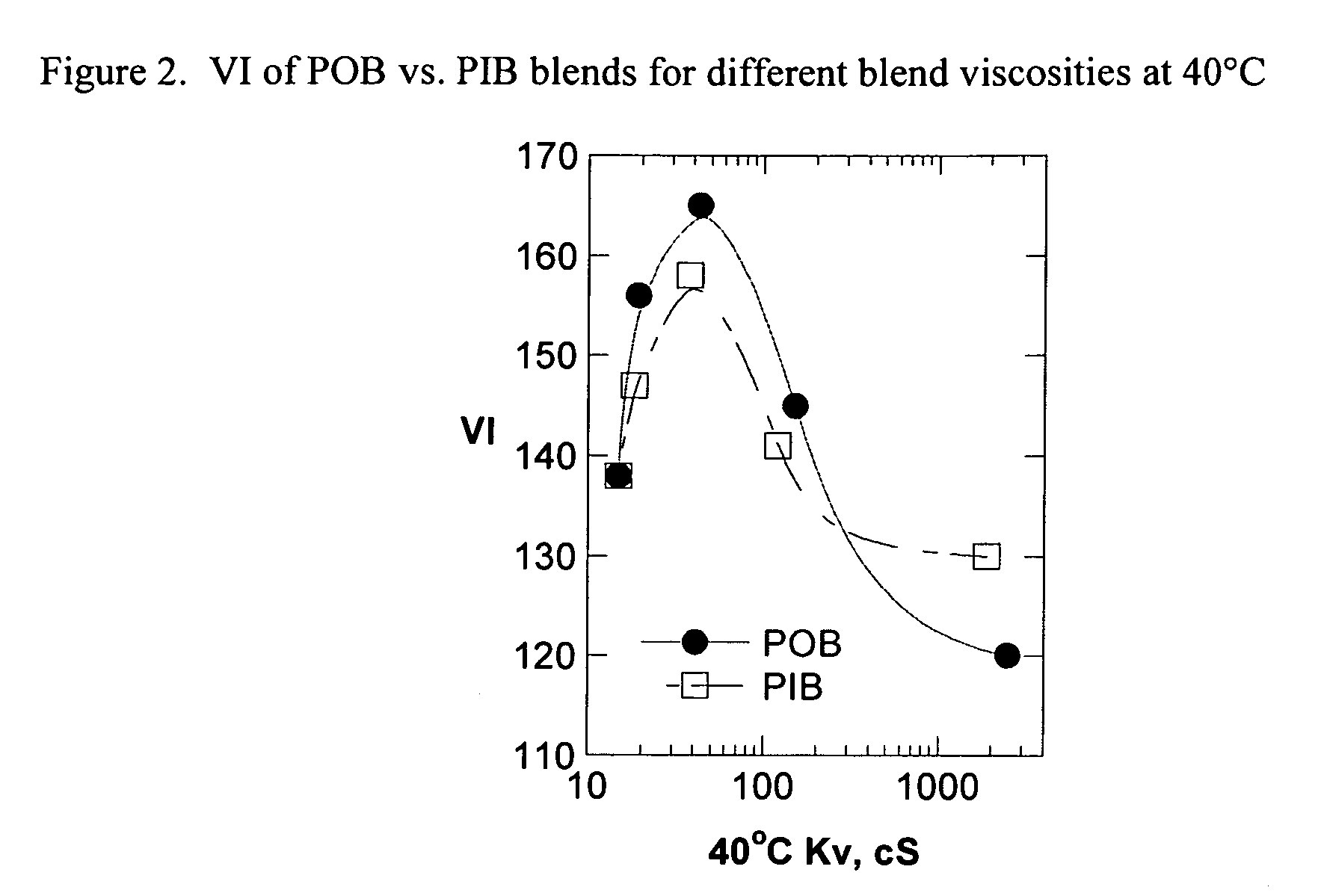
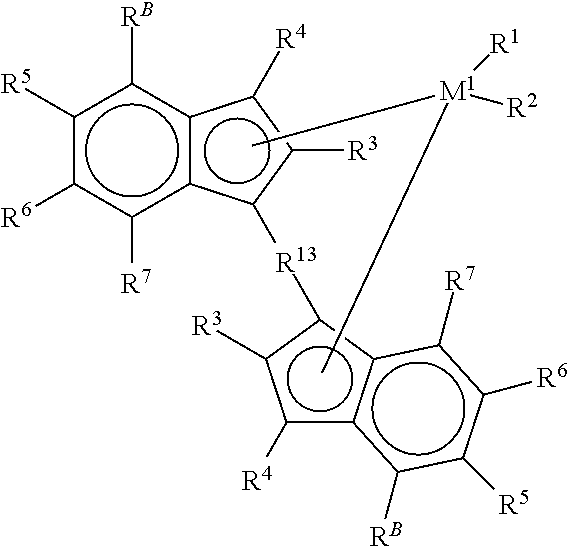
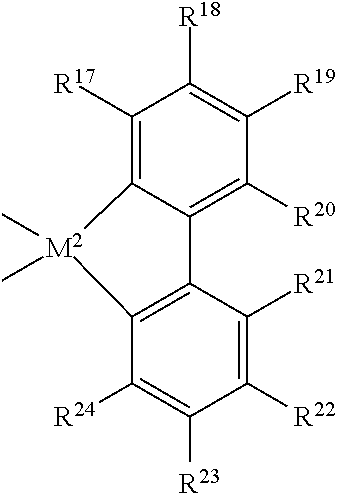
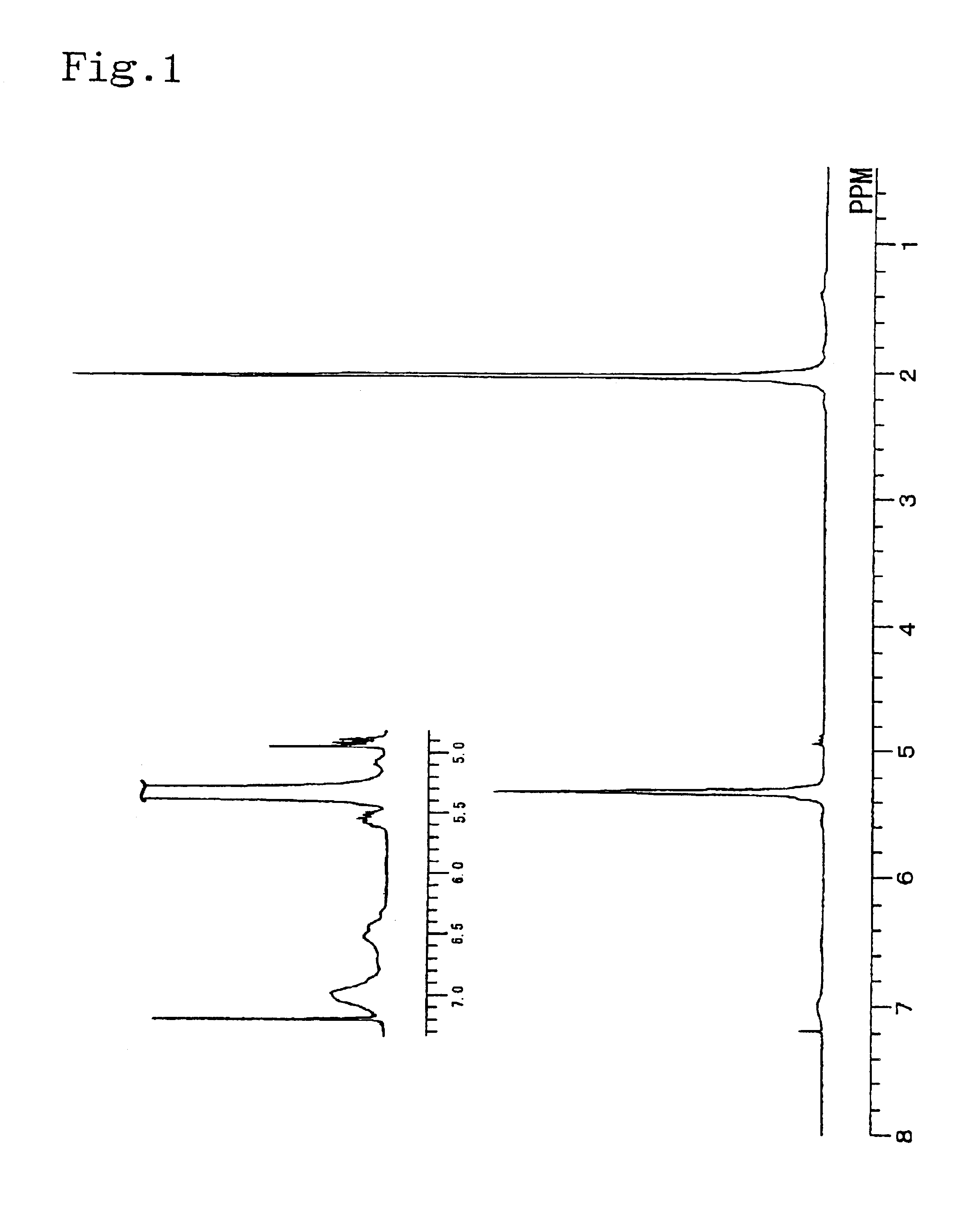
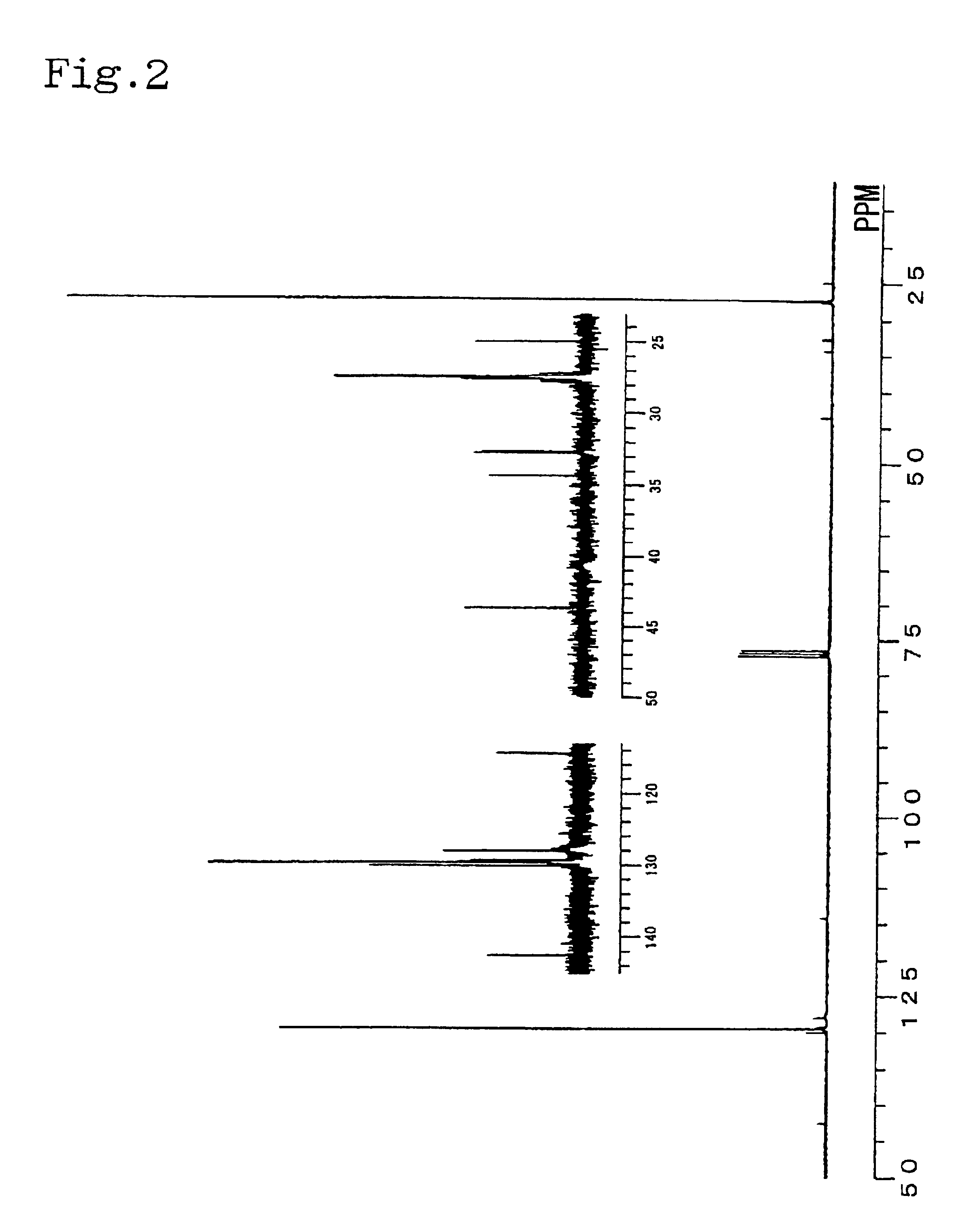
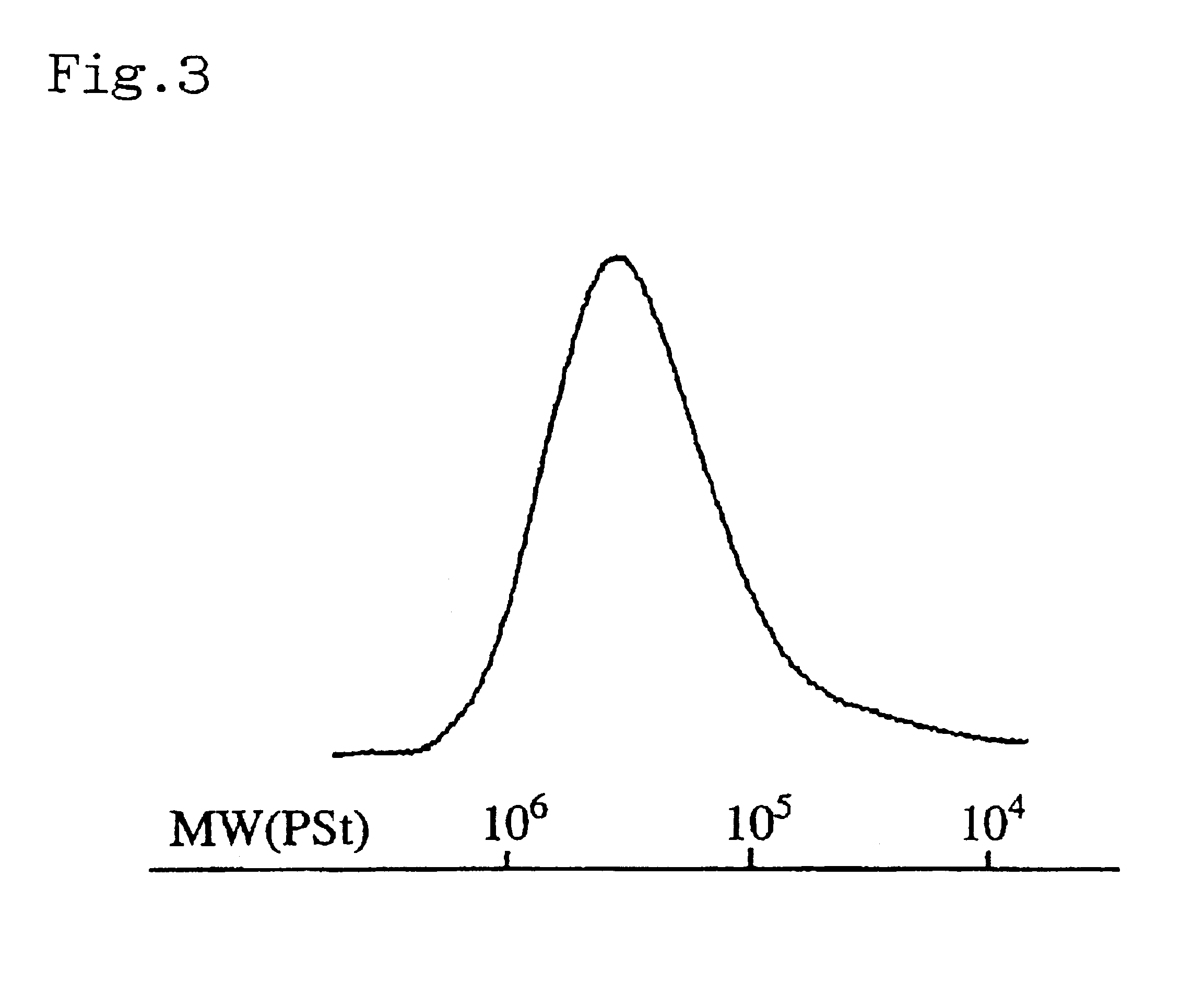
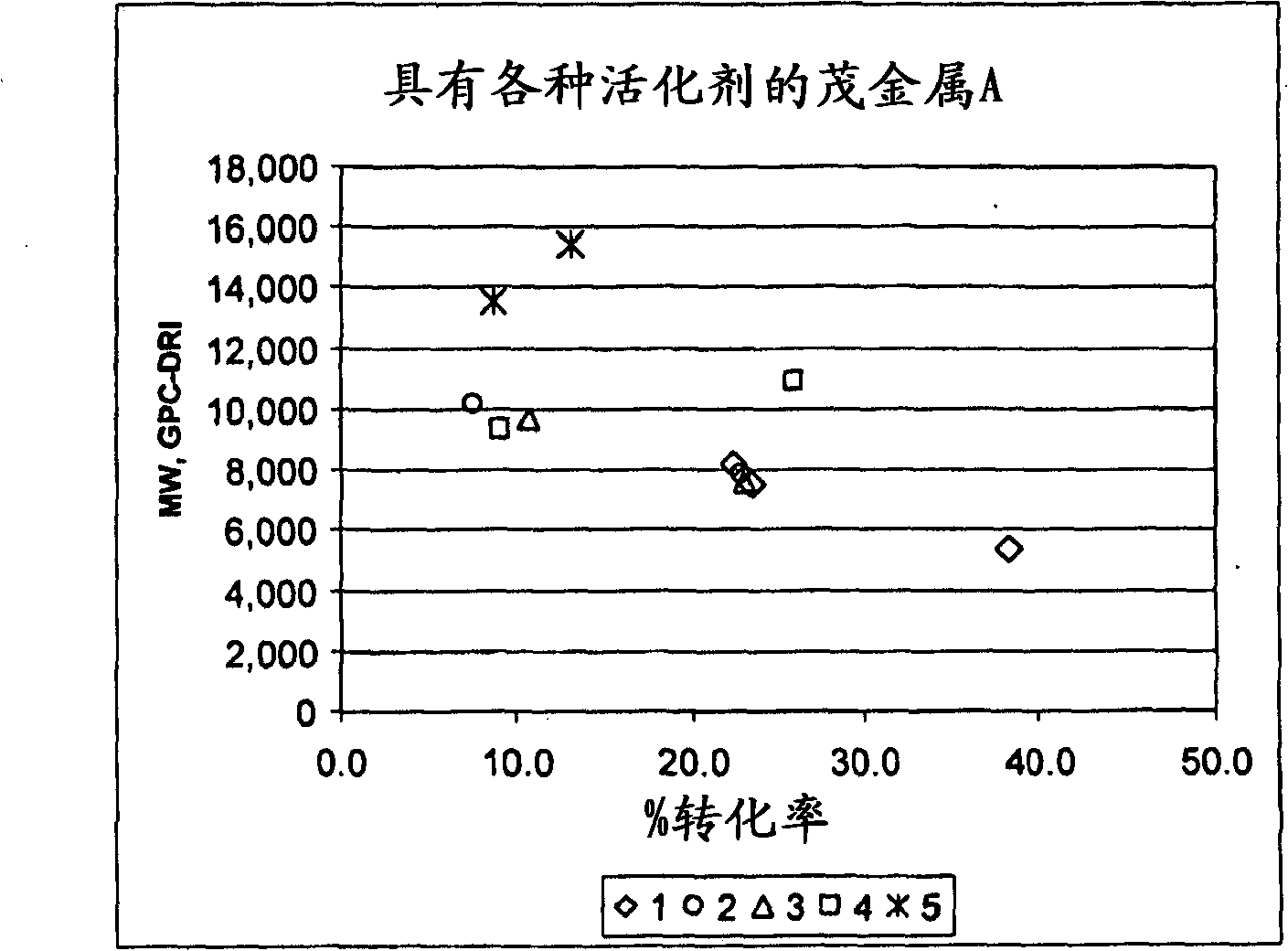
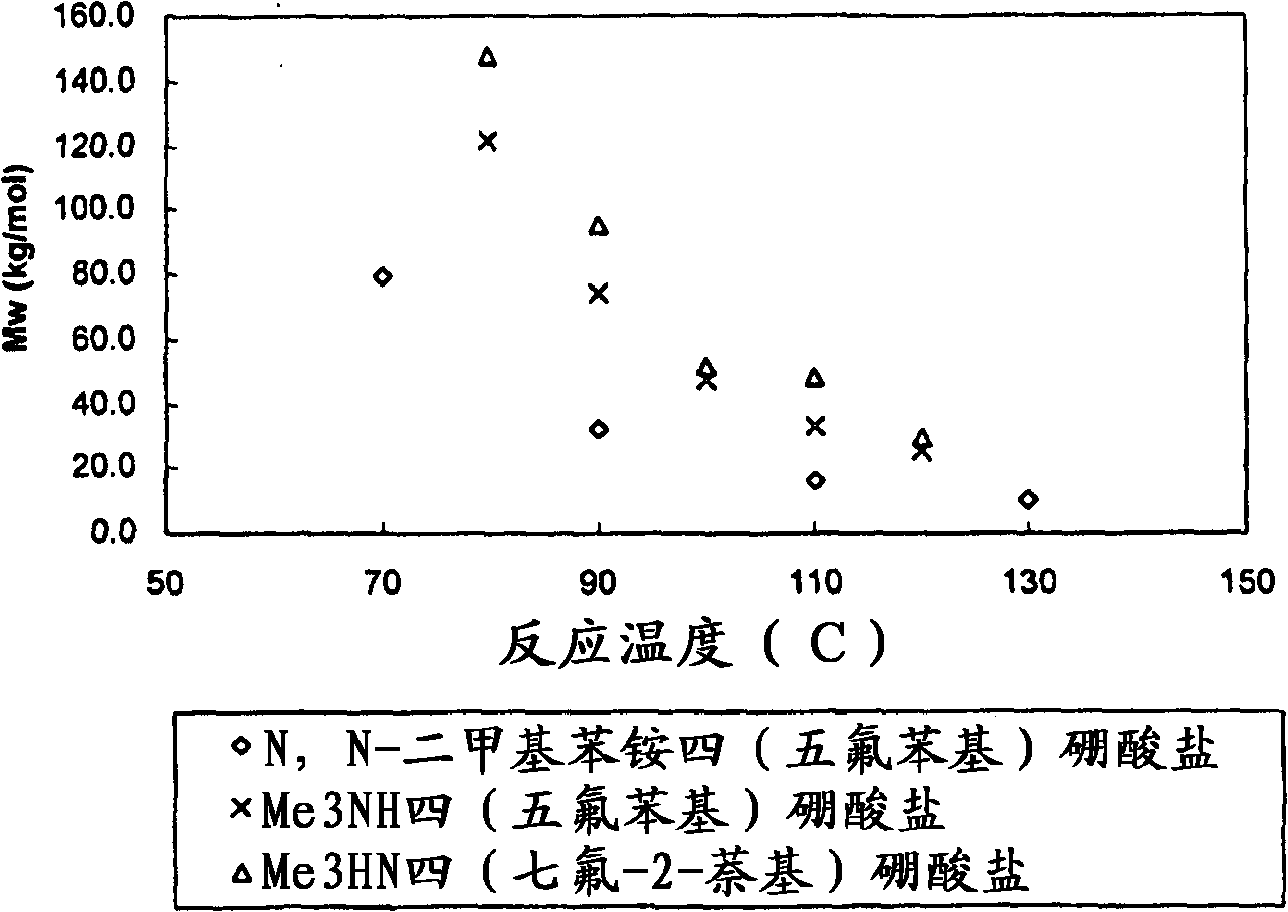
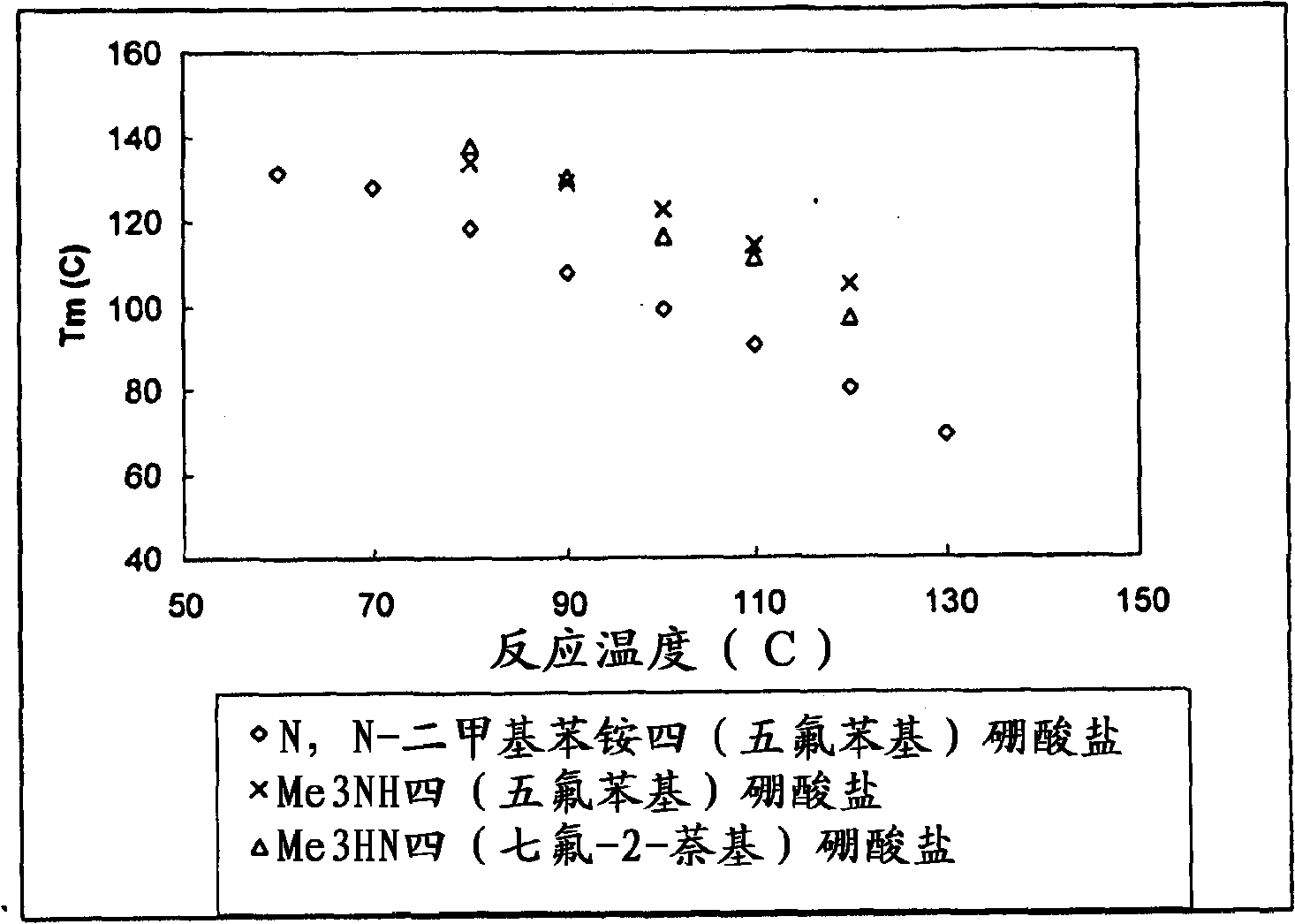
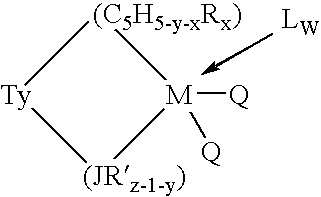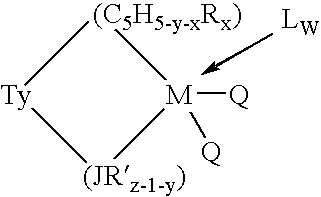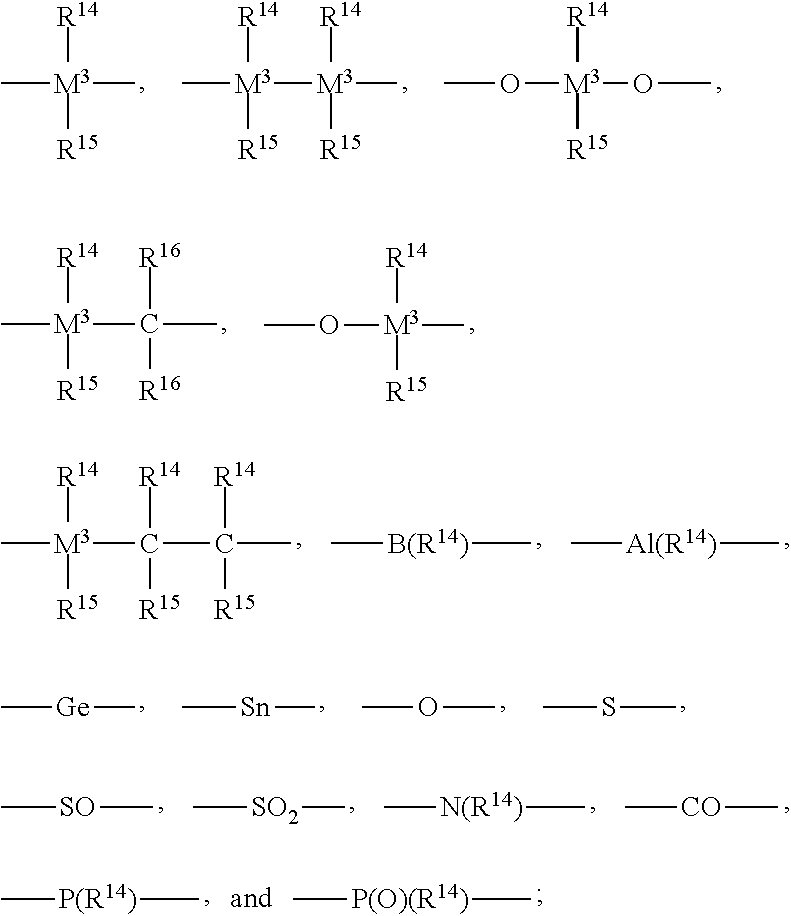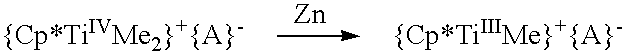Patents
Literature
72 results about "Non-coordinating anion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
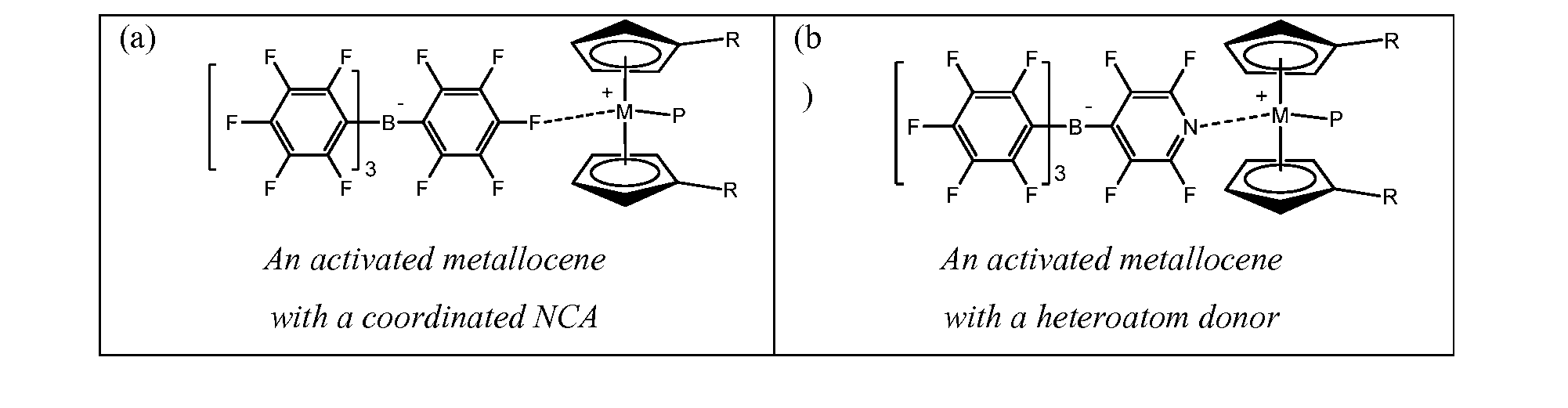
Anions that interact weakly with cations are termed non-coordinating anions, although a more accurate term is weakly coordinating anion. Non-coordinating anions are useful in studying the reactivity of electrophilic cations. They are commonly found as counterions for cationic metal complexes with an unsaturated coordination sphere. These special anions are essential components of homogeneous olefin polymerisation catalysts, where the active catalyst is a coordinatively unsaturated, cationic transition metal complex. For example, they are employed as counterions for the 14 valence electron cations [(C₅H₅)₂ZrR]⁺ (R = methyl or a growing polyethylene chain). Complexes derived from non-coordinating anions have been used to catalyze hydrogenation, hydrosilylation, oligomerization, and the living polymerization of olefins. The popularization of non-coordinating anions has contributed to increased understanding of agostic complexes wherein hydrocarbons and hydrogen serve as ligands. Non-coordinating anions are important components of many superacids, which result from the combination of Brønsted acids and Lewis acids.
Aluminum-free monocyclopentadienyl metallocene catalysts for olefin polymerization
ActiveUS7163907B1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetallocenesPolymer sciencePolyolefin
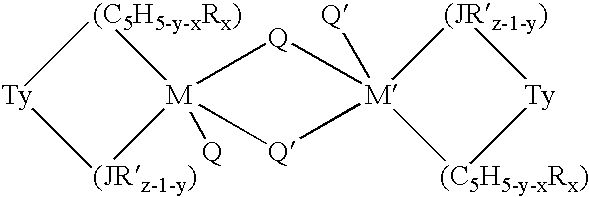
This invention relates to a catalyst system for the production of polyolefins comprising:(A) a Group IV B transition metal component represented by one of the two general formulaewherein(C5H5-y-xRx) is a cylopentadienyl ring(JR′z-l-y) is a heteroatom ligand in which J is an element with a coordination number of three from Group V-A or an element with a coordination number of two rom Group VI-A of the Periodic Table of Elements,each Q is independently, hydride, C1—C20 hydrocarbyl radicals, substituted hydrocarbyl radials wherein one or more hydrogen atoms is replaced by an electron withdrawing group, or C1—C20 hydrocarbyl-substituted metalloid radicals wherein the metalloid is selected from the group consisting of germanium and silicon, provided that Q is not a substituted or unsubstituted cyclopentadienyl ring, or both Q together may be an alkylidene, olefin, acetylene or a cyclometallated hydrocarbyl;“y” is 0 or 1; when “y” is 1, T is a covalent bridging group containing a Group IV-A or V-A element;L is a neutral Lewis base; and “w” is a number from 0 to 3;(B) an activator compound comprising (1) a cation; and (2) a compatible noncoordinating anion.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process to produce low viscosity poly-alpha-olefins
ActiveUS20070043248A1Hydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionPolyolefinAlpha-olefin
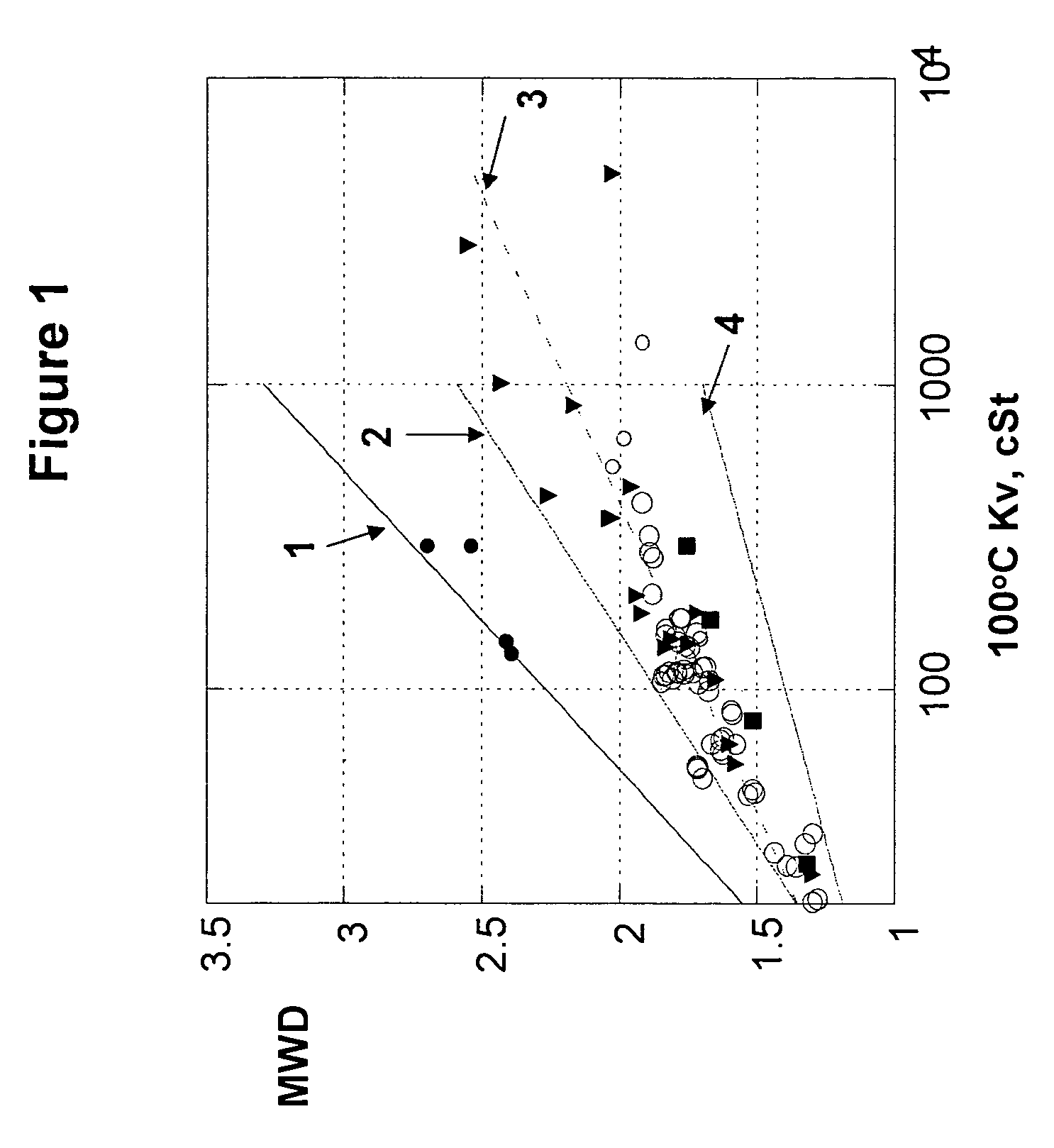
This invention relates to a process to produce a polyalpha-olefin comprising: 1) contacting one or more alpha-olefin monomers having 3 to 24 carbon atoms with an unbridged substituted bis cyclopentadienyl transition metal compound having: 1) at least one non-isoolefin substitution on both cyclopentadientyl rings, or 2) at least two substitutions on at least one cyclopentadienyl ring, a non-coordinating anion activator, and optionally an alkyl-aluminum compound, where the molar ratio of transition metal compound to activator is 10:1 to 0.1:1, and if the alkyl aluminum compound is present then the molar ratio of alkyl aluminum compound to transition metal compound is 1:4 to 4000:1, under polymerization conditions wherein: i) hydrogen is present at a partial pressure of 0.1 to 50 psi, based upon the total pressure of the reactor or the concentration of the hydrogen is from 1 to 10,000 ppm or less by weight; ii) wherein the alpha-olefin monomer(s) having 3 to 24 carbon atoms are present at 10 volume % or more based upon the total volume of the catalyst / activator / alkylaluminum compound solutions, monomers, and any diluents or solvents present in the reaction; iii) the residence time of the reaction is at least 5 minutes; iv) the productivity of the process is at least 43,000 grams of total product per gram of transition metal compound; v) the process is continuous or semi-continuous, and vi) the temperature in the reaction zone does not rise by more than 10° C. during the reaction; and vii) ethylene is not present at more than 30 volume % of the monomers entering the reaction zone; and 2) obtaining a polyalpha-olefin (PAO), optionally hydrogenating the PAO, wherein the PAO comprises at least 50 mole % of a C3 to C24 alpha-olefin monomer, and wherein the PAO has a kinematic viscosity at 100° C. of 20 cSt or less.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process To Produce Polyalphaolefins
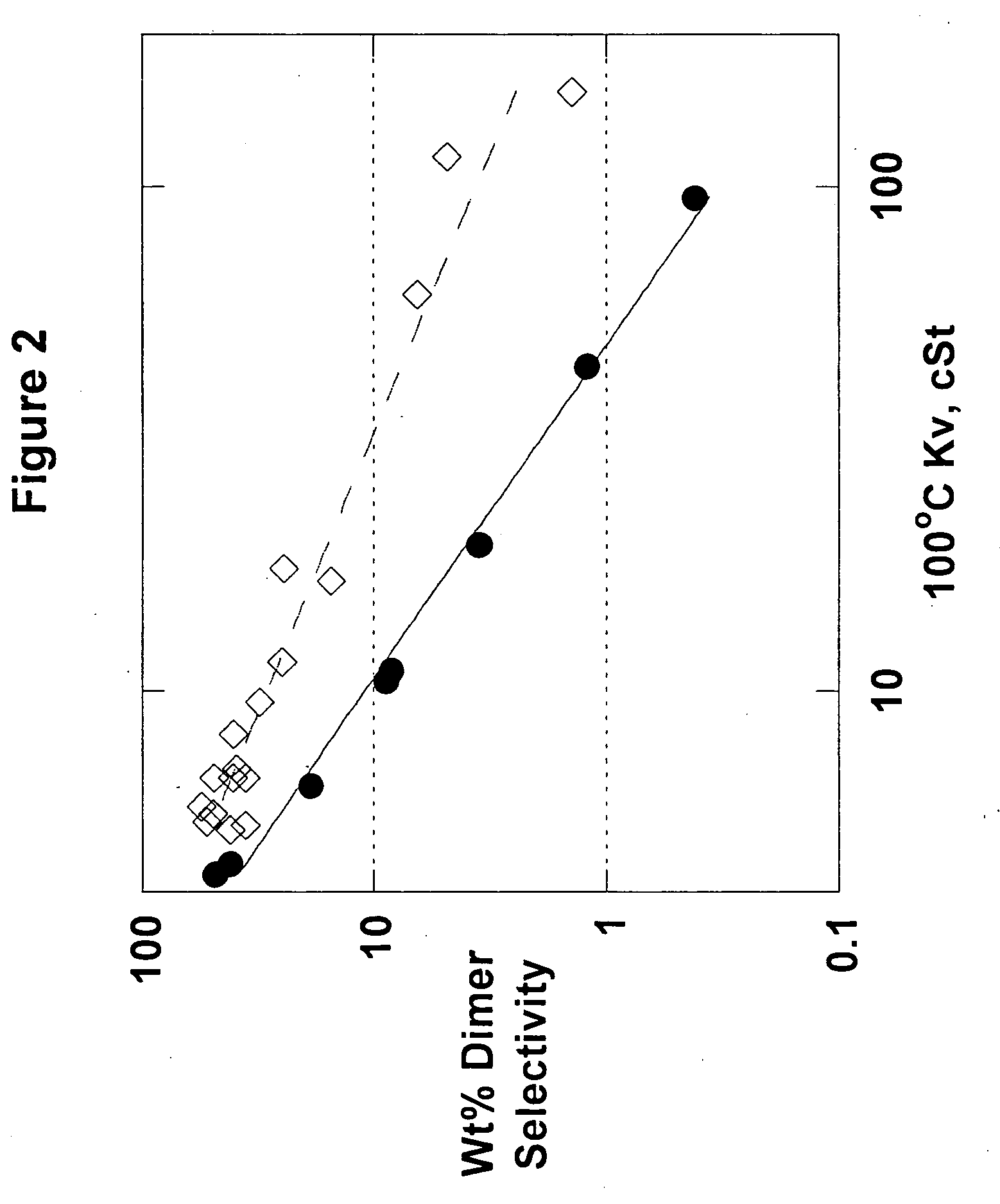
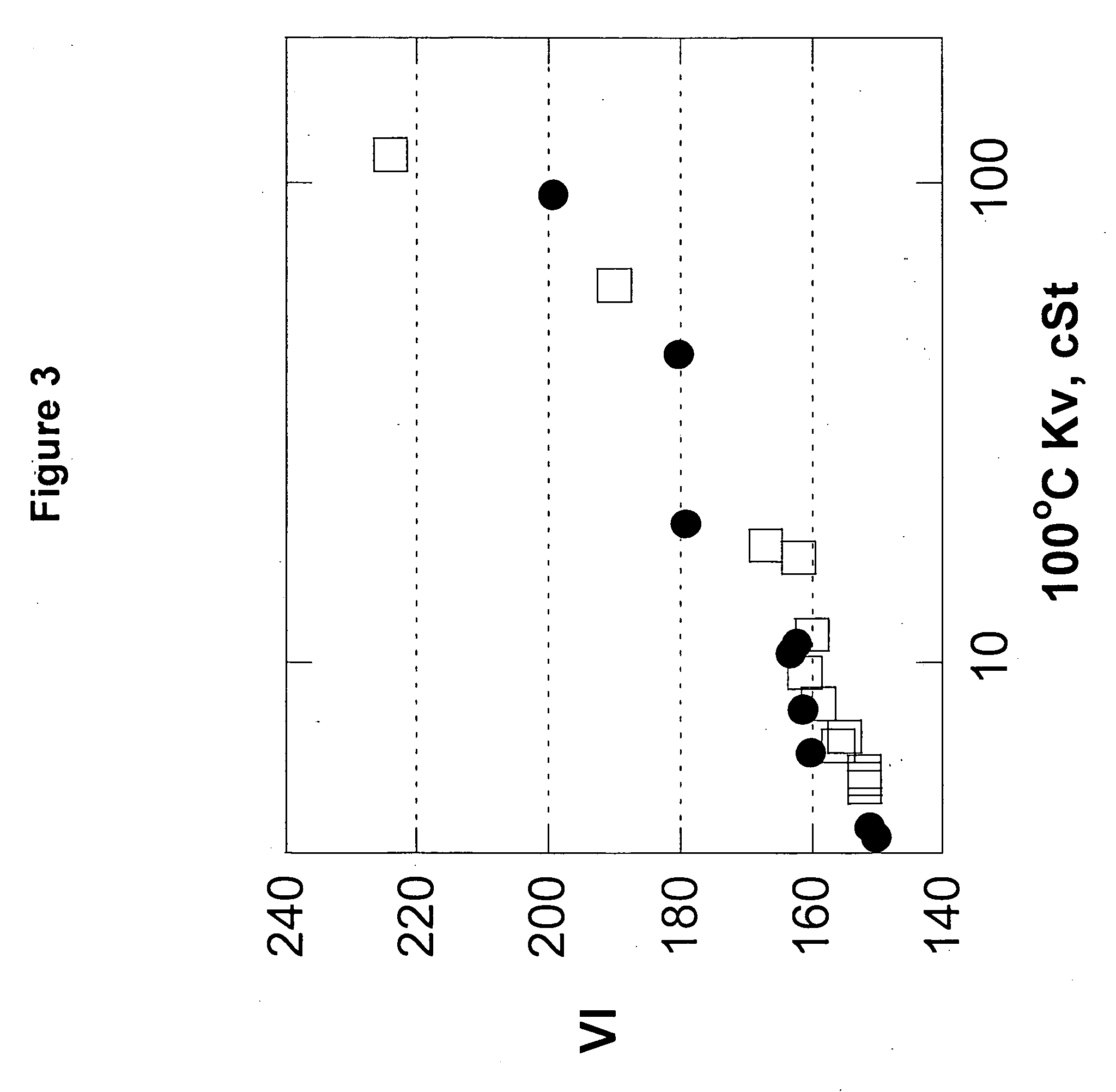
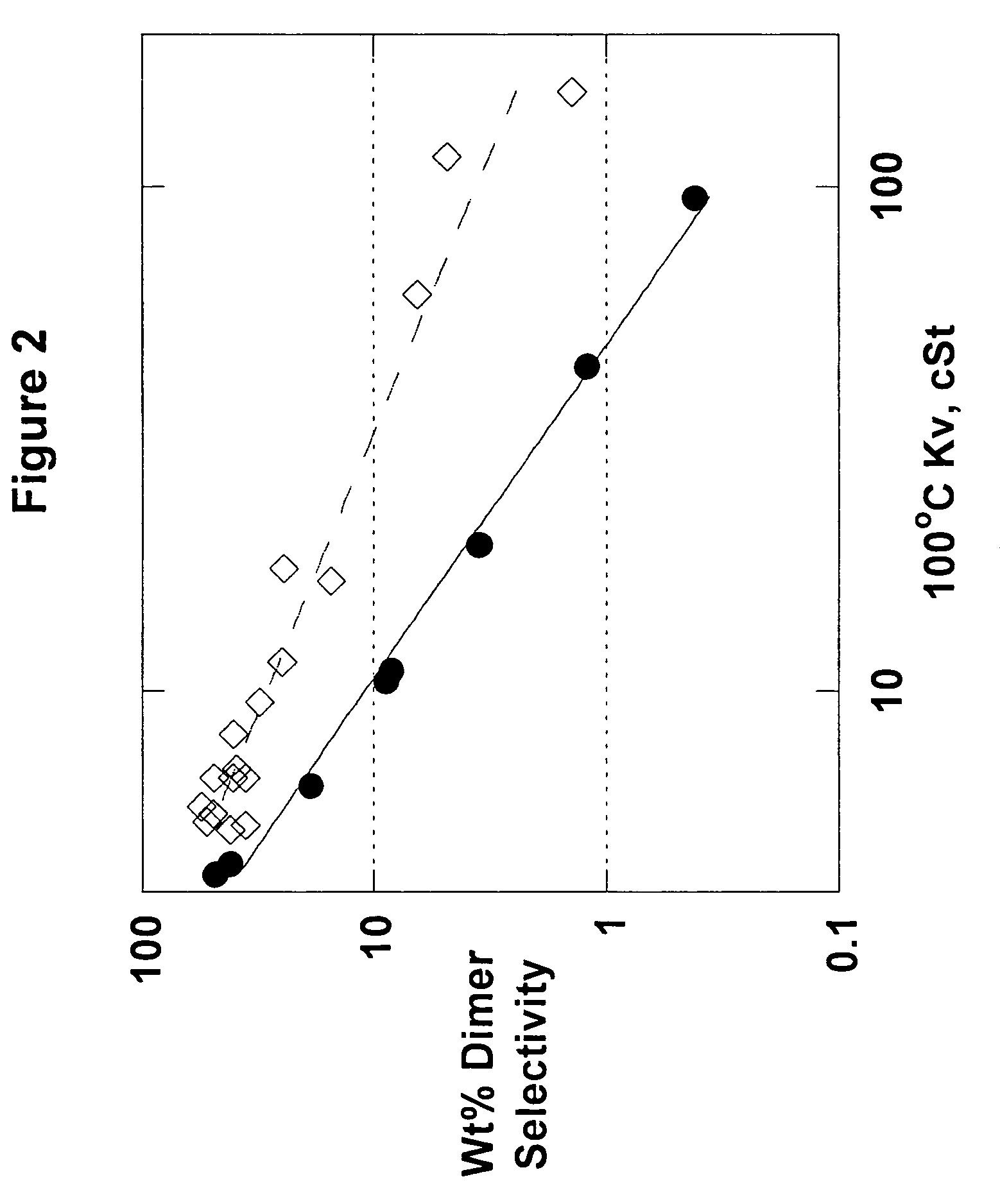
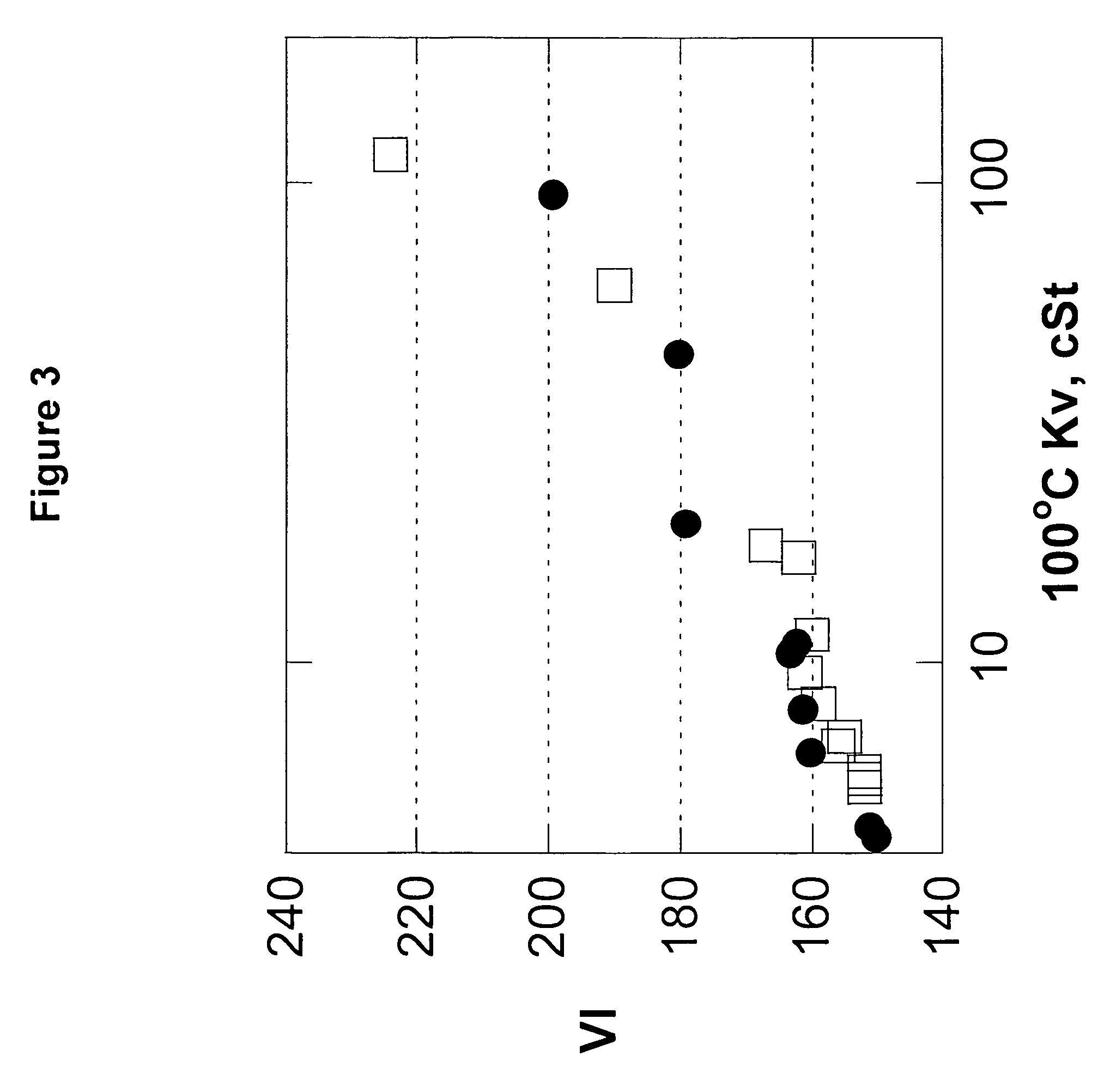
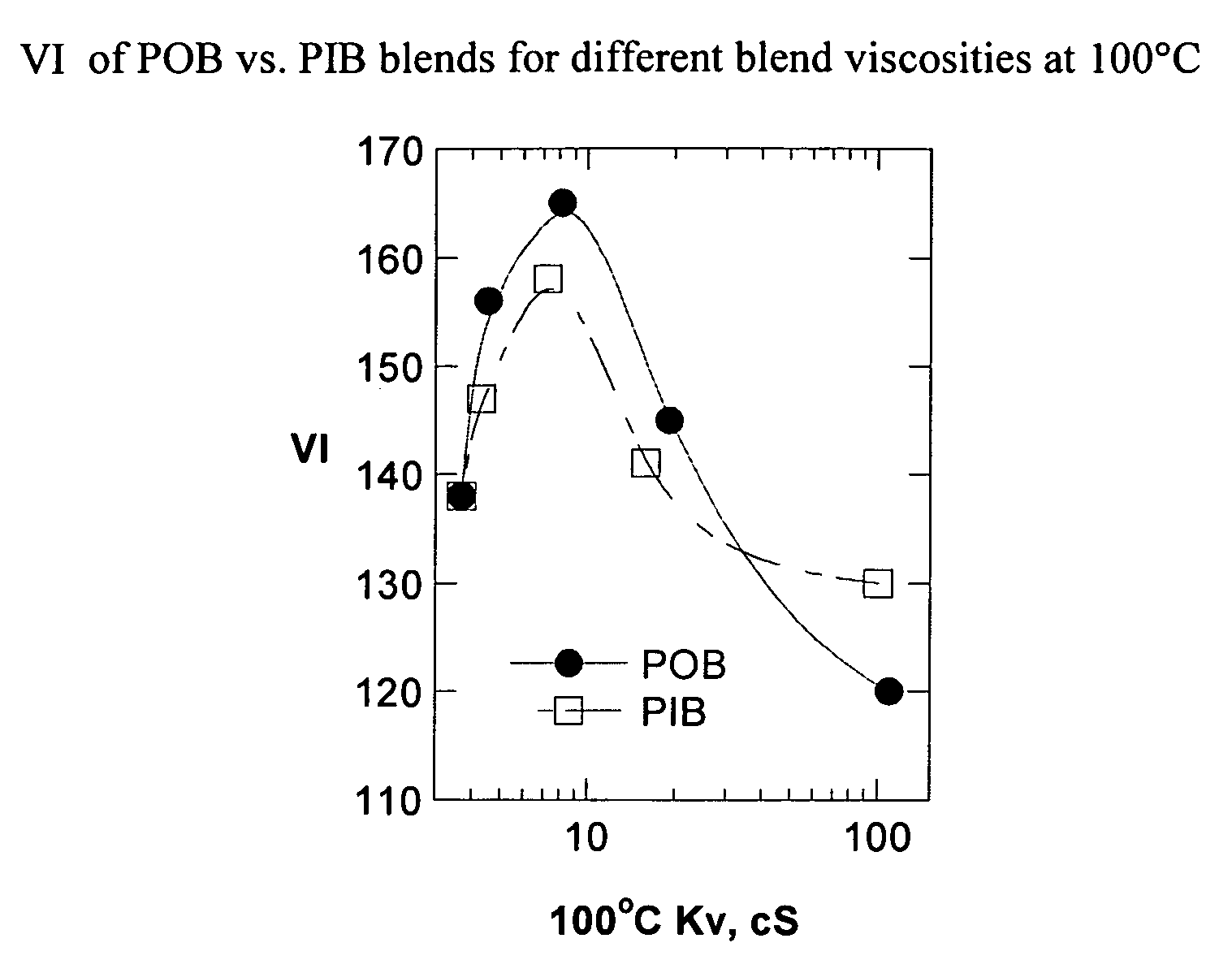
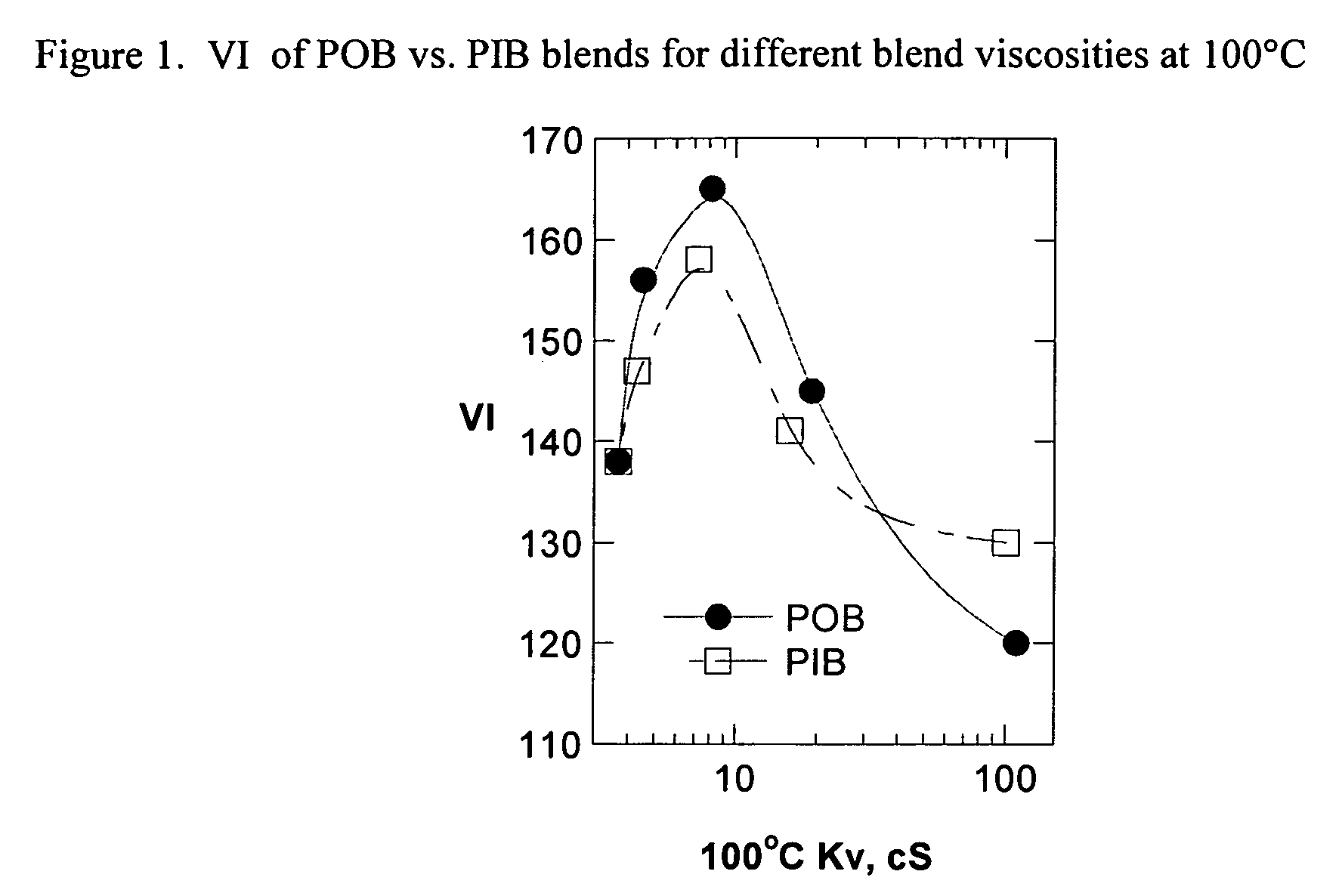
The present invention relates to processes to produce liquid poly-alpha-olefins comprising:a) contacting in a reaction zone, in the presence of from 0 to 60 psi hydrogen, one or more C3 to C20 alpha-olefin monomers with a non-coordinating anion activator, a single bridged meso-metallocene transition metal compound having less than about 35 wt % racemic isomer, and a co-activator selected from the group consisting of alkyl aluminum compounds and alkyl alumoxanes, provided that when the alkyl alumoxane is present it is present in a molar ratio of less than 0.1:1 of alkylalumoxane to meso-metallocene, and provided that when the alkyl aluminum compound is present it is present at a molar ratio of alkyl aluminum to meso-metallocene of from 2:1 to 10,000 to 1, where the molar ratio of activator to meso-metallocene is from 10:1 to 0.1:1, andprovided that ethylene is not present at more than 30 volume % of the monomers entering the reaction zone, and provided that the alpha-olefin monomers in the feed components are present in at least 20 wt % or more based upon the weight of the meso-metallocene, non-coordinating anion activator, co-activator, monomers, and solvent or diluent, andwhere: i) the productivity of the process is at least 50,000 g of total product per gram of transition metal compound (where the total product is defined to be the total amount of product exiting the reactor, minus unreacted monomers and solvents); and ii) no more than 5% monomer is converted from olefin to alkane; andb) obtaining a liquid polyalphaolefin product having a pour point of less than 25° C., a KV100 of 2 to 6000 cSt, 20 weight percent dimer or less and a viscosity index of 60 or more.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Carbon and/or silicon bridged binuclear metallocene catalyst for styrene polymerization
InactiveUS6010974AHigh catalytic activityHigh Molecular Weight DistributionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationArylSilylene
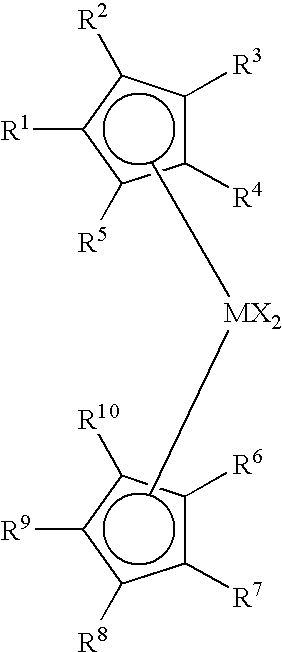
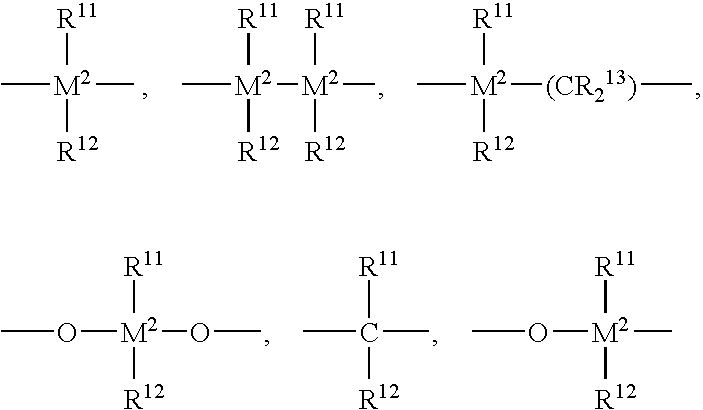
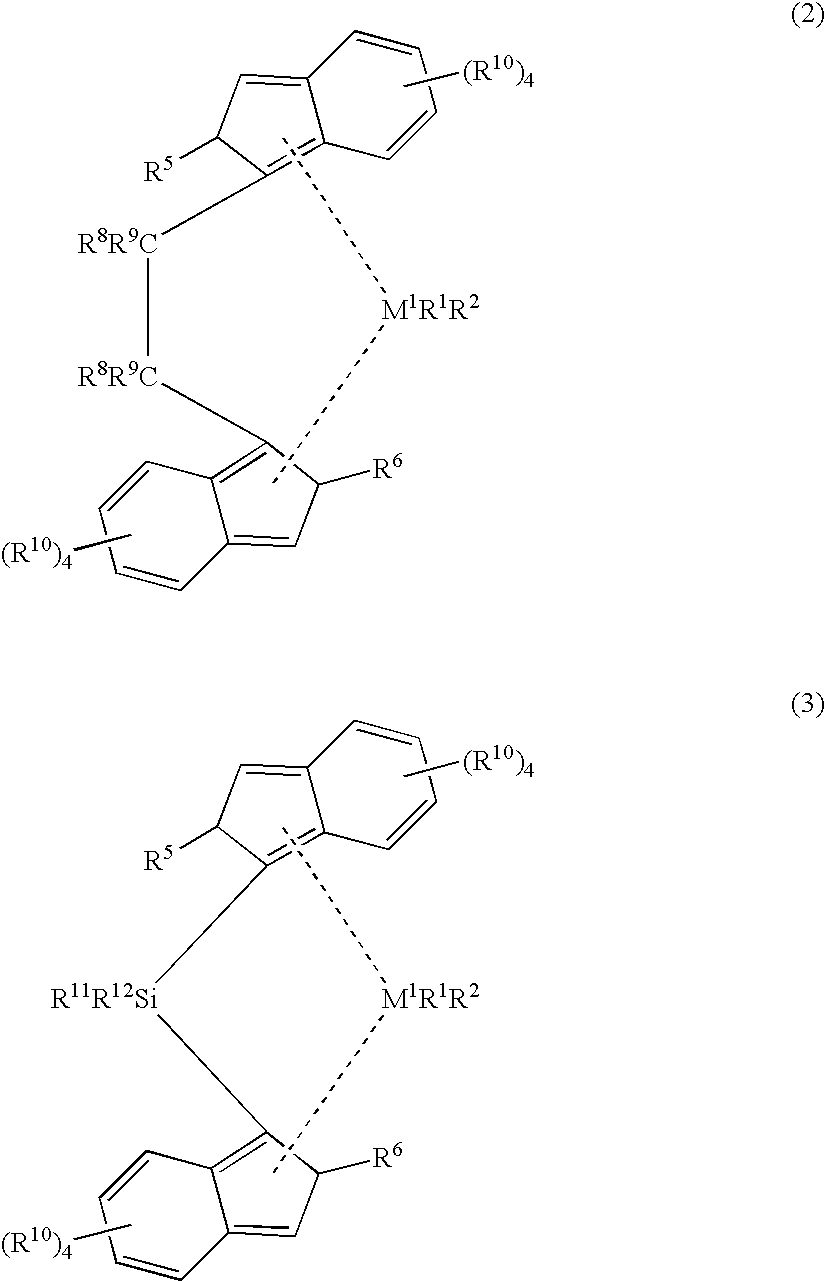
An alkylene and / or silylene bridged binuclear metallocene catalyst for styrene polymerization is represented by the following formula (I): where M1 and M2 are the same or different transition metal of Group IVb of the Periodic Table; Cp1 and Cp2 are the same or different cyclopentadienyl; alkyl, alkoxy, silyl or halogen substituted cyclopentadienyl; indenyl; alkyl, alkoxy, silyl or halogen substituted indenyl; fluorenyl; or alkyl, alkoxy, silyl or halogen substituted fluorenyl, which is capable of pi -electron, eta 5-bonding with M1 or M2; each of E1, E2 and E3, independently of one another, is a carbon atom or a silicon atom; m, p and q are integers of 0 to 15 and m+p+q> / =1; each of R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6, independently of one another, is a hydrogen, an alkyl, an aryl, an alkoxy or a halogen; X is a hydrogen, an alkyl, an alkoxy or a halogen; and n is 3. M1 and M2 may also be in cardin form by mixture of (I) with a compound which abstructs an X gray from each metal atom and substitution then with non-coordinating anions.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Process to produce high viscosity fluids
ActiveUS20080177121A1Hydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionHydrocarbonsPolyolefinPtru catalyst
This invention relates to processes to produce liquid poly-alpha-olefins (PAOs) having a kinematic viscosity at 100° C. of more than 20 cSt in the presence of a metallocene catalyst with a non-coordinating anion activator and hydrogen.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process to produce low viscosity poly-alpha-olefins
ActiveUS8207390B2Hydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionNon-coordinating anionAlpha-olefin
A low viscosity poly(alpha-olefin) (PAO) is produced by contacting one or more C3 to C24 alpha-olefins with an unbridged, substituted bis-cyclopentadienyl transition metal compound, a non-coordinating anion activator, and an alkyl-aluminum compound. The molar ratio of transition metal compound to activator is 10:1 to 0.1:1 and the molar ratio of alkyl aluminum compound to transition metal compound is 1:4 to 4000:1. The transition metal compound has either (a) at least one non-isoolefin substitution on both cyclopentadienyl rings, or (b) at least two substitutions on at least one cyclopentadienyl ring. The PAO is comprised of at least 50 mole % of C3 to C24 alpha-olefins, has a Mw / Mn between 1 and 1.4, and a kinematic viscosity at 100° C. of 20 cSt or less.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Base stocks and lubricant blends containing poly-alpha olefins
This disclosure relates to substantially atactic polymers of at least one of propylene, 1-butene or 1-pentene, processes for making such polymers and compositions including the polymers. The polymers may be used as lubricants or may be combined with low viscosity base stocks to form lubricants. The polymers may be made in the presence of a metallocene catalyst with a non-coordinating anion activator and optionally with hydrogen.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Polyolefins made by catalyst comprising a noncoordinating anion and articles comprising them
ActiveUS7511104B2Low mobilityReduce dielectric lossOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
Polymers made by transition metal catalyst systems comprising a bulky noncoordinating anion (NCA) as cocatalyst component. In comparison to polymers containing a conventional NCA, these polymers show a considerably lower dielectric loss, making them suitable for insulation applications such as for power cable.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Polypropylene fibers and fabrics
InactiveUS7081299B2Improve featuresShot levelFixed capacitor dielectricSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceNon-coordinating anion
The present invention is a meltblown fiber and a fabric manufactured from the fiber comprising reactor grade polypropylene having a melt flow rate of from 100 to 5000 and having less than 50 stereo defects per 1000 units. Further, the polypropylene is typically produced from a metallocene catalyzed process, the metallocene being at least one bridged 2,4 di-substituted indenyl metallocene in one embodiment, and a bridged 4-phenyl indenyl metallocene in another embodiment. The metallocene is part of a system that can include a fluorided support and a non-coordinating anion activator.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
High temperature olefin polymerization process
InactiveUS6291609B1Superior molecular weight and activity capabilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationReaction temperatureHafnium
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Catalyst Systems Comprising Multiple Non-Coordinating Anion Activators and Methods for Polymerization Therewith
ActiveUS20120316302A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsNitrogenBoron containing
This invention relates to a method to polymerize olefins comprising contacting olefins with a catalyst system comprising a transition metal catalyst compound and: 1) at least two NCA activators represented by the formula: Zd+(Ad−), where Z is a Bronsted acid or a reducible Lewis acid, Ad− is a boron containing NCA, d is 1, 2, or 3, and where Z is a Bronsted acid and Z is a reducible Lewis acid in the first and second NCA activators, respectively; or 2) at least two NCA activators, one as described in Formula I and one not as described in Formula I; or 3) two NCA activators as described in Formula I except that the N in the second NCA in the ArNHal is at a different position in the nitrogen containing aromatic ring than the N in the first NCA.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process to produce high viscosity fluids
ActiveUS7989670B2Hydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionHydrocarbonsHydrogenNon-coordinating anion
This invention relates to processes to produce liquid poly-alpha-olefins (PAOs) having a kinematic viscosity at 100° C. of more than 20 cSt in the presence of a metallocene catalyst with a non-coordinating anion activator and hydrogen.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Base stocks and lubricant blends containing poly-alpha olefins
This disclosure relates to substantially atactic polymers of at least one of propylene, 1-butene or 1-pentene, processes for making such polymers and compositions including the polymers. The polymers may be used as lubricants or may be combined with low viscosity base stocks to form lubricants. The polymers may be made in the presence of a metallocene catalyst with a non-coordinating anion activator and optionally with hydrogen.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Supported Metallocene Catalyst Systems and Methods of Preparation Thereof
InactiveUS20140121341A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationNon-coordinating anionMetal
This invention relates to a process to produce a supported metallocene catalyst system, the process comprising: (i) contacting a support material with an alkyl aluminum compound to provide an alkyl aluminum treated support material; wherein the alkyl aluminum compound is represented by the formula: R3Al; wherein each R group is, independently, a substituted or unsubstituted C1 to C12 alkyl group, Cl or F with the proviso that at least one R group is a C1 to C12 alkyl group; (ii) contacting the alkyl aluminum treated support material with an ionic stoichiometric activator, wherein the ionic stoichiometric activator is represented by the formula: (Z)d+Ad−; wherein (Z)d+ is a cation, where Z is a reducible Lewis Acid, Ad− is a non-coordinating anion having the charge d−, and d is 1, 2, or 3; (iii) contacting a metallocene compound comprising a group 4, 5, or 6 metal with the alkyl aluminum treated support material; and (iv) obtaining a supported metallocene catalyst system.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Non-symmetrical ligands and catalyst systems thereof for ethylene oligomerization to linear alpha olefins
InactiveUS7179871B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic chemistry methodsNon-coordinating anionAlpha-olefin
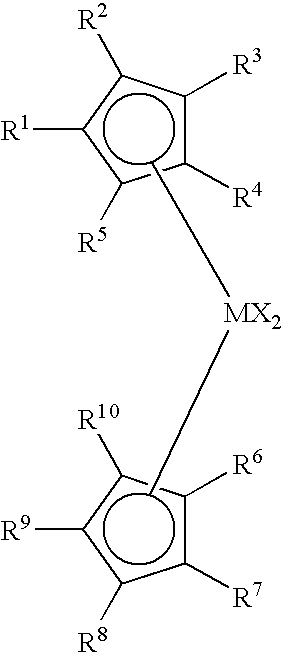
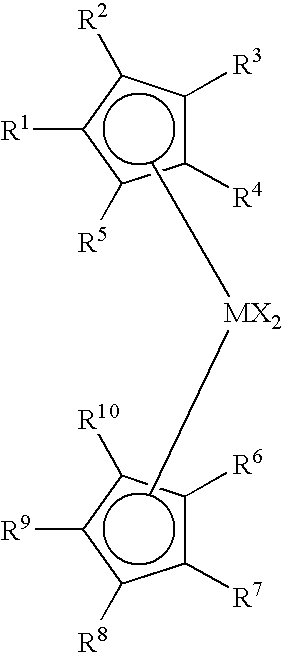
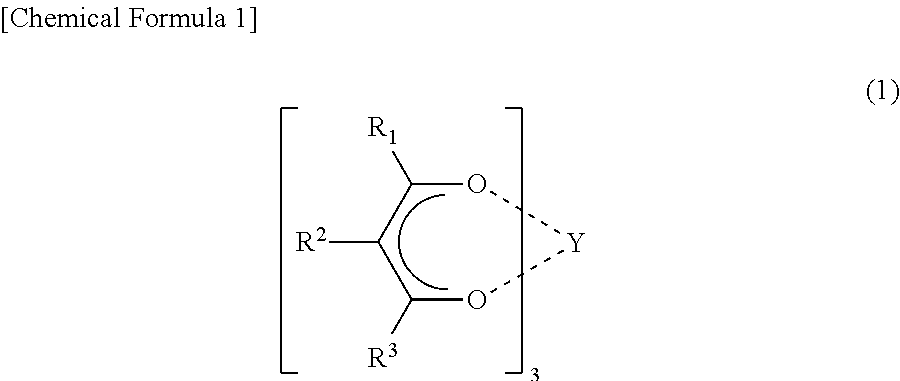
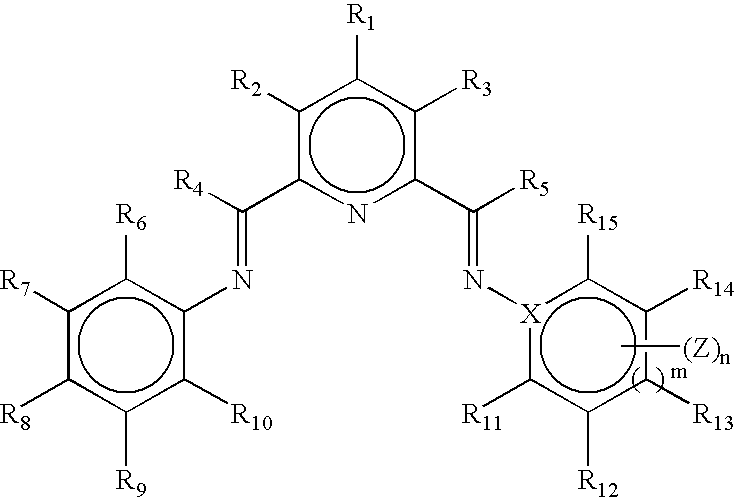
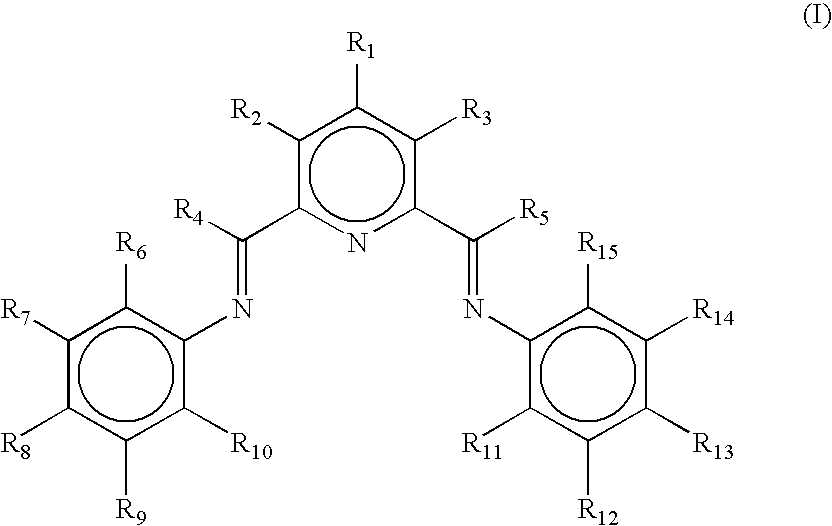
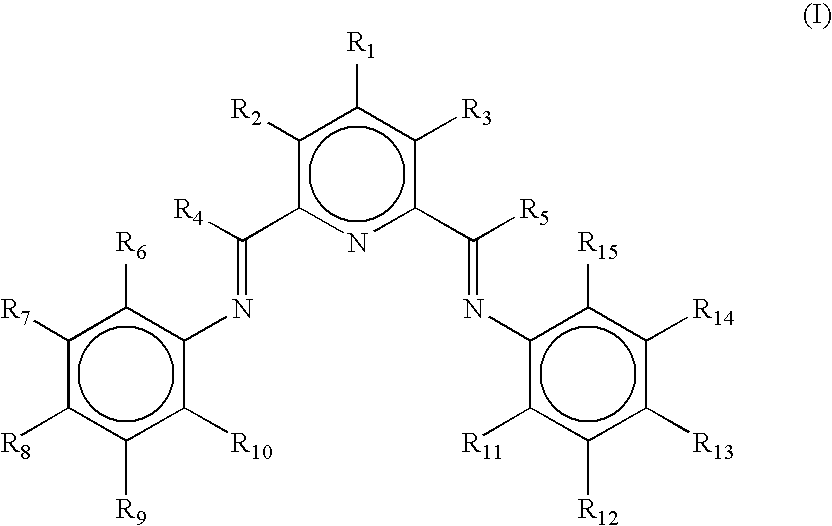
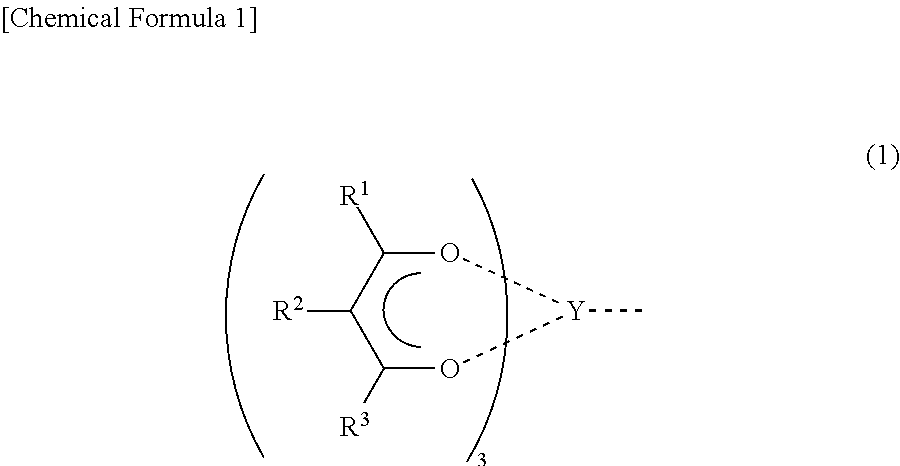
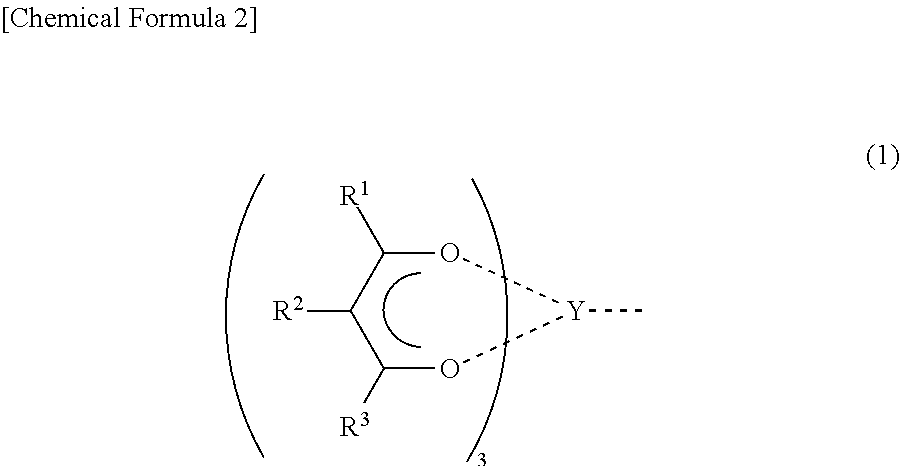
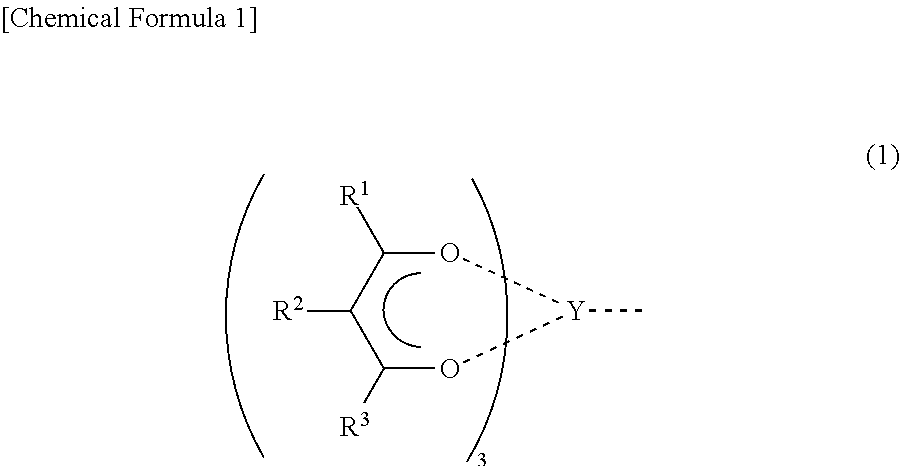
Non-symmetrical ligands of formula (I);bis-aryliminepyridine MXn complexes comprising a non-symmetrical ligand of formula (I), wherein M is a metal selected from Fe or Co, n is 2 or 3, and X is halide, optionally substituted hydrocarbyl, alkoxide, amide, or hydride; [bis-aryliminepyridine MYp.Ln+][NC−]q complexes, comprising a non-symmetrical ligand of formula (I), wherein Y is a ligand which may insert an olefin, M is Fe or Co, NC− is a non-coordinating anion and p+q is 2 or 3, matching the formal oxidation of the metal atom M, L is a neutral Lewis donor molecule and n=0, 1, or 2; and processes for the production of alpha-olefins from ethylene, using said complexes.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Cyclopentadienyl-containing low-valent early transition metal olefin polymerization catalysts
InactiveUS7119158B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsOxidation stateNon-coordinating anion
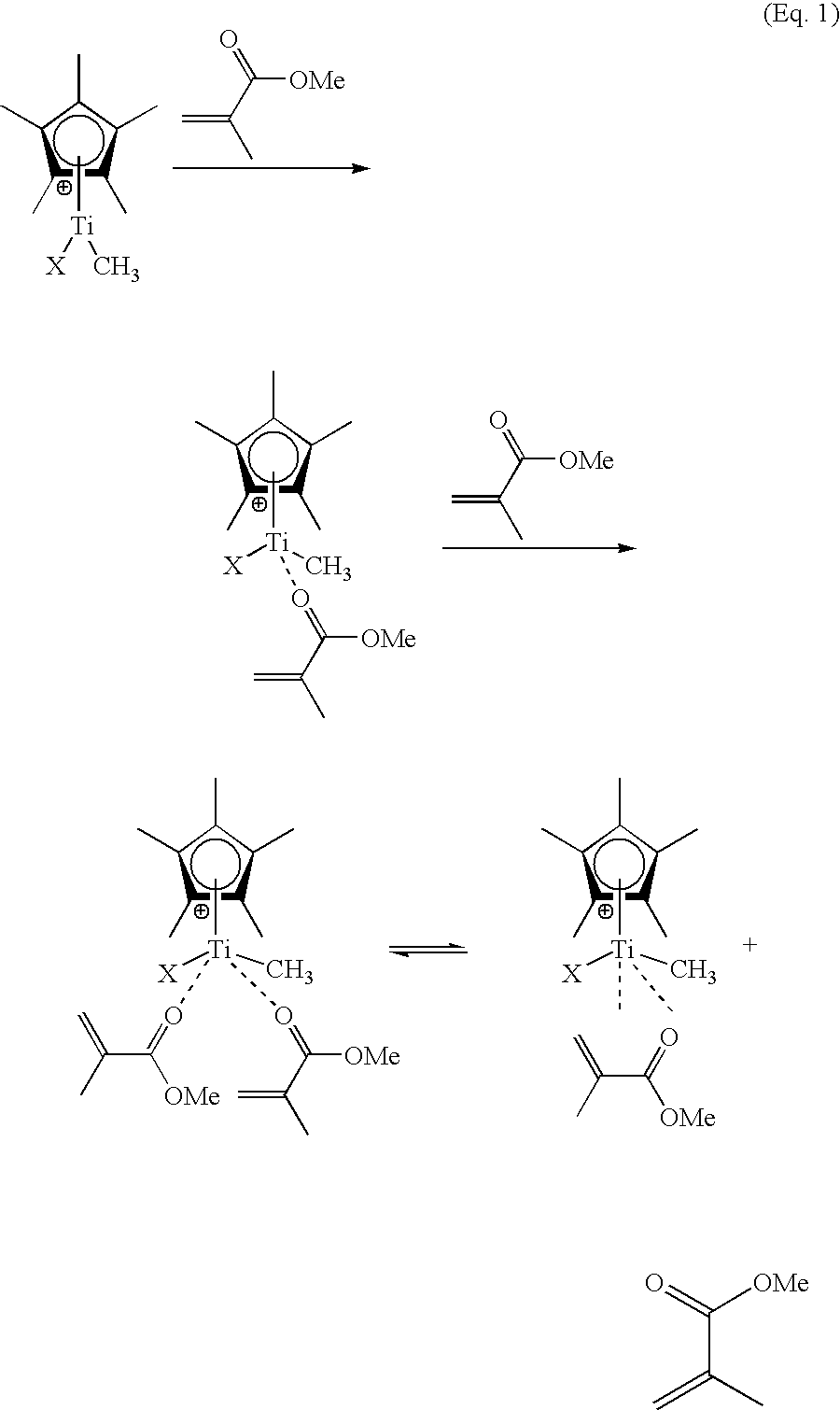
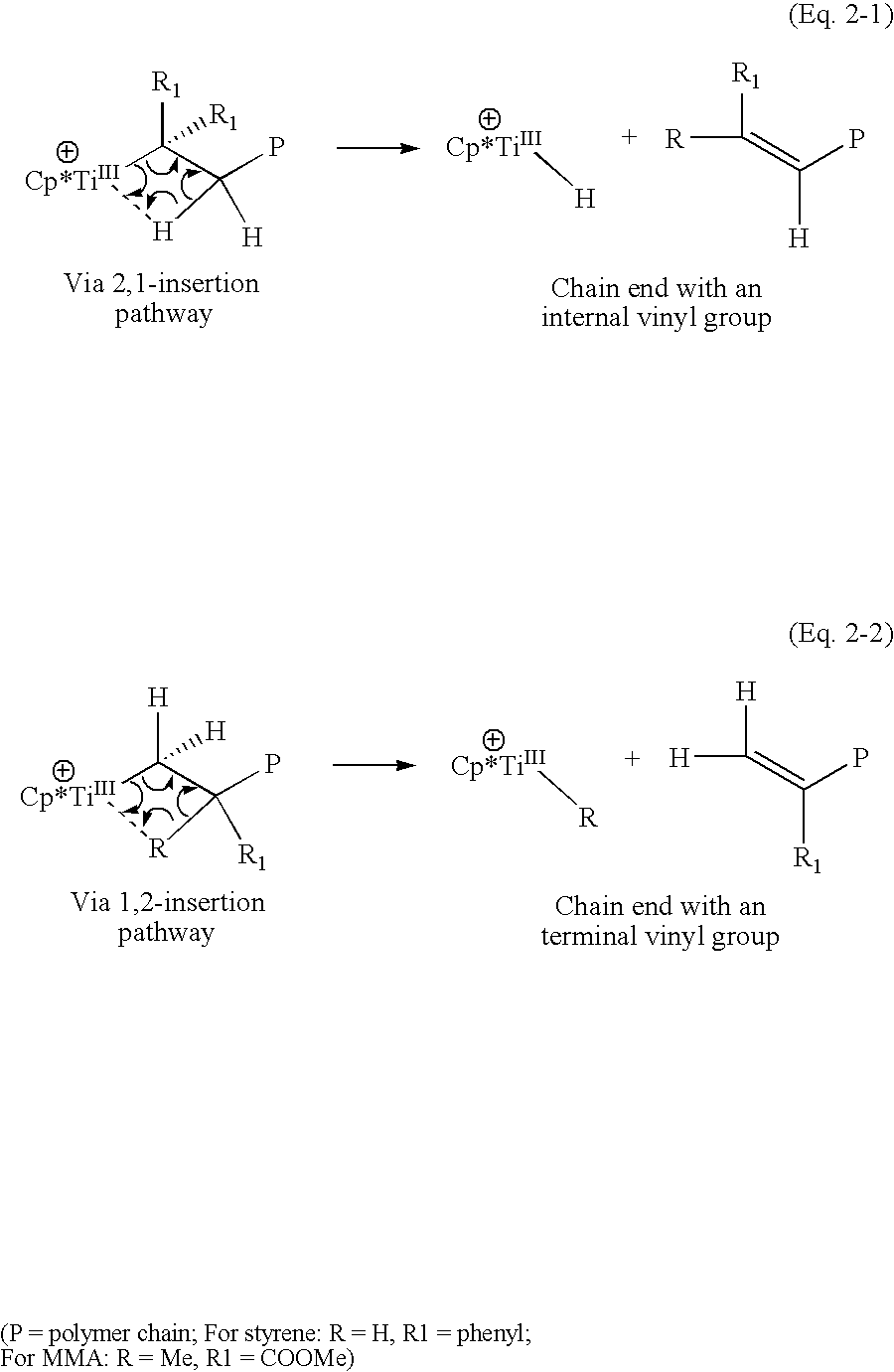
A catalyst system useful to polymerize and co-polymerize polar and non-polar olefin monomers is formed by in situ reduction with a reducing agent of a catalyst precursor comprising{Cp*MRR′n}+{A}−wherein Cp* is a cyclopentadienyl or substituted cyclopentadienyl moiety; M is an early transition metal; R is a C1–C20 hydrocarbyl; R′ are independently selected from hydride, C1–C20 hydrocarbyl, SiR″3, NR″2, OR″, SR″, GeR″3, SnR″3, and C═C-containing groups (R″=C1–C10 hydrocarbyl); n is an integer selected to balance the oxidation state of M; and A is a suitable non-coordinating anionic cocatalyst or precursor. This catalyst system may form stereoregular olefin polymers including syndiotactic polymers of styrene and methylmethacrylate and isotactic copolymers of polar and nonpolar olefin monomers such as methylmethacrylate and styrene.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Process for producing conjugated diene polymer
InactiveUS20110263803A1Efficient productionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsNon-coordinating anionHigh activity
Disclosed is a process for producing a conjugated diene polymer having a very high content of cis-1,4 structures by using an yttrium compound-containing catalyst that is relatively easy to handle and has a high activity. Specifically disclosed is a process for producing a conjugated diene polymer containing cis-1,4 structures at a ratio of 99% or higher, which is characterized by polymerizing a conjugated diene in the presence of a catalyst produced from (A) a specific yttrium compound, (B) an ionic compound consisting of a non-coordinating anion and a cation, and (C) an organoaluminum compound.
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Olefin polymerization catalysts derived from Group-15 cationic compounds and processes using them
InactiveUS6822057B2Effectively remove polar impurity from reactionReduced activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationProtonationOrganometallic catalysis
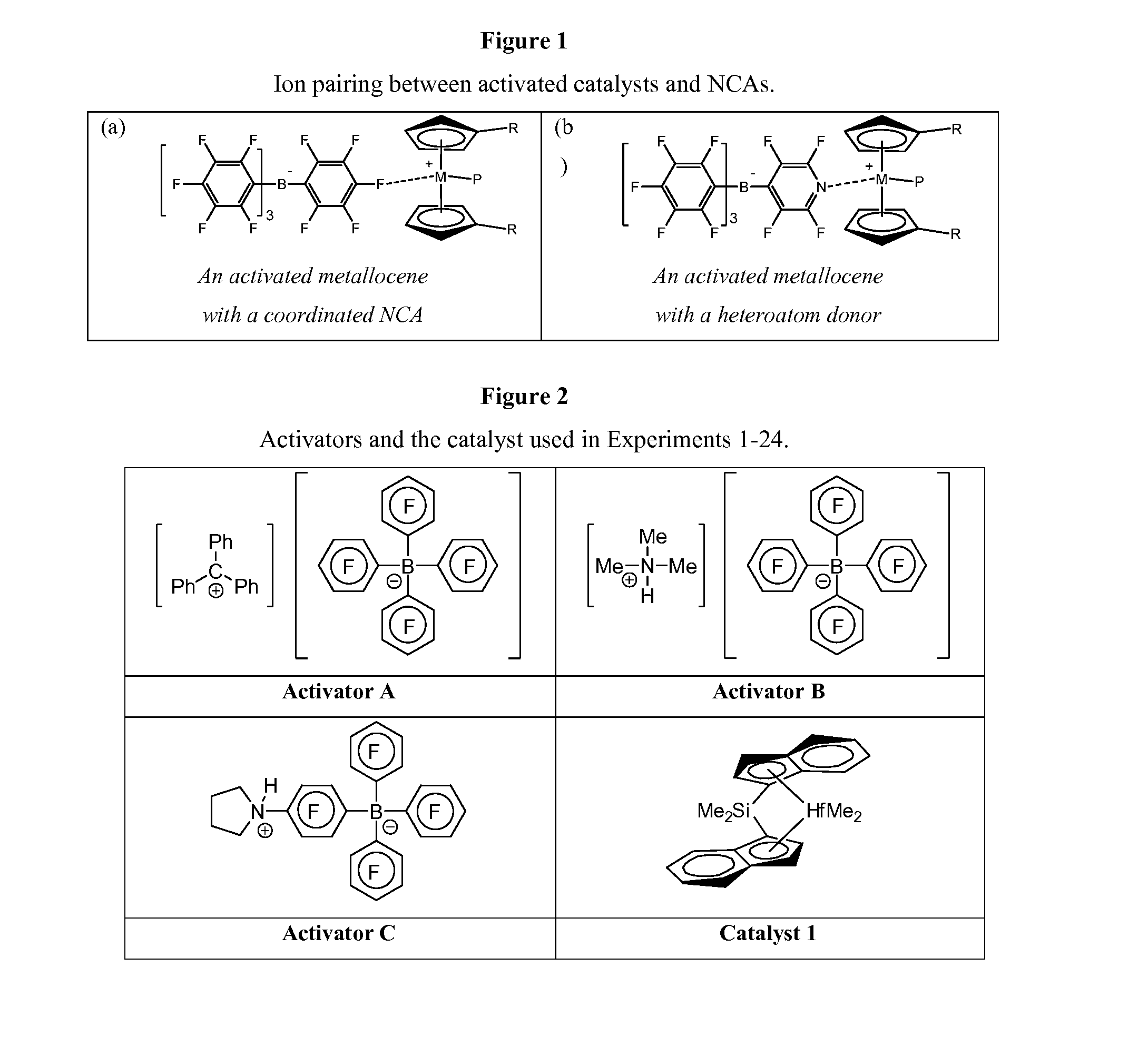
Fluorinated amine compounds, R'iArF-ER2, where ArF is a fluoroaryl substituent, E is nitrogen or phosphorous, each R is independently a C1-C20 hydrocarbyl substituent, or the two R's may be connected to form an unsubstituted or substituted C2-C20 cycloaliphatic substituent, R' is a C1-C20 hydrocarbyl or halogenated hydrocarbyl, and i is 0, 1 or 2 are disclosed. These compounds may be protonated and complexed with suitable substantially noncoordinating anions to prepare polymerization catalyst components. When these catalyst components are combined with organometallic catalyst precursors, the catalyst precursor is activated to a catalyst. This catalyst is combined with monomer under olefin polymerization conditions to prepare polymer. High number-average molecular weight polymers at high productivity rates were observed from using metallocene catalysts activated with [N-pentafluorophenyl pyrrolidinium][tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)borate].
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Transition metal complexes
InactiveUS20050215792A1Improve solubilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIron group organic compounds without C-metal linkagesSolubilityTransition metal atoms
A transition metal complex which is a bis-arylimine pyridine MXn complex or a [bis-arylimine pyridine MXp+][NC−]q complex comprising a bis-arylimine pyridine ligand and M is a transition metal atom; n matches the formal oxidation state of the transition metal atom M; X is halide, optionally substituted hydrocarbyl, alkoxide, amide, or hydride; NC− is a non-coordinating anion; and p+q matches the formal oxidation state of the transition metal atom M. The transition metal complexes of the present invention, their complexes with non-coordinating anions and catalyst systems containing such complexes have good solubility in non-polar media and chemically inert non-polar solvents especially aromatic hydrocarbon solvents. The catalyst systems can be used for a wide range of (co-)oligomerization, polymerization and dimerization reactions.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Polymeric supported catalysts for olefin polymerization
InactiveUS6426313B2Reduce pollutionEnhanced particle densityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationCross-linkProtonation
The described invention provides a low fouling, high particle density polymerization process and an olefin polymerization cocatalyst activator composition comprising a cross-linked polymer bead having a surface area of from about 1 to 20 m.sup.2 / g to which are bound a plurality of non-coordinating anions, where the polymeric support comprises ligands covalently bound to the central metal or metalloid atoms of said anions, and an effective number of cationic species to achieve a balanced charge. The invention also provides an olefin polymerization catalyst compositions comprising the reaction product of a) the foregoing cocatalyst activator, and b) an organometallic transition metal compound having ancillary ligands, at least one labile ligand capable of abstraction by protonation and at least one labile ligand into which an olefinic monomer can insert for polymerization. In a preferred embodiment, the polymeric support has a surface area of .ltoreq.10 m.sup.2 / g and is particularly suitable for use with high activity organometallic, transition metal catalyst compounds.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
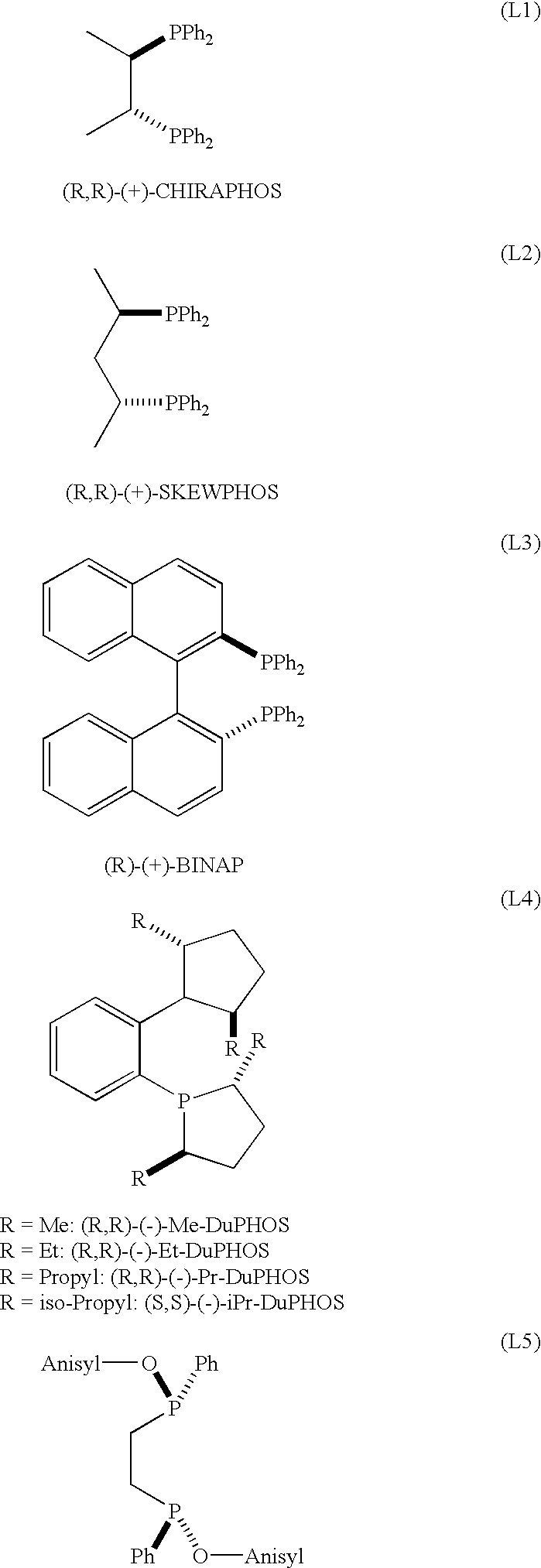
Ruthenium catalysts and their use in the asymmetric hydrogenation of weakly coordinating substrates
InactiveUS6214763B1Organic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAsymmetric hydrogenationDiphosphines
A catalyst of Ru comprising bidentate phosphine ligands is described which is obtained by a process that comprises treating equimolar amounts of an appropriate Ru complex and a bidentate diphosphine ligand with an acid of the formula H-Anion, wherein the anion is a non-coordinating anion, said acid being used in a ratio of 1 molar equivalent per mole of Ru complex and the treatment being carried out in a non-coordinating or weakly coordinating medium, under an oxygen-free atmosphere.Said catalyst is useful for the preparation of the preferred isomer of the Hedione(R), having the configuration (+)-(1R)-cis, and of many other substrates comprising highly hindered carbon-carbon double bonds.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Process to Produce Ethylene Propylene Copolymers
This invention relates to a copolymer prepared using two or more non-coordinating anion activators comprising a first C2 to C12 alpha olefin (such as ethylene), a second C3 to C12 alpha olefin (such as propylene) different from the first alpha olefin, and diene (such as ethylidene norbornene and / or vinyl norbornene), where the polymer has: a) first alpha olefin (ethylene) content of 35 to 90 mol %; b) second alpha olefin (propylene) content of 9.8 to 64.8 mol %; c) diene content of 0.2 to 5 mol %; d) a branching index g′ave of 0.95 or more; e) a complex viscosity ratio (eta*(0.01 rad / s) / eta*(100 rad / s), at 125° C.) greater than 1.1*Y0, where Y0=Y1+{[(Y2−Y1) / (X2−X1)](X0−X1)}, where X0 is the wt % of a first non-coordinating anion activator, NCA1, used to prepare the copolymer (based upon weight of NCA1 and a second non-coordinating anion activator, NCA2, used to prepare the copolymer), X1=0, X2=100, Y1=complex viscosity ratio of polymer made with 100% NCA1 and 0% NCA2, Y2 is complex viscosity ratio of polymer made with 100% NCA2 and 0% NCA1, where NCA1 has an Mw lower than the Mw of NCA2; f) an Mw / Mn of 4.0 or less; g) a melting point of 30° C. or less; and h) a Composition Distribution Breadth Index of 50% or more.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Ruthenium catalysts and method for making same
InactiveUS6455460B1Organic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDiphosphinesDouble bond
A catalyst of ruthenium (II) comprising bidentate phosphine ligands is described which is obtained by a process that comprises treating equimolar amounts of an appropriate Ru complex and a bidentate diphosphine ligand with an acid of the formula H-Anion, wherein the anion is a non-coordinating anion, said acid being used in a ratio of 1 molar equivalent per mole of Ru complex and the treatment being carried out in a non-coordinating or weakly coordinating medium, under an oxygen-free atmosphere. Said catalyst is useful for the preparation of the preferred isomer of the Hedione(R), having the configuration (+)-(1R)-cis, and of many other substrates comprising highly hindered carbon-carbon double bonds.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Process to produce polyalphaolefins
Liquid poly-alpha-olefins having a KV100 of 2 to 6000 cSt, 20 weight percent dimer or less and a viscosity index of 60 or more are obtained by contacting in a reaction zone, in the presence of from 0 to 60 psi hydrogen, C3 to C20 alpha-olefin monomers with a non-coordinating anion activator, a single bridged meso-metallocene transition metal compound having less than about 35 wt % racemic isomer, and a co-activator. The molar ratio of activator to meso-metallocene is from 10:1 to 0.1:1, and the alpha-olefin monomers in the feed components are present in at least 20 wt % or more based upon the weight of the meso-metallocene, non-coordinating anion activator, co-activator, monomers, and solvent or diluent. The productivity of the process is at least 50,000 g of total product per gram of transition metal compound and no more than 5% monomer is converted from olefin to alkane.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Polyolefins made by catalyst comprising a noncoordinating anion and articles comprising them
ActiveUS20050123778A1Low mobilityReduce dielectric lossOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
Polymers made by transition metal catalyst systems comprising a bulky noncoordinating anion (NCA) as cocatalyst component. In comparison to polymers containing a conventional NCA, these polymers show a considerably lower dielectric loss, making them suitable for insulation applications such as for power cable.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Conjugated diene polymer manufacturing method, polybutadiene, and rubber composition utilizing the same
InactiveUS20110269899A1Excellent rubber propertyImprove workabilitySpecial tyresPolymer scienceMooney viscosity
Provided by using a catalyst containing an yttrium compound is conjugated diene polymer with very low solution viscosity, improved workability, high degree of branching, and high content of cis-1,4 structures. Also provided is a rubber composition utilizing the polymer and allowing excellent dispersion of reinforcing agent. According to a method of manufacturing a conjugated diene polymer characterized by polymerizing a conjugated diene at 50 to 120° C. in the presence of a catalyst obtained from (A) an yttrium compound, (B) an ionic compound consisting of a non-coordinating anion and a cation, and (C) an organoaluminum compound, the conjugated diene polymer has the following characteristics that: (1) a ratio (Tcp / ML1+4) between a 5 wt % toluene solution viscosity (Tcp) measured at 25° C. and a Mooney viscosity (ML1+4) at 100° C. is 0.1 to 1.2; and (2) a content of cis-1,4 structures is 80% or higher, and a content of 1,2 structures is lower than 5%.
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Olefin polymerization catalysts derived from Group-15 cationic compounds and processes using them
InactiveUS20020115806A1Speed up the processAchieve benefitsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationProtonationOrganometallic catalysis
Fluorinated amine compounds, R'iArF-ER2, where ArF is a fluoroaryl substituent, E is nitrogen or phosphorous, each R is independently a C1-C20 hydrocarbyl substituent, or the two R's may be connected to form an unsubstituted or substituted C2-C20 cycloaliphatic substituent, R' is a C1-C20 hydrocarbyl or halogenated hydrocarbyl, and i is 0, 1 or 2 are disclosed. These compounds may be protonated and complexed with suitable substantially noncoordinating anions to prepare polymerization catalyst components. When these catalyst components are combined with organometallic catalyst precursors, the catalyst precursor is activated to a catalyst. This catalyst is combined with monomer under olefin polymerization conditions to prepare polymer. High number-average molecular weight polymers at high productivity rates were observed from using metallocene catalysts activated with [N-pentafluorophenyl pyrrolidinium][tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)borate].
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Catalyst composition
InactiveUS7196031B2Increase contentNarrow molecular weight distributionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationAluminoxaneRare earth metal compounds
A catalyst composition for polymerization of a conjugated diene or copolymerization of a conjugated diene and an aromatic vinyl compound, which comprises the following components: (A) a metallocene-type complex of a rare earth metal compound (samarium complex etc.), and (B) an ionic compound composed of a non-coordinate anion and a cation (triphenylcarbonium tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)borate etc.) and / or an aluminoxane. The catalyst composition is useful for producing a polymer having a high cis-1,4-configuration content in the microstructure and a narrow molecular weight distribution.
Owner:RIKEN
Catalyst composition and process for producing copolymer
InactiveUS6960631B2High molecular weightNarrow molecular weight distributionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationAluminoxaneRare earth metal compounds
A method for block copolymerization of a conjugated diene and an aromatic vinyl compound, which comprises the steps of carrying out homopolymerization of the conjugated diene in the presence of a catalyst composition comprising the following components: (A) a metallocene type complex of a rare earth metal compound, and (B) an ionic compound composed of a non-coordinate anion and a cation and / or an aluminoxane, and then adding the aromatic vinyl compound, and a catalyst composition for polymerization of a conjugated diene or copolymerization of a conjugated diene and an aromatic vinyl compound, which comprises the following components: (D) a neodymium complex, and (B) an ionic compound composed of a non-coordinate anion and a cation and / or an aluminoxane.
Owner:RIKEN
Catalyst system and process for olefin polymerization
InactiveCN102112499AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsPhotochemistryCarbon atom
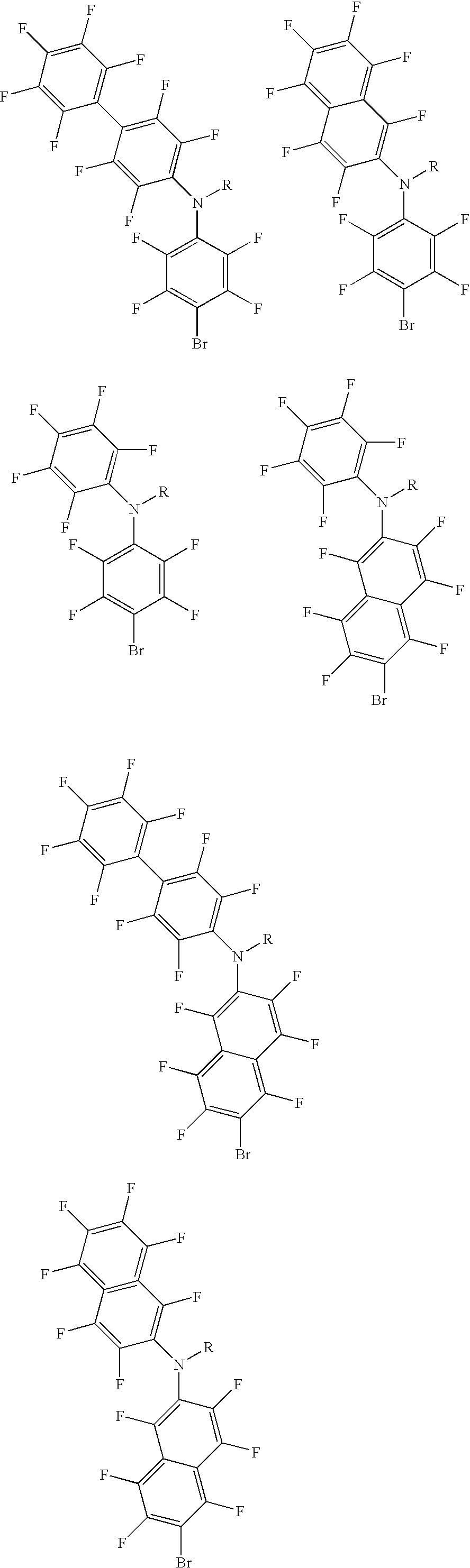
The present application relates to a new catalyst system for the polymerization of olefins, comprising a new ionic activator having the formula: [R<1>R<2>R<3>AH]<+>[Y]<->, wherein [Y]<-> is a non-coordinating anion (NCA), A is nitrogen or phosphorus, R<1> and R<2> are hydrocarbyl groups or heteroatom-containing hydrocarbyl groups and together form a first, 3- to 10-membered non-aromatic ring with A, wherein any number of adjacent ring members may optionally be members of at least one second, aromatic or aliphatic ring or aliphatic and / or aromatic ring system of two or more rings, wherein said at least one second ring or ring system is fused to said first ring, and wherein any atom of the first and / or at least one second ring or ring system is a carbon atom or a heteroatom and may be substituted independently by one or more substituents selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, halogen atom C1 to C10 alkyl, C5 to C15 aryl, C6 to C25 arylalkyl, and C6 to C25 alkylaryl, and R<3> is a hydrogen atom or C1 to C10 alkyl, or R<3> is a C1 to C10 alkylene group that connects to said first ring and / or to said at least one second ring or ring system. The present application also relates to a process for the polymerization of olefins, preferably propylene, using this and other catalyst systems, as well as to polymers made by said process.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com