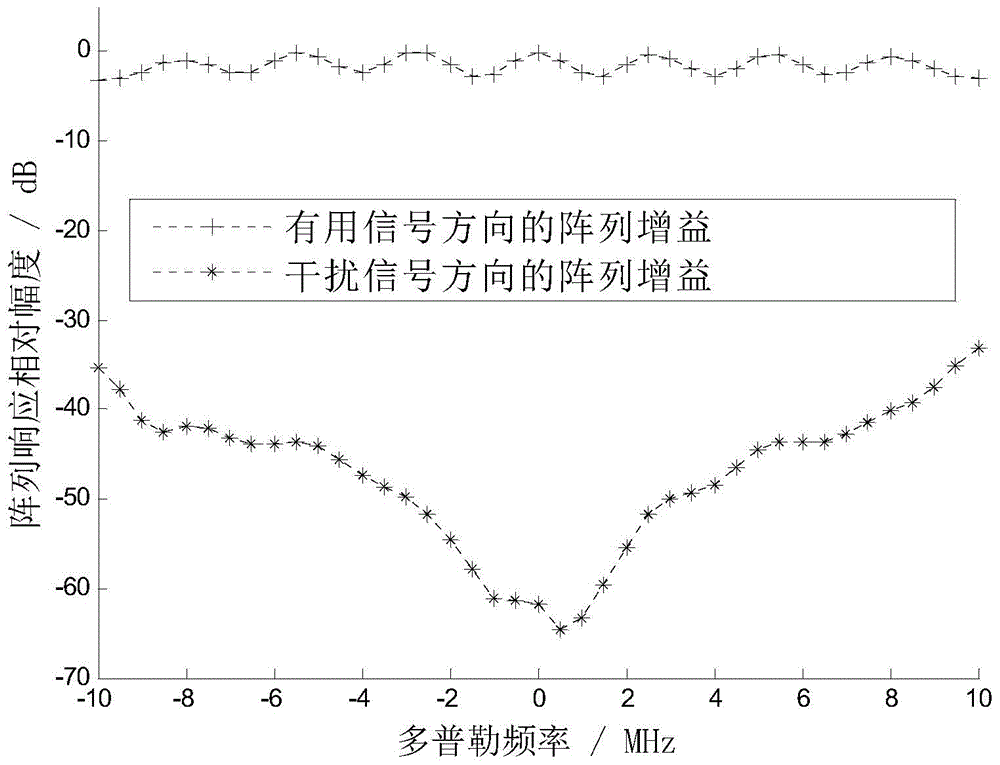
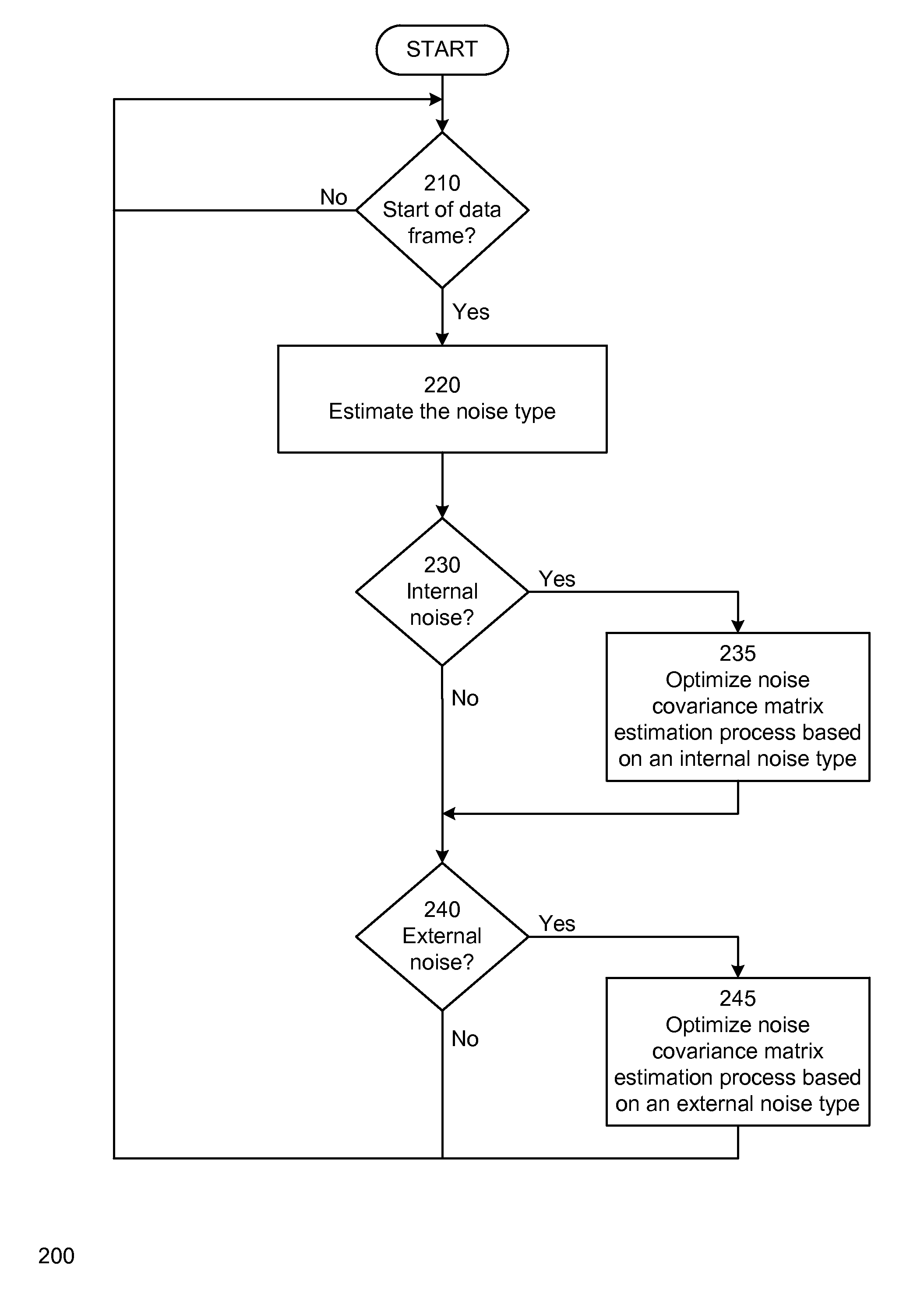
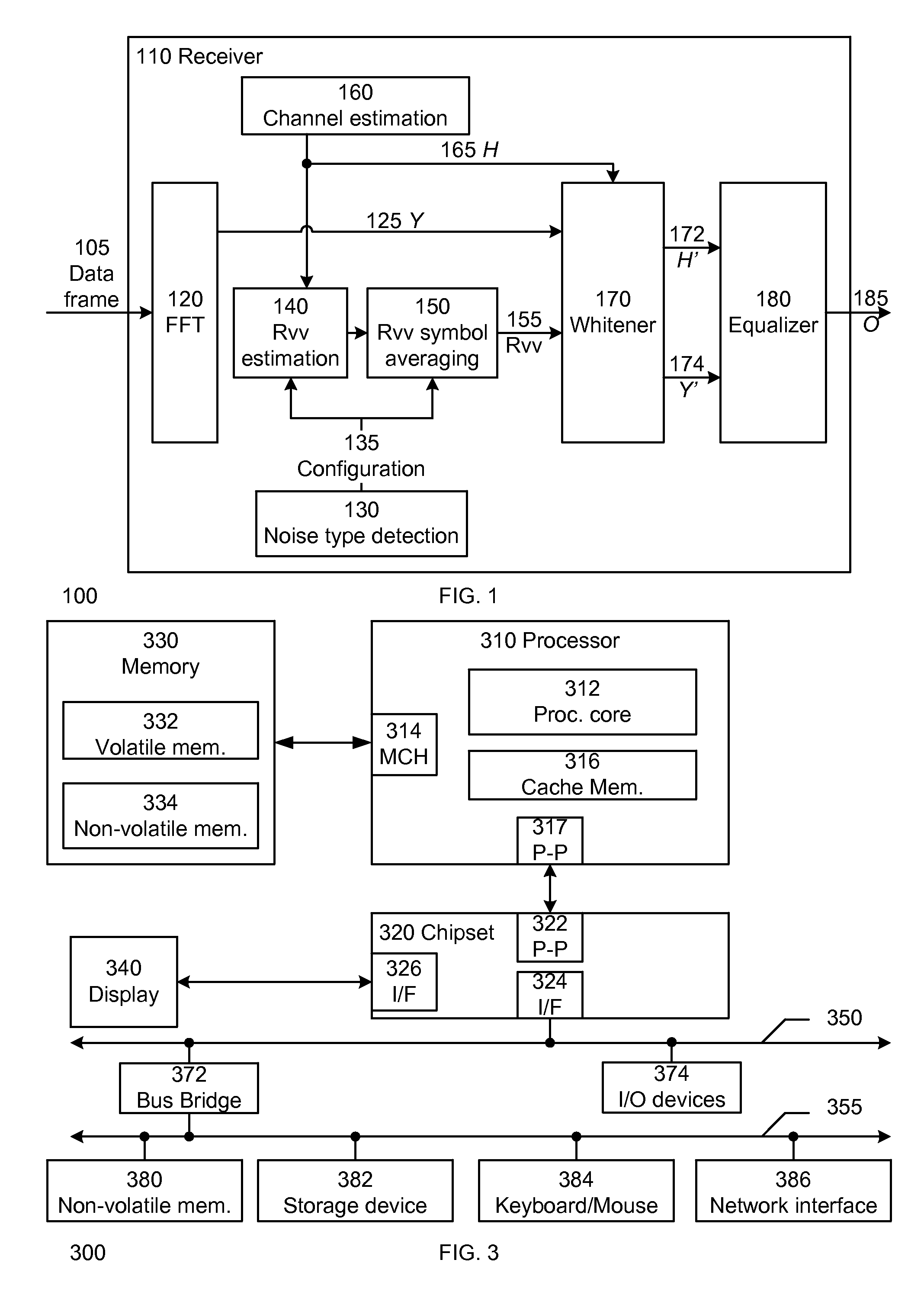
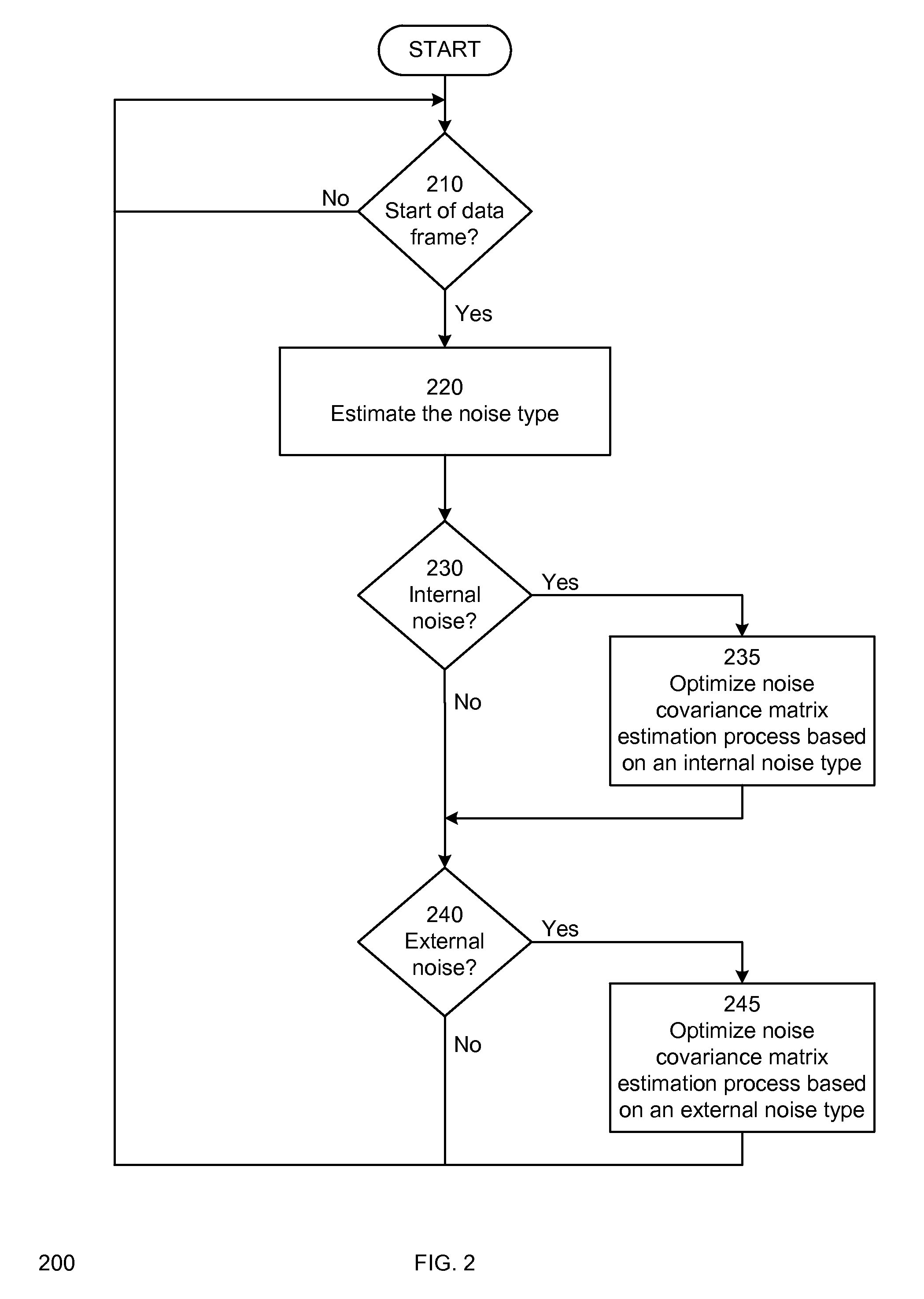
Method and apparatus for adaptive mitigation of noise interference
A method and system for adaptive mitigation of noise interference in a receiver. In one embodiment of the invention, the receiver determines the type of the dominant noise interference among one or more noise interferences. The receiver determines or optimizes the estimation and averaging process of the noise covariance matrix based on the type of the dominant noise interference in one embodiment of the invention. This allows dynamic selection and adaptation of the noise estimate covariance matrix based on the noise type in one embodiment of the invention.
Owner:APPLE INC
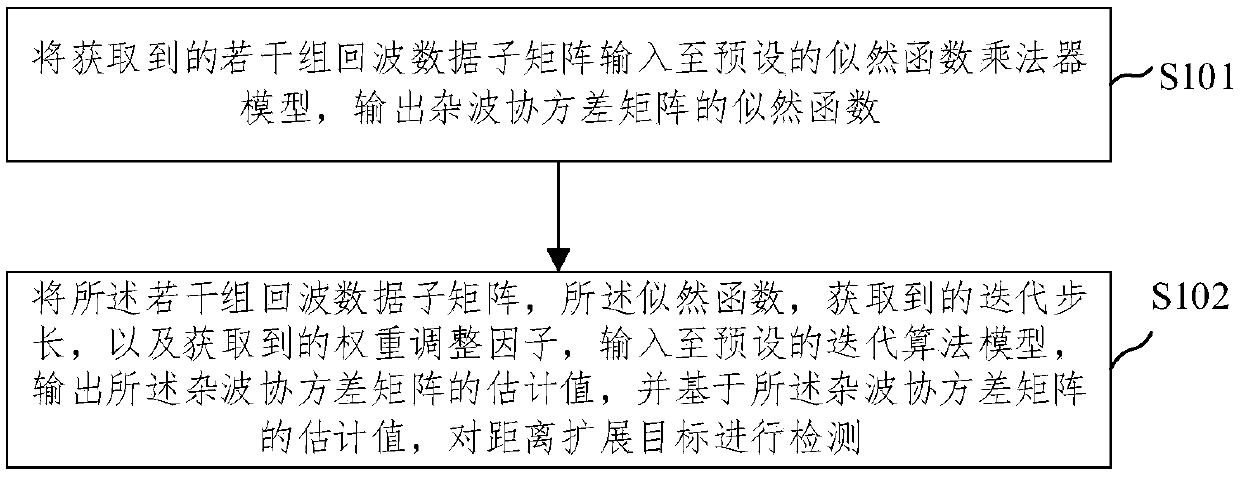
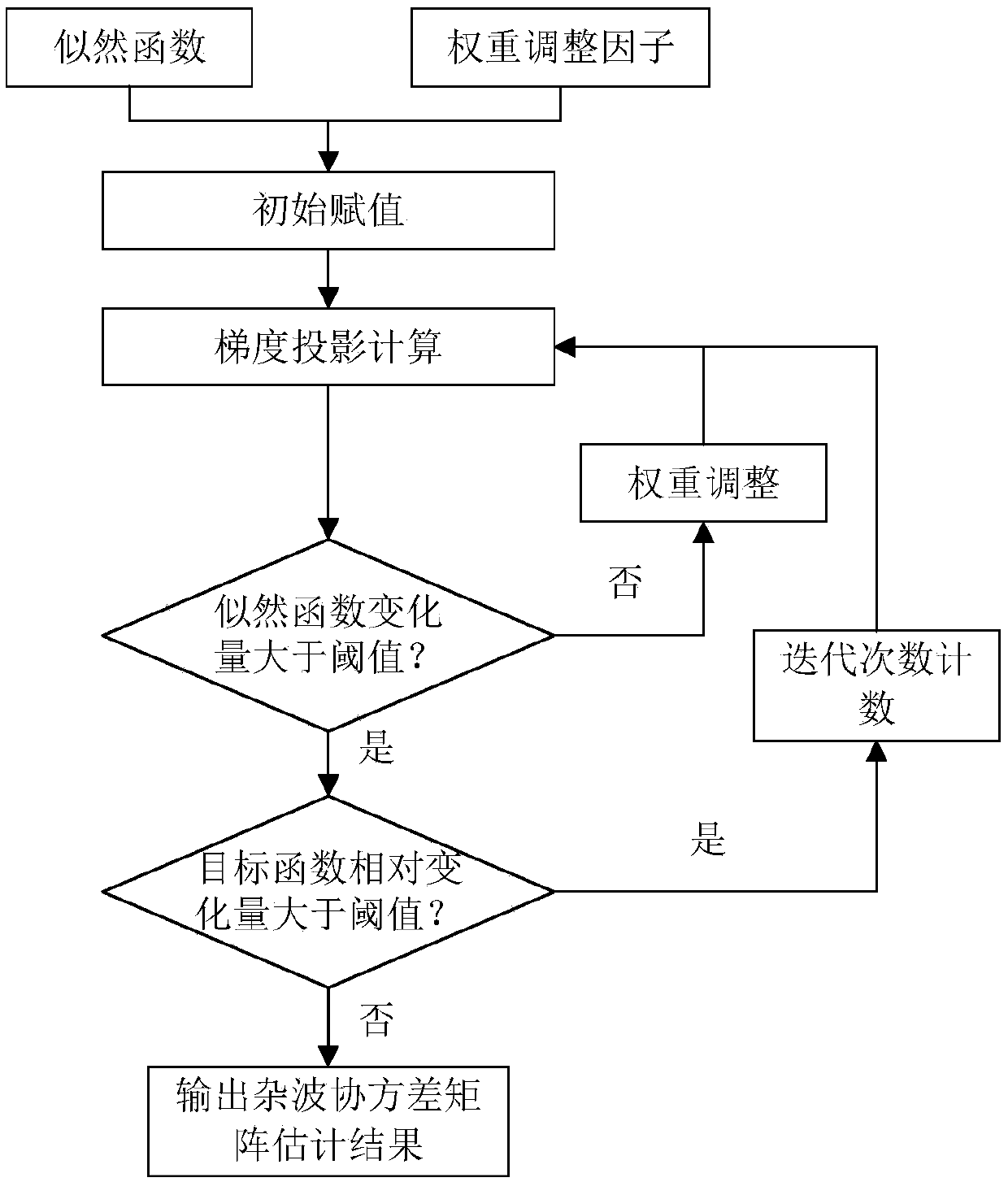
Distance extension target detection method and device based on clutter covariance matrix estimation
ActiveCN108896967AImprove estimation accuracyImprove detection accuracyWave based measurement systemsWeight adjustmentAlgorithm
The invention provides a distance extension target detection method and device based on clutter covariance matrix estimation. The method comprises inputting the obtained plurality of sets of radar echo data sub-matrices to a preset likelihood function multiplying unit model, and outputting a likelihood function of the clutter covariance matrix; inputting the plurality of sets of radar echo data sub-matrices, the likelihood function, the obtained iteration step size and the obtained weight adjustment factor to a preset iterative algorithm model, and outputting an estimated value of the cluttercovariance matrix. The distance extension target detection method and device based on the clutter covariance matrix estimation do not need auxiliary data, when parameter estimation is carried out under the non-complete observation, the likelihood function maximization and the clutter covariance matrix rank minimization, the weight is dynamically adjusted in the iterative solution process, and theestimation precision of the clutter covariance matrix is improved, so that the detection performance of the distance extension target is improved, and the detection precision and the detection accuracy are improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Non-iterative mixed signal source positioning method based on rank loss
ActiveCN110286352AReduce computational complexitySimple methodPosition fixationComplex mathematical operationsIterative methodSignal source
The invention discloses a non-iterative mixed signal source positioning method based on rank loss, and the method comprises the following steps of receiving and acquiring receiving data of a mixed signal source to be positioned through an array; calculating the estimated value of a covariance matrix R from the received data, calculating the direction of arrival angles of a near-field signal source and a far-field signal source in a mixed signal source, calculating the distance between the near-field signal source and the far-field signal source in the mixed signal source and classifying the mixed signal source into the far-field signal source and the near-field signal source; when the estimated value is obtained, the signal source is considered to be the near-field signal source, and K2 near-field signal sources are estimated; and obtaining far-field signal source candidates according to the estimated signal direction of arrival angle and distance of the near-field signal sources, and obtaining the direction of arrival angles of K1 far-field signal sources by utilizing a direction of arrival selection strategy. According to the method, the far-field and near-field mixed narrowband signals are positioned by utilizing second-order statistics of array data, and meanwhile, the saturation behavior in signal source positioning is overcome by a non-iterative method.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Civil aircraft flight control sensor signal reconstruction fault-tolerant control method
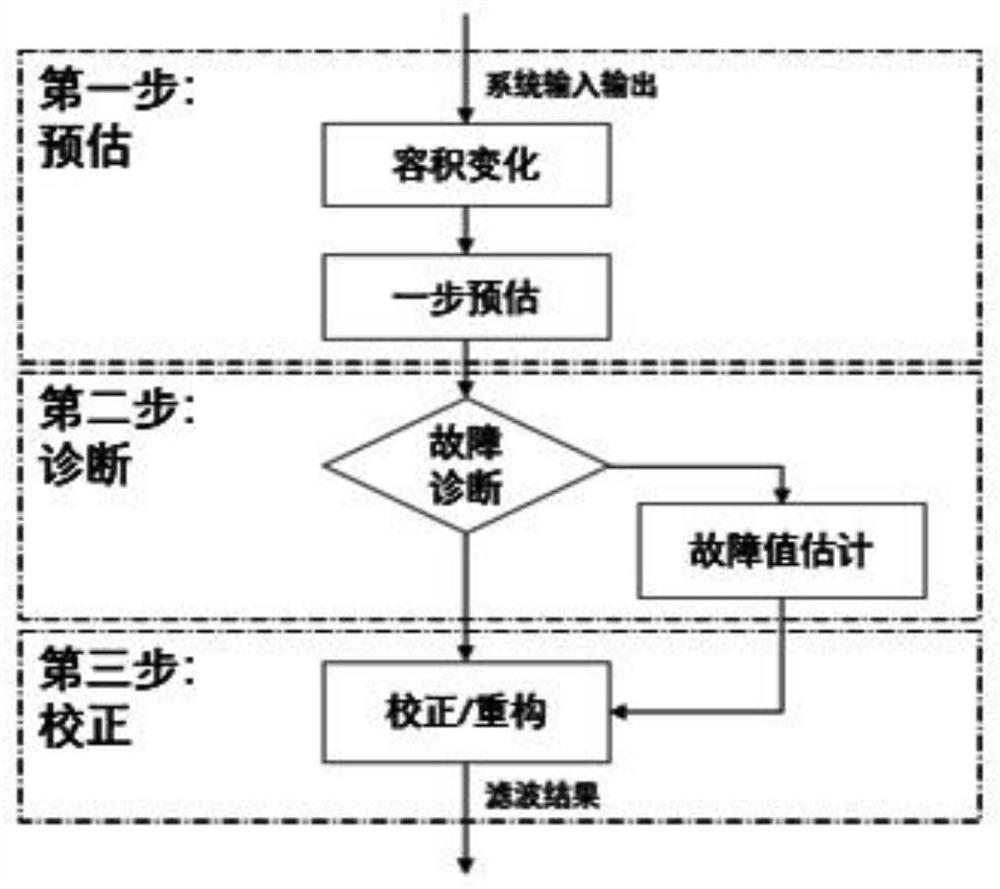
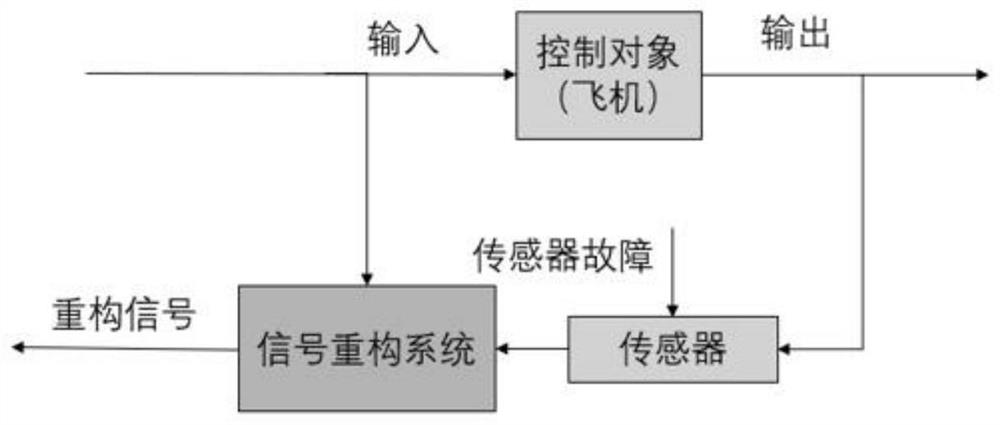
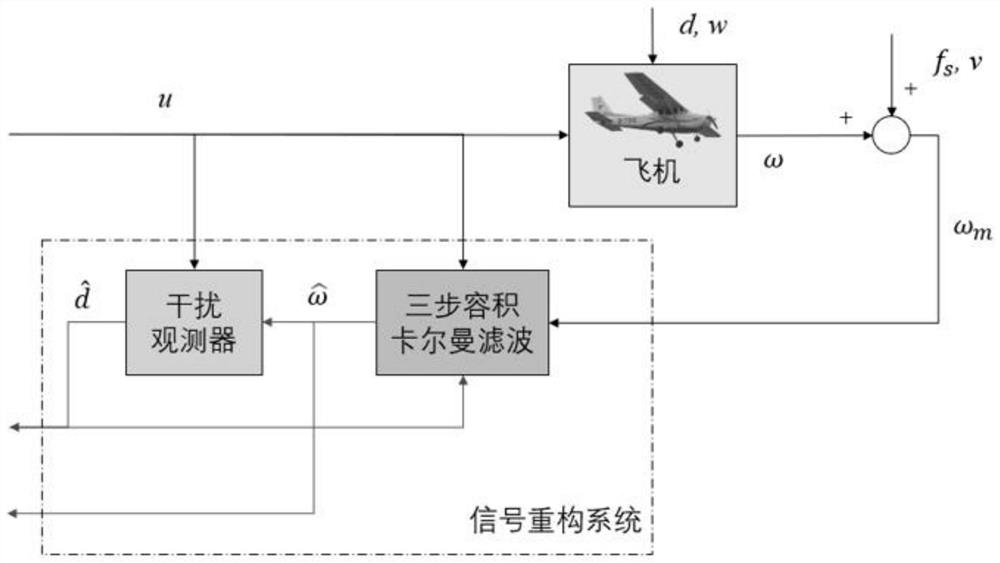
ActiveCN113128035ASolve the accuracy problemSolve the problem of cumbersome parameter adjustmentDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsSignal reconstructionFault tolerant control system
The invention relates to a civil aircraft flight control sensor signal reconstruction and fault-tolerant control method, which comprises the following steps: selecting a volume point for a nonlinear flight control system and calculating one-step estimation; and after fault diagnosis, isolation and estimation are performed, correcting the estimation of the system state according to the estimation of the covariance matrix, and then carrying out signal reconstruction or state updating according to a fault diagnosis result. According to the invention, effective tracking of a control instruction can be realized without being influenced by sensor faults and external interference; and compared with the prior art, the fault-tolerant control system has the advantages that parameter adjustment is simpler and more convenient, the precision is higher, the workload required during parameter adjustment is remarkably reduced, and the reconstruction precision and the control robustness when the system is disturbed are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
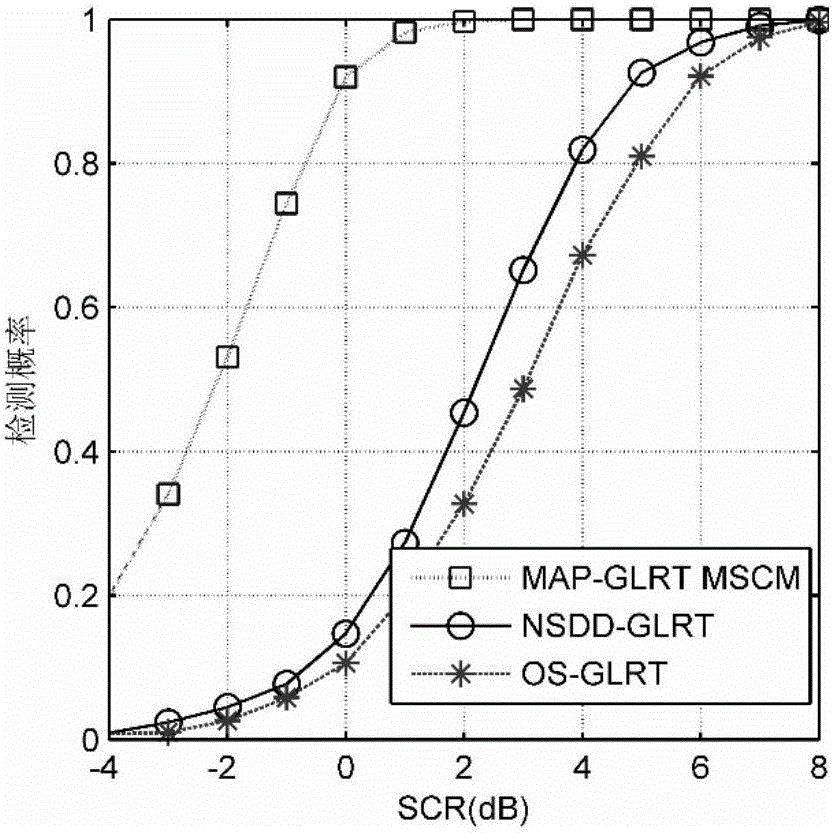
Correction sample covariance matrix estimate algorithm based on maximum posteriori
ActiveCN107179531AEasy to detectImprove estimation accuracyWave based measurement systemsAlgorithmSpatial covariance matrix
The invention discloses a correction sample covariance matrix estimate algorithm based on the maximum posteriori; the method comprises the following steps: 1, using a MAP-GLRT detector mathematics expression to serve as a mathematics prototype; 2, using a MSCM estimate algorithm based on the maximum posteriori as a clutter covariance matrix estimate algorithm; 3, replacing the covariance matrix in the MAP-GLRT detector mathematics expression as the MSCM, thus obtaining the MAP-GLRT detector corrected mode, i.e., the MAP-GLRT MSCM detector expression of the correction sample covariance matrix estimate algorithm based on the maximum posteriori. The invention imports the MAP-GLRT MSCM detector into the correction sample covariance matrix estimate algorithm based on the maximum posteriori, thus improving the covariance matrix estimate precision; the MAP-GLRT MSCM detector has a similar detection performance with the MAP-GLRT detector when an object is detected under the uniform sea clutter background; the correction sample covariance matrix estimate algorithm can comply with real clutter environment requirements, and the detector can obtain better detection performances in actual measurement sea clutter data tests.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
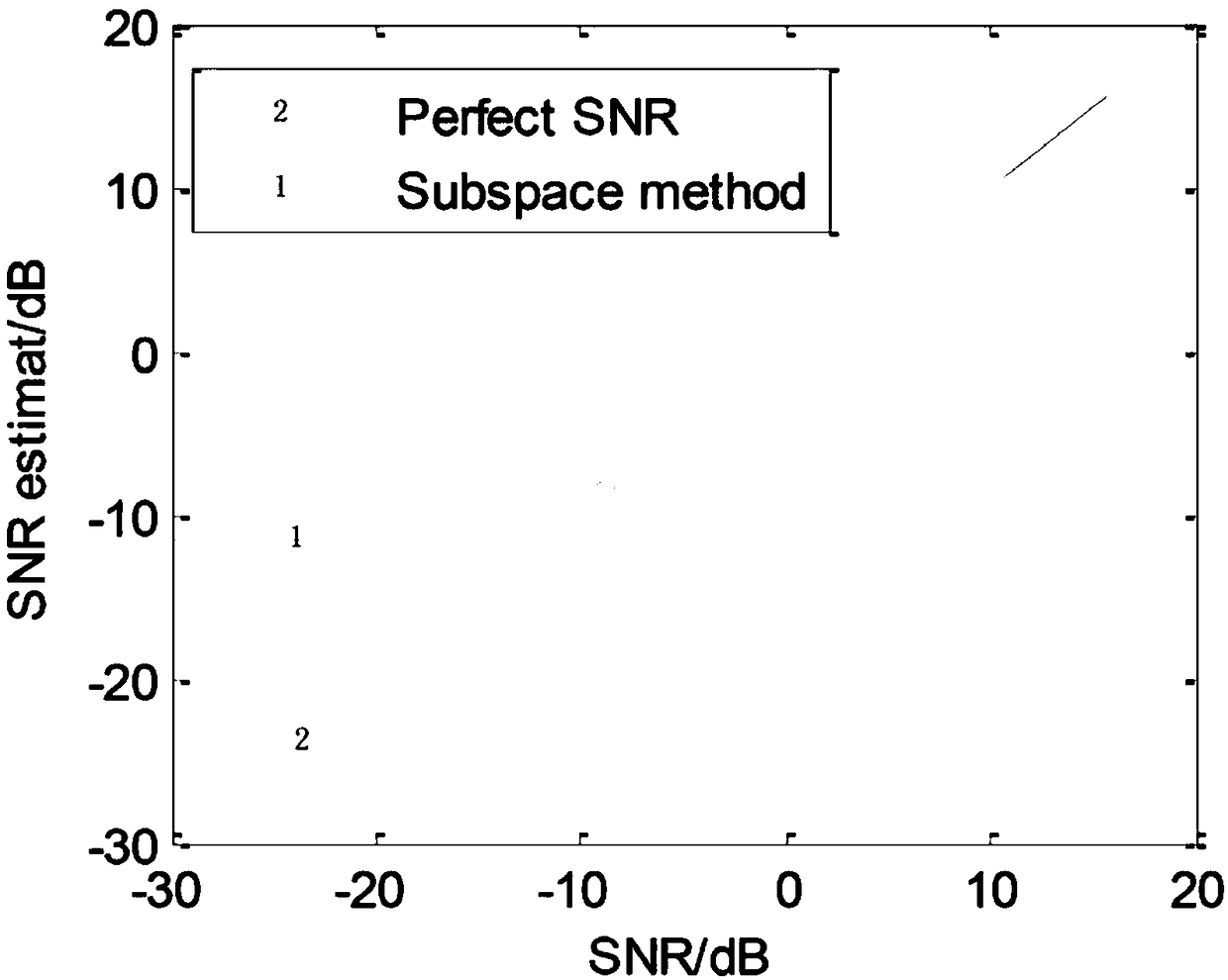
SNR estimation method based on sub space
ActiveCN109194422ASmall amount of calculationProcessing speedTransmission monitoringEstimation methodsDecomposition
The present invention discloses an SNR estimation method based on a sub space. The method comprises the following steps of: the step 1: solving an estimation value of a covariance matrix by employingreceiving signals obtained through a communication device; the step 2: solving dimensions of a signal sub space; the step 3: performing characteristic value decomposition for the estimation value of the covariance matrix obtained in the step 1, and performing descending order of the characteristic values according to the dimensions of the signal sub space; and the step 4: solving noise power and signal power according to the characteristic values obtained in the step 3 so as to obtain an estimation value of the SNR. The SNR estimation method based on the sub space is small in calculated amountand faster in processing speed, and has estimation performances being superior to that of other algorithms in the prior art.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Reduced rank beam forming method based on united alternative optimization
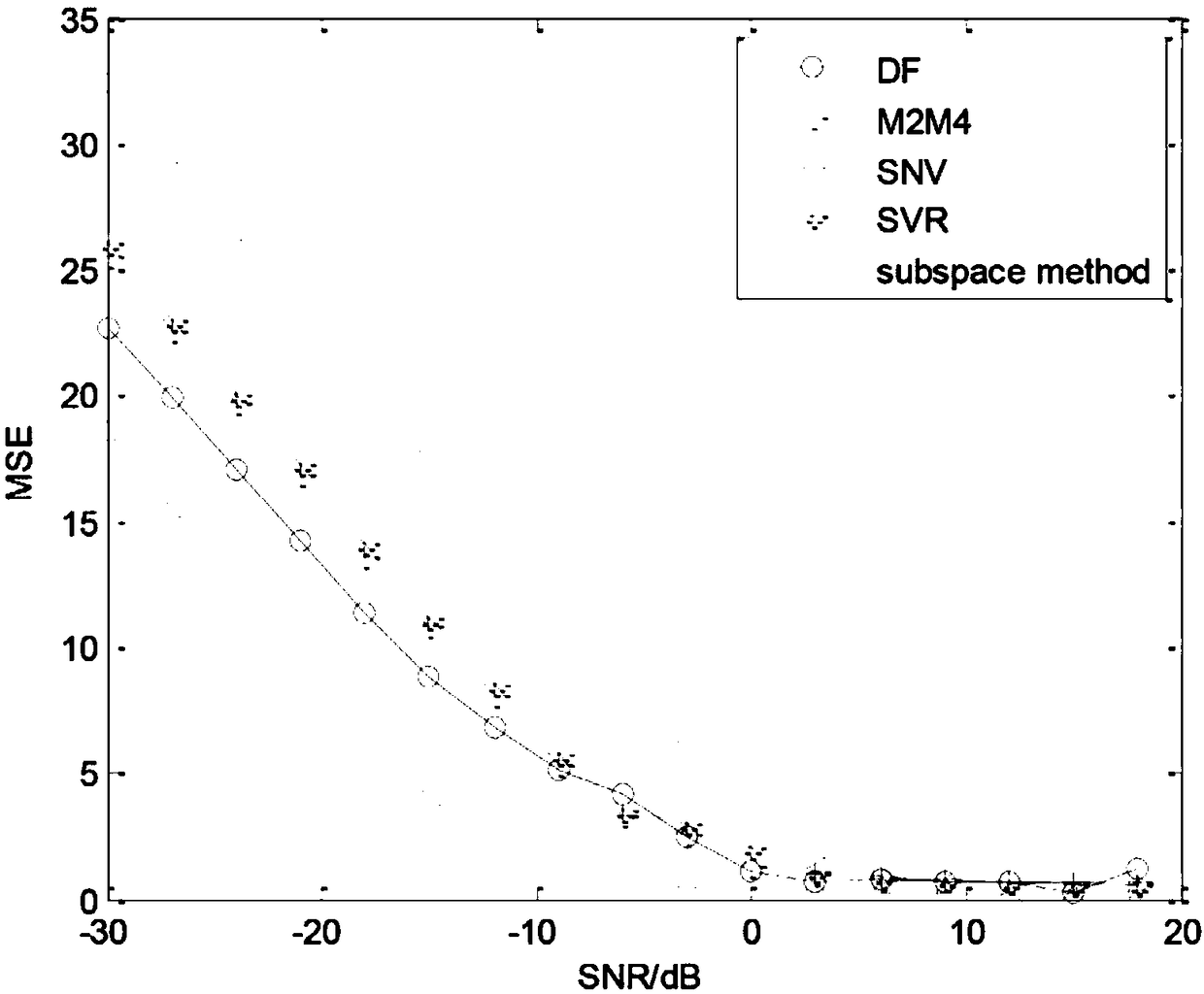
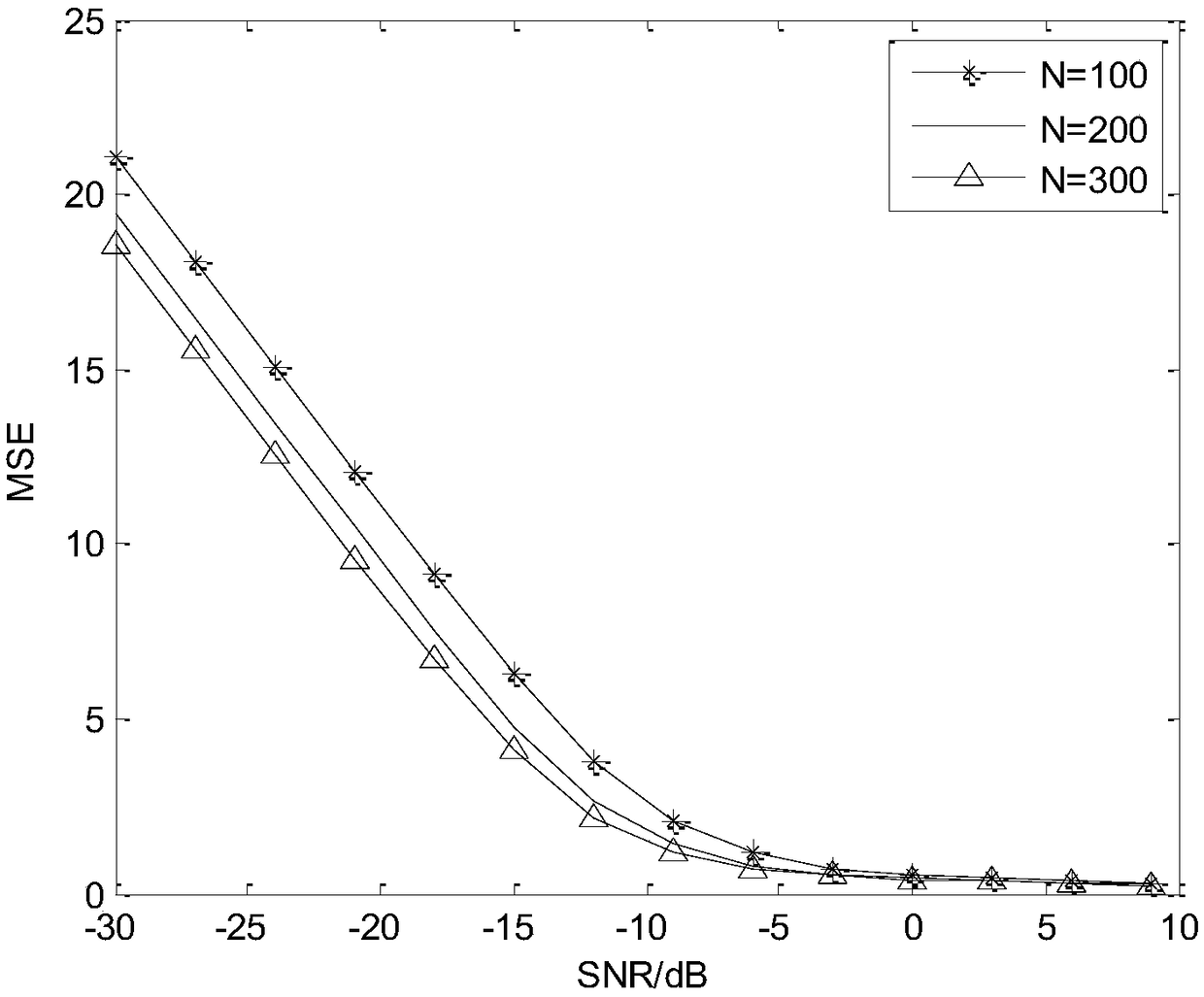
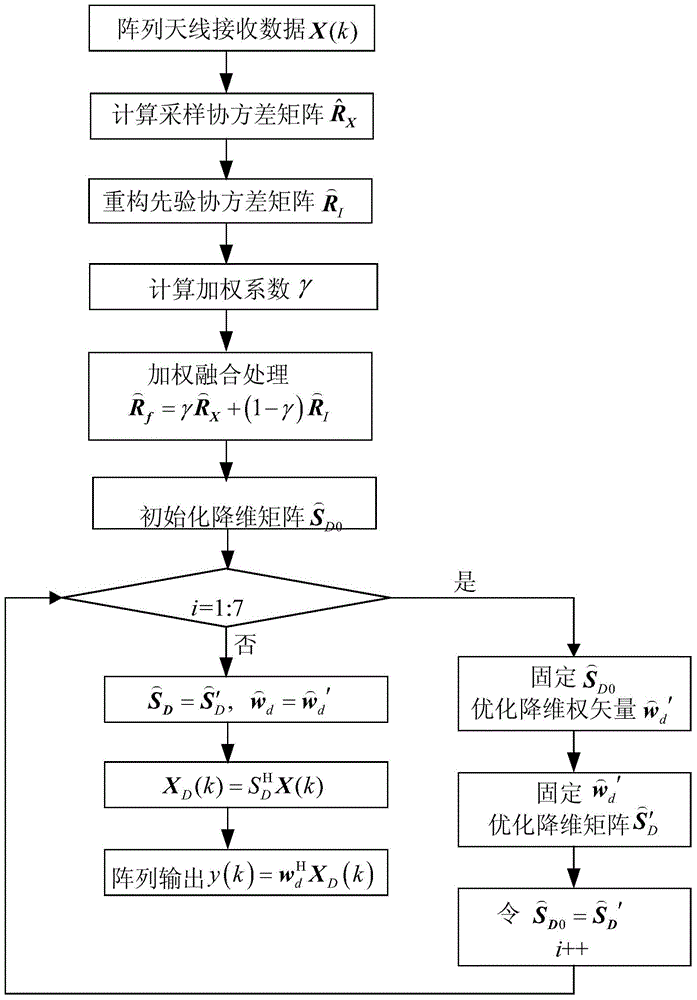
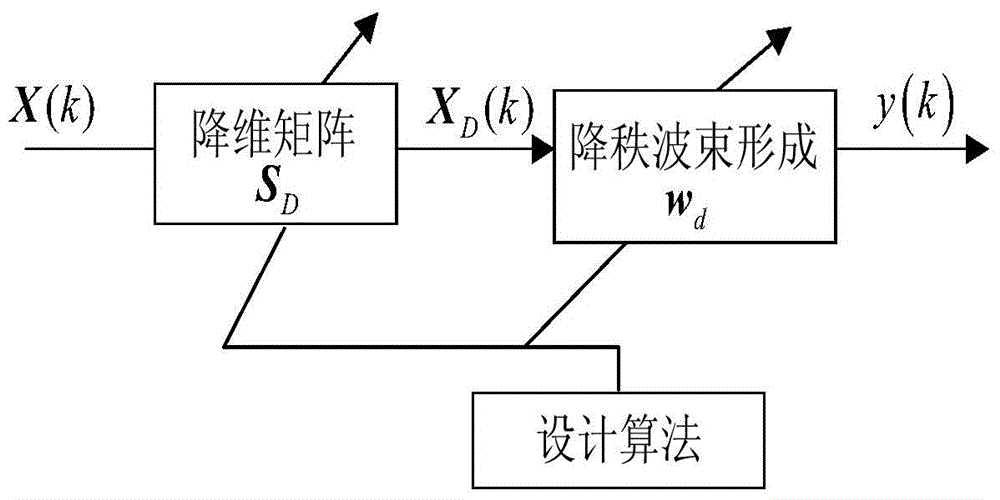
InactiveCN104459627AImprove estimation accuracyDimensionally robustWave based measurement systemsSmall sampleDimensionality reduction
The invention discloses a reduced rank beam forming method based on united alternative optimization. The method mainly aims to solve the problems that a full-dimensional adaptive beam former is heavy in computation and low in output SINR under a small sample condition. The implementation process of the method includes the steps that an array antenna receives data and calculates a sample covariance matrix; the sample covariance matrix updates a prior covariance matrix by the utilization of the spatial spectrum reconstruction technology; an estimation covariance matrix of array data is obtained by the adoption of a weight fusion processing method; an optimal dimensionality reduction matrix and an optimal dimensionality reduction weight vector are obtained through the estimation covariance matrix according to the linear linearly constrained minimum variance error criterion in the manner of adopting a united alternative optimization dimensionality reduction matrix and a dimensionality reduction weight vector. The method has the advantages of being light in computation burden and high in output SINR, and is used for estimating the covariance matrix under the small sample condition and forming an optimal reduced rank beam.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
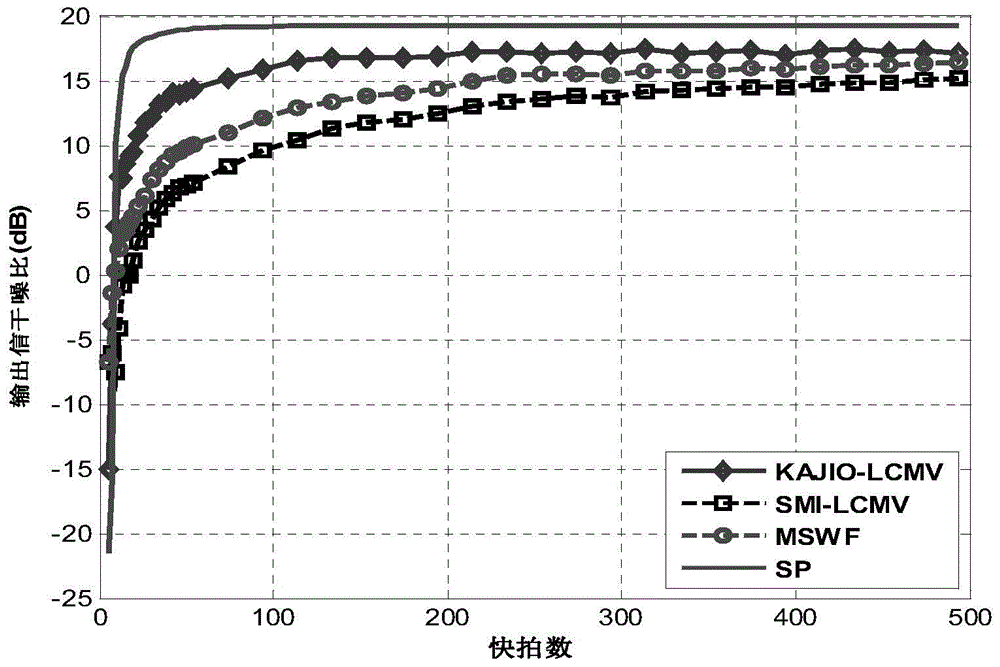
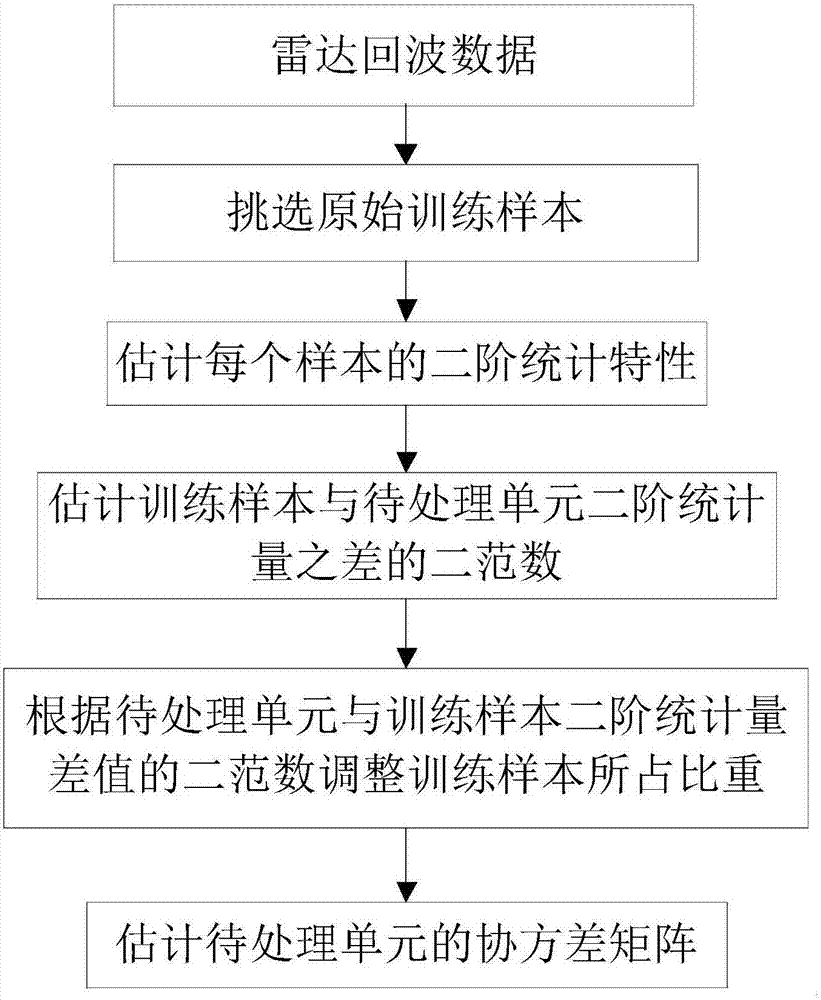
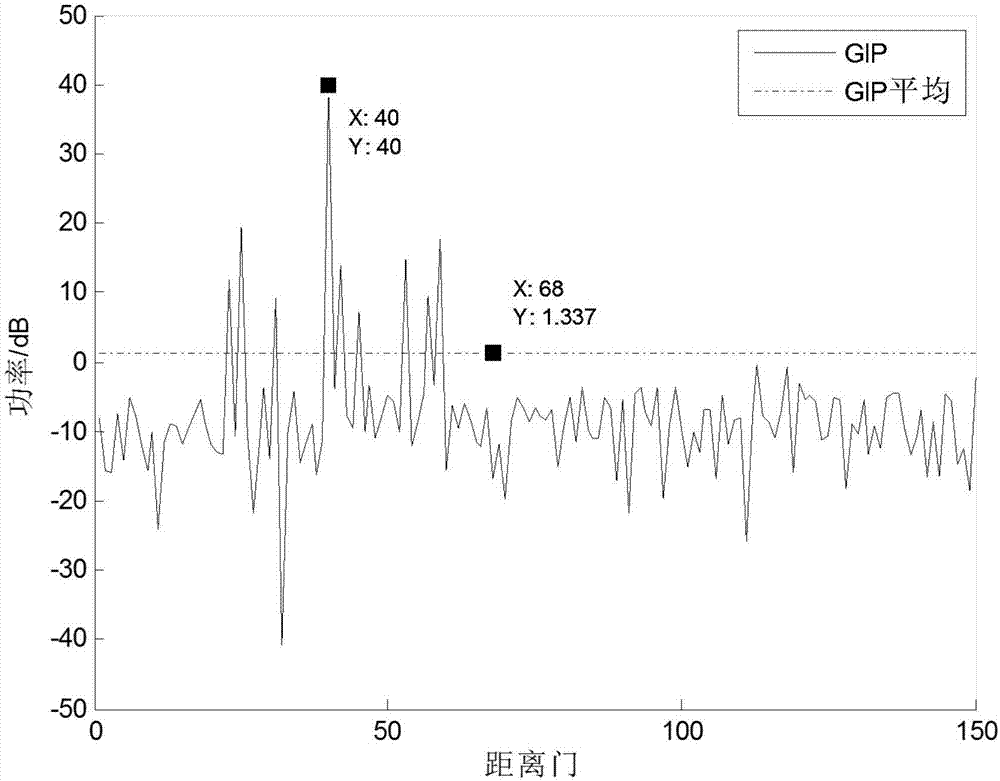
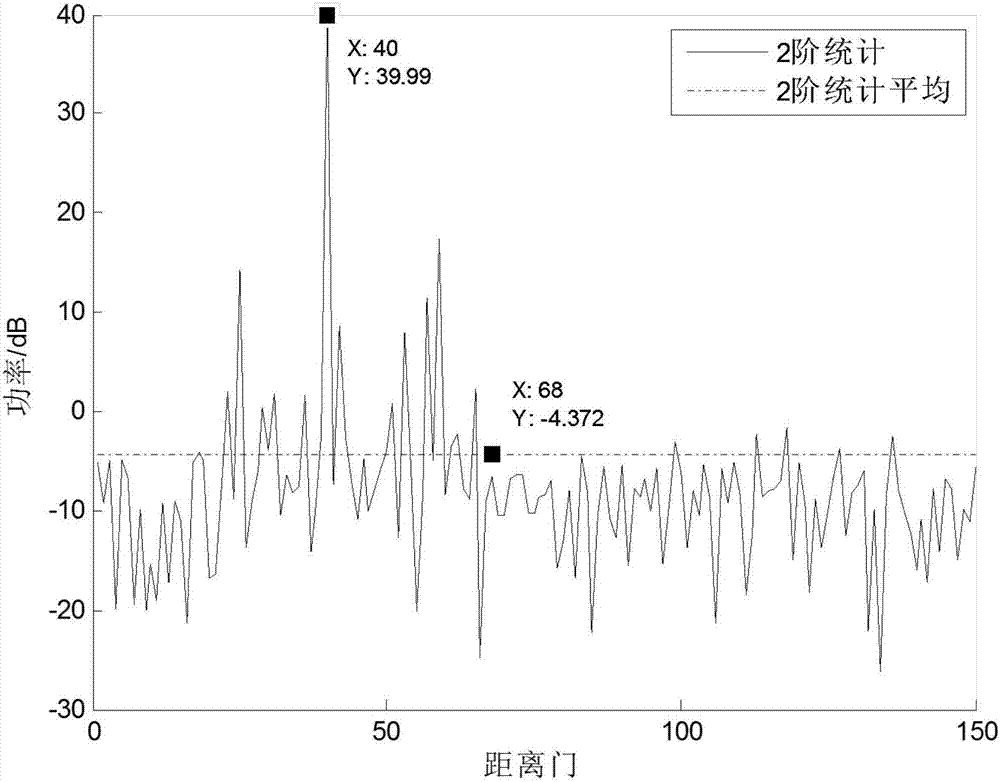
Clutter covariance matrix estimation method based on two-order statistics similarity
ActiveCN107315169AAccurate estimateImprove detection abilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionEstimation of covariance matrices
The invention relates to the technical field of signal processing, and particularly provides a clutter covariance matrix estimation method based on a two-order statistics similarity, so as to estimation of a clutter covariance matrix in the case of space-time adaptive processing. Original samples are taken near a to-be-processed unit in a sliding window mode firstly; then, the two-order statistics of each sample is estimated; then, according to the two-order statistics of the to-be-processed unit and the original sample, the similarity between the to-be-processed unit and the original sample is estimated; when the covariance matrix of the to-be-processed unit is estimated, the weight of the similarity is added before each training sample, if a certain sample is comparatively similar to the to-be-processed unit, the training sample occupies a large proportion when the covariance matrix of the to-be-processed unit is estimated, and thus, the clutter covariance matrix estimation precision of the to-be-processed unit is thus improved. The method can accurately estimate the covariance matrix of the to-be-processed unit, and the detection performance of an airborne radar is improved.
Owner:LEIHUA ELECTRONICS TECH RES INST AVIATION IND OF CHINA
An Adaptive Beamforming Method for Array Antennas Based on Diagonal Loading
ActiveCN104360338BEffective estimateReduced precision requirementsWave based measurement systemsSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringSpatial covariance matrix
The invention belongs to the technical field of adaptive beamforming, and particularly relates to a diagonal loading based adaptive beamforming method for an array antenna. The diagonal loading based adaptive beamforming method specifically includes acquiring sample data through the array antenna, calculating a covariance matrix of the sample data, taking the value of the covariance matrix as an estimated value of an interference and noise covariance matrix, improving the covariance matrix by an diagonal loading method, and solving a guide vector of a constrained optimization problem estimation desired signal. A final simulation result verifies effectiveness of two improvement methods.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Kalman filtering method with unknown process noise covariance matrix recursive estimation
The invention provides a Kalman filtering method with unknown process noise covariance matrix recursive estimation and aims at a discrete time time-invariant system and aims at solving the system state filtering estimation problem of the discrete time time-invariant system under the condition that an observation noise covariance matrix is completely unknown. The Kalman filtering method comprises step one, constructing a new statistical sequence {xik} according to an observation sequence {yk}; step two, calculating a covariance matrix recursion formula of {xik}; step three, calculating a process noise covariance matrix estimation sequence according to an algebraic relationship between real-time estimation values Covk(xi) of the observation noise covariance matrix and a new statistical sequence covariance matrix; step four, calculating an estimation sequence as the following formula of a covariance matrix according to the relationship between f(Q) and a process noise covariance matrix Q; substituting the process noise covariance matrix estimation sequence as the following formula replacing a truth value into a standard Kalman filtering method to calculate a system real-time state estimation and a state estimation deviation covariance matrix.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Mixed block similarity-based polarized SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image speckle reduction method
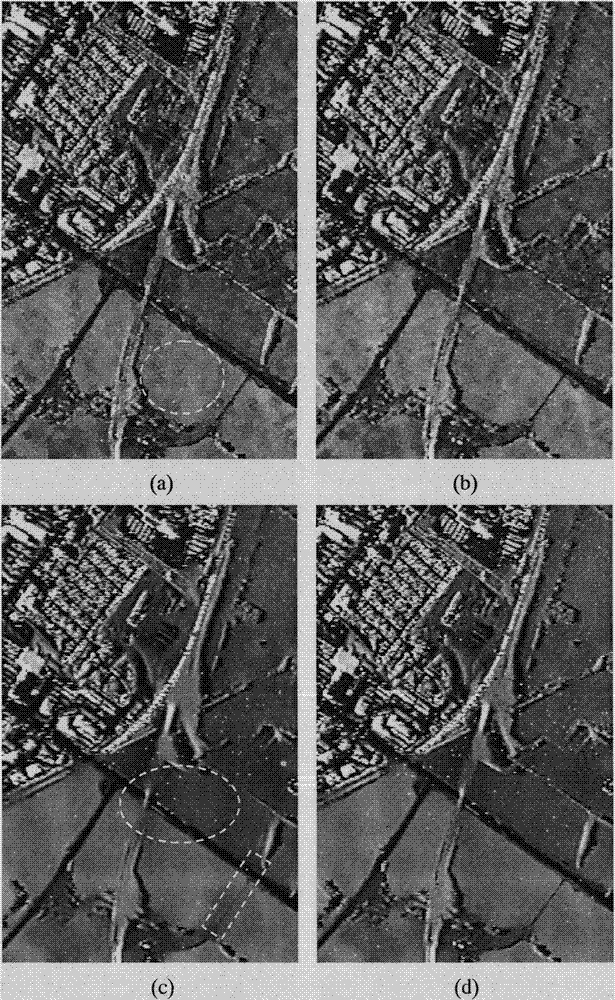
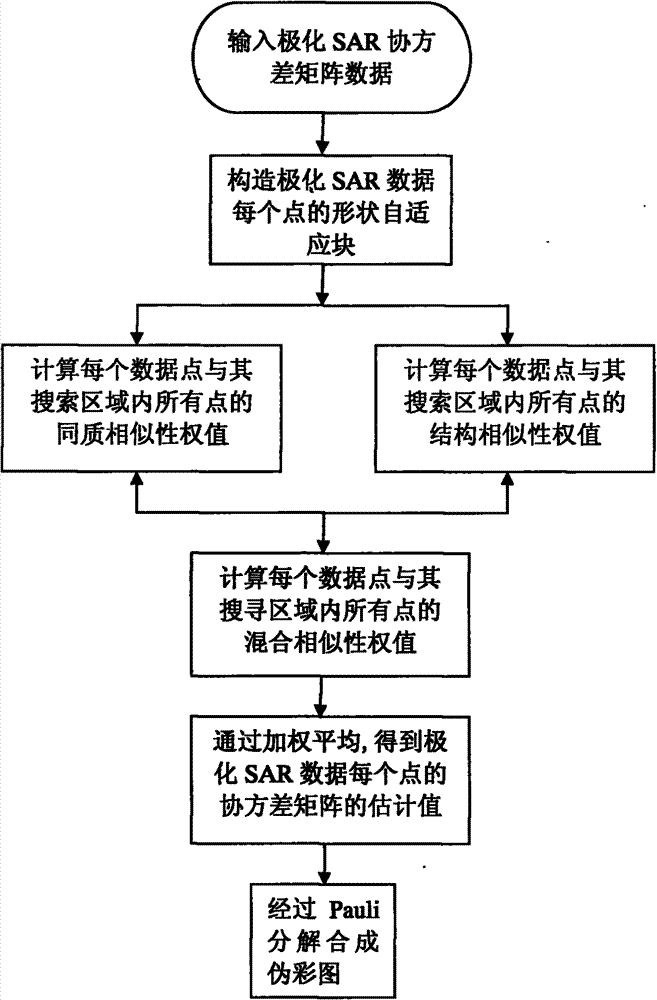
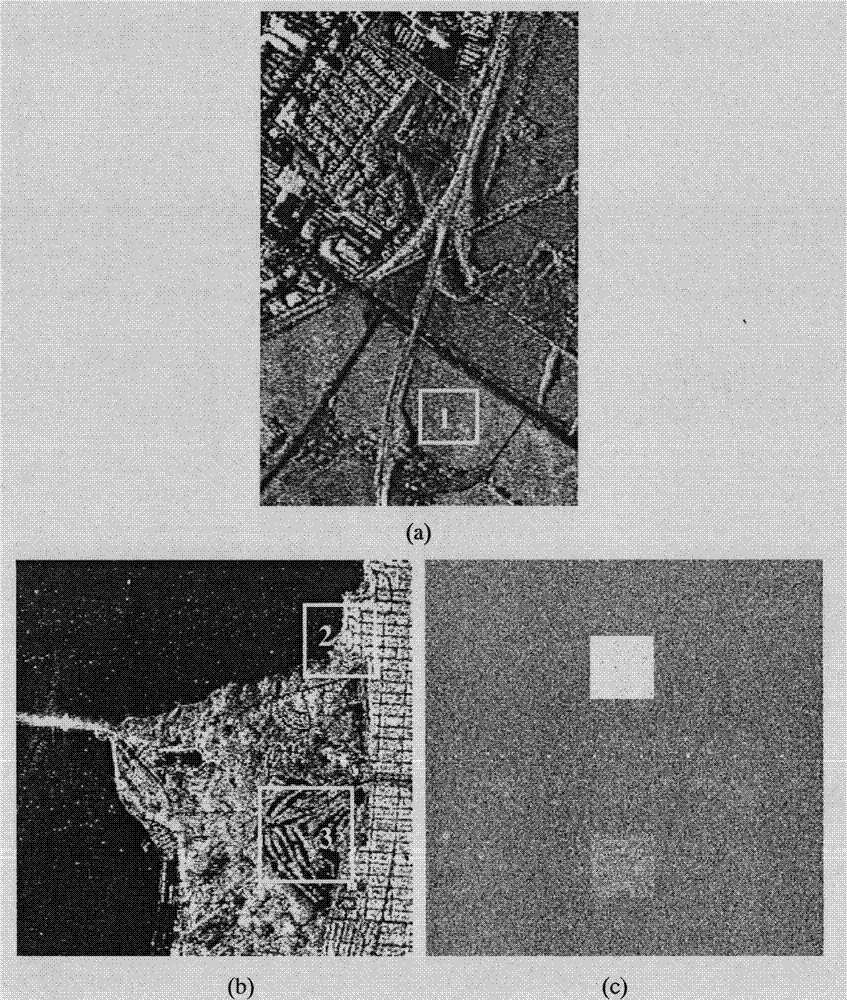
InactiveCN103400352AGuaranteed calculation accuracyAccurate collectionImage enhancementPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention discloses a mixed block similarity-based polarized SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image speckle reduction method, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The method comprises the following implementation processes: inputting polarized SAR covariance matrix data, and constructing a shape adaptive block of each point of the polarized SAR covariance matrix data; calculating homogeneous similarity weights and structural similarity weights of all points in the search area of each point of the polarized SAR data to obtain a mixed similarity weight; and obtaining the estimation values of the covariance matrix of each point of the polarized SAR data by weighted averaging, and performing Pauli decomposition to obtain a speckle-removed image of the polarized SAR data. By the method, the mixed similarity weight is introduced by combining the homogeneous similarity weights and the structural similarity weights, similar sets can be selected more accurately, and the problem that detail information remaining and speckle noise suppression cannot be balanced very well by a Pretest filter method is solved. The speckle reduction capacity of a polarized SAR image can be improved, and the detail information can be remained well; therefore, the method can be used for the speckle reduction processing of the polarized SAR image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com