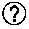Patents
Literature
32 results about "Mast cell stabilizer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mast cell stabilizers are chromone medications used to prevent or control certain allergic disorders. They block mast cell degranulation, stabilizing the cell and thereby preventing the release of histamine and related mediators. One suspected pharmacodynamic mechanism is the blocking of IgE-regulated calcium channels. Without intracellular calcium, the histamine vesicles cannot fuse to the cell membrane and degranulate.
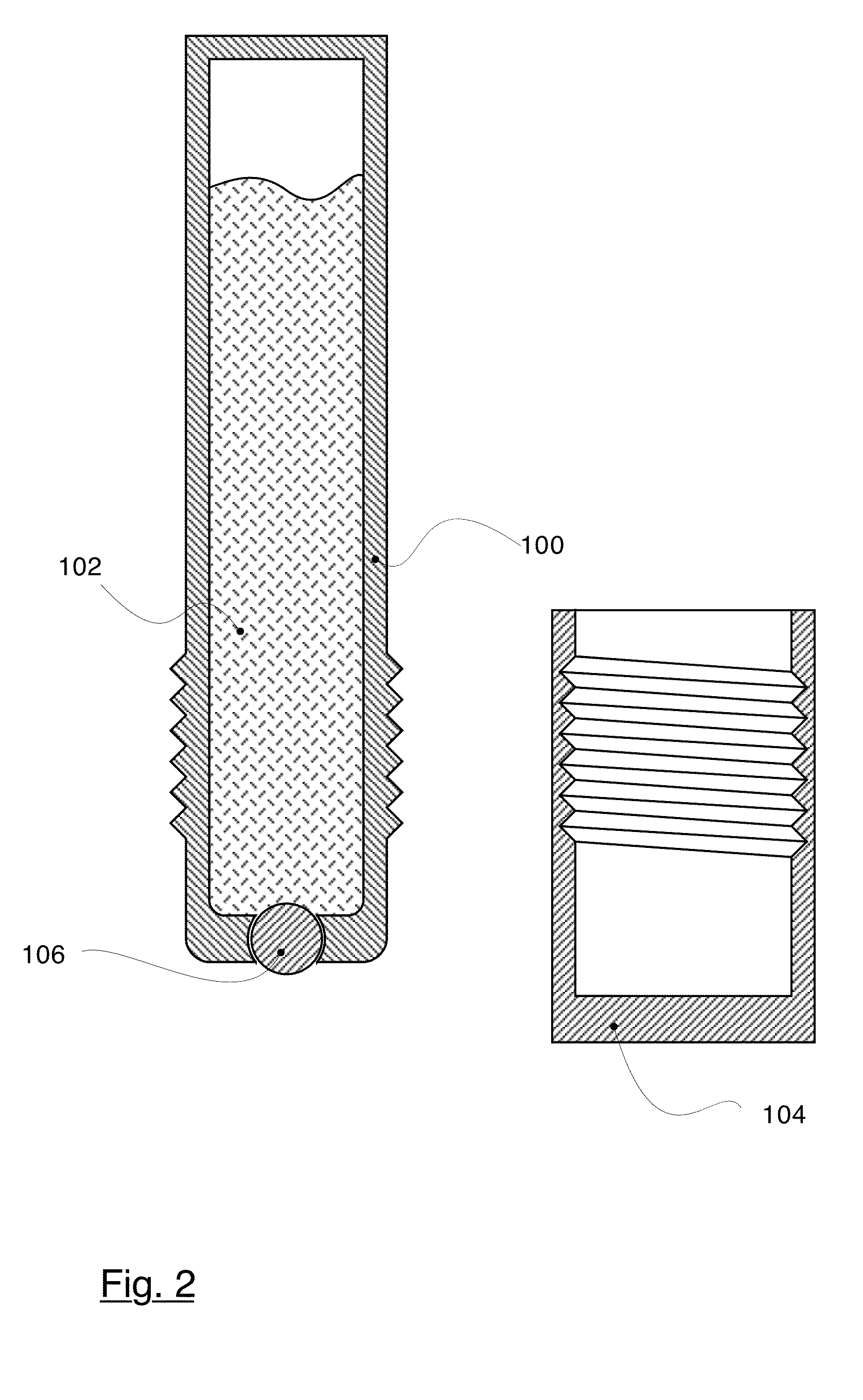
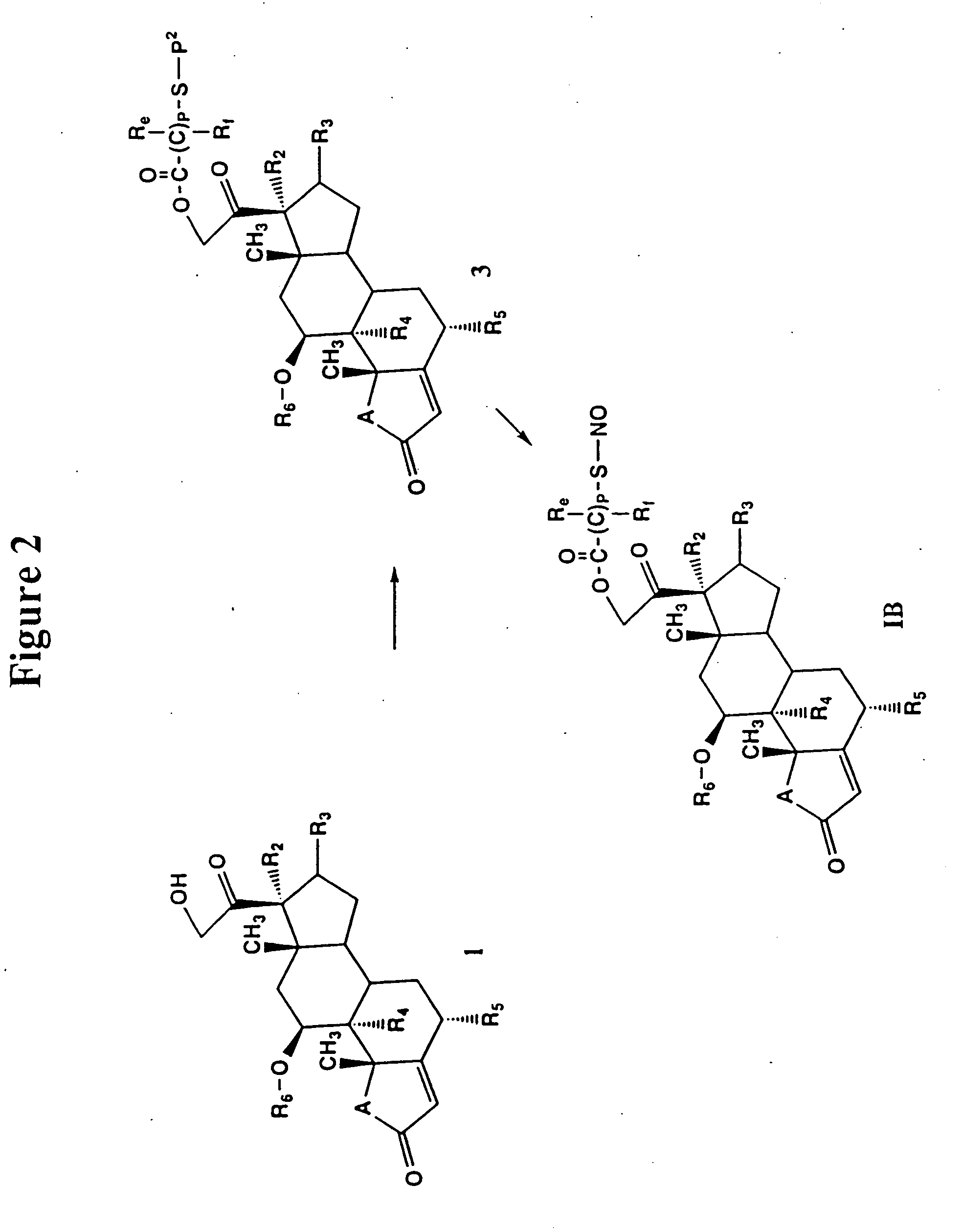
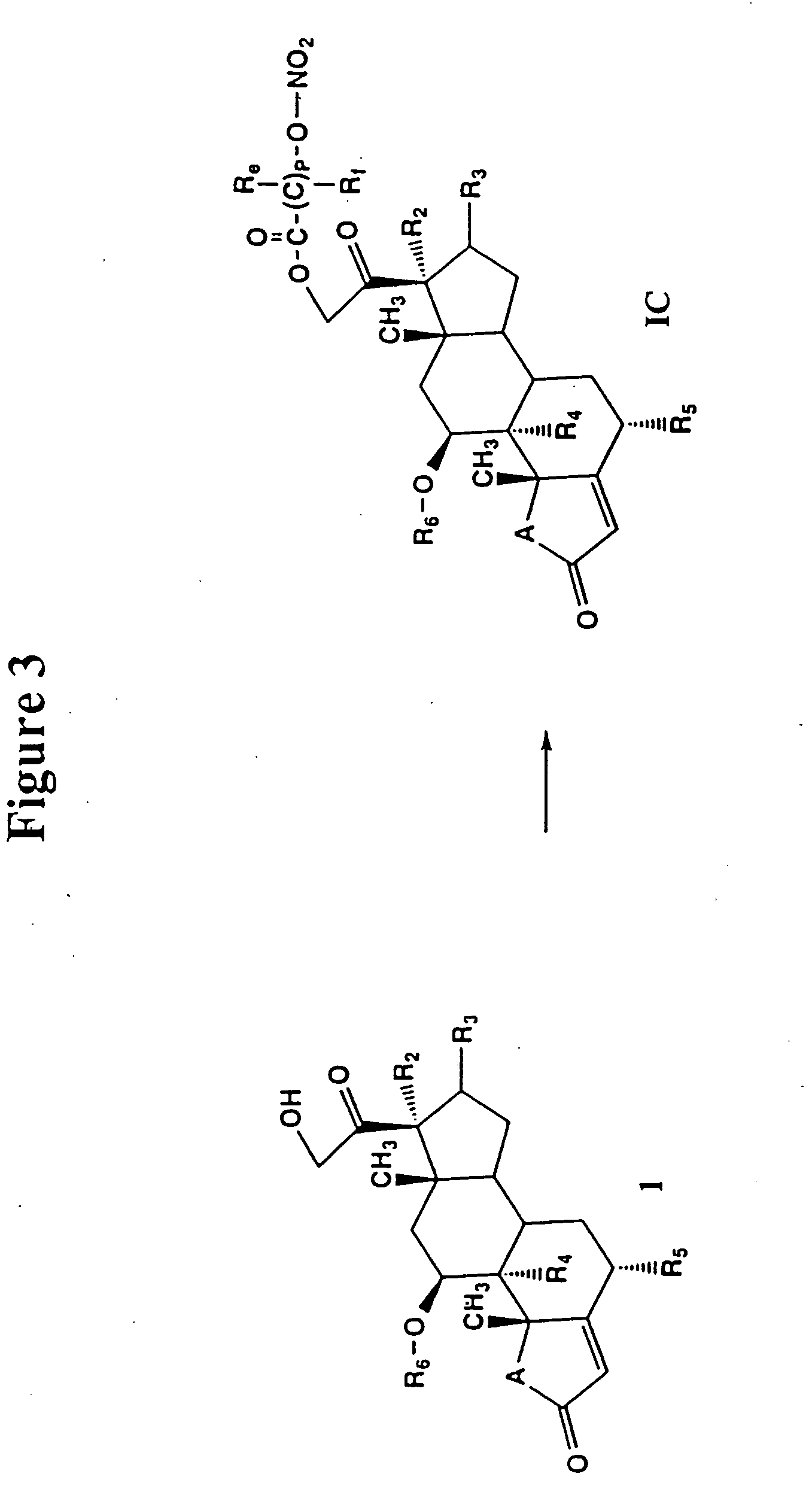
Use of connective tissue mast cell stabilizers to facilitate ocular surface re-epithelization and wound repair
InactiveUS20080139531A1Inhibition releaseOvercomes drawbackBiocideOrganic chemistryConjunctival woundDihydropyridine
Disclosed are methods of treating a wound in a subject that involve administering to the subject a pharmaceutically effective amount of a composition that includes one or more human connective tissue mast cell stabilizers, wherein administration of the composition results in treatment of the wound. In particular embodiments, the wound is an ophthalmic or dermal wound, such as a corneal epithelial defect, a conjunctival wound, or dermal abrasion. Administration, for example, may be by topical application of the composition to the ocular surface or skin. Exemplary mast cell stabilizers include olopatadine, variants of olopatadine, alcaftidine, derivatives of alcaftidine, dihydropyridines, and spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Owner:ALCON RES LTD
Compositions and methods for tolerizing the immune system to allergens
InactiveUS20160263212A1Reduce development riskReduce riskHydroxy compound active ingredientsAllergen ingredientsIMMUNE SUPPRESSANTSBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Compositions and methods can be used for tolerizing the immune system. The compositions can be physiologically acceptable and can include any of a wide variety of allergens that are designed to be administered in escalating doses to, for example, an infant. The compositions can include other active ingredients (e.g., one or more of a steroid, vitamin, mineral, vasodilator, hormone, decongestant, anticholinergic agent, leukotriene inhibitor, immunomodulator, mast cell stabilizer, expectorant, immune suppressant, anti-histamine, or anti-inflammatory agent) and / or a carrier.
Owner:STALLERGENES GREER PLC
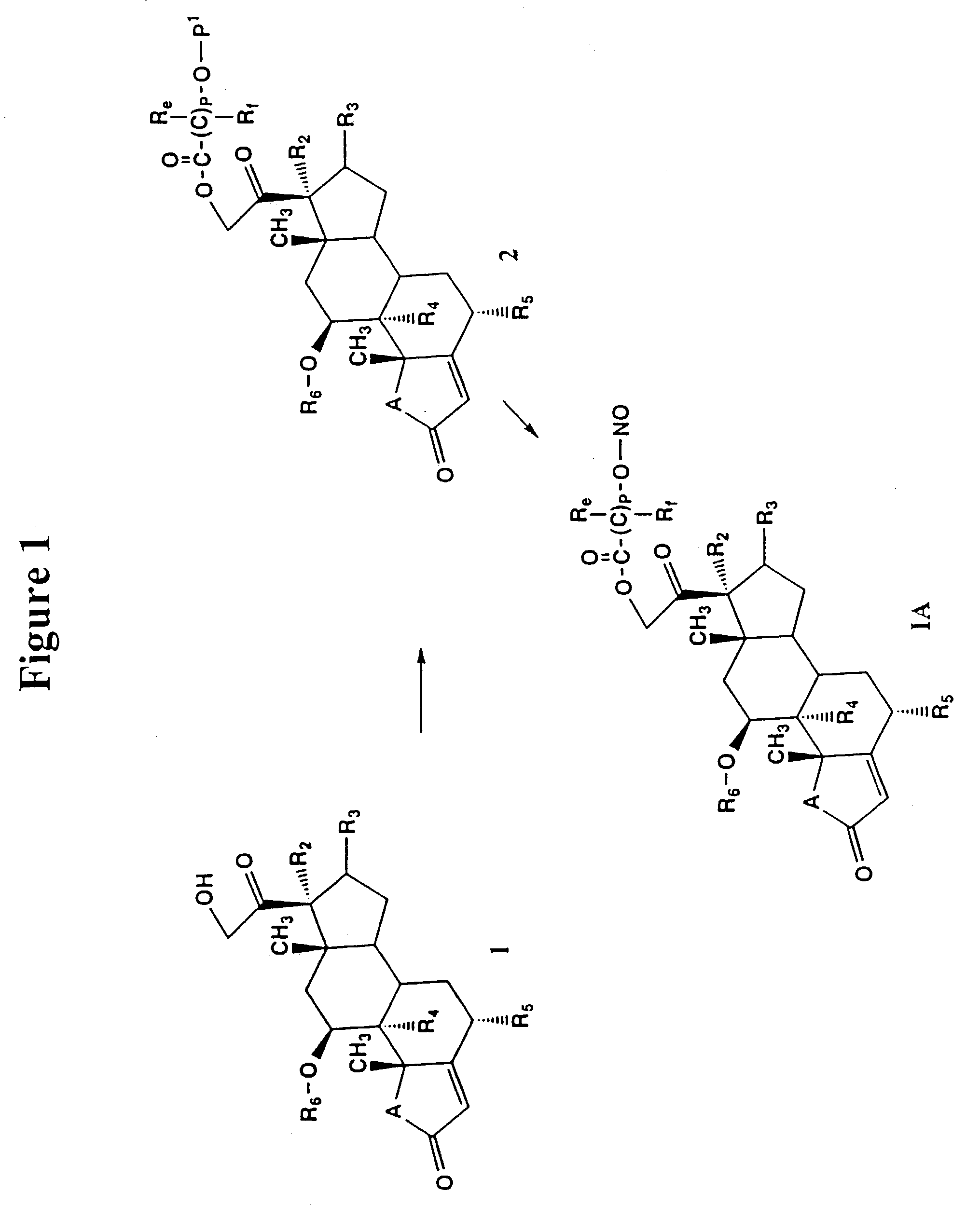
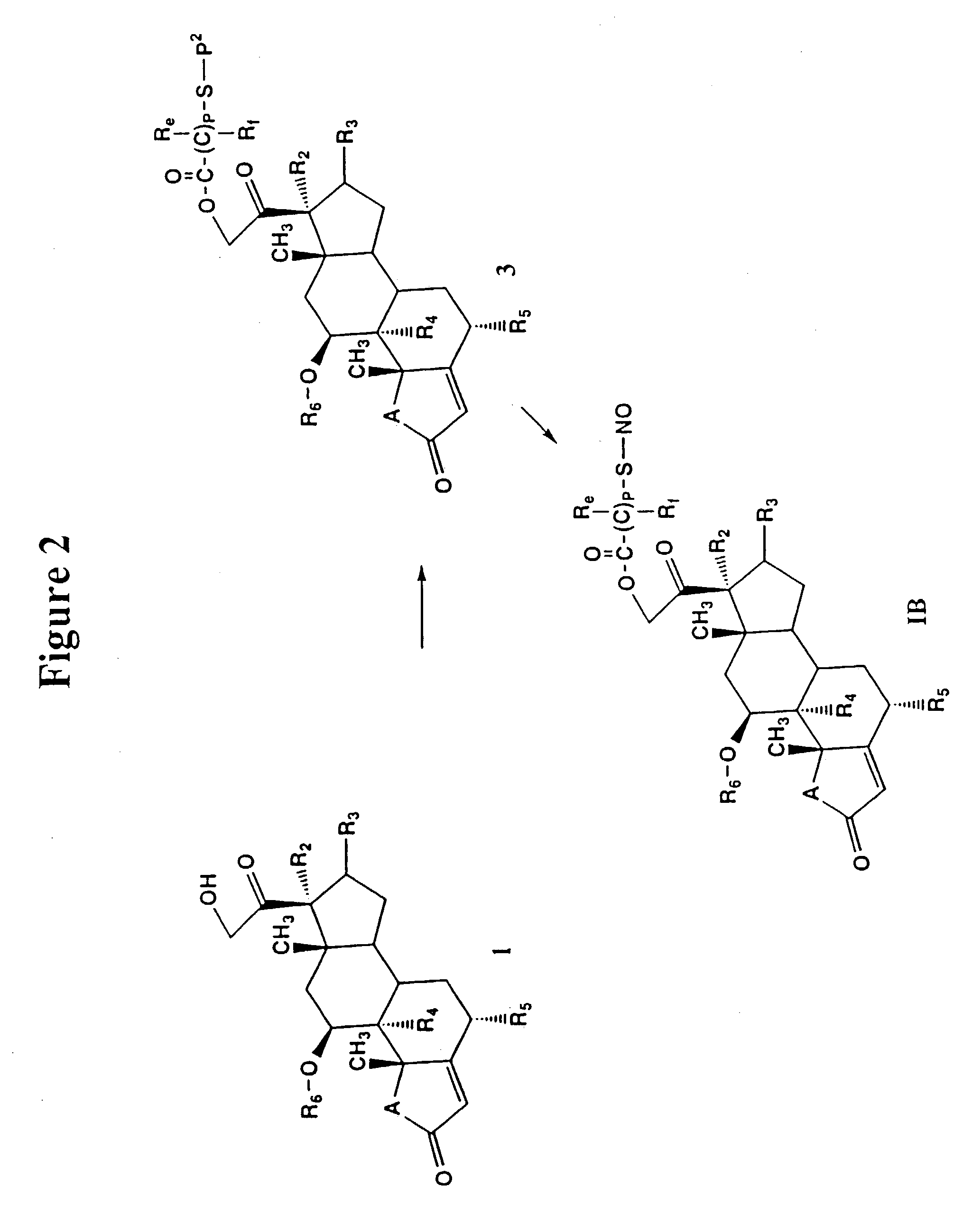
Nitrosated and nitrosylated compounds and compositions and their use for treating respiratory disorders
Disclosed are (i) compounds of a steroid, a β-agonist, an anticholinergic, a mast cell stabilizer and a phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor directly or indirectly linked to a NO or NO2 group or a group which stimulates endogenous production of NO or EDRF in vivo; (ii) compositions of steroids, β-agonists, anticholinergics, mast cell stabilizers and PDE inhibitors, which can optionally be substituted with at least one NO or NO2 moiety or a group which stimulates endogenous production of NO or EDRF in vivo, and a compound that donates, transfers or releases nitric oxide as a charged species, i.e., nitrosonium (NO+) or nitroxyl (NO−), or as the neutral species, nitric oxide (NO.) or that stimulates endogenous production of NO or EDRF in vivo; and (iii) uses for them in preventing and / or treating respiratory disorders.
Owner:ARBOR PHARMA LLC
Treating eczema with a combination of isotonic saline ocean(R) and nasal mast cell stabilizers
InactiveUS6596284B1Inhibits the release of histamineUseful in treatmentBiocideInorganic non-active ingredientsEczematous DisordersAqueous solution
The present invention relates to the prevention and treatment of atopic dermatitis and treatment of atopic dermatitis and other eczematous disorders by application of topical mast cell stabilizers including cromolyn sodium, nedocromil or lodoxamide, in a vehicle of a buffered isotonic saline solution (OCEAN(R)).
Owner:BAUSCH HEALTH IRELAND LTD
Methods
InactiveUS20100166804A1Ameliorating side effectSevere reactionBiocideAllergen ingredientsMetaboliteProphylactic treatment
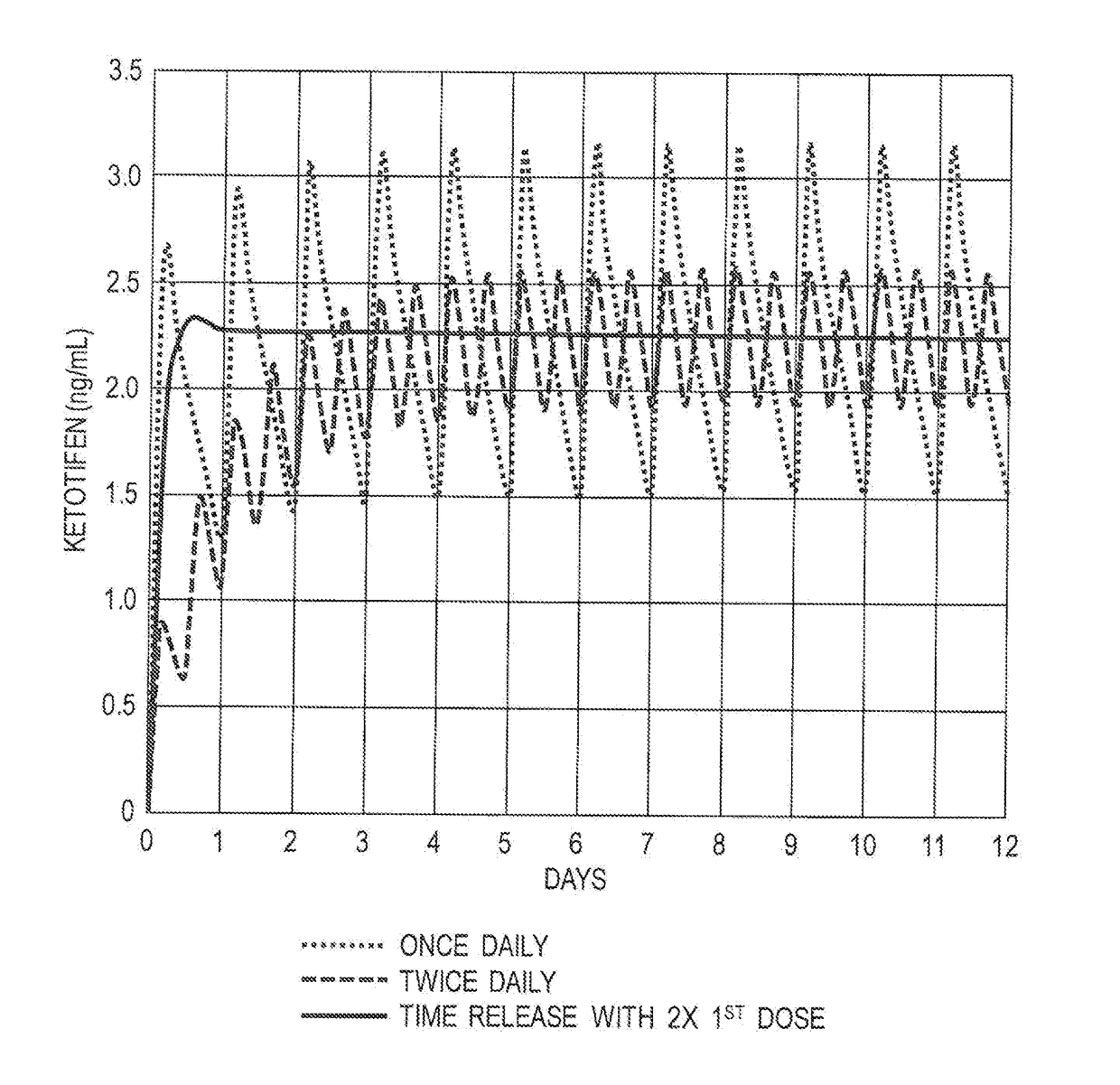
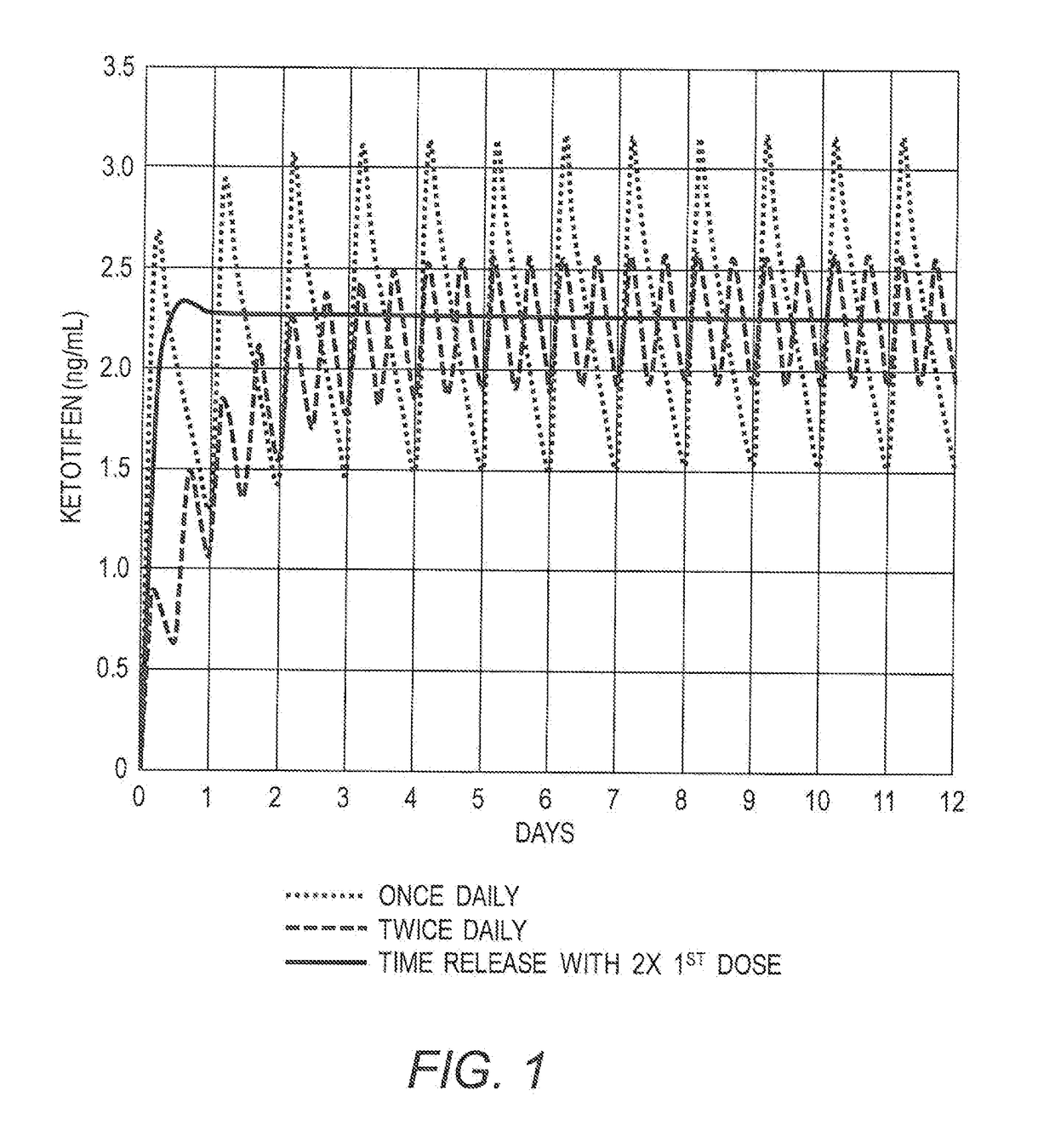
The present invention relates to methods of prophylactically treating, reducing, delaying or controlling severe allergic reaction, e.g., to food and / or hymenoptera allergen, e.g. peanut allergen or bee venom allergen, in patients at risk of systemic anaphylaxis, e.g., patients receiving allergen desensitization therapy, through the use of a mast cell stabilizer, e.g., ketotifen and / or its metabolites or derivatives in free or pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts thereof. The invention further provides methods to desensitize a patient to one or more allergens comprising administering (i) one or more allergen to induce tolerance and (ii) one or more mast cell stabilizers in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:MASTCELL PHARMA
Methods for the treatment of systemic disorders treatable with mast cell stabilizers, including mast cell related disorders
Owner:RESPIVANT SCI GMBH
Methods and treatment for allergies and inflammation associated with gastrointestinal diseases
InactiveUS20110206659A1Avoid developmentInhibit inflammationBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsAntigenProphylactic treatment
Methods of the prophylaxis of the development of allergy in a patient at risk of sensitization to an antigen(s) or allergen(s) due to impaired gastrointestinal functions include administering a mast cell inhibitor, e.g., ketotifen, e.g., ketotifen fumarate. Methods for prophylactically treating, reducing, delaying or controlling gastrointestinal disorders include administering a mast cell stabilizer, e.g., ketotifen to a patient in need thereof. Pharmaceutical preparation, composition for use in methods described, are also disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of prophylaxis or treating gastrointestinal and esophageal inflammation, and methods for the prophylaxis of the development of additional allergies to a newly introduced substance in a patient with a preexisting allergy. Such methods include delivery of a mast cell stabilizer, e.g., ketotifen. Oral and topical administration are contemplated within the scope of the methods.
Owner:MASTCELL PHARMA
Treatment and prevention of cardiovascular disease using mast cell stabilizers
The present invention is directed to methods of treating or preventing the development of cardiovascular disease by administering compounds that stabilize mast cells. In addition, it includes pharmaceutical compositions which have both a mast cell stabilizer and instructions regarding the use of the stabilizer in treating or preventing cardiovascular disease. The methods and compositions will be of particular value for preventing aneurysms of the abdominal aorta in individuals with atherosclerosis, diabetes, hypertension or a family history of aneurysms.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Method for the treatment and/or prevention of oral allergic symptions of the lips due to oral contact with a food allergen
InactiveUS20130030009A1Increase contact timePromote absorptionBiocideOrganic chemistryAllergic symptomsAllergic reaction
A method of applying a topical preparation of at least one of a mast cell stabilizer, an antihistamine, and a leukotriene inhibitor is disclosed for prevention and / or treatment of oral allergy syndrome of the lips, including lip itchiness and / or swelling. For example, topical application of Cromolyn Sodium to the lips can be used to prevent and / or treat allergic reaction to consumption or other contact with raw fruits and / or raw vegetables. The topical administration can be performed by using applicator devices that apply at least one of a mast cell stabilizer and an antihistamine in the form of a liquid, or a gel, or a butter, or a wax-like solid, or a liposome suspension. Applicator devices can include at least one of: a roller, a brush, a sponge, a swab, a tube, a lipstick. The taste of the at least one of a mast cell stabilizer and an antihistamine can be masked by flavors.
Owner:HARISH ZIV
Mast cell stabilizers for treatment of hypercytokinemia and viral infection
ActiveUS20180072796A1Little of responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsViral infectionCytokine
Owner:EMERGO THERAPEUTICS INC
Mast cell stabilizers in the treatment of obesity
ActiveUS20090093511A1Lose weightAvoid weight gainBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsObesityMast cell stabilizer
The present invention is directed to methods of treating or preventing the development of obesity by administering compounds that stabilize mast cells. In addition, it includes pharmaceutical compositions which have both a mast cell stabilizer and instructions regarding the use of the stabilizer in treating or preventing obesity.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Compound capable of inhibiting mast cell degranulation and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106632378AInhibition releaseInhibition of degranulationOrganic chemistry methodsRespiratory disorderDiseaseStructural formula
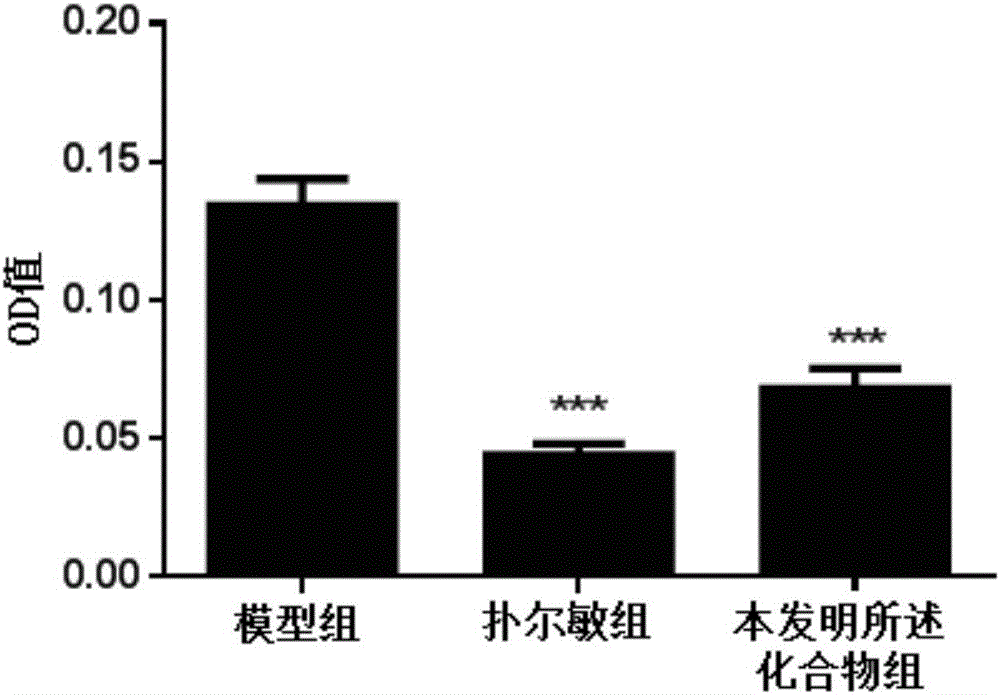
The invention discloses a compound capable of inhibiting mast cell degranulation and a preparation method and application thereof. The molecular formula of the compound is C22H2606, the molecular weight is 386.17, and the chemical structural formula is shown in the description. As proved by research results, the compound can significantly inhibit the release of beta-hexane in mast cells at the inhibition rate of 85.57 percent, has a significant inhibitory effect on mast cell degranulation, is expected to be used as an active ingredient in the preparation of a medicament for inhibiting mast cell mast cell degranulation, can be further used as an active ingredient in the preparation of a mast cell stabilizer medicament and the preparation of a medicament for preventing or / and treating allergic diseases, has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Mast cell stabilizers for treatment of chronic inflammatory conditions
ActiveUS20200215049A1Little of responseOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticBiochemistryBasophils+Mast cells
The present invention relates to methods for treating chronic inflammatory conditions using a mast cell stabilizing compound. The invention further relates to compositions and dosage forms comprising mast cell stabilizing agents.
Owner:EMERGO THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and treatment for allergies and inflammation associated with gastrointestinal diseases
ActiveUS20140302153A1Increase topical resident timeLonger local effectBiocideAntipyreticAntigenProphylactic treatment
Methods of the prophylaxis of the development of allergy in a patient at risk of sensitization to an antigen(s) or allergen(s) due to impaired gastrointestinal functions include administering a mast cell inhibitor, e.g., ketotifen, e.g., ketotifen fumarate. Methods for prophylactically treating, reducing, delaying or controlling gastrointestinal disorders include administering a mast cell stabilizer, e.g., ketotifen to a patient in need thereof. Pharmaceutical preparation, composition for use in methods described, are also disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of prophylaxis or treating gastrointestinal and esophageal inflammation, and methods for the prophylaxis of the development of additional allergies to a newly introduced substance in a patient with a preexisting allergy. Such methods include delivery of a mast cell stabilizer, e.g., ketotifen. Oral and topical administration are contemplated within the scope of the methods.
Owner:MASTCELL PHARMA
Sublingual immunotherapy with reduced oral itchiness
InactiveUS20140370086A1Consistent levelReduced and substantially no localized oral itchinessAllergen ingredientsPill deliveryCoated tabletsPatient compliance
Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) with reduced oral itchiness is disclosed. The improved sublingual immunotherapy combines a monotonically increasing dose of allergen, along with a constant dose of mast cell stabilizer, thereby substantially avoiding the oral itchiness and other uncomfortable adverse reactions typically experienced with SLIT, which can improve patient compliance. An antihistamine and / or a leukotriene inhibitor can also be added along with the mast cell stabilizer. Multi-layer and / or coated tablets, and flexible paired ampoules with special features to advantageously time the dose of the allergen relative to the dose of the mast cell stabilizer, have been provided to effectively administer the improved sublingual immunotherapy in a highly convenient manner. Methods, preparations, and apparatuses for administration of SLIT, apparatus for sequentially dispensing, methods for producing a sequence of allergen doses with reduced adverse reactions, methods for producing a stock solution for dilution, and methods for producing cooperative pre-filled vials are also disclosed.
Owner:HARISH ZIV
Mast cell stabilizers in the treatment of obesity
ActiveUS8445435B2Lose weightAvoid weight gainBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsObesityMast cell stabilizer
The present invention is directed to methods of treating or preventing the development of obesity by administering compounds that stabilize mast cells. In addition, it includes pharmaceutical compositions which have both a mast cell stabilizer and instructions regarding the use of the stabilizer in treating or preventing obesity.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
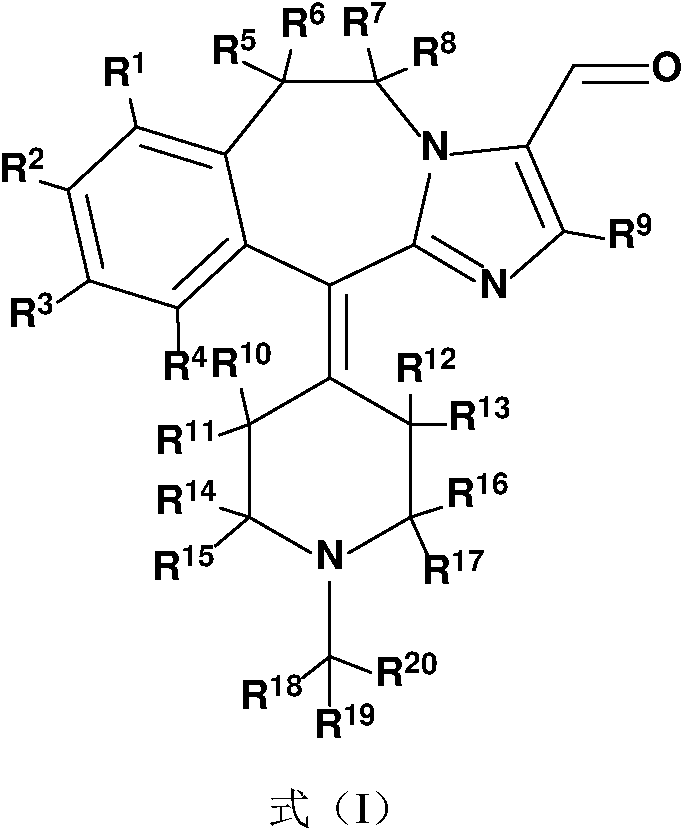
A substituted fused imidazole ring compound and its pharmaceutical composition
ActiveCN108368118BIncrease drug concentrationImprove securitySenses disorderOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical drugHistamine Receptor Antagonists
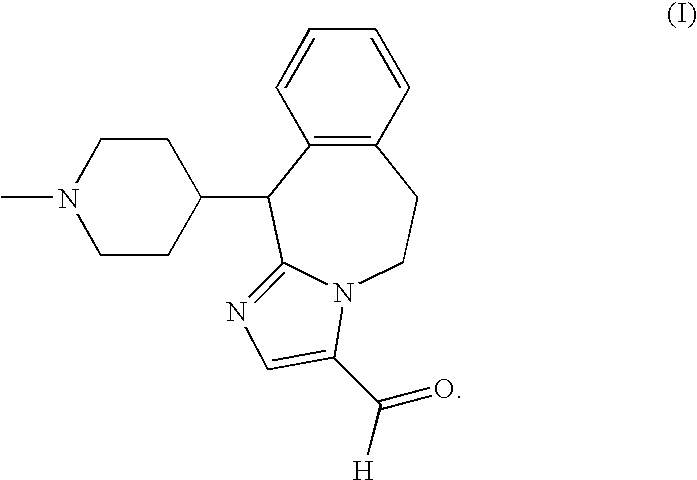
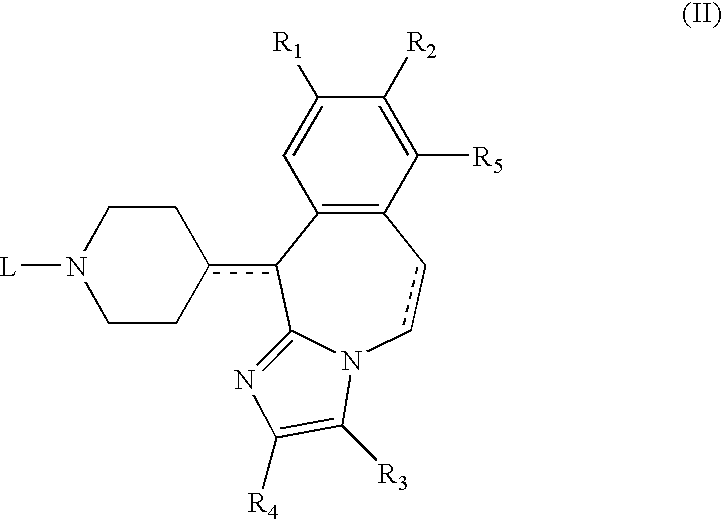
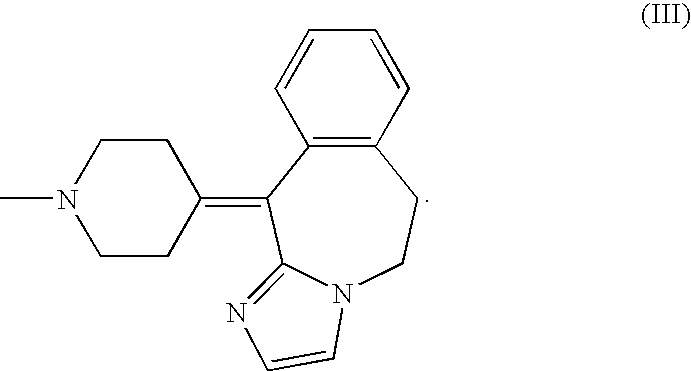
The invention relates to a substituted condensed imidazole ring compound, a composition containing the compound and applications thereof. Specifically, the invention discloses a fused imidazole ring compound represented by formula (), or a pharmaceutical composition of its crystal form, pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug, stereoisomer, hydrate or solvate. The compound of the present invention can be used as a histamine H1-receptor antagonist and a mast cell stabilizer, which can inhibit the release of histamine from mast cells and prevent the action of histamine, thereby alleviating allergic reactions. Formula (I).
Owner:SHENZHEN TARGETRX INC
Methods of treating cytokine release syndrome
PendingUS20220218652A1Improve throughputLimit deliveryNervous disorderOrganic chemistryTumor SyndromePharmaceutical medicine
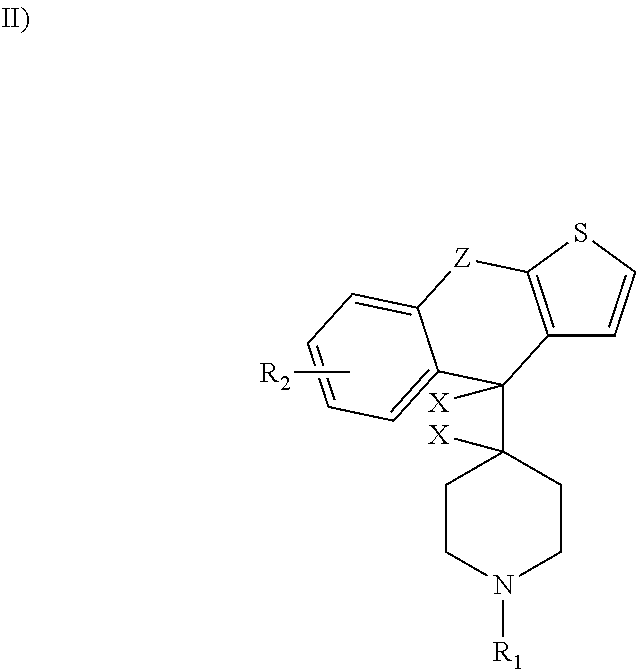
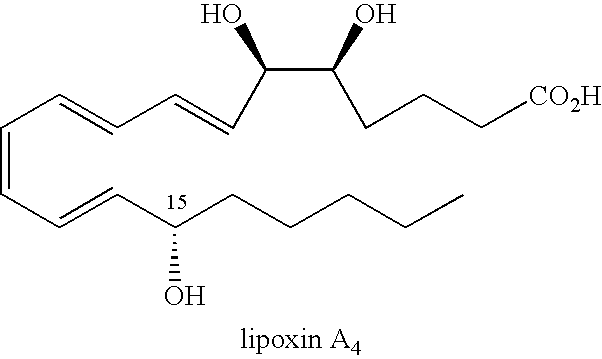
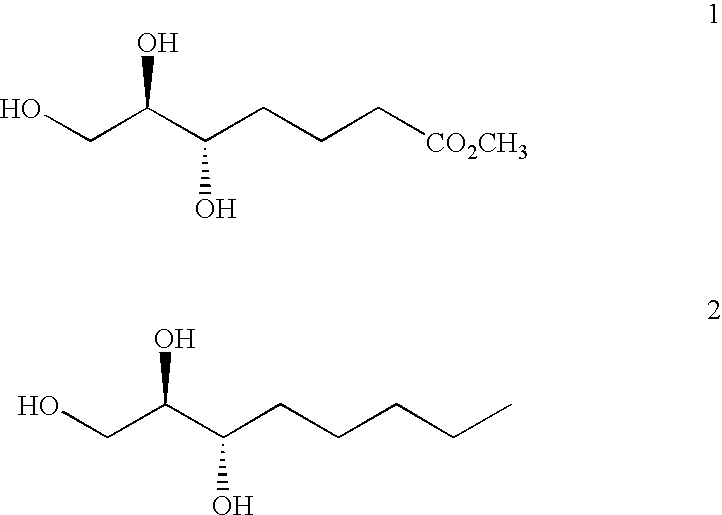
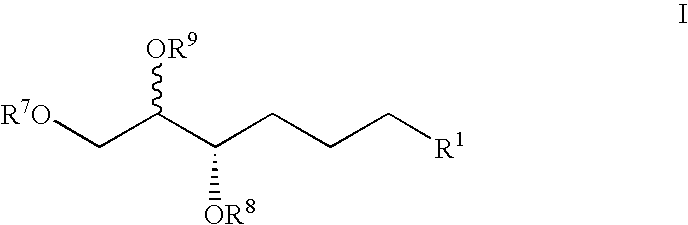
The present disclosure relates to a method of treating at least one Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS), cancer-related cognitive impairment, Infusion Reaction Syndrome (IRS), Capillary Leak Syndrome (CLS), Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS), Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS), Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS), Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS), Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD), Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), sepsis, Ebola, avian influenza, smallpox, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS), and Immune-related Adverse Events Syndrome (IrAES) in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering a mast cell stabilizer or a compound of Formula I or Formula II: Formula I, Formula II, wherein R1 is halogen, OH, or —OC(O)C1-5alkyl R2 and R3 are each independently selected from CO2R4 or CH2OR5; R4 is i L, Na, K, H, C1-5alkyl, or —CH2CO(C1-5alkyl); and R5 is H or C(O)(C1-5alkyl), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:AZTHERAPIES INC +1
Cromolyn Metal Complexes as enhanced pharmaceutical formulations and method of preparing the same
PendingUS20210338628A1Improve solubilityReduce penetrationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsDissolutionCrystallinity
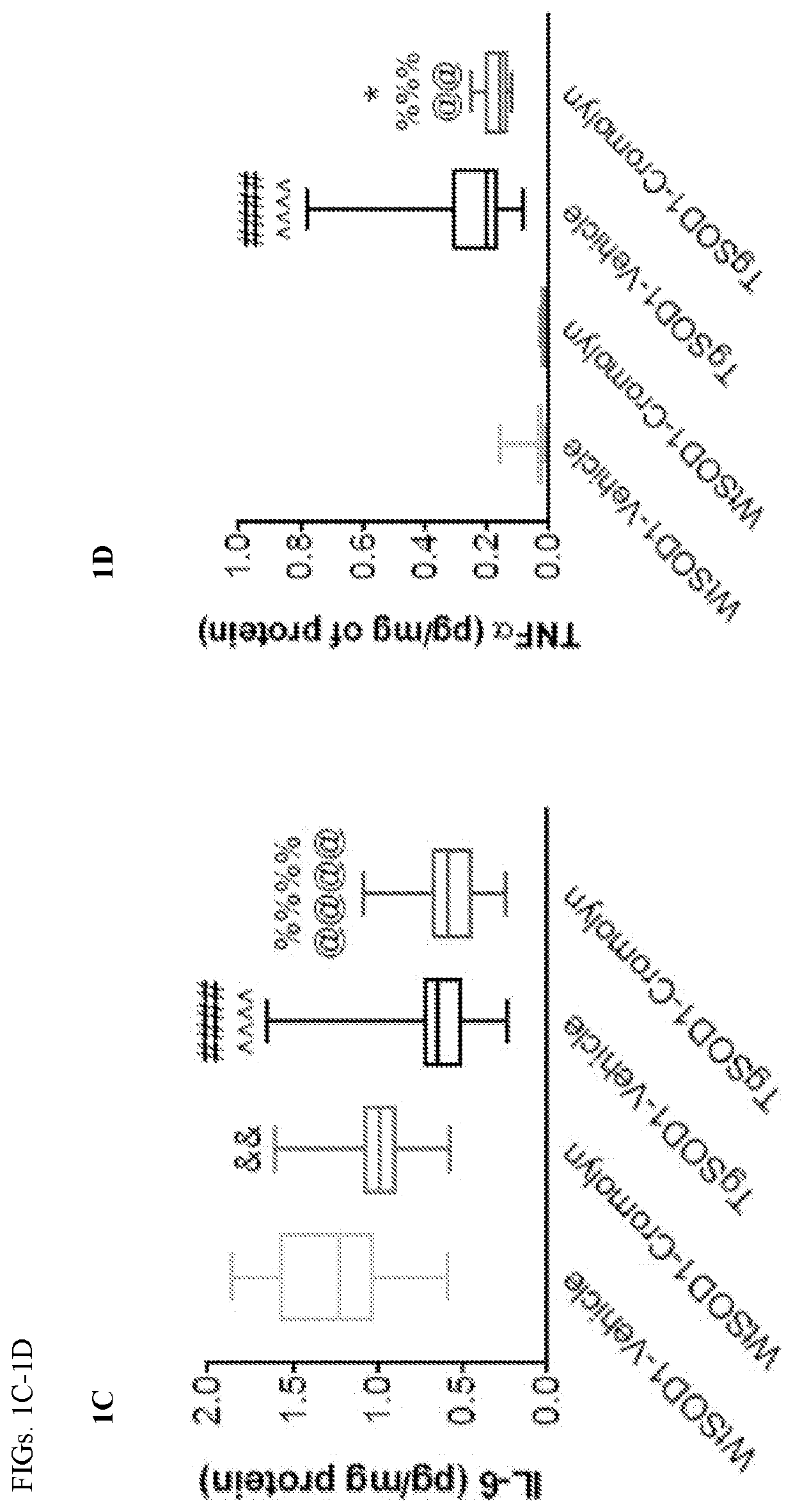
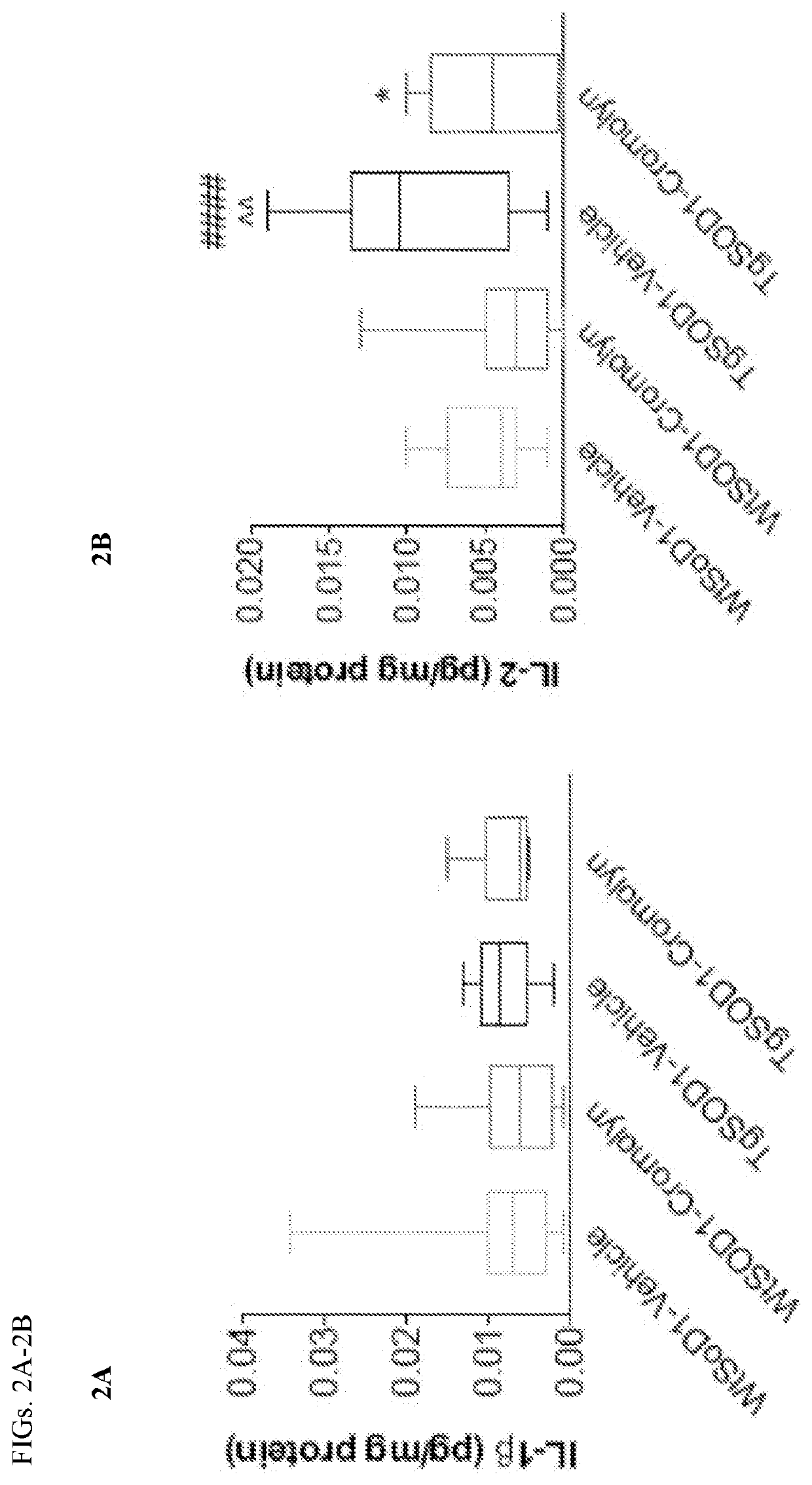
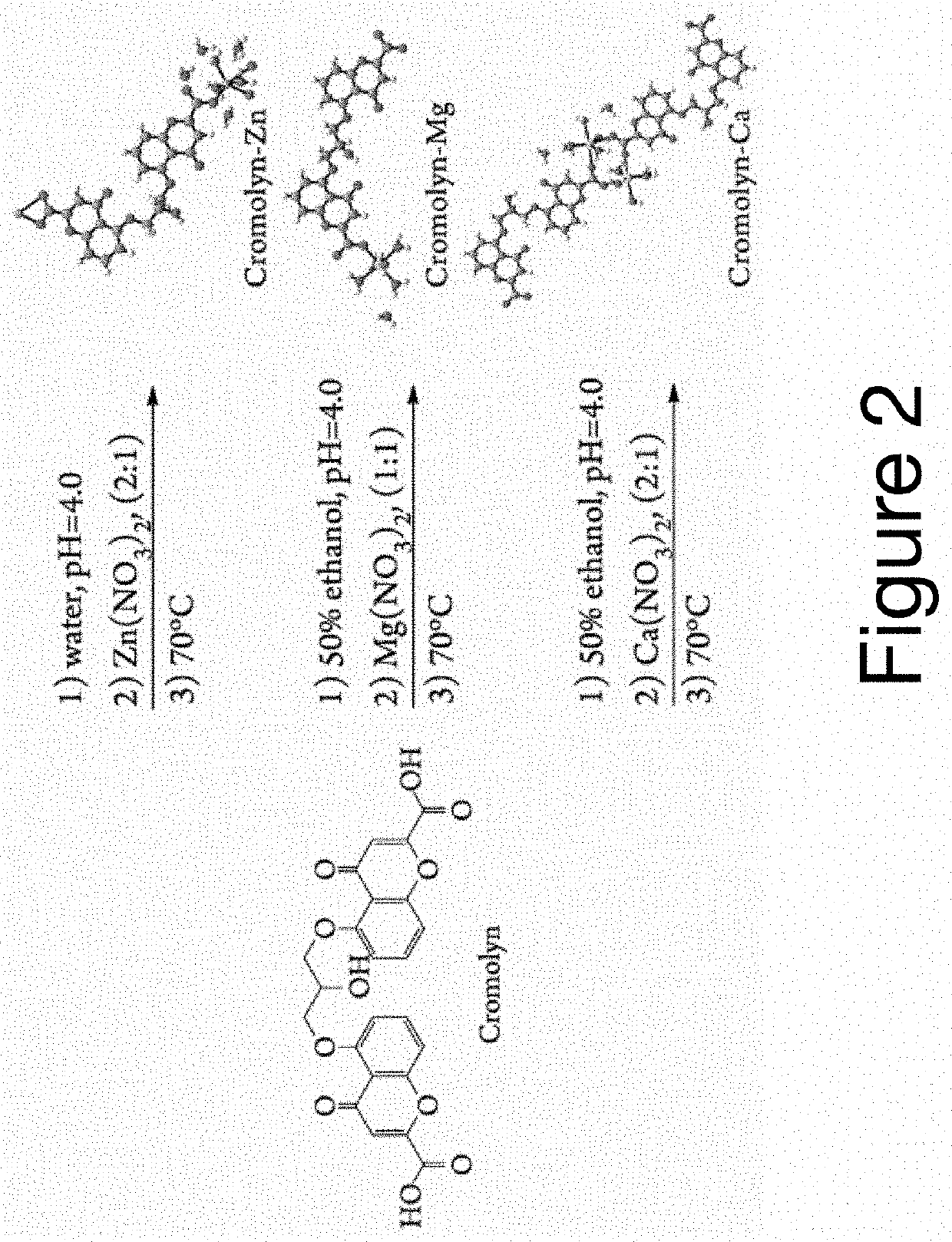
A series of pharmaceutical metal complexes (pMCs) were produced and characterized using the mast cell stabilizer, cromolyn, and bioactive metal ions (Zn+2, Mg+2, and Ca+2). Three novel pMCs, Cromolyn-Zn, Cromolyn-Mg, and Cromolyn-Ca were formed through reactions under controlled temperature and pH conditions. TGA demonstrated that these metal complexes showed an enhanced thermal stability due to the strong coordination with the ligand, cromolyn. PXRD data indicates a high degree of crystallinity as well as a unique packing arrangement for each pMCs. SEM analysis showed materials with well-defined morphologies while EDS presented elemental evidence for the unique composition of each pMCs. The crystal structure for these materials was elucidated through SCXRD, and a variety of binding modes and packing motifs were found within each respective metal complex. Only 2D structures were achieved under the conditions studied. Dissolution studies show high stability and slow degradation for the metal complexes, while a higher dissolution was observed for the drug compound in PBS. Neither CS nor the pMCs dissolved significantly in FaSSGF at 37° C.
Owner:LOPEZ MEJIAS VILMALI +3
Novel inhalant containing glucocorticoid and bronchodilator
ActiveCN102247597BLittle side effectsGood curative effectGranular deliveryRespiratory disorderStimulantGlucocorticoid
Owner:TIANJIN JINYAO GRP
A kind of purposes of abietane type diterpenoids
ActiveCN109419787BSuppress allergiesAnti-allergicOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderDiseasePharmacy
The invention discloses an application of abietane type diterpene compounds. The formula of the abietane type diterpene compounds is represented by the formula I. At least one of the compounds represented by the formula I, and hydrates, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, tautomer, stereoisomer, and precursor thereof is taken as an active component to prepare drugs or health care food for inhibiting mast cell de-granulation. The results of experiments show that the compounds represented by the formula I can prominently inhibit mast cell de-granulation, can be used as an active component to prepare drugs or health care food for inhibiting mast cell de-granulation, further can be used as an active component to prepare a mast cell stabilizer, and can be used to prepare drugs or health care food for preventing or / and treating allergic diseases caused by mast cell de-granulation.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Methods for reducing abnormal scar formation
PendingUS20210299116A1Reducing scar collagen abundance scar scarReducing scar scar width scarCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsProlyl HydroxylasesHif prolyl hydroxylase
This disclosure is directed to methods of reducing scar collagen abundance, scar width, and scar tissue contracture comprising administering to a subject in need of such treatment an effective amount of a mast cell stabilizer, or an effective amount of a HIF prolyl hydroxylase domain inhibitor, or an effective amount of a combination of a mast cell stabilizer and a HIF prolyl hydroxylase domain inhibitor.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Suppression of postoperative ileus
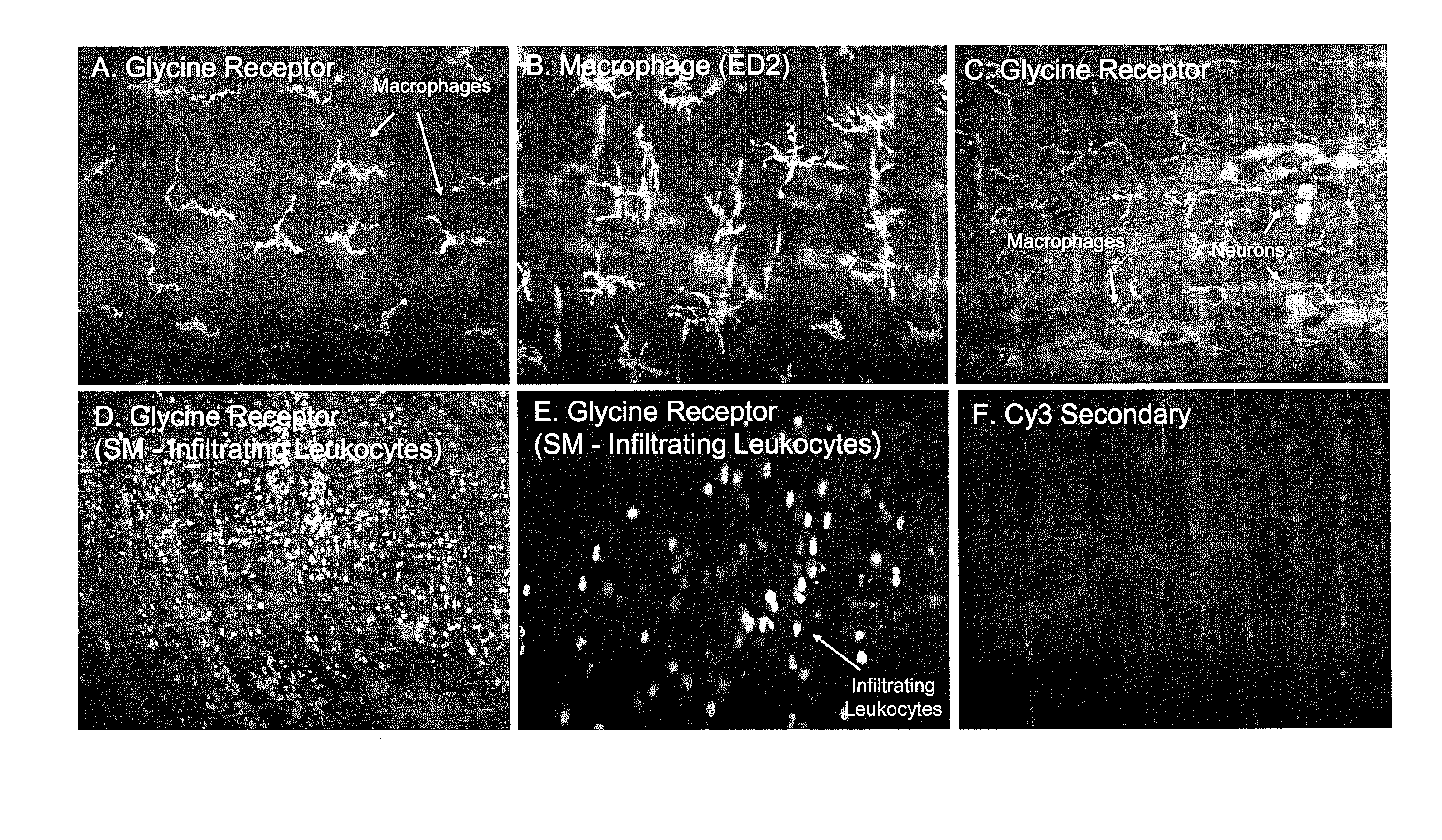
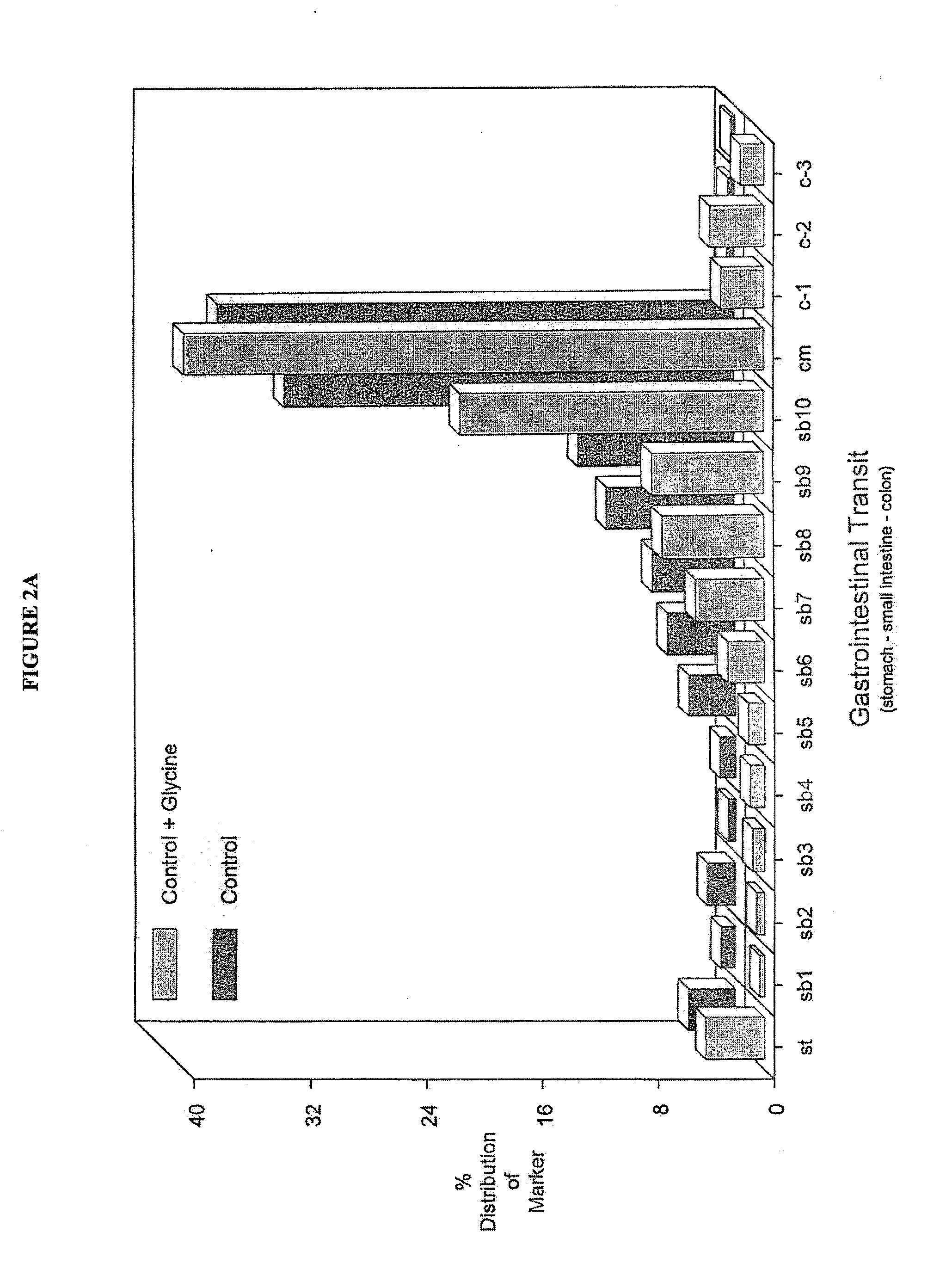
InactiveUS20090238792A1Facilitated releaseSuppressed increase in nitric oxide productionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycineInterleukin 10
The invention provides a method for suppressing postoperative ileus in connection with the performance of a surgical procedure on a patient. In accordance with the inventive method, interleukin-10 (IL-10), glycine, a COX-2 inhibitor and a mast cell stabilizer are administered to the patient undergoing the surgical procedure in an amount and at a location sufficient to therapeutically or prophylactically suppress postoperative ileus in the patient. The invention further provides a pharmaceutically acceptable composition comprising interleukin-10 (IL-10), glycine, a COX-2 inhibitor, a mast cell stabilizer and a pharmaceutically-acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Nitrosated and nitrosylated compounds and compositions and their use for treating respiratory disorders
Disclosed are (i) compounds of a steroid, a β-agonist, an anticholinergic, a mast cell stabilizer and a phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor directly or indirectly linked to a NO or NO2 group or a group which stimulates endogenous production of NO or EDRF in vivo; (ii) compositions of steroids, β-agonists, anticholinergics, mast cell stabilizers and PDE inhibitors, which can optionally be substituted with at least one NO or NO2 moiety or a group which stimulates endogenous production of NO or EDRF in vivo, and a compound that donates, transfers or releases nitric oxide as a charged species, i.e., nitrosonium (NO+) or nitroxyl (NO−), or as the neutral species, nitric oxide (NO.) or that stimulates endogenous production of NO or EDRF in vivo; and (iii) uses for them in preventing and / or treating respiratory disorders.
Owner:ARBOR PHARMA LLC
Compositions and methods for treating, controlling, reducing, ameliorating, or preventing allergy
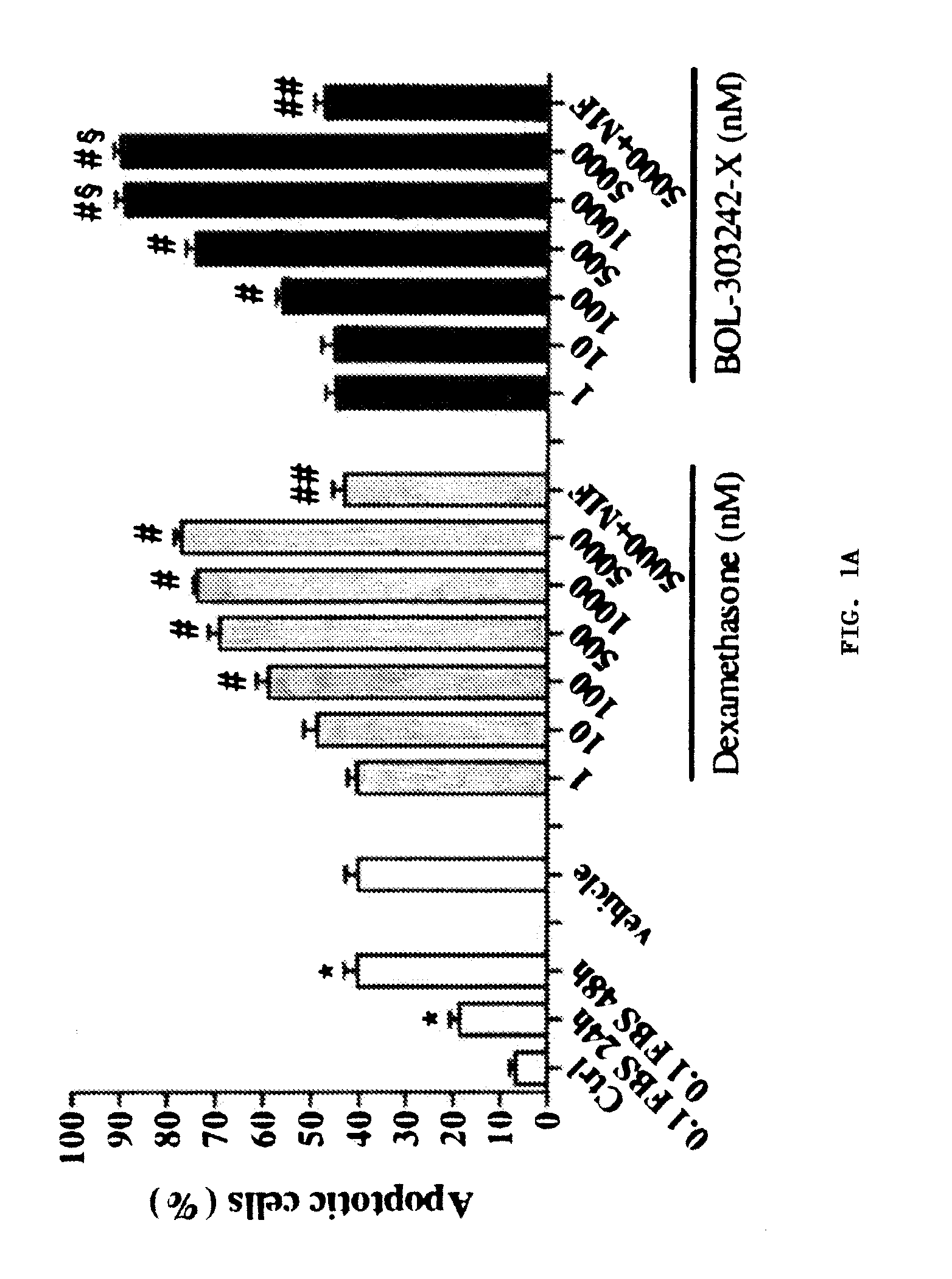
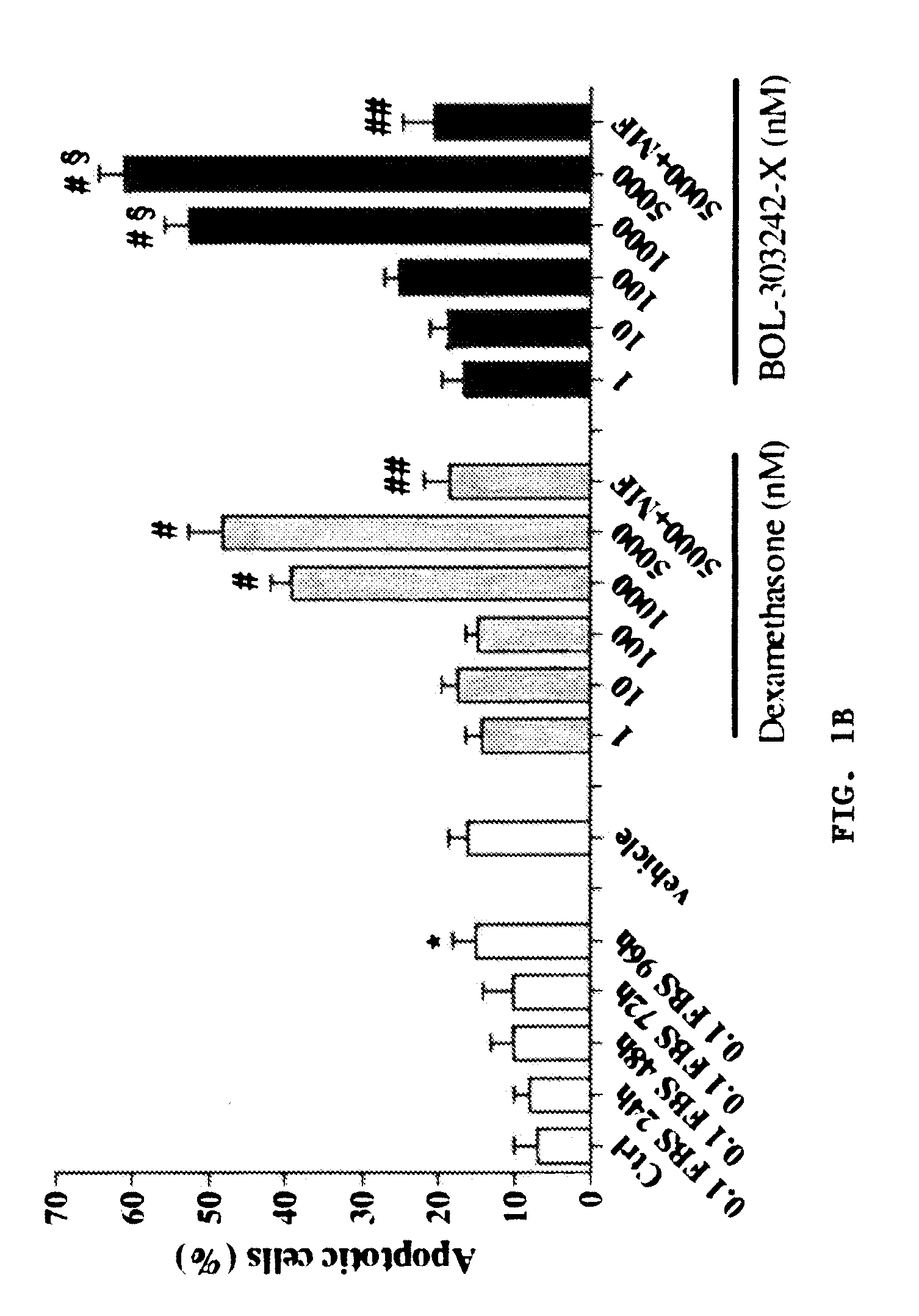
A composition for treating, controlling, reducing, ameliorating, or preventing allergy comprises a dissociated glucocorticoid receptor agonist ('DIGRA'), a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof. The composition can comprise an anti-allergic medicament and / or an additional anti-inflammatory agent and can be formulated for topicalapplication, injection, or implantation. The anti-allergic medicament can comprise an antihistamine, a mast-cell stabilizer, a leukotriene inhibitor, an immunomodulator, an anti-IgE agent, or a combination thereof.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Therapeutic or prophylactic agent for retinopathy of prematurity, testing method for retinopathy of prematurity, and screening method for therapeutic or prophylactic substance for retinopathy of prematurity
ActiveUS20150276718A1Highly effectiveOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderActive ingredientTryptase.beta
Provided are a therapeutic or prophylactic agent for retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) that is suited to the pathogenic mechanism of ROP and a method of testing for ROP. The therapeutic or prophylactic agent for ROP uses at least one substance from the group consisting of inhibitors against tryptase derived from mast cells and / or mast cell stabilizers as an active ingredient. The testing method for ROP includes detecting a marker substance that can be released by degranulation of mast cells in a biological sample originating from a patient and determining the presence or absence of ROP on the basis of the detected amount of the marker.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKYO UNIV OF AGRI & TECH +1
Methods of treating cytokine release syndrome
PendingCN113038945AIncreased transdermal fluxNervous disorderOrganic chemistryTumor SyndromePharmaceutical medicine
The present disclosure relates to a method of treating at least one condition selected from Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), Immune effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS), cancer-related cognitive impairment, Infusion Reaction Syndrome (IRS), Capillary Leak Syndrome (CLS), Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS), Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS), Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS), Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS), Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD), Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), sepsis, Ebola, avian influenza, smallpox, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS), and Immune-related Adverse Events Syndrome (IrAES) in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering a mast cell stabilizer or a compound of Formula I or Formula II shown in the specification, wherein R1 is halogen, OH, or -OC(O)C1-5alkyl, R2 and R3 are each independently selected from CO2R4 or CH2OR5; R4 is Li, Na, K, H, C1-5alkyl, or -CH2CO(C1-5alkyl); and R5 is H or -C(O)(C1-5alkyl), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Mast cell stabilizers for treatment of chronic inflammatory conditions
ActiveUS11478463B2Little of responseOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticBiochemistryBasophils+Mast cells
The present invention relates to methods for treating chronic inflammatory conditions using a mast cell stabilizing compound. The invention further relates to compositions and dosage forms comprising mast cell stabilizing agents.
Owner:EMERGO THERAPEUTICS INC
Compositions and Methods for Treating, Controlling, Reducing, Ameliorating, or Preventing Allergy
InactiveUS20110105559A1Treating and controlling and reducing and ameliorating and preventing allergyBiocideAntipyreticAllergyAgonist
A composition for treating, controlling, reducing, ameliorating, or preventing allergy comprises a dissociated glucocorticoid receptor agonist (“DIGRA”), a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable ester thereof. The composition can comprise an anti-allergic medicament and / or an additional anti-inflammatory agent and can be formulated for topical application, injection, or implantation. The anti-allergic medicament can comprise an antihistamine, a mast-cell stabilizer, a leukotriene inhibitor, an immunomodulator, an anti-IgE agent, or a combination thereof.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Method of treating ocular allergy
InactiveUS20100160298A1BiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsHistamine antagonistsOcular allergy
Owner:ALCON RES LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com