Patents
Literature
616 results about "Hot liquids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
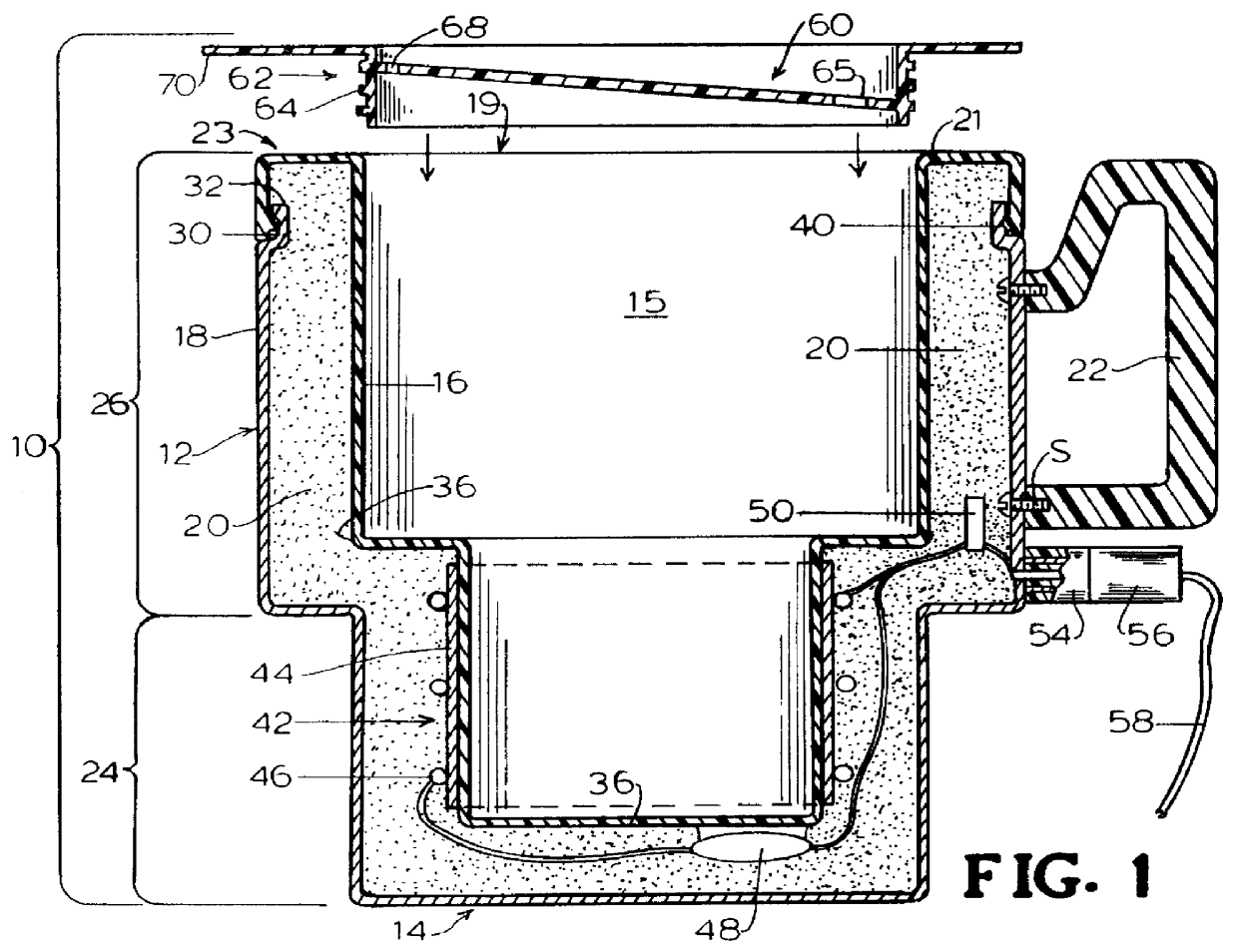
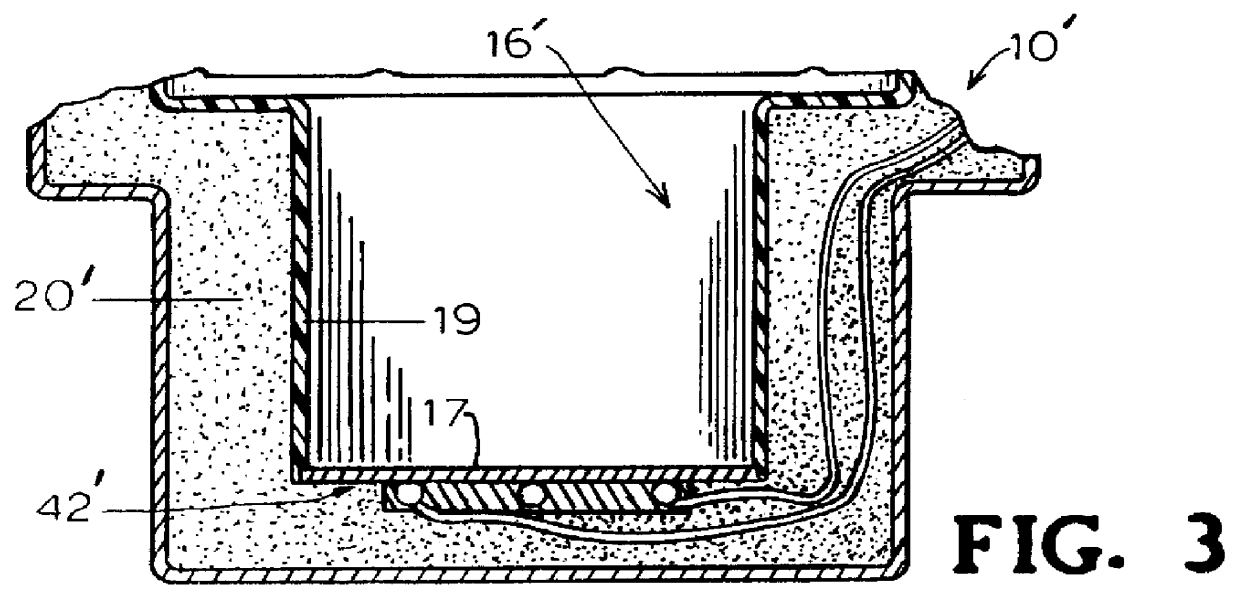
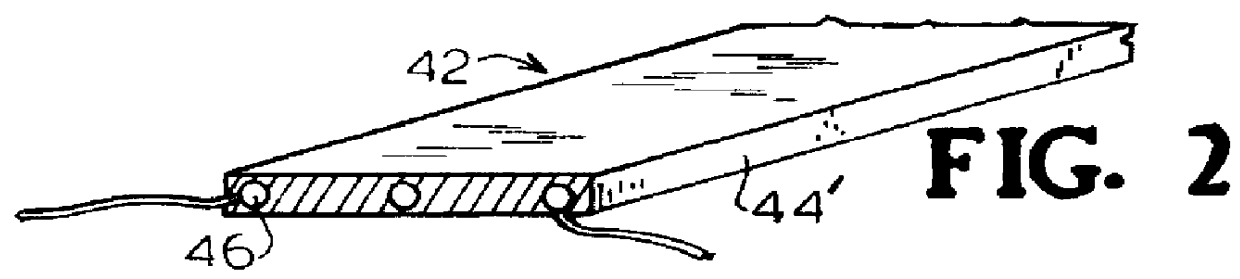
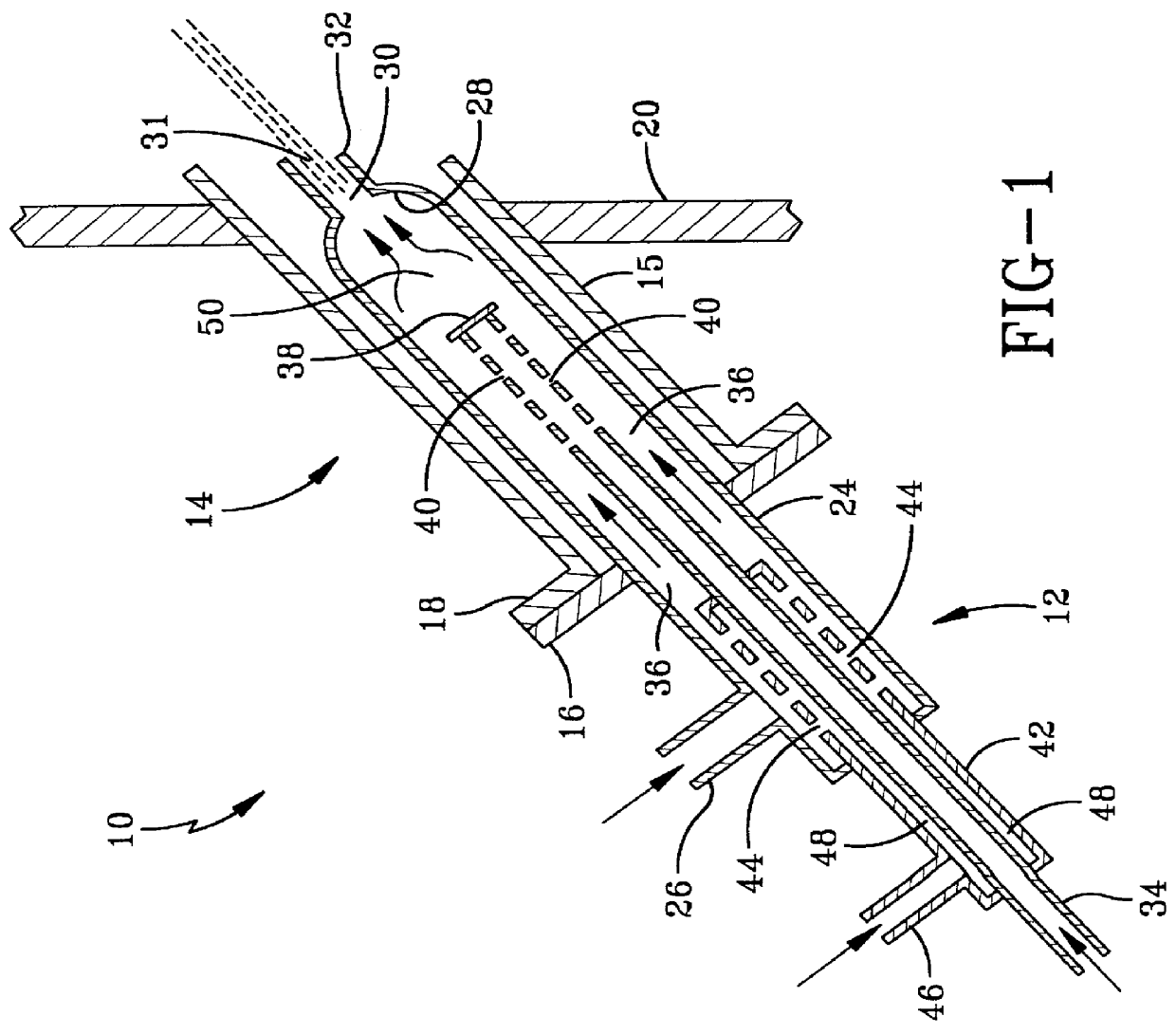
Electric drinking cup for vehicles
InactiveUS6140614ASafe to touchImparts strength and durabilityElectric heatingWater-boiling vesselsElectricityEngineering
An electric drinking cup for use while driving a vehicle comprised of a plastic inner liner, a metal outer shell, and an insulation-filled space therebetween. A heating element is associated with the bottom portion of the inner liner, and is electrically connected to a vehicle's electrical system. The plastic inner liner curves around the upper edge of the outer metal shell providing a cup lip, which does not get hot when containing a hot liquid. The plastic inner liner and heating element further provide a diffuse heat that heats liquid, such as coffee or hot chocolate, slowly to the desired temperature such that, when heated, the liquid does not become burned and distasteful. The outer metal shell provides durability.
Owner:GLOBAL SALES
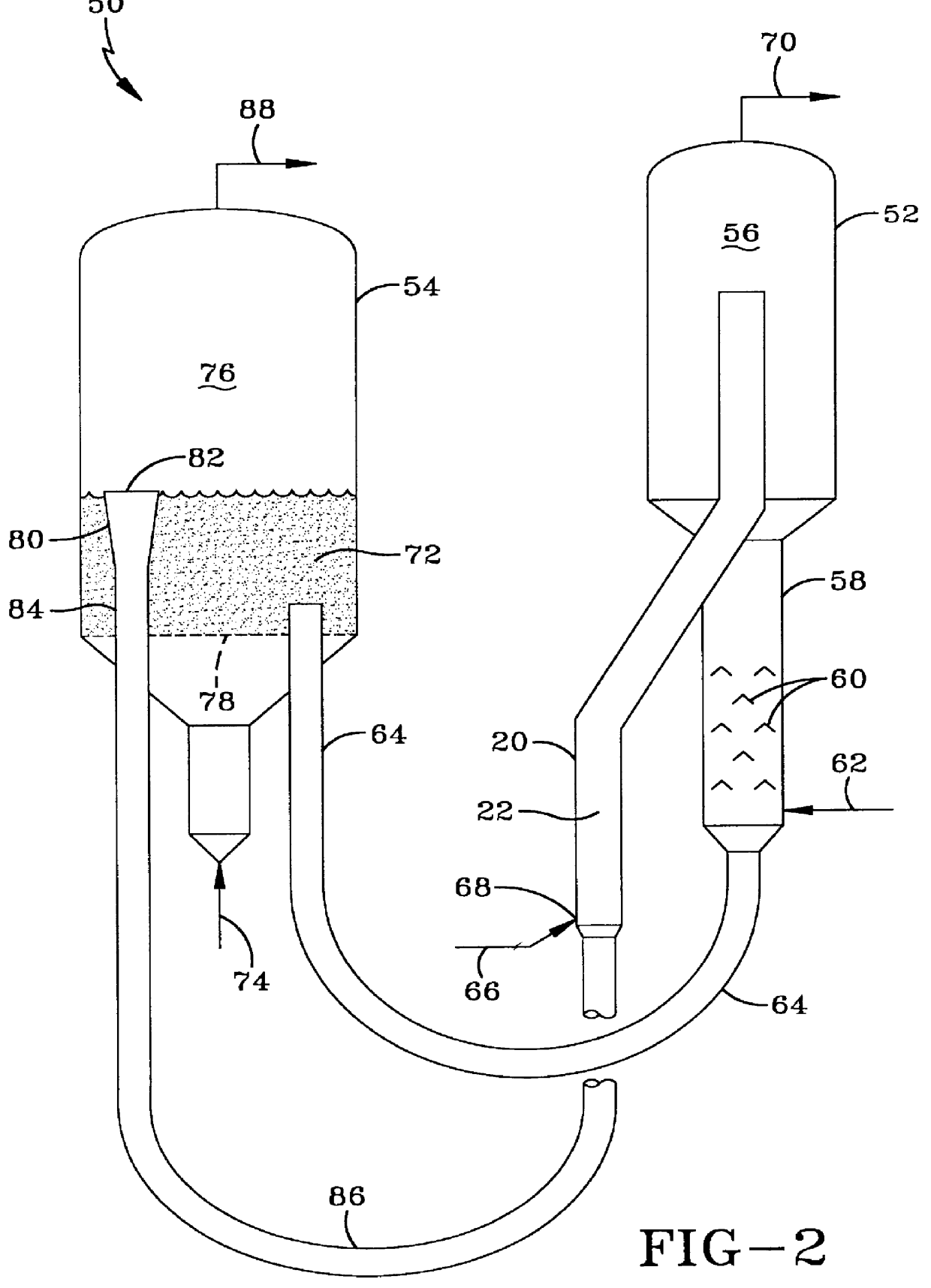
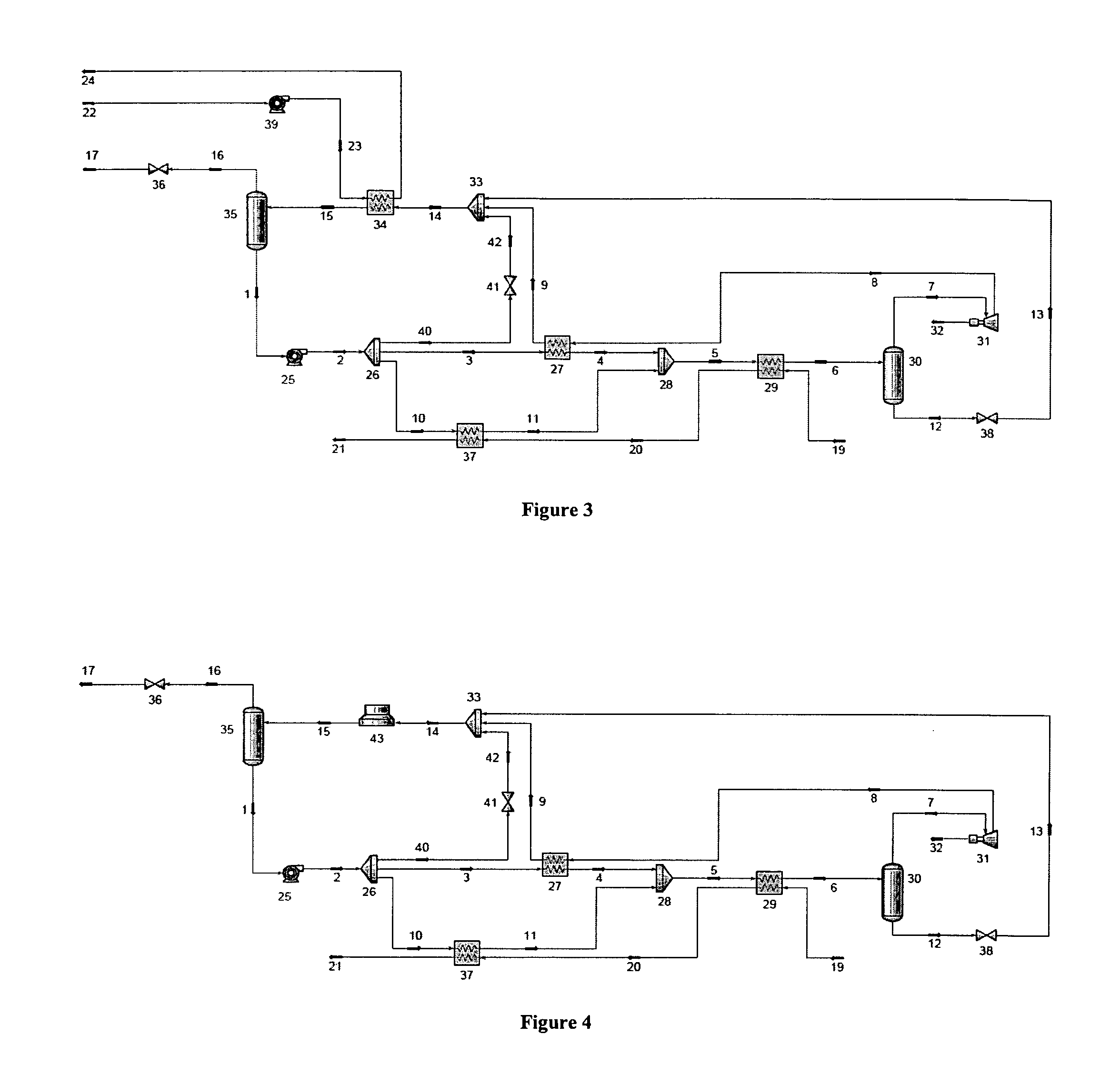
FCC feed injection using subcooled water sparging for enhanced feed atomization
Atomization of a high boiling point, hot liquid, such as a hydrocarbon feed oil for a fluid cat cracker, is enhanced by injecting subcooled water into the hot liquid, to form a two-phase fluid of the liquid and steam, upstream of the atomization. The hot liquid is at conditions of temperature and pressure effective for the injected, subcooled water to vaporize into steam, when the water contacts it. Typically this means that the hot liquid is hotter and at a lower pressure than the water. In an FCC process, the subcooled water is sparged into the flowing hot oil in a conduit in a riser feed injector. This produces a spray of hot oil in the riser reaction zone in which the oil drops are smaller and more uniformly distributed in the spray.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
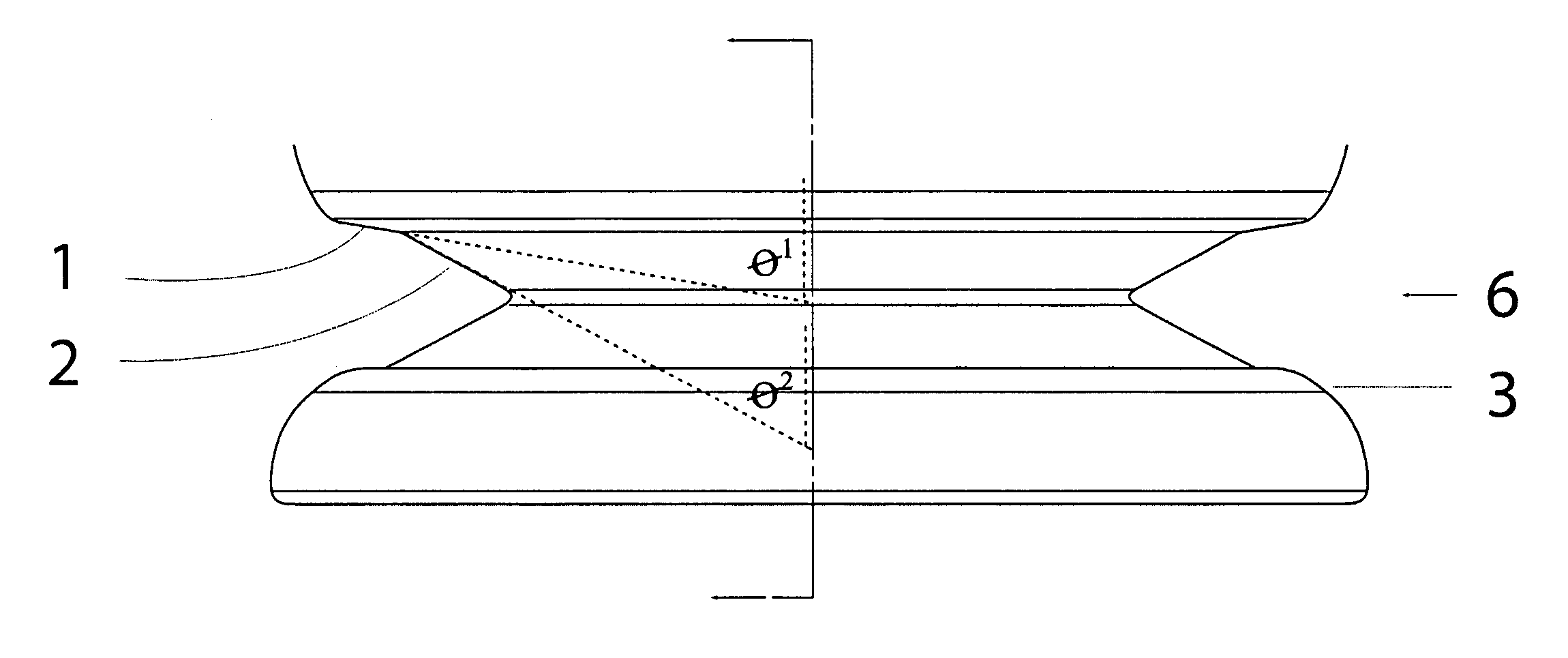
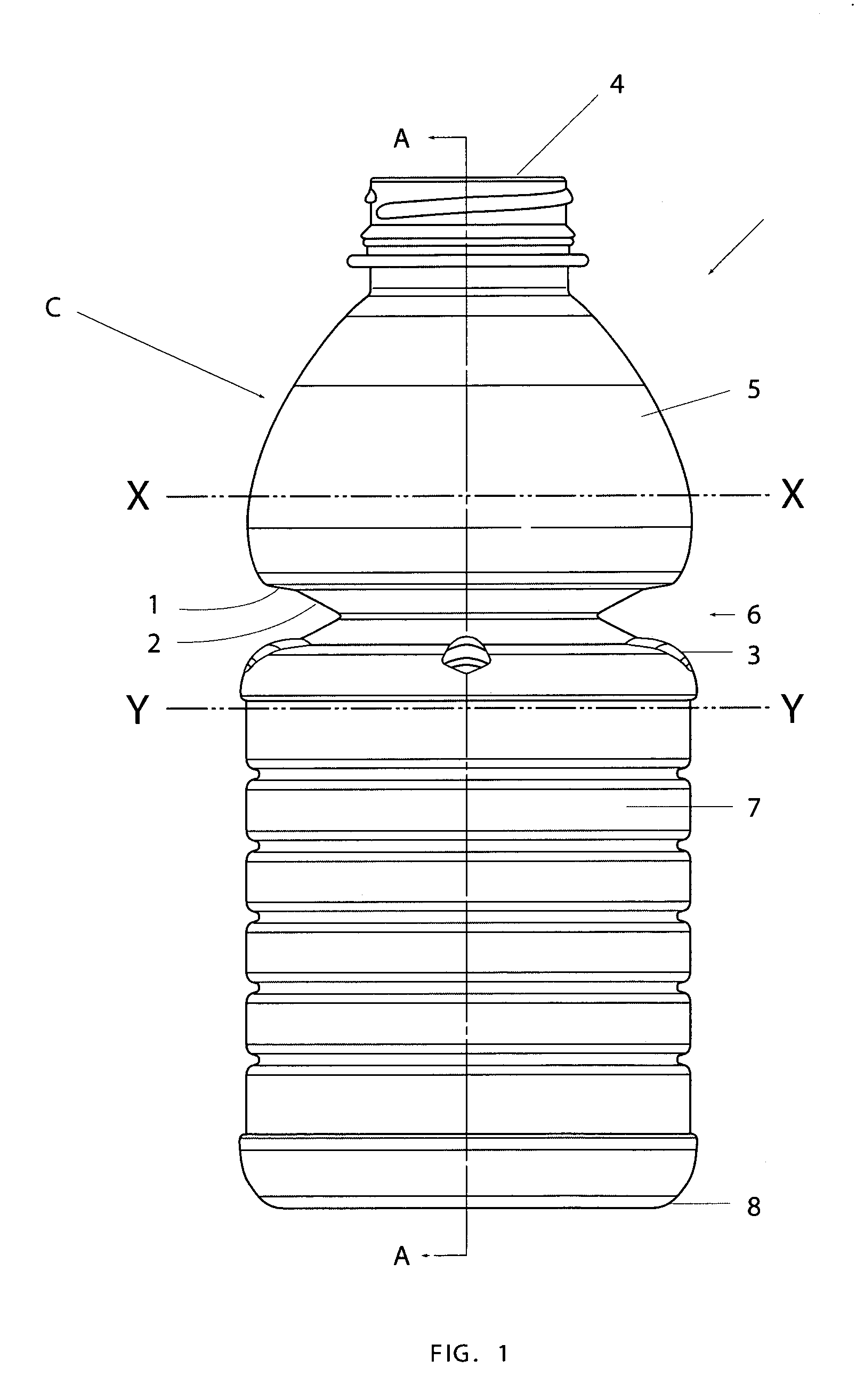
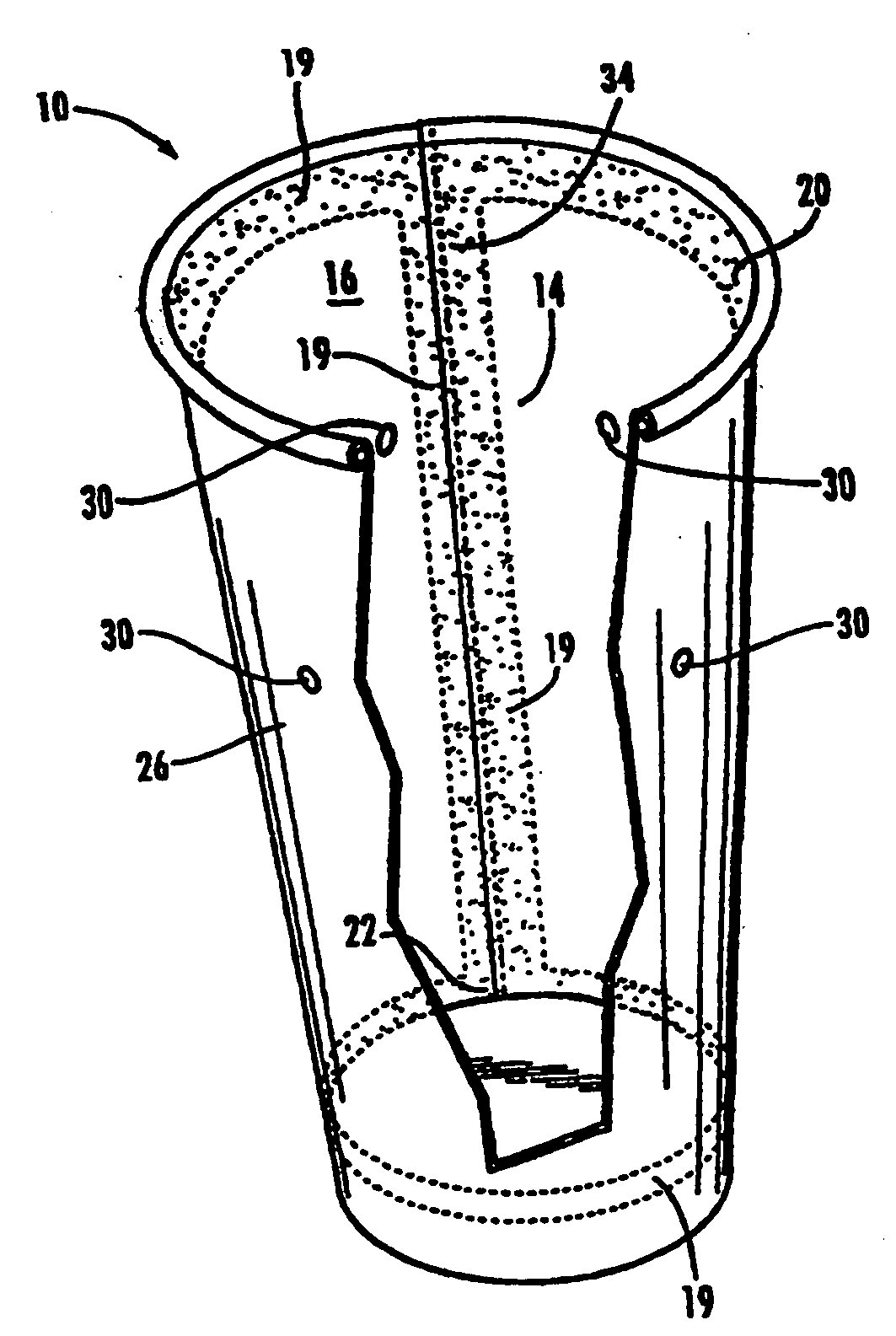
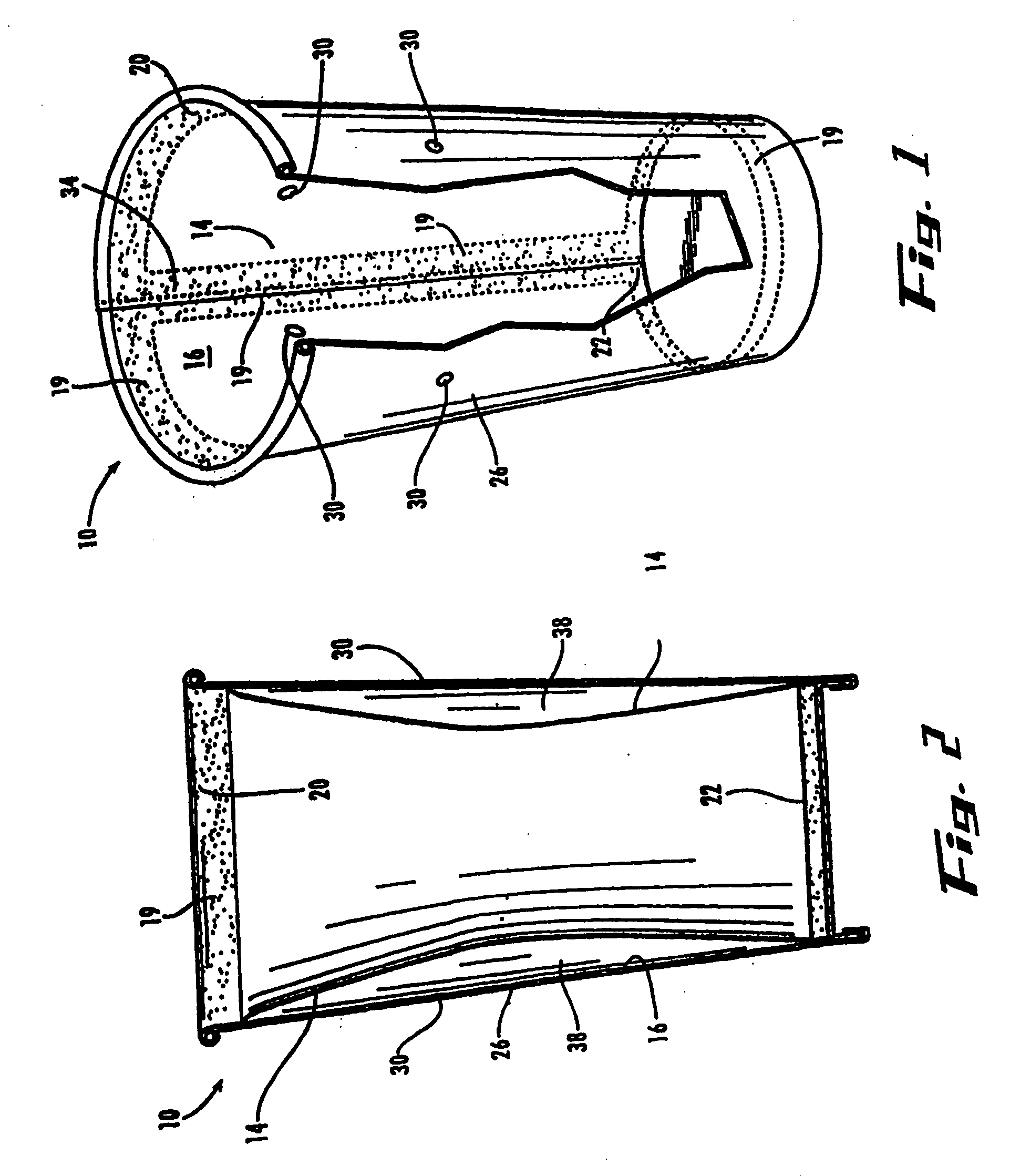
Semi-rigid collapsible container
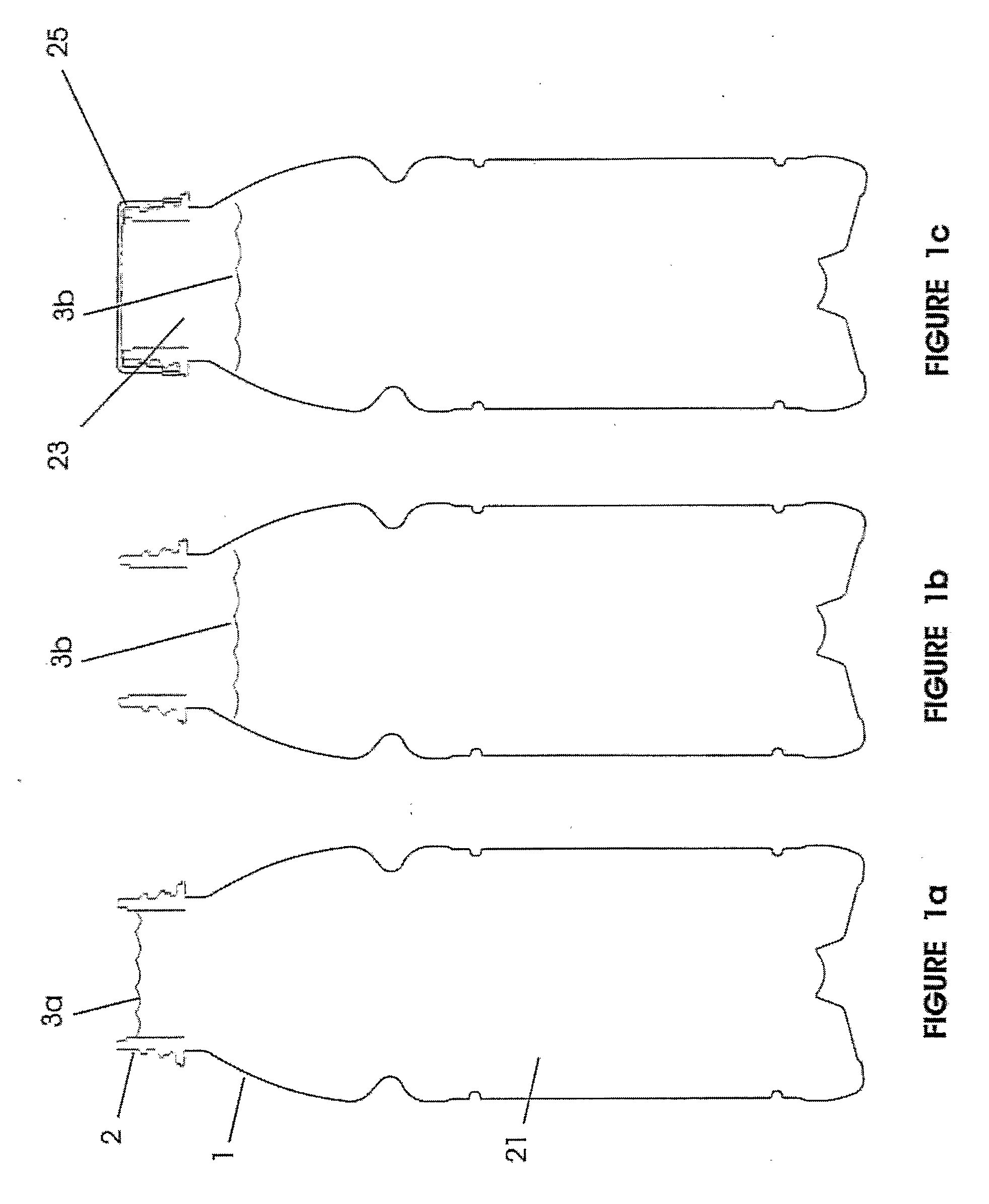
A semi-rigid collapsible container (10) has a side-wall with an upper portion (5), a central portion (6), a lower portion (7) and a base (8). The central protion (6) includes a vacuum panel portion having a control portion (2) and an initiator portion (1). The control portion (2) is inclined more steeply in a vertical direction, i.e. has a more acute angle relative to the longitudinal axis of the container (10), than the initiator portion (1). On low vacuum force being present within the container panel following the cooling of a hot liquid in the container (10), the initiator portion (1) will flex inwardly to cause the control protion (2) to invert and flex further inwardly into the container (10) and the central portion (6) to collapse. In the collapsed state upper and lower portions of the central portion (6) may be in substantial contact so as to contain the top-loading capacity of the container (10). Raised ribs (3) made an aditional support for the container in its collapsed state. In another embodiment the telescoping of the container back to its original position occurs when the vacuum force is released following removal of the container cap.
Owner:CO2 PAC
Hot beverage brewing apparatus
ActiveUS20090007792A1Easy to controlCompact and reliable and inexpensive to manufactureSteam generation heating methodsBoiler flue tubes/fire tubesProcess engineeringHot liquids
A hot beverage brewing apparatus. A pressurized hot liquid delivery system provides liquid under pressure within a range of acceptable brewing temperatures without any mechanical pump. Water is apportioned into sealable tank volumes, one of which is heated to boil the liquid and produce steam under pressure. The pressurized steam displaces the liquid from the tank volumes in proportion and at a temperature that is within the acceptable brewing range. The hot liquid under pressure is directed to a capsule receiving station to infuse a material in a capsule. The capsule dispenses the brewed beverage without contacting the brewing apparatus.
Owner:SOLABEV
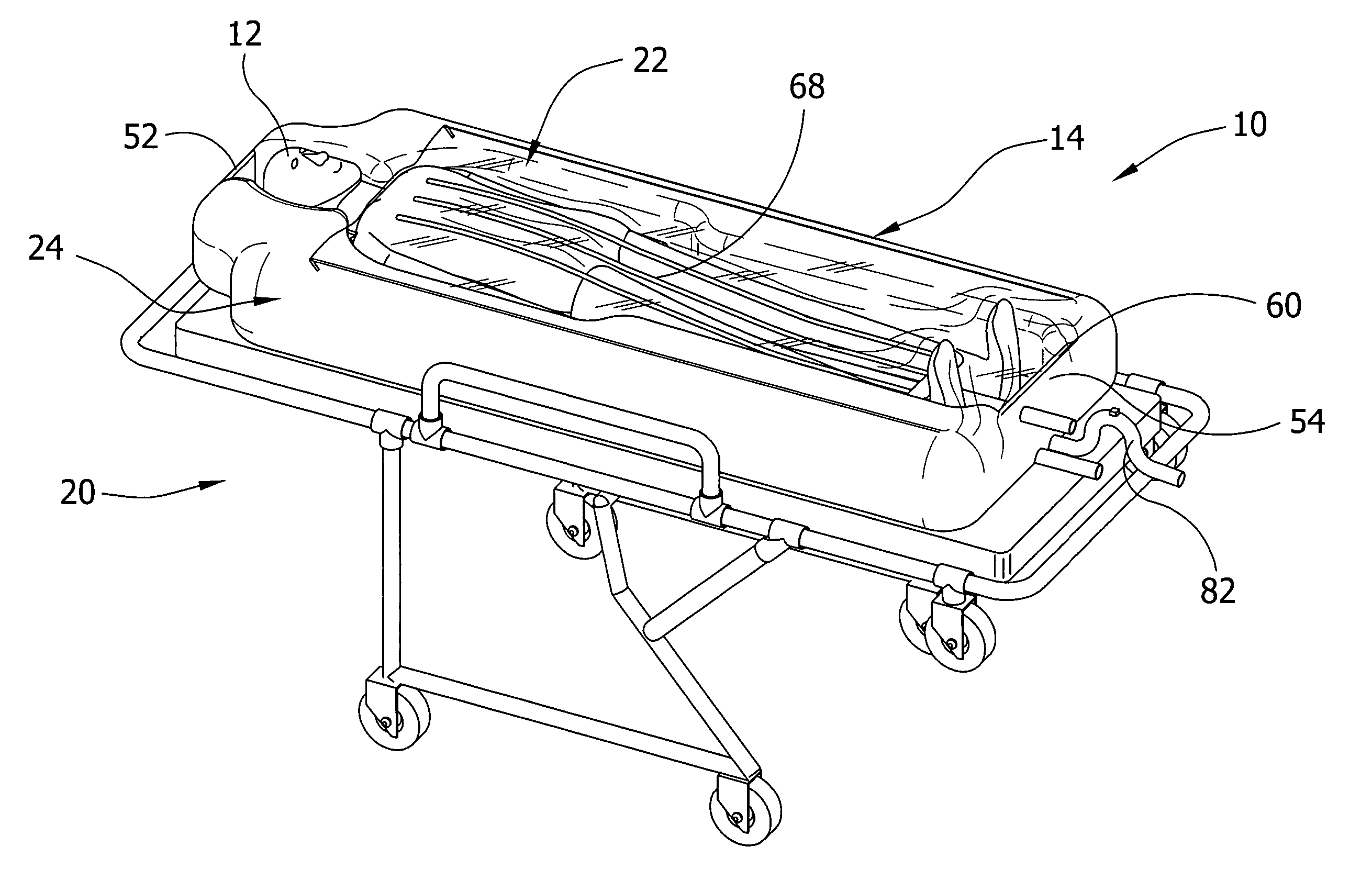
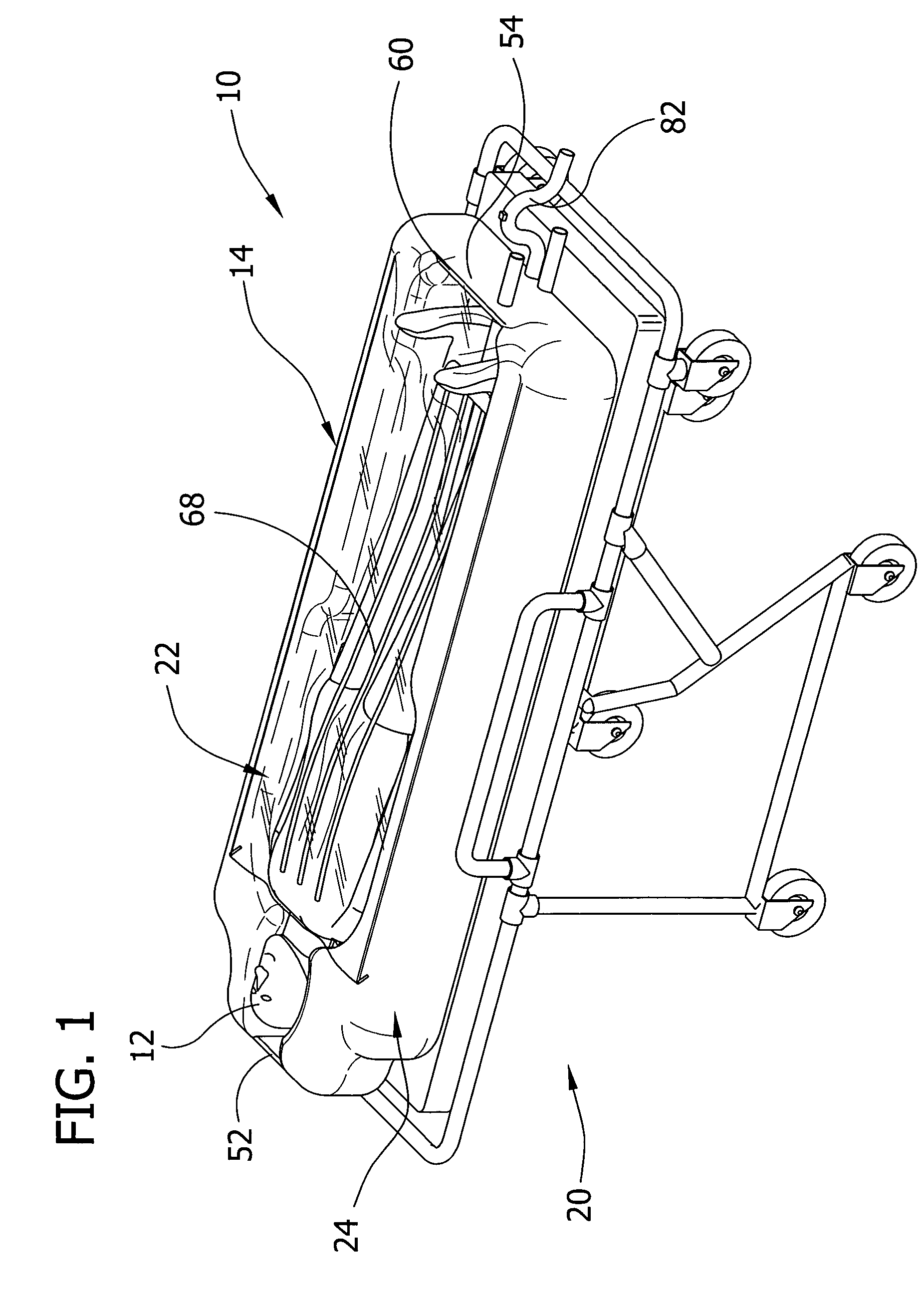
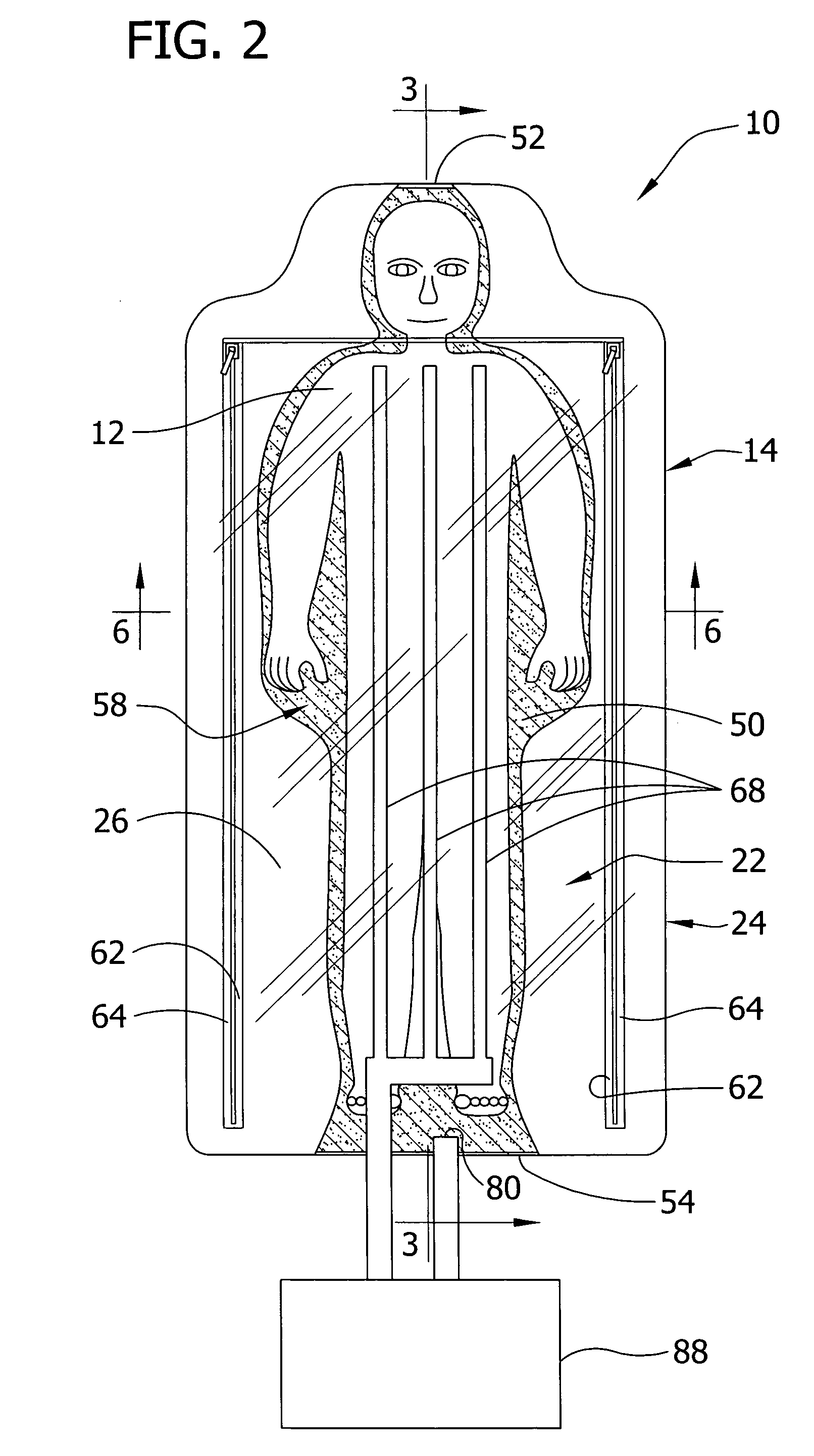
Apparatus for altering the body temperature of a patient
ActiveUS20060069418A1Improve heat transfer performanceTreatment roomsStretcherMedicineBiomedical engineering
Apparatus for altering the body temperature of a patient comprises a cover for covering at least a portion of a patient's body and a compliant support adapted to underlie and generally conform to the shape of the portion of the patient's body to define a well adjacent to the patient's body portion for accumulating heat transfer liquid. The cover and compliant support cooperatively define an enclosure for receiving the portion of the patient's body and are constructed to conduct a heat transfer liquid into direct contact with the portion of the patient's body received in the enclosure to promote heat transfer between the patient's body and the heat transfer liquid.
Owner:LIFE RECOVERY SYST HD
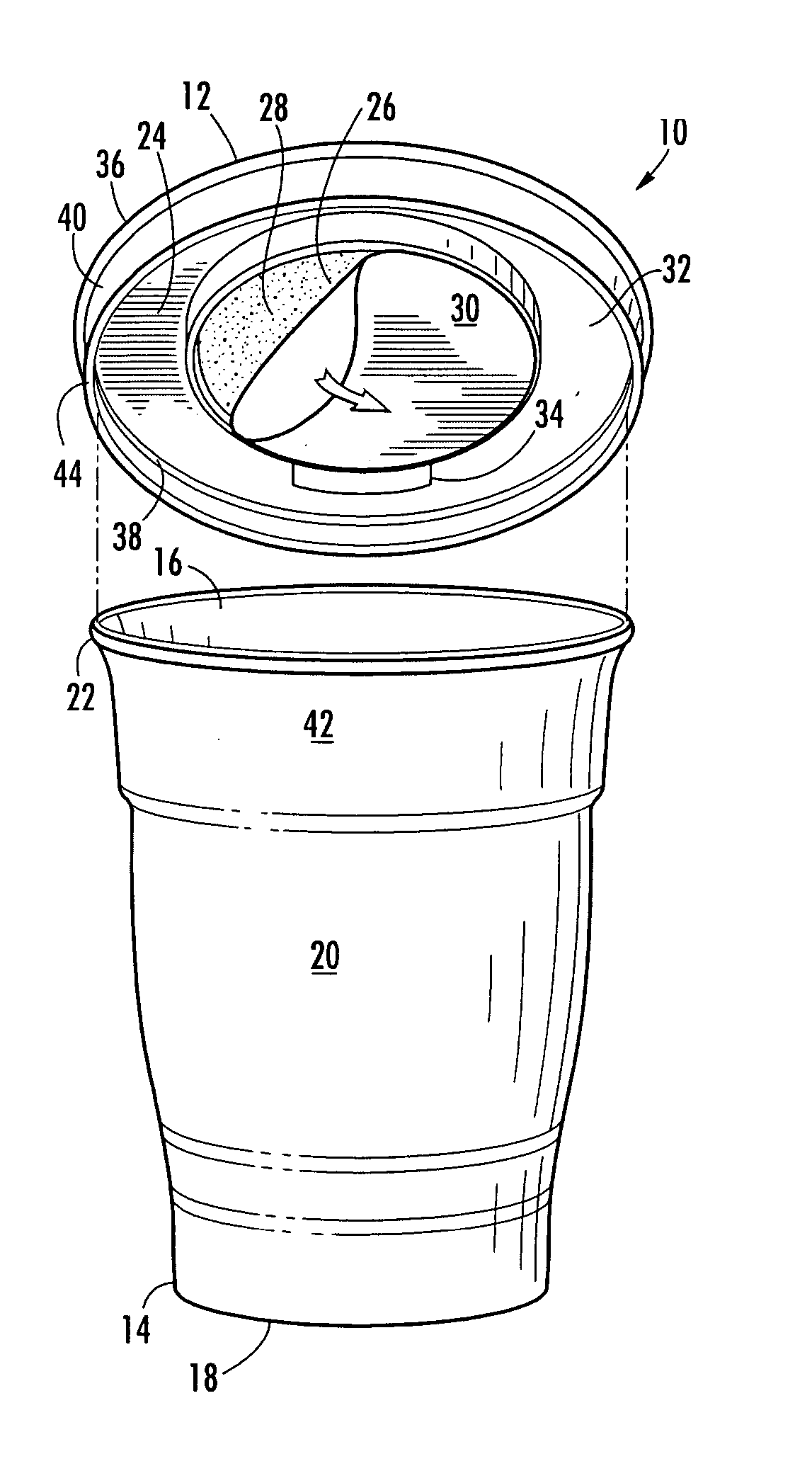
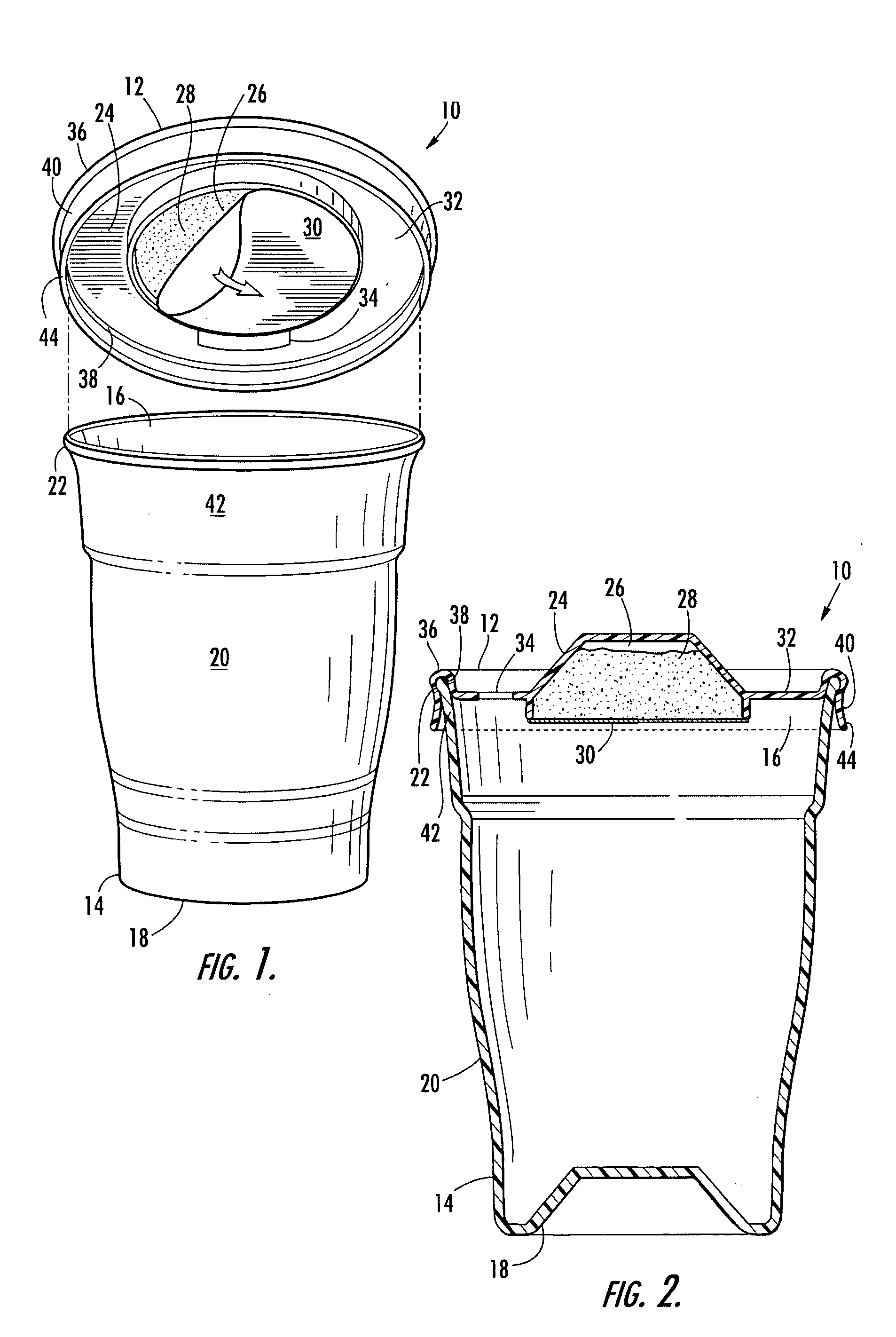
Beverage container lid having liquid cooling effect
InactiveUS20090108006A1Eliminate the problemIncrease volumeDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusCooling effectEngineering
Disclosed is a lid for a beverage container including external and internal covers, which may be coupled together to define a cooling reservoir there between to receive and cool hot liquids that may be held in the beverage container. The external cover having ventilation holes and a dispensing spout for dispensing the liquid therein to the user. The internal cover includes a plurality of walls used for directed the hot liquid that enters from the beverage container. A plurality of entrance apertures are disposed in the interior cover, allowing the hot liquid to enter the reservoir. A plurality of dispensing walls cooperate to direct the hot liquid entering through the entrance apertures and to separate the hot liquid from cooled liquid exiting the reservoir through a dispensing aperture disposed in the spout.
Owner:COOLLID CORP
Thermally insulated beverage glass
InactiveUS6405892B1Eliminates and reduces condensationWithout aggravation and disadvantage of condensation and sweatingDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusDouble wallPolystyrene
Owner:VOLAN KEN MICHAEL
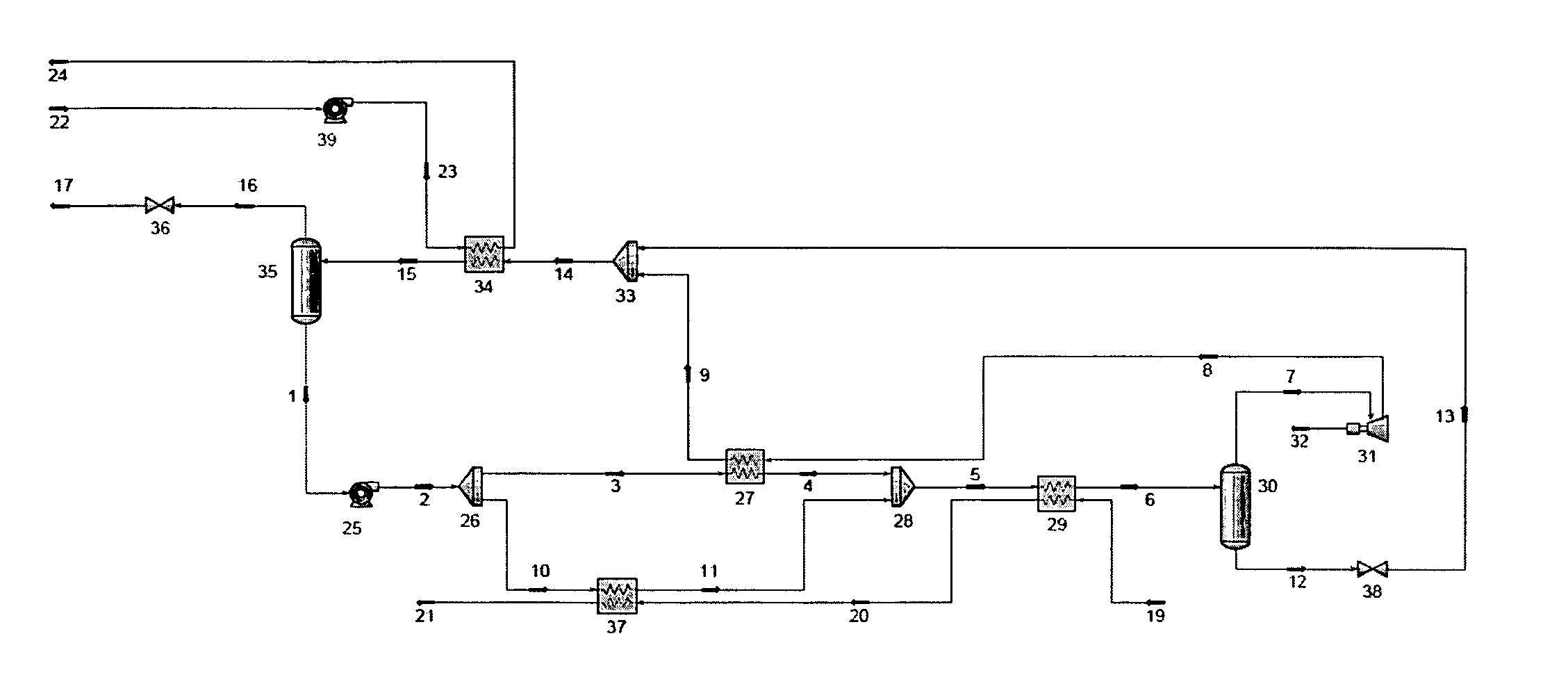
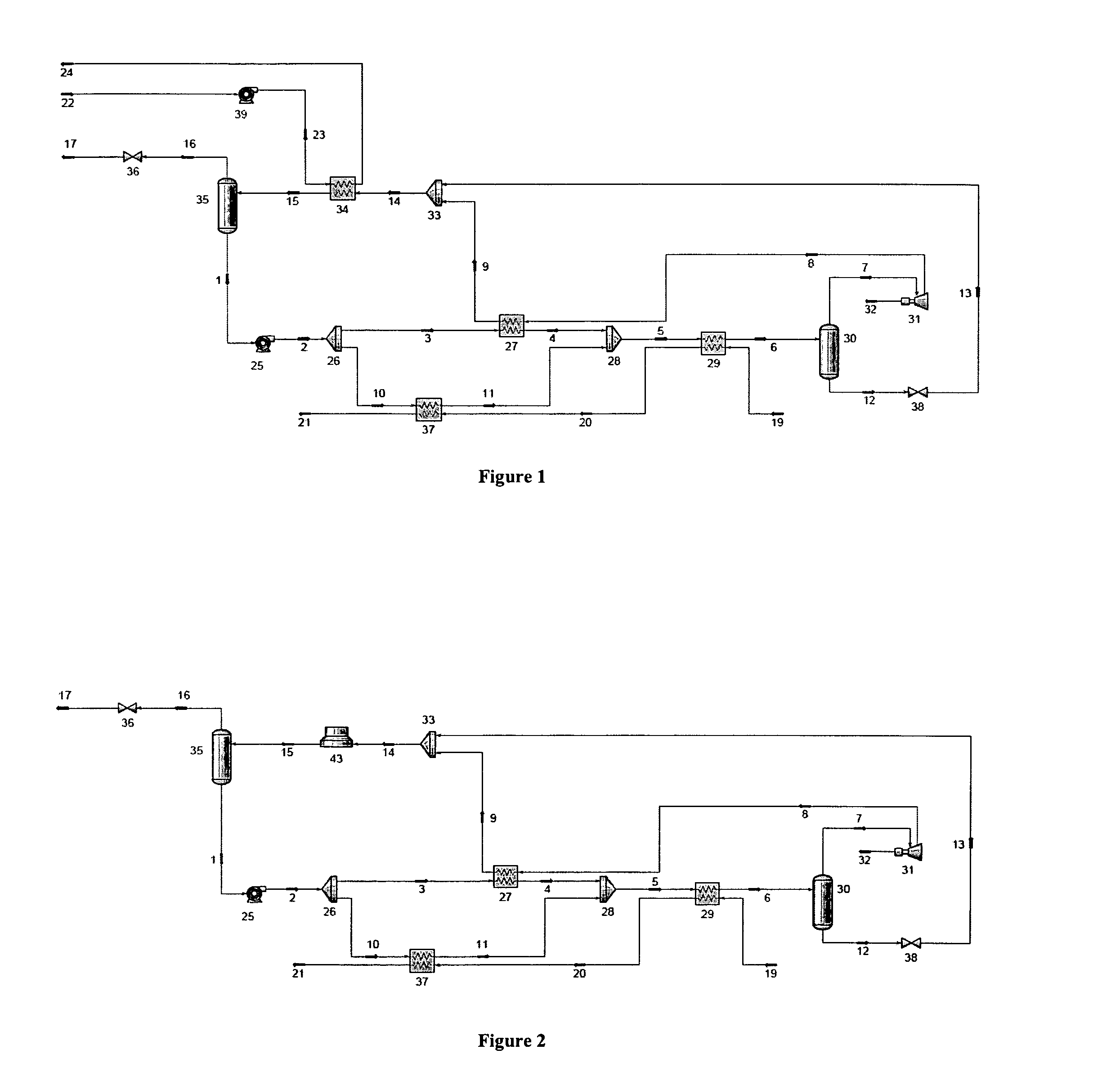
Power recovery and energy conversion systems and methods of using same
In various illustrative examples, the system may include heat recovery heat exchangers, one or more turbines or expanders, a desuperheater heat exchanger, a condenser heat exchanger, a separator, an accumulator, and a liquid circulating pump, etc. In one example, a bypass desuperheater control valve may be employed. The system comprises a first heat exchanger adapted to receive a heating stream from a heat source after passing through a second heat exchanger and a second portion of a working fluid, wherein, the second portion of working fluid is converted to a hot liquid via heat transfer. An economizer heat exchanger that is adapted to receive a first portion of the working fluid and the hot discharge vapor from at least one turbine may also be provided. The first and second portions of the working fluid are recombined in a first flow mixer after passing through the economizer heat exchanger and first heat exchanger, respectively. A second heat exchanger is provided that receives the working fluid from the first flow mixer and a hot heating stream from a heat source and convert the working fluid to a hot vapor. The hot vapor from the second heat exchanger is supplied to at least one turbine after passing through a separator designed to insure no liquid enters the said at least one turbine or expander. The hot, high pressure vapor is expanded in the turbine to produce mechanical power on a shaft and is discharged as a hot, low pressure vapor.
Owner:TAS ENERGY
On demand hot liquid dispenser
A system for quickly and accurately heating a liquid to a specified temperature and dispensing the liquid on demand. The system is particularly suited for brewing tea and preferably stores preset temperatures corresponding to different tea varieties. Also preferably, the system allows the user to set customized temperatures. The system also comprises a timer, also having preset and user customizable periods adapted for brewing different varieties of tea.
Owner:RABIN MICHELLE +1
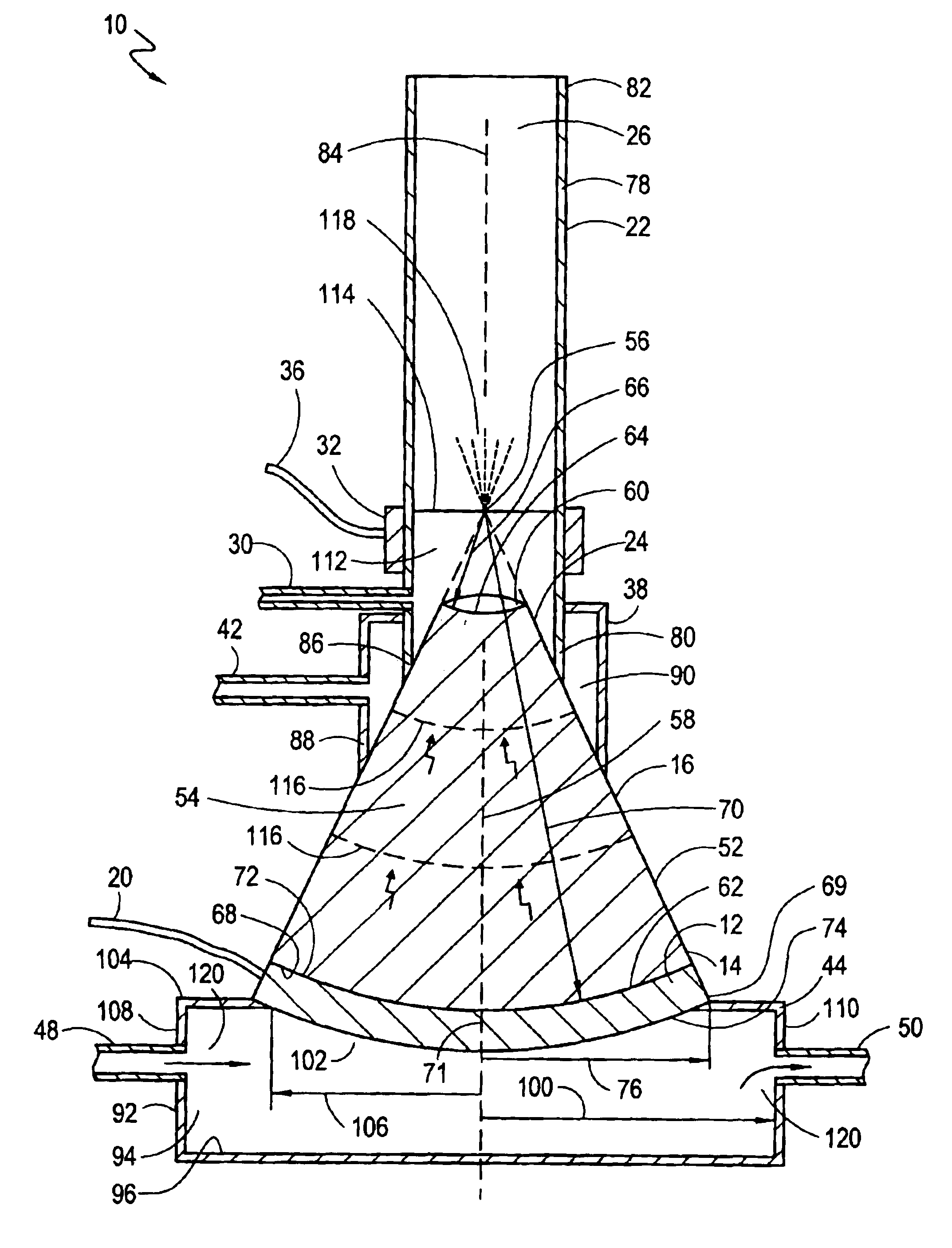
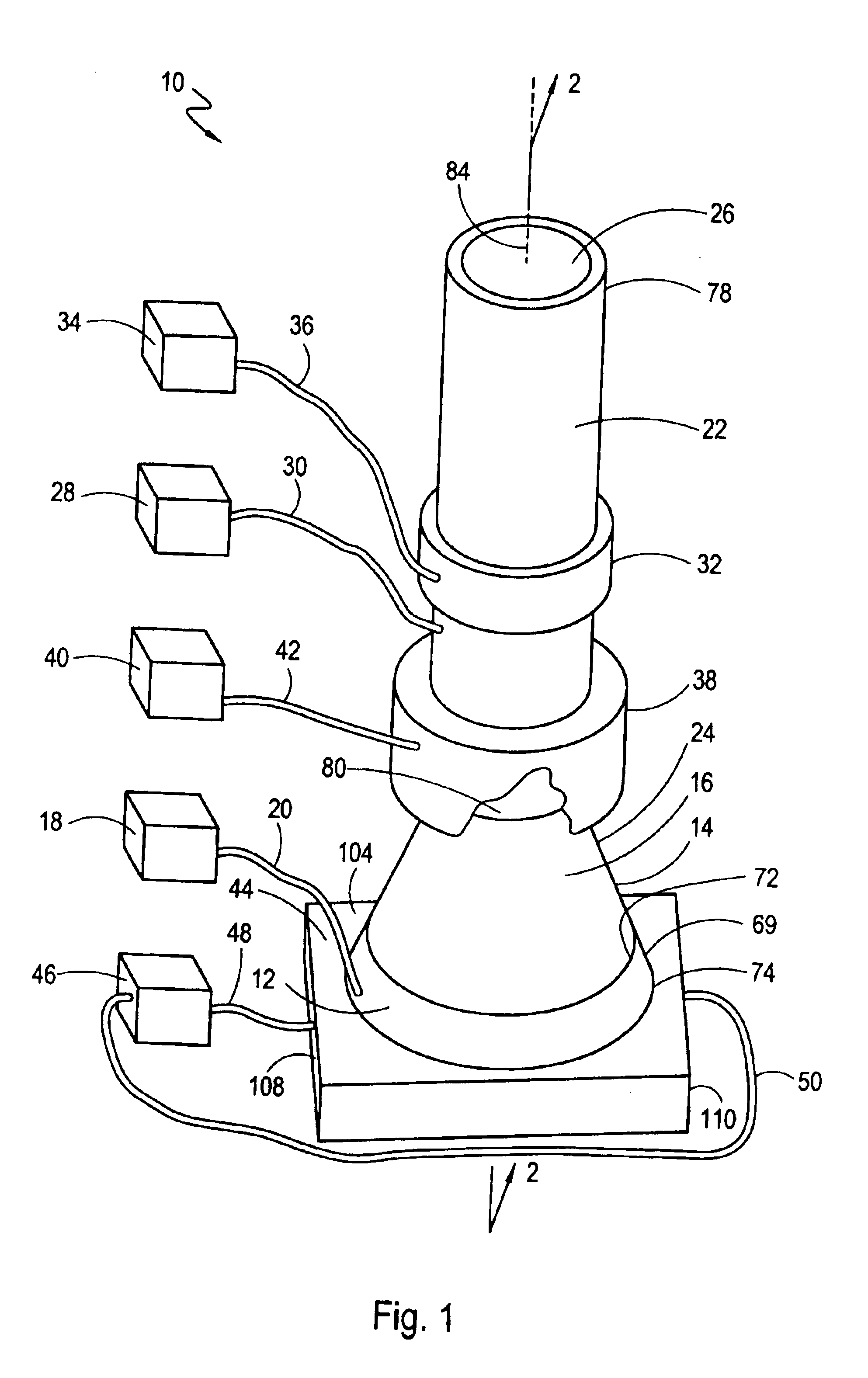
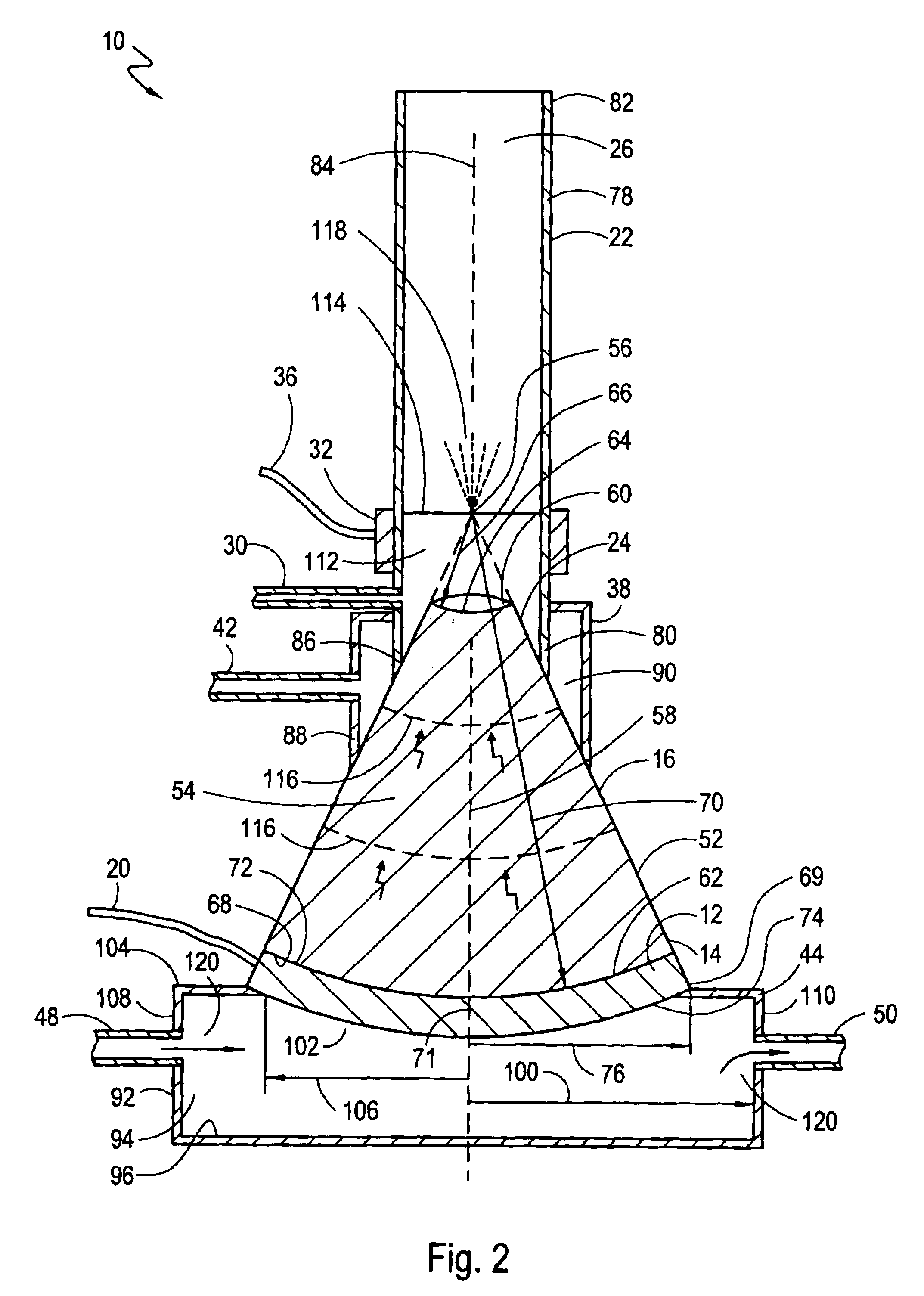
High frequency ultrasonic nebulizer for hot liquids
InactiveUS6883729B2Improve fluid tight sealEffective distanceMovable spraying apparatusChiropractic devicesSpherical shapedEngineering
A nebulizer for atomizing a high-temperature liquid includes a truncated, conical concentrator that defines a vertex and that has a small-diameter end and a large-diameter end. The small-diameter end has a spherical-shaped, concave surface and the large-diameter end has a spherical-shaped, convex surface. A piezoelectric transducer has a spherical-shaped, concave surface that is attached to the convex surface of the concentrator. A cylindrical-shaped droplet manifold is positioned over the small-diameter end of the concentrator to create a liquid chamber in the manifold with the vertex inside the liquid chamber. A feeding tube introduces the high-temperature liquid into the liquid chamber until the surface of the liquid reaches the vertex. With an activation of the transducer, acoustic waves that have spherical wavefronts are launched away from the concave surface of the transducer. The concentrator propagates and directs the spherical wavefronts for convergence at the vertex to nebulize the liquid.
Owner:ARCHIMEDES OPERATING
Power recovery and energy conversion systems and methods of using same
In various illustrative examples, the system may include heat recovery heat exchangers, one or more turbines or expanders, a desuperheater heat exchanger, a condenser heat exchanger, a separator, an accumulator, and a liquid circulating pump, etc. In one example, a bypass desuperheater control valve may be employed. The system comprises a first heat exchanger adapted to receive a heating stream from a heat source after passing through a second heat exchanger and a second portion of a working fluid, wherein, the second portion of working fluid is converted to a hot liquid via heat transfer. An economizer heat exchanger that is adapted to receive a first portion of the working fluid and the hot discharge vapor from at least one turbine may also be provided. The first and second portions of the working fluid are recombined in a first flow mixer after passing through the economizer heat exchanger and first heat exchanger, respectively. A second heat exchanger is provided that receives the working fluid from the first flow mixer and a hot heating stream from a heat source and convert the working fluid to a hot vapor. The hot vapor from the second heat exchanger is supplied to at least one turbine after passing through a separator designed to insure no liquid enters the said at least one turbine or expander. The hot, high pressure vapor is expanded in the turbine to produce mechanical power on a shaft and is discharged as a hot, low pressure vapor.
Owner:TAS ENERGY
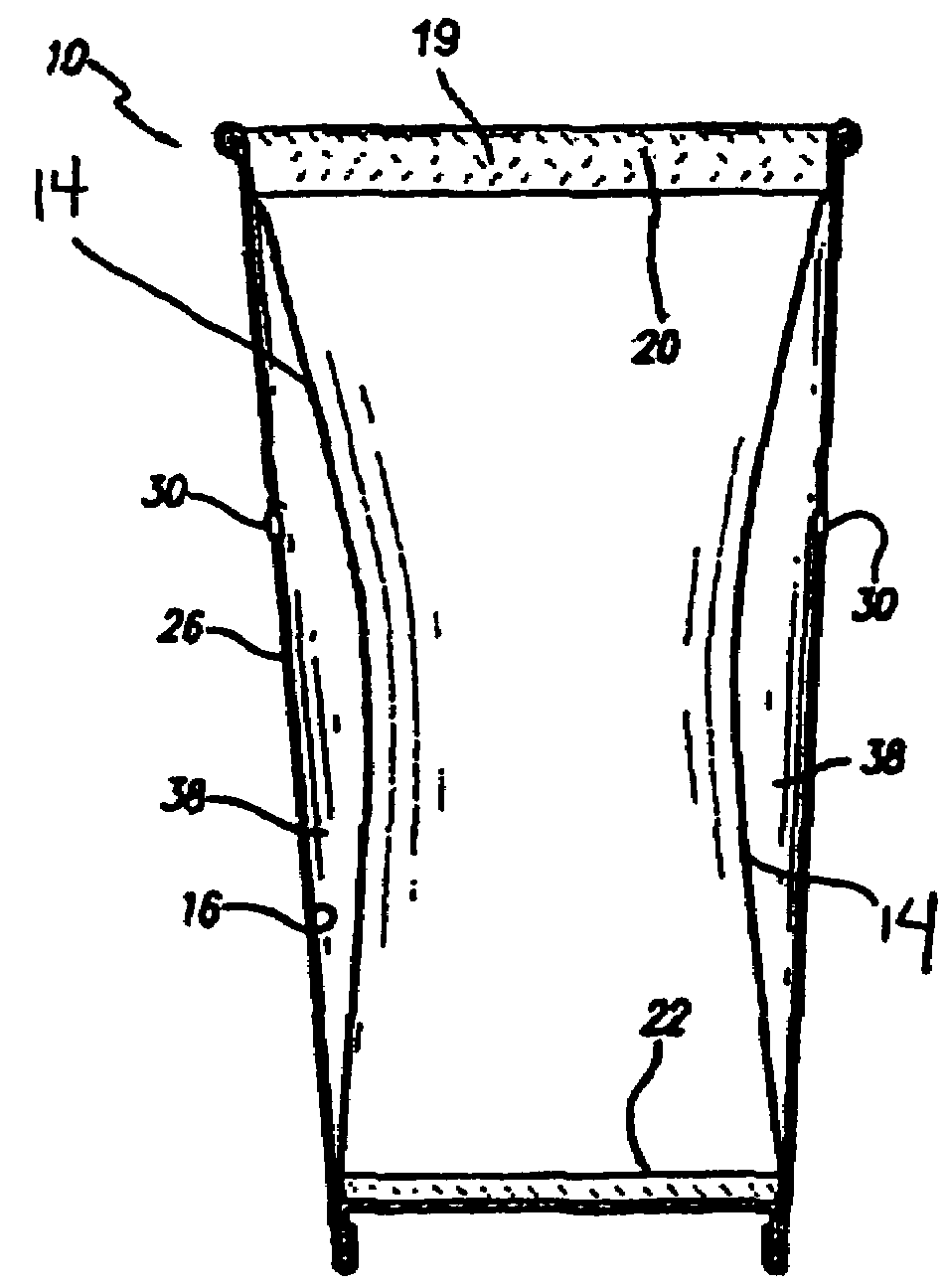
Container employing inner liner and vents for thermal insulation and methods of making same
InactiveUS7510098B2Improve insulation performanceBoxes/cartons making machineryDomestic cooling apparatusCardboardThermal insulation
The present invention provides a container suitable for providing insulation wherein the container has an inner shrink film liner. The sidewalls of the container, which can be made from paperboard or other suitable material, are vented to allow ambient air to freely flow through the sidewall of the container during activation of the shrink film with hot liquid or other suitable material. When the container is filled with material having a temperature of from about 130° F. to up to about 212° F., the shrink film is activated and the container provides excellent insulation, thereby allowing the container to be held in a consumer's hand for an extended period without causing burns or excessive discomfort. Methods of making this container are also provided.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Thermal receptacle with phase change material containing insert
A thermal receptacle having a side wall which has an inner surface and a spaced outer surface. An interstitial chamber may be defined by the space between the inner and outer surfaces. A phase change material containing insert is provided into the receptacle. The insert contains a phase change material or a plurality of different phase change materials. Phase change material may also be located within the interstitial chamber. The phase change material regeneratively absorbs thermal energy from a hot liquid in the receptacle thereby rapidly lowering the temperature of the liquid and then the material releases the thermal energy back to the liquid to maintain the temperature of the liquid.
Owner:WILLIAMS PRESTON NOEL +3
Electric tankless water heater
In various embodiments, the invention provides a system for heating a liquid, such as, for example, water, comprising a plurality of liquid heaters, the inlets and outlets of which are respectively connected in a parallel flow relationship by respective manifolds, and configured to provide liquid having a temperature of greater than about 90 degrees Fahrenheit at a flow rate of greater than about 10 gallons per minute. In various embodiments, the present invention provides an electric tankless liquid heater system capable of delivering hot liquids, and in particular water, at even higher flow rates and or temperatures, including, but not limited to, flow rates greater than about: (1) 12 gpm; (2) 18 gpm; (3) 20 gpm; and (5) 20 gpm; and / or temperatures of greater than about: (1) 100° F.; (2) 120° F.; (3) 140° F.; and (4) 180° F.
Owner:RHEEM MFG CO
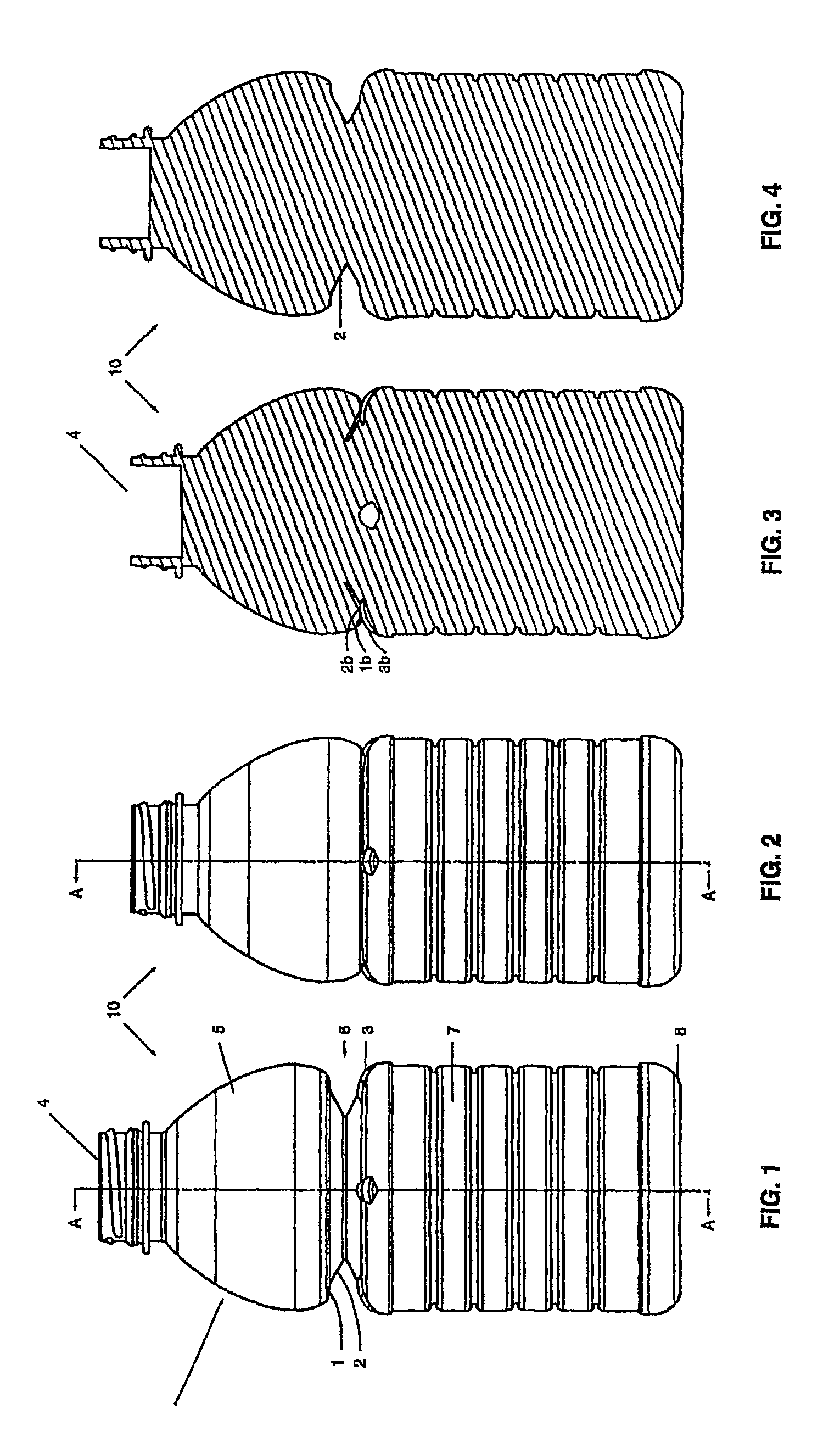
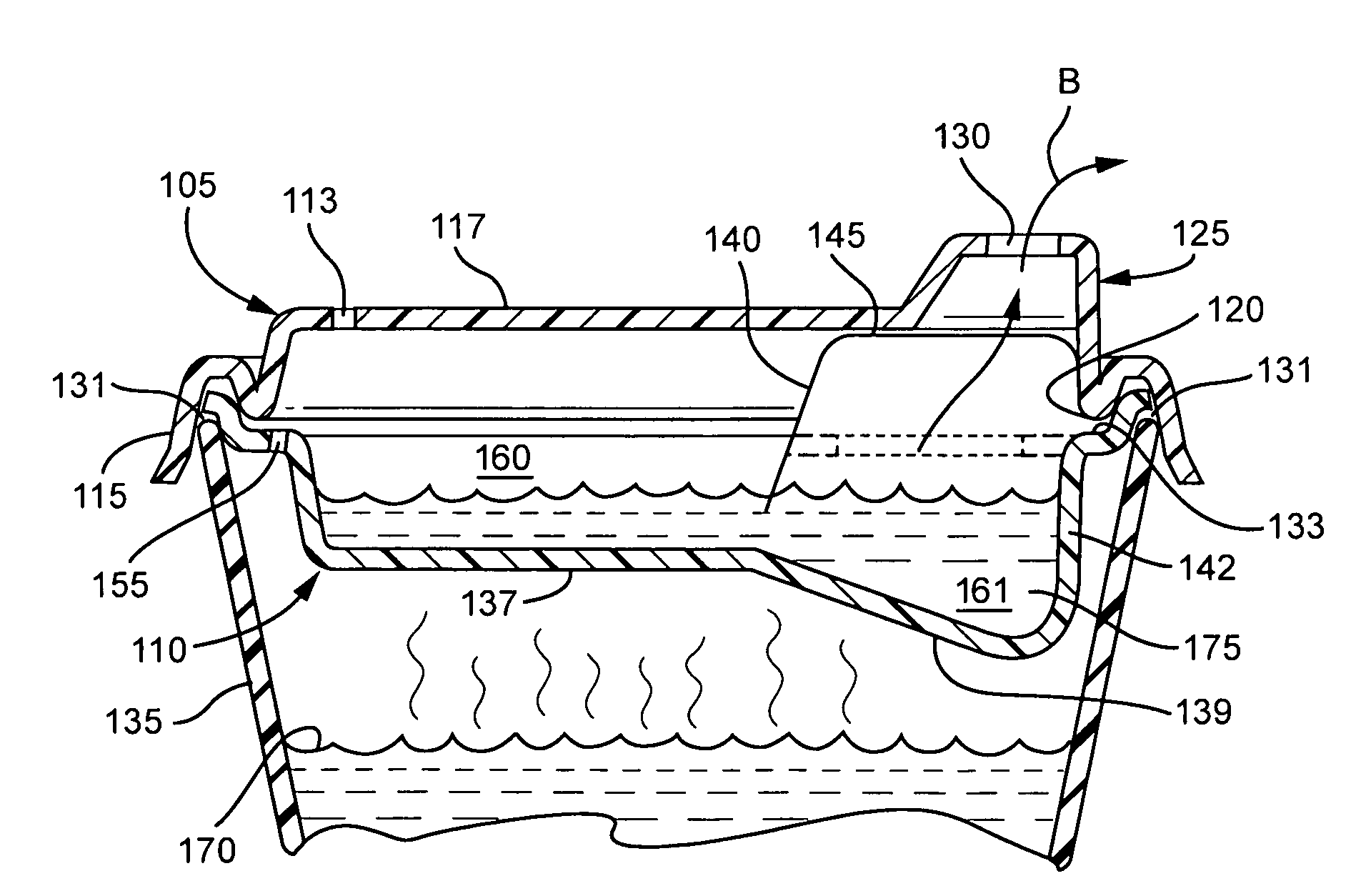
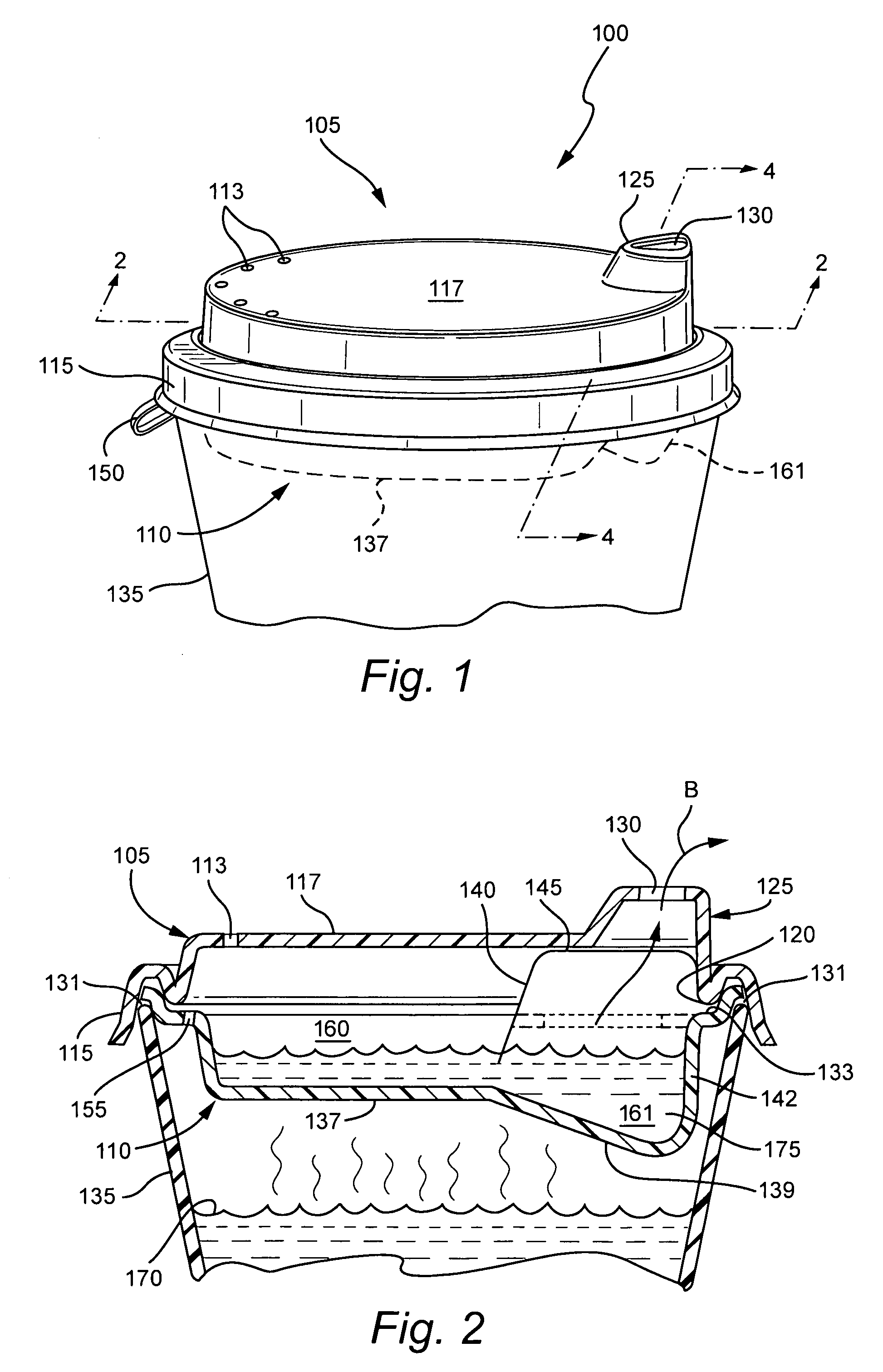
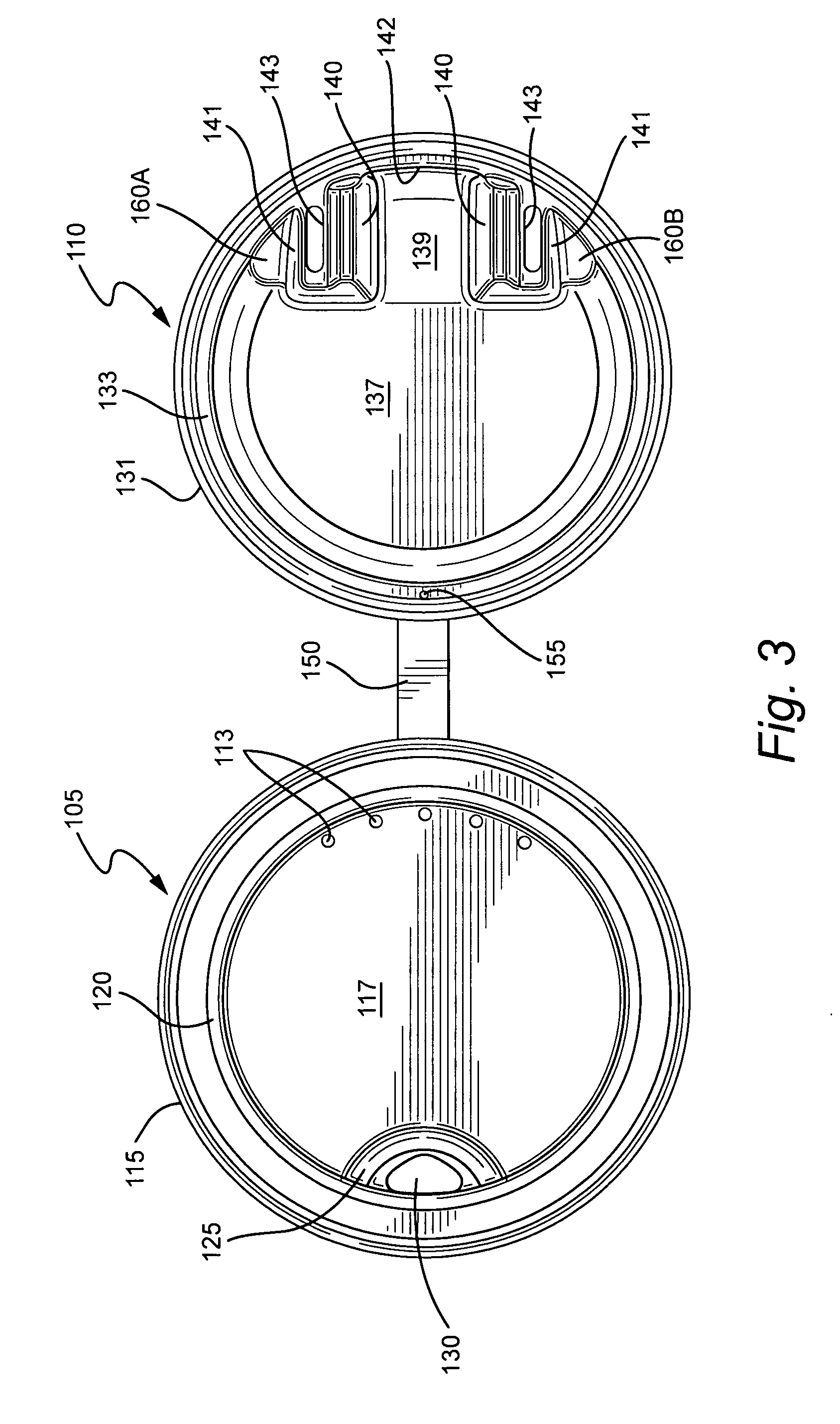
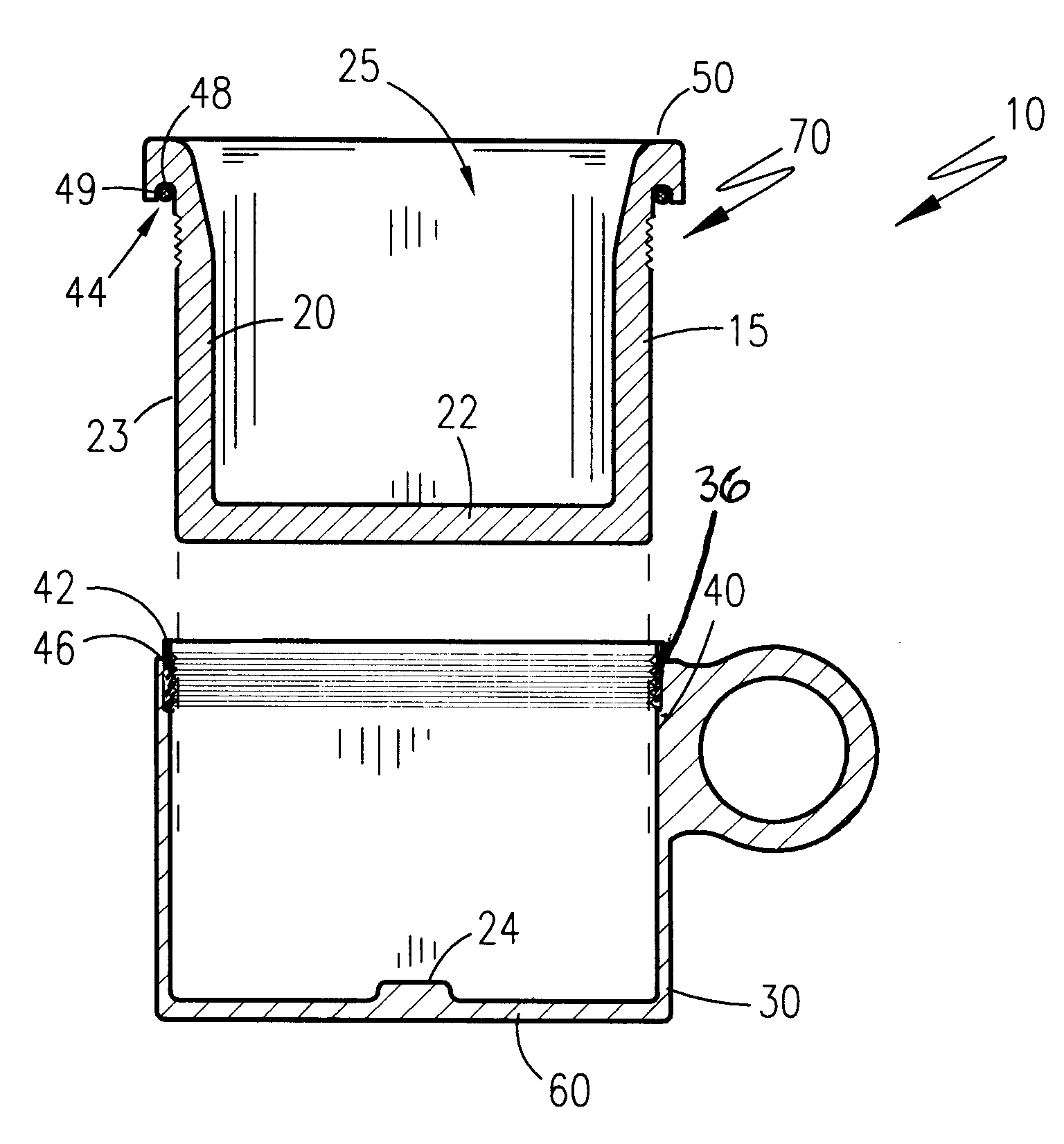
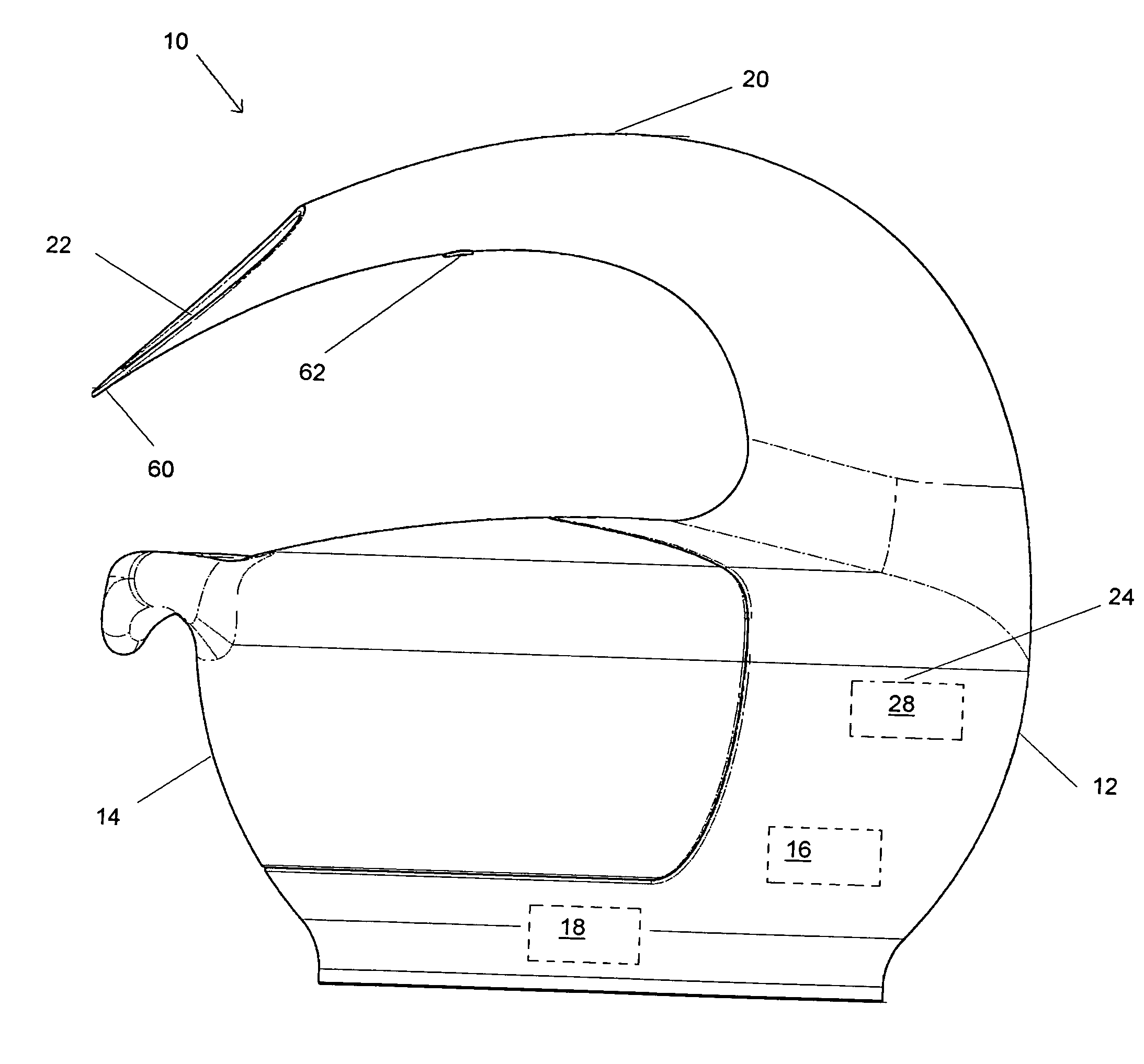
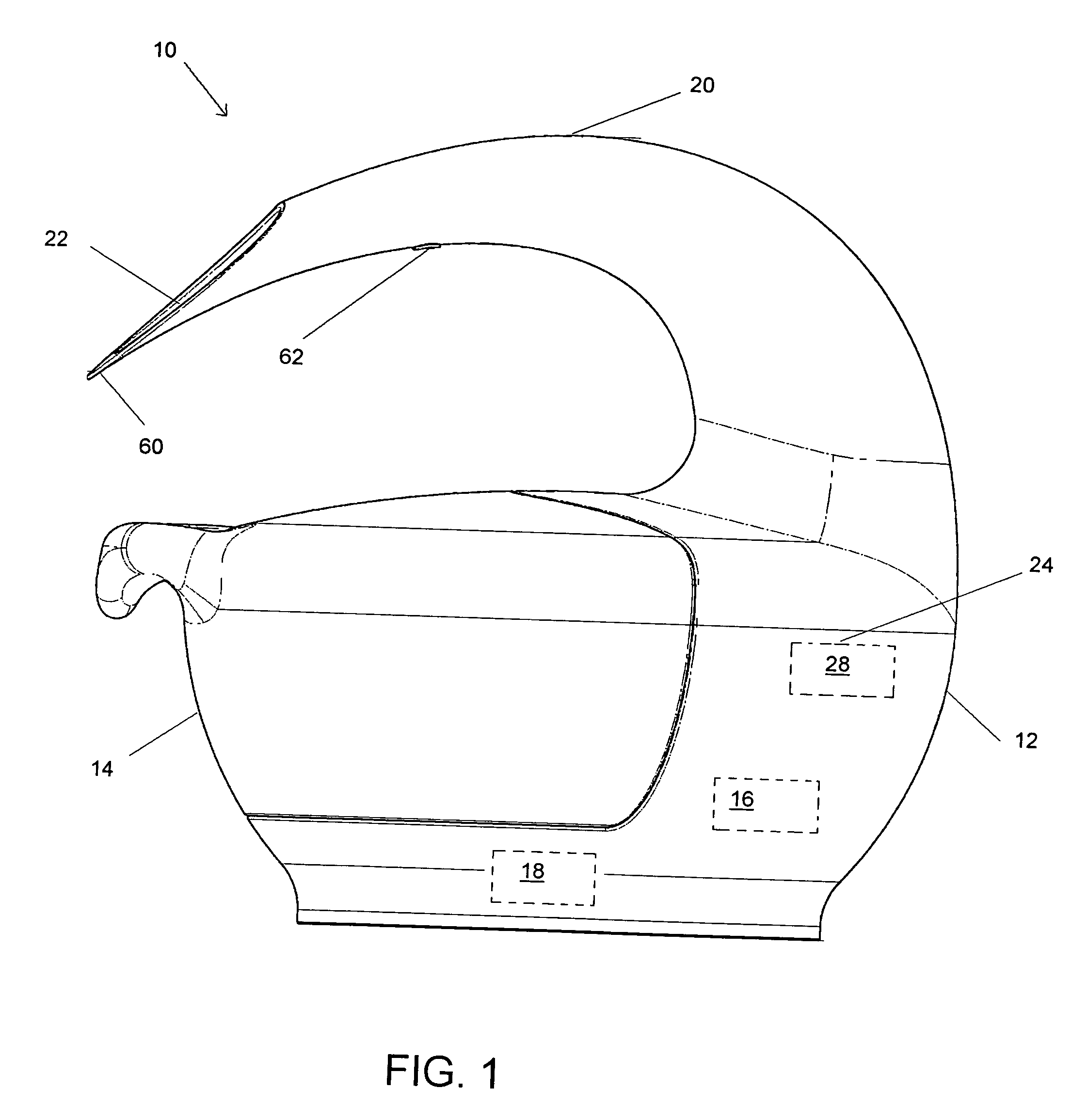
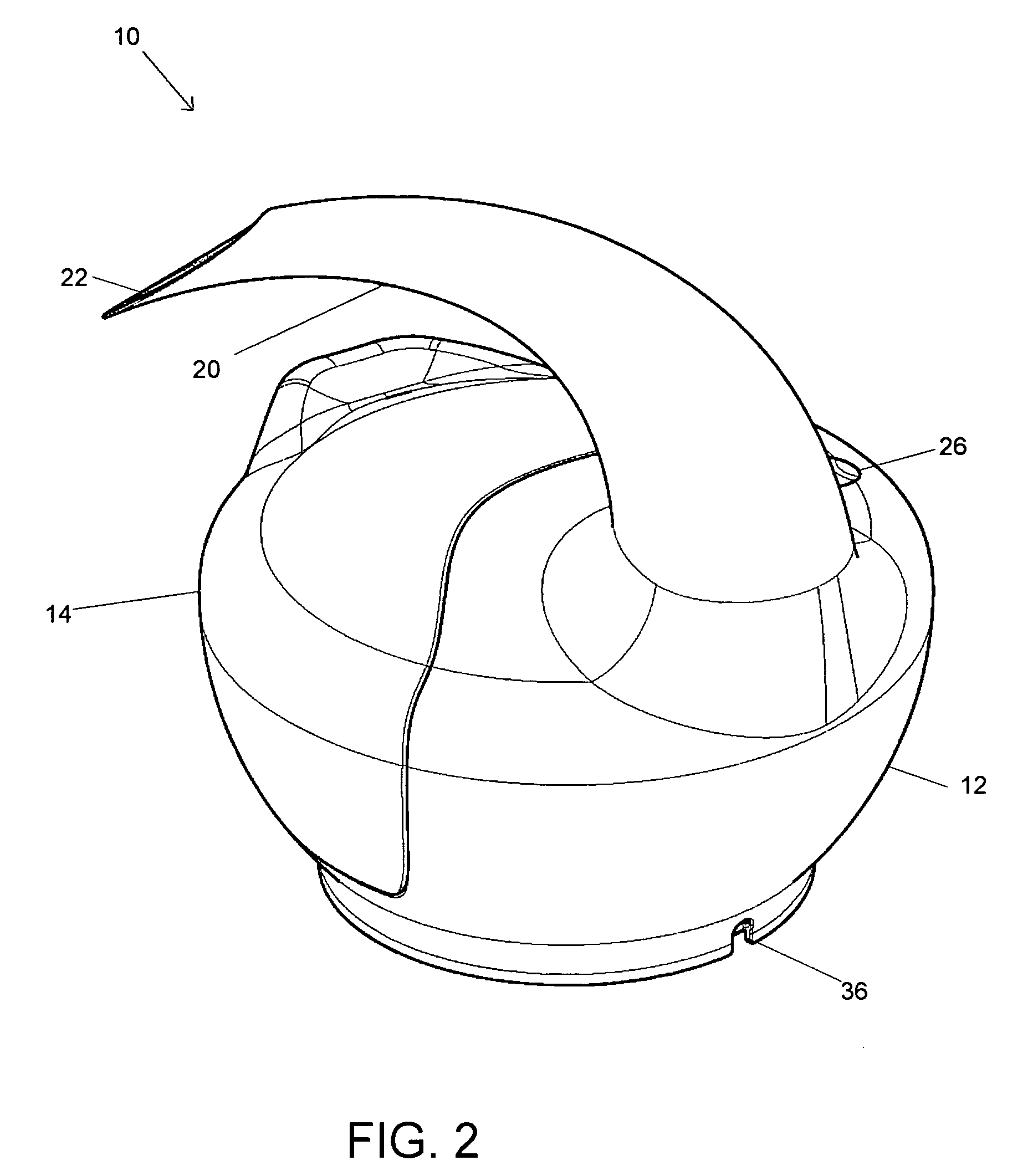
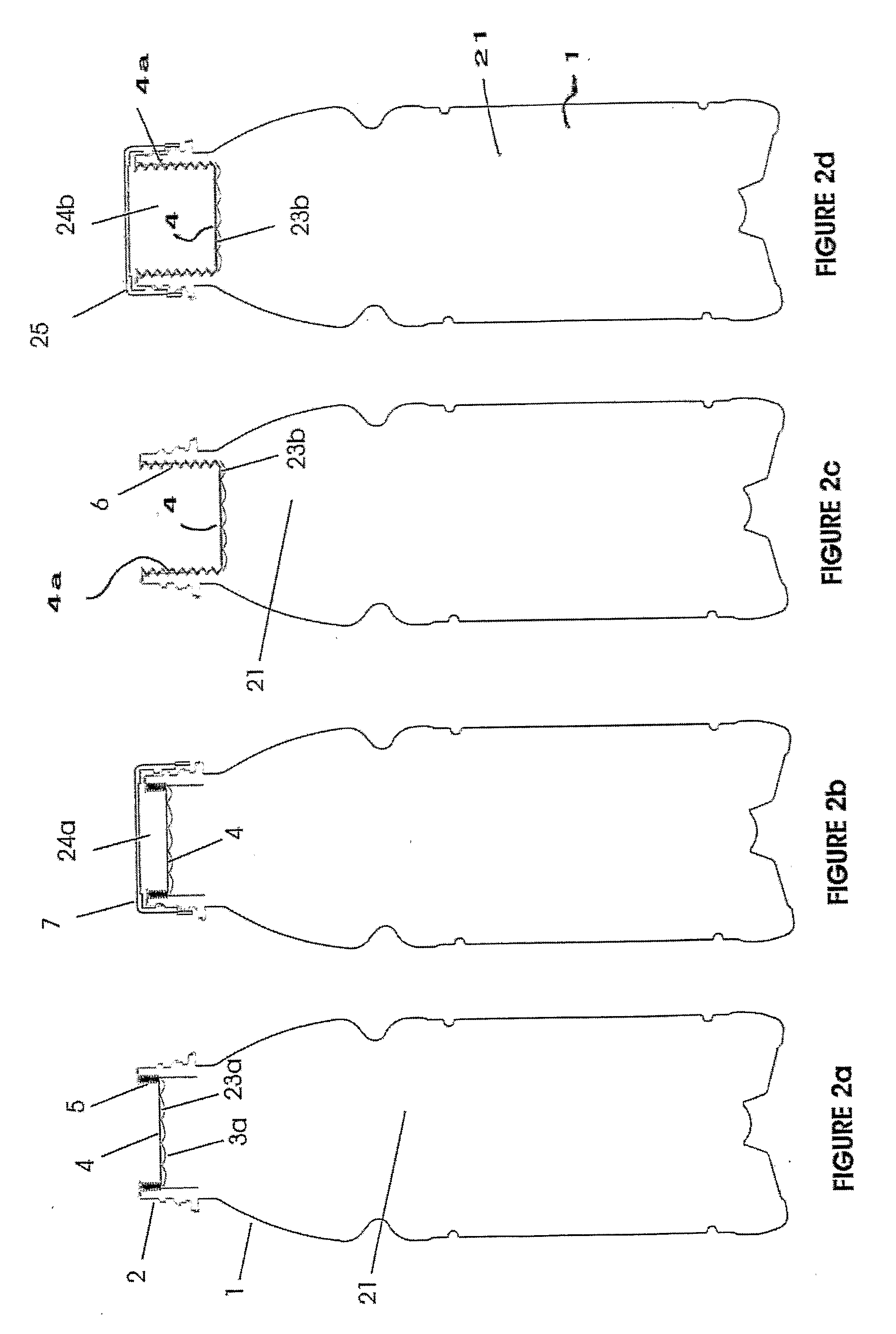
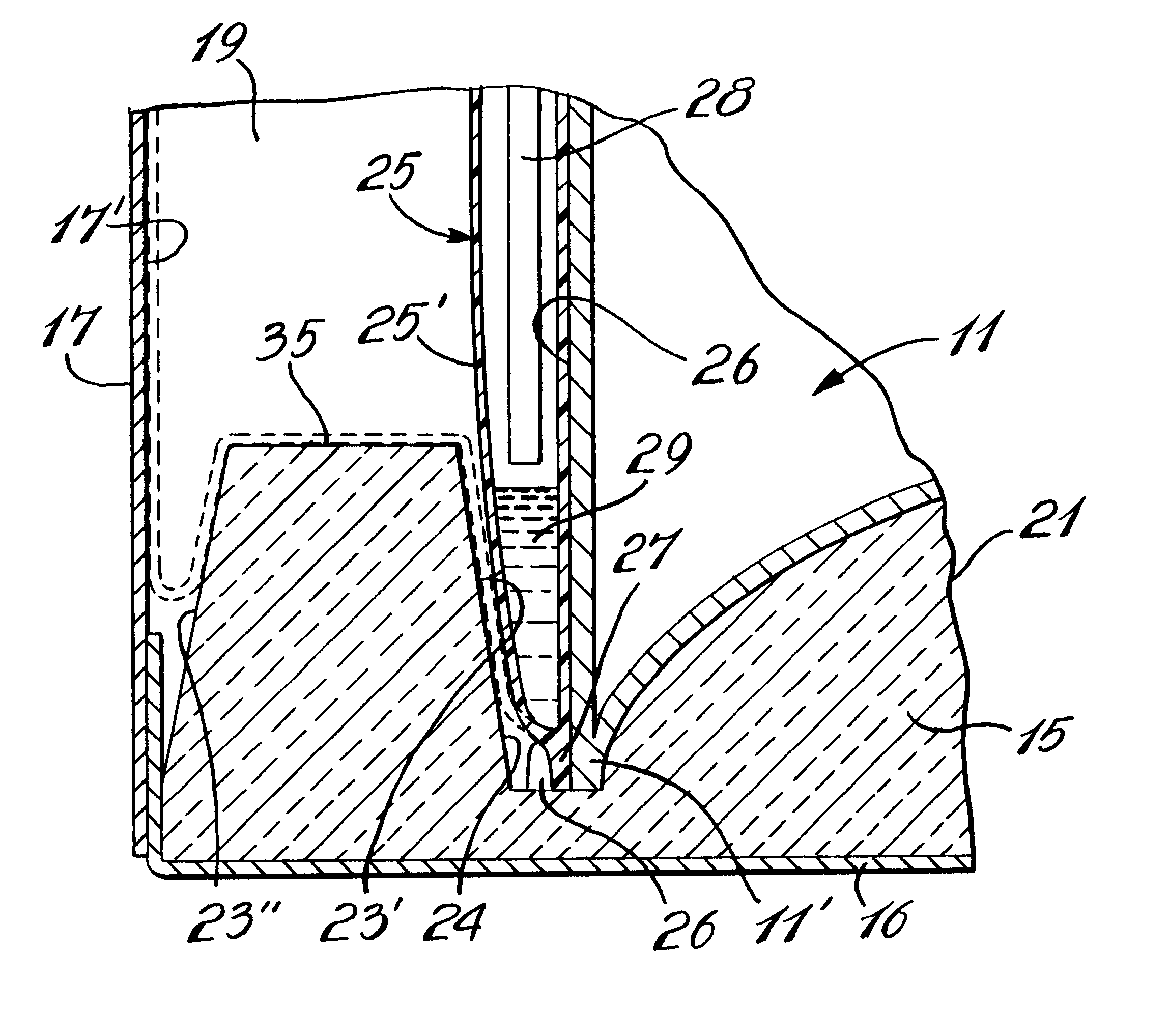
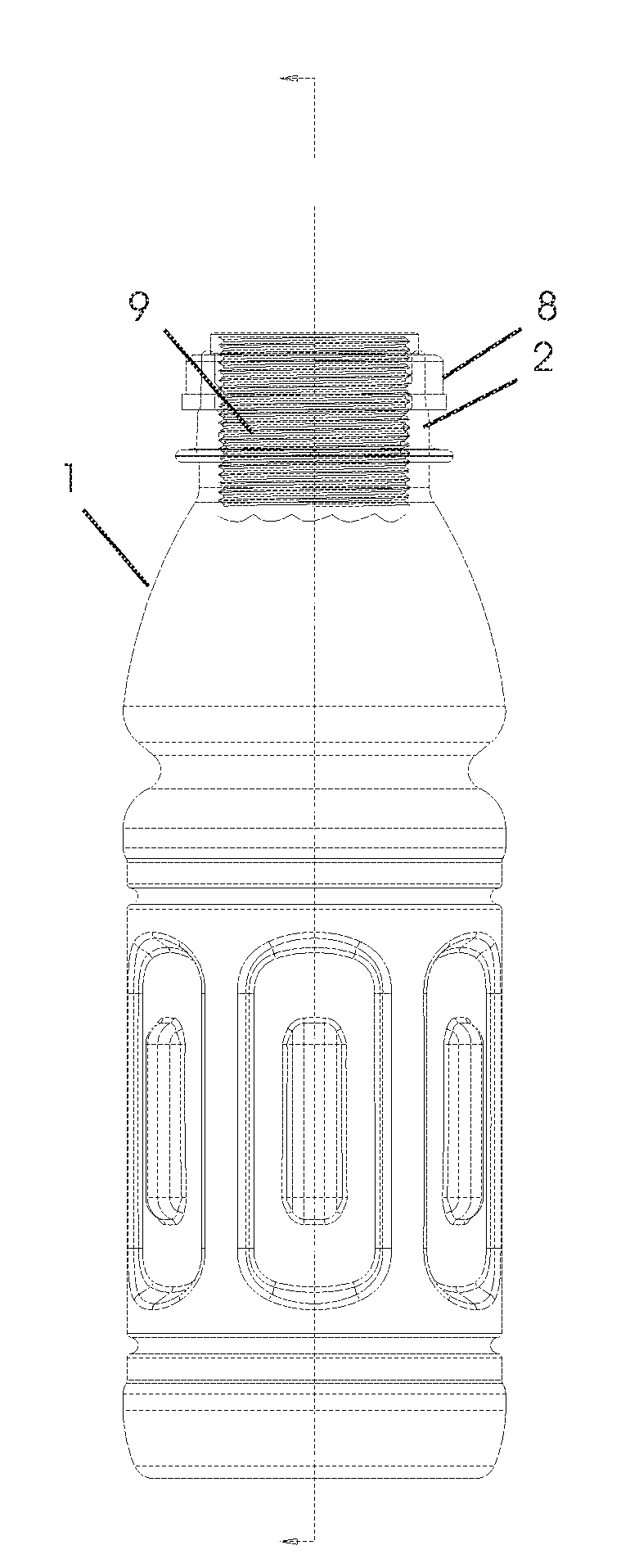
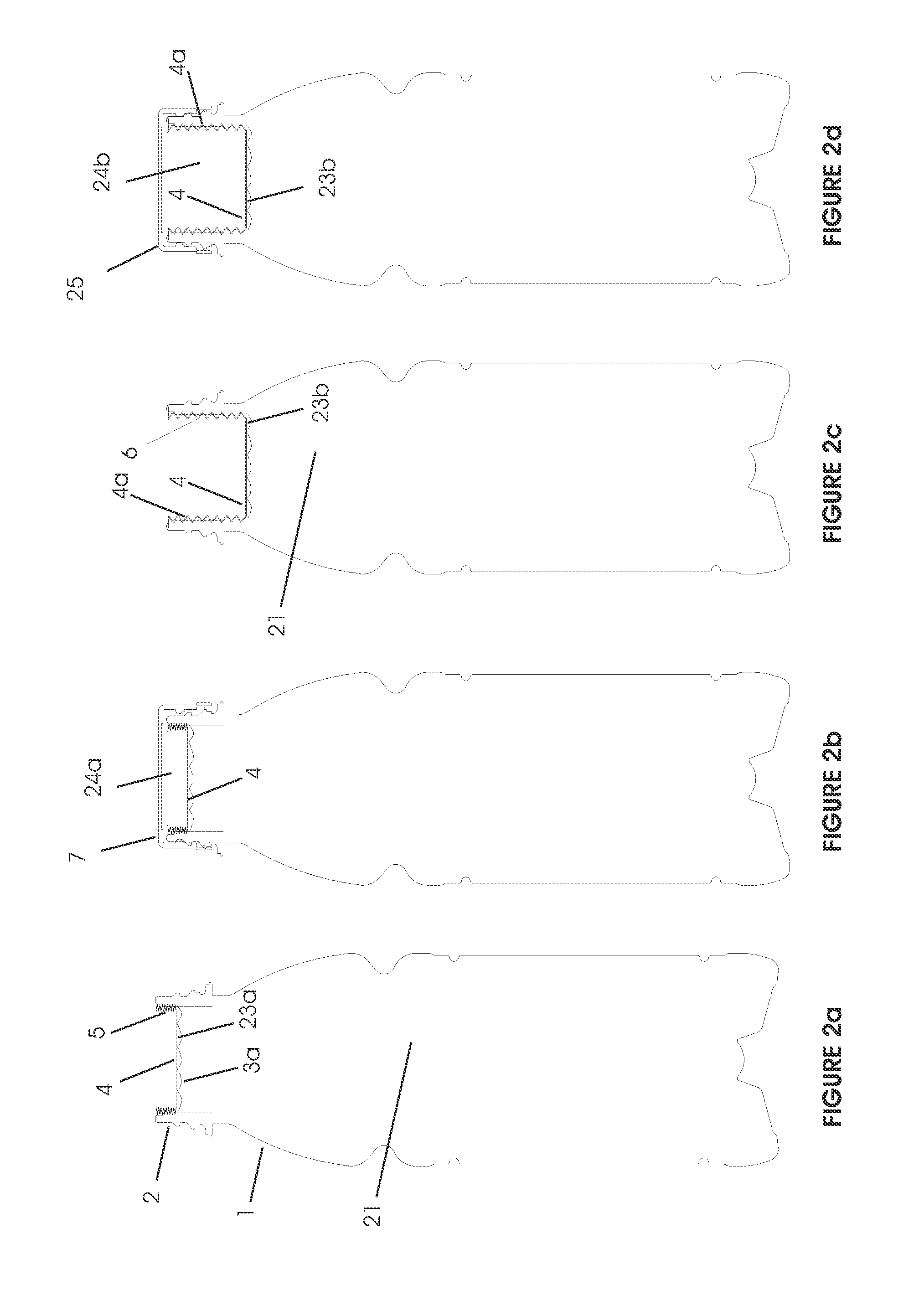
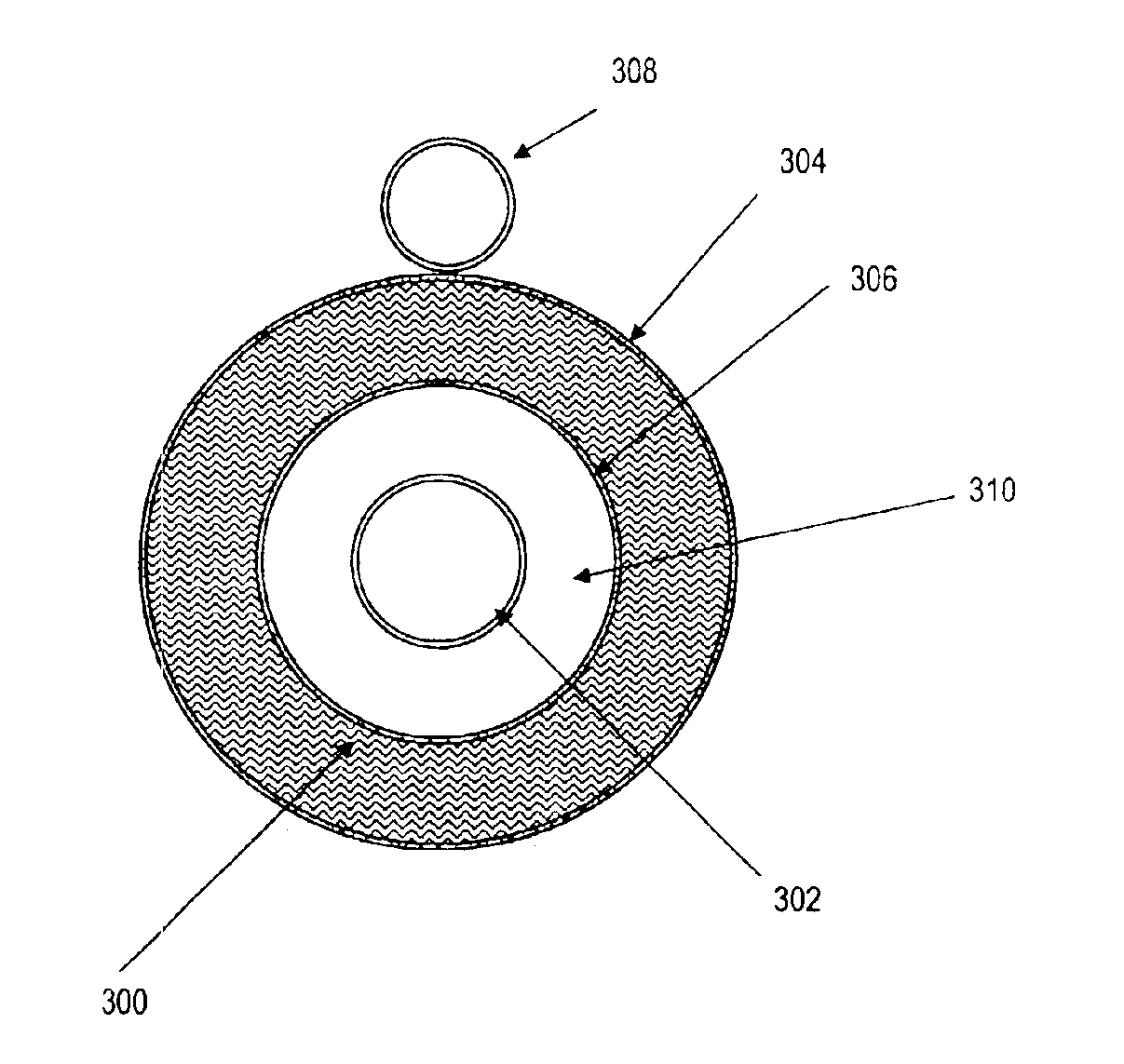
Headspace sealing and displacement method for removal of vacuum pressure
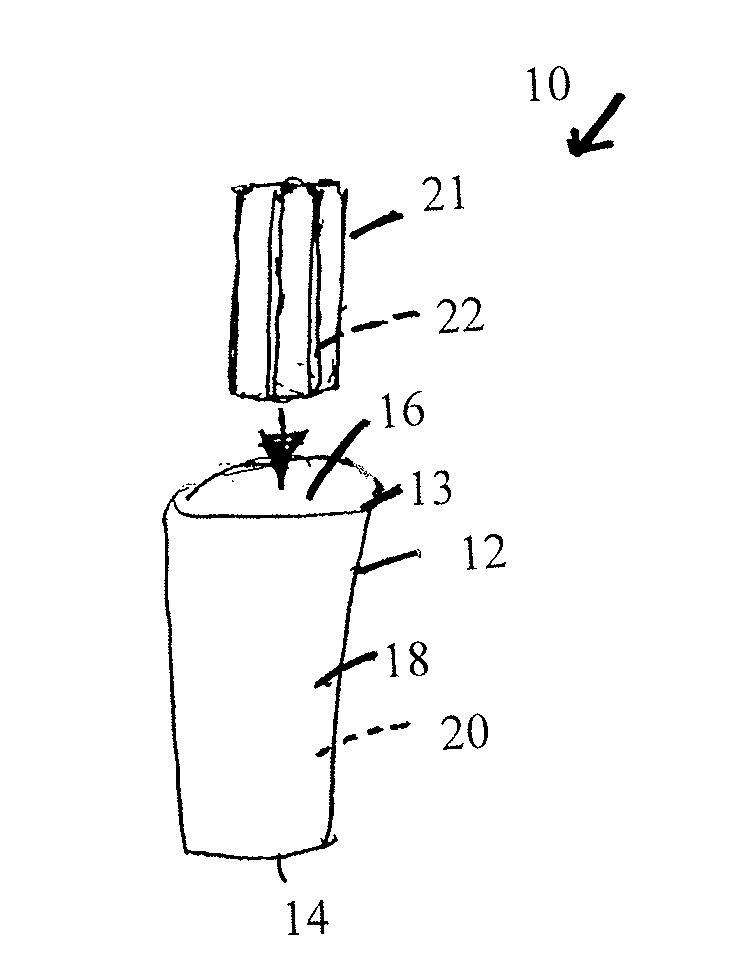
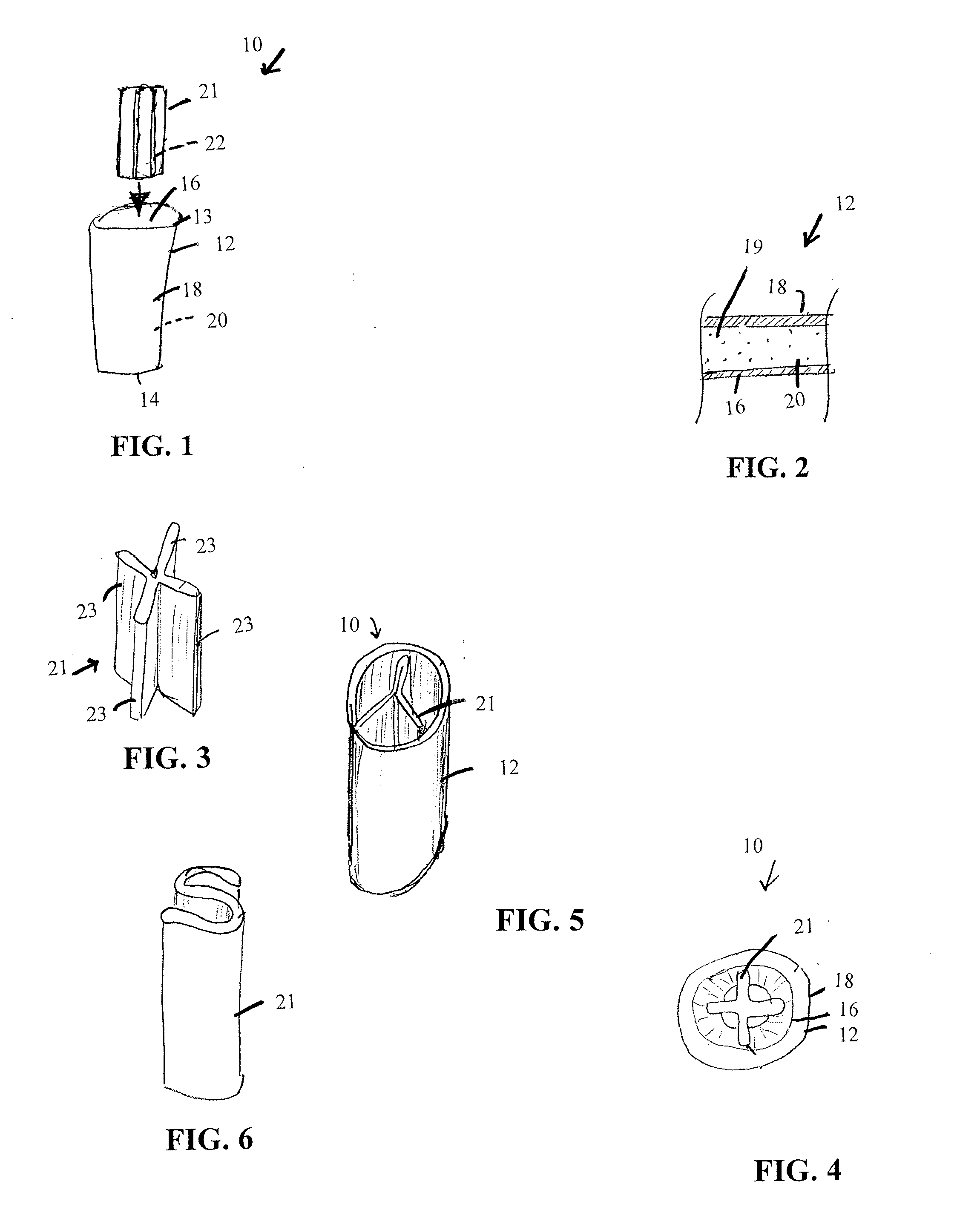
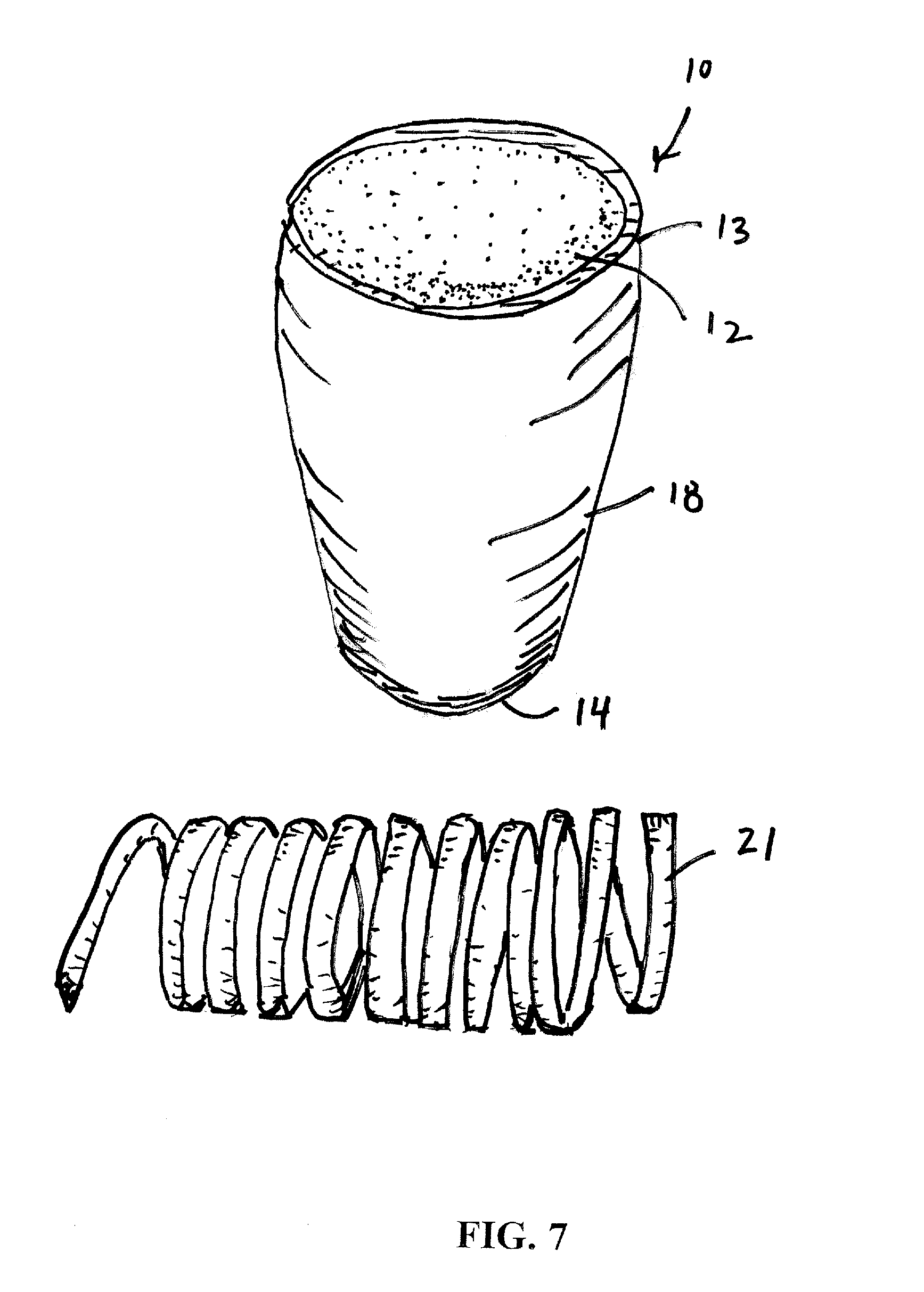
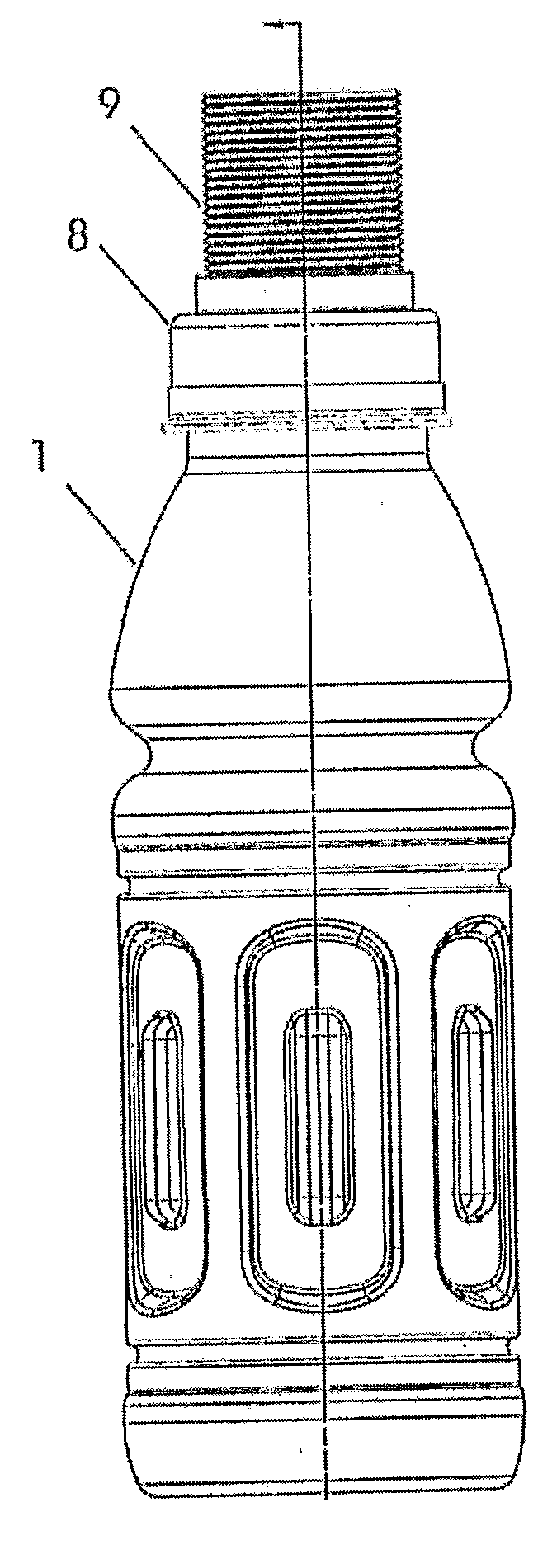
A container (1) is intended for filling with a hot liquid (21). The container (1) has a neck finish (2) with an opening closed off by a primary seal (4) which has an expandable side wall (4a). As the liquid (21) cools, the side wall (4a) is drawn into the container (1) to remove vacuum pressure created within the container (1). A permanent cap (25) can provide a secondary seal for the container and define a secondary headspace (24b) between the primary and secondary seals (4) (25). In other embodiments the seal (4) can be replaced by a mechanically movable seal which may be locked in its downward position. Also the secondary seal can be provided with a port or aperture to provide access into the secondary headspace for a commodity. Also a commodity such as a tablet or pill may be provided within the secondary headspace
Owner:MELROSE DAVID MURRAY
Hot drink cup lid with cooling air-flow
Owner:PITTS CONSTANCE LINDA
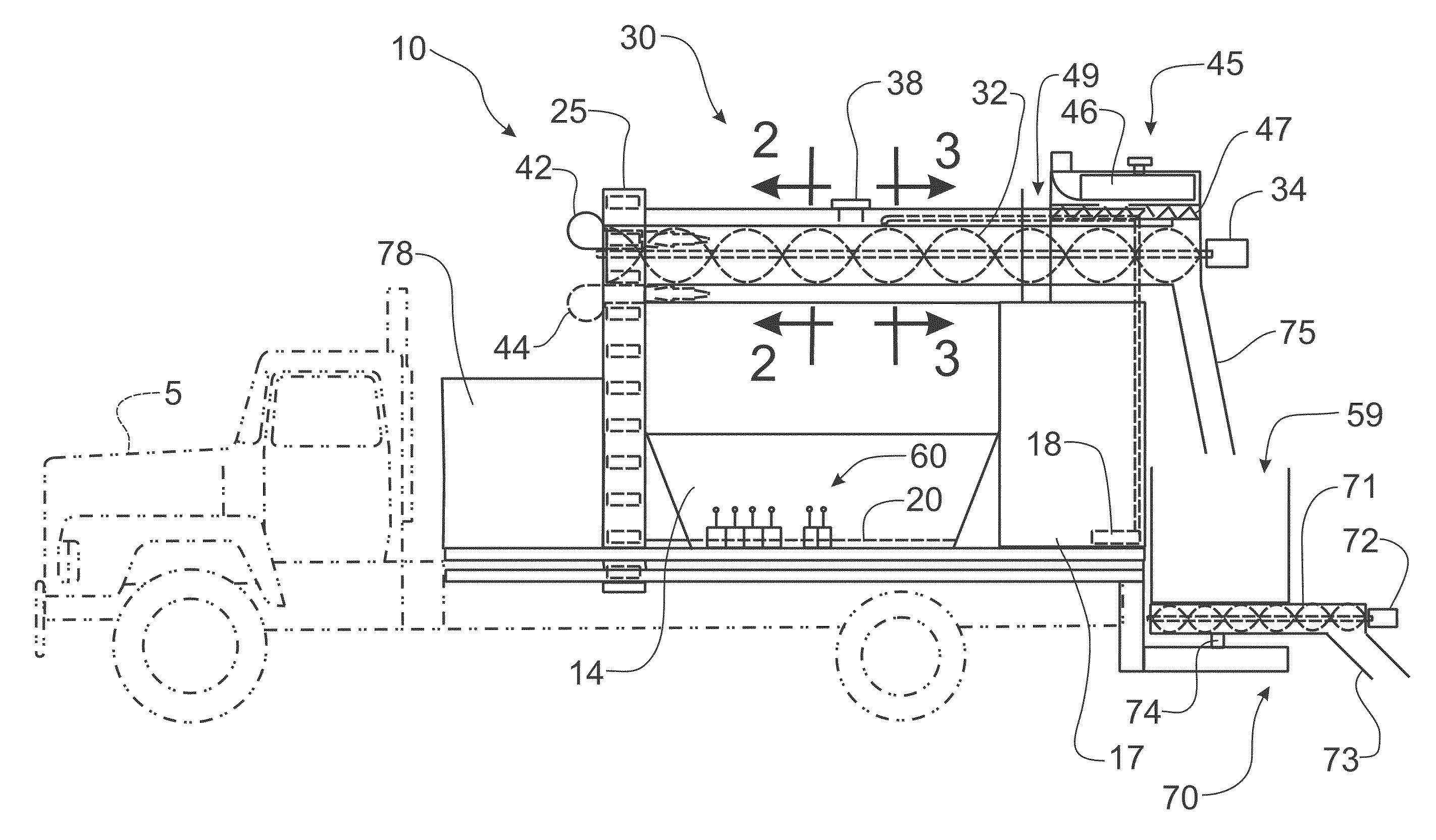
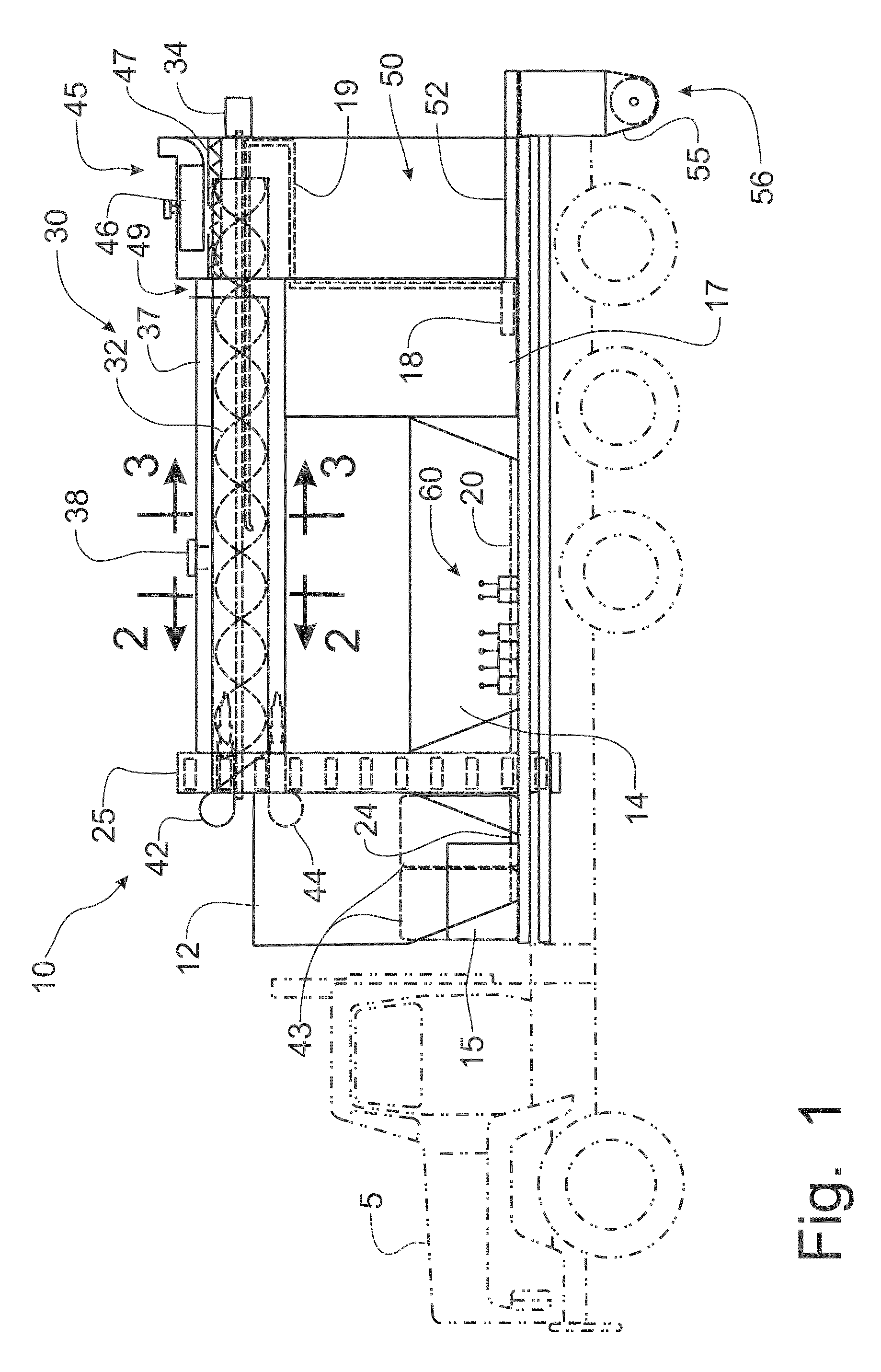
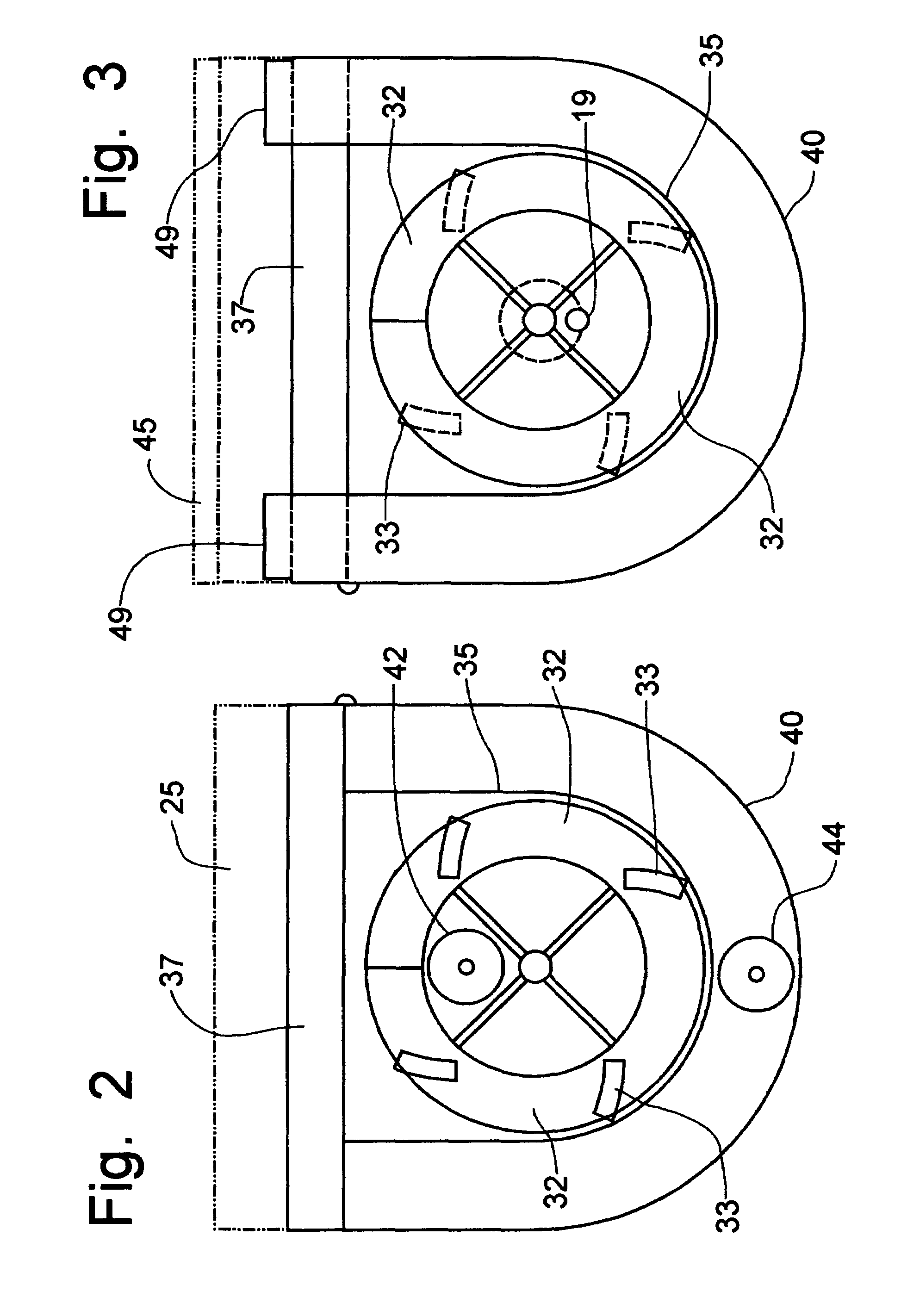
Mobile asphalt production machine
A mobile asphalt production machine mixes bituminous concrete at the job site through a mixing auger mechanism mounted in an insulated housing. Propane burners provide heat within the mixing auger mechanism and within the insulated housing to produce a hot-mix bituminous concrete in large or small batches. The components of the asphalt mixture are stored in separate bins that can be re-filled at the job site to provide a continuous supply of asphalt. Hot liquid bitumen is added to heated aggregate within the mixing auger mechanism. Recycled asphalt can be added through a port in the mixing auger for incorporation into the mixture. Controls permit the rate of flow of each individual component to be selectively varied in order to change the recipe for the mixture and to provide calibration of the component, while a master control will maintain the pre-established flow rates through a variable speed of operation.
Owner:ZIMMERMAN HAROLD M
Cavitated insulating support base for hot water tank
A hot water tank is comprised of a cylindrical disc-shaped support base on which is supported a cylindrical inner tank concentrically therewith. A circumferential ridge projects upwardly adjacent an outer peripheral edge of the support base and spaced from a lower edge portion of a circumferential side wall of the inner tank to form a circumferential containment channel between the ridge and the lower edge portion. The channel has a volume sufficient to receive a lower portion of a plastic film pouch wrapper disposed at least about a lower section of the inner casing as well as a pre-determined quantity of hot expandable liquid urethane placed therein in sufficient quantity to fill a space between the inner casing and an outer shell secured spaced about the inner casing when the urethane is expanded. The channel prevents the liquid urethane from flowing out of the lower portion of the wrapper located therein due to deterioration of the wrapper when exposed to the hot liquid urethane.
Owner:MICLAU S R I
Container assembly having an overcap with a storage compartment
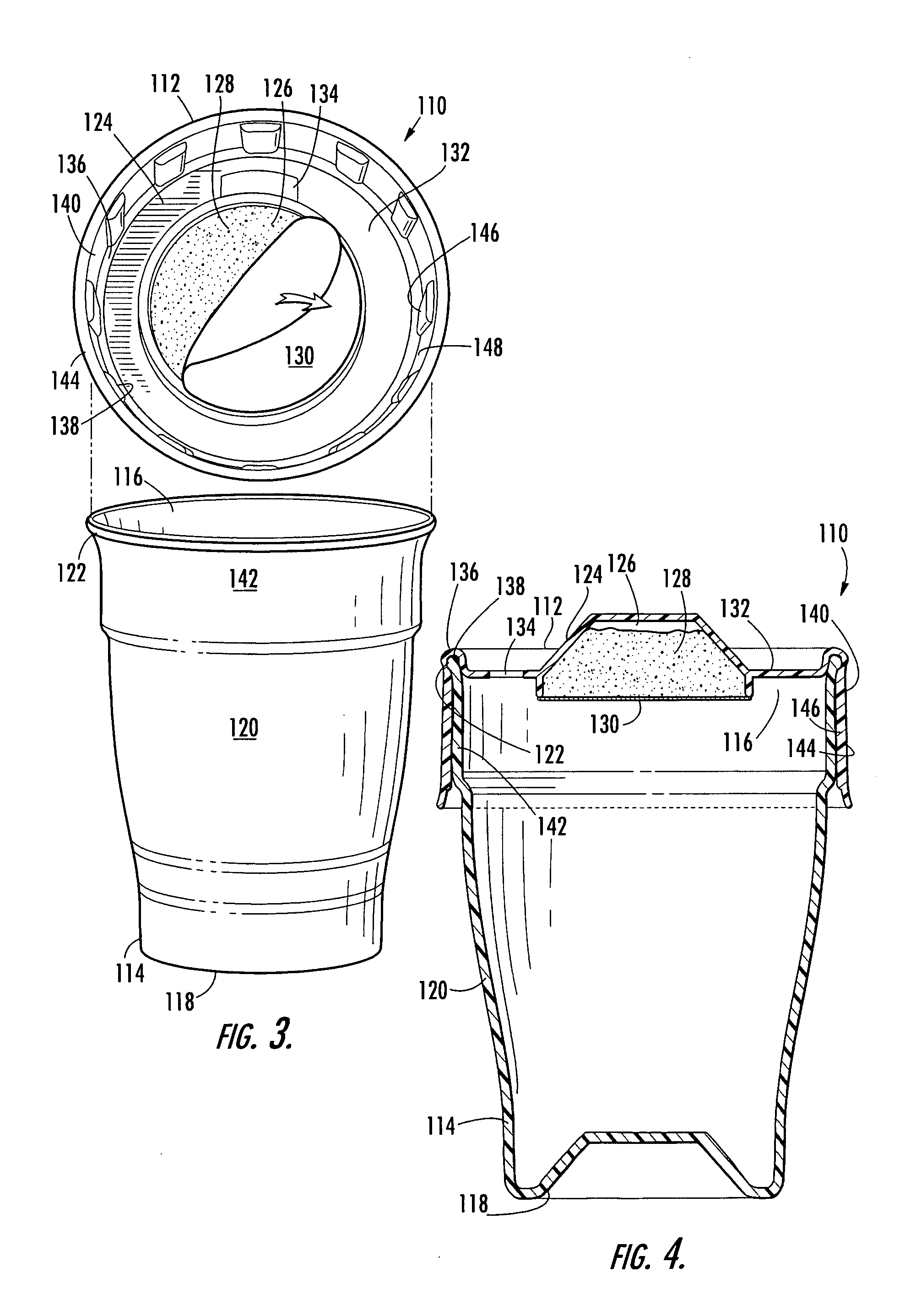
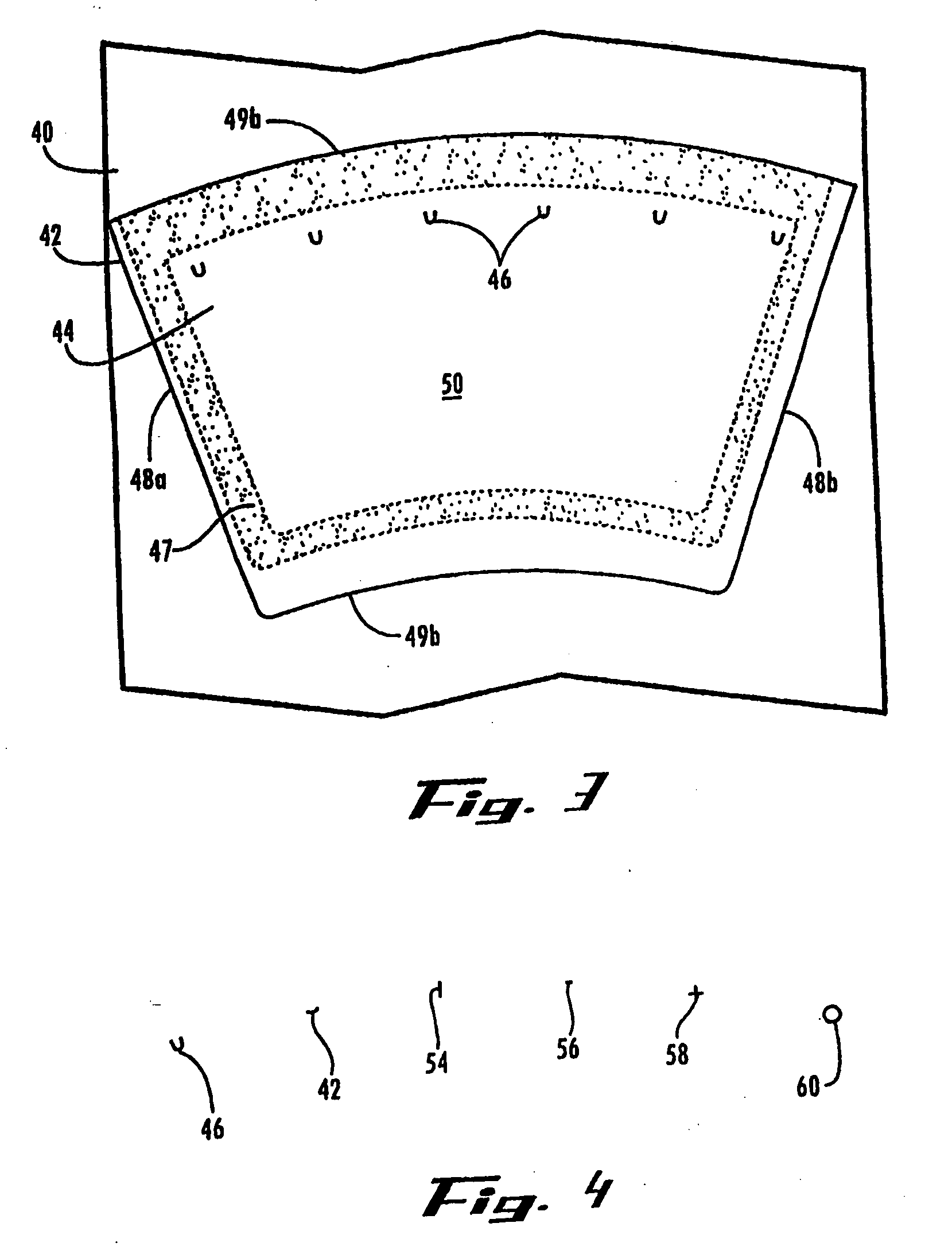
InactiveUS20050178677A1Easy accessClosure with auxillary devicesRigid containersEngineeringHot liquids
There is provided an overcap that includes a storage compartment for receiving a product to be mixed with a hot liquid. The overcap includes a top wall defining the storage compartment in an underside of the top wall surrounded by an annular portion. The overcap includes an aperture in the annular portion. The overcap also includes a skirt extending downward from a rim surrounding the annular portion. The skirt extends below a lowermost surface of the top wall and can define a grip surface which a consumer may use to hold the container assembly, such that the grip surface insulates against heat if a hot liquid is held in the container. The storage compartment is sealed with a membrane that is relatively impermeable to moisture. In addition, the skirt includes a plurality of spacers on the inside surface of the skirt that are circumferentially spaced apart and that extend downwardly from the rim of the overcap.
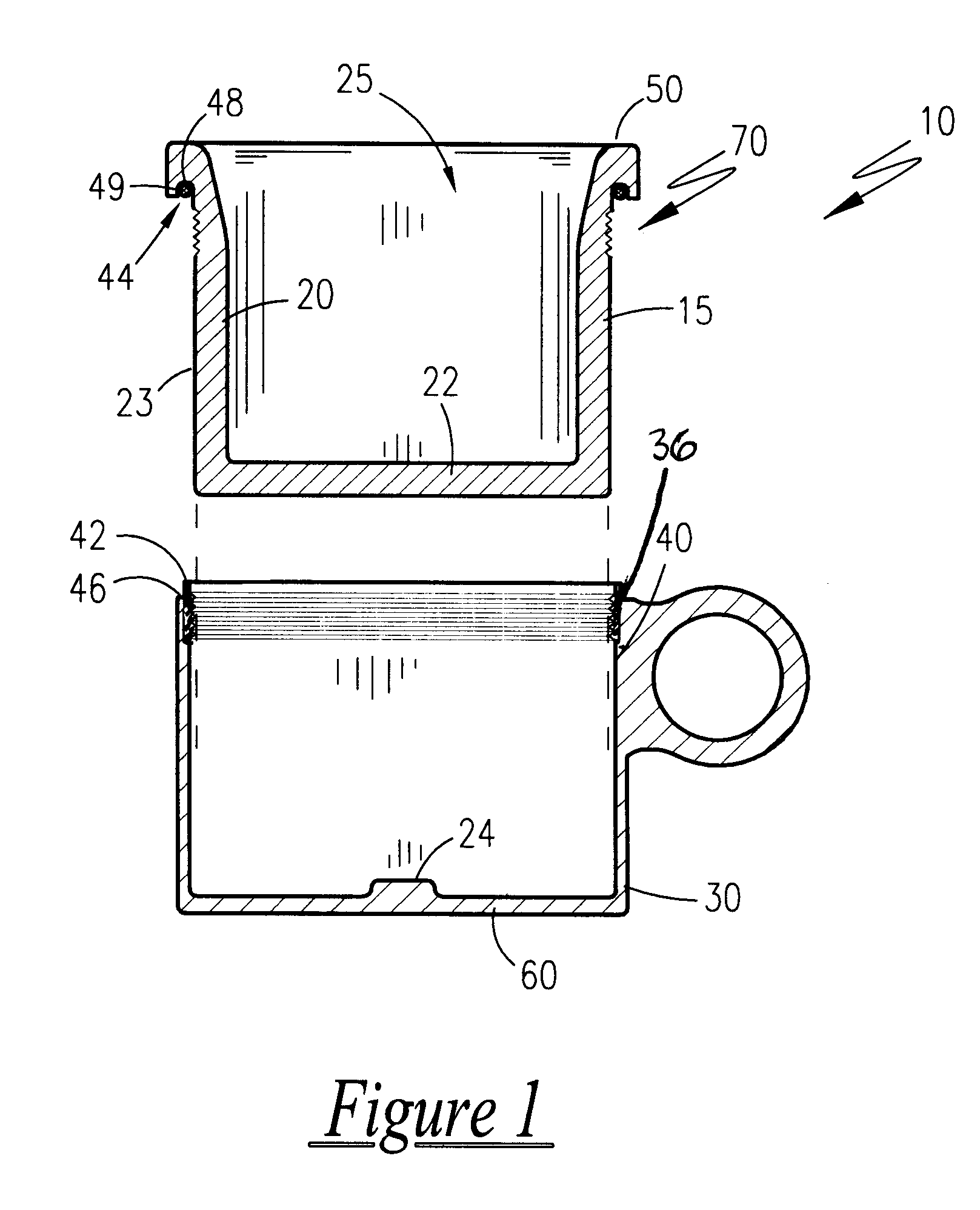
Headspace sealing and displacement method for removal of vacuum pressure
A container (1) is intended for filling with a hot liquid (21). The container (1) has a neck finish (2) with an opening closed off by a primary seal (4) which has an expandable side wall (4a). As the liquid (21) cools, the side wall (4a) is drawn into the container (1) to remove vacuum pressure created within the container (1). A permanent cap (25) can provide a secondary seal for the container and define a secondary headspace (24b) between the primary and secondary seals (4) (25). In other embodiments the seal (4) can be replaced by a mechanically movable seal which may be locked in its downward position. Also the secondary seal can be provided with a port or aperture to provide access into the secondary headspace for a commodity. Also a commodity such as a tablet or pill may be provided within the secondary headspace.
Owner:MELROSE DAVID MURRAY
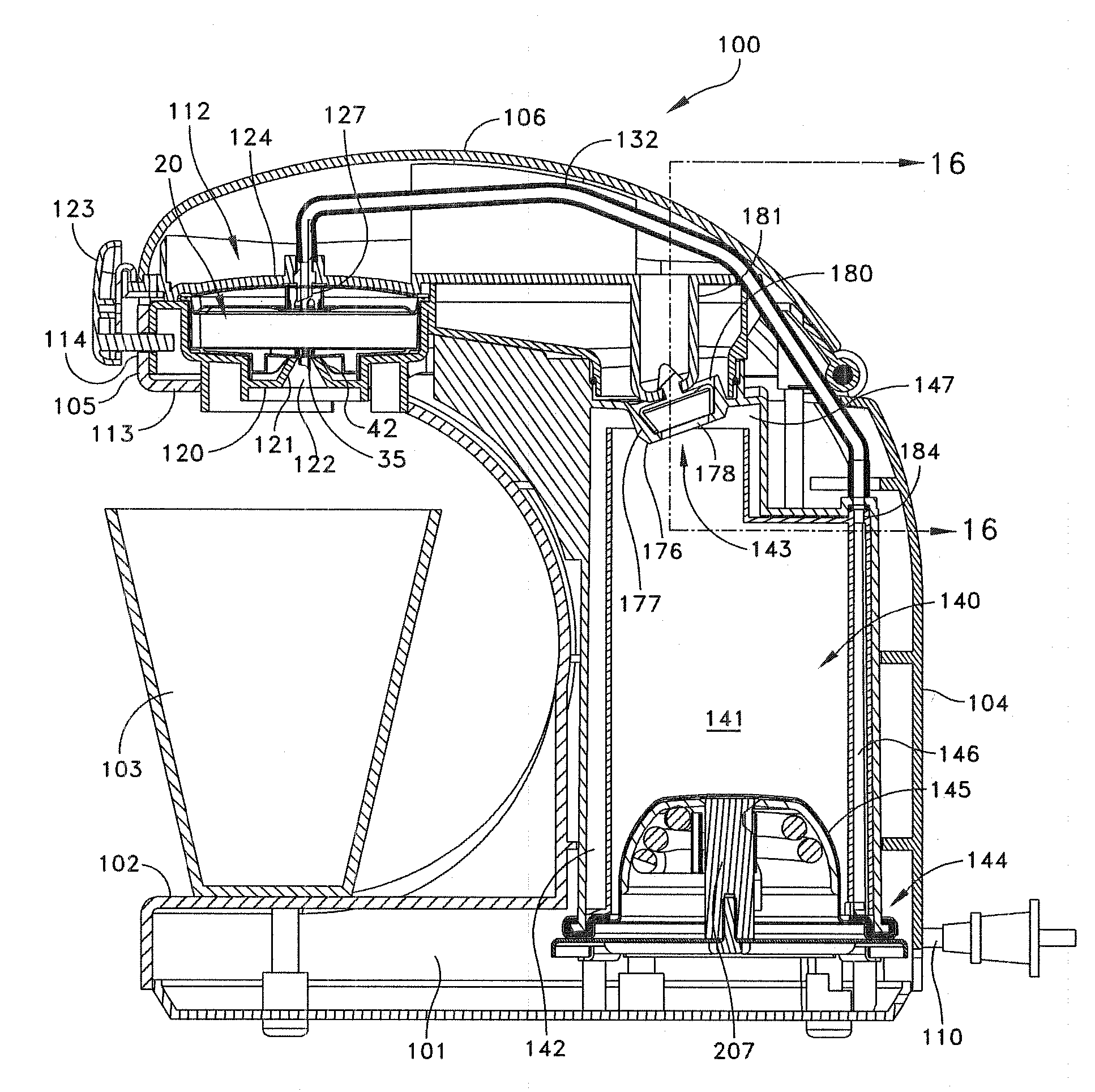
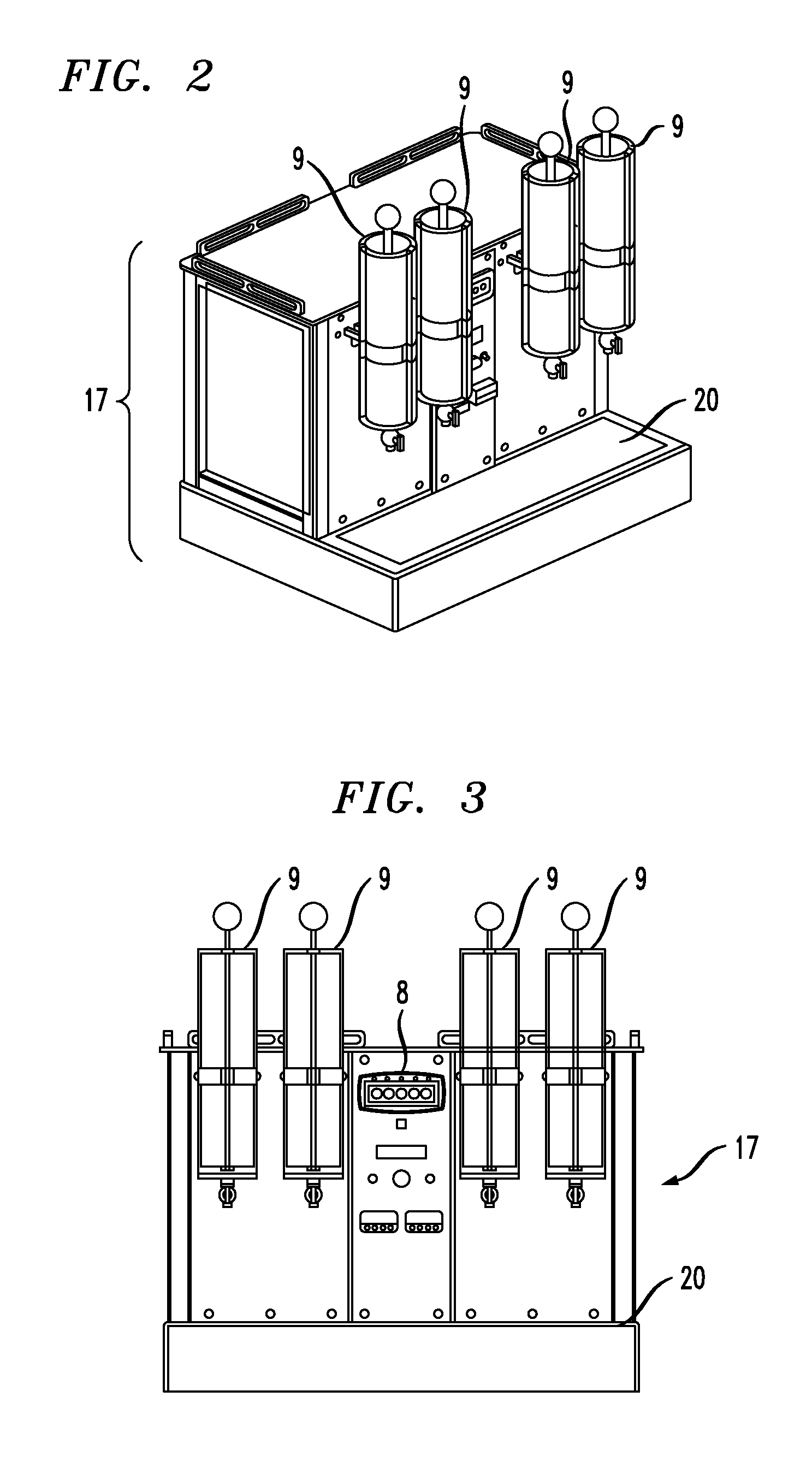
Hot beverage brewing system
In described embodiments, a hot liquid extraction system includes a brew chamber having a brew chamber upper end and a brew chamber lower end. A steam chamber is disposed below the brew chamber. A filtering base is removably inserted into the brew chamber. The filtering base has a diaphragm having a plurality of openings formed therein. The diaphragm is movable via fluid pressure between a first position in which the openings are open, thereby providing fluid communication between the brew chamber and the steam chamber and a second position in which the openings are closed, thereby precluding fluid communication between the brew chamber and the steam chamber.
Owner:ALPHA DOMINCHE HLDG INC
Apparatus and method for high temperature viscosity and temperature measurements
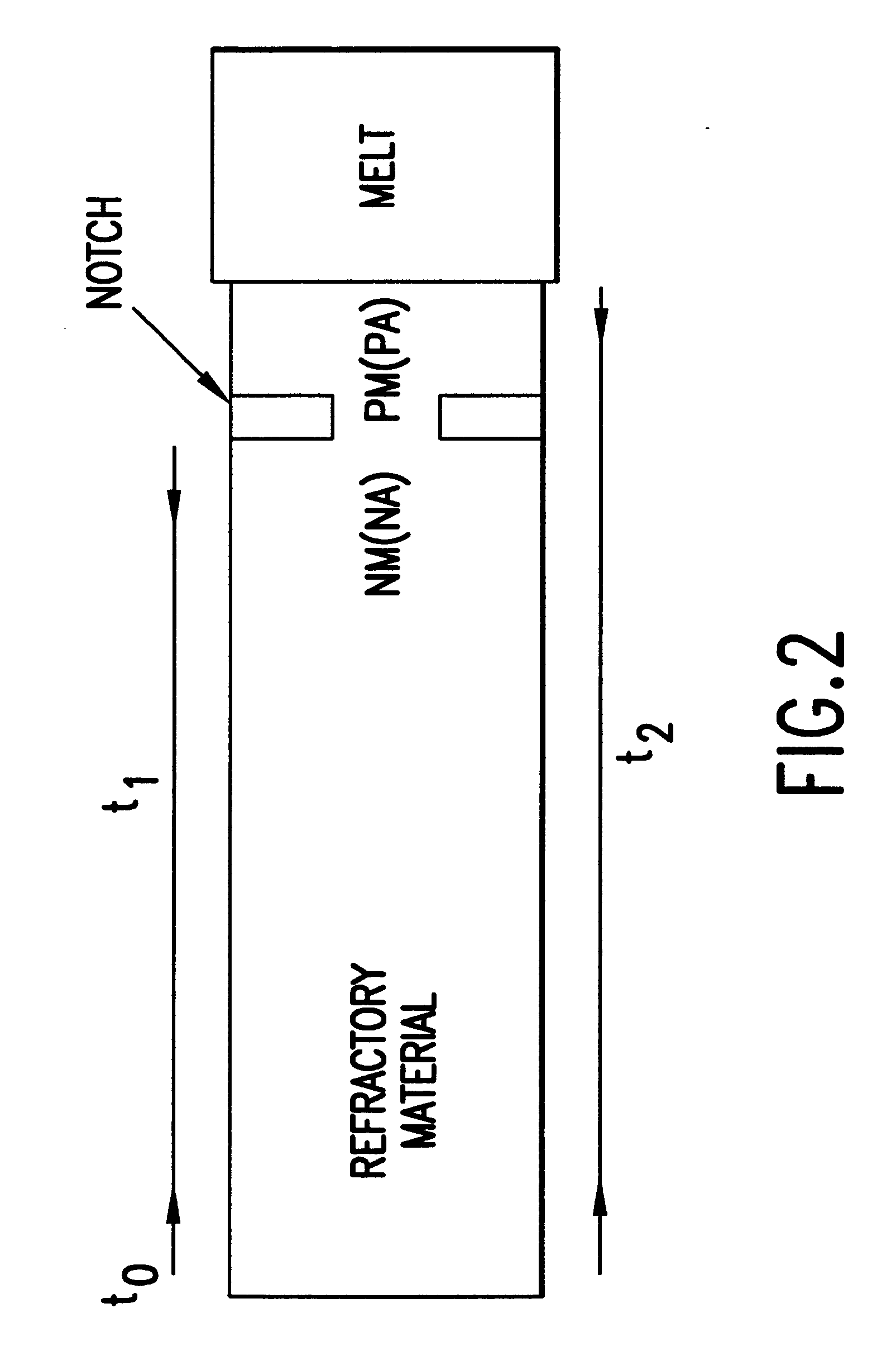
InactiveUS6296385B1Thermometer detailsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesRefractoryTransducer
A probe for measuring the viscosity and / or temperature of high temperature liquids, such as molten metals, glass and similar materials comprises a rod which is an acoustical waveguide through which a transducer emits an ultrasonic signal through one end of the probe, and which is reflected from (a) a notch or slit or an interface between two materials of the probe and (b) from the other end of the probe which is in contact with the hot liquid or hot melt, and is detected by the same transducer at the signal emission end. To avoid the harmful effects of introducing a thermally conductive heat sink into the melt, the probe is made of relatively thermally insulative (non-heat-conductive) refractory material. The time between signal emission and reflection, and the amplitude of reflections, are compared against calibration curves to obtain temperature and viscosity values.
Owner:MISSISSIPPI STATE UNIVERSITY
Hot beverage brewing system and use thereof
In described embodiments, a hot liquid extraction system includes a vessel, a controllable steam and water source external from the vessel which heats the liquid of the corresponding vessel, a filter assembly disposed within the vessel operable to filter and remove a solid from the brewed beverage, and a valve to dispense the filtered beverage from the base of the brew vessel. Some embodiments include one or more valves operable to regulate water flow and steam into the brewing vessel, and a filter operable to separate a brewed liquid from a flavor base and to remove a spent flavor base from the system. Some embodiments include processor control of the system, allowing for operation tailored to individual user requirements that might be downloaded to the processor through various wired and non-wired interfaces.
Owner:ALPHA DOMINCHE HLDG INC
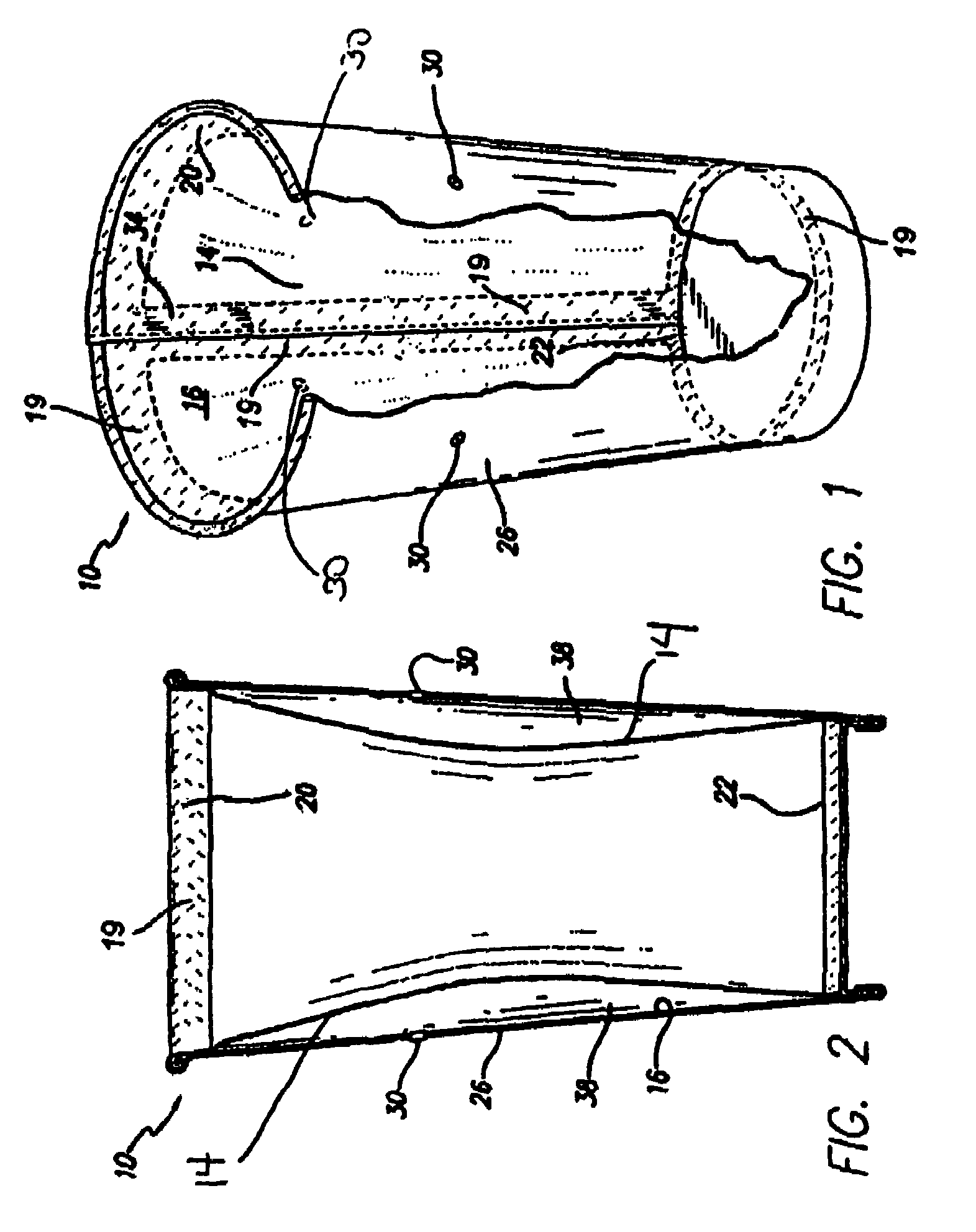
Method of making a container employing inner liner and vents for thermal insulation
InactiveUS20090170679A1Avoid layeringImprove insulation performanceMechanical working/deformationBoxes/cartons making machineryThermal insulationPaperboard
The present invention provides a container (10) suitable for providing insulation wherein the container has an inner shrink film (14) liner. The sidewalls of the container, which can be made from paperboard or other suitable material, are vented to allow ambient air to freely flow through the sidewall of the container during activation of the shrink film (14) with hot liquid or other suitable material. When the container is filled with material having a temperature of from about 130° F. to up to about 212° F., the shrink film (14) is activated and the container (10) provides excellent insulation, thereby allowing the container to be held in a consumer's hand for an extended period without causing burns or excessive discomfort. Method of making this container (10) are also provided.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Active heating of thermally insulated flowlines
InactiveUS6955221B2Cost-effective and reliableCost-effectiveInsulationFluid removalEngineeringHot liquids
Hydrocarbon liquids are transported from a subsea welihead to an above-surface hydrocarbon processing facility along a pipe-in-pipe flowline. The flowline is a pipe placed coaxially within an outer carrier pipe and the annulus between the pipes is filled with thermally insulating material. The hydrocarbon liquids have their temperature maintained above solidification / precipitation temperature by heat from an active heating system. Hot liquid, preferably hot water, is passed along the annulus, either along a single pipe or multiple pipes installed in the insulation-filled annulus, or along an inner annulus formed by a water pipe added concentrically around the hydrocarbon-transporting inner pipe, inside the outer insulation-filled annulus. The water or other suitable liquid can be heated in a heater at or adjacent the subsea wellhead, or by a water heater in the above-surface hydrocarbon processing facility.
Owner:SUBSEA 7 US
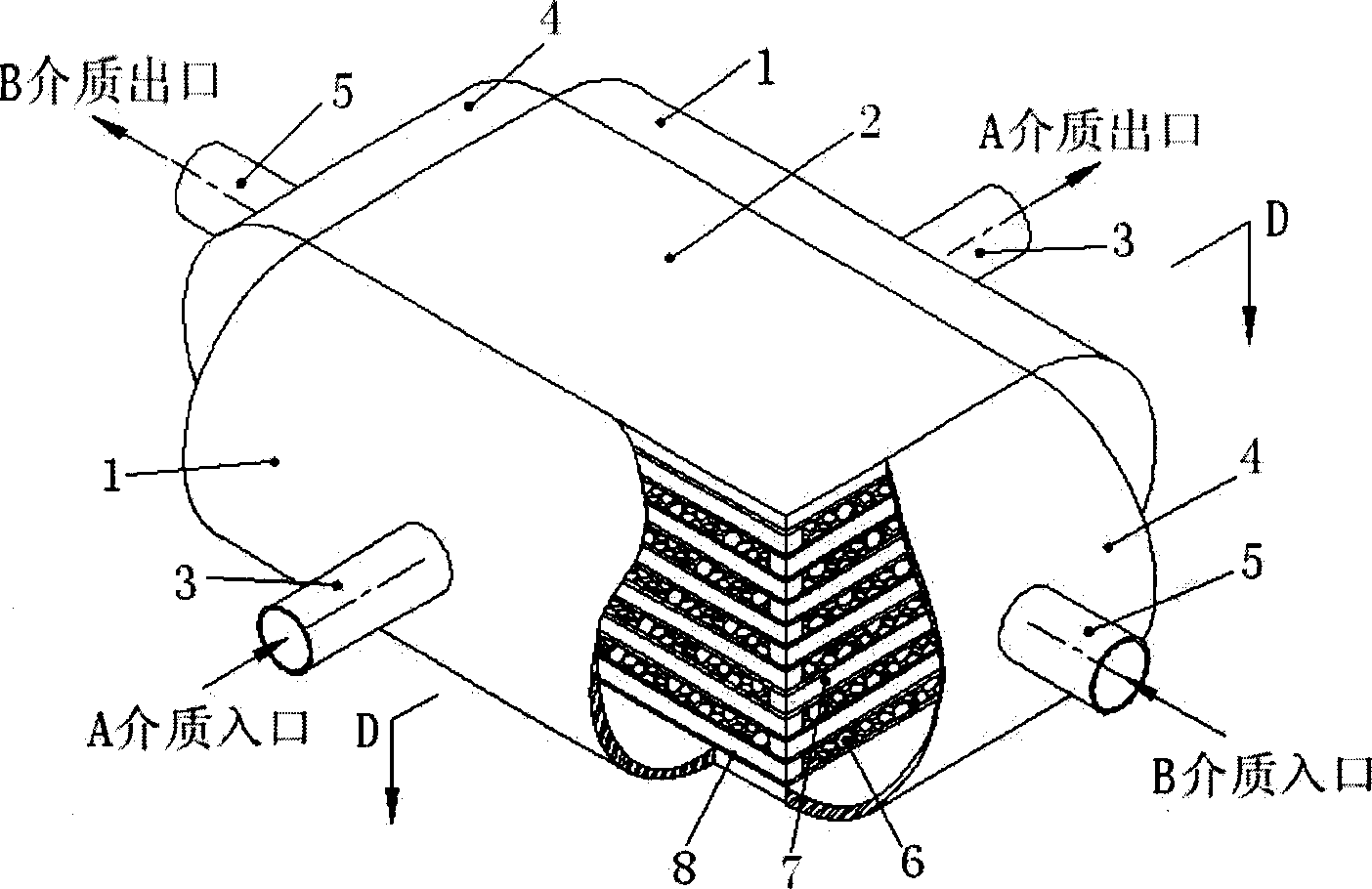
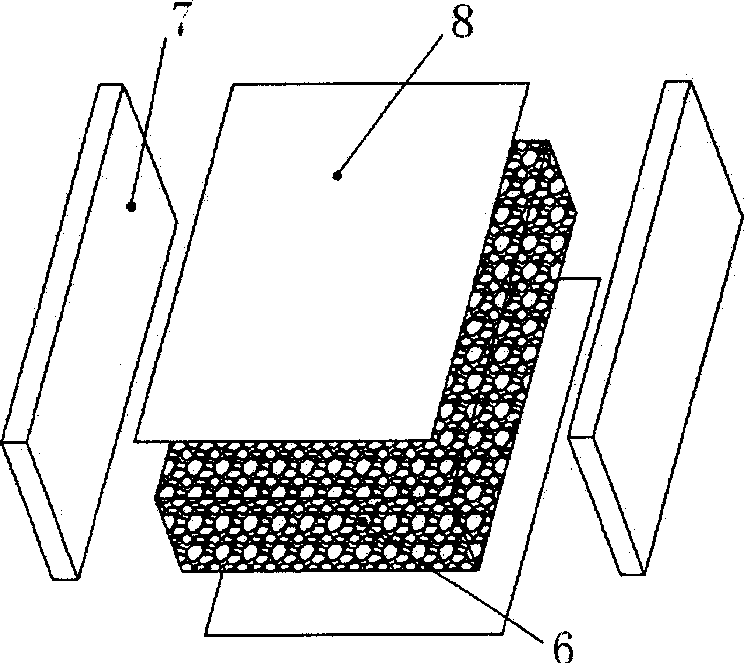
Band-bubble type heat-exchanger
InactiveCN1851377AImprove pressure bearing capacityDoes not create mutual leakage deficiencyLaminated elementsStationary plate conduit assembliesReticular formationEngineering
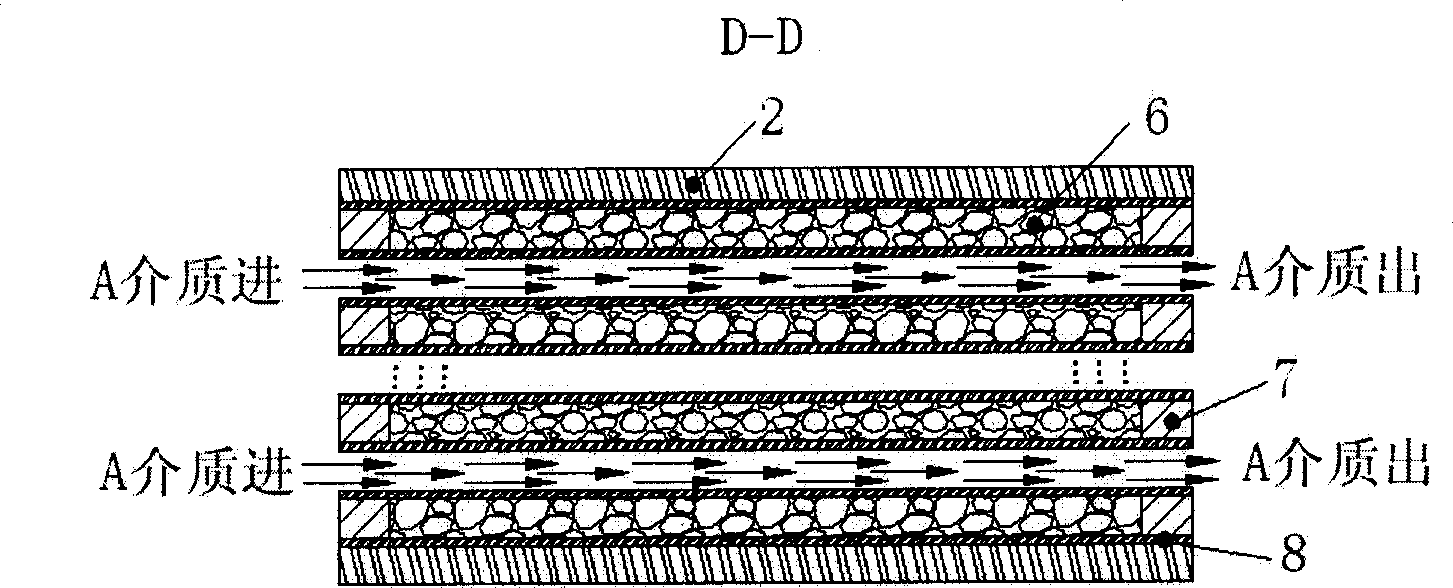
The invention relates to a heat exchanger with new type structure that has end plate, nipple, and core identity. And the end plate is set at the two sides of liquid channel. The core identity is formed by plural cool liquid channel and hot liquid channel. The liquid channel is formed by porous material of 3D solid reticular formation, and is sealed by guarantee strip. Catalyst coating layer is coated on the surface of the porous material liquid channel inner holes and make the exchanger has high heat efficiency.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Motor frame cooling with hot liquid refrigerant and internal liquid
InactiveUS20050235672A1Improve heat transfer performanceCompressorDomestic cooling apparatusElectric machineCooling effect
This invention presents the device and method for cooling electric machines with hot liquid refrigerant in a floating refrigerant loop and using an internal liquid such as oil for enhancing the cooling effects. The electric machine cooling apparatus has at least one refrigerant tube disposed in the electric machine. The refrigerant tube is in thermal communication with the electric machine. An internal liquid is disposed inside the frame of the electric machine. The internal liquid is in thermal communication with the electric machine and at least one refrigerant tube. The refrigerant is at least partially a hot liquid refrigerant supplied from a floating refrigerant loop.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Hot drink cup lid with cooling air-flow
Owner:PITTS CONSTANCE LINDA
High-purity pressure-maintaining deep sea hot liquid sampler
InactiveCN1453567ASolve water absorptionSolve the problem of non-sample seawater in the dead volume of the sampling valveWithdrawing sample devicesAutomatic controlEngineering
The present invention belongs to the field of marine technological instrument and equipment. One sample barrel with I-shaped sample cavity piston and one pressure accumulating barrel with pressure accumulating cavity piston are fixed to two ends of one containing body with axial small hole separately, to form pressure accumulating cavity, isolated water cavity, pre-sucking cavity and sample cavity. There are one one-way valve mechanism set in front of the sample cavity piston; varying-damp throttle mechanism comprising the throttle rod on pressure accumulating cavity piston and the small hole in the connecting body; valve plate, sampling valve and water sucking pipe in front end of the sample barrel; and inflating valve behind the pressure accumulating barrel. The present invention hashigh sample purity and automatically controlled sample speed, and is suitable for collecting deep sea hot liquid flow sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hot beverage brewing system and use thereof
In described embodiments, a hot liquid extraction system includes a vessel, a controllable steam and water source external from the vessel which heats the liquid of the corresponding vessel, a filter assembly disposed within the vessel operable to filter and remove a solid from the brewed beverage, and a valve to dispense the filtered beverage from the base of the brew vessel. Some embodiments include one or more valves operable to regulate water flow and steam into the brewing vessel, and a filter operable to separate a brewed liquid from a flavor base and to remove a spent flavor base from the system. Some embodiments include processor control of the system, allowing for operation tailored to individual user requirements that might be downloaded to the processor through various wired and non-wired interfaces.
Owner:ALPHA DOMINCHE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com