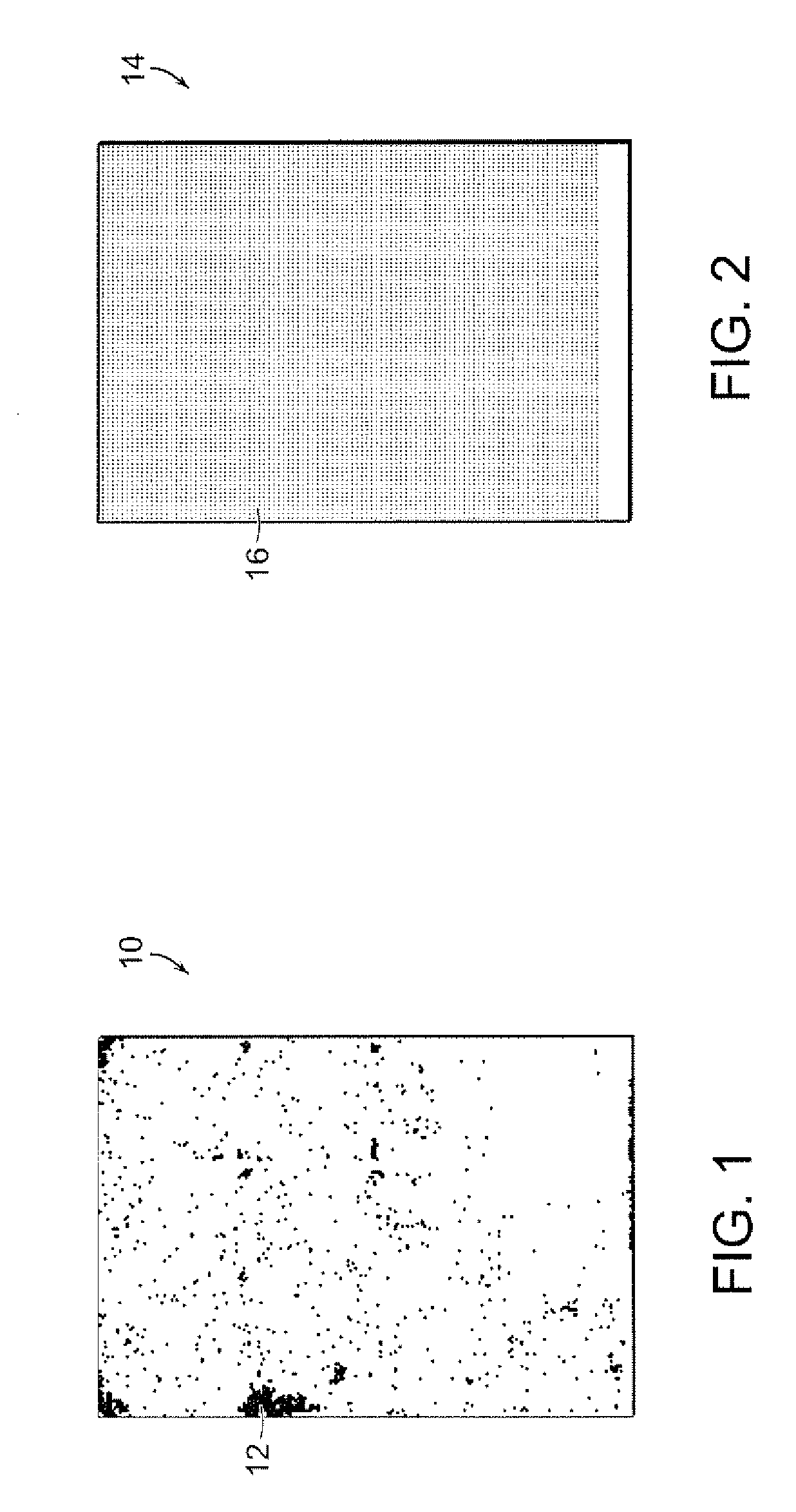
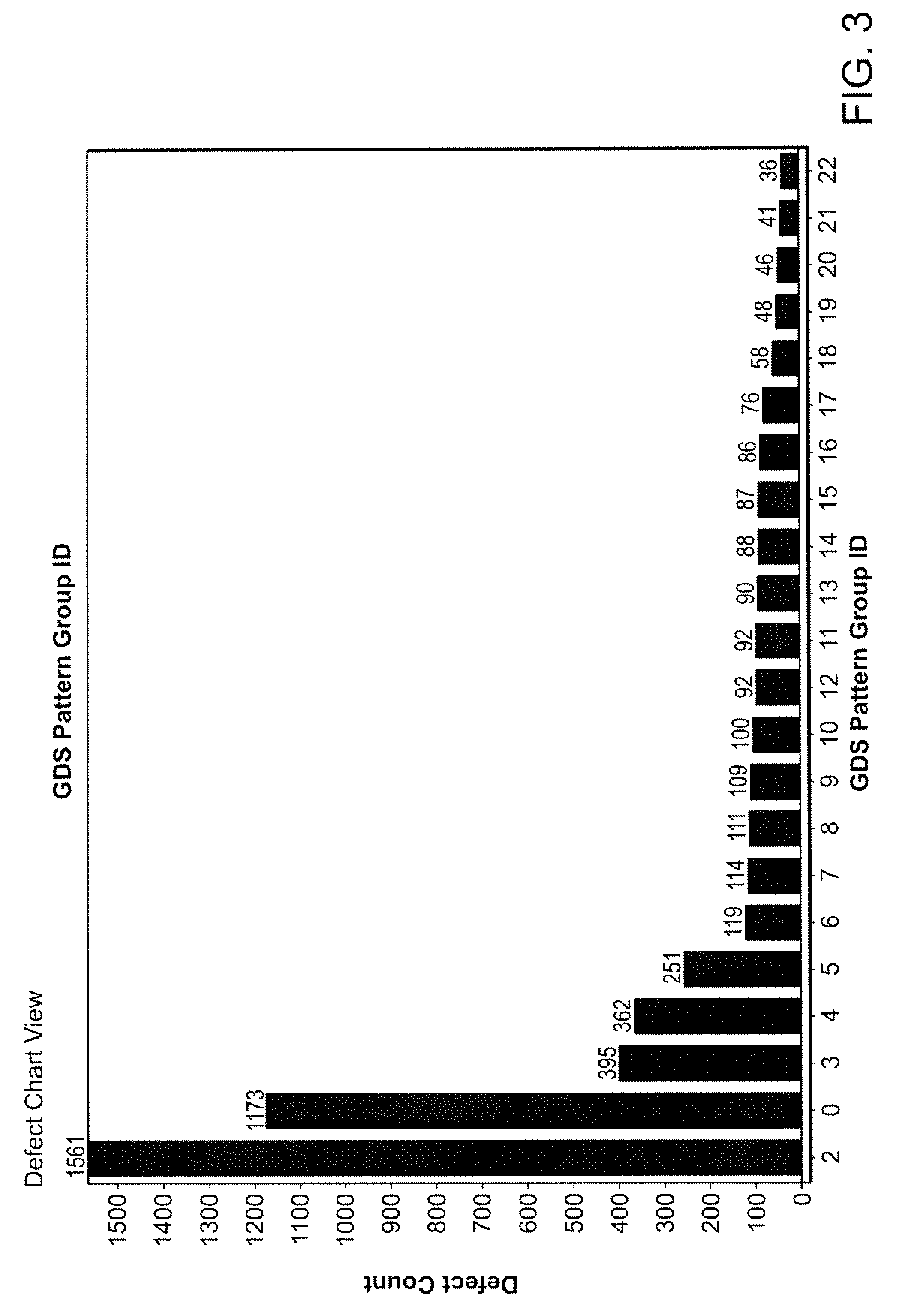
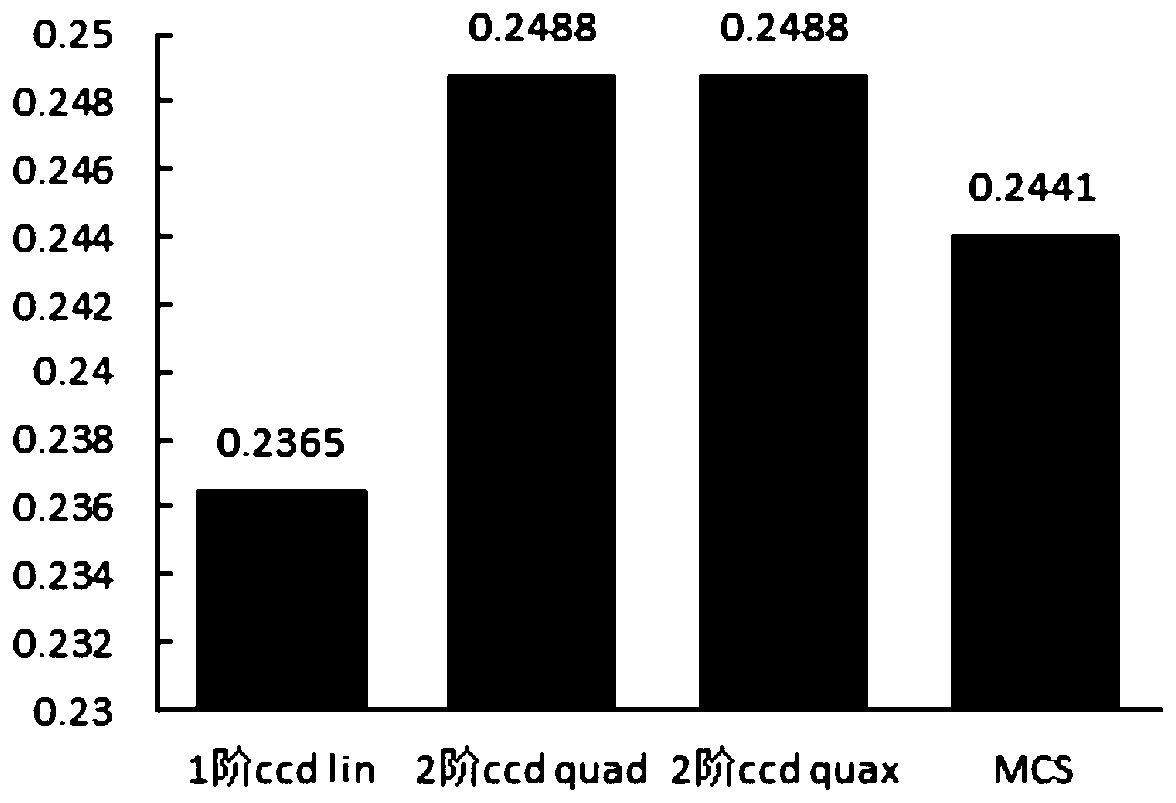
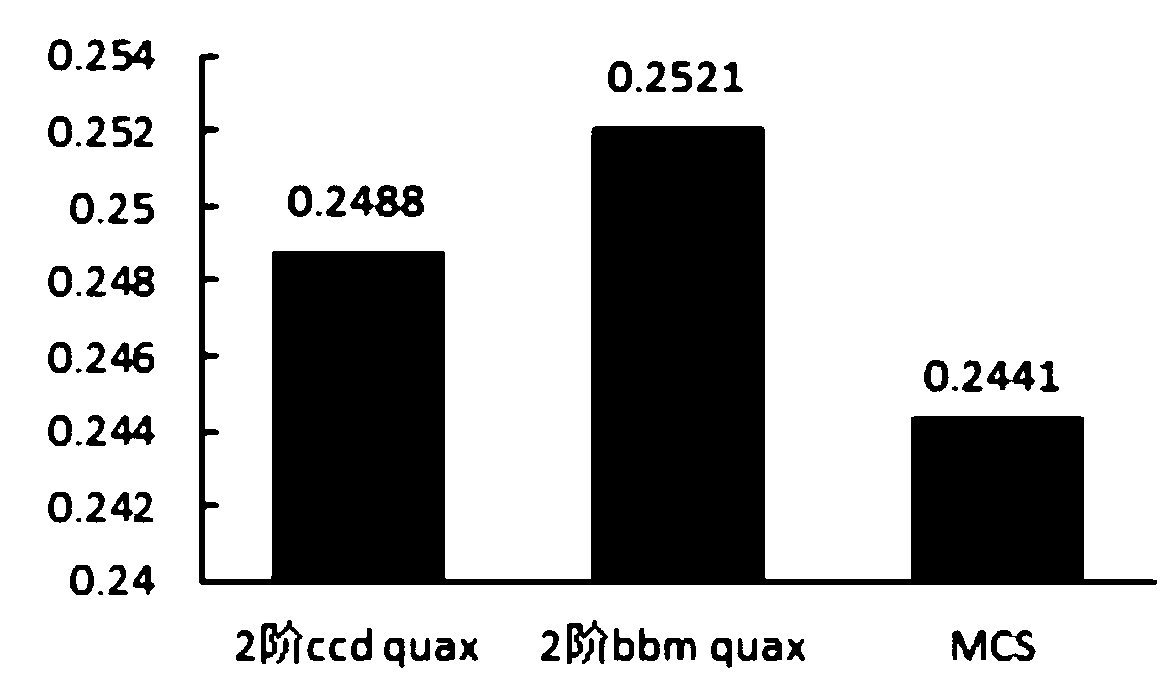
Patents
Literature
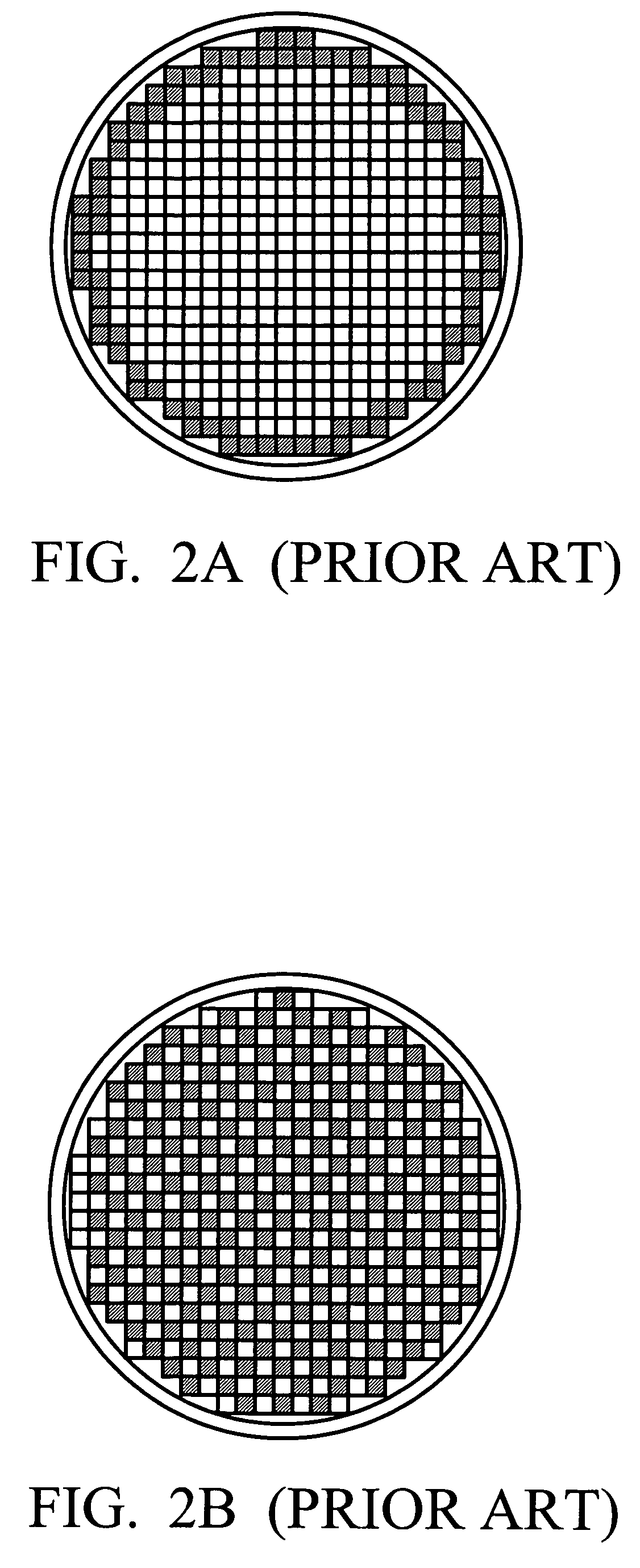
44 results about "Random defects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
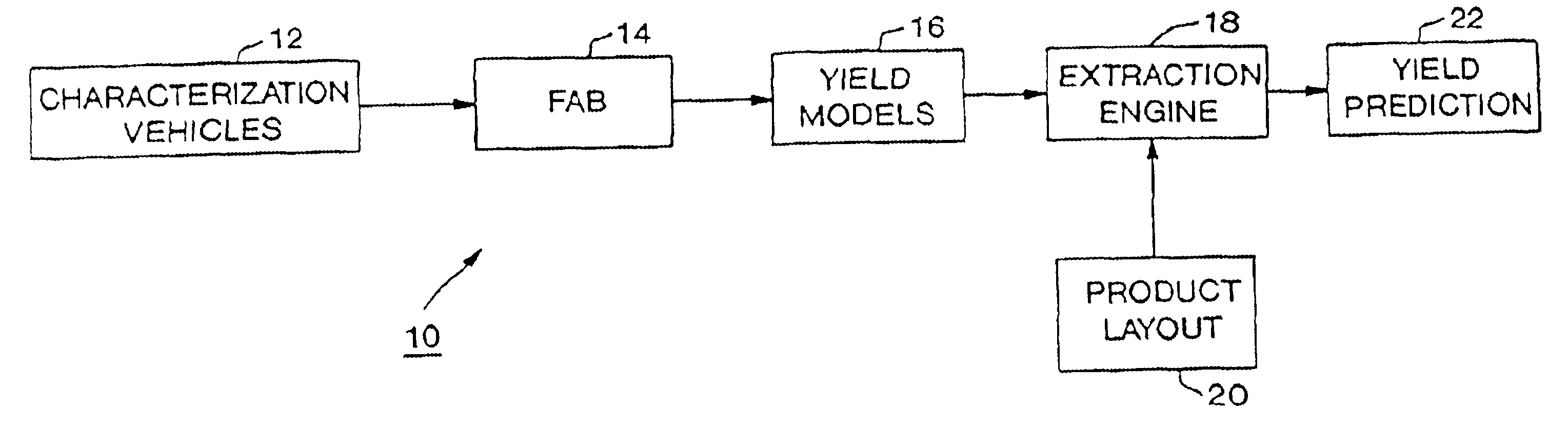
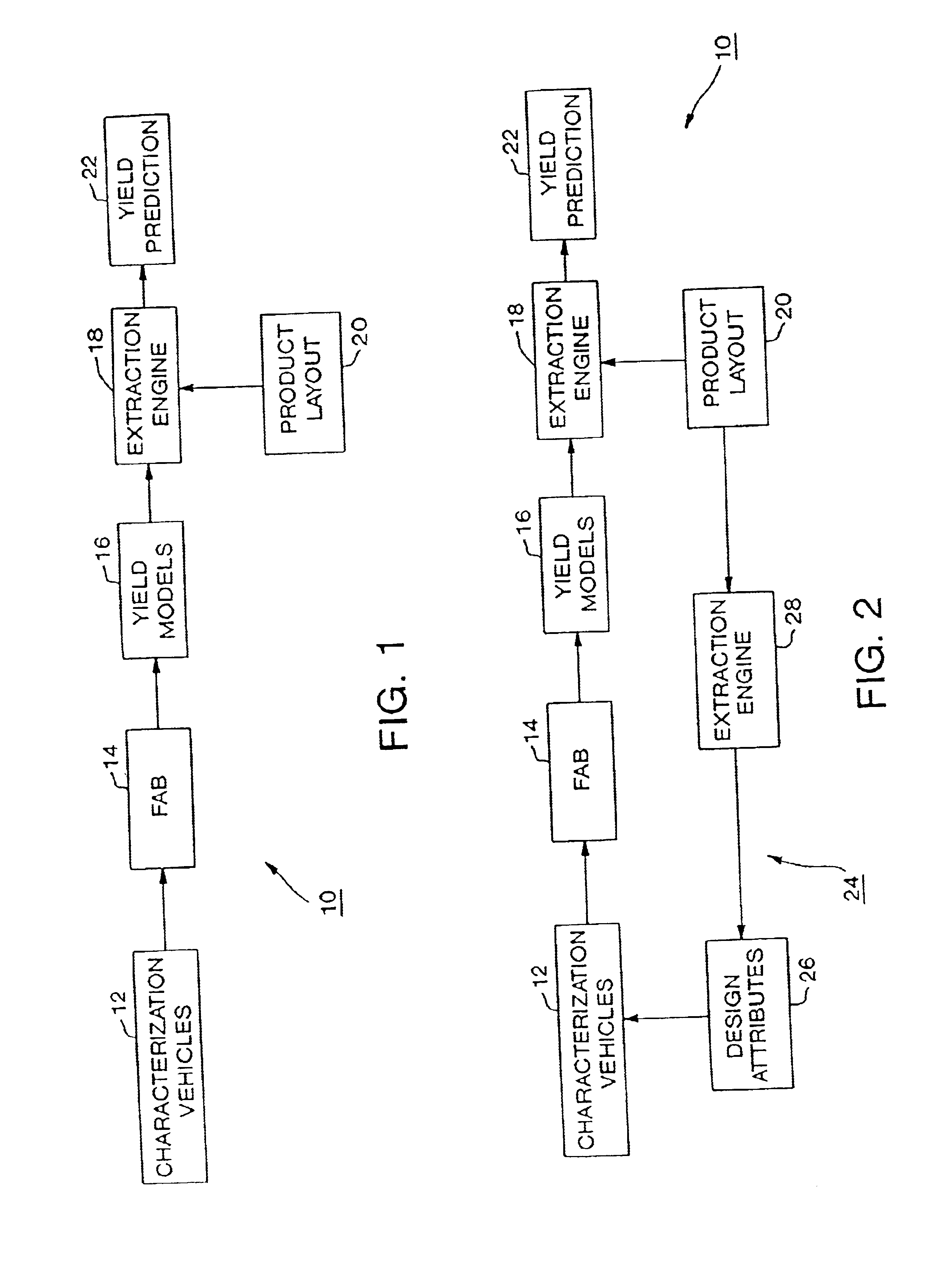
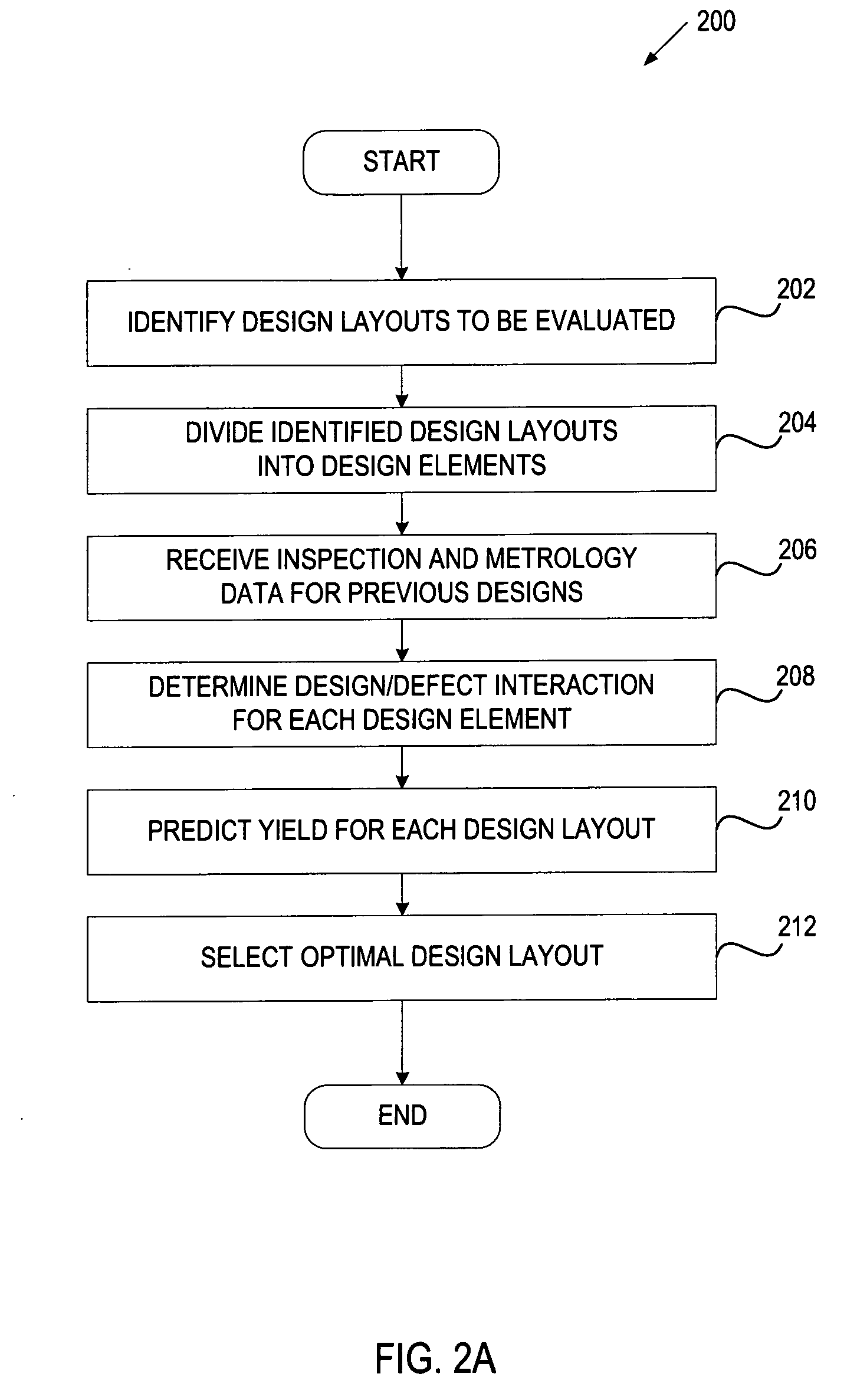
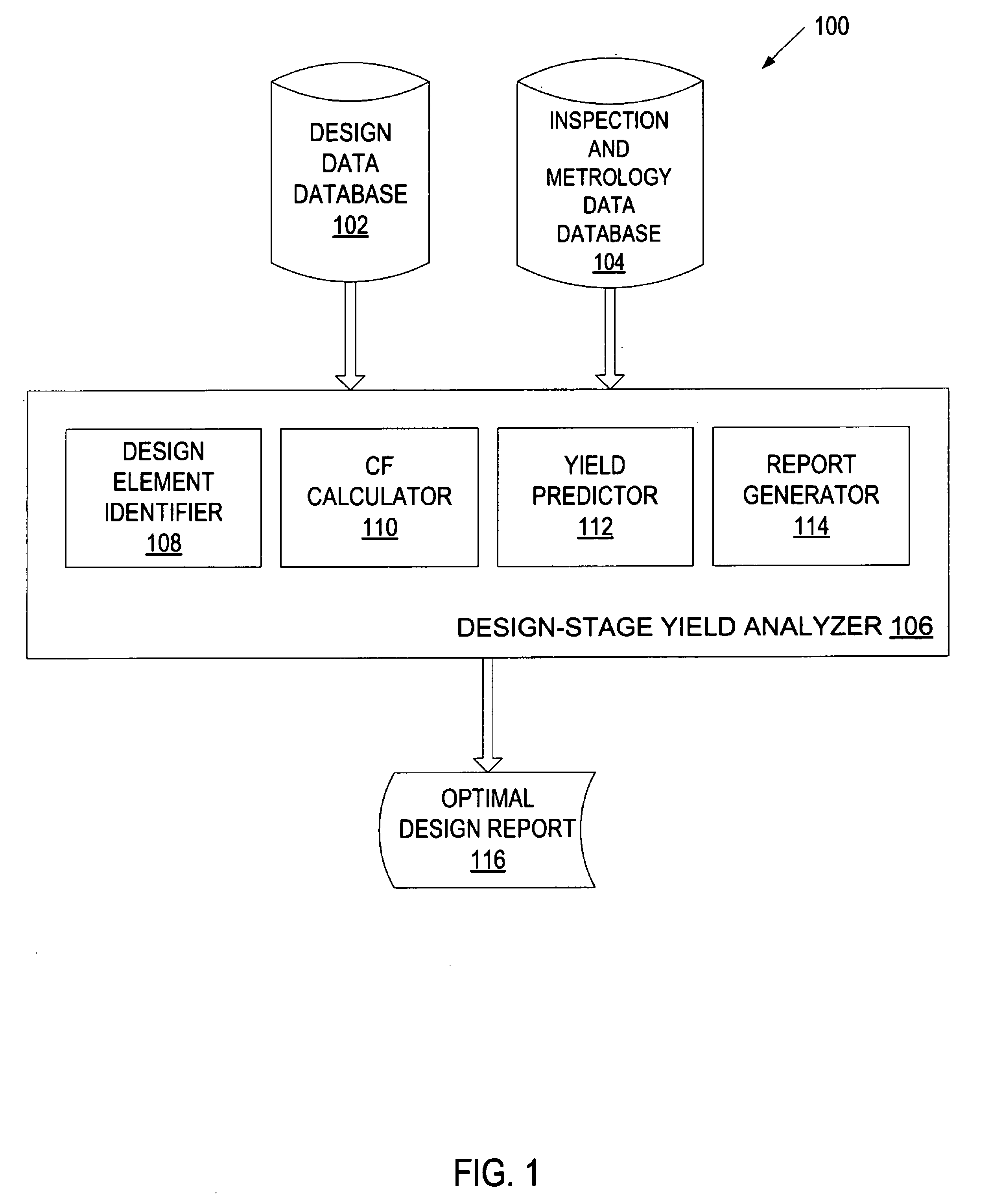
System and method for product yield prediction
InactiveUS6901564B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementComputer controlEngineeringRandom defects
A yield for an integrated circuit is predicted by processing a wafer to have a portion fabricated with at least one layout attribute of the integrated circuit. The portion of the wafer is analyzed to determine an actual yield associated with the at least one layout attribute. A systematic yield associated with the at least one layout attribute is determined based on the actual yield and a predicted yield associated with the at least one layout attribute. The predicted yield assumes that random defects are the only yield loss mechanism. A yield of an actual or proprosed product layout is predicted for the integrated circuit based on the systematic yield.
Owner:PDF SOLUTIONS INC
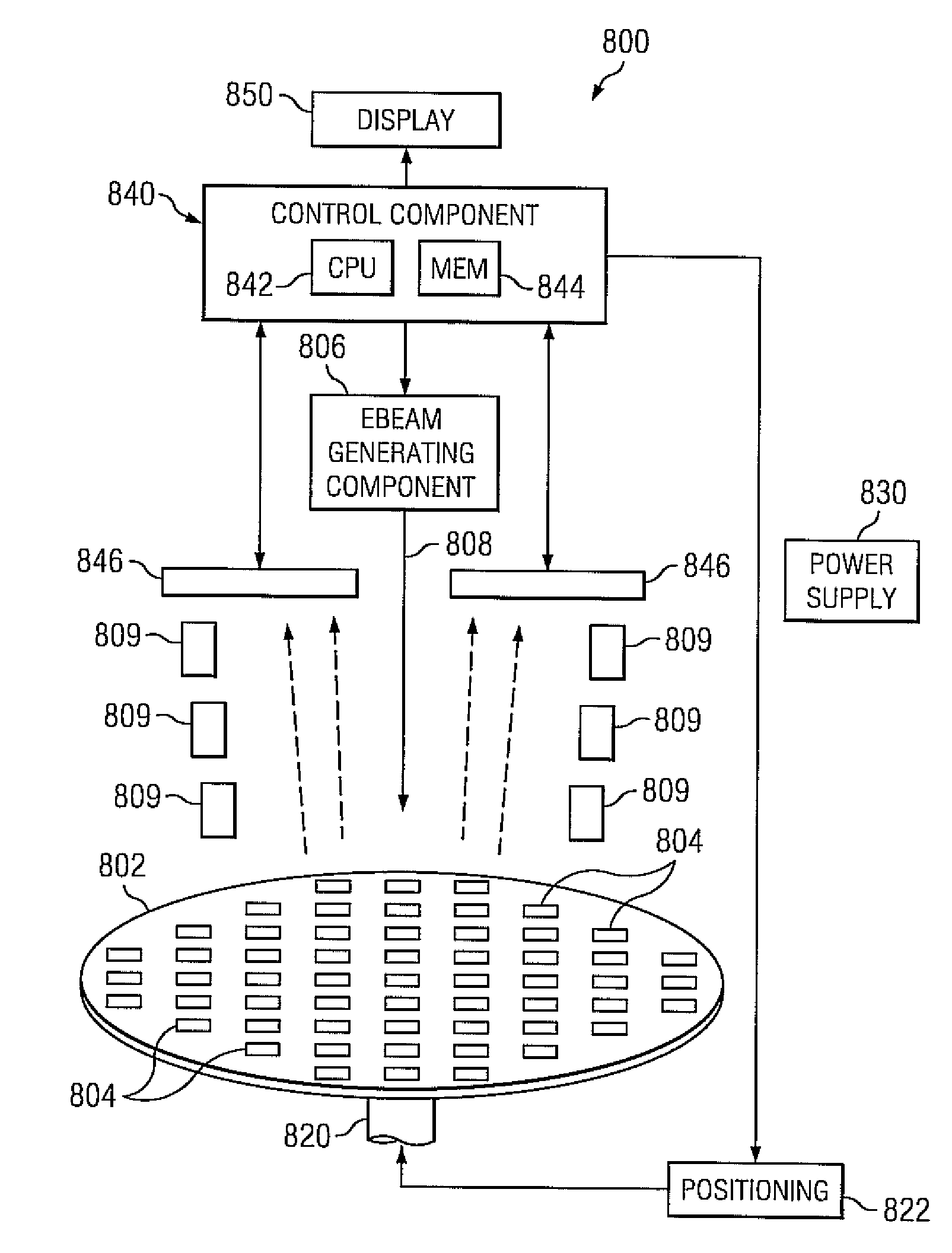
Test structures for e-beam testing of systematic and random defects in integrated circuits
InactiveUS20090102501A1Non-uniform stressMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectron beam testingDislocation
In accordance with the invention, there are electron beam inspection systems, electron beam testable semiconductor test structures, and methods for detecting systematic defects, such as, for example contact-to-gate shorts, worm hole leakage paths, holes printing issues, and anomalies in sparse holes and random defects, such as, current leakage paths due to dislocations and pipes during semiconductor processing.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
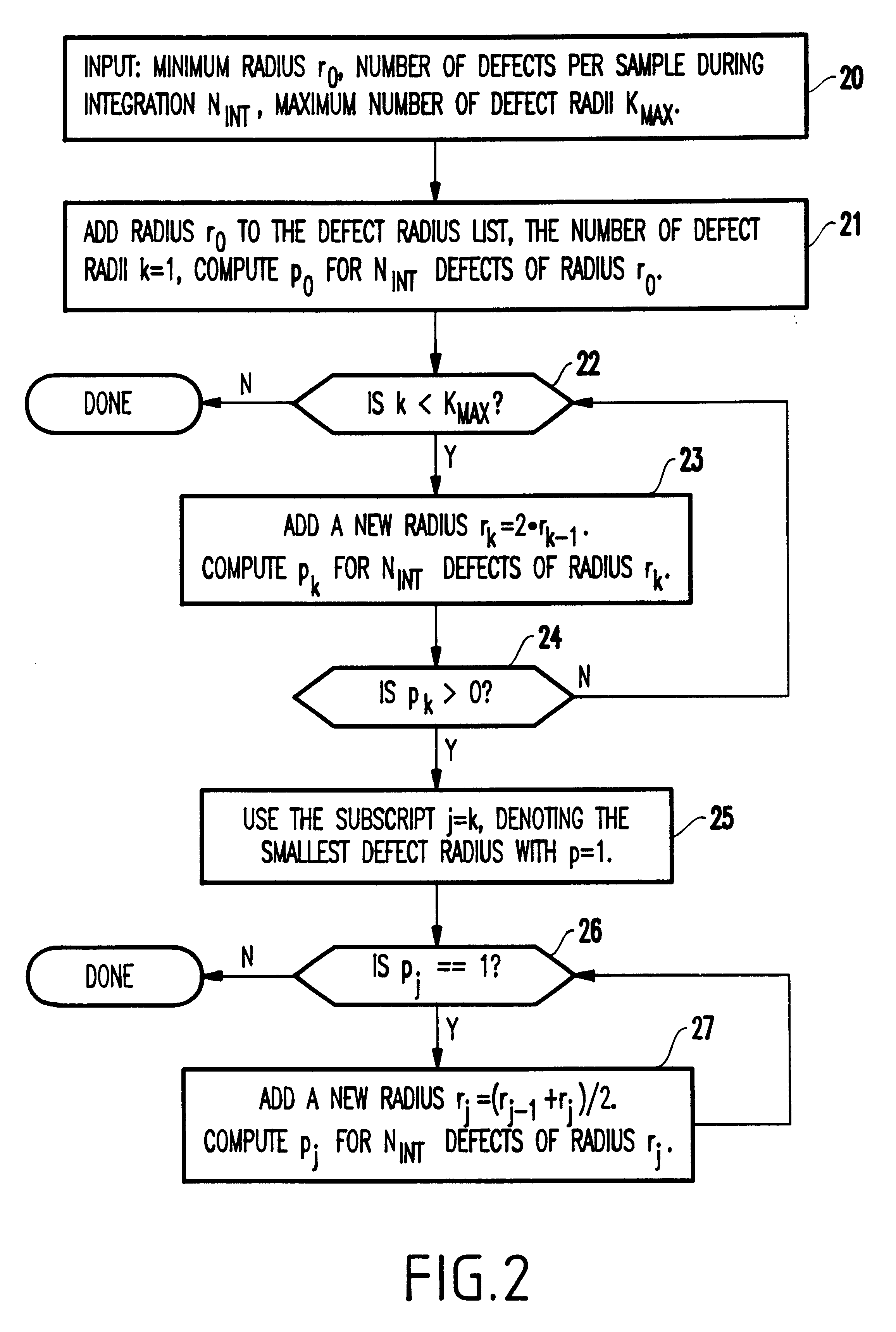
Method for prediction random defect yields of integrated circuits with accuracy and computation time controls
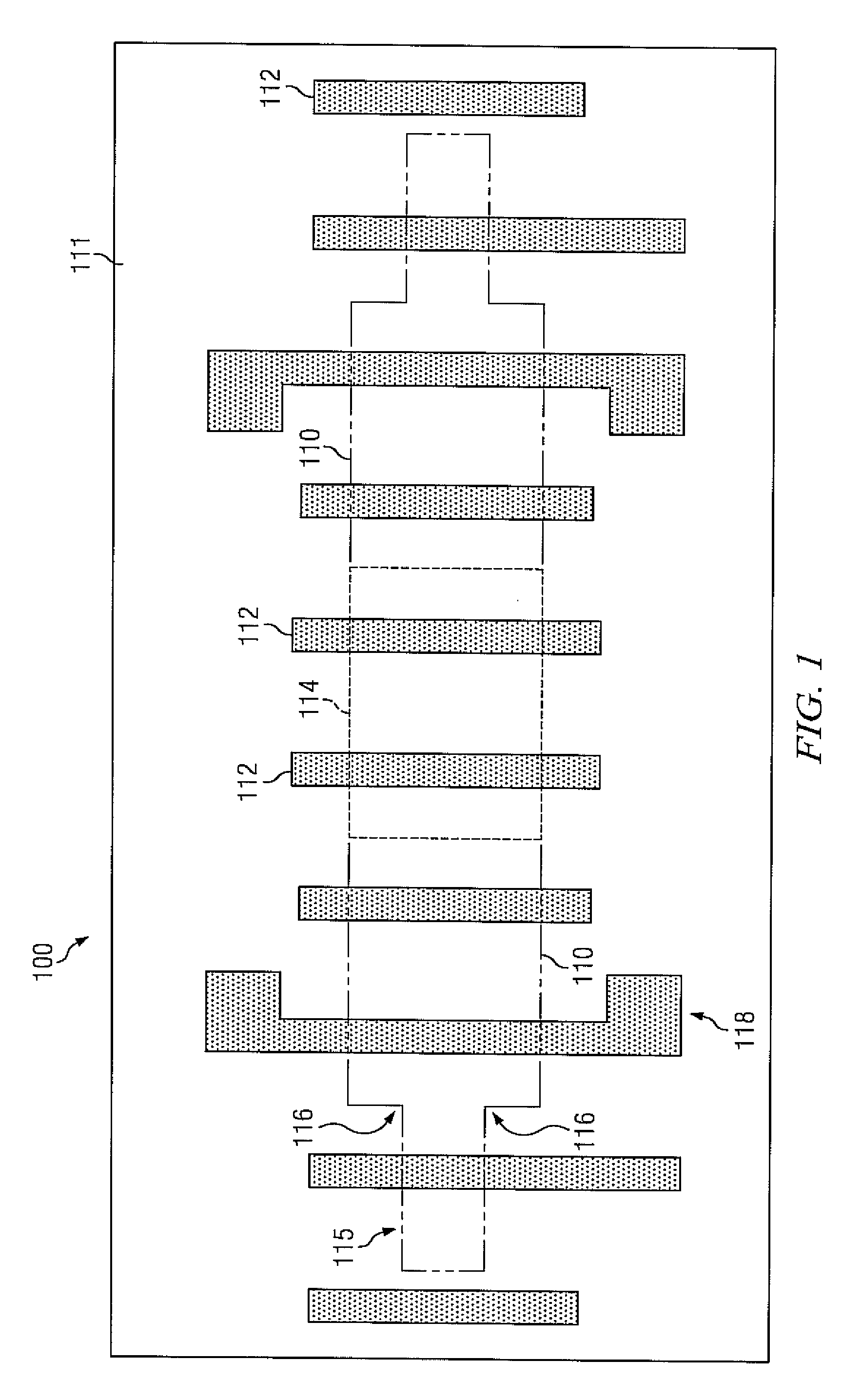
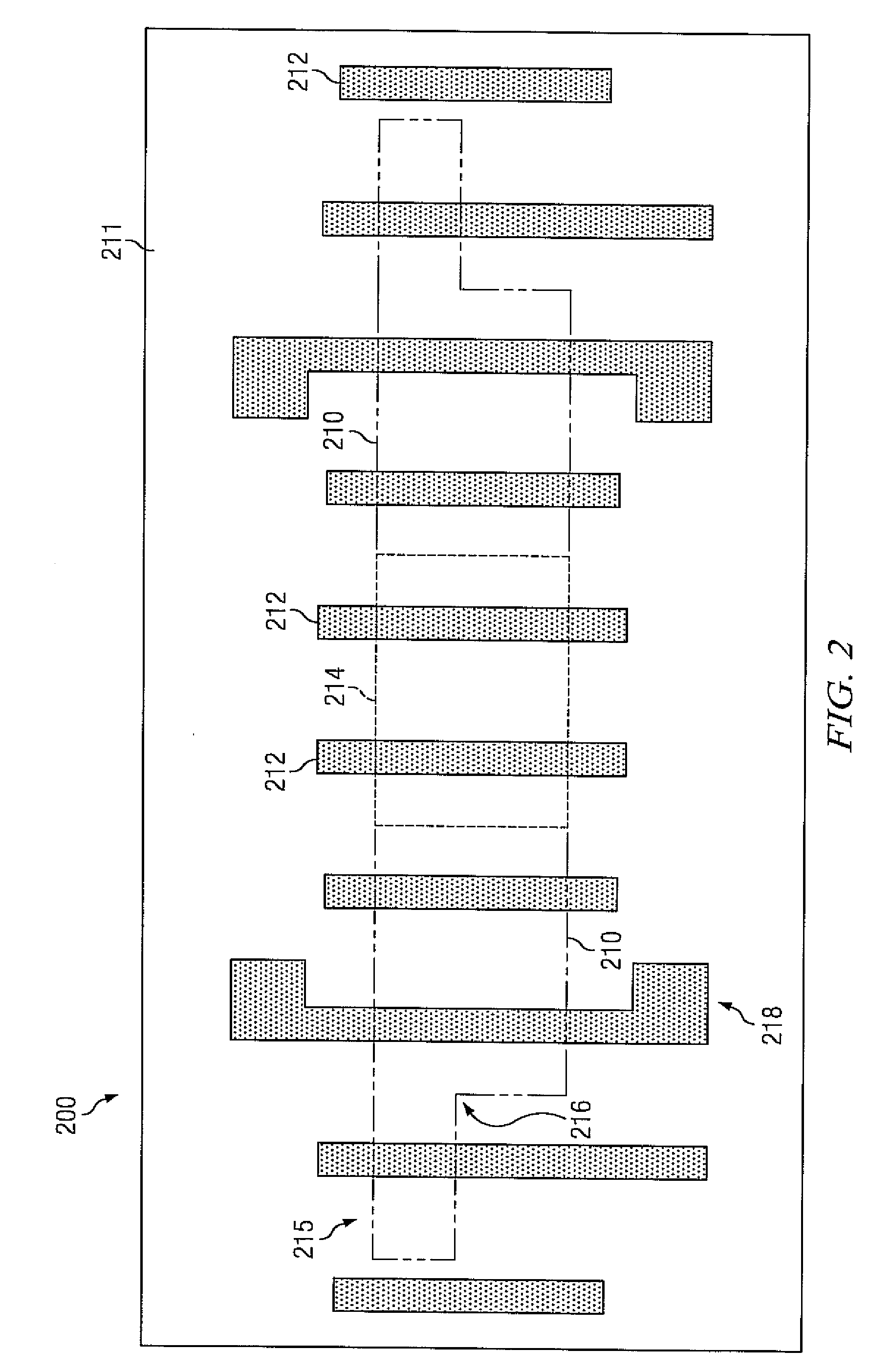
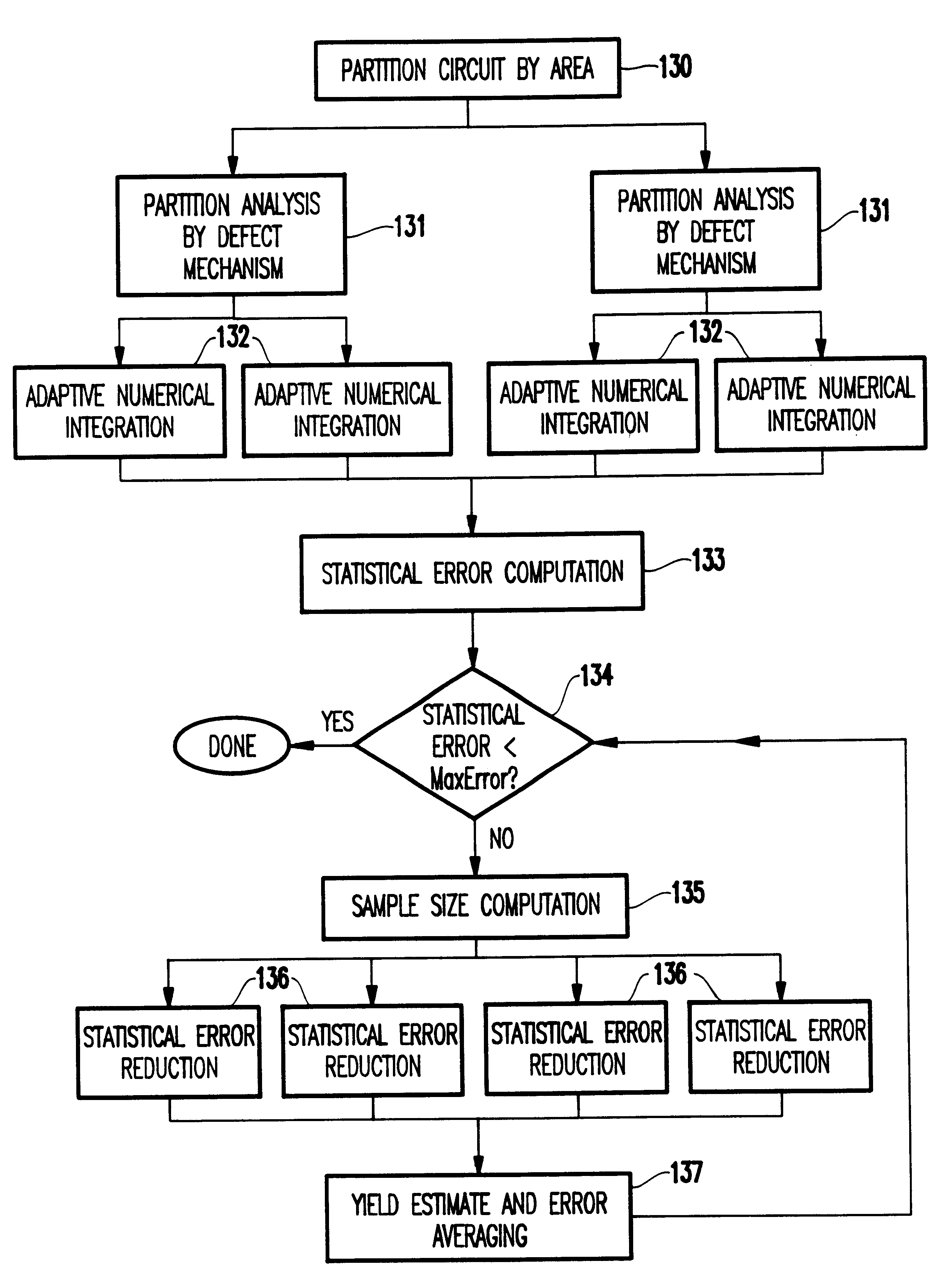
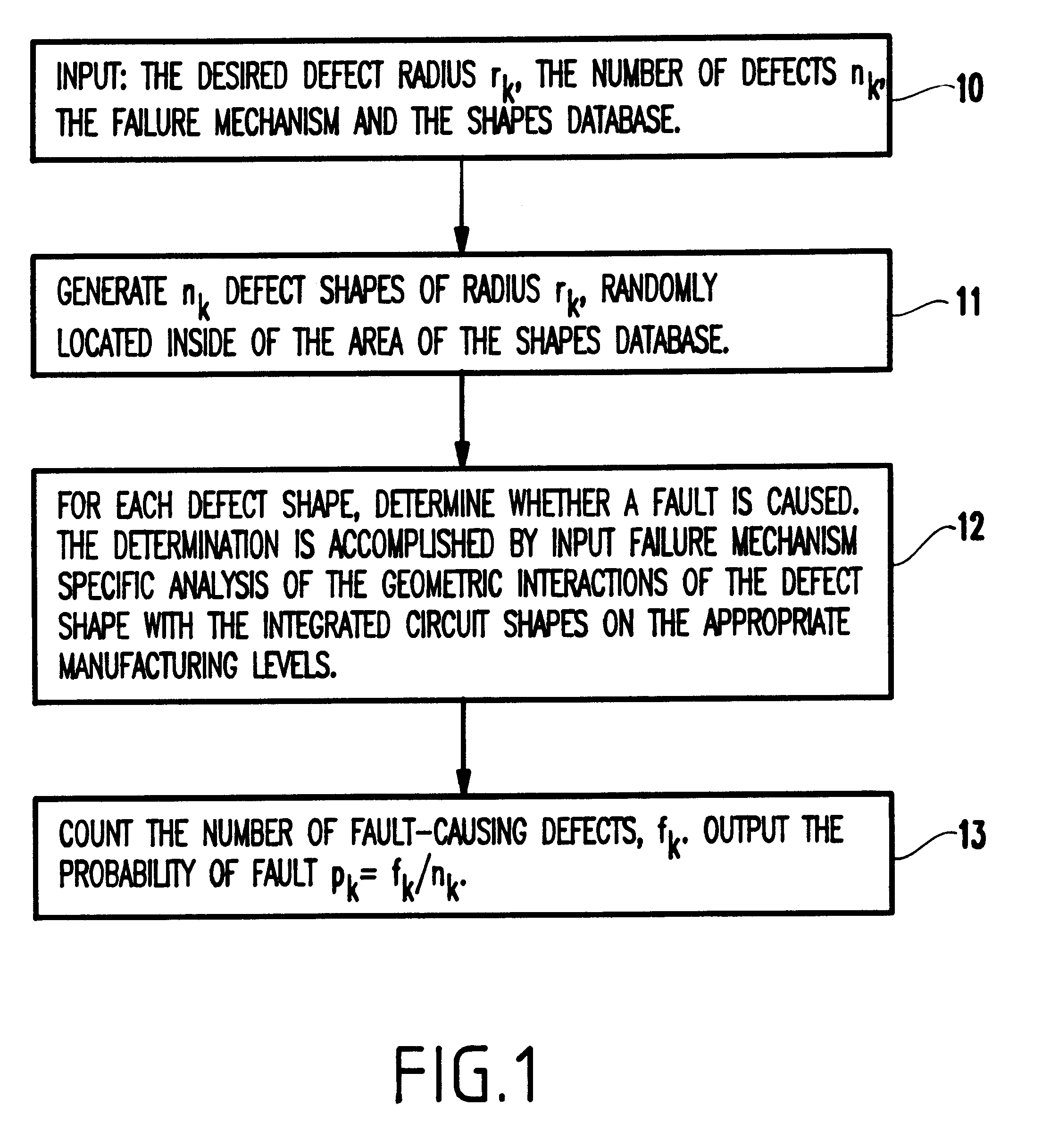
InactiveUS6738954B1Reduce the amount of calculationReduce errorsDigital circuit testingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDefect sizeIntegrated circuit layout
A method of computing a manufacturing yield of an integrated circuit having device shapes includes sub-dividing the integrated circuit into failure mechanism subdivisions (each of the failure mechanism subdivisions includes one or more failure mechanism and each of the failure mechanisms includes one or more defect mechanisms), partitioning the failure mechanism subdivisions by area into partitions, pre-processing the device shapes in each partition, computing an initial average number of faults for each of the failure mechanisms and for each partition by numerical integration of an average probability of failure of each failure mechanism, (the numerical integration produces a list of defect sizes for each defect mechanism, and the computing of the initial average includes setting a maximum integration error limit, a maximum sample size for a population of each defect size, and a maximum number of allowable faults for each failure mechansim), and computing a final average number of faults for the integrated circuit by iterativelly reducing a statistical error of the initial average number of faults for each of the failure mechanisms until the statistical error is below an error limit.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
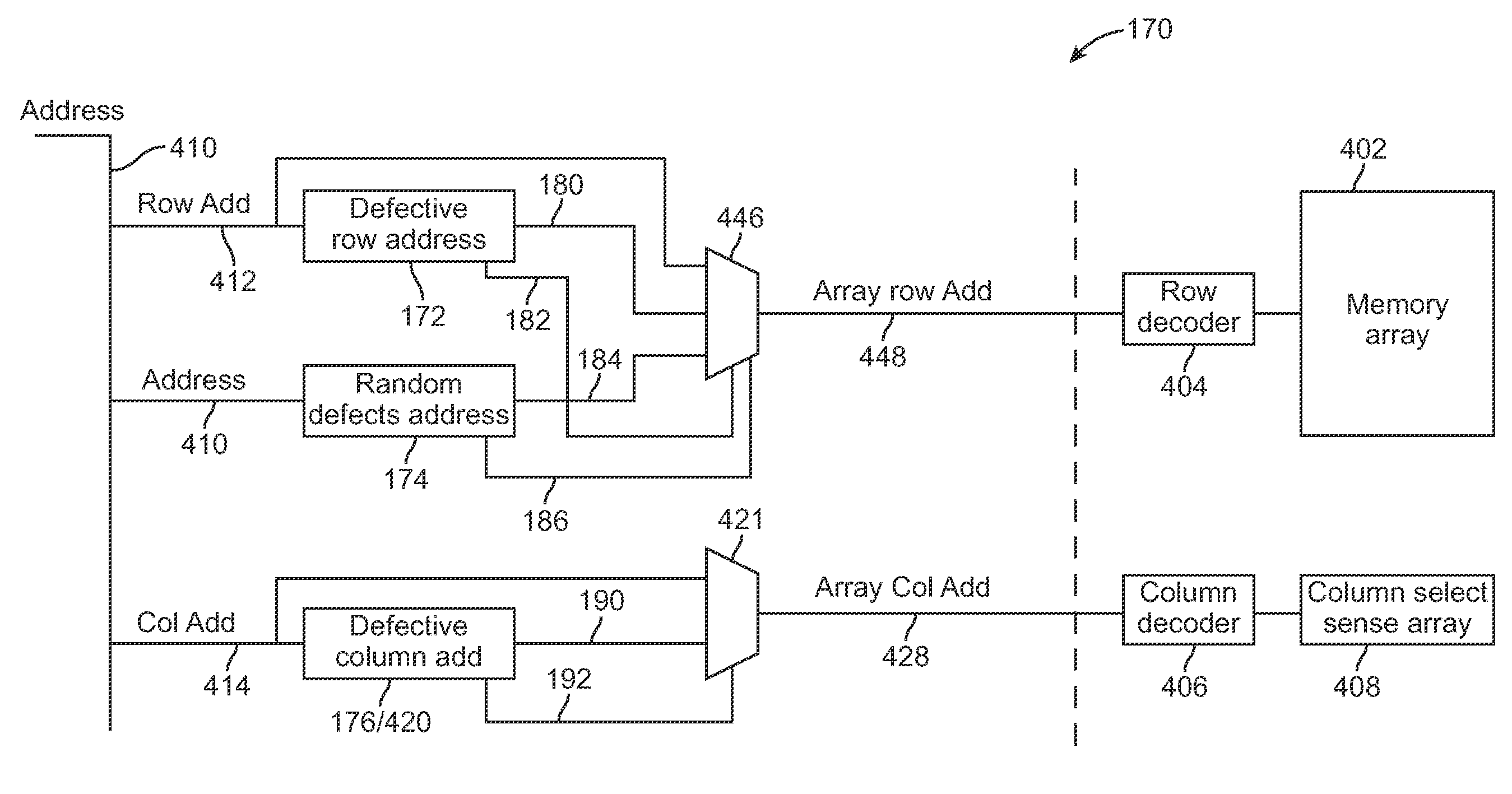
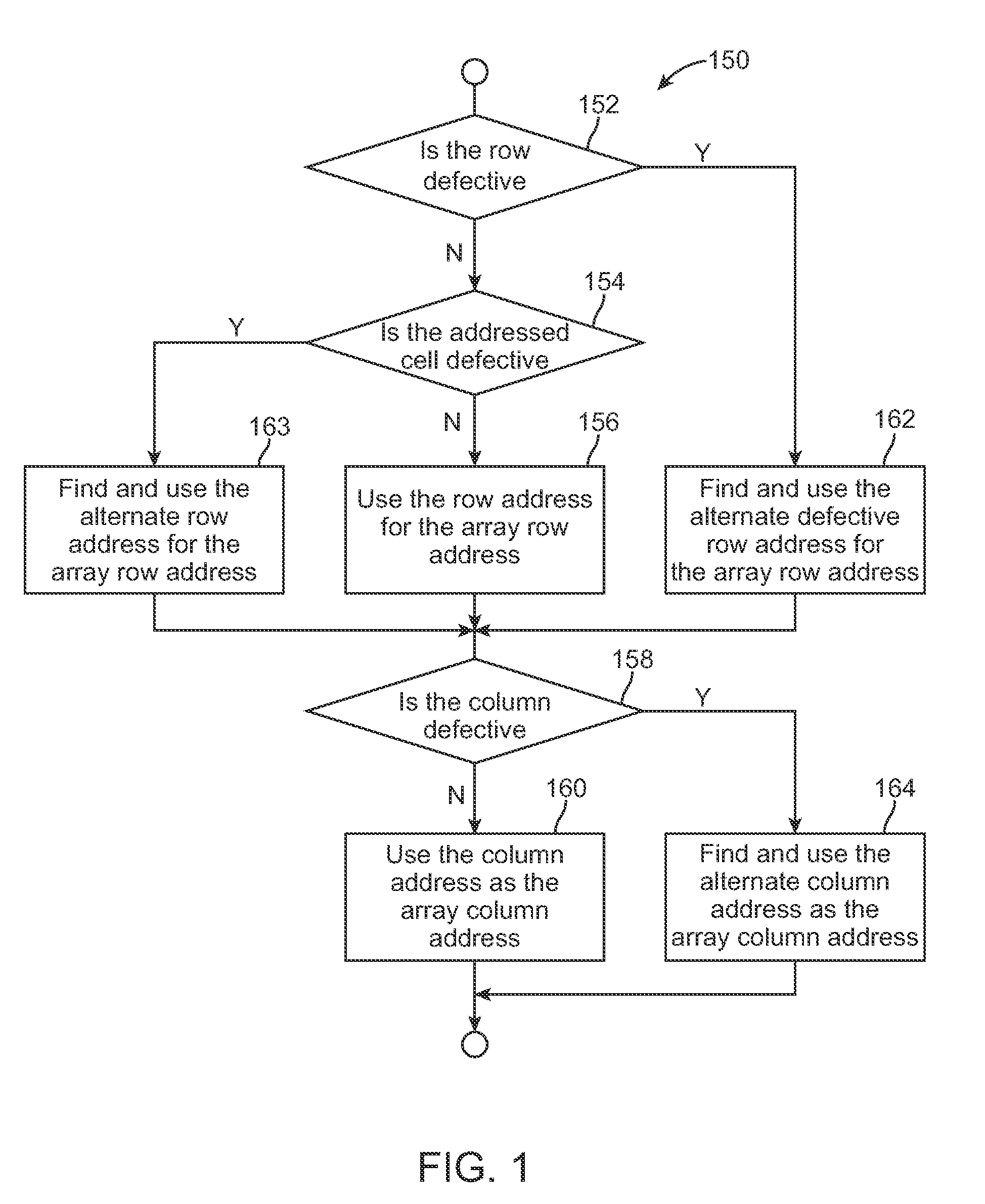
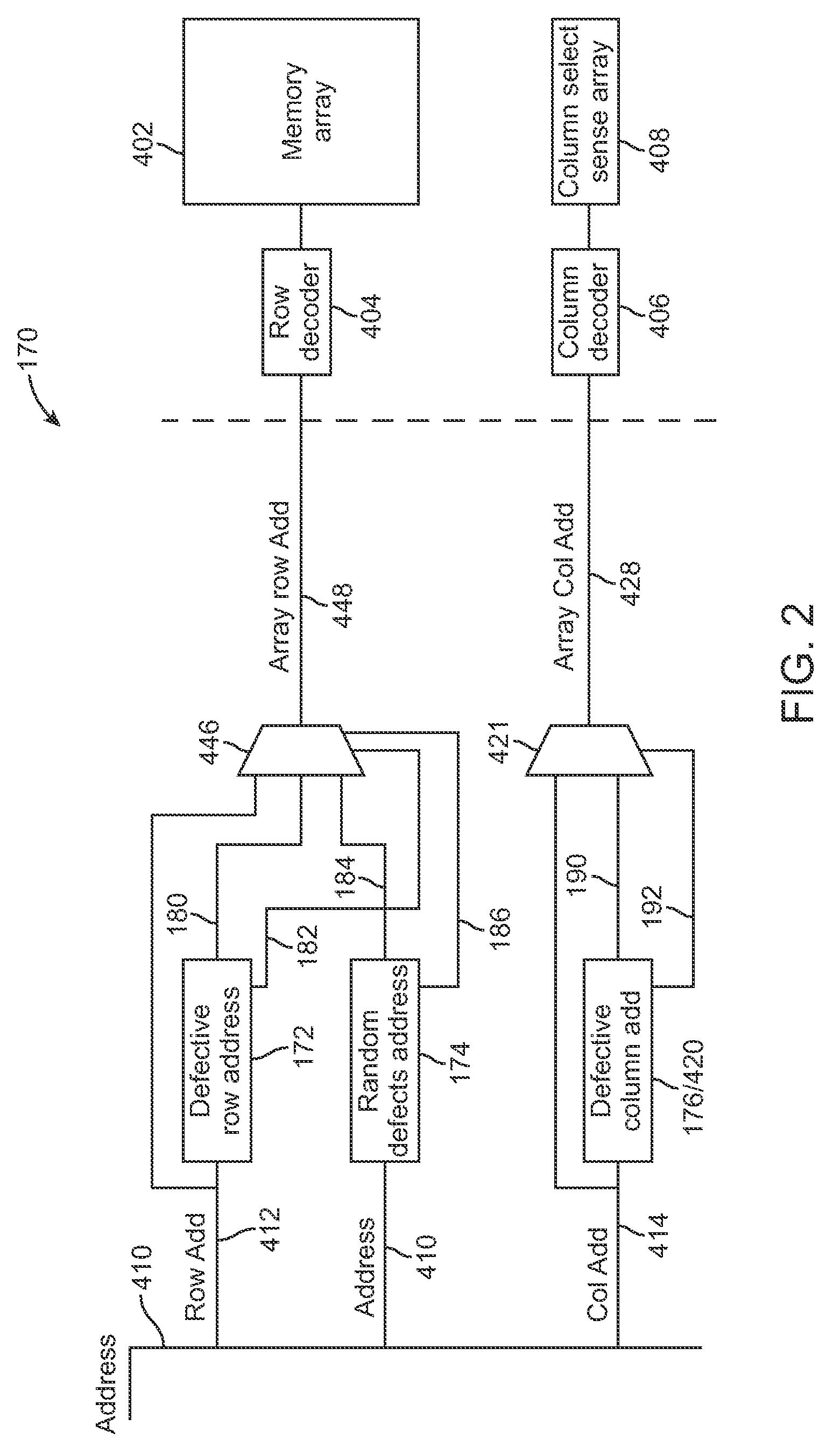
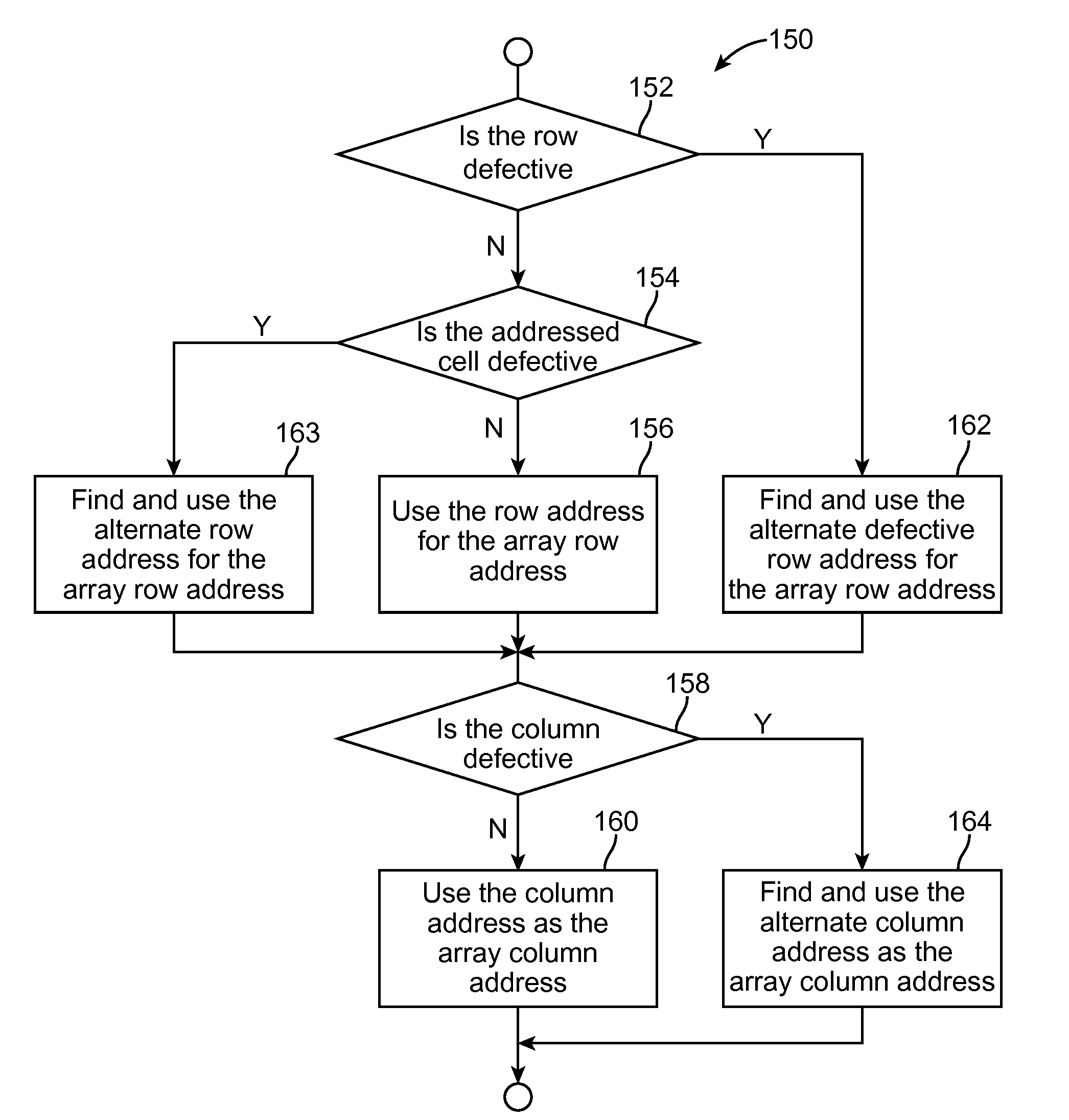
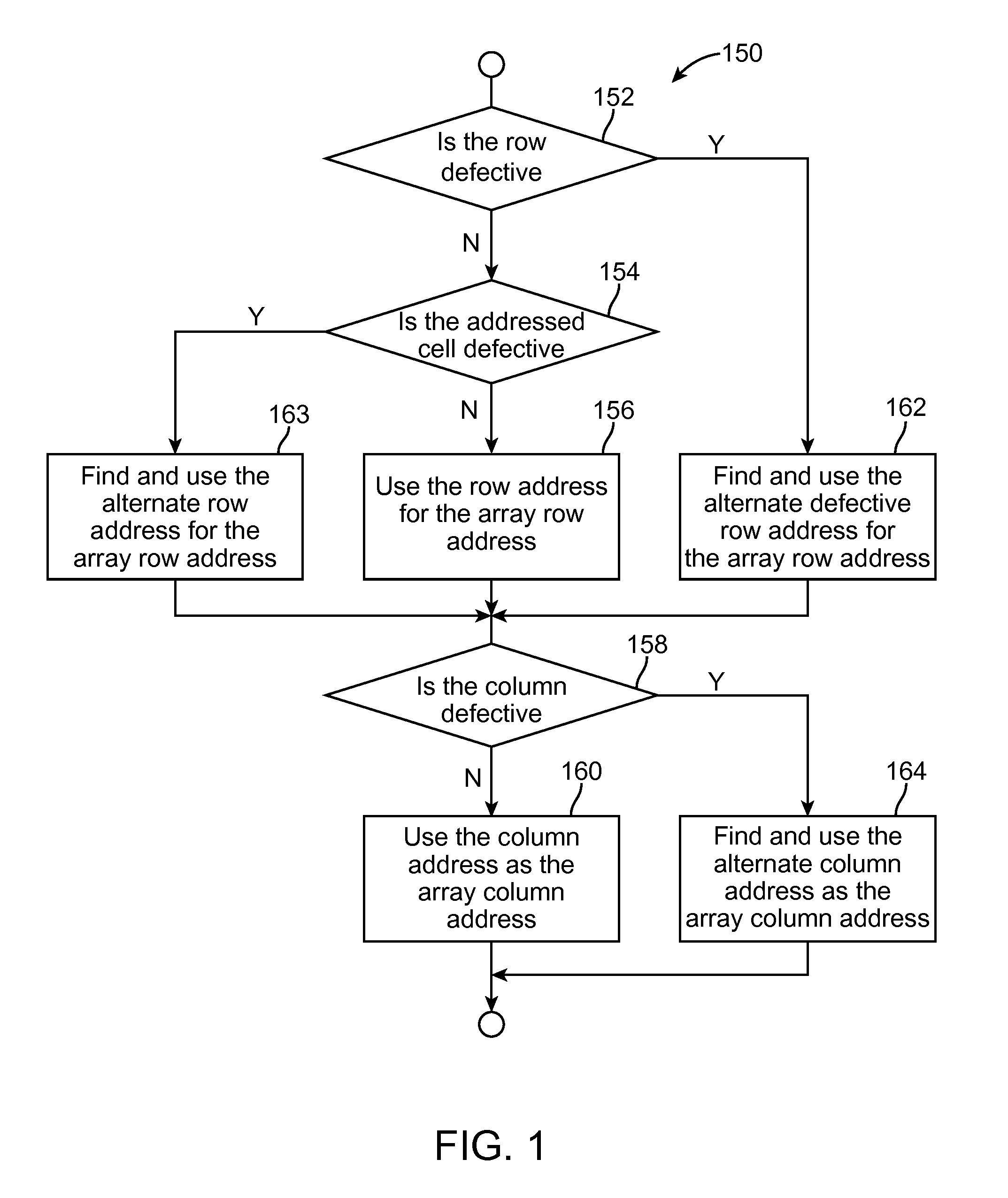
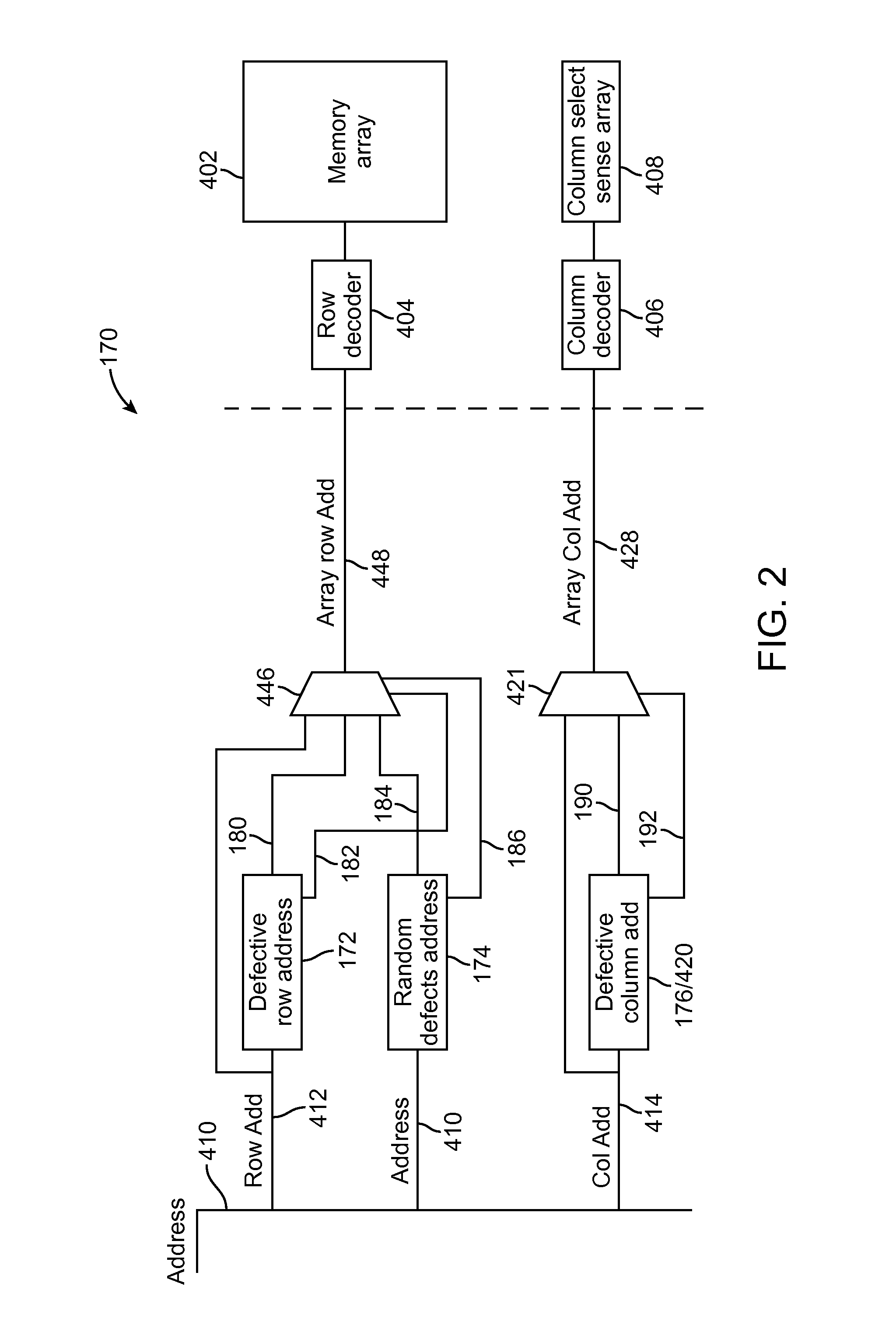
Mapping of random defects in a memory device
ActiveUS20130007544A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationStatic storageMemory cellParallel computing
A memory device includes a memory array with random defective memory cells. The memory array is organized into rows and columns with a row and column identifying a memory location of a memory cell of the memory array. The memory device includes a row address device and a column address device and is operative to use a grouping of either the row or the column addresses to manage the random defective memory cells by mapping the memory location of a defective memory cell to an alternate memory location.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
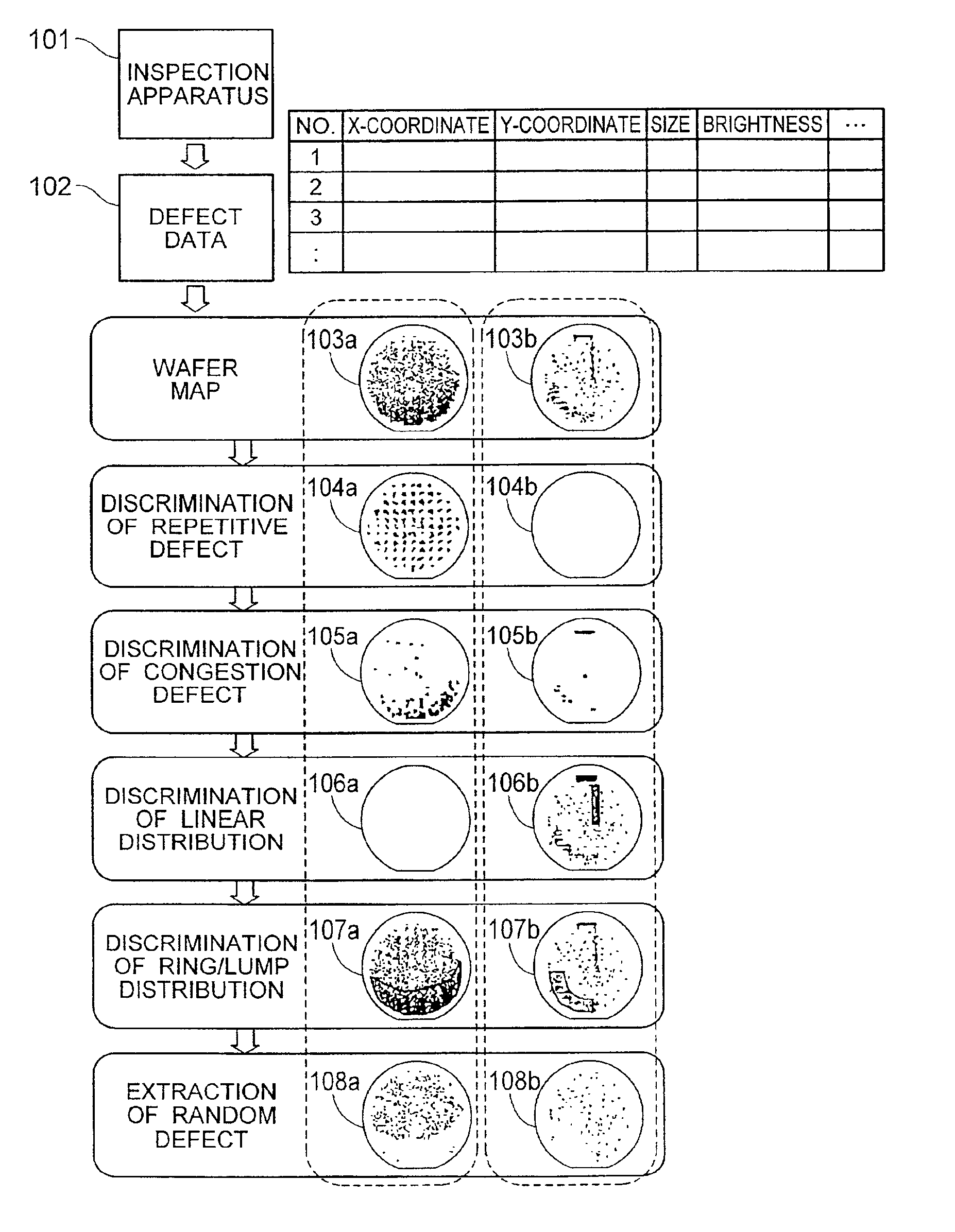
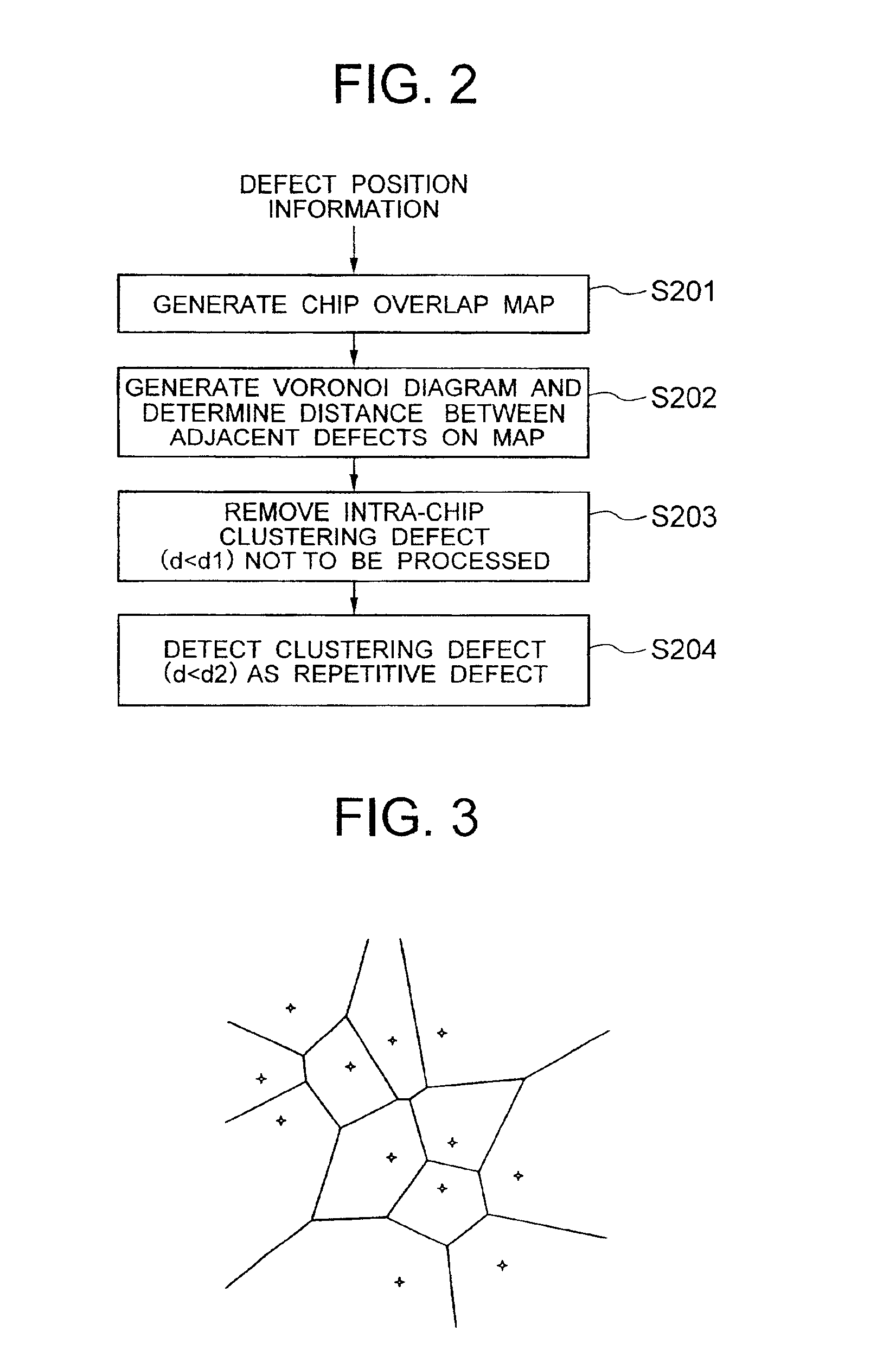
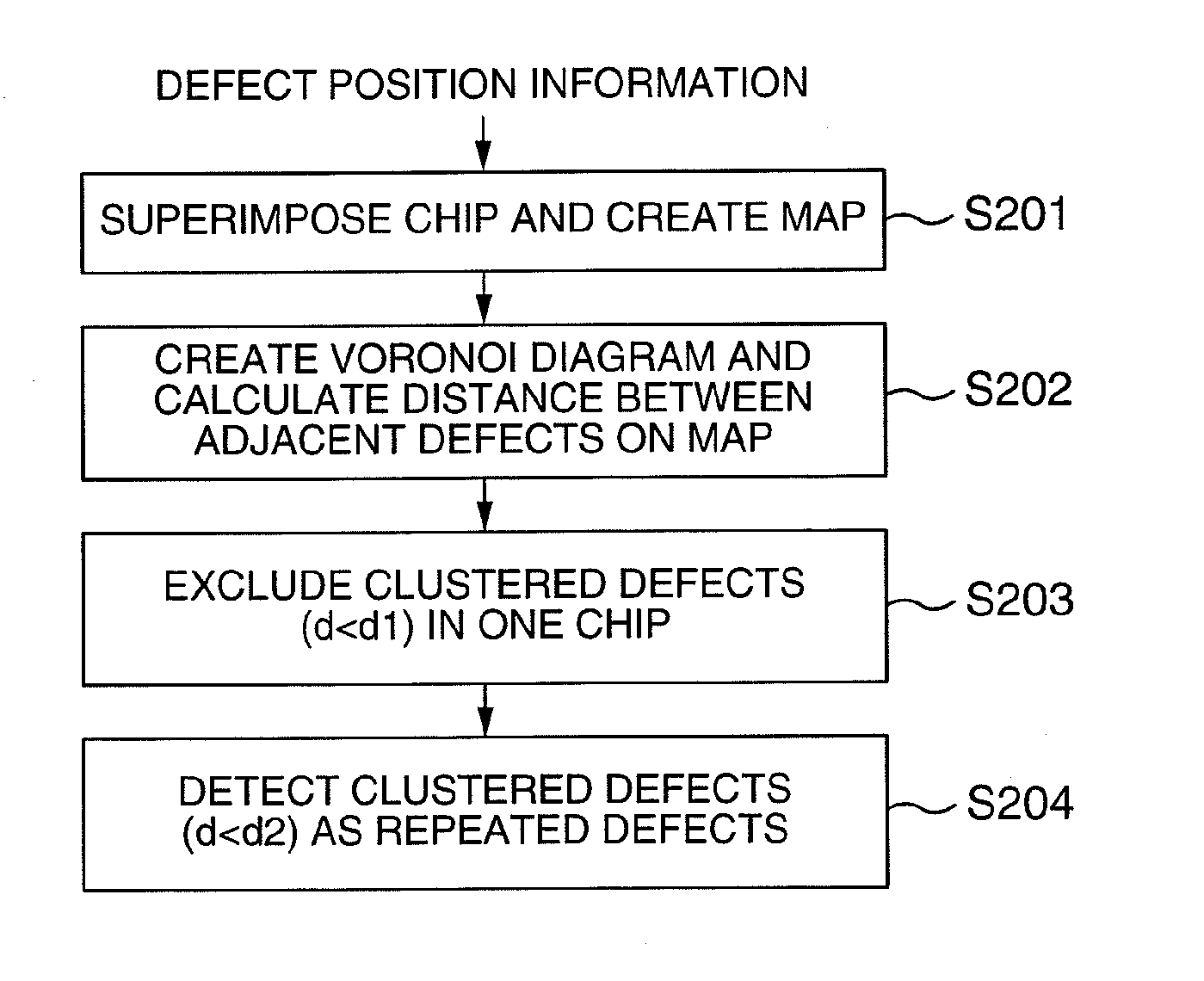
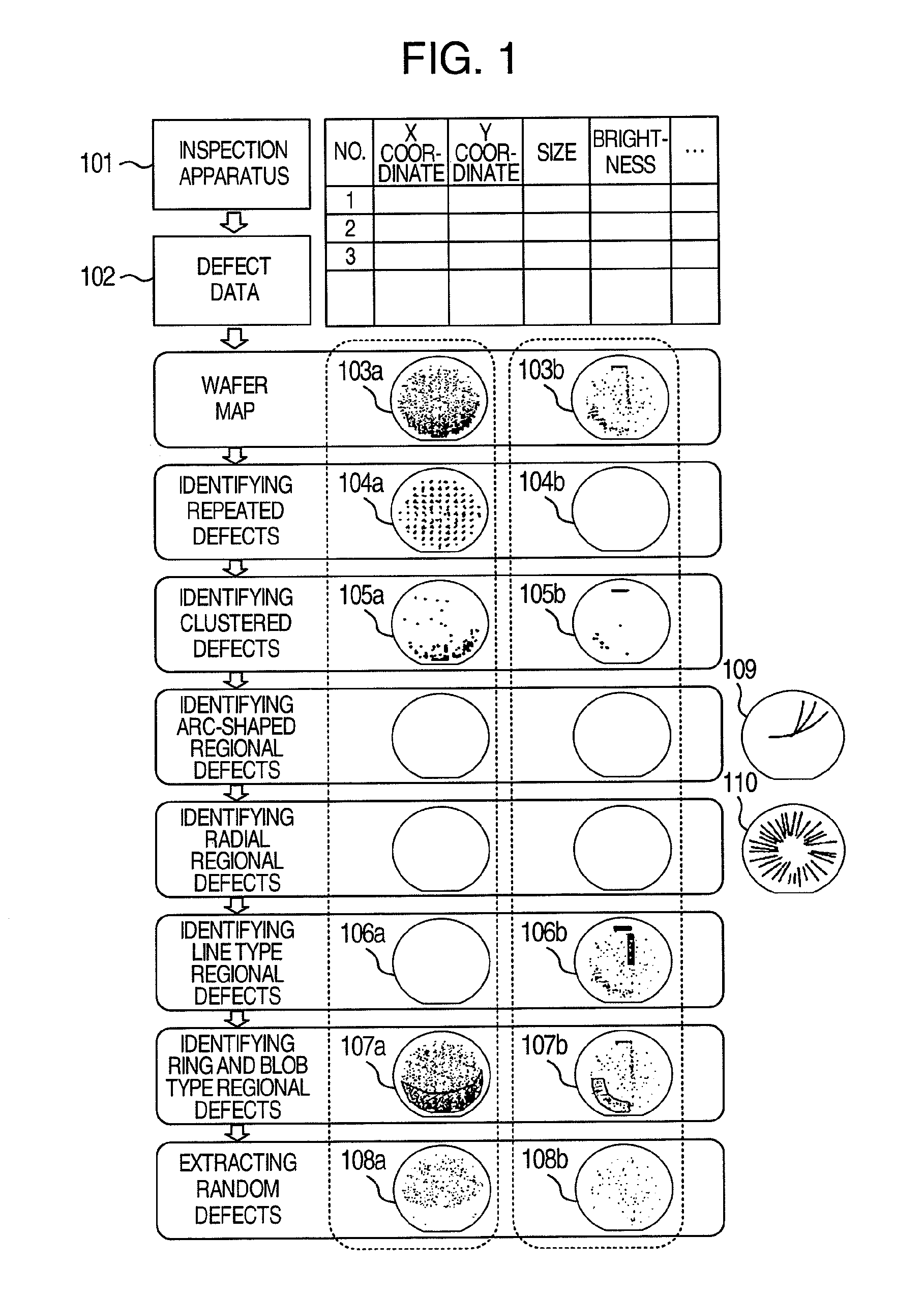
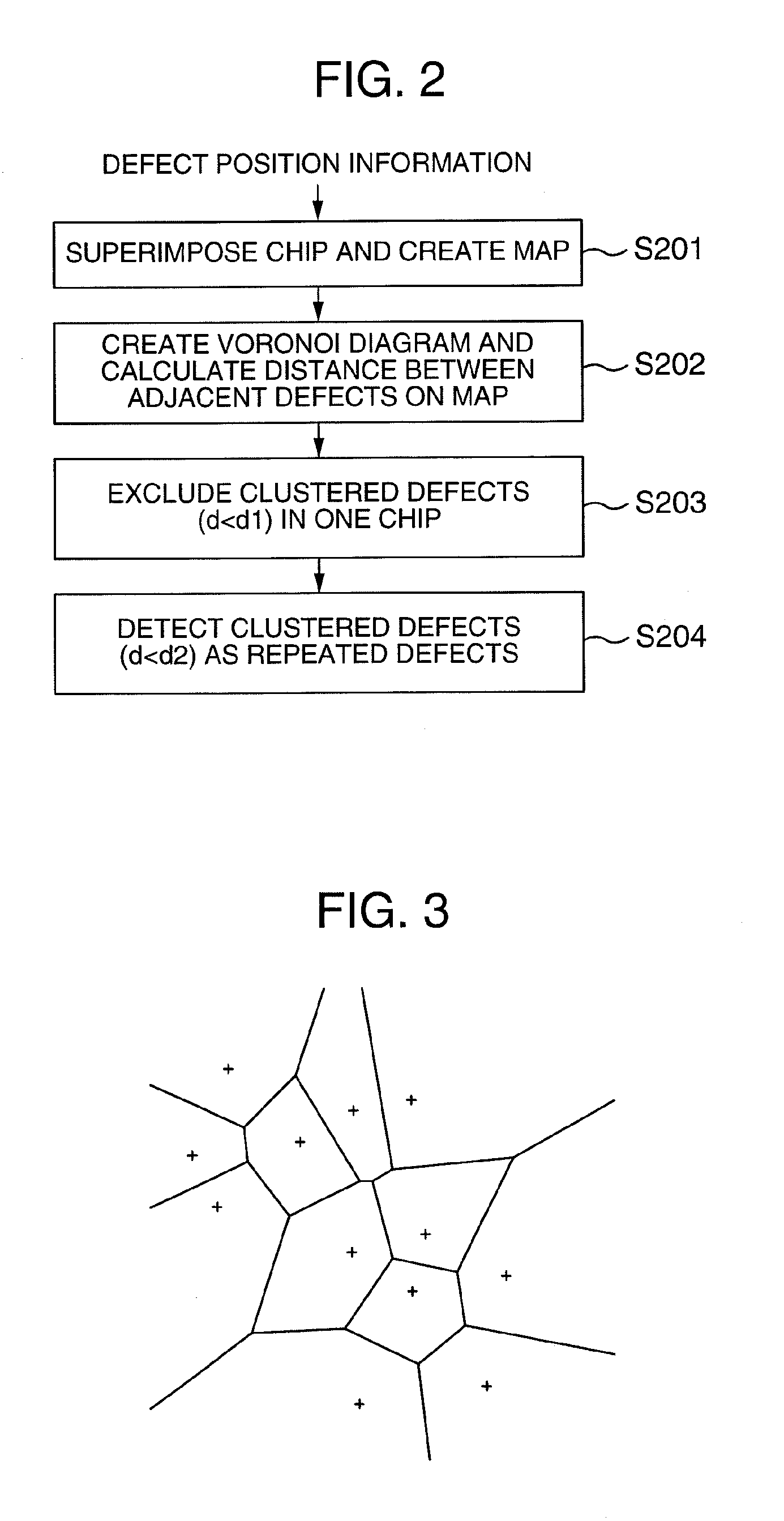
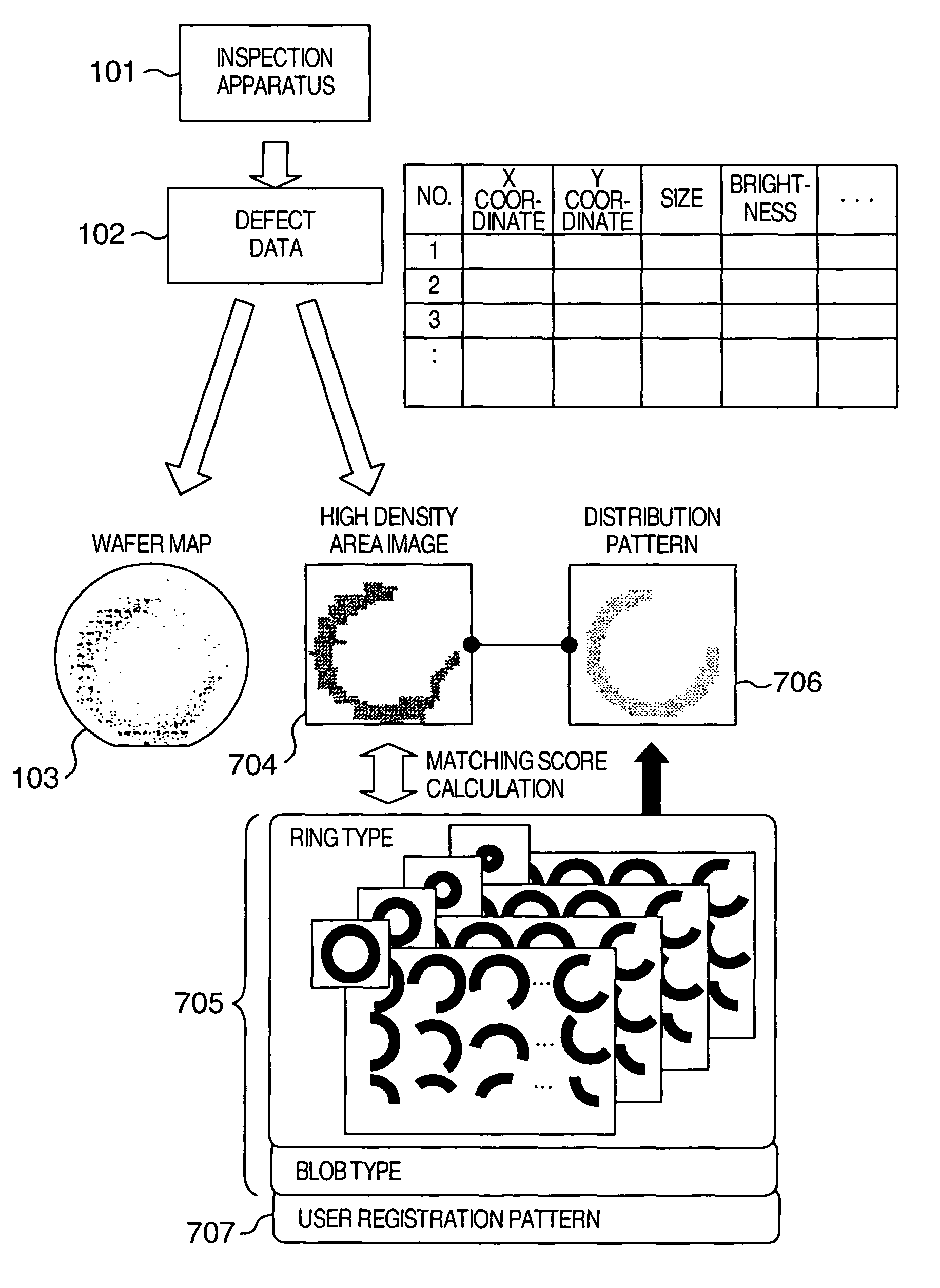
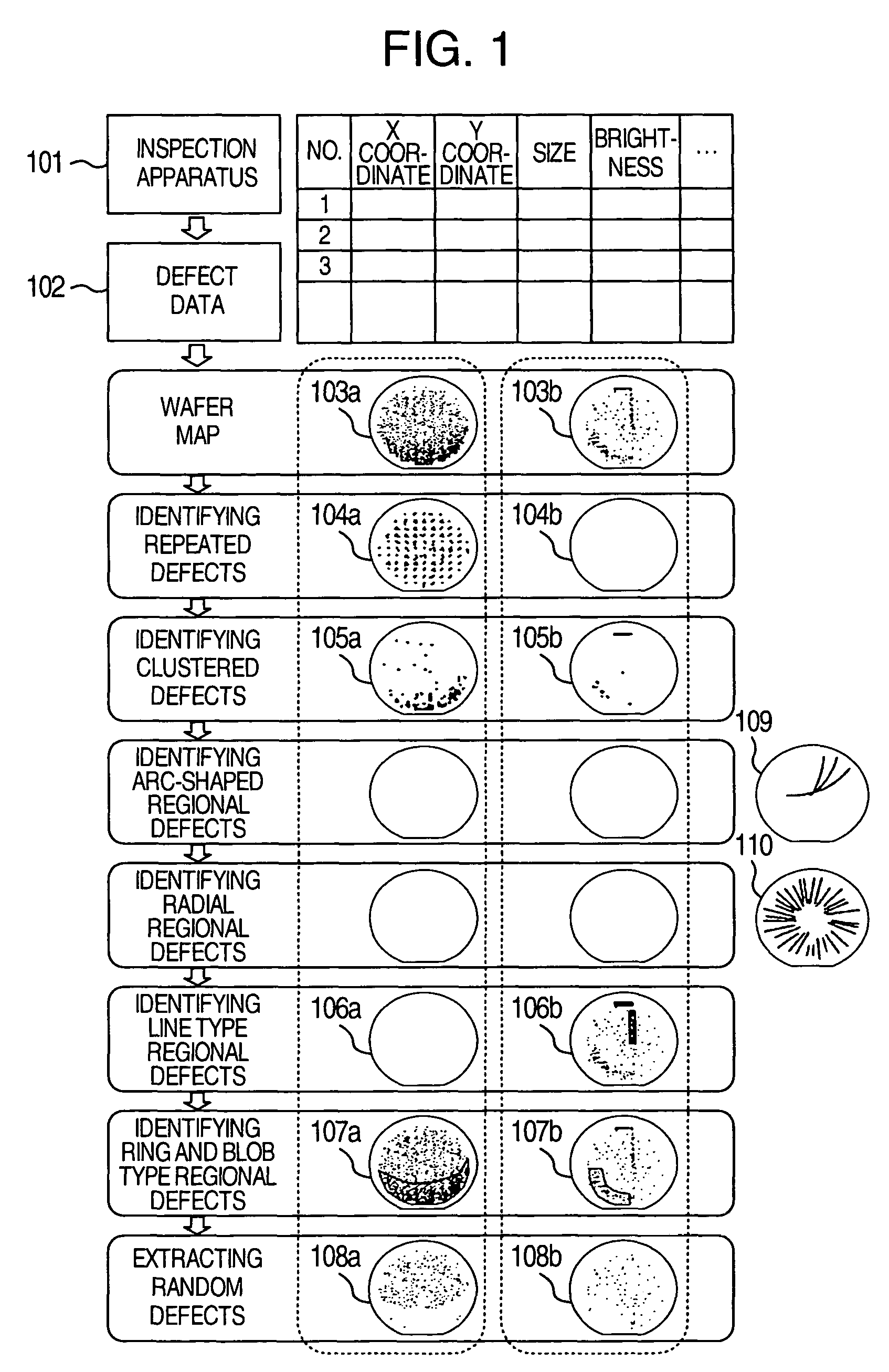
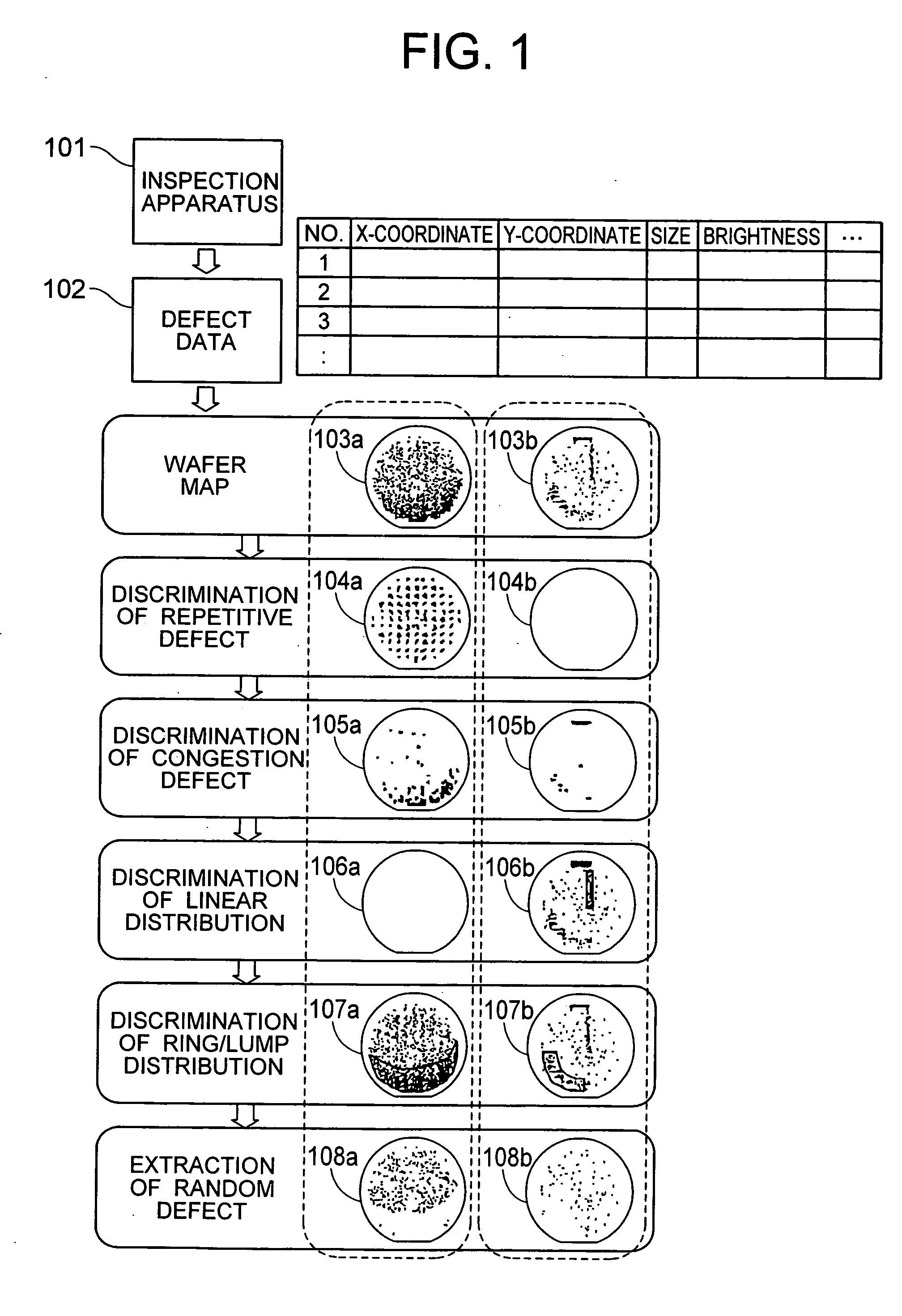
Method for analyzing defect data and inspection apparatus and review system
InactiveUS6876445B2Process defectEasy to identifyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceSemiconductor
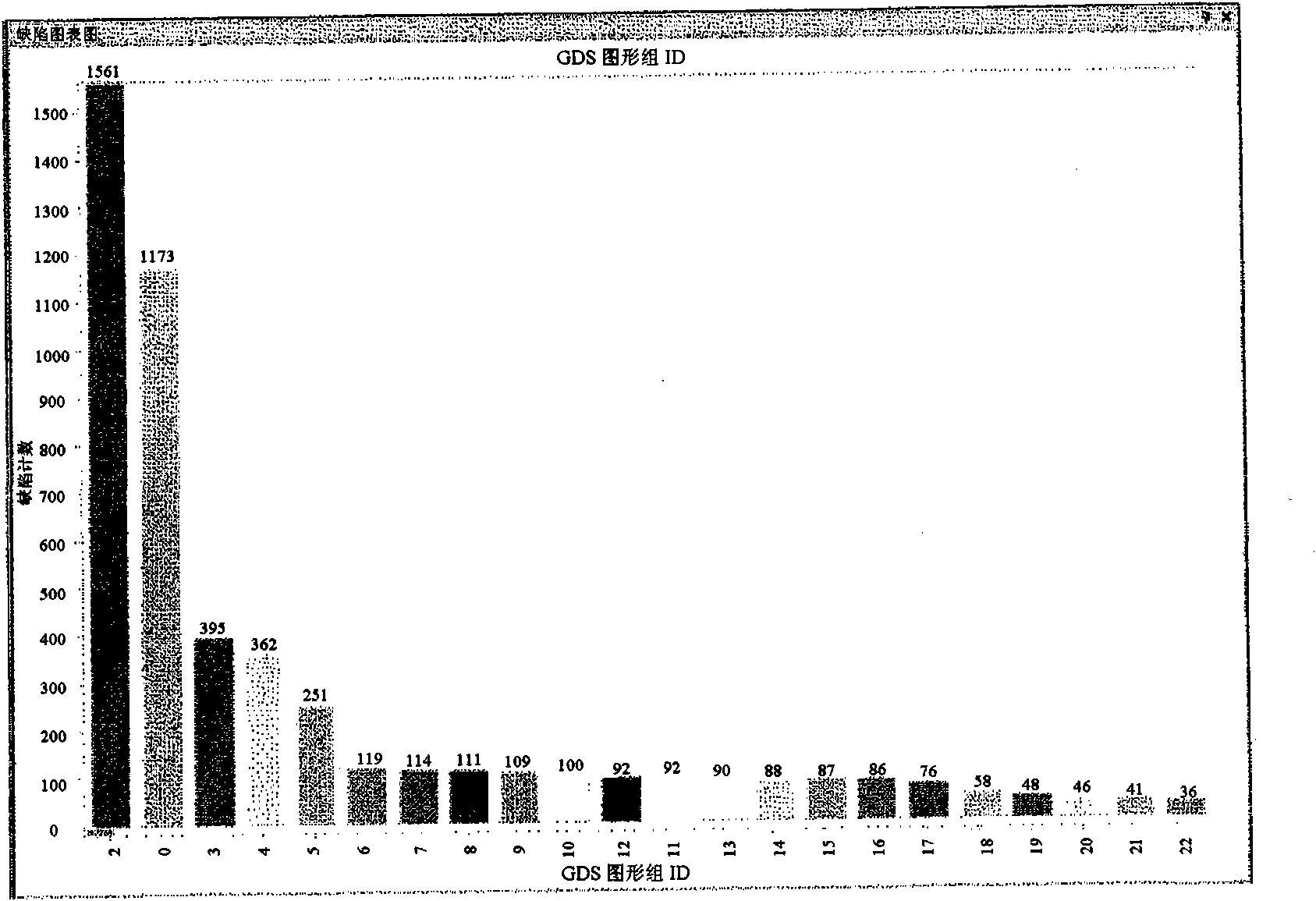
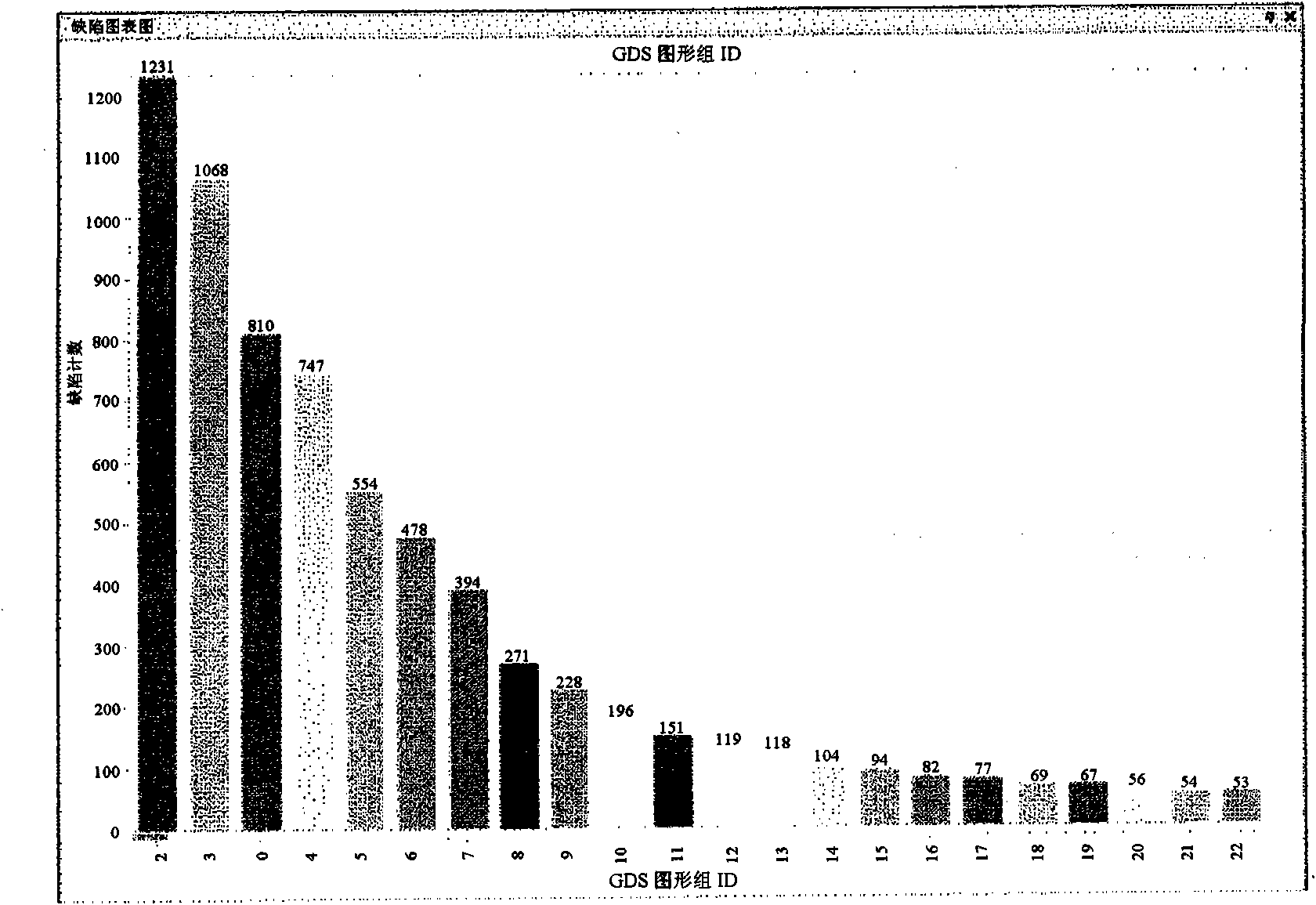
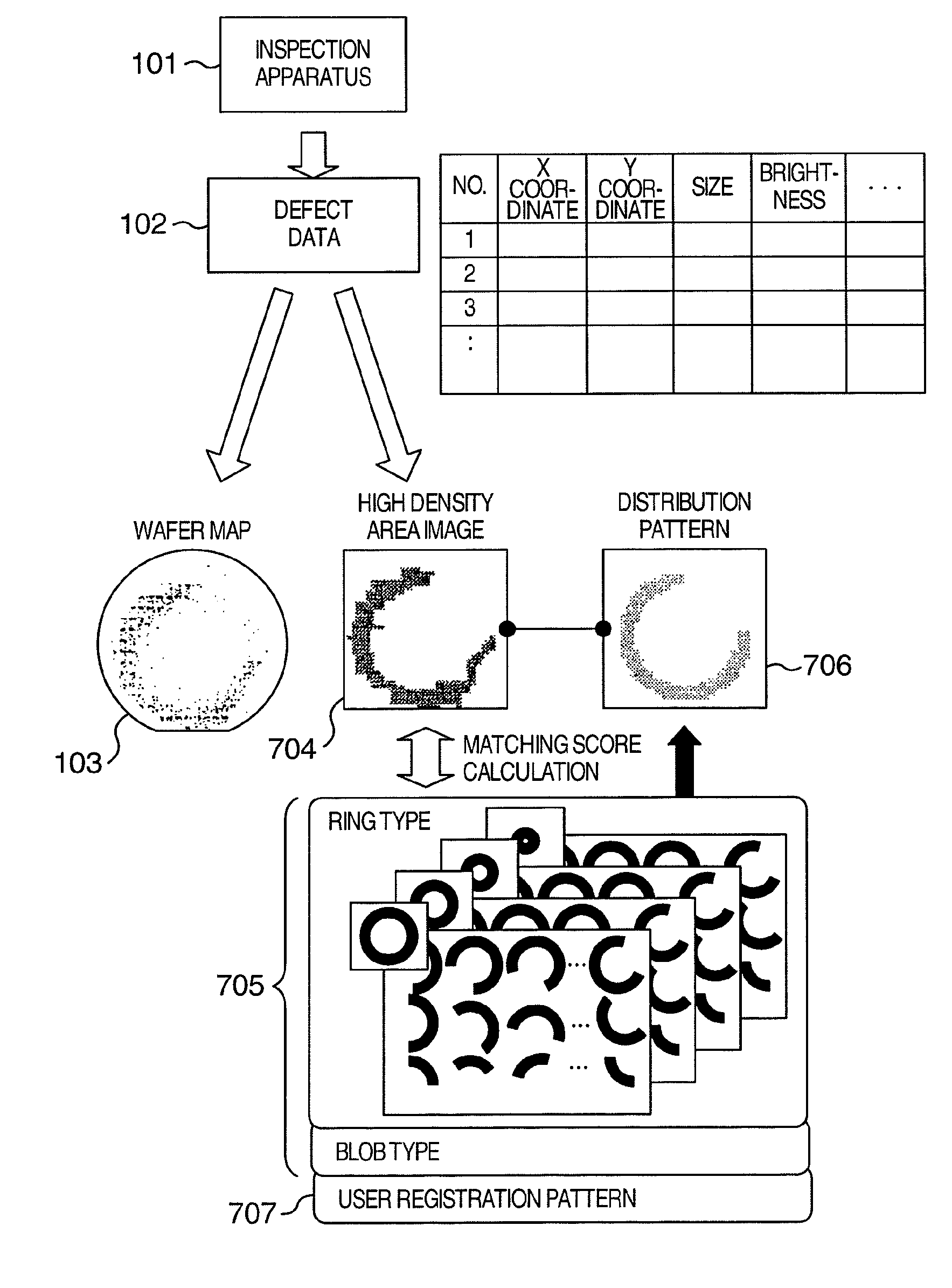
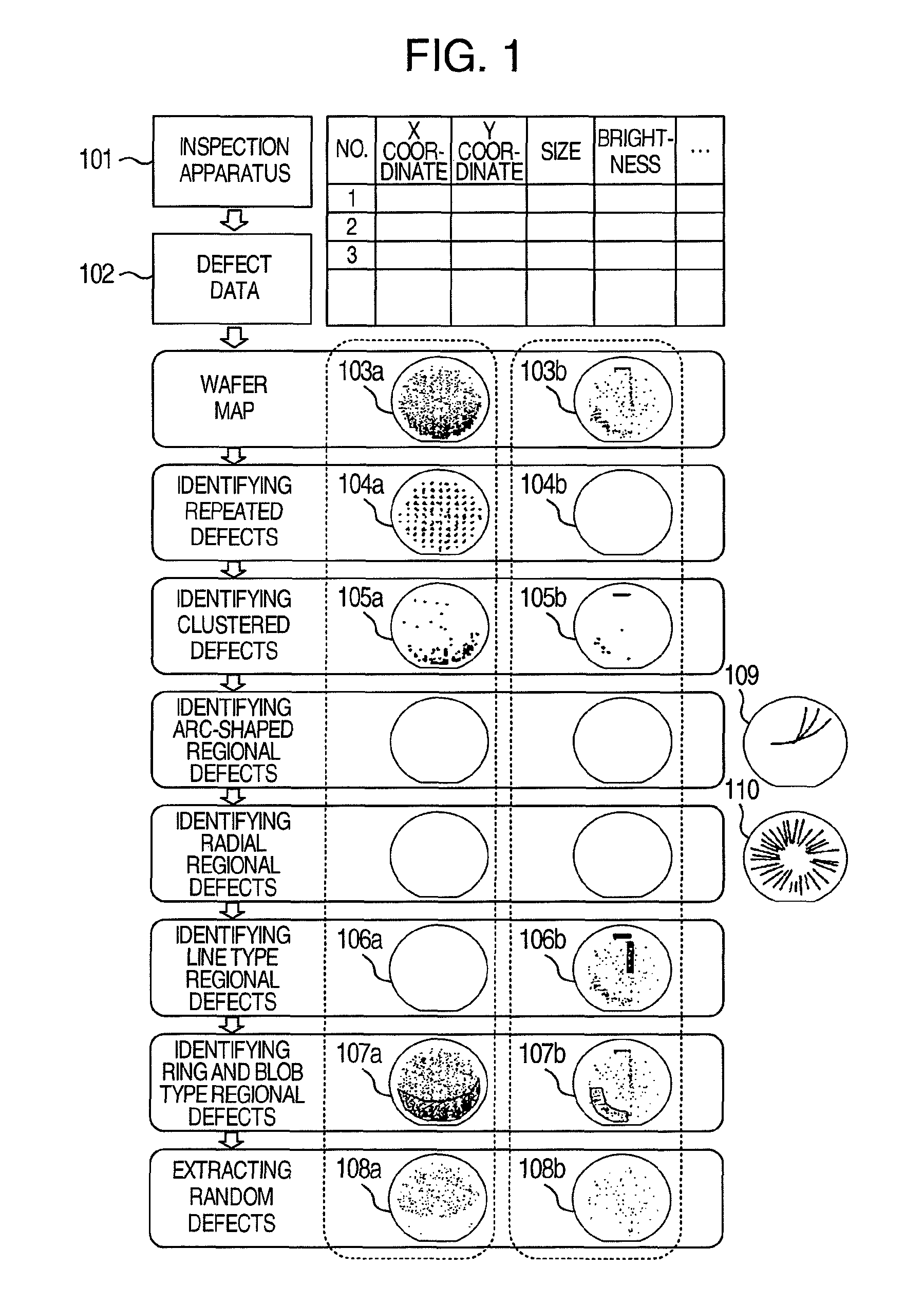
The distribution states of defects are analyzed on the basis of the coordinates of defects detected by an inspection apparatus to classify them into a distribution feature category, or any one of repetitive defect, congestion defect, linear distribution defect, ring / lump distribution defect and random defect. In the manufacturing process for semiconductor substrates, defect distribution states are analyzed on the basis of defect data detected by an inspection apparatus, thereby specifying the cause of defect in apparatus or process.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP +1
Computer-implemented methods for determining if actual defects are potentially systematic defects or potentially random defects
ActiveUS20090055783A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareElectrical testingComputer scienceRandom defects
Various computer-implemented methods for determining if actual defects are potentially systematic defects or potentially random defects are provided. One computer-implemented method for determining if actual defects are potentially systematic defects or potentially random defects includes comparing a number of actual defects in a group to a number of randomly generated defects in a group. The actual defects are detected on a wafer. A portion of a design on the wafer proximate a location of each of the actual defects in the group and each of the randomly generated defects in the group is substantially the same. The method also includes determining if the actual defects in the group are potentially systematic defects or potentially random defects based on results of the comparing step.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
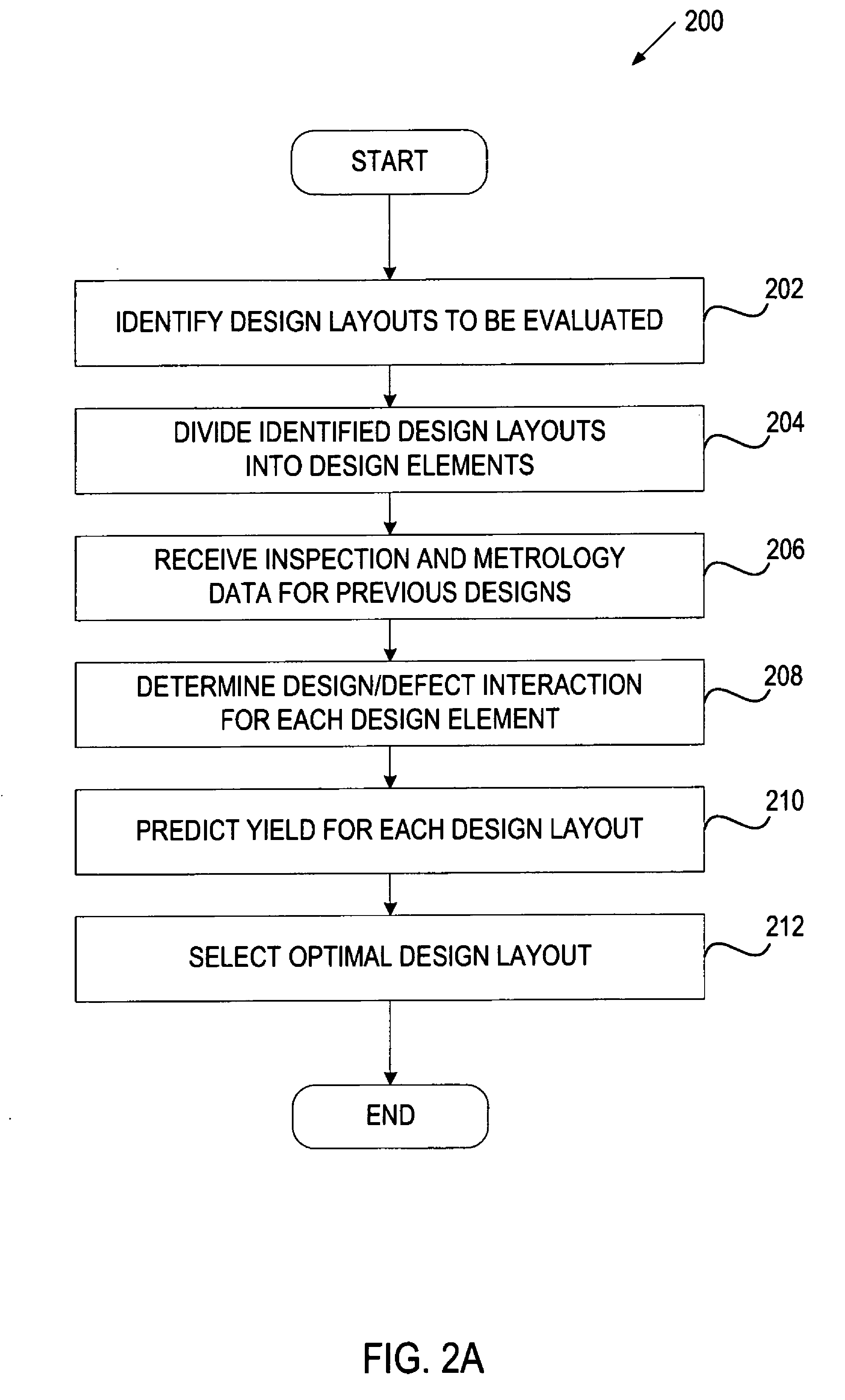
Stage yield prediction
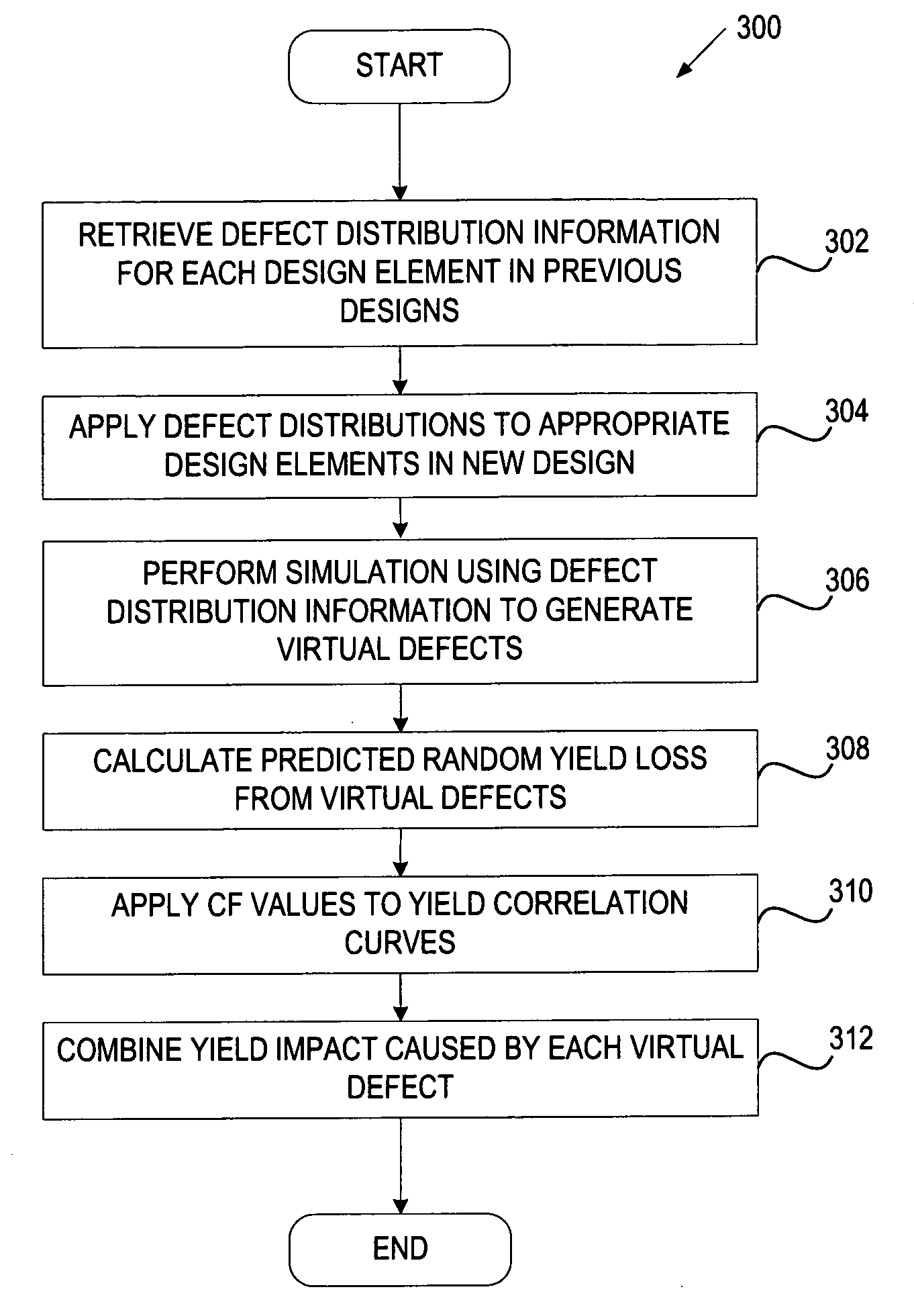
In one embodiment, a method for predicting yield during the design stage includes receiving defectivity data identifying defects associated with previous wafer designs, and dividing the defects into systematic defects and random defects. For each design layout of a new wafer design, yield is predicted separately for the systematic defects and the random defects. A combined yield is then calculated based on the yield predicted for the systematic defects and the yield predicted for the random defects.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and Apparatus for Analyzing Defect Data and a Review System
In a process for manufacturing a semiconductor wafer, defect distribution state analysis is performed so as to facilitate identification of the defect cause including a device cause and a process cause by classifying the defect distribution state according to the defect position coordinates detected by the inspection device, into one of the distribution characteristic categories: repeated defects, clustered defects, arc-shaped regional defects, radial regional defects, line type regional defects, ring and blob type regional defects, and random defects.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for analyzing defect data and a review system
ActiveUS7813539B2Increase speedImage enhancementImage analysisDistribution characteristicEngineering
In a process for manufacturing a semiconductor wafer, defect distribution state analysis is performed so as to facilitate identification of the defect cause including a device cause and a process cause by classifying the defect distribution state according to the defect position coordinates detected by the inspection device, into one of the distribution characteristic categories: repeated defects, clustered defects, arc-shaped regional defects, radial regional defects, line type regional defects, ring and blob type regional defects, and random defects.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
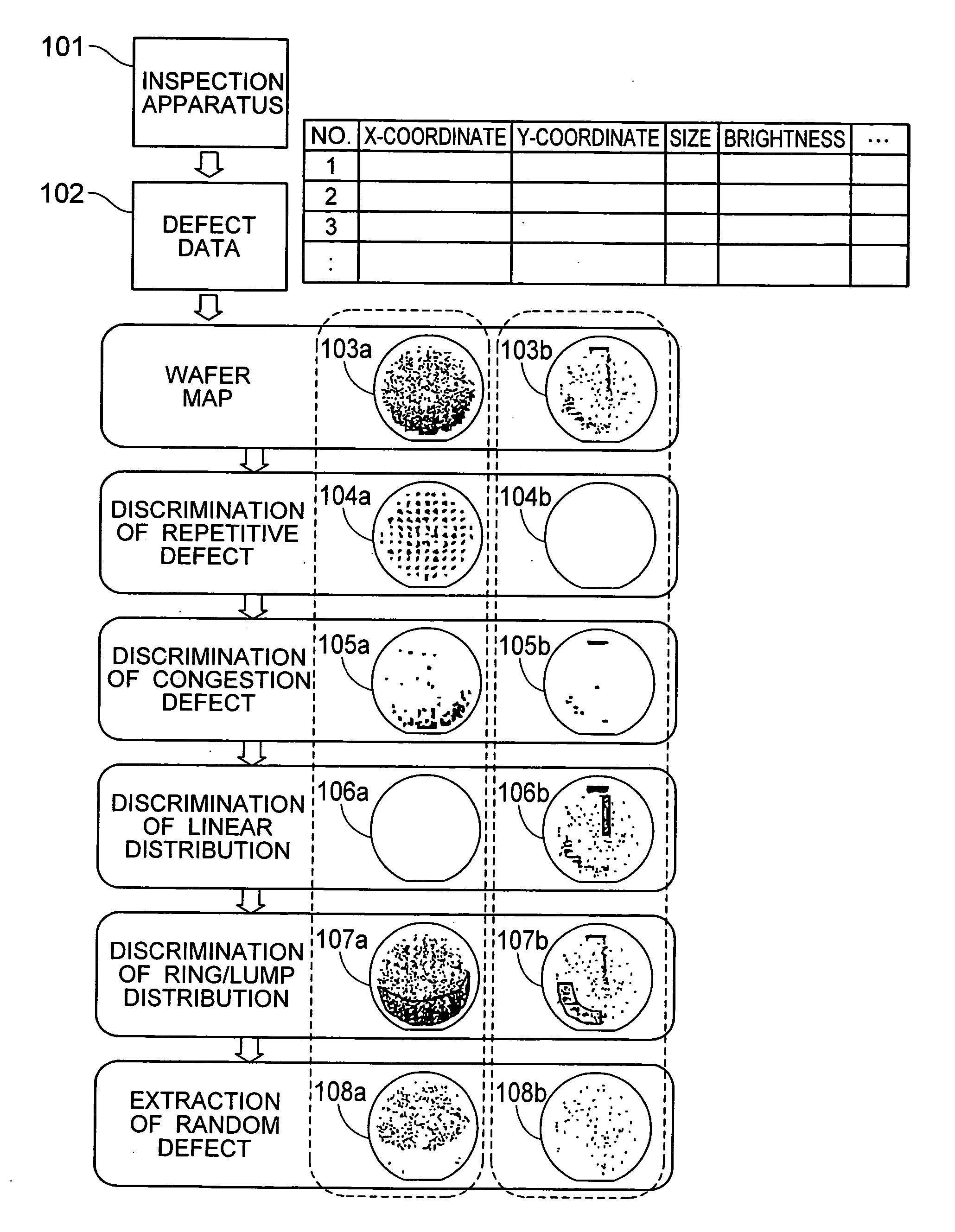
Method for analyzing defect data and inspection apparatus and review system
InactiveUS20050168731A1Quick classificationExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisLinearityComputer science
The distribution states of defects are analyzed on the basis of the coordinates of defects detected by an inspection apparatus to classify them into a distribution feature category, or any one of repetitive defect, congestion defect, linear distribution defect, ring / lump distribution defect and random defect. In the manufacturing process for semiconductor substrates, defect distribution states are analyzed on the basis of defect data detected by an inspection apparatus, thereby specifying the cause of defect in apparatus or process.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Pattern analysis method, pattern analysis apparatus, yield calculation method and yield calculation apparatus
InactiveUS20050273739A1Accurate acquisitionCAD circuit designProgram controlParallel computingCalculation methods
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
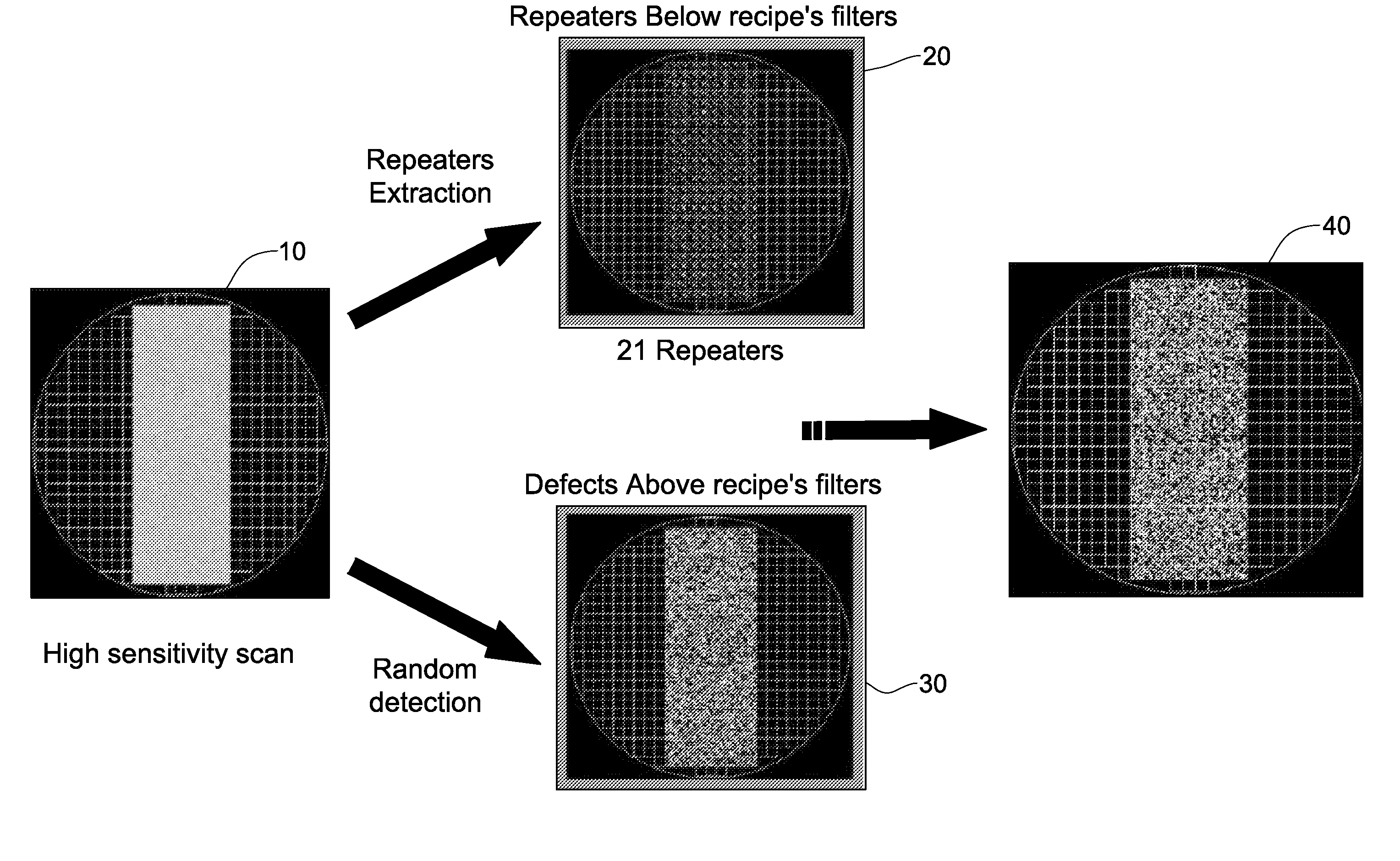
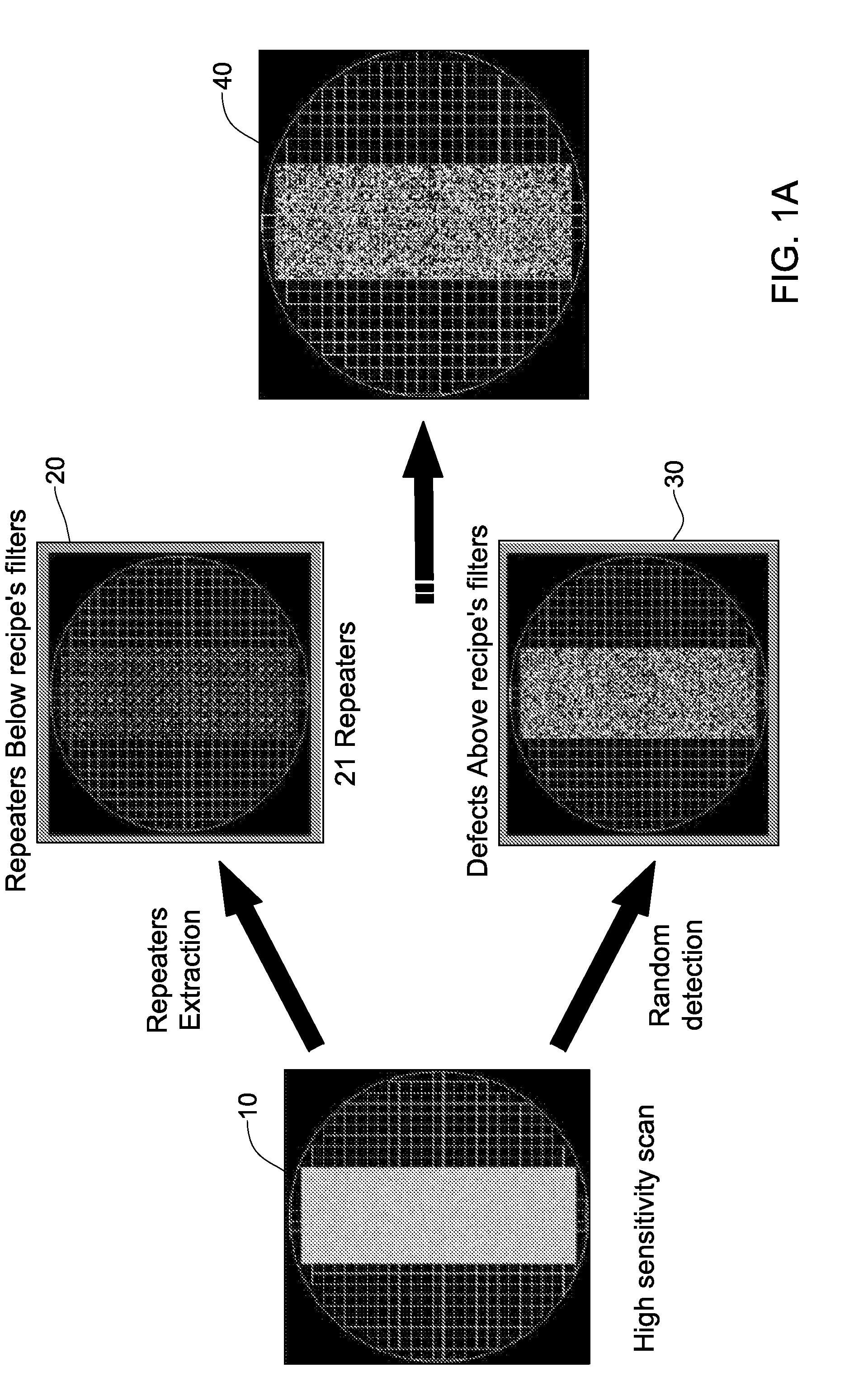
Wafer defect detection system and method
ActiveUS8255172B2Eliminate die-level systematic defectsMaterial analysis by optical meansSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionRepeater
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Yield analysis method
InactiveUS20060128039A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDigital computer detailsEngineeringAnalysis method
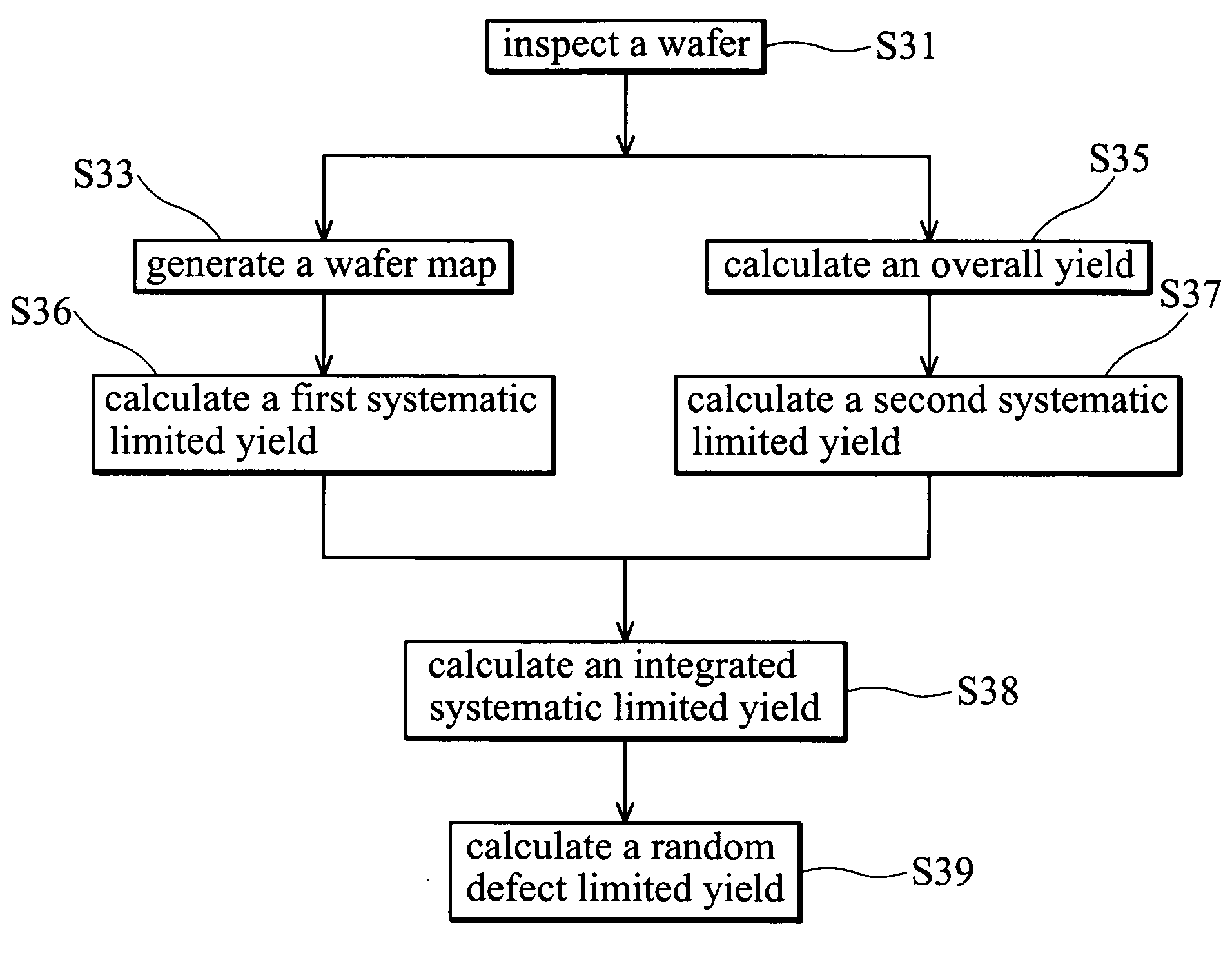
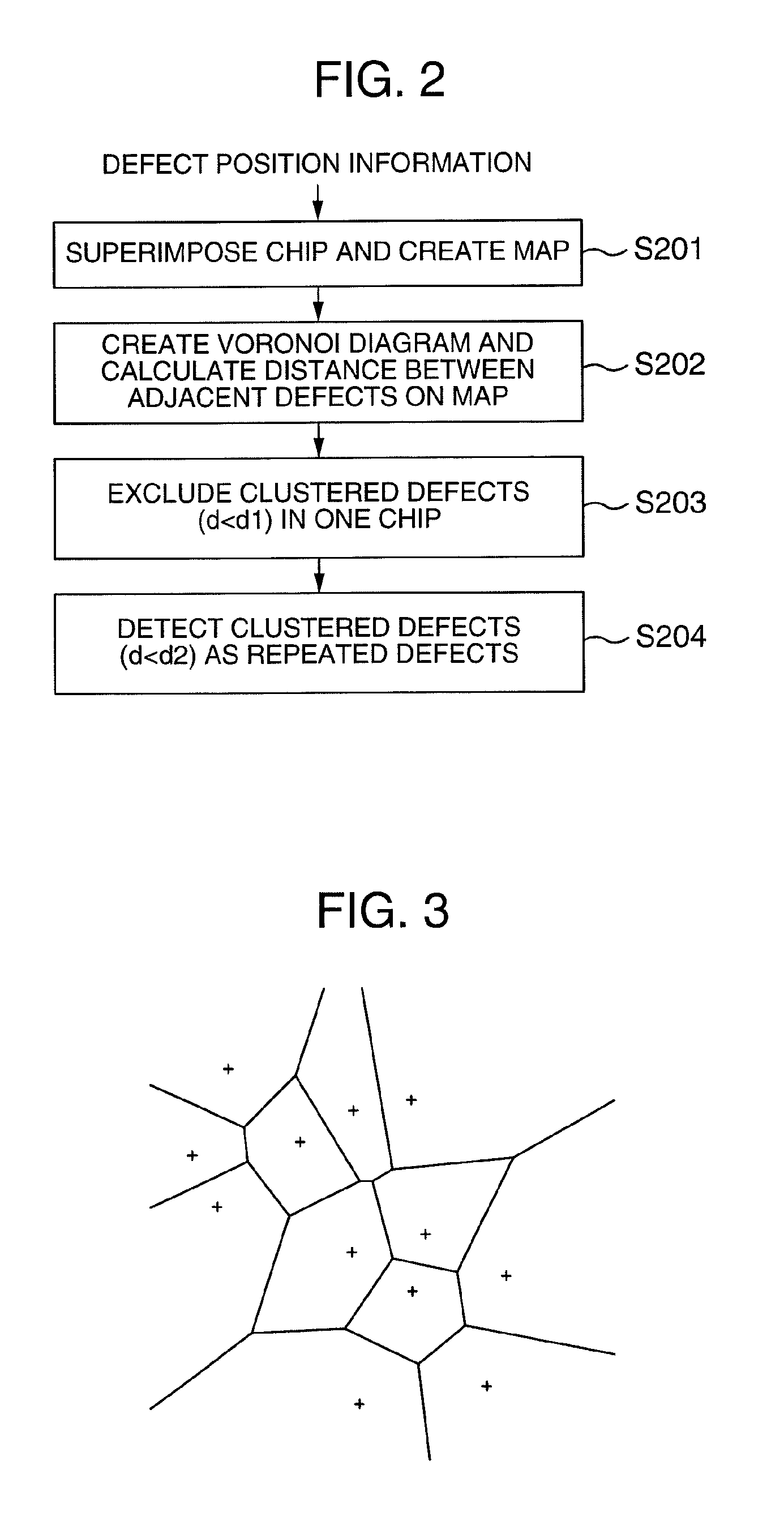
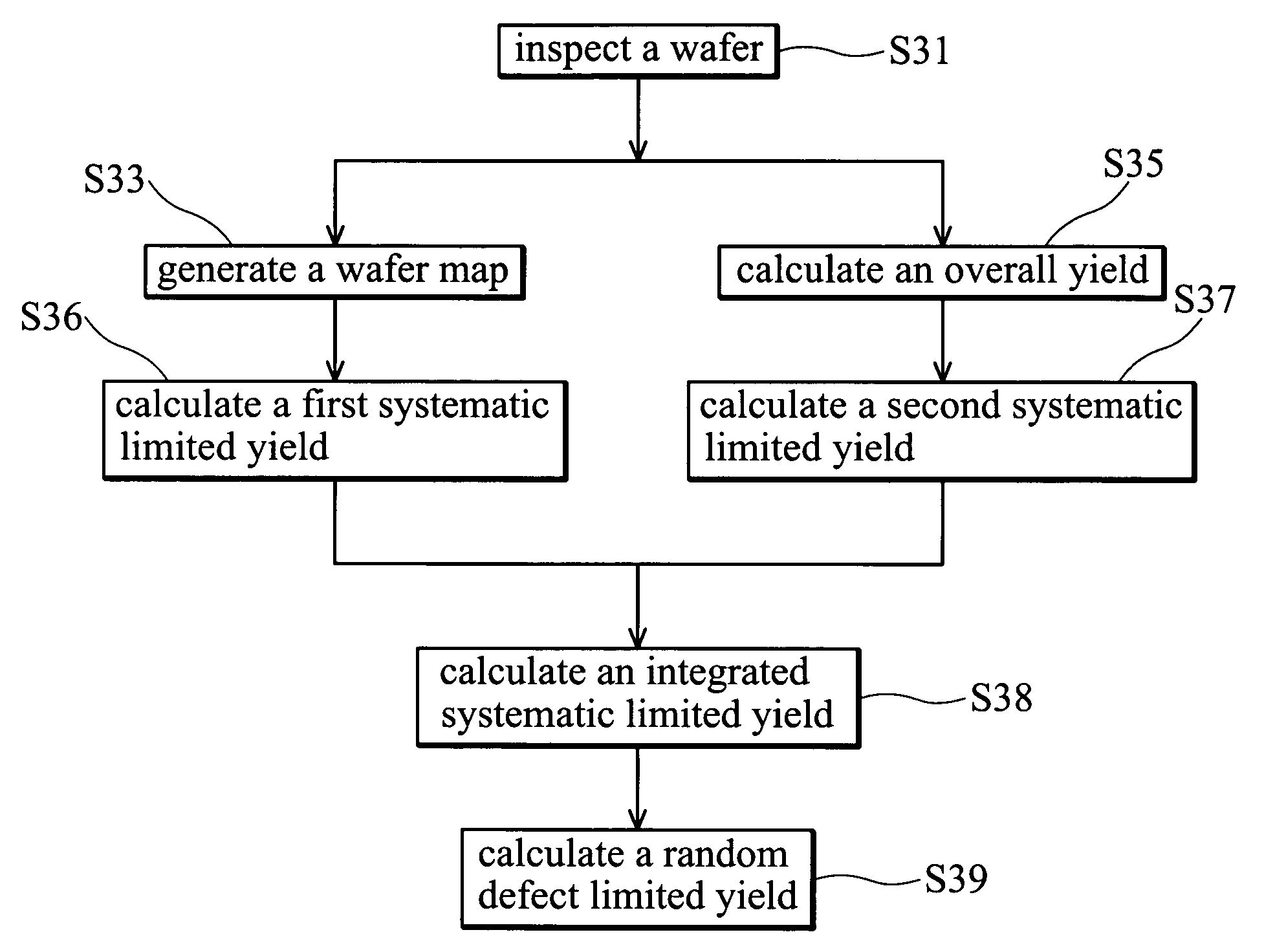
A yield analysis method. First, a wafer having multiple dies is inspected to obtain wafer defect data containing defect information for every die in the wafer. Then a wafer map and an overall yield are generated according to the wafer defect data. The wafer map displays defective dies and defect-free dies in the wafer. Then, first and second systematic limited yields are calculated in accordance with the wafer defect data and the wafer map, wherein the first systematic limited yield is calculated excluding defective dies with localized distribution, and the second systematic limited yield is calculated excluding defective dies with repeated distribution. Then a random defect limited yield is determined in accordance with the overall yield, the first systematic limited yield, and the second systematic limited yield.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Stage yield prediction
In one embodiment, a method for predicting yield during the design stage includes receiving defectivity data identifying defects associated with previous wafer designs, and dividing the defects into systematic defects and random defects. For each design layout of a new wafer design, yield is predicted separately for the systematic defects and the random defects. A combined yield is then calculated based on the yield predicted for the systematic defects and the yield predicted for the random defects.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Wafer defect detection system and method
ActiveUS20100076699A1Eliminate die-level systematic defectsMaterial analysis by optical meansSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionComputer science
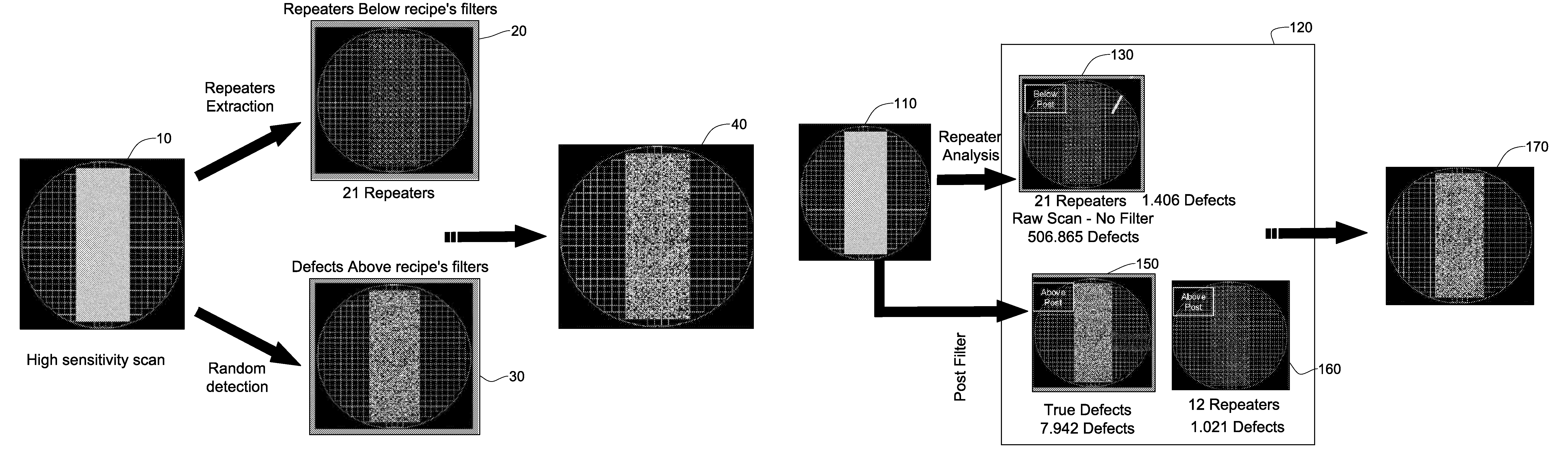
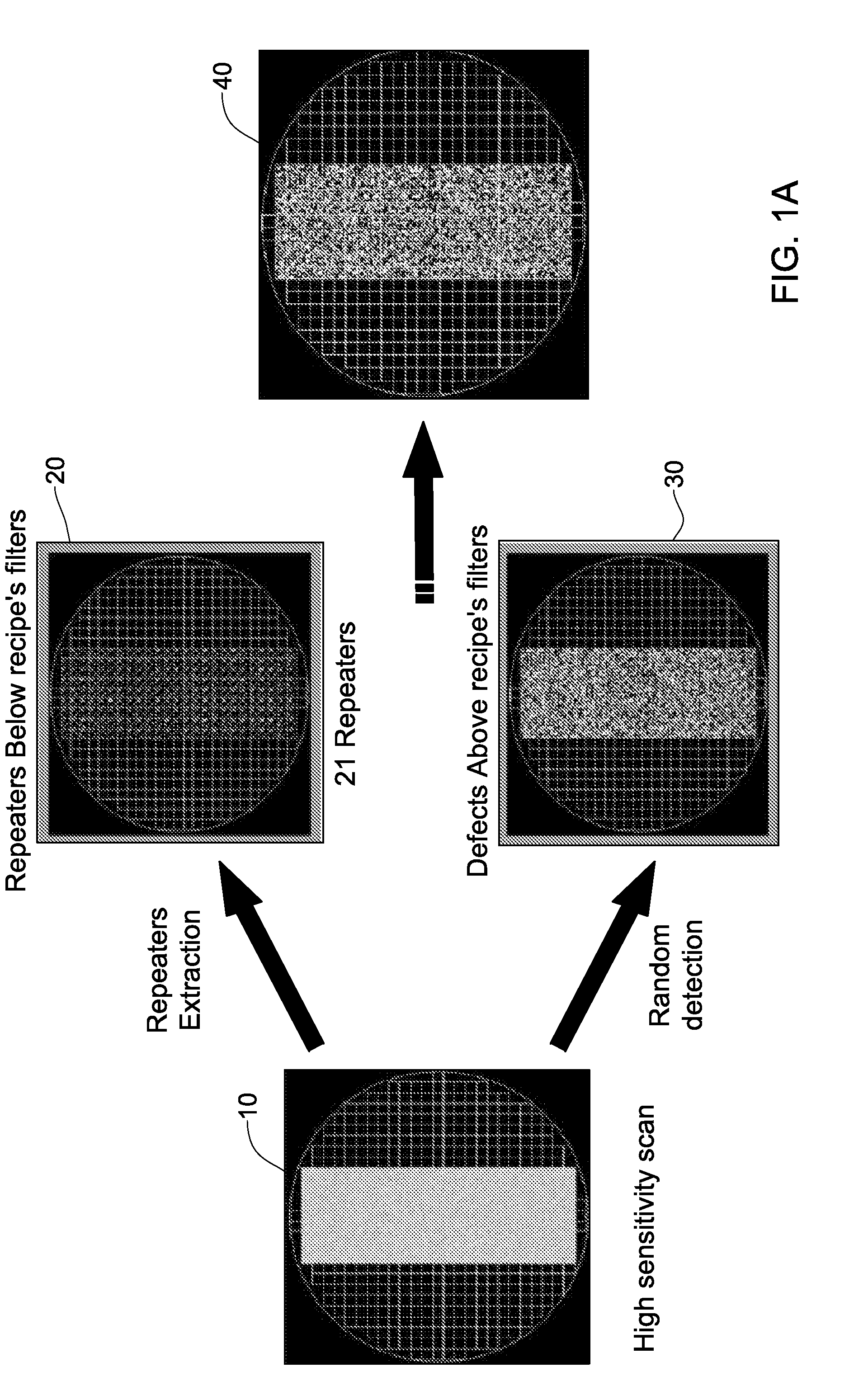
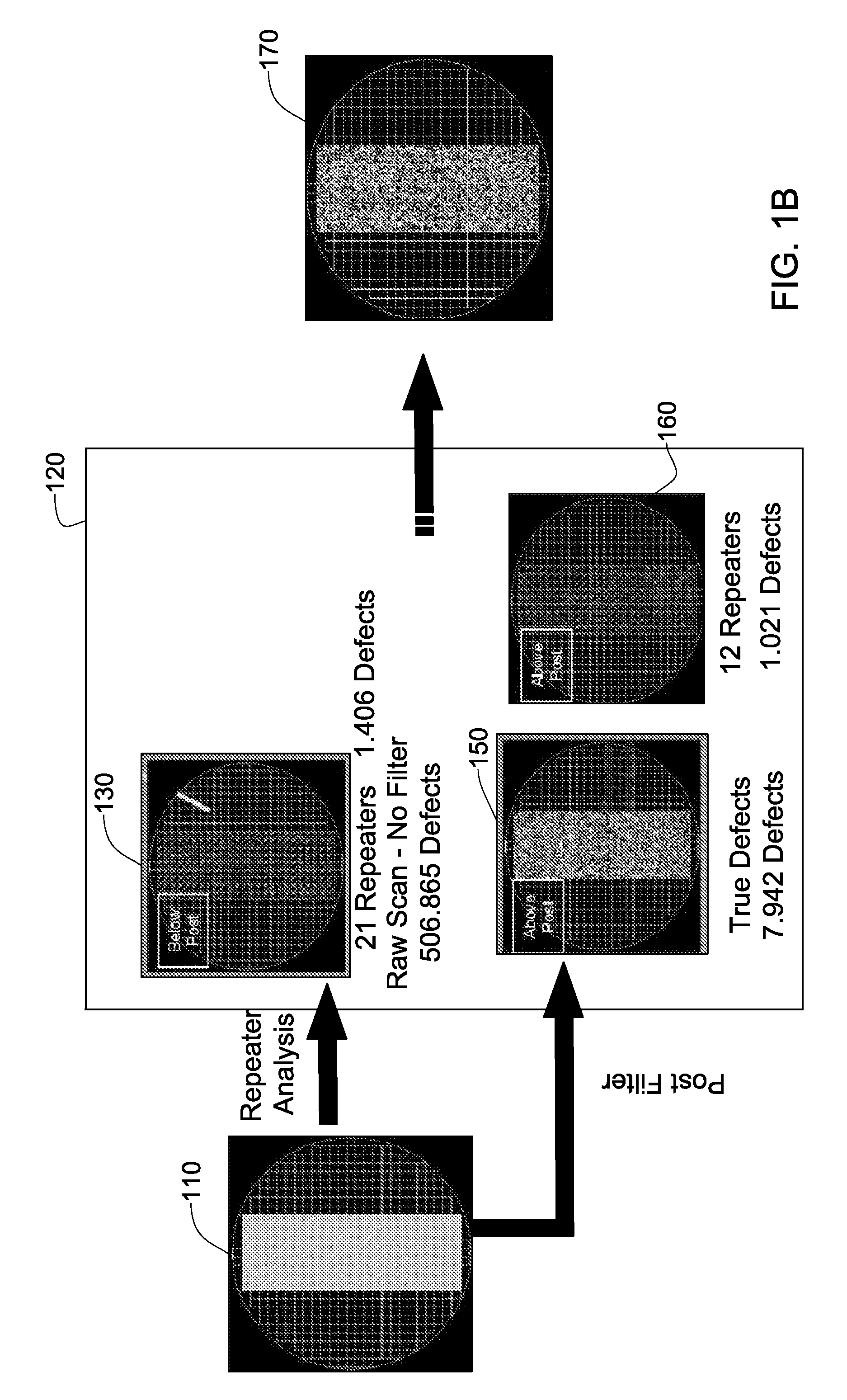
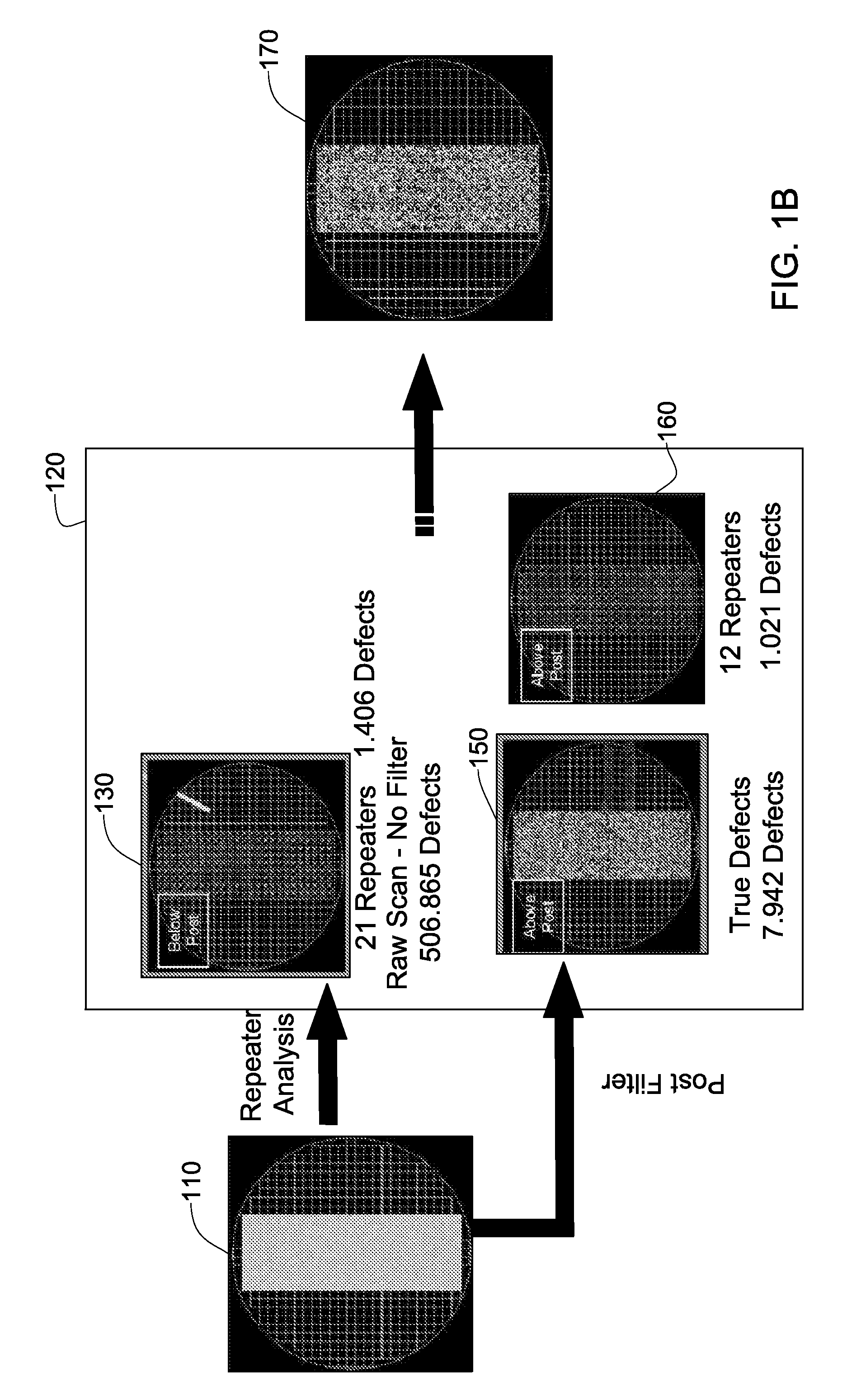
Random defects and repeaters accommodated on a wafer are detected using slice information obtained by scanning a plurality of wafer slices; analyzing defect information using a first set of filters selected to detect random defects, thereby generating a first set of defects per slice, analyzing the defect information using a second set of filters selected to detect repeaters, thereby providing a second set of defects per slice; analyzing a plurality of the second sets of defects per slice using a third set of filters selected to detect repeater families, thereby providing a set of repeaters per wafer; and optionally combining the set of repeaters per wafer with a plurality of the first sets of defects per slice, thereby generating one or more defect maps indicative of random defects and / or repeaters.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Three-dimensional reconstruction method for internal defect of alloy firmware
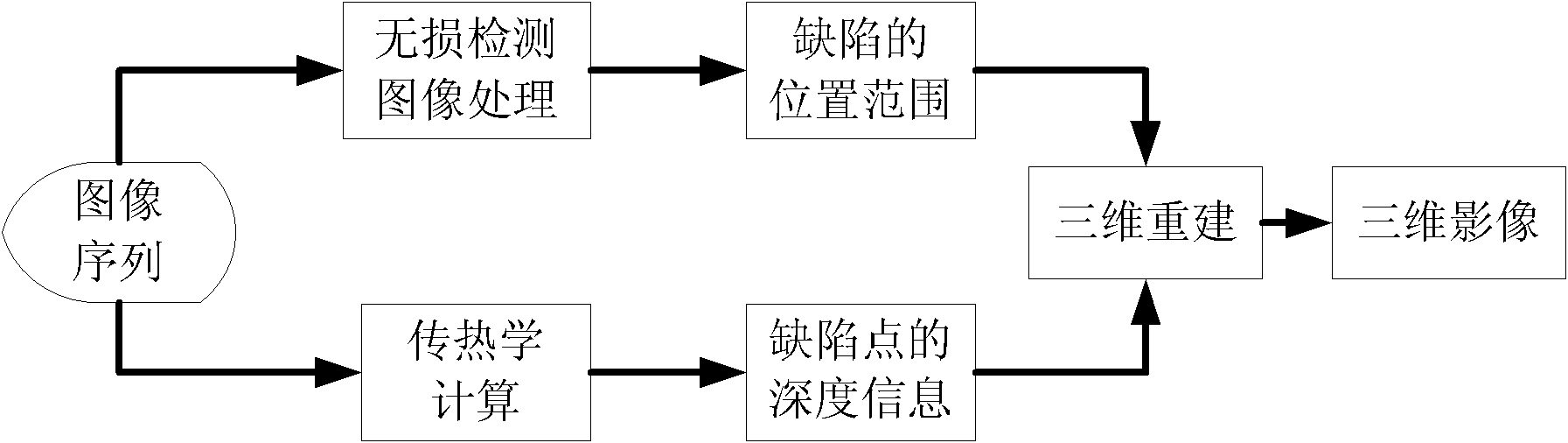
InactiveCN102486462AOptically investigating flaws/contaminationThree dimensional simulationReconstruction method
The invention relates to a three dimensional reconstruction method for internal defect of an alloy firmware, which comprises the following steps: using a nondestructive test device to generate an infrared image; in the infrared image, carrying out nondestructive test on the internal defect of the alloy firmware by a nondestructive test technology, determining the position scope of the defect and the color difference information; according to the defect position scope, determining the depth information of a random defect point by combining a heat transfer theory; according to the defect position scope and the depth information, completing the three-dimensional reconstruction through a visualization technology for realizing the three-dimensional simulation of the defect. According to the invention, the three-dimensional simulation is carried out for the internal defect of the alloy firmware, thereby the three-dimensional image of the internal defect can be presented in a visual and effective mode. The internal defect condition of the alloy firmware can be detected by the method, the firmware can not be damaged, the technicians can conveniently observe the three-dimensional image of the internal defect of the firmware from multi-direction and multi-level aspects. The method of the invention has important reality meaning and research value.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Computer-implemented methods for determining if actual defects are potentially systematic defects or potentially random defects
Various computer-implemented methods for determining if actual defects are potentially systematic defects or potentially random defects are provided. One computer-implemented method for determining if actual defects are potentially systematic defects or potentially random defects includes comparing a number of actual defects in a group to a number of randomly generated defects in a group. The actual defects are detected on a wafer. A portion of a design on the wafer proximate a location of each of the actual defects in the group and each of the randomly generated defects in the group is substantially the same. The method also includes determining if the actual defects in the group are potentially systematic defects or potentially random defects based on results of the comparing step.
Owner:KLA CORP
Method and apparatus for analyzing defect data and a review system
In a process for manufacturing a semiconductor wafer, defect distribution state analysis is performed so as to facilitate identification of the defect cause including a device cause and a process cause by classifying the defect distribution state according to the defect position coordinates detected by the inspection device, into one of the distribution characteristic categories: repeated defects, clustered defects, arc-shaped regional defects, radial regional defects, line type regional defects, ring and blob type regional defects, and random defects.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
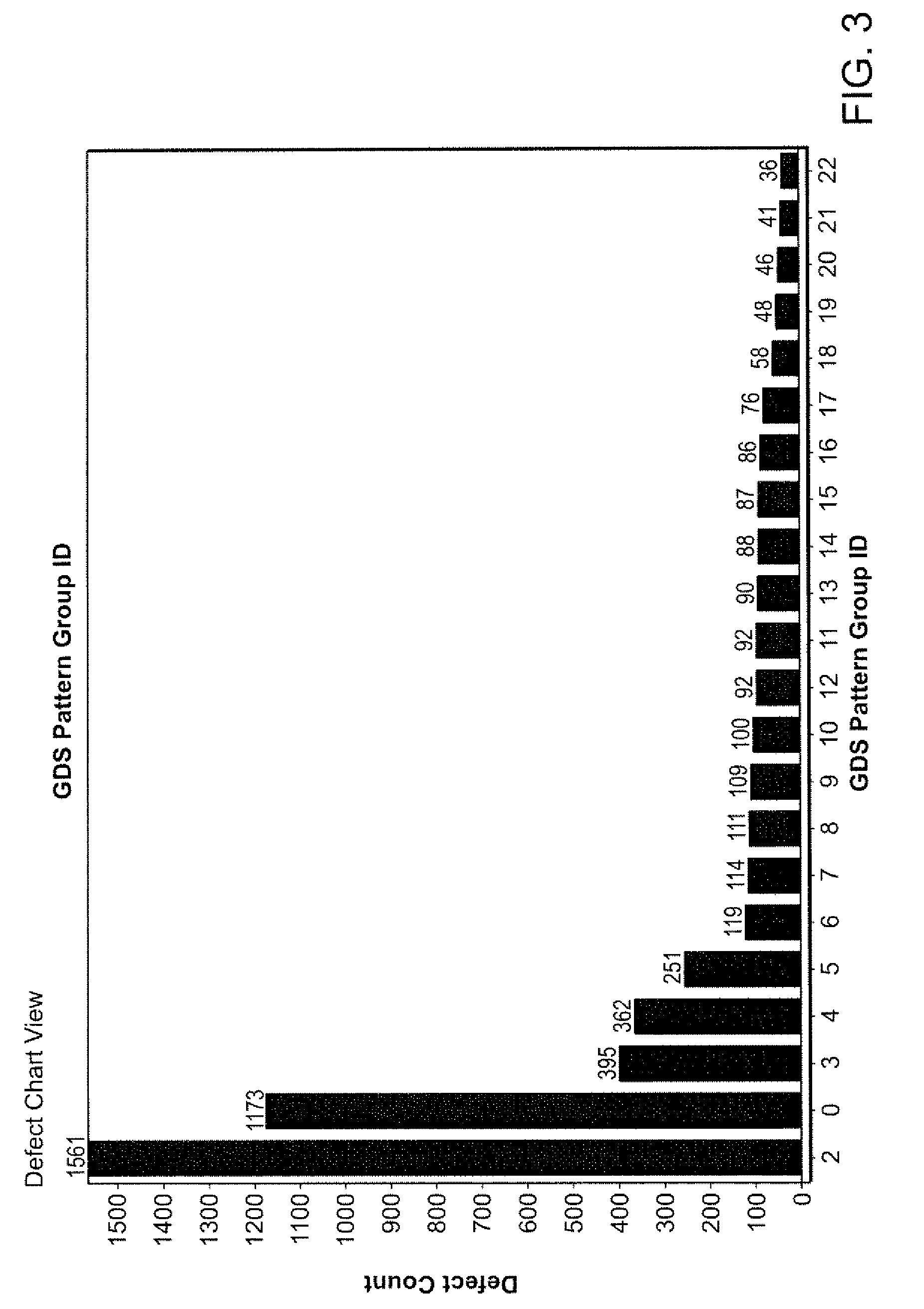
Criticality analysis augmented process window qualification sampling
ActiveUS20190072858A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansAlgorithmProcess window
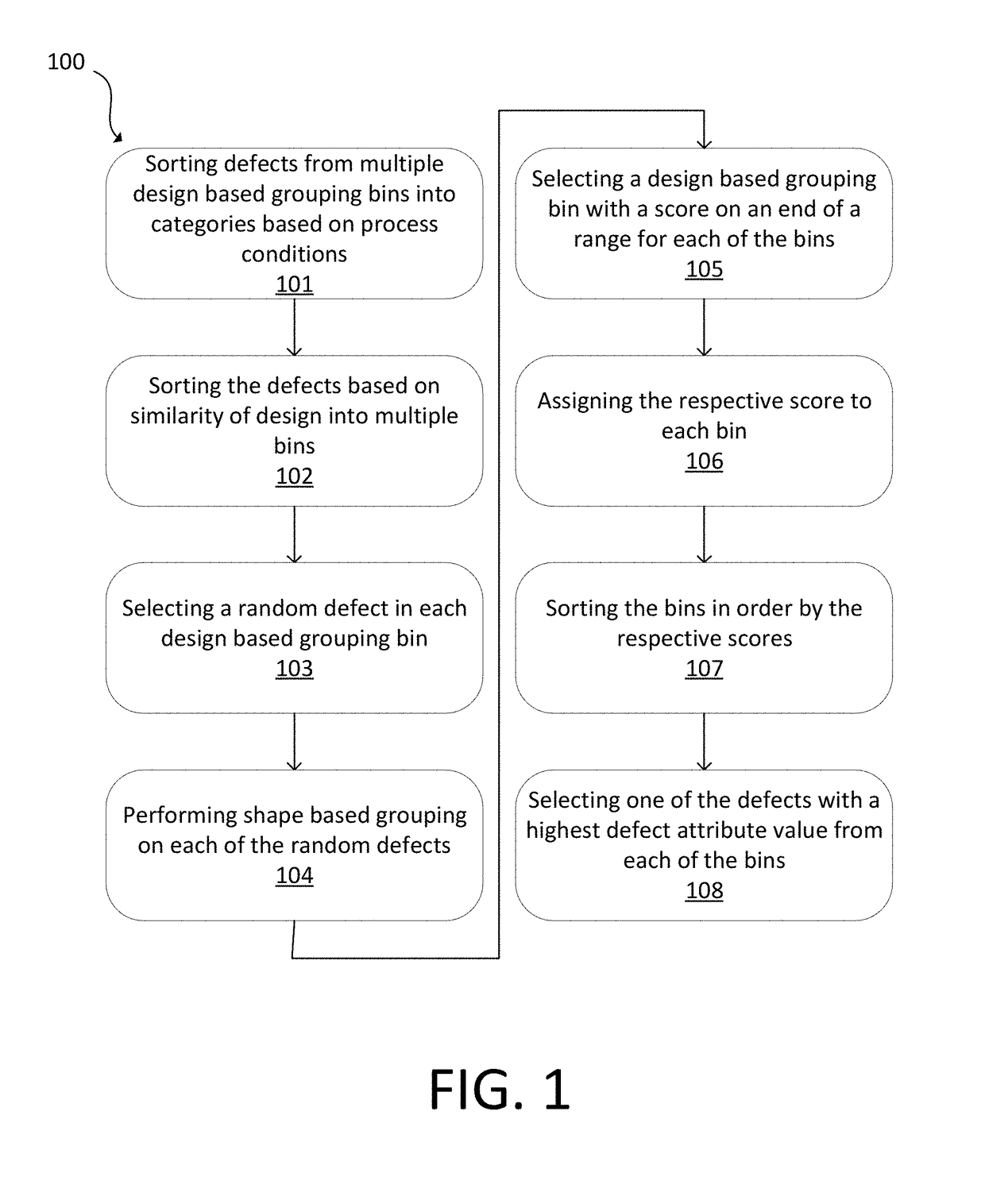
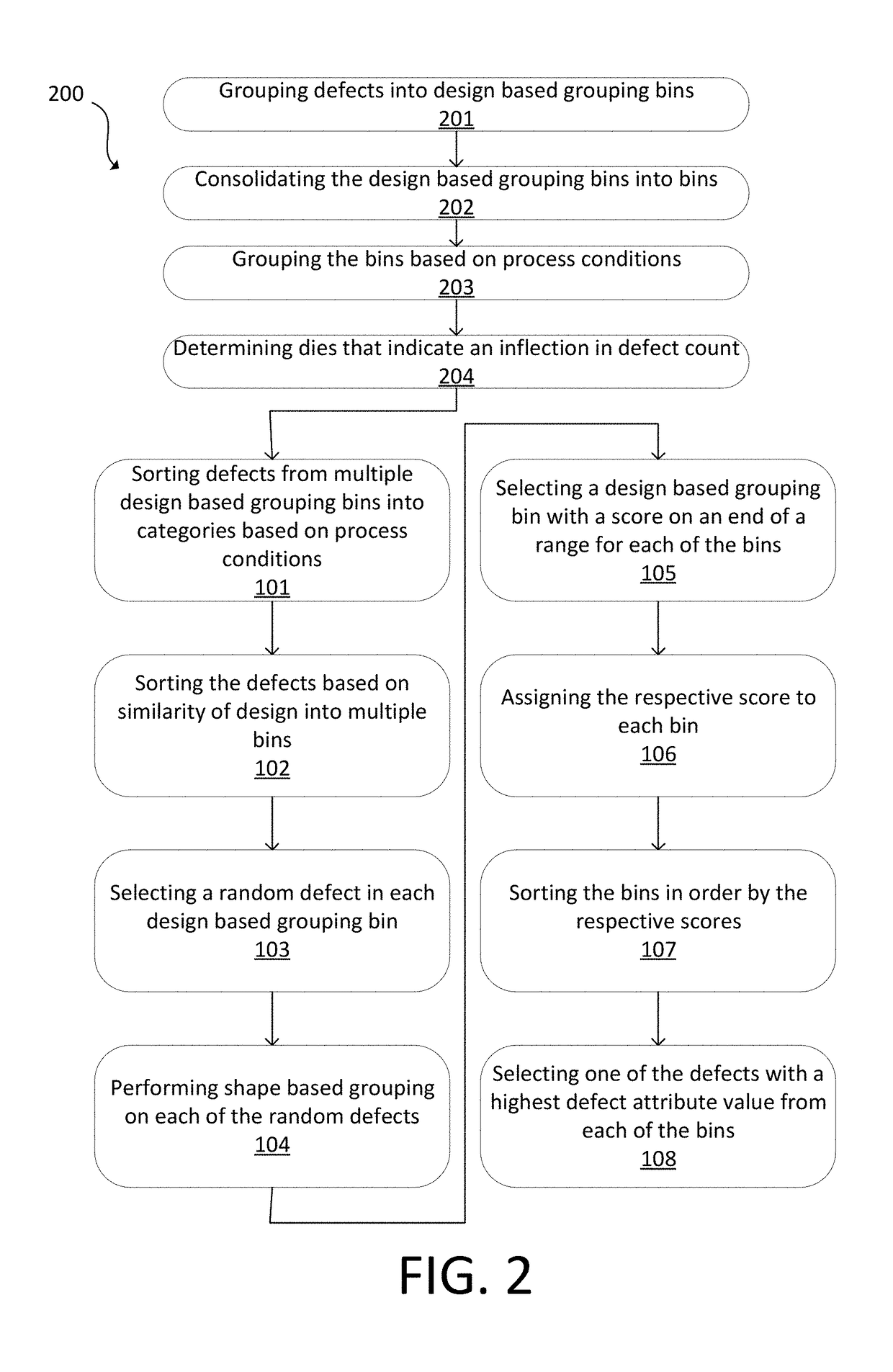
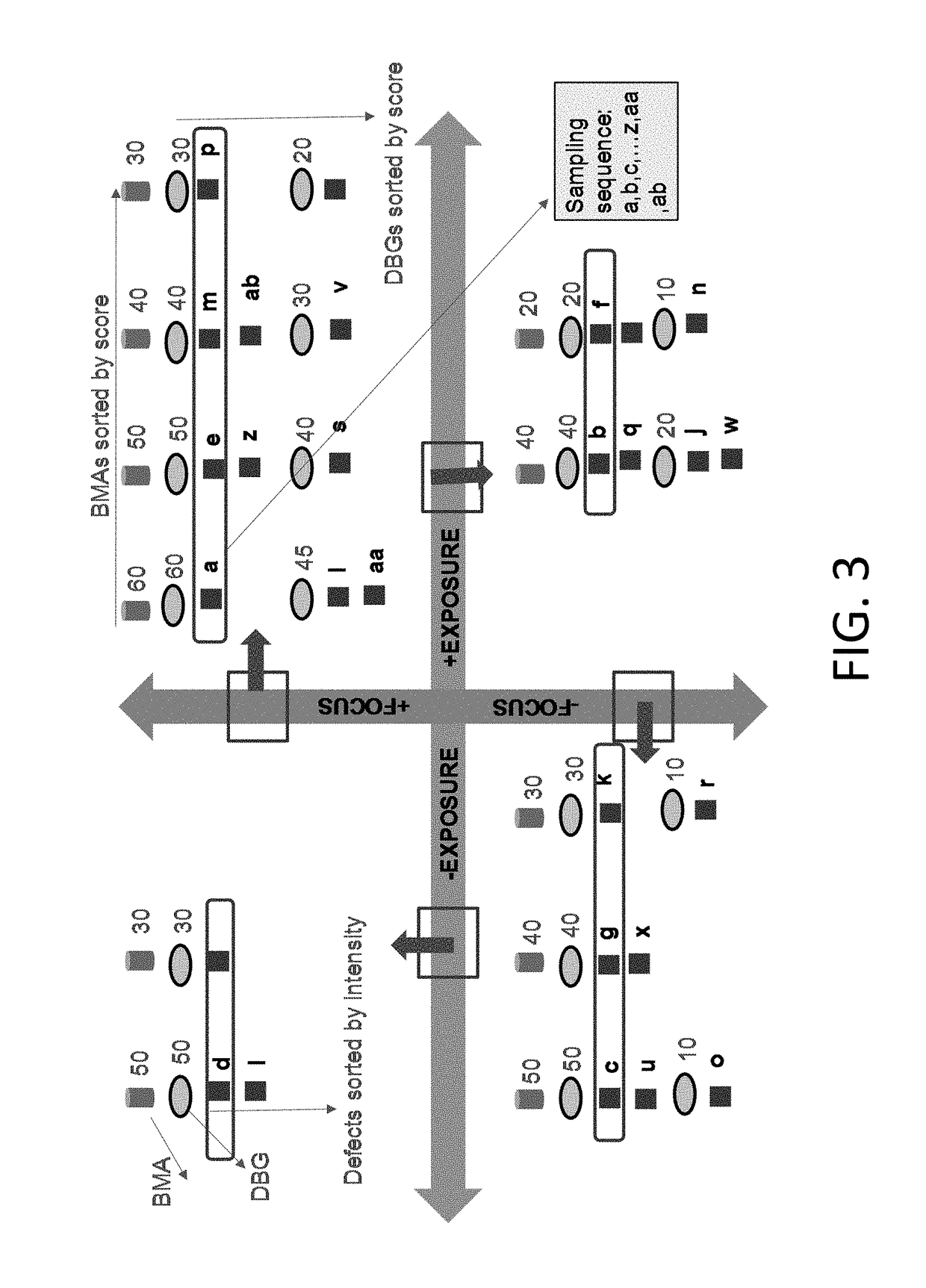
Techniques are provided that can select defects based on criticality of design pattern as well as defect attributes for process window qualification (PWQ). Defects are sorted into categories based on process conditions and similarity of design. Shape based grouping can be performed on the random defects. Highest design based grouping scores can be assigned to the bins, which are then sorted. Particular defects can be selected from the bins. These defects may be reviewed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Yield analysis method
InactiveUS7386418B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDigital computer detailsEngineeringAnalysis method
A yield analysis method. First, a wafer having multiple dies is inspected to obtain wafer defect data containing defect information for every die in the wafer. Then a wafer map and an overall yield are generated according to the wafer defect data. The wafer map displays defective dies and defect-free dies in the wafer. Then, first and second systematic limited yields are calculated in accordance with the wafer defect data and the wafer map, wherein the first systematic limited yield is calculated excluding defective dies with localized distribution, and the second systematic limited yield is calculated excluding defective dies with repeated distribution. Then a random defect limited yield is determined in accordance with the overall yield, the first systematic limited yield, and the second systematic limited yield.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method for preparing photo-curable bone repairing material from epoxy group-containing siloxane-clad modified hydroxyapatite
InactiveCN101966349AGood biocompatibilityImprove mechanical propertiesProsthesisEpoxyBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for preparing a photo-curable bone repairing material from epoxy group-containing siloxane-clad modified hydroxyapatite, which belongs to the field of research on biomedical composite materials. The method comprises the following steps of: performing surface grafting modification on the hydroxyapatite; cladding the modified hydroxyapatite in siloxane by a sol gel method; and performing UV photopolymerization. The photo-curable bone repairing material has high biocompatibility and mechanical property and hydrophilcity; moreover, the material is in a flowing viscous sol state before being cured, so the material can be combined with tissues and subjected to injection molding for repairing the random defects of the tissues in vivo.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for detecting random defects of silicon gate of CMOS process
InactiveCN101692430AEfficient use ofSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical testingChain typeInterconnection
The invention discloses a method for detecting random defects of a silicon gate of a CMOS process. The method comprises the following steps: designing a comb-shaped testing structure of a parametric transistor according to an orthogonal table L9 (34), and detecting leakage defects between a source electrode and a drain electrode of the transistor when the silicon gate is a control gate pole; designing a through-hole chain-type testing structure of the parametric transistor according to an orthogonal table L16 (45), and detecting broken circuit defects when the silicon gate and an upper metal are connected with each other; designing a snake-shaped testing structure of a parametric phase inverter according to an orthogonal table L16 (45), and detecting the broken circuit defects when the silicon gate is the gate pole for interconnection; and measuring an optical parameter of each testing structure by using a four electrode testing method, and analyzing the level combination of factors which remarkably affect the random defects of the silicon gate through a variance analysis method. The basic units of the testing structures are arranged by a compact mode, can effectively utilizes areas of the testing structures, and can emulate the defects of the silicon gate in an actual circuit, thereby determining the level combination of the factors which remarkably affect the optical parameters of the testing structures.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Modeling method of fully-graded concrete three-dimensional mesoscopic model containing random defects
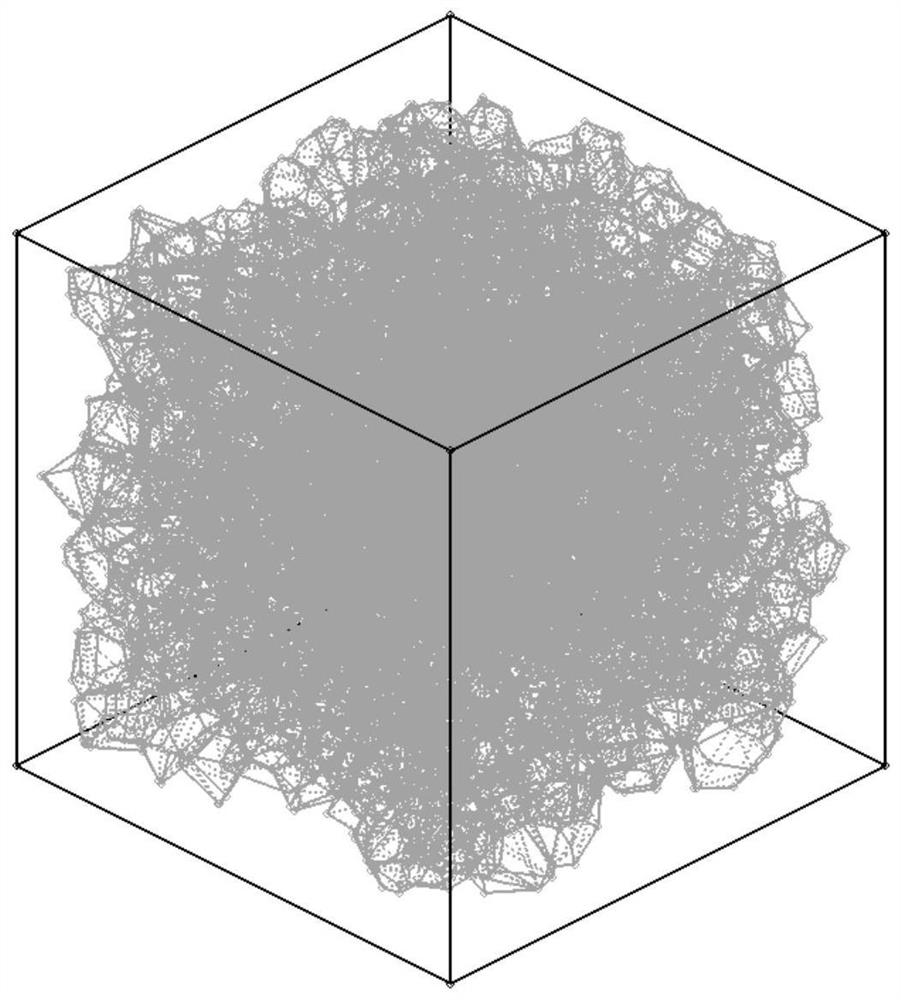
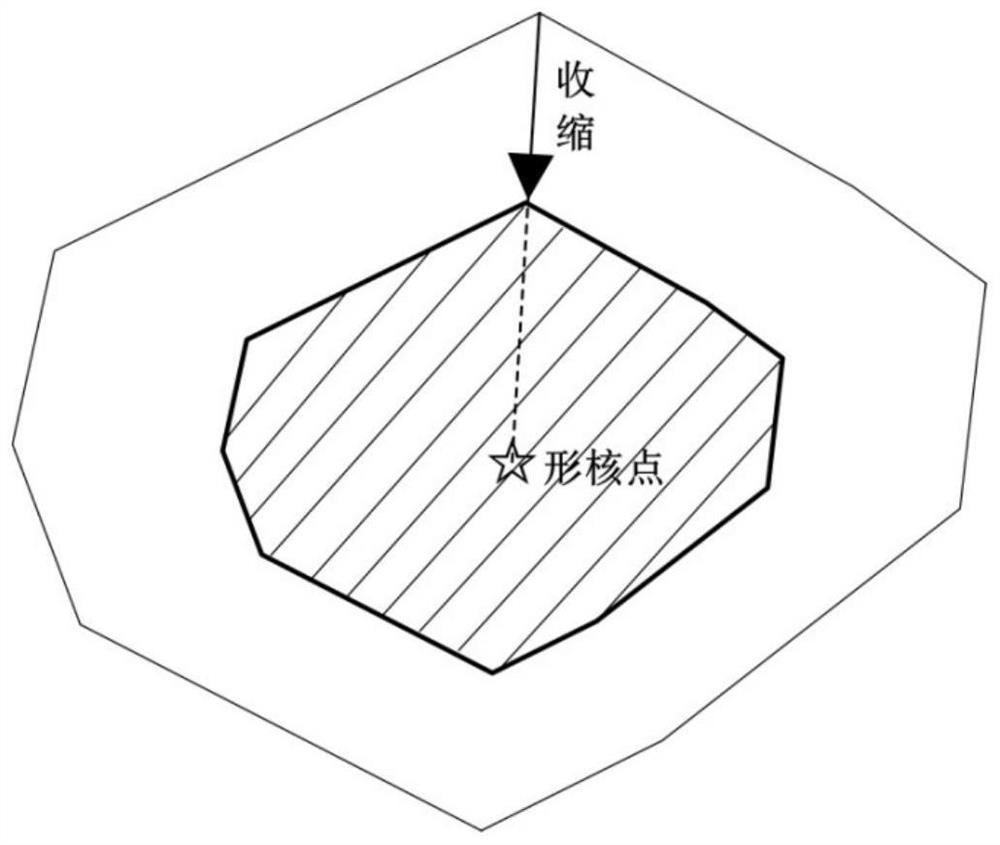
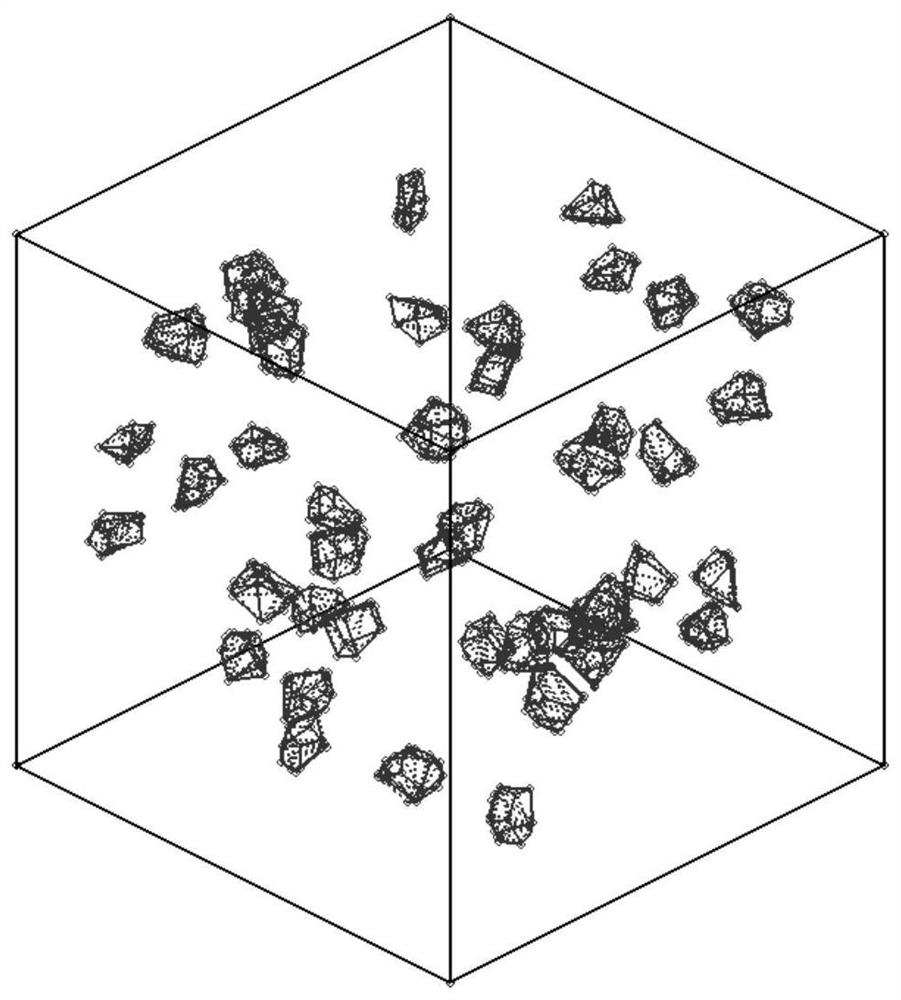
PendingCN113987750AAvoid convexity judgmentsAvoid contactDesign optimisation/simulationChemical data visualisationAlgorithmModelSim
The invention relates to a modeling method of a full-graded concrete three-dimensional mesoscopic model containing random defects. The modeling method mainly solves the important problems in the current concrete mesoscopic modeling process that (1) complex aggregate convexity judgment and aggregate intersection and overlapping judgment are difficult to avoid by most modeling methods; (2) a modeling method based on a traditional Voronoi technology is difficult to meet the requirement of aggregate grading; (3) random defects are difficult to introduce into the mesoscopic model; and (4) the modeling efficiency needs to be further improved. The method comprises the following steps: performing a random shrinkage process meeting aggregate grading requirements on each convex polyhedron cell element in a three-dimensional Voronoi graph by taking a corresponding nucleation point as a center, and generating a random aggregate model with four-grade distribution; and the random spherical pore defect with the required volume content is rapidly introduced outside the aggregate distribution area, and finally the full-graded concrete mesoscopic model containing the random defect is established. According to the modeling method, random defects are introduced. Meanwhile, the aggregate grading requirement can be accurately met, and the modeling method has the very obvious efficiency advantage.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
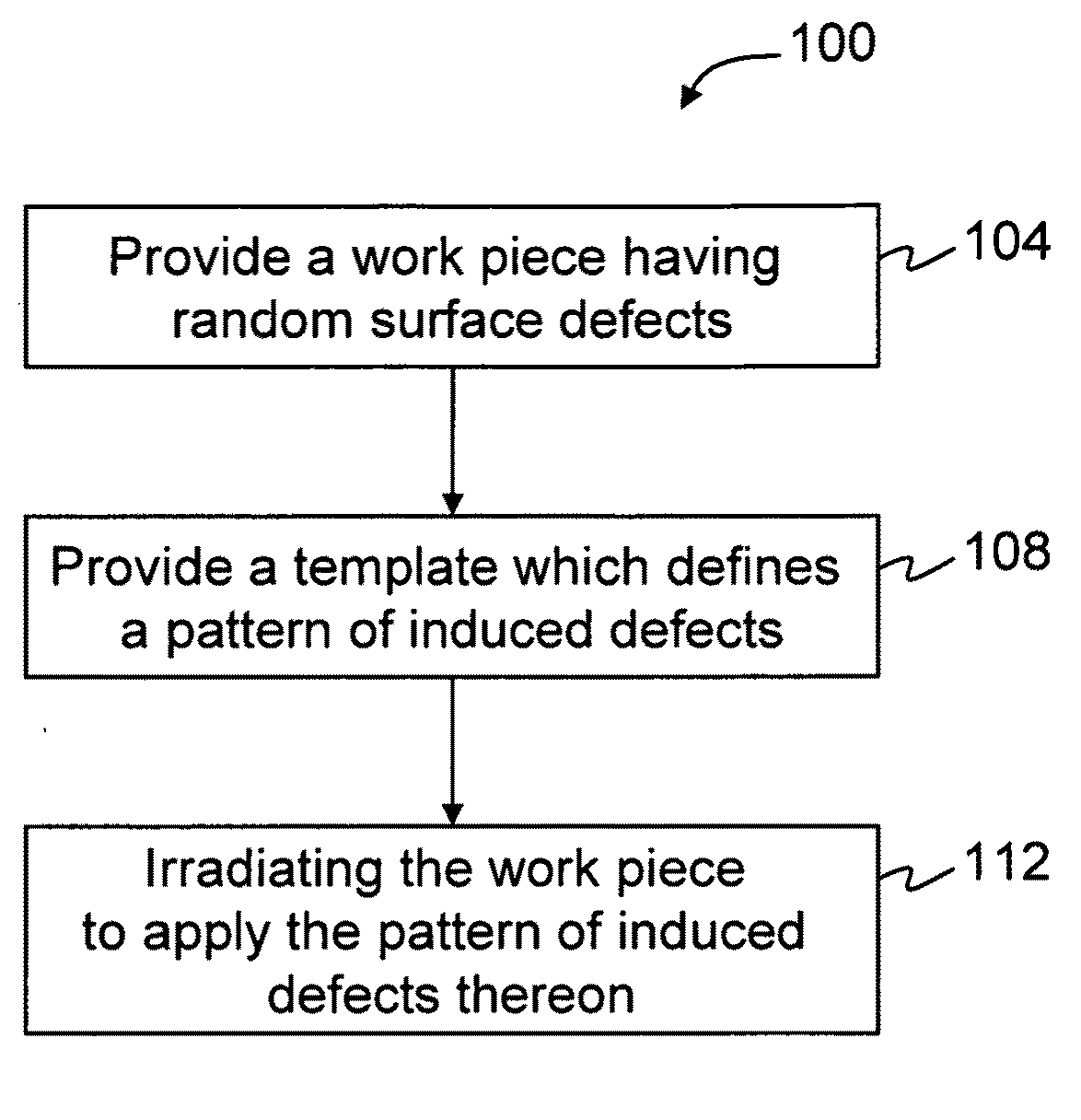
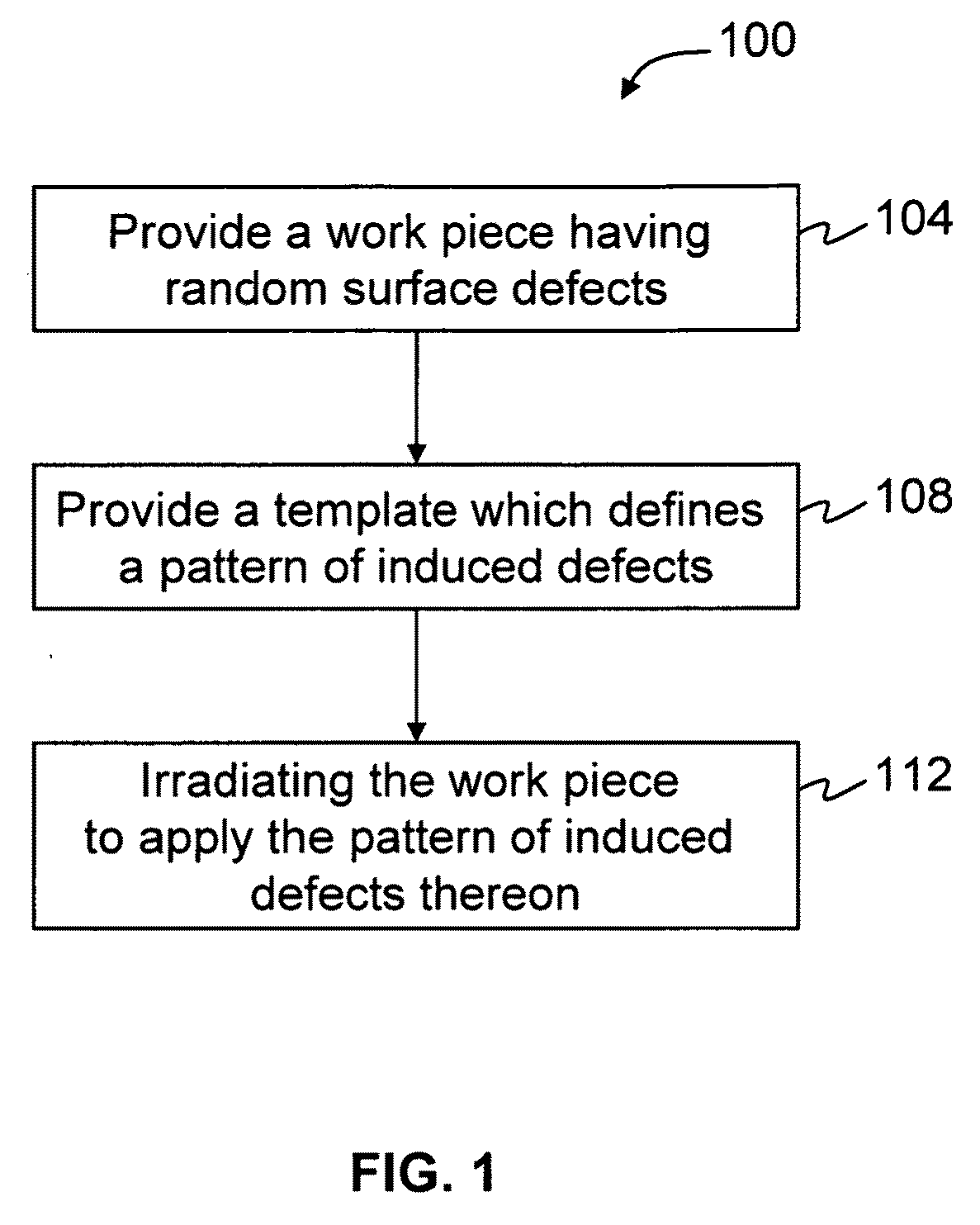
Methods for concealing surface defects
InactiveUS20100155625A1Electric discharge tubesWelding/soldering/cutting articlesRandom defectsMaterials science
Methods for removing random or uncontrolled surface defects from a work piece surface are provided, by applying a plurality of induced controlled defects over the random defects to alter the surface texture.
Owner:INTEL CORP
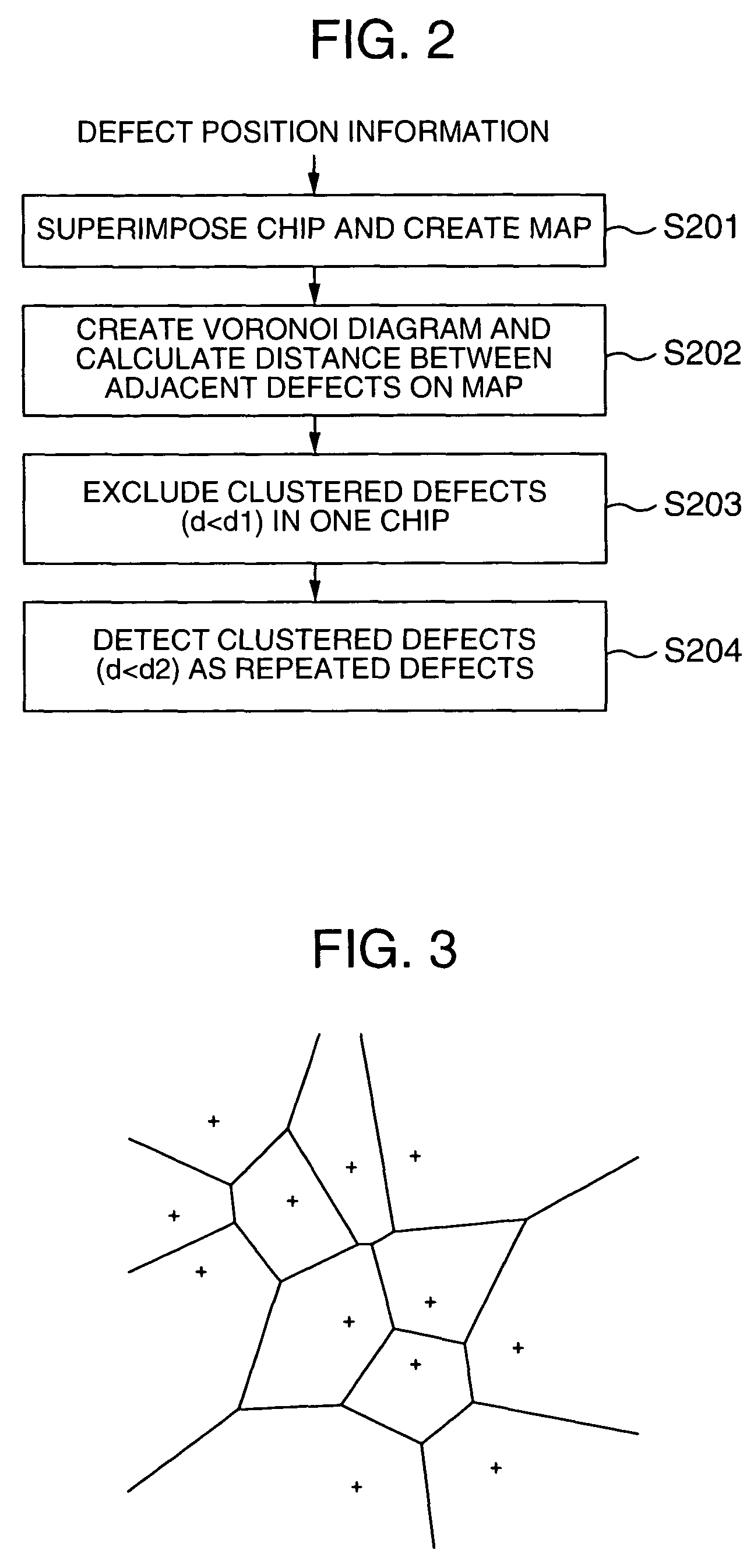
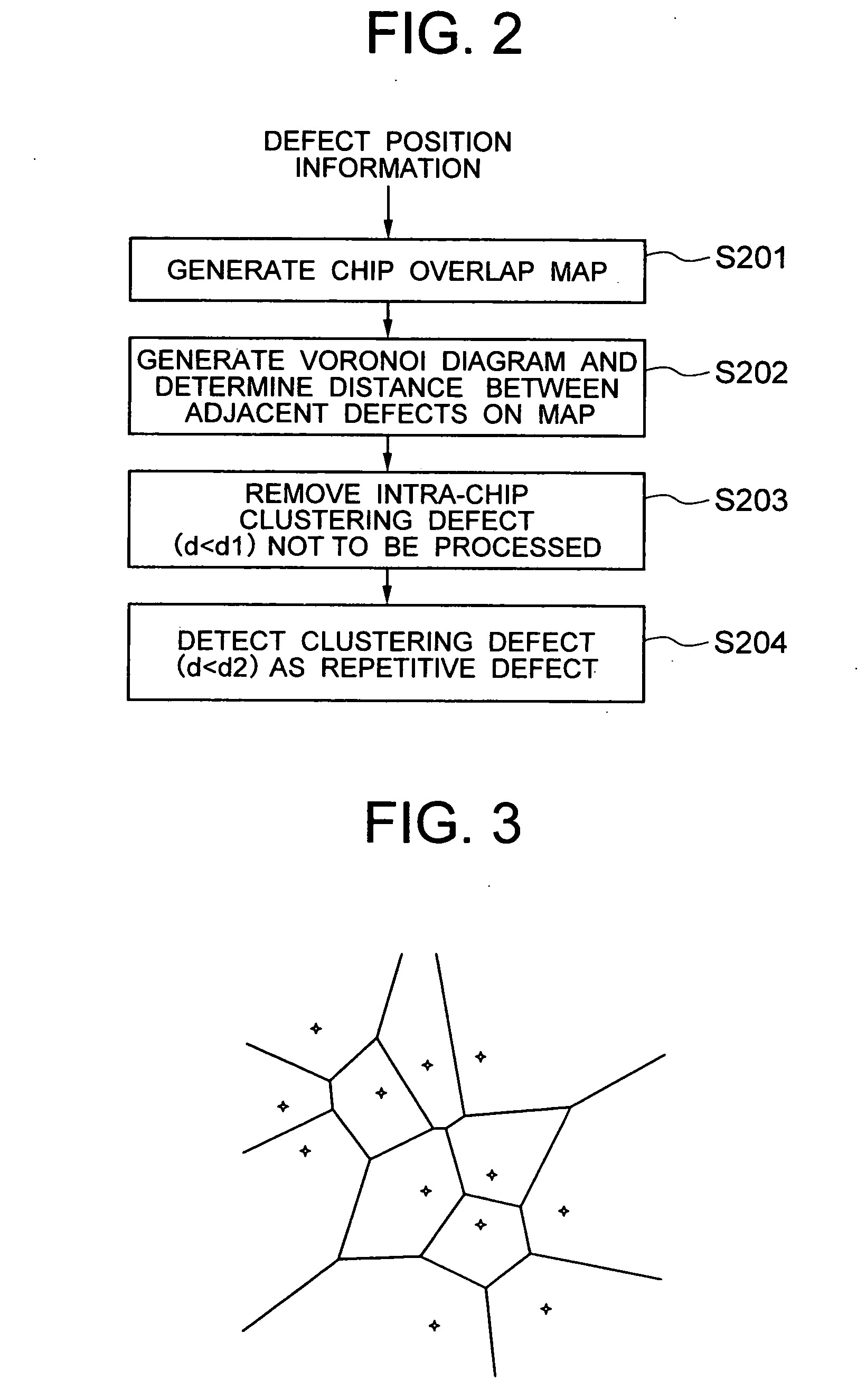
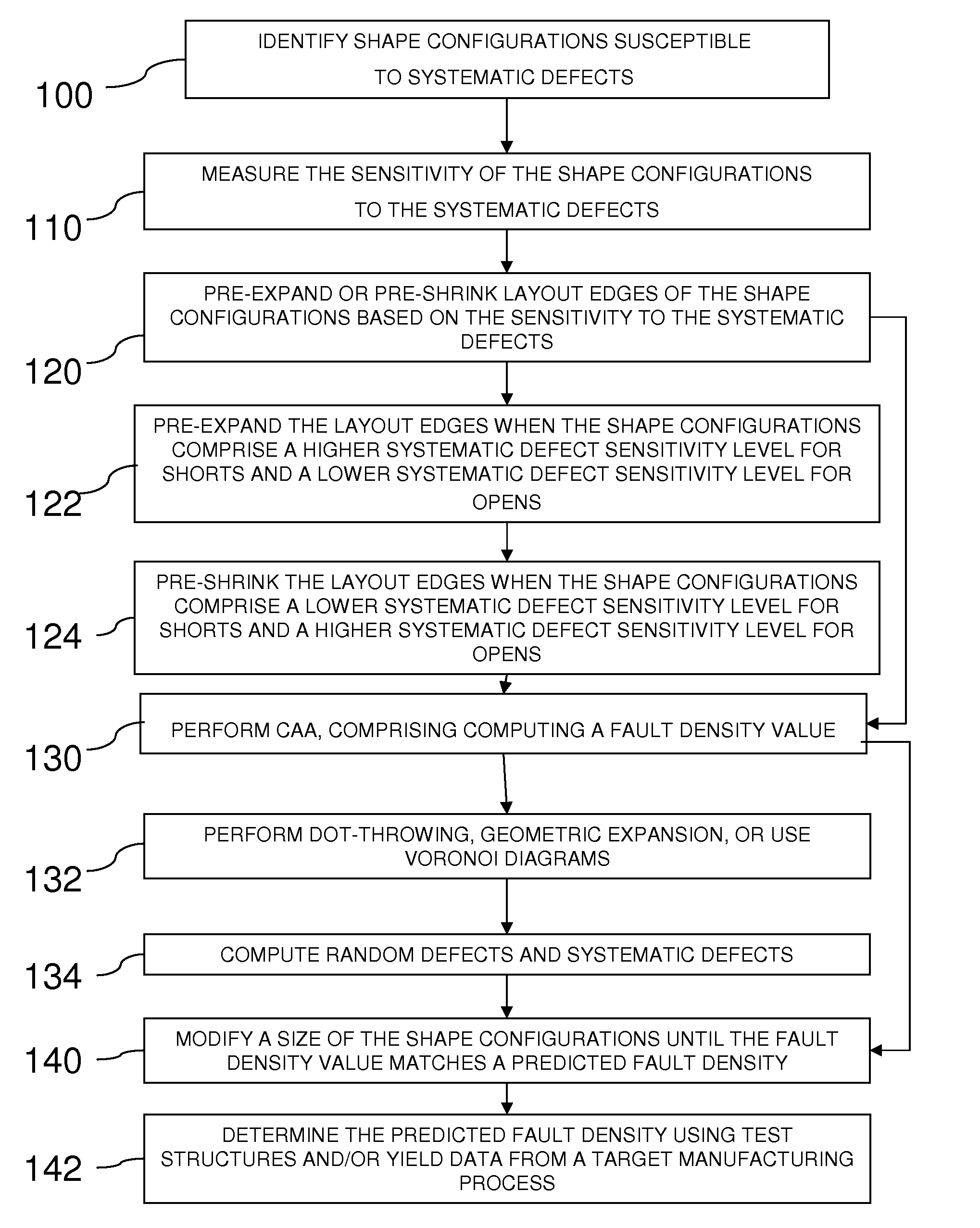
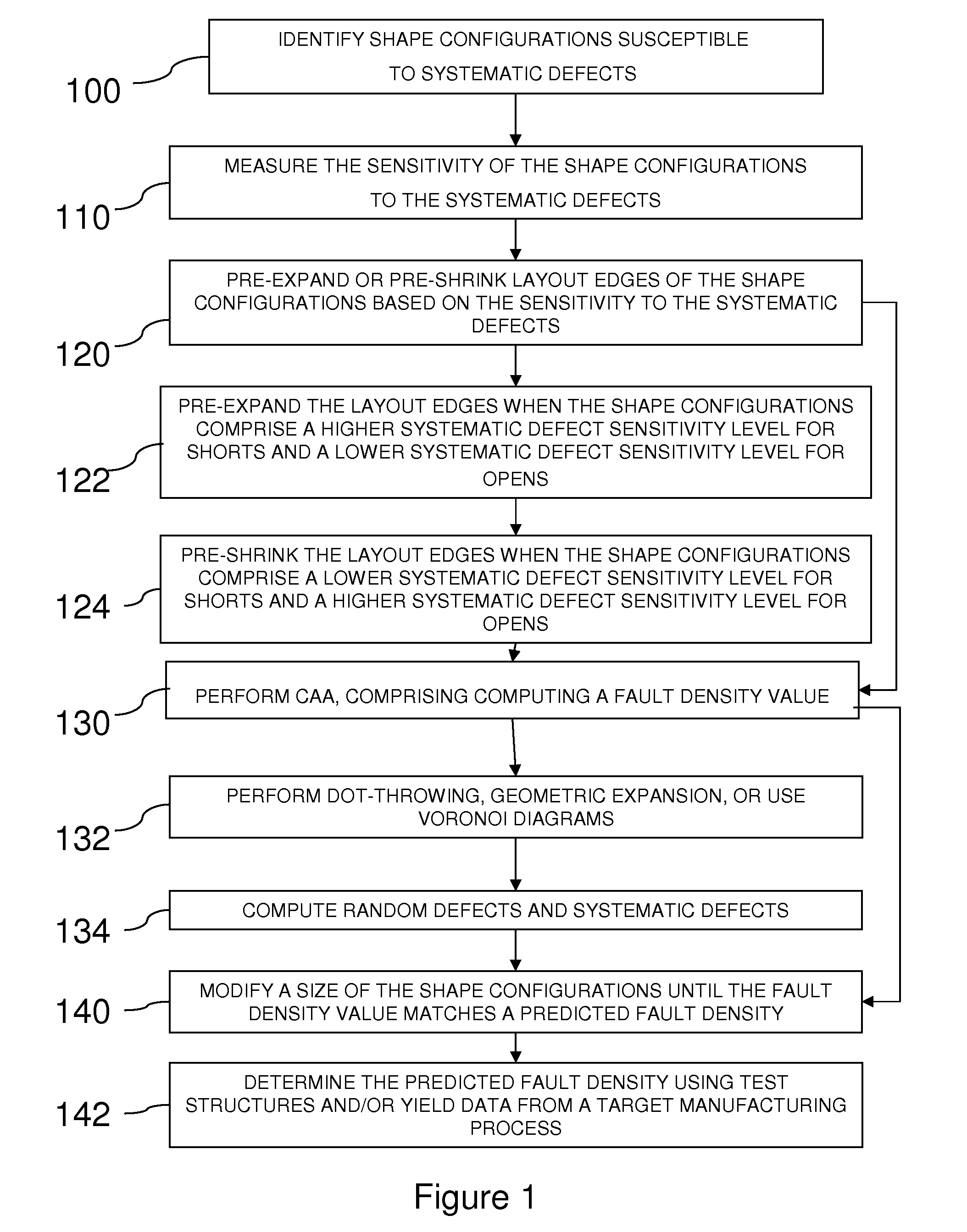
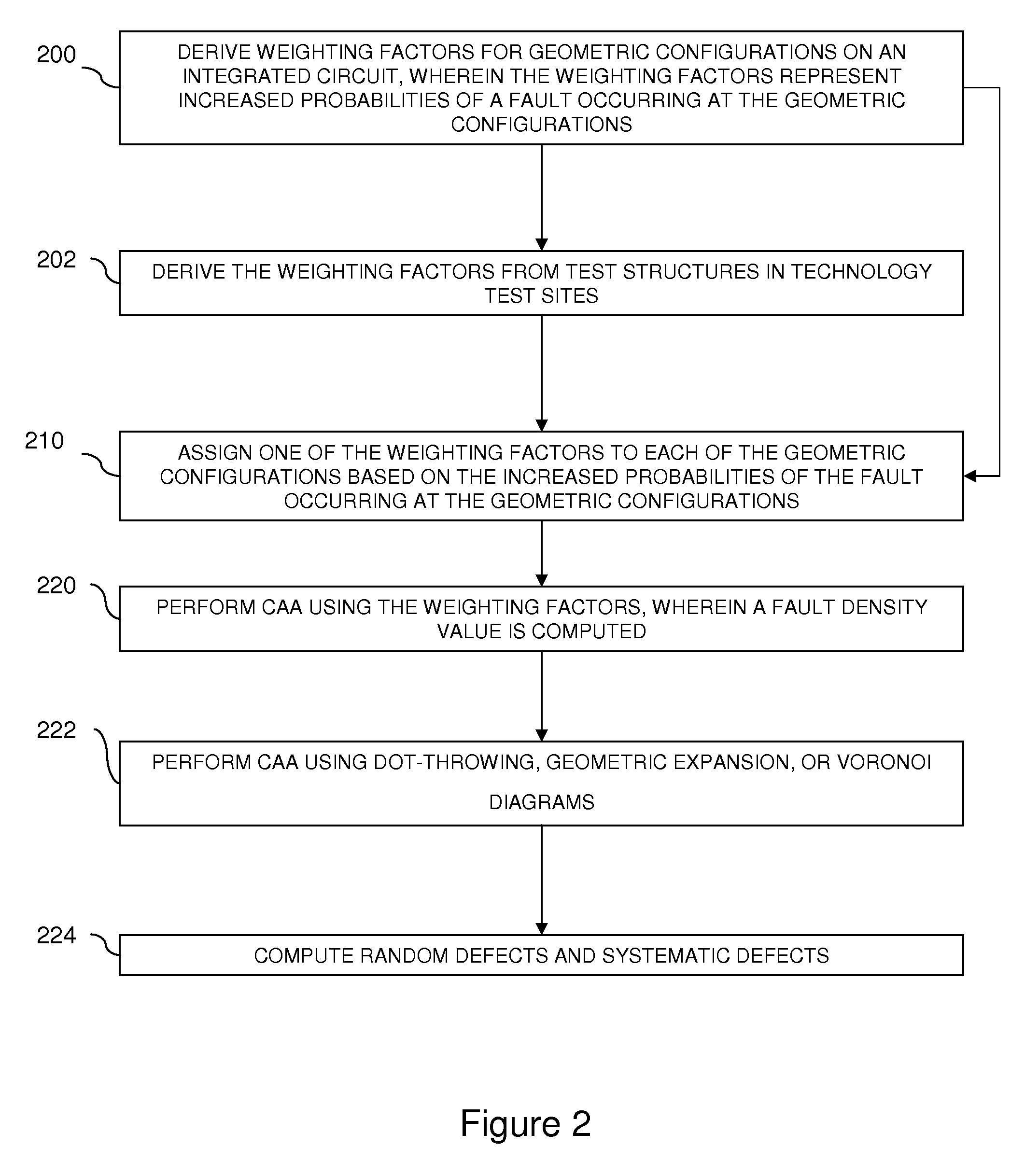
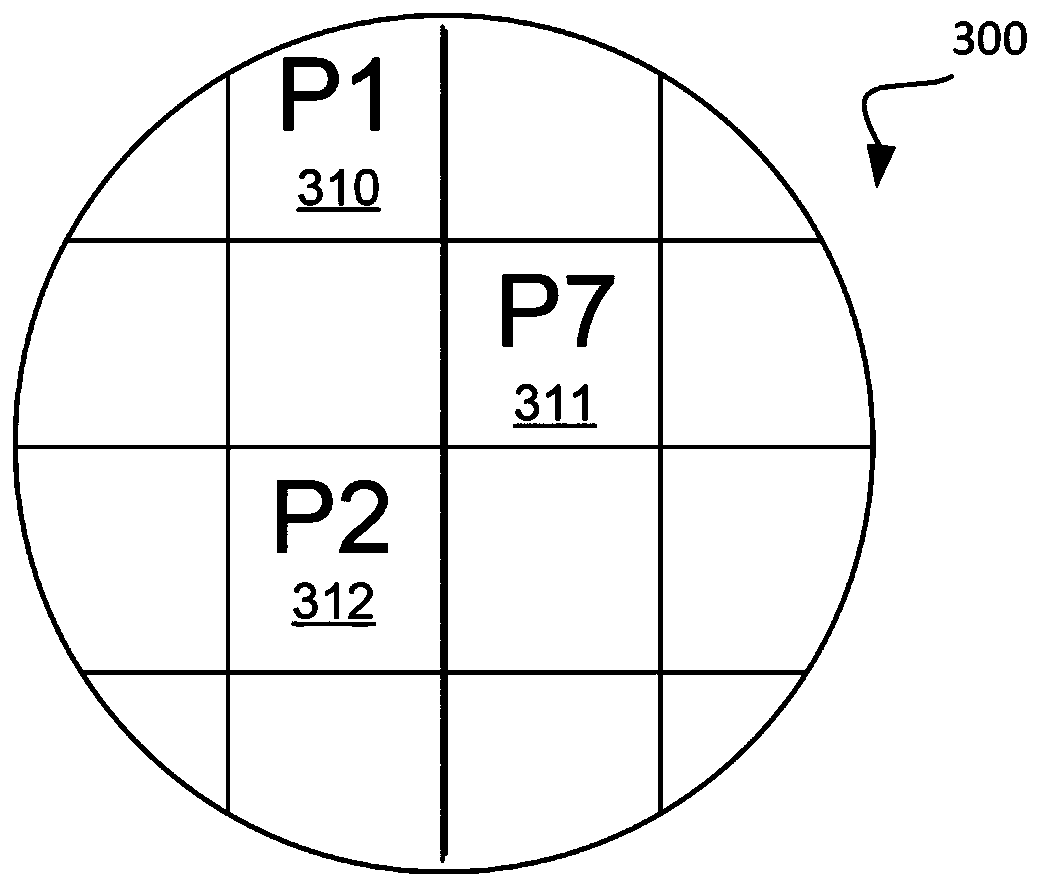
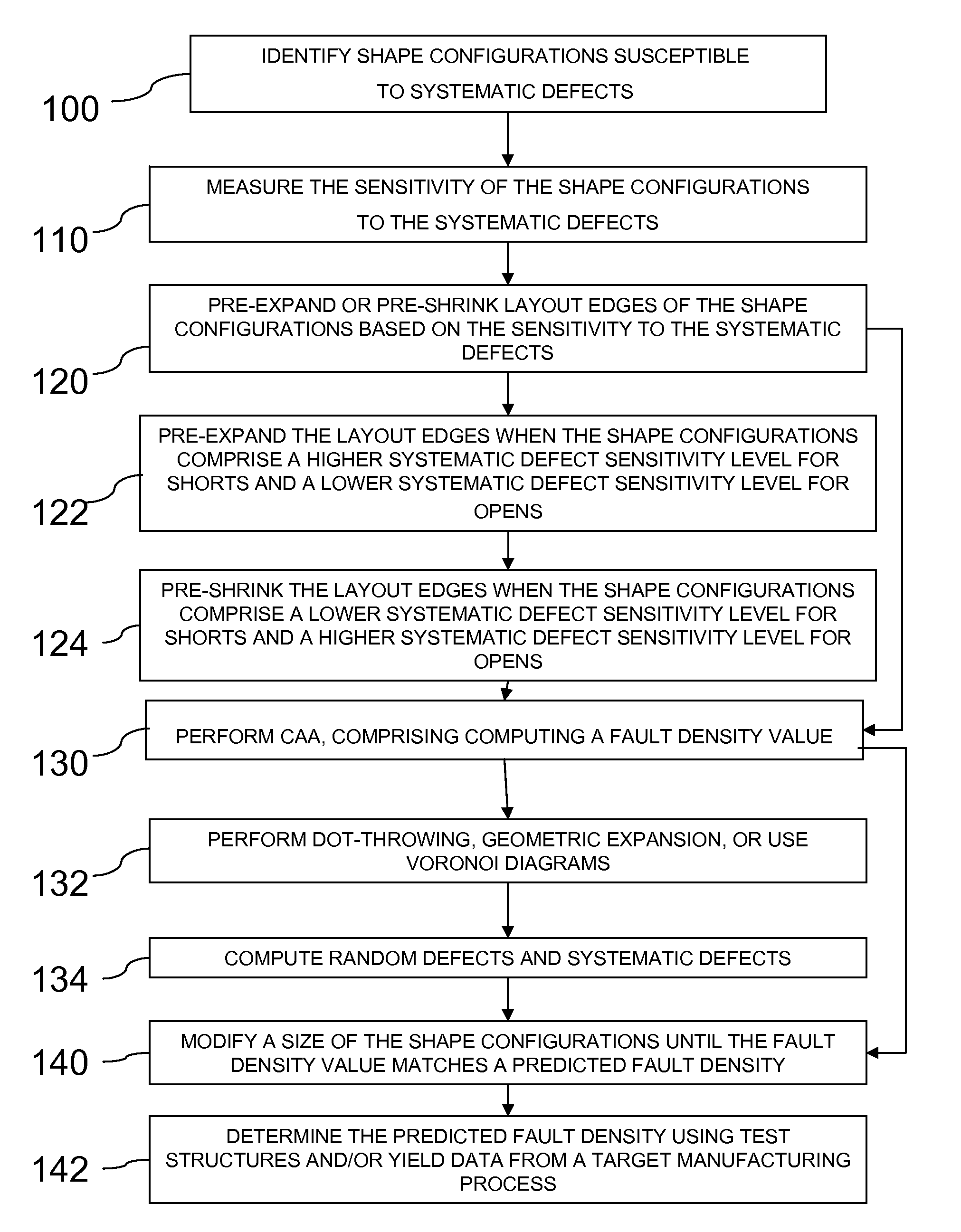
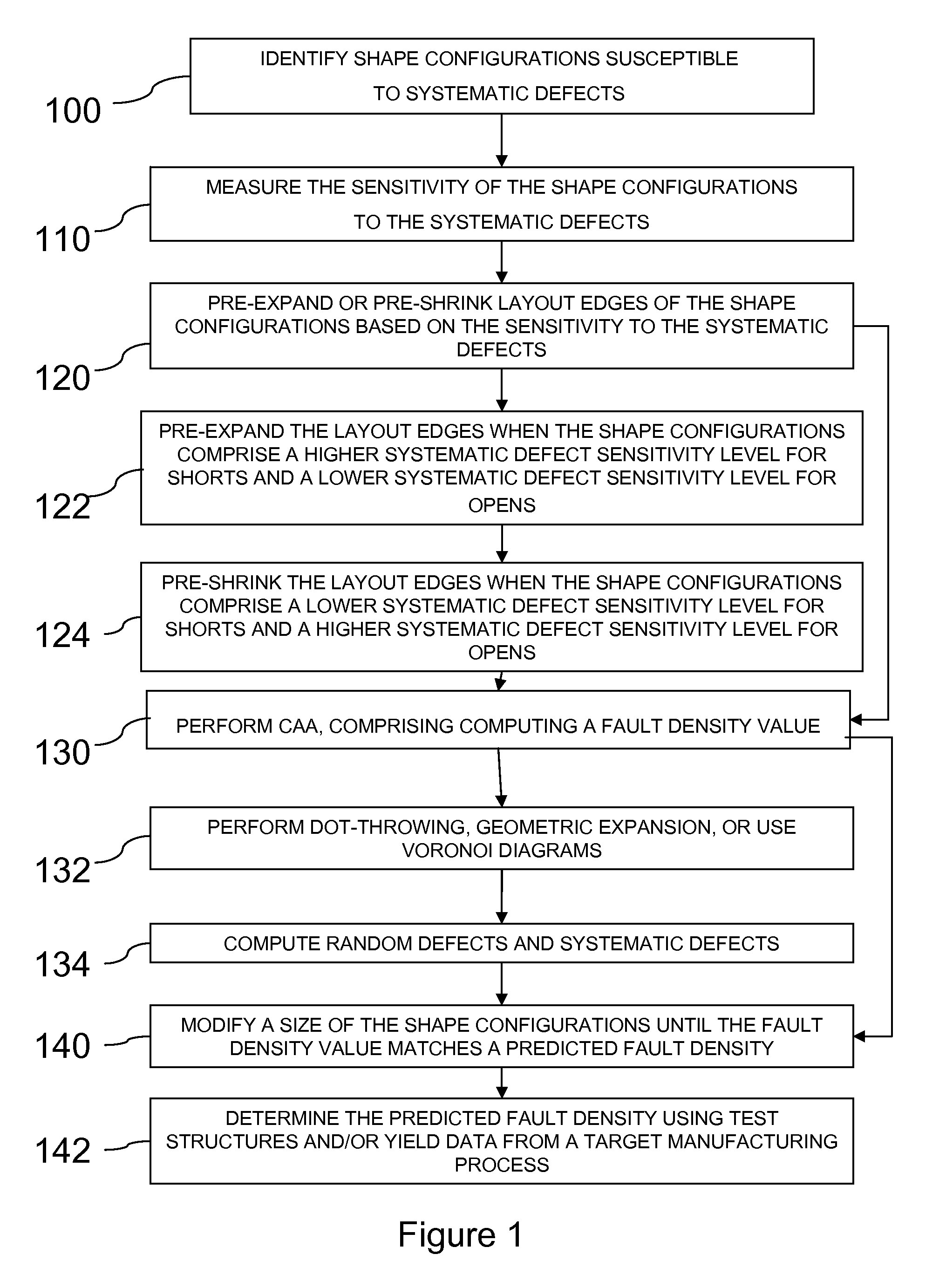
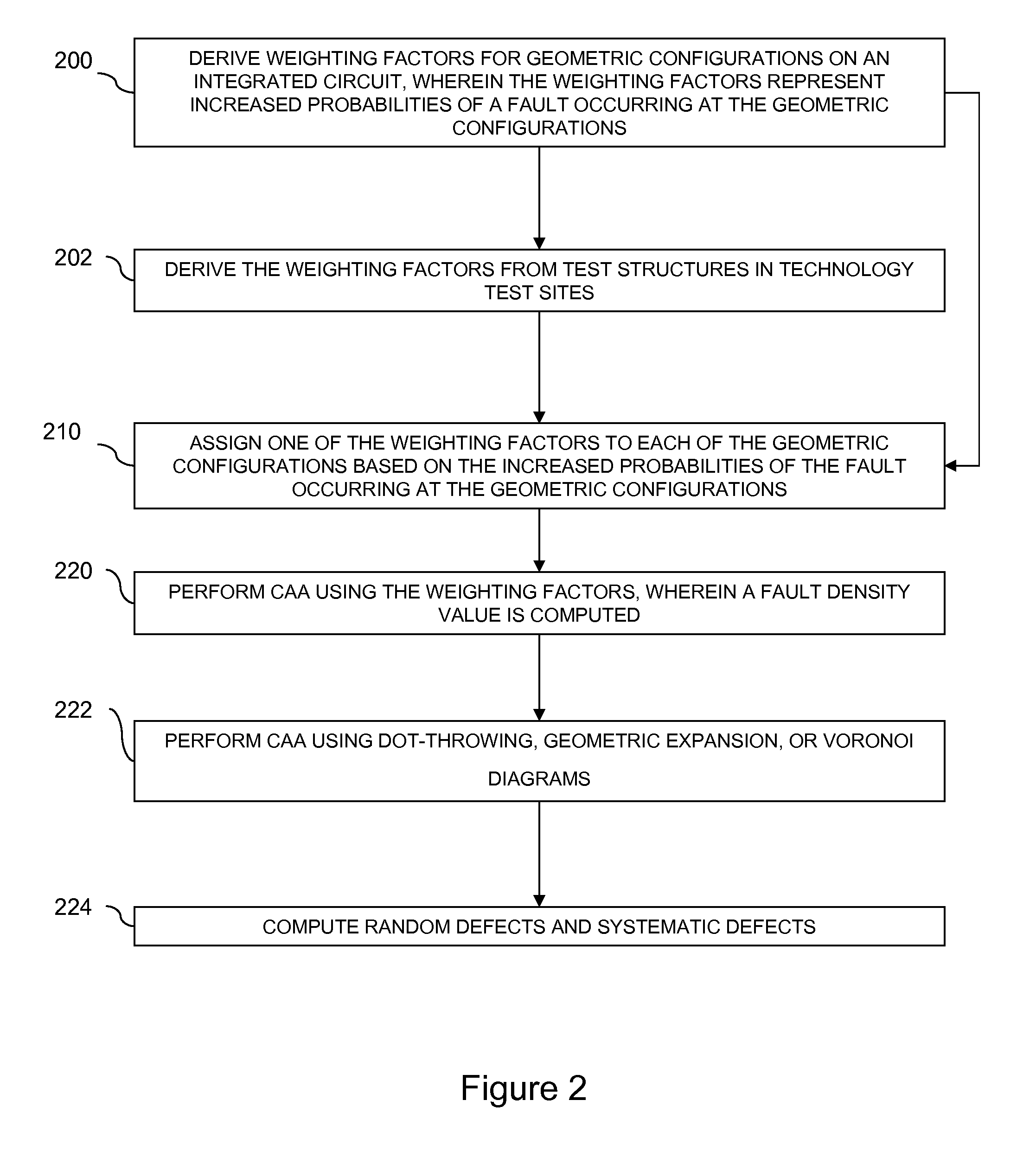
Method for computing the sensistivity of a VLSI design to both random and systematic defects using a critical area analysis tool
InactiveUS20090113360A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designAnalysis toolsIntegrated circuit layout
A method of estimating integrated circuit yield comprises providing an integrated circuit layout and a set of systematic defects based on a manufacturing process. Next, the method represents a systematic defect by modifying structures in the integrated circuit layout to create modified structures. More specifically, for short-circuit-causing defects, the method pre-expands the structures when the structures comprise a higher systematic defect sensitivity level, and pre-shrinks the structures when the structures comprise a lower systematic defect sensitivity level. Following this, a critical area analysis is performed on the integrated circuit layout using the modified structures, wherein dot-throwing, geometric expansion, or Voronoi diagrams are used. The method then computes a fault density value, random defects and systematic defects are computed. The fault density value is subsequently compared to a predetermined value, wherein the predetermined value is determined using test structures and / or yield data from a target manufacturing process.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
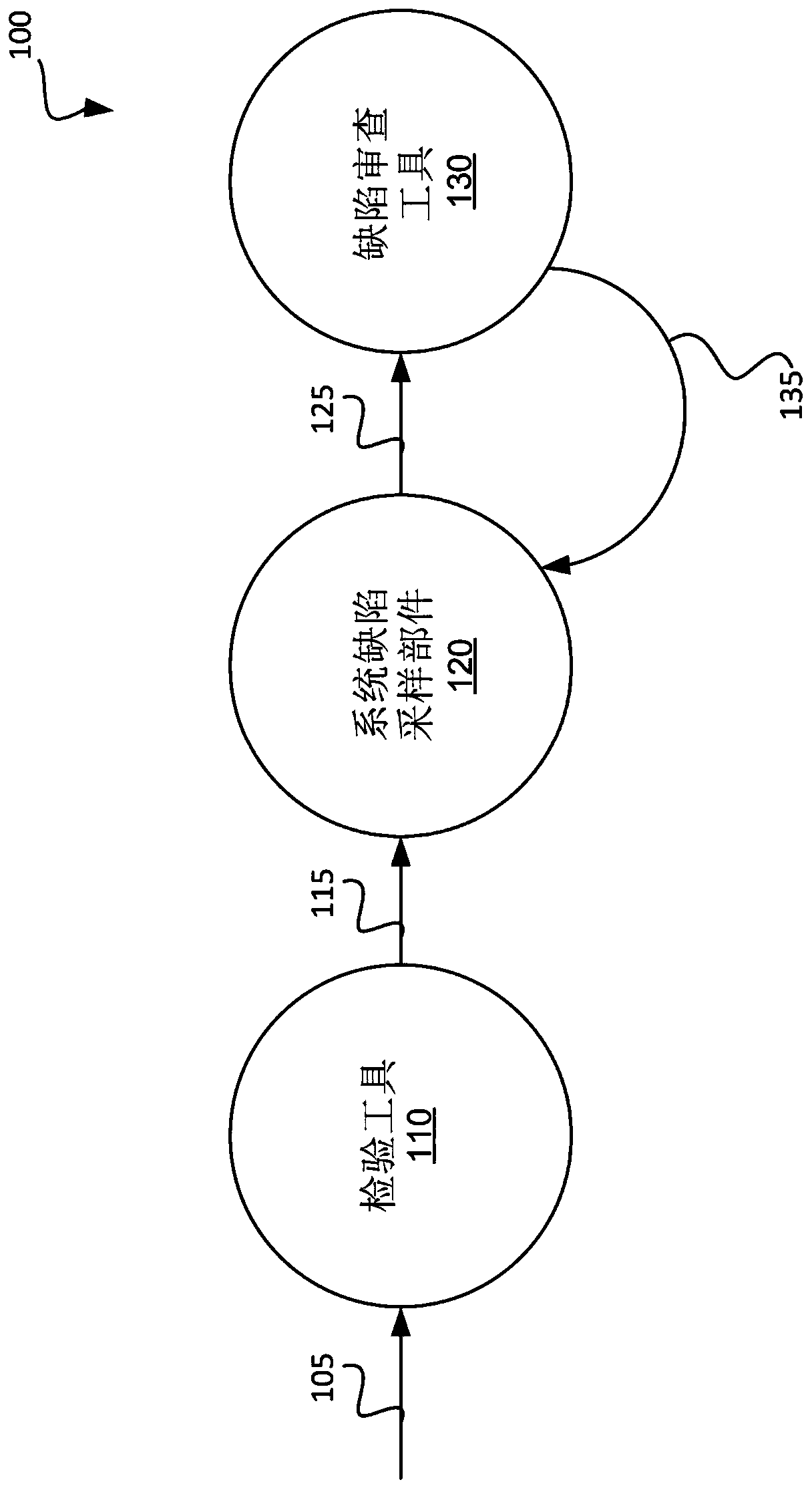
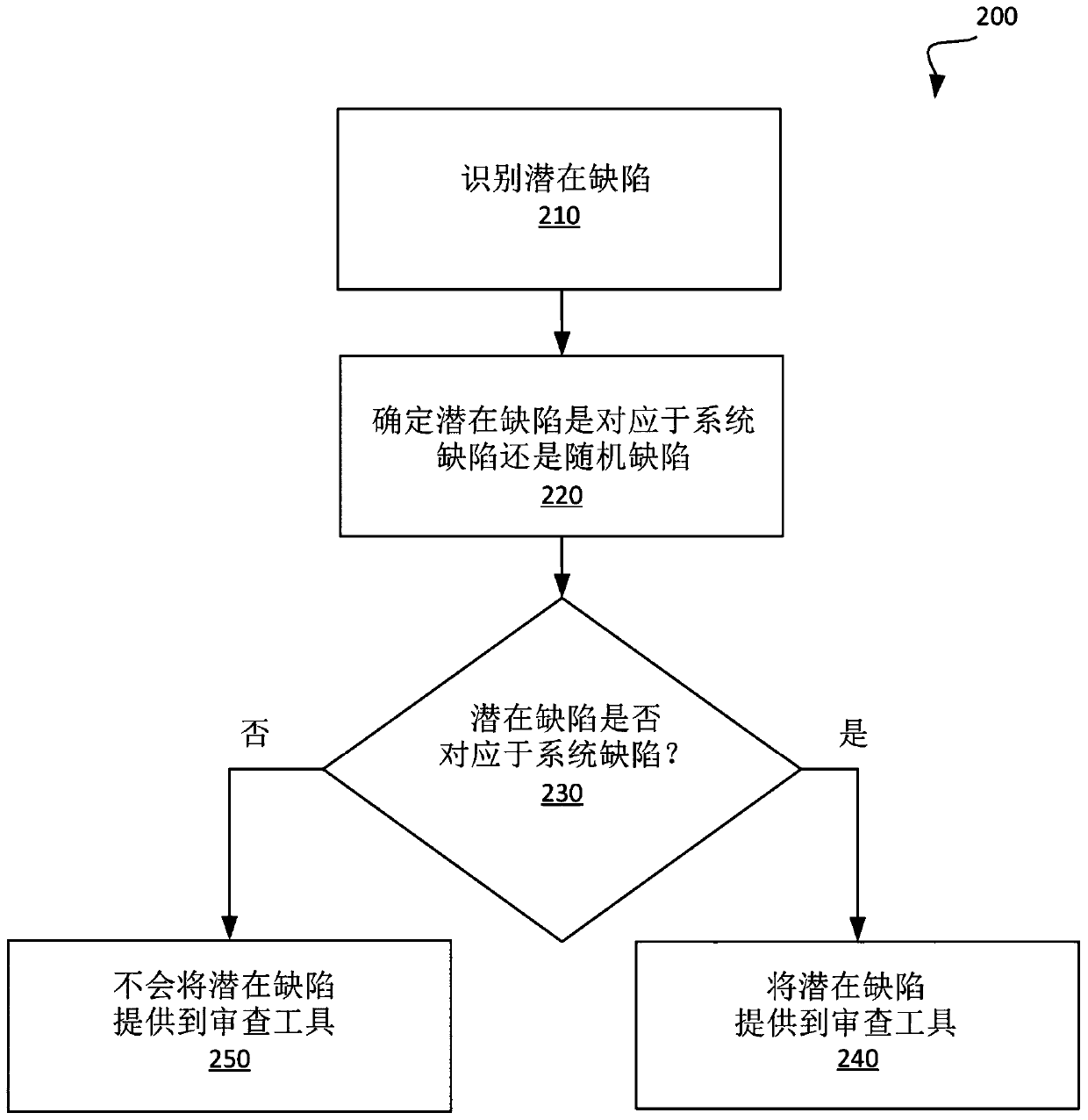
Guided inspection of a semiconductor wafer based on systematic defects
ActiveCN110660694ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingEngineering physics
A candidate defect may be identified at a semiconductor wafer. A determination may be made as to whether the candidate defect at the semiconductor wafer corresponds to a systematic defect or a randomdefect. In response to determining that the candidate defect at the semiconductor wafer corresponds to a systematic detect, the candidate defect at the semiconductor wafer may be provided to a defectreview tool for review by the defect review tool.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Method for computing the sensitivity of a VLSI design to both random and systematic defects using a critical area analysis tool
InactiveUS7487476B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designAnalysis toolsIntegrated circuit layout
A method of estimating integrated circuit yield comprises providing an integrated circuit layout and a set of systematic defects based on a manufacturing process. Next, the method represents a systematic defect by modifying structures in the integrated circuit layout to create modified structures. More specifically, for short-circuit-causing defects, the method pre-expands the structures when the structures comprise a higher systematic defect sensitivity level, and pre-shrinks the structures when the structures comprise a lower systematic defect sensitivity level. Following this, a critical area analysis is performed on the integrated circuit layout using the modified structures, wherein dot-throwing, geometric expansion, or Voronoi diagrams are used. The method then computes a fault density value, random defects and systematic defects are computed. The fault density value is subsequently compared to a predetermined value, wherein the predetermined value is determined using test structures and / or yield data from a target manufacturing process.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Mapping of random defects in a memory device
ActiveUS8887013B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionParallel computingRandom defects
A memory device includes a memory array with random defective memory cells. The memory array is organized into rows and columns with a row and column identifying a memory location of a memory cell of the memory array. The memory device includes a row address device and a column address device and is operative to use a grouping of either the row or the column addresses to manage the random defective memory cells by mapping the memory location of a defective memory cell to an alternate memory location.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Random defect mode superposition method based on response surface method
ActiveCN110991112AMake up for the shortcomings of large sample calculationsImprove stacking efficiencySustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationCritical loadStructural engineering
The invention provides a random defect mode superposition method based on a response surface method. The method comprises the following steps: expressing a critical load fitting expression in a polynomial form by utilizing a polynomial response surface method, calculating and determining an undetermined coefficient of the obtained expression according to the critical load fitting expression, and determining the critical load fitting expression according to the undetermined coefficient obtained by calculation; determining a critical load; and calculating the failure probability of structure critical load. According to the method, a probability model of a structural defect modal combination coefficient is established, a random variable is fitted by utilizing a polynomial, and stable bearingcapacity analysis is carried out on a classical reticulated shell and a reticulated shell with random defects, so the defect of large sample calculation amount of a random defect method and an improved random defect method is overcome, random defect mode superposition efficiency is improved, and problems in reliability of critical load designing is overcome.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com